Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Semiconductor radiation detectors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
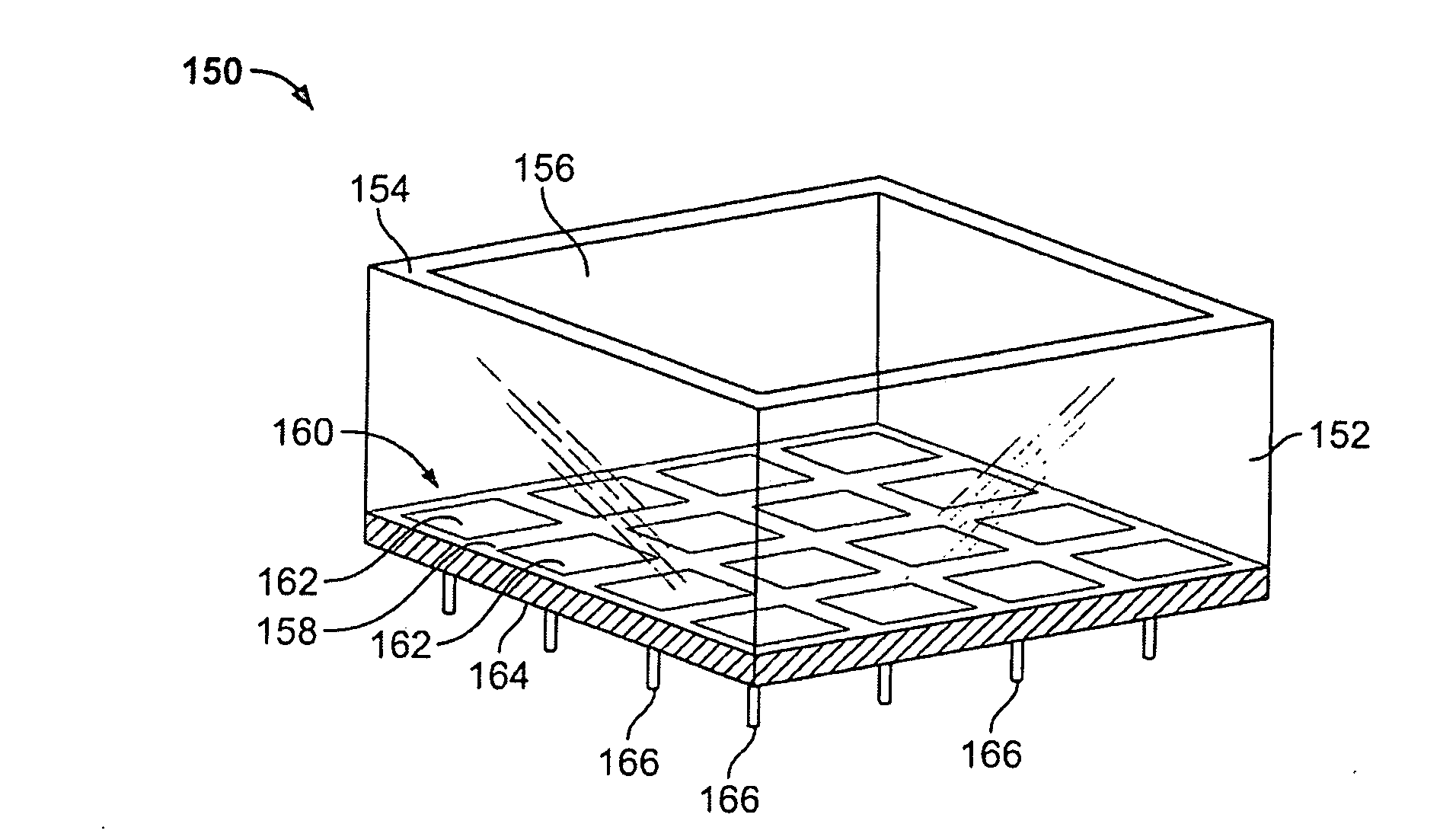
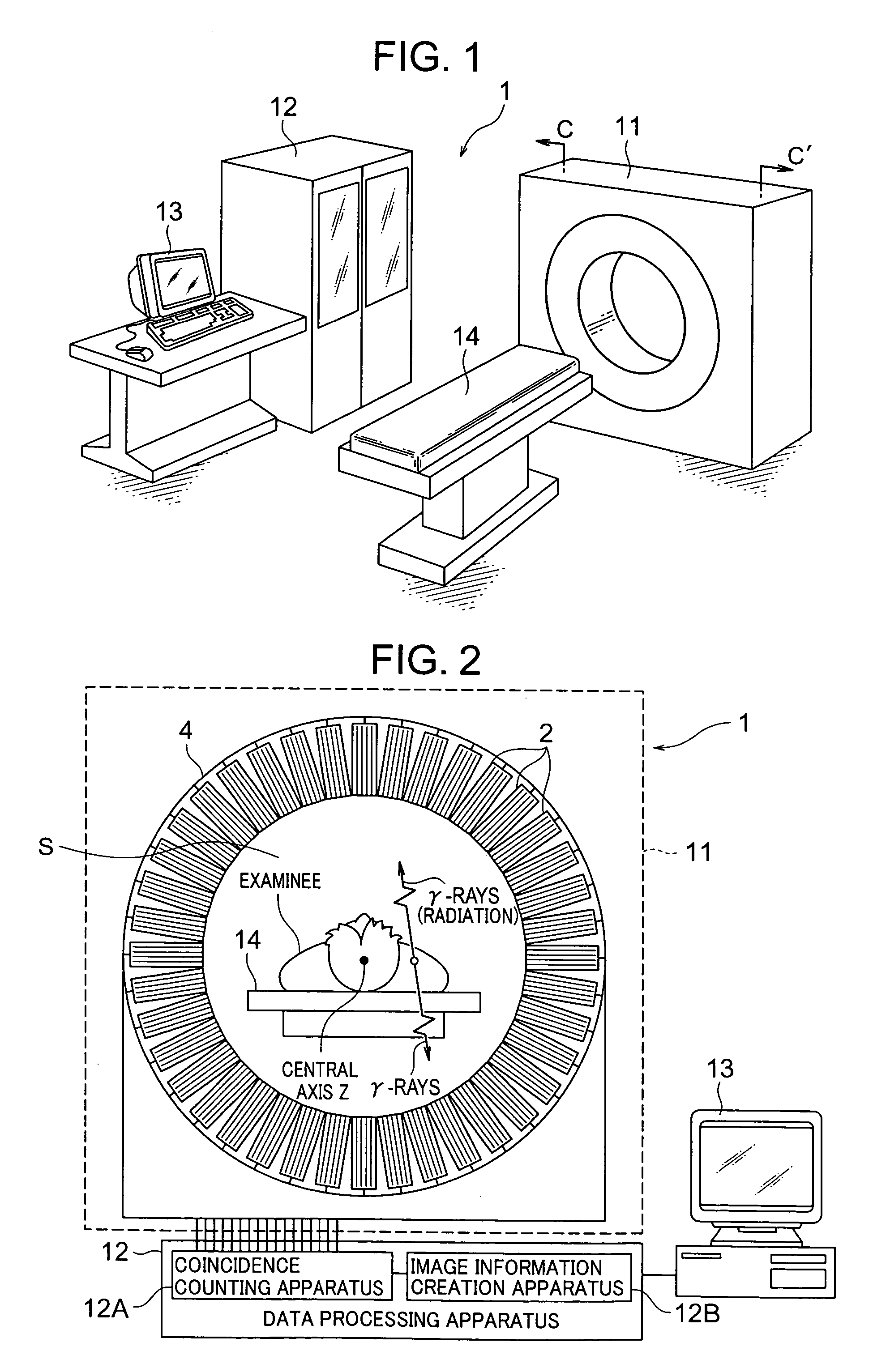
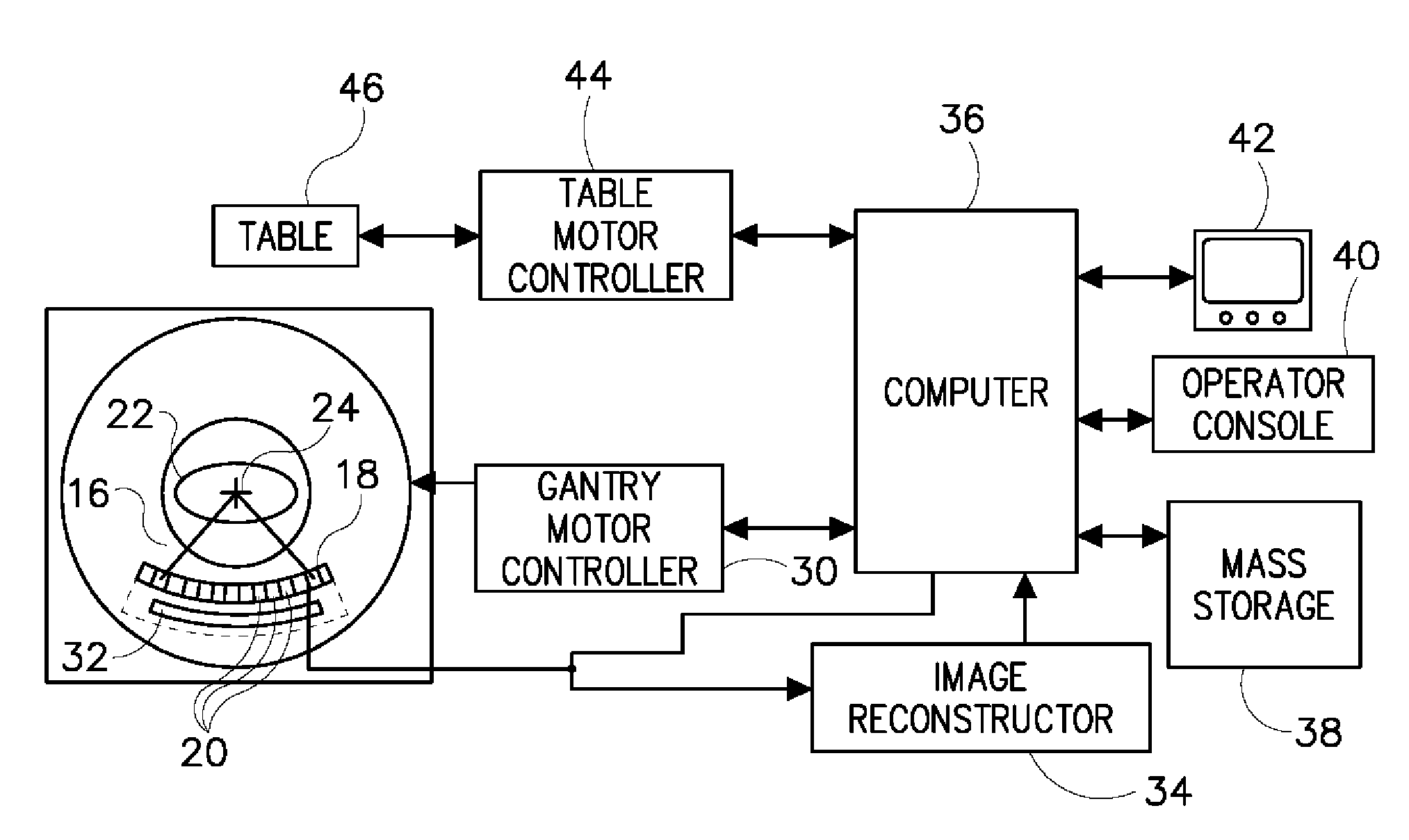
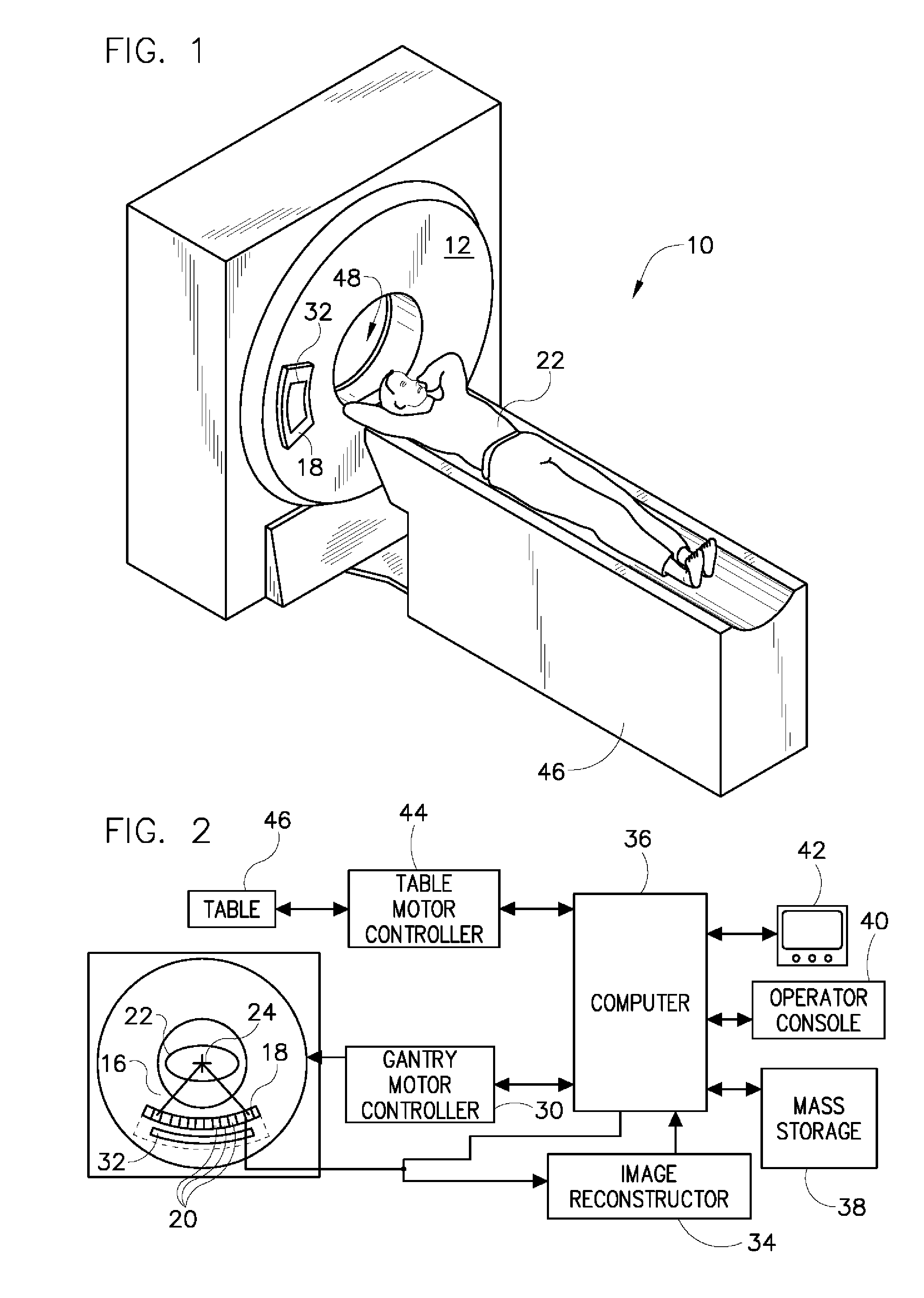
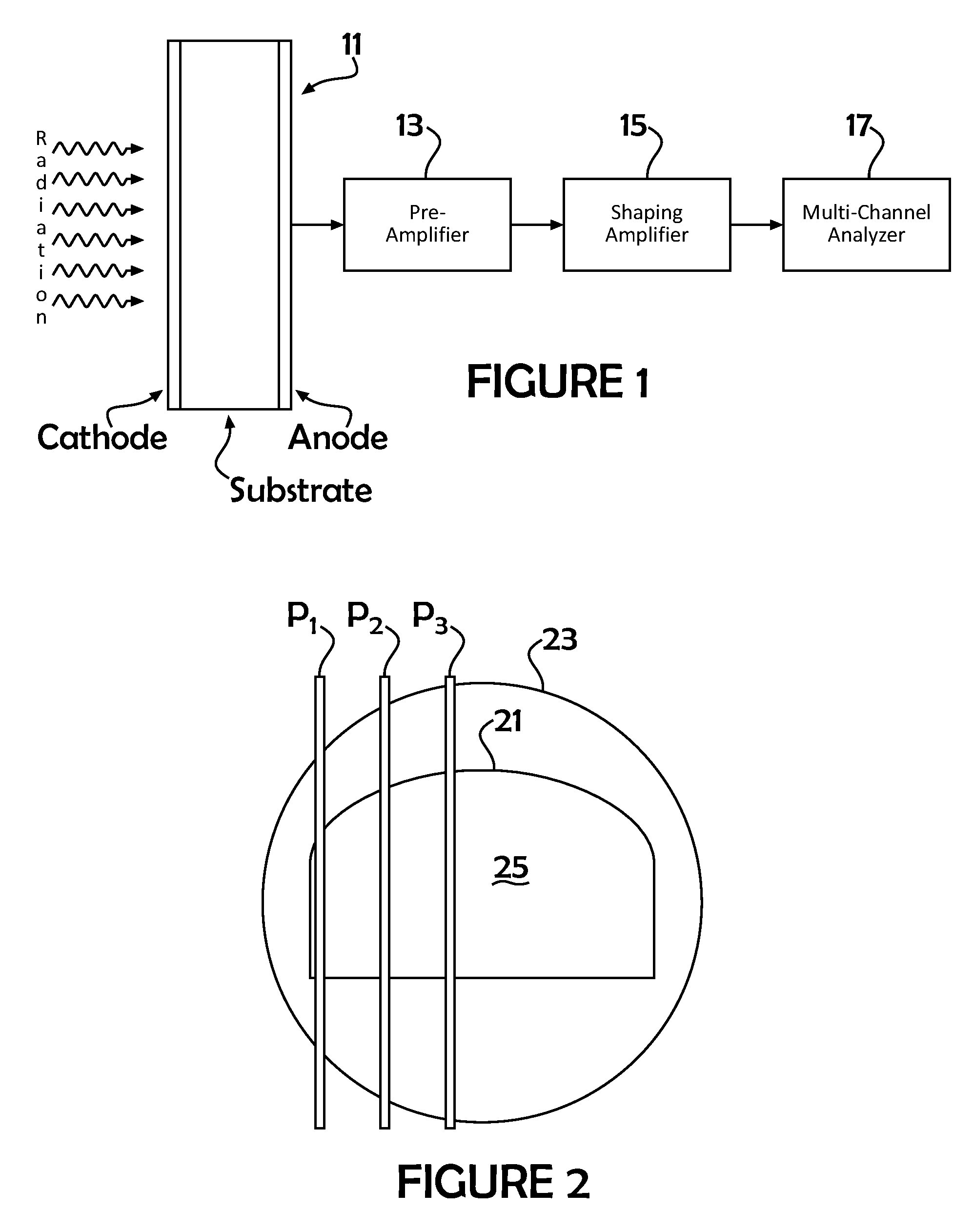
Nuclear medicine imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050067579A1Improve cooling efficiencyImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementSemiconductor radiation detectorsSemiconductor
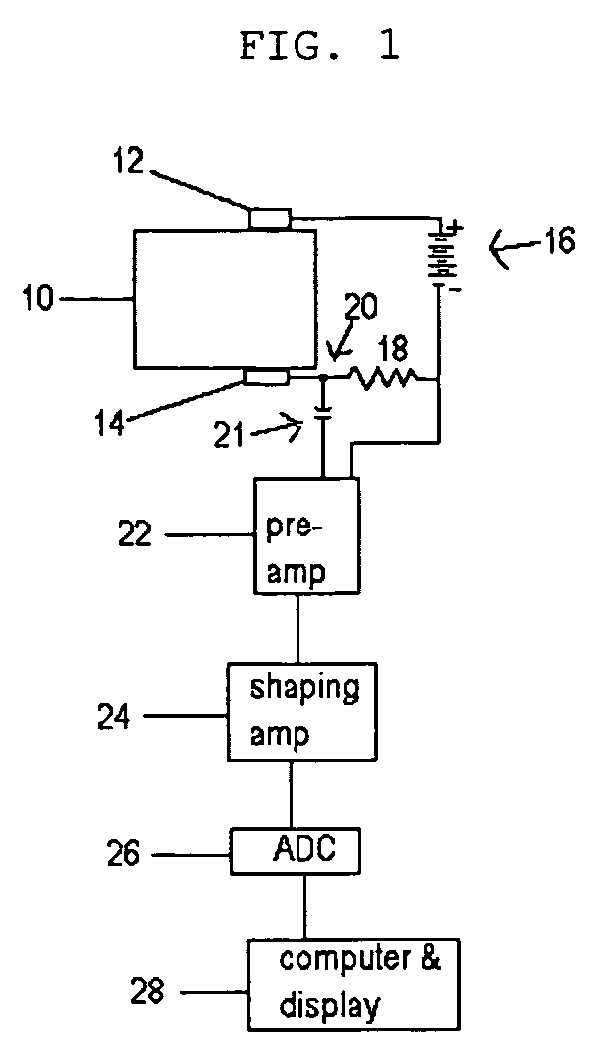
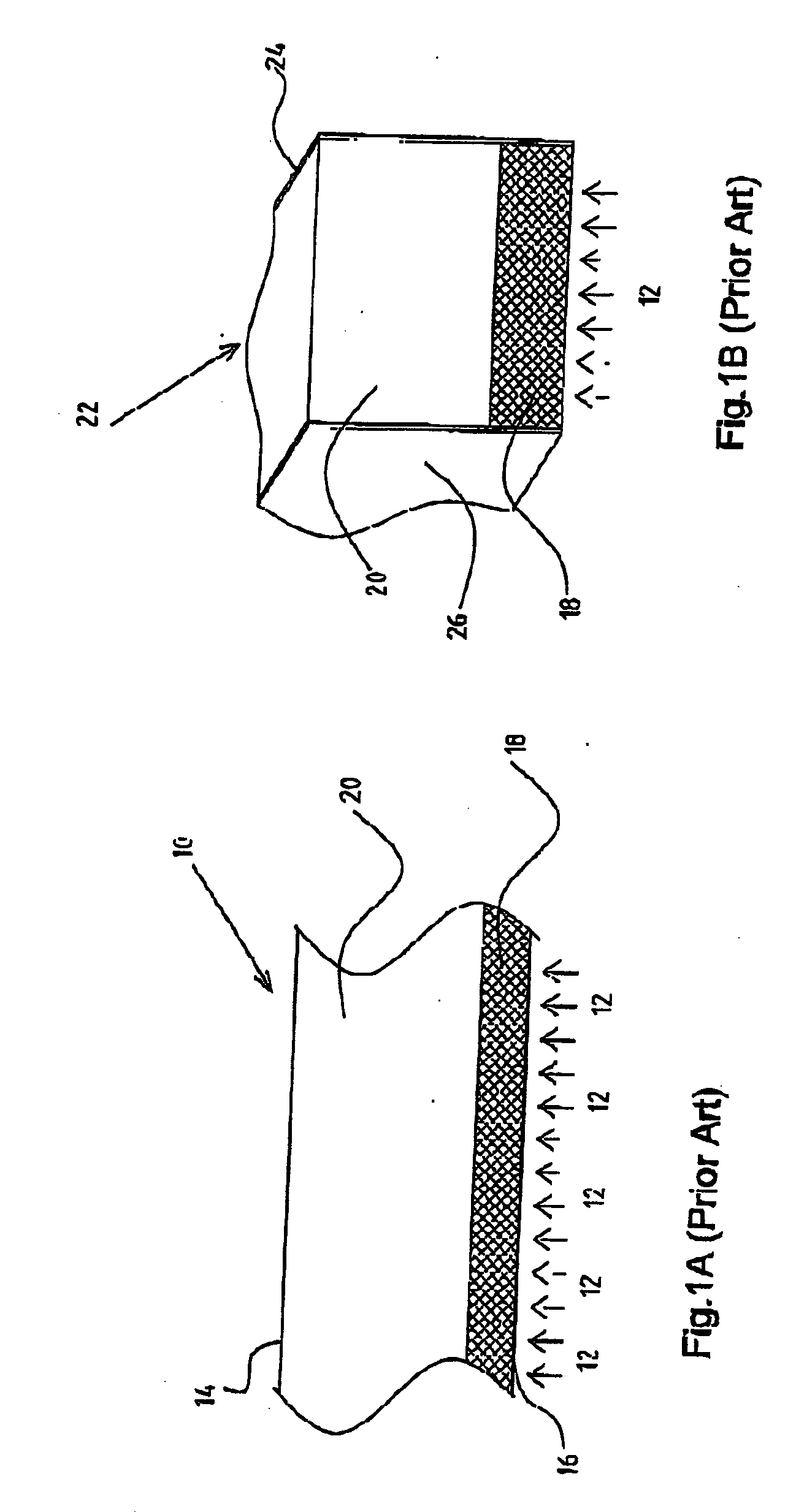
Semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled to improve accuracy in radiation detection. Semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled by heat conductance through heat conductive boards. In addition, the semiconductor radiation detectors are cooled by cooling medium filled or supplied to a heat insulating body covering the semiconductor radiation detectors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor radiation detector with guard ring, and imaging system with this detector
InactiveUS20070280409A1Reduce noiseImprove dynamic rangeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging qualityOpto electronic
A guard-ring electrode can be used at a suitable position for each of a plurality of imaging regions. Improvement in image quality and reduction in unnecessary radiation exposure, such as reduction in artifacts or noise, improvement in SNR, and expansion in dynamic range, are realized by reducing the cross-talk or the inflow of electrical