Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2405 results about "Iron salts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron salts are the most common type of supplemental iron for one major reason: their ability to break down in water. The extent to which they break down in water varies greatly, however, with some iron salts being much more soluble than others. Though most iron supplements are at least somewhat water-soluble, iron does not dissolve in water.
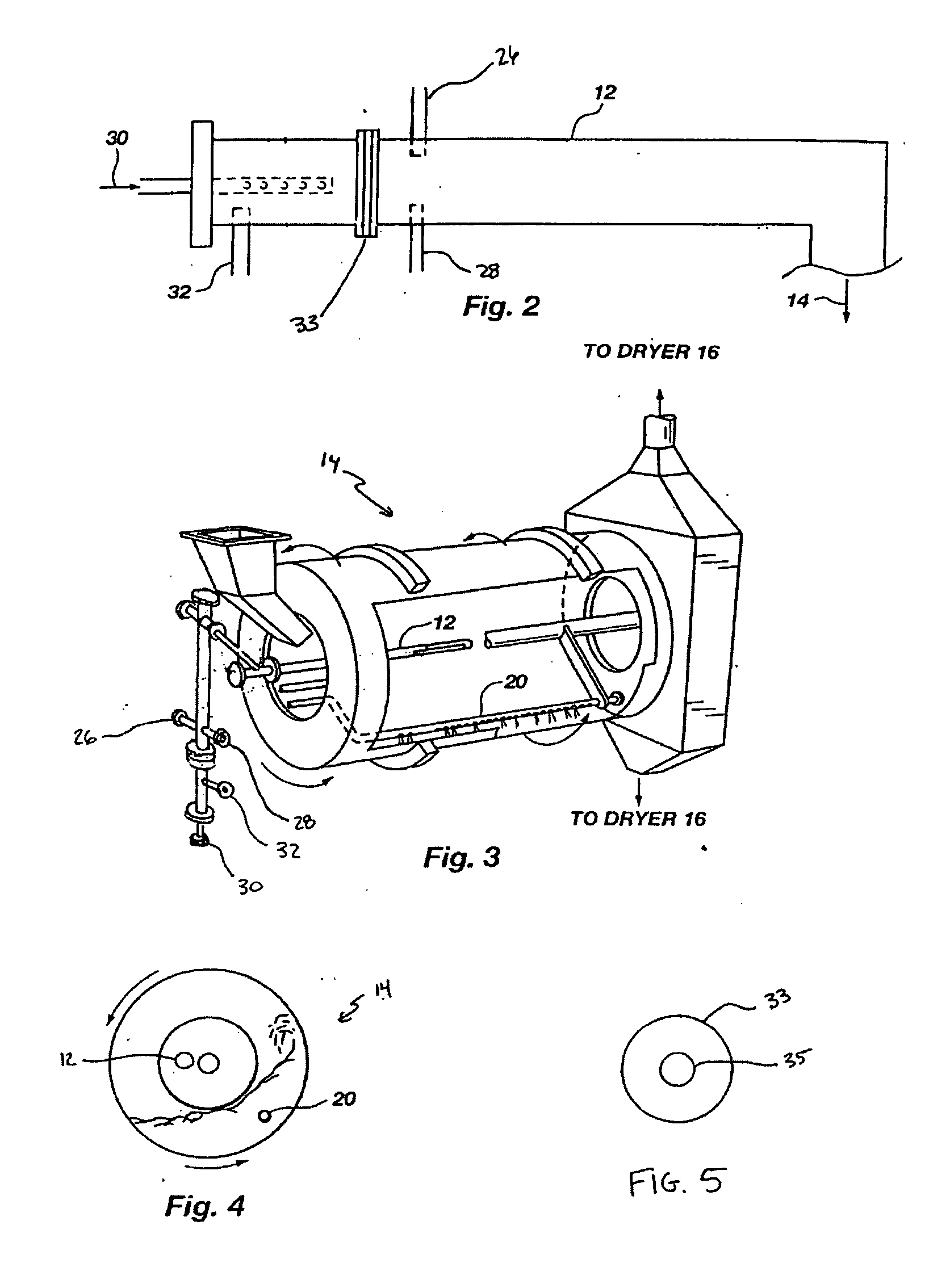
Iron-based ionic liquid catalysts for hydroprocessing carbonaceous feeds
InactiveUS6139723AIncrease hydrocracking ability of catalystIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid productIron salts
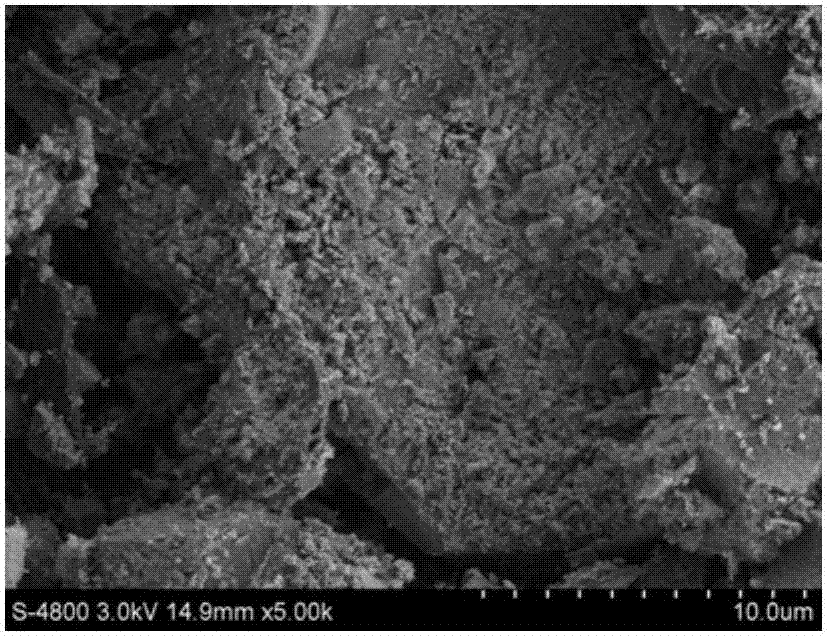
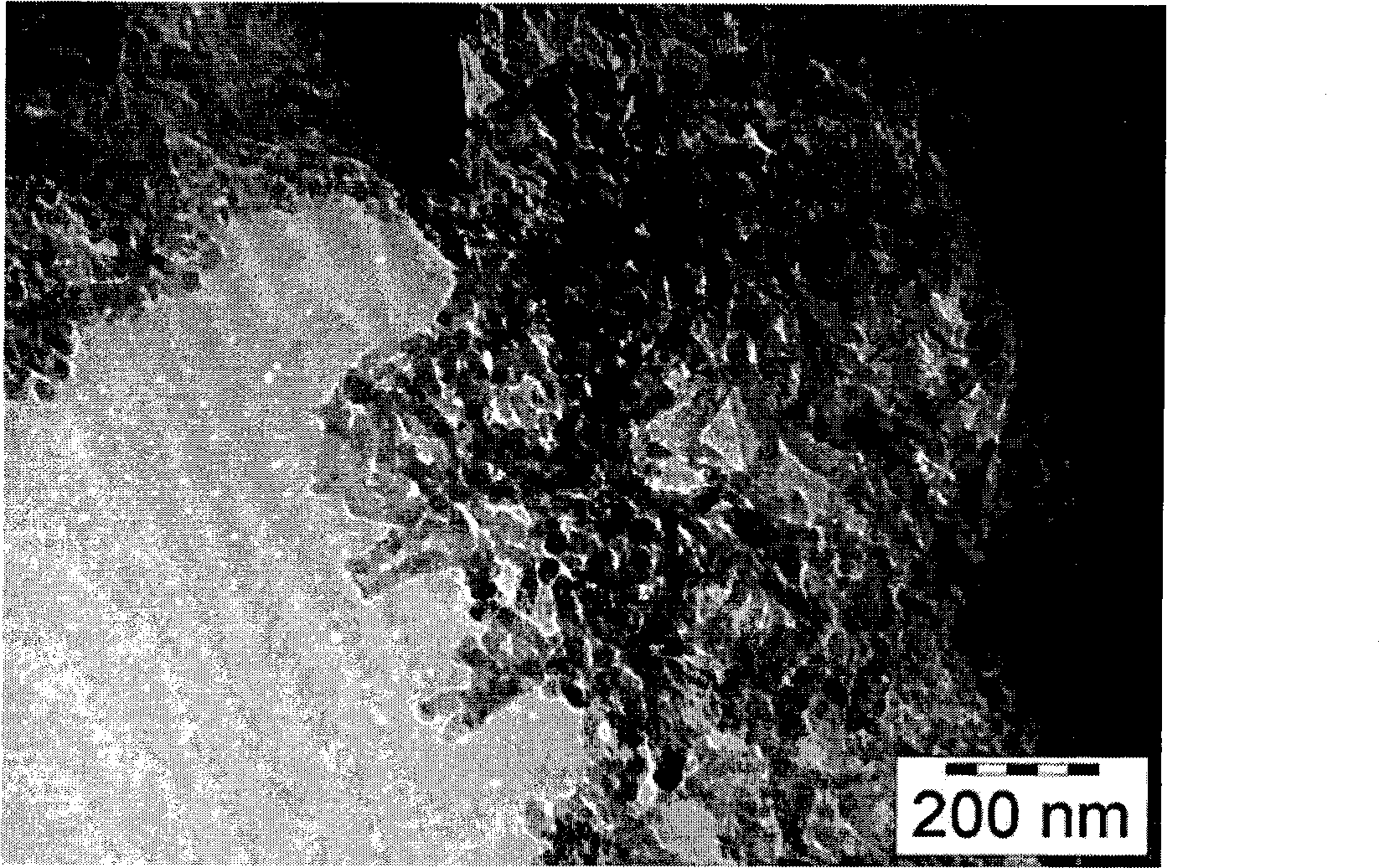
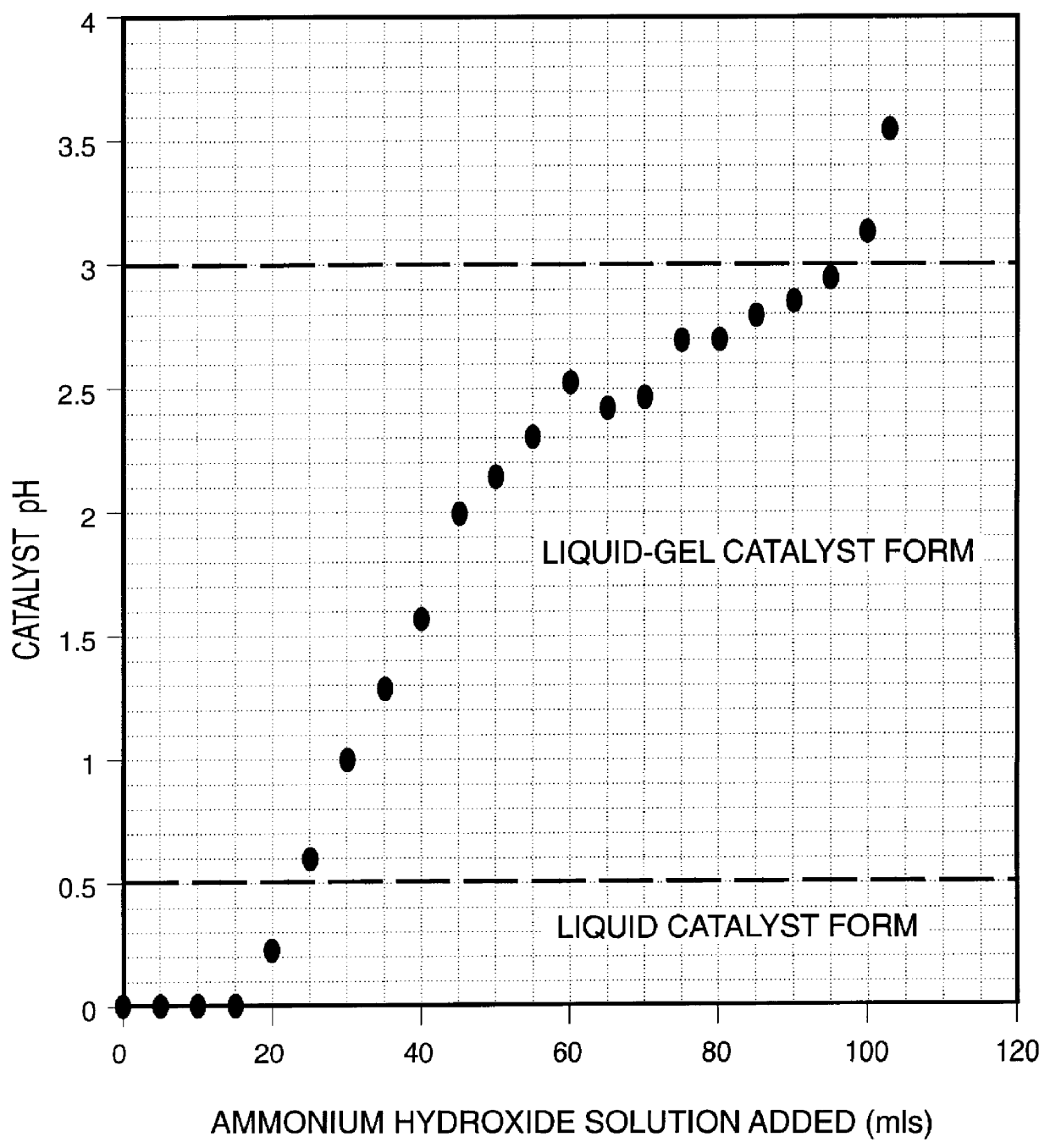
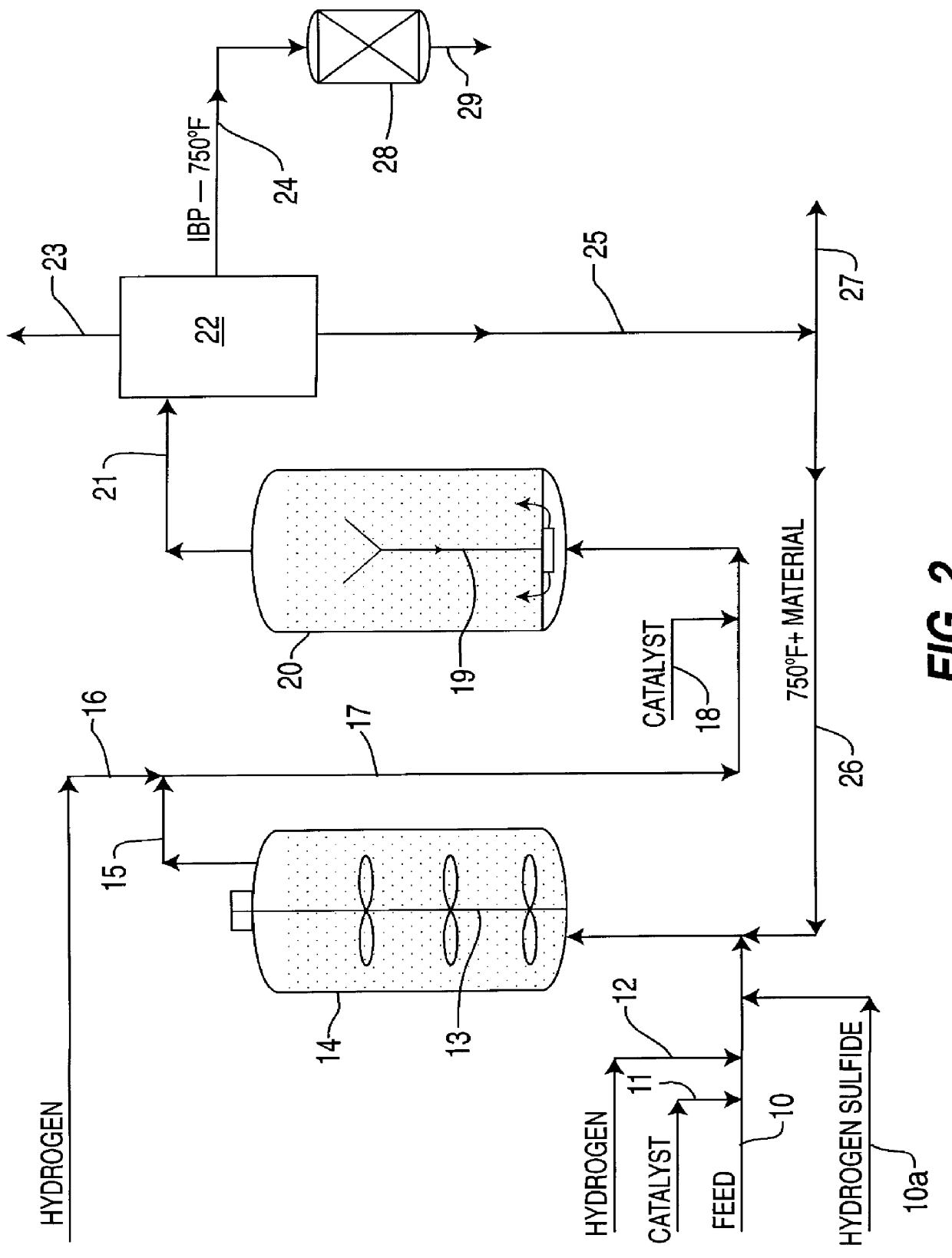
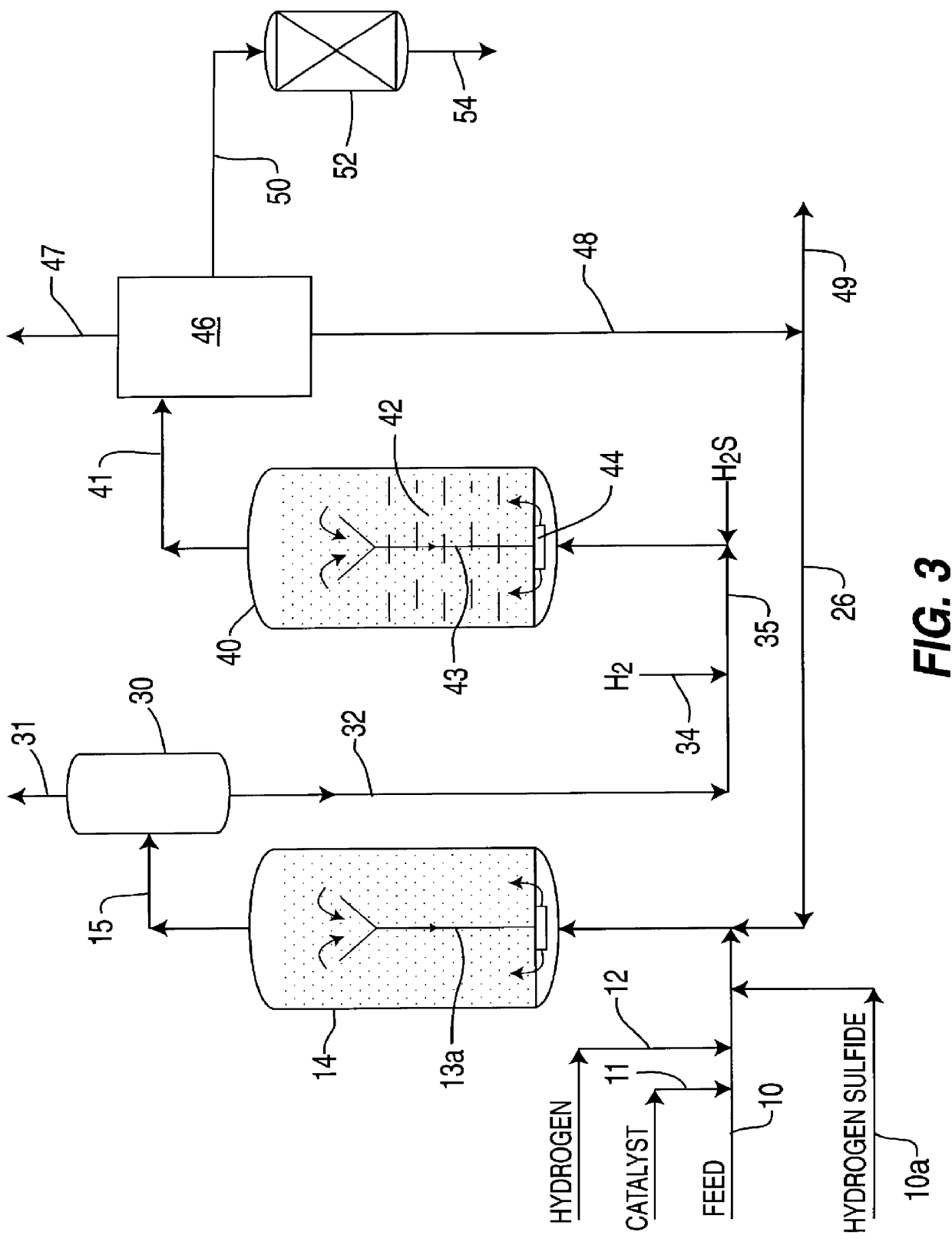
A highly dispersed iron-based ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst which may be anion-modified and metals-promoted has high catalytic activity, and is useful for hydrocracking / hydrogenation reactions for carbonaceous feed materials. The catalyst is produced by aqueous precipitation from saturated iron salt solutions such as ferric sulfate and ferric alum, and may be modified during preparation with anionic sulfate (SO42-) and promoted with small percentages of at least one active metal such as cobalt, molybdenum, palladium, platinum, nickel, or tungsten or mixtures thereof. The resulting catalyst may be used in a preferred ionic liquid form or in a liquid-gel form, and either fluidic form can be easily mixed and reacted with carbonaceous feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, mixed plastic waste, or mixtures thereof. The invention includes methods for making the ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst, and processes for using the fluidic catalysts for hydroprocessing the carbonaceous feed materials to produce desirable low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
Method for producing carbon coated nano stage lithium iron phosphate by precipitation
InactiveCN101393982AAvoid synthetic stepsEasy to controlElectrode manufacturing processesIron saltsPhosphate
