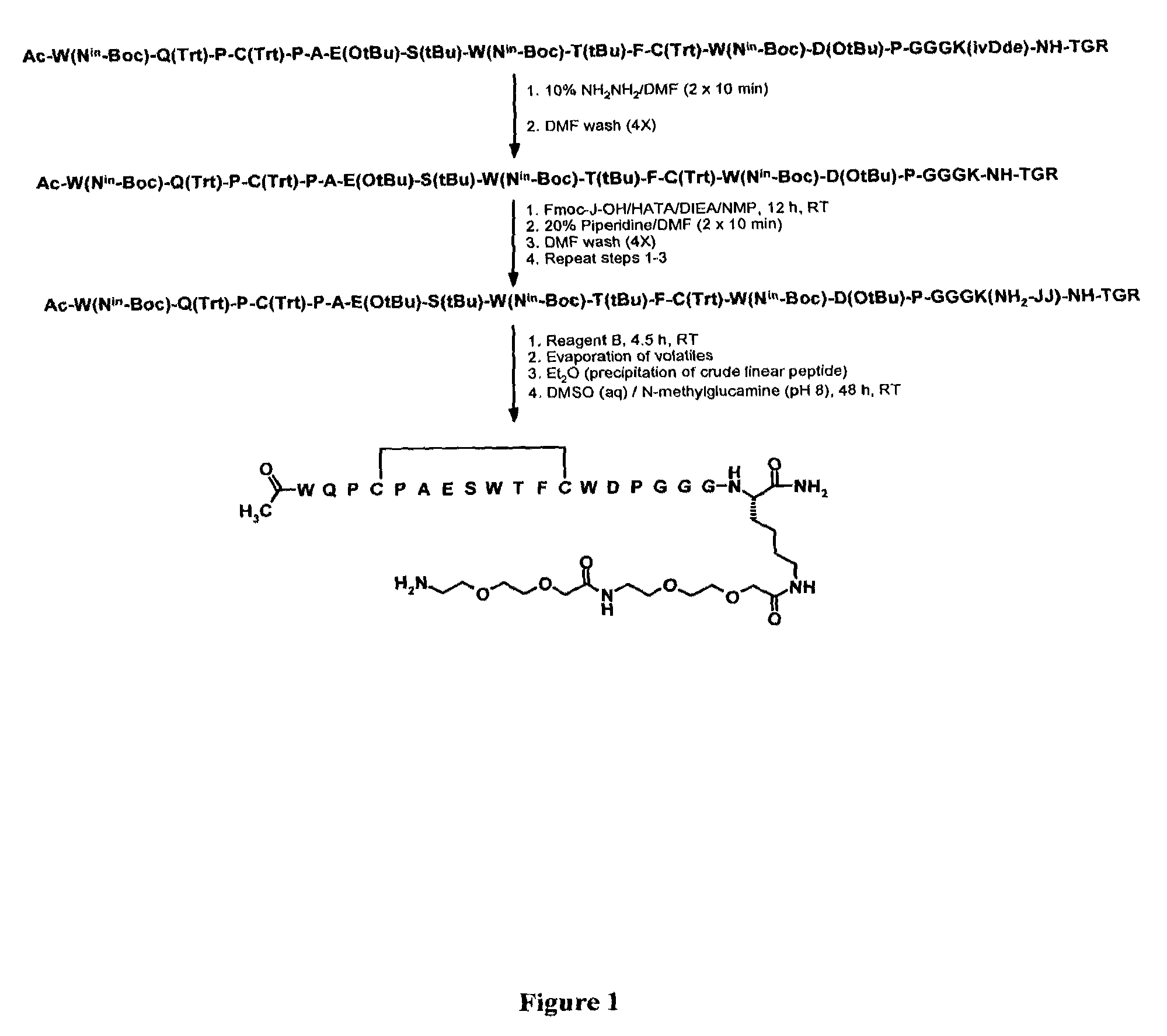
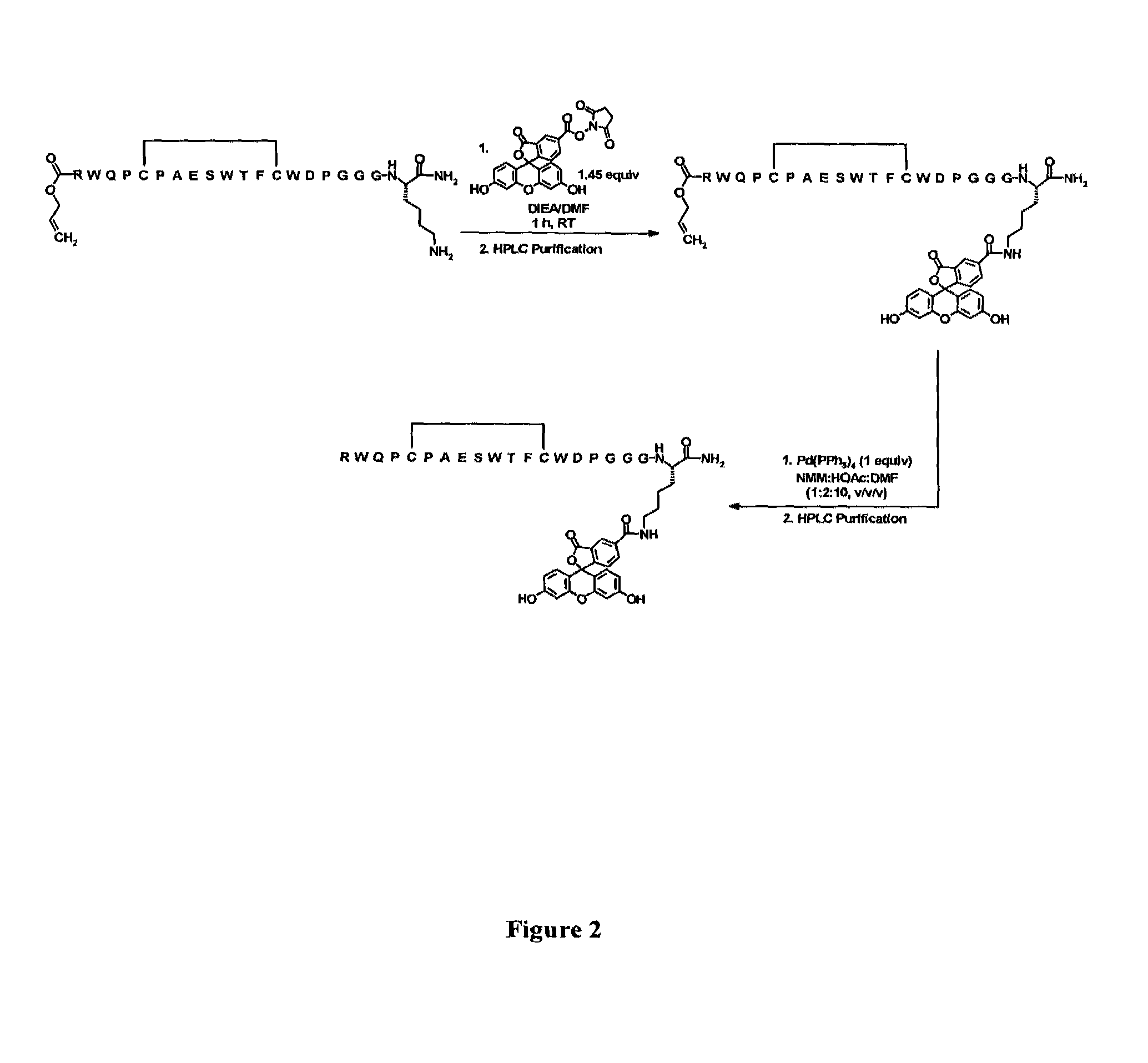
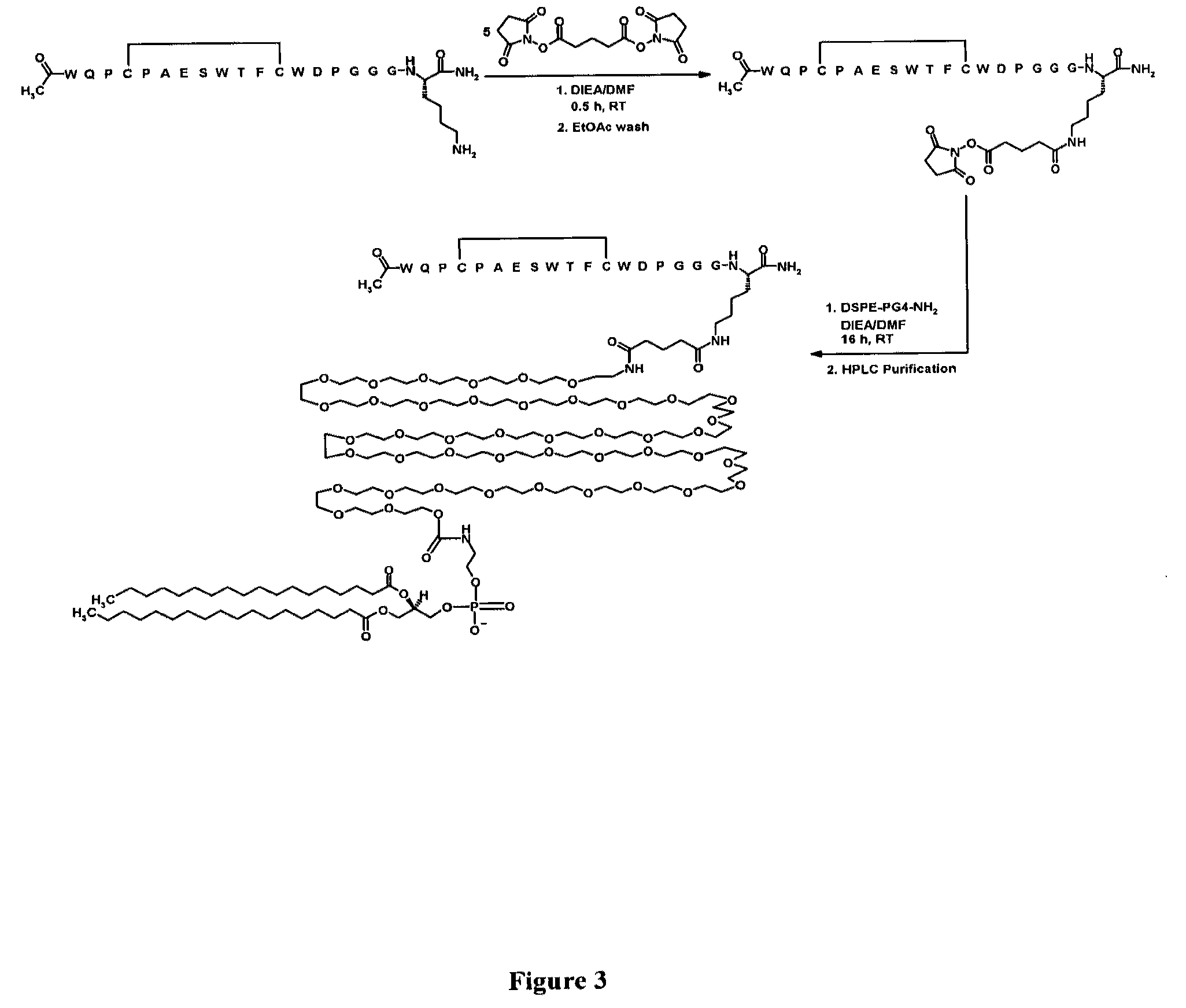
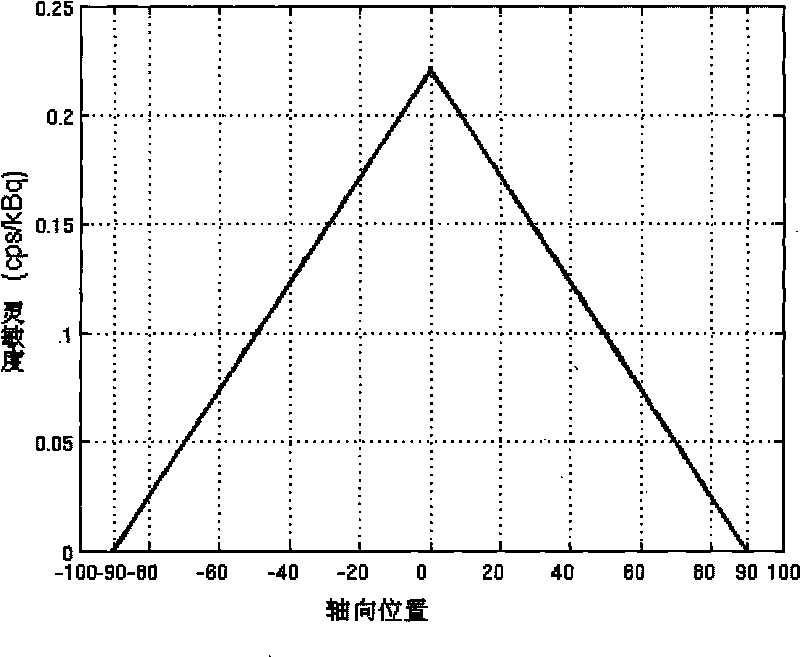
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223 results about "Nuclear medicine imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
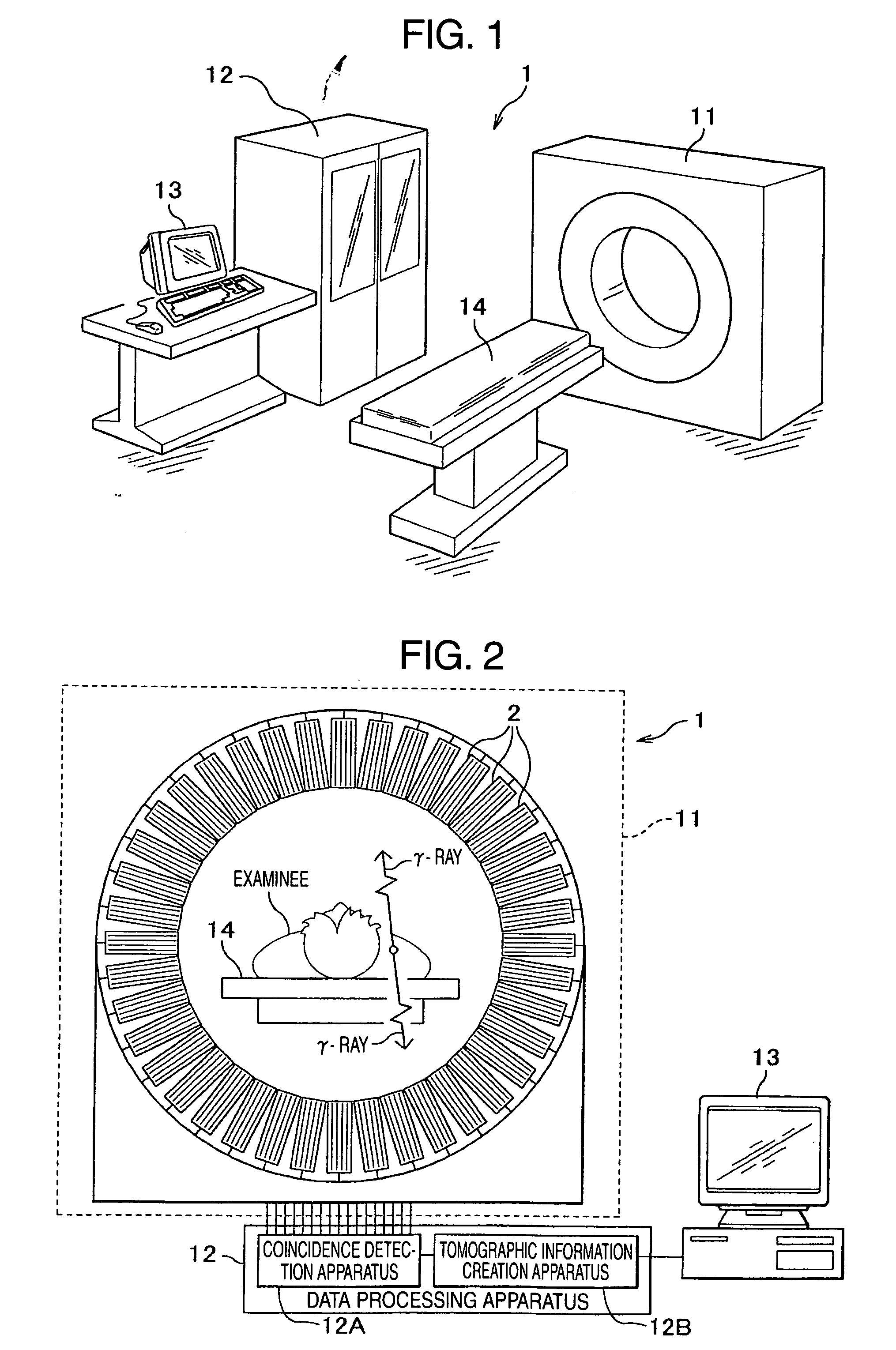
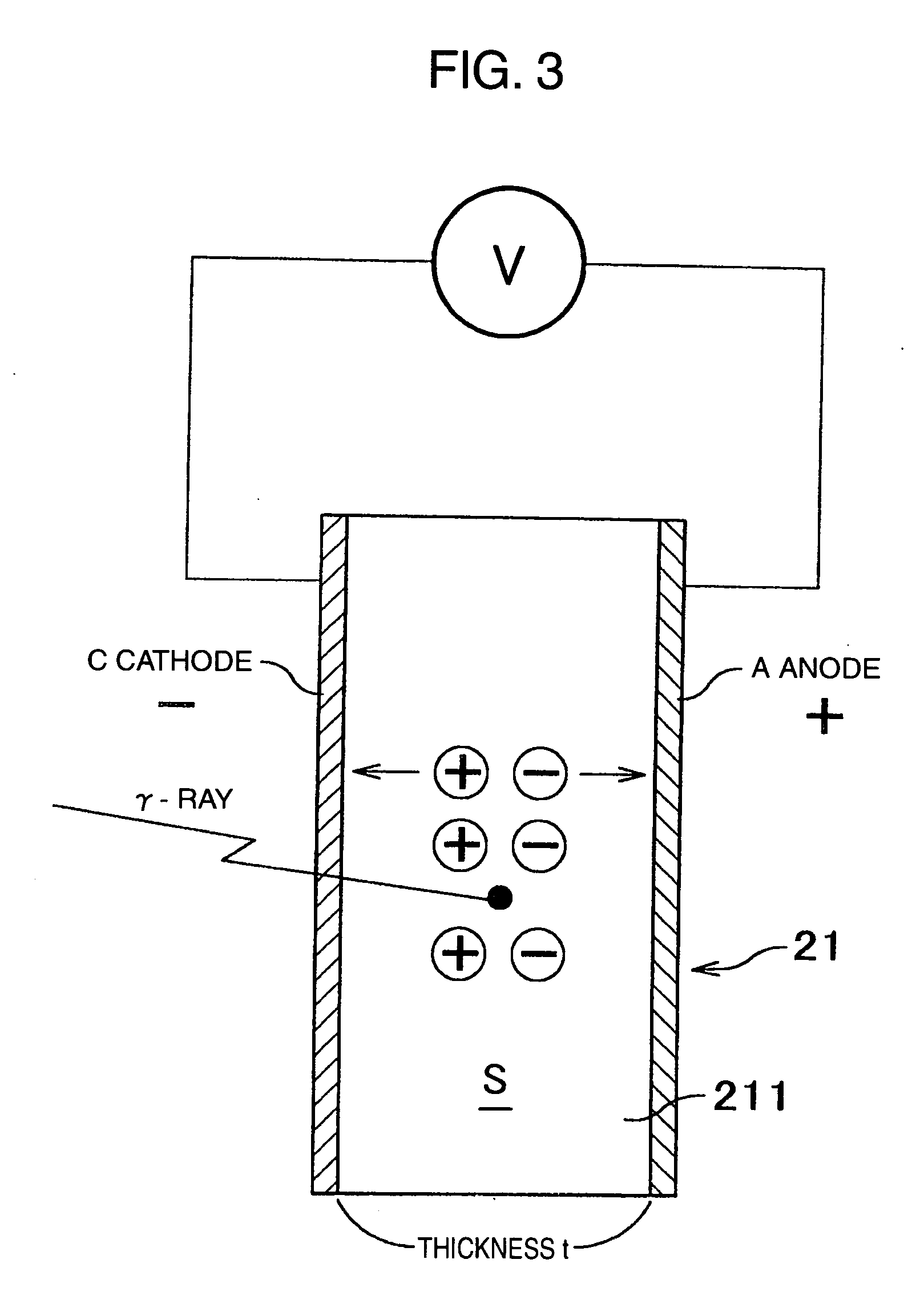
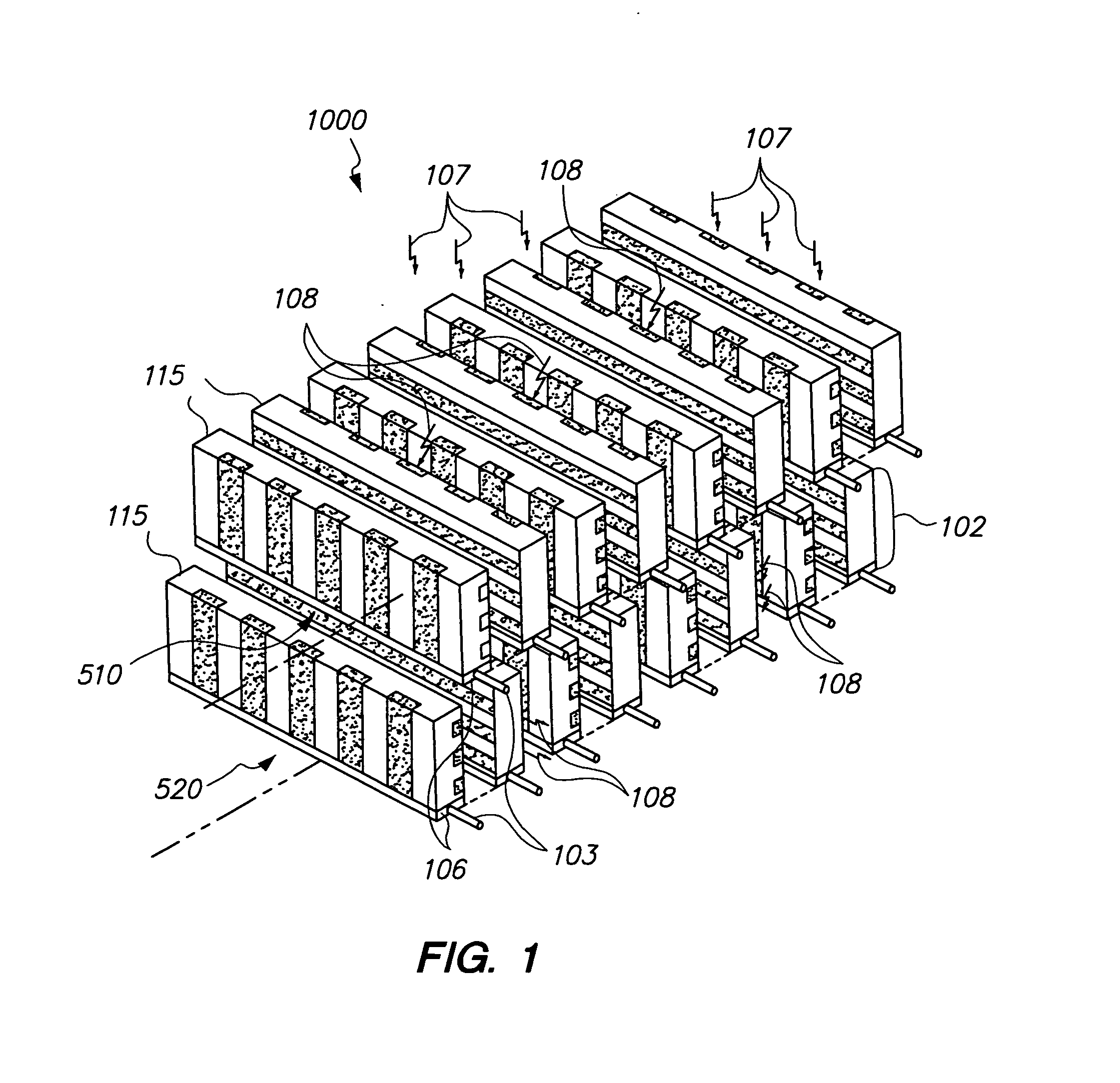
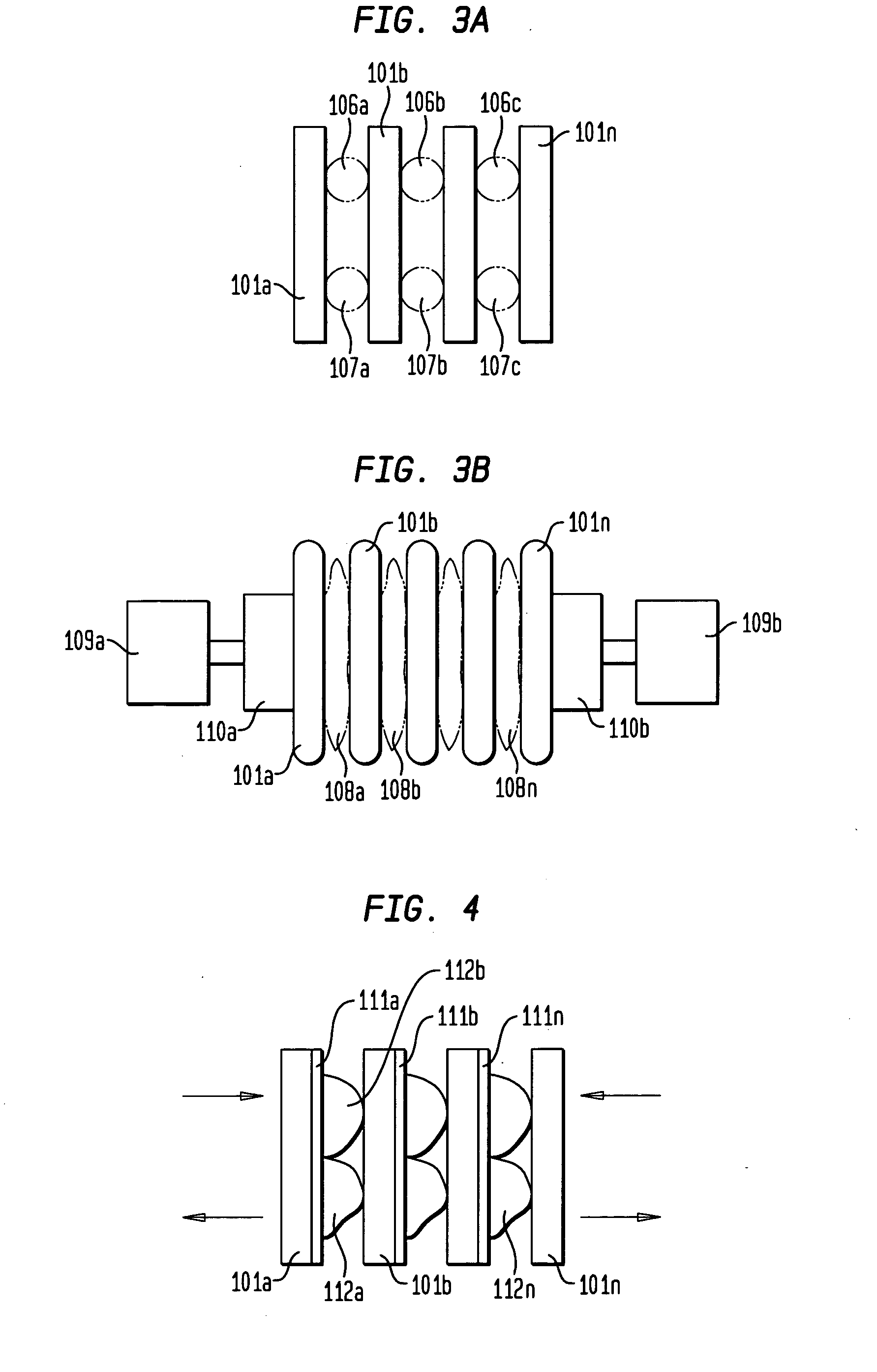
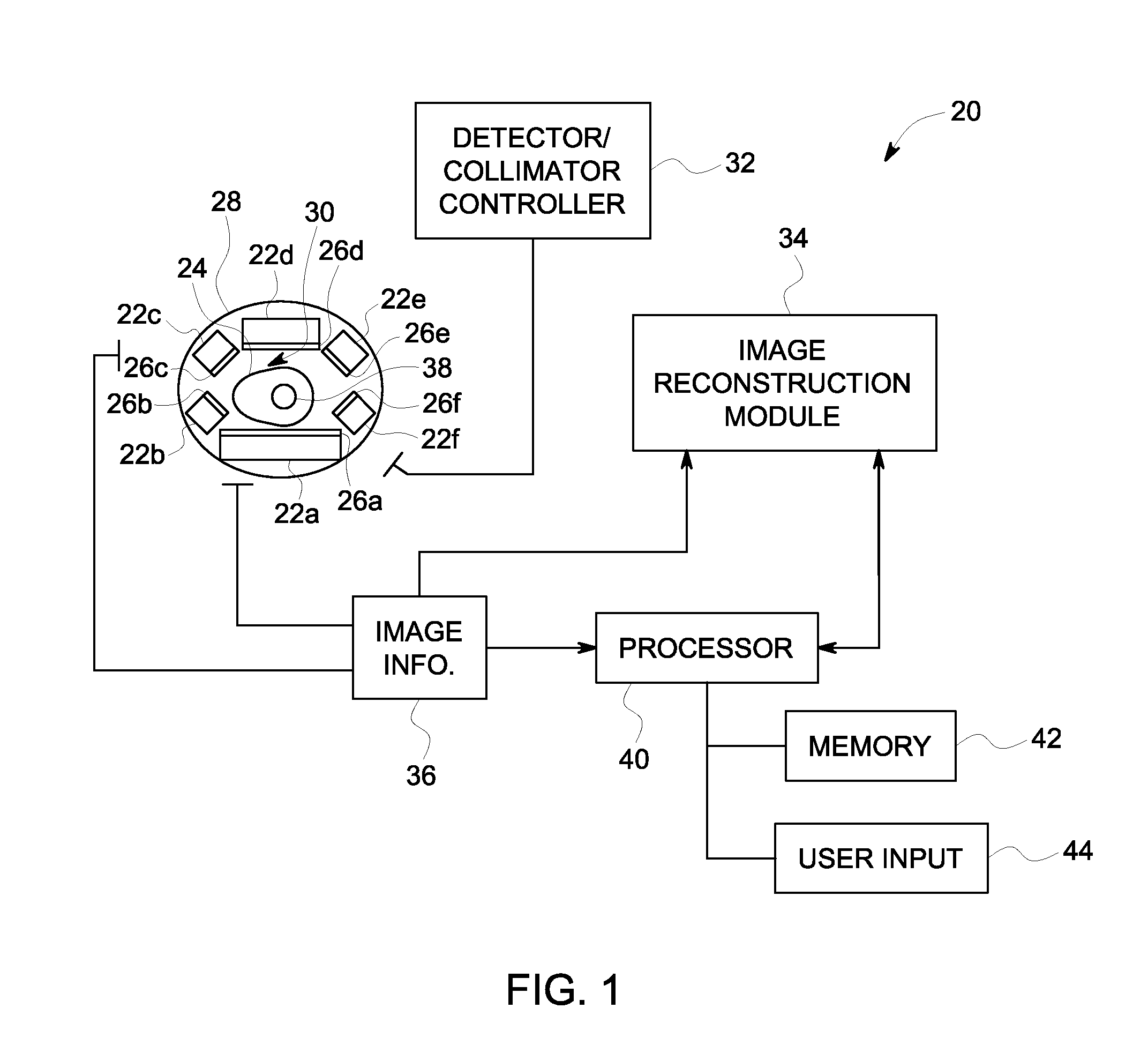
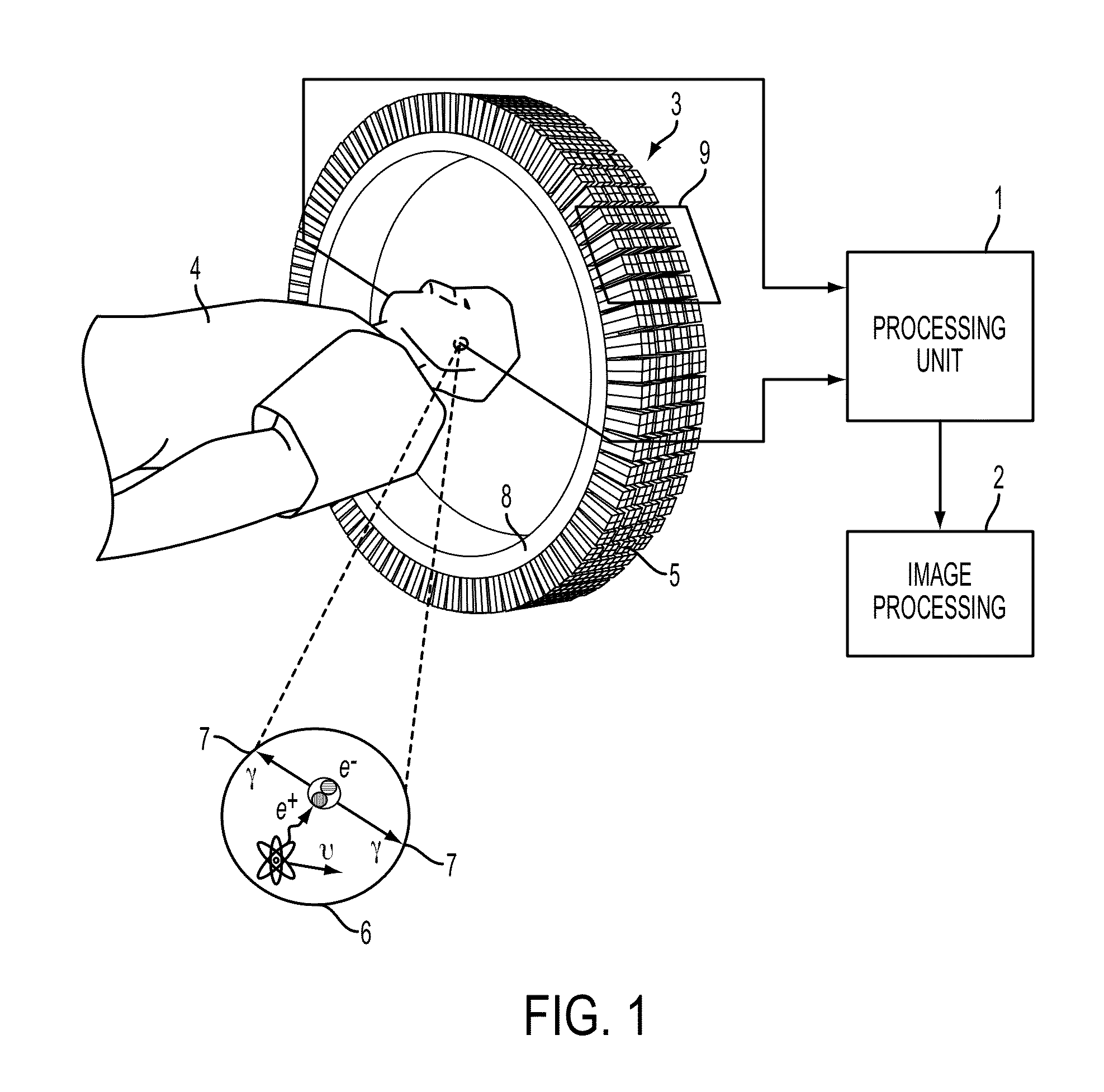
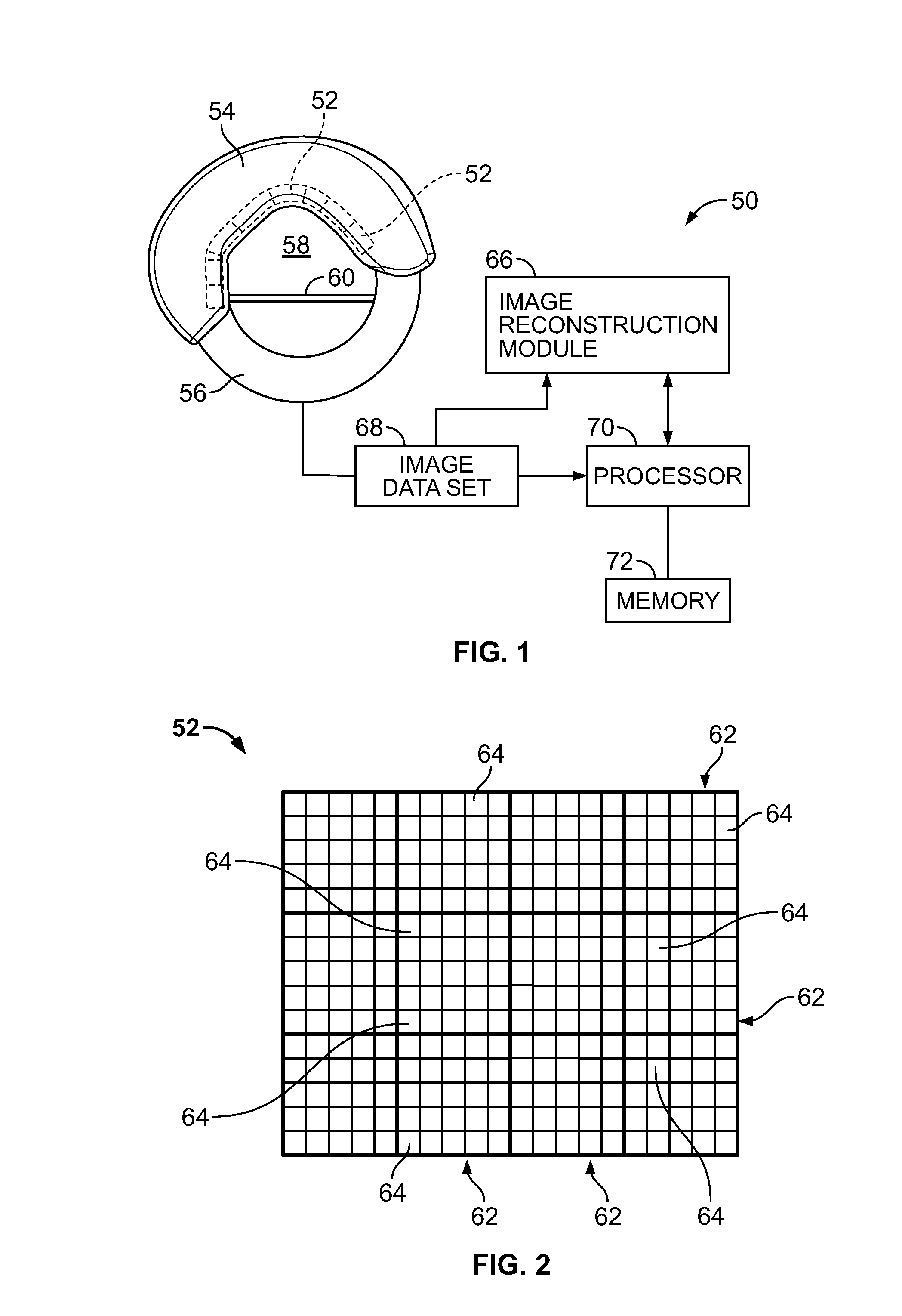
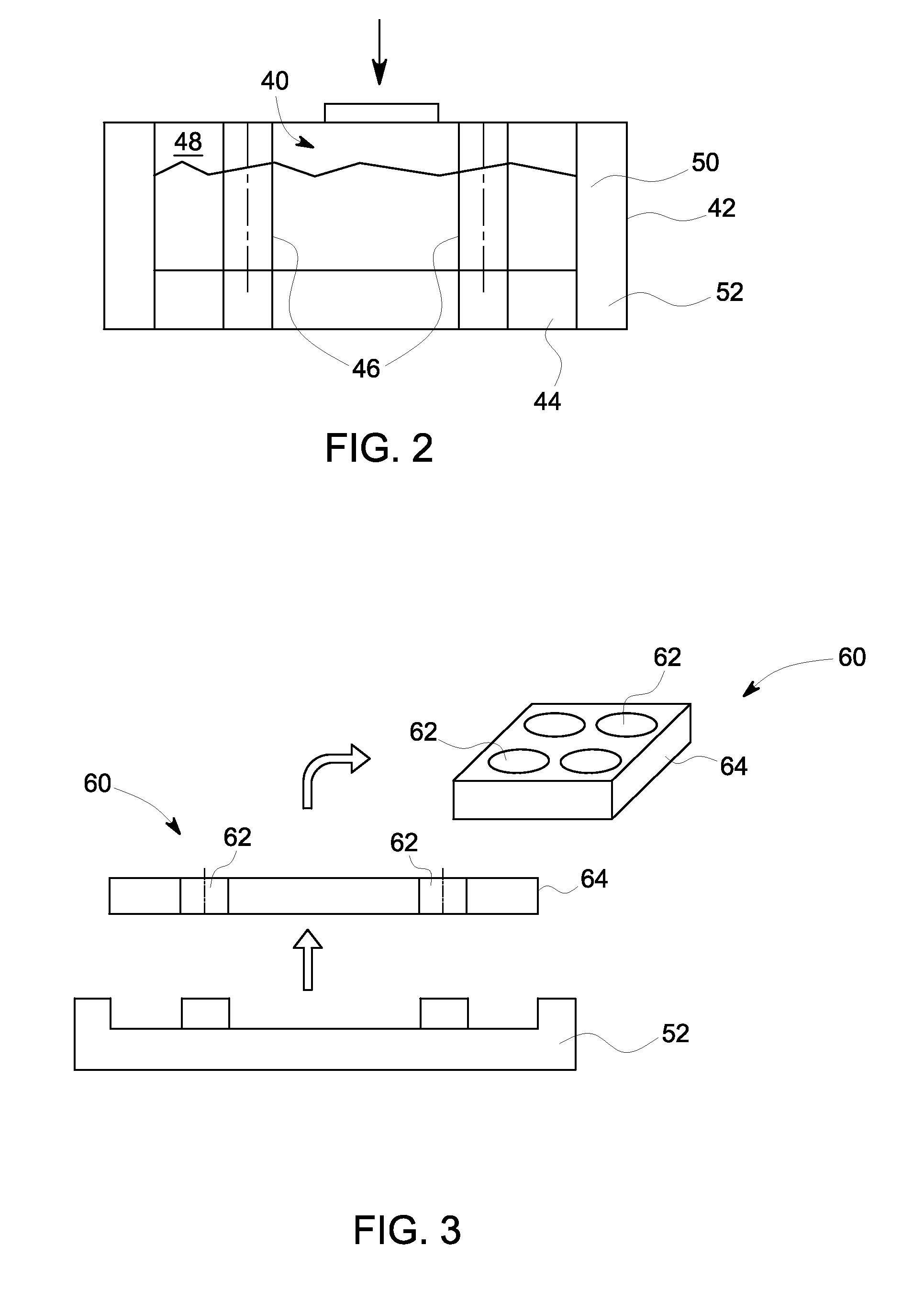
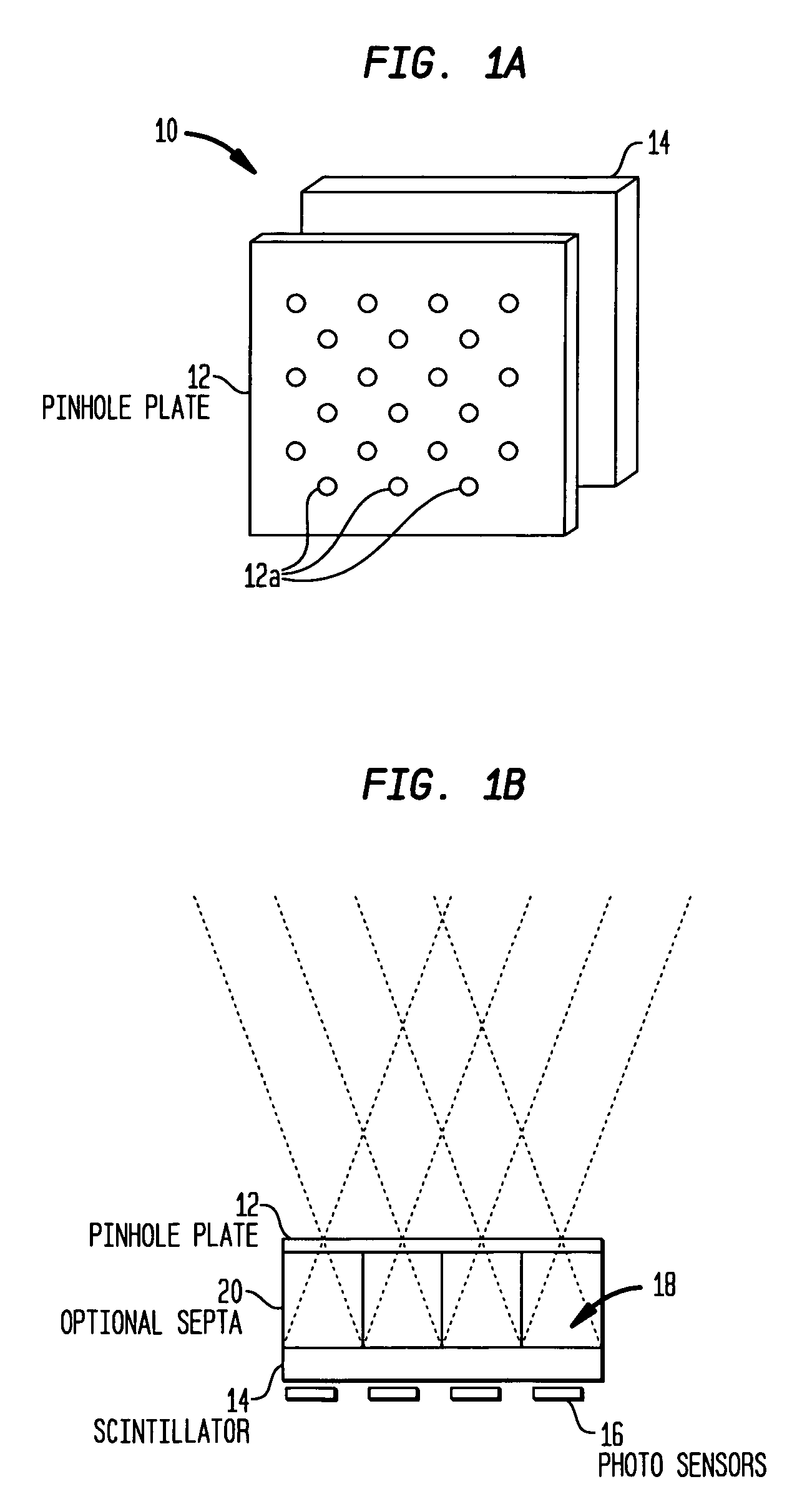
Nuclear medicine imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050067579A1Improve cooling efficiencyImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementSemiconductor radiation detectorsSemiconductor
Semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled to improve accuracy in radiation detection. Semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled by heat conductance through heat conductive boards. In addition, the semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled by cooling medium filled or supplied to a heat insulating body covering the semiconductor radiation detectors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
The invention provides novel Compton camera detector designs and systems for enhanced radiographic imaging with integrated detector systems which incorporate Compton and nuclear medicine imaging, PET imaging and x-ray CT imaging capabilities. Compton camera detector designs employ one or more layers of detector modules comprised of edge-on or face-on detectors or a combination of edge-on and face-on detectors which may employ gas, scintillator, semiconductor, low temperature (such as Ge and superconductor) and structured detectors. Detectors may implement tracking capabilities and may operate in a non-coincidence or coincidence detection mode.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Method for synthesizing labelled compounds
