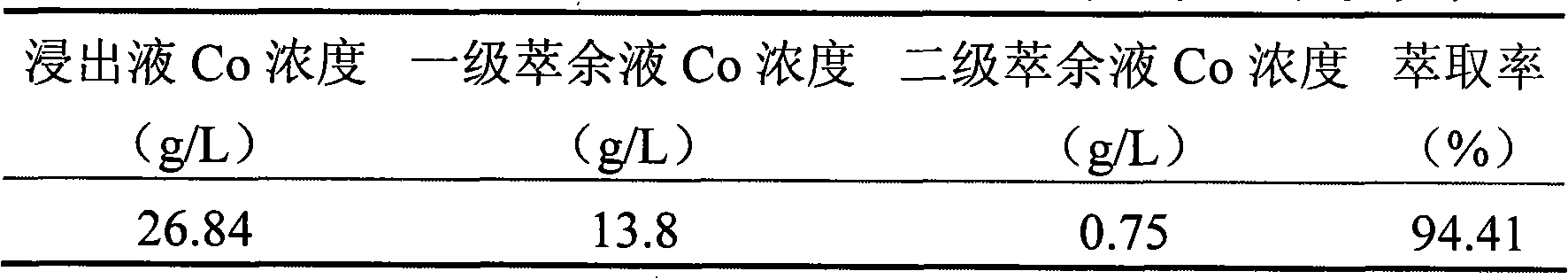
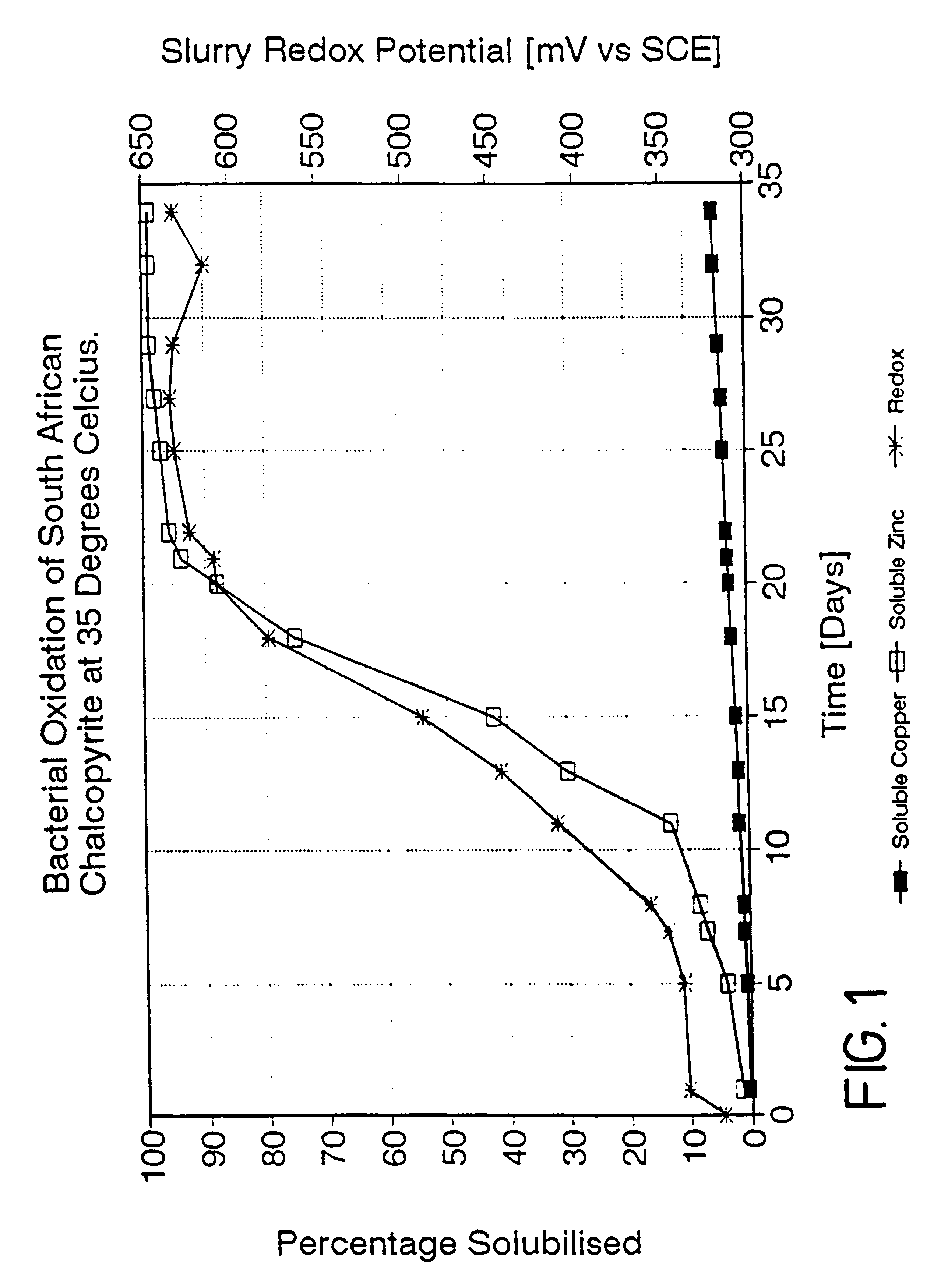
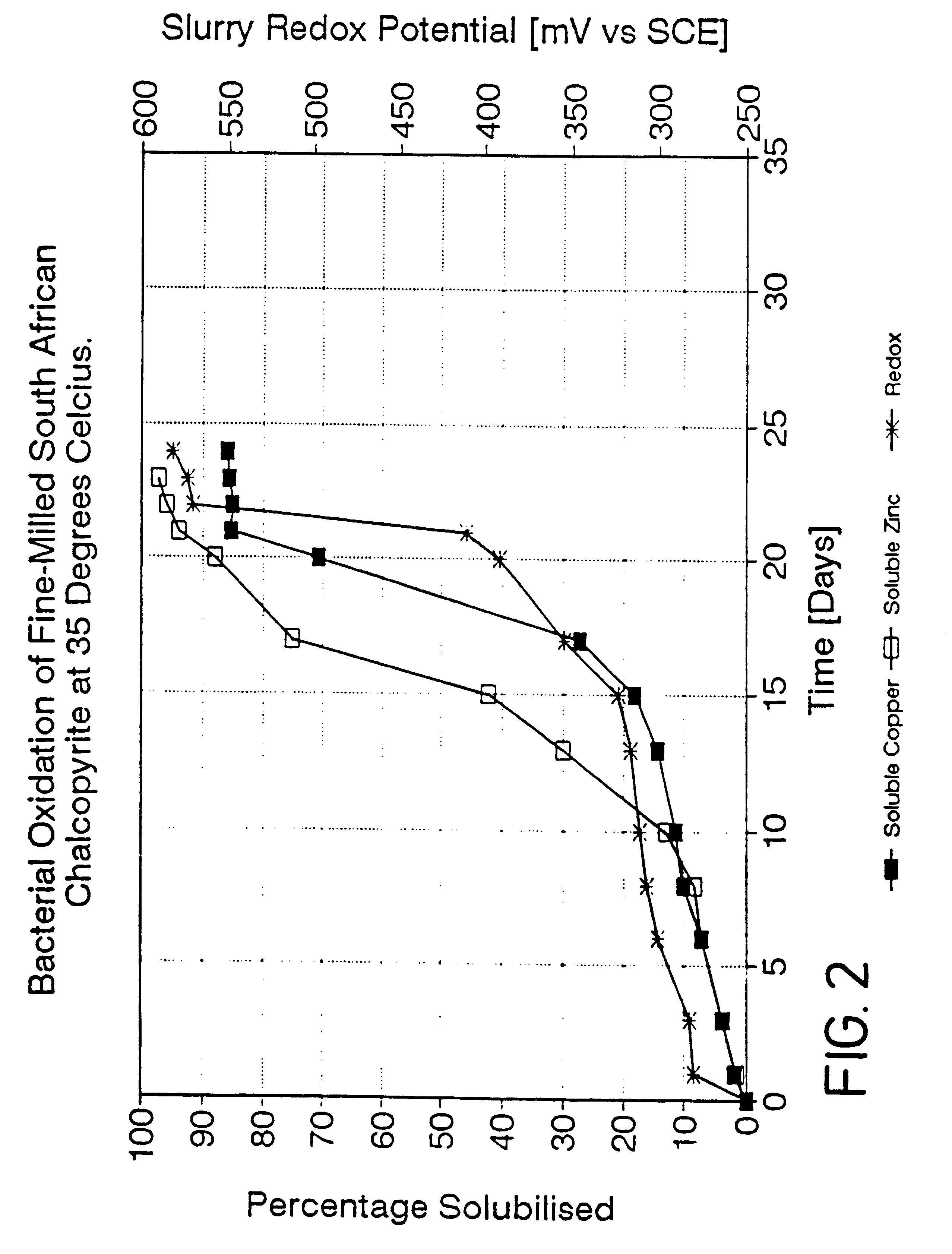
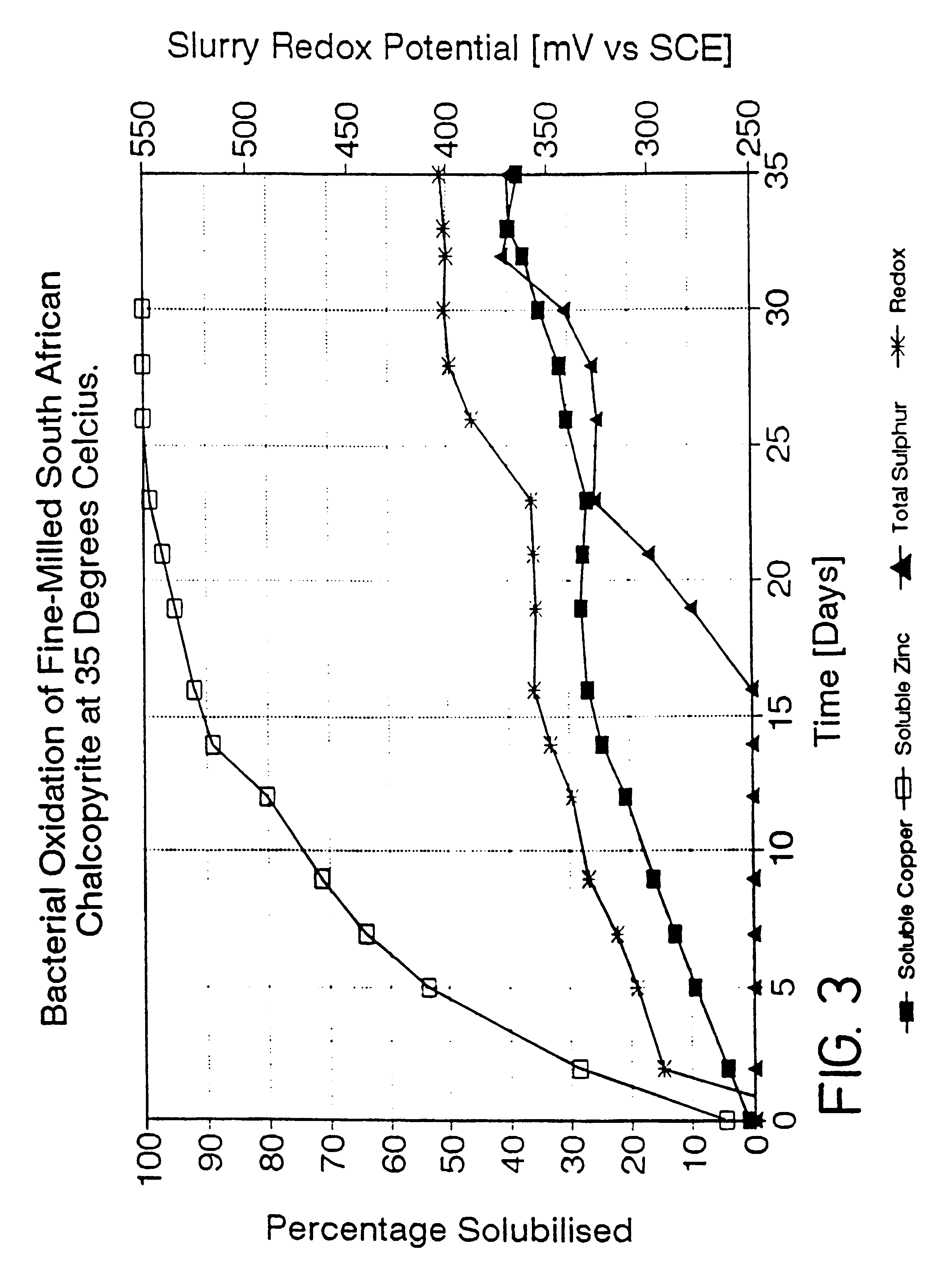
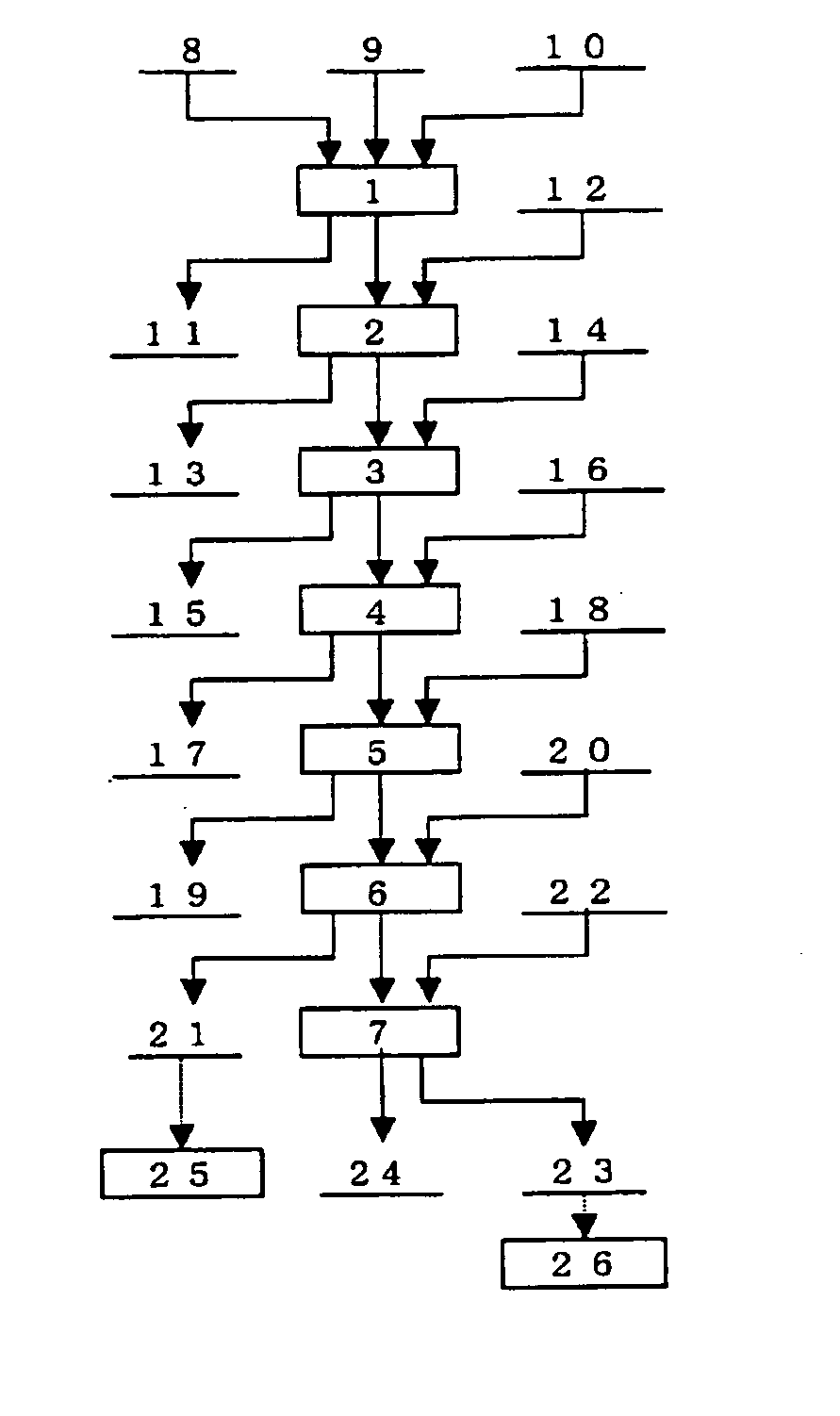
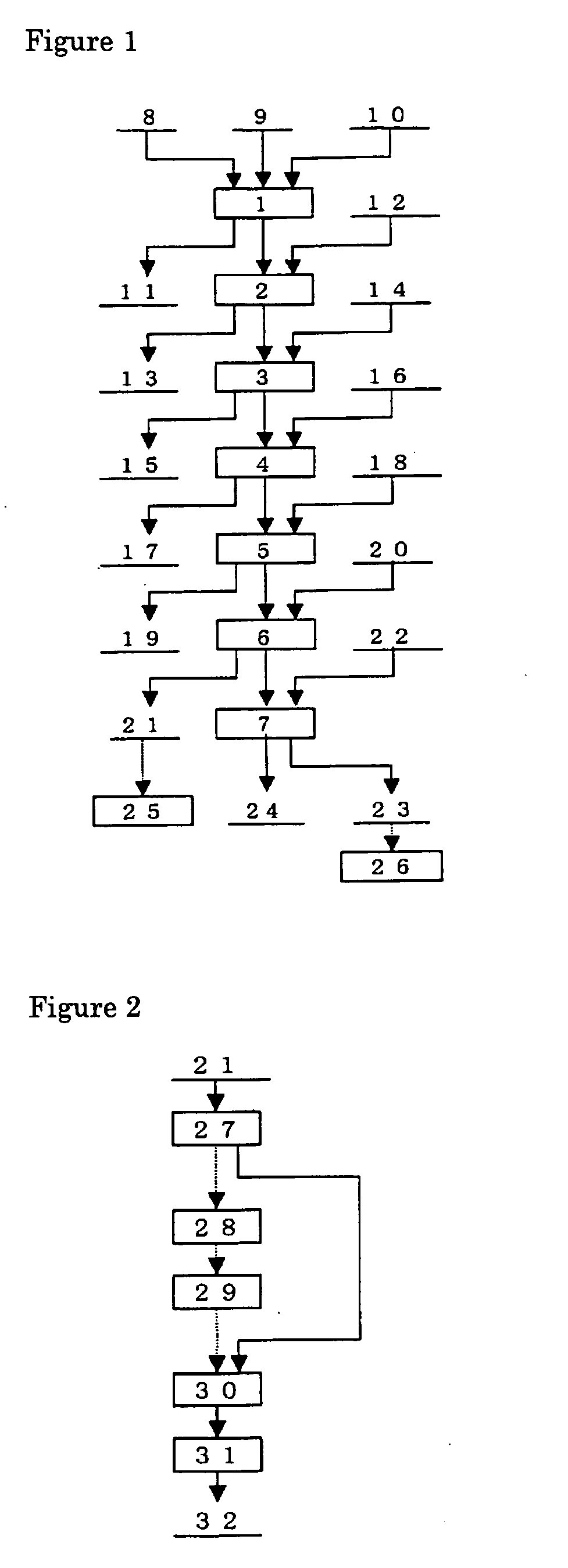
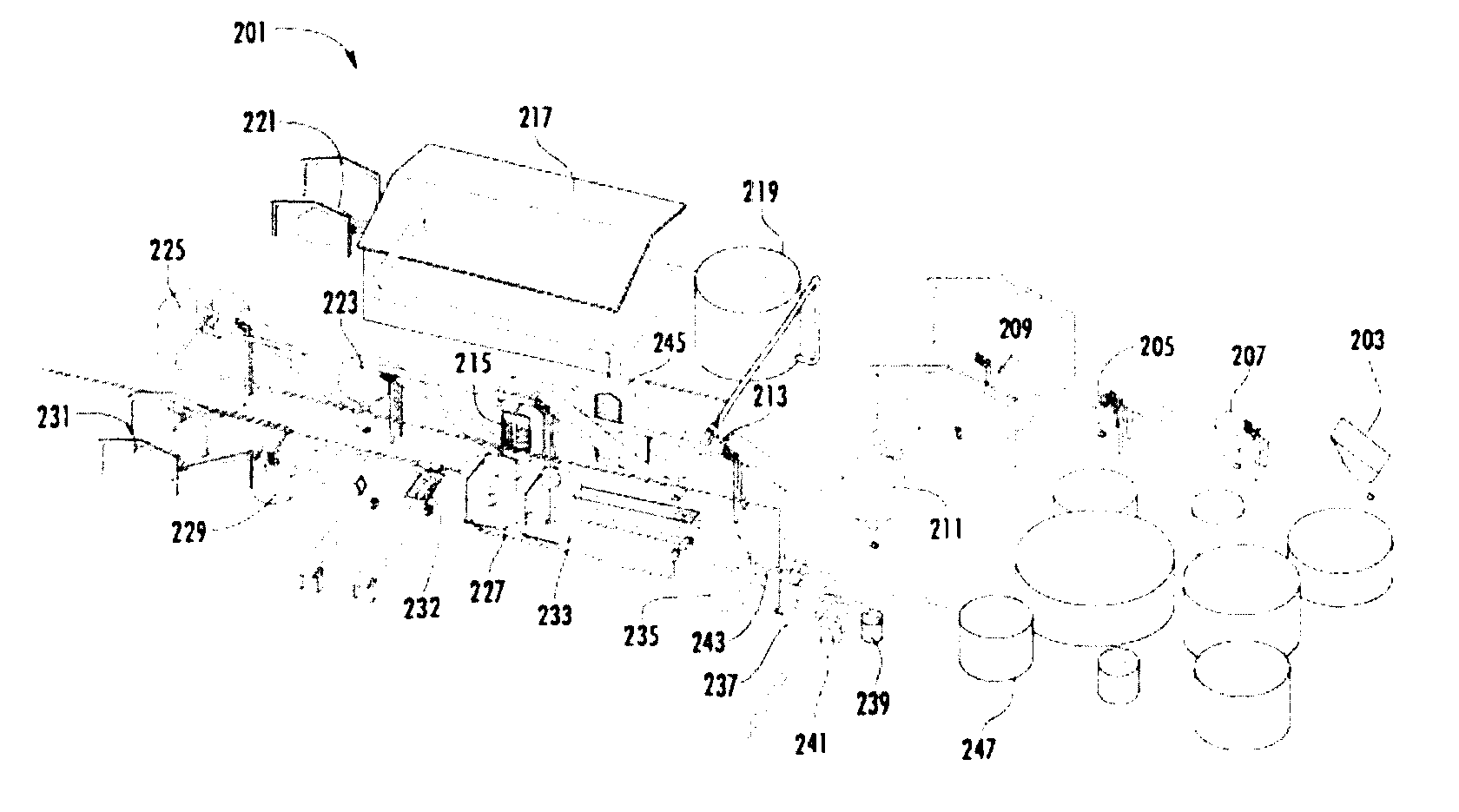
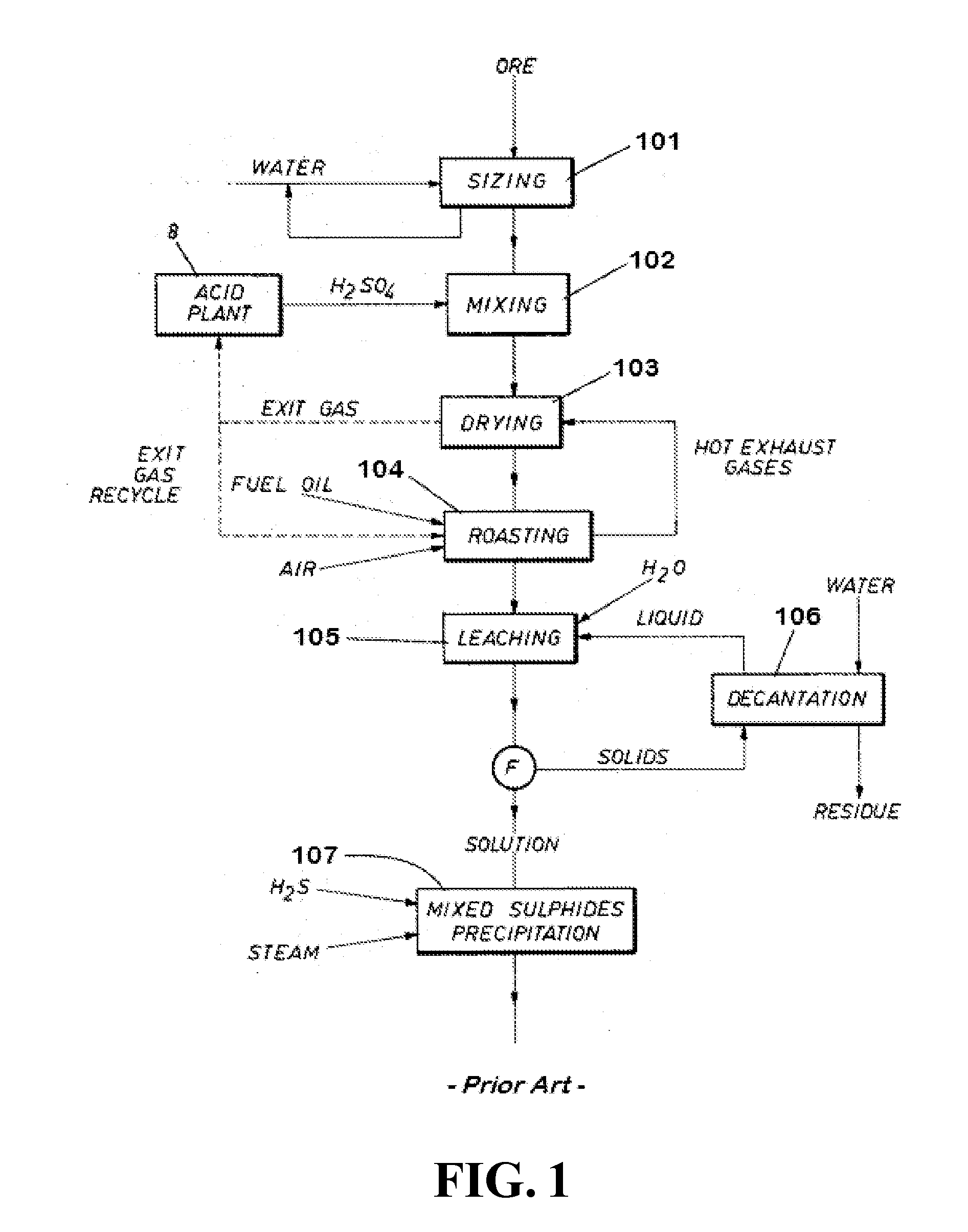
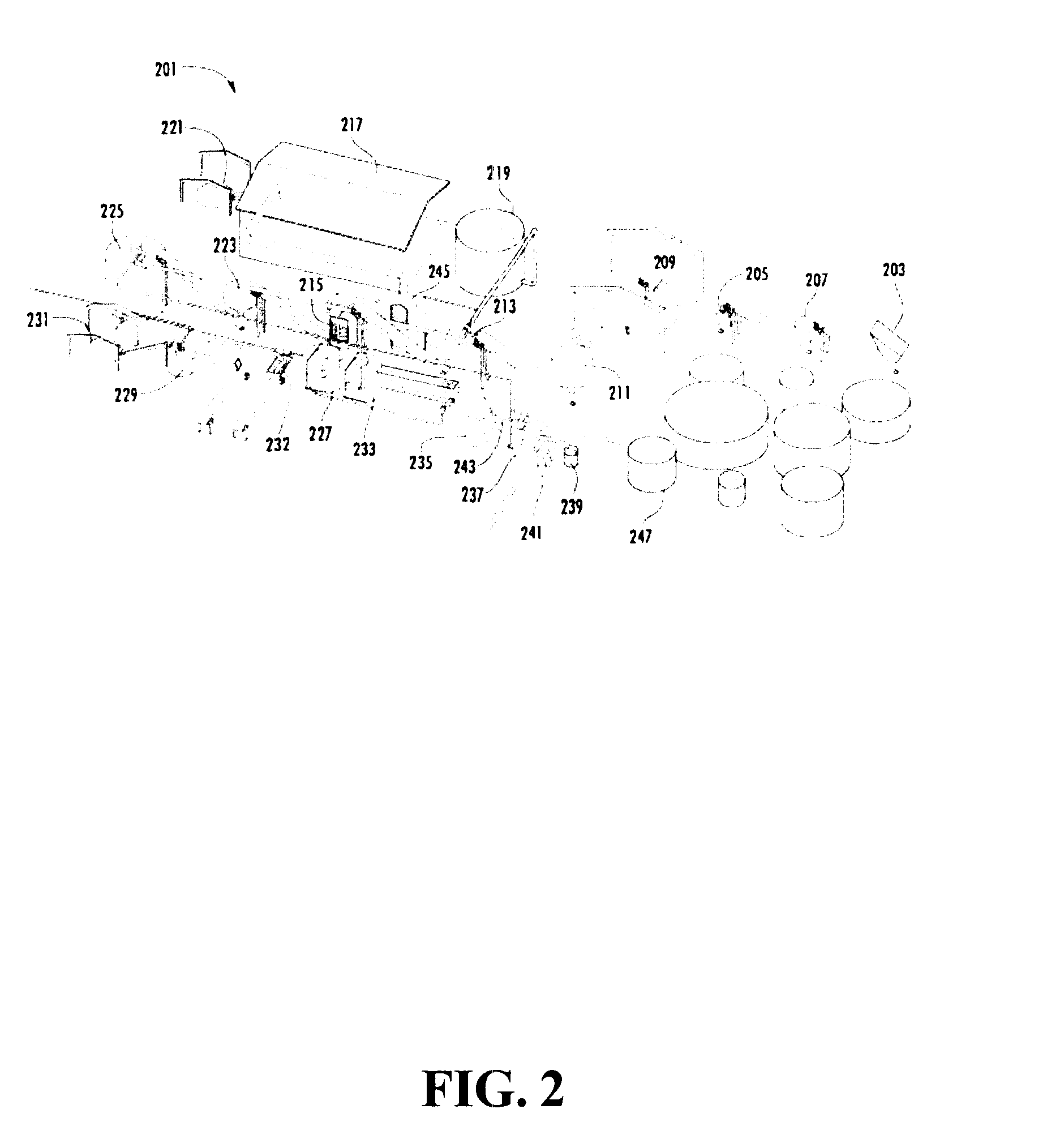
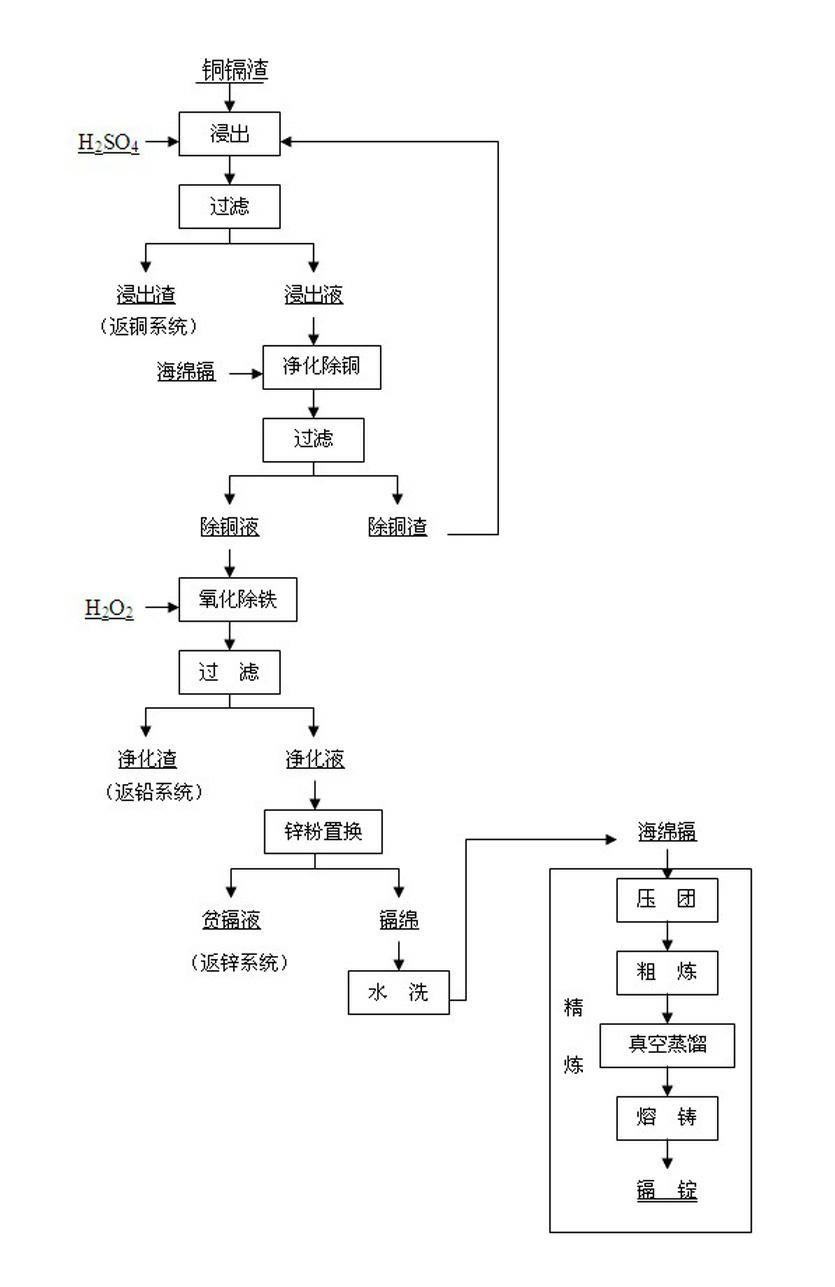
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3881 results about "Pregnant leach solution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
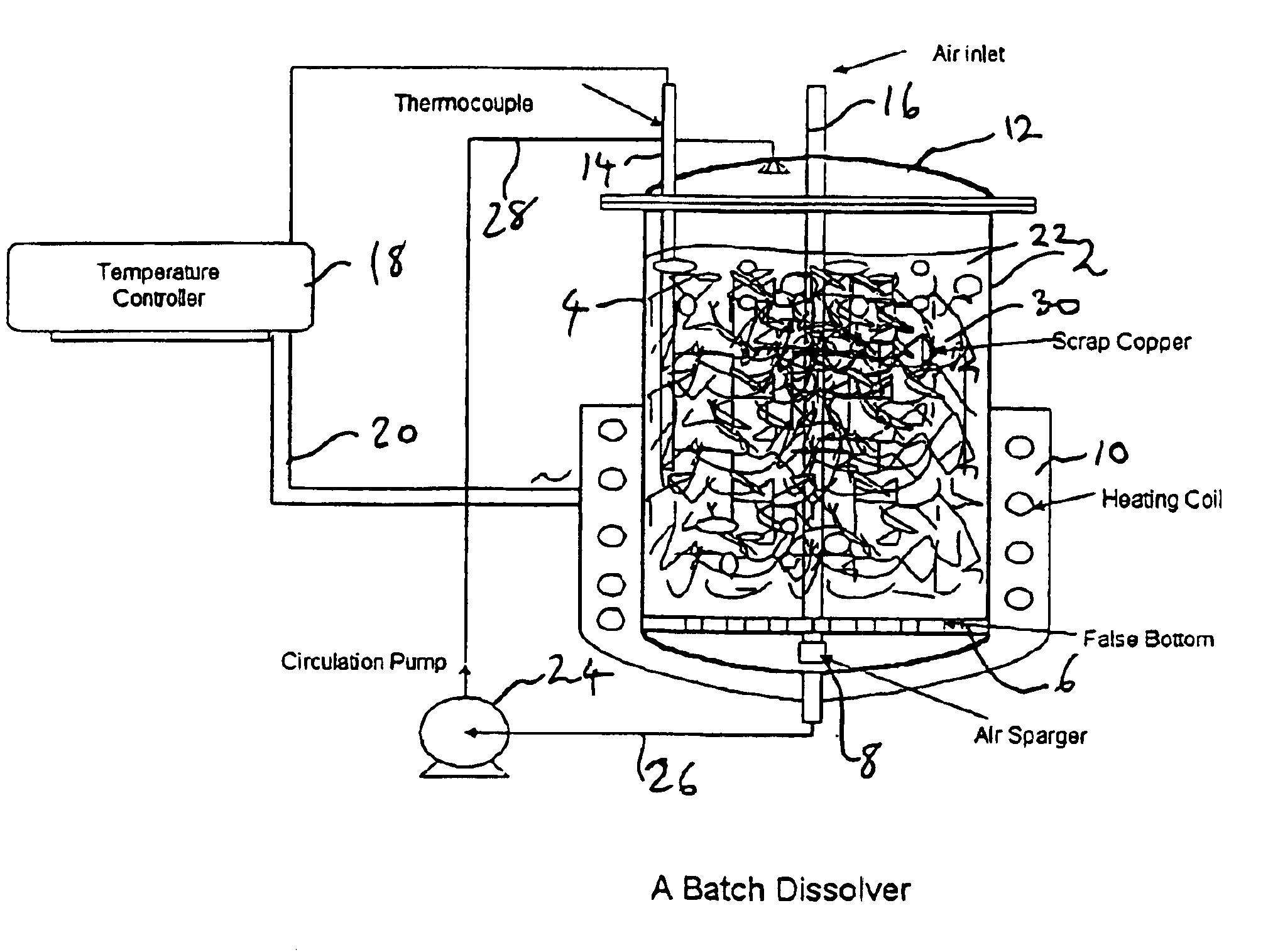
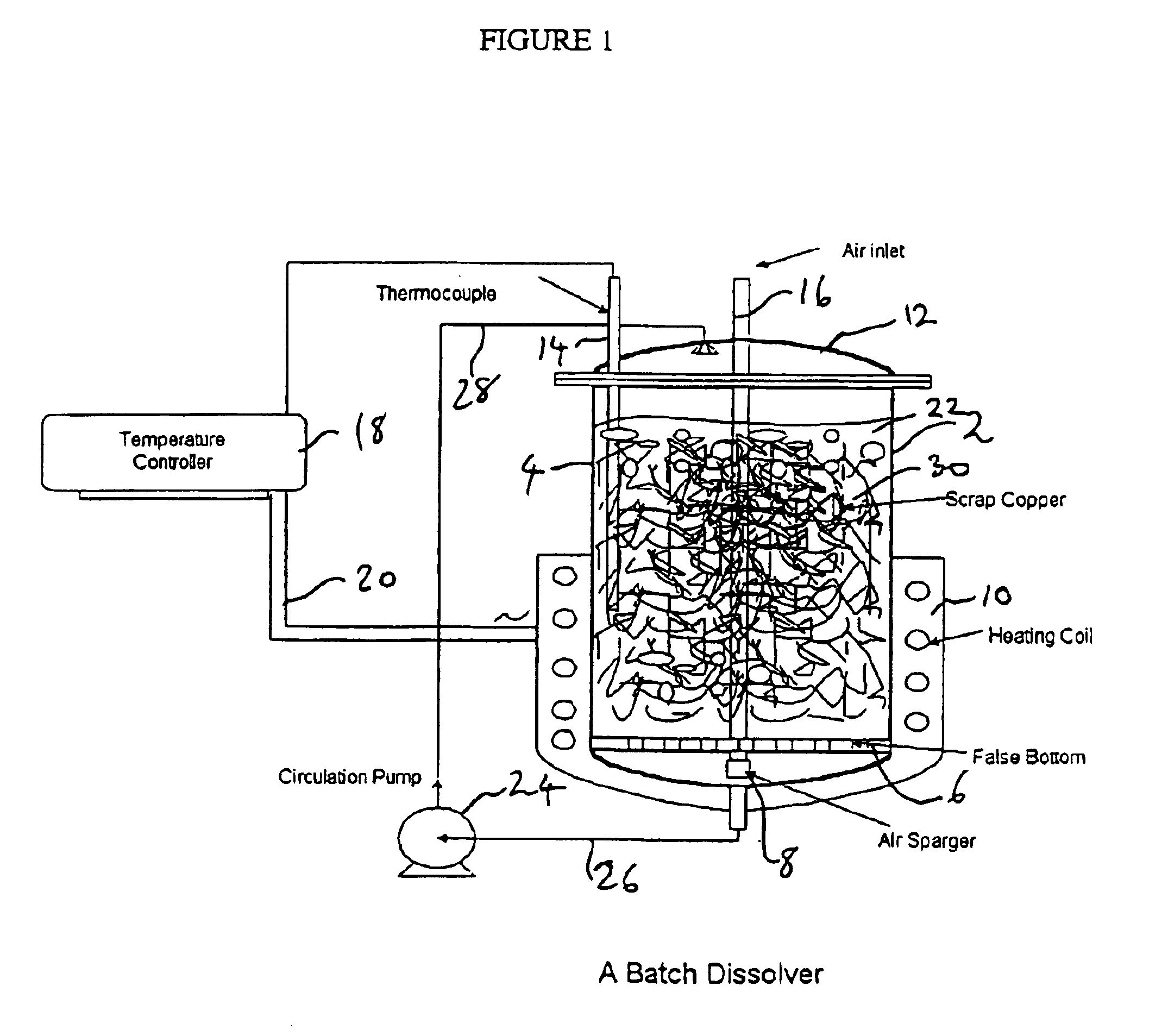
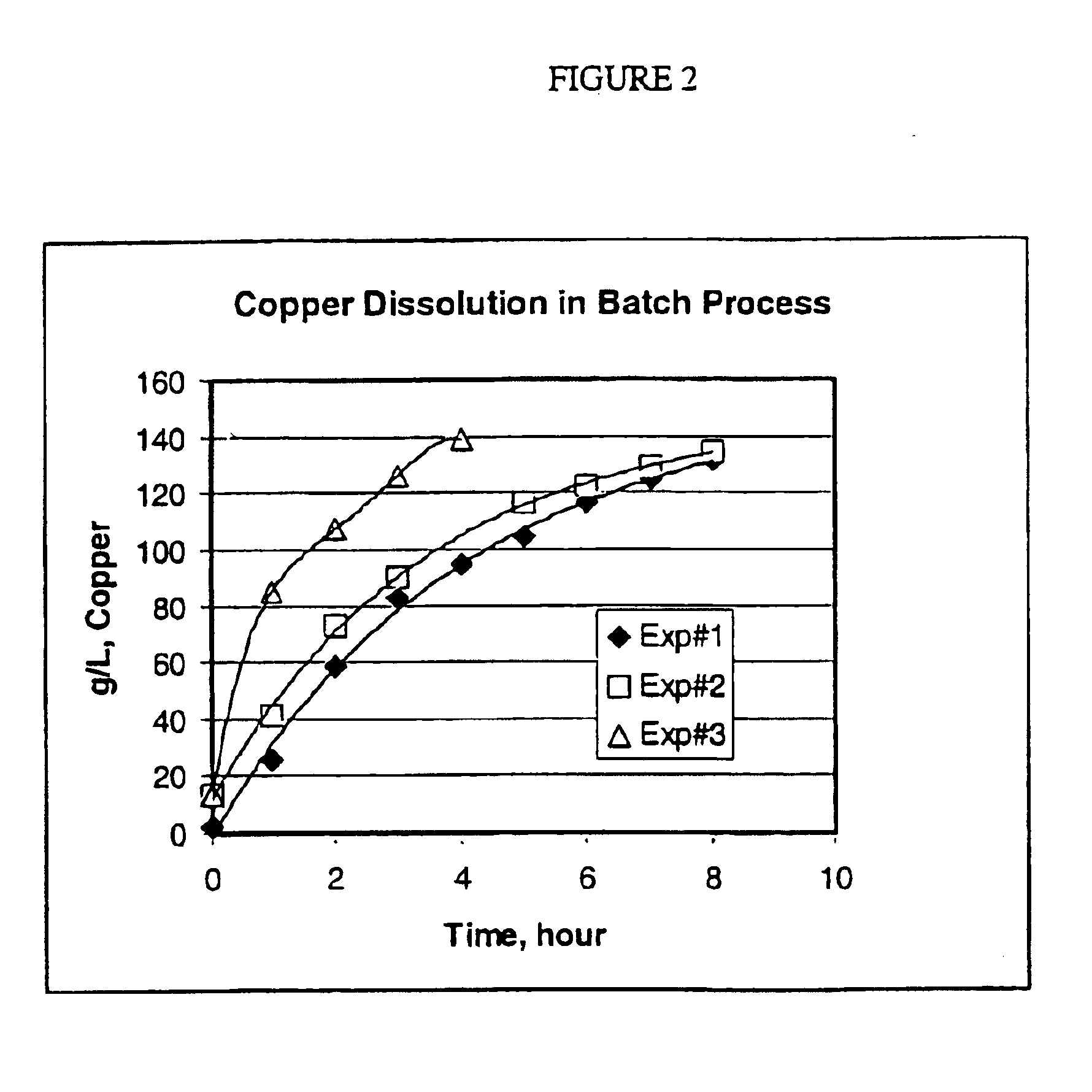
Pregnant Leach Solution (PLS) is acidic metal-laden water generated from stockpile leaching and heap leaching. Pregnant Leach Solution is used in the SX/EW process. The portion of an original liquid that remains after other components have been dissolved by a solvent is called raffinate.
