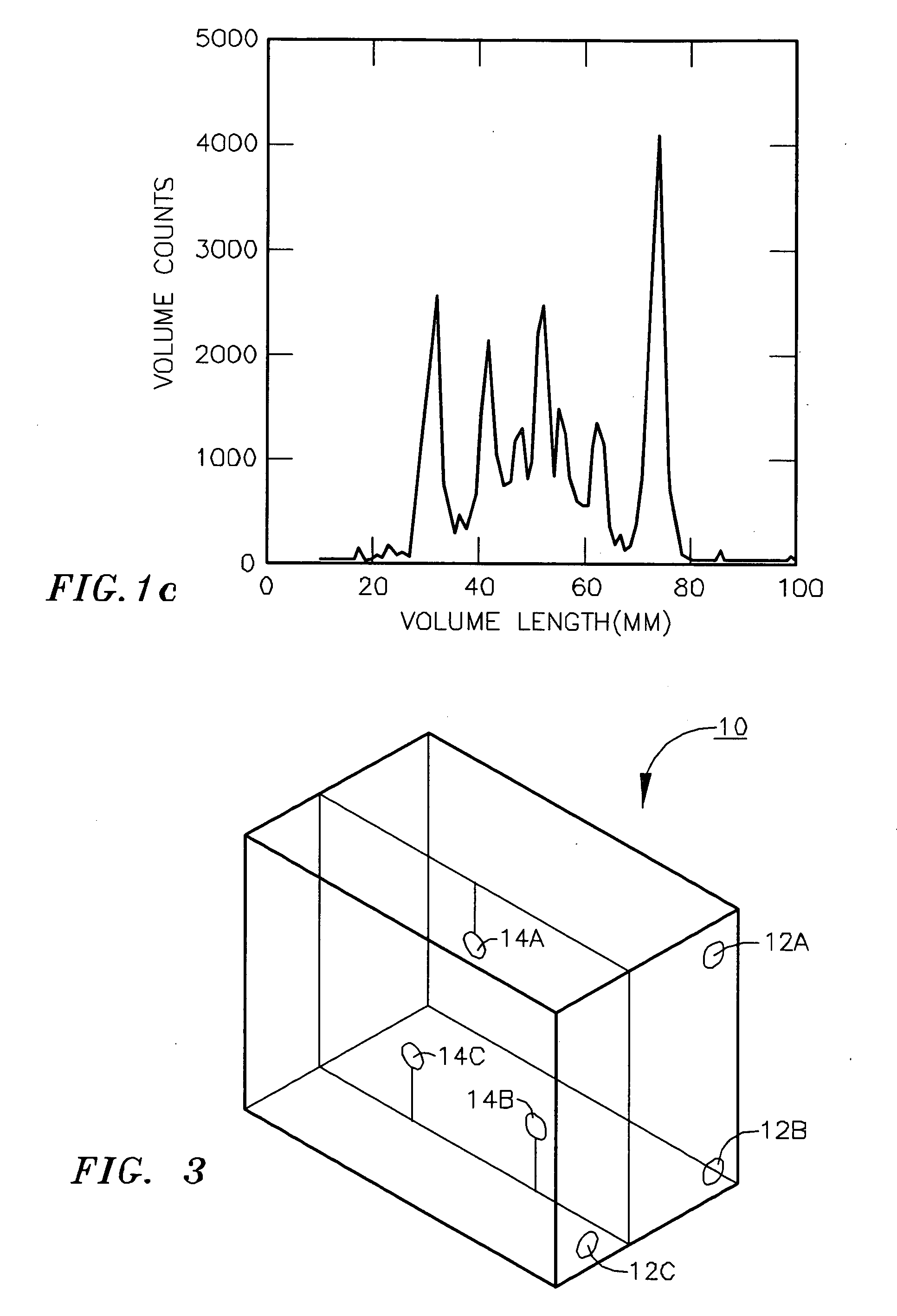
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
152 results about "Single photon emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, scintigraphy). but is able to provide true 3D information.
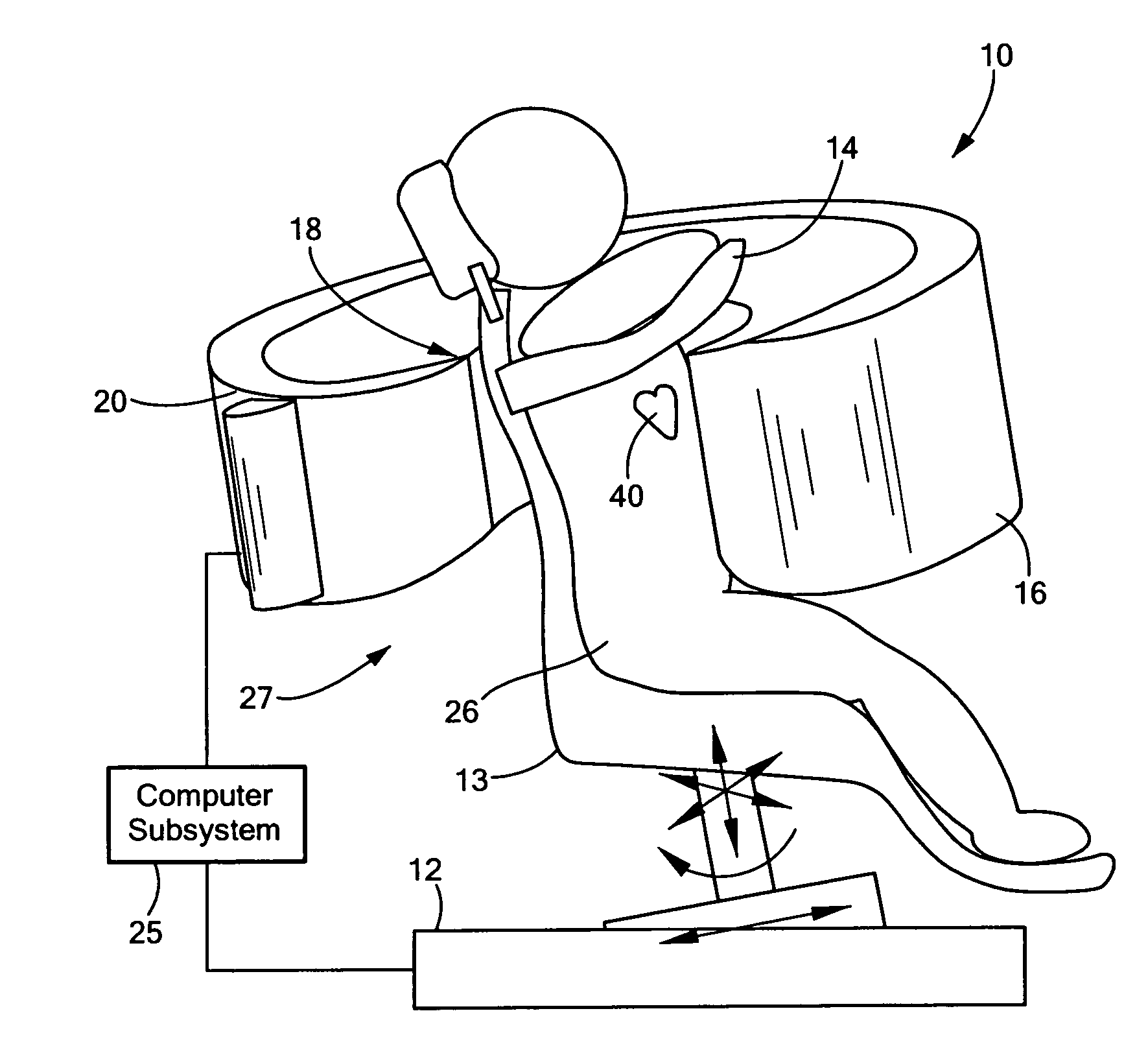
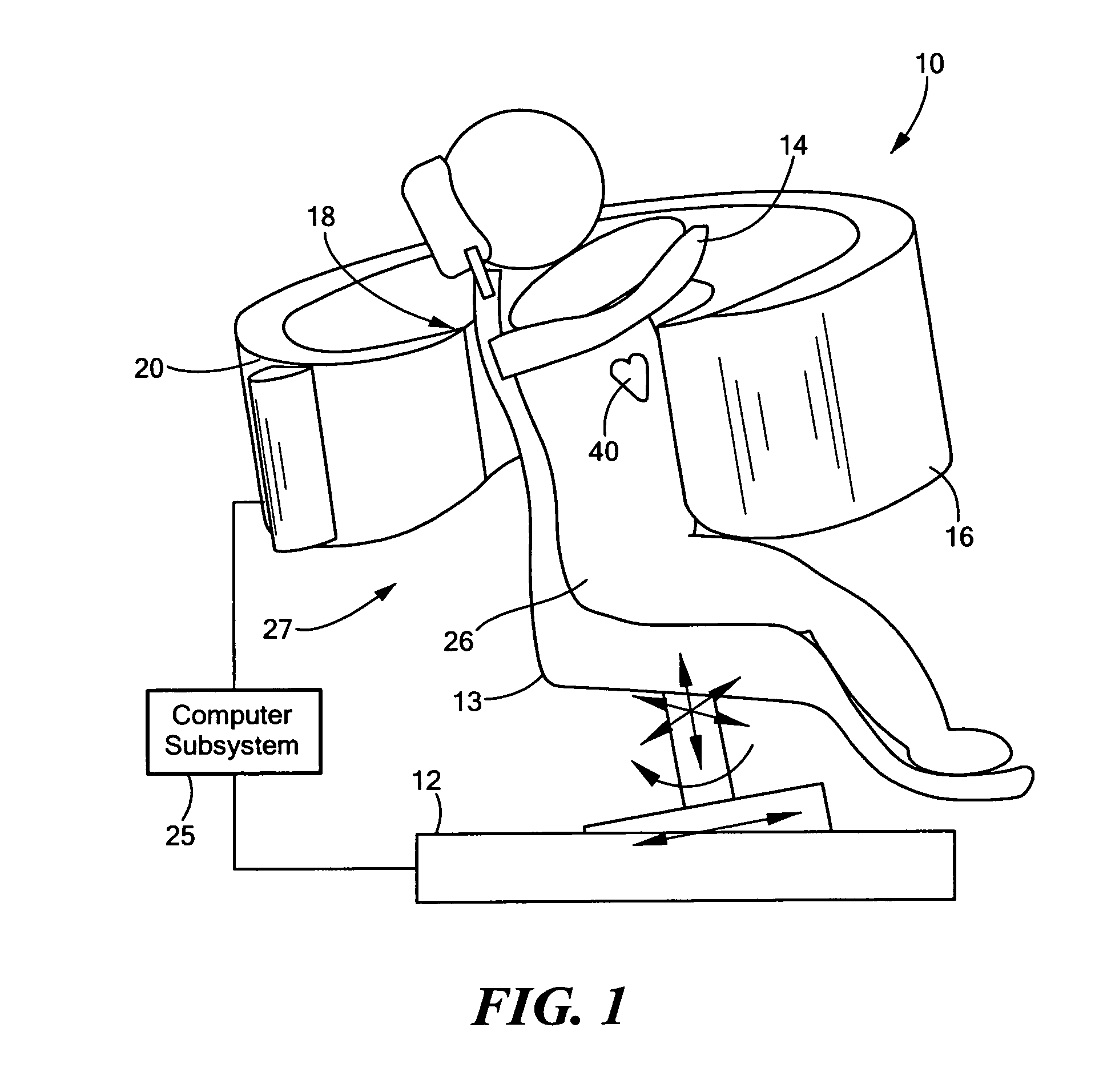
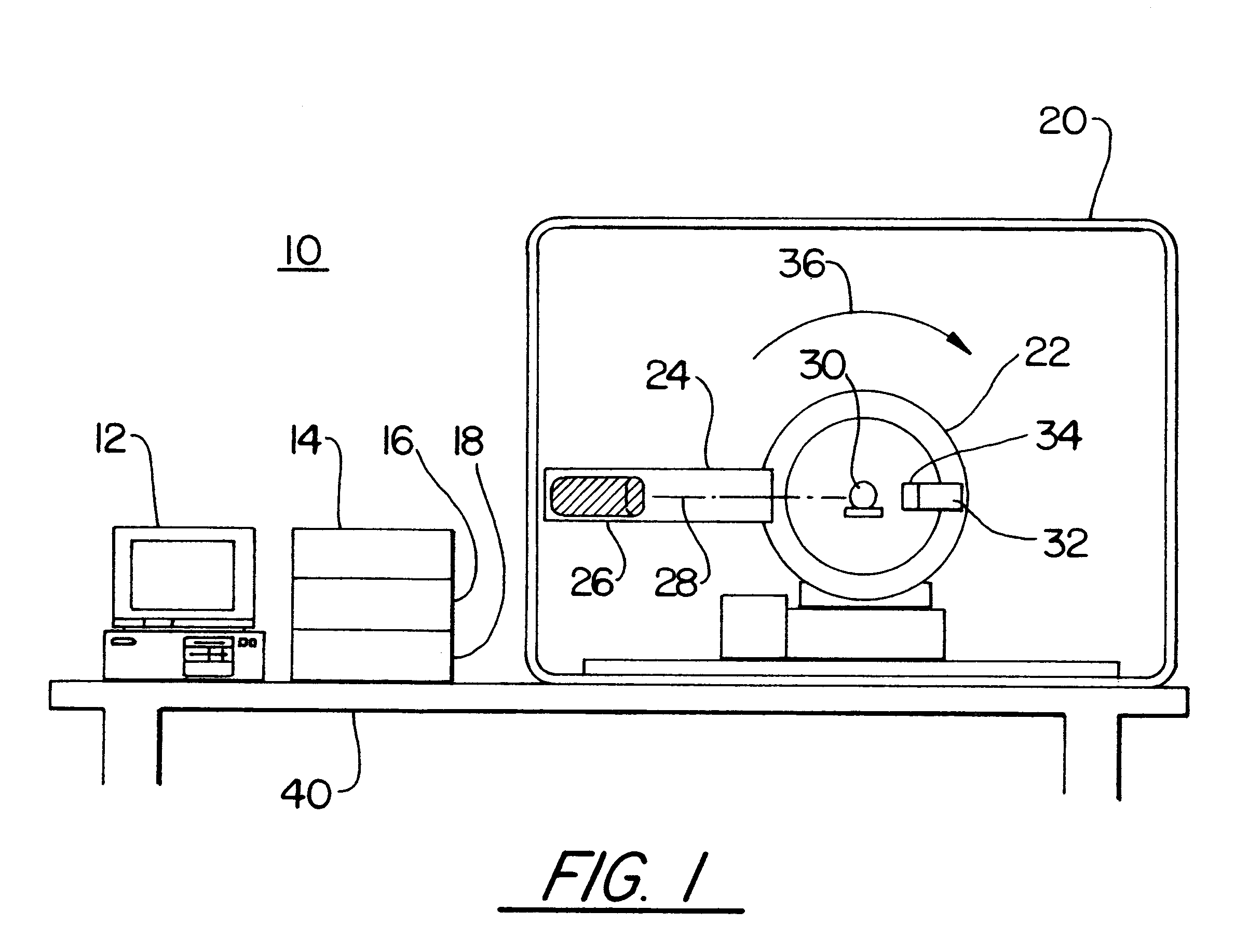
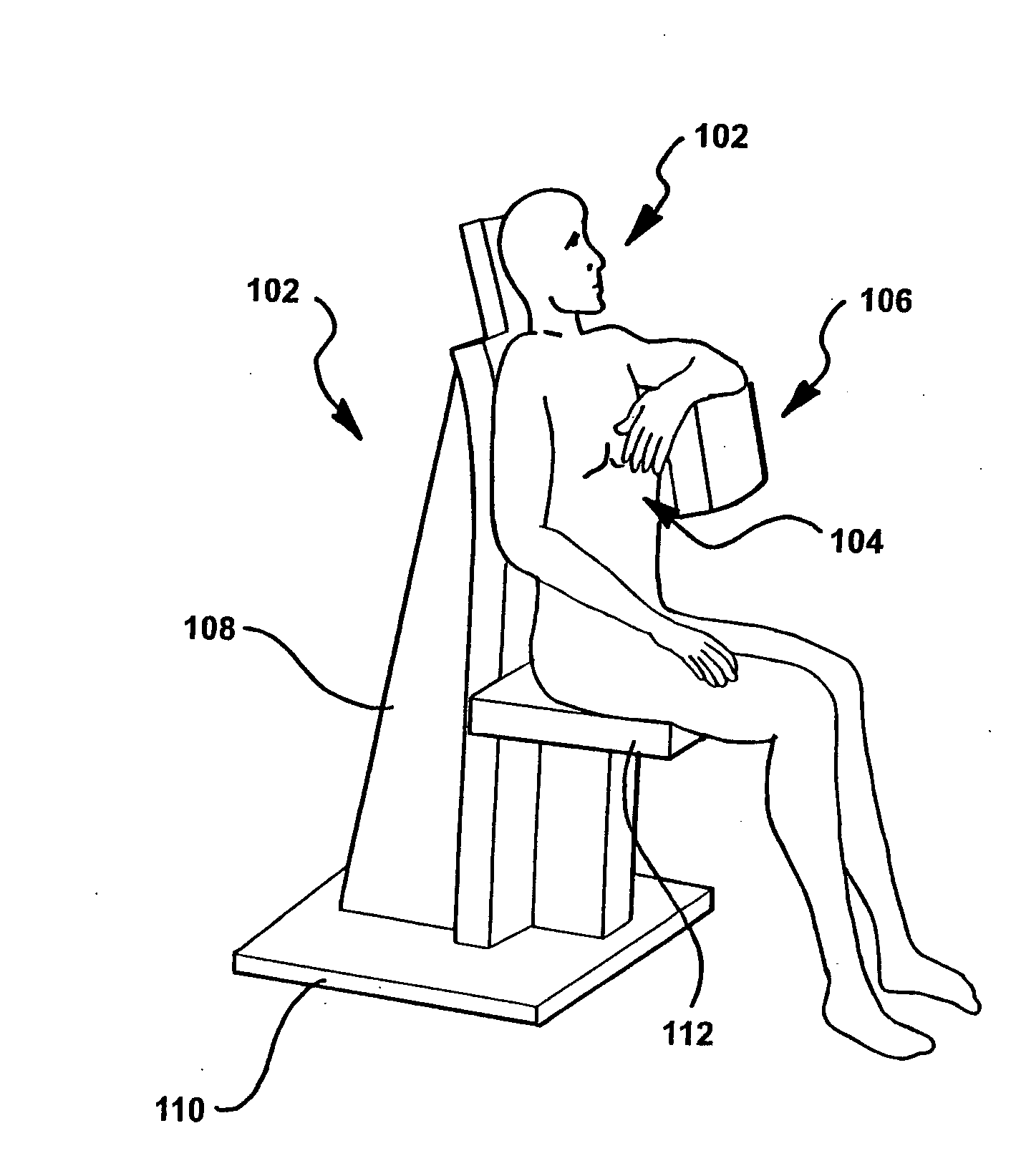
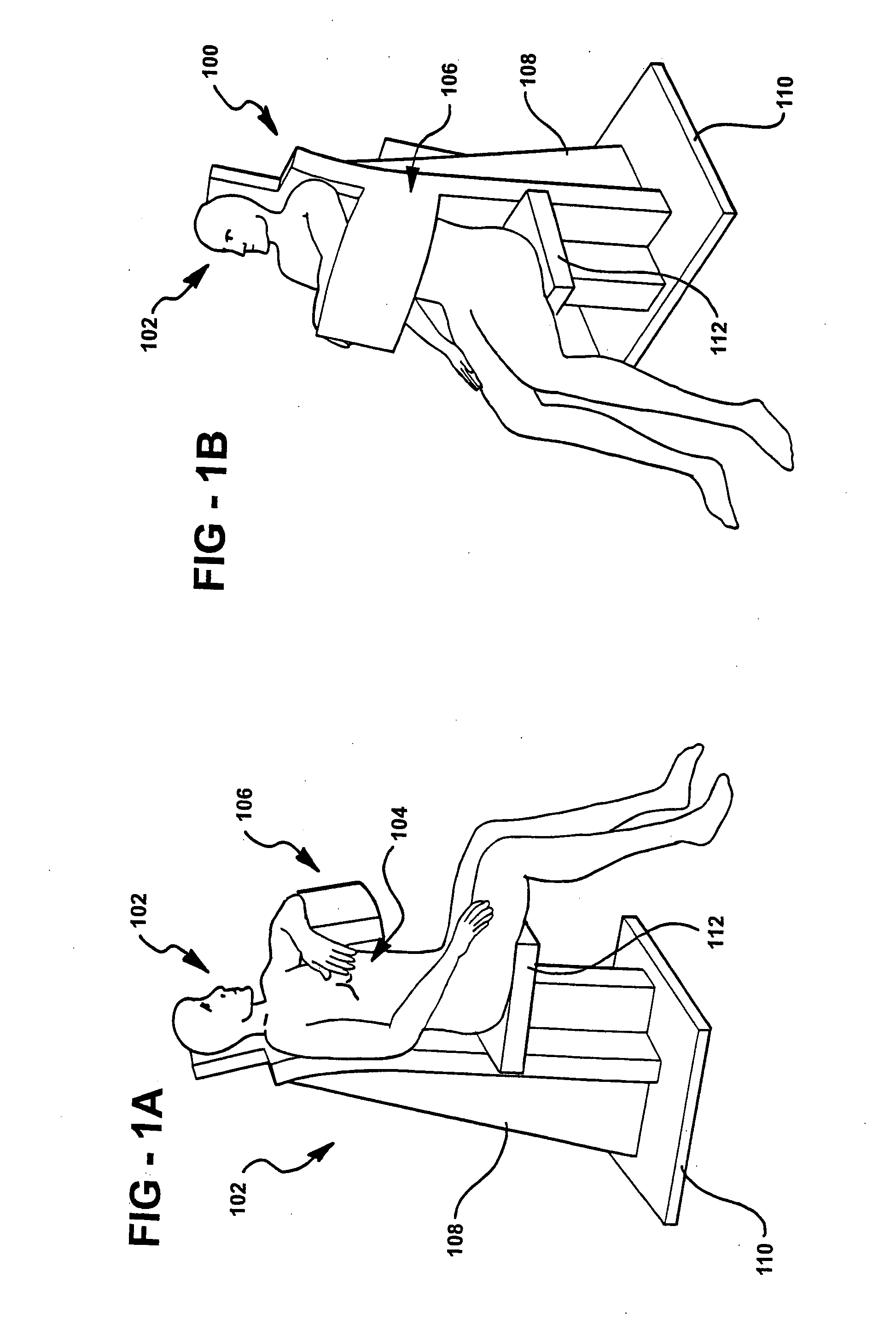
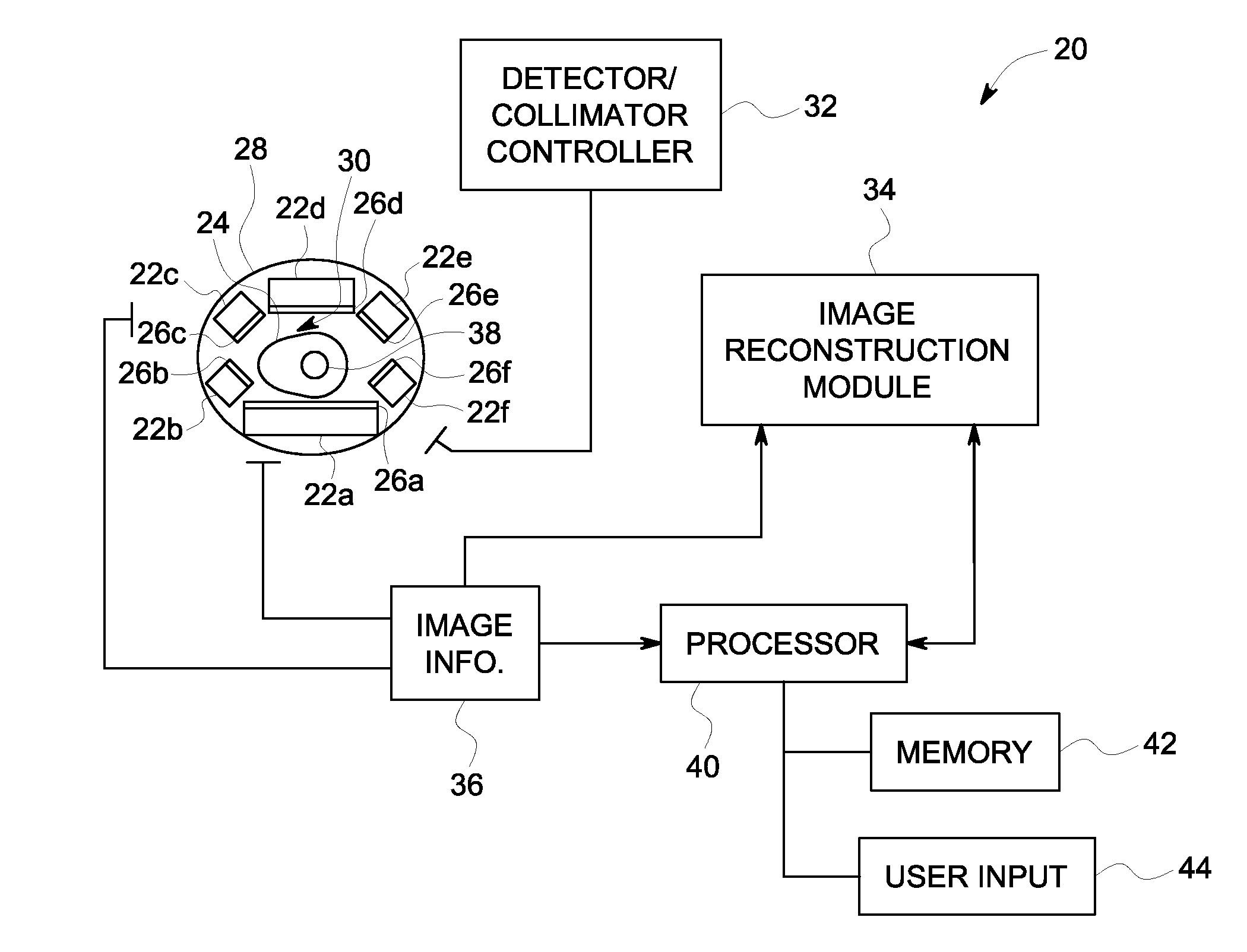
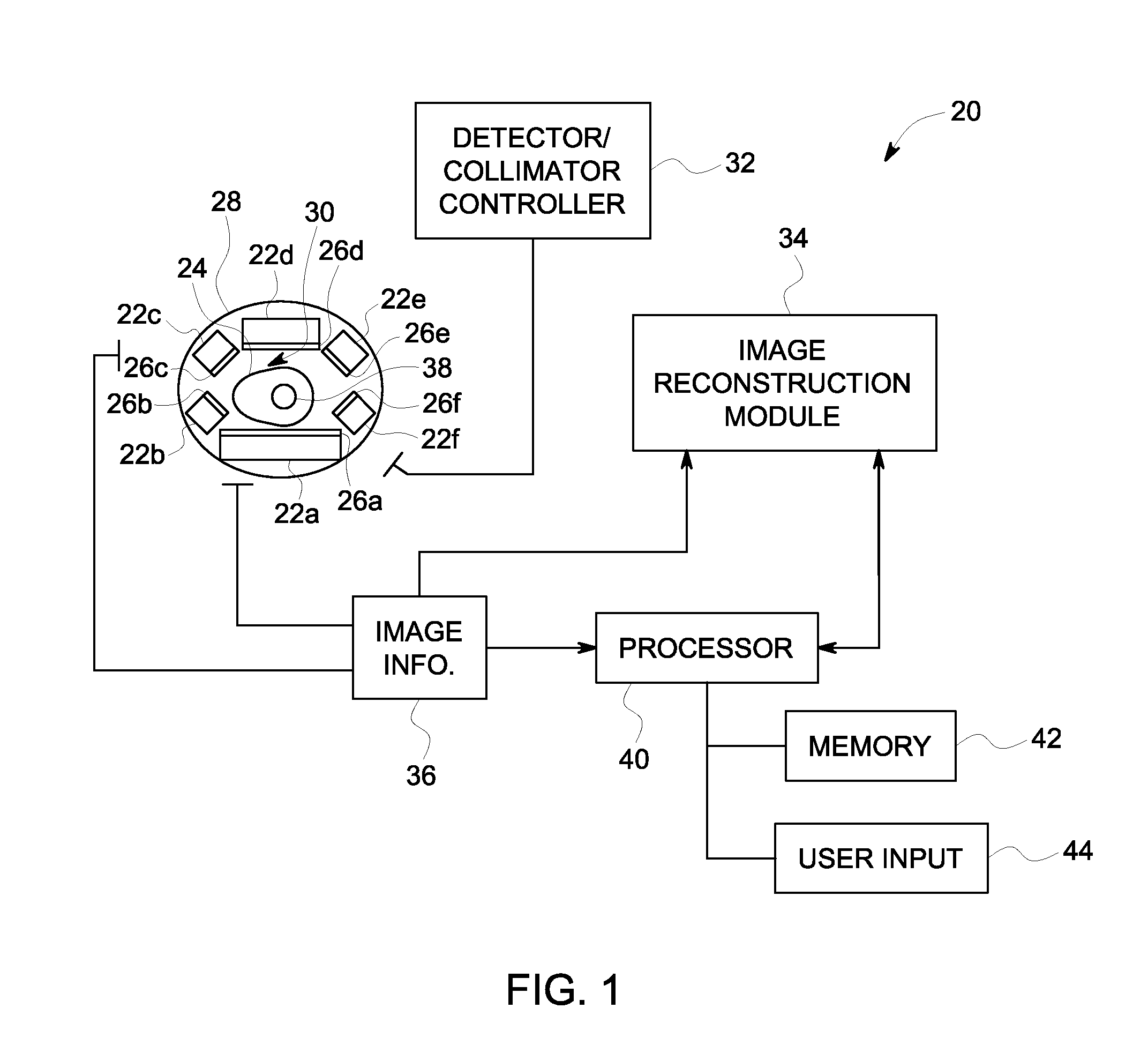
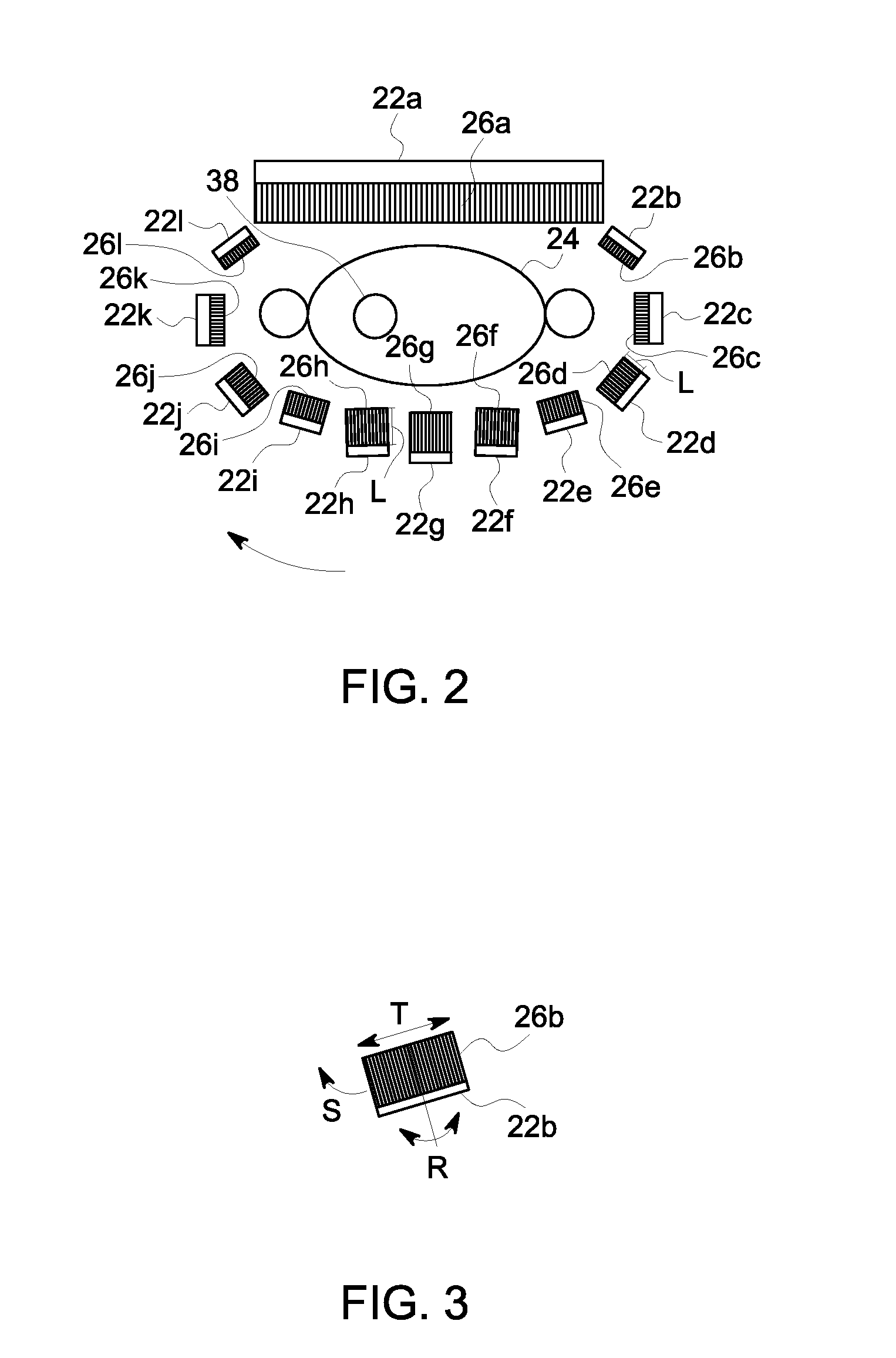
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7683331B2Optimize dataQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyGeometric efficiencyCardiac imaging
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Simultaneous CT and SPECT tomography using CZT detectors
A method for simultaneous transmission x-ray computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission tomography (SPECT) comprises the steps of: injecting a subject with a tracer compound tagged with a gamma-ray emitting nuclide; directing an x-ray source toward the subject; rotating the x-ray source around the subject; emitting x-rays during the rotating step; rotating a cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) two-sided detector on an opposite side of the subject from the source; simultaneously detecting the position and energy of each pulsed x-ray and each emitted gamma-ray captured by the CZT detector; recording data for each position and each energy of each the captured x-ray and gamma-ray; and, creating CT and SPECT images from the recorded data. The transmitted energy levels of the x-rays lower are biased lower than energy levels of the gamma-rays. The x-ray source is operated in a continuous mode. The method can be implemented at ambient temperatures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
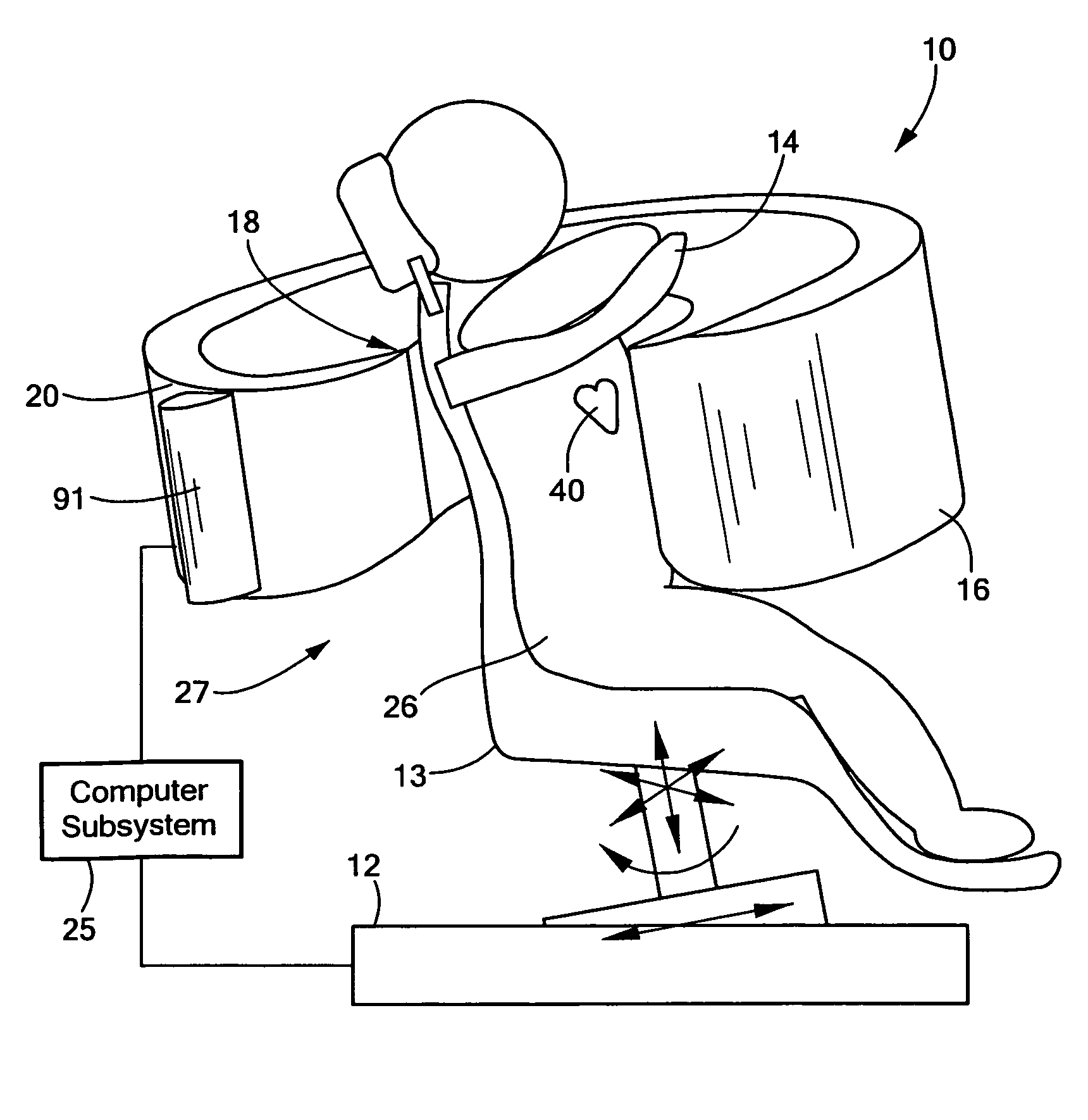
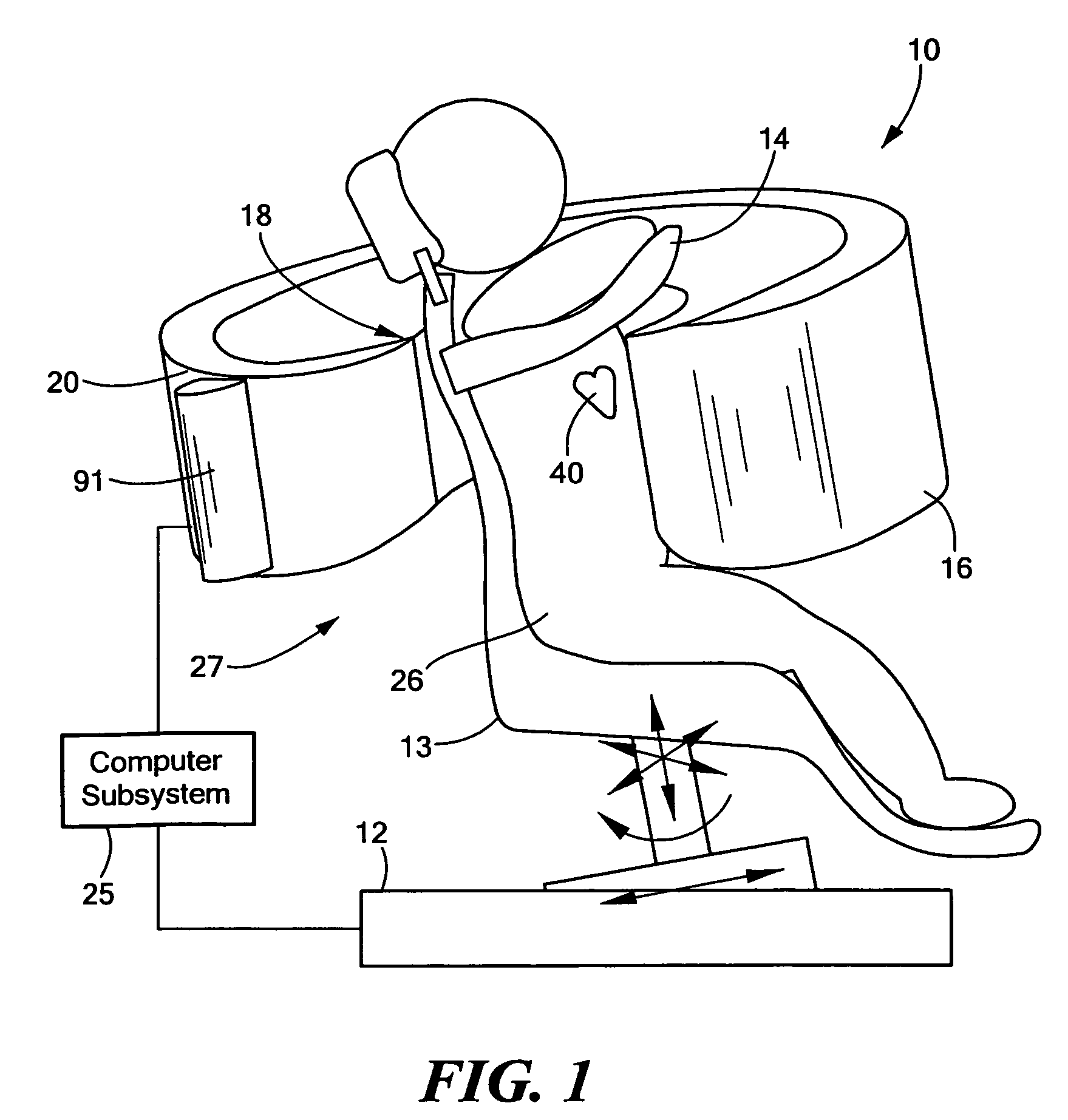
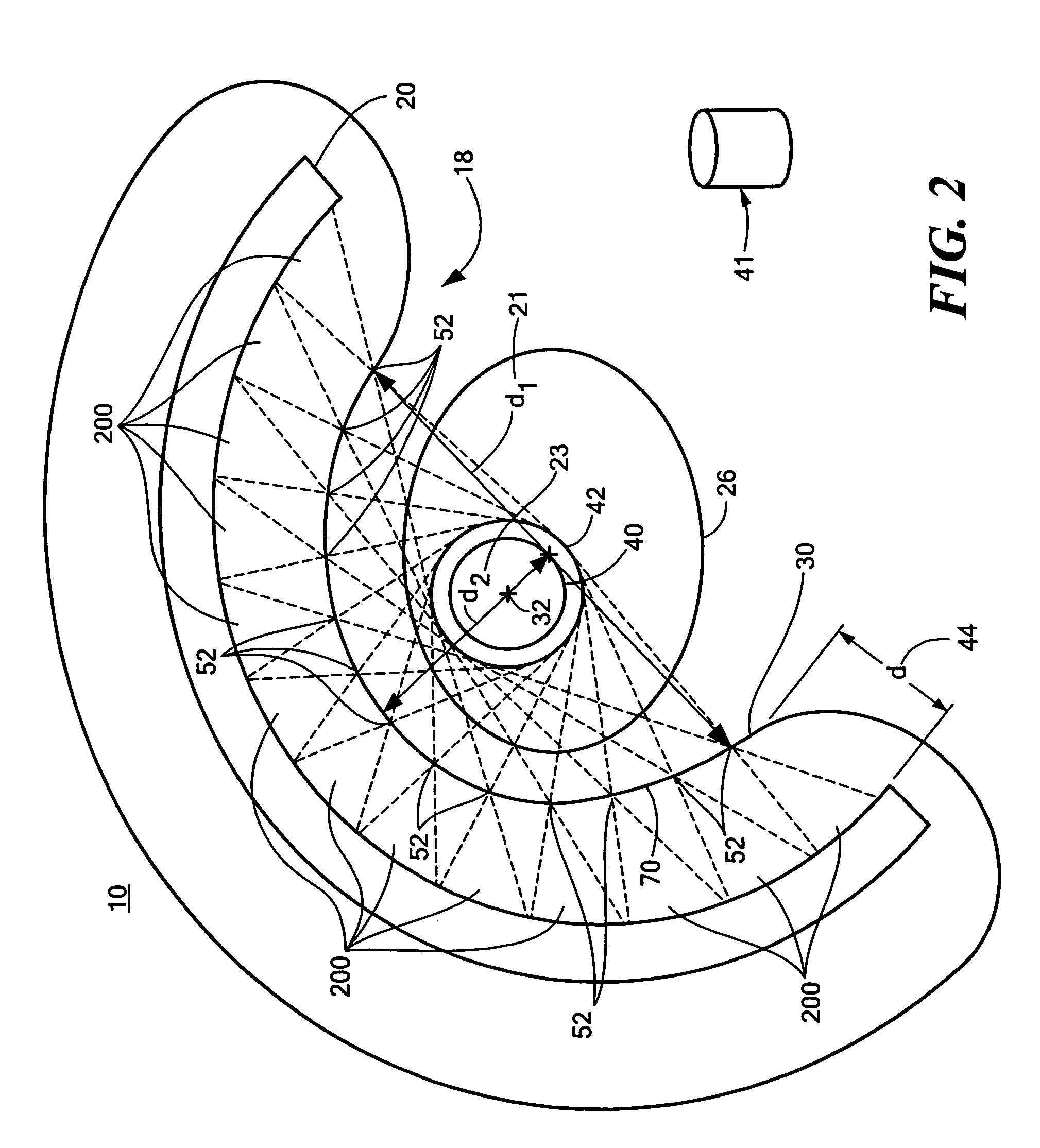
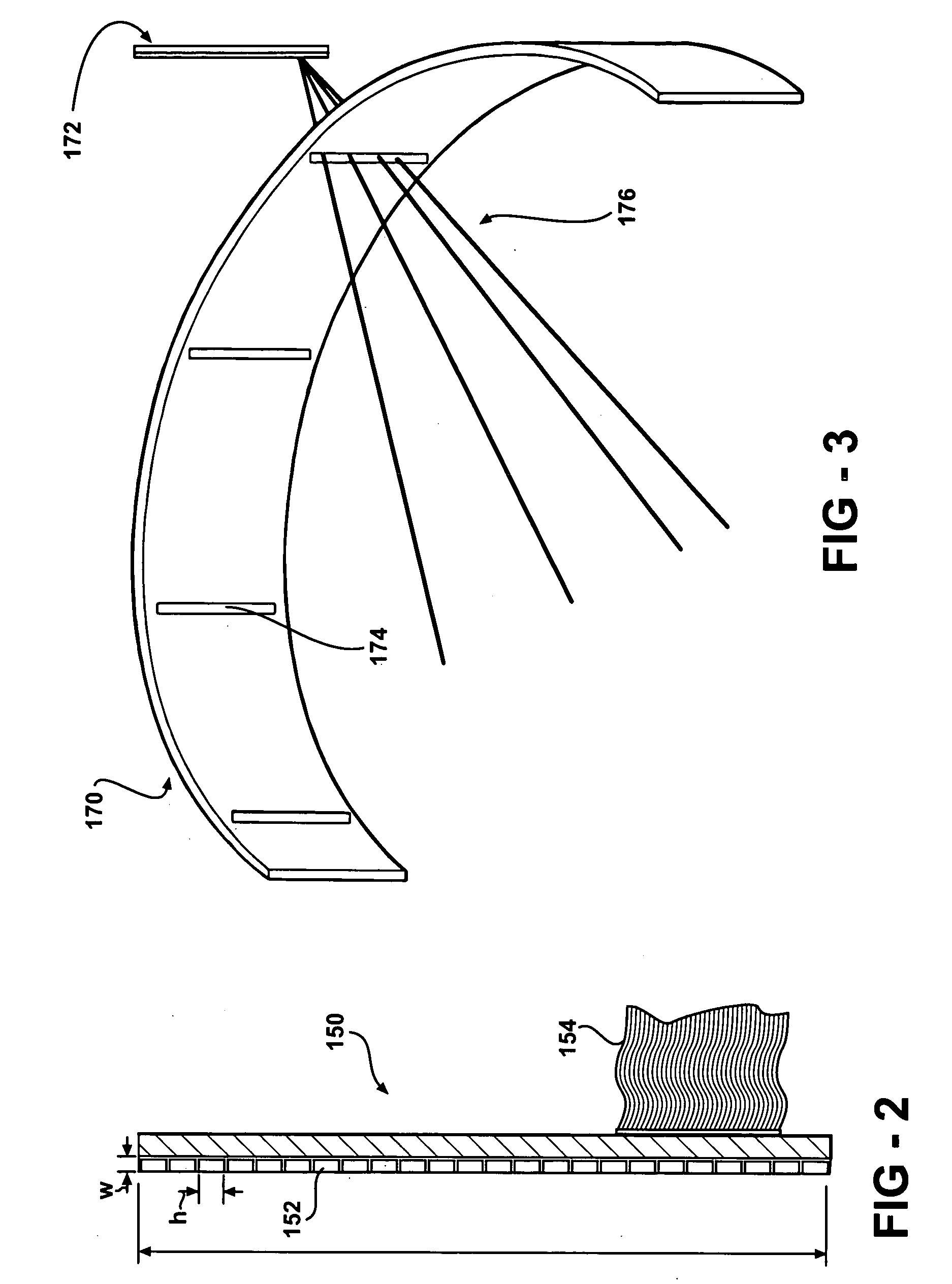
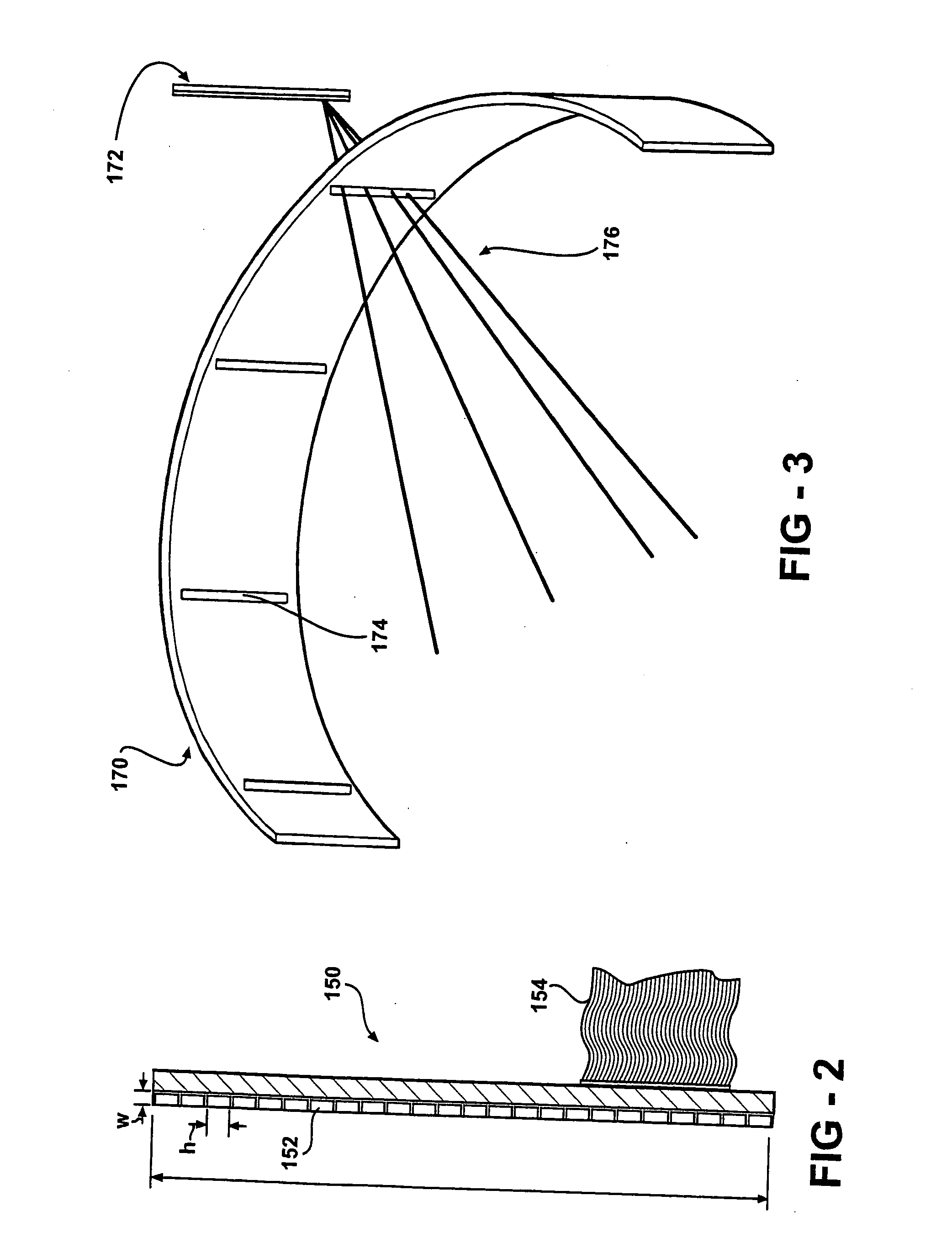
Integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7683332B2Improve image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTransmission Computed TomographyPatients position
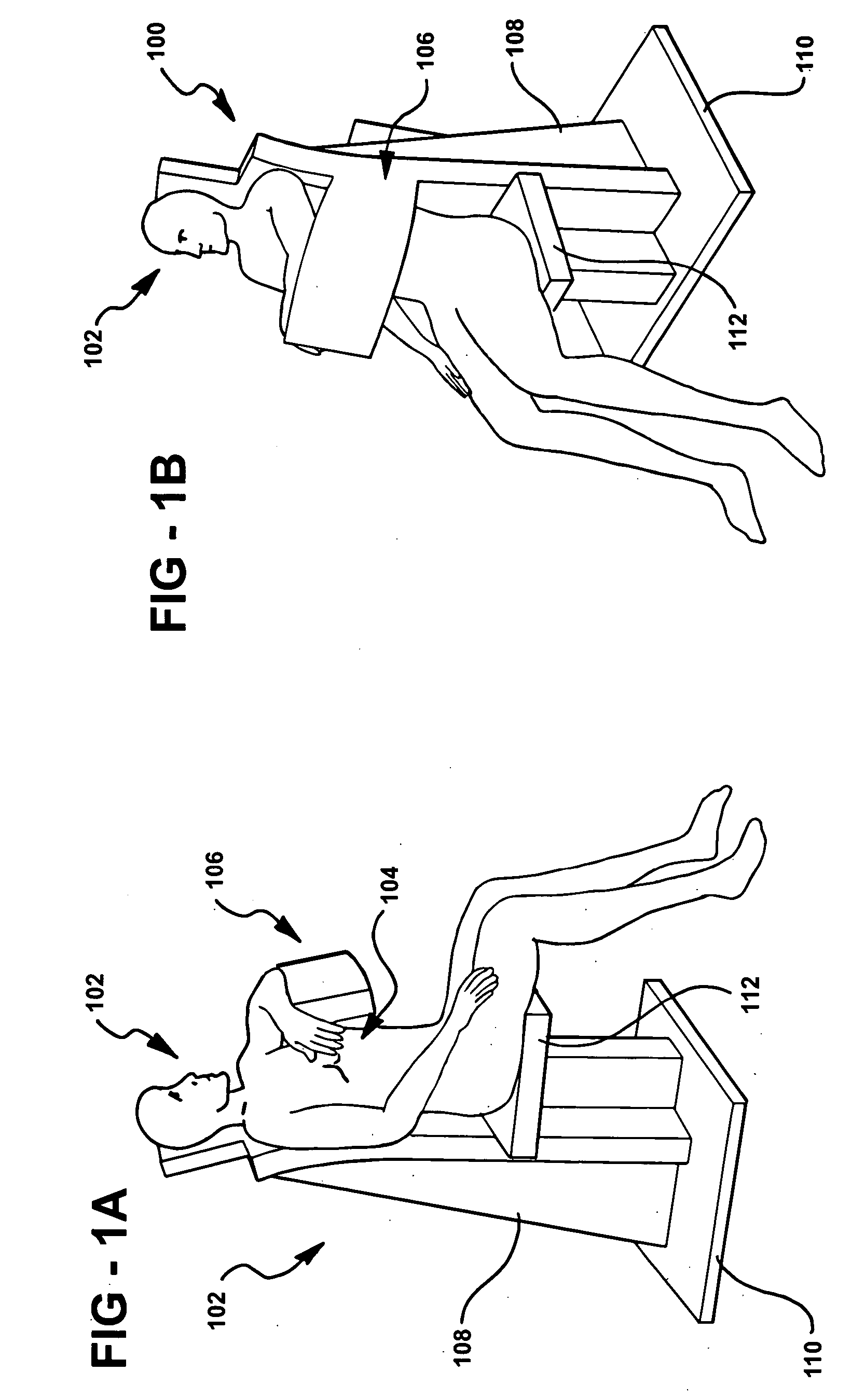
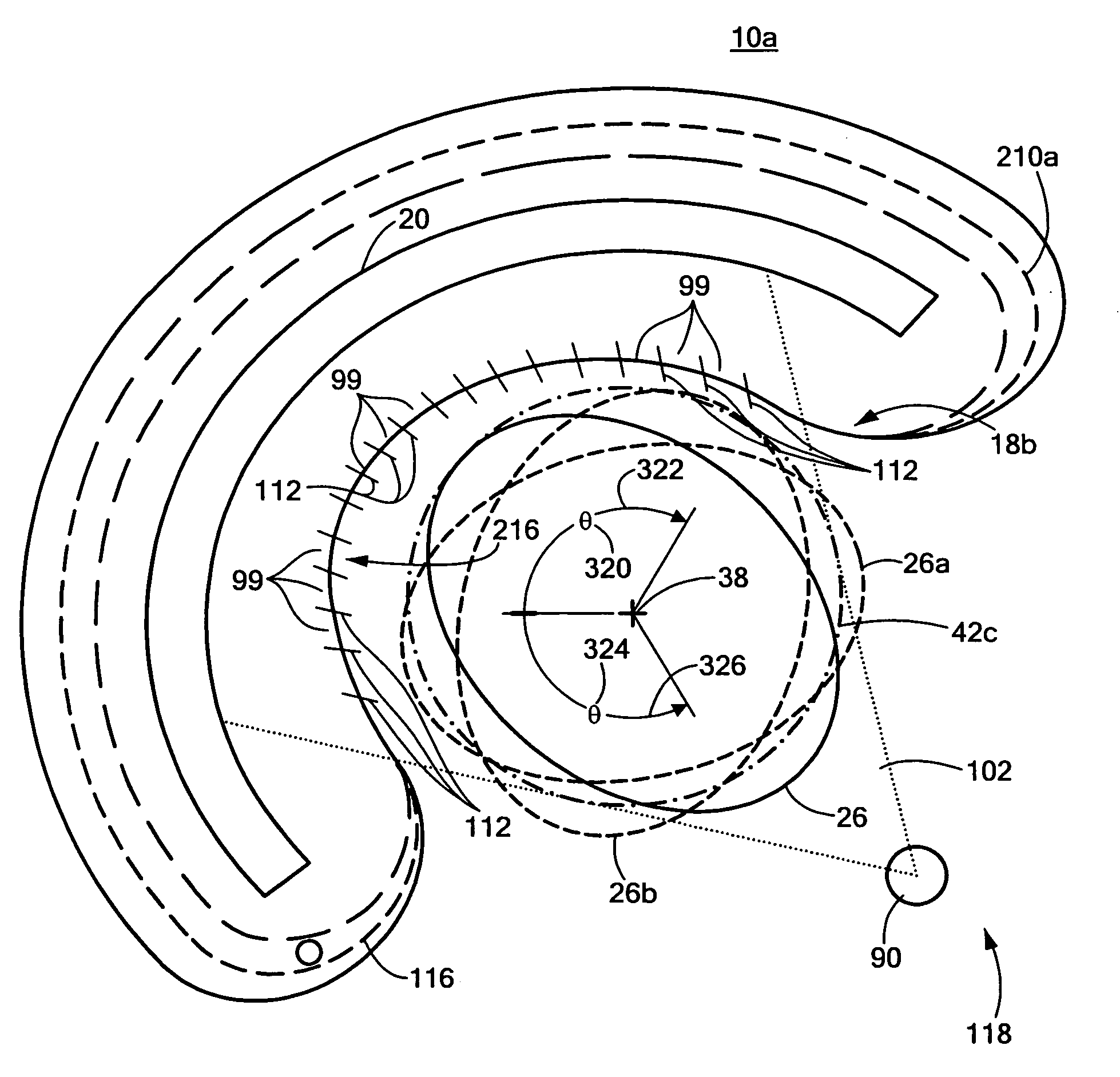
This invention features an integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) / transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging including an open arc-shaped frame. A collimator system is shaped to approximately match the thoracic contour of patients having different sizes and weights and shaped to surround and position the collimator closely proximate a heart of a patient of said patients encompassed by at least one predetermined image volume for optimizing collimation of radiation photons emitted from the heart. An arc-shaped detector system is coupled to the collimator subsystem having a shape closely matching the shape of the collimator subsystem for detecting collimated radiation photons from the collimator subsystem and generating output electrical signals. A patient positioning subsystem positions a patient to a predetermined central longitudinal axis of the three-dimensional imaging volume and for intermittently and incrementally rotating the patient about the predetermined central longitudinal axis for generating a plurality of TCT images.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
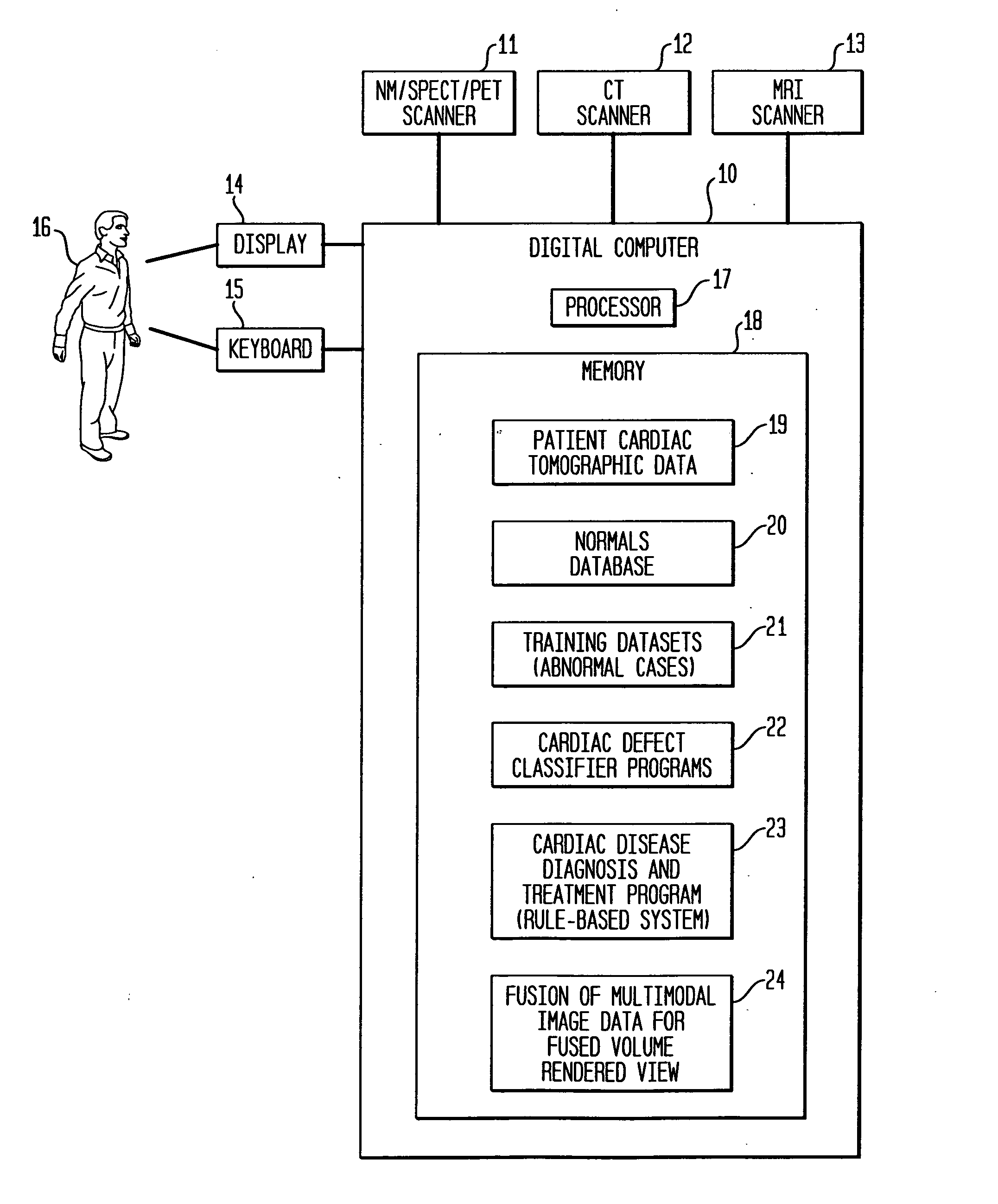
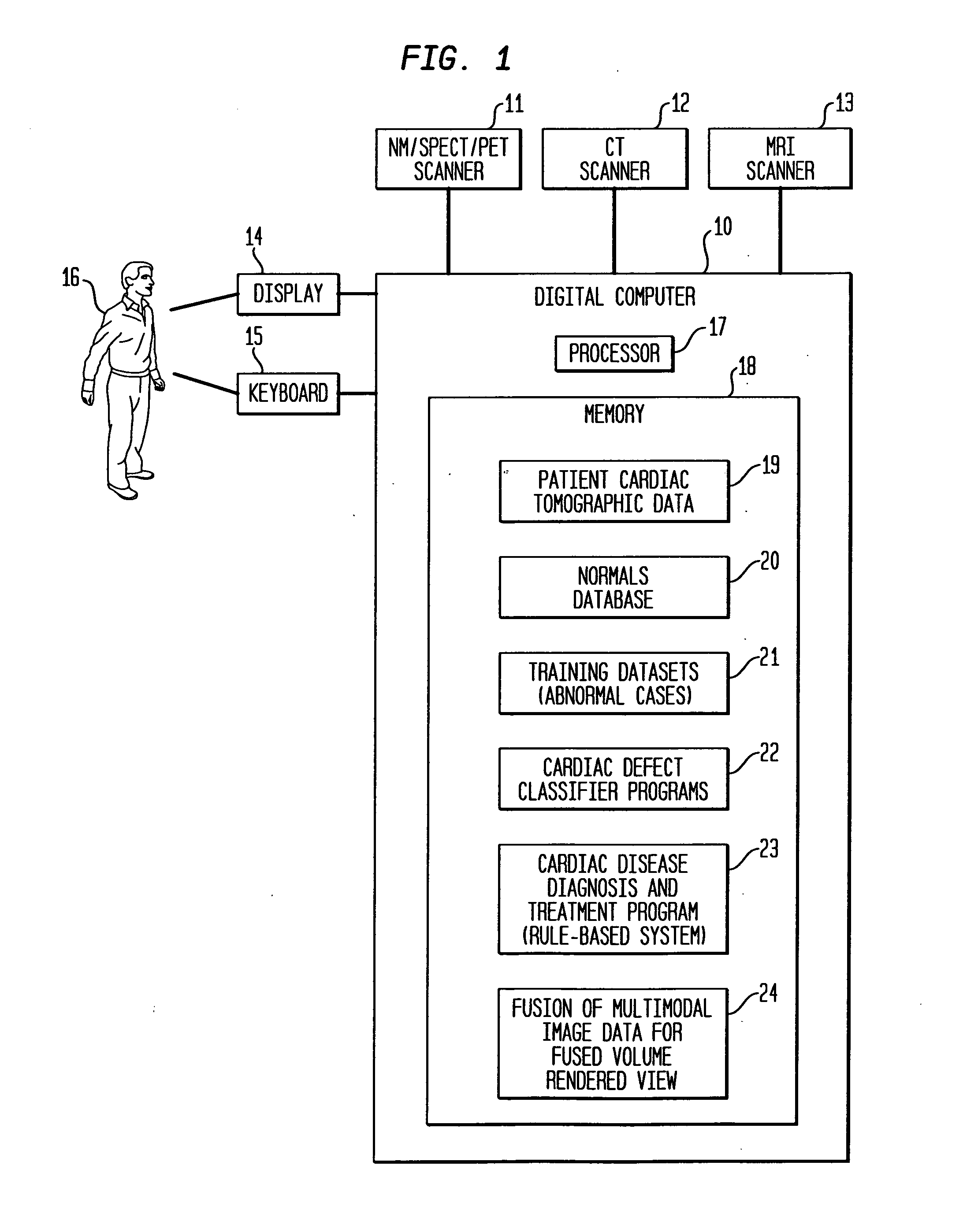
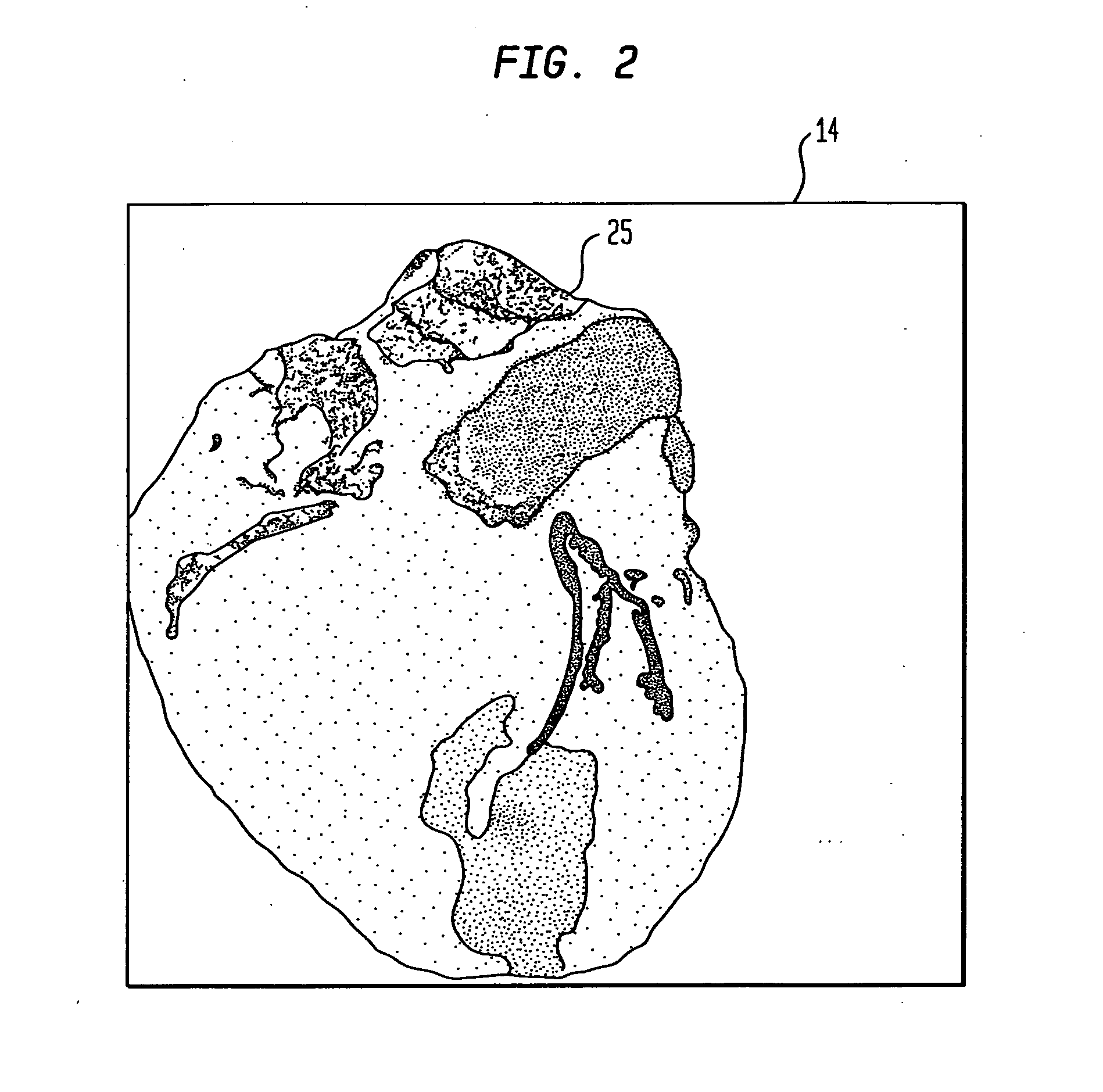
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
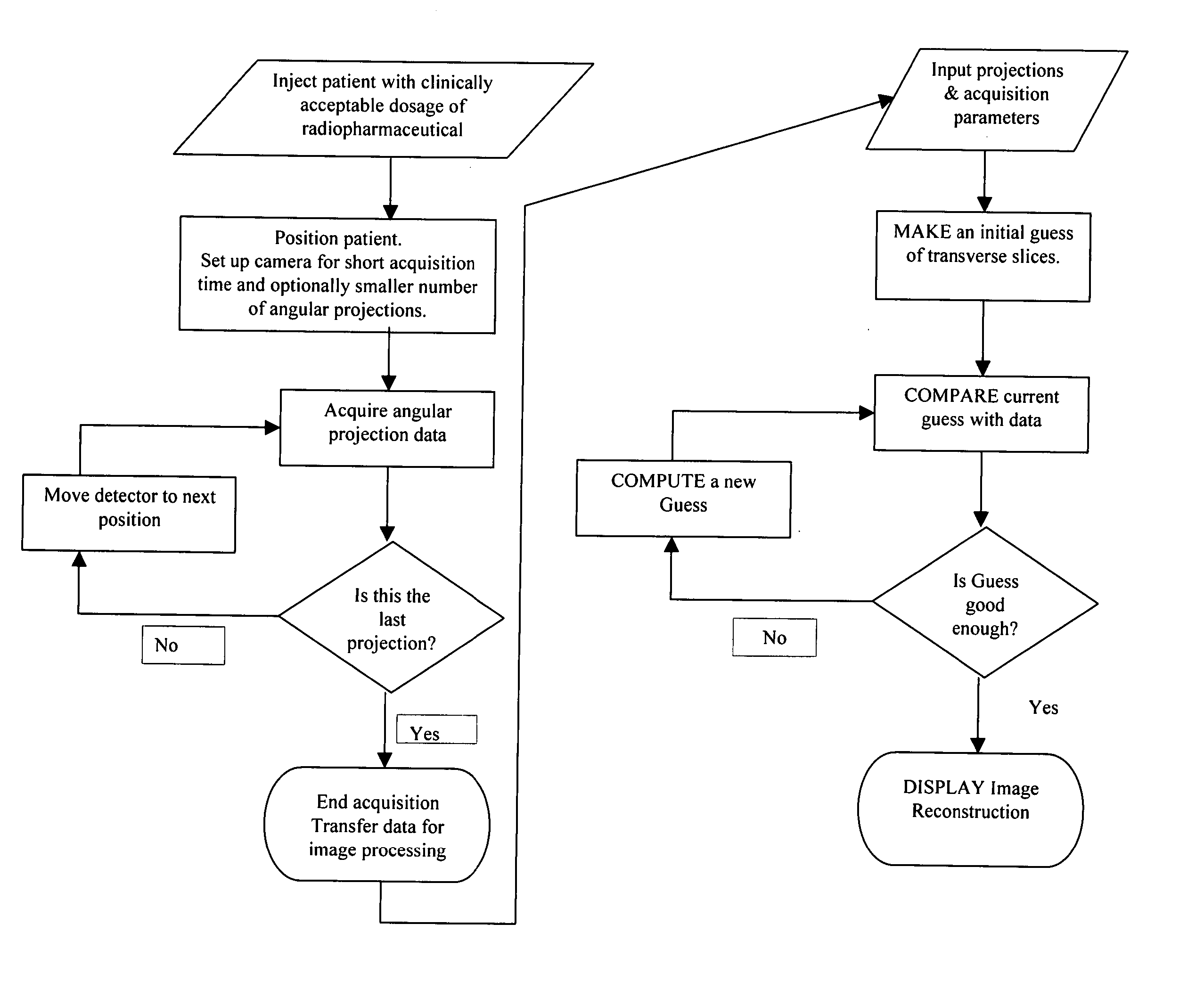
Efficient single photon emission imaging
InactiveUS7026623B2Shorten the timeImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive drugRadiology
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Efficient single photon emission imaging
InactiveUS20050145797A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansAcquisition timeGamma ray
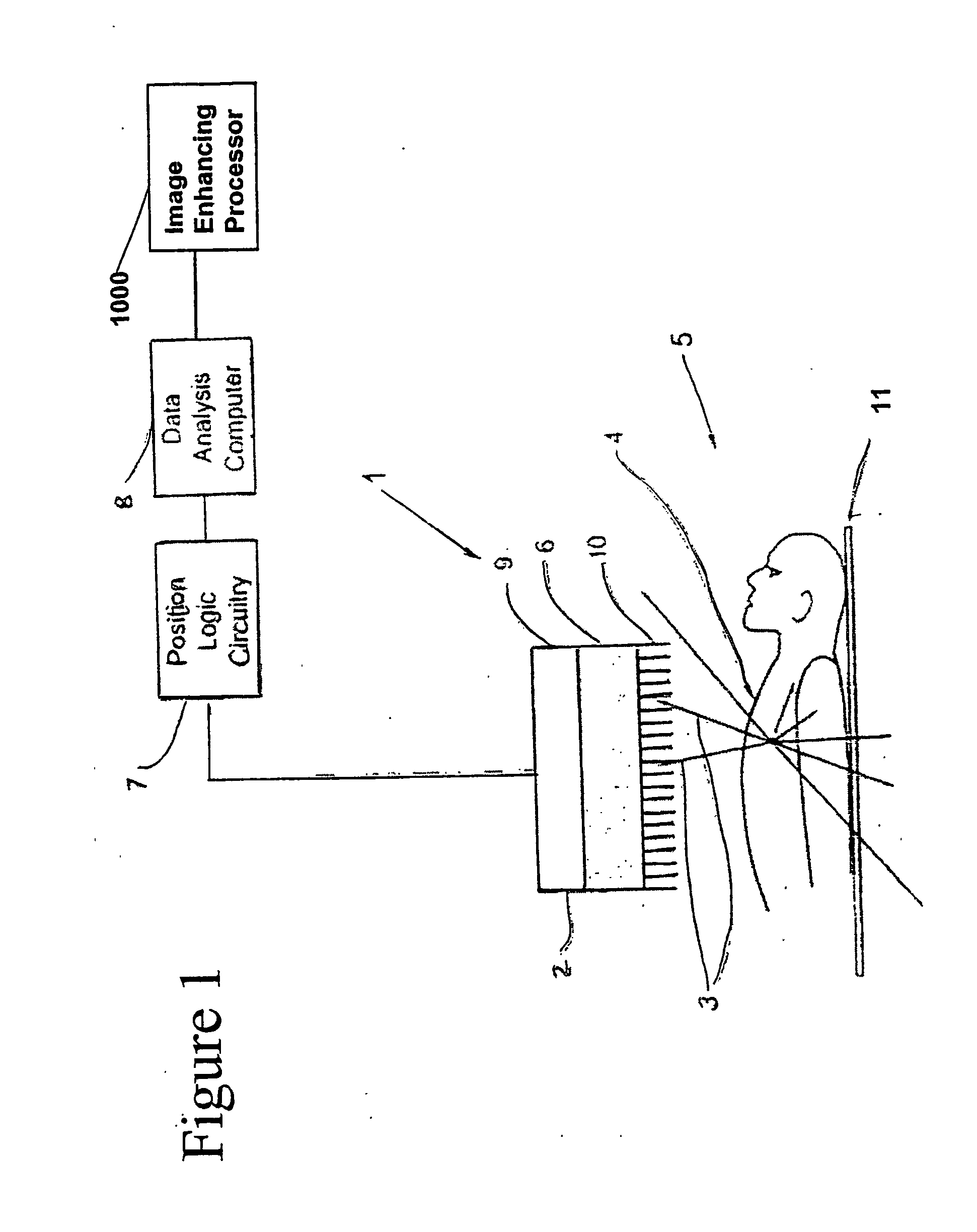
