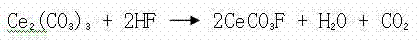Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
286results about "Zinc sulates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Group ii alloyed i-iii-vi semiconductor nanocrystal compositions and methods of making same
InactiveUS20080202383A1High Luminescence Quantum YieldMaterial nanotechnologyZinc sulatesLuminescence quantum yieldSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor nanocrystal composition that is stable and has high luminescent quantum yield. The semiconductor nanocrystal composition has a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a group II alloyed I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystal material. A method of making a semiconductor nanocrystal composition is also provides which includes synthesizing a semiconductor nanocrystal core of a group II alloyed I-III-VI semiconductor material.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
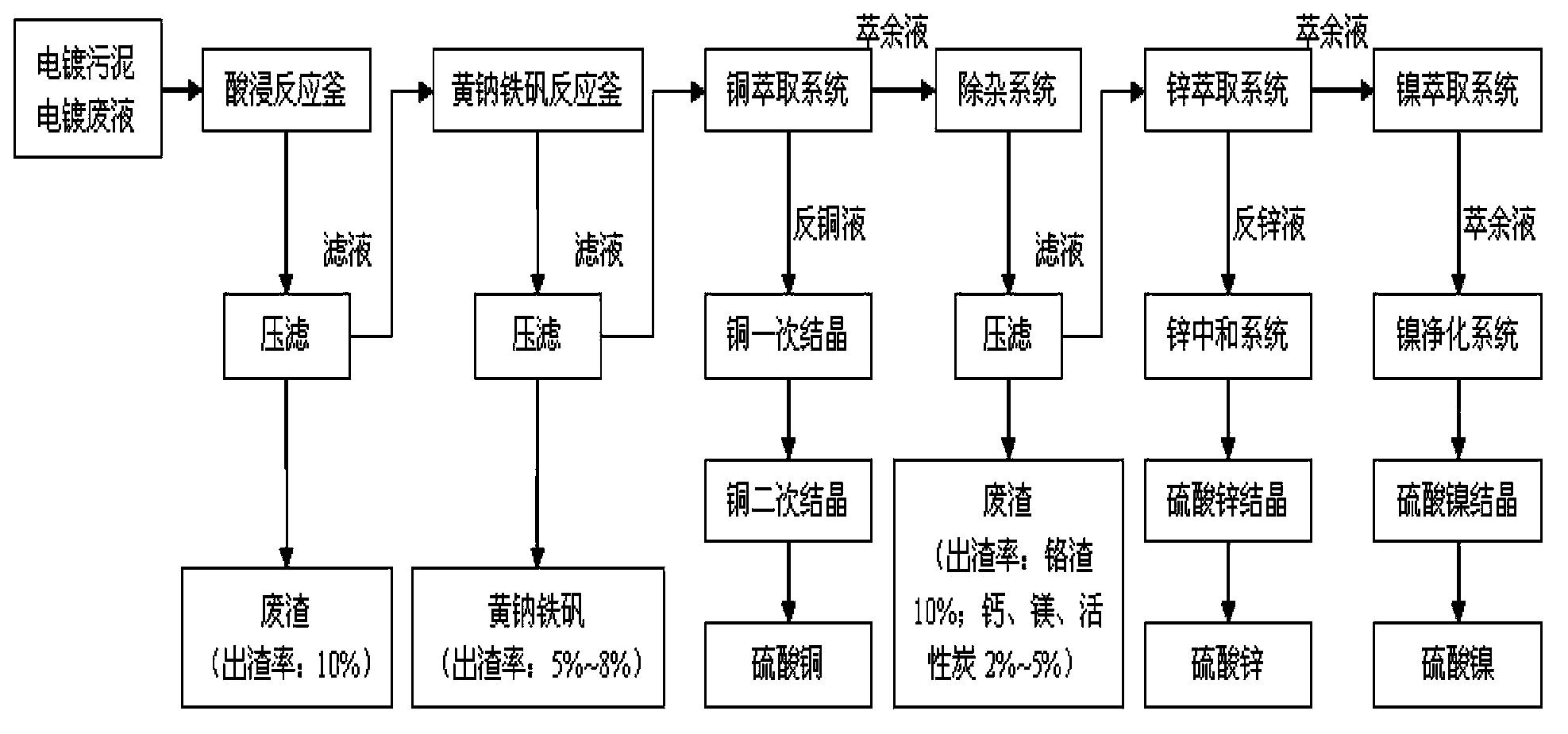
Method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge
The invention relates to a method for recycling copper, nickel, chromium, zinc and iron from plating sludge, belonging to the technical field of chemical engineering and metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: acid leaching, vulcanizing for separation and enrichment, hot-pressure leaching, extracting for separation, hot-press oxidizing chromium, purifying chromium solution, extracting ferric chloride and the like. The method has obvious advantages of strong adaptability to different kinds of plating sludge, high utilization of metal resources, high value-added content of product,less process waste residue, thorough deintoxication and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
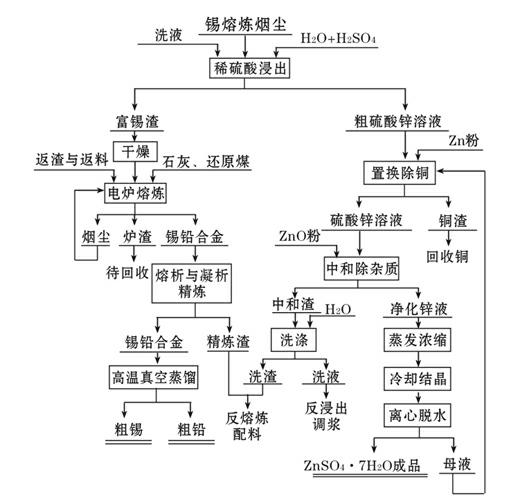
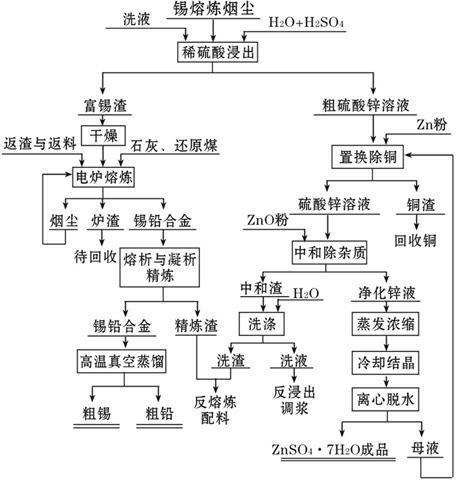
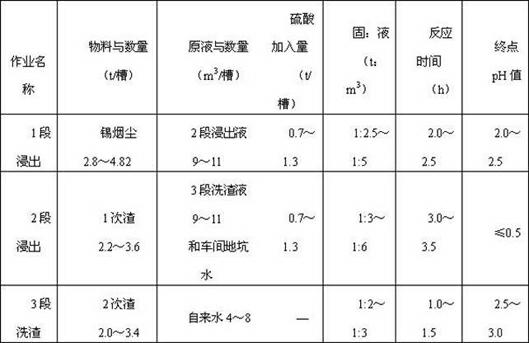
Method for producing zinc sulfate heptahydrate, crude tin and crude lead by using tin smelting dust
InactiveCN102352443AHigh recovery rateReasonable process structureZinc sulatesProcess efficiency improvementSulfateCopper
The invention discloses a method for producing zinc sulfate heptahydrate, crude tin and crude lead by using tin smelting dust. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pretreating the raw material; (2) leaching with a dilute sulphuric acid to separate out zinc; (3) purifying the crude zinc sulfate solution, preparing zinc sulfate heptahydrate; (4) performing electric furnace smelting on the tin-rich residue to prepare a tin-lead alloy; (5) adopting the conventional liquation process (the temperature is 500-600 DEG C) and the agglutination method (the temperature is 230-240 DEG C) to refine the tin-lead alloy and increase the Sn-Pb grade of the alloy to 94%-96%, and sending the refining residue back to the electric furnace to perform smelting and dosing treatment; and (6) performing high temperature vacuum distillation to produce crude tin and crude lead. By adopting the method, the tin smelting dust can be effectively utilized, the resource can be saved and metals such as tin,lead, zinc and copper can be recovered together.
