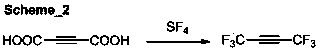Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198results about "Zinc halides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method
ActiveUS20060047132A1High yieldHigh purityZinc halidesGallium/indium/thallium compoundsCompound (substance)Impurity
Owner:UBE IND LTD
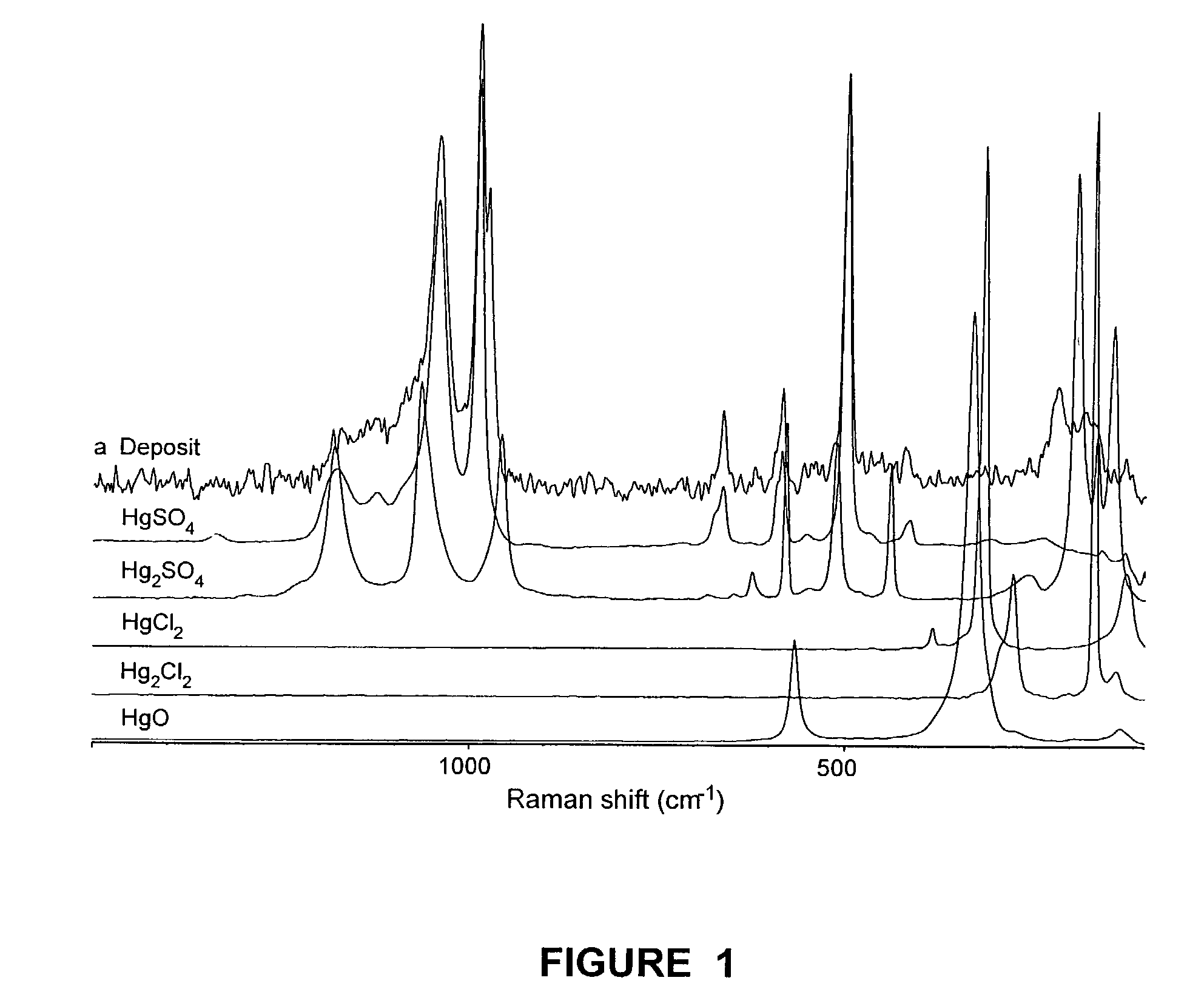
Method and apparatus for mitigating mercury emissions in exhaust gases
InactiveUS7517511B2Mitigating mercury emissionNitrogen compoundsUsing liquid separation agentMercury DichlorideExhaust fumes
Mercury emissions in an exhaust gas are mitigated. Mercury dichloride is formed upon a surface from a substantial portion of the mercury in the exhaust gas. The mercury dichloride sublimes from the surface, and the sublimed mercury dichloride is subsequently removed from the exhaust stream.
Owner:SCHOFIELD KEITH
Method for making organometallic compounds
Owner:UBE IND LTD
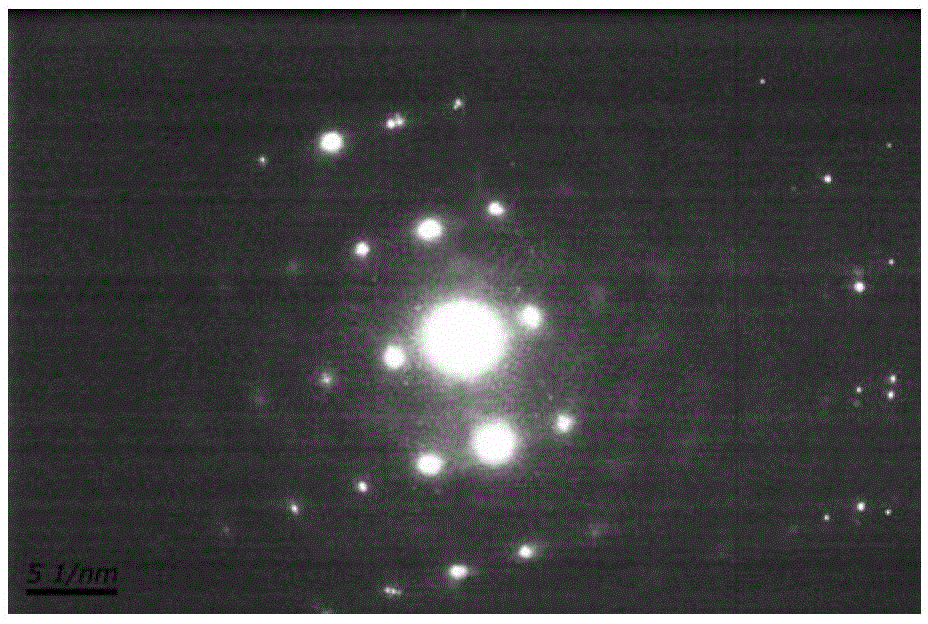
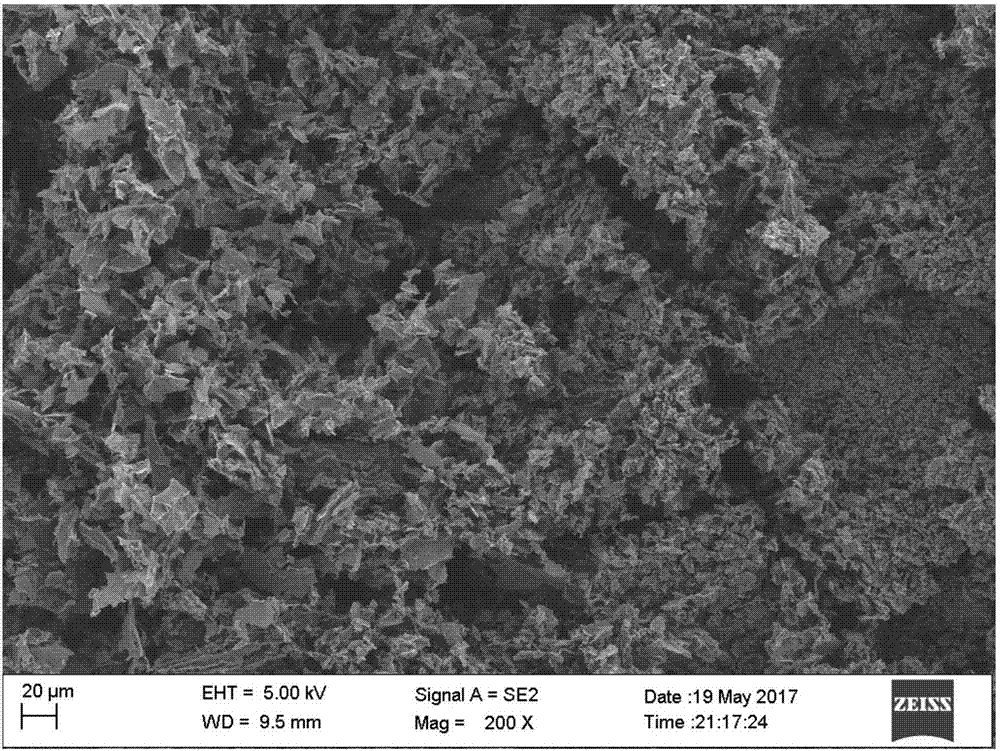
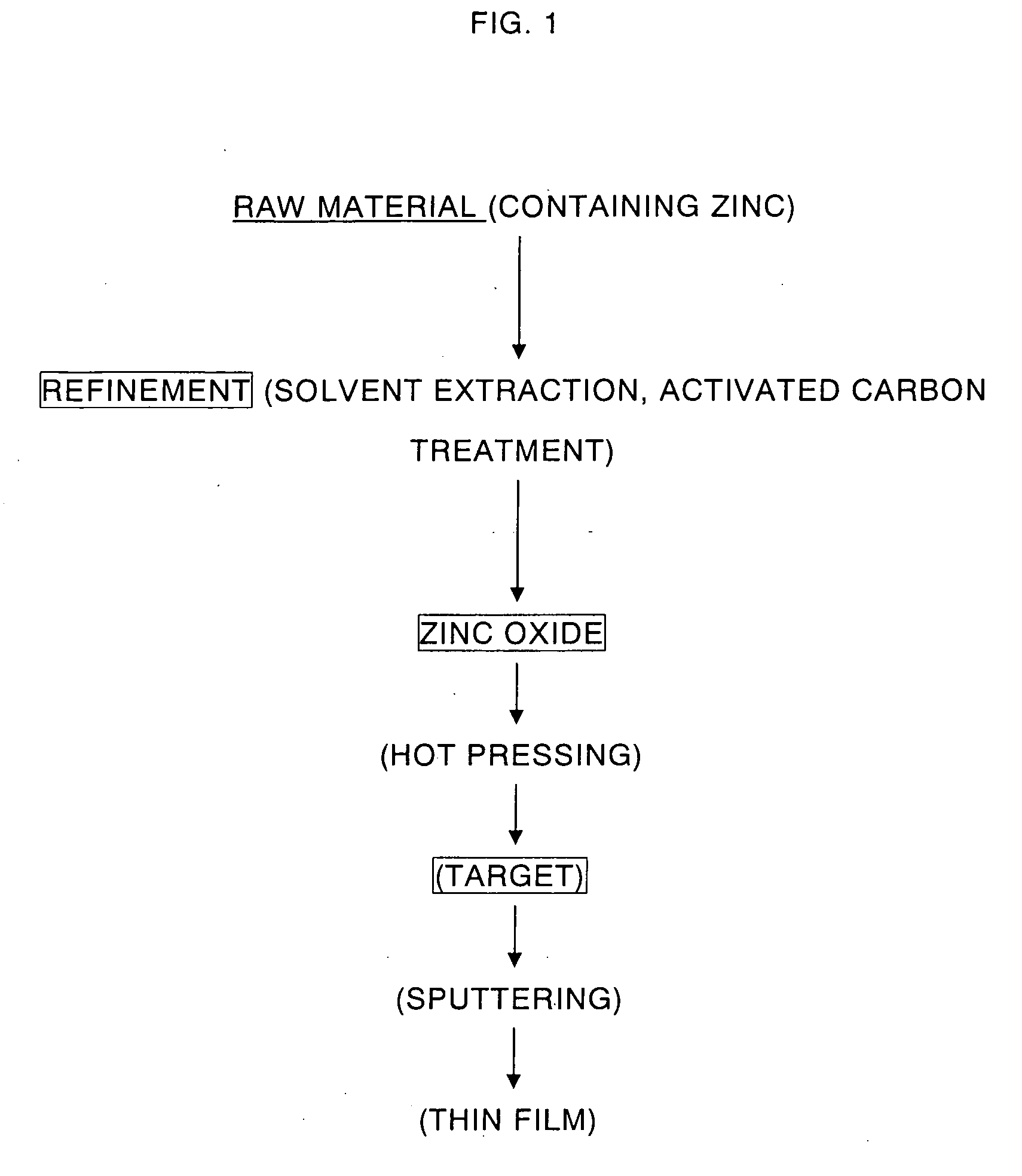
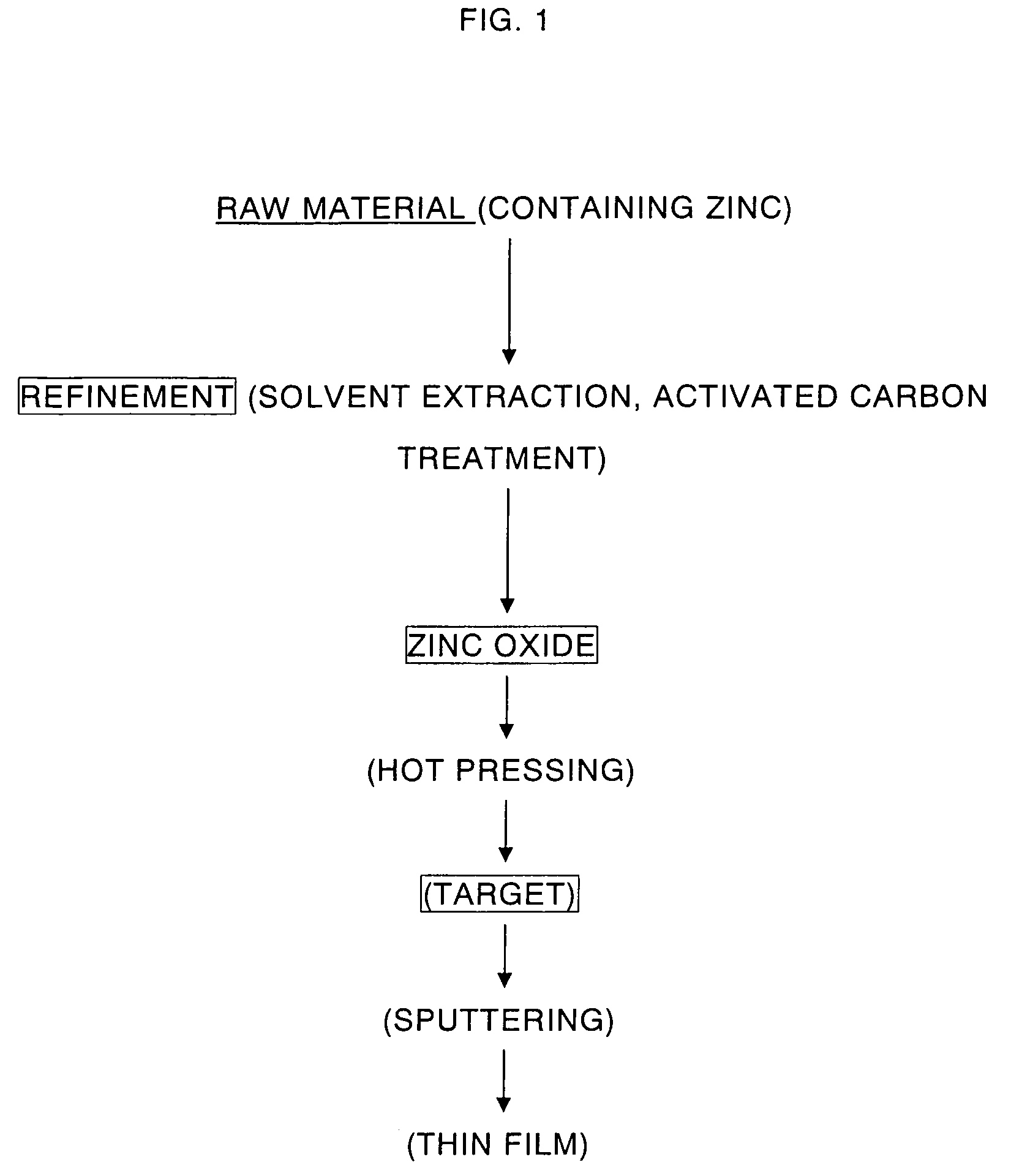
High purity zinc oxide powder and method for production thereof, and high purity zinc oxide target and thin film of high purity zinc oxide
InactiveUS20070098626A1High purityReduce manufacturing costCellsZinc halidesZinc hydroxideActivated carbon
Provided is a manufacturing method of high purity oxide powder including the steps of subjecting a raw material such as Zn-containing scrap to acid leaching or electrolytic extraction, thereafter performing solvent extraction and activated carbon treatment thereto in order to remove impurities, neutralizing the resultant solution freed of impurities with an alkaline solution to obtain zinc hydroxide, and firing the zinc hydroxide to obtain zinc oxide. Provided are high purity zinc oxide efficiently freed of impurities, in particular C, Cl, S and Pb impurities, at low cost and the manufacturing method thereof; a target manufactured by firing the high purity zinc oxide; and a high purity zinc oxide thin film obtained by the sputtering the target.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
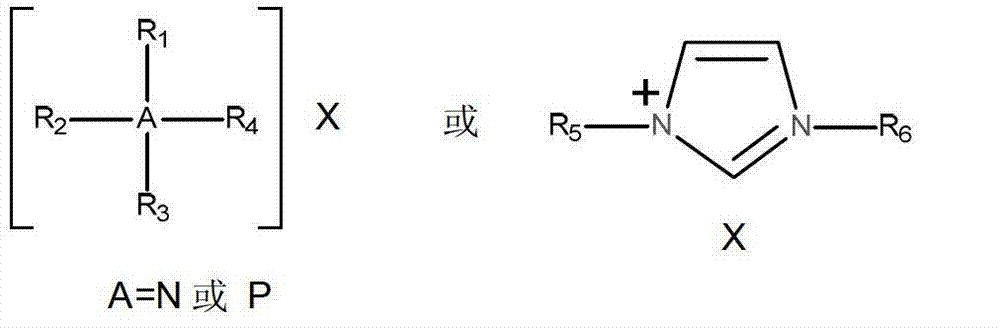
