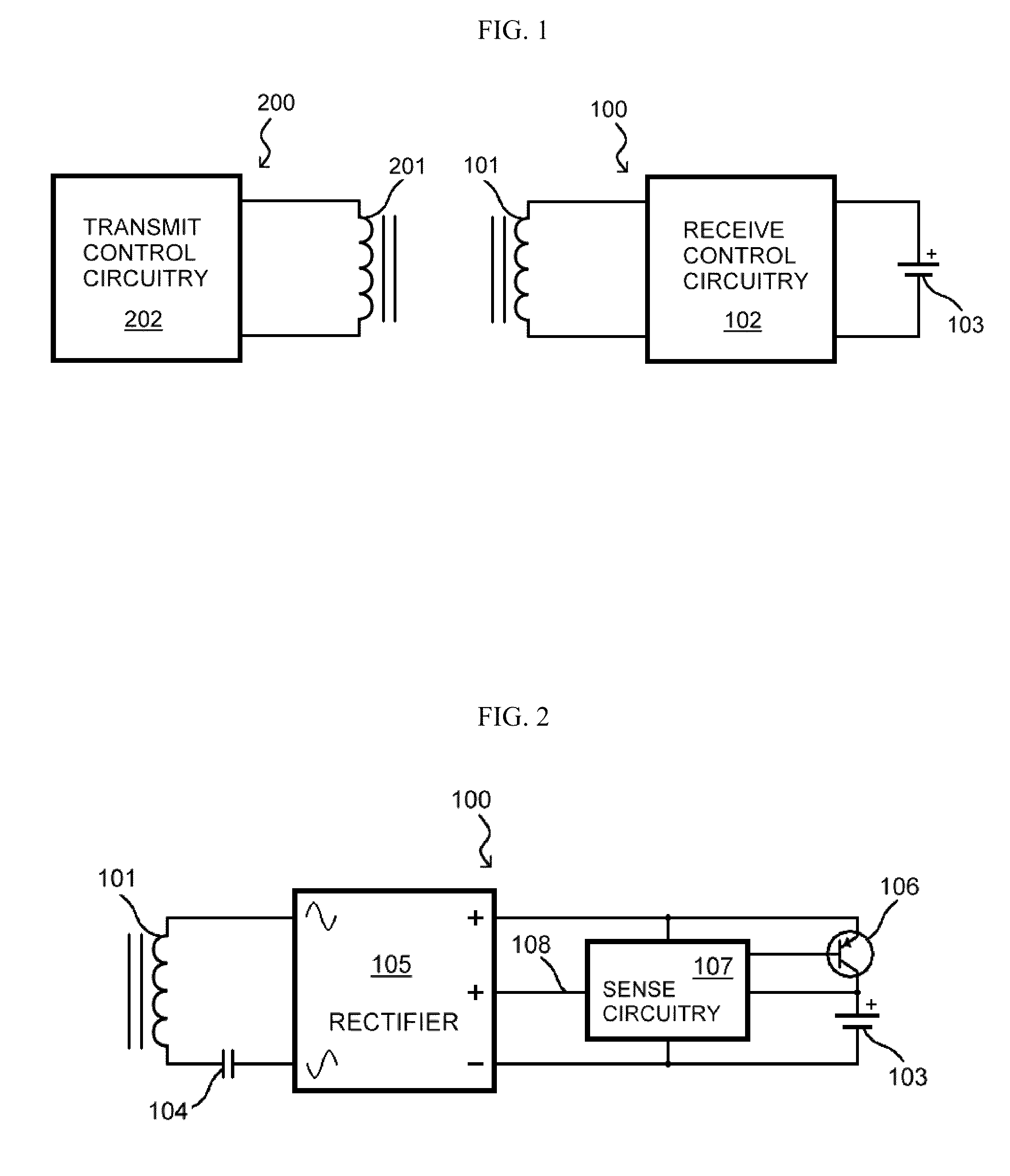
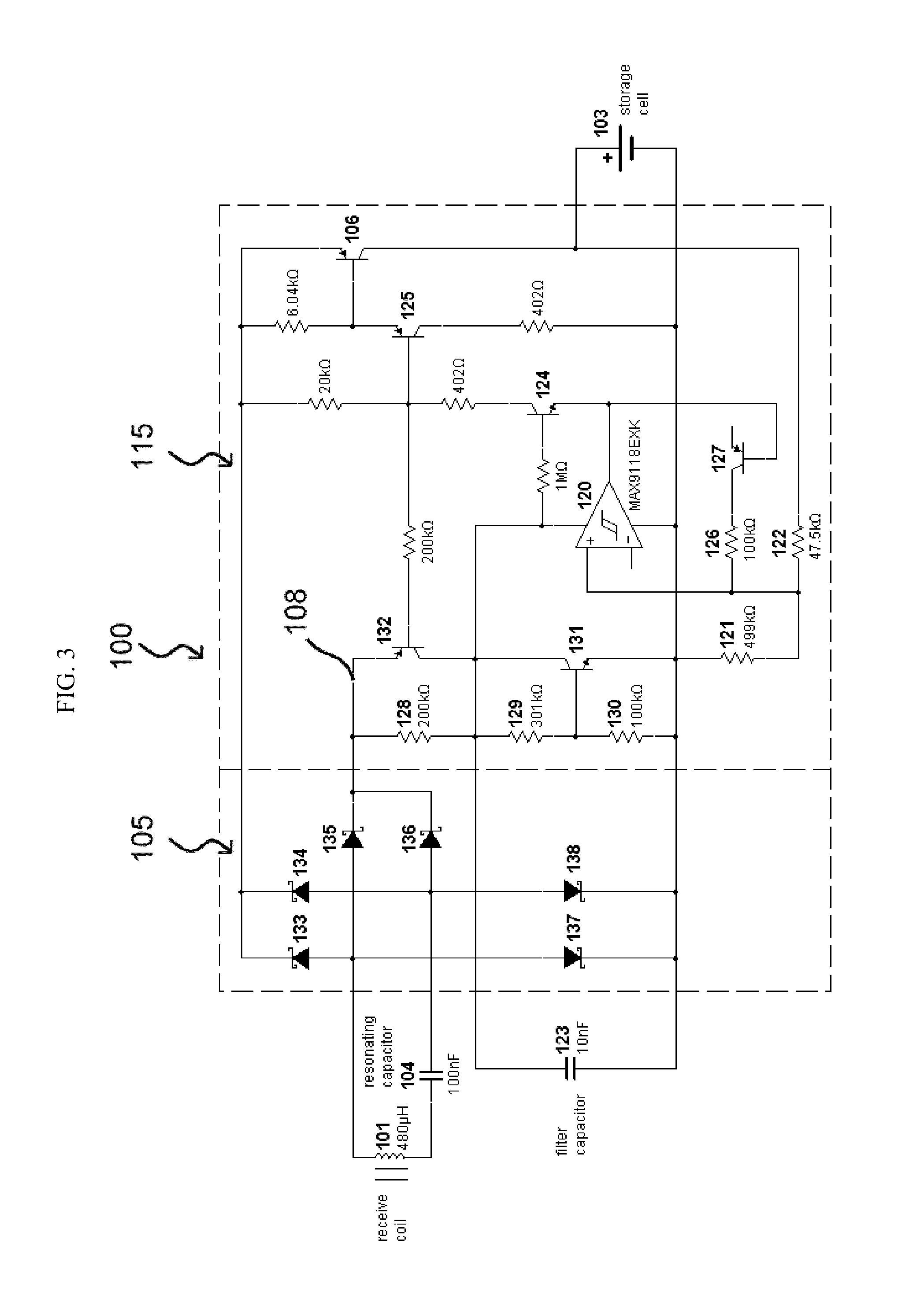
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
387results about "Computing operations for integration/differentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
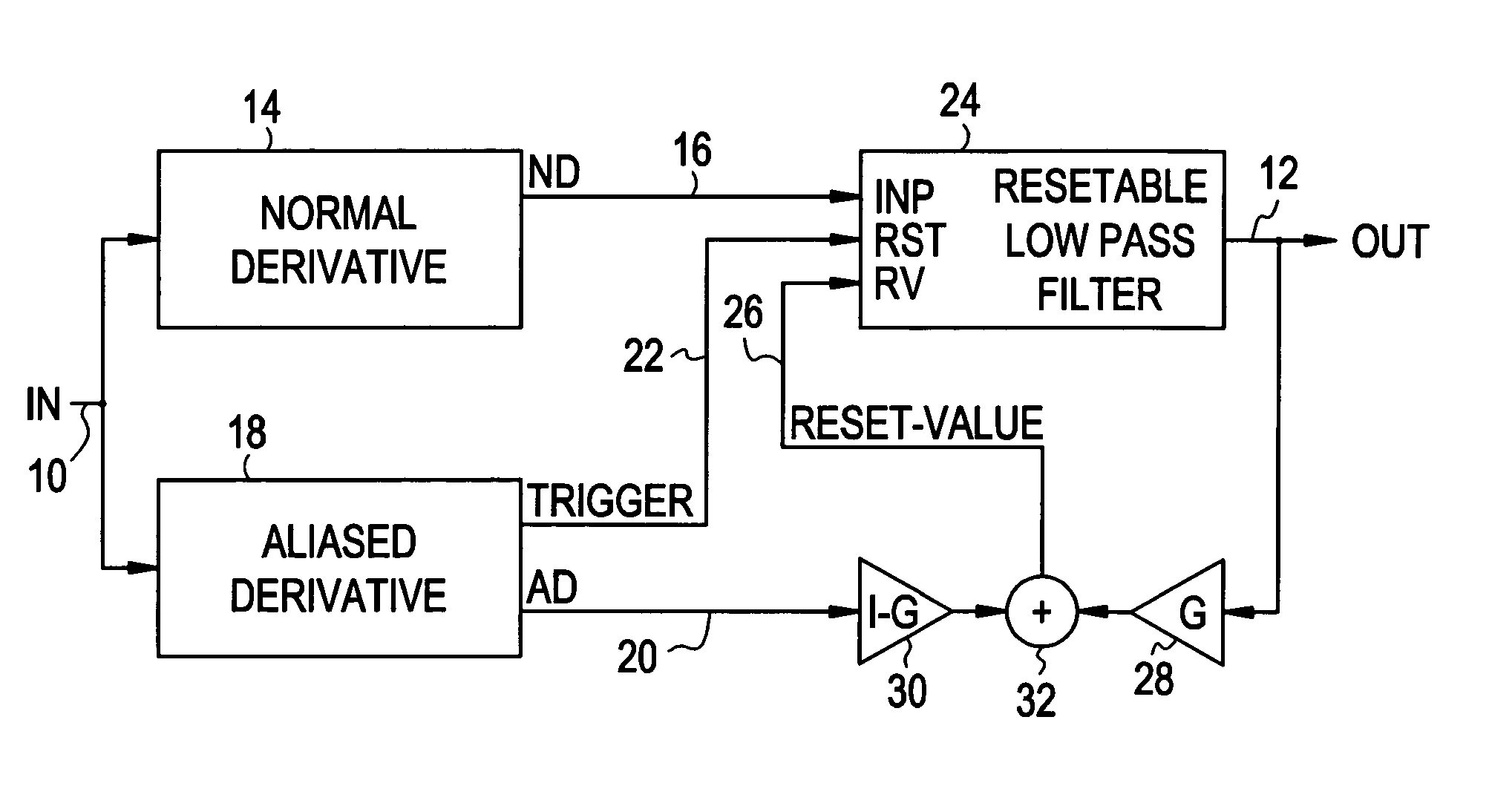
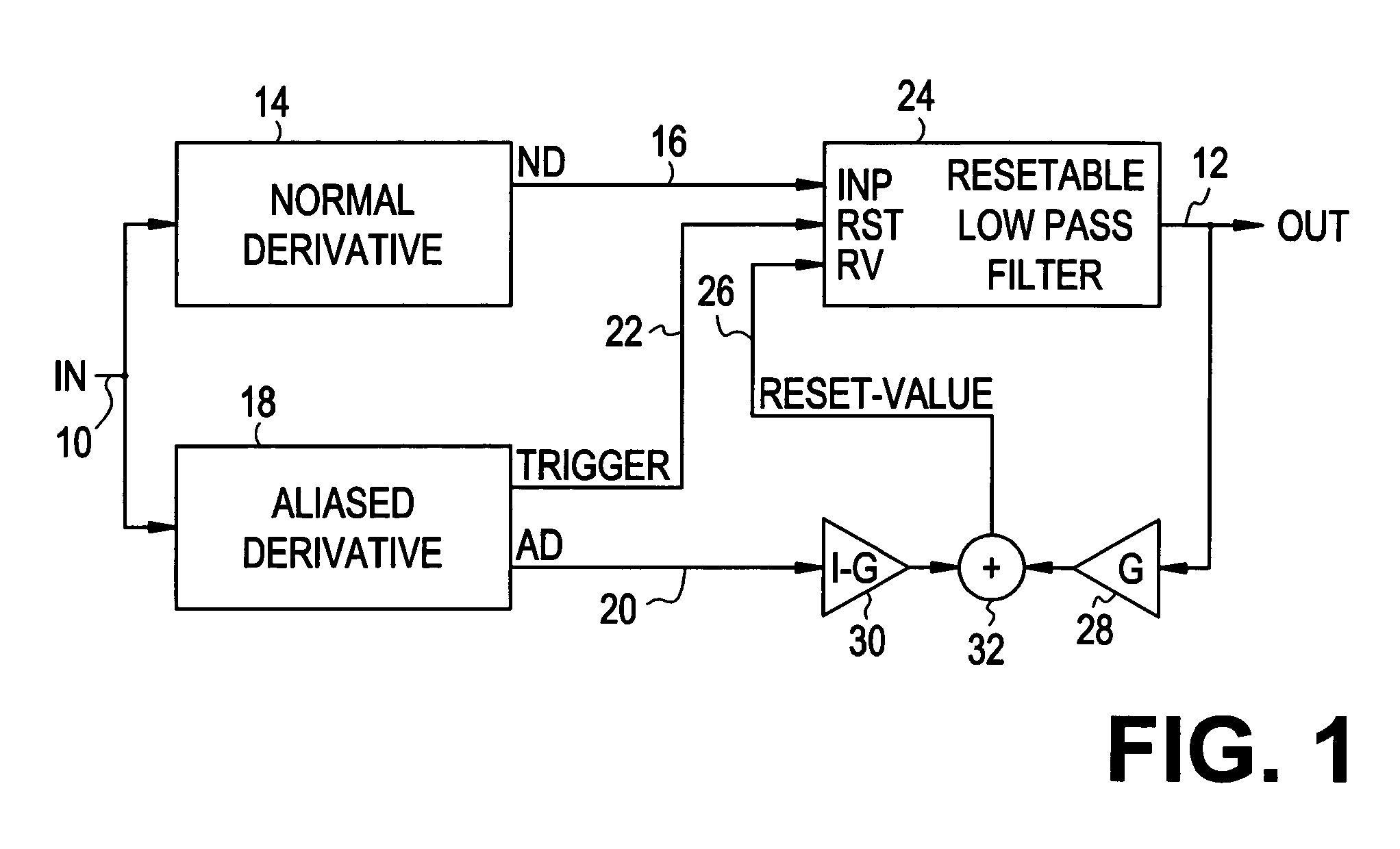
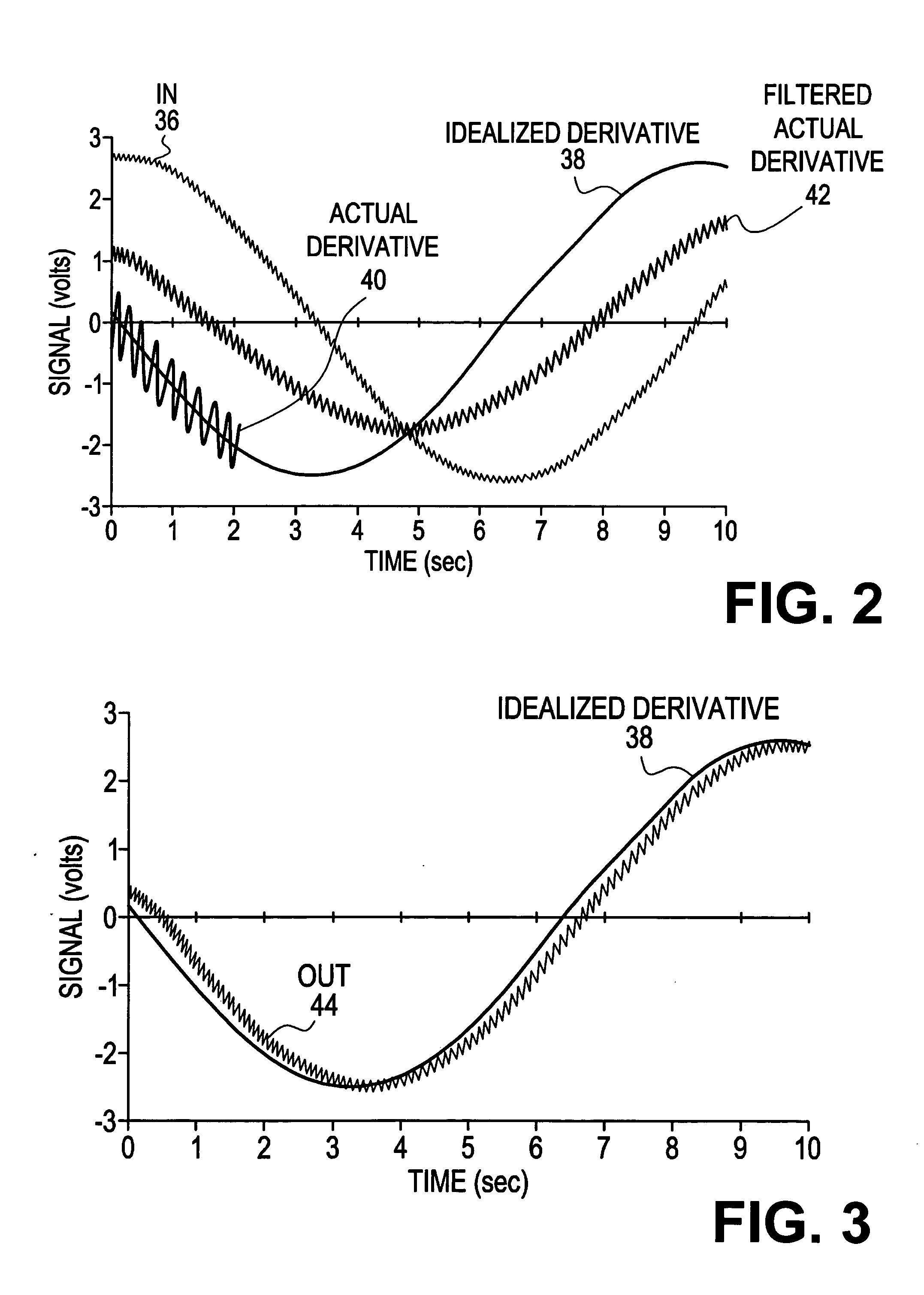
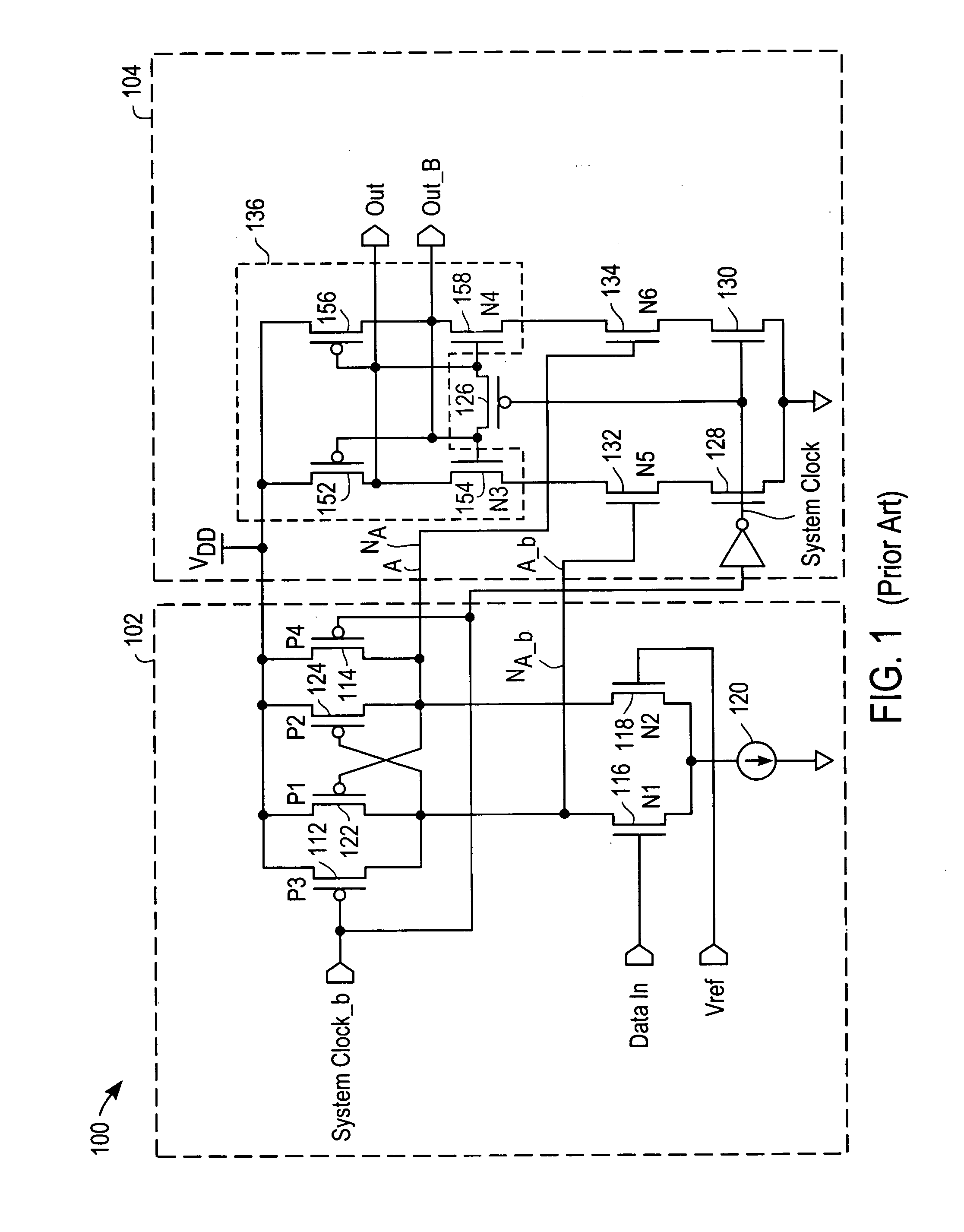
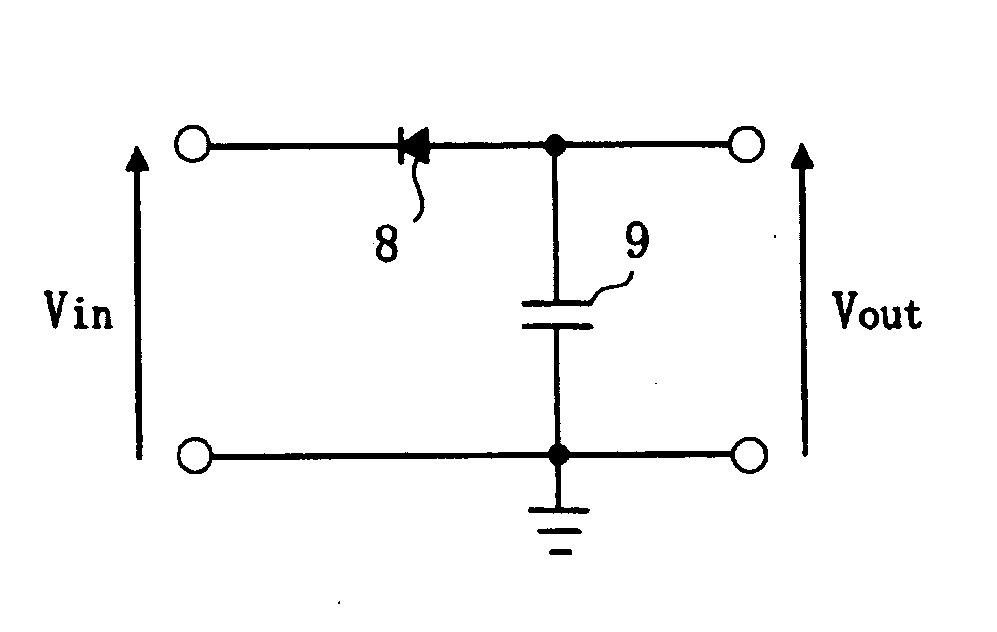
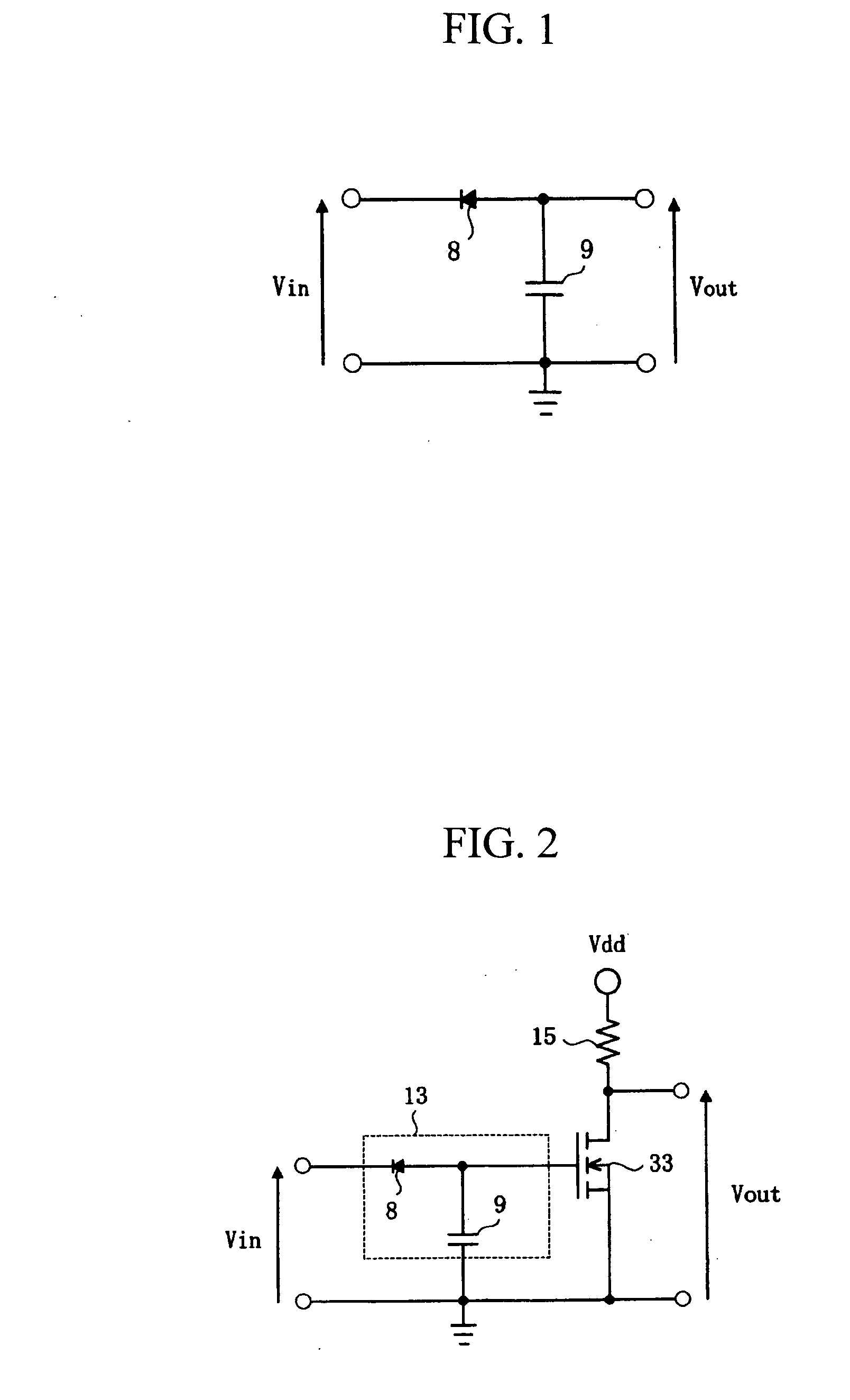
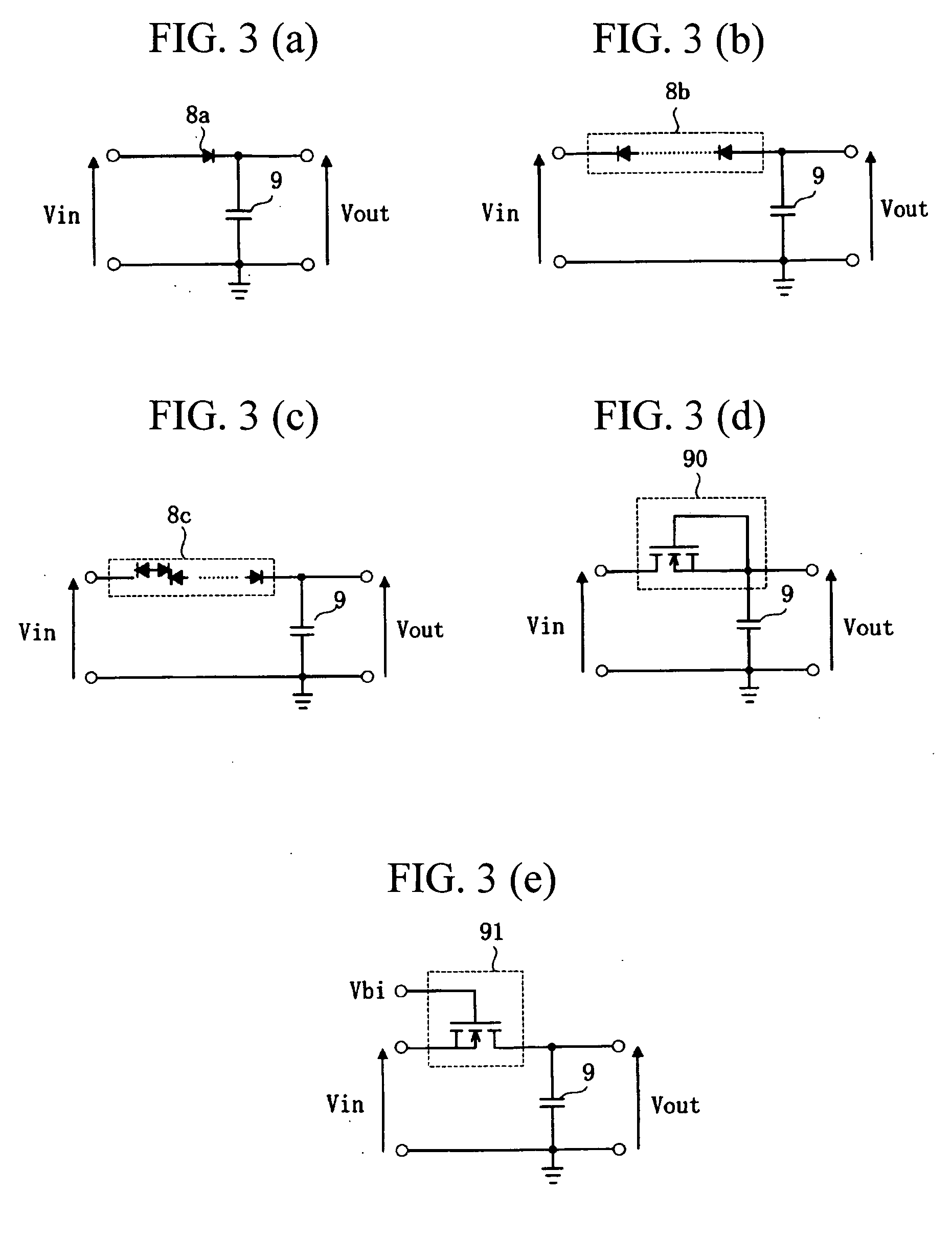
Method of determining the derivative of an input signal
InactiveUS20050256919A1Eliminate Phase Delay IssuesSimple methodComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationChemistry
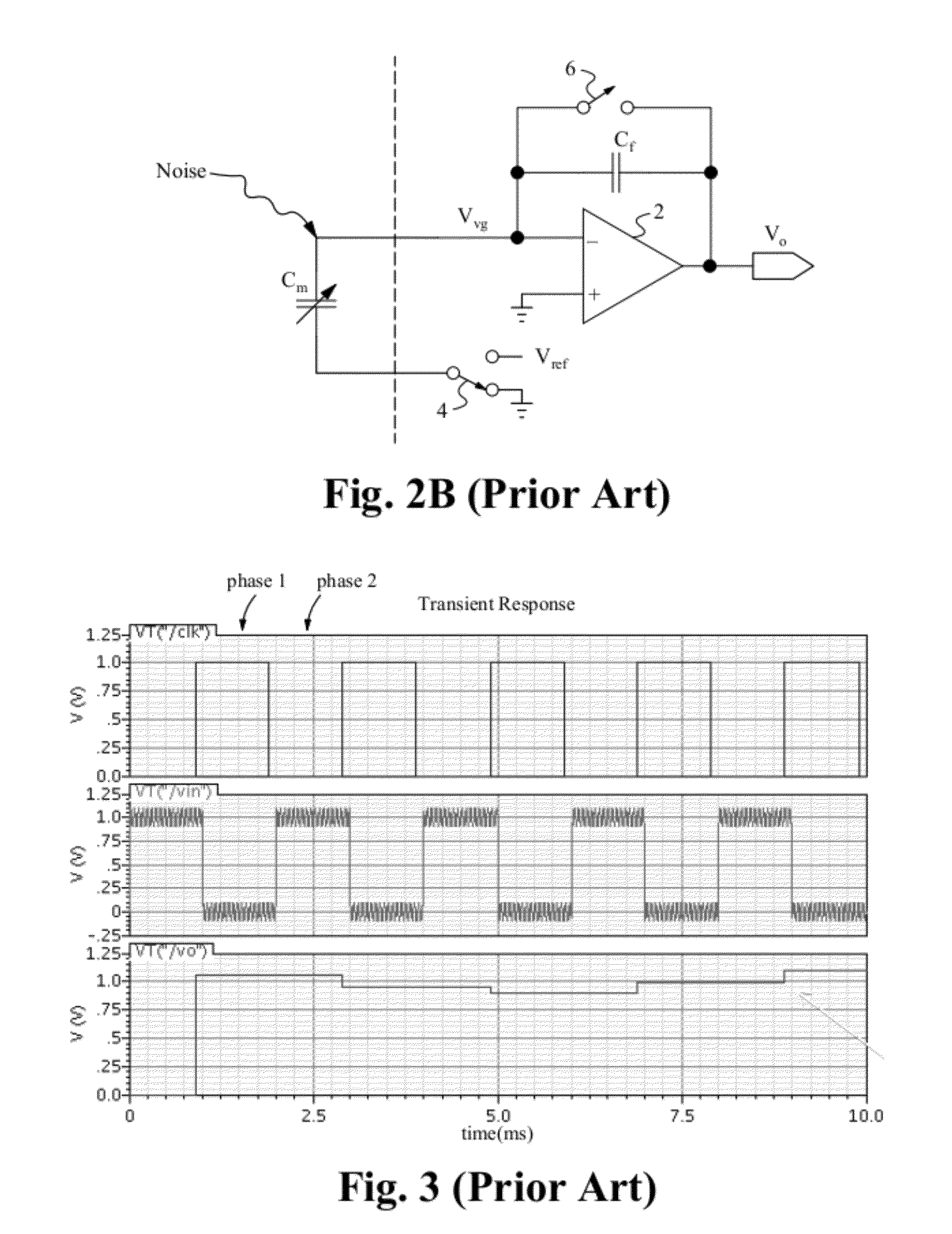
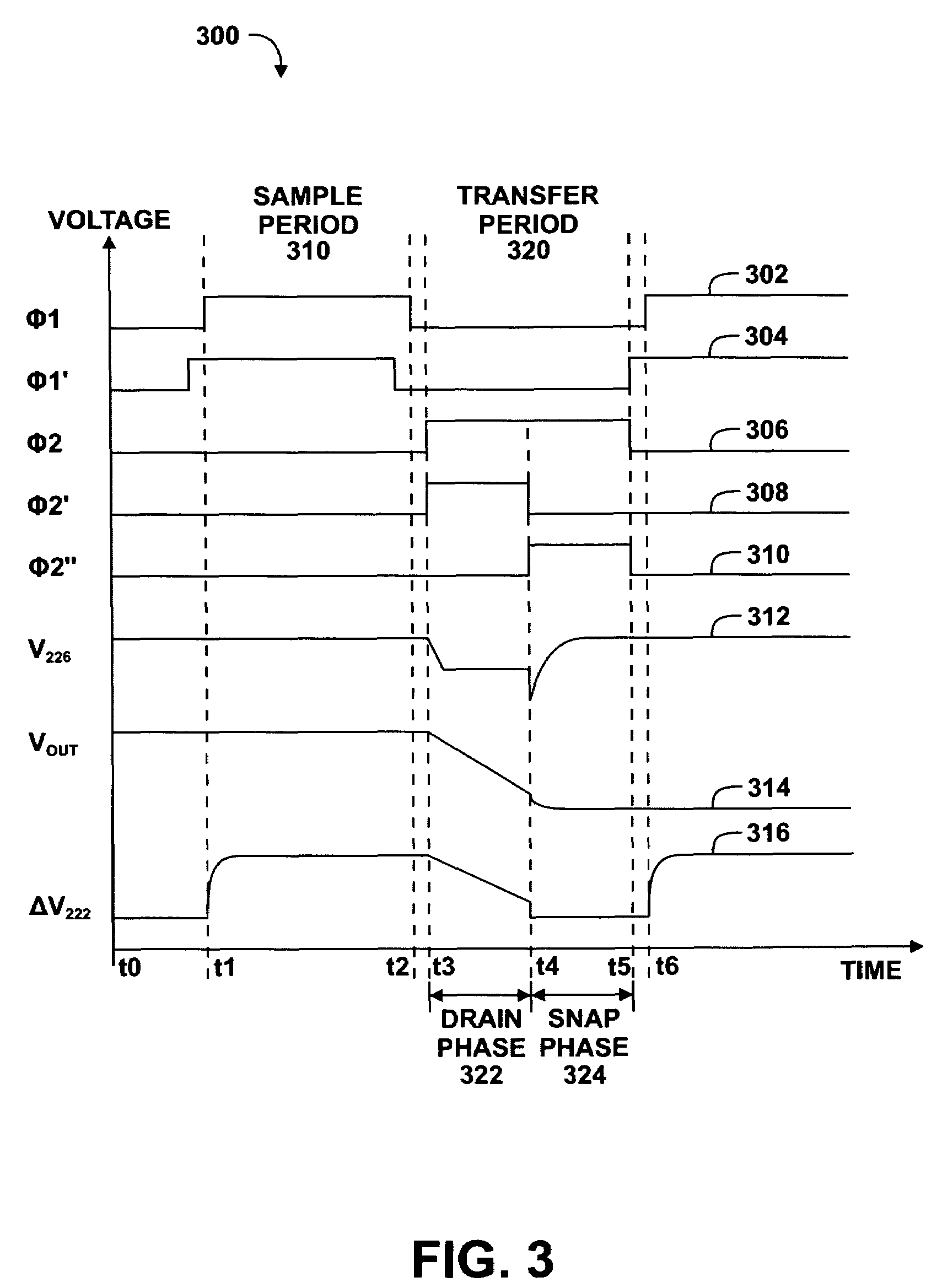
The derivative of a noise-containing input signal is determined by using an aliased derivative to periodically reset a filtered version of a normally determined derivative. The aliased derivative is calculated using a slower update or sampling rate than the normally determined derivative, and the filtered version of the normally determined derivative is reset to a reset value at each update of the aliased derivative. The reset value is based on a weighted sum of the aliased derivative and the filter output. The periodically reset filter output closely follows an idealized derivative of the input signal, substantially eliminating the phase delay introduced by conventional filtering.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
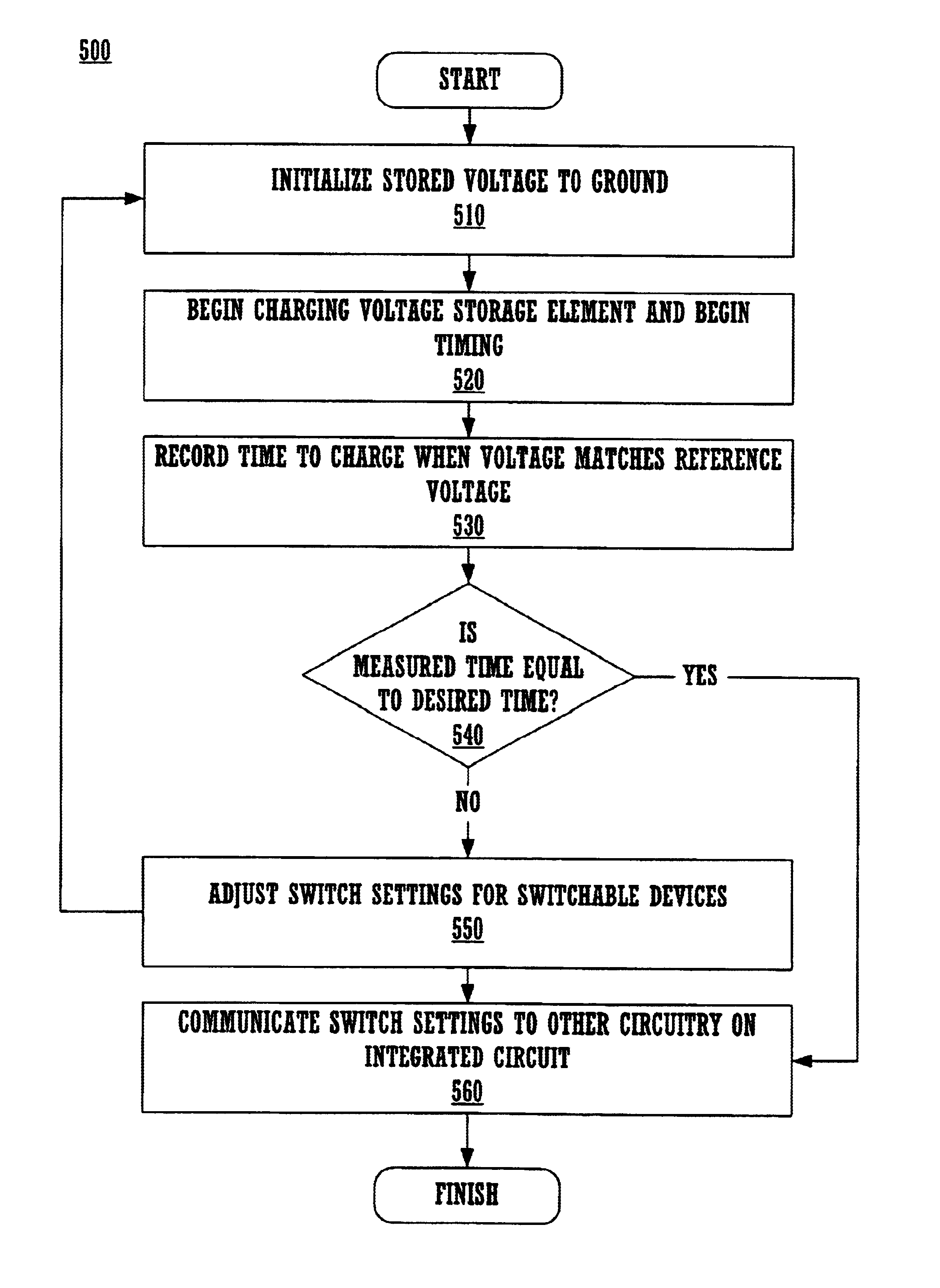
Calibration of integrated circuit time constants
InactiveUS6842710B1Computing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationRC time constantVoltage reference
A method and system for calibrating a time constant within an integrated circuit. A voltage storage element is charged, and the time required to achieve a reference voltage on the storage element is measured. The measured time is compared to a desired time. It necessary, an adjustable impedance is modified to change the charging time, and the cycle may be repeated until the charging time matches the desired time. In this novel manner, an actual RC time constant, as rendered in a particular integrated circuit, is measured and potentially adjusted to match a desired time constant. Advantageously, configuration information of the adjustable impedance may be communicated to other circuitry within the integrated circuit to enable such circuitry to implement the same RC time constant in analog signal processing. Consequently, embodiments of the present invention overcome incidences of wide tolerance in passive components implemented in integrated circuits. Beneficially, no external test equipment is required.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Apparatus for current-to-voltage integration for current-to-digital converter