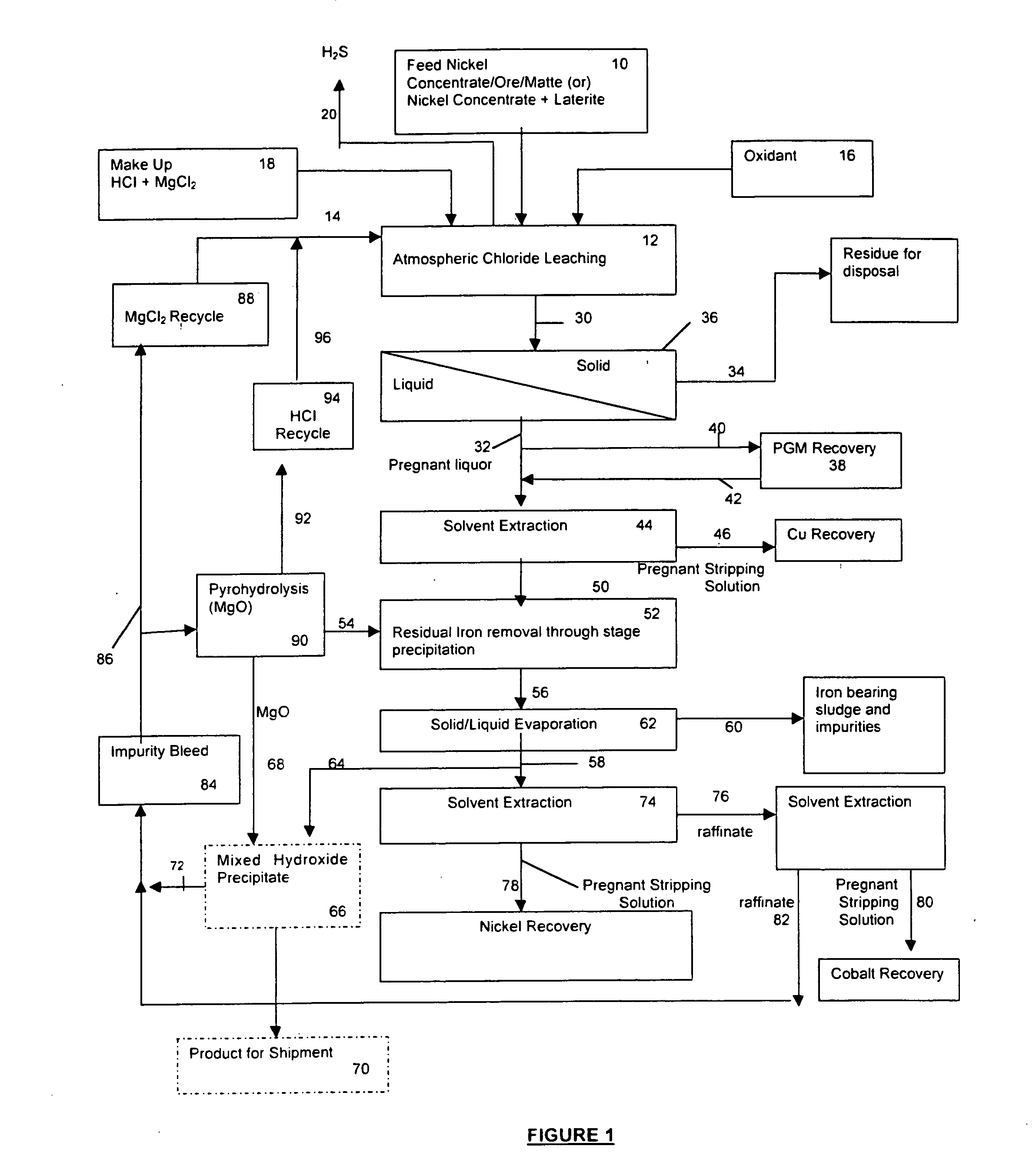
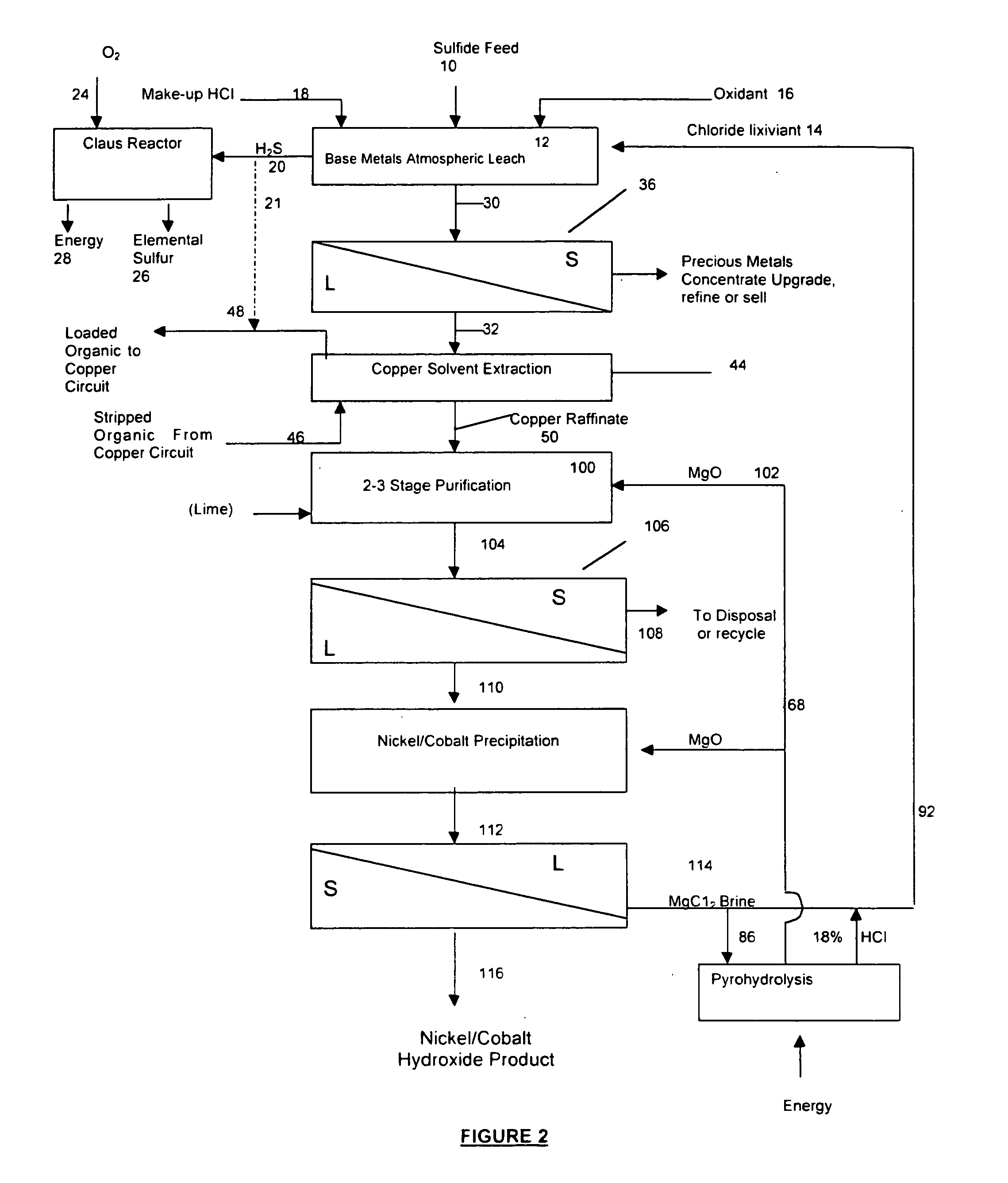
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS20050118081A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfideDissolution
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
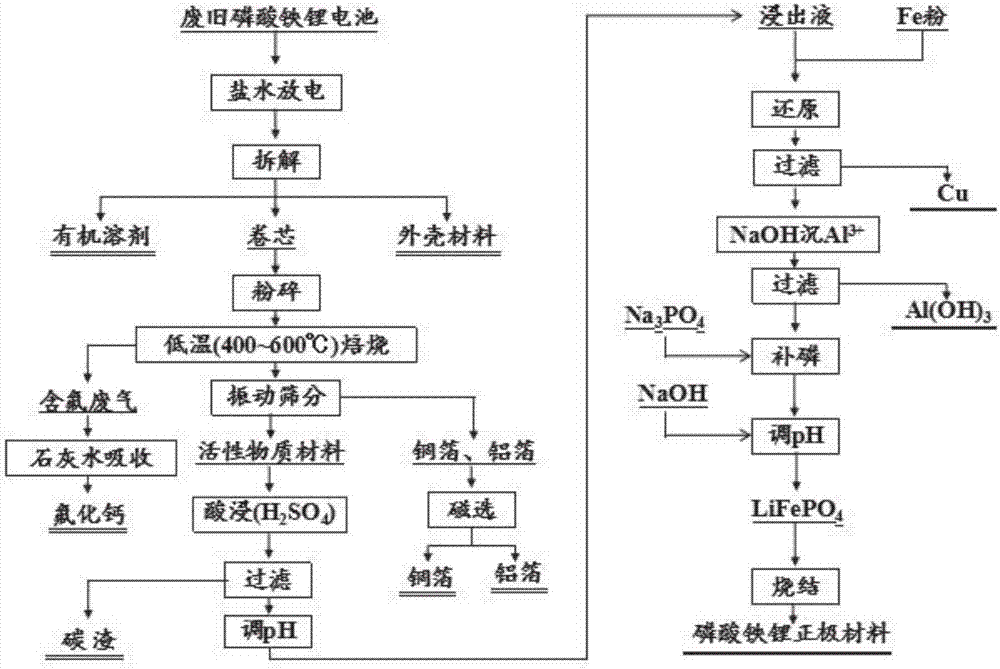
Method for regenerating positive active material from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries
ActiveCN106910889ARealize combination generationQuality assuranceCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingFiltrationCopper foil
The invention discloses a method for regenerating a positive active material from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) waste lithium iron phosphate batteries are discharged in saline water, and organic solvents, roll cores and casing materials are disassembled; 2) the roll cores are subjected to crushing, calcination and other steps, and active materials, copper foil and aluminum foil are separated through vibrating screening. Fluorine-containing waste gas is absorbed with lime water, the copper foil and the aluminum foil are separated with a magnetic separation method, the active materials are leached out with sulfuric acid, and a leachate and carbon residues are obtained through separation; 3) Cu<2+> in the leachate is reduced to elementary copper by adding iron powder, meanwhile, Fe<3+> is reduced to Fe<2+>, copper and excessive iron residues are filtered out, aluminum is removed through precipitation with an alkaline liquid, the filtrate is supplemented with a phosphorus source after filtration, the pH value is adjusted by adding the alkaline liquid, coarse lithium iron phosphate precipitates are produced, and finally, battery-grade lithium iron phosphate is obtained through sintering. Comprehensive utilization of the waste lithium iron phosphate batteries and regeneration of the active materials are realized with a simple, practical, economical and feasible method, no secondary pollution is produced, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Neutral inorganic composite material for dehydration, solidification and modification of high water content sludge
ActiveCN101955345ASolving Alkaline ProblemsHigh compressive strengthSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSolid waste managementHazardous substanceHigh water content
The invention discloses a neutral inorganic composite material for dehydration, solidification and modification of high water content sludge. The composite material comprises a powdery mixture consisting of the following components in part by weight: 100 parts of water hardened solidifying material consisting of hydrated gypsum and magnesium oxide, 80 to 120 parts of inorganic water absorption ash material, 20 to 40 parts of inorganic substance aid hardened material, 1 to 10 parts of high polymer coagulant and 1 to 5 parts of modifying functional agent. After being treated by the neutral inorganic composite material, the solidified sludge has high compressive strength; the pH of the lixivium is neutral, and meanwhile, harmful substances such as heavy metal and the like in the sludge can be effectively solidified; the treated sludge meets the requirement of landfill soil, soil for earthwork or soil for greening and farmlands; and the neutral inorganic composite material can be widely applied to the dehydration, solidification and modification of the high water content sludge such as sludge from waterworks, dredged bottom mud of rivers and lakes, residual building soil and the like.