InactiveUS6172207B1Reduce duration and complexityShorten the timeIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCompound aRoom temperature
A process and a device for synthesizing labeled compounds. The process involves preparing a labeling agent, labeling a precursor with the labeling agent, where the precursor is a protected substrate, and deprotecting the labeled precursor to convert the labeled precursor to a labeled compound by passing the labeled precursor through a solid support in a column or a cartridge. The process may be used to convert labeled tetraacetylfluoroglucose (TAFg) to labeled fluoro-deoxy-glucose (FDG) for use in nuclear medical imaging. The process is more rapid than conventional methods and is performed at room temperature rather than high temperature for conventional technology.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +2
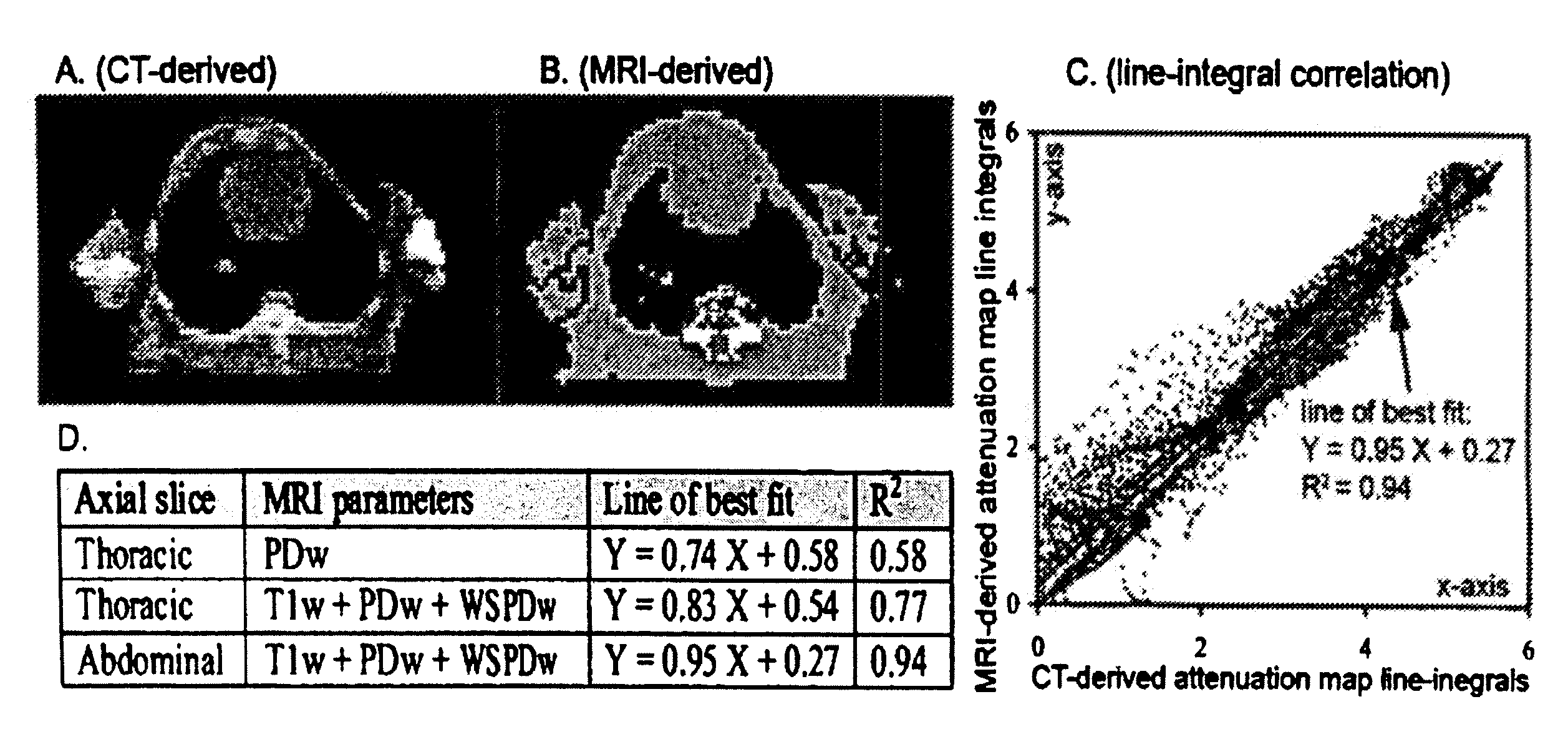
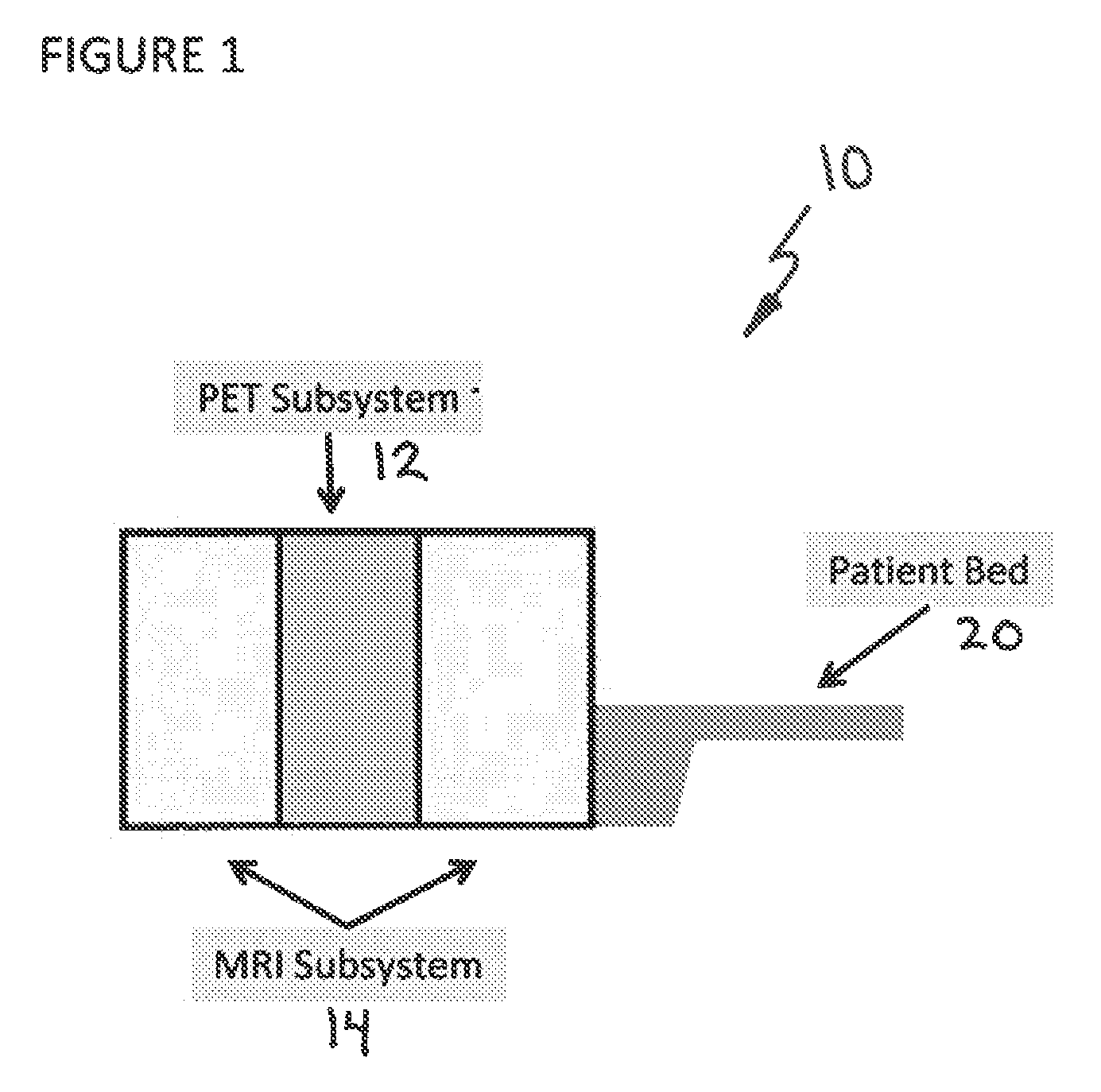
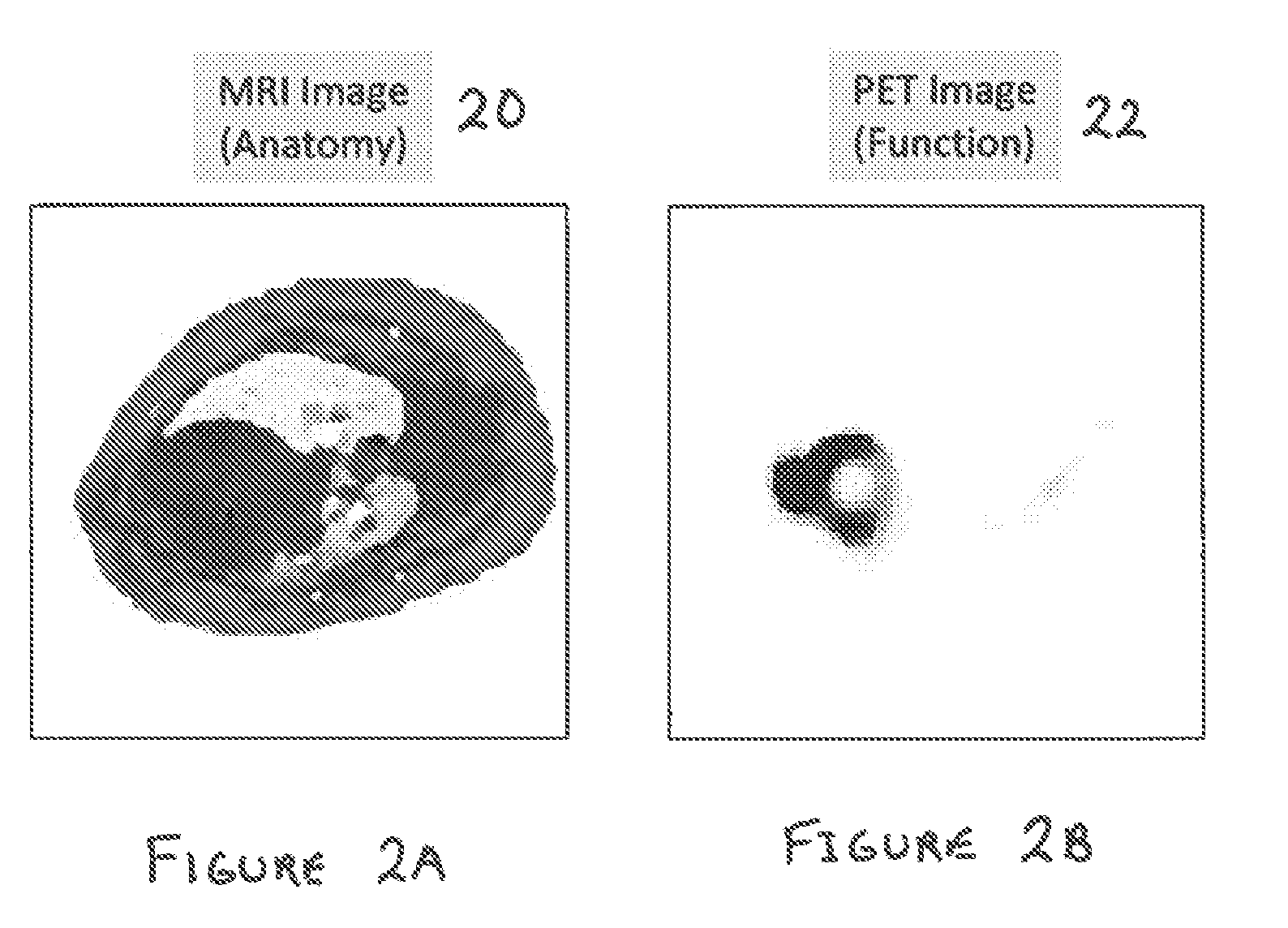
System and method for correcting attenuation in hybrid medical imaging
ActiveUS20100204563A1Facilitating non-uniform attenuation correctionImage analysisMagnetic measurementsUltrasound attenuationMedical imaging
A hybrid medical imaging system comprises a nuclear medicine imaging subsystem for capturing an image of a target region of a subject, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) subsystem for capturing an MRI image of the target region based on at least one MRI parameter and processing structure communicating with the subsystems. The processing structure processes the MRI image to estimate attenuation within the target region and uses the estimated attenuation to correct the image captured by the nuclear medicine imaging subsystem.