The invention discloses a precipitation method for preparing nanometer level iron phosphate lithium coated with carbon. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighing iron salt, deionized water and a compound of metallic elements; after the stirring and the mixing are performed, adding a phosphorous compound and citric acid diluted with water to the mixture; after the stirring is performed again, adding a precipitation agent to the mixture and controlling to the neutrality; stirring to react in a container, and after the static placement, respectively adding the deionized water, a carbon source and lithium salt to mix uniformly after the precipitate is filtered and washed; stirring again to react, and drying the water at 30 to 160 DEG C and warming up at the heating rate under the protection of non-oxidized gas after a product is crashed; baking at a constant temperature of 450 to 850 DEG C, cooling down to a room temperature at a cooling rate or with a stove, and finally obtaining the nanometer level ferric phosphate lithium coated with the carbon after crashing is performed. The precipitation method has the advantage that the raw material cost and the processing cost are low because bivalent iron is taken as the raw material. The iron phosphate lithium prepared by using the process has the characteristics of good physical processing performance and good electrochemistry performance, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:南京海泰纳米材料有限公司
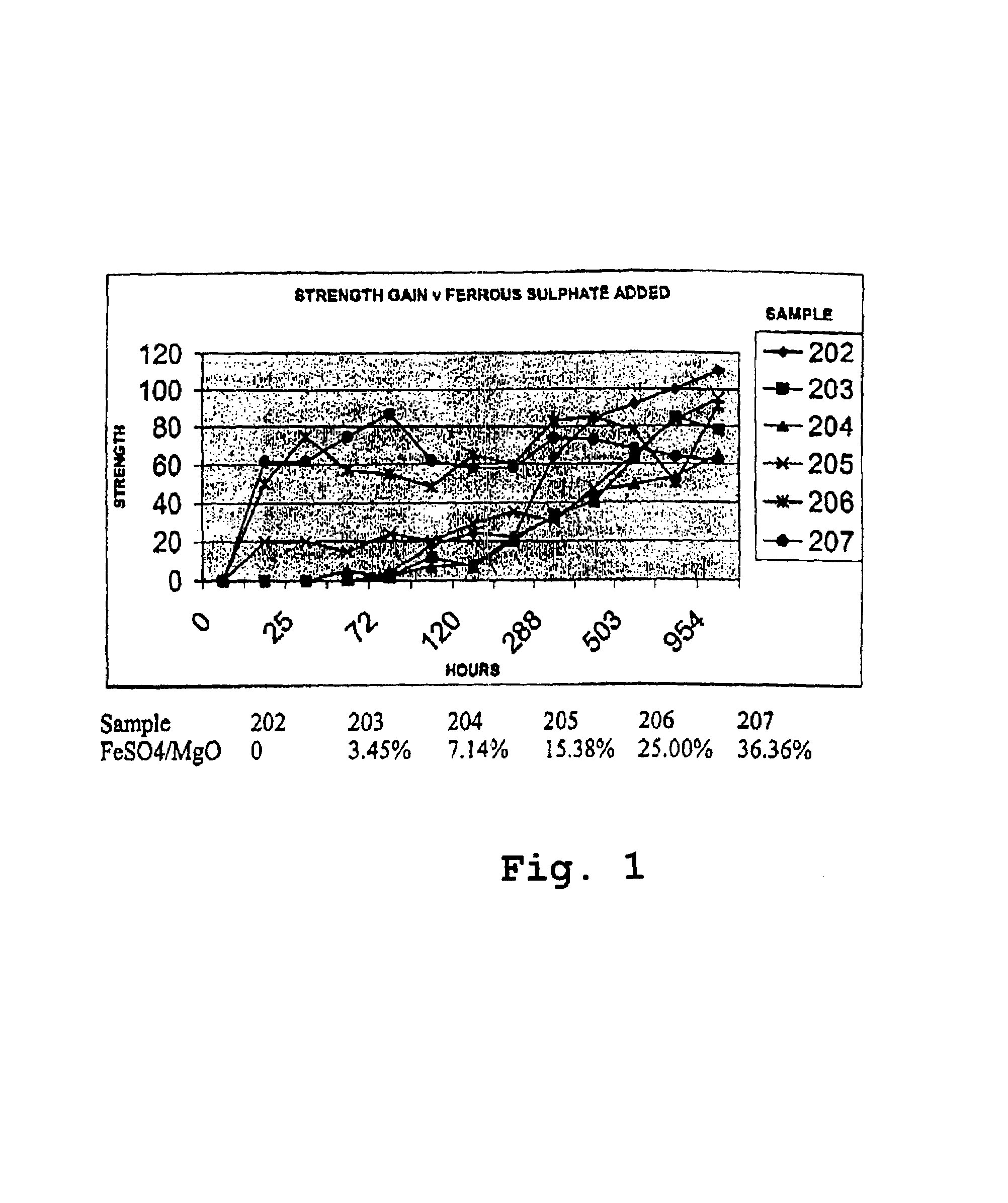
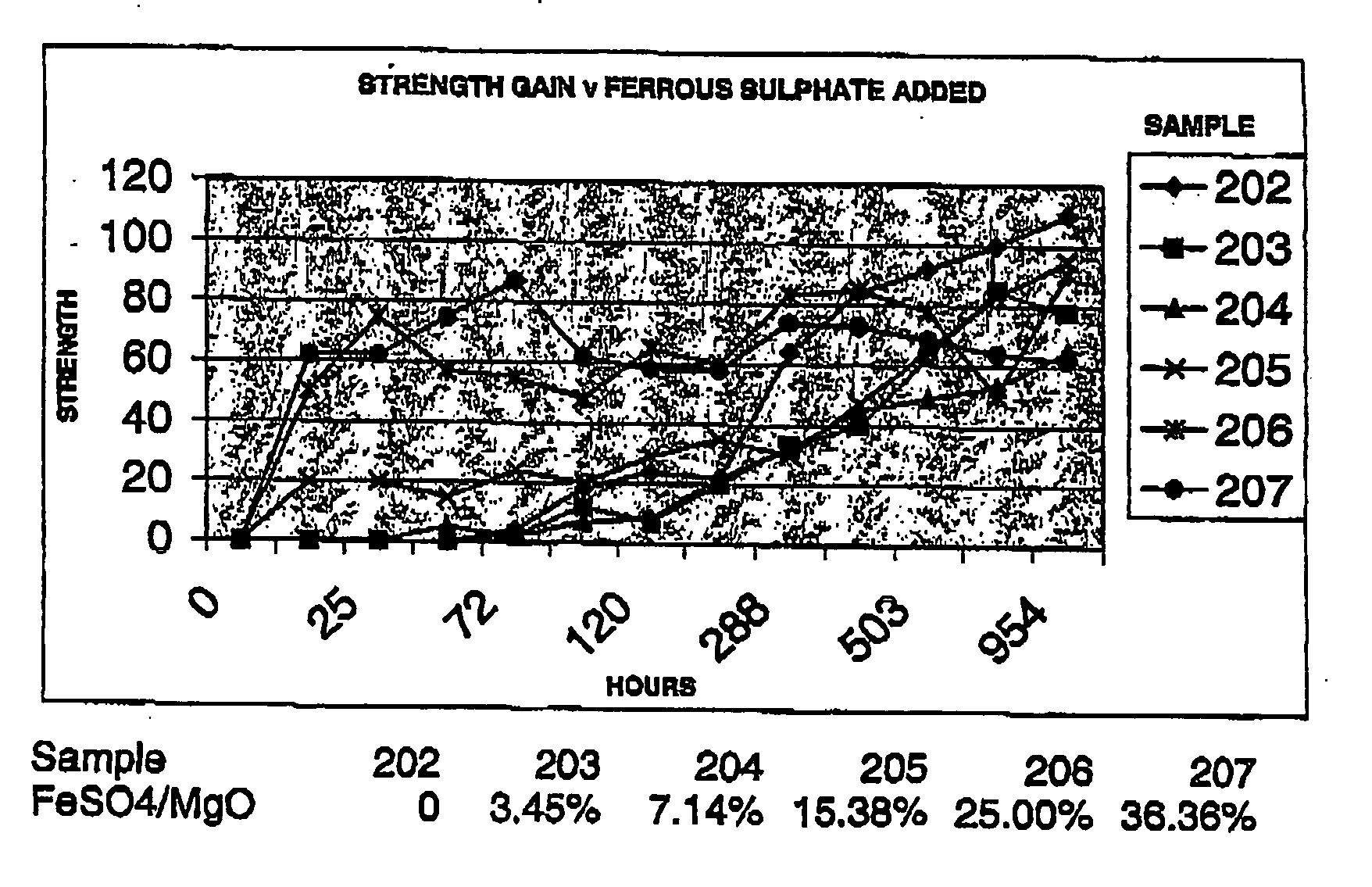
Reactive magnesium oxide cements
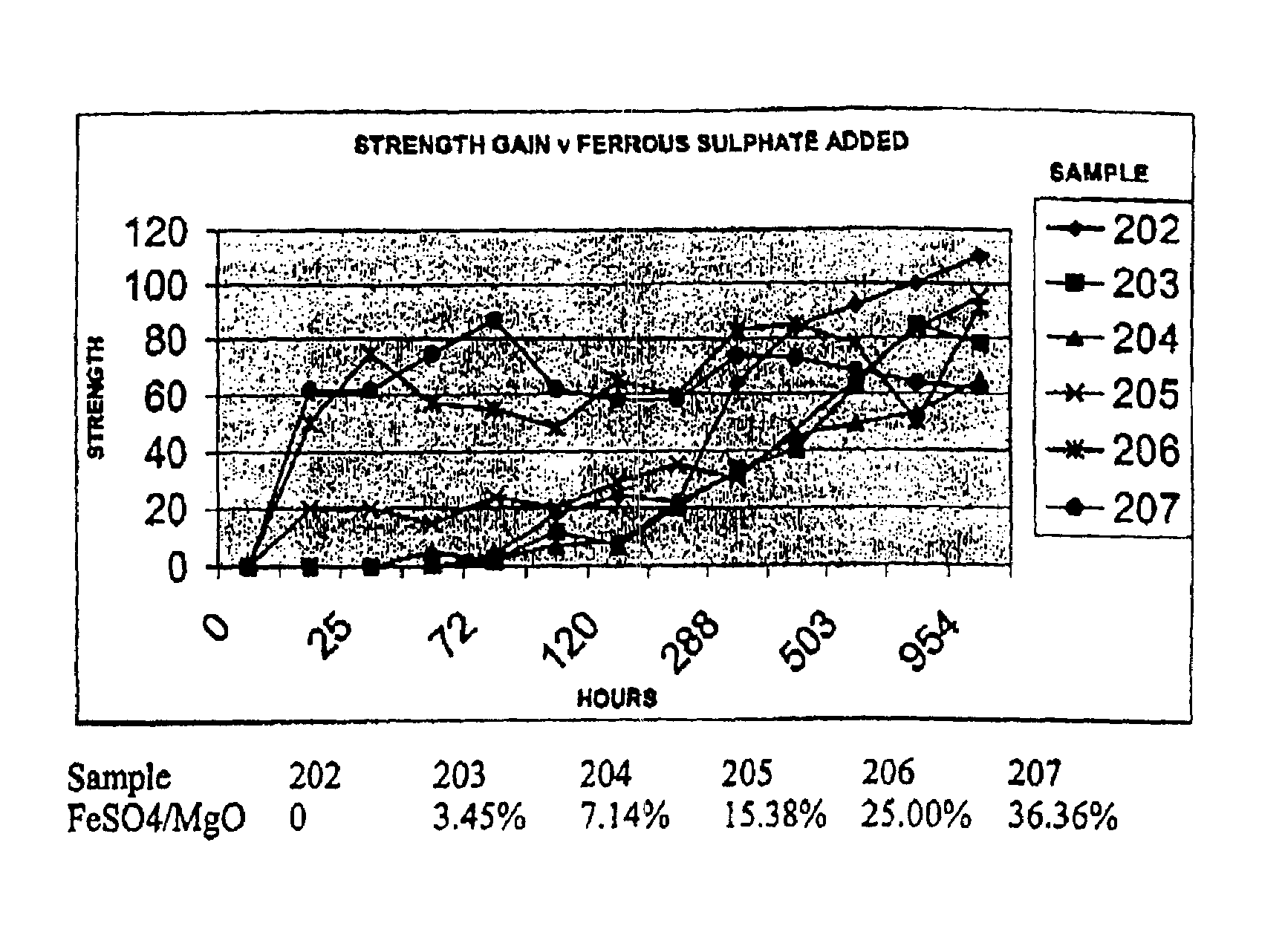
Novel hydraulic cements are disclosed that include reactive magnesium oxide prepared by low temperature calcination. The cements can be formulated to suit a large number of applications with various setting times, strength and levels of sustainability either by adding iron salts such as ferrous sulfate or blending with other compatible faster setting hydraulic cements such as Portland cement or by using both methods.The compositions are able to incorporate relatively large amounts of low cost pozzolans such as fly ash to advantage as well as wastes. Many excellent properties are exhibited and in particular good comprehensive strength and resistance to sulfates is able to be achieved.
