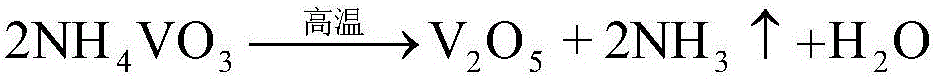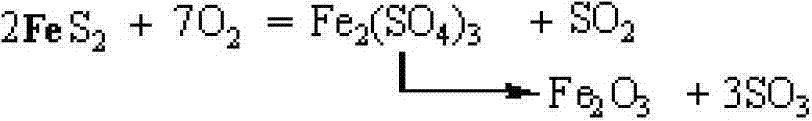Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
279results about How to "Efficient leaching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for selectively recycling lithium from lithium iron phosphate waste
ActiveCN106910959AEfficient leachingLow costWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementHypochloriteSelective leaching
The invention discloses a method for selectively recycling lithium from lithium iron phosphate waste through a direct oxidization method. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that the lithium iron phosphate waste is added into a water solution, meanwhile, an oxidizing agent is added, stirring is carried out, lithium iron phosphate and the oxidizing agent react to generate iron phosphate, lithium ions enter the solution, and therefore a pure lithium-containing solution and iron phosphate solids are obtained. The adopted oxidizing agent comprises one or a mixture of persulfate, ozone, oxygen, pypocholoride and hydrogen peroxide. The molar weight of the oxidizing agent is 0.6-20 times that of lithium iron phosphate. The lithium-containing solution can be directly used for preparing a high-purity lithium product. According to the method, efficient and selective leaching of lithium can be achieved simply by adding a certain amount of oxidizing agent, and the method is mild in reaction condition, short in process and simple in equipment.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH
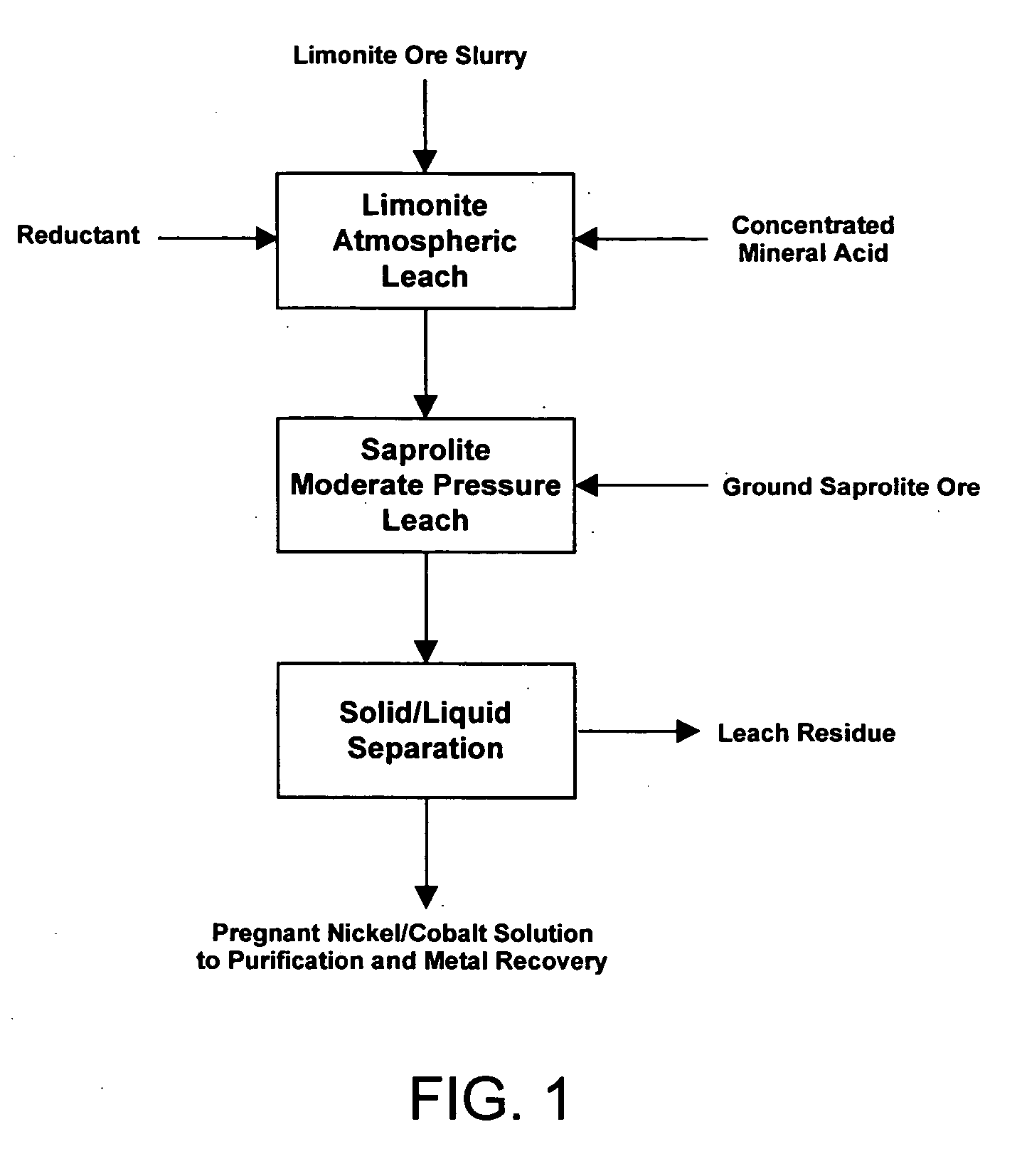
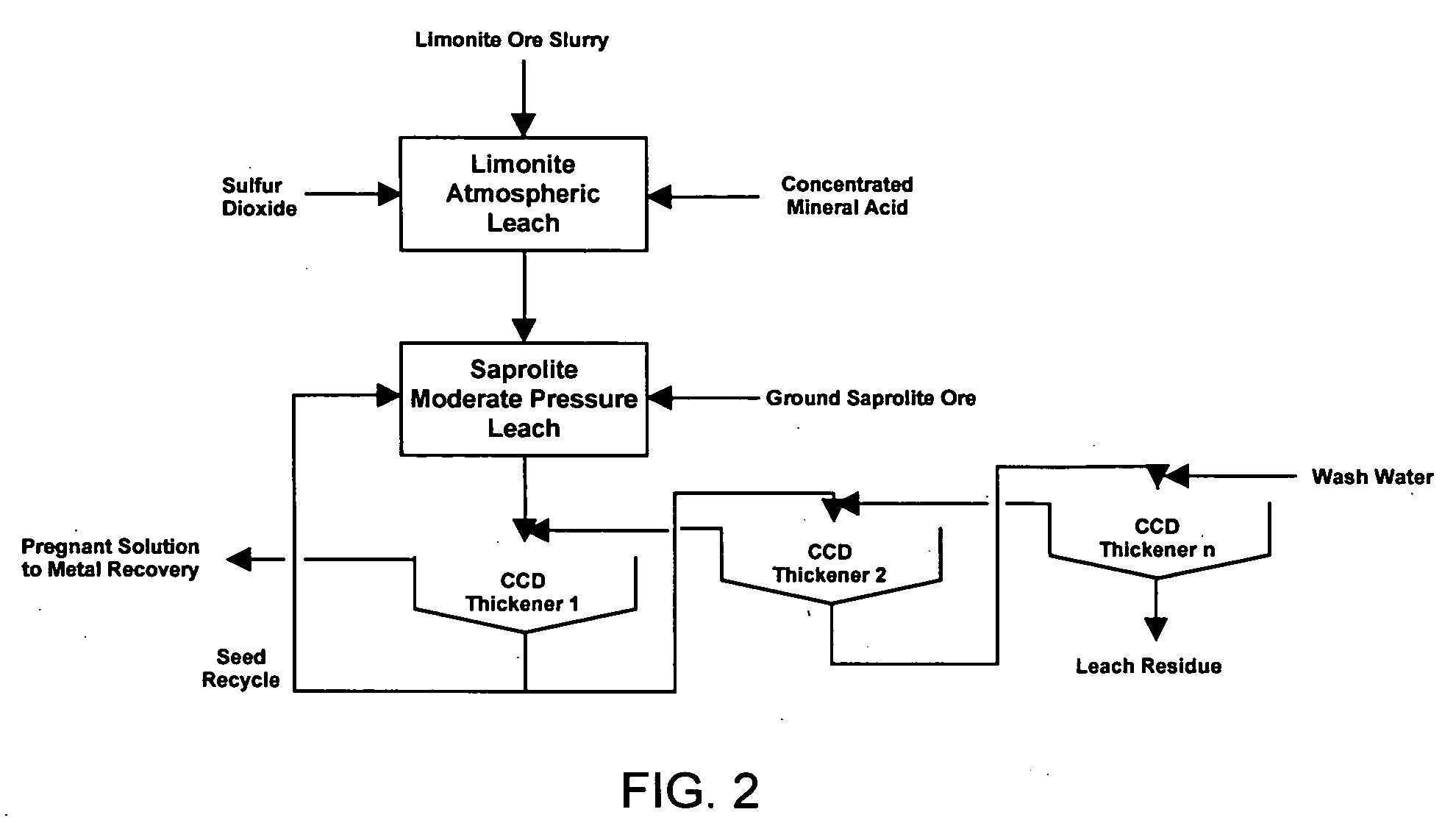
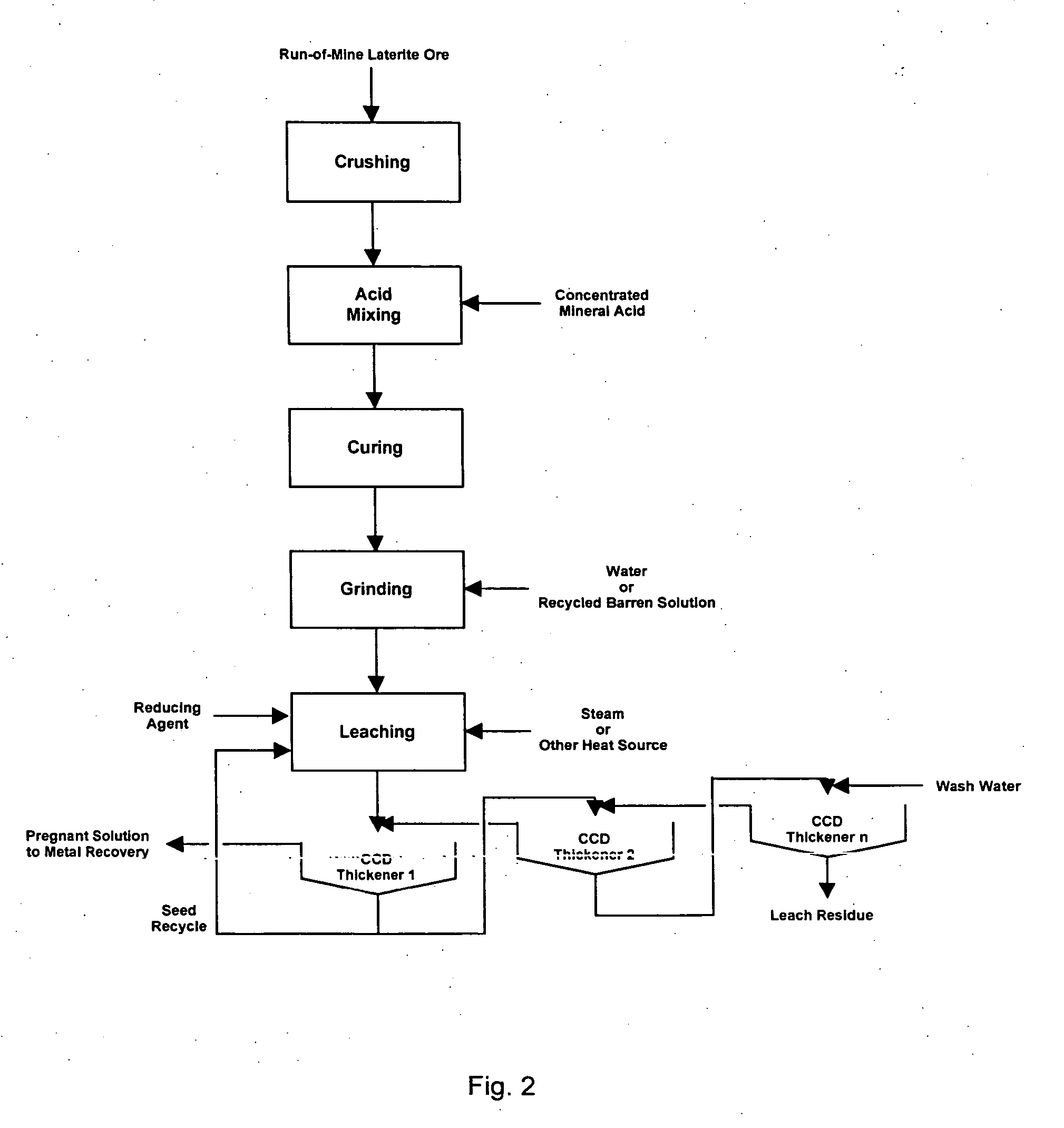
Method for nickel and cobalt recovery from laterite ores by combination of atmospheric and moderate pressure leaching
InactiveUS20060024224A1Efficient leachingEfficient separationIron compoundsCobalt compoundsRecovery methodIon exchange
A process for leaching laterite ores containing limonite and saprolite. Sufficient mineral acid is added to a slurry of limonite which is leached at atmospheric pressure to dissolve most of the soluble non-ferrous metals and soluble iron. After adding saprolite the slurry is further leached at a temperature above the normal boiling point and at a pressure above atmospheric pressure for a time sufficient to leach most of the contained nickel in the saprolite and to precipitate most of the iron in solution. The pressure of the slurry is then reduced, and nickel and / or cobalt is subsequently recovered from the leach solution by solvent extraction, resin-in-pulp or other ion exchange, sulfide or hydroxide precipitation, or other recovery method.