InactiveUS20090273386A1Reduce charge injectionReduce demandComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationDigital down converterIntegrator
Owner:CUSTOM ONE DESIGN
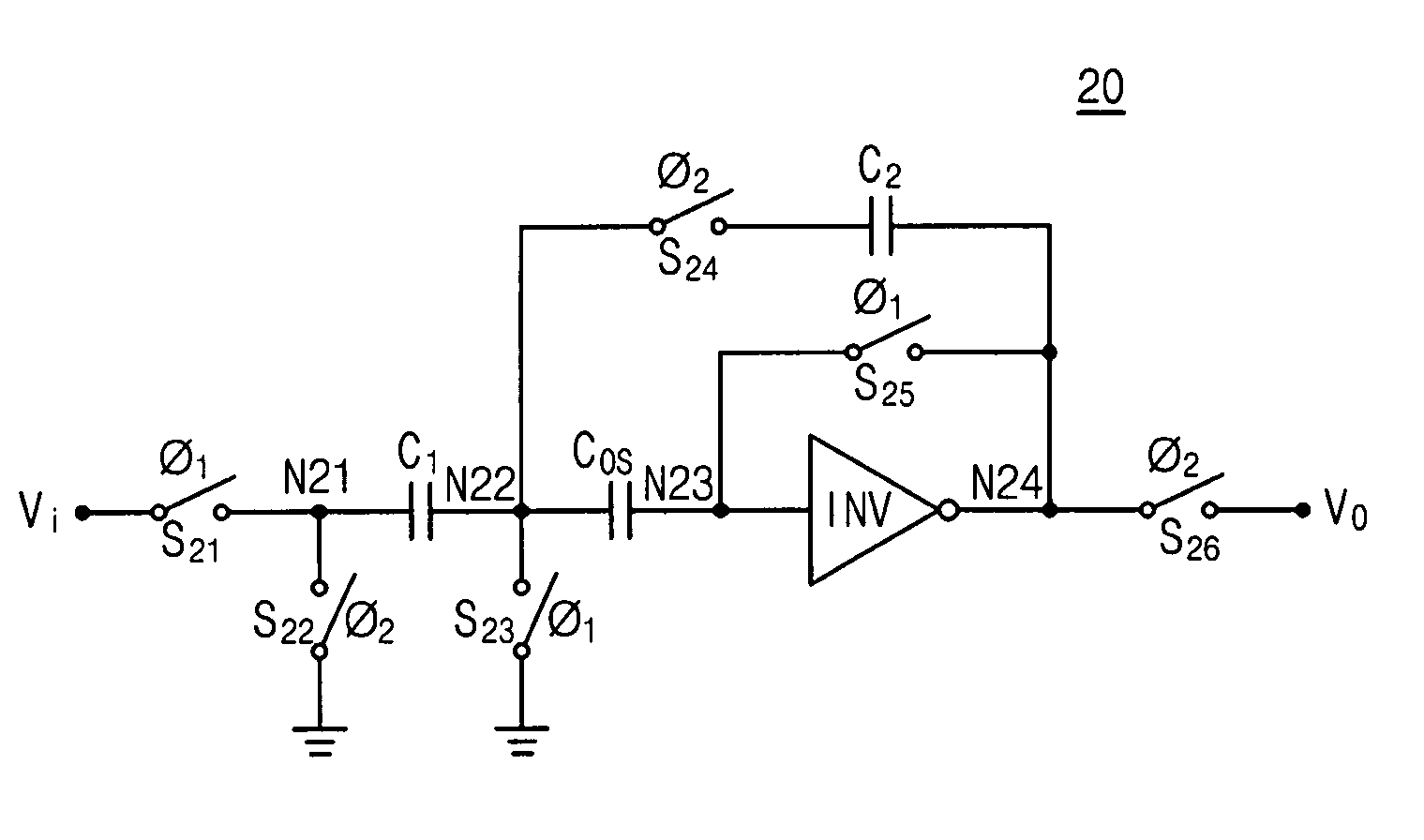
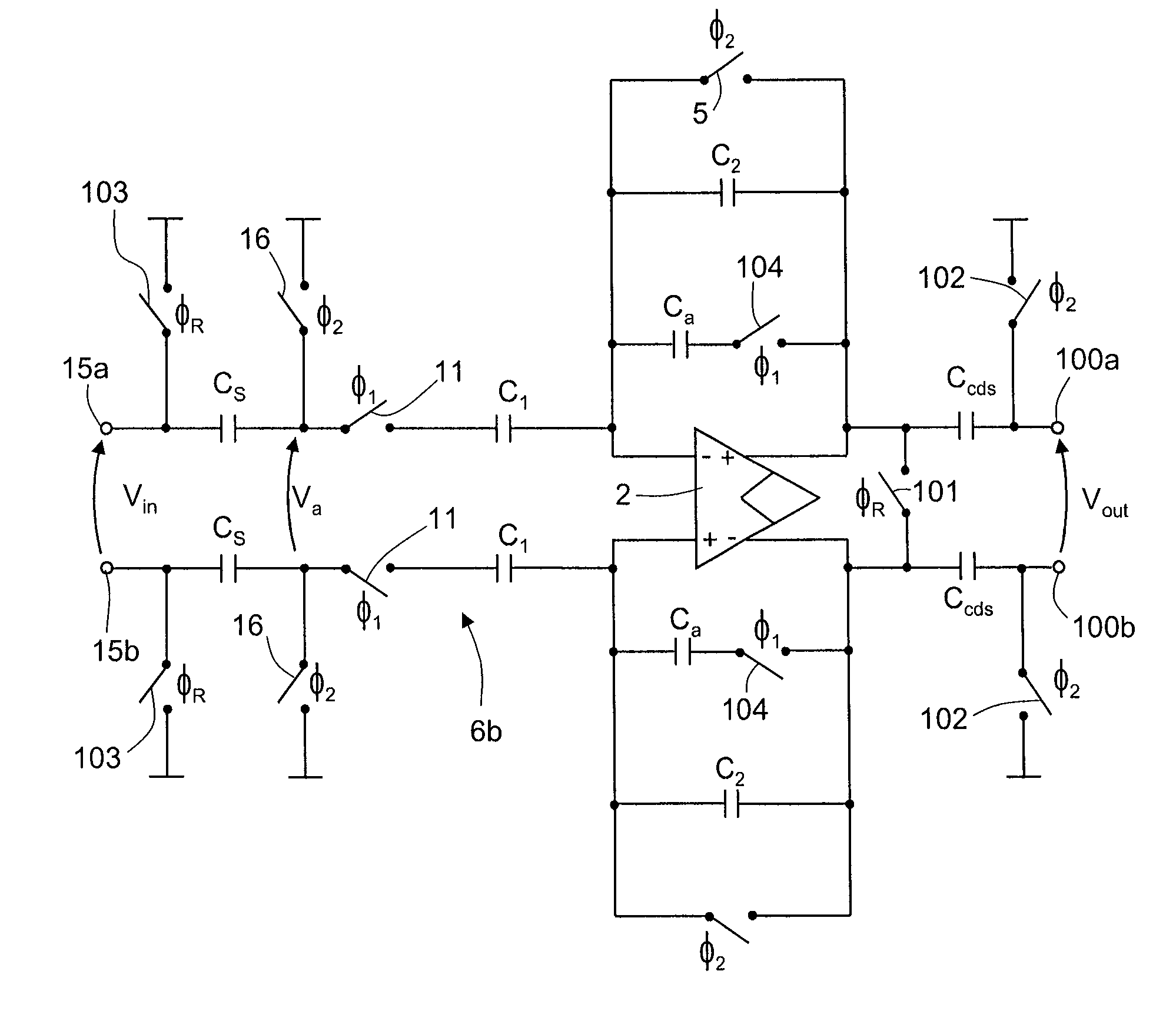
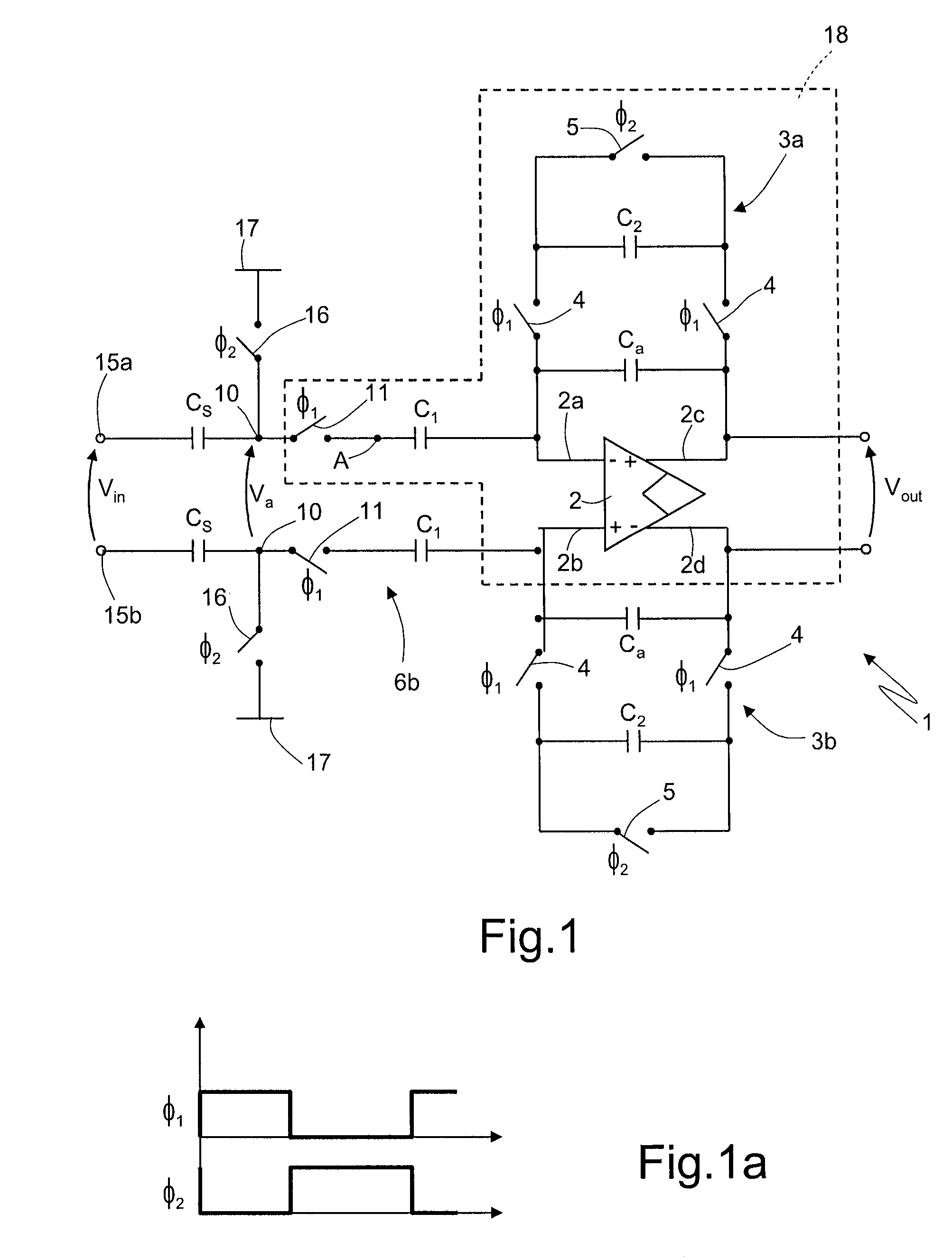
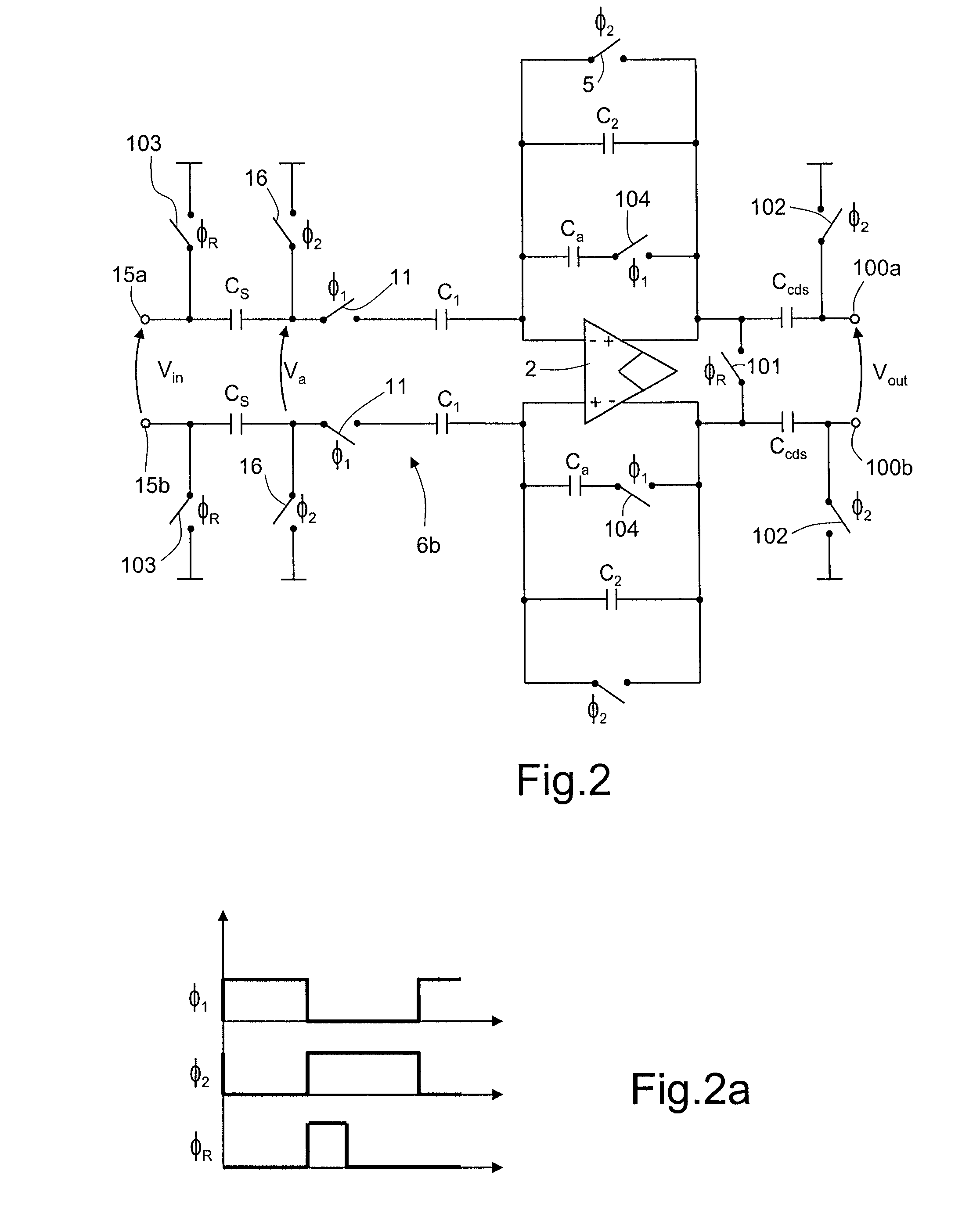
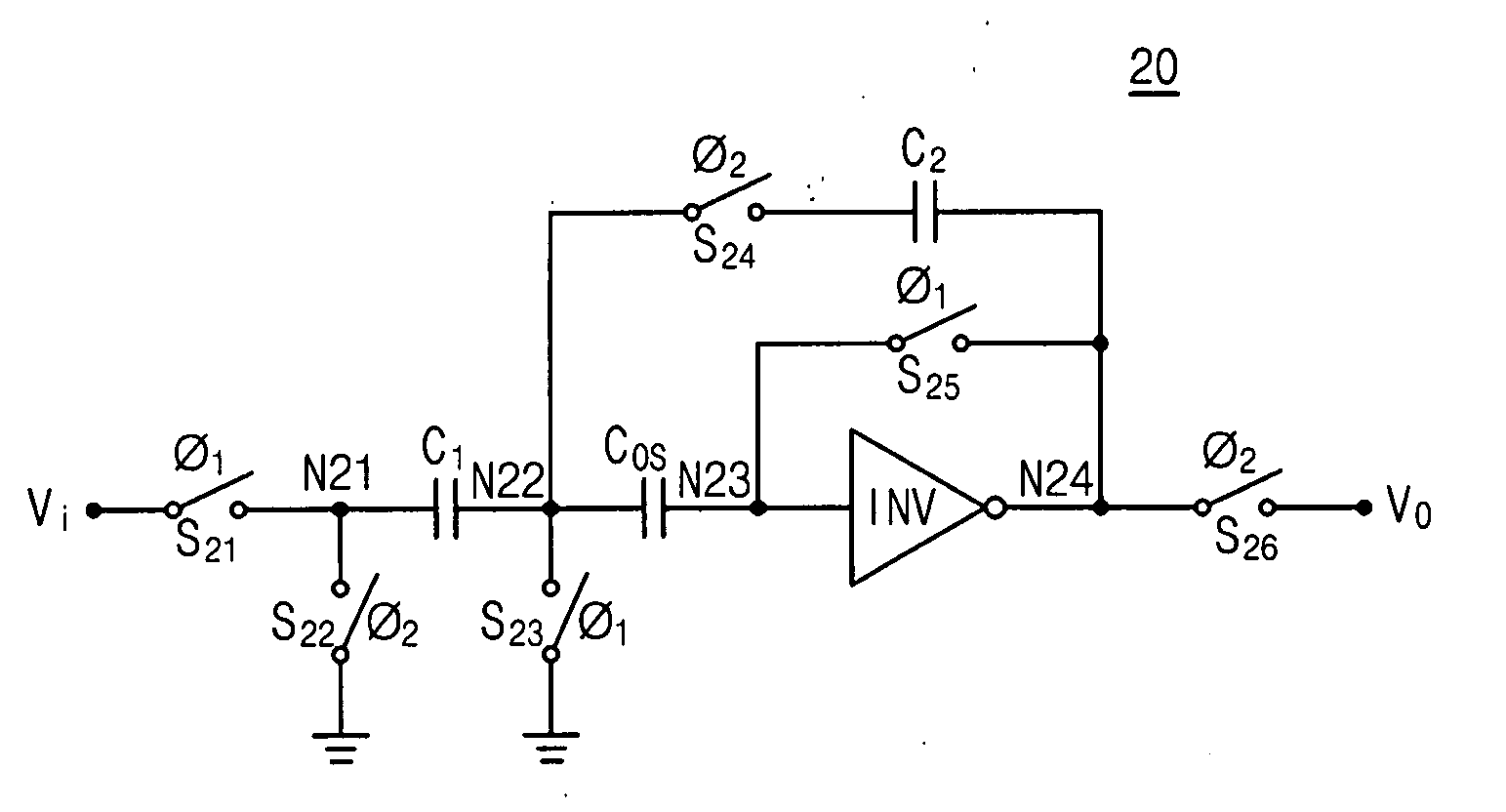
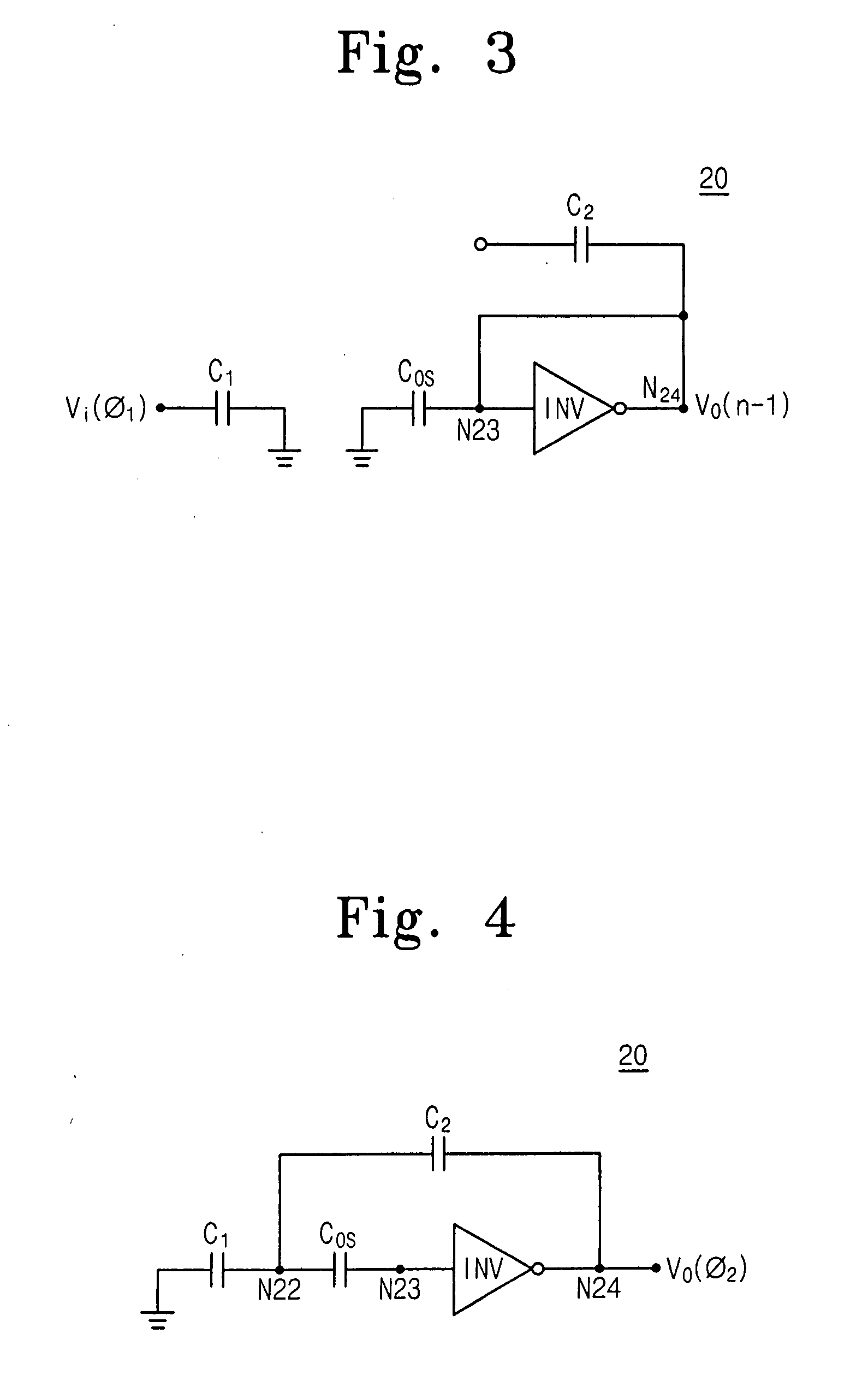
Switched capacitor circuit with inverting amplifier and offset unit
ActiveUS7800427B2Reduce power consumptionReduce circuit areaAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputing operations for integral formationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A switched capacitor circuit includes an amplifier, a charging unit, an offset unit, and an integrating unit. The charging unit is coupled between an input node and a first node, and is for accumulating charge corresponding to an input signal during a sampling mode. The offset unit is coupled between the first node and an input of the amplifier, and is for maintaining the first node to be a virtual ground during an integrating mode. The integrating unit is coupled between the first node and an output of the amplifier, and is for receiving charge from the charging unit during the integrating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
MEMS inertial sensor with frequency control and method
InactiveUS20100263445A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesComputing operations for integration/differentiationResonanceTransducer
An inertial sensor has a transducer with a sense resonator. The sense resonator is oscillated. A signal responsive to the oscillation is provided. A first baseband signal and a second baseband signal are provided responsive to the signal responsive to the oscillation of the sense resonator. A signal for controlling a resonance frequency of the sense resonator is provided responsive to performing a Goertzel algorithm on the first baseband signal and the second baseband signal. One use of controlling the resonance frequency is to control an offset between the resonance frequency of the sense resonator and the frequency of the oscillation of drive masses in the sense resonator. Using the Goertzel algorithm is particularly efficient in controlling the resonance frequency.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
