Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1942 results about "Iron content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Where the amount of iron ranges from 12.18 mg to 1.67 mg per 100g. The top vegetable is Mushrooms, morel, raw with the highest iron content, which in 100g contains 12.18 mg of iron. The total recommended daily allowance or RDA for iron is 14 mg.
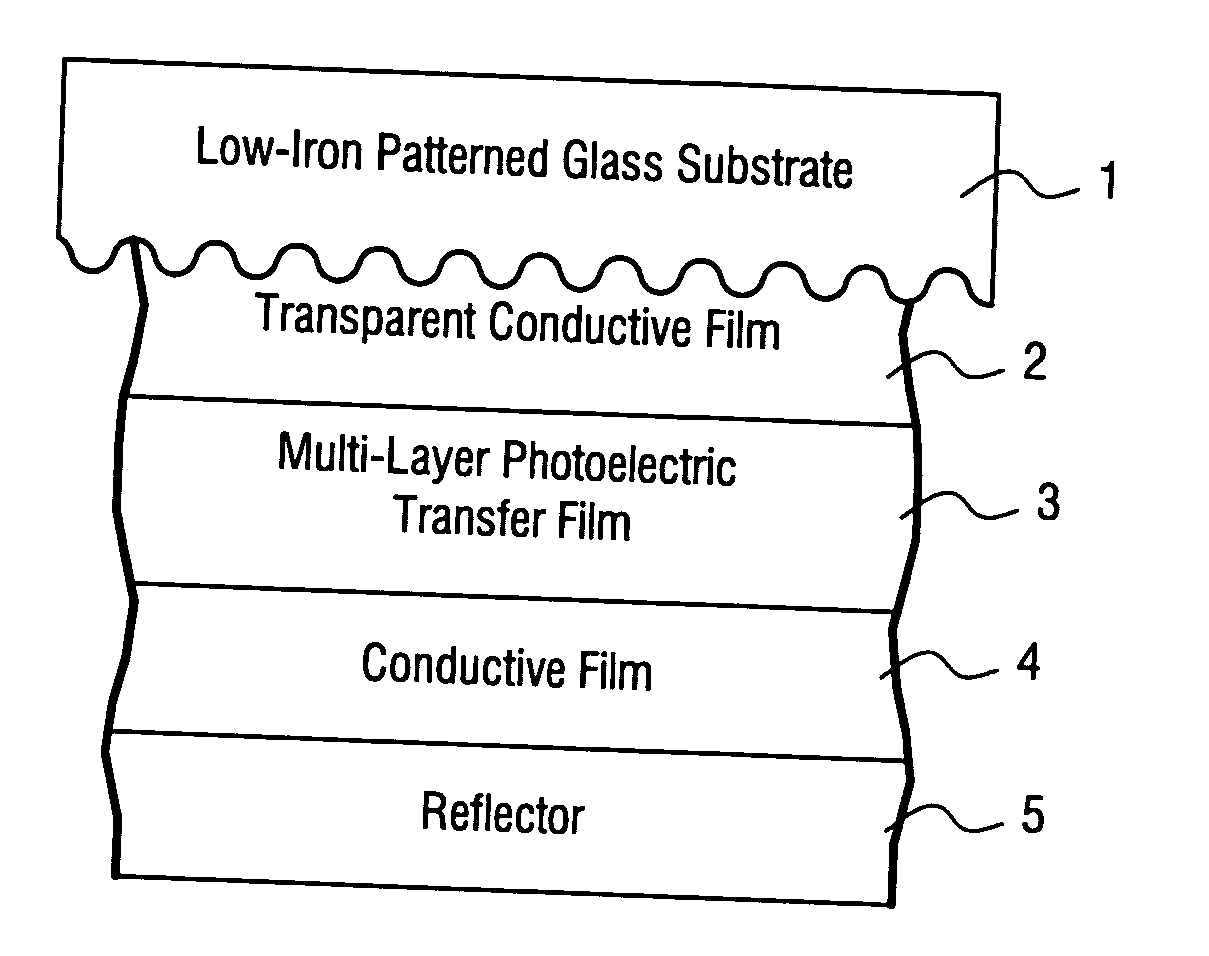
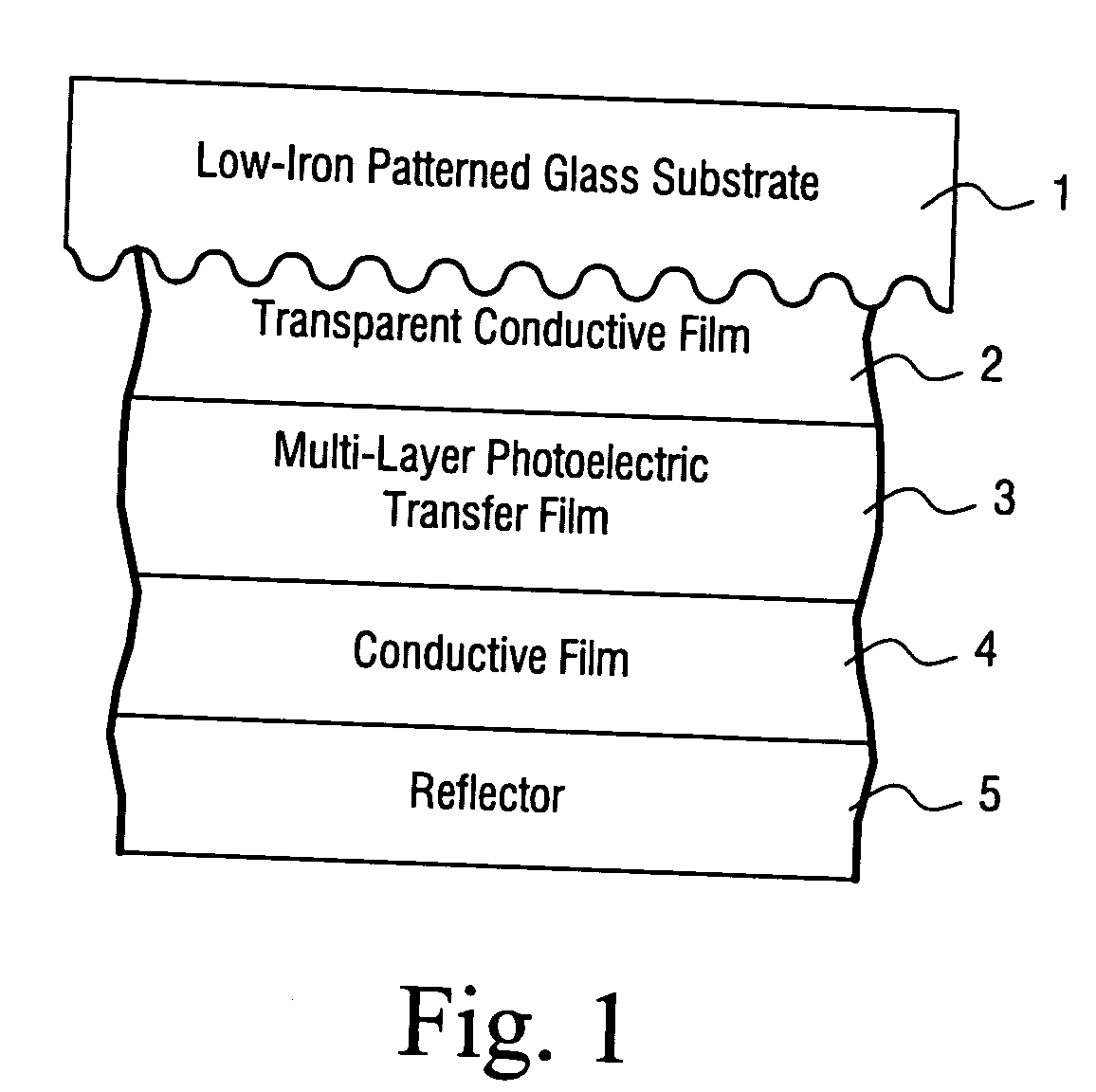
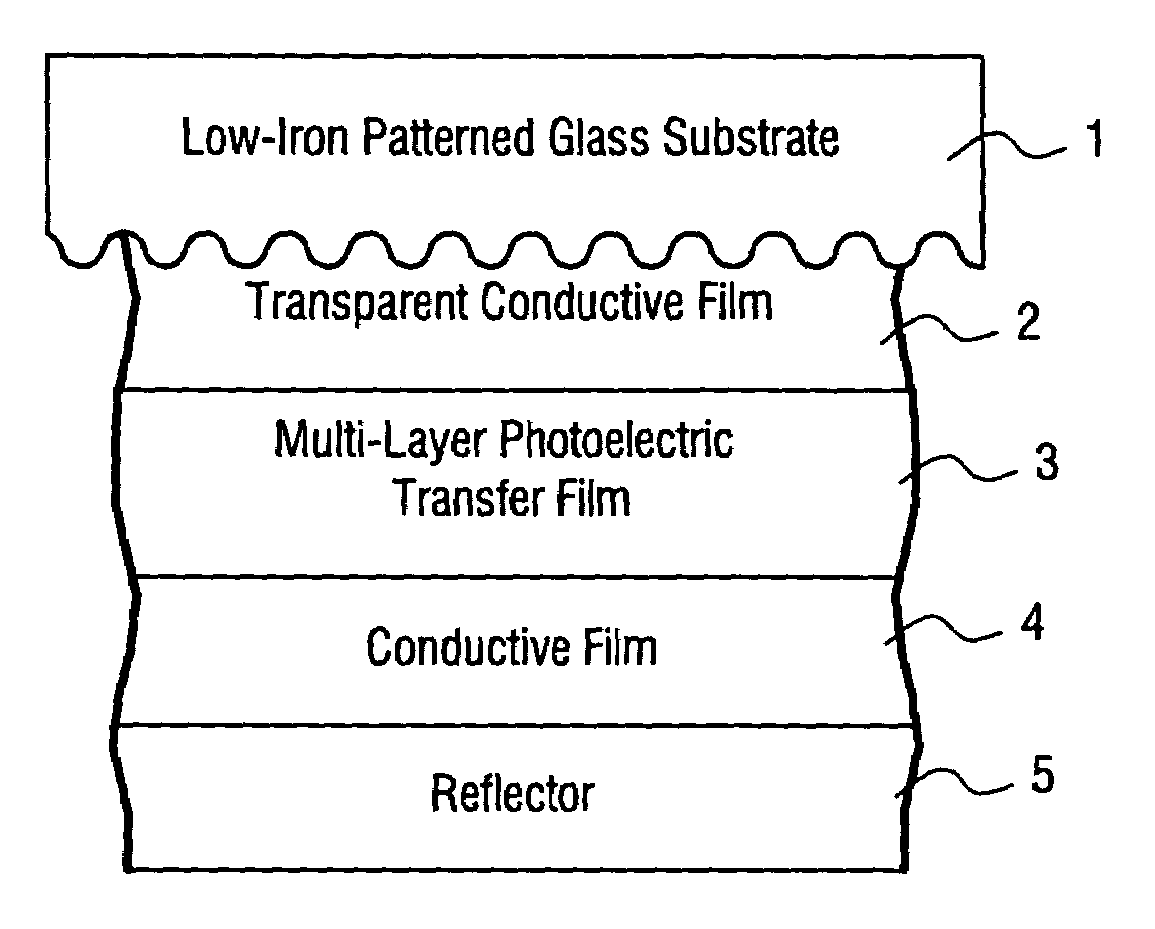
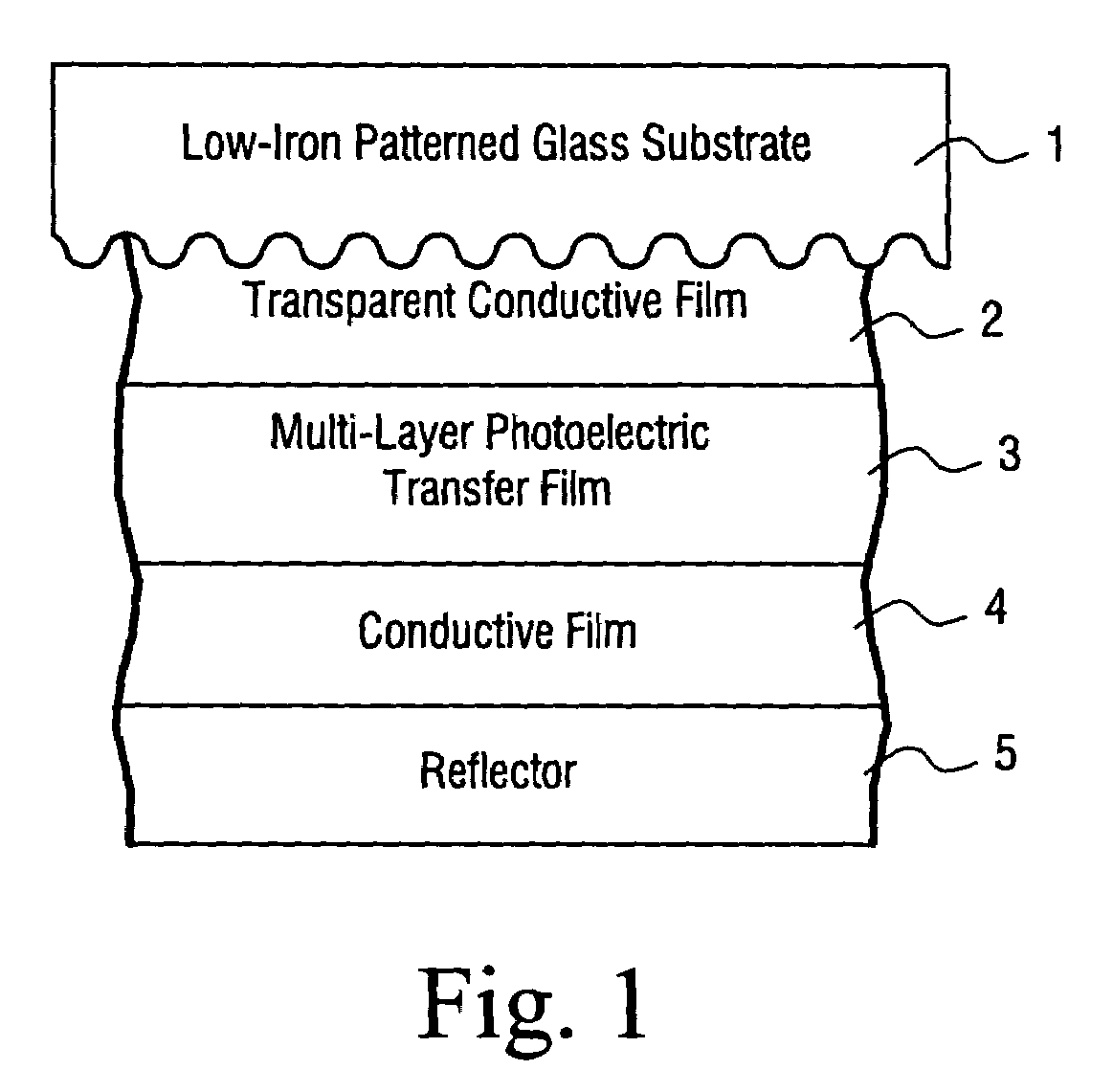
Solar cell using low iron high transmission glass with antimony and corresponding method
A high transmission and low iron glass is provided for use in a solar cell. The glass substrate may be patterned on at least one surface thereof. Antimony (Sb) is used in the glass to improve stability of the solar performance of the glass upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and / or sunlight. The combination of low iron content, antimony, and / or the patterning of the glass substrate results in a substrate with high visible transmission and excellent light refracting characteristics.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
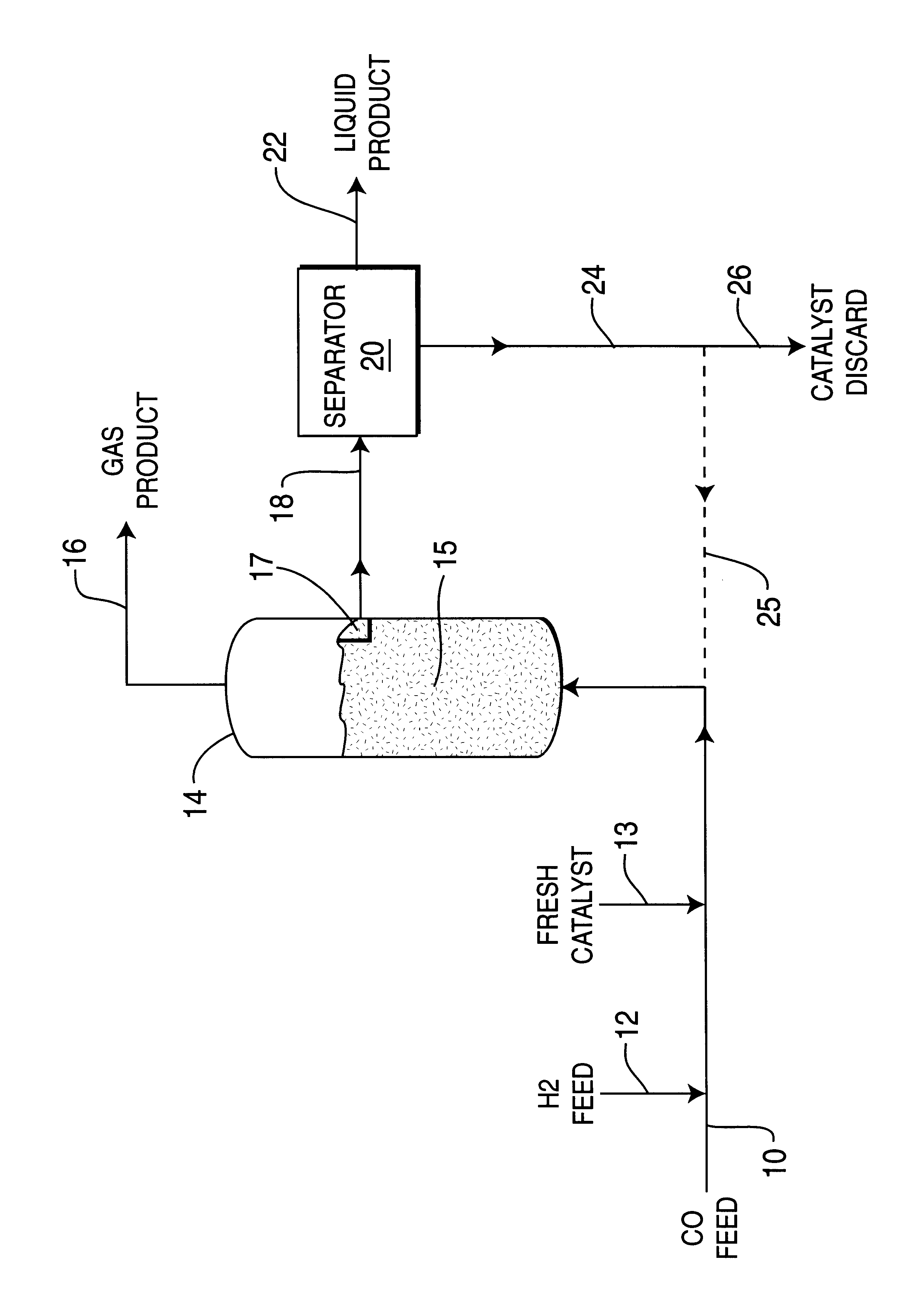
Skeletal iron catalyst having improved attrition resistance and product selectivity in slurry-phase synthesis processes
InactiveUS6277895B1High particle strengthGood attristion resistanceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationFixed bedSlurry
Particulate skeletal iron catalyst is provided which contain at least about 50 wt. % iron with the remainder being a minor portion of a suitable non-ferrous metal and having characteristics of 0.062-1.0 mm particle size, 20-100 m2 / g surface area, and 10-40 nm average pore diameter. Such skeletal iron catalysts are prepared and utilized for producing synthetic hydrocarbon products from CO and H2 feeds by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process. Iron powder is mixed with non-ferrous powder selected from aluminum, antimony, silicon, tin or zinc powder to provide 20-80 wt. % iron content and melted together to form an iron alloy, then cooled to room temperature and pulverized to provide 0.1-10 mm iron alloy catalyst precursor particles. The iron alloy pulverized particles are treated with NaOH or KOH caustic solution at 30-95° C. temperature to extract and / or leach out most of the non-ferrous metal portion, and then screened and treated by drying and reducing with hydrogen and to provide the smaller size skeletal iron catalyst material. Such skeletal iron catalyst is utilized with CO+H2 feedstream for Fischer-Tropsch reactions in either a fixed bed or slurry bed type reactor at 180-350° C. temperature, 0.5-3.0 mPa pressure and gas hourly space velocity of 0.5-3.0 L / g Fe / hr to produce desired hydrocarbon products.
Owner:INST OF COAL CHEM ICCCHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method of making iron and steel