charges from ineffective regions. Based on a radiation detector having a plurality of pixel electrodes 117 and a common electrode that sandwich a photoelectric conversion layer, an interelement guard-ring electrode 111 is adjacently disposed between the pixel electrodes 117 of the radiation detecting element, and the interelement guard-ring electrode 111 is switched between an electrically open-circuit state and a ground-potential connection state, so as to change the area in which the radiation detecting element detects radiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
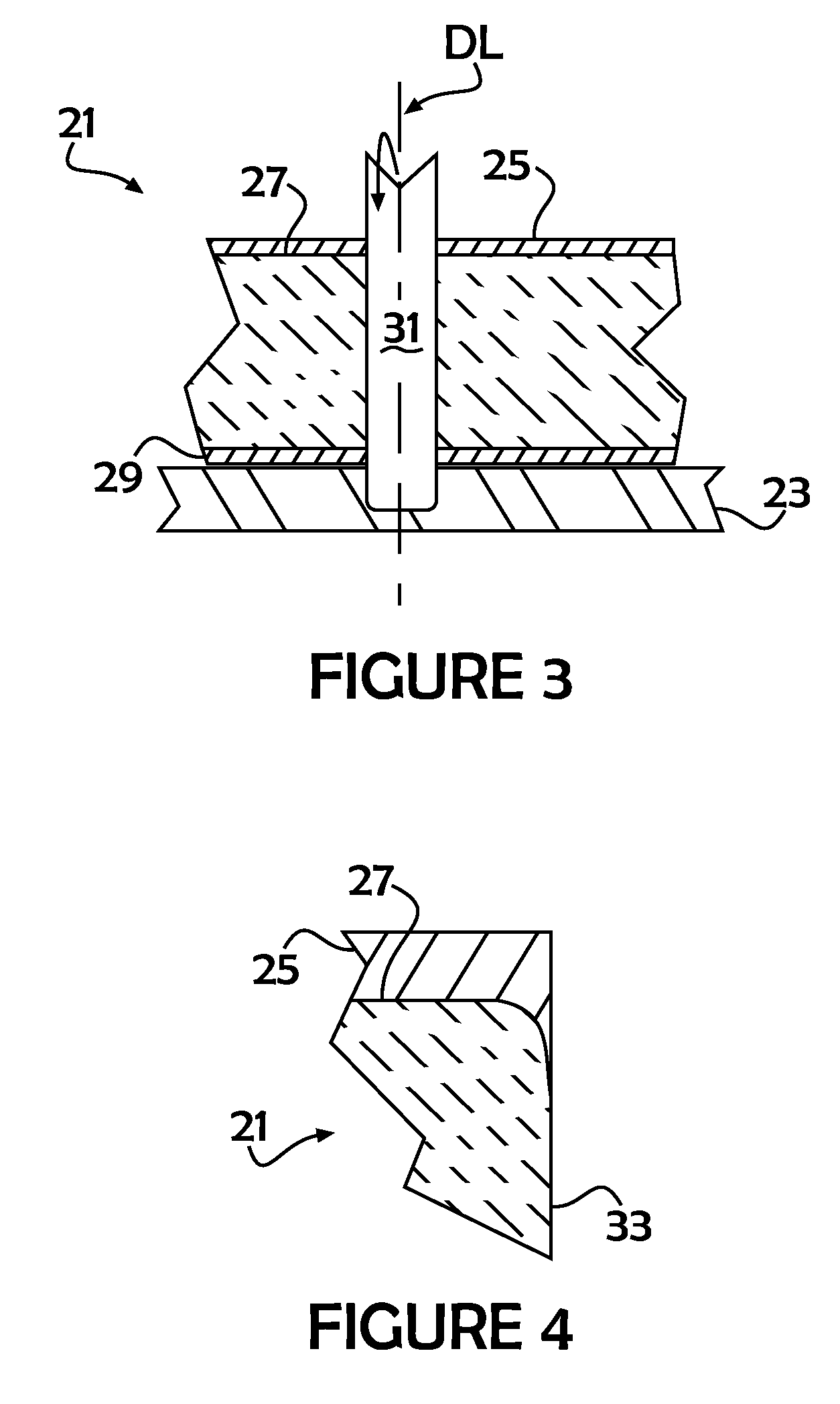
Segmented radiation detector with side shielding cathode
ActiveUS7223982B1Minimize electronic noiseGood detector energy resolutionFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesX-rayCounting efficiency
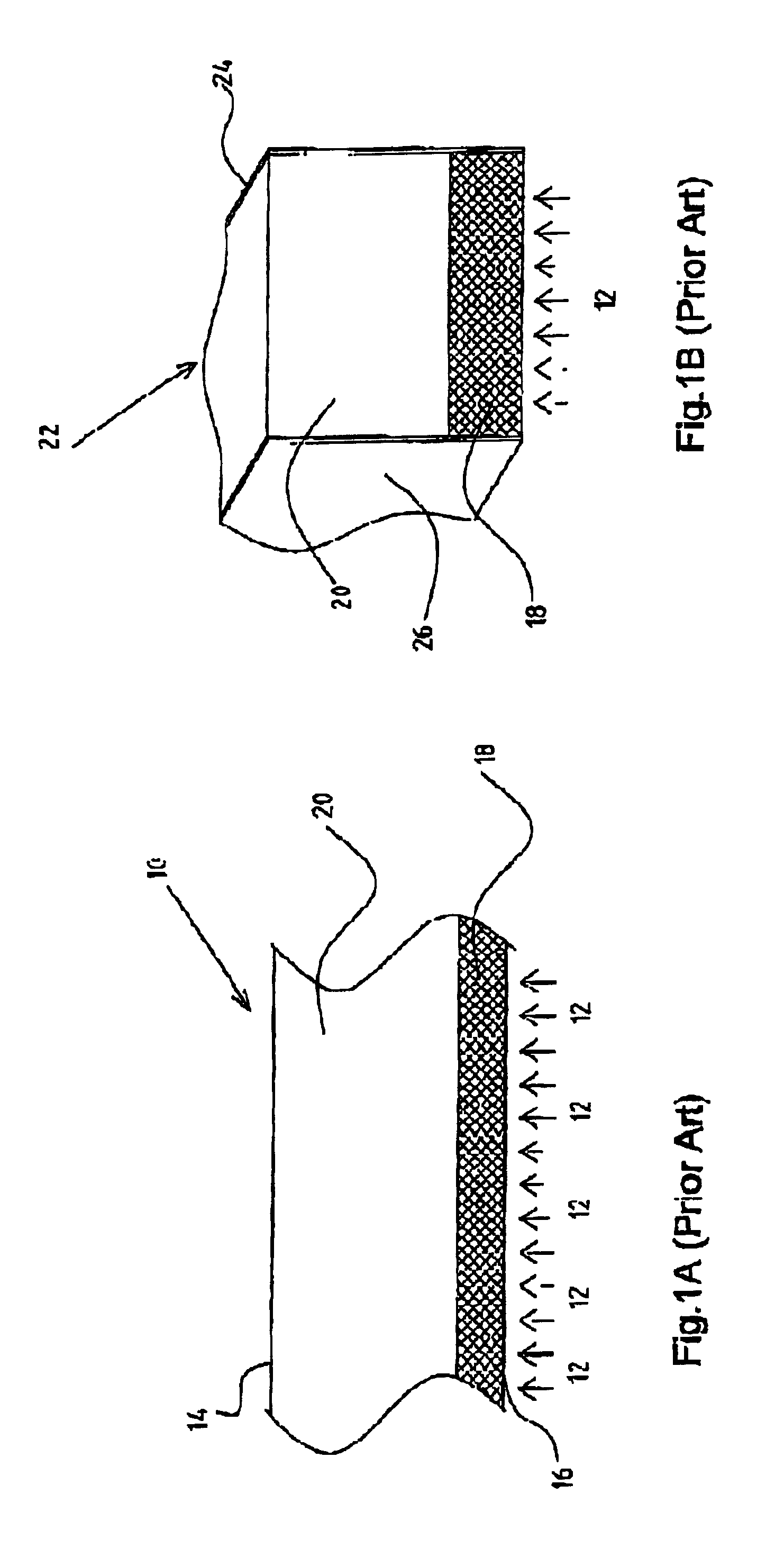
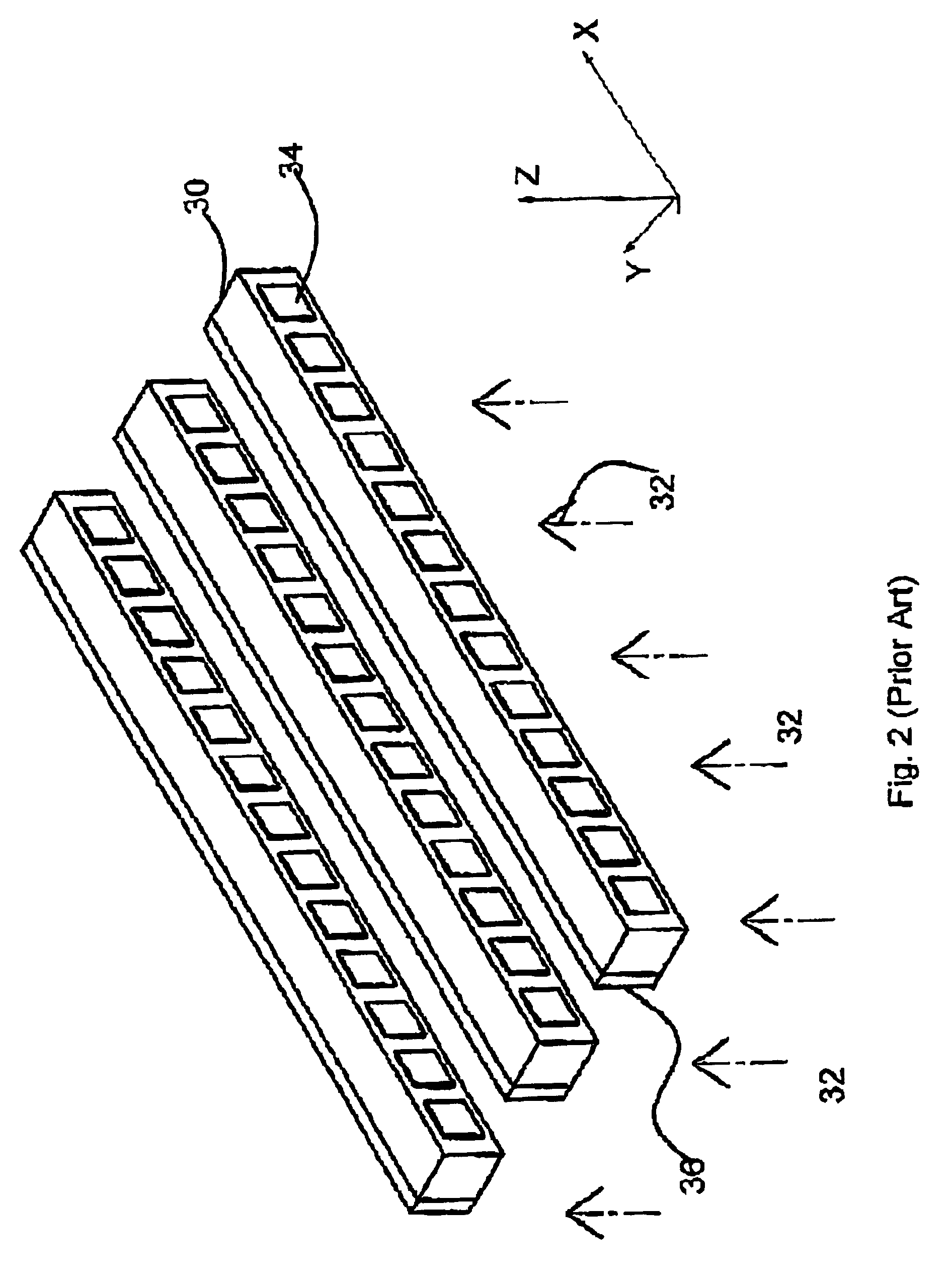
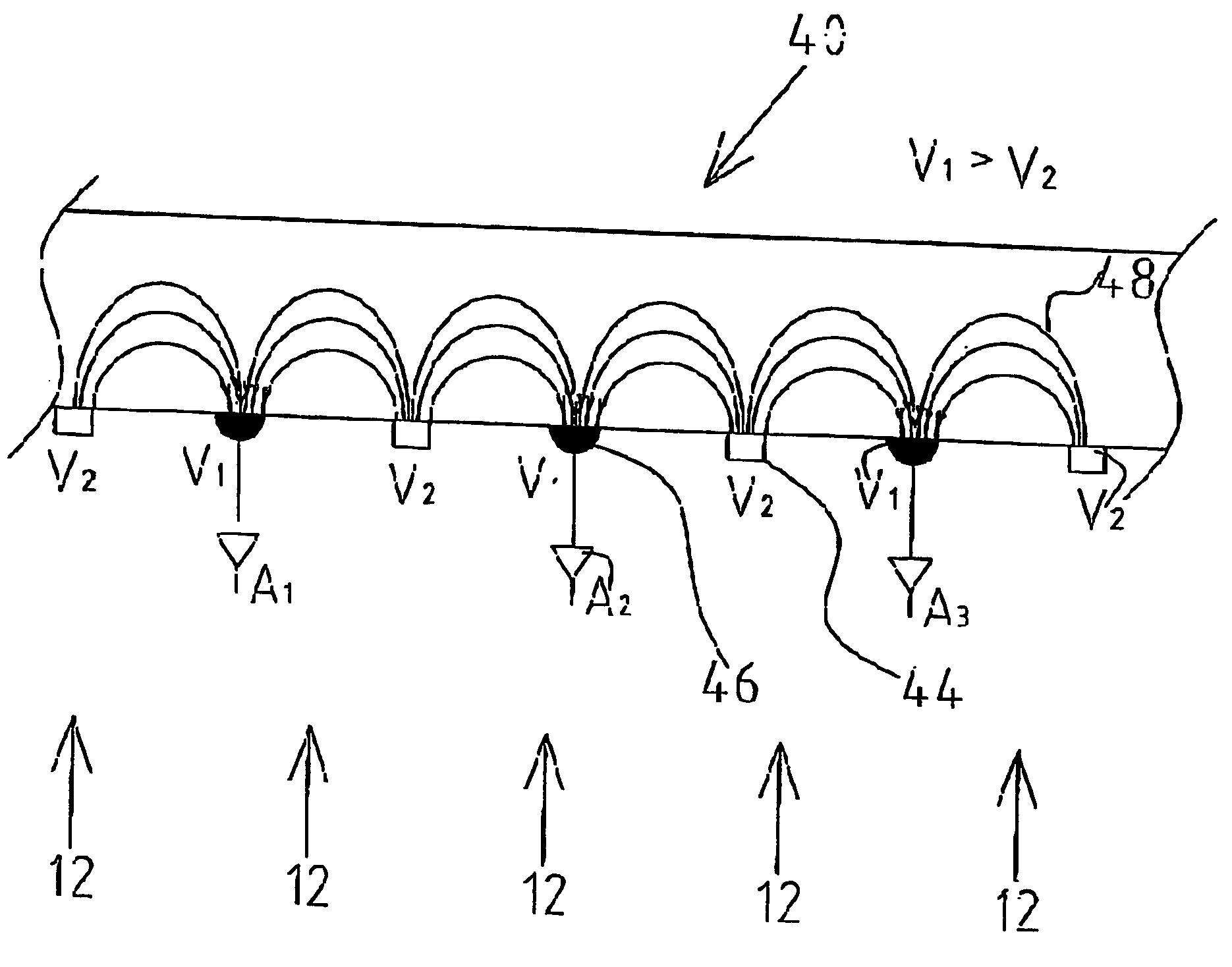
A semiconductor radiation detector is provided for improved performance of pixels at the outer region of the crystal tile. The detector includes a semiconductor single crystal substrate with two major planar opposing surfaces separated by a substrate thickness. A cathode electrode covers one of the major surfaces extending around the sides of the substrate a fraction of the substrate thickness and insulated on the side portions by an insulating encapsulant. An exemplary example is given using Cadmium Zinc Telluride semiconductor, gold electrodes, and Humiseal encapsulant, with the side portions of the cathode extending approximately 40-60 percent of the substrate