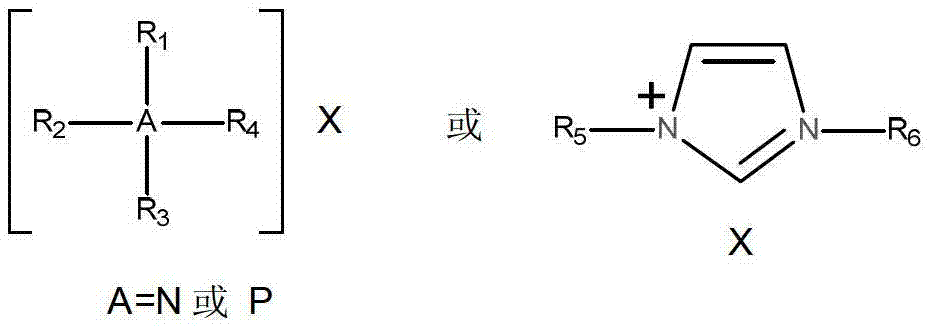
Three-ingredient eutectic ionic liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103193711ALow costWill not emitZinc halidesUrea derivatives preparationOrganic synthesisToxic material
The invention relates to three-ingredient eutectic ionic liquid and a preparation method thereof. The three-ingredient eutectic ionic liquid consists of ILX, MH and HBD, wherein ILX is ionic liquid with negative-monovalent halogen ions which serve as negative ions, MH is transition metal haloid, and HBD is a compound with multiple hydrogen bonds. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing ILX, MH and HBD according to the molar ratio of 1: 1: n (n= 0.5-4), heating up to the temperature of 100-140 DEG C, and then, carrying out heat preservation for 2-4 hours until a mixture is completely dissolved. According to the ionic liquid disclosed by the invention, the melting point is extremely low, the viscosity is low, the conductivity is high, the dissolution performance is good, and the ionic liquid has Lewis acidity and catalysis performance, so that the ionic liquid can be widely applied to organic synthesis reaction, the preparation of nano and mesoporous materials, gas absorption and the like; and the preparation process is simple, the raw materials are readily available, the cost is low, no organic solvents are used and no toxic substances are emitted during reaction, no byproducts are produced, and the ionic liquid is biodegradable, so that the ionic liquid is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
High purity zinc oxide powder and method for production thereof, and high purity zinc oxide target and thin film of high purity zinc oxide
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Application of lactam as solvent in nano-grade material preparation
ActiveCN103204525AIncrease added valueMeet the requirements of green environmental protectionMaterial nanotechnologySilicaSolventMacromolecule
Disclosed is an application of lactam as a solvent in nanomaterial preparation. The preparation method comprises a precipitation method, a sol-gel method or a high-temperature pyrolysis method. The method achieves recycling utilization of the lactam solvent, which meets the requirements of environmental protection.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
