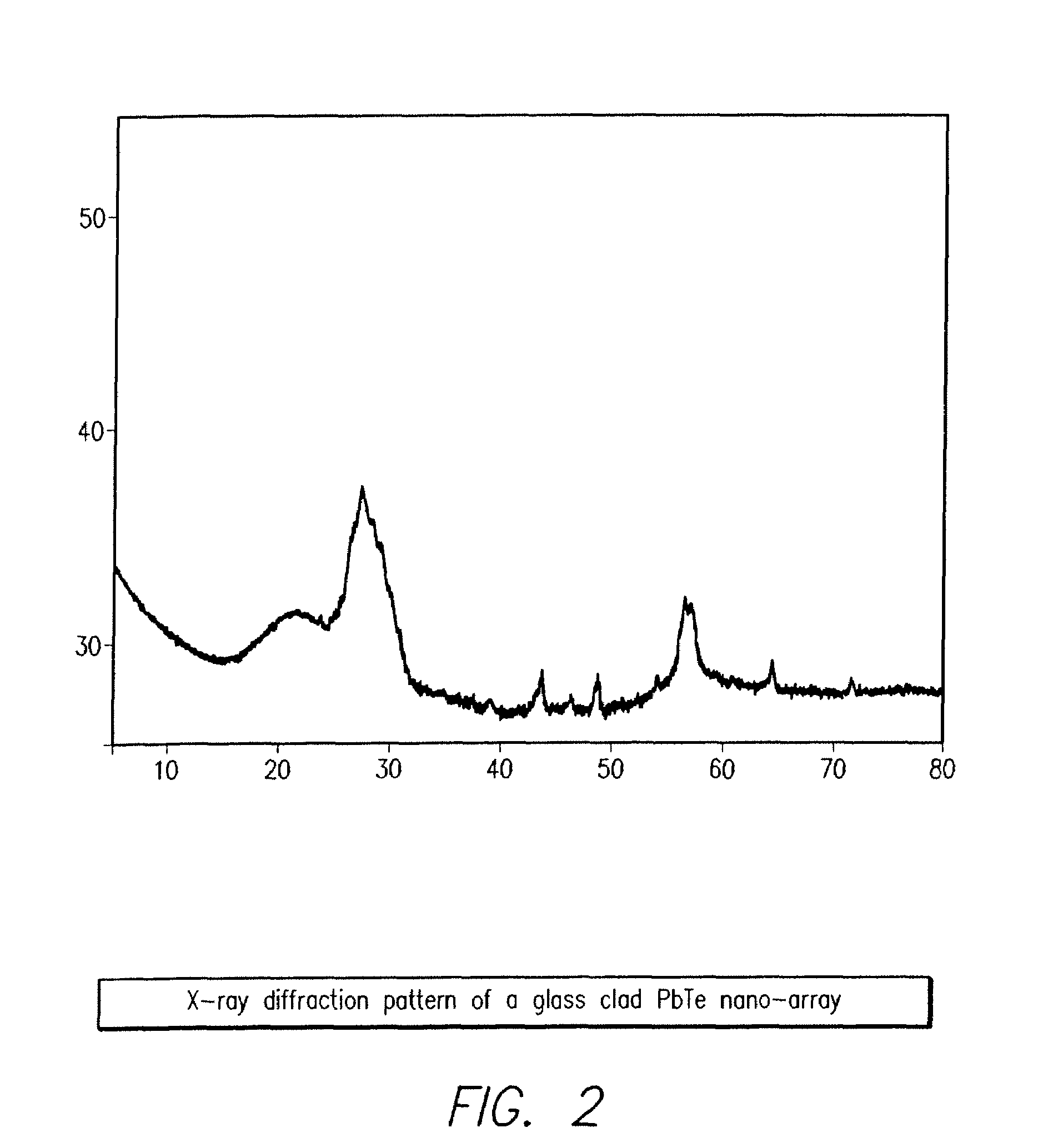
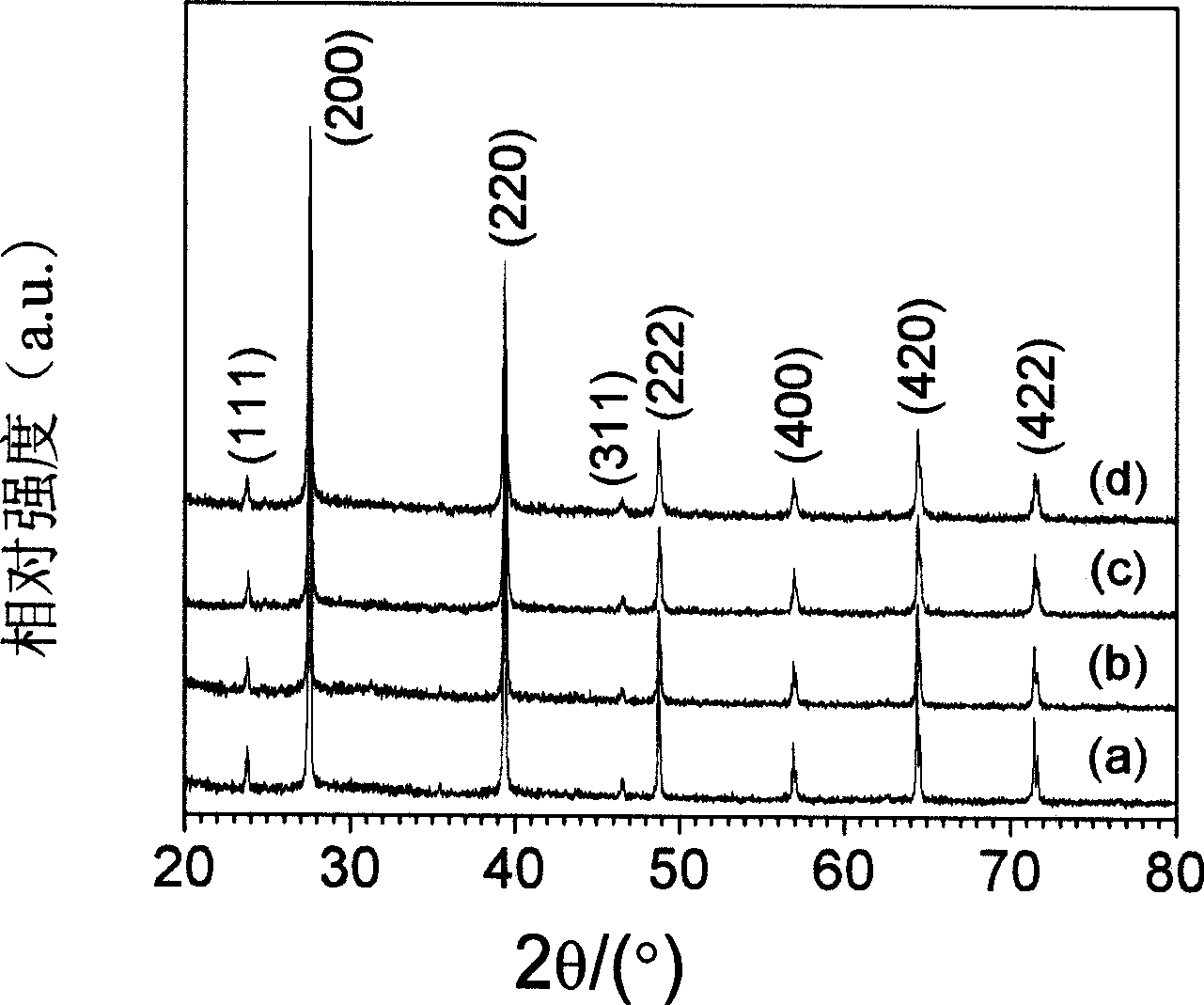
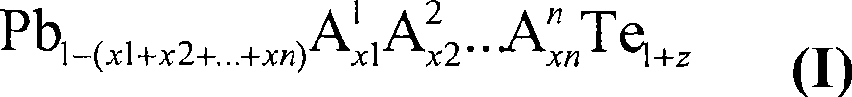Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Lead telluride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
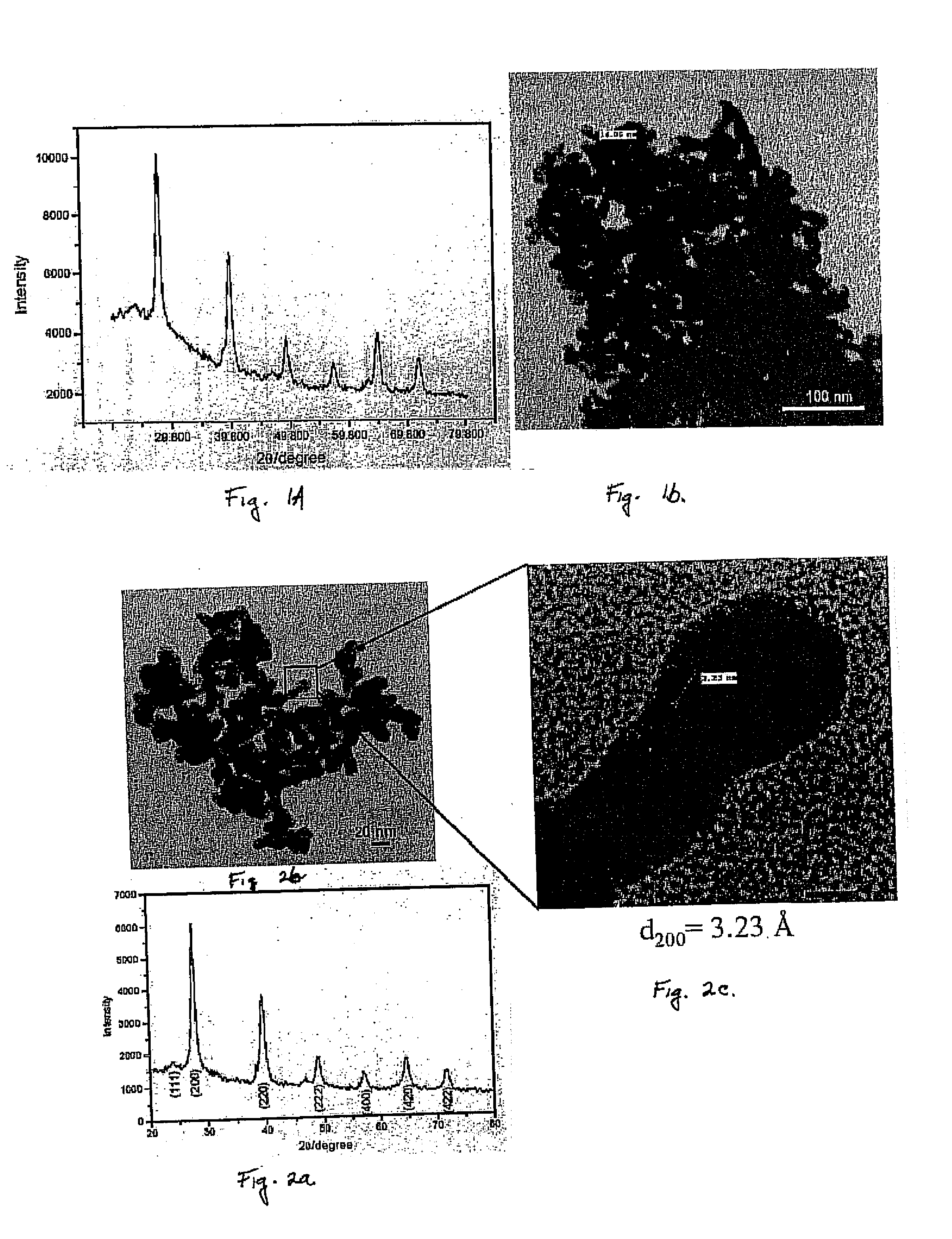
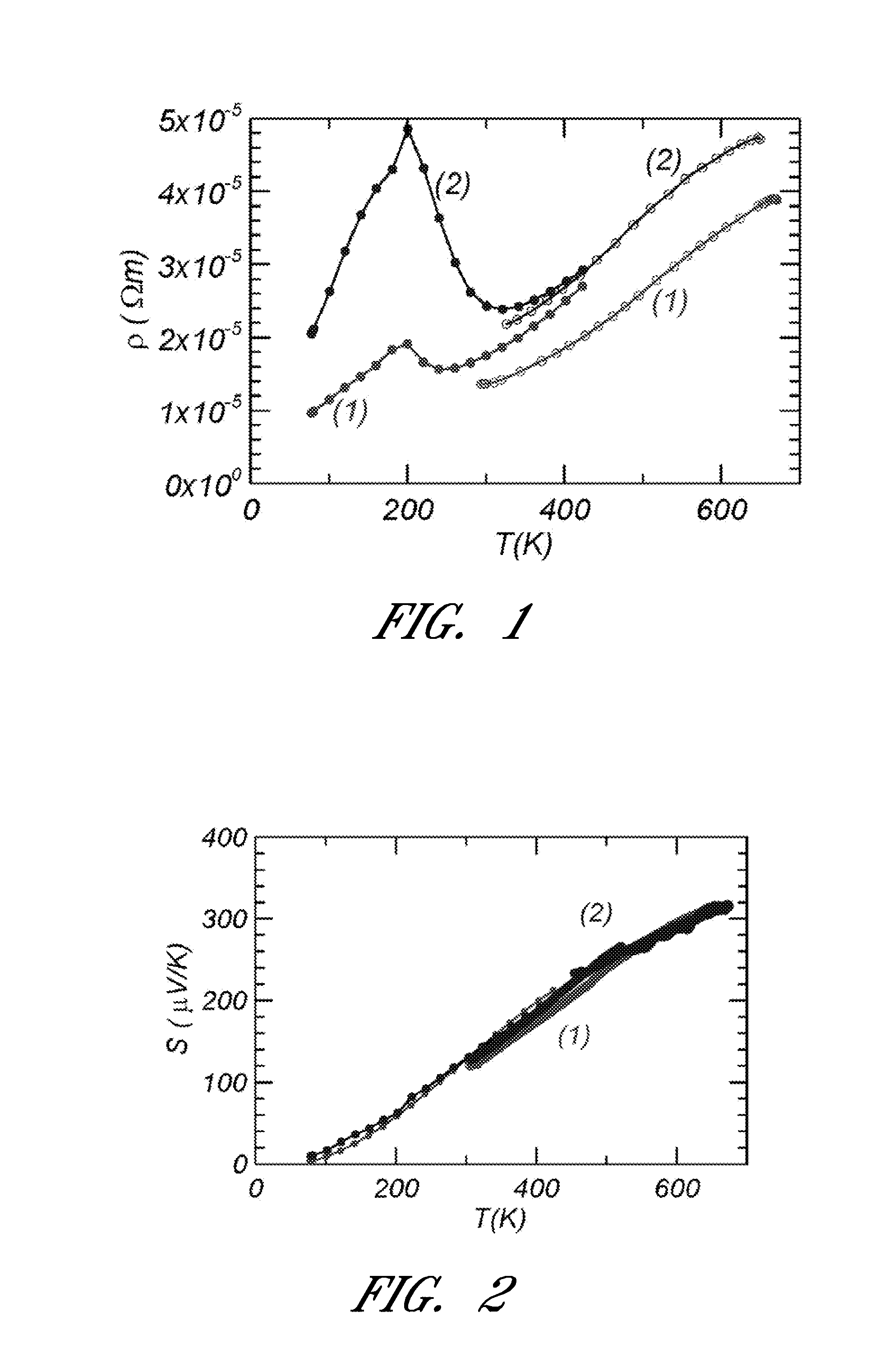
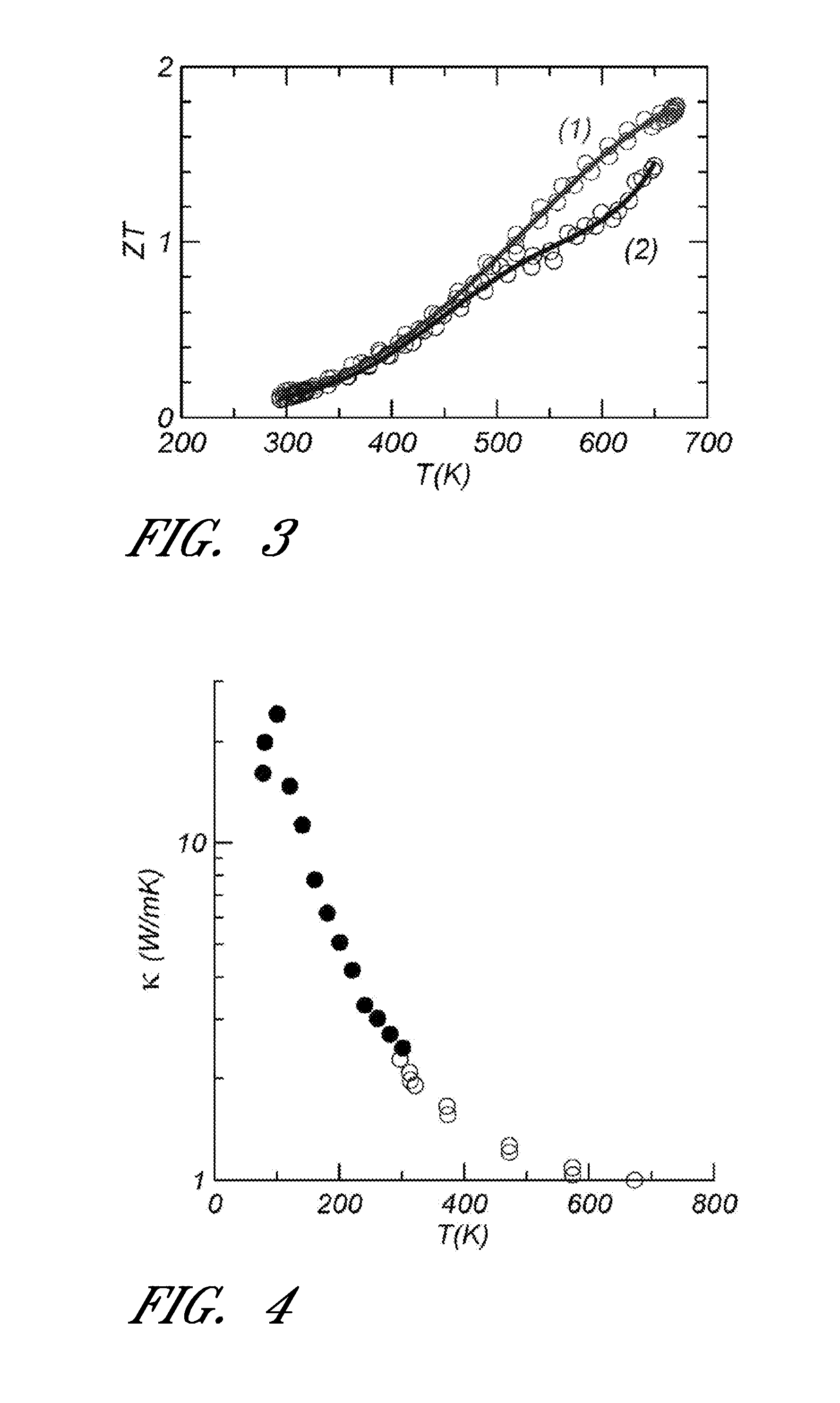
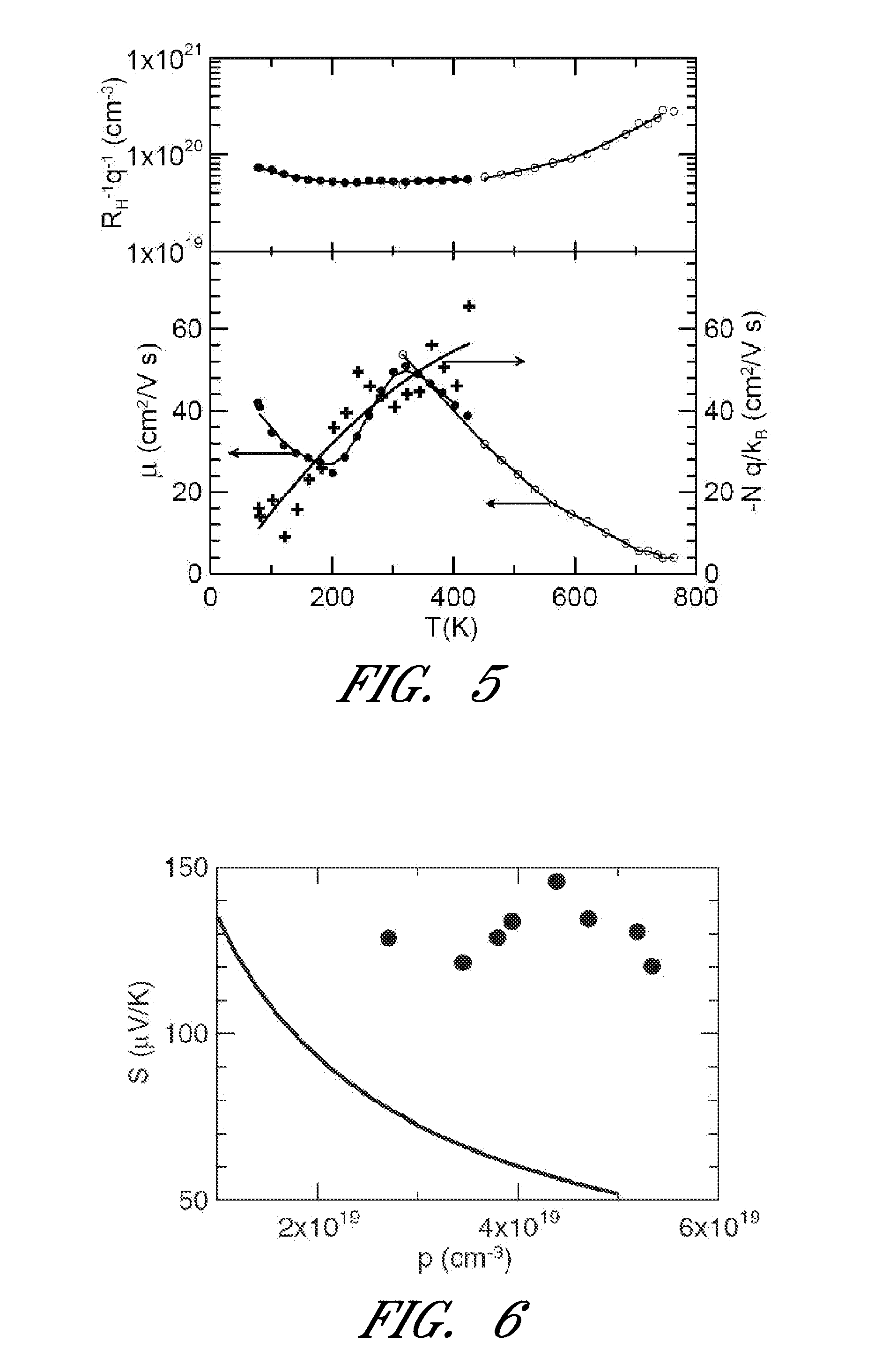
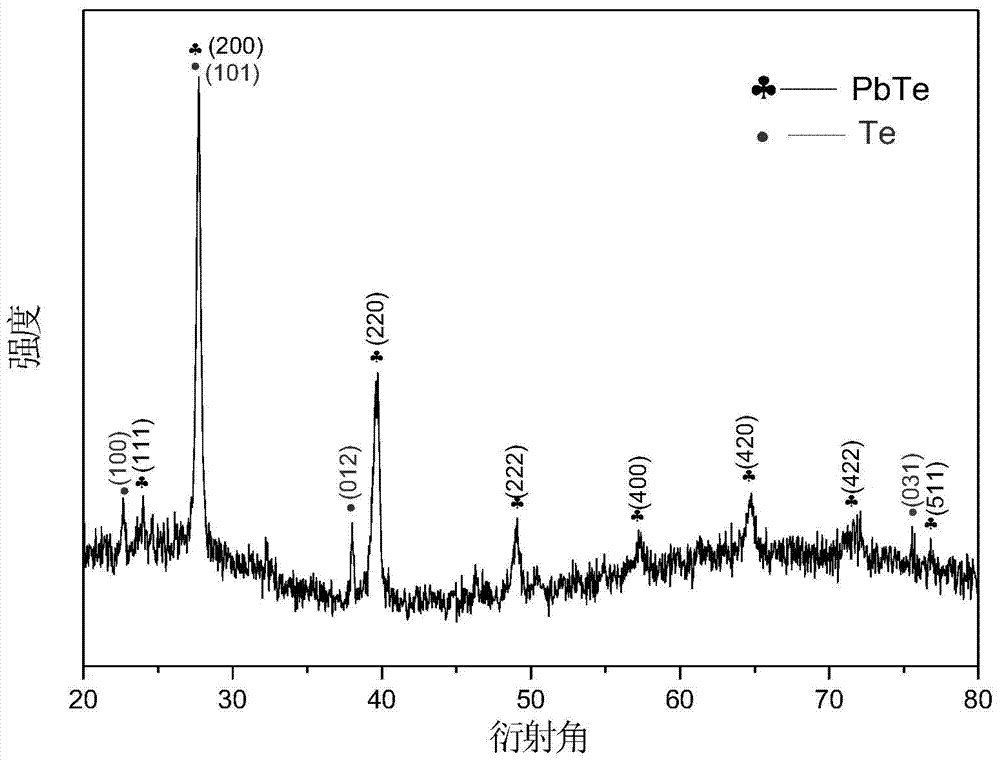
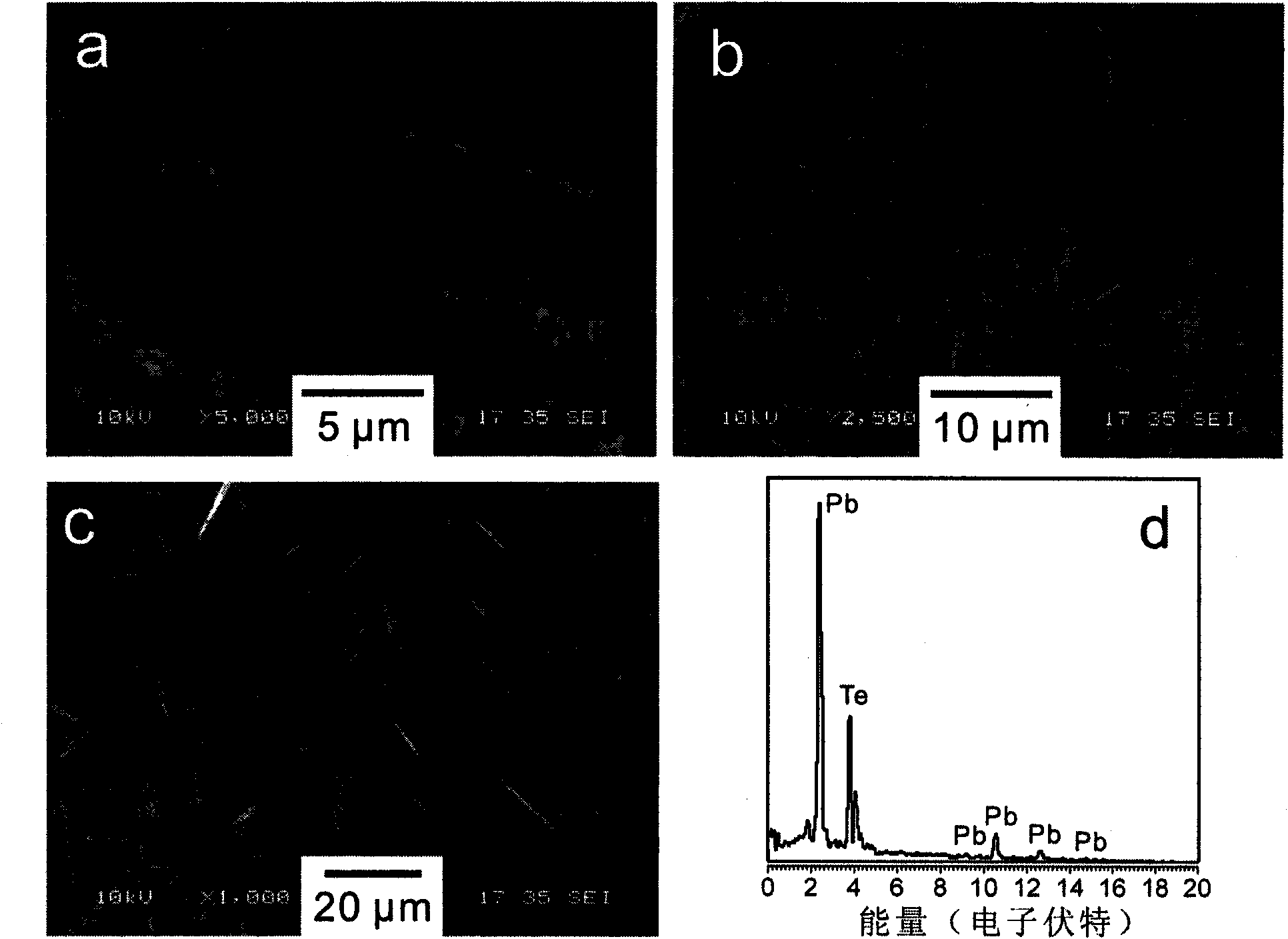
Lead telluride is a compound of lead and tellurium (PbTe). It crystallizes in the NaCl crystal structure with Pb atoms occupying the cation and Te forming the anionic lattice. It is a narrow gap semiconductor with a band gap of 0.32 eV. It occurs naturally as the mineral altaite.
Metal telluride nanocrystals and synthesis thereof
InactiveUS20080112877A1Material nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsBismuth tellurideLead telluride
A process for synthesizing a metal telluride is provided that includes the dissolution of a metal precursor in a solvent containing a ligand to form a metal-ligand complex soluble in the solvent. The metal-ligand complex is then reacted with a telluride-containing reagent to form metal telluride domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers. NaHTe represents a well-suited telluride reagent. A composition is provided that includes a plurality of metal telluride crystalline domains(PbTe)1-x-y(SnTe)x(Bi2Te3)y (I)having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive where x is between 0 and 1 inclusive and y is between 0 and 1 inclusive with the proviso that x+y is less than or equal to 1. Each of the metal telluride crystalline domains has a surface passivated with a saccharide moiety or a polydentate carboxylate. A densified mass having a density of greater than 95% of the theoretical density includes a plurality of lead telluride, tin telluride, bismuth telluride, or a combination thereof of domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive that have been subjected to hot isotactic pressing.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA +1
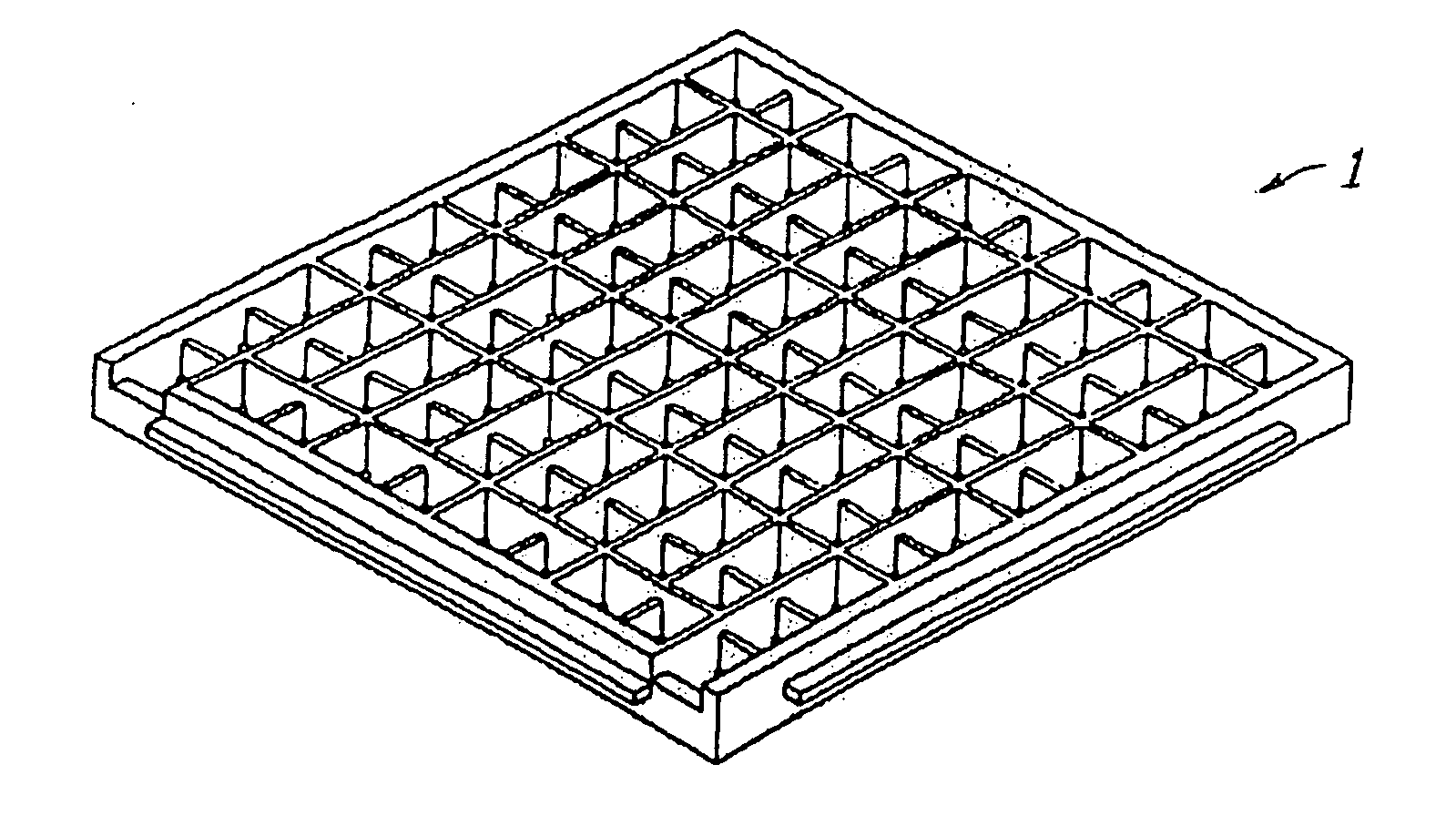
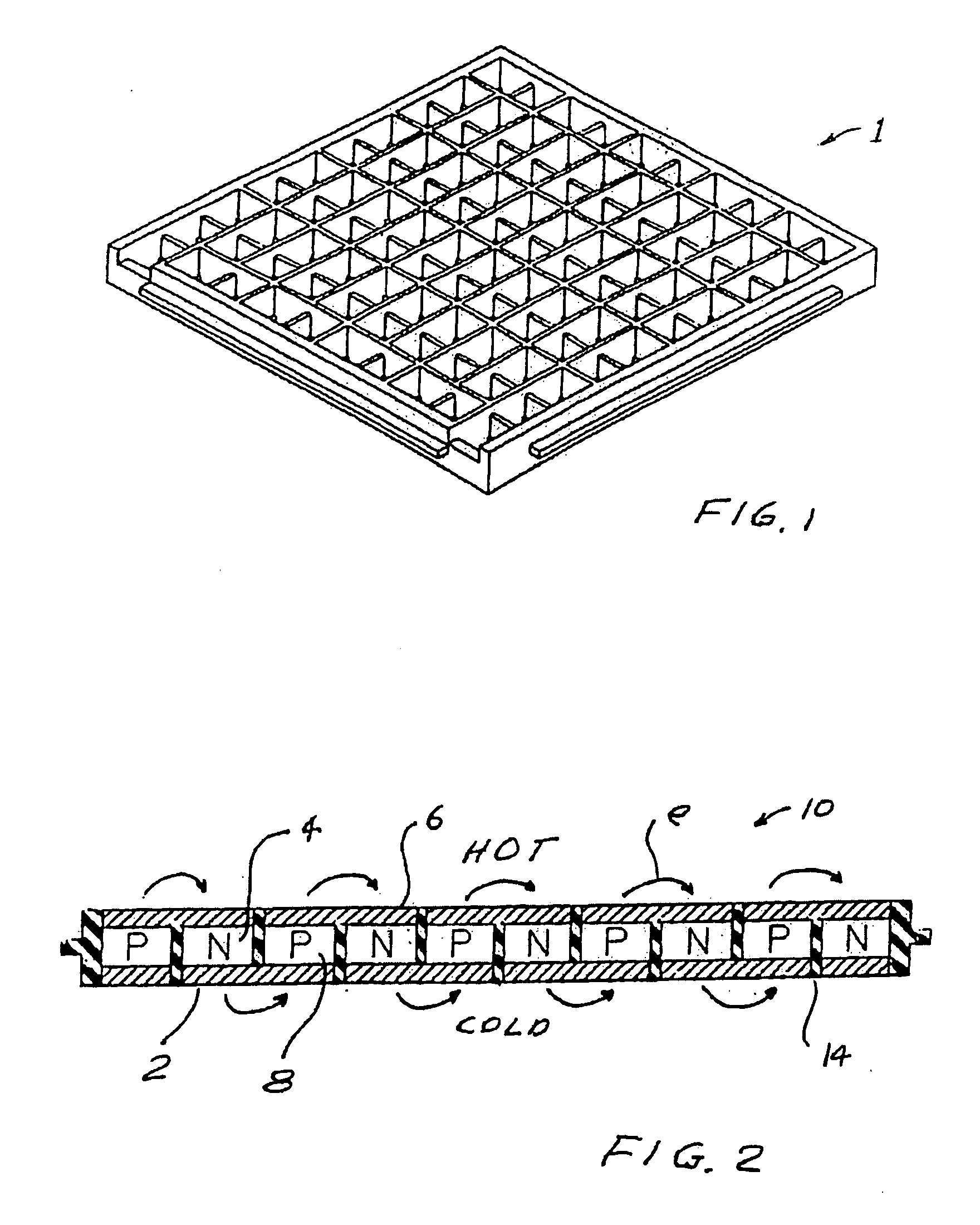
Segmented thermoelectric module with bonded legs
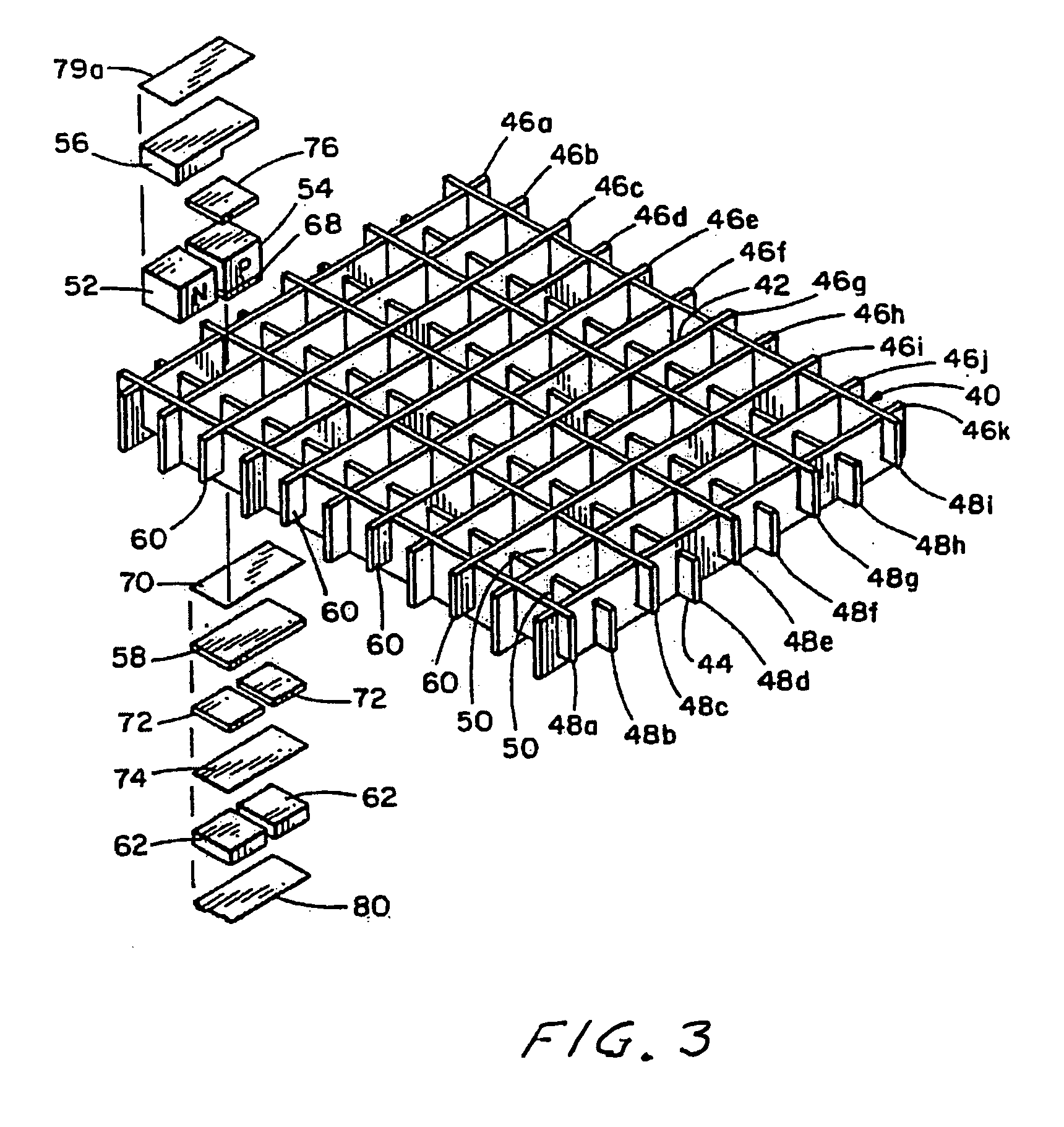
InactiveUS20120103381A1Effective applicationLow thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectExhaust apparatusElectricityLead telluride
A segmented lead telluride egg-crate thermoelectric module. In preferred embodiments N legs and P legs are segmented into at least two segments. The segments are chosen for their figure of merit in the various temperature ranges between the hot side and the cold side of the module. In preferred embodiments a low-temperature egg-crate, molded from a liquid crystal polymer material, having very low thermal conductivity holds in place and provides insulation and electrical connections for the thermoelectric N legs and P legs at the cold side of the module. A castable ceramic capable of operation at temperatures in excess of 500° C. is used to provide electrical insulation between the legs at the hot side of the module.
