Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
400 results about "Thallium compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
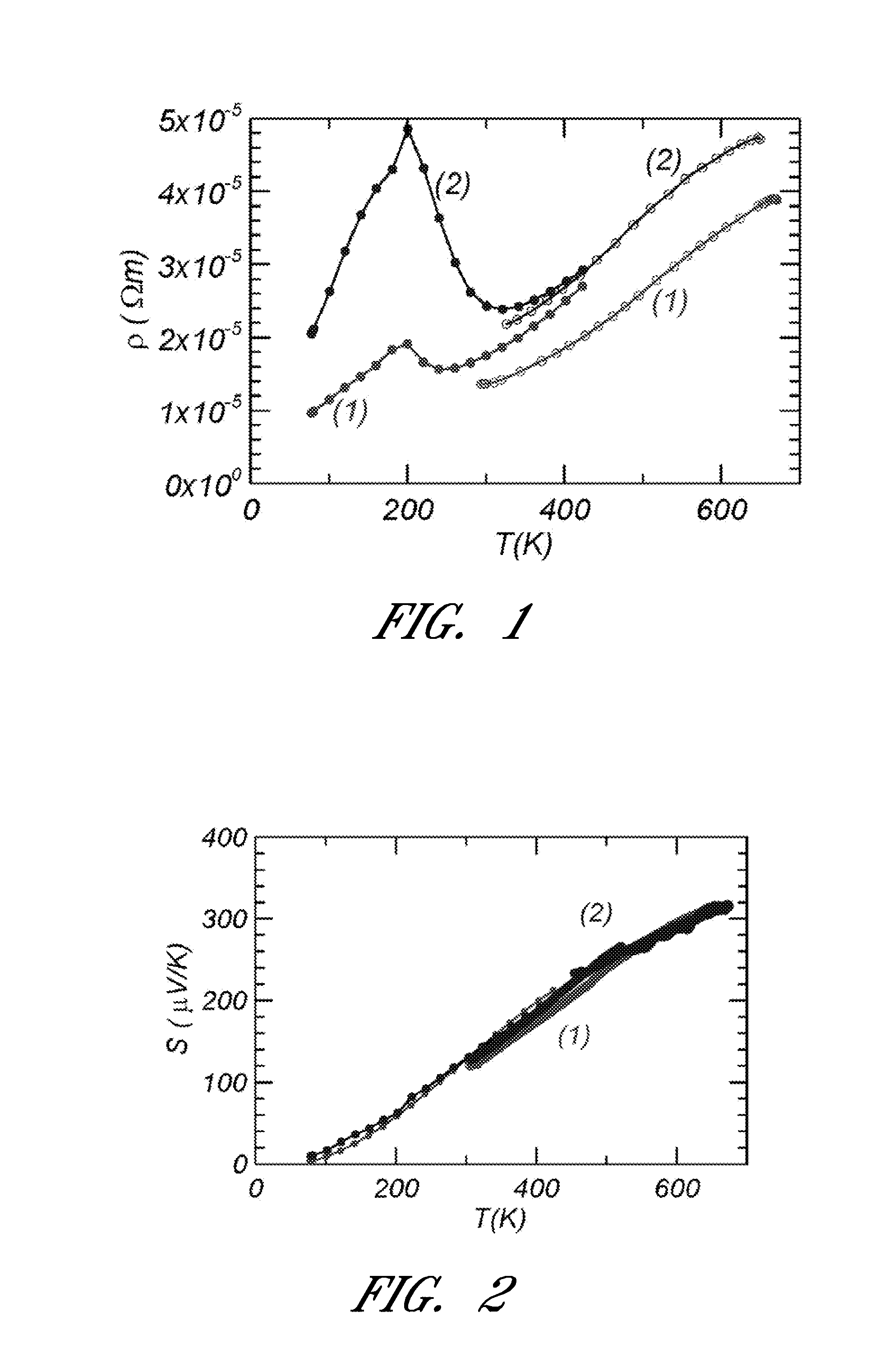
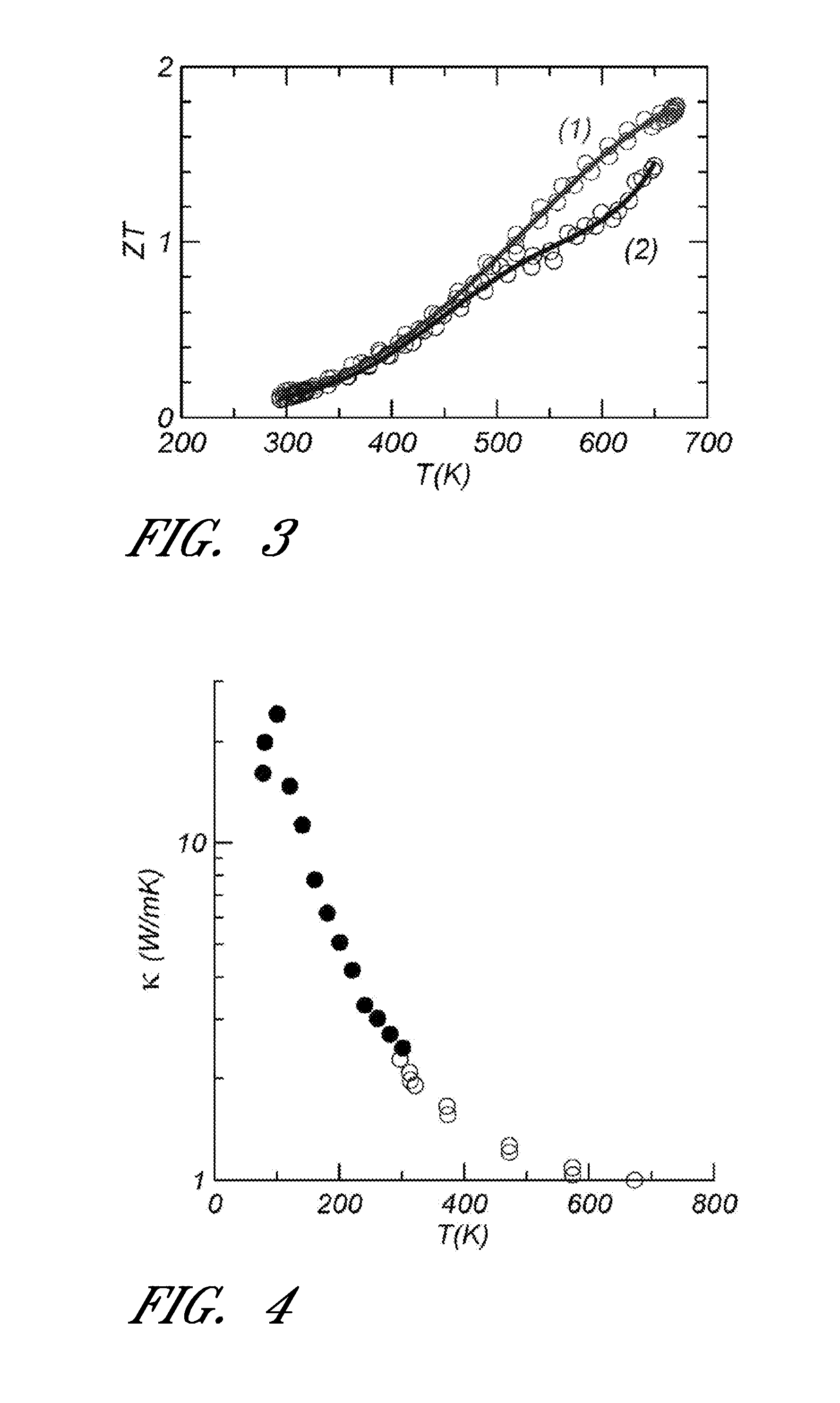
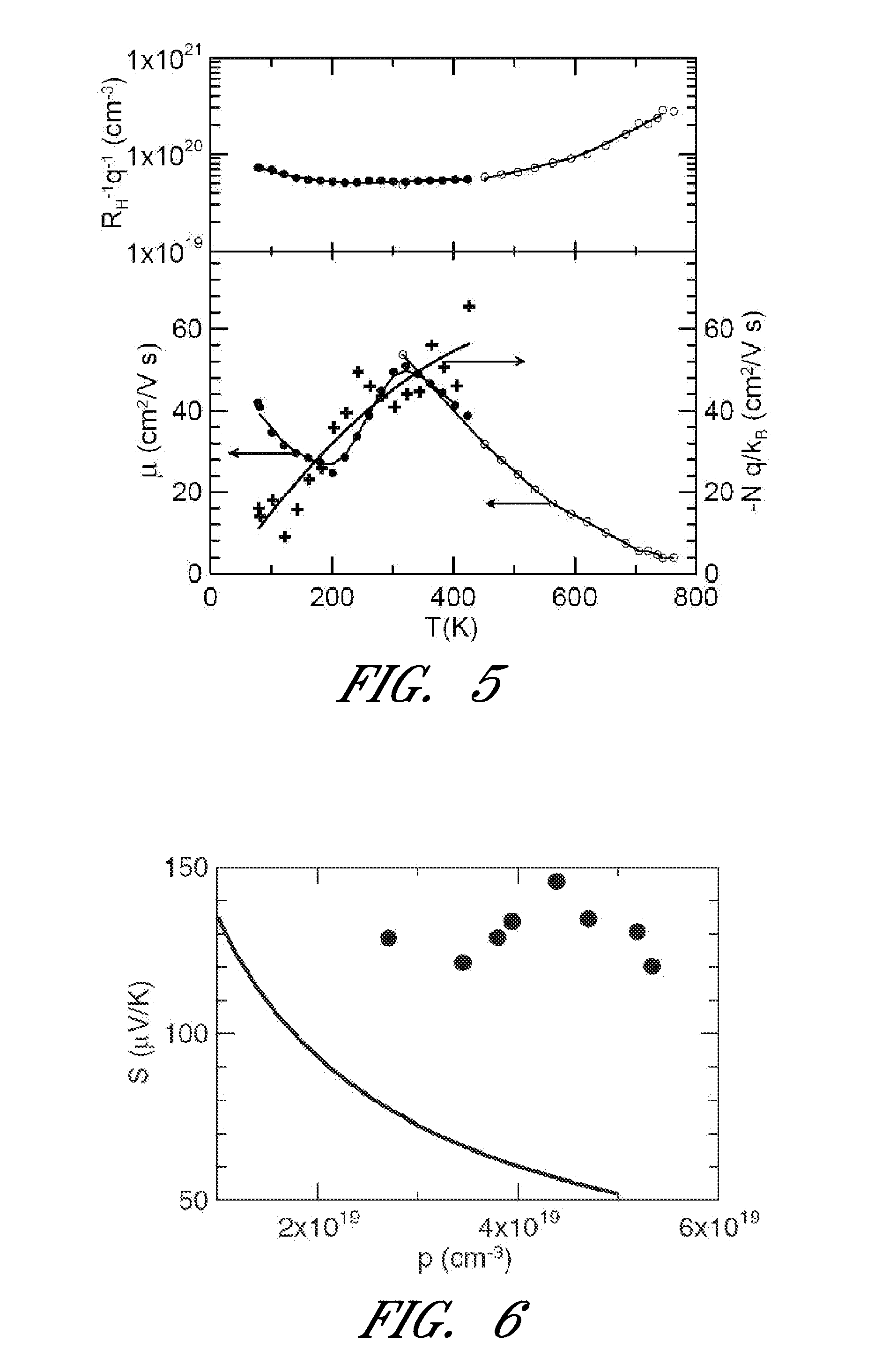
Thallium makes chemical compounds in two oxidation states: +1 and +3. The +1 state is more common and less reactive. Its chemical compounds are very similar to potassium or silver compounds. It makes a hydroxide that in a strong base when dissolved in water.