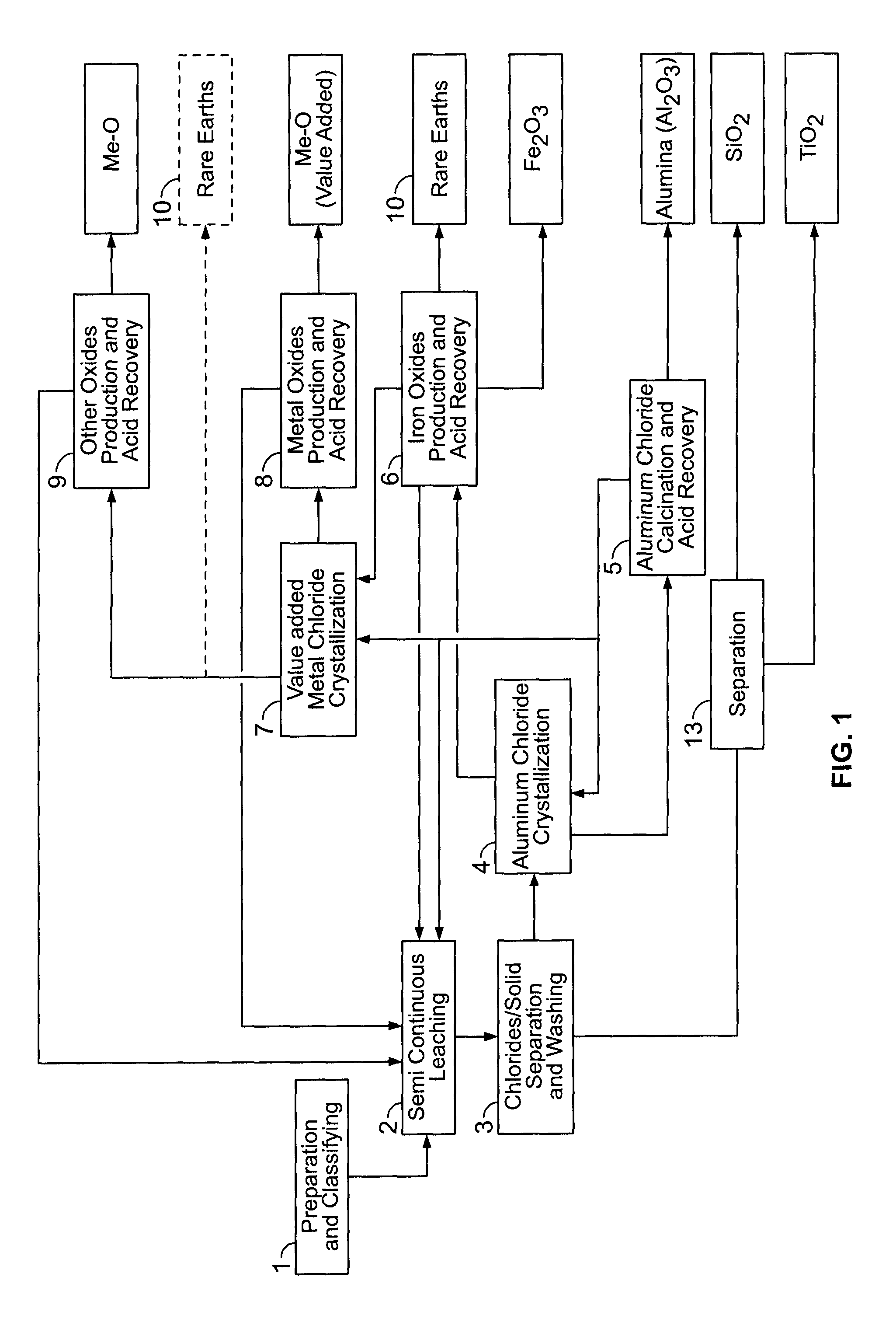
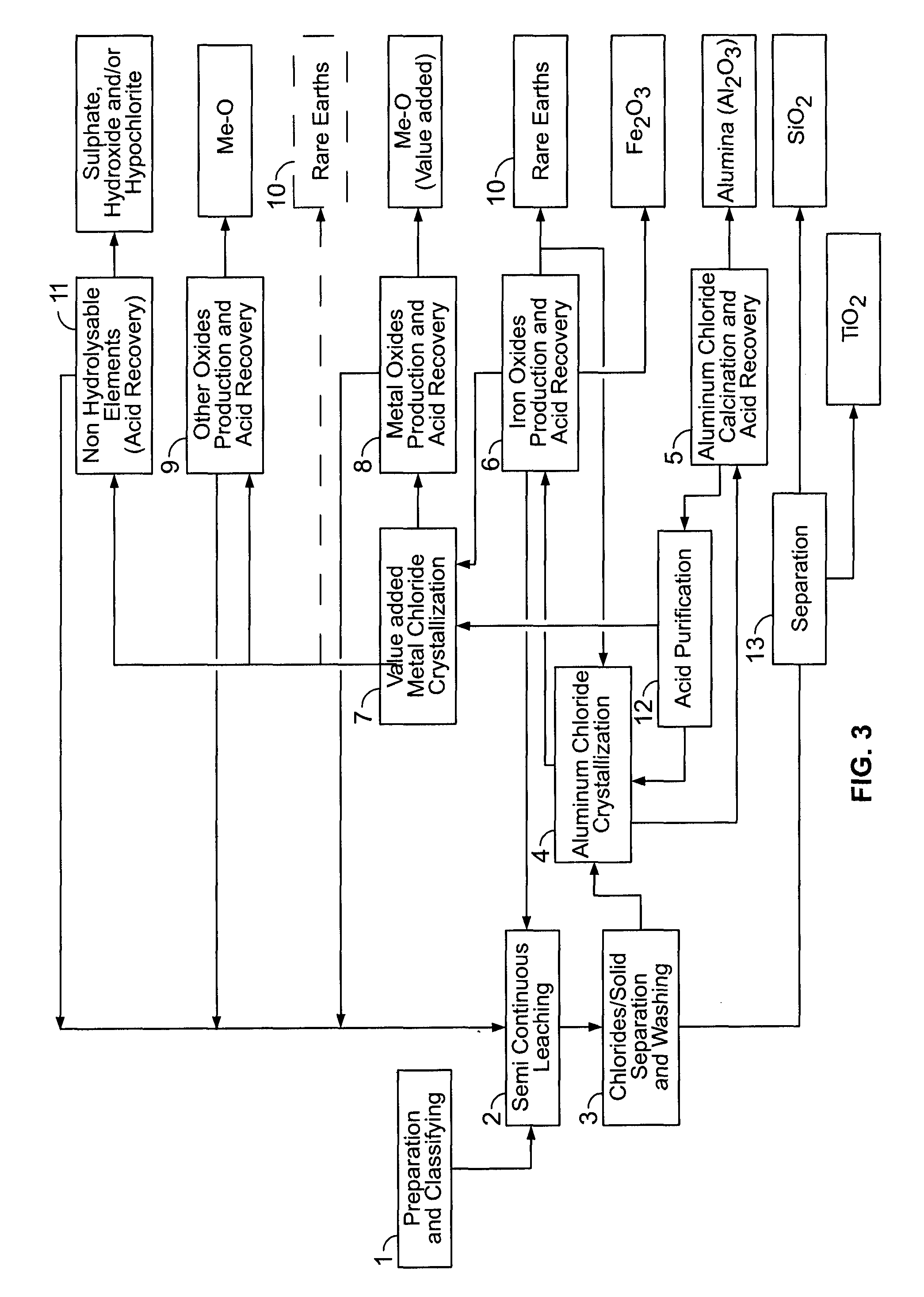
PROCESSES FOR PREPARING ALUMINA AND MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE BY HCl LEACHING OF VARIOUS MATERIALS
The disclosed processes can be effective for treating various materials comprising several different metals. These materials can be leached with HCl for obtaining a leachate and a solid. Then, they can be separated from one another and a first metal can be isolated from the leachate. Then, a second metal can further be isolated from the leachate. The first and second metals can each be substantially selectively isolated from the leachate. This can be done by controlling the temperature of the leachate, adjusting pH, further reacting the leachate with HCl, etc. The metals that can be recovered in the form of metal chlorides can eventually be converted into the corresponding metal oxides, thereby allowing for recovering HCl. The various metals can be chosen from aluminum, iron, zinc, copper, gold, silver, molybdenum, cobalt, magnesium, lithium, manganese, nickel, palladium, platinum, thorium, phosphorus, uranium, titanium, rare earth element and rare metals.
Owner:ORBITE ALUMINAE INC
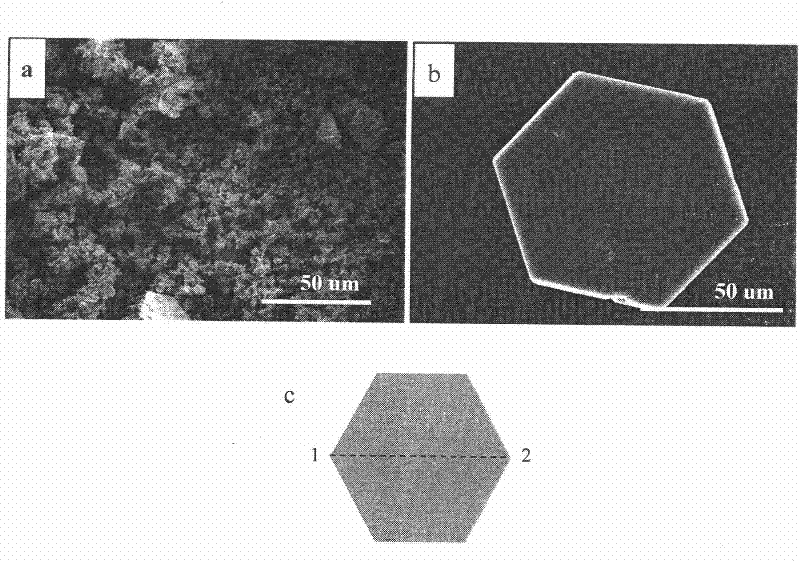
Method for preparing alkali zinc chloride nano-powder in hexagonal flake structures
The invention discloses a method for preparing alkali zinc chloride nano-powder in hexagonal flake structures, which is characterized by including steps: dissolving zinc chloride and hydroxyl reagent into water or water-alcohol mixed solution, adjusting the solution pH within a range of from 2.0 to 9.0, and obtaining the alkali zinc chloride nano-powder after chemical precipitation reaction under water bath at 50-99 DEG C or heating via an oven for 0.1-72 hours. The molecular formula of the alkali zinc chloride is Zn5(OH)8C12 (H2O), each flake is regularly hexagonal, the size of each flake ranges from 0.1 micrometer to 100 micrometer, and the thickness of each flake ranges from 20 nanometers to