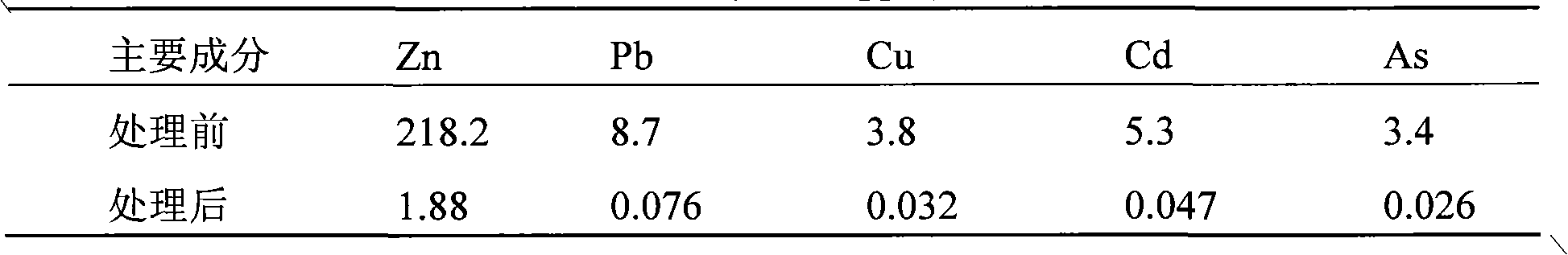Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
664 results about "Thorium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately hard, malleable, and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided.
Inorganic dopants, inks and related nanotechnology
InactiveUS6849109B2Facilitated DiffusionLower transition temperatureSelenium/tellurium compundsCell electrodesIndiumCerium
Ink compositions with modified properties result from using a powder size below 100 nanometers. Colored inks are illustrated. Nanoscale coated, uncoated, whisker inorganic fillers are included. The pigment nanopowders taught comprise one or more elements from the group actinium, aluminum, antimony, arsenic, barium, beryllium, bismuth, cadmuim, calcium, cerium, cesium, chalcogenide, cobalt, copper, dysprosium, erbium, europium, gadolinium, gallium, gold, hafnium, hydrogen, indium, iridium, iron, lanthanum, lithium, magnesium, manganese, mendelevium, mercury, molybdenum, neodymium, neptunium, nickel, niobium, nitrogen, oxygen, osmium, palladium, platinum, potassium, praseodymium, promethium, protactinium, rhenium, rubidium, scandium, silver, sodium, strontium, tantalum, terbium, thallium, thorium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
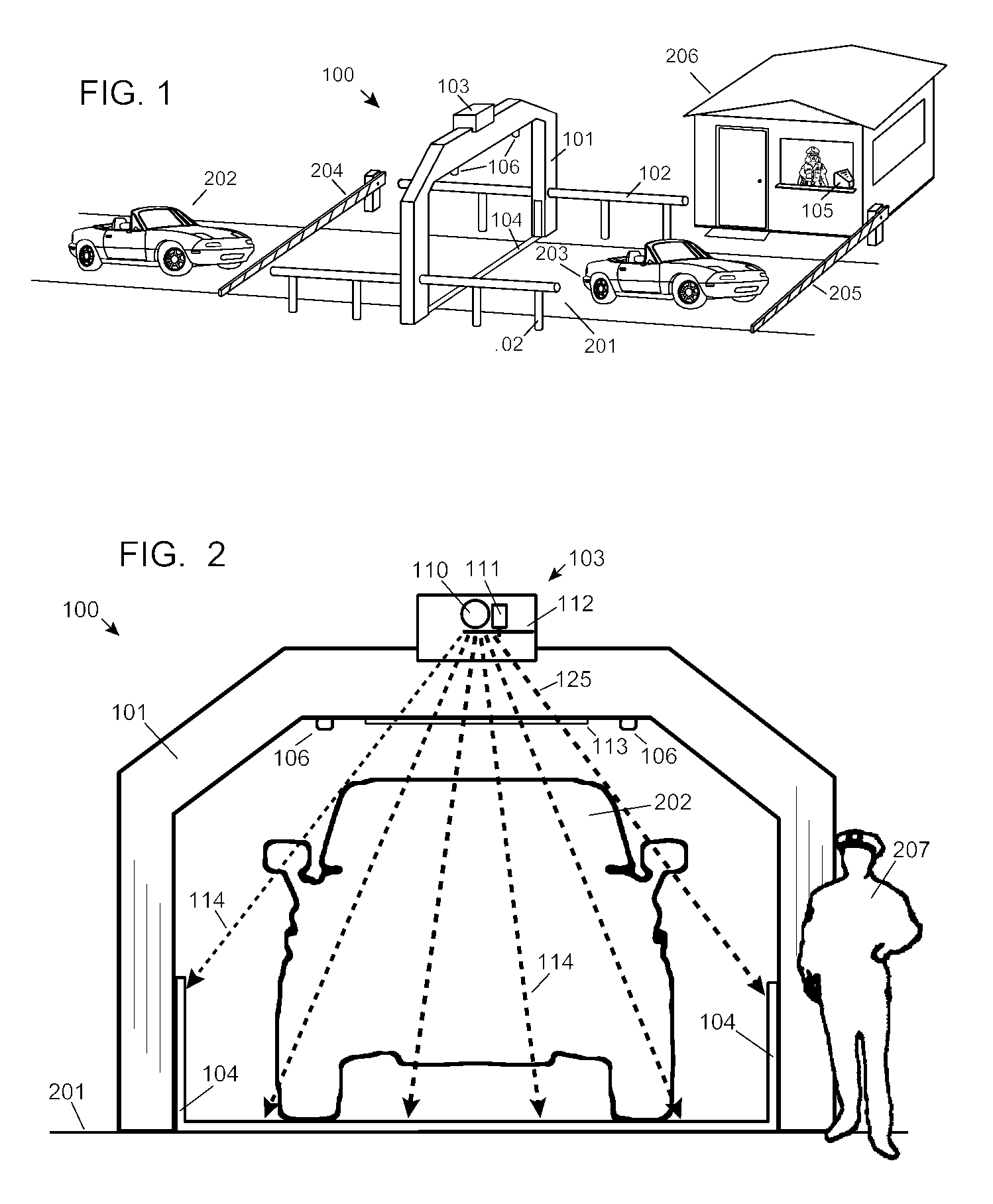
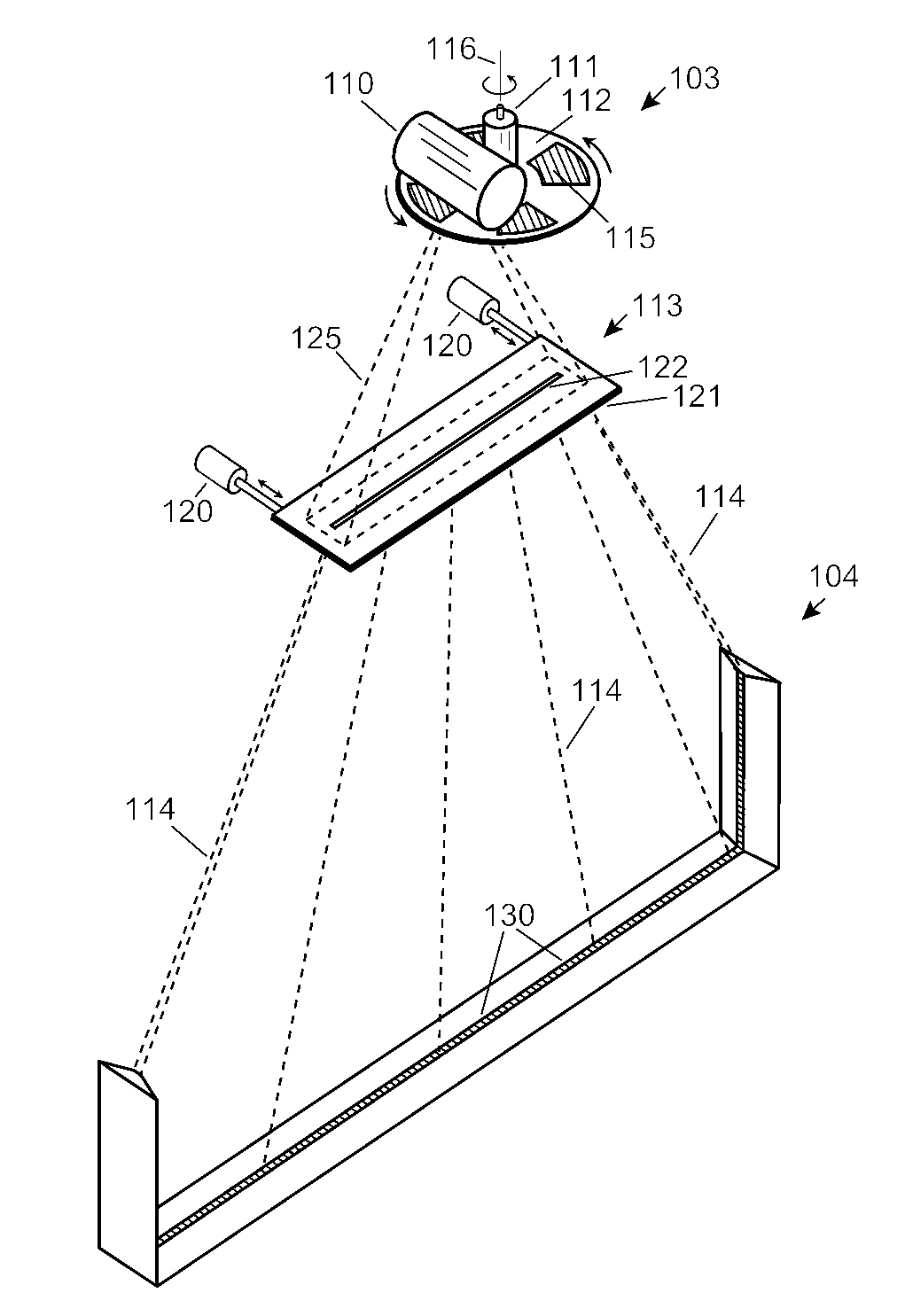
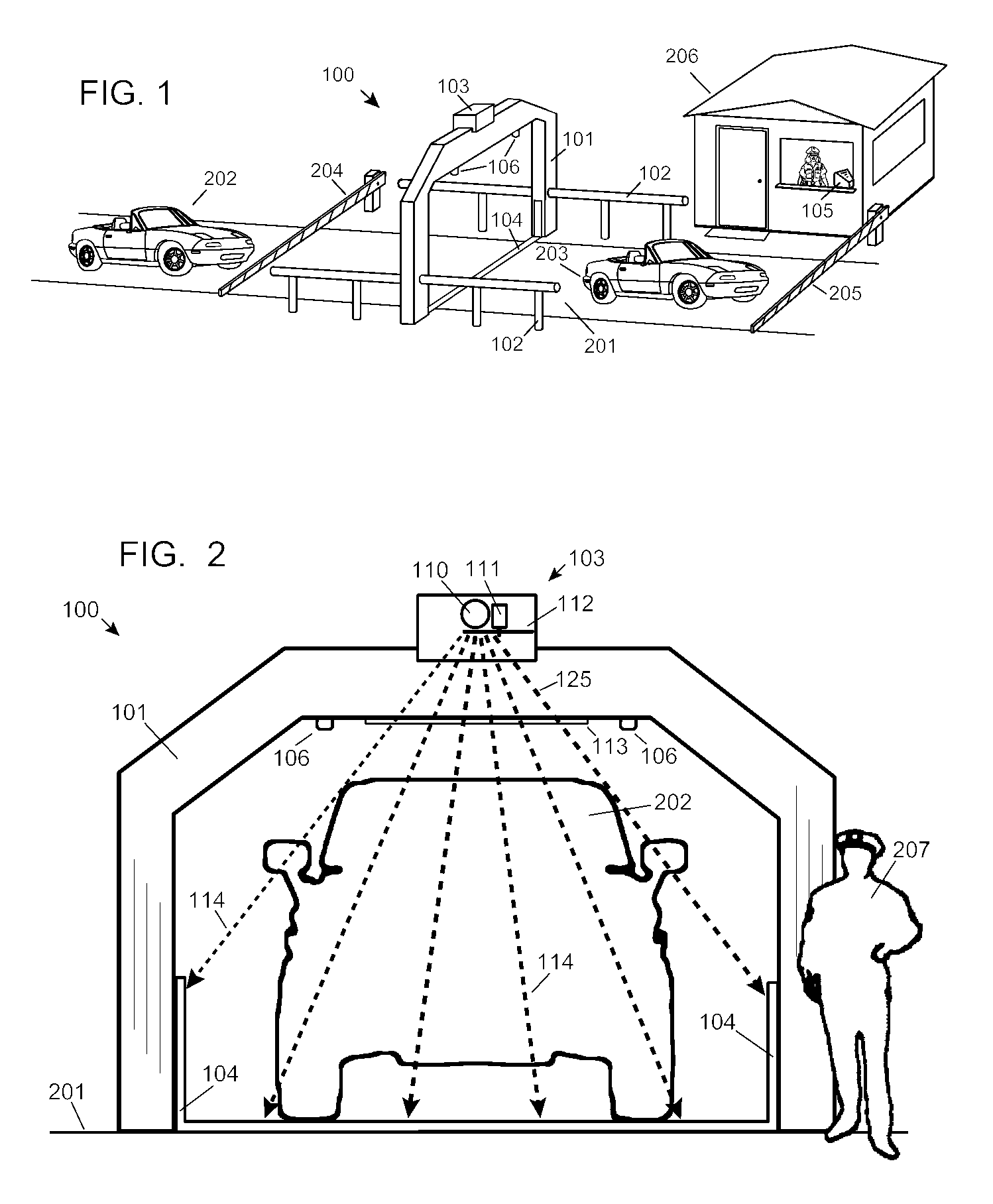
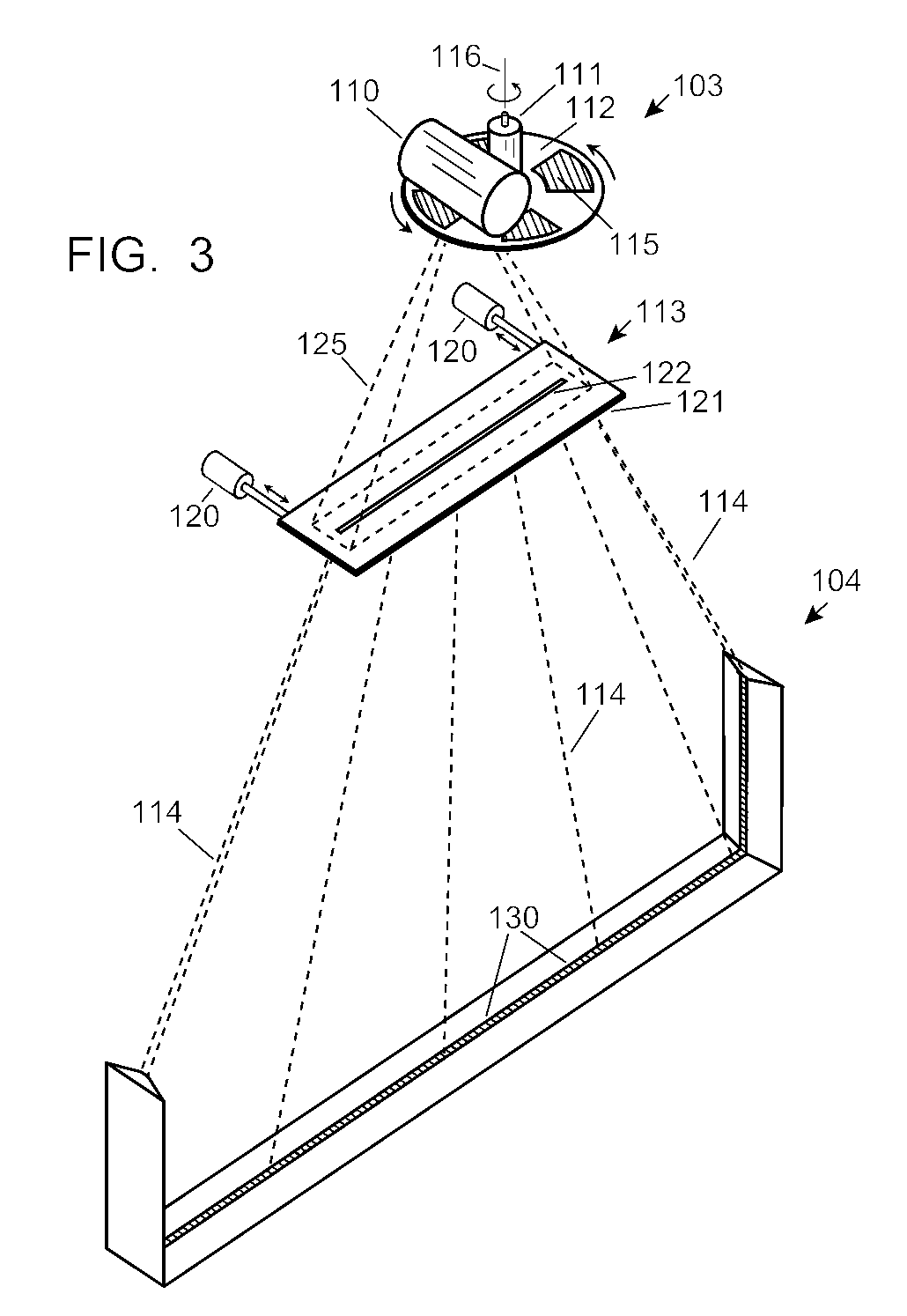
Automobile scanning system
ActiveUS7742568B2Easy to checkUniform exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Automobile Scanning System
ActiveUS20090086907A1Easy to checkUniform radiation exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Non Proliferating Thorium Nuclear Fuel Inert Metal Matrix Alloys for Fast Spectrum and Thermal Spectrum Thorium Converter Reactors
InactiveUS20080144762A1Improve heat transfer performanceRobust assemblyOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationHigh energyEpithermal neutron
A set of alloy formulations is disclosed to use with thorium based nuclear fuels in a fast spectrum reactor; with thorium based nuclear fuels in existing thermal spectrum power reactors; for medical isotope production in the epithermal, the fast, the fission spectrum and the thermal spectra; and to use as fuel in test and experimental reactors that are non proliferative. The alloys form inert metal matrixes to hold fine particles of dispersed thorium containing fuel. The formulations also are useful for the production of medical and commercial isotopes in the high energy, fast and epithermal neutron spectra.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Reactor tray vertical geometry with vitrified waste control
InactiveUS20060171498A1Reduce the amount of wasteNegative environmental impactConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationThermal energyVitrification
A nuclear-powered plant for systems of up to about 100 MWs with a confinement section where the reaction takes place in a core having a reactive thorium / uranium-233 composition, and where an external neutron source is used as a modulated neutron multiplier for the reactor core output. The core is housed in a containment structure that radiates thermal energy captured in a multiple-paths heat exchanger. The exchanger heat energy output is put to use in a conventional gas-to-water heat exchanger to produce commercial quality steam.
