Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
562results about "Tool workpiece connection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
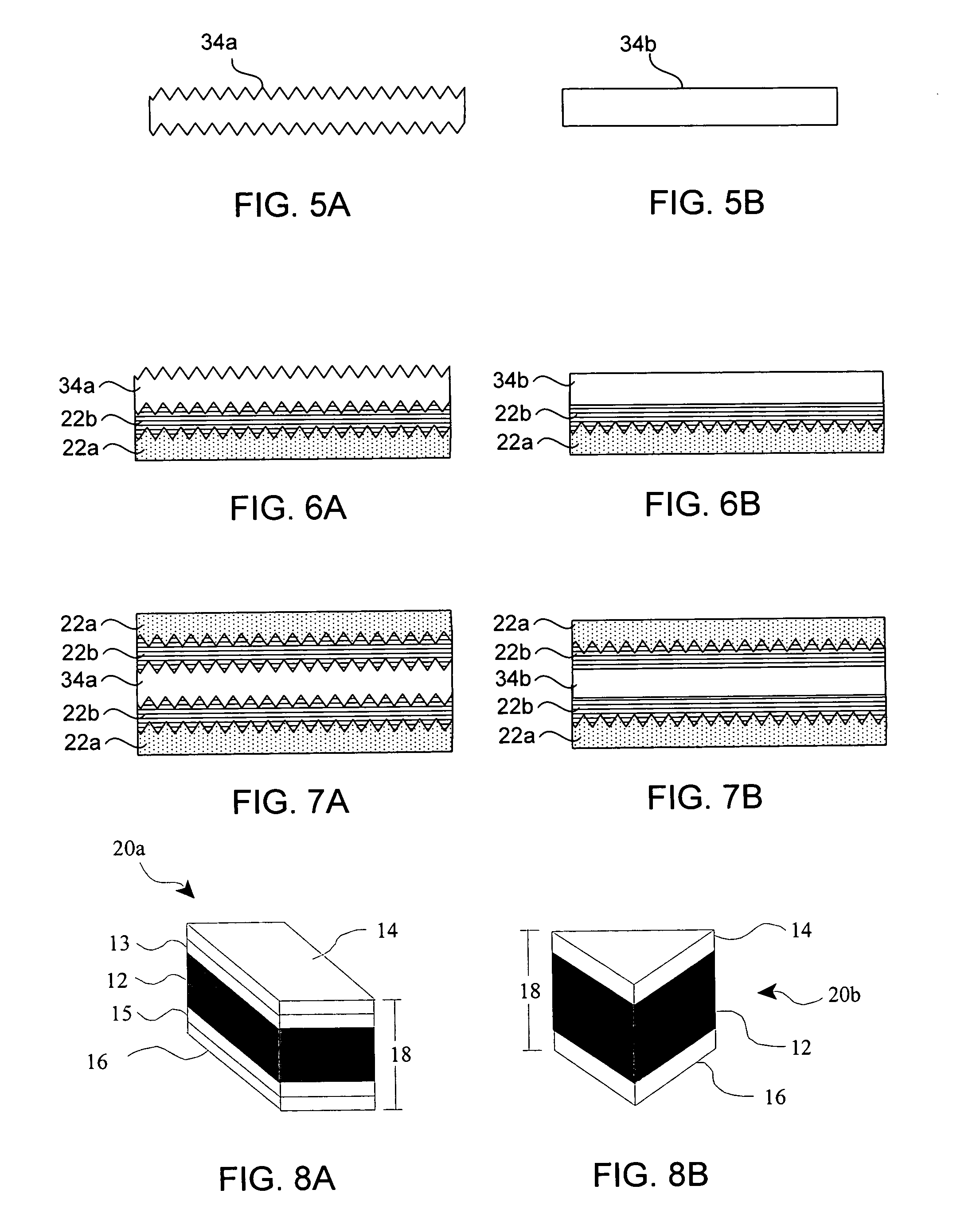
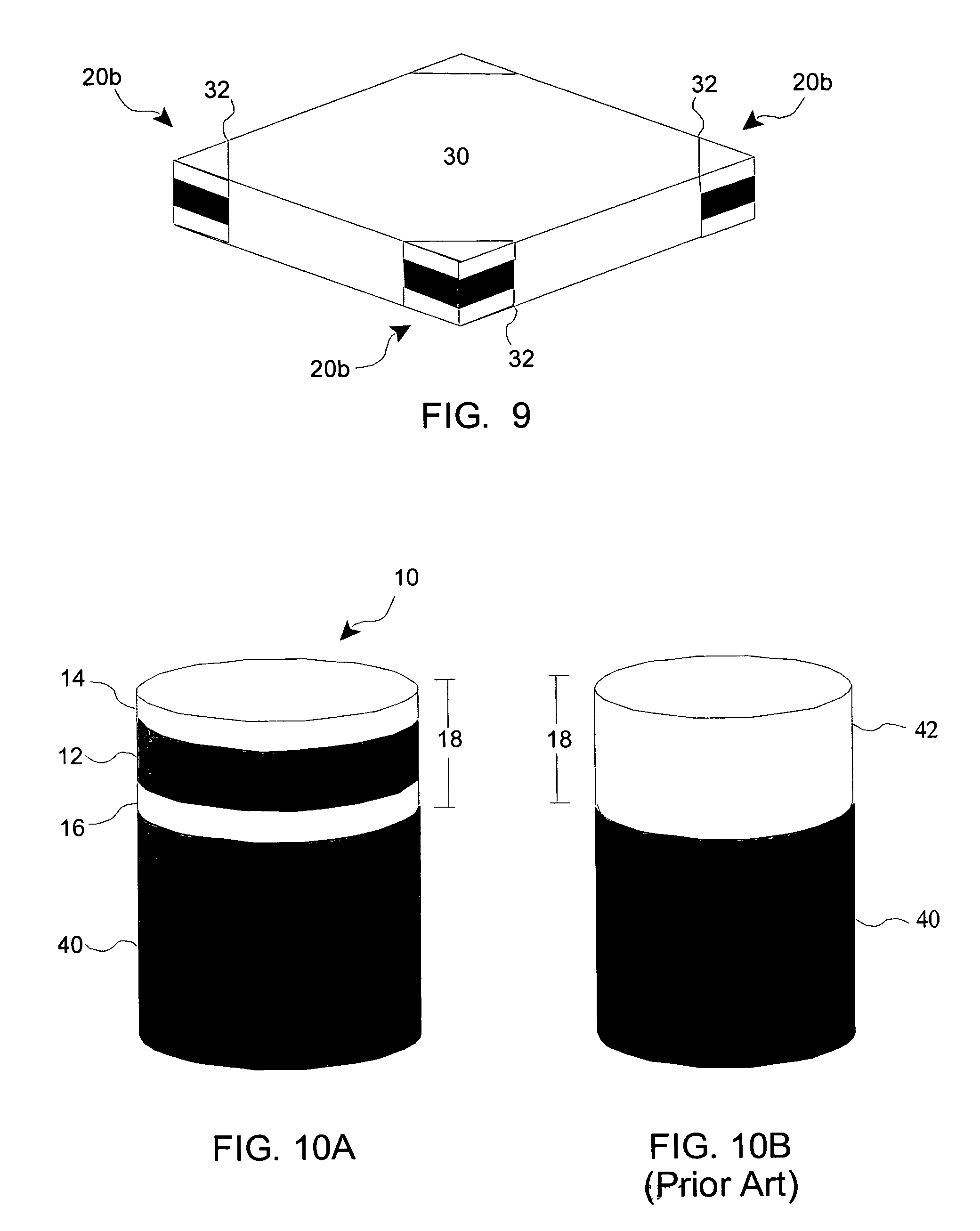
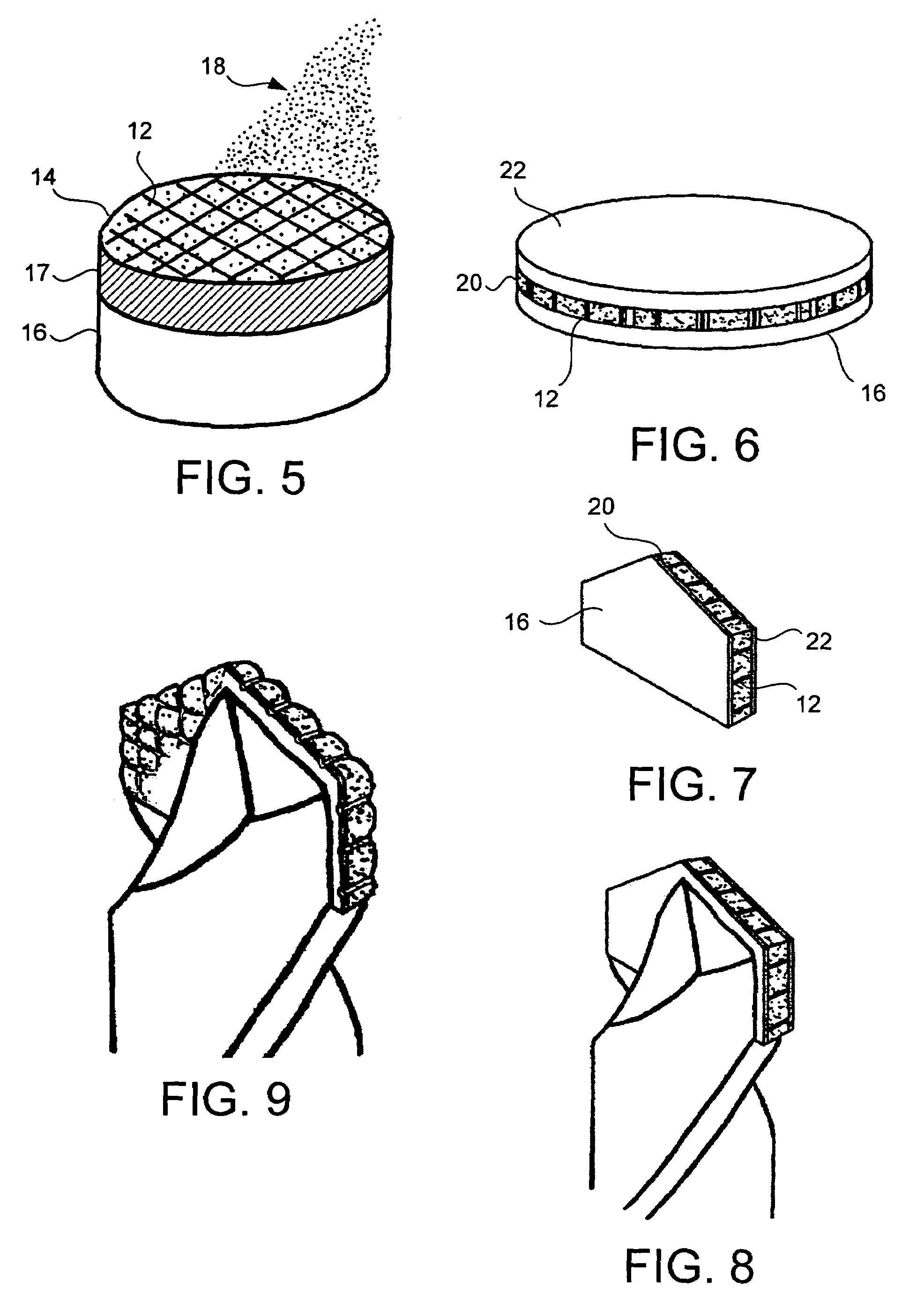
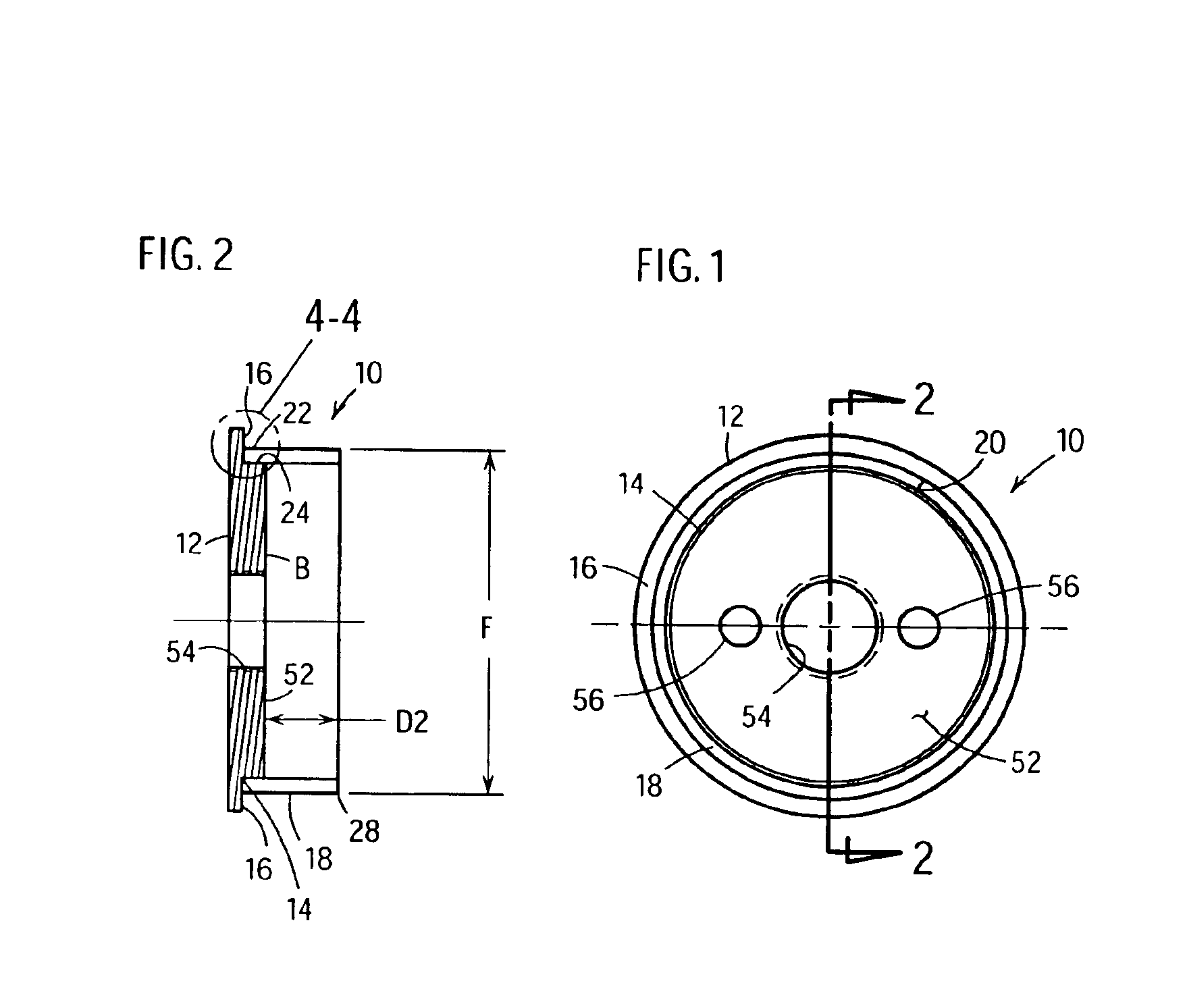
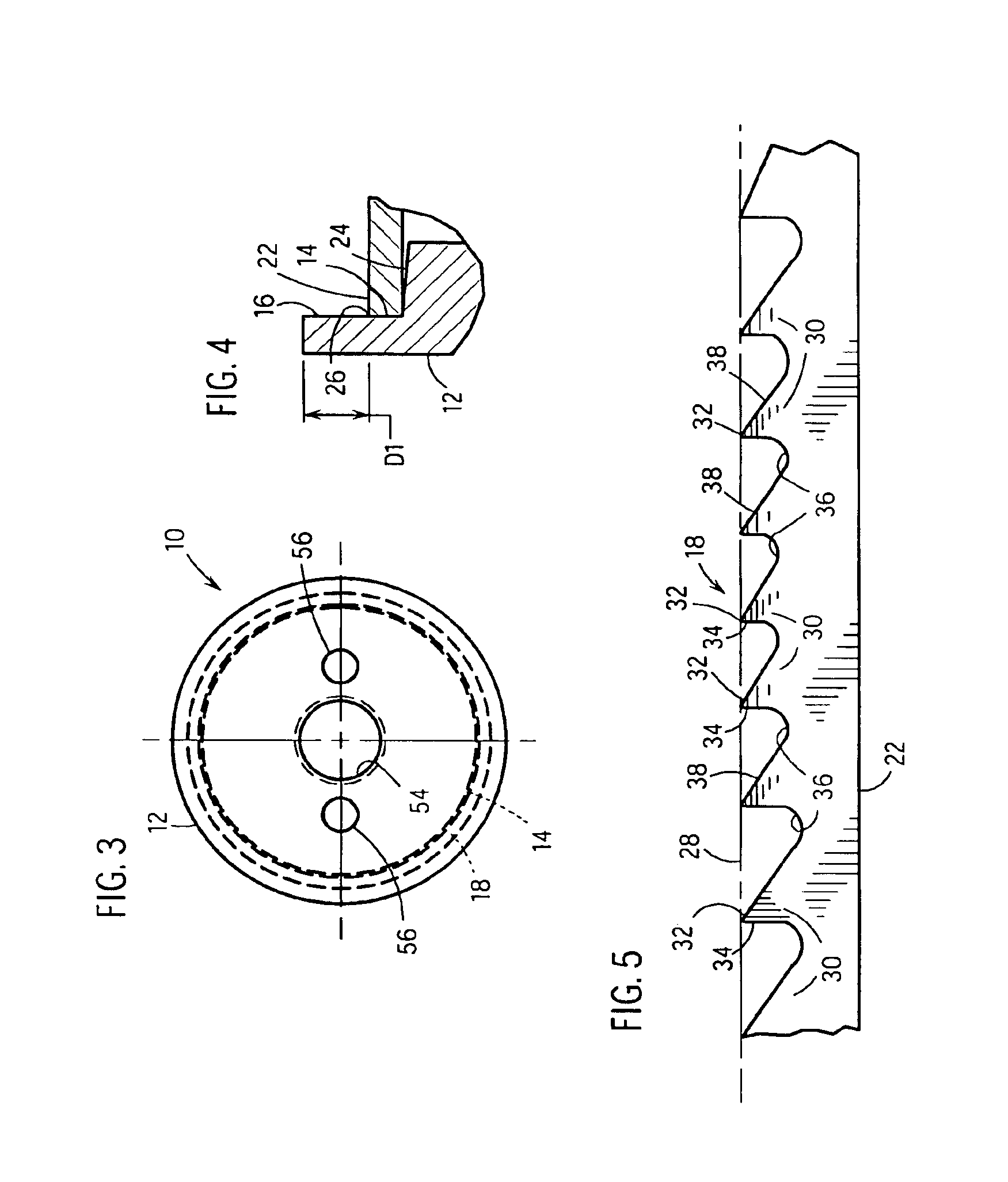
Doubled-sided and multi-layered PCD and PCBN abrasive articles
InactiveUS20050050801A1Improve propertiesIncreasing the thicknessPigmenting treatmentTool workpiece connectionHigh pressureMaterials science
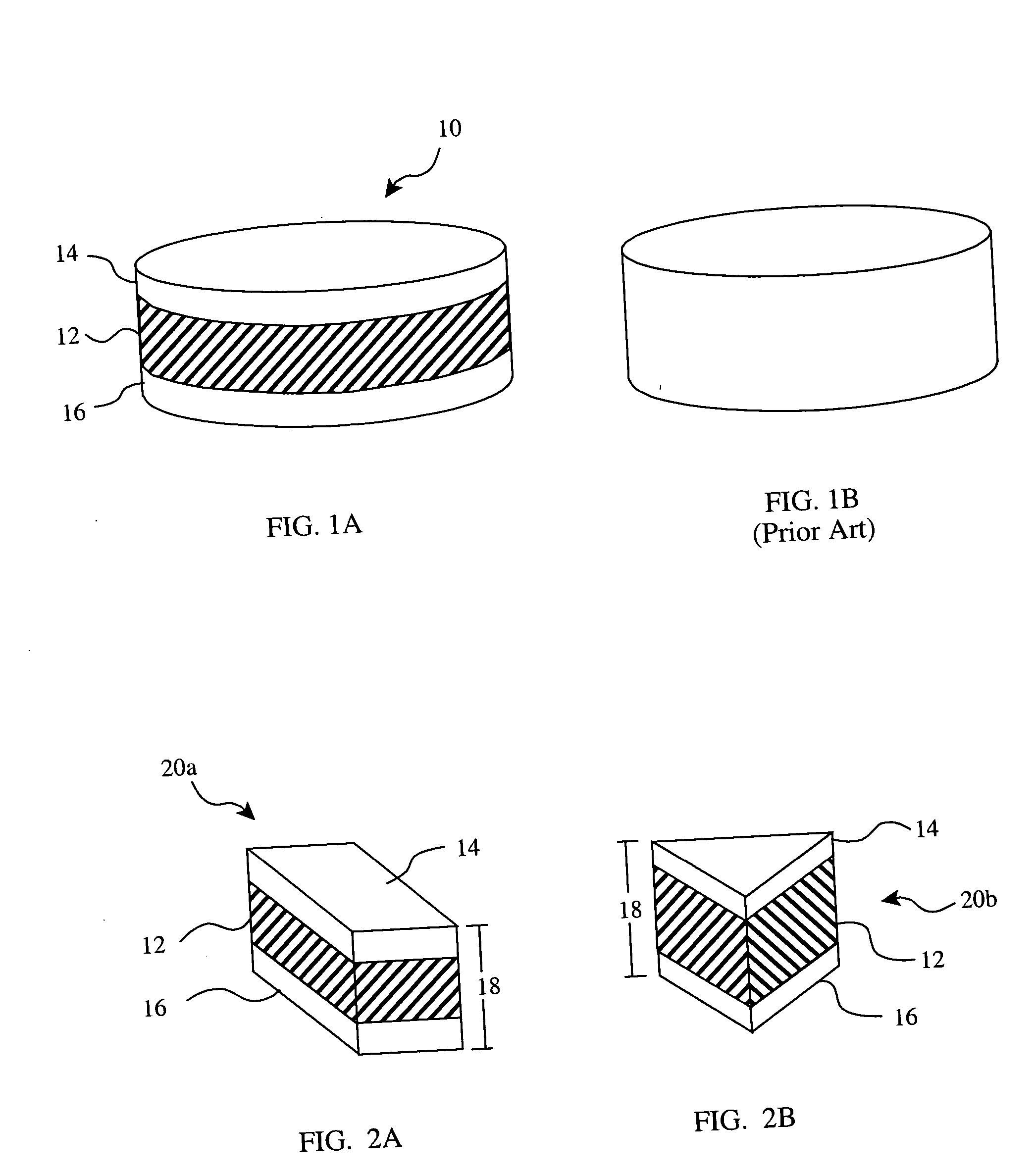
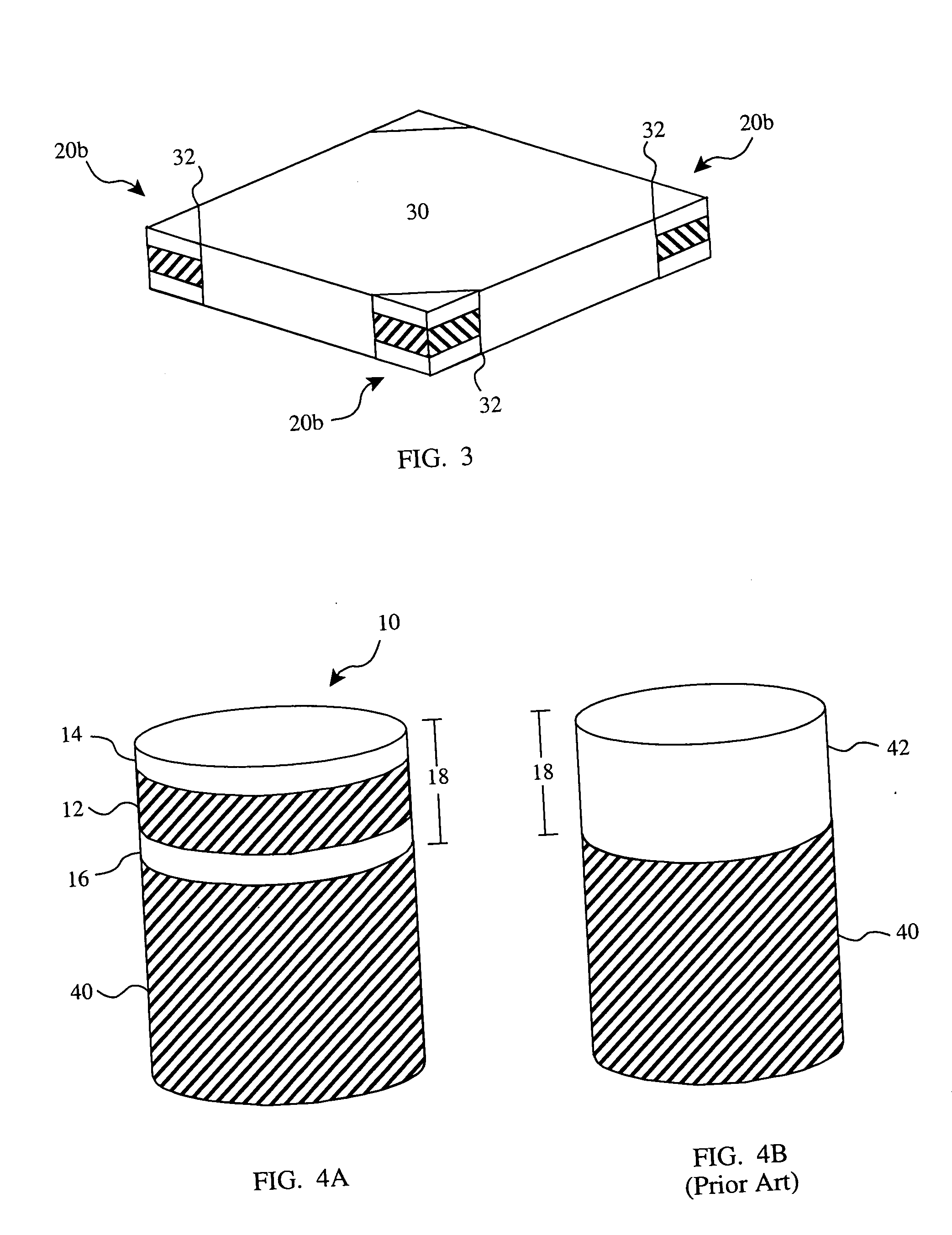
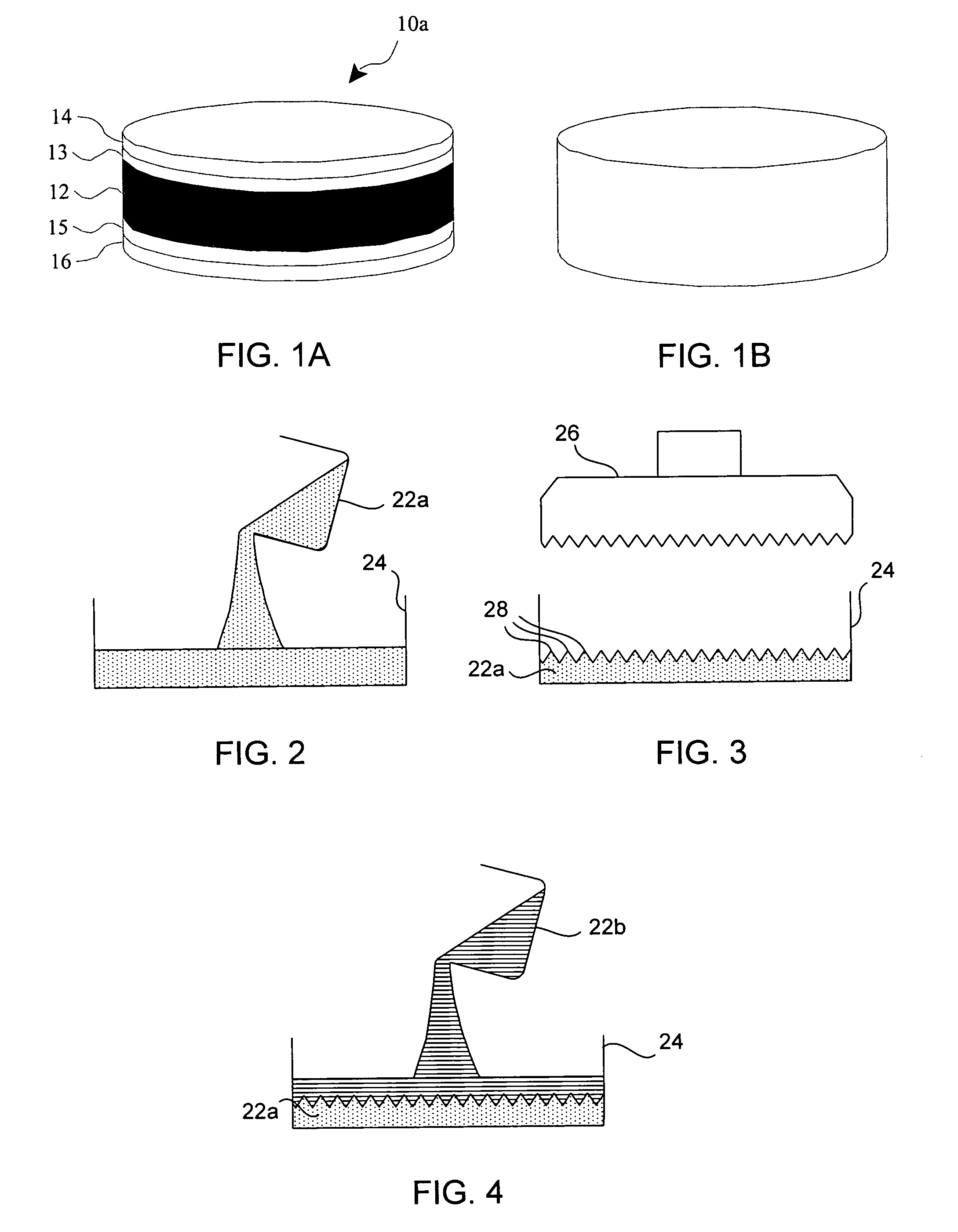
A doubled-sided PCD or PCBN compact as well as a new multi-layered PCD and PCBN can be produced using high pressure high temperature processes allowing for increased effective thickness of abrasive tools. A polycrystalline compact can include a substrate having a first surface and a second surface which are non-contiguous. Additionally, a first polycrystalline layer can be attached to the first surface of the substrate and a second polycrystalline layer attached to the second surface of the substrate. The first and second polycrystalline layers can include superabrasive particles bonded together by sintering or chemical bonding with an additional metal. Such double-sided PCD and PCBN compacts as well as a new multiple layered PCD and PCBN allow for increased effective thickness of a tool without suffering from non-homogenous results typical of standard PCD and PCBN compacts, regardless of superabrasive particle size. Each polycrystalline layer can include superabrasive particles of varying particle sizes such that the final tool is tailored for specific abrading characteristics. Such doubled-sided and / or multiple layered PCD and PCBN compacts can be incorporated into a wide variety of abrasive tools for use in cutting, milling, grinding, polishing, drilling and other similar abrasive applications.