A method of diagnostic imaging in a shortened acquisition time for obtaining a reconstructed diagnostic image of a portion of a body of a human patient who was administered with dosage of radiopharmaceutical substance radiating gamma rays, using SPECT. The method comprises acquiring photons emitted from said portion of the body, by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, wherein the total time of photon acquiring is substantially shorter than the clinically acceptable acquisition time; processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby deriving data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by iteratively processing said data.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
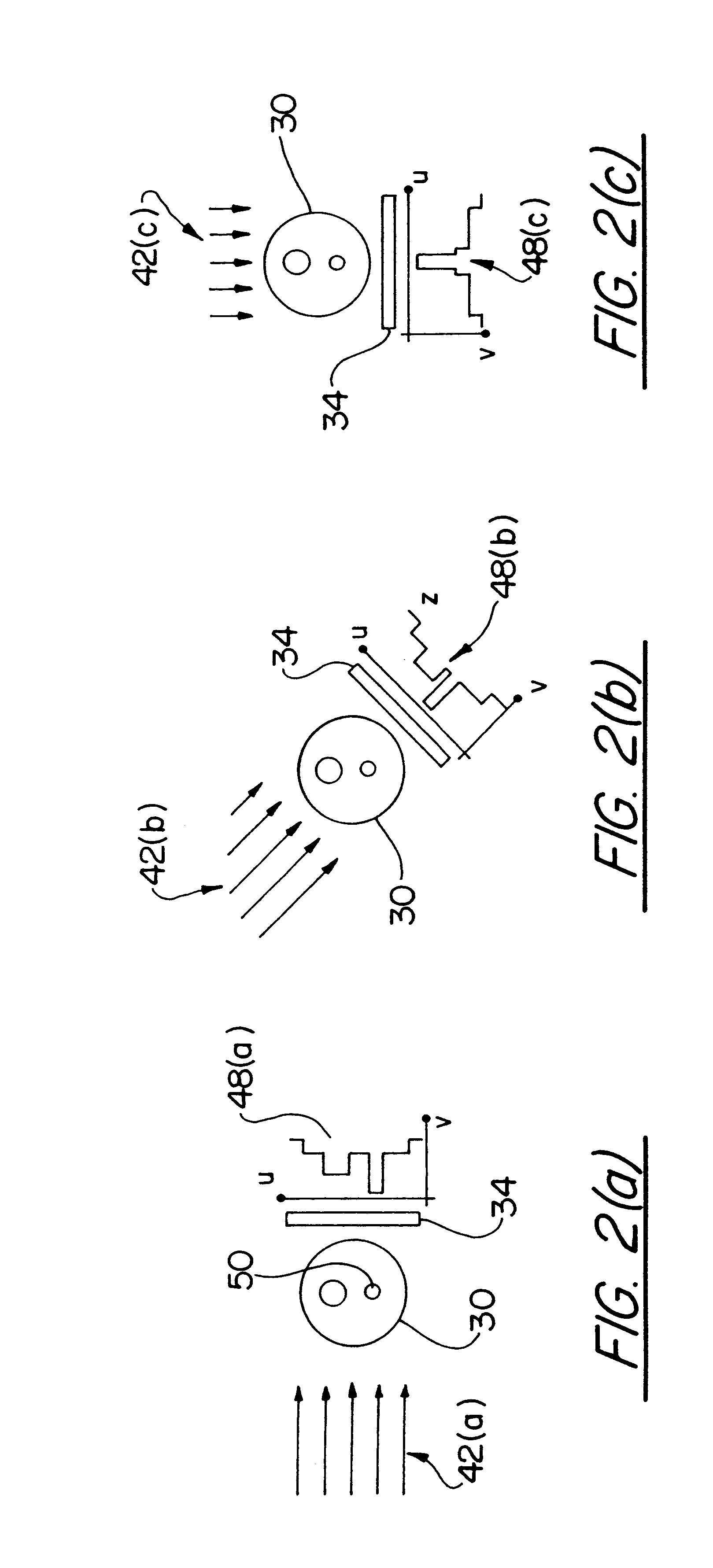
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS20050001170A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton attenuationField of view
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a base for supporting a patient and a detector assembly adjacent the field of view. The detector assembly detects photon strikes from the field of view. A photon-blocking member is disposed between the field of view and the detector and has an aperture slot that allows passage of photons aligned with the slot. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of collimating vanes formed of photon-attenuating material. A support assembly supports the collimating assembly and includes a first support member and a second support member with the collimating assembly being disposed therebetween. An adjustment assembly includes a first adjuster operable to adjust a first distance between the collimating assembly and the first support member and a second adjuster operable to adjust a second distance between the collimating assembly and the second support member.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS20050056788A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton attenuationField of view
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a base for supporting a patient and a detector assembly adjacent the field of view. The detector assembly detects photon strikes from the field of view. A photon-blocking member is disposed between the field of view and the detector and has an aperture slot that allows passage of photons aligned with the slot. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of collimating vanes formed of photon-attenuating material. A support assembly supports the collimating assembly and includes a first support member and a second support member with the collimating assembly being disposed therebetween. An adjustment assembly includes a first adjuster operable to adjust a first distance between the collimating assembly and the first support member and a second adjuster operable to adjust a second distance between the collimating assembly and the second support member.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Nuclear medicine imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors
ActiveUS20120248320A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyHelical computed tomographyNuclear medicine imaging
A Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors are provided. One NM imaging system includes a gantry, at least a first imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the first imaging detector is a non-moving detector, and at least a second imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the second imaging detector is a moving detector. The first imaging detector is larger than the second imaging detector and the first and second imaging detectors have different detector configurations. The NM imaging system further includes a controller configured to control the operation of the first and second imaging detectors during an imaging scan of an object to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information such that at least the first imaging detector remains stationary with respect to the gantry during image acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and imaging method
ActiveCN102764138AImage results are accurateImage results are reliableComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData acquisition