Owner:太仓市南仓金属材料有限公司
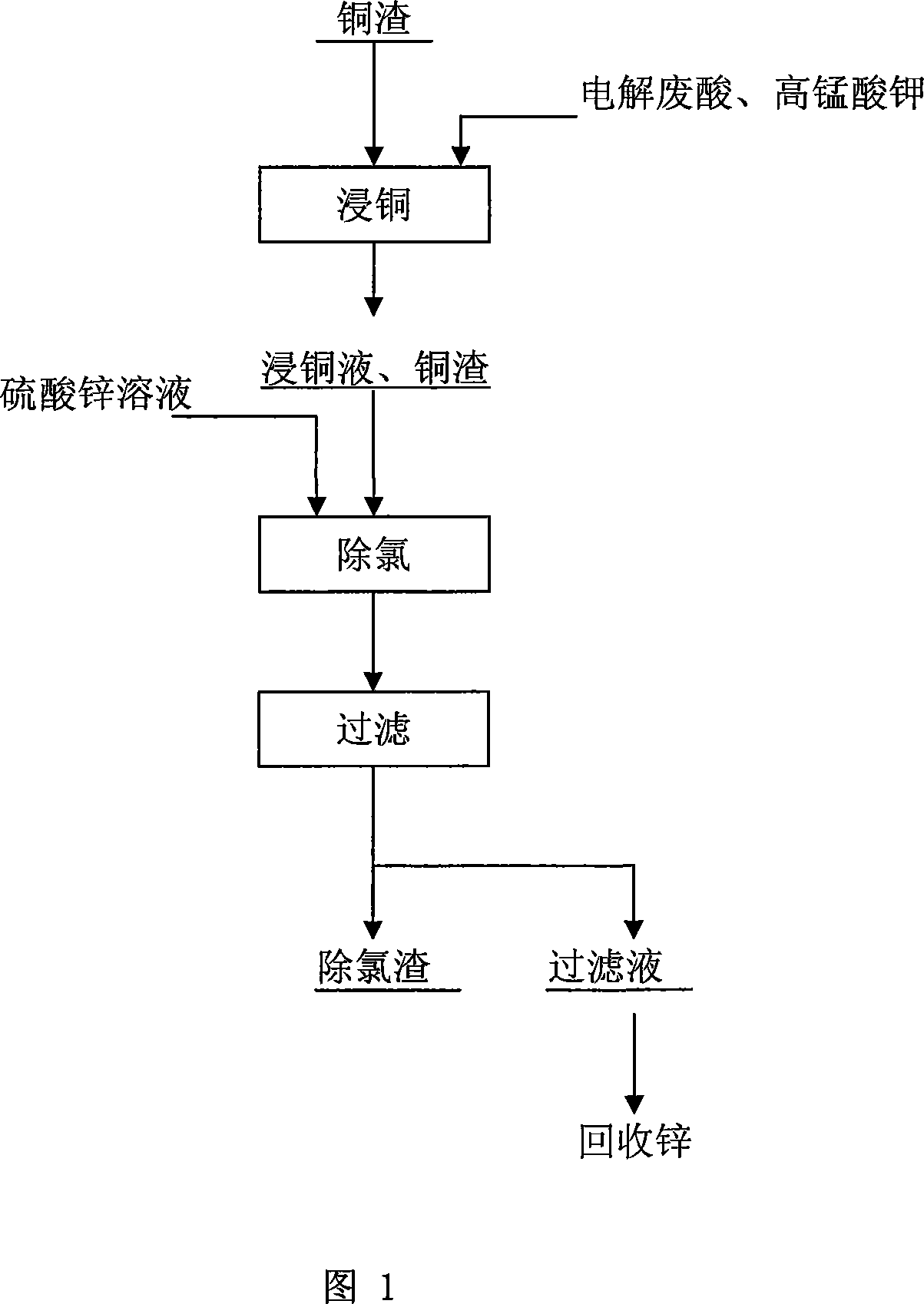
Method for removing chlorine from zinc sulfate solution
InactiveCN101113015ATake advantage ofNo pollution in the processZinc sulatesSulfatePhysical chemistry
A method to remove chlorine from zinc sulfate solution pertains to nonferrous metallurgy. The chlorine in the zinc sulfate solution is removed through elementary copper in copper slug and Cu2+ generated from oxidation of copper slug react with chloride ion to get insoluble CuCl precipitation. The invention makes a further use of copper slug generated from wet zinc melting method, first partial elementary copper in the copper slug is oxidized and then Cu2+ ion is obtained without adding copper sulfate, realizing the effect that elementary copper and Cu2+ ion are both supplied by the slug to involve in chlorine removal reaction. When in the chlorine removal process, no copper sulfate is added and the copper slug is made a full use, therefore, production cost is reduced, operation process is simplified, no waste slug, waste gas and waste water are added and no pollution is done to the environment and as materials involved in the invention are ordinary materials and are not needed and consumed in a large amount, the invention has remarkable economic effect.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
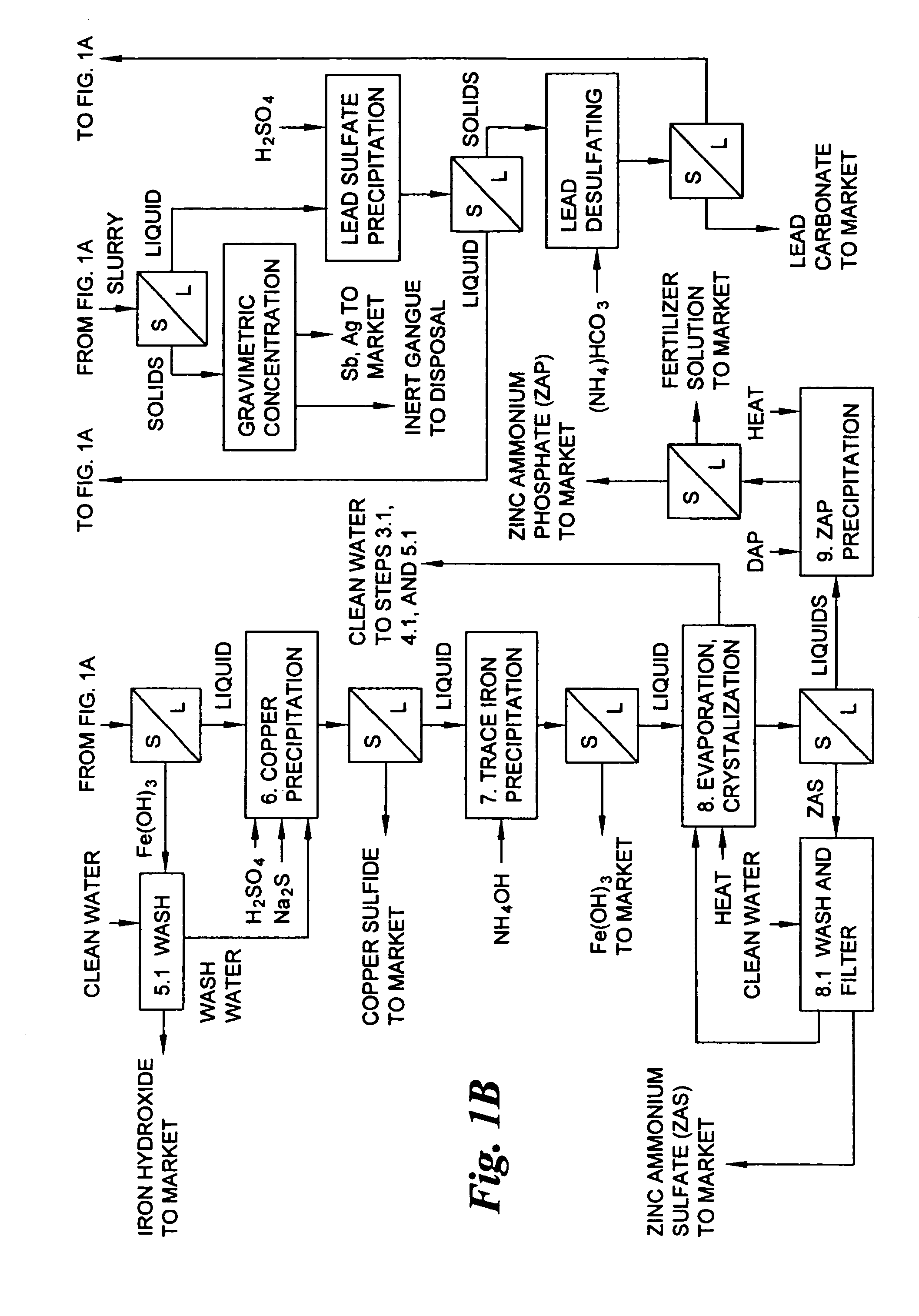
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
Electroplating sludge recycling technology
InactiveCN104099474AReduce dosageGuaranteed leaching rateZinc sulatesSludge treatmentLiquid wasteSludge
The invention discloses an electroplating sludge recycling technology. The technology comprises the steps of acid dipping, iron removal, copper extraction, impurity removal, zinc extraction, nickel extraction, low acid leaching and high acid leaching, tailings are washed with water, the iron removal step is carried out through a sodium jarosite process, copper extraction adopts two stage extraction, two stage water washing, four stage back extraction, and second stage extraction is carried out after first stage extraction, precipitation, washing and acid dissolution. The technology has the advantages of technological period shortening, guarantee of the product purity through multiple stage extraction, effective use of the waste resource, and reduction of the emission of a waste liquid.