Owner:D B I CENTURY FUELS & AEROSPACE SERVICES
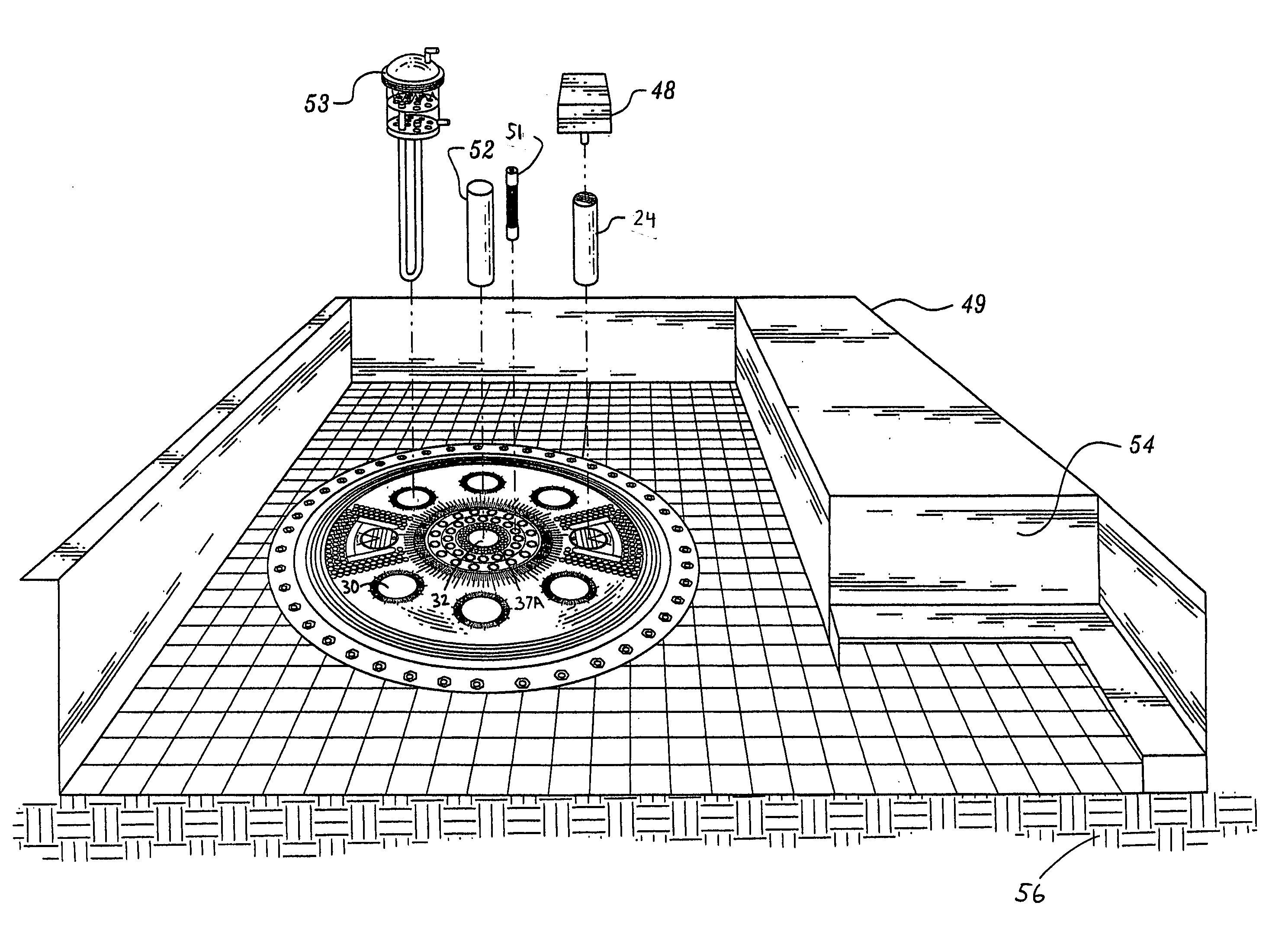
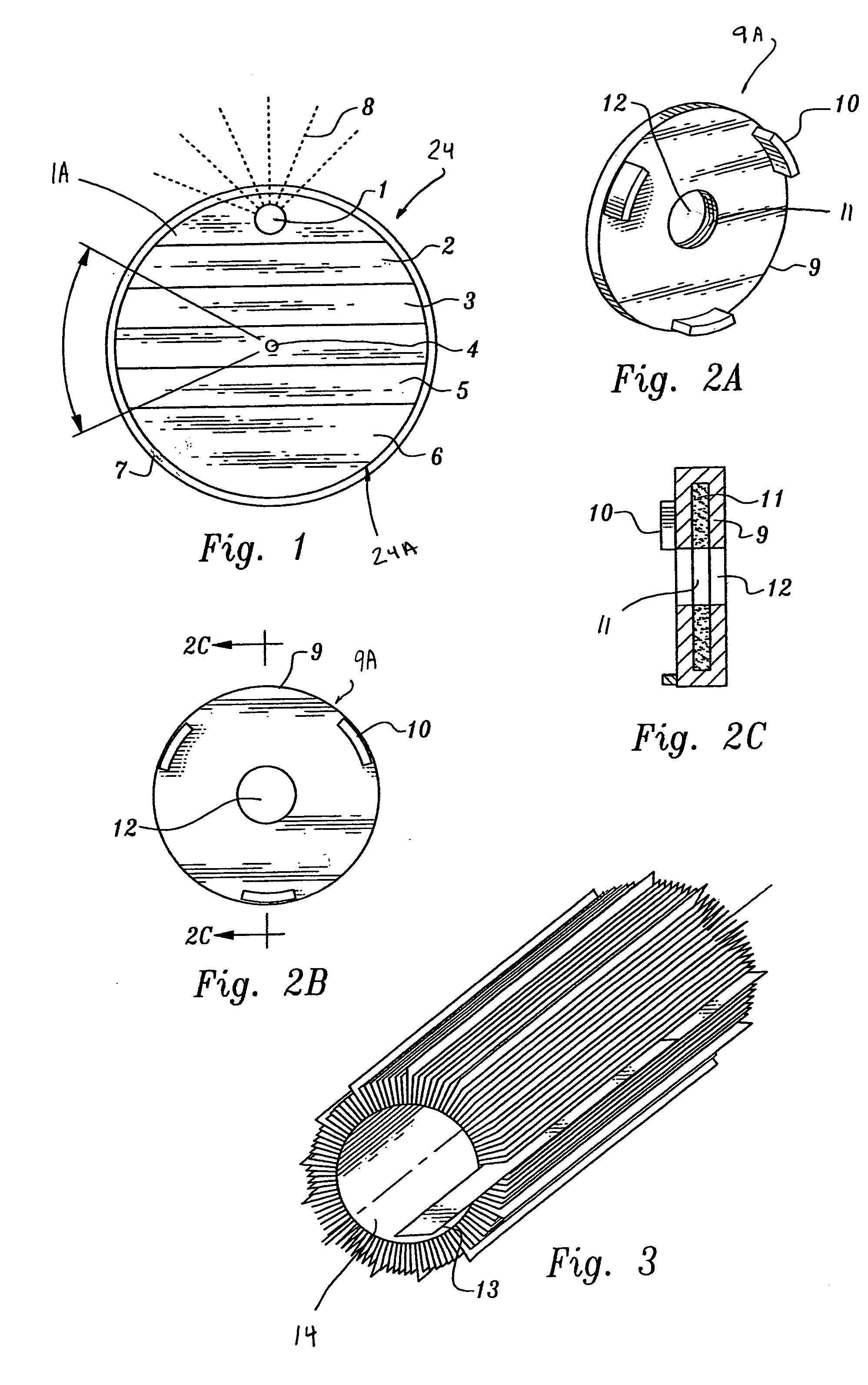
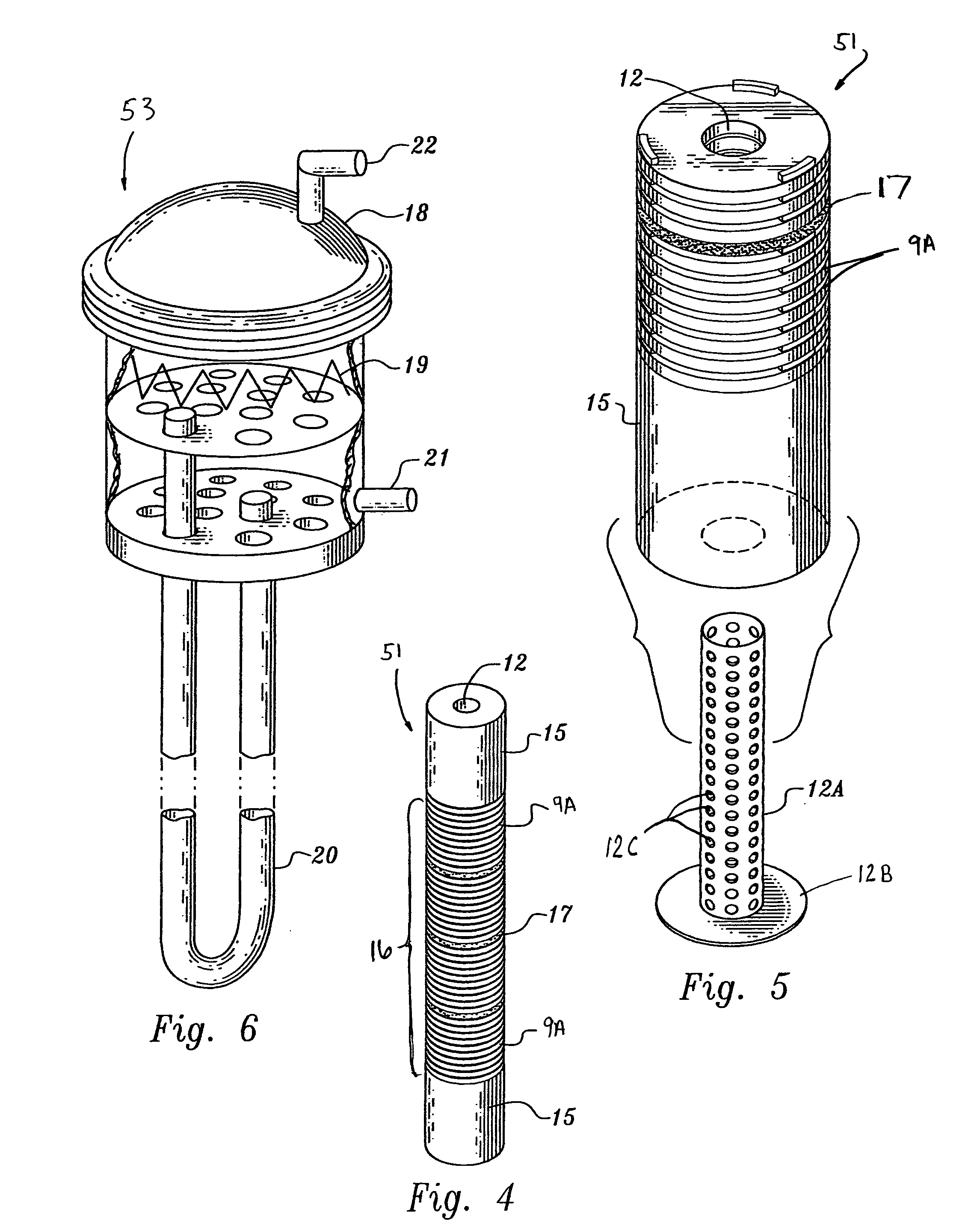
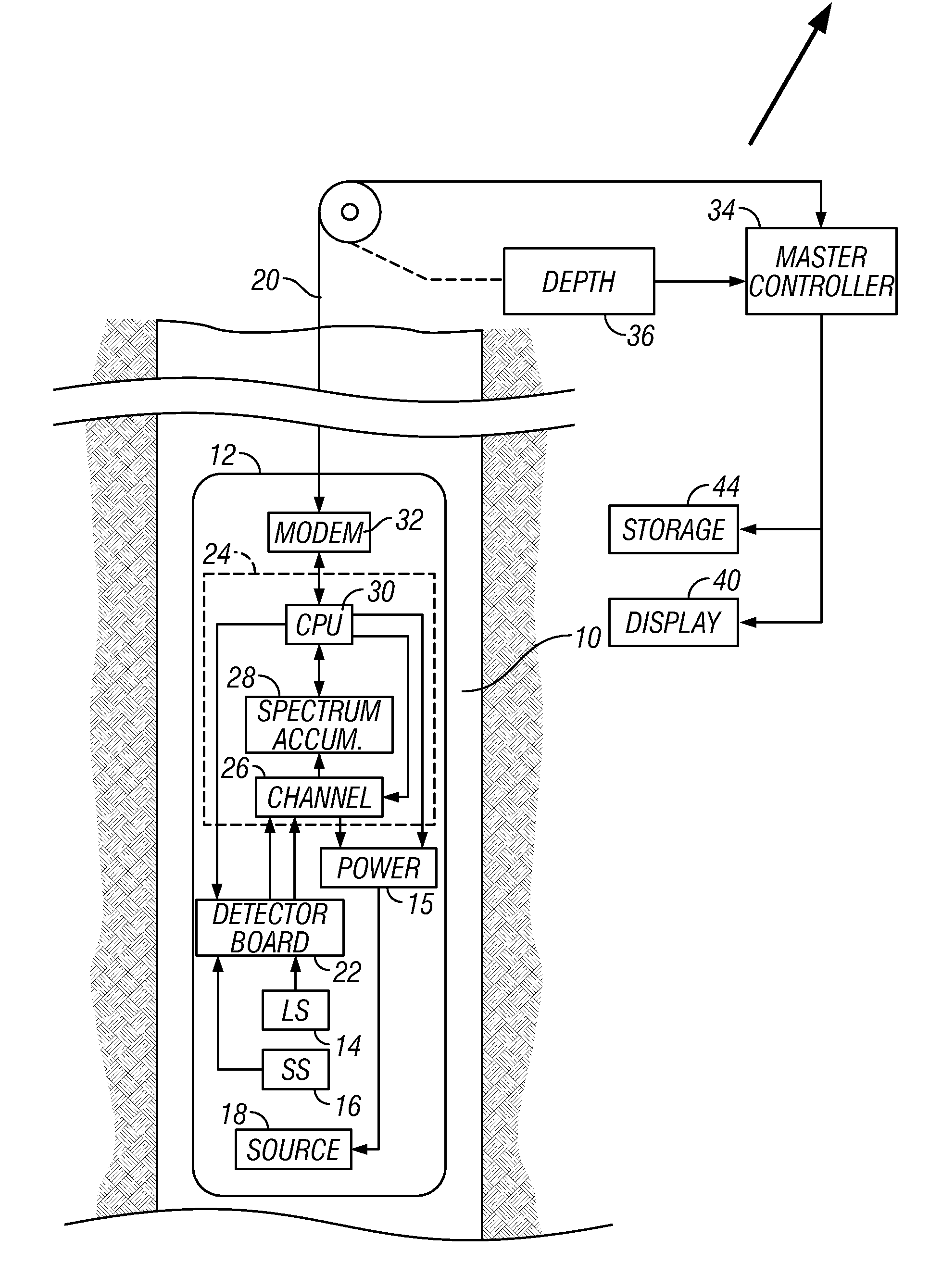
Spectral gamma ray logging-while-drilling system
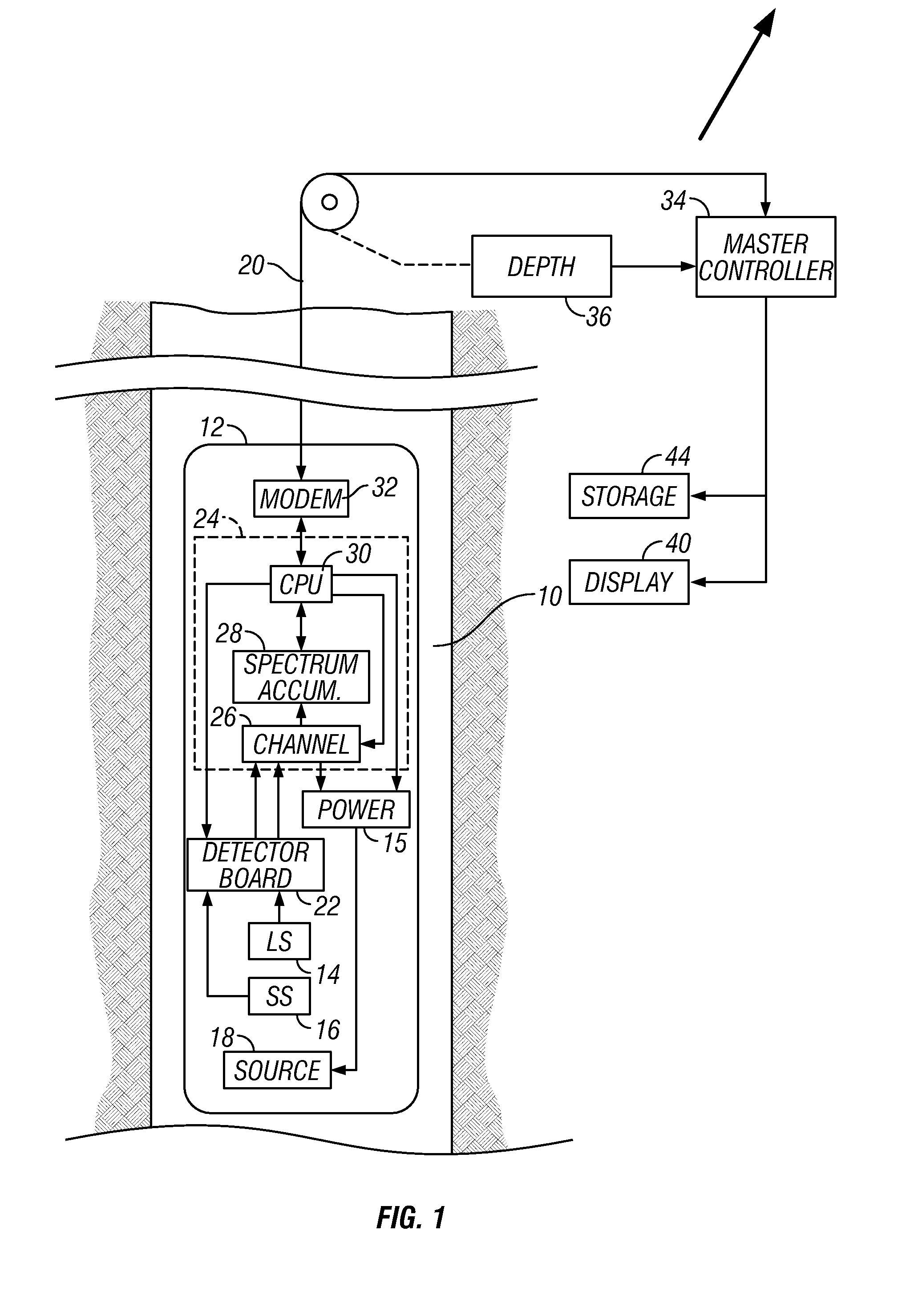
ActiveUS20050199794A1Minimize degradationMaximizing counting rateCalibration apparatusBorehole/well accessoriesPotassiumDrilling system
A method for determining concentrations of naturally occurring radioactive elements in earth formation by analysis of gamma ray energy spectra measured by at least one gamma ray detector while the borehole is being drilled. Gain of the gamma ray detector is controlled automatically through analysis of the spectra. The one or more gamma ray detectors are disposed at the periphery of the downhole instrumentation to maximize sensitivity. Elemental concentrations of naturally occurring radioactive elements such as potassium, uranium and thorium are measured either as a function of depth in the borehole, or as a function of aximuthal sectors around the borehole wall, or as a function of both depth and azimuthal sectors.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA
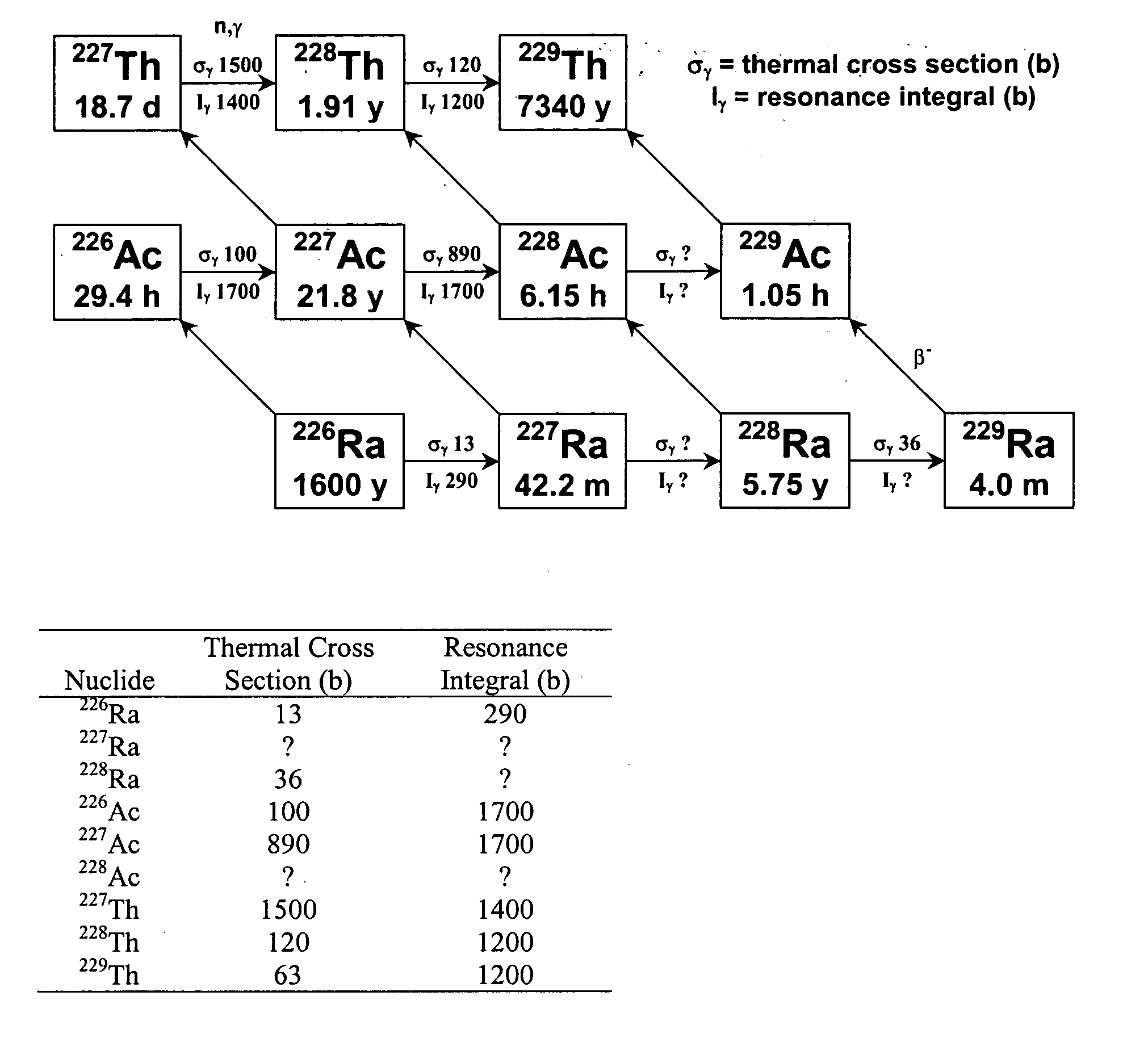
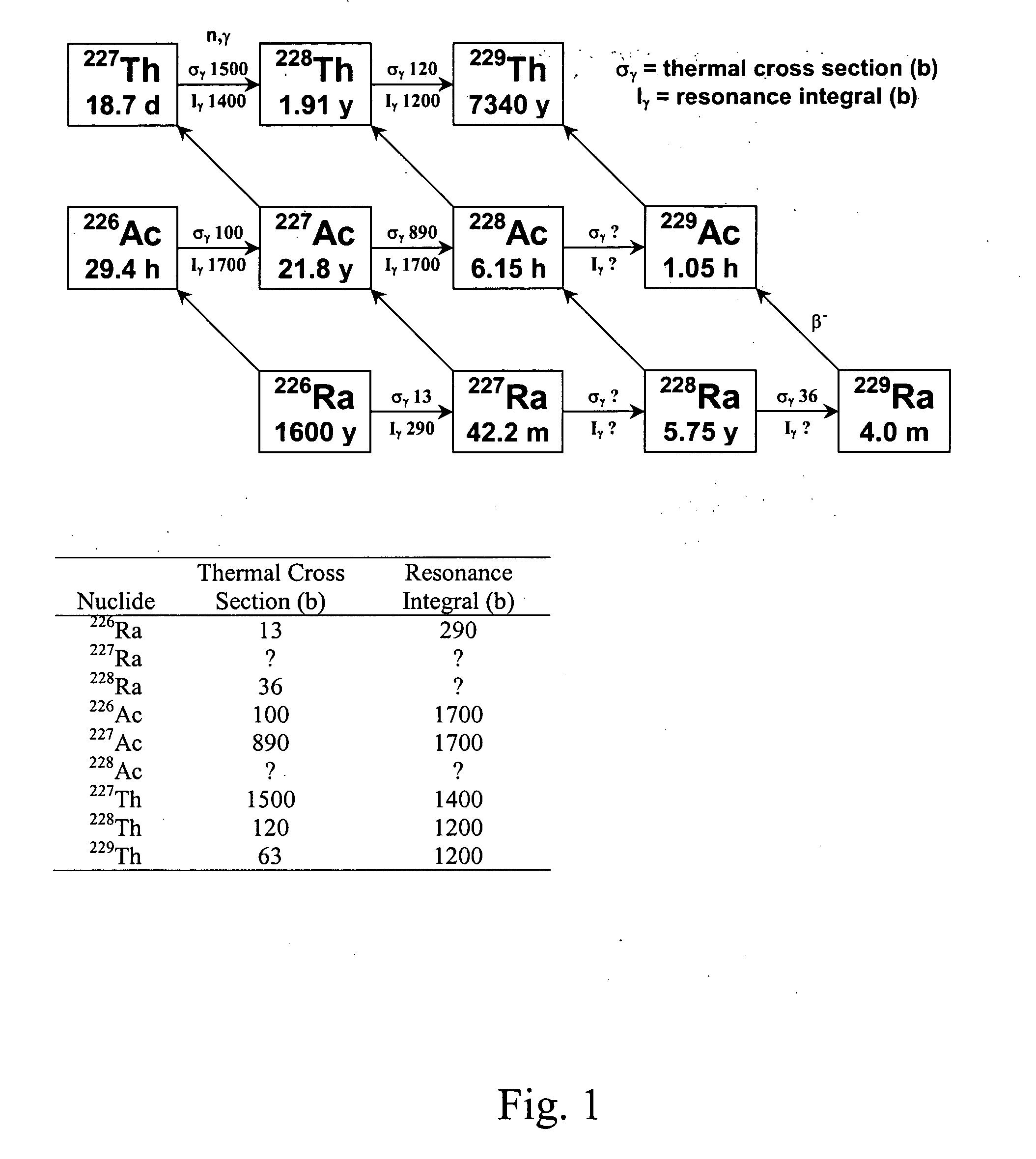
Production of thorium-229
InactiveUS20050105666A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesNeutron captureAlpha particle
