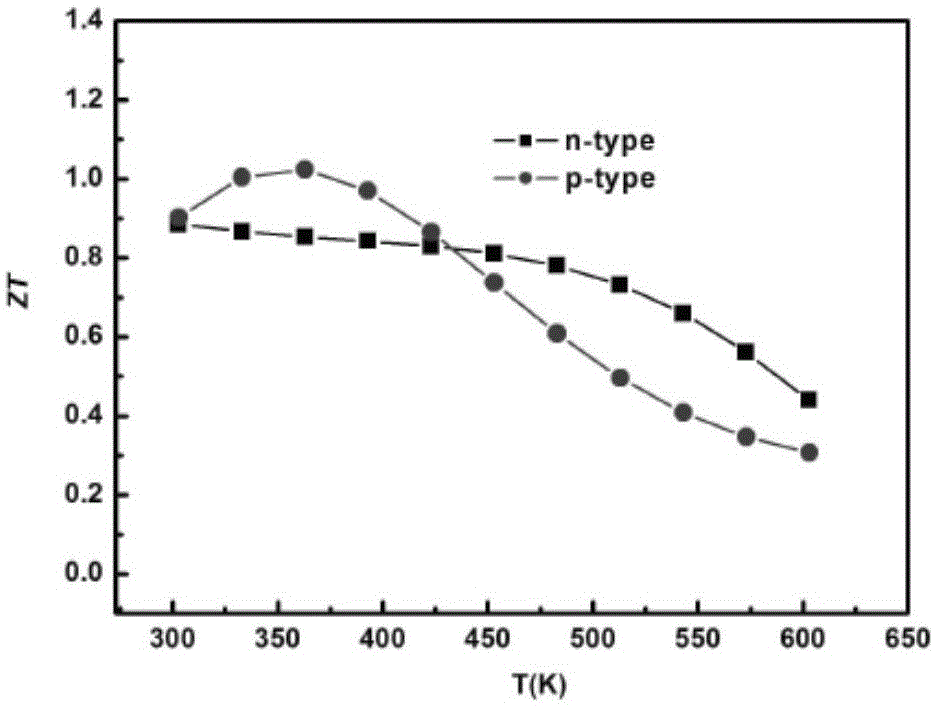
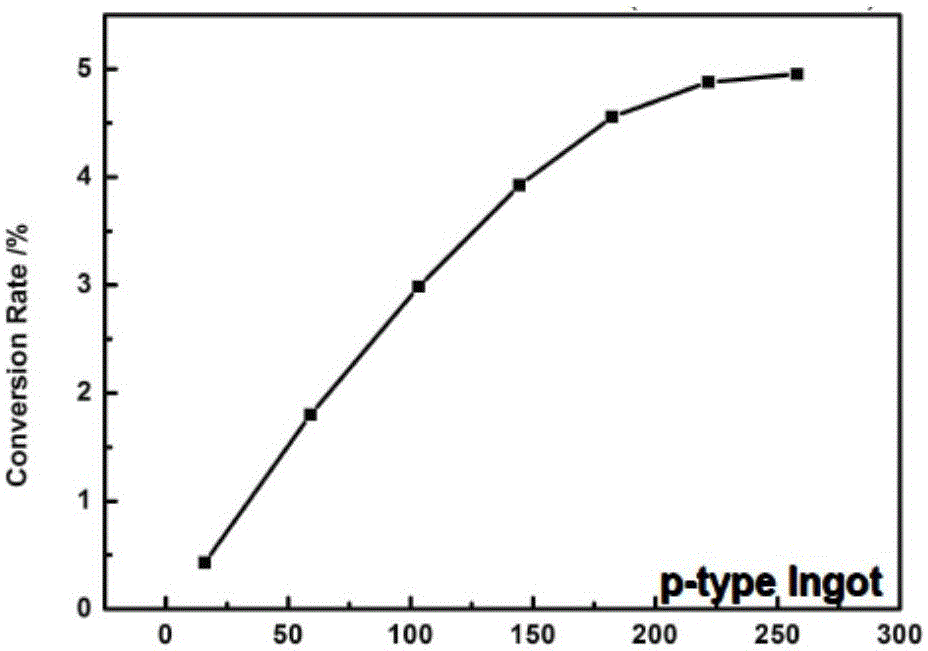
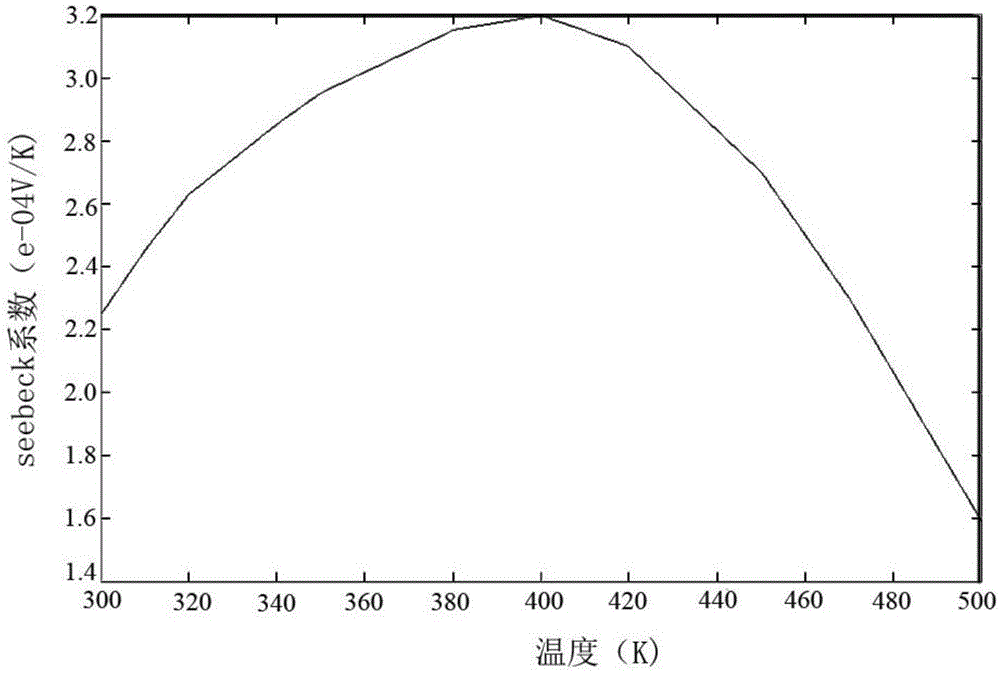
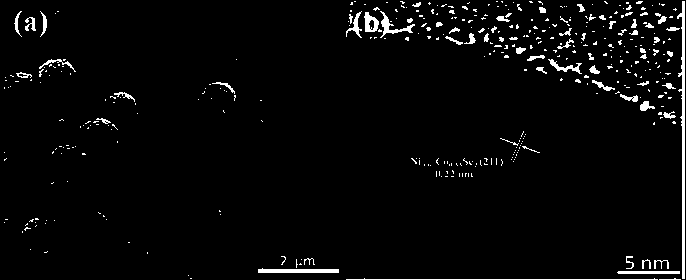
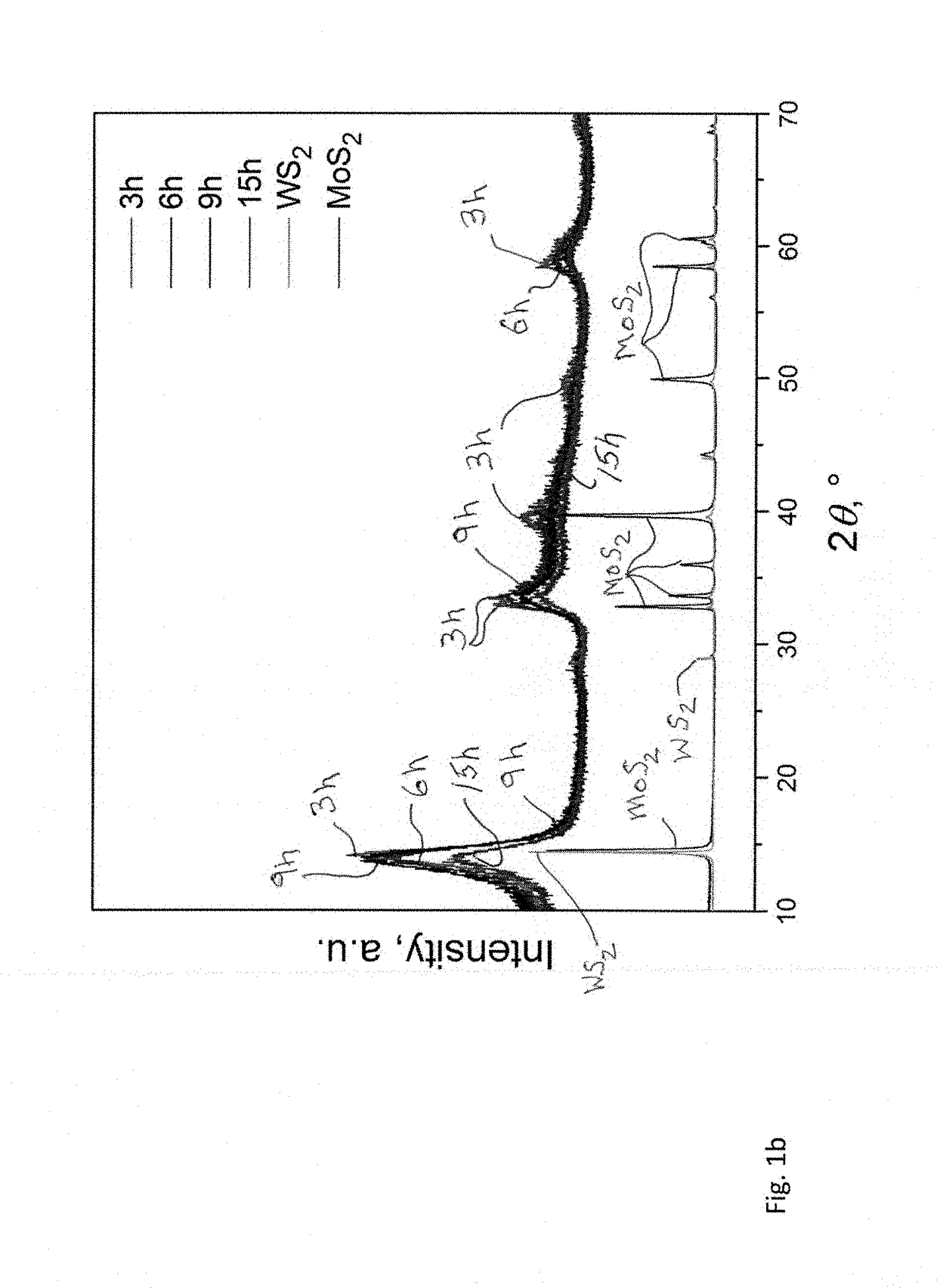
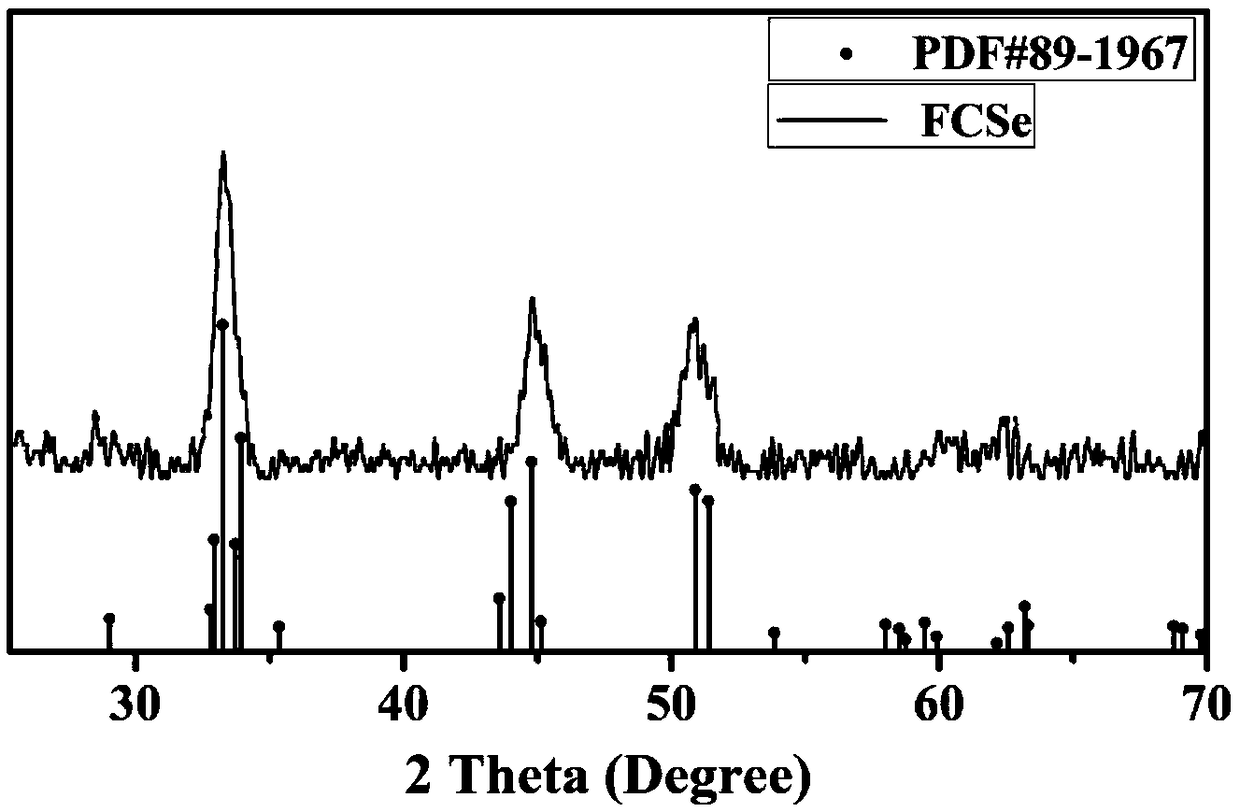
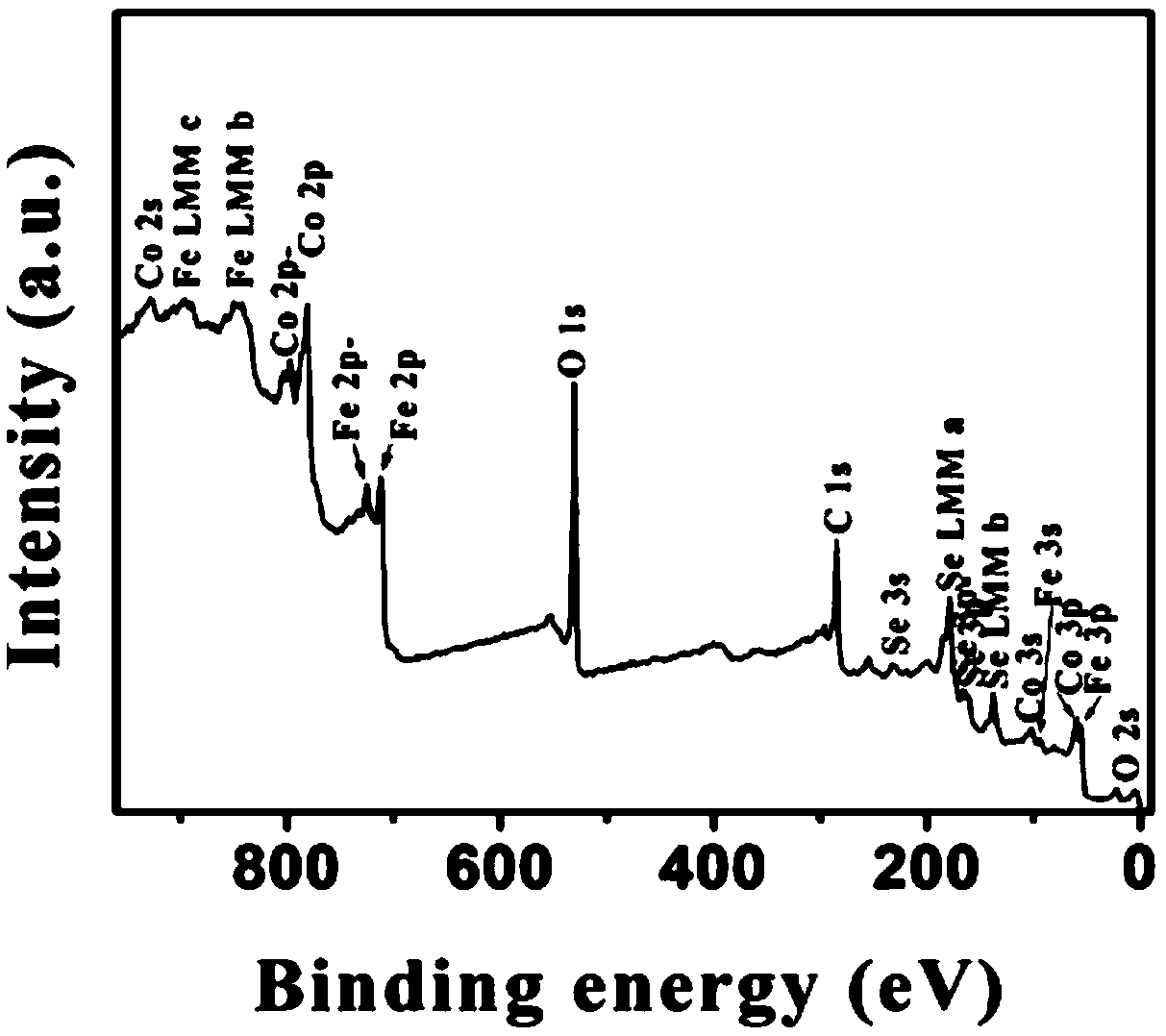
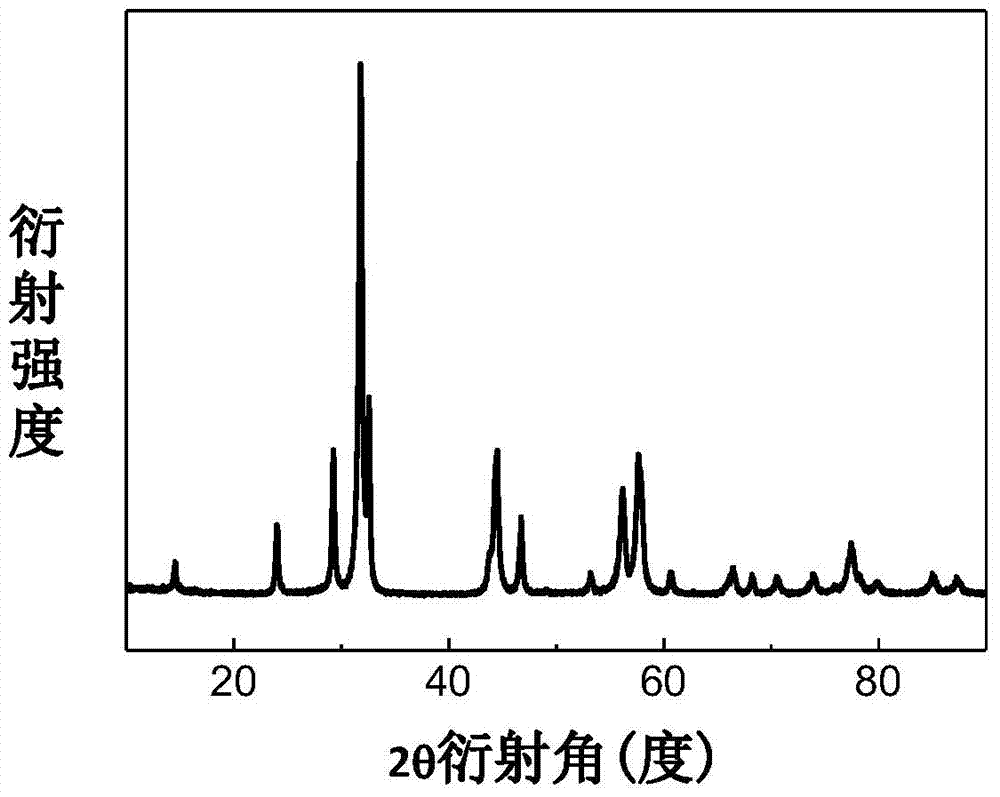
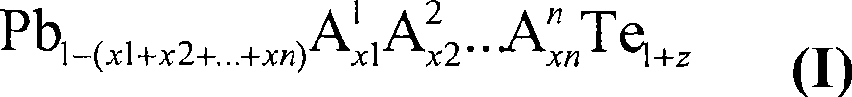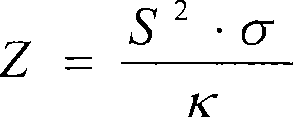Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
460results about "Selenium/tellurium compounds with other elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
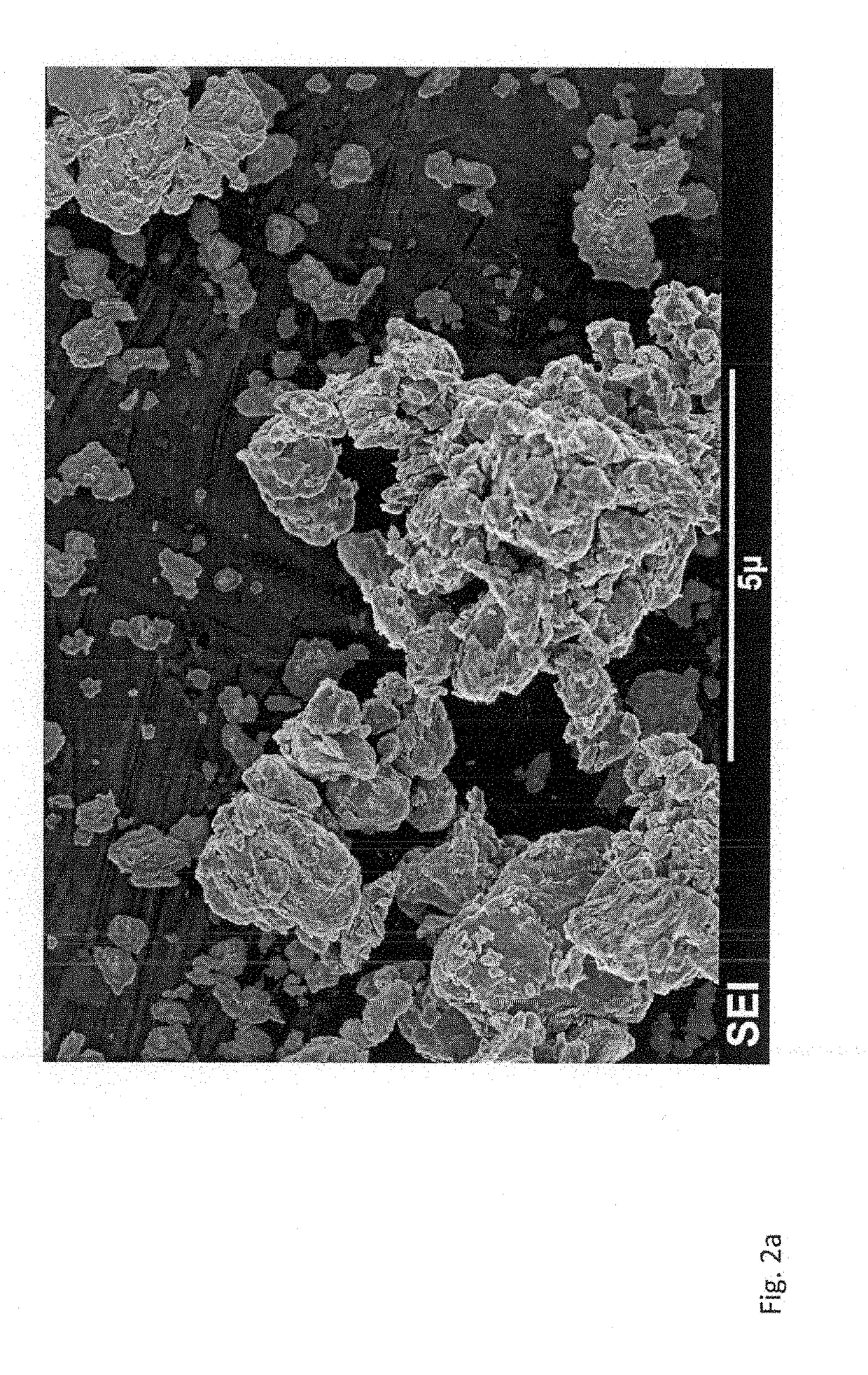
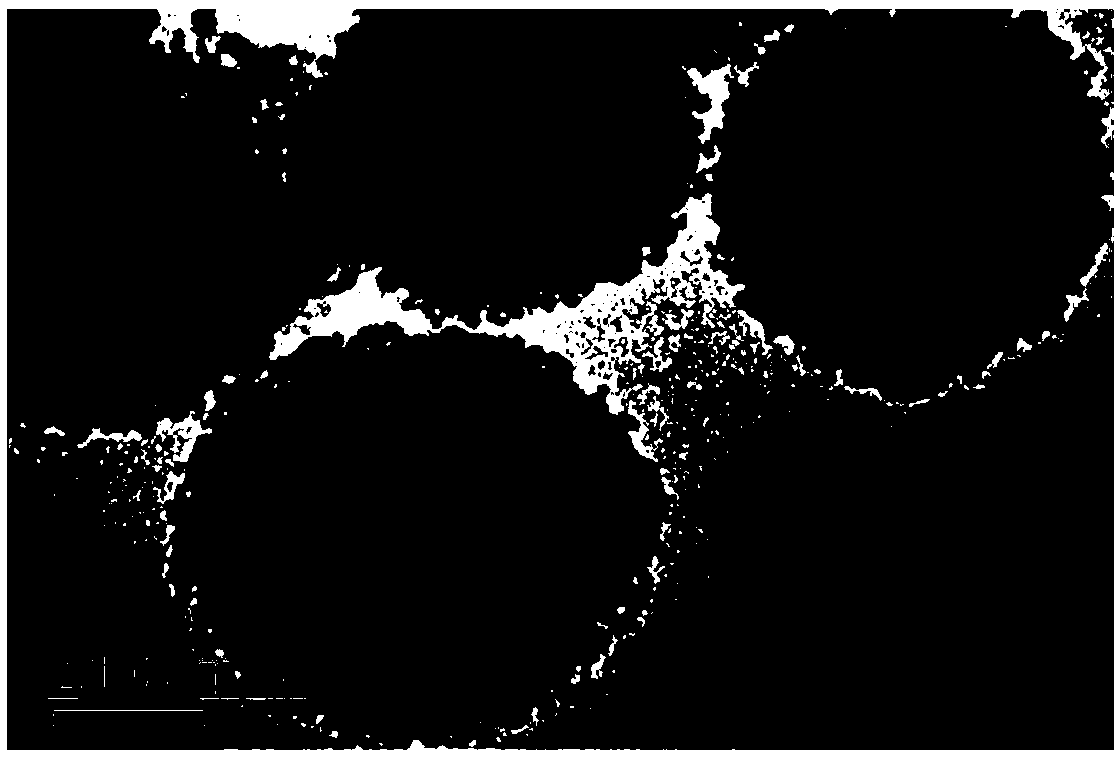
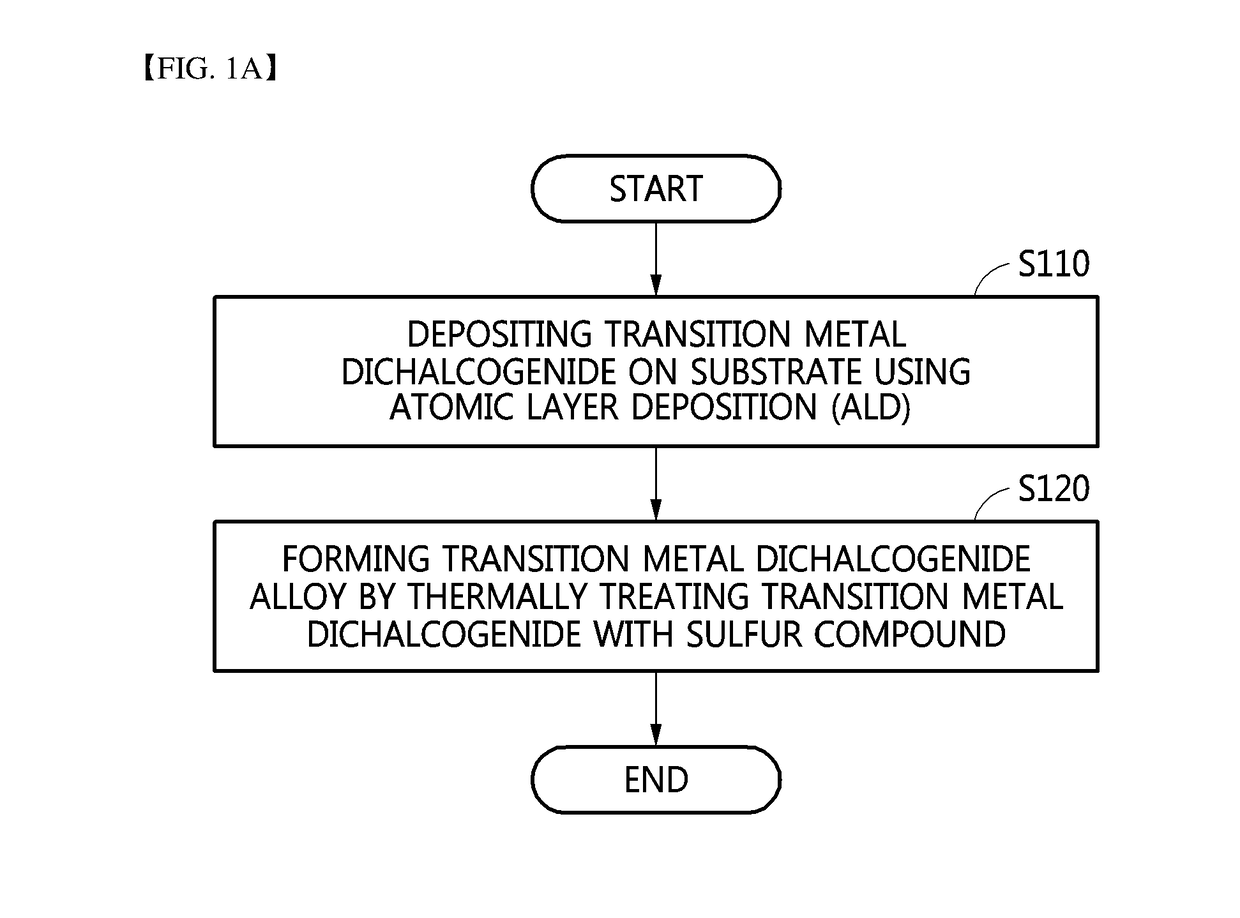
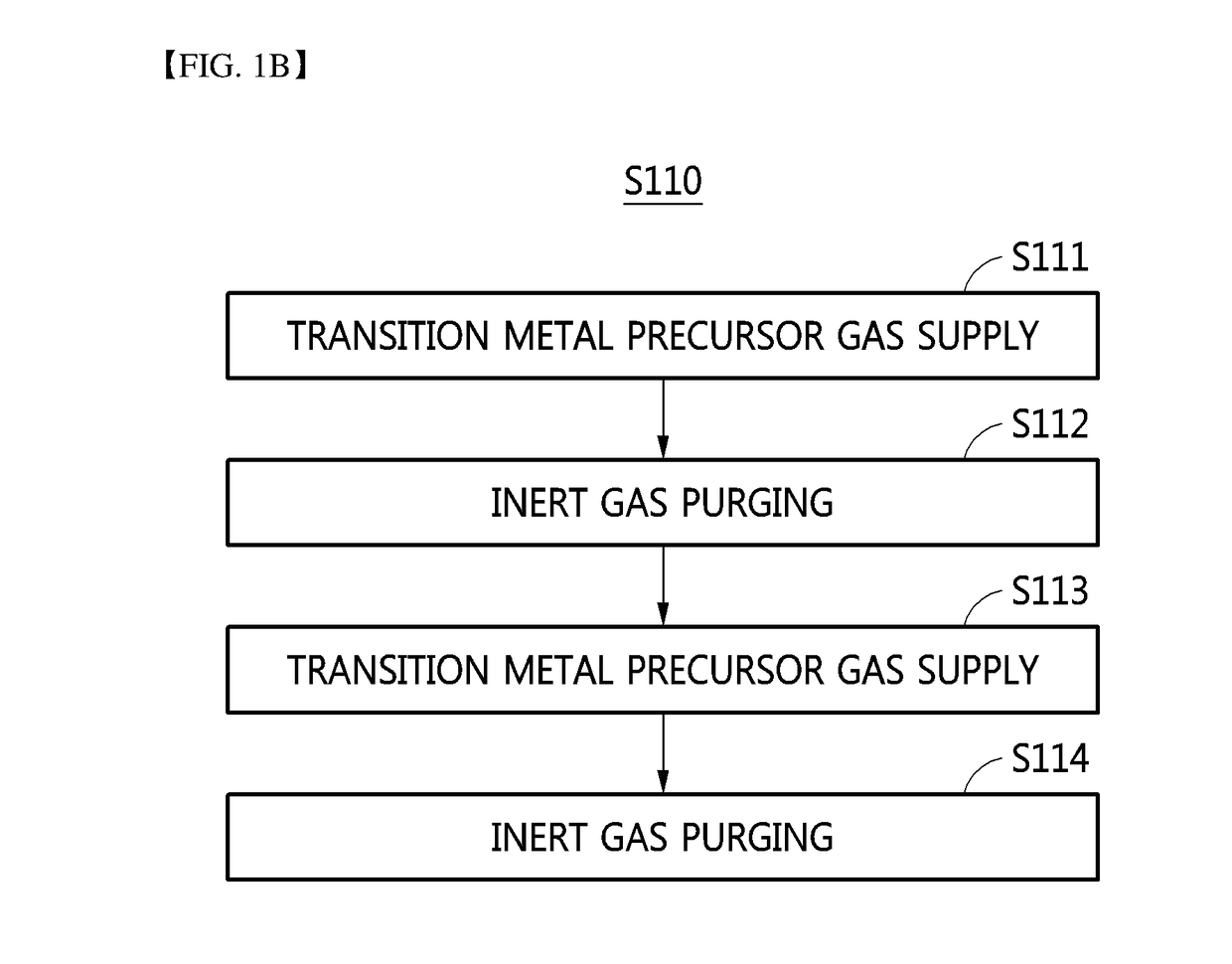
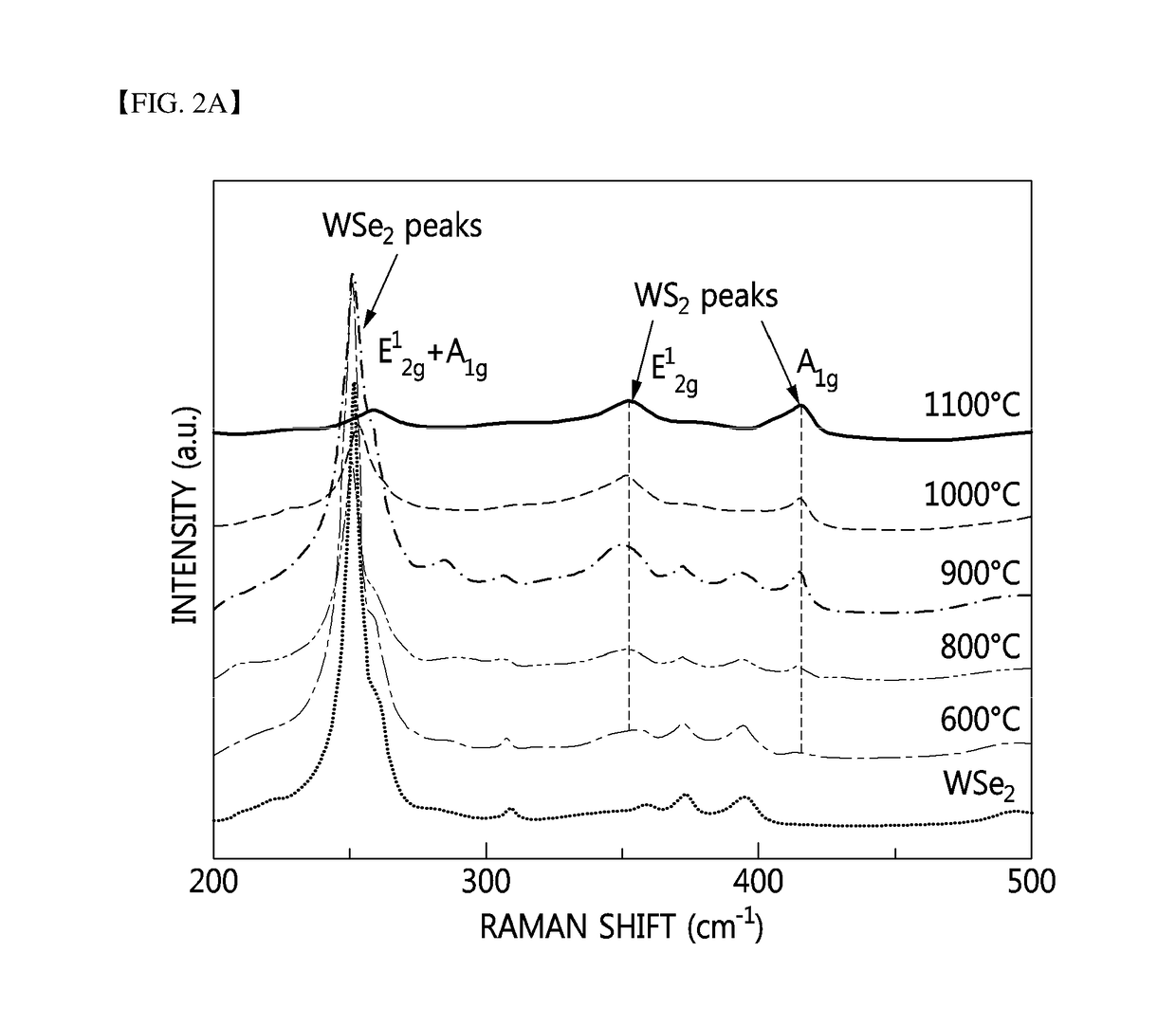
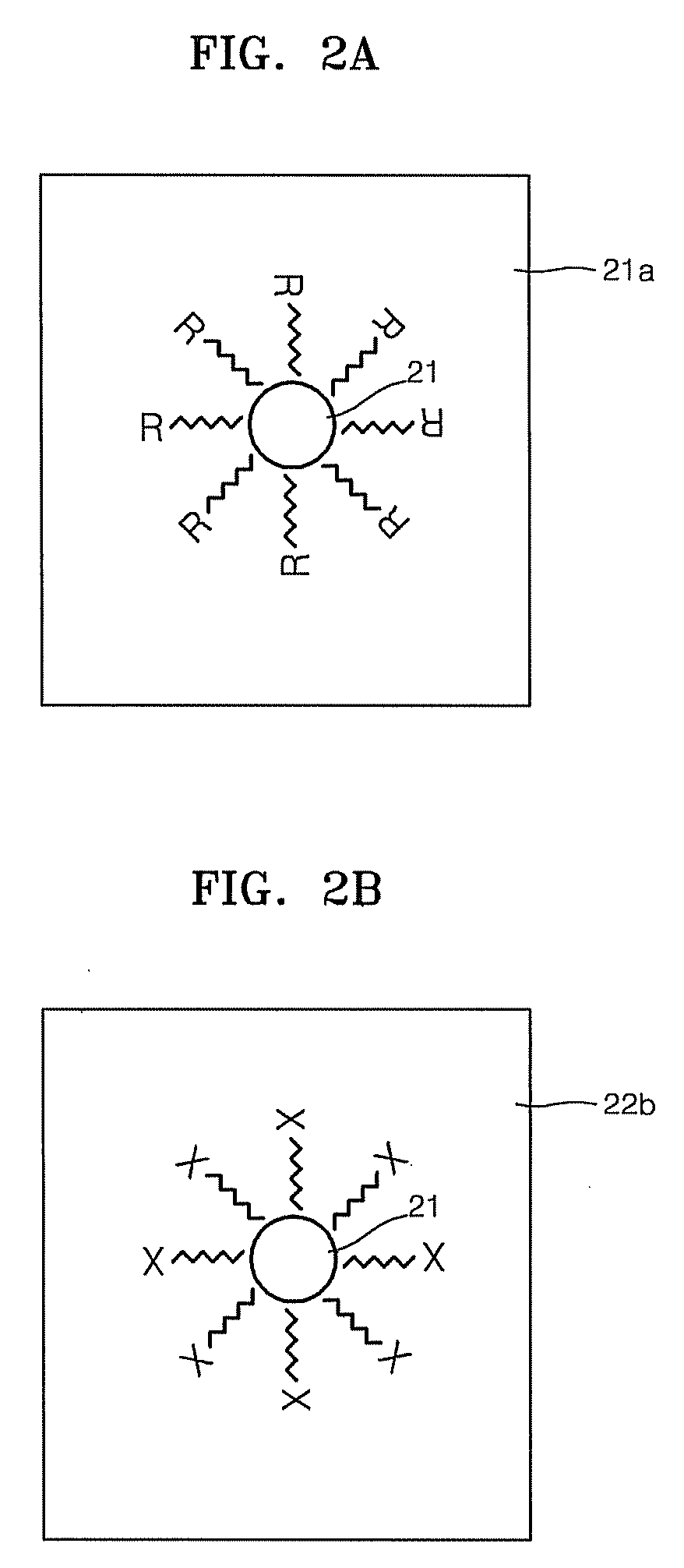
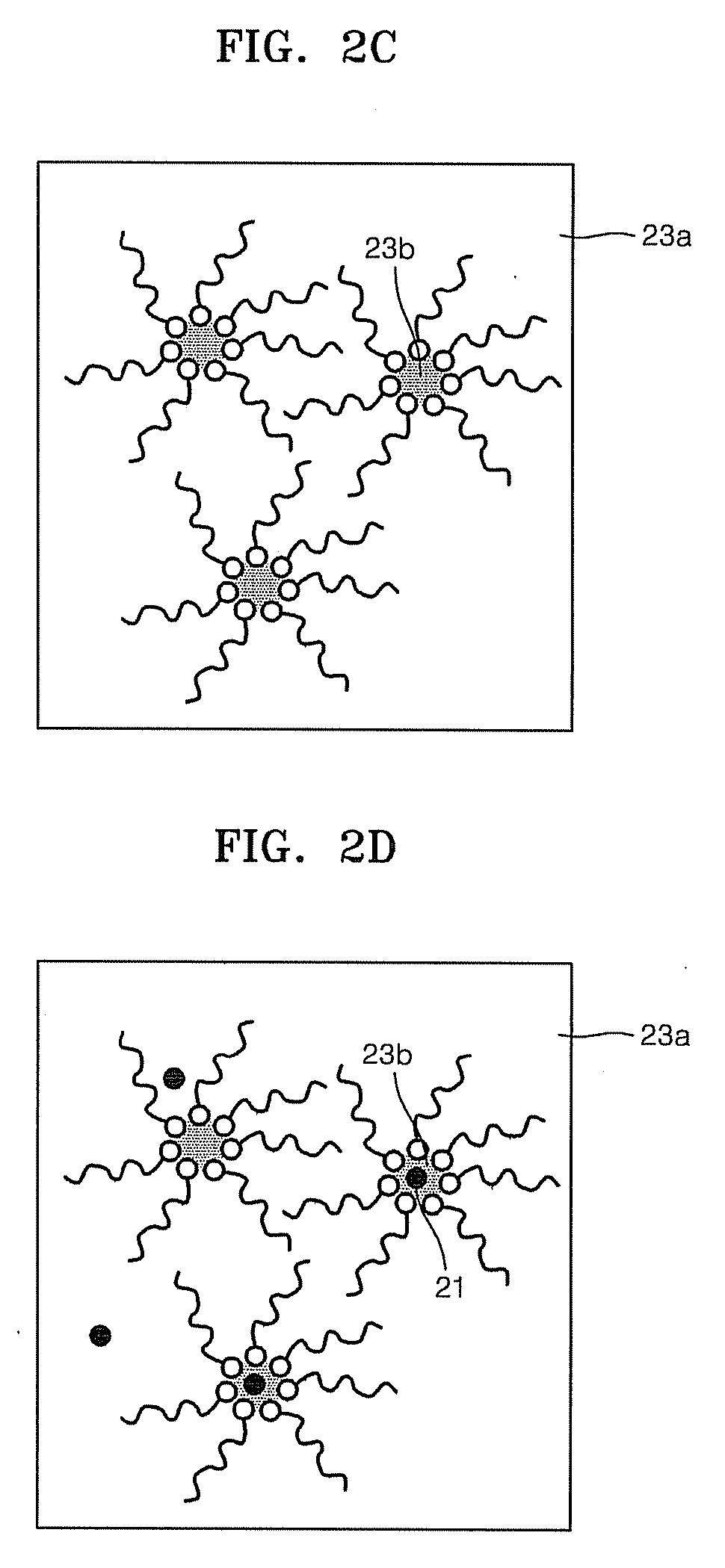
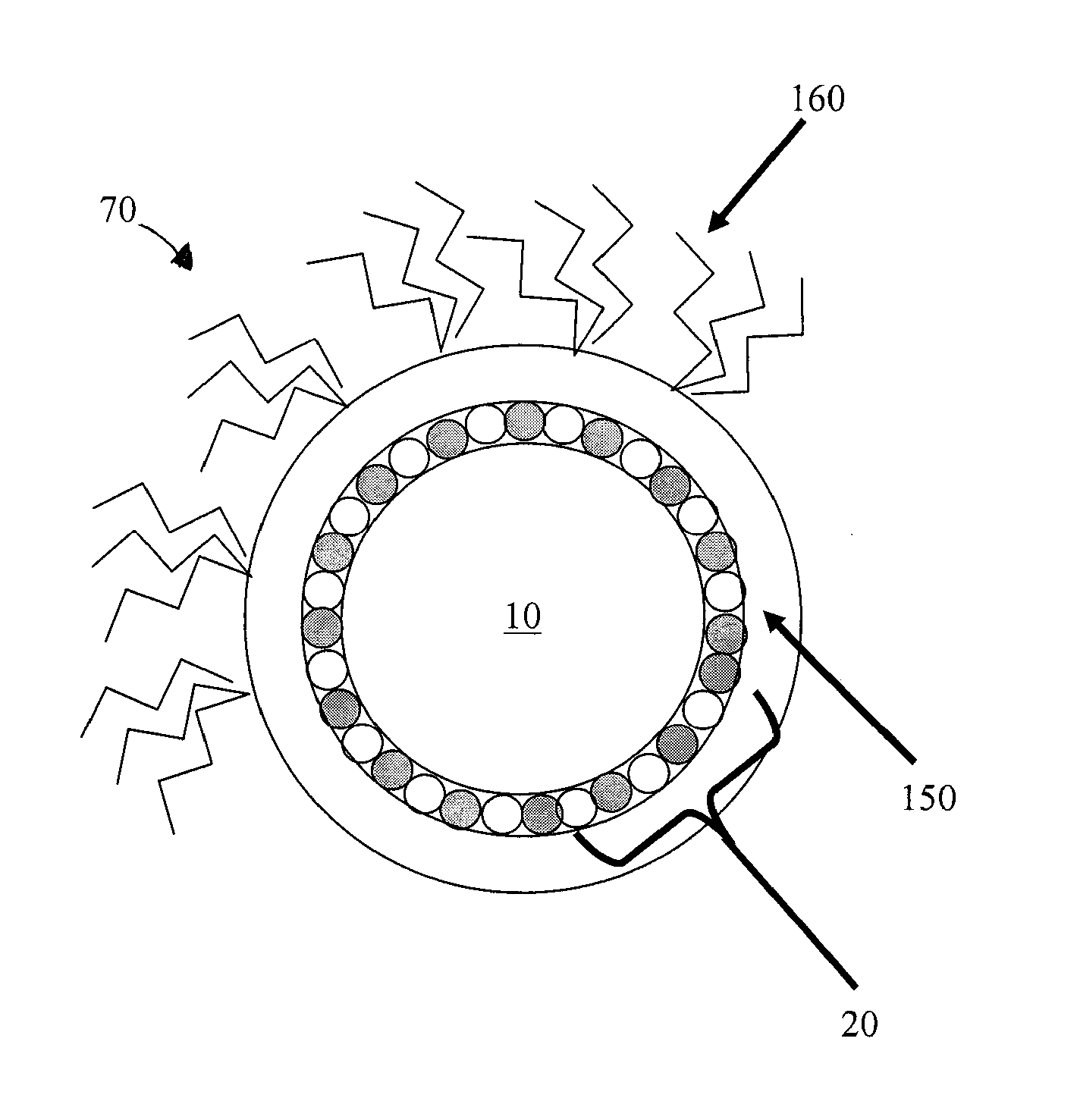
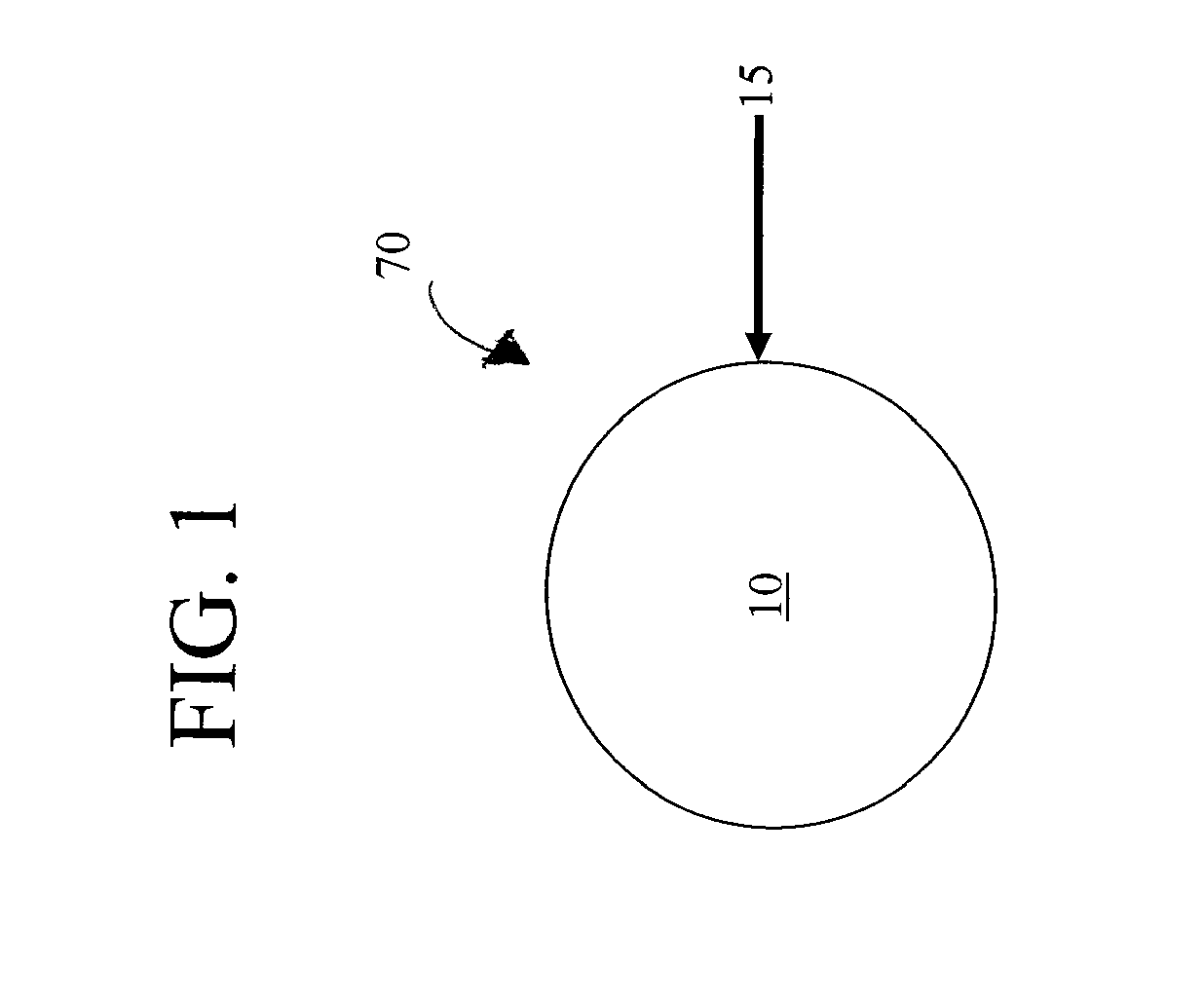
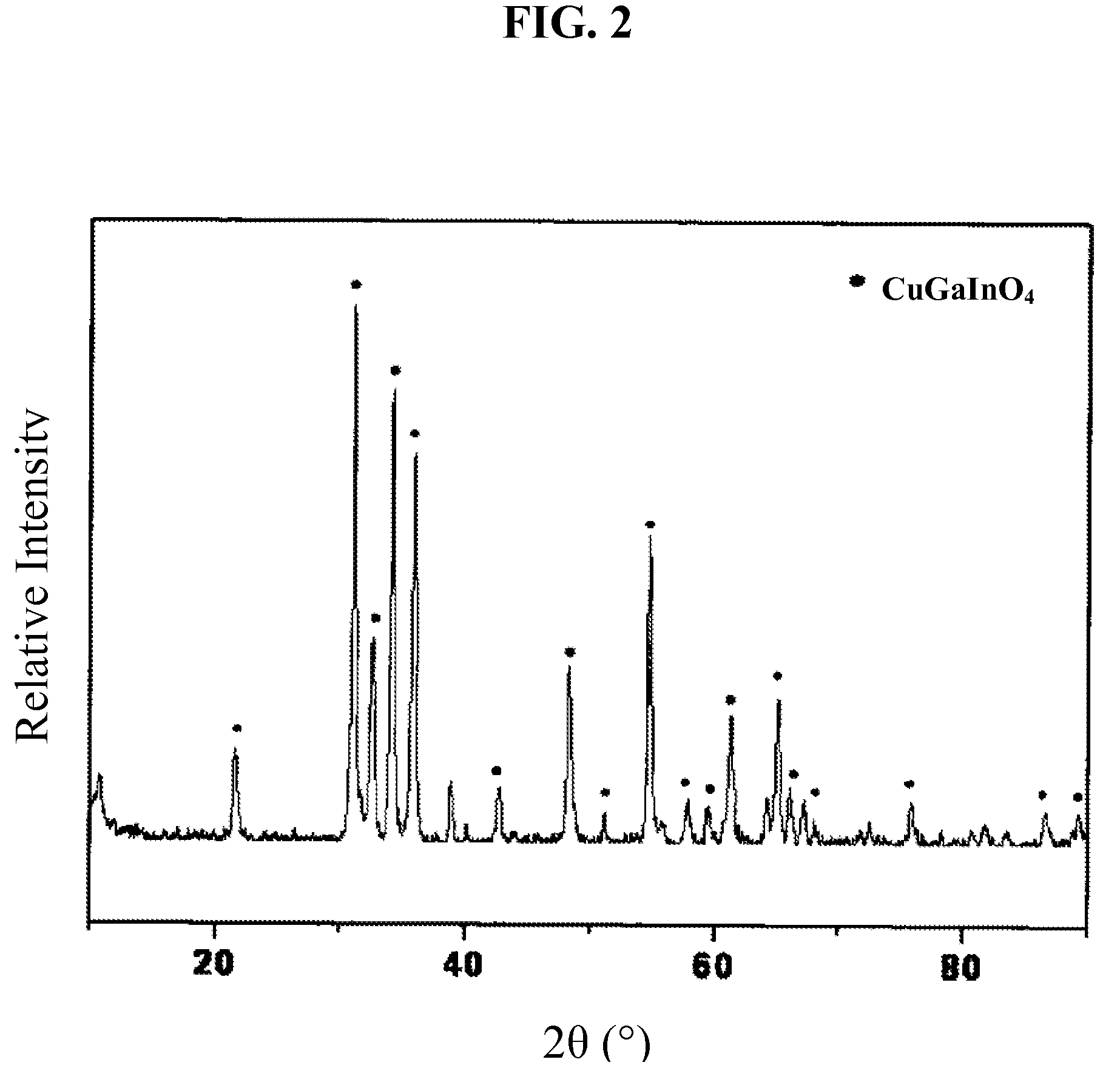
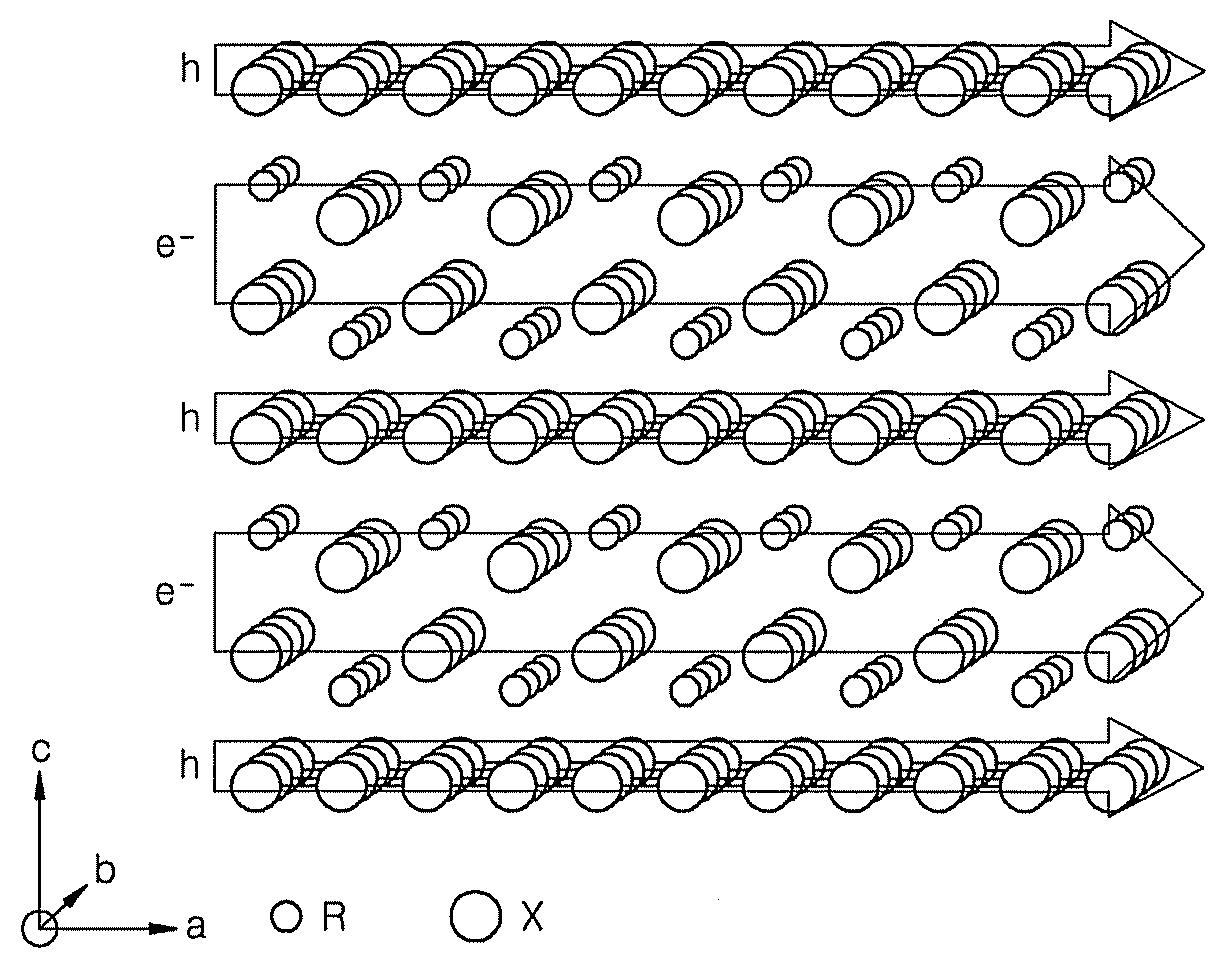
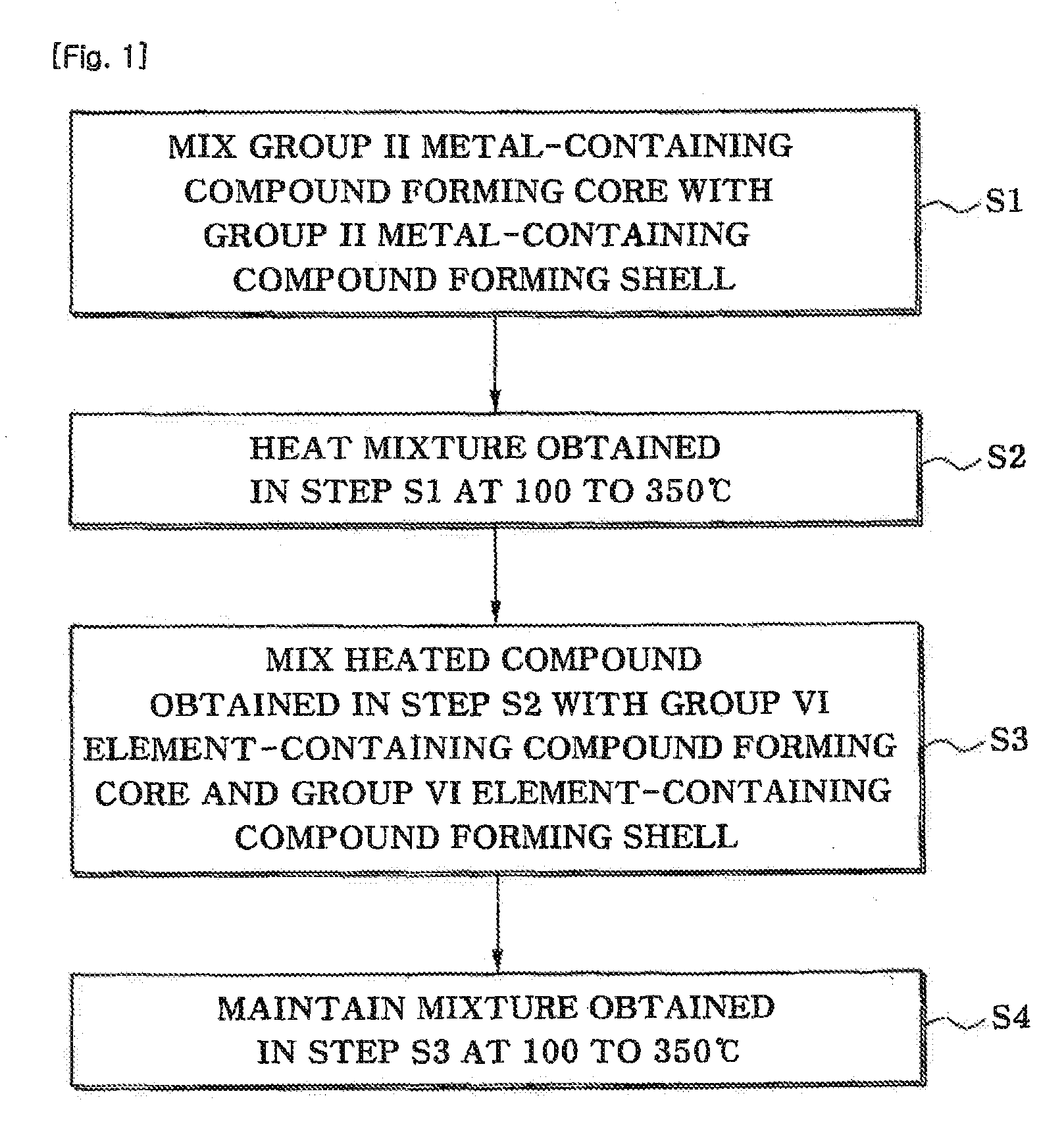
Transition metal dichalcogenide alloy and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170267527A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsSulfurAlloy
Disclosed are a transition metal dichalcogenide alloy and a method of manufacturing the same. A method of manufacturing a transition metal dichalcogenide alloy according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes a step of depositing transition metal dichalcogenide on a substrate using atomic layer deposition (ALD); and a step of forming a transition metal dichalcogenide alloy by thermally treating the transition metal dichalcogenide with a sulfur compound.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
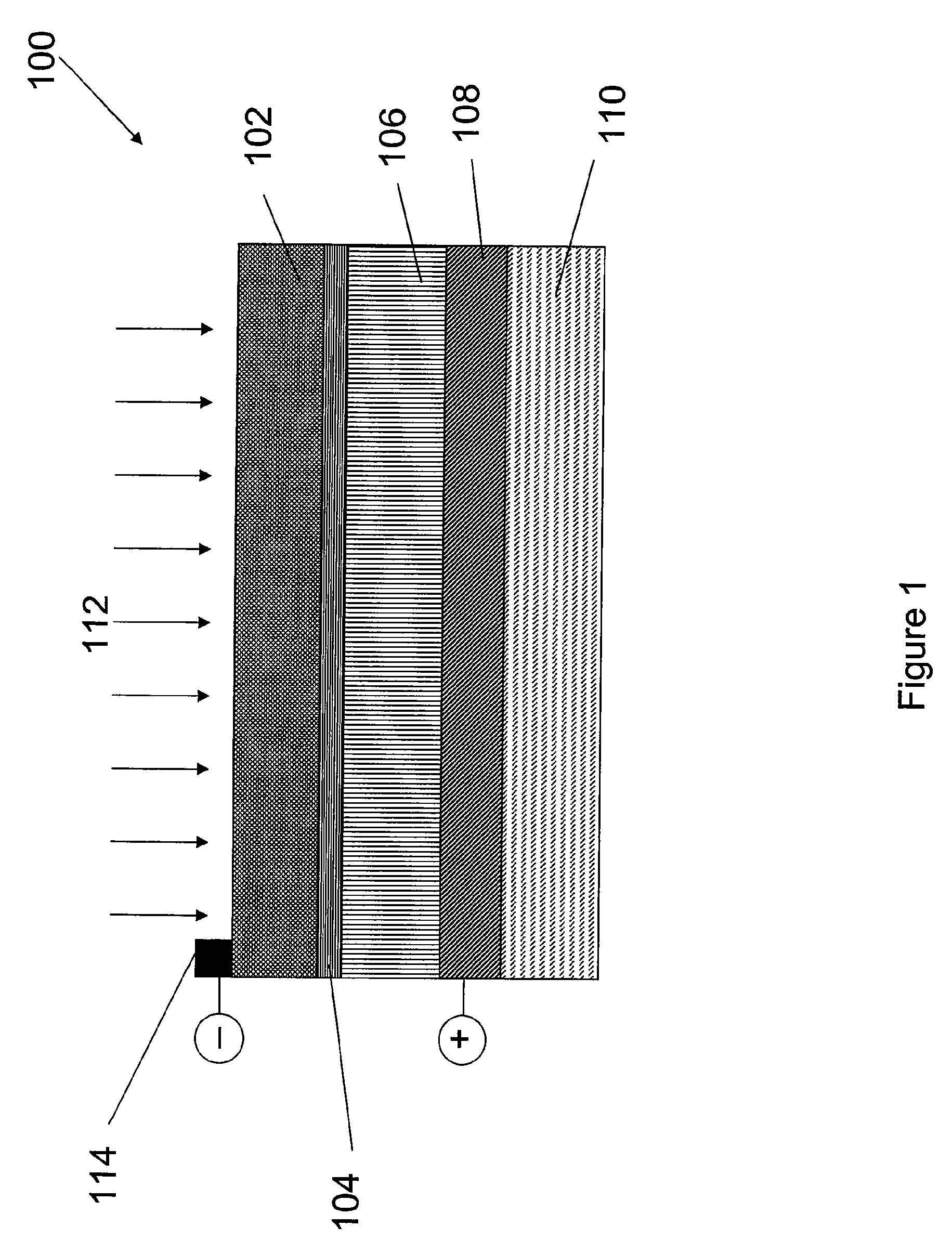
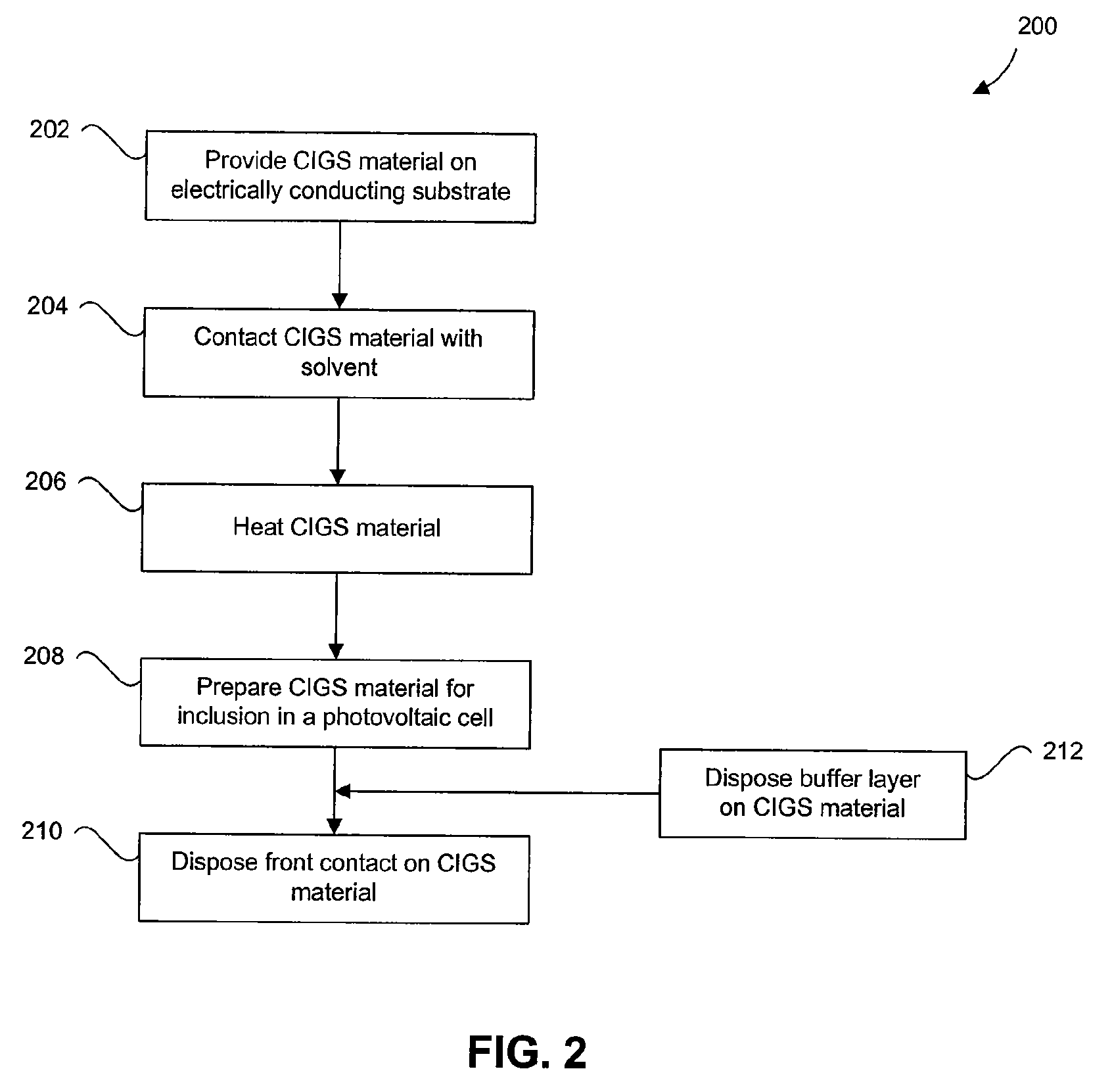
Chemical Treatments to Enhance Photovoltaic Performance of CIGS
InactiveUS20090235987A1Enhance solar cell conversion efficiencyReduce surface defect densityLighting and heating apparatusPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsChemical treatmentSolvent
The present invention provides method of treating semiconductor surfaces (e.g., CIGS) using various solvents (including ionic solvents and eutectics), and methods preparing photovoltaic cells comprising treated CIGS materials.
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