Owner:ZHENJIANG HUAKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
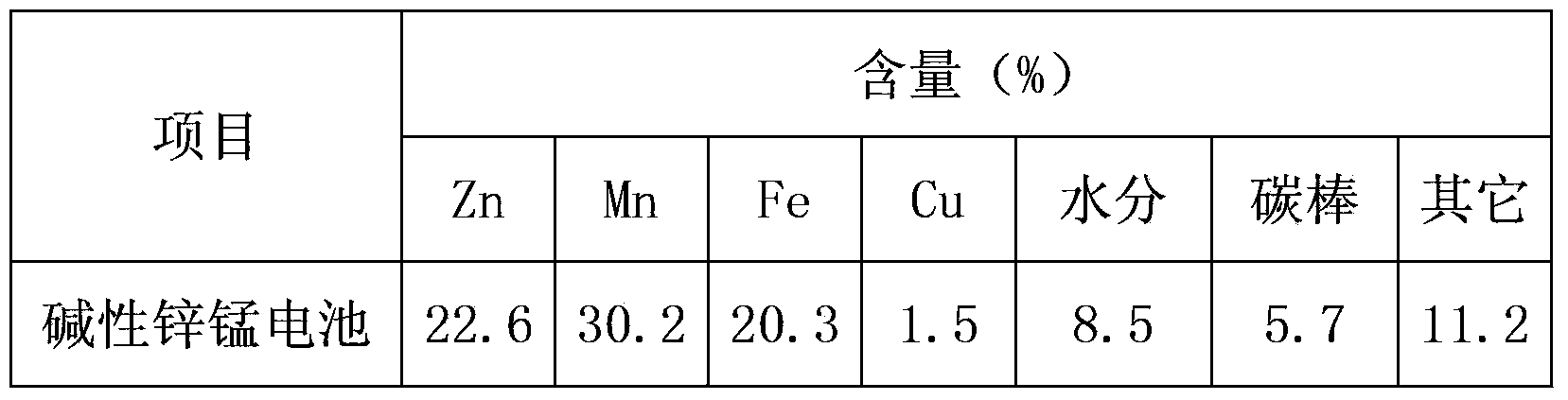
Method for preparation of high purity manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate from waste zinc-manganese batteries
ActiveCN104229898AStrong ability to useEfficient recyclingZinc sulatesManganese sulfatesChemical industryResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for preparation of high purity manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate from waste zinc-manganese batteries. Zinc-manganese batteries mainly contain manganese, zinc, iron, copper and other valuable metal components, and by means of sulfuric acid dissolution, iron powder replacement, oxidation neutralizing for iron removal, extraction purification and separation, crystallization and other processes, high purity manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate products can be prepared. The high purity manganese sulfate obtained by the invention can be used for preparation of battery materials, and the high purity zinc sulfate can be used for medicine, feed, food, chemical industry and other fields. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high resource utilization and recovery rate, and high product quality, etc.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Method for pretreating incineration ash of circuit board and recovering bromine
ActiveCN108118157AEasy to recycleNo emissionsZinc sulatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesRecovery methodBromine
The invention discloses a method for pretreating incineration ash of a circuit board and recovering bromine, belongs to the field of comprehensive recovery of ash whole-wet valuable metal and particularly relates to a method for recovering valuable metal, enriching precious metal and recovering bromine salt in the pretreatment process of incineration ash of the circuit board. The method mainly comprises the steps: extracting mixed alkali; recovering copper by copper extraction and back extraction; carrying out neutralization and precipitation to separate lead and zinc; evaporating and crystallizing bromine; regenerating mixed alkali extracting liquor; removing zinc by acid pickling; evaporating and crystallizing zinc; carrying out zinc and copper removal on mixed alkali extracting residuesand the like. Compared with a traditional ash comprehensive process, the technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages that recovery of valuable metals such as copper, zinc and lead and enrichment of precious metal such as silver in the pretreatment process of the ash is realized to the maximum extent; meanwhile, the bromine salt is separated and recovered; the method has the characteristics of high recovery added value, no tail liquid drainage and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Treatment method of zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid
The invention relates to a treatment method of a zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid. The method comprises the following steps: adding a reducing agent to the zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid, and fully reacting to obtain a reducing liquid; filtering the reducing liquid to collect a first filtrate; adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the first filtrate, and uniformly stirring to obtain a mixed liquid; evaporating and concentrating the mixed liquid at 90-110 DEG C to obtain a concentrated liquid; filtering the concentrated liquid at 70-100 DEG C to obtain a mixture with solids of FeSO4.H2O and ZnSO4.H2O. A certain amount of zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is added into the filtered second filtrate for a concentration and crystallization process in the next cycle. According to the treatment method of the zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid, heavy metal ions are replaced to single substances, and after solid impurities in the reducing liquid are filtered to remove, the concentrated sulfuric acid is added. The mixture is evaporated, concentrated and filtered to obtain the crystal mixture with solids of FeSO4.H2O and ZnSO4.H2O. The crystal mixture can be used as a mineral additive for feed. According to the treatment method of the zinc-containing and iron-containing waste acid, the recovery rates of zinc and iron are higher, and the product has broad market prospect.
