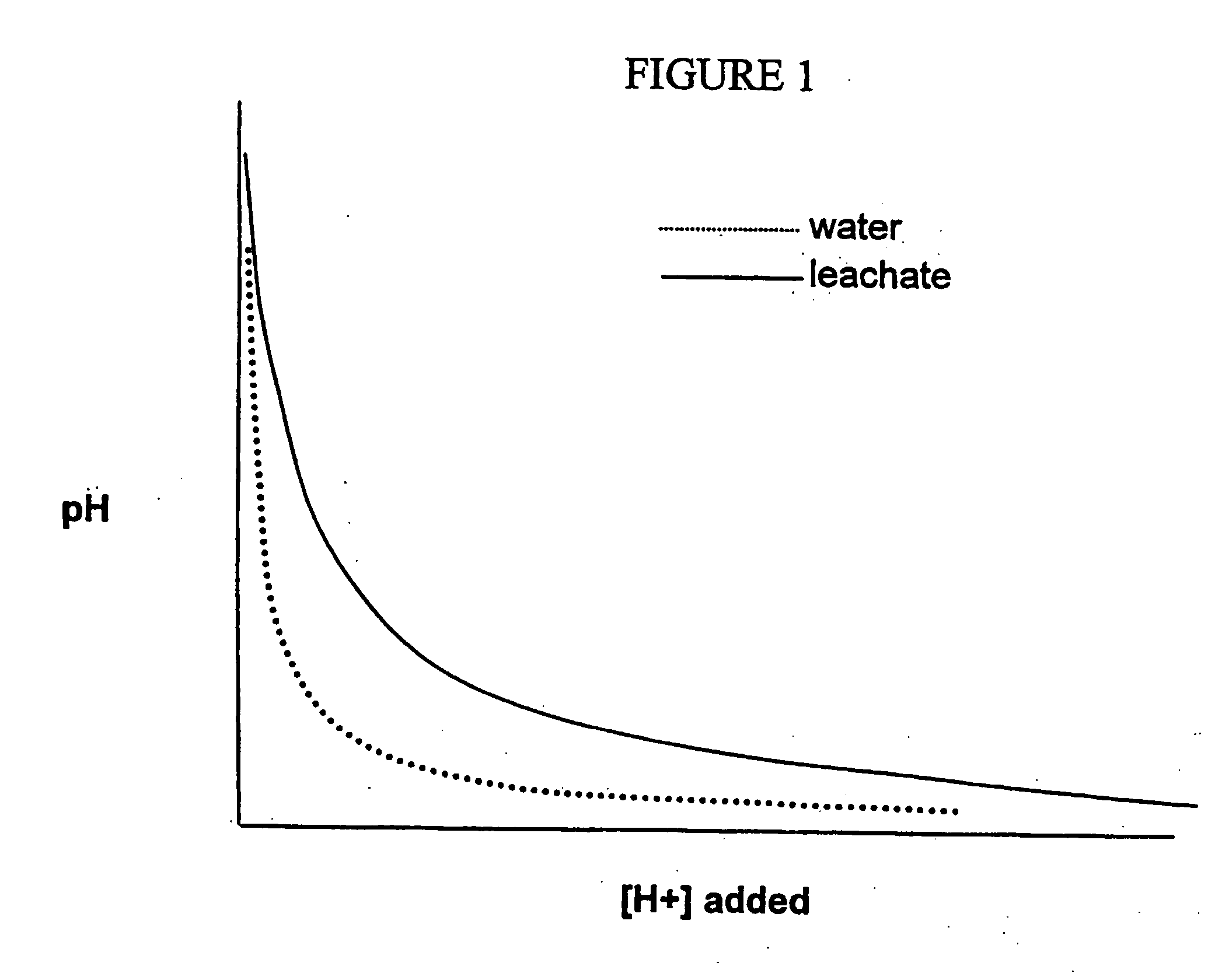
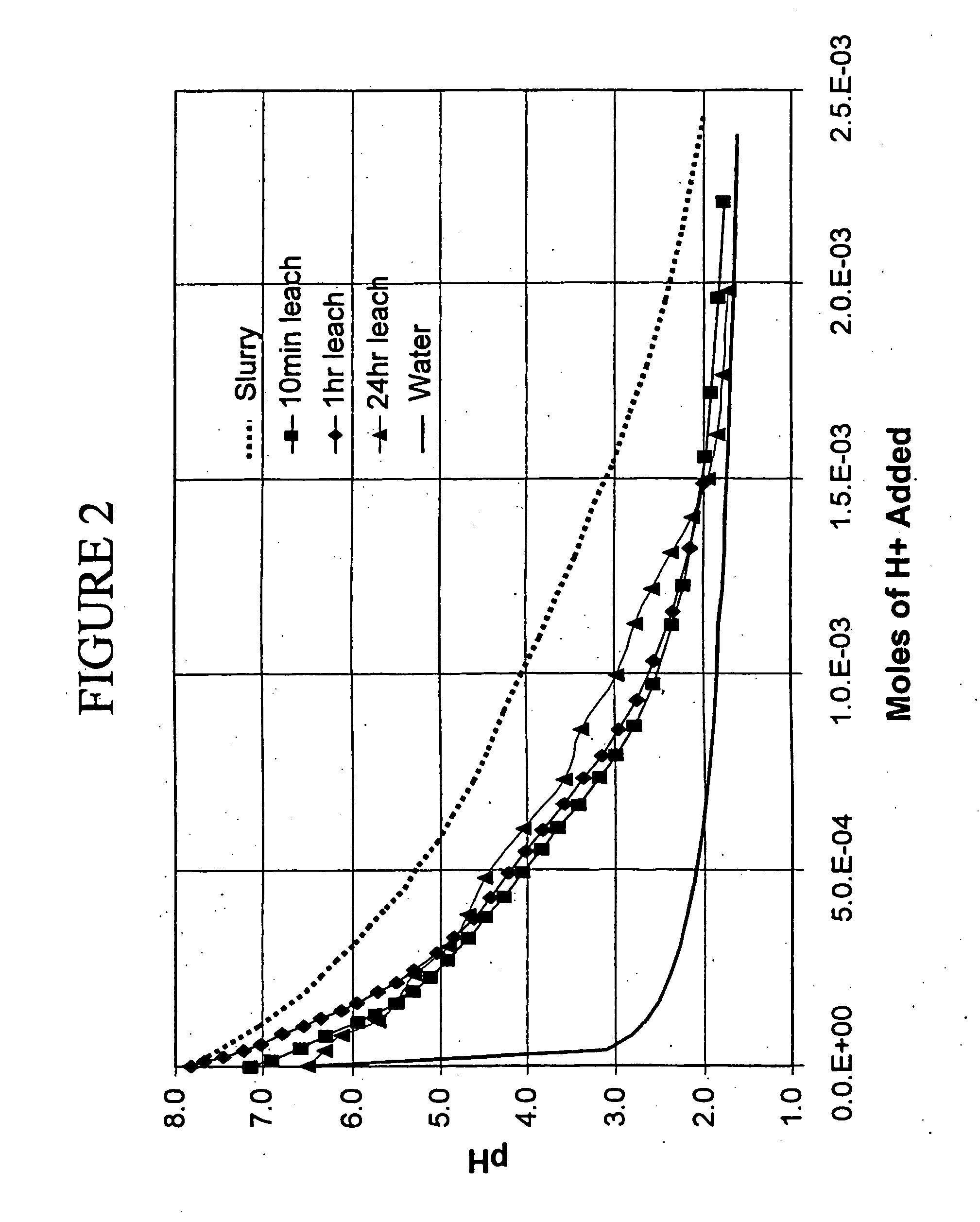
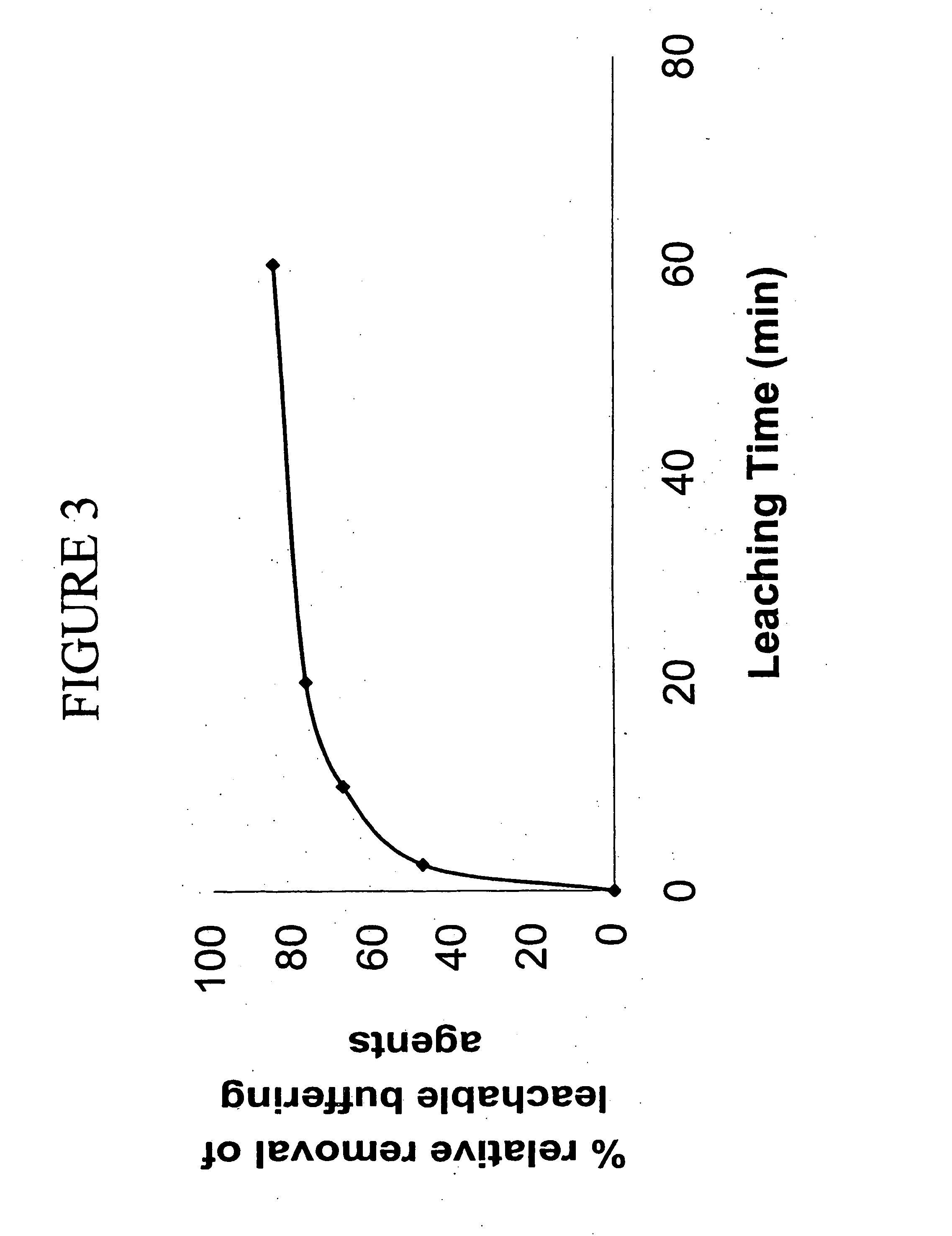
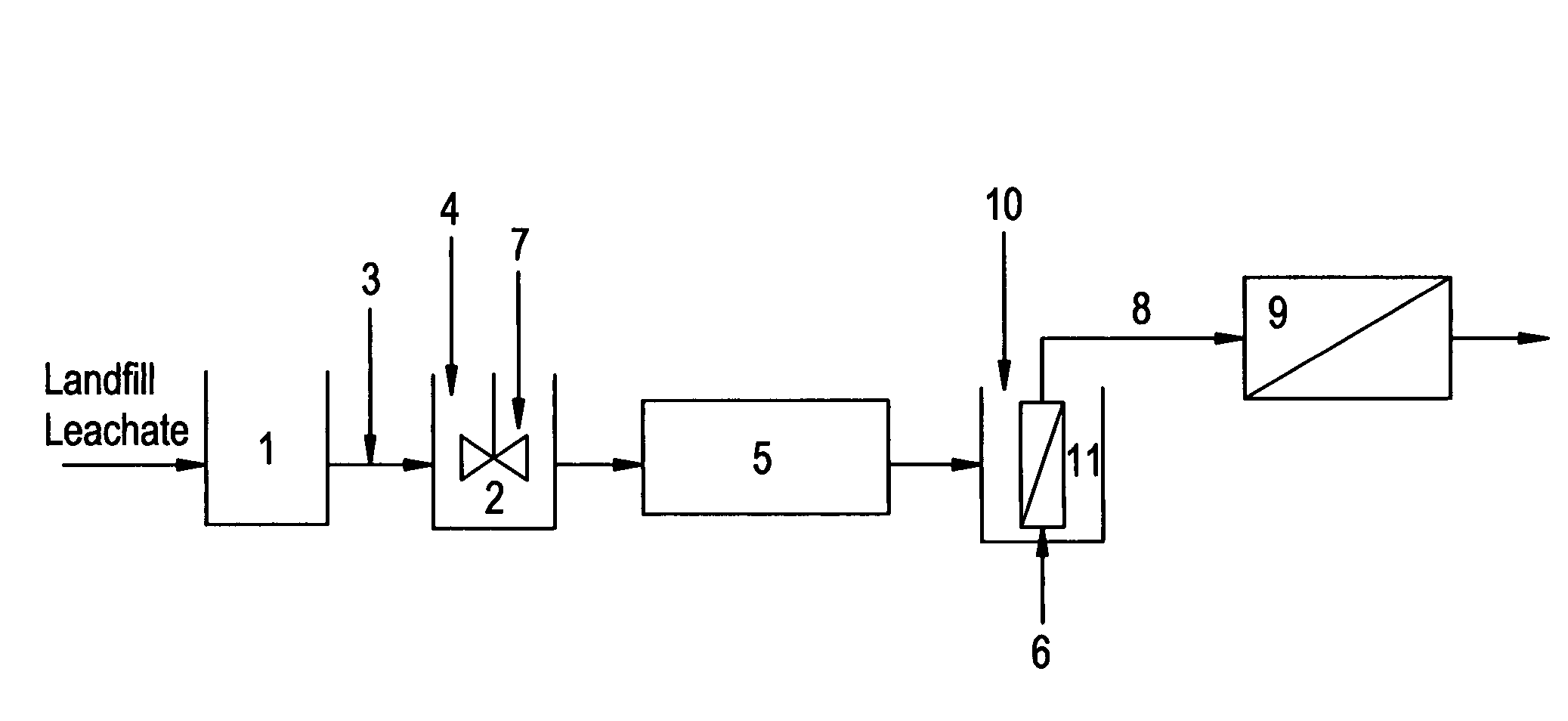
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5584 results about "Leachate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
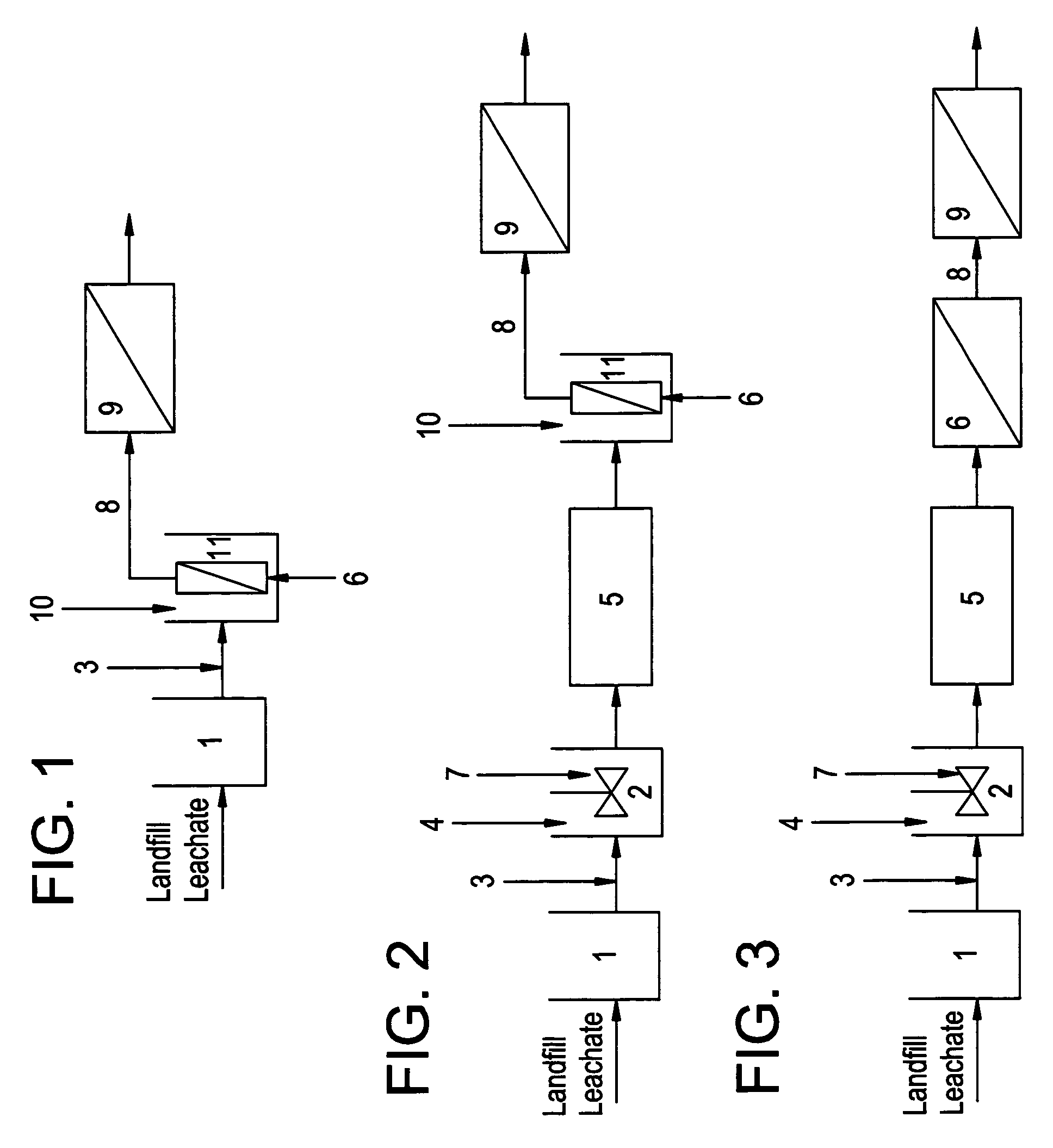
A leachate is any liquid that, in the course of passing through matter, extracts soluble or suspended solids, or any other component of the material through which it has passed. Leachate is a widely used term in the environmental sciences where it has the specific meaning of a liquid that has dissolved or entrained environmentally harmful substances that may then enter the environment. It is most commonly used in the context of land-filling of putrescible or industrial waste.