Owner:SKYE RESOURCES
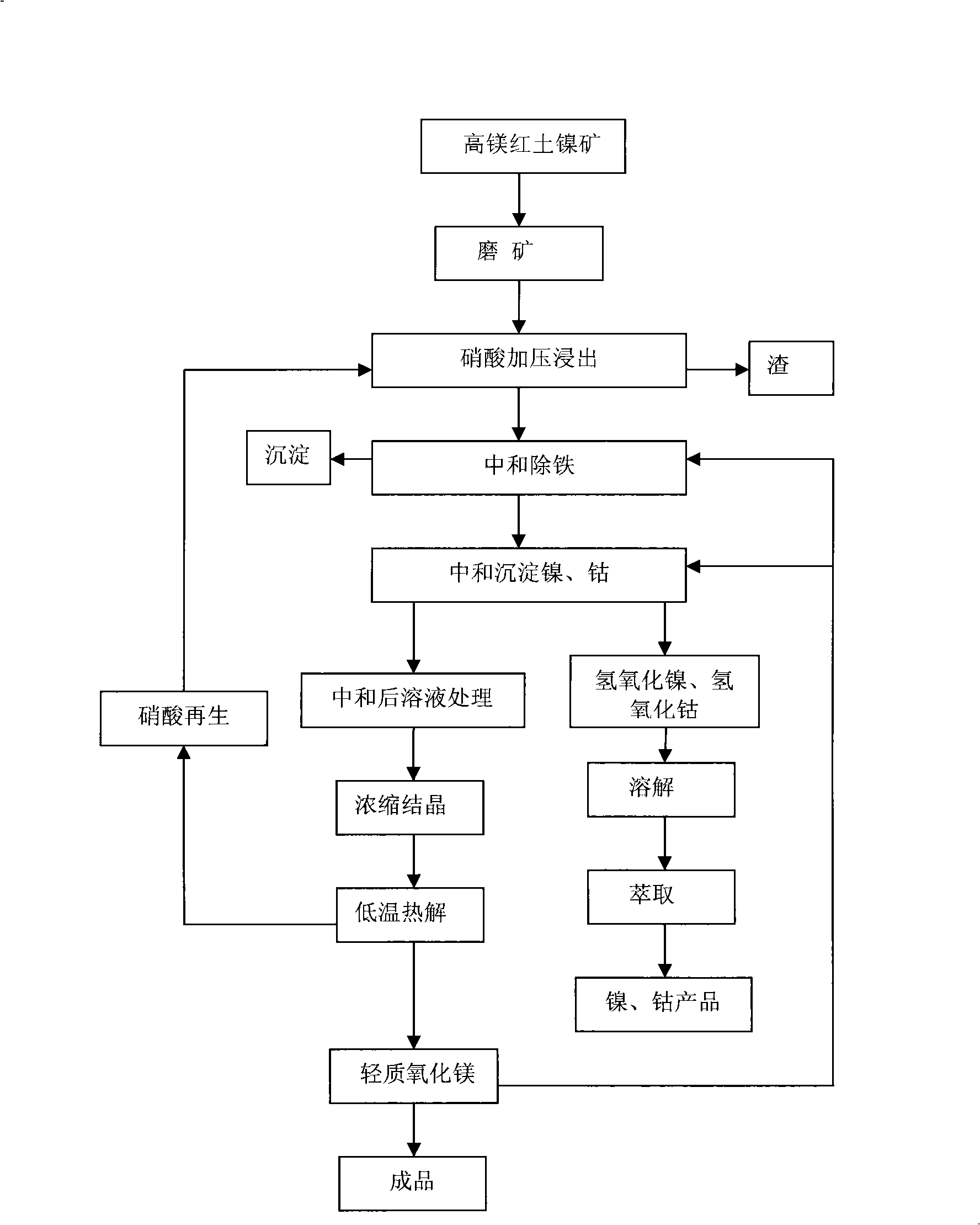
Treating method for high magnesium laterite nickel mine
InactiveCN101289704AEfficient extractionEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHigh magnesium
The invention discloses a method for treating high magnesium laterite-nickel ores. The method comprises the following steps of preliminary treatment of ore, pressurized leaching, iron purification of leach solution, deposition of nickel and cobalt, condensation and crystallization, production of light magnesium oxide by low-temperature thermal decomposition of crystals and regeneration of nitric acid. Under mild conditions of low temperature and pressure, leaching ratios of nickel and cobalt both reach 95 percent, the leaching ratio of magnesium reaches 98 percent, the iron content in the leach solution is less than 1g / L, and no silicon dioxide is leached out. The method can fully recover nickel, cobalt and magnesium, and the magnesium is generated in the form of light magnesium oxide, and the leaching agent-nitric acid can be recovered and regenerated for n, thereby better resolving the problems of highly efficient leaching-out of nickel and cobalt and reasonable utilization of magnesium; moreover, the technical flow is simple and has low requirements on equipment, and in the process of leaching out, the scab phenomenon does not occur in a high-pressure pan, so that the method is applied to the large-scale industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
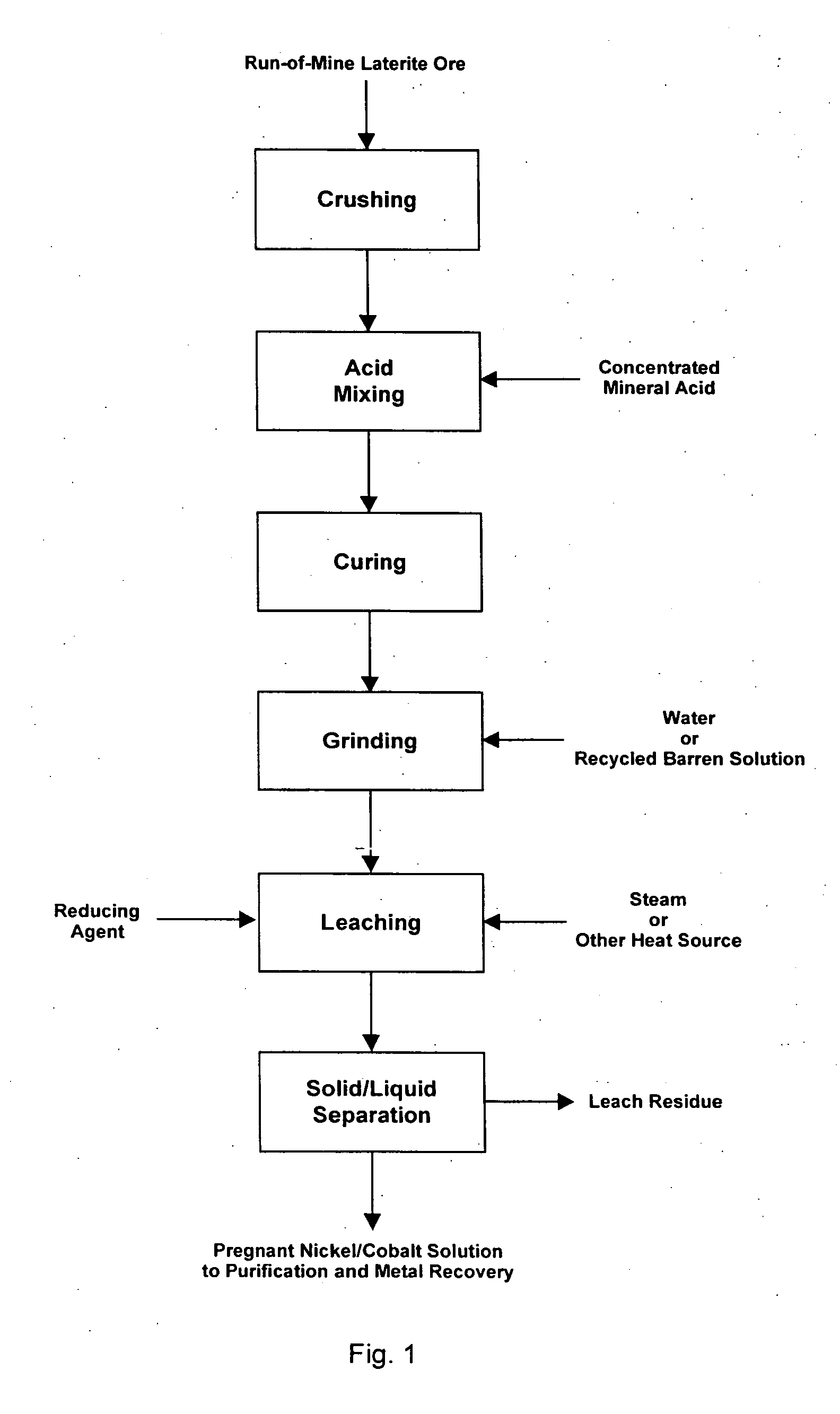
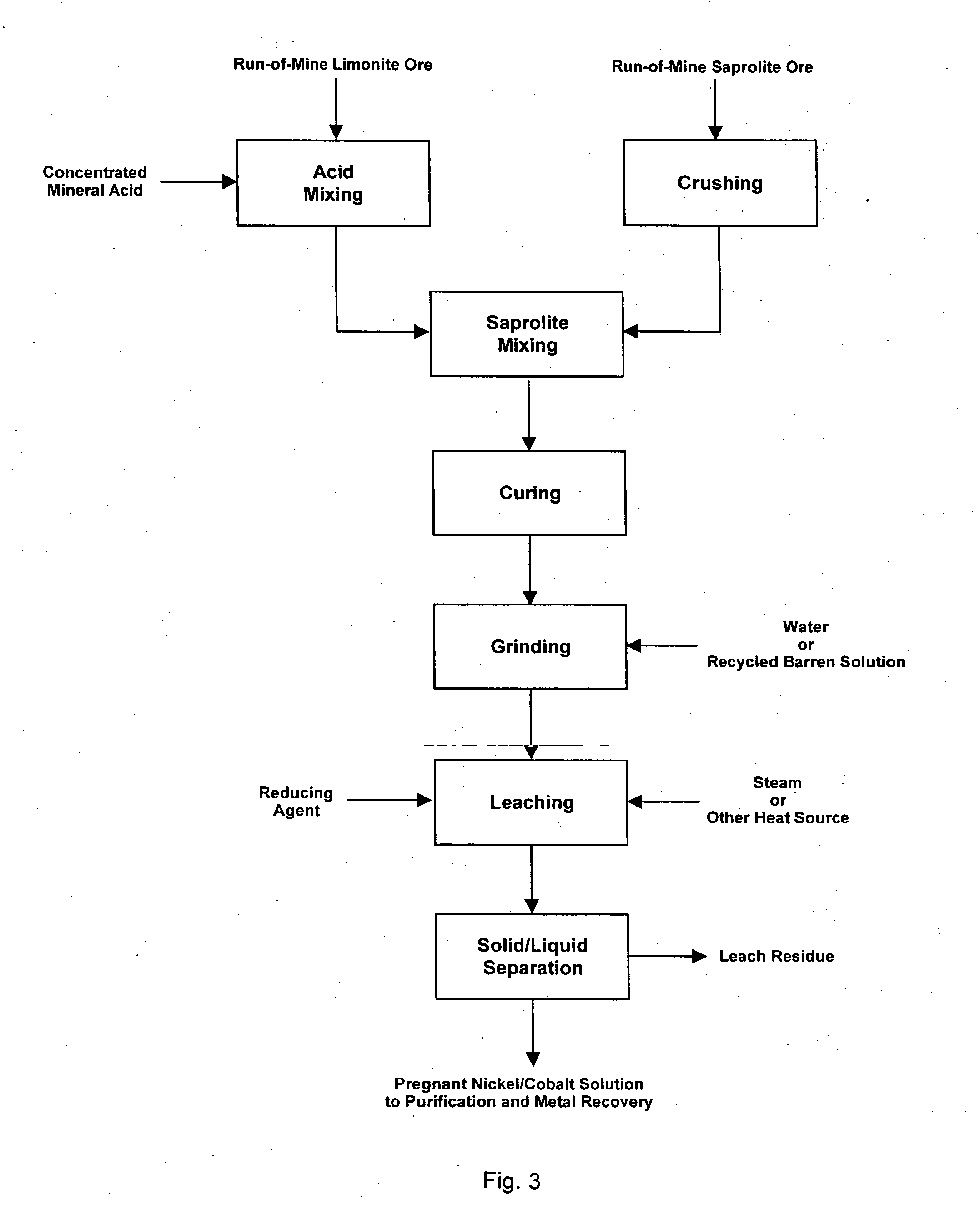
Method for nickel and cobalt recovery from laterite ores by reaction with concentrated acid and water leaching
InactiveUS20060002835A1Efficiently separateEfficient leachingIron compoundsCobalt compoundsJarositeOxide
A process for leaching laterite ores containing limonite and saprolite in a two stage process. The first stage consisting of mixing and reacting the ore with concentrated mineral acid, and the second stage consisting of preparing a slurry of the acid / ore mixture in water and leaching the mixture to dissolve nickel and cobalt. Iron is efficiently separated from nickel and cobalt in the solid leach residue primarily as an oxide or hydroxide of ferric iron other than jarosite.
Owner:SKYE RESOURCES
Method for preparing aluminum oxide from coal series kaolinite rock or coal gangue
InactiveCN101234774AReduce energy consumptionSave resources and energyAluminium compoundsCoal gangueKaolinite