Owner:3R ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Fluorine-removing process for zinc sulphate solution
InactiveCN1966407ADoes not affect electrowinningHigh fluoride removal rateZinc sulatesSulphate IonFlow sheet
The invention relates to the technology of removing fluorine by zinc sulphate solution, which belongs to the way of removing fluorine in the neutral extracted supernatant during the wet process of refining zinc. In the invention, after adding Al3+ and PO43- to the neutral extracted supernatant which contains fluorine, the fluorine is precipitated so it can be removed from the solution. The advantages of the invention: short technological flow-sheet, easy to operate, high fluorine-removing rate, less loss of elements with valence, more available to the cheap accessories and low operating cost.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
Method for producing battery-grade manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate with waste and used zinc-manganese batteries
ActiveCN107815550AHigh recovery rateAchieve recyclingZinc sulatesProcess efficiency improvementManganeseDissolution
The invention discloses a method for producing battery-grade manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate with waste and used zinc-manganese batteries and belongs to the technical field of waste and used battery utilization. The method comprises the steps that the waste and used zinc-manganese batteries are crushed, and the zinc-manganese batteries are placed into a crusher to be crushed into powder with the particle size being 200 microns or below; the zinc-manganese battery powder material is dissolved, and an acid and a reducing agent are added for dissolution; the pH is adjusted to remove iron and aluminum; zinc and manganese are separated, the zinc sulfate is prepared, and the zinc is extracted and separated through a P204 extraction agent; impurities are removed, a heavy metal trapping agent and fluoride are added, and heavy metal, calcium and magnesium are removed; a manganese sulfate solution is prepared, the manganese is extracted and separated through P507, then an obtained pure manganese solution is concentrated and crystallized, and the battery-grade manganese sulfate is obtained. By means of the method for producing the battery-grade manganese sulfate and the zinc sulfate with the waste and used zinc-manganese batteries, the battery-grade manganese sulfate and high-purity zinc sulfate crystals can be obtained, the obtained manganese sulfate crystals are in a particle shape and are free of the agglomeration phenomenon, the process is simple, and full-ingredient recycling is achieved.
Owner:蒋央芳
Method for manufacturing zinc sulfate by utilizing high-grade arsenic zinc oxide and zinc ash from steel works
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing zinc sulfate by utilizing high-grade arsenic zinc oxide and zinc ash from steel works, which comprises the following steps: calculating the use amount of the two raw materials: high-grade arsenic zinc oxide and zinc ash from steel works according to the lab results of the elements arsenic, ferrum and zinc in the two raw materials; mixing the rawmaterials; and evaporating and crystallizing after pulpifying, lixiviating, adjusting pH value, oxidizing to remove ferrum and arsenic, neutralizing, filtering by pressing and purifying to obtain qualified zinc sulfate products. The invention is highly adaptable to high-grade arsenic materials and can process zinc oxide materials containing 1.5-2.5 percent of arsenic. The manufacturing process issafe and reliable, and no such personal injury caused by accidents as AsH3 poisoning occurs, thus clean manufacturing can be realized to prevent arsenic from causing secondary pollution; the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the products have high quality meeting the II class standard (zinc sulfate heptahydrate) respectively in HG 2934-2000 (feed-grade zinc sulfate) and HG / T2326-2005 (industrial zinc sulfate).
Owner:CHANGNING YANJIANG ZINC IND
Method for preparing manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate from waste batteries containing manganese and zinc
ActiveUS20110123419A1Simple processEconomical efficiencyZinc sulatesCell electrodesCyclic processManganese
A method for preparing manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate from waste batteries containing manganese and zinc, and more particularly to a method for preparing manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate from waste batteries containing manganese and zinc. Zinc powder and activated carbon are added to a leached solution obtained from a continuous leaching process so as to remove heavy metals and organic materials from the leached solution, and then the leached solution is spray-dried to simultaneously obtain manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate at high-purity by a simple process without generating wastewater. An environmentally friendly waste battery recycling process is thereby provided, because it is not required to use additional chemical substances for neutralization titration or impurity removal in recovering manganese sulfate and zinc sulfate by leaching a waste battery powder.
Owner:ECONIX
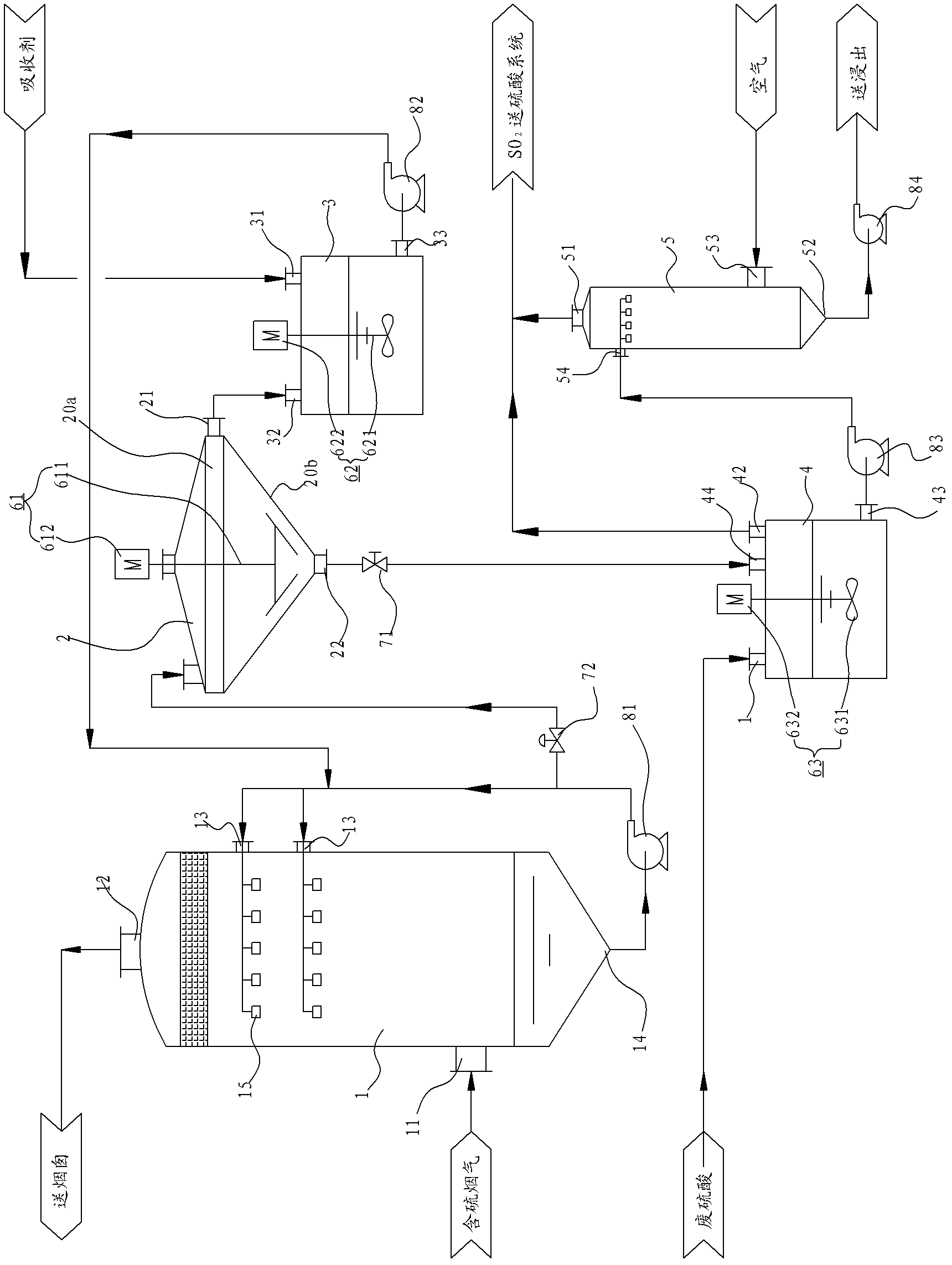
Desulfurization method for fume gas containing low-concentration sulfur dioxide
ActiveCN103506001ASolve the blockageRealize pollution control without pollutionZinc sulatesDispersed particle separationLiquid wasteElectrolysis
The invention discloses a desulfurization method for fume gas containing low-concentration sulfur dioxide. The desulfurization method comprises the following steps: making zinc hypoxide powder into absorption slurry with a predetermined concentration, making the absorption slurry reversely contact the fume gas containing low-concentration sulfur dioxide in a reverse-injection material feeding pipe of a dynamic wave washing tower, conversing sulfur dioxide into zinc sulfite by utilizing the reactions between zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide, then decomposing zinc sulfite into zinc sulfate through an electrolysis waste liquid, recycling the sulfur dioxide generated by the decomposition into a sulfuric acid producing system, and finally filtering so as to obtain zinc sulfate for leaching.