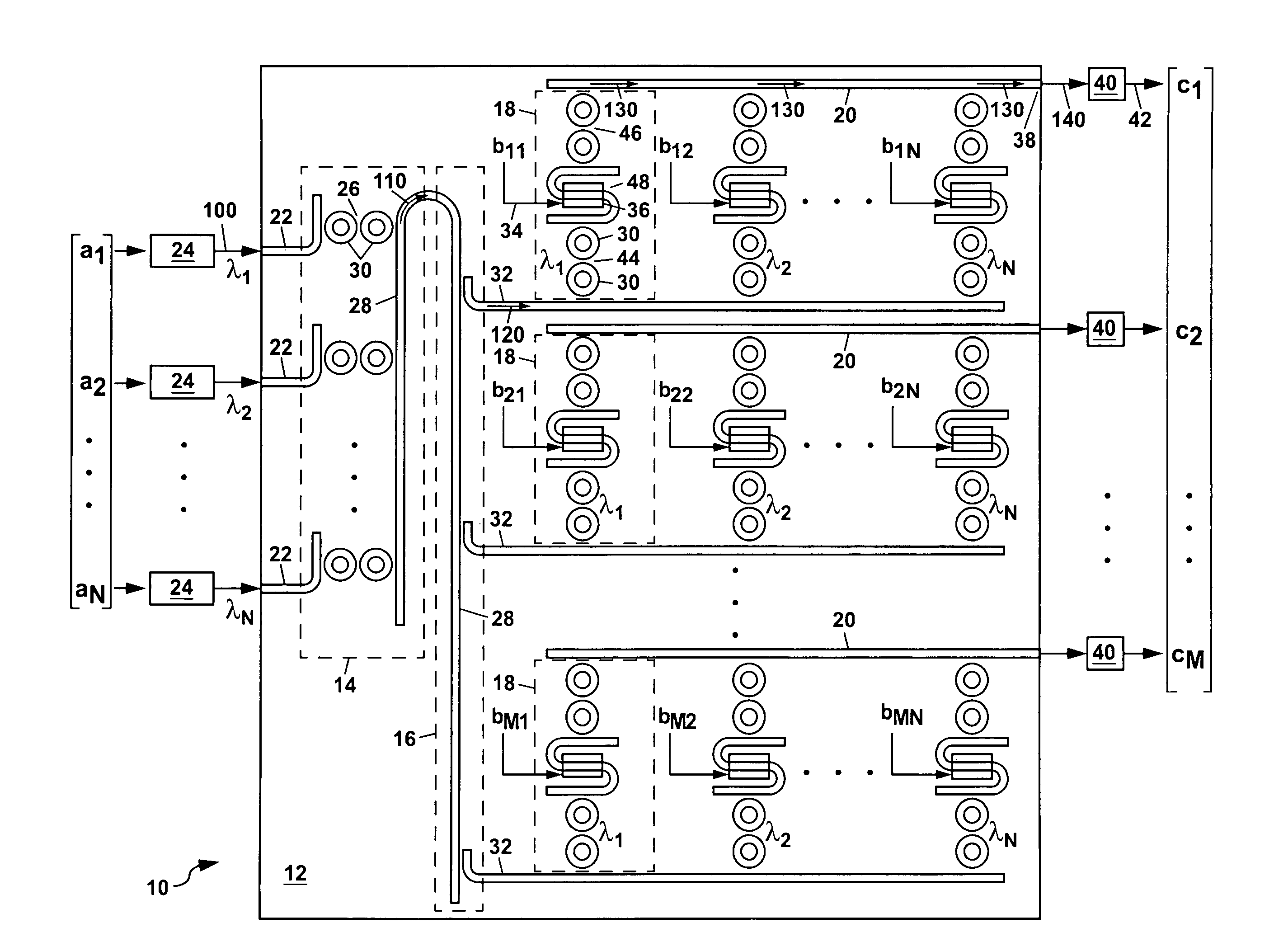
Integrated optic vector-matrix multiplier
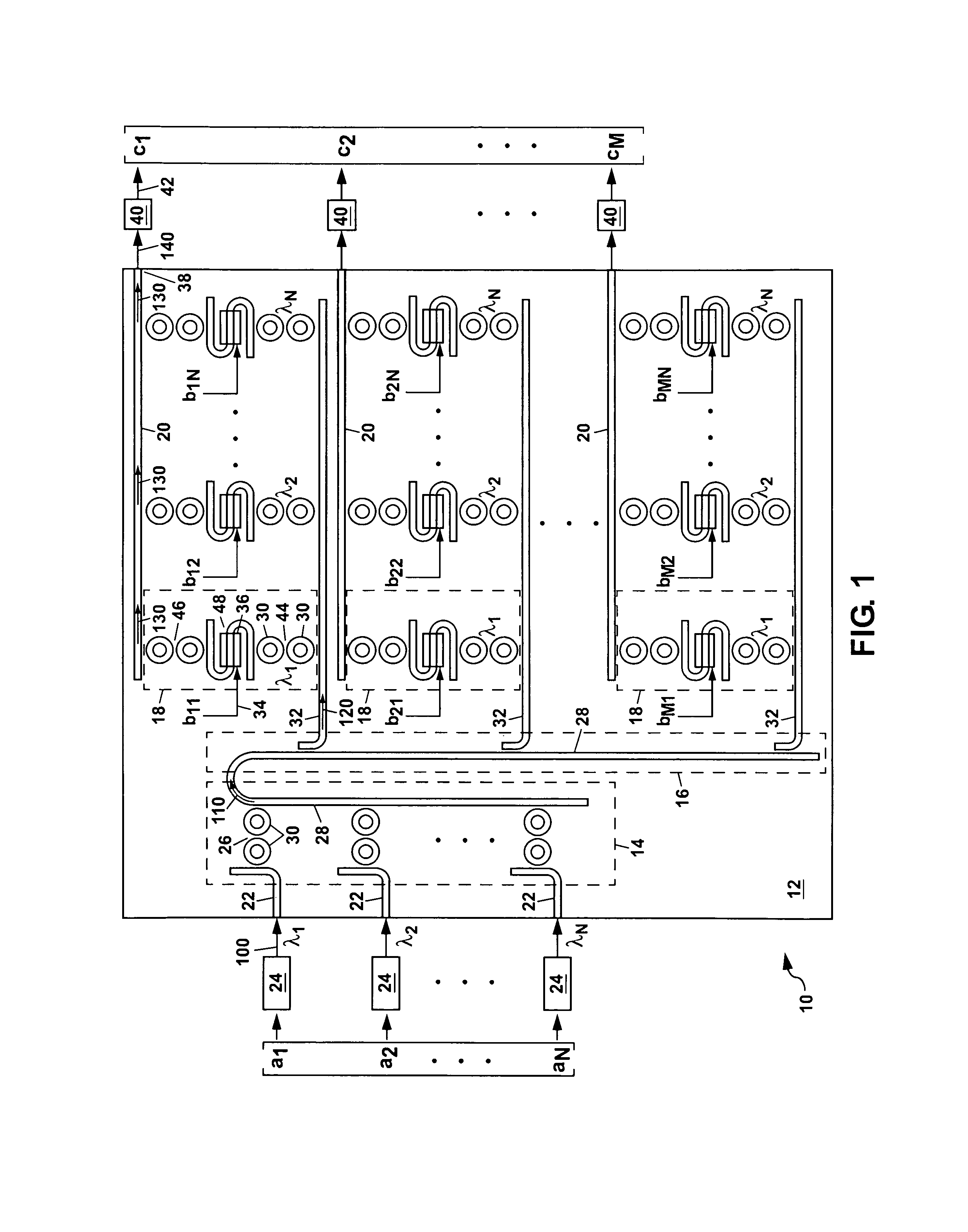
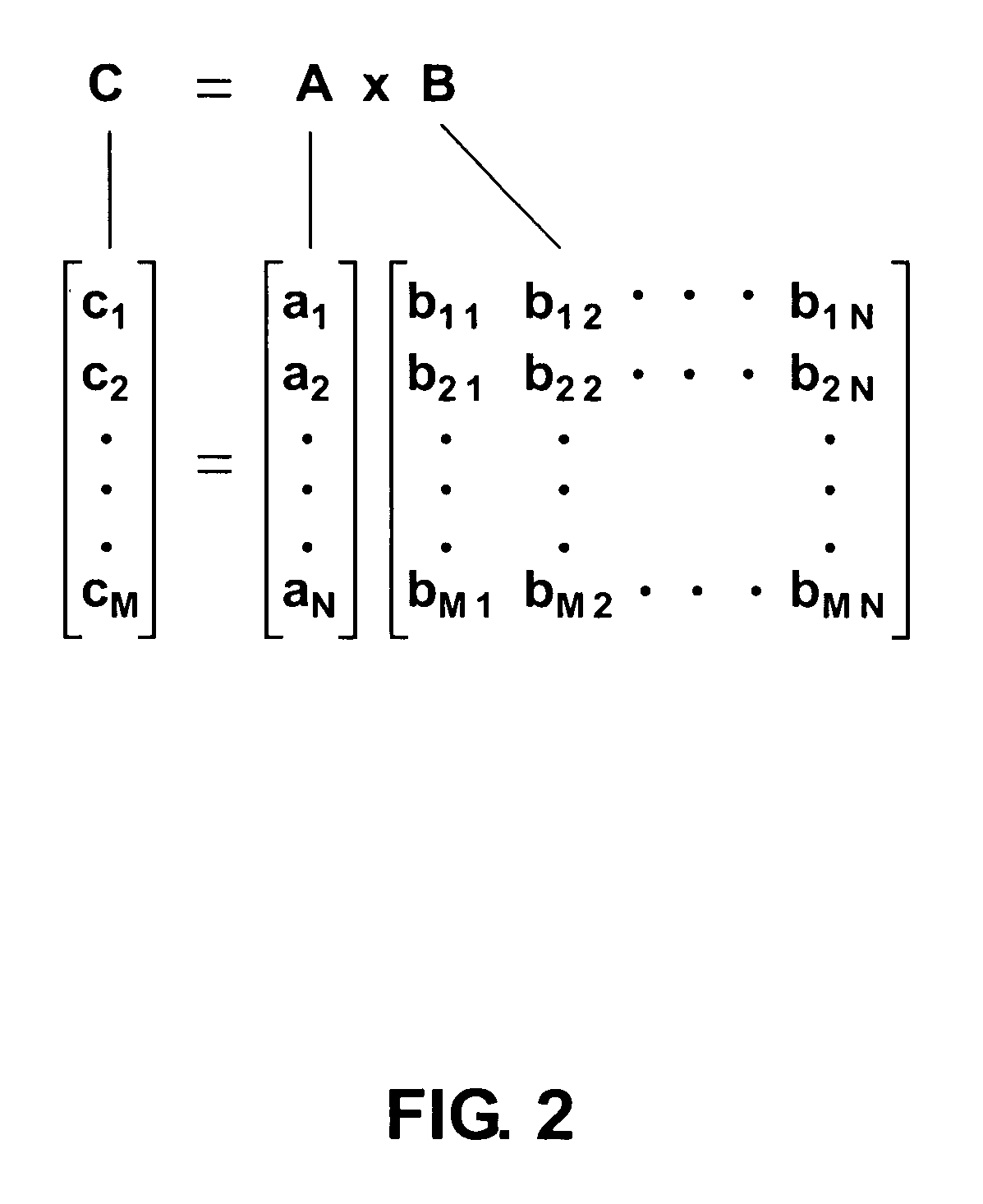
ActiveUS8027587B1Computing operations for integration/differentiationWavelength-division multiplex systemsMatrix multiplierLength wave
A vector-matrix multiplier is disclosed which uses N different wavelengths of light that are modulated with amplitudes representing elements of an N×1 vector and combined to form an input wavelength-division multiplexed (WDM) light stream. The input WDM light stream is split into N streamlets from which each wavelength of the light is individually coupled out and modulated for a second time using an input signal representing elements of an M×N matrix, and is then coupled into an output waveguide for each streamlet to form an output WDM light stream which is detected to generate a product of the vector and matrix. The vector-matrix multiplier can be formed as an integrated optical circuit using either waveguide amplitude modulators or ring resonator amplitude modulators.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
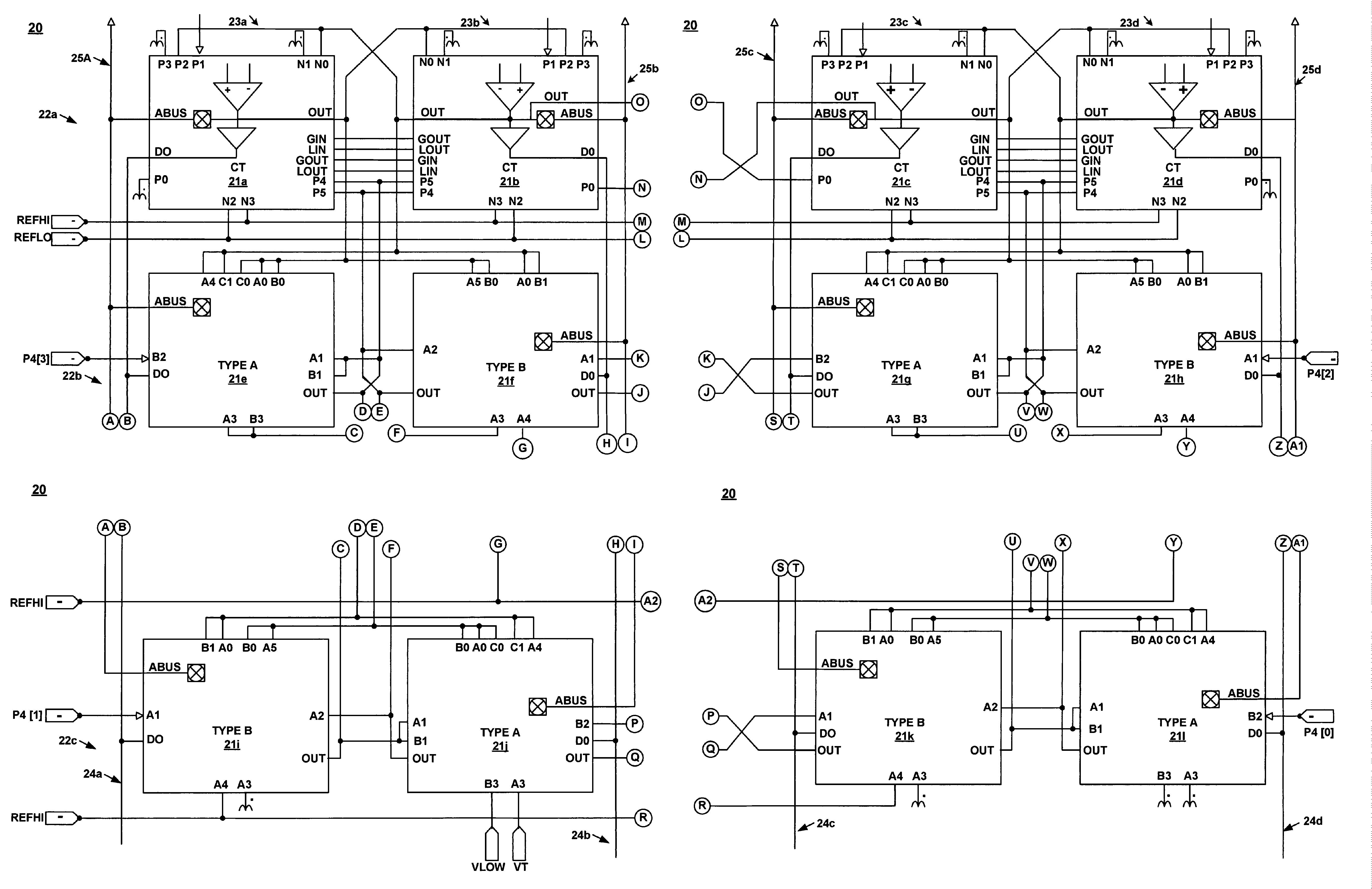
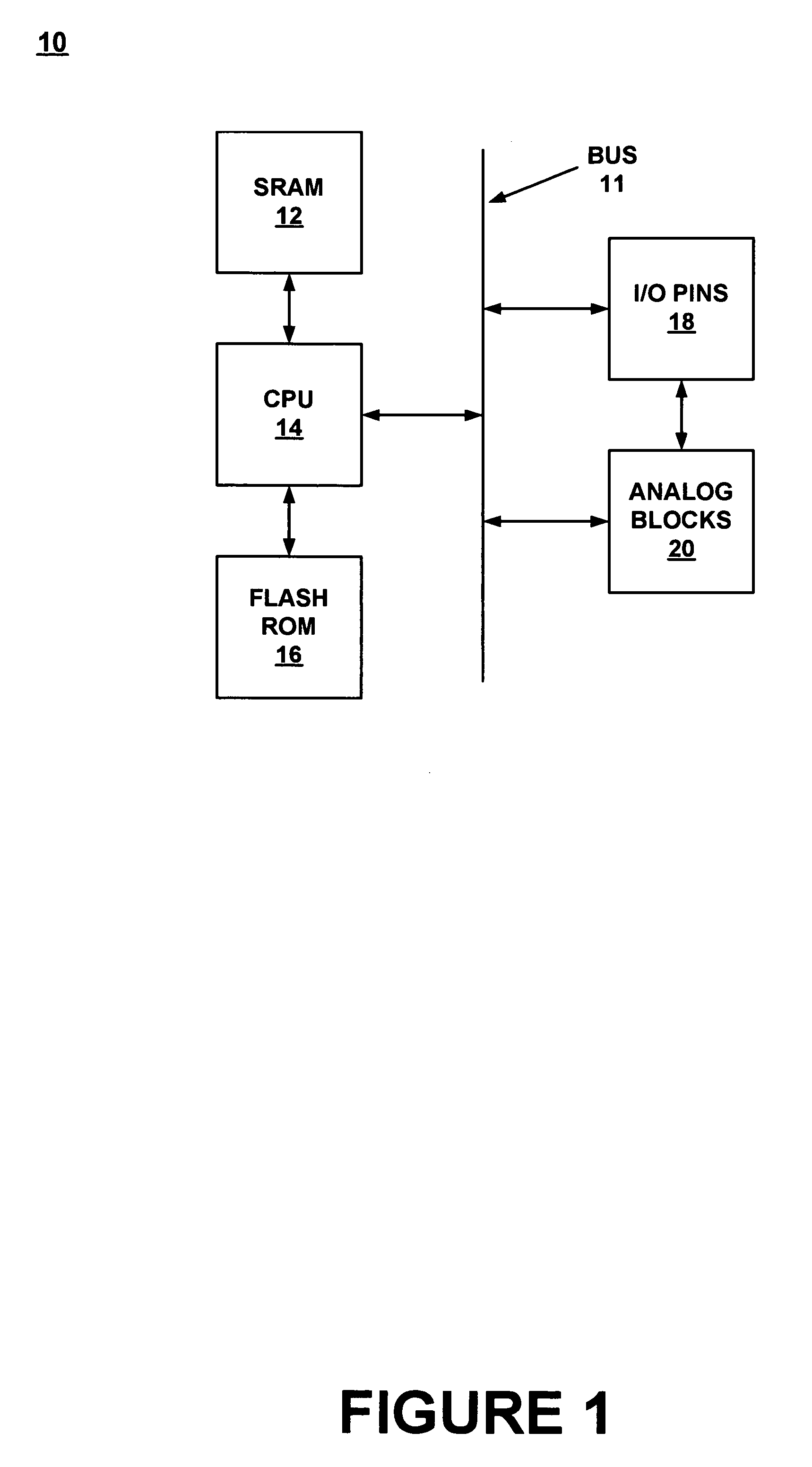
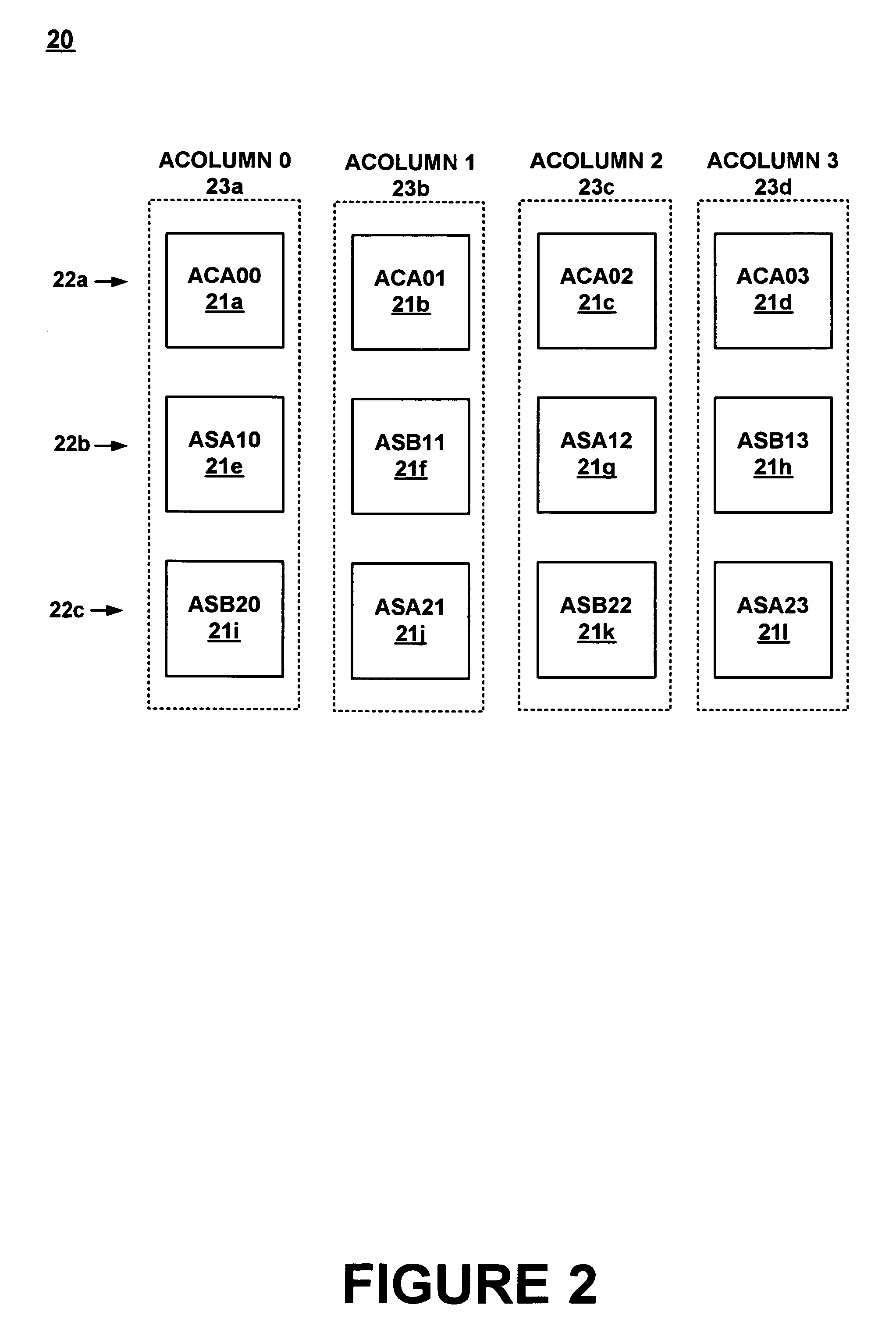
Method for synchronizing and resetting clock signals supplied to multiple programmable analog blocks
InactiveUS6967511B1Efficiently usLow costComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationA domainComputer science
A method for establishing frequency and phase alignment of clock signals across a domain of analog blocks coupled in a single integrated circuit. Different analog functions are implemented by selectively and electrically coupling different combinations of analog blocks. The analog blocks may be arrayed in a number of columns. A synchronized clock signal is supplied to all of the analog blocks in a combination of blocks, even when the blocks are in different columns. The frequency of the clock signal can be changed dynamically depending on the analog function to be achieved.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
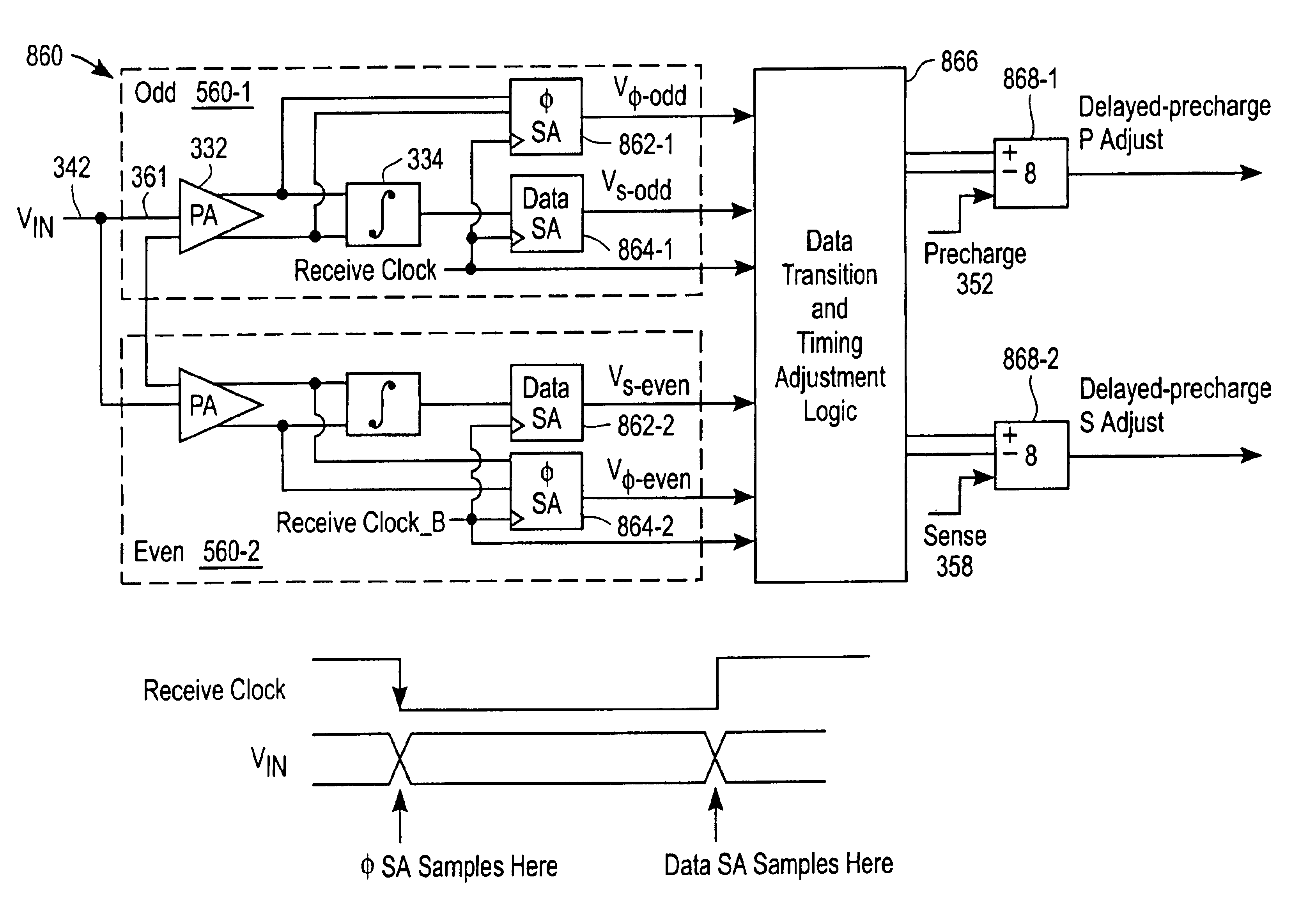
Method and apparatus for receiving high speed signals with low latency
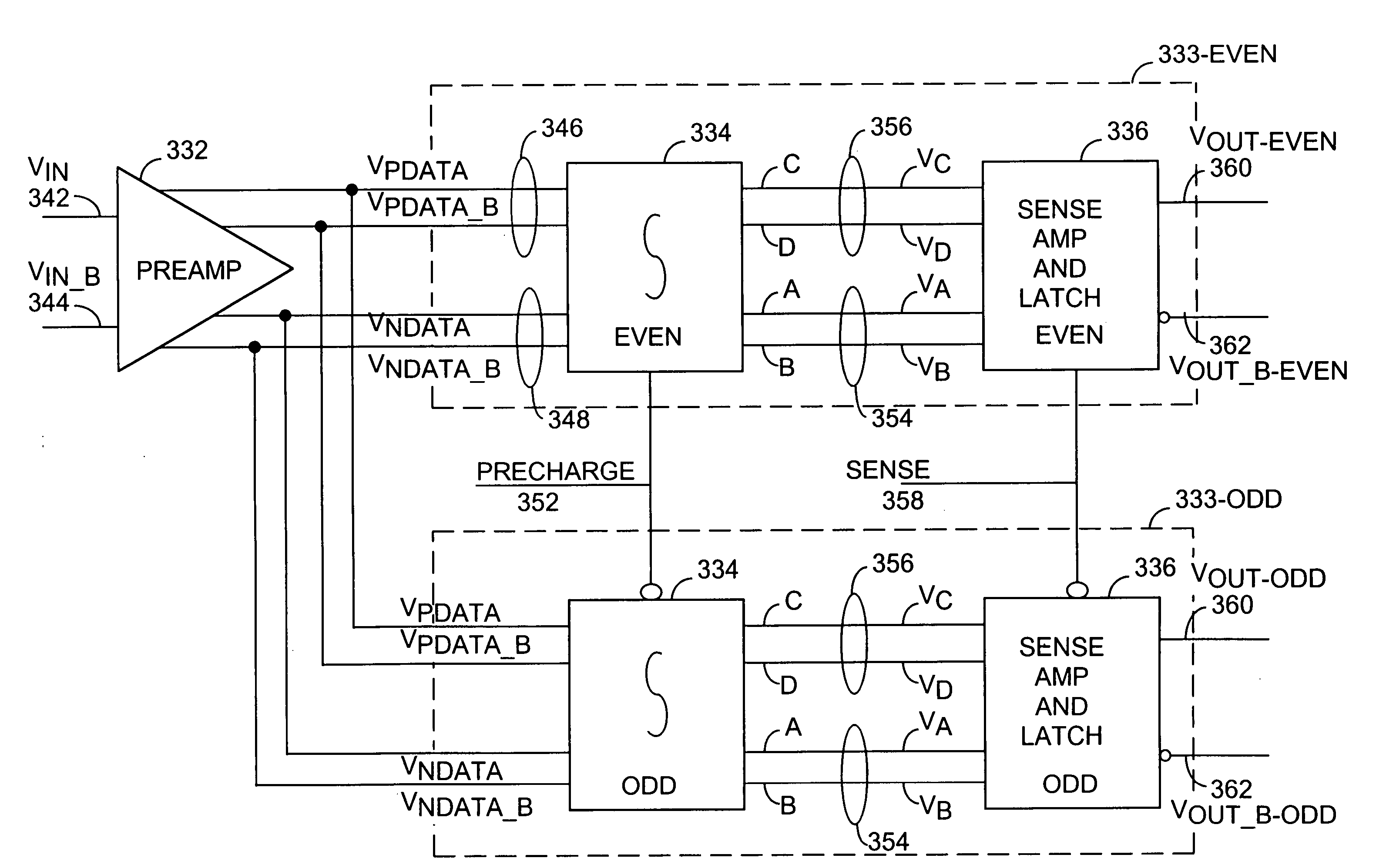
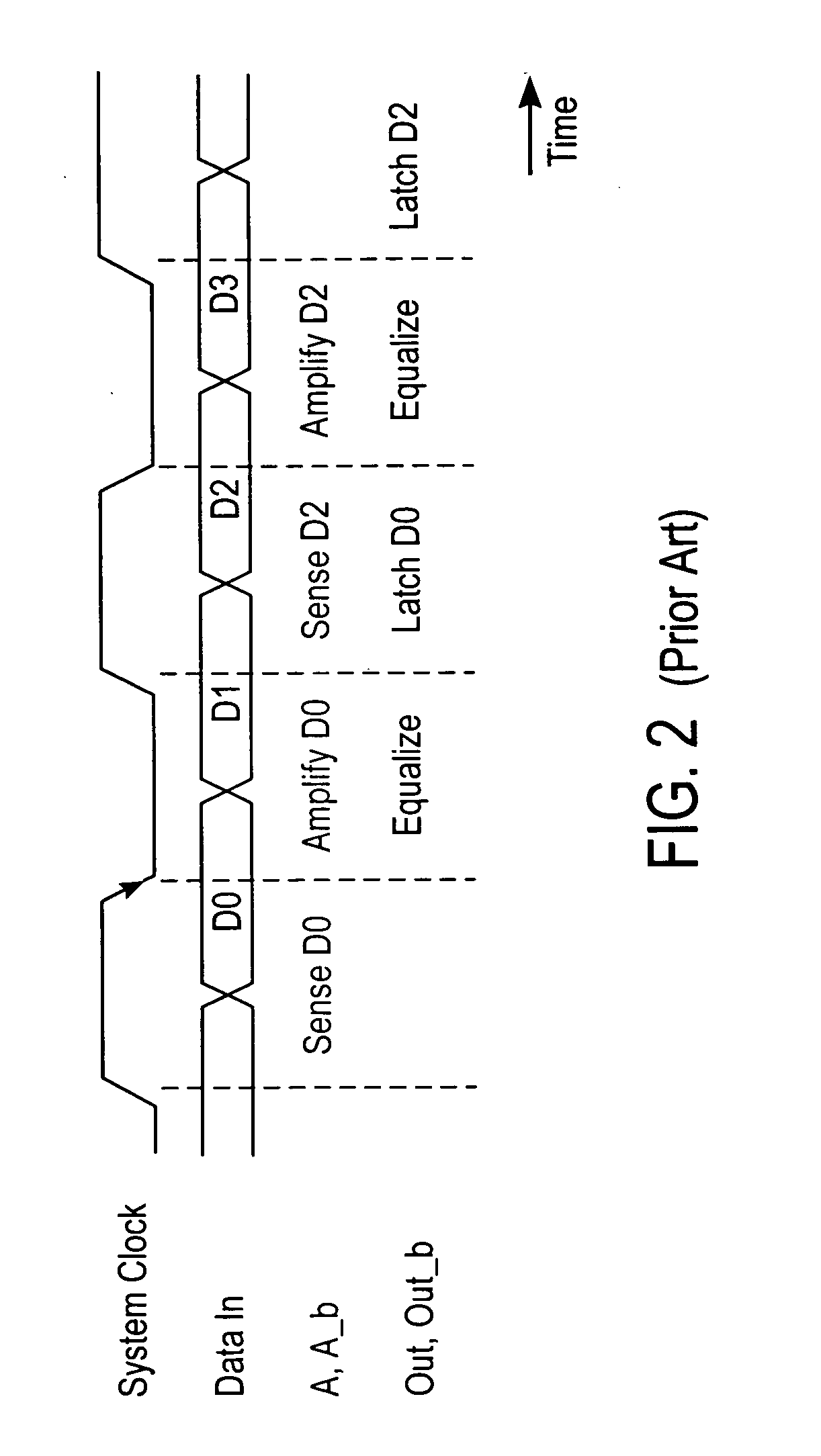