thickness. The example with CZT allows use of monolithic CZT detectors in X-ray and Gamma-ray applications at high bias voltage. The shielding electrode design is demonstrated to significantly improve gamma radiation detection of outer pixels of the array, including energy resolution and photopeak counting efficiency. The detector has performance of detector leakage current density less than 6 nA / mm2 at a bias potential of substantially 1400V, and responsive to gamma radiation such that the energy resolution full width half maximum of more than 90% of the pixels is less than 6%.
Owner:REDLEN TECH
Method and apparatus for electron-only radiation detectors from semiconductor materials
InactiveUS6069360AElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesElectrode potentialSemiconductor materials
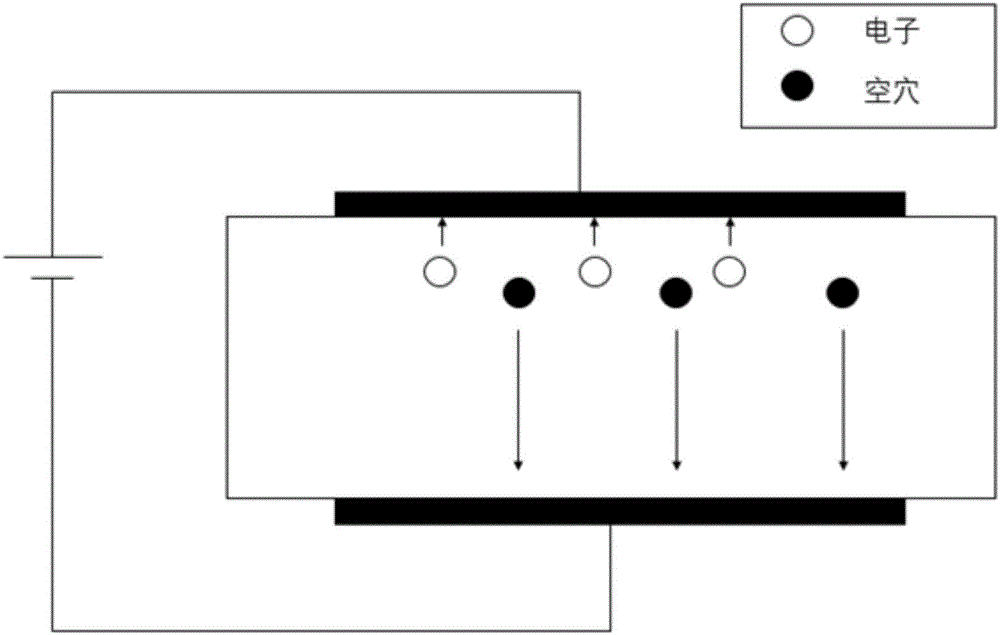
A system for obtaining improved resolution in room temperature semiconductor radiation detectors such as CdZnTe and Hgl2, which exhibit significant hole-trapping. A electrical reference plane is established about the perimeter of a semiconductor crystal and disposed intermediately between two oppositely biased end electrodes. The intermediate reference plane comprises a narrow strip of wire in electrical contact with the surface of the crystal, biased at a potential between the end electrode potentials and serving as an auxiliary electrical reference for a chosen electrode-typically the collector electrode for the more mobile charge carrier. This arrangement eliminates the interfering effects of the less mobile carriers as these are gathered by their electrode collector.