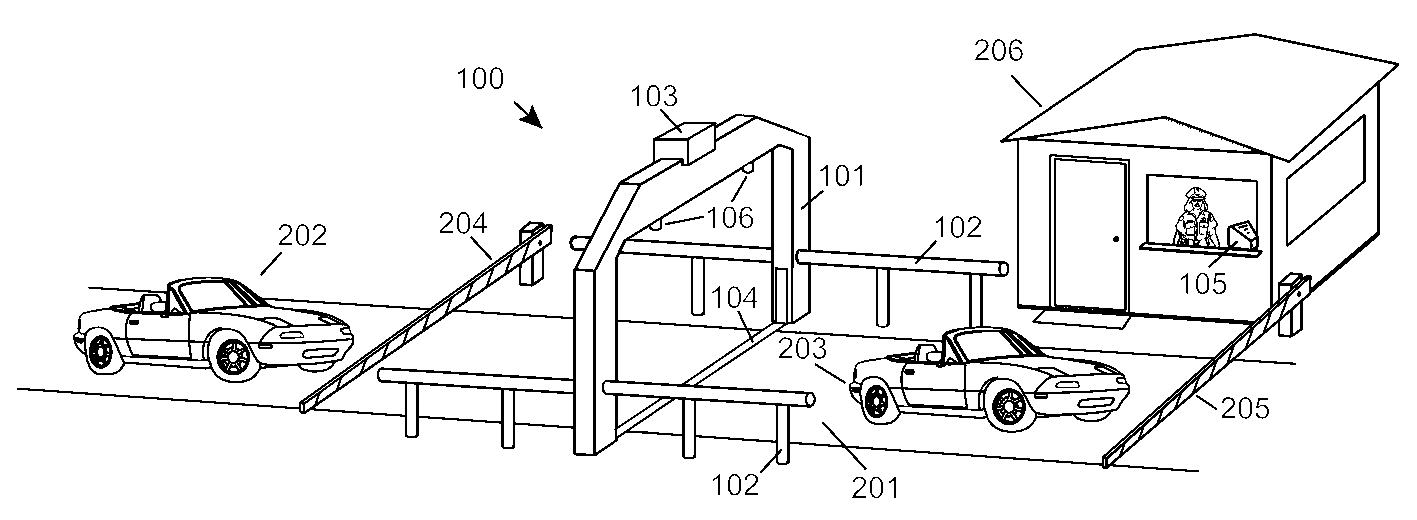
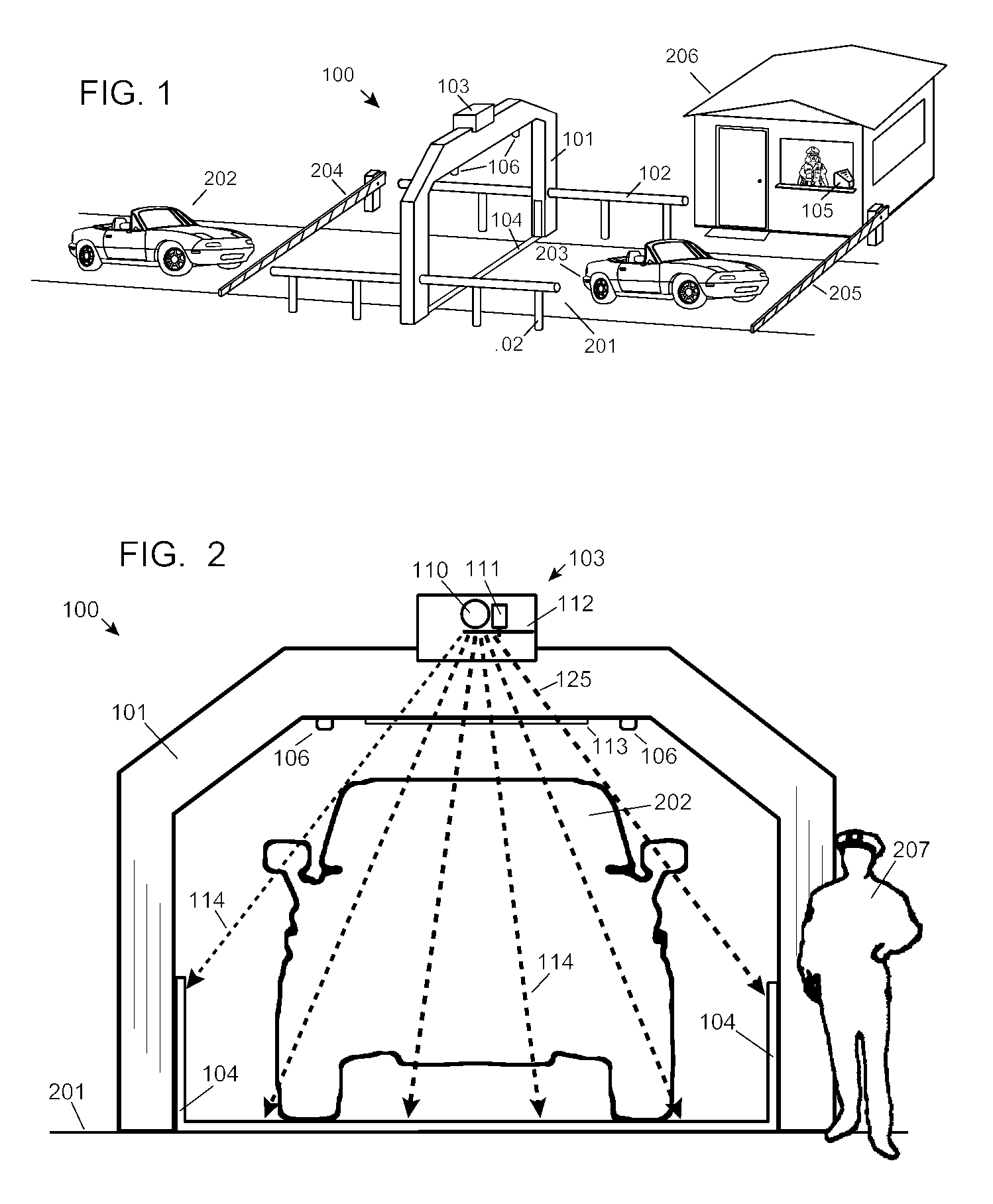
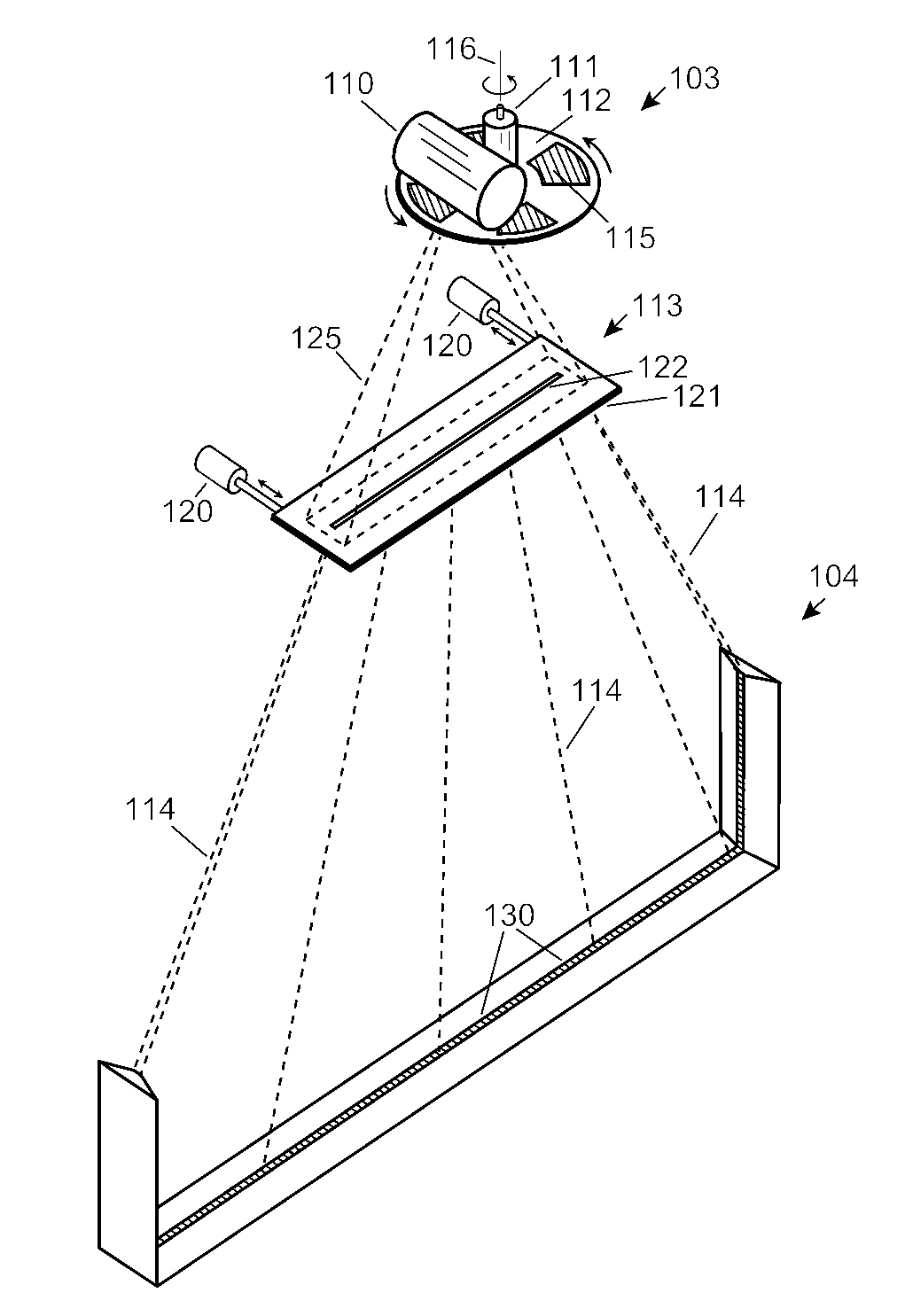
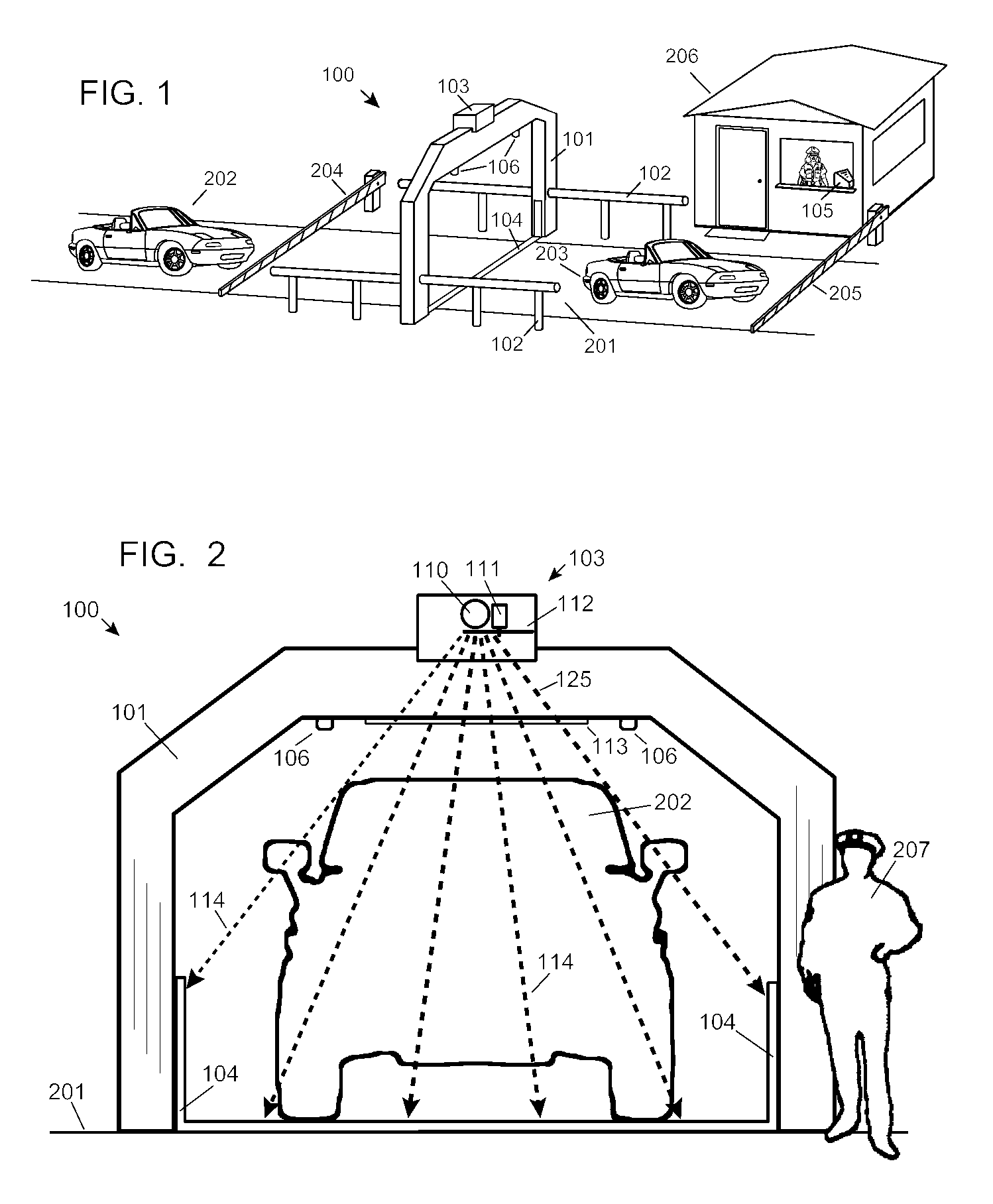
Automobile scanning system
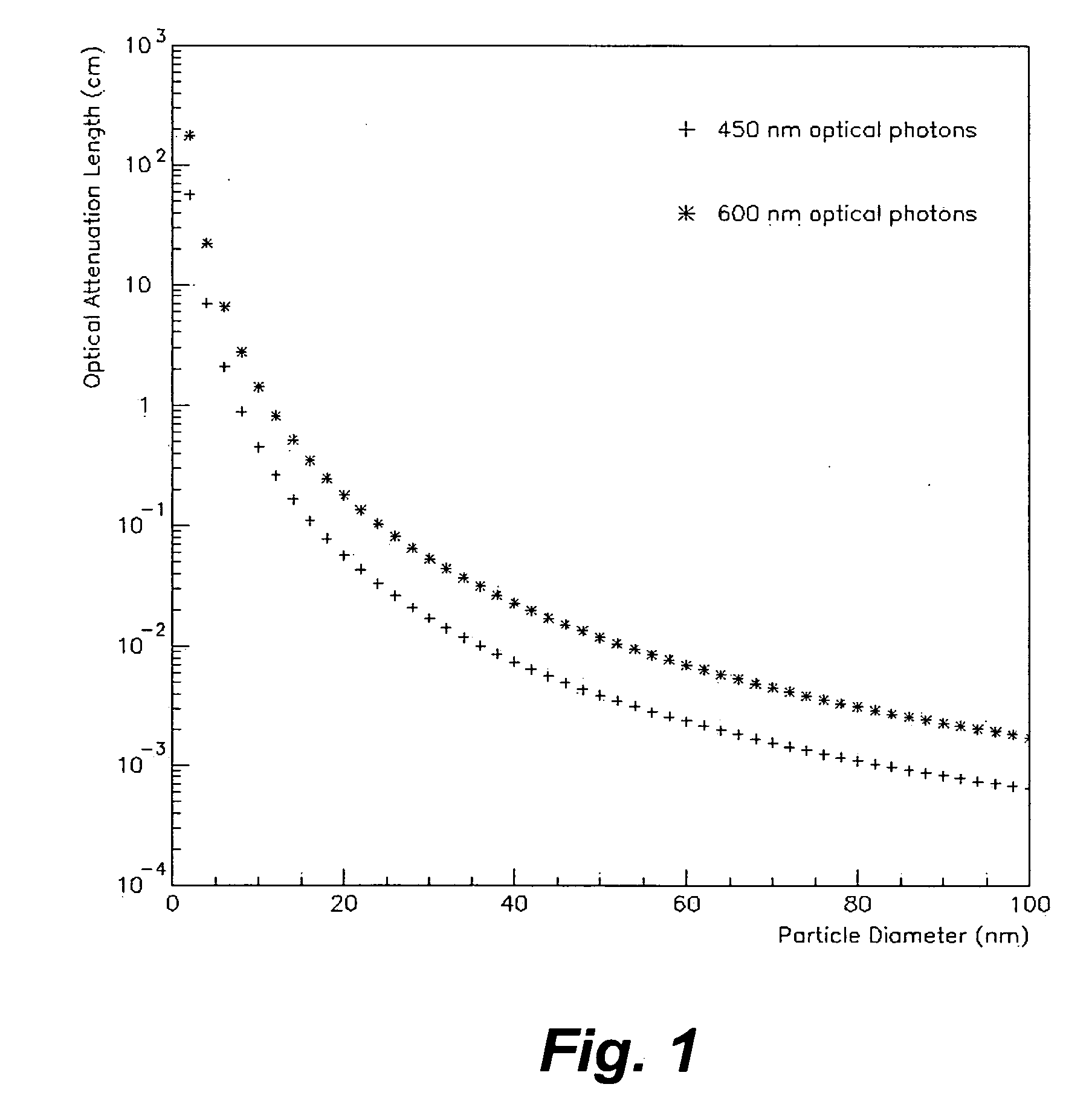
ActiveUS7742568B2Easy to checkUniform exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Automobile Scanning System
ActiveUS20090086907A1Easy to checkUniform radiation exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
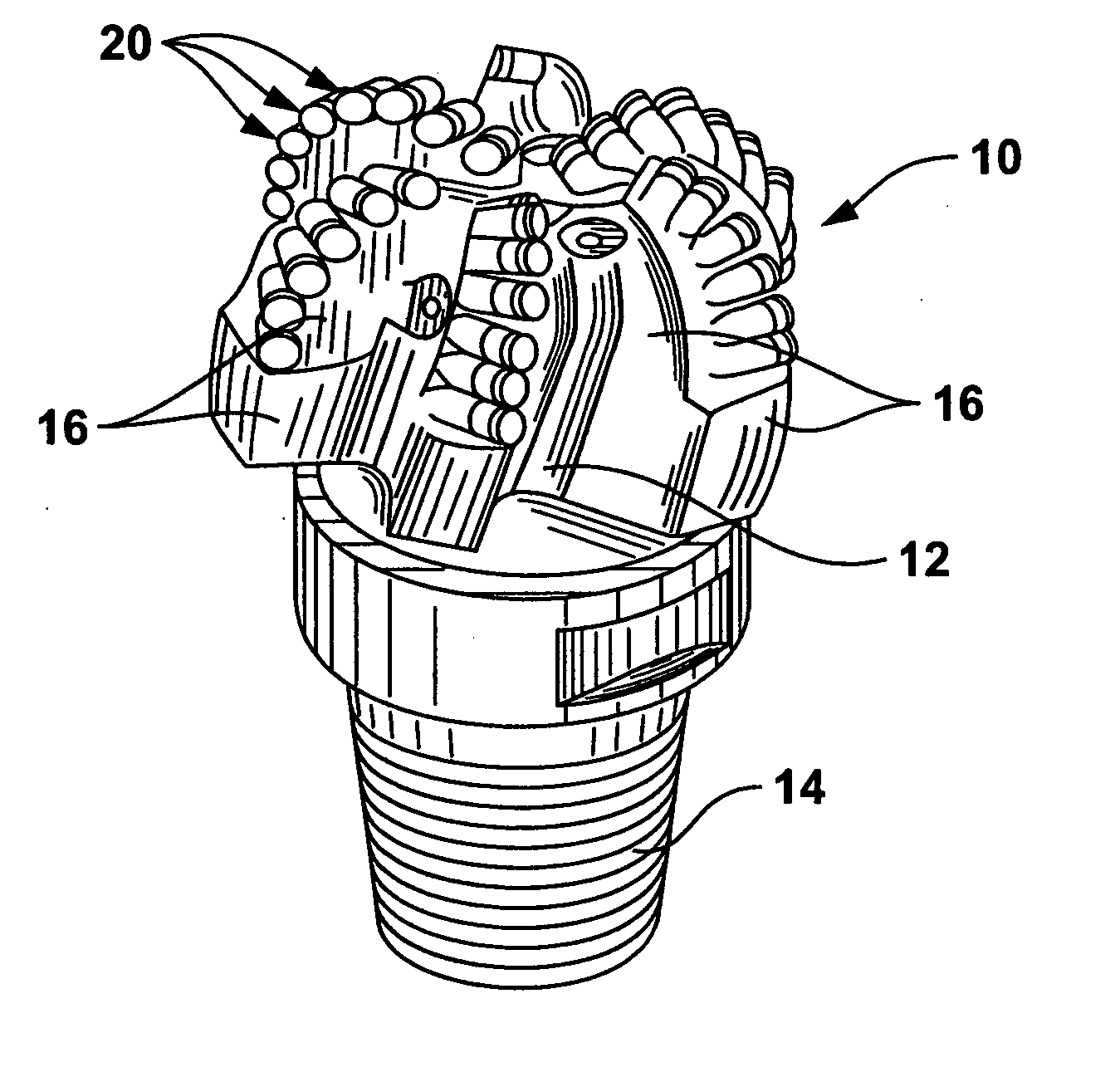
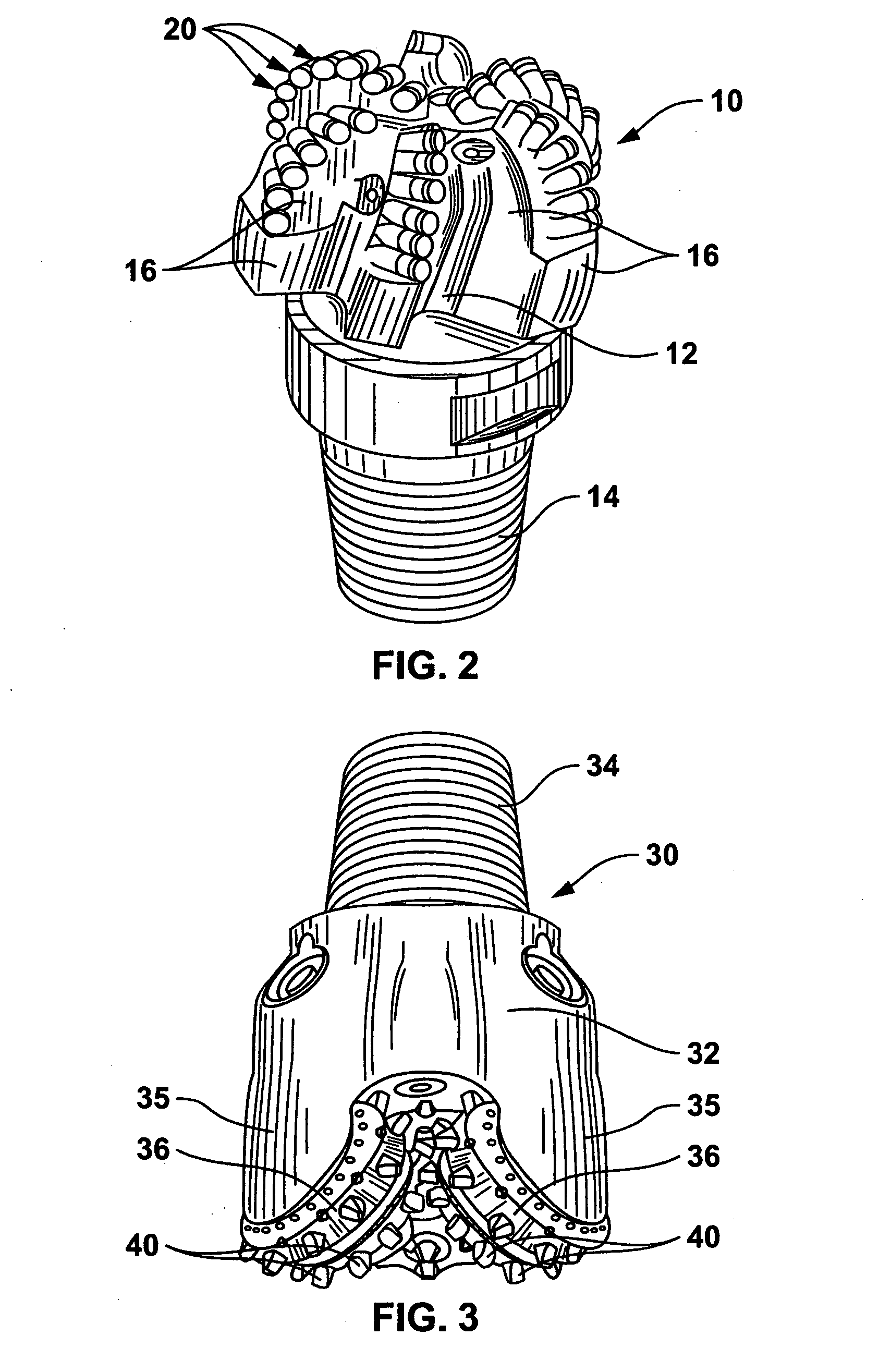
Braze alloy for drilling applications
A down hole cutting tool includes a cutting element support structure. The cutting element support structure has at least one cavity formed therein. A cutting element is disposed in the cavity. Braze alloy is also disposed in the cavity between the cutting element and the cutting element support structure. The braze alloy comprises between about 0.5% and about 10% by weight of at least one selected from the group of gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl). Methods for building a down hole tool using the braze alloy are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC +1
Braze alloy
A braze alloy is described which includes indium and / or thallium as alloying elements. For example, between about 0.5% and about 10% by weight of indium (In) and / or thallium (Tl) can be added to a braze alloy to reduce the braze temperature without substantially effecting braze strength. Braze alloys that are alloyed to including indium (In) and / or thallium (Tl) can be use in brazing cutting elements to drilling tools. These alloying elements may also be added to braze alloys used for other applications to reduce braze temperature.
Owner:KEMBAIYAN KUMAR T
Nanocomposite scintillator, detector, and method
InactiveUS20080093557A1Material analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsSodium iodideTungstate