Catalytic Gasification Particulate Compositions
ActiveUS20090229182A1Efficient use ofBiofuelsGas modification by gas mixingPtru catalystPetroleum coke
Particulate compositions are described comprising a carbonaceous material, such as petroleum coke and / or coal, treated or otherwise associated with a gasification catalyst, where the catalyst is at least in part derived from a leachate from a biomass char, for gasification in the presence of steam to yield a plurality of gases including methane and at least one or more of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other higher hydrocarbons are formed. Processes are also provided for the preparation of the particulate compositions and converting the particulate composition into a plurality of gaseous products.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Composition and method for forming a sprayable materials cover
InactiveUS20050084334A1Improve performanceImprove adhesionSolid waste disposalLandfill technologiesWater dispersibleSlurry
An alternative cover for landfill may be formed from a slurry mixture of water, cementitious binder, adhesion enhancing admixture and fiber. These constituents may be mixed and applied to cover landfilled wastes, granular material piles or for soil erosion control. The cover will harden to minimize water infiltration, wind blown dust, odor and affinity to birds, flies and other insects. The water may include tap water, landfill leachate and wastewater. The binder may include Portland cement, blended cement, cement kiln dust, class C fly ash, and / or calcium sulphate hemihydrate. The adhesion enhancing admixture includes water-dispersible polymers. The fibers may comprise shredded paper or wood or plastic fibers.
Owner:CJS TECH
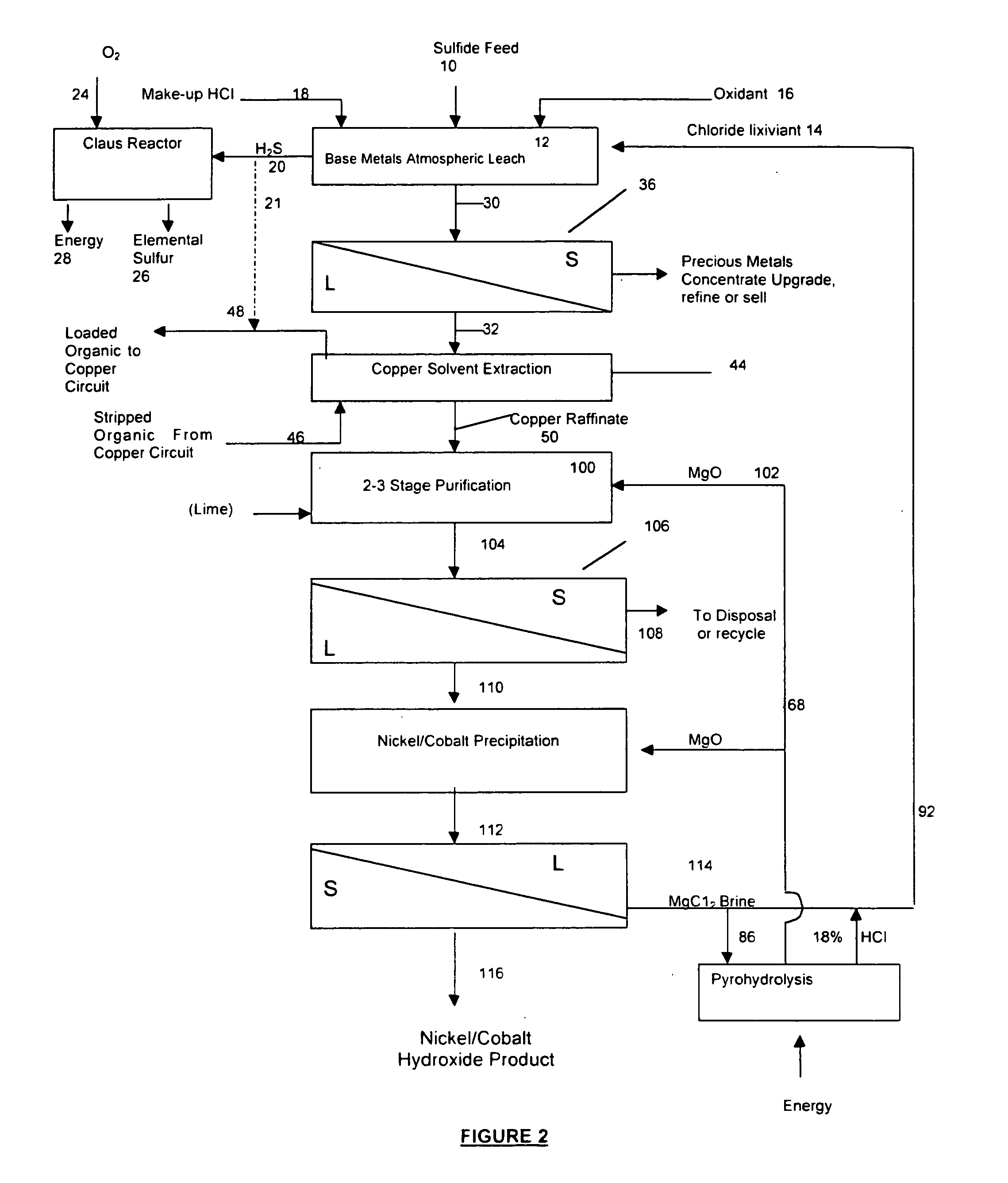
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS20050118081A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfideDissolution
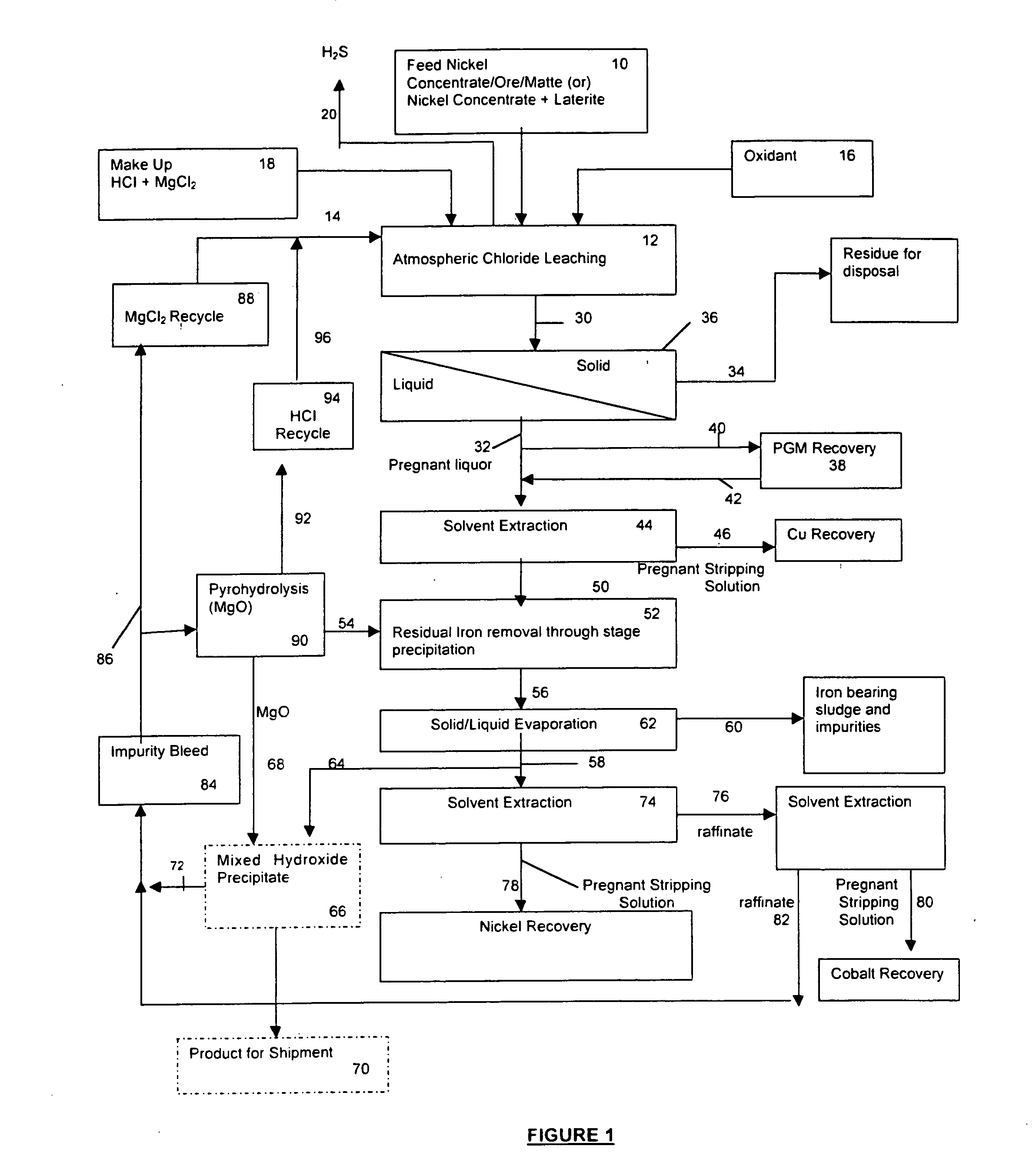
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
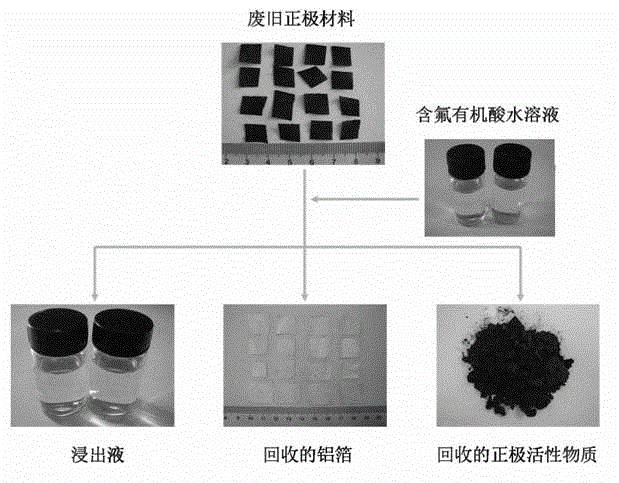
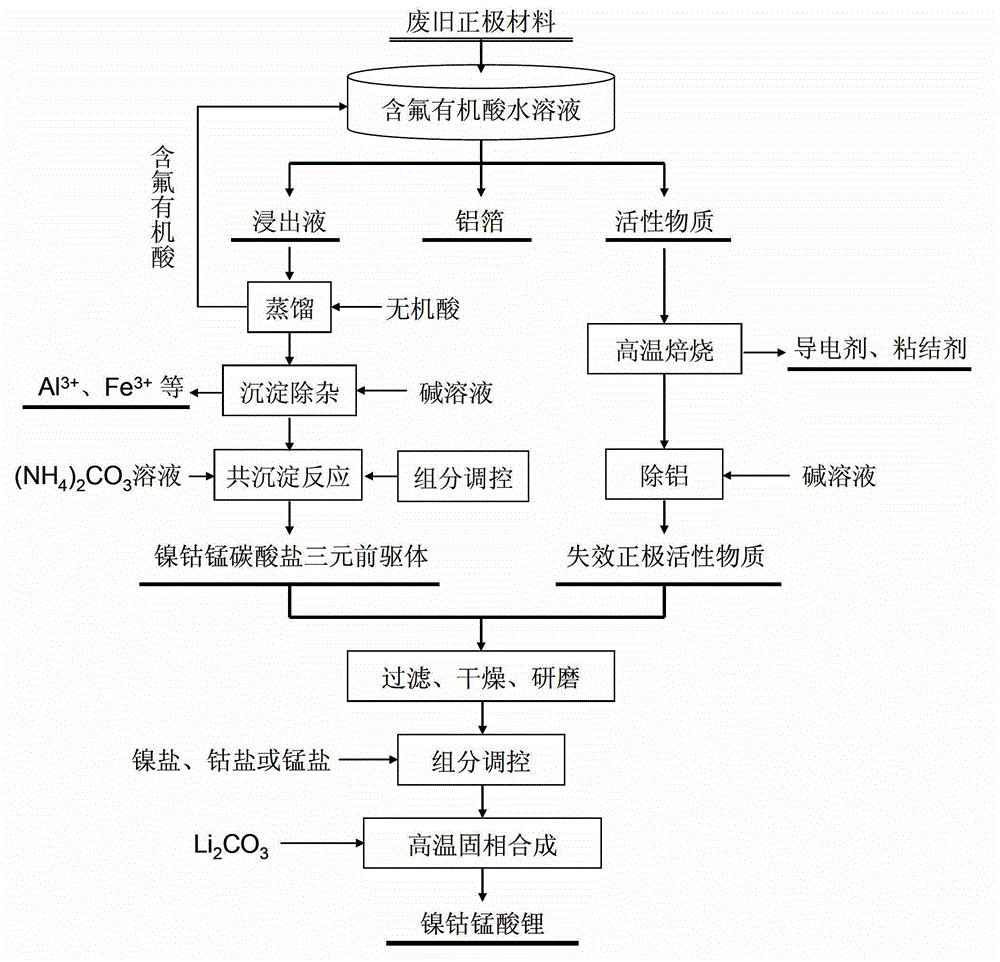
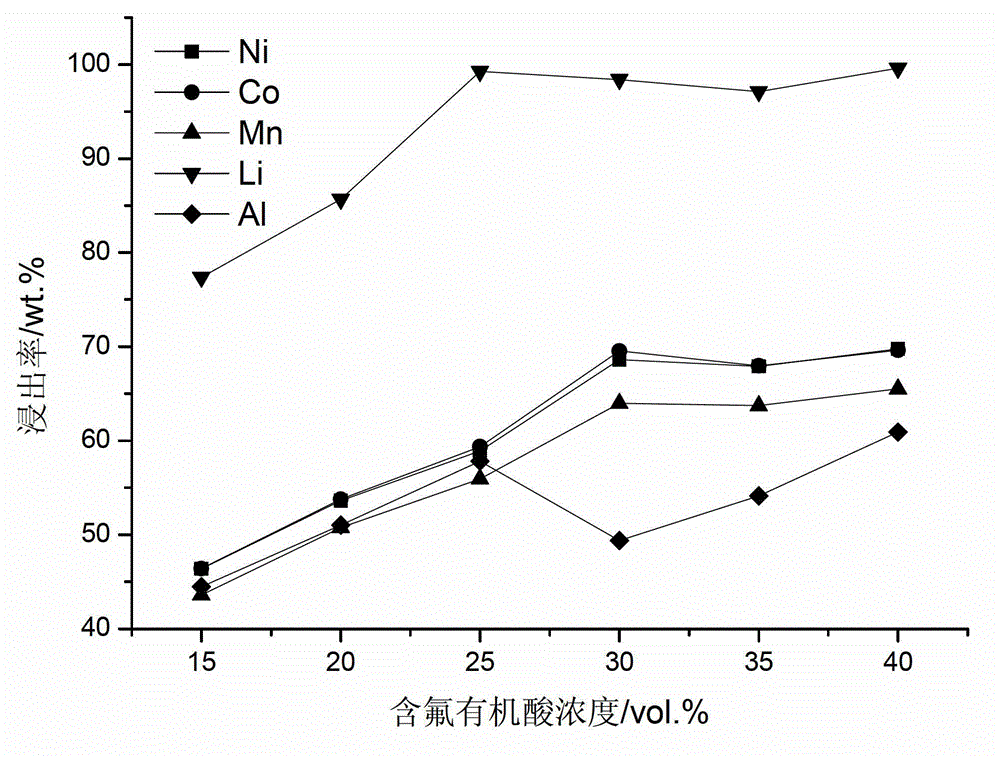
Full-component resource reclamation method for waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN102751549AAvoid secondary pollutionImprove separation efficiencyWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingRecovery methodDistillation
The invention provides a full-component resource reclamation method for waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the following steps: 1) separating active substances and aluminum foils in waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries by using an aqueous solution of fluorine-containing organic acid and carrying out liquid-solid-solid separation so as to obtain leachate, the lithium-containing active substances and the aluminum foils; 2) respectively carrying out high temperature roasting and impurity removal with alkali liquor on the lithium-containing active substances; 3) respectively carrying out recovery of the fluorine-containing organic acid through addition of acid and distillation, deposition of impurity ions through addition of alkali and ammonium carbonate coprecipitation on the leachate so as to prepare nickel-cobalt-manganese carbonate ternary precursor; and 4) carrying out component regulation on a mixture of the treated active substances and the nickel-cobalt-manganese carbonate ternary precursor, adding lithium carbonate in a certain proportion and carrying out high temperature solid phase sintering so as to prepare a lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide ternary positive electrode material. The method provided in the invention has the following advantages: the application scope of the method is wide; separation efficiency of the lithium-containing active substances and the aluminum foils is high; short-flow direct re-preparation of positive electrode materials in waste lithium ion batteries is realized; and the method is applicable to large-scale resource reclamation of waste lithium ion batteries.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrasonic combined waste water treatment process and system of refuse leachate
InactiveCN102139990ASimple processCompact structureWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsMultistage water/sewage treatmentEmission standardCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to an ultrasonic combined waste water treatment process of refuse leachate, relating to the technical field of waste water treatment and recycling of resources and environmental protection. The ultrasonic combined waste water treatment process of the refuse leachate comprises the following steps of: enabling waste water to enter a regulating pond; treating colloids, amphoteric substances and heavy metals in a coagulation sedimentation pond; eliminating ammonia nitrogen in an ultrasonic catalytic oxidation pond; sequentially sedimentating through biological treatment in an ABR (Acrylate Butadience Rubber) baffle plate anaerobic pond, a hydrolytic pond, a facultative pond and an aerobic pond; filtering in a CMBR (Chatter Membrane Bioreactor); eliminating waste gases and stench in a carbon filter pond; disinfecting in a contact disinfection pond; and filtering in an RO (Reverse Osmosis) membrane reverse osmosis system so as to obtain water meeting the requirements for emission standards. The invention also provides a treatment system for the ultrasonic combined waste water treatment process. The ultrasonic combined waste water treatment process and system can obtain the outflow water with stable quality by treating the refuse leachate; the treatment system has the advantages of small size and occupying area, high efficiency, low energy consumption and easy realization for mechanical-electrical integration control and management; and in addition, the invention is beneficial to the protection of the original landscapes of a construction party by adopting a non-buried type structure and also reduces the influence of the operation of the treatment system on an office area.