Owner:SANDIA
Apparatus and methods for calibrating pixelated detectors
ActiveUS20100193696A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsPixel based
An apparatus and methods for calibrating pixelated detectors are provided. A method includes acquiring energy response data for a plurality of pixels of the pixelated semiconductor radiation detector and performing at least one of energy calibration and sensitivity calibration on each of the plurality of pixels based on the acquired energy response data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
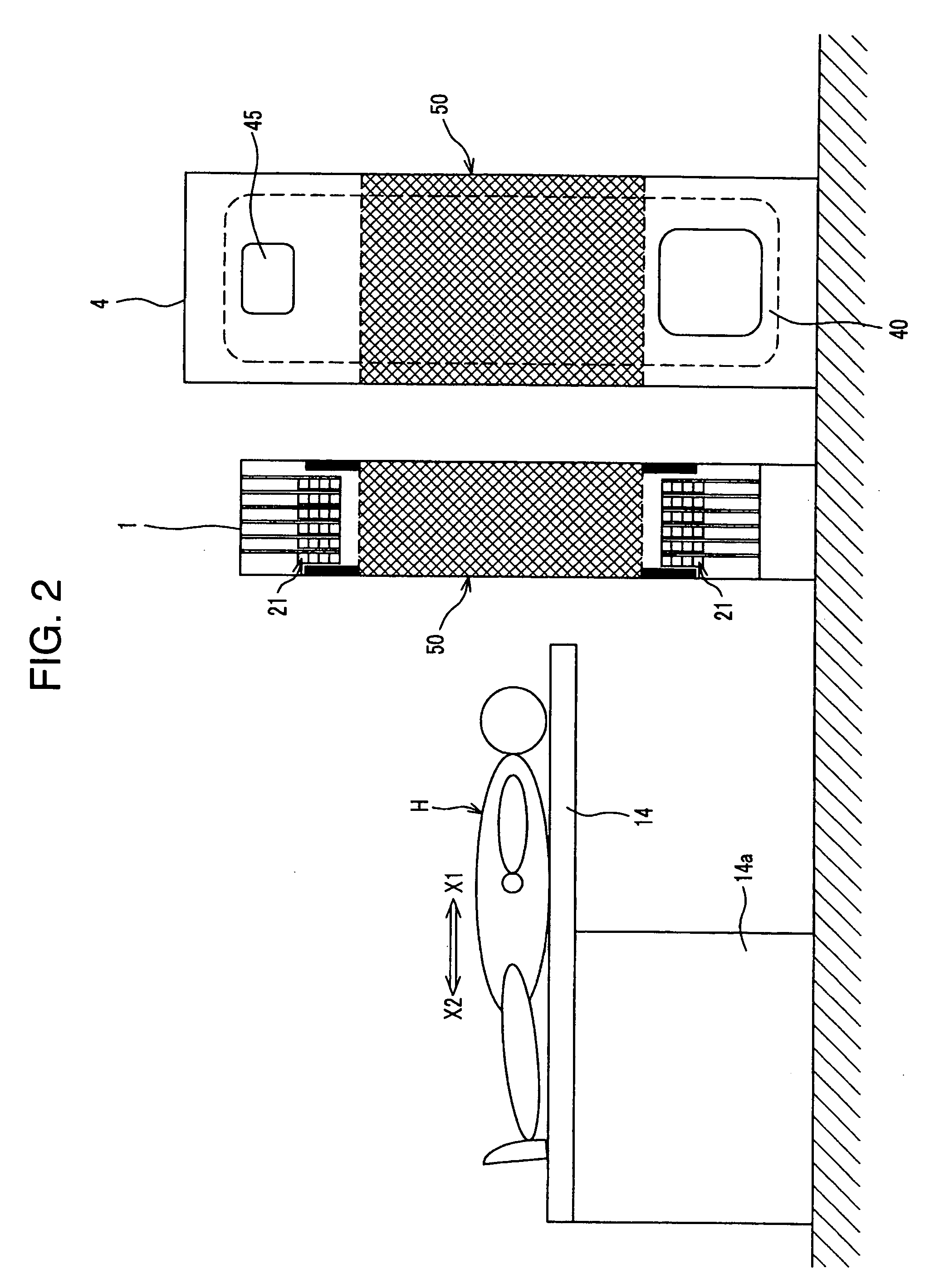
Radiological imaging system
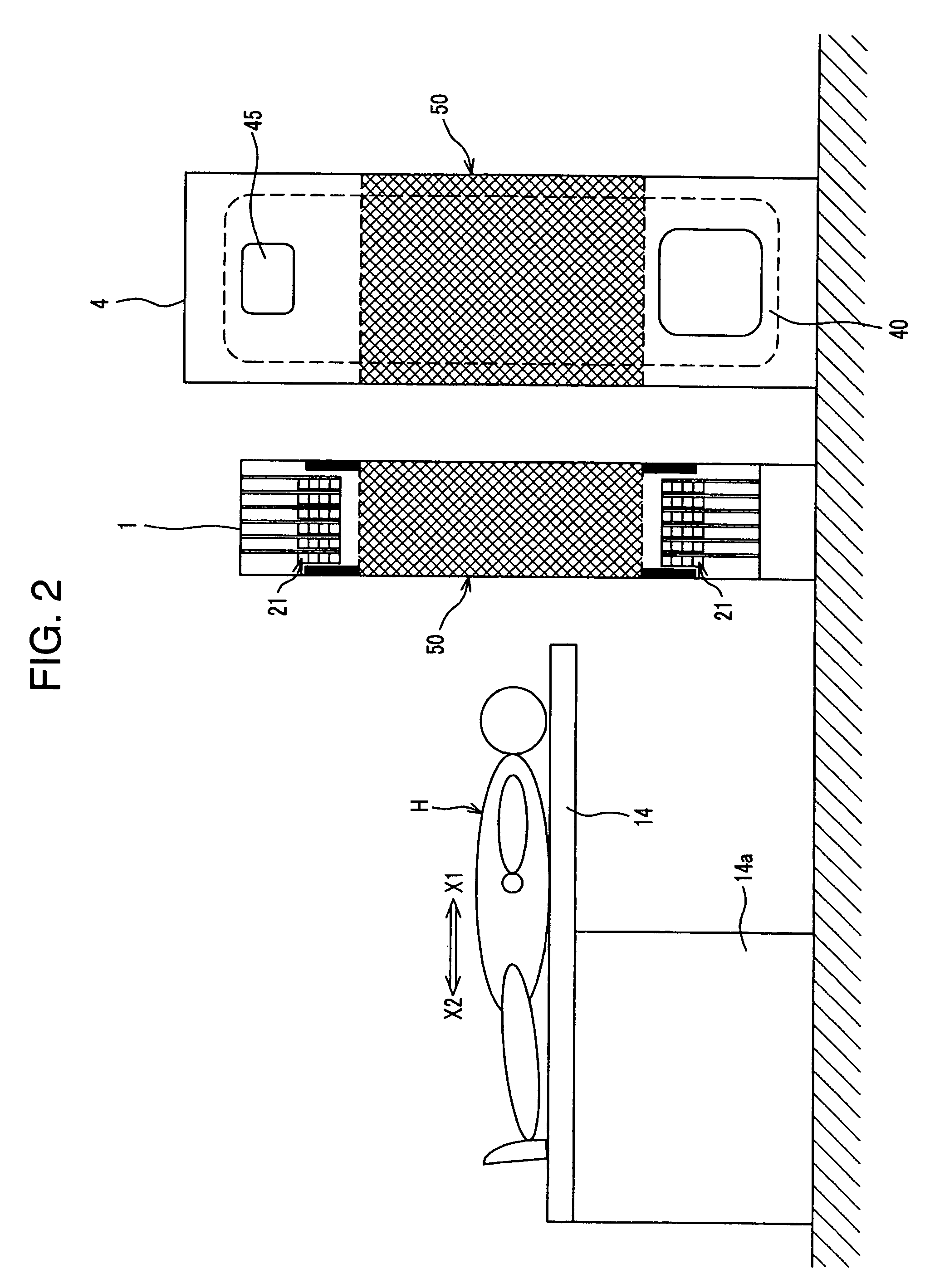
InactiveUS20050067578A1Less intimidatingSmall sizeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
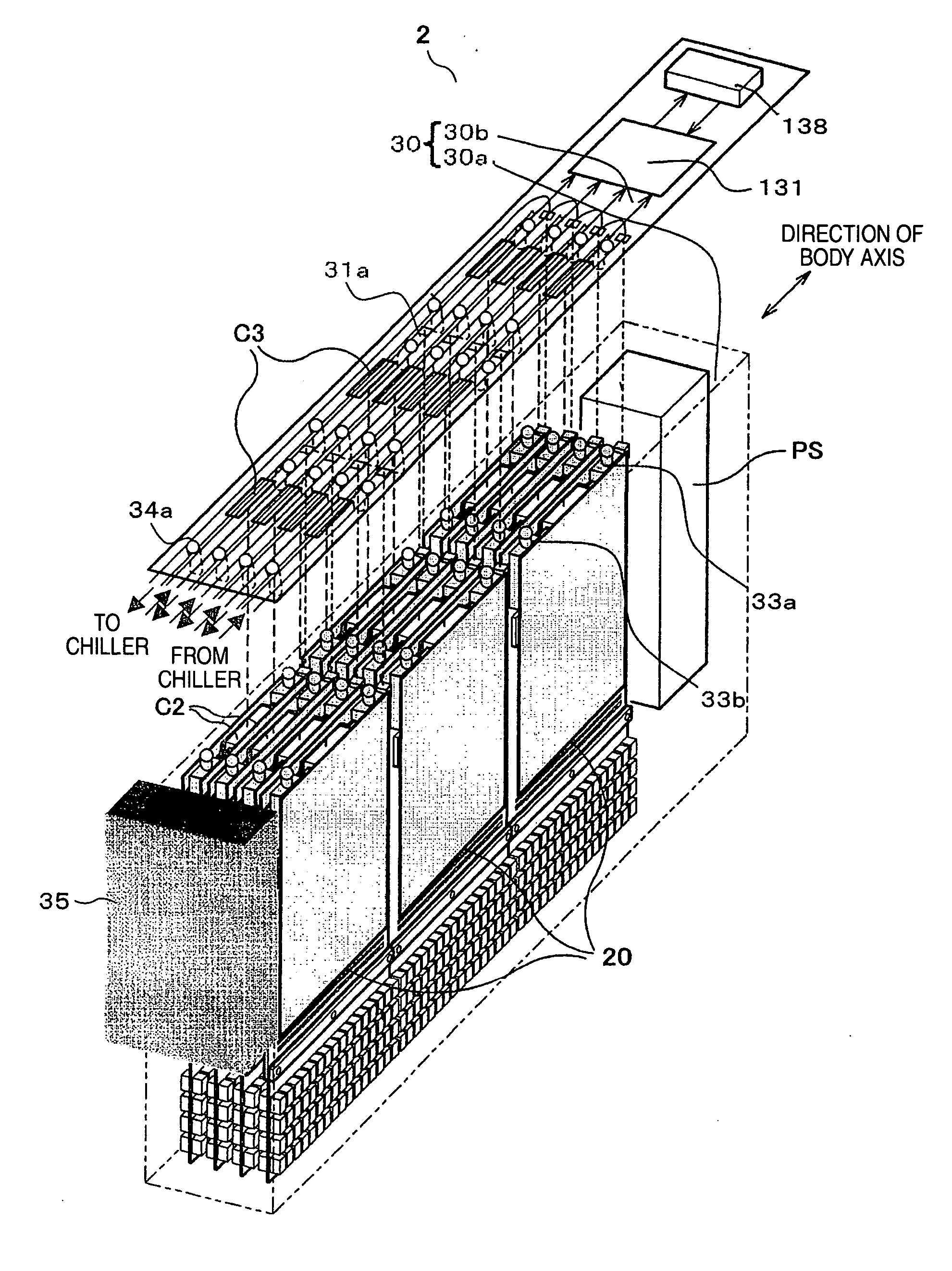
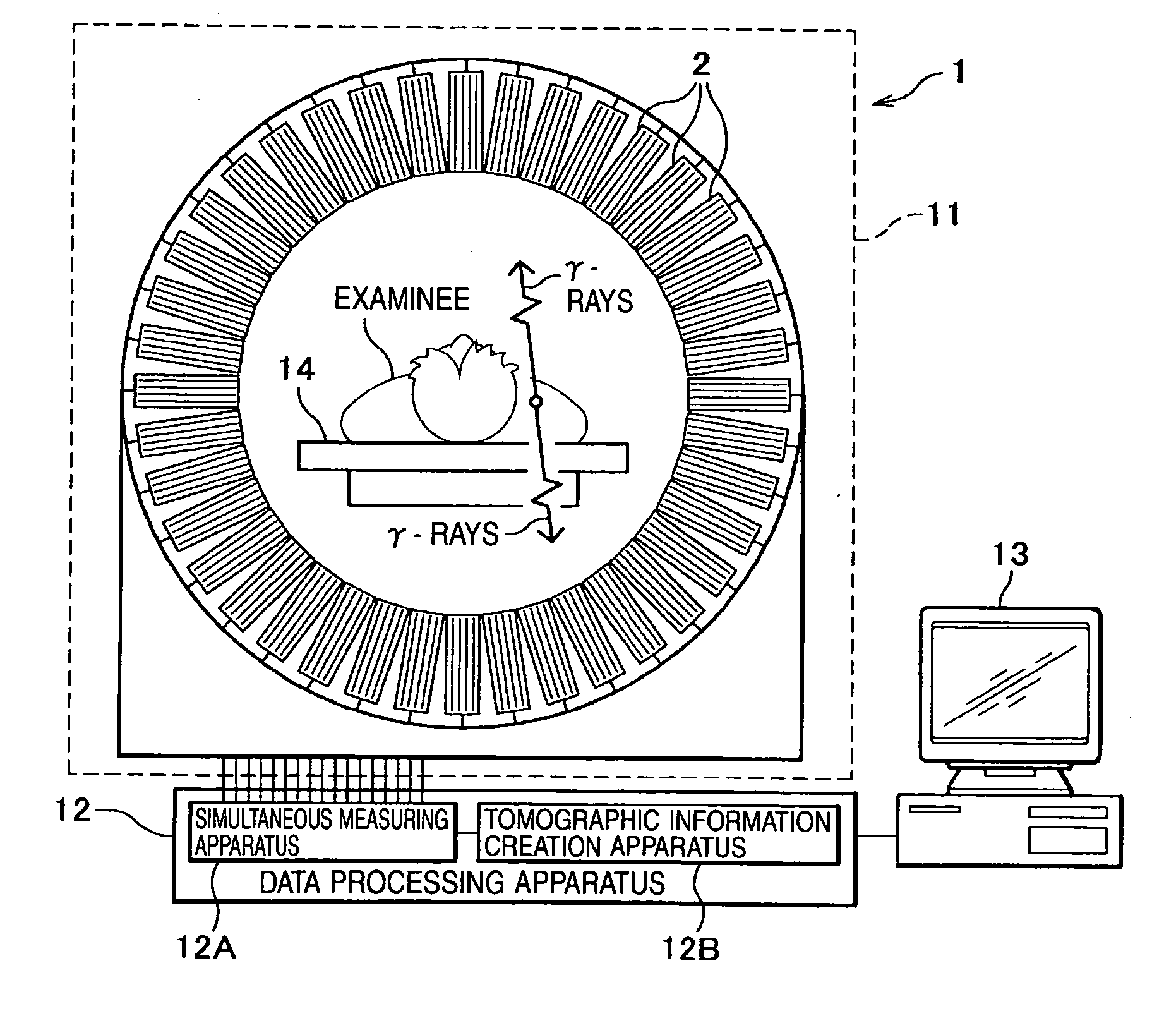
The radiological imaging system which can improve an energy resolution and perform a diagnosis with high accuracy includes a bed for carrying an examinee H, first and second imaging apparatuses and disposed along the longitudinal direction of the bed. The first imaging apparatus has a plurality of semiconductor radiation detectors for detecting γ-rays emitted from the examinee H, arranged around the bed, the second imaging apparatus has an X-ray source for emitting X-rays to the examinee H and a radiation detector for detecting X-rays which have been emitted from the X-ray source and passed through the examinee H, and the bed is shared by the first imaging apparatus and the second imaging apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
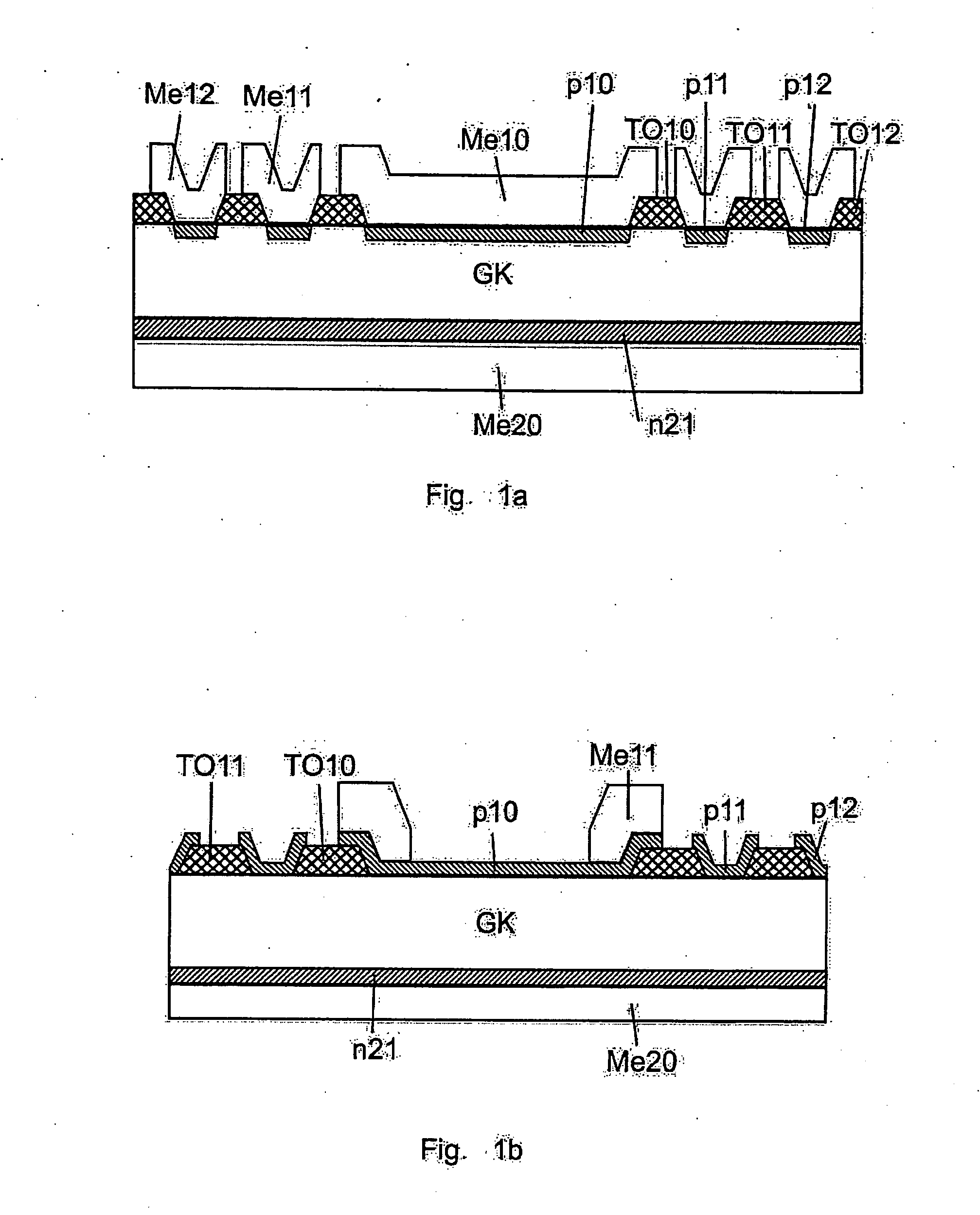
Semiconductor radiation detectors and method for fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20070072332A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSemiconductor radiation detectors
The invention relates to a method for fabricating semiconductor radiation detectors comprising a bulk of a first conductivity type for detecting radiation with further semiconductor layers of a second and a first conductivity type patterned thereon, at least one of the further semiconductor layers being deposited by epitaxy. The invention relates further to integration of electronic components in radiation detectors in employing epitaxy, as well as to radiation detectors of a great variety in which epi layers are deposited as thin radiation entrance windows, as guard structures and as resistive layers.