Owner:TECECO
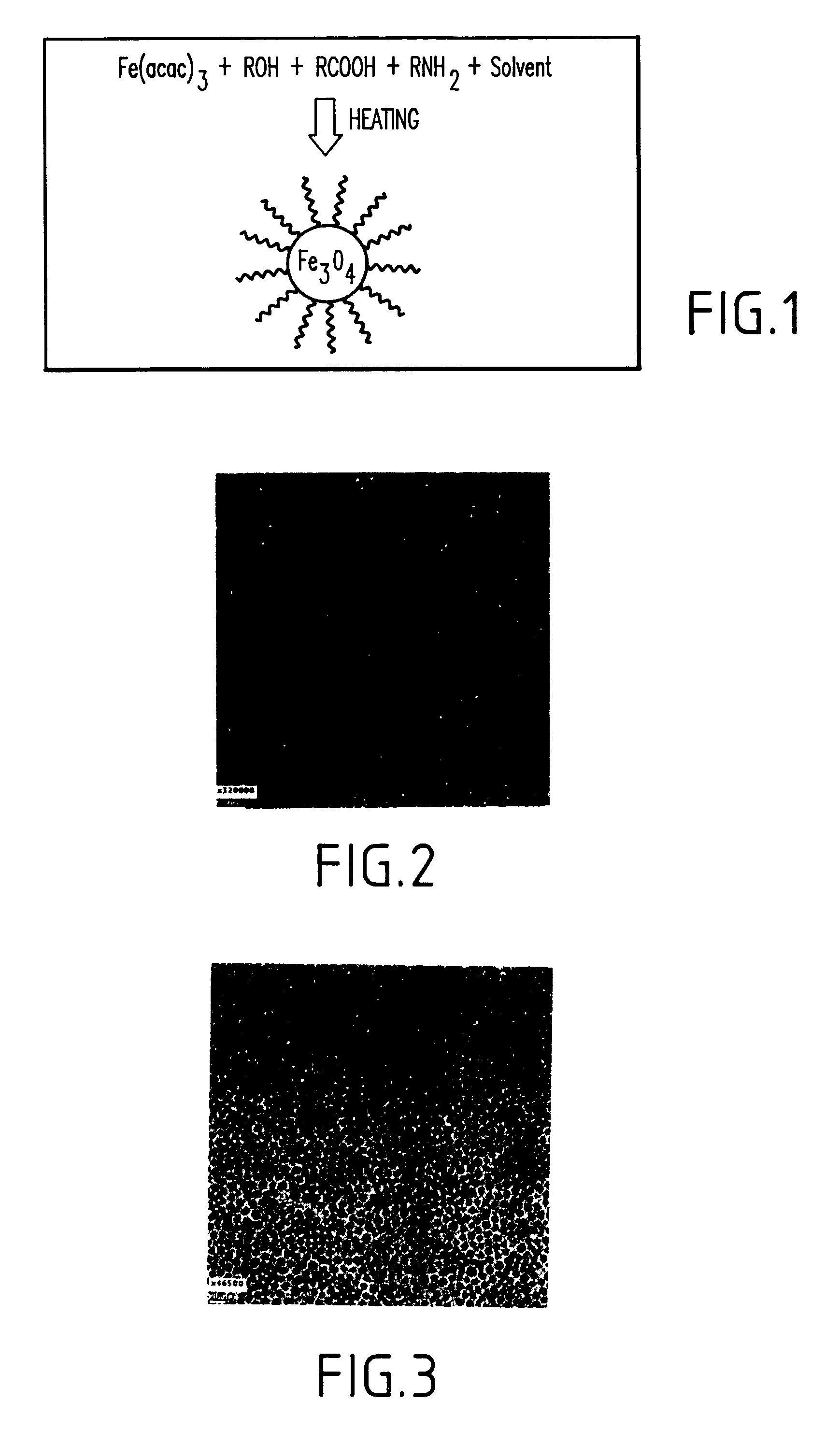
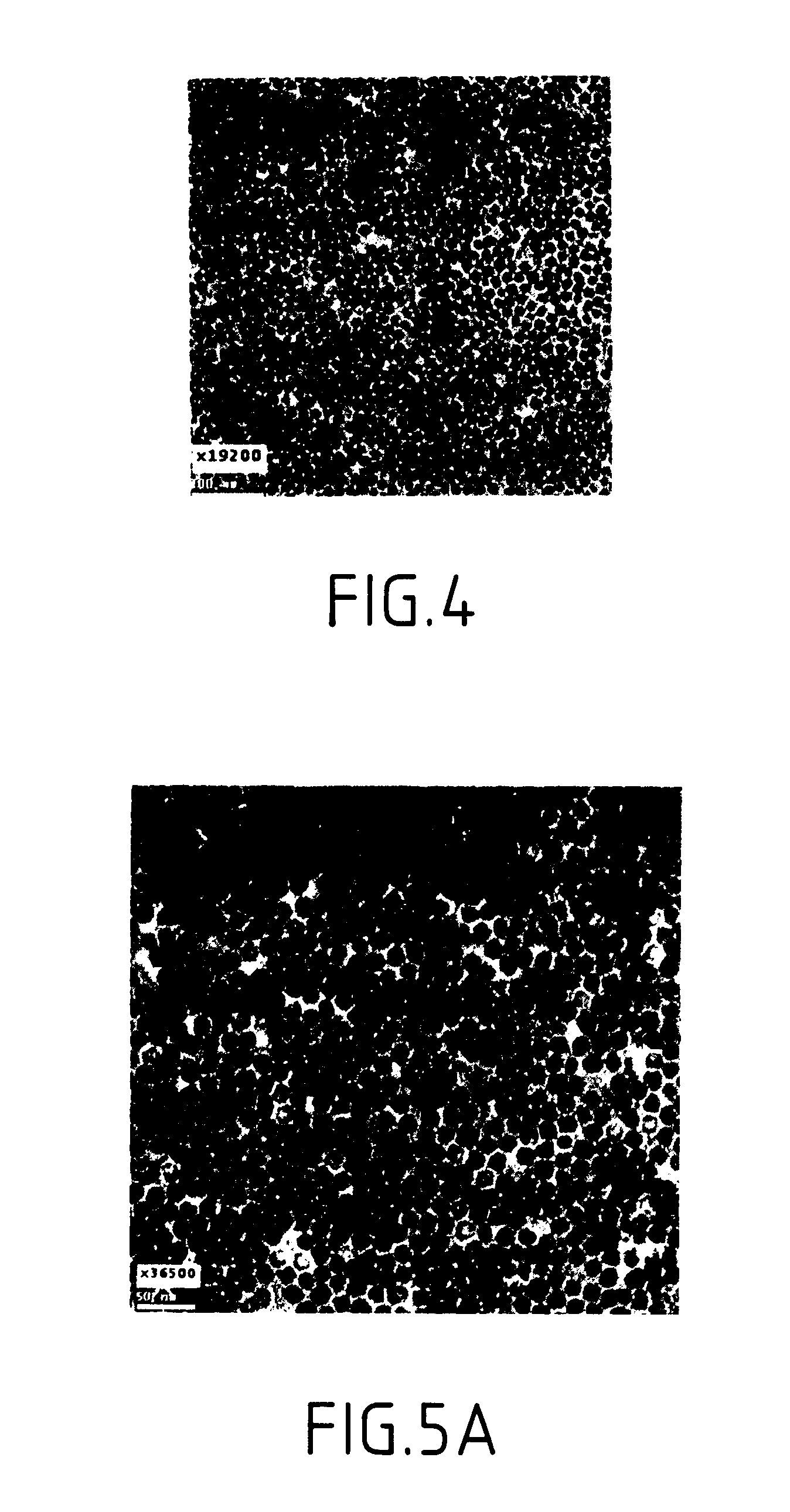
Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles and the process of forming Fe-based nanomaterials
InactiveUS6962685B2Small sizeNarrow size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismIron saltsMagnetite Nanoparticles
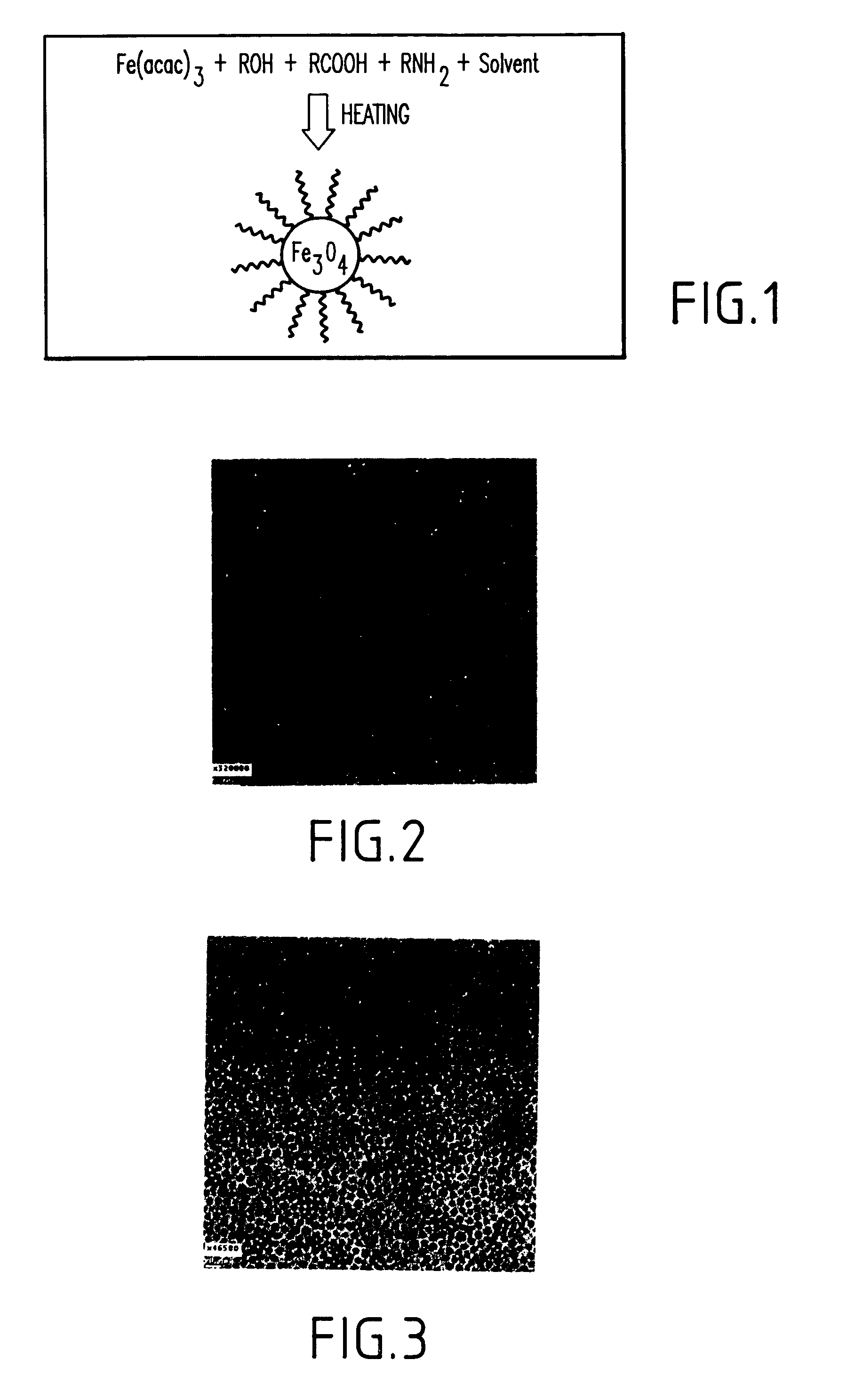
A method and structure for making magnetite nanoparticle materials by mixing iron salt with alcohol, carboxylic acid and amine in an organic solvent and heating the mixture to 200–360 C is described. The size of the particles can be controlled either by changing the iron salt to acid / amine ratio or by coating small nanoparticles with more iron oxide. Magnetite nanoparticles in the size ranging from 2 nm to 20 nm with a narrow size distribution are obtained with the invention. The invention can be readily extended to other iron oxide based nanoparticle materials, including M Fe2O4 (M=Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ti, Ba, Mg) nanomaterials, and iron oxide coated nanoparticle materials. The invention also leads to the synthesis of iron sulfide based nanoparticle materials by replacing alcohol with thiol in the reaction mixture. The magnetite nanoparticles can be oxidized to γ-Fe2O3, or α-Fe2O3, or can be reduced to bcc-Fe nanoparticles, while iron oxide based materials can be used to make binary iron based metallic nanoparticles, such as CoFe, NiFe, and FeCoSmx nanoparticles.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
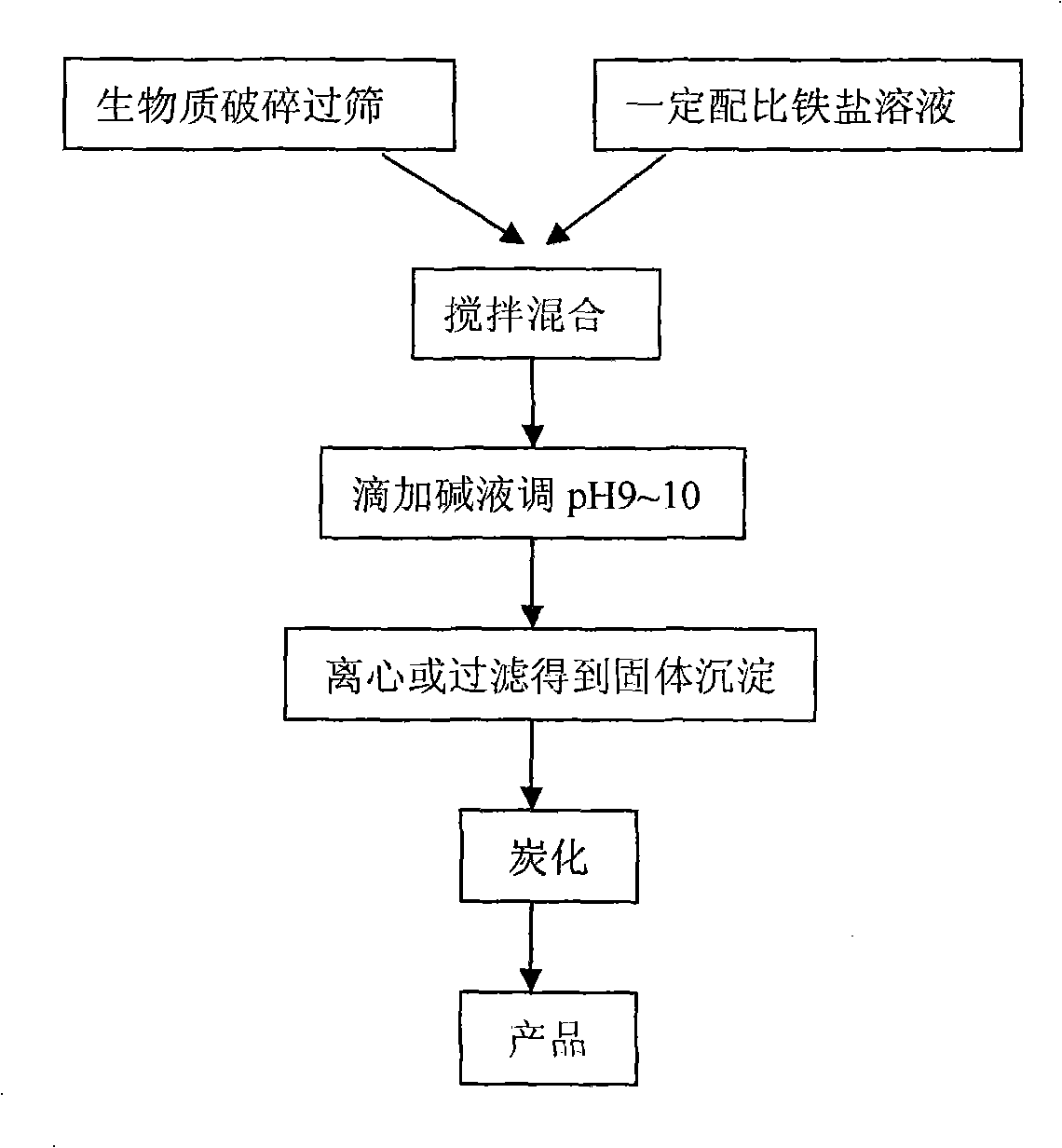
Method for preparing magnetic biological carbon adsorbing material and usage thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnetic biological carbon adsorbing material and the usage thereof. The method comprises the steps: 1) drying and crushing waste biomass, and sieving by20-100 meshes; 2) putting the sieved biomass into 0.1-0.5mol / L of iron salt solution with the weight percent of the biomass being 1-10% of the total quantity; under stirring, dripping 3-6mol / L of NaOH solution until the pH value of the solution is 9-10; 3) filtering, drying and compacting the solid precipitate, and then limiting oxygen carbonizing for 1-5h at the temperature of 100-700 DEG C, thus obtaining the magnetic biological carbon adsorbing material; 4) putting the magnetic biological carbon adsorbing material into waste water, and simultaneously removing organic pollutant and phosphate radical in the waste water. The method realizes synchronization of preparation of the adsorbing material and the process of magnetization, and is simple in preparation process, rich in the source ofthe biomass material and low in cost; furthermore, the prepared magnetic adsorbent is covered by biological carbon or embedded with magnetic nano Fe3O4 granules, has special structure and stable existence, can effectively remove the organic pollutant and phosphate in the waste water, and is easy for magnetic separation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dry-powder-type culturing substrate and preparing method
InactiveCN101070531AEasy to manufactureLow costHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureIron saltsTrace element
Powder type culture medium is from plenty of element kinds , trace element and iron salt and vitamin kind of composition, after processing manufacture the original powder that makes powder culture medium. The various components of the medium and the final product were dry powder. The preparation Method: First, concentrate all plenty of elements to collect reserve; Mix trace element and vitamin kind totally to wrap to attach , and then mix the thin medicine and plenty of elements of trace element totally, under the role with centrifugal high speed, making it even scatter and wrap up to glue to unite. So, make the original powder of powder culture medium for manufacture. This medium-dry powder manufacturing easier, does not require the use of complex machines and equipment, and low-cost easy to promote. The product is of high quality in existing product. It can be used in plant breeding, tissue culture and molecular biology research, and can be used for various commercial purposes.