Owner:CHO HYUN SAM +2
Doubled-sided and multi-layered PCBN and PCD abrasive articles
InactiveUS20050210755A1Improve propertiesIncreasing the thicknessPigmenting treatmentTool workpiece connectionWear particleHigh pressure
A doubled-sided PCBN and / or PCD compact can be produced using high pressure high temperature processes allowing for increased effective thickness of abrasive tools, decreased delamination, and increased useful service life. A polycrystalline compact can include a substrate having a first surface and a second surface which are non-contiguous. Additionally, a first polycrystalline layer can be attached to the first surface of the substrate and a second polycrystalline layer attached to the second surface of the substrate. The first and second polycrystalline layers can be attached to the substrate via an intermediate layer containing superabrasive particles. Such double-sided PCBN and PCD compacts allow for increased effective thickness of a tool without suffering from non-homogenous results typical of standard PCD and PCBN compacts, regardless of superabrasive particle size. Each polycrystalline layer can include superabrasive particles of varying particle sizes such that the final tool is tailored for specific abrading characteristics. Such doubled-sided PCBN and PCD compacts can be incorporated into a wide variety of abrasive tools for use in cutting, milling, grinding, polishing, drilling and other similar abrasive applications.
Owner:ADICO ASIA POLYDIAMOND
Cutting tool inserts and methods to manufacture
The present invention relates to cutting tool inserts. A cutting tool insert includes an abrasive tip of a hard material, an abrasive or superabrasive material. A cutting tool insert is bonded to an insert body by mechanical force. The mechanical forces are generated through deformation of mating geometric features on the abrasive tip and insert body.
Owner:DIAMOND INNOVATIONS INC
Hole-saw assembly including two hole-saws
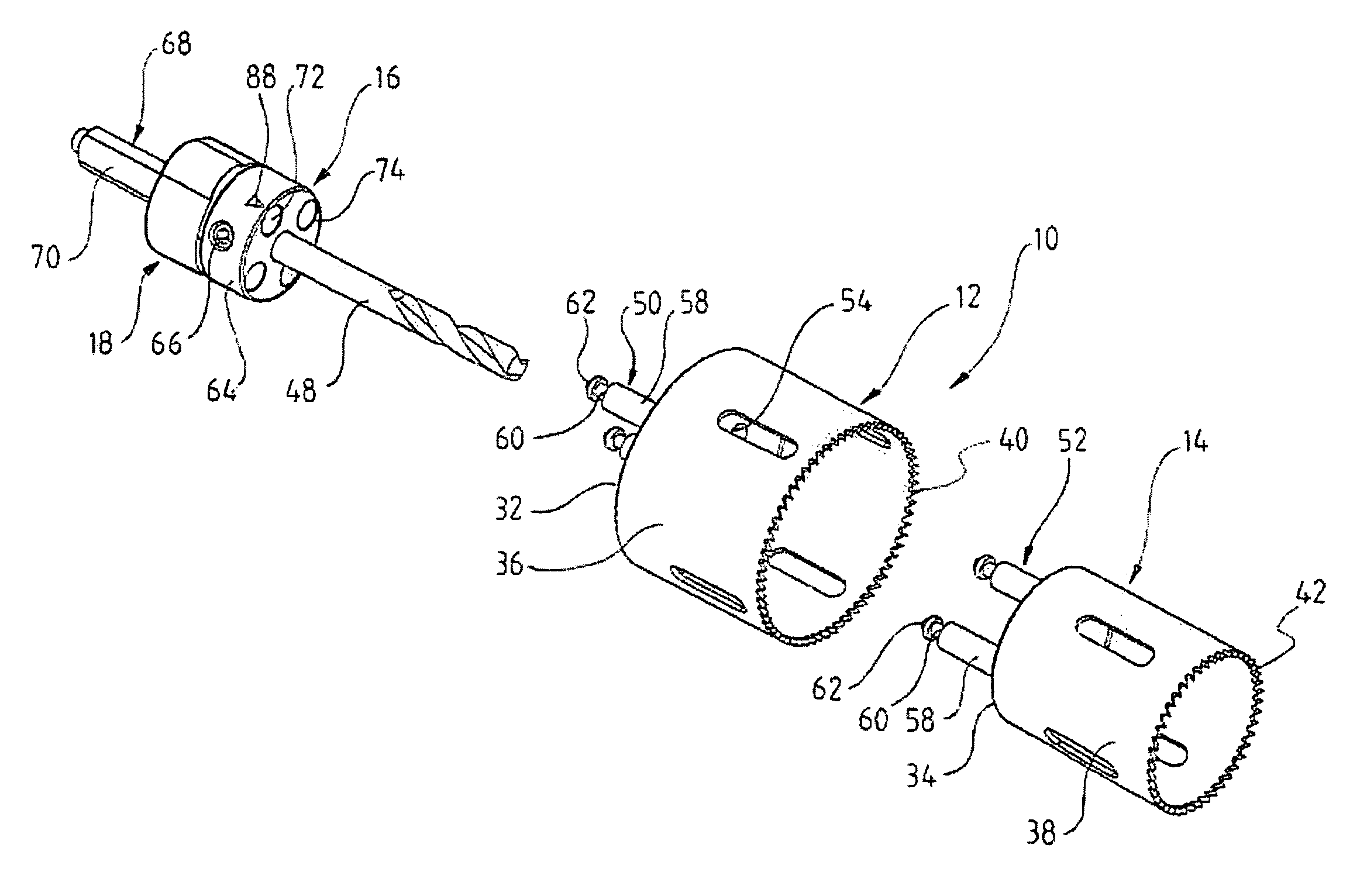
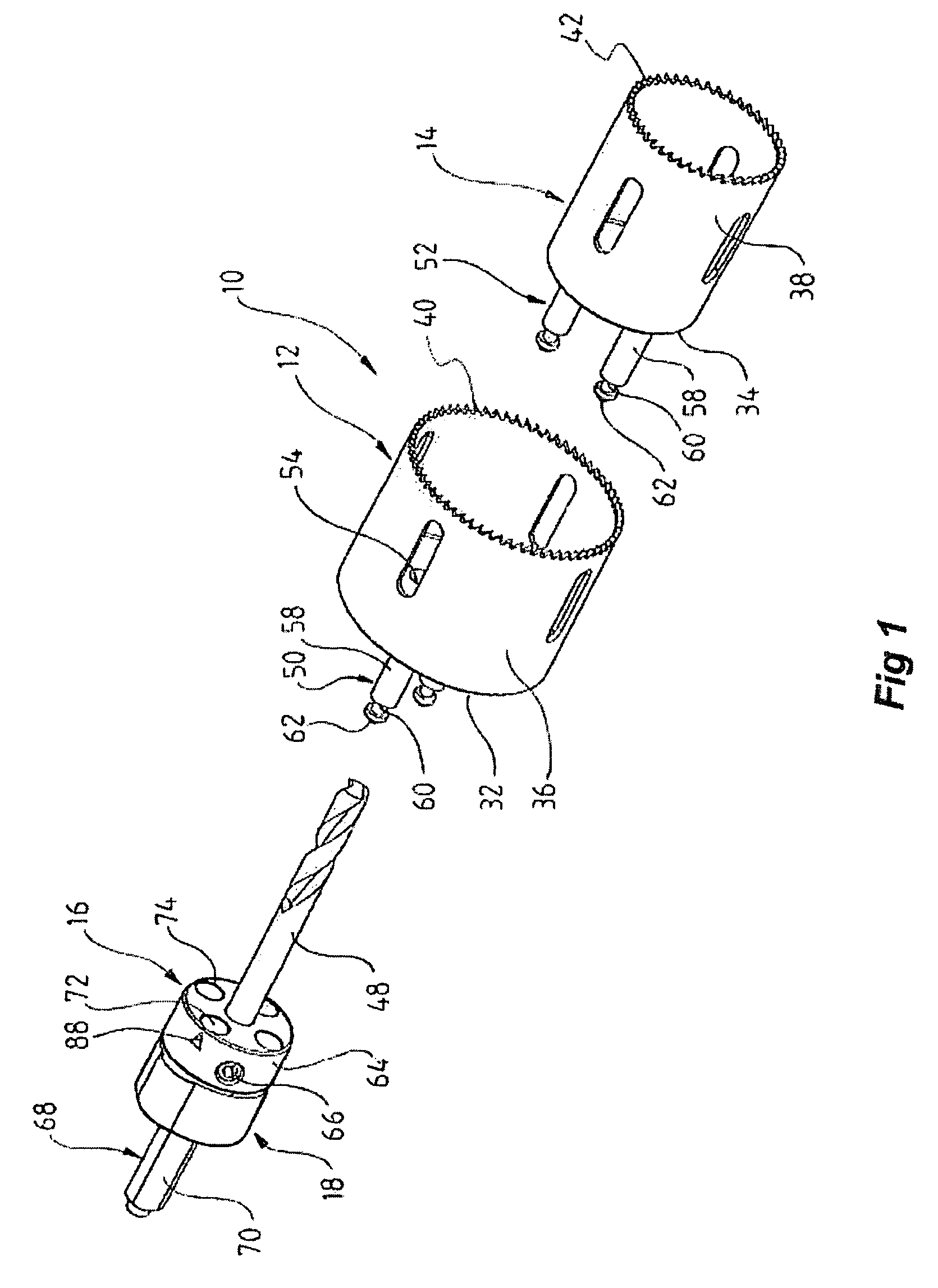
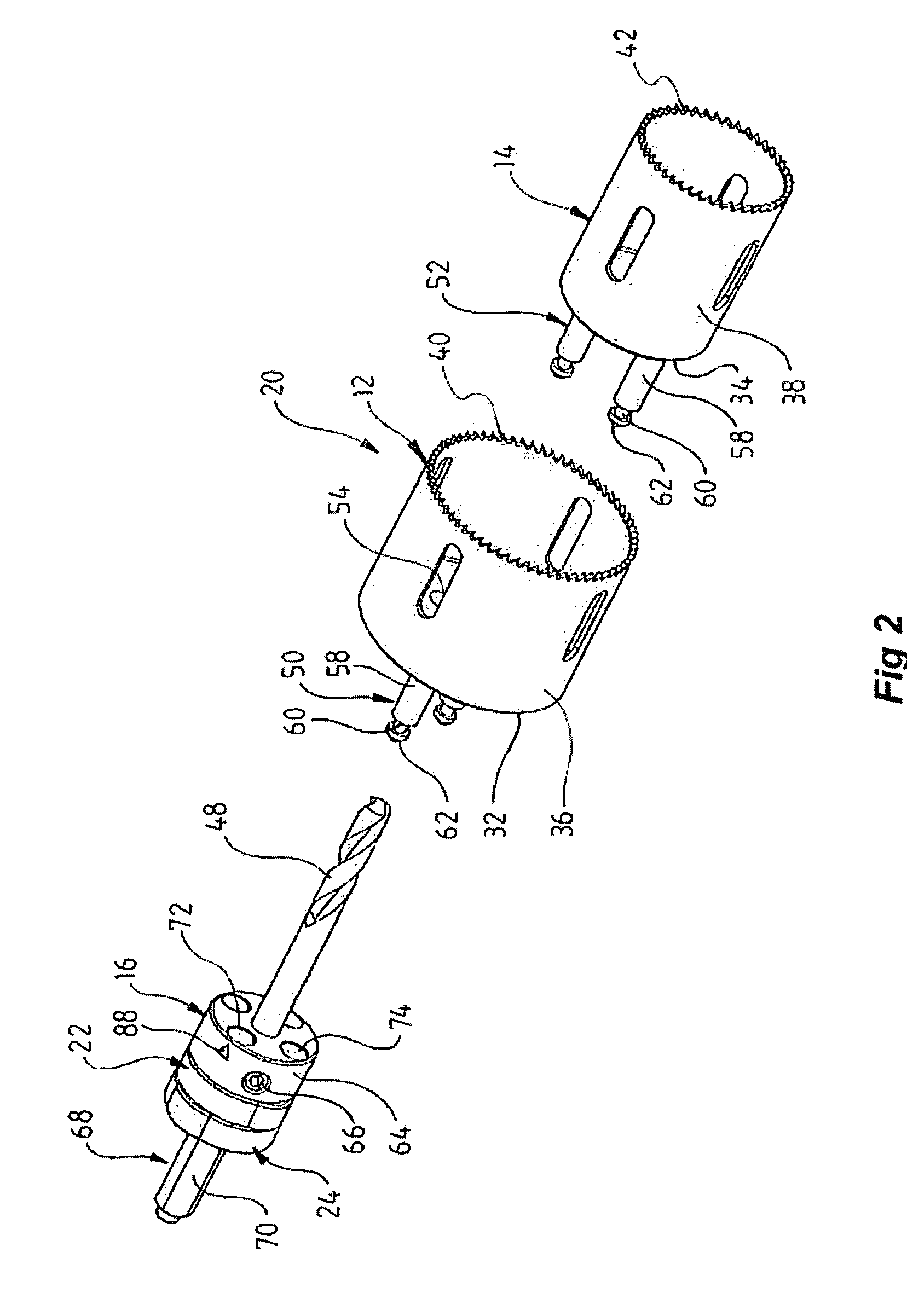
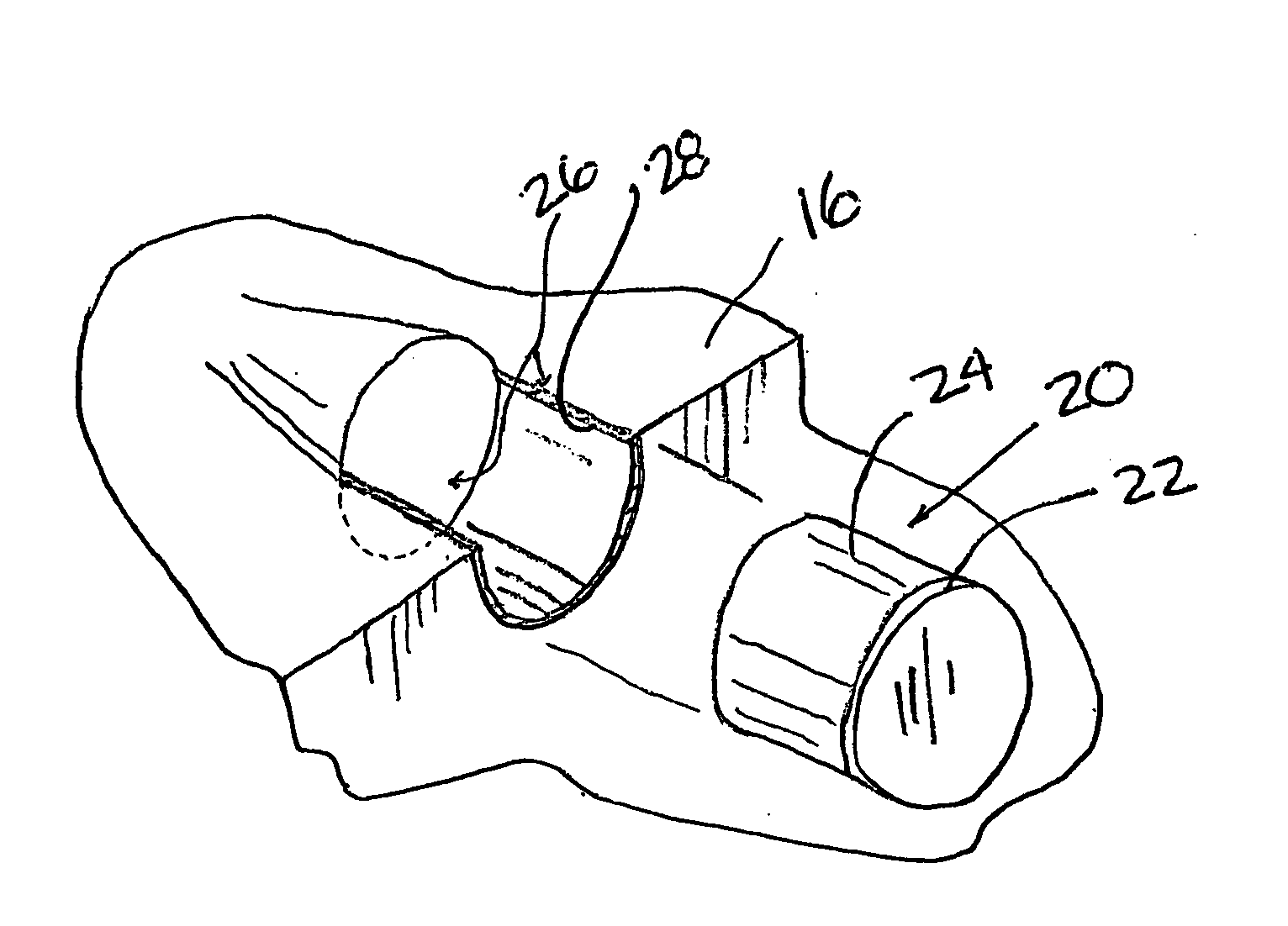
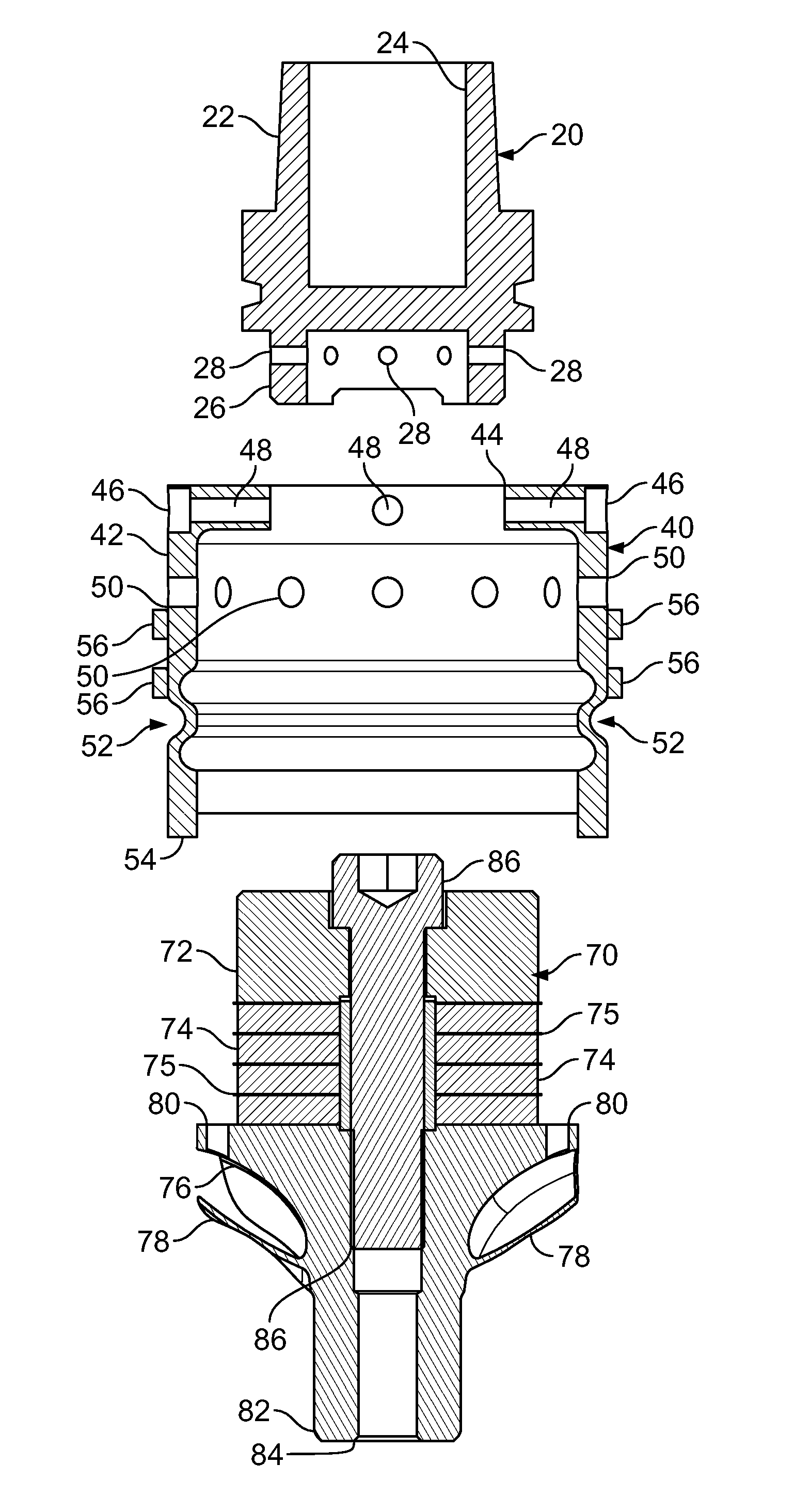
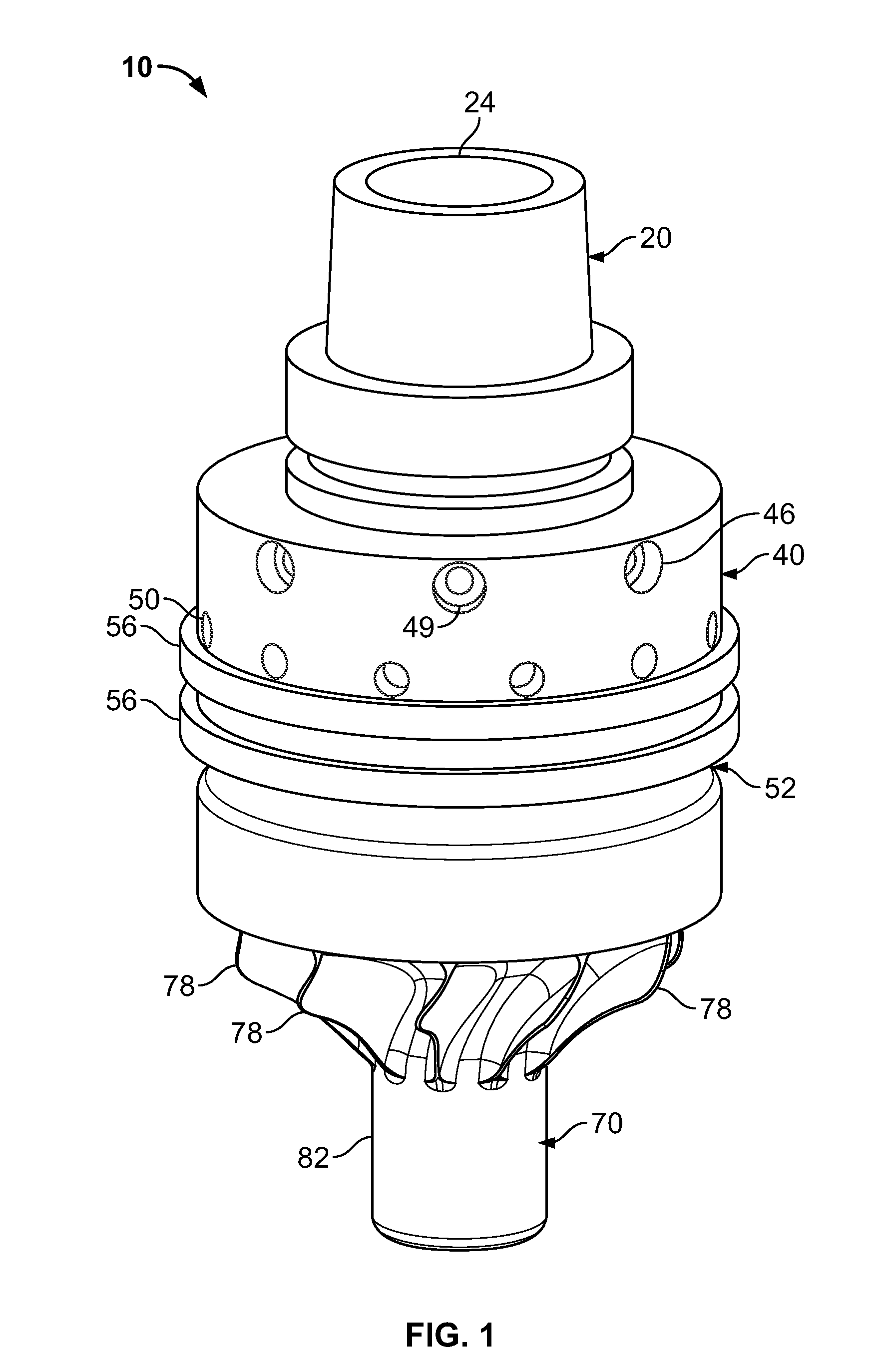
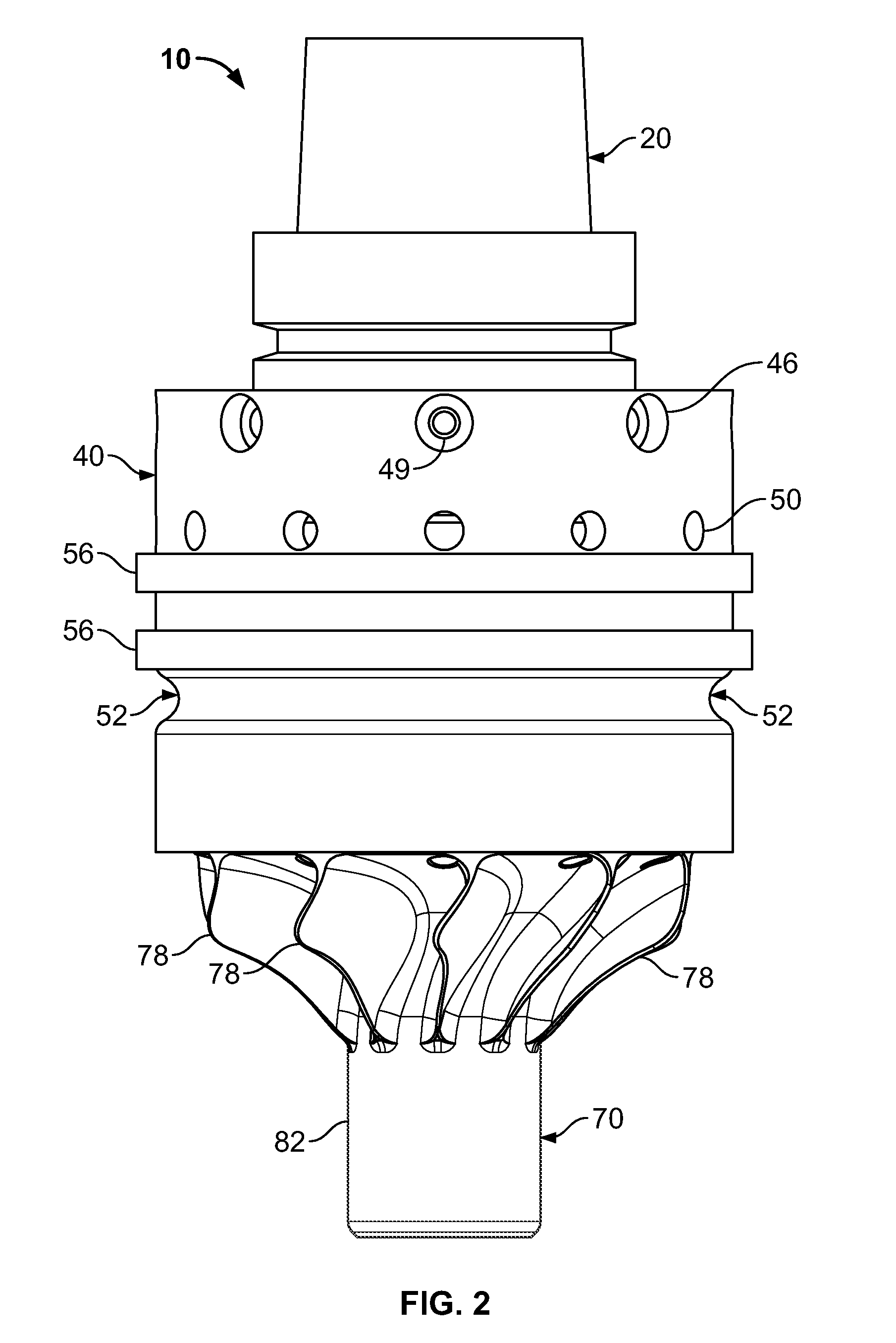
The present invention relates to an improved hole-saw assembly and in particular, to a mandrel engageable by a drill and including at least one locking ring or annulus that allows for the base of two hole-saws of different diameter to be quickly and easily mountable and demountable from the mandrel. The hole-saw assembly includes a first hole-saw having a base that includes a pair of drive-pins extending outwardly therefrom and a pair of apertures for insertion therethrough of the drive pins of a second hole-saw. The drive pin pairs are then inserted through corresponding apertures in the mandrel to engage an annulus coupled to the mandrel. The present invention provides for each drive pin to be engaged by the annulus despite the difference in longitudinal length of the drive pins beyond the base of the first hole-saw. The hole-saws are snap-fit within the annulus and may be disengaged by simply rotating the annulus to a second position. A further embodiment of the present invention further allows one to insert the hole-saws into any one of the mandrel insertion points without being concerned about whether it contains the correct engaging means or not. A still further embodiment of the invention prevents slight longitudinal movement which is known to occur when the hole-saws are coupled to the mandrel.
