Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
280 results about "Neutron capture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
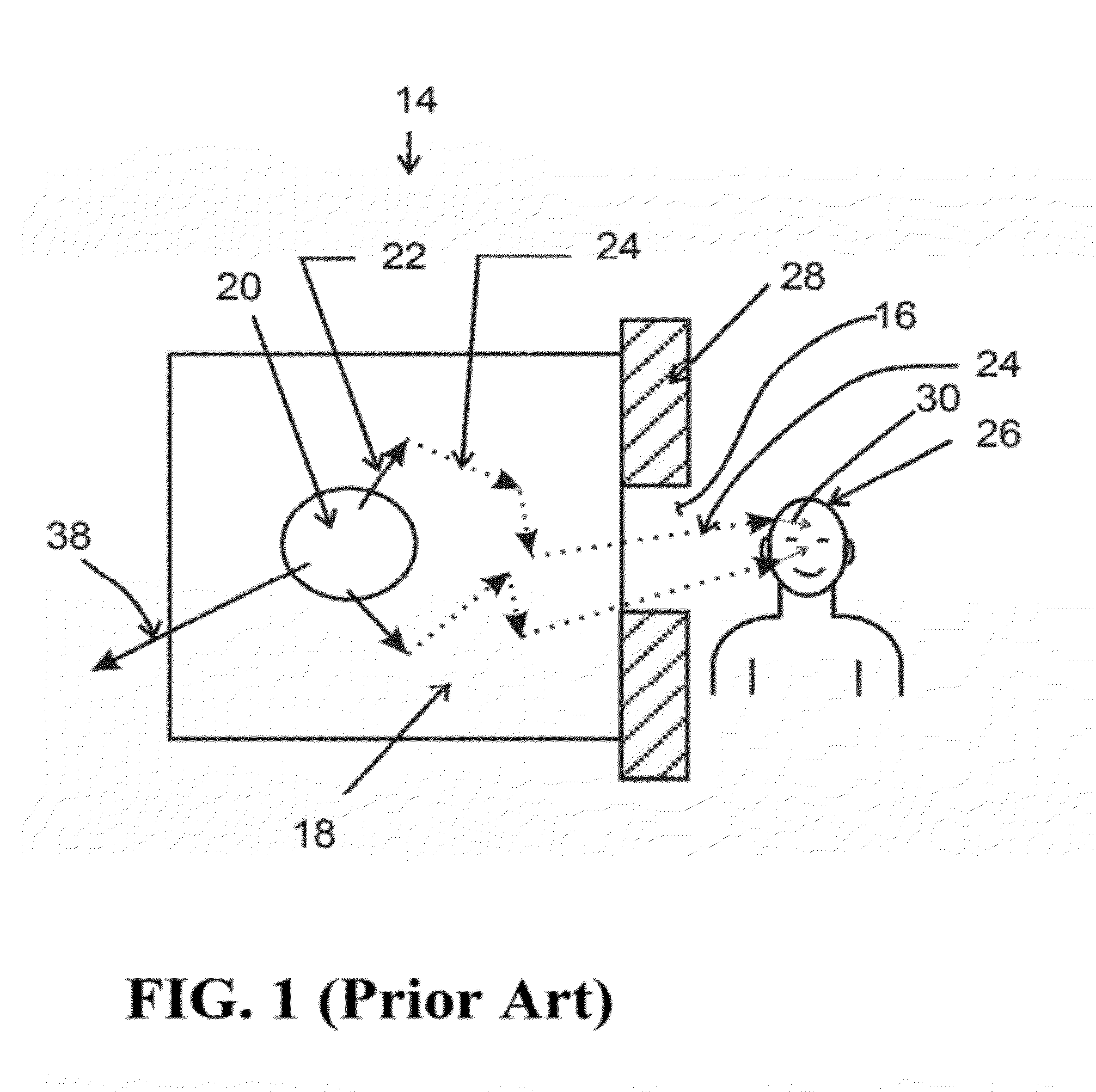
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, which are repelled electrostatically.
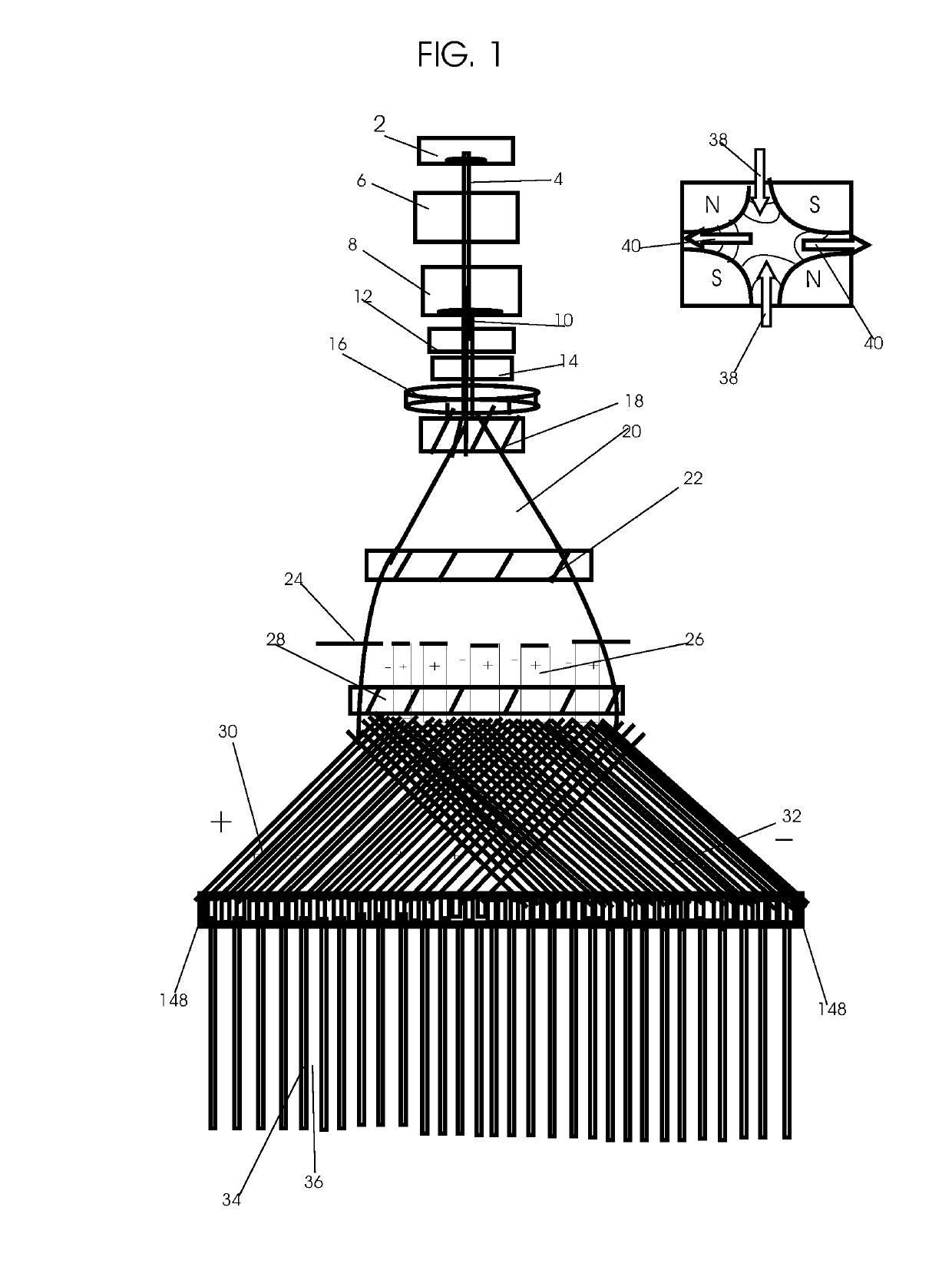
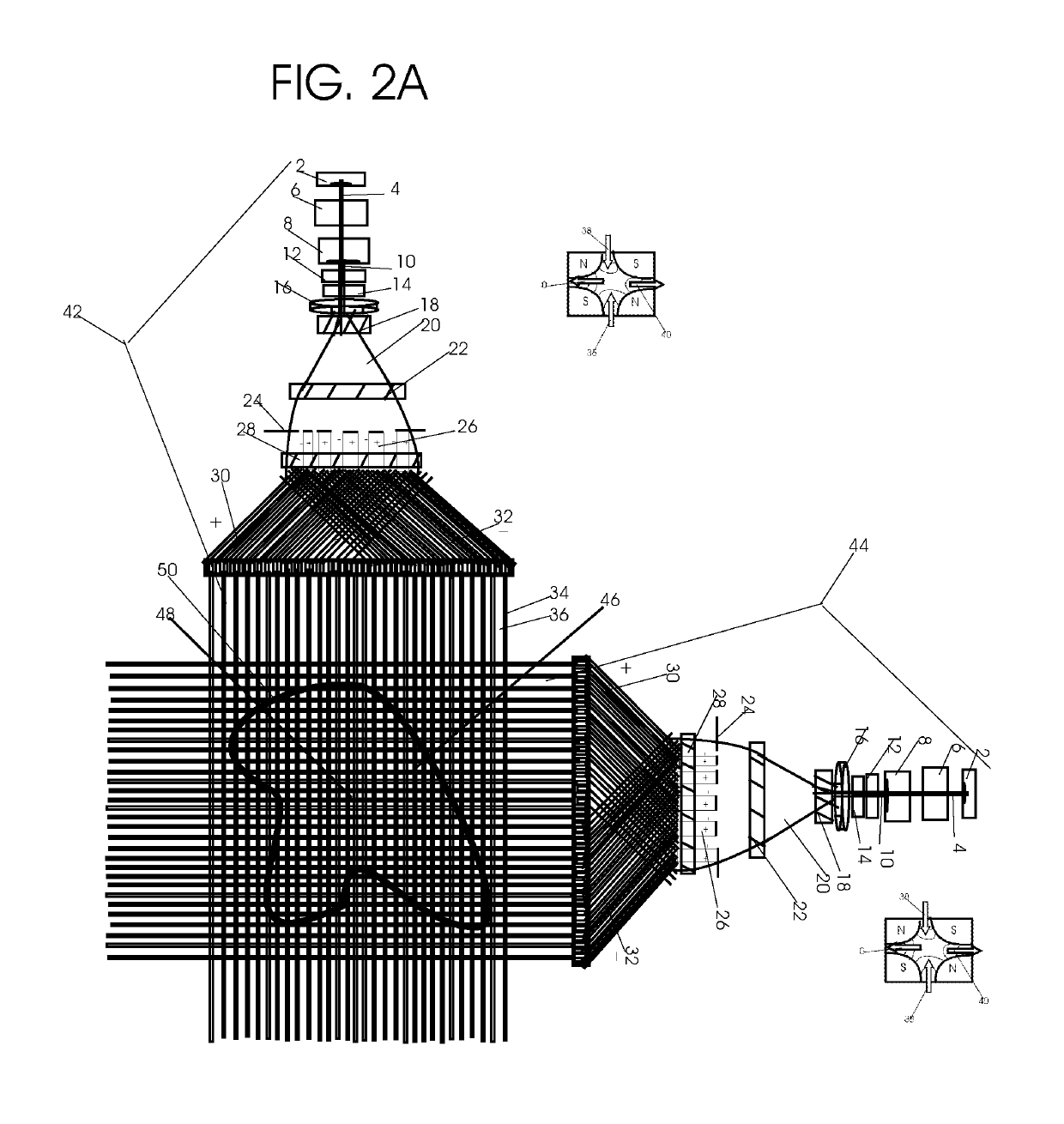
High-current DC proton accelerator
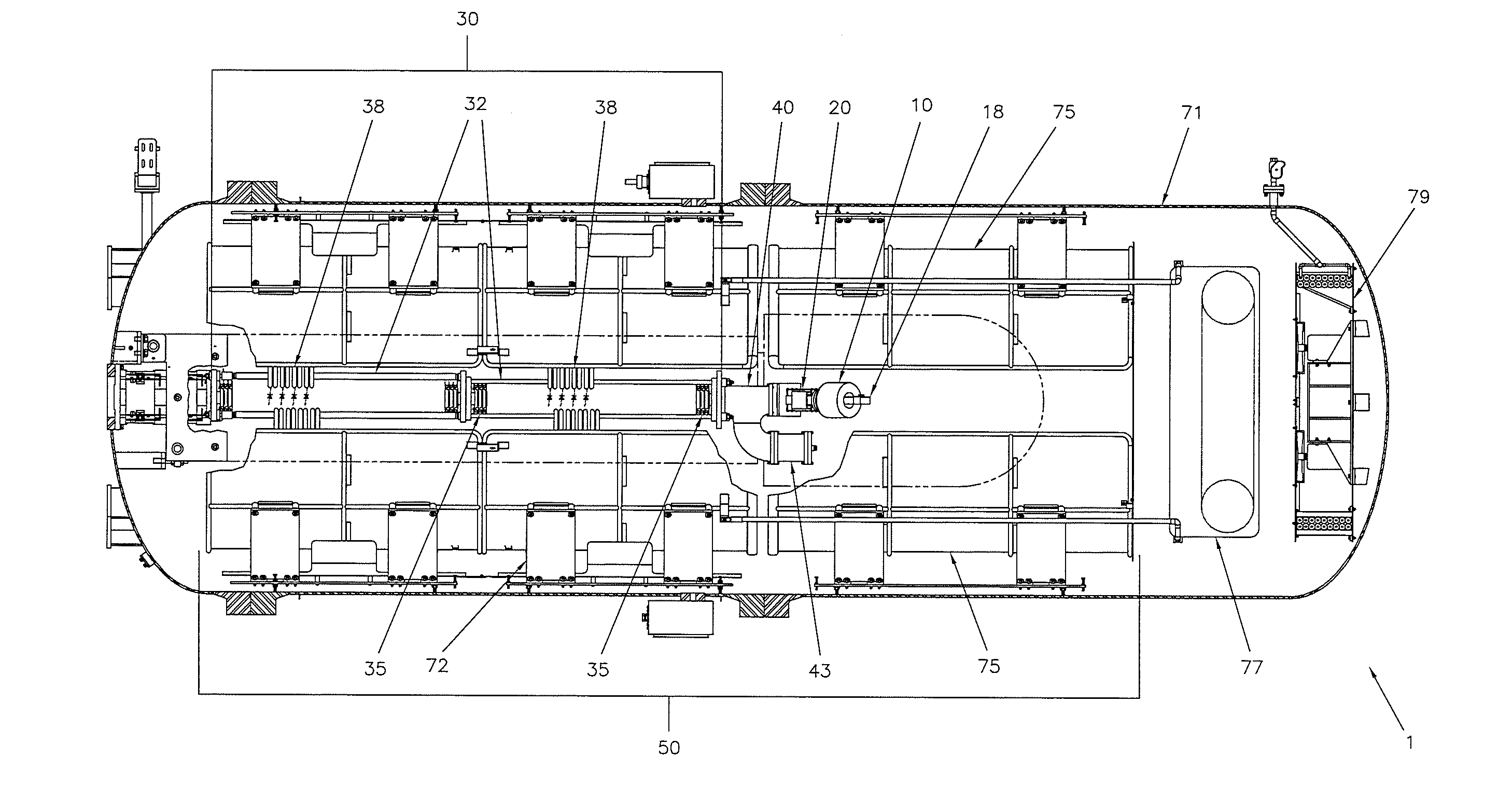
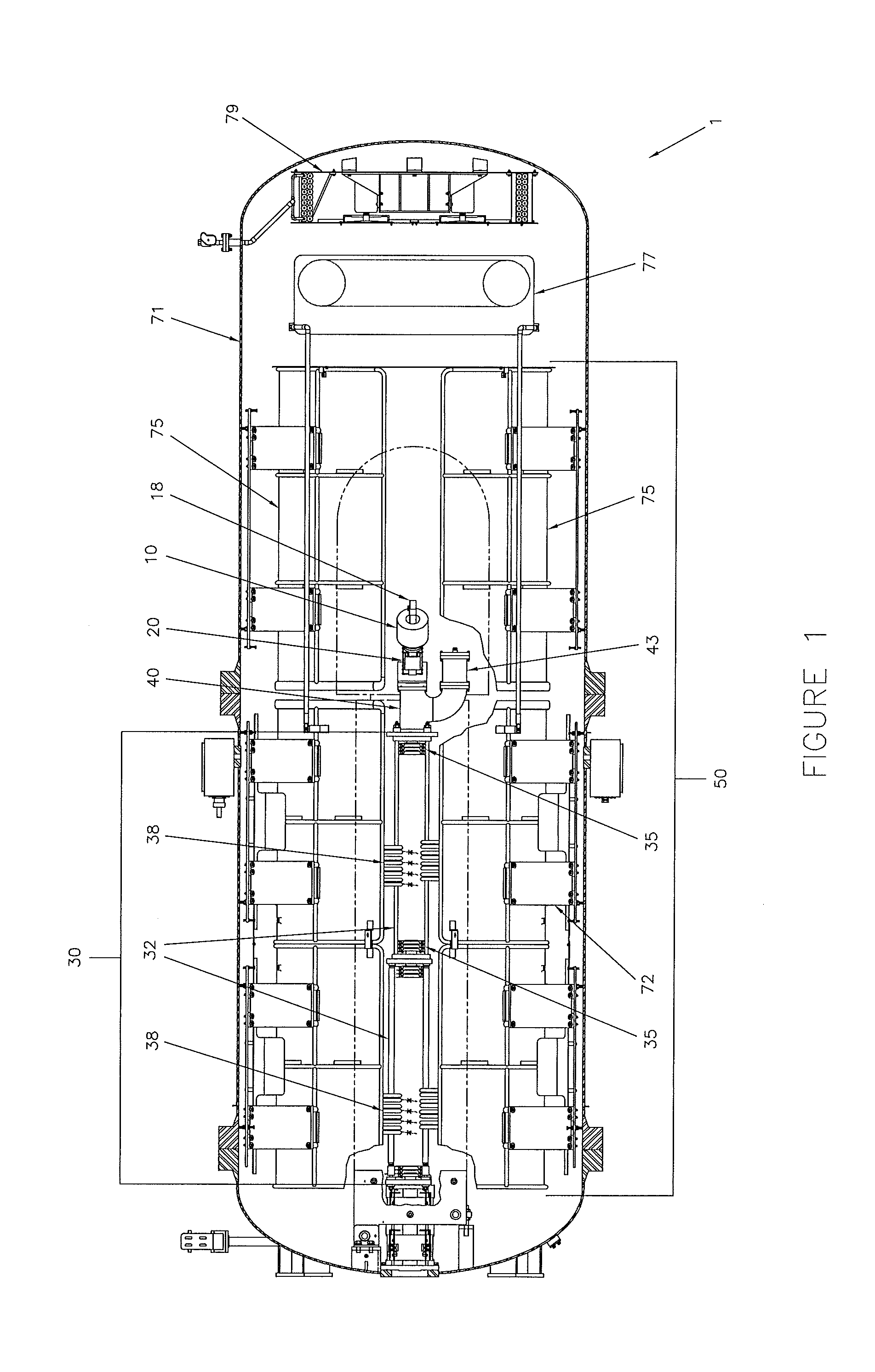
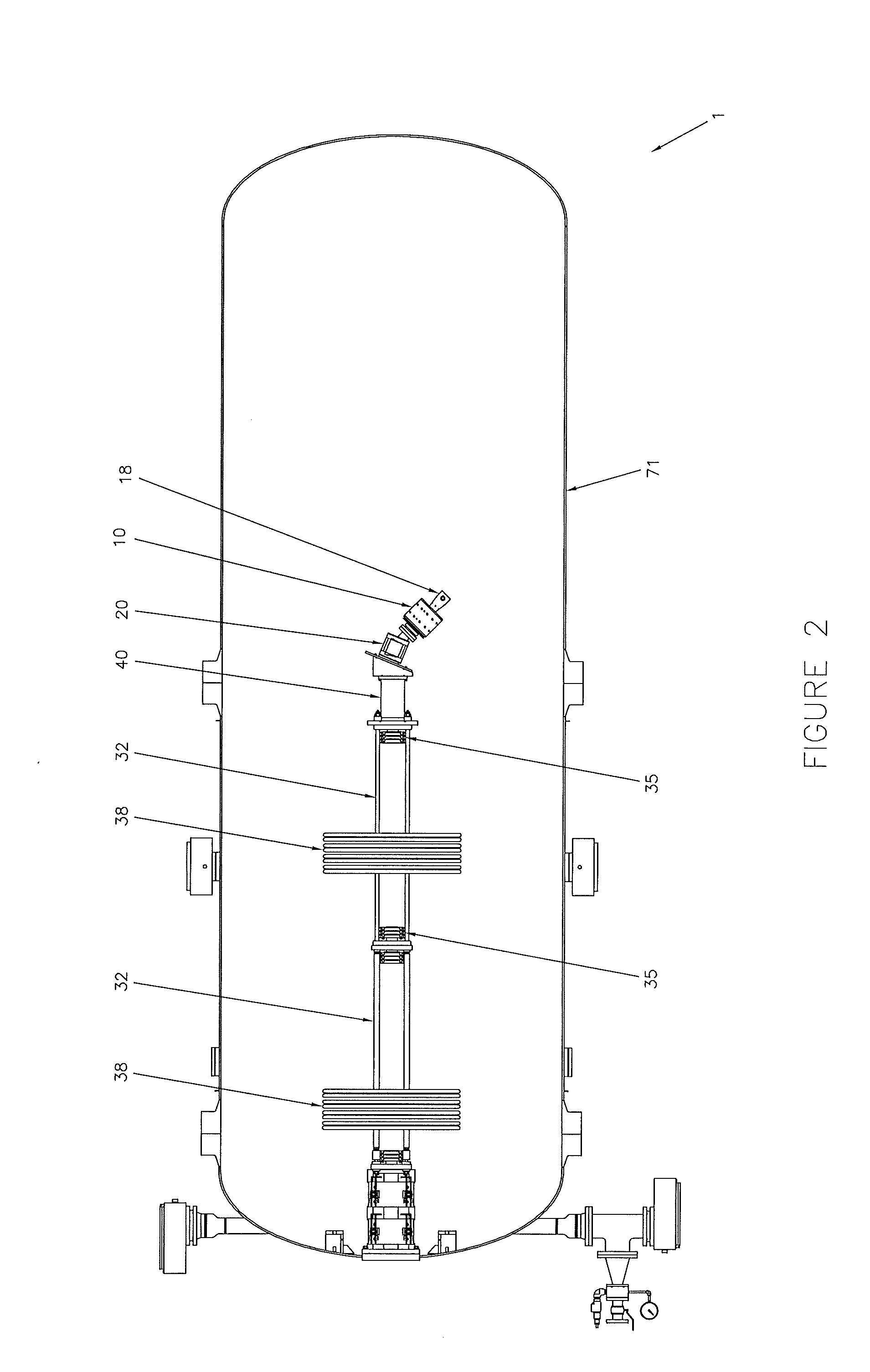
InactiveUS20100033115A1Reduce harmful effectsLimit divergence of beamTransit-time tubesDirect voltage acceleratorsHigh energyNeutron capture
A dc accelerator system able to accelerate high currents of proton beams at high energies is provided. The accelerator system includes a dc high-voltage, high-current power supply, an evacuated ion accelerating tube, a proton ion source, a dipole analyzing magnet and a vacuum pump located in the high-voltage terminal. The high-current, high-energy dc proton beam can be directed to a number of targets depending on the applications such as boron neutron capture therapy BNCT applications, NRA applications, and silicon cleaving.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
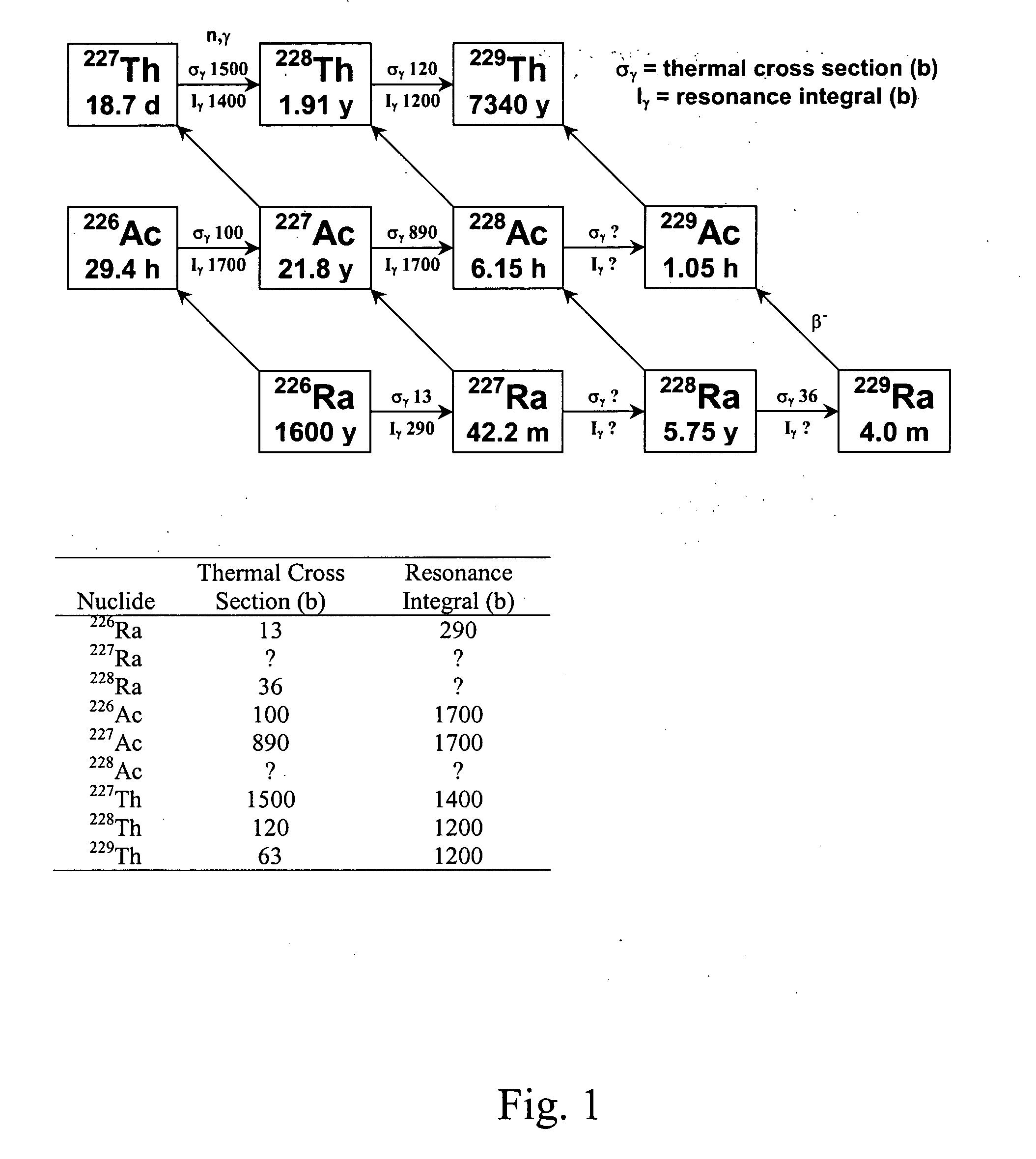
Production of thorium-229
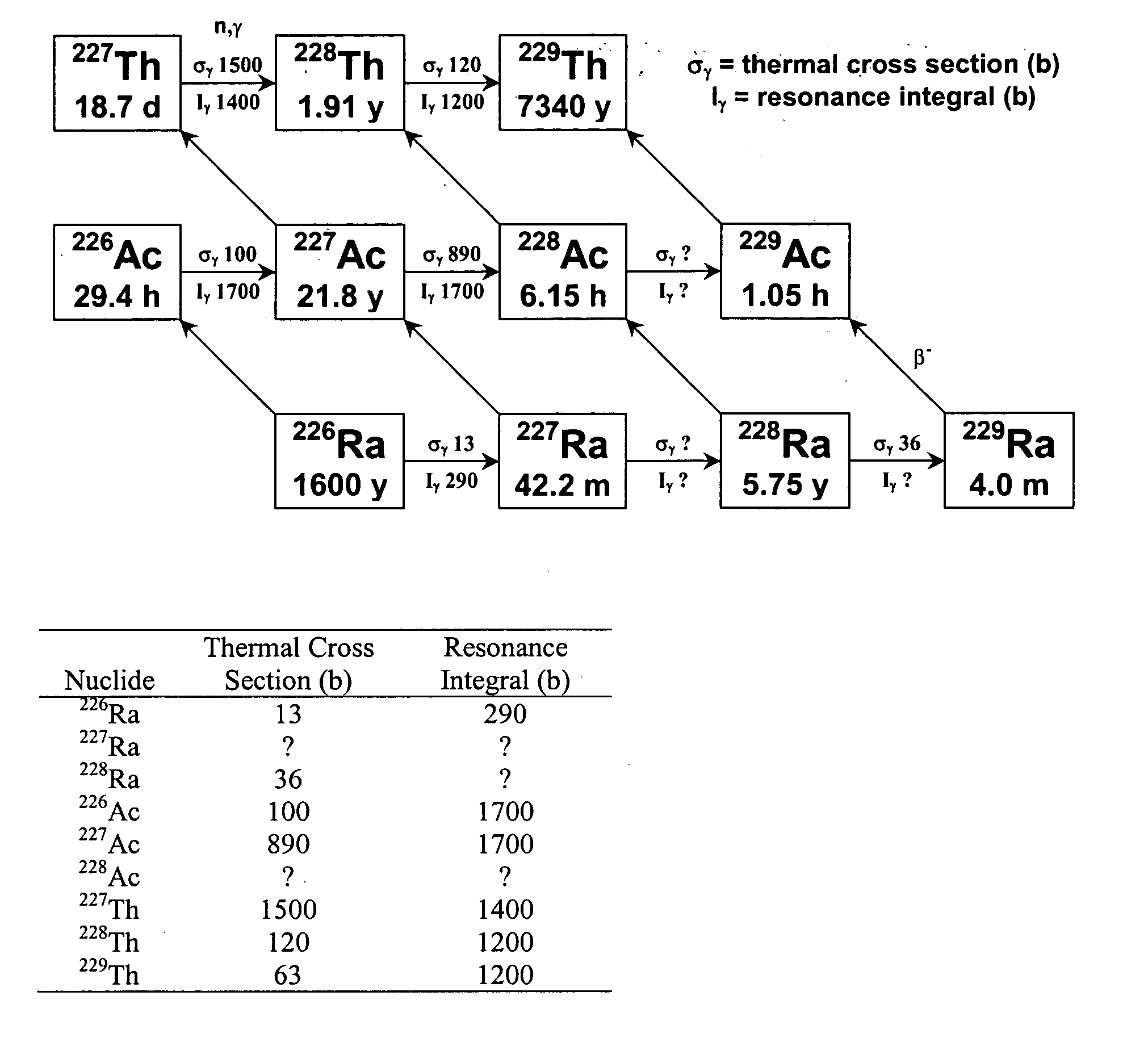
InactiveUS20050105666A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesNeutron captureAlpha particle
A method for producing 229Th includes the steps of providing 226Ra as a target material, and bombarding the target material with alpha particles, helium-3, or neutrons to form 229Th. When neutrons are used, the neutrons preferably include an epithermal neutron flux of at least 1×1013 n s−1·cm−2. 228Ra can also be bombarded with thermal and / or energetic neutrons to result in a neutron capture reaction to form 229Th. Using 230Th as a target material, 229Th can be formed using neutron, gamma ray, proton or deuteron bombardment.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
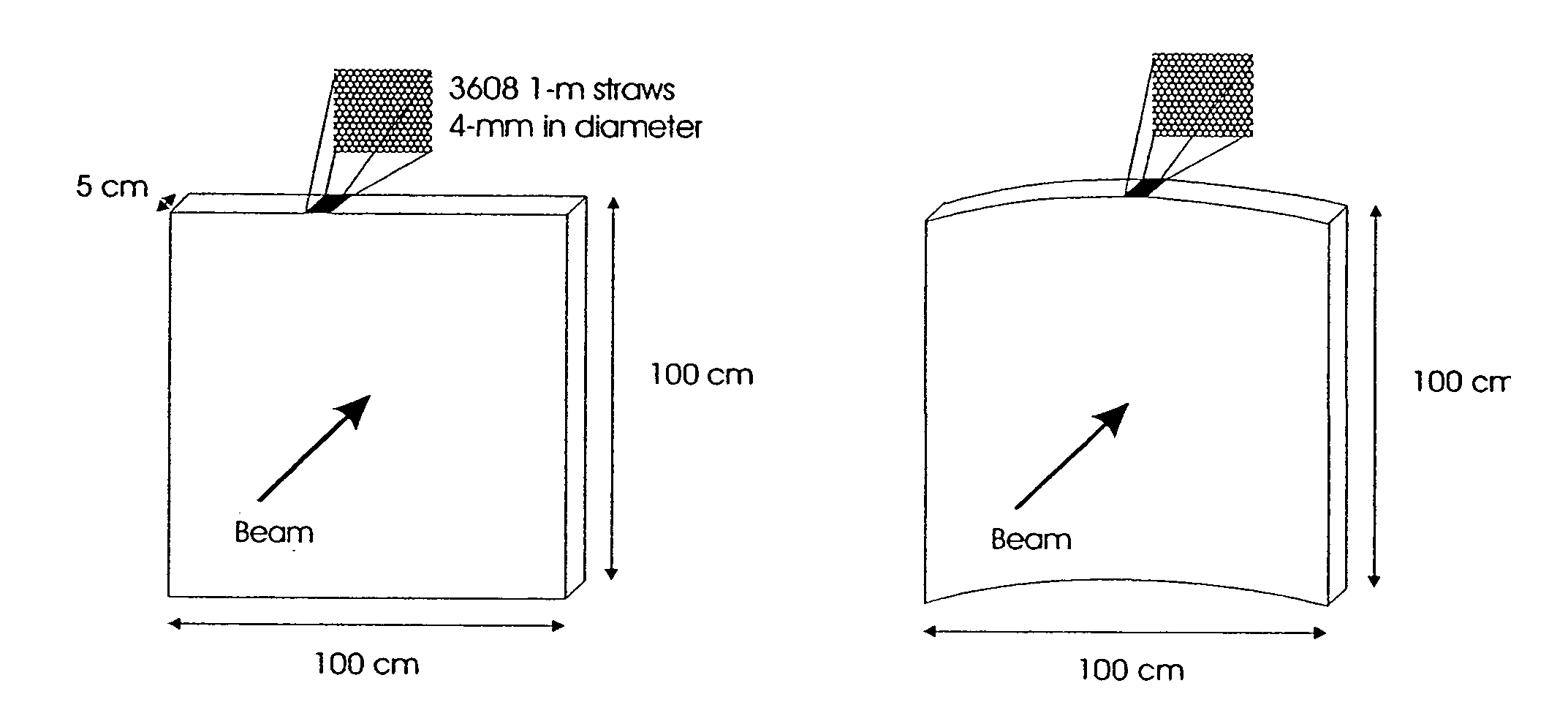
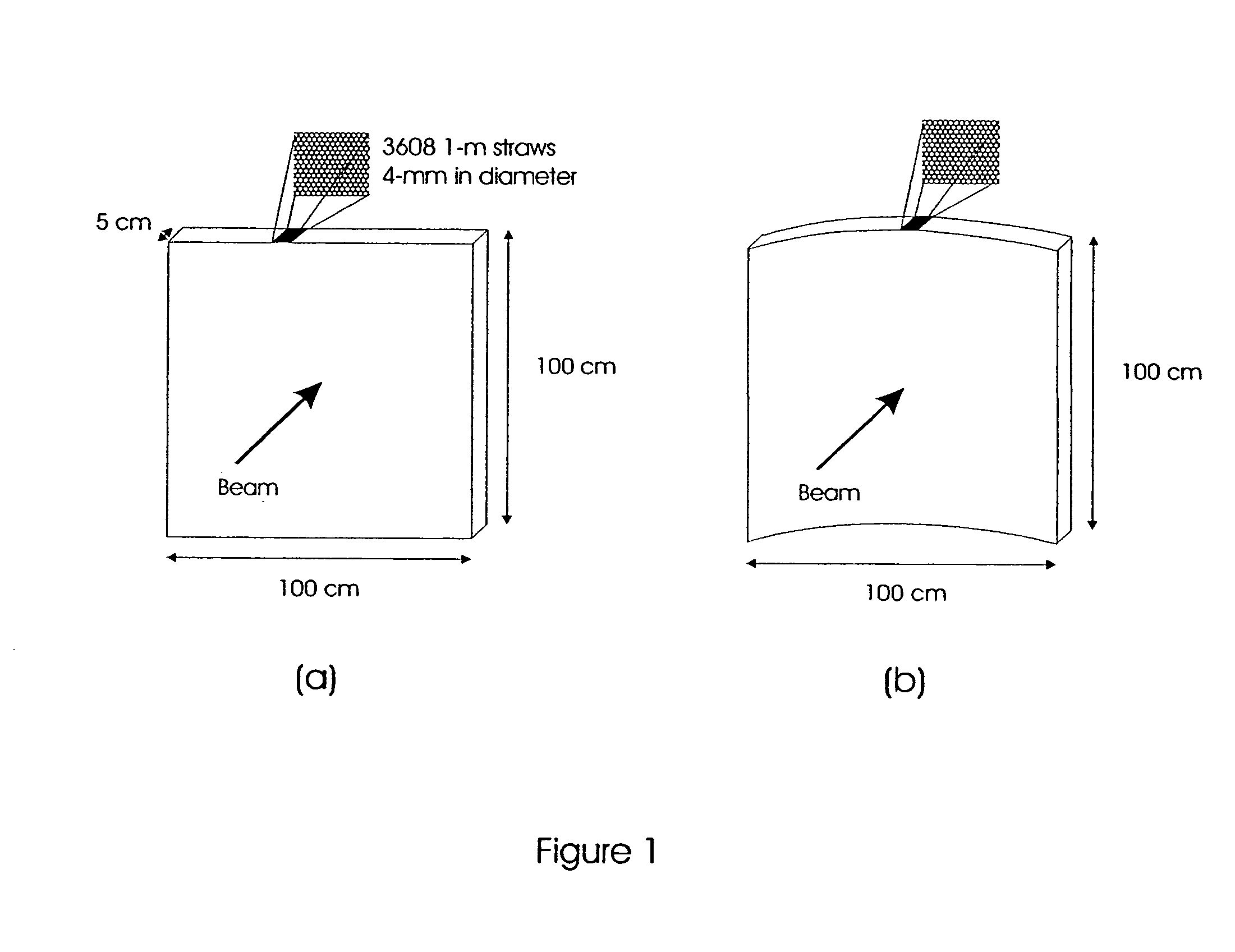
Boron coated straw neutron detector
ActiveUS7002159B2Sensitive to radiationImpression capsElectric discharge tubesElectronCharge division