Owner:江苏艾特克环境工程有限公司
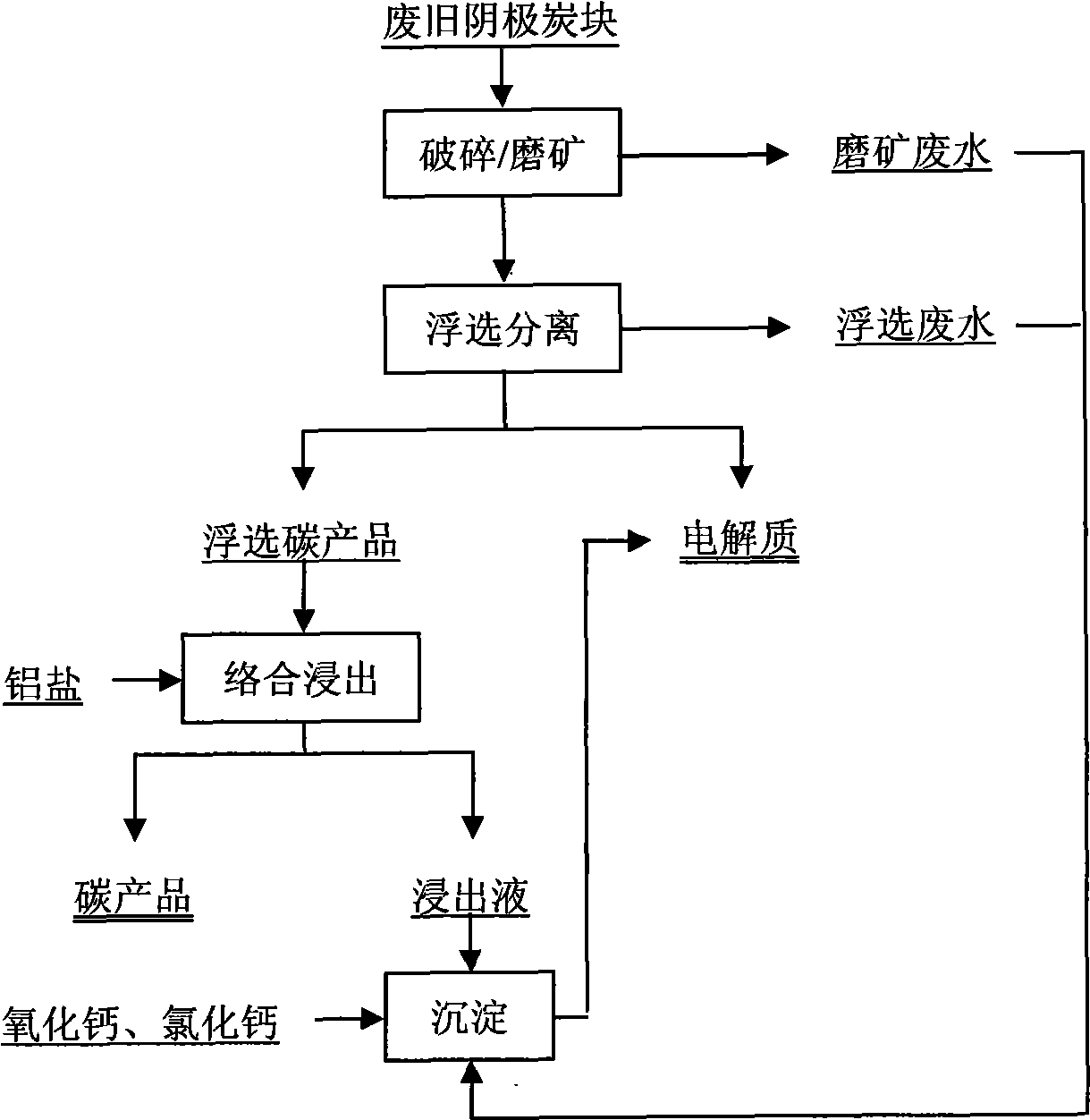
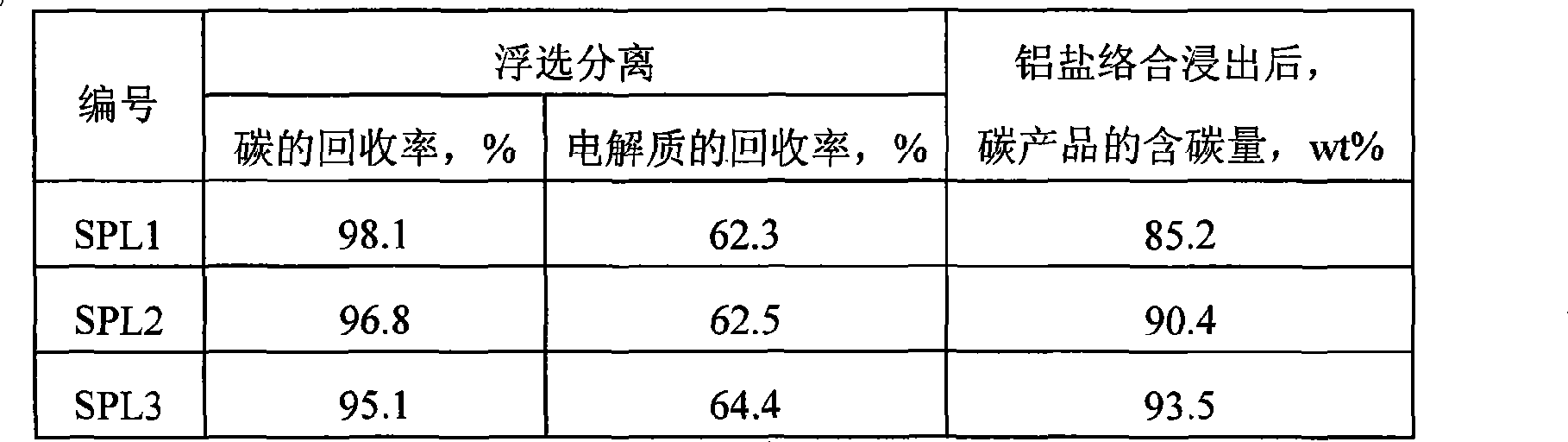
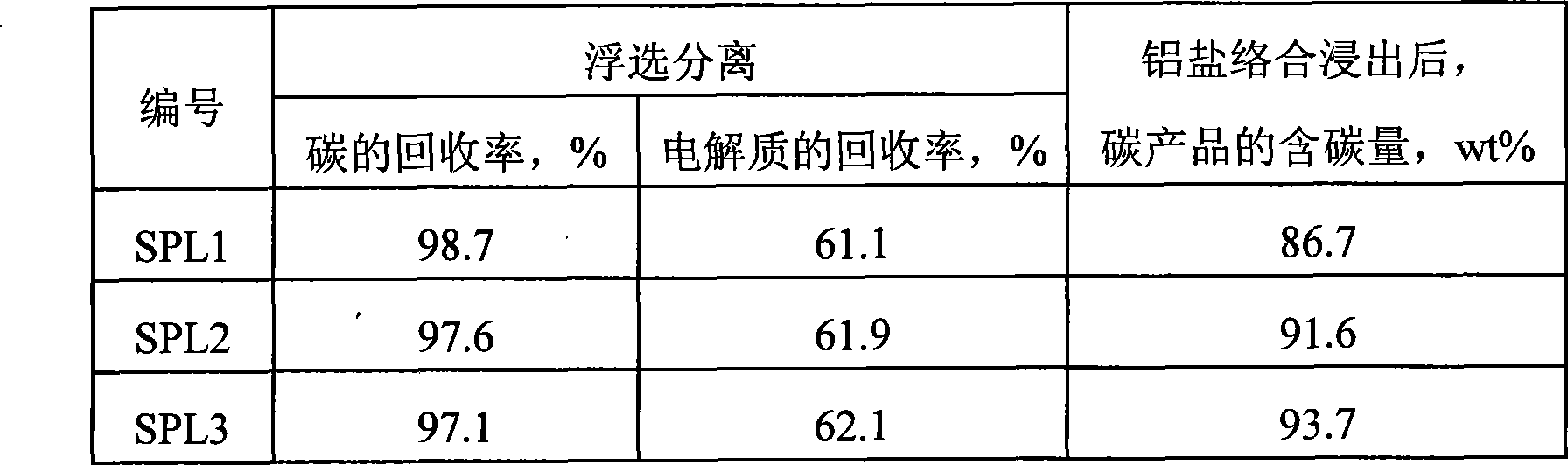
Method for electrolyzing waste and old cathode carbon block by comprehensive utilization of aluminum
ActiveCN101480658ARealize flotation separationHigh carbon contentFluoride preparationWaste processingPregnant leach solutionHigh carbon
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively using aluminium to electrolyze a waste cathode carbon block, which belongs to the technical field of environment protection and comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding the waste cathode carbon block; adjusting the concentration and the PH value of ore slurry after the grinding, then using floatation equipment to carry out floatation treatment, and separating electrolyte and carbon which are contained in the waste cathode carbon block; using an aluminium salt solution to soak for extracting the electrolyte contained in a carbon product obtained from the floatation, and further improving the grade of a high-carbon product; mixing the grinding waste water, the floatation waste water and the soaking solution, and adding CaO and CaCl2 to precipitate and recover aluminium and fluothane in the mixture. The method for comprehensively using aluminium to electrolyze a waste cathode carbon block has simple operating condition, low energy consumption, high recovery ratio of valuable substances and good application prospect.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag clinker leached by ammonium carbonate
ActiveCN102560086ALow costImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag clinker leached by ammonium carbonate. The method comprises the following steps of: calcifying and roasting vanadium slag of which the molar ratio of CaO to V2O5 is (2-3):1 at the temperature of between 700 and 900 DEG C, grinding the vanadium slag clinker, sieving, and leaching by an ammonium carbonate solution at the leaching temperature of between 60 and 98 DEG C for 30 to 120 minutes, filtering to obtain vanadium-containing leachate, performing vanadium deposition on the vanadium-containing leachate to obtain a vanadium finished product, wherein when the ammonium carbonate solution is leached, the concentration of the ammonium carbonate solution is between 200 and 800 g / L, and a liquid / solid ratio of the ammonium carbonate solution to the vanadium slag clinker is (5-30):1. According to the method, a leaching process is easy to operate and low in cost, and has low requirement on the equipment; and a leaching agent is low in cost and can be recycled, so that the production cost is reduced. By the method, the leaching rate of the vanadium is high, namely is over 90 percent, impurity elements and particularly a phosphorus element in the leachate are reduced, and the leaching rate of phosphorus is less than 10 percent.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
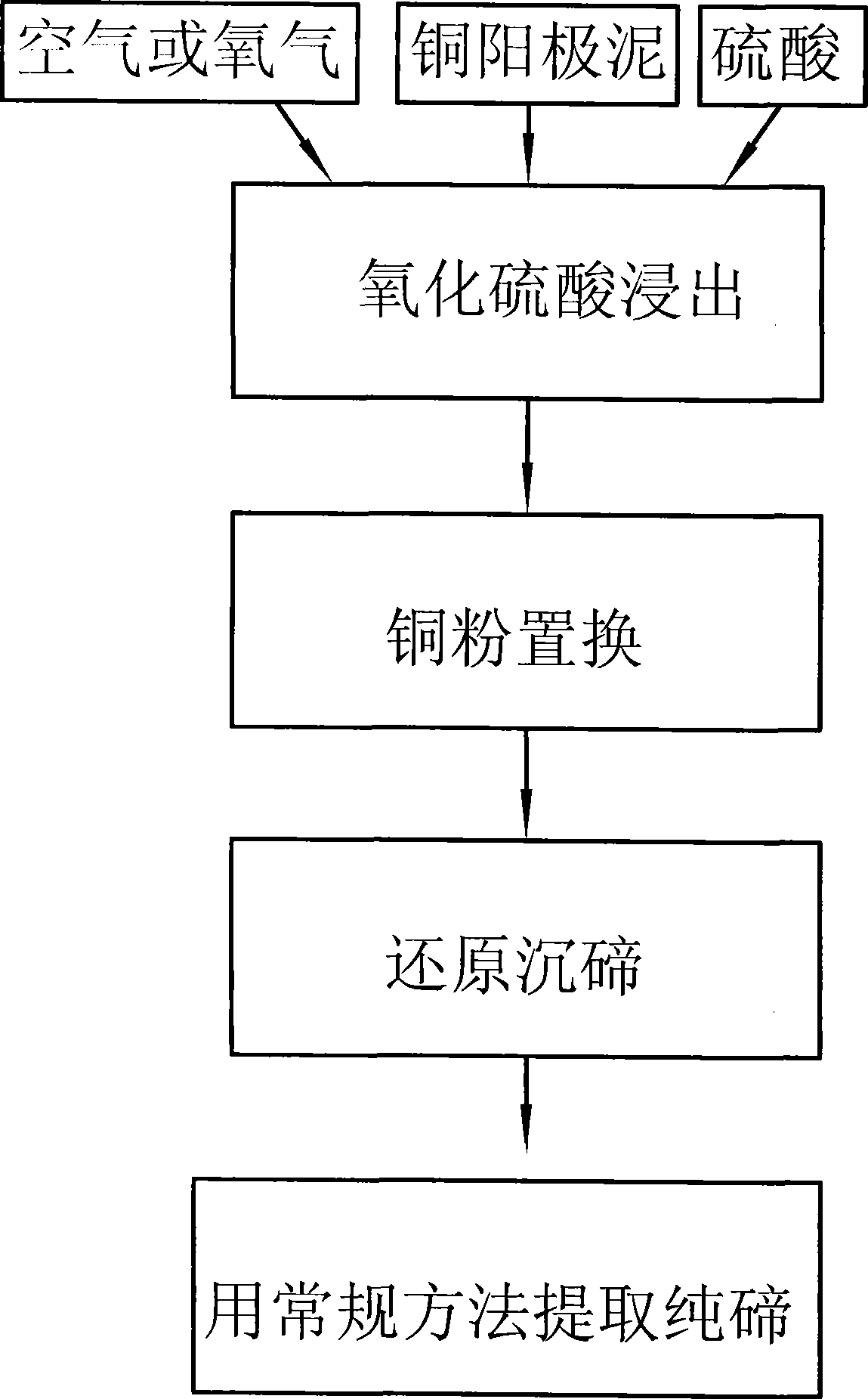
Process for extracting tellurium from copper anode mud
ActiveCN101434385AReduce consumptionEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumTe elementOxygen
The invention discloses a technology for extracting tellurium from copper anode slime, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) the copper anode slime is put into a sulfuric acid solution, oxygen is introduced into the sulfuric acid solution for oxidation sulfuric acid leaching; solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain leachate containing copper and tellurium; and the leaching process being finished in a closed high-pressure device; (2) copper powder is added into the leachate to remove silver or selenium in the leachate by substitution, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out; (3) sulfur dioxide is introduced into the leachate obtained from the step (2) to precipitate the tellurium by reduction, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain crude tellurium; and (4) the crude tellurium is processed according to a conventional method to extract pure tellurium. The technology adopts one-section oxidation acid leaching to leach the copper and tellurium out, copper powder to remove the impurities of silver, selenium and the like by substitution, and sulfur dioxide to precipitate the tellurium by reduction (obtaining tellurium dioxide), and the tellurium dioxide precipitation is alkali-dissolved and then electrolyzed to obtain the tellurium, therefore, the flow is simple, the consumption of the copper powder is remarkably reduced, and the simplification of the technology is beneficial to improve the recovery ratio of the tellurium, which can achieve more than 90 percent.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
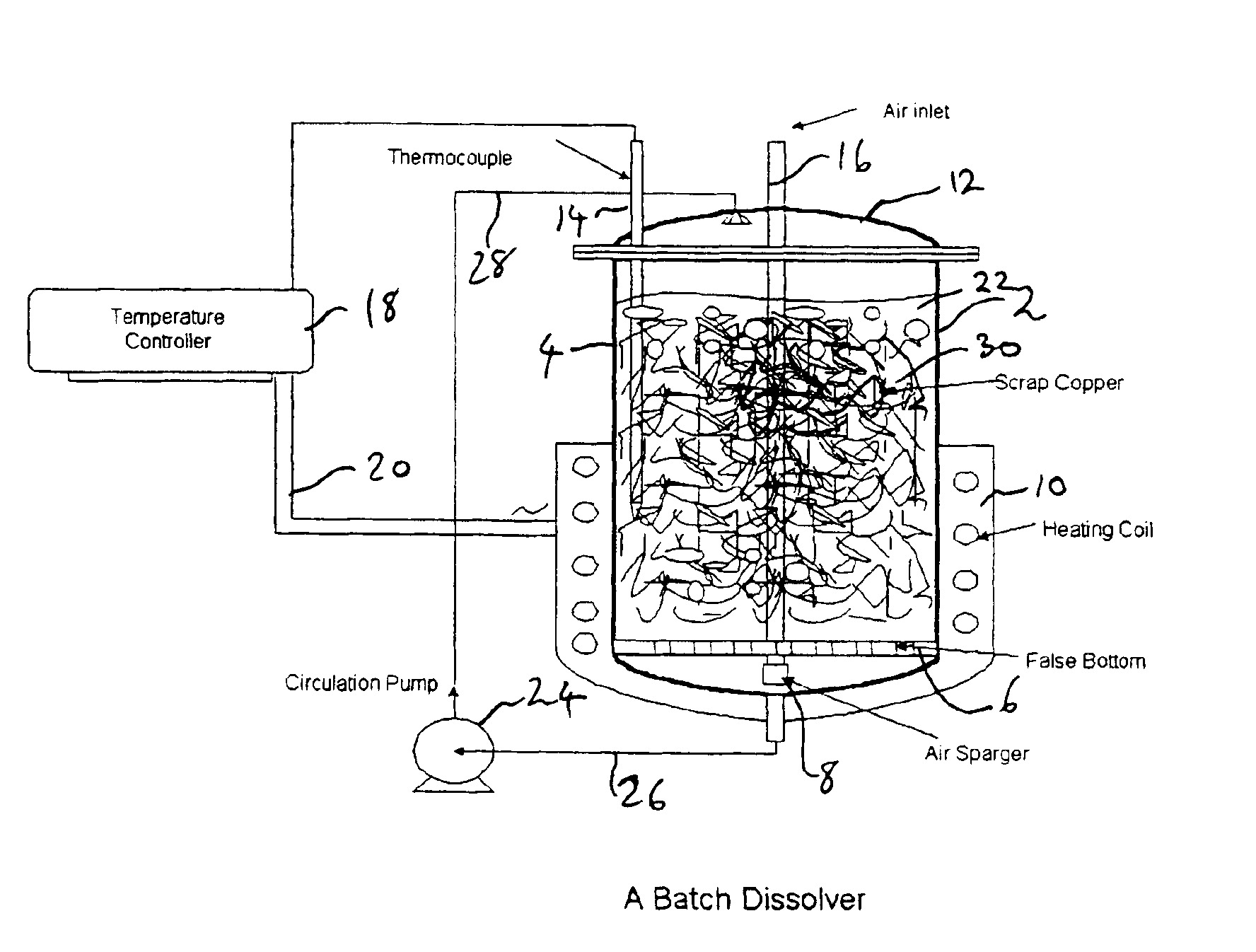
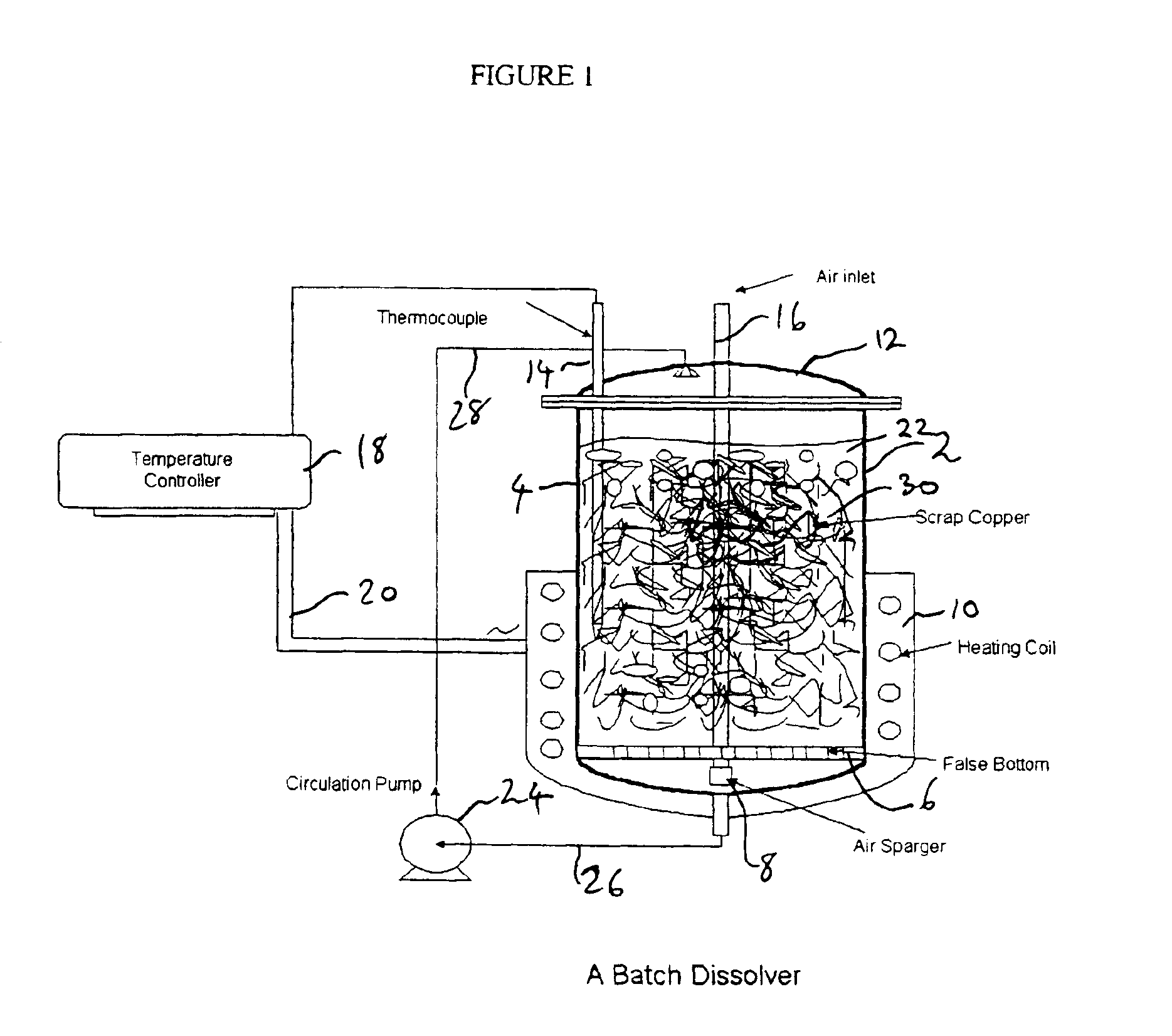
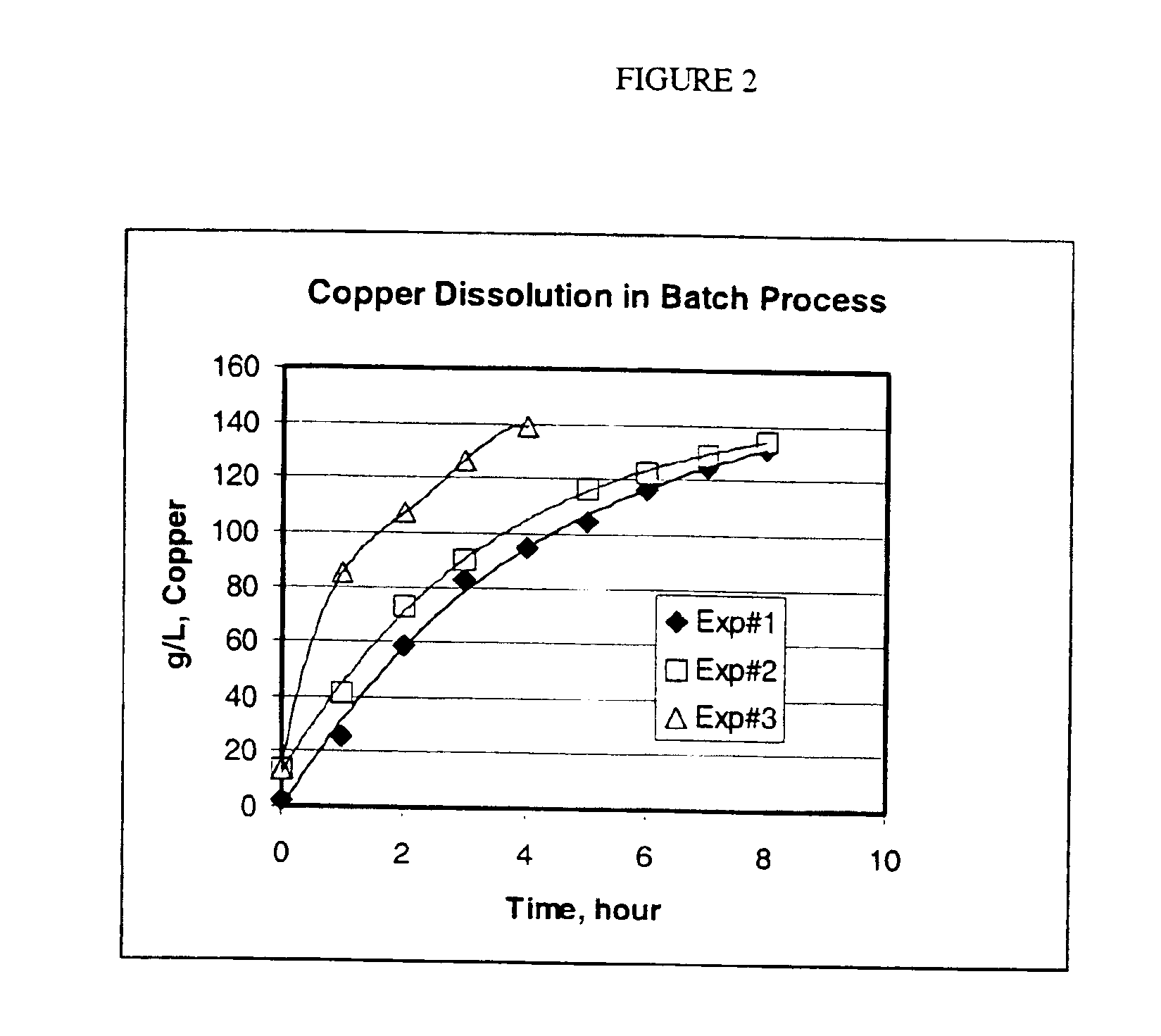
Process for the dissolution of copper metal
InactiveUS6905531B2Efficient productionCopper organic compoundsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processPregnant leach solutionDissolution
Process for producing a copper-containing aqueous solution, in which a copper mass is dissolved in the presence of an oxidant in an aqueous leach liquor containing monoethanolamine and (HMEA)2CO3. The leach liquor is produced by partially carbonating the monoethanolamine.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
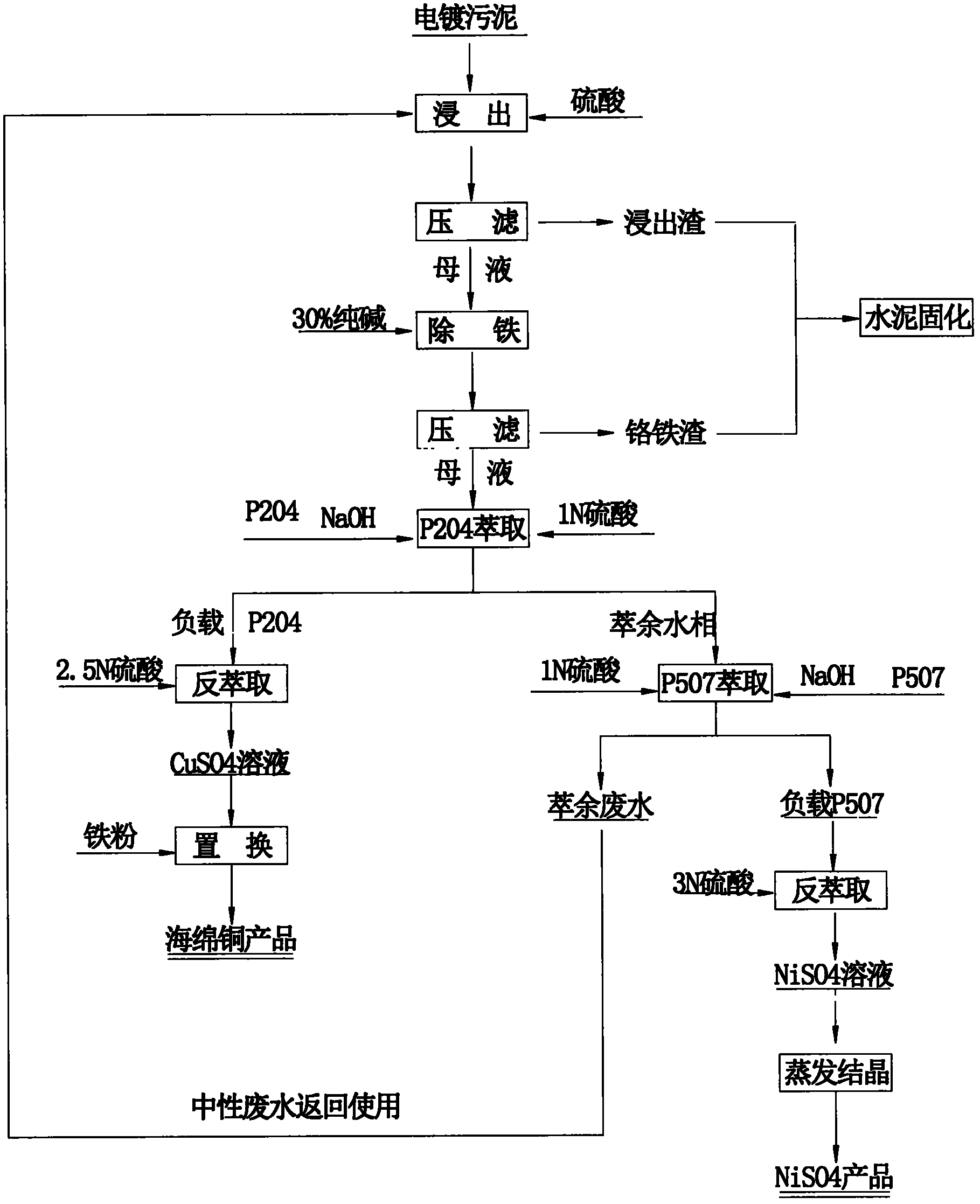
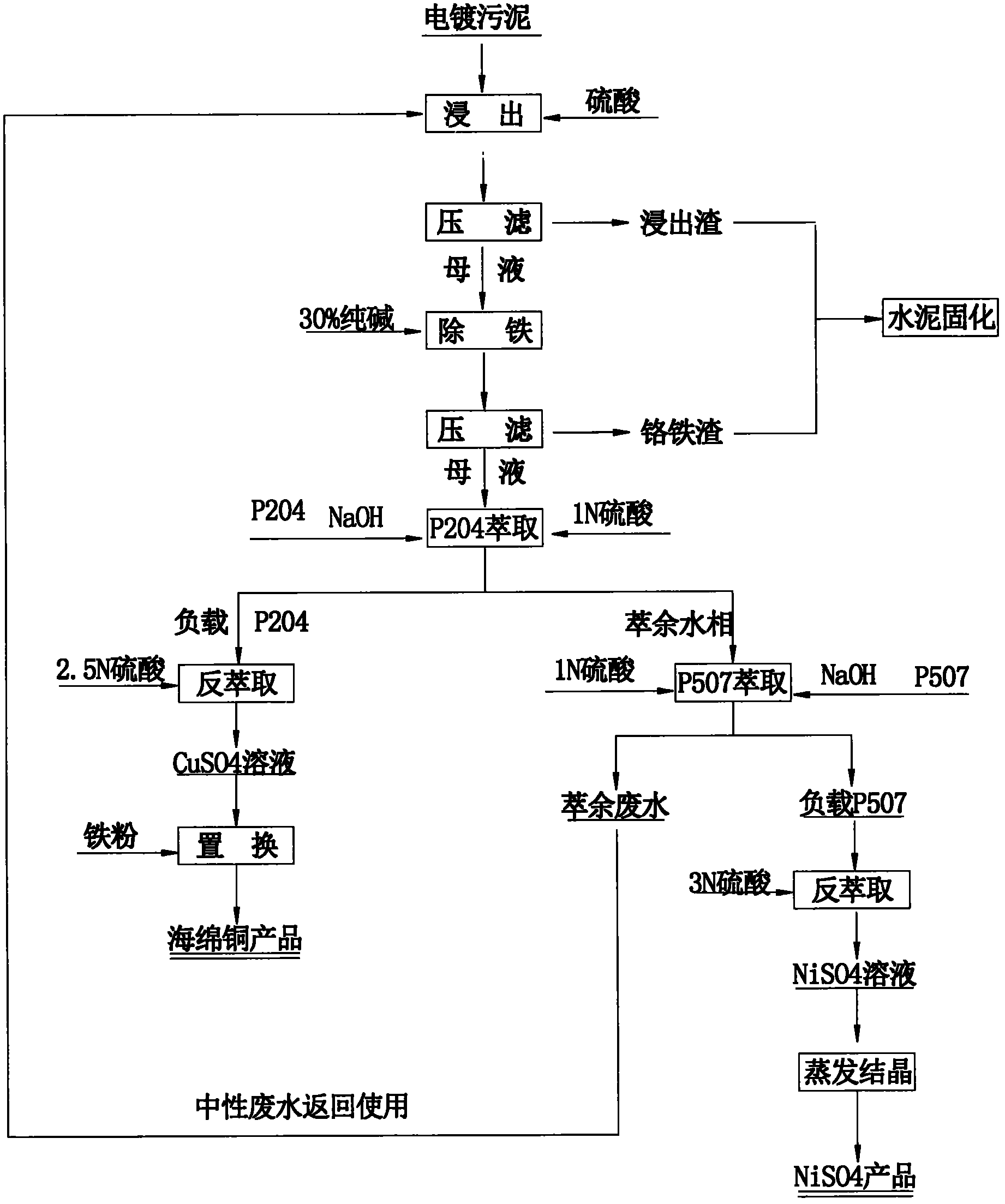
Method for recovering valuable metal from electroplating sludge
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from electroplating sludge. Electroplating sludge is used as a raw material; advanced theories and scientific means of leaching principle, redox principle, extraction principle, iron filing displacement principle and evaporation crystallization principle in a wet method metallurgy are integrally utilized; and a technology of ''acid decomposition of electroplating sludge-leachate purification to remove ferrochrome-P204 impurity removal-P507 enrichment-condensation crystallization'' is employed. Meanwhile, calcium and magnesium are removed by an extraction method, which substitutes a traditional sodium fluoride method for removing calcium and magnesium. A recovery rate of nickel reaches 95%, and copper content of recovered copper sponge is larger than 80%. Besides, acid dissolved slag and purifying slag can be solidified to reach requirements of environmental protection and will not cause secondary pollution; waste water can be recycled and has a strong technological versatility. The method is suitable for treating various routine electroplating sludge, has easily controllable technical conditions and low operating cost and is easy for realizing large scale production; therefore, the method is a practical novel technology for treating electroplating sludge in a way of quantitative reduction, harmlessness and resource.
Owner:朱小红
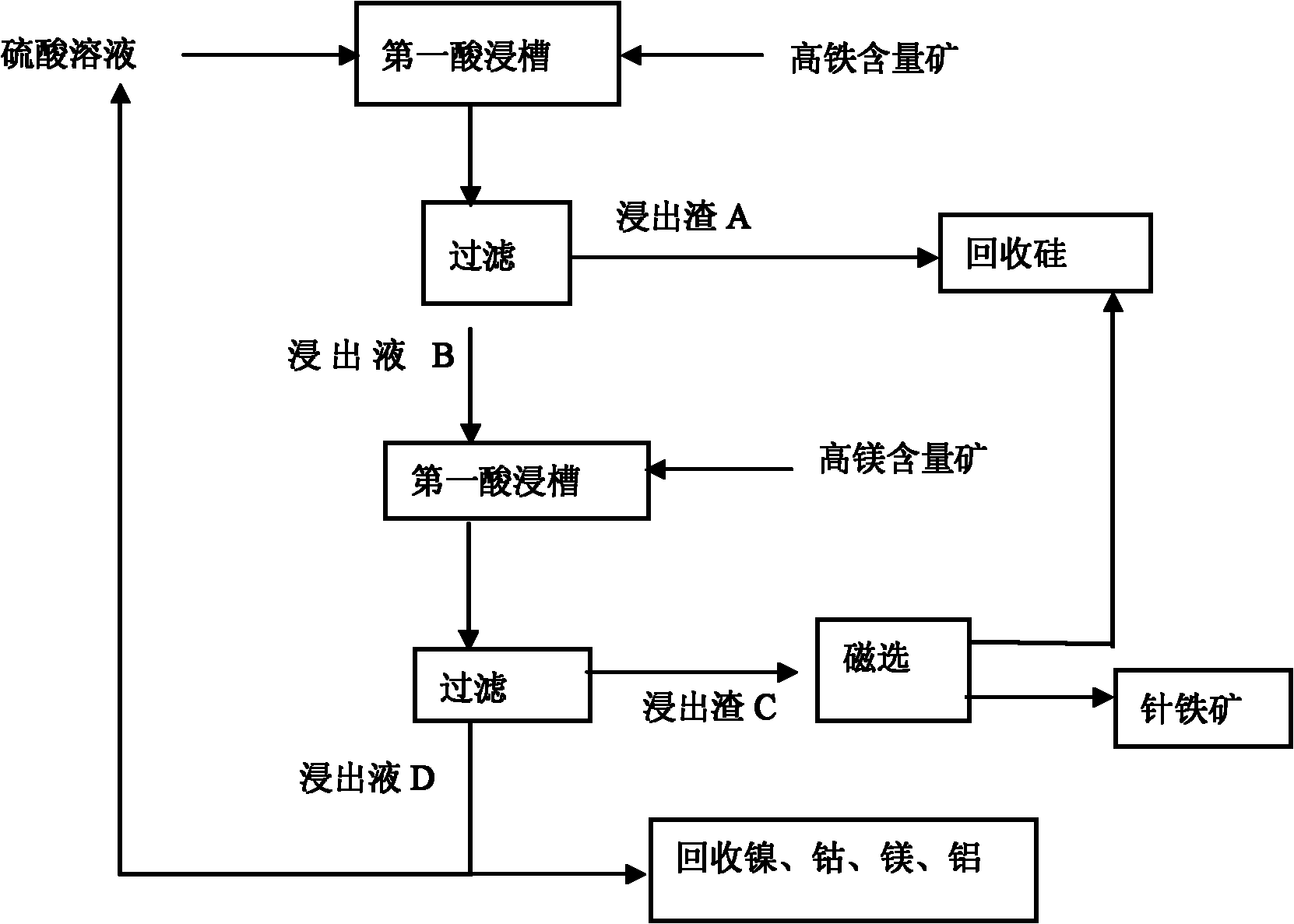
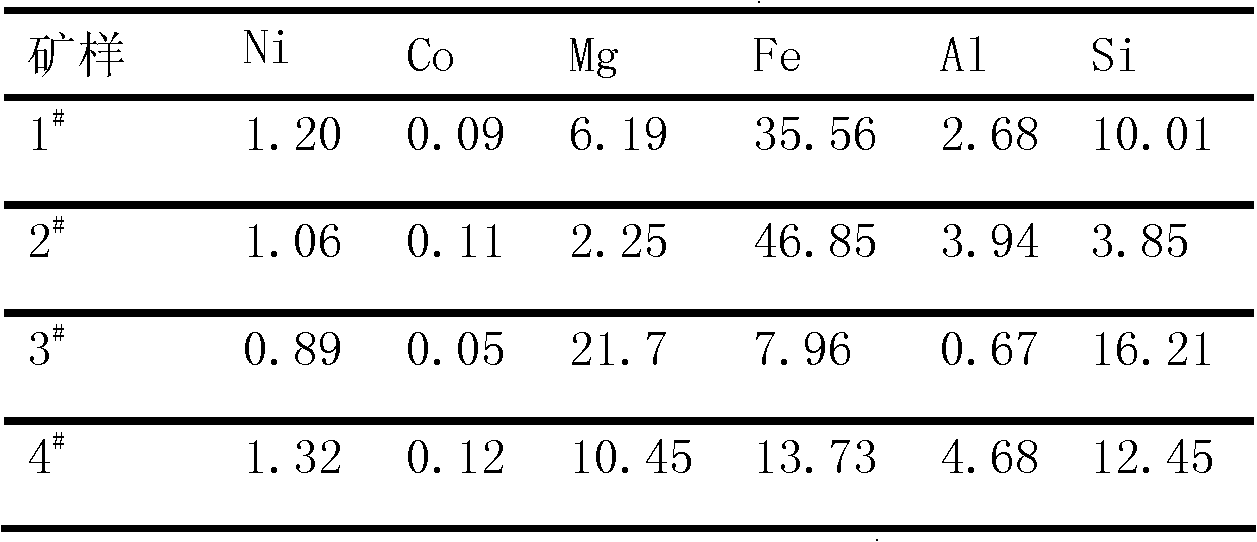
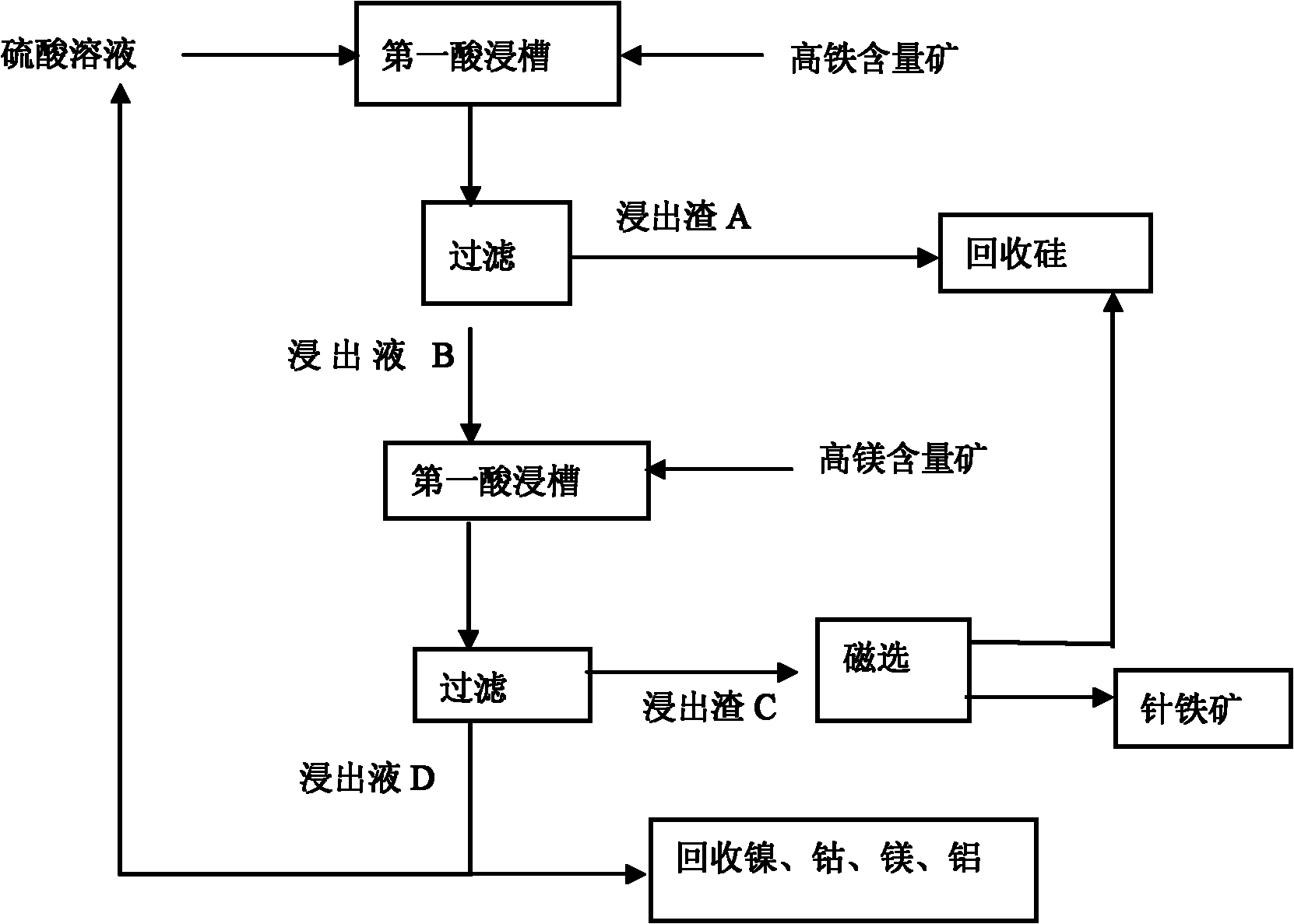
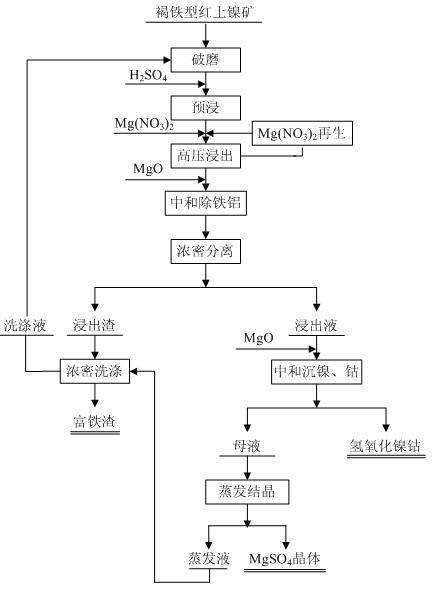
Normal-pressure leaching method for simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content
InactiveCN102206749AOvercoming the disadvantage of requiring autoclave leachingOvercome the drawbacks of leachingIron oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementLateriteNon magnetic