Owner:KEMMER JOSEF
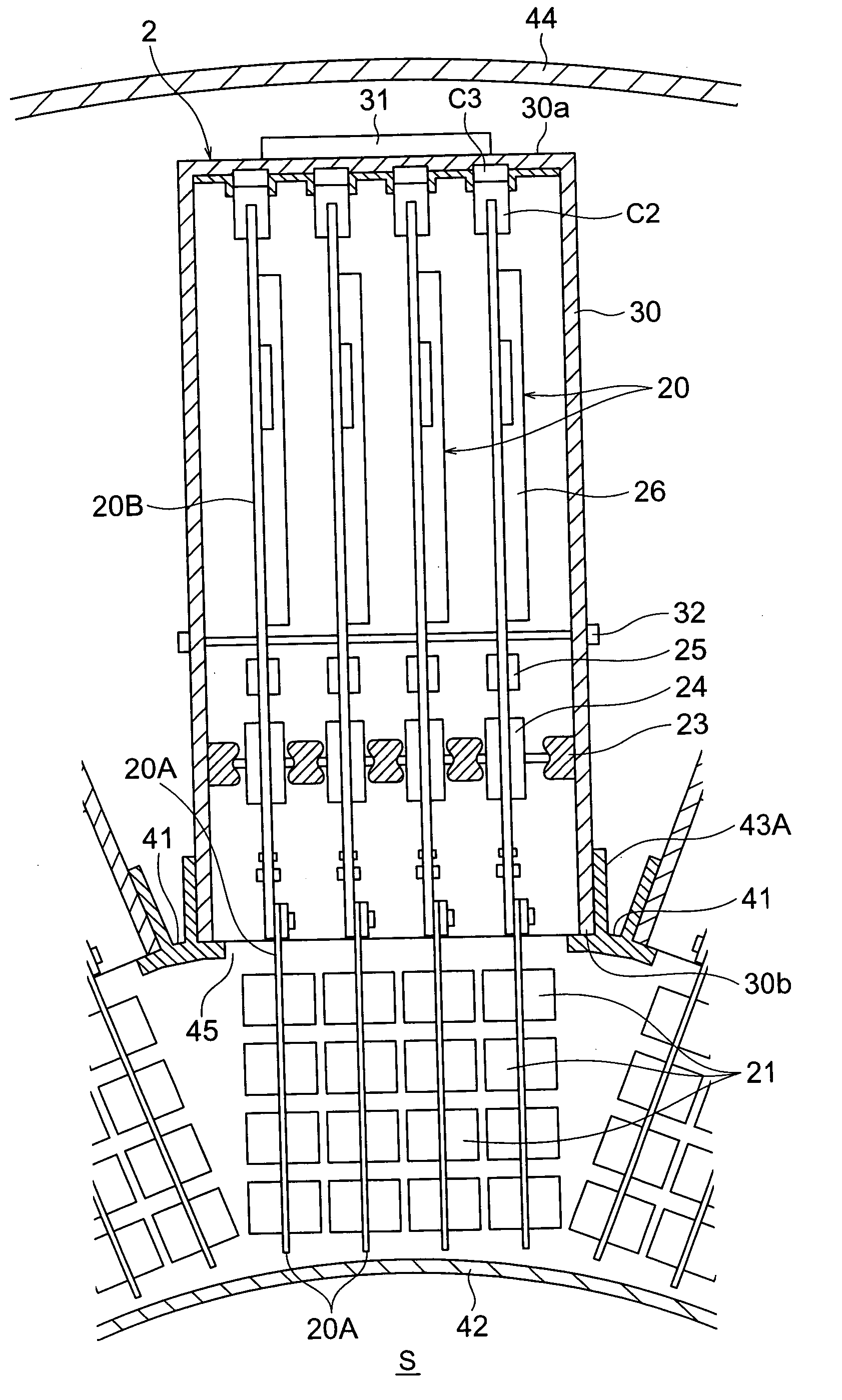
Semiconductor radiation detector and radiological imaging apparatus
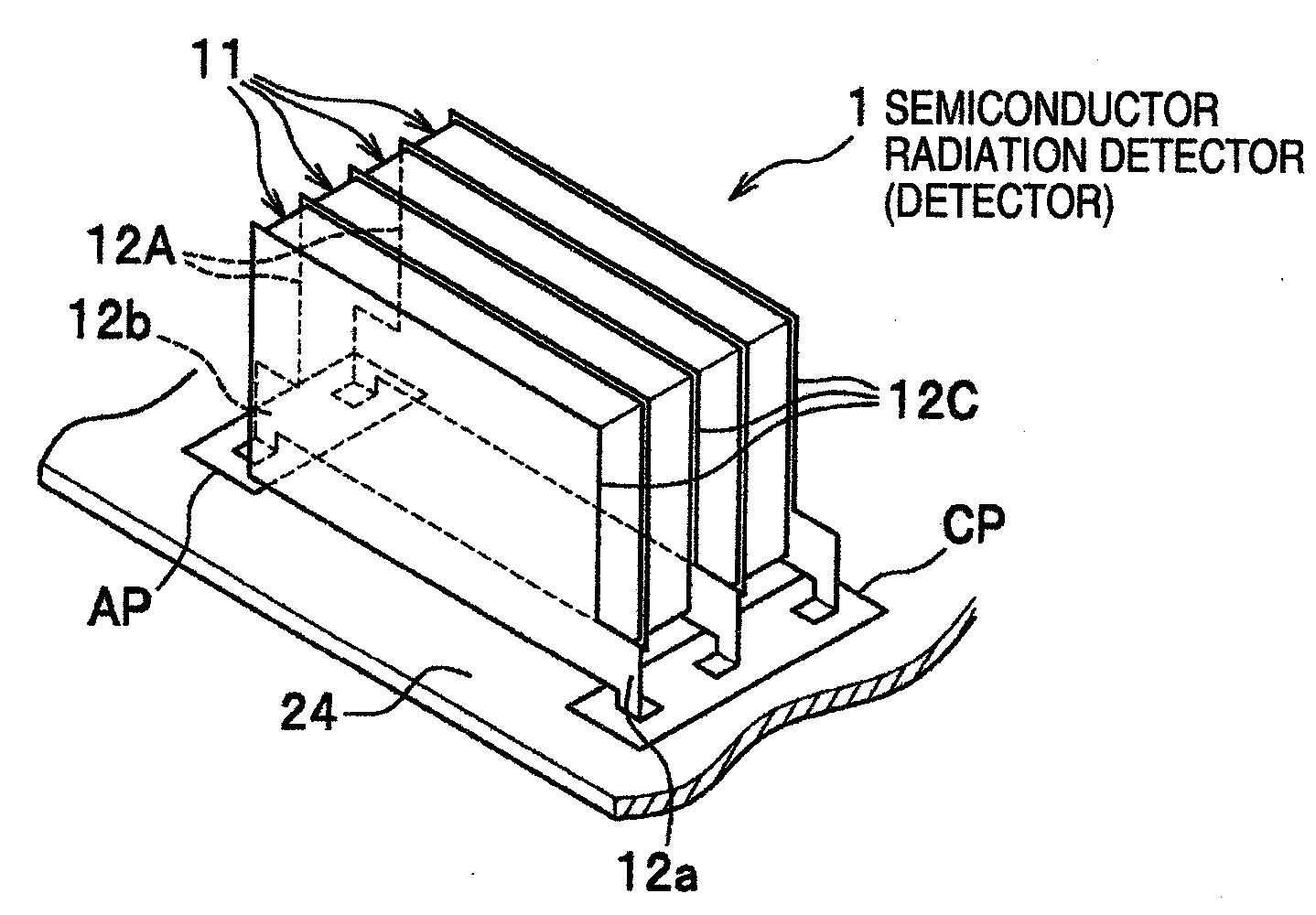
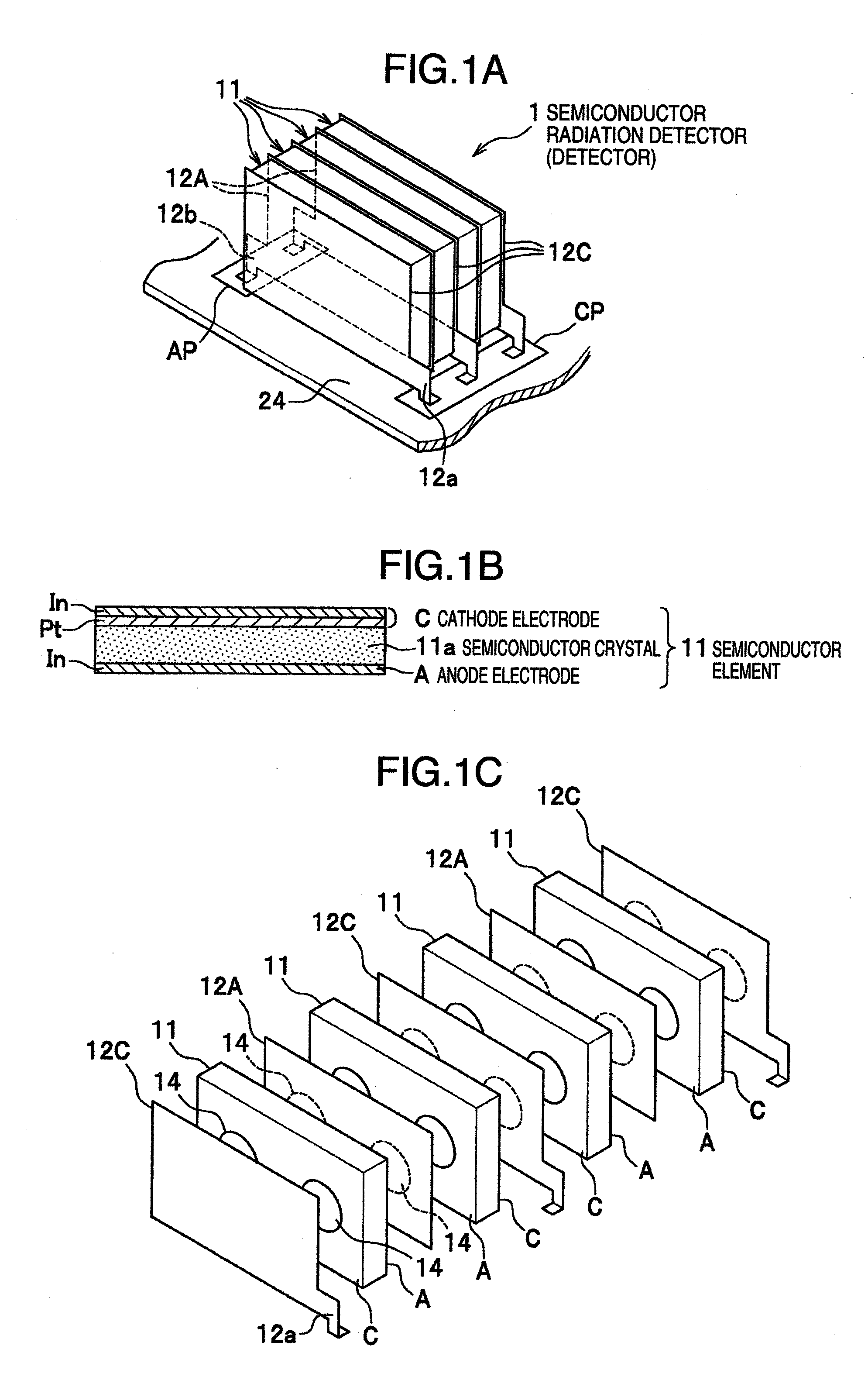
InactiveUS20050067577A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
A radiation imaging apparatus with high spatial resolution including semiconductor radiation detectors arranged on a wiring board capable of detecting γ-rays by separating their positions in the direction of incidence of γ-rays is provided. A semiconductor radiation detector is constructed by including five semiconductor devices made up of, for example, CdTe rectangular parallelepiped plates, a cathode electrode on one side of the semiconductor device, an anode electrode on the other side of the semiconductor device and an insulator for coating five semiconductor detection devices from the outside. The semiconductor radiation detector is mounted on a wiring board using an anode pin and a cathode pin.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radiation detector and radiation apparatus
InactiveUS20050098730A1Rapidly and efficiently collectSolve the low detection efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
A practical semiconductor radiation detector capable of collecting electrons rapidly with a large volume is disclosed. A multiple layers of grid electrodes around an anode formed on a semiconductor element limits the generation of the induced charge signal for the anode to the space in the neighborhood of the anode, while at the same time making it possible to collect the electrons rapidly. As a result of limiting the space for generating the induced charge by the grid electrodes, the energy resolution is improved even for a thick semiconductor element. Also, the capability of rapidly collecting the electrons due to the high field strength generated by the grid electrodes makes a sensitive volume of the whole semiconductor and thus achieves a high radiation detection efficiency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Two-dimensional radiation detector
InactiveUS6946660B2Improve efficiencyLower levelSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsAnode spot
A two-dimensional, pixellated, monolithic semiconductor radiation detector, in which each detector pixel is essentially a perpendicular mode detector. This is achieved by an arrangement of anode spots, one for each pixel located on the flux-exposed front surface of the detector substrate, surrounding by a cathode array preferably in the form of a network of lines, such that the field between the anodes and cathodes on this front surface has a major component in the direction parallel to the surface, and hence perpendicular to the incident photon flux. The conductivity of the substrate is high near this front surface, since this is where the highest level of absorption of photons takes place, and a significant photoconductive current is thus generated between cathodes and anodes. The conductivity is proportional to the incoming photon flux, and decays exponentially with depth into the detector. Since all of the conduction paths are in parallel to each other, the resultant conductance between each anode and its surrounding cathode is the summation of all those conductances.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