A method for producing 229Th includes the steps of providing 226Ra as a target material, and bombarding the target material with alpha particles, helium-3, or neutrons to form 229Th. When neutrons are used, the neutrons preferably include an epithermal neutron flux of at least 1×1013 n s−1·cm−2. 228Ra can also be bombarded with thermal and / or energetic neutrons to result in a neutron capture reaction to form 229Th. Using 230Th as a target material, 229Th can be formed using neutron, gamma ray, proton or deuteron bombardment.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
High flux sub-critical reactor for nuclear waste transmulation
InactiveUS20080232533A1Improve distributionImprove economyConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationHigh fluxPu element
A process to safely convert about 95% of the nuclear waste into a usable fuel source is disclosed. The process, involving a sub-critical power reactor and a proliferation-resistant fuel cycle, consumes depleted uranium or thorium fuel with fissionable fuel, including reactor or weapons-grade plutonium. The reactor is comprised of coaxial neutron and energy-amplifying regions separated by moderating and thermal neutron absorbing layers. Control of the water or gas-cooled reactor is provided by plutonium-helium loops with a variable volume flow rate and an external source of neutrons that quickly reacts to any fluctuations of the reactor parameters. A second embodiment of the invention is a compact sub-critical propulsion reactor utilizing fission electric cell and thermo-acoustic technology for electrical power generation.