Owner:深圳市万山红环保实业有限公司
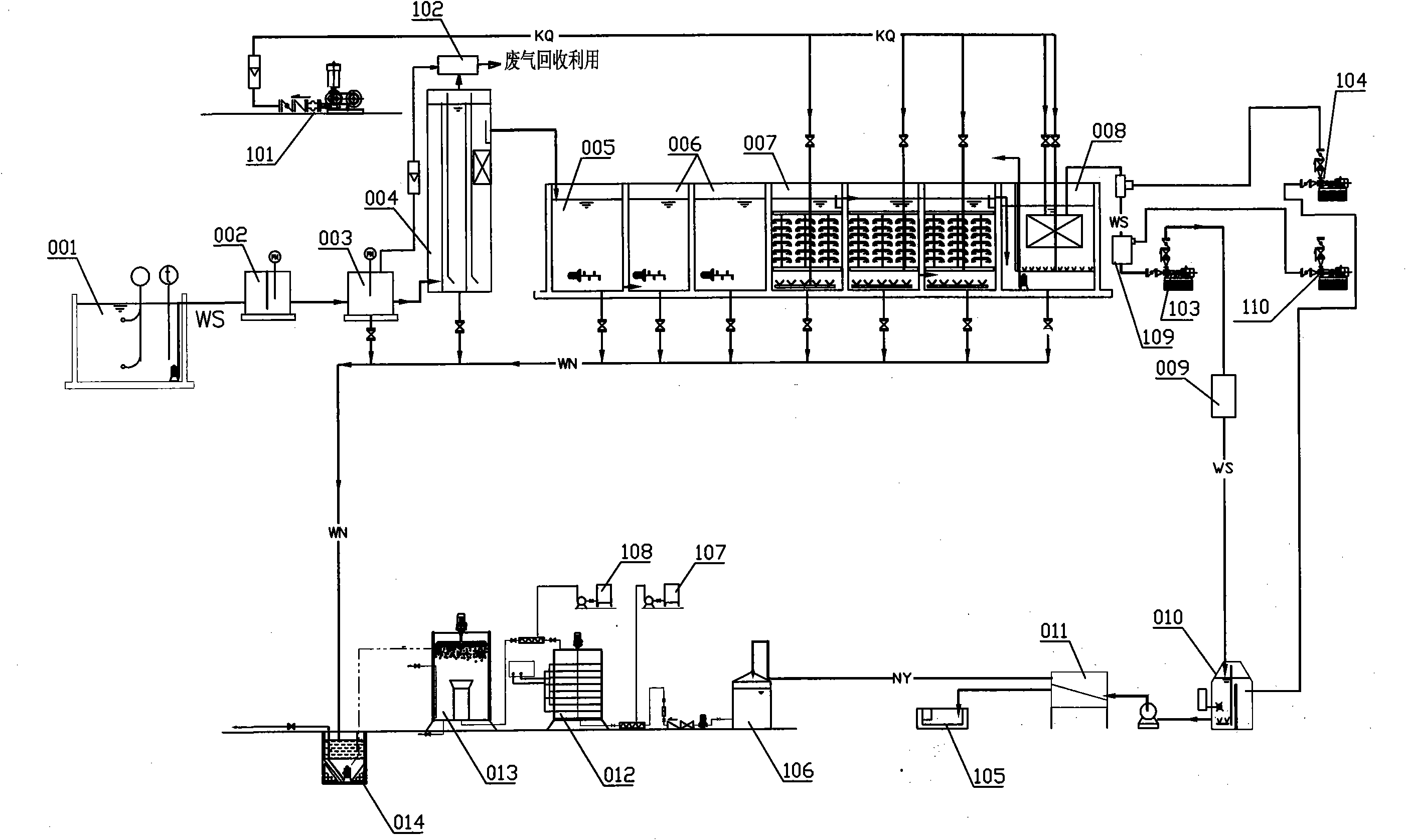
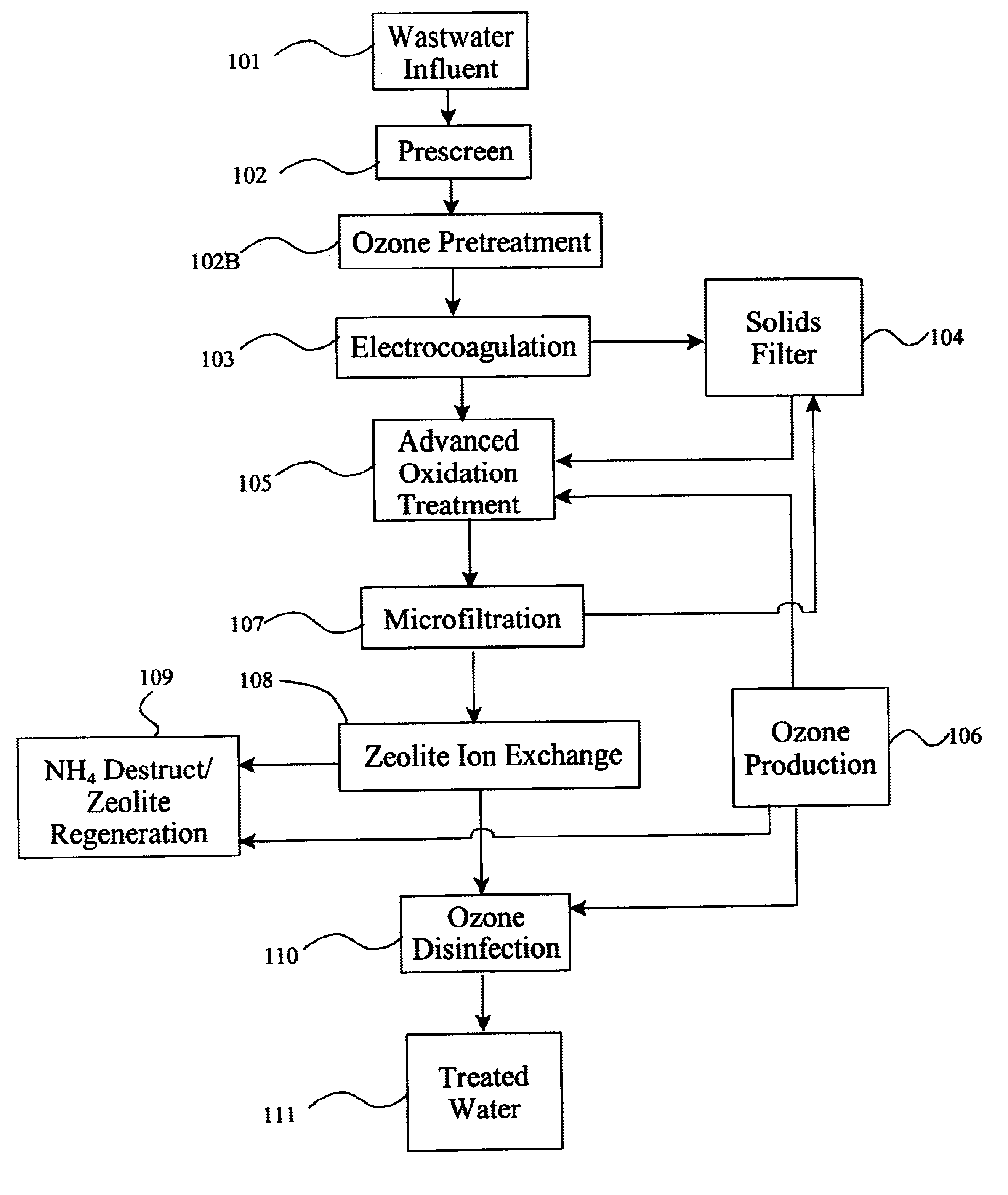
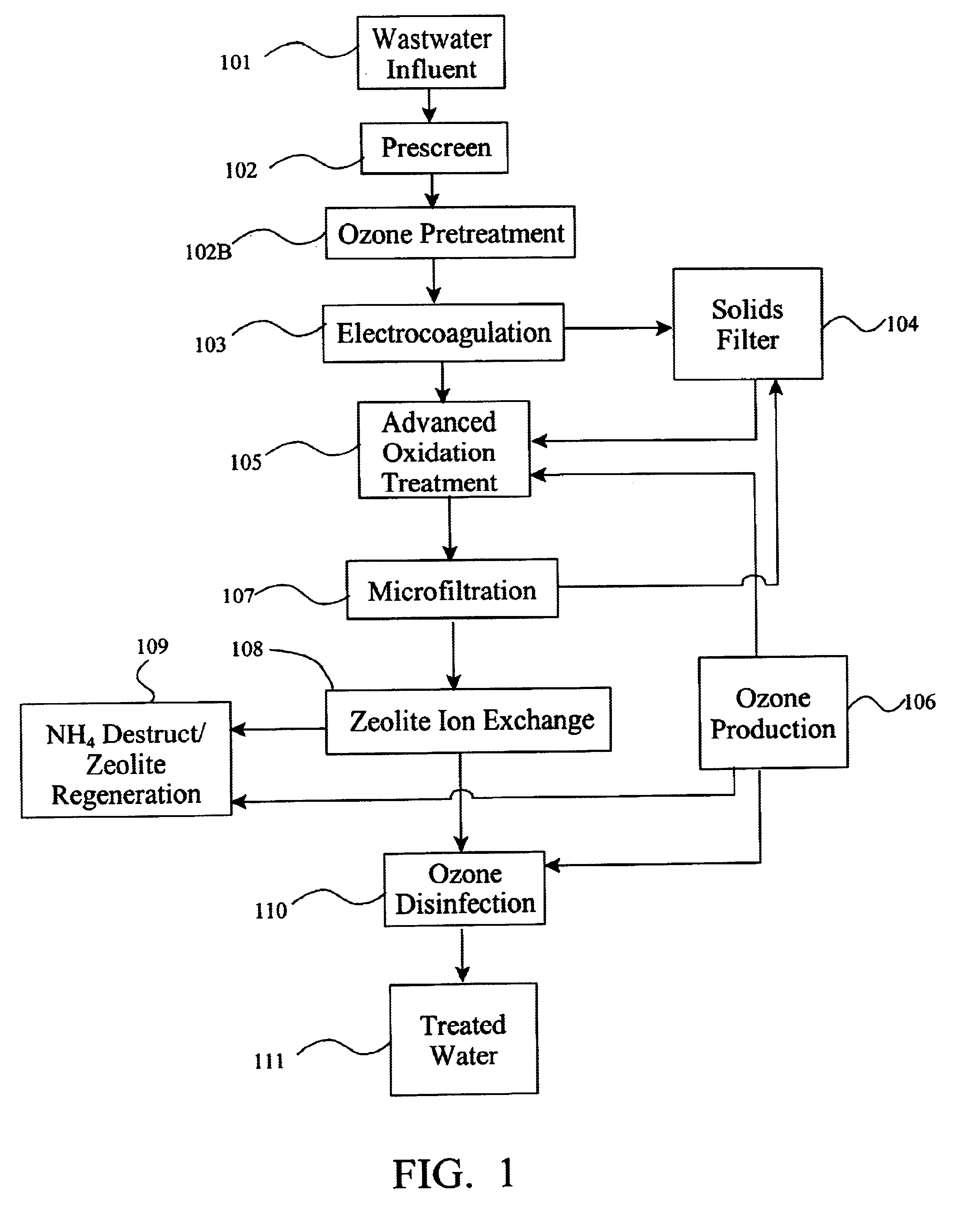
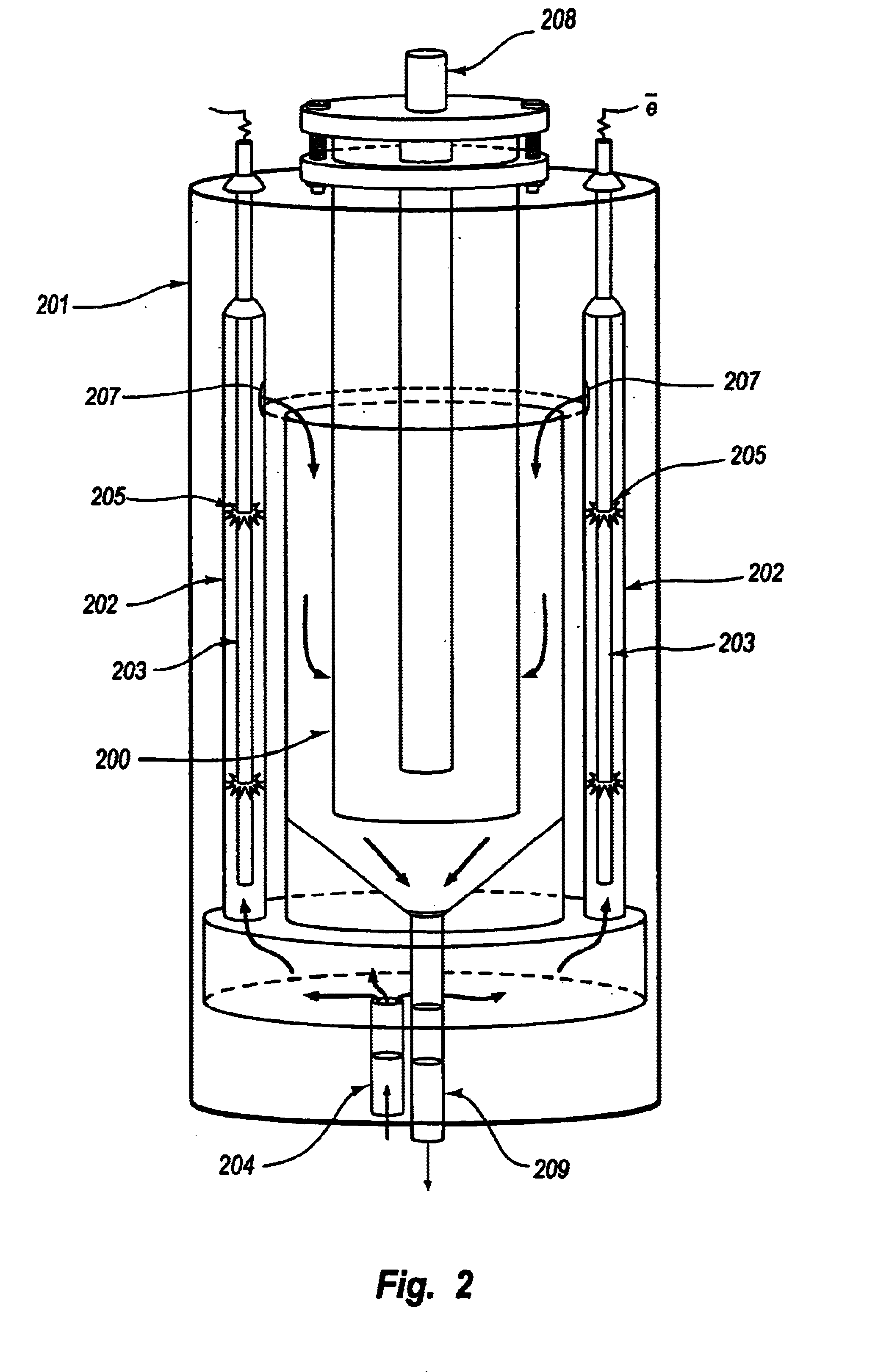
Leachate and wastewater remediation system
InactiveUS6960301B2Effective amount of reactionMany difficultyLiquid separation by electricityFlow mixersAdvanced oxidation processFiltration
A compact portable modular wastewater treatment system which integrates several processing technologies to provide a substantially purified water source. A wastewater stream is sent through an initial filtration step. The filtered wastewater is then subjected to electrocoagulation and then further filtered. The resulting stream containing substantially only organics is then treated in an advanced oxidation process which can include passing an electrical current through the water during the oxidation process. The partially treated water is then passed through ion-exchange columns to polish ammonium and other contaminants. The ion-exchange columns are cycled through regeneration cycles to provide continuous ion-exchange medium. The ammonium rich brine solution used in regeneration is subjected to an ammonium destruct process and then reused in regenerating ion-exchange columns. The water can then be sent through a final disinfection oxidation process to destroy or inactivate pathogens and / or remove any remaining colorants or odor to provide a water source suitable for almost any use.