InactiveUS6149709AEasy to getLess impurity contentProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceHigh energyRefractory
Molten iron is prepared by (1) providing iron oxide and a carbonaceous reducing agent, (2) preparing a shaped product from the carbonaceous reducing agent and the iron oxide, (3) preparing solid reduced iron from the shaped product, wherein the solid reduced iron has a metallization of at least 60%, a specific gravity of at least 1.7, and a carbon content of at least 50% of the theoretical amount required for reducing the iron oxide remaining in the solid reduced iron, and, (4) before substantial cooling occurs, heating the solid reduced iron in an arc heating-type melting furnace at a high temperature. The molten iron can be prepared efficiently from iron ores of relatively low iron content without causing erosion of refractories, at high energy and high reduction efficiencies, and by a simple operation in a simple facility.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Solar cell using low iron high transmission glass with antimony and corresponding method
A high transmission and low iron glass is provided for use in a solar cell. The glass substrate may be patterned on at least one surface thereof. Antimony (Sb) is used in the glass to improve stability of the solar performance of the glass upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and / or sunlight. The combination of low iron content, antimony, and / or the patterning of the glass substrate results in a substrate with high visible transmission and excellent light refracting characteristics.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Soda-lime-silicate glass composition
A neutral-colored soda-lime-silicate glass with high light transmission in the visible region. The glass has a basic composition which contains at least the following constituents: SiO2, 66-75 weight %; Na2O, 10-20 weight %; CaO, 5-15 weight %; MgO, 0-6 weight %; Al2O3, 0-5 weight %; and K2O, 0-5 weight %; and incorporates a colorant portion comprising the following constituents: Co, 0.1-1 ppm; Fe2O3, <=0.03 weight % (total iron content); and FeO / Fe2O3, >0.4. The glass possesses a light transmittance (illuminant D 65 according to DIN 67 507) of at least 89% at a reference thickness of 4 mm.
Owner:PILKINGTON DEUTLAND
Water-absorbing resin composition
InactiveUS20060074160A1Excellent in stability of gelImprove the immunityAbsorbent padsBaby linensFiberInorganic salts
A water-absorbent resin composition comprising an oxygen-containing reducing inorganic salt and a water-absorbent resin, wherein the iron content in the resin composition is at most 1 ppm; an absorbent having the above-mentioned water-absorbent resin composition and a hydrophilic fiber; and an absorbent article comprising the above-mentioned absorbent interposed between a liquid-permeable sheet and a liquid-impermeable sheet.