The invention relates to a method for preparing alumina by using kaolinite in coal measures or coal gangue as raw material with simple process and low energy consumption; by utilizing special influence of inner heat source (carbon) in the kaolinite in coal measures or coal gangue on calcination performance of the kaolinite in coal measures, the alumina is prepared after crashing, low temperature calcination, hydrochloric acid leaching, filtration, purification and fractional-step pyrolysis by fractional steps. The method for preparing the alumina has the advantages that the problems that calcination temperature of the prior art is high or calcination time is long as well as leaching temperature is high or leaching time is long are solved; process energy consumption is reduced; intermediate product of the purified and separated watery alumina is not required to be dried; the alumina is prepared directly by using the method of the pyrolysis by fractional steps; the process is simplified and operability is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
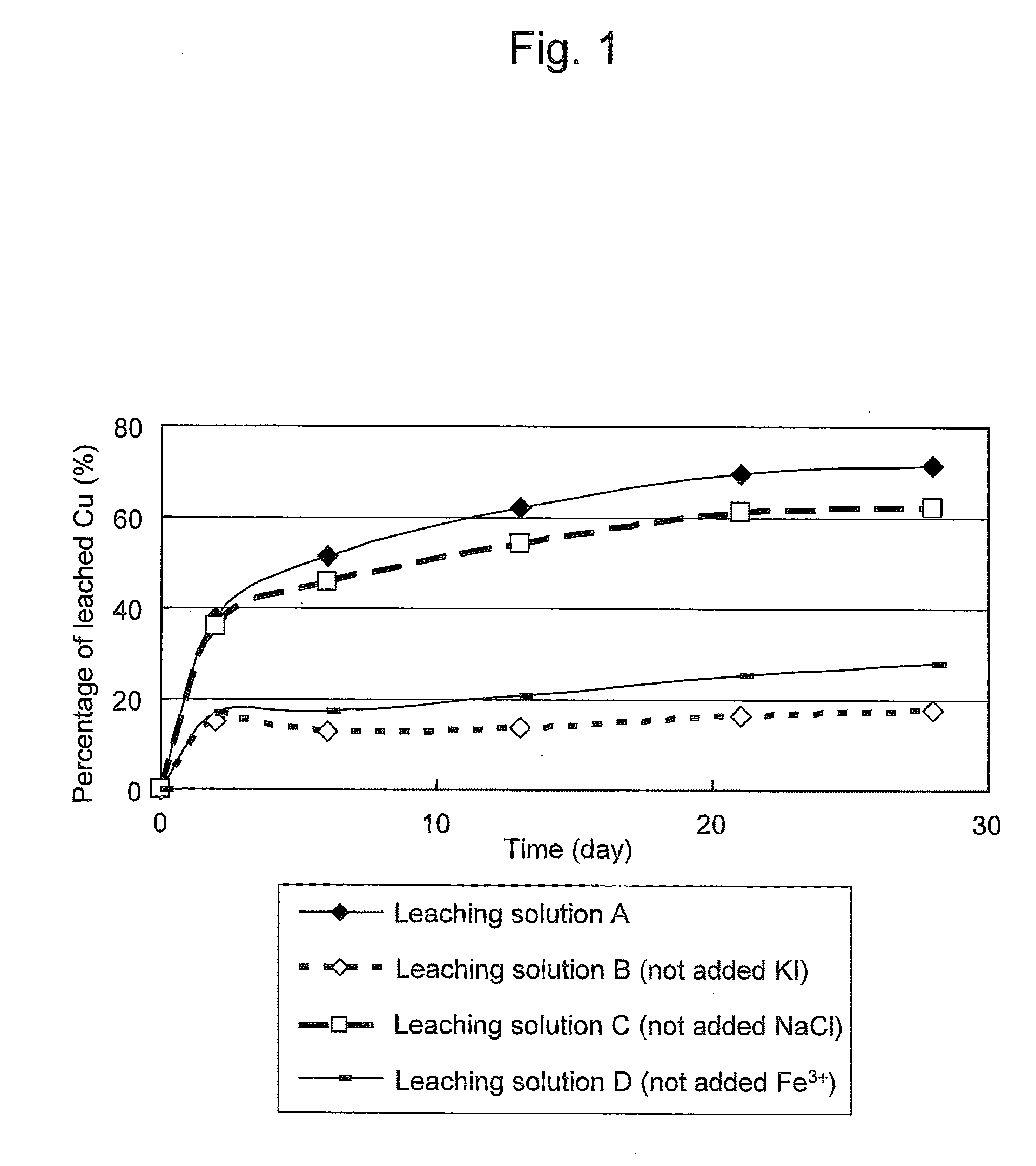
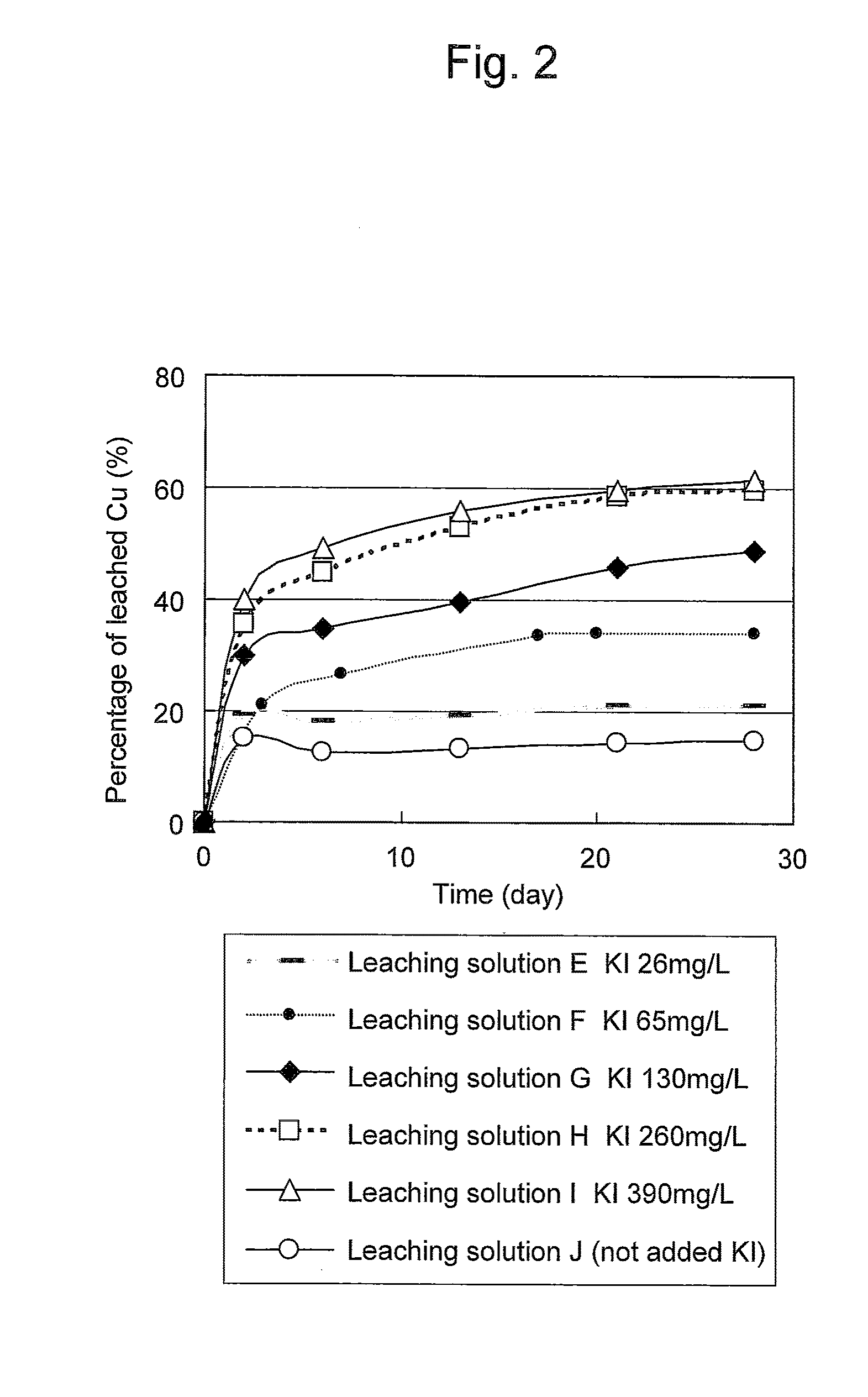
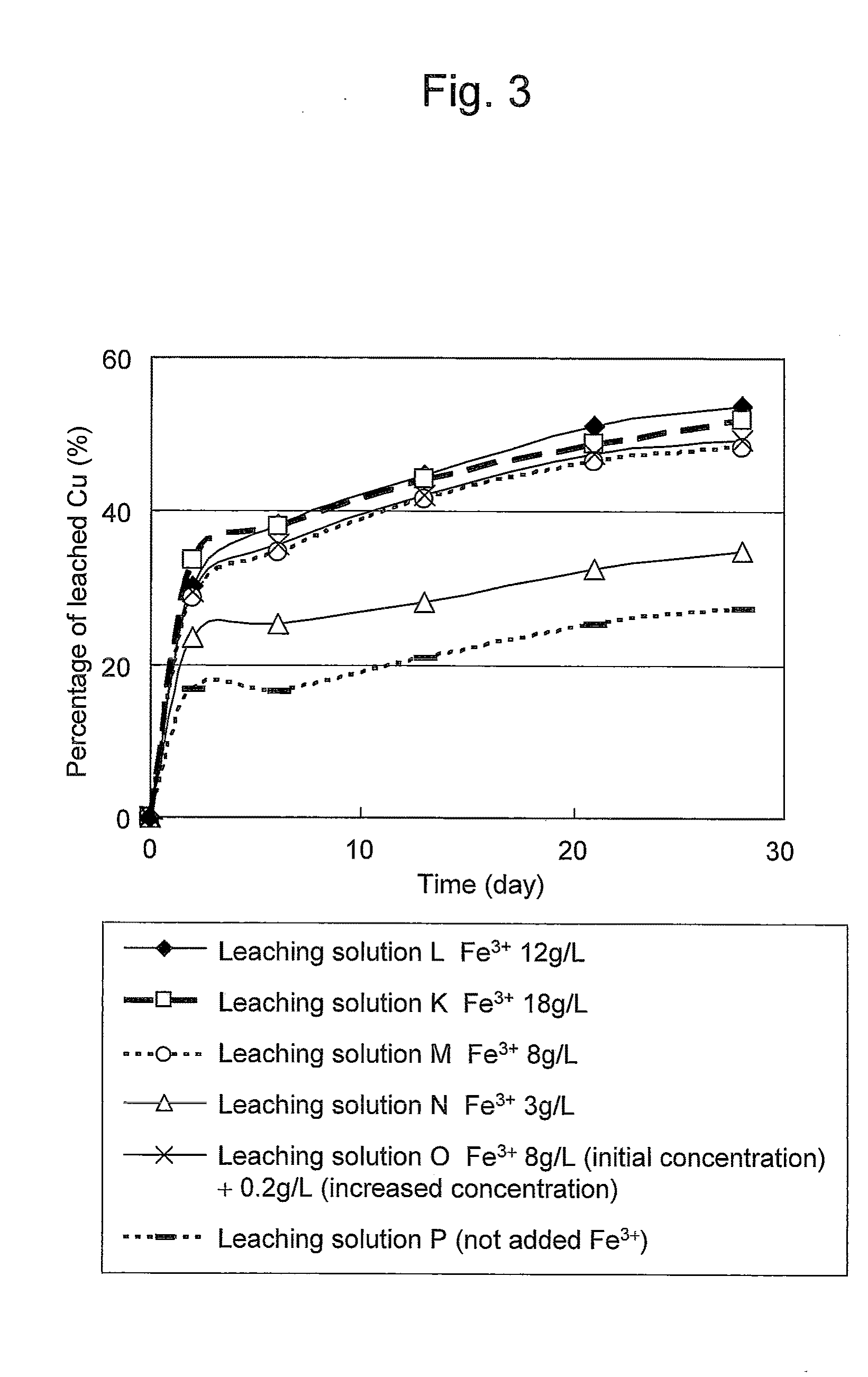
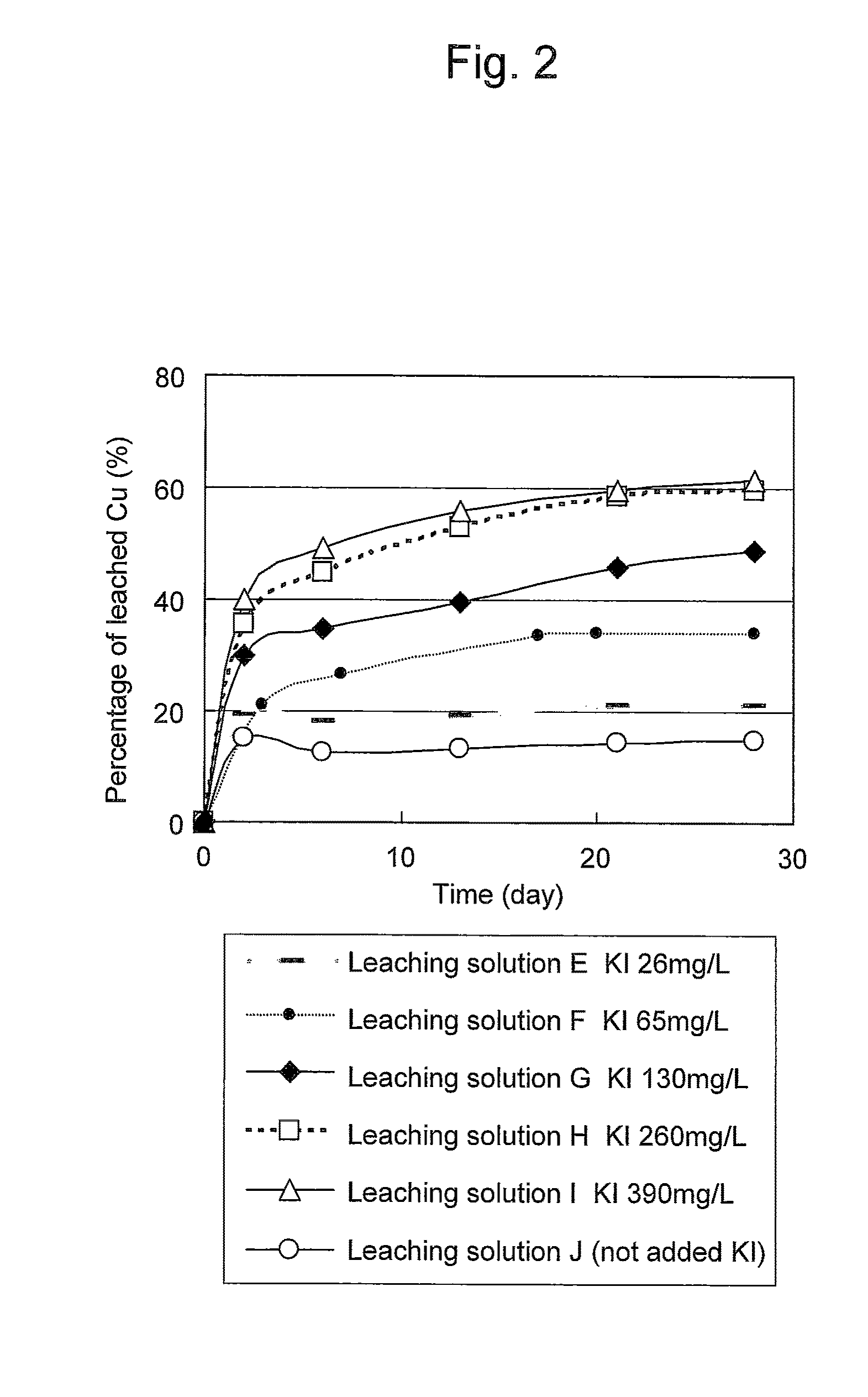
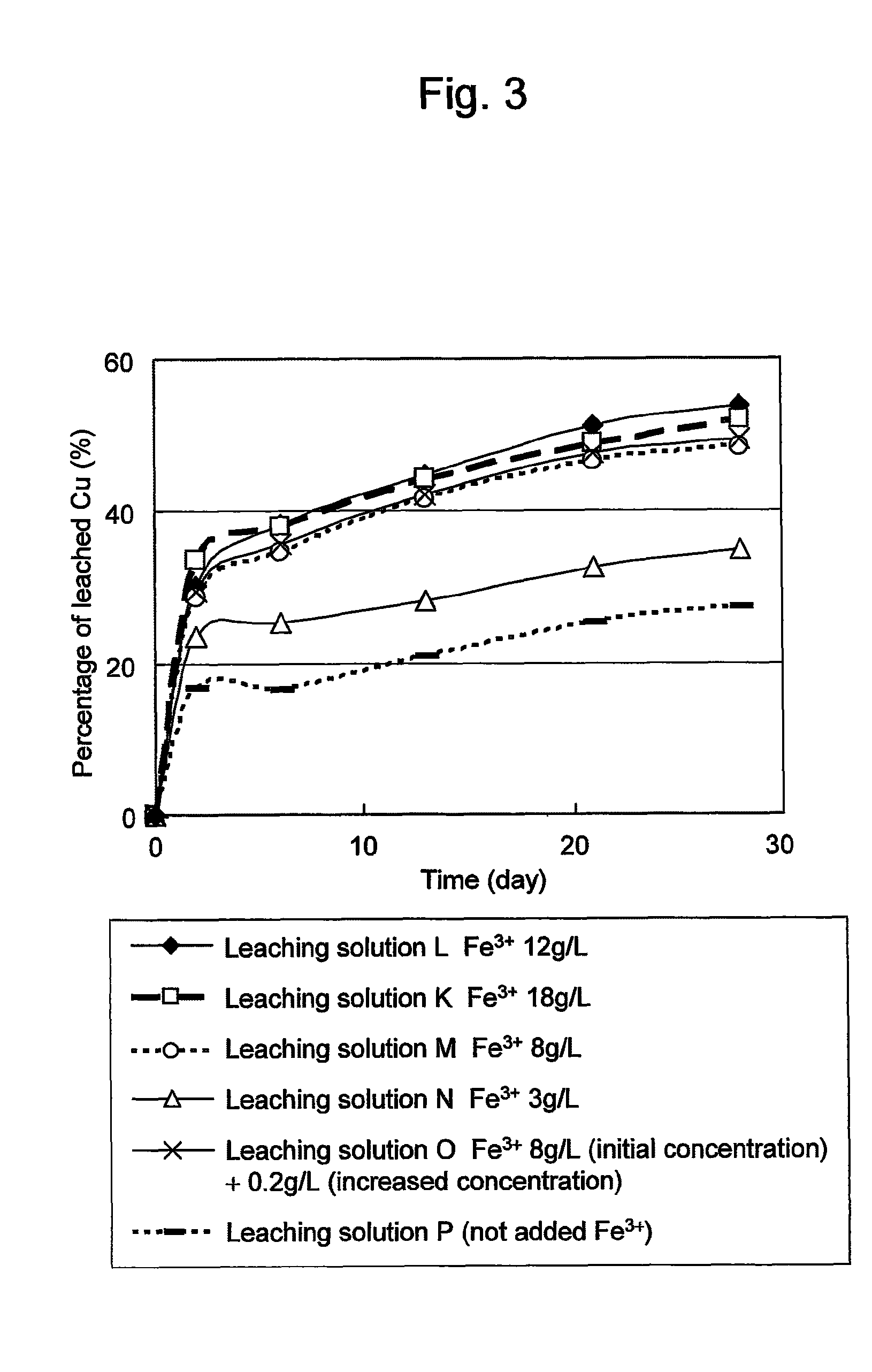
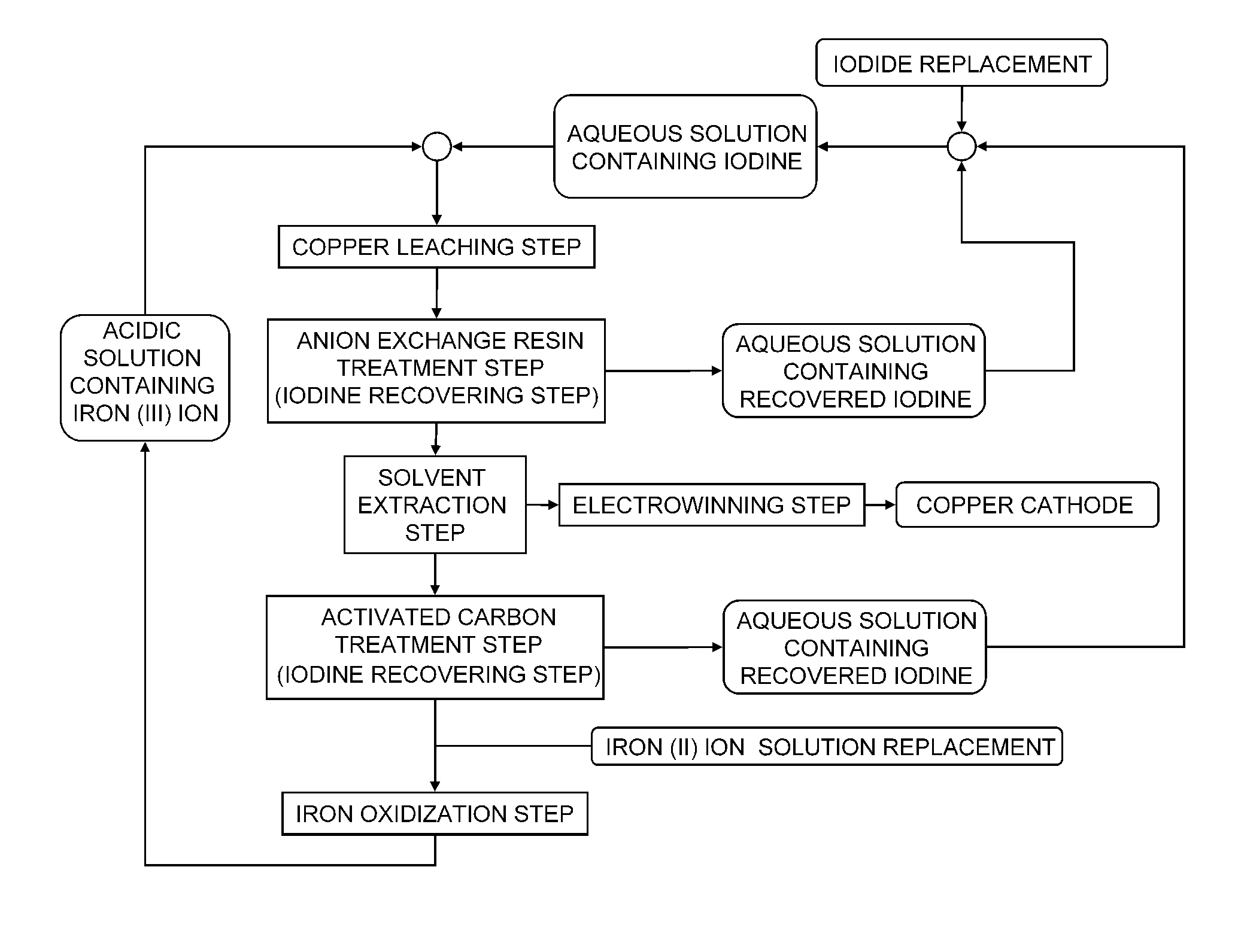
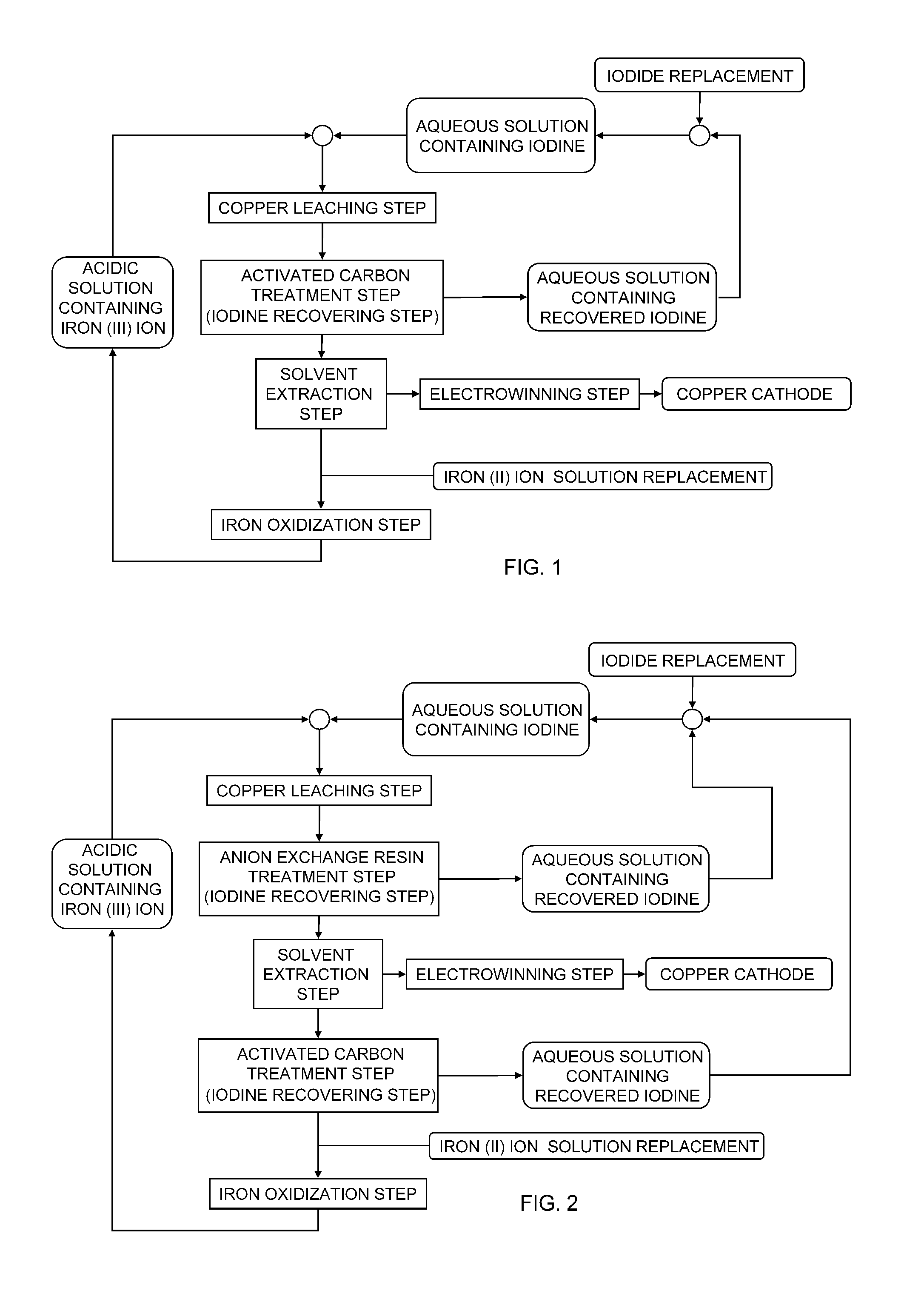
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
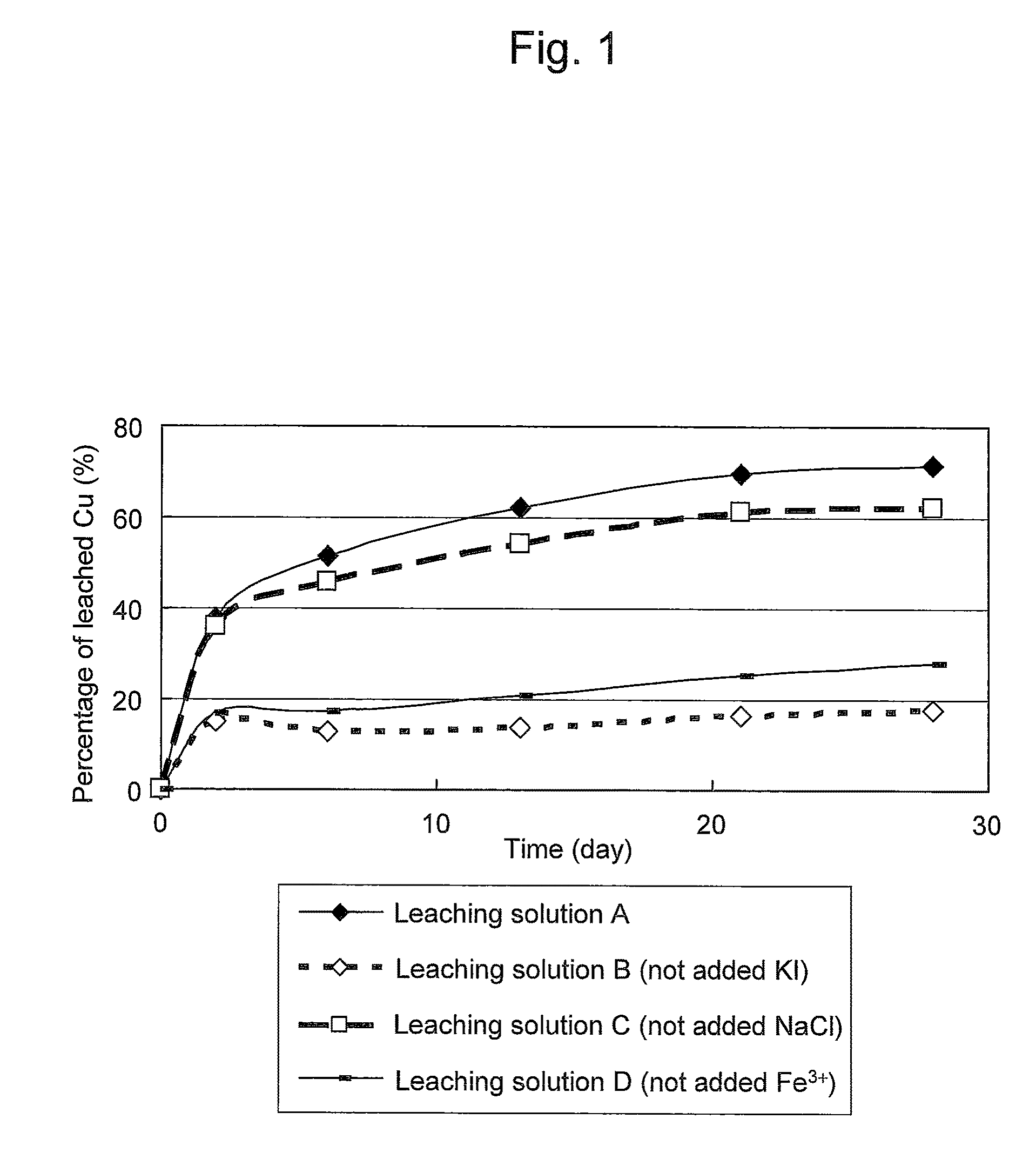
ActiveUS20100018349A1Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
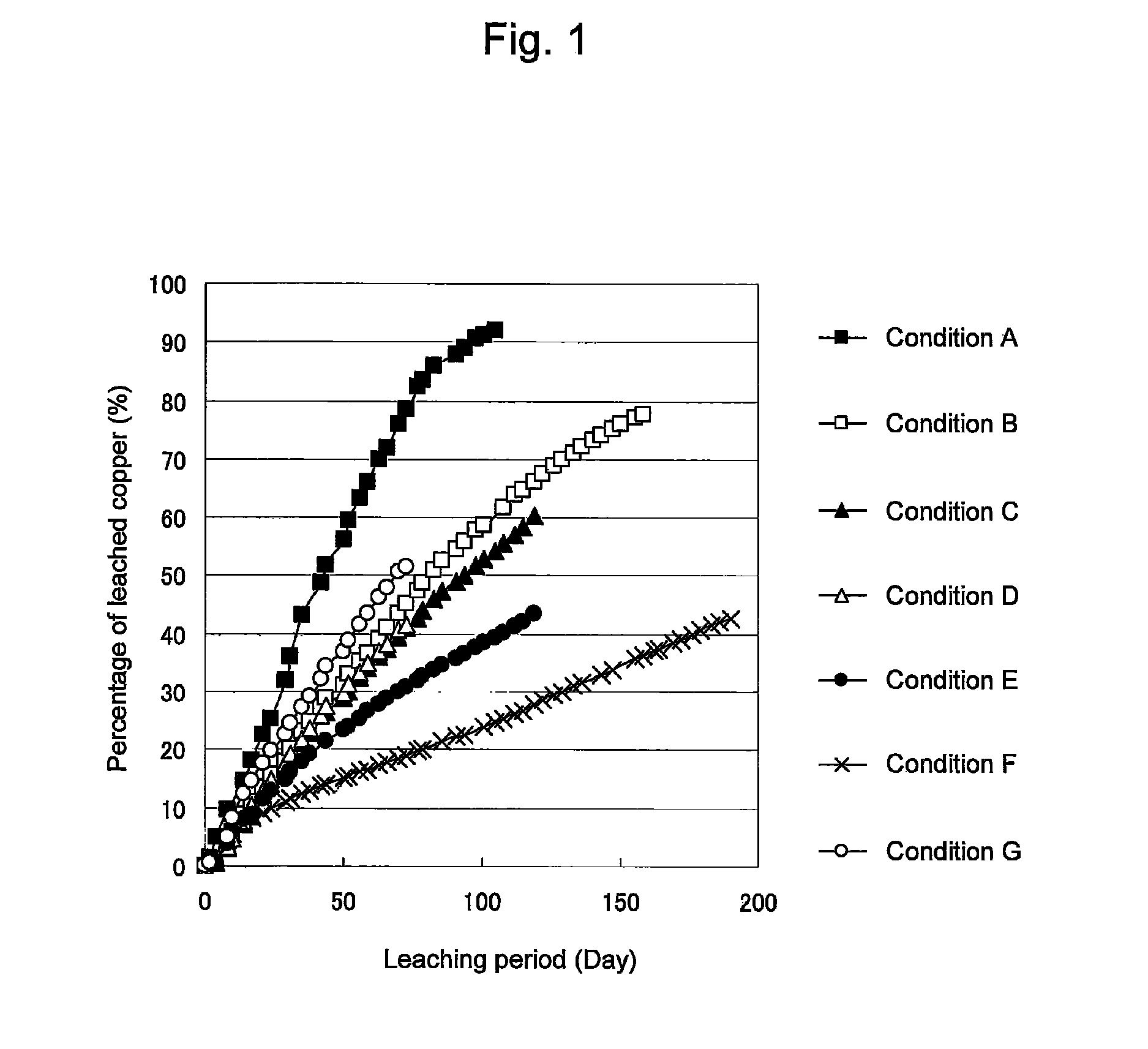
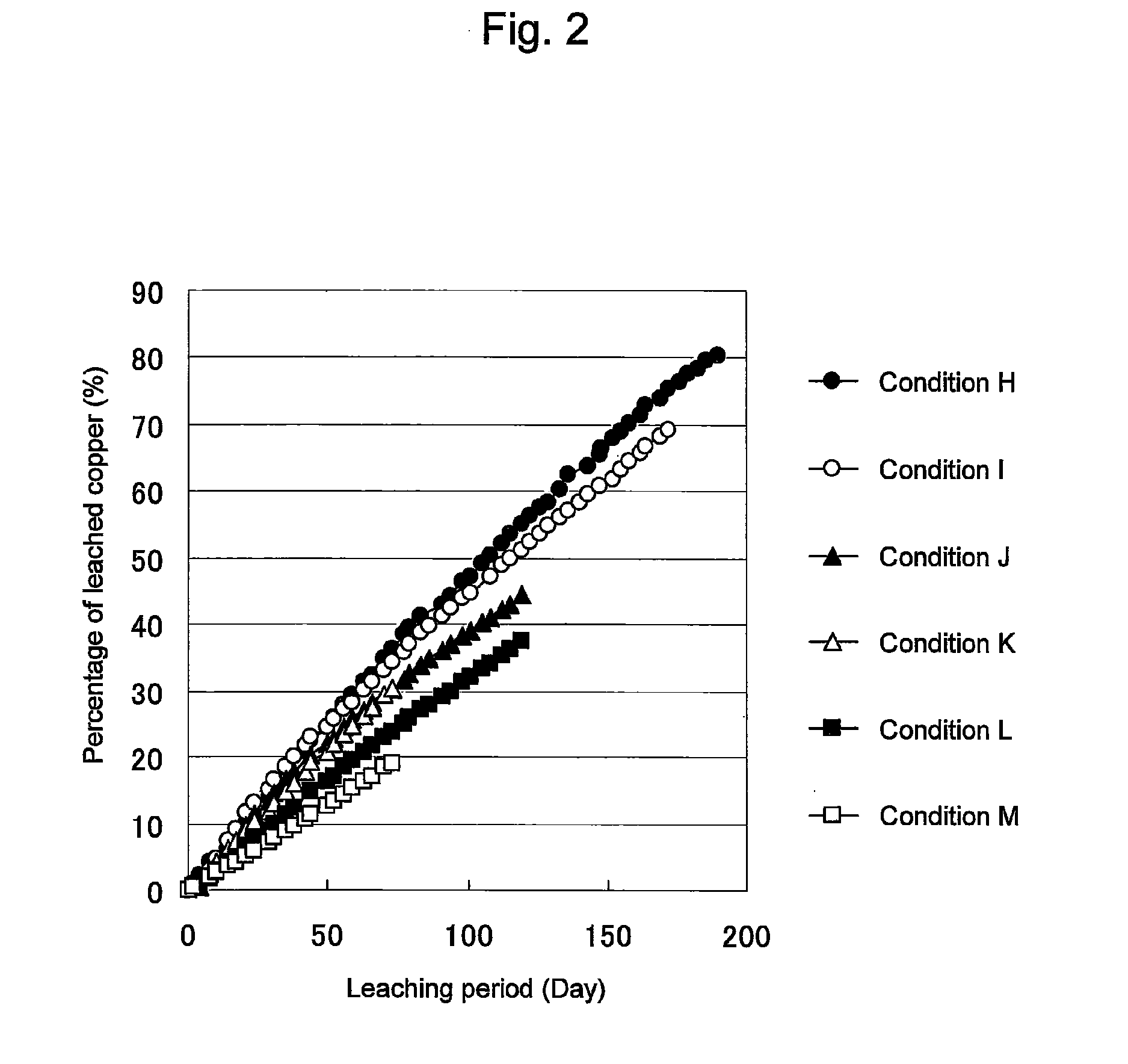
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
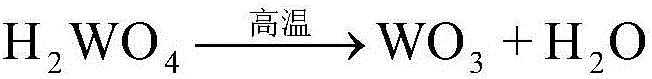
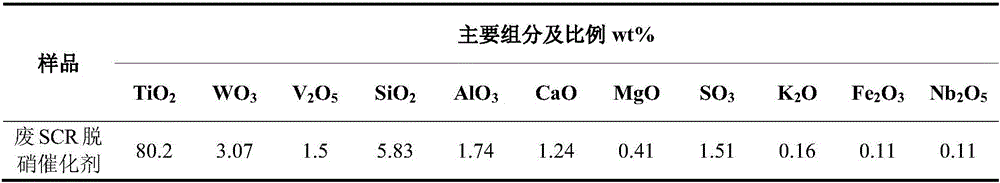
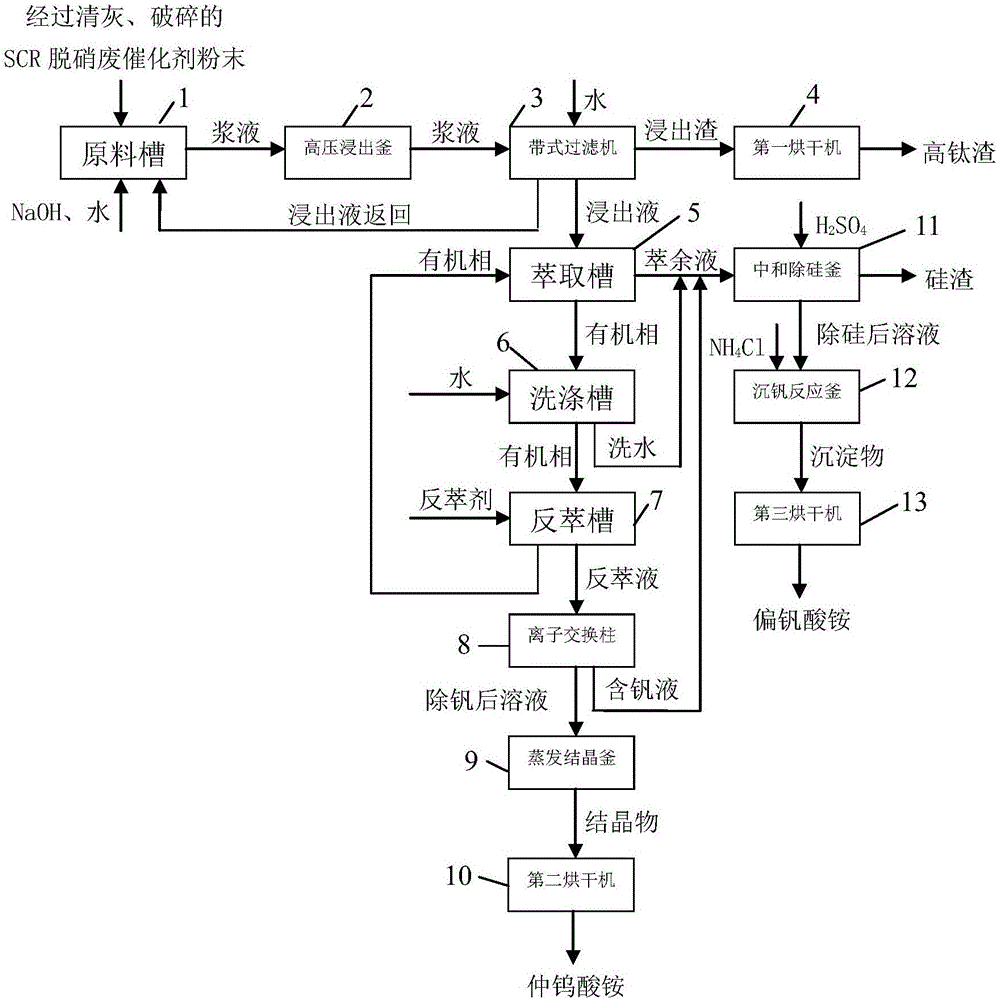
Separating and recovering method for W and V in waste SCR denitration catalyst
ActiveCN106048230AEfficient leachingHigh selectivityProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionKerosene
The invention discloses a separating and recovering method for W and V in a waste SCR denitration catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of recovery of waste catalysts. The separating and recovering method comprises the specific steps that at first, after being smashed and dried, the SCR catalyst is uniformly mixed with Na2CO3 to obtain a mixture, the mixture is calcined at high temperature to obtain a calcined product, and the calcined product is placed in dilute sulphuric acid to leach W and V; then, W and V in the leachate are extracted with a trioctylamine-isodecanol kerosene solution, and are separated out from an extracted organic phase with NaOH as a back-extractant; next, H2SO4 is added in a back extraction solution to regulate pH, excessive NH4C1 is added to realize vanadium precipitation, and ammonium metavanadate precipitates obtained through filtering are calcined to obtain a V2O5 product; and at last, sulfuric acid is continuously added in a secondary filtrate obtained after vanadium precipitation to regulate pH, excessive CaCl2 is added to realize tungsten precipitation, CaWO4 