A neutron detector technology based on 10B thin film conversion of neutrons and detection of neutron capture reaction products in a counter gas within a thin straw tube detector body is described. This neutron detector is based on gas-filled thin wall straw tubes, modified for the conversion of neutrons in a very thin coating, or layer, of 10B, applied for example as a sputter-coated film of 10B4C, that lines the interior, or inside of the straw tube surface; and the subsequent detection of the neutron reaction products in the counter gas. One embodiment of this invention employs a closely-packed array of 10B4C-lined straw tubes employing a very thin and therefore high efficiency 10B4C layer, hence removing the barrier to efficient neutron capture reaction product escape while still providing for efficient neutron capture by providing a plurality of very thin 10B converters, each individual converter element providing efficient reaction product escape. Using such densely packed straw tube detectors of small diameter, a reasonable stack depth allows a high neutron detection efficiency to be achieved on the 1–10Å wavelength range of thermal neutrons. The position of each interacting neutron can be accurately obtained with for example, resistive charge division readout combined with straw decoding electronics to determine the identity of the struck straw.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
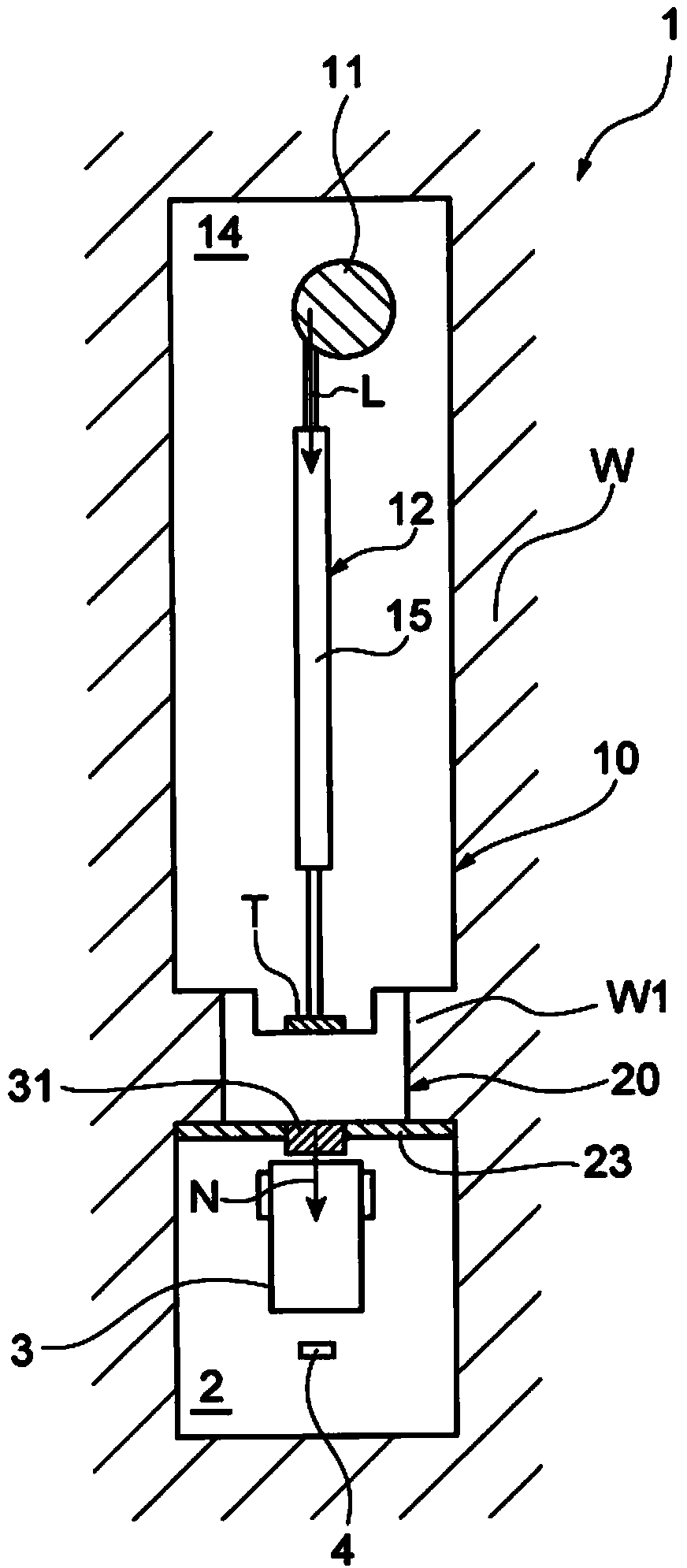
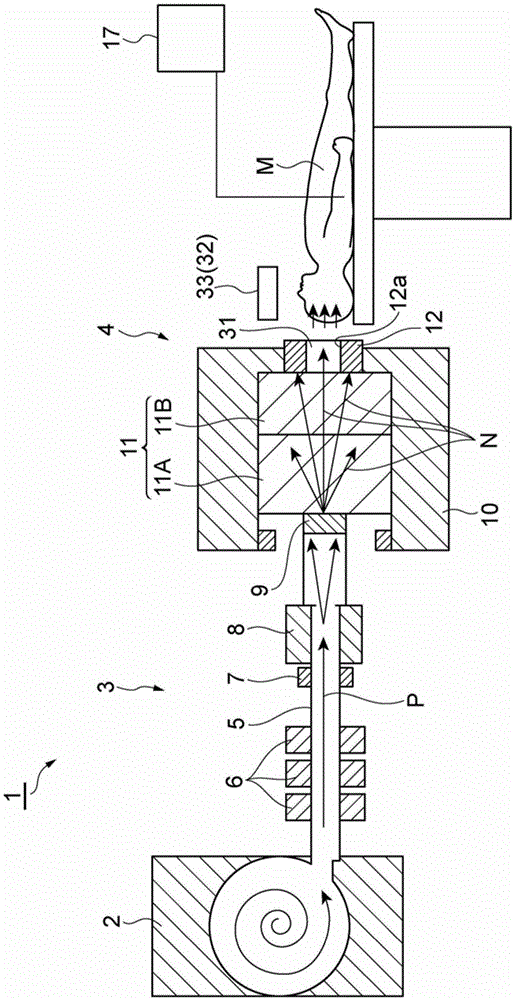
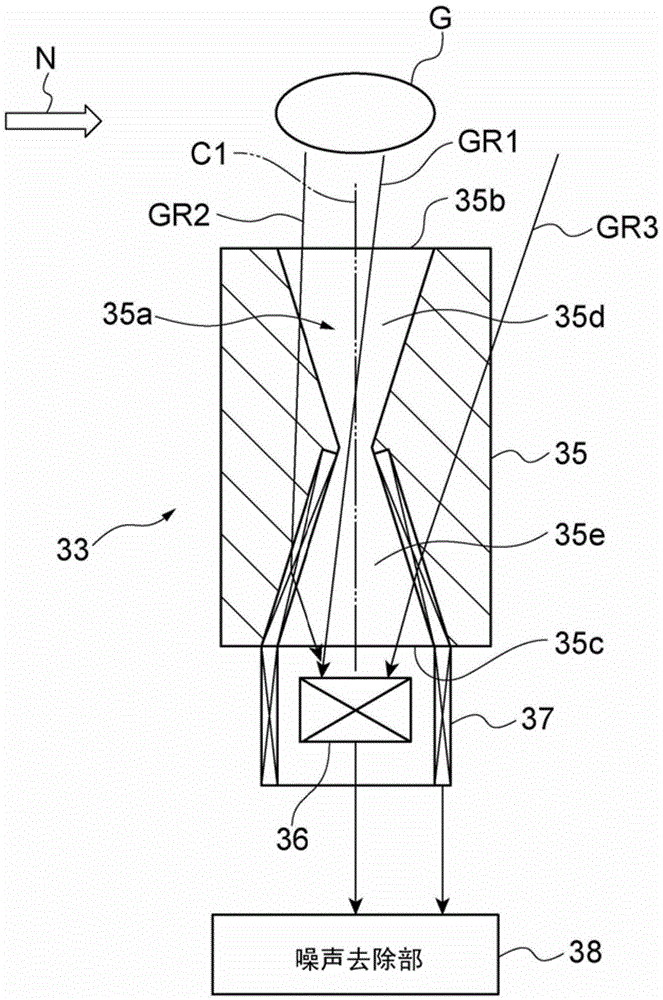
Neutron capture therapy apparatus and neutron beam measuring method
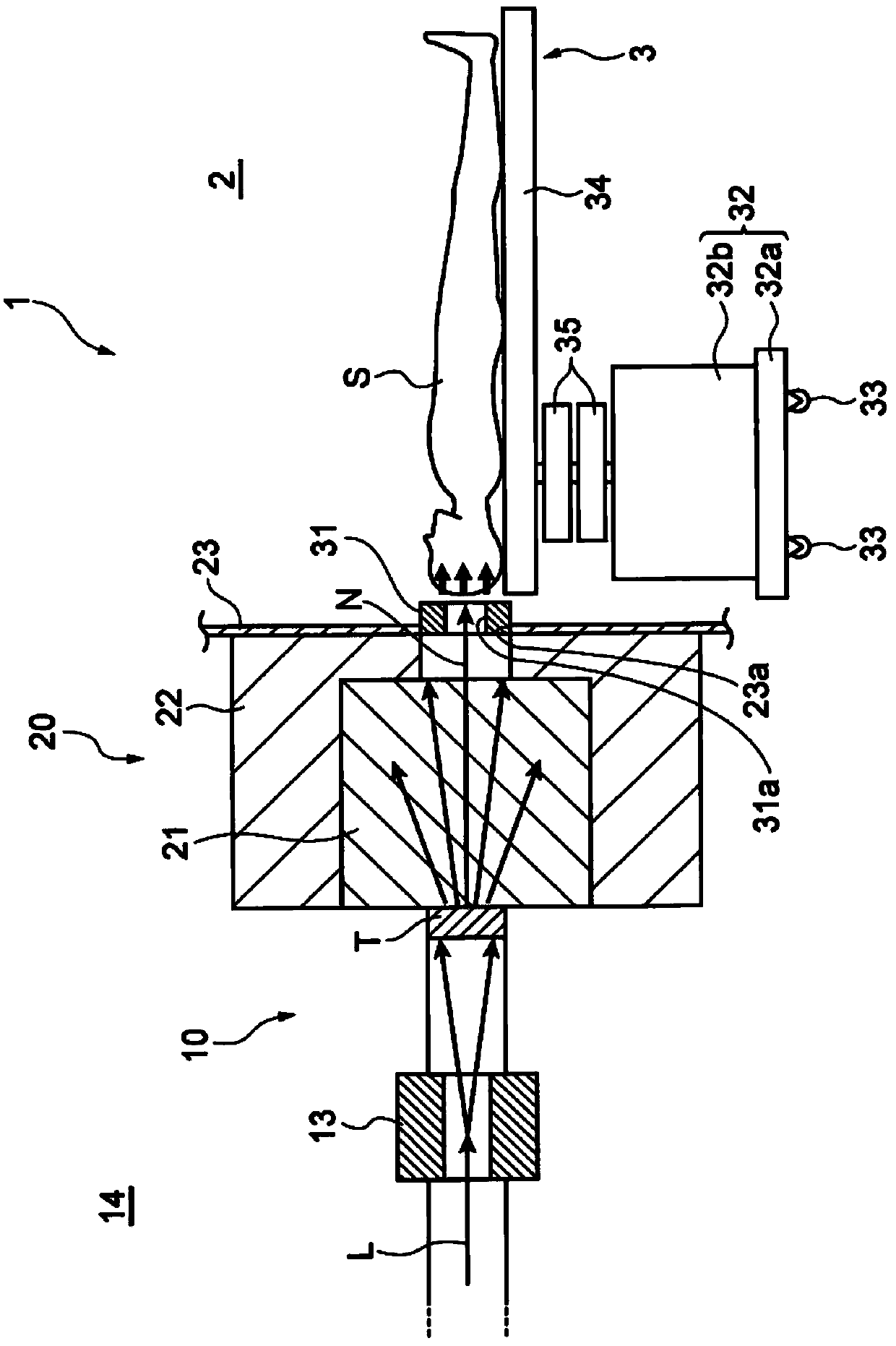
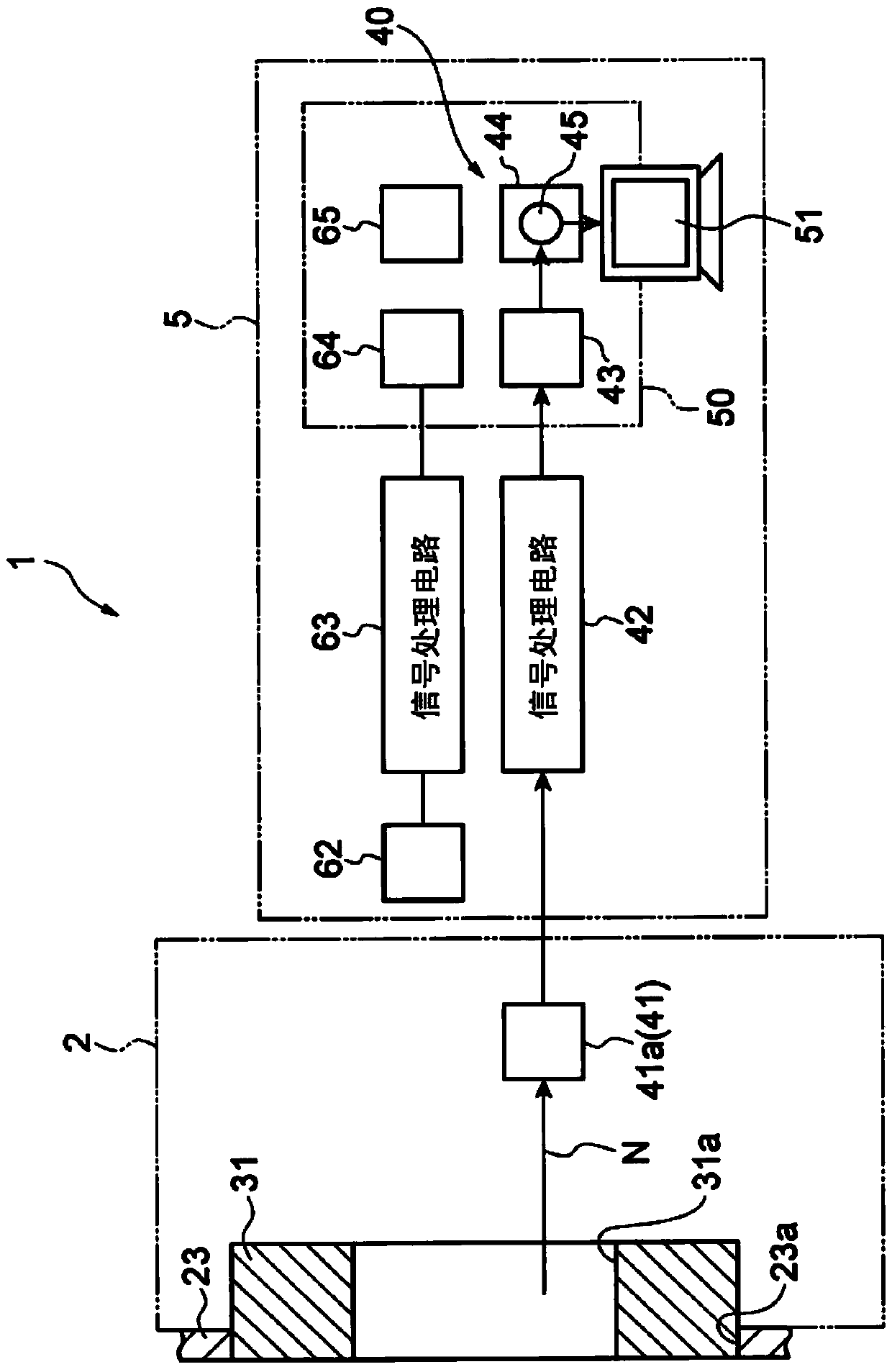
ActiveCN104174121AReal-time measurementDecreased measurement accuracyMeasurement with scintillation detectorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron doseNeutron capture
There is provided a neutron capture therapy apparatus (1) capable of measuring the neutron dose in real time while suppressing a reduction in the measurement accuracy of a neutron beam (N). A real-time dose output unit (40) including a scintillation detector (41), which detects the neutron beam (N) and outputs a signal in real time, and a neutron dose output unit (44), which converts the signal, output from the scintillation detector (41) into a neutron dose using a correction coefficient (45) and outputs the neutron dose in real time, and a correction coefficient setting unit (60) that sets the correction coefficient 45 are provided. The correction coefficient setting unit (60) includes a gamma ray detection section (62) that detects a gamma ray emitted from a gold wire (61) activated by irradiation of the neutron beam (N), and modifies the correction coefficient (45) based on a signal, which is output from the scintillation detector (41) by irradiation of the neutron beam (N), and a dose of the neutron beam (N), which is acquired based on the gamma ray detected by the gamma ray detection section (62).