Owner:SUMITOMO SEIKA CHEM CO LTD
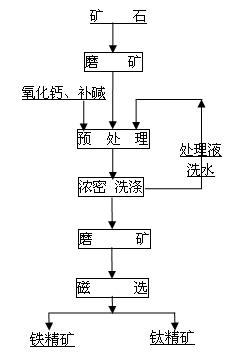
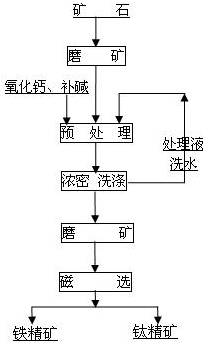
Beneficiating method for ilmenite
ActiveCN102181626AIncrease alkali concentrationHigh in ironBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementMagnetiteIlmenite
The invention discloses a beneficiating method for ilmenite, relating to a method for preparing titanium concentrate and iron concentrate by beneficiating crude ilmenite. The method is characterized in that: a beneficiating process of the method orderly comprises the following steps of: (1) grinding the crude ilmenite; (2) performing alkaline leaching pretreatment under the conditions of heating, oxygenating and pressurizing; (3) filtering pulp which is subjected to the alkaline leaching pretreatment; (4) washing filter residue and grinding; and (5) performing magnetic separation to obtain the titanium concentrate and the iron concentrate. In the method provided by the invention, the characteristic of iron and titanium compact symbiosis and the isomorphism occurrence characteristic of vanadium are damaged from the source of vanadium titano-magnetite by adopting the pretreatment process, so that mineral transformation of the vanadium titano-magnetite is realized, dissociation on lattice layers of titanium and iron is realized, high-quality iron concentrate and titanium concentrate with lower iron content are obtained through grinding and the magnetic separation process, an alkaline medium used in the pretreatment can be recycled, and the process has a small influence on environment and a bright application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
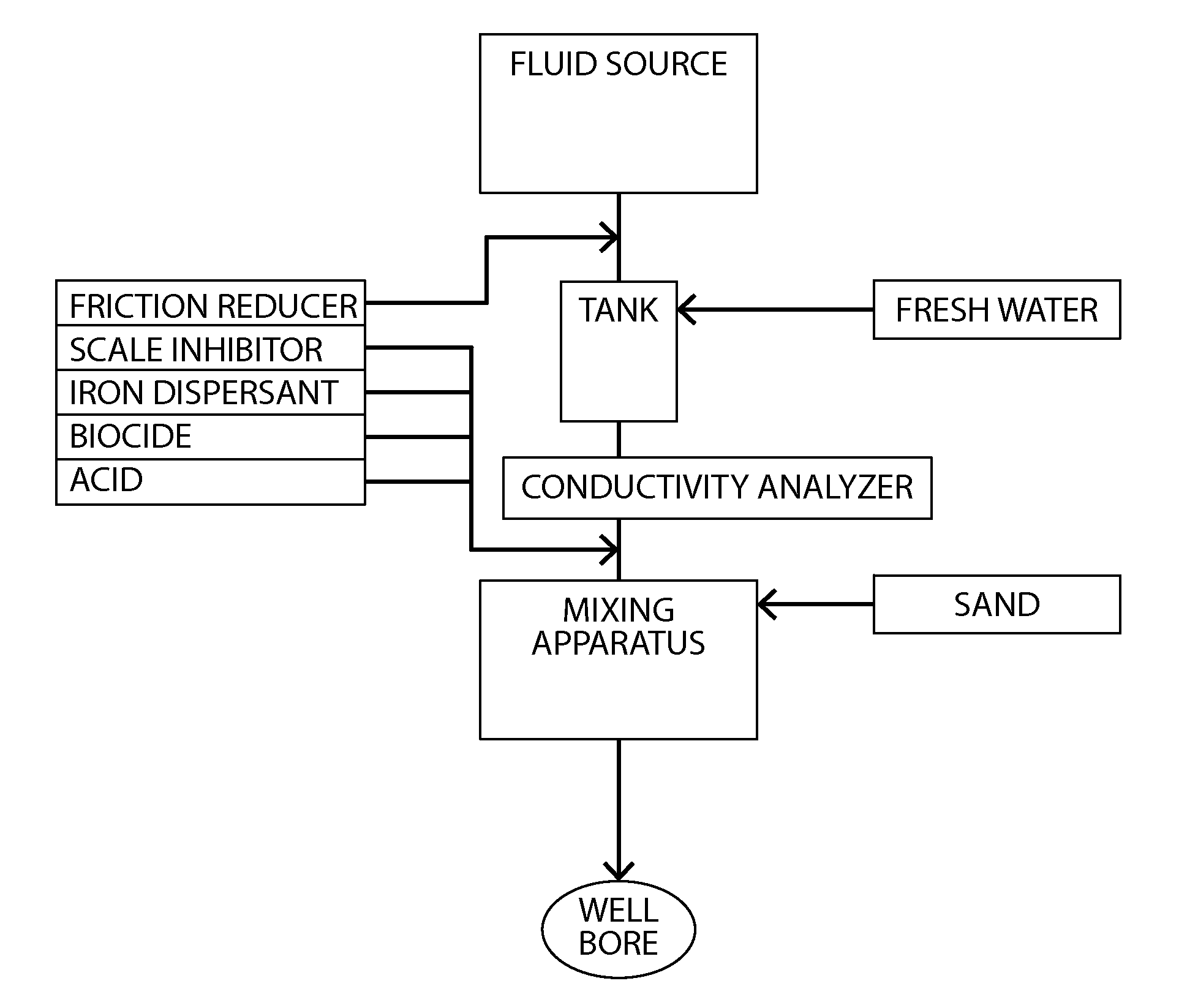
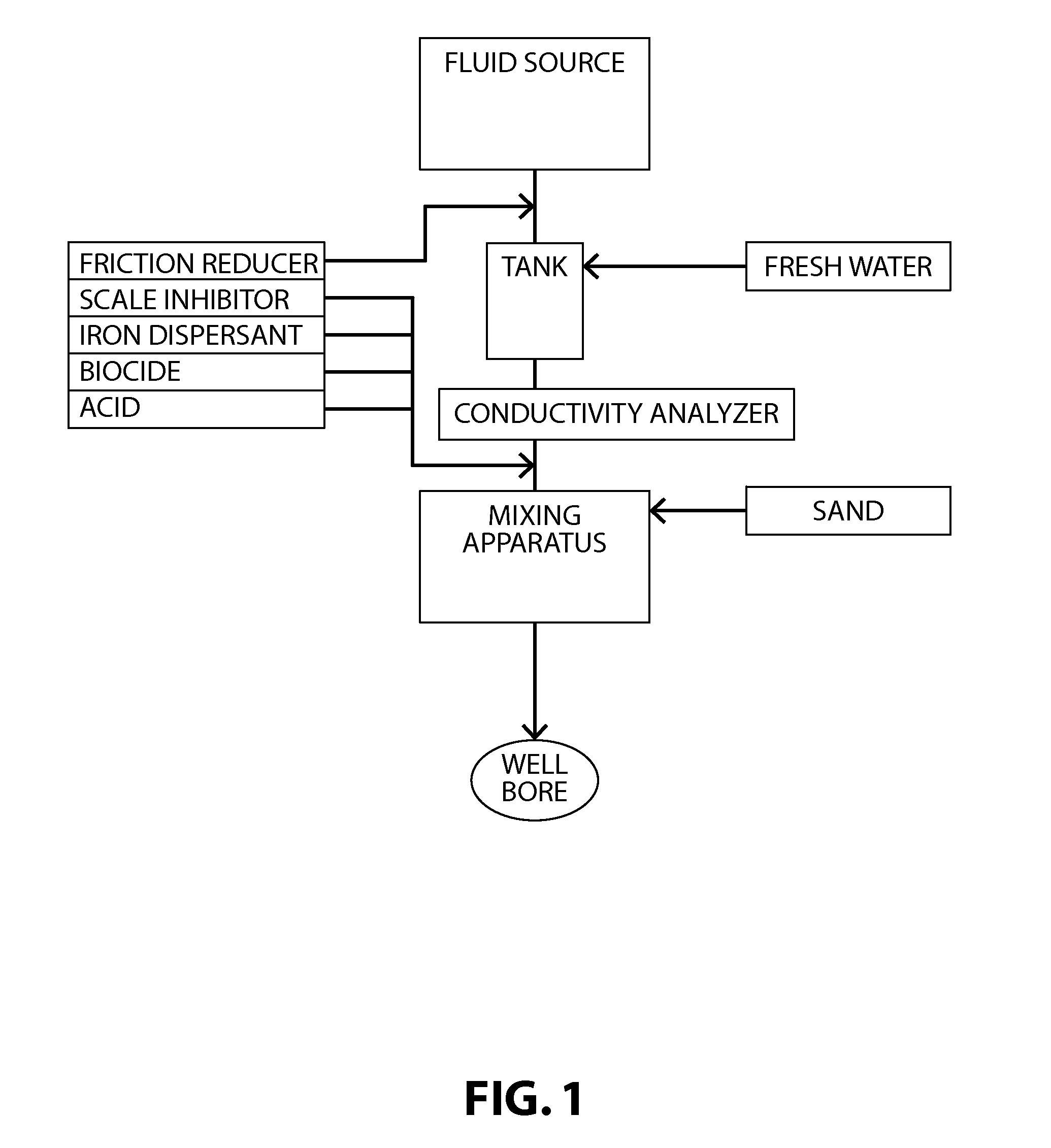
Fracturing fluid water reuse system and method
ActiveUS20120024525A1Low costIncreasing well productionFluid removalMixer accessoriesFracturing fluidHydraulic fracturing
Methods of processing a fluid recovered from an oil or gas extraction operation for reuse in a hydraulic fracturing fluid are described. The methods include providing an amount of a produced fluid composition containing iron and suspended solids and controlling at least one of the conductivity, iron content, oxidative strength, and pH of the composition, such that Fenton's reagent is formed in situ. Also described are hydraulic fracturing fluids produced using fluid recovered from an oil or gas production process and treated in accordance with the methods described herein as well as systems for preparing a hydraulic fracturing fluid having, as a fluid source, fluid recovered from an oil or gas production process that has been treated in accordance with the methods described herein.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
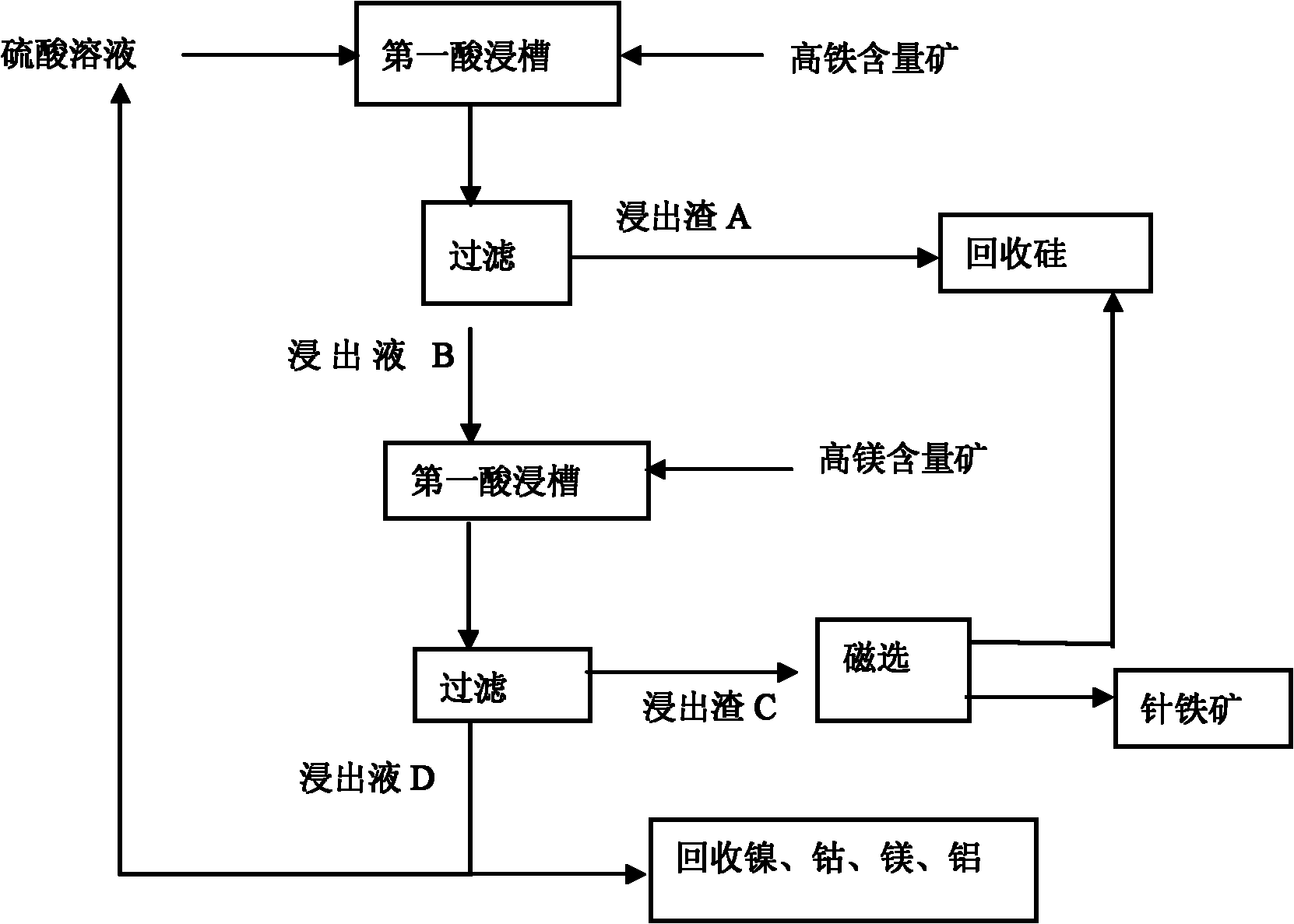
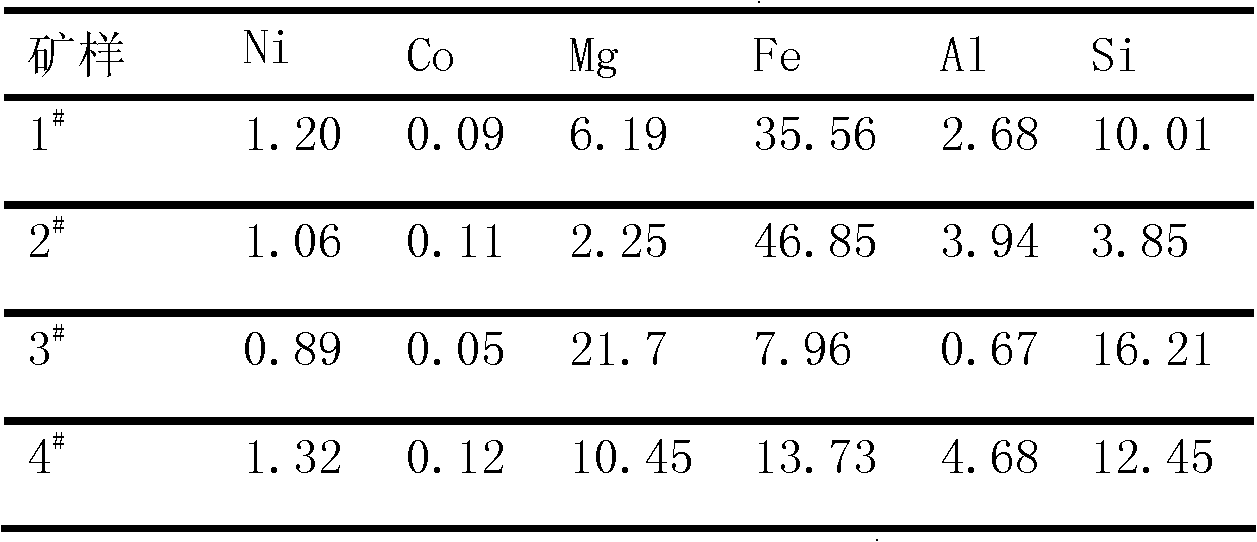
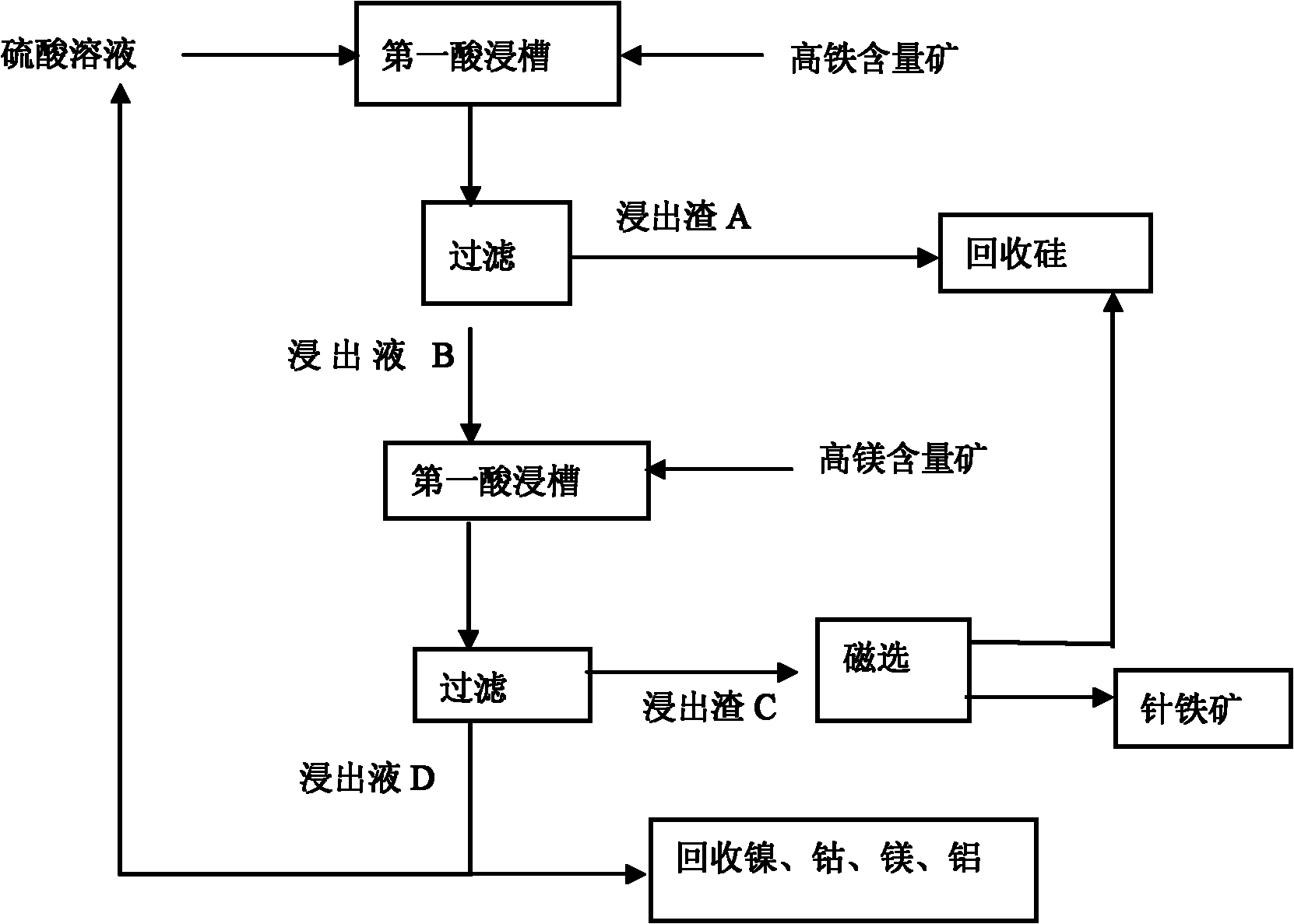
Normal-pressure leaching method for simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content
InactiveCN102206749AOvercoming the disadvantage of requiring autoclave leachingOvercome the drawbacks of leachingIron oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementLateriteNon magnetic
The invention discloses a normal-pressure leaching method simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content, comprising the following steps of: screening the laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content; adding sulfuric acid to the laterite with high iron content for leaching so as to obtain leaching residue A and a leaching solution B; adding the laterite with high magnesium content to the leaching solution B, leaching to obtain leaching residue C and a leaching solution D; carrying out magnetic separation on the leaching residue C, wherein a magnetic part E is recovered as an iron product, and a non-magnetic part F and the leaching residue A are mixed to be used for recovering silicon products; delivering a part of the leaching solutionD into a purifying and recovering process, and returning the other part of the