The invention discloses a multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and an imaging method thereof. The device comprises an X-ray computer tomography (CT) system, a positron emission tomography (PET) system, a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system, a fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT) system, a rotating rack system, a little animal bed system, a data acquisition system and a computer, various imaging systems are sampled and stored by the data acquisition system through a data line into the computer, and various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft. According to the multi-mode little animal molecular image imaging device and the imaging method, various imaging systems share one little animal bed system and the same inspection shaft, an installing fusion molecular medicine image of four modes of X-ray CT, PET, SPECT and FMT can achieve complementary advantages of different image devices, and the obtained image result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
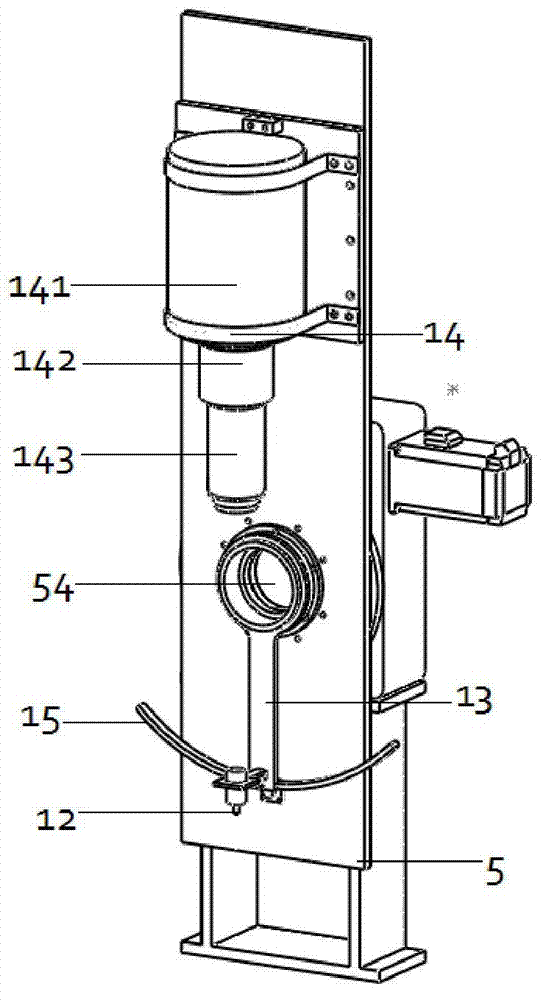
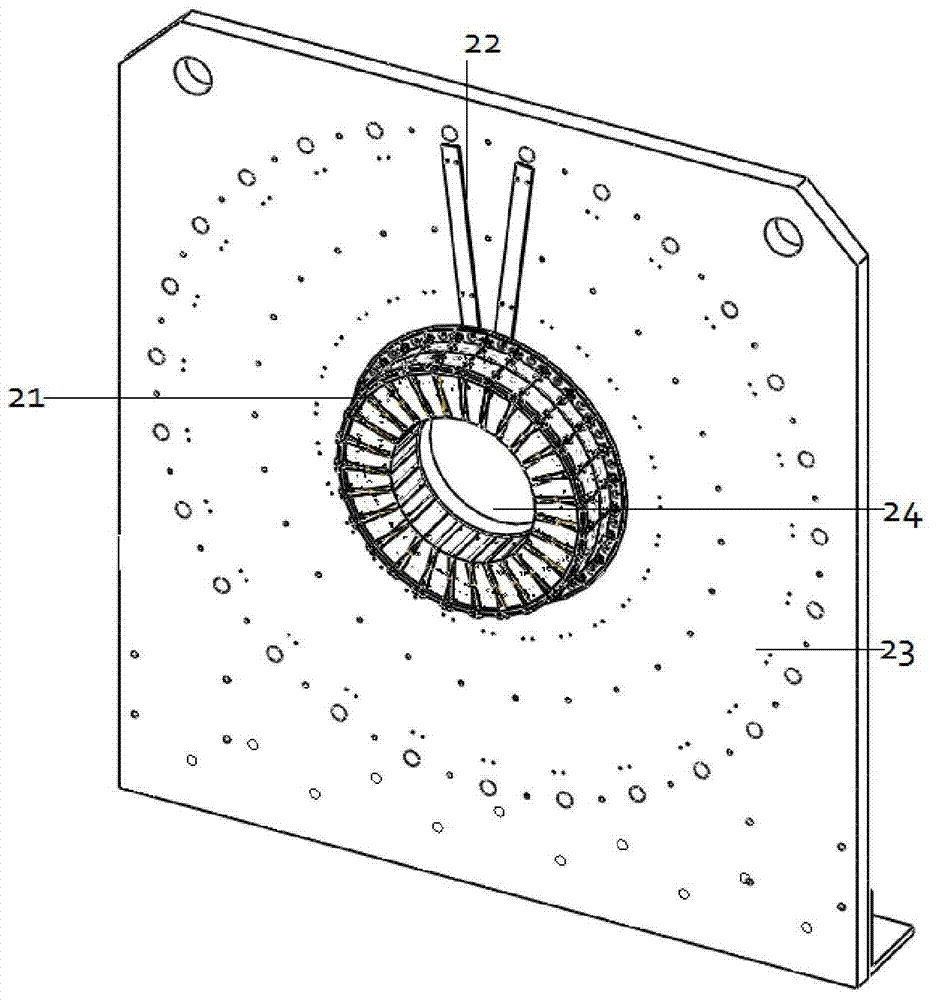
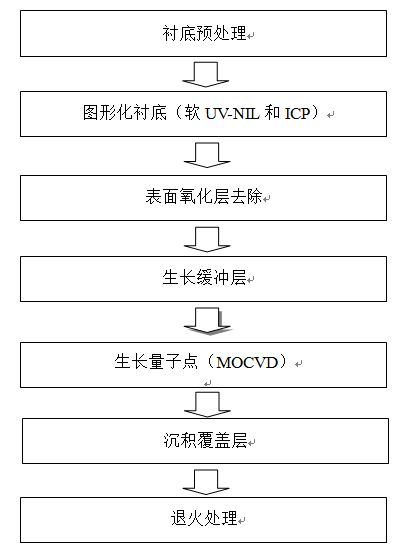
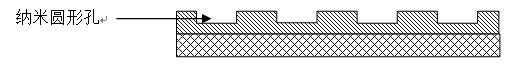
Manufacture method of large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array
InactiveCN101830430AReduce sizeSmall sizeNanostructure manufactureUltravioletInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a manufacture method of a large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a nanopore graphic array on a substrate by adopting soft ultraviolet nano imprint lithography (UV-NIL) and an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) technology; and growing quantum dots in a self-organizing way by using a prepared graphical substrate as a template and using a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) system. The invention realizes the low-cost, consistent and batched preparation of the large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array and can be applied to manufacture of devices such as quantum dot lasers, quantum dot memories, quantum dot solar batteries, quantum dot LEDs, single photon emitters, and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
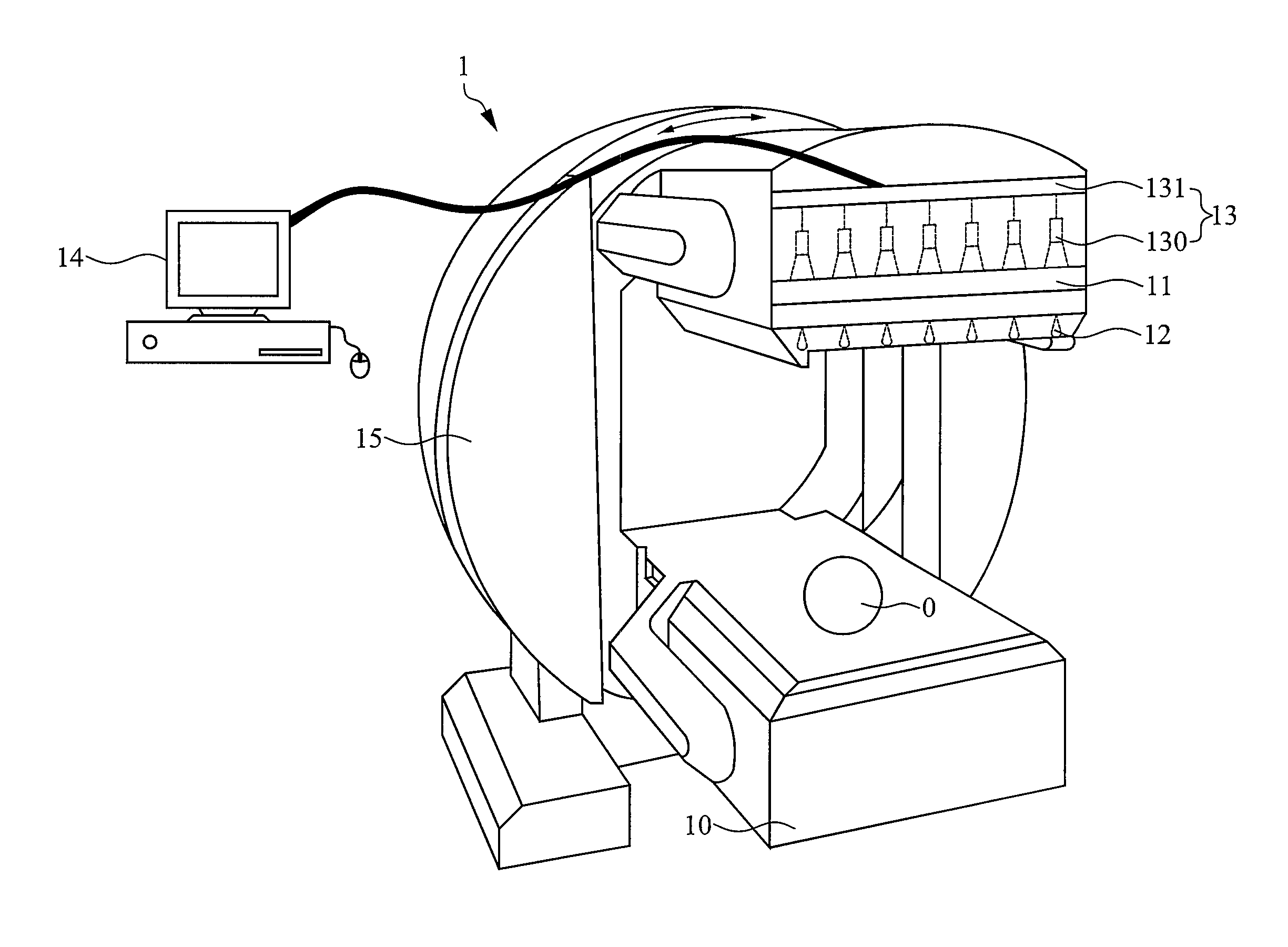
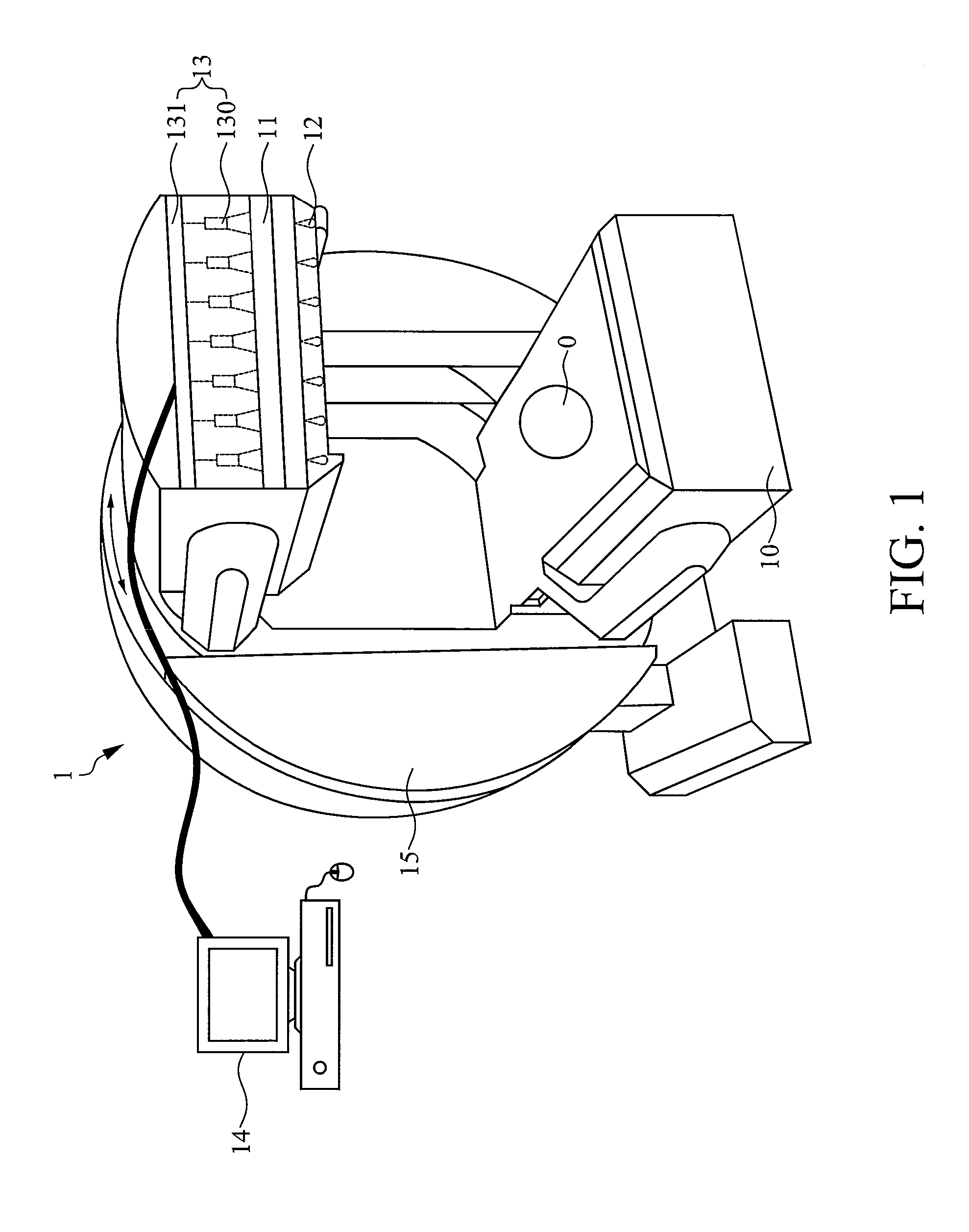
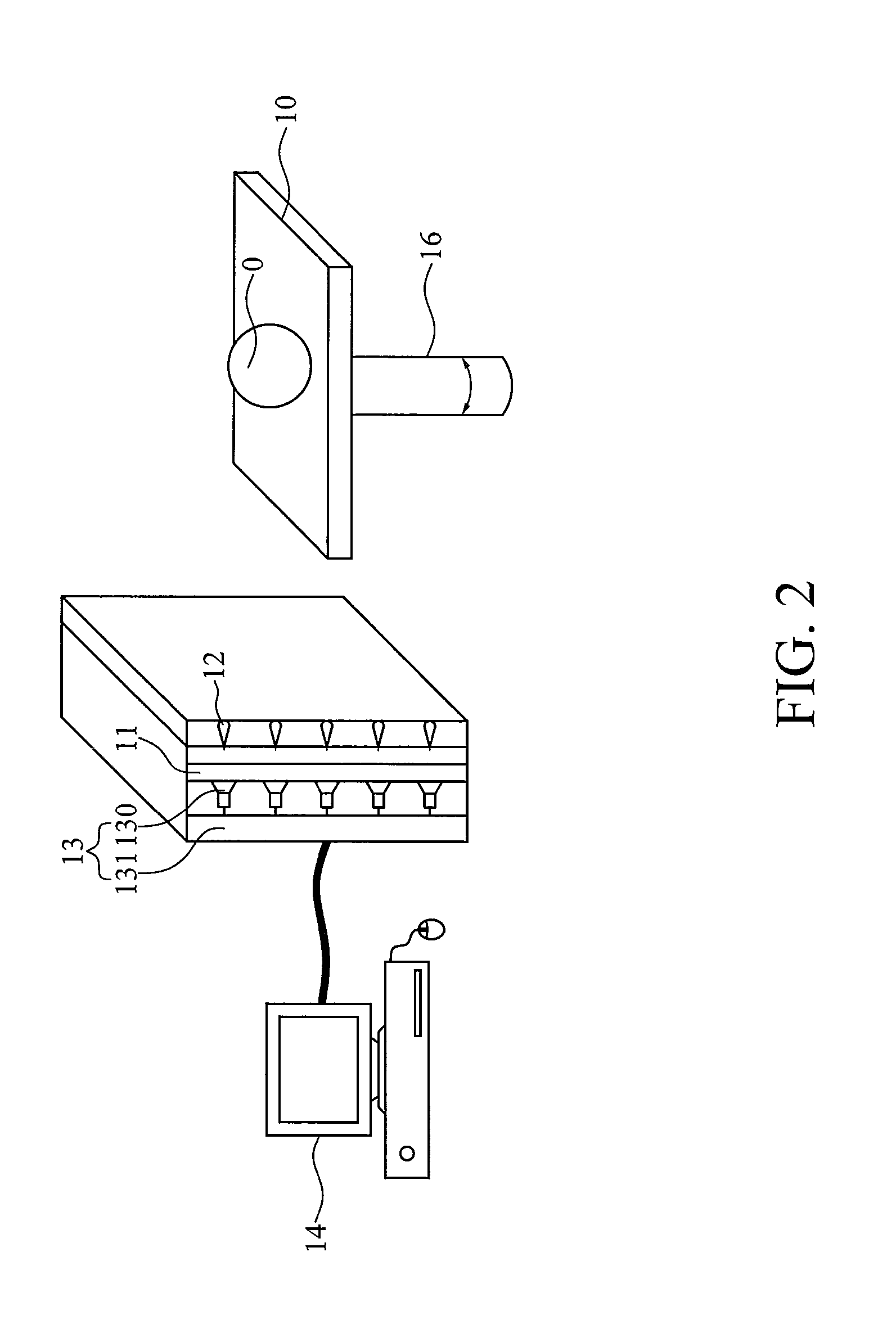
Single photon emission computed tomography instrument and the operating method thereof
A single photon emission computed tomography instrument is provided, which has a platform, at least one detector, at least one beam stopper, a signal processing device and a computer. The at least one detector is disposed at one side of the platform, and the at least one beam stopper is disposed between the platform and the detector. The signal processing device is electrically communicated with the at least one detector, and the computer is electrically communicated with the signal processing device. The present disclosure further provides an operating method which the beam stopper is added or removed respectively while scanning an analyze by the single photon emission computed tomography instrument in different angles. The projection dataset emitted from the focus could be estimated by subtracting the projecting data without the beam stopper from that with the beam stopper, and high resolution image could be obtained by using image reconstruction program.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
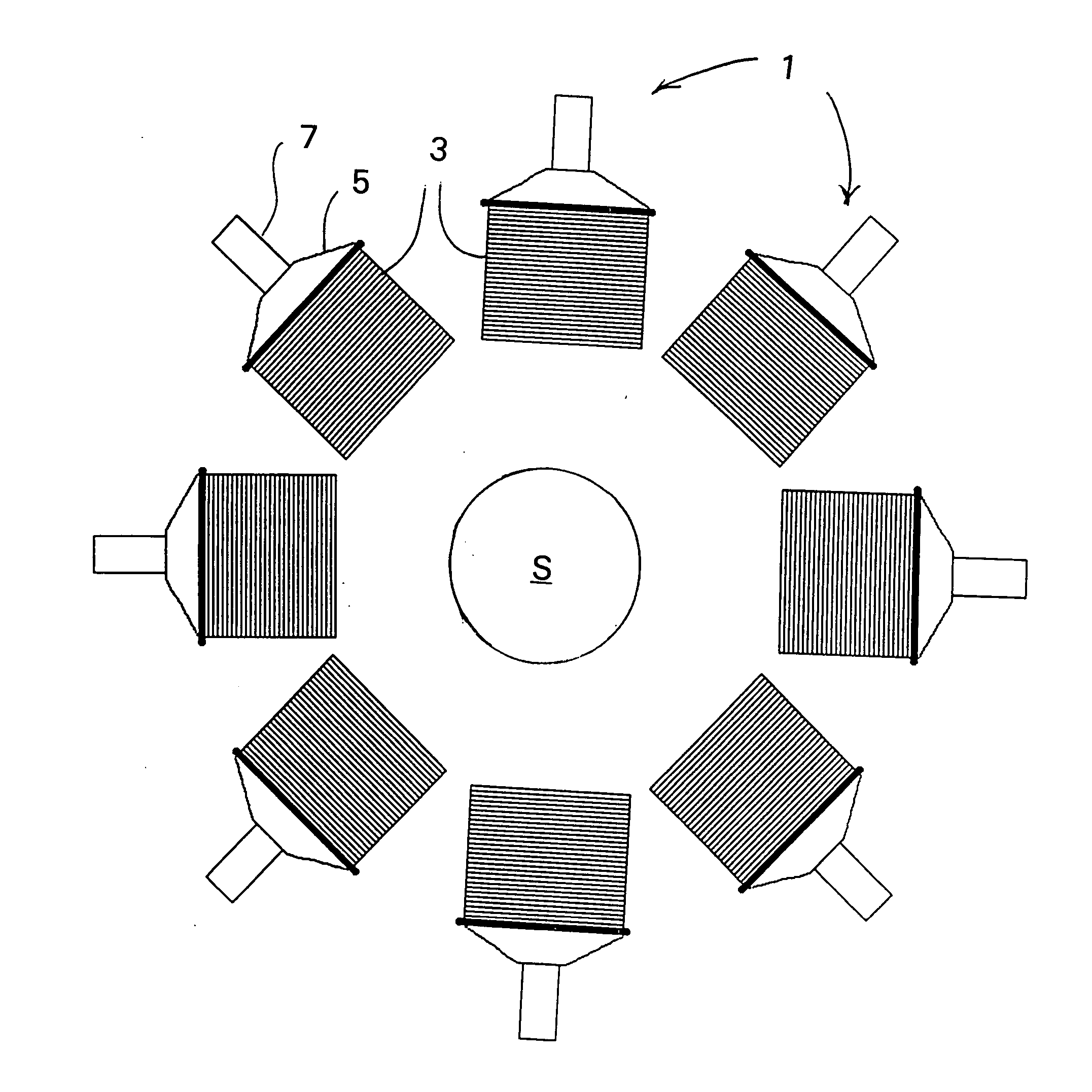
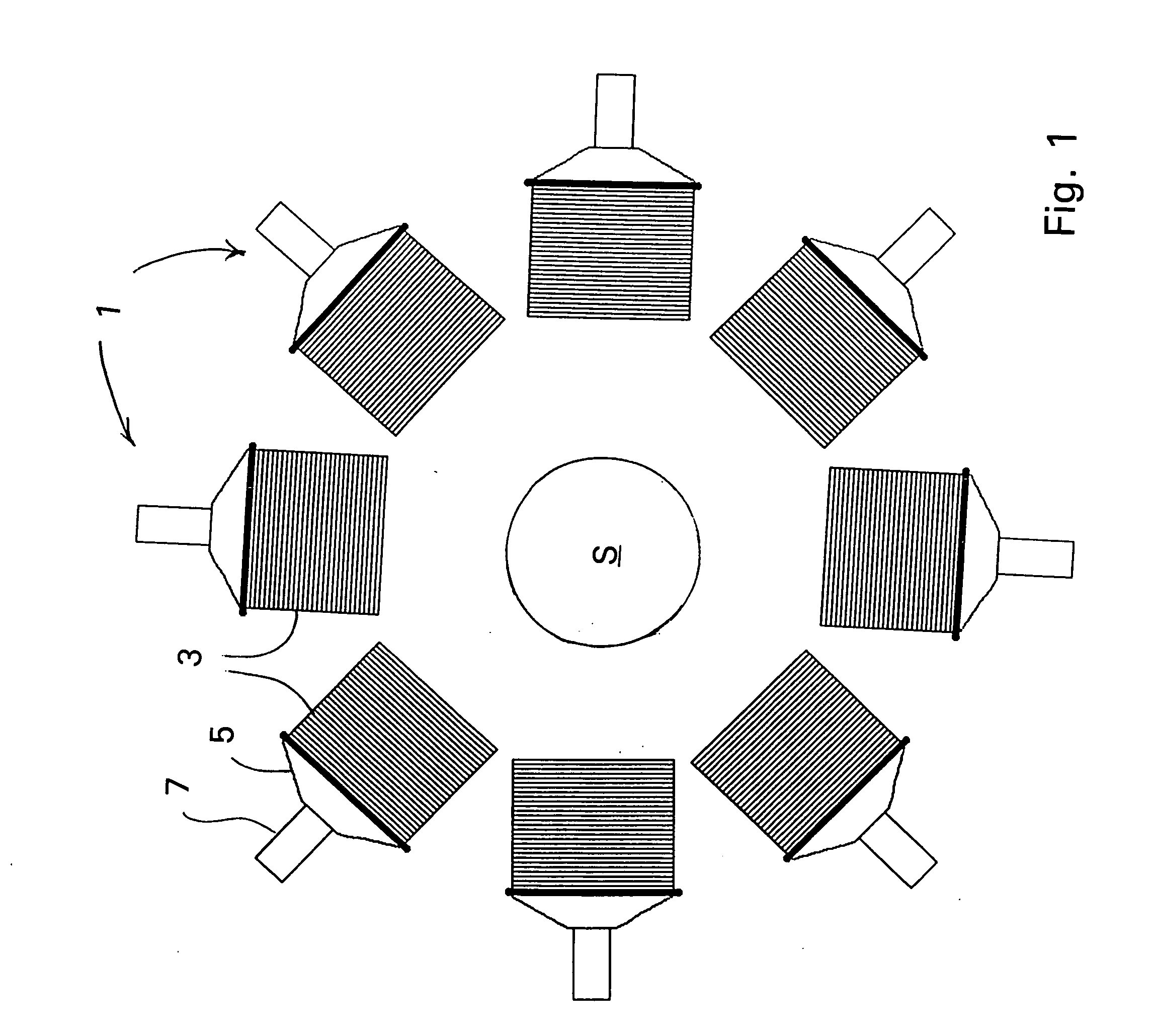
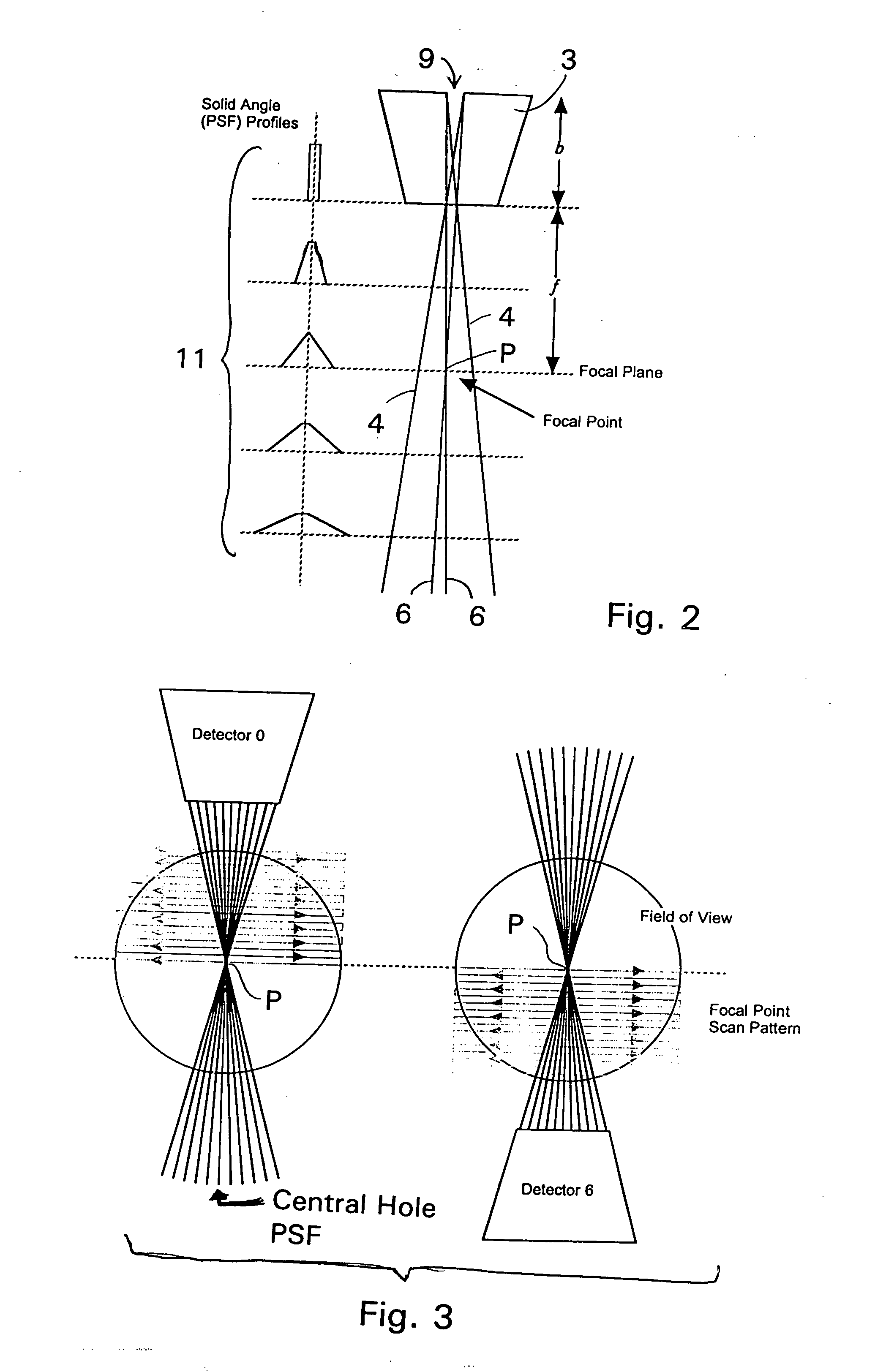
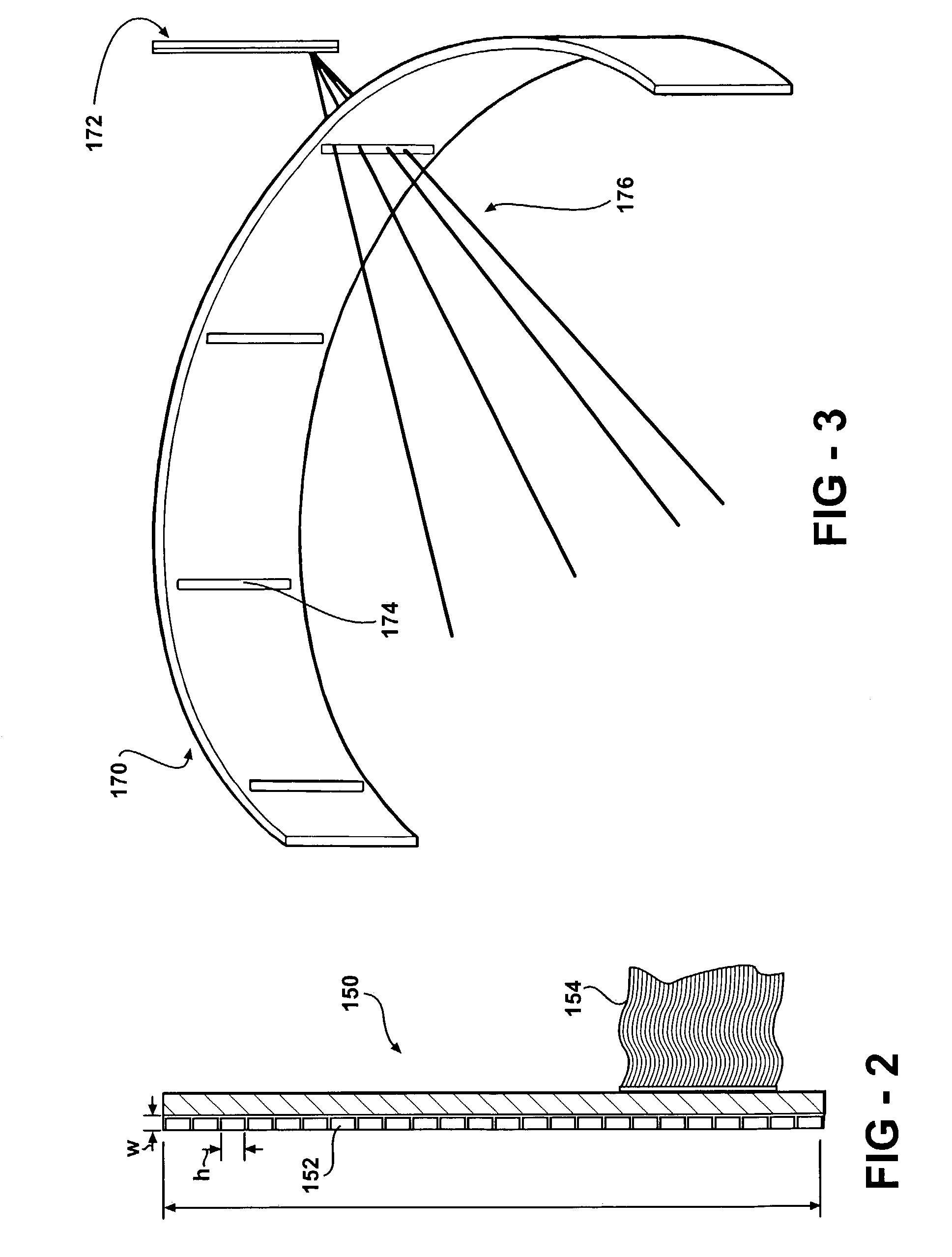
Scanning focal point apparatus
ActiveUS20070029491A1Maximizing spatial resolutionMaximizing sensitivitySolid-state devicesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhoton emission
A collimator, and in particular a method for making a collimator for use with a small high resolution single-photon emission computed tomographic (SPECT) imaging tool for small animal research. The collimator is sized, both functionally and structurally, particularly smaller than known collimators and appropriately scaled to achieve a highly sensitive collimator which facilitates desired reconstruction resolutions for small animals, as well as compliments other functional imaging modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and event-related potential (ERP), magneto-encephalography (MEG), and near-infrared optical imaging.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
Geometric calibration method for SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) system
ActiveCN104173074AImprove image qualityExact geometric parametersComputerised tomographsTomographySingle photon emission ctImaging quality