Owner:KEIGHTLEY KYM JOHN
Braze alloy for drilling applications
A down hole cutting tool includes a cutting element support structure. The cutting element support structure has at least one cavity formed therein. A cutting element is disposed in the cavity. Braze alloy is also disposed in the cavity between the cutting element and the cutting element support structure. The braze alloy comprises between about 0.5% and about 10% by weight of at least one selected from the group of gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl). Methods for building a down hole tool using the braze alloy are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC +1
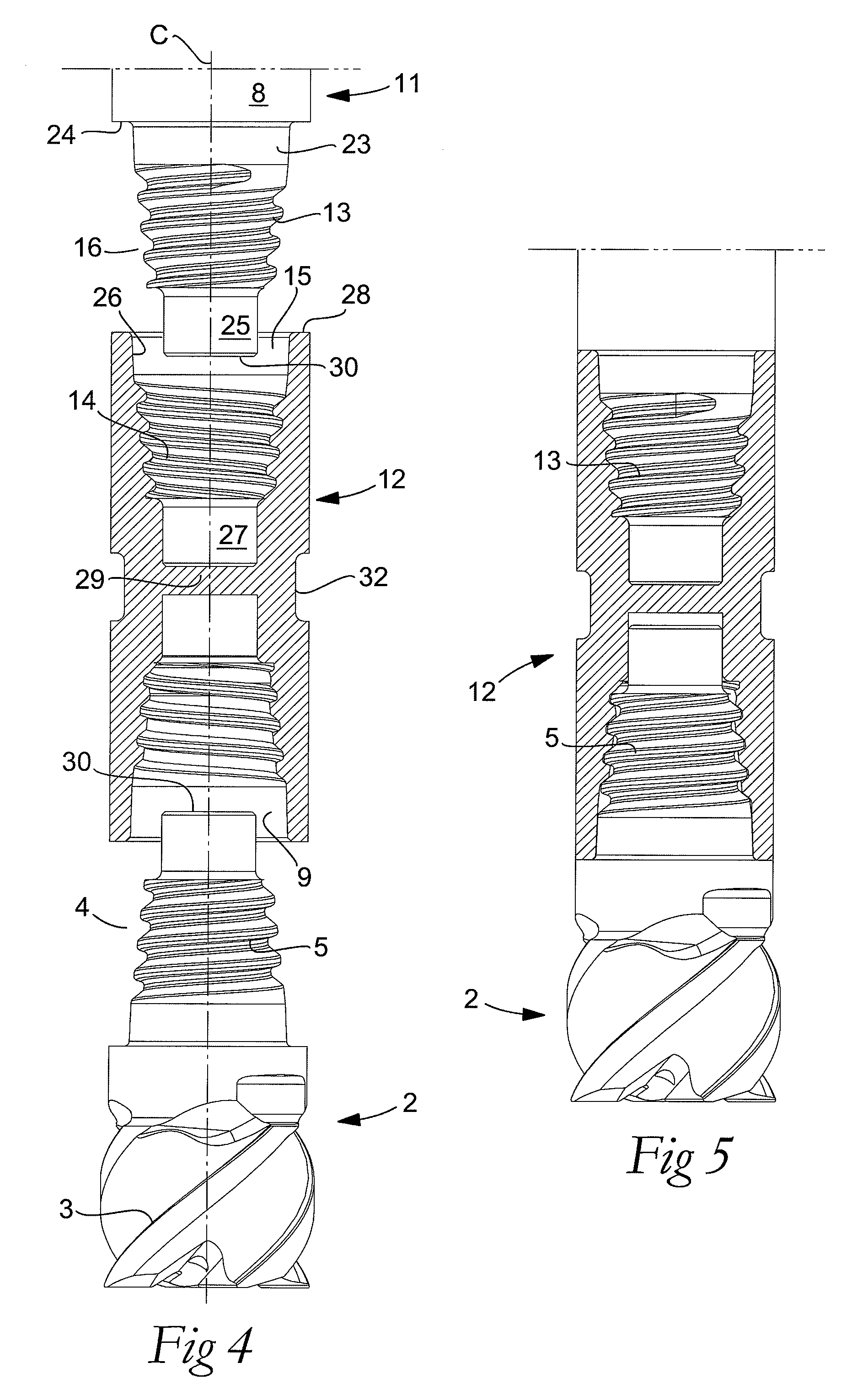
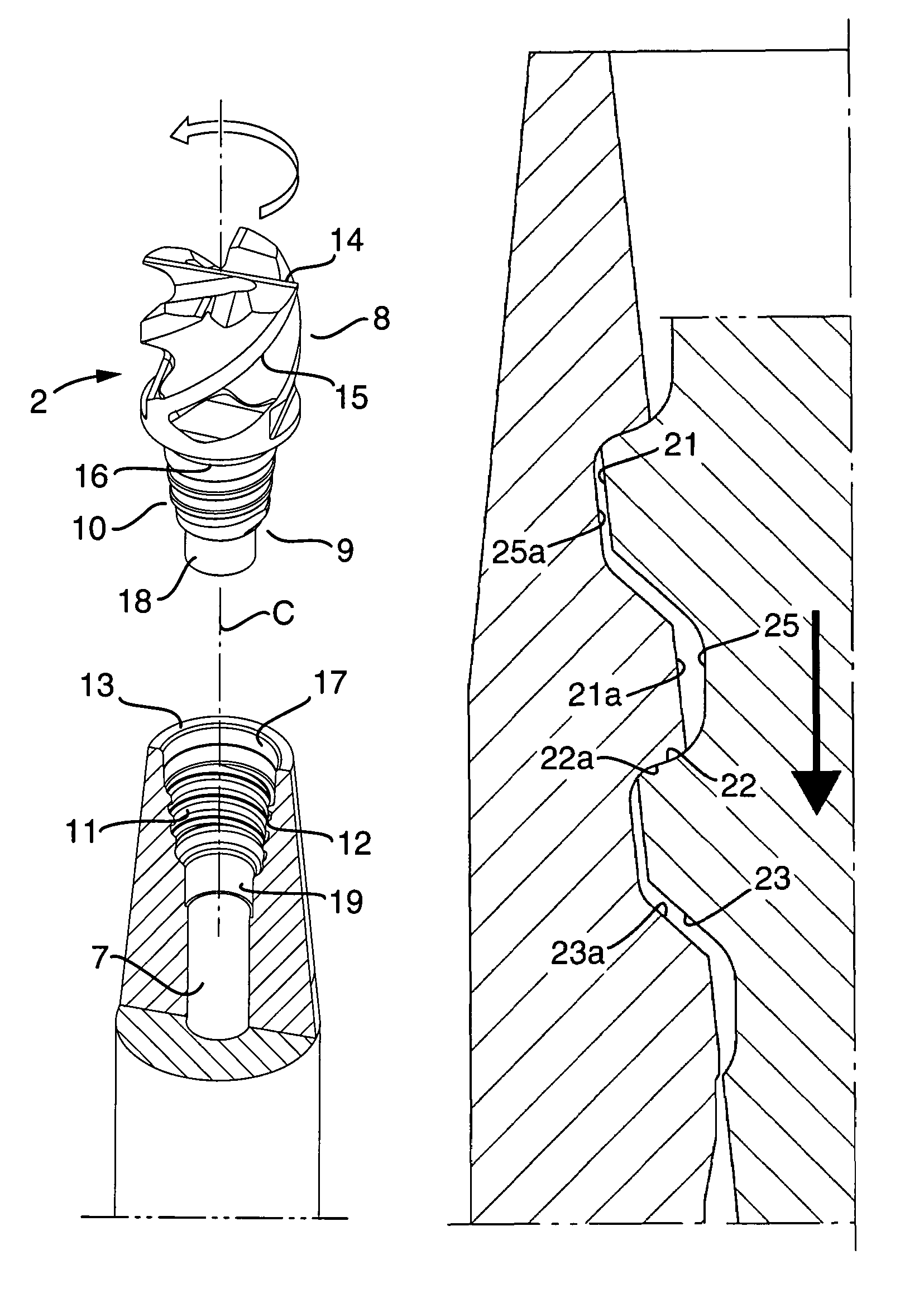
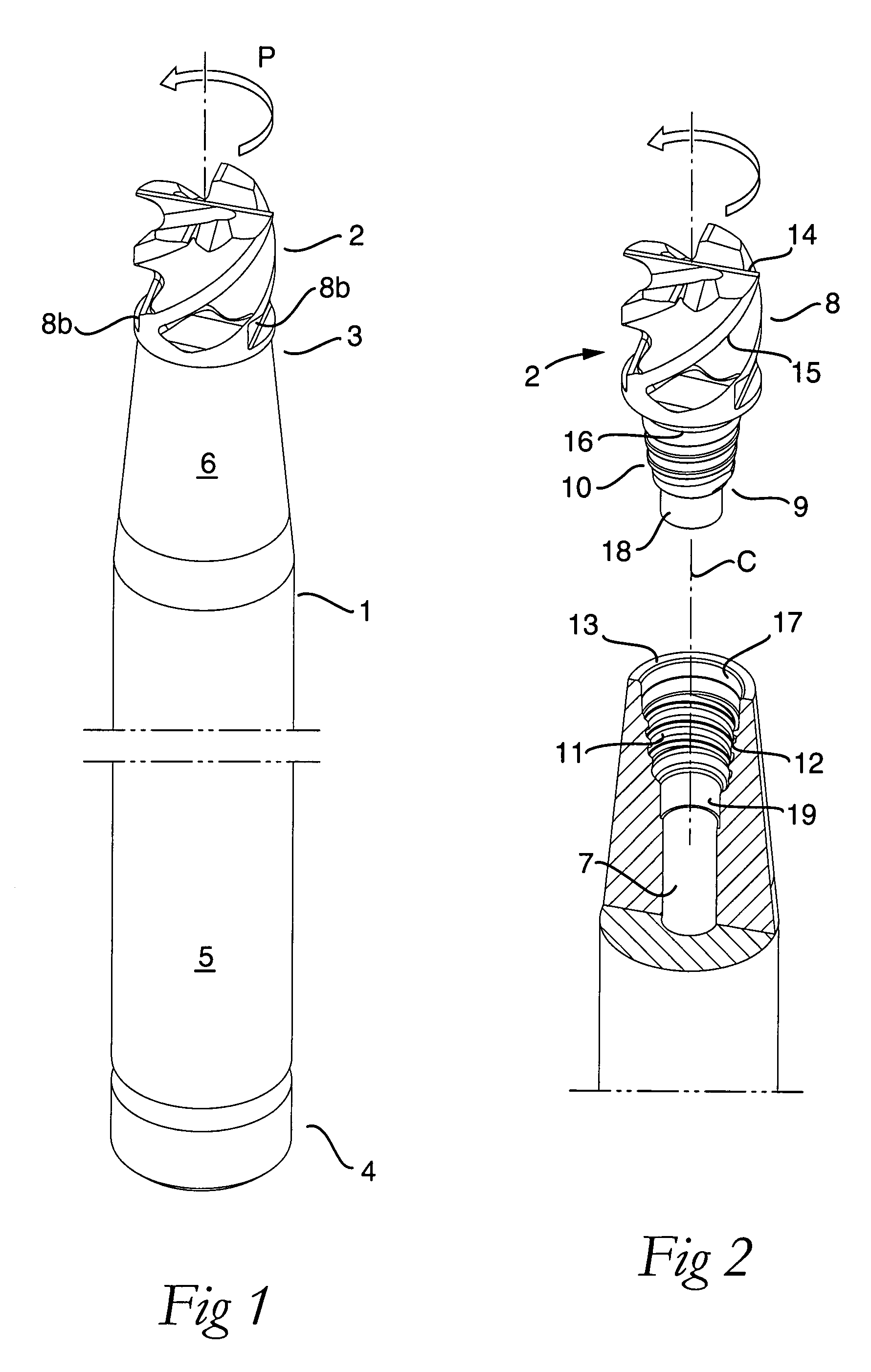
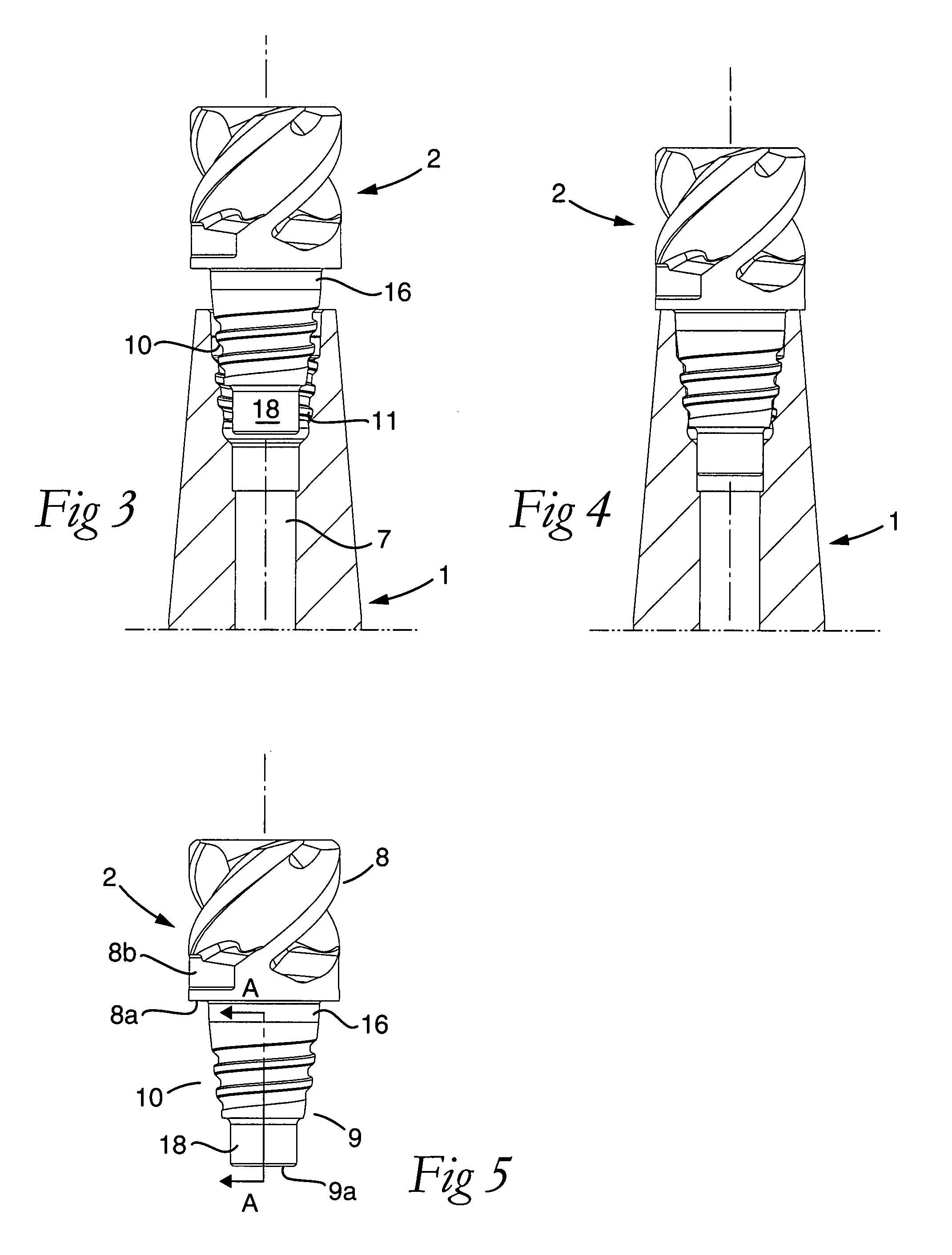
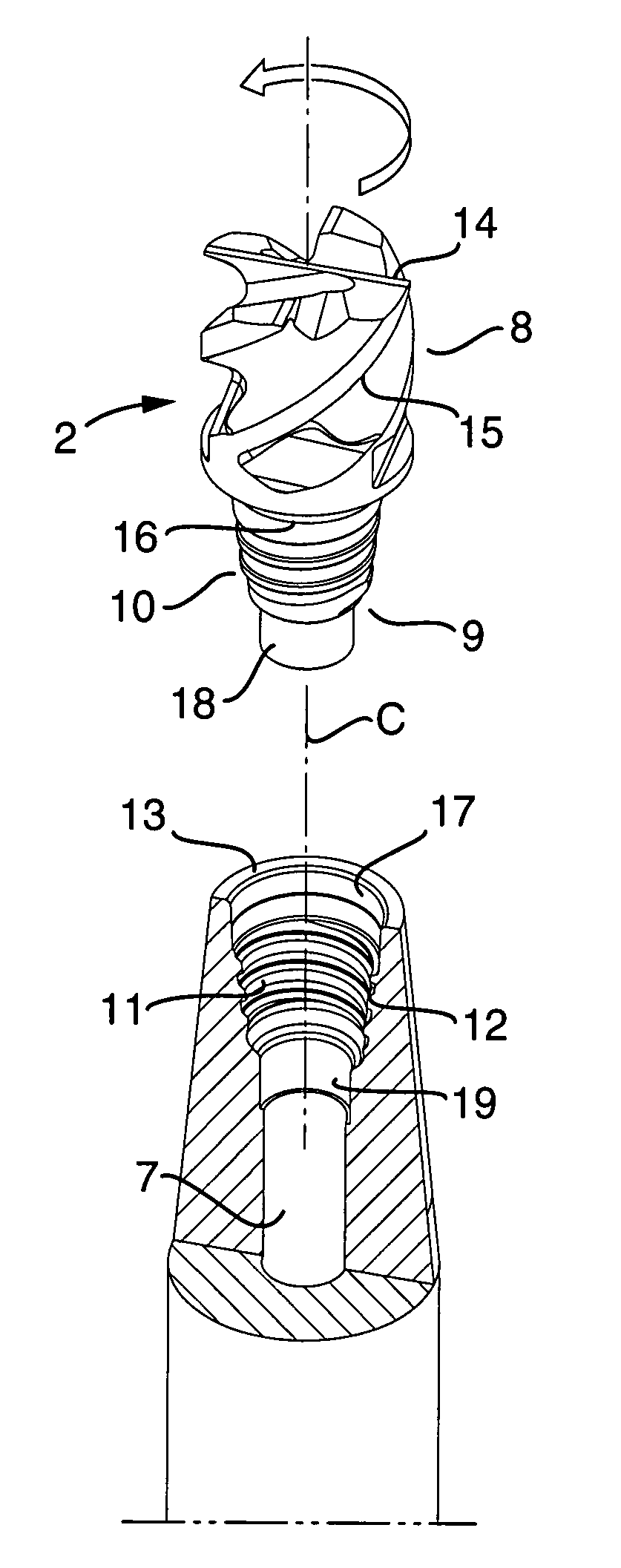
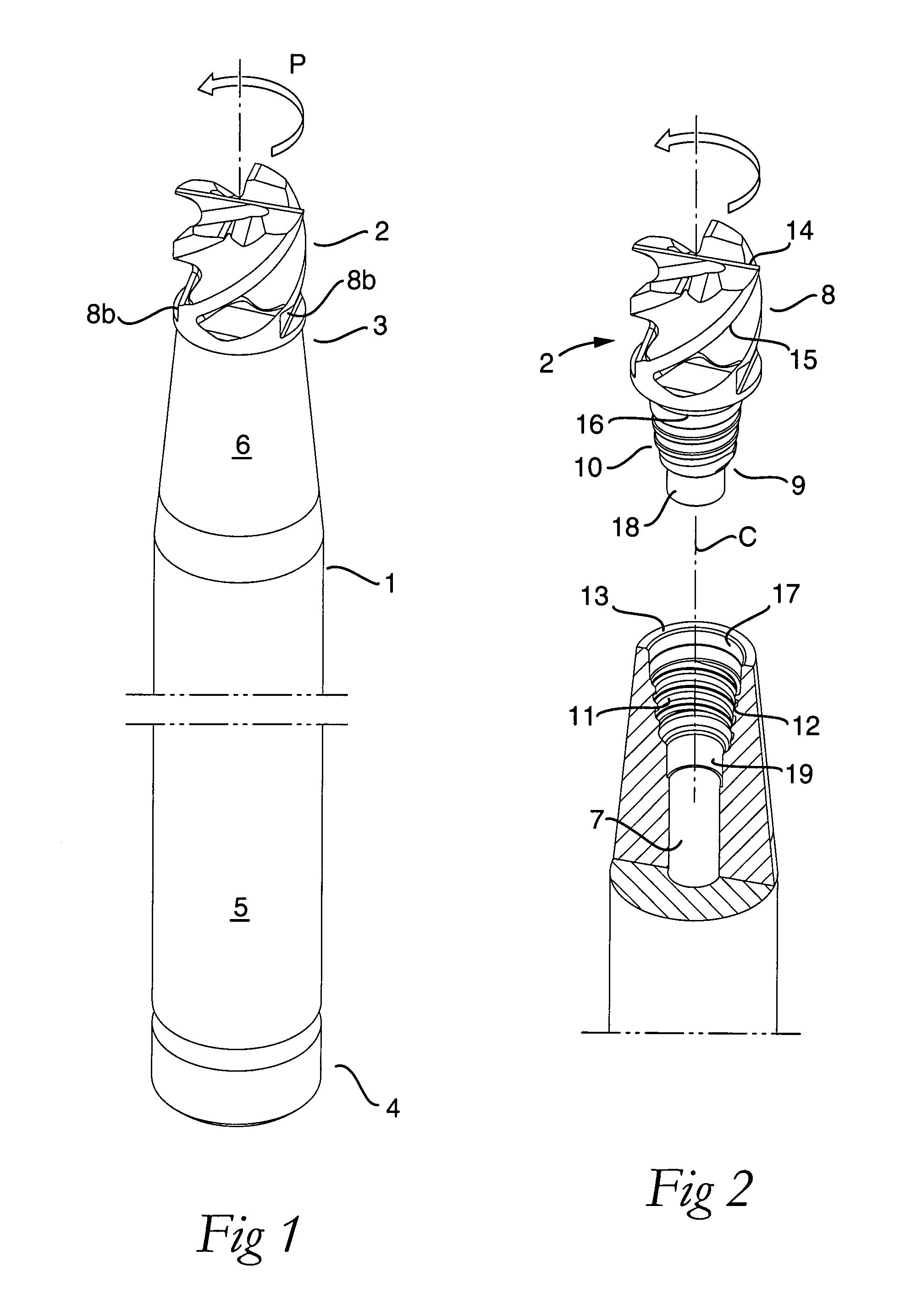
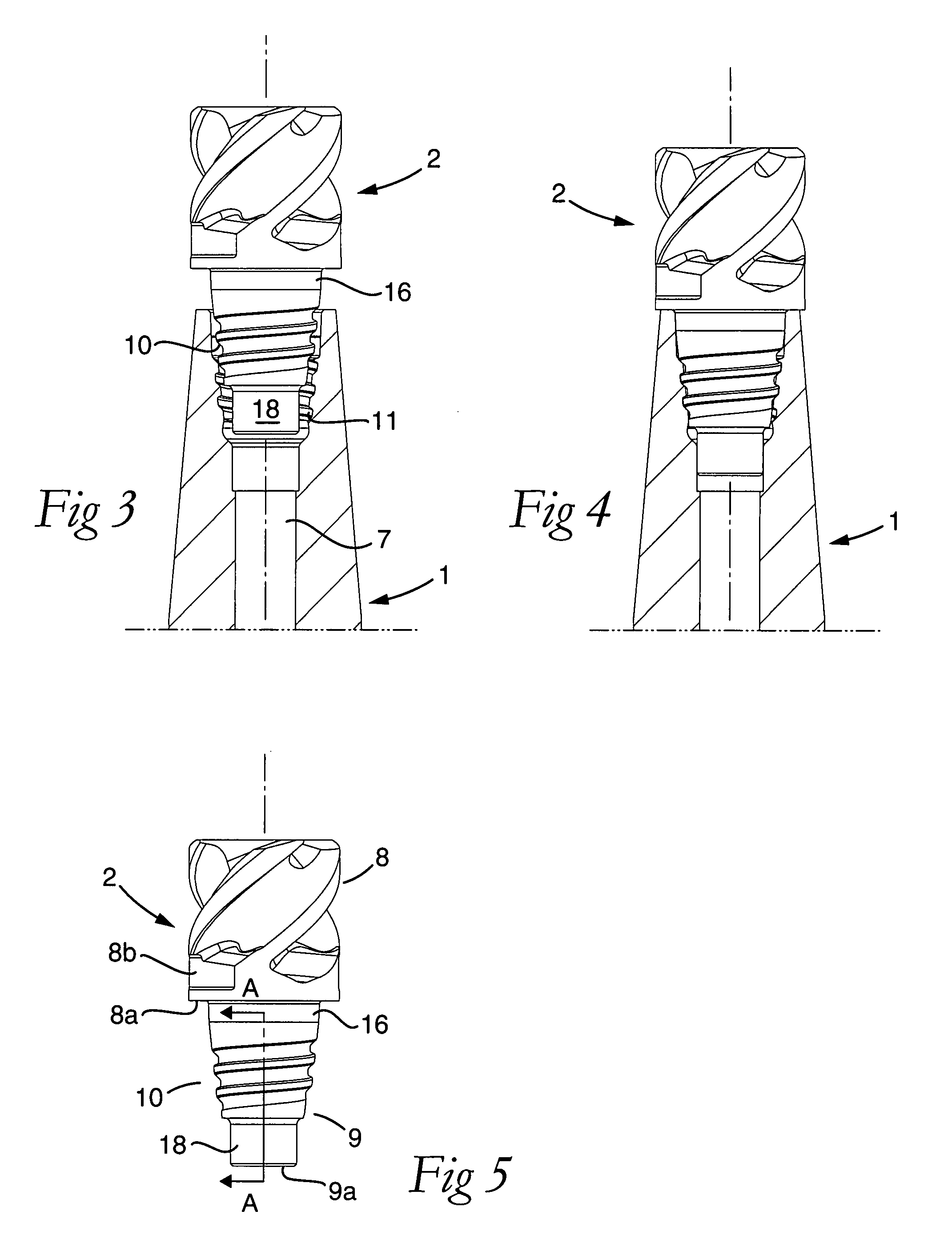
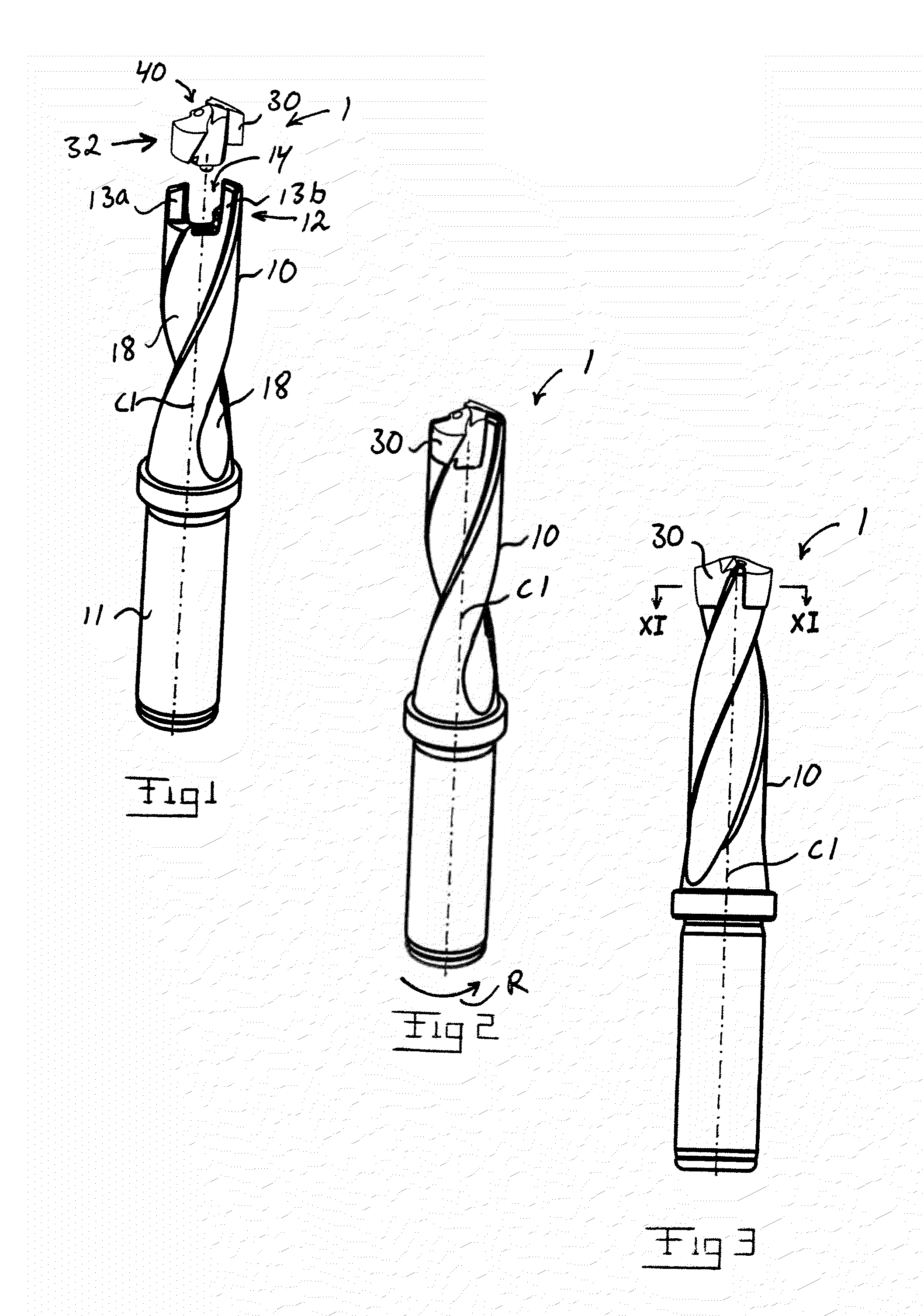
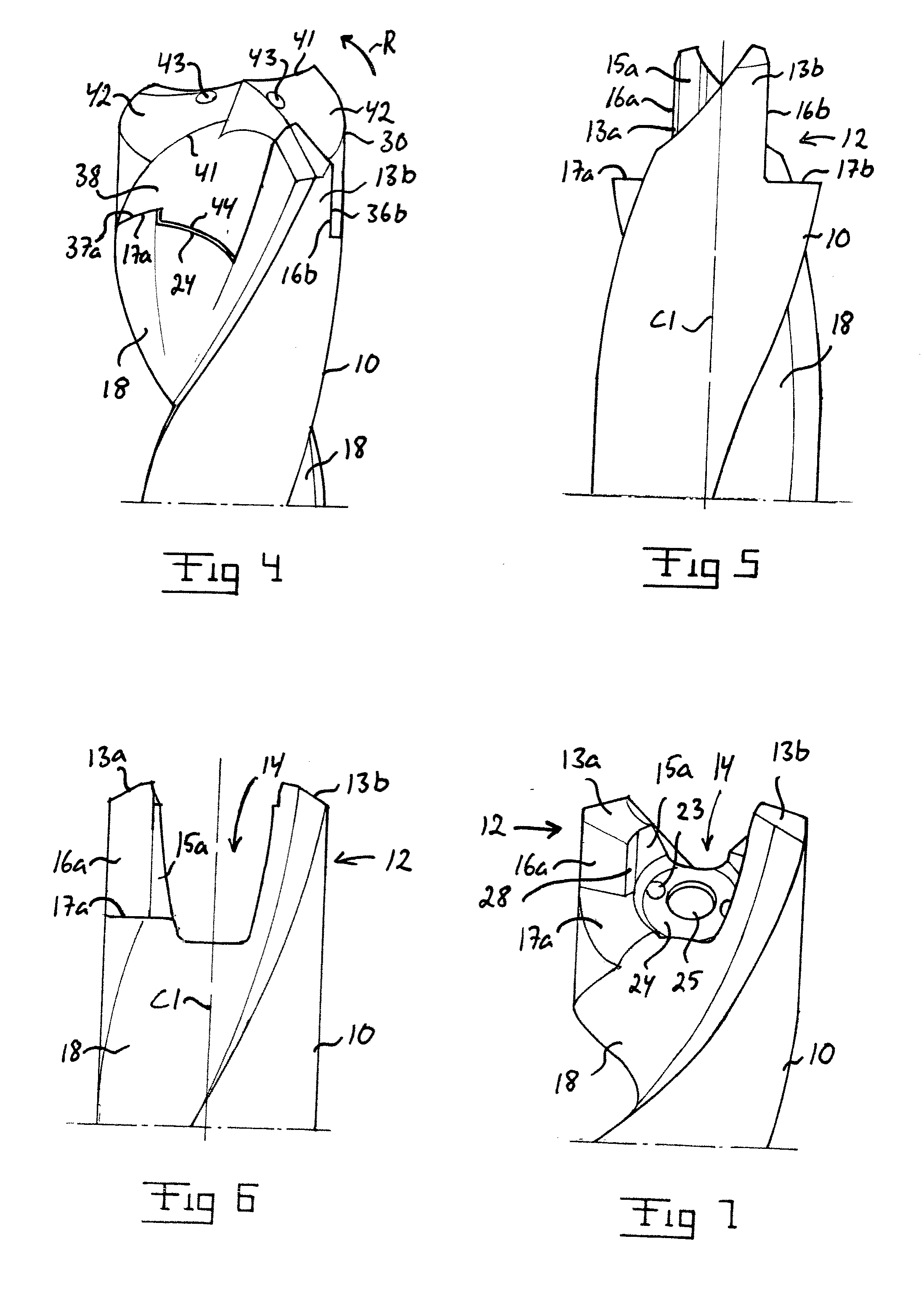
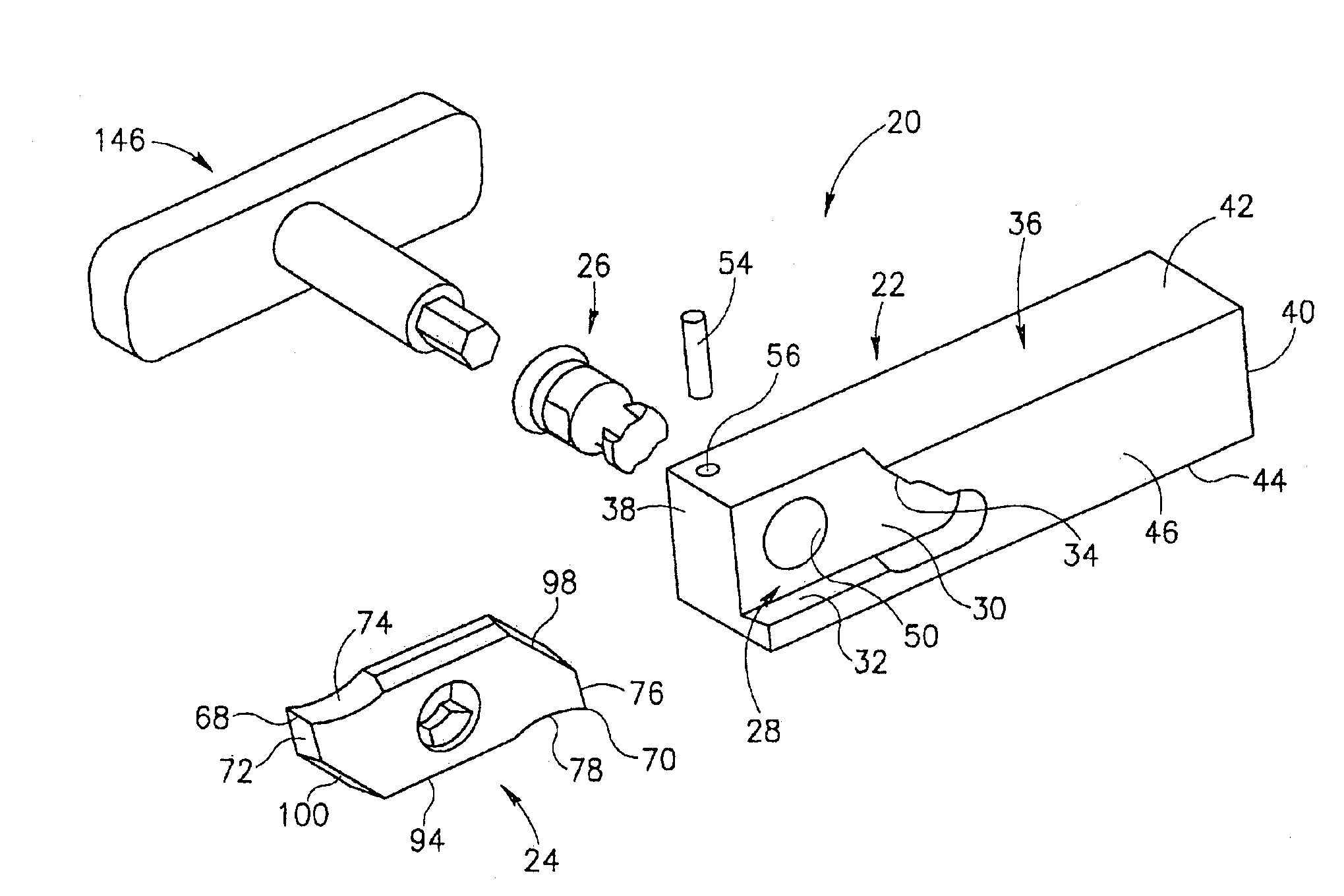
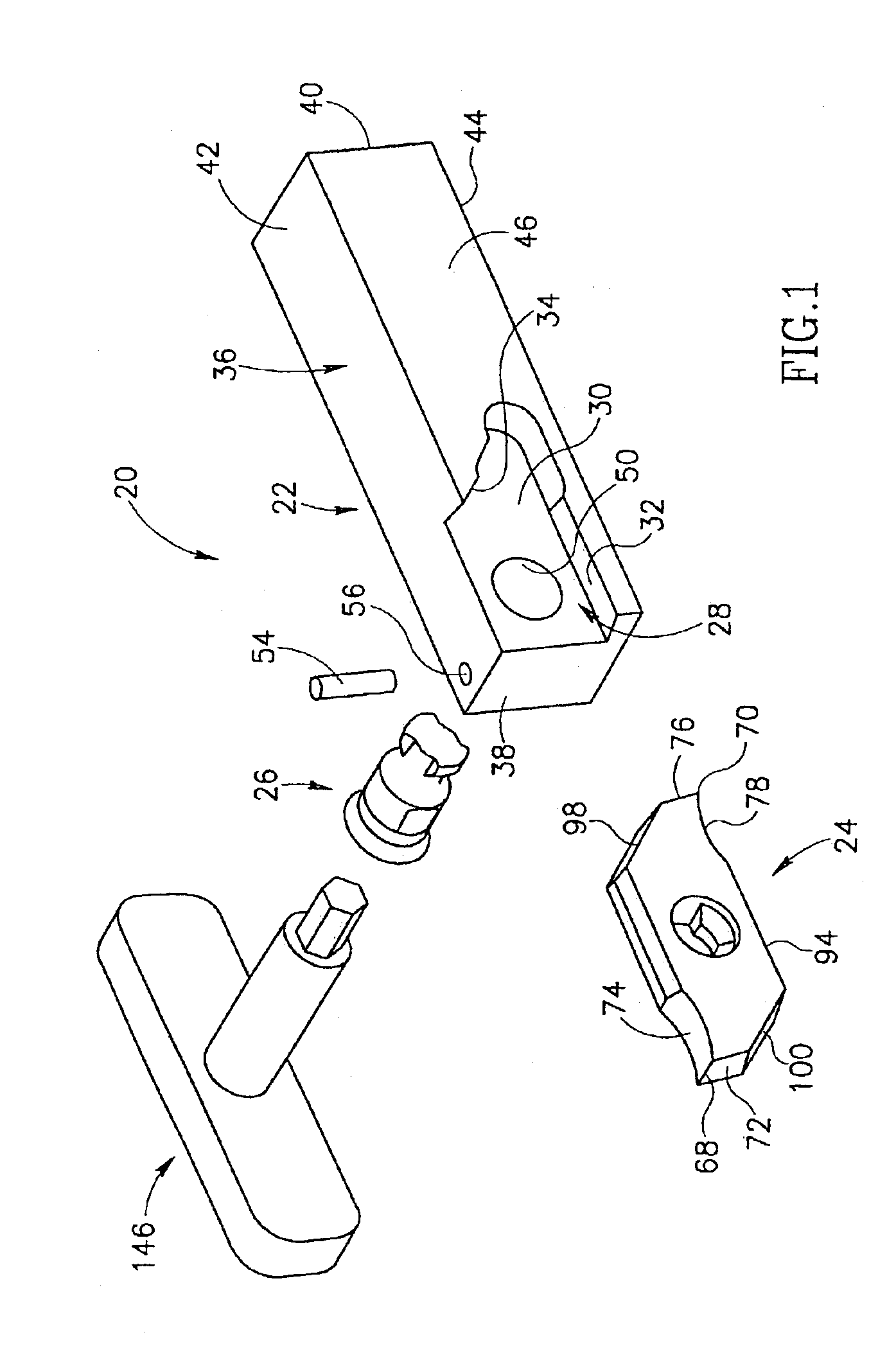
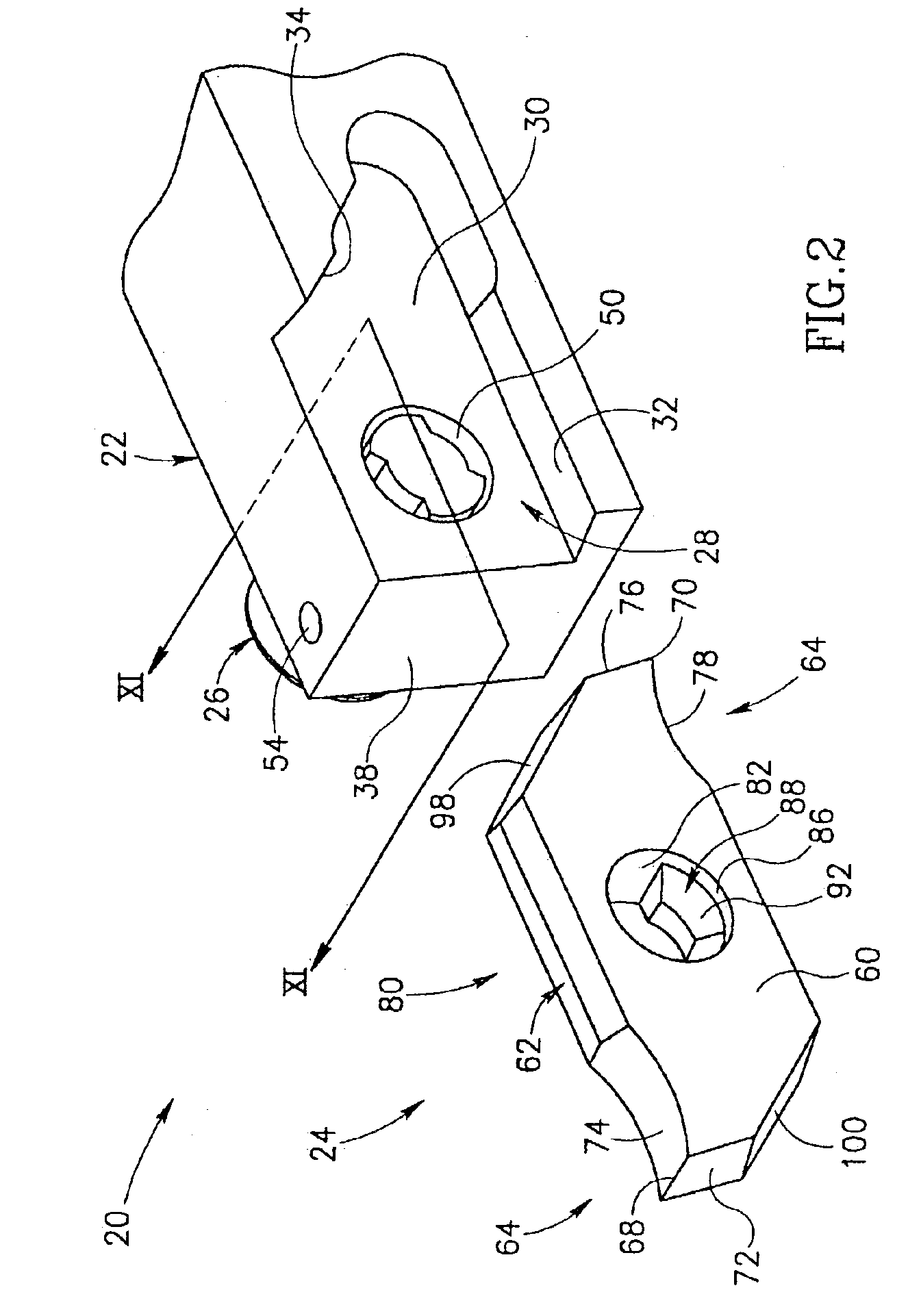
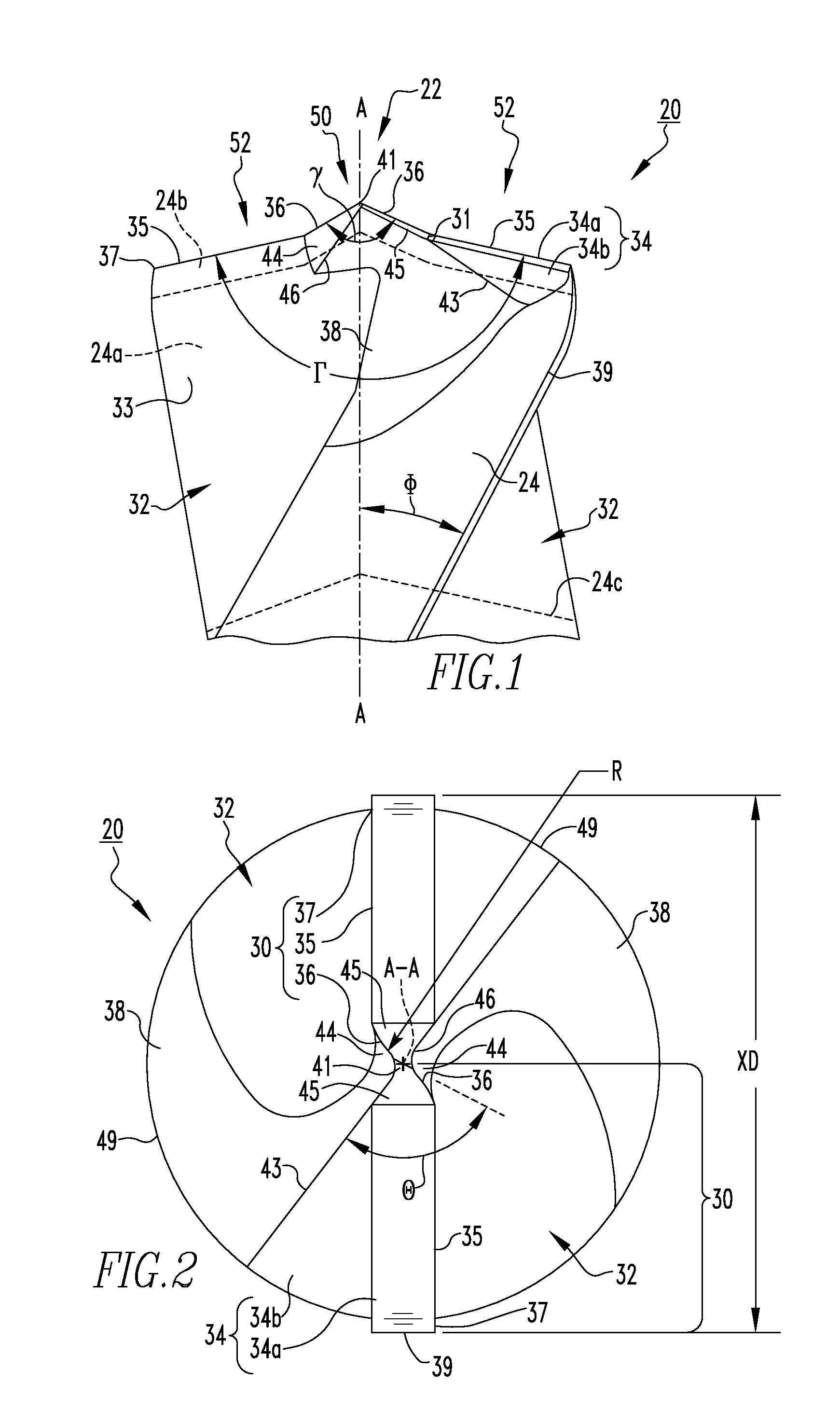
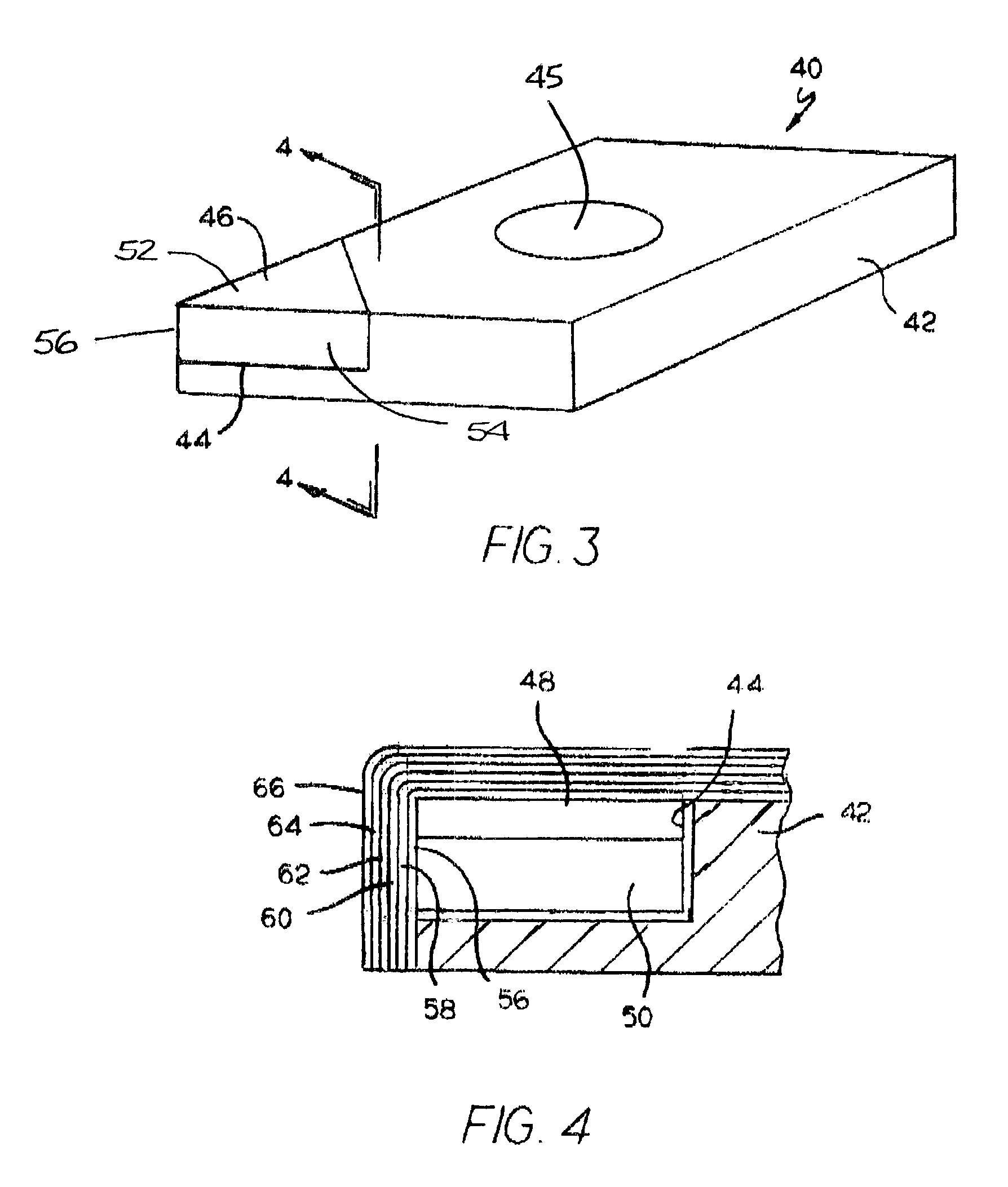
Tool for chip removing machining as well as a basic body therefore
InactiveUS7713004B2Easy to processImprove accuracyTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingCouplingAxial force
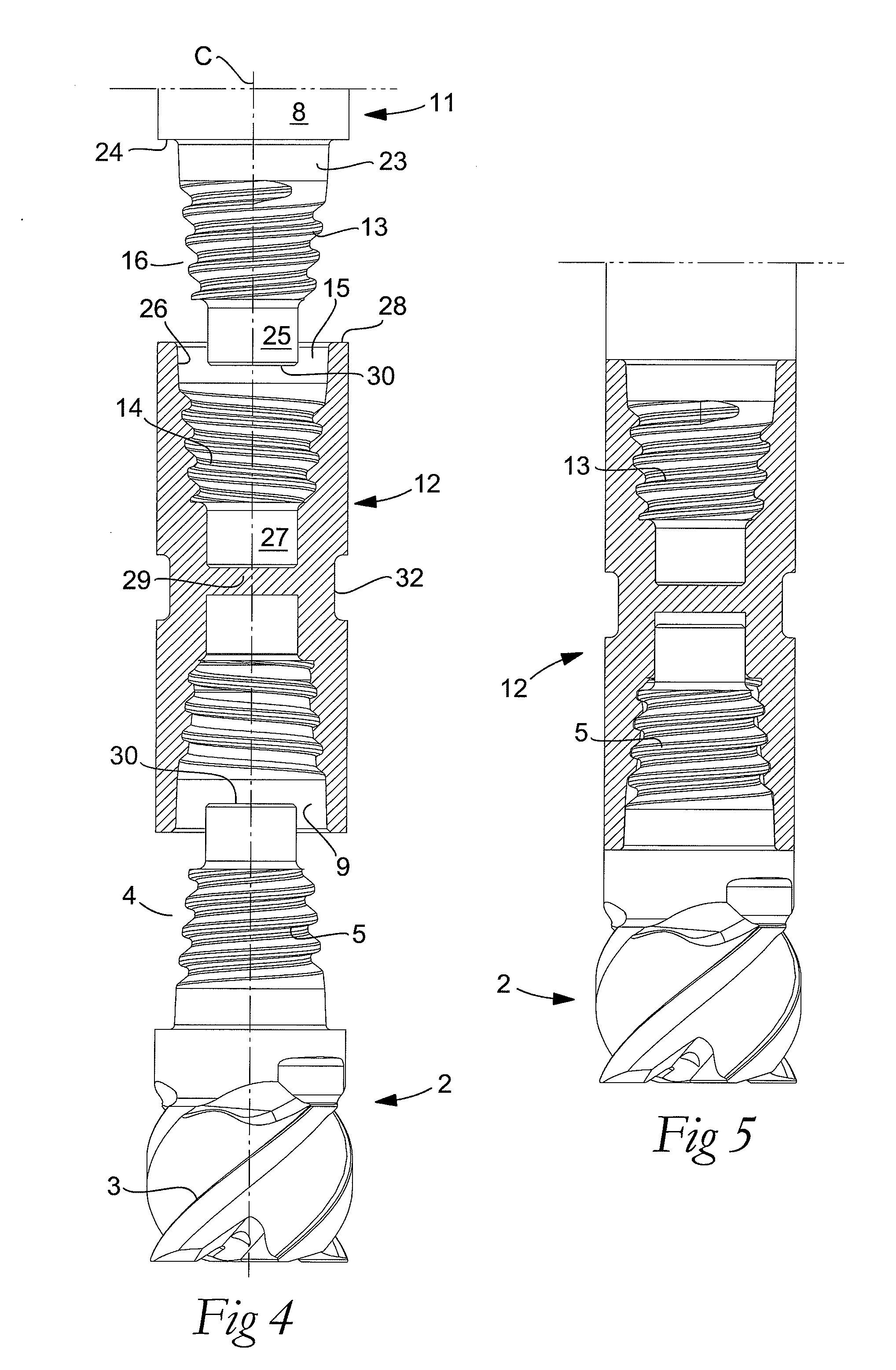
A tool for chip removing machining, including a long narrow basic body having an envelope surface which is concentric with a center axis, and two opposite ends, and a replaceable loose top which is connected to the basic body via a first coupling that includes a first seating formed in one end of the basic body and a first male element formed in one end of the loose top. The basic body includes a primary part body made of a first material having a first modulus of elasticity, and a secondary part body which includes the first seating and is made of a second material having a second modulus of elasticity which is lower than the first modulus of elasticity. The two part bodies of the basic body are interconnected via a second coupling which includes a second seating in the secondary part body as well as a second male element that is formed on the primary part body and has one or more precision machined flank surfaces that are arranged to apply, together with one or more co-operating and precision machined flank surfaces of the second seating, joining axial forces to the part bodies by turning the part bodies in relation to each other.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Hole cutter and method for producing
InactiveUS20050105981A1Low costOvercome disadvantagesTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingHole sawAnnular cutter
A hole cutter machine tool combines the characteristics and properties of a low-cost hole saw with the speed and performance of an annular cutter. The hole cutter comprises a cutter ring portion similar to an end portion of existing annular cutters with a carrier portion similar to the cup of a hole saw. In one embodiment the hole cutter has a threaded aperture which enables use with a standard hole saw arbor or with a replaceable arbor having an annular cutter shank. An embodiment of the method of making the hole saw includes a joining process in which the cutter ring is simultaneously attached to the carrier portion and heat treated.