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
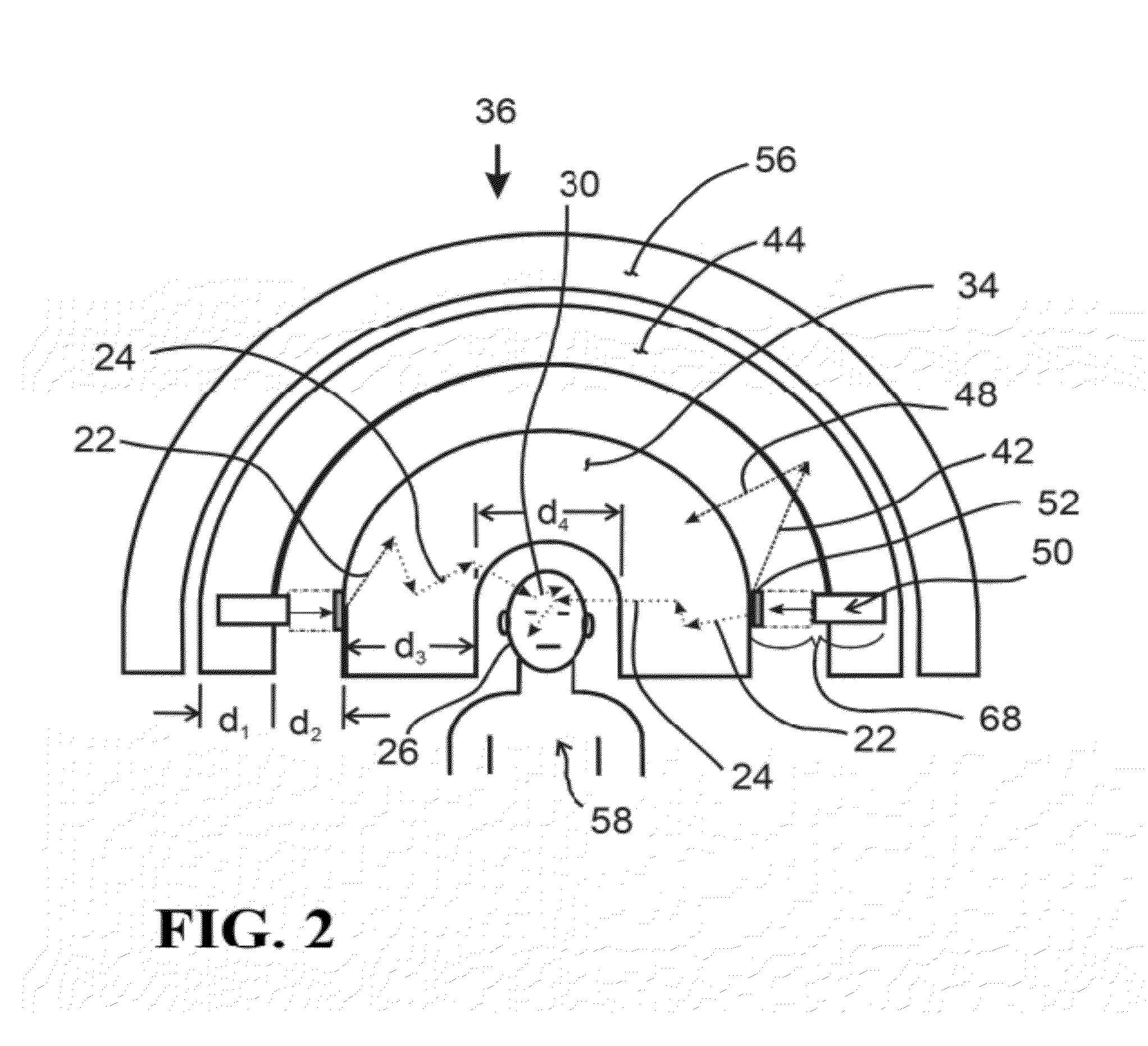
Neutron Source for Neutron Capture Therapy
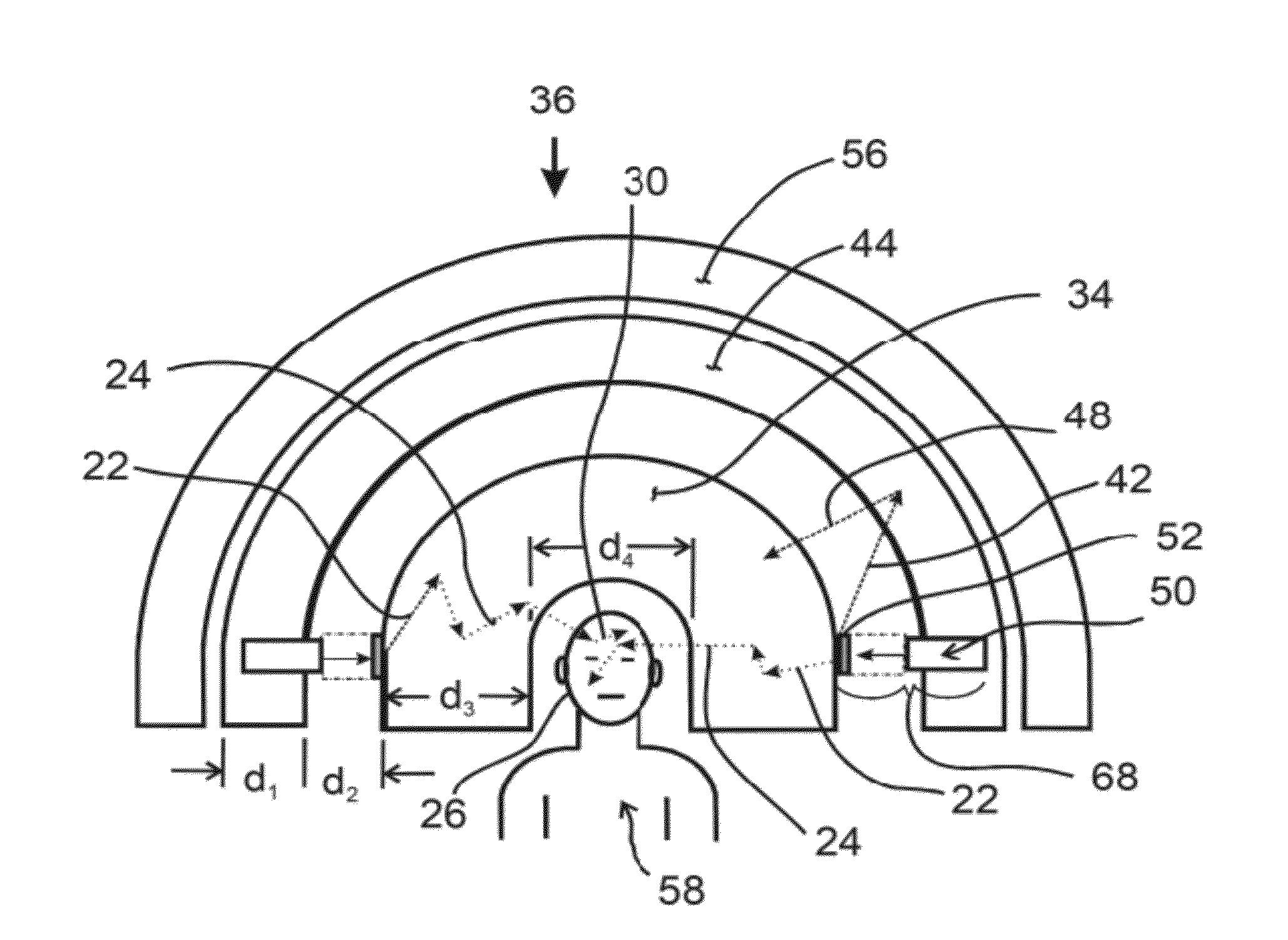
InactiveUS20120330084A1Reduce electric powerReact SafeNeutron sourcesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyNeutron captureGamma ray
A therapy apparatus for producing thermal neutrons at a tumor site in a patient has a plurality of fast neutron sources surrounding a moderator, a fast neutron reflecting media around the fast neutron sources, a gamma-ray and neutron shielding media surrounding the fast neutron reflecting media, and a patient chamber positioned inside the moderator. The fast neutron sources are positioned around the moderator to maximize and direct the neutron flux to said tumor site.
Owner:ADELPHI TECH INC
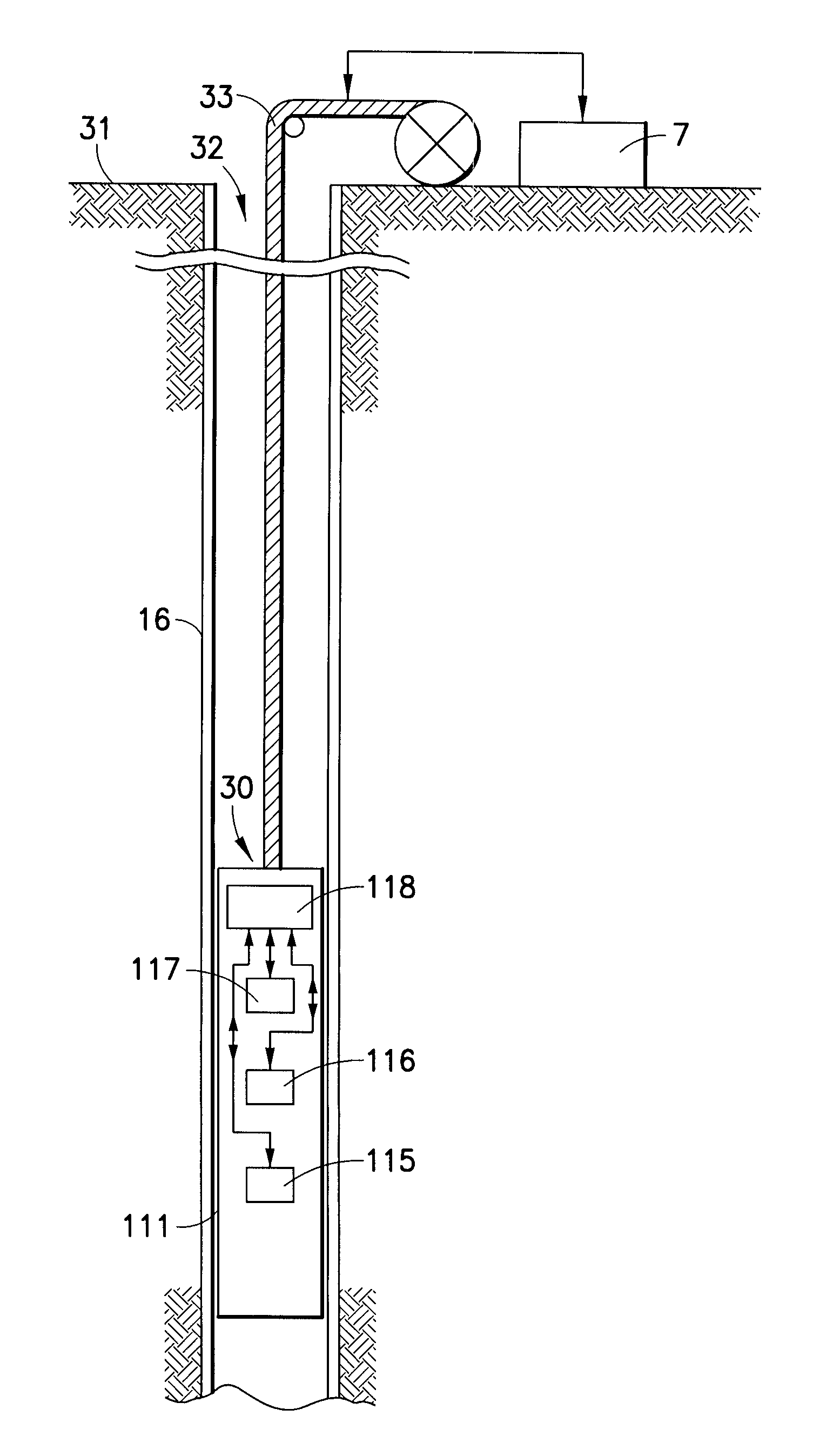
Well logging method for determining formation characteristics using pulsed neutron capture measurements
ActiveUS7408150B1Repeatable smooth behaviorPoorly repeatable resultNuclear radiation detectionFrequency spectrumNeutron capture
A method for determining thermal capture cross-sections of formations surrounding an earth borehole, including the following steps: providing a logging device that is moveable through the borehole; transmitting, from the logging device, bursts of neutrons into the formations; detecting, at the logging device, resultant gamma ray counts, and deriving a measurement spectrum from the gamma ray counts; deriving a forward model comprising a combination of model exponential components having respective model decay times and model amplitudes; deriving an error function that depends on comparison between the forward model and the measurement spectrum; and determining, by regularized inversion, optimized exponential components of the model that substantially minimize the error function; the optimized exponential components being indicative of the thermal capture cross-sections of the formations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Moldable neutron sensitive compositions, articles, and methods
ActiveUS20090140158A1Sufficient flowabilityOther chemical processesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron captureChemistry
Moldable neutron sensitive compositions containing an inorganic scintillating component, and neutron capture component, and a moldable resin component, are described. They are prepared with optimized compositions for maximized thermal neutron sensitivity. Methods for preparing such compositions, and articles and radiation detectors made from them are described as well.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Compound isotope target assembly for production of medical and commercial isotopes by means of spectrum shaping alloys
InactiveUS20090274258A1Increase local populationLow neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron captureResonance
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S +1
Moldable neutron sensitive compositions, articles, and methods
ActiveUS7800073B2Other chemical processesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron captureChemistry
Moldable neutron sensitive compositions containing an inorganic scintillating component, and neutron capture component, and a moldable resin component, are described. They are prepared with optimized compositions for maximized thermal neutron sensitivity. Methods for preparing such compositions, and articles and radiation detectors made from them are described as well.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Neutron Source for Neutron Capture Therapy