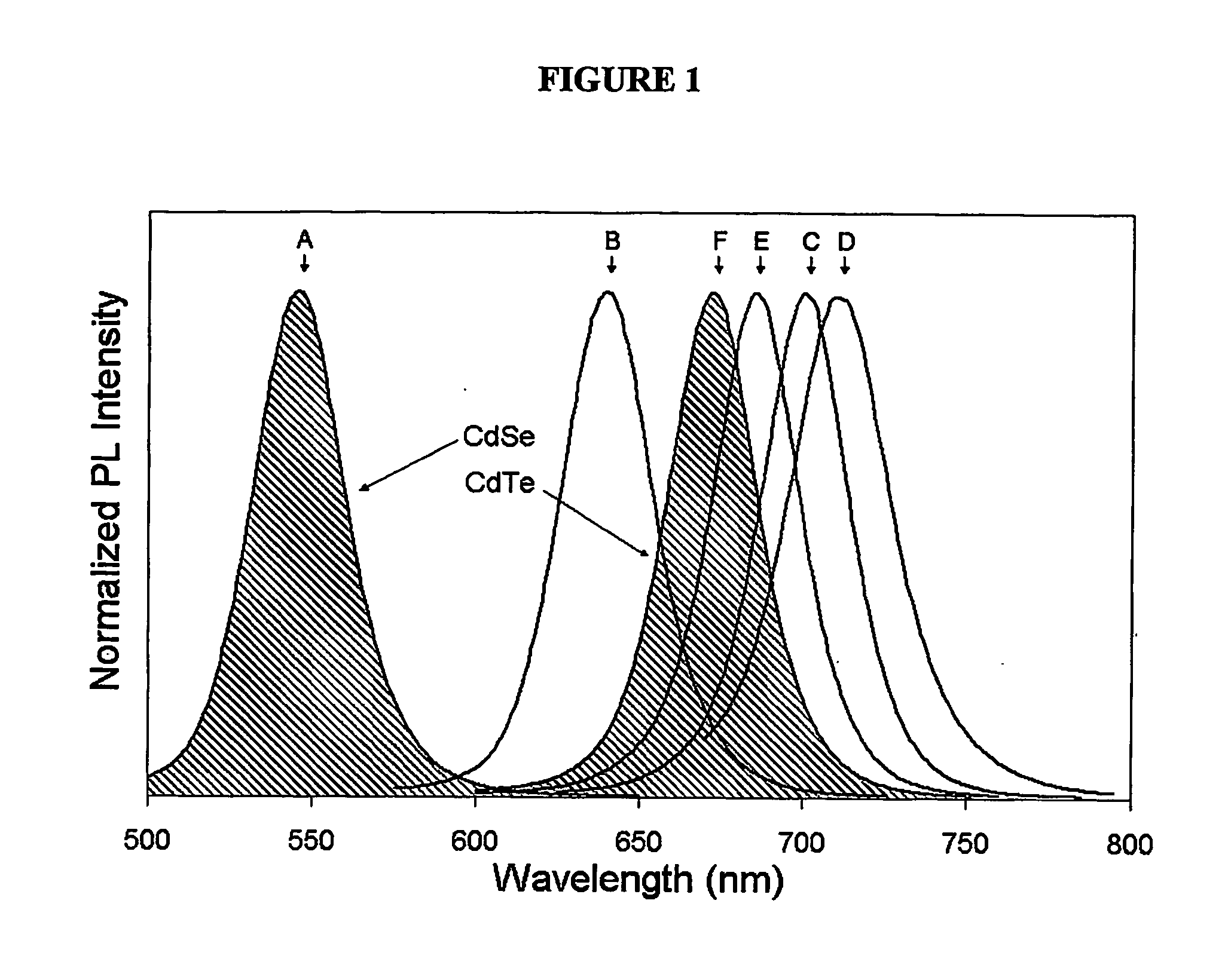
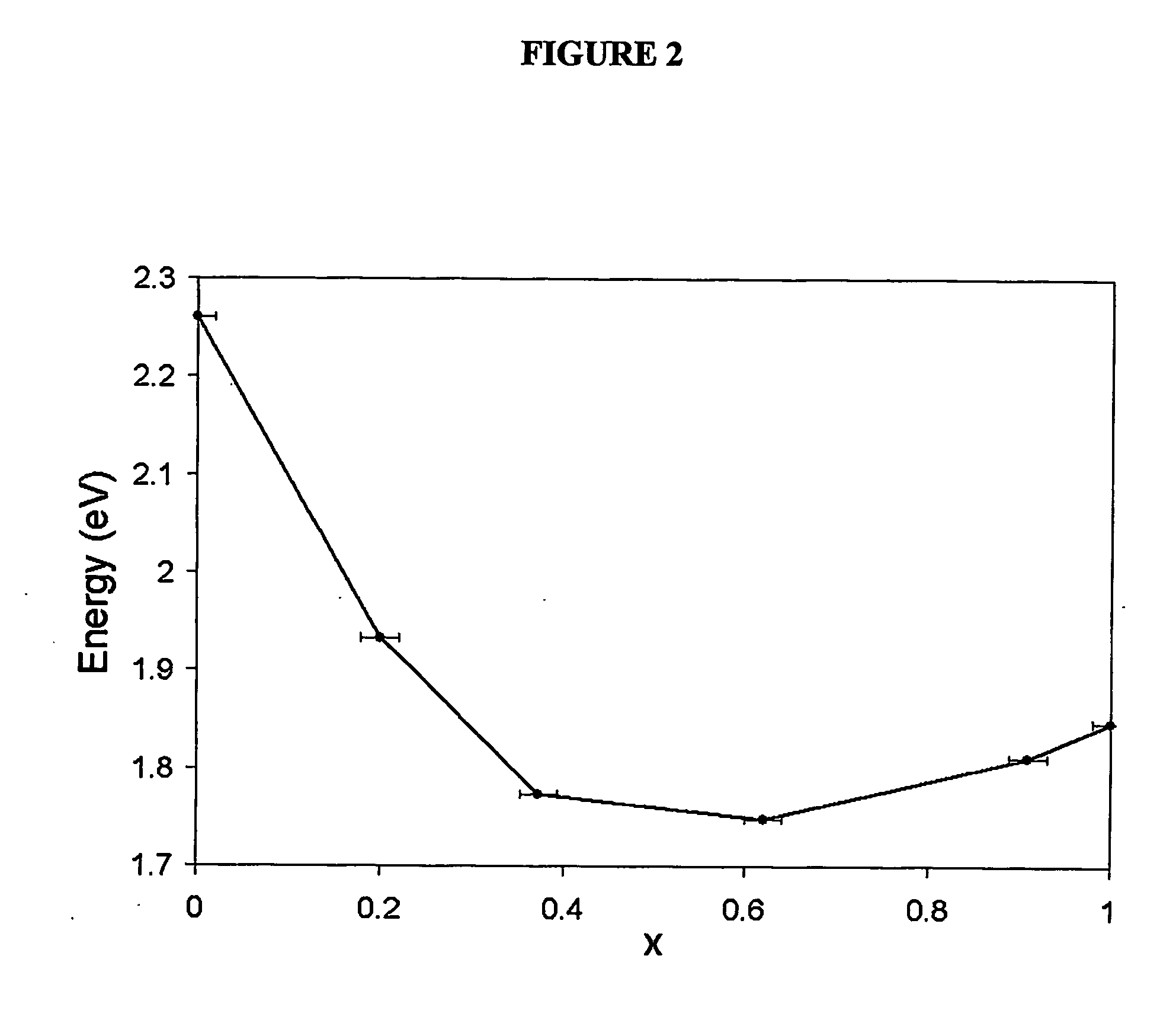
Alloyed semiconductor quantum dots and concentration-gradient alloyed quantum dots, series comprising the same and methods related thereto
An alloyed semiconductor quantum dot comprising an alloy of at least two semiconductors, wherein the quantum dot has a homogeneous composition and is characterized by a band gap energy that is non-linearly related to the molar ratio of the at least two semiconductors; a series of alloyed semiconductor quantum dots related thereto; a concentration-gradient quantum dot comprising an alloy of a first semiconductor and a second semiconductor, wherein the concentration of the first semiconductor gradually increases from the core of the quantum dot to the surface of the quantum dot and the concentration of the second semiconductor gradually decreases from the core of the quantum dot to the surface of the quantum dot; a series of concentration-gradient quantum dots related thereto; in vitro and in vivo methods of use; and methods of producing the alloyed semiconductor and concentration-gradient quantum dots and the series of quantum dots related thereto.