Owner:NEW EARTH SYST
Method of processing lignocellulosic feedstock for enhanced xylose and ethanol production
ActiveUS20070148751A1Improve accessibilityHigh yieldBiofuelsFermentationAqueous solutionHemicellulose
The present invention provides a method of producing xylose from lignocellulosic feedstock. The method comprises disrupting lignocellulosic feedstock; leaching the lignocellulosic feedstock by contacting the feedstock with at least one aqueous solution for a period greater than about 2 minutes to produce a leached feedstock and a leachate; removing the leachate from the leached feedstock; acidifying the leached feedstock to a pH between about 0.5 and about 3 to produce an acidified feedstock, and; reacting the acidified feedstock under conditions which disrupt fiber structure and hydrolyze a portion of hemicellulose and cellulose of the acidified feedstock, to produce a composition comprising xylose and a pretreated feedstock. The xylose may be purified from the pretreated feedstock or it may be converted to ethanol with the pretreated feedstock.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Method of improving performance of ultrafiltration or microfiltration membrane process in landfill leachate treatment
A method of processing landfill leachate by use of a membrane separation process is disclosed. Specifically, the following steps are taken to process landfill leachate: collecting landfill leachate in a receptacle suitable to hold said landfill leachate; treating said landfill leachate with one or more water soluble polymers, wherein said water soluble polymers are selected from the group consisting of: amphoteric polymers; cationic polymers; zwitterionic polymers; and a combination thereof; optionally mixing said water soluble polymers with said landfill leachate; passing said treated landfill leachate through a membrane, wherein said membrane is an ultrafiltration membrane or a microfiltration membrane; and optionally back-flushing said membrane to remove solids from the membrane surface.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Method for regenerating positive active material from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries
ActiveCN106910889ARealize combination generationQuality assuranceCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingFiltrationCopper foil
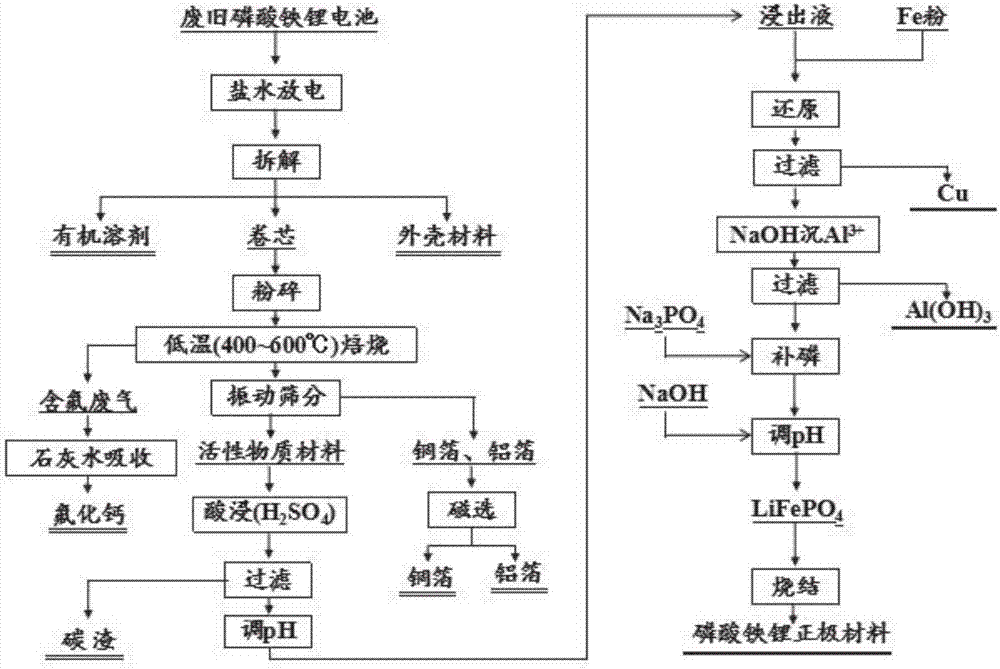
The invention discloses a method for regenerating a positive active material from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) waste lithium iron phosphate batteries are discharged in saline water, and organic solvents, roll cores and casing materials are disassembled; 2) the roll cores are subjected to crushing, calcination and other steps, and active materials, copper foil and aluminum foil are separated through vibrating screening. Fluorine-containing waste gas is absorbed with lime water, the copper foil and the aluminum foil are separated with a magnetic separation method, the active materials are leached out with sulfuric acid, and a leachate and carbon residues are obtained through separation; 3) Cu<2+> in the leachate is reduced to elementary copper by adding iron powder, meanwhile, Fe<3+> is reduced to Fe<2+>, copper and excessive iron residues are filtered out, aluminum is removed through precipitation with an alkaline liquid, the filtrate is supplemented with a phosphorus source after filtration, the pH value is adjusted by adding the alkaline liquid, coarse lithium iron phosphate precipitates are produced, and finally, battery-grade lithium iron phosphate is obtained through sintering. Comprehensive utilization of the waste lithium iron phosphate batteries and regeneration of the active materials are realized with a simple, practical, economical and feasible method, no secondary pollution is produced, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
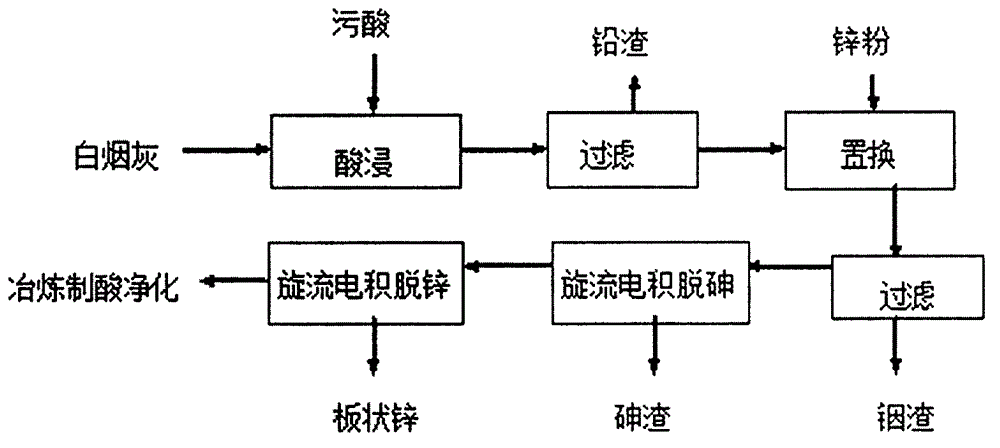
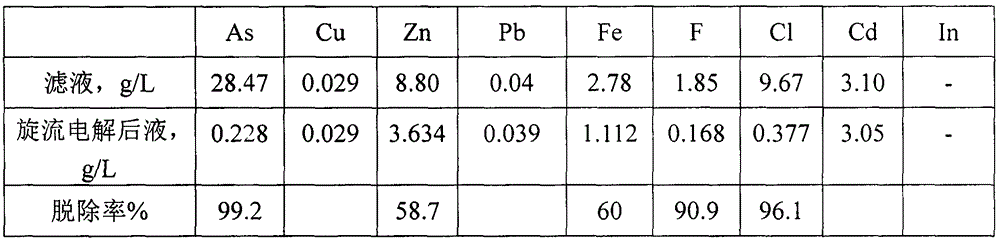
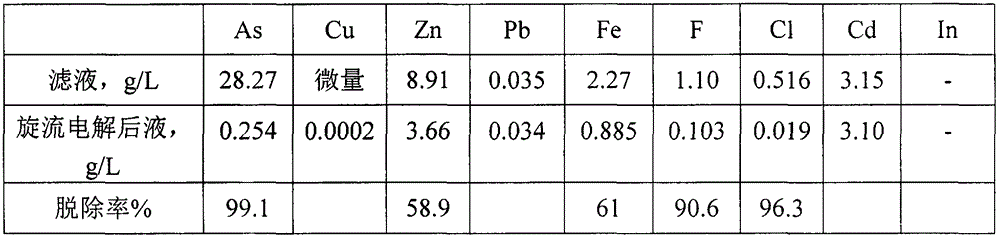
Method of recycling valuable metals from arsenic-containing soot
The invention relates to a method of recycling valuable metals from arsenic-containing soot. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing acidic wastewater with white soot, controlling the pH value to 2.5-3.0, performing acid leaching at a temperature of 70-80 DEG C, and filtering to obtain leachate and lead slag; (2) replacing indium for the leachate by using zinc powder, and filtering to obtain indium slag; (3) performing rotational-flow electrodeposition arsenic removal and zinc removal on filtrate in sequence to obtain arsenic slag and zinc slag. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for purifying the acidic wastewater to reach a condition for recycling the acidic wastewater to a smelting acid manufacturing and purifying section, so that the treated acidic wastewater can be directly returned to the acid manufacturing and purifying section, and therefore, the gypsum slag is completely removed to truly achieve the purpose of zero emission. Meanwhile, the method disclosed by the invention can also be used for achieving the treatment of white soot and recycling the valuable metals, so that environmental protection and resource comprehensive utilization are achieved.
Owner:五矿铜业(湖南)有限公司 +3
Method of processing lignocellulosic feedstock for enhanced xylose and ethanol production
The present invention provides a method of producing xylose from lignocellulosic feedstock. The method comprises disrupting lignocellulosic feedstock; leaching the lignocellulosic feedstock by contacting the feedstock with at least one aqueous solution for a period greater than about 2 minutes to produce a leached feedstock and a leachate; removing the leachate from the leached feedstock; acidifying the leached feedstock to a pH between about 0.5 and about 3 to produce an acidified feedstock, and; reacting the acidified feedstock under conditions which disrupt fiber structure and hydrolyze a portion of hemicellulose and cellulose of the acidified feedstock, to produce a composition comprising xylose and a pretreated feedstock. The xylose may be purified from the pretreated feedstock or it may be converted to ethanol with the pretreated feedstock.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
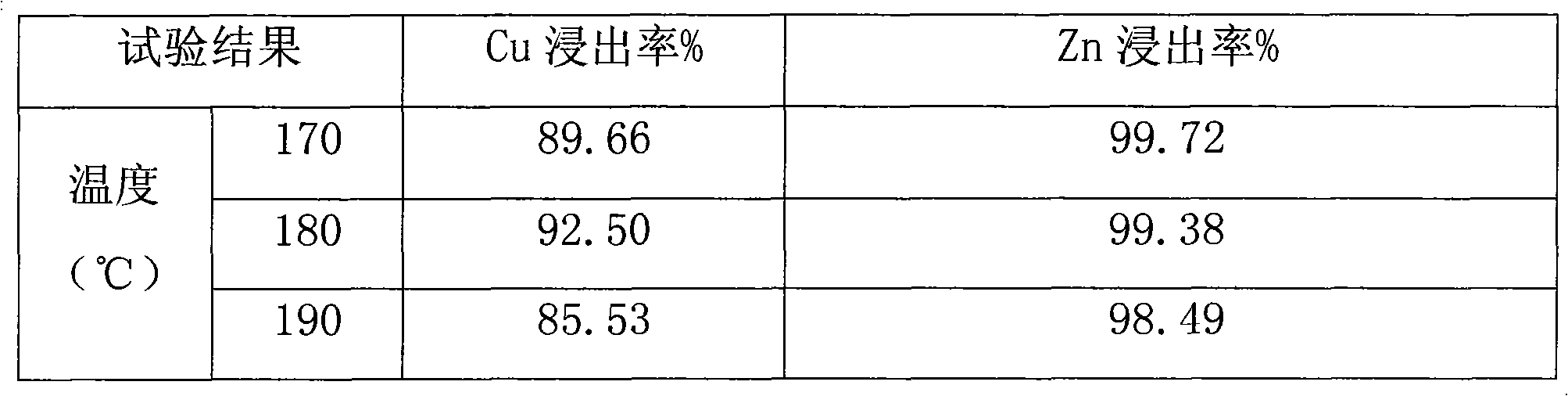
Method for recovering waste SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration catalyst
ActiveCN104805298AHigh activityDispersed particle separationChemical recyclingEconomic benefitsTitanium
The invention relates to a method for recovering a waste SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration catalyst. According to the method, the waste SCR denitration catalyst is subjected to pretreatment firstly so as to remove impurities and catalysis ingredients, such as activated vanadium, tungsten and molybdenum, and then, the waste SCR denitration catalyst is subjected to leaching, so as to obtain titanium-rich leached residue and a tungsten-molybdenum-vanadium-containing leachate; valuable elements in the leachate can be subjected to resource treatment through two methods: the first method comprises the steps of synchronously purifying the valuable elements in the leachate, then, proportionally adjusting the content of each substance so as to prepare a mixture of the catalysis ingredients, and further preparing a new catalyst so as to realize remanufacturing; the second method comprises the steps of separating and purifying each valuable element in the leachate, thereby preparing different products. The method can be used for recovering the valuable elements in the waste SCR denitration catalyst, and the environmental and economic benefits are remarkable.
Owner:BOTREE CYCLING SCI &TECH CO LTD
Methods of recovering hydrocarbons from hydrocarbonaceous material with reduced non-carbonaceous leachate and co2 and associated systems
ActiveUS20080190816A1Avoid insufficient heatingInhibition formationThermal non-catalytic crackingUnderground chambersLeachateMaterials science
A method of recovering hydrocarbons from hydrocarbonaceous materials can include forming a stationary permeability control infrastructure. This constructed infrastructure defines a substantially encapsulated volume. A comminuted hydrocarbonaceous material can be introduced into the control infrastructure to form a permeable body of hydrocarbonaceous material. The permeable body can be heated sufficient to remove hydrocarbons therefrom within a temperature range which is sufficient to substantially avoid formation of carbon dioxide or non-hydrocarbon leachates. During heating the hydrocarbonaceous material is substantially stationary as the constructed infrastructure is a fixed structure. Removed hydrocarbons can be collected for further processing, use in the process, and / or use as recovered.