InactiveUS6965262B2Reduces input-to-output latencyReduce static power consumptionDigital differential analysersDigital storageIntegratorAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and method for receiving high-speed signals having a wide common-mode range with low input-to-output latency. In one embodiment, the receiver includes an integrator to accumulate charge in accordance with an input signal during an integration time interval to produce an output voltage. A sense amplifier samples and converts the output voltage of the integrator to a logic signal; and a latch stores the logic signal. In an alternate embodiment, a preamplifier conditions the input signal prior to being integrated. In another embodiment using multiple receivers, circuitry is added to the receiver to compensate for timing errors associated with the distribution of the timing signals. In yet another embodiment, the integrator is coupled to an equalization circuit that compensates for intersymbol interference. In another embodiment, another circuit compensates for accumulated voltage offset errors in the integrator.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Switched-capacitor high-pass mirrored integrator
InactiveUS7038532B1Improve noise characteristicsComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
In a high-pass (mirrored) integrator structure that employs chopper modulation, the input and output of the mirrored integrator are connected to the input and output ports of the operational amplifier, bypassing the chopper stabilization modulators. The mirrored integrator can be used in sigma-delta analog-to-digital converters.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Integrator circuitry for single channel radiation detector
InactiveUS7411198B1Wide dynamic rangeComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationIntegratorAudio power amplifier
Input circuitry is provided for a high voltage operated radiation detector to receive pulses from the detector having a rise time in the range of from about one nanosecond to about ten nanoseconds. An integrator circuit, which utilizes current feedback, receives the incoming charge from the radiation detector and creates voltage by integrating across a small capacitor. The integrator utilizes an amplifier which closely follows the voltage across the capacitor to produce an integrator output pulse with a peak value which may be used to determine the energy which produced the pulse. The pulse width of the output is stretched to approximately 50 to 300 nanoseconds for use by subsequent circuits which may then use amplifiers with lower slew rates.