The invention discloses geometric calibration method for a SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) system. The method comprises the steps as follows: a collimator is measured to obtain geometric parameters of a pinhole or a slot in the collimator; the collimator and a PET (position emission tomography) detector are assembled to form the SPECT system; the collimator is controlled to move, and the PET detector is used for measuring multi-group background coincidence events when the collimator moves to a plurality of target positions; and position coordinates of the collimator in the SPECT system are obtained according to the multi-group background coincidence events. According to the method, the geometric parameters of the SPECT system can be accurately calibrated, accurate geometric parameters are provided for image reconstruction of tomography, and accordingly, the imaging quality of the SPECT system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
In vivo imaging of amyloid plaques in glaucoma using intravenous injectable dyes
InactiveUS20050214222A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLuminescence/biological staining preparationNervous systemFluorescence
In vivo imaging may be used to assess a condition (e.g., a state of glaucoma or a state of ocular hypertension) of an eye of a living animal. A dye may be intravenously injected into the living animal. The dye may bind to amyloid in the nervous system of the animal. Images may be taken of a retina, an optic nerve head, an optic nerve, the lateral geniculate nucleus, and / or the visual cortex. Images may be taken using methods such as fluorescent angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, positron emission tomography, and / or single photon emission computed tomography. The condition of the eye and / or retinal ganglion cells in the eye may be assessed from one or more of the images. The condition of the eye may be assessed based on the presence of amyloid in one or more of the images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
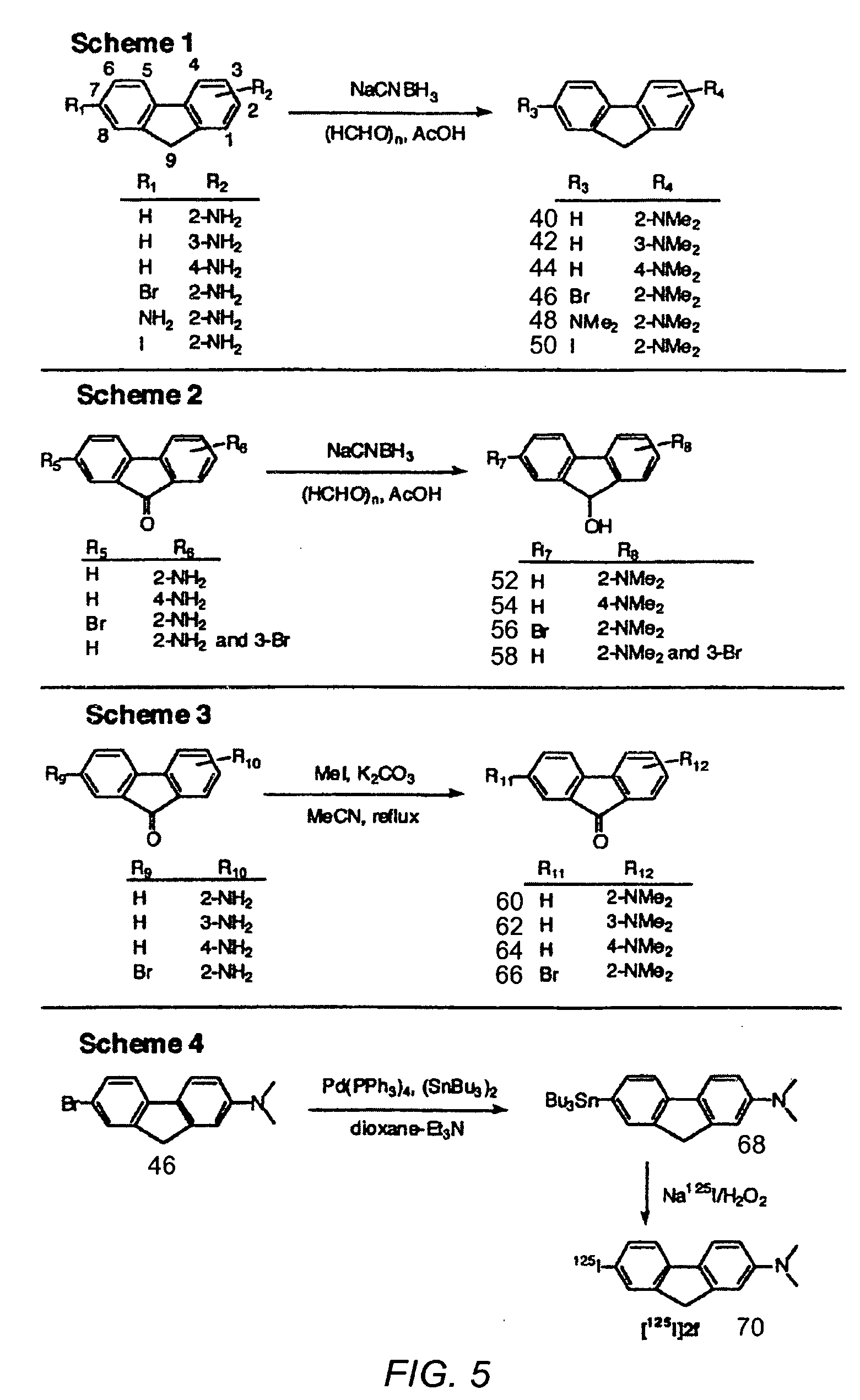
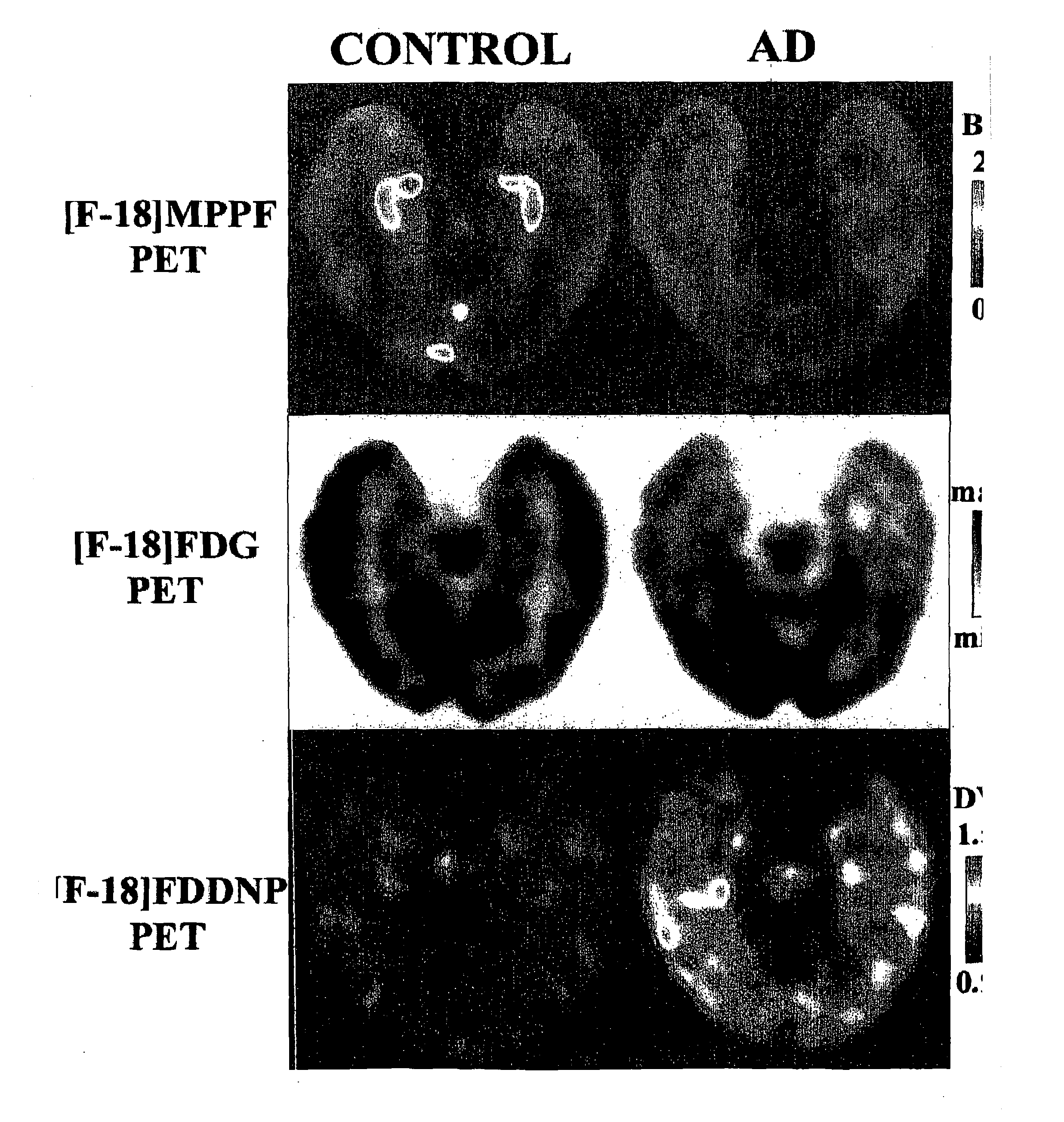
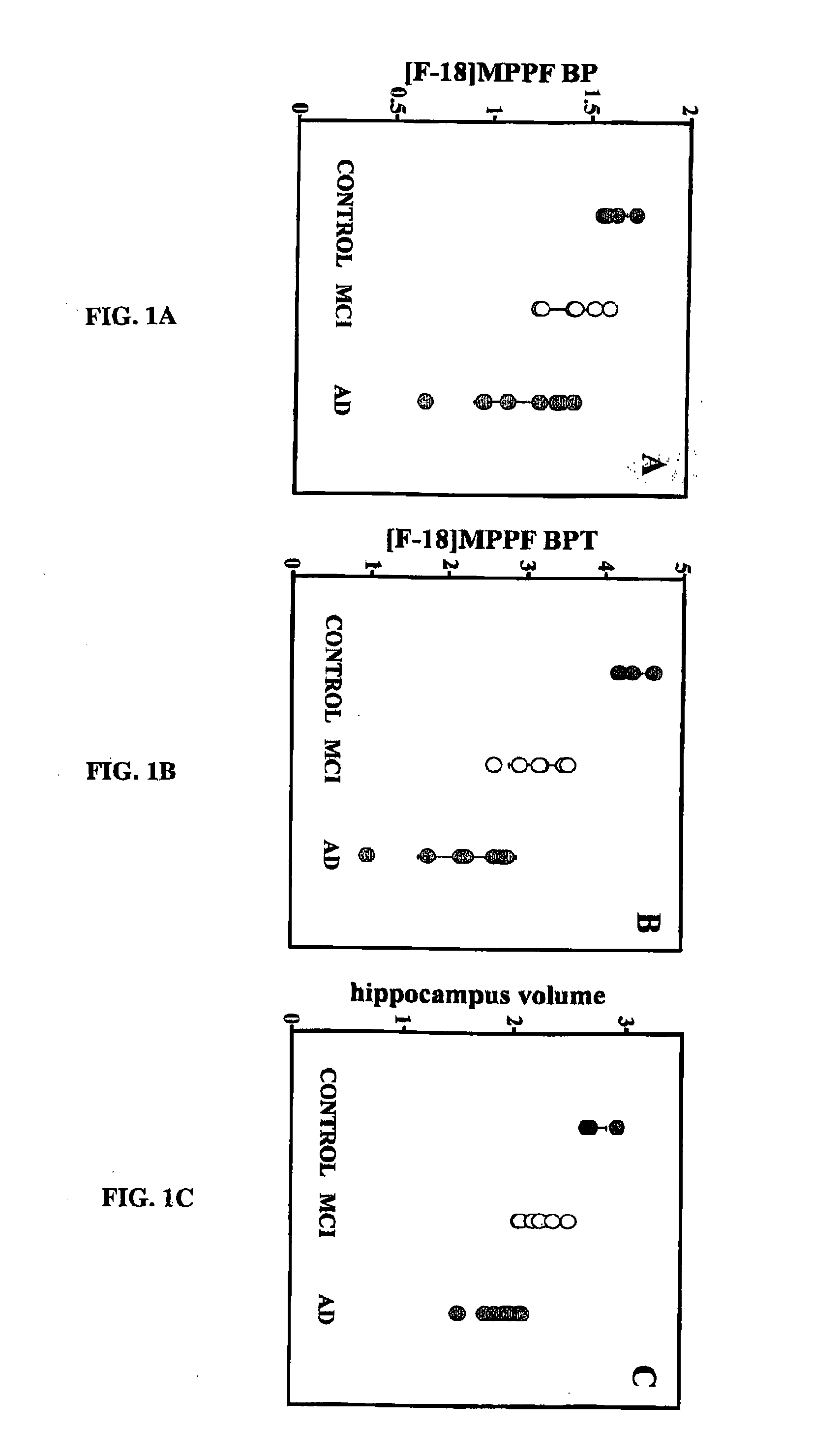
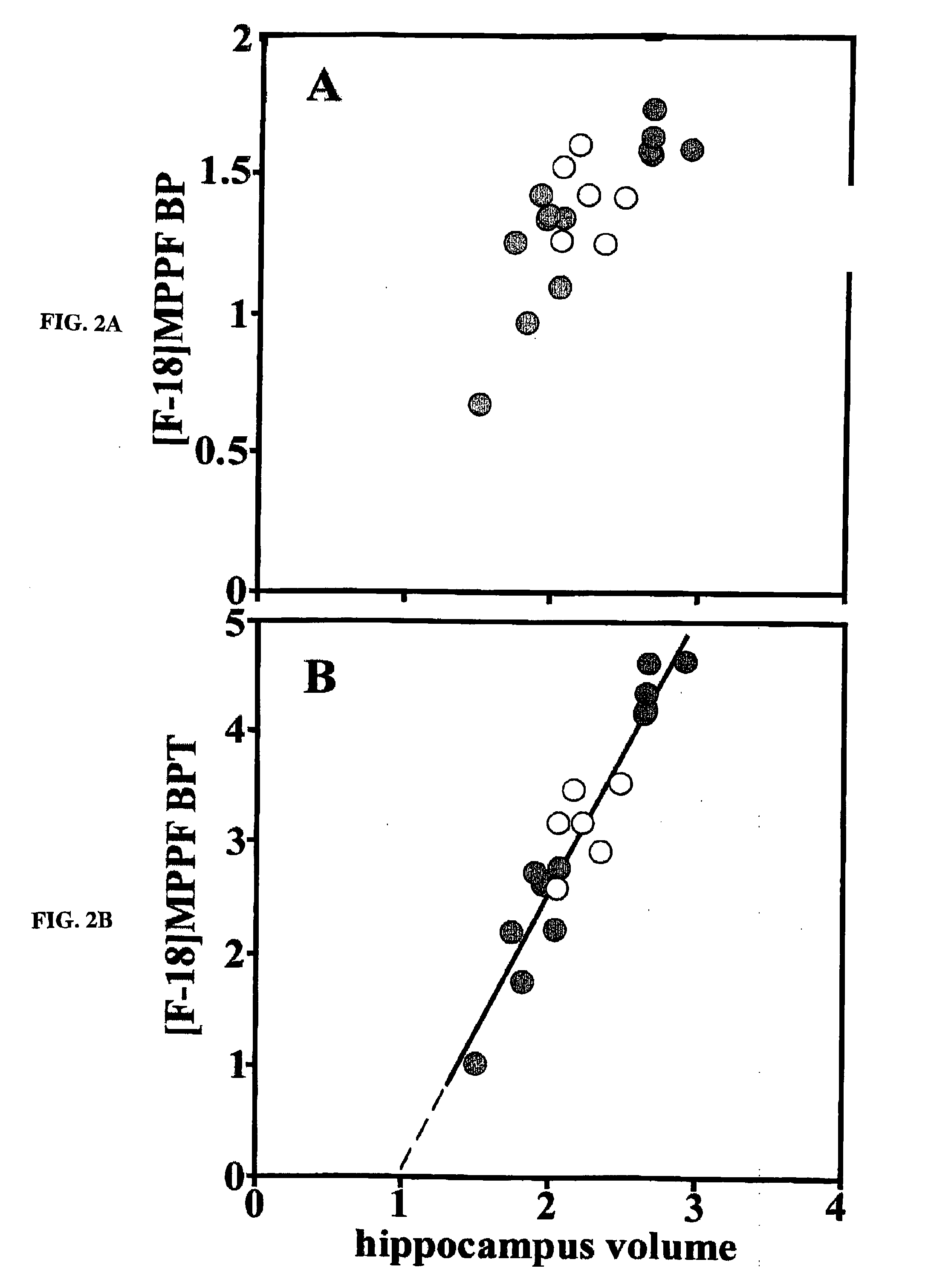
Method for Detecting Alzheimer's Disease and other Forms of Dementia, and Measuring Their Progression
The invention provides a method for detecting or monitoring Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia using positron emission tomography (PET) or single-photon emission computed tomagraphy (SPECT) and radiolabeled, serotonin 5-HT1A receptor-specific tracers (such as [F-18]MPPF, [F-18]FCWAY, [C-11]WAY-100635, and other radiolabeled compounds having agonistic or antagonistic effect on serotonin receptors), for detection or monitoring of pathological changes (i.e., neuronal cell loss) associated with dementia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
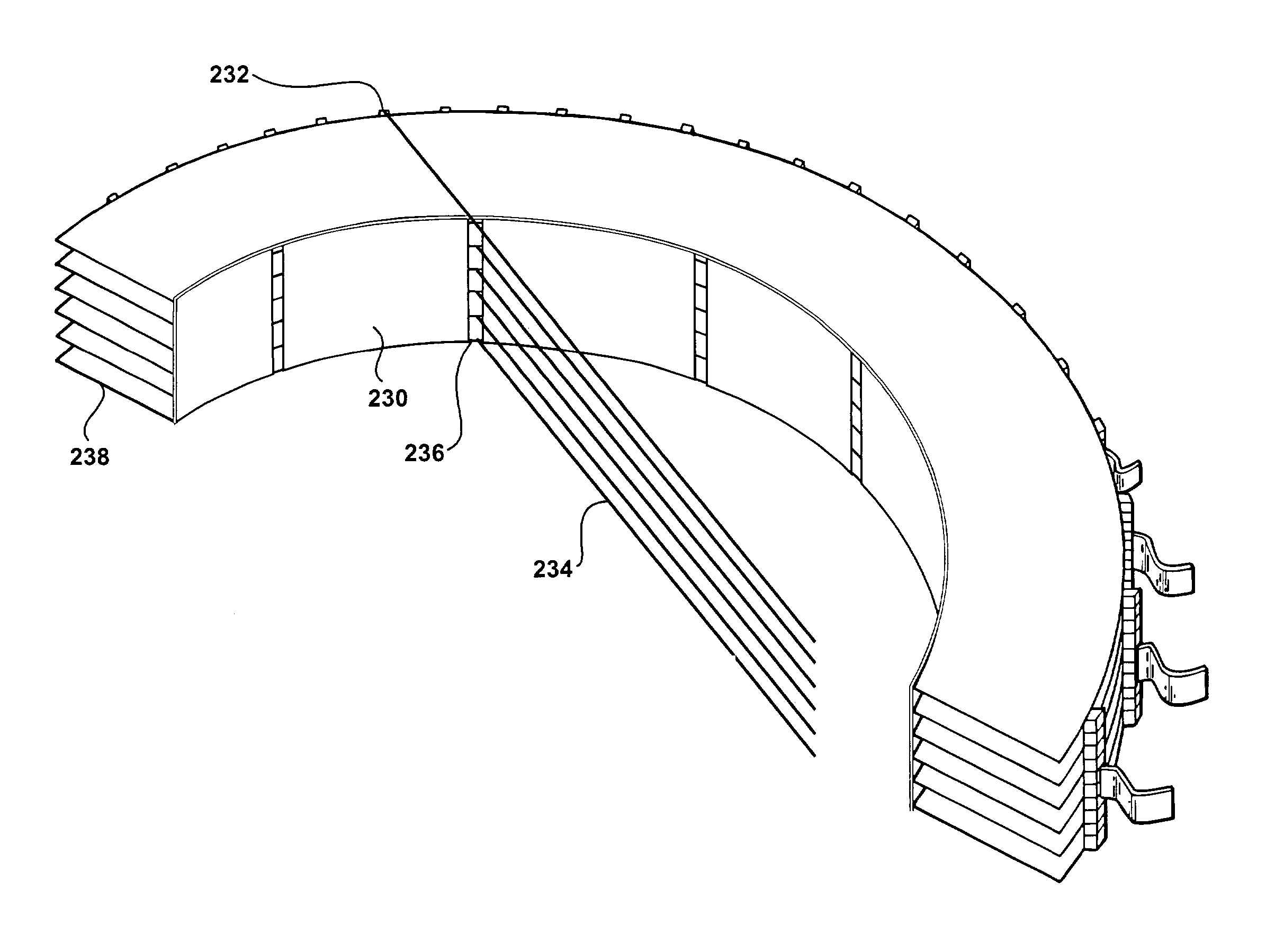
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS7015476B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansLines of responseFront edge
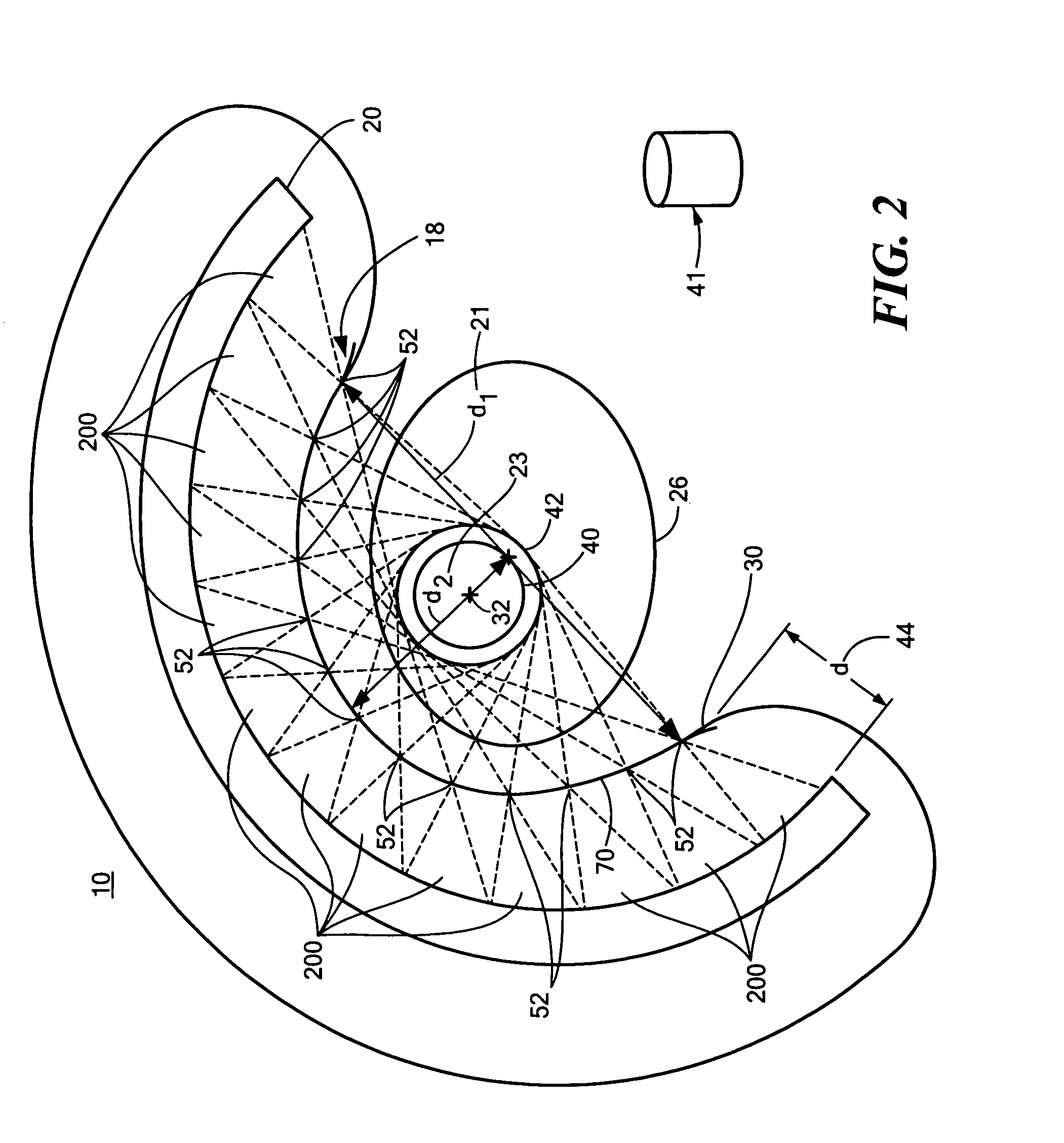
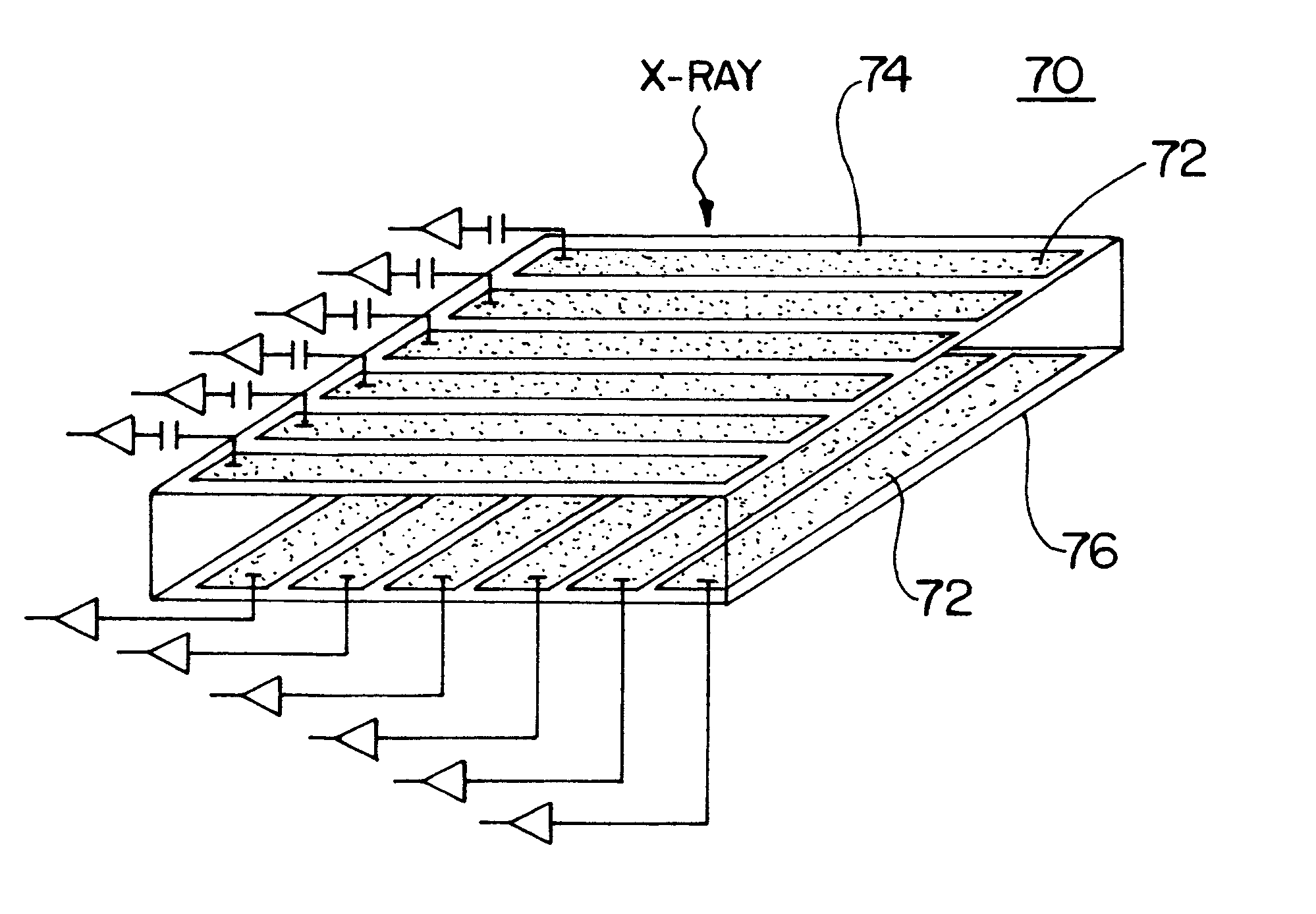
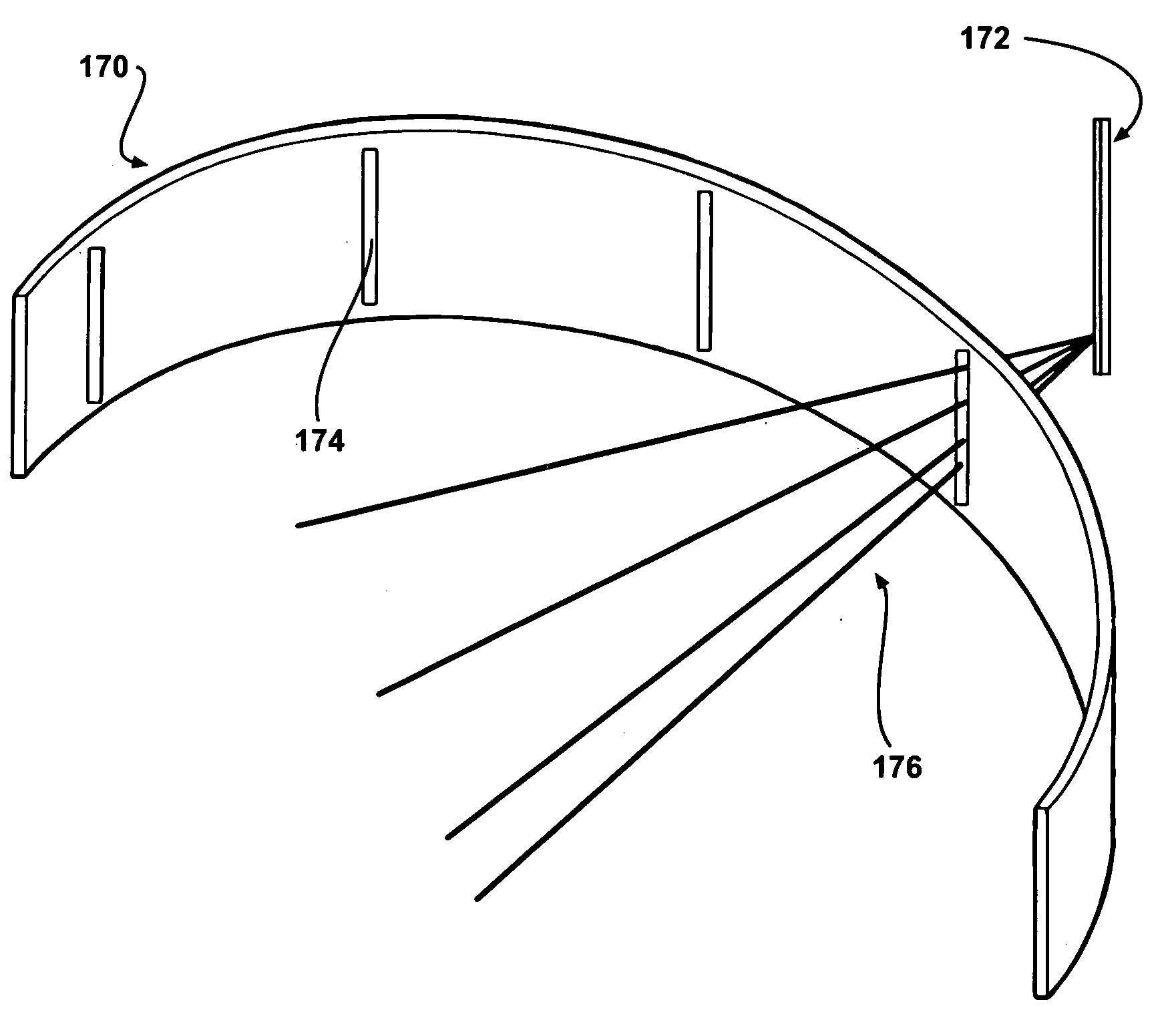
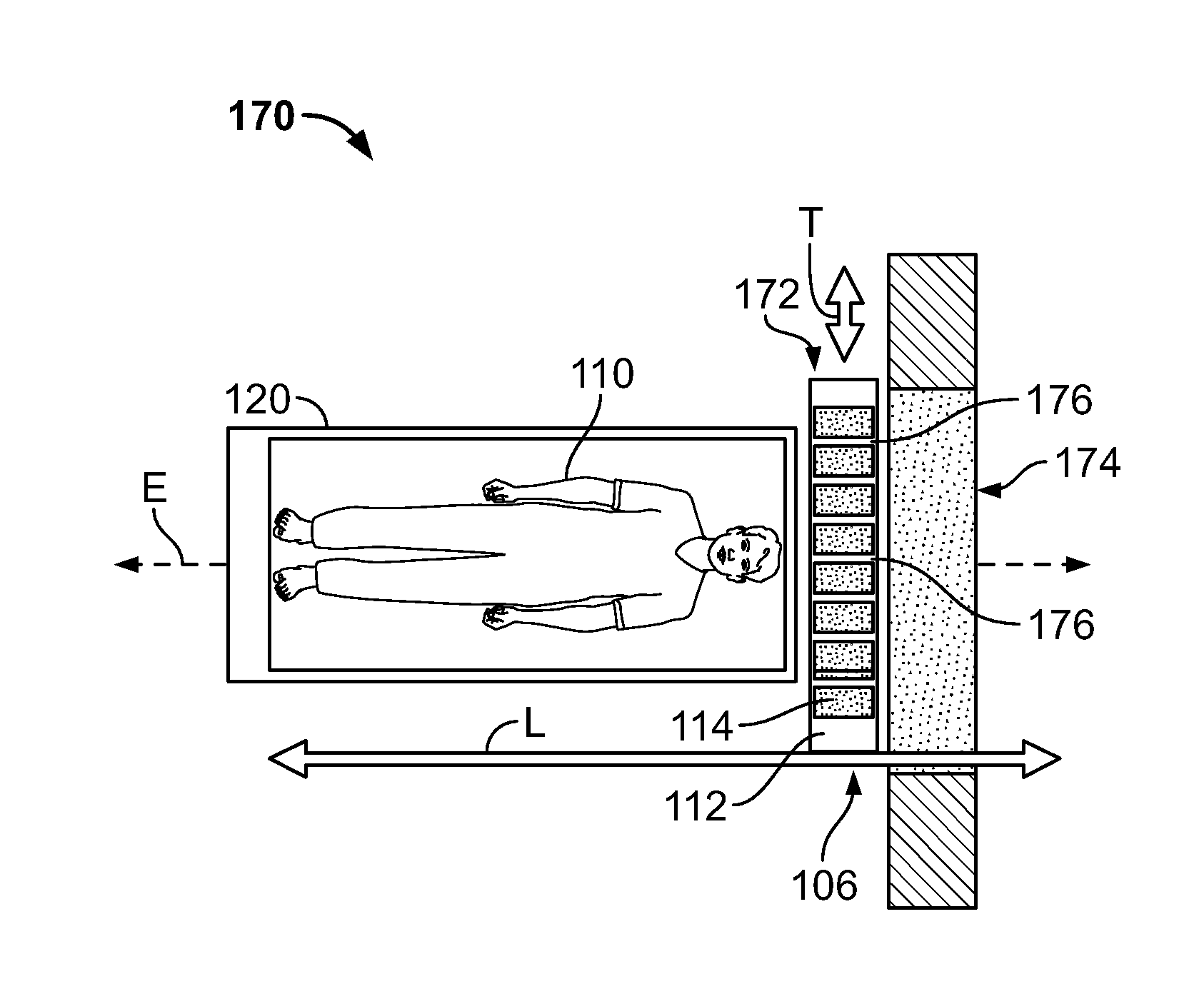
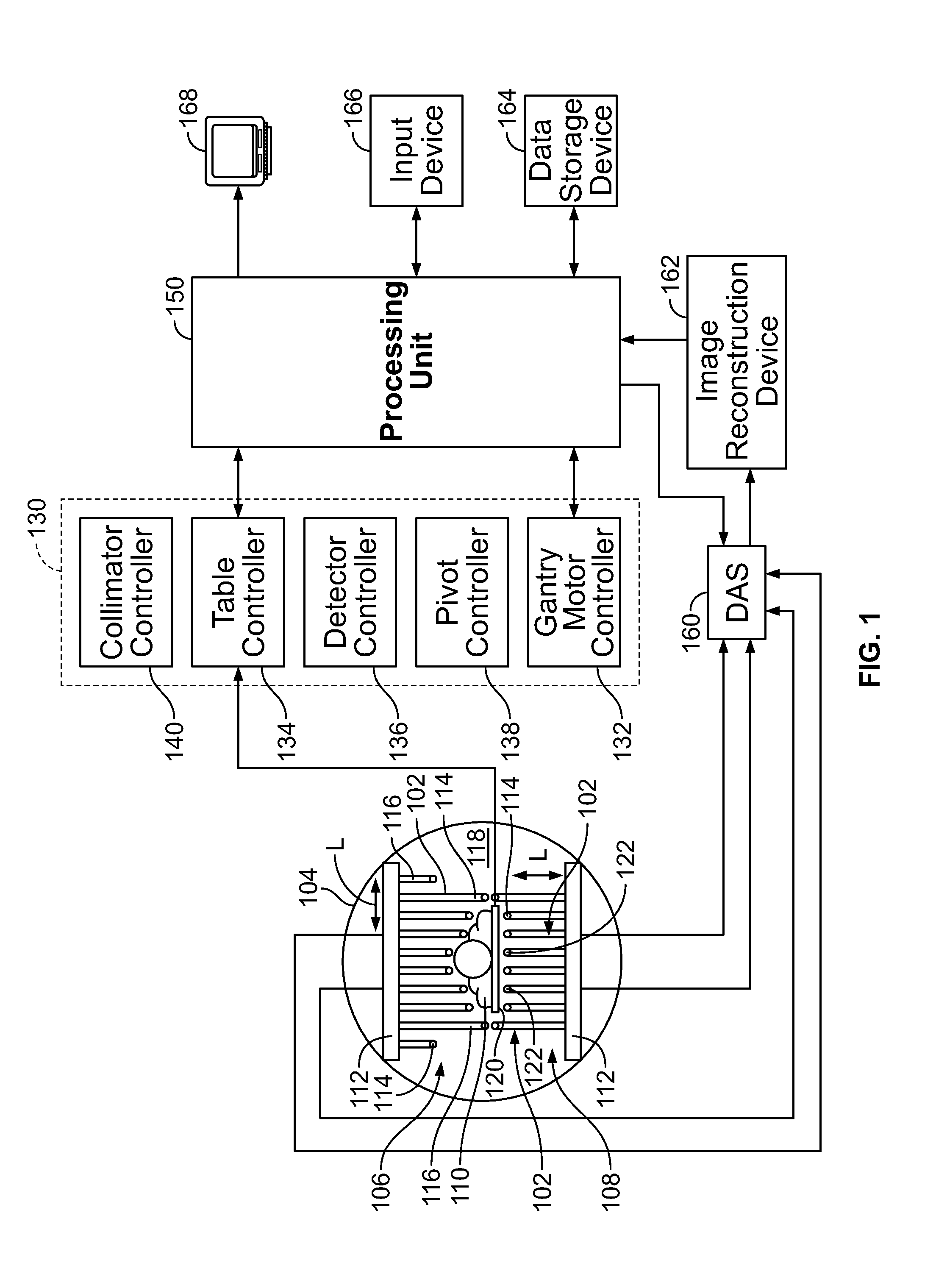
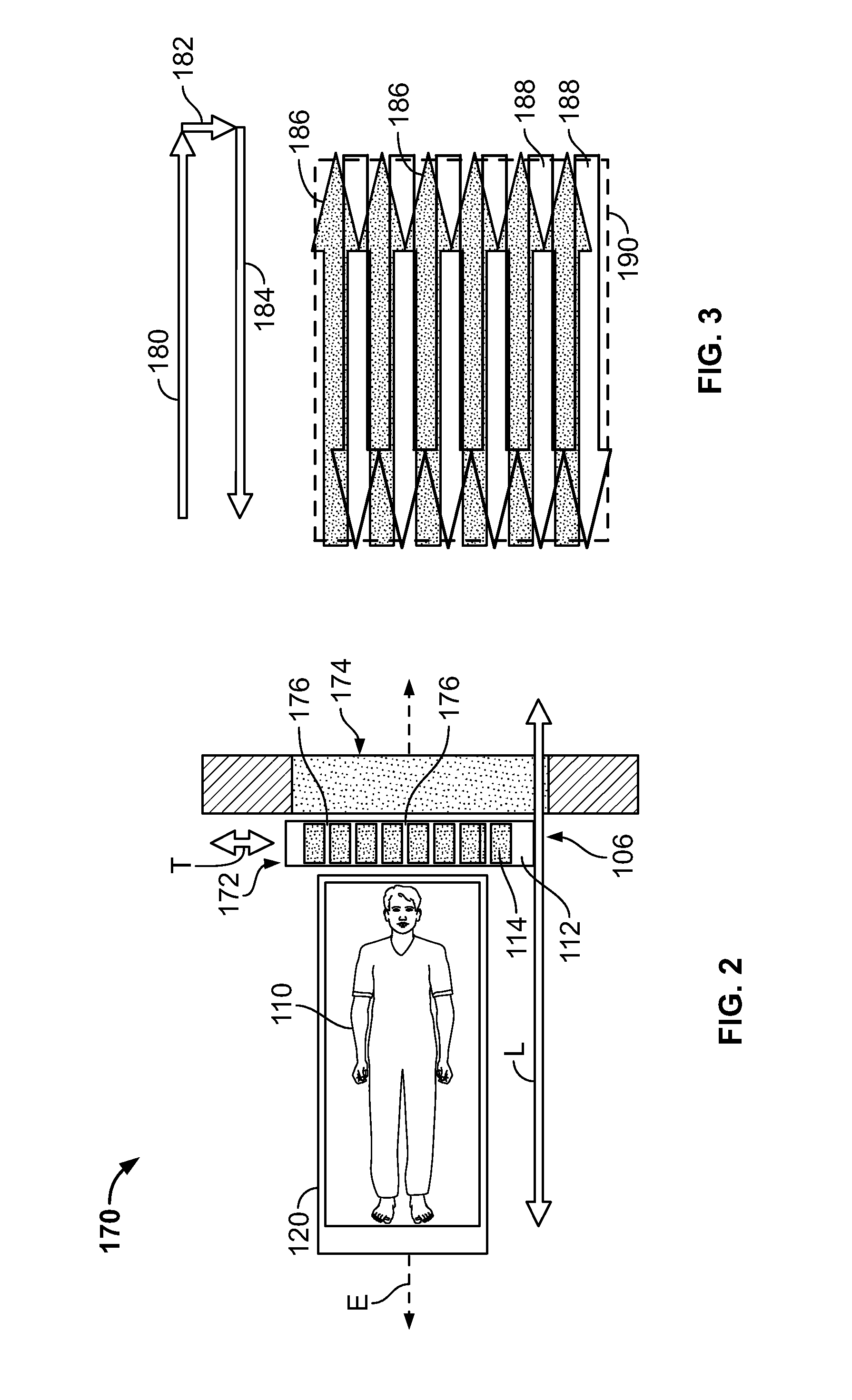
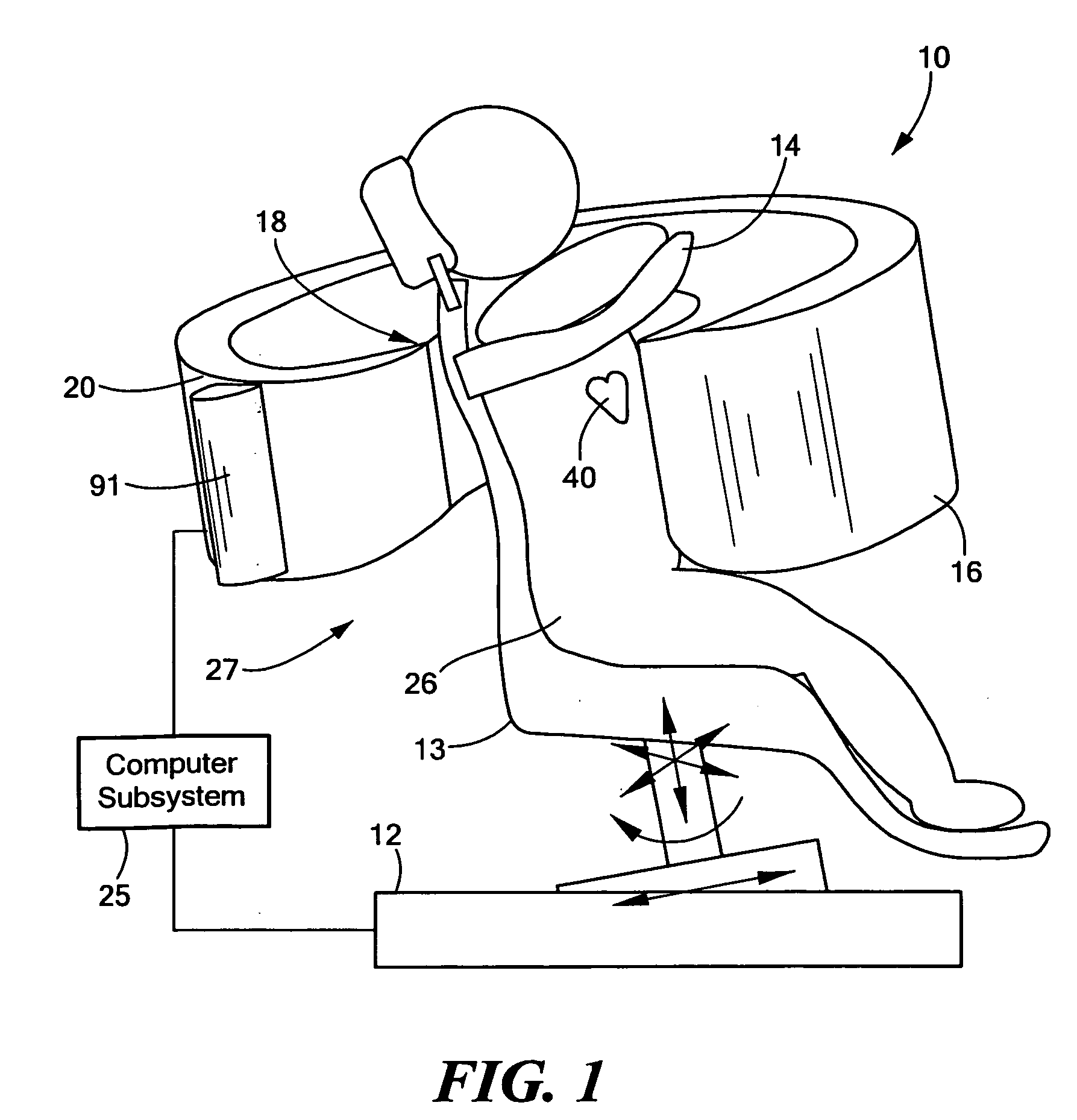
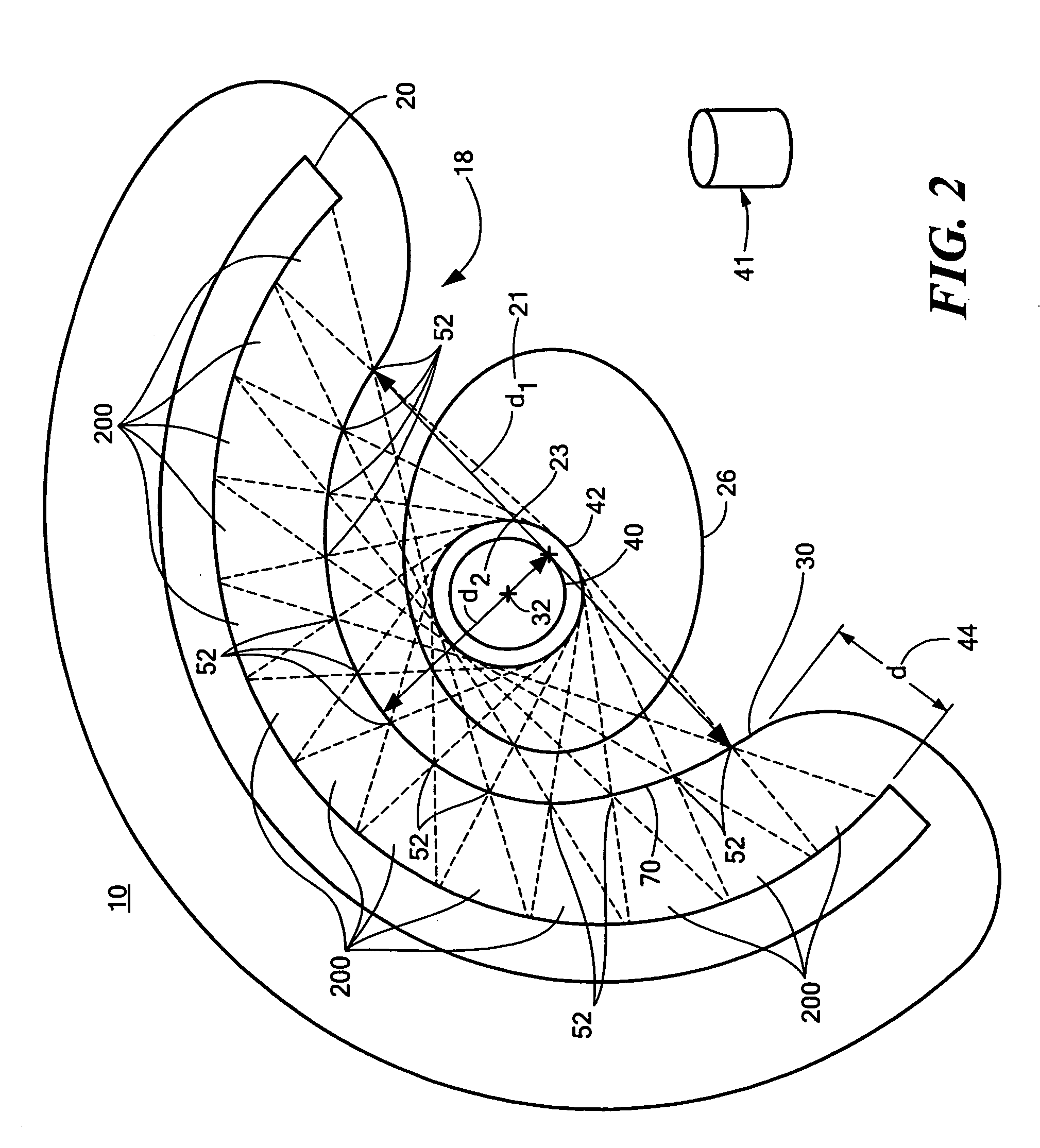
A single photon emission computed tomography system produces multiple tomographic images of the type representing a three-dimensional distribution of a photon-emitting radioisotope. The system has a base including a patient support for supporting a patient such that a portion of the patient is located in a field of view. A longitudinal axis is defined through the field of view. A detector module is adjacent the field of view and includes a photon-responsive detector. The detector is operable to detect if a photon strikes the detector. A photon-blocking member is positioned between the field of view and the detector. The blocking member has an aperture slot for passage of photons aligned with the aperture slot. A line of response is defined from the detector through the aperture. A collimating assembly includes a plurality of generally parallel