The invention discloses a normal-pressure leaching method simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content, comprising the following steps of: screening the laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content; adding sulfuric acid to the laterite with high iron content for leaching so as to obtain leaching residue A and a leaching solution B; adding the laterite with high magnesium content to the leaching solution B, leaching to obtain leaching residue C and a leaching solution D; carrying out magnetic separation on the leaching residue C, wherein a magnetic part E is recovered as an iron product, and a non-magnetic part F and the leaching residue A are mixed to be used for recovering silicon products; delivering a part of the leaching solutionD into a purifying and recovering process, and returning the other part of the leaching solution D into the leaching process of the laterite with high iron content, and carrying out a next leaching period; repeating the leaching period for 4-5 times, and completely delivering a leaching solution I obtained from a last leaching period into the recovering processes of nickel, cobalt, aluminum and magnesium. The normal-pressure leaching method has the advantages of low cost and acid consumption and high leaching efficiency of the nickel and the cobalt and realizes the efficient separation and the recycling of iron, silicon, the nickel and the cobalt and the discharge without acid liquor.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
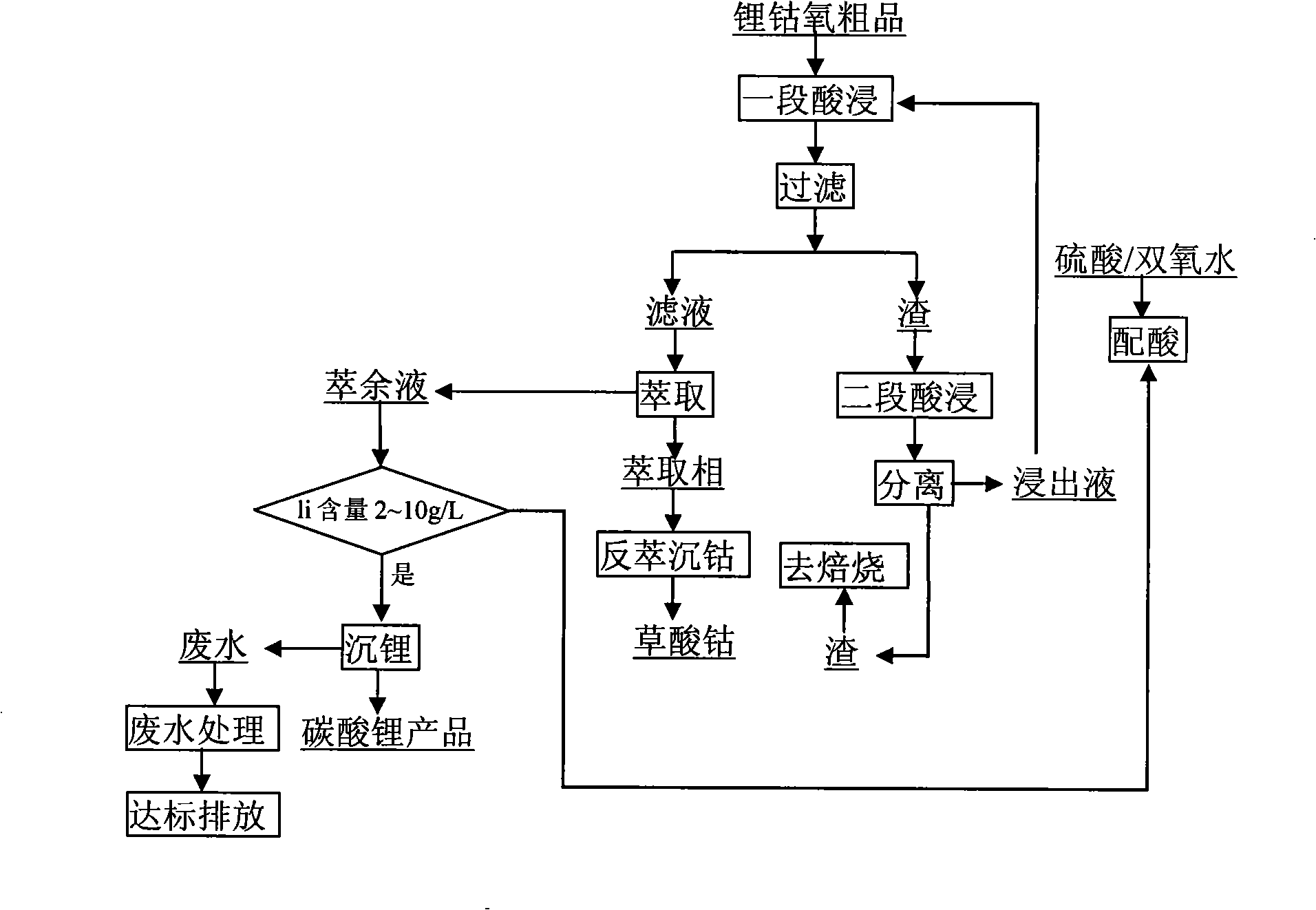
Environment-friendly acid leaching-extraction process in waste lithium battery recovery
InactiveCN101280357AEmission reductionReduce alkali consumptionSolid waste disposalProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionWastewater
The invention discloses an environment protective acid leaching-extraction process for the waste lithium battery recovery, lithium cobaltate and carbon power material can be obtained by splitting waste lithium electrically, a multi-section contra-flow acid leaching can be performed in sulphuric acid / oxydol mixed solution, two to four sections can be in counter current percolation extraction, the pH value of the leach solution is 2 to 6, and extracting process can be promoted by the leach liquor; after sulphuric acid / oxydol and washing water are dropped into the raffinade, back to acid leaching section; the raffinade can be used circularly, after lithium is concentrated to 2 to 10g / L in the raffinade, deposit lithium, then the waste water can be discharged and processed. The multi-section counter current percolation extraction is adopted by the invention, thus the pH value of the raffinade meets the requirement of the P507 extraction exactly, one hand, the consumption of alkali is reduced, on the other hand, the raffinade can be used circularly after extraction, water consumption in the process can be saved, and 5 to 15 times of discharge amount of the waste water can be reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for the rapid leaching of chalcopyrite in the absence of catalysts
InactiveUS6277341B1Increase surface areaImprove misalignmentSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
Owner:MINTEK
Method for preparing ternary positive electrode material through recovering waste ternary lithium battery
ActiveCN111206148AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling costsCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingManganese sulphatePregnant leach solution
The invention provides a method for preparing a ternary positive electrode material through recovering a waste ternary lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps of 1) mixing pretreatednickel cobalt lithium manganate waste positive electrode powder with sulfate, and roasting to obtain a roasted product; 2) immersing the roasted product in water to obtain water immersion liquid andwater immersion slag; wherein the water immersion liquid contains lithium salt; 3) reacting the water immersion slag with an acid solution and hydrogen peroxide to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese leaching solution; 4) removing impurities from the nickel-cobalt-manganese leaching solution, then extracting cobalt, manganese and nickel, and saponifying and reversely extracting obtained organic phaseto obtain a nickel sulfate solution, a cobalt sulfate solution and a manganese sulfate solution; and 5) co-precipitating the nickel sulfate solution, the cobalt sulfate solution and the manganese sulfate solution with a sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia water, mixing obtained precursor with lithium carbonate, sintering, and screening iron to obtain the ternary positive electrode material. According to the method, lithium is extracted firstly, so that the influence of a lithium element on subsequent nickel-cobalt-manganese extraction is reduced, the impurity content in the ternary positiveelectrode material is reduced, and the recovery rate of nickel-cobalt-manganese is greatly improved; and meanwhile the recovery rate of the lithium can be improved.
Owner:NINGBO RONBAY LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
Process for the dissolution of copper metal
InactiveUS6905532B2Efficient productionCopper organic compoundsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processPregnant leach solutionDissolution
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
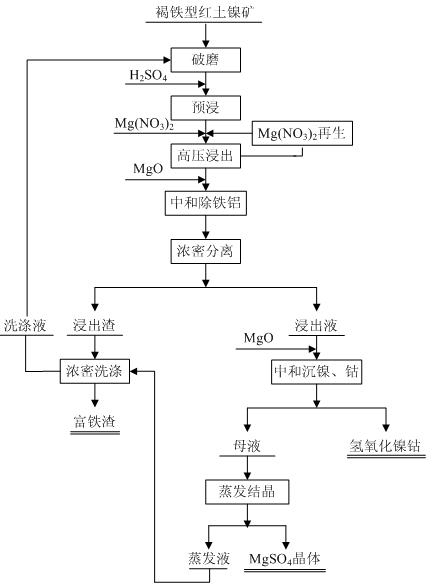
Method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN102534206AReduce consumptionEasy to operate and controlProcess efficiency improvementSlagSlurry
The invention discloses a method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore and relates to a process method for recovering nickel, cobalt and iron through treatment of laterite nickel ore by wet process. The method is characterized in that the technical process comprises: (1) grinding raw limonitic laterite nickel ore into fine powder, making slurry, adding sulfuric acid, heating the slurry and leaching the slurry; (2) adding Mg(NO3)2 into the pre-leached slurry, heating with stirring, pressurizing the slurry and leaching the slurry; 3) at the end of leaching, neutralizing the slurry, removing iron and aluminum from the slurry, and separating to obtain a leaching solution and a leaching residue; and 4) washing the leaching residue to obtain washing liquid and iron-enriched slag, neutralizing the leaching solution, precipitating nickel and cobalt, obtaining nickel and cobalt hydroxides, evaporating a mother solution from which nickel and cobalt are separated to crystallize magnesium sulfate and comprehensively recovering magnesium sulfate. The method realizes the high-efficiency selective leaching of nickel and cobalt, the leaching rate reaches over 90 percent, the iron leaching rate is lower than 0.8 percent and iron-enriched slag with an iron content of over 55 percent is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Recovery method of copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel
ActiveCN103184338ASimple processEasy to operatePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodElectrolysis
The invention provides a recovery method of a copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel. The method comprises the steps that: the copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel is crushed into pieces; the pieces are soaked by using a H2SO4+H2O2 system, such that a soaking liquid is obtained; the soaking liquid is filtered, such that a first leachate is obtained; with a first phase ratio of 1, the first leachate is extracted by using an extraction agent; separation is carried out, such that a first extraction liquid and a first raffinate are obtained; the extraction agent is composed of 30% of P2O4 and 70% of kerosene by volume percentage, the extraction and balance time is 5-20min; an HCl solution is adopted as a stripping agent, and the first extraction liquid is striped by using a second phase ratio, such that In and stripping residual liquid are obtained; a reducing agent is added into the first raffinate; when a reduction reaction is finished, crude Se and a second leachate are obtained by filtering; alkali is added into the second leachate, and a pH value is regulated such that the pH value is constantly higher than 14; when a reaction is finished, filtering is carried out, such that a filtering slag comprising a hydroxide of Cu and a water solution comprising Ga are obtained; the alkali is NaOH, the pH value adjustment process is to add the NaOH in the reaction process after pH=14 so that the pH is always kept more than 14 during the reaction process, and the reaction time is kept for 0.5-2h; and the water solution is electrolyzed.
Owner:FIRST SEMICON MATERIALS
In-situ uranium leaching and mining treatment method by adding O2 into CO2
The invention provides an in-situ uranium leaching and mining treatment method by adding O2 into CO2. The invention comprises the steps of (1) adding O2 into leaching solution, then injecting an underground mine-water contained layer into a liquid injection pipeline, and preparing the leaching solution by adopting different oxygenation concentrations according to different underground leaching periods; (2) adding 100-300mg / L of CO2 into the leaching solution containing uranium; (3) conducting ion exchange adsorption on the leaching solution containing uranium, adopting macroporous styrene strong-base anion exchange resin, adsorbing to obtain saturated resin adsorption tail solution; and (4) washing saturated resin by adopting an eluting agent, and then analyzing uranyl carbonate ion solution to obtain Na2U2O7 sediment slurry and sediment mother liquor. According to the method, a high-temperature heating device is eliminated, so that the energy consumption and equipment investment are lowered greatly, the alkali consumption is lowered, control parameters are refined, the consumption of alkali is saved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
Process for mutual separation of platinum group metals
ActiveUS20050066774A1Avoid high levels of impuritiesReduce impurityRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsLiquid solutions solvent extractionIridiumDecomposition
A process for mutual separation of platinum group metals (PGM), wherein highly stable compounds and steps are used to efficiently remove impurity elements while preventing increase of impurity content relative to that of the PGM in the mother liquor and also preventing decomposition of a chloro complex, and palladium, platinum, iridium, ruthenium and rhodium are separated mutually in such a way that each of the separated PGM has a sufficient purity to be a commercial product. A process for mutual separation of PGM, comprising the first step for leaching a raw material containing PGM and impurity elements, second step for removing the impurity elements from the leach liquor by solvent extraction, third step for recovering palladium from the raffinate, fourth step for removing cationic impurity elements from the raffinate by solvent extraction, fifth step for recovering platinum from the raffinate by hydrolysis, sixth step for recovering ruthenium from the precipitate by leaching, and seventh step for recovering iridium by solvent extraction to prepare the stripping liquor containing iridium and raffinate containing rhodium.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
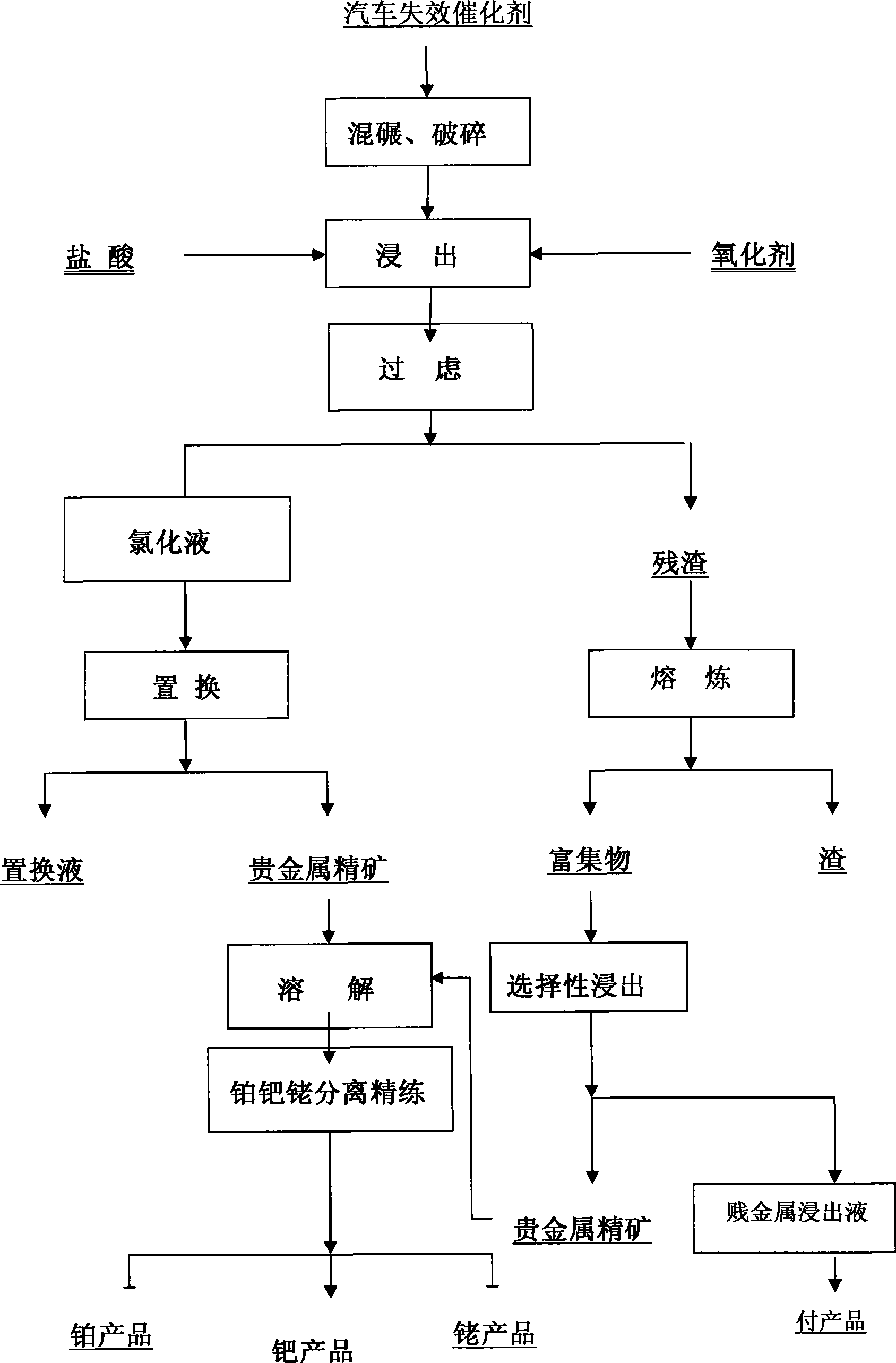
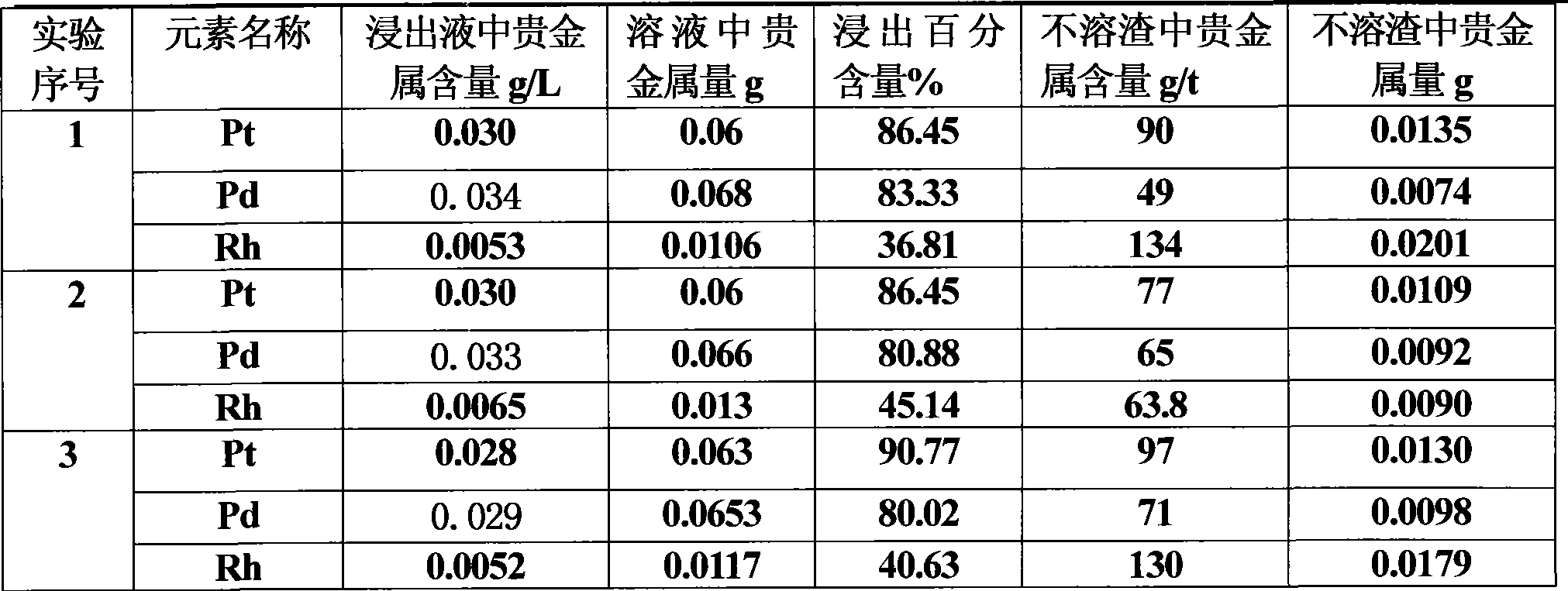
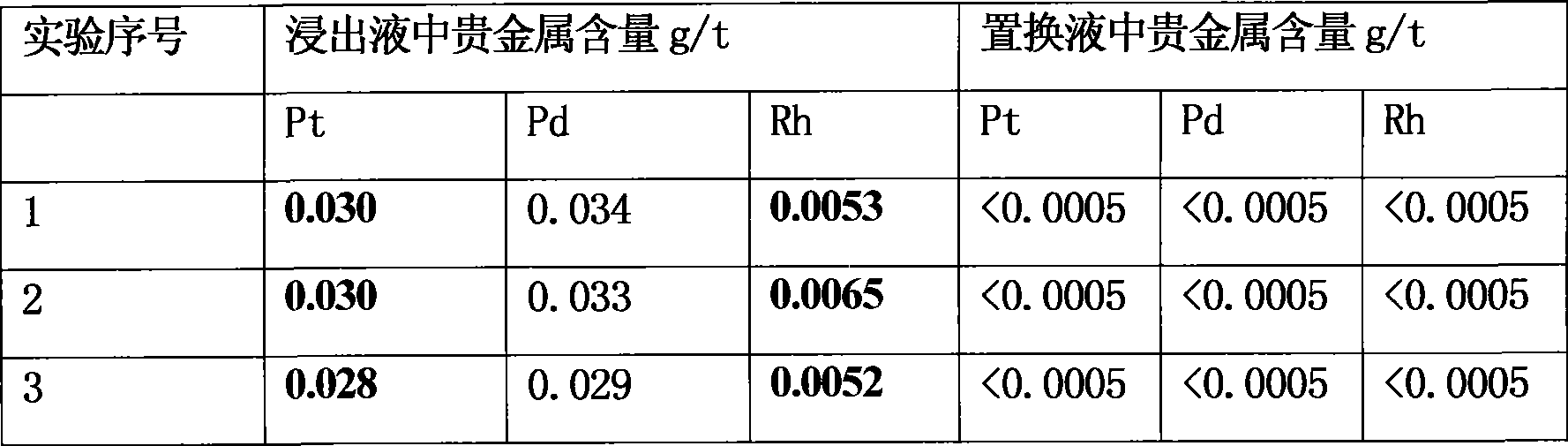
Method for extracting precious metal from auto-exhaust catalyst by hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy complex process
InactiveCN101519725ALoose process conditionsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPlatinum
The invention relates to a method for extracting precious metal from a disabled auto-exhaust catalyst, which comprises the following steps: 1. lixiviating precious metal from the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst by a hydrometallurgy process and obtaining precious metal concentrates after permuting lixivium; 2. lixiviating slag, collecting precious metal of the slag by a pyrometallurgy process to obtain a precious metal phase and selectively lixiviating base metal in the precious metal phase to obtain precious metal concentrates; and 3 combining the precious metal concentrates obtained in the first two steps and refining the precious metal concentrates to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The invention compensates the deficiency that the percent recovery of the precious metal is low by simply treating the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst with the hydrometallurgy process and has the advantages that the contents of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are smaller than 1g / t and the product purity reaches 99.95 percent.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
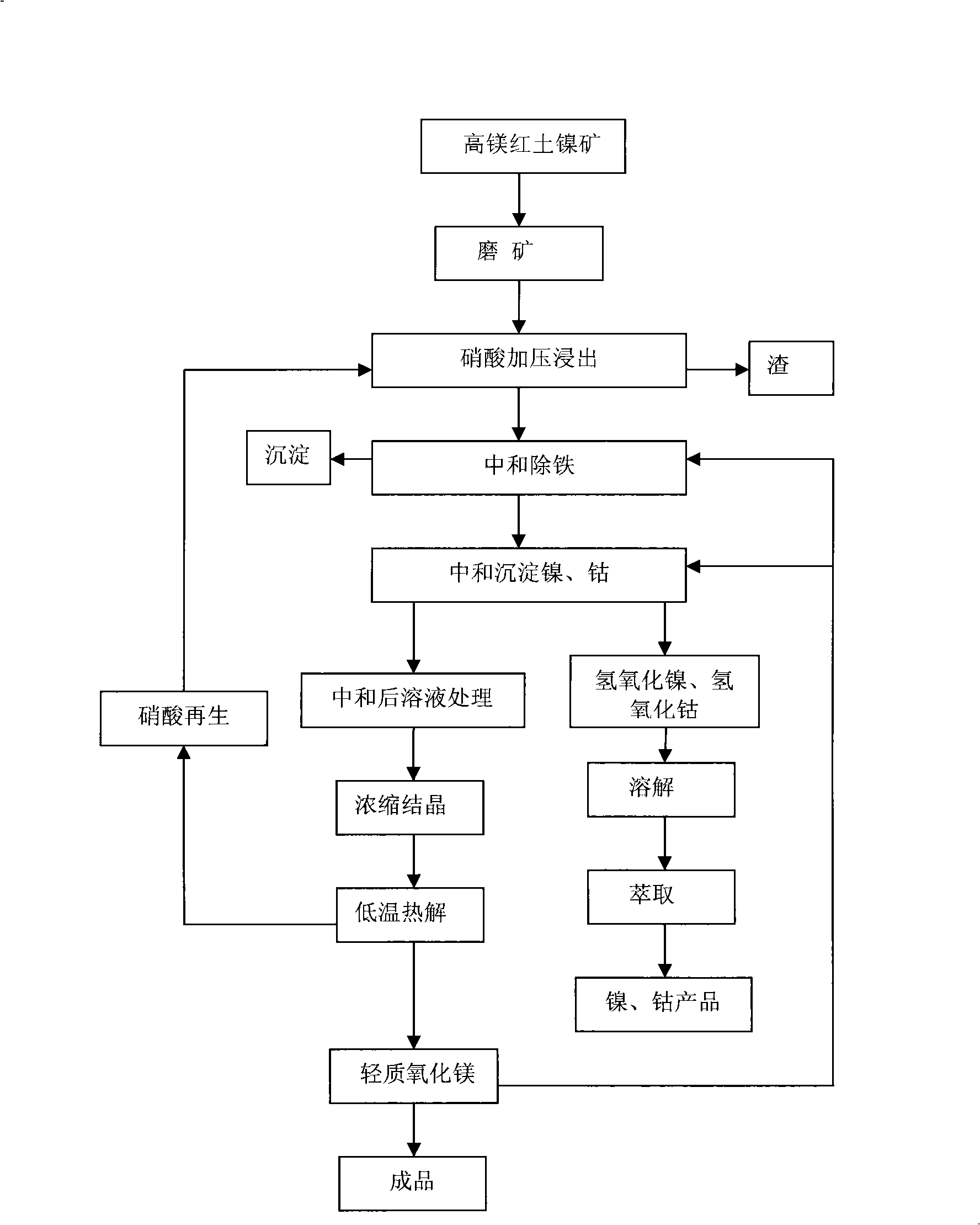
Treating method for high magnesium laterite nickel mine
InactiveCN101289704AEfficient extractionEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHigh magnesium
The invention discloses a method for treating high magnesium laterite-nickel ores. The method comprises the following steps of preliminary treatment of ore, pressurized leaching, iron purification of leach solution, deposition of nickel and cobalt, condensation and crystallization, production of light magnesium oxide by low-temperature thermal decomposition of crystals and regeneration of nitric acid. Under mild conditions of low temperature and pressure, leaching ratios of nickel and cobalt both reach 95 percent, the leaching ratio of magnesium reaches 98 percent, the iron content in the leach solution is less than 1g / L, and no silicon dioxide is leached out. The method can fully recover nickel, cobalt and magnesium, and the magnesium is generated in the form of light magnesium oxide, and the leaching agent-nitric acid can be recovered and regenerated for n, thereby better resolving the problems of highly efficient leaching-out of nickel and cobalt and reasonable utilization of magnesium; moreover, the technical flow is simple and has low requirements on equipment, and in the process of leaching out, the scab phenomenon does not occur in a high-pressure pan, so that the method is applied to the large-scale industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
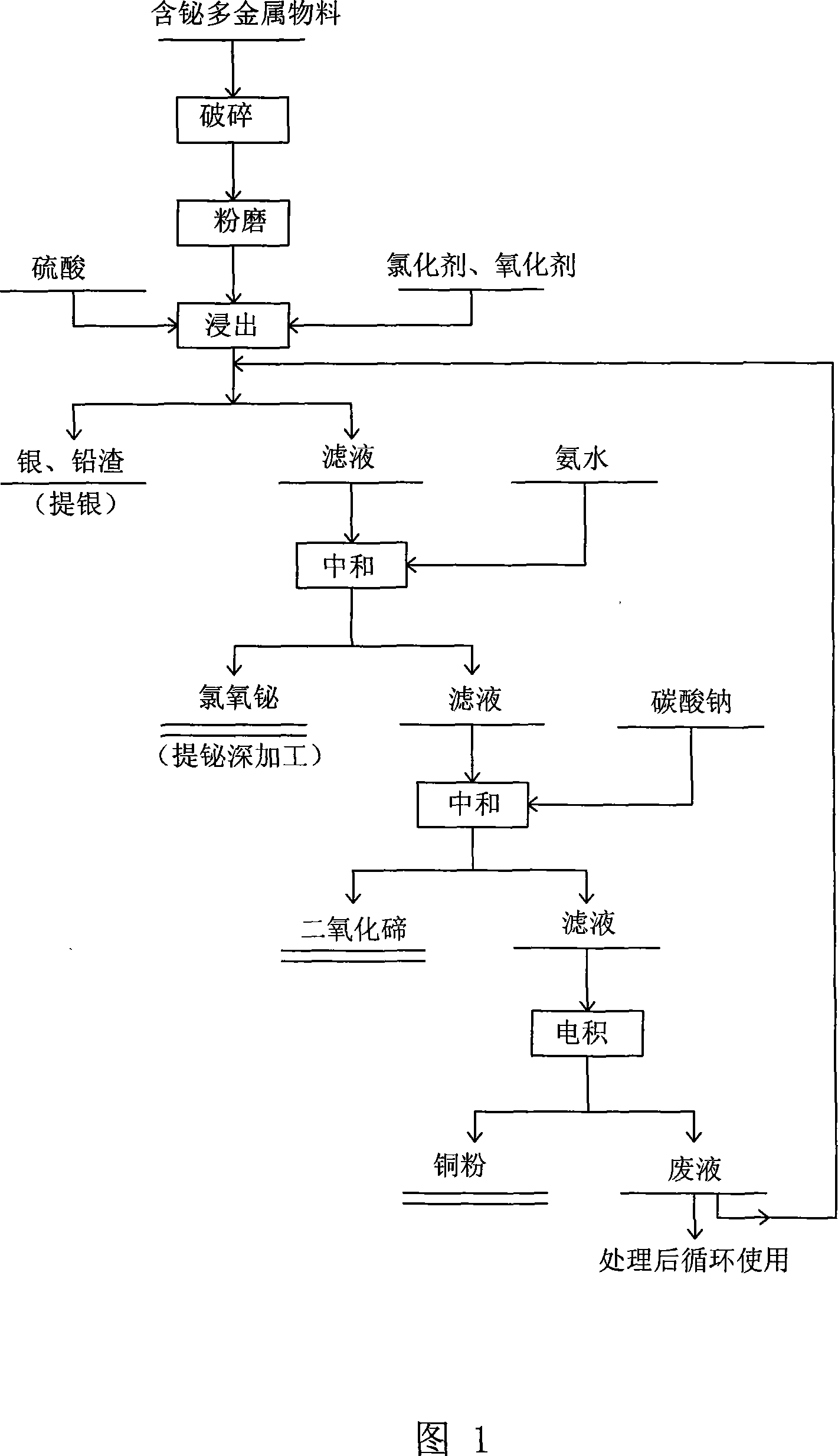
Comprehensive extraction of valent metal from bismuth-containing polymetallic material
InactiveCN101029353AHigh recovery rateImprove product added valuePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSesquioxideTe element
A method for extracting metal from bismuth-contained multi-metal material is carried out by leaching out copper and tellurium from bismuth-contained multi-metal by sulfuric acid, adding into chlorinating agent and oxidant to leach out metal bismuth, extracting silver from leaching-out slag with AgCl, PbSO4 and PbC12, adding ammonia water into leaching-out liquid, adjusting pH value to 1.5 to obtain bismuth oxychloride slag with 70% bismuth content, smelting into coarse bismuth by firing method or machining to obtain high-purity bismuth sesquioxide, adjusting pH value to 4.5 by Na2CO3, depositing tellurium to obtain tellurium dioxide and copper-contained solution, and electrically depositing to obtain copper powder with copper-contained content90%. It adopts wetting and firing metallurgical technology, has higher metal recovery rate and excellent leaching-out separation effect and effluent circulating utilization and no environmental pollution.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