Owner:BASF SE & HI Z TECH
High temperature compact thermoelectric module with gapless eggcrate
InactiveUS20100024437A1Low thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentBismuth tellurideLead telluride
A high-temperature thermoelectric module. The module includes a two part molded egg-crate for holding in place and providing insulation and electrical connections for a number of thermoelectric n-legs and p-legs. A first part of the egg-crate is comprised of a ceramic material capable of operation at temperatures in excess of 600° C. and a second part comprised of a thermoplastic material having very low thermal conductivity. In preferred embodiments the high temperature ceramic is zirconia and the thermoplastic material is DuPont Zenite. The thermoelectric legs are also comprised of high-temperature and low-temperature material. In preferred embodiments the high temperature thermoelectric material is lead telluride and the low temperature material is bismuth telluride. In preferred embodiments metal felt spacers are provided in each leg to maintain proper electrical contacts notwithstanding substantial temperature variations. Preferably the module is sealed in an inert gas filled insulating capsule.
Owner:HI Z TECH +1
Thermoelectric figure of merit enhancement by modification of the electronic density of states
InactiveUS20110248209A1Heat-exchange elementsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsDopantChemical compound
A thermoelectric material and a method of using a thermoelectric material is provided. The thermoelectric material can include at least one compound. For example, the at least one compound may be a Group IV-VI compound such as lead telluride. The at least one compound may further include one or more dopants such as sodium, potassium, and thallium. The method of using a thermoelectric material can include exposing at least one portion of the at least one compound to a temperature greater than about 700 K.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV +1
Doped lead tellurides for thermoelectric applications
InactiveCN101421185AEnergy inputSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsSemiconductor materialsLead telluride
A p- or n-conductive semiconductor material comprises a compound of the general formula Pb1-(x1+x2+ . . . +xn)A1x1A2x2 . . . AnxnTe1+z (I) where: in each case independently n is the number of chemical elements different from Pb and Te, 1 ppm<=x1 . . . xn<=0.05, -0.05<=z<=0.05 and n>=2, A1 . . . An are different from one another and are selected from the group of the elements Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, As, Sb, Bi, S, Se, Br, I, Sc, Y, La, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu or n=1, and A1 is selected from Ti, Zr, Ag, Hf, Cu, Gr, Nb, Ta.