precipitates obtained through filtering are pickled with hydrochloric acid to obtain a pickled product, and the pickled product is calcined to obtain a WO3 product. The separating and recovering method can realize efficient separation and recovery of W and V in the waste SCR catalyst, the process is simple, the pollution is less, and the separating and recovering method has a relatively high engineering application value.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
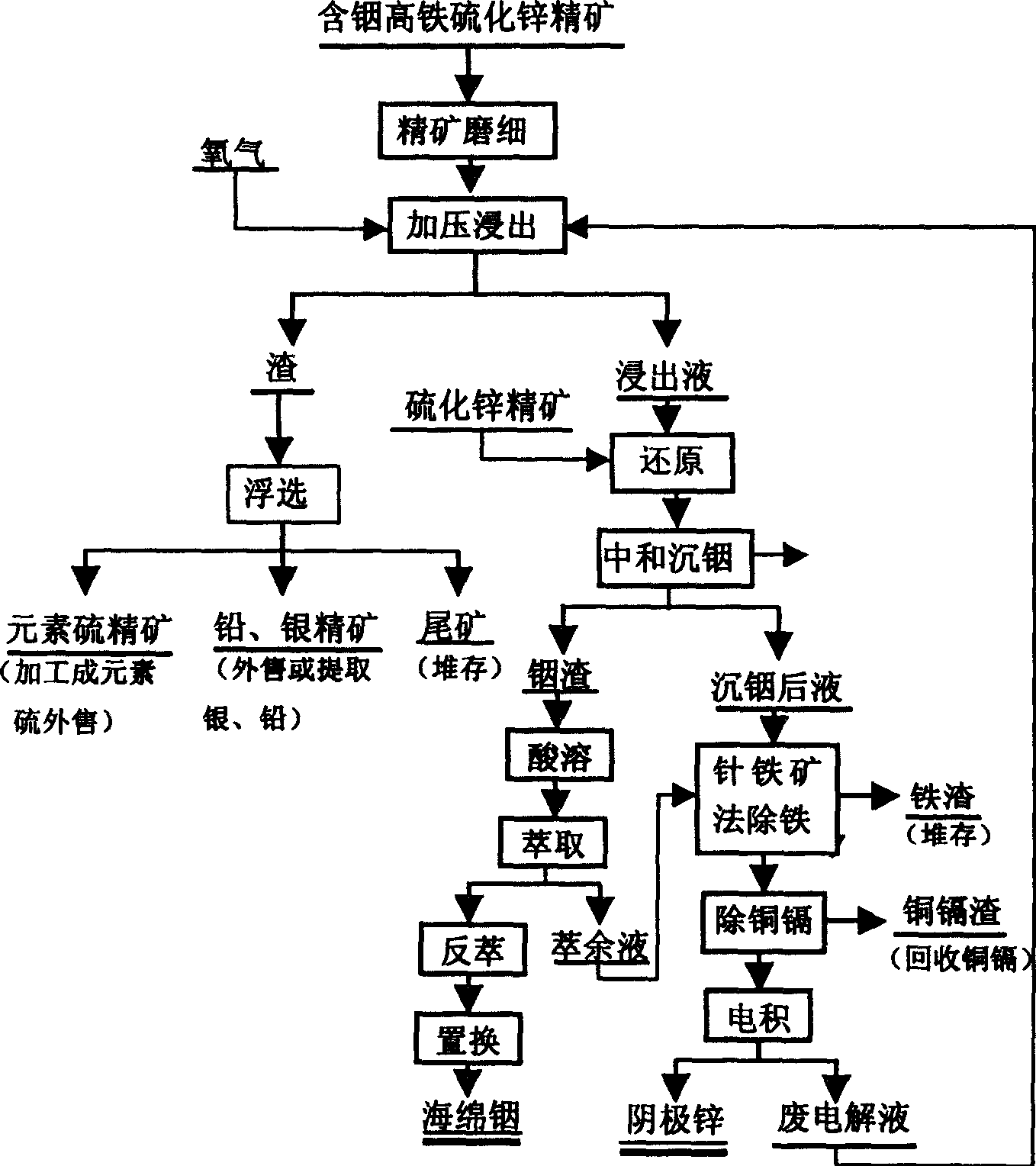
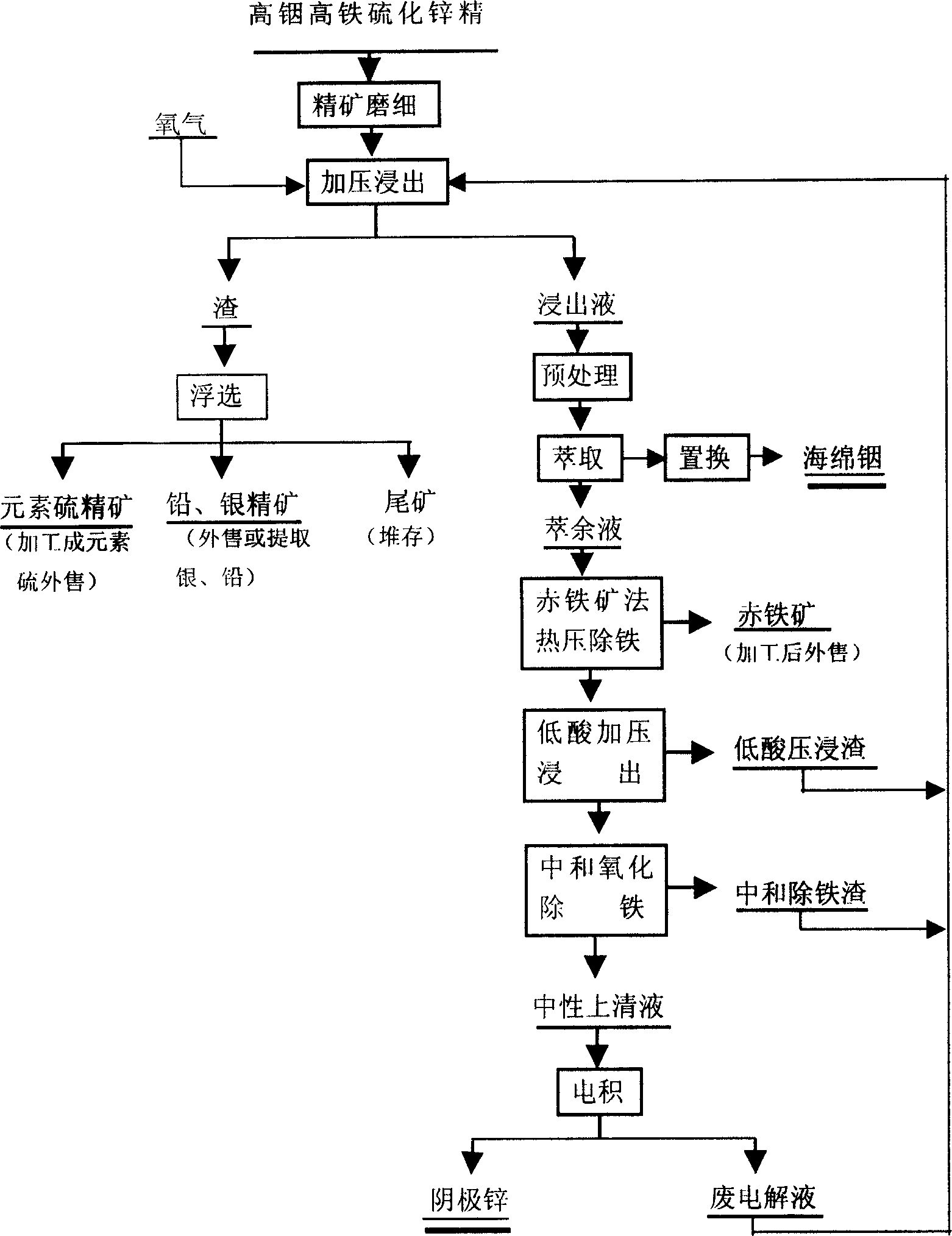
Production method of zinc indium by pressurized acid leaching neutralization precipitation separation indium from indium containing high iron zinc sulfide concentrate
A process for preparing zinc and indium from the In contained high-Fe zinc sulfide ore concentrate includes such steps as grinding, mixing with the waster electrodeposition liquid of Zn to obtain slurry, loading in pressurizing reactor, acid extracting for extracting Zn by more than 99% and In by more than 92%, neutralizing and depositing to separate In, removing Fe from the extracting liquid, solution cleaning, electrodeposition, and fusion-casting to obtain Zn.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL GROUP
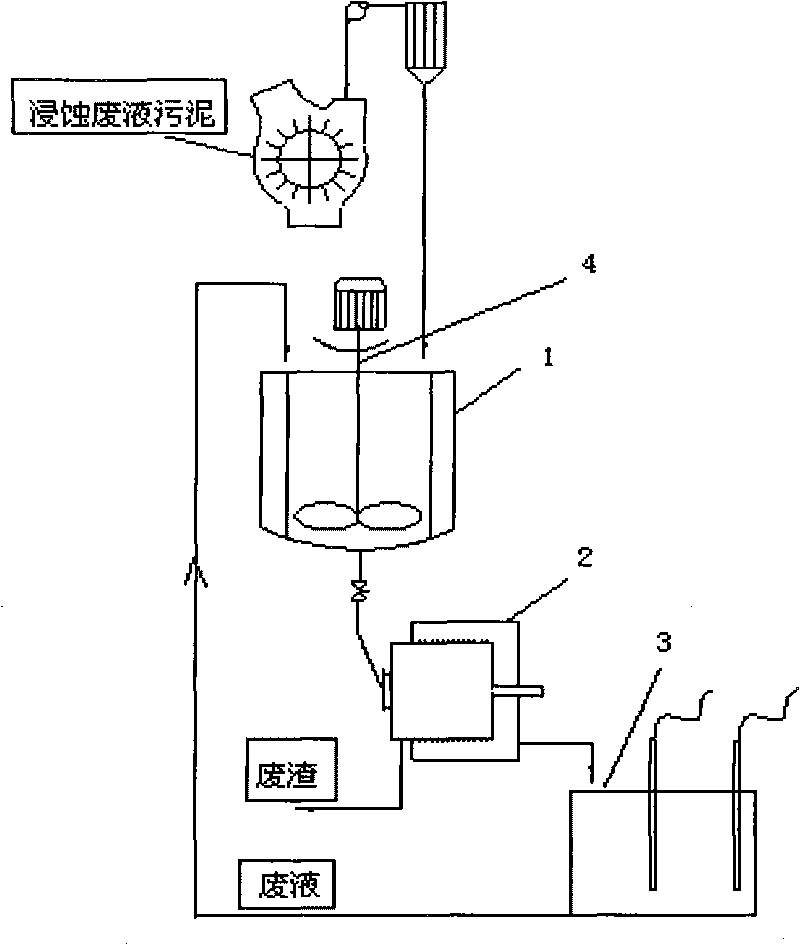
Method for recovering metallic copper in mud by using microorganism and special device
InactiveCN101760619AIncreased content of metal elementsIncrease element contentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementHeating systemMetal leaching
The invention relates to a method for recovering metallic copper in mud generated after production of a circuit board and / or treatment of electroplating rinse-waste water by using a microorganism and a special device. The method comprises the following steps: A, adding a culture medium into a reactor, inoculating a pre-cultured T.f bacteria and T.t bacteria inoculation liquid, starting a heating system and pre-culturing the mixture for 1+ / -0.5 day to obtain a reaction liquid; B, adding the mud into the reaction liquid obtained in the step A with stirring, starting an aeration machine to culture the mixture for 3 to 10 days, opening a valve at the bottom of the reactor, then pumping a leaching agent which contains mud granules from the reactor with stirring, filtering the mud granules with a filter press to obtain the metallic leaching agent; and C, after extracting and condensing the metallic leaching agent obtained in the step B, allowing the metallic leaching agent to enter an electrolytic bath for electrolysis to obtain copper with the purity of over 99 percent, or directly evaporating the concentrated liquor to obtain high-purity CuSO4. The method has the advantages of simple technique, low cost and environmental friendliness.