ActiveUS20140179978A1Uniform dosingUniform ratioNeutron sourcesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyNeutron captureGamma ray
A therapy apparatus for producing thermal neutrons at a tumor site in a patient has a plurality of fast neutron sources surrounding a moderator, a fast neutron reflecting media around the fast neutron sources, a gamma-ray and neutron shielding media surrounding the fast neutron reflecting media, and a patient chamber positioned inside the moderator. The fast neutron sources are positioned around the moderator to maximize and direct the neutron flux to said tumor site.
Owner:ADELPHI TECH INC
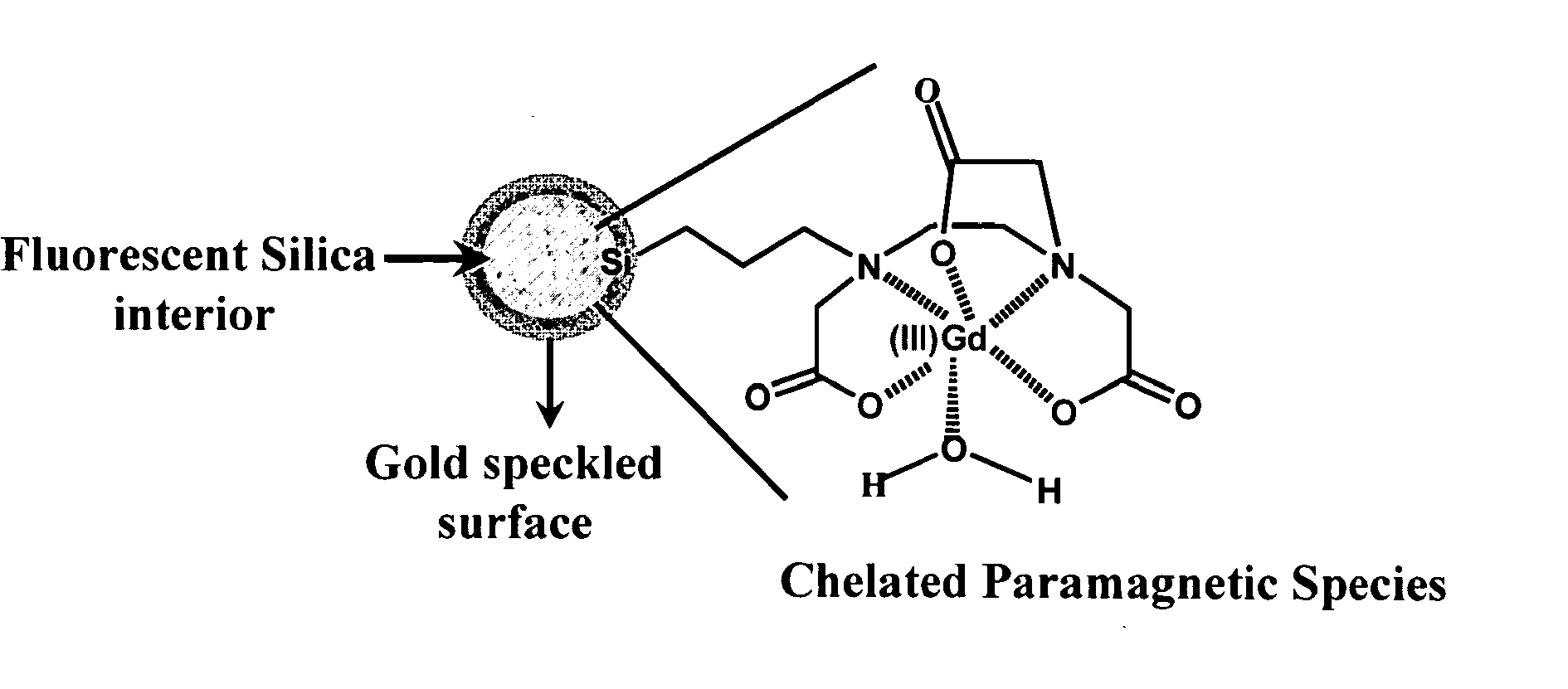
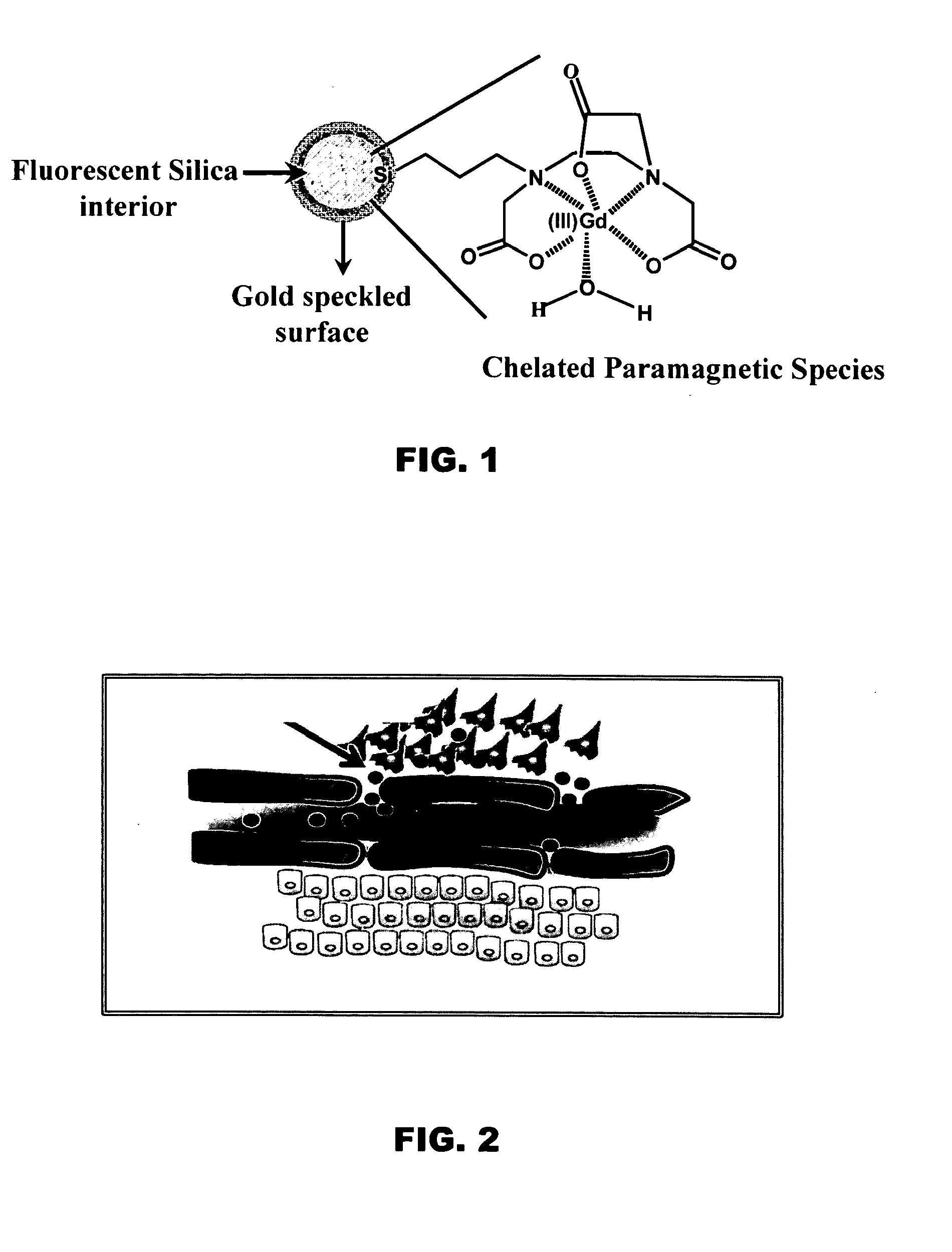
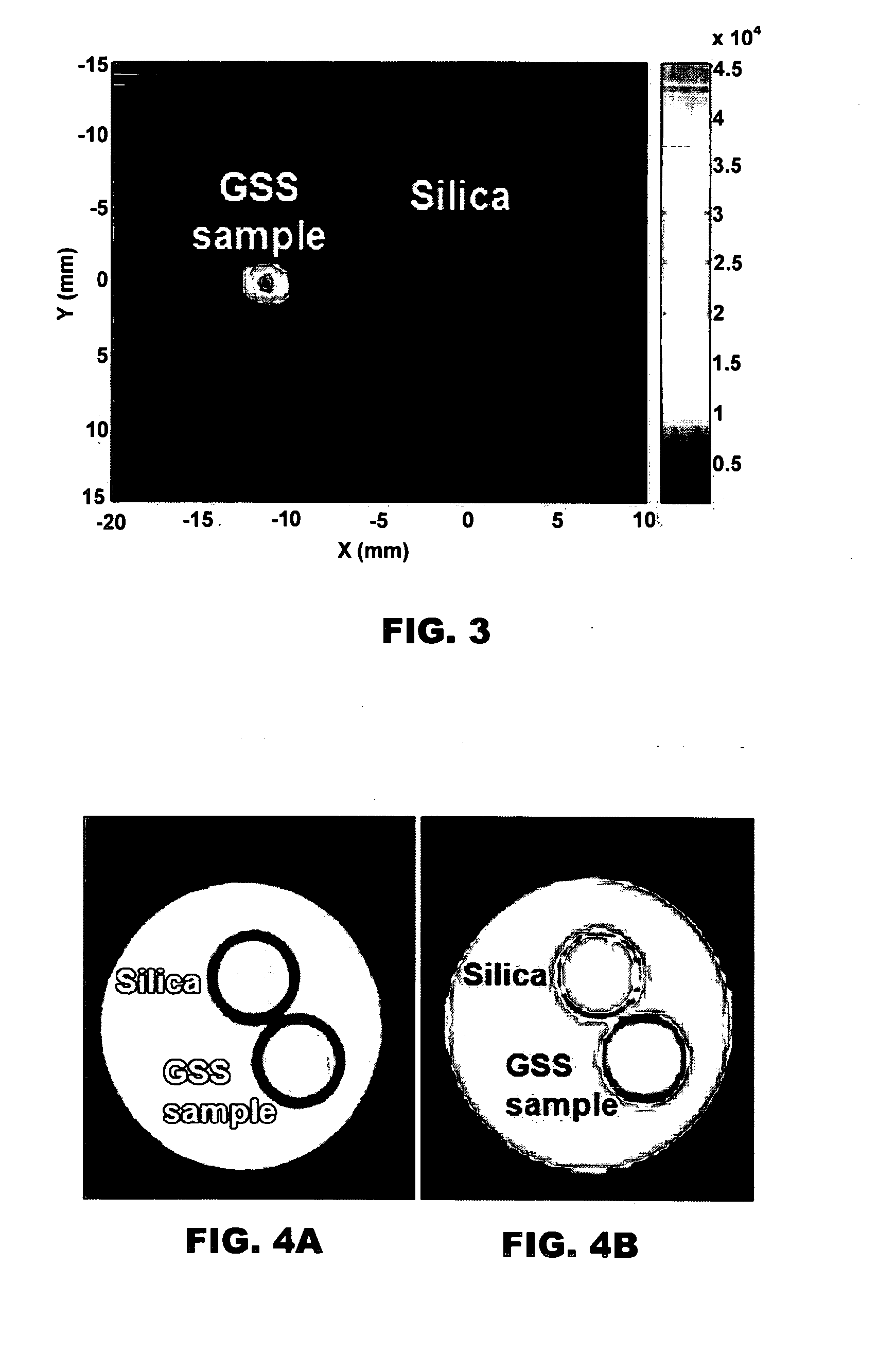
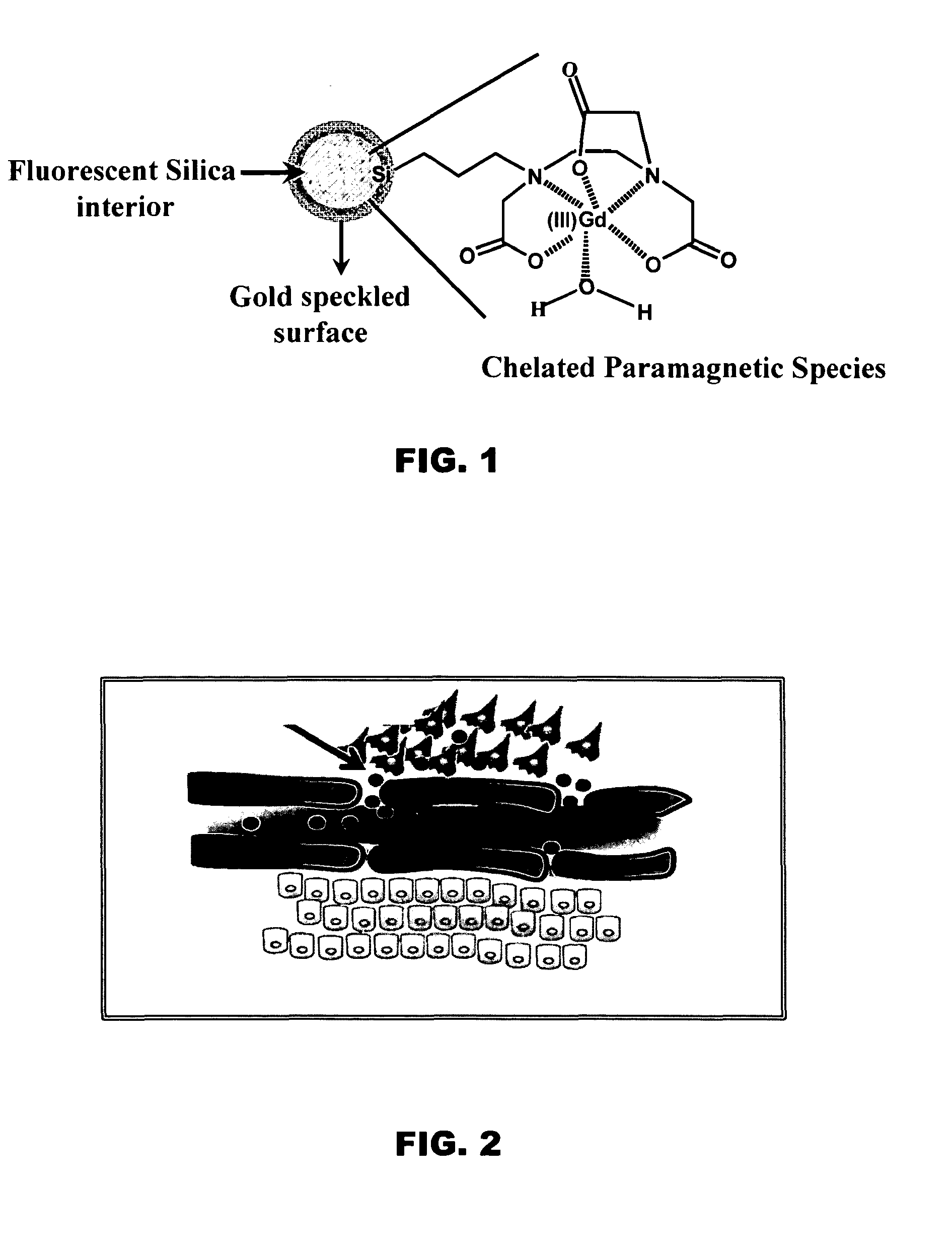
Multimodal nanoparticles for non-invasive bio-imaging
InactiveUS20100254911A1Increase contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideMetal coatingNeutron capture
Multimodal nanoparticles are nanoparticles containing contrast agents for PAT and one or more of luminescence imaging, x-ray imaging, and / or MRI. The multimodal nanoparticles can have a dielectric core comprising an oxide with a metal coating on the core. The particles can be metal speckled. The multimodal nanoparticles can be used for therapeutic purposes such as ablation of tumors or by neutron capture in addition to use as contrast agents for imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Neutron radiating device in hospital
InactiveCN1509777ASelf-stabilizingPower optimizationSurgical instrument detailsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyReaction layerNeutron capture
Owner:周永茂
Multimodal nanoparticles for non-invasive bio-imaging
InactiveUS8361437B2Increase contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideMetal coatingNeutron capture
Multimodal nanoparticles are nanoparticles containing contrast agents for PAT and one or more of luminescence imaging, x-ray imaging, and / or MRI. The multimodal nanoparticles can have a dielectric core comprising an oxide with a metal coating on the core. The particles can be metal speckled. The multimodal nanoparticles can be used for therapeutic purposes such as ablation of tumors or by neutron capture in addition to use as contrast agents for imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
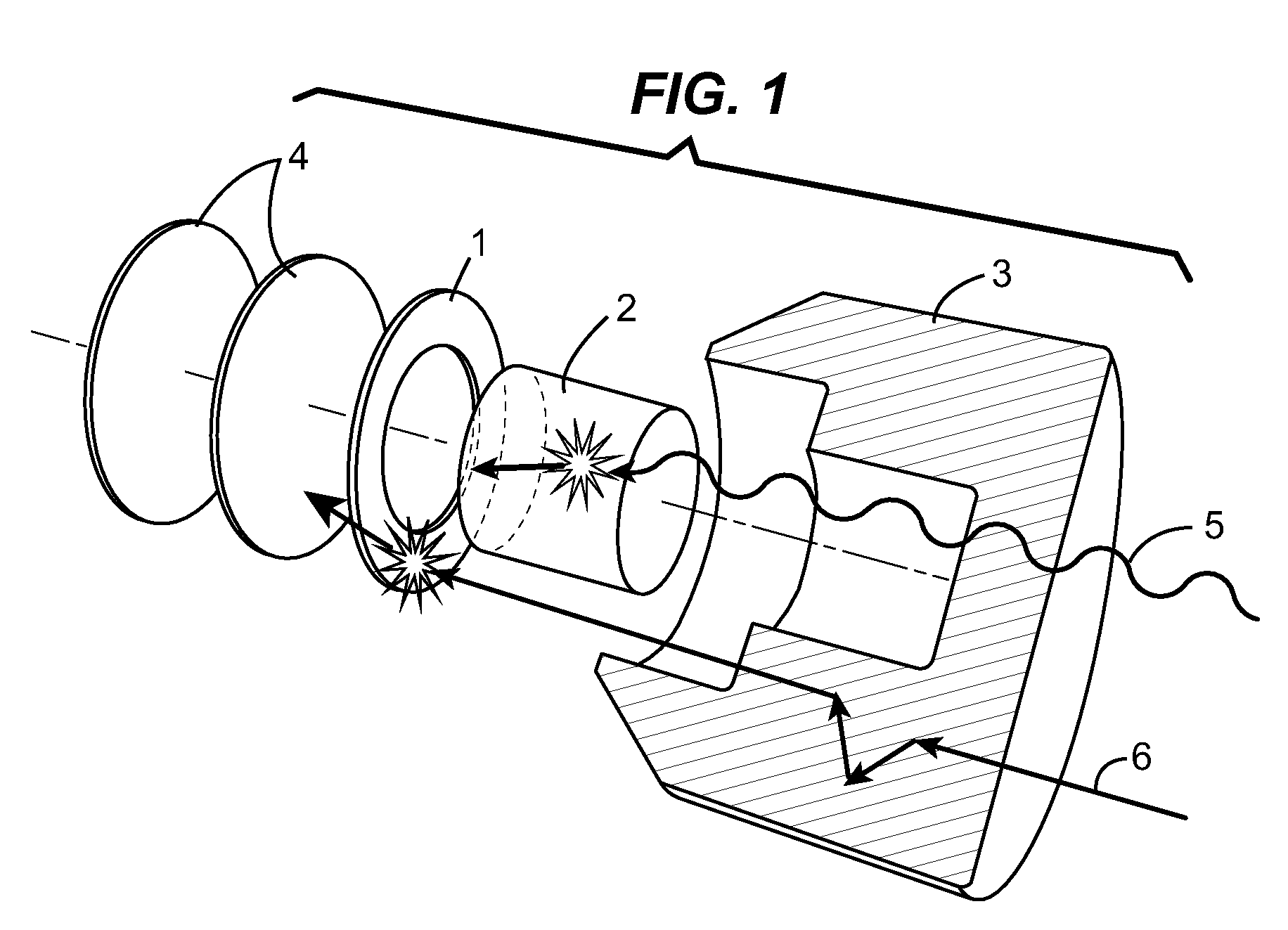
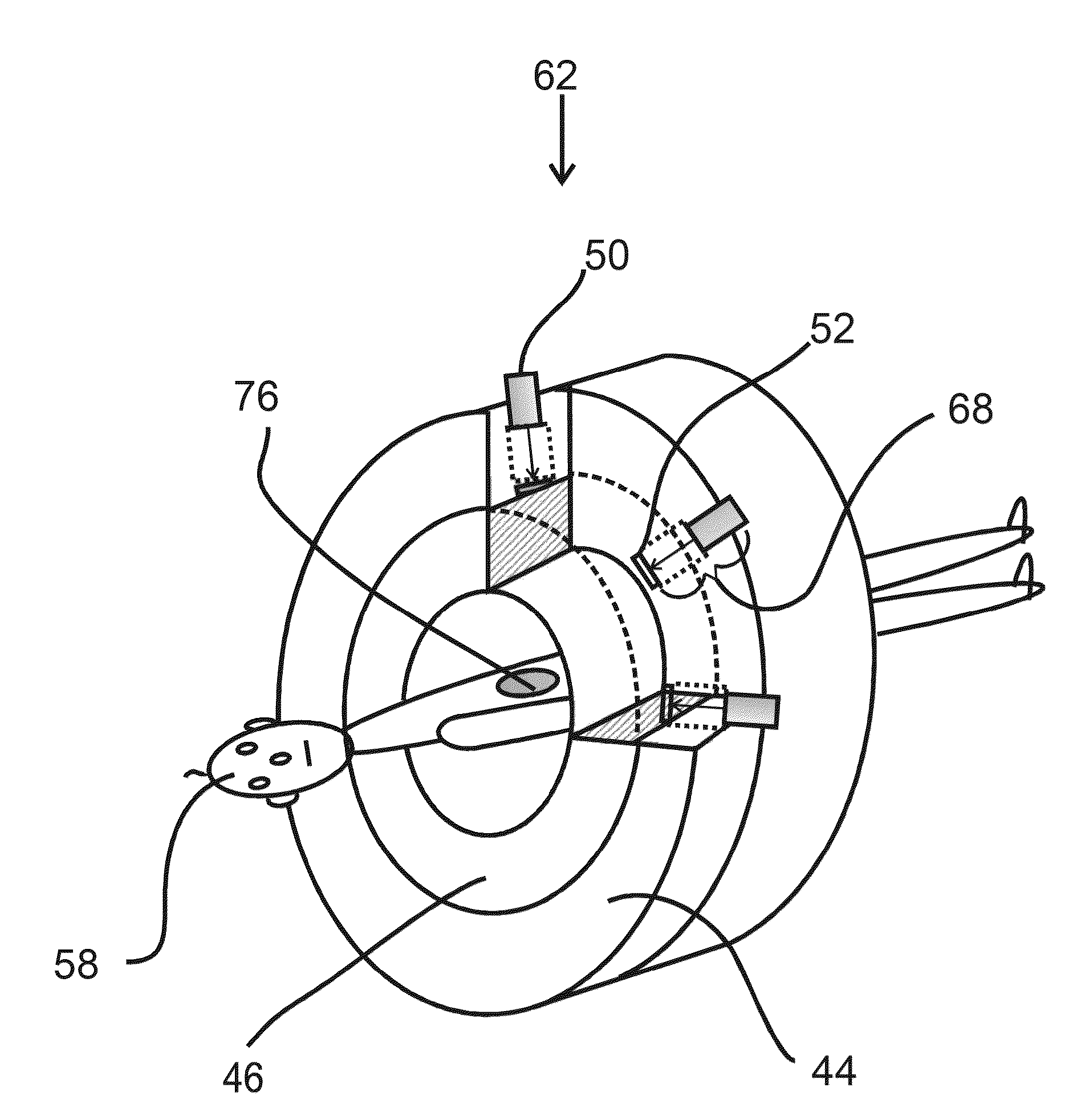
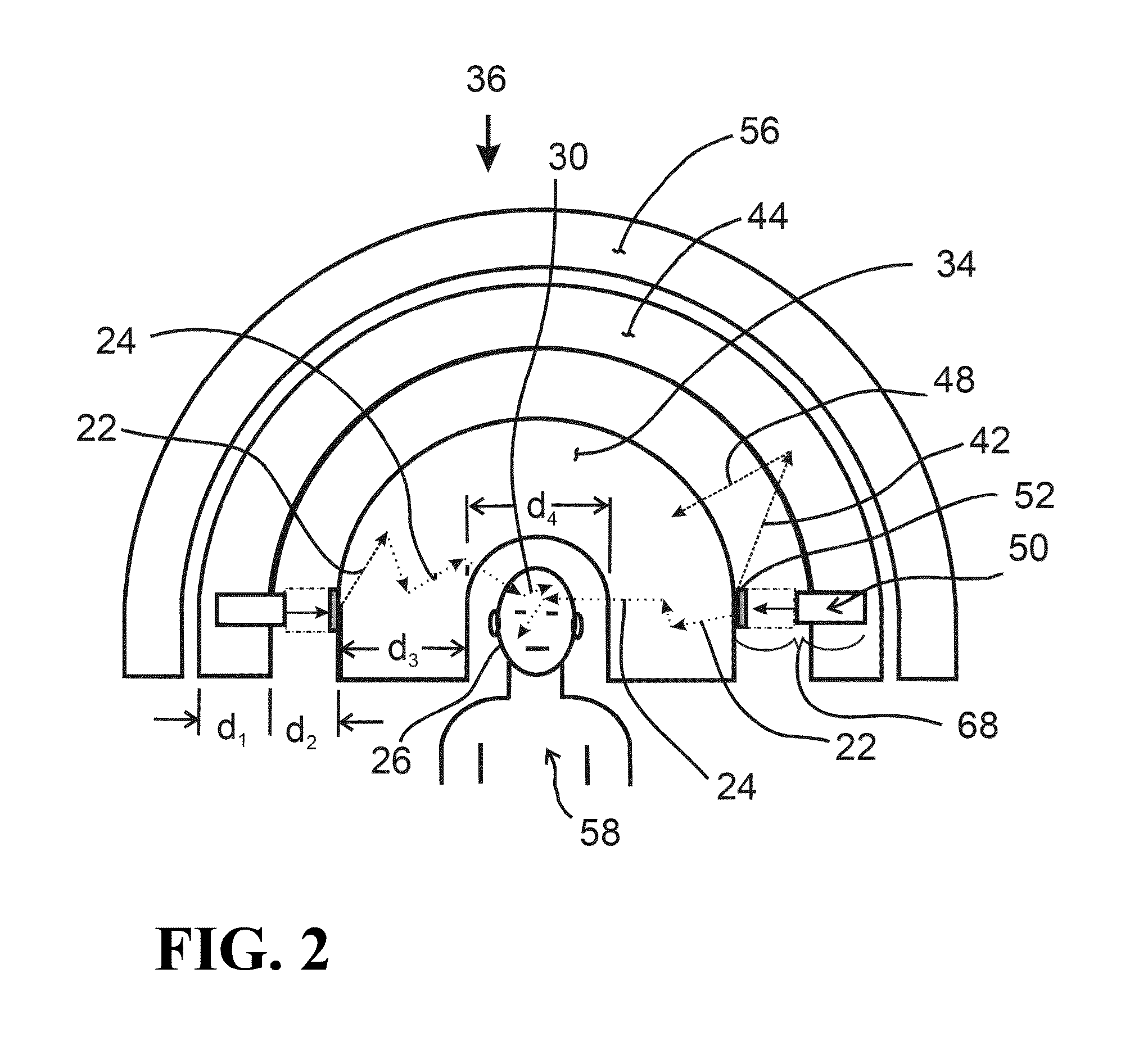
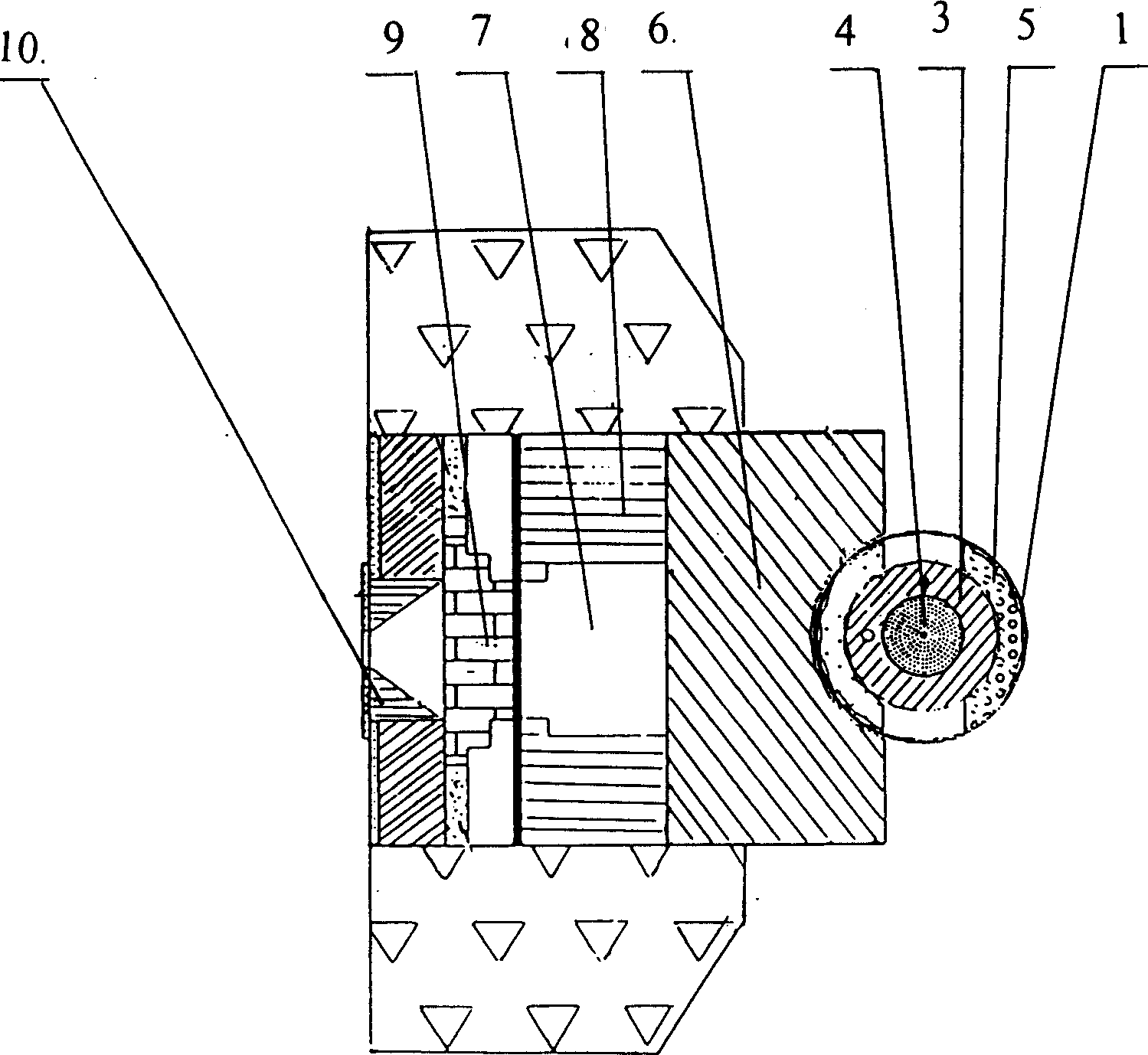
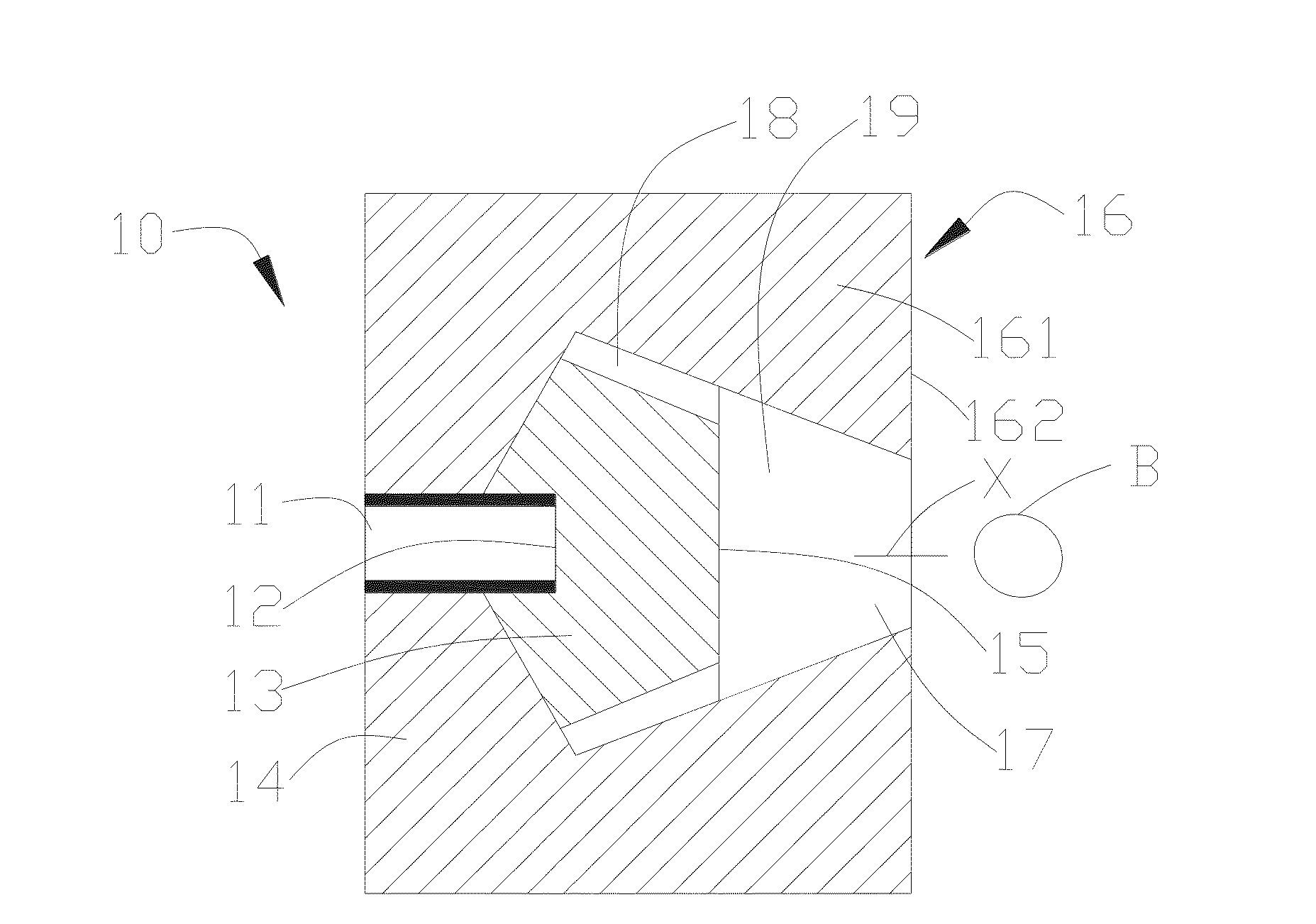
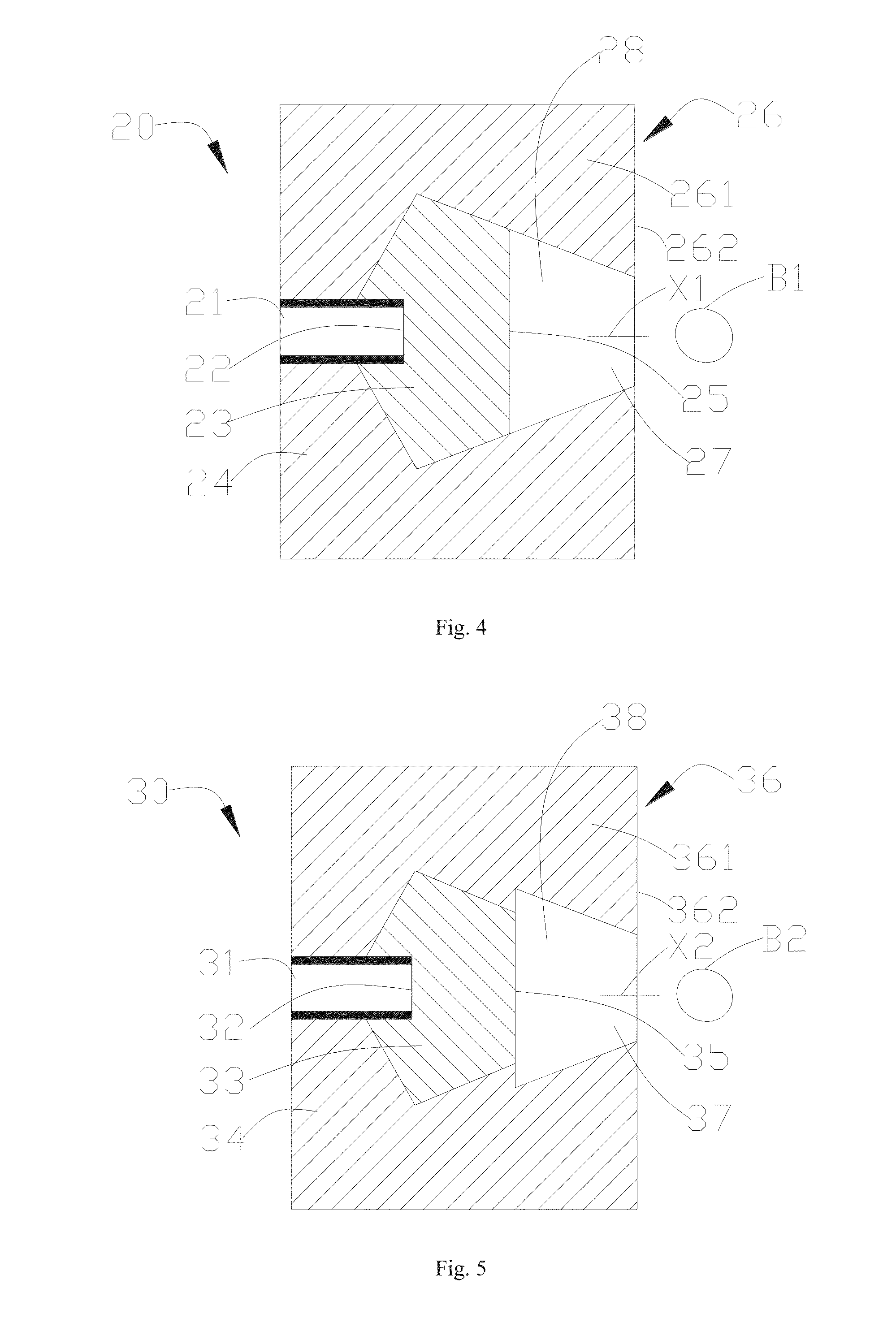
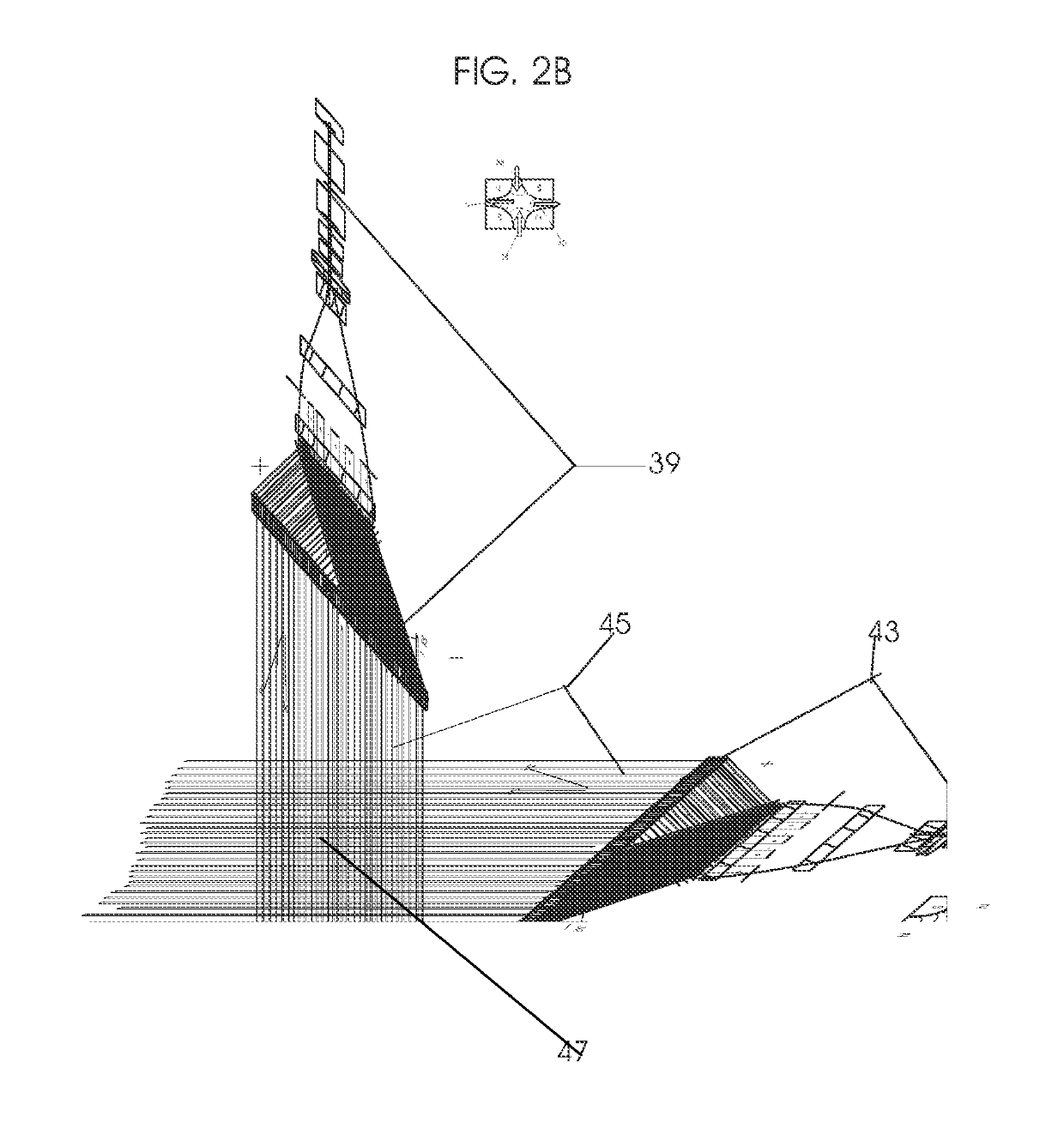
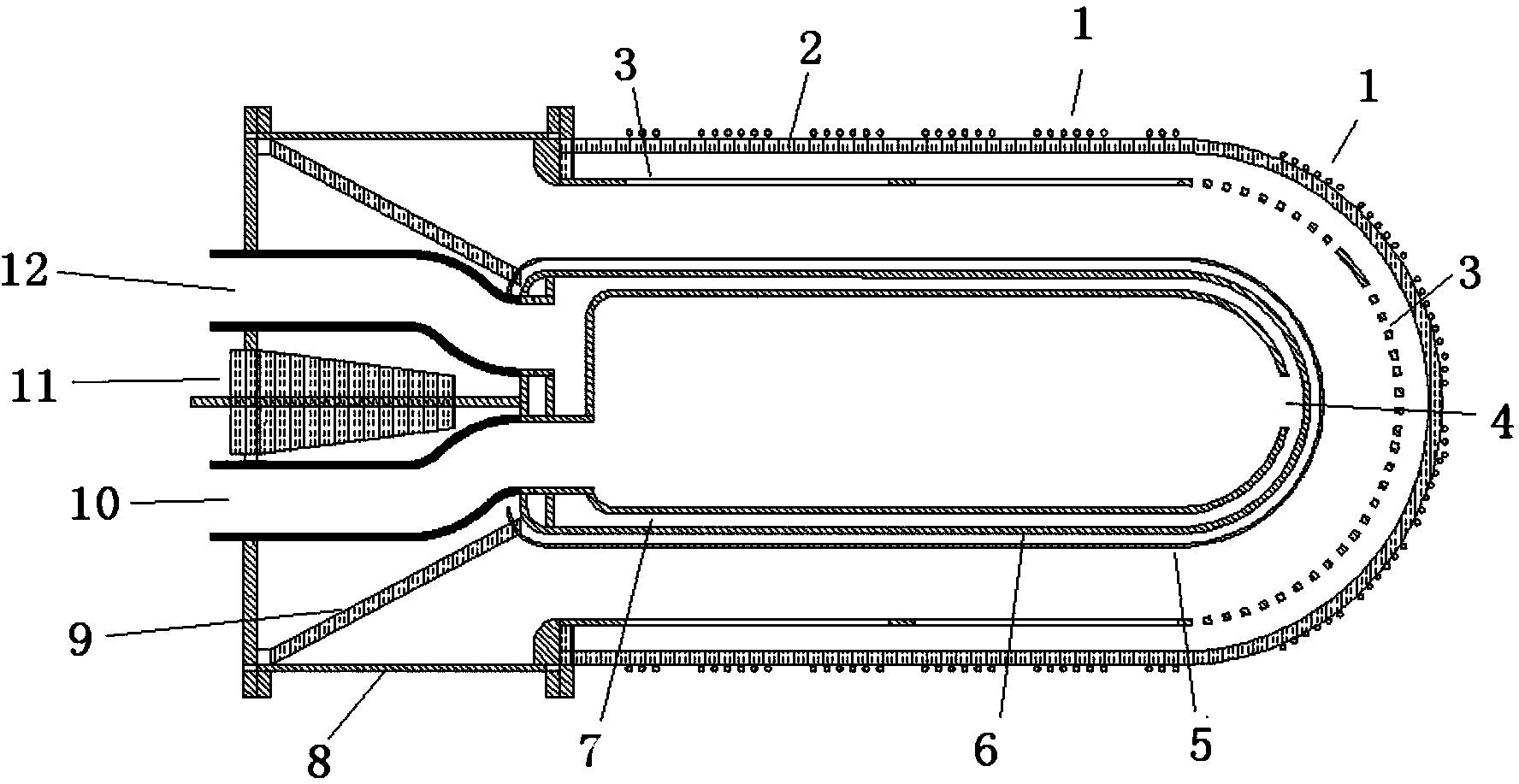
Beam shaping assembly for neutron capture therapy
ActiveUS20160158579A1Increase fluxQuality improvementRadiation/particle handlingDirect voltage acceleratorsReduced doseNuclear reaction