Owner:RED LEAF RESOURCES
Formula of toadstool culturing materials and toadstool natural culturing method
InactiveCN101628834AMaintain natural ecological characteristicsIncrease productionCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersNutrition supplementationHypha
The invention discloses two toadstool natural culturing methods belonging to one general invention conception. The first method comprises the following steps of mixing toadstool cultivated species with toadstool culturing materials and soil evenly, forming the mixture of the toadstool cultivated species, culturing materials and soil, sowing the mixture containing the toadstool cultivated species in a land and covering with soil with the thickness of 0.5cm-2.5cm; the toadstool culturing materials comprise herbaceous plant in grass family, crop straws, bran and KH2PO4, MgSO4, urea and other nutrient substances. The second method is as follows: hole sowing the toadstool cultivated species in the land directly and covering with soil with the thickness of 0.5cm-2.5cm. For the above two methods, at least one time of nutrition supplementation is carried out when mycelial is mature, and the nutrient supplementary solution is prepared by grass ash leachate, KH2PO4, MgSO4 and urea.
Owner:CHENGDU JINYI REAL ESTATE
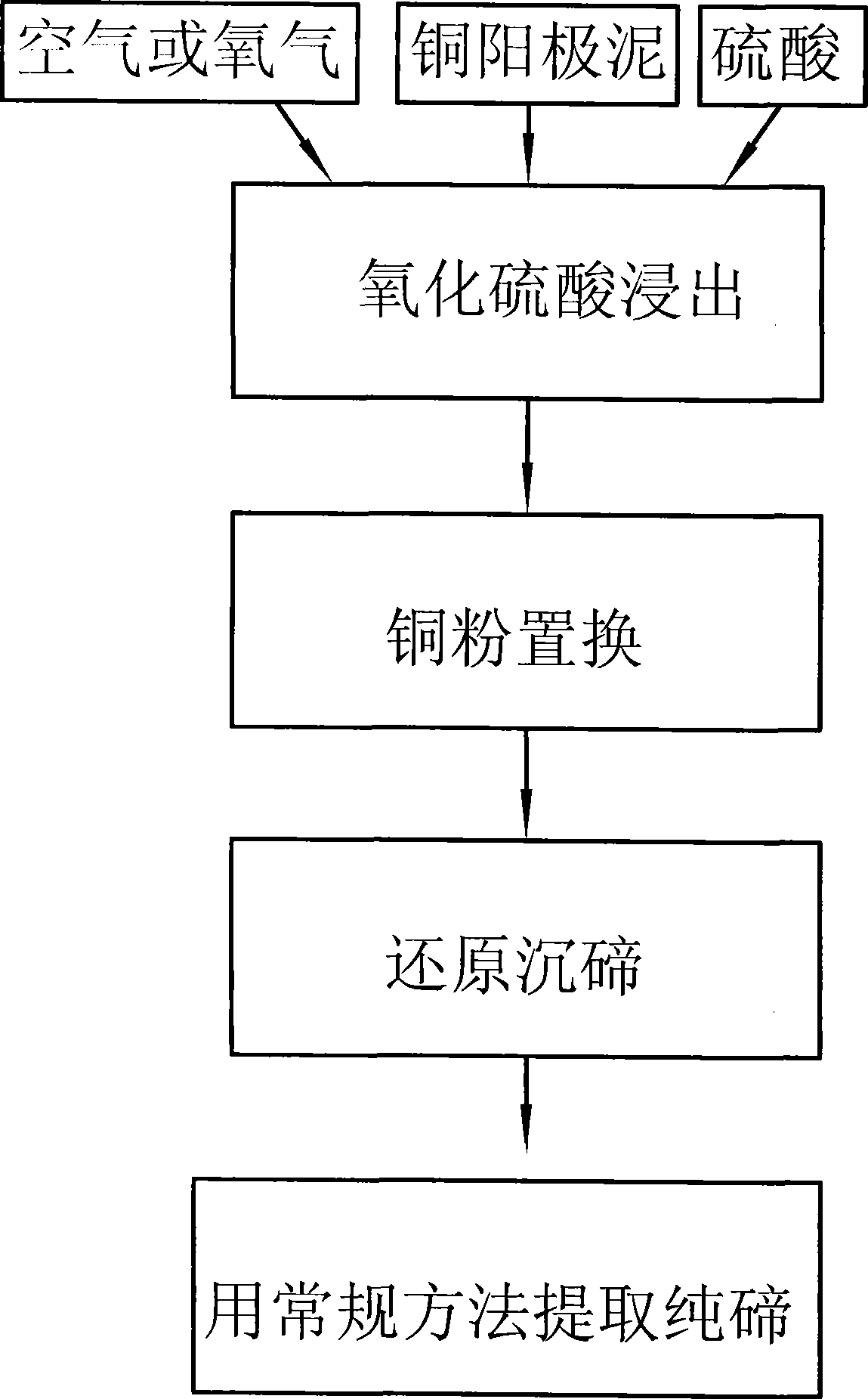
Process for extracting tellurium from copper anode mud
ActiveCN101434385AReduce consumptionEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumTe elementOxygen
The invention discloses a technology for extracting tellurium from copper anode slime, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) the copper anode slime is put into a sulfuric acid solution, oxygen is introduced into the sulfuric acid solution for oxidation sulfuric acid leaching; solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain leachate containing copper and tellurium; and the leaching process being finished in a closed high-pressure device; (2) copper powder is added into the leachate to remove silver or selenium in the leachate by substitution, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out; (3) sulfur dioxide is introduced into the leachate obtained from the step (2) to precipitate the tellurium by reduction, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain crude tellurium; and (4) the crude tellurium is processed according to a conventional method to extract pure tellurium. The technology adopts one-section oxidation acid leaching to leach the copper and tellurium out, copper powder to remove the impurities of silver, selenium and the like by substitution, and sulfur dioxide to precipitate the tellurium by reduction (obtaining tellurium dioxide), and the tellurium dioxide precipitation is alkali-dissolved and then electrolyzed to obtain the tellurium, therefore, the flow is simple, the consumption of the copper powder is remarkably reduced, and the simplification of the technology is beneficial to improve the recovery ratio of the tellurium, which can achieve more than 90 percent.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
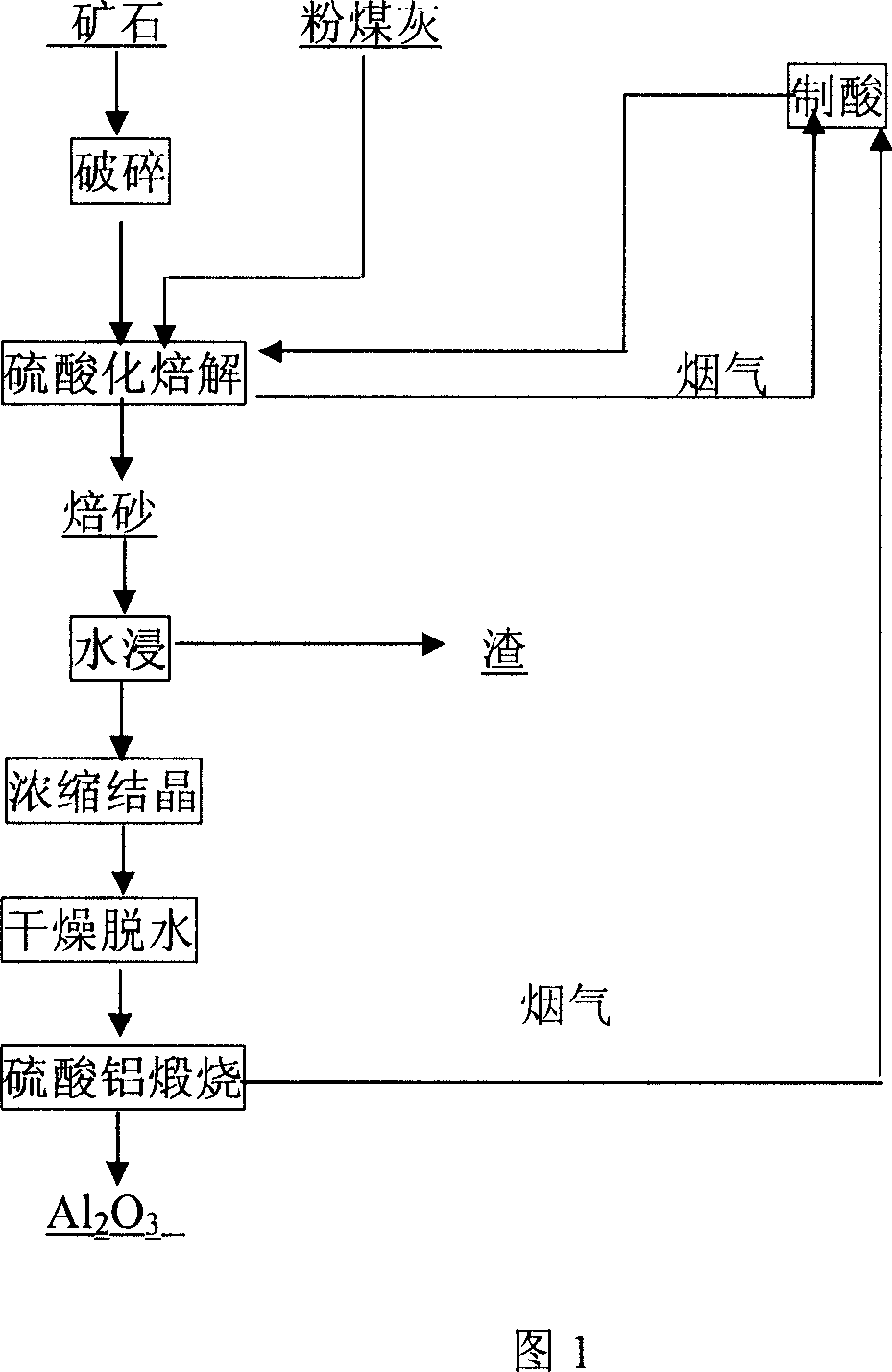
Method of acid extracting aluminium from high-silicon alumina-containing raw mineral materials
The invention relates the method of extracting aluminium from high-silicon siliceous mineral. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the aluminous ore and sulfuric acid, baking, leaching with water, filtering leachate, getting aluminium sulphate solvent, thickening filter liquor, separating out aluminium sulphate, drying, dewatering, getting anhydrous aluminium sulphate; calcining aluminium sulphate, and getting Al2O3. The invention can extracte aluminium from high-silicon siliceous mineral, coal gangue, coal ash, China clay, andalusite, feldspath, ganister, nepheline and vermiculite without baking. The method has the advantages of simple technology, little corrosion, easy operation and high recovery ratio.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Production method for manganese sulfate by using biological cellulose and low-grade manganese ores
The invention discloses a production method for manganese sulfate by using low-grade manganese ores. According to the method, manganese sulfate with high purity can be produced by using waste low-grade manganese ores with manganese content of 10% to 20%, manganese tailing or manganese-containing solid waste residue. The method comprises the steps of preparation of raw materials, a slaking reaction, a leaching reaction, neutralization and purification of leachate, etc. According to the invention, production of manganese sulfate is not restricted by the grade of manganese ores, and low-grade manganese oxide ores with a grade greater than 10%, manganese tailing or manganese-containing solid waste residue can be fully utilized; produced manganese sulfate has high yield and high purity and is a very important industrial fundamental product; almost no external heat supply is needed, low energy consumption is achieved, production cost is low, it does not need to turn over and mix materials in the process of the reactions, the reactions are smooth, no toxic gas is generated, and no environmental pollution is produced; discharge of three wastes (waste gas, waste water and industrial residue) reaches national discharge standards for environmental protection, and there is no dust pollution in a workshop.
Owner:陈昆先 +1
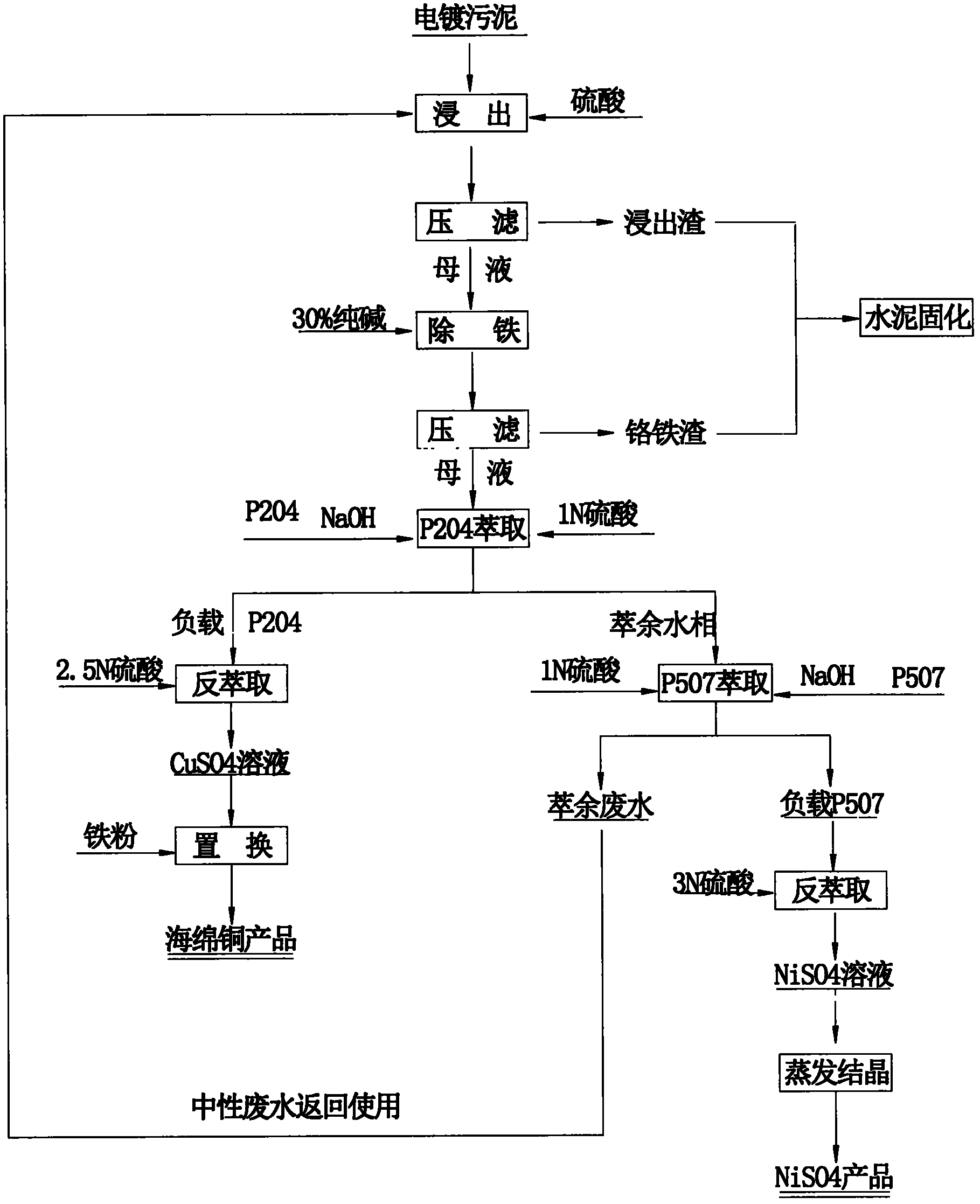
Method for recovering valuable metal from electroplating sludge
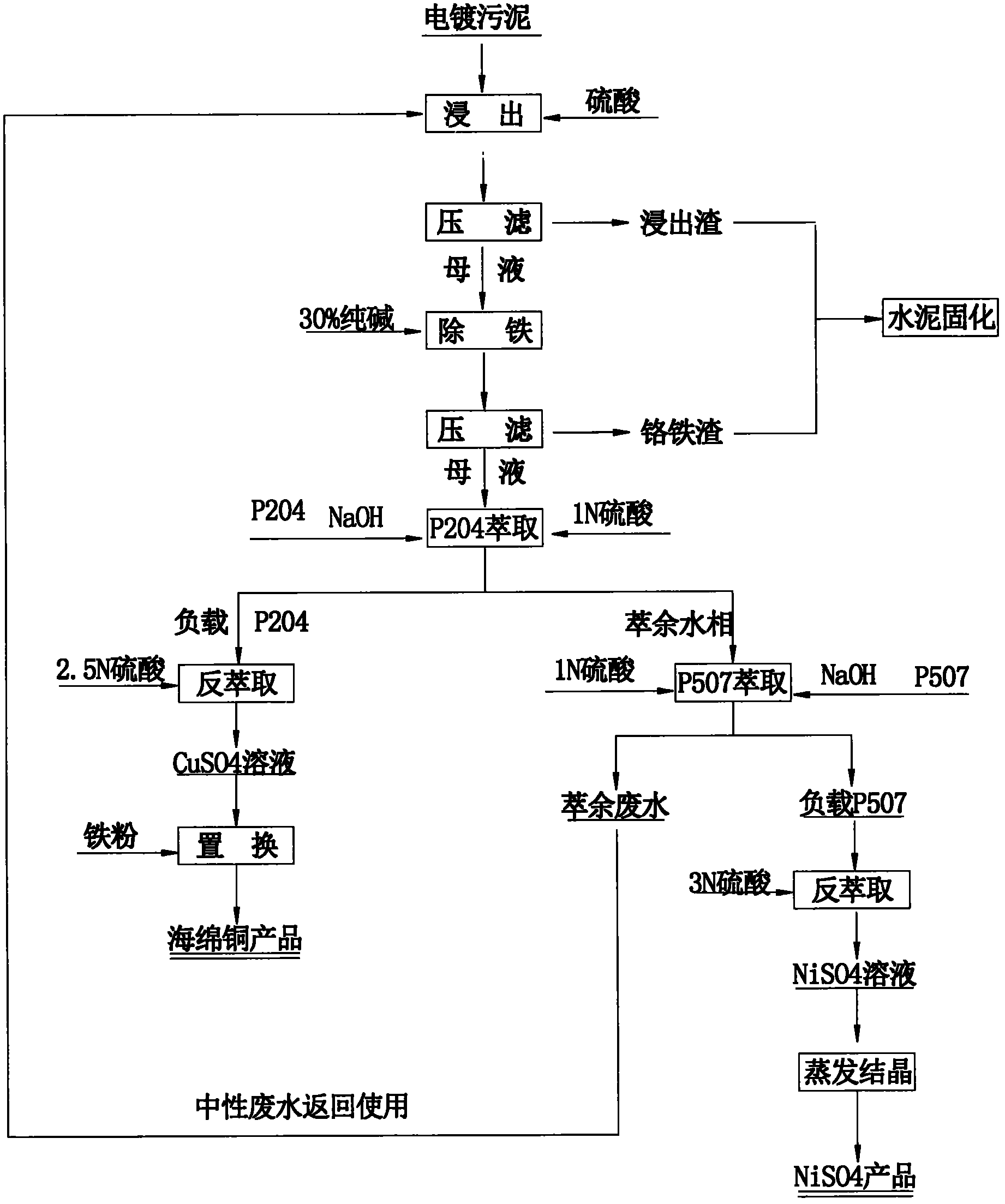
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from electroplating sludge. Electroplating sludge is used as a raw material; advanced theories and scientific means of leaching principle, redox principle, extraction principle, iron filing displacement principle and evaporation crystallization principle in a wet method metallurgy are integrally utilized; and a technology of ''acid decomposition of electroplating sludge-leachate purification to remove ferrochrome-P204 impurity removal-P507 enrichment-condensation crystallization'' is employed. Meanwhile, calcium and magnesium are removed by an extraction method, which substitutes a traditional sodium fluoride method for removing calcium and magnesium. A recovery rate of nickel reaches 95%, and copper content of recovered copper sponge is larger than 80%. Besides, acid dissolved slag and purifying slag can be solidified to reach requirements of environmental protection and will not cause secondary pollution; waste water can be recycled and has a strong technological versatility. The method is suitable for treating various routine electroplating sludge, has easily controllable technical conditions and low operating cost and is easy for realizing large scale production; therefore, the method is a practical novel technology for treating electroplating sludge in a way of quantitative reduction, harmlessness and resource.