Owner:BASF AG
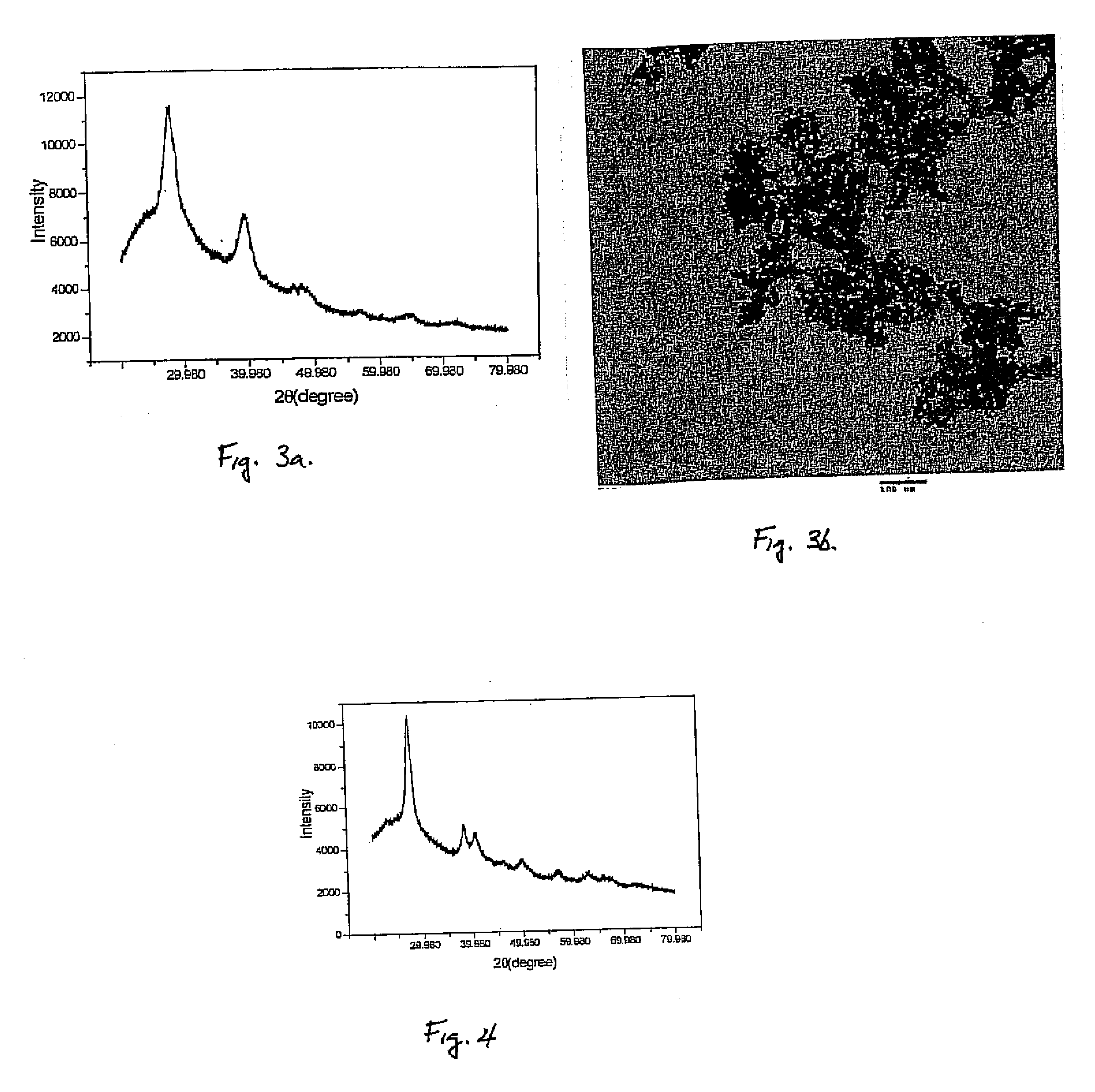
Method for producing selenide and telluride nano-material with composite base metal hydroxide solvent
InactiveCN101219779ALow costSimplify operating proceduresBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsLead tellurideSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing nanometer crystal material of selenide and telluride, suitable for preparing nanometer crystal materials such as zinc selenide, lead selenide, cadmium selenide, cuprous selenide, zinc and cadmium selenide, silver telluride and lead telluride. The method is characterized by replacing water or organic solvent in the prior hydrothermal / solvent thermal synthetic method with fused compound hydroxide of alkali metals, and carrying out chemical reaction under normal pressure of temperature of 100 to 300 DEG C. All materials are soluble inorganic metal salts, selenide powders and telluride powders. The synthetic process has low cost; various parameters (such as temperature, pressure, concentration, etc.) in the reaction process are easy to monitor and control; the reaction system is good in uniformity, simple in technology and easy in production expansion. The obtained crystal products have good crystallinity, clean surface and uniform size, thus suitable for intrinsic property research and function exertion of the nanometer crystal material to the maximum limit.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Metal telluride nanocrystals and synthesis thereof
InactiveUS20080036101A1Material nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsCarboxylic saltCarboxylic acid
A process for synthesizing a metal telluride is provided that includes the dissolution of a metal precursor in a solvent containing a ligand to form a metal-ligand complex soluble in the solvent. The metal-ligand complex is then reacted with a telluride-containing reagent to form metal telluride domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers. NaHTe represents a well-suited telluride reagent. A composition is provided that includes a plurality of metal telluride crystalline domains(PbTe)1-x-y(SnTe)x(Bi2Te3)y (I)having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive where x is between 0 and 1 inclusive and y is between 0 and 1 inclusive with the proviso that x+y is less than or equal to 1. Each of the metal telluride crystalline domains has a surface passivated with a saccharide moiety or a polydentate carboxylate. A densified mass having a density of greater than 95% of the theoretical density includes a plurality of lead telluride, tin telluride, bismuth telluride, or a combination thereof of domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive that have been subjected to hot isotactic pressing.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Preparation method and application of two-dimensional lead telluride nano sheet and nano material