Owner:惠州市雄越保环科技有限公司
Preparation method of environment-friendly type precious metal beneficiation agent
ActiveCN103937986AAvoid pollutionEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementLead saltSodium cyanide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a low-toxic environment-friendly type novel precious metal beneficiation agent. Raw materials of the low-toxic environment-friendly type novel precious metal beneficiation agent comprise a cyanate, sodium hydroxide, sodium sulfate, sodium ferrocyanide, a bromide, and a lead salt. The preparation method comprises following steps: sodium cyanate, sodium hydroxide, sodium sulfate, and sodium ferrocyanide are mixed at a certain ratio; an obtained mixture is delivered into a smelting pot which is heated to be slightly red, and is heated to 650 to 750 DEG C so as to obtain a fused material, temperature is maintained to be 750 DEG C for 30 to 50min of reaction, and then an obtained product is collected and cooled; the obtained product is smashed, the bromide and the lead salt are added for stirring, and the environment-friendly type precious metal beneficiation agent is obtained via combination. The environment-friendly type precious metal beneficiation agent can be widely used for precious metal beneficiation metallurgy of nonferrous metals ores, contains no hypertoxic compounds, is safe for human and animal, and is friendly to the environment. Compared with other metal beneficiation agents, the environment-friendly type precious metal beneficiation agent is excellent in effects, stable in performance, and low in production cost; the preparation method is simple; and environmental protection can be realized.
Owner:广西河池鑫银环保科技有限公司
Method for producing manganese sulfate by acid leaching under pressure of pyrolusite and pyrite
The invention discloses a method for producing manganese sulfate from the acid leaching of pyrolusite and pyrite under pressure, which includes the following steps: (1) after the pyrolusite and pyrite are mixed according to the proportions of 1:0.3 to 0.5 based on the mass ratio of the pyrolusite and pyrite, sulfate with the acidity of 100 to 220g / l is adopted for size mixing; (2) after the size mixing is finished, the materials are added into an autoclave, and the pressure in the autoclave is controlled from 0.3 to 1.0MPa, and the temperature is controlled from 100 to 110 DEG C for the manganese leaching reaction under pressure; after the time of reaction is for 60 to 180 minutes, the slag is discharged and the slag liquid is separated. The method can leach the manganese in the pyrolusite within a short time with different acidities under certain pressure and higher temperature and the leaching rate of the manganese is about 95 percent and the content of manganese in the slag is less than 1.5 percent.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Process and device for alkaline extraction and recovery from waste catalysts in SCR (selective catalytic reduction) denitrification
ActiveCN106435197AAchieve recyclingEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium paratungstateTitanium
The invention discloses a process and a device for alkaline extraction and recovery from waste catalysts in SCR (selective catalytic reduction) denitrification. By adoption of NaOH solution, tungsten and vanadium in the waste catalysts in SCR denitrification are leached into leach liquid while titanium is remained in leach residues, so that separation of titanium from tungsten and vanadium is realized; then an alkaline extraction process is adopted for separating tungsten and vanadium in the leach liquid; finally, a refining process including steps of crystallizing, dewatering, drying and the like is carried out to obtain high-purity ammonium paratungstate and ammonium metavanadate in accordance with national standards, and by-product titanium-rich residues are obtained at the same time. By the process and the device for alkaline extraction and recovery from the waste catalysts in SCR denitrification, valuable metals in the waste catalysts in SCR denitrification can be recovered, and the high-purity ammonium paratungstate and ammonium metavanadate in accordance with the national standards are obtained while the by-product titanium-rich residues are obtained as well.
Owner:武汉恒合嘉创环境工程有限公司
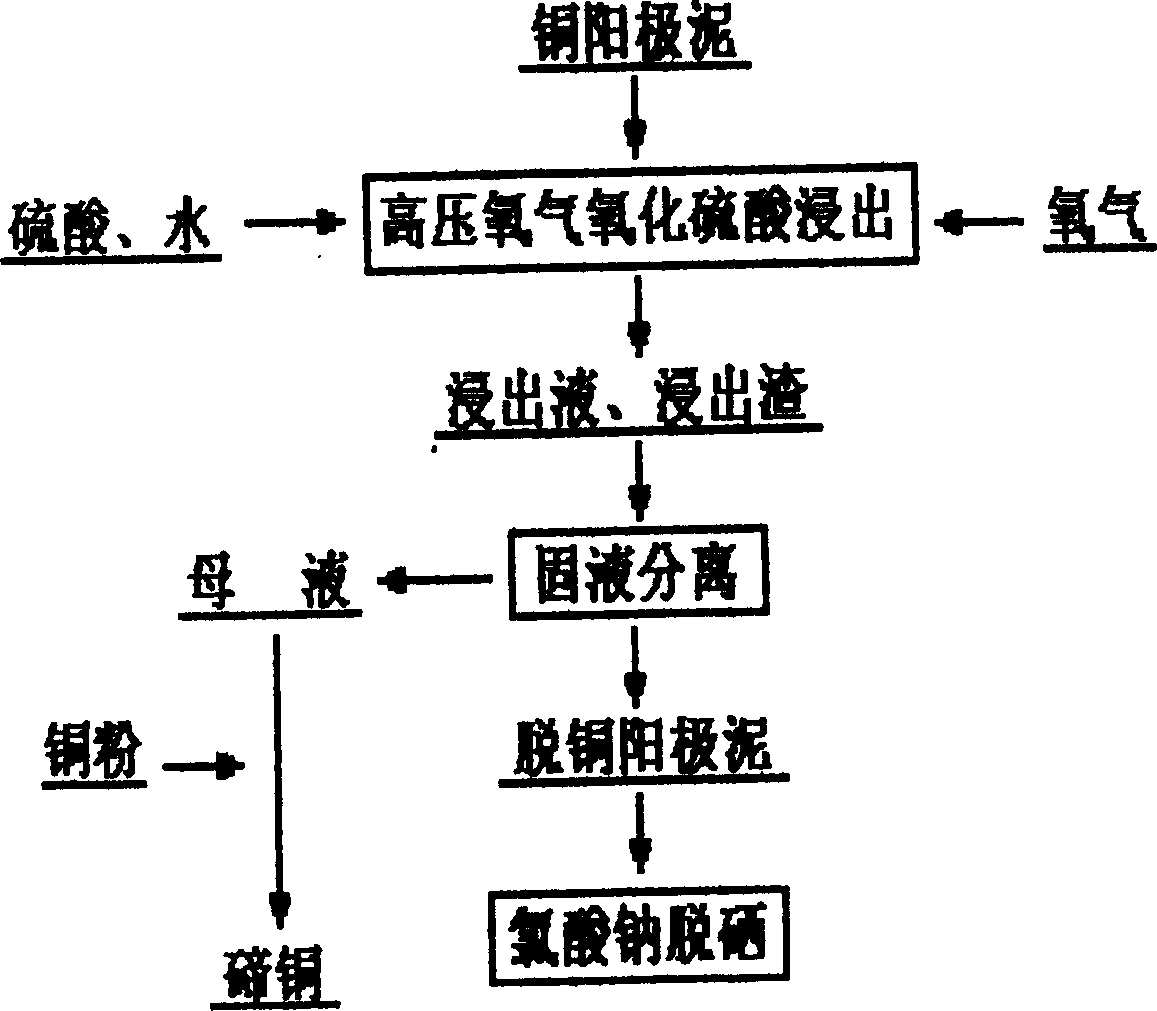
Method for leaching tellurium from copper anode mud using pressurized acid leaching process
InactiveCN1821060AEfficient leachingImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumPregnant leach solutionTe element
The present invention relates to pressurizing and acid leaching process for leaching out tellurium from copper anode mud, and belongs to the field of wet metallurgical technology of rare dispersion element. The process includes the following steps: mixing water and anode mud in 1-40 wt% to prepare slurry, filtering to eliminate large grain and sand, mixing with sulfuric acid solution of 70-300 g / L concentration, heating in a high pressure reactor at 100-180 deg.c, introducing gaseous oxidizing medium, regulating and maintaining the pressure at 0.5-1.6 MPa for direct acid leaching reaction for 60-120 min, solid-liquid separation to obtain the tellurium leachate. The present invention has simple technological process, less needed apparatus, reinforced process, short leaching period and high tellurium leaching rate.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL GROUP
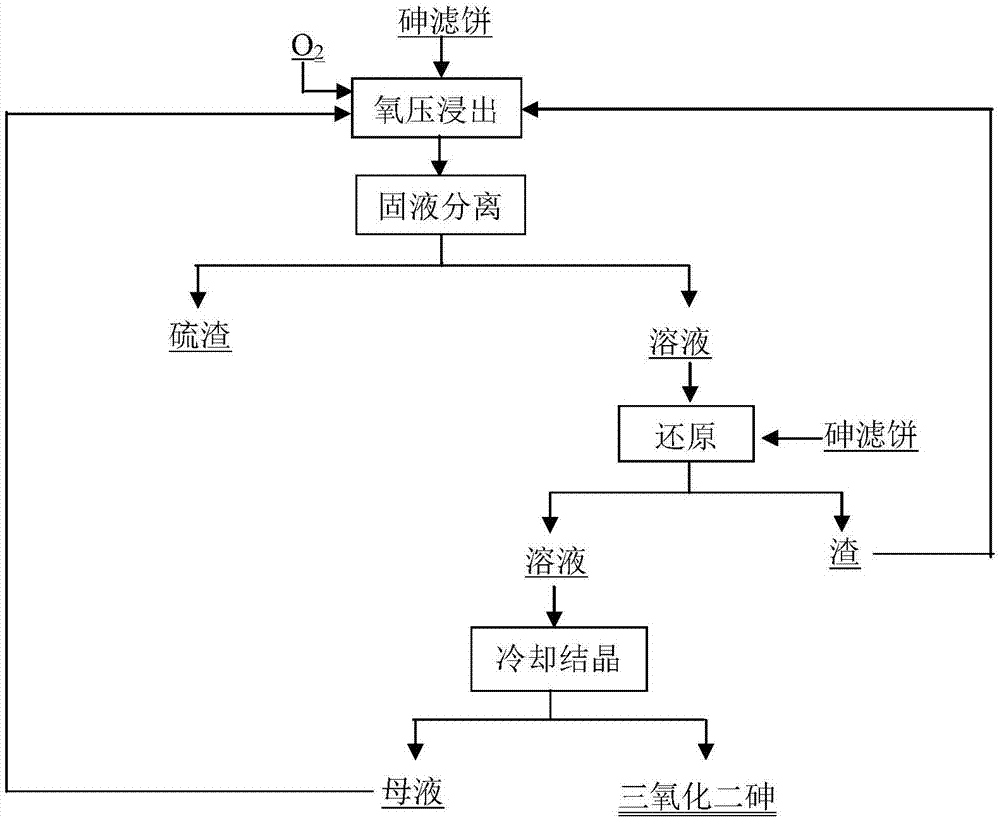
Process of extracting arsenic from arsenic sulfide waste residue by adopting whole wet method
The invention discloses a process of extracting arsenic from arsenic sulfide waste residue by adopting the whole wet method. The process comprises the following steps: arsenic sulfide waste residue is subjected to oxygen pressure leaching and solid-liquid separation to obtain sulfur slag and an oxygen pressure leach solution containing pentavalent arsenic and H2SO4; arsenic sulfide waste residue is taken as a reducing agent to obtain pentavalent arsenic by reduction, and solid-liquid separation is carried out, so as to obtain a solution containing trivalent arsenic and a slag phase; the solution containing trivalent arsenic is subjected to cooling crystallization and drying to obtain a opaque glass product, and the slag phase is returned to be subjected to oxygen pressure leaching. The process has the advantages of being short in process flow, economic and practical, good in operating environment and capable of realizing closed circulation of the solution; arsenic and sulfur are recovered in the forms of a arsenic trioxide product and sulfur, the problem that the conventional SO2 reduction causes acid swelling is solved, and the industrial popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:郴州金铖环保科技有限公司
High-efficiency leaching process of nickel from laterite-nickel ore
InactiveCN101338377AReduce usageEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlurry
The invention discloses an effective extraction technique for the nickel in a lateritic nickel ore. The invention takes the lateritic nickel ore of silicate as the raw material and takes vitriol as an extraction agent after being cracked and screened to add the extraction materials into the extraction liquid with a certain concentration for reacting for a certain period of time under a certain temperature and stirring speed; after the reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is instantly carried out to obtain the extraction liquid rich in nickel. The invention carries out stirring extraction reaction under a normal pressure and realizes the effective extraction of the nickel in the lateritic nickel ore by selecting a proper extraction ore slurry concentration and adjusting the extraction reaction time, the temperature and the rotating speed of a stirrer; the technique of the invention has the advantages of low acid consumption and less corrosion to devices, etc. Besides, the technique of the invention is applicable for batch production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of recovering lithium and copper from waste lithium iron phosphate battery selectively
ActiveCN111187913AEfficient leachingAvoid leachingWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLithium iron phosphateIron phosphate