Owner:朱小红
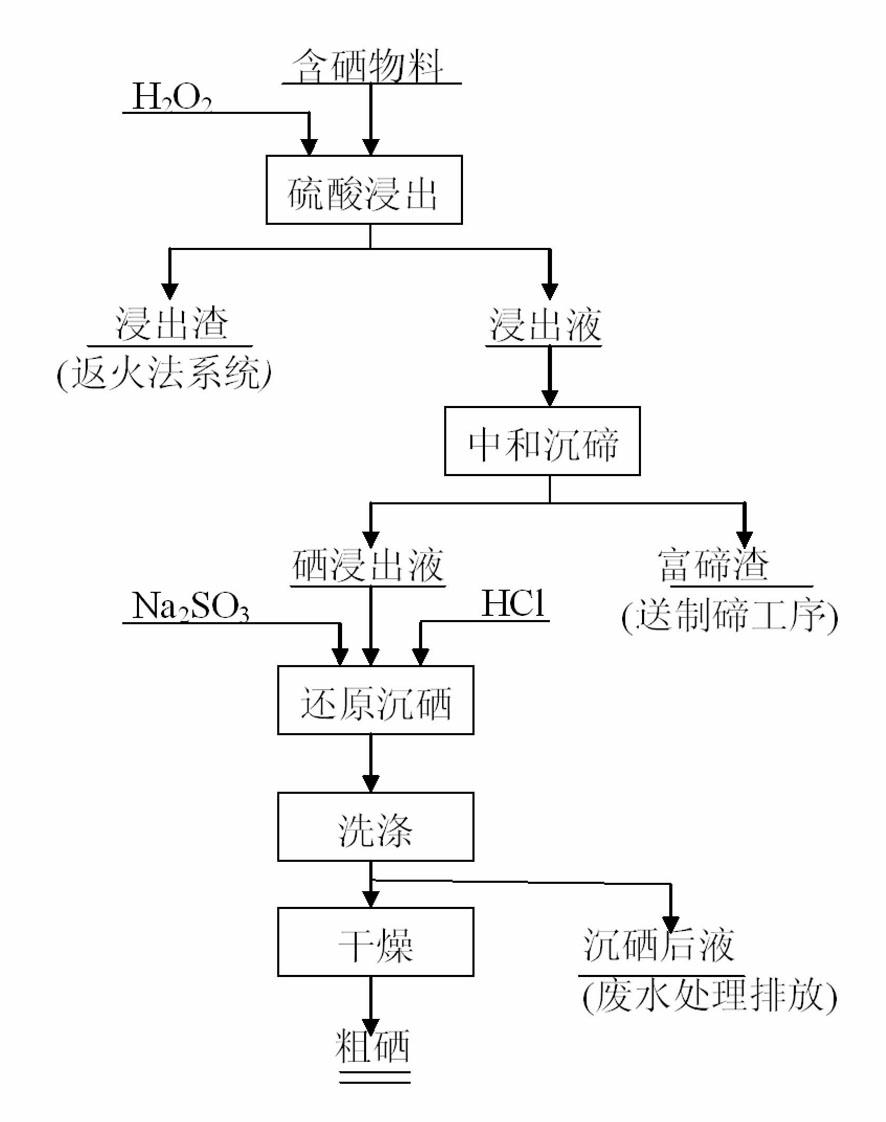
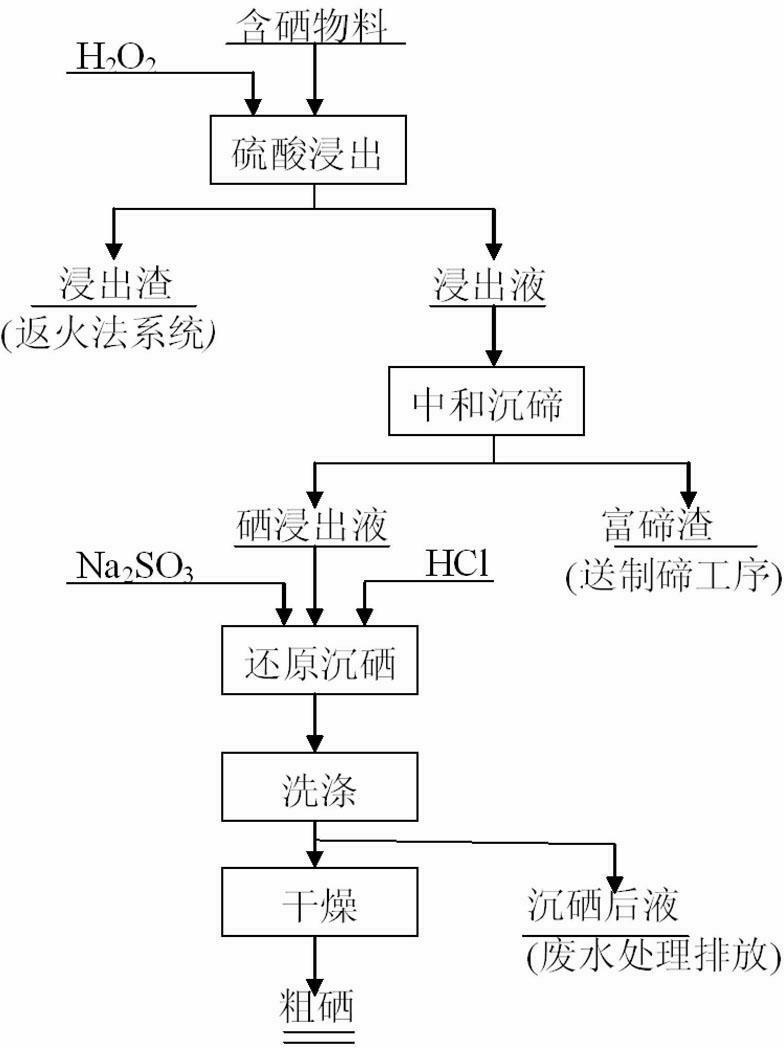
Process for separating and recovering selenium from selenium-containing material
The invention relates to a process for separating and recovering selenium from a selenium-containing material. The process comprises the following steps: dissolving the selenium-containing material into a sulfuric acid solution, adding 10% H2O2 into the mixture, filtering and separating to get leachate and residue containing silver, lead, copper and other valuable metals; separating the selenium from tellurium in the oxidation leachate by using sodium hydroxide; and acidifying the selenium leachate with hydrochloric acid, adding sodium sulfite to reduce the settled selenium, washing and drying to get crude selenium with the grade of not lower than 90%. The crude selenium which is separated by the process is higher in purity and can be directly refined, so that the process flow of recovering selenium is shortened, the recovery rate of selenium is improved, the production cost is reduced and the energy is saved; and the sodium sulfite is used for substituting sulfur dioxide to perform reduction, the control is easy and the environmental pollution is further reduced. The process has very important significance in both aspects of recovering resources and protecting an environment.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Silver anode mud treatment process
InactiveCN102041393AReduce lossLow costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDissolution
The invention relates to a silver anode mud treatment process. The process is characterized by leaching silver anode mud with nitric acid, wherein silver, palladium and base metals enter into solution while gold and platinum remain in residue; after roasting the leaching residue and removing impurities, using a cast gold anode plate to electrolyze the leaching residue to obtain gold No. 1 and using electrolyte for recycling platinum; regulating the pH value of leachate and adding mixed precipitator A solution to selectively precipitate palladium to obtain palladium precipitate residues; solution after palladium precipitation mainly being AgNO3 solution and returning the AgNO3 solution to undergo silver electrolysis; dissolving the palladium precipitate residues with aqua regia and filtering the dissolved solution to obtain the filter residue which is mainly AgCl, reducing the filter residue with hydrazine hydrate to obtain crude silver powder and returning the crude silver powder to a cast silver anode plate; and concentrating and carrying out ammonium on the solution after dissolution to obtain (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate, dissolving the (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate with ammonia and acidizing the (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate with hydrochloric acid to obtain Pd(NH3)2Cl2 precipitate, then reducing the Pd(NH3)2Cl2 precipitate with hydrazine hydrate and then drying the reduction product to obtain spongy palladium, wherein the produced filtrate is returned to the concentration process. The invention has the advantages of less precious metal loss, low cost, strong practicability, high comprehensive recoverability and obvious economic benefit.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Infiltration method for treating garbage
InactiveCN1872745AEasy to handleEasy to manageTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFlocculationAfter treatment
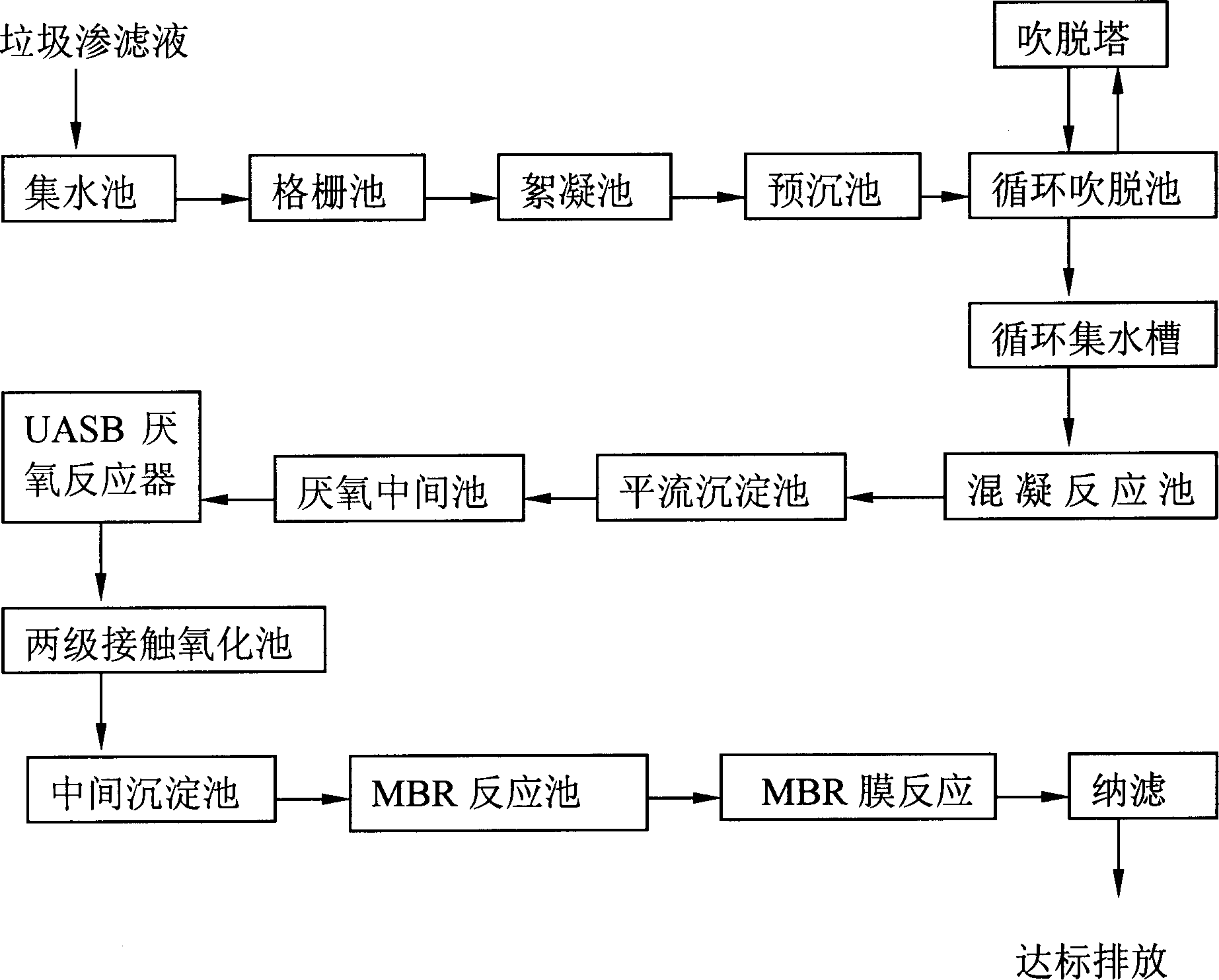
This invention discloses a method for treating the leachate of garbage. The method comprises: (1) adding flocculant to the leachate of garbage under a basic condition, and performing flocculation and preprecipitation; (2) performing partial denitrification in a circulatory aeration tank and an aeration column; (3) performing anaerobic treatment in an upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor; (4) performing aerobic treatment by two-step contact oxidation; (5) treating the leachate in a membrane bioreactor; (6) performing nanofiltration. Water after treatment has a COD value not higher than 10 mg / L, and electrical conductivity not higher than 1000 mus cm, and can satisfy the standard for domestic water.