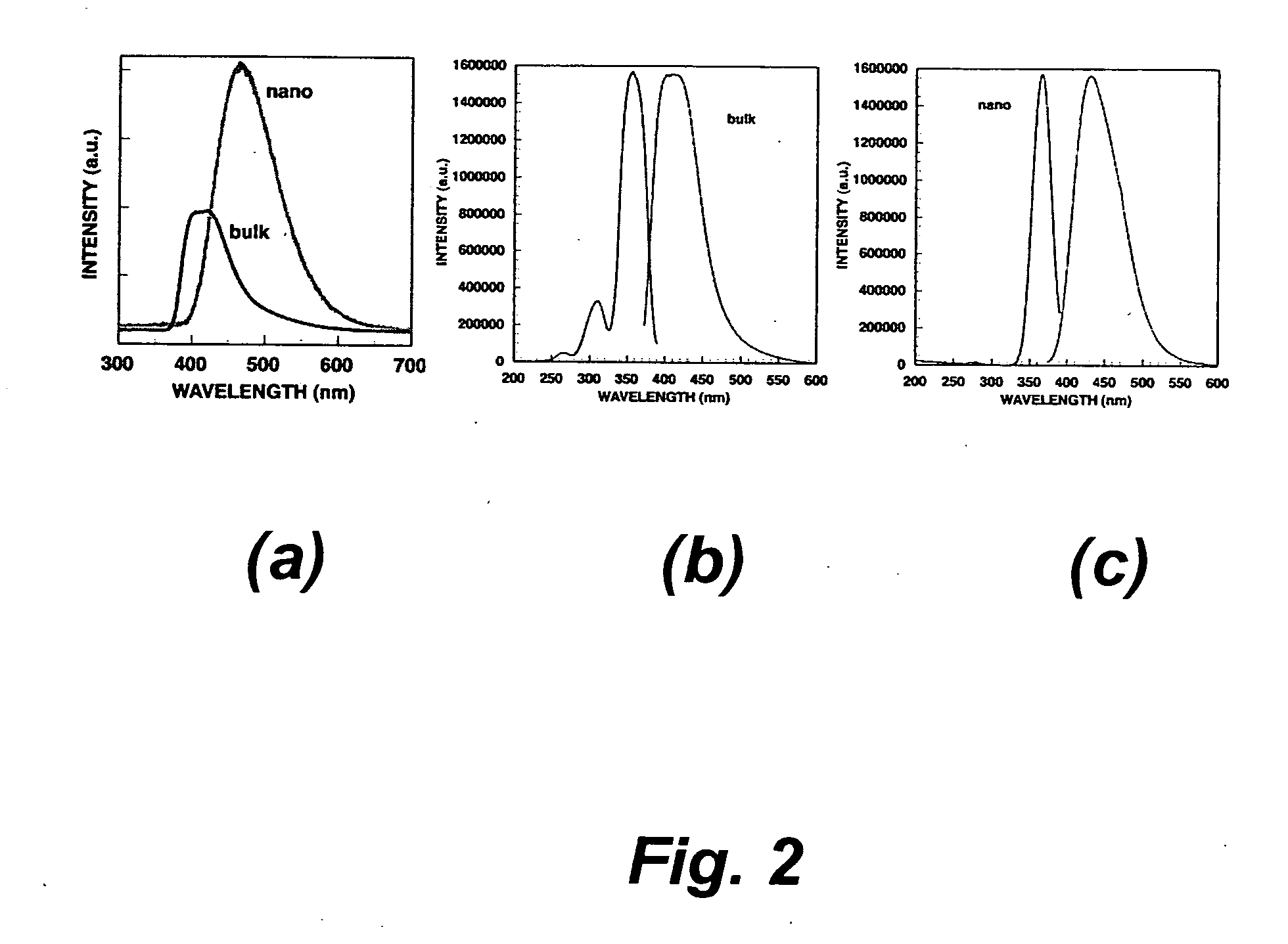
A compact includes a mixture of a solid binder and at least one nanopowder phosphor chosen from yttrium oxide, yttrium tantalate, barium fluoride, cesium fluoride, bismuth germanate, zinc gallate, calcium magnesium pyrosilicate, calcium molybdate, calcium chlorovanadate, barium titanium pyrophosphate, a metal tungstate, a cerium doped nanophosphor, a bismuth doped nanophosphor, a lead doped nanophosphor, a thallium doped sodium iodide, a doped cesium iodide, a rare earth doped pyrosilicate, or a lanthanide halide. The compact can be used in a radiation detector for detecting ionizing radiation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
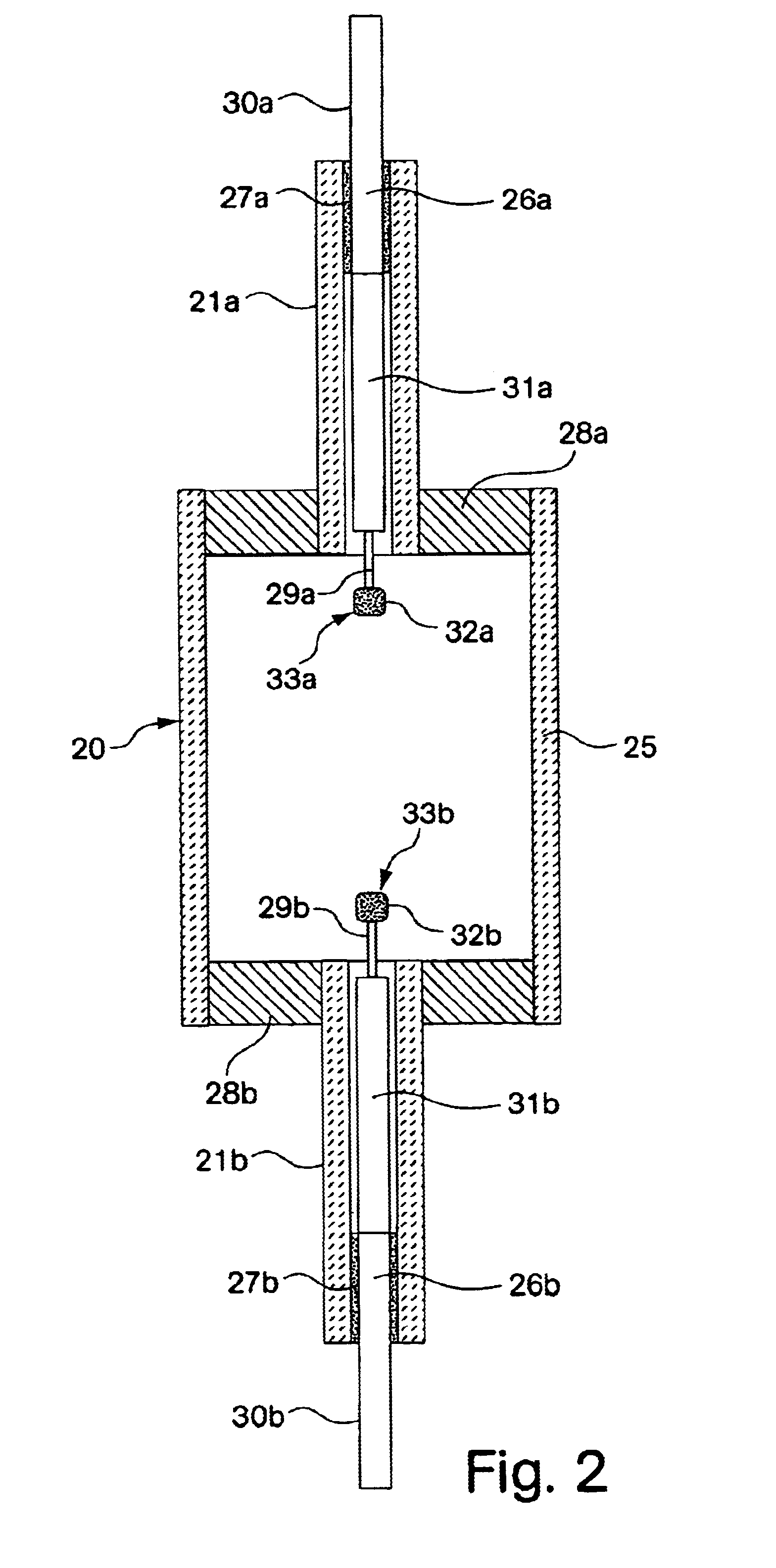
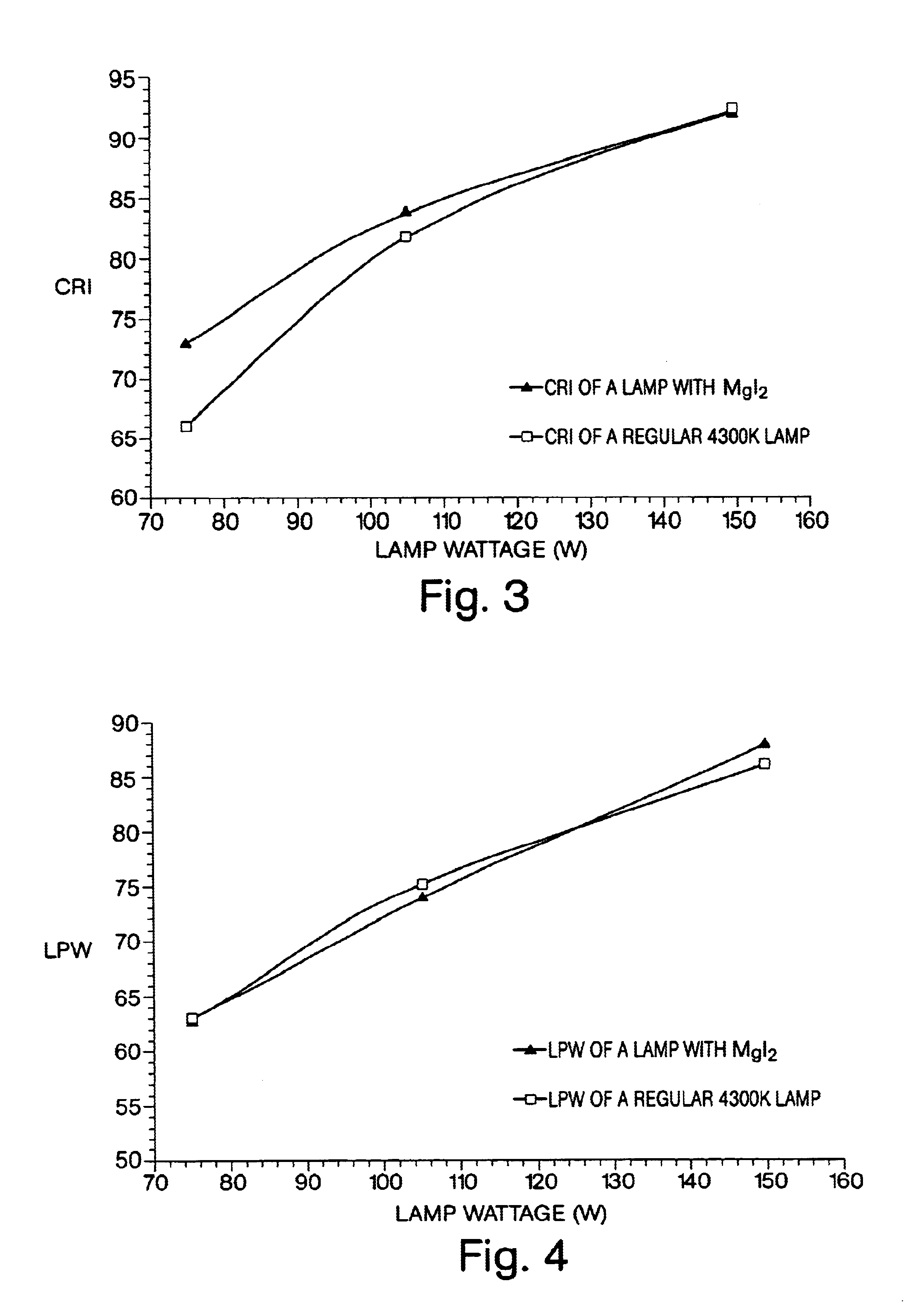
Thallium free-metal halide lamp with magnesium and cerium halide filling for improved dimming properties
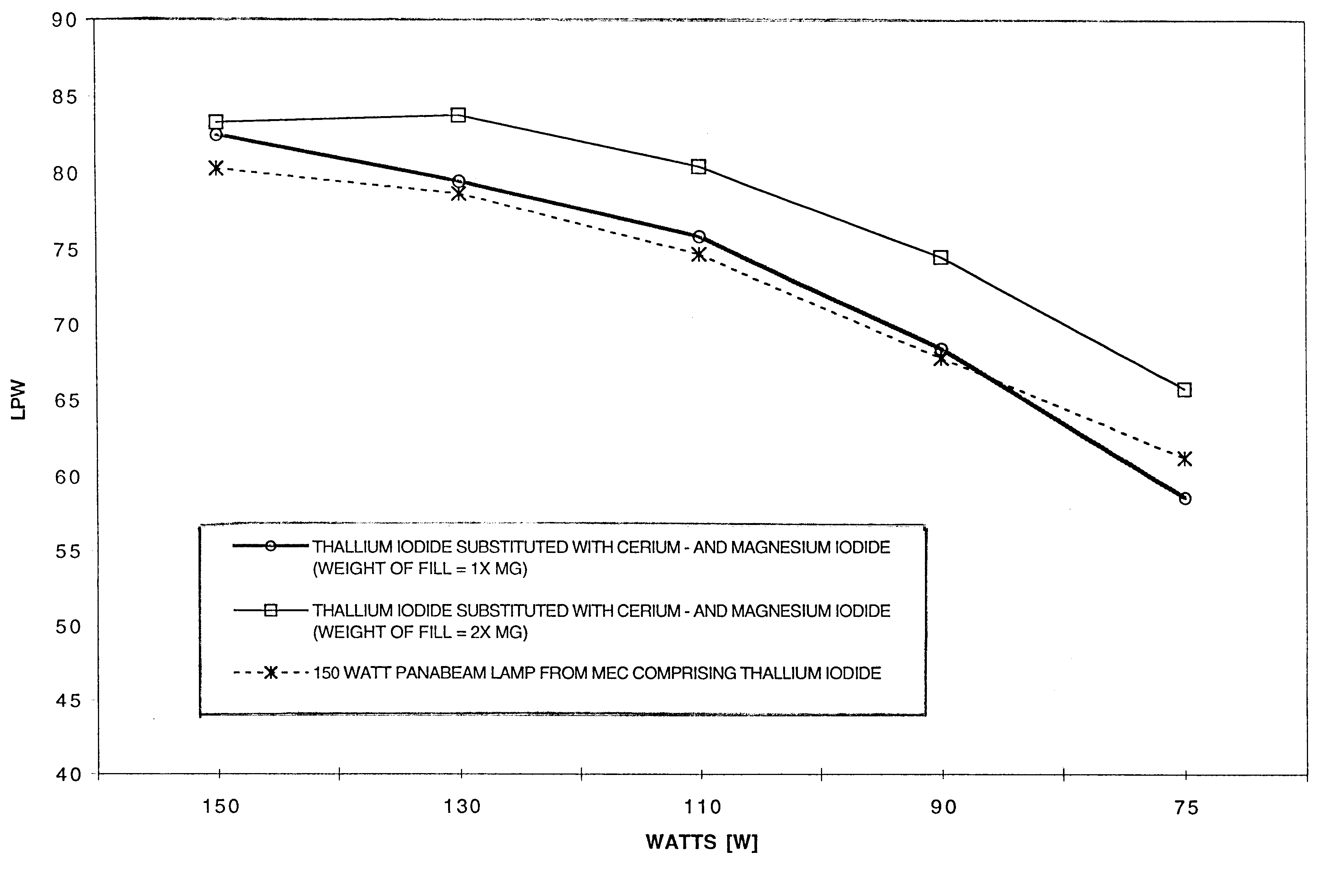
InactiveUS6501220B1Increase vapor pressureReduce the temperatureSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsMetal-halide lampCerium
A thallium-free high pressure ceramic metal halide lamp having superior dimming characteristics with a fill composition comprising MgI2 and CeI3. In addition, the fill chemistry comprises NaI and the halides of rare earth metals such as Dy, Ho and Tm.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
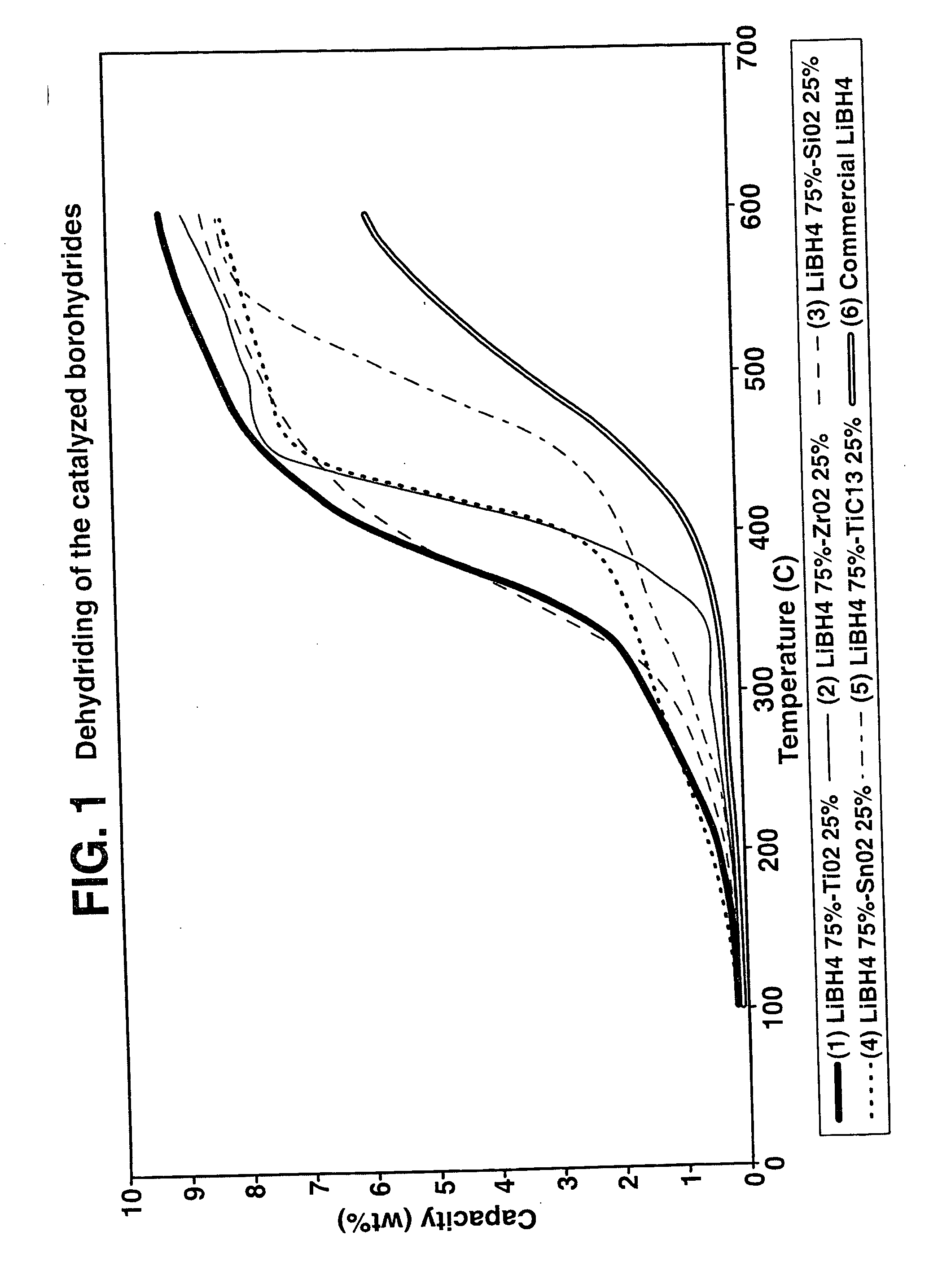
Destabilized and catalyzed borohydrided for reversible hydrogen storage
InactiveUS20060194695A1Reduce the temperatureImproved hydrogen binding/release kineticsHydrogenPhysical/chemical process catalystsIndiumCobalt
A hydrogen storage material and process is provided in which catalyzed alkali borohydride materials and partially substituted borohydride materials are created and which may contain effective amounts of catalyst(s) which include transition metal oxides, halides, and chlorides of titanium, zirconium, tin, vanadium, iron, cobalt