Owner:陈曦
Methods to improve heteroatom lattice substitution in large and extra-large pore borosilicate zeolites
InactiveUS6790433B2Controlled catalytic propertyAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsIron saltsAluminosilicate
The invention, in one embodiment, is a method for preparing crystalline zeolites by (a) contacting a calcined essentially aluminum free borosilicate zeolite with an aqueous acid solution, thereby producing an at least partially deboronated zeolite; (b) contacting said at least partially deboronated zeolite with a solution selected from the group consisting of an aqueous aluminum salt solution, thereby producing an aluminosilicate zeolite; an aqueous gallium salt solution, thereby producing a gallosilicate zeolite; an aqueous iron salt solution, thereby producing a ferrosilicate zeolite; and mixtures thereof; and (c) where the contacting in step (b) occurs at a pH of not greater than about 3.5. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a method for preparing crystalline zeolites by contacting a calcined essentially aluminum free large or extra-large pore borosilicate zeolite with a solution selected from the group consisting of an aqueous aluminum salt solution, thereby producing an aluminosilicate zeolite; an aqueous gallium salt solution, thereby producing a gallosilicate zeolite; an aqueous iron salt solution, thereby producing a ferrosilicate zeolite; and mixtures thereof; and where the contacting occurs at a pH of not greater than about 3.5.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Catalyst and method for reduction of nitrogen oxides
InactiveUS20060029535A1Efficient workSelective catalytic reductionNitrous oxide captureNitrogen compoundsCerium nitrateIron salts
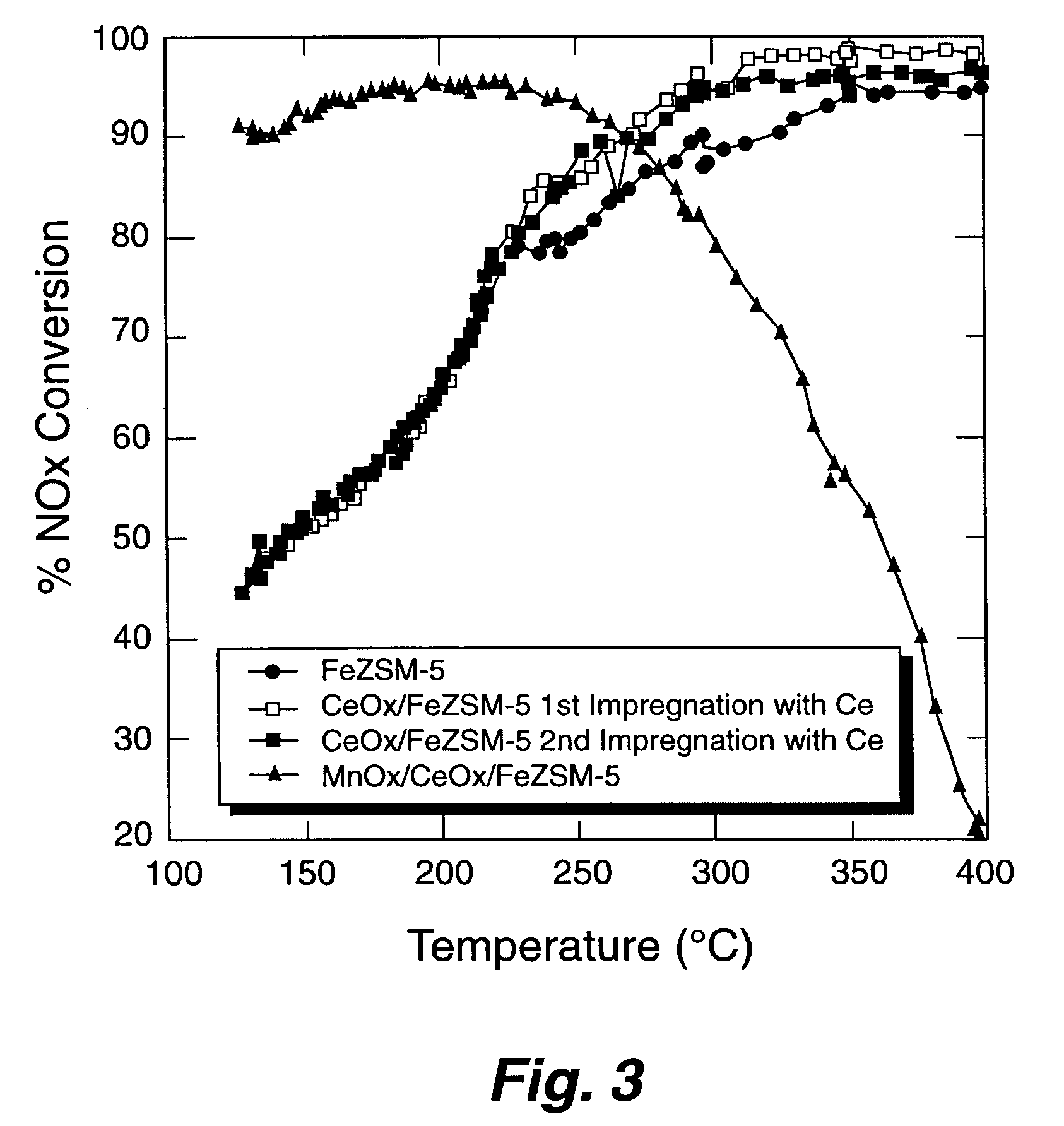
A Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) catalyst was prepared by slurry coating ZSM-5 zeolite onto a cordierite monolith, then subliming an iron salt onto the zeolite, calcining the monolith, and then dipping the monolith either into an aqueous solution of manganese nitrate and cerium nitrate and then calcining, or by similar treatment with separate solutions of manganese nitrate and cerium nitrate. The supported catalyst containing iron, manganese, and cerium showed 80 percent conversion at 113 degrees Celsius of a feed gas containing nitrogen oxides having 4 parts NO to one part NO2, about one equivalent ammonia, and excess oxygen; conversion improved to 94 percent at 147 degrees Celsius. N2O was not detected (detection limit: 0.6 percent N2O).
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Hydrothermally stable metal promoted zeolite beta for NOx reduction
InactiveUS6914026B2Increasing Fe(OH) content of catalystGood hydrothermal stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationIron saltsIon exchange
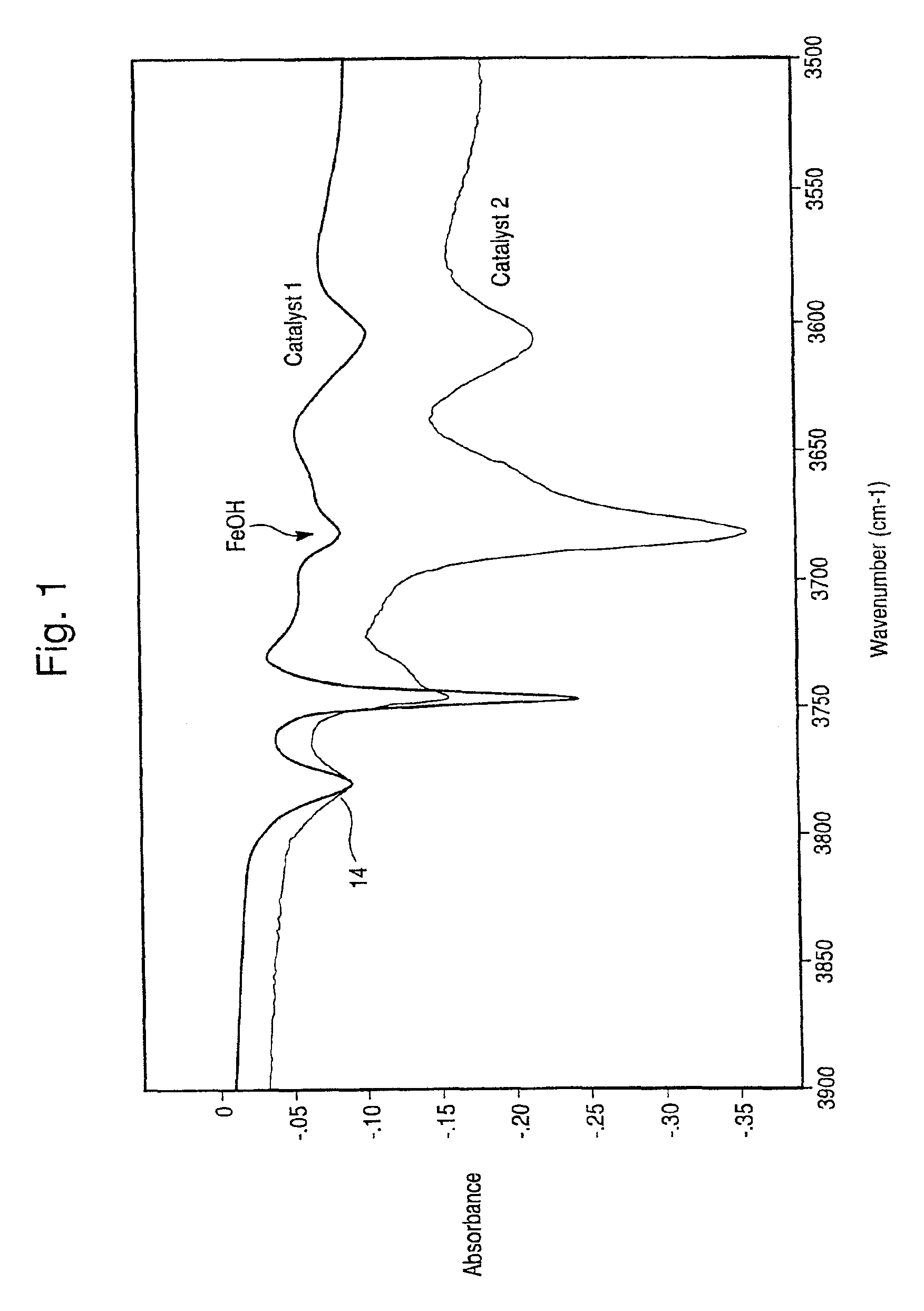
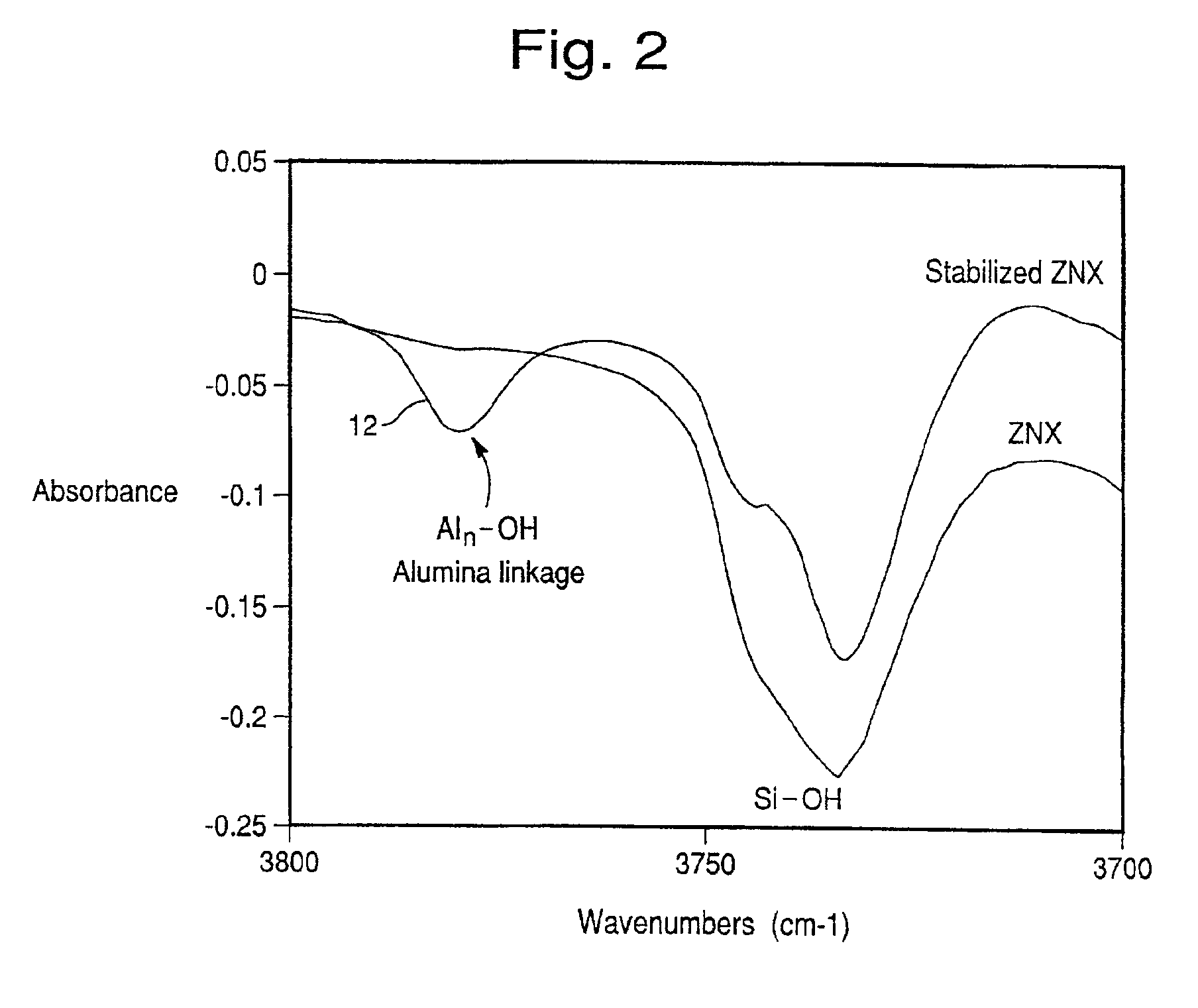
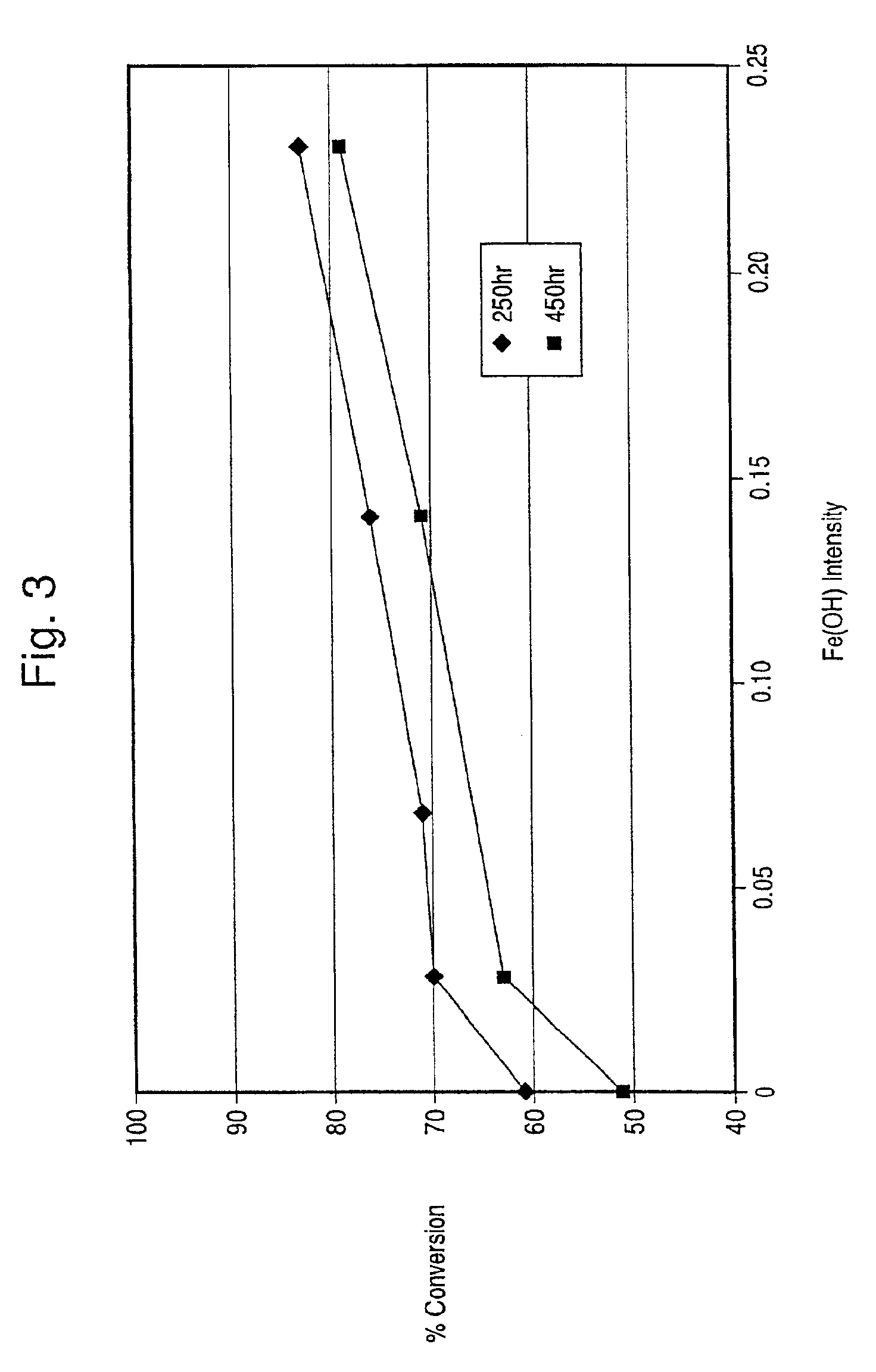
The present invention is directed to an iron-promoted zeolite beta catalyst useful in the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia in which the iron-promoted zeolite beta is treated so as to provide increased amounts of the iron promoter in the form of Fe(OH).The stabilized zeolite is formed by cation exchange of an iron salt into a zeolite beta which has a reduced sodium content such as by exchanging a sodium beta with ammonium or hydrogen cations. A zeolite beta having a reduced carbon content and a Si / Al ratio of no more than 10 also increases the Fe(OH) content of the iron-promoted catalyst. The iron-promoted catalyst which has the iron in the form of Fe(OH) is characterized by a peak at 3680±5 cm−1 in the IR spectra.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Method for preparing iron lithium phosphate by recovering water-system waste lithium-ion power battery
ActiveCN101916889AReduce manufacturing costSolving Recycling ProblemsWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingPower batteryIron salts
The invention discloses a method for preparing iron lithium phosphate by recovering water-system waste lithium-ion power batteries, comprising the following steps: 1) cutting and brushing a water-system waste lithium-ion power battery, processing by deionized water, sieving and drying to recover the mixture of an electrode material and a conductive agent; 2) adding inorganic acid to the dried mixture of the electrode material and the conductive agent to process, filtering to obtain acid solution containing Li+, Fe2+ and PO43-; 3) adding lithium salt or iron salt to the acid solution containing Li+, Fe2+ and PO43-, adding ascorbic acid and stirring, controlling the pH value to equal to 3-7, and filtering to obtain precipitation; and 4) adding the crude product LiFePO4 obtained in step 3) to a water solution of cane sugar for ball milling, drying and calcining to obtain a regenerative LiFePO4 material. The method has low cost, simple operation and no secondary pollution.