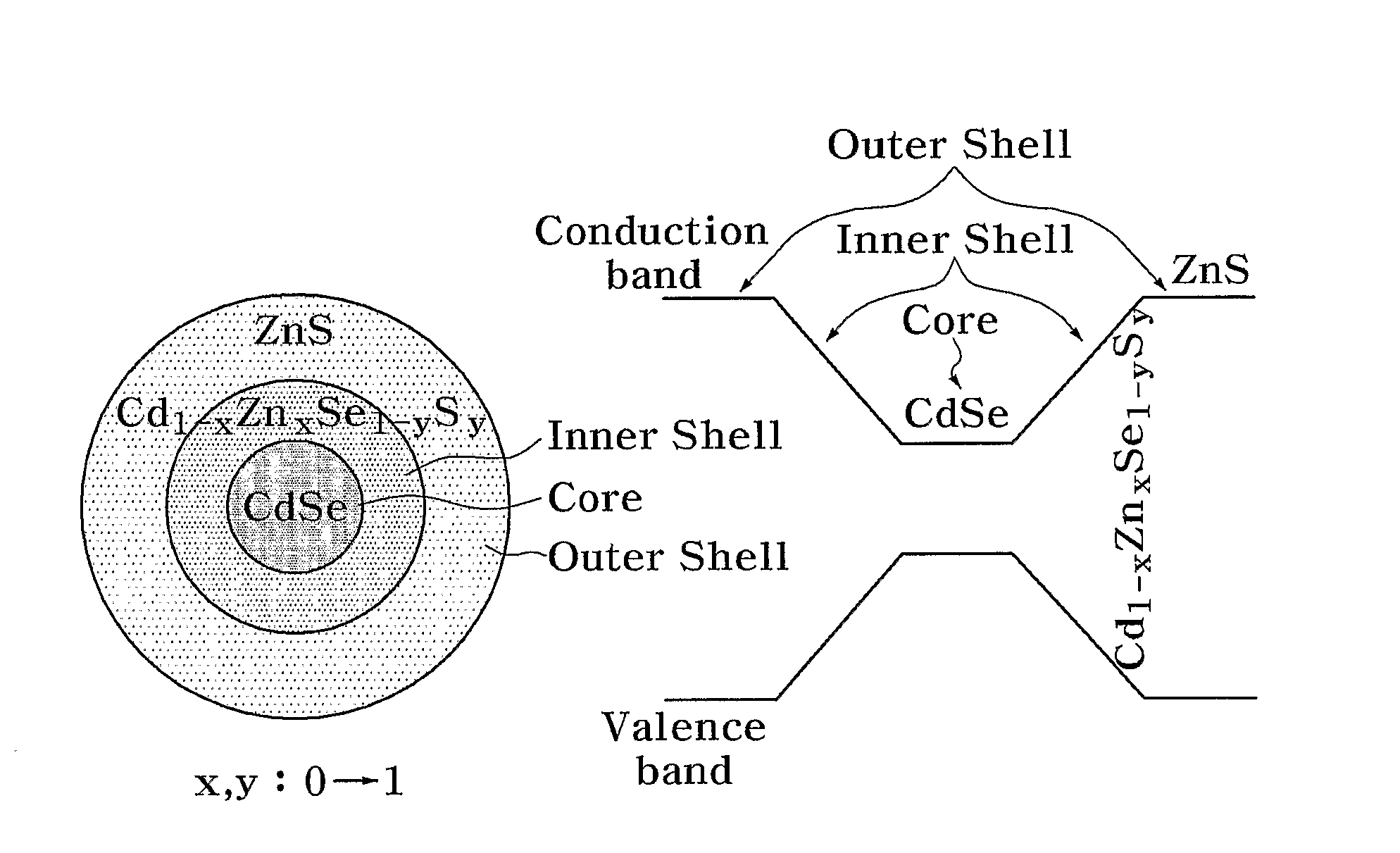
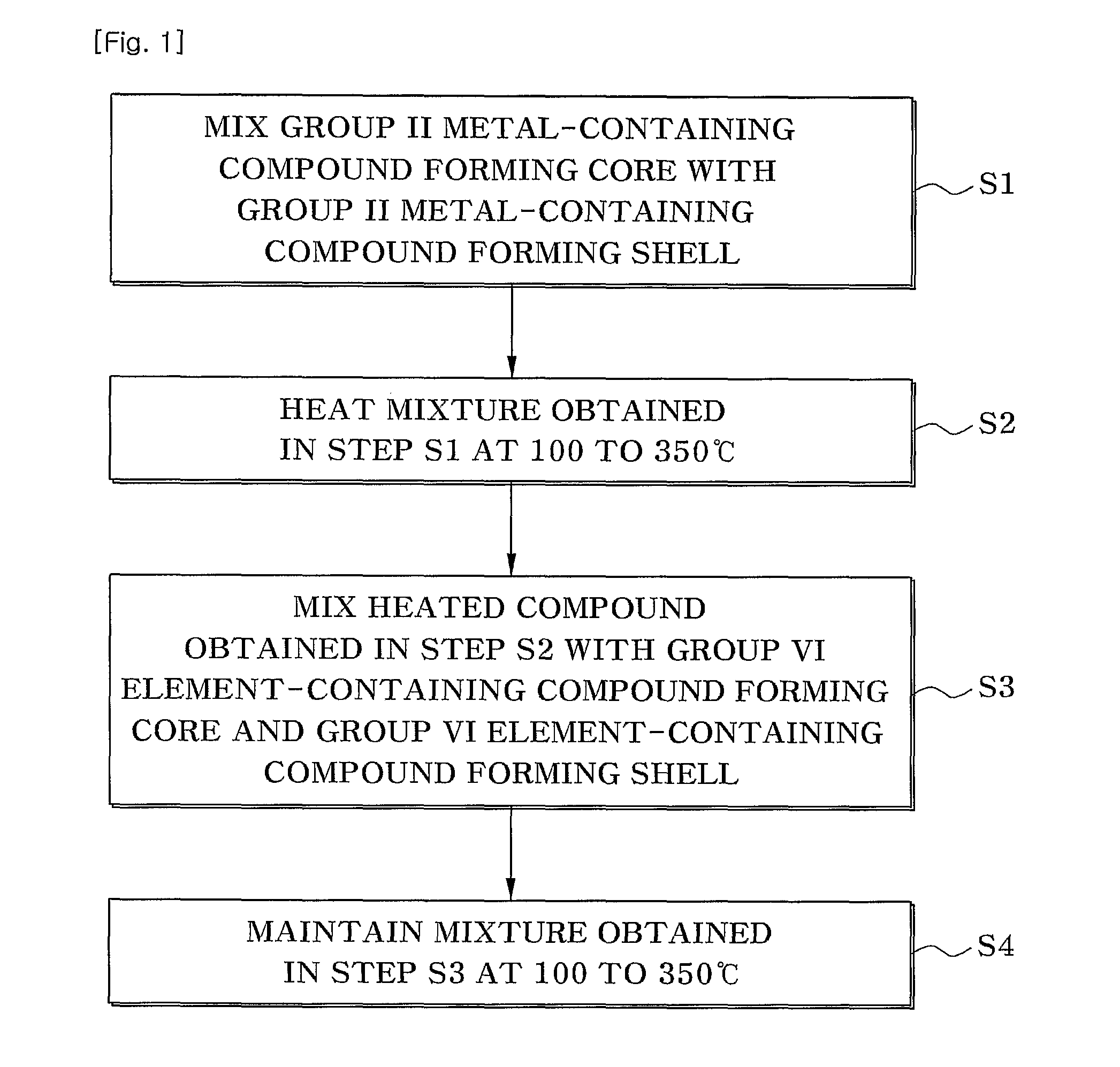
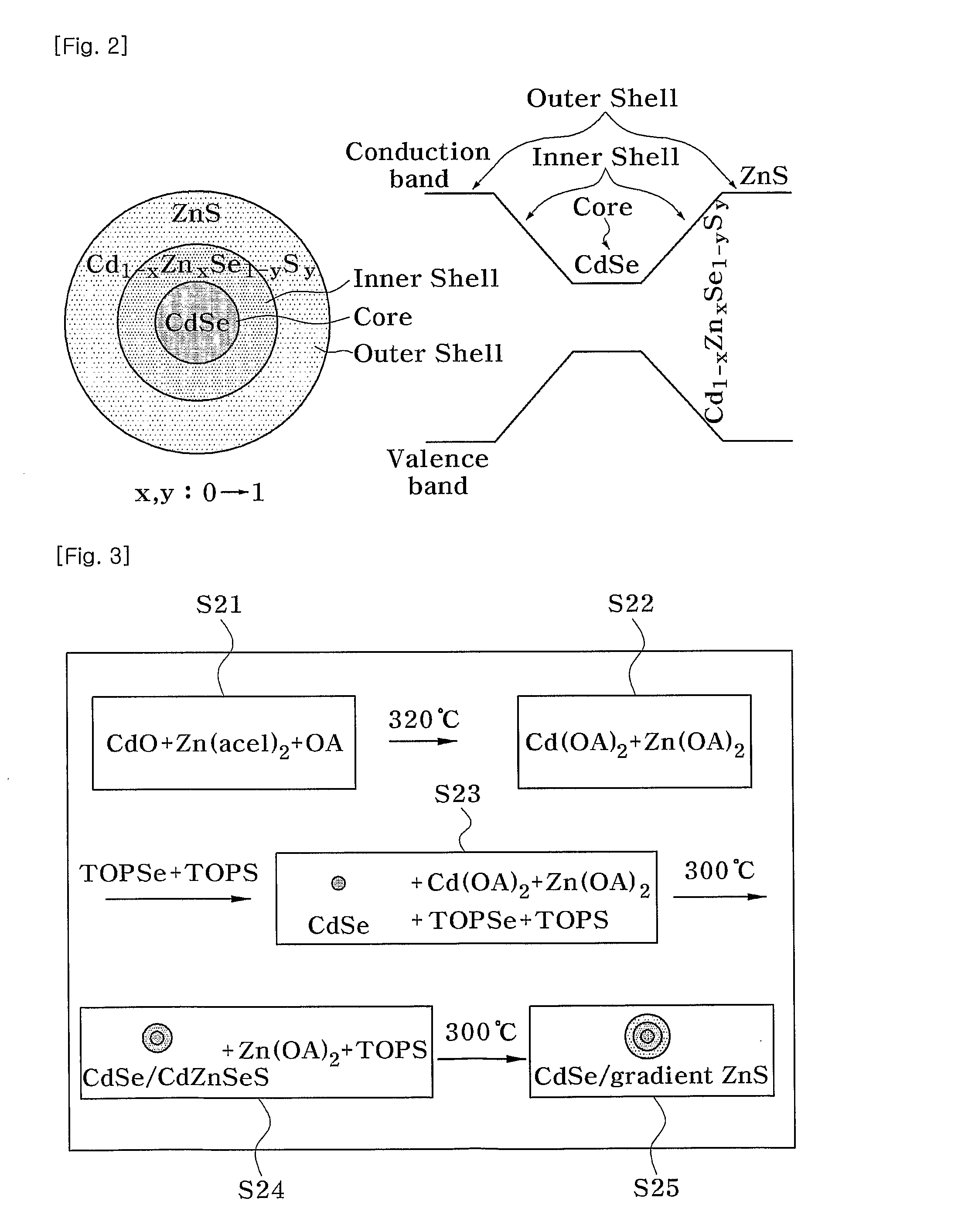
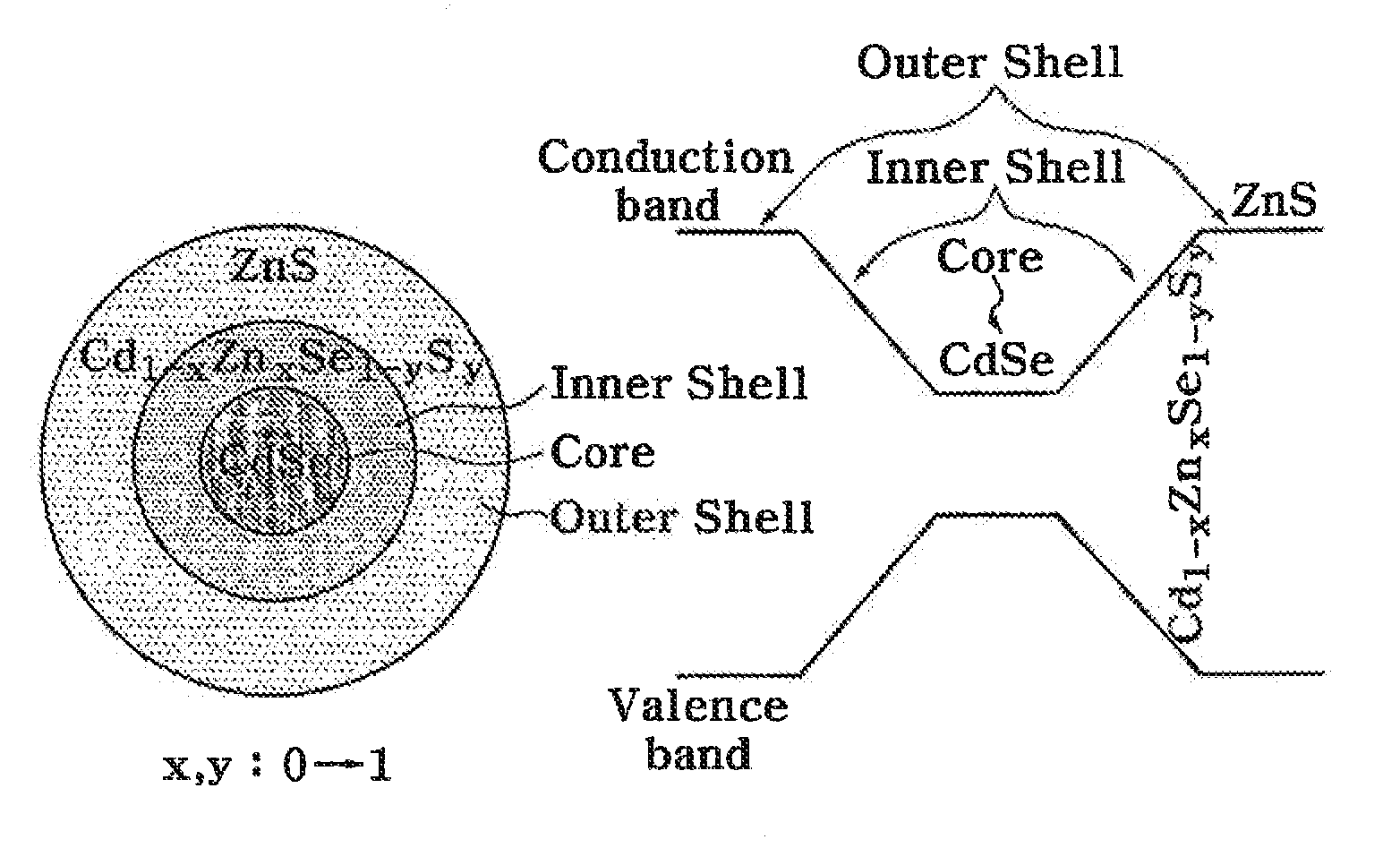
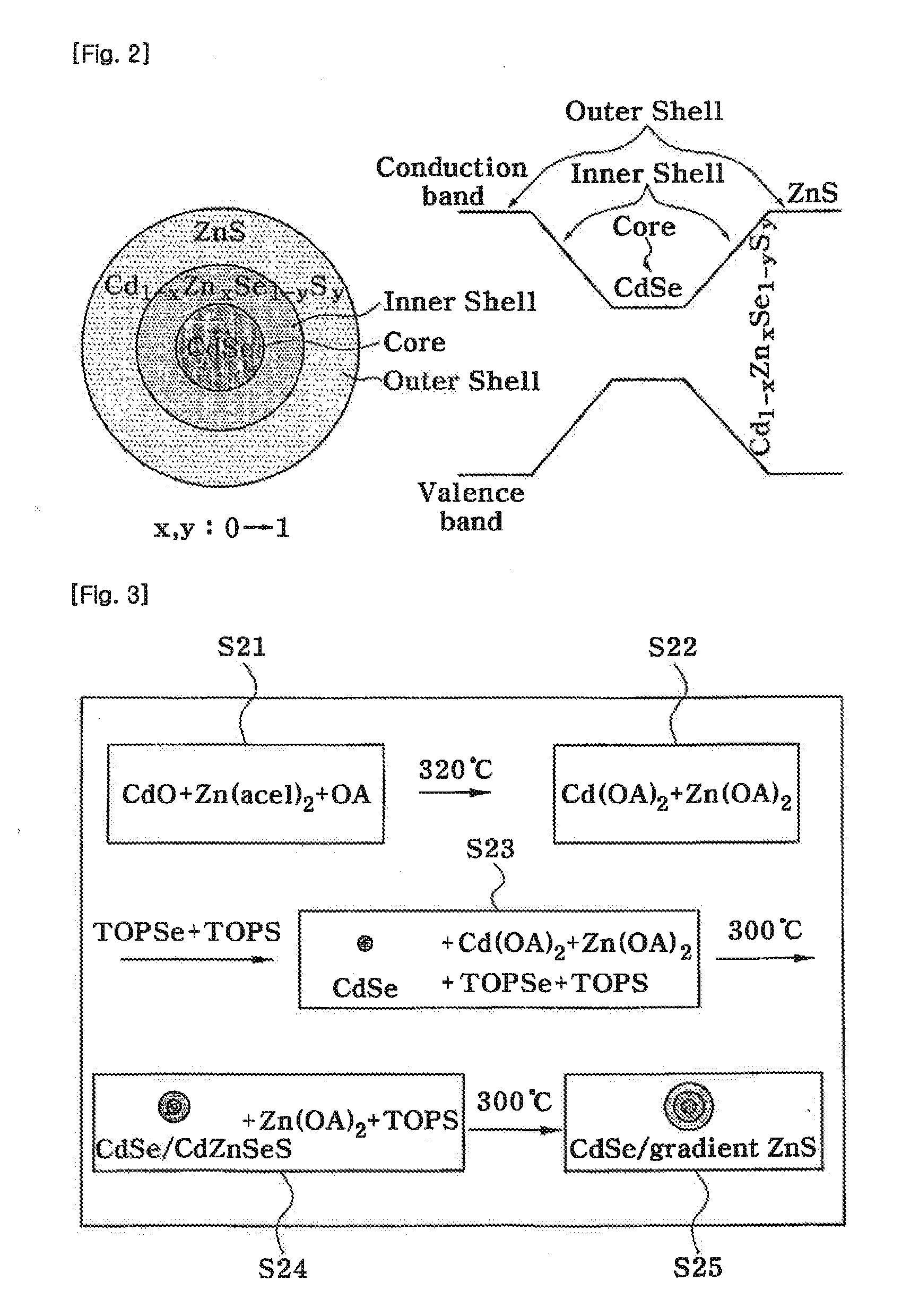
Quantum dots having composition gradient shell structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100140586A1Low costSolve low luminous efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyCadmium sulfidesElectron holeLattice mismatch
Provided are quantum dots having a gradual composition gradient shell structure which have an improvedluminous efficiency and optical stability, and a method of manufacturing the quantum dots in a short amount of time at low cost. In the method, the quantum dots can be manufactured in a short amount of time at low cost using a reactivity difference between semiconductor precursors, unlike in uneconomical and inefficient conventional methods where shells areformed after forming cores and performing cleaning and redispersion processes. Also, formation of the cores is followed by formation of shells having a composition gradient. Thus, even if the shells are formed to a large thickness, the lattice mismatch between cores and shells is relieved. Furthermore, on the basis of the funneling concept, electrons and holes generated in the shells are transferred to the cores to emit light, thereby obtaining a high luminous efficiency of 80% or more. The quantum dot structure is not limited to Group II-IV semiconductor quantum dots but can be applied to other semiconductors quantum dots, such as Group III-V semiconductors quantum dots and Group IV-IV semiconductors quantum dots. Also, the manufacturing method can be utilized in the development of semiconductor quantum dots having different physical properties, and in various other fields.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
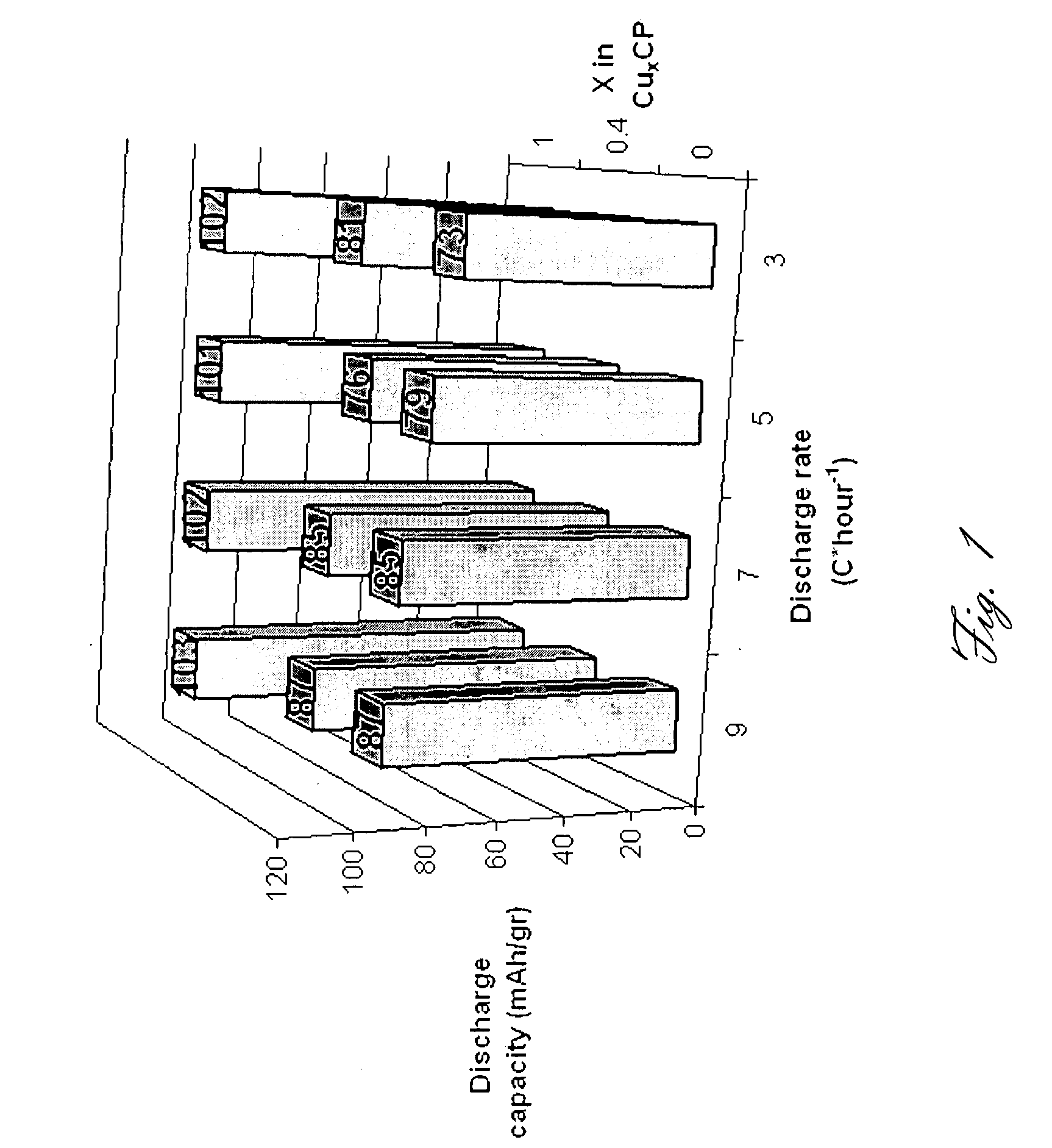
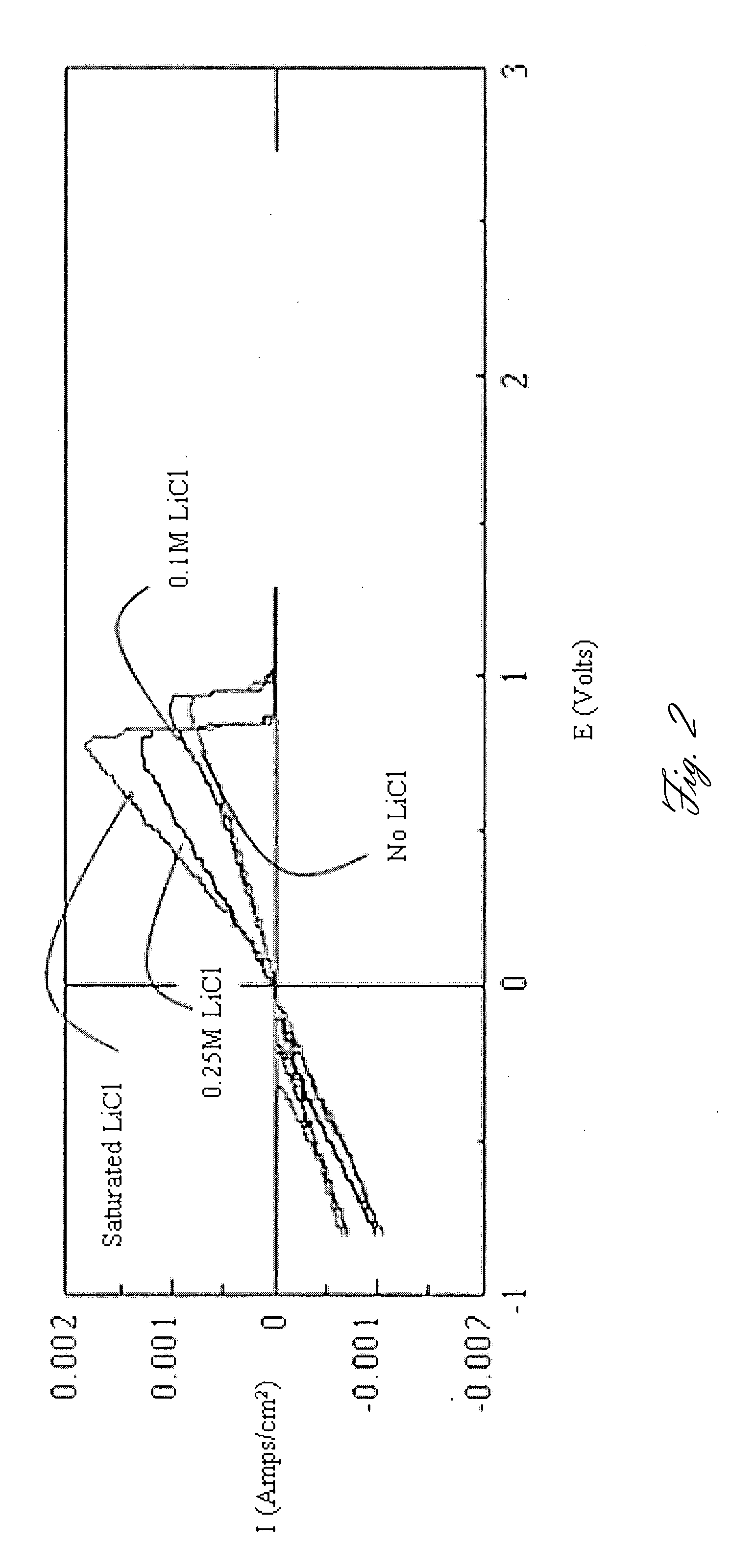
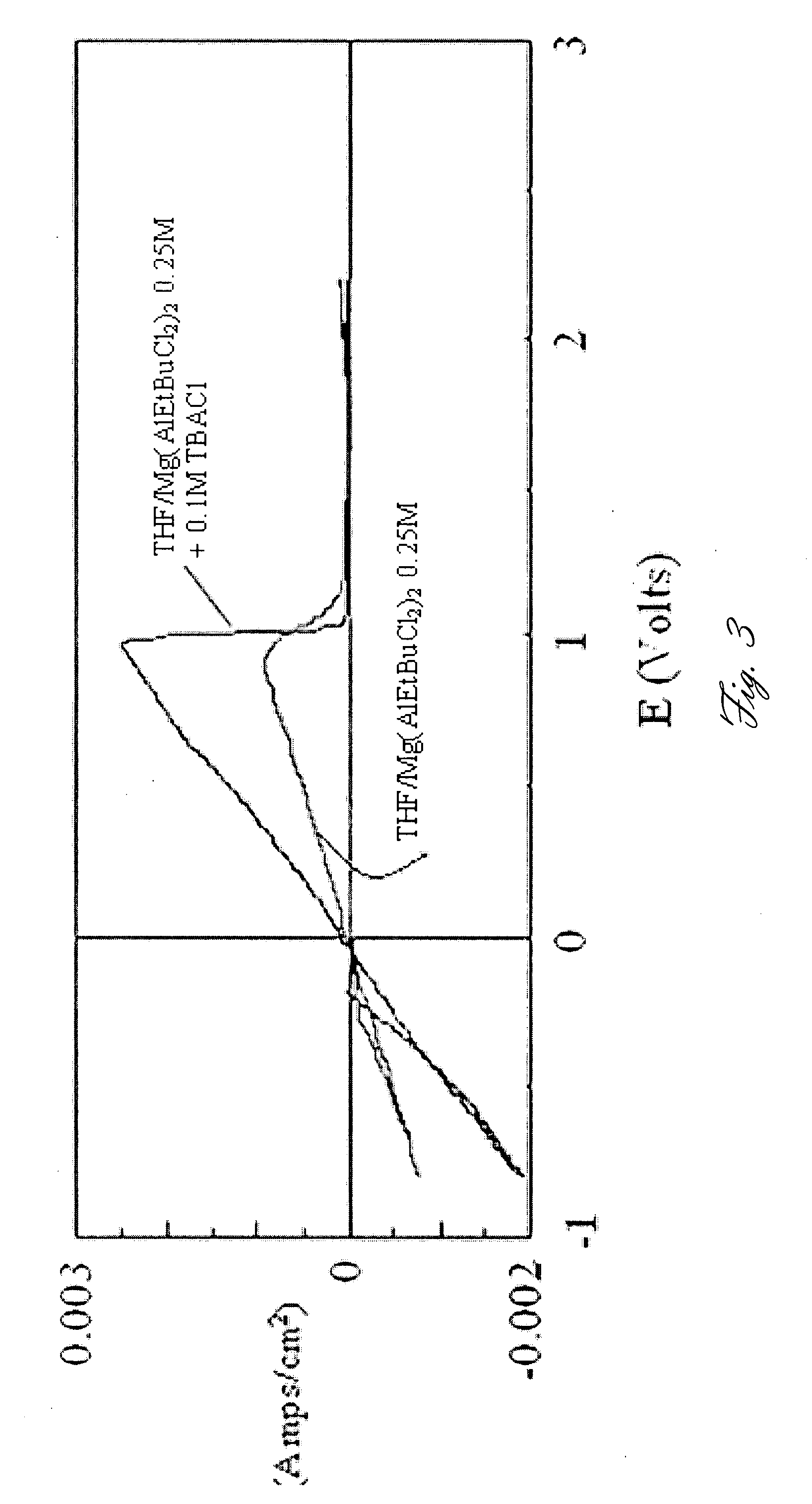
Rechargeable magnesium battery
ActiveUS20080182176A1Improved kineticsImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsElectrochemical windowCopper
This invention generally relates to electrochemical cells utilizing magnesium anodes, new solutions and intercalation cathodes. The present invention is a new rechargeable magnesium battery based on magnesium metal as an anode material, a modified Chevrel phase as an intercalation cathode for magnesium ions and new electrolyte solution from which magnesium can be deposited reversibly, which have a very wide electrochemical window. The Chevrel phase compound is represented by the formula Mo6S8-YSeY in which y is higher than 0 and lower than 2 or by the formula MXMo6S8 in which M is selected from the group comprising of copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), silver (Ag) and / or any other transition metal; further wherein x is higher than 0 and lower than 2.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Method of coating nanoparticles