Owner:M K MORSE COMPANY THE
Tool for chip removing machining as well as a part and threaded joint therefor
ActiveUS7611311B2Improved propertyGenerating large tightening forces without jeopardizing the durability of the thread ridgesTool workpiece connectionThread cutting machinesPull forceEngineering
A cutting tool, and a loose top therefore, includes two parts detachably connected to each other via a threaded joint in which co-operating male and female threads are included in the form of helicoidal ridges. The profile shape of each helicoidal ridge is defined by a top and two flanks, which delimit a helicoidal groove having a bottom. The first flank is inclined in relation to a center axis of the tool at a first angle that is smaller than a second angle of the second flank in relation to the center axis. Accordingly, the thread ridge is reinforced in comparison with thread ridges having a symmetrical profile shape, whereby larger tensile forces than compressive forces can be applied to the threaded joint while avoiding damage to the thread ridges.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Reversible saw tooth
A replaceable saw tooth for a rotary cutting machine. The saw tooth comprises more than two cutting edges on each of two opposed faces thereof. More specifically, the saw tooth may comprise a body having two cutting faces disposed opposite each other and spaced apart by at least four side faces which are each parallel to an opposite one of the side faces. The side faces are parallel to a central axis extending between the two cutting faces. Four cutting edges are defined between the side faces and each of the two cutting faces.
Owner:QUADCO
Braze alloy
A braze alloy is described which includes indium and / or thallium as alloying elements. For example, between about 0.5% and about 10% by weight of indium (In) and / or thallium (Tl) can be added to a braze alloy to reduce the braze temperature without substantially effecting braze strength. Braze alloys that are alloyed to including indium (In) and / or thallium (Tl) can be use in brazing cutting elements to drilling tools. These alloying elements may also be added to braze alloys used for other applications to reduce braze temperature.
Owner:KEMBAIYAN KUMAR T
Polycrystalline superabrasive composite tools and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20080023230A1Wide applicationProperty is limitedPigmenting treatmentDrill bitsCarbideHigh pressure
A polycrystalline superabrasive composite tool can be produced using high pressure high temperature processes allowing for increased thermal resistance, wear resistance and toughness of abrasive tools, and additionally allowing for increased effective thickness of abrasive tools. A polycrystalline superabrasive compact can include a support substrate and a superabrasive polycrystalline layer having a diffusion bridge embedded therein that includes a carbide former. Additionally, a working layer can be attached adjacent to the superabrasive polycrystalline layer and opposite the support substrate to form a drill bit sandwich segment. The diffusion bridge matrix of the present invention allows for a new welding phase at each interface between the superabrasive polycrystalline layer and support substrate and between the polycrystalline layer and the metal working layer, thus eliminating delamination failure at the interfaces. The superabrasive polycrystalline layer can include superabrasive particles of varying particle sizes such that the final composite tool is tailored for specific abrading characteristics. The polycrystalline superabrasive composite tools can be incorporated for use in machining, drilling, grinding, cutting, polishing and similar abrasive applications.
Owner:ADICO ASIA POLYDIAMOND
Ultrasonic machining module
A device for use in a machining system, including an ultrasonic transducer, wherein the ultrasonic transducer is adapted to receive a tool bit; a housing adapted to be both compatible with the machining system and to receive the ultrasonic transducer, wherein the housing is operative to isolate all radial and other vibrations generated by the ultrasonic transducer except the axial vibrations transmitted to the tool bit; and a tool holder, wherein the tool holder and the top portion of the housing are mechanically coupled to one another.
Owner:EDISON IND INNOVATION
Braze alloy and method of use for drilling applications
A down hole cutting tool includes a cutting element support structure. The cutting element support structure has at least one cavity formed therein. A cutting element is disposed in the cavity. Braze alloy is also disposed in the cavity between the cutting element and the cutting element support structure. The braze alloy comprises between about 0.5% and about 10% by weight of at least one selected from the group of gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl). Methods for building a down hole tool using the braze alloy are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC +1
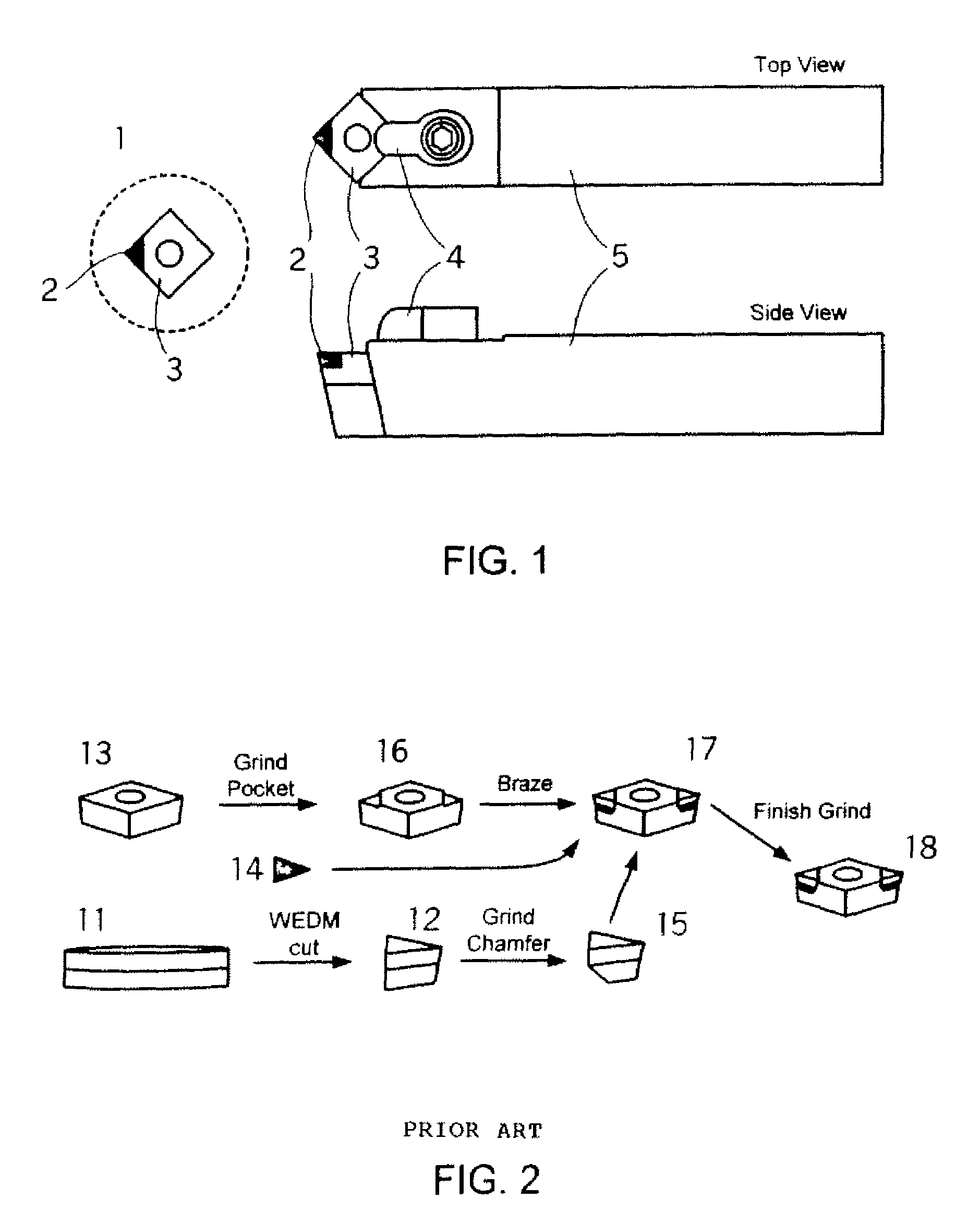
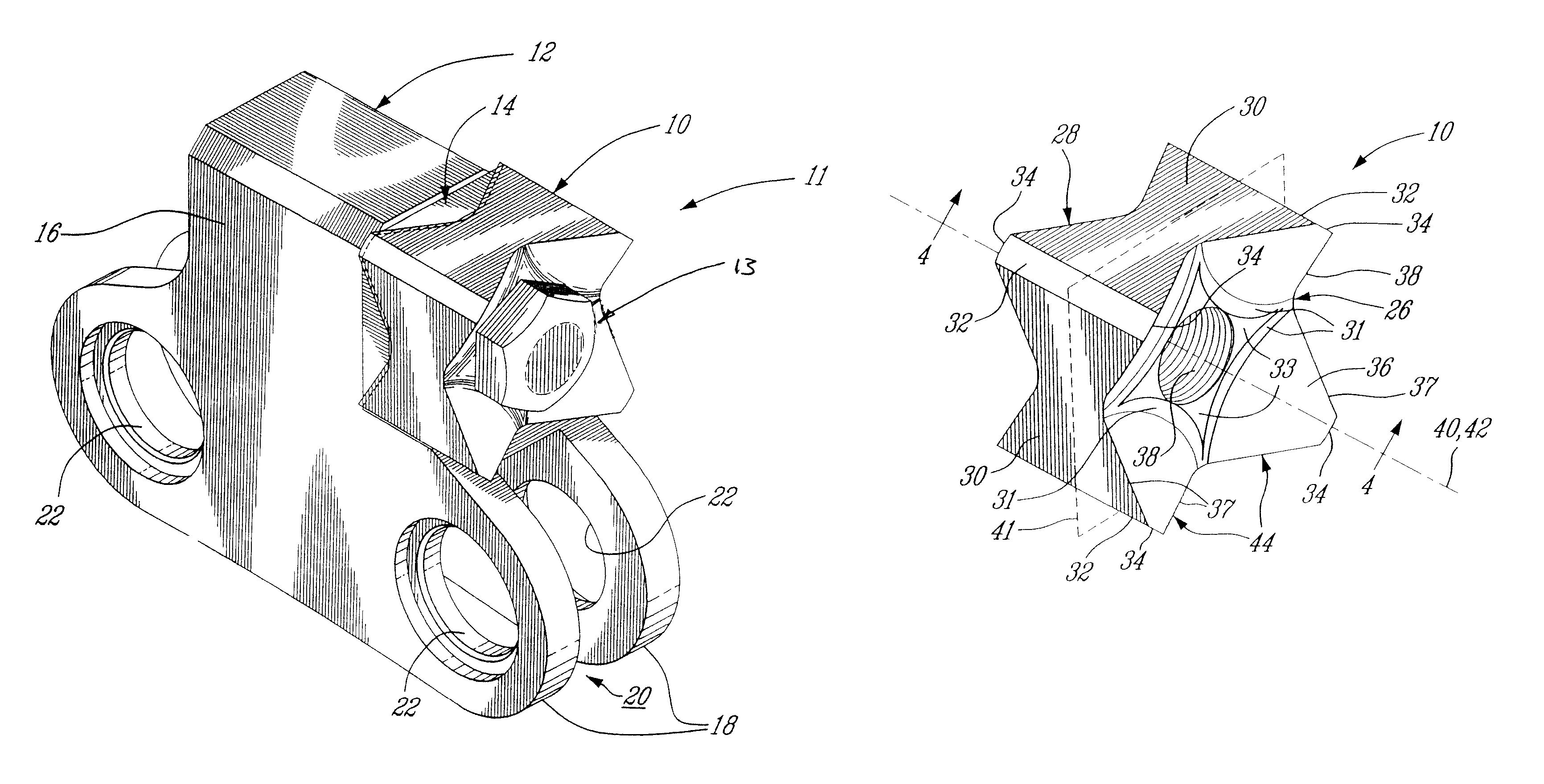
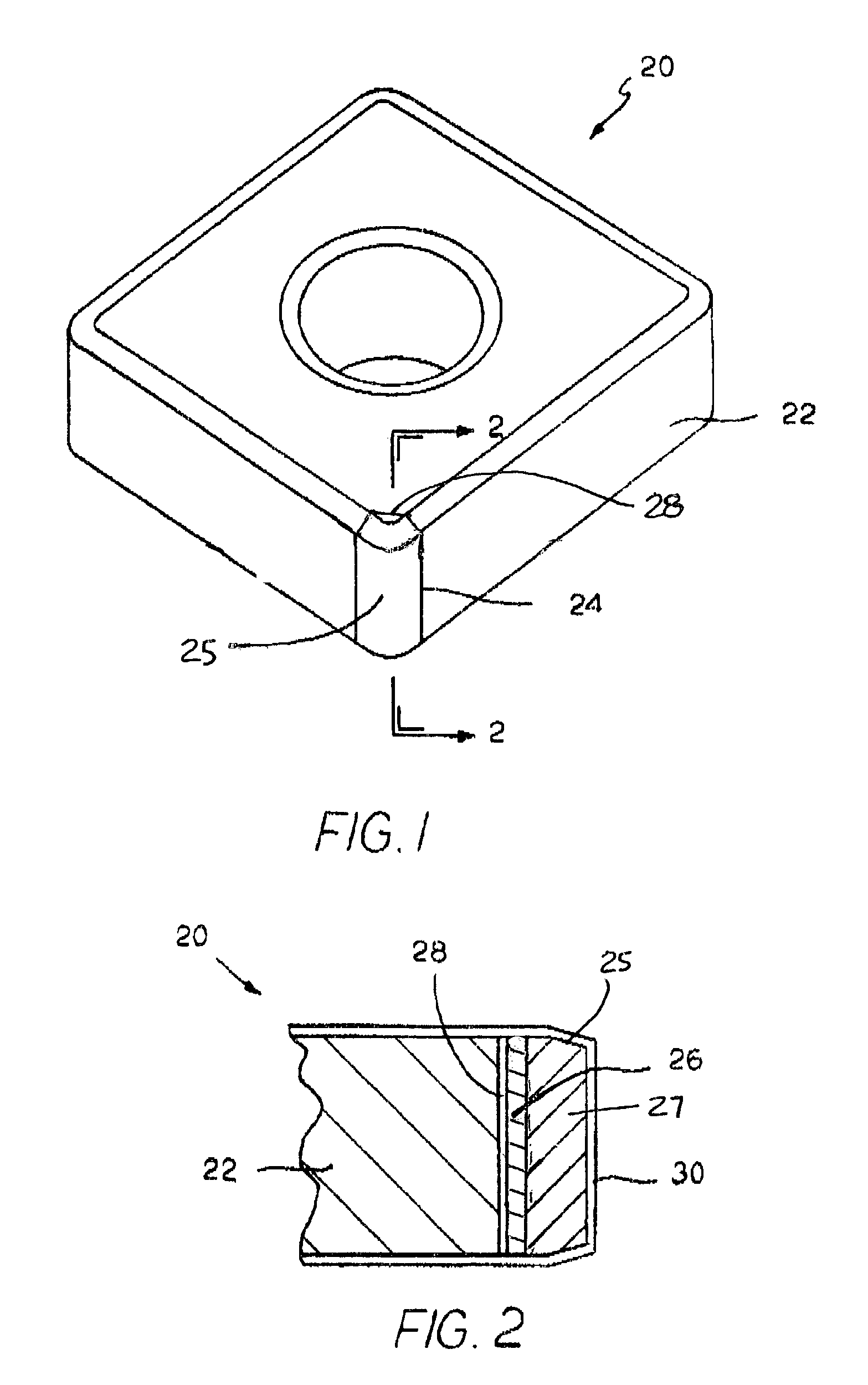
Indexable cutting inserts and methods for producing the same
A cutting insert has a body formed of a superhard material or a superhard material and a cemented carbide, and has a hole through said body and a preformed hole inlay in said hole to allow securing of the insert to a holder. The method of making same is also disclosed.