Owner:云南云铜锌业股份有限公司
Method for treating sludge containing trivalent chromium and recovering heavy metal
ActiveCN103011537ARemove hidden dangers of pollutionHigh purityZinc sulatesSludge treatmentSludgeResource recovery
The invention discloses a method for treating sludge containing trivalent chromium and recovering heavy metal. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing the content of components in sludge containing chromium to dilute the sludge containing chromium; and treating the sludge containing chromium by ammonium salt, ammonia water, alkali and acid to obtain pigment grade chromium oxide, single metal or other products. The method is applied to the disposal and recovery process of the sludge containing chromium generated in the industries, such as steel, electroplating and tanning to achieve a good pollution control and resource recovery effect.
Owner:武汉巍川环保科技有限责任公司
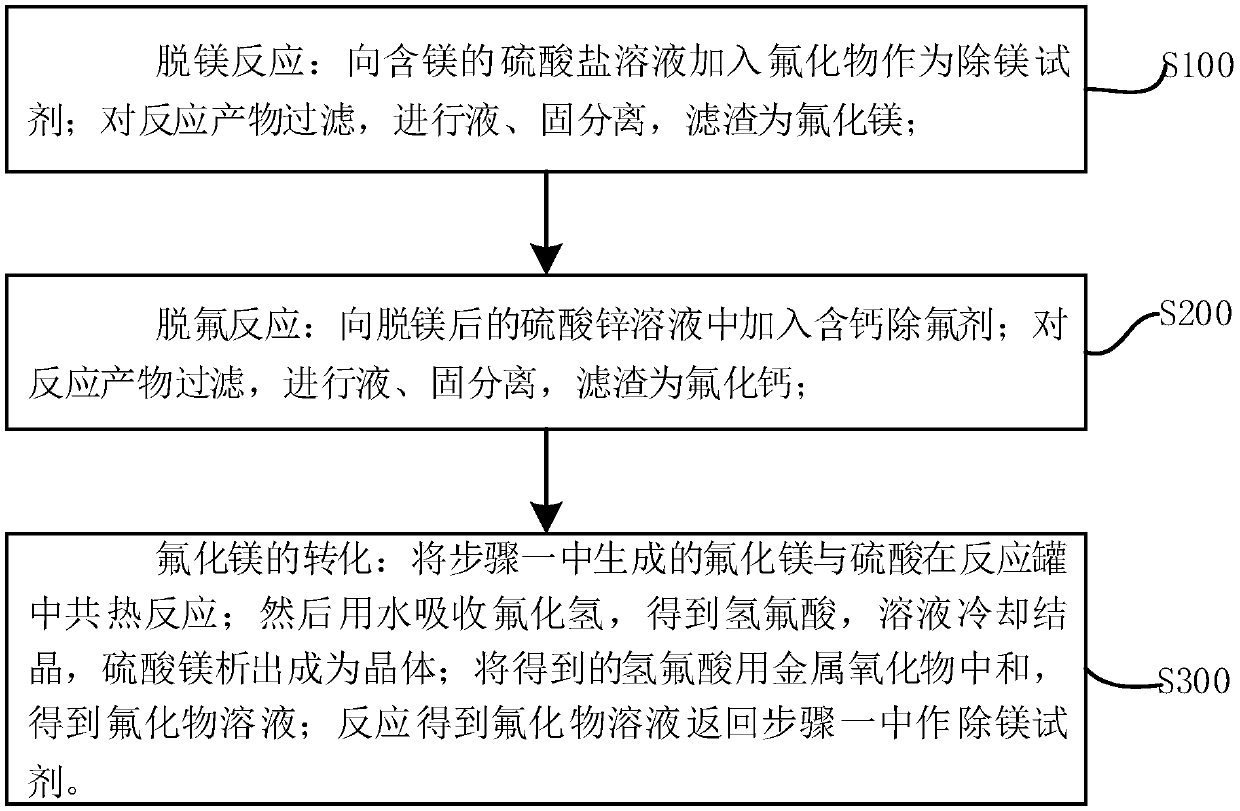
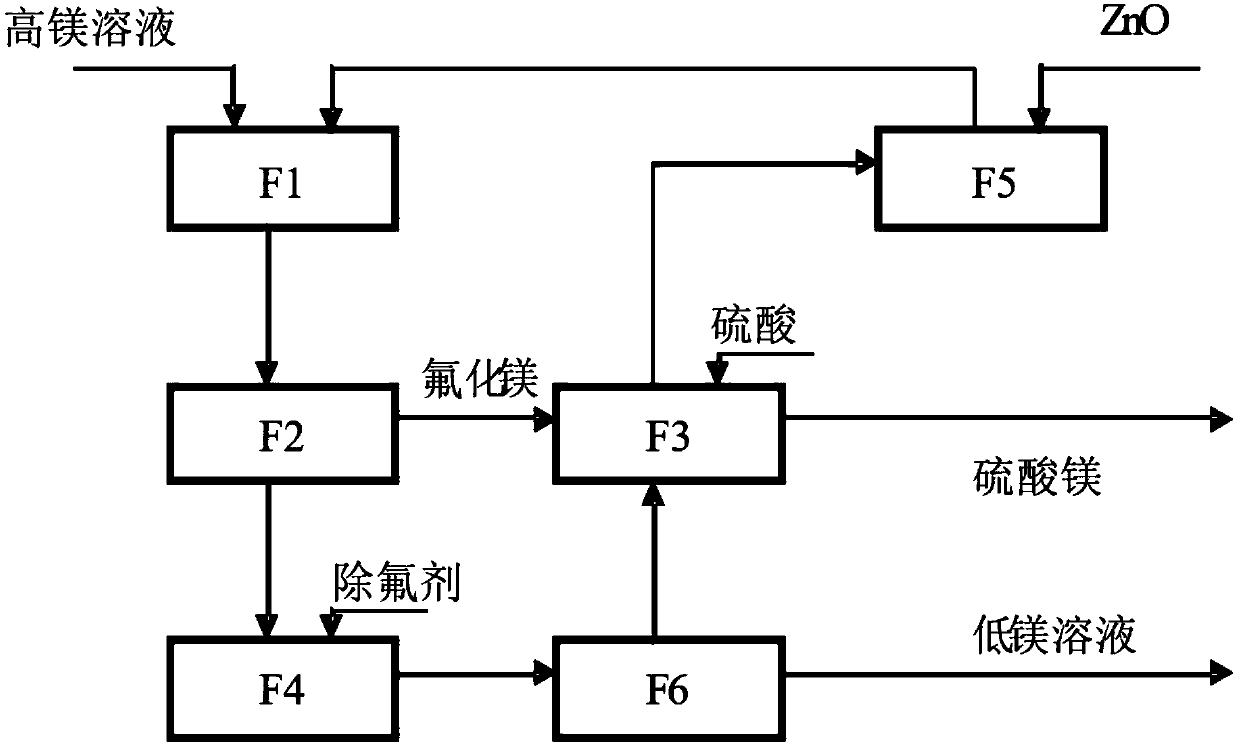
System and process for fluorine-circulation magnesium removal of sulfate solution
PendingCN109665501ARealize recyclingAchieve recyclingZinc sulatesSulfate preparationTreatment costsLiquid solid
The invention discloses a system and process for fluorine-circulation magnesium removal of sulfate solution. The process includes: step one, magnesium removal, to be more specific, adding a fluoride serving as a magnesium removal agent into magnesium-containing sulfate solution, filtering a reaction product, and performing liquid-solid separation, wherein filter residue is magnesium fluoride; steptwo, defluorination, to be more specific, adding a calcium-containing fluorine removal agent into zinc sulfate solution subjected to magnesium removal, filtering a reaction product, and performing liquid-solid separation, wherein filter residue is calcium fluoride; step three, magnesium fluoride conversion, to be more specific, subjecting sulfuric acid and magnesium fluoride generated in the stepone to co-heating reaction in a reaction tank, absorbing hydrogen fluoride by water to obtain hydrofluoric acid, cooling the solution to crystallize, separating out magnesium sulfate crystal, neutralizing obtained hydrofluoric acid by a metal oxide to obtain fluoride solution, and returning the fluoride solution obtained in reaction to the step one to serve as the magnesium removal agent. Therefore, the process realizes fluorine recycling, so that treatment cost is sharply reduced.