Owner:长春劲能科技集团有限公司
Carbon and electrospun nanostructures
InactiveUS20050025974A1Material nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingIron saltsElectrospun nanofibers
The present invention is directed to the production of nanostructures, e.g., single wall carbon nanotubes (“SWNT”) and / or multi-wall carbon nanotubes (“MWNT”), from solutions containing a polymer, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN). In particular, the invention is directed to the production of nanostructures, for example, SWNT and / or MWNT, from mixtures, e.g., solutions, containing polyacrylonitrile, polyaniline emeraldine base (PANi) or a salt thereof, an iron salt, e.g., iron chloride, and a solvent. In one embodiment, a mixture containing polyacrylonitrile, polyaniline emeraldine base or a salt thereof, an iron salt, e.g., iron chloride, and a solvent is formed and the mixture is electrospun to form nanofibers. In another embodiment, the electrospun nanofibers are then oxidized, e.g., heated in air, and subsequently pyrolyzed to form carbon nanostructures.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Catalytic conversion of hydrocarbons to hydrogen and high-value carbon
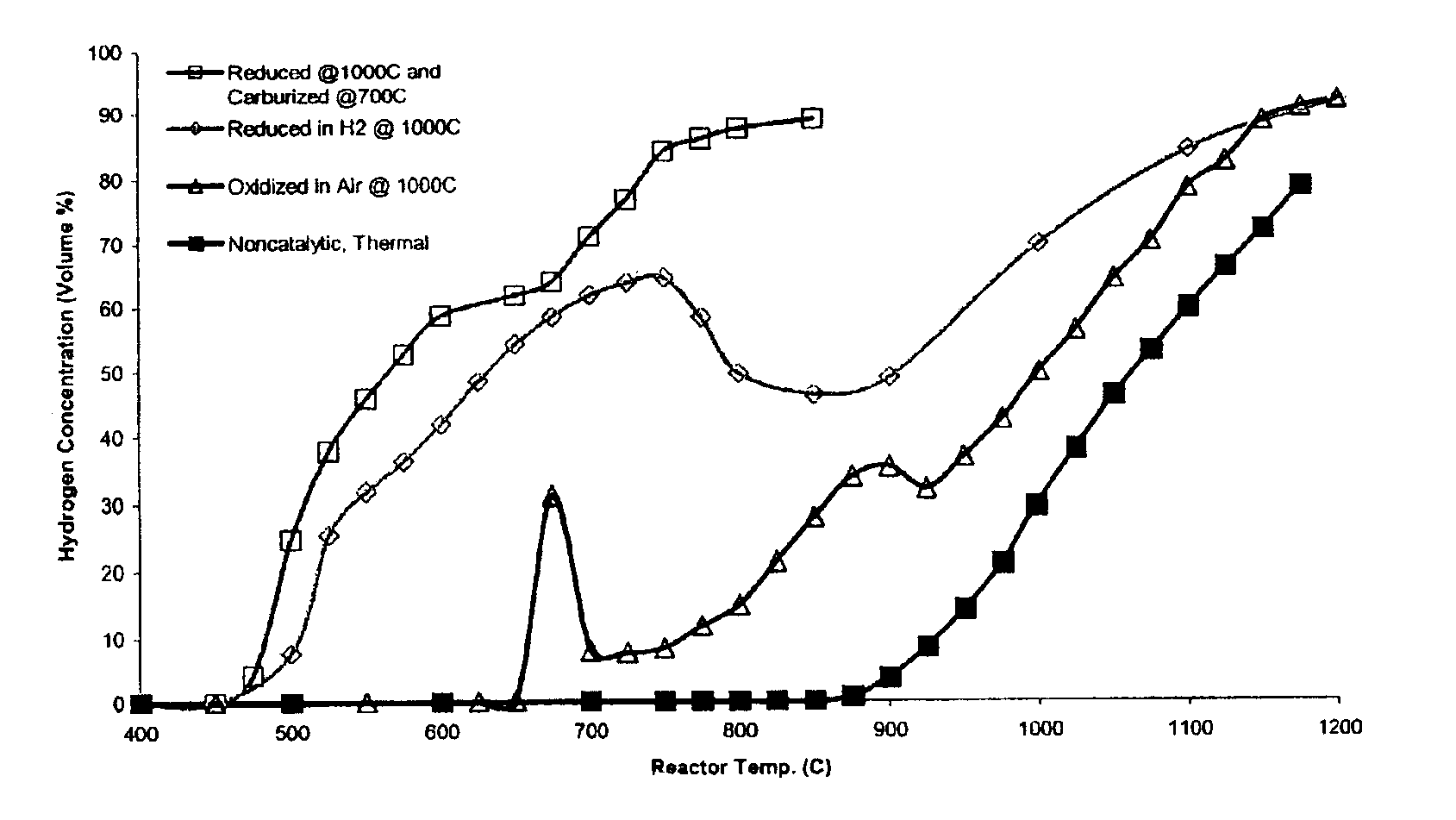
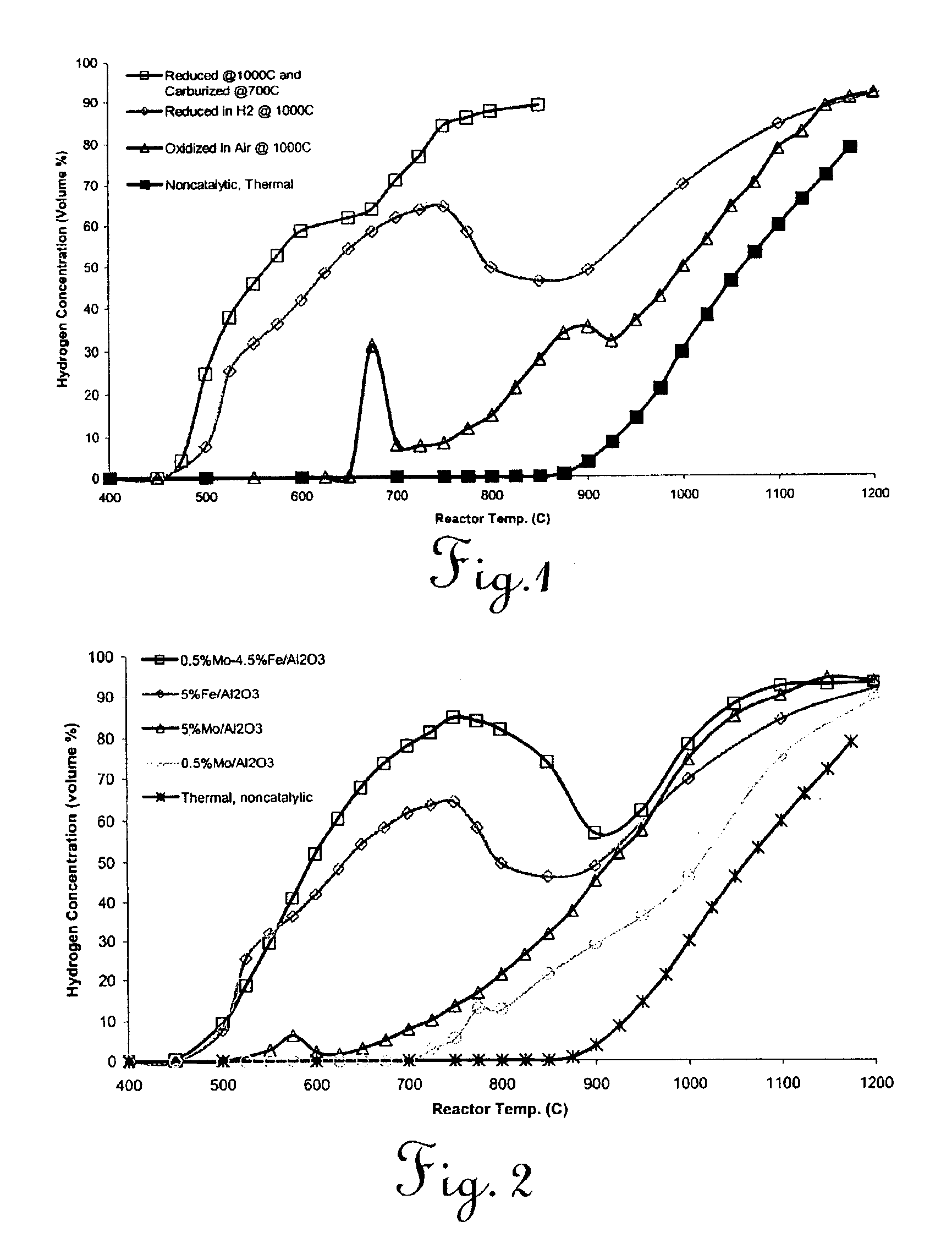
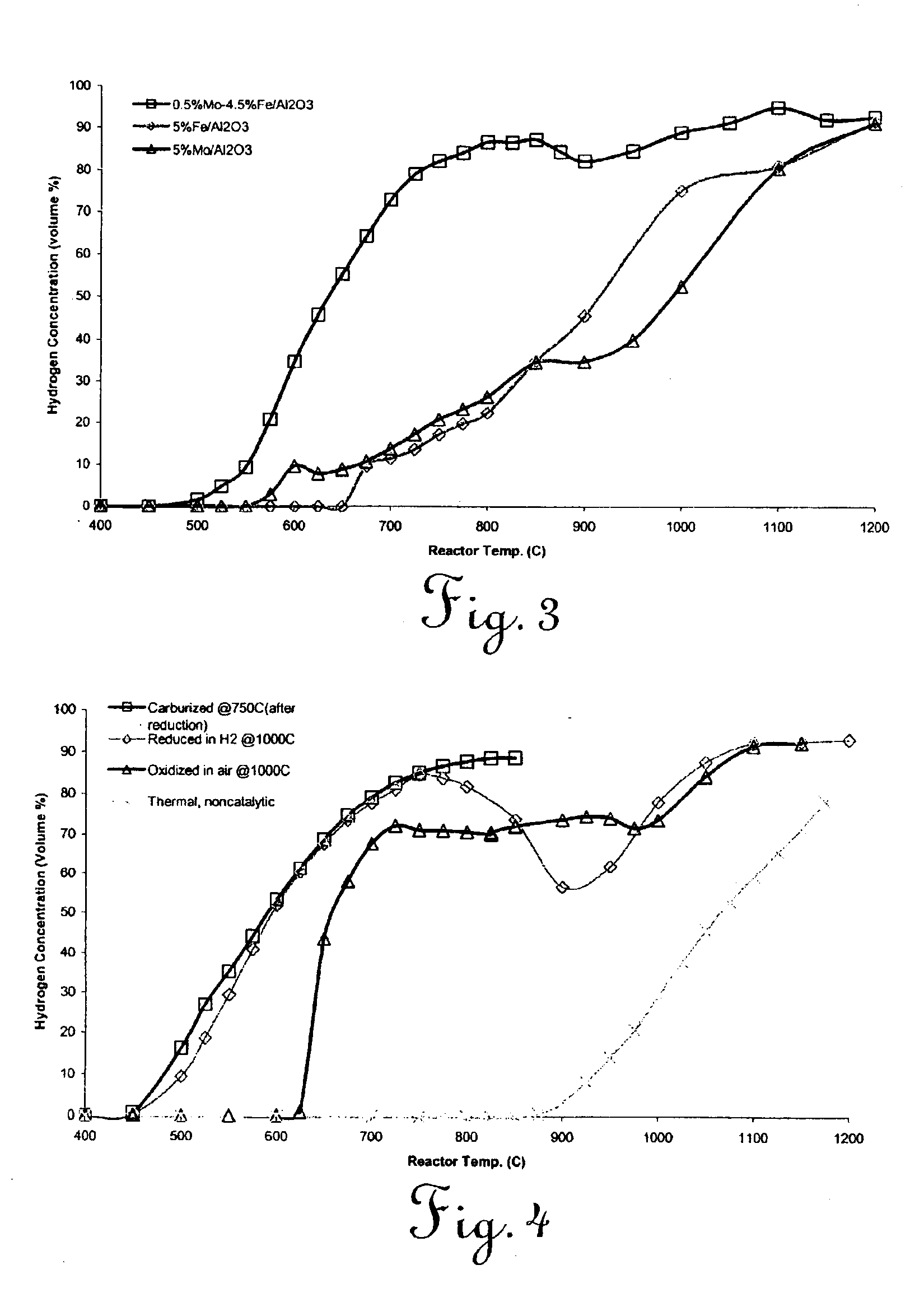
The present invention provides novel catalysts for accomplishing catalytic decomposition of undiluted light hydrocarbons to a hydrogen product, and methods for preparing such catalysts. In one aspect, a method is provided for preparing a catalyst by admixing an aqueous solution of an iron salt, at least one additional catalyst metal salt, and a suitable oxide substrate support, and precipitating metal oxyhydroxides onto the substrate support. An incipient wetness method, comprising addition of aqueous solutions of metal salts to a dry oxide substrate support, extruding the resulting paste to pellet form, and calcining the pellets in air is also discloses. In yet another aspect, a process is provided for producing hydrogen from an undiluted light hydrocarbon reactant, comprising contacting the hydrocarbon reactant with a catalyst as described above in a reactor, and recovering a substantially carbon monoxide-free hydrogen product stream. In still yet another aspect, a process is provided for catalytic decomposition of an undiluted light hydrocarbon reactant to obtain hydrogen and a valuable multi-walled carbon nanotube coproduct.
Owner:KENTUCKY UNIV RES FOUND OF
Antimicrobial Composition
Disclosed herein are antimicrobial compositions comprising an effective concentration of a metal salt combined with a plant extract. In some embodiments the composition comprises a copper salt and / or an iron salt and / or a nickel salt and / or a cobalt salt; and an extract of a plant selected from a group consisting of Punka granatum, Viburnum plicatum, Camellia sinensis, and Acer spp. The invention extends to uses of such compositions as medicaments, and to methods of treating microbial infections. The invention extends to methods for preventing microbial infections by coating objects and surfaces with the compositions.
Owner:NATURE THERAPEUTICS
Organic recycling with metal addition
InactiveUS20050039508A1Reduce slurry viscosityAvoid flowAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSolubilityIron sulfate
The invention is directed to methods for producing a granular nitrogen fertilizer from an organic material comprising adding a metallic salt to said organic material to form a slurry. Preferably the organic material comprises dewatered biosolids and contains water from a scrubber. Metallic salts that can be used comprise a salt of iron, zinc, or a mixture thereof. Preferred iron salts comprises ferric sulfate or ferric oxide, and preferred zinc salts comprises zinc sulfate or zinc oxide. Preferably, the metallic salt is mixed with an acid such as sulfuric acid to form an acidified metal salt. Slurry pH ranges from approximately 2-2.5. The acidified metal salt is added to the organic material in sufficient quantity to lower viscosity of the slurry such that the resulting fluid does not hinder fluid flow during operation. When the metallic salt comprises acidified ferric sulfate or ferrous sulfate, sufficient iron can be present to produce a fertilizer product with 0.1 weight percent to 10 weight percent iron sulfate calculated on a dry weight basis. The invention is also directed to fertilizer products made by the methods of the invention. Preferred products are granules and the metallic salt increases product hardness. Fertilizer granules preferably contain metal that is bioavailable to a plant when used as a fertilizer. Solubility of the metal of the product in water is enhanced, and the product is low staining.
Owner:UNIFIED ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES GROUP +1
Process for producing iron phosphate for producing iron lithium phosphate material
The preparation method of iron phosphate used for preparing lithium iron phosphate material in the present invention relates to heavy metal phosphate, and the steps are: dissolving analytically pure soluble iron salt in distilled water to prepare a 0.05-5M aqueous solution, and the added mass is the iron salt mass 0.01~3% of anionic surfactant, then add analytically pure phosphoric acid according to the molar ratio of Fe3+:PO43-=1:0.8~1.2 and stir evenly, and slowly add alkaline solution with a concentration of 1~9M under stirring , the feeding time is more than 1 hour, until the pH value of the solution reaches 6-7, the iron phosphate precipitate is filtered, and the filtered iron phosphate is washed 3-5 times with distilled water 2-5 times its weight. Dry at ~90°C to obtain the product FePO4·2H2O powder. The iron phosphate product with two crystal waters prepared by the method of the invention has high reactivity, and the performance of the lithium iron phosphate material made by using it is better than that of the lithium iron phosphate material made by commercially available iron phosphate products.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Reactive magnesium oxide cements
Novel hydraulic cements are disclosed that include reactive magnesium oxide prepared by low temperature calcination. The cements can be formulated to suit a large number of applications with various setting times, strength and levels of sustainability either by adding iron salts such as ferrous sulfate or blending with other compatible faster setting hydraulic cements such as Portland cement or by using both methods. The compositions are able to incorporate relatively large amounts of low cost pozzolans such as fly ash to advantage as well as wastes. Many excellent properties are exhibited and in particular good comprehensive strength and resistance to sulfates is able to be achieved.