Disclosed herein is a method of coating nanoparticles with a metal oxide. The method includes substituting surfaces of hydrophobic nanoparticles with an organic substance having a hydrophilic group effective to render the nanoparticles hydrophilic; and injecting the hydrophilic nanoparticles and a precursor of the metal oxide into an organic solvent including an amphiphilic surfactant to coat the nanoparticles with a metal oxide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Group ii alloyed i-iii-vi semiconductor nanocrystal compositions and methods of making same
InactiveUS20080202383A1High Luminescence Quantum YieldMaterial nanotechnologyZinc sulatesLuminescence quantum yieldSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor nanocrystal composition that is stable and has high luminescent quantum yield. The semiconductor nanocrystal composition has a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a group II alloyed I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystal material. A method of making a semiconductor nanocrystal composition is also provides which includes synthesizing a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a group II alloyed I-III-VI semiconductor material.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
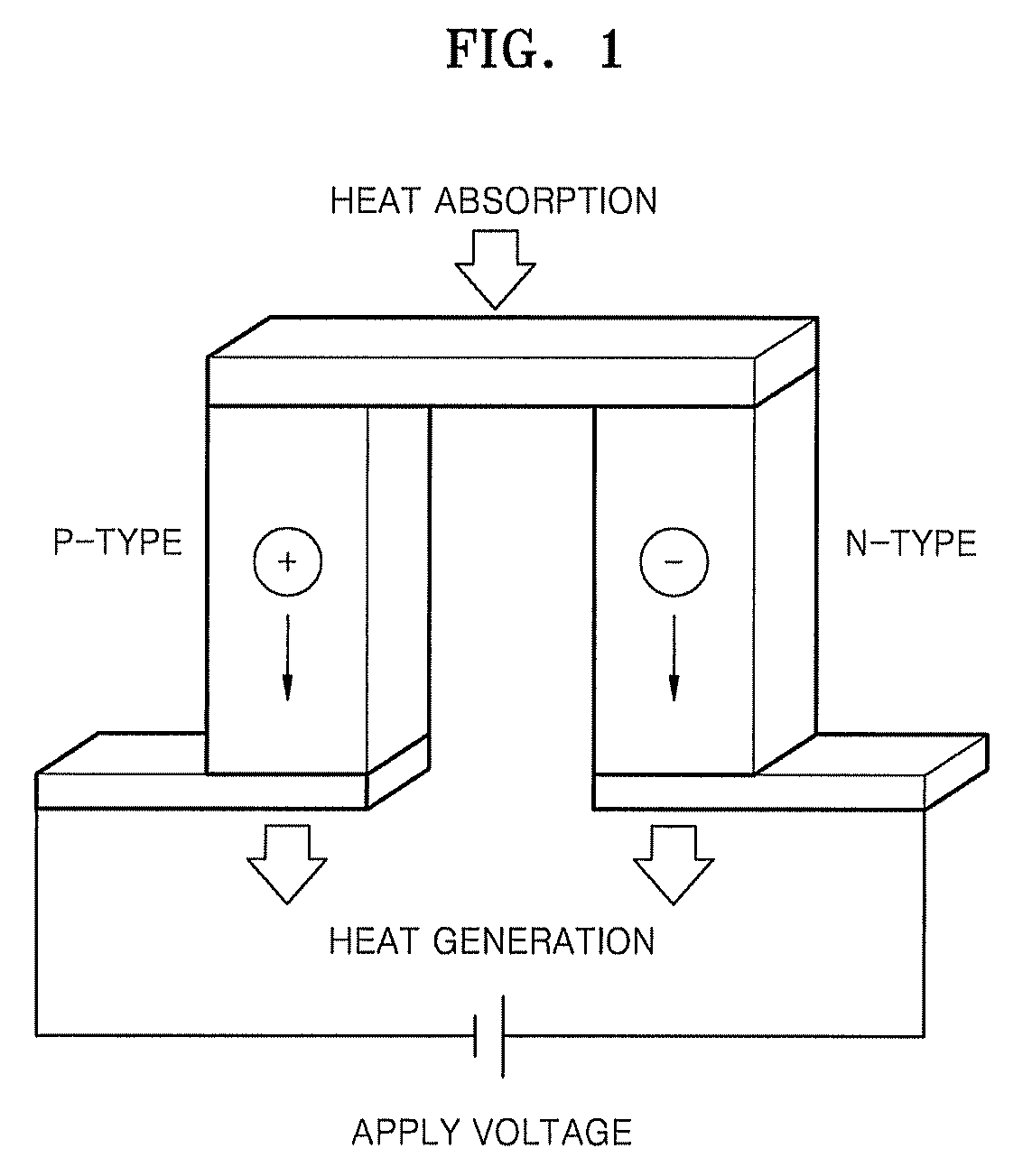
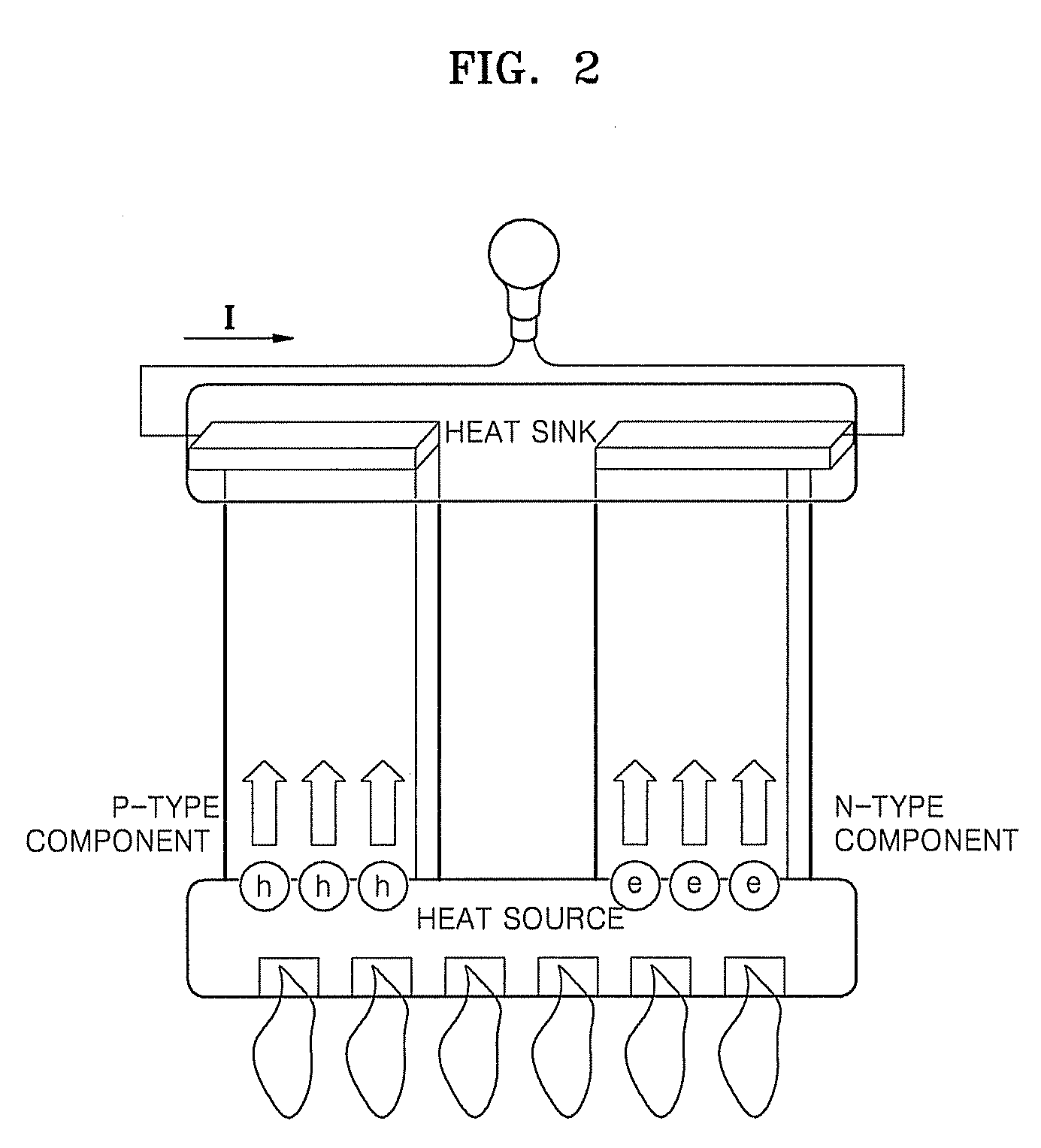
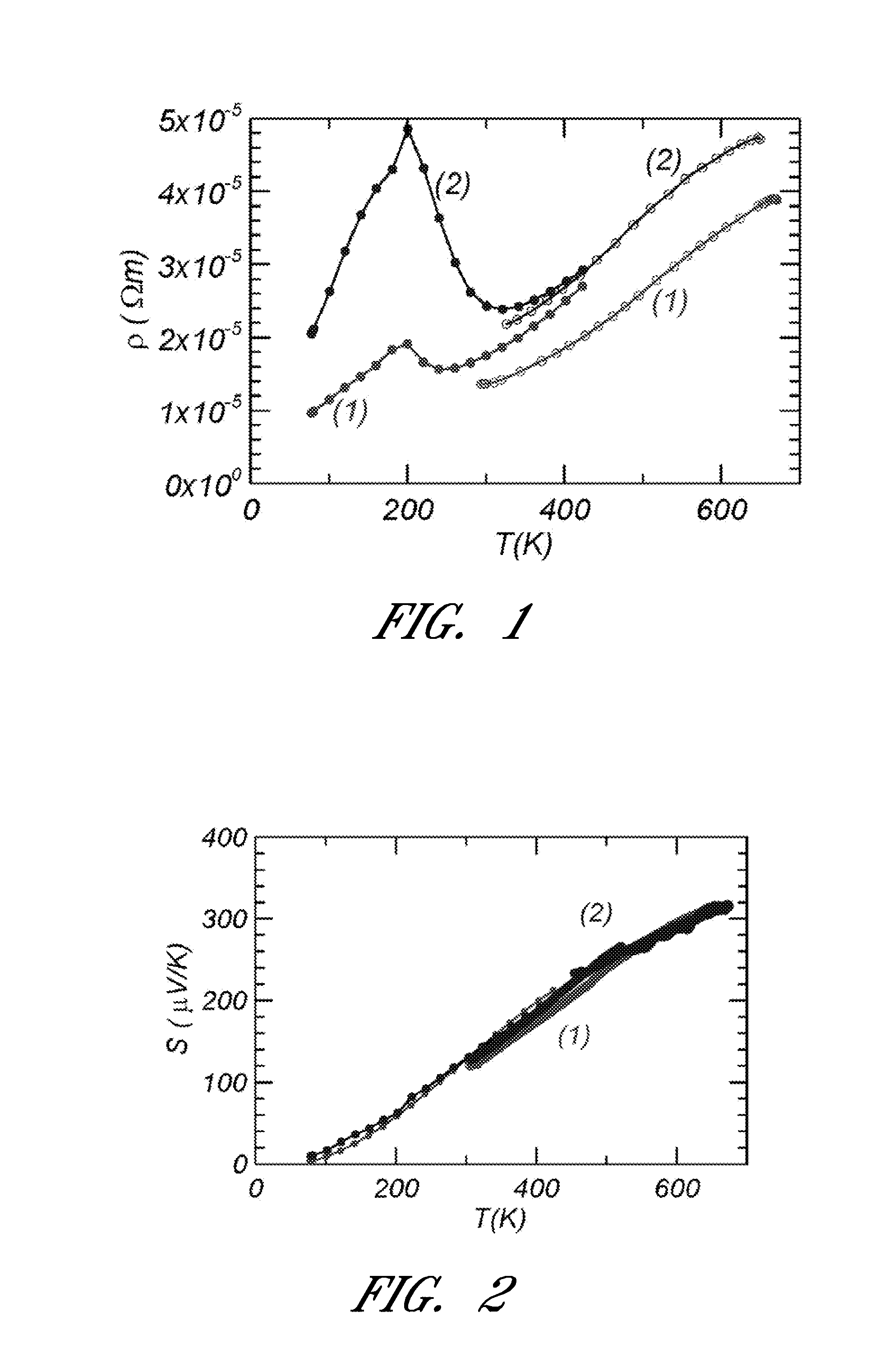
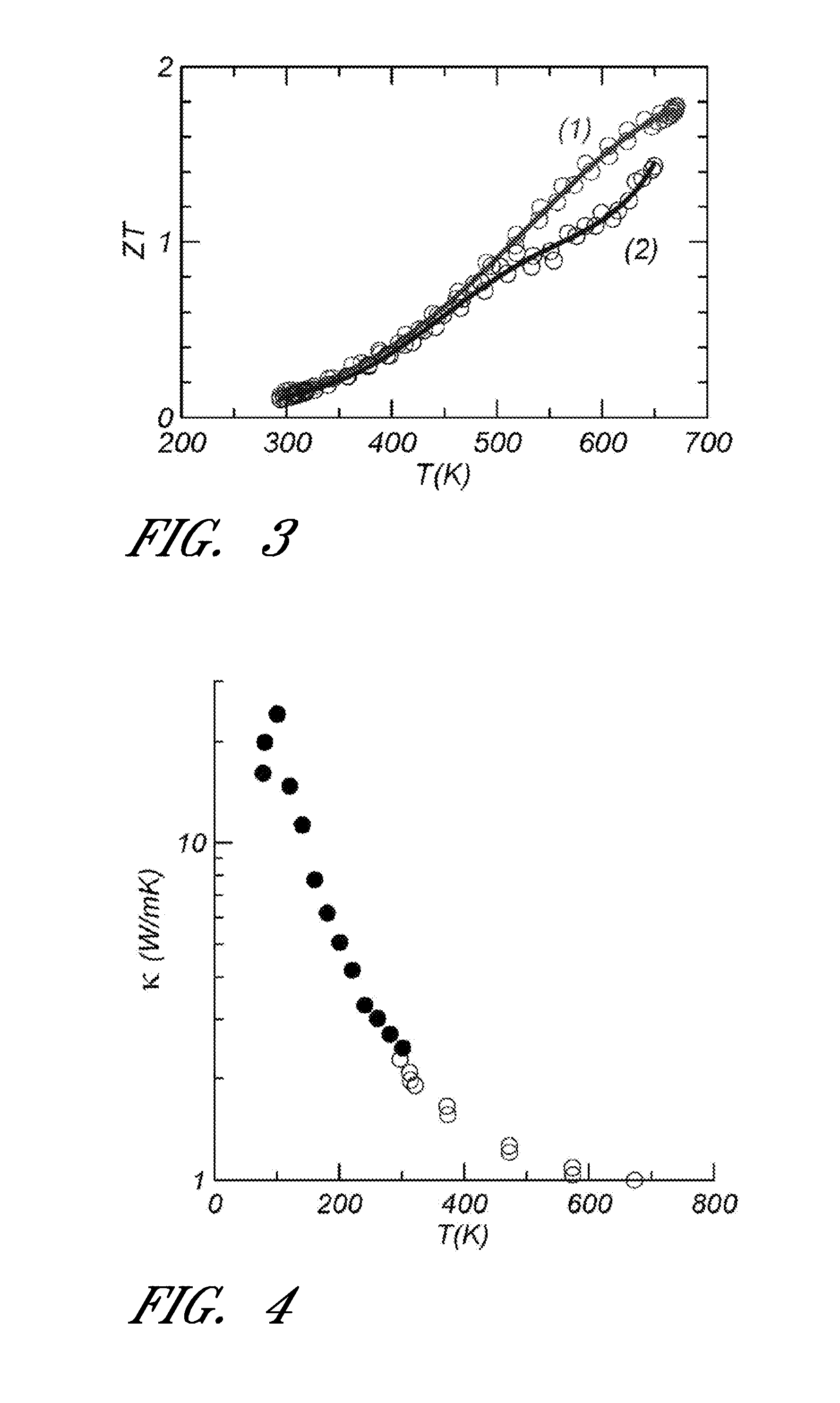
Thermoelectric material and thermoelectric converting element using the same
Compounds are expressed by general formula of AxBC2-y where 0<=x<=2 and 0<=y<1, and have CdI2 analogous layer structures; A-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Ir, Pt, Au, Sc, rare earth elements containing Y, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Sn, Pb and Bi; B-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W, Ir, and Sn; C-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of S, Se and Te; the compounds exhibit large figure of merit so as to be preferable for thermoelectric generator / refrigerator.
Owner:NEC CORP
Coated nano particle and electronic device using the same
ActiveUS20070087197A1Improve luminous efficiencyMinimizing lost lightMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoparticleRefractive index
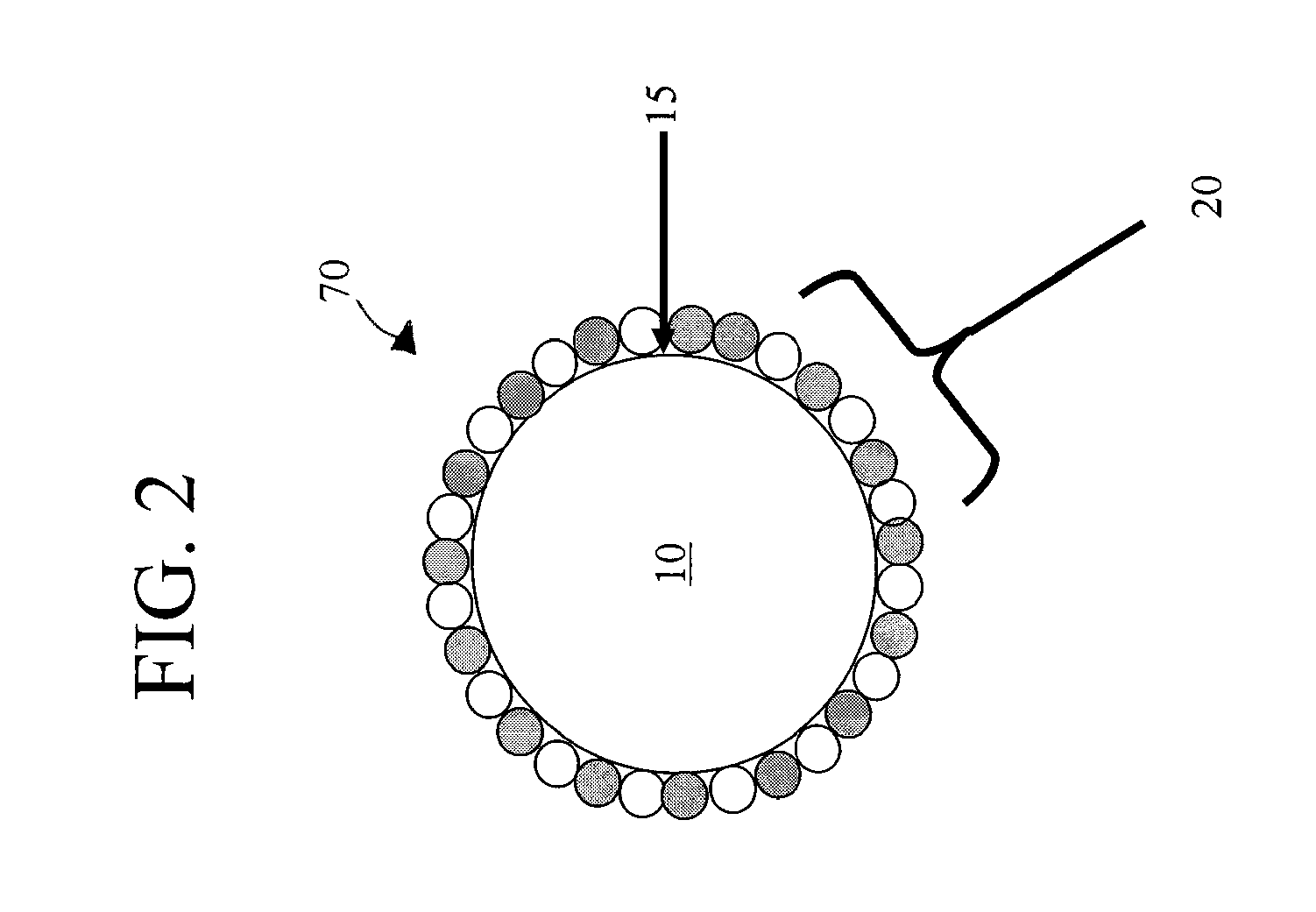
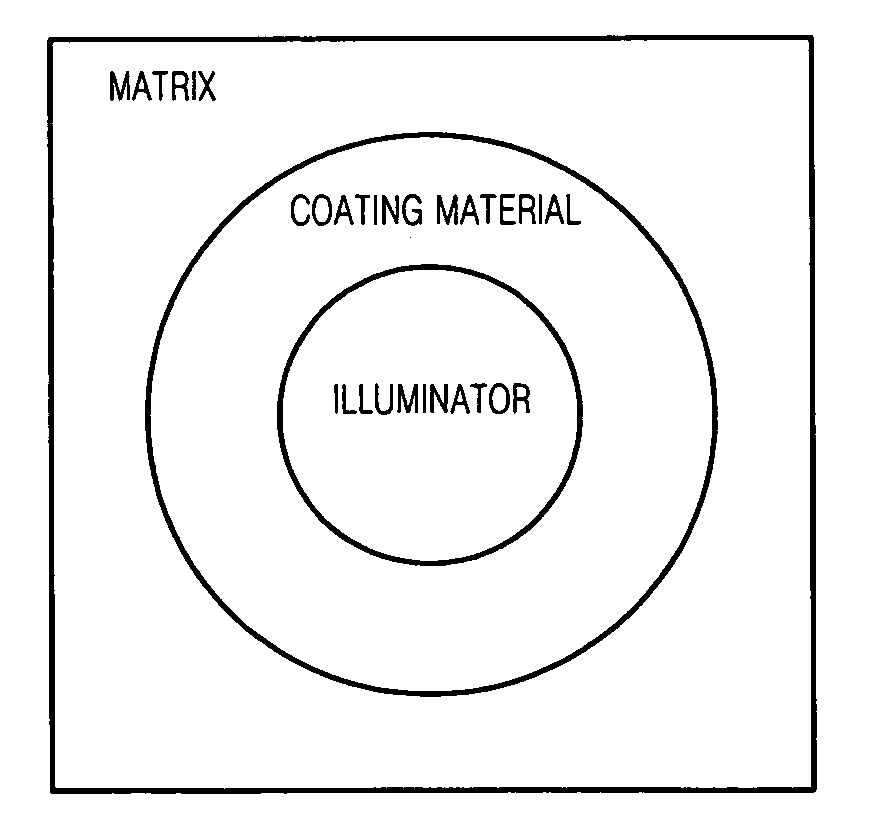
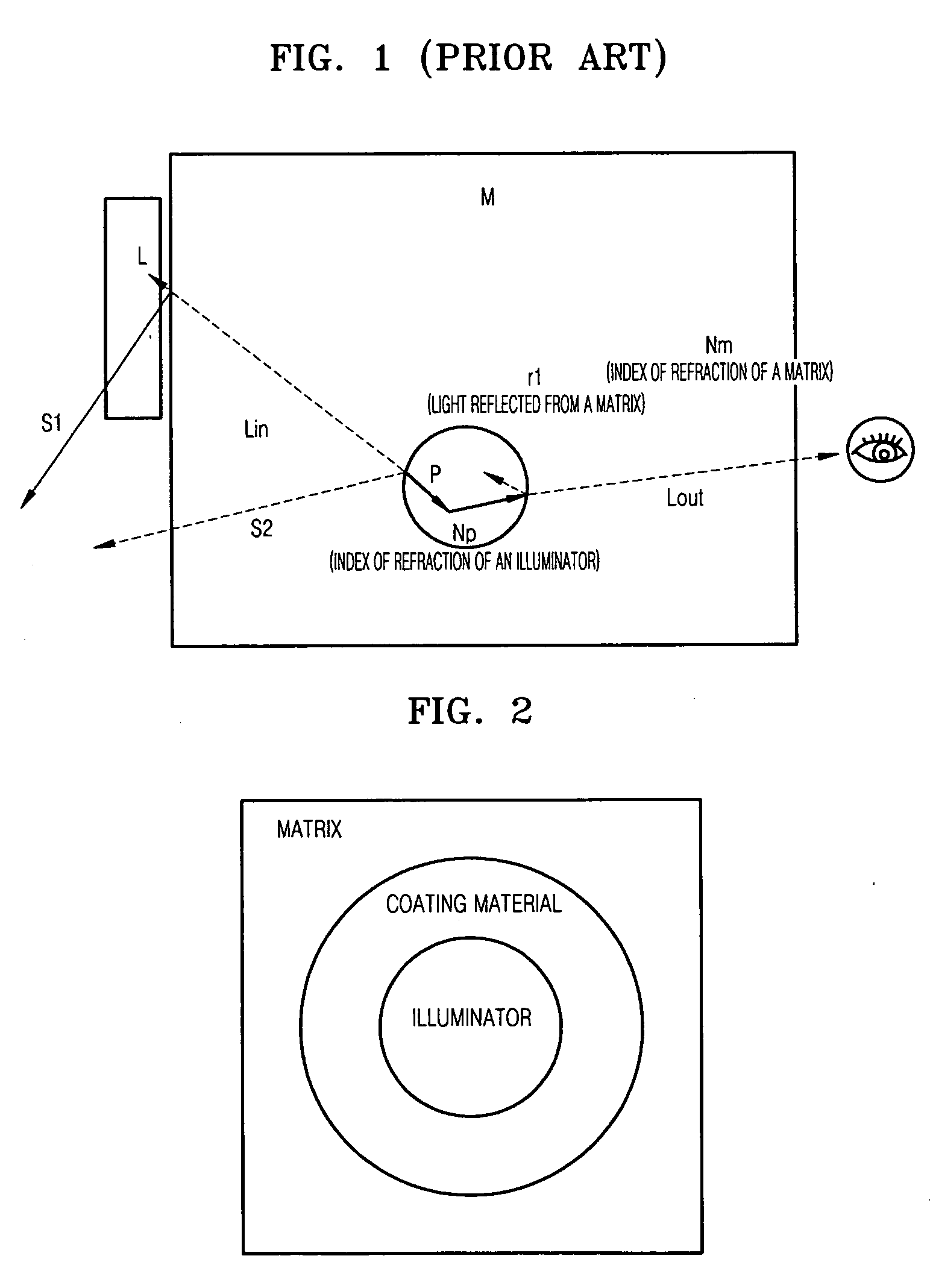
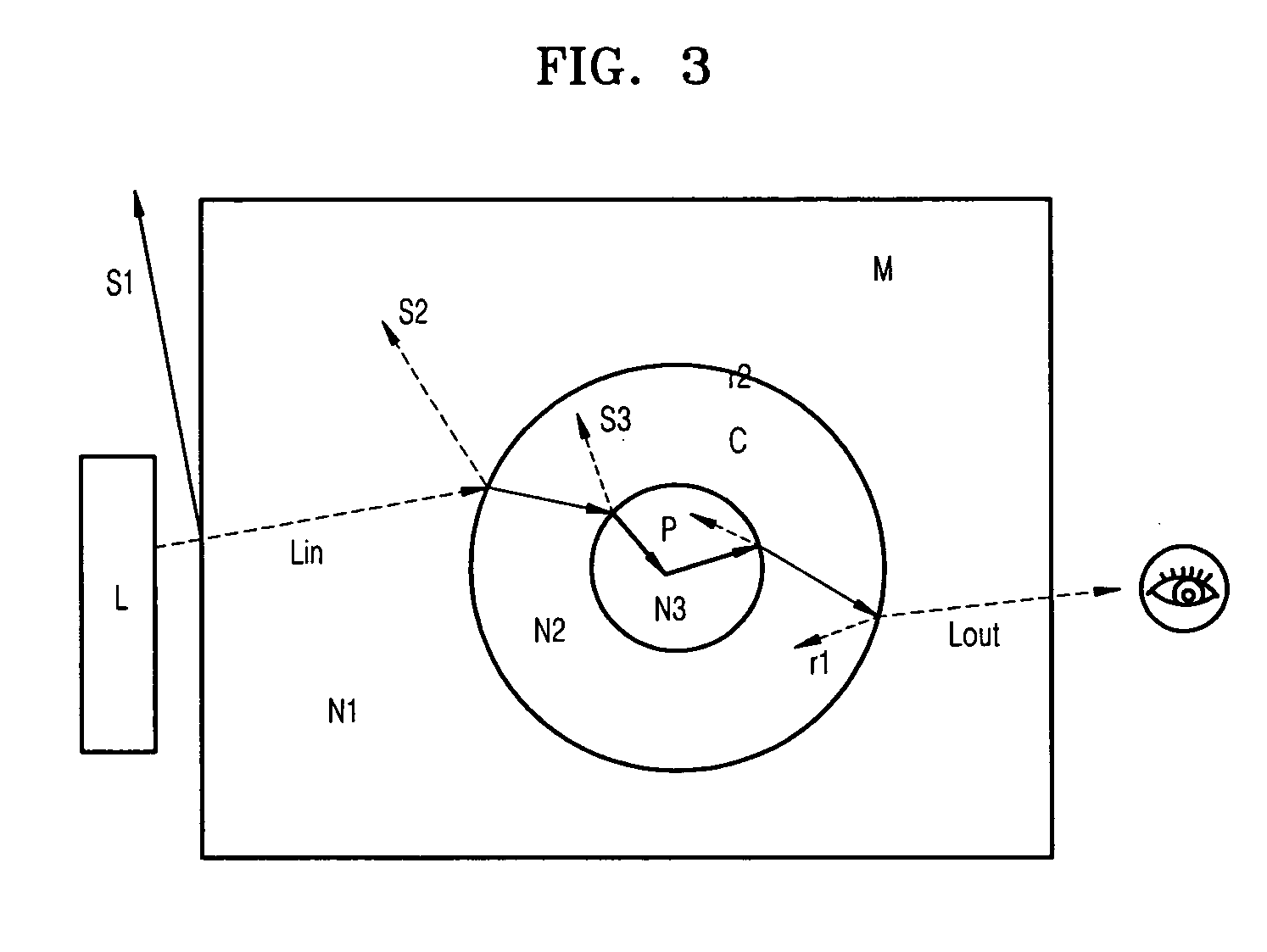
A coated nano particle and an electronic device using the composite nano particle as an illuminator are provided. The composite nano particle includes a nano particle receiving light and emitting light; and a coating material formed on a surface of the nano particle and having an index of refraction different from that of the nano particle. The coated nano particle is made by coating a surface of the nano particle with a material having an index of refraction, which has an intermediate value between an index of refraction of a matrix and an index of refraction of the nano particle as an illuminator, with a predetermined thickness. The light emitted from the nano particle is efficiently transferred to the outside as the light reflected from the matrix and absorbed by the nano particle is suppressed. Therefore, a luminous efficiency of the illuminator is improved, and an electronic device using the illuminator is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Quantum dots, rods, wires, sheets, and ribbons, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140252316A1Improve stand-alone performanceImprove mobilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsQuantum dotNanocrystal