Owner:吴红
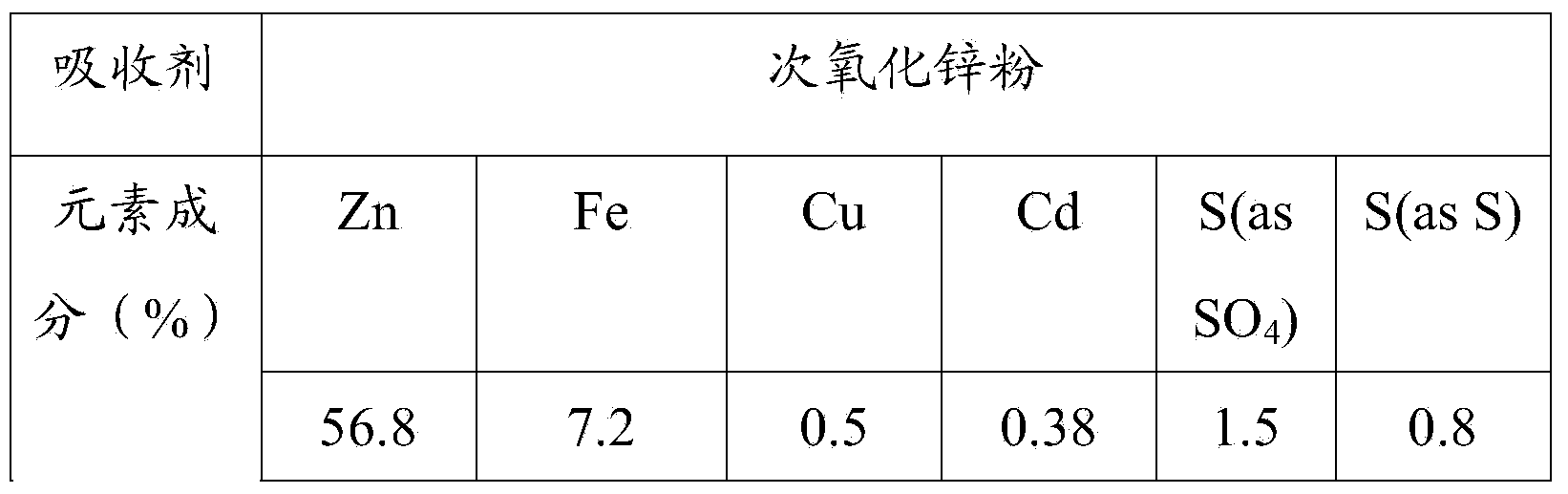
Zinc oxide desulfuration technology
InactiveCN102423622ALow costMeet the needs of environmental protectionZinc sulatesDispersed particle separationDesorptionSlurry
The invention discloses a zinc oxide desulfuration technology, which comprises the following steps of: reversely contacting sulfurous flue gas with a zinc-oxide-contained absorption solution in an absorption tower so as to remove sulfur from the sulfurous flue gas; conveying the desulfurated absorption solution into a settling tank and carrying out settling so as to obtain solid impurities and a supernatant; stirring and pulpifying the supernatant and a zinc-oxide-contained absorbent in a pulpifying tank, and then, conveying the mixture back the absorption tower; subjecting the solid impurities and a waste acidic solution to reacting in an acidifying tank so as to produce SO2 and acidified serous fluid; reversely contacting the acidified serous fluid with air in a sulfur dioxide desorption tower so as to desorb the SO2 from the acidified serous fluid and obtain SO2-desorbed serous fluid; and carrying out acid making by using the produced SO2. According to the zinc oxide desulfuration technology disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the cost for raw materials in each system is saved, and no waste gas, waste liquid and waste solid are discharged in the whole system, so that the totally-closed operation is realized, and the requirements on environmental protection are met. In addition, the technology is simple, the process is short, further, the operation is convenient, and the continuous operation can be realized.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Zinc oxide desulphurization system
ActiveCN102389705AReduce foulingReduce cloggingZinc sulatesDispersed particle separationLiquid wasteDesorption
The invention discloses a zinc oxide desulphurization system comprising an absorption tower, a settling tank, a slurrying tank, an acidifying tank and a sulfur dioxide desorption tower, wherein the absorption tower is provided with an air inlet, an air outlet, an absorption liquid inlet and an absorption liquid outlet; the settling tank is communicated with the absorption liquid outlet; the slurrying tank is communicated with the settling tank, so that absorbent and supernatant liquor are sent to the absorption tower after being stirred; the acidifying tank is connected with a solid-contained slurry outlet of the settling tank; and the sulfur dioxide desorption tower is connected with the acidifying tank. According to the zinc oxide desulphurization system, by the control on the solid content and the pH value of the absorption liquid in the absorption tower, the problems of equipment blockage and scaling are obviously reduced and the absorption efficiency of SO2 is not influenced. In addition, without the discharge of any waste gas, waste liquid and waste solid, fully-closed operation is achieved. The equipment is simple, the operation and the maintenance are convenient and the cost is low; and compared with the traditional zinc oxide desulphurization, the zinc oxide desulphurization of the invention is short in process, convenient to operate and capable of realizing continuous operation.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Green utilization method of waste acid
ActiveCN103588240ALow costImprove adsorption capacityZinc sulatesChemical industryZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
The invention discloses a green utilization method of a waste acid, and belongs to the fields of the metallurgy and the chemical industry. The method comprises the following steps: adding zinc oxide powder to neutralize sulfuric acid in the waste acid and generate zinc sulfate; adding zinc powder to replace heavy metal ions comprising lead ions, cadmium ions, copper ions and the like in the waste acid to enrich most heavy metals in the waste acid; adding ferrous sulfate to precipitate arsenic, and utilizing the strong adsorption and flocculation capability characteristics of hydroxide of iron to further remove a small amount of harmful heavy metal ions comprising lead ions, cadmium ions, copper ions and the like residual in the waste acid; and carrying out concentrating crystallization, centrifugation and drying of an arsenic-precipitated filtrate to obtain zinc sulfate heptahydrate. The method has the advantages of short process flow, reduction of the waste acid treatment cost of traditional methods, economic benefit and good application prospect.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Method for preparing zinc sulphate monohydrate from zinc-containing waste residues
The invention discloses a method for preparing zinc sulphate monohydrate from zinc-containing waste residues. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1), acid leaching; (2), oxidation for iron removal; (3), extraction of copper; (4), replacement for cadmium removal; (5), concentration and crystallization. The method for preparing the zinc sulphate monohydrate from the zinc-containing waste residues is a low-carbon and environmentally-friendly scheme, the preparation raw material is low in cost, waste is reutilized, the environmental problem that existing zinc-containing waste residues cannot be recycled and utilized is solved, the preparation process is energy-saving and environmentally-friendly, no waste gas or waste water is generated, a reagent unfriendly to the environment is not used, meanwhile metal, such as the copper and cadmium, is recycled, and the waste residues are reutilized.