The invention discloses a method of recovering lithium and copper from a waste lithium iron phosphate battery selectively and relates to the technical field of electronic waste recovery processing. The method comprises the following steps of mixing the waste lithium iron phosphate battery with an inorganic acid and oxygen to react at 96-150 DEG C, and carrying out solid-liquid separation after thereaction to obtain a lixivium and an iron phosphate leaching residue mixing the lixivium with a separator to separate copper in the lixivium, and then adding an alkaline substance to adjust the pH toremove impurities iron and aluminum to obtain a purified liquid; and precipitating the purified liquid and sodium salt to obtain a lithium product. According to the method, a waste lithium iron phosphate electrode material structure is damaged in a high-temperature oxidant acidic environment. In particular, at 96-150 DEG C, it is only needed to add a small amount of inorganic acid to leach lithium and copper efficiently while Fe is hardly leached, so that lithium and copper with high value can be recovered. The method is short in process flow, simple in equipment and low in reagent cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF RARE METALS
Lithium resource recycling method on waste lithium ion battery negative plate
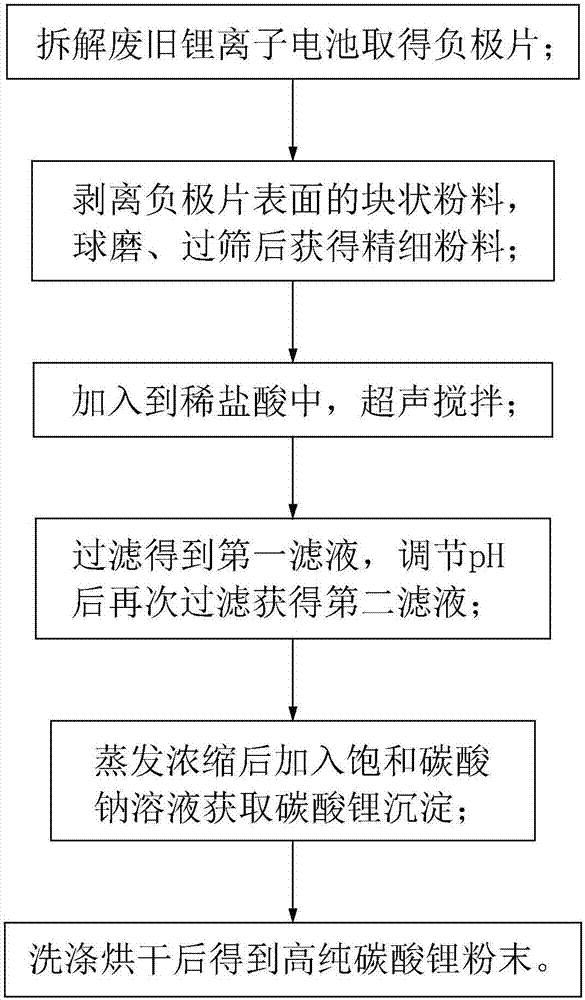
InactiveCN107394298AEase of bulk recyclingEfficient leachingWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLithium carbonateChemistry
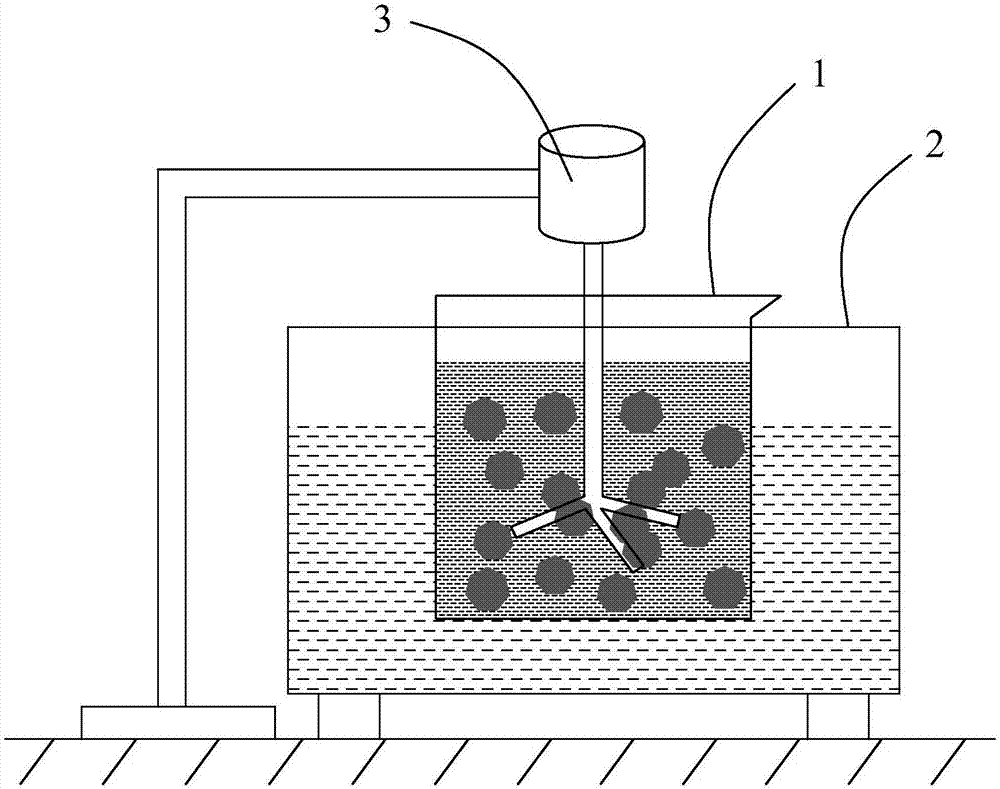
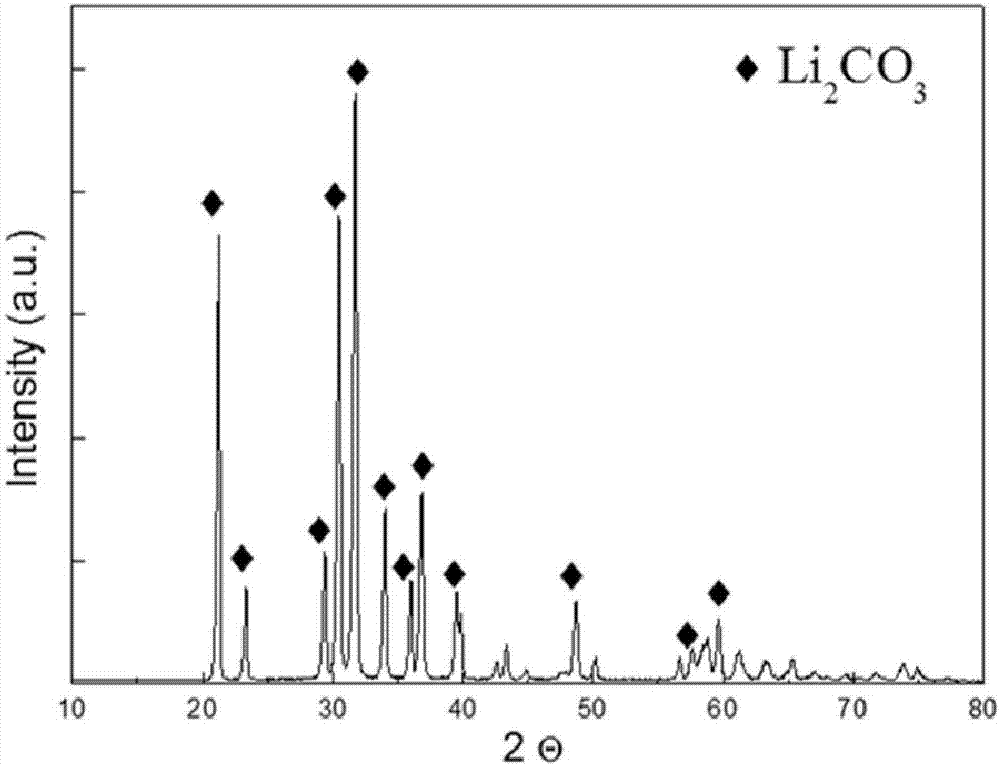
The invention provides a lithium resource recycling method on a waste lithium ion battery negative plate. The method comprises the following steps: firstly manufacturing the massive powder on the surface of the negative plate as fine powder, and supplementing with the ultrasonic stirring in the reaction process with the diluted hydrochloric acid, thereby realizing the efficient leaching of the lithium resource. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple in process flow, low in cost, easy to recycle lithium ion battery negative plate in batch and realize the industrial application; and the high-pure lithium carbonate powder obtained through the recycling method provided by the invention can be directly used for industrial production, and the economic value of the recycling is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS8163063B2Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Method for extracting indium from high-indium high-iron zinc sulphide concentrates by pressure acid leach and solvent extraction
InactiveCN1664131AEfficient leachingHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionIndium
The invention relates to an indium extraction method by acid dipping and solvent extraction under high pressure from zine sulfide clean ore with high component of indium and iron. After jevigating process of zine sulfide clean ore with high component of indium and iron, pasting the powder with zinc electrodeposition discard solution, sending the mixture to pressure pan to do acid dipping directly, in which zinc leaching ratio approaches to 99% or higher while indium leaching ratio approaches to 96% or higher, extracting more than 95% of indium in leachate by solvent, so recovery ratio of sponge indium from zine clean ore approaches to 85% or more, processing leachate, from which indium is extracted, to produce sine by wet zinc smelting technology such as deironing, extraction in neutral condition, solution purification, electrodeposition and fusion casting. This invention has the properties of simplifying process, high recovery ratio of indium and zine and high-activity processing of complex zinc clean ore with high component of indium.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL GROUP
Recovery method for waste lithium ion battery anode materials based on mechano-chemical method
ActiveCN110791652AEfficient leachingHazard reductionWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementMetallic lithiumChemical reaction
The invention discloses a recovery method for waste lithium ion battery anode materials based on a mechano-chemical method, and belongs to the field of waste lithium ion battery recycling. The waste lithium ion battery anode materials are ground into powder, the powder is sufficiently and evenly mixed with an activating agent and an organic reducing agent, the activating agent can generate activefree radicals, a mixture is obtained, the mixture is subjected to ball grinding, the waste lithium ion battery anode materials generate plastic deformation, lattice imperfection is generated in crystal particles, and the crystal particles generate crystal transfer or are not crystallized; and products obtained after ball grinding are added into deionized water, and valuable metal ions are leached.The method does not depend on high-concentration strong acid, strong base, strong oxidization reducing reagents, expensive organic acid and the like, the mechano-chemical reaction in a solid phase isadopted as a reaction body, and efficient leaching of valuable metal lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese and the like in the waste lithium ion battery anode materials is achieved under the mild leaching environment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for innocent treatment of low-concentration arsenic-containing waste residue and recovery of arsenic
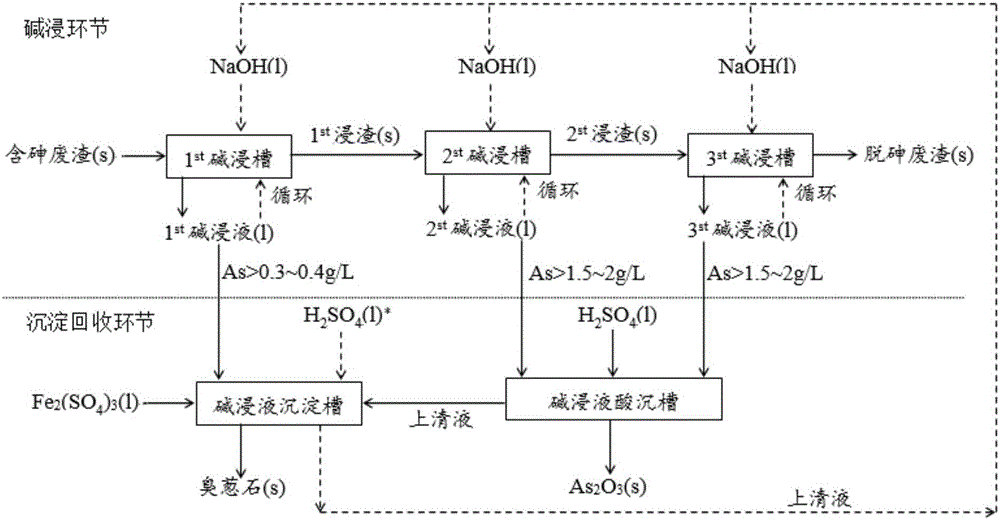
ActiveCN106011475AEfficient leachingReduce arsenic levelsArsenic oxides/hydroxides/oxyacidsIron compoundsResource utilizationMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for innocent treatment of low-concentration arsenic-containing waste residue and recovery of arsenic. Aiming at low-concentration arsenic-containing waste residue, according to the invention, a multistage alkaline leaching method is adopted, wherein mechanical stirring is performed for 10-12h in the environment of 60-80 DEG C, three-stage successive leaching is adopted, the arsenic leaching rate reaches more than 80%, the arsenic content of waste residue after treatment is less than 0.05%, which is lower than the hazardous waste identification limiting value, and therefore, the waste residue can be used as making material of building materials. As2O3 in an arsenic-containing alkaline leaching solution can be recovered by acid neutralization and sedimentation, and ferric sulfate is added to a leaching solution after filtering and sedimentation so as to produce FeAsO4.2H2O sedimentation, the comprehensive arsenic removing rate of the arsenic-containing alkaline leaching solution can reach 99%, and filter liquor can be recycled. Compared with the prior art, according to the invention, no wastewater discharge is caused in the whole process, the technology is simple, and the material is easily available, and the method can be widely popularized and applied to treatment and resource utilization of low-concentration arsenic-containing solid waste.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method of separating and recovering valuable metals from waste lithium battery materials and application thereof
InactiveCN109666799AReduce usageEfficient leachingWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementGrape seedChemistry
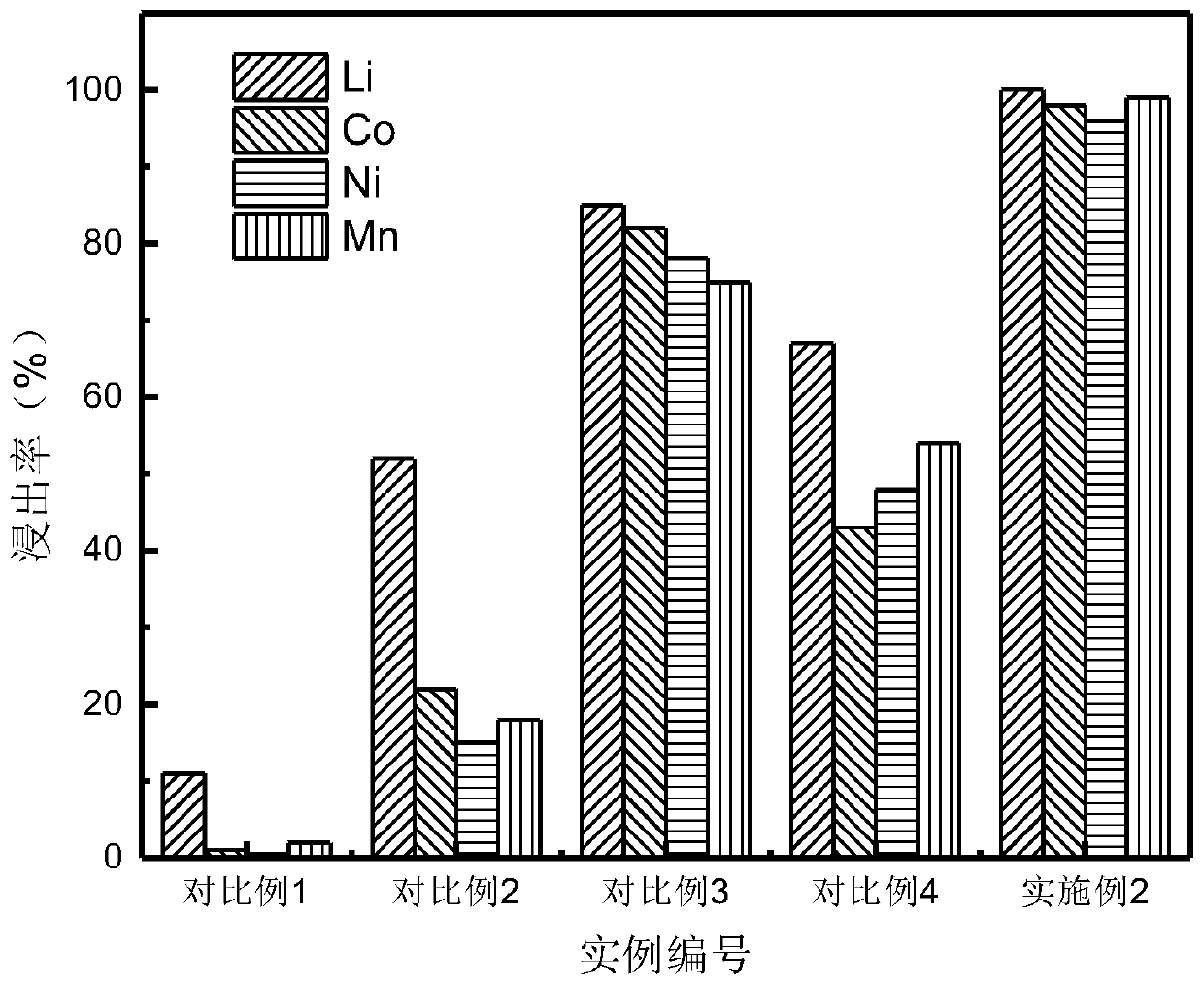
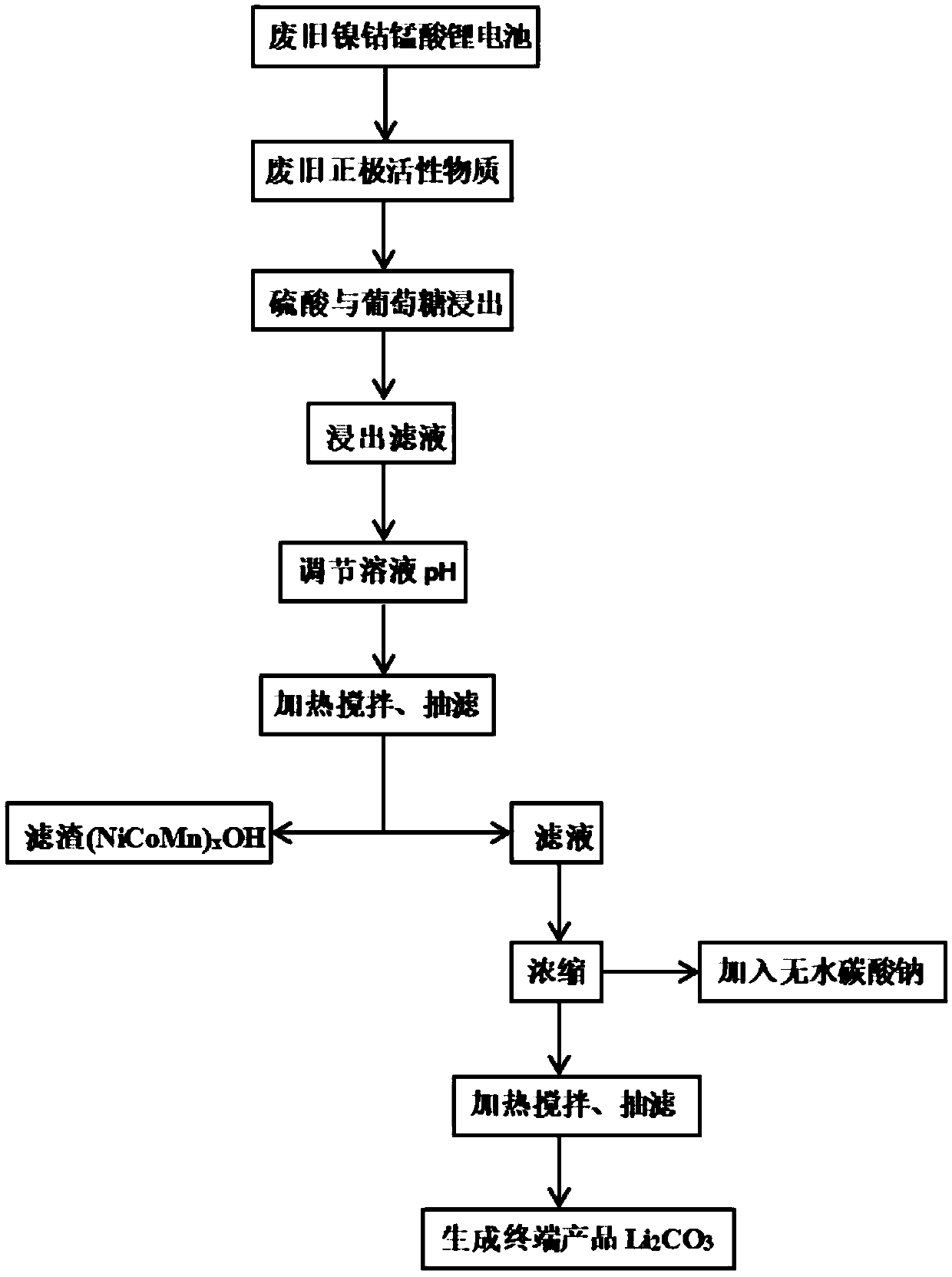
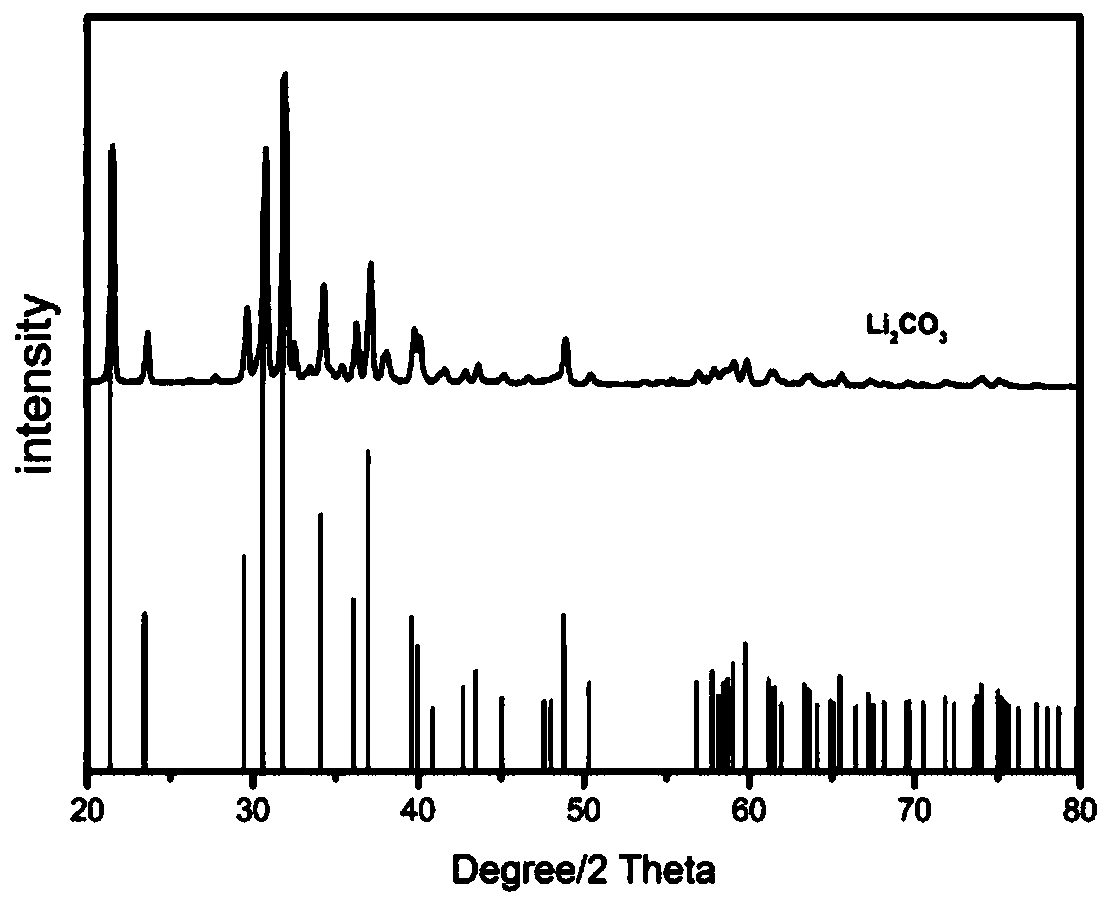
The invention discloses a method of separating and recovering valuable metals from waste lithium battery materials. The method comprises the following steps that a positive electrode material of a battery is leached by using sulfuric acid and a reducing agent, and filtering is carried out after the reaction is completed to obtain a leachate, wherein the reducing agent is one kind or multiple kindsof glucose, cane sugar, vitamin C, grape seeds, sodium thiosulfate and sodium sulfite; an additive is added into a leaching solution so as to adjust the pH value of the leaching solution in the rangeof 10-12, nickel, cobalt and manganese ions in the leaching liquid are enabled to be co-precipitated, and filtering is carried out to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese-containing precipitate and a lithium-ion solution after the reaction is finished; and the lithium-ion solution is concentrated to 20-45 g / L, excessive anhydrous sodium carbonate is added into the concentrated lithium-ion solution for reaction to obtain precipitate lithium carbonate; and the invention further discloses application of the product prepared by the method in battery production. According to the method and the application, leaching efficiency is high the process is simple, the waste liquid can be treated to prepare the terminal product lithium carbonate, and the pollution caused by the waste lithium battery to theenvironment can be effectively reduced.