Owner:NASA
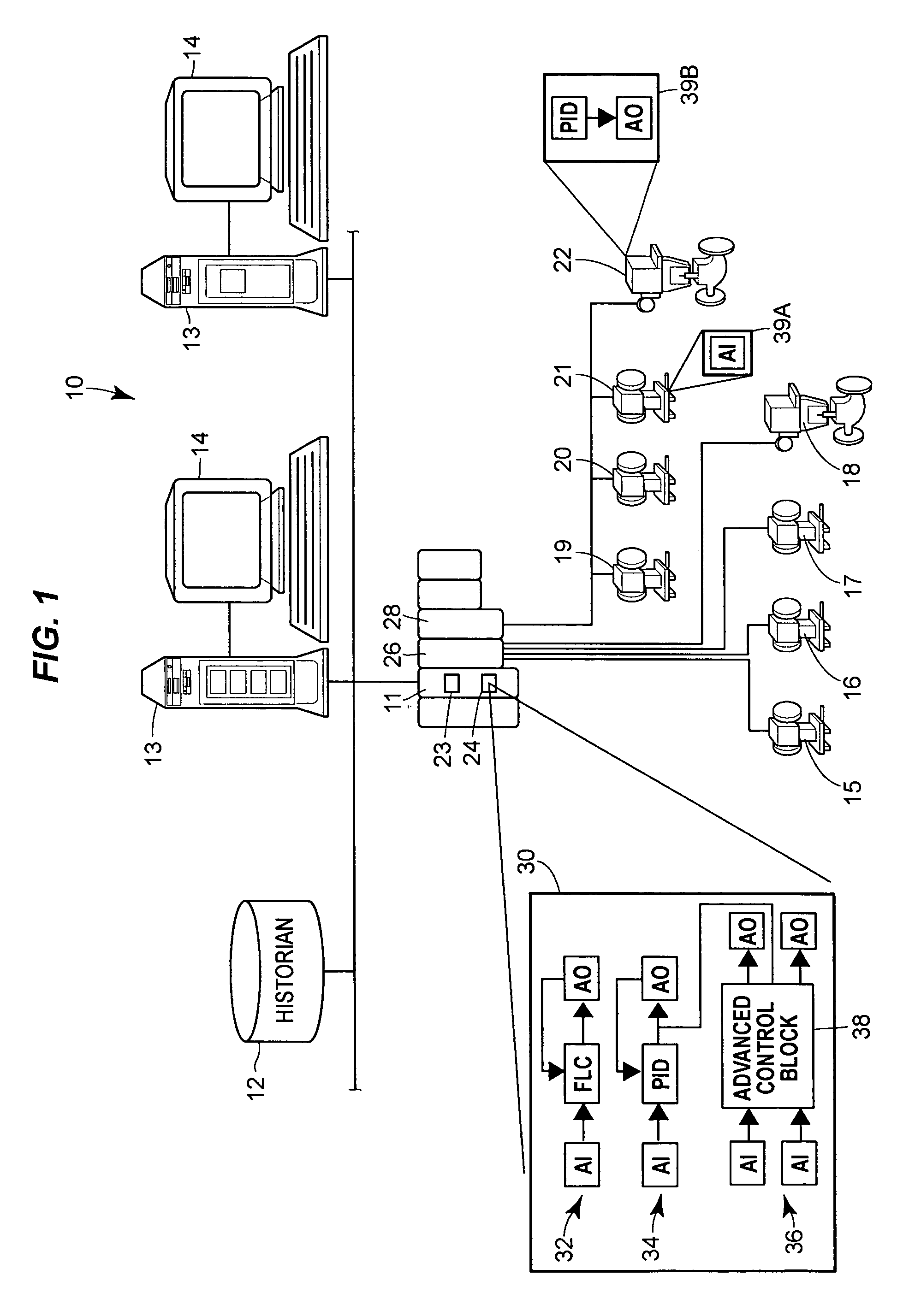
Process control with unreliable communications
ActiveUS7620460B2Programme controlComputing operations for integration/differentiationControl signalEngineering
Disclosed are methods and devices for controlling a process with a control signal. Iterations of a control routine are implemented to generate the control signal, and when an indication of a response to the control signal is unavailable, a feedback contribution to the control signal is maintained over one or more of the iterations of the control routine. The feedback contribution is then modified upon receiving the response indication, in which the feedback contribution is determined in accordance with an elapsed time between the received response indication and a previous communication of the response indication.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
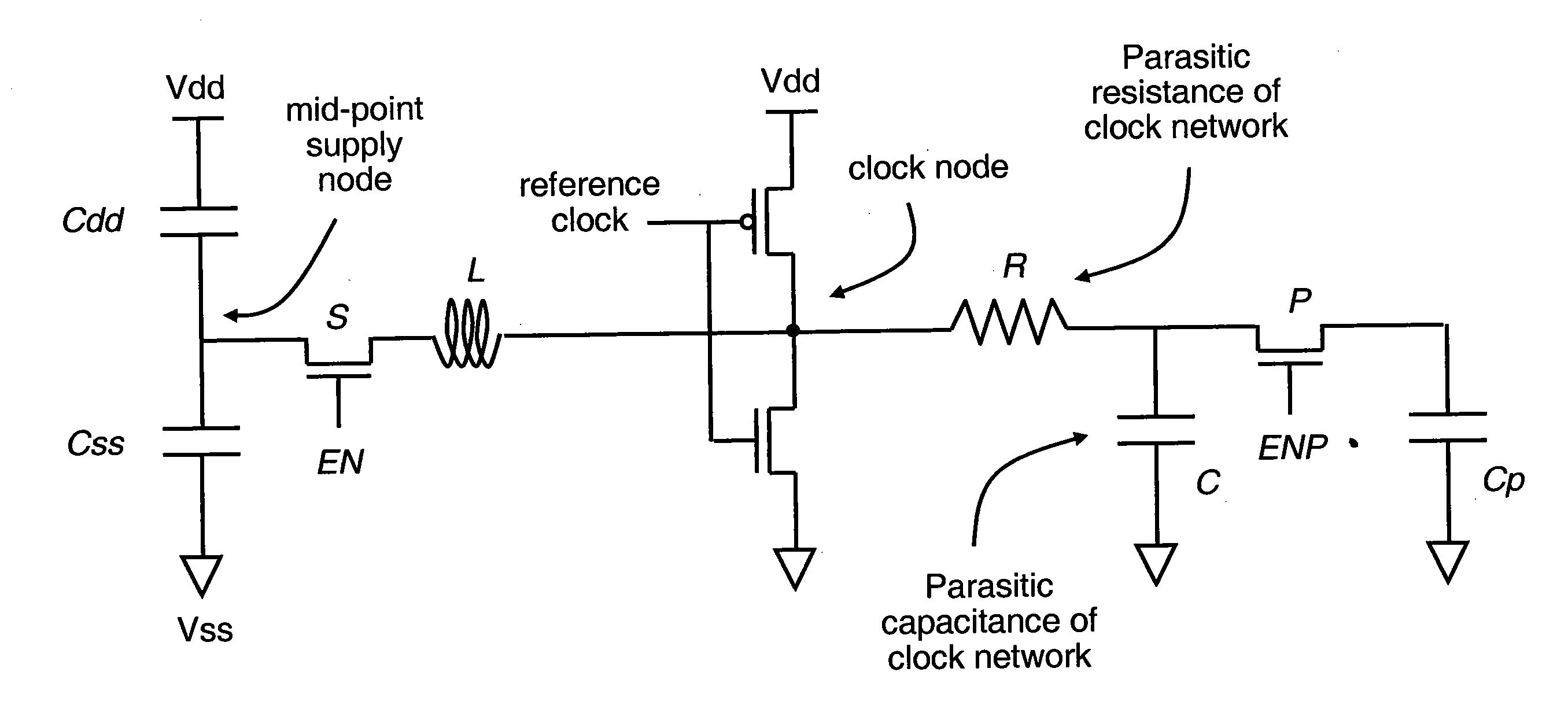
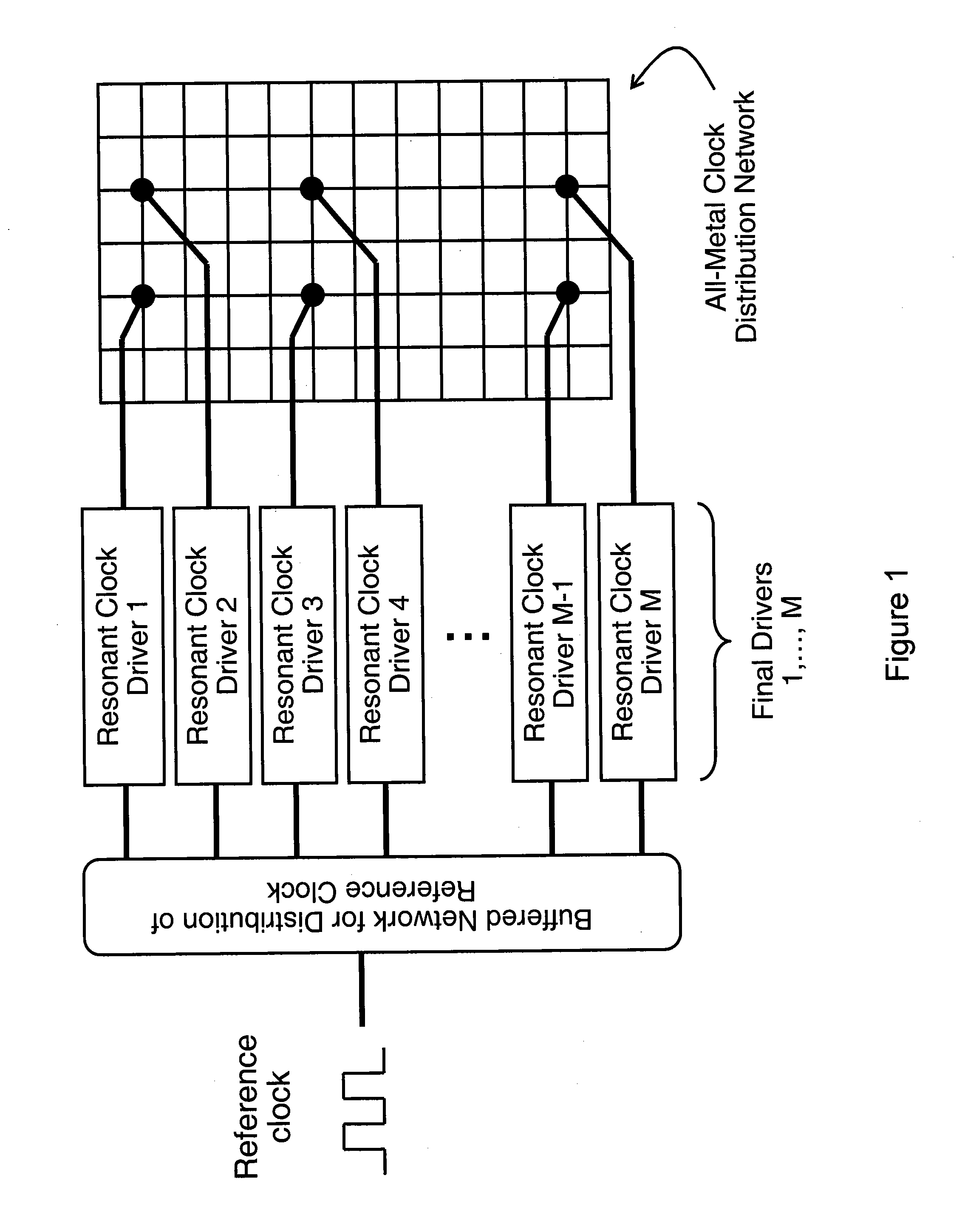
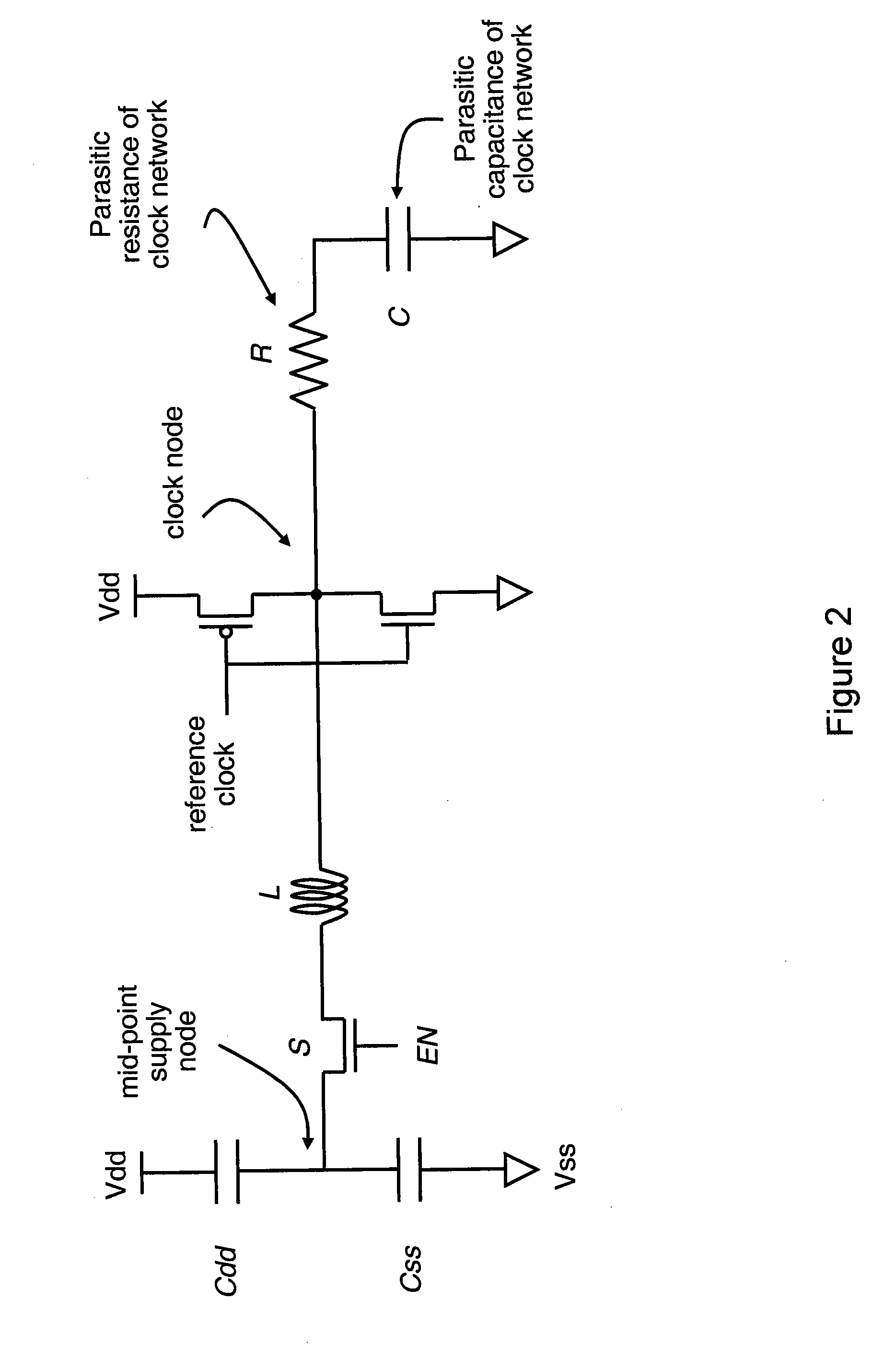
Architecture for adjusting natural frequency in resonant clock distribution networks
ActiveUS20110090018A1Run energy savingReduce overheadComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationSemiconductorDistribution networks
An inductor architecture for resonant clock distribution networks is proposed. This architecture allows for the adjustment of the natural frequency of a resonant clock distribution network, so that it achieves energy-efficient operation at multiple clock frequencies. The proposed architecture is primarily targeted at the design of integrated inductors and exhibits relatively low area overheads. Such an architecture is generally applicable to semiconductor devices with multiple clock frequencies, and high-performance and low-power clocking requirements such as microprocessors, ASICs, and SOCs. Moreover, it is applicable to the binning of semiconductor devices according to achievable performance levels.
Owner:CYCLOS SEMICON
Switched-capacitor band-pass filter of a discrete-time type, in particular for cancelling offset and low-frequency noise of switched-capacitor stages
ActiveUS8497746B2Eliminate offsetReduce flicker noiseComputing operations for integral formationMultiple-port networksCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A band-pass filter made up by an operational amplifier and by an input circuit. The input circuit is formed by a capacitive filtering element, connected to the input of the operational amplifier; a coupling switch, coupled between an input node and the capacitive filtering element; a capacitive sampling element, coupled between the input of the filter and the input node; and a sampling switch, coupled between the input node and a reference-potential line. The coupling switch and the input sampling switch close in phase opposition according to a succession of undesired components sampling and sensing steps, so that the capacitive sampling element forms a sampler for sampling the undesired component in the undesired components sampling step, in the absence of the component of interest, and forms a subtractor of the undesired components from the input signal in the sensing step.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
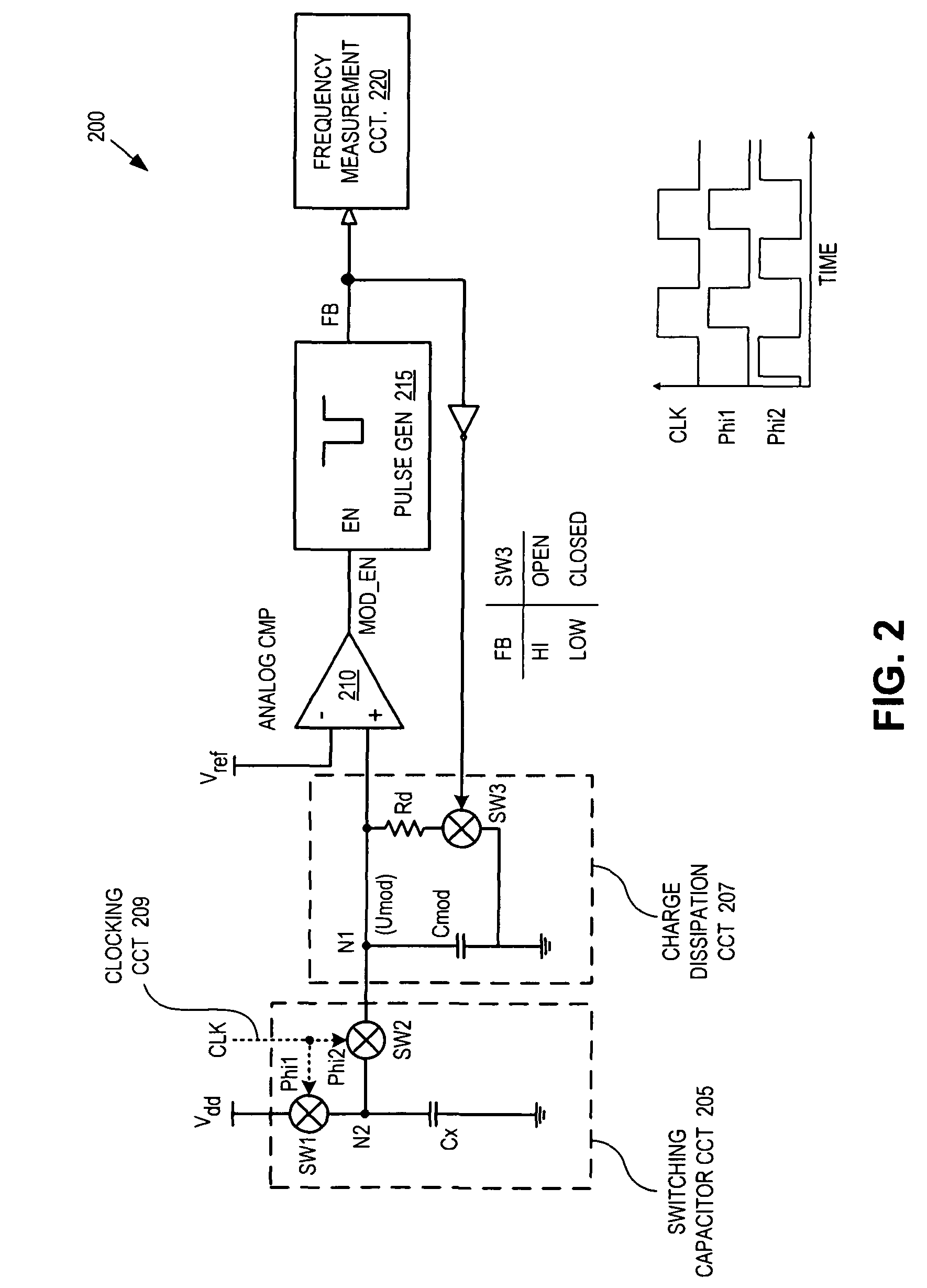
Capacitance to frequency converter
ActiveUS8169238B1Computing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceFrequency changer
A capacitance to frequency converter includes a switching capacitor circuit, a charge dissipation circuit, a comparator, and a signal generator. The switching capacitor circuit charges a sensing capacitor and transfers charge from the sensing capacitor to a circuit node of the charge dissipation circuit. The comparator is coupled to the charge dissipation circuit to compare a potential at the circuit node to a reference voltage. The signal generator is coupled to an output of the comparator and to the charge dissipation circuit. The signal generator is responsive to the output of the comparator to generate a signal fed back to control the charge dissipation circuit. A frequency of the signal is proportional to a capacitance of the sensing capacitor.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
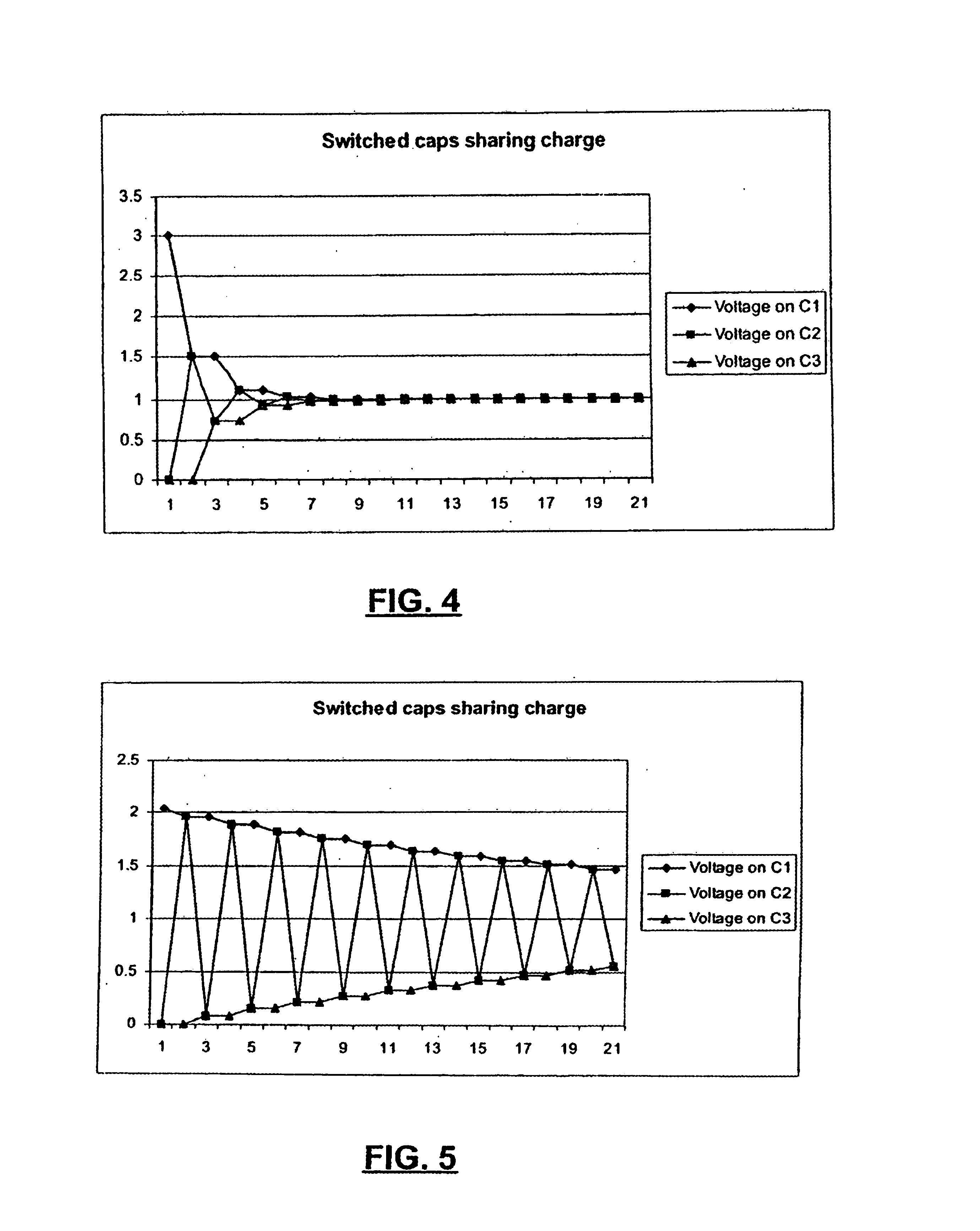
Switched capacitor circuit compensation apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050140422A1Easy to useIncrease currentElectric analogue storesDigital differential analysersCapacitanceLoop control
A compensated switched capacitor circuit comprises a switched capacitor circuit and a compensation circuit. The compensation circuit generates a reference current that varies under closed loop control to maintain a targeted slew rate for charging a reference capacitor that is determined by the input clock frequency. The switched capacitor circuit's output amplifier is configured such that its output current varies in proportion to the reference current. Thus, by configuring the reference capacitor to track the effective capacitance of the switched capacitor circuit, the settling time of the switched capacitor circuit may be made relatively insensitive to the value of and changes in the effective capacitance over a range of clock frequencies. The compensation circuit may include a clock reconditioning circuit to ensure that the switched capacitor circuit is clocked at a desired duty cycle.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