Owner:台山市化工厂有限公司
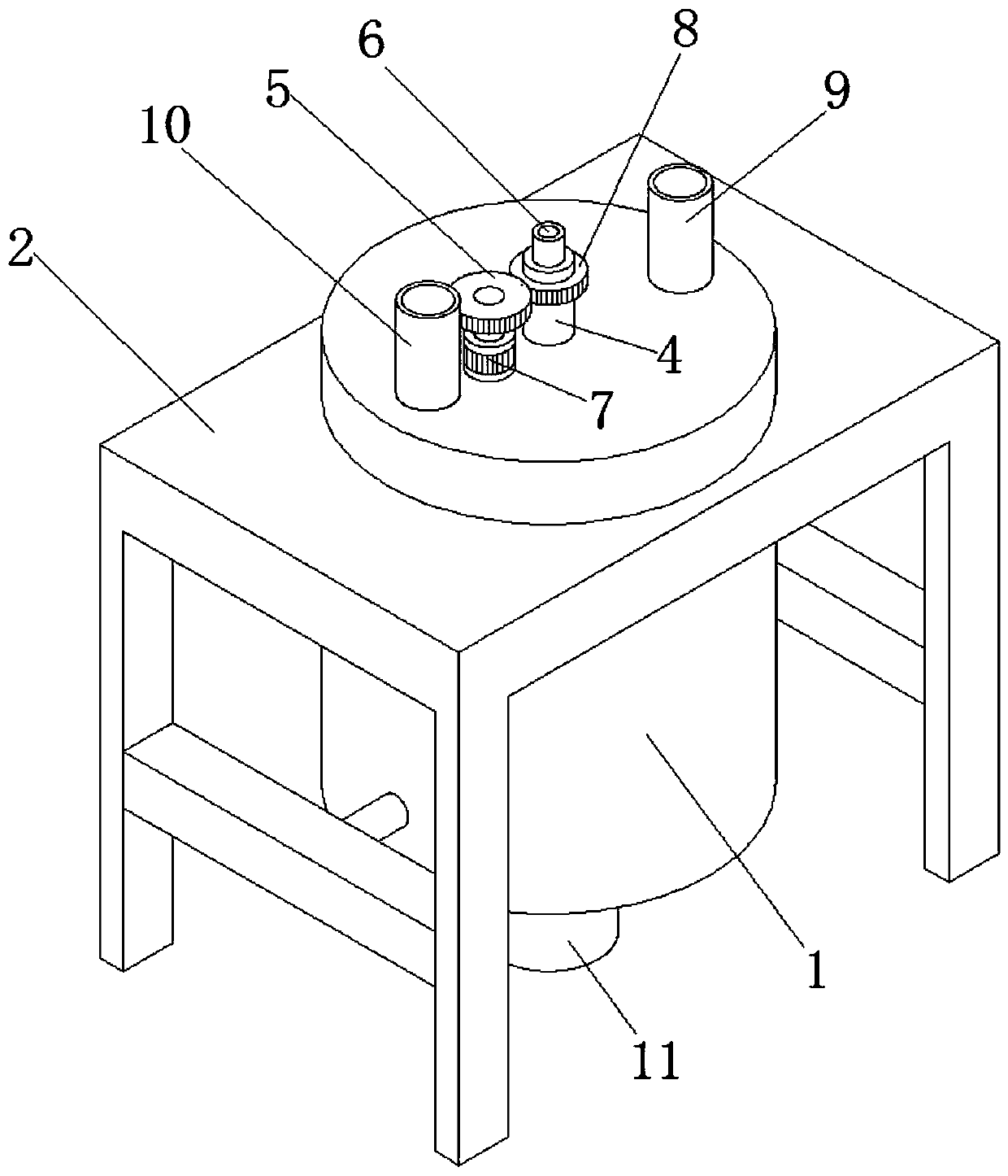
Convenient-to-clean reaction kettle for zinc sulfate production
InactiveCN110918031AAvoid interferenceCause interferenceZinc sulatesHollow article cleaningSulfate zincEngineering
The invention discloses a convenient-to-clean reaction kettle for zinc sulfate production. The reaction kettle comprises a kettle body and a rack for fixing the kettle body, wherein the kettle body isfixed on a supporting plate at the upper end of the rack; the outer side of the bottom end of the kettle body is fixedly connected with a cross beam between two groups of support legs of the rack through fixing rods; a feeding pipe, an adding pipe and a rotating shaft are mounted at the top end of the kettle body; the bottom end of the kettle body is arc-shaped; a discharge port is formed in themiddle of the kettle body; a discharge pipe is fixedly mounted on the discharge port; the rotating shaft is fixedly inserted into the middle position of the kettle body through a bearing; the bottom end of the rotating shaft is connected with a bottom wiping plate through an electric push rod; stirring fan blades and nozzles are symmetrically mounted at the lower end of the rotating shaft, and cleaning assemblies are arranged at parts, on both sides of the rotating shaft, of the interior of the kettle body. According to the convenient-to-clean reaction kettle for zinc sulfate production, sediments attached to the inner wall are scraped and cleaned, and in cooperation with the nozzles mounted on the rotating shaft, when the kettle body is cleaned, scraping and water spraying can be conducted at the same time, and the cleaning effect of the reaction kettle is improved.
Owner:HUNAN LIHONG NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Mine acid wastewater utilization and deep purification method
ActiveCN105439357AEfficient recyclingLess slagZinc sulatesMultistage water/sewage treatmentPurification methodsVulcanization
The invention relates to a mine acid wastewater utilization and deep purification method which comprises the following steps: (1) adjusting the pH value of mine acid wastewater using a neutralizer to recover gypsum; (2) recovering iron through two-stage neutralization; (3) recovering copper and zinc through an efficient vulcanization reaction; (4) leaching the copper and zinc residue with acid and separating copper and zinc to obtain a zinc sulfate solution and copper-rich residue; recovering the vulcanizing agent; drying the zinc sulfate solution by an MVR technology to prepare zinc sulfate; and applying the vulcanizing agent to the step (3) for the efficient vulcanization reaction; and (5) performing deep treatment and reusing the effluent or discharging when the effluent reaches the standard. By adopting the method, the recovery efficiency of copper in the mine acid wastewater can reach 85% or more, and the recovery rate of zinc is 95% or over while high-purity gypsum can be produced at the same time; compared with traditional technology, the residue quantity can be reduced by 20% or over, and the utilization of the mine acid wastewater is realized; and the new technology has the advantages of efficient purification and low cost and brings remarkable economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for preparing lead chloride and zinc sulfate by using mid low grade zinc oxide ores and zinc oxide-lead oxide paragenetic ores
The invention discloses a method for preparing lead chloride and zinc sulfate by using mid low grade zinc oxide ores and zinc oxide-lead oxide paragenetic ores, comprising the following steps: (1) crushing zinc ores and levigating, then mixing the levigated zinc ores with ammonium sulfate and roasting; (2) dissolving out clinkers obtained by roasting, carrying out iron precipitation and aluminium precipitation on the obtained filtrate, and further separating lead from the residues of zinc extraction; (3) boiling down a zinc sulfate solution obtained after iron precipitation and aluminium precipitation for electrolysis; and (4) leaching the residues of zinc extraction with an NaCl solution to obtain a filtrate, condensing the filtrate, cooling down and crystallizing out PbCl2 crystals, and returning the NaCl solution to the leaching process. According to the invention, circulation utilization is realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for rapidly removing arsenic in high arsenic zinc oxide through zinc ash and sodium carbonate peroxide in iron and steel plants and producing zinc sulfate
InactiveCN103274449ATo achieve the purpose of comprehensive recycling at the same timeTo achieve the purpose of comprehensive recyclingZinc sulatesFiltrationHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for rapidly removing arsenic in high arsenic zinc oxide through zinc ash and sodium carbonate peroxide in iron and steel plants and producing zinc sulfate, which rapidly removes arsenic in high arsenic zinc oxide through zinc ash and sodium carbonate peroxide in iron and steel plants and simultaneously also produces zinc sulfate. By adopting the property that Fe(OH)3 can produce FeAsO4 with arsenic acid when the pH value of Fe(OH)3 is 3.0 to 5.4, iron in raw material is leached out, and Fe(OH)3 is produced through oxidation reaction and hydrolysis reaction, so that the purpose that arsenic is removed from solution is realized. The method comprises the concrete steps of calculating usage amount of high arsenic zinc oxide and zinc ash in iron and steel plants according to laboratory reports of arsenic, iron and zinc elements in the high arsenic zinc oxide and the zinc ash in iron and steel plants, mixing the raw material, slurrying, leaching, pH value adjusting, removing iron and arsenic trough sodium carbonate peroxide oxidation, neutralization, pressure filtration, purification, evaporative crystallization, and finally obtaining qualified zinc sulfate products. Arsenic is subjected to smelting waste solidification during the smelting process, so that hazard-free treatment is realized.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Chemical extraction and recovery method for carbon black after waste rubber decomposition
The invention provides a chemical extraction and recovery method for carbon black after waste rubber decomposition. The chemical extraction and recovery method at least comprises following steps: providing a decomposed solid which is obtained through waste rubber decomposition; providing an acid solution, placing the acid solution and the decomposed solid in a stirring device, carrying out a firststirring process, and generating a first mixed solution; separating the first mixed solution into a first solution and a first precipitate through a first separation process, and obtaining a first metallic compound from the first solution through a first dehydration process; providing an alkaline solution, placing the alkaline solution and the first precipitate in the stirring device, carrying out a second stirring process, and generating a second mixed solution; separating the second mixed solution into a second solution and a second precipitate through a second separation process, and obtaining a second metallic compound from the second solution through a second dehydration process; and obtaining carbon black from the second precipitate through a third dehydration process.