Owner:深圳市百斯特环保工程有限公司
Garbage leachate treatment technique
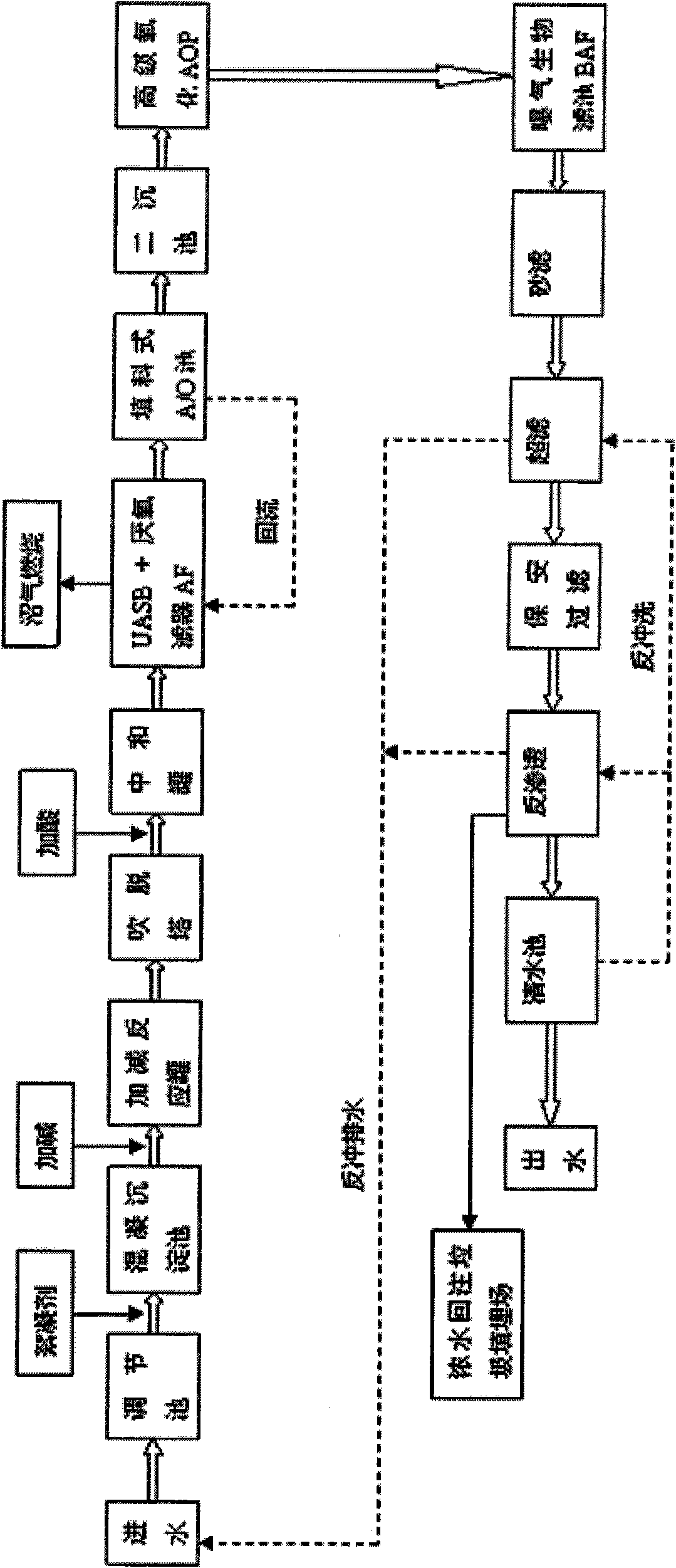
ActiveCN101671095AEfficient separationEfficient degradationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisWater qualitySewage
The invention discloses a garbage leachate treatment technique, comprising: homogenizing the water quality of garbage leachate by an adjusting tank, and then leading the garbage leachate to enter a coagulative precipitation tank; then, alkalifying and deaminizing, and lifting into a UASB+AF tank through pump; after that, removing a great deal of organic matter, and leading the effluent to enter apacked A / O tank together with the sewage processed by the original sewage plant; removing the organic matter and the ammonia nitrogen which are difficult to degrade, and then passing through a secondary sedimentation tank and entering an advanced oxidation system for deep oxidation; leading the effluent to enter a biological aerated filter, processing by a sand filtering system and then entering amembrane processing system; and finally, ensuring the water quality of the effluent to be stable and reach the standard. As the garbage leachate treatment technique adopts the technology of 'biochemistry+ physical chemistry+ membrane separation' to treat the leachate, the effluent can reach the first grade discharge standard (GB16889-1997).
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN
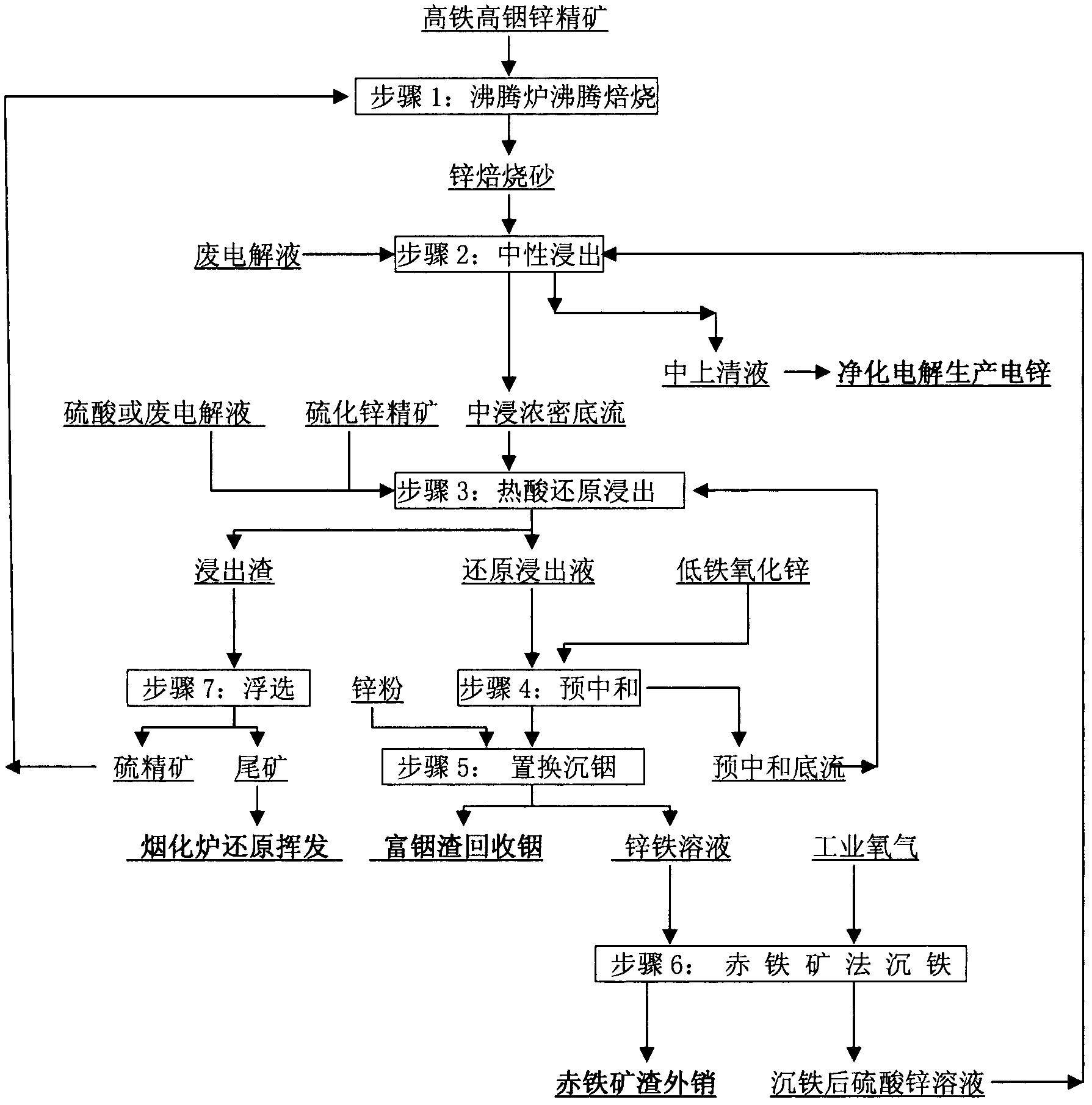
Method for extracting zinc indium and recovering iron from high-iron high indium zinc concentrate
InactiveCN102312083AHigh recovery rateReasonable and orderly separationProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSulfur
A method for extracting zinc indium and recovering iron from high-iron high indium zinc concentrate comprises the following steps: roasting high-iron high indium zinc concentrate which comprises 13-20% of Fe and 0.05-0.25% of In to produce zinc calcine; performing neutral leaching of zinc calcine; performing hot acid reduction and leaching of the neutral leached residues; performing preneutralization of the hot acid reduced leachate by zinc oxide; performing replacement and indium deposition of the preneutralized solution by zinc powder; performing iron deposition of the solution after indium deposition by oxygen-compressed hematite to produce hematite slag with 55-65% of iron; separating sulfur concentrate and flotation tailings from the hot acid reduced leached residues by a flotation method, returning the sulfur concentrate for boiling and roasting treatment, allowing the tailings to enter a fuming furnace for reduction and volatilization treatment.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Apparatus and method for nitrogen removal by combining garbage leachate SBR and anaerobic ammoxidation
ActiveCN102515350AEfficient biological denitrificationLow running costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPeristaltic pumpNitrogen removal
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for nitrogen removal by combining garbage leachate SBR and anaerobic ammoxidation, which belongs to the low carbon nitrogen (CN) ratio high density ammonia nitrogen garbage leachate biological denitrogenation technical field. The apparatus comprises an integrated water tank, a SBR short distance nitrated reactor and an anaerobic ammoxidation reactor; a preposition water tank and a postposition water tank in the integrated water tank are communicated with a peristaltic pump and the SBR short distance nitrated reactor, the postposition water tank is connected with the bottom of the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor through the outlet pipe and the peristaltic pump, an self-circulation pipeline is provided on the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor, and is connected with the SBR preposition water tank through the outlet pipe and the peristaltic pump. The method comprise the following steps starting the SBR short distance nitrated reactor, starting the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor, and an operation is in series of the SBR short distance nitrated reactor and the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor is carried out. The apparatus of the present invention is suitable for organic matter removal and short distance nitrogen removal of the garbage leachate at late period in the garbage landfill, the process is advanced, and the advantages of energy saving and consumption reduction is obvious.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Recovery method of copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel
ActiveCN103184338ASimple processEasy to operatePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodElectrolysis
The invention provides a recovery method of a copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel. The method comprises the steps that: the copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel is crushed into pieces; the pieces are soaked by using a H2SO4+H2O2 system, such that a soaking liquid is obtained; the soaking liquid is filtered, such that a first leachate is obtained; with a first phase ratio of 1, the first leachate is extracted by using an extraction agent; separation is carried out, such that a first extraction liquid and a first raffinate are obtained; the extraction agent is composed of 30% of P2O4 and 70% of kerosene by volume percentage, the extraction and balance time is 5-20min; an HCl solution is adopted as a stripping agent, and the first extraction liquid is striped by using a second phase ratio, such that In and stripping residual liquid are obtained; a reducing agent is added into the first raffinate; when a reduction reaction is finished, crude Se and a second leachate are obtained by filtering; alkali is added into the second leachate, and a pH value is regulated such that the pH value is constantly higher than 14; when a reaction is finished, filtering is carried out, such that a filtering slag comprising a hydroxide of Cu and a water solution comprising Ga are obtained; the alkali is NaOH, the pH value adjustment process is to add the NaOH in the reaction process after pH=14 so that the pH is always kept more than 14 during the reaction process, and the reaction time is kept for 0.5-2h; and the water solution is electrolyzed.