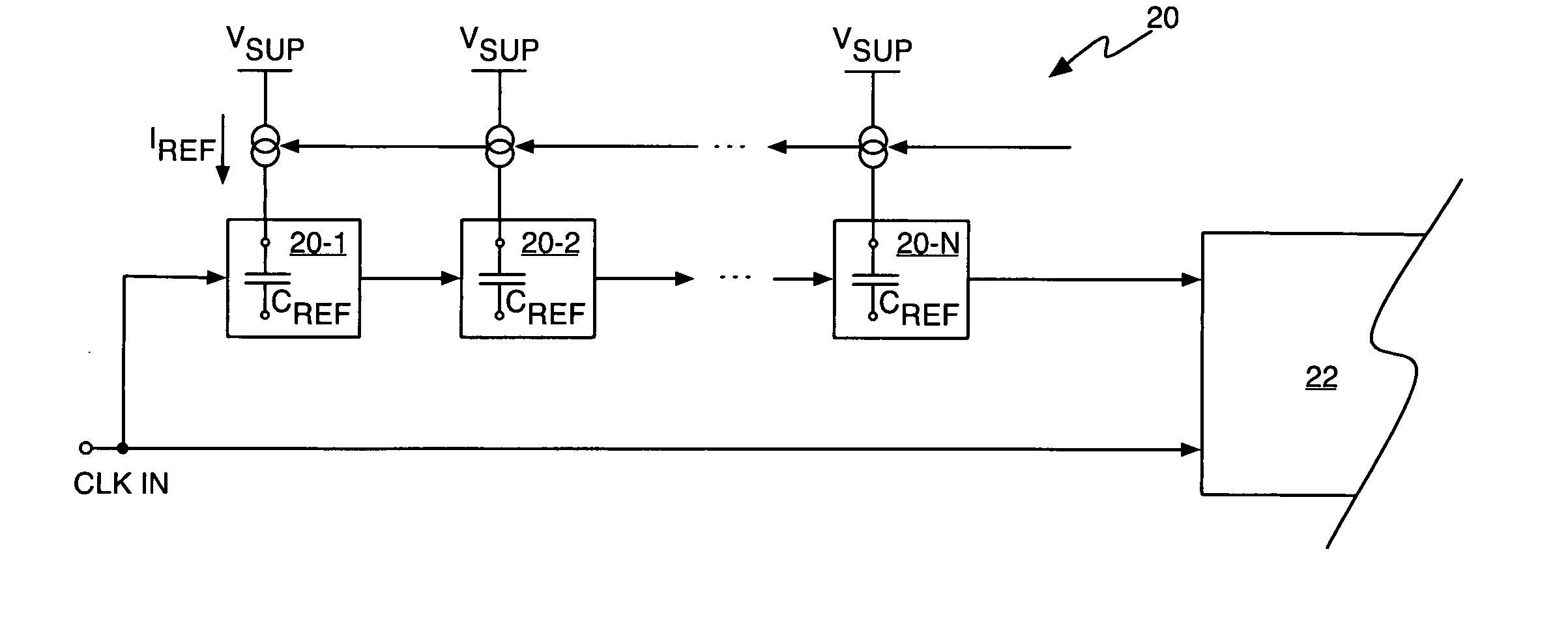
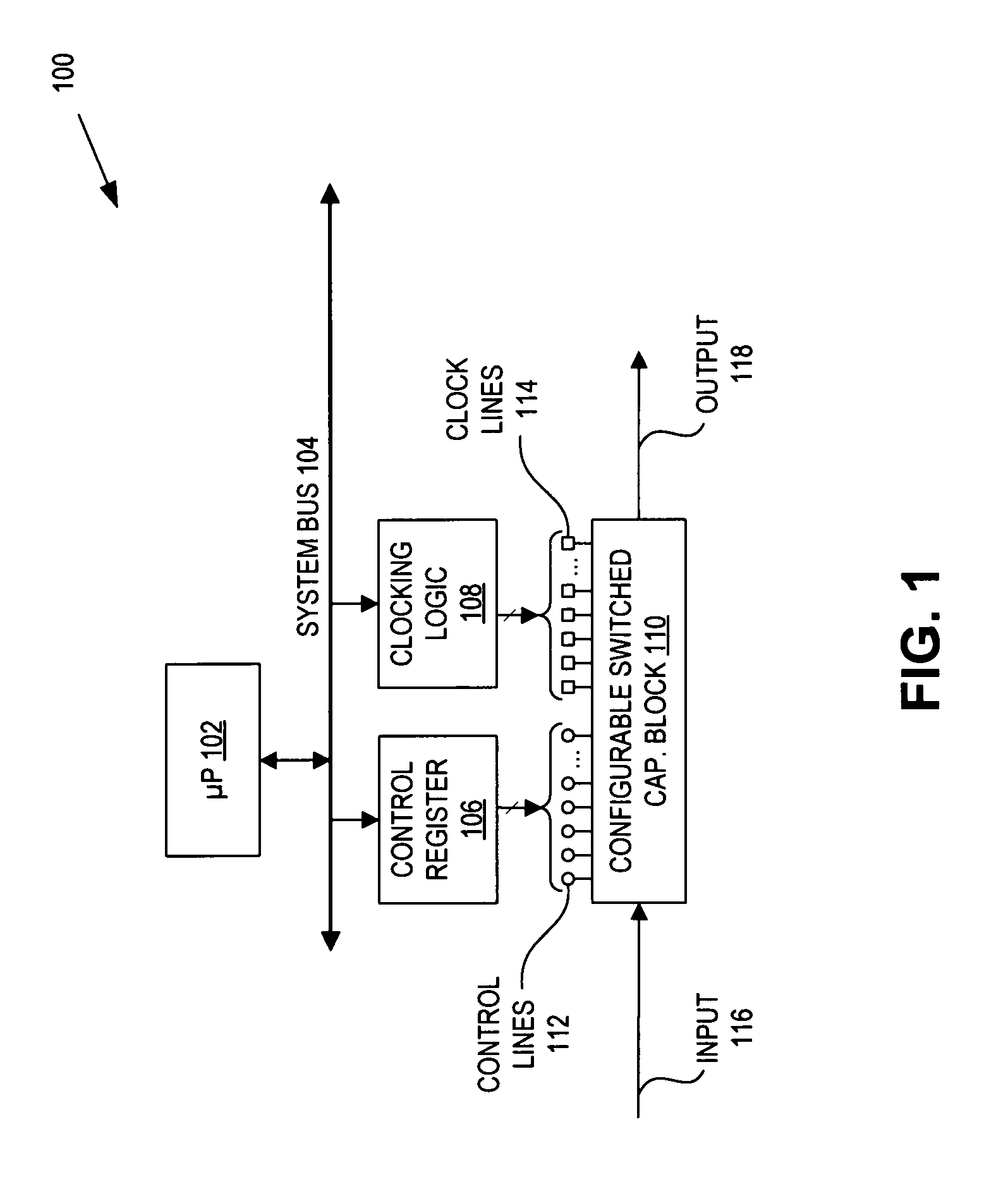
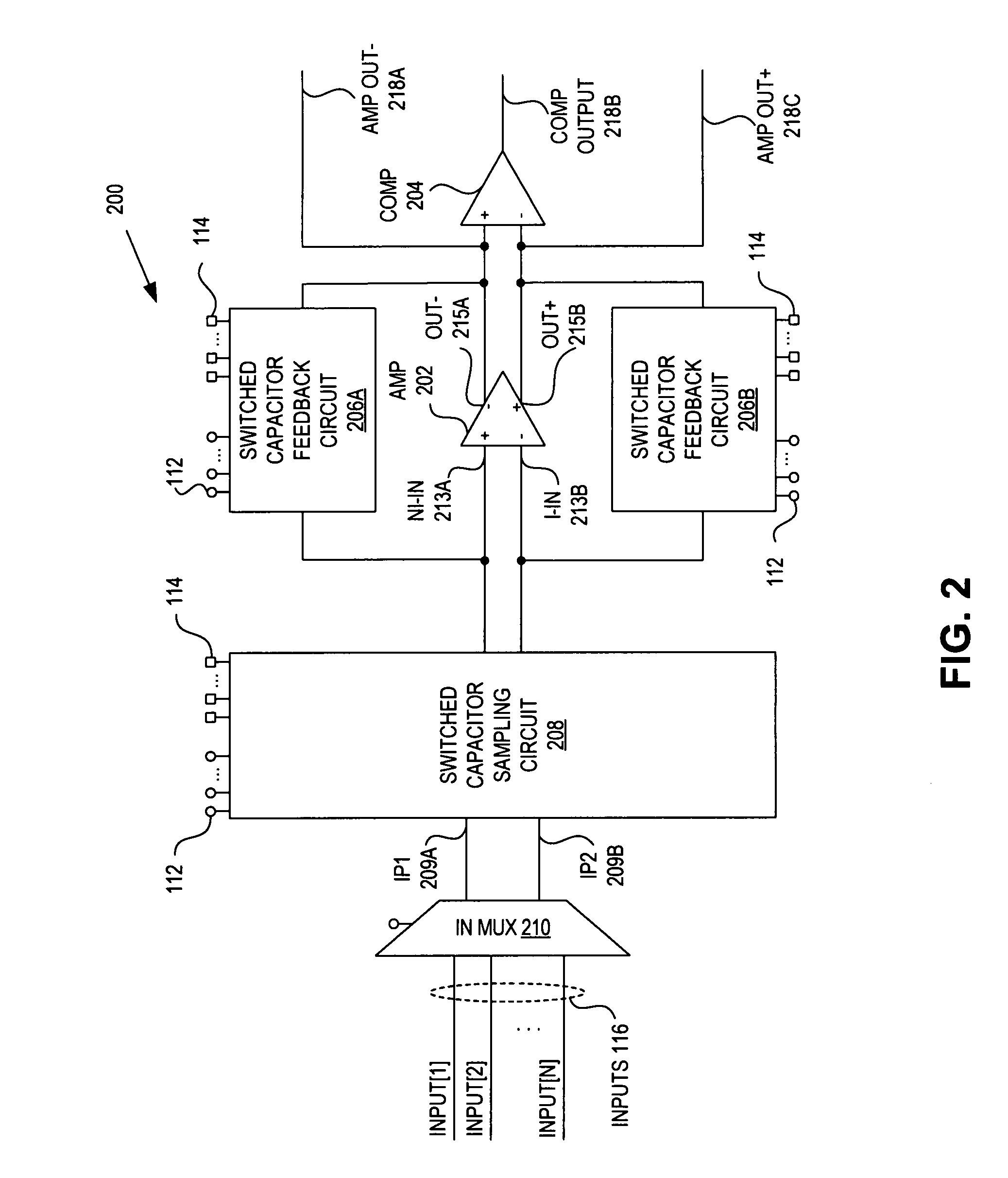
Configurable switched capacitor block
ActiveUS7679422B1Computing operations for integral formationElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierFeedback circuits
A configurable switched capacitor block includes a switched-capacitor (SC) sampling circuit, a fully differential amplifier, an SC feedback circuit, and a comparator. The SC sampling circuit is coupled to receive an input signal and to selectively generate a sampled signal to a differential input of the amplifier. The SC feedback circuit is coupled between the differential inputs and the differential outputs of the amplifier to selectively control a feedback of the amplifier. The comparator is coupled to the differential outputs of the amplifier to generate an output signal. The configurable switched capacitor block has multiple modes of operation which are selectable by programming the SC sampling circuit and the SC feedback circuit.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Calibration for mixed-signal integrator architecture
ActiveUS20120218020A1Decreases integrated output voltageIncrease costComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationIntegratorDisplay device
A mixed signal correlator utilizes coherent detection within a capacitance measurement application. In some applications, the mixed signal correlator is used to measure capacitance of a touch screen display. An external capacitor whose capacitance is measured is kept small for improved sensitivity and can be used for a variety of applications having varied integration periods for measurement. The external capacitor is kept small and can be used for varied applications by adjusting the output voltage within a range that is less than the supply voltage, and maintaining a count of the adjustments to later reconstruct an actual output voltage for the integration period. An output is a weighted sum of an analog integrator output and a digital counter output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
At frequency phase shifting circuit for use in a quadrature clock generator
InactiveUSRE37452E1Enhance the shake effectComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationPhase shiftedClock generator
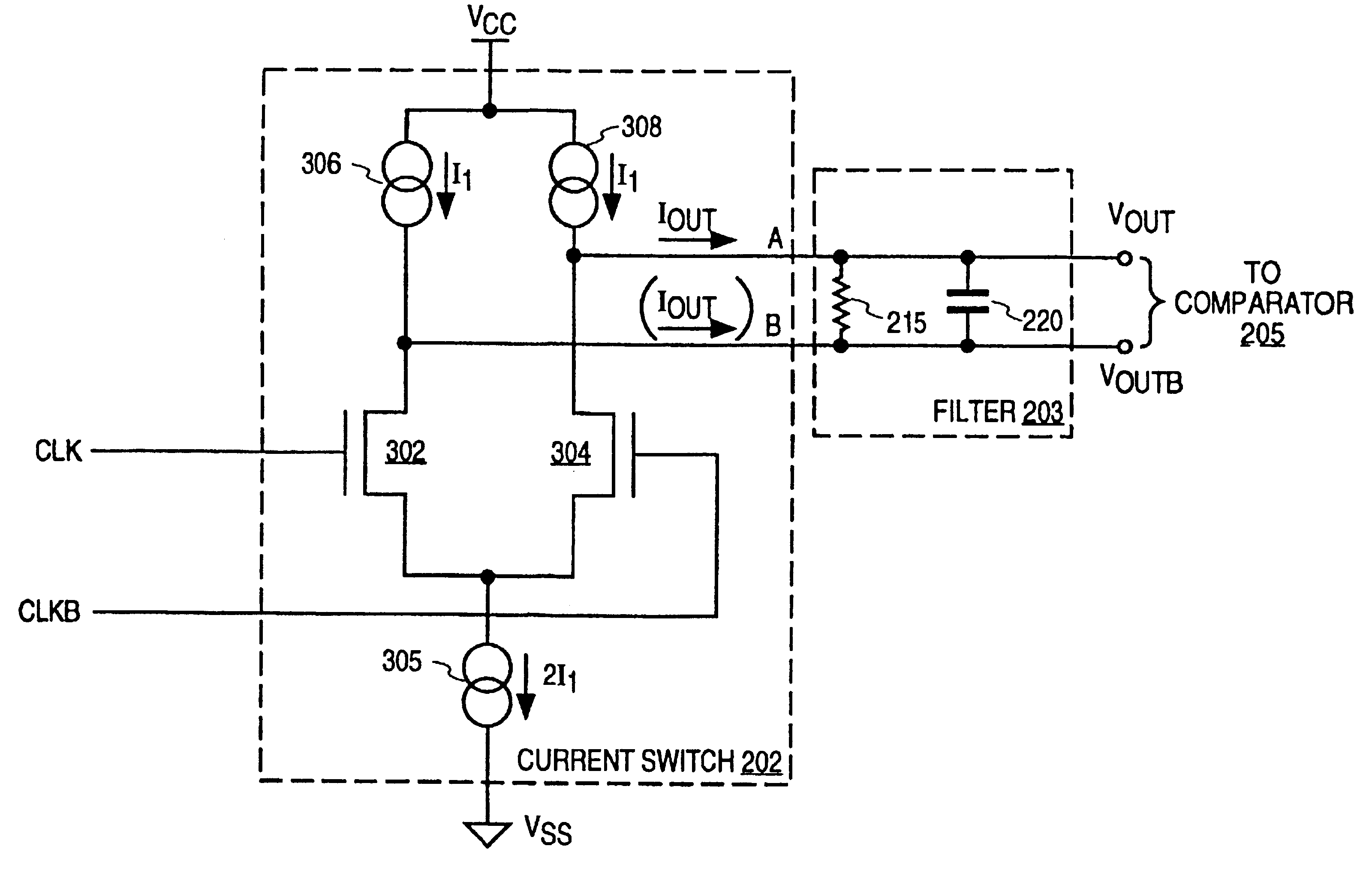
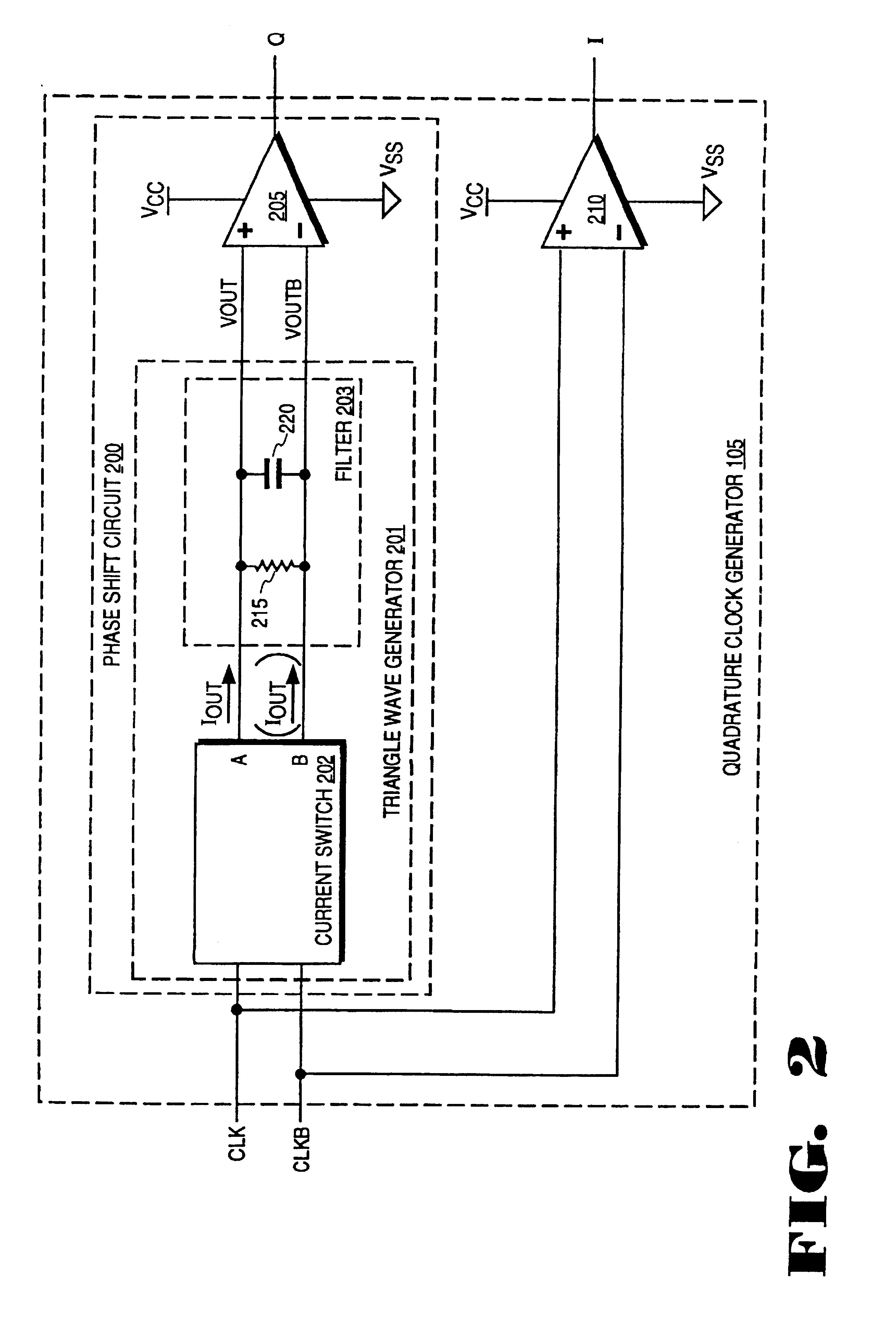
A phase shifting circuit that may be used as part of a quadrature clock generator. The phase shifting circuit comprises a triangle wave generator coupled to receive an input reference signal. The triangle wave generator outputs a pair of complementary triangle wave signals in response to the input reference signal. A comparator having a pair of inputs is coupled to receive the pair of complementary triangle wave signals. The comparator outputs an output signal having a predetermined phase relationship with the input reference signal in response to a comparison between the pair of complementary triangle wave signals.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method and apparatus for receiving high speed signals with low latency
InactiveUS20060061405A1Reduce signal delayDigital differential analysersDigital storageIntegratorAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and method for receiving high-speed signals having a wide common-mode range with low input-to-output latency. In one embodiment, the receiver includes an integrator to accumulate charge in accordance with an input signal during an integration time interval to produce an output voltage. A sense amplifier samples and converts the output voltage of the integrator to a logic signal; and a latch stores the logic signal. In an alternate embodiment, a preamplifier conditions the input signal prior to being integrated. In another embodiment using multiple receivers, circuitry is added to the receiver to compensate for timing errors associated with the distribution of the timing signals. In yet another embodiment, the integrator is coupled to an equalization circuit that compensates for intersymbol interference. In another embodiment, another circuit compensates for accumulated voltage offset errors in the integrator.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
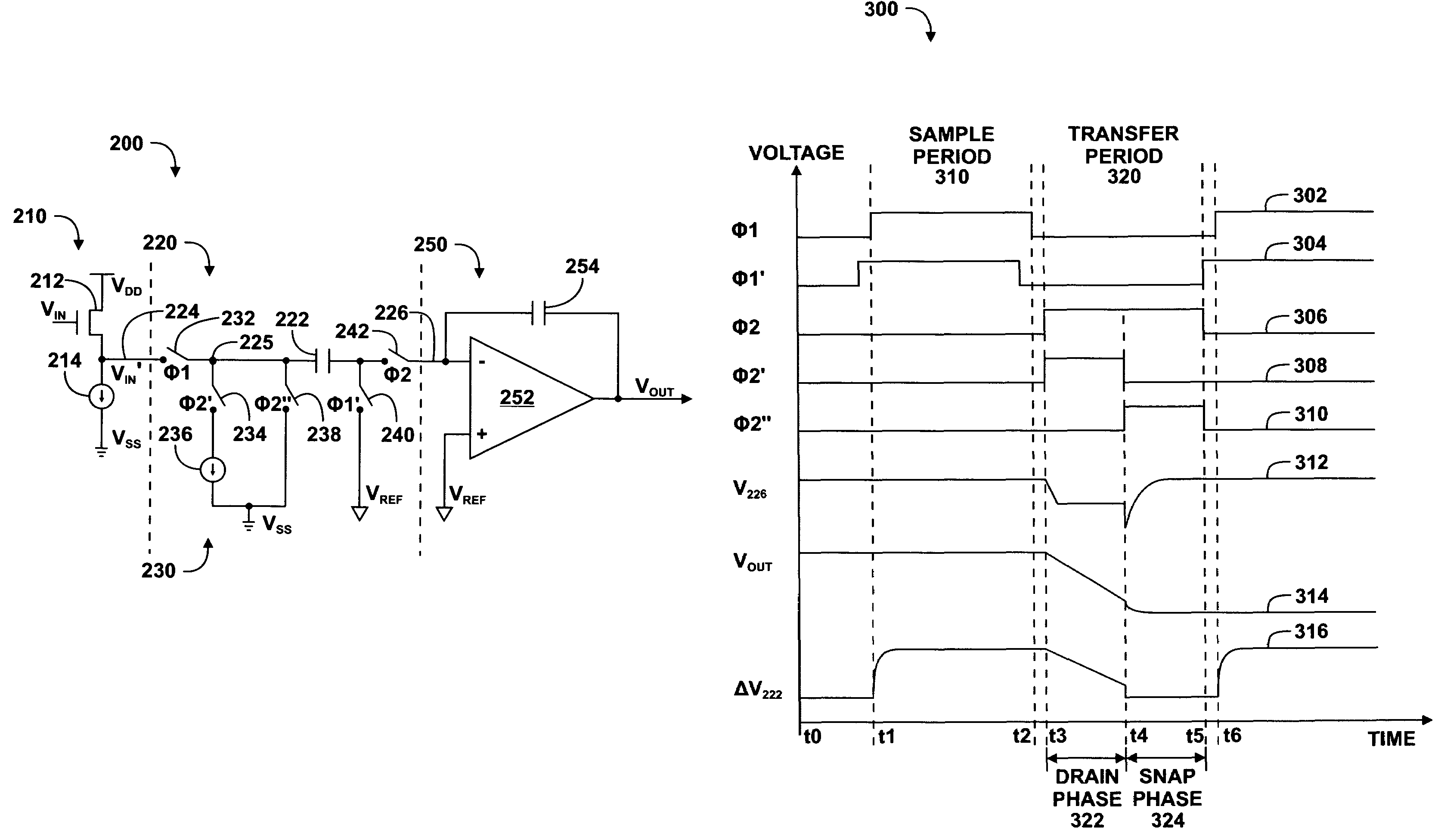
Switched capacitor input circuit and method therefor
InactiveUS7157956B2Computing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationIntegratorEngineering
A switched capacitor input circuit (200) includes an input buffer (210), a switched capacitor sampler circuit (220), and an integrator (250). The input buffer (210) has an input terminal for receiving an input voltage, and an output terminal. The switched capacitor sampler circuit (220) has an input terminal coupled to the output terminal of the input buffer (210), and an output terminal. The switched capacitor sampler circuit (220) includes a capacitor (222) and stores a charge proportional a voltage at the output terminal of the input buffer (210) in the capacitor (222) during a sample period, and transfers the charge from the capacitor (222) to the output terminal thereof during a transfer period subsequent to the sample period in a plurality of charge portions corresponding to a like plurality of phases of the transfer period. The integrator (250) has an input terminal coupled to the output terminal of the switched capacitor sampler circuit, and an output terminal for providing an output voltage signal.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Analog PLL with switched capacitor resampling filter
InactiveUS7078946B2Reduce noiseComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationSwitched capacitorPhase-locked loop
A resampler filter for use in an analog phase-locked loop has a charge pump and one or more switched capacitors switched by signals derived from a voltage controlled oscillator in the phase locked loop.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
Switched capacitor circuit with inverting amplifier and offset unit
ActiveUS20080116966A1Reduce power consumptionReduce circuit areaComputing operations for integral formationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAudio power amplifierSample Mode
A switched capacitor circuit includes an amplifier, a charging unit, an offset unit, and an integrating unit. The charging unit is coupled between an input node and a first node, and is for accumulating charge corresponding to an input signal during a sampling mode. The offset unit is coupled between the first node and an input of the amplifier, and is for maintaining the first node to be a virtual ground during an integrating mode. The integrating unit is coupled between the first node and an output of the amplifier, and is for receiving charge from the charging unit during the integrating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
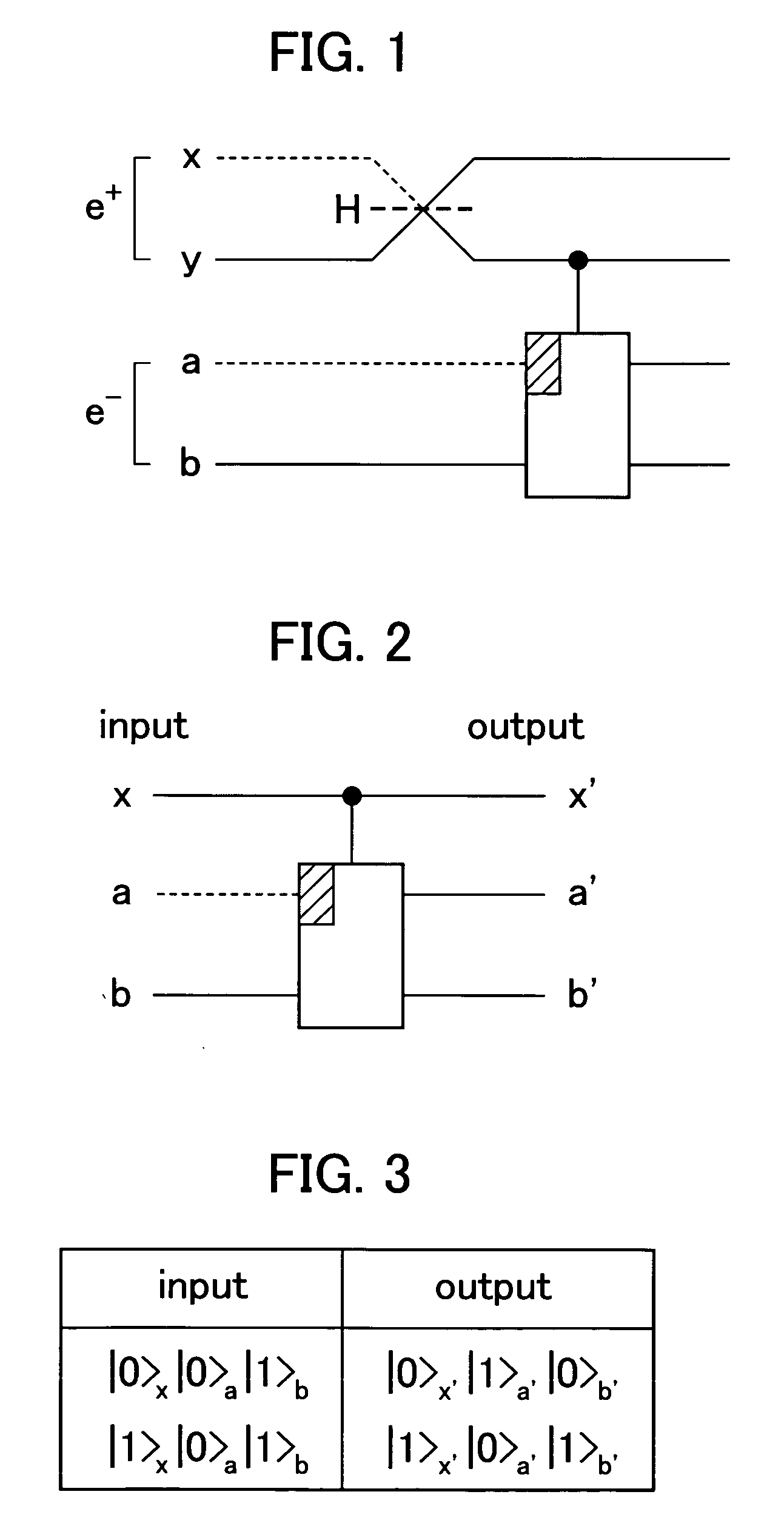
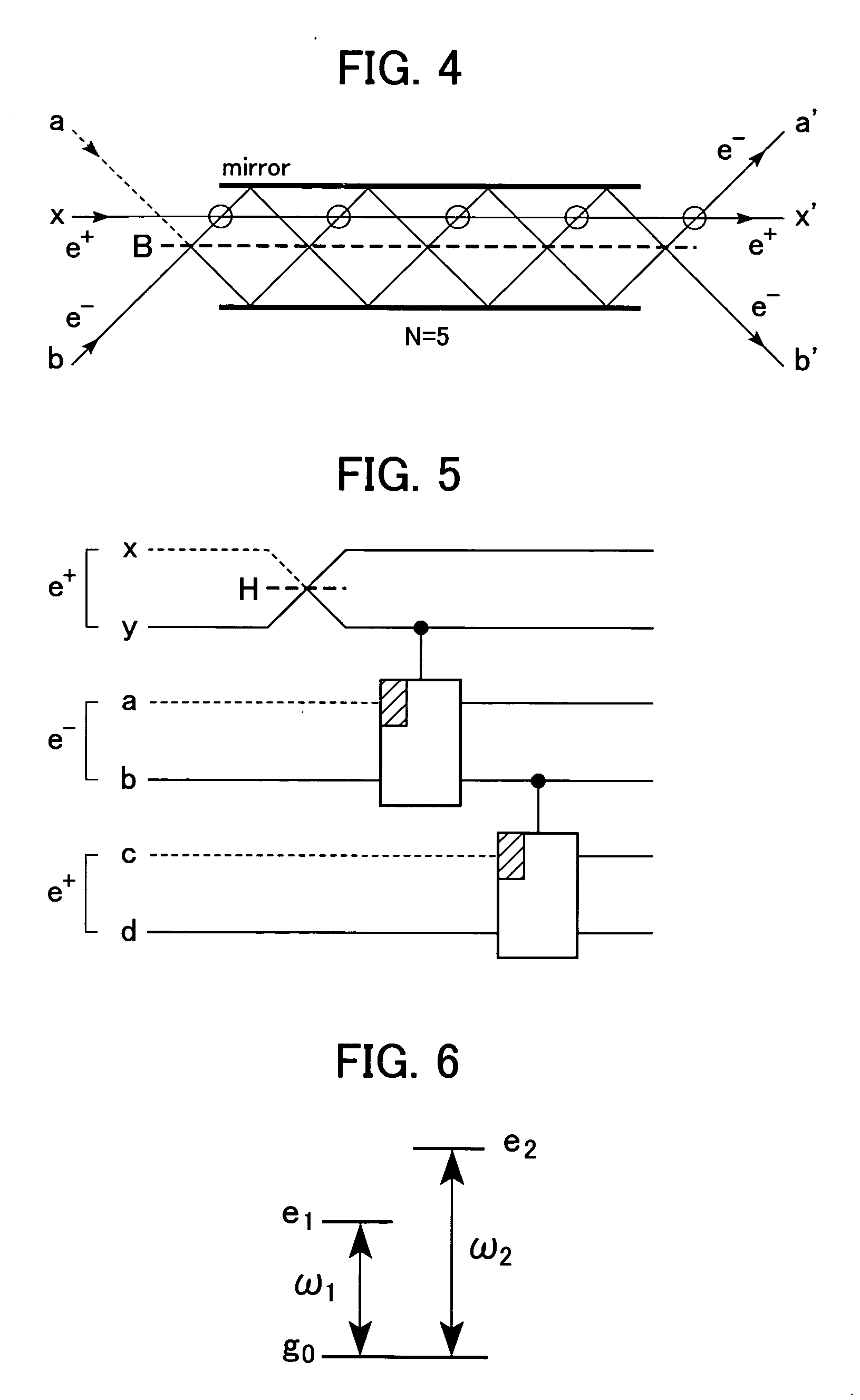
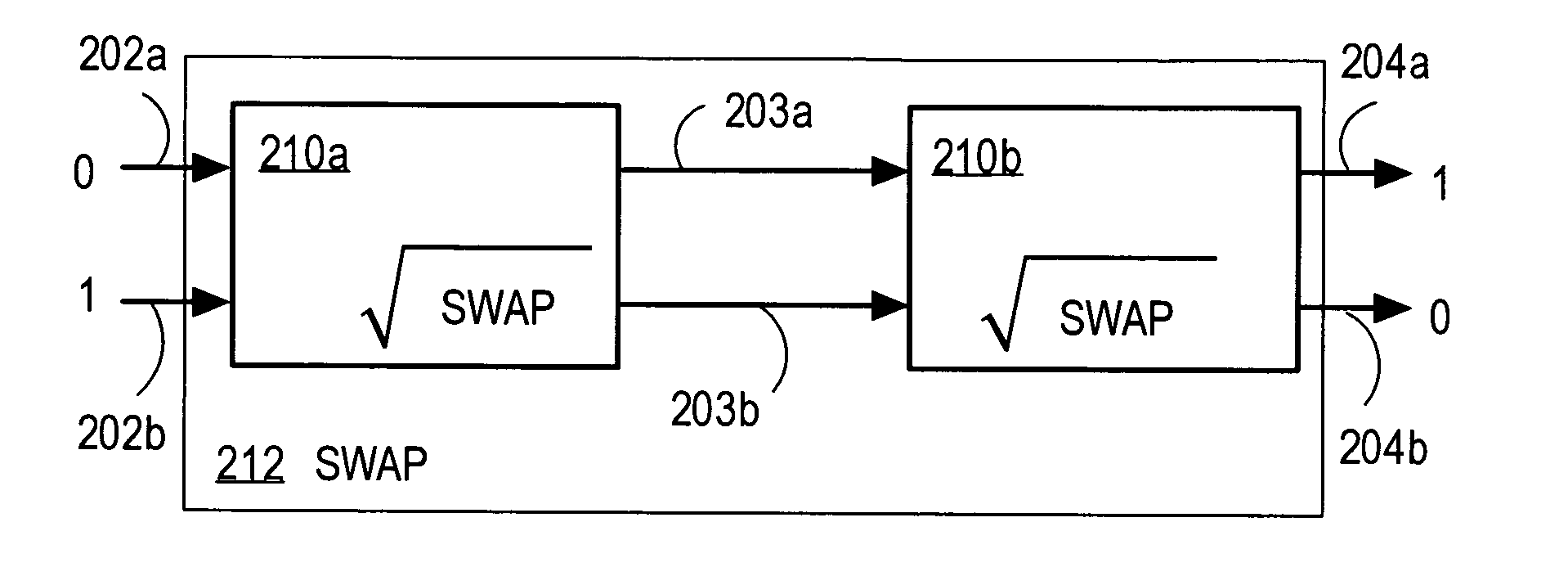
Quantum-state-generating apparatus, Bell measurement apparatus, quantum gate apparatus, and method for evaluating fidelity of quantum gate
InactiveUS20050133780A1Promote generationQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationBell stateBeam splitter
An apparatus for generating a quantum state of a two-qubit system including two qubits, each qubit being represented by a particle which invariably travels through one of two paths, includes a quantum gate composed of an interferometer for implementing an-interaction-free measurement. The apparatus receives two particles having no correlation and generates a Bell state with asymptotic probability 1. A Bell measurement of a state of a two-qubit system is performed by observing a quantum gate composed of the interferometer after the quantum gate has processed the state and selecting the state from the Bell bases. An approximate fidelity of a quantum gate composed of the interferometer is calculated, if an absorption probability with which a first particle absorbs a second particle in the interferometer is less than 1, under the condition that the number of times the second particle hits beam splitters in the interferometer is sufficiently large.
Owner:CANON KK
Integration circuit, decrement circuit, and semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20060022609A1Reduce areaSmall sizeComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationMOSFETPower flow
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Systems and methods for maintaining a drive signal to a resonant circuit at a resonant frequency
ActiveUS8022775B2Computing operations for integral formationBatteries circuit arrangementsPhase detectorPhase difference
Systems and methods for maintaining a drive signal to a resonant circuit at a resonant frequency are provided. A system for maintaining a drive signal to a resonant circuit at a resonant frequency can include: an oscillator configured to provide an output to a phase comparator and a drive circuit, the drive circuit configured to provide a drive signal to a resonant circuit; a phase detector configured to receive a filtered version of the drive signal from the resonant circuit and provide a phase-indicating signal to the phase comparator; and the phase comparator, wherein the phase comparator is configured to provide a signal based on the phase difference between the oscillator output and the phase-indicating signal, wherein the signal from the phase comparator is used to control the frequency of the oscillator such that the phase difference converges to a fixed value.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
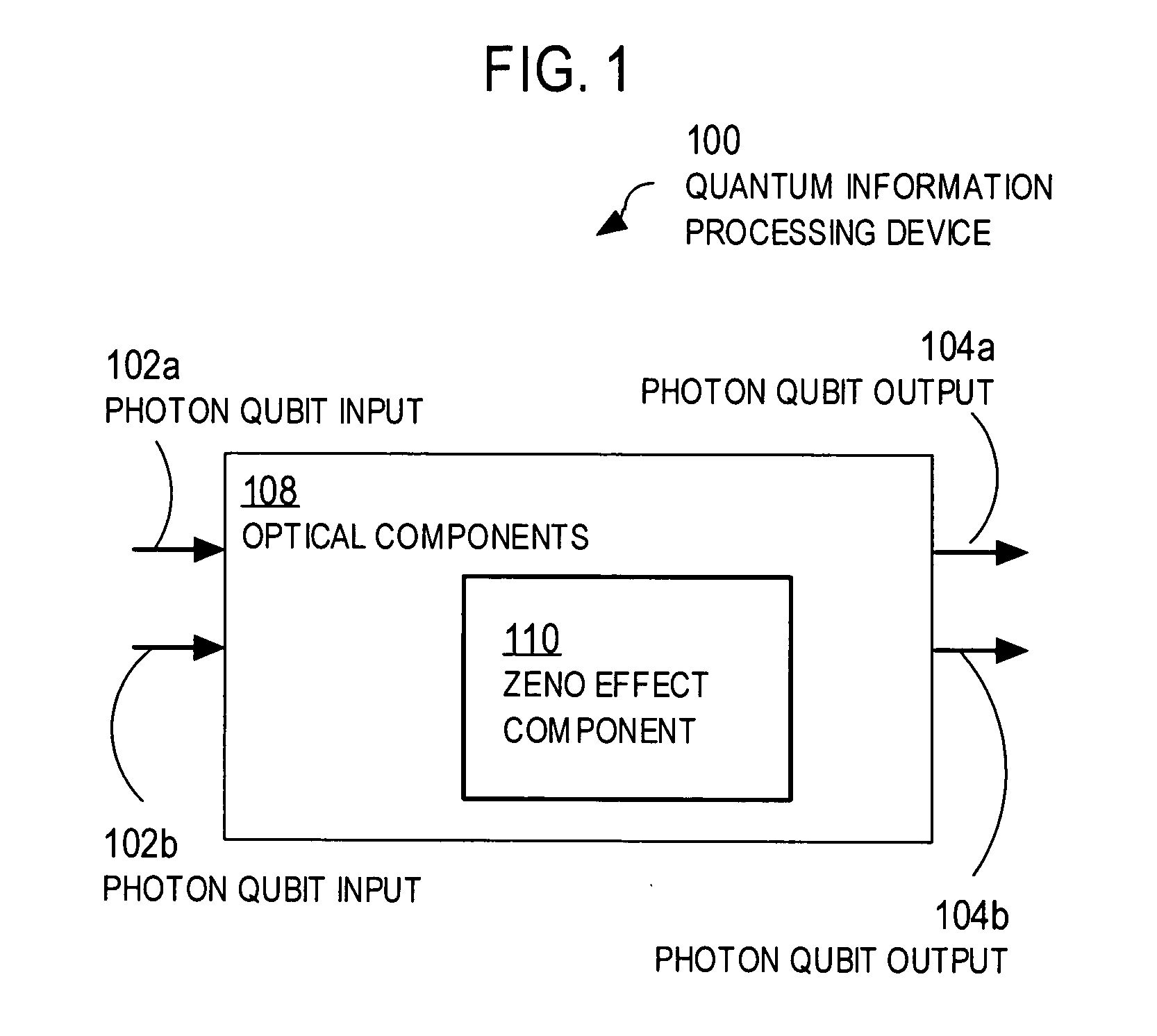
Techniques for quantum processing with photons and the Zeno effect
ActiveUS20050117836A1Small spacingReduce error rateQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationInformation processingQuantum Zeno effect