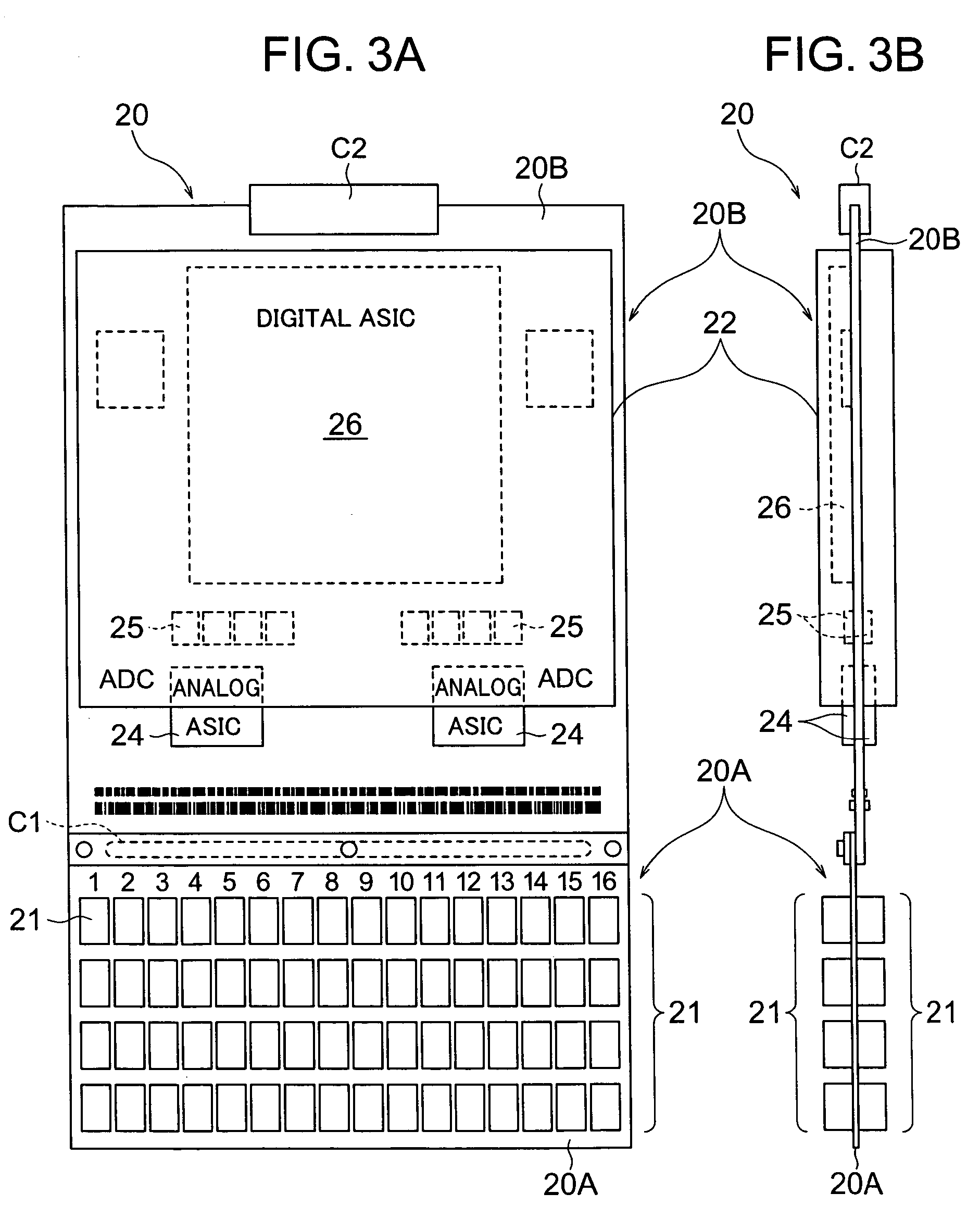
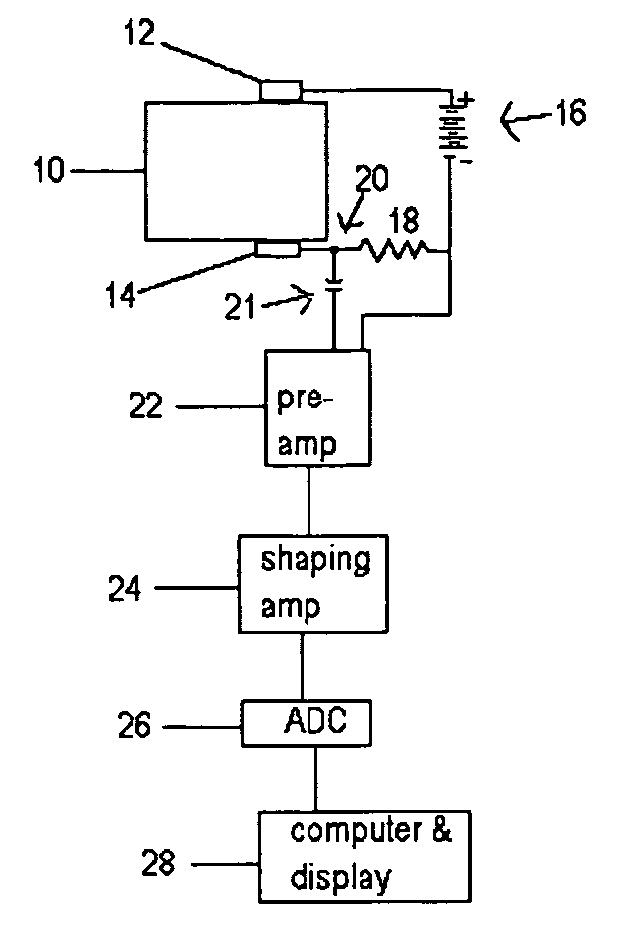
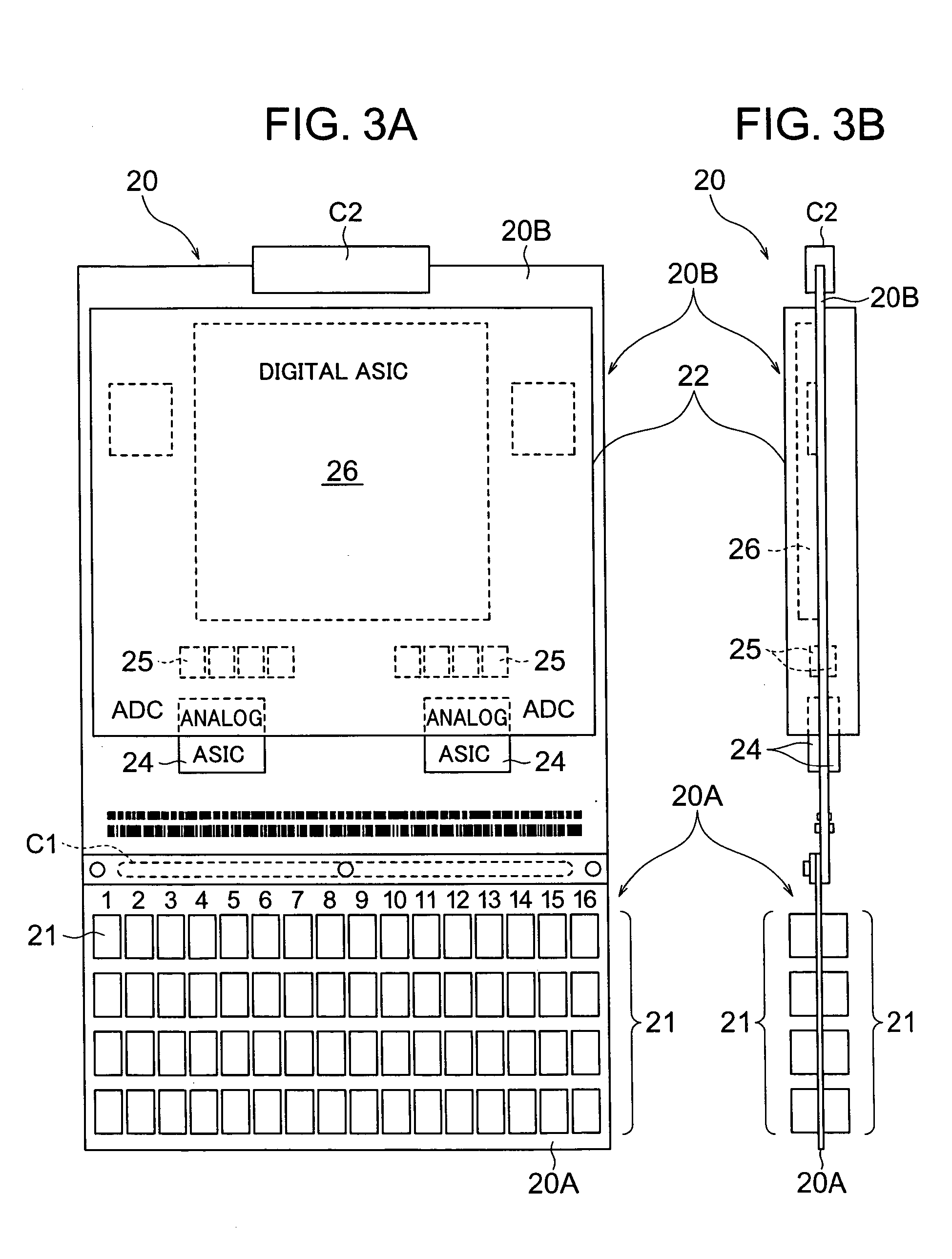
Data acquisition system for photon counting and energy discriminating detectors
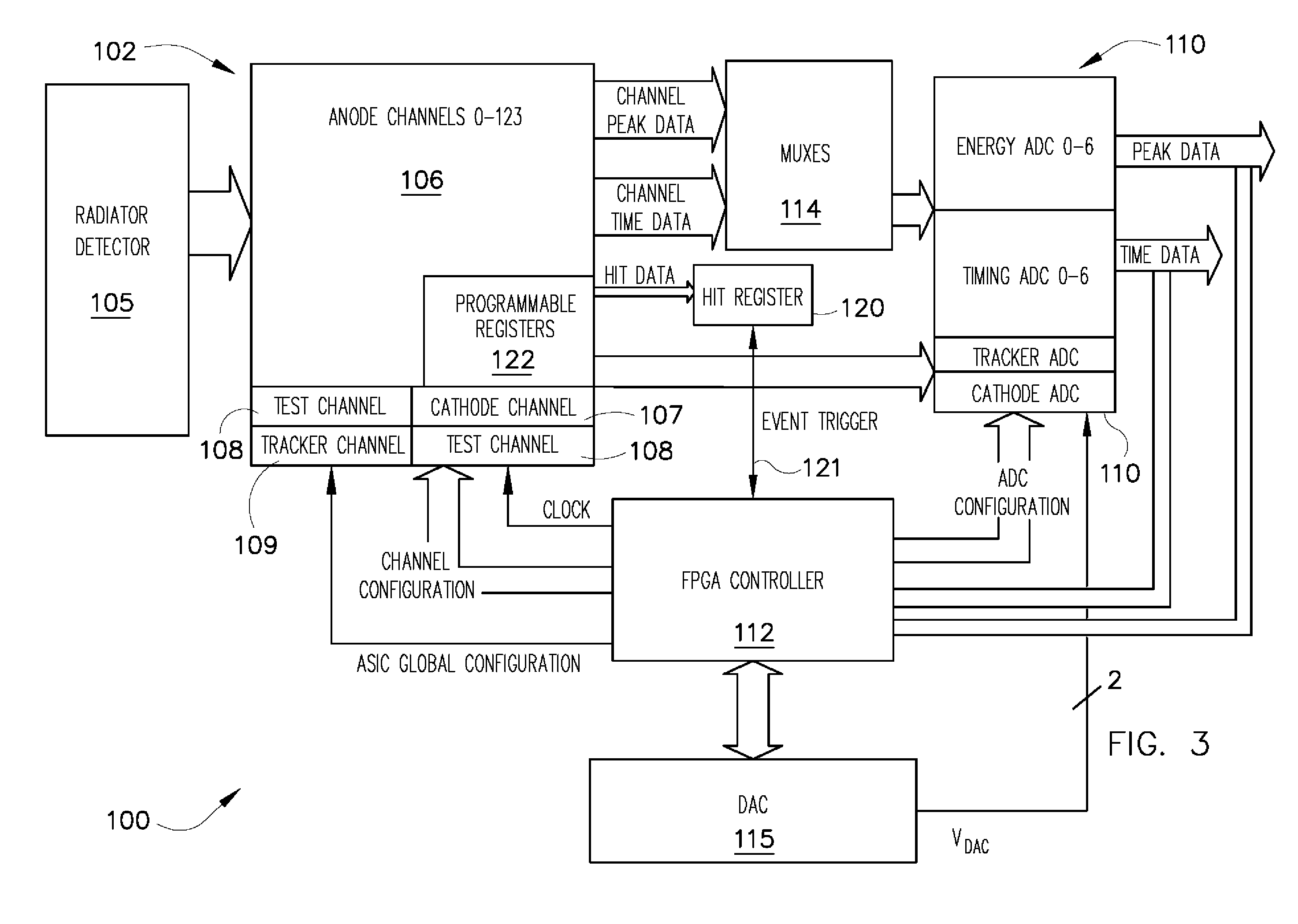
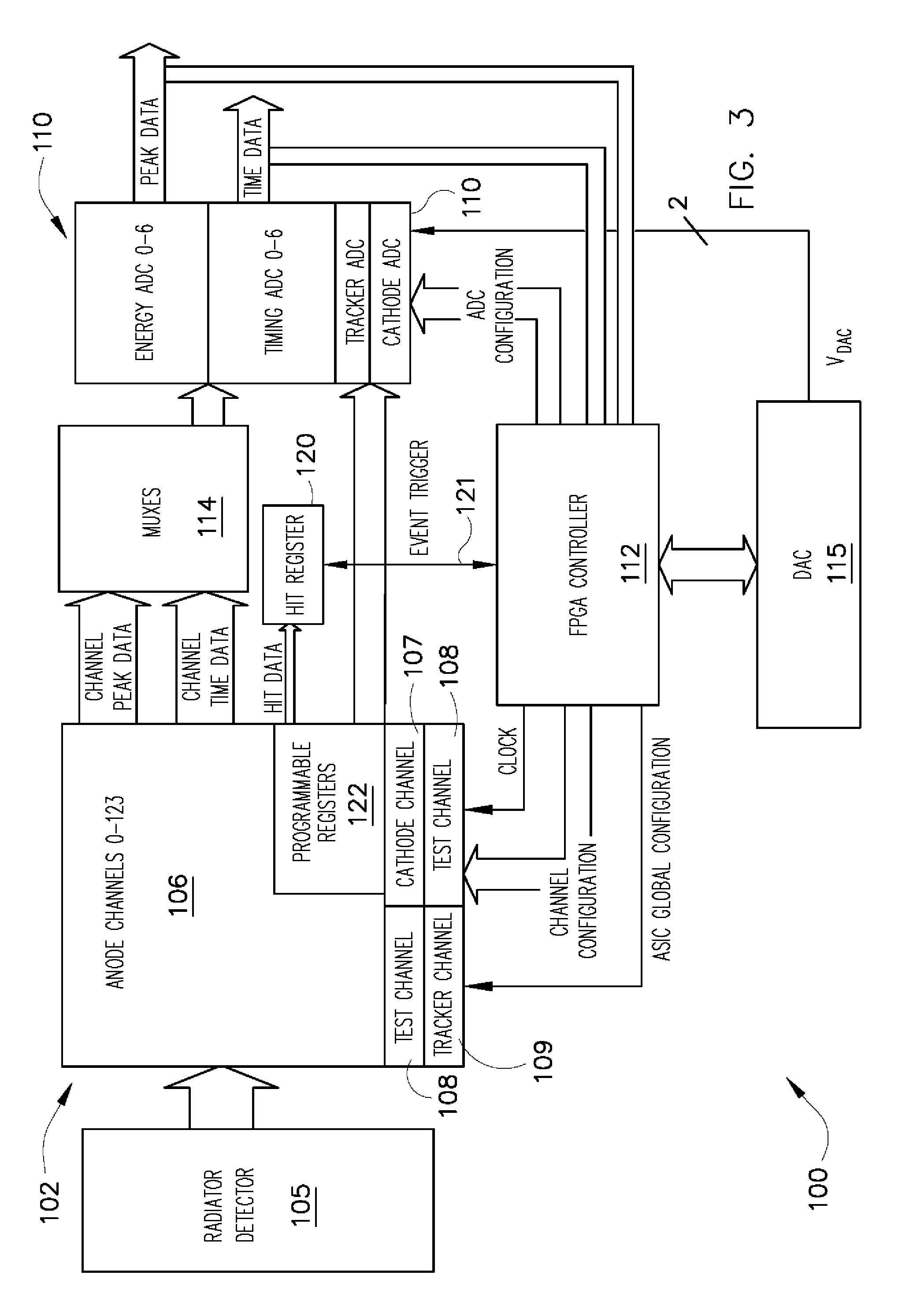
ActiveUS7760123B2Electric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData acquisitionSemiconductor radiation detectors
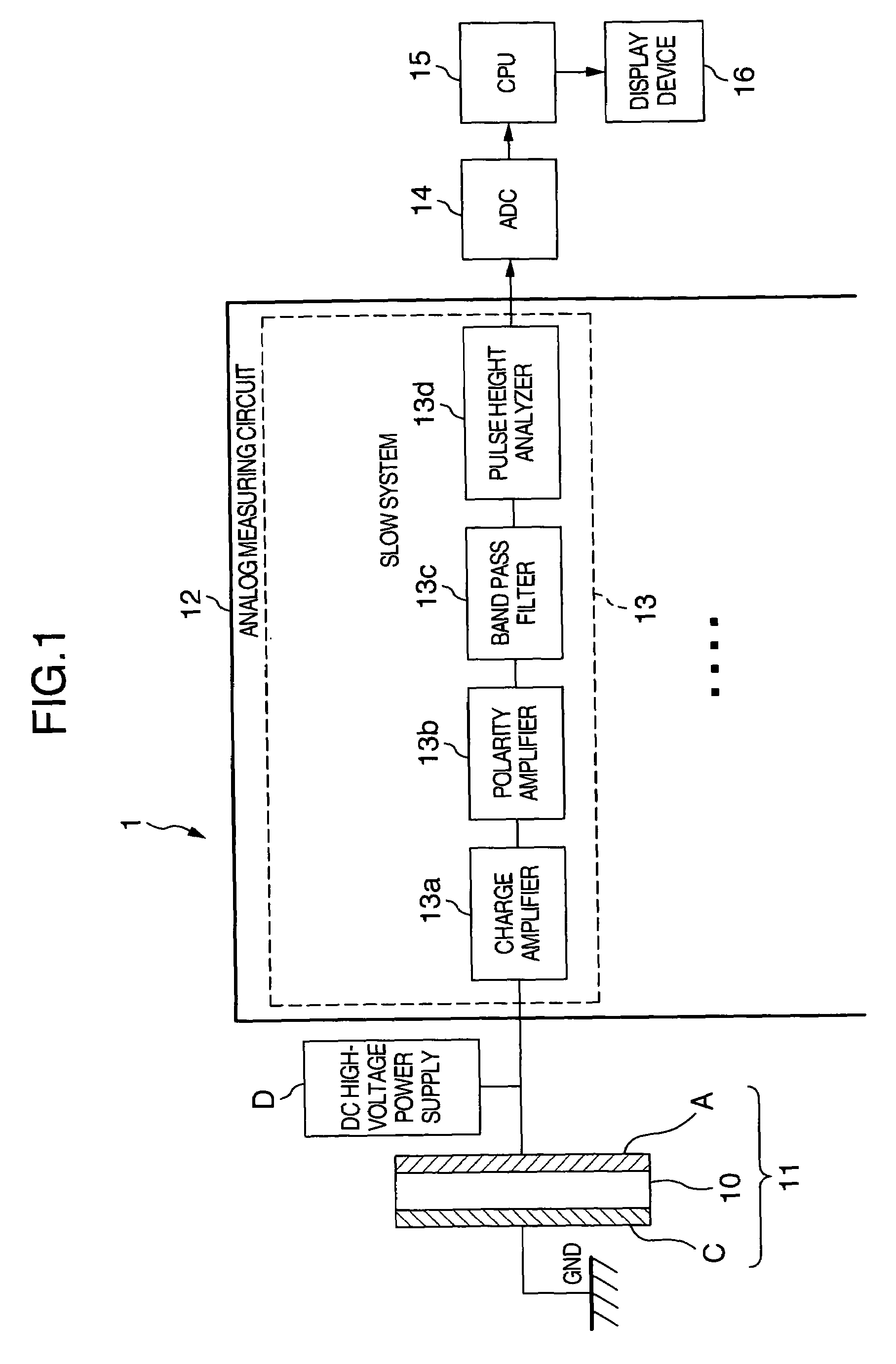
A data acquisition system including a readout Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) having a plurality of channels, each channel having a time discriminating circuit and an energy discriminating circuit, wherein the ASIC is configured to receive a plurality of signals from a semiconductor radiation detector. The data acquisition system also includes a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) electrically coupled to the ASIC and configured to provide a reference signal to the ASIC used in the generation of digital outputs from the ASIC, and a controller electrically coupled to the ASIC and to the DAC, the controller configured to instruct the DAC to provide the reference signal to the ASIC.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
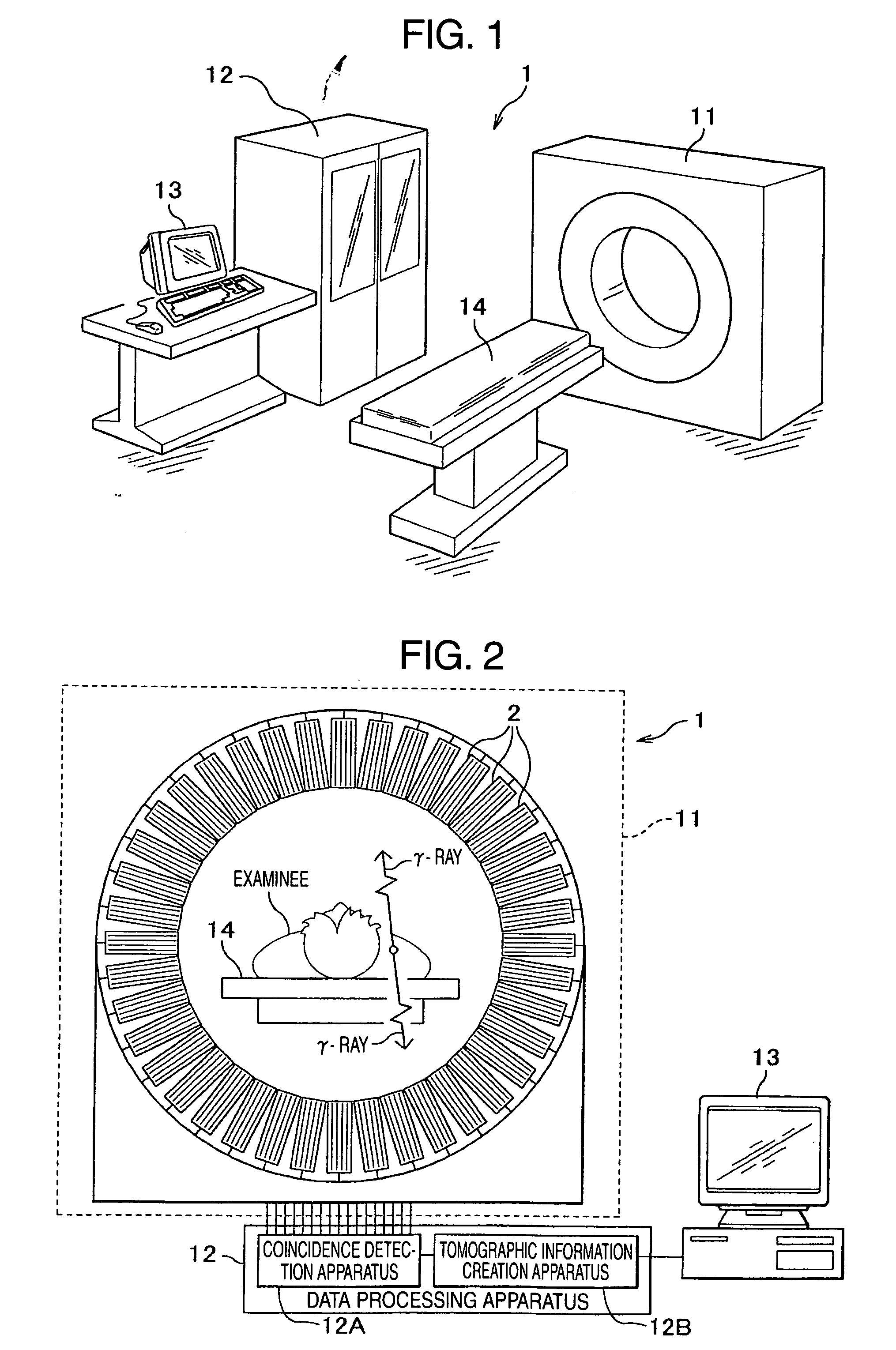
Semiconductor radiation detector, positron emission tomography apparatus, semiconductor radiation detection apparatus, detector unit and nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus
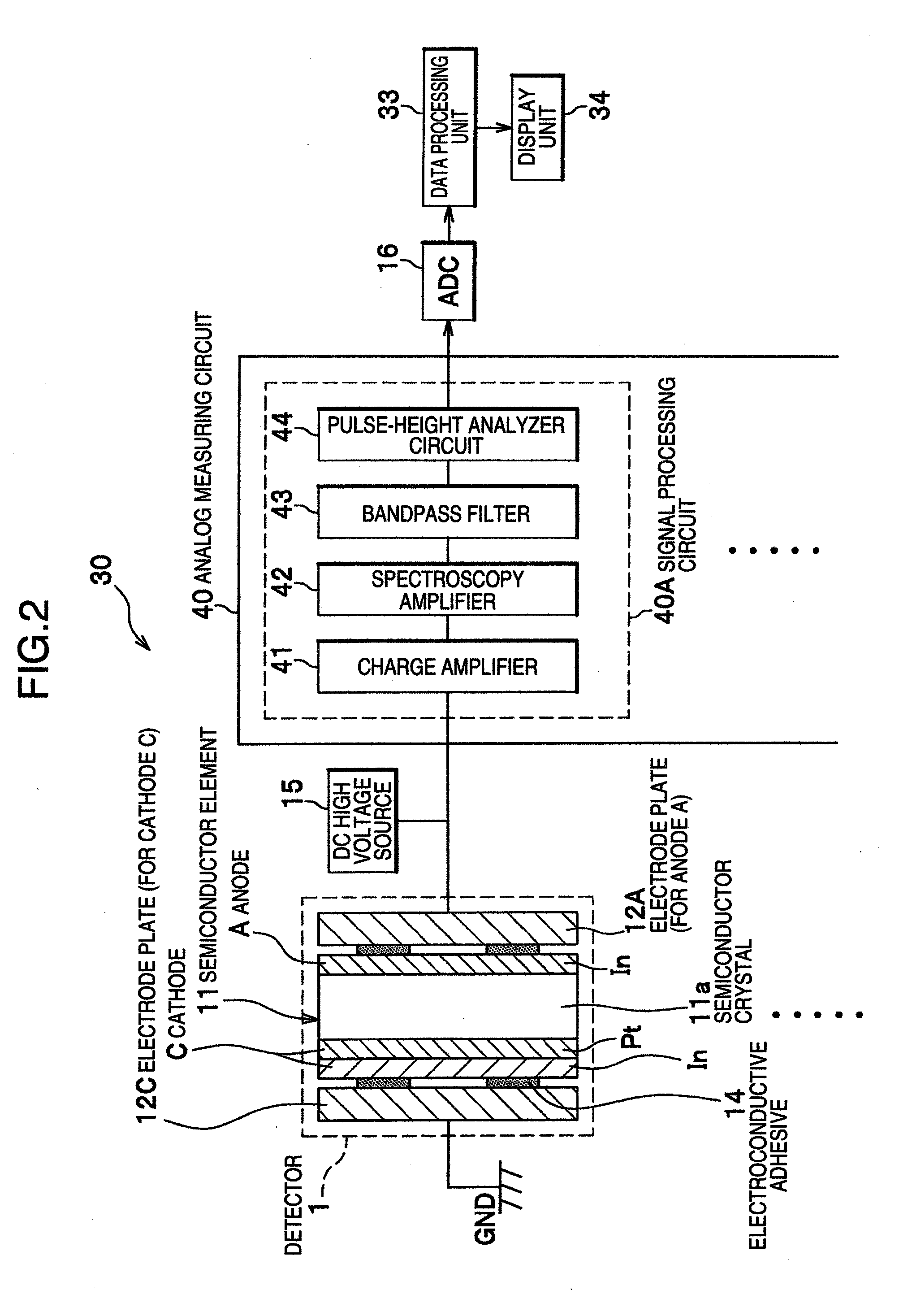
InactiveUS20050067572A1Shorten the timeEasy maintenancePhotometrySolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor radiation detectors
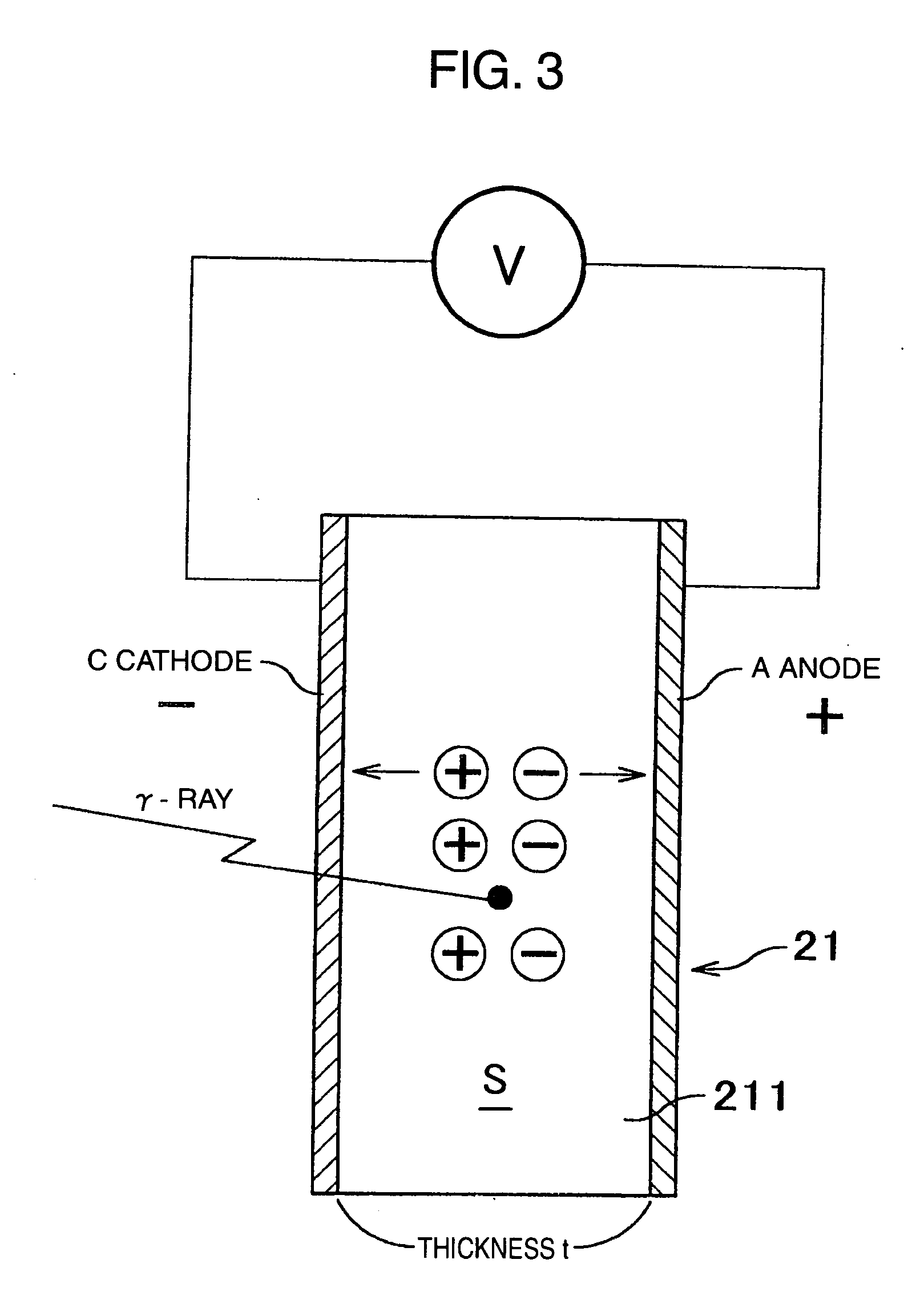
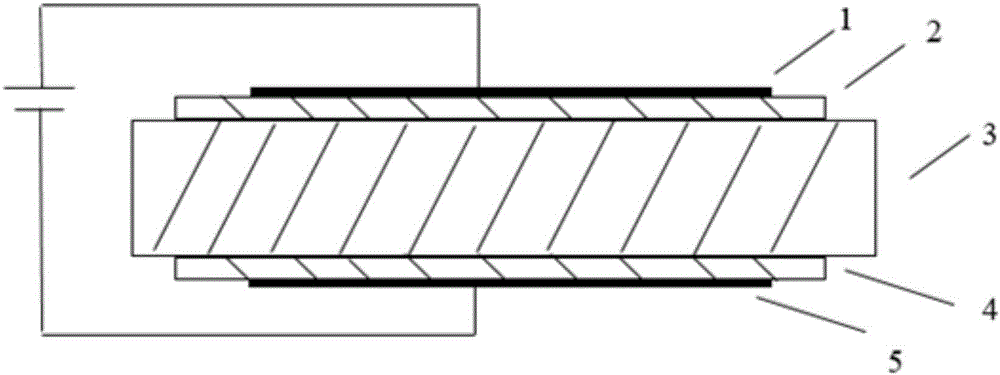
Each semiconductor radiation detector used for a nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus (PET apparatus) is constructed with an anode electrode A facing a cathode electrode C sandwiching a CdTe semiconductor member S which generates charge through interaction with γ-rays. Then, a thickness t of the semiconductor member S sandwiched between these mutually facing anode electrode A and cathode electrode C is set to 0.2 to 2 mm. Furthermore, the devices are mounted (laid out) on substrates in such a way that the distance (distance of conductor) between the semiconductor radiation detector and an analog ASIC which processes the signal detected by this detector is shortened. Furthermore, the substrates on which the detectors are mounted are housed in a housing as a unit (detector unit).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor radiation detector based on Bi-based quaternary halide single crystal, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106711272AImprove stabilityModerate band gapSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor radiation detectorsContact layer