ActiveCN109650354AIncrease the areaReduce surface roughnessNanotechnologyPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic detectorsDecomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of nano materials, in particular to a preparation method and application of a two-dimensional lead telluride nano sheet and a nano material. The method comprises the steps that a reaction raw material which is used for the growing of the lead telluride nano sheet is weighed; a sheet-like material with a surface with an atomic level smoothness is taken as a growing substrate; the reaction raw material is thermostatically heated to perform vapor deposition in a protective gas flow after programmed temperature increasing; the substrate is allowed to bequenched after the decomposition process is completed, and the two-dimensional lead telluride nano sheet is obtained on the substrate. The thickness of the nano sheet is 5 nm-200 nm, the width or length is 0.1-70 microns, and the nano sheet is provided with a monocrystalline structure. The nano sheet is of a face-centered cubic crystal, and the exposed crystal face of the nano sheet belongs to {100} crystal face family and is provided with a sheet-like rectangular morphology; the ultra-thin two-dimensional lead telluride nano sheet with large area, uniform orientation and morphology and crystallinity can be obtained through a Van der waals epitaxy technology, and the two-dimensional lead telluride nano sheet can be applied to the fields of infrared ray photoelectric detectors and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method of drawing a glass clad multi core lead telluride wire
InactiveUS7530239B2Large ZT factorCost-effectively integrated into everyday heatingGlass making apparatusThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectFiberLead telluride
The present invention provides a method of drawing nanowires, comprising sealing off one end of a glass tube such that the tube has an open end and a closed end, introducing a nanowire material inside the glass tube and evacuating the tube by attaching the open end to a vacuum pump, heating a portion of the glass tube such that the glass partially melts under the vacuum such that the partially melted glass tube provides an ampoule containing the nanowire material to be used in a first drawing operation, introducing the ampoule containing the nanowire material into a heating device, increasing the temperature within the heating device such that the glass tube melts just enough for it to be drawn and drawing fibers of glass clad nanowire material. The invention further provides a method for bunching together such fibers and redrawing them one or more times to produce arrays of nanowires clad in glass.