and combinations of the various catalysts and the destabilization agents which include metals, metal hydrides, metal chlorides and complex hydrides of magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium and combinations of the various destabilization agents. When the catalysts and destabilization agents are added to an alkali borodydride such as a lithium borohydride, the initial hydrogen release point of the resulting mixture is substantially lowered. Additionally, the hydrogen storage material may be rehydrided with weight percent values of hydrogen of at least about nine percent.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
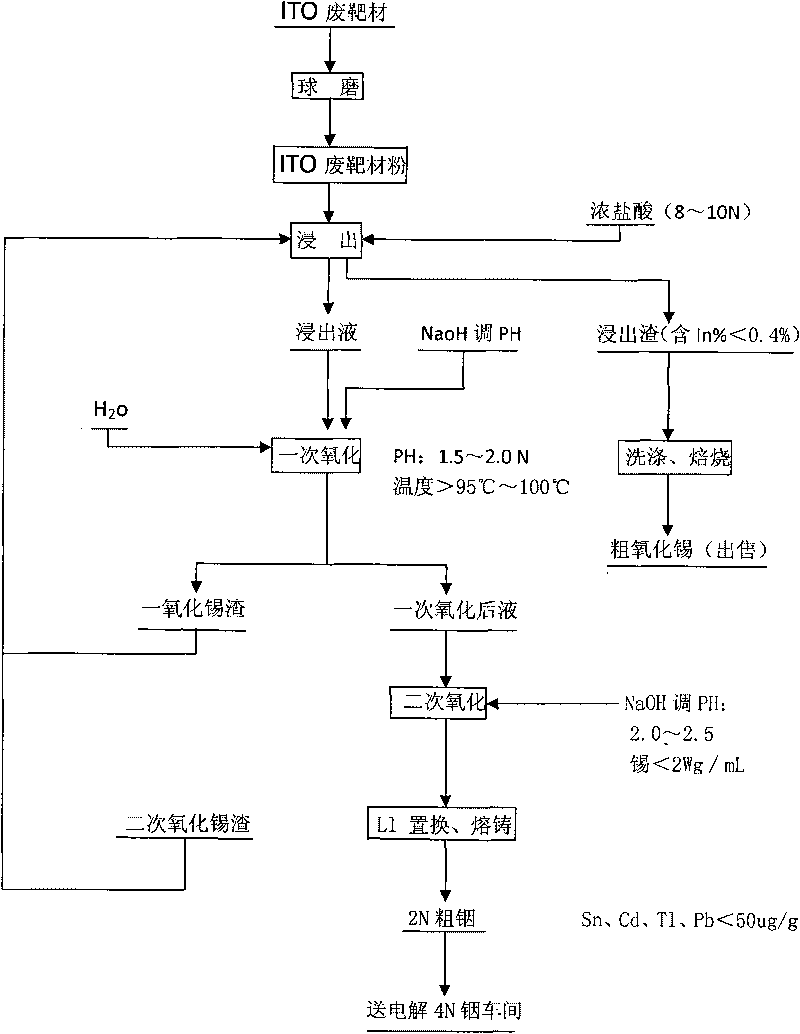
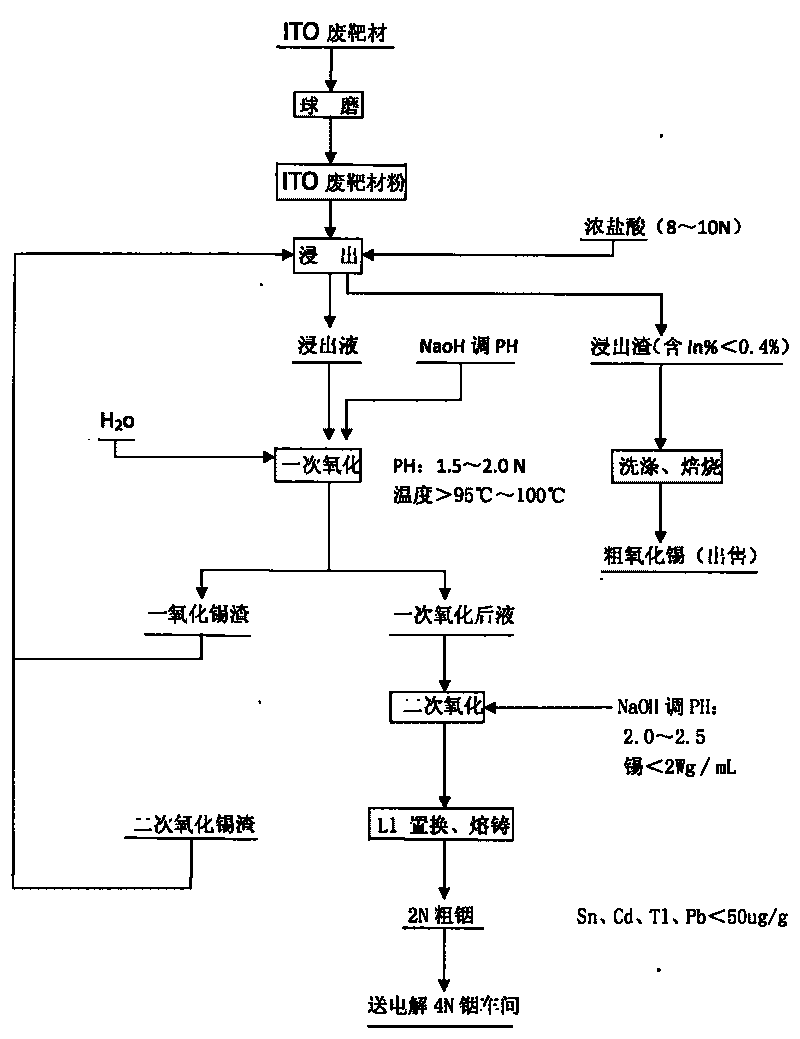
Method for recovering indium and tin from ITO waste targets by utilizing oxidation method
InactiveCN101701292AStable recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationIndium
The invention utilizes the characteristics that tin has two states of bivalence and tetravalence in the solution, and the difference of the pH values is great when the tetravalent tin and trivalent indium ions precipitate in the solution, so the tetravalent tin and trivalent indium ions can be controlled under a certain pH value; oxidant is utilized to oxidize tin ions into tetravalence to generate hydrolysis precipitation, while indium still remains in the water solution, thus achieving the complete separation of indium from tin. At the moment, the tin contained in the indium solution is lowered to 2ppm, aluminium cutter replacement can be directly carried out after vulcanization to ensure that the content of tin, cadmium, thallium and lead is less than 100 PPM, and the content of indium is greater than 99%; while the oxidized tin dregs return and leach, and finally coarse tin oxide can be obtained for sale after washing and roasting the leached dregs, and the grade of indium content is lower than 0.2%.