Owner:BLANOVSKY ANATOLY
Method for removing metal ions from aqueous solution by use of hydrotalcite
InactiveCN102336461AImprove removal efficiencyHigh ion exchange capacityOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMetal ions in aqueous solutionRadioactive agent
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, specifically to a method for removing metal ions from an aqueous solution by the use of hydrotalcite. The method provided by the invention comprises the step of removing metal ions from an aqueous solution by the use of hydrotalcite. The metal ions, which refer to heavy metal ions or radioactive substance ions, comprise one or more selected from the group consisting of mercury, chromium, lead, arsenic, cadmium, tin, copper and zinc heavy metal ions. The radioactive substance ions comprise uranium, thorium and radium ions. According to the invention, hydrotalcite is applied in metal ions-containing sewage processing, leading to high metal ion removing efficiency and obvious effects. In the meanwhile, raw material sources for the preparation of hydrotalcite are extensive, the cost is low, the preparation method is simple, energy consumption is low and the investment is also low. Therefore, the method provided by the invention has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
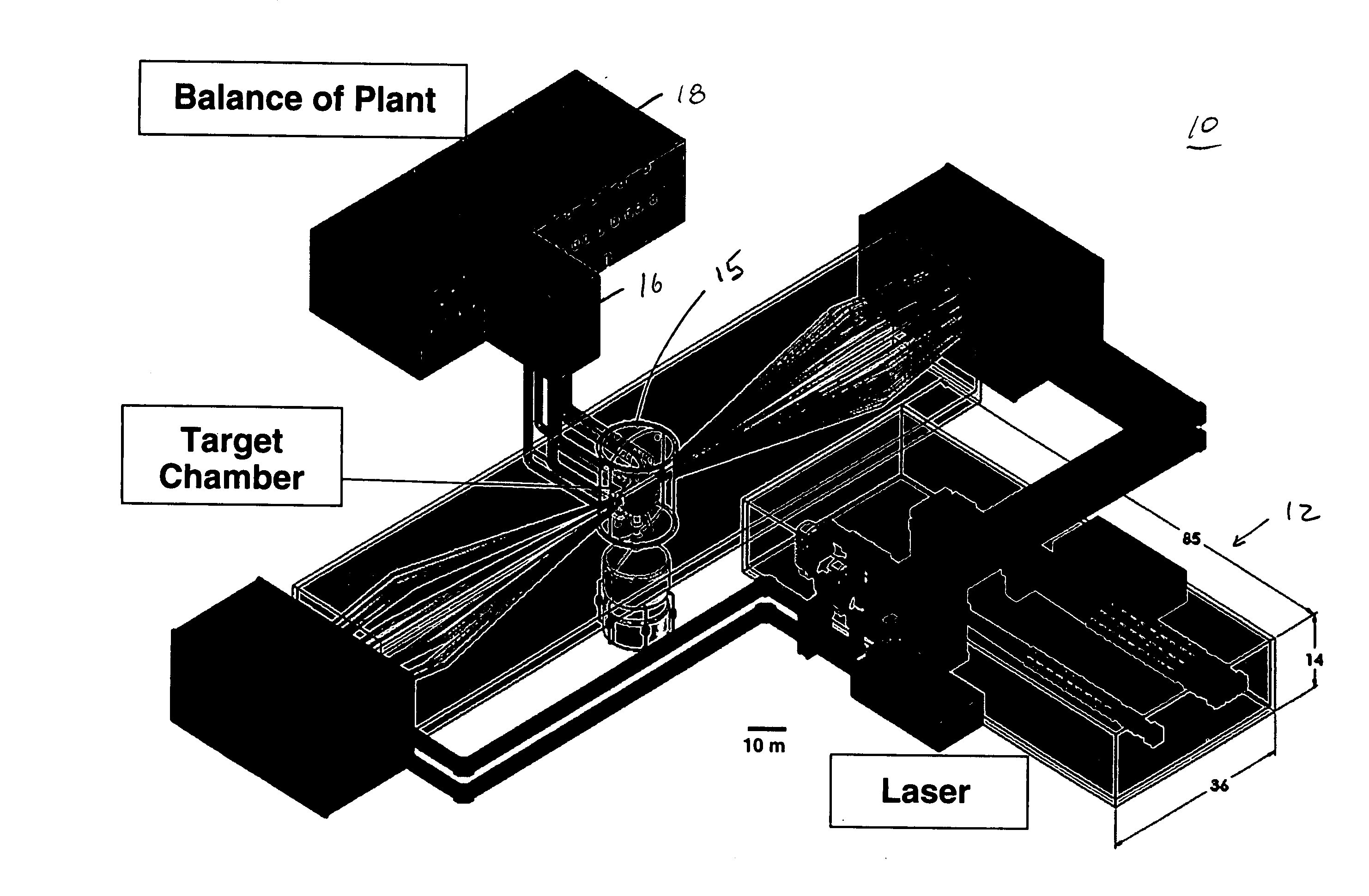
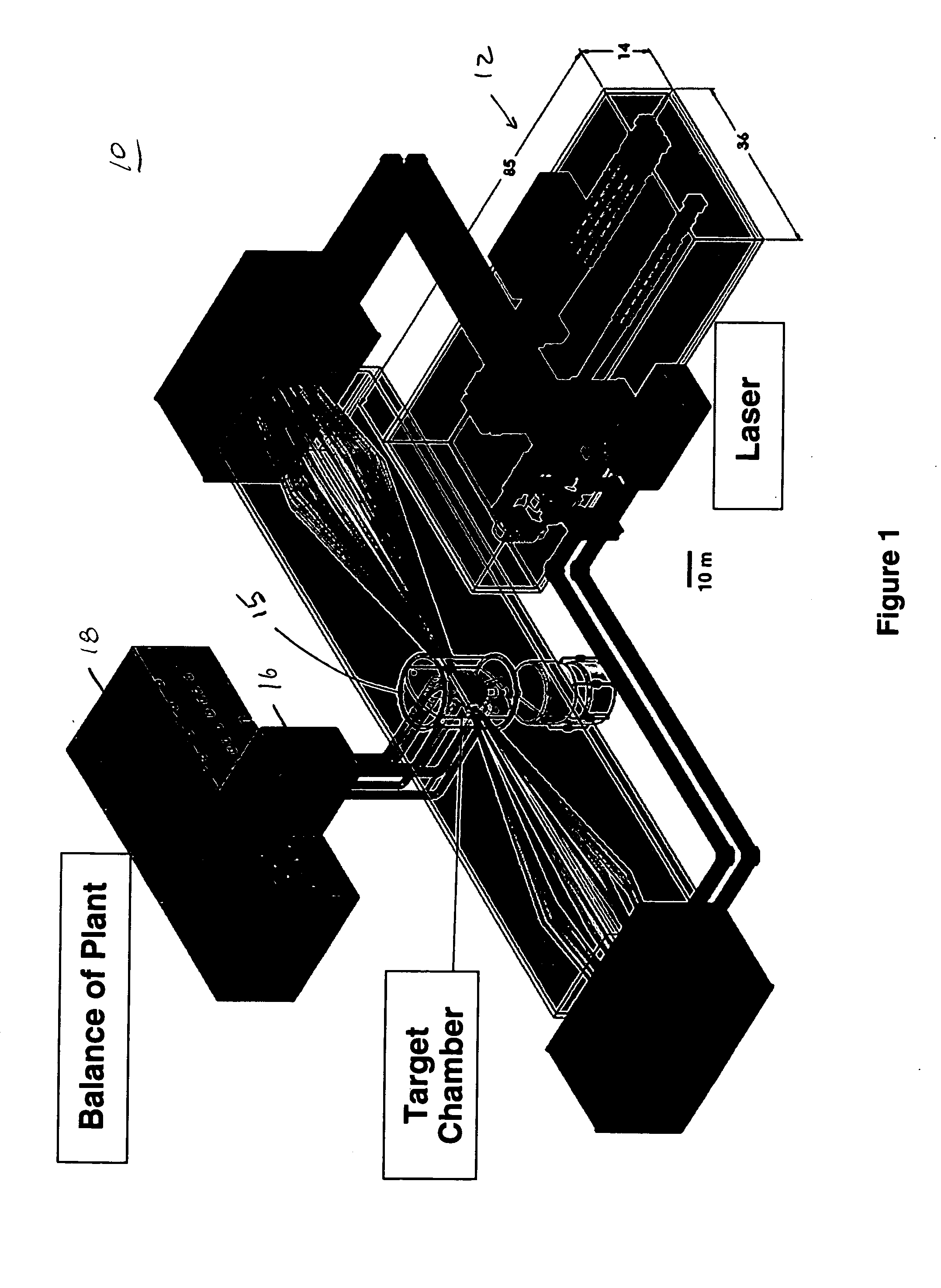
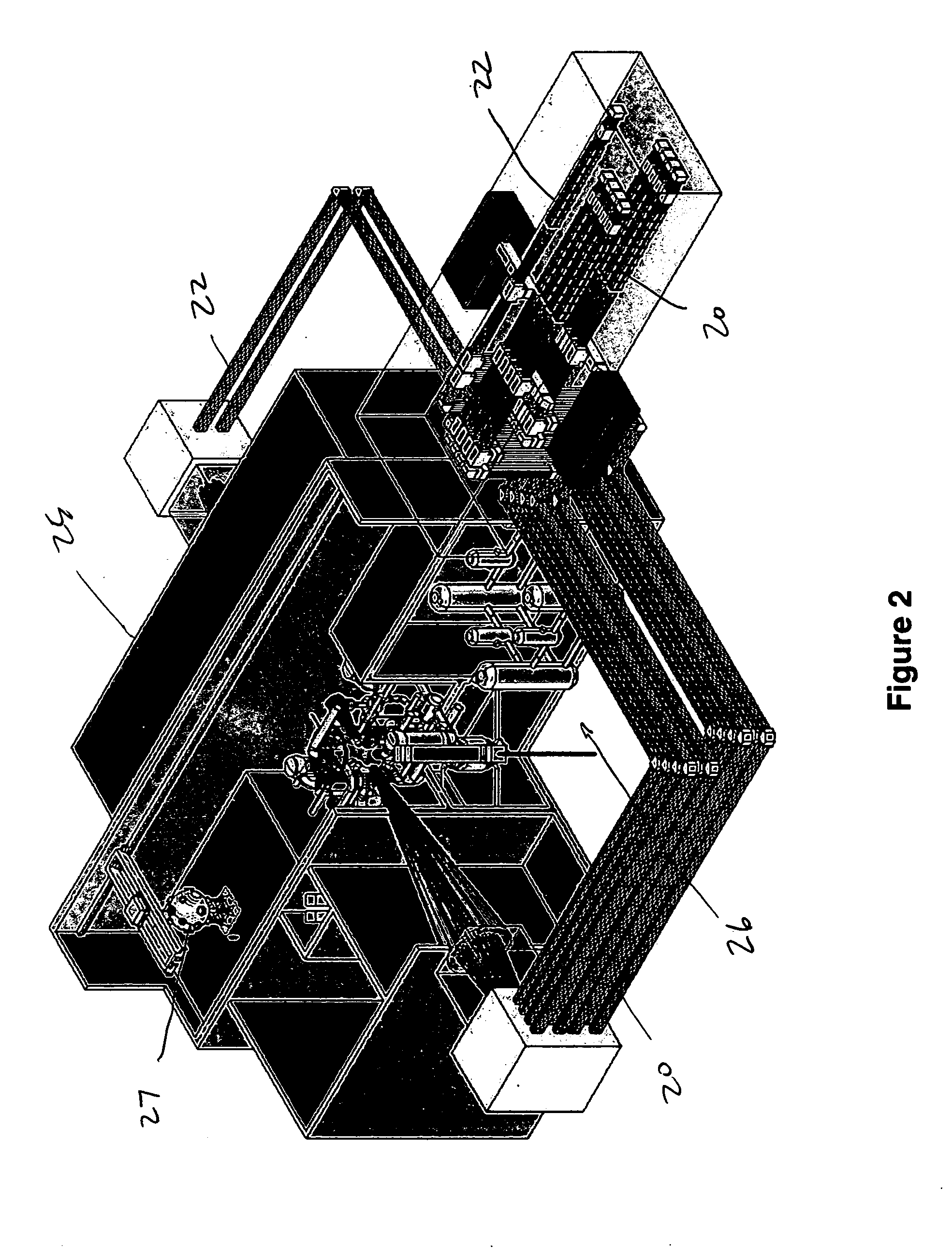
Control of a Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion-Fission Power Plant
ActiveUS20110286563A1Extended service lifeReduce spreadNuclear energy generationWaste based fuelFusion fissionEngineering
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Composite inorganic membrane for separation in fluid systems
InactiveUS20070251389A1Improve throughputHigh selectivityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPorous substrateNiobium
A composite membrane for separating components of fluid mixtures including either a porous, essentially continuous, vacuum-deposited ceramic layer, supported by a porous substrate, the ceramic layer comprising at least one oxide selected from aluminum, titanium, tantalum, niobium, zirconium, silicon, thorium, cadmium and tungsten oxides, wherein the average width of the substrate pores is greater than that of the ceramic layer pores, subject to stated conditions; or a multi-layer system of at least two such ceramic layers, disposed on at least one side of, and supported by, a porous substrate, the ceramic layers comprising at least one of the above-specified oxides, wherein between successive ceramic layers, there is disposed a vacuum-deposited metallic layer wherein the porosity and (or) average pore width of the metallic layer is less than those of the ceramic layer. The invention further relates to the application of similar membranes to TLC and column chromatography.
Owner:ACKTAR
Method of producing inorganic aerogels under subcritical conditions
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 04250 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 14, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 14, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 30, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 13721 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 17, 1997Preparation of inorganic aerogels based on oxides of the metals magnesium, aluminum, silicon, tin, lanthanum, titanium, zirconium, chromium and / or thorium by producing a hydrogel in a sol / gel process, replacing the water in the hydrogel by an organic solvent, and drying the solvent-moist gel, takes place by conducting the drying step by exposing the solvent-moist gel to an ambient temperature which is above the boiling temperature of the solvent and at a pressure which is below the supercritical pressure of the solvent in such a way that the solvent within the gel is heated up very rapidly and evaporates.
Owner:BASF AG
Fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method and nuclear reactor for same
InactiveCN105023621AInherently safeReduce engineering difficultyFuel elementsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreInherent safety