x micrometers. The alkali zinc chloride nano-powder which is a zinc-contained compound in a special hexagonal flake structure is expected to be applied in fields of chemical synthesis, chemical catalysis, photocatalysis, sensors, nano devices and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process to produce simonkolleite, zinc oxide and zinc hydroxide
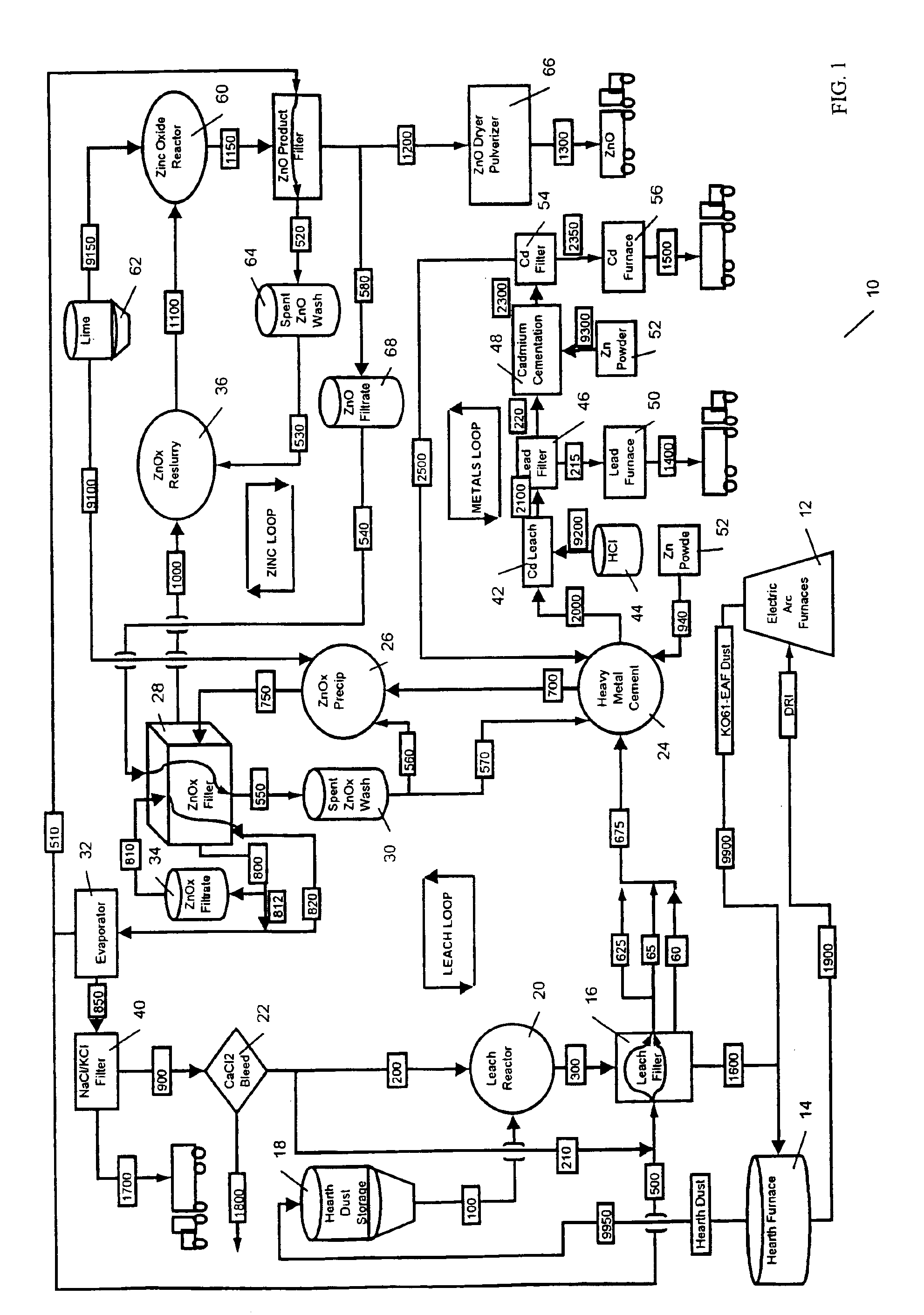
A hydrometallurgical process utilizing an atmospheric calcium chloride leach to selectively recover from various metal feed stocks (consisting of elemental metals, metal oxides, metal ferrite, metal hydroxide, metal carbonates, metal sulfate / sulfur compounds, and their hydrates, specifically including but not limited to EAF Dust K061) zinc, lead, cadmium, silver, copper and other valuable metals to the exclusion of iron, magnesium, halogen salts and other unwanted elements. The process solves the problem of iron and magnesium leach solution contamination because iron is unexpectedly converted to magnetite. The heavy metals are cemented out of solution using zinc or other selected dust at a pH of 6 or greater under unique and unexpected conditions, which do not require acid. Simonkolleite / zinc- oxychloride / zinc-hydroxide is produced from the purified zinc chloride complex pregnant leach solution and is converted directly to high purity active rubber grade 99+% zinc oxide having small particle size and high surface area. The products are metal concentrates suitable for: metal refiner / processors, production of elemental metal, or other conversion processes. The process removes Arsenic and Fluorides in the feed material. The process also solves the problem of chloride contamination in the zinc oxide and prevents heavy metal contaminants in the hydrometallurgically produced zinc oxide derived from feed stocks containing chlorides or when chlorides are used to leach the metal bearing feed stocks. In one embodiment, calcium and / or magnesium compounds are added to the iron bearing waste to increase the recovery of zinc and other non-ferrous metals and to produce an iron bearing flux. The process is environmentally friendly and fully recycles all streams.