Owner:LAWSON HEALTH RES INST
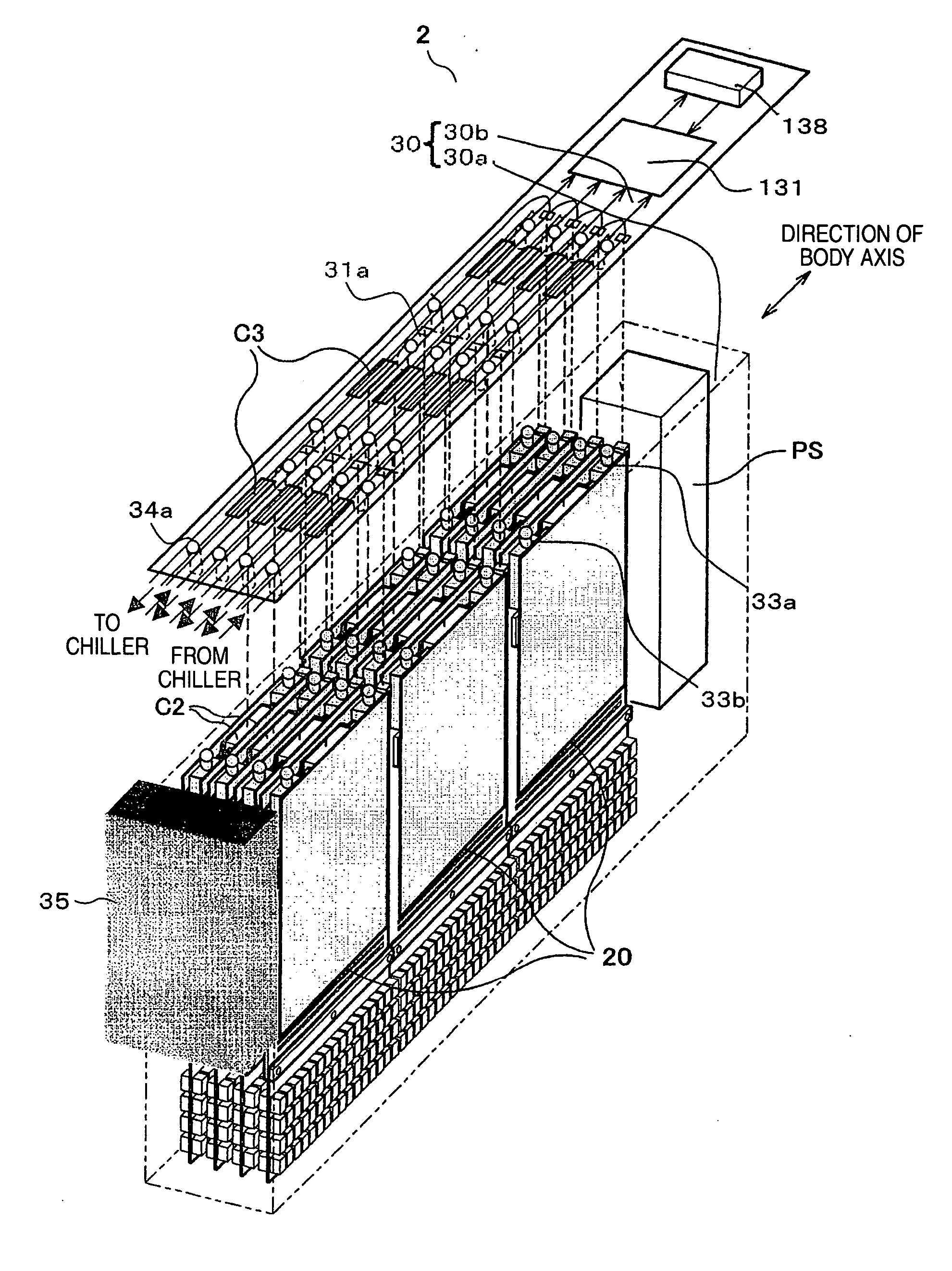
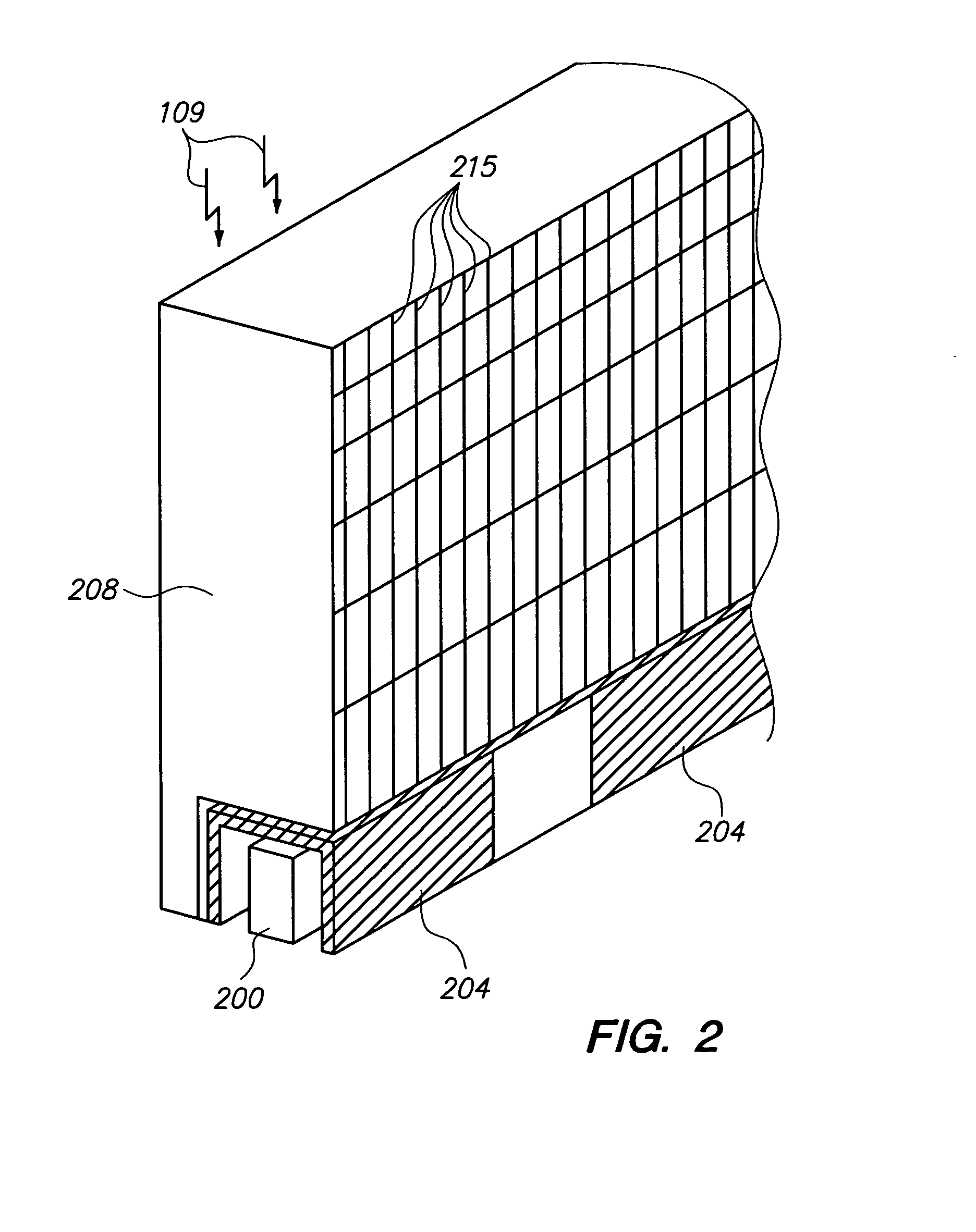
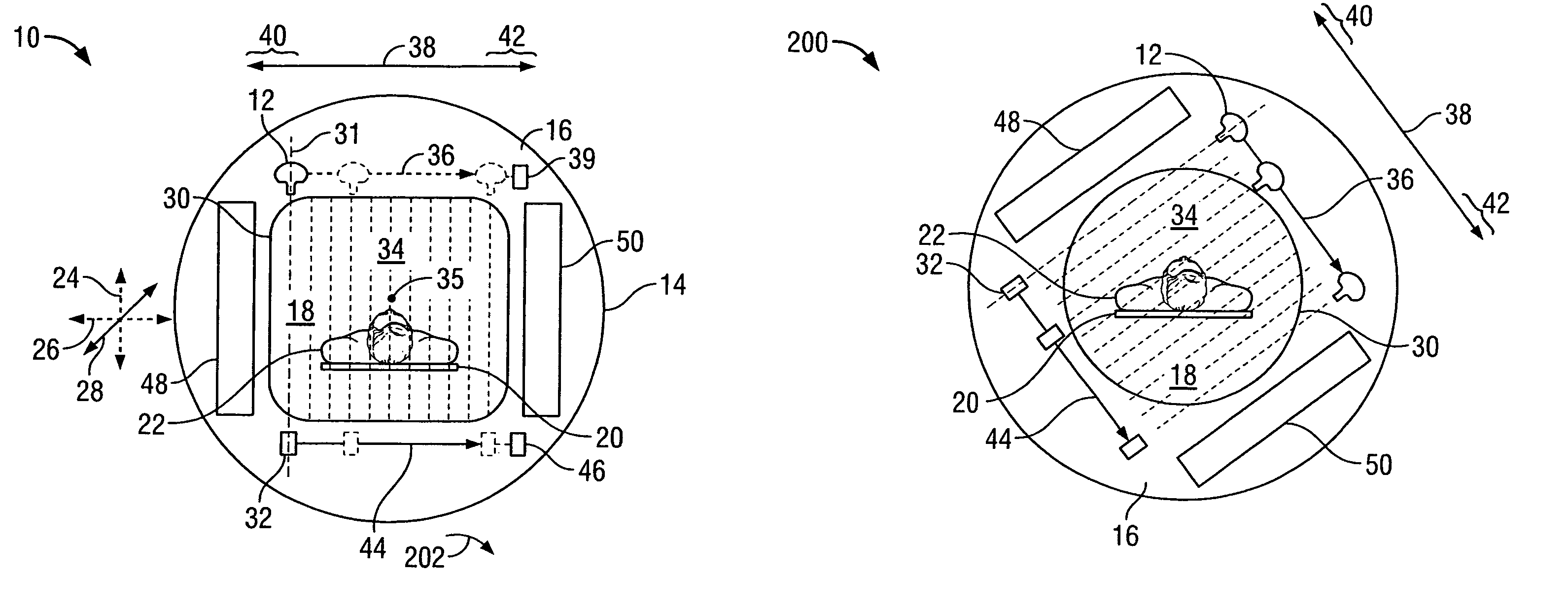
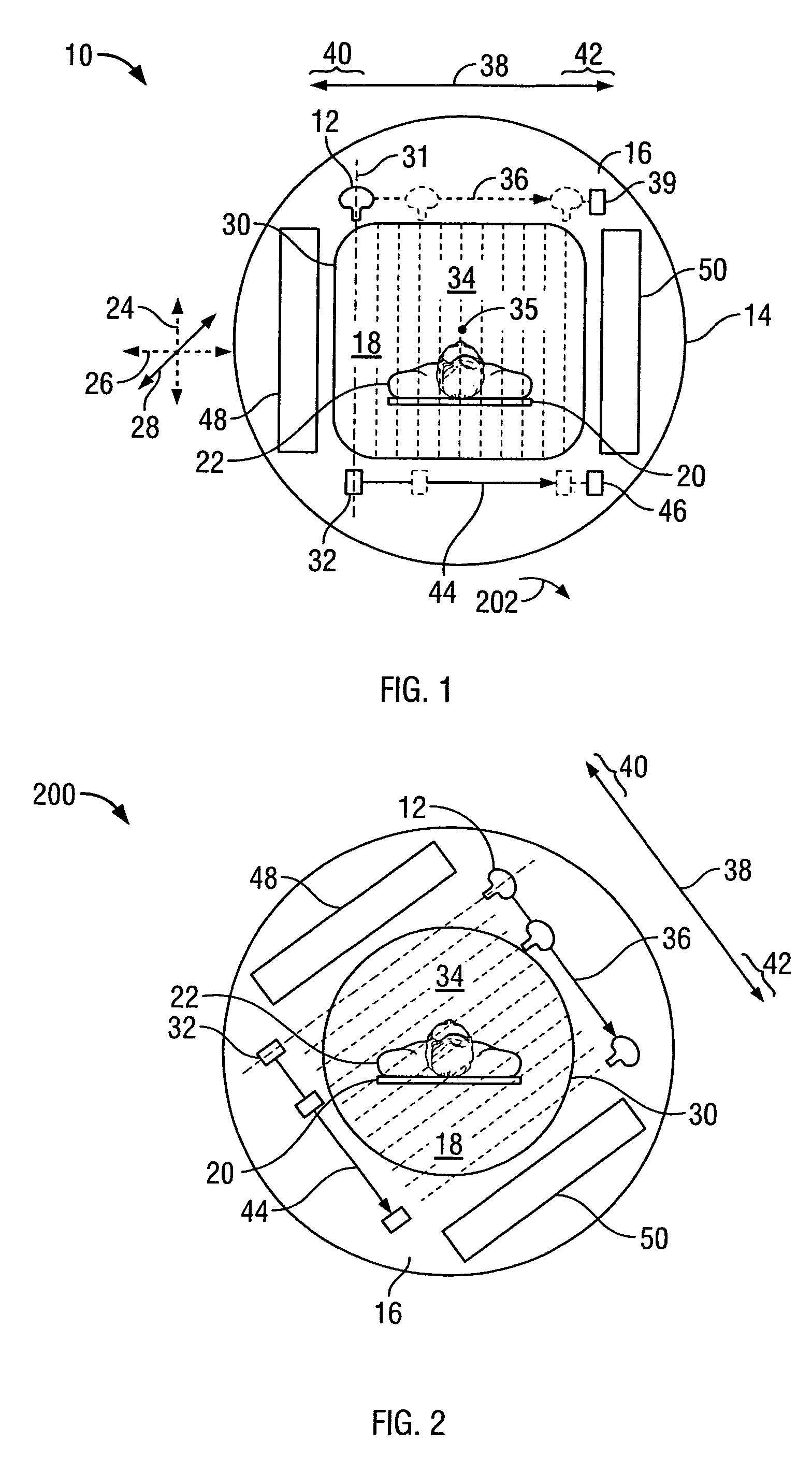
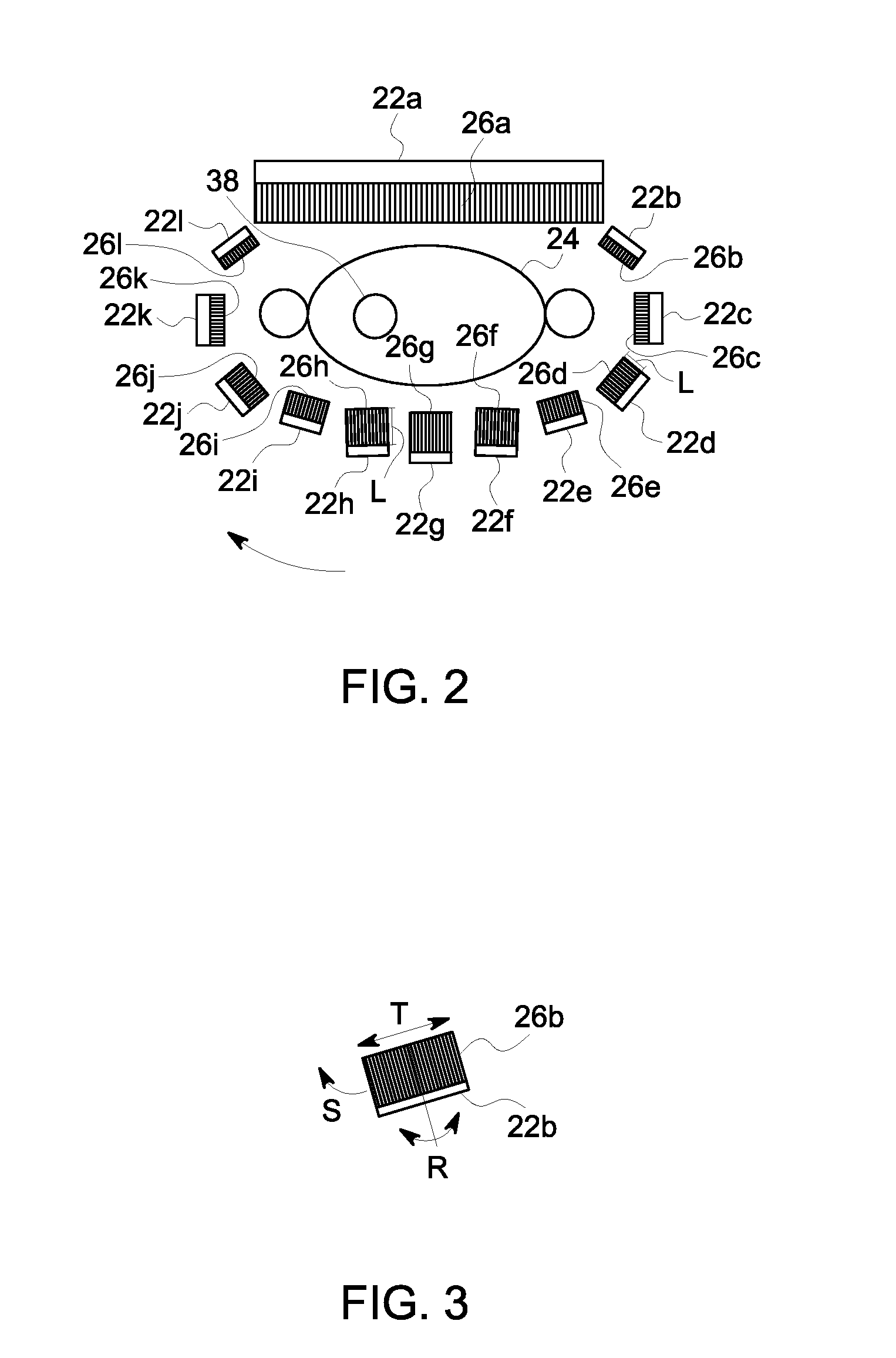
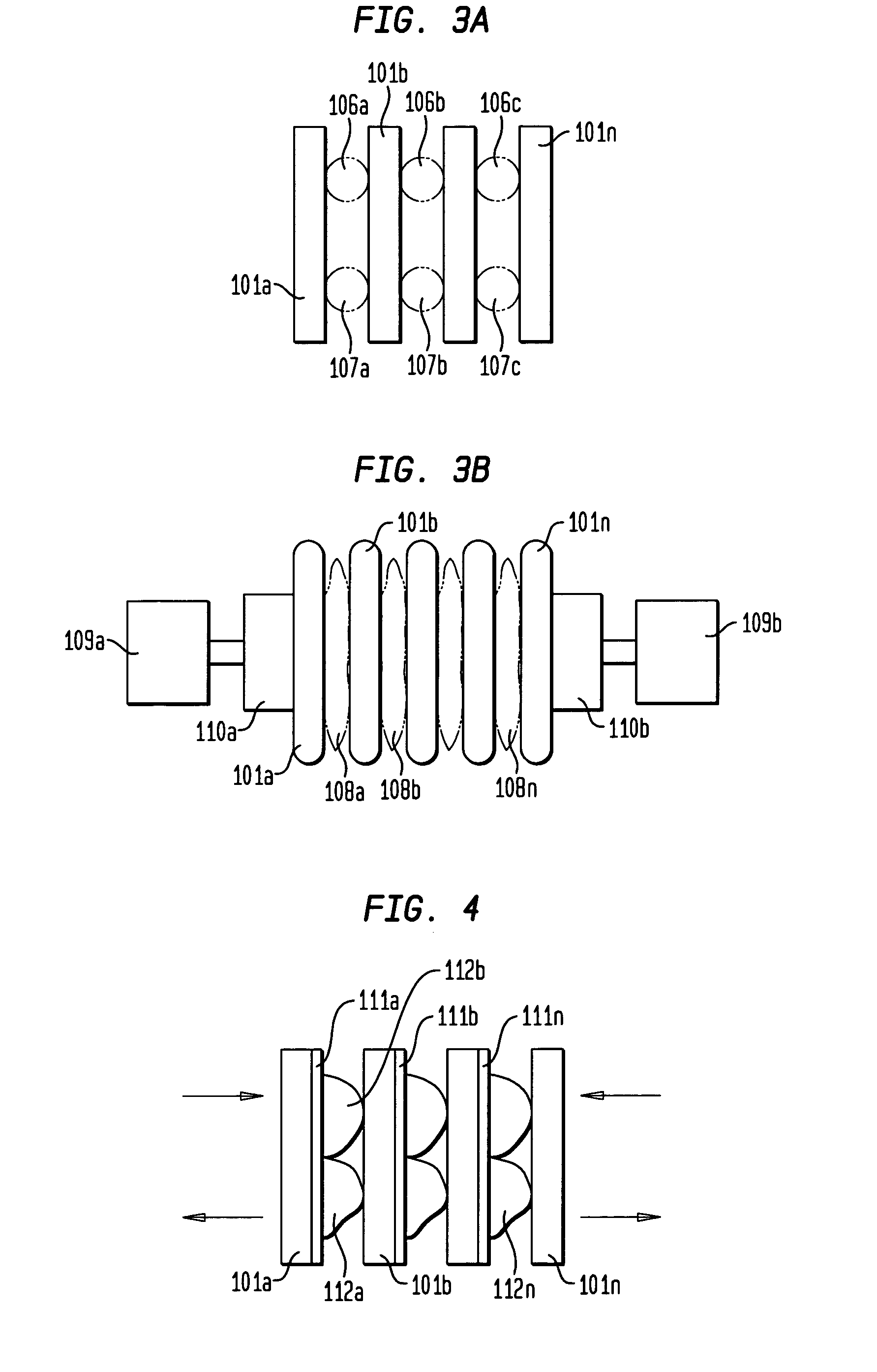
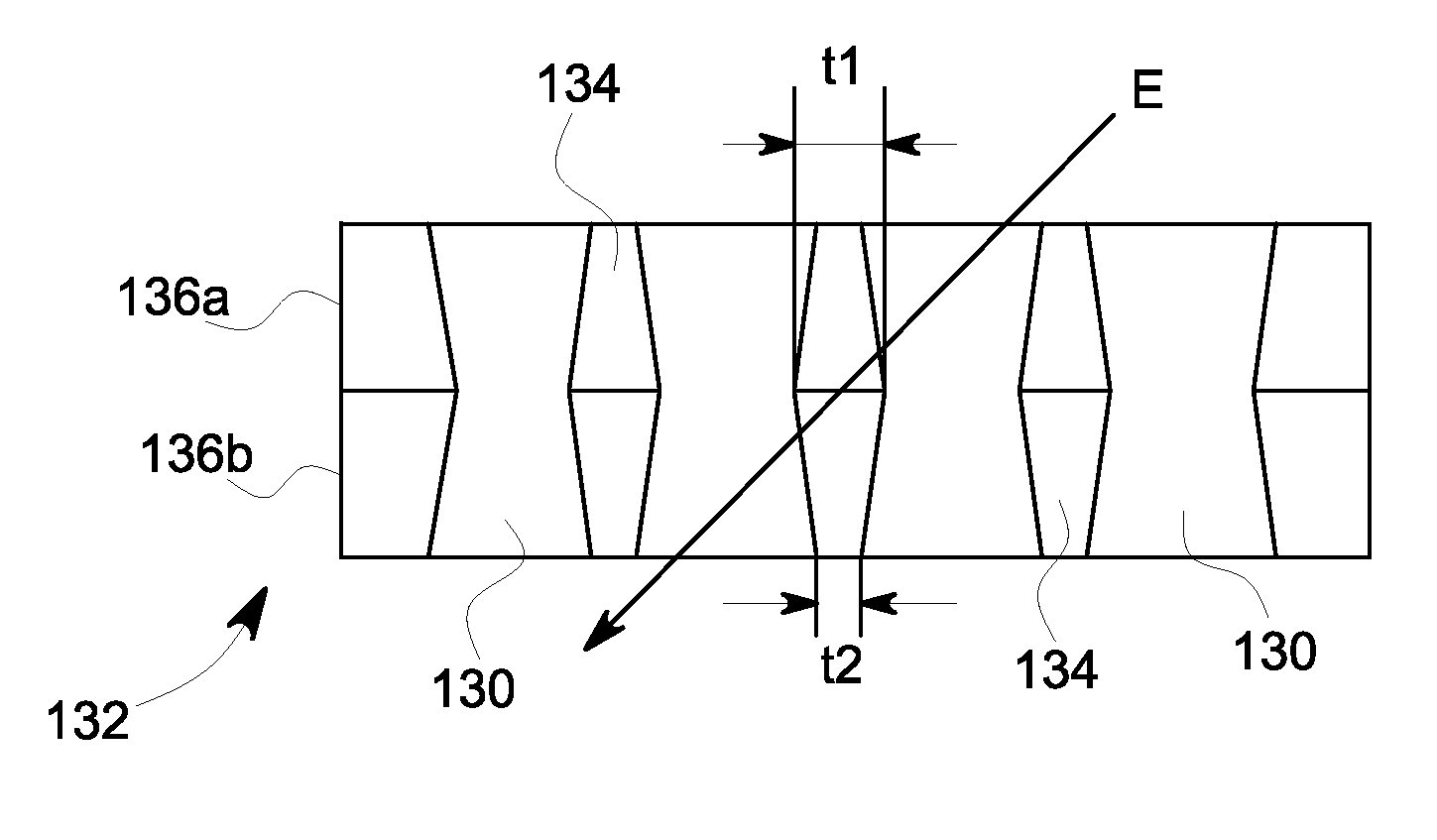
Collimator with variable focusing and direction of view for nuclear medicine imaging
ActiveUS20060145081A1Enhance the imageHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation attenuationNuclear medicine imaging
According to the present invention, a novel slat collimator for use in nuclear medicine imaging is provided. The slat collimator comprises a first layer comprising a plurality of spaced apart elongated slats and a second layer comprising a plurality of spaced apart elongated slats. The slats of the second layer are positioned orthogonally with respect to the slats of the first layer. The slats are constructed of a radiation attenuation material and the spaces between the slats may be non-variable or variable.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods and systems for multi-modality imaging
InactiveUS6956925B1Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputed tomography
A method of examining a patient is provided. The method includes imaging a patient utilizing a computed tomography imaging modality, the patient between the pencil-beam x-ray source and the x-ray detector, and imaging the patient between the pencil-beam x-ray source and the x-ray detector using a nuclear medicine imaging modality.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
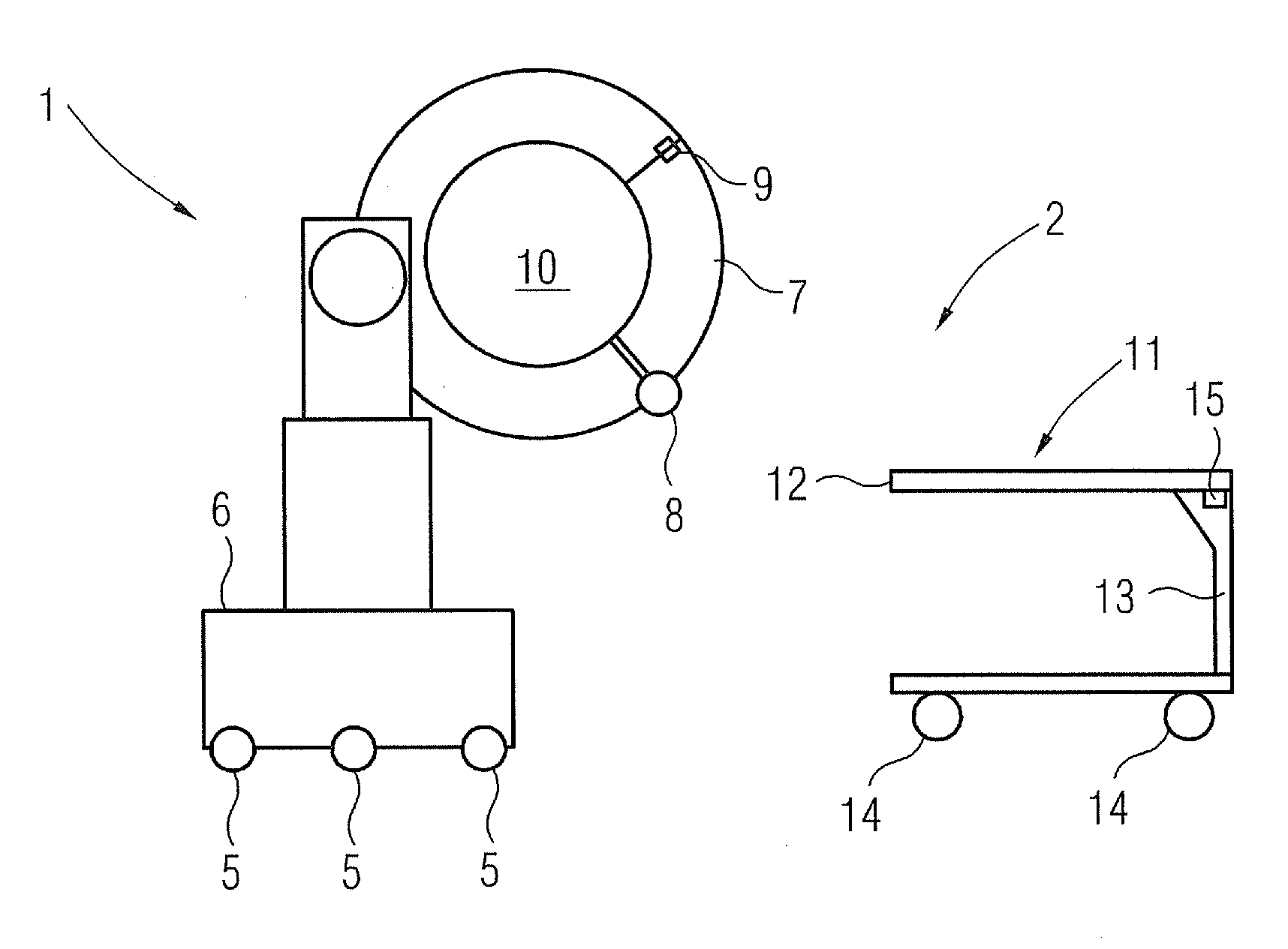
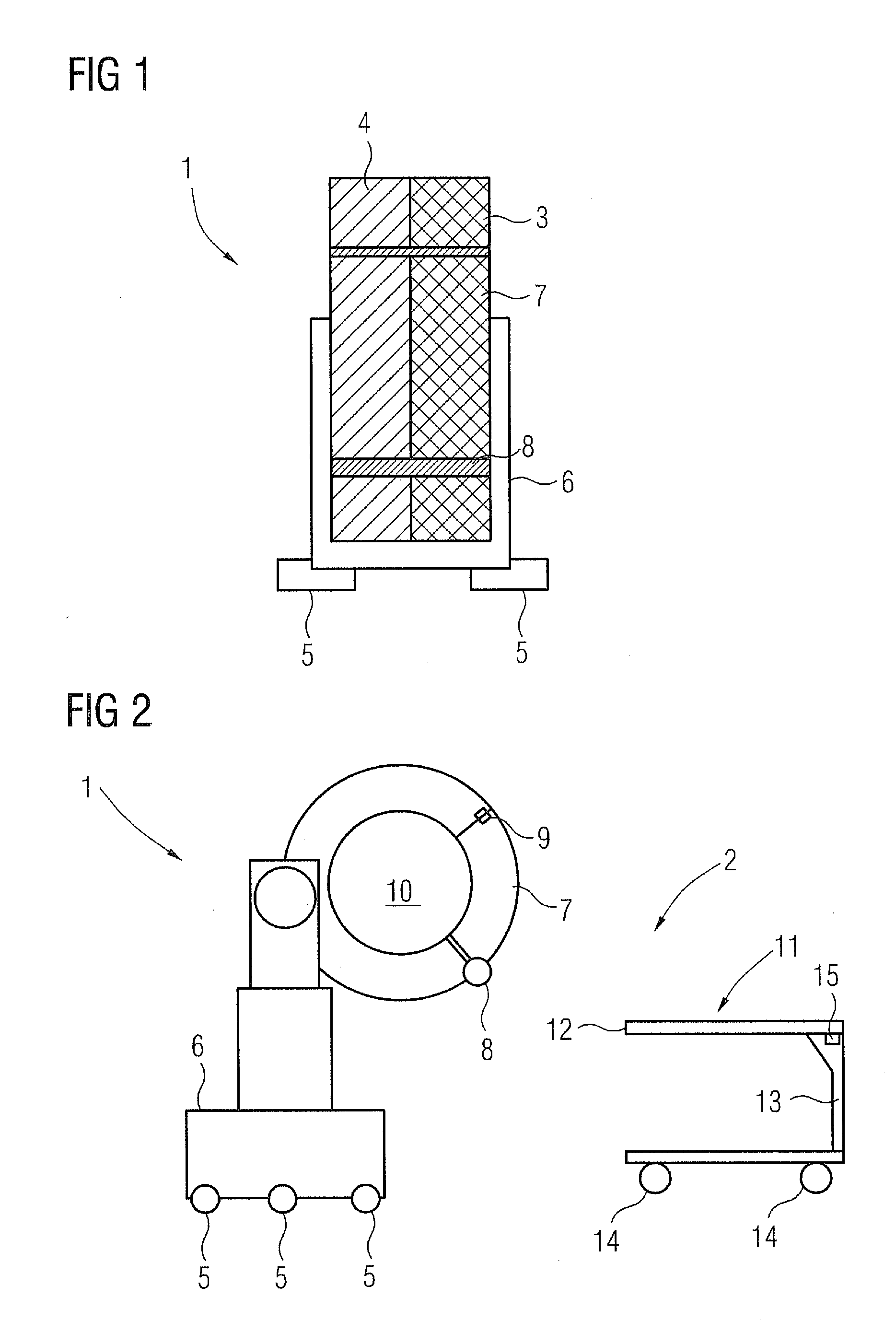
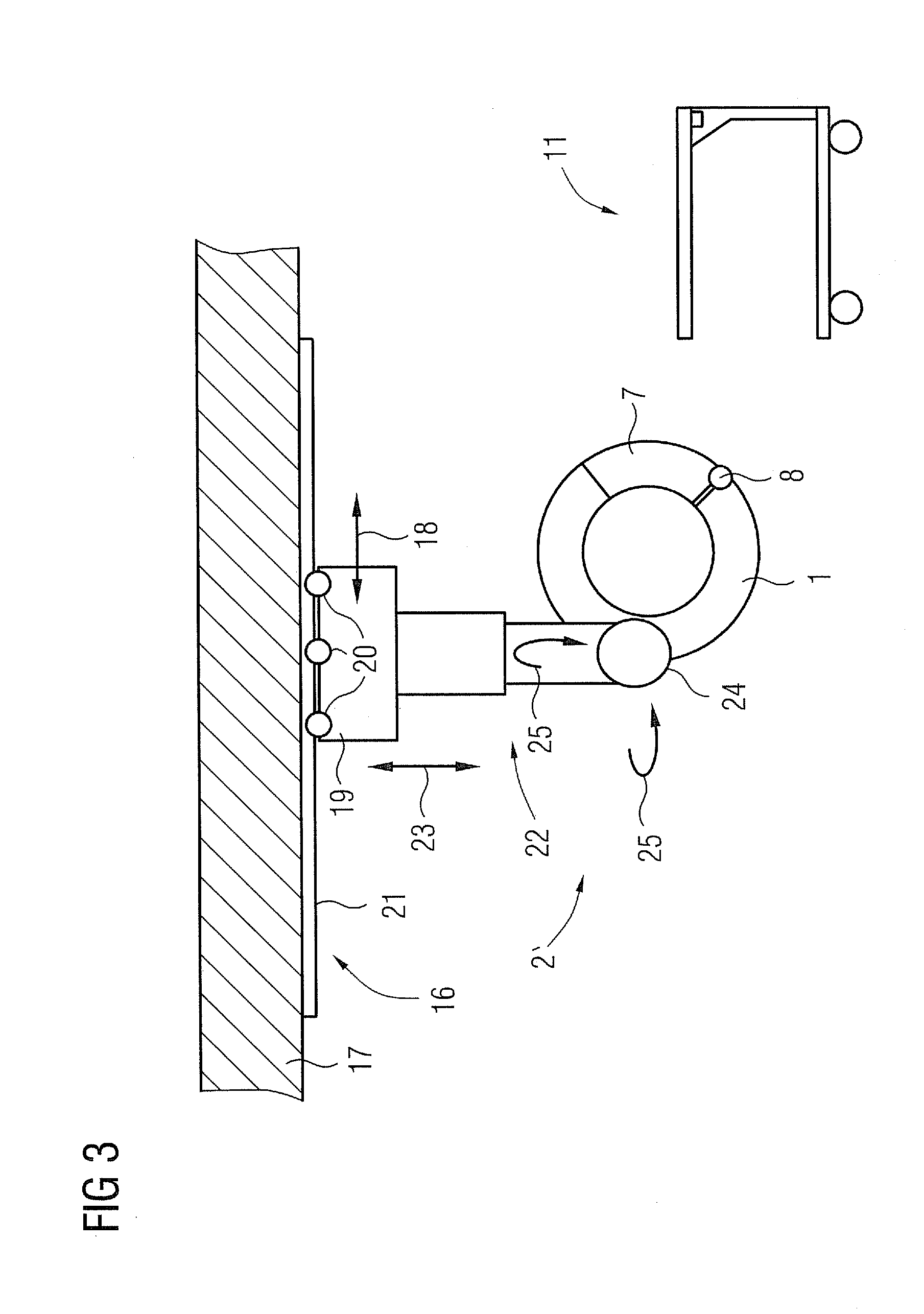
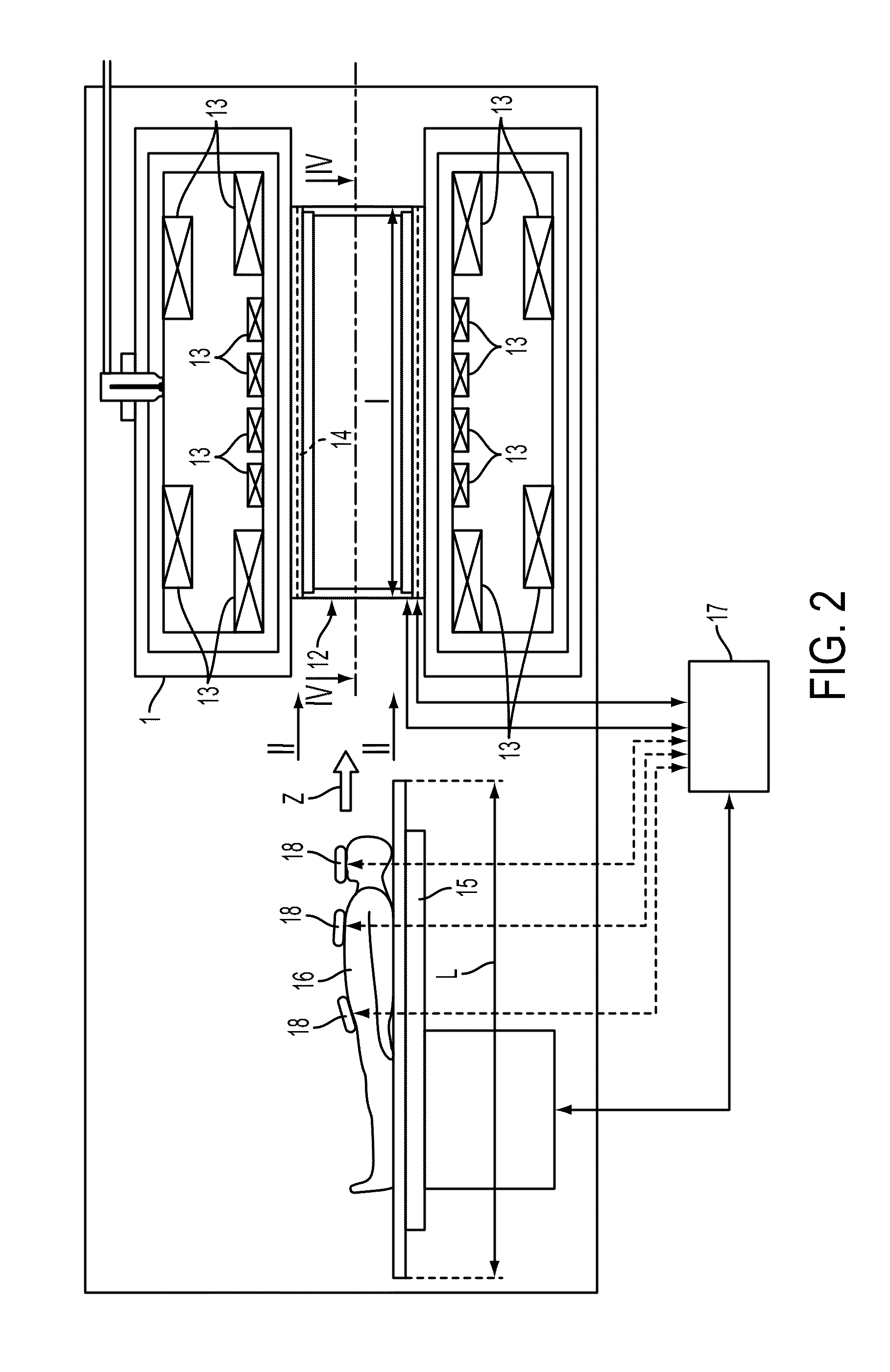
Medical examination device for CT imaging and for nuclear medical imaging
InactiveUS20110280364A1Enhance the imageSharp contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedical imagingCt imaging
A medical examination device for CT imaging and for nuclear medical imaging is provided. The medical examination device has an essentially ring-shaped gantry with a CT imaging arrangement and a nuclear medical imaging arrangement. The gantry has an especially laterally arranged, fold-out or removable segment for creating an access opening to the interior of the gantry.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Nuclear medicine imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors
ActiveUS20120248320A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyHelical computed tomographyNuclear medicine imaging
A Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors are provided. One NM imaging system includes a gantry, at least a first imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the first imaging detector is a non-moving detector, and at least a second imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the second imaging detector is a moving detector. The first imaging detector is larger than the second imaging detector and the first and second imaging detectors have different detector configurations. The NM imaging system further includes a controller configured to control the operation of the first and second imaging detectors during an imaging scan of an object to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information such that at least the first imaging detector remains stationary with respect to the gantry during image acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
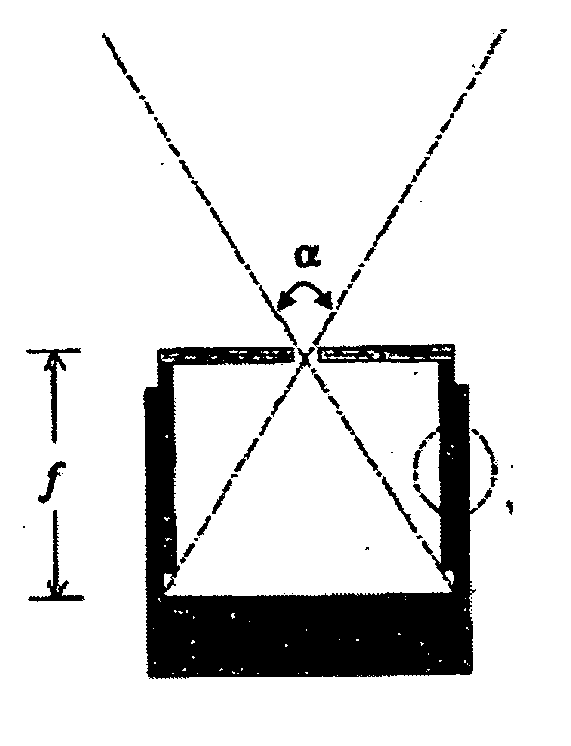