Described are ZnxCd1-xSySe1-y / ZnSzSe1-z core / shell nanocrystals, CdTe / CdS / ZnS core / shell / shell nanocrystals, optionally ally doped Zn(S,Se,Te) nano- and quantum wires, and SnS quantum sheets or ribbons, methods for making the same, and their use in biomedical and photonic applications, such as sensors for analytes in cells and preparation of field effect transistors.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Rapid synthesis of ternary, binary and multinary chalcogenide nanoparticles
InactiveUS20100003187A1Rapid responseEasy to handleMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsOrganic solventSulfur
A method for synthesizing a chalcogenide nanoparticle is provided. The method comprises reacting a metal component with an elemental chalcogen precursor in the presence of an organic solvent. The chalcogenide nanoparticles include ternary, binary and / or multinary chalcogenide nanoparticles and the metal component comprises metal halides or elemental metal precursors. The alkylamine solvent has a normal boiling temperature of above about 220° C. and an average particle size of from about 5 nm to about 1000 nm.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
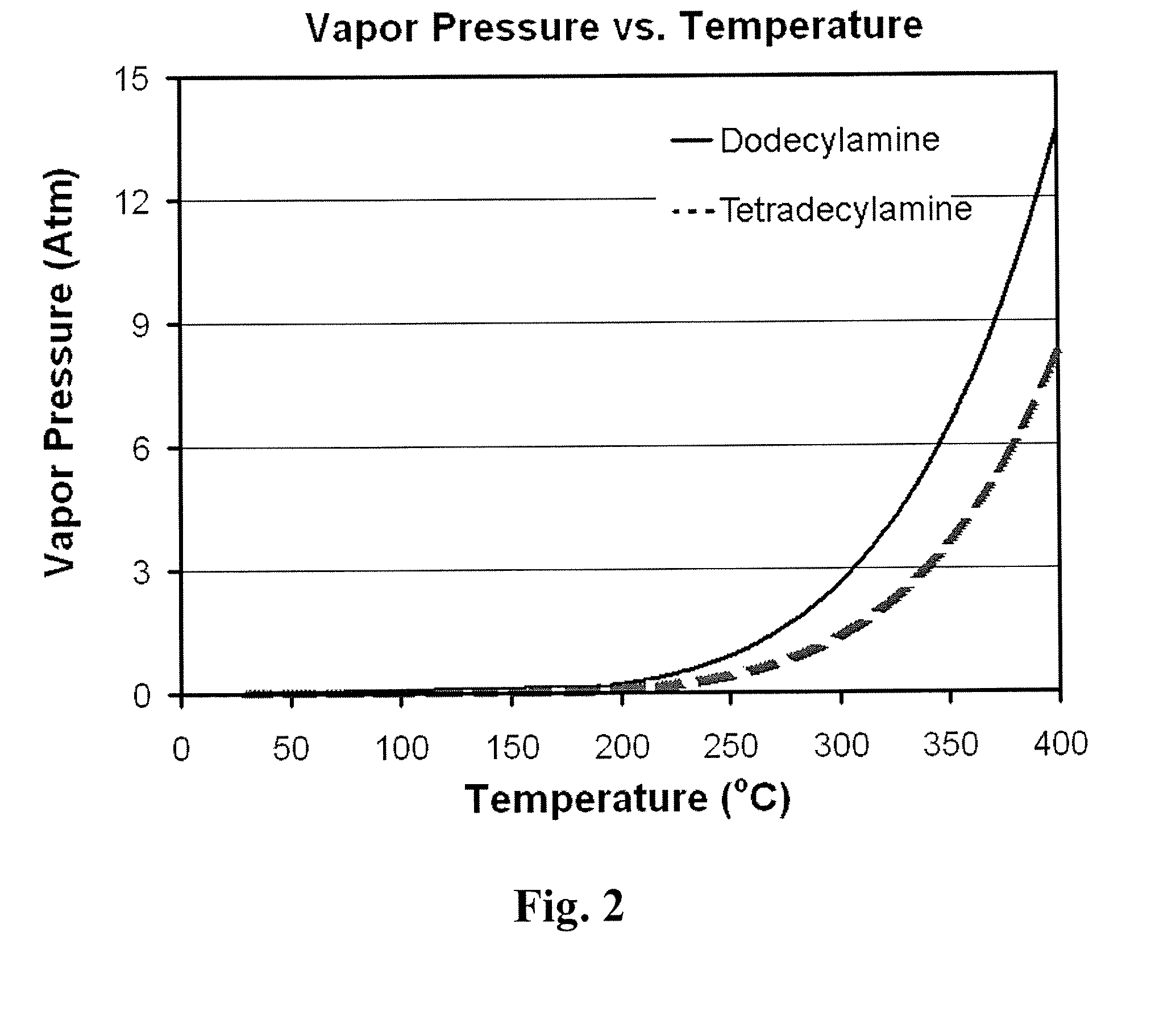
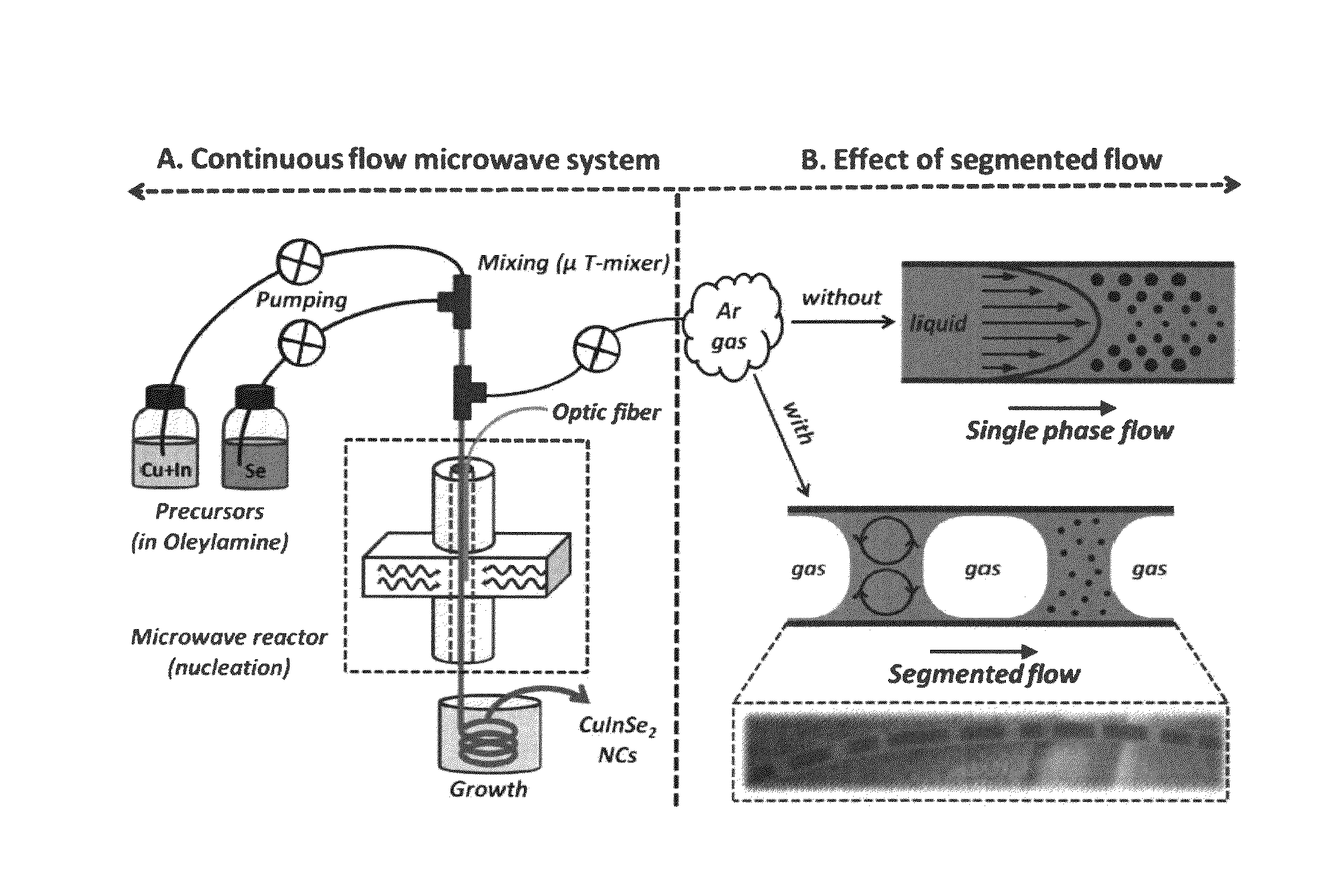
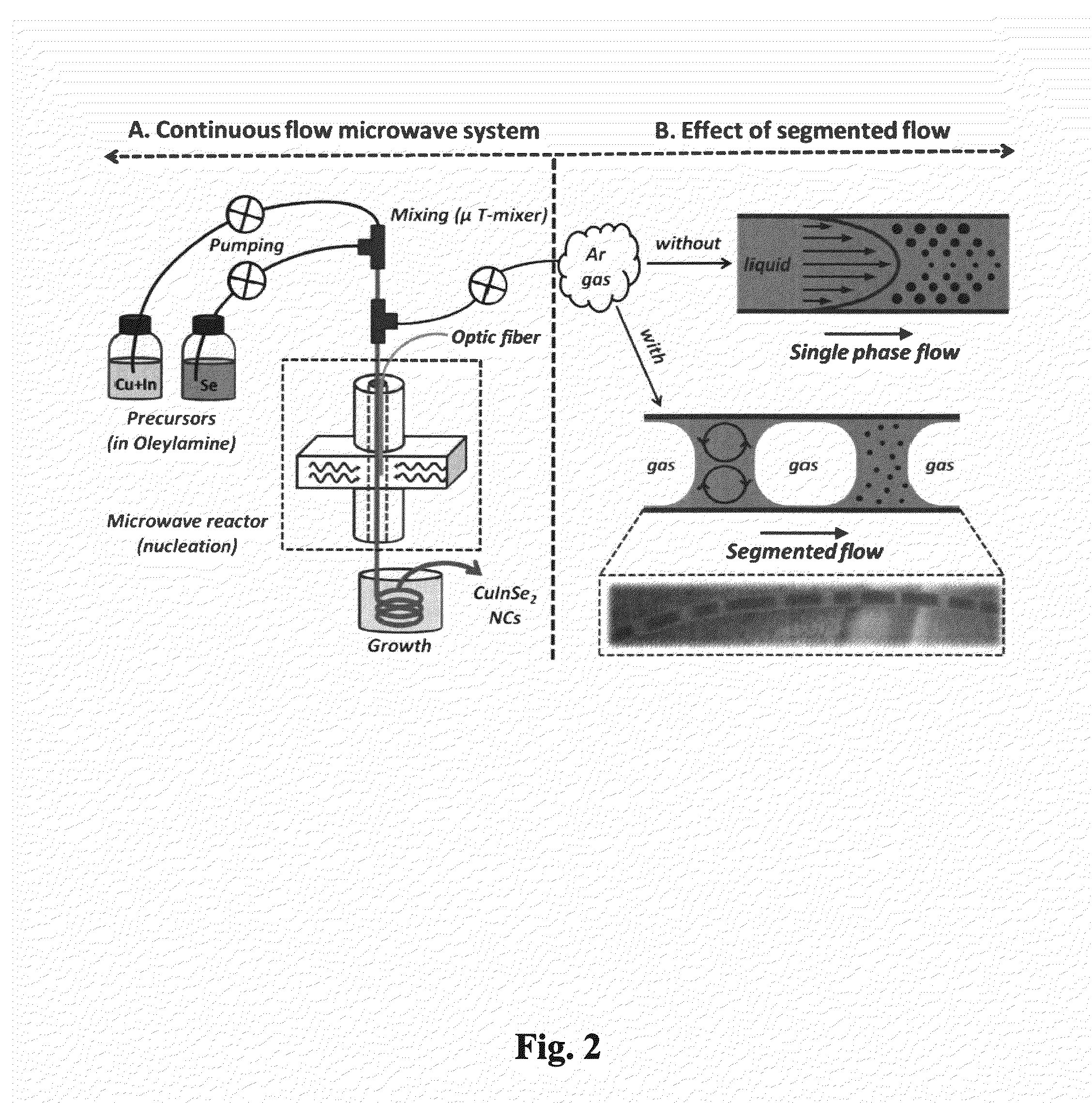
Continuous microwave-assisted segmented flow reactor for high-quality nanocrystal synthesis
ActiveUS20150182936A1Quality improvementTin compoundsPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsProcess engineeringContinuous flow
Systems and methods for synthesizing high-quality nanocrystals via segmented, continuous flow microwave-assisted reactor were developed.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
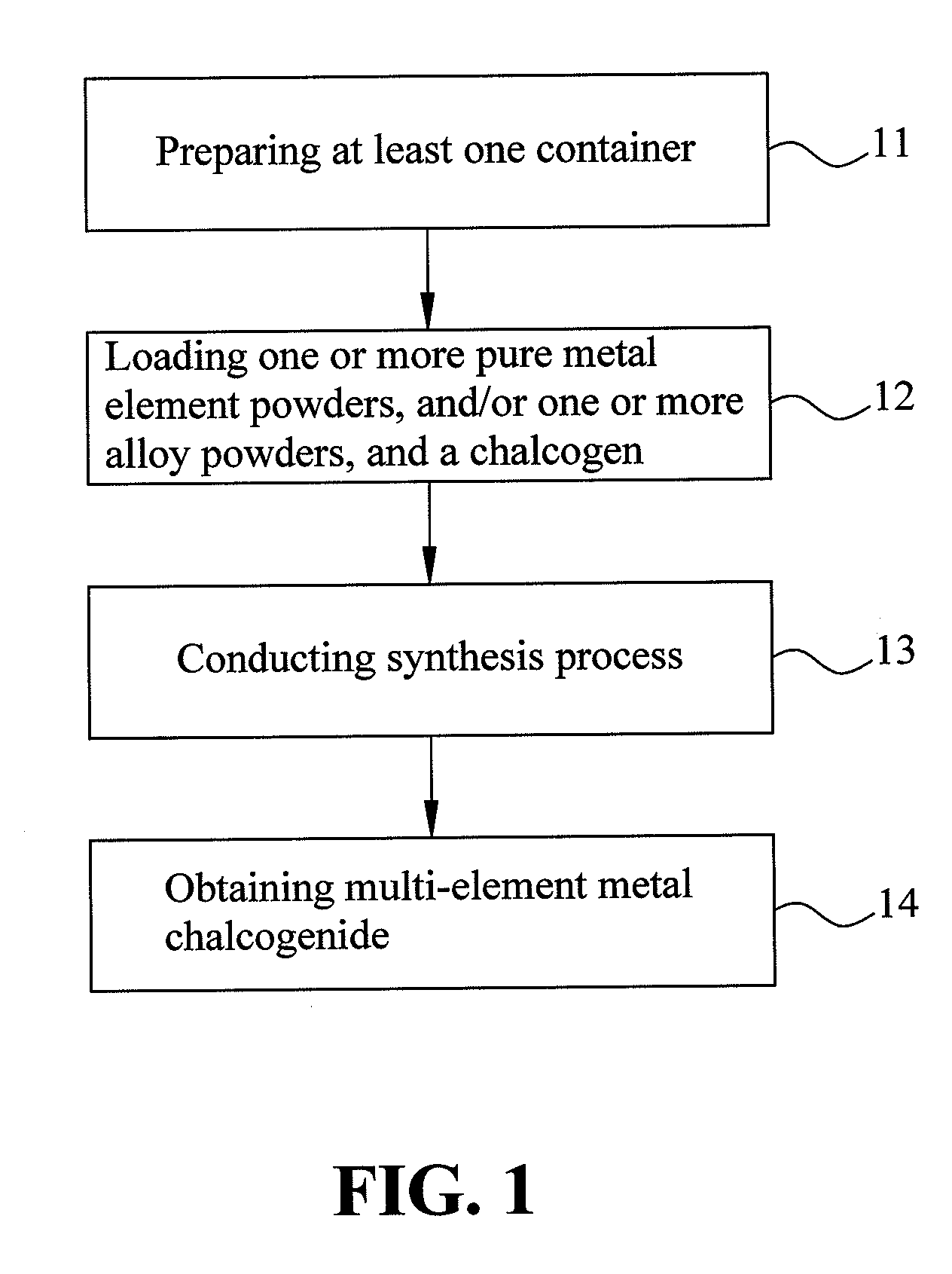
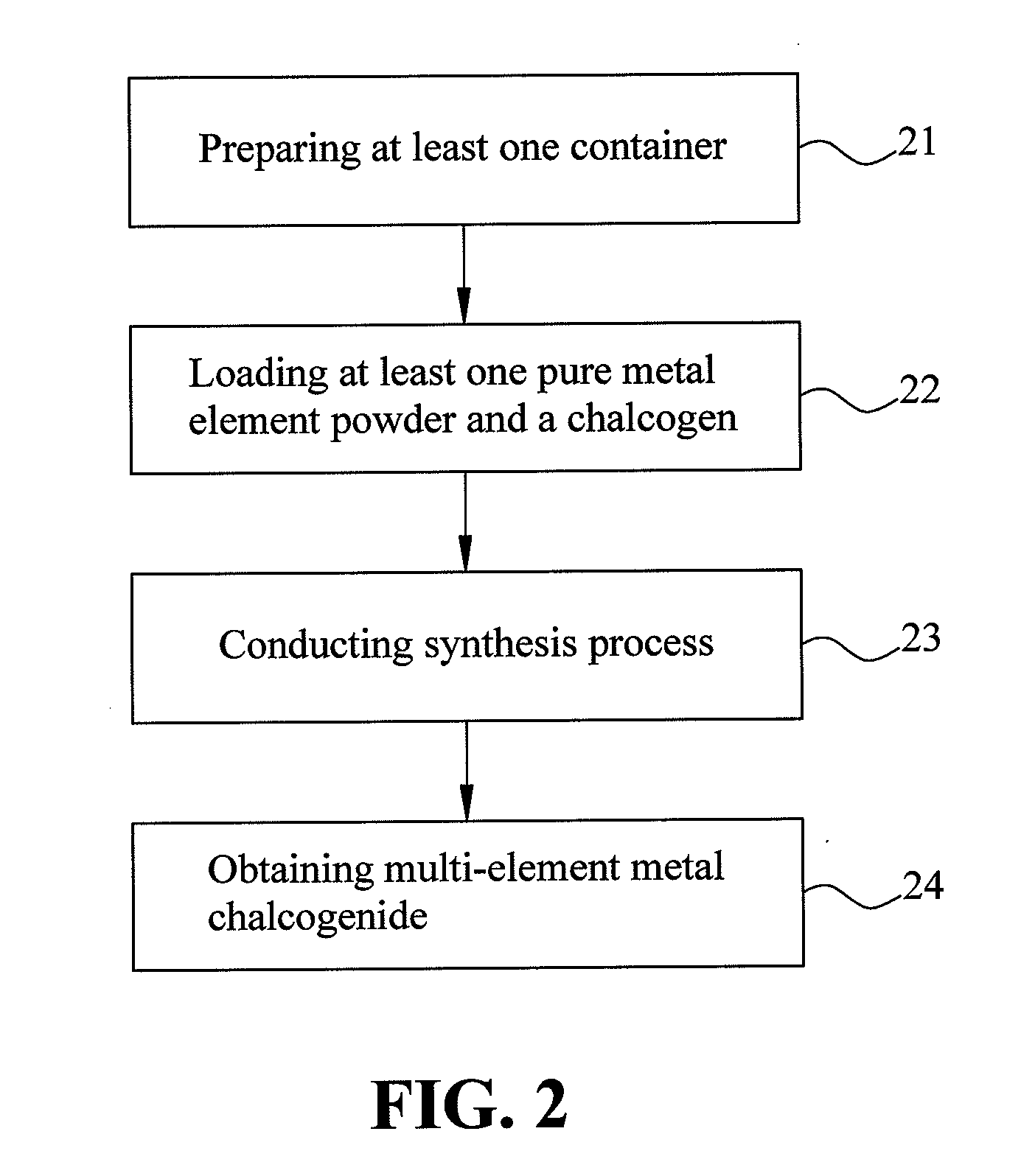
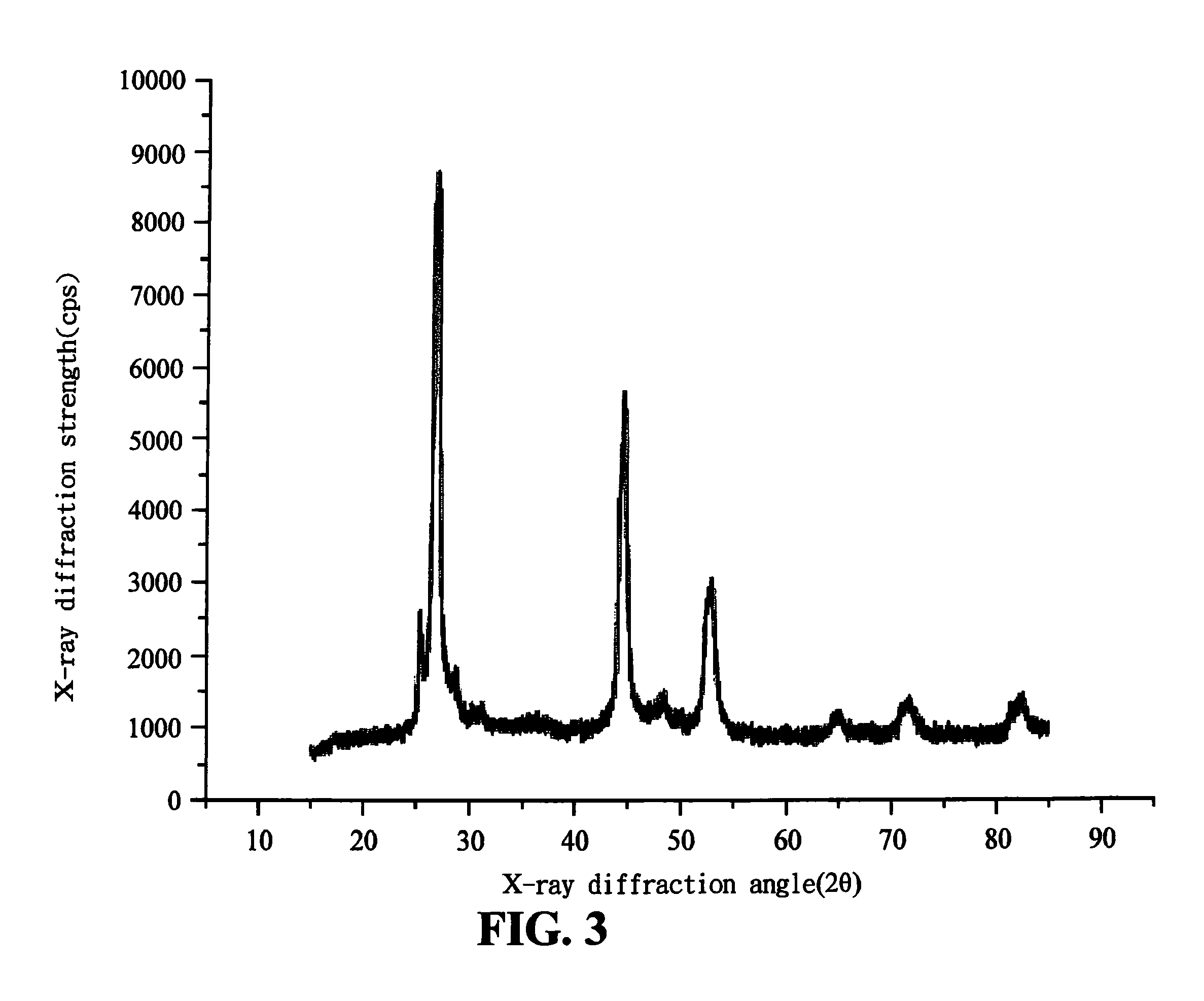
Multi-element metal chalcogenide and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20100227066A1Simple processLow production costNanotechFinal product manufactureSolution phase synthesisMetal chalcogenides
A multi-element metal chalcogenide and a method for preparing the same are provided. According to the present invention, the multi-element metal chalcogenide includes multiple metal elements. According to the present invention, a multi-element metal chalcogenide powder is prepared, and all of the multiple metal elements of the multi-element metal chalcogenide are derived from simple substance powders of the metal elements, and / or one or more alloy powders mixed in accordance with a mole ratio. Then, a solution phase synthesis of the powder of the multi-element metal chalcogenide is conducted under the normal pressure to prepare the multi-element metal chalcogenide. The multi-element metal chalcogenide can be coated to obtain a film or used to make a target and then bombard the target for sputtering a film. In such a way, a selenization process which is conventional in fabricating the semiconductor solar cell is eliminated, thus improving the production yield and efficiency.
