Method of separating and recovering valuable metals from waste lithium battery materials and application thereof
A waste lithium battery, separation and recycling technology, applied in battery recycling, recycling technology, waste collector recycling and other directions, can solve the problems of short leaching time, low pollution, high price, and achieve high-efficiency leaching, low cost, and high-efficiency preparation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
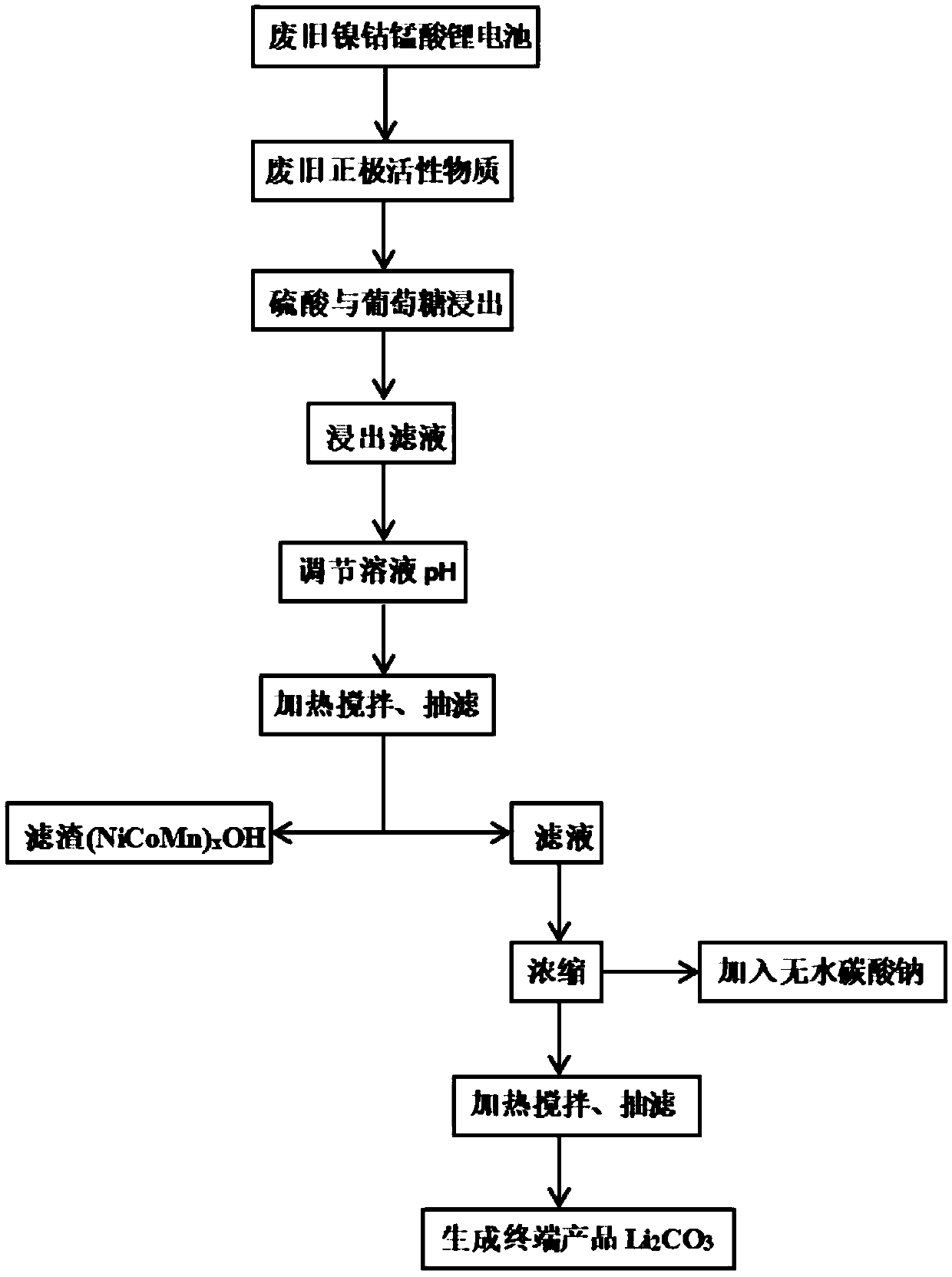
[0050] A method for separating and recovering valuable metals from waste battery materials and preparing lithium carbonate, the steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) discharging, disassembling and separating the battery material to obtain a battery positive electrode material;
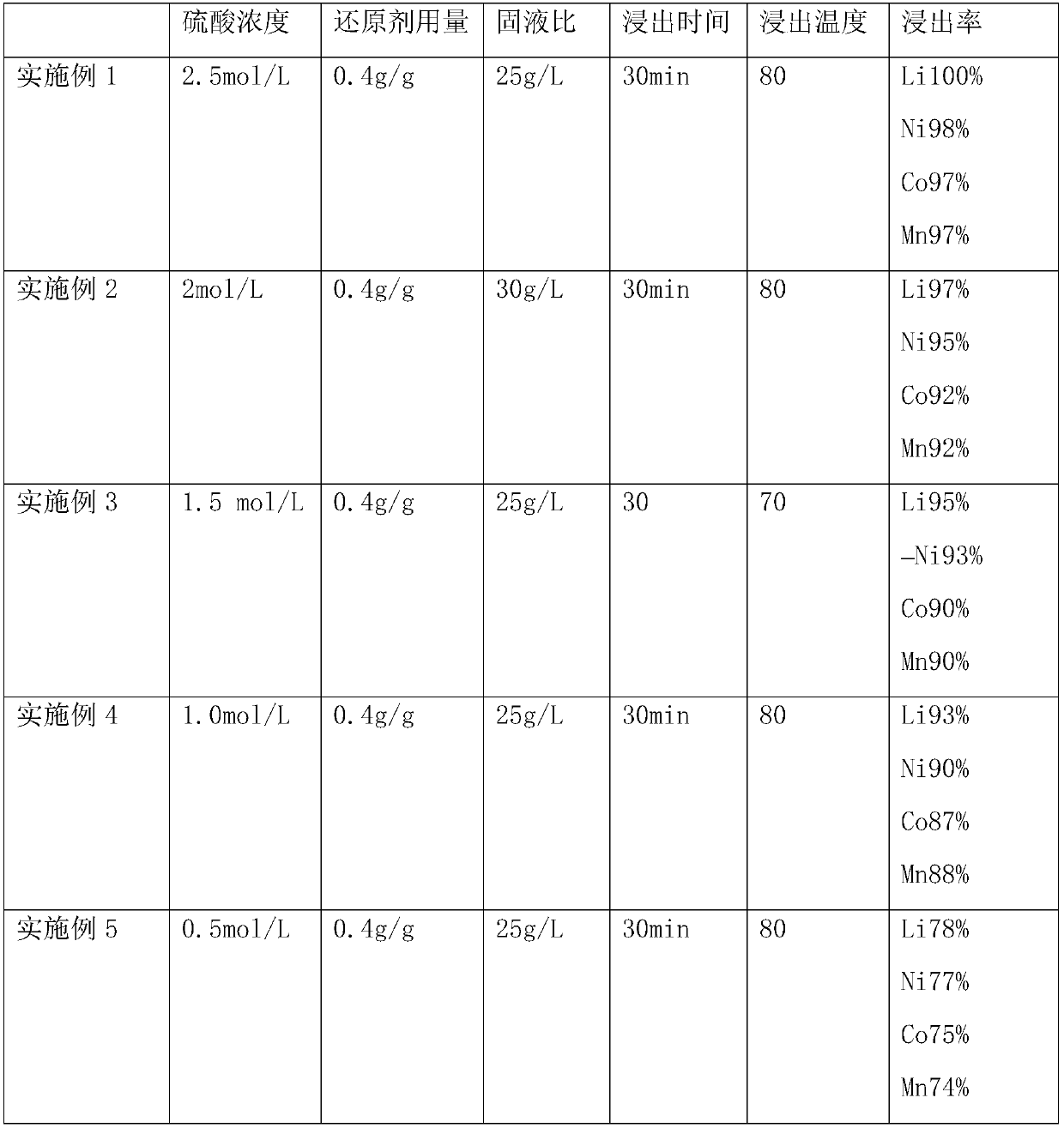
[0052] (2) leaching the battery cathode material obtained in step (1) with 2.5 mol / L sulfuric acid and 0.4 g / g glucose, wherein the leaching time is 30 min, the leaching temperature is 80° C., the solid-liquid ratio is 25 g / L, and the leaching time is 30 min. Stirring is carried out during the process, and the reaction is filtered to obtain the leachate;