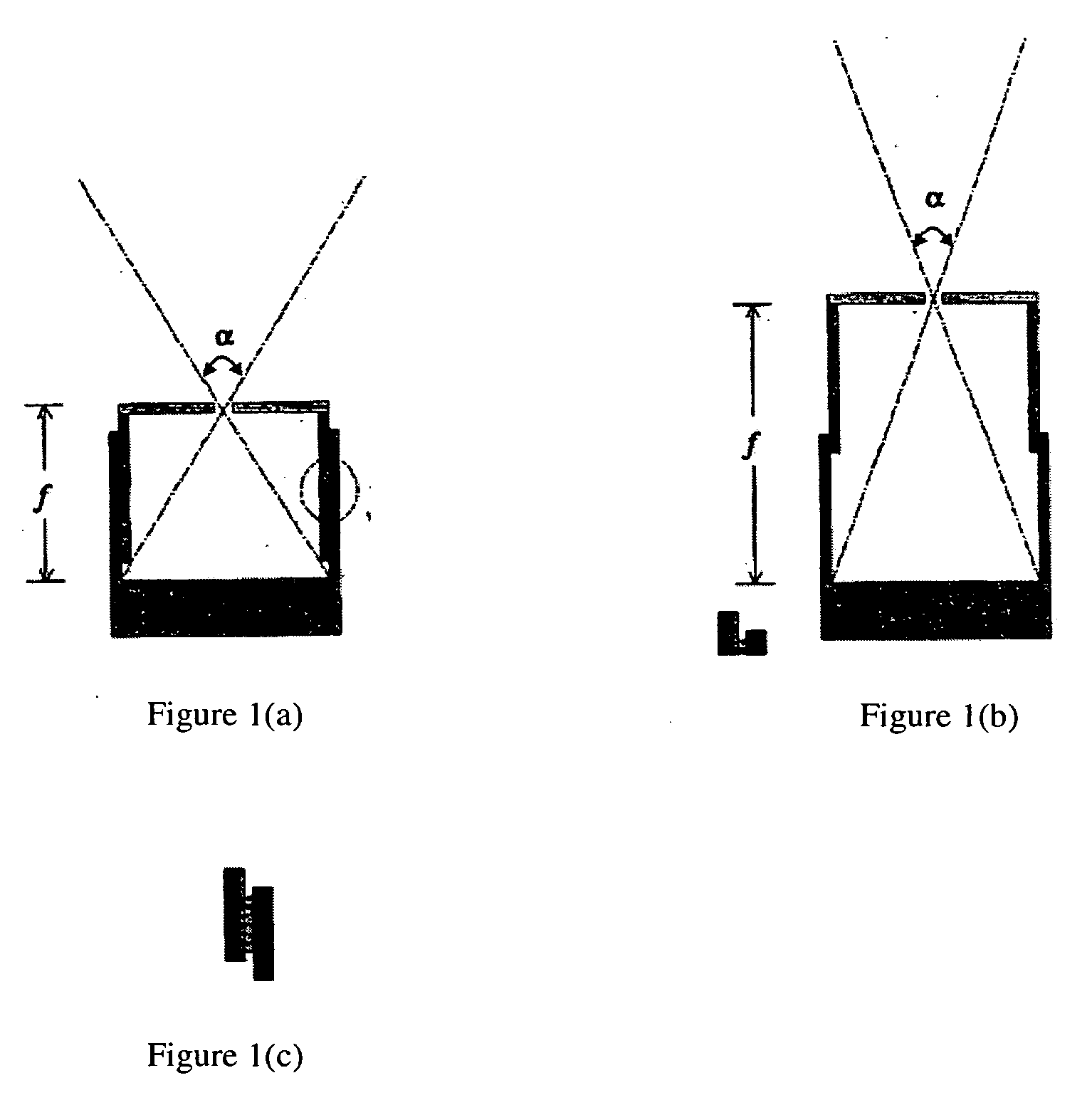
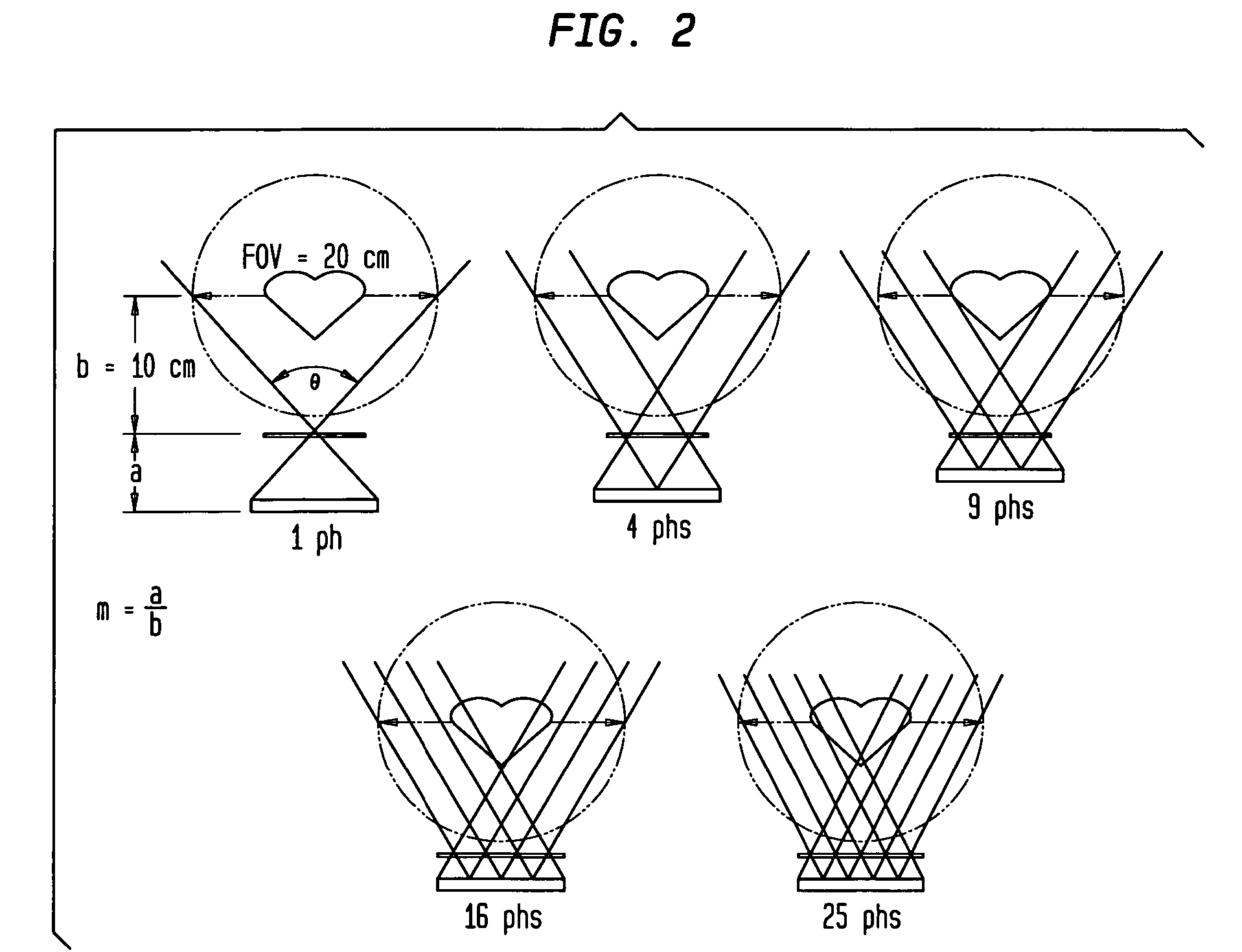
Adjustable focal length pinhole collimator
ActiveUS20070221853A1Eliminates and least minimizes needMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImage resolutionHand held
A pinhole collimator is provided that eliminates or at least minimizes the need for collimator exchange, to manage system sensitivity versus spatial resolution tradeoff, and to control imaging FOV (field of view) depending on object size by controlling the focal length of the collimator. There is also provided a detector system is that includes a detector, a collimator, and means for changing the focal length. Various means for changing the focal length are also identified. The collimator can have a plurality of apertures in a top plate, each aperture with its own collimator septa. Additionally, there is provided a medical imaging system that includes the detector system and collimator of the present invention. The nuclear medical imaging systems can have a hand-held detector assembly and be portable.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Nuclear medical imaging device
InactiveUS20060050845A1Accurate correctionExtension of timeVolume/mass flow measurementHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayGamma imaging
An apparatus for imaging a field of view, according to an embodiment of the present invention, comprises an x-ray source positioned adjacent to the field of view, a source mask located between the x-ray source and the field of view having at least one source aperture defined therethrough, and an emission detector, such as a gamma camera, adjacent to the field of view. The apparatus may allow substantially concurrent x-ray imaging and gamma imaging of the field of view.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Methods and systems for multi-modality imaging
InactiveUS20050213705A1Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsComputed tomographyImaging modalities
A method of examining a patient is provided. The method includes imaging a patient utilizing a computed tomography imaging modality, the patient between the pencil-beam x-ray source and the x-ray detector, and imaging the patient between the pencil-beam x-ray source and the x-ray detector using a nuclear medicine imaging modality.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
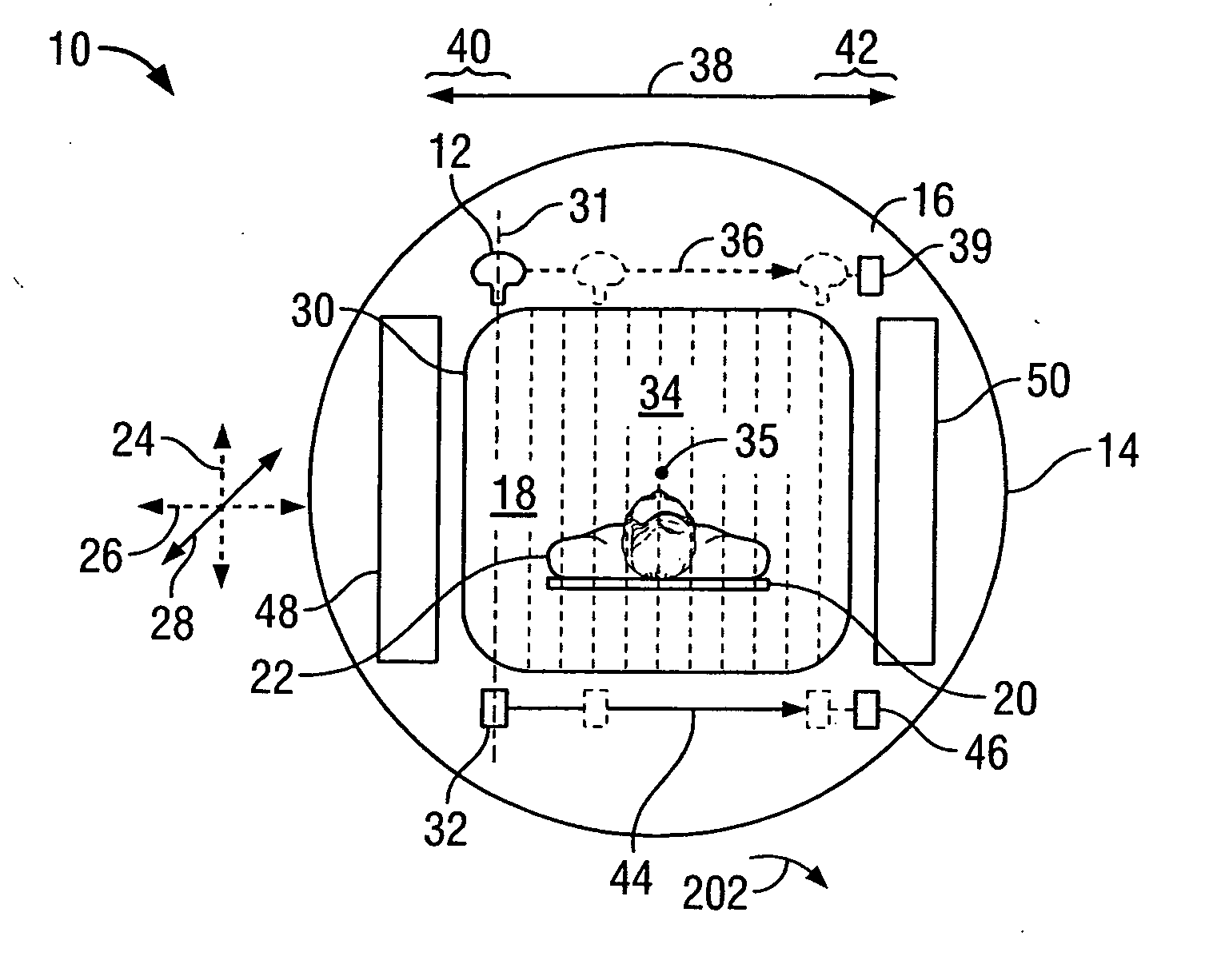
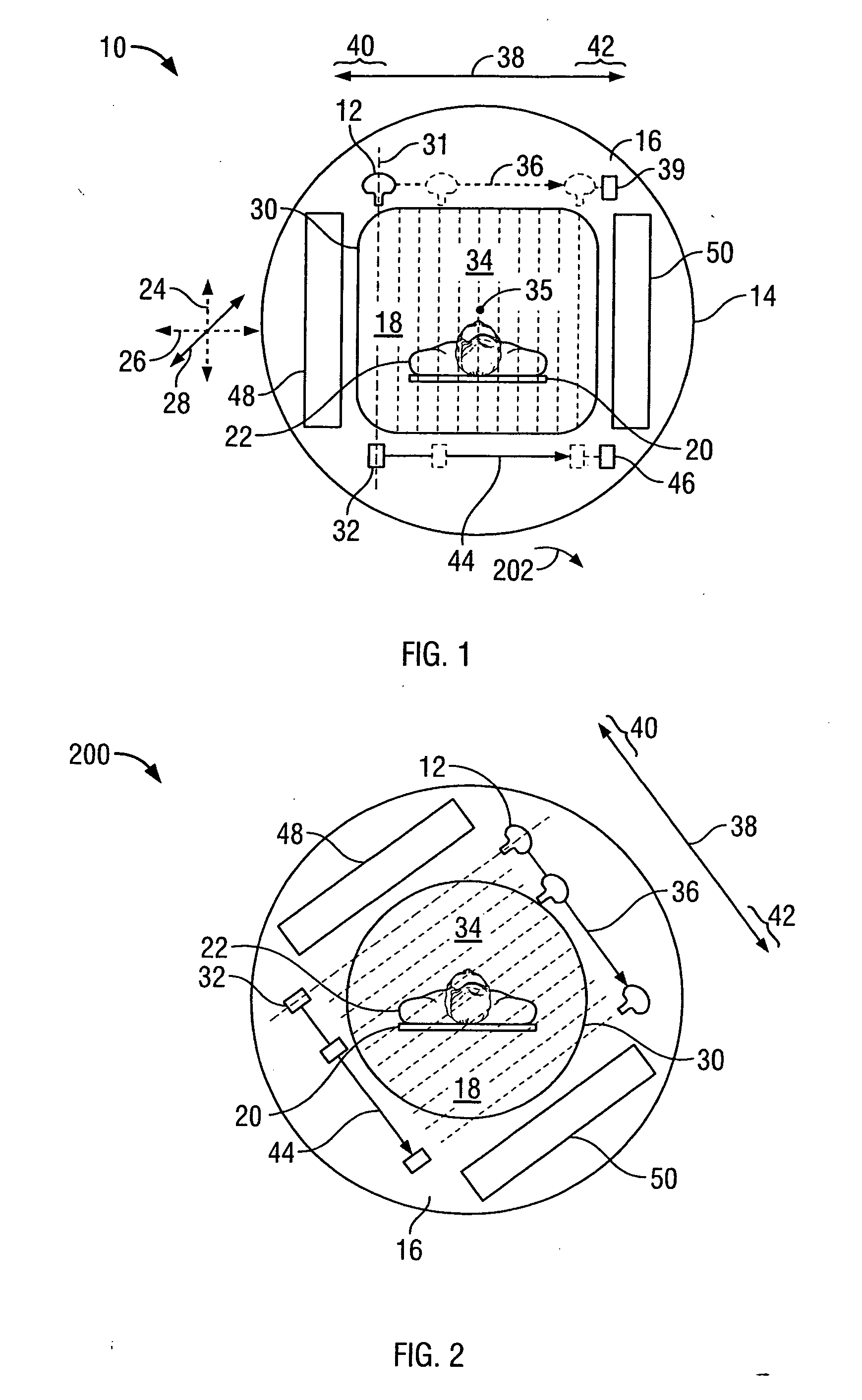
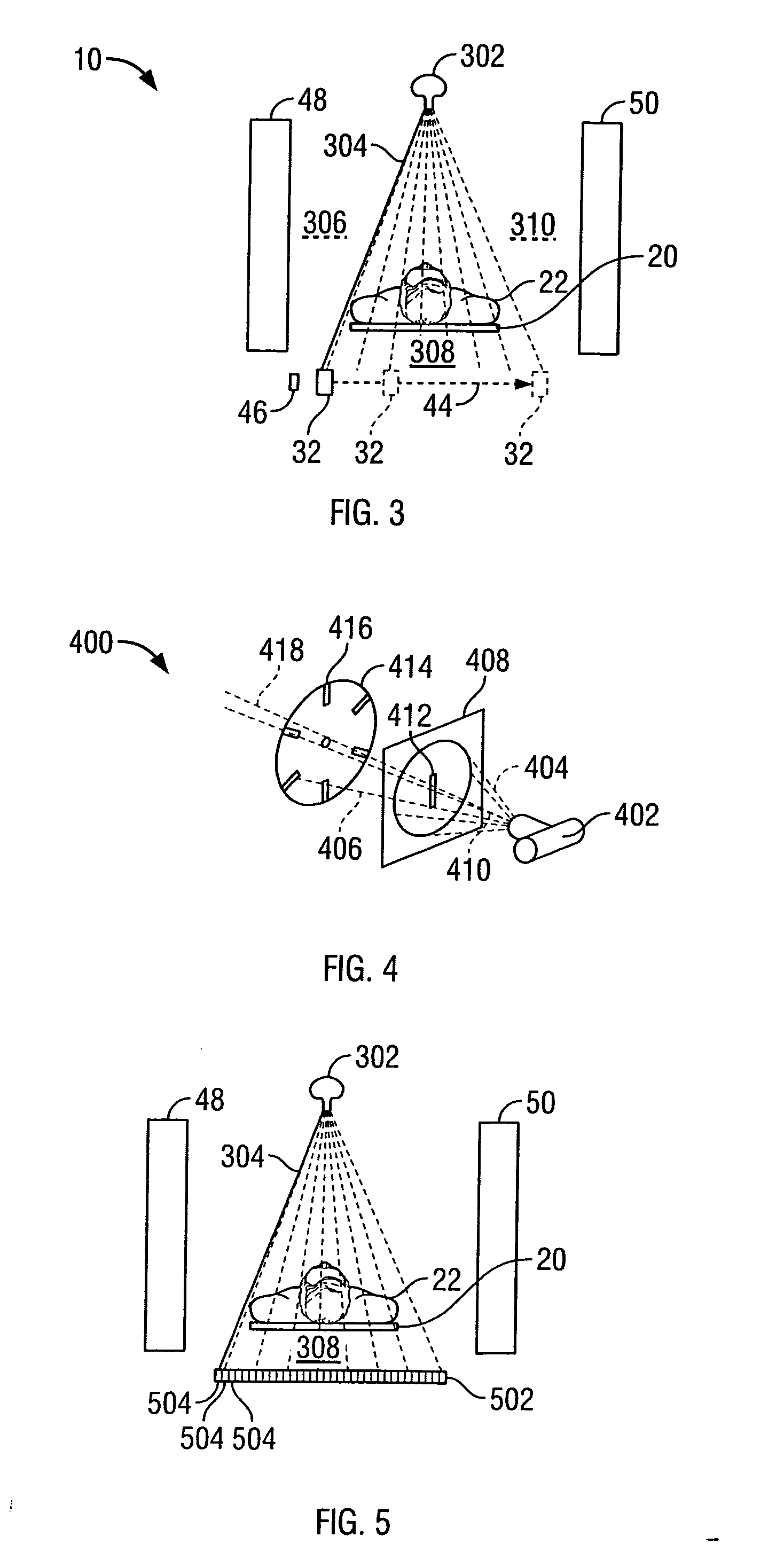
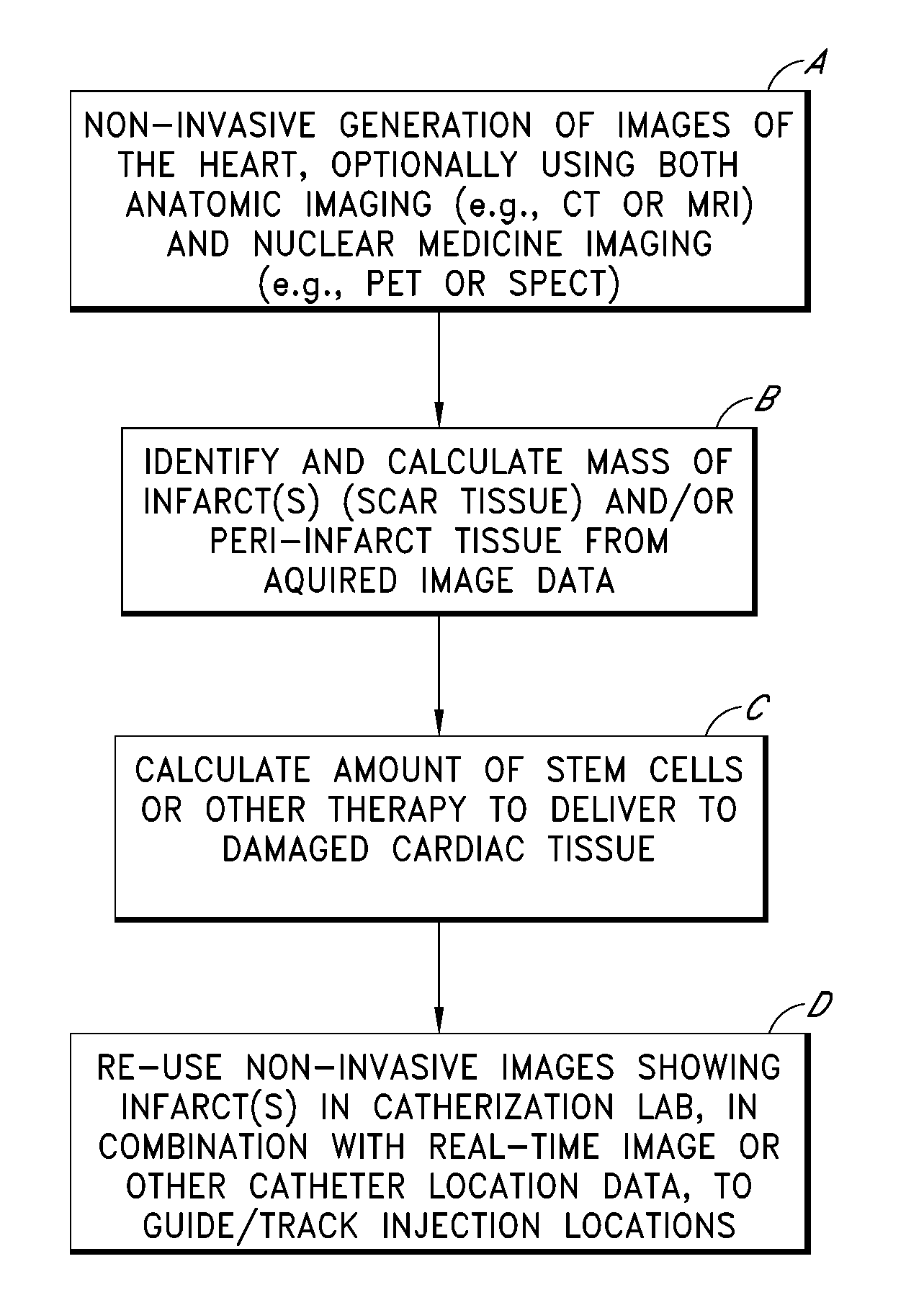
Medical imaging processes for facilitating catheter-based delivery of therapy to affected organ tissue
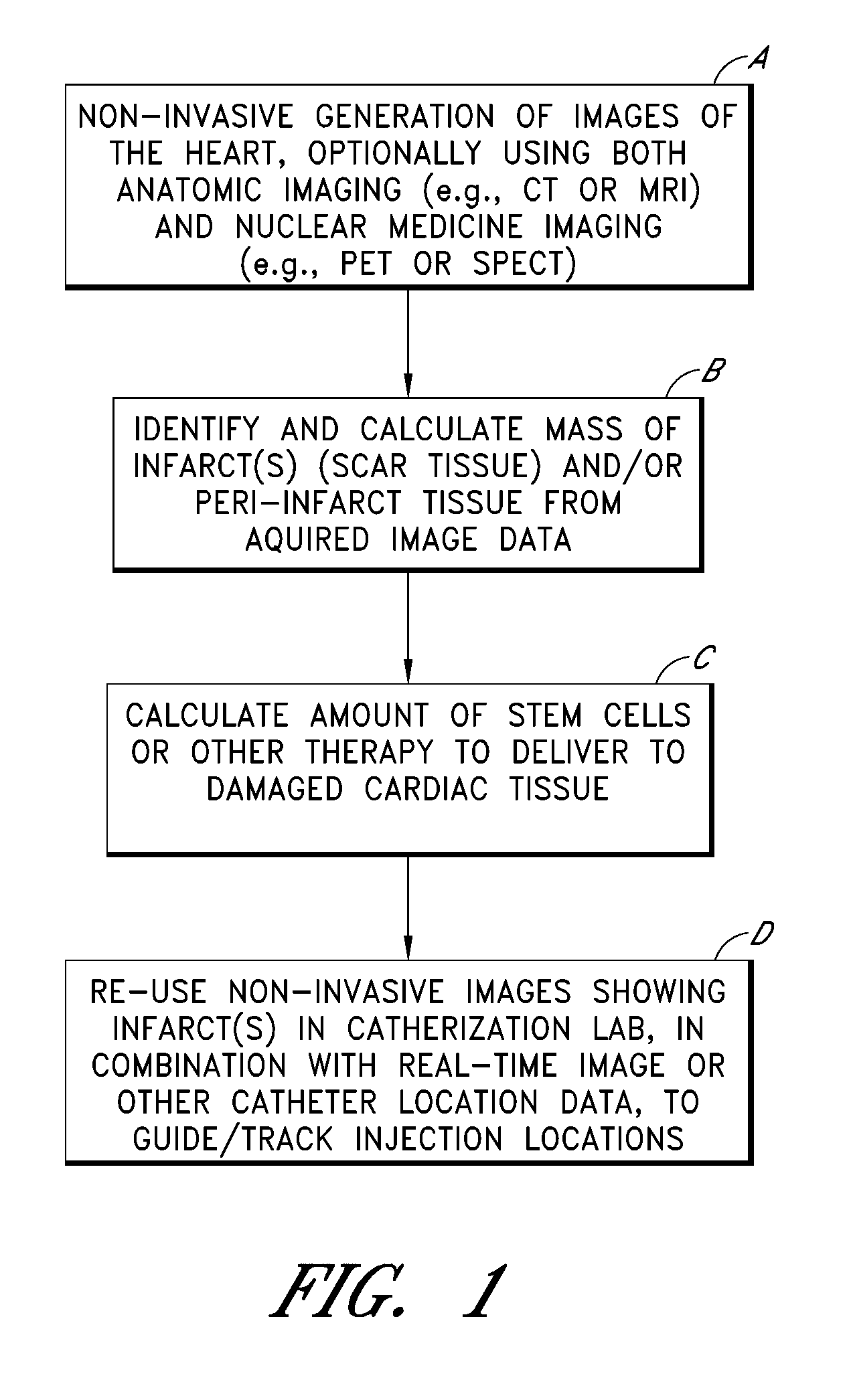
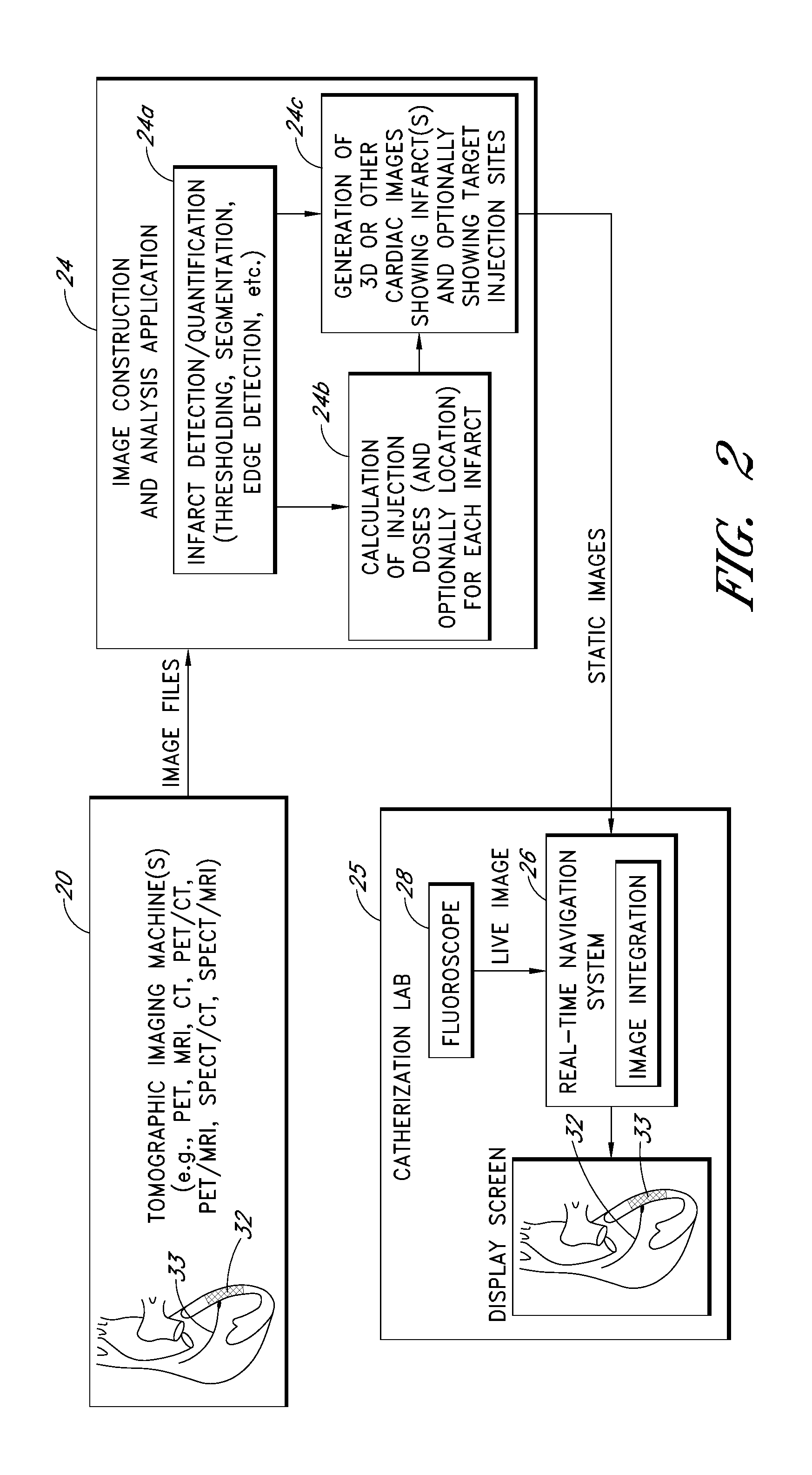
Medical imaging processes are disclosed for facilitating the catheter-based delivery of stem cells or other therapy to affected organ tissue, including myocardial infarct and peri-infarct tissue. The disclosed processes include the integration of static image data showing the affected tissue with a live / moving image (e.g., a fluoroscopy image) to generate a hybrid view showing the real time location of an injection catheter relative to the affected tissue. The static image data may include or be derived from one or more noninvasive nuclear medicine imaging scans (e.g., PET or SPECT) generated prior to the catheterization procedure. The live image may also be augmented with visual markers showing target and / or actual injection locations. Also disclosed are methods for calculating amounts of therapy to deliver to the affected tissue.