Owner:WHITMAN CHESTER W
Method for recycling germanium, gallium, indium and selenium in waste diode
ActiveCN102951618AReduce pollutionHigh recovery rateZinc halidesSolid waste disposalIndiumMineral Sources
The invention relates to treatment of waste metal materials, and in particular relates to a method for recycling germanium, gallium, indium and selenium in a waste diode. The recycling method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing the waste diode; (2) separating plastic powder from metal powder; (3) oxidizing roasting; (4) recycling selenium; and (5) recycling gallium, indium and germanium. By using the method, the pollution of the diode on the environment is reduced, valuable elements of selenium, indium, gallium and germanium are recycled, and mineral resources are saved; and the method is simple to operate, lower in cost, high in recycling rate of selenium, indium, gallium and germanium elements and very high in purity of recycling products.
Owner:JIANGXI GREEN ECO MFG RESOURCE CYCLE
Method for preparing basic zinc chloride
ActiveCN101704545AHigh purityImprove absorption and utilizationZinc halidesAnimal feeding stuffZinc hydroxideChloride
The invention discloses a method for preparing basic zinc chloride, which comprises the following steps: adding zinc hydroxide slurry into zinc chloride solution in a molar ratio of the zinc hydroxide to the zinc chloride being 3-4.5:1 to perform reaction at the temperature between 70 and 105DEG C and a pH value between 5 and 9, and obtaining a reaction product after the reaction; washing the reaction product with water, and centrifuging and drying the reaction product to obtain the basic zinc chloride. The preparation method has sample and safe operation, low waste emission and low production cost; and the product has better quality.
Owner:XINGJIA BIO ENG CO LTD
Synthesis method of basic zinc chloride monocrystal nanorods
InactiveCN102745737AAvoid problems such as increased reaction energy consumptionLow costZinc halidesMaterial nanotechnologyChemical synthesisSynthesis methods
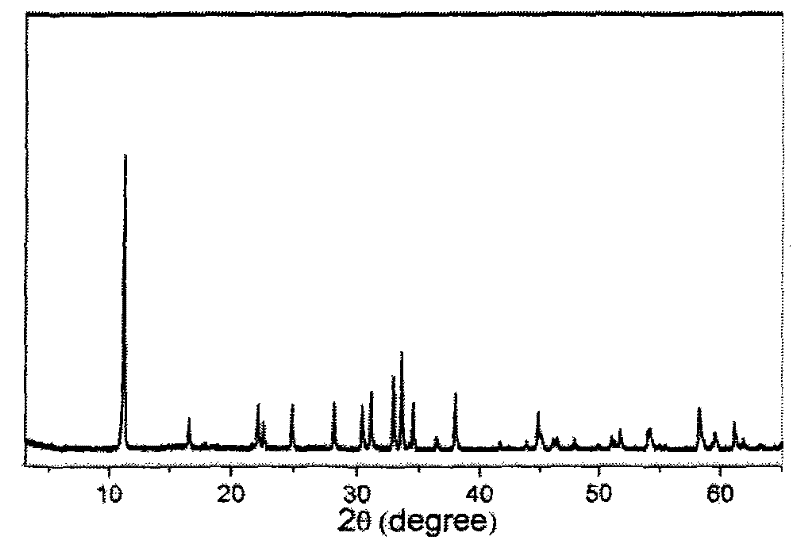
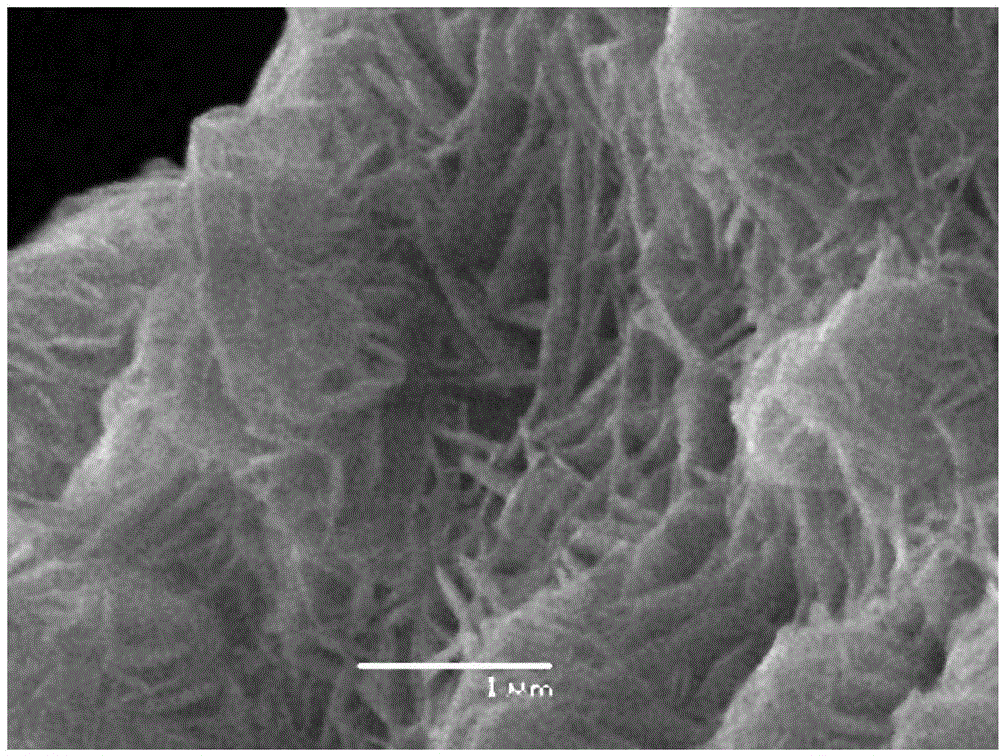
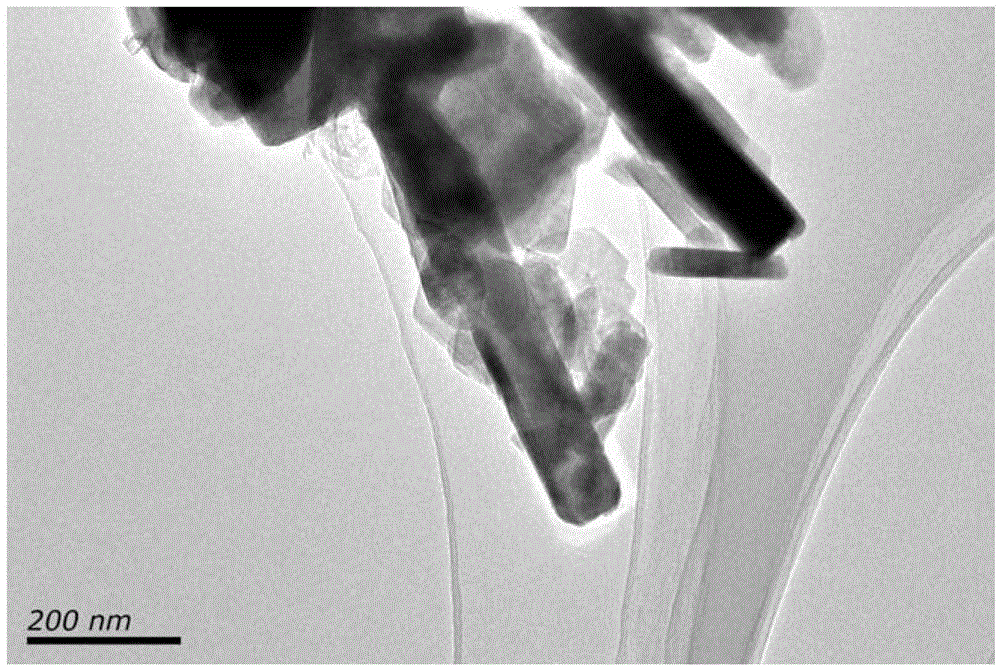
The invention discloses a synthesis method of basic zinc chloride monocrystal nanorods. The synthesis method is characterized by comprising the following steps: taking zinc chloride and ammonia water as raw materials and reacting the raw materials at the room temperature; washing with deionized water, and centrifuging; adding deionized water which is 10-20 times of the volume of a sample, heating in an oven at 80 DEG C for 2 hours and then standing still; washing the sample with absolute ethyl alcohol, and then centrifuging; and drying in the oven at 40 DEG C for 6 hours to prepare the basic zinc chloride Zn5(OH)8Cl2.H2O monocrystal nanorods with diameters of about 70 nm and lengths of 400nm. The product prepared by the synthesis method has a wide application prospect and can be applied to various fields such as chemical synthesis, photocatalysis, sensors and nano devices, and the synthesis method is in no need of any additives or expensive equipment, and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, easiness in control and industrialization, low production cost, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Basic zinc chloride particulate matter and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107857291ALarge particle sizeImprove liquidityZinc halidesAccessory food factorsParticulatesWastewater
The invention discloses a basic zinc chloride particulate matter and a preparation method thereof. The basic zinc chloride particulate matter mainly consists of basic zinc chloride particles. D10 of the basic zinc chloride particles is greater than 100 mu m, D95 of the basic zinc chloride particles is greater than 450 mu m, and the basic zinc chloride particles do not contain a binder. The appearance of the basic zinc chloride particles contained in the basic zinc chloride particulate matter is mostly spherical, and the basic zinc chloride particles having a particle diameter of greater than 500 mum in the basic zinc chloride particle matter accounts for 1% or lower of the total weight of the basic zinc chloride particulate matter. The basic zinc chloride particulate matter has a relatively large particle size and good flowability, does not cause dust flying and flows easily during use, and solves the problems that more dust appears in the work environment and a premix is difficult touniformly mix in the process of preparing the premix by using basic zinc chloride by the existing feed enterprise. The preparation process provided by the invention uses ammonium chloride as an inducer without additional introduction of impurities, the production wastewater can be completely recycled, the production cost is low, and the production process is environmentally friendly and economical.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KECHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for comprehensive treatment and utilization of high-zinc-content waste acid
ActiveCN106745151ARealize processing utilizationEfficient separationZinc halidesCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesChlorideZinc
The invention relates to a method for comprehensive treatment and utilization of high-zinc-content waste acid. By reasonably designing process steps and reaction agents of the method for comprehensive treatment and utilization of the high-zinc-content waste acid, effective separation, recycling and reutilization of iron and zinc are achieved, iron and zinc resource waste is avoided, a by-product industrial calcium chloride solution having a wide industrial application value and meeting the national quality standard is also obtained, comprehensive treatment and utilization of the high-zinc-content waste acid is successfully achieved, and the method is simple in process, lower in cost, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:TANGSHAN 3R CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of basic zinc chloride
ActiveCN103121706ALow priceEasy to handleZinc halidesZinc oxides/hydroxidesCalcium hydroxideWastewater
The invention discloses a preparation method of basic zinc chloride. The invention relates to basic zinc chloride, and in particular relates to a preparation method of basic zinc chloride of a feed additive. The invention aims to provide a preparation method of basic zinc chloride lower in cost and safe and environment-friendly. The method is characterized in that the basic zinc chloride is prepared by reaction of zinc chloride and calcium hydroxide. According to the invention, the basic zinc chloride is successfully prepared by reaction of zinc chloride and calcium hydroxide. The preparation method is simple, the process flow is short, the reaction cost is low and wastewater generated by the reaction is easy to process and save and environment-friendly. Contents of zinc and chlorine as well as arsenic, lead and cadmium in a basic zinc chloride product prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention completely meet the national standard of feed grade basic zinc chloride, and the basic zinc chloride can be directly used as the feed additive.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENTOU ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Graphite intercalation compound preparation method
The invention discloses a graphite intercalation compound preparation method. The method includes: mixing graphite with metal halides in air, sealing in a reactor, heating to a certain temperature, keeping the temperature for a period of time to allow the metal halides to diffuse to graphite intercalation so as to form a graphite intercalation compound with the metal halides as an intercalator, and converting the metal halide type intercalator into metal sulfide or metal phosphide to obtain a graphite intercalation compound with the metal sulfide / phosphide as the intercalator, so that the metal sulfide / phosphide can exist in graphite intercalation in a molecular level. Insertion of different substances in graphite intercalation can be realized, so that different characteristics of products can be achieved; a preparation process has advantages of low material consumption, low energy consumption, product quality stability, high technical repeatability and the like, the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production, and final products are applied to fields of next-generation energy storage materials, solar cell materials, electro-catalysis and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for recycling metals in sludge from wire rope production
ActiveCN107098556AReduce processing burdenZinc halidesWaste water treatment from metallurgical processEnvironmental resistanceSludge
The invention belongs to environmental protection and resource recycling projects and relates to a method for recycling metals in sludge from wire rope production; sludge and acid waste from wire rope manufacturers have a high content of heavy metal lead (2000 ppm and above), which usually does not meet the economic requirement of industrial extraction, and are unable to be treated by the wire rope manufacturers. By using mixing reaction of sludge with the acid waste and electrochemical methods, the problem that the sludge and acid waste are difficult to treat is well solved.
Owner:江苏荣信环保科技有限公司
Porous material and method for producing the same
InactiveCN1798703AExcellent fluorination catalytic abilityHigh porosityMagnesium fluoridesCobalt halidesHydrogen fluoridePhysical chemistry
The present invention provides a raw material composition suitably used for synthesizing a porous metal fluoride having a large surface area and being stable even in a corrosive gas environment or the like. The porous metal fluoride obtained by reacting this raw material composition with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride has a larger surface area and is stable in a corrosive gas environment, etc., and can be used, for example, as a fluorination catalyst.
Owner:权恒道
Preparation method of basic zinc chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of basic zinc chloride, comprising the following steps of: adding sodium hydroxide or ammonia water into zinc chloride solution with the mol ratio of the sodium hydroxide or ammonia water to zinc chloride solution of 7.5-8.5:5, reacting under the condition that the temperature is 60-105 DEG C and the pH value is 5-9, and obtaining reaction products after the reaction is finished; and washing with water, centrifuging and drying reaction products to obtain the basic zinc chloride. The preparation method is simple and safe in operation, and has the advantages of little waste emission, low production cost and excellent product quality.