Owner:南京中锗科技有限责任公司
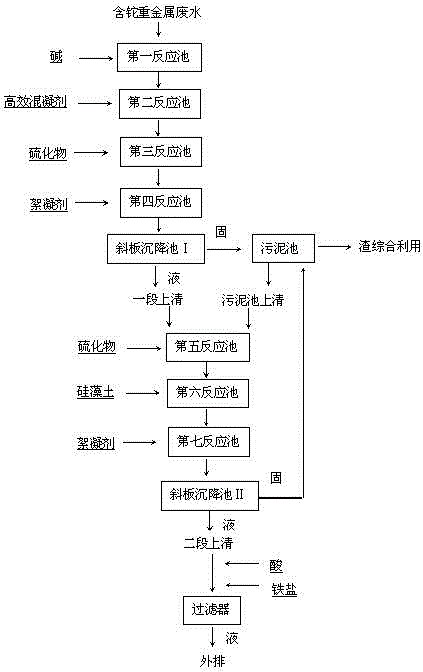
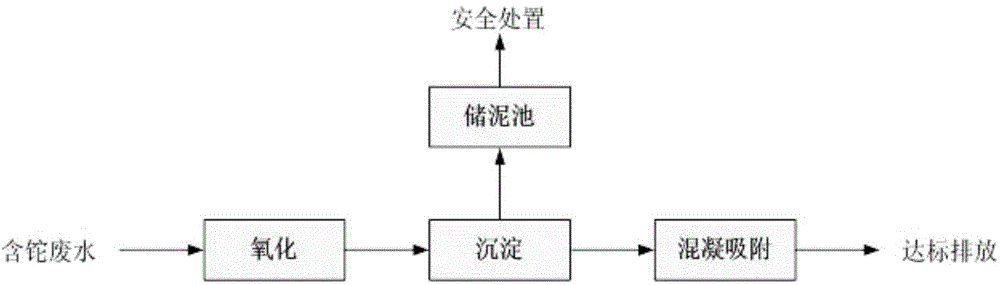
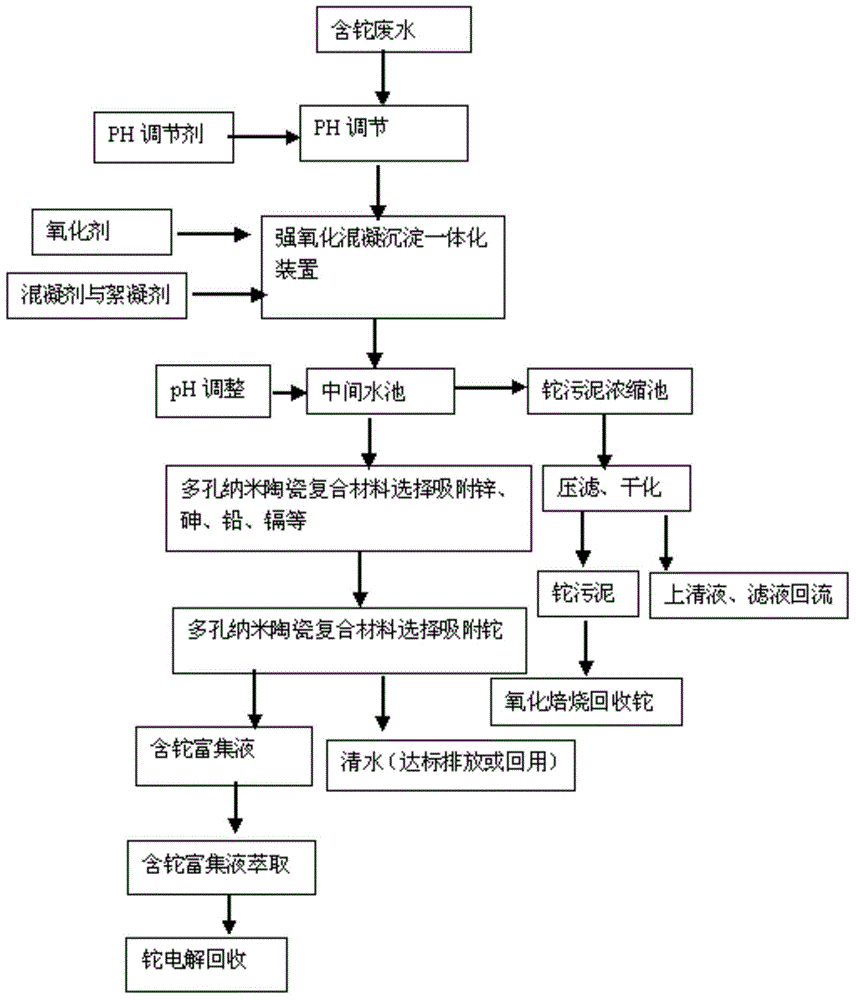
Process for removing thallium from thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater through neutralization and flocculation
InactiveCN104445732AGuaranteed deep removalRealize deep purificationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationIron salts
The invention discloses a process for removing thallium from thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater through neutralization and flocculation. The process comprises the following steps: performing primary treatment, namely adjusting the pH value of thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater to be more than 7through acid and alkali, adding an efficient coagulant, sulfide and a flocculant, and performing solid-liquid separation through a slanting board sedimentation pool; performing secondary treatment, namely adding sulfide, diatomite and the flocculant into supernatant purified water after primary treatment, and performing solid-liquid separation through the slanting board sedimentation pool; adjusting the purified water subjected to secondary treatment to be neutral, adding iron salt, and finally filtering through a filter and directly discharging to the outside. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme, the removal rate of thallium and other heavy metal ions in the heavy metal wastewater can be effectively increased, the environmental pollution can be avoided, and the medicament cost can be reduced.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Dehydrogenation catalyst composition
Owner:UOP LLC
Scintillator materials which are useful for detecting radiation, and related methods and articles
A scintillator composition is described, including a matrix material and an activator. The matrix material includes at least one alkali metal or thallium; at least one alkaline earth metal or lead; and at least one halide compound. The activator is usually cerium, praseodymium, or mixtures thereof. Radiation detectors which include the scintillator composition are also described. Methods for detecting high-energy radiation also form part of this disclosure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Catalyst for preparing olefin from low-carbon alkane by dehydrogenation and preparation method of catalyst
ActiveCN105214657AImprove carbon storage capacityImprove stabilityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkaneIndium
The invention provides a catalyst for preparing olefin from low-carbon alkane by dehydrogenation. The catalyst comprises an aluminum oxide carrier and the following active components with the carrier as datum by mass: 0.1 to 2.0% of a group-VIII metal, 0.1 to 2.0% of a second metal component, 0.5 to 5.0% of a group-IA metal and 0.3 to 10.0% of halogen, wherein the aluminum oxide carrier has a pore volume of pores with a diameter of 2 to 10 nanometers accounting for 4 to 15% of a total pore volume, a pore volume of pores with a diameter of 10 to 20 nanometers accounting for 40 to 60% of the total pore volume, a pore volume of pores with a diameter of 20 to 50 nanometers accounting for 1.0 to 5.0% of the total pore volume, and a pore volume of pores with a diameter of more than 50 nanometers and less than 10 microns accounting for 20 to 50% of the total pore volume; and the second metal component is selected from the group consisting of tin, germanium, lead, indium, gallium or thallium. The catalyst is applied to preparation of propylene from propane by dehydrogenation and has high activity and selectivity and low coke deposition rate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
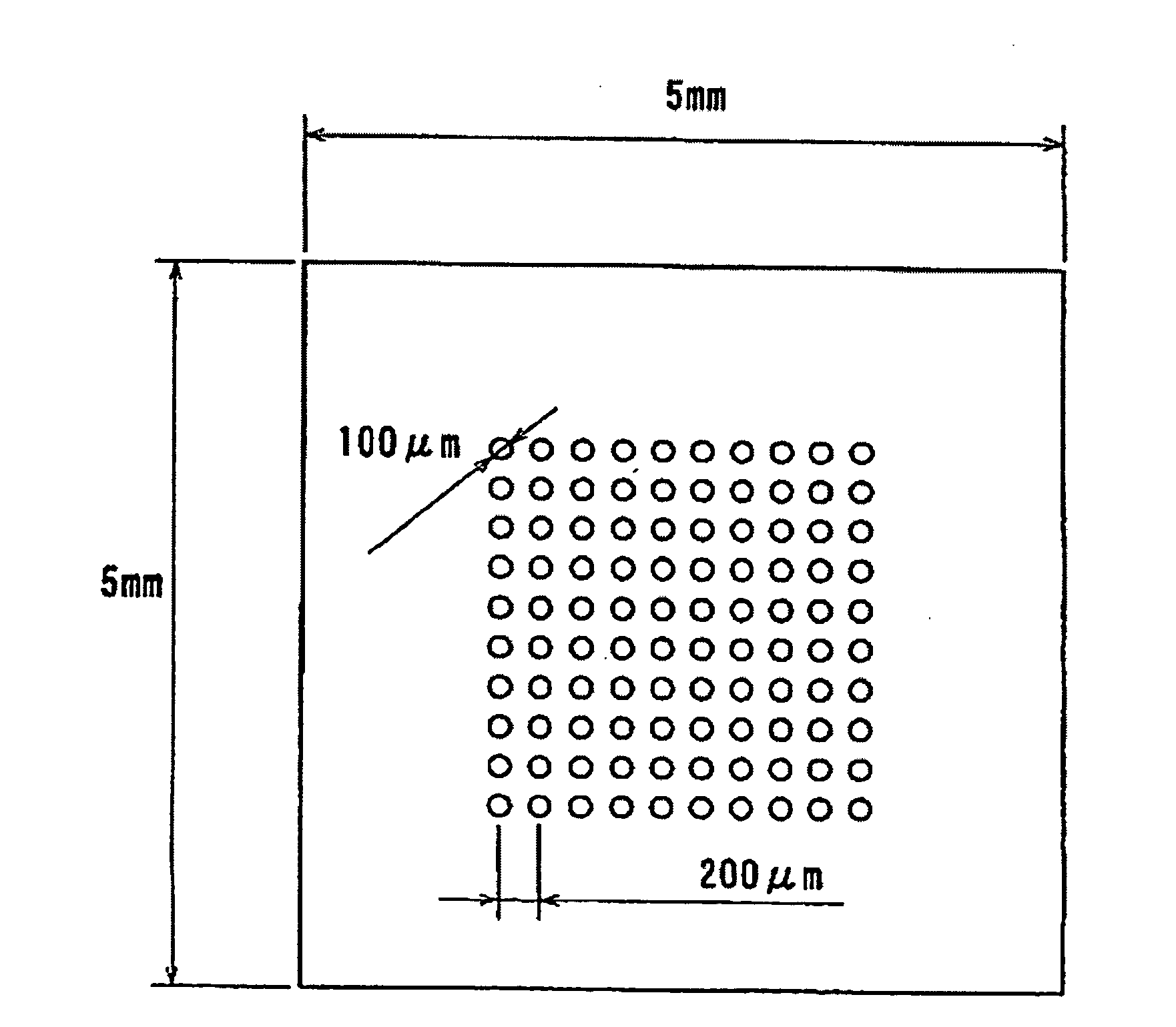
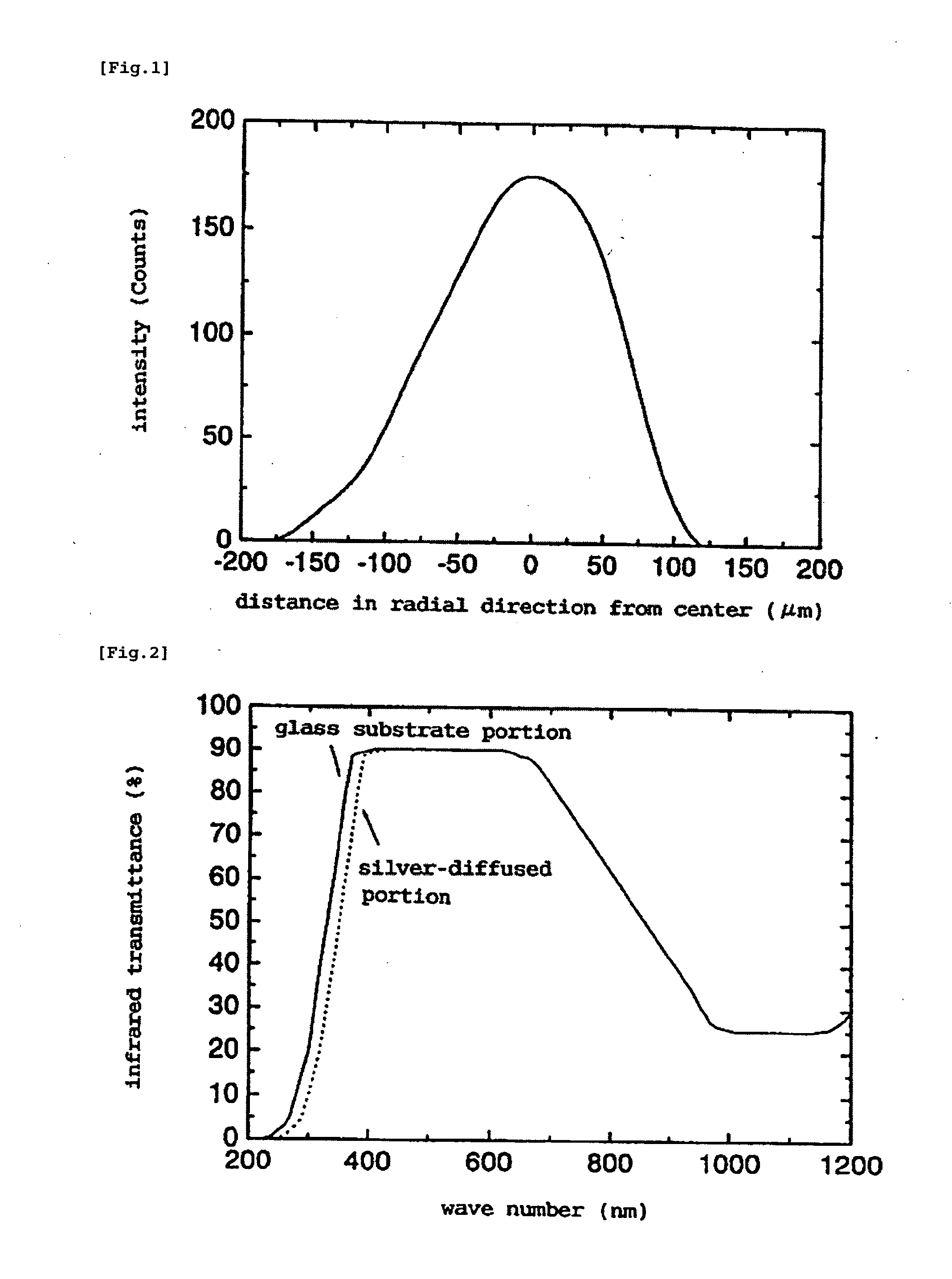
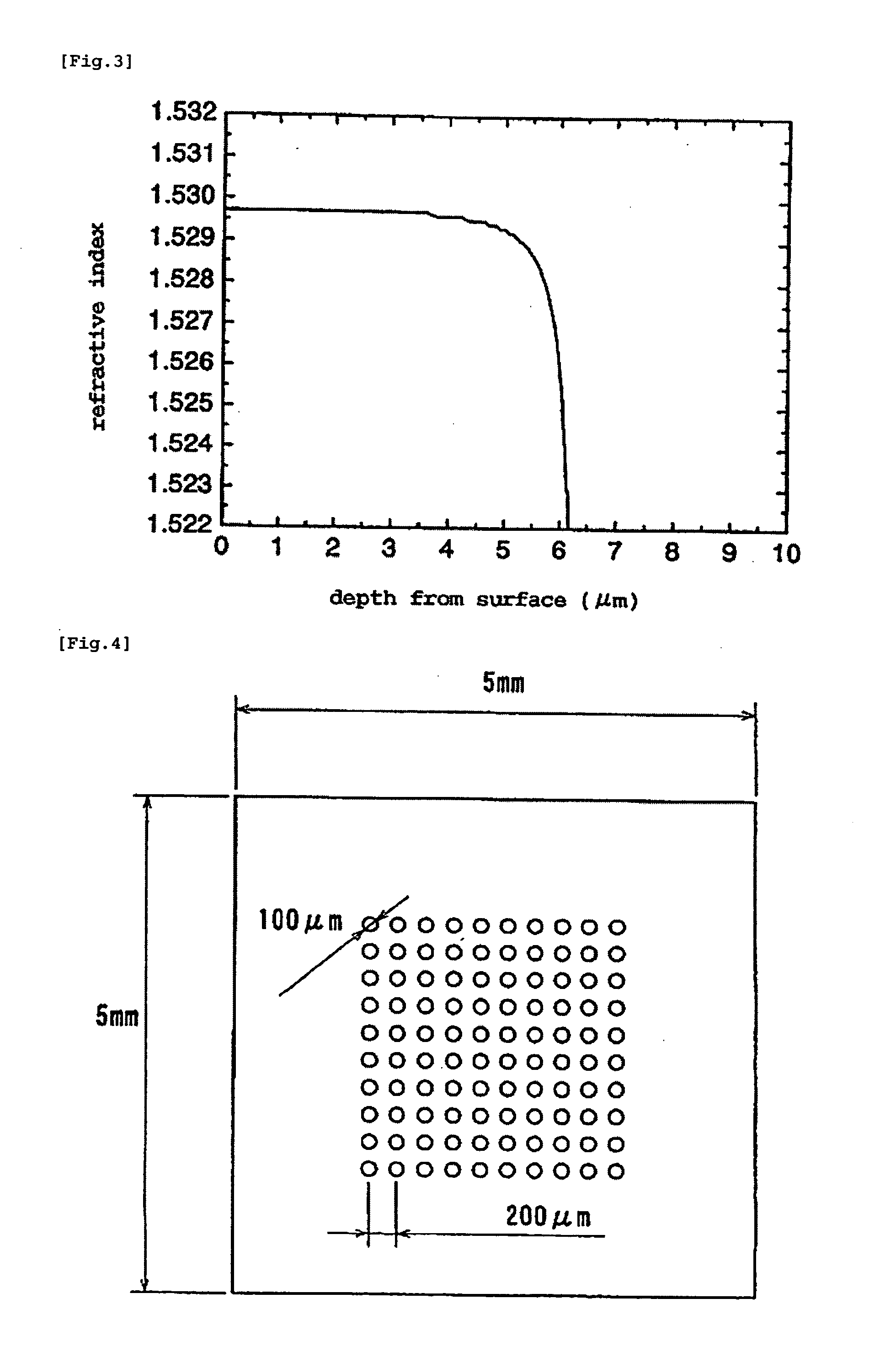
Method for Manufacturing Gradient-Index Optical Element Having Infrared Absorbing Ability
InactiveUS20100165454A1Low costProductionElectrostatic spraying apparatusCoatingsRubidium compoundGradient-index optics
A method of readily producing a gradient optical element having infrared absorbing ability by easily forming a refractive index distribution in a desired portion of a glass substrate having infrared absorbing ability without requiring a specific treatment atmosphere nor using a molten salt.More specifically, the present invention provides a method for producing a gradient-index optical element having infrared absorbing ability, the method comprising applying a paste containing an organic resin, an organic solvent, and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of lithium compounds, potassium compounds, rubidium compounds, cesium compounds, silver compounds, copper compounds, and thallium compounds onto a glass substrate containing an alkali metal component, at least one member selected from the group consisting of iron, copper, cobalt and vanadium, and over 3 wt. % of iron, when contained singly among iron, copper, cobalt and vanadium, on an Fe2O3 basis, taking the total weight of the glass as 100 wt. %, and heating the glass substrate at a temperature below the softening temperature of the glass substrate.