collimating vanes formed of a photon attenuating material. The vanes are spaced apart so as to find a plurality of gaps, with the gaps each having a height. Each of the vanes has a front edge directed toward the field of view and a back edge directed towards the detector. The front-to-back depth of each of the vanes is greater than 10 times the height of the gaps. The plurality of vanes is disposed between the detector and the field of view such that only photons passing through one of the gaps can travel from the field of view to the detector. A displacement device moves either the detector module or the photon-blocking member relative to the other so that the aperture is displaced relative to the detector and the line of response is swept across at least a portion of the field of view.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
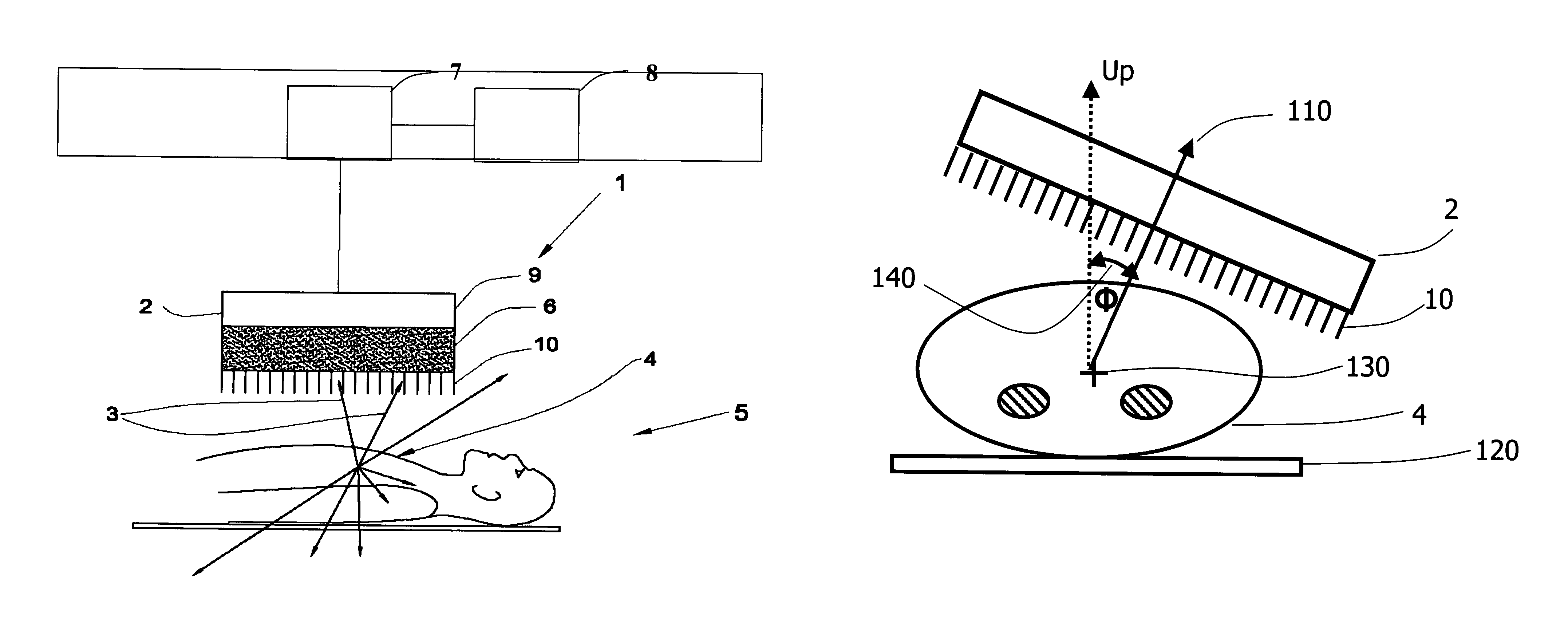
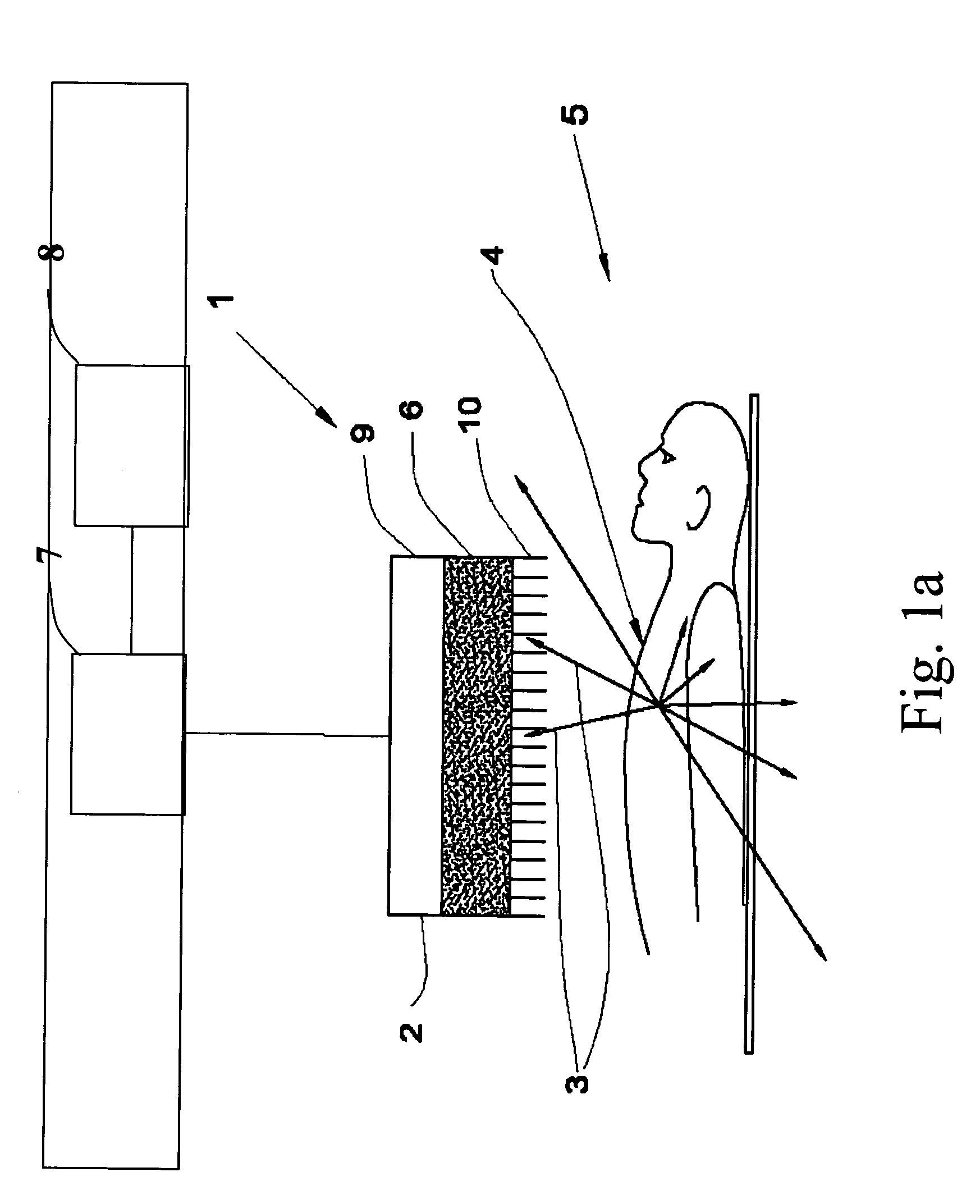
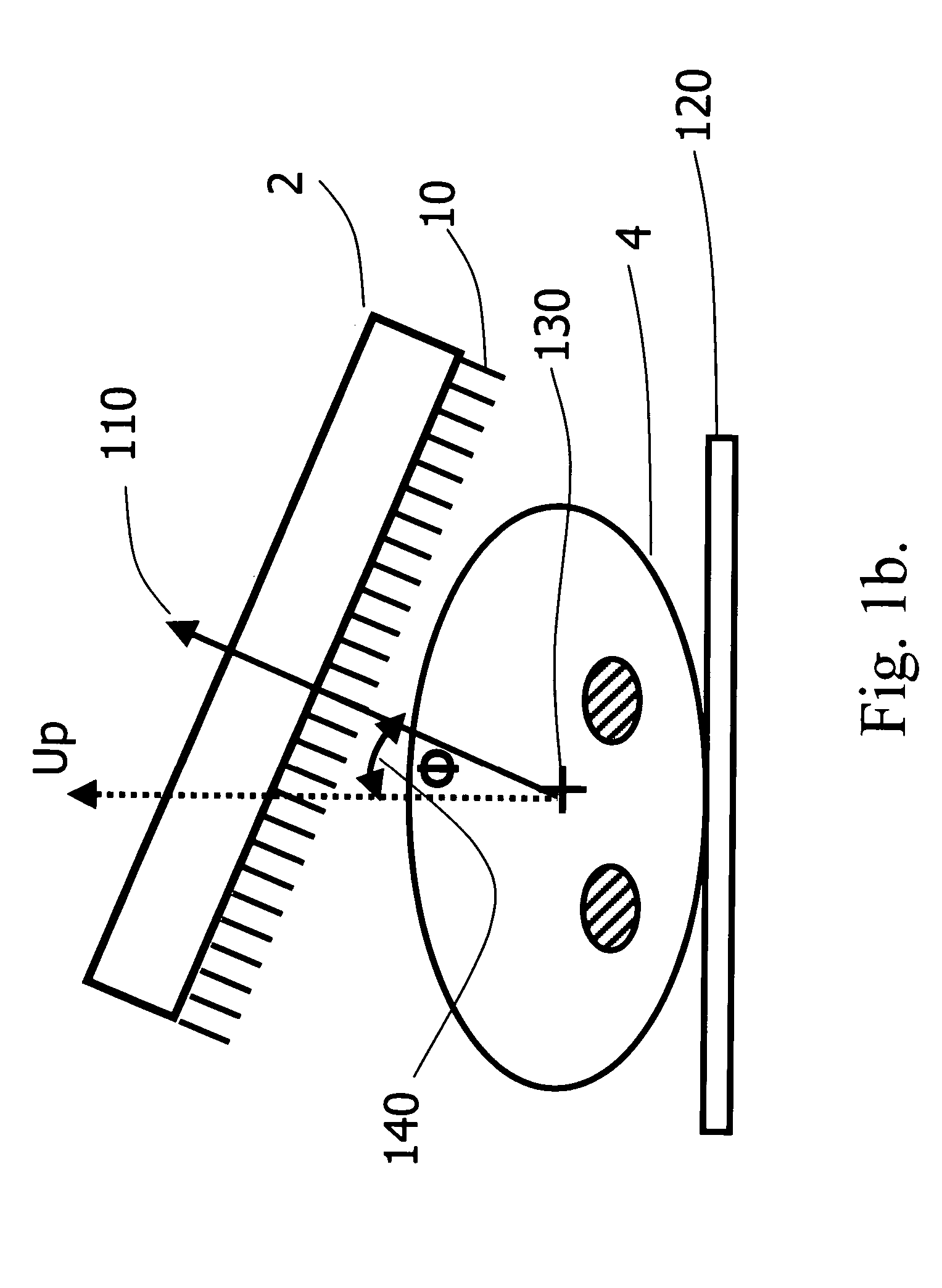
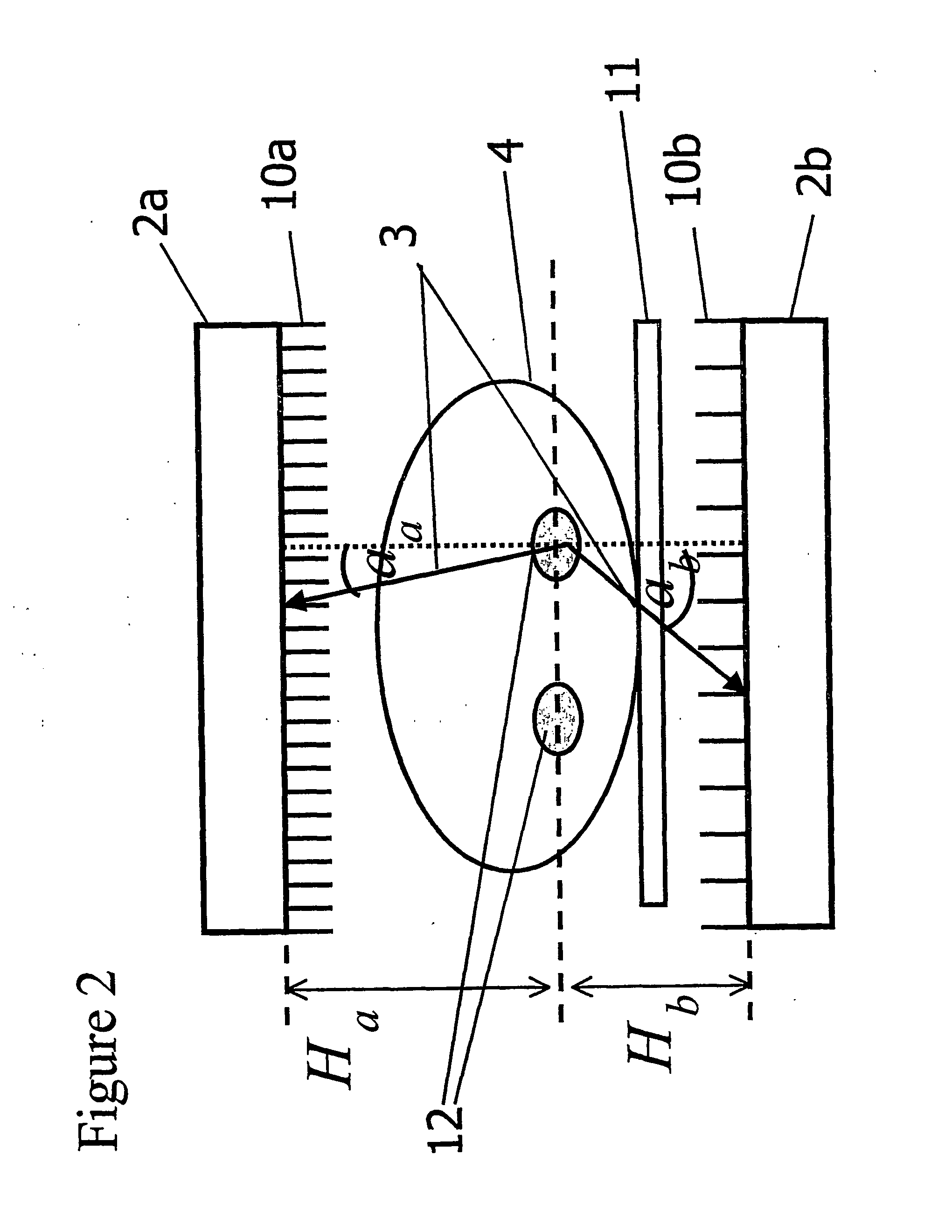
Enhanced Planar Single Photon Emission Imaging
InactiveUS20070217666A1Improve image qualityImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityGamma ray
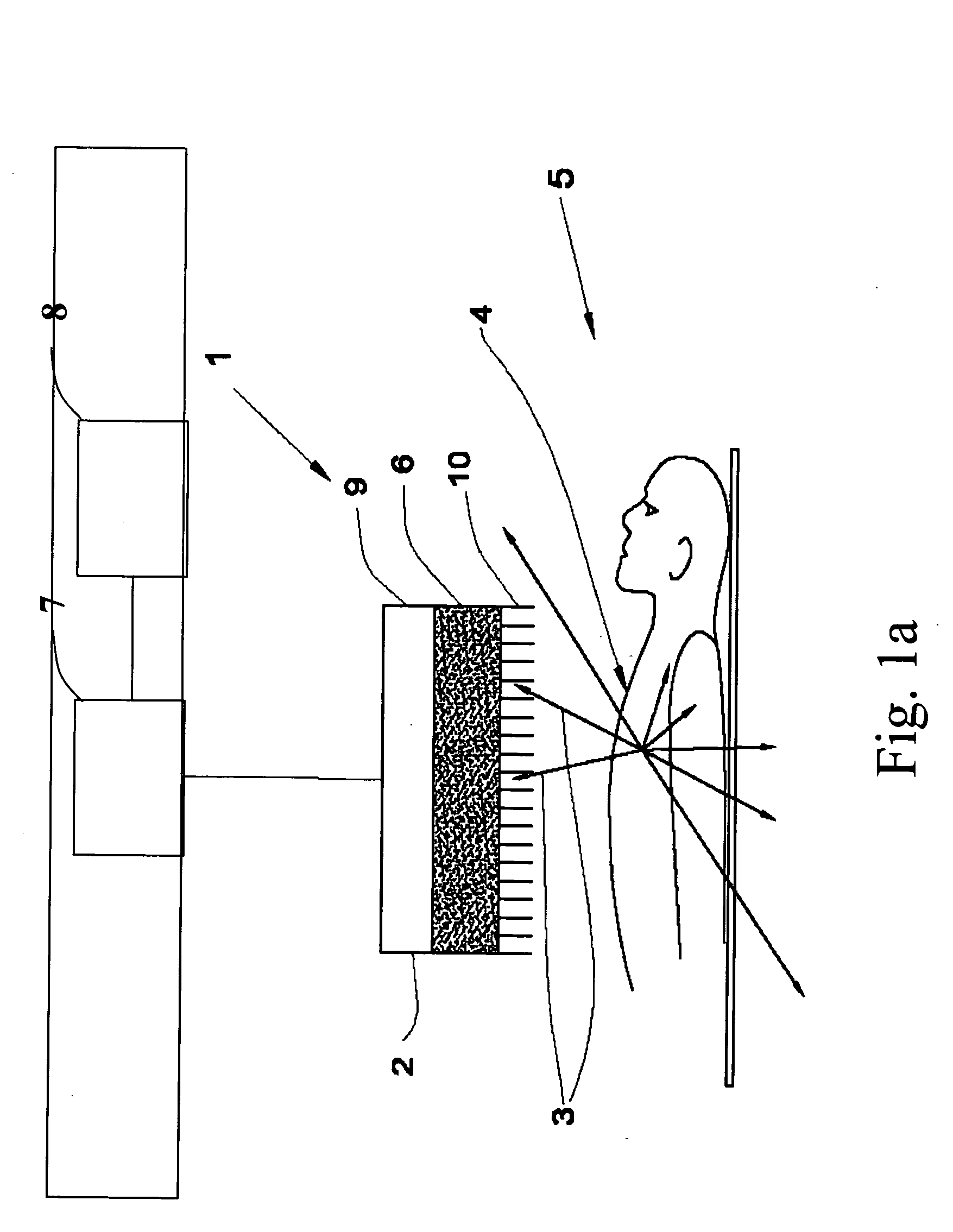
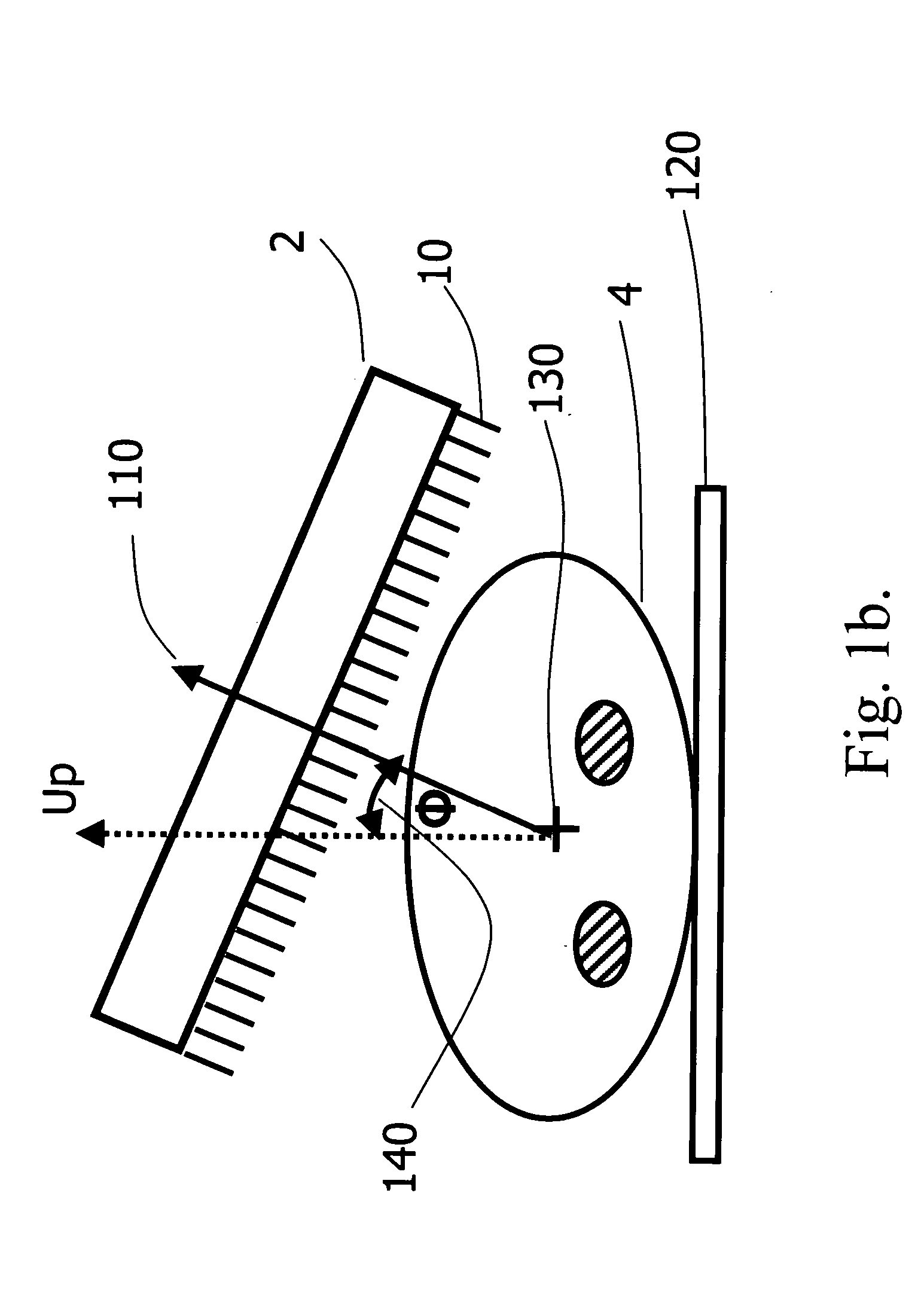
An apparatus and method for obtaining a planar image of a portion (4) of a body (5) and enhancing image quality of at least one specific organ or volume of interest located within the portion (4) of the body (5), administered with radiopharmaceutical substance radiating gamma rays, by using single photon emission imaging, for determination of functional information thereon, comprising: (a) acquiring at least one projection data of the portion (4), by means of a gamma camera detector (2); (b) determining the effective distance between the detector (2) and the specific organ of interest; (c) calculating weight values taking into account acceptance angles of the gamma camera detector (2) and the effective distance; and (d) obtaining a two dimensional image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion (4) by mathematically analyzing the data in conjunction with weight values.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Multi-aperture single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080116386A1Reduce image noiseSolve the low detection efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansResearch ObjectImaging quality
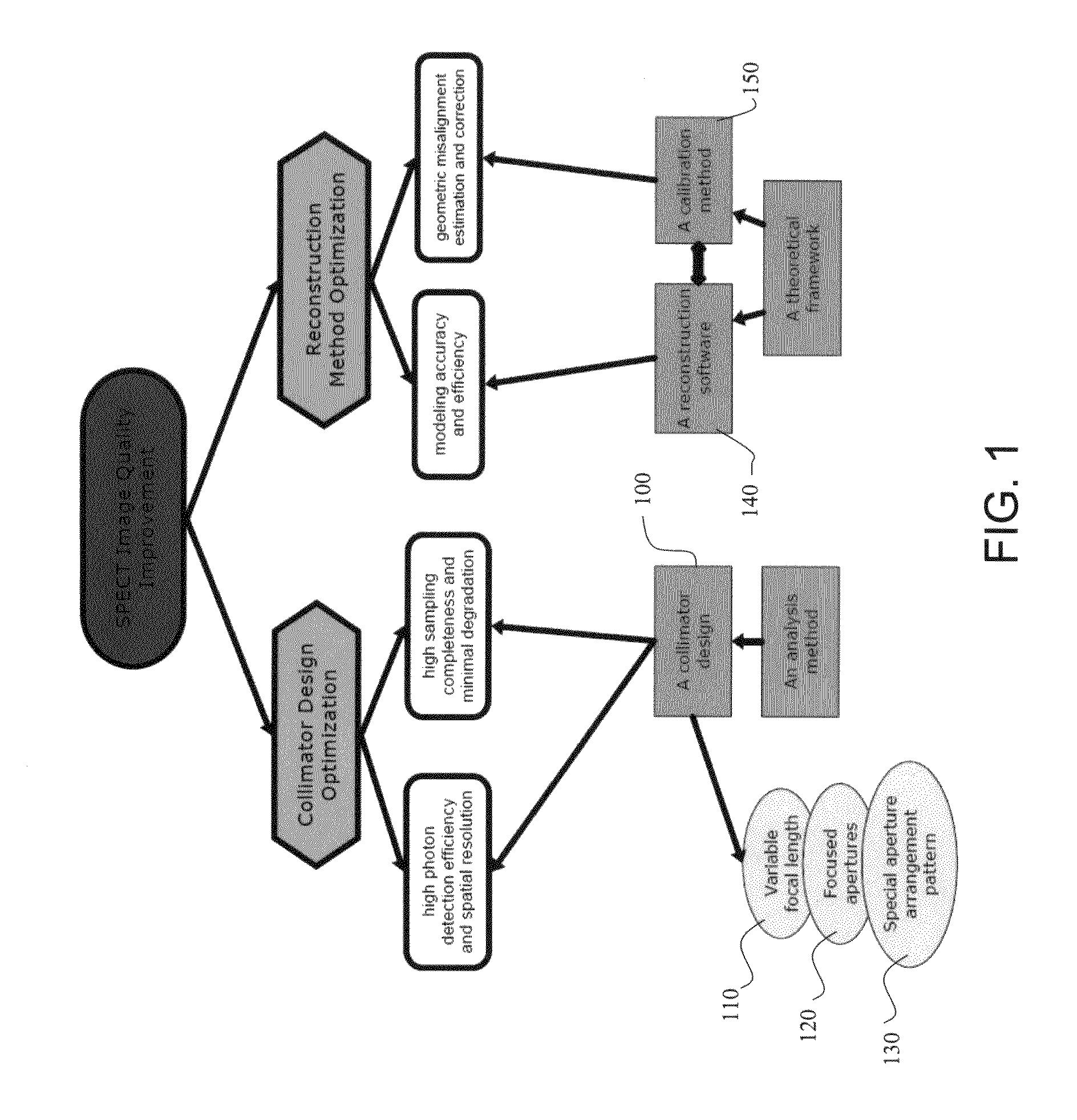
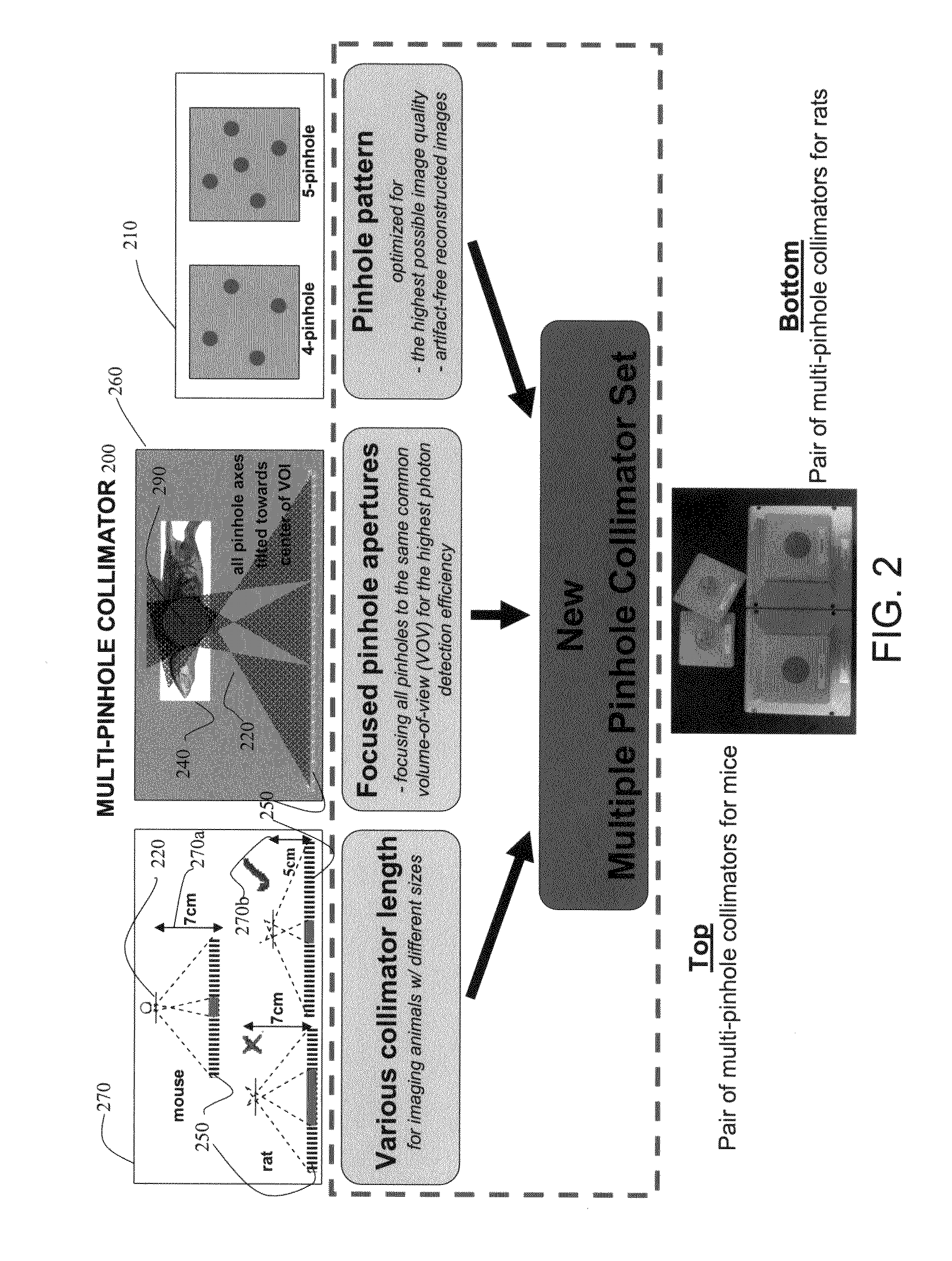
Methods and systems for improving image quality of single photon nuclear imaging systems, such as single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) systems for imaging of an object under study, such as small objects including small animals of different sizes using synthetic apertures. The methods and systems include processes and instrumentations for high-resolution, high detection efficiency leading to lower image noise and artifact-free synthetic aperture single photon nuclear images, such as SPECT images. Also, the method and systems provide design parameters, hardware settings, and data acquisition processes for optimal imaging of objects having different sizes.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA IDEAS
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving detector heads
ActiveUS20150094573A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsPhotonSingle-photon emission computed tomography
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving heads are provided. One system includes a gantry having an opening therethrough, a patient table movable through the opening of the gantry along an examination axis, and a plurality of detector units mounted to the gantry and aligned in a row transverse to the examination axis. The plurality of detector units are spaced apart from each other, wherein the spacing forms gaps between adjacent detector units. The plurality of detector units are configured to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) data. The system further includes a controller configured to control movement of the patient table and the plurality of detector units to acquire two-dimensional (2D) SPECT data, wherein the plurality of detector units remain in a fixed relative orientation with respect to each other when acquiring the 2D SPECT data and move together to acquire the 2D SPECT data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Intergrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20080137806A1Easy to replaceEasy to handleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTransmission Computed TomographyPatients position