Owner:CHUNG JUN WEN +1
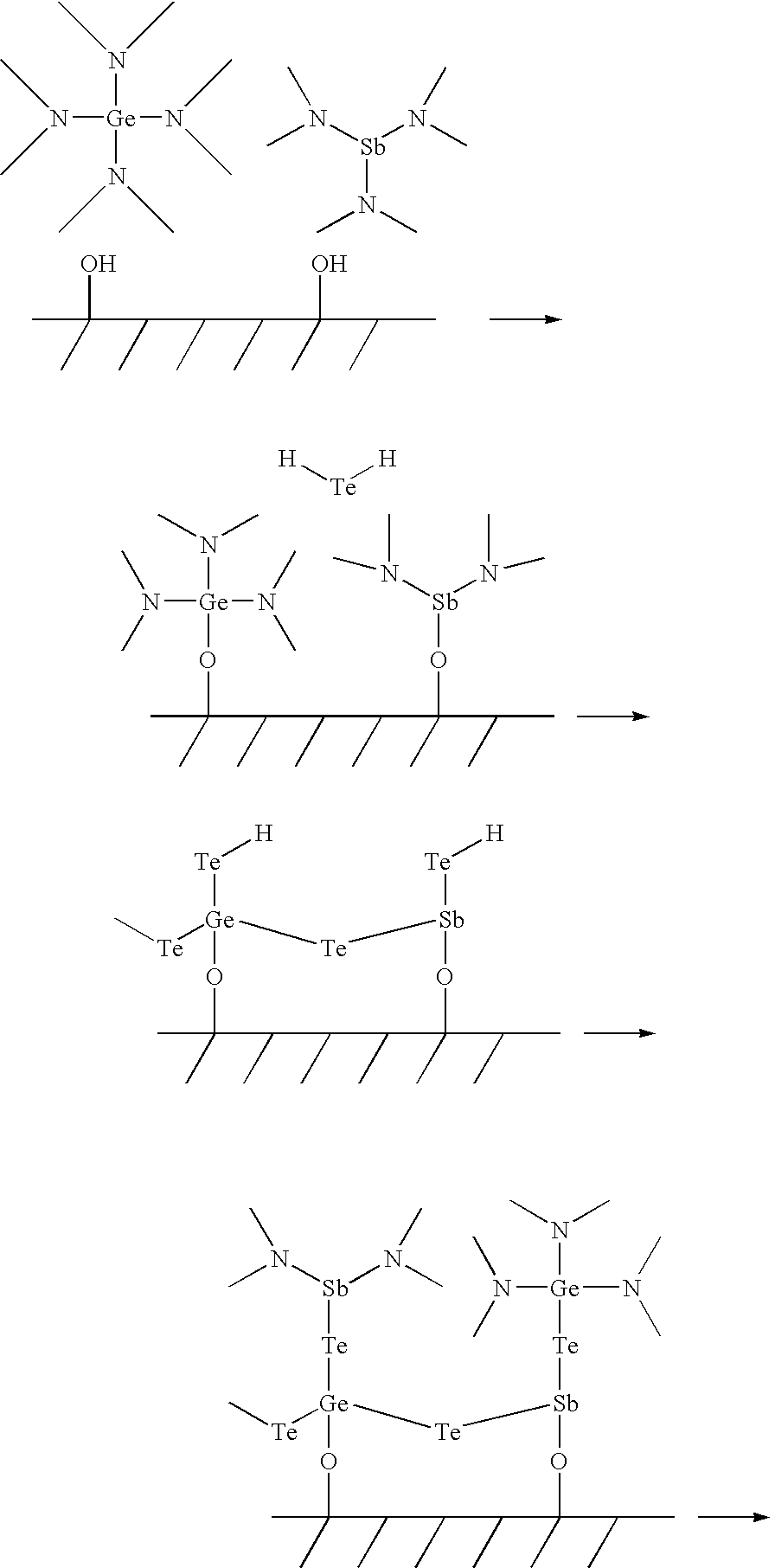
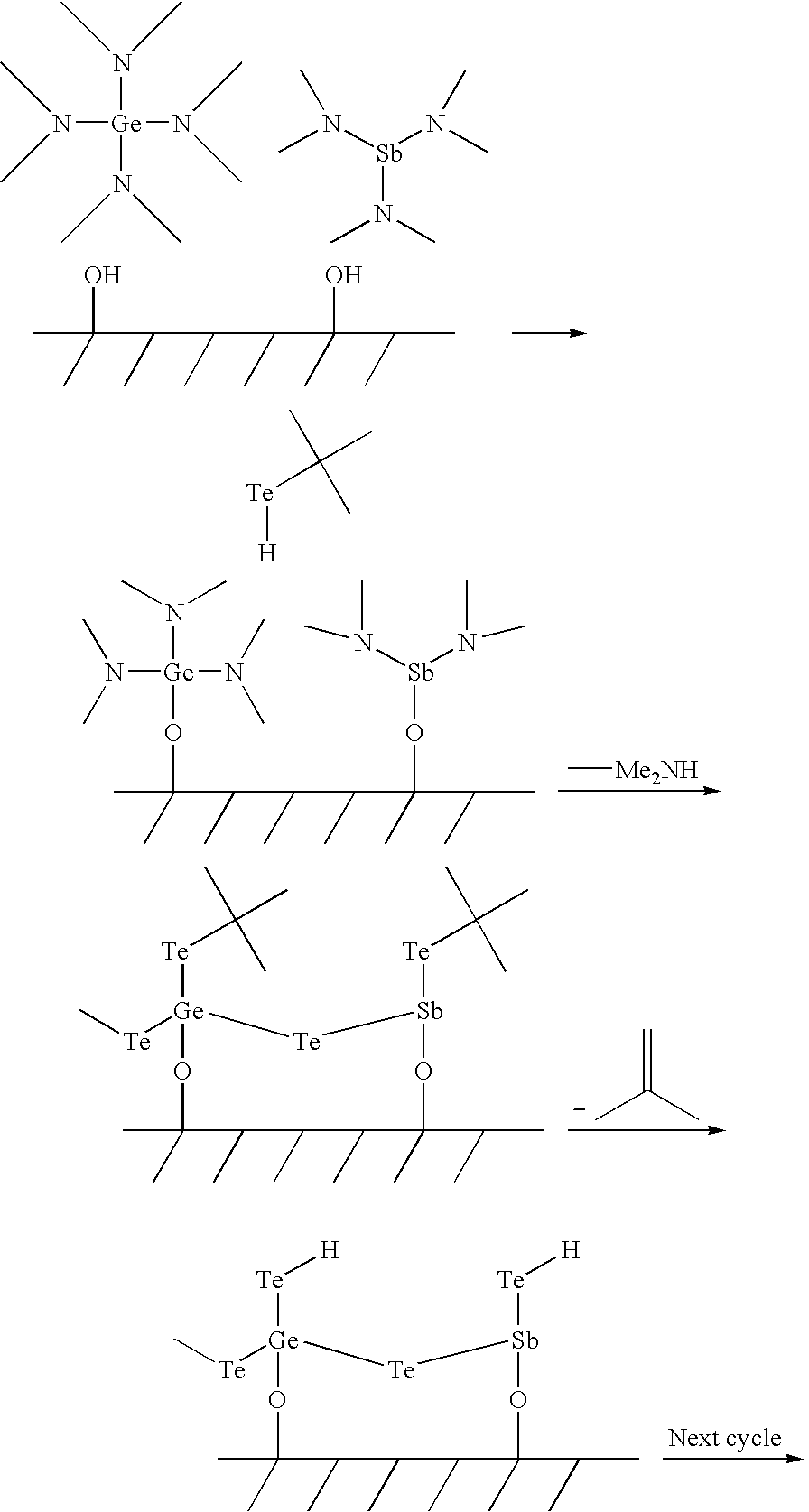
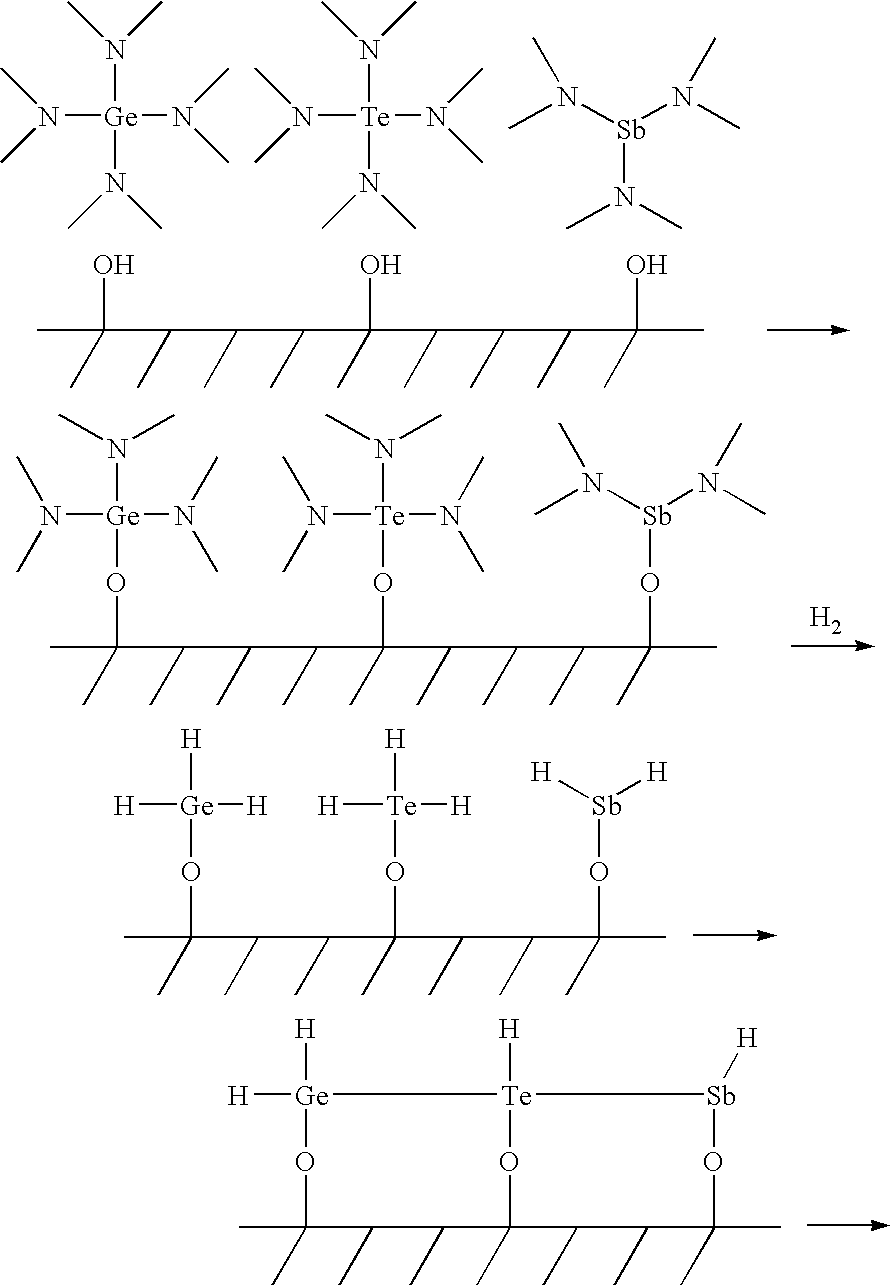
Tellurium (Te) Precursors for Making Phase Change Memory Materials
InactiveUS20090142881A1Satisfies needSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsotope introduction to organic compoundsPhase-change memoryTe element
Tellurium (Te)-containing precursors, Te containing chalcogenide phase change materials are disclosed in the specification. A method of making Te containing chalcogenide phase change materials using ALD, CVD or cyclic CVD process is also disclosed in the specification in which at least one of the disclosed tellurium (Te)-containing precursors is introduced to the process.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
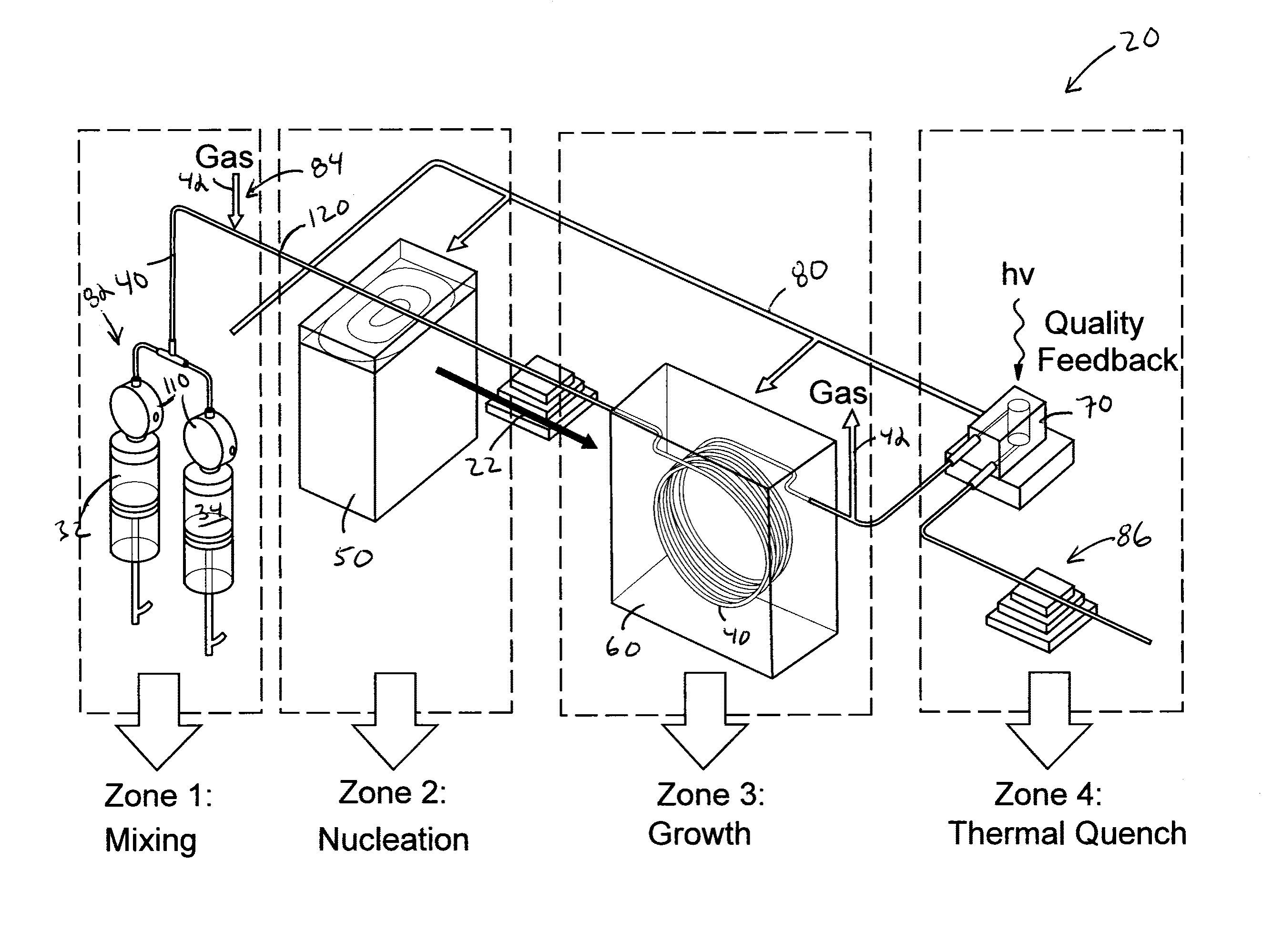
Continuous flow reactor for the synthesis of nanoparticles
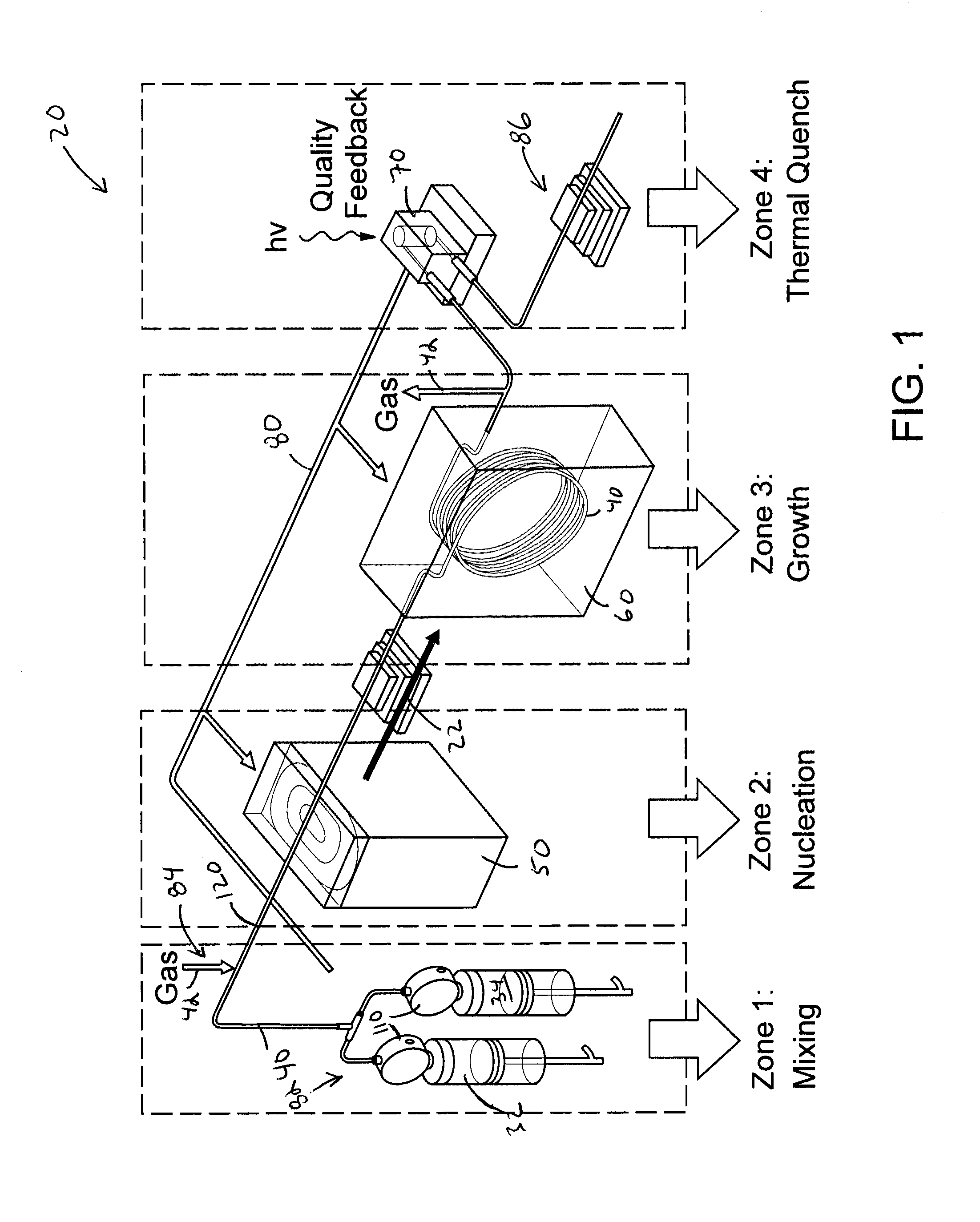
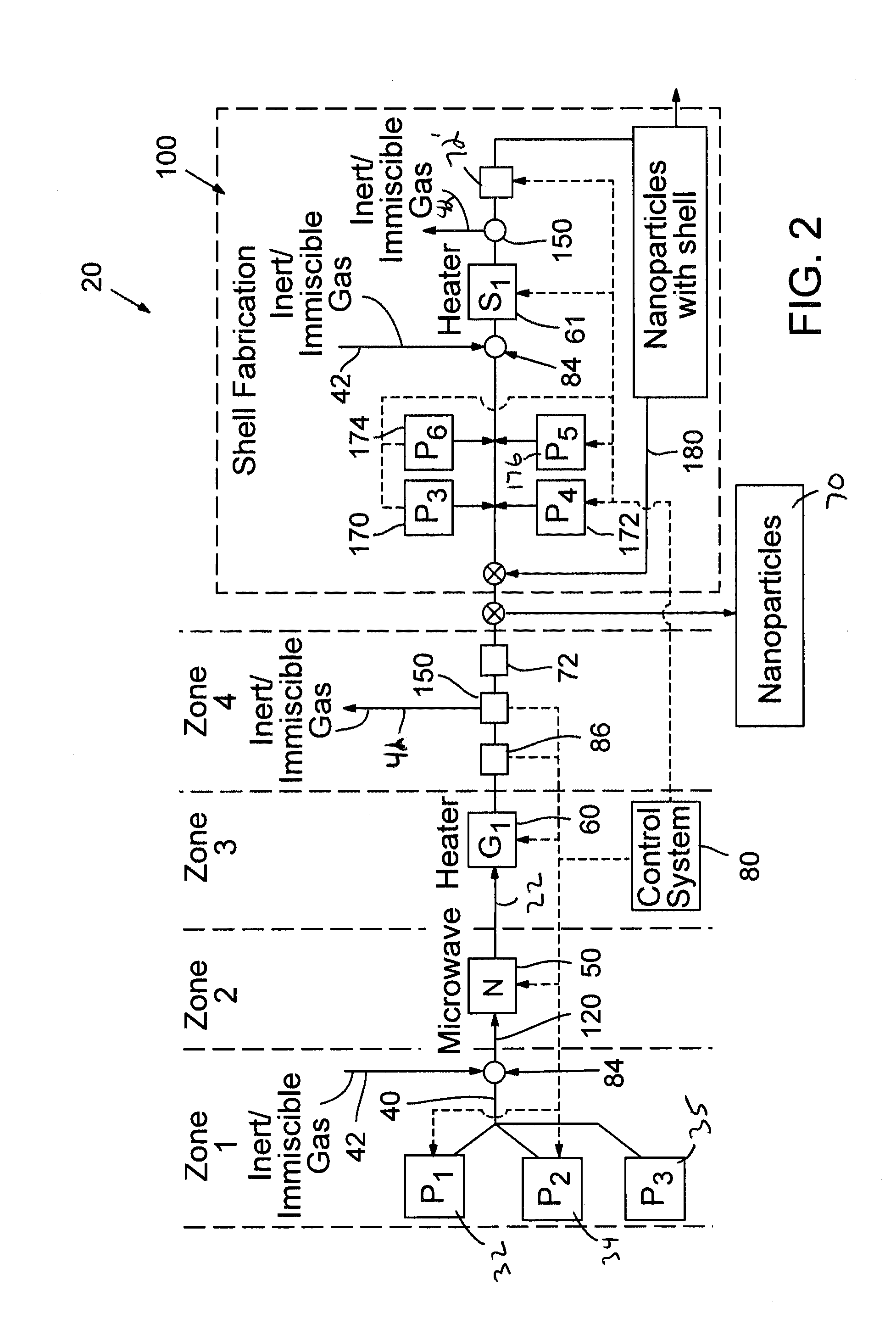
ActiveUS20140264171A1Enhance electronic and optical propertyIncreased durabilityRadiation applicationsCell electrodesEnergy absorptionEngineering
A continuous flow reactor for the efficient synthesis of nanoparticles with a high degree of crystallinity, uniform particle size, and homogenous stoichiometry throughout the crystal is described. Disclosed embodiments include a flow reactor with an energy source for rapid nucleation of the procurors following by a separate heating source for growing the nucleates. Segmented flow may be provided to facilitate mixing and uniform energy absorption of the precursors, and post production quality testing in communication with a control system allow automatic real-time adjustment of the production parameters. The nucleation energy source can be monomodal, multimodal, or multivariable frequency microwave energy and tuned to allow different precursors to nucleate at substantially the same time thereby resulting in a substantially homogenous nanoparticle. A shell application system may also be provided to allow one or more shell layers to be formed onto each nanoparticle.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
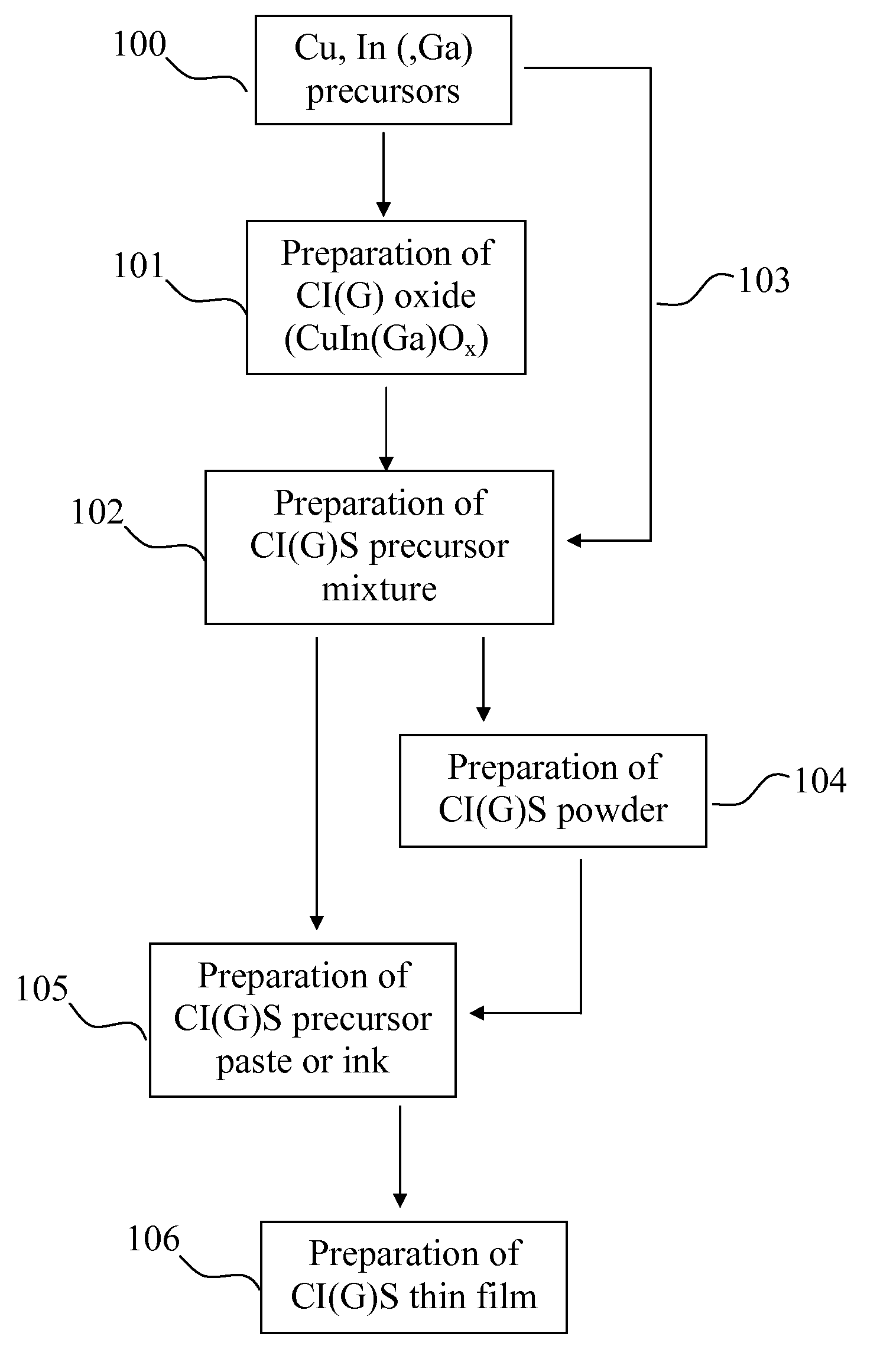
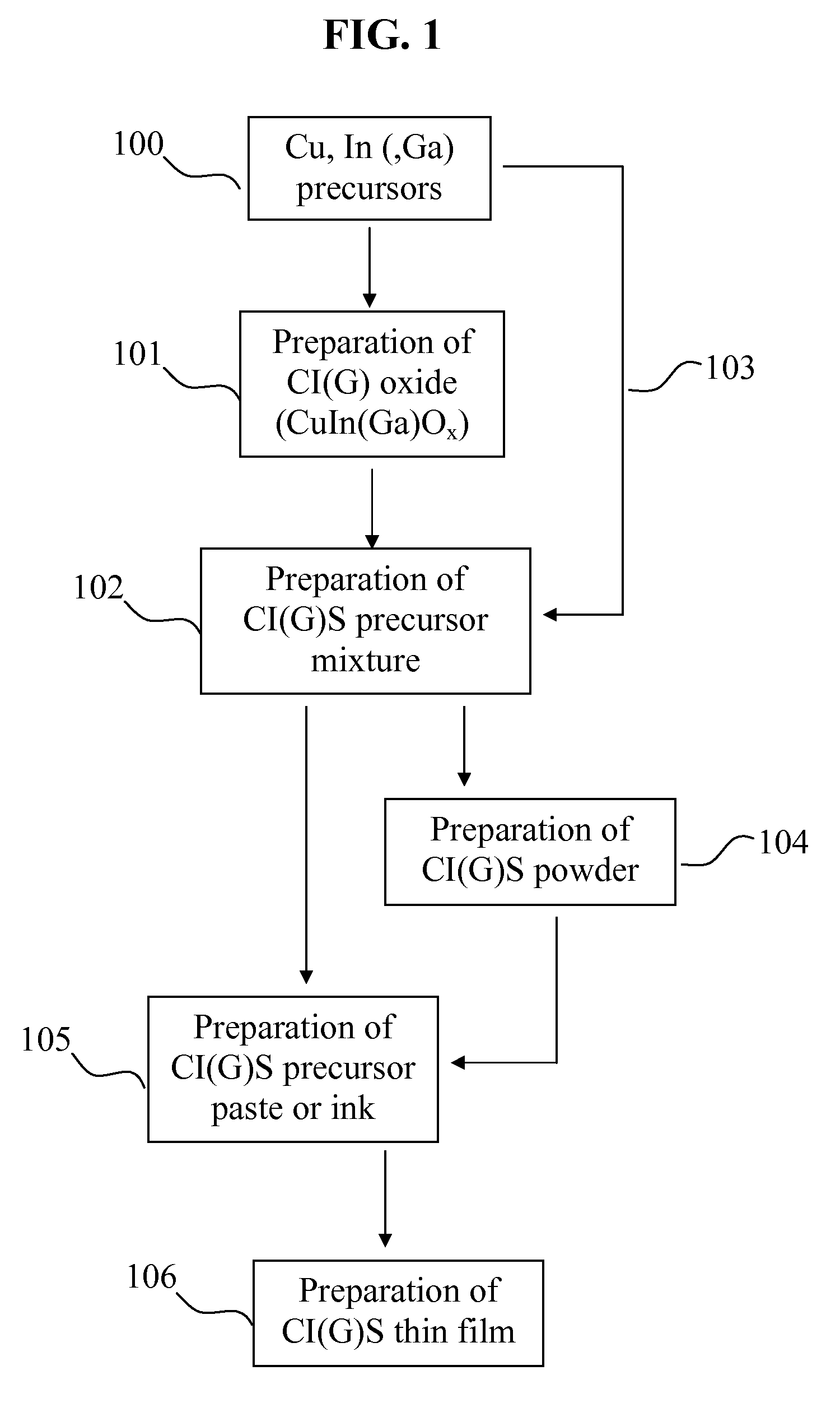
Preparation of thin film for solar cell using paste
InactiveUS20090214763A1Low costEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsToxic gasSolar cell
A preparation method of a CIS-based or CIGS-based thin film for a light absorption layer of a solar cell, which uses a paste prepared by mixing precursors of Cu, In, Se, and optional Ga in a solvent, minimizes the raw material loss, does not produce a toxic gas during the process, and is suitable for producing a large scale film at a low production cost.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Nanoparticles and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130092885A1Improve electrical performanceLess securityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureHydrazine compoundSulfur
A method of manufacturing nanoparticles including: providing a metal chalcogenide complexes (MCC) hydrazine hydrate solution; providing a first organic solution of nanoparticles with first organic ligands; forming a mixed solution by mixing the MCC hydrazine hydrate solution and the first organic solution of nanoparticles capped with the first organic ligands; and replacing the first organic ligands of the nanoparticles with ligands of the MCC hydrazine hydrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dichalcogenide thermoelectric material
InactiveUS20090250651A1Low thermal conductivityLarge power factorSulfide/polysulfide preparationSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsThermoelectric materialsRare earth
A dichalcogenide thermoelectric material having a very low thermal conductivity in comparison with a conventional metal or semiconductor is described. The dichalcogenide thermoelectric material has a structure of Formula 1 below:RX2-aYa Formula 1wherein R is a rare earth or transition metal magnetic element, X and Y are each independently an element selected from the group consisting of S, Se, Te, P, As, Sb, Bi, C, Si, Ge, Sn, B, Al, Ga, In, and a combination thereof, and 0≦a<2.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Quantum dots having composition gradient shell structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120315391A1Easily substitutedShort amount of timeMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsQuantum dotSemiconductor
Provided are quantum dots having a gradual composition gradient shell structure which have an improved luminous efficiency and optical stability, and a method of manufacturing the quantum dots in a short amount of time at low cost. In the method, the quantum dots can be manufactured in a short amount of time at low cost using a reactivity difference between semiconductor precursors, unlike in uneconomical and inefficient conventional methods where shells are formed after forming cores and performing cleaning and redispersion processes. Also, formation of the cores is followed by formation of shells having a composition gradient.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Thermoelectric figure of merit enhancement by modification of the electronic density of states
InactiveUS20110248209A1Heat-exchange elementsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsDopantChemical compound
A thermoelectric material and a method of using a thermoelectric material is provided. The thermoelectric material can include at least one compound. For example, the at least one compound may be a Group IV-VI compound such as lead telluride. The at least one compound may further include one or more dopants such as sodium, potassium, and thallium. The method of using a thermoelectric material can include exposing at least one portion of the at least one compound to a temperature greater than about 700 K.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV +1
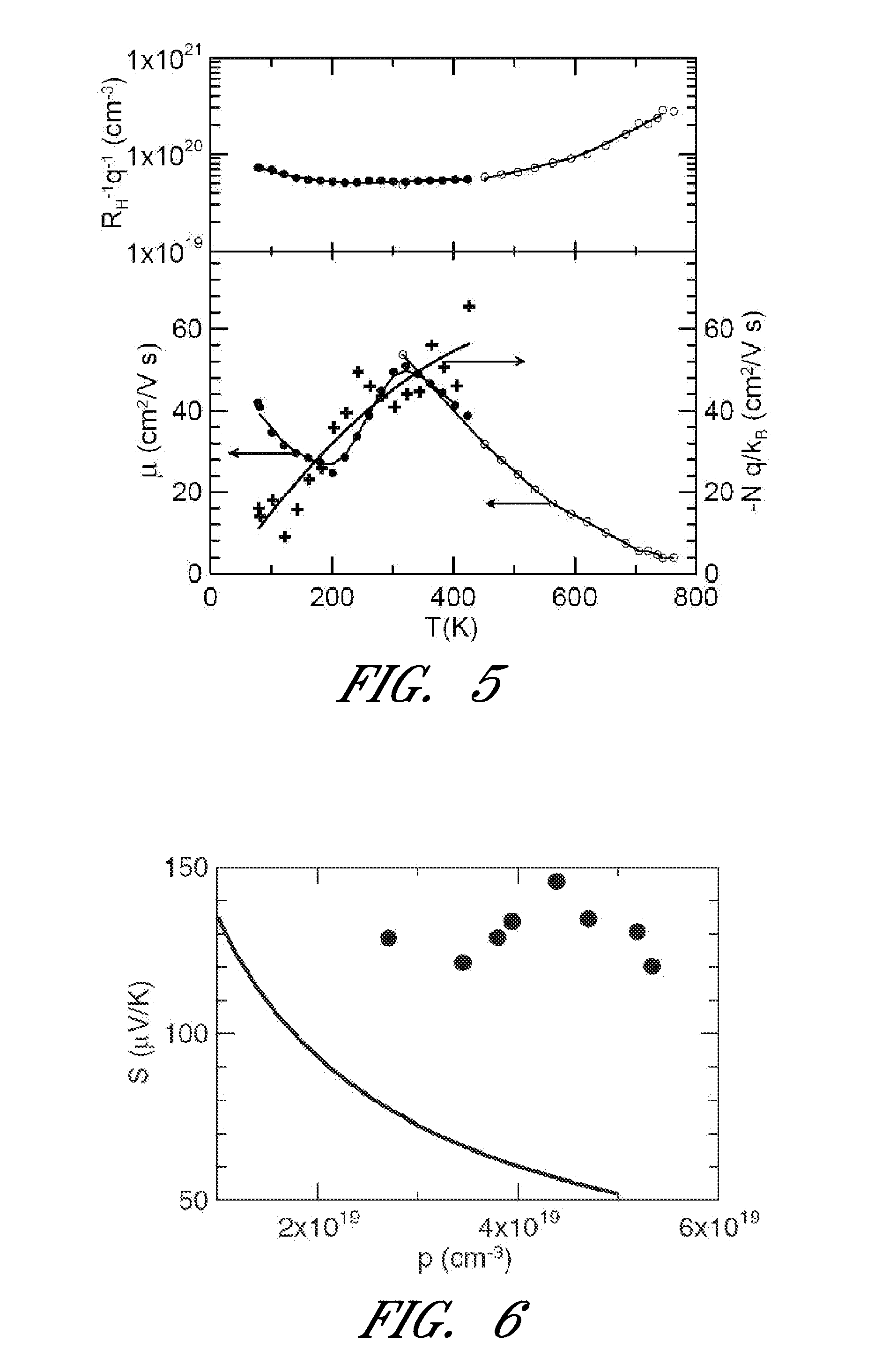
Doped lead tellurides for thermoelectric applications
InactiveCN101421185AEnergy inputSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsSemiconductor materialsLead telluride
A p- or n-conductive semiconductor material comprises a compound of the general formula Pb1-(x1+x2+ . . . +xn)A1x1A2x2 . . . AnxnTe1+z (I) where: in each case independently n is the number of chemical elements different from Pb and Te, 1 ppm<=x1 . . . xn<=0.05, -0.05<=z<=0.05 and n>=2, A1 . . . An are different from one another and are selected from the group of the elements Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, As, Sb, Bi, S, Se, Br, I, Sc, Y, La, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Re, Fe, Ru, Os, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Hg, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu or n=1, and A1 is selected from Ti, Zr, Ag, Hf, Cu, Gr, Nb, Ta.