Owner:ISUZU GLASS +1
Water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and/or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ
ActiveCN102145947AHigh electronegativityLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFerric hydroxideWater source
The invention discloses a water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ, relating to a water treatment method of thallium and / or cadmium-containing source water and solving the problems of complex process, high running cost and low removing efficiency of thallium and / or cadmium existing in the conventional water treatment technology specific to thallium and / or cadmium-polluted source water. The method comprises the following steps of: adding permanganate and ferrous salt into Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+>-containing water; stirring to obtain a mixed solution; adding a coagulant; and performing conventional water treatment. A nanometer ferric hydroxide-manganese dioxide oxide composite adsorbent which has a large specific surface area and high electronegativity and is easy for precipitation separation is produced in situ by making permanganate react with the ferrous salt, so that Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> can be removed effectively andspecifications in the national Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water are met. The method has the advantages of high removing efficiency, simple process, flexibility and convenience for operation, no change of the original treatment process of a water plant, low running cost and the like, and can be applied to emergency treatment of a water pollution event.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Catalyst for the oxidation of a mixed aldehyde feedstock to methacrylic acid and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20070021296A1Improve distributionOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsIndiumCerium
A heteropolyacid catalyst for oxidation of isobutyraldehyde, methacrolein or mixtures or combinations thereof to methacrylic acid is disclosed where the heteropolyacid catalyst includes at least molybdenum (Mo), phosphorus (P), vanadium (V), and a first component including bismuth (Bi) and / or boron (B). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also optionally include a second component including potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and / or thallium (Tl) and optionally a third component including antimony (Sb), cerium (Ce), niobium (Nb), indium (In), iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), arsenic (As), silver (Ag), zinc (Zn), germanium (Ge), gallium (Ga), zirconium (Zr), magnesium (Mg), barium (Ba), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), titanium (Ti), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), and / or lanthanum (La). The heteropolyacid catalyst can also include an ammonium-containing compound designed to increase a value of medium pores in the final heteropolyacid catalyst. A method for oxidizing isobutanal to methacrylic acid using the heteropolyacid catalyst is also disclosed.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
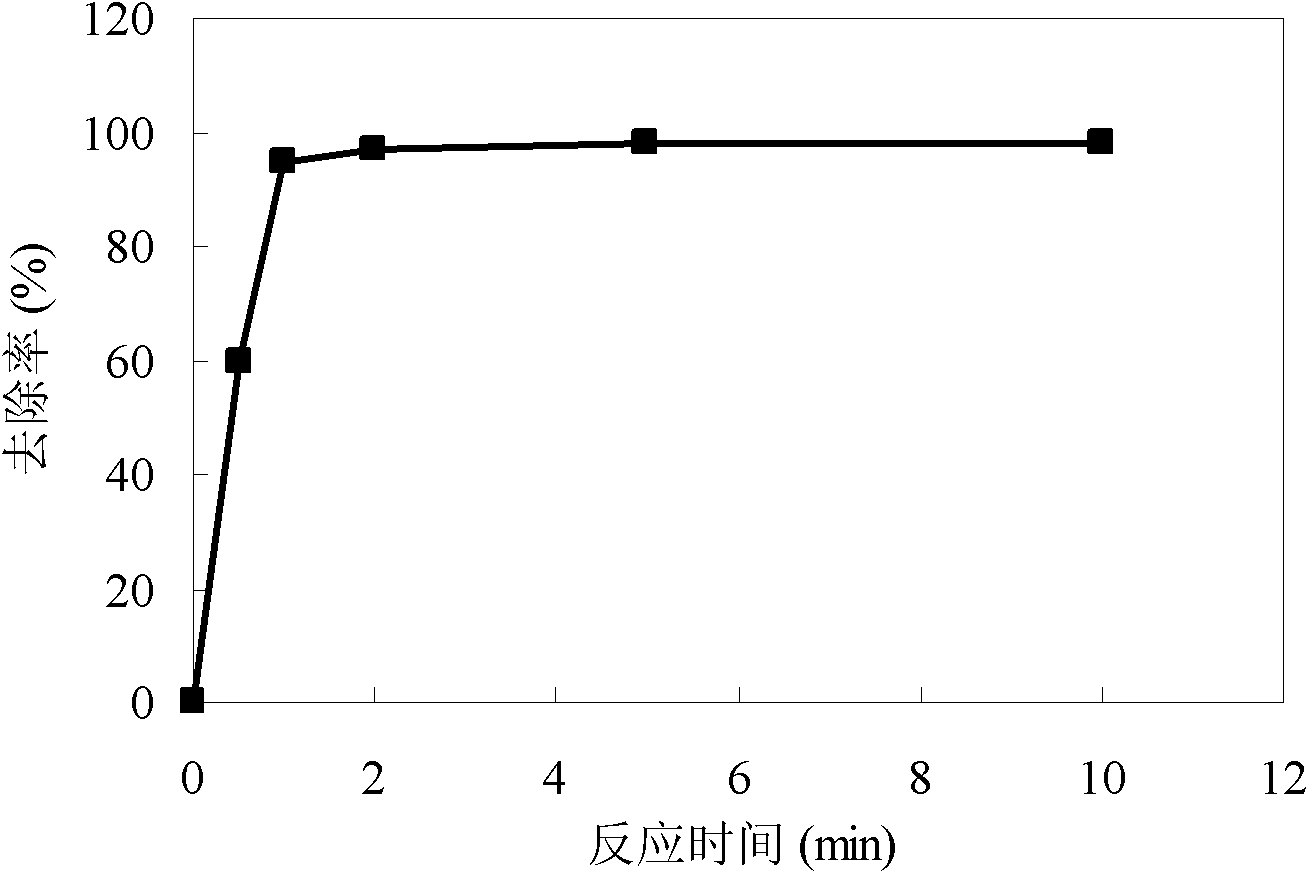
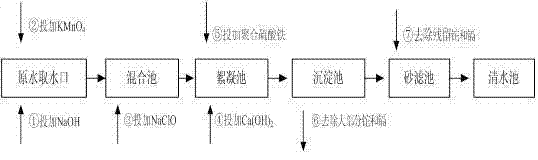
Method for simultaneous removal of cadmium and thallium in raw water
ActiveCN103693774ASimple processEasy to implementWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentCadmium CationTreated water
The invention provides a method for simultaneous removal of cadmium and thallium in raw water. The method comprises the following steps: step A, adding sodium hydroxide into raw water, adjusting a pH value to alkalescence and then adding potassium permanganate with a concentration of 0.3 to 0.8 mg / L; step B, adding sodium hypochlorite or liquid chlorine, wherein the concentration of added sodium hypochlorite or liquid chlorine is 0.5 to 2.5 mg / L in term of effective chlorine; step C, adding limewash into raw water having undergone a full oxidation reaction and adjusting a pH value to 8.5 to 9.0; step D, adding a flocculating agent, carrying out a flocculation reaction for 10 to 20 min and then carrying out deposition for at least 0.5 h so as to remove cadmium, thallium and colloids of manganese hydroxide and iron hydroxide through coprecipitation, wherein the pH value of water after precipitation drops to 7.0 to 8.5; and step E, filtering raw water obtained after precipitation by using quartz sand. The invention has the following beneficial effects: cadmium concentration of treated water is as small as the limit of a detection method, i.e., 0.02 mu g / L, or less than 0.02 mu g / L; thallium concentration of treated water is as small as the limit of a detection method, i.e., 0.01 mu g / L, or less than 0.01 mu g / L; and the pH value, manganese ions and iron ions of the treated water all meet requirements prescribed in drinking water quality standards.