Owner:TECECO
Preparation and application of greenly synthesized biochar supported zero-valent iron nanomaterial
InactiveCN108043361AHigh reactivityImprove stabilityWater treatment parameter controlOther chemical processesEnvironmental resistanceWater baths
The invention relates to the technical field of metal nanoparticles, in particular to preparation and an application of greenly synthesized biochar supported metal nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving biochar powder and iron salt (divalent or trivalent) in ethanol water to obtain a biochar and iron ion mixed solution; performing water bath on the biocharand iron ion mixed solution at 30-80 DEG C, adding a green tea extract solution under mechanical stirring, and continuously stirring the mixture for 10-30 min to obtain a greenly synthesized biochar supported zero-valent iron nano-solution; performing separation with a suction filtration method to obtain a precipitate, and drying the precipitate at 40-80 DEG C for 36-72 h to obtain the greenly synthesized biochar supported zero-valent iron nanomaterial. The method has the advantages that the process is simple, the method is green, the cost is low, and the like; the prepared greenly synthesizedbiochar supported zero-valent iron nanomaterial can effectively repair underground water polluted by Cr (VI) ions, cannot cause secondary pollution, is safe to use and has huge application value.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Composite reagent for treating recycled water of printing and dyeing wastewater and application method of composite reagent
InactiveCN104108775AAchieve efficiencyAchieve economyWaste water treatment from textile industryWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSolubilityFlocculation
The invention discloses a composite reagent for treating recycled water of printing and dyeing wastewater and an application method of the composite reagent. The composite reagent comprises the following components by weight percent: 20% to 70% of aluminum salt coagulant, 5% to 30% of iron salt coagulant, 5% to 40% of mineral material and 5% to 45% of activated carbon. The method comprises the following steps: preparing the composite reagent for treating the recycled water of the printing and dyeing wastewater into powder or an aqueous liquid in which the content of effective components accounts for 5% to 30%; regulating a pH value of effluent in a printing and dyeing wastewater biochemical system to be within 3 to 9; adding the powder or the aqueous liquid of the composite reagent into the effluent in the printing and dyeing wastewater biochemical system under the condition that the adding quantity of the effective components is between 20mg / L and 1000mg / L after the pH value of the effluent is regulated; and stirring for 0.2 to 2 hours and then standing so as to obtain the recycled water conforming to the water quality standard in textile industry. According to the method, macromolecular colloidal pollutants in the biochemical effluent of the printing and dyeing wastewater, which are difficult to degrade, can be removed by utilizing the coagulation / flocculation performance of aluminum salts and iron salts in the composite reagent; and meanwhile, soluble inert pollutants in the wastewater are removed by utilizing the adsorbability of the activated carbon and the mineral material in the composite reagent.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
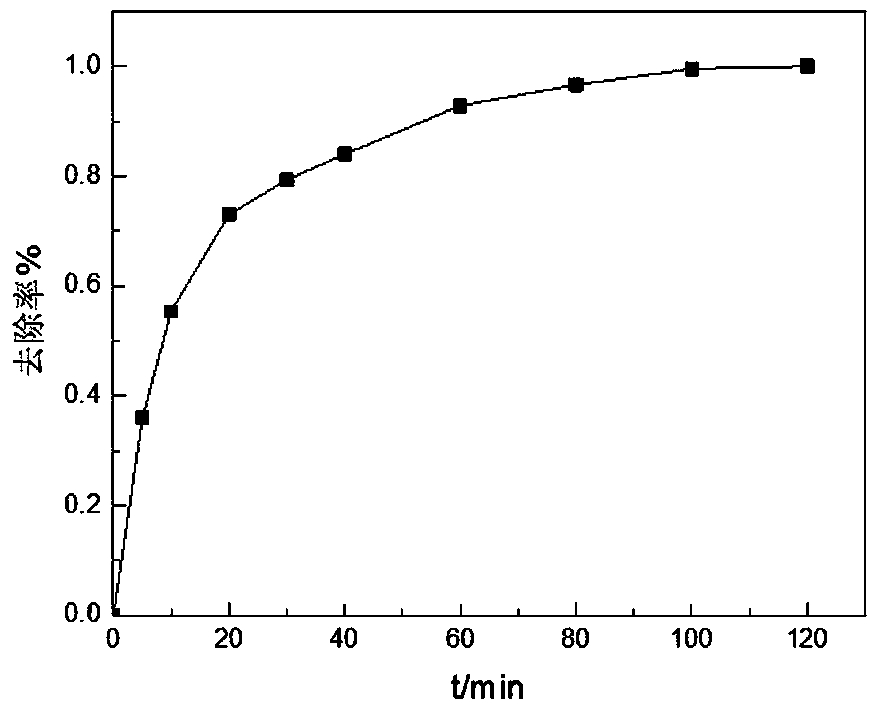
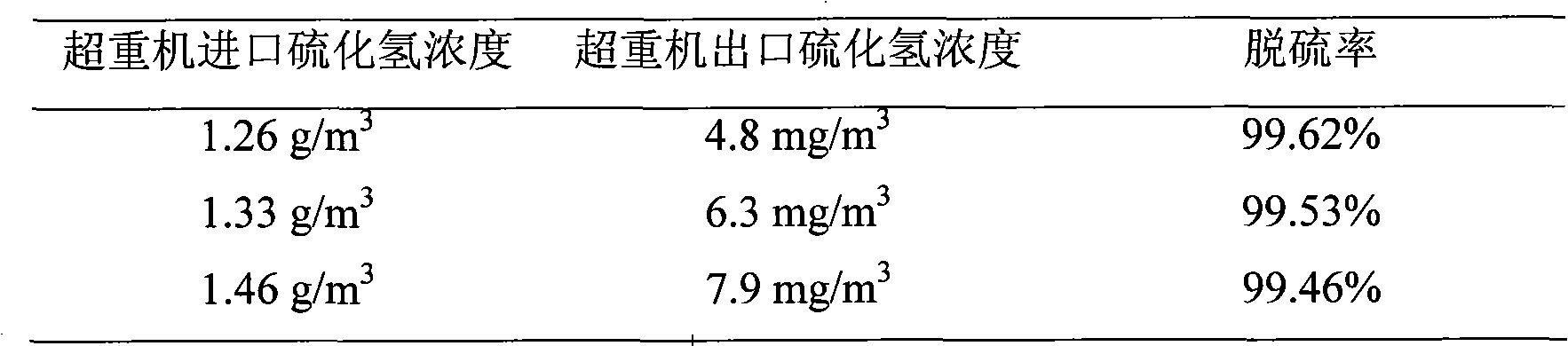
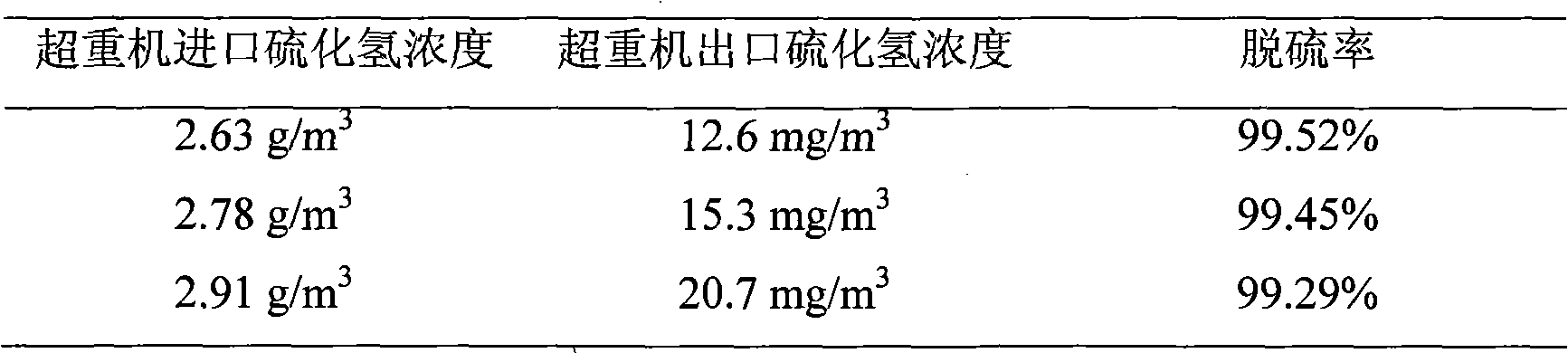
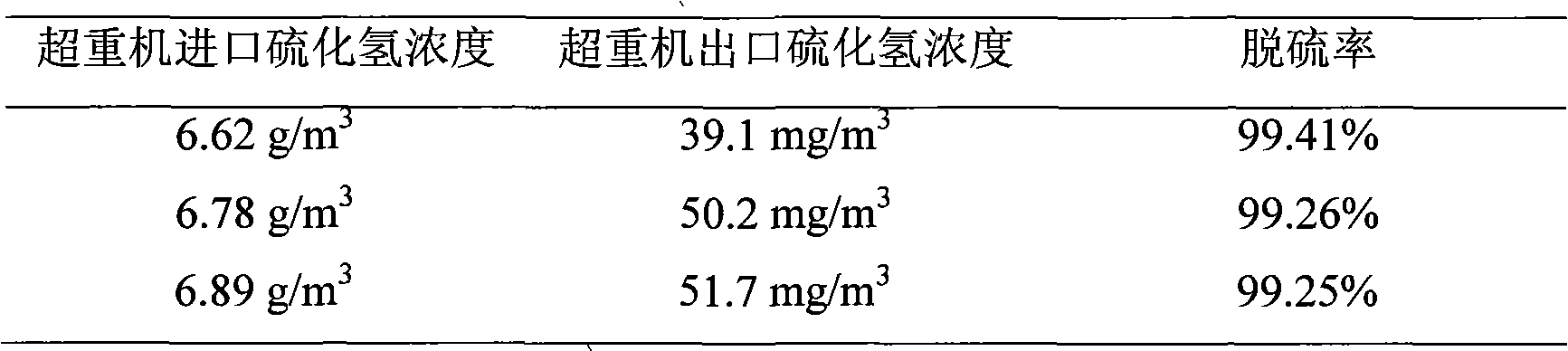
Iron complex desulfurizer suitable for super-gravity desulfurization
ActiveCN101874968AReduce corrosionReduce corrosion rateDispersed particle separationSulfur granulesIron salts
The invention belongs to the technical field of gas purification, and in particular relates to an iron complex desulfurizer suitable for super-gravity desulfurization. The active ingredients of the iron complex desulfurizer are the following components: a soluble iron salt, an iron salt complexing agent, hydrosulfide absorbants comprising alkaline matters and alcamines, and additives comprising astabilizing agent, a synergist, a sulfur granule settling agent and a corrosion inhibitor. The iron complex desulfurizer has the advantages of large accumulative saturation sulfur capacity (reaching 0.60g / L), high absorption speed, high efficiency, stable solution performance without degradation, easy recovery of sulfur, less side reactions, low running cost and the like; and the accumulative saturation sulfur capacity and the absorption speed are obviously improved, so the iron complex desulfurizer is suitable for the characteristics of small liquid circulating volume and short retention time of the super-gravity desulfurization, fully takes the obvious advantages of the super-gravity technology in the wet desulphurization, and is a high-efficiency, economic, practical and environment-friendly iron complex desulfurizer.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles and the process of forming fe-based nanomaterials
InactiveUS20050191231A1Small sizeNarrow size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureIron saltsMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method and structure for making magnetite nanoparticle materials by mixing iron salt with alcohol, carboxylic acid and amine in an organic solvent and heating the mixture to 200-360 C. is described. The size of the particles can be controlled either by changing the iron salt to acid / amine ratio or by coating small nanoparticles with more iron oxide. Magnetite nanoparticles in the size ranging from 2 nm to 20 nm with a narrow size distribution are obtained with the invention. The invention can be readily extended to other iron oxide based nanoparticle materials, including MFe2O4 (M=Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ti, Ba, Mg) nanomaterials, and iron oxide coated nanoparticle materials. The invention also leads to the synthesis of iron sulfide based nanoparticle materials by replacing alcohol with thiol in the reaction mixture. The magnetite nanoparticles can be oxidized to γ-Fe2O3, or α-Fe2O3, or can be reduced to bcc-Fe nanoparticles, while iron oxide based materials can be used to make binary iron based metallic nanoparticles, such as CoFe, NiFe, and FeCoSmx nanoparticles.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for treating waste acid by gypsum sedimentation, arsenic oxidizing sedimentation and iron salt neutralization and co-precipitation
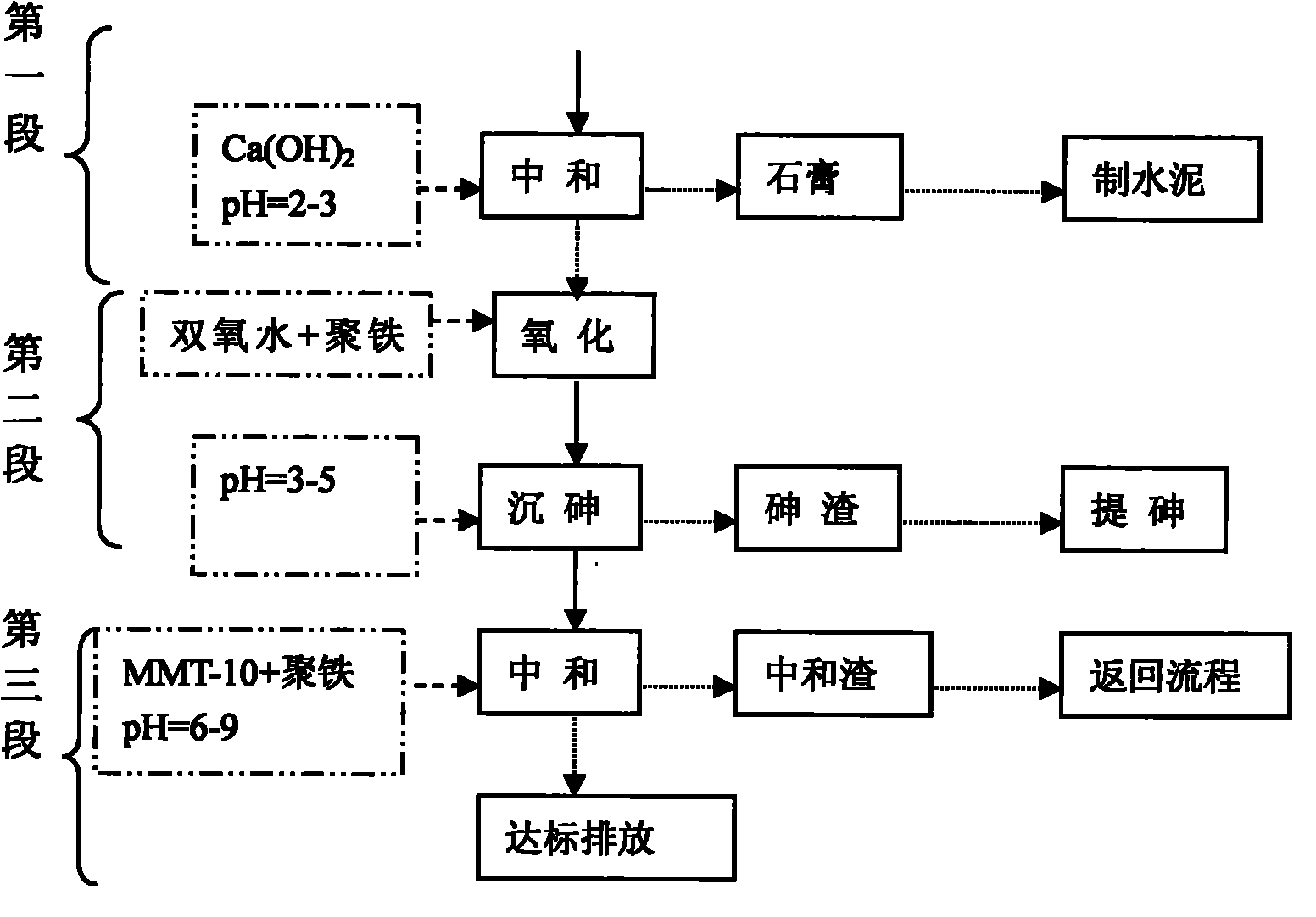
ActiveCN101830583AAchieving zero emissionsRealize resource utilizationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentIron saltsSlag
The invention discloses a method for treating waste acid by gypsum sedimentation, arsenic oxidizing sedimentation and iron salt neutralization and co-precipitation. The method comprises the following steps of: the first section: gypsum sedimentation, namely putting lime cream into the waste acid, and removing most sulfuric acid from the waste acid through neutralization reaction to generate CaSO4sediment and gypsum; the second section: arsenic oxidizing sedimentation, namely performing solid-liquid separation after the gypsum reaction, adding polymeric iron into supernate, adding hydrogen peroxide oxidant into the supernate to oxidize Fe2+ into Fe3+ and oxidize As3+ into As6+ under the condition of low pH, and removing most arsenic from the waste acid through oxidizing sedimentation reaction so as to enrich the arsenic in the waste acid and produce arsenic slag; and the third section: iron salt neutralization and co-precipitation, namely performing solid-liquid separation after the arsenic reaction, adding polymeric iron and heavy metal ion hunting agent into the supernate, and removing residual arsenic and heavy metal ions from the waste acid to generate neutralized slag and water meeting the national discharge standard. The method has the advantages of short flow, simplicity, practicability, good pollution control effect and good gypsum byproduct, and the removal rate of arsenic is up to 99.999 percent.
Owner:YUNNAN COPPER CO LTD
Carbon-based composite material for arsenic and cadmium polluted soil remediation and application of composite material
ActiveCN107115840AImprove performanceIncrease load strengthOther chemical processesWater contaminantsIron saltsCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a carbon-based composite material for arsenic and cadmium polluted soil remediation and application of the composite material. The carbon-based composite material disclosed by the invention is prepared by the steps: taking crop straws as raw materials, and charring to prepare charcoal; mixing with an iron salt solution according to a certain solid-liquid ratio, regulating the pH value of the solution in the process so as to realize coprecipitation of the two materials; performing pyrolysis, thereby obtaining the carbon-based composite material. The carbon-based composite material prepared in the invention is applied to arsenic and cadmium compound polluted soil, and methods such as turning over, watering and the like are combined, so that the content of arsenic and cadmium in an effective state can be obviously reduced; therefore, the arsenic and cadmium in the soil can be transferred to a direction with low biotoxicity and migration, the physicochemical properties of the soil can be improved to a certain degree, and the composite material is suitable to be applied to multiple types of soil. The arsenic and cadmium ions in a water body can be effectively removed, the preparation process is simple in operating steps, and the material is wide in source, low in production cost and environment-friendly.