A beam shaping assembly for neutron capture therapy includes a beam inlet, a target having nuclear reaction with an incident proton beam from the beam inlet to produce neutrons forming a neutron beam defining a main axis, a moderator adjoining to the target, a reflector surrounding the moderator, a thermal neutron absorber adjoining to the moderator, a radiation shield arranged inside the beam shaping assembly and a beam outlet. The neutrons are moderated to epithermal neutron energies. An outer surface of the moderator includes at least a first tapered section. The reflector leads the neutrons deviated from the main axis back. The thermal neutron absorber is used for absorbing thermal neutrons so as to avoid overdosing in superficial normal tissue during therapy. The radiation shield is used for shielding leaking neutrons and photons so as to reduce dose of the normal tissue not exposed to irradiation.
Owner:NEUBORON MEDTECH
Device and methods for adaptive resistance inhibiting proton and carbon ion microbeams and nanobeams radiosurgery
ActiveUS10413755B1Eliminate inefficienciesGood prospectsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDiamond-like carbonCarbon ion
This invention relates to adaptive resistance inhibiting 100 to 10,000 Gy, single fraction proton and carbon ion microbeam and nanobeam radiosurgery, proton spray chemotherapy and proton spray gadolinium and boron neutron capture therapy with least normal tissue toxicity. Secondary neutrons, protons, ions and radiation from the accelerator and the patient specific collimator are removed with tissue equivalent collimator that also generates proton and carbon ion microbeam and nanobeam. Laser interaction with micrometer and nanometer thick metallic and diamond like carbon targets are also used for proton and carbon ion beam generation. Polyenergetic proton beam is spatially separated. Ion beam and Laser ion beam is accelerated in a hybrid RF accelerator. It is split into microbeam and nanobeam. Secondary neutrons, protons and gamma radiation are removed with tissue equivalent collimators that also generate microbeams and nanobeams. Adaptive resistance to cancer treatment is inhibited by dual target radiation, DNA strands break and enzymes inactivation.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
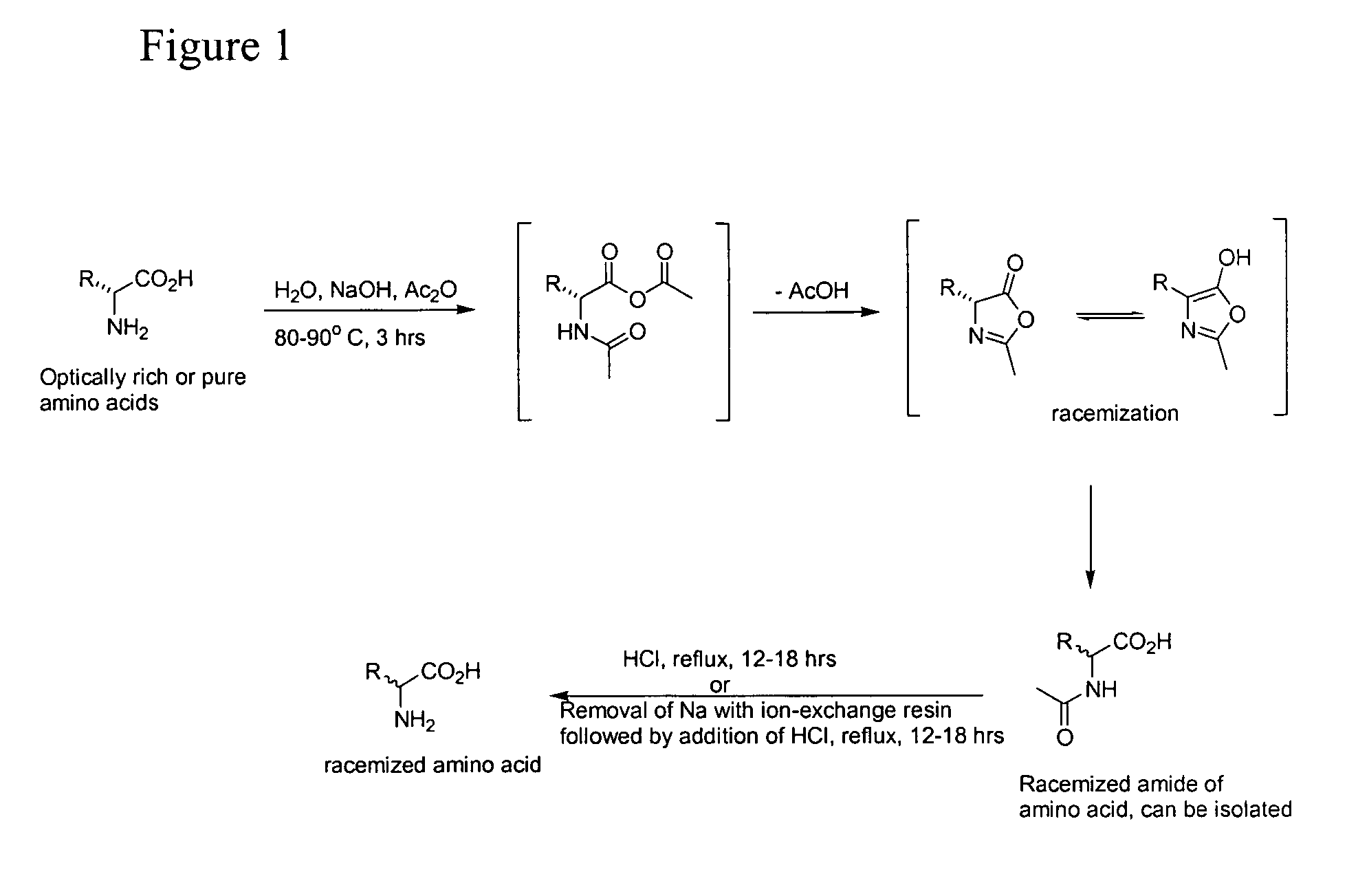
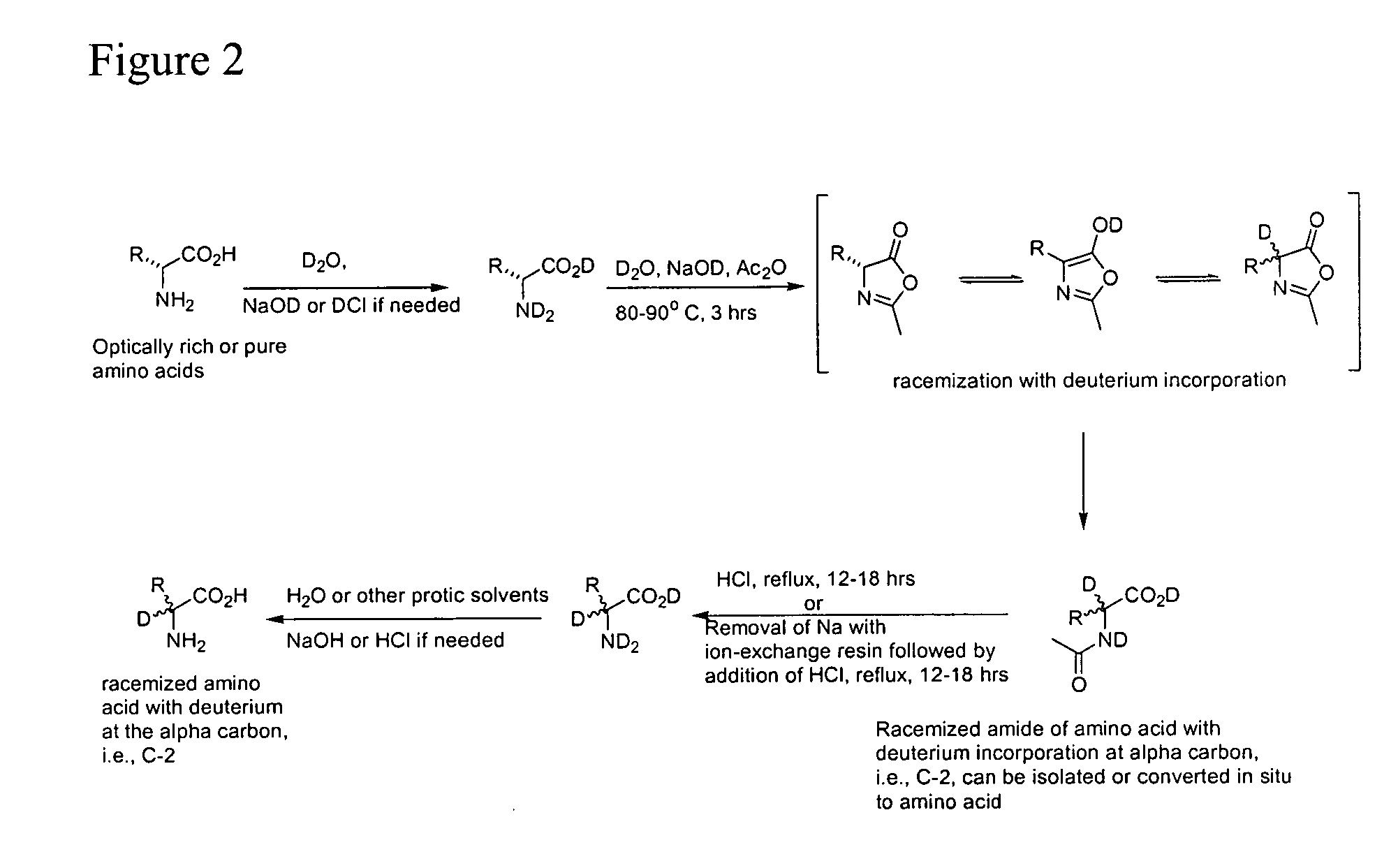
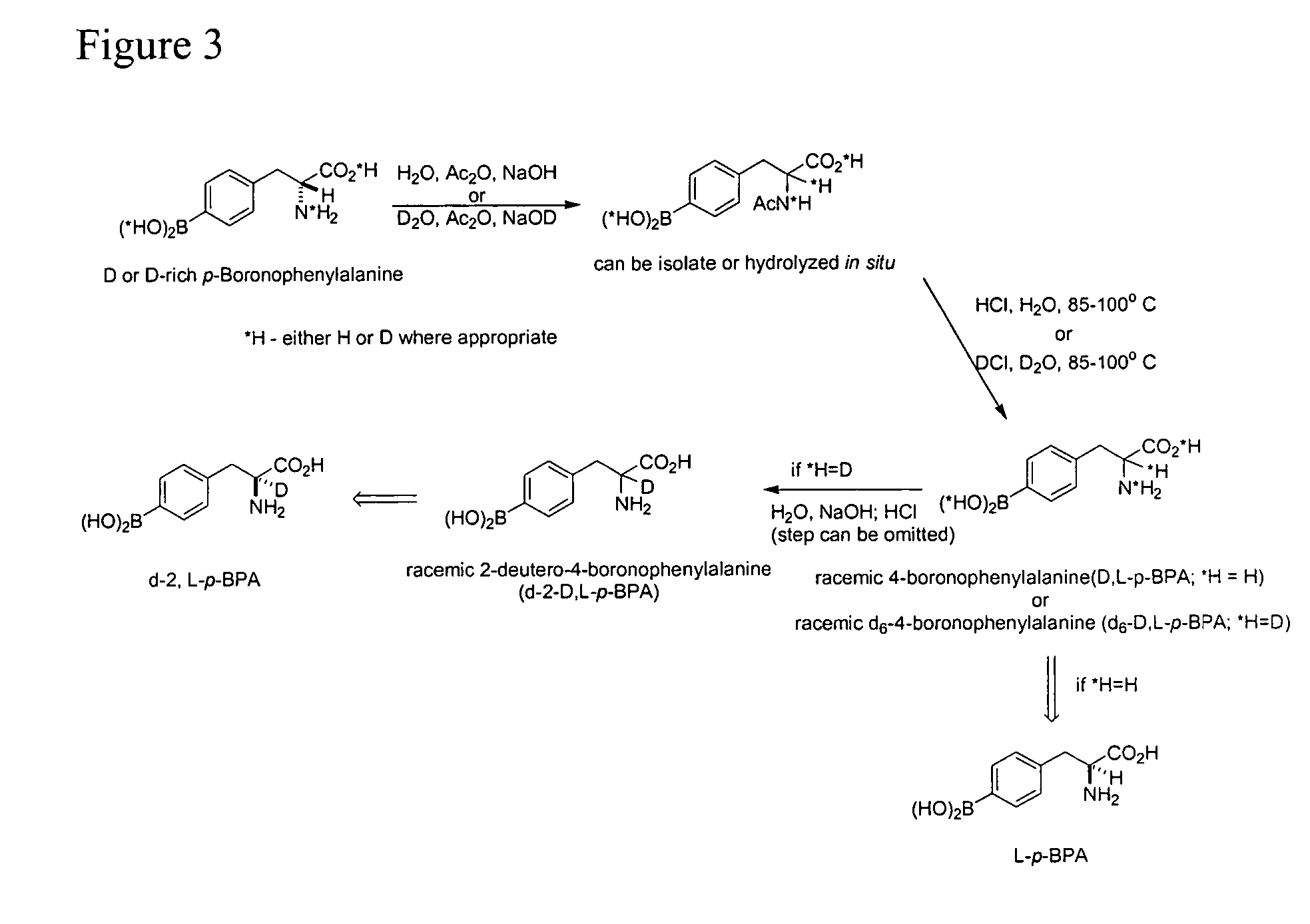
Compositions, methods of preparing amino acids, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070104648A1Group 3/13 element organic compoundsDiagnostic recording/measuringSugar amino acidMammalian tissue
The present invention relates to amino acids, complexes, and compounds comprising deuterium and tritium isotopes preferably alpha deuterated amino acids, polypeptides, antibodies, derivatives and saccharide-amino acid complexes and conjugates. In some embodiments, the invention relates to methods of using compounds comprising deuterium for imaging biochemical concentrations and distributions in mammalian tissues using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In some embodiments, the invention relates to the used of said amino acids derivatives and complexes in boron neutron capture therapy. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to the preparation of amino acids, polypeptides, antibodies, derivatives and saccharide complexes / conjugates comprising heavy hydrogen isotopes. In some embodiments, the invention relates to racemizing amino acids starting from compositions of any optical purity. In further embodiments, the invention relates to the preparation of amino acids and their N-acyl counterparts with deuterium incorporated at the alpha carbon.