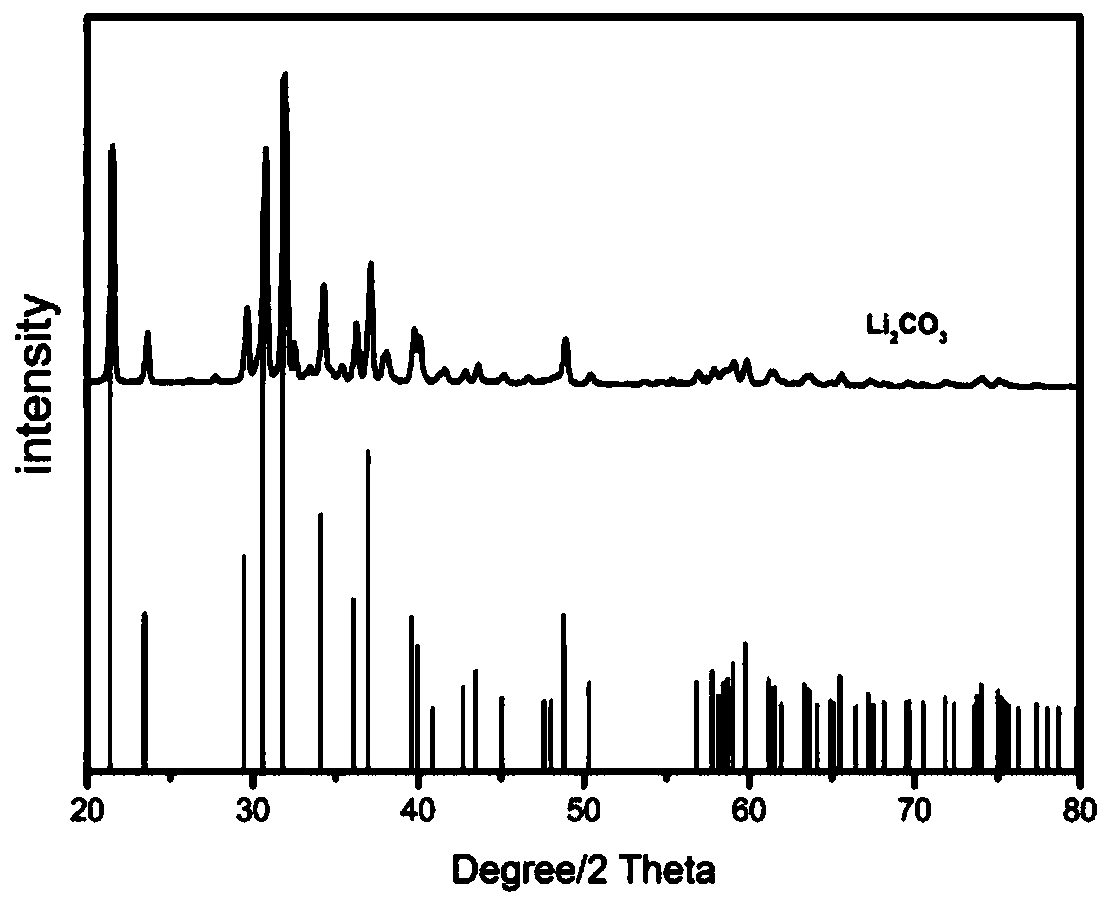
[0053] (3) adding additives to the leaching solution obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 11, so that nickel, cobalt and manganese ions in the leaching solution are precipitated, the temperature of the precipitation reaction is 30 ° C, and the reaction time is 90 min. Filtration to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese-conta...
Embodiment 2
[0058] A method for separating and recovering valuable metals from waste battery materials and preparing lithium carbonate, the steps are as follows:
[0059] (1) discharging, disassembling and separating the battery material to obtain a battery positive electrode material;
[0060] (2) leaching the battery cathode material obtained in step (1) with 2 mol / L sulfuric acid and 0.4 g / g glucose, wherein the leaching time is 30 min, the leaching temperature is 80° C., and the solid-liquid ratio is 30 g / L. The leaching process Stirring is carried out in the reaction, and the leaching solution is obtained by filtration after completion of the reaction;
[0061] (3) adding additives to the leaching solution obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 11, so that nickel, cobalt and manganese ions in the leaching solution are precipitated, the temperature of the precipitation reaction is 50 ° C, and the reaction time is 45 min. Filtration to obtain nickel-co...
Embodiment 3
[0066] A method for separating and recovering valuable metals from waste battery materials and preparing lithium carbonate, the steps are as follows:
[0067] (1) discharging, disassembling and separating the battery material to obtain a battery positive electrode material;
[0068] (2) leaching the battery cathode material obtained in step (1) with 1.5 mol / L sulfuric acid and 0.4 g / g glucose, wherein the leaching time is 30 min, the leaching temperature is 80 °C, the solid-liquid ratio is 25 g / L, and the leaching time is 30 min. Stirring is carried out during the process, and the reaction is filtered to obtain the leachate;
[0069] (3) adding additives to the leaching solution obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 11, so that nickel, cobalt and manganese ions in the leaching solution are precipitated, the temperature of the precipitation reaction is 70 ° C, and the reaction time is 90 min. Filtration to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese-contai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com