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor radiation detector and radiation detection apparatus
InactiveUS7157716B2High resistivityLattice defects in the single crystal are also decreasedSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLattice defectsSignal processing circuits
The present invention provides a semiconductor radiation detector and radiation detection apparatus capable of improving energy resolution and the semiconductor radiation detection apparatus includes a semiconductor radiation detector and a signal processing circuit which processes a radiation detection signal output from the semiconductor radiation detector. The semiconductor radiation detector is provided with anode electrodes A and cathode electrodes C disposed so as to face each other with semiconductor radiation detection elements placed in-between. The semiconductor radiation detection element is made up of a single crystal of thallous bromide containing trivalent thallium (e.g., tribromobis thallium). The semiconductor radiation detector containing such a semiconductor radiation detection element reduces lattice defects in the single crystal and thereby increases charge collection efficiency.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Semiconductor radiation detector and radiation detection equipment
InactiveUS20080157255A1Inhibit deteriorationReduce hardnessSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor radiation detectorsHardness
A semiconductor radiation detector and a radiation detection equipment capable of suitably preventing the deterioration of the detection characteristics are disclosed. The semiconductor radiation detector 1 includes a semiconductor crystal 11a formed of at least one of CdTe, CdZnTe, GaAs and TlBr held between the electrodes of a cathode C and an anode A. At least one of the electrodes is a stack structure including a plurality of metals. The first layer is formed of Pt or Au, and the second layer is formed of a metal lower in hardness than Pt or Au, as the case may be, of the first layer. The second layer of In, for example, is formed by the electroless plating method. Also, a metal may be further stacked on the second layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radiological imaging system
InactiveUS20070057191A1Improve quantitativenessImprove detection accuracyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
The radiological imaging system which can improve an energy resolution and perform a diagnosis with high accuracy includes a bed for carrying an examinee H, first and second imaging apparatuses and disposed along the longitudinal direction of the bed. The first imaging apparatus has a plurality of semiconductor radiation detectors for detecting γ-rays emitted from the examinee H, arranged around the bed, the second imaging apparatus has an X-ray source for emitting X-rays to the examinee H and a radiation detector for detecting X-rays which have been emitted from the X-ray source and passed through the examinee H, and the bed is shared by the first imaging apparatus and the second imaging apparatus.