Owner:CELL GENETICS
Nuclear medical imaging method and device
ActiveCN102755172AEnhance the imageComputerised tomographsTomographyLines of responseDepth of interaction
The invention provides a nuclear medical imaging method and device for obtaining optimal images. The nuclear medical imaging method comprises a first determining step of determining a line of response set by the positions of a pair detector crystals, a defining step of defining an array of radiation points corresponding to the line of response, a second determining step of determining a solid angle with the bottom surface being surfaces of the pair of detector crystals defining the line of response for each point in the array of the radiation points corresponding to the line of response, a generating step of averaging the solid angle for generating an average solid angle, a third determining step of determining a position factor related to depth-of-interaction, and a calculation step of multiplying the reciprocal of the average solid angle by the position factor for calculating a geometric corrective factor for the line of response.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
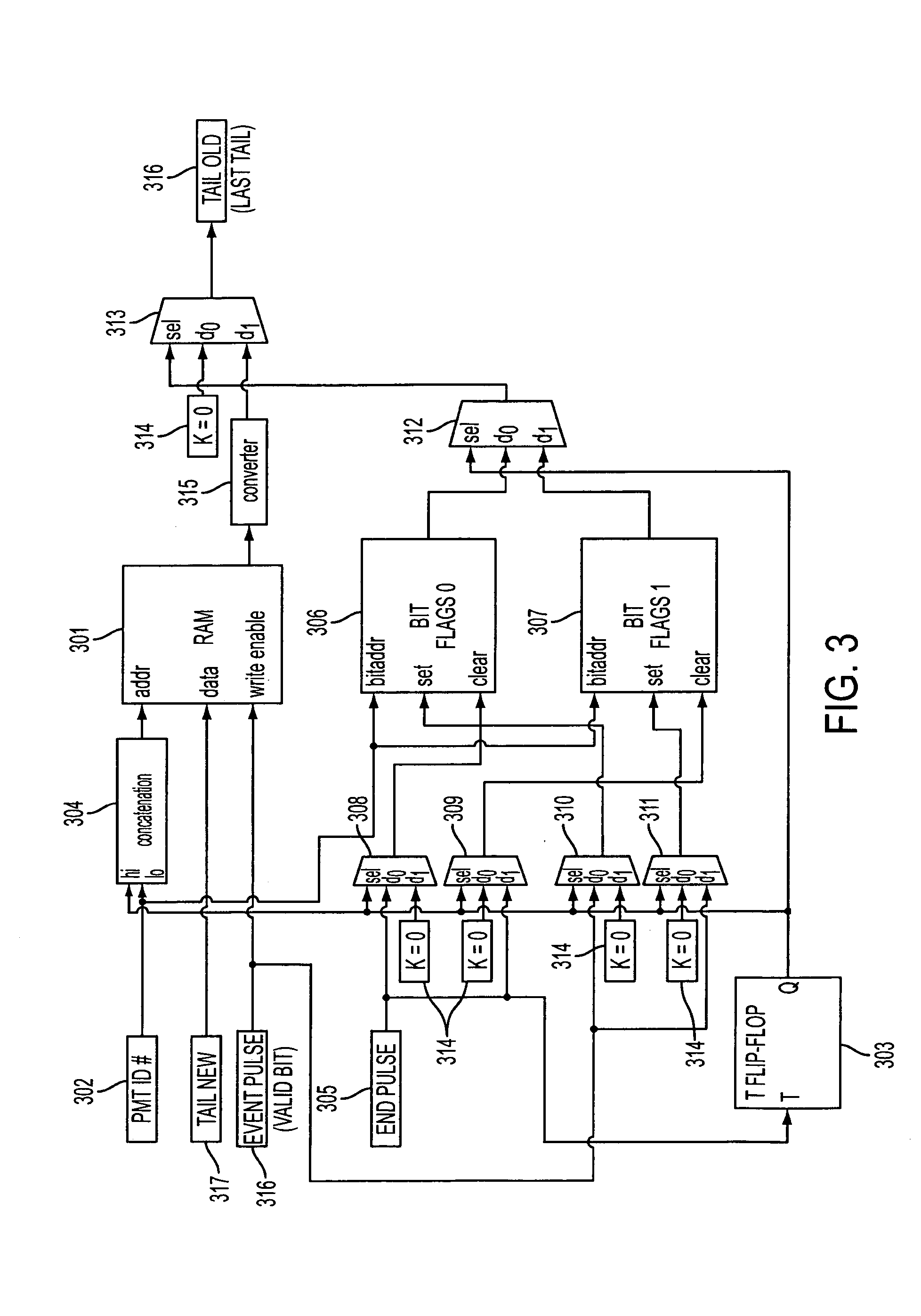
Pipeline processing of pulse pile-up correction in a nuclear medicine imaging system
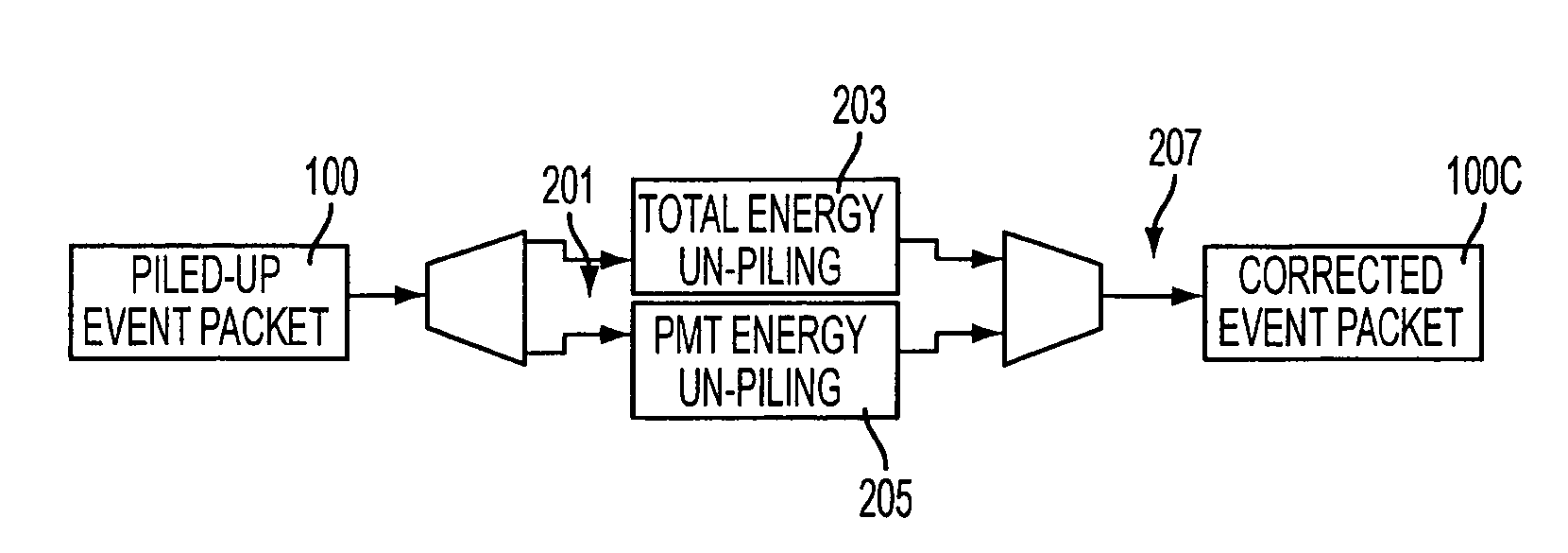
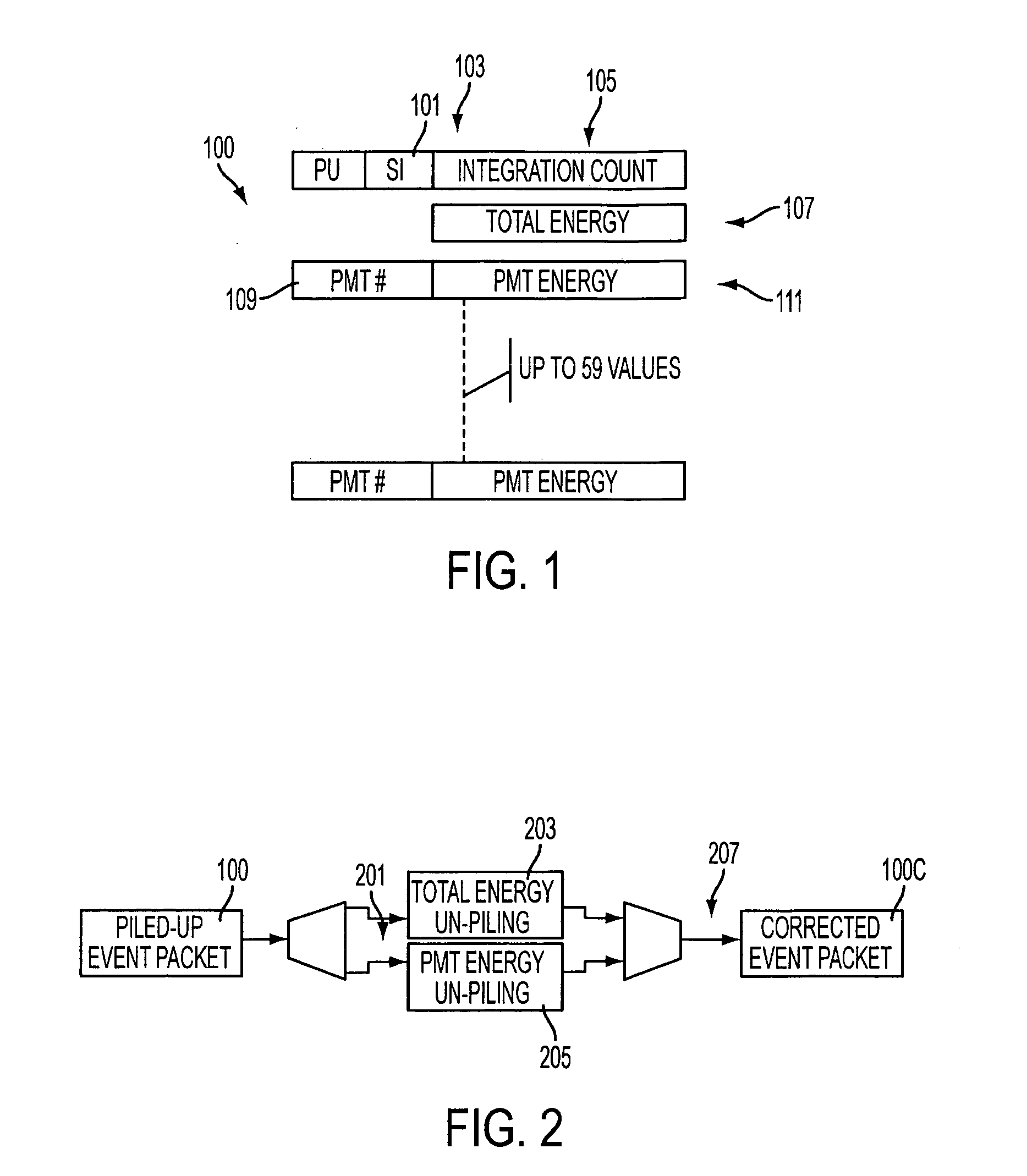
ActiveUS7439515B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCorrection algorithmEvent data
Correction of scintillation event data from a nuclear medicine imaging system for effects of pulse pile-up is carried out by separating event data packets into total energy and individual detector energy data packets, executing pile-up correction algorithms on each of the separated packets simultaneously using a pipeline processing architecture, and reassembling the corrected data packets into corrected scintillation event data packets. Pulse tail correction information for each individual detector is stored in a storage medium for a present event and immediately preceding event for which correction information exists, which allows individual detector correction information to be retrieved by using a look-up procedure, thereby enabling correction to be performed within a single processor cycle.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
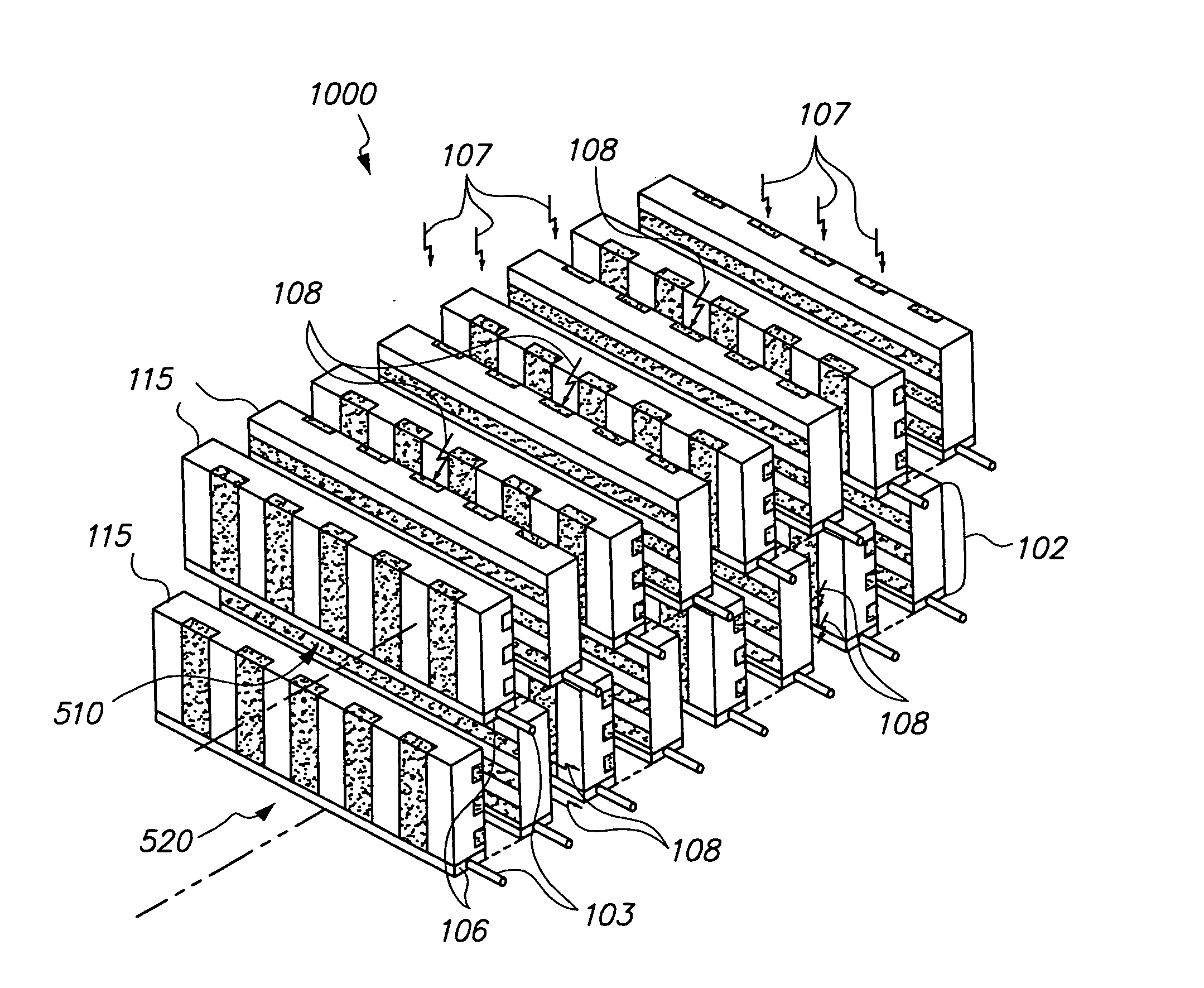
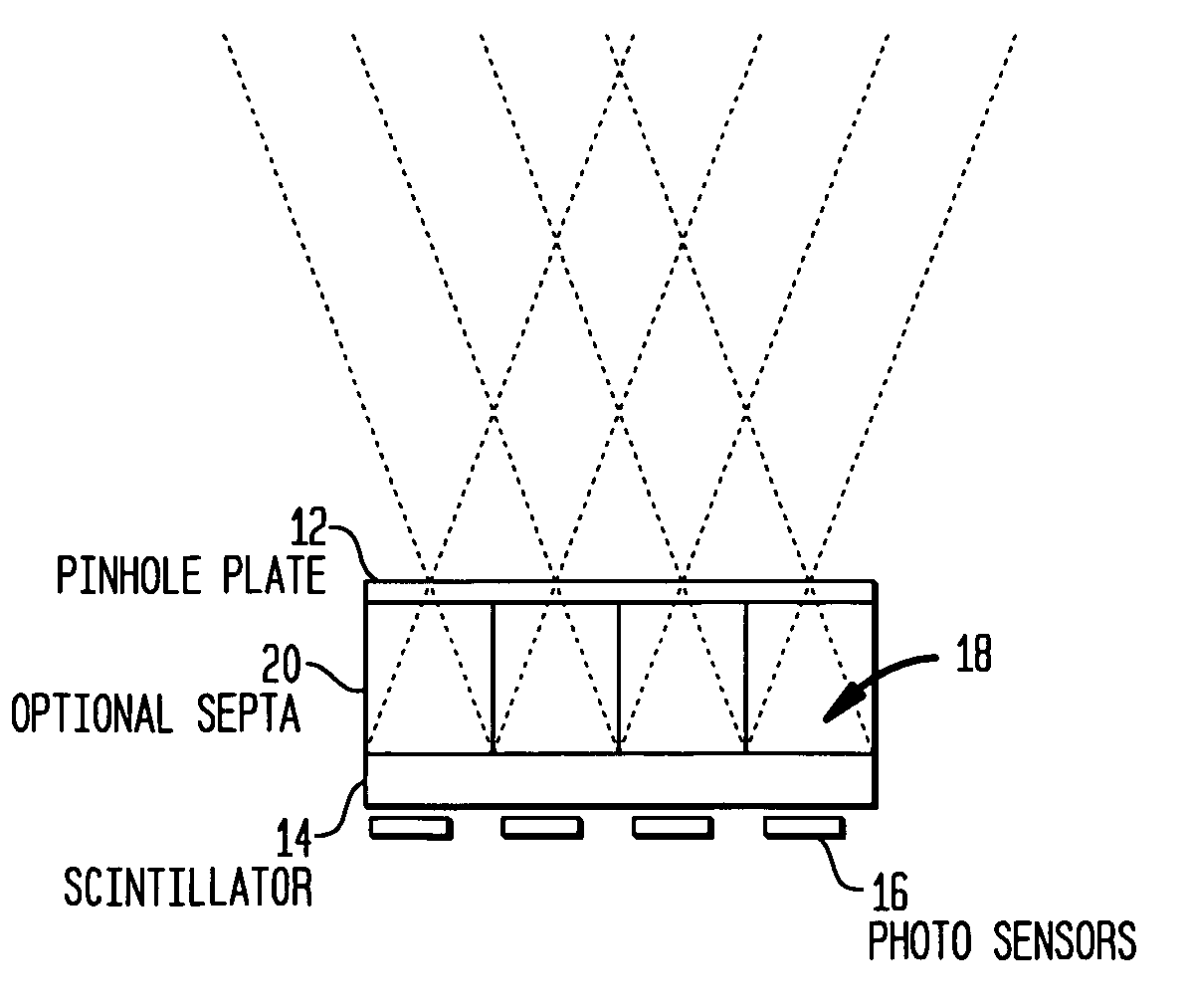
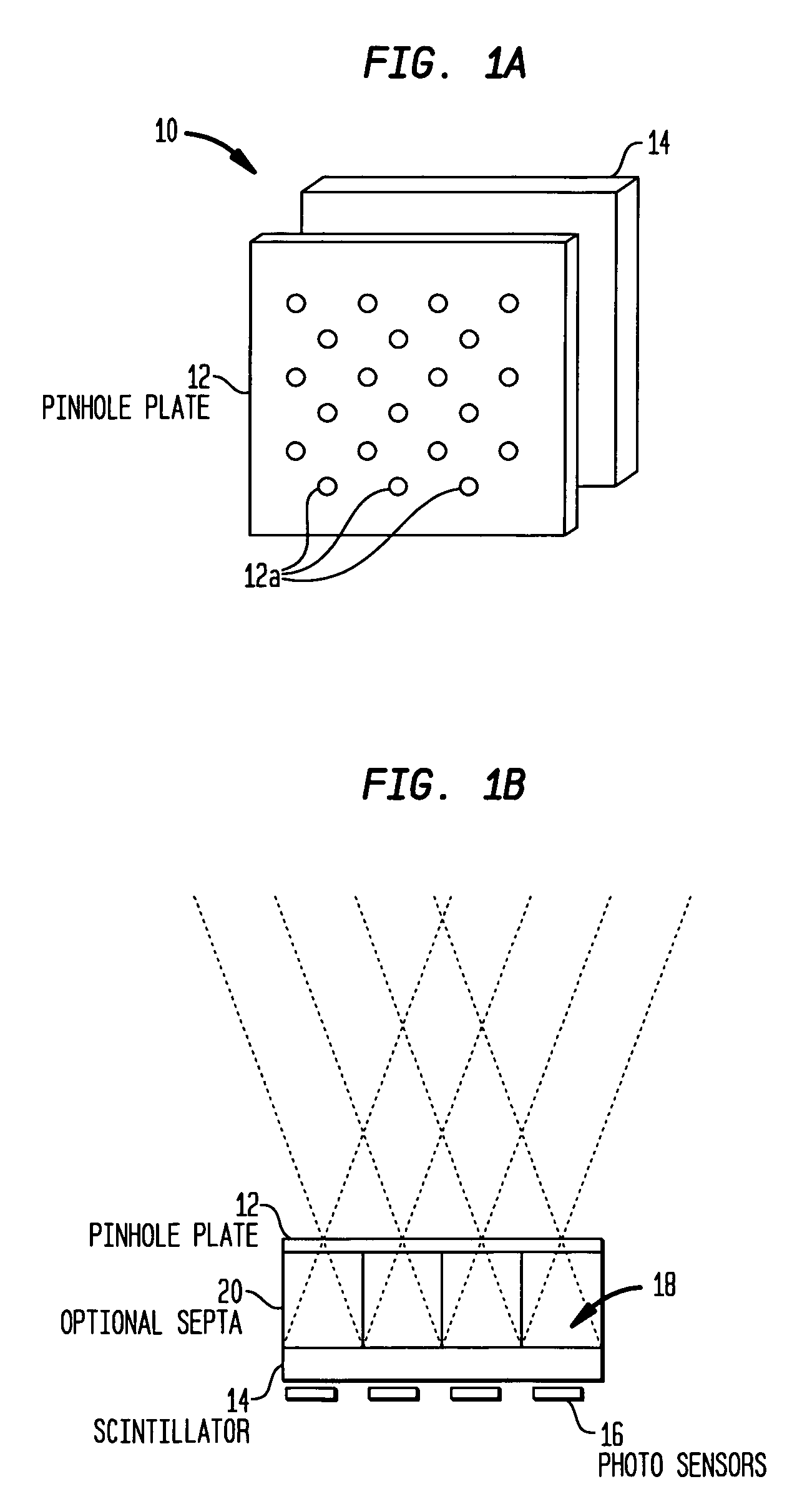
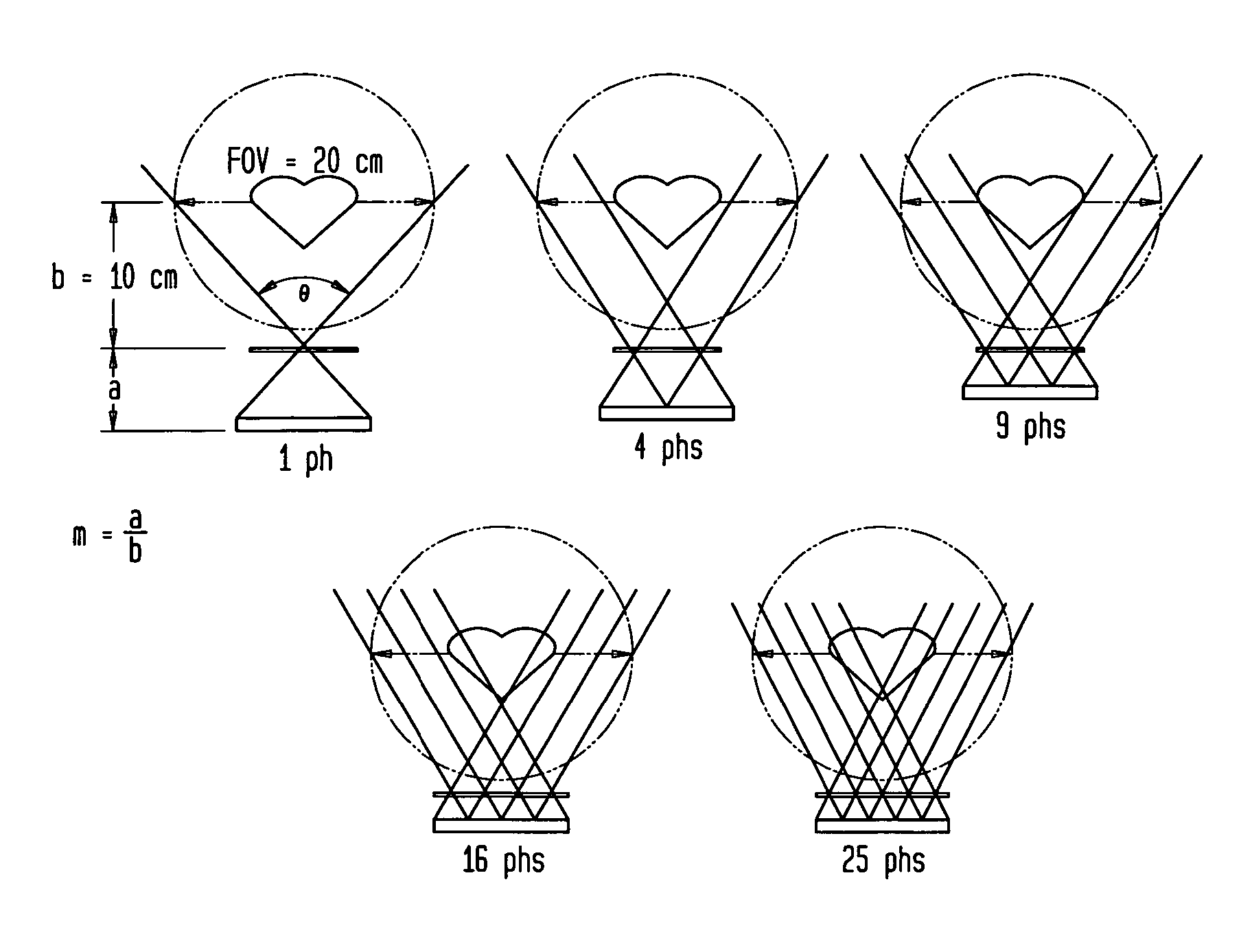
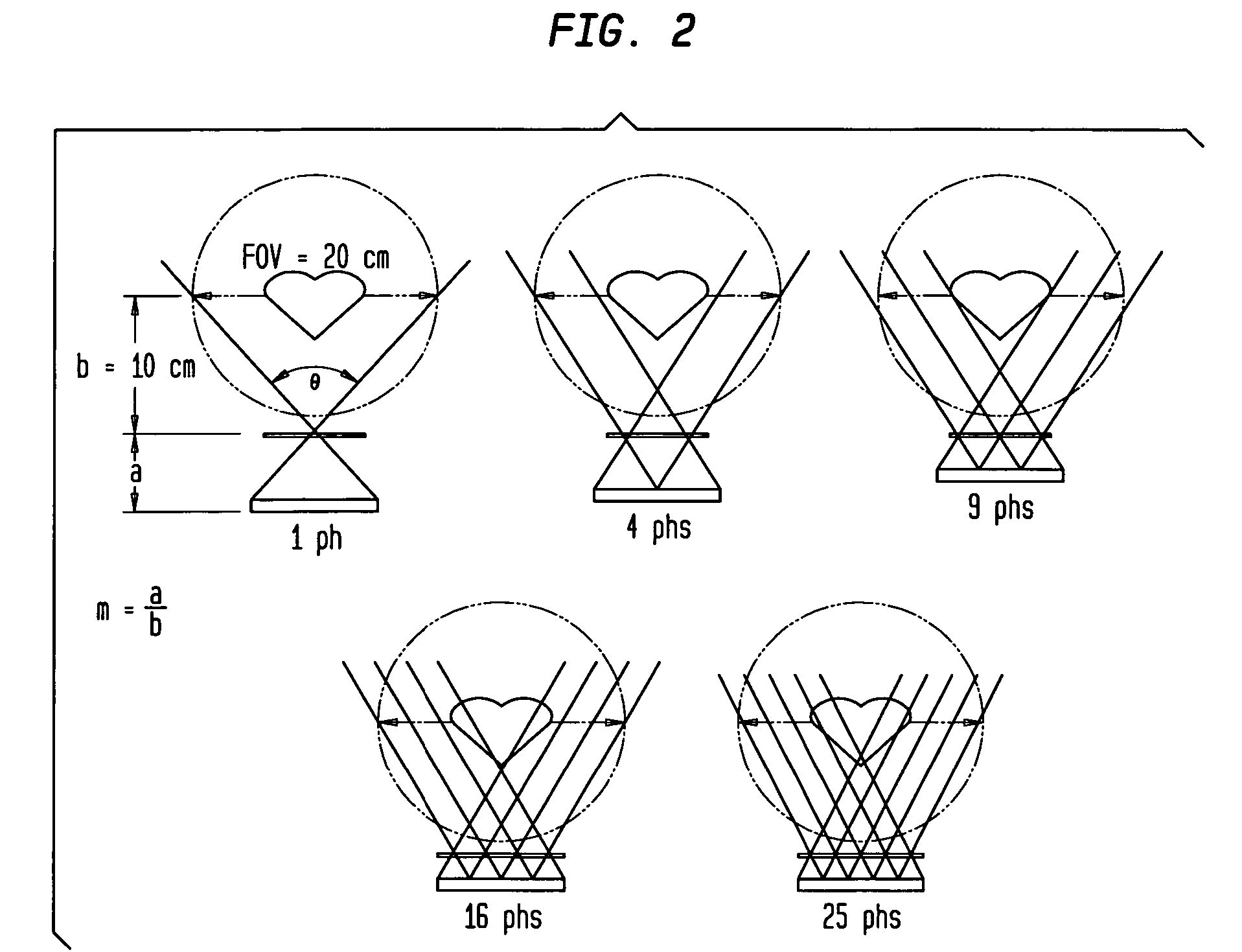
Multi-pinhole collimation for nuclear medical imaging
ActiveUS20060000978A1Reduce spacingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansMedical imagingNuclear medicine imaging
A multi-pinhole collimator nuclear medical imaging detector divides a target object space into many non-overlapping areas and projects a minified image of each area onto a segmented detector, where each segment functions as an independent detector or imaging cell. Septa may be provided between the collimator and the detector, to physically isolate the segments.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
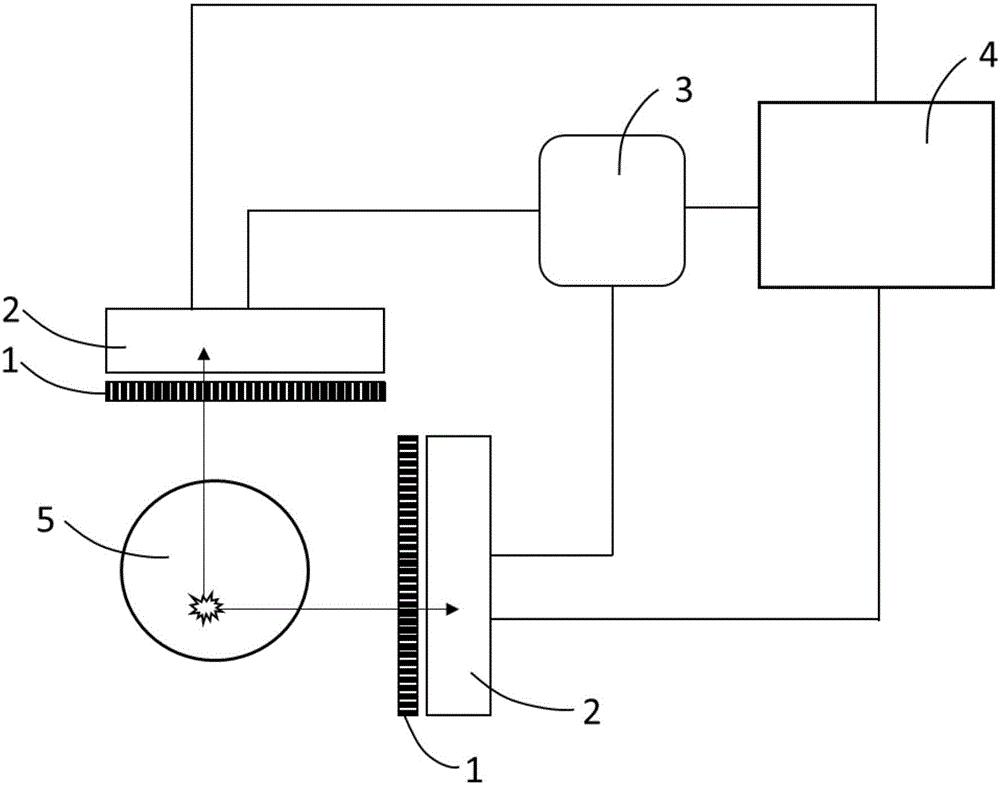
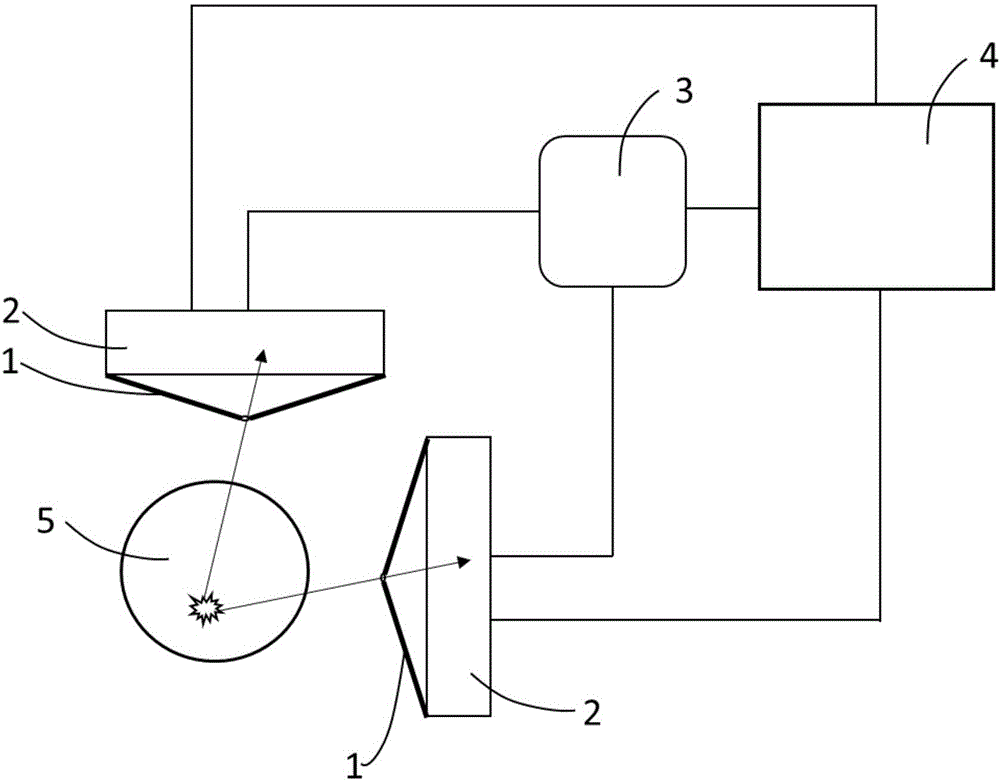
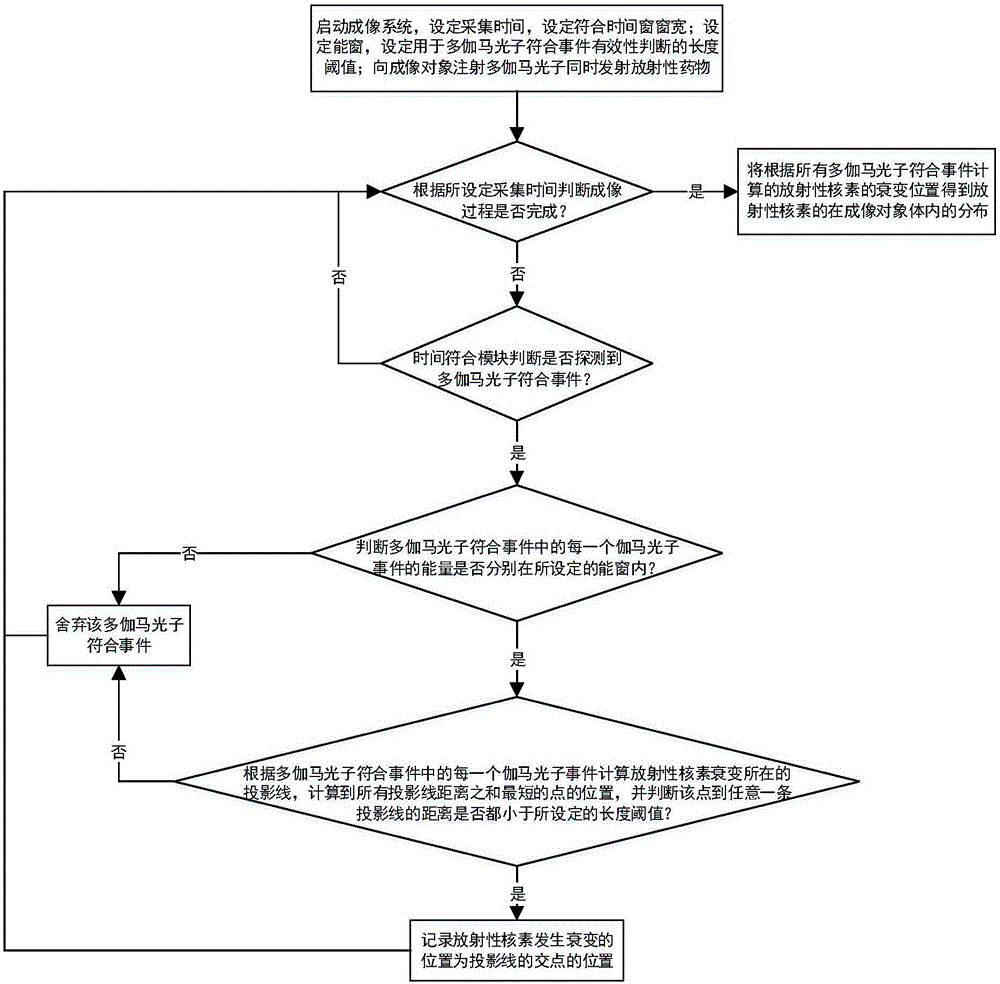
Multi-gamma-photo simultaneous medicine emission time coincidence nuclear medical imaging system and method
ActiveCN106108934AGet the distributionImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation diagnostic device controlComputerised tomographsReconstruction algorithmNuclear medicine imaging
The invention discloses a multi-gamma-photo simultaneous medicine emission time coincidence nuclear medical imaging system and method, and belongs to the field of nuclear medical images. The system comprises multiple detector probes arranged in non-parallel mode, a time coincidence module and a computer platform. Each detector probe is composed of a collimator and a gamma photo detector with a time measuring function. Multiple gamma photos radiated by detection radionuclides within a short time form multiple gamma-photo coincidence events. The point with the smallest sum, of distances of projection lines determined by the multiple gamma-photo coincidence events, calculated by the method is the disintegration position of radionuclides, and the distribution of radionuclides in living bodies can be obtained by accumulating a certain number of mult-gamma-photo coincidence events. By means of the imaging system and method, reconstruction algorithm is simplified, the signal to noise ratio of reconstructed images is improved, the requirement for the gamma photo total count is lowered, and the irradiation risk to patients is lowered.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