Owner:BASF AG
BiSbTeSe-based thermoelectric material
InactiveCN105047808ALow thermal conductivityImprove thermoelectric performanceSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsAlloy
The invention discloses a BiSbTeSe-based thermoelectric material. The formula of the BiSbTeSe-based thermoelectric material is Bi<m>Sb<n>Te<x>Se<y>M<z>, wherein m=0.4-0.6, n=1.4-1.6, x=2.7-2.9, y=0.075-0.3, z=0.02-0.15, and M is one or two kinds of elements selected from S, Si, P, Ge, Sn, Ce, Li, I, Br, Al, Cu, Ag, Yb, Tm, La, Gd and Dy. Steps such as powder mixing and alloy smelting are adopted to prepare the BiSbTeSe-based thermoelectric material. The BiSbTeSe-based thermoelectric material of the invention has the advantages of low thermal conductivity, excellent thermoelectric properties, extended application range and the like.
Owner:LEIZIG GUANGDONG THERMOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Carbon-coated nickel cobalt selenide nano material with excellent water electrolysis performance and preparation method of carbon-coated nickel cobalt selenide nano material
InactiveCN108486605AExcellent water electrolysis performanceLow priceMaterial nanotechnologySelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsN dimethylformamideElectrolysis
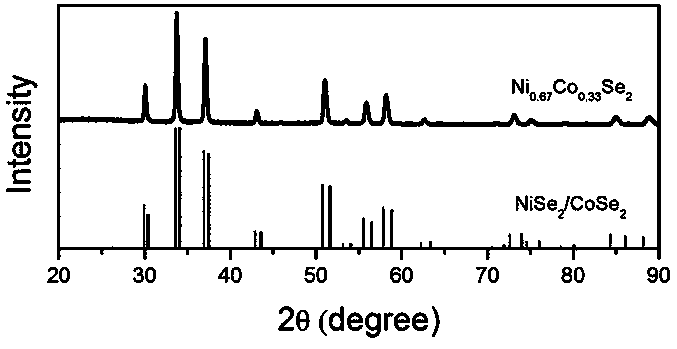
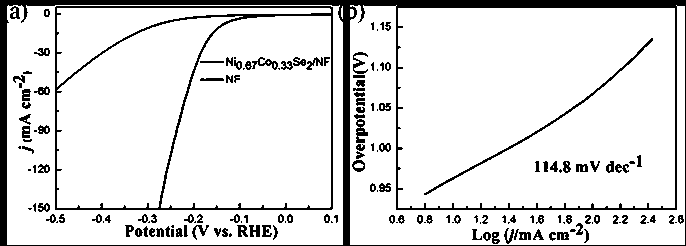
The invention provides a carbon-coated nickel cobalt selenide (Ni0.67Co0.33Se2) nano material with excellent water electrolysis performance and a preparation method of the carbon-coated nickel cobaltselenide (Ni0.67Co0.33Se2) nano material. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving Co(NO3)2.6H2O, Ni(NO3)2.6H2O, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-K30) and terephthalic acid in a mixed solution ofN,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and ethanol at first; then transferring the solution into an autoclave with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner; after a Co-Ni-MOFs material is synthesized by high-temperaturereaction, washing, drying and grinding the Co-Ni-MOFs material, mixing the Co-Ni-MOFs material with selenium powder and then placing the mixture in a tube furnace; and carrying out high-temperature annealing treatment in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the carbon-coated nickel cobalt selenide (Ni0.67Co0.33Se2) nano material. The obtained carbon-coated Ni0.67Co0.33Se2 nano material has excellent characteristics of high preparation speed, high yield, good stability and the like, and has high application value in the aspect of water electrolysis catalysis under the alkaline condition.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
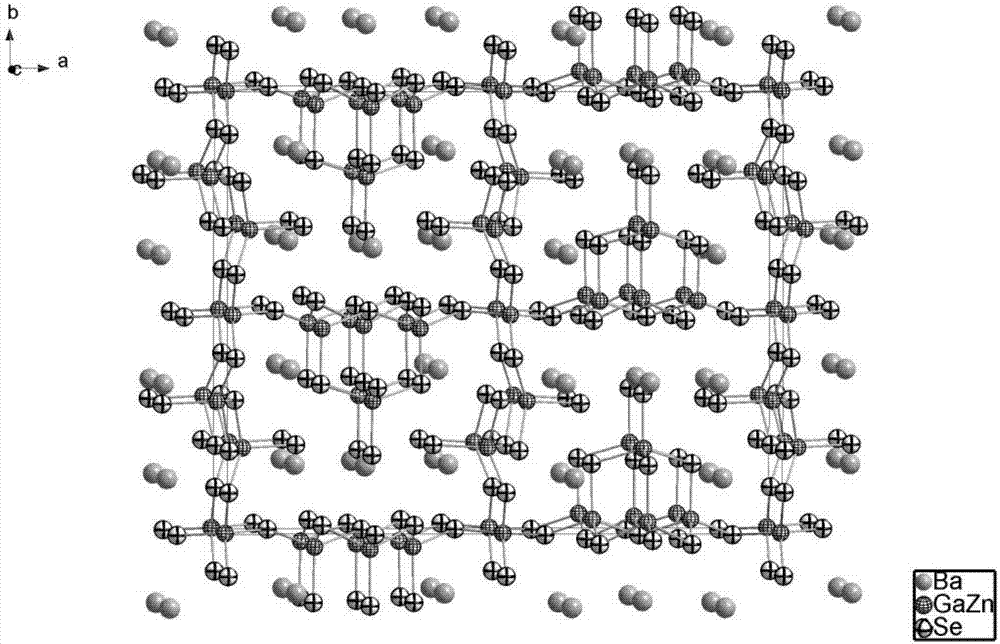
Selenium gallium zinc barium compound, selenium gallium zinc barium infrared nonlinear optical crystal, and preparation methods and purposes thereof
InactiveCN107021462AUse large sizeLong growth cyclePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsNonlinear optical crystalMechanical property
The invention discloses a selenium gallium zinc barium compound, which has a chemical formula of Ba5ZnGa6Se15. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the selenium gallium zinc barium compound. In addition, the invention also discloses a selenium gallium zinc barium crystal, and a preparation method and application thereof. In the growth process of a selenium gallium zinc barium infrared nonlinear optical crystal, the crystal can easily grow up and is not covered; the advantages of high growth speed, low cost, easy acquisition of large-size crystal and the like are realized. The obtained selenium gallium zinc barium infrared nonlinear optical crystal has the advantages that the infrared light transmission wave bands are wide; the mechanical properties are good; the processing and the storage are easy, and the like. The selenium gallium zinc barium crystal can be used for manufacturing an infrared laser frequency conversion device.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS +1
Inclusion free cadmium zinc tellurium and cadmium tellurium crystals and associated growth method
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for crystal growth of cadmium zinc tellurium (CZT) and cadmium tellurium (CdTe) crystals with an inverted growth reactor chamber. The inverted growth reactor chamber enables growth of single, large, high purity CZT and CdTe crystals that can be used, for example, in X-ray and gamma detection, substrates for infrared detectors, or the like. The inverted growth reactor chamber enables reductions in the presence of Te inclusions, which are recognized as an important limiting factor in using CZT or CdTe as radiation detectors. The inverted growth reactor chamber can be utilized with existing crystal growth techniques such as the Bridgman crystal growth mechanism and the like. In an exemplary embodiment, the inverted growth reactor chamber is a U-shaped ampoule.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Preparation of metal chalcogenides
ActiveUS20190039913A1Simple and inexpensive and scalable waySelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsGrain treatmentsSulfurMetal chalcogenides
A method embodiment involves preparing single metal or mixed transition metal chalcogenide using exfoliation of two or more different bulk transition metal dichalcogenides in a manner to form an intermediate hetero-layered transition metal chalcogenide structure, which can be treated to provide a single-phase transition metal chalcogenide.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Double metal selenide Fe2CoSe4 material of porous structure and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108892111AUniform particle sizeImprove conductivityCell electrodesSecondary cellsOrganic solventSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a double metal selenide Fe2CoSe4 material of a porous structure and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out a solvothermal reaction on ionic salt of ferrum and ionic salt of cobalt in an organic solvent to form a ferric and cobalt precursor; then selenizing the precursor to obtain a porous sphericalmaterial, the diameter of which is 200-260 nm, wherein the specific surface area of the material is 81.21 m<2> / g. The volume change of a cathode material in a charging process can be accommodated effectively. The conductivity of the material can be improved well as a result of the mesoporous property and large specific surface area of the material, and the volume change of the cathode material inthe charging process can be accommodated effectively, so that good electrochemical properties can be generated. The material as the cathode material of a sodium ion battery shows excellent cyclic stability, and is good in capacity retaining rate and is slow in capacity fading.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Bi2O2Se-based thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104261357ASignificant change in performanceHeating evenlySelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsThermoelectric materialsOxide ceramic
The invention belongs to the field of oxide ceramic materials and preparation methods thereof and particularly relates to a Bi2O2Se-based thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of firstly, weighing Bi2O3 powder, Bi powder, Se powder and SnO2 powder according to the stoichiometric ratio: Bi2-xSnxO2Se (0<=x<=0.10), mixing, then, carrying out vacuum tube sealing, and calcining to finish a phase forming stage; and compacting the calcined powder, and sintering by using SPS discharge plasmas to obtain the pure-phase and Sn doped Bi2O2Se-based thermoelectric material. Compared with the traditional hot-pressed sintering method, the preparation method has the advantages of uniformity in heating, high heating speed, short sintering time and the like; the defects of long reaction time, high sintering energy consumption, high operation difficulty and the like in the prior art can be effectively overcome; and the performance of a sintered sample is obviously changed, and the ZT value of the Bi2O2Se-based thermoelectric material can be greatly increased after Sn is doped.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
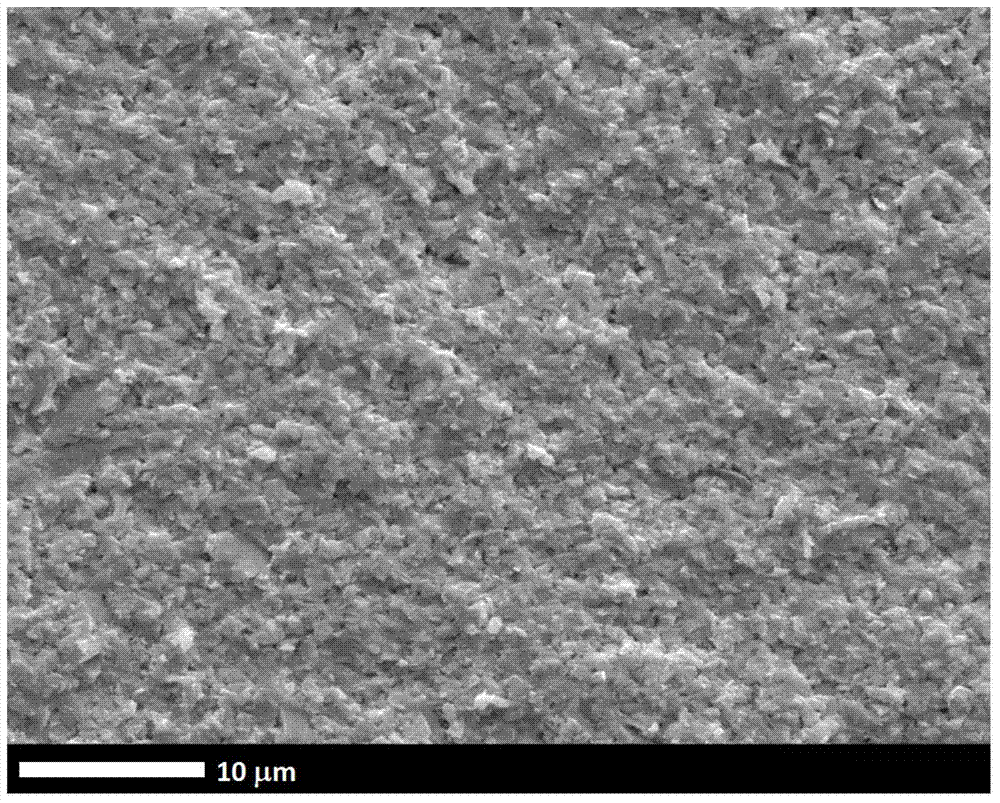
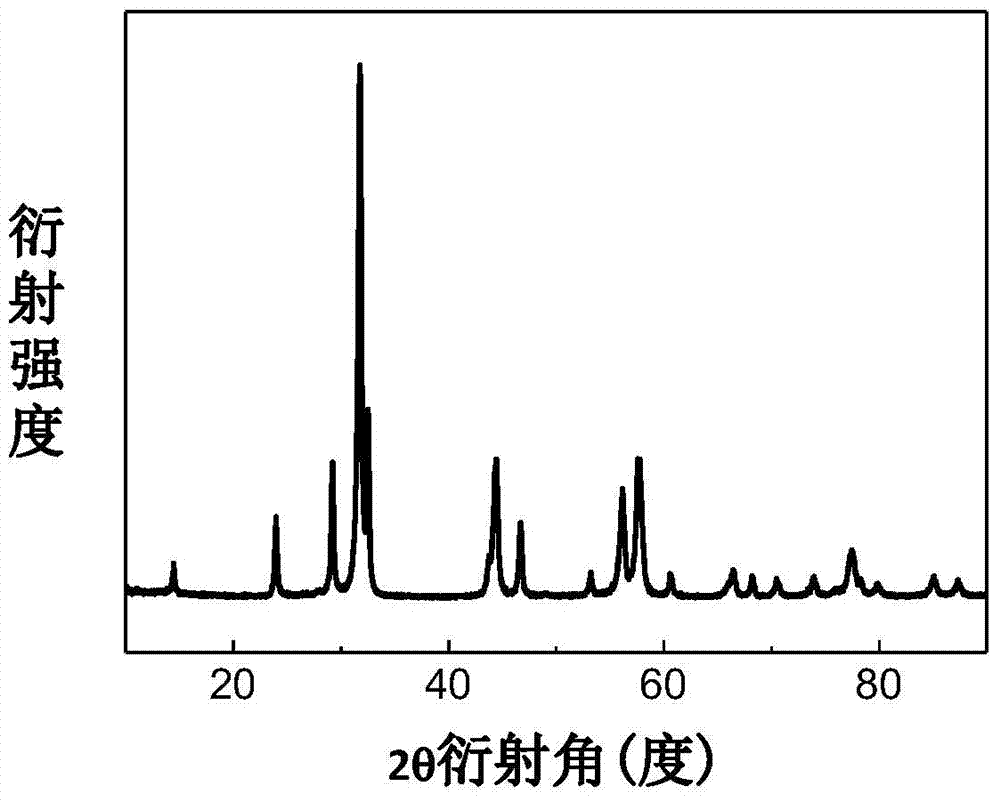
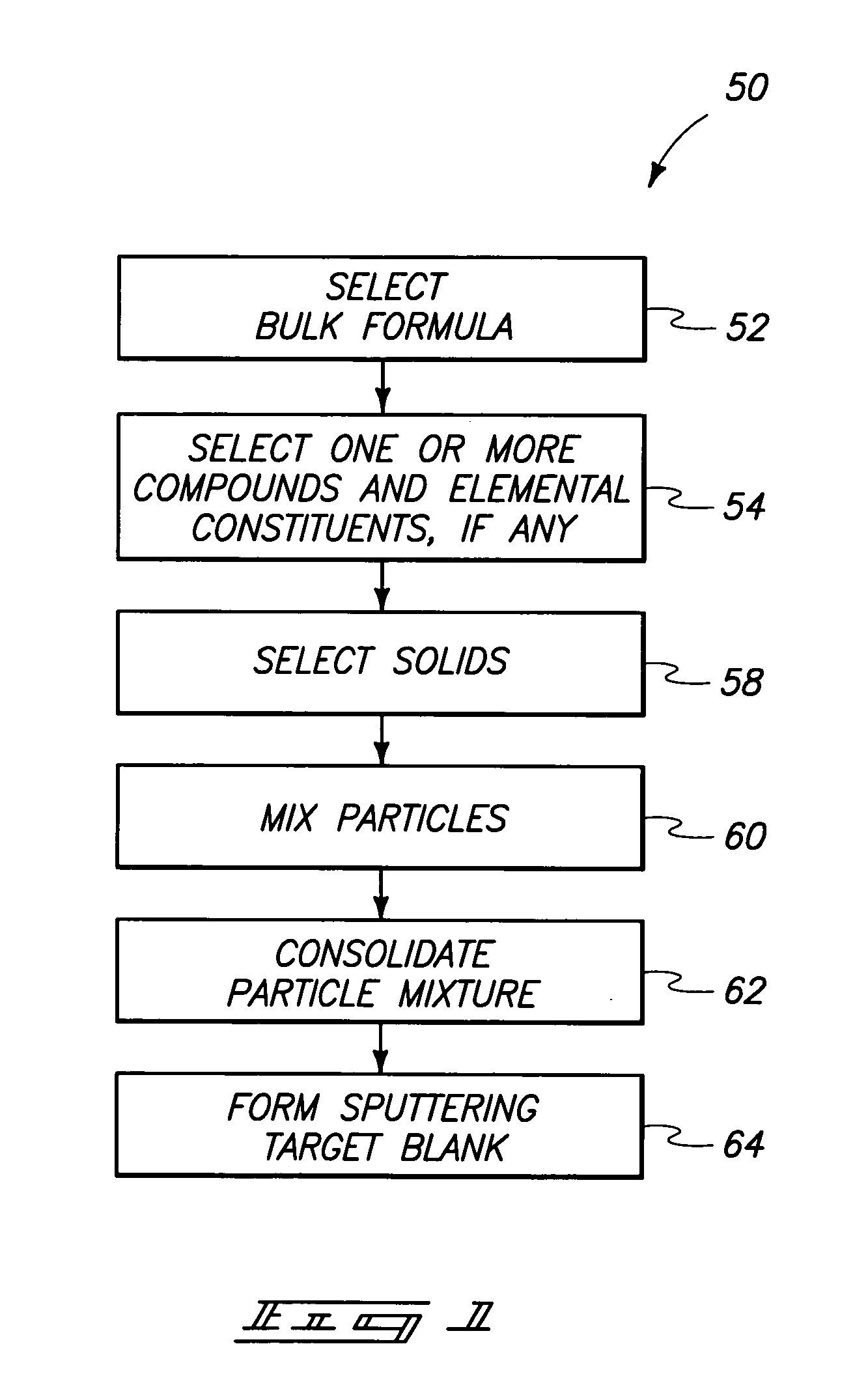
Alloy casting apparatuses and chalcogenide compound synthesis methods
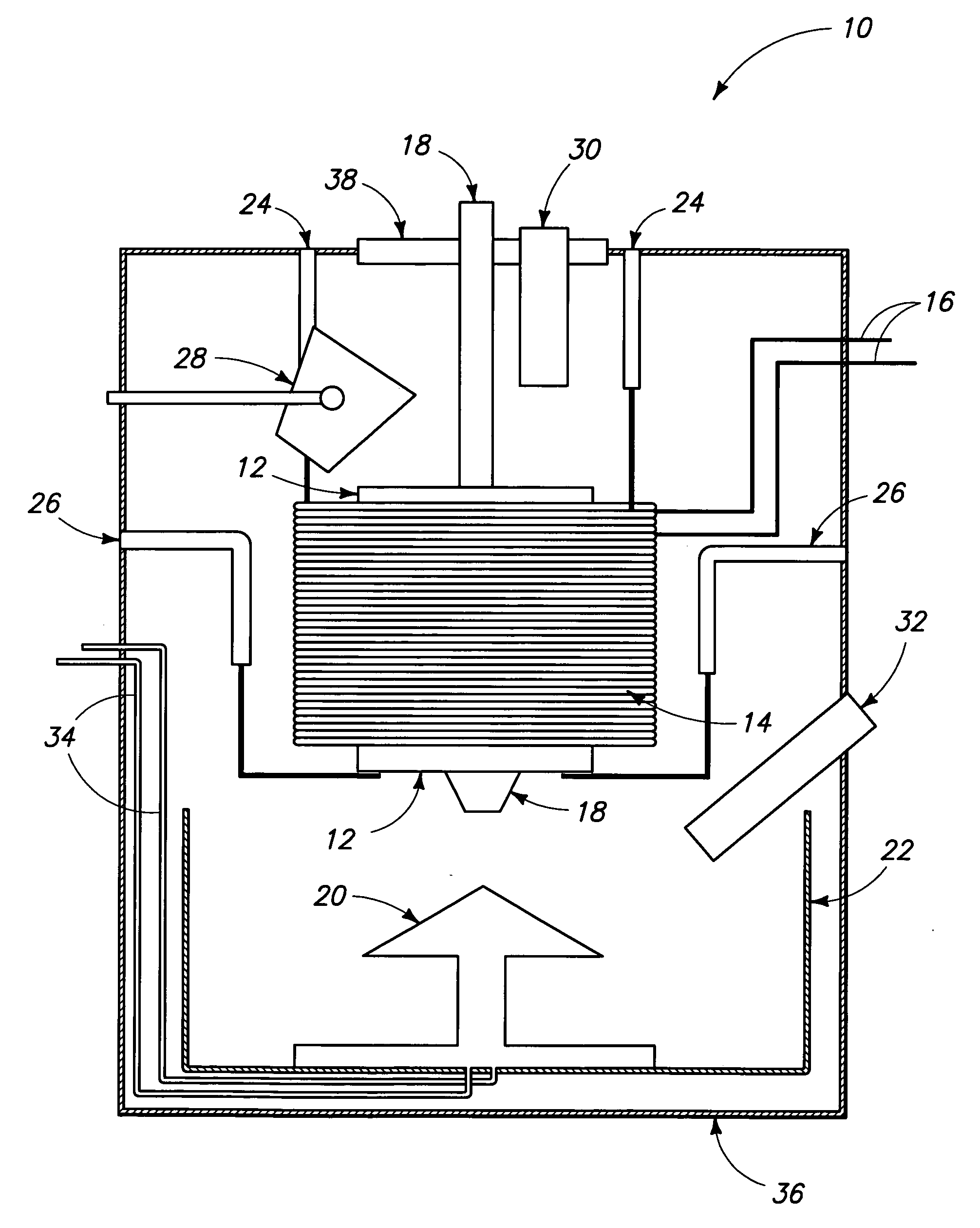
A chalcogenide compound synthesis method includes homogeneously mixing solid particles and, during the mixing, imparting kinetic energy to the particle mixture, heating the particle mixture, alloying the elements, and forming alloyed particles containing the compound. Another chalcogenide compound synthesis method includes, under an inert atmosphere, melting the particle mixture in a heating vessel, removing the melt from the heating vessel, placing the melt in a quenching vessel, and solidifying the melt. The solidified melt is reduced to alloyed particles containing the compound. An alloy casting apparatus includes an enclosure, a heating vessel, a flow controller, a collection pan and an actively cooled quench plate. The heating vessel has a bottom-pouring orifice and a pour actuator. The flow controller operates the pour actuator from outside the enclosure. The quench plate is positioned above a bottom of the collection pan and below the bottom-pouring orifice.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Synthesis of multinary chalcogenide nanoparticles comprising cu, zn, sn, s, and se
InactiveCN102459063ASimple compositionFacilitate exchange reactionsNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
Nanoparticle compositions and methods for synthesizing multinary chalcogenide CZTSSe nanoparticles containing Cu, Zn, and Sn in combination with S, Se or both are described. The nanoparticles may be incorporated into one or more ink solutions alone or in combination with other chalcogenide-based particles to make thin films useful for photovoltaic applications, including thin films from multilayer particle films having a composition profile. The composition and stoichiometry of the thin films may be further modified by subjecting the particle films to gas or liquid phase chalcogen exchange reactions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com