Owner:GLYCONIX CORP
Absolute elemental concentrations from nuclear spectroscopy
ActiveCN102084271AX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
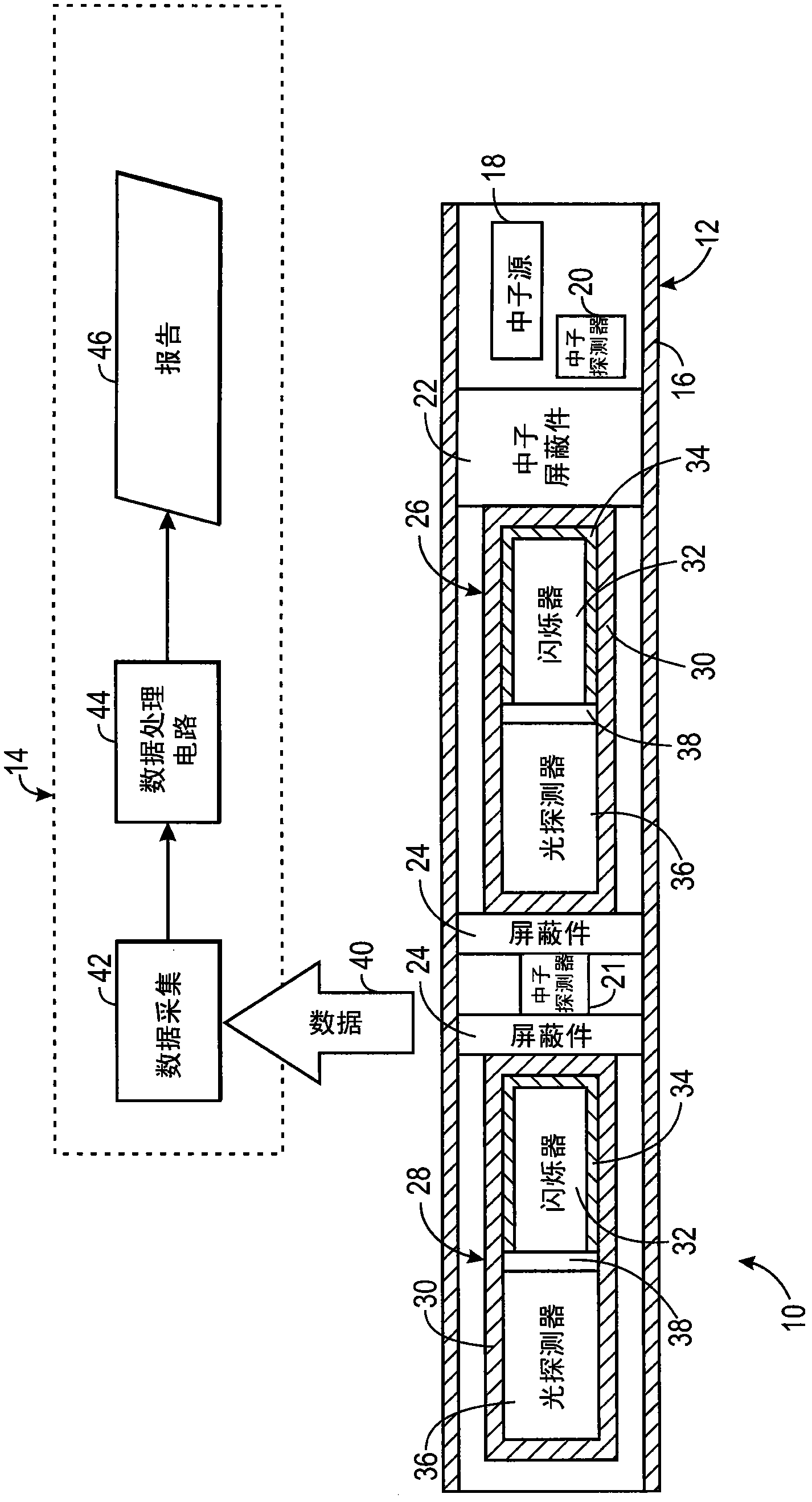
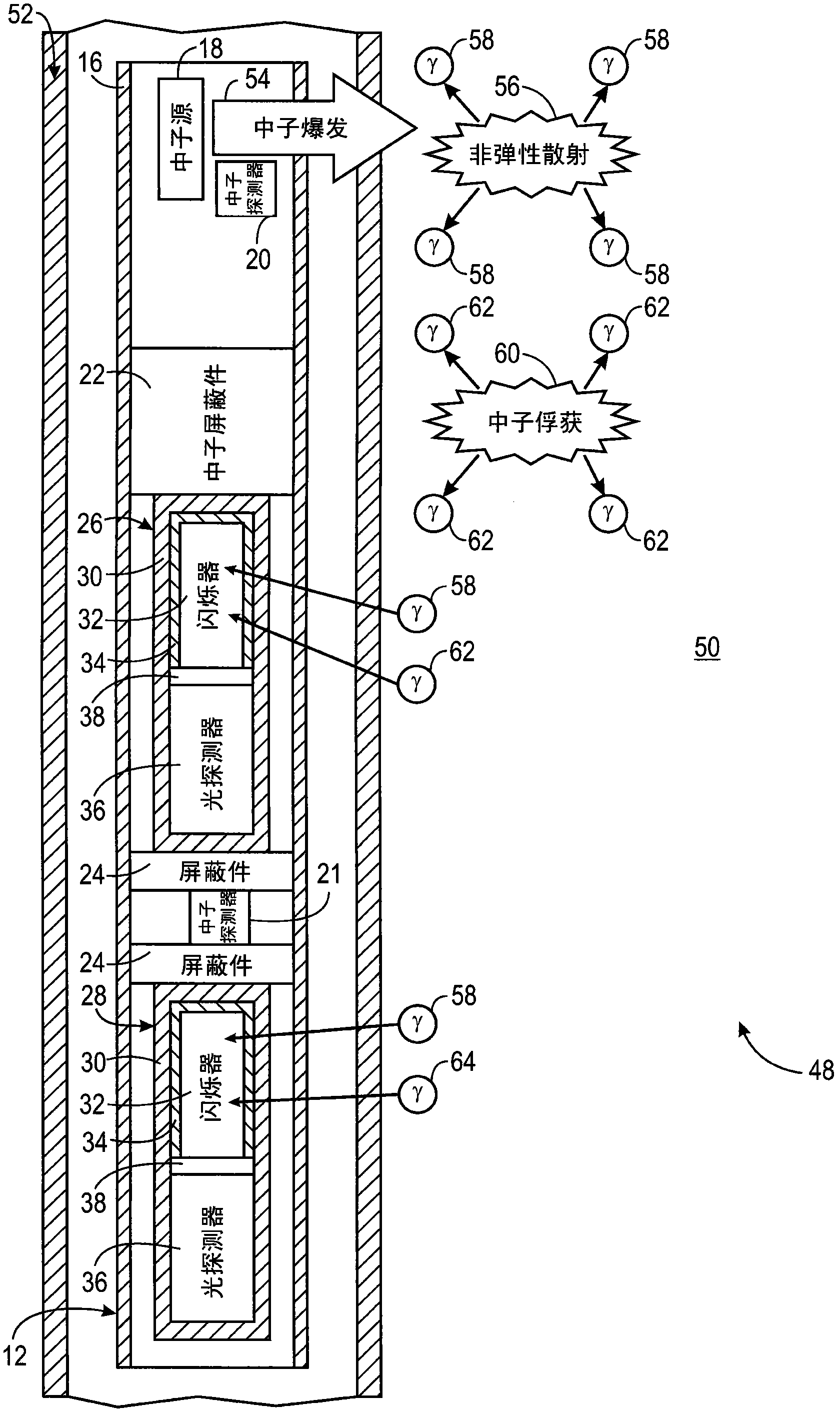
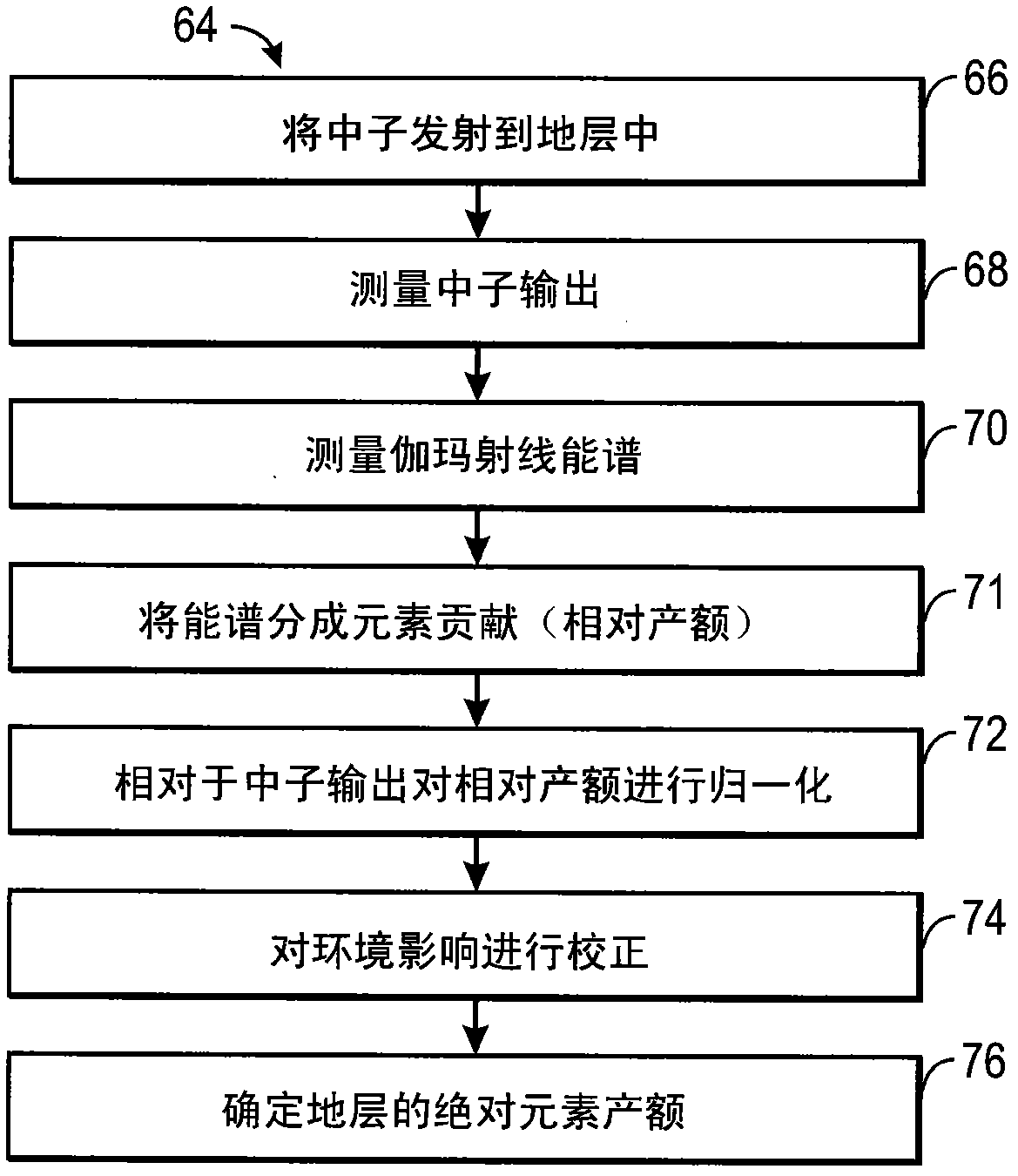
The present invention discloses a system and method for estimating absolute elemental concentrations of a subterranean formation from neutron-induced gamma-ray spectroscopy. In one example, a system (10) for estimating an absolute yield of an element in a subterranean formation may include a downhole tool (12) and data processing circuitry (14). The downhole tool may include a neutron source (18) to emit neutrons into the formation, a neutron monitor (20) to detect a count rate of the emitted neutrons, and a gamma-ray detector (26,28) to obtain gamma-ray spectra deriving at least in part from inelastic gamma- rays produced by inelastic scattering events and neutron capture gamma-rays produced by neutron capture events. The data processing circuitry may be configured to determine a relative elemental yield from the gamma-ray spectra and to determine an absolute elemental yield based at least in part on a normalization of the relative elemental yield to the count rate of the emitted neutrons.
Owner:PRAD RES & DEV LTD
Formation element capture gamma-ray spectra measurement method and device
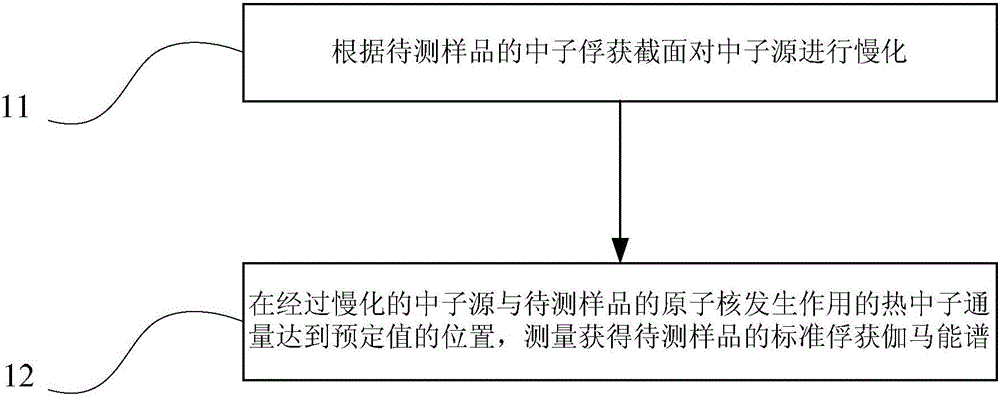
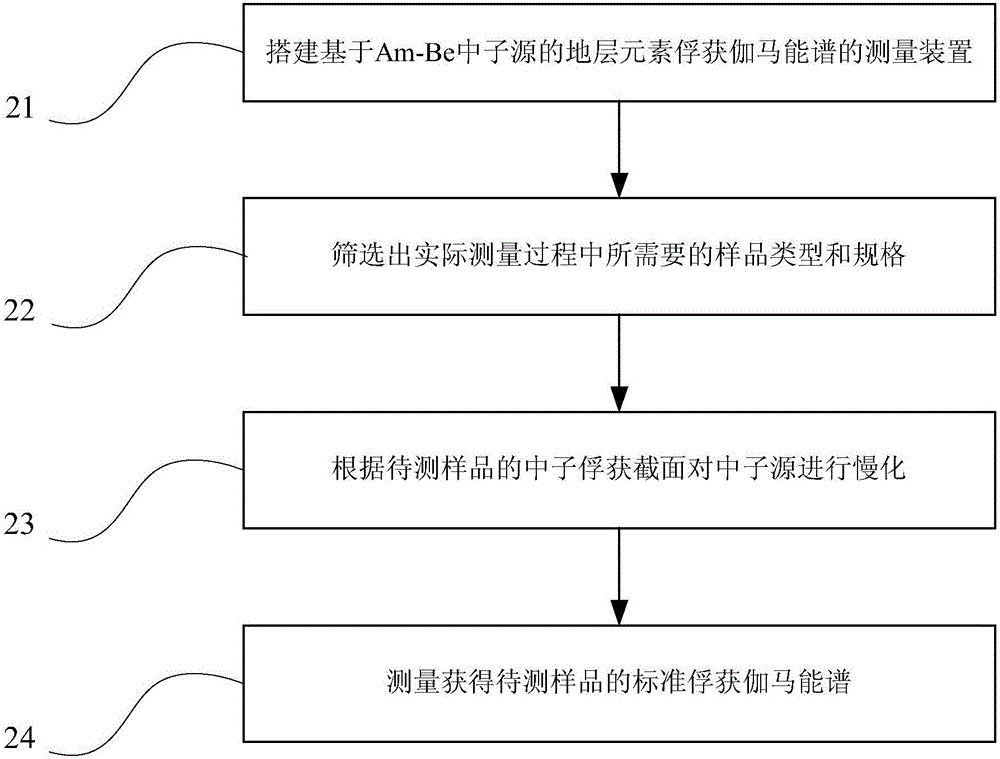
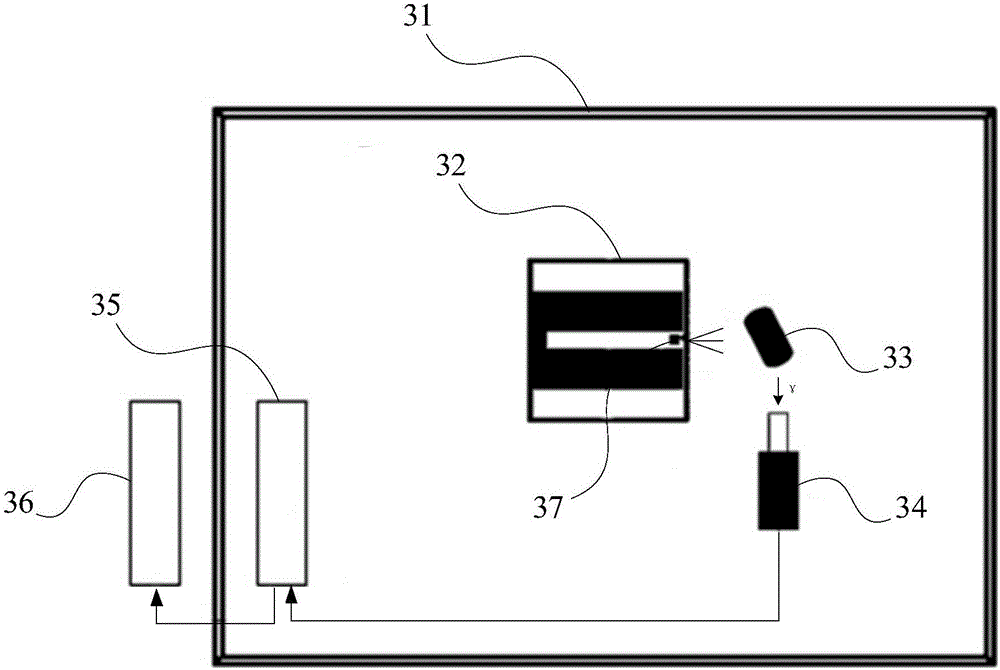
ActiveCN105093343AImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNuclear radiation detectionThermal neutron fluxNeutron capture
The invention provides a formation element capture gamma-ray spectra measurement method and device, and belongs to the technical field of oil-gas exploration logging. The method comprises the steps that a neutron source is slowed down according to the neutron capture cross section of samples to be measured; and standard capture gamma-ray spectra of the samples to be measured can be acquired through measurement when thermal neutron flux of reaction of the neutron source through slowing down and the atomic nucleus of the samples to be measured reaches the position of the preset value. The neutron source is slowed down according to the neutron capture cross section of different samples to be measured so that the element capture gamma-ray spectra of the samples to be measured can be acquired through measurement, and multiple types of formation element capture gamma-ray spectra with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
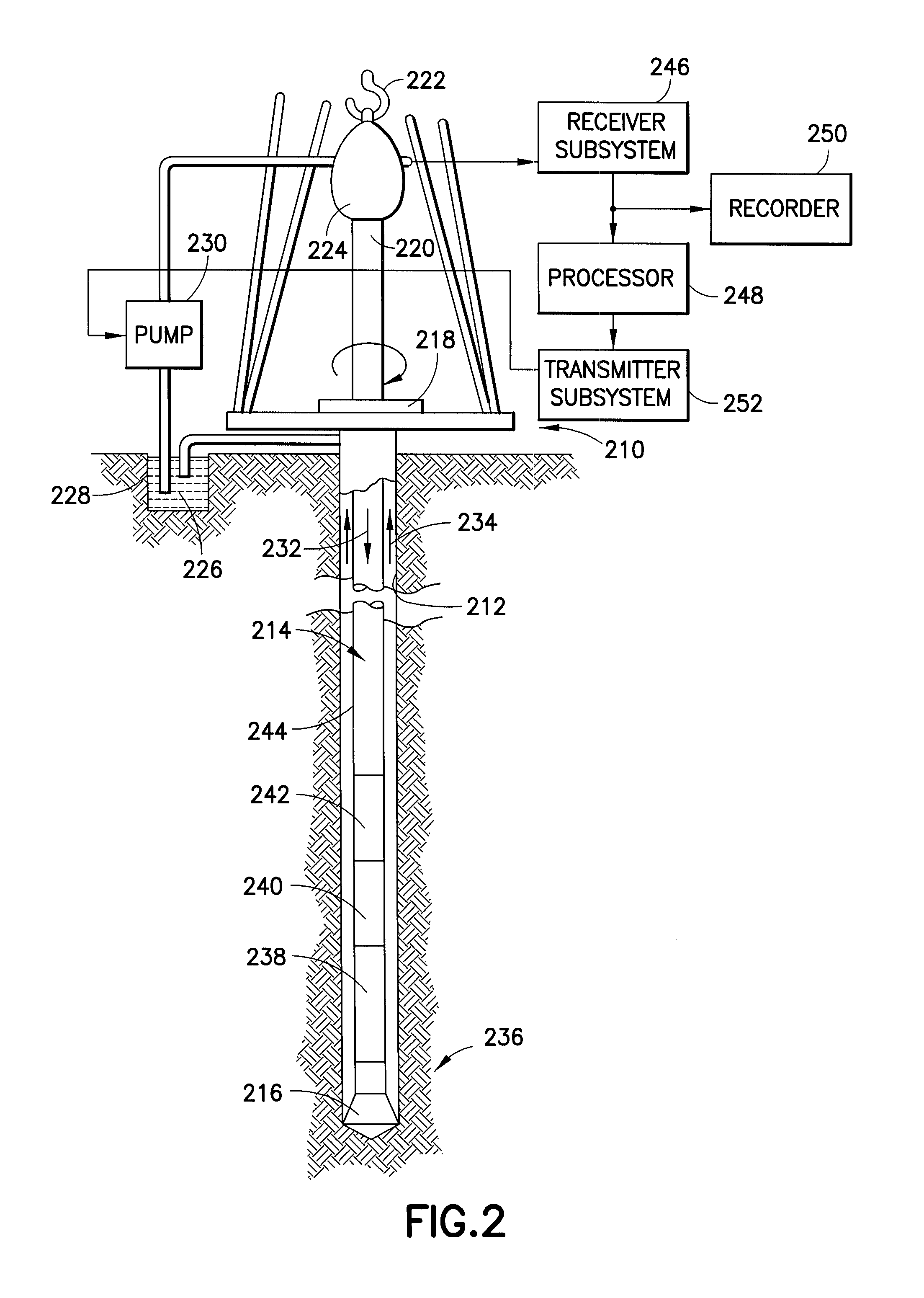
Method for monitoring or tracing operations in well boreholes
The present invention relates to novel methods for monitoring or tracing a job operation performed in a borehole, such as well boreholes traversing a geological formation. In one embodiment, the novel methods of the invention comprise the steps of: (a) disposing into the borehole a neutron absorber during the performance of the job operation; (b) logging the borehole with an instrument capable of measuring a neutron capture in and around the borehole after performance of the job operation; and (c) monitoring or tracing the job operation performed in the borehole by comparing the measured neutron capture with a baseline neutron capture in and around the borehole. The methods of the present invention pose small or no risk from a health safety and environment perspective and are useful for monitoring or tracing hydraulic fracturing, cementing operation in well boreholes, production logging or subsurface location of downhole collars, float shoes and other jewellery.