Owner:武昌首义学院
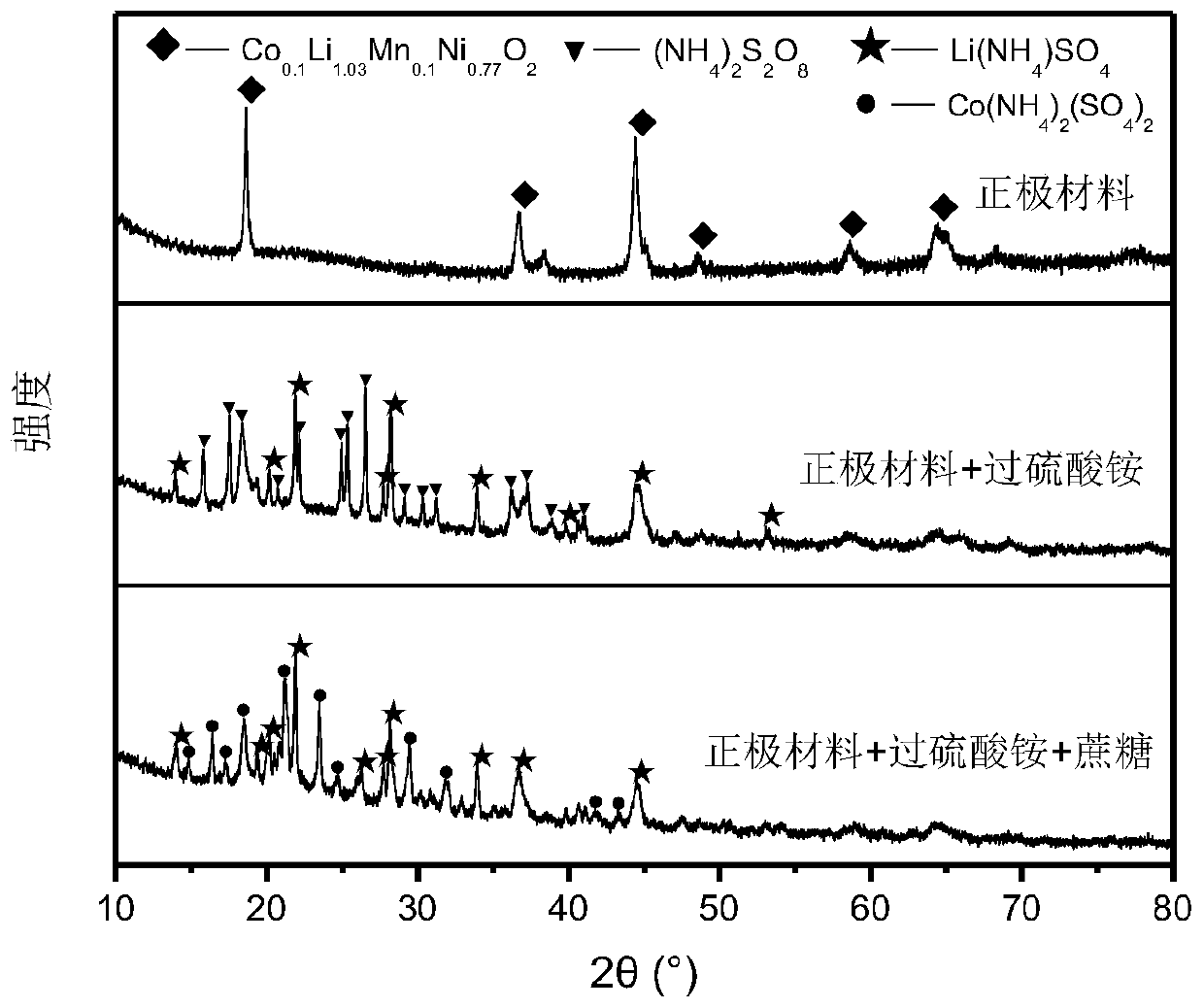
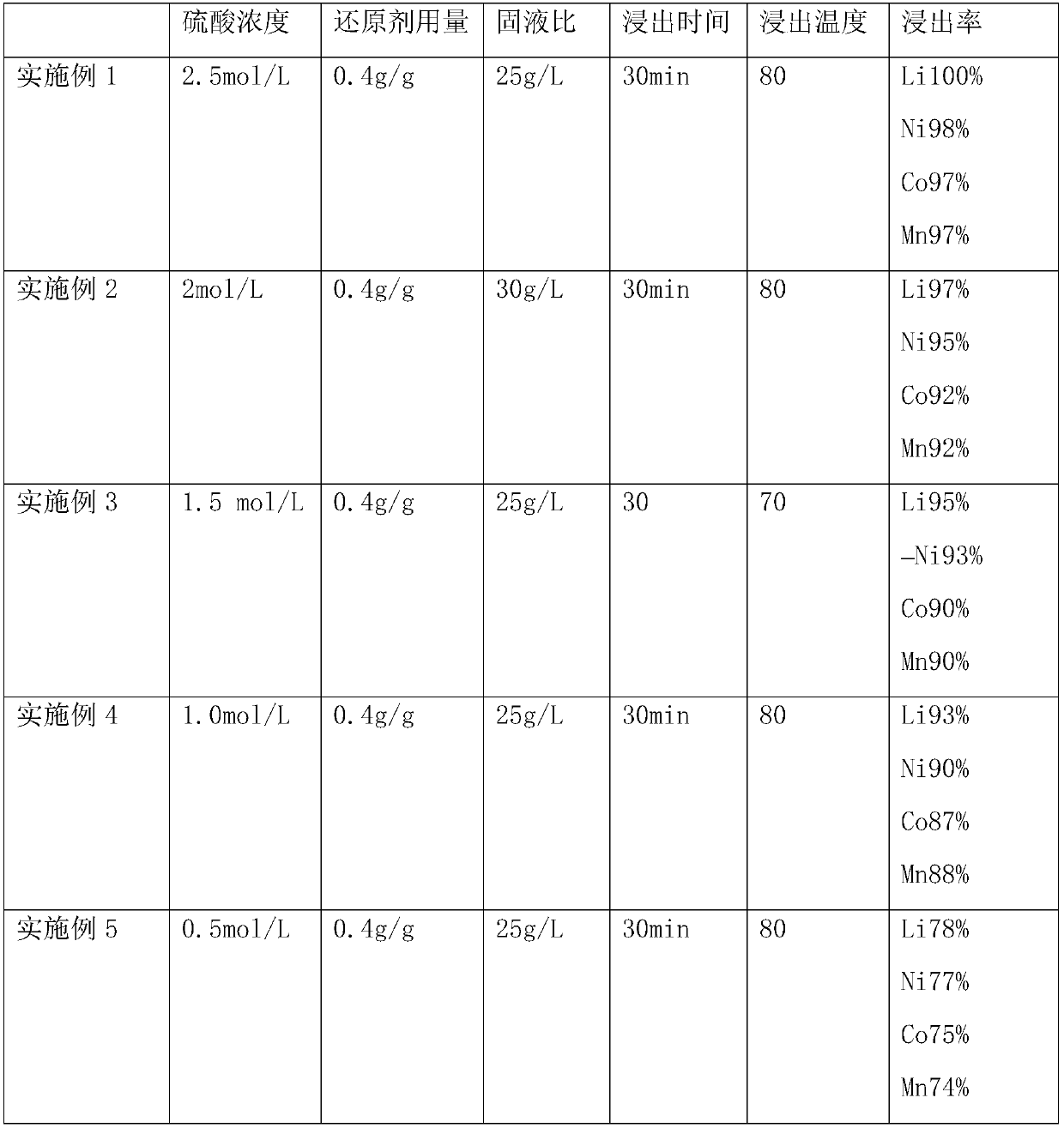
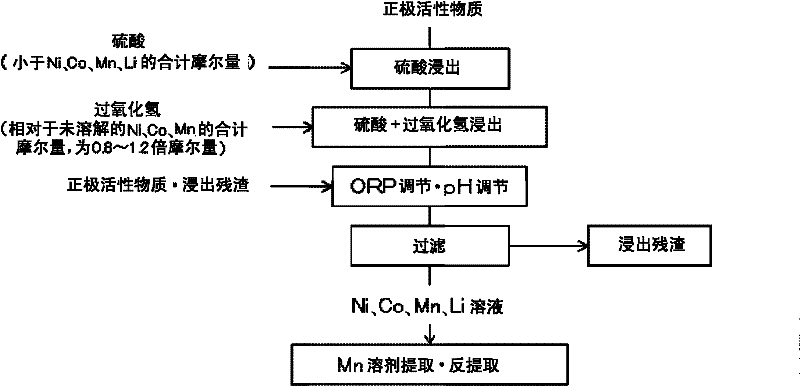
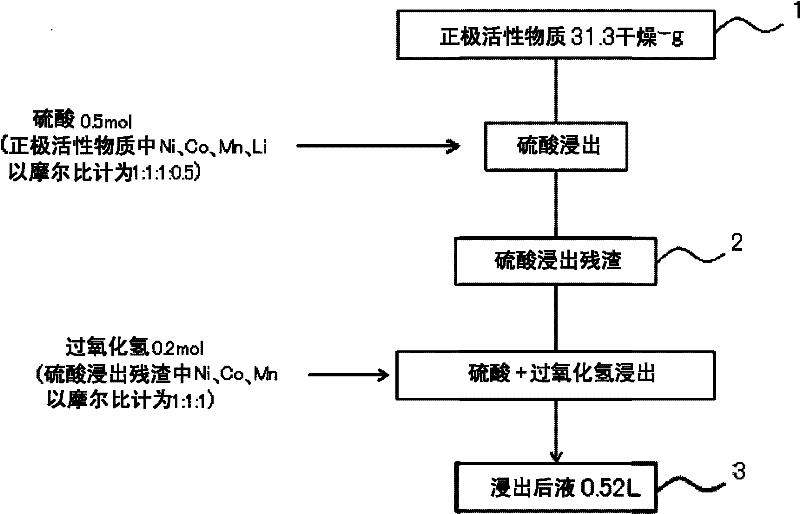
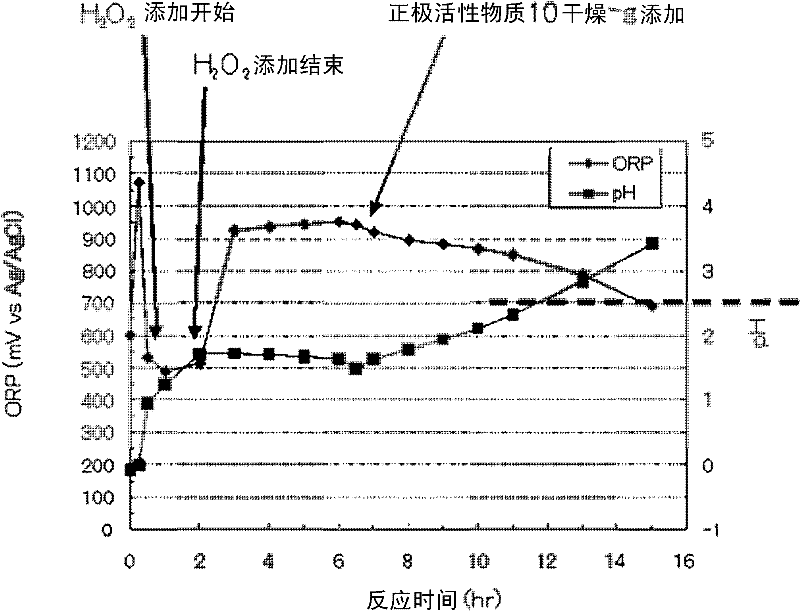
Method for leaching positive electrode active material
ActiveCN102544628ADoes not generate chlorine gasReduce usageWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementManganeseSlurry
Nickel, cobalt and lithium are efficiently leached from the positive electrode active material of lithium-ion secondary cell, obtaining solution suitable for isolating various metals. The invention relates to a method for leaching positive electrode active material which leaches valued metals from the positive electrode active materials of a lithium-ion formed by composite oxide having transition metals including at least manganese. The method comprises a first process which is to dissolve soluble parts of sulfuric acid solution in the positive electrode active material, and a second process which is no solid-liquid separation is conducted after the first process, and adding hydrogen peroxide in sulfuric acid leaching slurry solution, and leaching unleached parts in the left sulfuric acid leaching slurry.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
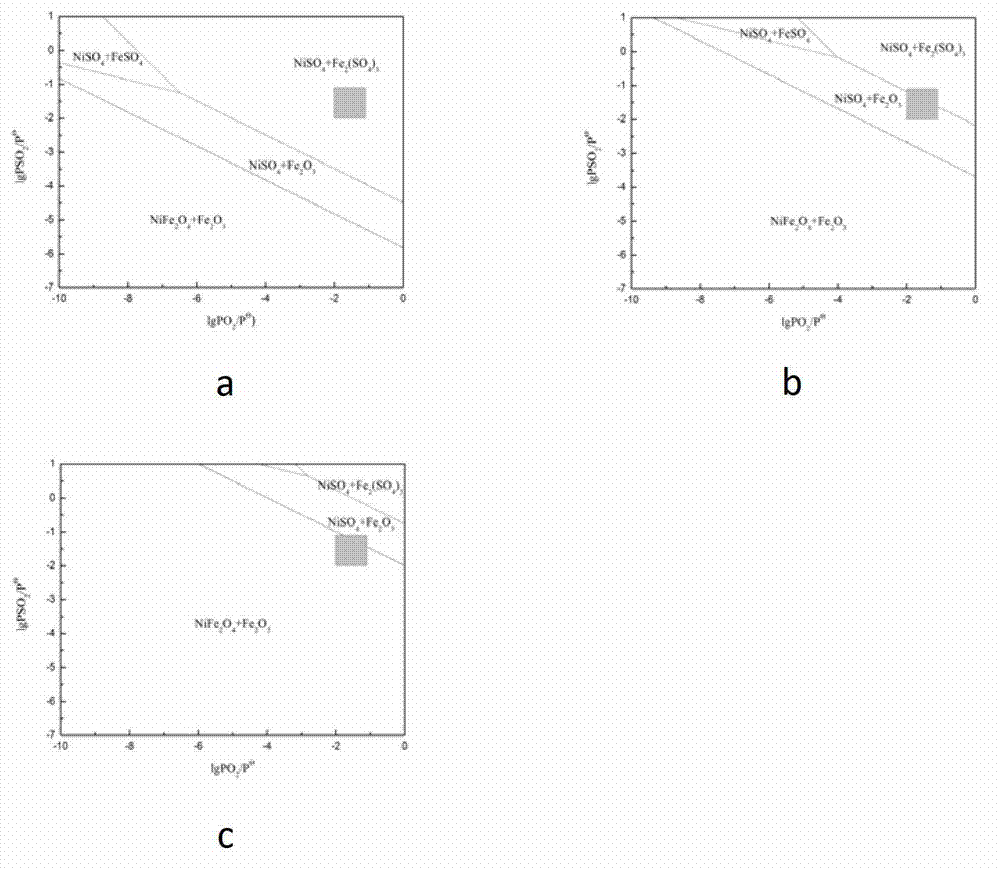
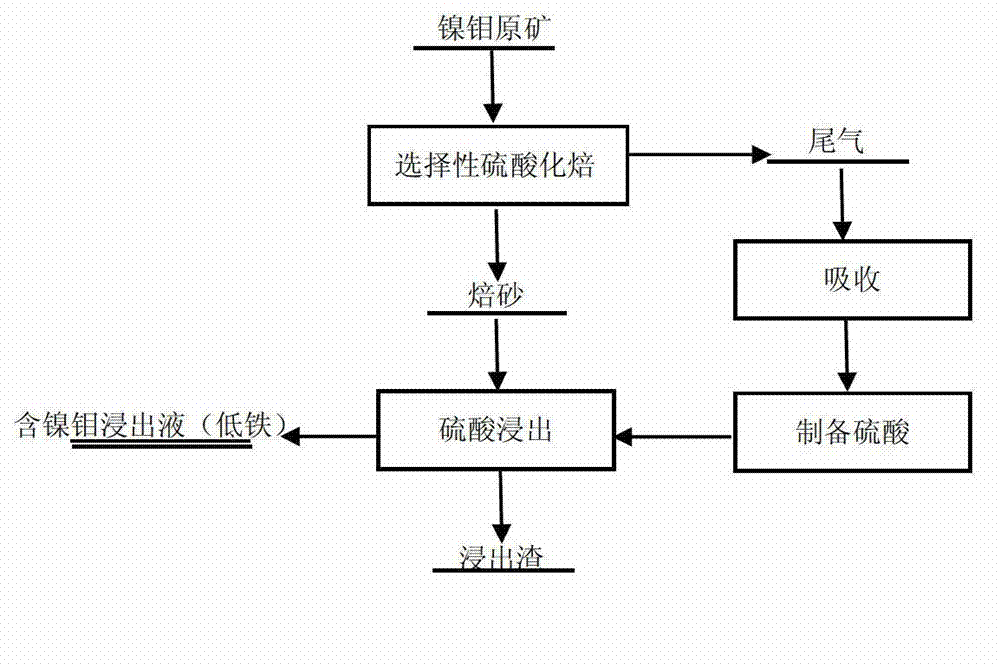
Method for selectively leaching nickel and molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ore
ActiveCN103088210AAvoid leachingReduce the difficulty of subsequent impurity removalSulfur compoundsProcess efficiency improvementImpurityFerric
The invention discloses a method for selectively leaching nickel and molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ore. Particularly, in the method, the selective sulfating roasting of the nickel-molybdenum ore is realized by controlling roasting atmosphere and temperature; amd a roasted product obtained through roasting is leached by using a sulphuric acid solution. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low leaching ratio of iron impurities, no environment pollution and low cost, can be used for high-selectively simultaneously leaching nickel and molybdenum from the nickel-molybdenum ore and can be widely applied to industrialized production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for the production of oryzanol enriched fraction from rice bran oil soapstock
InactiveUS20040192948A1Easy to handleIncrease temperatureFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiocideRice Bran ExtractRice bran oil
The present invention relates to an improved process for the production of oryzanol enriched fraction from rice bran oil soapstock; the present invention particularly relates to saponification, dehydration and leaching of rice bran oil soapstock for production of oryzanol enriched fraction.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for recovering germanium from germanium-containing materials
InactiveCN103952575AEfficient leachingImprove solubilityProcess efficiency improvementStrong acidsHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a method for recovering germanium from germanium-containing materials, particularly relates to a method for recovering germanium from germanium-containing materials of non-ferrous smelting industry, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the steps of leaching germanium-containing materials as raw materials of which the particle sizes are 100 meshes with inorganic strong acid as an leaching agent of which the concentration is 50-120g / L and an aid-leaching agent at 35-95 DEG C and filtering to obtain a germanium-containing leaching solution, adjusting the pH value of the germanium-containing leaching solution to be 6-9, stirring and carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain germanium residues, and calcining the germanium residues at 350-500 DEG C to obtain a crude germanium dioxide product, wherein the aid-leaching agent is one of tartaric acid, water-soluble tartrate, citric acid, water-soluble citrate, oxalic acid and water-soluble oxalate. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple process, easiness in operation, high recovery ratio of germanium, large enrichment ratio, and convenience in industrial production and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
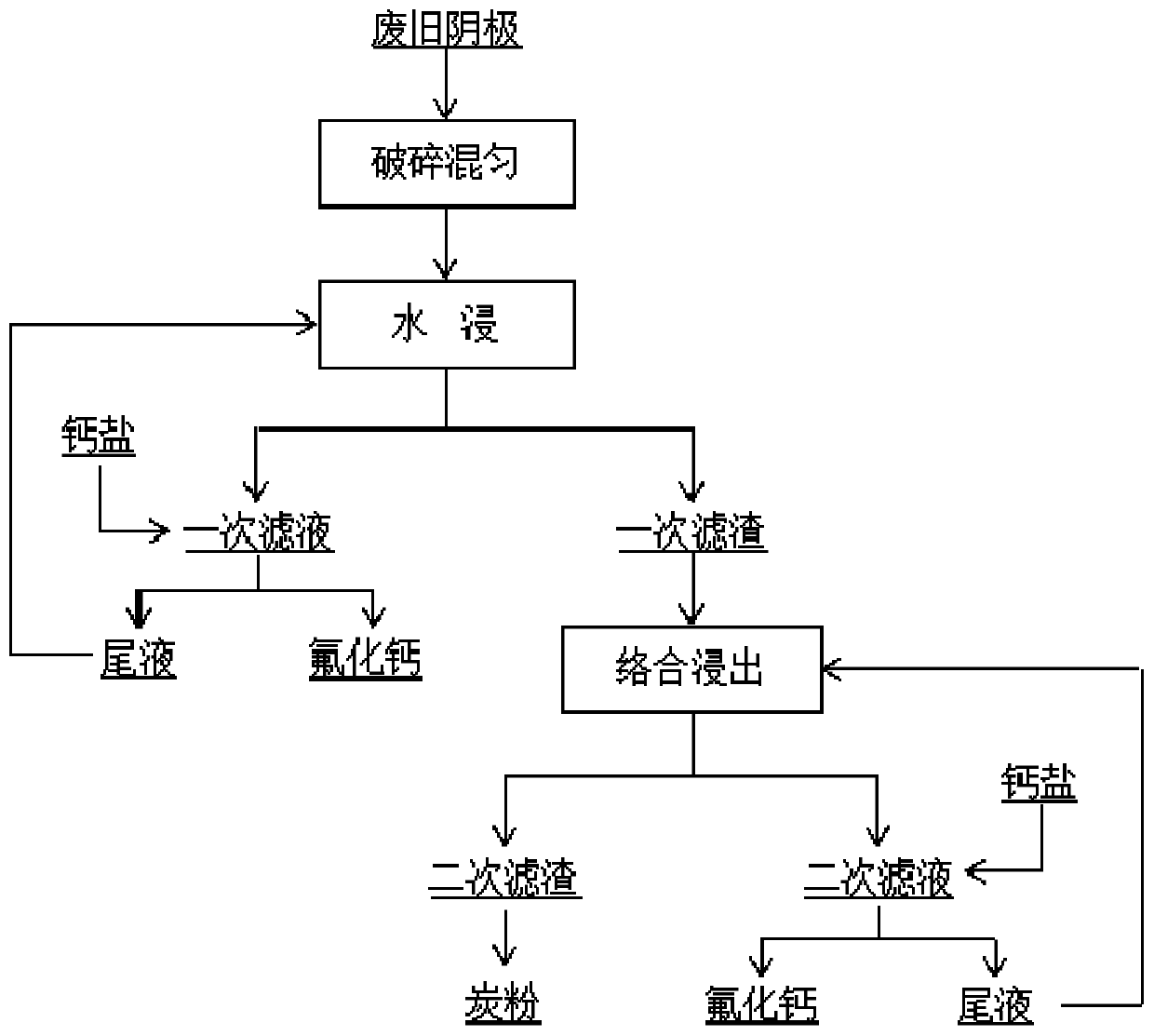
Method for leaching and recycling fluorine in aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode
ActiveCN109734115AEfficient leachingRealize harmless treatmentCalcium/strontium/barium fluoridesElectrolysisIron salts