Owner:FIRST SEMICON MATERIALS
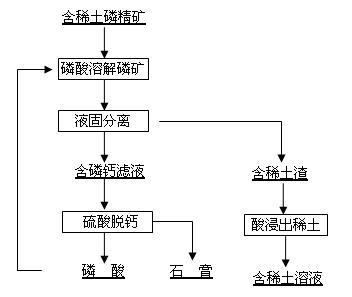
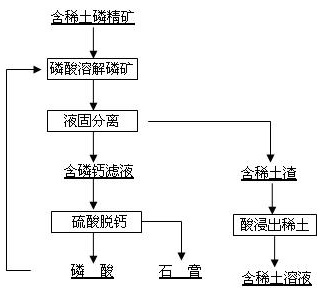
Method for separating tombarthite from phosphorus ore
The invention discloses a method for separating tombarthite from phosphorus ore and relates to the method for separating the tombarthite from the phosphorus ore containing the tombarthite. The method is characterized in that the process steps are as follows: (1) mixing phosphate concentrate containing the tombarthite with a phosphoric acid solution for performing reaction; (2) filtering for getting a reaction solution and slag containing the tombarthite; (3) adding acid into the slag containing the tombarthite for leaching for getting leachate containing the tombarthite, and further recycling the tombarthite through one or more of an extraction method, an ion exchange adsorption method, a precipitation method and a crystallization method; and (4) performing decalcification on the reaction solution obtained by filtration and then returning to the step (1). By adopting the method, the precipitation rate of the tombarthite in the phosphorus ore is greater than 85%, the slag rate is small, the grade of the tombarthite in the slag is high, the leaching rate of the tombarthite in the slag is high, no additives are added during the process and the product quality of the phosphoric acid is not affected; and furthermore, the phosphoric acid used during the process can be self-produced and can also be circulating dilute phosphoric acid, dilute phosphoric acid and the like generated during the production process of the phosphoric acid, thereby being tightly linked with the production process of the phosphoric acid through the sulfuric acid method.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
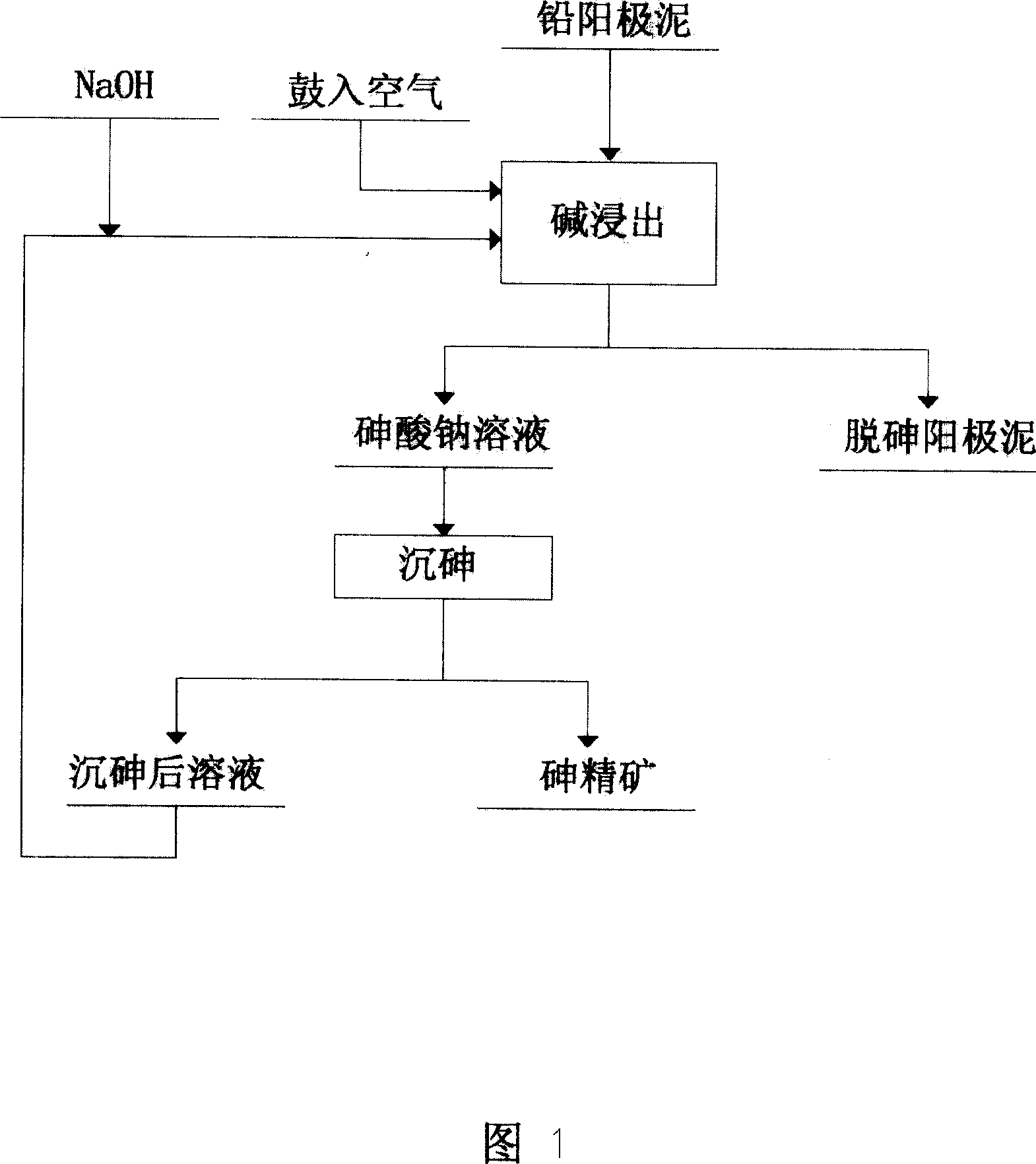
Method of removing arsenic for anode mud with high arsenic and lead content
The invention discloses a method to remove arsenic with high arsenic lead anode mud in noble metal metallurgical technical domain, which comprises the following steps: adding alkali liquor into high arsenic lead anode mud; leaching with alkali under the condition of air-blowing and heating; removing the arsenic; getting lead anode mud; reclaiming god and silver and other valuable metal with known craft; incorporating sodium arsenate in the leachate; depositing arsenic with lime; reclaiming arsenic clean ore; supplementing alkali liquor for the solution after depositing arsenic; backing to alkaline leaching process. This invention can make arsenic of anode mud decrease to below 1% and does not need any alteration for original craft.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
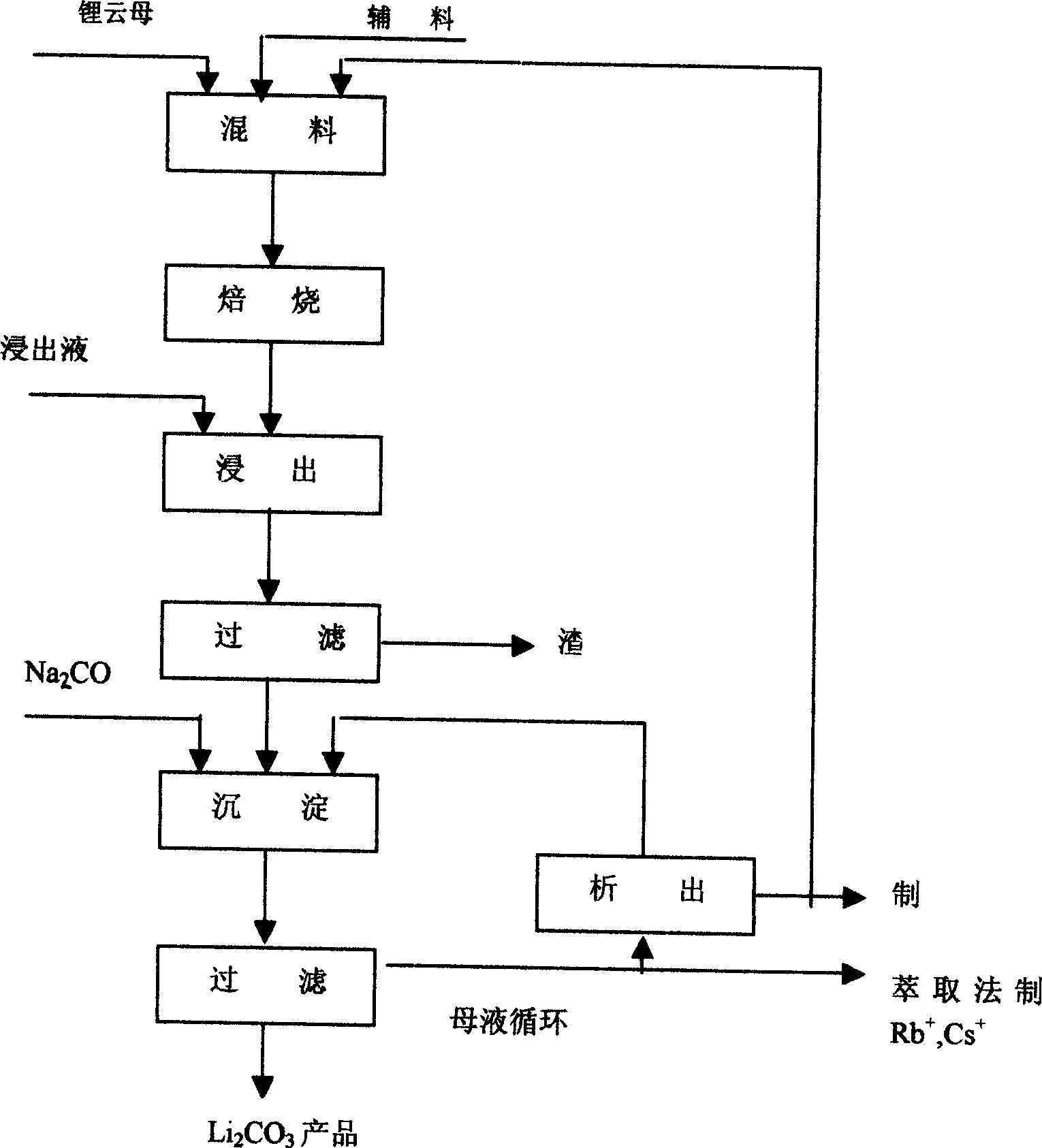
Process for preparing lithium chlorate by lithium extracted from lepidolite
InactiveCN1827527AReduce energy consumptionReduce investmentLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium carbonateSulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparation of lithium carbonate extracting lithium from lithionite. The invention consists of milling, leaching and filtering after modifying by broasting lithonite ore together with the additive findings such as calcium fluoride, calcium sulfate and sodium sulfate at a certain temperature, adding sodium carbonate into the leachate to deposite lithium ion forming the deposition of lithium carbonate, and washing and drying the solid gained by filtering to get the product of lithium carbonate. The filtered mother liquid returns to the circulation to deposit lithium ion. After secondary circulation, we get the mixed salts of potassium sulfate and sodium sulfate as the educts by washing and drying the aforementioned filtered mother liquid. Some of the mixed salts return as findings roasted with lithonite ore for circulation use, while others can be used as raw material for preparation of potassium sulfate.
Owner:钟辉
Method and device for treating garbage percolate
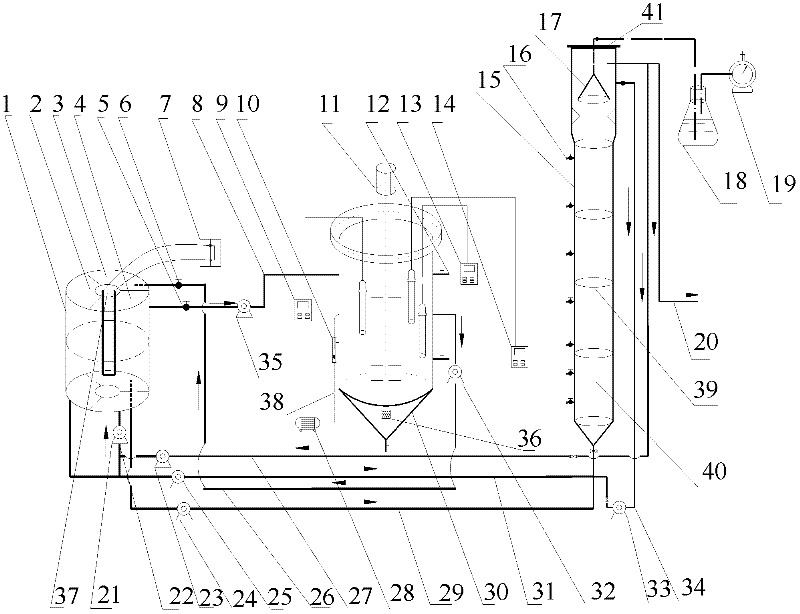
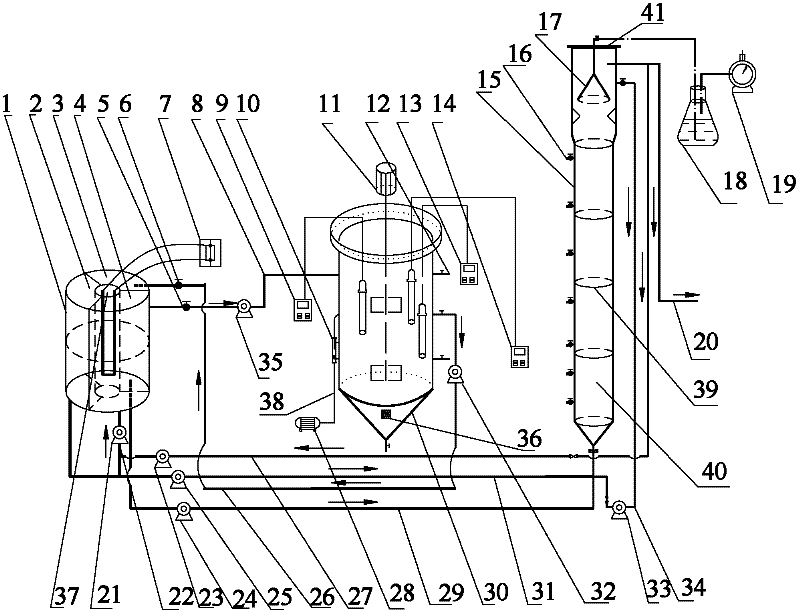
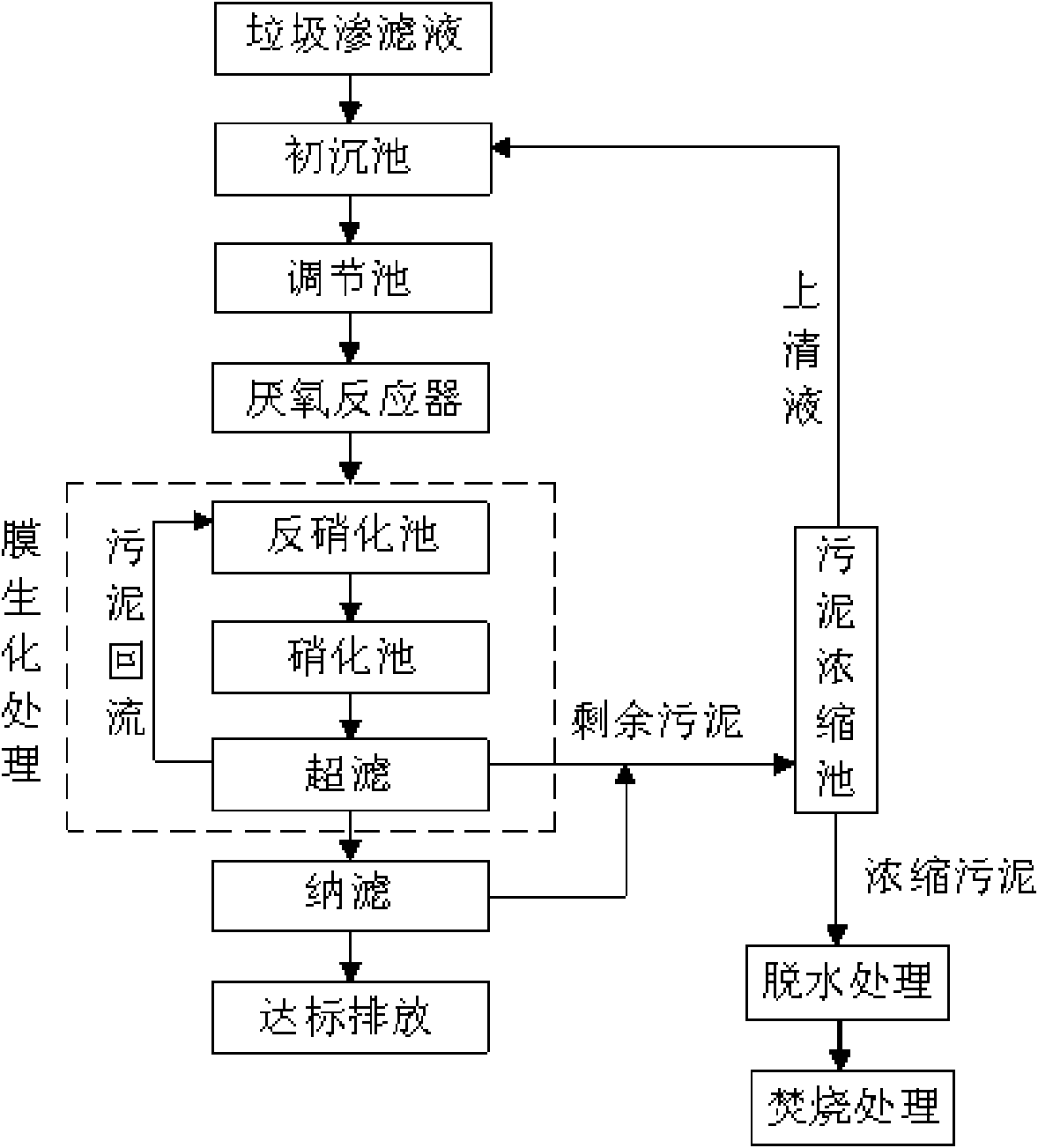
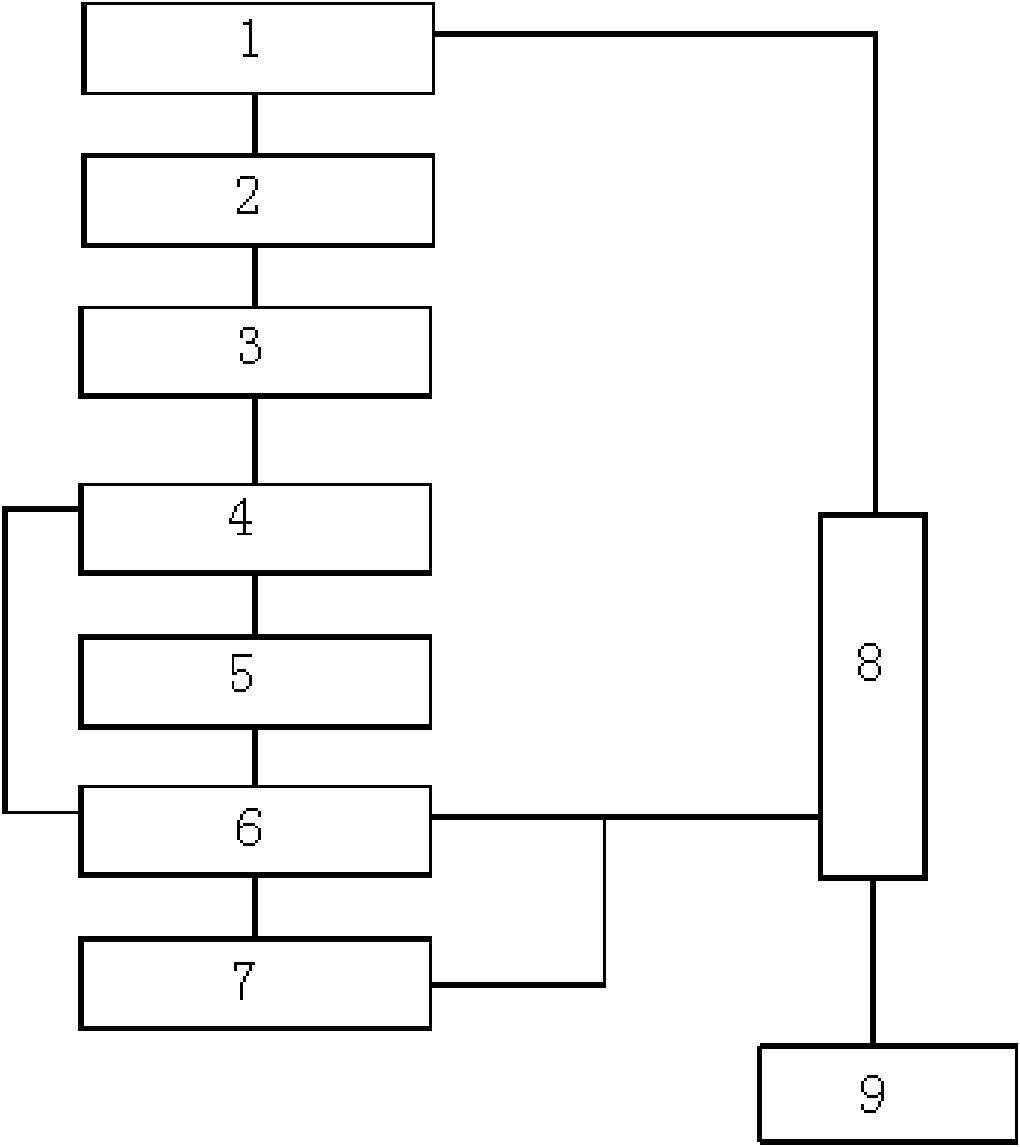
ActiveCN101597131AAchieving zero emissionsRelieve stressSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHigh concentrationAfter treatment
The invention discloses a method and a device for treating garbage percolate, wherein the method comprises the steps of pretreatment, anaerobic treatment, membrane biochemical treatment, nanofiltration treatment, sludge treatment and the like; the device comprises a primary sedimentation tank (1) and an adjusting tank (2), the adjusting tank (2) is connected with an anaerobic reactor (3), the anaerobic reactor (3) is connected with a denitrification tank (4), and the denitrification tank (4) is communicated with a nitrification tank (5); and the nitrification tank (5) is connected with an ultrafiltration apparatus (6), and the ultrafiltration apparatus (6) is connected with a nanofiltration device (7). The method and the device achieve COD degradation of high-concentration wastewater so that the COD of high-concentration COD of 50,000 reaches about 50 after treatment and reaches the standard of industrial reuse water, thus the method and the device achieve zero discharge of the percolate, initiate a new attempt to treat high-concentration percolate, and fill up the domestic blank.
Owner:汕头市澄海洁源垃圾发电厂有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com