Owner:张瑞永
Feed additives containing yeast microelement chelate and production thereof
InactiveCN1423959APromote digestion and absorptionImprove immunityFungiZinc sulatesFood additiveHigh survival rate
A feed additive containing yeast, trace element chelate and inorganic metallic salt is prepared through adding yeast and said inorganic salt, regulating pH value to 5, chelating reaction at 60-90 deg.C for 90 min, and spray drying. Its advantages are high biological utilization rate, high effect on improving immunity and quality of animal, high survival rate and high laying rate or weight increasing rate.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Production technique of zinc sulfate monohydrate
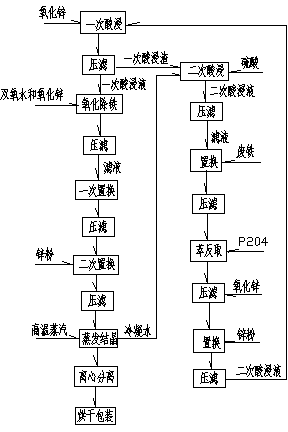
InactiveCN103708531ATo achieve the purpose of removing cadmiumReduce contentZinc sulatesFiltrationSlag
The invention discloses a production technique of zinc sulfate monohydrate, which comprises the following steps: reacting zinc oxide and a sulfuric acid solution, carrying out pressure filtration to form a primary acid leaching solution and primary acid leaching slag, adding oxydol and zinc oxide into the primary acid leaching solution to oxidize and precipitate iron, adding the primary acid leaching slag into a sulfuric acid solution to perform secondary acid leaching, carrying out pressure filtration to form a secondary acid leaching solution and secondary acid leaching slag, adding scrap iron and P204 into the secondary acid leaching solution, reacting the secondary acid leaching solution and zinc oxide to perform iron removal and neutralization, adding zinc powder for replacement and purification, and adding the secondary acid leaching solution subjected to replacement and purification into the primary acid leaching solution; and carrying out triple effect evaporation crystallization by using hot vapor to obtain the zinc sulfate monohydrate crystal. The technique enhances the zinc content in the acid leaching solution, lowers the cadmium content in the acid leaching solution, improves the product quality, and enhances the raw material utilization ratio and product yield; and meanwhile, the acid leaching solution is subjected to triple effect evaporation crystallization to reduce the hot vapor required by evaporation crystallization, thereby lowering the thermal energy consumption.
Owner:PINGXIANG BAOHAI FEED ADDITIVE
Lignocellulose ester catalysis method for preparing zinc sulfate from alkylation waste sulfuric acid
A lignocellulose ester catalysis method for preparing zinc sulfate from alkylation waste sulfuric acid is as below: adding alkylation waste sulfuric acid to zinc oxide or zinc hydroxide for reaction until a pH value is in a weak acid range to obtain a mixed solution; filtering the mixed solution to obtain leaching residue was and a reaction solution; then adding a catalyst of lignocellulose ester and an oxidant in the reaction solution to conduct a redox reaction; completely converting the organic matters in the alkylation waste sulfuric acid into CO2, H2O, N2 and other innocuous small molecules; conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain a fibrous residue and a purified liquid; and finally crystallizing the refined liquid to obtain a zinc sulfate product with industrial grade or feed grade purity. The lignocellulose ester not only has a catalytic function, but also has the function of an activating oxidant and adsorption decoloration; the production process does not introduce other impurities, and does not cause secondary pollution; the organic matters in the waste acid is completely oxidized and degraded; all the mother liquor is reused; and product quality is not affected.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
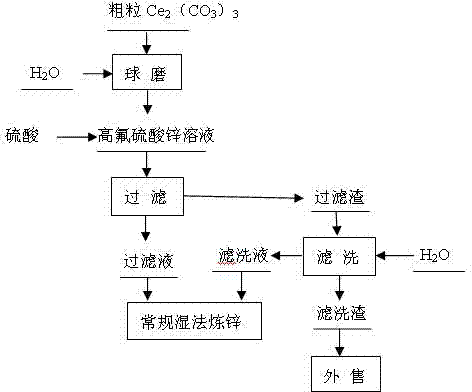
Defluorination method for zinc sulphate solution
InactiveCN102336429AHigh recovery rateQuality improvementZinc sulatesRare earth metal compoundsSulfate zincPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a defluorination method for a zinc sulphate solution, comprising the following ordered steps of: A, a ball-milling process: milling coarse grains Ce2(CO3) with water by a ball mill, wherein the Ce2(CO3) is milled to have the grain size of less than 1 micrometer so as to form slurry, and the slurry is used for a sedimentation defluorination process; B, the sedimentation defluorination process: adding the slurry formed by the step A into the zinc sulphate solution with the pH value of 5.0-5.4, adding sulfuric acid to regulate the pH value to be 3.0-4.5, making the Ce2(CO3) react with the fluorine in the zinc sulphate solution to generate the CeCO3F sediment, wherein the concentration of fluorine ions in the solution is reduced to be less than 0.1g / L, the solution is filtered, the filtrate is used for regular zinc hydrometallurgy, and the filter residue is used for a sedimentation residue filtering and washing process; C, the sedimentation residue filtering and washing process: adding water for filtering and washing the filter residue obtained by the step B, wherein the filtered and washed liquid is used for the regular zinc hydrometallurgy, and the filtered and washed residue is sold. The method provided by the invention is featured by being short and easy, low in energy consumption, pollution free, low in technical operation difficulty, excellent in defluorination effect, low in operating cost, remarkable in economic benefits, and the like.
Owner:孙位成
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com