Owner:XINGJIA BIO ENG CO LTD
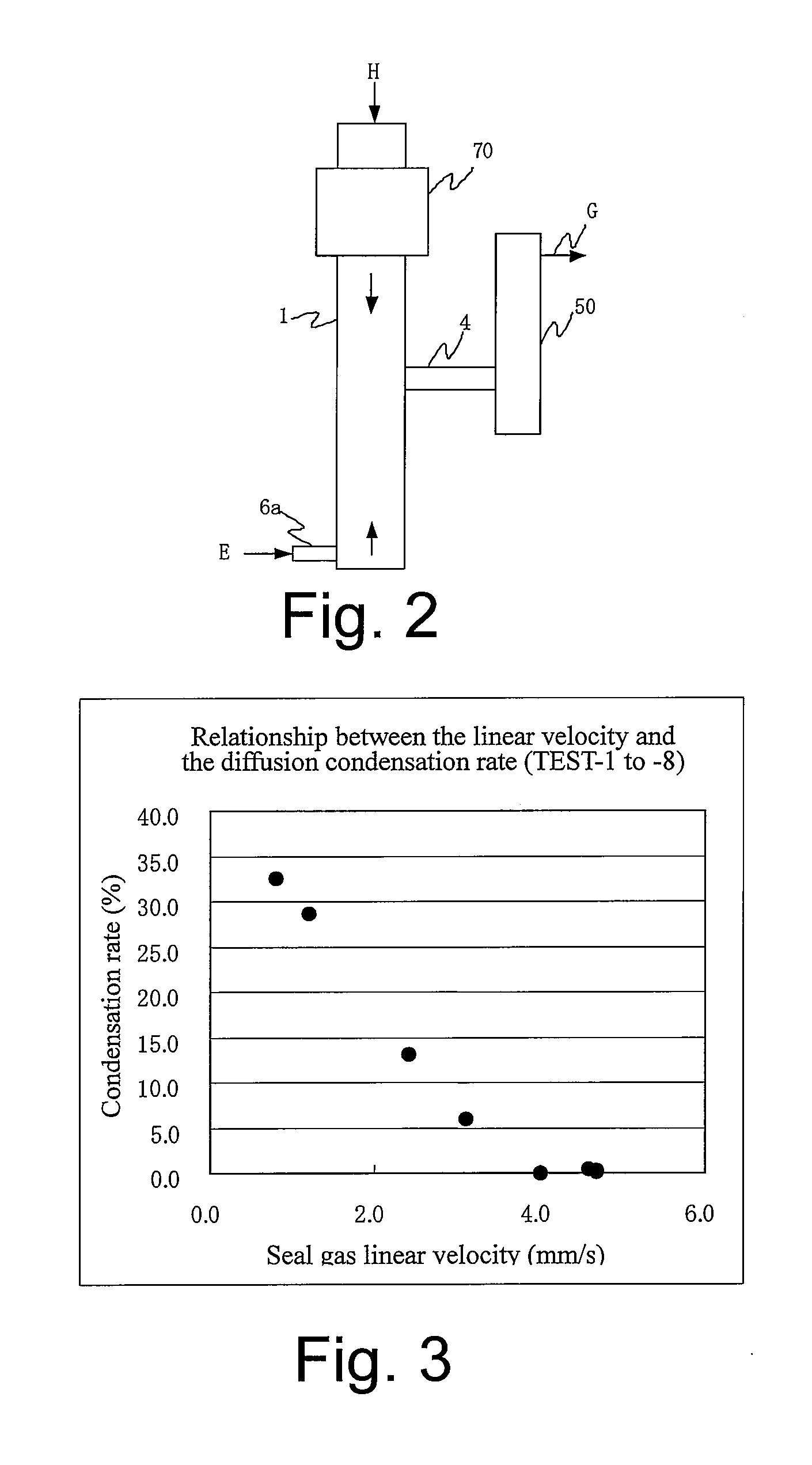
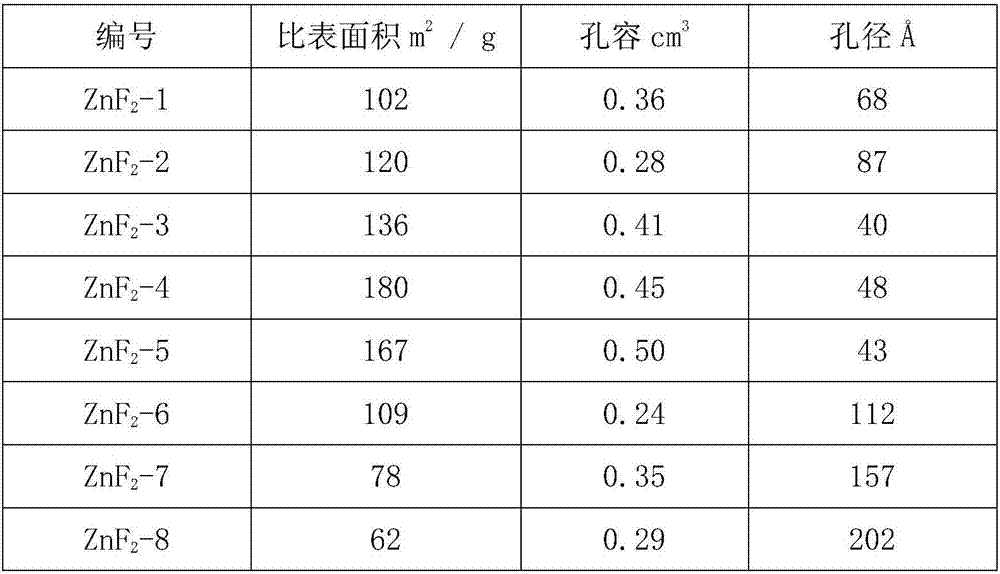
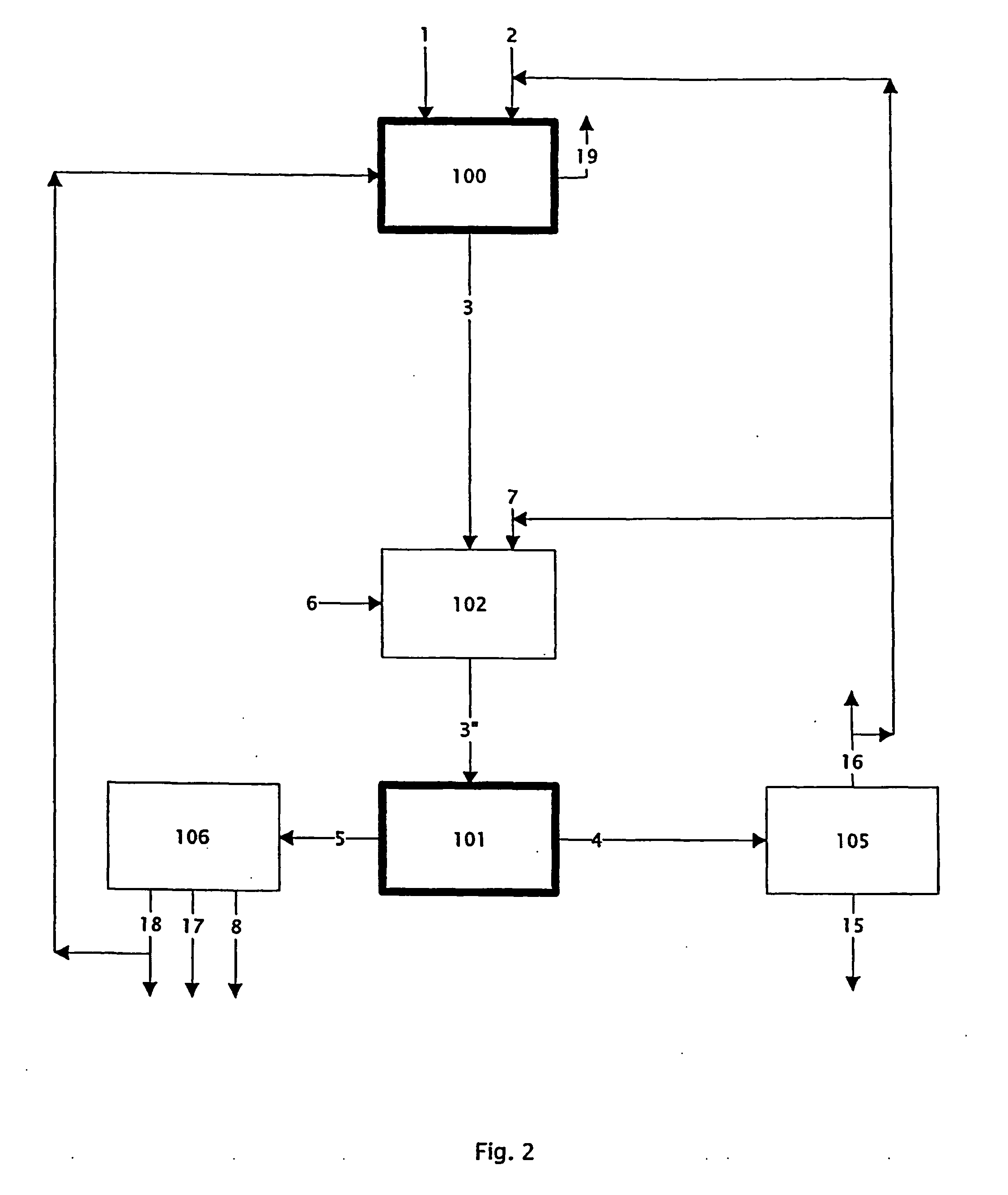
Method and apparatus for producing solid product
InactiveUS20080226531A1High purityAvoid quality lossAfter-treatment apparatusZinc halidesHigh densityProduct gas
Provided is a production method and a production apparatus using a method for producing a solid product by a reaction of gaseous raw materials with a plurality of components including a step of conducting the reaction using a reactor disposed in a vertical direction; a step of feeding the gaseous raw materials with a plurality of components from the upper part of the reactor; a step of, in the lower part of the reactor, forming a seal gas layer composed of a gas having a high density and fed continuously from the lower part of the reactor; a step of discharging an exhaust gas containing a by-product gas generated by the reaction and unreacted gaseous raw materials from somewhere in the upper part of the formed seal gas layer; and a step of accommodating a solid product in the seal gas layer of the lower part.