The present invention relates to a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method and a nuclear reactor for same. The main contents comprise: a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reaction implementation method, a reactor modular design approach, a fast reactor type coupling nuclear reactor, a reactor core, a fuel element, a nuclear control system, and a proliferation fuel system. The fast reactor type coupling nuclear reactor mainly combusts thorium and nuclear waste, and has inherent security. The reactor main container is composed of a fission pool and a moderating pool that are completely isolated from each other but coupling to each other. A primary coolant is separated from a moderator. A thermal insulation layer is disposed between the fission pool and the moderating pool so that both can perform neutron exchange but heat exchange is blocked. Fast neutrons produced by the fission pool and moderated neutrons reflected by the moderating pool may enable the reactor core to simultaneously perform coupling nuclear reaction of the two types of neutrons. The moderating pool may be provided with the nuclear control system, and ex-core coupling core control may be implemented. The moderating pool is provided with a thorium purification fuel system, and on-line extraction of the purification fuel can be performed, and separation of nuclide is safe and simple, thereby providing a solution to the technical bottleneck of "thorium reactor".
Owner:陈安海
Application and method of neutral phosphamide extraction agent for extracting and separating thorium
ActiveCN104131164AImprove extraction abilityEfficient separation and recoveryProcess efficiency improvementPurification methodsThorium
The invention relates to a thorium separation and purification method and in particular relates to an application of a neutral phosphamide extraction agent shown as a general formula I in the specification for extracting and separating thorium, as well as a method for extracting and separating thorium by using the neutral phosphamide extraction agent.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
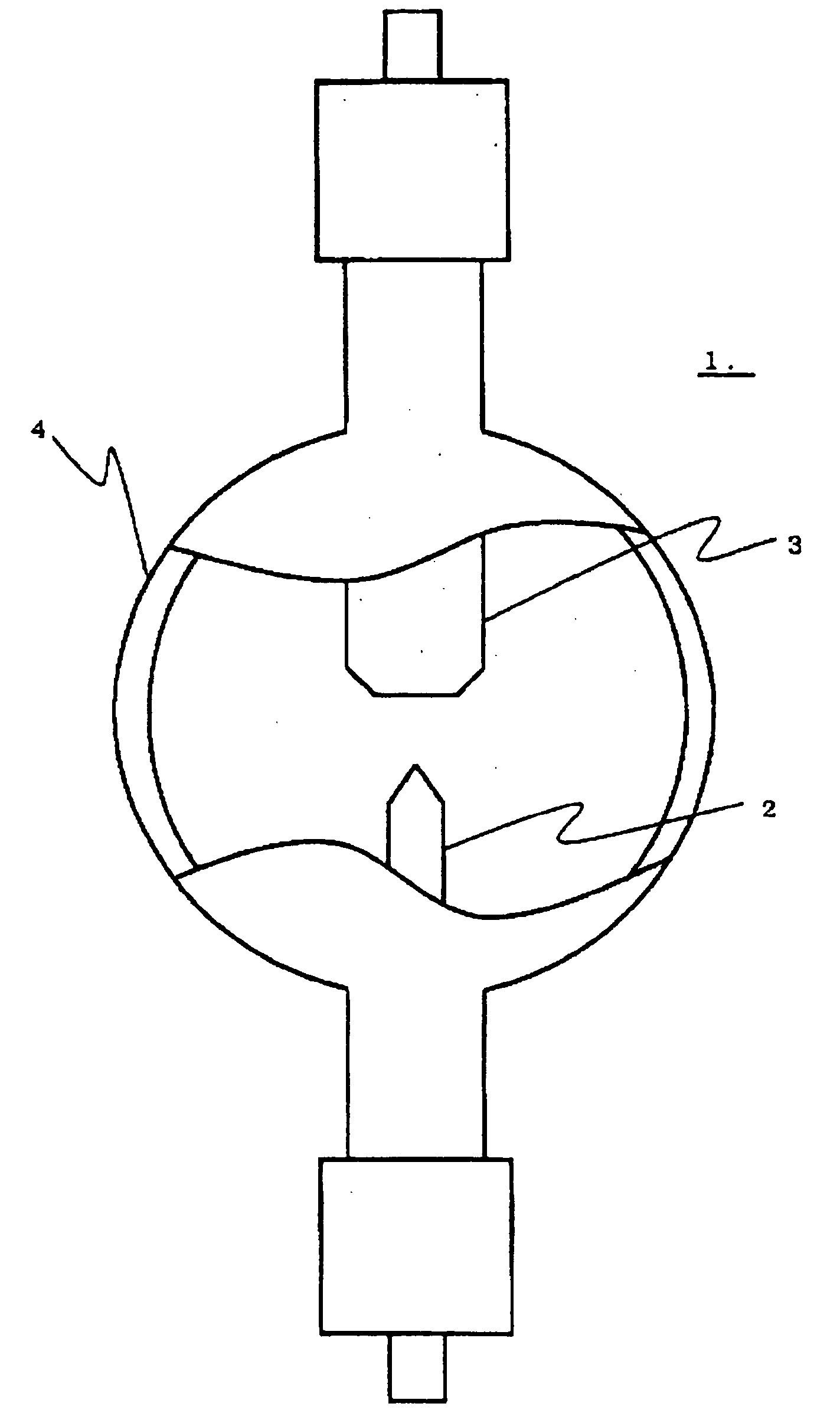
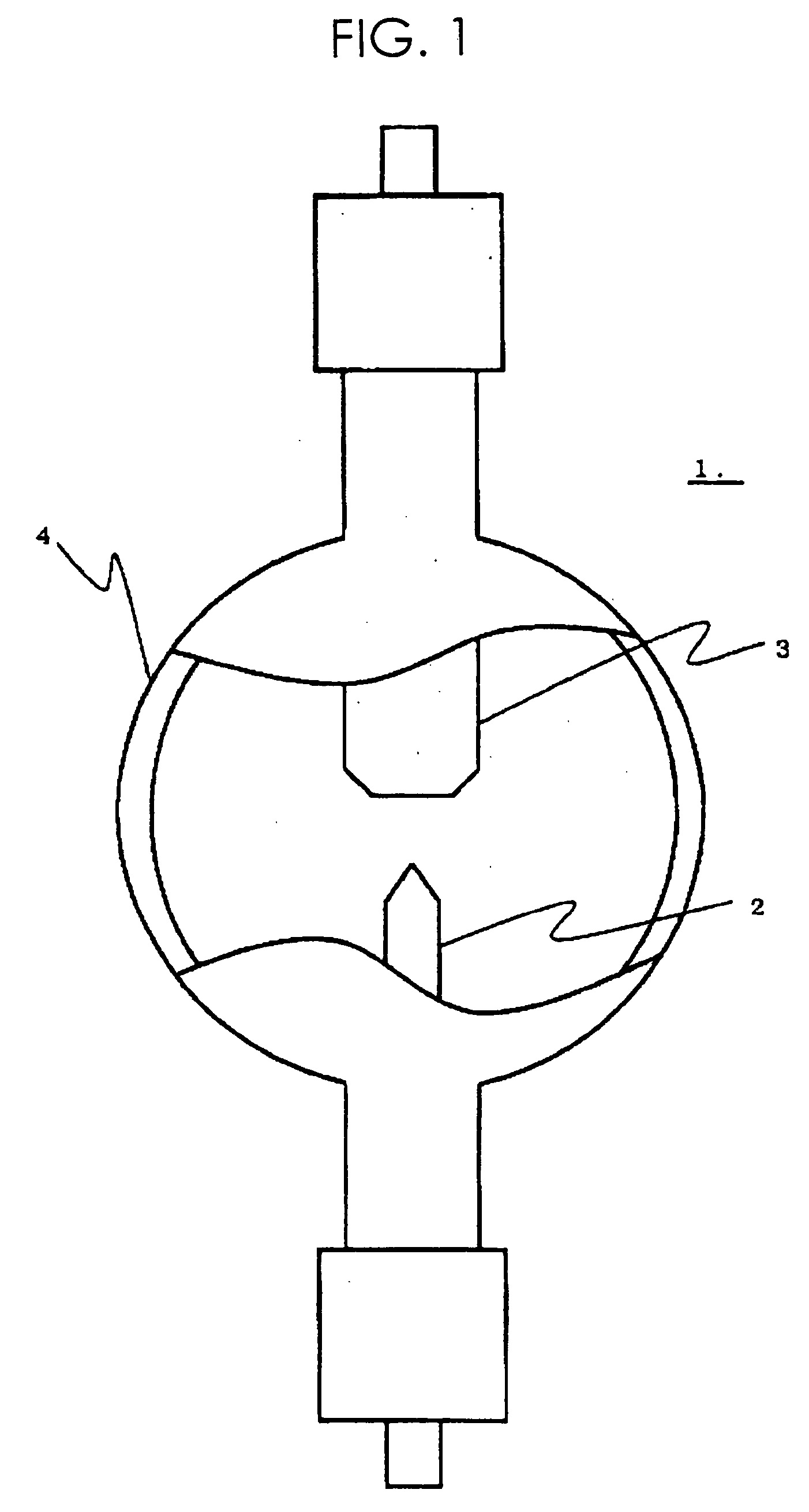
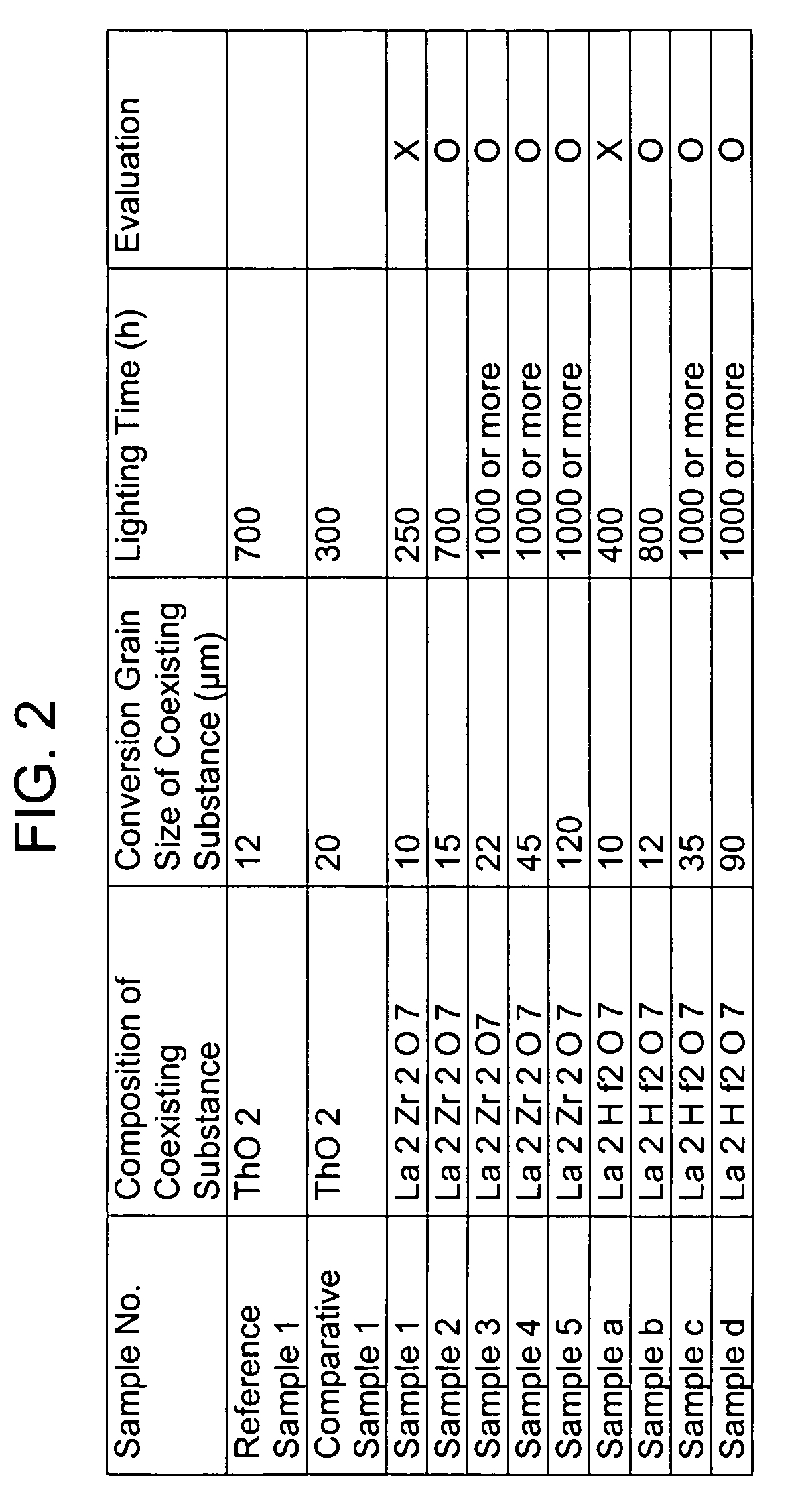
High-load and high-intensity discharge lamp
ActiveUS20060220559A1Long life-timeImprove stabilityWork-feeding meansSolid cathode detailsNiobiumCerium
The present high-load and high-intensity discharge lamp includes a cathode made of a material which does not (substantially) include thorium but can be used as a cathode material of high heat load, so that a long lifetime and high stability corresponding to those of thoriated-tungsten can be realized. Specifically, the cathode is made of a metal base having a high melting point which mainly consists of tungsten and includes a coexisting substance in which an oxide of at least one kind of metal selected from lanthanum, cerium, yttrium, scandium, and gadolinium and an oxide of at least one kind of metal selected from titanium, zirconium, hafnium, niobium, and tantalum are coexistent. The conversion grain size of the coexisting substance is 15 μm or greater, and the plurality of coexisting substances are present in the metal base with a high melting point.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
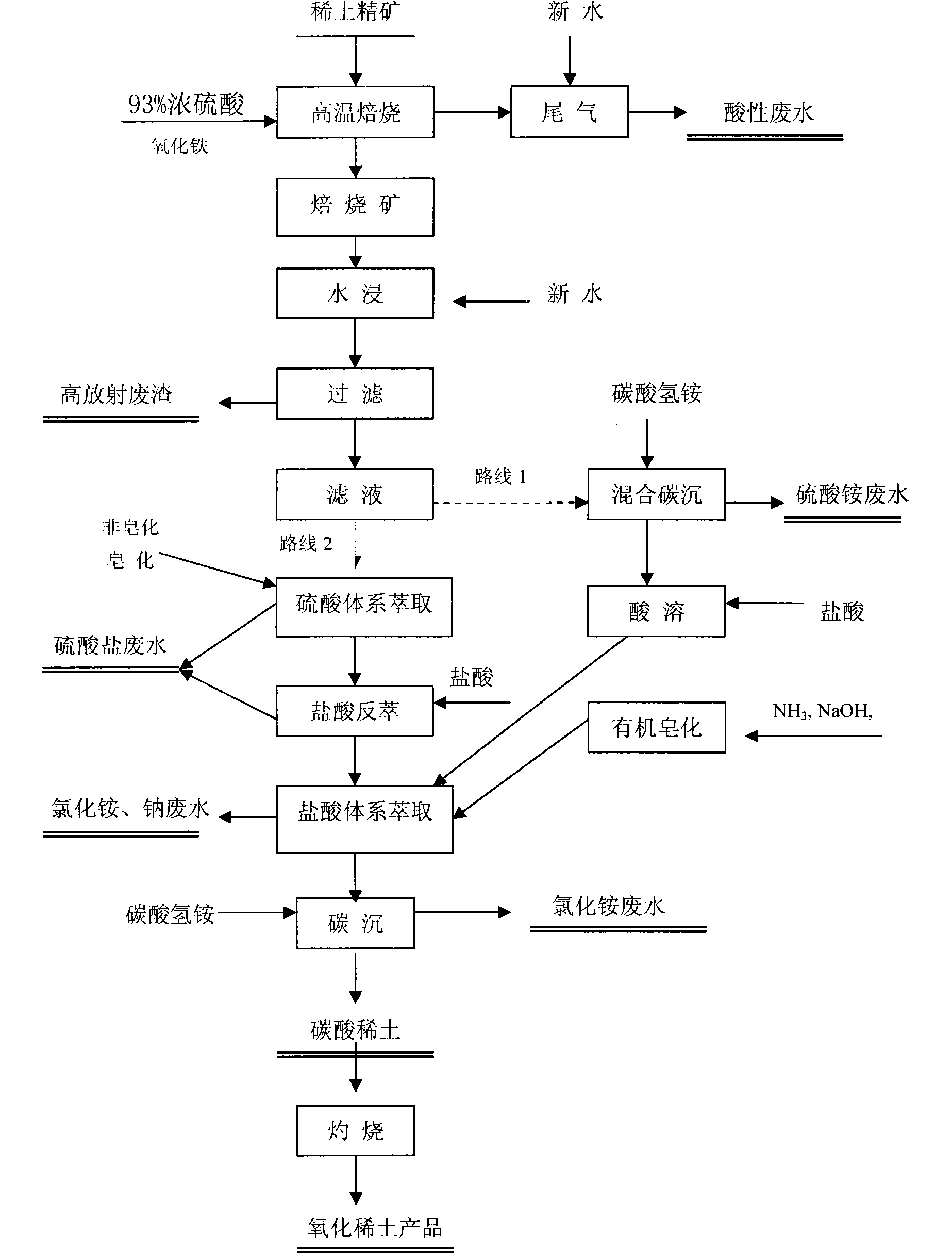
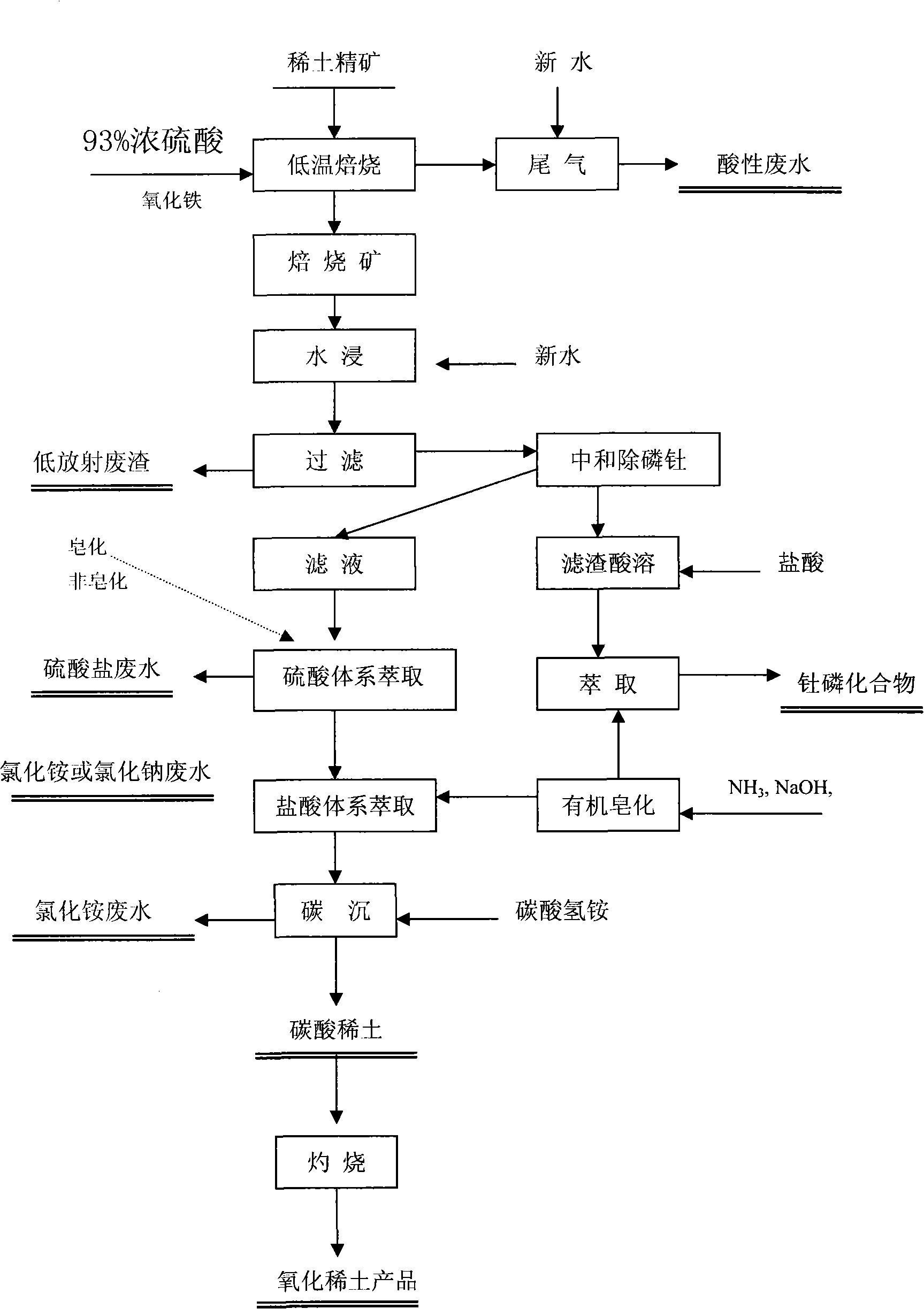
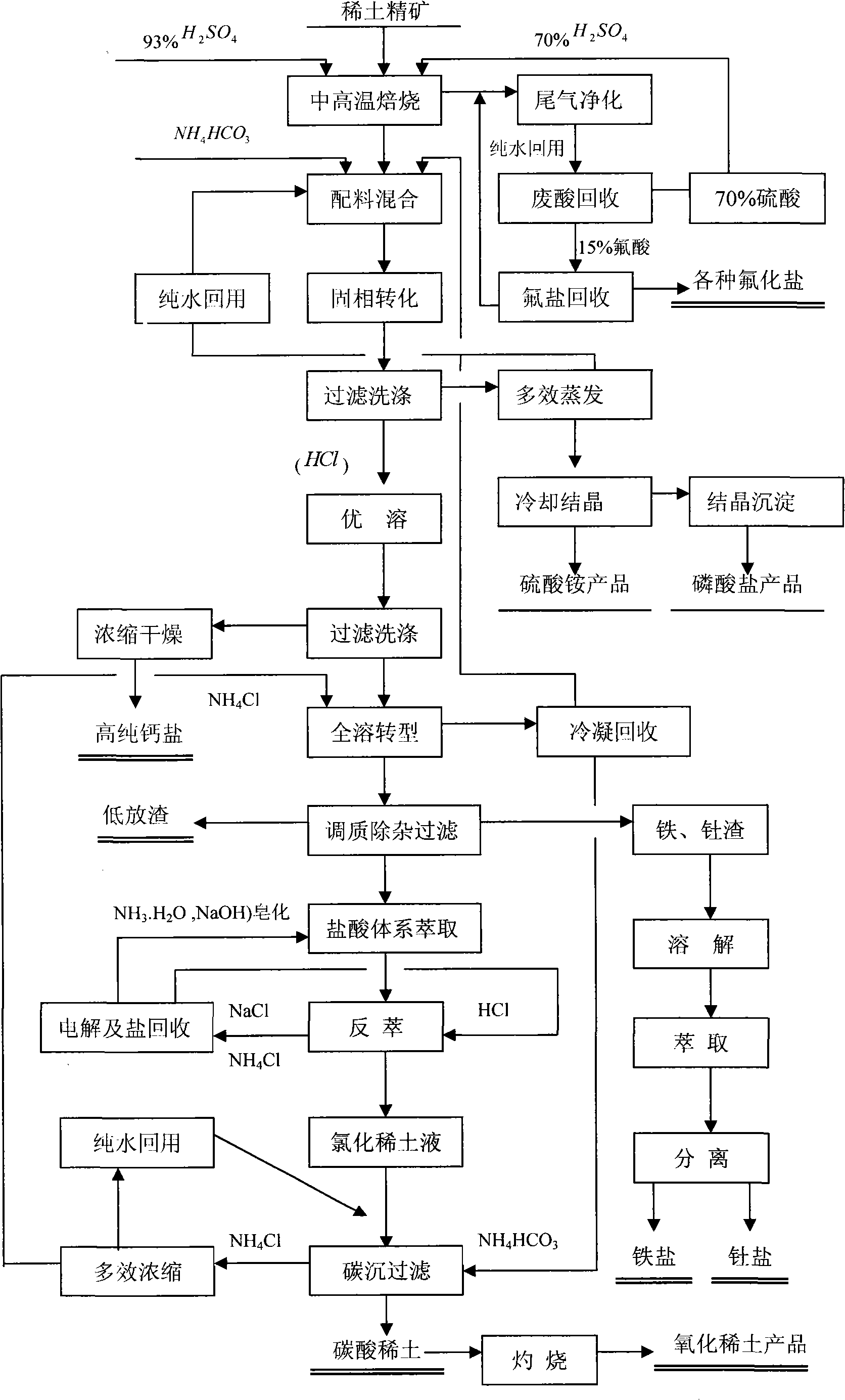
Process for rare-earth smelting resource reclamation and cyclic production
InactiveCN101880782AAchieve governanceAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementIndustrial waste waterSmelting process
The invention relates to a process for rare-earth smelting resource reclamation and cyclic production. The process has the main characteristic of comprehensively and systematically solving the problems of environmental protection and industrial promotion of the whole rare-earth industrial chain by adopting innovative integrated technical means. The process mainly comprises administration and comprehensive utilization of waste gas, waste water and waste slag, revolution of a rare-earth smelting process, and reclamation and repeated utilization of various important resources such as sulfur, fluorine, ammonium, thorium, phosphorus, calcium and the like so as to achieve smokeless and harmless treatment of the waste gas, full utilization of the resources and zero discharge of industrial waste water and fulfill the final goal of cyclic production. The process radically solves the maximum environment-friendly bottleneck problem in a sustainable development process of the Baotou rare-earth industry from resource advantage to industrial advantage, in particular the historical key environment-friendly technical problem, reduces energy consumption of a large amount of resources and pollutiondischarge, greatly reduces the production cost, upgrades the rare-earth industry, and extends the larger industrial chain at the same time.