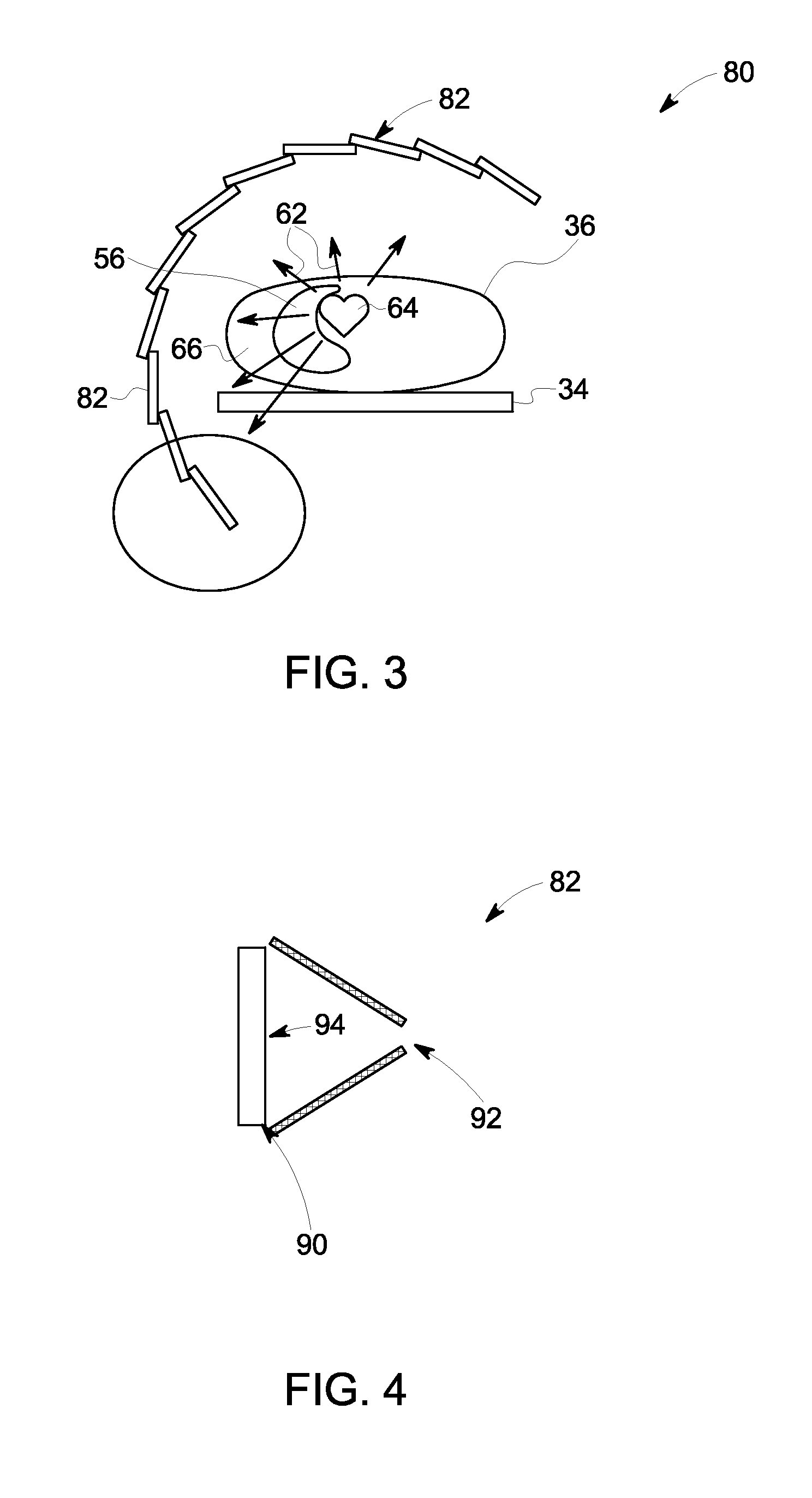
Imaging system using independently controllable detectors
ActiveUS9029791B1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton emissionTomography
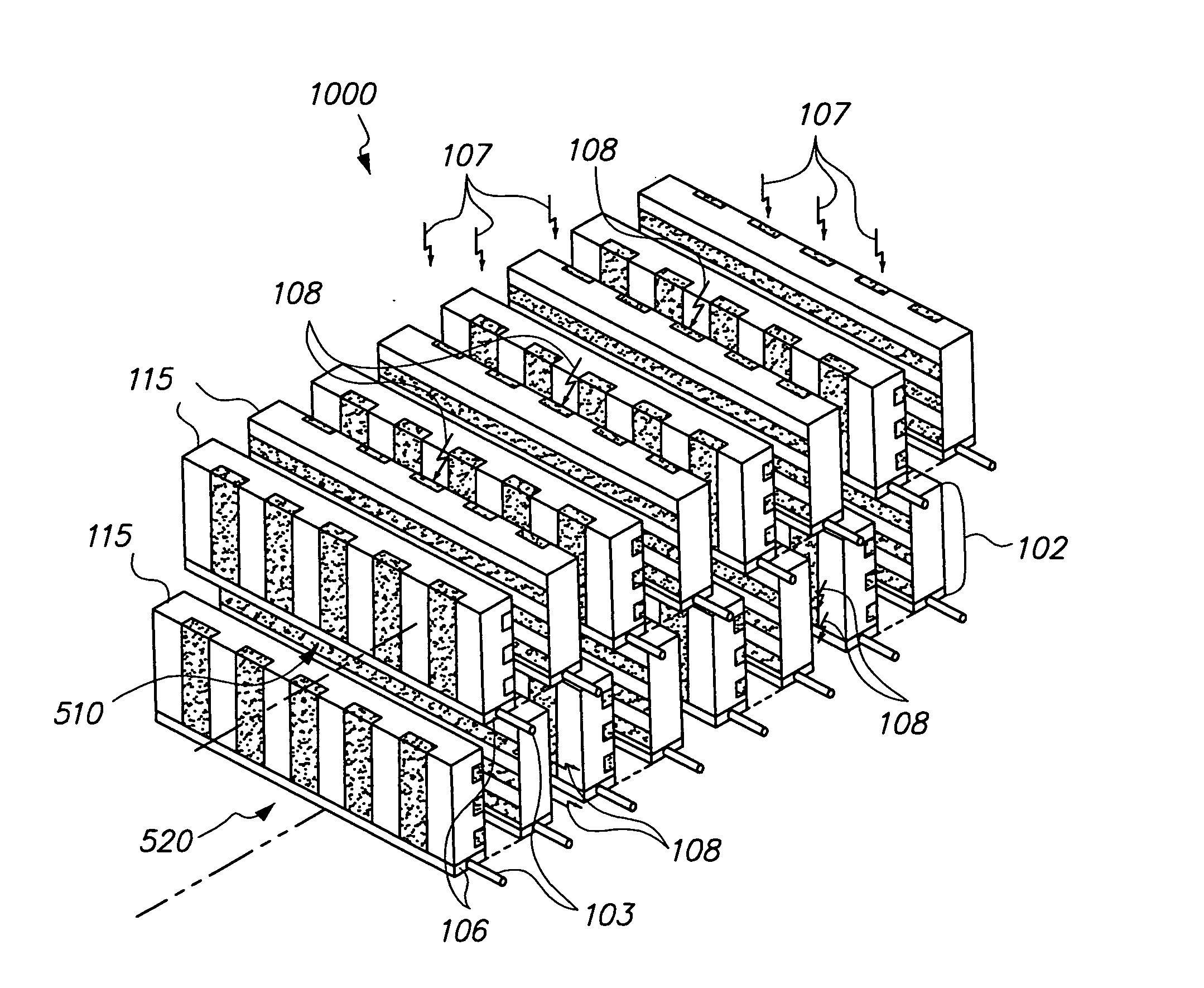
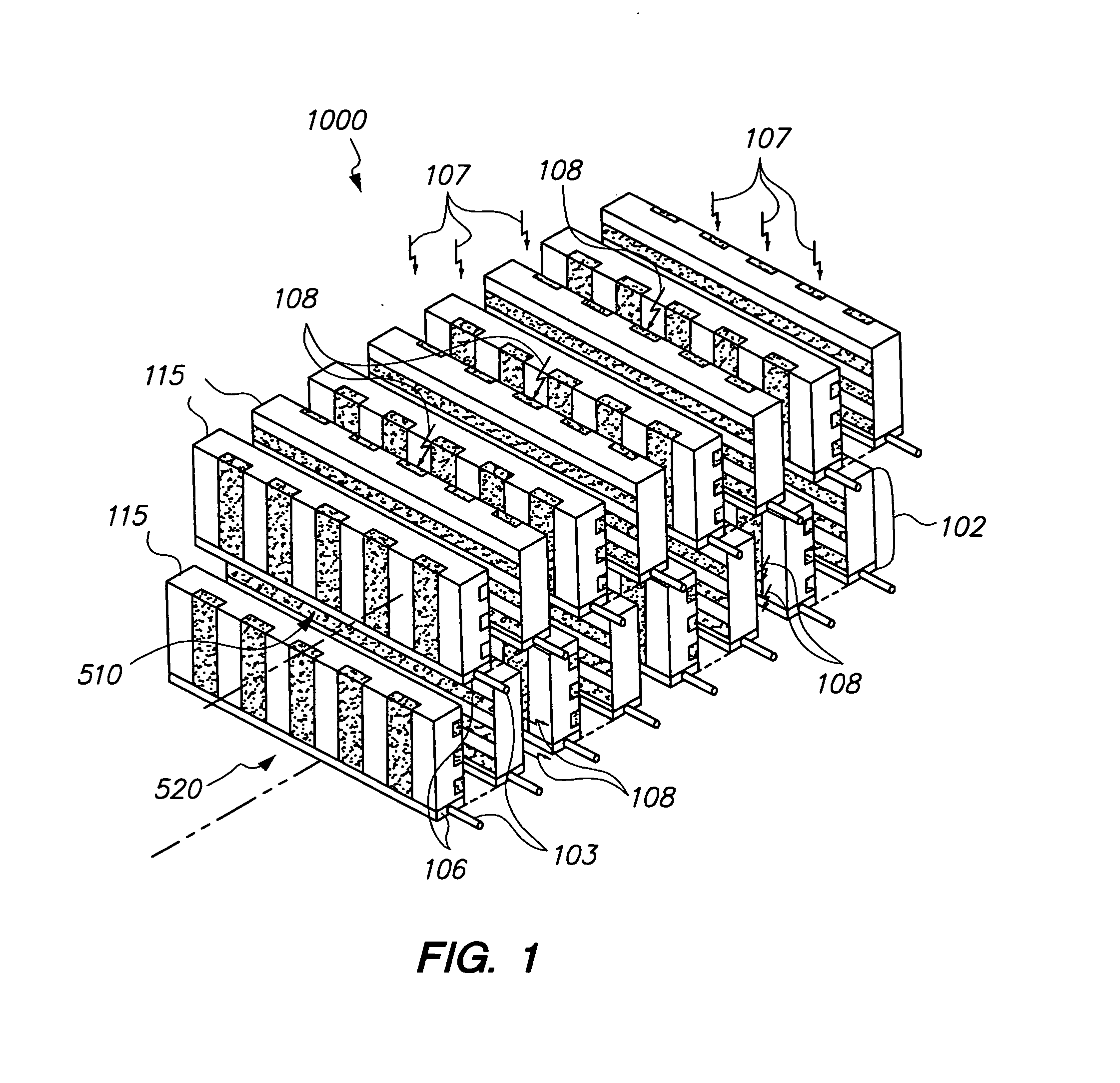
A customizable and upgradable imaging system is provided. Imaging detector columns are installed in a gantry to receive imaging information about a subject. Imaging detector columns can extend and retract radially as well as be rotated orbitally around the gantry. The gantry can be partially populated with detector columns and the detector columns can be partially populated with detector elements. The system can automatically adjust an imaging operation based on installation information related to partial population or other factors such as scan type or subject specific information. This system can be a Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Collimator with variable focusing and direction of view for nuclear medicine imaging
ActiveUS7345282B2Enhance the imageHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation attenuationNuclear medicine imaging
According to the present invention, a novel slat collimator for use in nuclear medicine imaging is provided. The slat collimator comprises a first layer comprising a plurality of spaced apart elongated slats and a second layer comprising a plurality of spaced apart elongated slats. The slats of the second layer are positioned orthogonally with respect to the slats of the first layer. The slats are constructed of a radiation attenuation material and the spaces between the slats may be non-variable or variable.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Systems and methods for attenuation compensation in nuclear medicine imaging based on emission data
ActiveUS20130248719A1Reconstruction from projectionMedical imagingUltrasound attenuationEnergy window
Systems and methods for attenuation compensation in nuclear medicine imaging based on emission data are provided. One method includes acquiring emission data at a plurality of energy windows for a person having administered thereto a radiopharmaceutical comprising at least one radioactive isotope. The method also includes performing a preliminary reconstruction of the acquired emission data to create one or more preliminary images of a peak energy window and a scatter energy window and determining a body outline of the person from at least one of the reconstructed preliminary image of the peak energy window or of the scatter energy window. The method further includes identifying a heart contour and segmenting at least the left lung. The method additionally includes defining an attenuation map based on the body outline and segmented left lung and reconstructing an image of a region of interest of the person using an iterative joint estimation reconstruction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
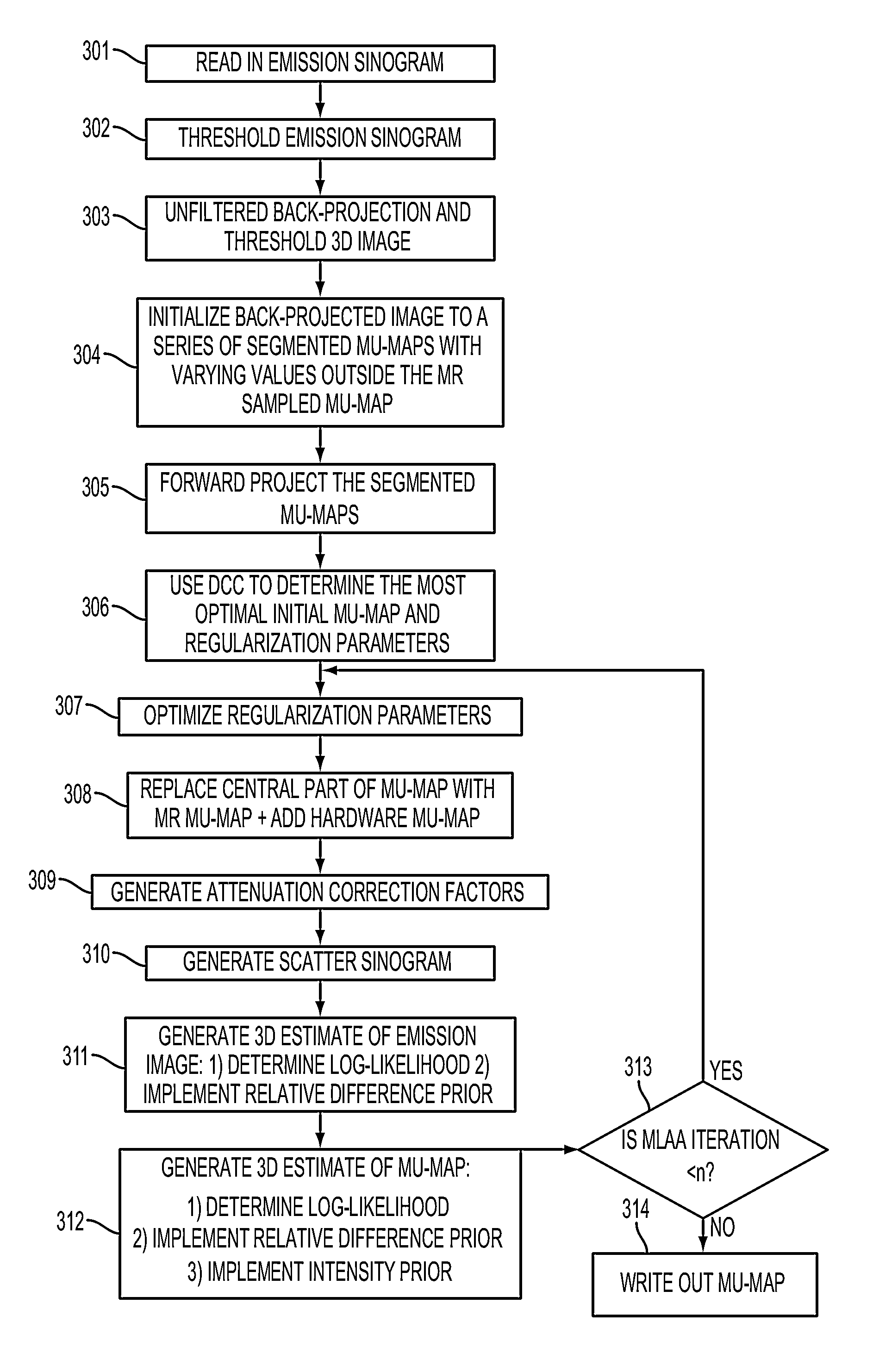
Generating Attenuation Correction Maps for Combined Modality Imaging Studies and Improving Generated Attenuation Correction Maps Using MLAA and DCC Algorithms
ActiveUS20140056500A1Reduce noiseReduce the numberReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionWhole bodyCompanion animal
The DCC (Data Consistency Condition) algorithm is used in combination with MLAA (Maximum Likelihood reconstruction of Attenuation and Activity) to generate extended attenuation correction maps for nuclear medicine imaging studies. MLAA and DCC are complementary algorithms that can be used to determine the accuracy of the mu-map based on PET data. MLAA helps to estimate the mu-values based on the biodistribution of the tracer while DCC checks if the consistency conditions are met for a given mu-map. These methods are combined to get a better estimation of the mu-values. In gated MR / PET cardiac studies, the PET data is framed into multiple gates and a series of MR based mu-maps corresponding to each gate is generated. The PET data from all gates is combined. Once the extended mu-map is generated the central region is replaced with the MR based mu-map corresponding to that particular gate. On the other hand, in dynamic PET studies the uptake in the patient's arms reaches a steady state only after the tracer distributes throughout the body. Hence, for dynamic scans, the projection data of all frames is summed and used to generate the MLAA based extended mu-map for all frames.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
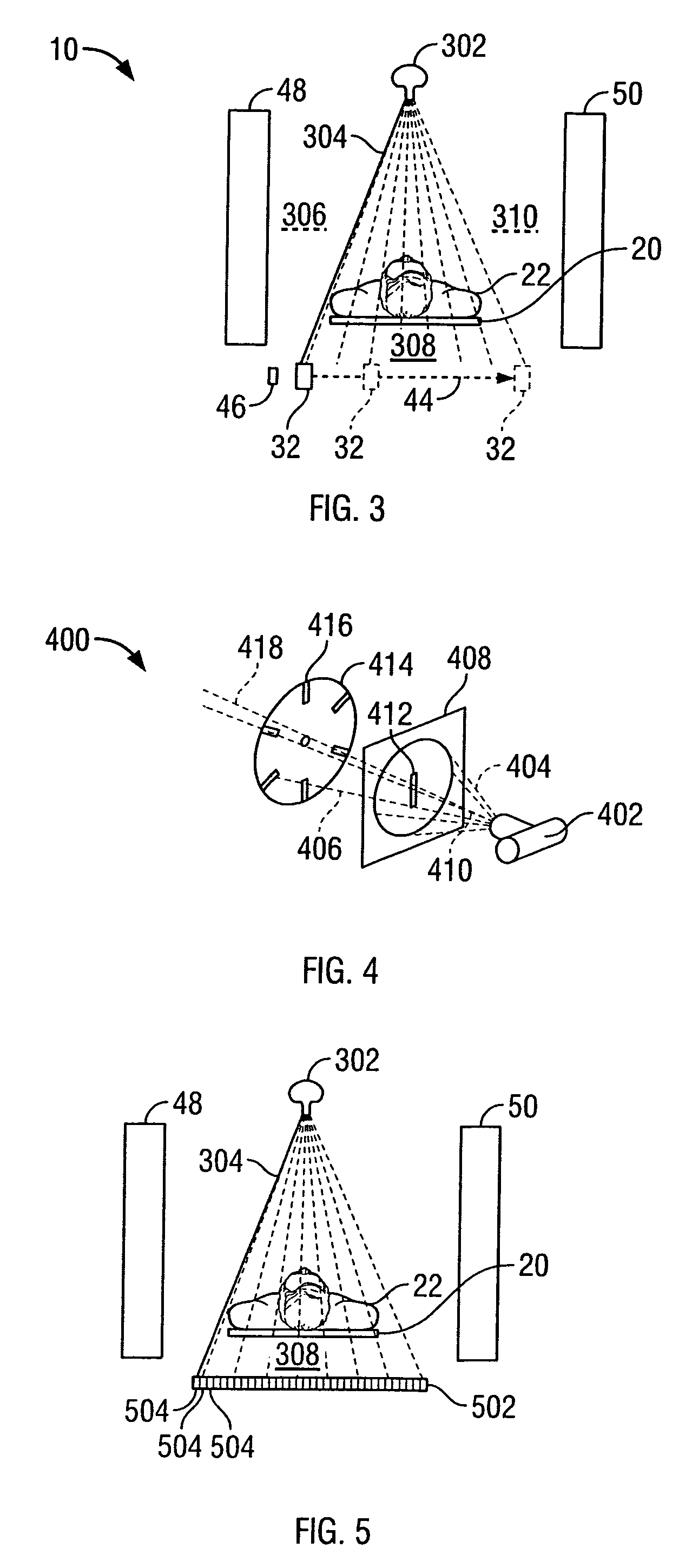
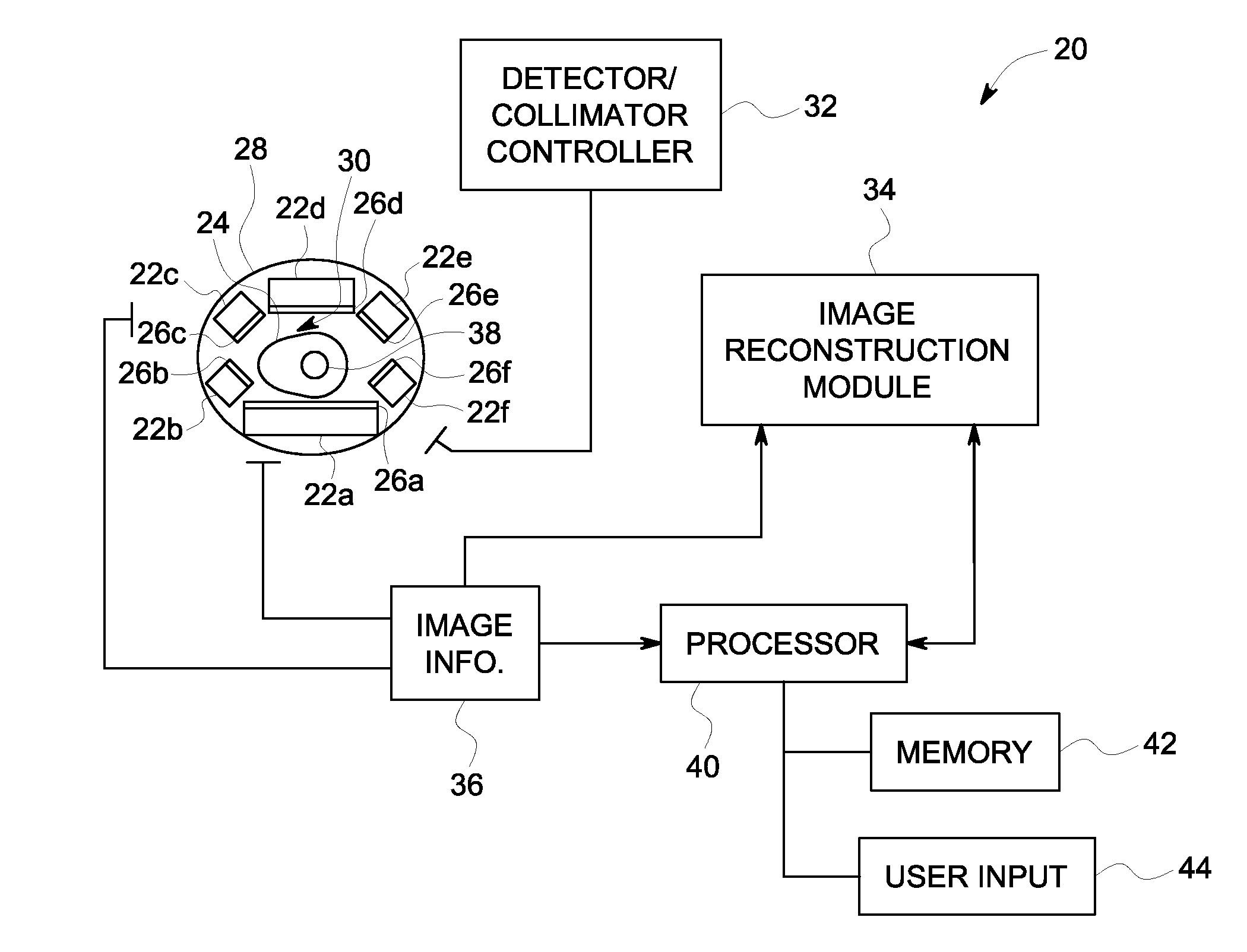
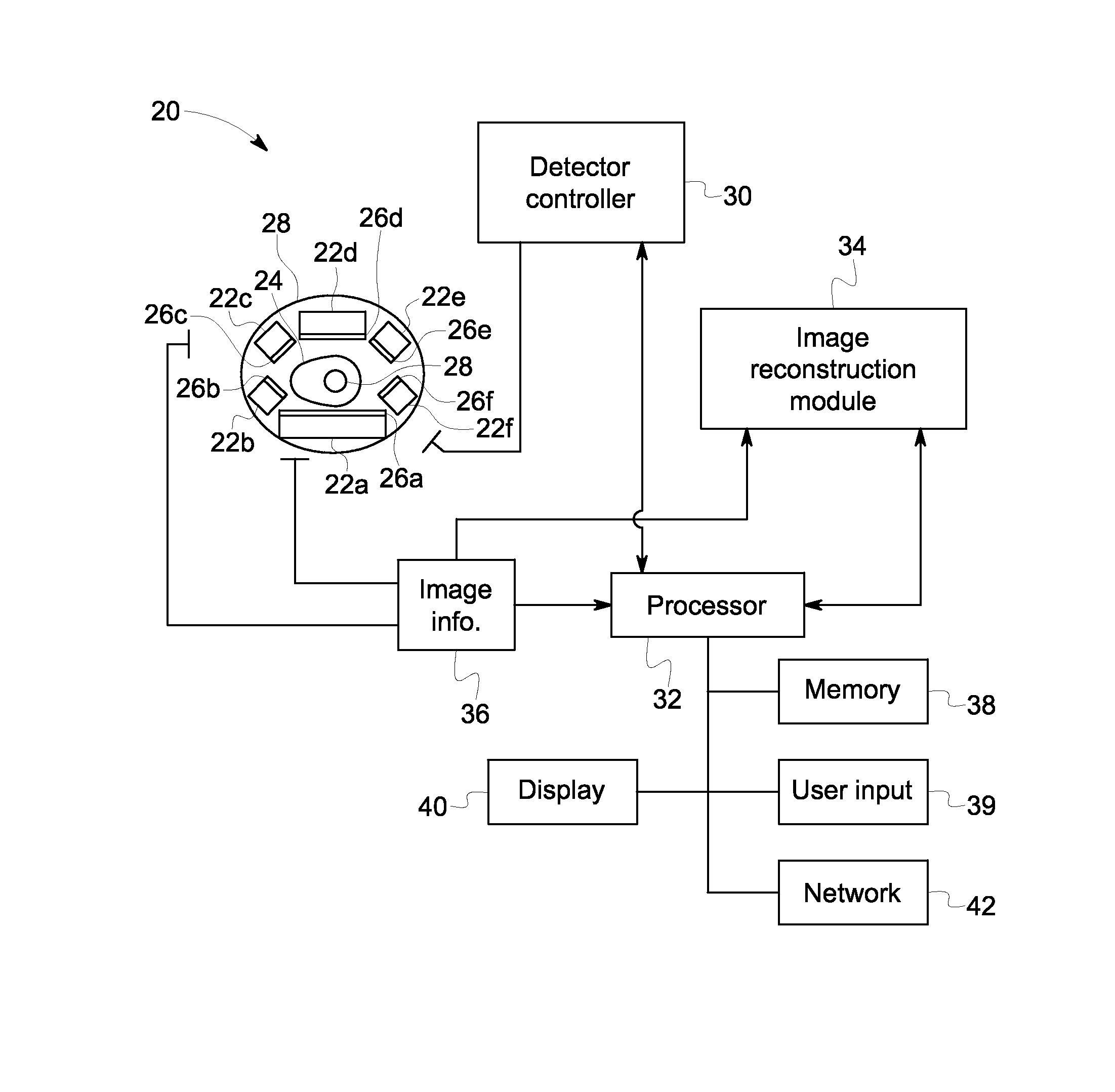
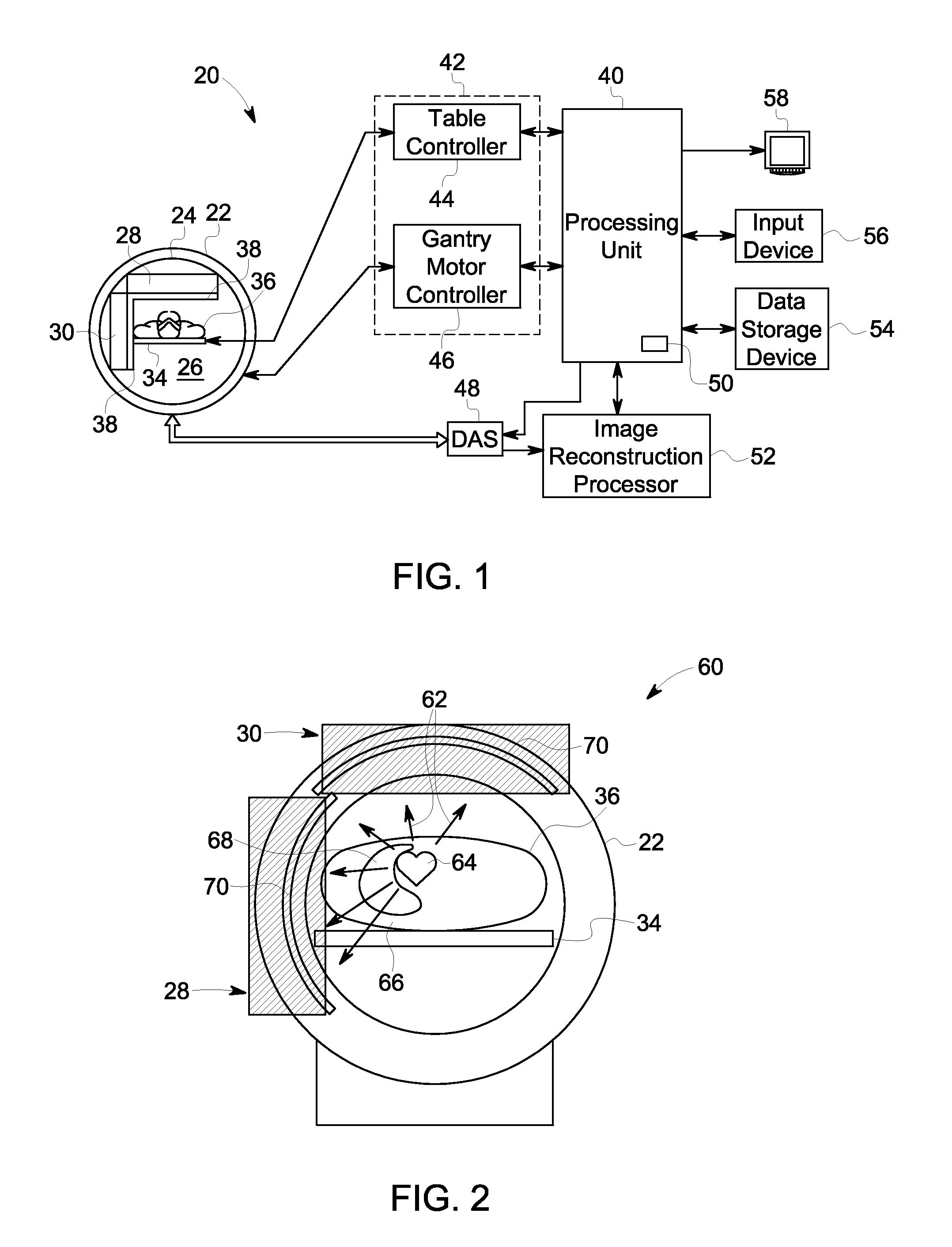
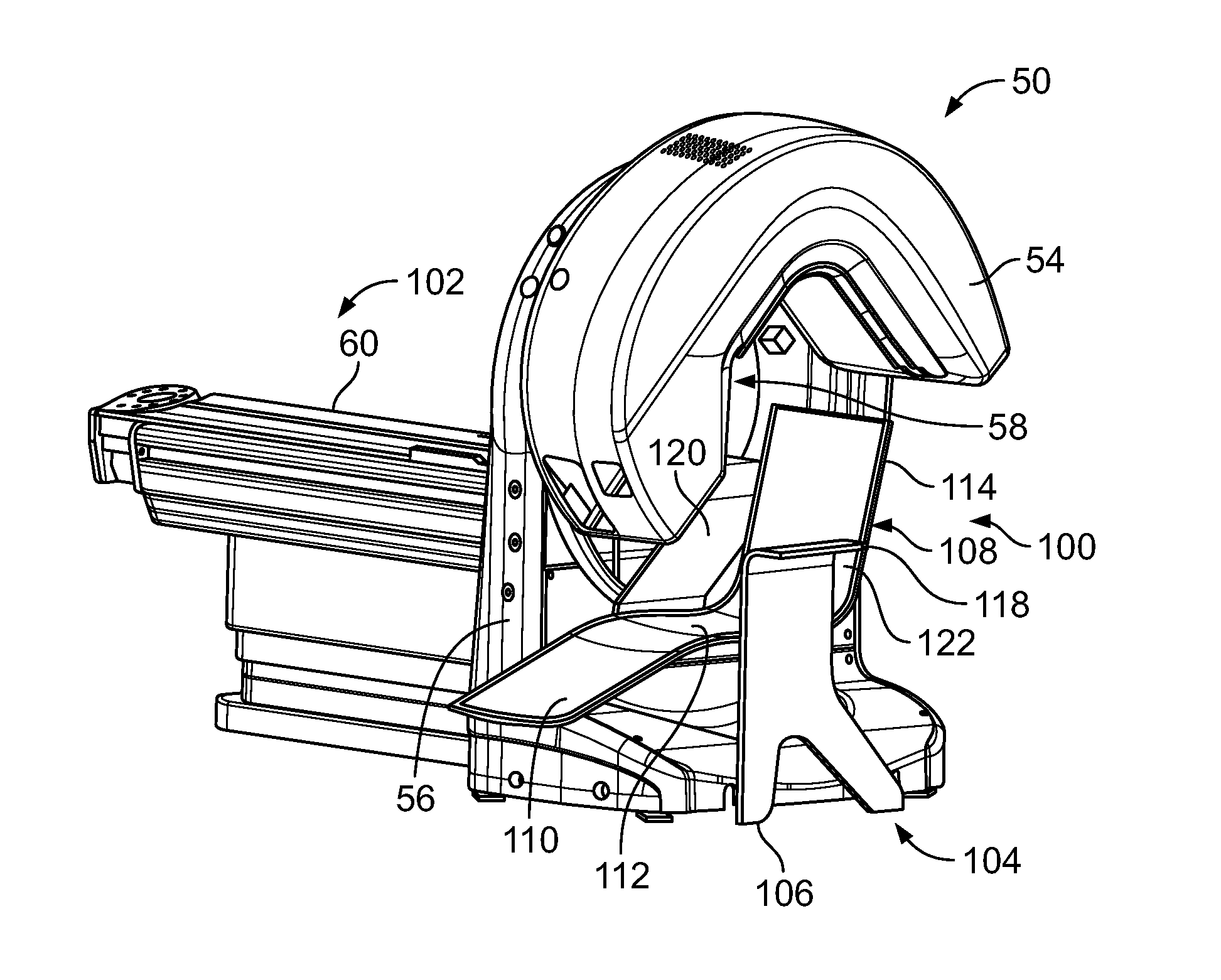
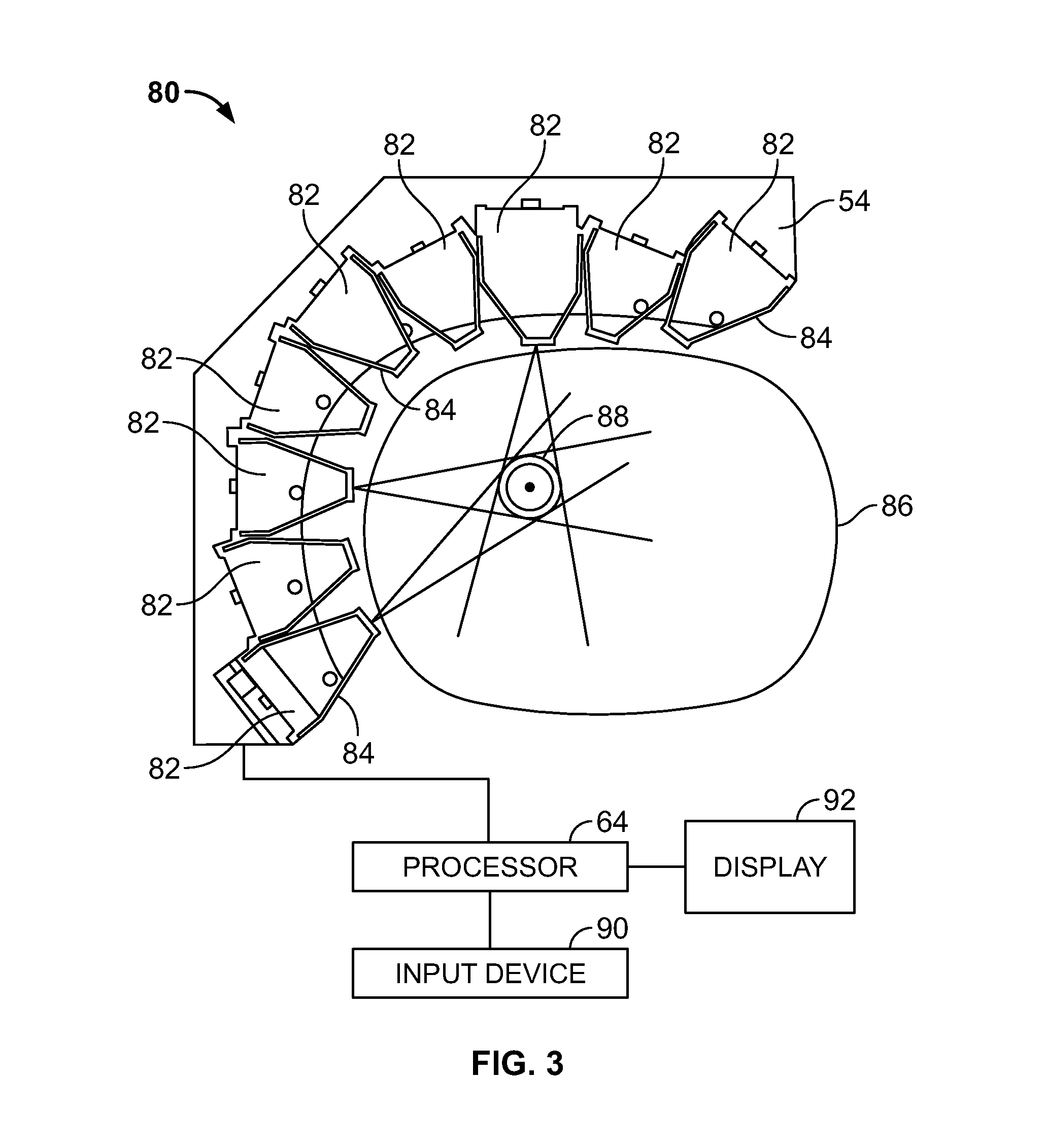