Techniques are provided that use the quantum Zeno effect to implement practical devices that use single photons as the qubits for quantum information processing. In the quantum Zeno effect, a randomly-occurring event is suppressed by frequent measurements to determine whether the event has occurred. The same results can be obtained by using atoms or molecules or ions to react to the occurrence of the event. Techniques include directing one or more input qubits onto a device and applying a quantum Zeno effect in the device. The quantum Zeno effect is applied by consuming one or more photons in the device under conditions in which photons, that would otherwise be output by the device, do not represent a result of a particular quantum information processing operation. Devices implemented using the quantum Zeno effect can operate with low error rates without the need for high efficiency detectors and large number of ancilla.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Subrange analog-to-digital converter and method thereof
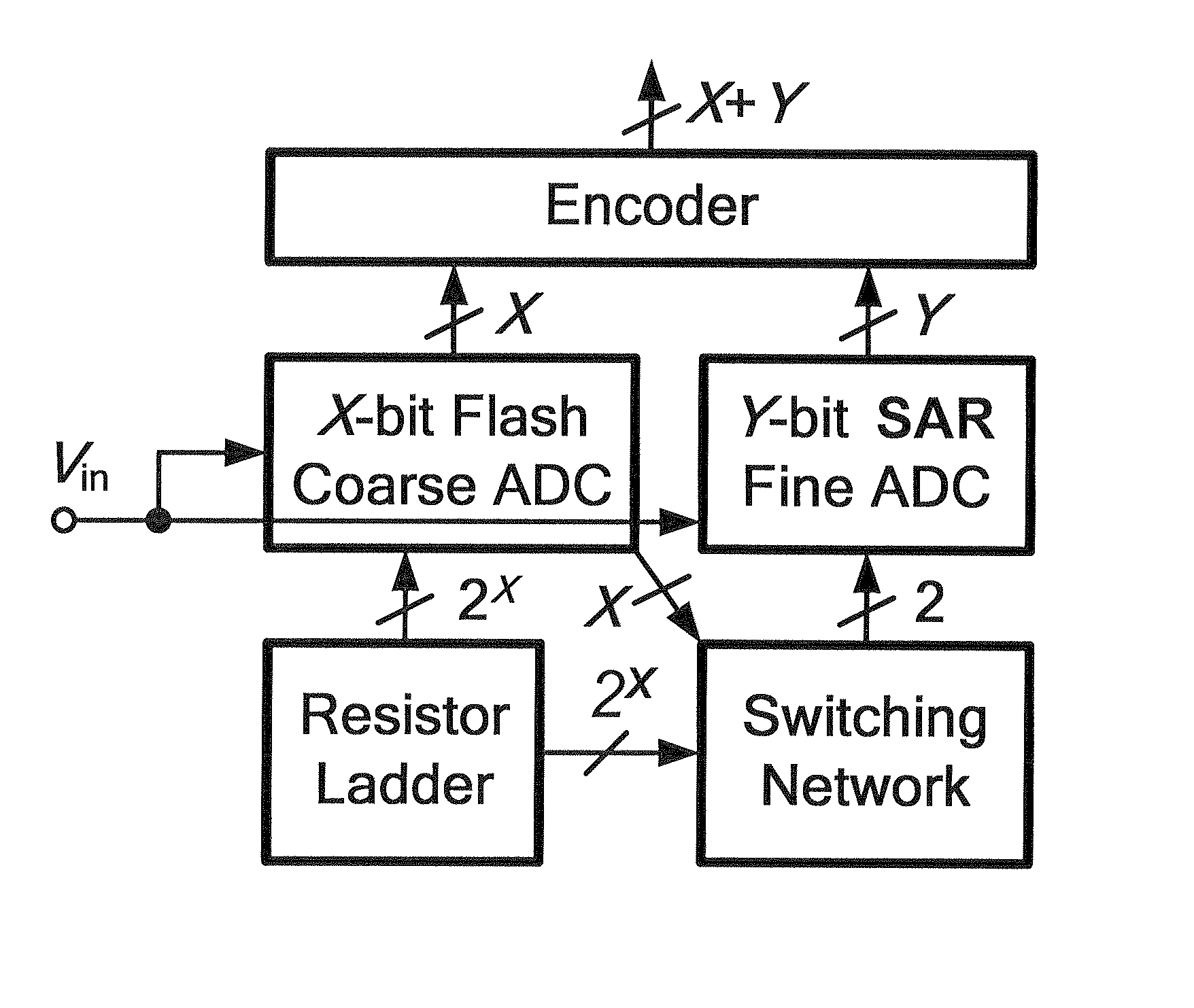
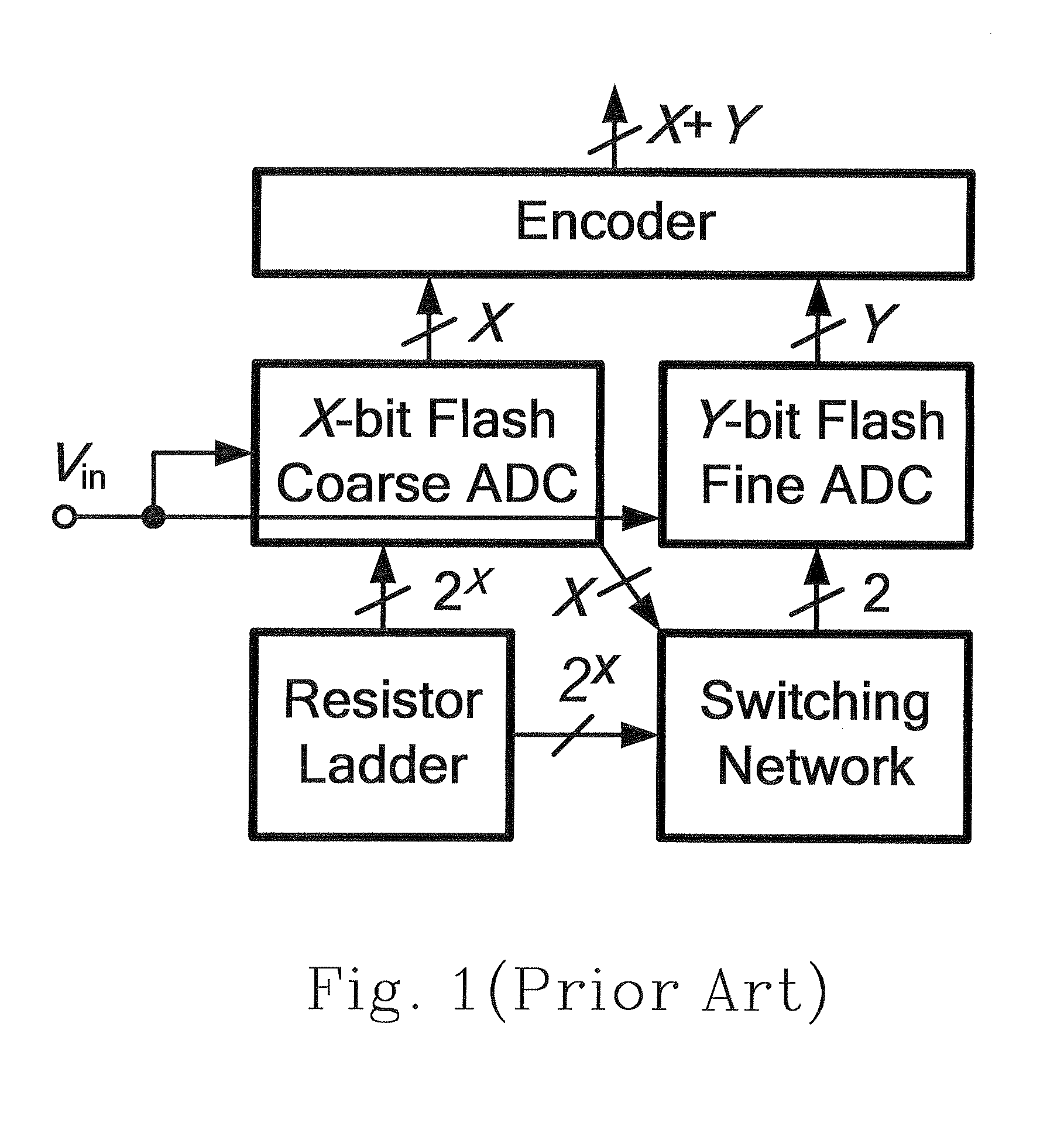
InactiveUS20120154193A1Improves differential non-linearity (DNL)Fast sampling speedComputing operations for integral formationElectric signal transmission systemsDigital down converterEngineering
The configurations and adjusting method of a subrange analog-to-digital converter (ADC) are provided. The provided subrange ADC includes a X.5-bit flash ADC, a Y-bit SAR ADC and a (X+Y)-bit segmented capacitive digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
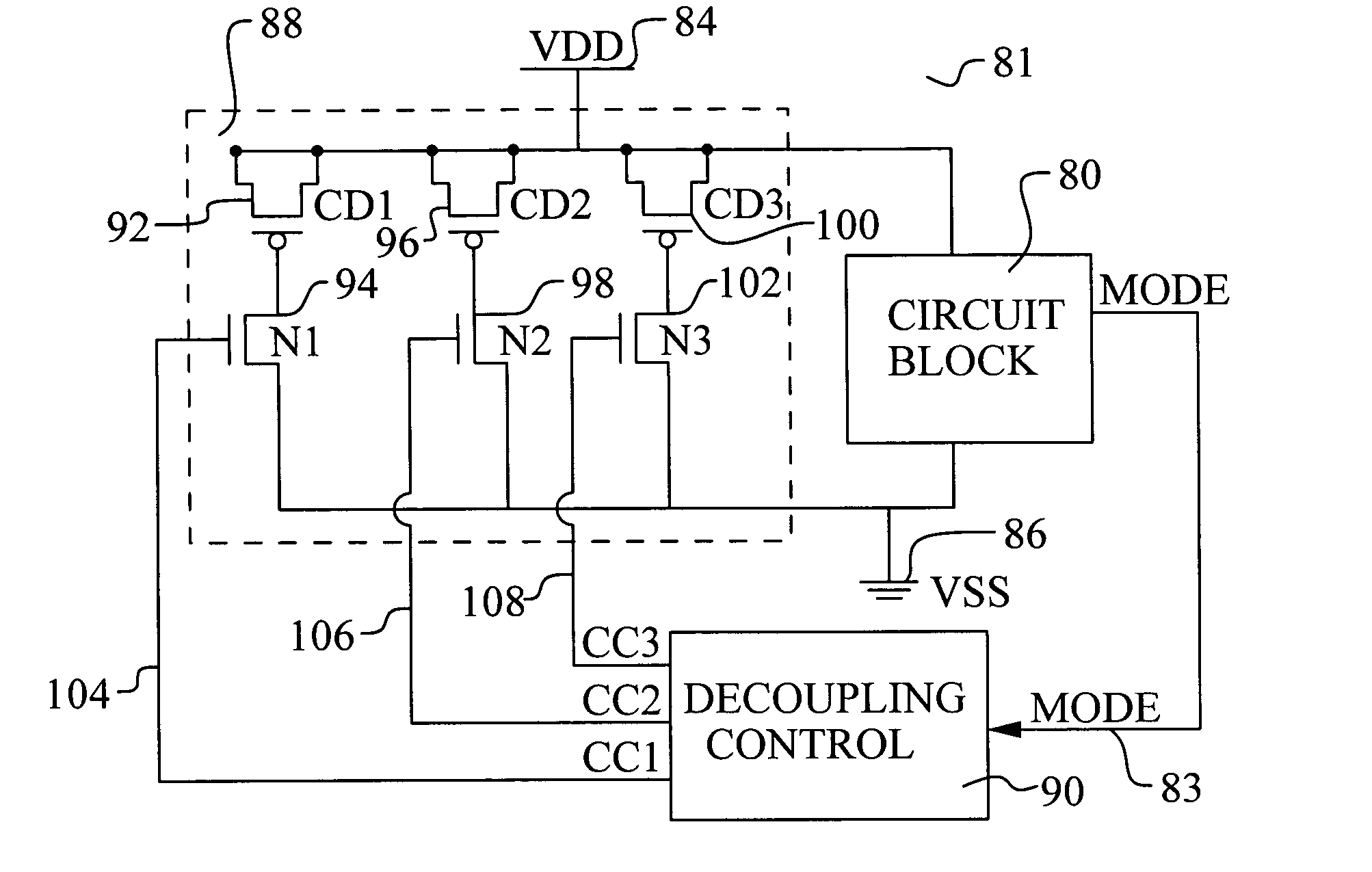
Dynamically adjustable decoupling capacitance to reduce gate leakage current
InactiveUS20050062523A1Reduce switching noiseCurrent is limitedComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceGate leakage current
A new method to reduce switching noise on an integrated circuit device is achieved. The method comprises providing an integrated circuit device comprising a power supply, a ground, and a plurality of switchable capacitors. Each switchable capacitor is connected from the power supply to ground. The operating mode of the integrated circuit device is tracked. An optimal capacitance value is selected based on the operating mode. A set of switchable capacitors from the plurality of switchable capacitors is selected to thereby connect the optimal capacitance value from the power supply to ground.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
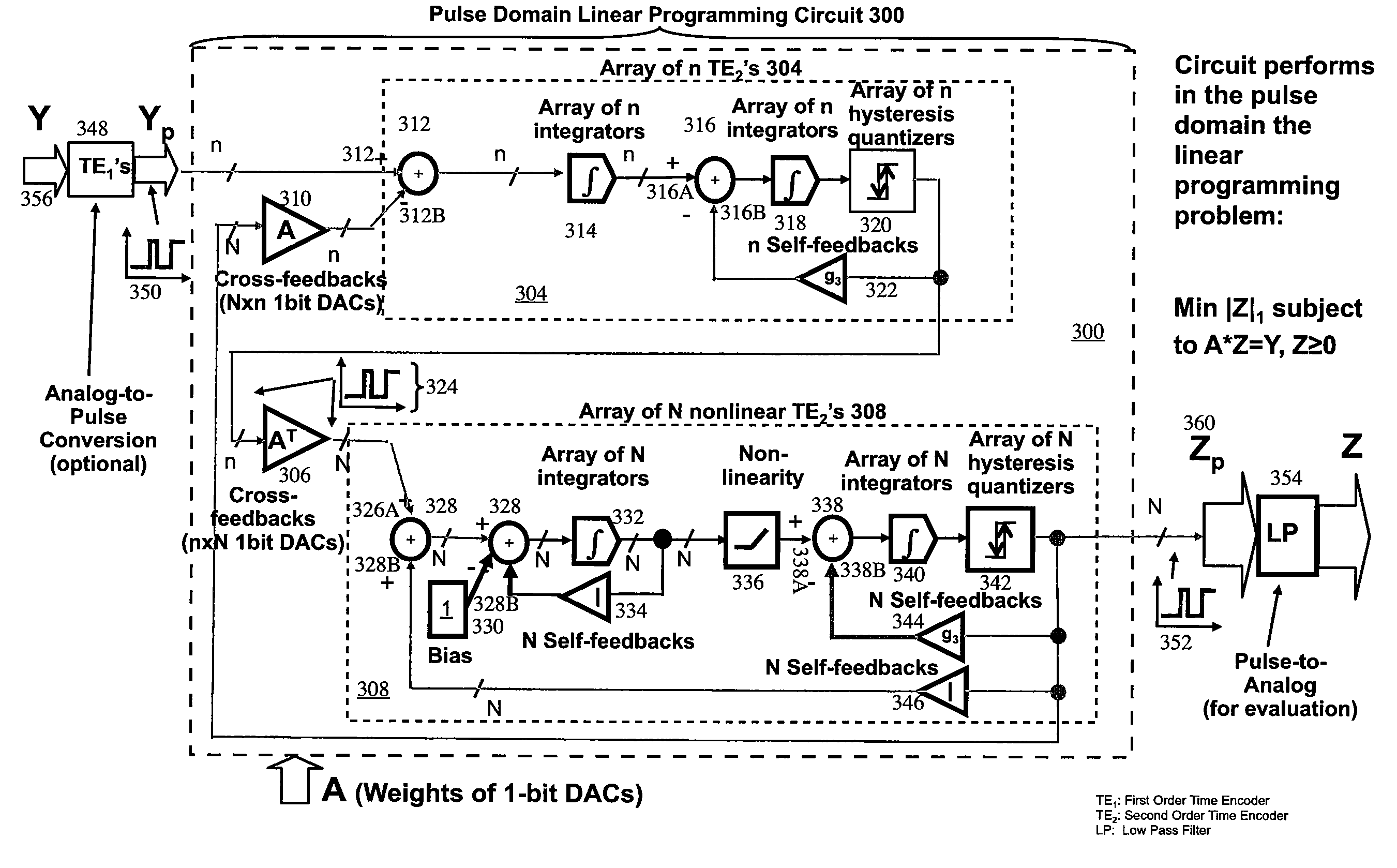
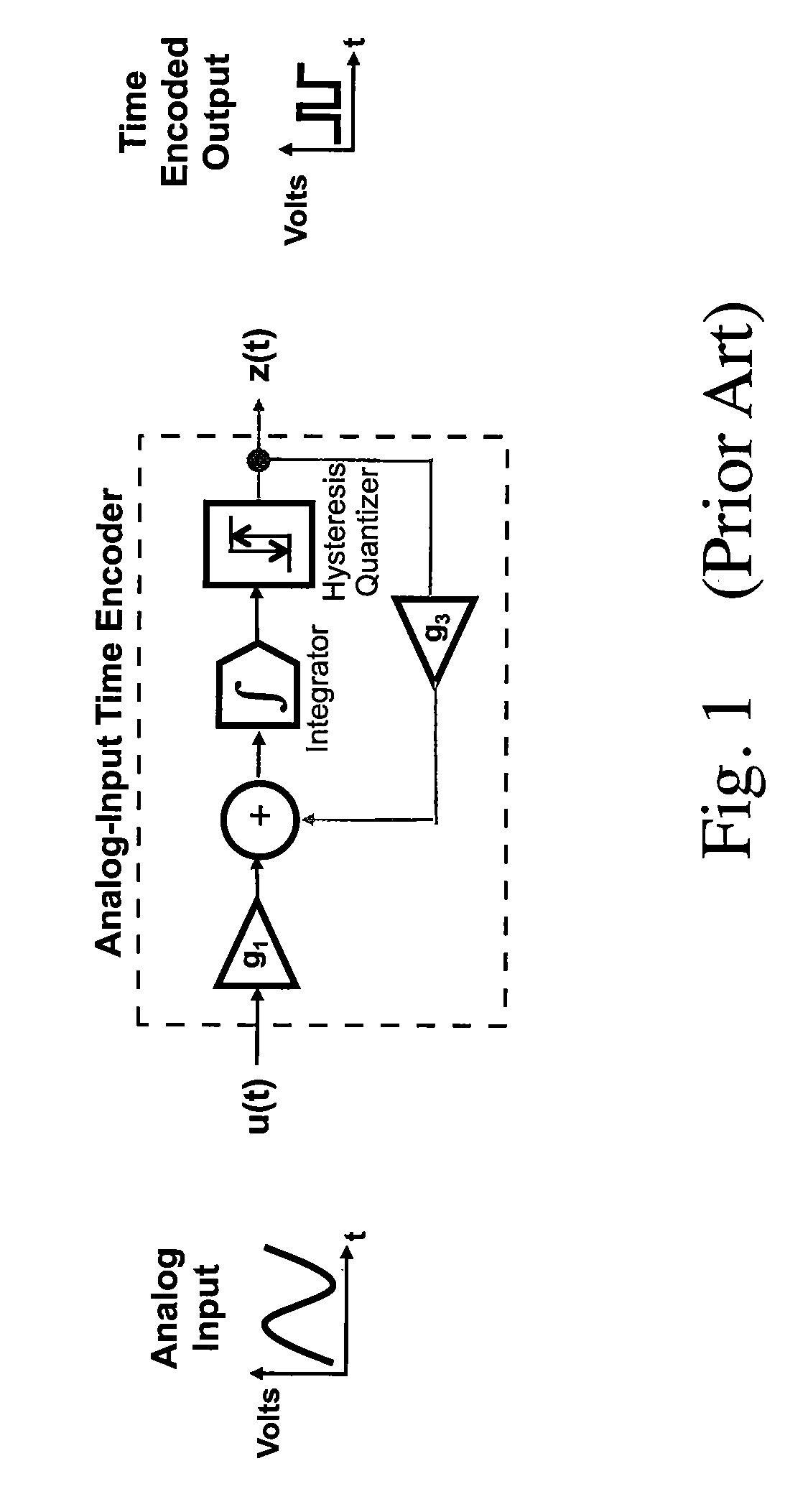
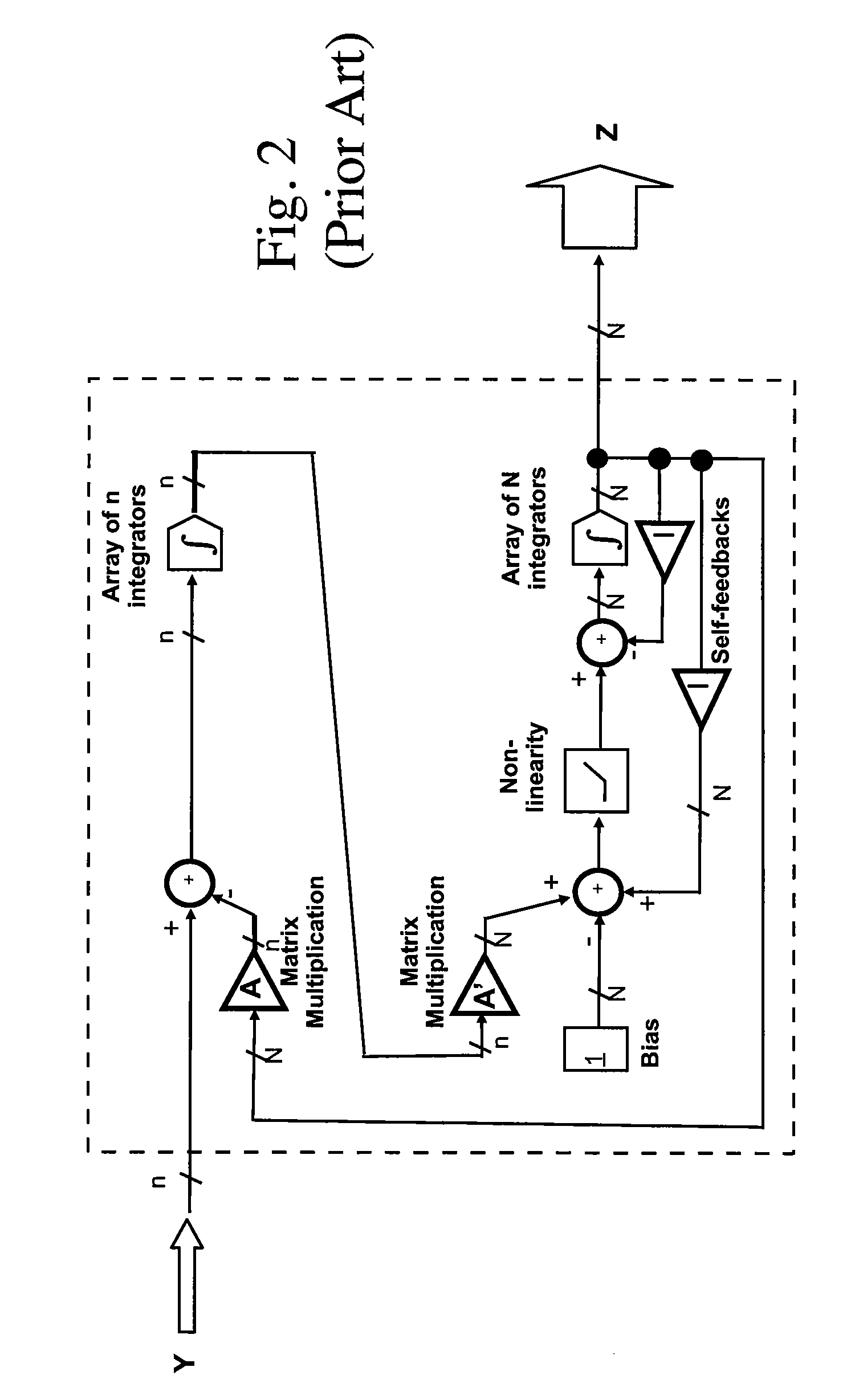
Pulse domain linear programming circuit
ActiveUS7724168B1Electric signal transmission systemsComputing operations for integration/differentiationHysteresisIntegrator
A system for making a pulse domain linear programming circuit. The inputs and the outputs to the pulse domain linear programming circuit are time encoded pulse signals. The circuit includes arrays of two types of cross-coupled time encoding elements. The first type of elements includes two integrators, adders, a hysteresis quantizer, and a 1-bit self-feedback DAC. The second type of elements includes a bias element, a leaky integrator, adders, a fixed memory-less non-linearity, a regular integrator, a hysteresis quantizer and a 1-bit self-feedback DAC. The cross-coupling signals between the two types of elements are pulse time-encoded signals. All of the cross-coupling weights are set via 1-bit DACs having variable gains. The cross-coupling weights are used to set a constraint equation of a pulse domain linear programming problem. Methods to make the foregoing circuit are also described.
Owner:HRL LAB
High Q linear controlled variable capacitor using translinear amplifier
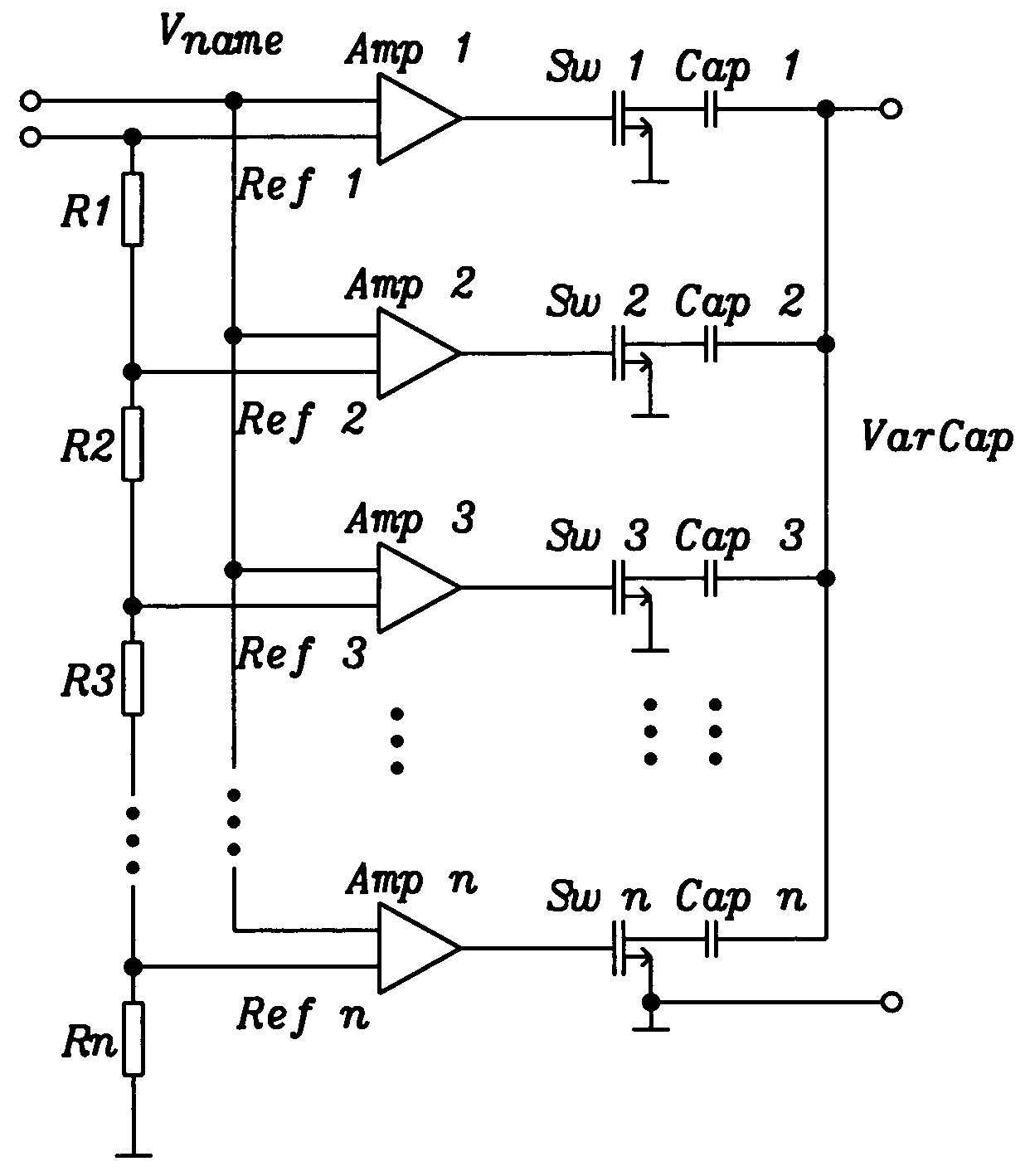
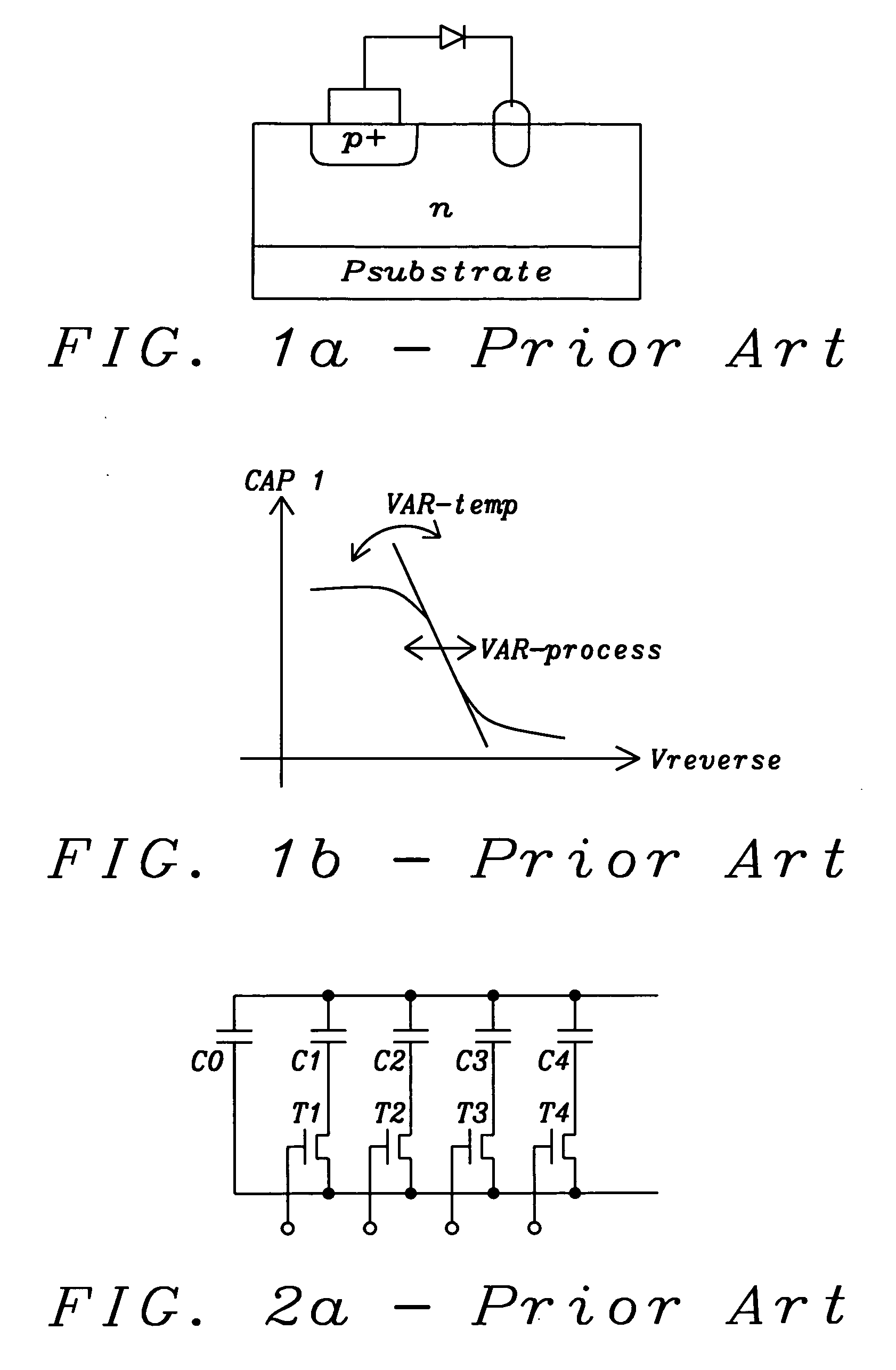
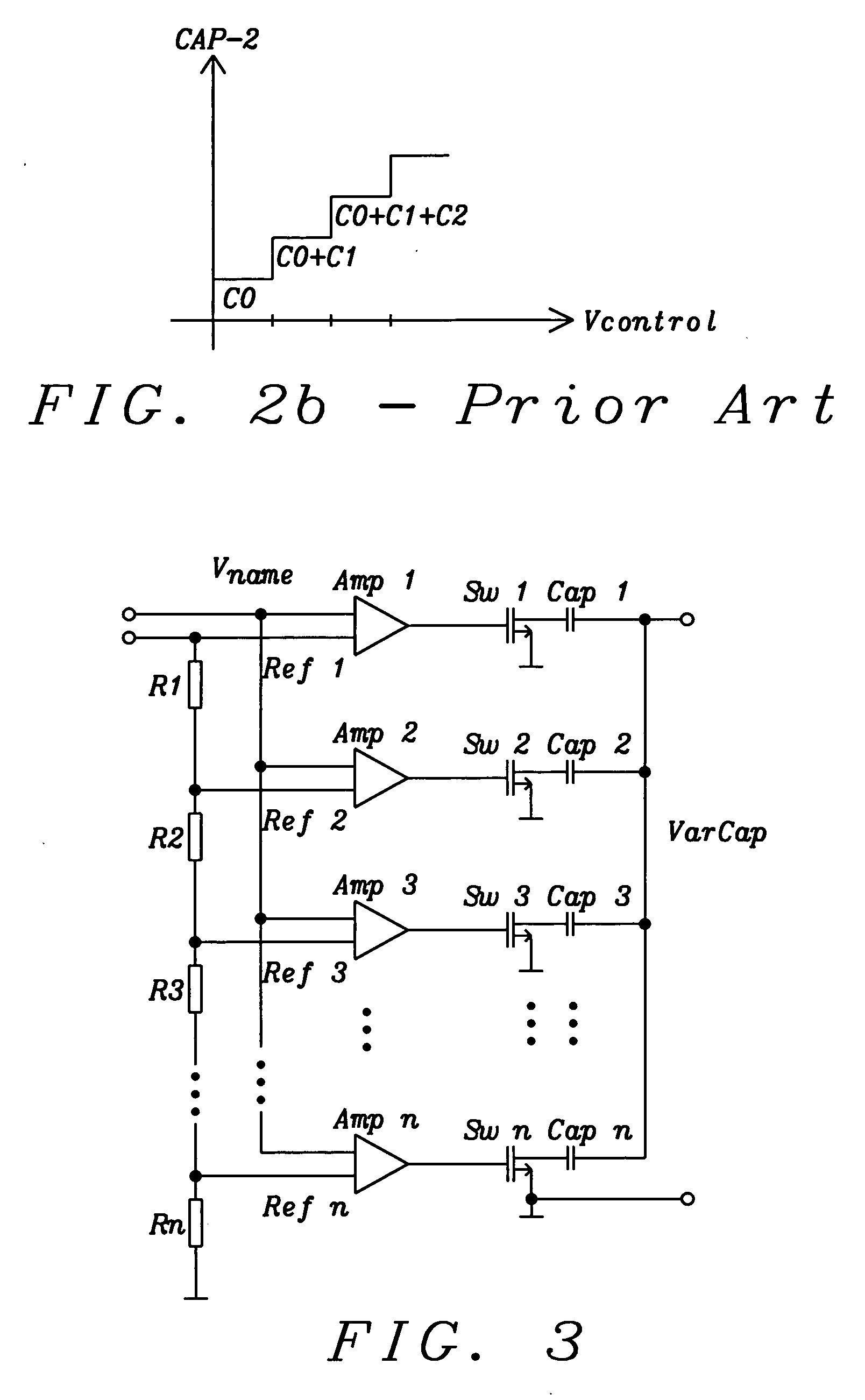
InactiveUS20050151575A1Many degrees of freedomMinimize impactComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationQ factorLinear control
A voltage controlled variable capacitor, formed of a larger number of fixed capacitor segments and a corresponding number of switching elements, uses translinear amplifiers to control each switching element. Each translinear amplifier linearly switches from the fully off to the fully on state; a minimum number of switching stages (ideally only one) is in the mode-of-change at any one time with a minimum overlap. The arrangement achieves a nearly linear change of capacitance at linear tuning voltage change, while resulting in high Q-factor due to the low RDSon and high RDSoff of the fully switched stages. The invention eliminates temperature and voltage dependencies of other solutions like varactor diodes.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR
Popular searches
Measurement arrangements for variable Acceleration measurement Mitigation of undesired influences Computation using denominational number representation Resistance/reactance/impedence Electronic circuit testing Frequency selective two-port networks Special data processing applications Tunable filters Switched capacitor networks
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com