Owner:INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Resource treating method for oil-containing sludge
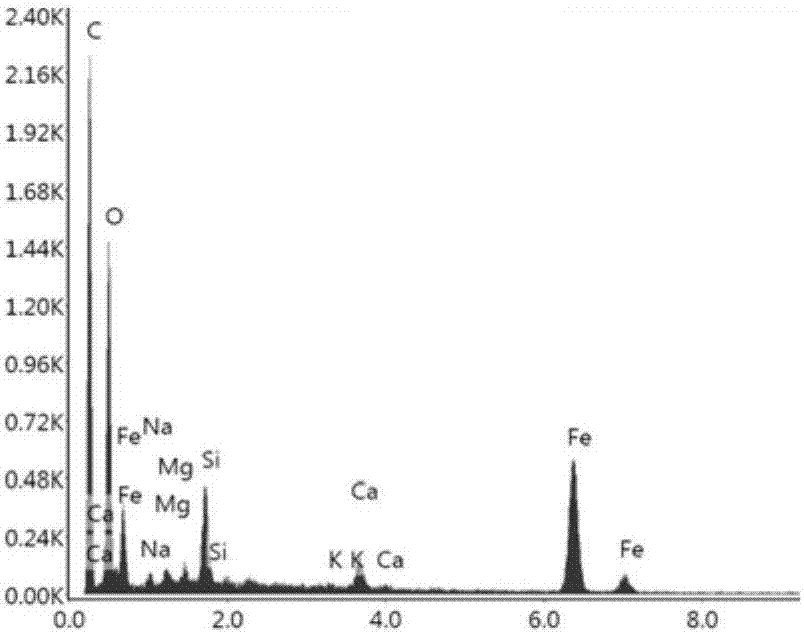
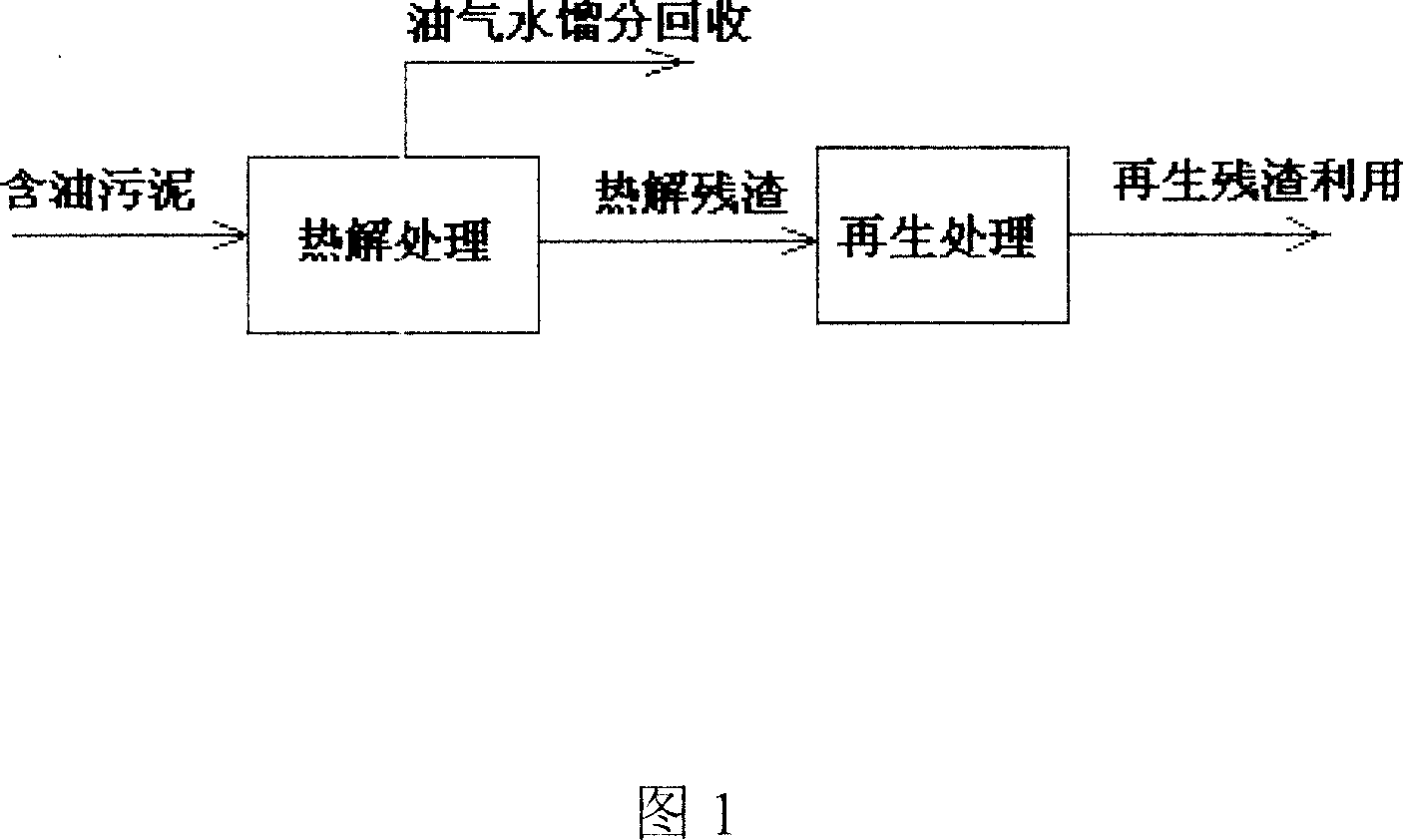
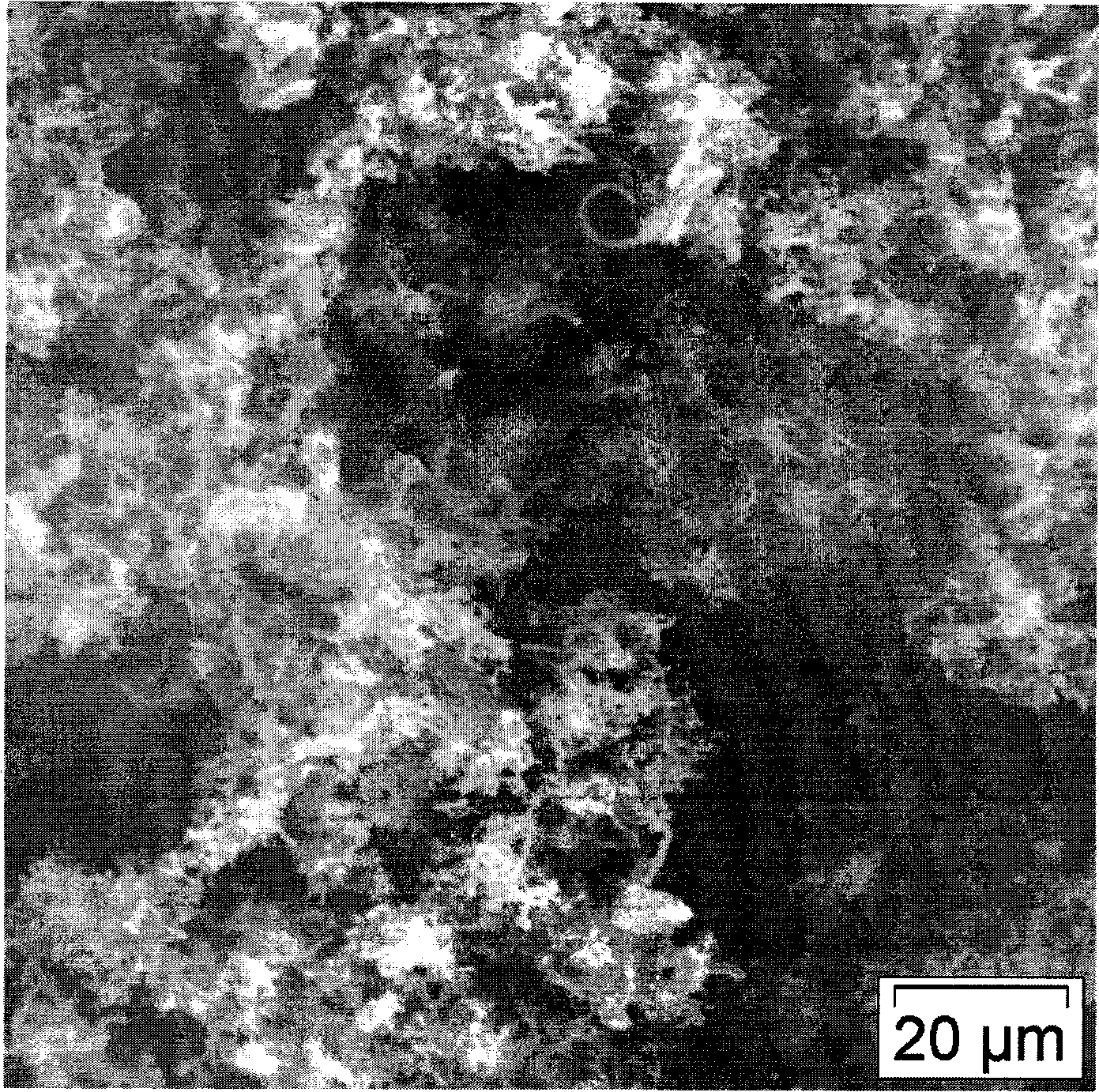
ActiveCN101113067ASolve pollutionReduce doseSludge treatment by pyrolysisByproduct vaporizationClay mineralsIron salts
The invention relates to a resource processing method for oily sludge. First, the oily sludge is sent to a closed retorting cracking furnace to be pyrolyzed, and the pyrolyzed period is 1-5 hours under 200-600 DEG C, then the oil, gas, and water are recovered. Second, sulfate or hydrochloride is put into the pyrobitumen of sludge containing inorganic aluminum salt or iron salt flocculant according to the chemical equivalent of the aluminum salt or iron salt 1 to 1-1.5 to do acid-soluble processing. The products after the two processes can be reclaimed and used as the flocculant of the sewage processing system, or reclaimed as the concentrating agent of sludge. The pyrobitumen containing mostly clay mineral can be used as decolorizing and absorbing material of waste water and oil, or used as absorbent for lube-oil complementing and refining process. The method used in oilfield gathering transportation and treatment system can realize zero discharge in course of the gathering transportation and treatment, and can effectively solve the pollution problem of the oily sludge and find the automate answer for the oily sludge. Meanwhile, by adopting the method, the cost for the treatment of sewage flocculation and for adding sludge concentration agent can be reduced and the energy material can be reclaimed from sludge and the wastage of oil can be reduced.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for preparing lithium iron phosphate/nanometer carbon composite anode material
InactiveCN101533904AEffective contactReduce usageElectrode manufacturing processesFiberCarbon composites
The invention provides a method for preparing lithium iron phosphate / nanometer carbon composite anode material, which is characterized by comprising the steps as follows: 1) a precursor is pretreated, raw materials are weighed according to the components and weight percentage as follows: 0.2%-15% of catalyst, 5%-15% of lithium salt, 40%-60% of iron salt and 25%-45% of phosphate; the catalyst is one or several kinds of metal Fe, Co and Ni; the raw materials are added with dispersant and then are ball-milled in a ball grinder to prepare the precursor; 2) a carbon nano tube or carbon fiber grows; and 3) lithium iron phosphate or adulterant lithium iron phosphate is prepared. The invention solves the problem that the carbon nano tube is difficult to be dispersed in high-viscosity high-solid lithium iron phosphate slurry, and the invention provides the method for growing the carbon nano tube or the carbon fiber synchronously during the process of preparing the lithium iron phosphate and improves the specific capacity and the cycle life of the lithium iron phosphate under the condition of charging and discharging.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Iron base catalyst used for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101811047AIncreased synthetic reactivityLow selectivityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst activation/preparationIron saltsMetal salts
The invention discloses an iron base catalyst used for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and a preparation method and the application thereof. The catalyst comprises iron, reducing auxiliary agents of IB family metal Cu and / or Ag oxides, electronic auxiliary agents of IA family metal Li, Na, K or Rb, hydrogenation auxiliary agents of VIII family noble metal Ru, Rh, Pd or Pt and structural auxiliary agents of SiO2. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: using alkaline compounds for carrying out fast coprecipitation on iron salts or a mixture of the iron salts or reducing auxiliary agents of IB family metal salt solutions; carrying out secondary pulping after precipitate washing; adding IA family metal salt solutions and silica sol, or adding IA family metal silicate in the pulp; carrying out spray drying forming on pulp; then, soaking obtained materials in VIII family noble metal salt solution; and obtaining the catalyst of the invention after drying roasting. The catalyst is applicable to the technical process for producing hydrocarbon through low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction, and has high heavy hydrocarbon product yield, wherein the methane selectivity is very low, and the olefin selectivity is also obviously reduced.
Owner:SYNFUELS CHINA TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing magnetic biochar from straw
InactiveCN105536700AOptimize structural configurationMeet greenOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesIron saltsCarbonization
A method for preparing magnetic biochar from straw includes the step of selecting of a straw material, wherein wheat straw, corn straw, rice straw or cotton straw is selected as the straw material, the straw material is pretreated by cleaning, then the straw material is dipped with a trivalent iron salt solution, and filtered by vacuum, then a filter cake is dried, and a finished magnetic biochar product can be obtained by carbonization treatment in inert gas conditions. The magnetic biochar can be obtained by dipping the straw material in the trivalent iron salt solution by a pyrolysis process, and a new way for the use of straw is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
Process for recovering heavy metallic salt and inorganic acid in pickling waste liquid
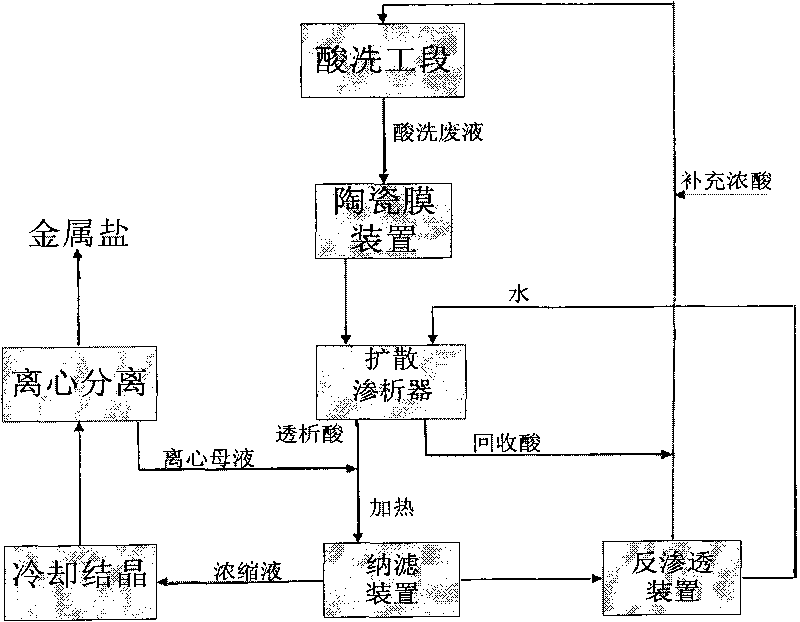
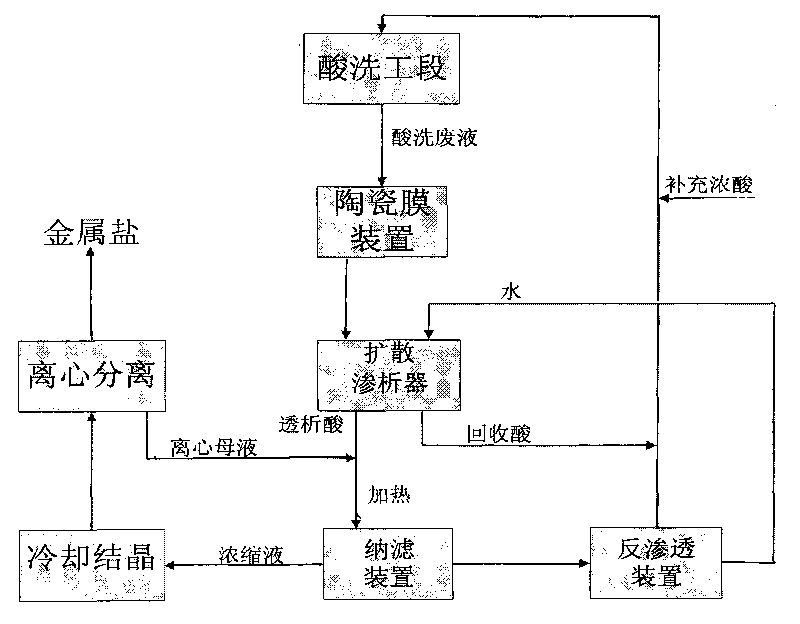