Owner:JNC CORP
Process for preparing basic zinc chloride of trace mineral supplement
The invention discloses a method for preparing alkali zinc chloride, a trace element additive, which is prepared from zinc oxide and zinc chloride by the mol ratio of 4:1 at 75-95 deg. C, controlling pH=6-8, reacting 1.5-3 hours under normal pressure condition, then carrying out centrifugal separation, washing, drying, disintegrating, and packaging.
Owner:XINGJIA BIO ENG CO LTD
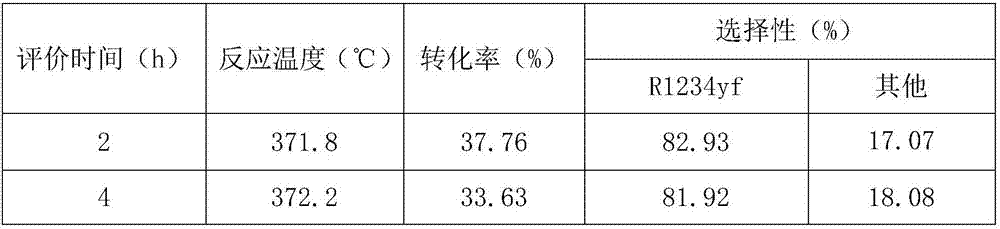
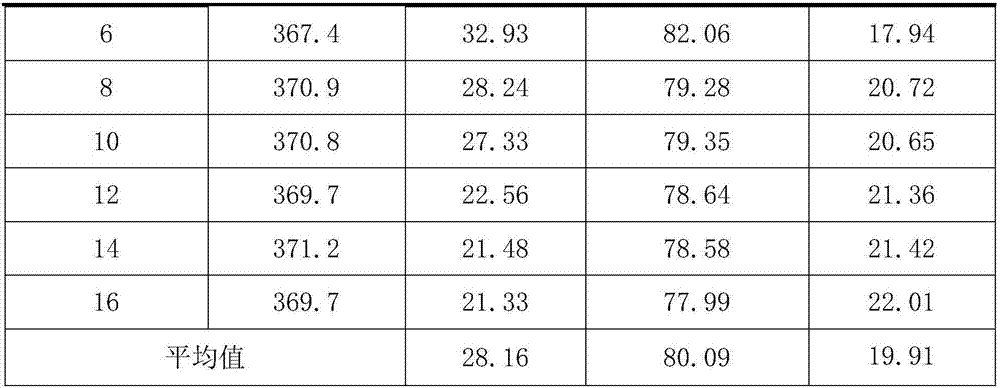
High specific surface area catalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN107540011AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityZinc halidesPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHigh selectivityZinc fluoride
The present invention discloses a zinc fluoride-containing catalyst having high specific surface area and used for fluorine-chlorine exchange reactions, wherein the specific surface area is 80-180 m<2> / g, the pore volume is 0.15-0.50 cm<3>, and the pore size is 20-100 angstrom. According to the present invention, with the application of the catalyst in fluorine-chlorine exchange reactions, the catalyst has advantages of high conversion rate, high selectivity and low cost in the.
Owner:SINOCHEM MODERN ENVIRONMENTAL CHEM INDAL XI ANCO +1
Chloride melt process for the separation and recovery of zinc
InactiveUS20050006247A1Easy to controlIncrease flexibilityZinc halidesChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideBoiling pointChloride
Process for the production of ZnCl2 from a Zn bearing primary and / or secondary material comprising the steps of reacting the Zn bearing material with a chlorinating agent such as Cl2 to convert metals into chlorides and vaporising the volatile components of the reaction product at a temperature between the melting point of said reaction product and the boiling point of ZnCl2, thereby recovering a Zn rich chlorinated melt, and thereafter distilling ZnCl2 from this Zn rich chlorinated melt, thereby recovering purified ZnCl2 and a Zn-depleted chlorinated melt.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Method for preparing active carbon from biomass, and prepared active carbon
InactiveCN107337206AReduce pollutionRecycling reducesZinc halidesCarbon compoundsActivated carbonAcid washing
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for utilizing magnesium resource in wet zinc smelting process
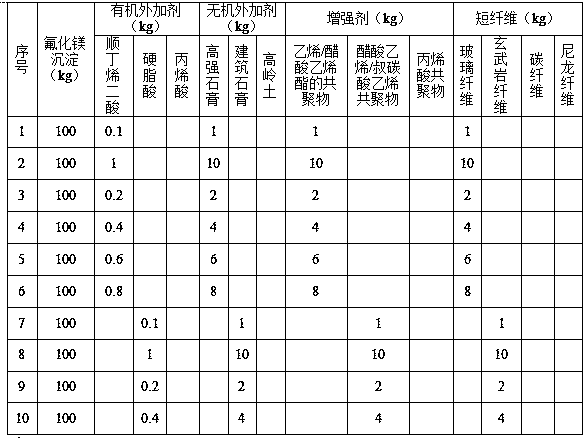
ActiveCN109867463AWide range of usesConducive to in-situ resource utilizationZinc halidesProcess efficiency improvementFiberSoot
The patent discloses a method for utilizing magnesium resources in a wet zinc smelting process. The method comprises the steps of adding magnesium fluoride seed crystals and zinc fluoride to a magnesium-containing zinc sulfate solution to obtain coarse grains crystals of a magnesium fluoride precipitate, and conducting liquid-solid separation; adding concentrated sulfuric acid to the magnesium fluoride precipitate to obtain hydrogen fluoride gas and magnesium sulfate; introducing the hydrogen fluoride into a container containing zinc oxide soot to obtain zinc fluoride; adding a catalyst and anatmosphere regulating agent to the magnesium sulfate, and conducting heating and decomposing to obtain magnesium oxide; and adding magnesium sulfate, an an organic admixture, an inorganic admixture,a reinforcing agent and short fiber to the magnesium oxide, and conducting uniform mixing, so as to obtain magnesium oxysulfate cement. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of low production cost, high production efficiency and good product quality.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne
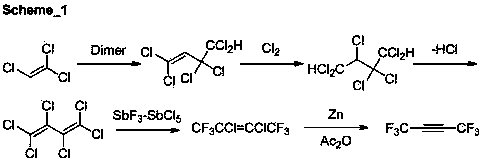
ActiveCN103420783ALow purity requirementHigh yieldZinc halidesPreparation by dehalogenationButeneOrganosolv
The invention discloses a preparation method of 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne. In the present of an organic solvent and under the action of a reaction auxiliary agent, 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2,3-dichloro-2-butene and zinc powder are subjected to carry out a reductive dechlorination reaction so as to obtain 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butyne. The preparation method has the advantages of low raw material cost, simple operation, mild reactions, quick reaction speed, high yield, low cost, and high selectivity.
Owner:SINOCHEM LANTIAN +1
Technique for recovering zinc chloride from waste water in reduction process of isooctyl thioglycolate
ActiveCN101445268ARealize harmless treatmentEliminate pollutionZinc halidesWater/sewage treatmentLow speedFiltration
The invention discloses a technique for recovering zinc chloride from waste water in reduction process of isooctyl thioglycolate, which is suitable for waste water treatment for the reduction process of the isooctyl thioglycolate. The technique comprises the following steps: firstly, the waste water is pumped into a storage tank by a vacuum pump and stands at normal temperature for precipitation and impurity removal; then the deslagging is carried out on the rest solution through a pumping filtration tank, the precipitation tank stands at the normal temperature for precipitation, and the BaCl2 is added and stirred at the normal temperature; the rest solution is pumped into a concentration kettle by using a corrosion-resistant centrifugal pump, and after temperature rising at low speed and vacuum treatment, and the KMnO4 and the NaOH tablet are added in, stirred and precipitate. The hydrogen chloride gas in the concentration kettle becomes muriate acid through a condenser, is put into a hydrochloric acid finished product storage tank, and the concentrated ZnCl2 solution in the concentration kettle is pumped to a zinc chloride finished product storage tank by using the vacuum pump after temperature reduction. By adopting the technique, not only all the zinc chloride and all the hydrogen chloride in the waste water are recovered, the pollution of the waste water in the original technique is eliminated, but also the wastes are reduced, the economic income is added, and the economic benefit is remarkable; and the technique is simple, easy to be operated and is feasible for popularization.
Owner:三门峡奥科化工有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com