Owner:ZT3 TECH INC
Preparation of lead telluride base block thermoelectric material
InactiveCN101486450AImprove thermoelectric performanceGood orientationSelenium/tellurium compundsTe elementImpurity
The invention relates to a method for preparing block thermoelectric material of lead telluride base. Relevant salts are taken as raw materials, PbTe thermoelectric material containing Ag, Sb and Se is prepared by adopting a hydrothermal method combined with the technique of vacuum melting; the thermoelectric material refers to Ag1-xPbn-2SbTen-ySey, wherein, n is equal to or more than 12, x is equal to or more than 0 and less than 1 and y is equal to or more than 0 and equal to or less than 0.1n. The preparation method is as follows: firstly, a silver soluble salt, a lead soluble salt, a compound containing antimony, a compound containing tellurium, and selenium powder are taken as raw materials, alkali metal borohydride or diamide is taken as a reducing agent, the raw materials react at the temperature of 150 DEG C to 200 DEG C for 20 hours to 40 hours by adopting the hydrothermal method and lead telluride powder with impurities is prepared. Then, the obtained powder is put into a graphite crucible and sealed in a quartz glass tube under vacuum. The well-sealed glass tube is put into a resistance furnace with the temperature rising to 900 DEG C to 1000 DEG C, the heat is preserved for hours, then the temperature slowly drops to 450 DEG C which is kept for hours, and then the glass tube is cooled down to room temperature so as to obtain the compact block thermoelectric material. The preparation method of block thermoelectric material of telluride lead base is simple and economical and the prepared block thermoelectric material shows certain orientation and has fairly good thermoelectric property.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing superlattice nanowire array assembled by tellurium-lead telluride nanocrystals
InactiveCN103757688AEasy to prepareLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsTe elementTwo step
The invention relates to a method for preparing superlattice nanowire array assembled by tellurium-lead telluride nanocrystals and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: selecting porous anodized alumina (PAA) prepared by utilizing a two-step anodization method as a template; applying a negative bias voltage in electrolyte containing Pb and Te ions by virtue of a pulse electrochemical deposition technique, and alternatively carrying out electrochemical deposition of PbTe and Te elements in pore paths of the PAA, so as to finally obtain the superlattice nanowire array assembled by Te-PbTe nanocrystals. The method has the effects and the advantages that a product is an orderly-arranged superlattice nanowire array which is assembled by the tellurium-lead telluride nanocrystals and is alternatively formed by two different materials, namely tellurium nanocrystals and lead telluride nanocrystals; the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the components and structure of the array are easy to adjust and control; the superlattice nanowire array has important potential application prospects in the fields of energy sources, thermoelectricity, optics, electrics and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for leaching tellurium in tellurium slag in co-oxidation mode
ActiveCN105925811AImprove leaching effectEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumSlagMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for leaching tellurium in tellurium slag in a co-oxidation mode. The method comprises the following steps that 1, sodium chloride is added into a sulfuric acid solution and heated to 60 DEG C-90 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted, then, ozone is introduced, the tellurium slag is added, and stirring is conducted; and 2, under the condition that stirring is kept, hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the solution processed in the step 1, the solution and the ozone are subjected to oxidizing leaching in a synergetic mode, and solid-liquid separation is conducted after reaction lasts for 2-8 h, so that leaching slag and leaching liquid containing the tellurium are obtained. According to the method for leaching the tellurium in the tellurium slag in the co-oxidation mode, hydroxyl radicals very high in oxidizing capacity are produced under an O3 / H2O2 system; the stable structure of lead telluride and the stable structure of bismuthic acid copper are opened through the high oxidizing property of the hydroxyl radicals, so that the tellurium, bismuth and copper are exposed; the chlorine benignity characteristic of the tellurium and the bismuth is utilized, so that the leaching effect of the tellurium, the bismuth and the copper in the tellurium slag is good, the leaching rate of the tellurium reaches 99%, the leaching rate of the bismuth reaches 96%, and the leaching rate of the copper reaches 99%; and accordingly, the tellurium in the complex tellurium slag is efficiently and directly leached, and step-by-step recycling of the tellurium, the bismuth, the copper and antimony is facilitated.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of lead telluride nano crystal and micron crystal
InactiveCN101602495AHigh crystallinityHigh purityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsThermoelectric materialsLead salt