leaching solution D into the leaching process of the laterite with high iron content, and carrying out a next leaching period; repeating the leaching period for 4-5 times, and completely delivering a leaching solution I obtained from a last leaching period into the recovering processes of nickel, cobalt, aluminum and magnesium. The normal-pressure leaching method has the advantages of low cost and acid consumption and high leaching efficiency of the nickel and the cobalt and realizes the efficient separation and the recycling of iron, silicon, the nickel and the cobalt and the discharge without acid liquor.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
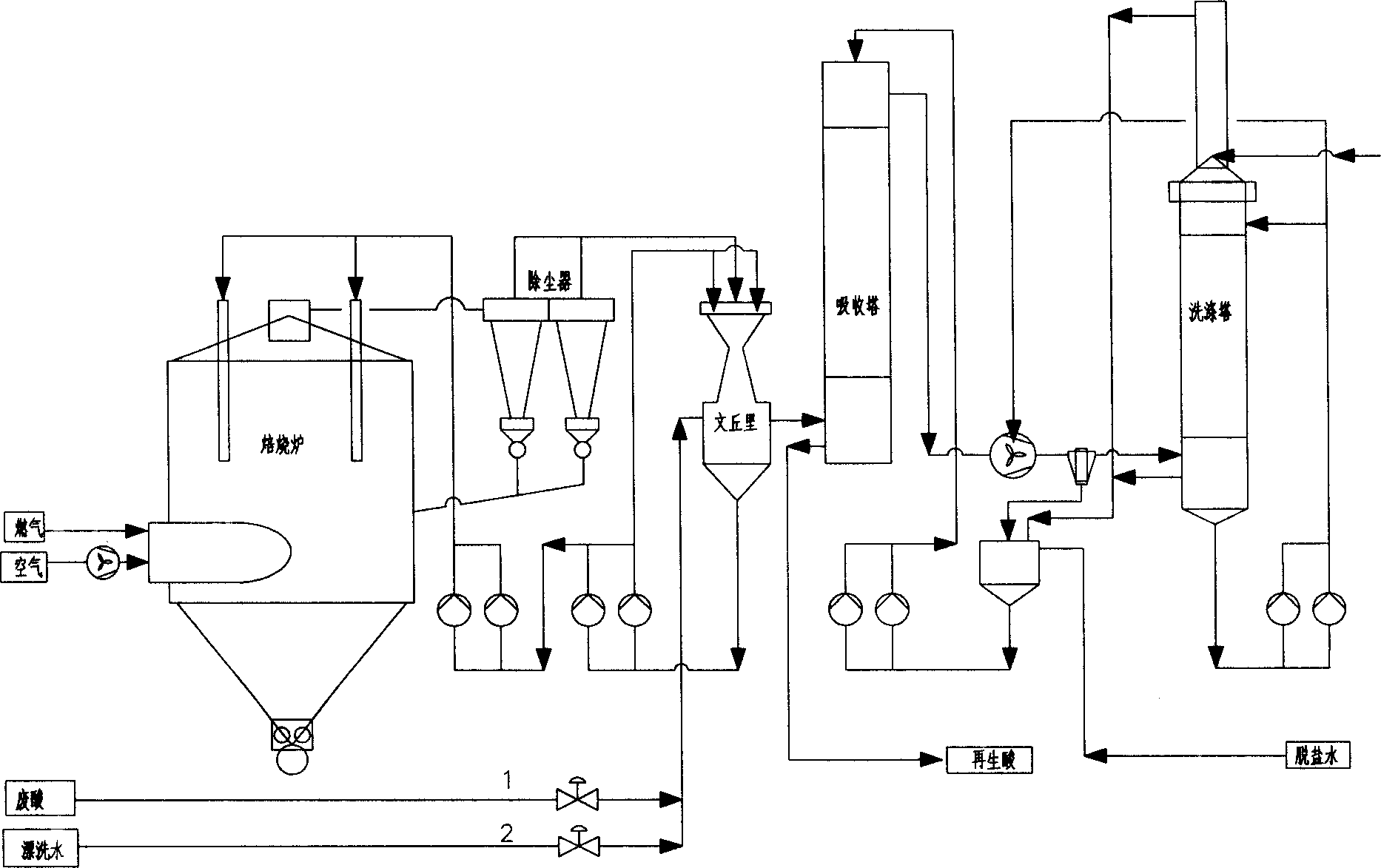
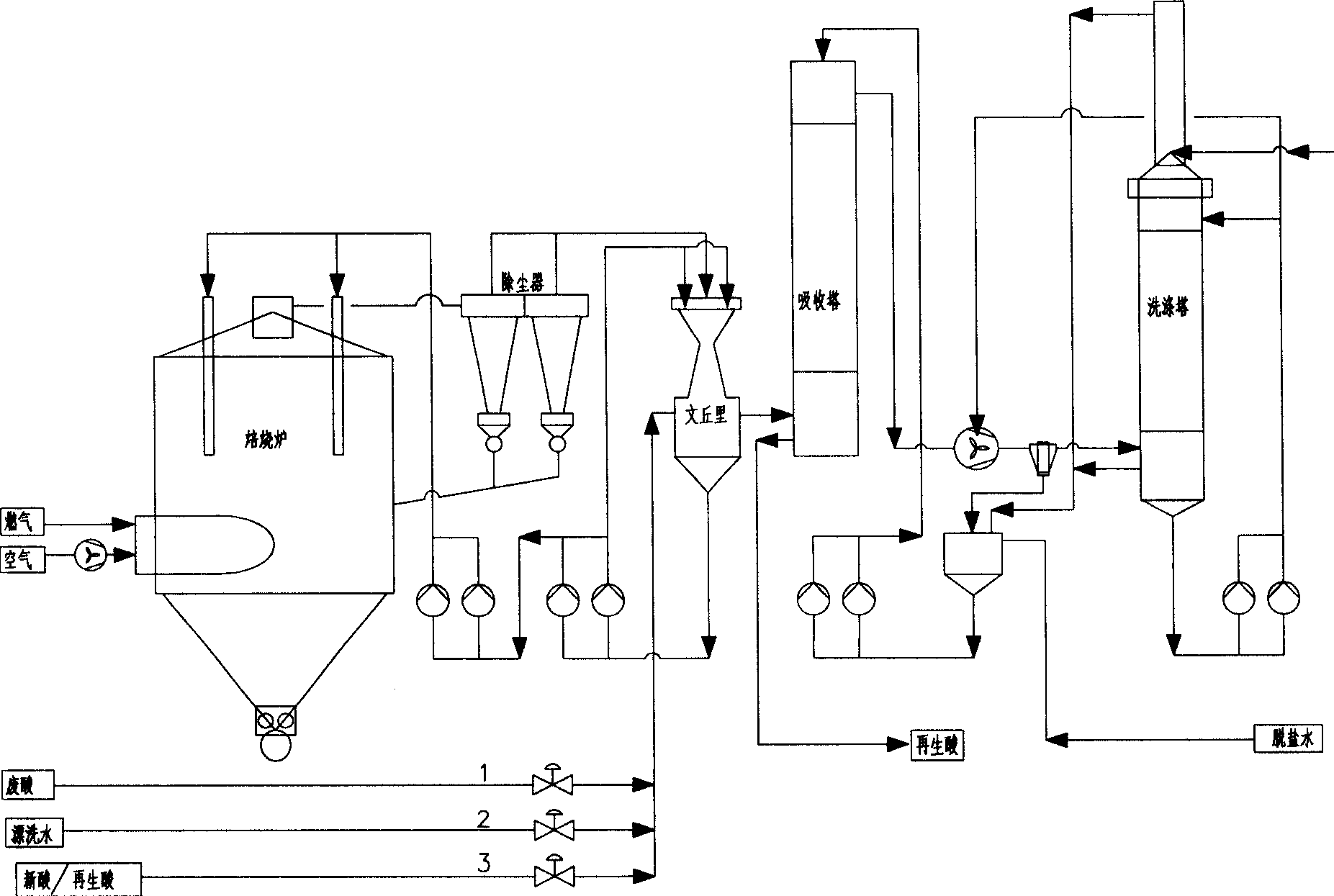
Hydrochloride waste regenerating process for spray roasting
ActiveCN1851320AReduce the concentration of iron oxide powderLower iron levelsIncinerator apparatusVolumetric Mass DensityHydrogen chloride
The invention relates to hydrochloric acid exhausted liquid reclaiming process. It includes the following steps: water operation after 390 centigrade degree; adding 18-20 percent hydrochloric acid before acid operation 5-10 minutes; acid operation; and blowing out. It can reduce brown iron oxide density of discharging gas, and the iron content in reclaimed acid.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Catalyst for synthesizing gasoline and diesel fraction selected by synthesis gas
InactiveCN1418933AHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryActivated carbonAdjuvant
The catalyst for directly preparing high-grade gasoline and diesel oil clean liquid fuel by using synthetic gas and utilizing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis reaction is formed from three portions of active component, adjuvant and carrier, in which its active component is metal iron, the adjuvant is formed from metal elements of Cu, Ce, K, Co and Ru, etc. and its carrier can use apricot stone activatedcarbon or coconut activated carbon, the specific surface area of active carbon is 200 sq.m / g-2000 sq.m / g, its pore volume is 0.3-1.5 cu.cm / g, pore size distribution is 4-1000 A, the metal iron content is 4-40% of total weight of catalyst, the adjuvant element content is 0.01-20.0% of total weight of the catalyst. The addition of adjuvant element can effectively improve the reaction and stability property of catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing zinc-iron-selenium enriched bio-fertilizer and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101225006AImprove the level ofSimple methodBio-organic fraction processingFertilising methodsFermentationSe element
The invention relates to a preparation method for a zinc-iron-selenium-rich biological fertilizer and a usage, which belongs to the technical field of crop production. Water is added into pig manure, silkworm excrement, human excrement and colza cakes for a fermentation to get mother liquor of the biological fertilizer; zinc sulfate, green copperas, sodium selenite are added into the mother liquor for reactions to get zinc-iron-selenium-rich biological foliar fertilizer for the rice. The fertilizer is separately sprayed in the booting stage and the full heading stage of the rice, with an amount of 1000ml per mu. The function rice, with zinc content 19.4 to 28.7mg / kg, iron content 7.0 to 20.2mg / kg, and selenium content 0.08 to 0.15 mg / kg, measures up to the limit standards of zinc, iron, and selenium in the national food standards. Organic selenium accounts for more than 99% of the total selenium in the zinc-iron-selenium-rich function nutritive rice. The preparation method for the zinc-iron-selenium-rich biological fertilizer proves effective, economical, safe and non-polluted through twice foliage sprays with zinc-iron-selenium fertilizer for the rice as an experiment.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
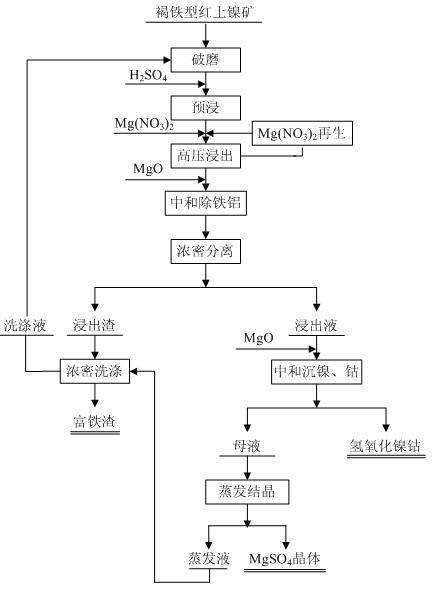
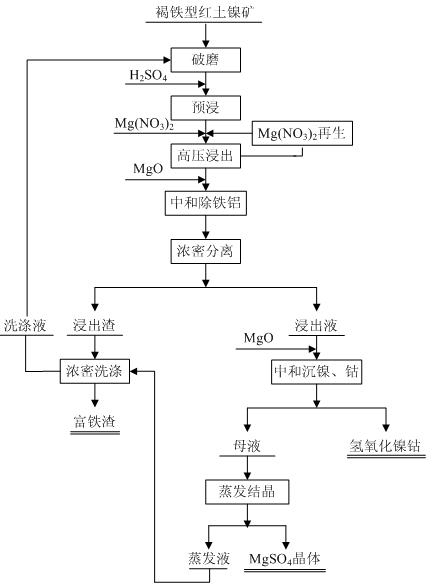