Owner:MASNYK ROBERT MICHAEL +1
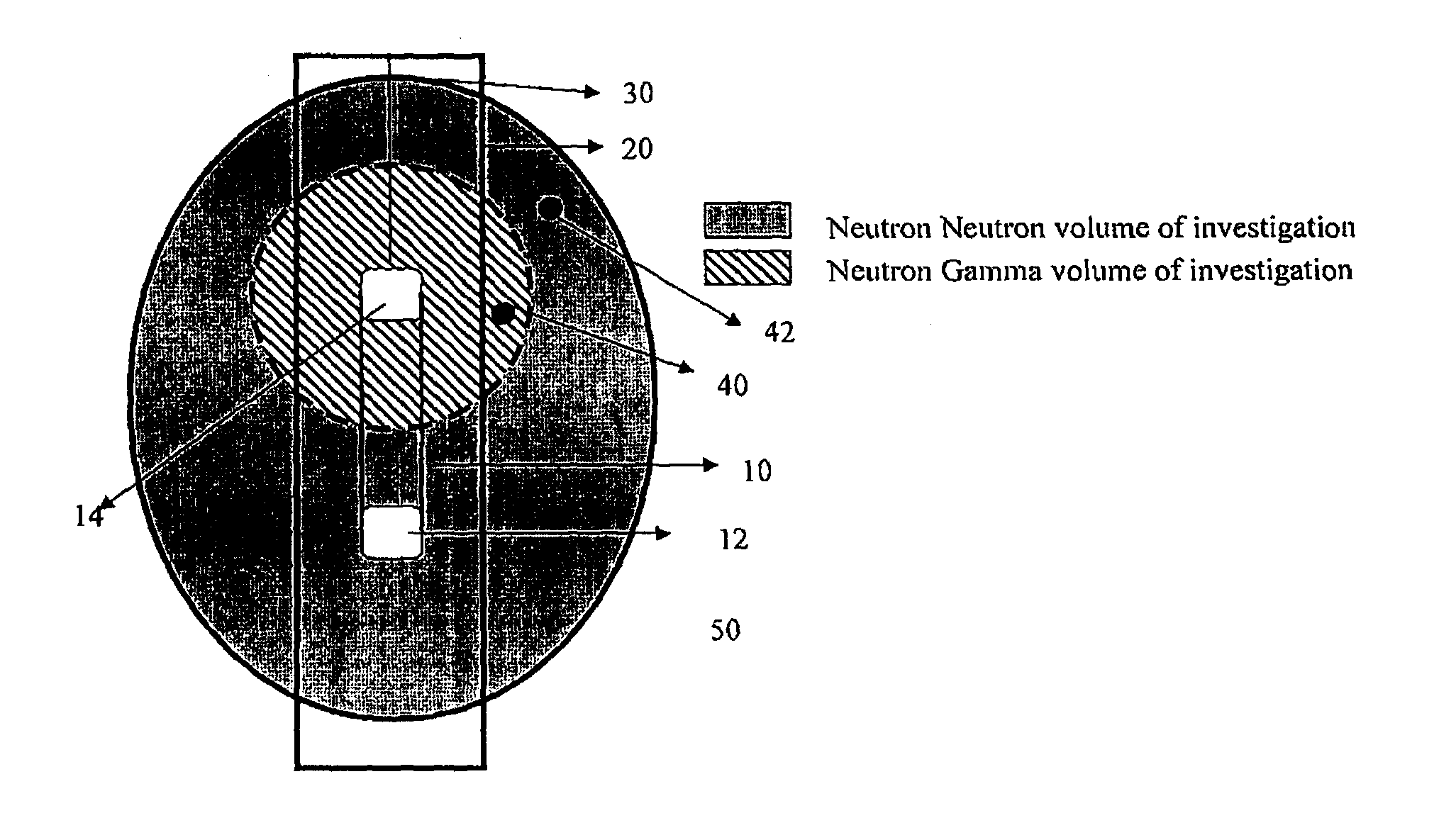
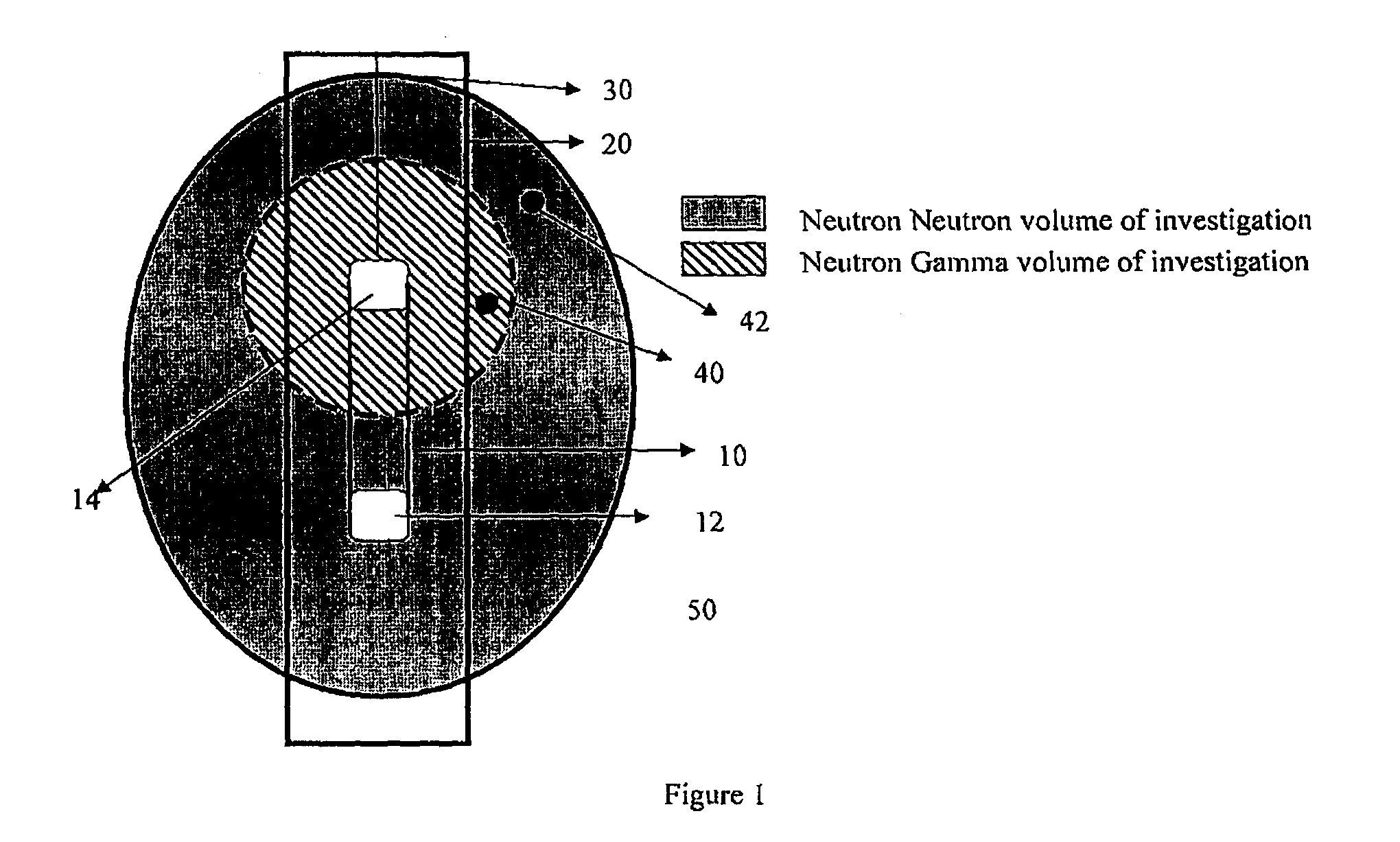
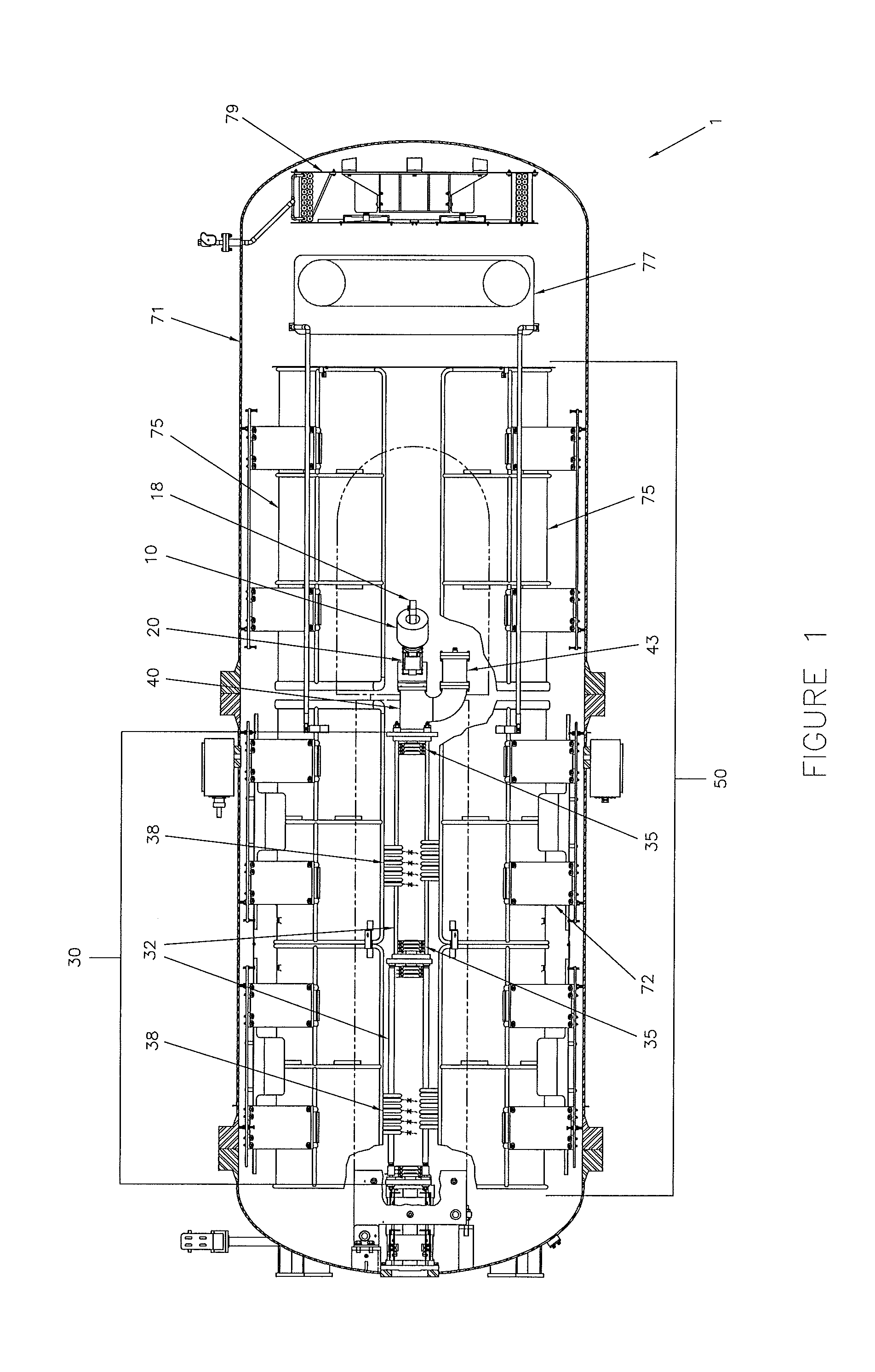
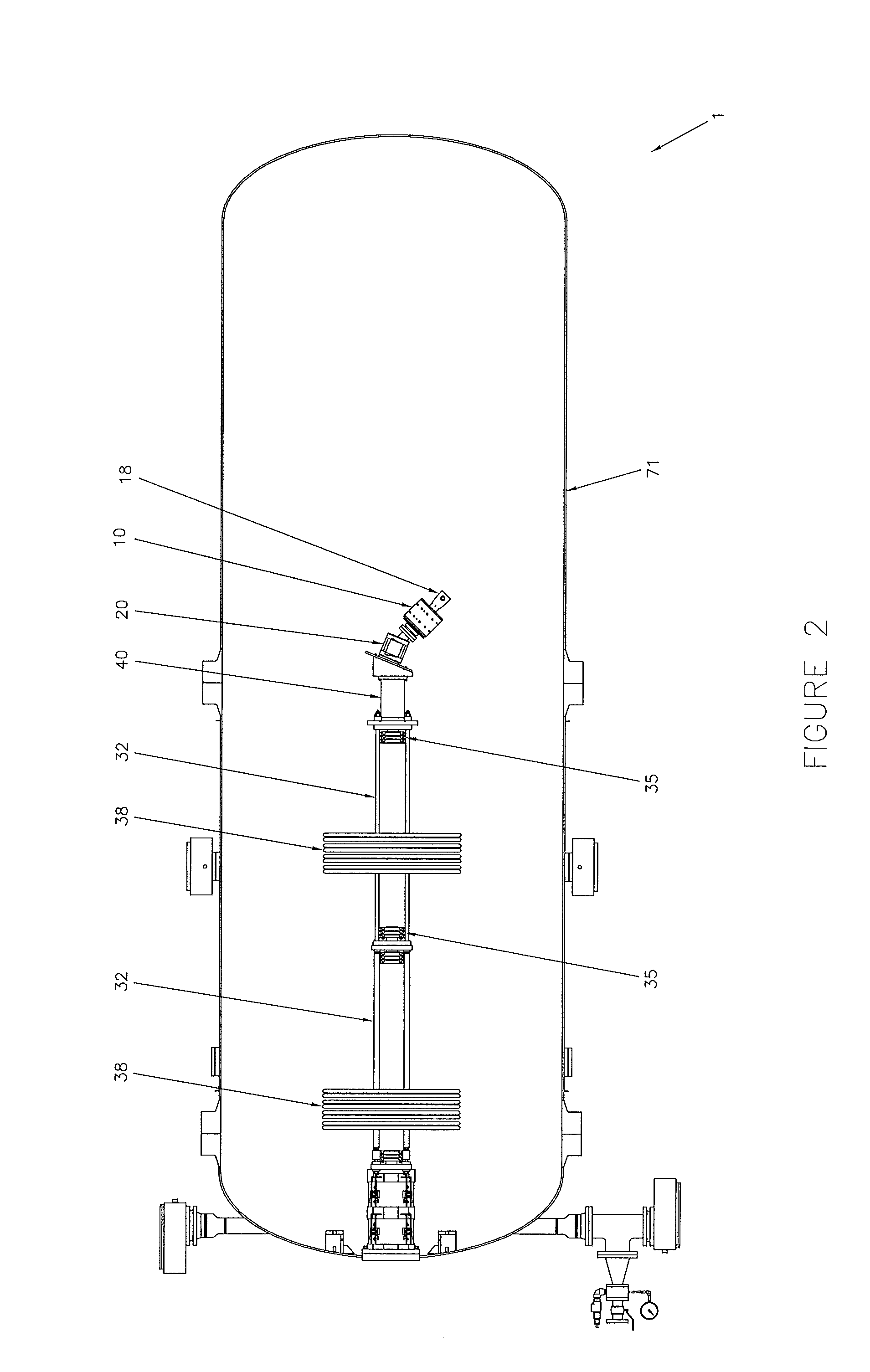
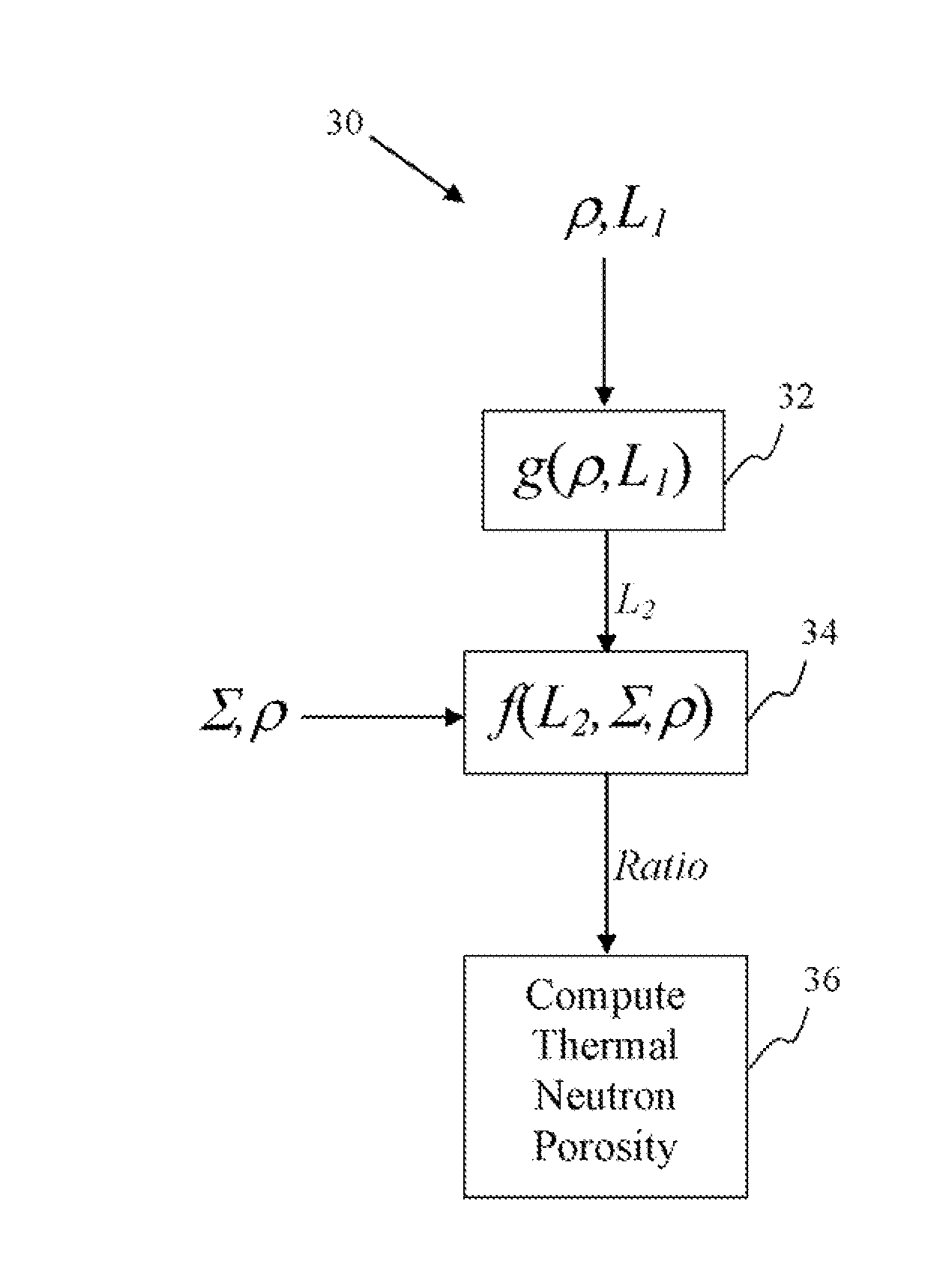
Thermal neutron porosity from neutron slowing-down length, formation thermal neutron capture cross section, and bulk density
A method for determining at least one formation property calculated from neutron measurements acquired with a downhole tool includes emitting neutrons from a source in the tool into the formation, detecting neutrons with at least one detector in the downhole tool, calculating a first slowing-down length (L1) based on the detected neutrons, and deriving a second slowing-down length (L2) based on the first slowing-down length (L1). Further steps include deriving a correlation function for relating slowing-down lengths from a first tool to slowing-down lengths associated with a different source, wherein the correlation function depends on formation properties such as bulk density; and applying the correlation function to the slowing-down length of the first tool to derive the slowing-down length of the second tool. A method for determining a thermal neutron formation porosity based on a slowing-down length from epithermal neutron measurements from an electronic neutron source includes converting the slowing-down length into a computed neutron slowing-down length from thermal neutron measurements from a chemical neutron source, wherein the converting uses a correlation function that depends on formation bulk density; deriving a thermal neutron countrate ratio based on the computed neutron slowing-down length, wherein the deriving uses a function that depends on the formation bulk density and formation sigma; and computing the thermal neutron formation porosity from the thermal neutron countrate ratio.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Boron carrying agent for integrating tumor diagnosis and treatment
InactiveCN109053781AHigh enrichment efficiencyEasy to prepareEnergy modified materialsBoron compound active ingredientsImage diagnosisNeutron capture
The invention relates to a boron carrying agent for integrating tumor diagnosis and treatment. The boron carrying agent is tyrosine boron trifluoride (FBY) obtained by replacing a carboxyl group witha boron trifluoride group on the basis of tyrosine. FBY can be used for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for treating malignant tumors; radioactive <18>F-labeled FBY can also be used for positronemission tomography (PET) imaging diagnosis. <18F>-FBY can simultaneously achieve imaging diagnosis and precise treatment of cancers.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
High-current DC proton accelerator
InactiveUS8148922B2Reduce harmful effectsReduce the amount requiredTransit-time tubesDirect voltage acceleratorsHigh energyNeutron capture
A dc accelerator system able to accelerate high currents of proton beams at high energies is provided. The accelerator system includes a dc high-voltage, high-current power supply, an evacuated ion accelerating tube, a proton ion source, a dipole analyzing magnet and a vacuum pump located in the high-voltage terminal. The high-current, high-energy dc proton beam can be directed to a number of targets depending on the applications such as boron neutron capture therapy BNCT applications, NRA applications, and silicon cleaving.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Thermal Neutron Porosity from Neutron Slowing-Down Length, Formation Thermal Neutron Capture Cross Section, and Bulk Density
A method for determining at least one formation property calculated from neutron measurements acquired with a downhole tool includes emitting neutrons from a source in the tool into the formation, detecting neutrons with at least one detector in the downhole tool, calculating a first slowing-down length (L1) based on the detected neutrons, and deriving a second slowing-down length (L2) based on the first slowing-down length (L1). Further steps include deriving a correlation function for relating slowing-down lengths from a first tool to slowing-down lengths associated with a different source, wherein the correlation function depends on formation properties such as bulk density; and applying the correlation function to the slowing-down length of the first tool to derive the slowing-down length of the second tool. A method for determining a thermal neutron formation porosity based on a slowing-down length from epithermal neutron measurements from an electronic neutron source includes converting the slowing-down length into a computed neutron slowing-down length from thermal neutron measurements from a chemical neutron source, wherein the converting uses a correlation function that depends on formation bulk density; deriving a thermal neutron countrate ratio based on the computed neutron slowing-down length, wherein the deriving uses a function that depends on the formation bulk density and formation sigma; and computing the thermal neutron formation porosity from the thermal neutron countrate ratio.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
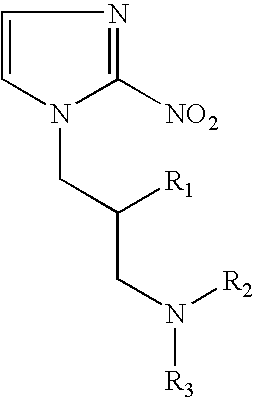
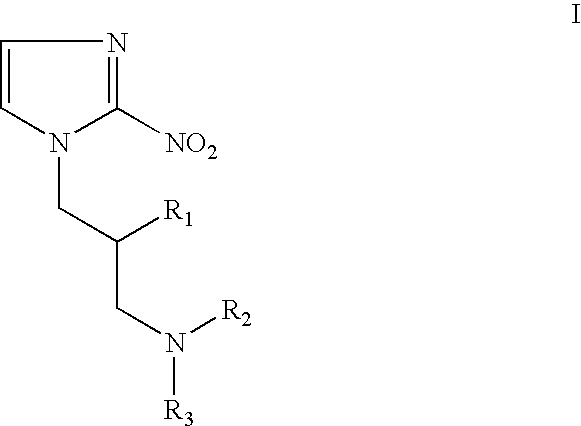
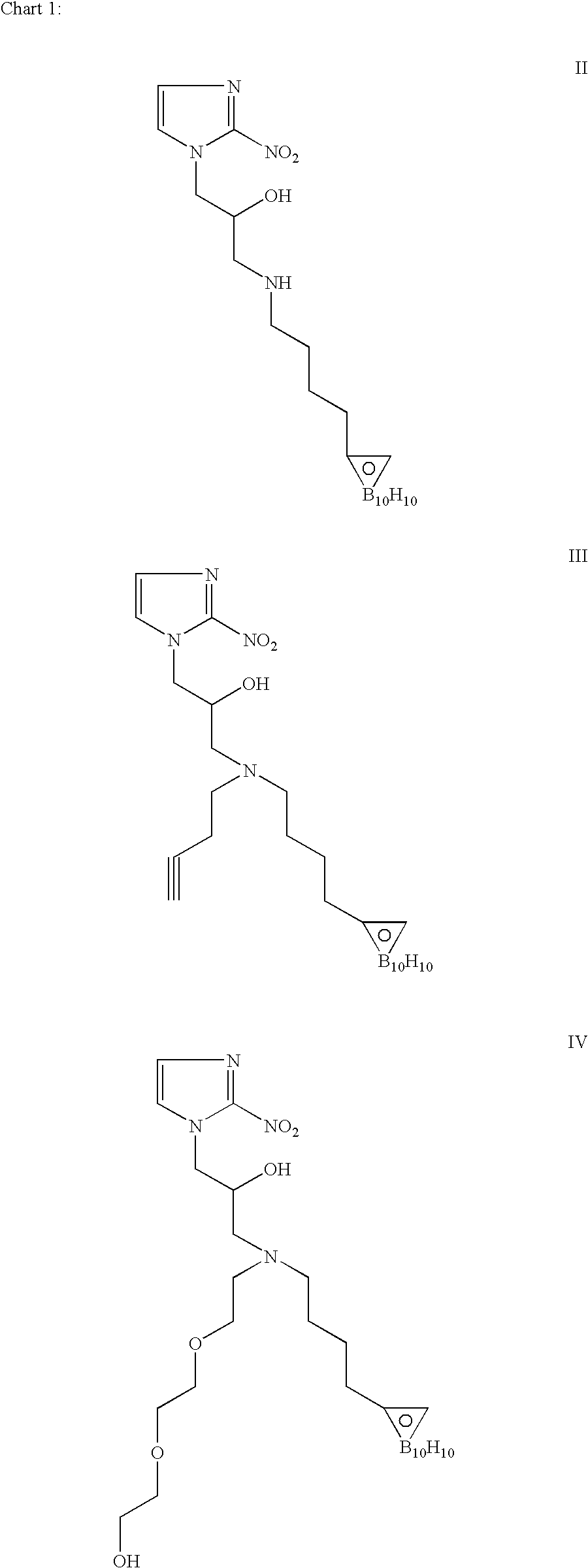
Hypoxia-selective, weakly basic 2-nitroimidazole delivery agents and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080102026A1Reduce deliveryImprove solubilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNitroimidazoleTissue concentrations
The invention features a class of 2-nitroimidazole compounds with a secondary basic nitrogen atom and a linker bearing one or more therapeutic agents, cytotoxic agents, detectable labels, or chelating groups. In particular, the invention provides 2-nitroimidazole compounds containing a cluster of boron atoms for use in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). The 2-nitroimidazole compounds can be used to treat hypoxic conditions, including, e.g., cancer, inflammation, and ischemia. The weakly basic 2-nitroimidazole compounds target to hypoxic tissue and provide increased tissue concentration overall.