The invention relates to a preparation method of lead telluride nano crystal and micron crystal, belonging to the thermoelectric material technical field. In the method, soluble lead salt and compound containing tellurium are taken as raw materials, borohydride of alkali metal is taken as reducing agent, mixed hydroxides are adopted as reaction medium, and reaction is carried out for 0.5-12h at 170-200 DEG C at normal atmosphere, thus obtaining the PbTe nano crystal and micron crystal. The preparation method related in the invention has the characteristics of simple device and process, low cost and high reaction speed and is easy for industrialized production. The invention can obtain nano and micron PbTe products in different appearances by simply controlling reaction time. The obtained product has good crystallinity, and the surface is clean and smoother, thus having potential application value in preparation of nano and micro thermoelectric devices.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing lead telluride nano-wire
InactiveCN101225548AHigh puritySimple processPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsSemiconductor materialsLead telluride
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lead telluride nano-wire, belonging to the technical field of thermoelectric semiconductor materials, which comprises the following steps: first, prepare a Te nano-wire with the diameter of 3-20 nanometers; second, add Pb (NO3)2 with the same molar ratio with Na2TeO3 to the solution of Te nano-wire, seal in an autoclave at 90-100 DEG C to react for 9-12 hours, and get PbTe nano-wire with uniform diameter and the length of 1 micron to 100 microns. The preparation method of a lead telluride nano-wire has the advantages that: PbTe nano-wire with uniform diameter and average length smaller than the exciton Bohr radius can be produced through controlling the growth temperature, the lead salt concentration and the reaction time; the PbTe nano-wire prepared with the method can be used as an ideal scientific research material, laying good basis for preparing and realizing thermoelectric nanometer devices in the future.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
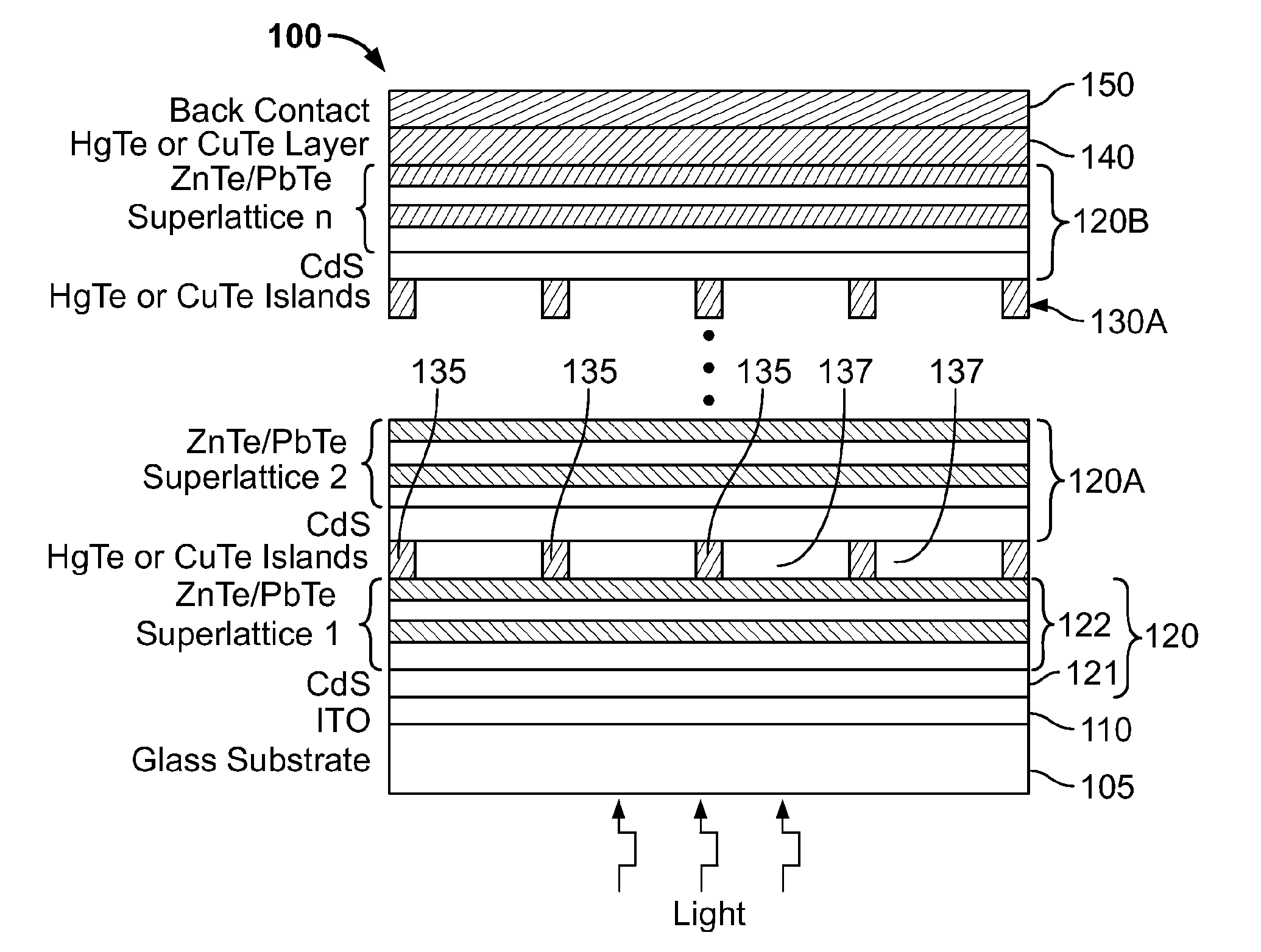
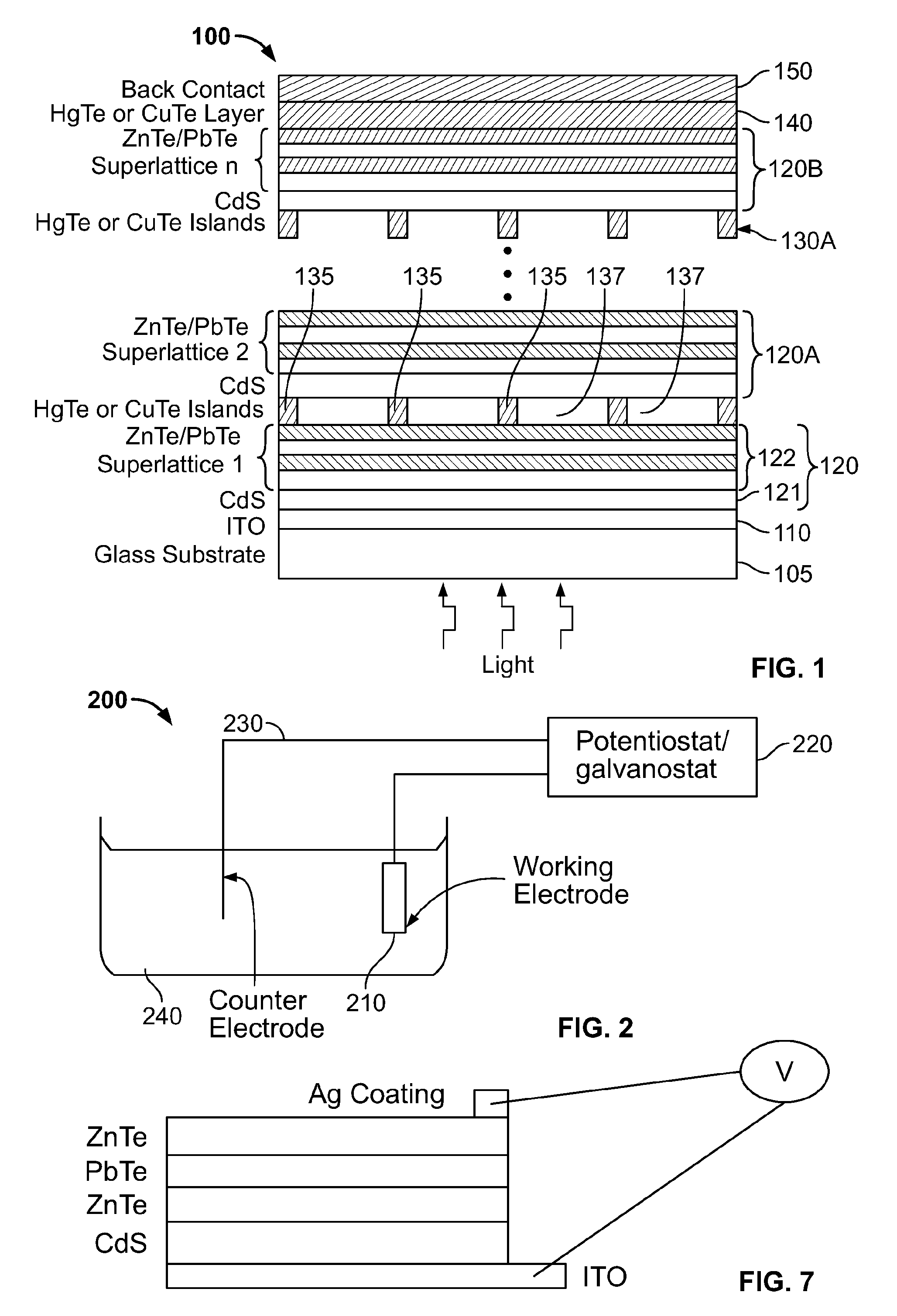
Solar cells and method of making solar cells
InactiveUS20110155207A1PV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc tellurideElectrical battery
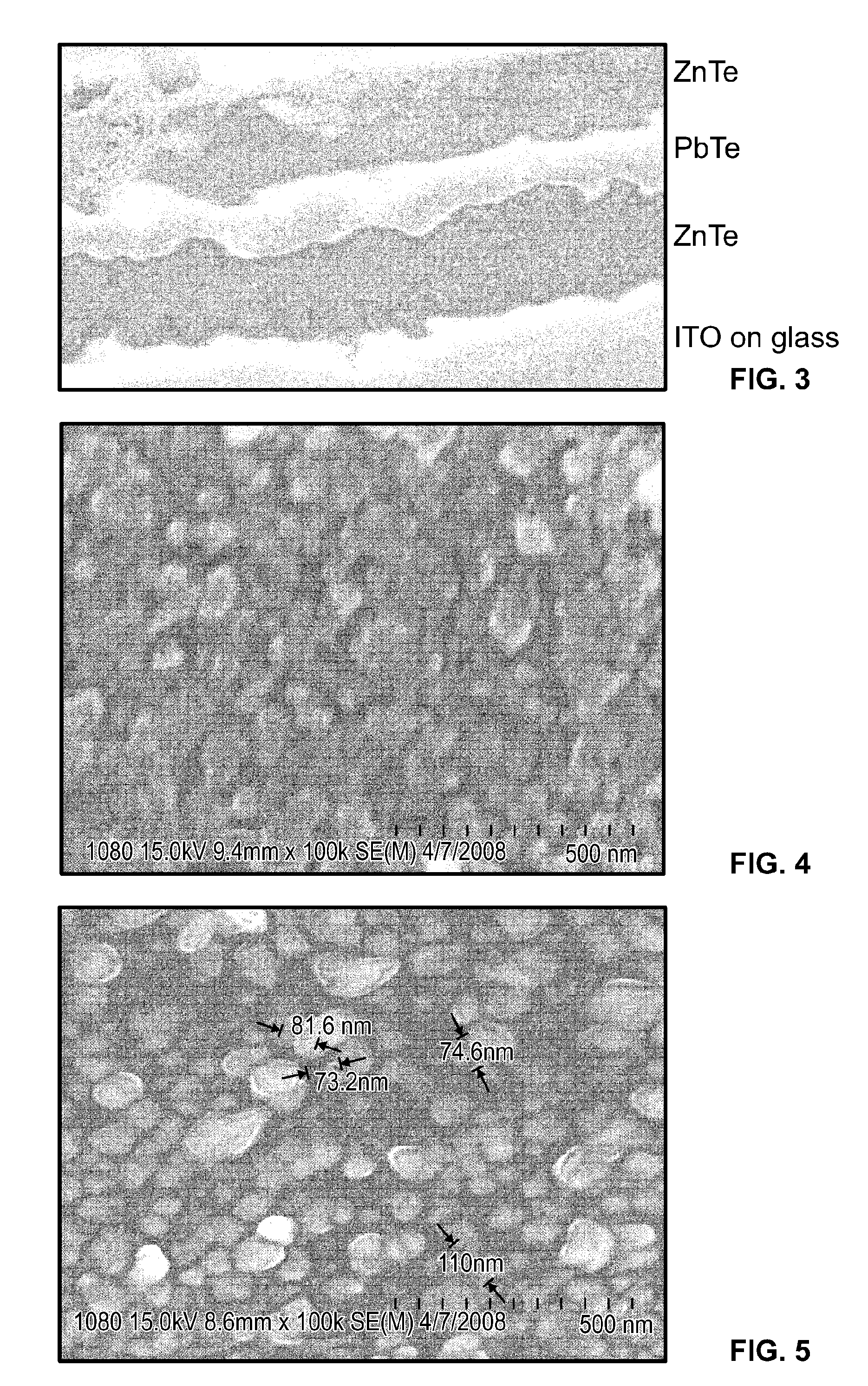
A multi junction photovoltaic cell includes at least two P-N junctions electrically connected to each other in series. Each P-N junction includes a P-type absorber layer and a N-type emitter layer, each P-type absorber layer including a plurality of alternating thin film layers of zinc telluride and lead telluride, wherein zinc telluride and lead telluride have respective bandgaps when in bulk thickness and the effective bandgap of each P-type absorber layer is between the respective bandgaps, The effective bandgap of at least one P-type absorber layer is different from that of at least one other P-type absorber layer.
Owner:VILLANOVA UNIVERSITY
Infrared Bandpass Filters with High Rectangularity Transmission Curves
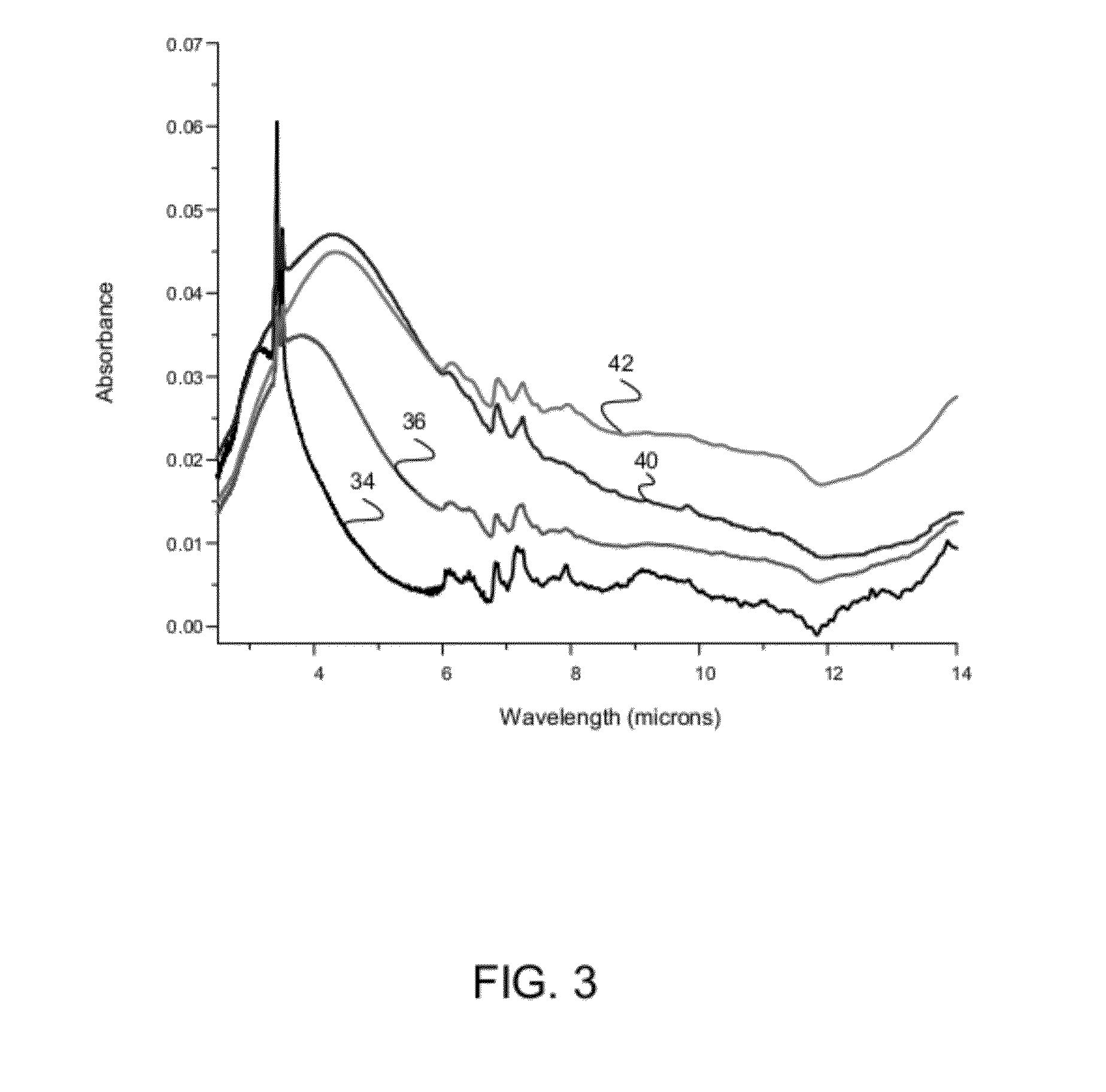
InactiveCN102269835AImprove resolutionGood rectangular shapeOptical filtersBandpass filteringOptical radiation
The invention discloses an infrared bandpass filter with a high squareness transmittance curve. The filter uses germanium as a base, zinc selenide and lead telluride as film materials, and is prepared by a vacuum thin film deposition method. The main film system adopts five resonant cavity precision film structure. It consists of a front film system, a substrate and a back film system. It has good band-pass transmission performance and can suppress optical radiation interference in other bands. It is applied to a space infrared scanning radiation instrument to meet the detection requirements for the infrared radiation of atmospheric targets.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple layer synthesis furnace device
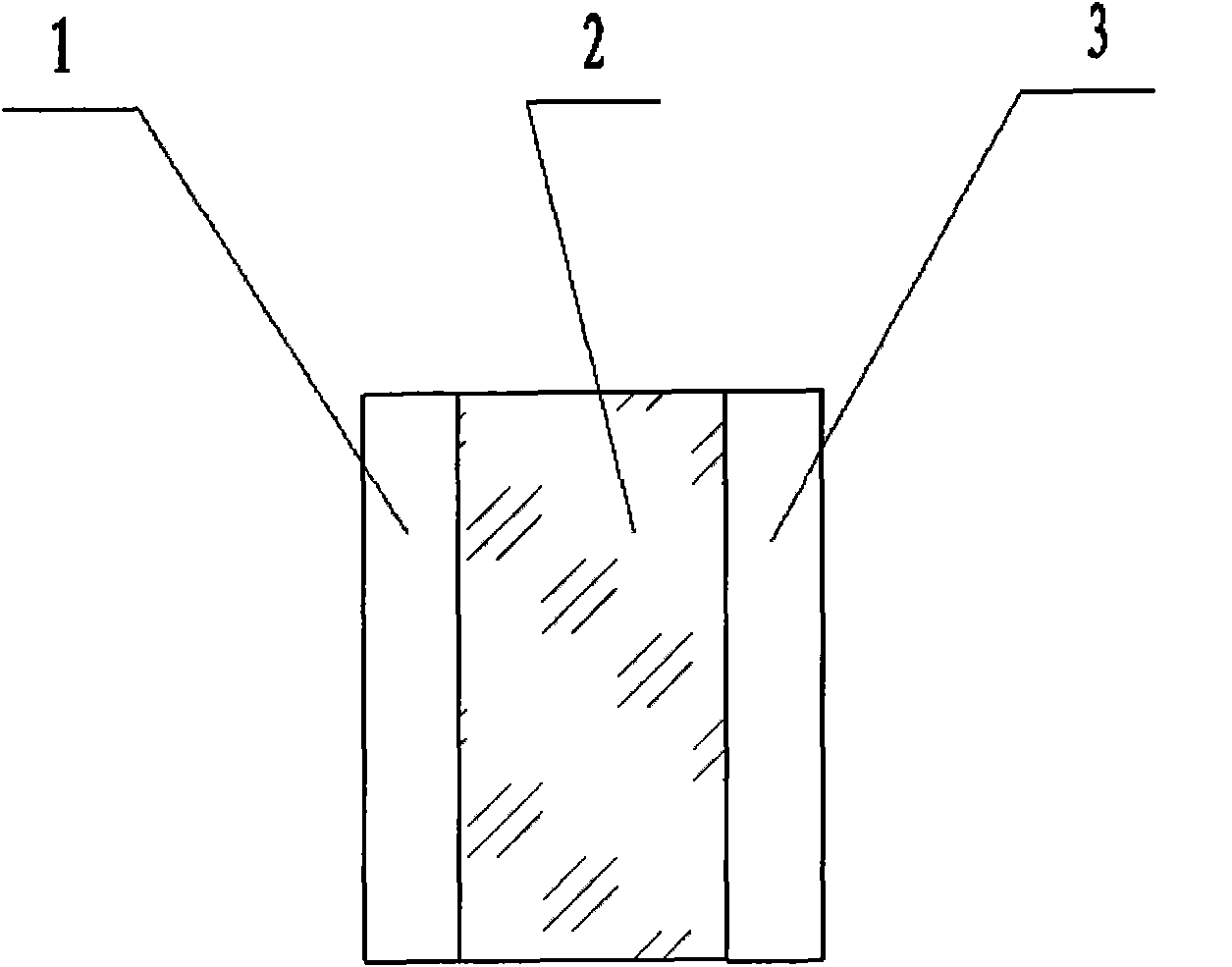
InactiveCN101118111AEnsure safetyEnsure production capacityMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesZinc tellurideInsulation layer
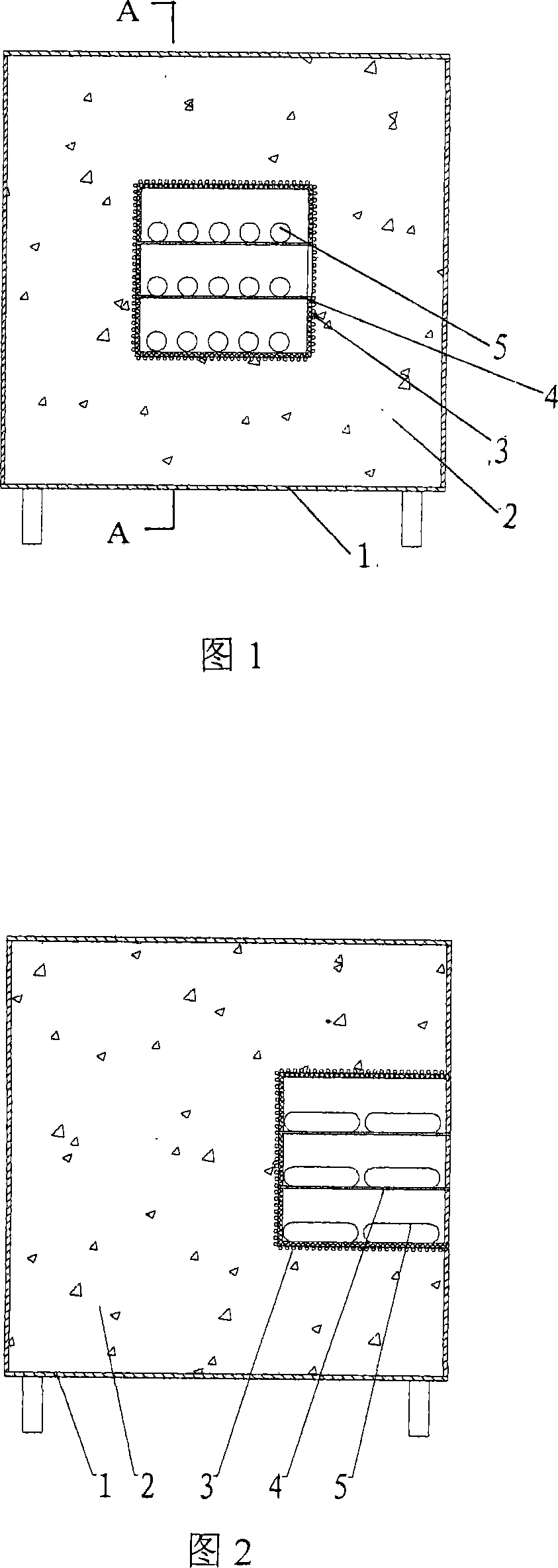
The present invention relates to a multilayer compound synthetic furnace device, which is characterized in that an insulation layer (2), a heating wire (3), an insulation board (4) and a synthetic reaction tube (5) are arranged in a synthetic furnace (1), the furnace chamber of the synthetic furnace is divided into a plurality of synthetic chambers with the insulation board, and a plurality of synthetic reaction tubes (5) are put in each synthetic chamber, the thermal field temperature gradient of the furnace chamber is controlled in less or equal to plus or minus 5 DEG C, and each synthetic chamber being separated ensures the security during the synthetic process. The multilayer compound synthetic furnace device is applied to the synthesis of cadmium telluride, zinc telluride and lead telluride.
Owner:四川鑫龙碲业科技开发有限责任公司
Synchronic preparation method of lead telluride thin film and nano powder
InactiveCN101602496ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getSimple processPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsPotassium borohydrideFluorescence
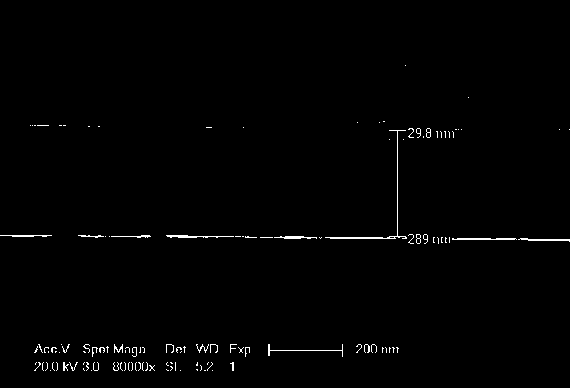