Owner:SANDVIK INTPROP AB
Cemented carbide cutting insert having integral structure for securing the insert in a holder
InactiveUS6273650B1High strengthEasy to operateTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingAlloyEngineering
A cutting insert intended for chip removing machining includes a body forming at least one cutting edge, a securing structure such as a helical thread disposed at one side of the body, and a key grip such as a profiled recess disposed at an opposite side. The insert is formed of injection molded cemented carbide such that the body, the securing structure, and the key grip are all integral with one another. The insert is secured in a holder by rotating the insert using a key which engages the key grip, whereupon the securing structure engages a complementary securing structure on the holder to pull the insert body against the holder.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Tool for chip removing machining as well as a part and threaded joint therefor
ActiveUS20070248421A1Avoid damageStrong pullTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingPull forceEngineering
A cutting tool, and a loose top therefore, includes two parts detachably connected to each other via a threaded joint in which co-operating male and female threads are included in the form of helicoidal ridges. The profile shape of each helicoidal ridge is defined by a top and two flanks, which delimit a helicoidal groove having a bottom. The first flank is inclined in relation to a center axis of the tool at a first angle that is smaller than a second angle of the second flank in relation to the center axis. Accordingly, the thread ridge is reinforced in comparison with thread ridges having a symmetrical profile shape, whereby larger tensile forces than compressive forces can be applied to the threaded joint while avoiding damage to the thread ridges.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Tool, tool body and cutting head
ActiveUS20100021253A1High standardComplicate to achieveThread cutting toolsTool workpiece connectionCouplingMachining
A tool for rotary cutting machining includes a tool body and a replaceable cutting head detachably attachable to the tool body. The cutting head has a coupling portion which is receivable in a space between two axially projecting coupling legs of the tool body. Cylindrical internal gripping surfaces are arranged in said space and designed for engagement with corresponding cylindrical external gripping surfaces of the cutting head. The gripping surfaces of the cutting head and the gripping surfaces of the tool body are dimensioned so as to prevent, by engagement with each other, the cutting head from being displaced in axial direction away from the tool body when the cutting head is attached to the tool body. A tool body and a cutting head included in such a tool are also disclosed.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
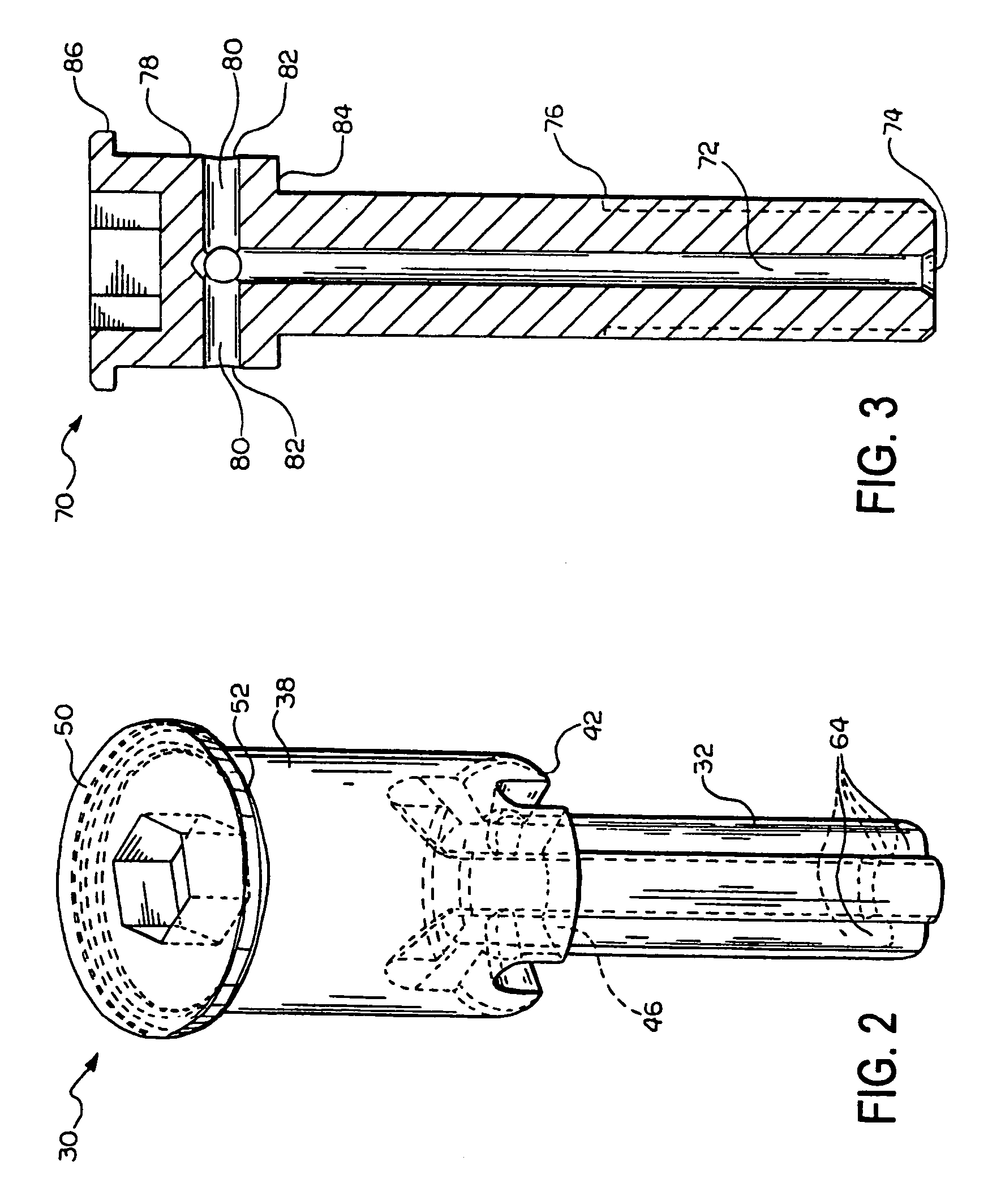
Tool for chip removing machining as well as a basic body therefore
InactiveUS20080304923A1Easy to processGood surface smoothnessTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingCouplingAxial force
A tool for chip removing machining, including a long narrow basic body having an envelope surface which is concentric with a center axis, and two opposite ends, and a replaceable loose top which is connected to the basic body via a first coupling that includes a first seating formed in one end of the basic body and a first male element formed in one end of the loose top. The basic body includes a primary part body made of a first material having a first modulus of elasticity, and a secondary part body which includes the first seating and is made of a second material having a second modulus of elasticity which is lower than the first modulus of elasticity. The two part bodies of the basic body are interconnected via a second coupling which includes a second seating in the secondary part body as well as a second male element that is formed on the primary part body and has one or more precision machined flank surfaces that are arranged to apply, together with one or more co-operating and precision machined flank surfaces of the second seating, joining axial forces to the part bodies by turning the part bodies in relation to each other.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
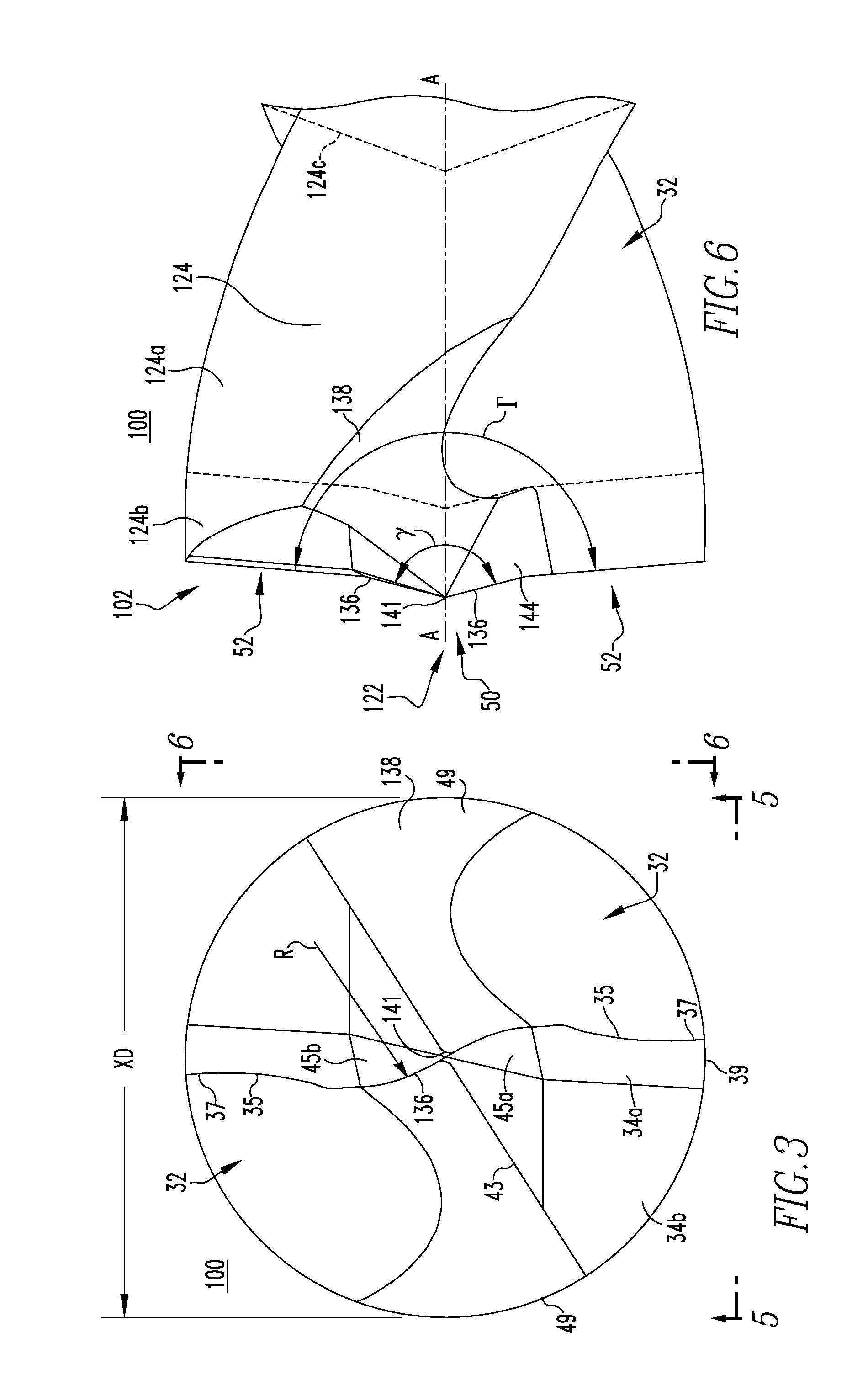
Contoured pcd and pcbn segments for cutting tools containing such segments
Contoured helical solid polycrystalline PCD and PCBN superabrasive segments are provided for attachment to cutting tool substrates such as twist drill tips, reamers, burrs and endmills. Segments are provided in near to net shape for attachment to a tool substrate thereby requiring reduced finishing steps and providing increased tailorability of grade and quality of final polycrystalline segments. Cutting tools comprising cutting tool substrates having attached thereto a contoured helical solid polycrystalline PCD and PCBN superabrasive segments are also disclosed.
Owner:CHO H SAM +4
Cutting tool
A cutting tool has a tool body in which a cutting insert is secured to an insert pocket in the tool body by a fastener. In contrast to the use of a threaded clamping screw, the fastener remains in engagement with the tool body during all stages of the attachment and clamping, or unclamping and removal of the cutting insert. The fastener is rotatable between a clamping position and a non-clamping position by means of one of two keys. One key being capable of engaging one of the fastener's ends, and the other key being capable of engaging the other of the fastener's ends. This is particularly convenient for circumstances where the approach to one or the other of the fastener's ends may be obstructed.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