Owner:UENO YUUICHIROU +7
Radiological imaging system
InactiveUS7683338B2Improve quantitativenessImprove detection accuracyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
The radiological imaging system which can improve an energy resolution and perform a diagnosis with high accuracy includes a bed for carrying an examinee H, first and second imaging apparatuses and disposed along the longitudinal direction of the bed. The first imaging apparatus has a plurality of semiconductor radiation detectors for detecting γ-rays emitted from the examinee H, arranged around the bed, the second imaging apparatus has an X-ray source for emitting X-rays to the examinee H and a radiation detector for detecting X-rays which have been emitted from the X-ray source and passed through the examinee H, and the bed is shared by the first imaging apparatus and the second imaging apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
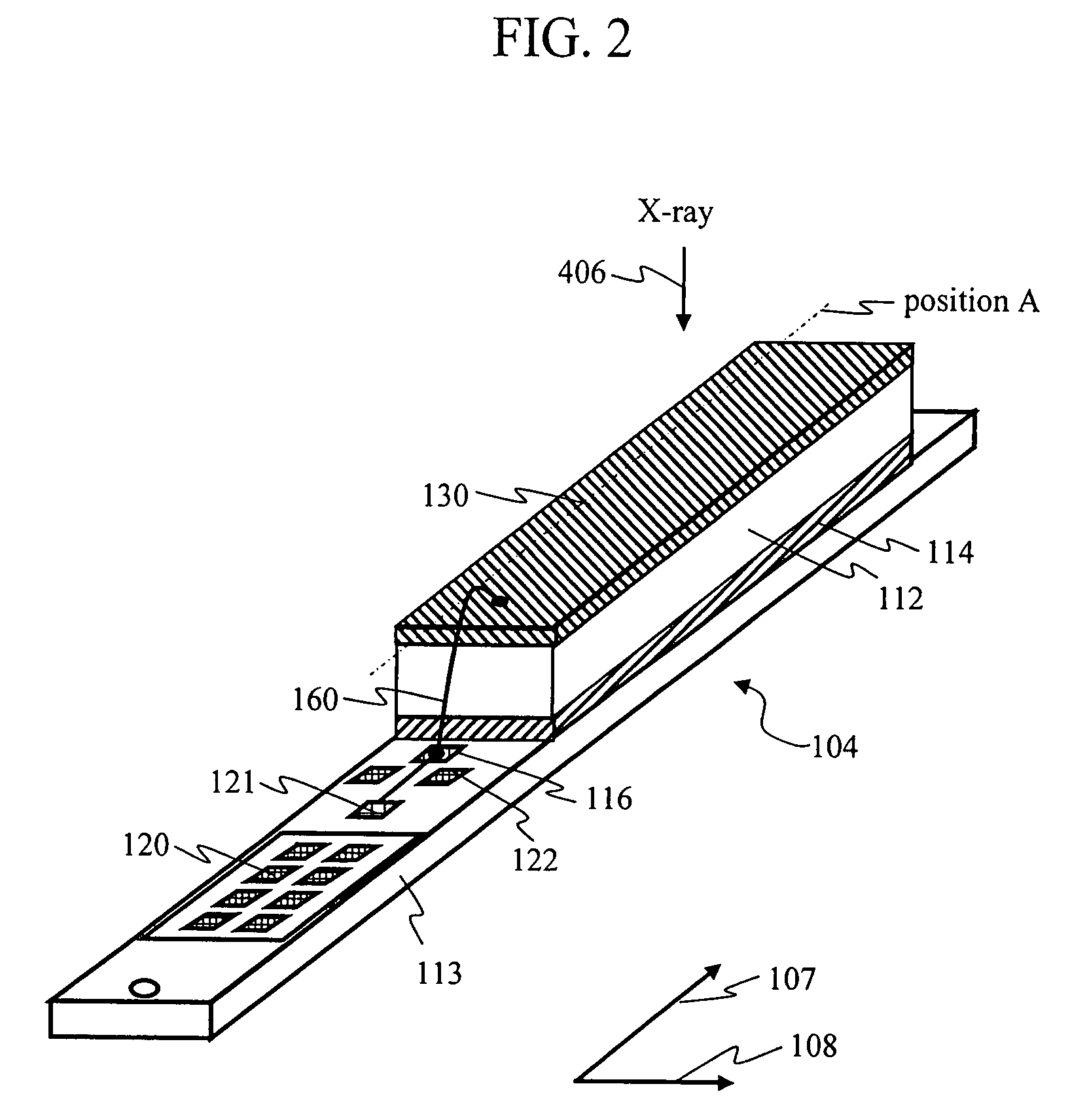
Method of fabricating patterned CZT and CdTe devices
ActiveUS20110156198A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSolder mask
A method of making a semiconductor radiation detector includes the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate having front and rear major opposing surfaces, forming a solder mask layer over the rear major surface, patterning the solder mask layer into a plurality of pixel separation regions, and after the step of patterning the solder mask layer, forming anode pixels over the rear major surface. Each anode pixel is formed between adjacent pixel-separation regions and a cathode electrode is located over the front major surface of the substrate. The solder mask can be used as a permanent photoresist in developing patterned electrodes on CdZnTe / CdTe devices as well as a permanent reliability protection coating. The method is very robust and ensures long-term reliability, outstanding detector performance, and may be used in applications such as medical imaging and for demanding other highly spectroscopic applications.
Owner:REDLEN TECH
Radiation detection equipment and nuclear medicine diagnosis device
InactiveUS20130324847A1Improve responseImprove performanceTomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentPt elementThallium compounds
Provided is radiation detection equipment including: a semiconductor radiation detector which has a semiconductor crystal made of thallium bromide; a capacitor which applies a voltage to the semiconductor radiation detector; and at least one DC power source which accumulates positive charges and negative charges in either of electrodes of the capacitor. Herein, a cathode and an anode in the semiconductor radiation detector are formed of at least one kind of a metal selected from gold, platinum and palladium. Further, the DC power source periodically reverses a voltage of accumulating the positive charges and a voltage of accumulating the negative charges in either of the electrodes of the capacitor per interval shorter than 10 min, thereby to apply the resulting voltage thereto.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Wafer bonded silicon radiation detectors
InactiveUS20060118728A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectron holeSemiconductor radiation detectors
An apparatus and method for operating a direct wafer bonded semiconductor radiation detector includes bonding a plurality of wafers, receiving a radiation signal from a radiation source thereby producing electron and hole pairs via the radiation signal interacting with the detecting device. A voltage source produces a voltage across the direct bonded wafers, thereby drifting the electrons and holes through the plurality of bonded layers. The drifted electrons and / or holes include total drifted charge information of the detector and are collected and processed either at the detector or remote from the detector.
Owner:PHLIPS BERNARD +3
Semiconductor radiation detector
InactiveUS7687780B2Measurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor radiation detectorsElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:BABCOCK & WILCOX TECH SERVICES Y-12 LLC +1
Two-dimensional radiation detector
InactiveUS20050242292A1Improve efficiencyLower levelElectric discharge tubesPhotometrySemiconductor radiation detectorsAnode spot
A two-dimensional, pixellated, monolithic semiconductor radiation detector, in which each detector pixel is essentially a perpendicular mode detector. This is achieved by an arrangement of anode spots, one for each pixel located on the flux-exposed front surface of the detector substrate, surrounding by a cathode array preferably in the form of a network of lines, such that the field between the anodes and cathodes on this front surface has a major component in the direction parallel to the surface, and hence perpendicular to the incident photon flux. The conductivity of the substrate is high near this front surface, since this is where the highest level of absorption of photons takes place, and a significant photoconductive current is thus generated between cathodes and anodes. The conductivity is proportional to the incoming photon flux, and decays exponentially with depth into the detector. Since all of the conduction paths are in parallel to each other, the resultant conductance between each anode and its surrounding cathode is the summation of all those conductances.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Radiological imaging apparatus and its detector unit
InactiveUS7217931B2Increase the arrangement densityEasy to detectSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsSignal processing
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radiation cassette carrier and portable radiation imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8834022B2Maintain operabilityMaintain performanceRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSolid-state devicesRadiation imagingSemiconductor radiation detectors
A cassette carrier for containing a cassette incorporating a semiconductor radiation detector includes a rectangular recessed portion formed for containing the cassette with an irradiation surface exposed. The recessed portion is formed by a first frame that forms a side wall of one side thereof and includes a handle that a user holds, and a second frame forming a side wall of another side of the recessed portion. In the side wall formed by the first frame, an opening is provided in an opposite position opposing a connector unit of the cassette with the cassette attached to the recessed portion. The first frame has a space in communication with the opening, and connection / disconnection of an external cable to / from the connector unit is possible through the space with the cassette attached, and the space is large enough to contain an entire connector housing of the external.
Owner:CANON KK
Data acquisition system for photon counting and energy discriminating detectors
ActiveUS20090129537A1Low powerLittle noiseElectric signal transmission systemsComputing operations for integration/differentiationDigital analog converterSemiconductor radiation detectors
A data acquisition system including a readout Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) having a plurality of channels, each channel having a time discriminating circuit and an energy discriminating circuit, wherein the ASIC is configured to receive a plurality of signals from a semiconductor radiation detector. The data acquisition system also includes a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) electrically coupled to the ASIC and configured to provide a reference signal to the ASIC used in the generation of digital outputs from the ASIC, and a controller electrically coupled to the ASIC and to the DAC, the controller configured to instruct the DAC to provide the reference signal to the ASIC.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Semiconductor radiation detector
InactiveUS20070080301A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor radiation detectorsElectromagnetic radiation
A semiconductor detector for ionizing electromagnetic radiation, neutrons, and energetic charged particles. The detecting element is comprised of a compound having the composition I-III-VI2 or II-IV-V2 where the “I” component is from column 1A or 1B of the periodic table, the “II” component is from column 2B, the “III” component is from column 3A, the “IV” component is from column 4A, the “V” component is from column 5A, and the “VI” component is from column 6A. The detecting element detects ionizing radiation by generating a signal proportional to the energy deposited in the element, and detects neutrons by virtue of the ionizing radiation emitted by one or more of the constituent materials subsequent to capture. The detector may contain more than one neutron-sensitive component.
Owner:BABCOCK & WILCOX TECH SERVICES Y-12 LLC +1
Semiconductor radiation detector with guard ring, and imaging system with this detector
InactiveUS7391845B2Reduce noiseVolume of data can be compressedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging qualityRadiation exposure
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of making a semiconductor radiation detector
ActiveUS20130264669A1Improve artInhibit deteriorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor radiation detectorsOptoelectronics
A method of making a semiconductor radiation detector wherein the metal layers which serve as the cathode and anode electrodes are recessed from the designated prospective dice lines which define the total upper and lower surface areas for each detector such that the dicing blade will not directly engage the metal during dicing and therefore prevent metal from intruding upon (smearing) the vertical side walls of the detector substrate.
Owner:PRODUCE
Radiological imaging apparatus and its detector unit
InactiveUS20050151087A1Improve shielding effectSuppresses superimposition of noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor radiation detectorsSignal processing
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Yttrium contacts for germanium semiconductor radiation detectors
ActiveUS20110298131A1Easy to optimizeEasy to divideSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSpectroscopyGamma ray
A germanium semiconductor radiation detector contact made of yttrium metal. A thin (˜1000 Å) deposited layer of yttrium metal forms a thin hole-barrier and / or electron-barrier contact on both p- and n-type germanium semiconductor radiation detectors. Yttrium contacts provide a sufficiently high hole barrier to prevent measurable contact leakage current below ˜120 K. The yttrium contacts can be conveniently segmented into multiple electrically independent electrodes having inter-electrode resistances greater than 10 GΩ. Germanium semiconductor radiation detector diodes fabricated with yttrium contacts provide good gamma-ray spectroscopy data.
Owner:HULL ETHAN +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com