Method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN102534206AReduce consumptionEasy to operate and controlProcess efficiency improvementSlagSlurry
The invention discloses a method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore and relates to a process method for recovering nickel, cobalt and iron through treatment of laterite nickel ore by wet process. The method is characterized in that the technical process comprises: (1) grinding raw limonitic laterite nickel ore into fine powder, making slurry, adding sulfuric acid, heating the slurry and leaching the slurry; (2) adding Mg(NO3)2 into the pre-leached slurry, heating with stirring, pressurizing the slurry and leaching the slurry; 3) at the end of leaching, neutralizing the slurry, removing iron and aluminum from the slurry, and separating to obtain a leaching solution and a leaching residue; and 4) washing the leaching residue to obtain washing liquid and iron-enriched slag, neutralizing the leaching solution, precipitating nickel and cobalt, obtaining nickel and cobalt hydroxides, evaporating a mother solution from which nickel and cobalt are separated to crystallize magnesium sulfate and comprehensively recovering magnesium sulfate. The method realizes the high-efficiency selective leaching of nickel and cobalt, the leaching rate reaches over 90 percent, the iron leaching rate is lower than 0.8 percent and iron-enriched slag with an iron content of over 55 percent is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
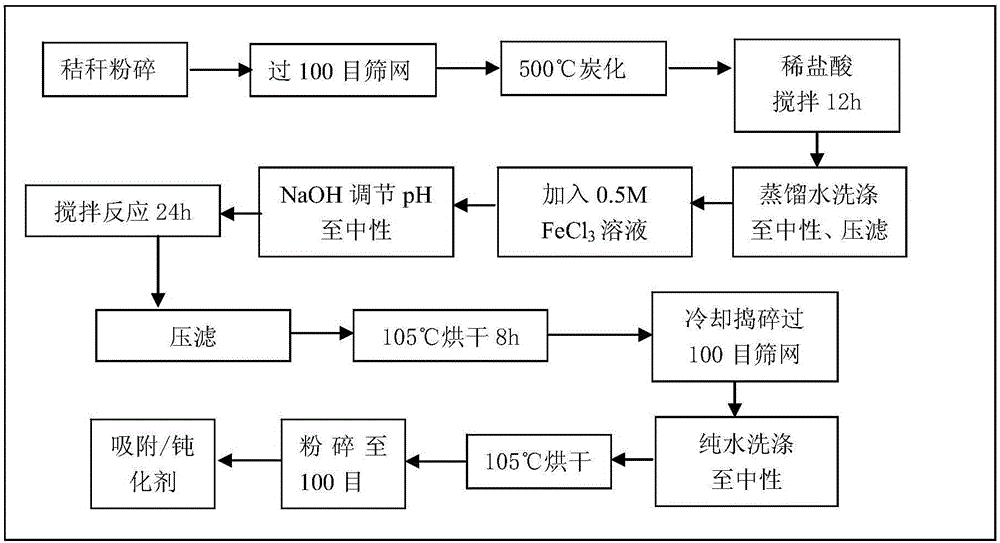
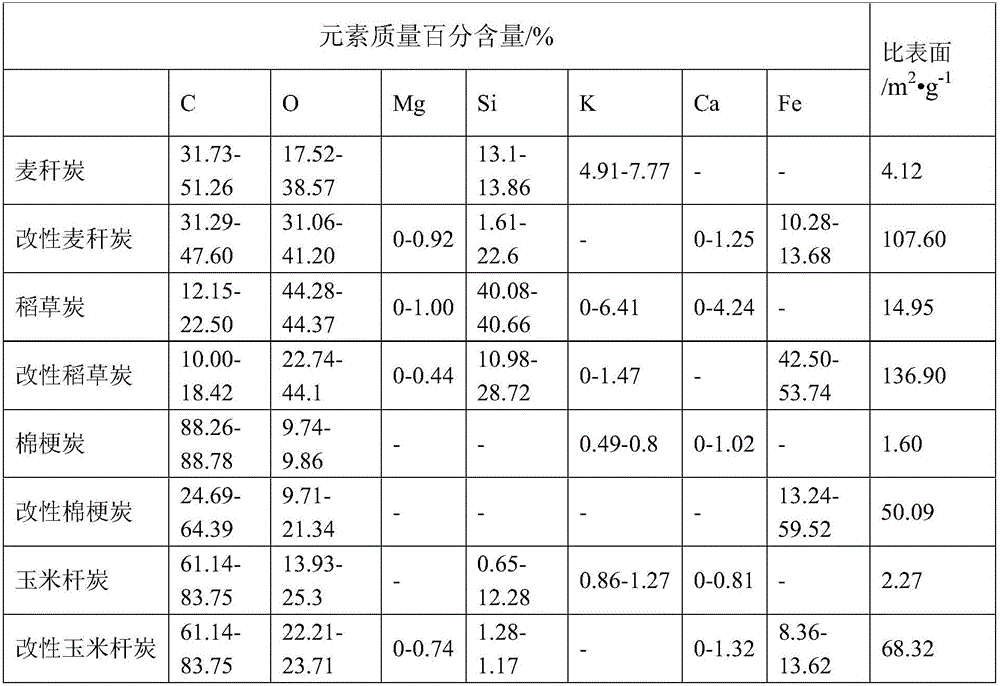
Modified biomass charcoal for treating arsenic pollution as well as preparation method and application of modified biomass charcoal
InactiveCN105944668AImprove stabilityLow carbonization temperatureOther chemical processesWater contaminantsArsenic pollutionFood safety
The invention provides modified biomass charcoal for treating arsenic pollution as well as a preparation method and an application of the modified biomass charcoal. The preparation method of the modified biomass charcoal comprises steps as follows: (1) biomass raw materials are charred, and the biomass charcoal is obtained; (2) the biomass charcoal is subjected to a reaction with a hydrochloric acid solution, solid-liquid separation is performed, a solid substance is obtained, is washed till the pH is neutral and then is dried, and the pretreated biomass charcoal is obtained; (3) the pretreated biomass charcoal and a FeCl3 solution are subjected to a reaction under the condition that the solution pH is neutral, solid-liquid separation is performed after the reaction, and mud cake is obtained; (4) the mud cake is dried and then washed till the pH is neutral, solid-liquid separation is performed, an obtained solid is dried for a second time, and the modified biomass charcoal is obtained. The modified biomass charcoal has large specific surface area and high iron content; the preparation method is simple and easy to operate; the modified biomass charcoal can be applied to treatment of arsenic waste and passivation of arsenic in farmland soil, and food safety is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for raising iron content and reducing silicon in concentrate by means of low-intensity magnetic separation process
InactiveCN103447144ARealize the purpose of increasing iron and reducing siliconSimple processWet separationOperational costsScreening method
The invention discloses a method for raising iron content and reducing silicon in concentrate by means of a low-intensity magnetic separation process. Aimed at the problems of floatation (reverse flotation) in the prior art in terms of raising iron content and reducing silicon in concentrate, a magnetic field screening method for separation and corresponding crashing and grinding process and equipment are adopted in order to achieve the goal of raising iron content and reducing silicon in concentrate. The method has the advantages of simple process, advanced equipment, low operating cost and remarkable economic benefit.