ActiveCN101759250AOptimizing the integration processReduce pollutionSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisLiquid wasteIron salts
The invention relates to a process for separating and recovering heavy metallic salt and inorganic acid in pickling waste liquid by a membrane method, which comprises the following concrete steps: filtering and removing solid suspended substances in pickling waste liquid through an inorganic ceramic membrane; separating acid from salt in the ceramic membrane penetrating liquid through diffusion dialysis; and heating the dialysis liquid of a diffusion dialyzer, then introducing the dialysis liquid into a nanofiltration membrane, and cooling and crystallizing the concentrated liquid of a nanofiltration device and then centrifuging the crystal of the concentrated liquid to obtain iron salt, wherein the penetrating liquid of the nanofiltration device passes through a reverse osmosis membrane device, the concentrated liquid of the reverse osmosis device returns to a pickling section, and the water discharged from the reverse osmosis device enters a diffusion dialysis section for recycling. The invention has the characteristics that the pickling waste liquid is completely used as resources, the recovery process is simple, the recovery ratio of metallic salt and acid is high, and water is recycled. The process of the invention can be coupled with various pickling sections to realize continuous and stable automated operation, and the supplemented acid amount can be quantitatively controlled according to the acid amount consumed by the crystallized metallic salt.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/sulfonated graphene composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102558772APorous Structure RegulationEasy to controlElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceIron salts
The invention relates to a method for preparing poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) / sulfonated graphene composite hydrogel with a porous structure through supramolecular self-assembly. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving sodium polystyrene sulfonate and sulfonated graphene in water, stirring, performing ultrasonic dispersion to ensure that the sodium polystyrene sulfonate and thesulfonated graphene are dissolved, adding a 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene monomer, uniformly stirring, adding polyvalent iron salt, standing at room temperature and reacting to obtain blocky poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) / sulfonated graphene composite hydrogel. The poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) / sulfonated graphene composite hydrogel with a controllable and porous structure is prepared by using the interaction and electrostatic action of a hydrogen bond and a pi-pi bond among the sulfonated graphene, the sodium polystyrene sulfonate and 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene through supramolecular self-assembly. The prepared composite hydrogel has high electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, and high specific capacitance and cycle stability in electroactive electrolyte.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Preparation method of magnetic-alloy-loaded porous carbon sphere composite wave-absorbing material
The invention relates to a preparation method of a magnetic-alloy-loaded porous carbon sphere composite wave-absorbing material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a precursor solution containing two or more magnetic metal ion salts; 2) stirring the porous carbon spheres in the precursor solution for impregnation; 3) filtering out the porous carbon spheres, washing and drying; 4) calcining the dried porous carbon spheres in an inert atmosphere; and 5) cooling to room temperature in an inert atmosphere to obtain the magnetic-alloy-loaded porous carbon sphere composite wave-absorbing material. The iron salt / cobalt salt, iron salt / nickel salt and cobalt salt / nickel salt mixed precursor solution are introduced to the inside of the ducts of the carbon spheres by using the high specific area and strong adsorptivity of the porous carbon spheres through the capillary actions and are combined with the hydrophilic oxygen-containing functional group; and finally, the drying and sintering treatment in the inert atmosphere are performed to obtain the iron-cobalt / iron-nickel / cobalt-nickel-alloy-loaded porous carbon sphere composite material. The whole preparation process is simple in technique and convenient to operate, and has low requirements for the production equipment.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
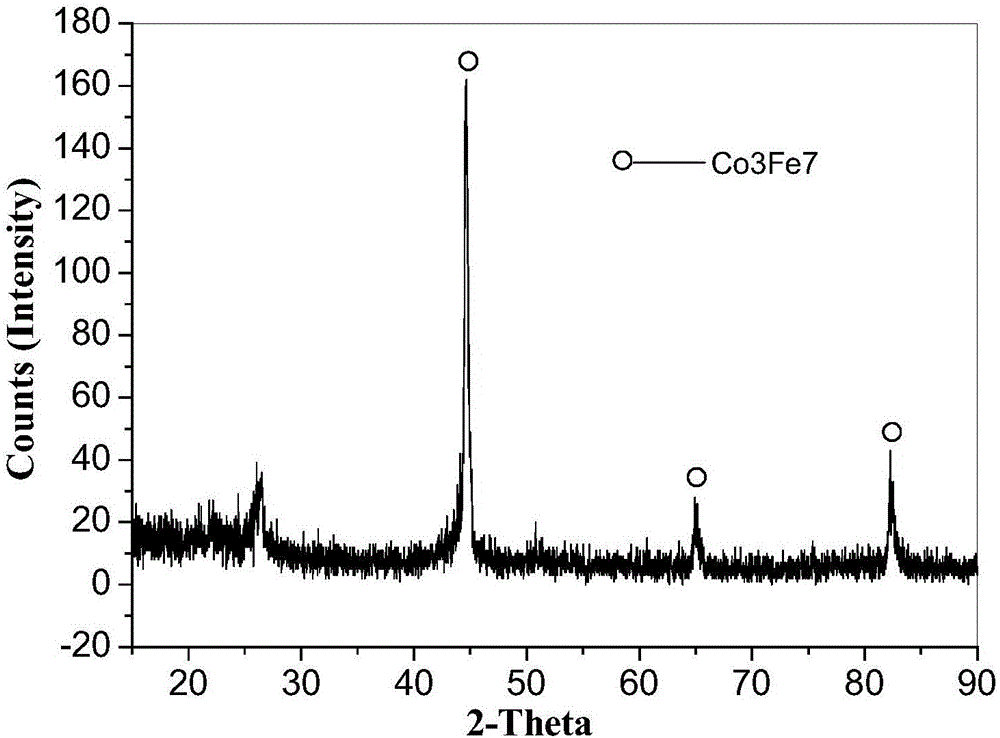
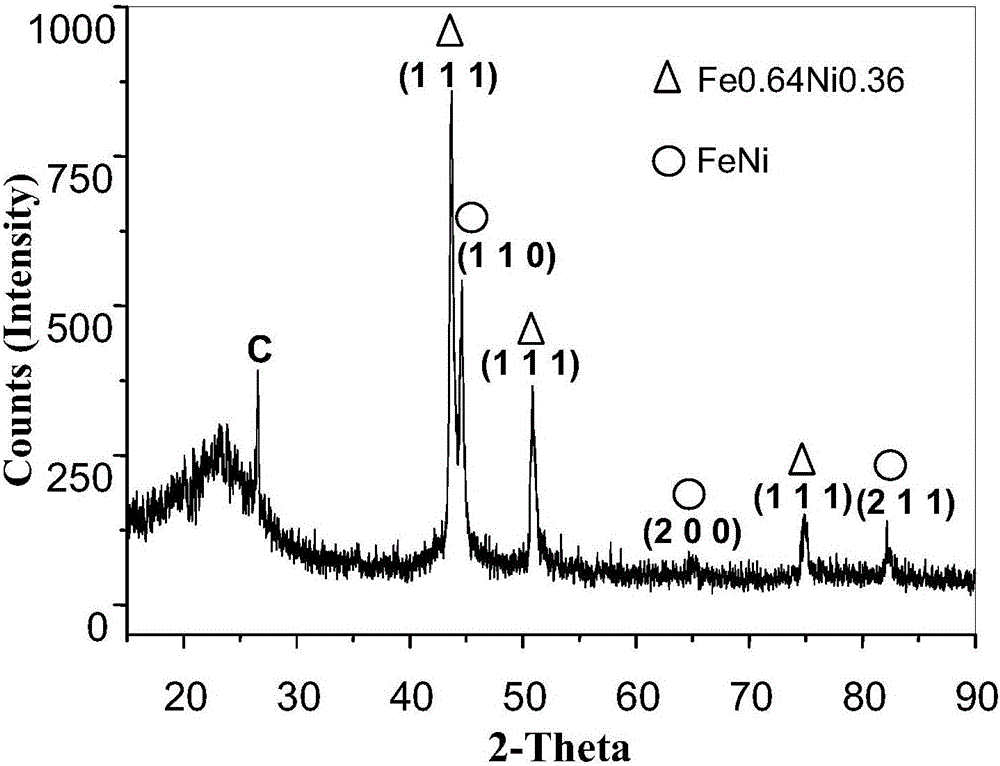
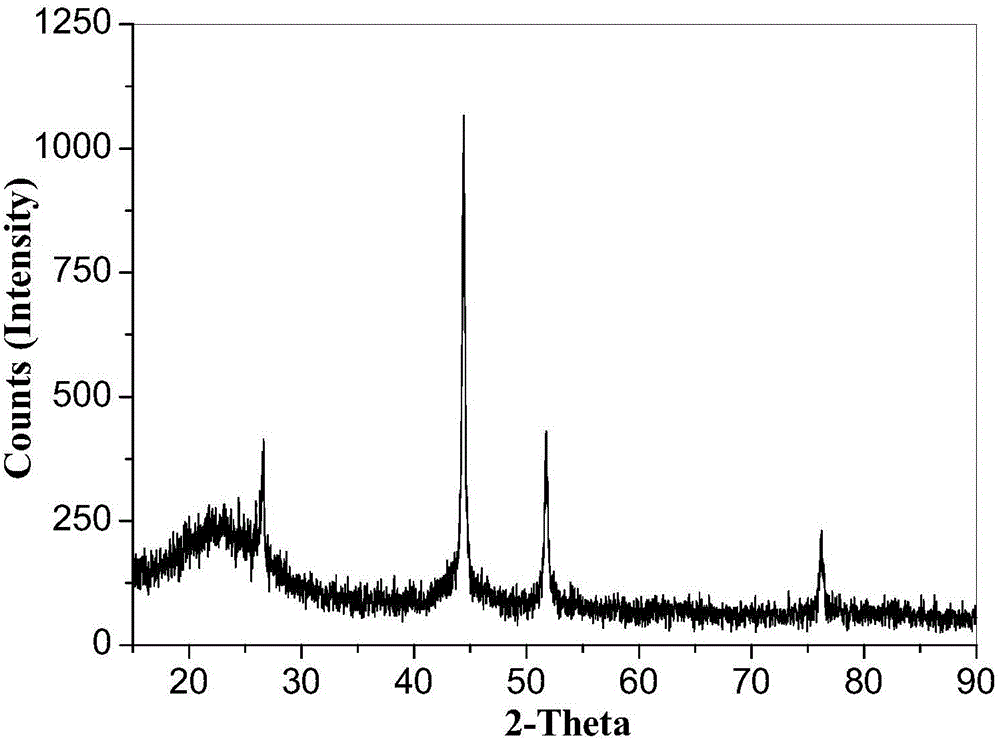
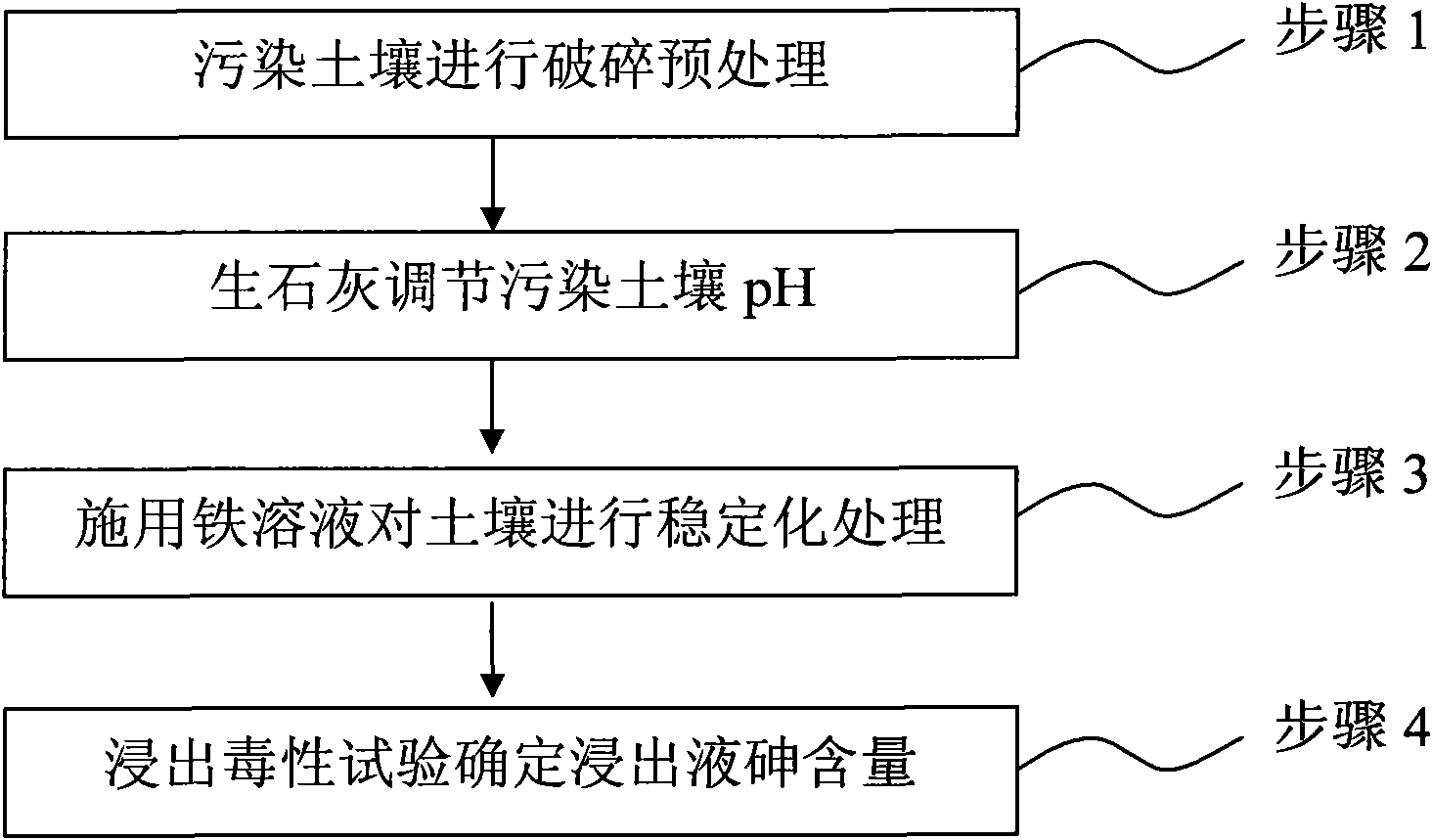
Method for remedying arsenic polluted soil
InactiveCN101879521AEasy to handleSimple operation and managementContaminated soil reclamationArsenateArsenic pollution
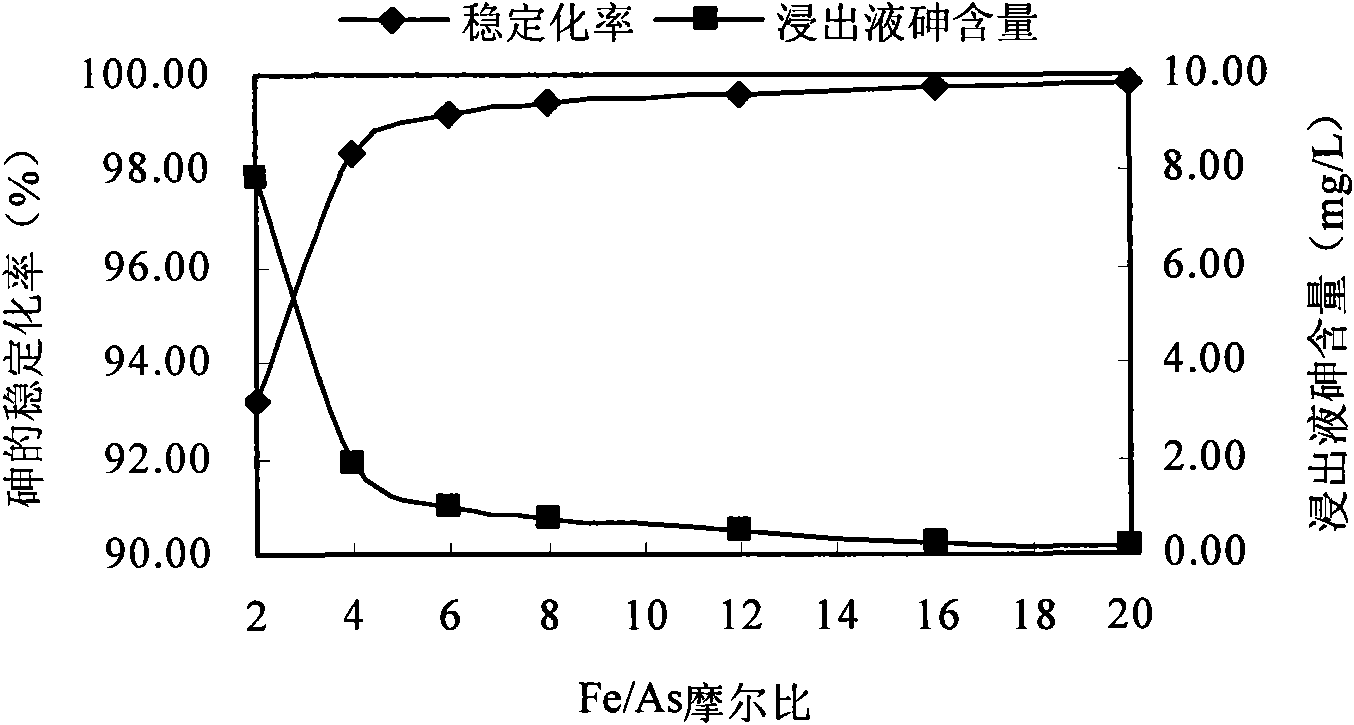
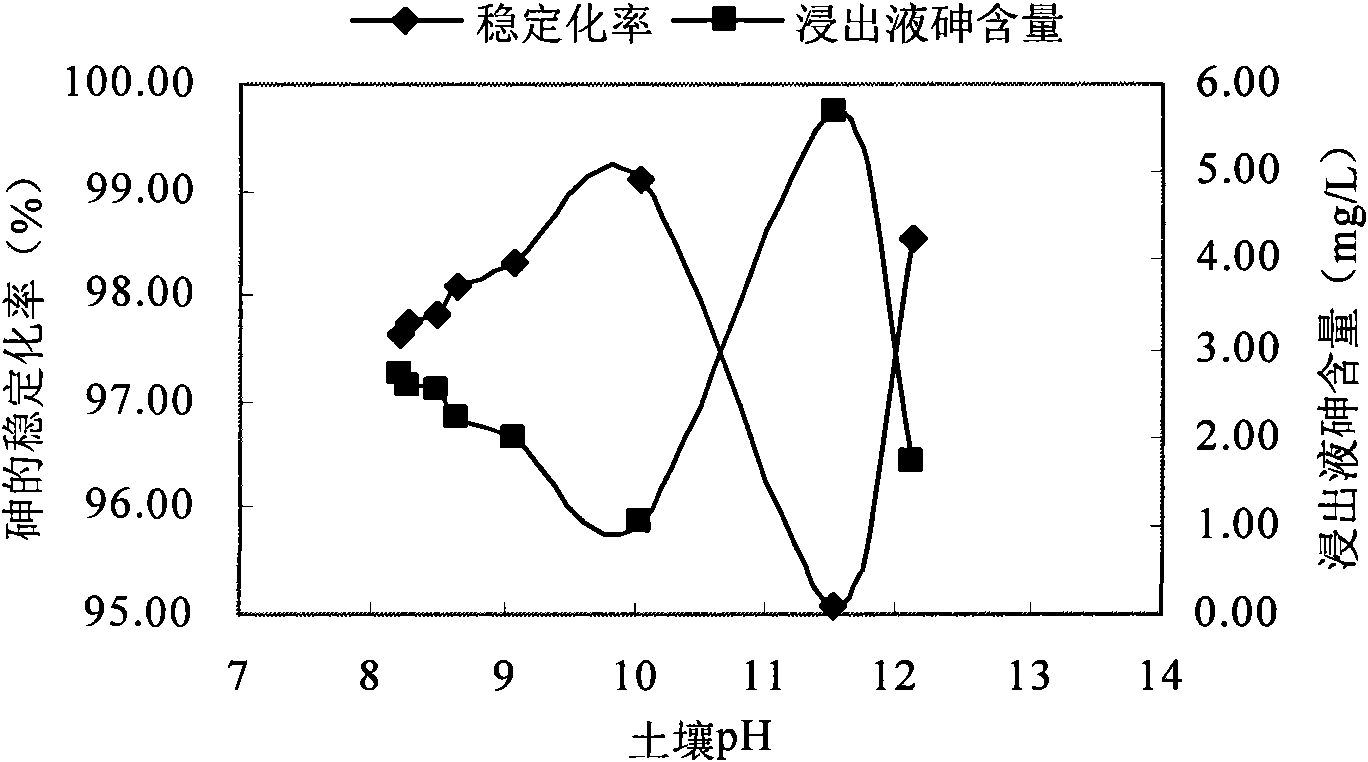
The invention discloses a method for remedying arsenic polluted soil. The method comprises a step of adding iron salt solution into the arsenic polluted soil so that the iron salt solution is reacted with arsenic in the soil to form arsenate FeAsO3 or FeAsO4 of iron. Before the iron salt solution is added, the method also comprises a step of crushing the arsenic polluted soil and steps of adjusting the pH of the arsenic polluted soil and measuring the arsenic content of the arsenic polluted soil. The method can quickly and efficiently treat the arsenic polluted soil, has simple operation and management and is suitable for major unexpected arsenic pollution remediation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com