The invention belongs to the lead telluride (PbTe) thin film and nano powder preparation method field. In a low temperature aqueous solution synchronic synthesis method of PbTe thin film and nano powder, inorganic salt containing lead and tellurium dioxide or sodium tellurite are taken as raw materials, potassium borohydride or sodium borohydride is taken as reducing agent, and PbTe thin film and nano powder are simultaneously synthesized in alkaline aqueous solution at room temperature to 50 DEG C. The invention initially synthesizes PbTe thin film and nano powder at normal atmosphere and below 100 DEG C, the prepared thin film is flat, compact and uniform; and powder product is small in grain diameter uniform in grain fineness distribution, and grain diameter size can be controlled by controlling reaction temperature. The raw materials used in the whole technology are available, the technology is simple, scale production is easy to realize, and organic solvent is not used in the reaction process, thus being beneficial to environmental protection. The synthesized PbTe thin film and nano powder can be widely applied to thermoelectric device, solar battery, fluorescence device, infrared optical element, infrared thin film device, semiconductor detector and the like and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Nanomaterial having tunable infrared absorption characteristics and associated method of manufacture
ActiveUS20120082848A1Facilitate tuning absorption characteristicLong IR wavelengthMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsChemical physicsLead telluride
A quantum nanomaterial having a bandgap that may be tuned to enable the quantum nanomaterial to detect IR radiation in selected regions including throughout the MWIR region and into the LWIR region is provided. The quantum nanomaterials may include tin telluride (SnTe) nanomaterials and / or lead tin telluride (PbxSn1-xTe) nanomaterials. Additionally, a method of manufacturing nanomaterial that is tunable for detecting IR radiation in selected regions, such as throughout the MWIR region and into the LWIR region, is also provided.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for synthesizing large-size lead telluride monocrystalline thermovoltaic material
InactiveCN108301048AAddress high-quality needsSingle crystal performance is stablePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsLead tellurideMaterial synthesis
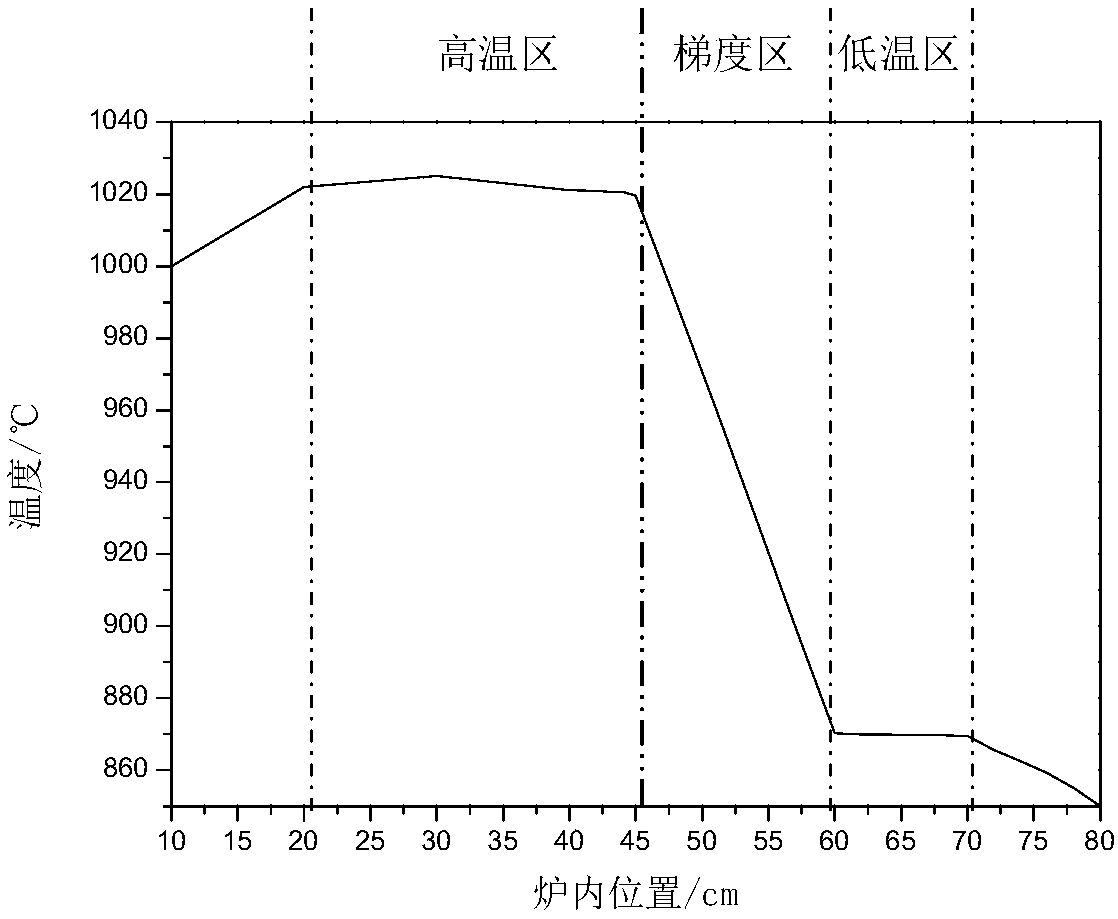
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a large-size lead telluride monocrystalline thermovoltaic material. According to the method, elemental tellurium and lead are served as raw materials, lead telluride polycrystalline positive and negative thermovoltaic materials are prepared firstly, and then, the large-size lead telluride thermovoltaic material is synthesized. During the preparation of the polycrystalline positive and negative thermovoltaic materials, the stoichiometric ratio of lead and the stoichiometric ratio of tellurium are 0.99: 1 and 1: 0.998 separately. During the synthesis of lead telluride, the polycrystalline positive and negative thermovoltaic materials are separately loaded into a large-size quartz growth ampule, and the large-size quartz growth ampule is vacuumized and sealed and then placed into a growth furnace. The bottommost end of the growth ampule is placed at a position of 30cm to 50cm of the furnace firstly, is slowly lowered at a rate of 0.3mm / hto 0.5mm / h after 30 to 50 hours of standing, is stopped lowering until the bottommost end of the quartz ampule reaches a position of 60cm to 80cm and is cooled, the growth ampule is taken out, the growth ampule goes through a high-temperature area, a gradient area and a low-temperature area along with change of a furnace-inside position, and the temperature range is 830 DEG C to 1,020 DEG C. According to the method, the blank in the prior art that lead telluride monocrystalline thermovoltaic materials cannot be produced in a large-size and large-scale manner is filled up. The product performance is stable and reliable, and the thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT value) reaches up to 1 or more.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
High-effect potassium-doped lead telluride-lead sulfide alloy thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104064666ALow thermal conductivityImprove energy conversion efficiencyThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsLead telluridePotassium
The invention provides a high-effect potassium-doped lead telluride-lead sulfide alloy thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. The high-effect potassium-doped lead telluride-lead sulfide alloy thermoelectric material is composed as shown in the formula: Ky (lower coordinate)PB(1-y) (lower coordinate)Te (1-x) (lower coordinate) Sx (lower coordinate), wherein x ranges from 0.1 to 0., and y ranges from 0.05 to 005 to 0.05. The high-effect potassium-doped lead telluride-lead sulfide alloy thermoelectric material has relatively high seebeck coefficient and conductivity and small heat conductivity, and therefore, high thermoelectric performance optimum value and energy conversion efficiency are high; when x is 0.3 and y is 0.025, the thermoelectric performance optimum value (ZT) within a wide temperature range from 673 to 923k is more than 2; the average thermoelectric performance optimum value is 1.56 under the temperature gradient from 300 to 900k, and the corresponding energy conversion efficiency is up to 20.7%.