Owner:安徽大昌矿业集团有限公司
Method for producing iron concentrate by brown hematite and siderite and reduction roaster
The present invention discloses a method for adopting the limonite and the siderite to produce iron powder and a reduction roaster. The material adopts the limonite and the siderite or the specularite, the hematite, and the sulphuric acid slag, the inclined rotary reduction roaster is used, the pressure of the furnace chamber is 250 to 350 Pa, under the deoxidizing atmosphere, the inert solid is rotated and moved to 650 to 900 DEG C from the low temperature, and is cooled and magnetized, and lastly become the iron powder through the dressing by magnetic separation. The present invention is adopted to produce the iron powder, the resources is rich and the production cost is low, and through the utilization of the powder metallurgy art, the iron content of the iron powder is controlled and the activation energy of the iron powder is reduced, and the chemical reaction ability is increased, thereby the output of iron powder is high, the quality is good, the iron powder is loose and porous, the specific surface is big, the apparent density is large, the manufacture cost of pellets sinter and steel smelting can be reduced greatly, and the iron powder can use directly to produce iron oxide red as well as H and N synthetic iron catalyst, or produce ultrapure iron powder.
Owner:郭元杰
Converter dephosphorizing and steelmaking method
The invention provides a converter dephosphorizing and steelmaking method. The method comprises the following steps of: a, adding slag making materials which consist of active lime, high-magnesium lime and a composite slagging agent into a converter molten pool; blowing and slagging by a dephosphorizing oxygen lance oxygen blowing process and an inert gas bottom blowing process to remove phosphorus in molten steel; and pouring 60 to 80 percent of slag out when the molten pool temperature in a converter is between 1,420 and 1,450 DEG C, the alkalinity of the slag is between 2.0 and 2.5 and the total iron content in the slag is between 10 and 15 weight percent; and b, adding the slag making materials into the converter molten pool; blowing and slagging by a normal oxygen lance oxygen blowing process and the inert gas bottom blowing process to further remove the phosphorus in the molten steel; pouring the slag out when the molten pool temperature in the converter is between 1,680 and 1,700 DEG C, the alkalinity of the slag is between 3.2 and 4.2 and the total iron content in the slag is between 16 and 23 weight percent to obtain the molten steel with the phosphorus element content of not more than 0.009 weight percent. By the method, the dephosphorizing efficiency and the dephosphorizing effect of the converter are improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
Method for recycling iron from steel slag
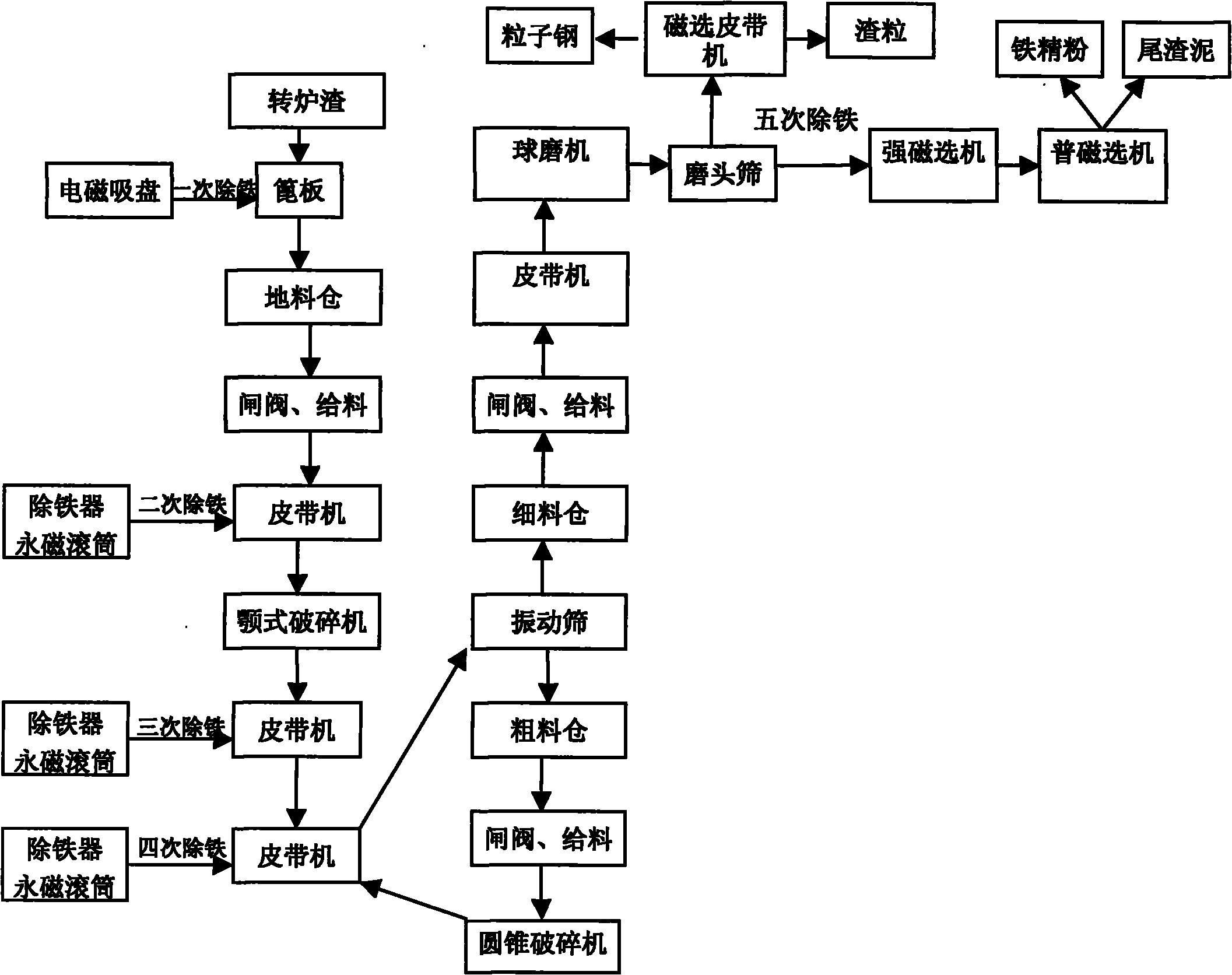
InactiveCN101864501AEasy to separateAvoid artificial unluckyRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementSlagGranularity
The invention belongs to the field of recycling of steel slag, in particular to a method for recycling iron from steel slag. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pouring steel slag into a grate plate with the length and the width of 180 mm respectively, leading the steel slag with granularity smaller than 180 mm to enter an underground material bin and carrying out first iron recycling on the steel slag with granularity larger than 180 mm by an electromagnetic sucking disk; (2) magnetically separating and crushing the steel slag with granularity smaller than 180 mm, wherein the crushed granularity is smaller than 60 mm; (3) magnetically separating the crushed steel slag; (4) screening by a vibrating screen, leading steel slag with granularity larger than 25 mm to enter a cone crusher for carrying out second crushing with the crushed granularity smaller than 25 mm, and magnetically separating; (5) grinding steel slag with granularity smaller than 25 mm, screening by a cylinder screen with granularity of 2 mm and remelting particle steel with granularity larger than 2 mm for utilizing; and after magnetically separating steel slag with granularity smaller than 2 mm by a wet magnetic separator, separating iron fine powder and tailings. The invention can recycle iron in the steel slag and reduce the iron content of the steel slag below 0.5 percent.
Owner:XINXING HEBEI ENG & RES INC
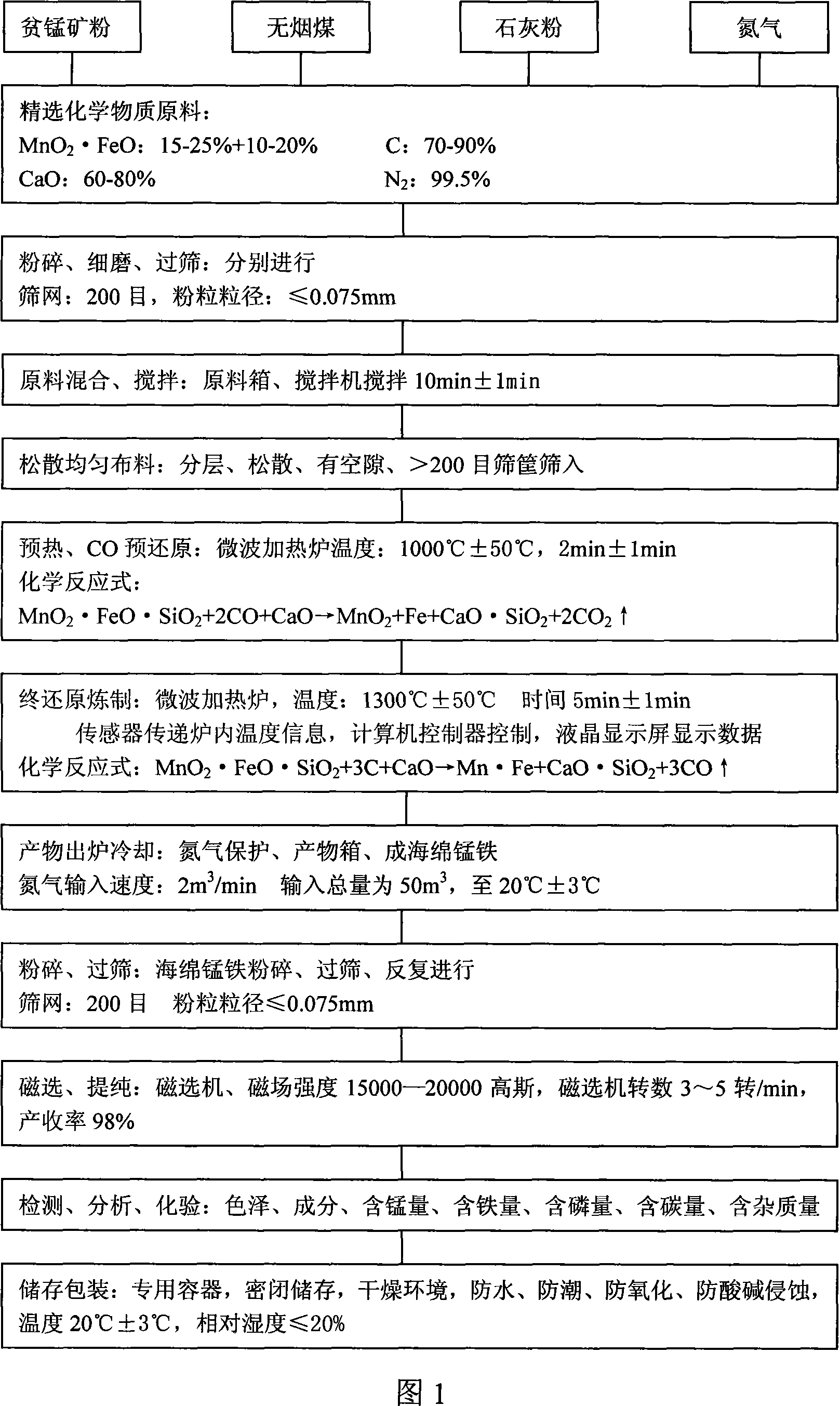
Method for preparing low-carbon metal manganese iron by using manganese-poor powdered ore
The invention relates to a low-carbon ferromanganese production method using low-grade manganese mineral powder. The low-grade manganese mineral powder which has rich reserves is heated by a micro-wave oven, reduced by carbon, smelted at high temperature, purified by magnetic separation to directly prepare low-carbon ferromanganese. And the production method saves sintered agglomeration process with large energy consumption and serious pollution. The low-carbon ferromanganese with high purity is made through the steps that: the material is carefully chosen, crushed, fine- grinded, sieved, mixed, stirred, preheated by the micro-wave oven, pre-reduced through carbon monoxide, finally reduced, smelted at high temperature, cooled under the protection of nitrogen and purified by magnetic separation. The preparation method has the advantages of short technological process, less using equipment, being suitable for large- scale industrialization production, the yield rate can reach 98 percent, wherein manganese content is 75 percent and iron content is 20 percent, and the content of carbon is less than 0.5 percent; the content of harmful material sulfur is also less than 0.5 percent; the content of phosphor is less than 0.2 percent. The products have the advantages of low carbon, low phosphor and sulfur containing, no agglomeration, no pollution to environment. The method is the ideal ferromanganese direct production method using low-grade manganese mineral powder and fills up a scientific research blank in the field in China.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Efficient magnetic separation method for quartz sand
InactiveCN102626668AIncrease production capacityReduce unit energy consumptionWet separationPurification methodsNo production
The invention discloses an efficient purification method for quartz sand. In the method, two-section smashing (rough smashing and fine smashing) and ore milling with a rod mill are adopted, so that the production capacity is increased greatly, unit energy consumption is lowered, and the method is suitable for large-scale production. A method for removing weakly-magnetic minerals and intergrowth quartz with high iron content from quartz sand through advanced ore washing and weakly magnetic-high gradient strongly magnetic combined magnetic separation before ore milling is adopted, so that the purity of quartz sand is increased greatly. The method has the advantages of simple process flow, easiness for operating, low cost, high purification efficiency, stable performance and environmental friendliness of a produced product, no use of any chemical substance in an entire production process, no production of any waste water, waste residues and waste gas, true realization of zero emission, no production of waste and prevention of pollution. The method is not limited by the production scale, various quartz sand products of low, medium and high grades can be produced, the enterprise profit can be maximized, and the method has a wide application prospect on the aspect of purification of quartz sand.