Owner:马克印 +1
Low absorption coatings for infrared laser optical elements
InactiveUS6020992AEffective and practical low absorptionReduce absorptionMirrorsOptical filtersOptoelectronicsOptic system
A thorium-free low absorption coating for infrared CO2 laser optics comprises an interior BaF2 layer formed on a substrate and an exterior layer formed over the interior layer to a predetermined thickness sufficient to substantially prevent water adsorption by the interior layer. Generally, the predetermined thickness is greater than about 11000 ANGSTROM , and in one embodiment of a two-layer low absorption coating designed for antireflection at 10.6 microns, the exterior layer has a physical thickness in a range between about 24600 ANGSTROM and 22800 ANGSTROM , and preferably about 24000 ANGSTROM . In the preferred two-layer AR coating embodiment, the exterior layer defines a cover layer and an absentee layer, and the interior layer is relatively thin. The preferred exterior layer and the preferred substrate consist essentially of ZnSe. Multilayer stacked coatings of more than two layer can also be formed to provide low absorption partially reflective or totally reflective coatings as well as AR coatings.
Owner:II VI
Thermonuclear plasma reactor for rocket thrust and electrical generation
InactiveUS20090000268A1Easy to triggerDownsize working reactionCosmonautic vehiclesNuclear energy generationHigh energyNuclear engineering
A reactor system produces plasma rocket thrust using alpha-initiated atomic fuel pellets without the need for a critical mass of fissionable material. The fuel pellets include an outer layer reactive material to alpha particles to generate neutrons (e.g., porous lead or beryllium), an under-layer of fissionable material (e.g., thorium or enriched uranium), and an optional inner core of fusion material (e.g., heavy water ice, boron hydride). The pellets are injected one at a time into a charged reaction chamber containing a set of alpha beam channels, possibly doubling as ion accelerators, all directed toward a common point. Alpha particles converging on each successive pellet initiate an atomic reaction in the fissionable under-layer, via a neutron cascade from the pellet outer layer, producing plasma that is confined within the chamber. This may be enhanced by atomic fusion of the optional inner core. The resulting high-energy plasma creates electrostatic pressure on the chamber and is allowed to exit the chamber through a port. An ion accelerator at the exhaust port of the chamber accelerates outgoing plasma ions, possibly with added reaction mass, to generate the rocket thrust. An electric circuit that includes the charged chamber may collect the electrons in the plasma to help power the ion accelerator(s).
Owner:YURASH GREG J
Reactor tray vertical geometry with vitrified waste control
InactiveUS20050069075A1Reduce riskReduce the amount of wasteConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationVitrificationThermal energy
A nuclear-powered plant for systems of up to about 100 MWs with a confinement section where the reaction takes place in a core having a reactive thorium / uranium-233 composition, and where an external neutron source is used as a modulated neutron multiplier for the reactor core output. The core is housed in a containment structure that radiates thermal energy captured in a multiple-paths heat exchanger. The exchanger heat energy output is put to use in a conventional gas-to-water heat exchanger to produce commercial quality steam.
Owner:D B I CENTURY FUELS & AEROSPACE SERVICES
Use of Thorium-Uranium Ratio as an Indicator of Hydrocarbon Source Rock
A low value of Th / U ratio as determined from natural gamma radiation is indicative of deepwater sedimentation. This, together with estimates of total organic carbon from pulsed neutron measurements, is used to characterize source rocks. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understand that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
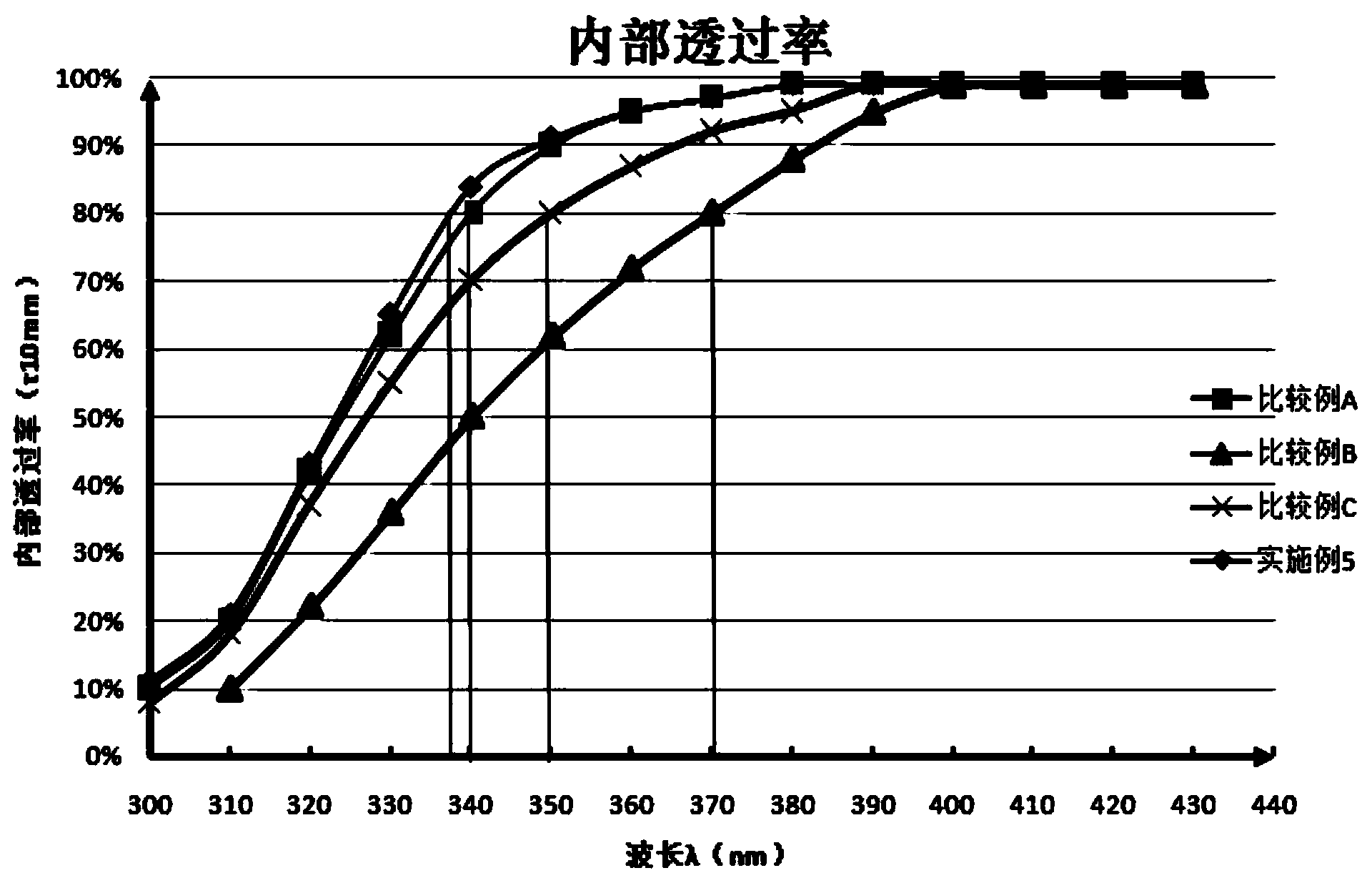
Optical glass
The present invention provides an optical glass having a refractive index (nd) and an Abbe number (vd) which are within an area surrounded by the straight lines which are drawn by connecting point A (nd=1.835, vd=46.5), point B (nd=1.90, vd=40.0), point C, (nd=1.90, vd=35.0) and point D (nd=1.835, vd=38.0) in a sequence of A, B, C, D and A as border lines in x-y coordinates shown in fig 1, in which X-axis is the Abbe number (vd) and Y-axis is the refractive index (nd), the area including the border line. The optical glass has low glass transition temperature (Tg), and suitable for precision mold pressing. The optical glass which has the refractive index (nd) and Abbe number (vd) within the above-described area, where the area includes the border lines, has the composition of SiO2-B2O3-La2O3-Gd2O3-Li2O-F system, the transition temperature (Tg) of 550 to 650 DEG C., and is free from lead, cadmium, thorium, Y2O3, P2O5 and TeO2.
Owner:OHARA
Gamma energy spectrum-based method for identifying clay shale reservoir and uranium ore occurrence on spot
ActiveCN102621588AQuick identificationQuick evaluationNuclear radiation detectionCounting rateUranium ore
The invention relates to a gamma energy spectrum-based method for identifying clay shale reservoir and uranium ore occurrence on the spot, which comprises the following steps that: rock debris in corresponding depth of drilling fluid is continuously sampled or a core acquired through the core drilling is sampled according to corresponding depths; the rock debris sample or the core sample is placed into a matched lead tank, and a gamma energy spectrum probe is used for measuring the rock debris sample or the core sample inside the lead tank; then counting rates and activity of uranium (U), radium (Ra), thorium (Th) and kalium (K) and a total gamma value are acquired according to the measurement result, so that the real content of U(Ra), Th and K in the rock can be calculated; and finally, a variation curve of the contents of U(Ra), Th and K is drawn according to the calculation results, and the clay shale reservoir and the uranium ore occurrence are identified according to variation characteristics of the curve. Gamma energy spectrum measurement and analysis on rock debris or the core which are acquired from the drilling are directly performed, so that the clay shale reservoir and the uranium ore occurrence can be rapidly identified and evaluated. The method is an economical and efficient method. The gamma energy spectrum measurement is performed on the drilling site, so that influence of an external environment on the rock sample can be avoided, and the accuracy of the measurement result can be guaranteed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Lanthanum flint optical glass and preparation method thereof
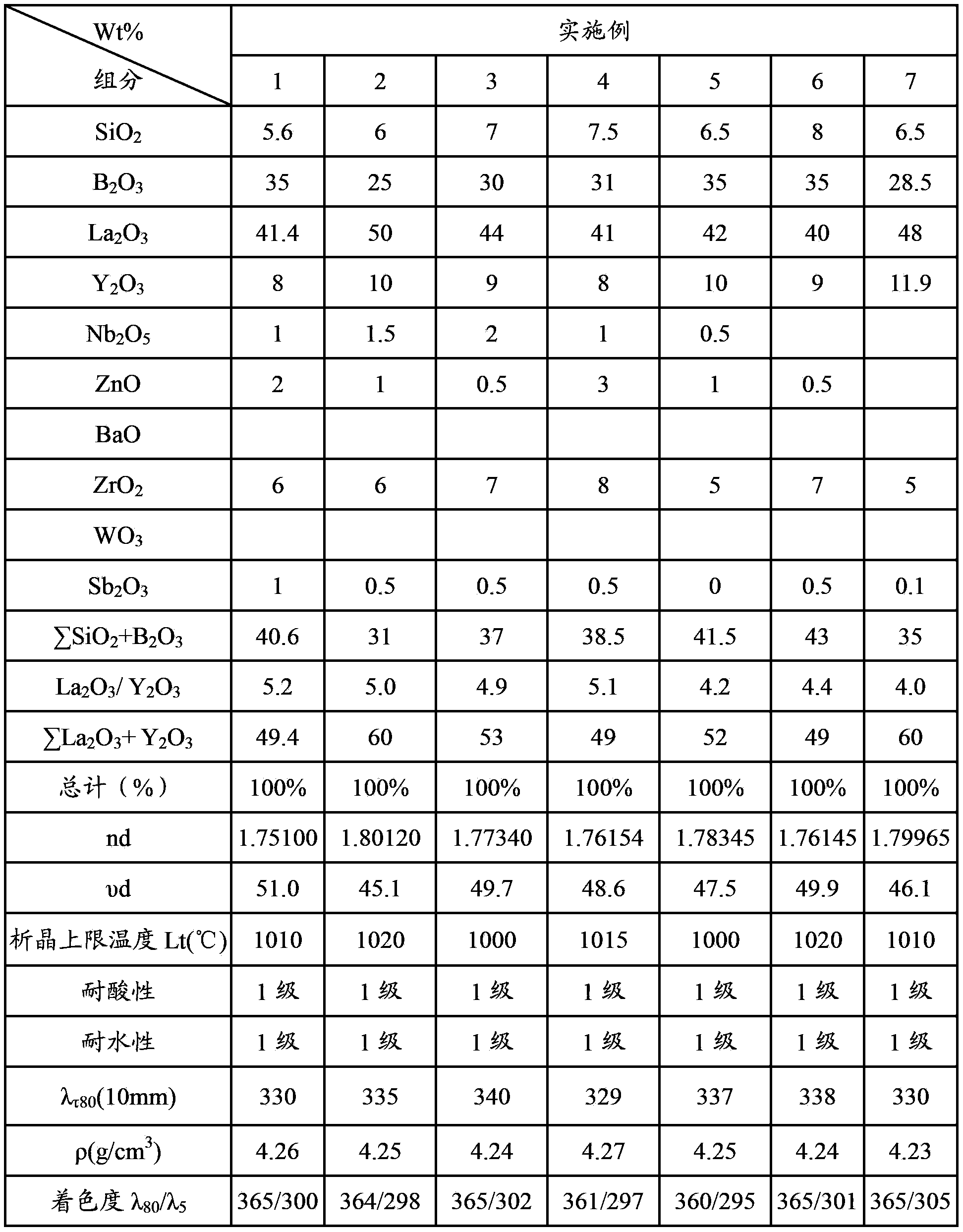
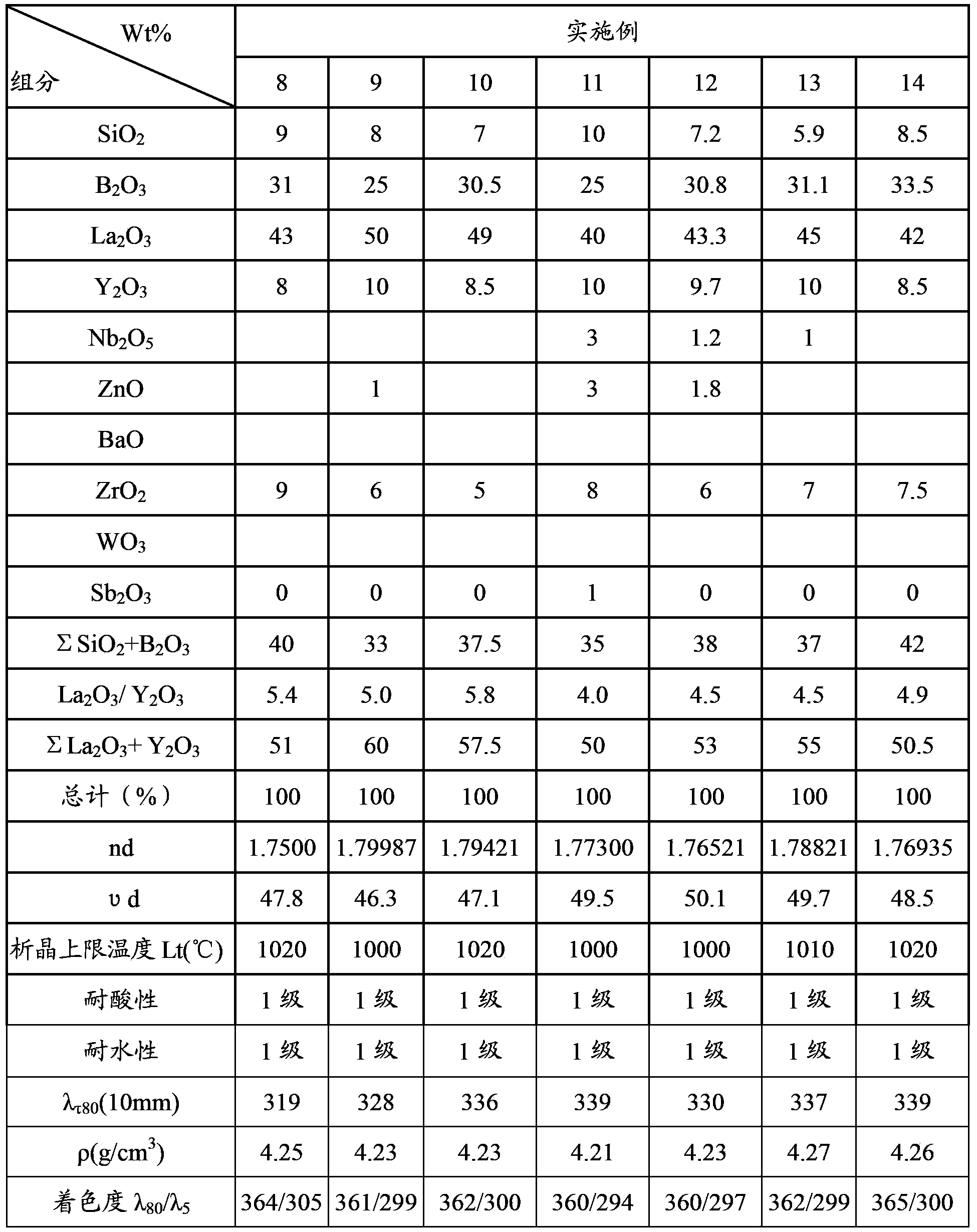
The invention provides lanthanum flint optical glass which takes Si2O, B2O3 and La2O3 as main components and a preparation method thereof. The lanthanum flint optical glass is free of thorium, cadmium and arsenic. The refractivity of the optical glass is 1.75-1.80, the Abbe number is 45-51, and the optical glass has excellent chemical stability. The optical glass comprises the following compounds in percentage by mass: 5.6-10% of SiO2, 25-35% of B2O3, 40-50% of La2O3, more than 8% and less than 12% of Y2O3, 5-10% of ZrO2, 0-3% of ZnO, 0-3% of Nb2O5, 0-1% of Sb2O3, 30-44% of Sigma(SiO2+B2O3) and 45-60% of Sigma(La2O3+Y2O3). The optical glass is free of Ta2O5, Gd2O3, Yb2O3, TiO2, Li2O, PbO, WO3 and BaO. The optical glass has low cost, low specific gravity and high internal transmittance, thus having great market competition advantages.