Owner:NATURAL PHARMACIA INT
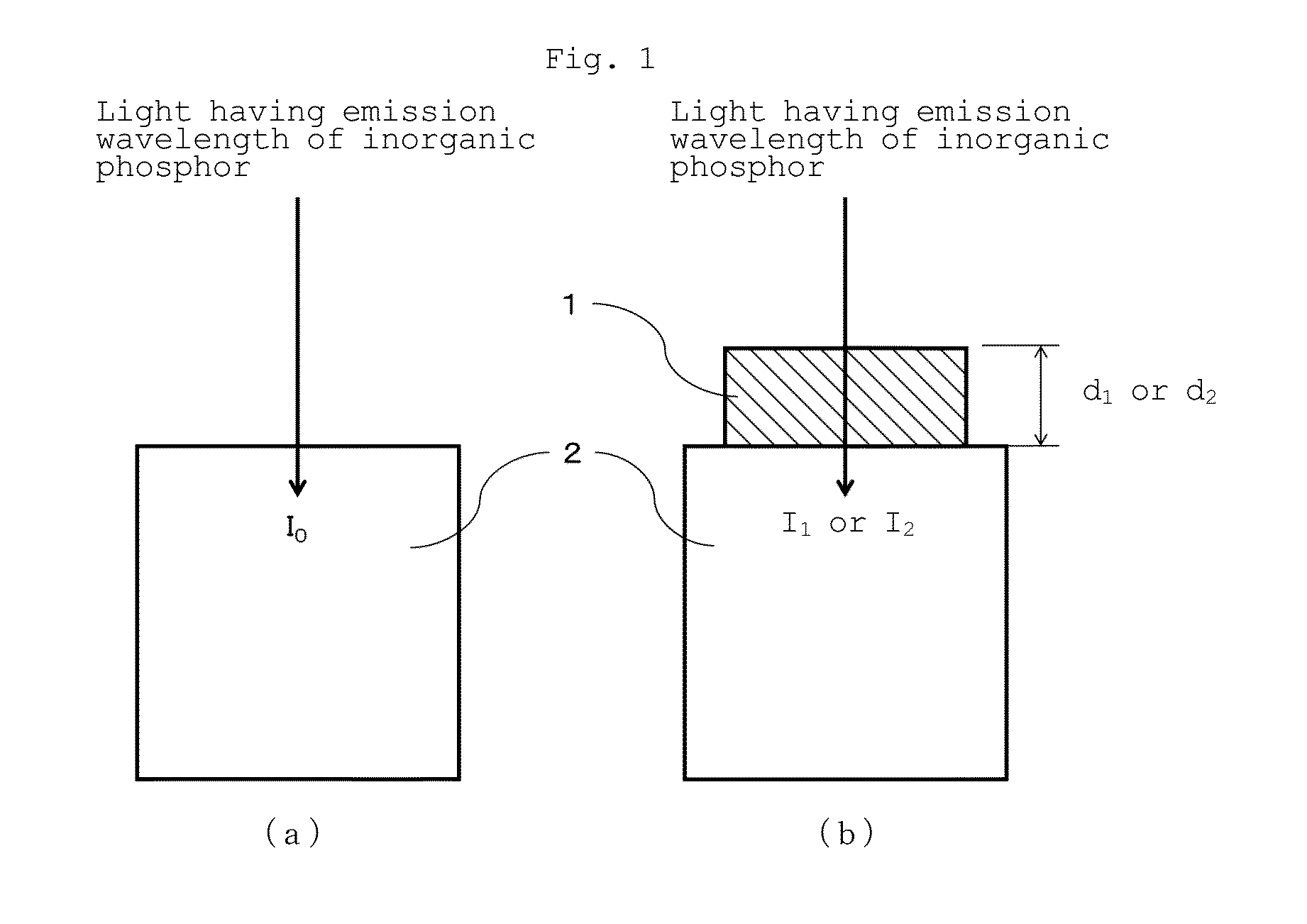
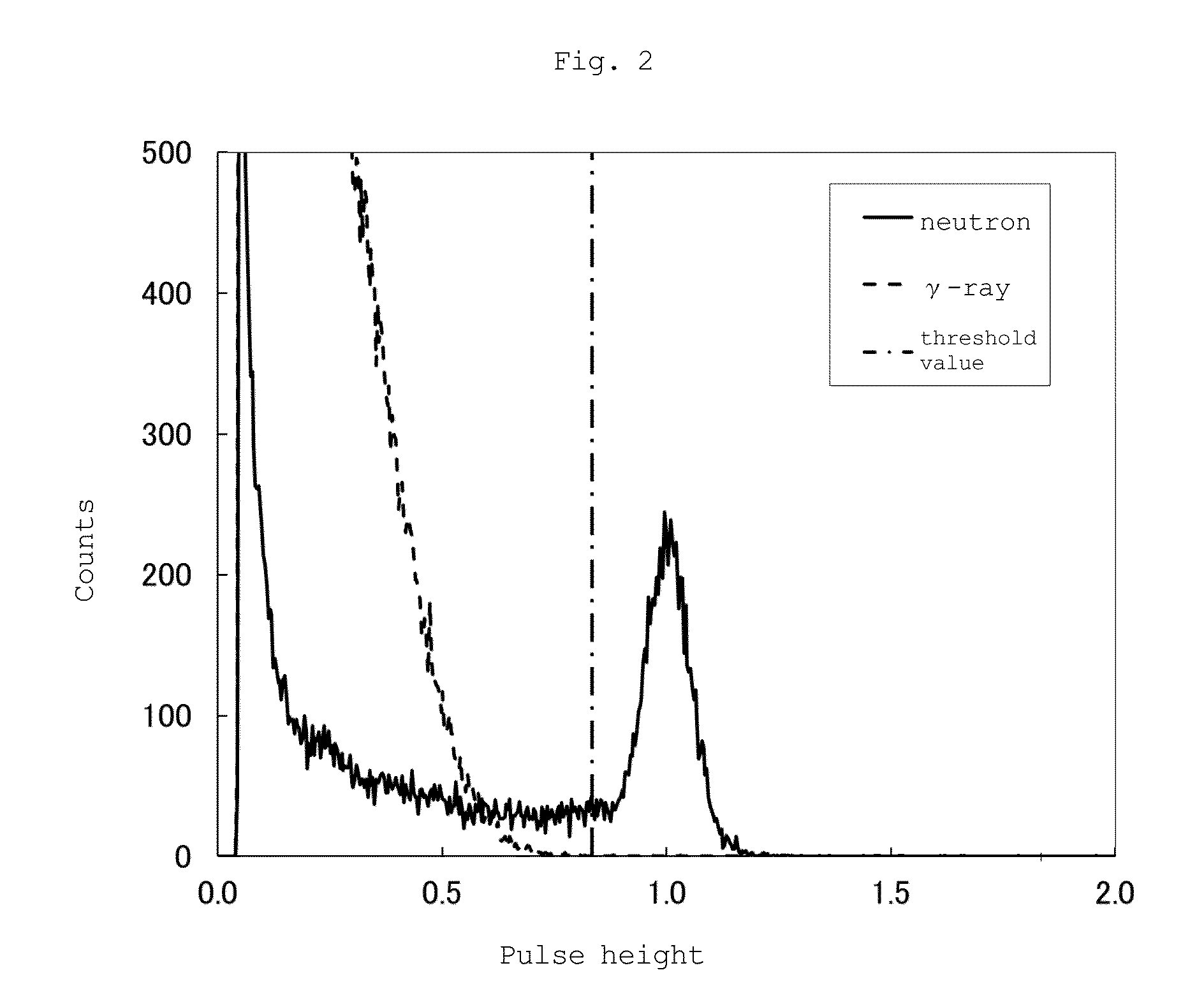
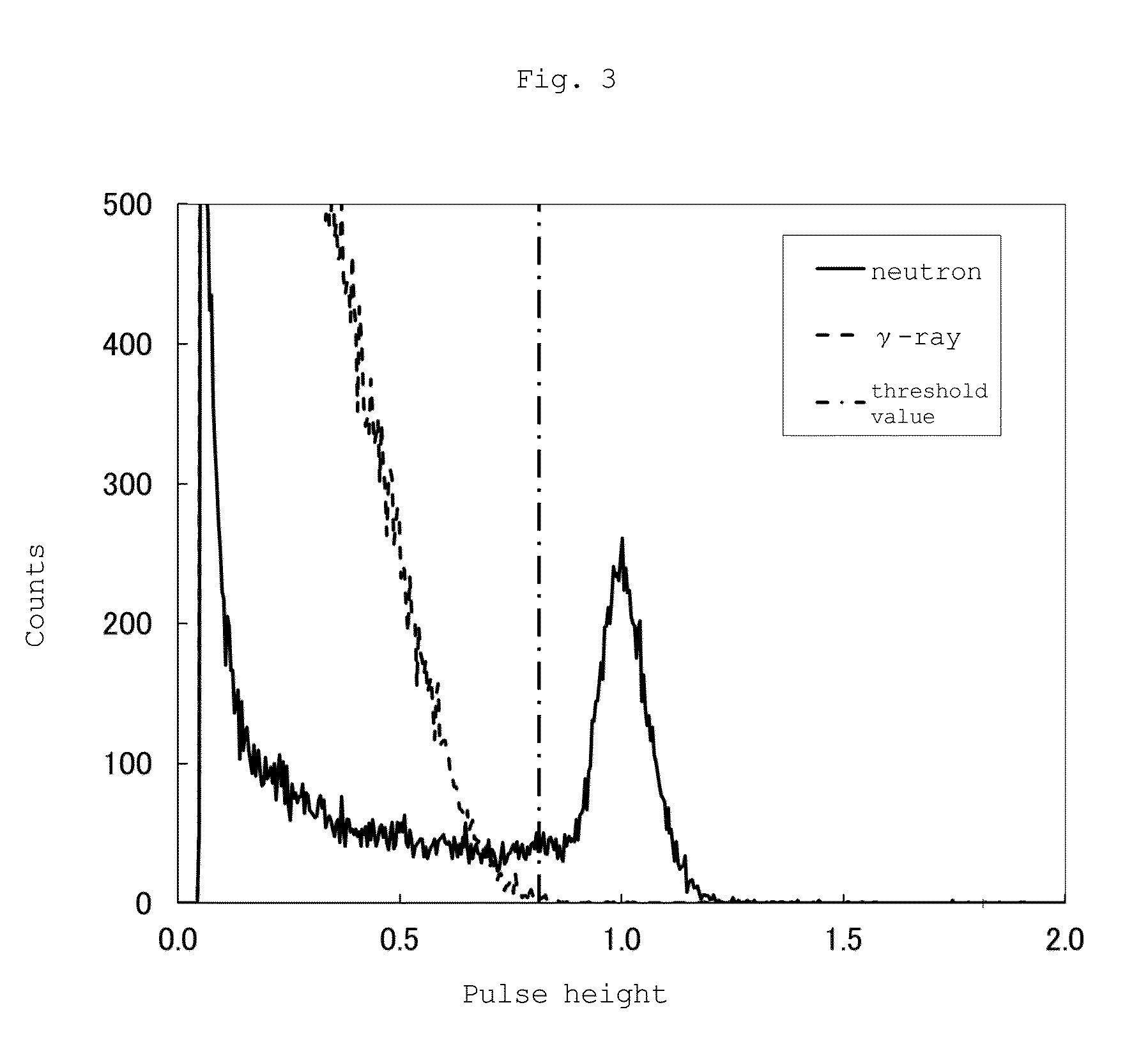
Neutron scintillator, neutron detection method and neutron detector
InactiveUS20150307777A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansLithiumPhosphor
A neutron scintillator composed of a resin composition comprising (A) an inorganic phosphor containing at least one neutron capture isotope selected from lithium 6 and boron 10 and (B) a resin, whereinthe inorganic phosphor is a particle having a specific surface area of 50 to 3,000 cm2 / cm3, and the internal transmittance based on 1 cm of the optical path length of the resin composition is 30% / cm or more at the emission wavelength of the inorganic phosphor.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
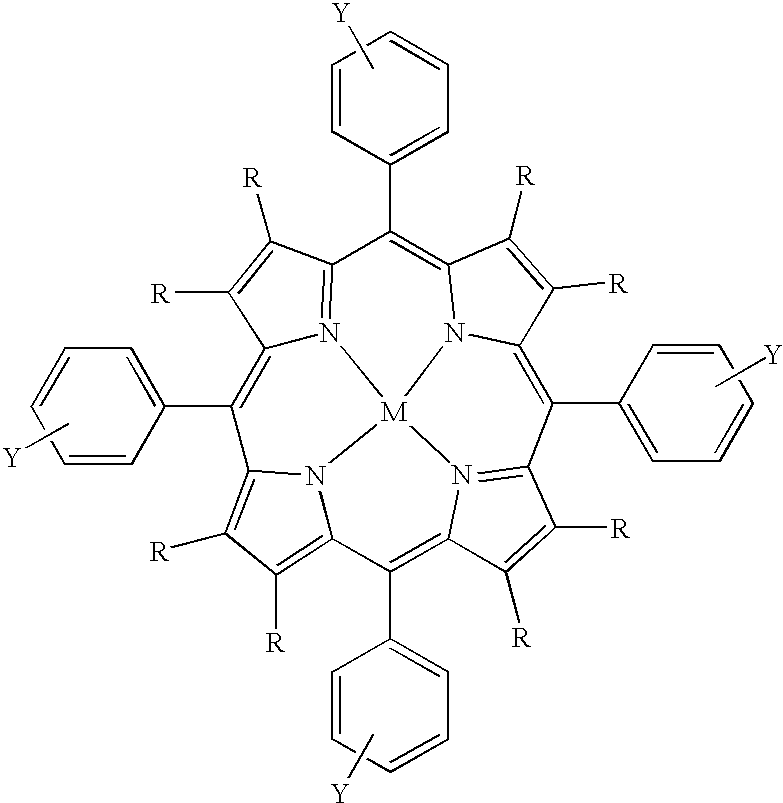
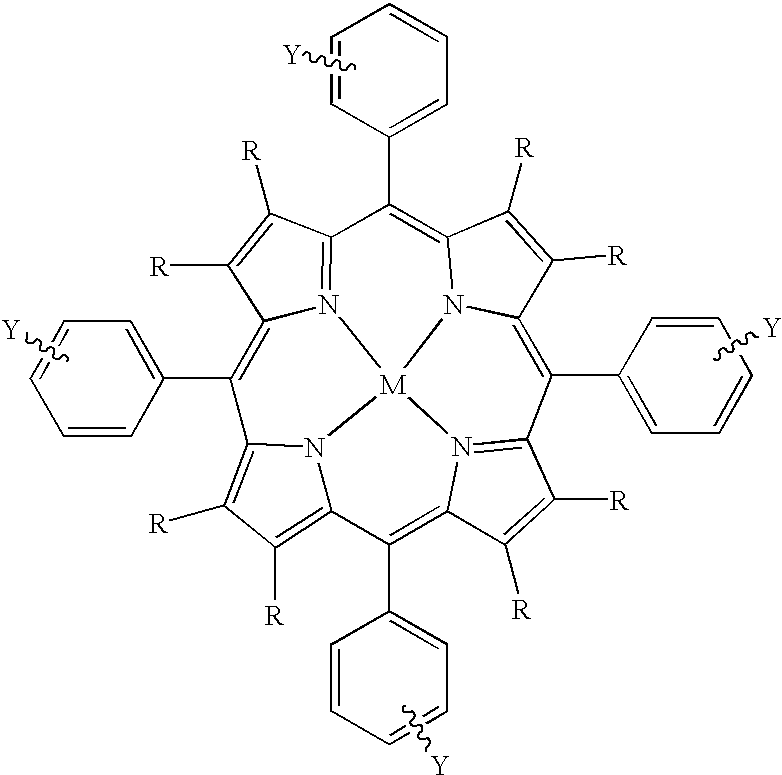
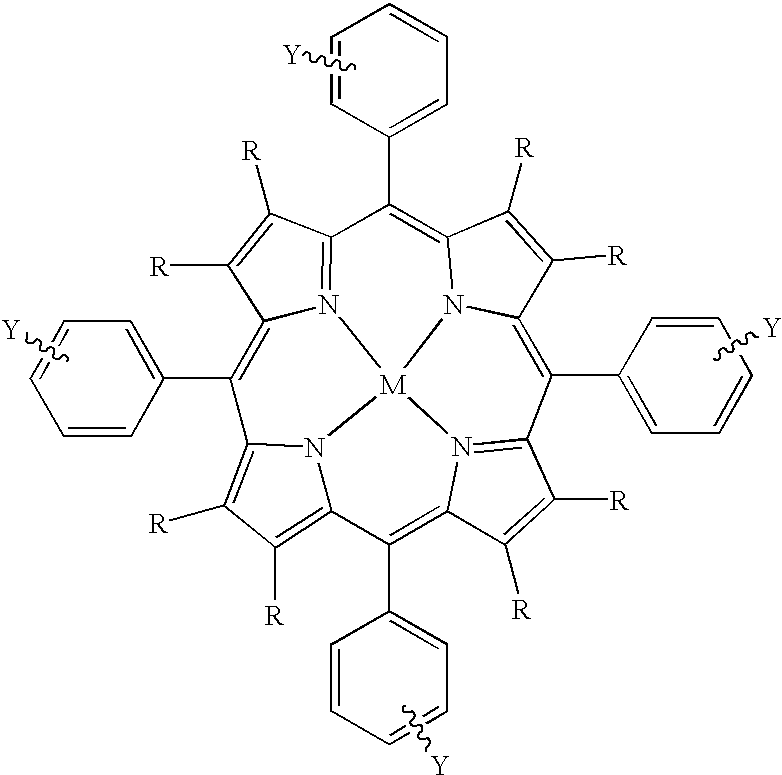
Metalloporphyrins and their uses as radiosensitizers for radiation therapy
The present invention covers radiosensitizers containing as an active ingredient halogenated derivatives of boronated porphyrins containing multiple carborane cages having the structurewhich selectively accumulate in neoplastic tissue within the irradiation volume and thus can be used in cancer therapies including, but not limited to, boron neutron-capture therapy and photodynamic therapy. The present invention also covers methods for using these radiosensitizers in tumor imaging and cancer treatment.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
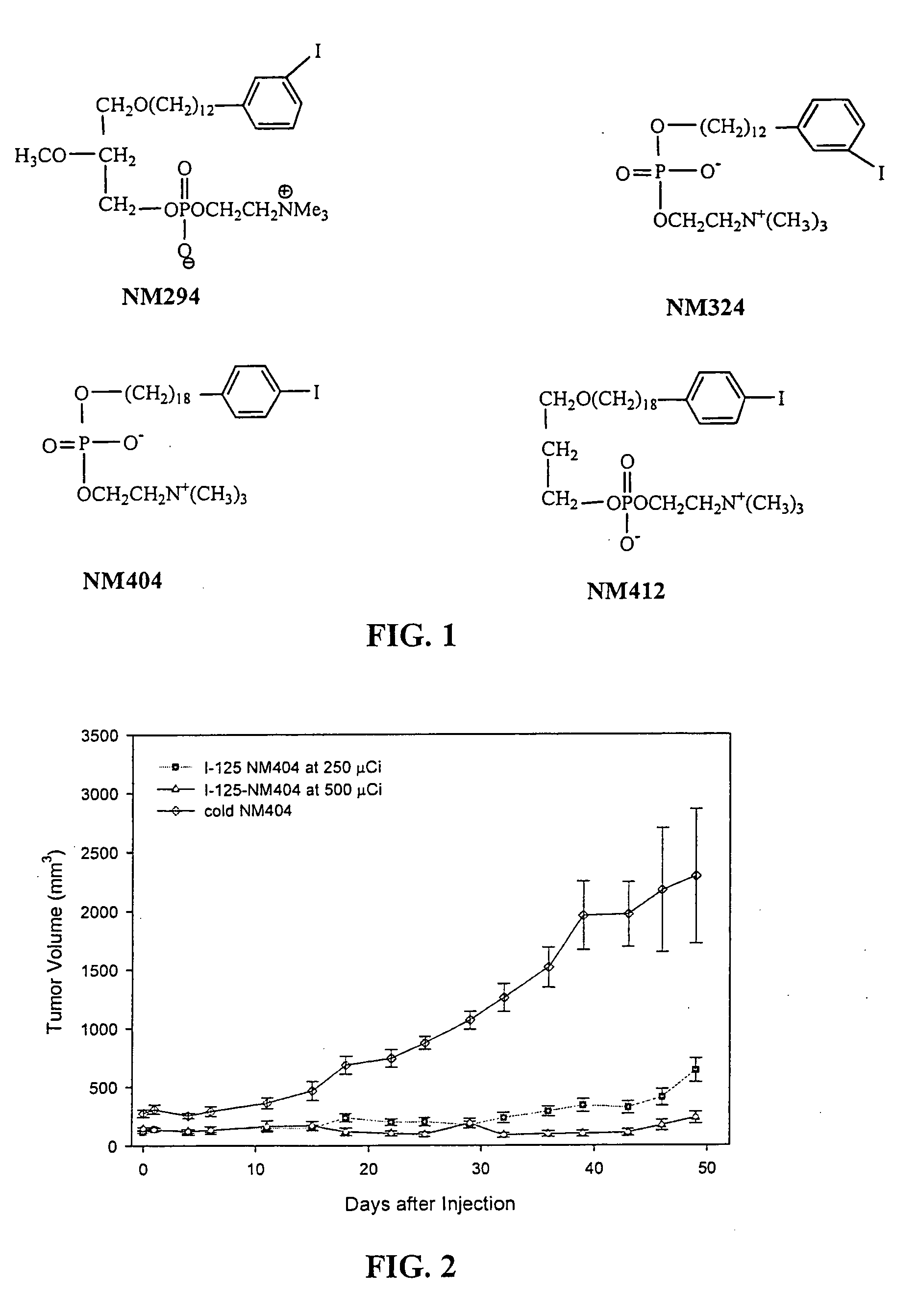
Compositions of phospholipid ether boronic acids and esters and methods for their synthesis and use
ActiveUS20090018357A1Reduce the overall heightSilicon organic compoundsBiocideCancer cellNeutron capture
The present invention discloses boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs and methods for their synthesis and use. The boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs described herein can be used in treating cancer and in particular can be used in conjunction with radiation therapy, such as external beam radiation therapy and neutron capture therapy to specifically target and kill cancer cells.
Owner:CELLECTAR
Gadolinium-Doped Water Cerenkov-Based Neutron and High Energy Gamma-Ray Detector and Radiation Portal Monitoring System
InactiveUS20110024639A1High sensitivityImprove scalabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron radiation measurementTime correlationHigh energy
A water Cerenkov-based neutron and high energy gamma ray detector and radiation portal monitoring system using water doped with a Gadolinium (Gd)-based compound as the Cerenkov radiator. An optically opaque enclosure is provided surrounding a detection chamber filled with the Cerenkov radiator, and photomultipliers are optically connected to the detect Cerenkov radiation generated by the Cerenkov radiator from incident high energy gamma rays or gamma rays induced by neutron capture on the Gd of incident neutrons from a fission source. The PMT signals are then used to determine time correlations indicative of neutron multiplicity events characteristic of a fission source.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Small high-yield deuterium-deuterium neutron generator
InactiveCN104244560AReduce exposure timeReduce volumeDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron irradiationDeuterium ions
The invention discloses a small high-yield and deuterium-deuterium neutron generator. Modular distributed high-frequency ion sources are adopted and evenly distributed on the outer surface of a ceramic cylinder with the spherical end, and deuterium ion beams distributed evenly are output, wherein the flow intensity of the deuterium ion beams is larger than 1 A, and the single atom proportion is larger than 80%; the deuterium ion beams are accelerated in a cylindrical accelerating electric field with the spherical end and bombard a cylindrical metal or ceramic self-forming target to cause a deuterium / deuterium reaction and then generate neutrons of 2.45 MeV, and the self-forming target is located at the high-potential end and provided with the spherical end. The number of the modular distributed high-frequency ion sources and the area of the self-forming target are not limited, the yield of the neutrons of the deuterium / deuterium reaction is larger than 1011 n / s, and no radioactive pollutants are discharged. The neutron generator is suitable for commercialized application such as the fields of boron neutron capture treatment, neutron radiography, on-line material component neutron detection, neutron irradiation modification and californium neutron source substitute products.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
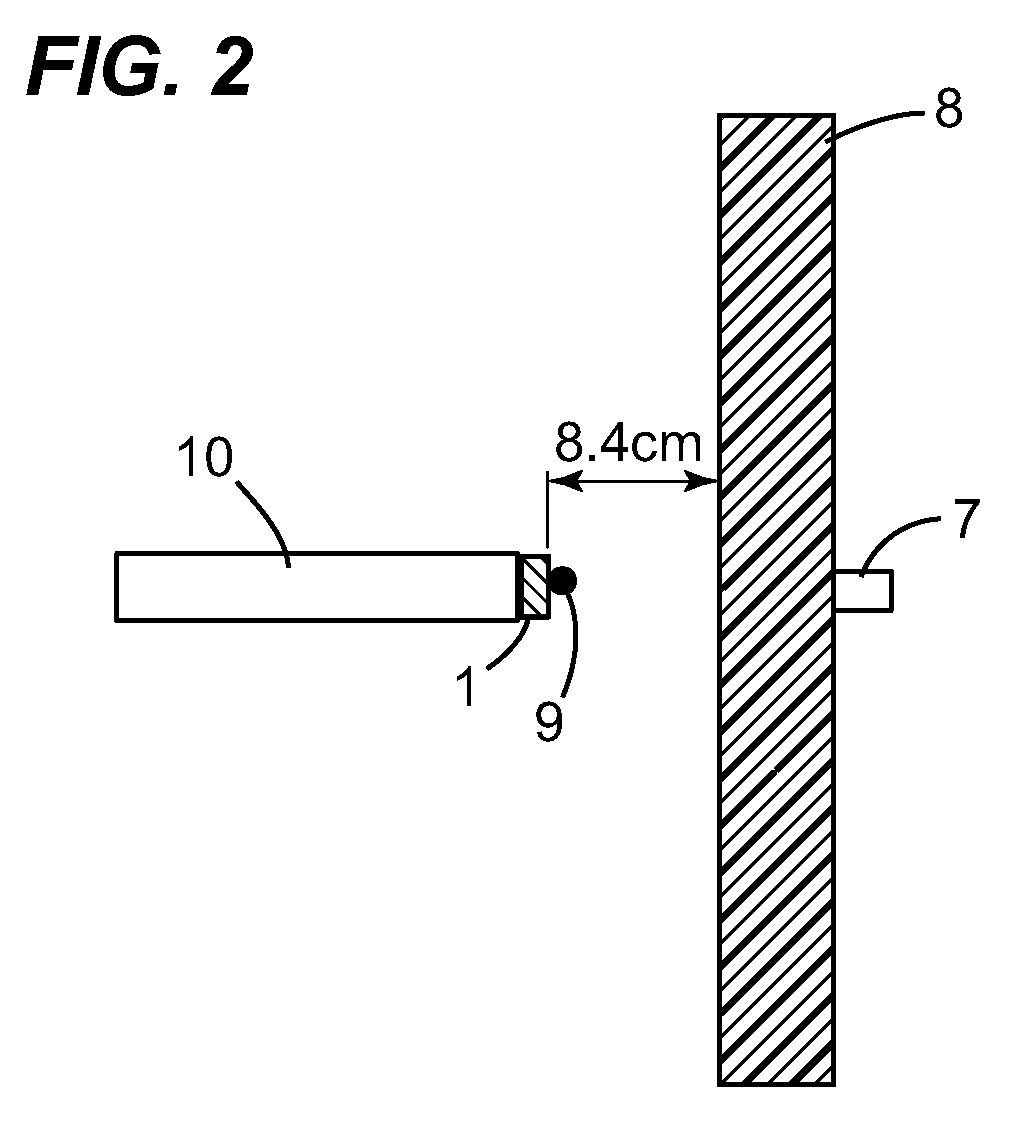
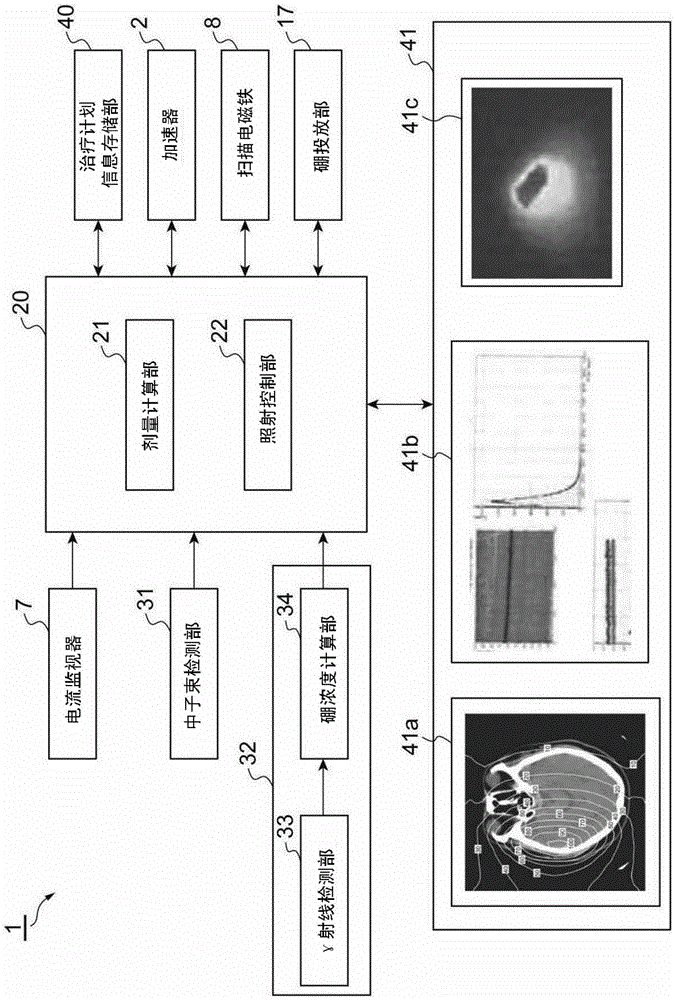
Neutron capture therapy device
ActiveCN105938731AImprove reliabilityDirect voltage acceleratorsIrradiation devicesNeutron captureBoron concentration
The invention provides a neutron capture therapy device which is capable of improving reliability of a boron neutron capture therapy. The neutron capture therapy device (1) in the invention is radiates neutron beams onto a object to be radiated (M), and boron in the radiated object (M) is enabled to react with the neutrons. The neutron capture therapy device (1) has a neutron beam radiating part (4) used for radiating the neutron beams (N) onto the object to be radiated (M) and a boron concentration measuring part (32) used for measuring in real time the concentration of boron in the object to be radiated (M) when the neutron beam radiating part (4) radiates the neutron beams (N).
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com