This invention features an integrated single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) / transmission computed tomography (TCT) system for cardiac imaging including an open arc-shaped frame. A collimator system is shaped to approximately match the thoracic contour of patients having different sizes and weights and shaped to surround and position the collimator closely proximate a heart of a patient of said patients encompassed by at least one predetermined image volume for optimizing collimation of radiation photons emitted from the heart. An arc-shaped detector system is coupled to the collimator subsystem having a shape closely matching the shape of the collimator subsystem for detecting collimated radiation photons from the collimator subsystem and generating output electrical signals. A patient positioning subsystem positions a patient to a predetermined central longitudinal axis of the three-dimensional imaging volume and for intermittently and incrementally rotating the patient about the predetermined central longitudinal axis for generating a plurality of TCT images.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Methods for improved single photon emission computed tomography using exact and stable region of interest reconstructions
InactiveUS20110105880A1Few artifactAccurate and reliable processReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
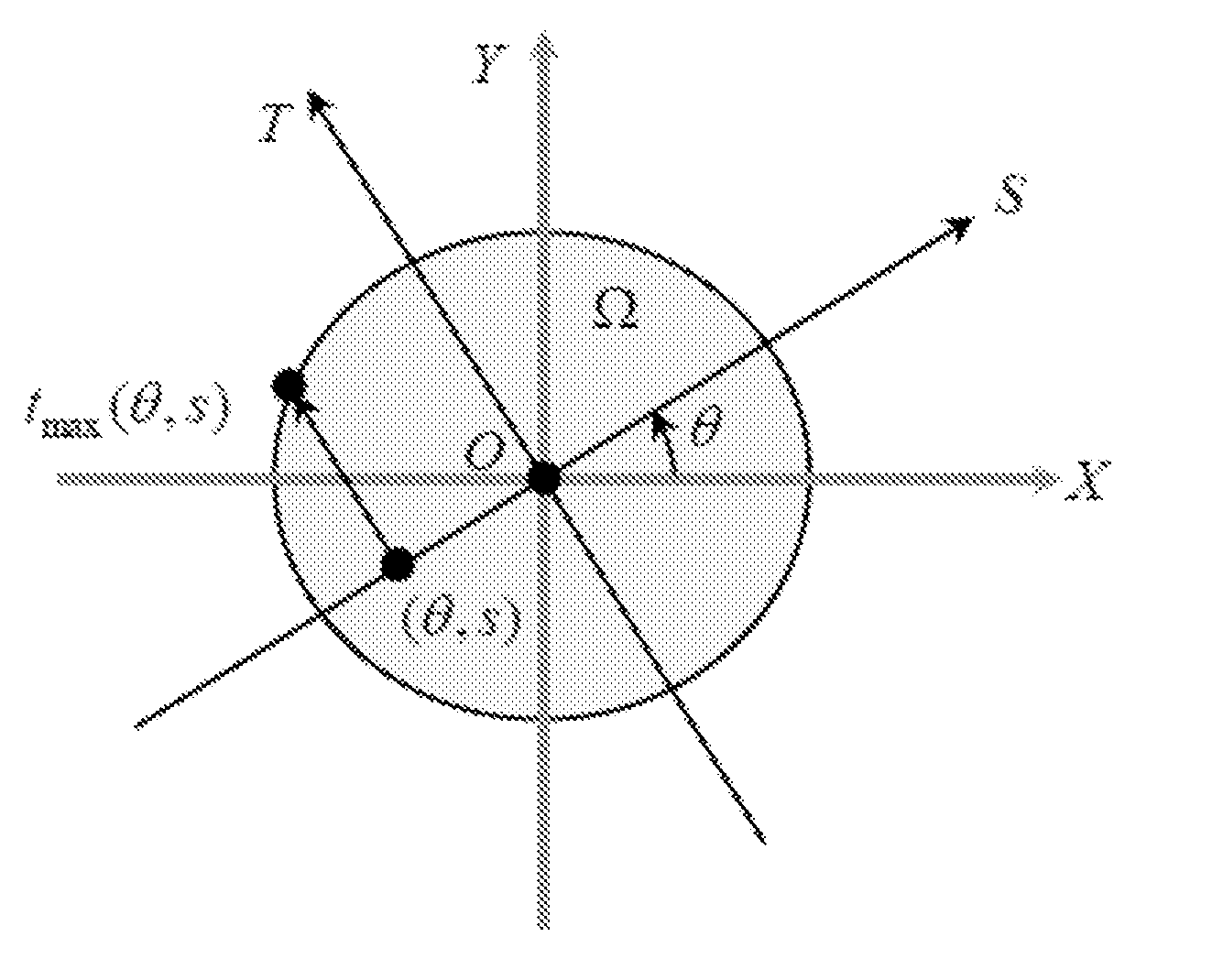
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices for improved computed tomography (CT) and, more specifically, to methods for improved single photon computed tomography (SPECT) using exact and stable region of interest (ROI) reconstructions. This technology can be extended across all tomographic modalities. Embodiments provide a method and a system for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a single photon emission computed tomography scanner comprising: identifying a region of interest in an object; defining an attenuation coefficient and object boundary; computing the generalized Hilbert transform of the data through the defined region of interest and a known subregion; and reconstructing the image with improved temporal resolution at lower radiation doses, wherein the reconstructing comprises performing a reconstruction method that yields an exact and stable reconstruction. Embodiments also provide a method and a system for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a single photon emission computed tomography scanner comprising: identifying a region of interest in an object; defining an attenuation coefficient and object boundary; and reconstructing the images by minimizing the high order total variation while minimizing the data discrepancy.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method for image reconstruction of moving radionuclide source distribution
InactiveUS20100316275A1Eliminate artifactsEliminate relative motionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall animalRadioactive tracer
A method for image reconstruction of moving radionuclide distributions. Its particular embodiment is for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging of awake animals, though its techniques are general enough to be applied to other moving radionuclide distributions as well. The invention eliminates motion and blurring artifacts for image reconstructions of moving source distributions. This opens new avenues in the area of small animal brain imaging with radiotracers, which can now be performed without the perturbing influences of anesthesia or physical restraint on the biological system.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Tumor imaging compounds
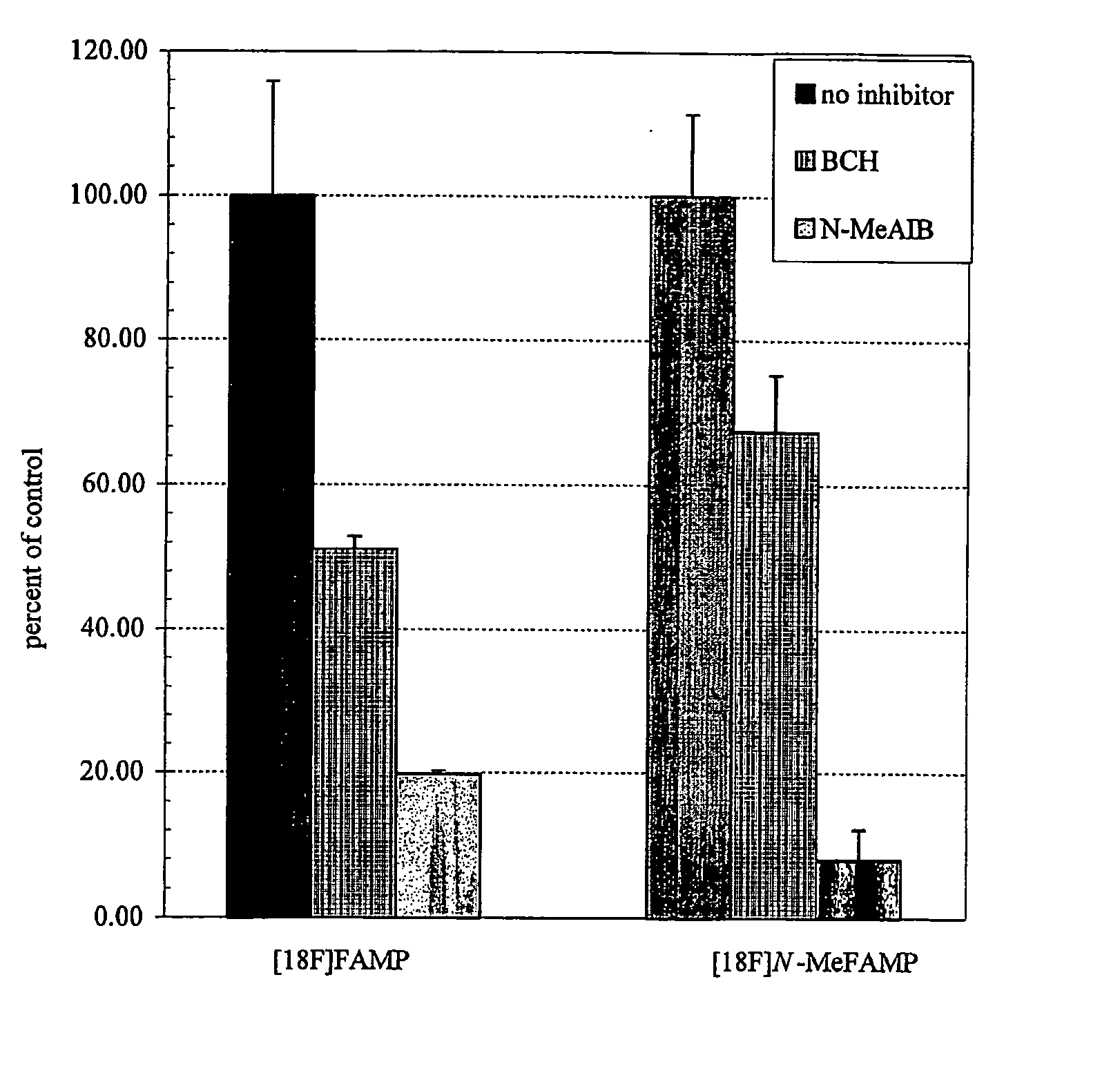
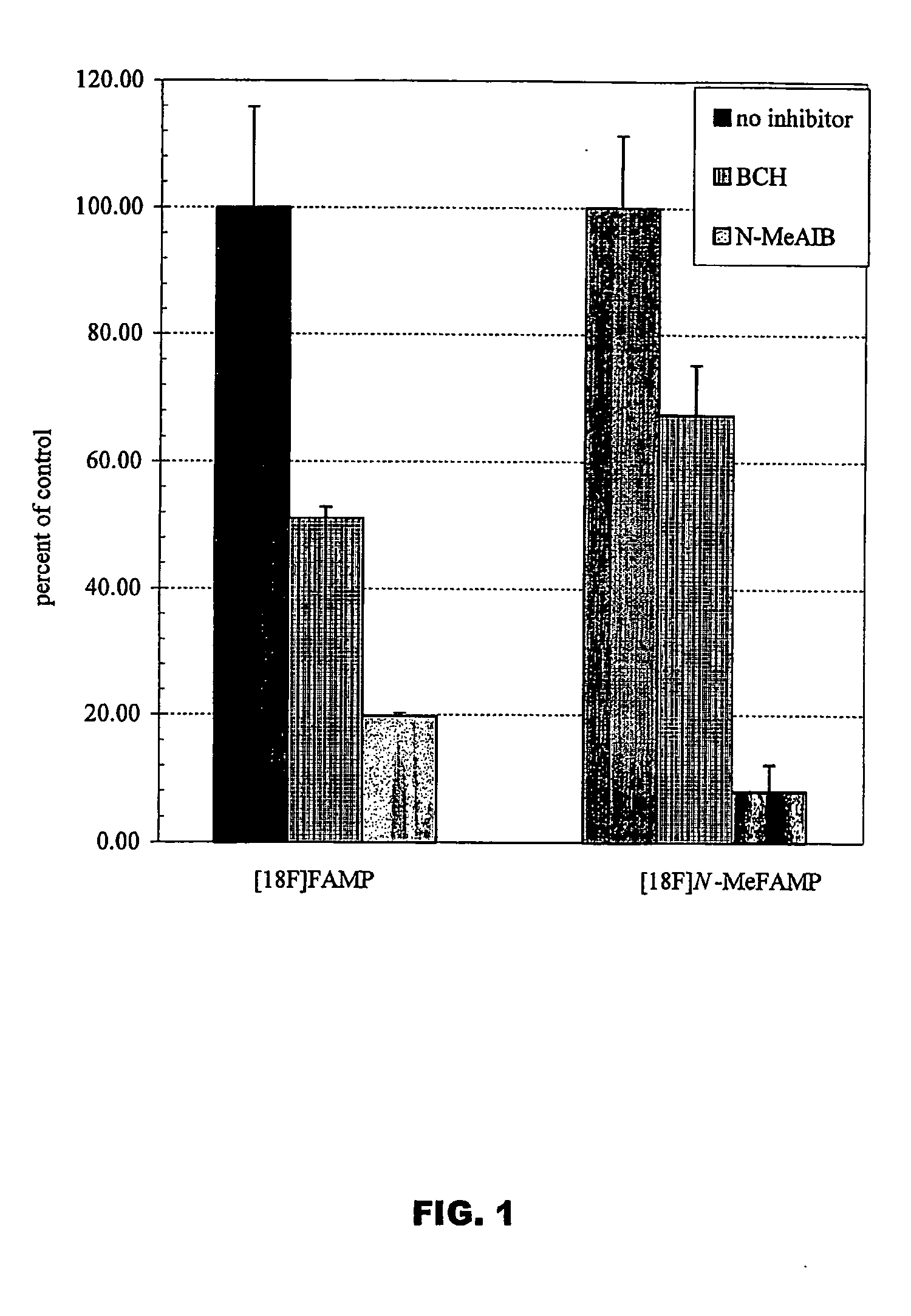
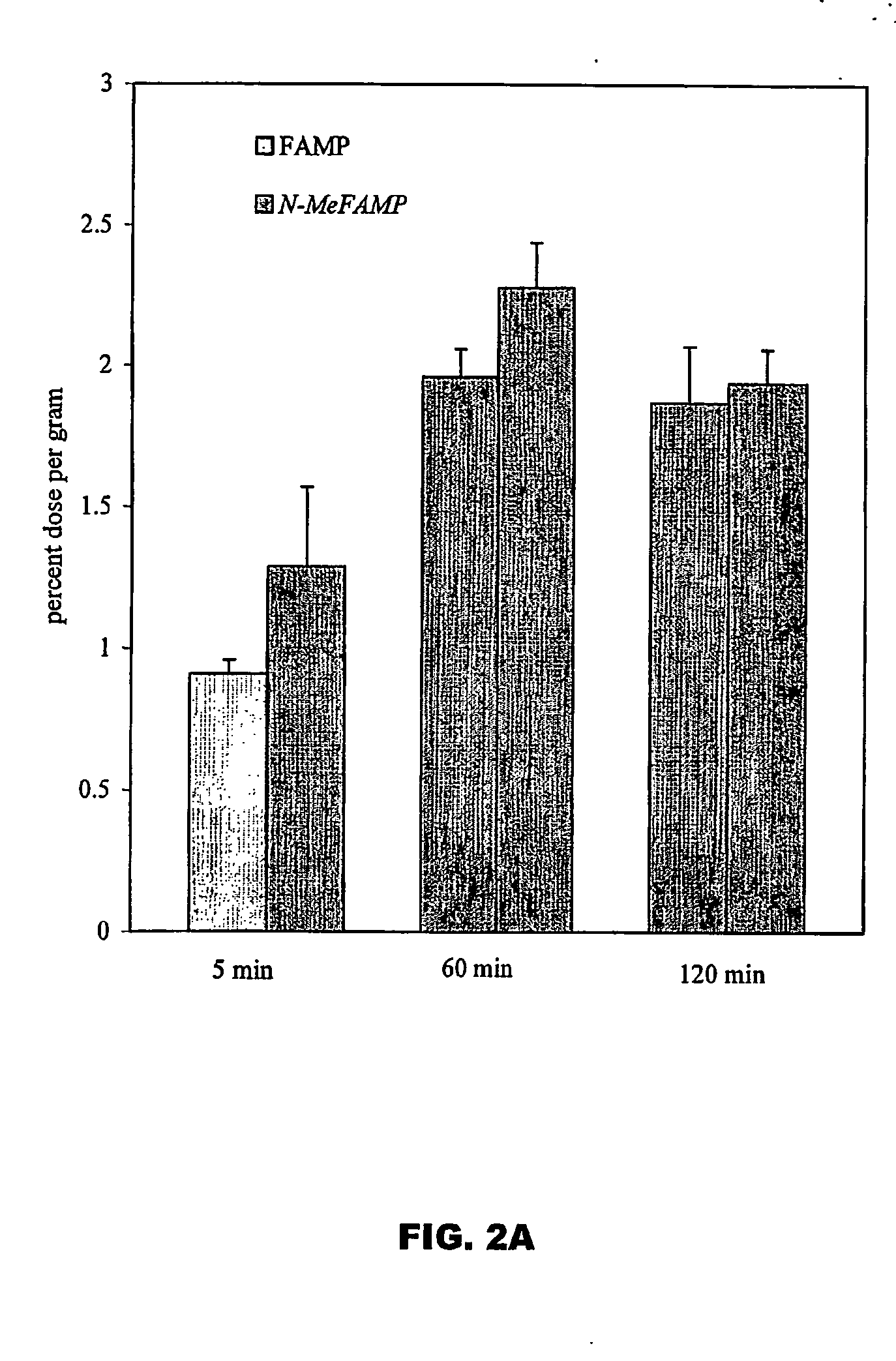
ActiveUS20050192458A1Rapid uptakeHigh retention rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRhenium
The invention provides novel amino acid compounds of use in detecting and evaluating brain and body tumors. These compounds combine the advantageous properties of α-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) analogs namely, their rapid uptake and prolonged retention in tumors with the properties of halogen sustituents, including certain useful halogen isotopes such as fluorine-18, iodine-123, iodine-124, iodine-125, iodine-131, bromine-75, bromine-76, bromine-77, bromine-82, astatine-210, astatine-211, and other astatine isotopes. In addition the compounds can be labeled with technetium and rhenium isotopes using known chelation complexes. The amino acid compounds disclosed herein have a high specificity for target sites when administered to a subject in vivo. Preferred amino acid compounds include [18F] FAMP, ([18F]5a) and [18F]N-MeFAMP, ([18F]5b). The invention further features pharmaceutical compositions comprised of an α-amino acid moiety attached to eiher a four, five or a six member carbon-chain ring. The labeled amino acid compounds are useful as imaging agents in detecting and / or monitoring tumors in a subject by Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computer Tomography (SPECT).
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Multi-modal homomorphic isochronic medical image imaging system and method
ActiveCN103815925AConducive to complementary advantagesRealize multi-modal dynamic acquisitionComputerised tomographsTomographyDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
The invention discloses a multi-modal homomorphic isochronic medical image imaging system and a multi-modal homomorphic isochronic medical image imaging method. The imaging system comprises an X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) device, a positron emission tomography (PET) device, a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) device, a rotating device, a scanning table device, a data acquisition system and a computer, wherein the X-ray CT device, the PET device and the SPECT device are arranged on the same rotating device, and share one scanning table device and the same scanning area to form the multi-modal imaging system. The same sampling angle is subjected to time-share scanning in three modes and is rotated by one circle, multi-modal homomorphic isochronic imaging is realized, different imaging equipment complements advantages of one another, the acquired image results are more accurate and reliable, multi-modal dynamic acquisition in real sense is realized.
Owner:北京锐视康科技发展有限公司
Single-photon-emission apparatus
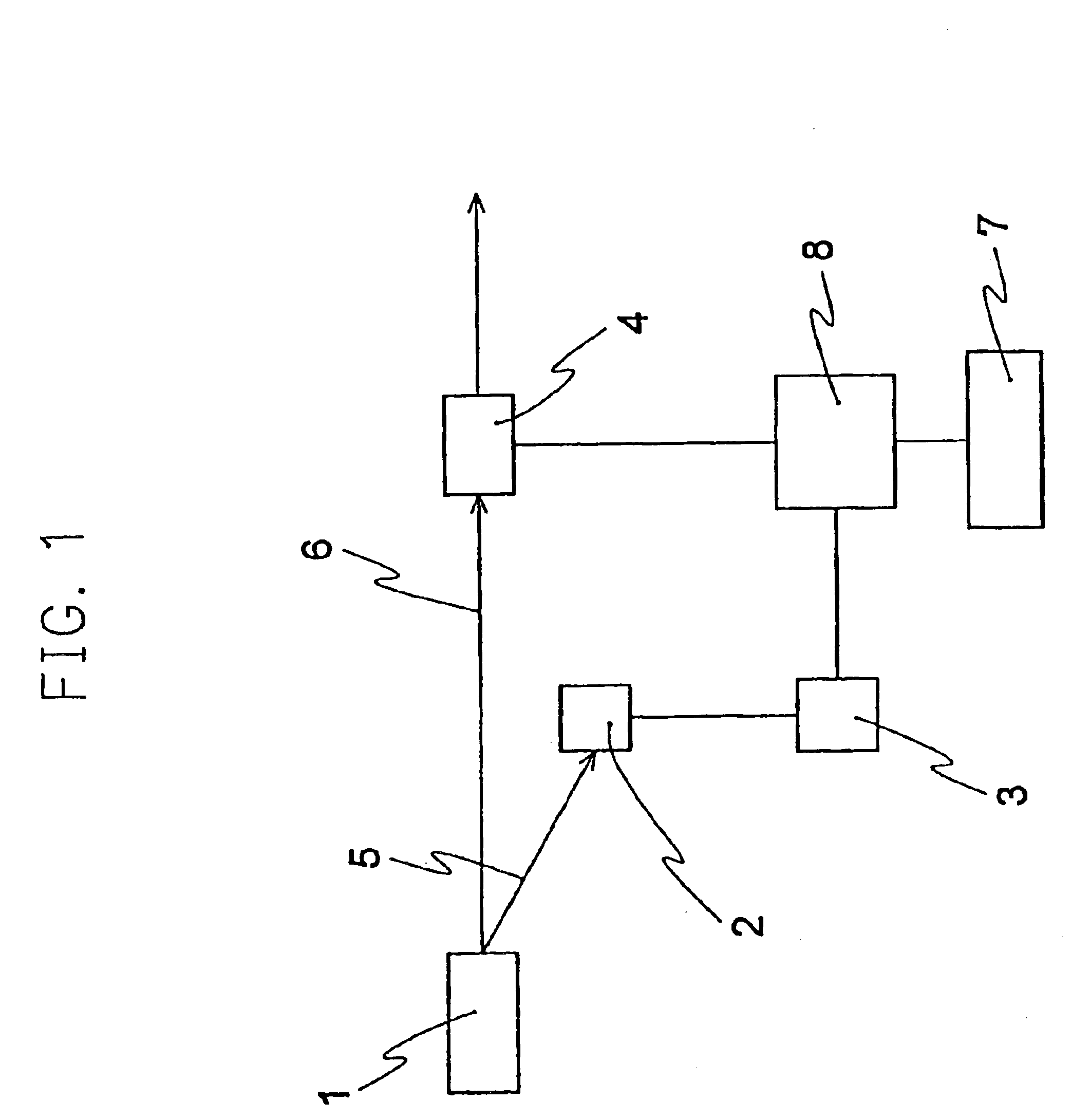
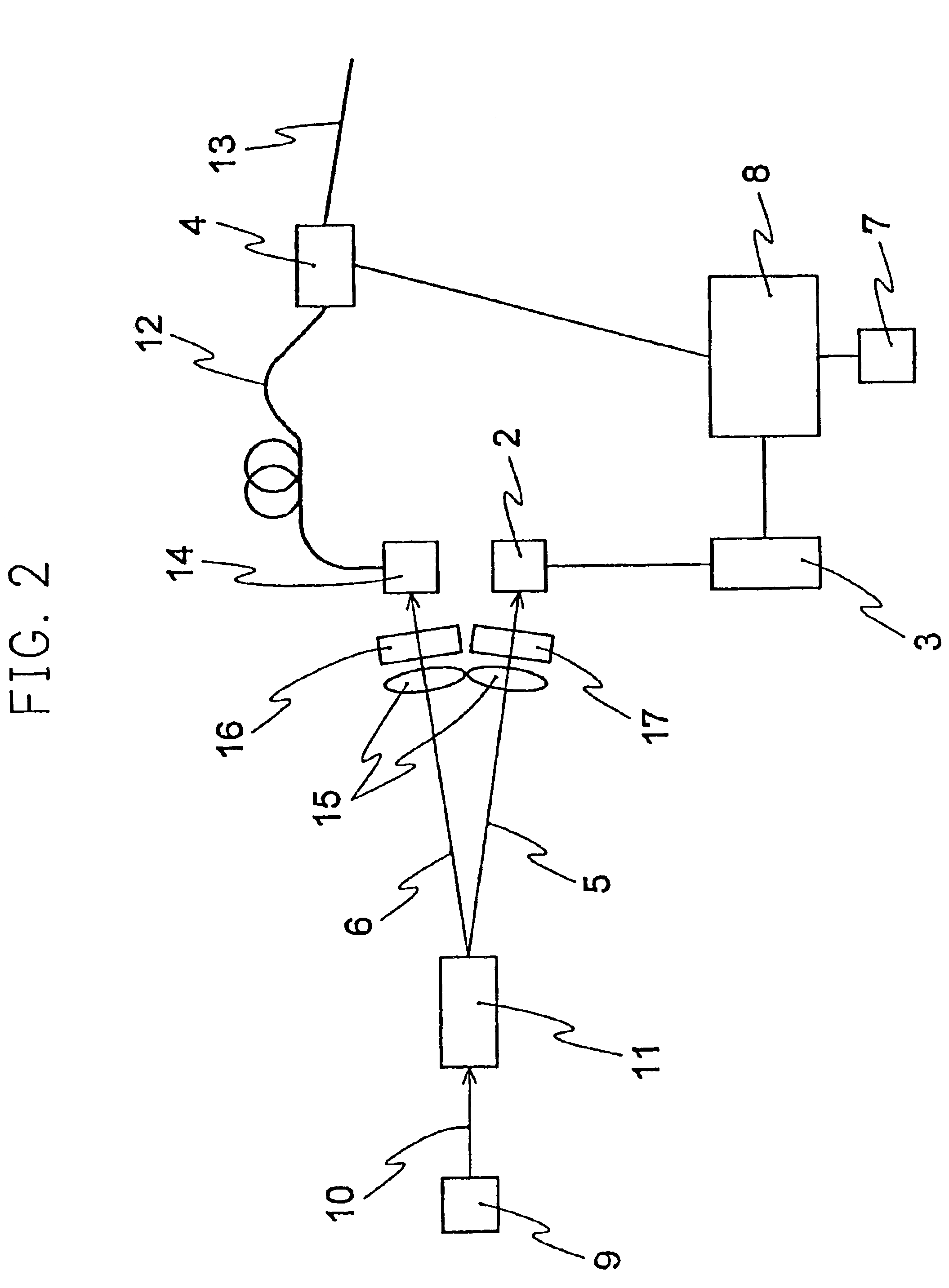
InactiveUS7088824B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPhysicsSingle photon emission
The apparatus includes a photon pair source for generating a photon pair that contains a signal photon and an idler photon and correlates with the generating time, photon detectors for detecting a incidence of idler photons, a clock generator, a gate device controller for generating signals for opening or closing a gate device in a frequency lowering a specific number of times within a specified time defined by the clock, and a gate device for opening or closing the gate in response to the signals from the gate device controller.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multi-doped lutetium based oxyorthosilicate scintillators having improved photonic properties
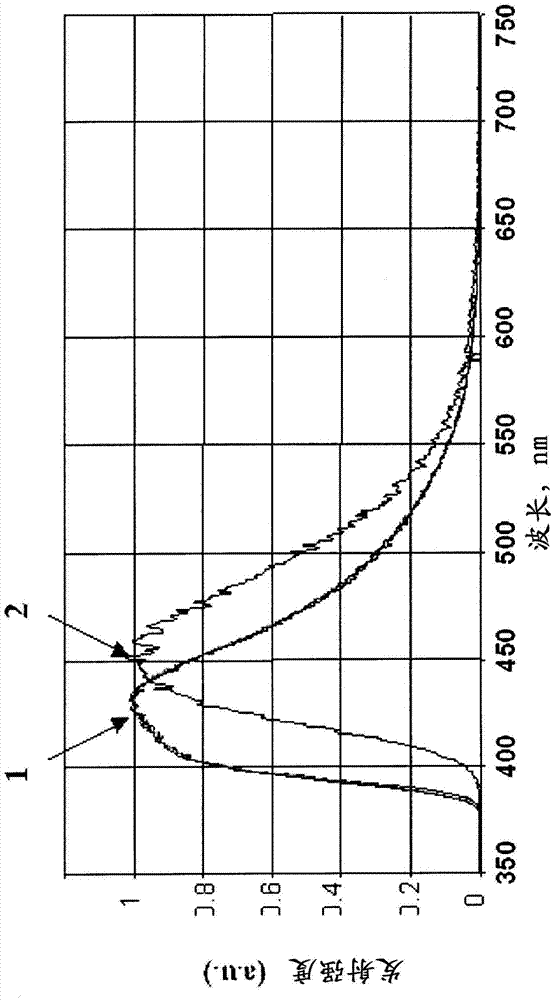
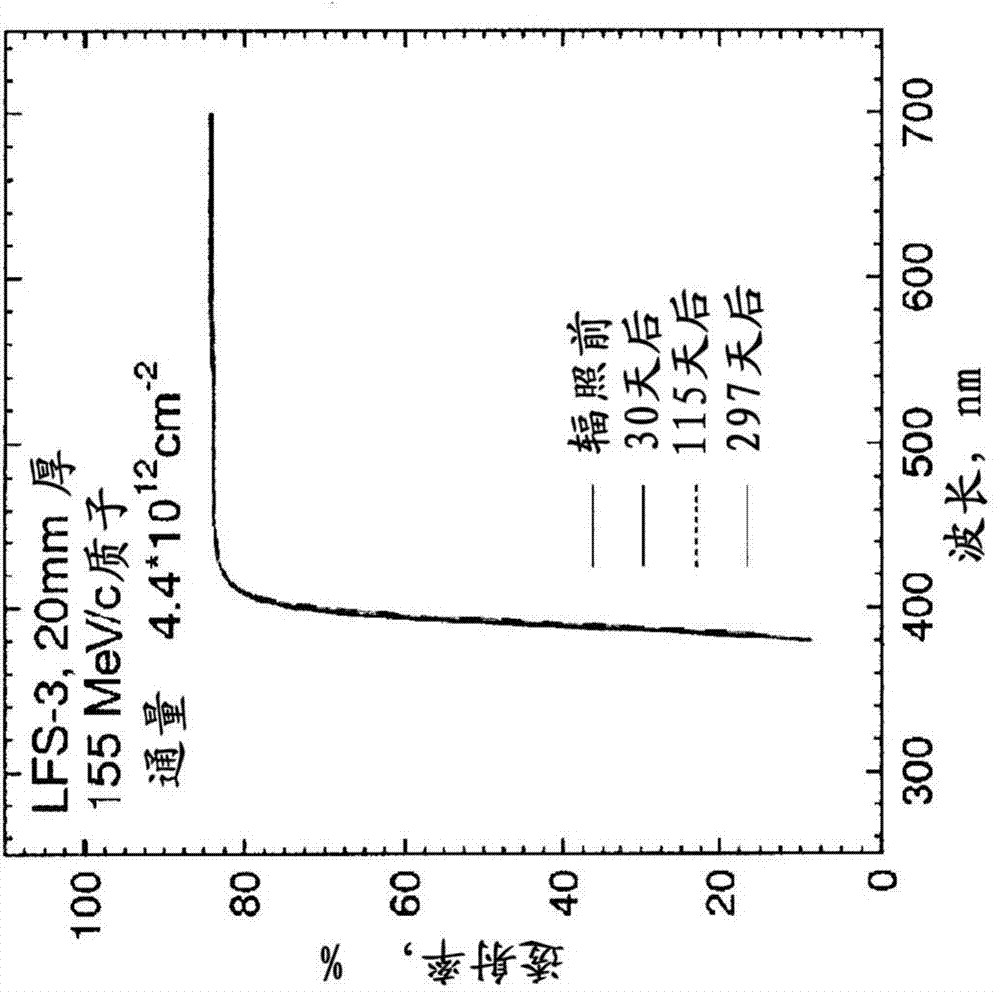
InactiveCN104508192ALow costIncrease concentrationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHigh energyCerium
The present invention relates to a set of multi-doped cerium-activated scintillation materials of the solid solutions on the basis of the rare earth silicate, comprising lutetium and having compositions represented by the chemical formulas: (Lu2-w-x+2yAwCexSi1-y)1-zMezJjOq and (Lu2-w-x-2yAwCexSi1+y)1-zMezJjOq. The invention is useful for detection of elementary particles and nuclei in high-energy physics, nuclear industry; medicine, Positron Emission Tomography (TOF PET and DOI PET scanners) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), Positron Emission Tomography with Magnetic Resonance imaging (PET / MR); X-ray computer fluorography; non-destructive testing of solid state structure, including airport security systems, the Gamma-ray systems for the inspection of trucks and cargo containers.