The invention relates to a method for leaching and recycling fluorine in an aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode, and belongs to the field of aluminum electrolysis solid waste source recycling. The method includes the steps: crushing and finely grinding aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode carbon blocks, and leaching soluble fluoride in the carbon blocks by water solution; complexing filter residue after leaching by iron salt solution, and leaching insoluble fluoride in the filter residue; filtering mixture to obtain powdered carbon with low content of the fluoride; adding calcium saltor calcium-containing compound into primary filter liquor and secondary filter liquor to generate calcium fluoride, recycling fluorine sources, and returning tail liquid after filtering to corresponding working sections to be recycled. According to the method, the fluoride in the waste cathode can be efficiently separated, secondary pollution is omitted, the purity of the prepared calcium fluoride is higher than 65%, the calcium fluoride can be used for metallurgy industry, the content of carbon in the recycled carbon powder is higher than 80%, and follow-up utilization is facilitated. The method is short in process procedure, harmless treatment of the aluminum electrolysis cell waste cathode carbon blocks is achieved, and the fluorine has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
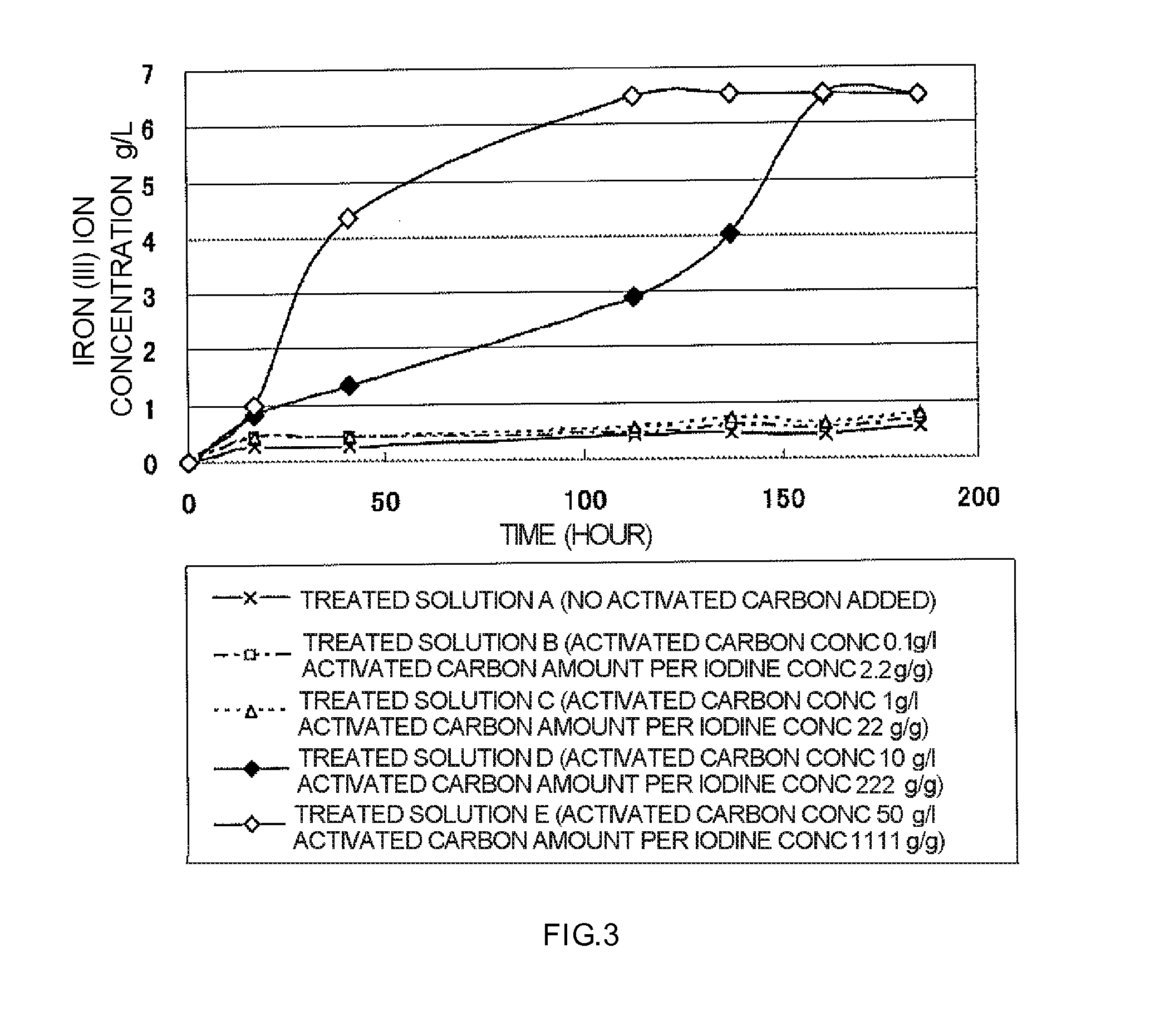
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore
ActiveUS20110229385A1Fast progressLow costSolvent extractionSolid sorbent liquid separationActivated carbonCopper sulfide
A method of leaching copper sulfide ore includes leaching copper from copper sulfide ore using a sulfuric acid solution comprising iodide ion and iron (III) ion surplus to the iodide ion as a leaching solution; reducing iodine in a solution obtained after the leaching step to less than 1 mg / L by an activated carbon treatment; and oxidizing iron (II) ion or newly added iron (II) ion in a solution obtained after the iodine reduction step by using iron oxidizing microbes to recover iron (III) ion.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
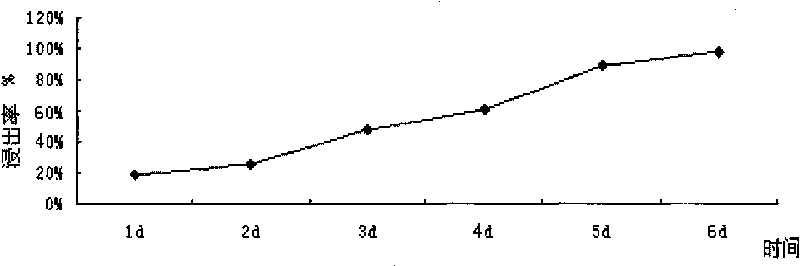
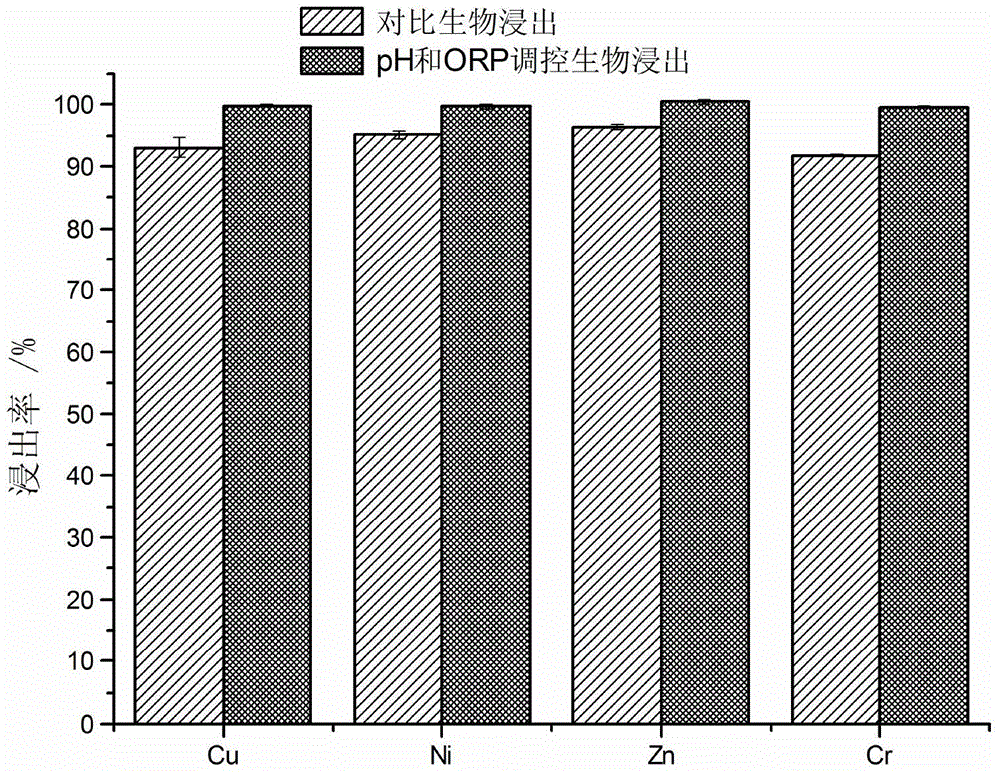
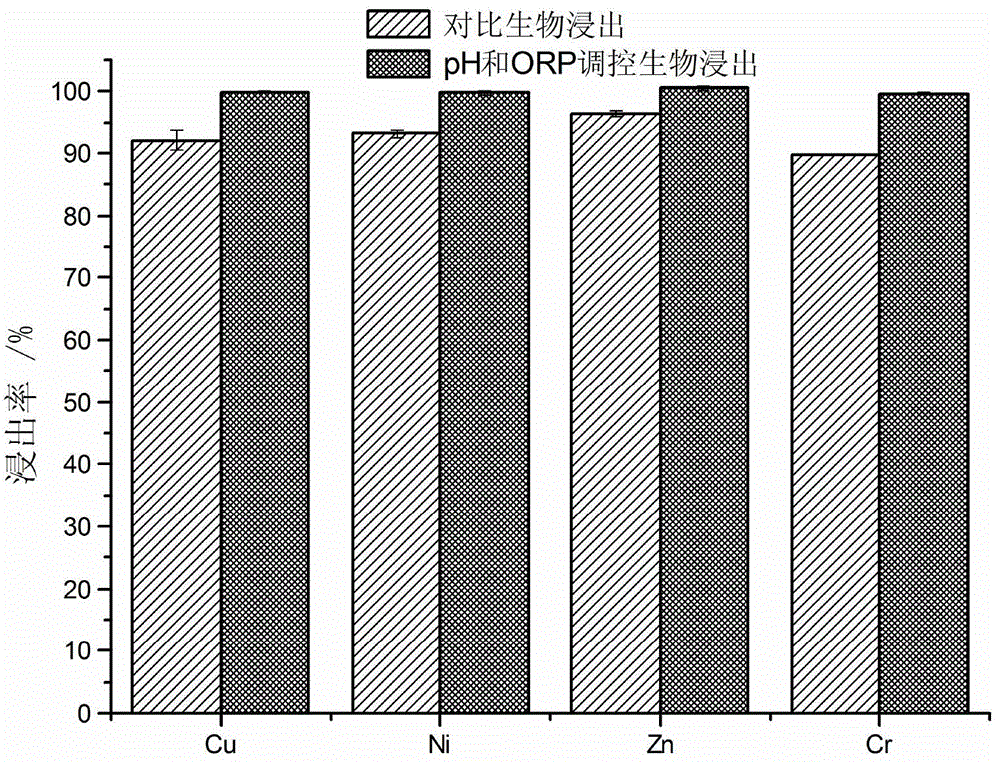
Method for biologically leaching heavy metal from heavy metal-contained waste based on pH and potential co-regulation
ActiveCN104862474AAvoid interactionEfficient DissolutionProcess efficiency improvementCo-regulationSludge
The invention discloses a method for biologically leaching heavy metal from a heavy metal-contained waste based on pH and potential co-regulation. The method comprises the following steps: in a process of leaching out the heavy metal-contained waste by an acidophilic iron oxide microbial agent, the pH value of the leaching system is controlled within 1.0-4.0 in the whole process; meanwhile, an oxidizing agent is combined with a reducing agent to regulate the redox potential of the leaching system, so that the redox potential of the leaching system is controlled within 420-650 mV; the pH value of the leaching system is gradually increased phase by phase in the leaching process; the redox potential of the leaching system is gradually increased phase by phase; the total leaching time is within 8 hours; and finally, the efficient leaching of the heavy metal from the heavy metal-contained waste by the acidophilic iron oxide microbial agent is realized. The method can accelerate biologic leaching of metal from sludge to shorten the leaching time and to reduce the acid consumption, and can greatly improve the biologic leaching efficiency.
Owner:厦门资生环保科技有限公司
Method of heap or dump leaching of copper from copper sulfide ore
ActiveUS8287623B2Efficient leachingIncrease ratingsSolvent extractionGold compoundsDump leachingHeap leaching
Disclosed is a method of efficiently leaching copper not only from a readily-soluble copper ore but also a poorly-soluble copper sulfide ore partially containing or consisting of chalcopyrite and / or covellite by means of ore heap leaching under versatile conditions for actual operation. Also disclosed is a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, including leaching copper from an ore including a copper sulfide ore by heap or dump leaching with the use of a sulfuric acid solution containing ferric (III) ions and iodide ions at a total iodine concentration of 8 to 100 mg / L as a leaching solution.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com