Owner:HUBEI NEW HUAGUANG NEW INFORMATION MATERIALS CO LTD
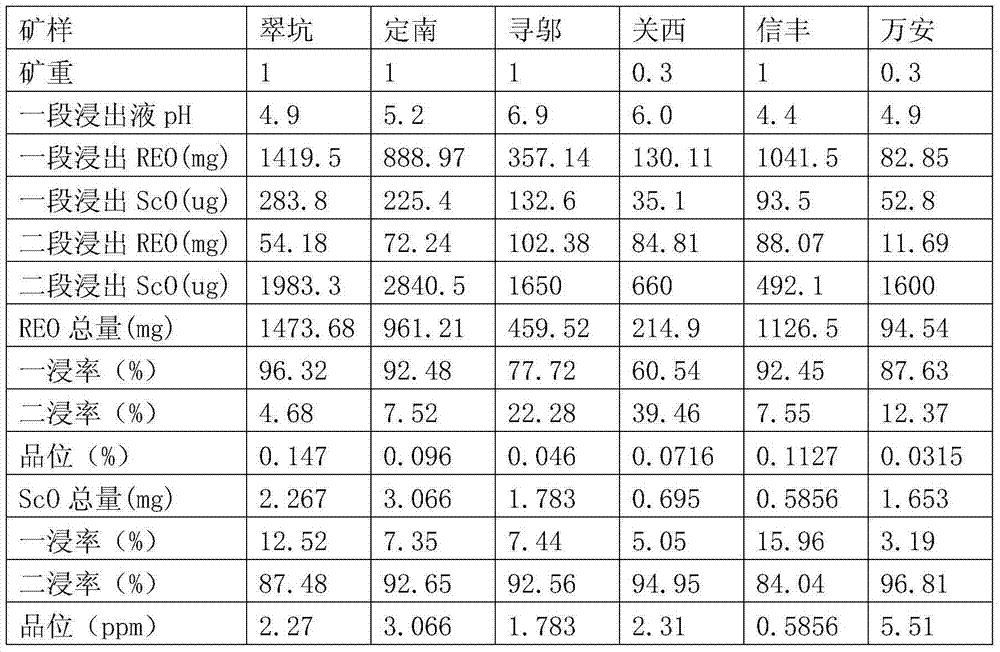
Technique for extraction separation of quadravalence cerium, thorium, fluorine and cerium less tervalence rare earth from sulphuric acid rare earth solution
ActiveCN101294244ANo pollution in the processReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementSulfate
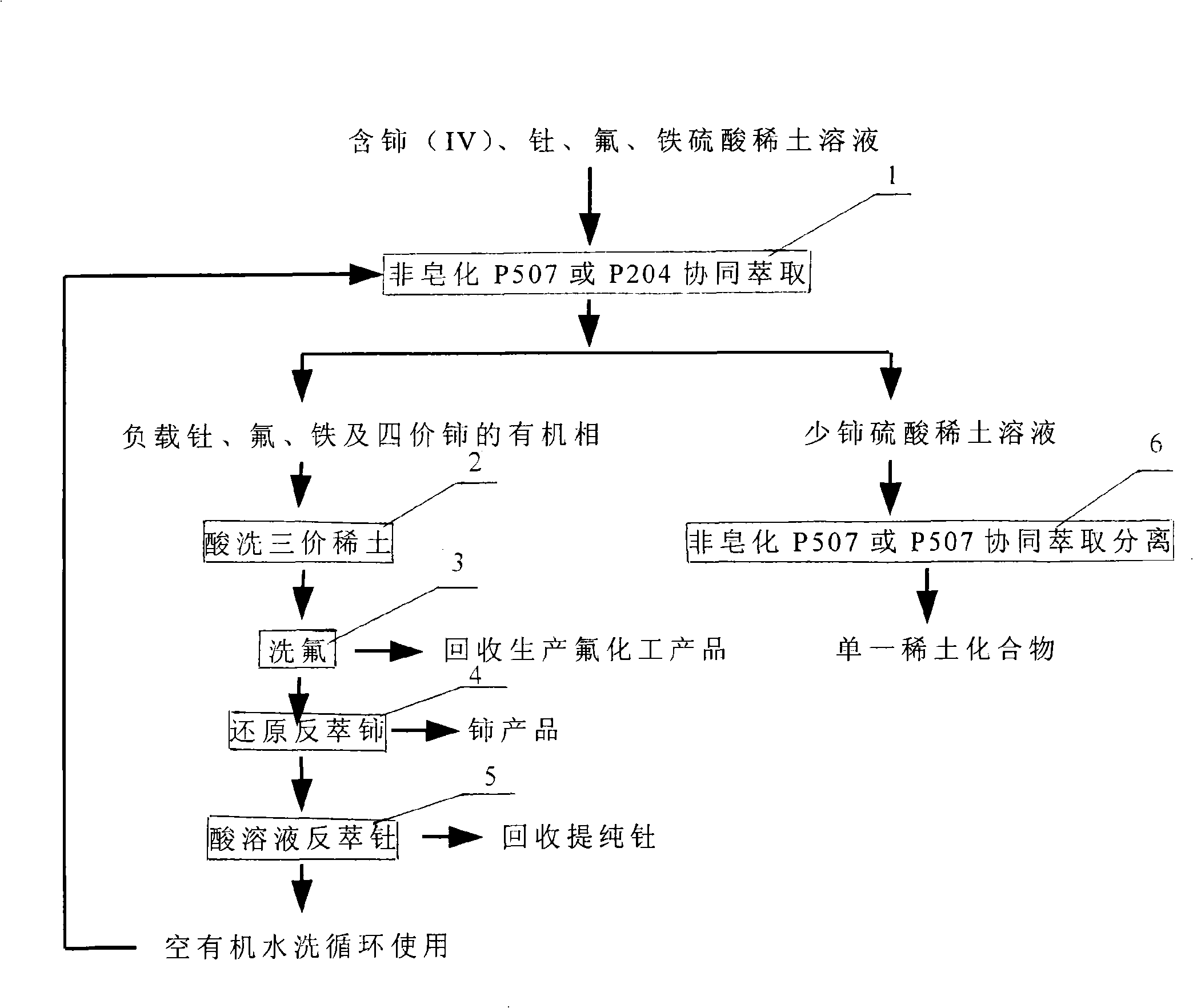
The invention relates to a technological method for extracting and separating quadrivalent cerium, thorium, fluorine and less-cerium trivalent rare-earth from rare earth sulfate solution. The rare earth sulfate solution, which is obtained through processing the rare-earth ores and contains high-valence cerium, the fluorine, the thorium and ferrum, is used as raw material; synergistic extraction agent basing on P507 and P204 is adopted for extracting and separating; the cerium (1V), the thorium, the fluorine, and the ferrum are extracted into an organic phase, then selective washing and back extraction are performed step by step to obtain three products that are the cerium, the fluorine, and the thorium, the trivalent rare-earth is left in a water phase, and then unsaponifiable P507 or the synergistic extraction agent basing on P507 is adopted to perform multistage fractional extraction to separate single rare earth elements. The technological method has the characteristics that the synergistic extraction agent basing on P507 and P204 is adopted, the thorium is easy to perform the back extraction, and extraction capacity is large, and the emulsification is not generated during the extraction process; the cerium (1V), the thorium, the fluorine, the ferrum and the trivalent rare-earth are extracted and separated in the same extraction system; both extraction and the separation adopt unsaponifiable extraction agent, and ammonia-nitrogen wastewater is not generated; in addition, the thorium and the fluorine are recovered as products, and the pollutions caused by thorium-containing waste residue, fluoride-containing wastewater and the ammonia-nitrogen wastewater are eliminated from headstream. Therefore, the technological method has the advantages of simple procedures, green environmental protection, and low manufacturing cost.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for improving ionic rare earth extraction rate and mine tailing safety
InactiveCN103695670AEnhanced exchange leachingImprove leaching efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSulfateRare earth
The invention discloses a method for improving an ionic rare earth extraction rate and mine tailing safety. According to the characteristics of ionic rare earth ore, 1, most of rare earth is subjected to extraction according to a ratio of rare earth raw ore to a nearly neutral ammonium salt ore-leaching agent and then an acid sulfate ore-leaching agent is supplied so that rare earth having high leaching difficulty is extracted by leaching, rather than at the beginning, a pH value of the ore-leaching agent is adjusted to less than 4, and 2, after acid sulfate ore-leaching agent-based extraction, tailings are cared respectively by water and a lime milk aqueous solution so that residual acid in the ore is neutralized and adsorbed excess ammonium is transferred to the solution and thus ammonium residues in the tailings are reduced and an ammonium recovery utilization rate is improved. Through the method, rare earth extraction efficiency is improved by 2-30% and the rare earth extraction efficiency is related to content of difficult exchange ingredients in ore, ammonium consumption is reduced by about 20%, content of rare earth and ammonium residues in mine tailings is reduced by above 50%, and content of rare earth, ammonium, uranium and thorium in mine tail water is reduced by above 70%. The method guarantees a tail water pH value of 7 and reduces risk of landslip caused by mine tailing puffing.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Production method of nuclear fuel clad element
ActiveCN104628395AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove thermal conductivityOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationComposite ceramicSlurry
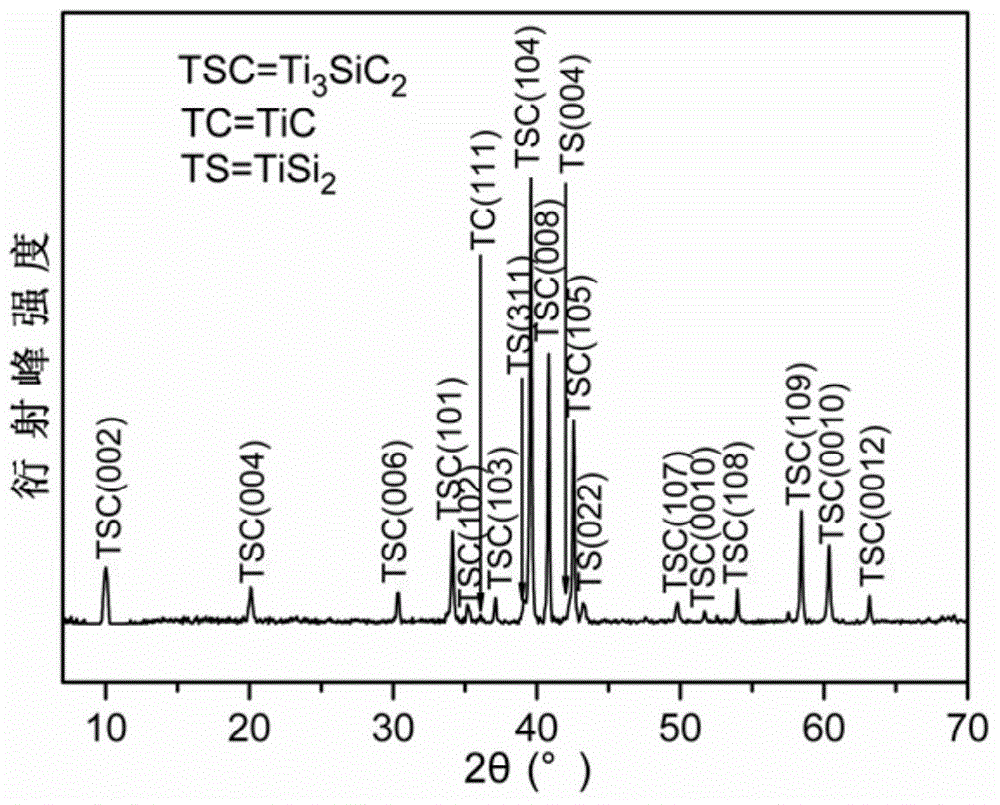
The invention provides a production method of a nuclear fuel clad element. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an MAX phase ceramic material, silicon carbide, an MAX phase-based composite ceramic material or a silicon carbide-based composite ceramic material, processing the above ceramic material to prepare a slurry, carrying out vacuum defoaming, making a ceramic film with the thickness of 10[mu]m-10mm on a base band through a curtain coating or draw-off process, winding to make a clad element blank, drying, carrying out rubber discharging, sintering, and carrying out surface treatment to obtain the nuclear fuel clad element. The production method has the advantages of simplicity, easy implementation, low cost, overcoming of the disadvantage of difficult processing of ceramic materials, high production efficiency, short cycle and easy industrialization. When the ceramic material is a Ti3SiC2-baed ceramic material, the ceramic material can resist molten fluorine salt corrosion, and can be used as a fluorine salt fuel clad element material in a nuclear reactor, so practical demands of a thorium-based fourth generation fission reactor nuclear energy system on the structure material are met.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Hamartite smelting separation process
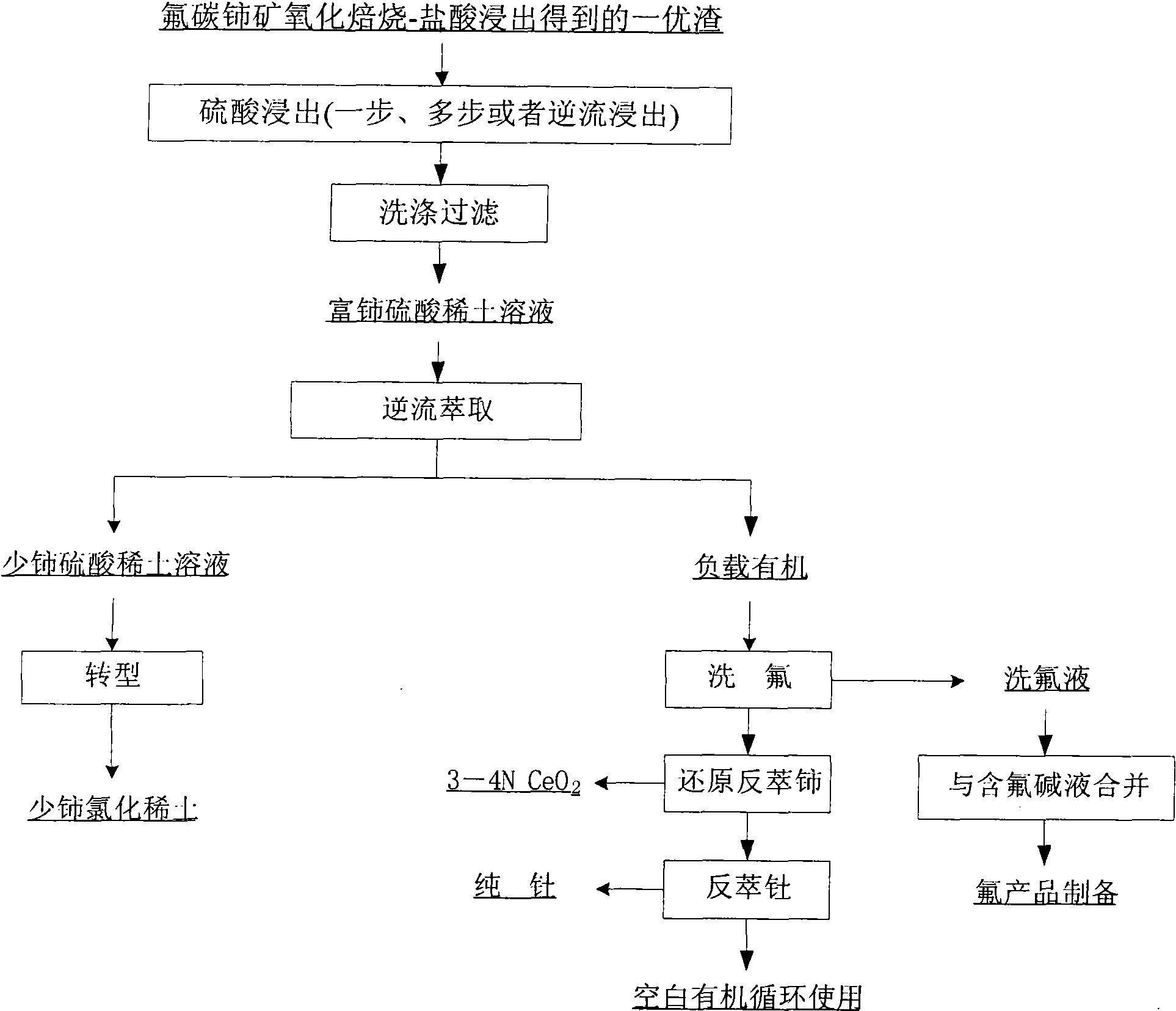
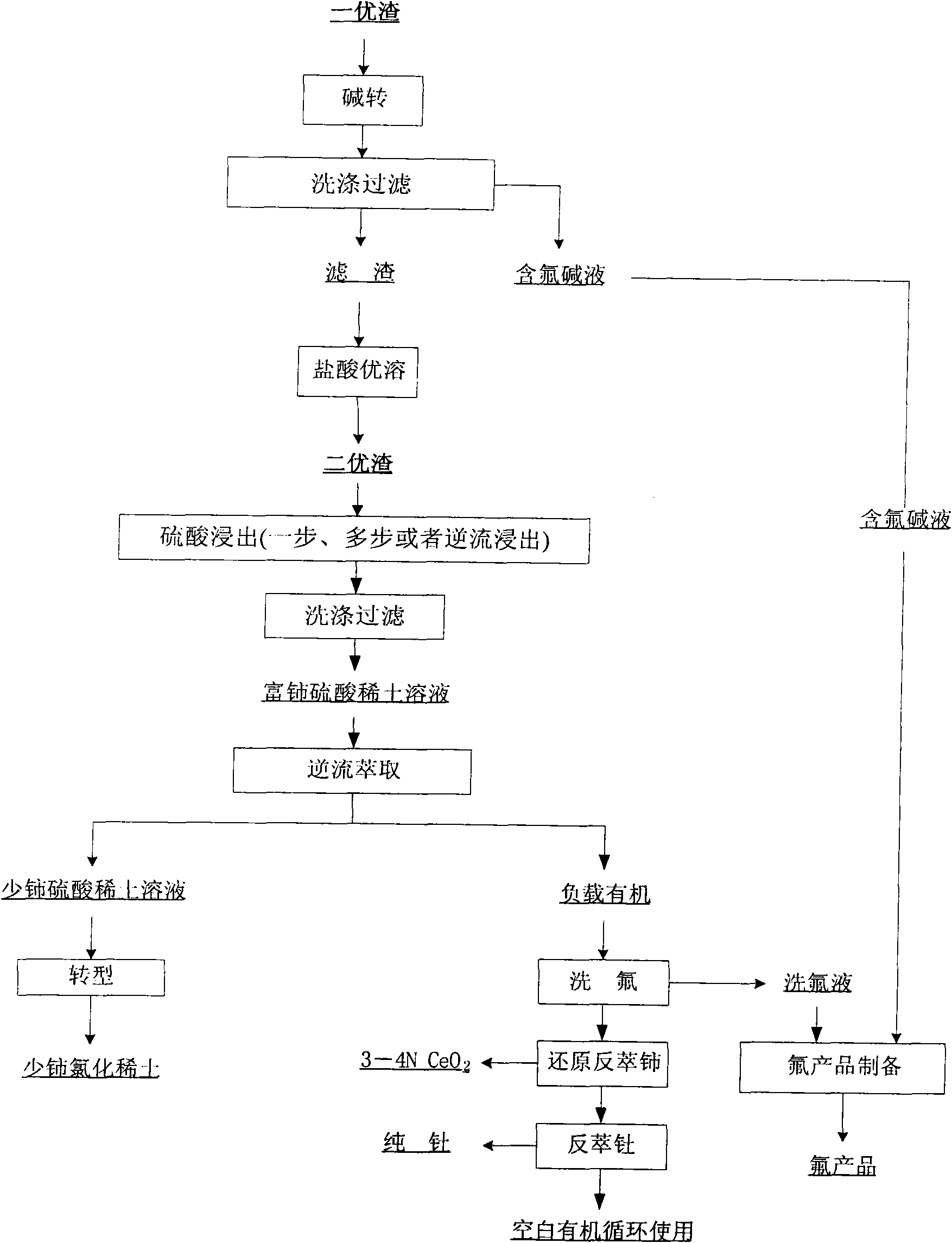
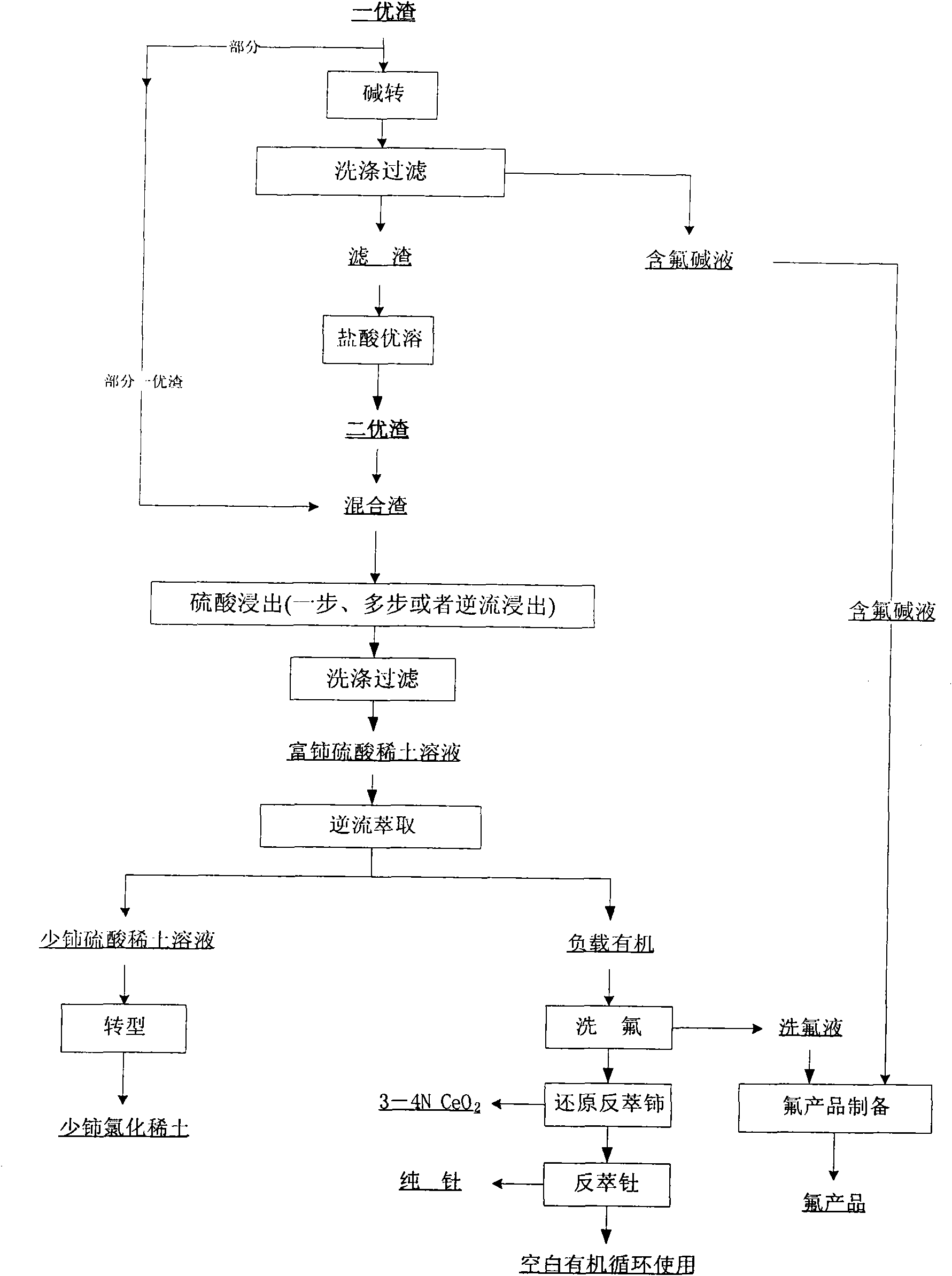
ActiveCN102146512AAchieve recyclingIncrease the added value of resourcesFluoride preparationProcess efficiency improvementFluoride productsSlag