System and Method for Recovery of Nickel Values From Nickel-Containing Ores
InactiveUS20120204680A1Photography auxillary processesSolvent extractionPregnant leach solutionIon-exchange resin
A method is provided for extracting nickel values from nickel-containing ores. The method comprises (a) treating a nickel-containing ore with an acid, thereby producing an acid treated ore; (b) baking the acid treated ore, thereby producing a baked ore; (c) leaching nickel from the baked ore to form a leachate; and (d) extracting nickel values from the leachate through the use of an ion exchange resin.
Owner:SCANDIUM INT MINING
Method for recovering cadmium from copper cadmium residues
InactiveCN102517455ASolve complexityResolve recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionIngot
The invention provides a method for recovering cadmium from copper cadmium residues. The method comprises the following steps: A, carrying out leaching by using sulfuric acid: the copper cadmium residues are leached by using sulfuric acid, and a filtering treatment is performed to obtain a leachate; B, carrying out purifying to remove copper: fresh cadmium sponge is added to the leachate from the step A to replace the copper in the leachate, and a filtering treatment is performed to obtain a copper-removed solution; C, carrying out oxidizing to remove iron: hydrogen peroxide is added to the copper-removed solution from the step B, and a filtering treatment is performed to obtain an iron-removed liquid; D, carrying out zinc powder replacement: sulfuric acid is added to the iron-removed liquid from the step C, zinc powder is added under a stirring state, treatments of filtering and washing are performed to obtain the sponge cadmium, and then a refining treatment is performed to obtain the cadmium ingot. The method of the present invention has the following advantages that: the process is simplified, the cadmium recovery rate is high, the zinc powder consumption is reduced, and no pollution is generated to the environment.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Method for extracting rhenium from eluate of flue ash generated by baking enriched ore of molybdenum
This invention relates to a method for extracting Re from flue dust and tail gas rinsing solution of Mo concentrate calcination. The method comprises: (1) adding water to flue dust, leaching out Re in the flue dust to obtain Re-containing leaching solution; (2) adjusting the pH value of the Re-containing leaching solution and tail gas rinsing solution to 5 with ammonium bicarbonate so that Mo, Fe, Cu and Zn ions are converted into hydroxides, separated from Re and precipitated, and filtering to obtain Re-containing solution for extraction; (3) extracting with extractant so that Re enters into the extractant, which is named enriched oil; (4) back-extracting the enriched oil with 3 N ammonia solution so that Re enters into the back extraction solution; (5) adding the back extraction solution into an ion exchange system so that Re is adsorbed onto the resin; (6) preparing 5-10% ammonium thiocyanate solution, adding ammonia solution to adjust the pH value to 8-9, and desorbing Re adsorbed onto the resin to obtain Re-containing desorption solution; (7) evaporating the desorption solution, concentrating, and crystallizing to obtain ammonium perrhenate product.
Owner:锦州沈宏实业集团有限公司
Method for collecting nickel and cobalt from laterite-nickel ore lixivium
ActiveCN101298638AHigh extraction rateReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
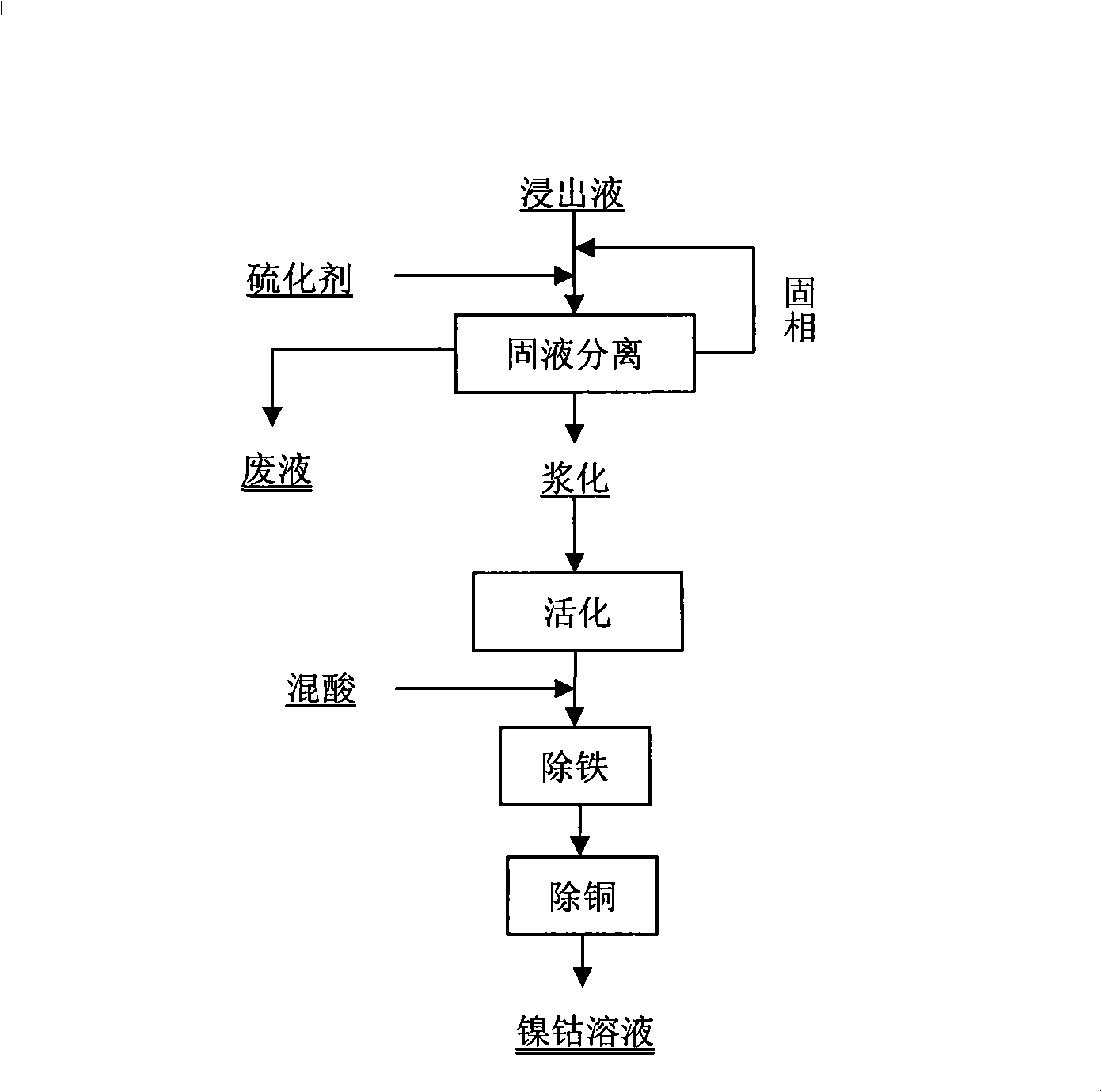
The invention discloses a method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from a laterite nickel ore lixivium, which comprises the following steps: after solid and liquid separation between the laterite nickel ore lixivium and ore slag is implemented, a vulcanizing agent is added into the lixivium, the solid and the liquid are separated after reaction precipitation, and precipitated solid is washed by a new lixivium, thus obtaining sulfide precipitate; after the sulfide precipitate is pulpified, sulphuric acid and solution of nitric acid and mixed acid are added so as to implement oxidizing leaching; the goethite method is adopted for removing iron from a superior pickle liquor; a sodium thiosulfate solution is added so as to implement copper removing; a filtering liquor that is the enriched nickel and cobalt solution is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from the laterite nickel ore lixivium is implemented at normal temperature and normal pressure, does not need a high-pressure caldron, has less device investment, low running cost, simple technical path, short process and controllable production scale; the vulcanizing agent and acids that are used in the technique can be recycled to the utmost extent and do not have emissions and environment pollution; the extraction yield of nickel and cobalt can achieve over 95 percent, and the method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from the laterite nickel ore lixivium has low production cost and easy industrialization.
Owner:福建常青新能源科技有限公司
Method for preparing ternary material precursor and recovering lithium by using spent lithium-ion battery ternary cathode materials
ActiveCN108878866AGuaranteed uniformityHigh recovery rateCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingManganeseCobalt
The invention belongs to the technical field of ternary material precursor preparation, and particular to a method for preparing a ternary material precursor and recovering lithium by using spent lithium-ion battery ternary cathode materials. Spent lithium-ion battery anode materials are roasted and screened to obtain ternary anode materials and aluminum foil; the ternary anode materials are leached out of a caustic soda solution and filtered to obtain filtrate and filter residues; carbonate is added to the filtrate to react to obtain lithium carbonate solid; the filter residues are leached with volatile acid; a reducing agent is added to the leaching solution and the volatile acid is removed by heating the solution to a boil; the molar ratios of nickel, cobalt and manganese in leaching solution are adjusted; and the leaching solution after adjusting the molar ratios of the nickel, the cobalt and the manganese is flow into a reaction kettle containing an ammonia water solution togetherwith the ammonia water solution and caustic solution, and coprecipitation is performed under inert gas protection. The method for preparing the ternary material precursor and recovering the lithium by using the spent lithium-ion battery ternary cathode materials realizes the preparation of the ternary material precursor and the recovery of the lithium at the same time, the production cost is reduced, product quality is high, economy is good, and the directional circulation of nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium resources is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Process For Metal Recovery From Catalyst Waste
InactiveUS20120156116A1Lanthanum oxide/hydroxidesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsPregnant leach solutionRare earth
A method for recovering rare earth metals from zeolite-containing waste FCC catalysts comprises an acid leaching step to remove the rare earth metals from the catalyst to form a leachate containing dissolved rare earth metals and separating the rare earth metals from the leachate such as by precipitation.