Methods and systems for positioning detectors for nuclear medicine imaging
ActiveUS20130320234A1Radiation measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansComputer scienceNuclear medicine imaging
Methods and systems for positioning detectors for Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging are provided. One system includes a gantry supporting one or more imaging detectors, wherein the gantry has a portion configured for movable operation. The system also includes a table on one side of the gantry configured to support a patient thereon, wherein the table is further configured to move within an opening of the gantry. The system further includes a patient support device movably positioned on an opposite side of the gantry from the table, wherein the patient support device is configured for movable operation.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
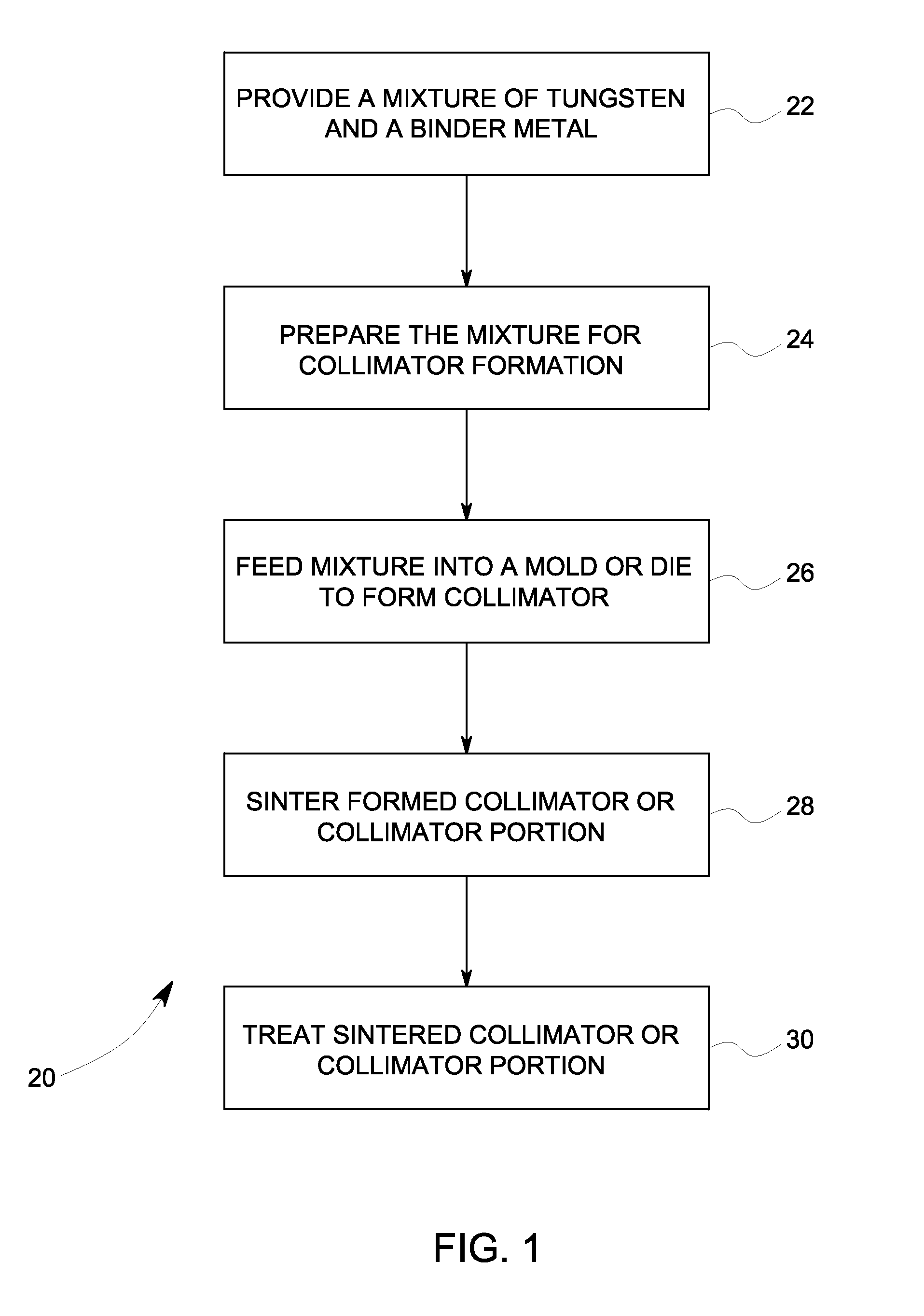
Collimators and methods for manufacturing collimators for nuclear medicine imaging systems
InactiveUS20120085942A1Transportation and packagingElectrode and associated part arrangementsTungstenNuclear medicine imaging
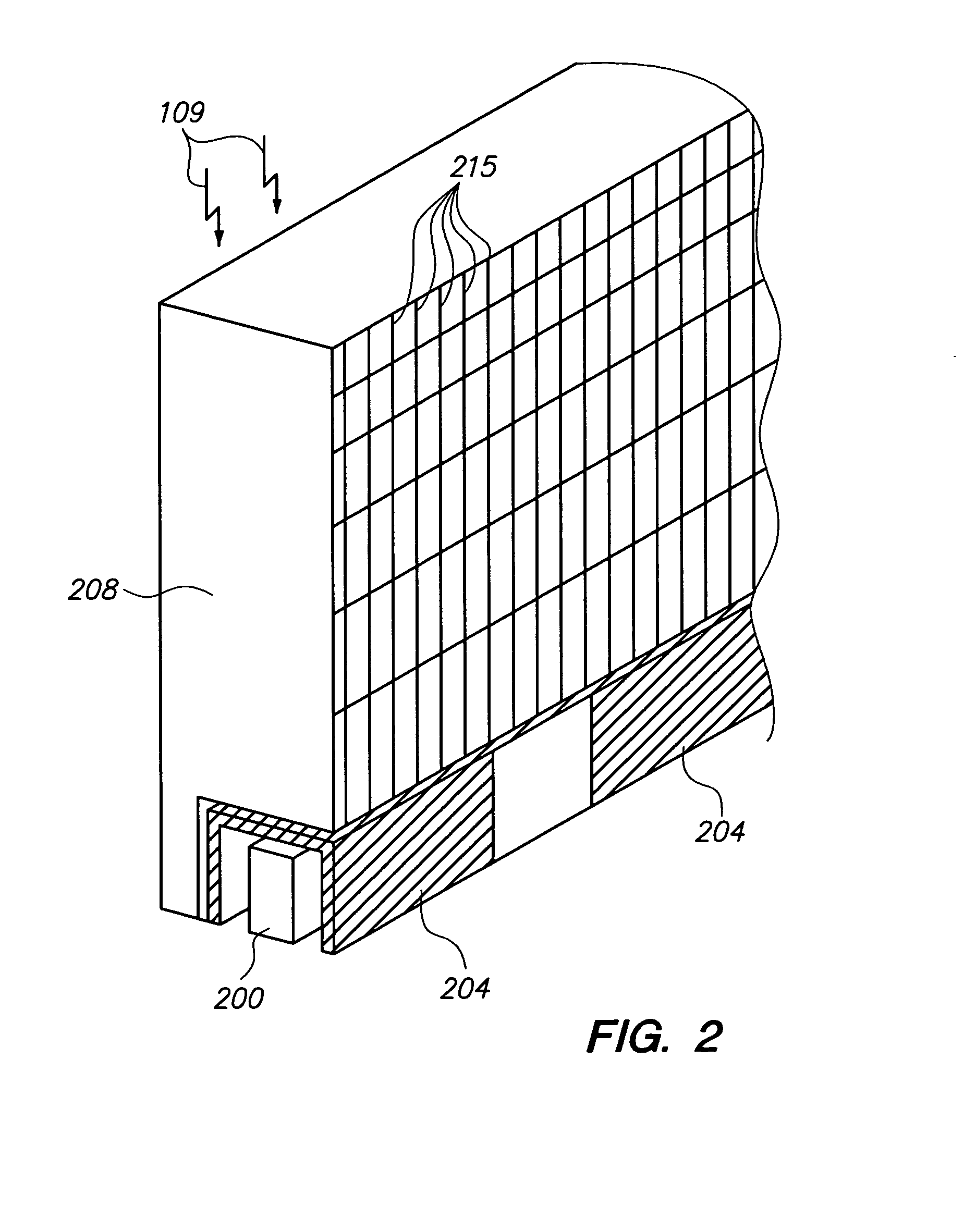
Collimators and methods for manufacturing collimators for nuclear medicine (NM) imaging systems are provided. One method includes forming a plurality of collimator segments from powdered tungsten, wherein the plurality of collimator segments have opposing faces with edges therebetween. The method also includes sintering the powdered tungsten segments and joining the plurality of sintered powdered tungsten segments at least at one or more of the edges to form the collimator for the NM imaging system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
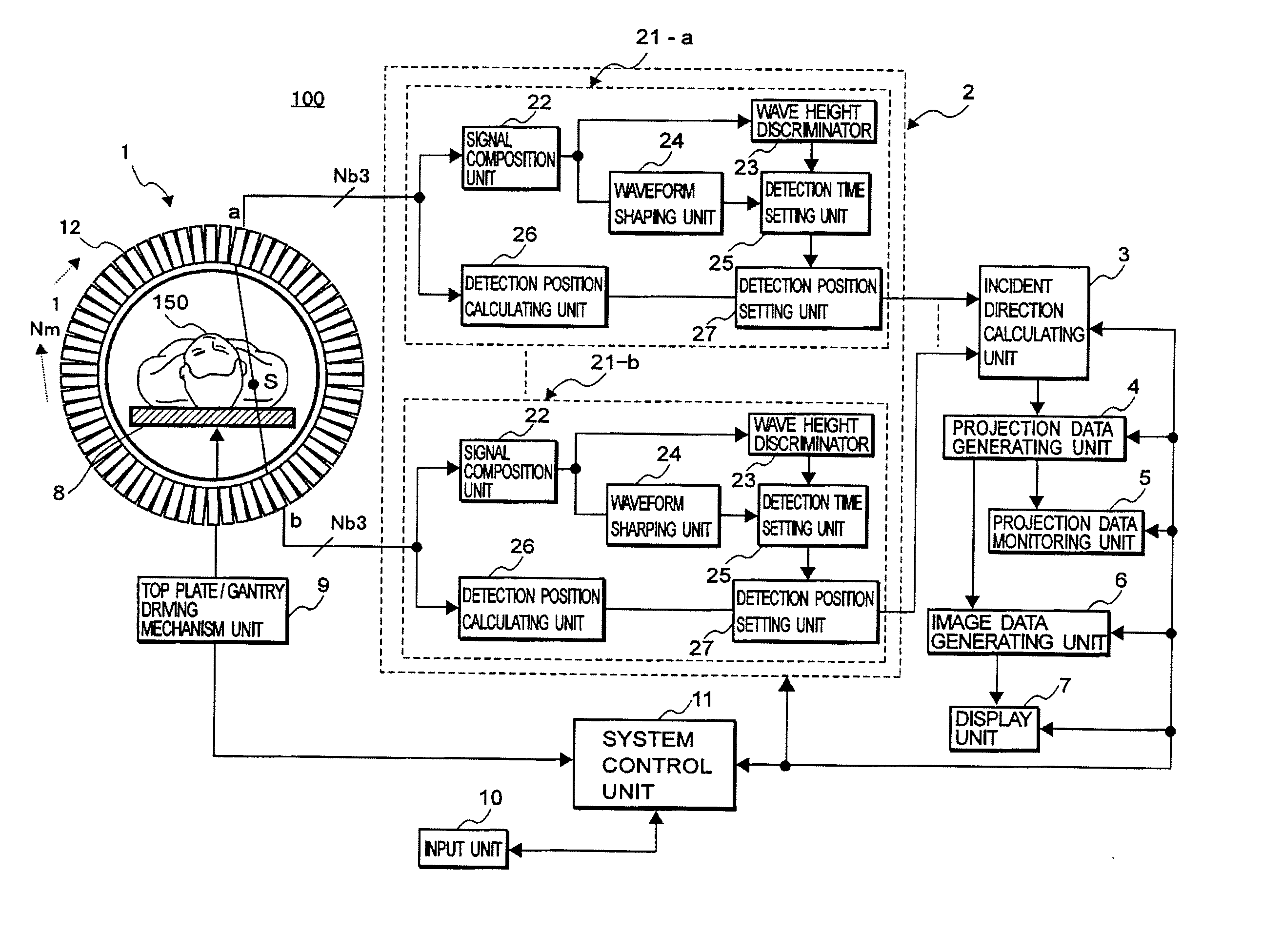
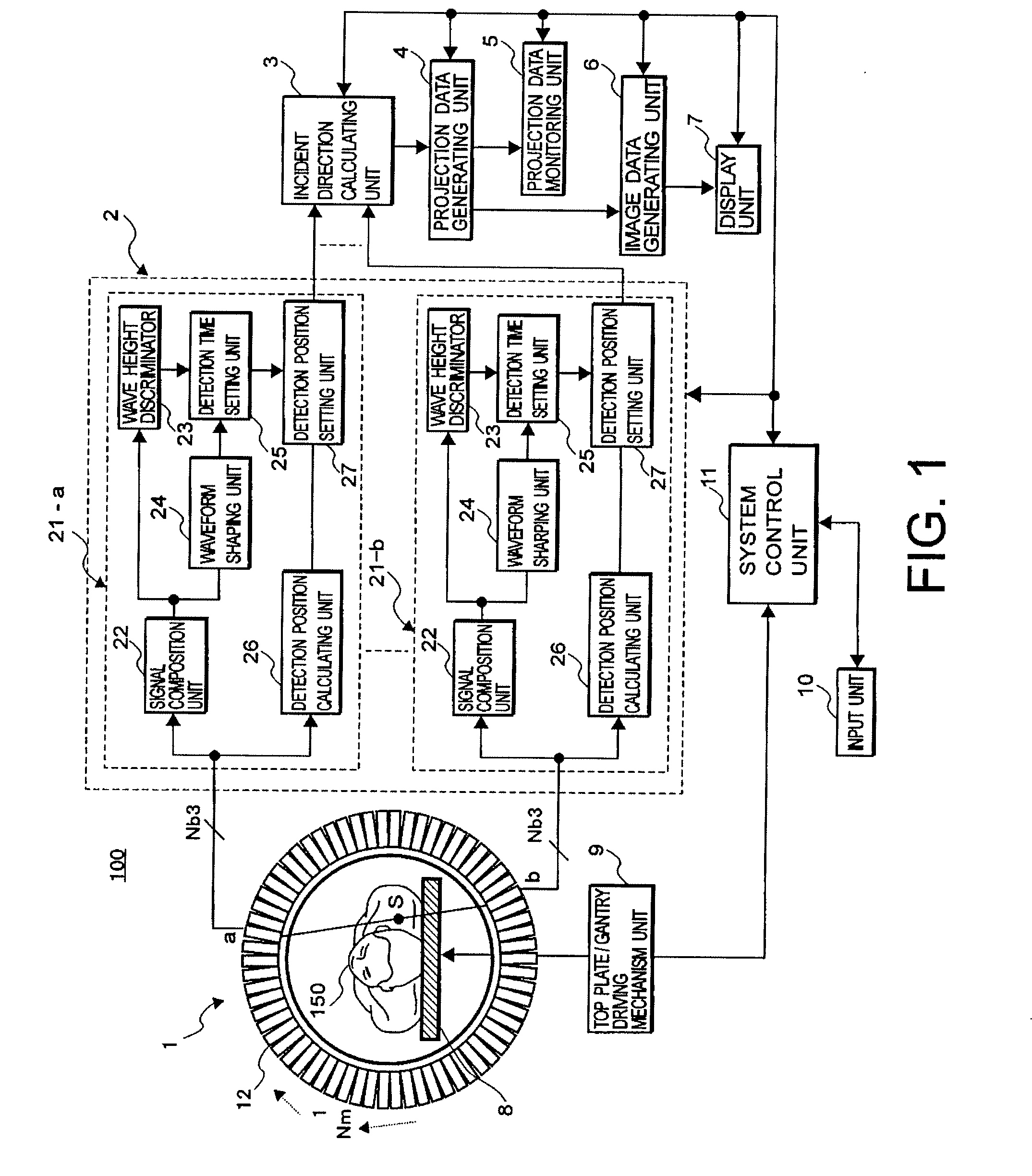
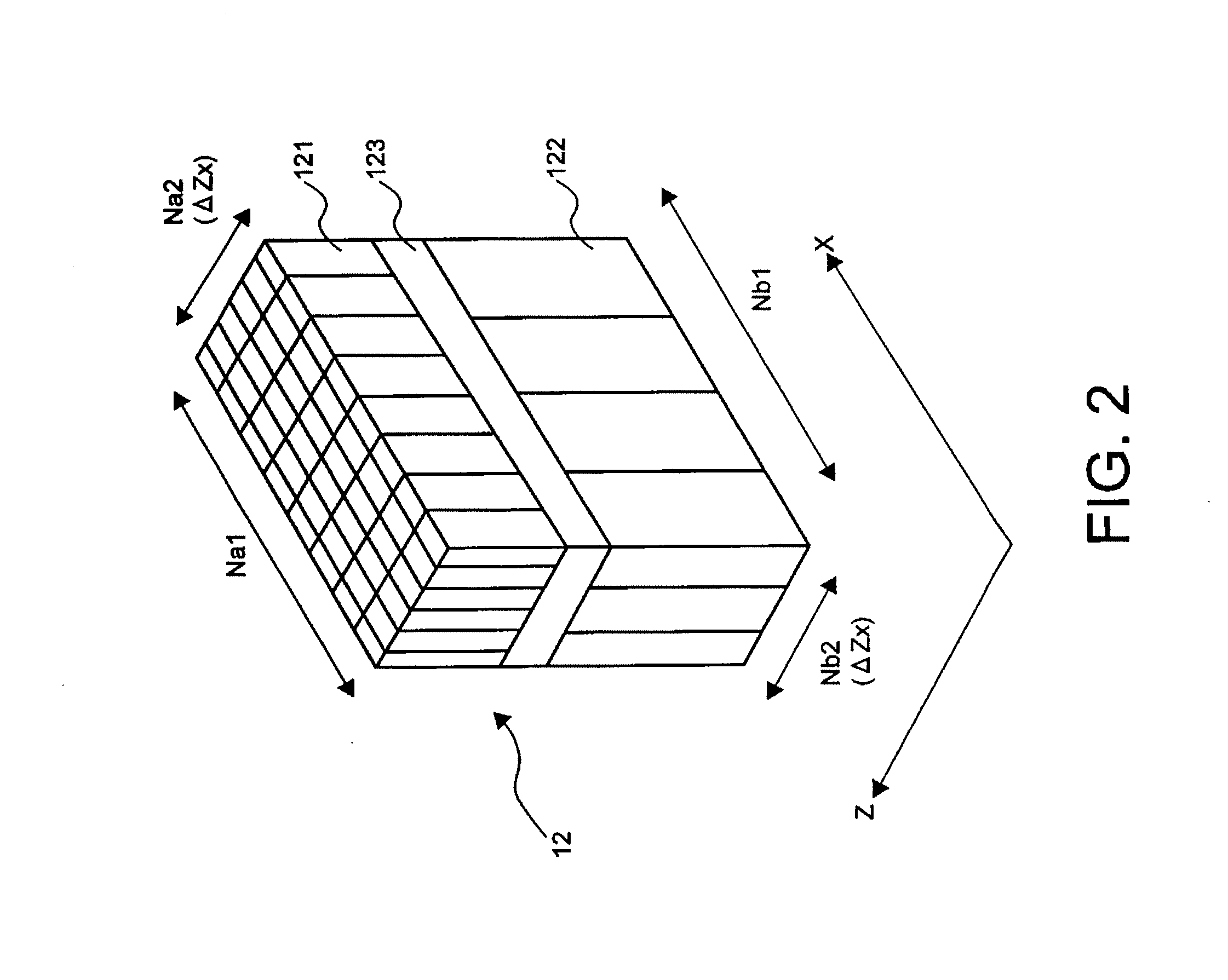
Nuclear medicine imaging apparatus and a method for generating image data
ActiveUS20070096028A1Improve test efficiencyReduce the burden onMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentBody movementGamma ray detection
The present invention provides a nuclear medicine imaging apparatus and image data generation method that achieves restarting of the generation of projection data and at an early stage while monitoring a variation of count values for detecting an occurrence of non-permissible body movement of a patient. The image processing apparatus consistent with the present invention detects a pair of gamma-rays successively emitted from an object with a radioactive isotope through a pair of detector modules in a data detecting unit. A data processing unit and an incident direction calculating unit in the image processing apparatus respectively calculate a gamma-ray detection position and a gamma-ray incident direction based on the acquired detection signals. A projection data generating unit in the apparatus generates monitoring projection data based on each count value of the detection signals in correspondence to the gamma-ray detection position and the gamma-ray incident direction. A projection data monitoring unit calculates a body movement index of the object by comparing count values of the monitoring projection data that are generated in each of two preferably adjoining monitoring periods. A system control unit generates an alarm signal for performing repetition of the monitoring projection data when the body movement index exceeds a threshold value and displays the alarm signal on a display unit.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Fibrin-binding peptides and conjugates thereof
ActiveUS8278274B2High degreeSuperior fibrin specific bindingAntibacterial agentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBinding peptideThrombus
Fibrin-binding peptides having high binding affinity and excellent physical characteristics compared to previously known fibrin-binding peptides are provided. These fibrin-binding peptides may be conjugated to a detectable label or a therapeutic agent and used to detect and facilitate treatment of pathological conditions associated with the presence of fibrin such as thrombic, angiogenic and neoplastic conditions. These peptides may be used in imaging processes such as MRI, ultrasound and nuclear medicine imaging (e.g. PET, scintigraphic imaging, etc.). The peptides may also be used therapeutically. The present invention also provides processes and methods for making and using such peptides and conjugates thereof.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Respiration correction technique in positron emission tomography
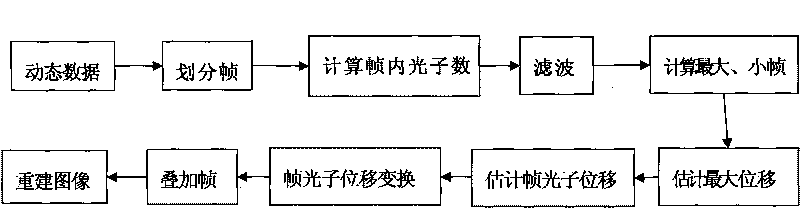
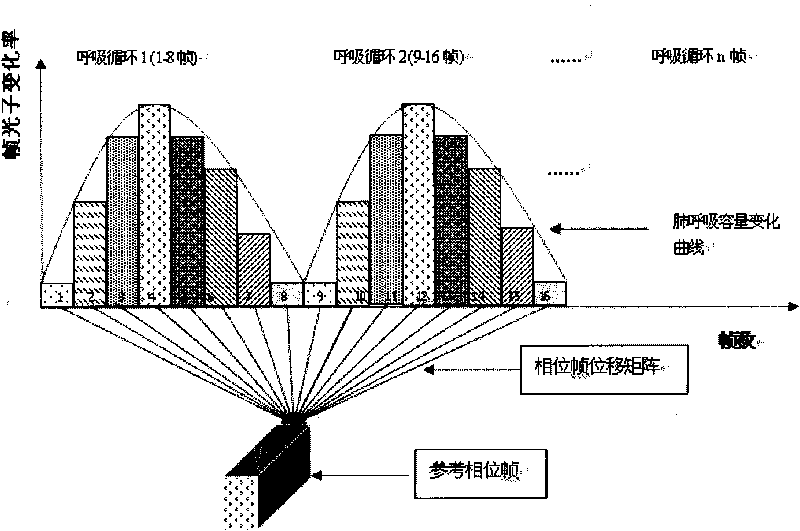
InactiveCN101702232AImprove the correct diagnosis rateCompensate for image artifactsImage enhancement3D-image renderingDetector geometryCorrection technique