Owner:ZECOTEK PHOTONICS INC
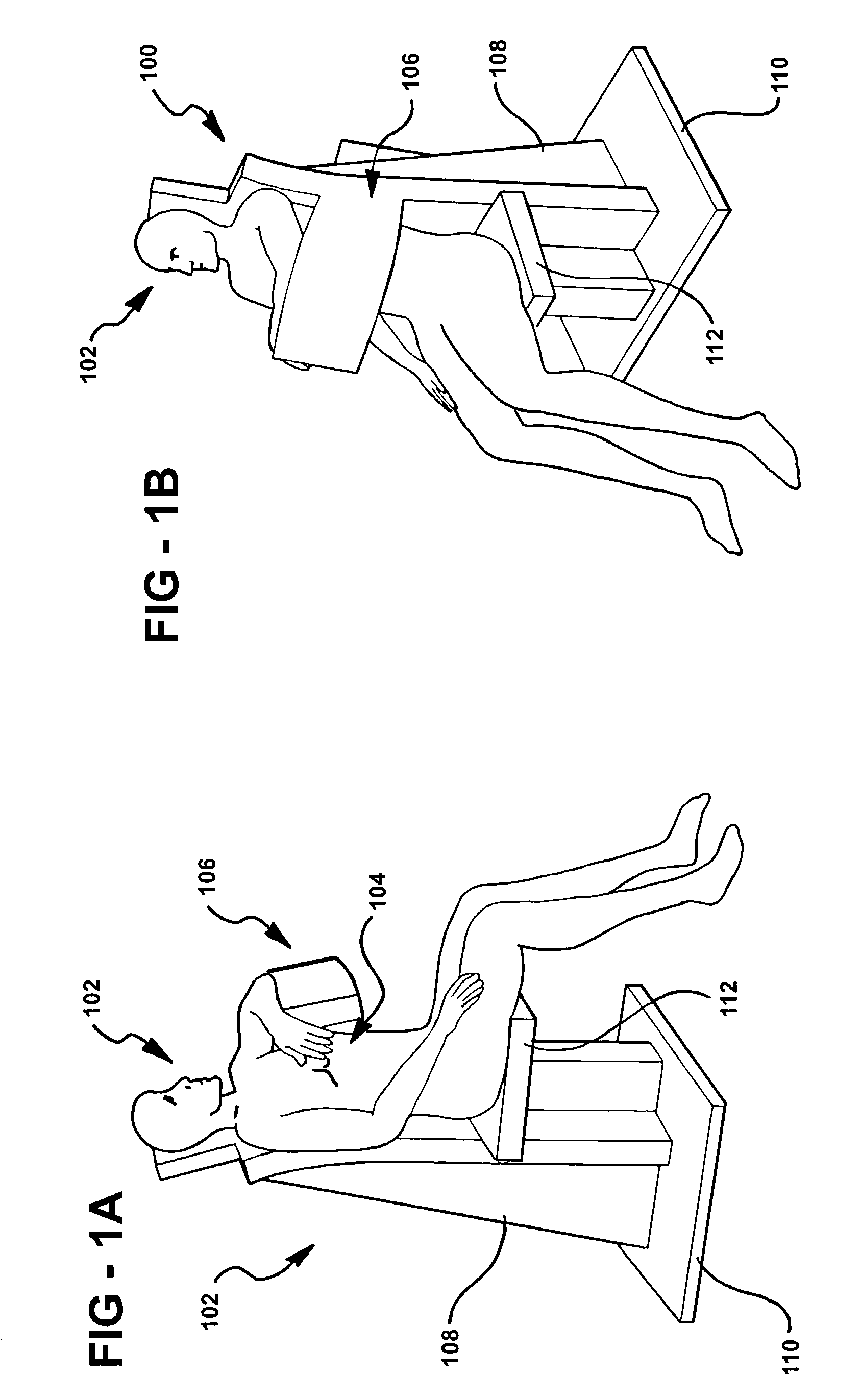
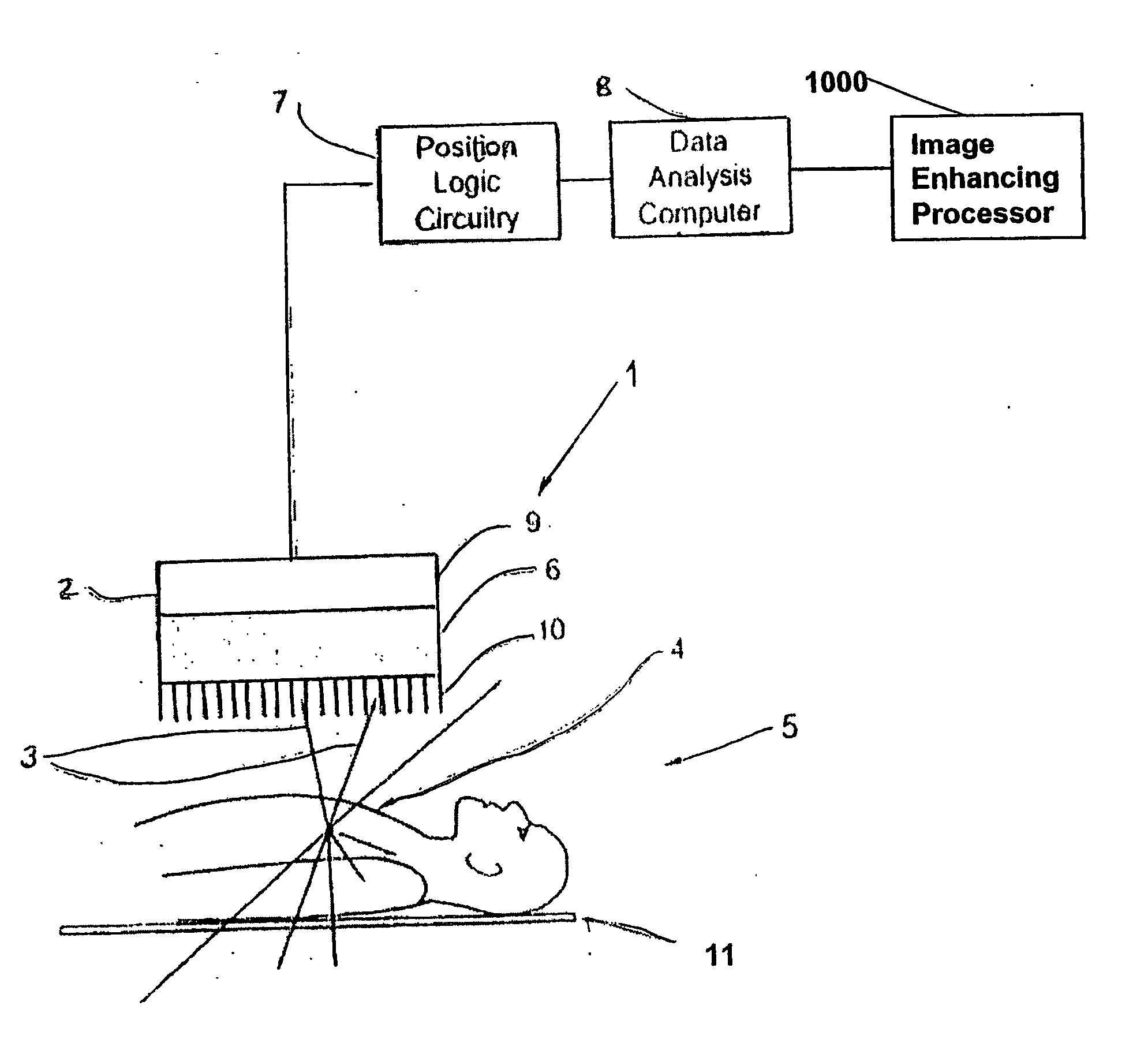
Diagnosis device for radiographic and nuclear medical examinations
InactiveUS20070102645A1Enhance the imageHigh registration precisionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital imagingX-ray
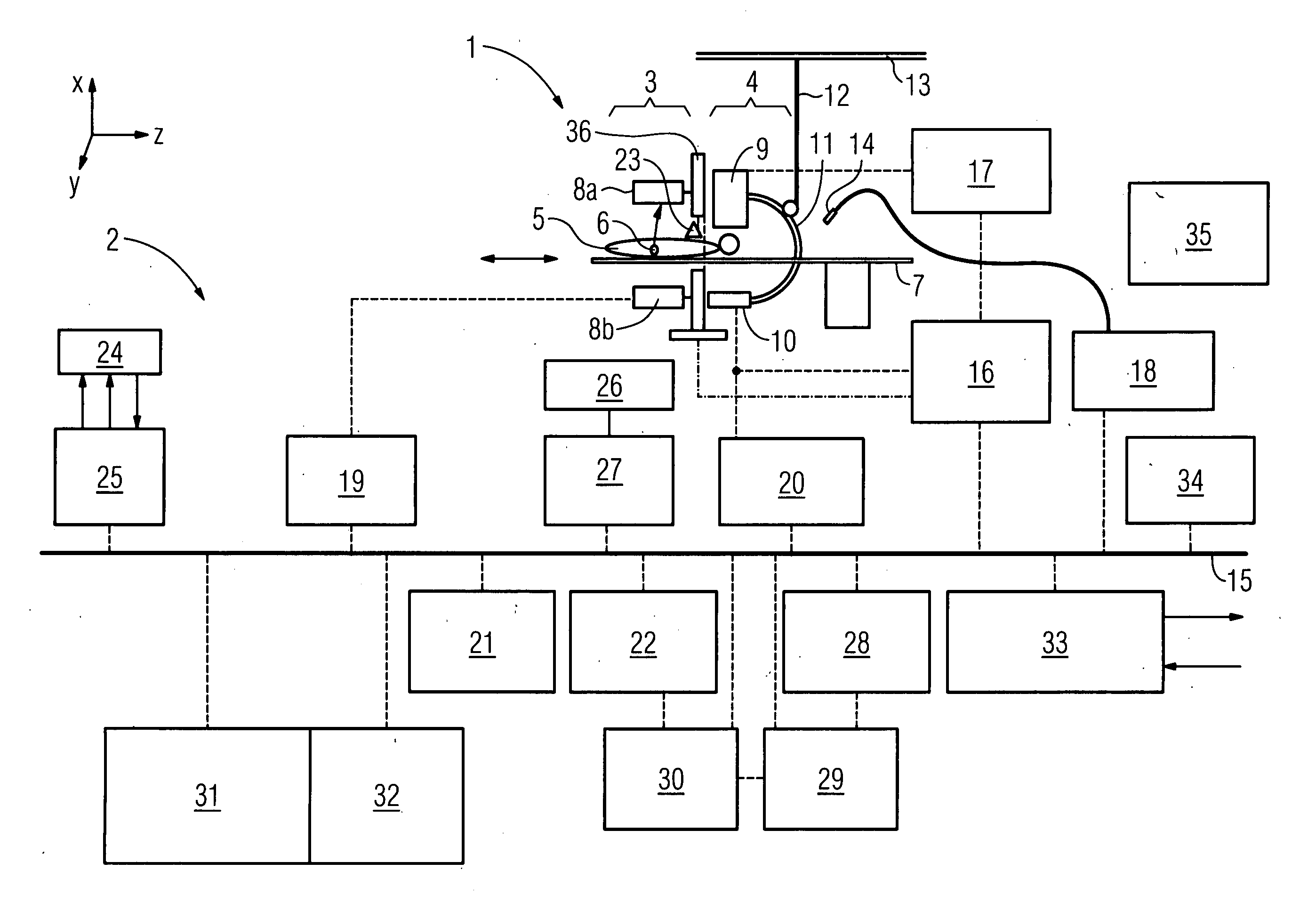
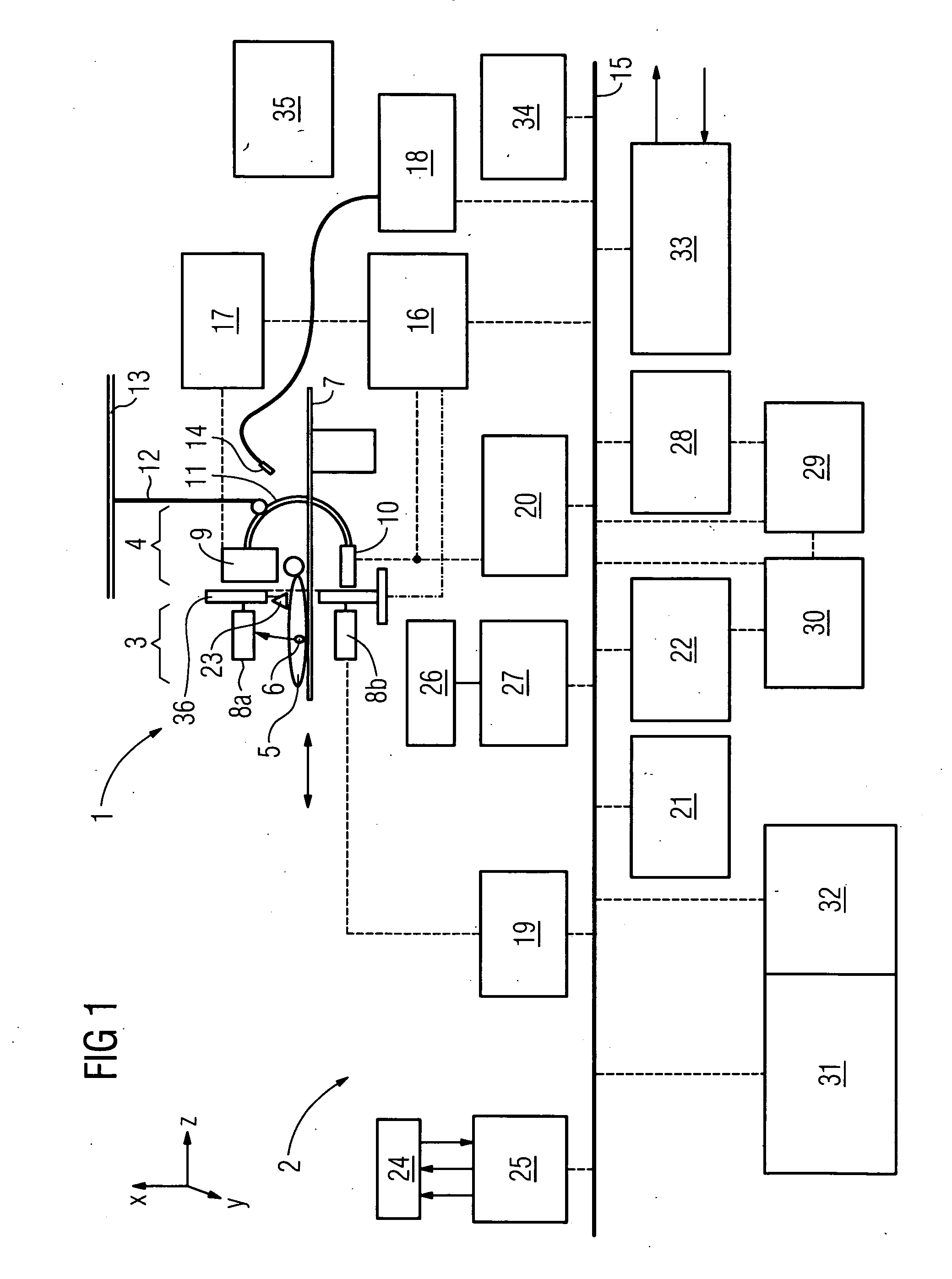
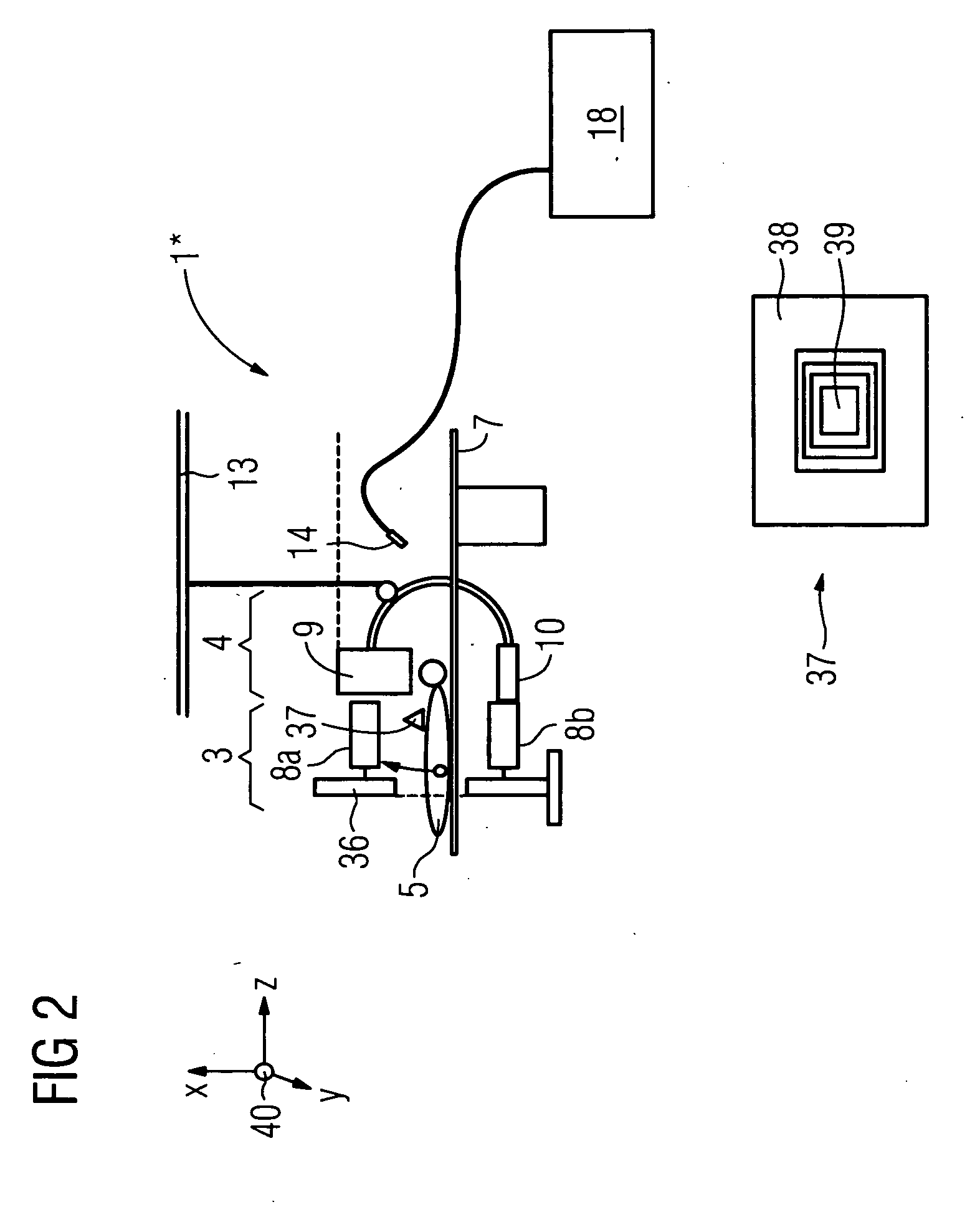
Diagnosis device for combined and / or combinable radiographic and nuclear medical examinations Digital imaging methods have now become common practice in medical diagnostics. Methods of this type have been used for some time, e.g. in computer tomography, for magnetic resonance examinations, ultrasound examinations and for nuclear medical methods. The object underlying the invention is to propose a diagnosis device for increasing accessibility to a patient. To this end, a diagnosis device (1) is proposed for combined and / or combinable radiographic and nuclear medical examinations with an x-ray source (9), with an examination room for accommodating a patient (5), with a gamma radiation source (6) arranged in the body, with the diagnosis device (1) being designed in order to carry out the radiographic examination by evaluating the measurement of the x-rays, and in order to carry out a single photon emission (SPE) examination as a nuclear medical examination by evaluating the gamma radiation, with a detector system (8a,b, 10) which has a detector surface for simultaneously measuring the x-ray and gamma radiation without changing the patient's position and / or which is designed to record a two-dimensional locally-resolved and object-imaging individual x-ray projection image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
SPECT examination device
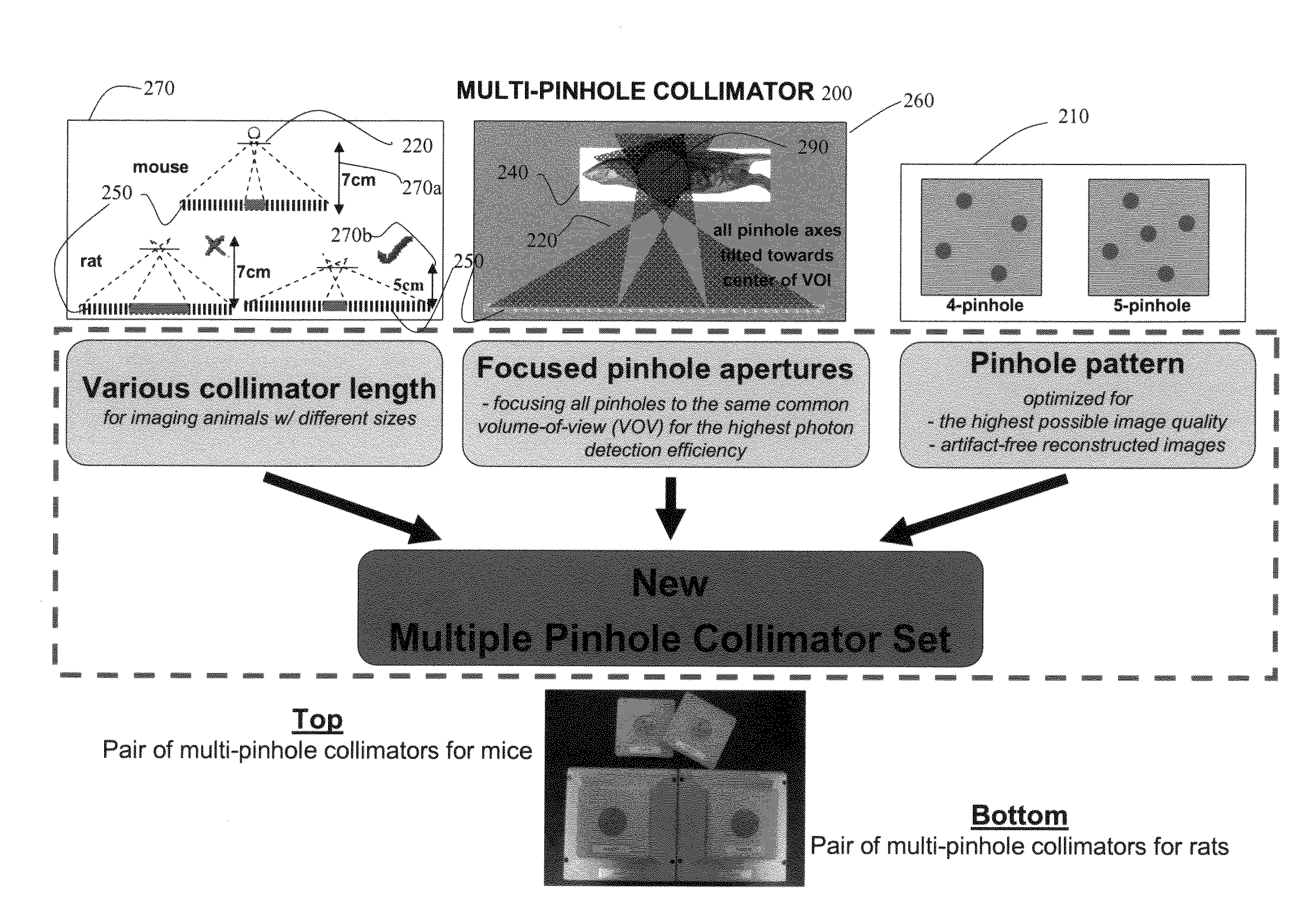
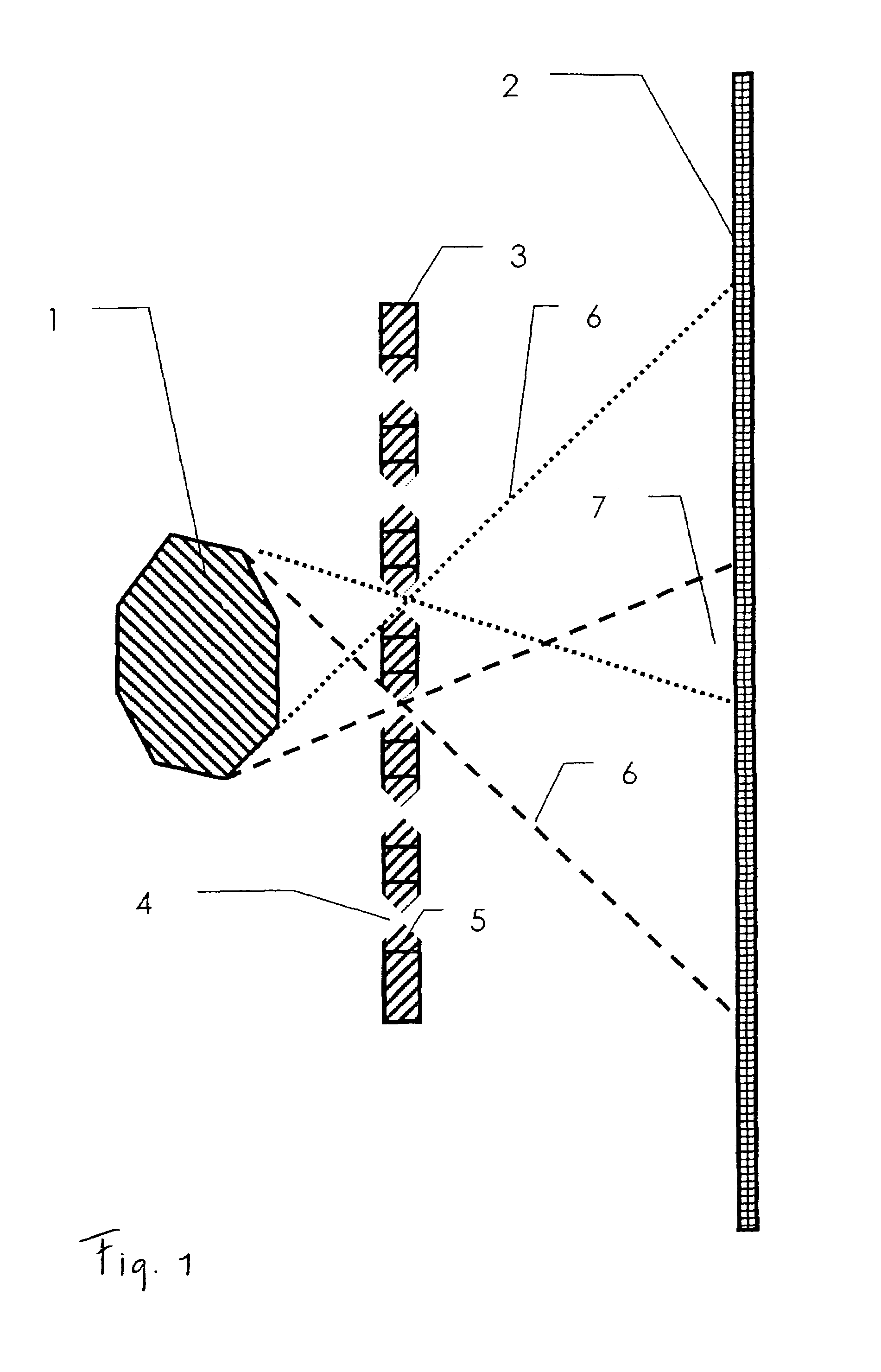
InactiveUS7199371B2Increase positioning resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansTomographyPhoton
A tomography device, particularly for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), comprises a multi-pinhole collimator and a detector for detecting gamma quanta or photons that penetrate the multi-pinhole collimator. In a tomographic method using the device, the distance between the object and the multi-pinhole collimator is selected to be smaller than the distance between the multi-pinhole collimator and the surface of the detector.
Owner:SCIVIS +1
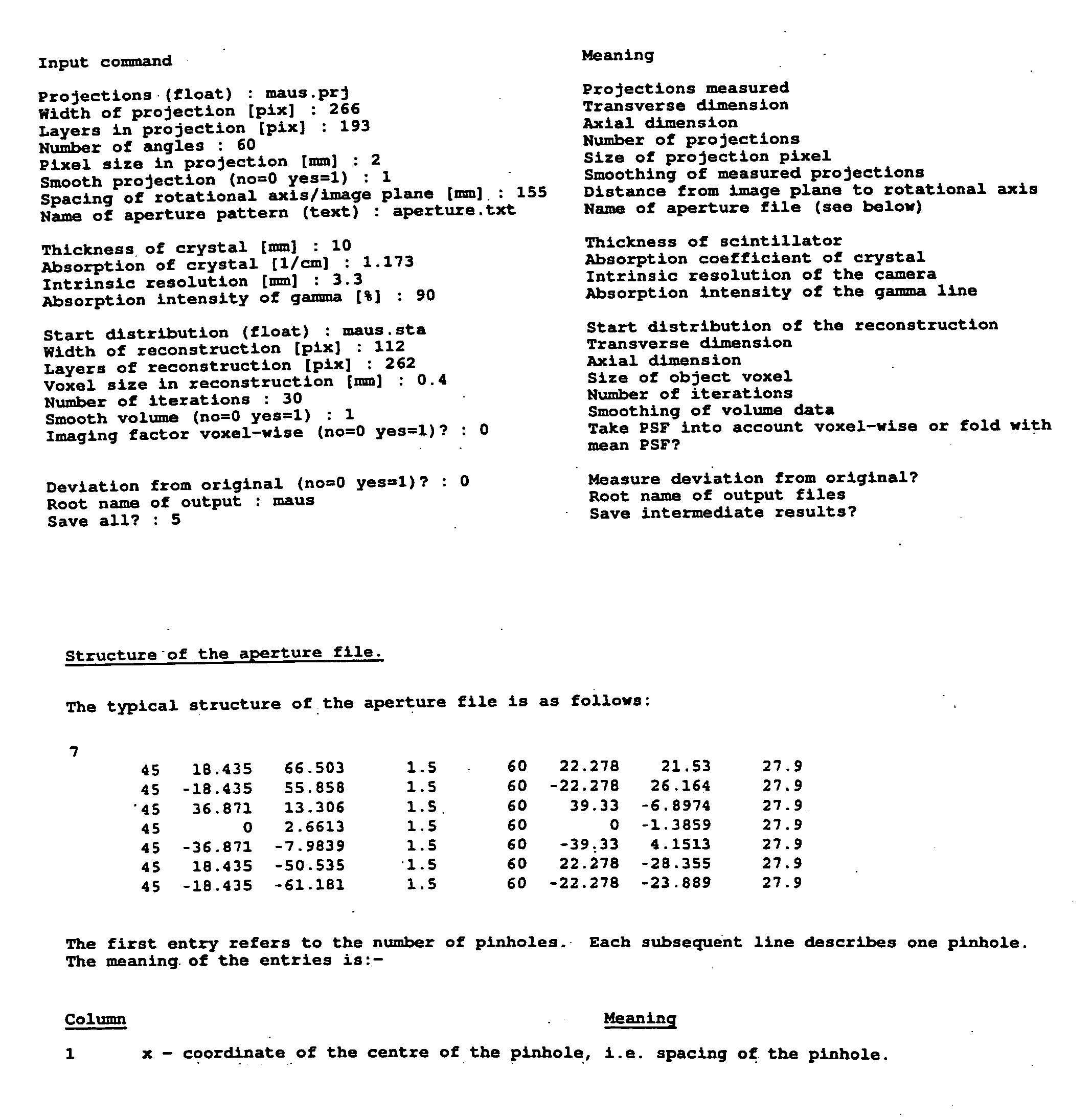
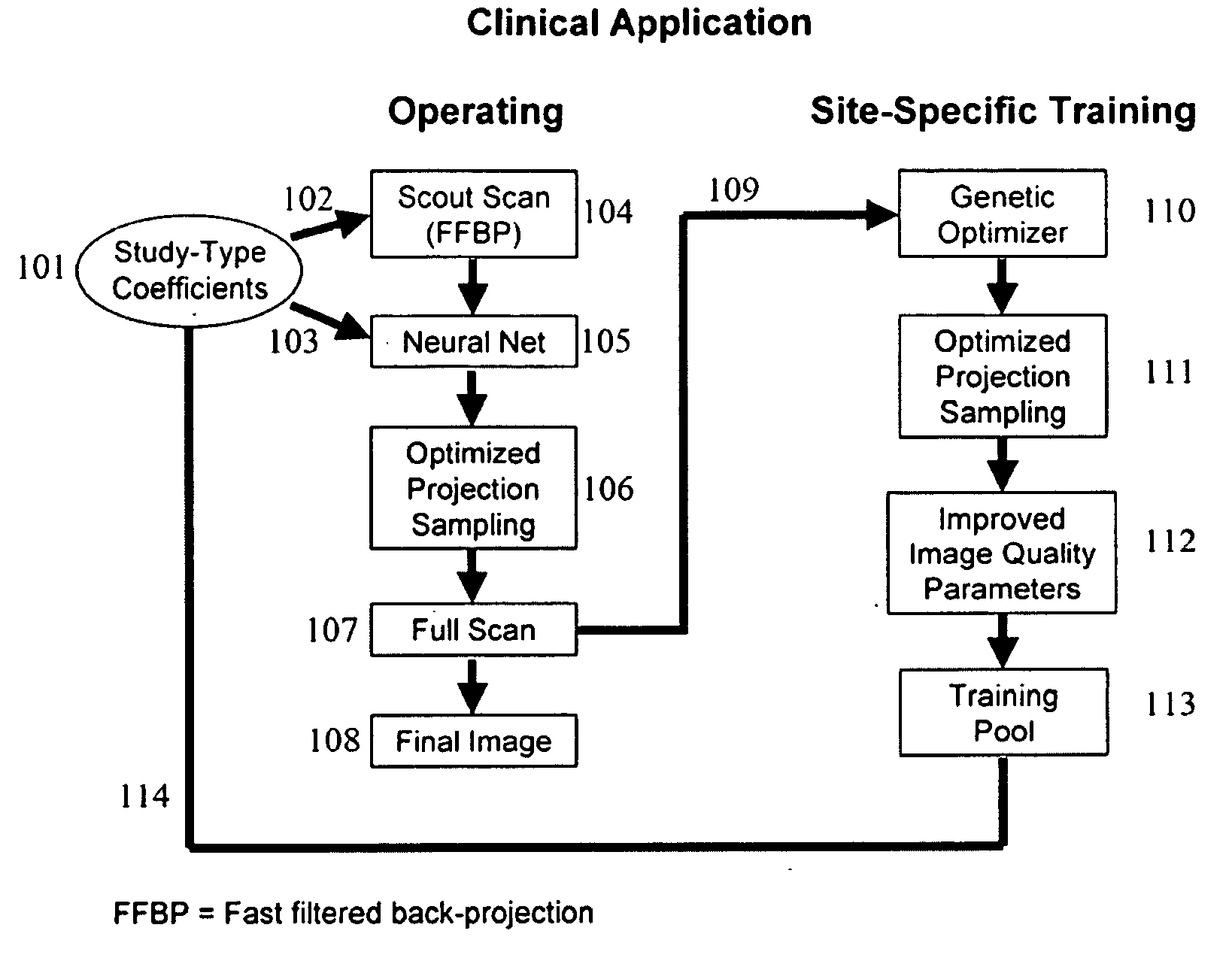
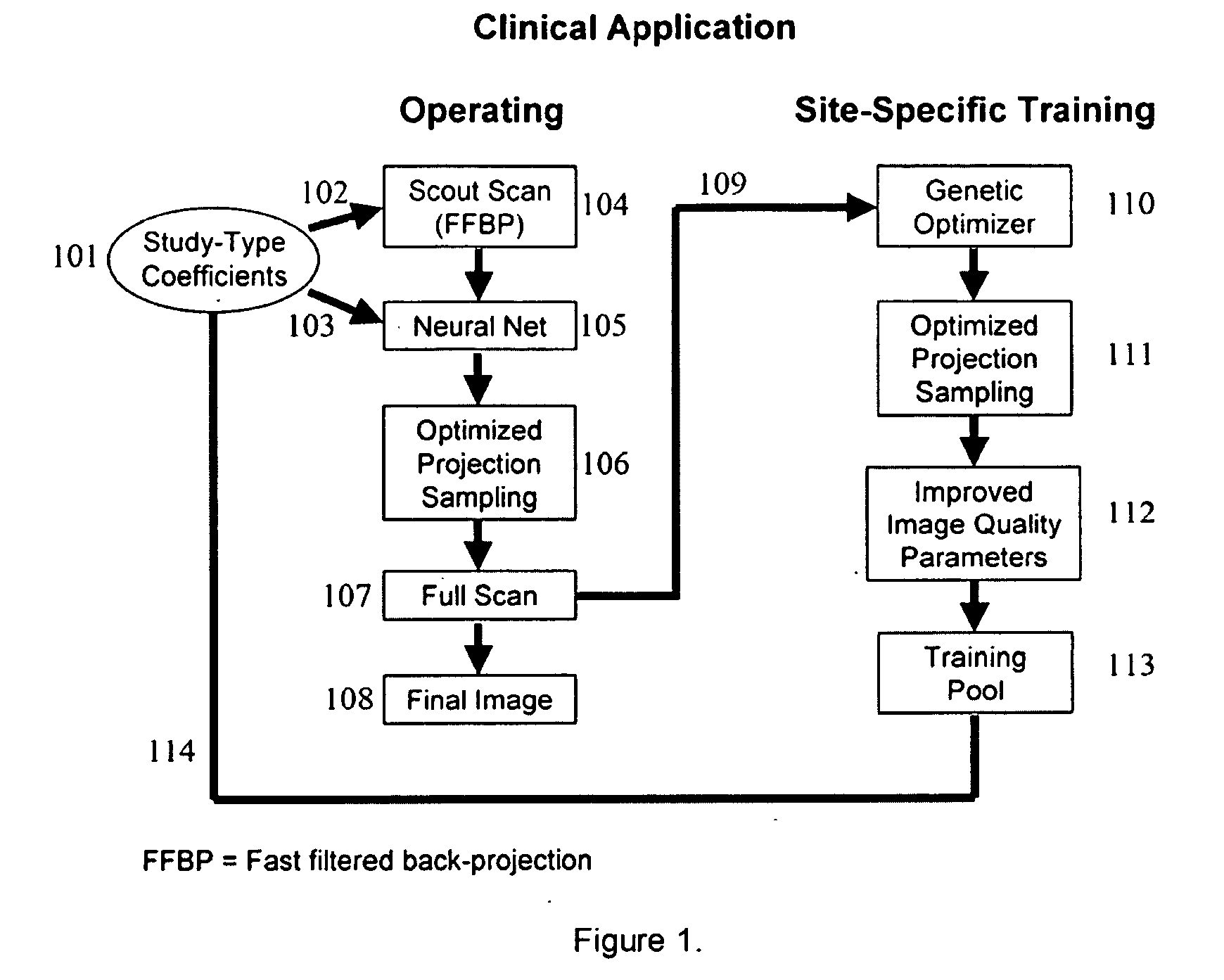
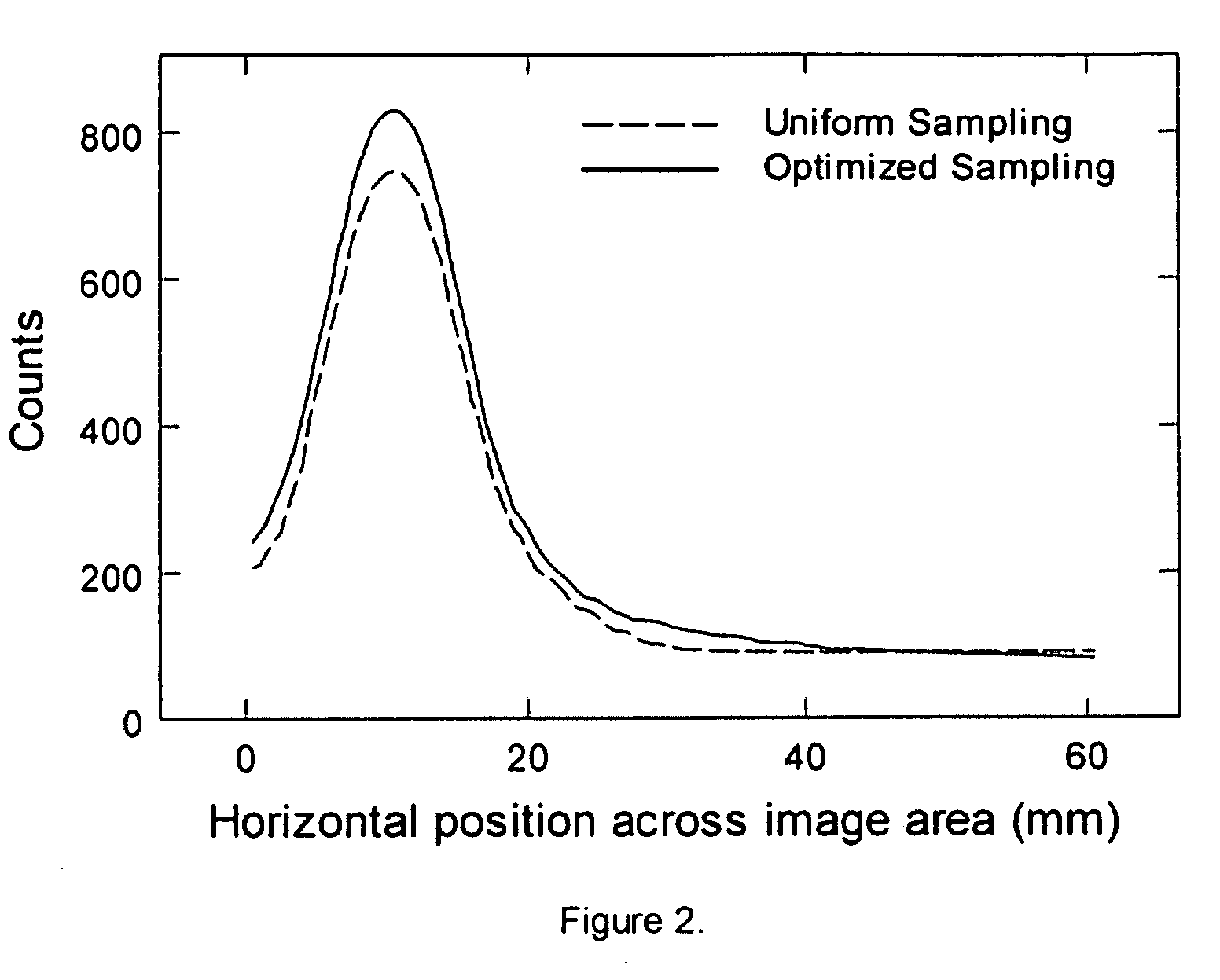
Optimized case specific spect sampling
InactiveUS20100155608A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentObject basedData acquisition
A method for improving single photon emission computed tomography by controlling acquisition parameters specific to the imaging goals and specific to the individual case under study. Data acquisition is modulated by scanning to adapt to the particular signal to noise characteristics of each object. A preliminary acquisition quickly scans the object of interest. The preliminary data is analyzed to optimize the secondary scan. The secondary scan is then acquired with optimized sampling of the object based on its own particular image characteristics. The system is able to learn, incorporating site specific data into a triaging set.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com