Rotary cutting tool having pcd cutting tip
A rotary cutting tool comprises an elongate body disposed about a longitudinal axis, the elongate body including a helical flute and a polycrystalline-diamond cutting tip. The cutting tip comprises an inner portion having an inner point angle and an outer portion having an outer point angle different from the inner point angle.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Polycrystalline superabrasive composite tools and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS7585342B2Property is limitedWide applicationPigmenting treatmentDrill bitsCarbideHigh pressure
A polycrystalline superabrasive composite tool can be produced using high pressure high temperature processes allowing for increased thermal resistance, wear resistance and toughness of abrasive tools, and additionally allowing for increased effective thickness of abrasive tools. A polycrystalline superabrasive compact can include a support substrate and a superabrasive polycrystalline layer having a diffusion bridge embedded therein that includes a carbide former. Additionally, a working layer can be attached adjacent to the superabrasive polycrystalline layer and opposite the support substrate to form a drill bit sandwich segment. The diffusion bridge matrix of the present invention allows for a new welding phase at each interface between the superabrasive polycrystalline layer and support substrate and between the polycrystalline layer and the metal working layer, thus eliminating delamination failure at the interfaces. The superabrasive polycrystalline layer can include superabrasive particles of varying particle sizes such that the final composite tool is tailored for specific abrading characteristics. The polycrystalline superabrasive composite tools can be incorporated for use in machining, drilling, grinding, cutting, polishing and similar abrasive applications.
Owner:ADICO ASIA POLYDIAMOND
Coated cutting tool with brazed-in superhard blank
ActiveUS7592077B2Tool workpiece connectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBoron nitrideBraze alloy
A coated cutting tool that comprises a body containing a pocket. The tool further includes a polycrystalline cubic boron nitride blank that is brazed into the pocket using a braze alloy. The braze alloy has a liquidus temperature of at least about 900 degrees Centigrade. There is a coating applied to the cutting tool.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Cutting tool including a locking screw and adapter with coolant delivery
A cutting tool has a cutter body, which carries a cutting insert, and an adapter, which has a longitudinal adapter axis, wherein a locking screw attaches the cutter body to the adapter. A coolant volume is defined in a vicinity of a meeting of the cutter body, the adapter and the locking screw. The adapter contains an axial adapter bore. The locking screw contains a transverse locking screw bore in fluid communication with the axial adapter bore. The locking screw further contains a peripheral transverse locking screw bore passage in fluid communication with the coolant volume and the transverse locking screw bore. The coolant volume and the transverse locking screw bore are in fluid communication with the cutter body coolant passage.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Sheet metal hole cutter
ActiveUS6939092B2Less expenseEqual and cutting performanceTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingAcute angleMechanical engineering
A sheet metal hole cutter has a cap plate defining a substantially circular peripheral groove and an annular shelf extending radially outwardly from the peripheral groove. An elongated band forming an approximately circular shape with opposite ends of the band contacting each other defines a base edge received within the circular peripheral groove in an abutting relationship with an inner edge of the groove. The band defines an axial depth of about ½ of an inch or less, and an outer diameter within the range of about 9 / 16 of an inch through about 6 inches. A weld region fixedly secures the base edge of the band to the cap plate. The annular shelf of the cap plate extends radially outwardly from the base edge of the band and defines a radial depth of at least approximately 1 / 16 of an inch in order to prevent over-feeding of the hole cutter through a work piece. A plurality of teeth are disposed along a cutting edge of the band, and each tooth defines a cutting surface extending between an outer edge and an inner edge of the tooth. Each cutting surface is oriented at an acute angle relative to the plane of the cap plate such that the outer edge of the respective tooth is spaced further away from the cap plate than the inner edge to thereby preferentially cut the work piece with the outer edge and create a substantially burr-free hole in the work piece.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
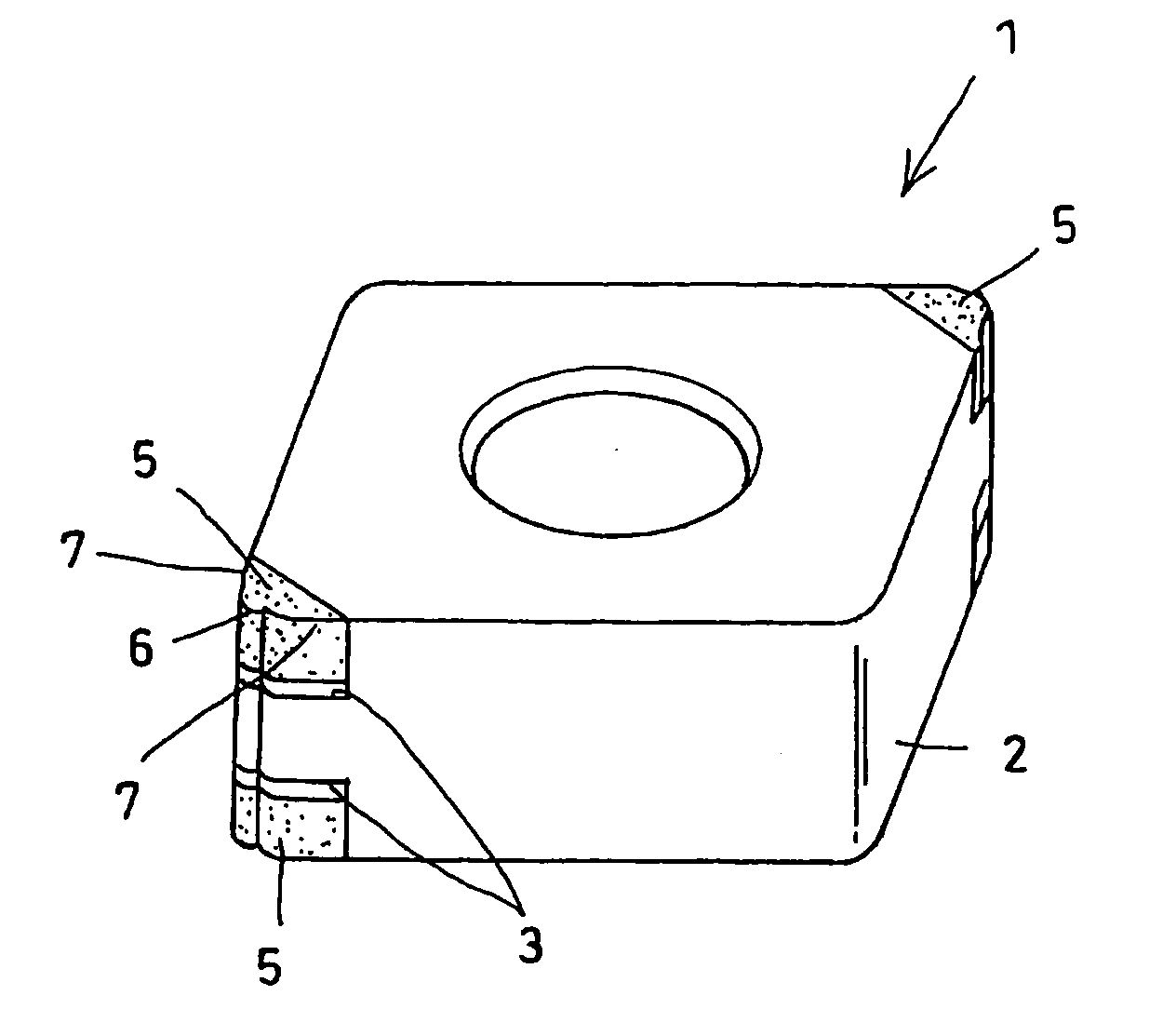
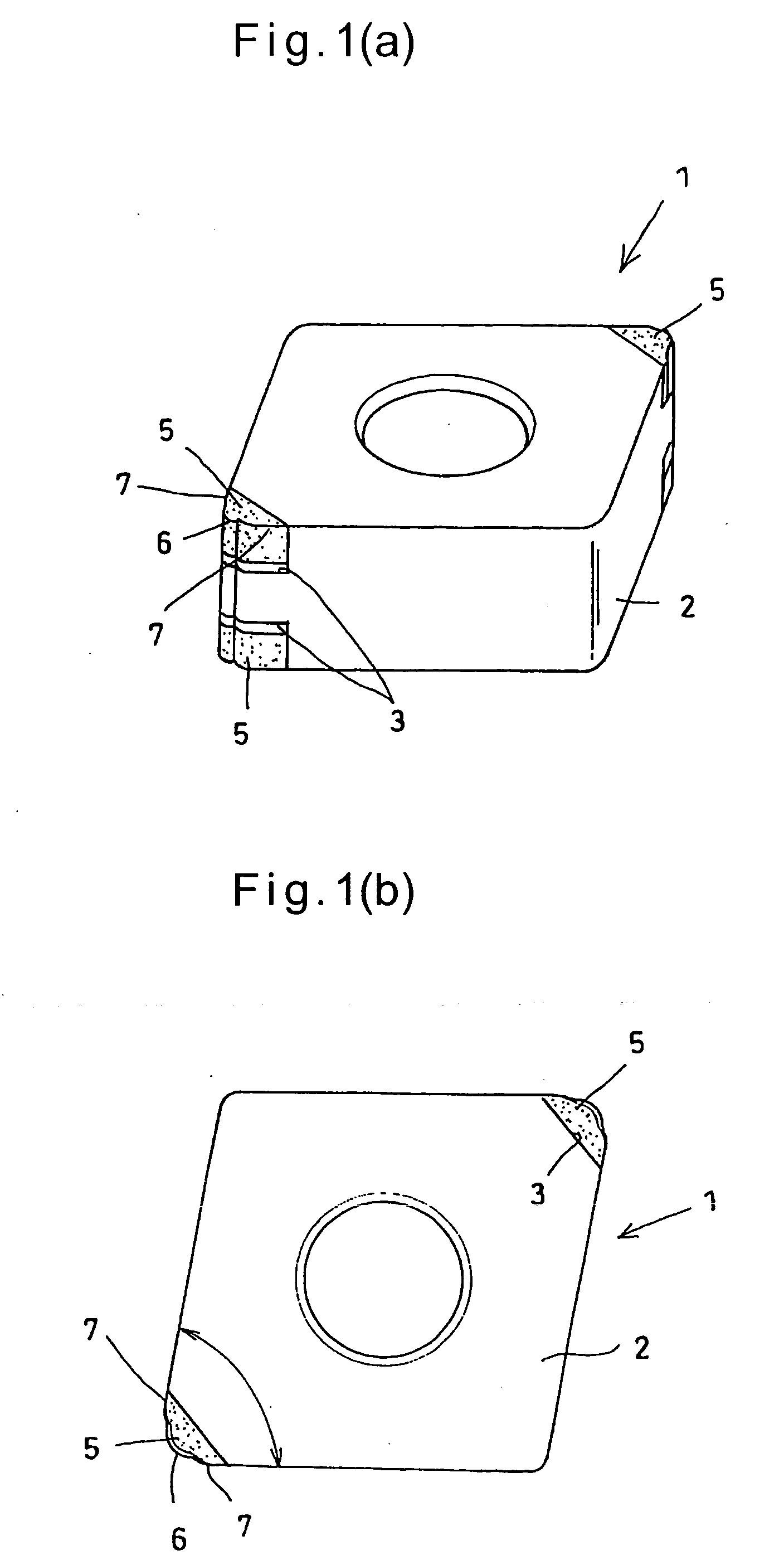
Cutting Tool for High-Quality High-Efficiency Machining and Cutting Method Using the Same
ActiveUS20080292415A1Improve machine efficiencyLarge widthTool workpiece connectionCutting insertsHardened steelEngineering
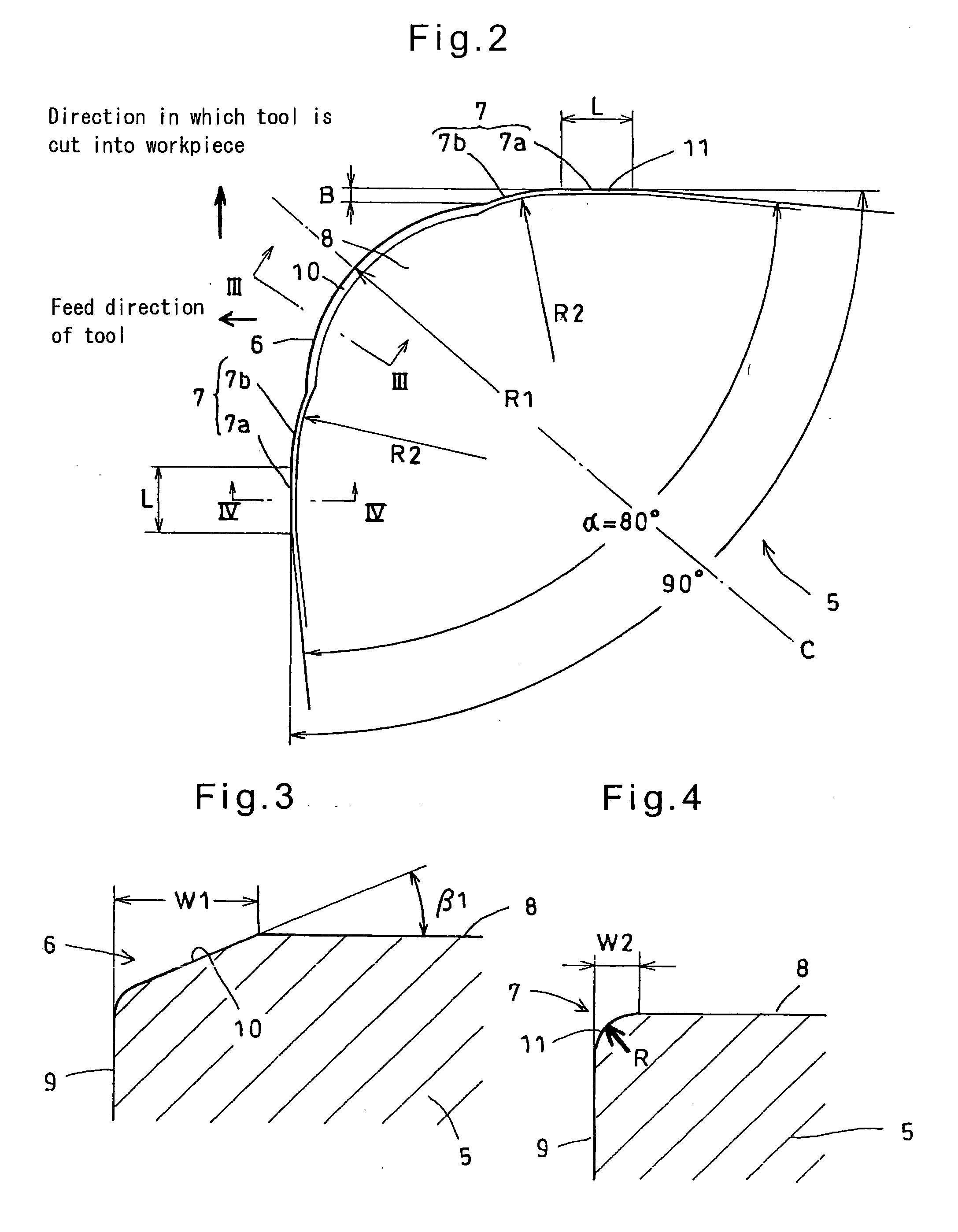
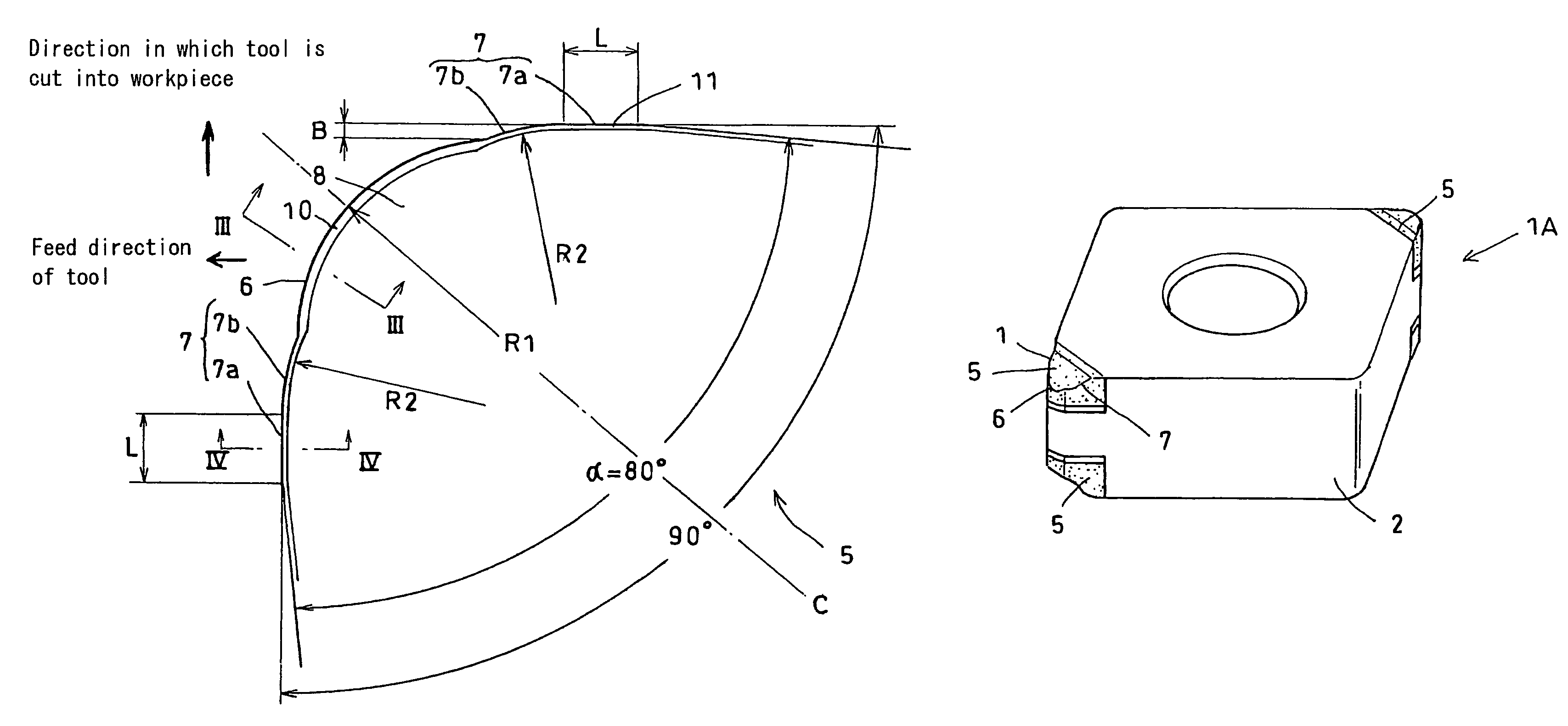
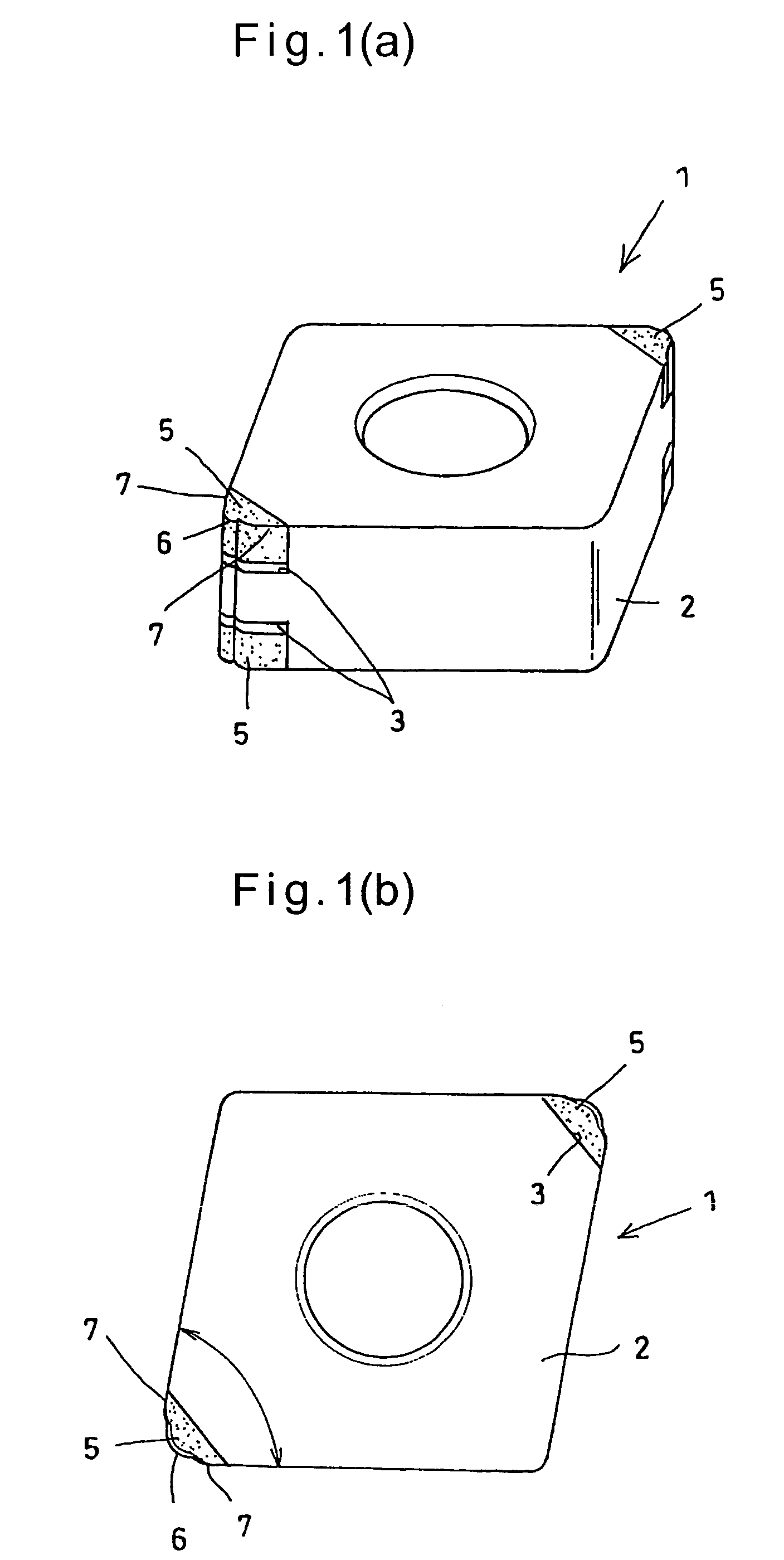
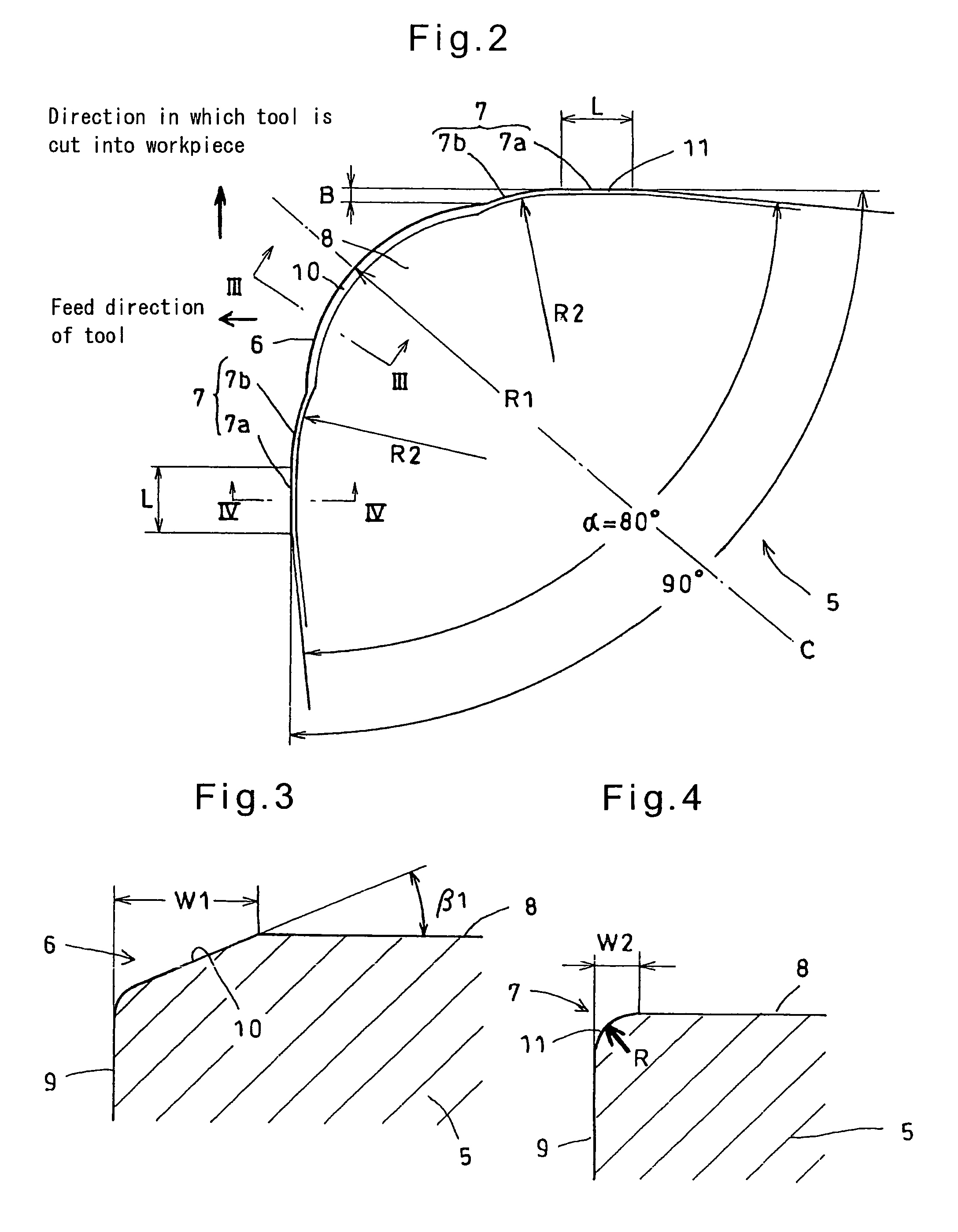