Owner:BASF CORP
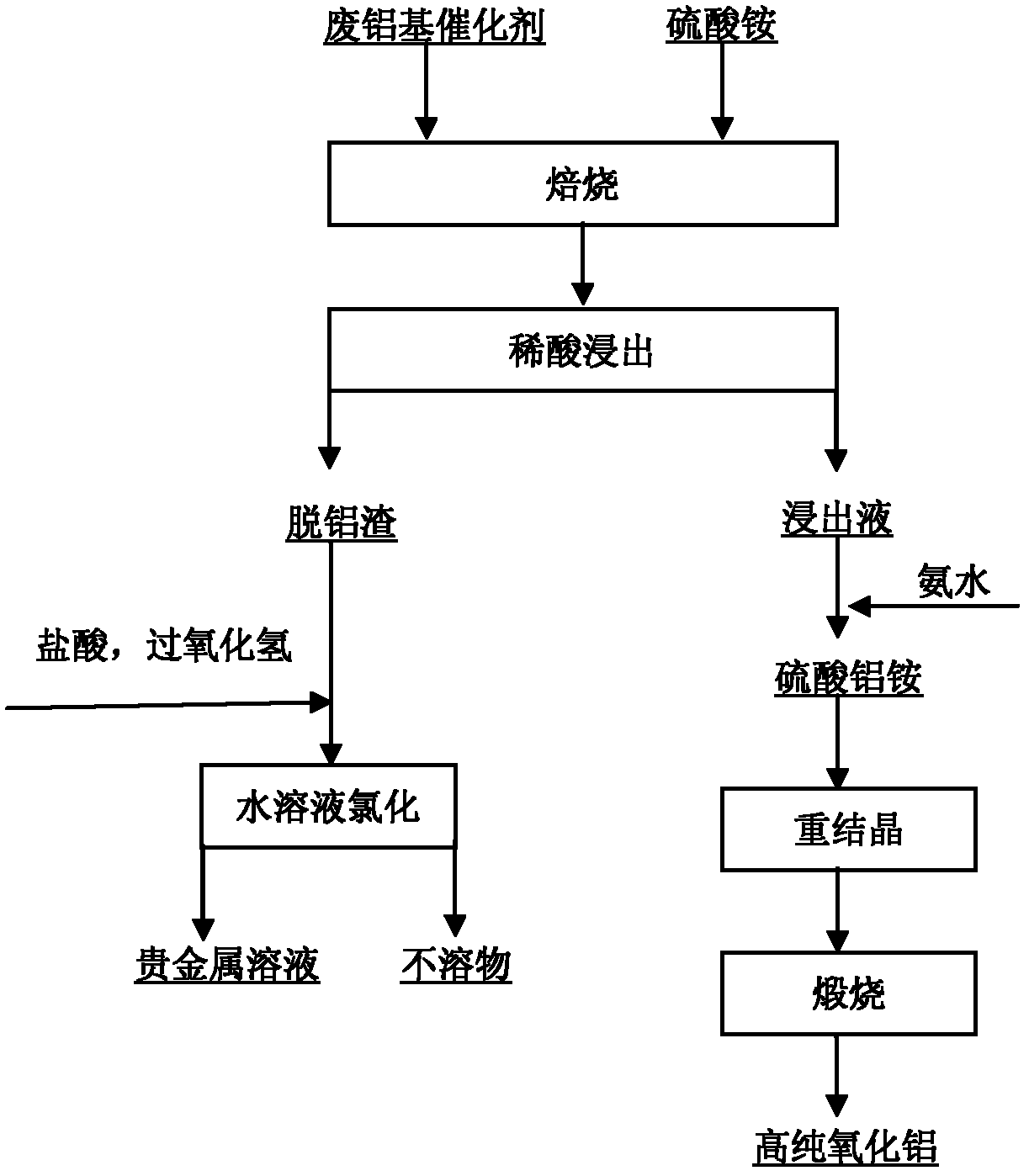
Method for recovering precious metal from waste aluminum-based catalyst and preparing high-purity alumina
InactiveCN102560129AAchieve recyclingReasonable processProcess efficiency improvementSlagAmmonium aluminium sulfate
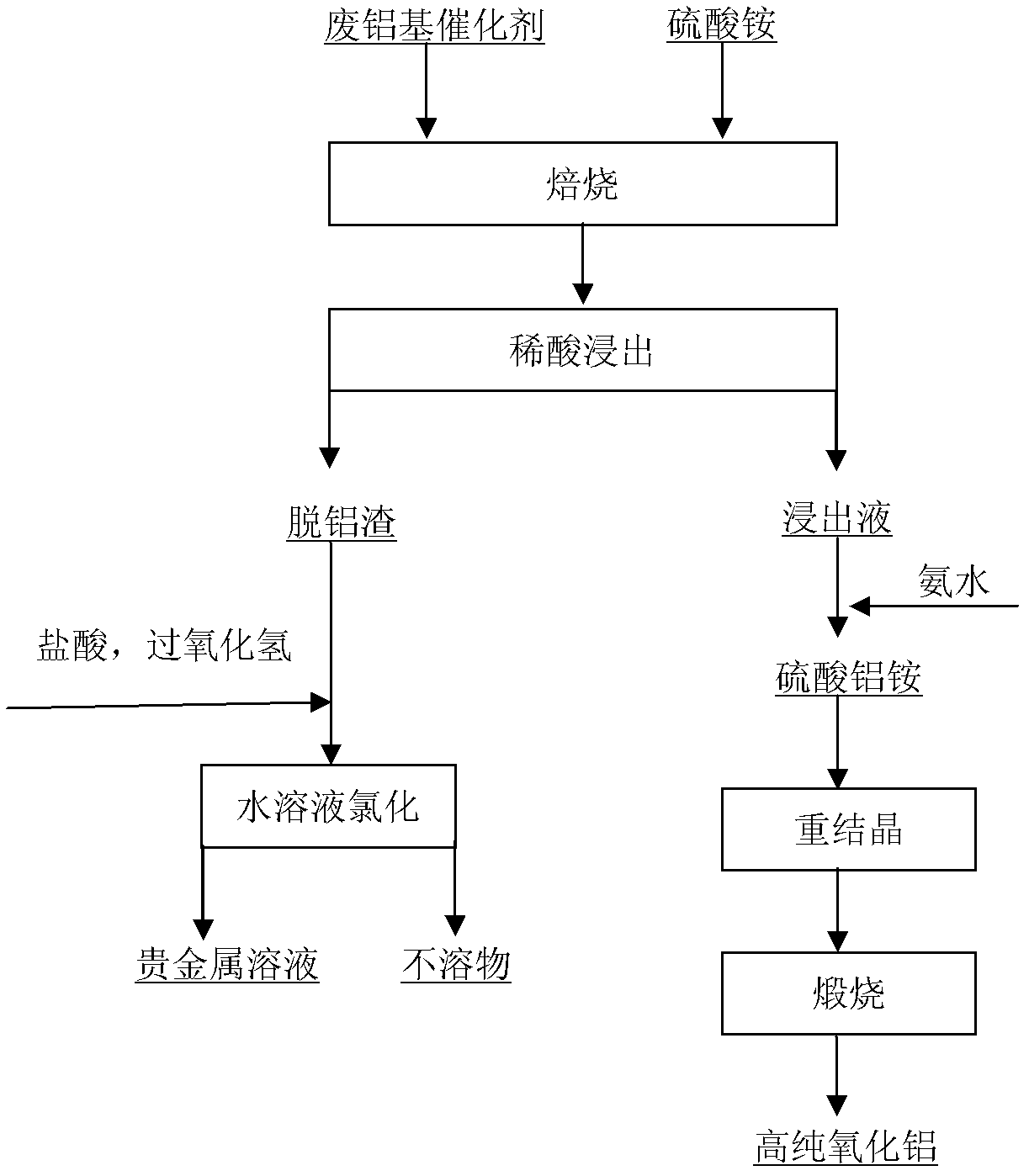
The invention discloses a method for recovering precious metal from a waste aluminum-based catalyst and preparing high-purity alumina. The method mainly comprises the processes of: roasting, leaching to remove aluminum by using dilute sulfuric acid, recovering the precious metal from slag from which the aluminum is removed by an aqueous solution chlorination method, adding ammonia water into leachate to precipitate an ammonium aluminum sulfate coarse crystal, recrystallizing, and calcining and decomposing to prepare the high-purity alumina. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing the finely ground waste aluminum-based catalyst (40mu m) and ammonium sulfate in a weight ratio of 1:(1.3-1.5), roasting at the temperature of between 300 and 500 DEG C for 2 to 4 hours, performing fluidization leaching on a roasting product by using 1mol / L dilute sulfuric acid for 2 hours, performing solid-liquid separation, and recovering the precious metal from the slag from which the aluminum is removed by the traditional aqueous solution chlorination method, wherein the recovery rate of the precious metal is over 99 percent; and adding the ammonia water into the leachate to regulate the pH value and precipitate the ammonium aluminum sulfate coarse crystal, recrystallizing, and calcining and decomposing to prepare the high-purity alumina, wherein the purity is over 99.99 percent, and the recovery rate is over 95 percent. The invention has the advantages that: the process is reasonable, the method is easy to operate, the added value of a product is high, pollution is light, mass production is convenient to implement, and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for recycling value metal from lithium cell slag containing Co, Ni, Mn
ActiveCN101509071AIncrease contact areaIncrease the areaPhotography auxillary processesWaste accumulators reclaimingPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention relates to a method for recycling valuable metals from lithium battery residues containing Co, Ni and Mn. Valuable metals such as Mn, Co, Ni and Li are recycled from ternary system Li metal salt of lithium battery residues. The lithium battery residues containing generally equivalent lithium acid metal salt of Co, Ni and Mn are stirred and dipped with hydrochloric acid solution in the concentration of more than 250g / l, or stirred and dipped with sulfuric acid solution in the concentration of more than 200g / l while heating till the temperature of 65 to 80 DEG C, or stirred and dipped for processing with the solution mixed with sulfuric acid solution in the concentration of more than 200g / l and hydrogen peroxide solution in the concentration of more than 20g / l. More than 98% of the three metals of Mn, Co and Ni are extracted with acidic extractant solvent from leach liquor so that the solution containing each metal is produced; therefore, the valuable metals such as Mn, Co, Ni and Li are recycled from these solutions and remaining liquid containing Li after extraction.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
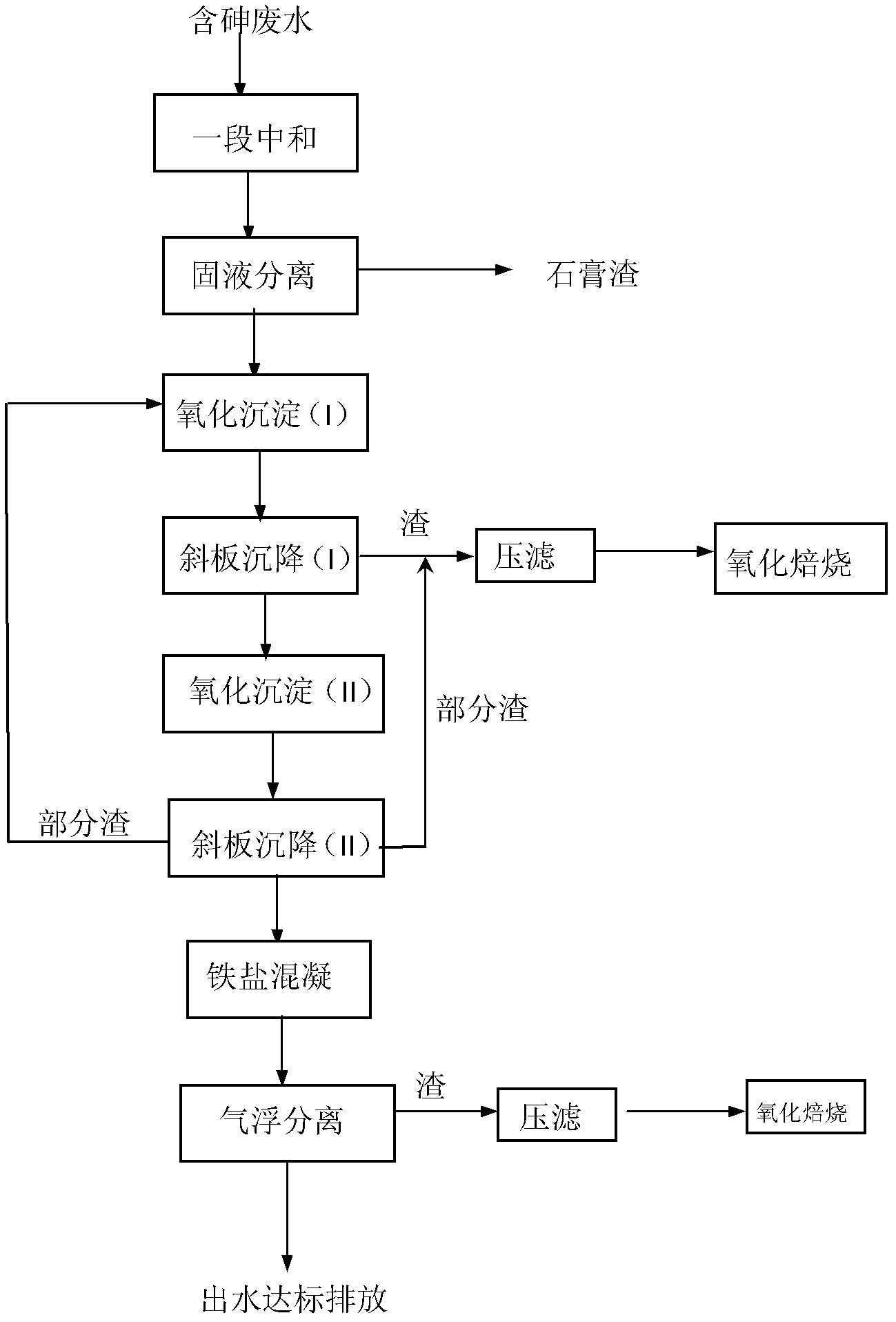
Treatment method for high-concentration arsenic waste water
ActiveCN103030233ARealize solid-liquid separationEfficient curingWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationFiltration
The invention discloses a treatment method for high-concentration arsenic waste water, and relates to the technical field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out pH neutralization adjustment, and executing solid-liquid separation after neutralization; 2, oxidizing sedimentation (I): treating the arsenic waste water with an alkaline coagulant, then, executing oxidization, and carrying out inclined plate settling to realize solid-liquid separation; 3, oxidizing sedimentation (II): adding lime or lime milk in the neutralized waste water, executing oxidization simultaneously, and carrying out inclined plate settling to realize solid-liquid separation; 4, ferric salt coagulation: adding an inorganic coagulant in water solution, stirring, and then, adding an organic flocculant; and 5, air floatation separation: adding a surface active agent, separating iron and arsenic slag, executing pressure filtration and drying, and carrying out oxidizing roasting. The method has the beneficial effect that the effluent As concentration of the treated waste water can meet the national emission standard; the As concentration of the leach liquor of the oxidized and roasted arsenic waste residue buried underground is far below the national stipulated limit, and arsenic is cured effectively.
Owner:深圳市明登科技有限公司
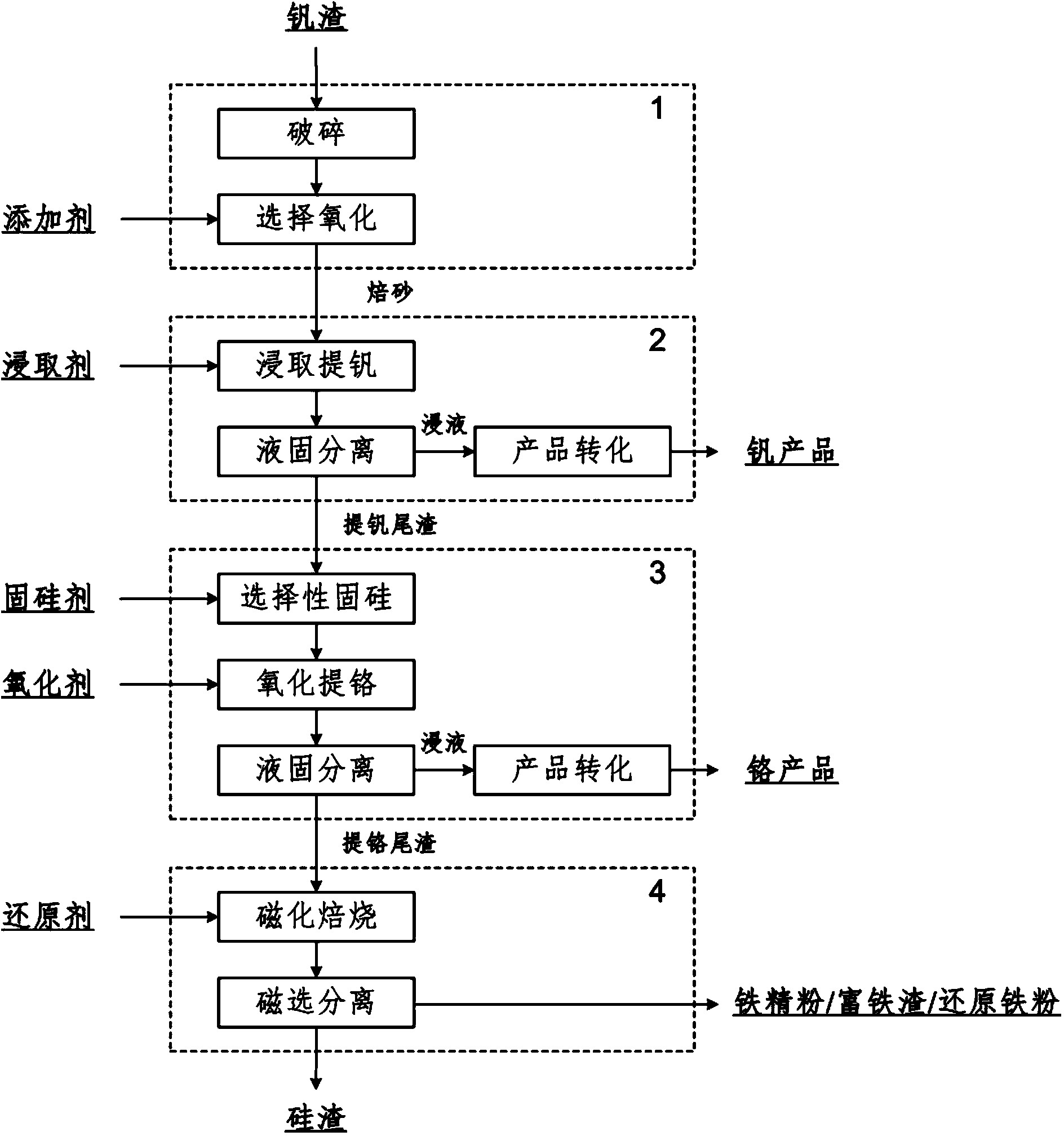
Clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step
The invention relates to a clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step. The clean process method comprises the following steps of: selectively oxidizing the vanadium slag to obtain a roasted product; leaching the obtained roasted product by using a leaching agent to extract vanadium, carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain vanadium-containing leach liquor and vanadium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the vanadium-containing leach liquor to prepare vanadium series products; adding the obtained vanadium-extracted tailings and a silicon fixing agent to a sodium hydroxide solution, selectively fixing silicon, then oxidizing to extract chromium, then carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain chromium-containing leach liquor and chromium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the chromium-containing leach liquor to prepare chromium series products; mixing the chromium-extracted tailings with a reducing agent, and carrying out magnetizing roasting and magnetic separation to obtain silicon slag and ion concentrate powder / iron-enriched slag / reduced iron powder. The clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the step-by-step extraction and high-efficiency separation of valuable components such as vanadium, chromium and iron which are contained in the vanadium slag, prevents the mutual entrainment of vanadium, chromium and iron products; in addition, the clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the near zero discharge of waste water and the recycling of final slag and is clean and pollution-free.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com