Owner:SHENZHEN WATER GRP CO LTD
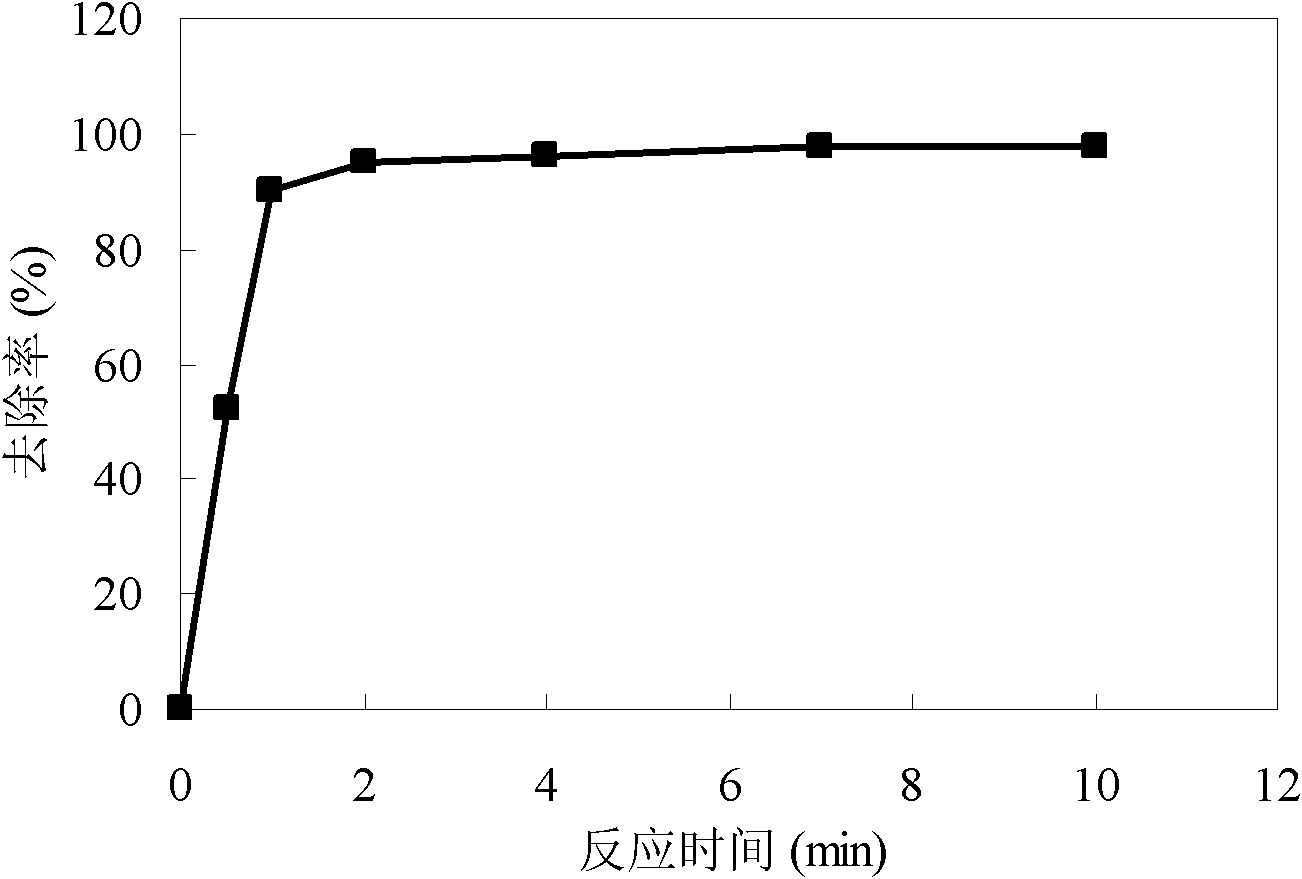
Method adopting combined technology of pre-oxidation and coagulating sedimentation to process wastewater containing thallium and ammonia-nitrogen
InactiveCN105293775AShort operating timeLess investmentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogen gasHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method adopting a combined technology of pre-oxidation and coagulating sedimentation to process wastewater containing thallium and ammonia-nitrogen. According to the method, a sodium hypochlorite oxidizing agent is added into a wastewater collecting tank so as to oxidize metal ions in wastewater, the monovalent thallium is fully oxidized into trivalent thallium, monovalent thallium is converted into complex under the effect of strong oxidant, and at the same time, the nitrogen in ammonia-nitrogen is degraded and removed in the form of nitrogen gas. After pre-oxidation, the wastewater is lifted to an integral processing facility through a self-sucking pump; ferrous sulfate and poly aluminum chloride (PAC) are added to form alumen ustum flocculus in a precipitation unit, the precipitate is wrapped, the thallium complex is adsorbed, then quicklime is added to adjust the solution to an alkaline environment; in the alkaline environment, Fe<3+>, Al<3+>, and prepolymer products thereof carry out hydrolysis quickly to form Fe(OH)3 flocculus and Al(OH)3 flocculus; before the flocculus becomes big, the adsorption sites on the surface of flocculus form covalent bonds with Ti<3+>, the flocculus becomes bigger and bigger very quickly and goes on absorbing Ti<3+> in water; at the same time, Ti<3+>, Fe<3+>, Al<3+>, Zn<2+>, lead, and cadmium carry out co-precipitation reactions, and thus the heavy metal ions in water are removed.
Owner:HUNAN LIHONG NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
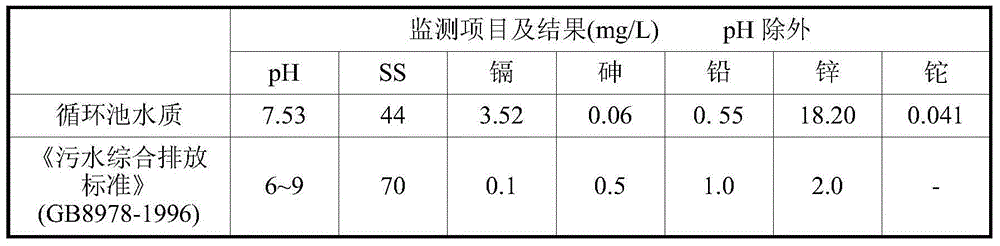
Thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater advanced treatment method
ActiveCN103693819AEliminate secondary pollutionLow costMultistage water/sewage treatmentPretreatment methodFiltration
The invention belongs to a thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater advanced treatment method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating thallium-containing heavy metal wastewater: adjusting the pH value of wastewater to 9.5-11.5 with alkaline, and adding a chemical thallium removing agent according to the mass ratio of the chemical thallium removing agent to thallium of (0.5-1.5):1; (2) medicating according to the mass ratio of the chemical thallium removing agent to wastewater after the reaction in step (1) for 15-30 minutes, and carrying out mixed reaction for 15-30 minutes; (3) adding liquid alkaline into the solution obtained from the step (2), adjusting the pH value to 11.0-11.5, reacting for 10-20 minutes, adding 5-50g / m<3> of flocculating agents, reacting for 10-20 minutes, carrying out solid-liquid separation by oblique plate deposition or plate frame press filtration, standing for 1-2 hours, and discharging or recycling supernate. The thallium contained heavy metal wastewater treatment method is simple in process, has no secondary pollution, is high in treatment efficiency, runs stably and low in cost, and has very high practicability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
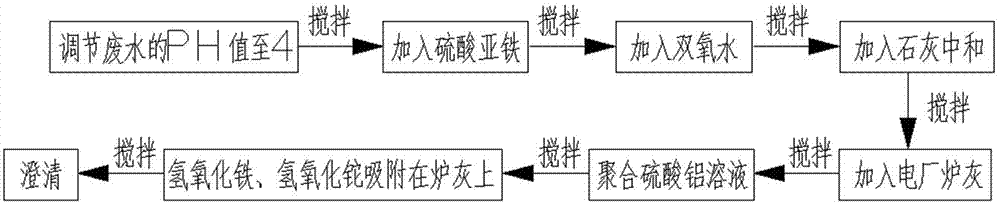
Method for removing trace of thallium in sewage
InactiveCN104773878AStrong oxidizingImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFenton reagentSulfate
The invention relates to a method for removing a trace of thallium in sewage. The method includes the process steps of regulating the PH value of the thallium-contained sewage to 4, adding a ferrous sulfate solution to the sewage, evenly mixing the sewage with the ferrous sulfate solution, adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage again, conducting stirring, oxidizing fluorosis univalence thallium (T1+) in the sewage into tervalence thallium (T13+), mixing ferrous iron and hydrogen peroxide into a fenton reagent, adding lime to the sewage and evenly conducting stirring so that the PH value of the sewage can be neutralized to be 7 to 9, hydrolyzing tervalence iron (Fe3+) in the sewage at the same time to form flocculent ferric hydroxide, adding an appropriate amount of power plant stove ash (electric duct collector stove ash) to the sewage, evenly conducting stirring, and adding a polyaluminium sulfate solution so that ferric hydroxide and thallium hydroxide can be adsorbed to the stove ash. Flocculent sediment generated through hydrolysis has the great surface area and quite strong adsorption capacity; the power plant stove ash can adsorb the flocculent sediment and colloid particles in the sewage and sink.
Owner:广东云测环境科技有限公司
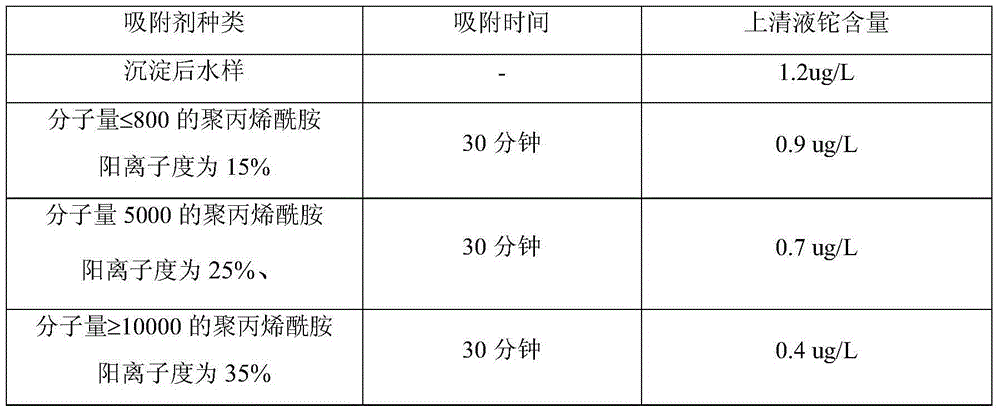
Method for removing metal thallium in wastewater
InactiveCN104528985AGuaranteed removal effectTake into account investmentWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsSorbentThallium
The invention discloses a method for removing metal thallium in wastewater, and the method is applicable to process wastewater with the thallium content of 0.05 mg / L or less. The method comprises the steps: step 1, oxidizing, namely, adding a strong oxidant into thallium-containing wastewater, so as to oxidize monovalent thallium ion in wastewater to form trivalent thallium ion; step 2, precipitating, namely, adding an alkali solution and adjusting the pH value to be 12 or more, so as to perform precipitation; and step 3, coagulating and adsorbing, namely, filtering, then adjusting pH of the filtrate to be 6-9, and pouring an adsorbent for coagulation and adsorption. The method is a comprehensive processing technology employing oxidation, precipitation and coagulation adsorption, is capable of guaranteeing the removal effect of thallium ion, has the removal rate of 97% or more, enables processed water to reach national discharge standard, also gives consideration to both investment and running cost, and is convenient for running and maintenance.