It is an object to provide a cutting tool which can perform high-quality, high-efficiency machining of a workpiece such as hardened steel.The cutting tool includes a finishing cutting edge 6 which initially cuts into the workpiece, and superfinishing cutting edges 7 for finishing the workpiece cut by the finishing cutting edge. The superfinishing cutting edges 7 project from the finishing cutting edge by a predetermined amount B in such a direction that the depth of cut of the superfinishing cutting edges increases. Each superfinishing cutting edge includes a burnishing portion 7a having a predetermined width L in the feed direction of the tool, and a wiper portion 7b. The superfinishing cutting edges 7 burnish the finished surface formed by the finishing cutting edge, while removing a affected layer formed by the finishing cutting edge.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
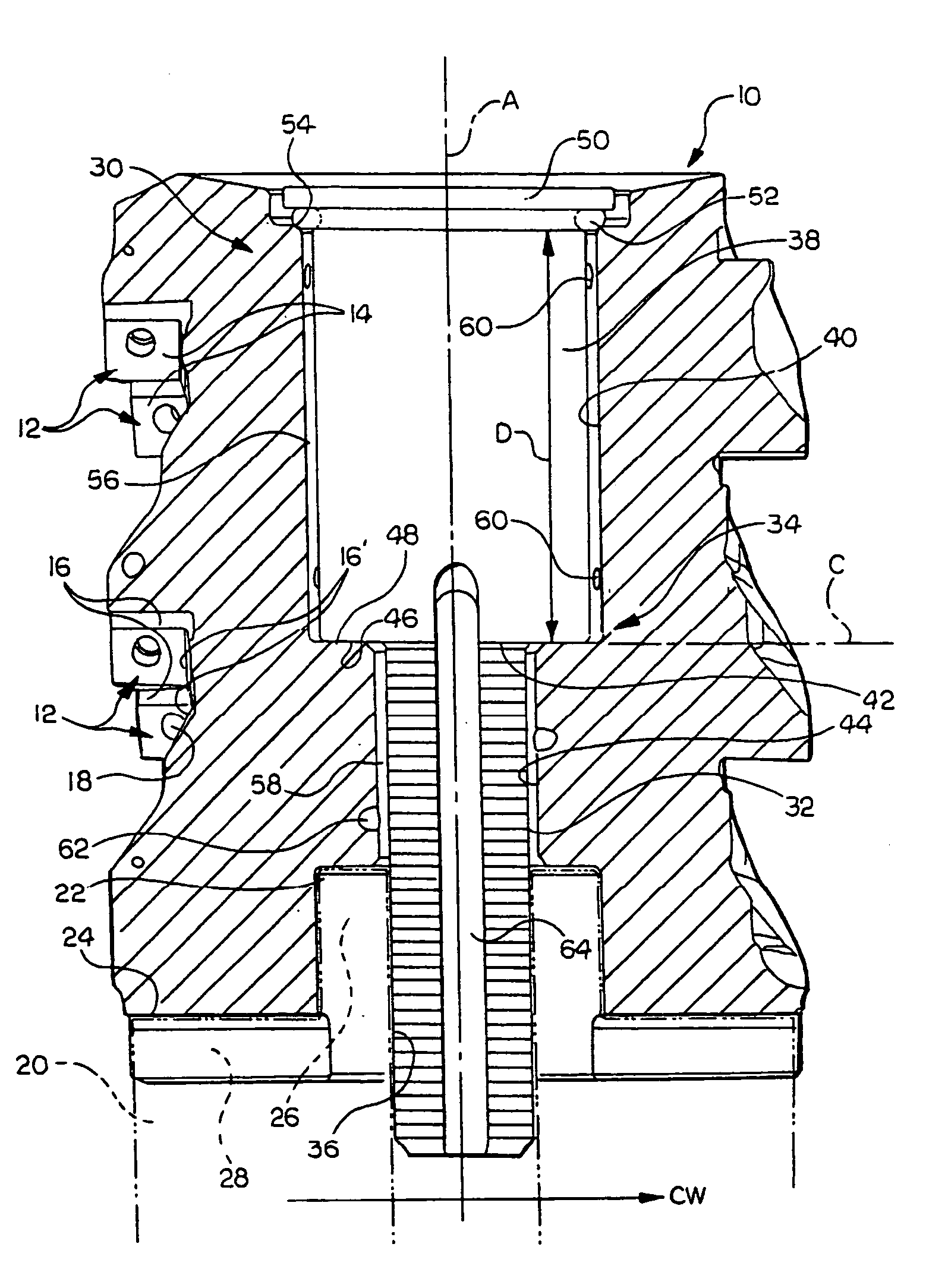
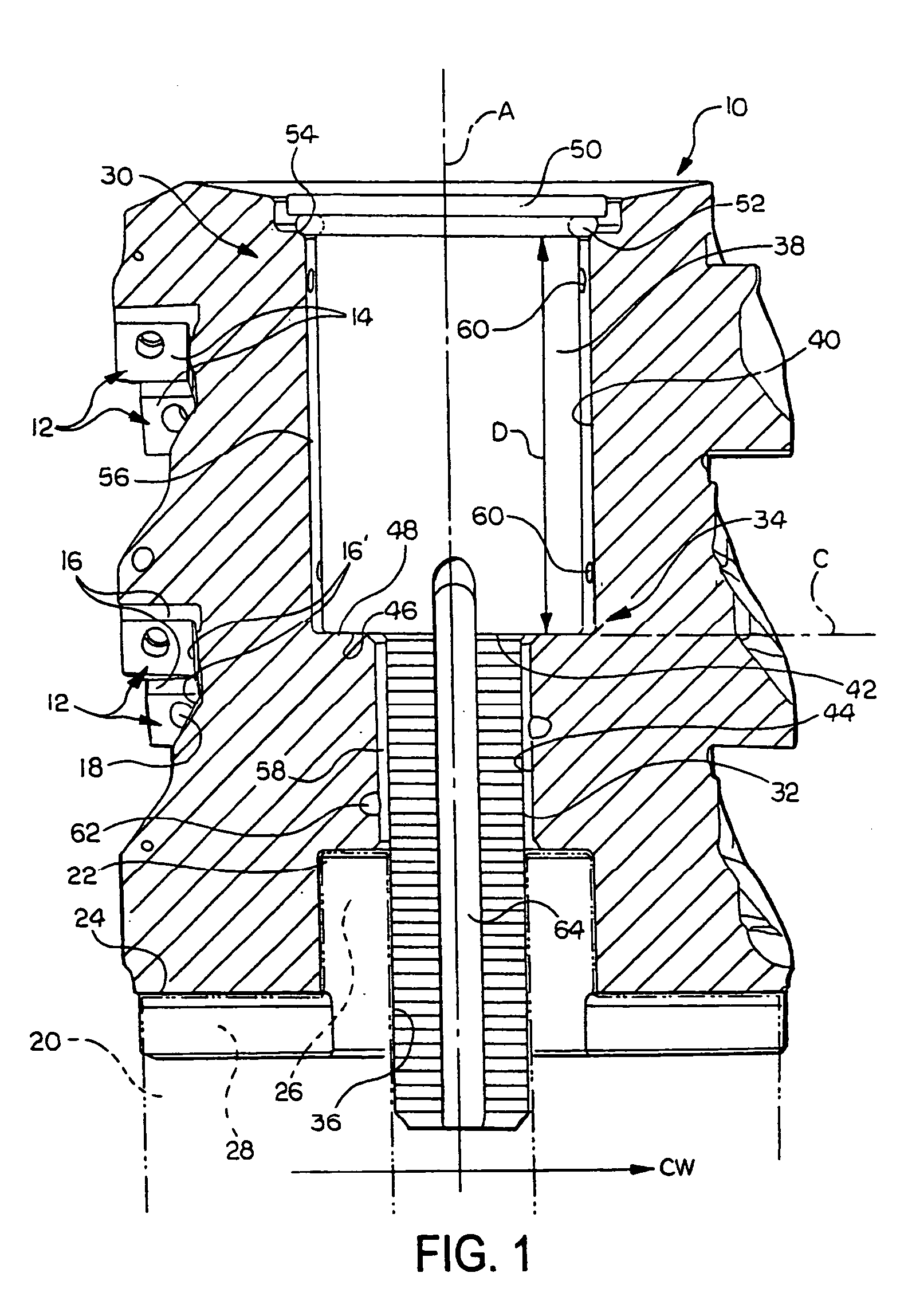
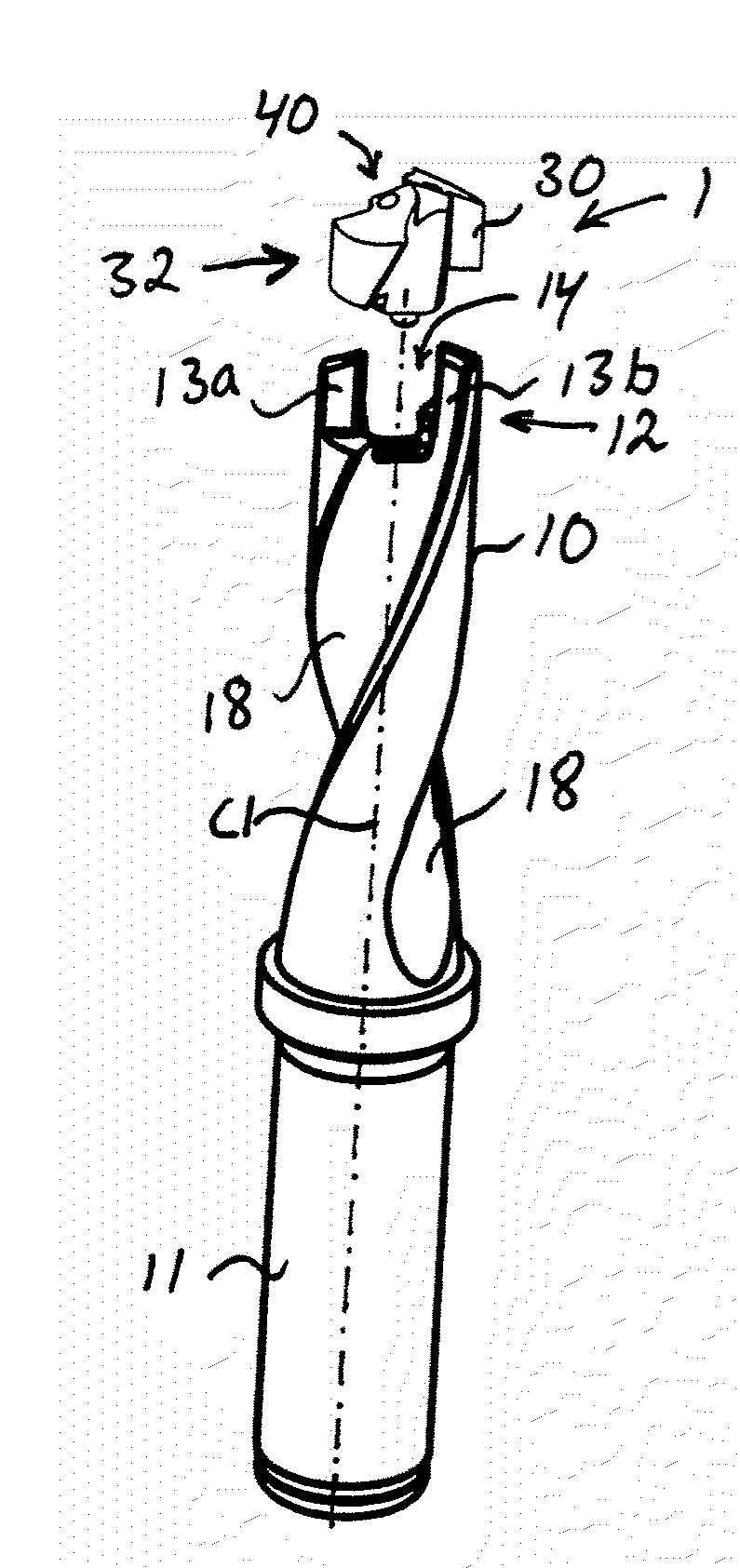
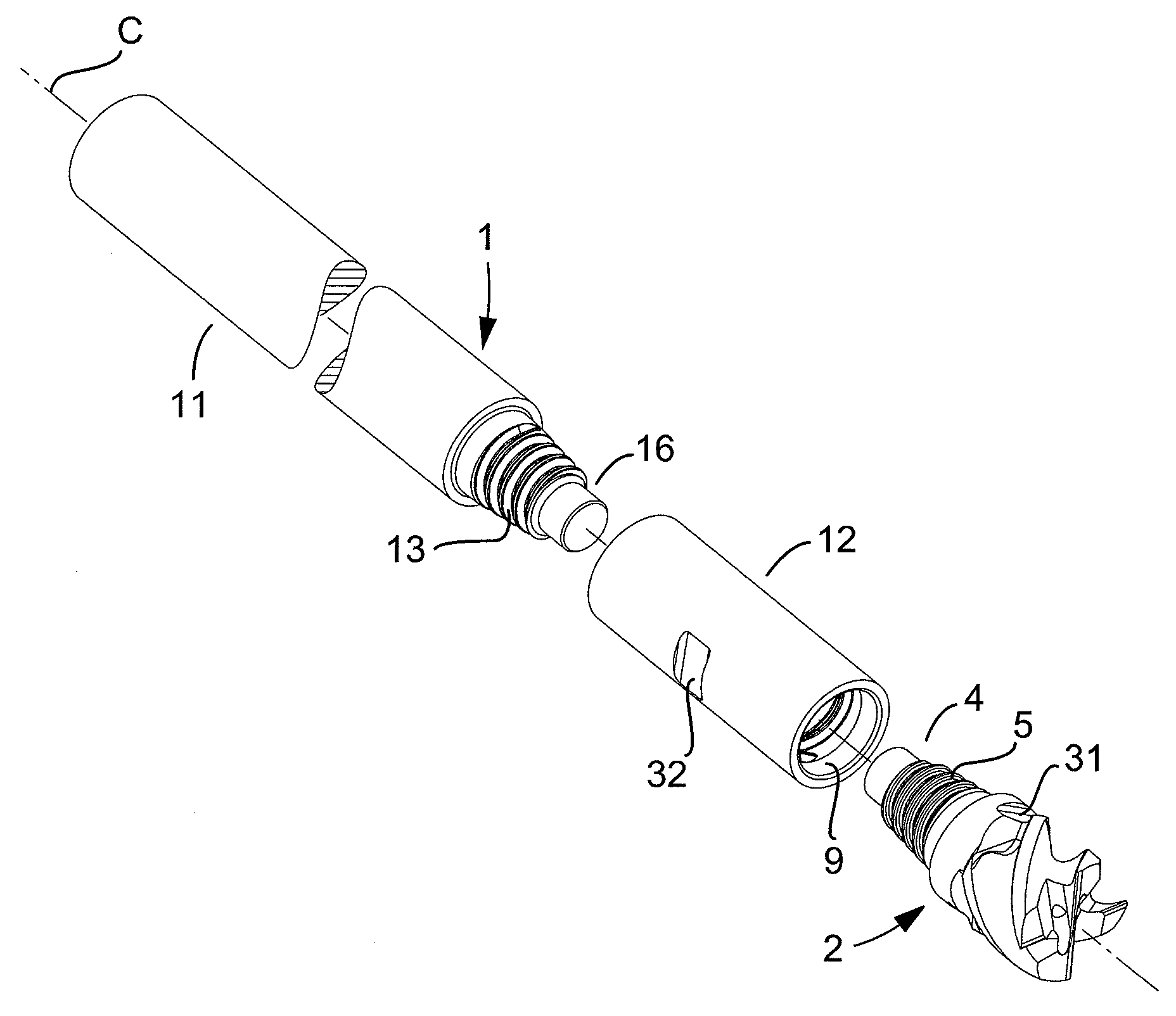
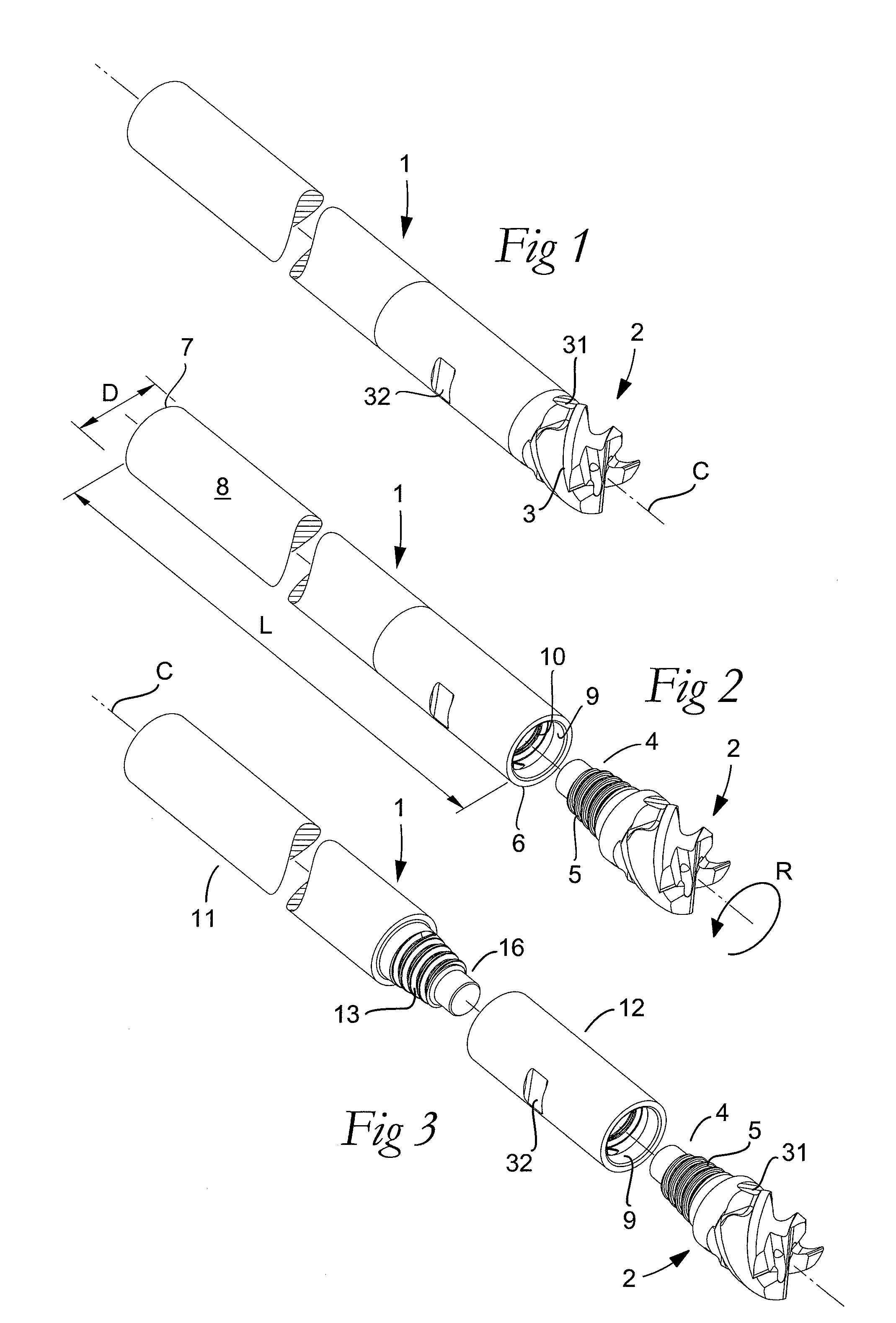
Rotatable tool for chip removing machining as well as a loose top and a basic body therefor
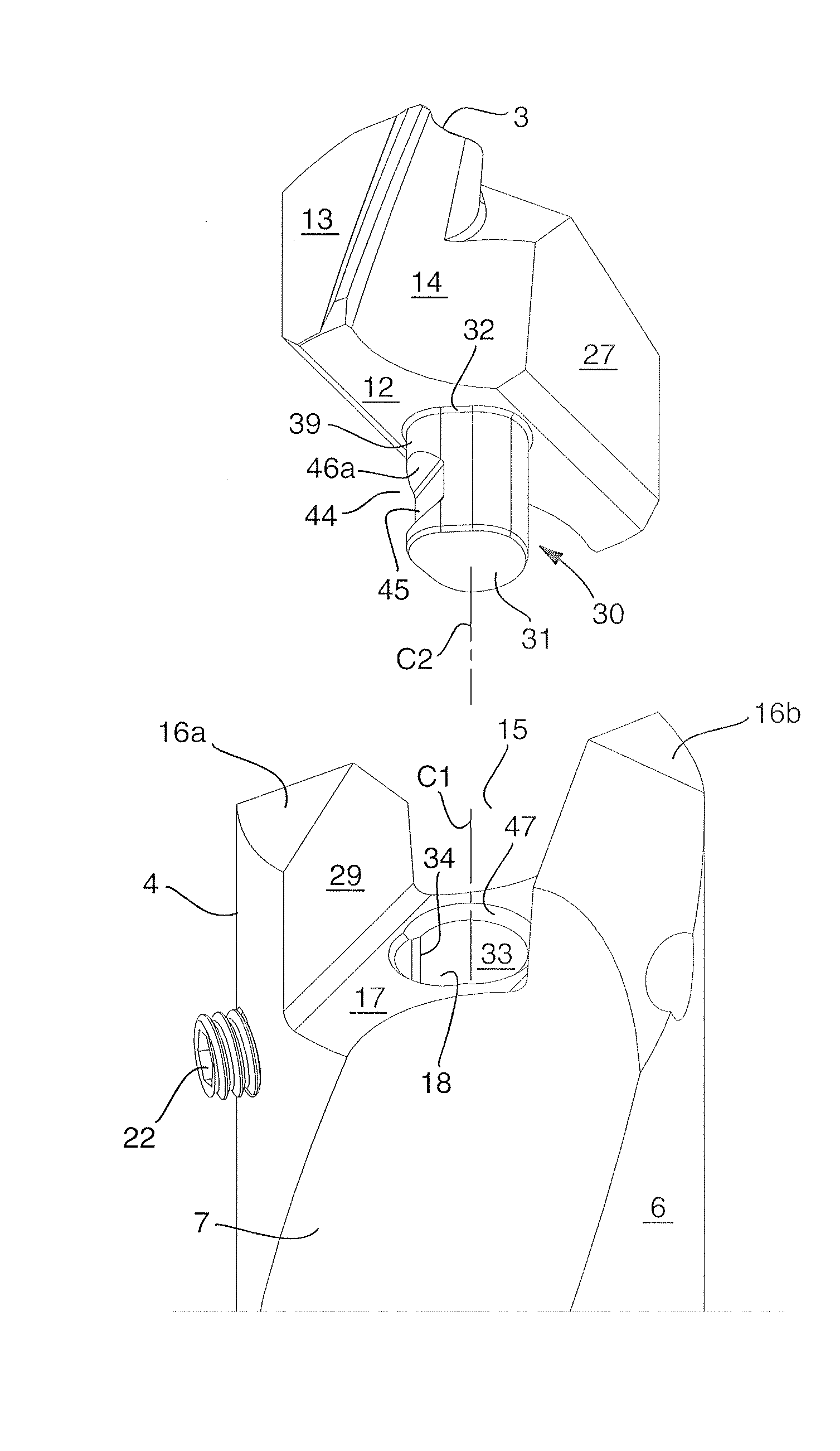
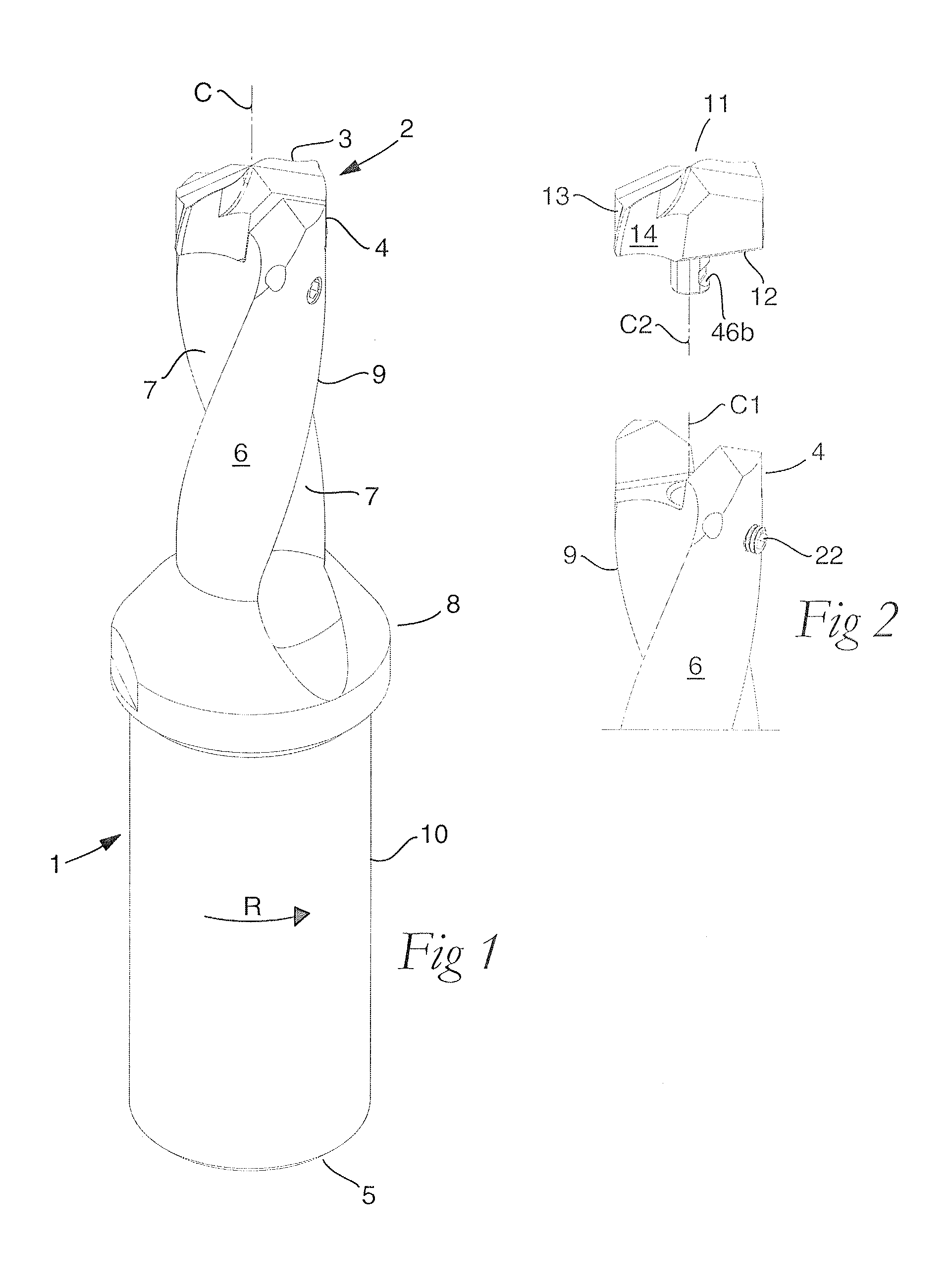
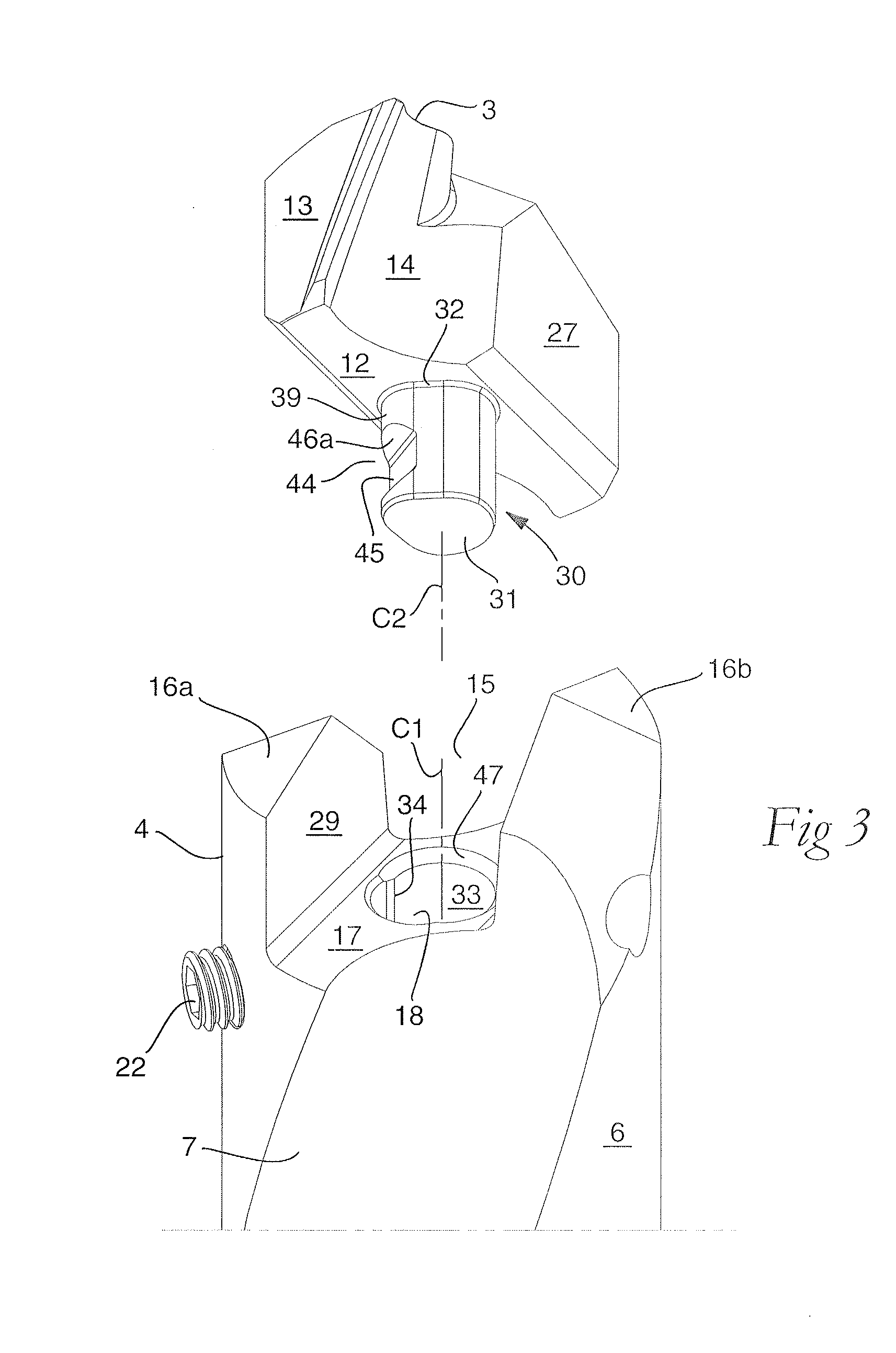
ActiveUS20110236145A1Strong and robustTool workpiece connectionTransportation and packagingEngineeringFront and back ends
A rotatable tool for chip removing machining, including a basic body having front and rear ends between which there extends a first geometrical center axis (C1) around which the basic body is rotatable in a predetermined direction of rotation, and a loose top having front and rear ends between which a second geometrical center axis (C2) extends. The front end of the basic body includes a jaw, which is delimited by two drivers and an intermediate bottom and in which a part of the loose top is received. A centering pin protrudes axially rearward from the loose top and is inserted in an axial center hole, which mouths in the bottom of the jaw and in which a threaded hole mouths for a screw co-operating with the center pin. The center hole includes a cylindrical support surface, which is concentric with the center axis (C1) of the basic body and against which the centering pin of the loose top is pressed by the screw. The centering pin of the loose top includes first and second diametrically opposed, external surfaces, each having an axial extension and a peripheral extension, the first external surface forming a contact surface that is pressed against the support surface of the center hole and extends tangentially between two axially extending boundary generatrices, which are situated along an imaginary circumscribed circle (S2) having a center (MP2) coinciding with the center axis (C2) of the loose top, and between which an arc angle (β) is less than 180°, the second external surface forming a clearance surface that lacks contact with the inside of the center hole as a consequence of the cross-sectional area of the centering pin being smaller than the cross-sectional area of the center hole. The circumscribed circle (S2) has a radius (r2) that is equally great as the radius (r1) of an inscribed circle (S1) along the cylindrical support surface of the center hole. A greatest radial distance (RD2) between the center axis (C2) of the loose top and a point on the clearance surface of the centering pin is greater than the radius (r2) of the circumscribed circle (S2) but smaller than a corresponding distance (RD1) between the center axis (C1) of the basic body and a clearance surface situated in the center hole and opposite the support surface.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
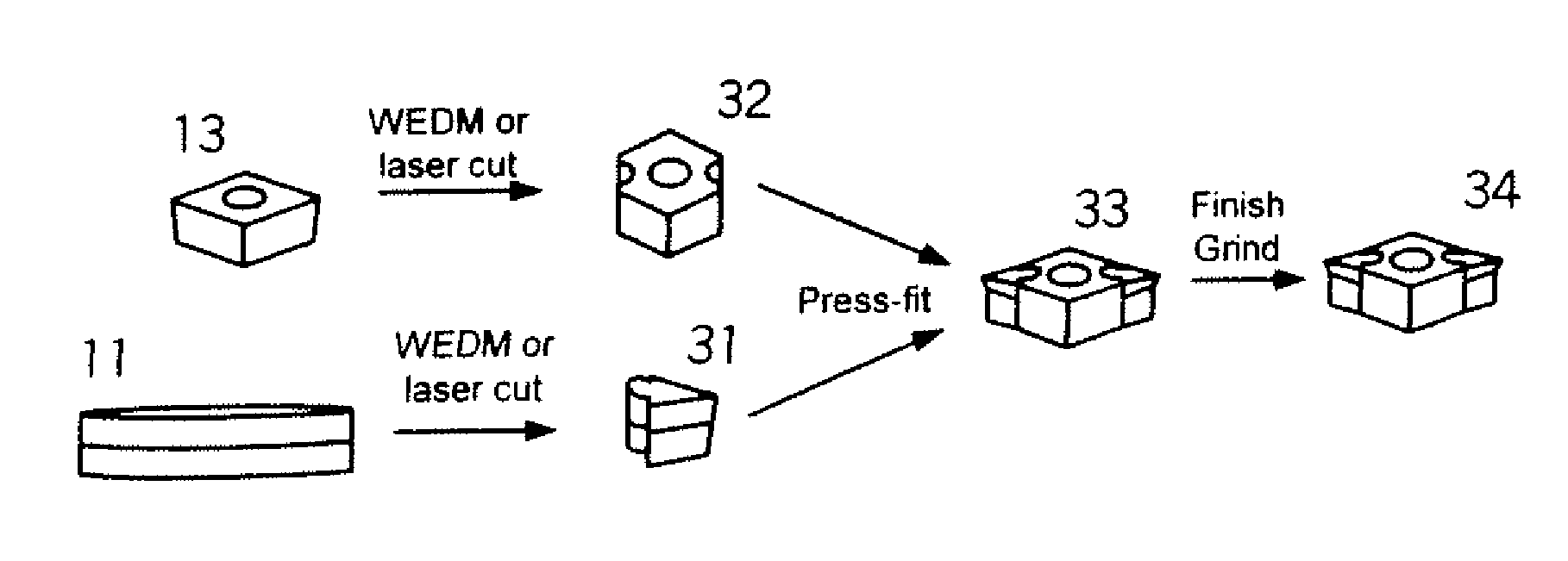
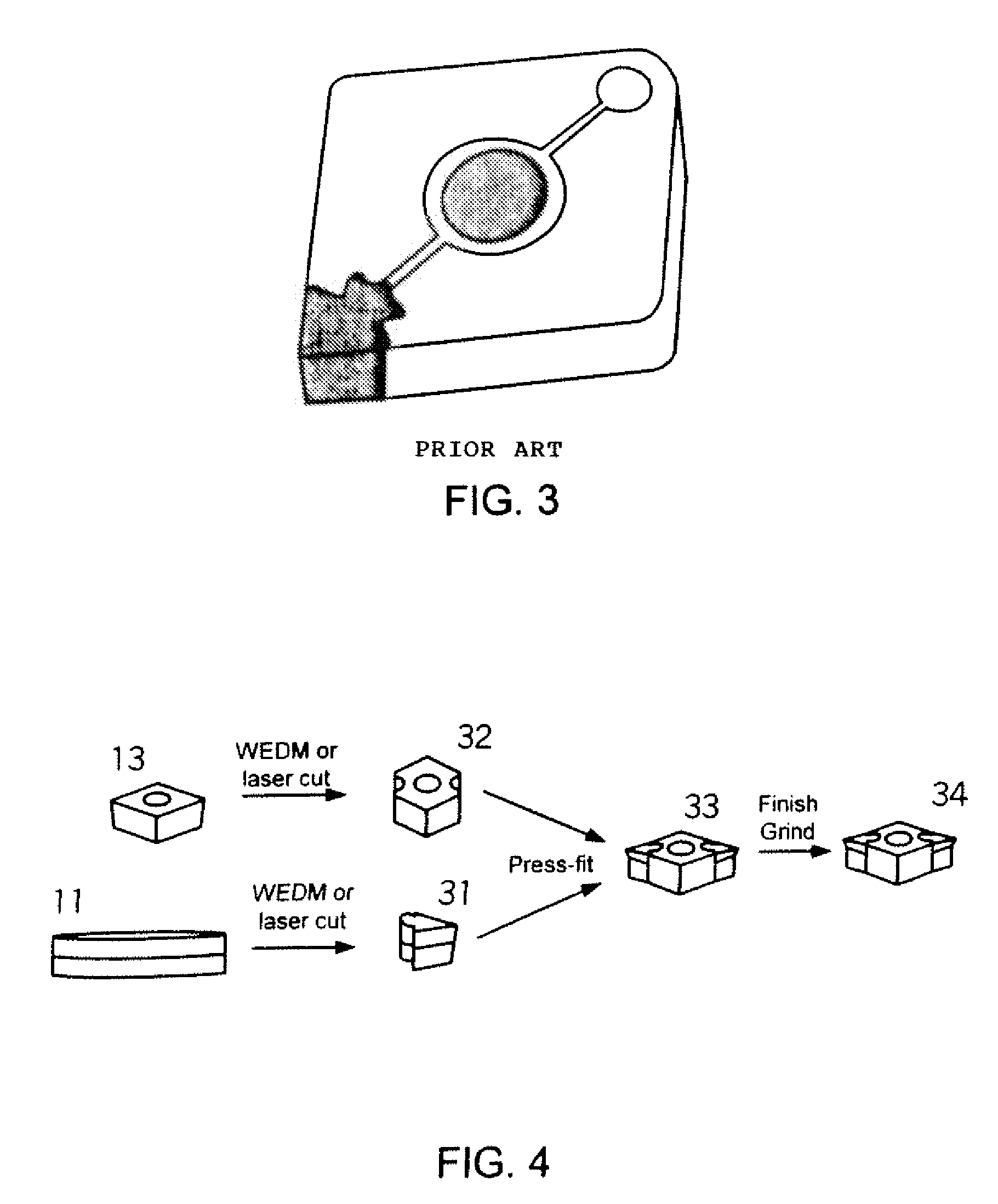
Indexable cutting inserts and methods for producing the same
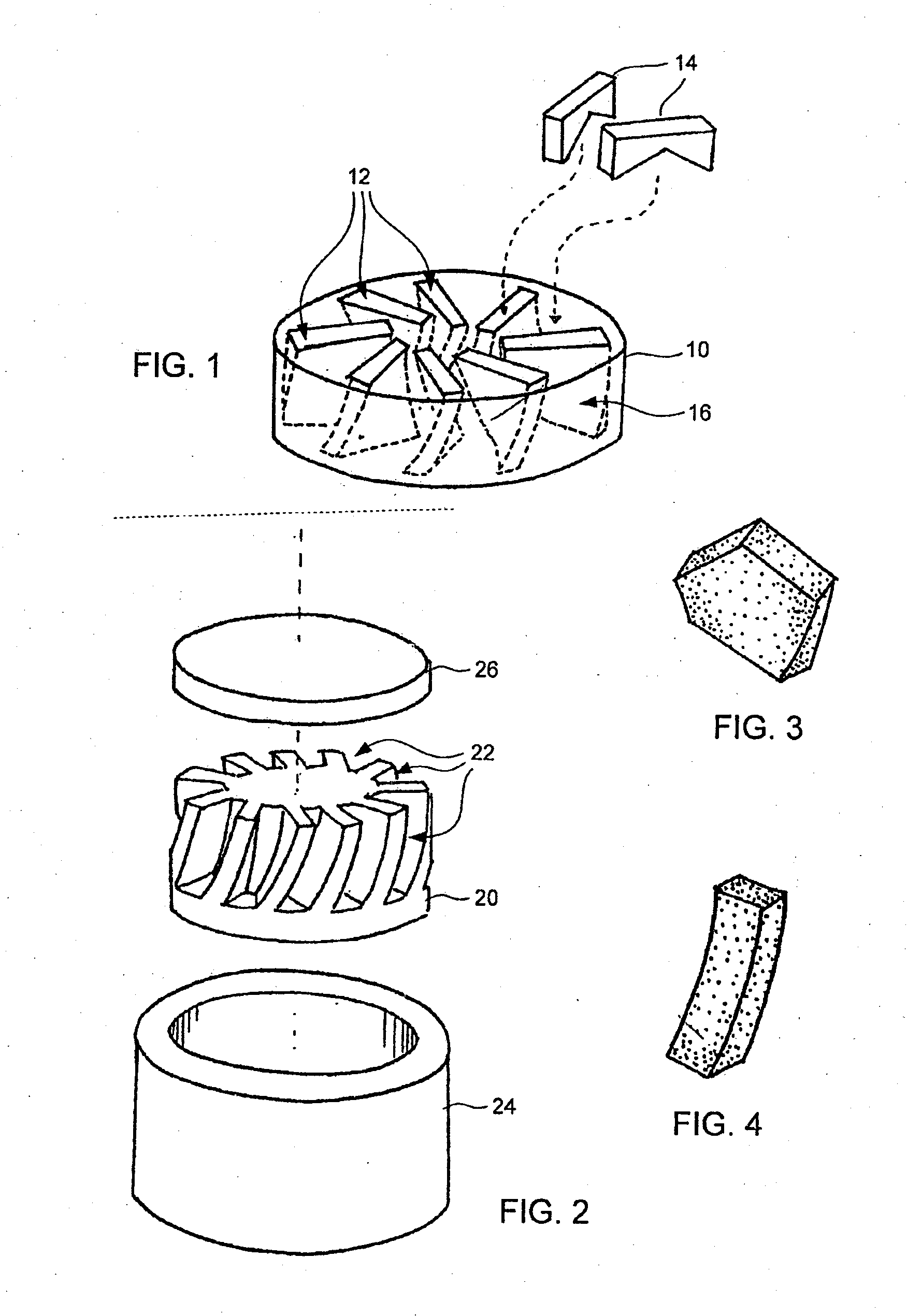
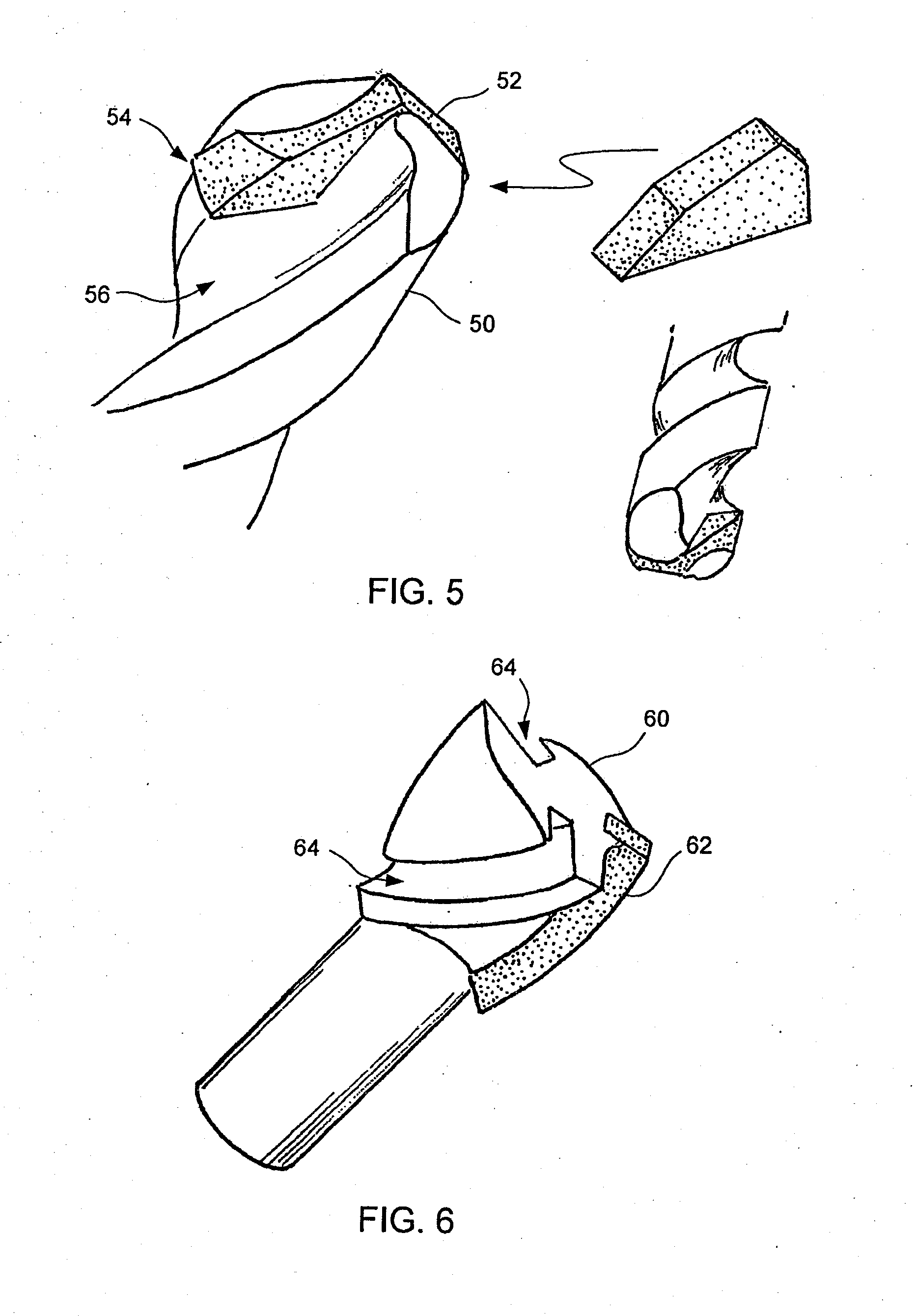
InactiveUS20050183893A1Produced in advanceDrill bitsTool workpiece connectionSuperhard materialEngineering
A method of making a cutting insert includes: (i) forming a blank having a substrate and superhard material, the substrate having more than 4 pockets, the superhard material disposed within the pockets; (ii) removing cutting tips from the blank by cutting the blank along cutting lines; (iii) providing a cutting insert body having a plurality of cavities for receiving a corresponding number of cutting tips; (iv) inserting a cutting tip into each of the plurality of cavities; and (v) brazing the cutting tips to the cutting insert body. A related cutting insert includes: a cutting insert body having a plurality of cavities formed therein; a plurality of cutting tips, each of the plurality of cutting tips disposed in a respective cavity, the cutting tips having a geometry that provides a mechanical retention or lock when inserted into the cavities of the cutting insert body, said geometry including a generally trapezoidal anchor portion with its base substantially flat and spaced away form the cutting edge of the body, the cutting tips further being brazed in the cutting insert body.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Cutting tool for high-quality high-efficiency machining and cutting method using the same
It is an object to provide a cutting tool which can perform high-quality, high-efficiency machining of a workpiece such as hardened steel.The cutting tool includes a finishing cutting edge 6 which initially cuts into the workpiece, and superfinishing cutting edges 7 for finishing the workpiece cut by the finishing cutting edge. The superfinishing cutting edges 7 project from the finishing cutting edge by a predetermined amount B in such a direction that the depth of cut of the superfinishing cutting edges increases. Each superfinishing cutting edge includes a burnishing portion 7a having a predetermined width L in the feed direction of the tool, and a wiper portion 7b. The superfinishing cutting edges 7 burnish the finished surface formed by the finishing cutting edge, while removing a affected layer formed by the finishing cutting edge.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com