The invention discloses a hamartite smelting separation process. First optimal slag or / and second optimal slag mainly containing cerium (IV), thorium (IV) and fluorine, obtained by oxidative roasted salt acid leaching of hamartite, is / are used as raw materials, and extraction and separation of rare earth are performed. The process comprises the following steps of: 1) leaching the first optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; or leaching the second optimal slag obtained by alkali conversion-hydrochloric acid dissolution of the first optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; or leaching the mixed slag of the first optimal slag and the second optimal slag by using sulfuric acid to obtain sulfuric acid-rare earth solution and filter residue; 2) performing extraction separation on the sulfuric acid-rare earth solution obtained in the step 1) to obtain a rare earth compound,fluorine washing liquor, a pure cerium product and a thorium product; and 3) synthesizing a fluoride product by using the fluorine-containing alkali wastewater obtained by alkali conversion in the step 1) and the fluorine washing liquor obtained by the extraction separation in the step 2). The process has the advantages that: the recovery rate of the rare earth is obviously improved, the fluorineand the thorium (IV) are effectively reclaimed in a product form, the high-purity cerium product is obtained, reclamation of the rare earth and associated resources is realized, and the additional values of the resources are improved; and the process flow is simple, the consumption of acid and alkali is low, the production cost is low, and the process is environmentally-friendly.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for extracting high-purity uranium, thorium and mixed rare earths from excellent molten slag
ActiveCN104775026ASimple processEase of mass productionProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationRare earth
The invention discloses a method for extracting high-purity uranium, thorium and mixed rare earths from excellent molten slag, which comprises the following steps: acid pickling: adding urdite excellent molten slag into an acid solution, stirring at normal temperature for some time, clarifying, and carrying out siphoning on the supernate to obtain a solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earths; and (2) pressure filtration and water washing: adding the slurry subjected to supernate siphoning into a plate and frame filter press, carrying out pressure filtration until no solution flows out, merging the filtrate with the supernate in the step (1), washing the filter residue of the plate and frame filter press with water until the pH value of the filtrate is 2.0-3.0, and merging the water washing solution with the supernate in the step (1) to obtain a clarified water solution containing uranium, thorium and rare earths and a filter residue. The method is simple in technical process, only adopts liquid-liquid extraction and uses one organic extractant, and thus, can easily implement large-scale production. The chemical materials are common and are low in consumption. The method can effectively extract single uranium and thorium products and mixed rare earths from the urdite excellent molten slag, and the overall yield is up to 90% above. The method is environment-friendly, and has obvious social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:JIANGXI JIEQIU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
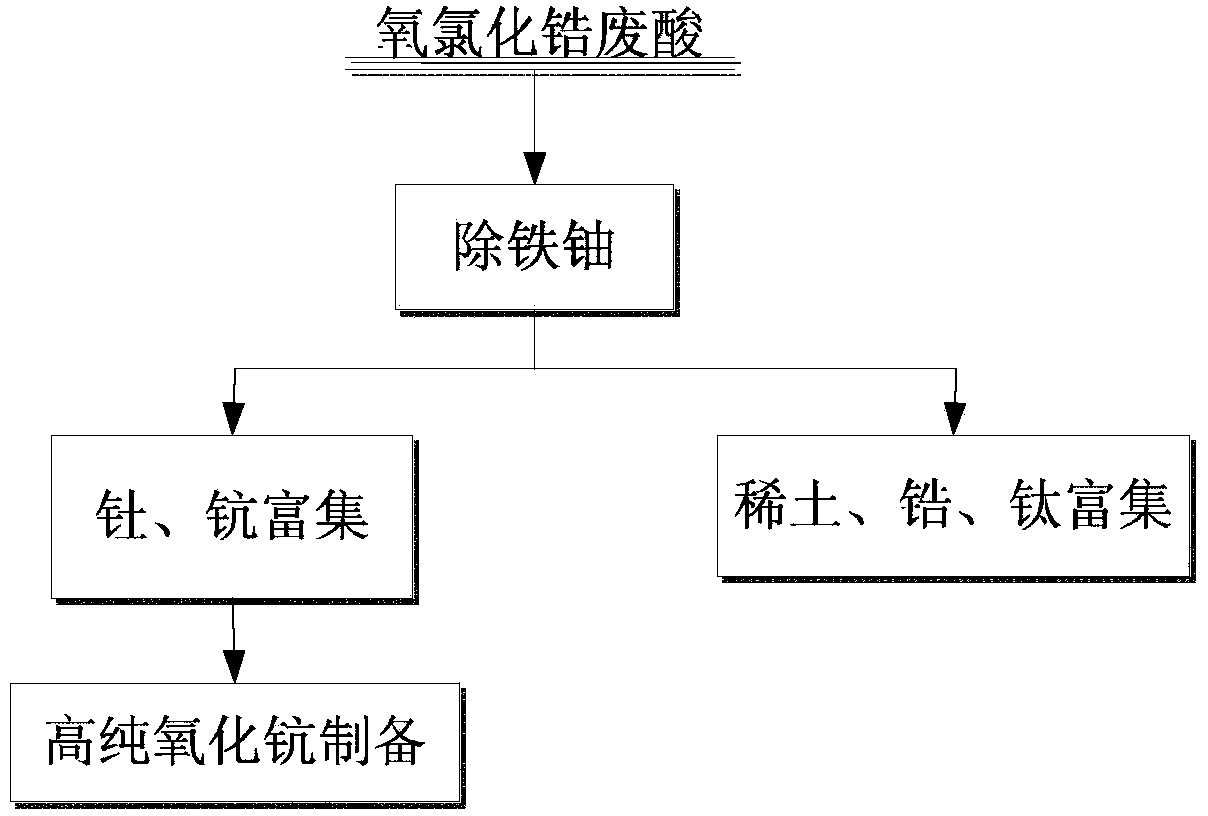
Method for comprehensively recovering multiple elements from zirconium oxychloride liquid waste
The invention provides a method for comprehensively recovering multiple elements from zirconium oxychloride liquid waste. The method comprises the following steps: (1) removing iron and uranium on zirconium oxychloride; (2) gathering scandium and thorium; (3) preparing a high-purity scandium oxide; and (4) gathering rare earth, zirconium and titanium. According to the method provided by the invention, through reasonable configuration of the recovering order of various elements from the zirconium oxychloride liquid waste, scandium enrichment capable of improving the purity by a subsequent purification method can be obtained just by virtue of a cheap extracting agent; and the adverse effects on purity improvement of the subsequently obtained scandium caused by irremovable zirconium and titanium, and radioactive elements thorium and uranium are avoided.
Owner:HUNAN RARE EARTH METAL MATERIAL RES INST
Method for producing diuranate by extracting uranium from rare earth slag containing uranium
The invention relates to a method for producing diuranate by carrying out uranium-thorium separation by using rare earth slag and a preparation method of a used reagent. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out uranium lixiviation on the rare earth slag; regulating the pH of uranium lixivium; carrying out reflux uranium extraction under the action of trifatty amine and mixed alcohol so as to achieve the purpose of the uranium-thorium separation; and carrying out reextraction and sedimentation to obtain a diuranate product with quality meeting or exceeding the standard requirements of diuranate technical conditions (EJ / T803-93). The invention successfully solves the difficulties in producing the diuranate by carrying out the uranium-thorium separation by using the rare earth slag, breaks through the technical bottleneck of difficult industrialization realization, reduces the environmental protection pressure, expands the channels of uranium production raw materials and saves the resources.
Owner:李志伟 +2
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com