The invention relates to a respiration correction technique in positron emission tomography, in particular to a technique for correcting the artifact of respiration tomography on the basis of the sensitivity characteristics of a three-dimensional positron emission detector, belonging to the field of nuclear medical tomography. The correction method provided by the invention can effectively compensate for the image artifact caused by respiration, thereby improving the diagnostic accuracy of doctors. The correction method comprises the following steps: frame segmentation is carried out on the acquired dynamic data by using the variation characteristics of the geometric sensitivity of a scanning detector in the three-dimensional PET, wherein the number of intra-frame photons can reflect the phase position of the organ motion, and the number of photons of each phase position has a linear relation with the motion displacement thereof; accordingly, each phase position is moved to certain reference phase position point for correcting; and the image reconstructed at last constitutes the image artifact caused by the respiration in the PET improved by correction. Compared with the prior art like the gating correction technique, the method of the invention dispenses with hardware equipment and extra preparation by patients or clinic before scanning, therefore, the method is easier, more effective and more reliable in actual application.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Shifted transmission mock for nuclear medical imaging
InactiveUS20070090300A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMedical imagingFor Attenuation Correction
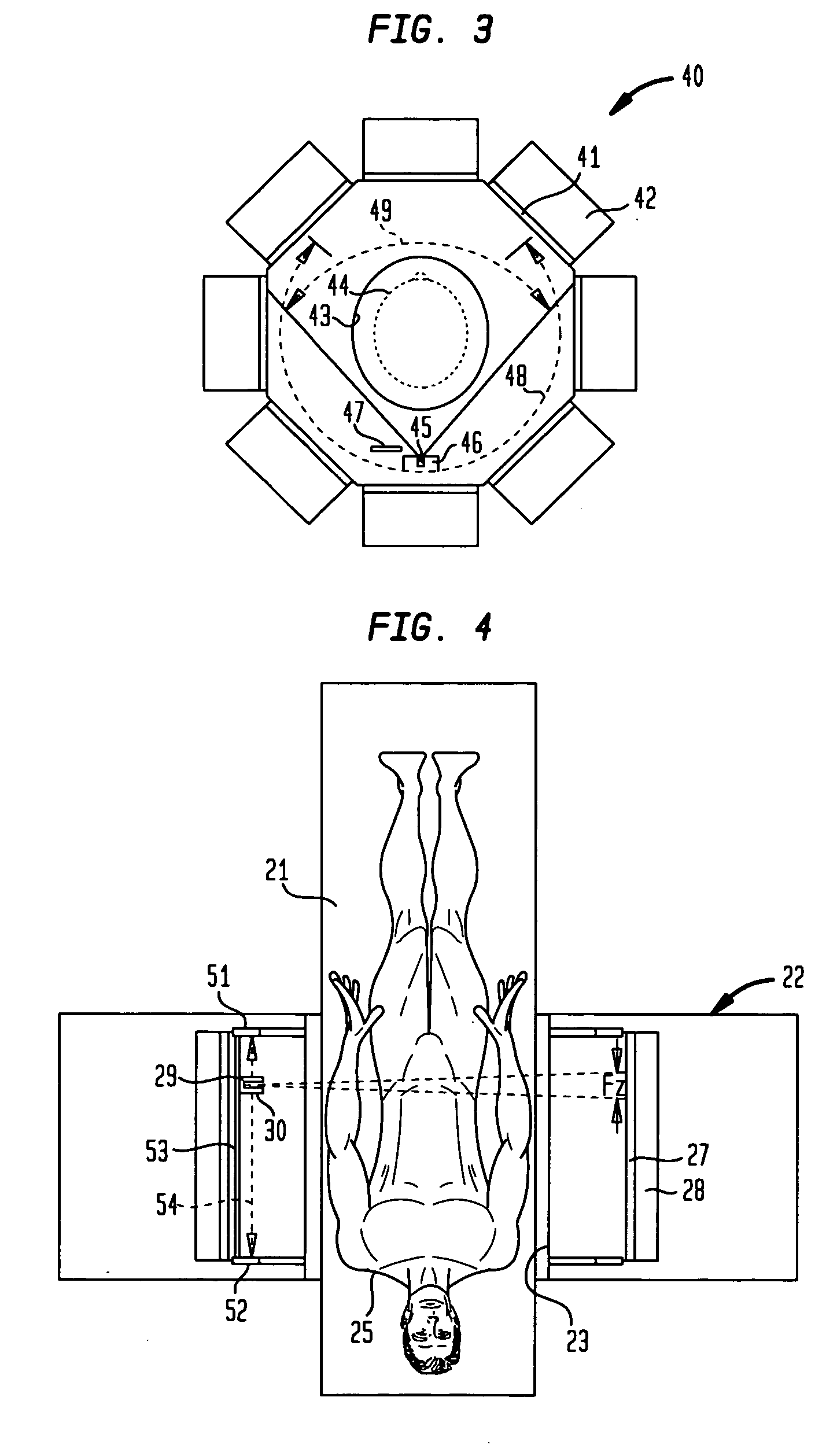
Emission contamination data are collected in a shifted mock scan simultaneous with the collection of transmission data during a transmission scan of a patient with a collimated gamma point source, the transmission data are corrected with the emission contamination data, and the corrected transmission data are used for attenuation correction of emission data for reconstruction of an emission image of the patient. In a preferred implementation, when the point source is at a particular axial location and illuminates an axial beamwidth of “Fz” over the gamma detector, emission contamination data are collected from the gamma detector over an axial separated region “Fz′” having about the same axial extent but axially displaced by about half of the axial field of view (FOV).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multi-pinhole collimation for nuclear medical imaging
ActiveUS7166846B2Reduce spacingMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMedical imagingNuclear medicine imaging
A multi-pinhole collimator nuclear medical imaging detector divides a target object space into many non-overlapping areas and projects a minified image of each area onto a segmented detector, where each segment functions as an independent detector or imaging cell. Septa may be provided between the collimator and the detector, to physically isolate the segments.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
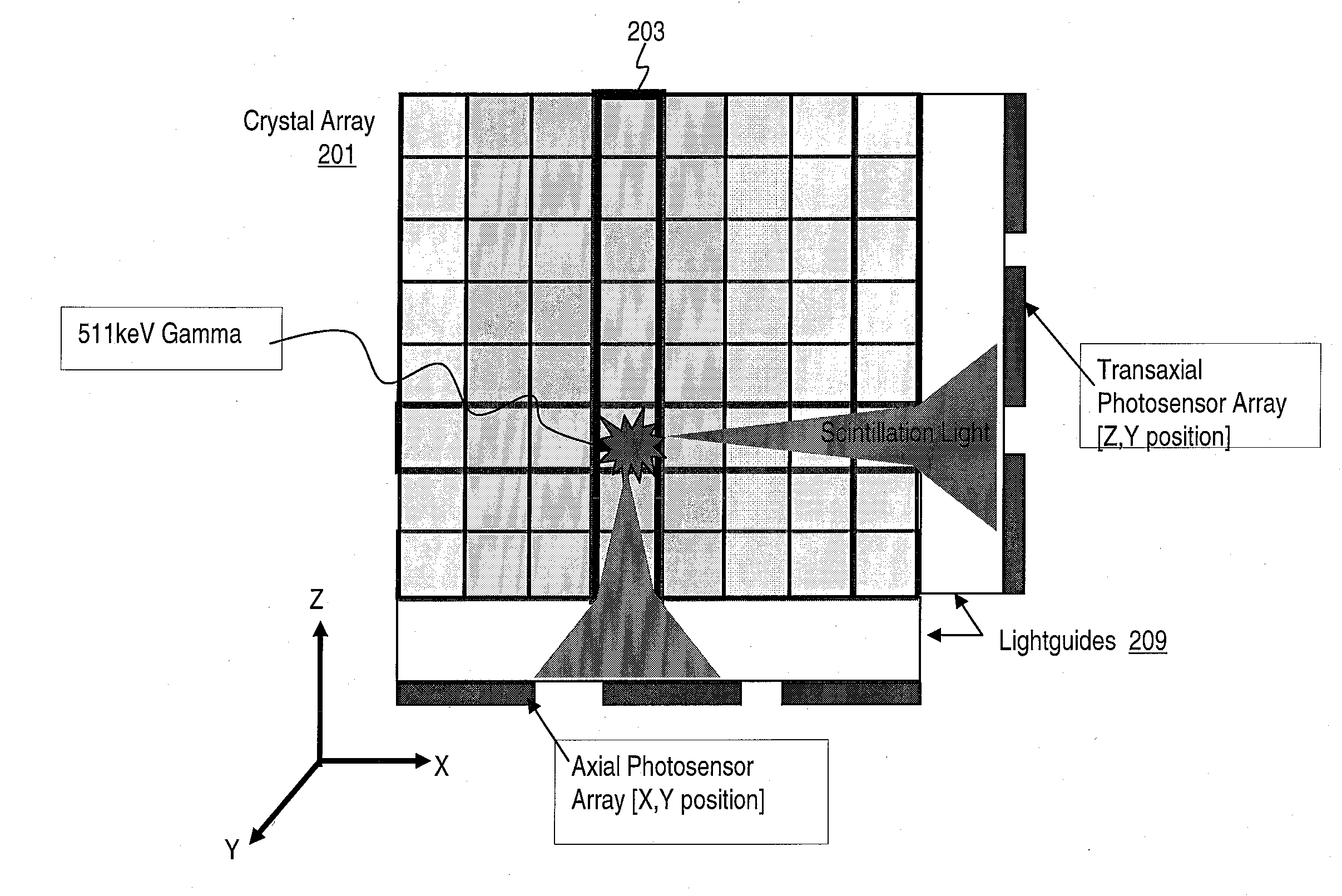
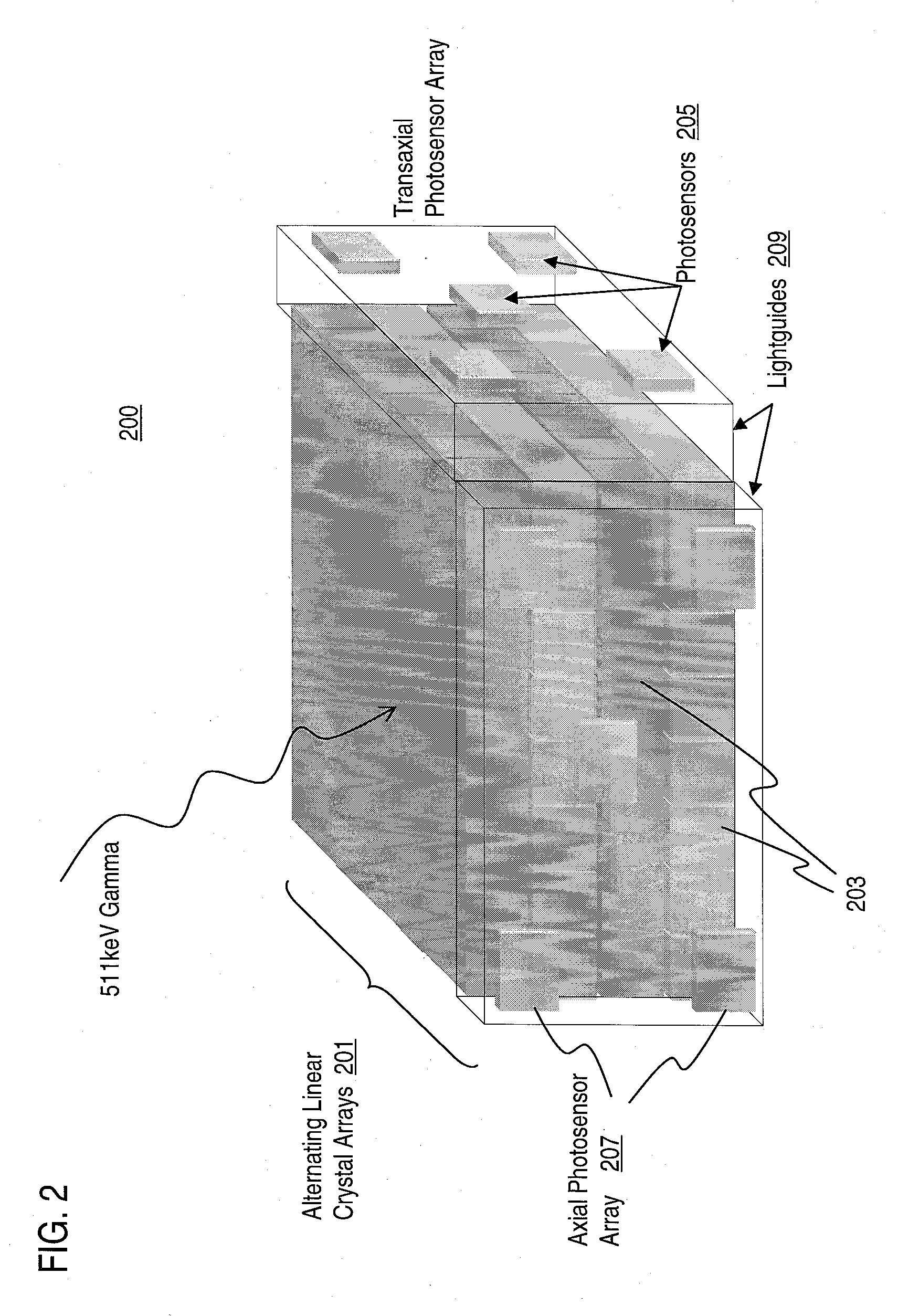
Method and Apparatus for Providing Depth-of-Interaction Detection Using Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
ActiveUS20090008562A1Minimizes edge effectHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyDepth of interactionOpto electronic
A detector is provided for nuclear medicine imaging. Scintillator pixels form an axial array and a transaxial array. A first photosensor is positioned along the axial array; and a second photosensor is positioned along the transaxial array, wherein the first photosensor and the second photosensor provide dual event localization for nuclear medicine imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Systems and methods for calibrating a nuclear medicine imaging system
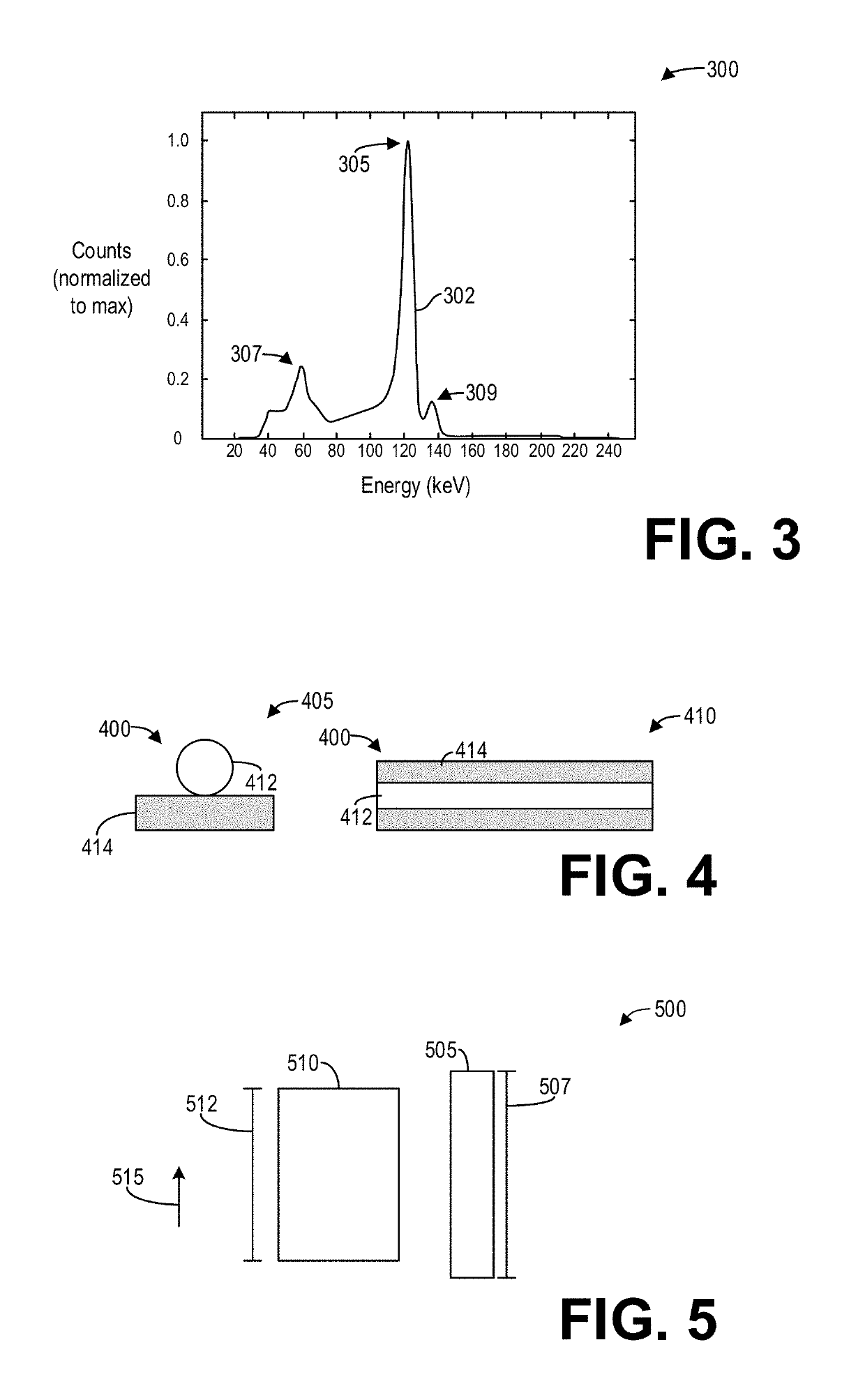
Methods and systems are provided for calibrating a nuclear medicine imaging system. In one embodiment, a method comprises: detecting, with a plurality of detectors, photons emitted by a calibration source comprising a radioactive line source and a fluorescence source, while pivoting one or more detectors of the plurality of detectors; and calibrating, with a processor communicatively coupled to the plurality of detectors, each detector of the plurality of detectors based on energy measurements of the detected photons. In this way, a two-point energy calibration of detectors can be performed with a single isotope, and without removing or adjusting a collimator attached to the detector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com