Owner:深圳热电新能源科技有限公司
Medium-wave infrared narrow band filter with wavelength of 5.25 microns
The invention discloses a medium-wave infrared narrow band filter with a wavelength of 5.25 microns, which is prepared by taking an aluminum oxide crystal as a substrate and taking zinc selenide and lead telluride as film layer materials through a vacuum film deposition method. A main film system is in a multi-half-wave and high-order separating layer film system structure and is matched with a secondary peak cutting-off film system with high cutting-off depth, thus the main film system has good effect on inhibiting interference of other gases. The filter is a critical component of a nitric oxide infrared analyzer and is suitable for batch production. The optical performance of a product and the physical strength of a film layer meet the actual use requirements. The invention is suitable for trace nitric oxide gas analyzers in the fields of environmental protection, petrochemical industry and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for lead telluride-based thermoelectric coating material
ActiveCN102995088AThickness is easy to controlUniform compositionElectrolytic inorganic material coatingThermoelectric materialsDopant
The invention belongs to the field of a thermoelectric material and in particular relates to a preparation method for a lead telluride-based thermoelectric coating material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: using graphite as an anode, Cu, Ni, Al, Au, Ag or graphite as a cathode; carrying out electro-deposition for 3-8 hours in an electrolyte solution at a temperature of 25 DEG C to 65 DEG C; depositing on the surface of the cathode to obtain a PbTe or PbTeTl thermoelectric coating. The electro-deposition method provided by the invention has high efficiency, can obtain PbTe with a controllable thickness and uniform components and a PbTe-based thermoelectric material containing dopant; the electric potential of the electro-deposition or current density is controlled to realize the co-deposition of two or more metals, and to form the PbTe or the PbTeTl coating. The preparation method has low cost, high efficiency and strong operability.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Thermoelectric nanocrystal coated glass fiber sensors
InactiveUS20140144477A1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsGlass fiberLead telluride
This disclosure examines using lead telluride nanocrystals as well as other materials suitable for thermoelectric conversion, particularly materials with high Figure of Merit values, as coatings on flexible substrates. This disclosure also examines using flexible substrates with lead telluride nanocrystal coatings as sensors.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Environment-friendly sulfur group stannide thermoelectric material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106676322AImprove thermoelectric performanceImprove thermoelectric conversion efficiencyElectricityLead telluride
The invention relates to a high-performance environment-friendly sulfur group stannide thermoelectric material and a preparing method thereof. The chemical general formula of the thermoelectric material is Sn1.03-yMgyTe(Cu2Te)x(0<x<=0.05, 0<y<=0.12). According to the preparing method, a metal elementary substance with purity larger than 99% is used as a raw material, material matching is carried out according to the stoichiometric ratio of Sn1.03-yMgyTe(Cu2Te)x, after vacuum packaging, high-temperature melting and annealing heat treatment are carried out, the material is ground into powder, and after vacuum hot-press sintering and slow cooling are carried out, a sheet material is obtained and is the novel sulfur group stannide thermoelectric material of the target component. According to the design, in the SnTe material, collaborative optimization of an electrical transport property and a hot transport property is achieved to improve thermoelectric performance of the material. Compared with the prior art, the invention develops a novel high-performance environment-friendly Sn1.03-yMgyTe(Cu2Te)x thermoelectric material, the zT value reaches 1.4 at 900 K, and the material is an environment-friendly high-performance thermoelectric material with potentials for replacing a traditional p-type lead telluride material.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Far infrared wave band optical film optical filter with CVD diamond being a substrate
ActiveCN106842401AImprove performanceLow average transmittanceOptical filtersZinc selenideRefractive index
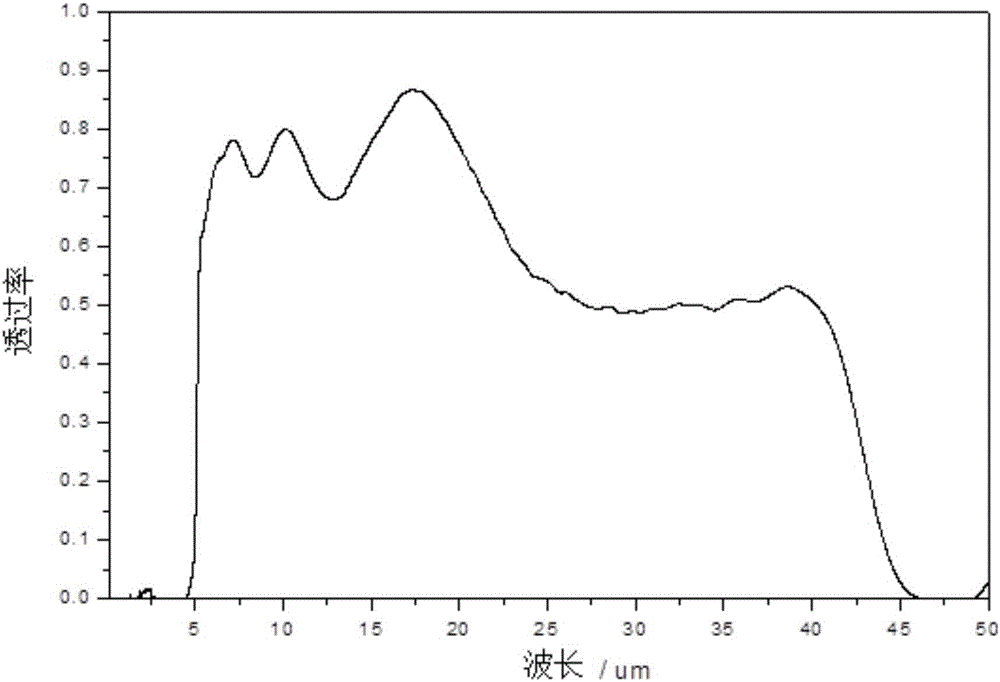
The invention discloses a far infrared wave band optical film optical filter with CVD diamond being a substrate. With lead telluride (PbTe) and zinc selenide (ZnSe) being a high-low refraction index film material, multiple layers of membranes are deposited on the two sides of the CVD diamond substrate by the adoption of a thermal evaporation deposition method in the vacuum environment of 1-2*103Pa and at the deposition temperature of 200+ / -2 DEG C; with the far infrared optical filter, wave bands with wave length smaller than 5 micrometers can be intercepted, the average transmittance is lower than 1%, and the average transmittance of wave bands of 5-45 micrometers is larger than 71%. The far infrared wave band optical film optical filter can be applied to the fields of far infrared target recognition in earth radiation detection and deep space detection and other fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
P-n type lead telluride/polypyrrole double-layer thermoelectric thin film material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109166958AExcellent thermoelectric performanceLow costThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsGas phasePolypyrrole
The invention provides a p-n-type lead telluride / polypyrrole double-layer thermoelectric film material and a preparation method thereof are disclose. That p-type lead telluride / polypyrrole double-layer thermoelectric film material is prepared by a hydrothermal method and a gas phase method. N-type lead telluride / polypyrrole bilayer thermoelectric thin film, the thickness of the lead telluride layer thin film is 20 nm-300 nm, and the thickness of the polypyrrole film is 20 nm-300nm. The lead telluride / polypyrrole double-layer thermoelectric thin film material prepared by the method has good thermoelectric performance, can be used for portable wireless sensor power supply, refrigeration of integrated circuit chips, refrigeration of light emitting diodes and photodetectors and other fields, has the advantages of simplicity, low cost, convenience and rapidity, and can be produced on a large scale.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Far-infrared optical thin film window with medium wave infrared cut-off function
ActiveCN107153231AImprove performanceLow average transmittanceOptical filtersRefractive indexOptical thin film
The invention discloses a far-infrared optical thin film window with a medium wave infrared cut-off function. The optical thin film window takes lead telluride (PbTe) and cesium iodide (CsI) as high and low refractive index film materials, and is prepared by adopting a steam-resistant thermal evaporation deposition method to deposit a plurality of layers of films respectively at the two sides of a chemical vapor deposited (CVD) diamond substrate at the deposition temperature of 180+ / -2 DEG C in a vacuum environment with a pressure of (1-2)*10<-3>Pa; the far-infrared optical thin film window can realize the cut-off of light waves which are 5 microns away from the front of a medium-wave infrared ray; after the light waves are cut off, the average transmittance of the light waves is less than 0.5%, anti-reflection for light within a wave band of 5-50 microns is realized, and the average transmittance is greater than 76 .8%. The far-infrared optical thin film window can be applied to the fields such as deep space detection, far infrared object identification and earth radiation detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lead selenide coated lead telluride dendritic crystal composite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103482588AReduce the temperatureImprove reaction efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsAqueous sodium hydroxide
The invention provides a lead selenide coated lead telluride dendritic crystal composite and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a thermoelectric material. The lead selenide coated lead telluride dendritic crystal composite and the preparation method provided by the invention have the advantages that the preparation method is low in reaction temperature, simple in process and friendly to environment, and the synthesized powder is high in purity and good in morphology. The lead selenide coated lead telluride dendritic crystal composite is composed of lead telluride and lead selenide, wherein PbTe in a stoichiometric proportion is coated with PbSe in a stoichiometric proportion. The preparation method comprises the steps that Pb(CH3COO)2.3H2O, TeO2 and SeO2 are dissolved in a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution in the mol ratio of Pb: Te: Se=2: 1: 1; NaBH4 is added to the solution and mixed together to obtain a precursor solution; next, the precursor solution is transferred into a reaction kettle and preserved with heat for 18-22 h at a temperature ranging from 160 to 200 DEG C and then the reaction is stopped; after the reaction temperature is reduced to the room temperature, precipitate is separated out, washed until neutrality and dried at a constant temperature; finally, the lead selenide coated lead telluride dendritic crystal composite is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Metal telluride nanocrystals and synthesis thereof
InactiveUS7790137B2Material nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsBismuth tellurideLead telluride
A process for synthesizing a metal telluride is provided that includes the dissolution of a metal precursor in a solvent containing a ligand to form a metal-ligand complex soluble in the solvent. The metal-ligand complex is then reacted with a telluride-containing reagent to form metal telluride domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers. NaHTe represents a well-suited telluride reagent. A composition is provided that includes a plurality of metal telluride crystalline domains(PbTe)1-x-y(SnTe)x(Bi2Te3)y (I)having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive where x is between 0 and 1 inclusive and y is between 0 and 1 inclusive with the proviso that x+y is less than or equal to 1. Each of the metal telluride crystalline domains has a surface passivated with a saccharide moiety or a polydentate carboxylate. A densified mass having a density of greater than 95% of the theoretical density includes a plurality of lead telluride, tin telluride, bismuth telluride, or a combination thereof of domains having a mean linear dimension of from 2 to 40 nanometers inclusive that have been subjected to hot isotactic pressing.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com