Owner:赣州金环磁选科技装备股份有限公司
Zinc hydrometallurgy production process
InactiveCN102876888AReduce lossesHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementCement factoryIndium
The invention relates to a zinc hydrometallurgy production process. According to the zinc hydrometallurgy production process provided by the invention, reduction leached supernate is subjected to preneutralization, then zinc dust is added for replacing indium, after the indium is separately removed, oxygen with the concentration being not lower than 98 percent is filled into liquid obtained after the indium is deposited, controlling the temperature in the range of 160 to 200 DEG C and controlling the pressure in the range of 1,000 to 2,000kPa, so that iron precipitates in the liquid obtained after the indium is deposited enter slags. The iron removed liquid obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process has the iron content being lower than 1.2g / l, the iron removed liquid can be directly returned to be subjected to neutral leaching, and the system has stable production working conditions and is beneficial to stable production; in the iron slags obtained by the zinc hydrometallurgy production process, the zinc content is lower than 1 percent, the zinc loss is low and the zinc recovery rate is high; the iron slags can be directly sold to a cement plant and an iron and steel plant to be used as the raw materials without being stacked in a slag field, so that the zinc hydrometallurgy production process is beneficial to environmental-protection and the comprehensive utilization of resources and mineral resources are saved.
Owner:广西华锡集团股份有限公司 +1
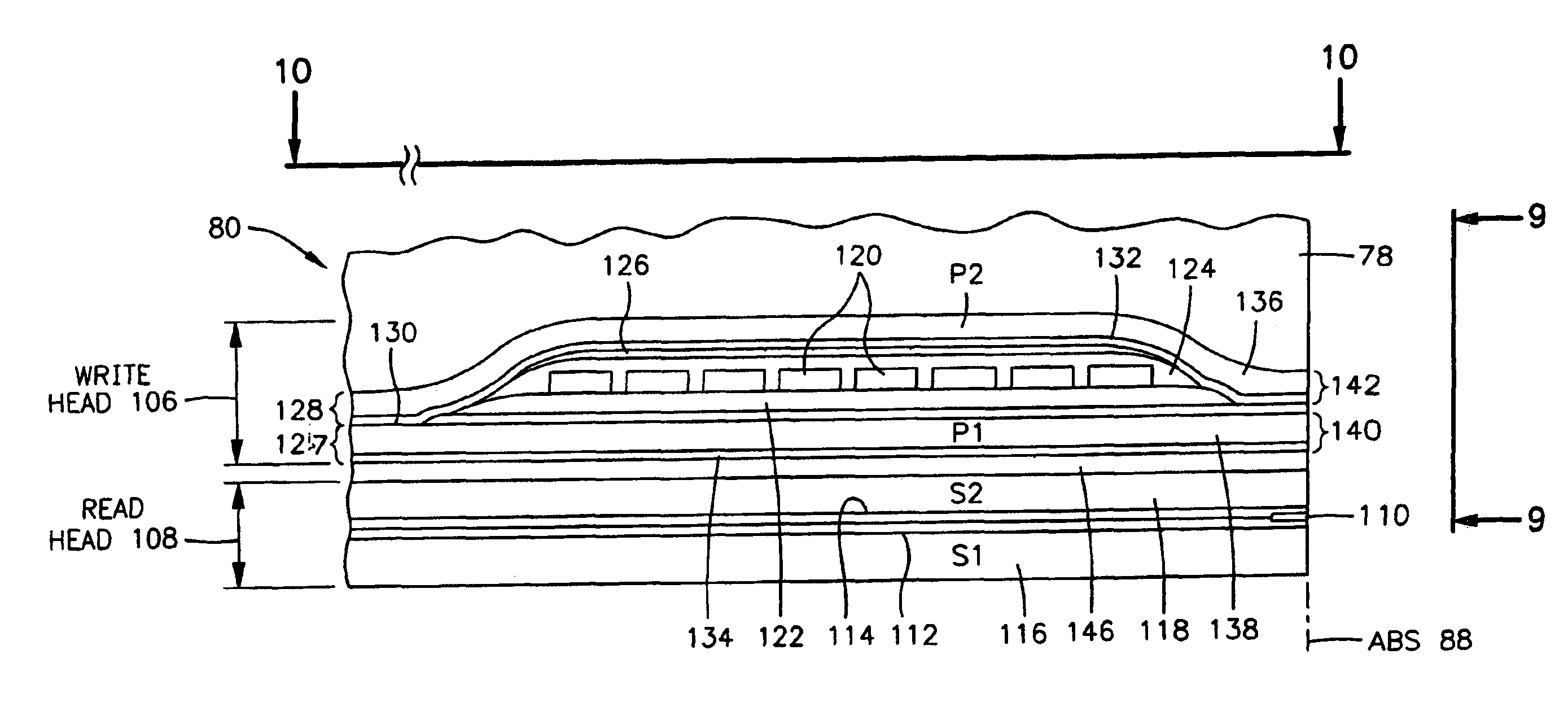
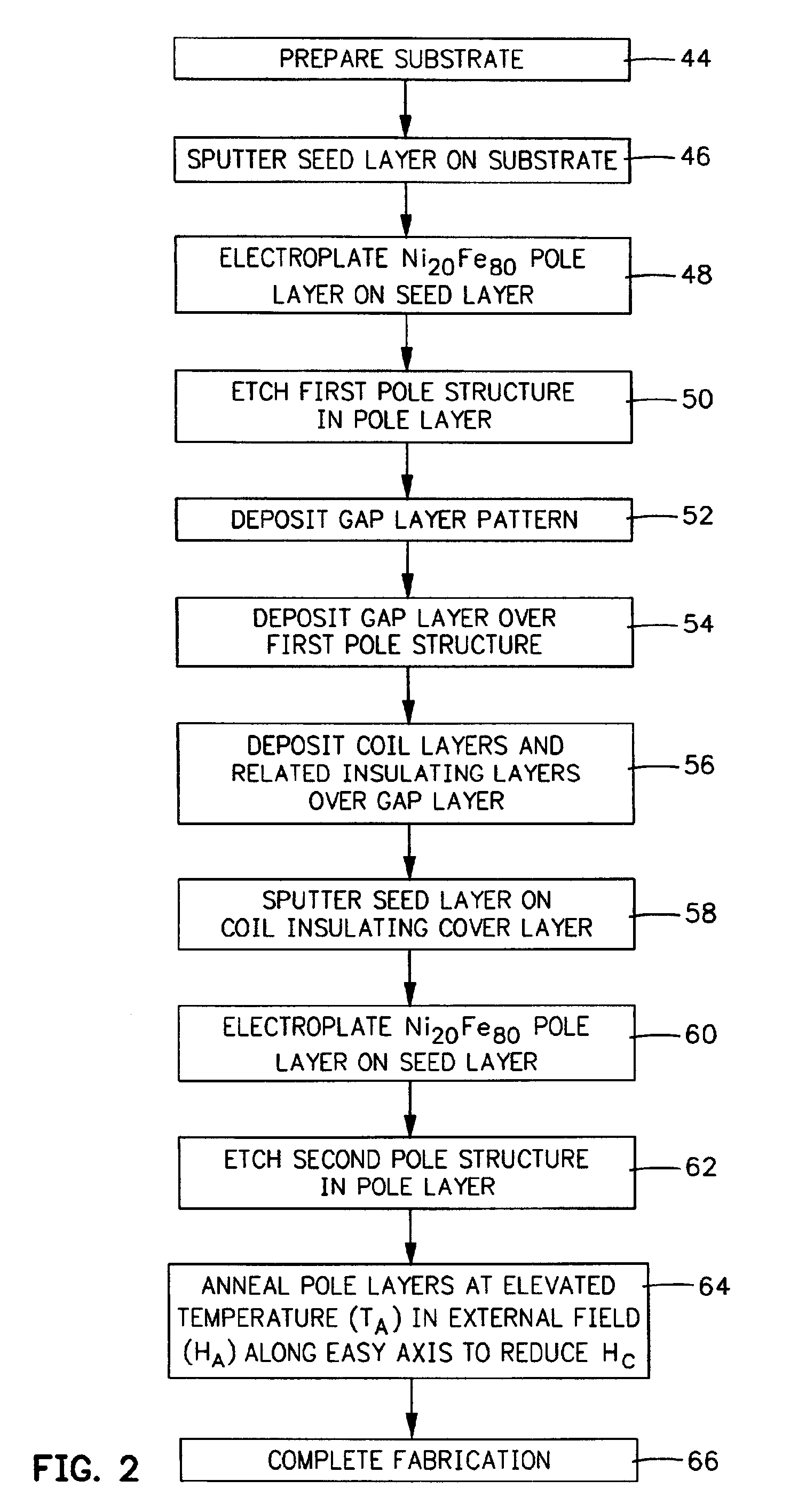
High-saturation thin-film write head for high-coercivity magnetic data storage media
InactiveUS6876507B2High level of magnetic fluxImproving data storage densityConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceMagnetic anisotropyAlloy
A thin-film write head employing pole pieces formed of an electroplated body-centered cubic (BCC) nickel-iron alloy with a saturation flux density (BS) of 1.9 to 2.3 T (19 to 23 kG) and an acceptable coercivity (HC) of about 80 to about 160 A / m (1-2 Oe). The iron content of the electroplated nickel-iron alloy is from 64% to 81% by weight. The two-layer pole fabrication process holds magnetic anisotropy and coercivity to useable values while improving saturation flux density and optimizing magnetostriction. This is accomplished by first electroplating a BCC nickel-iron layer onto an underlying seed layer and then annealing the two layers to reduce coercivity to less than about 160 amps / meter and raise magnetization to acceptable levels.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optimized process for processing steel slag by magnetic separation
The invention relates to an optimized process for processing steel slag by magnetic separation, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) screening steel slag by using a No.1 vibrating screen, separating out the steel slag and slag steel by using a No.1 magnetic separator to separate the oversize material, feeding the slag steel to a slag steel tank, and feeding the steel slagto a jaw crusher; (2) feeding the screen underflow of the No.1 vibrating screen and the discharge of the jaw crusher to a No.2 vibrating screen together, separating the oversize material by using a No.2 magnetic separator, feeding the separated slag steel to a rod mill, and stripping steel slag on the slag steel by the vibration effect of the rod mill; (3) feeding the steel slag separated out by the No.2 magnetic separator to a No.3 vibrating screen, feeding the oversize material to a large-size tailing storeroom, and feeding the screen underflow to a medium-size tailing storeroom; and (4) feeding the discharge of the rod mill to a No.4 vibrating screen, feeding the oversize material the iron content of which is no less than 90% to the slag steel tank, feeding the screen underflow to a No.3 magnetic separator, feeding the separated steel slag magnetic separation powder to a magnetic separation powder storeroom, and feeding the steel slag to a small-size tailing storeroom. By using theinvention, high-quality slag steel the iron content of which is more than 90% can be obtained, thereby fully recovering the iron in the steel slag.
Owner:鞍钢绿色资源科技有限公司
Graphite electrode for electrothermic reduction furnaces, electrode column, and method of producing graphite electrodes
InactiveUS20050254545A1Low production costElectric discharge heatingConductive materialGraphite electrodeCrystal structure
A graphite electrode for an electrothermic reduction furnace is formed from anode grade coke and graphitized at a graphitization temperature below 2700° C. The resulting electrode is particularly suited for carbothermal reduction of alumina. It has an iron content of about 0.05% by weight, a specific electrical resistivity of above 5 μOhm·m, and a thermal conductivity of less than 150 W / m·K. The graphite electrode is manufactured by first mixing calcined anode coke with a coal-tar pitch binder, and a green electrode is formed from the mixture at a temperature close to the softening point of the pitch binder. The green electrode is then baked to carbonize the pitch binder to solid coke. The resultant carbonized electrode, after further optional processing is then graphitized at a temperature below 2700° C. for a time sufficient to cause the carbon atoms in the carbonized electrode to organize into the crystalline structure of graphite.