Owner:HUNAN MUKUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Process for the selective conversion of alkanes to unsaturated carboxylic acids
The invention disclosed is a process for the selective conversion of an alkane to an unsaturated carboxylic acid in a one-step process with a mixed metal oxide catalyst composition having the general formula:MoVaNbbTecSbdMeOx wherein M is optional and may be one or more selected from silver, silicon, sulfur, zirconium, titanium, aluminum, copper, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, gallium, phosphorus, iron, rhenium, cobalt, chromium, manganese, arsenic, indium, thallium, bismuth, germanium, tin, cerium or lanthanum. This catalyst may be prepared by co-precipitation of metal compounds which are calcined to form a mixed metal oxide catalyst.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Dehydrogenation catalyst composition
A catalyst composite is disclosed. Also disclosed is its use for dehydrogenation reactions. The catalyst composite comprises a Group VIII noble metal component, a Group IA or IIA metal component, and a component selected from the group consisting of tin, germanium, lead, indium, gallium, thallium, or mixtures thereof, all on an alumina support comprising essentially theta-alumina, having a surface area from 50 to 120 m2 / g, an apparent bulk density of at 0.5g / cm3 and a mole ratio of the Group VIII noble metal component to the component selected from the group consisting of tin, germanium, lead, indium, gallium, thallium or mixtures thereof in the range from 1.5 to 1.7.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for preparing and extracting carotenoid from microbial thalli
ActiveCN102732049AReduce dosageShort processHydrocarbon purification/separationNatural dyesHigh pressureFermentation
The invention which belongs to bioengineering and bioseparation engineering fields relates to a method for preparing and extracting carotenoid from microbial thalli. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting the microbial thalli, separating the resulting fermentation solution and the thalli to obtain wet thalli, guiding the wet thalli to an explosion tank through a material flow pipeline, and carrying out high-pressure explosion wall breaking; dehydrating the wet thalli with disrupted cells to obtain a filter cake formed by thallium fragments; adding 10-25L of an organic solvent to each 1kg of the filter cake, and carrying out stirring extraction at 30-55DEG C for 20-50min; filtering to obtain an organic solvent extraction containing carotenoid grease; and carrying out vacuum concentration on the extraction at 40-60DEG C, and recovering the organic solvent to obtain the carotenoid grease. The extraction yield one time reaches above 90%. The method has the advantages of omission of dehydration drying and thallium crushing operations in traditional technologies, short process flow, high extraction yield and short time each time, reduced organic solvent application amount, substantially reduced energy consumption and other costs, simple whole process, and controllable quality, and is suitable for industrialized production applications.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Thermoelectric figure of merit enhancement by modification of the electronic density of states
InactiveUS20110248209A1Heat-exchange elementsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsDopantChemical compound
A thermoelectric material and a method of using a thermoelectric material is provided. The thermoelectric material can include at least one compound. For example, the at least one compound may be a Group IV-VI compound such as lead telluride. The at least one compound may further include one or more dopants such as sodium, potassium, and thallium. The method of using a thermoelectric material can include exposing at least one portion of the at least one compound to a temperature greater than about 700 K.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV +1
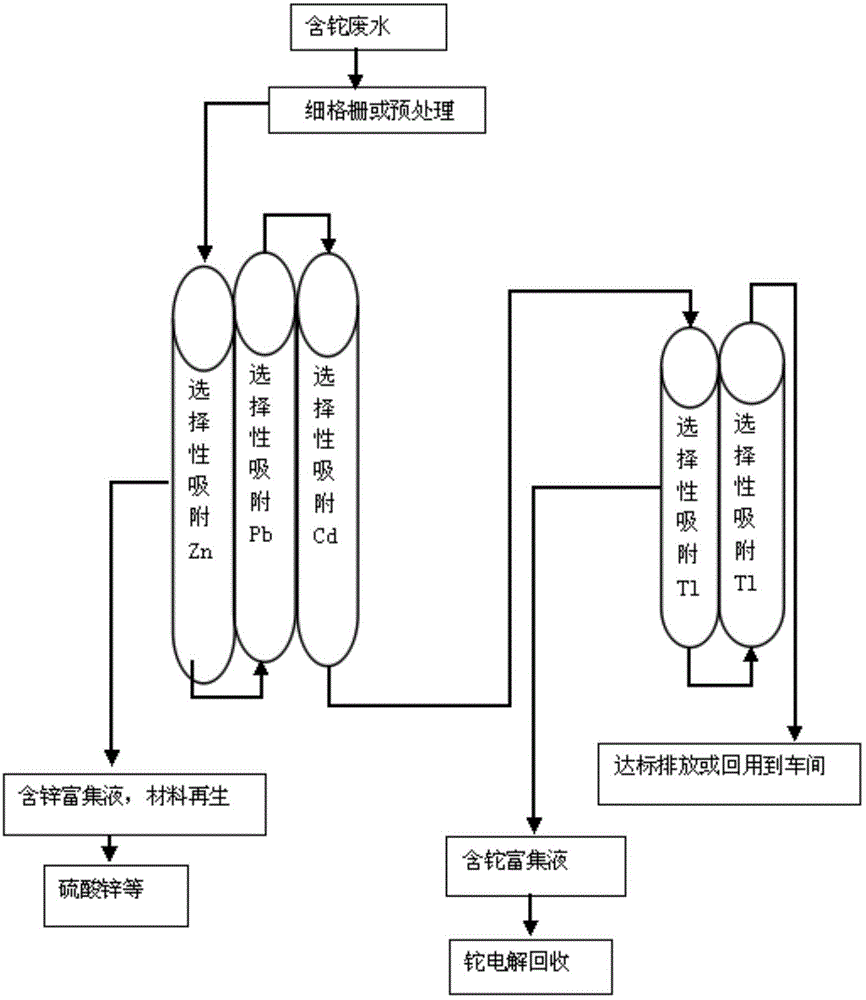
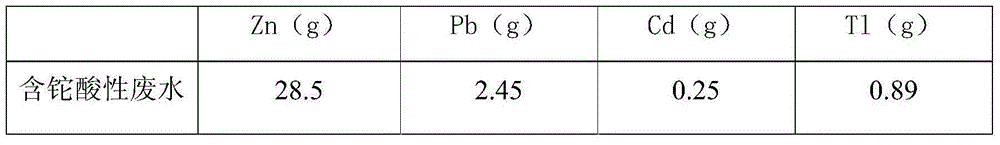
Thallium-containing wastewater strongly oxidizing, coagulating, adsorbing and recovering process
ActiveCN104310672AHighly selective adsorptionLarge specific surface areaWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatmentFiltrationSludge
The invention provides a thallium-containing wastewater strongly oxidizing, coagulating, adsorbing and recovering process. The process includes the following procedures: thallium-containing wastewater concentration, pH regulation, strong oxidization, coagulation, flocculation, precipitated sludge treatment, pH regulation, solid impurity filtration, removal of Zn, Pb, Cd and Tl, and the like. The process has the beneficial effects that the process has the advantages of advanced technology, maturity, good effluent quality, stability in operation, conciseness in process, strong practicability, easiness in start and stop, convenience in maintenance and management, small investment, low operating cost, small floor area for construction, short construction period and large application ranges of projects; treatment of heavy metal ion polluted sewage is not limited by temperatures; the limitation that a biological method can not be used in cold regions in the north can be overcome.
Owner:HUNAN JINGYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
X-ray detecting panel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106206636AThe detection went wellAvoid damageSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesIodideDetector array
The embodiment of the invention discloses an X-ray detecting panel and a preparation method thereof, relates to the field of detecting instruments, and provides the X-ray detecting panel with non-thallium-doped scintillator film layer as the scintillator. The injuries of thallium and iodide thereof to human bodies can be avoided, and meanwhile the preparation cost of the X-ray detecting panel is greatly reduced. The X-ray detecting panel comprises a lining substrate, a switch array arranged on the lining substrate, a photoelectric detector array arranged on the switch array, a cover plate, a scintillator film layer arranged on the cover plate, and a colloid quantum dot film layer arranged between the scintillator film layer and the photoelectric detector array, wherein the scintillator film layer is used for converting X-rays into near ultraviolet light, the colloid quantum dot film layer is used for converting near ultraviolet light converted by the scintillator film layer into visible light to be output, and the photoelectric detector array is used for converting the visible light converted by a wavelength converting unit into electric signals to be output.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
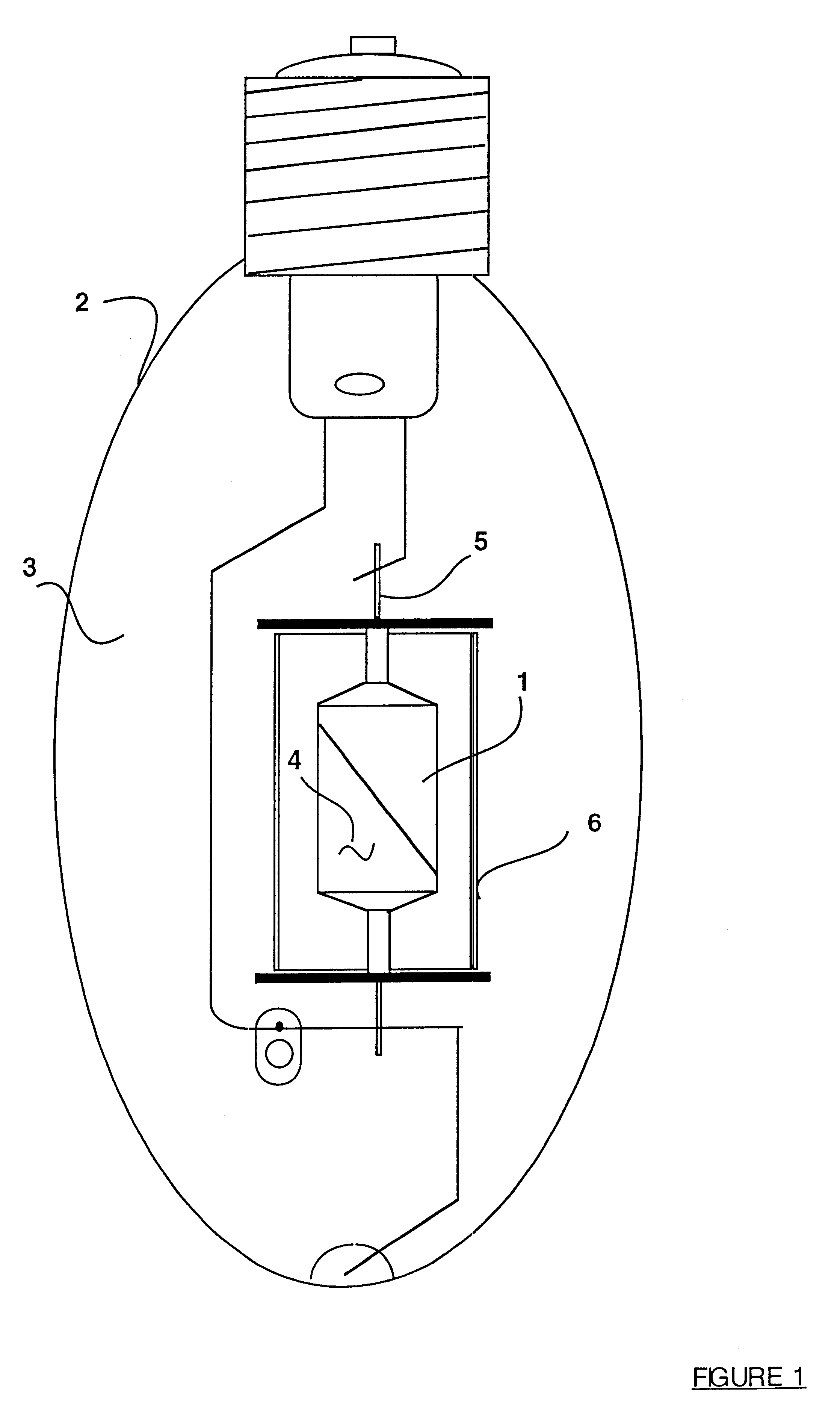
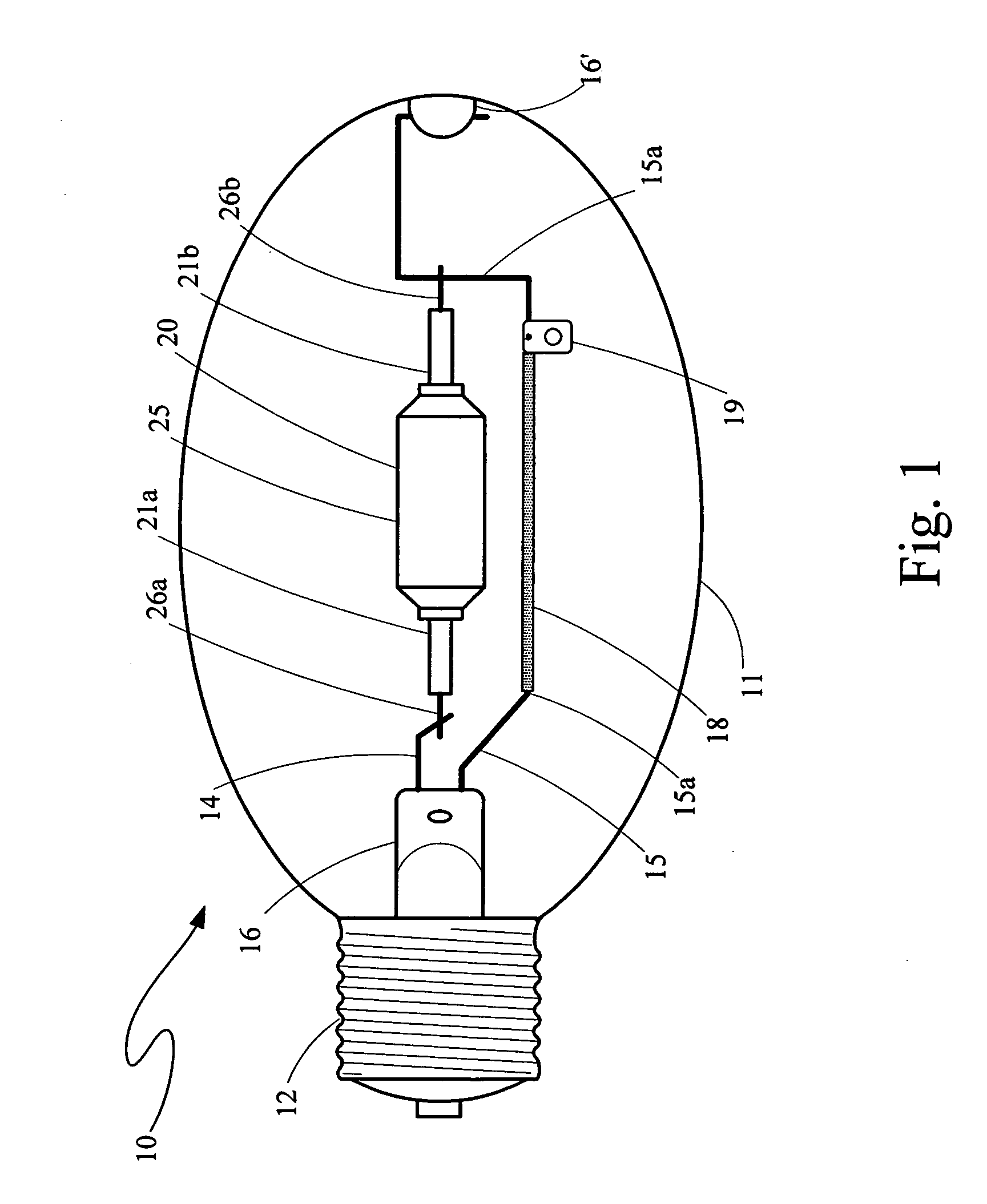
High red color rendition metal halide lamp
An arc discharge metal halide lamp for use in selected lighting fixtures having a discharge chamber with light permeable walls of a selected shape bounding a discharge region of a selected volume through which walls a pair of electrodes are supported with ionizable materials being provided in the discharge region of the discharge chamber comprising at least one member selected from a group consisting of halides of cerium, dysprosium, holmium, lithium, sodium, praseodymium, thallium and thulium, and further comprising a halide of calcium in a selected fraction of that weight total of all halides present in the discharge chamber with this selection depending also on the addition or not of a halide of aluminum. Others of the foregoing halides that are present are provided in amounts with certain limits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
In situ modification of molybdenum-based catalysts
A process for the conversion of a hydrocarbon selected from the group consisting of propylene, isobutylene, propane, isobutane or mixtures thereof, to acrylonitrile, methacrylonitrile, or mixtures thereof, the process comprising the step of reacting in the vapor phase at an elevated temperature and pressure said hydrocarbon with a molecular oxygen-containing gas and ammonia, in the presence of a molybdenum-based ammoxidation catalyst and a catalyst modifier, wherein said catalyst modifier comprises a molybdate or a polymolybdate of at least one element M selected from the group consisting of cesium, rubidium, potassium, sodium, thallium, lithium, nickel, cobalt, iron, chromium, copper, magnesium, manganese, cerium and phosporus, and wherein the ratio of the M elements to Mo in the molybdate or polymolybdate is greater than the ratio for these M elements to Mo in the molybdenum-based catalyst. The catalyst modifier is useful in modifying the performance of molybdenum-based catalyst and inhibiting molybdenum oxide loss for such catalysts.
Owner:INEOS EURO LTD
Thallium free-metal halide lamp with magnesium halide filling for improved dimming properties
InactiveUS6717364B1Lowering indexLamp performanceSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsMetal-halide lampThallium
A [thallium free] high pressure ceramic metal halide lamp having superior dimming characteristics with a fill composition including MgI2 and / or MgBr2.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Method of fabricating liquid for oxide thin film
ActiveUS20100251936A1Simple and low-costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolten casting coatingZinc compoundsIndium
A method of fabricating a liquid for an oxide thin film is provided, which includes mixing at least two kinds of dispersoids selected from the group consisting of a Zinc compound, an Indium compound, a Gallium compound, a Tin compound and a Thallium compound, with dispersion media corresponding to the selected dispersoids to form a dispersion system, and stirring and aging the dispersion system at a predetermined temperature for a predetermined time, wherein a molar ratio of the Zinc compound to each of the Indium compound, Gallium compound, Tin compound and Thallium compound is 1:0.1 to 1:2. According to the present invention, the liquid for the oxide thin film may be fabricated by a sol-gel method making it capable of being implemented in mass production in a simple and low-cost manner as opposed to the conventional vacuum deposition method.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com