Owner:SGL CARBON SE
Molten steel casting residue treatment and recycling method
ActiveCN102978305APromote expansion and pulverizationSolve the separation problemSievingScreeningSlagMolten steel
The invention discloses a molten steel casting residue treatment and recycling method which comprises the circular treatment steps of slaking, screening, magnetic separation and the like. The f-CaO in casting residue is slaked by vapor to accelerate the expansion and efflorescence of the casting residue, thereby solving the problem on the separation of the casting residue from a tank body and reducing dust nuisance. According to the method, a mixture of water spray casting residue and pyrolytic steel slag is used as the raw material, and the pyrolytic steel slag has the advantage of low f-CaO content, thereby ensuring that the f-CaO content of the final product can meet the requirements of cement and construction material industries; and a rod grinder treatment process is used, thereby achieving favorable grinding effect and ensuring that the product is uniform and stable in particle size. For the product disclosed by the invention, slag steel of which the grade is greater than 80% can be returned for steel making; purified steel shots and magnetic separation powder of which the grade is greater than 42% can be used for a sintering procedure; and steel tailings of which the iron content is smaller than 2% and the f-CaO content is smaller than 3% can be used for producing steel slag powder, steel slag cement, construction material products and road materials. The invention maximally recycles the metal material in the casting residue, realizes the zero discharge of industrial solid waste and ensures that the casting residue can be recycled 100% at a high added value.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
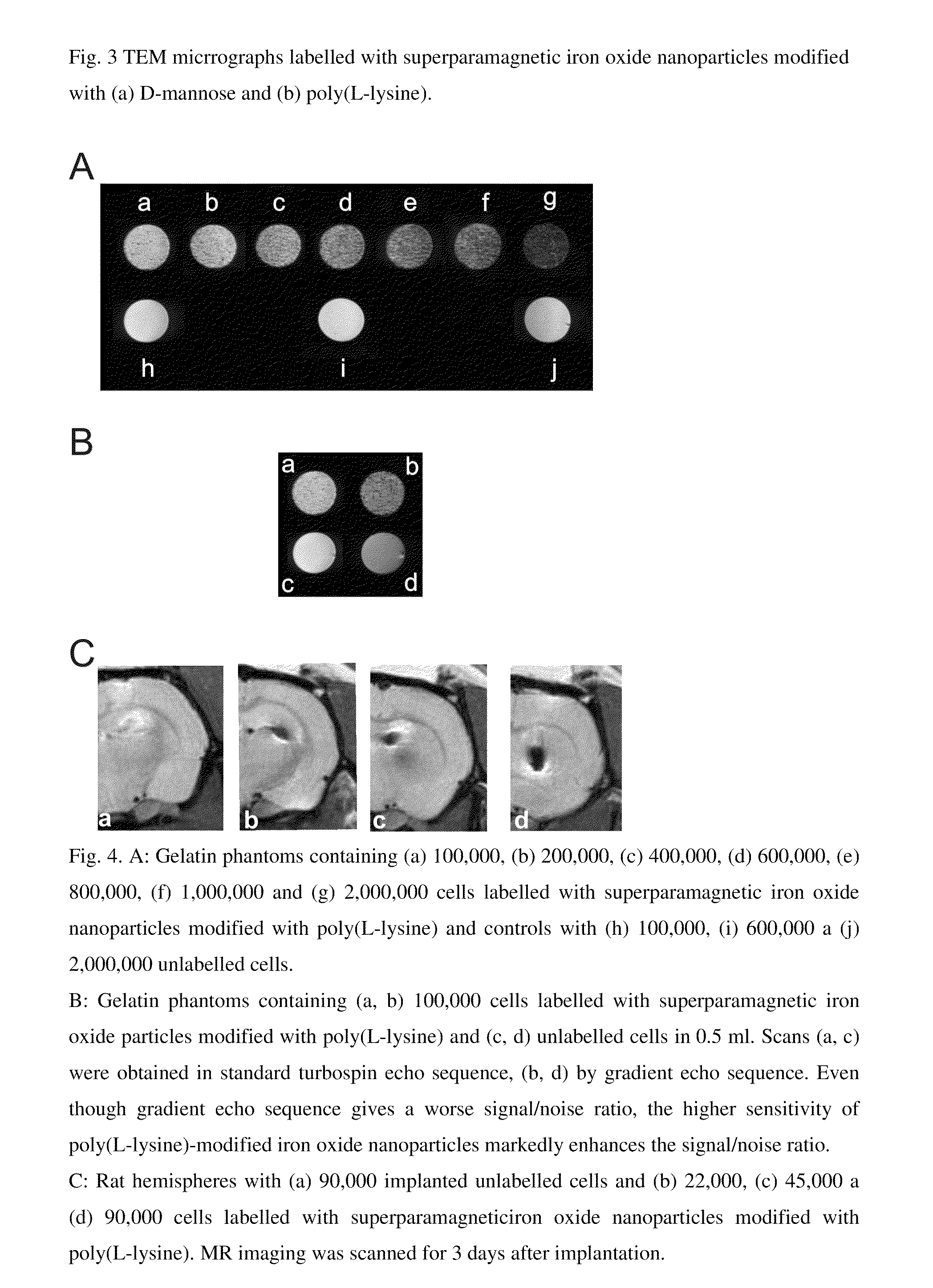
Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides with Modified Surface, Method of Their Preparation and Application
InactiveUS20090309597A1Less loadImprove abilitiesPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyArginineDextran
The subject of the invention is superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes based on iron oxides, to advantage magnetite or maghemite, with modified surface, coated with mono-, di- or polysaccharides from the group including D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextrans and dextrins, or with amino acids or poly(amino acid)s from the group including alanine, glycine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, arginine, L-lysine, aspartic and glutamic acid or with synthetic polymers based on (meth)acrylic acid and their derivatives selected from the group containing poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-dimethylmethacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylmethacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide), which form a colloid consisting of particles with narrow distribution with polydispersity index smaller than 1.3, the average size of which amounts to 0.5-30 nm, to advantage 1-10 nm, the iron content is 70-99.9 wt. %, to advantage 90 wt. %, the modification agent content 0.1-30 wt. %, to advantage 10 wt. %.The particles of size smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 can be obtained by a modified method of preparation.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention are prepared by pre-precipitation of colloidal Fe(OH)3 by the treatment of aqueous 0.1-0.2M solution of Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl3, with less than an equimolar amount of NH4OH, at 21° C., under sonication, to which a solution of a Fe(II) salt, to advantage FeCl2, is added in the mole ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2 under sonication and the mixture is poured into five- to tenfold, to advantage eightfold, molar excess of 0.5M NH4OH. The mixture is left aging for 0-30 min, to advantage 15 min, and then the precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, magnetically separated and washed with deionized water. Then 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.1 M aqueous solution of sodium citrate is added and then, dropwise, 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.7 M aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite. The precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, washed with deionized water under the formation of colloidal maghemite to which, after dilution, is added dropwise, to advantage under 5-min sonication, an aqueous solution of a modification agent, in the weight ratio modification agent / iron oxide=0.1-10, to advantage 0.2 for amino acids and poly(amino acid)s and 5 for saccharides.The particles smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 are prepared by mixing at 21° C. 1 volume part of 10-60 wt. %, to advantage 50 wt. %, of an aqueous solution of a saccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide, such as D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextran and dextrins, and 1 volume part of aqueous solution of a Fe(II) and Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl2 and FeCl3, where the molar ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2. A 5-15%, to advantage 7.5%, solution of NH4OH is added until pH 12 is attained and the mixture is heated at 60° C. for 15 min. The mixture is then sonicated at 350 W for 5 min and then washed for 24 h by dialysis in water using a membrane with molecular weight cut-off 14,000 until pH 7 is reached. The volume of solution is reduced by evaporation so that the final dry matter content is 50-100 mg / ml, to advantage 80 mg per 1 ml.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention can be used for labelling cells used in magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring their movement, localization, survival and differentiation especially in detection of pathologies with cell dysfunction and of tissue regeneration and also for labelling and monitoring cells administered for cell therapy purposes, in particular embryonal stem cells, fetal stem cells, stem cells of an adult human including bone marrow stem cells, olfactory glial cells, fat tissue cells, in the recipient organism by magnetic resonance.The preparation of labelled cells proceeds by adding to the complete culture medium 5-20 μl, to advantage 10 μl, of a colloid containing 0.05-45 mg iron oxide per ml, to advantage 1-5 mg iron oxide per ml of the medium, and culturing the cells for a period of 1-7 days, to advantage for 1-3 days, at 37° C. and 5% of CO2.
Owner:INST OF MACROMOLECULAR CHEM ASCR V V I +1
Toner and image forming method
InactiveUS6447969B1Improve charging effectHigh image densityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusElectron microscopeFerric
A toner is formed of toner particles each comprising a binder resin and iron oxide particles dispersed therein. The toner particles are characterized by uniform but non-surface-exposed dispersion of the iron oxide particles within the toner particles as represented by (i) a carbon content (A) and an iron content (B) giving a ratio B / A<0.001 at surfaces of the toner particles as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, (ii) an average circularity of at least 0.970, and (iii) at least 50% by number of toner particles satisfying D / C<=0.02, wherein C denotes a projection area-equivalent circular diameter of each toner particle and D denotes a minimum distance of iron oxide particles from a surface of the toner particle, based on a sectional view of the toner particle as observed through a transmission electron microscope (TEM).
Owner:CANON KK
Preparation method of solar ultrawhite ultrathin glass and product thereof
InactiveCN102219376AIron sulfide reductionHigh whitenessGlass furnace apparatusGlass rolling apparatusFragilityIron sulfide
The invention relates to the field of production of ultrawhite rolled glass, in particular to a preparation method of solar ultrawhite ultrathin glass and a product thereof. The preparation method of the solar ultrawhite ultrathin glass comprises the following steps of: selecting and preparing raw materials; conveying the raw materials; melting; forming glass; annealing; detecting; and cutting and packaging. In the preparation method, iron content is controlled by taking different measures in the steps of selecting and conveying the raw materials, so that iron sulfide in the final solar glass is greatly reduced and the whiteness of the glass is improved; in the melting process, bubbles in the melted glass liquid is reduced by exhausting air and debubbling, controlling temperature and adding a glass clarifying agent, so that absorption rate is reduced and light transmittance is improved; and the annealing step of the glass finished product is a key link of the production process and plays an important role in the quality of the ultrathin glass product, so the defects that the ultrathin glass is easy to harden and easy to break during production and has high fragility are overcome by controlling rolling velocity, temperature and annealing rate in the process of glass forming and glass annealing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINGXING SOLAR ENERGY TECH
Method for comprehensively recovering gold, iron and sulphur resource from gold-containing sulfurous iron ore
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering gold sulfurous iron resources from gold-bearing sulfurous iron ore, comprising the following steps: middle and low-grade sulfurous iron ore containing micro-gold and enclosed gold is grinded, and gold-bearing high-grade sulfur ore concentrate is obtained after sulfate dipping, mixture, floatation and concentration for a plurality of times; the ore concentrate undergoes high-temperature overoxidation roasting in a fluid-bed furnace to prepare sulfuric acid after flue gas undergoes dust removal and purification, and cinder becomes high-iron low-sulfur gold-bearing slag; the cinder is added with a pellet adhesive and a chlorating agent for grinding, and a pellet is prepared; the pellet is dried and then undergoes high-temperature chlorination-evaporation roasting; the flue gas is roasted and gold concentrate is obtained after dust collection; and the roasted pellet ore is a high-quality iron-making raw material the iron content of which is more than 60 percent and the gold content of which is less than 0.2 grams per ton. The technology highly efficiently recovers a large amount of gold resources which is lost in the sulfurous iron ore due to difficult cyanidation and leaching caused by containing the micro-gold and the enclosed gold through mixture and floatation of gold and sulfur, concentrate for a plurality of times, high-temperature overoxidation roasting deep desulfurization and high-temperature chlorination roasting degolding, obtains high-quality iron pellet ore while obtaining the sulfuric acid, and highly efficiently utilizes iron resources.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Silica heat-proof firebrick
ActiveCN101139210AExcellent physical and chemical indicatorsHigh temperature resistantSlurryRaw material
The present invention relates to the fireproof material technology field, in particular to a silicon heat insulation fireproof brick adaptable to be used in coke oven and carbon stove. The present invention can solve the shortcomings in the prior clay heat-insulation and fireproof brick that load distortion temperature is low; the material is easy to be shrunk in the high temperature; the heat conductivity ratio is much larger and the heat preservation effect is much worse and so on. The components and the relative weight ratio in the present invention are that: 81-85 percent of silica powder, 15-19 percent of perlite, and the following assistant materials, whose weight ratio occupied in the main raw materials is as follow: 045-0.55 percent of iron scale powder, 0.9-1.1 percent of cement, 6.5-7.5 percent of lime milk, 1.95-2.2 percent of paper slurry. The silica powder and the perlite with the stated matched ratio are added into a humid grinder and then the iron scale powder and the cement are added into to be grinded for 1-2 minutes; and then the water with the weight ratio occupied in the main raw material 1.8-2.2 percent is added, and then the lime milk is also added to be grinded and pressed for 10-15 minutes. Finally, the paper slurry is added to be grinded and pressed for 10-15 minutes. The mixture is taken out from the grinder to be molded. Each physical and chemical index of the silicon heat insulation fireproof brick in the present invention is better than the national standard; the present invention has the advantages of heat-resisting, low heat conductivity, low iron content, large compression strength and much better heat stability and so on. The present invention can be directly used as the inner bushing for the industrial stove.
Owner:山西盂县西小坪耐火材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com