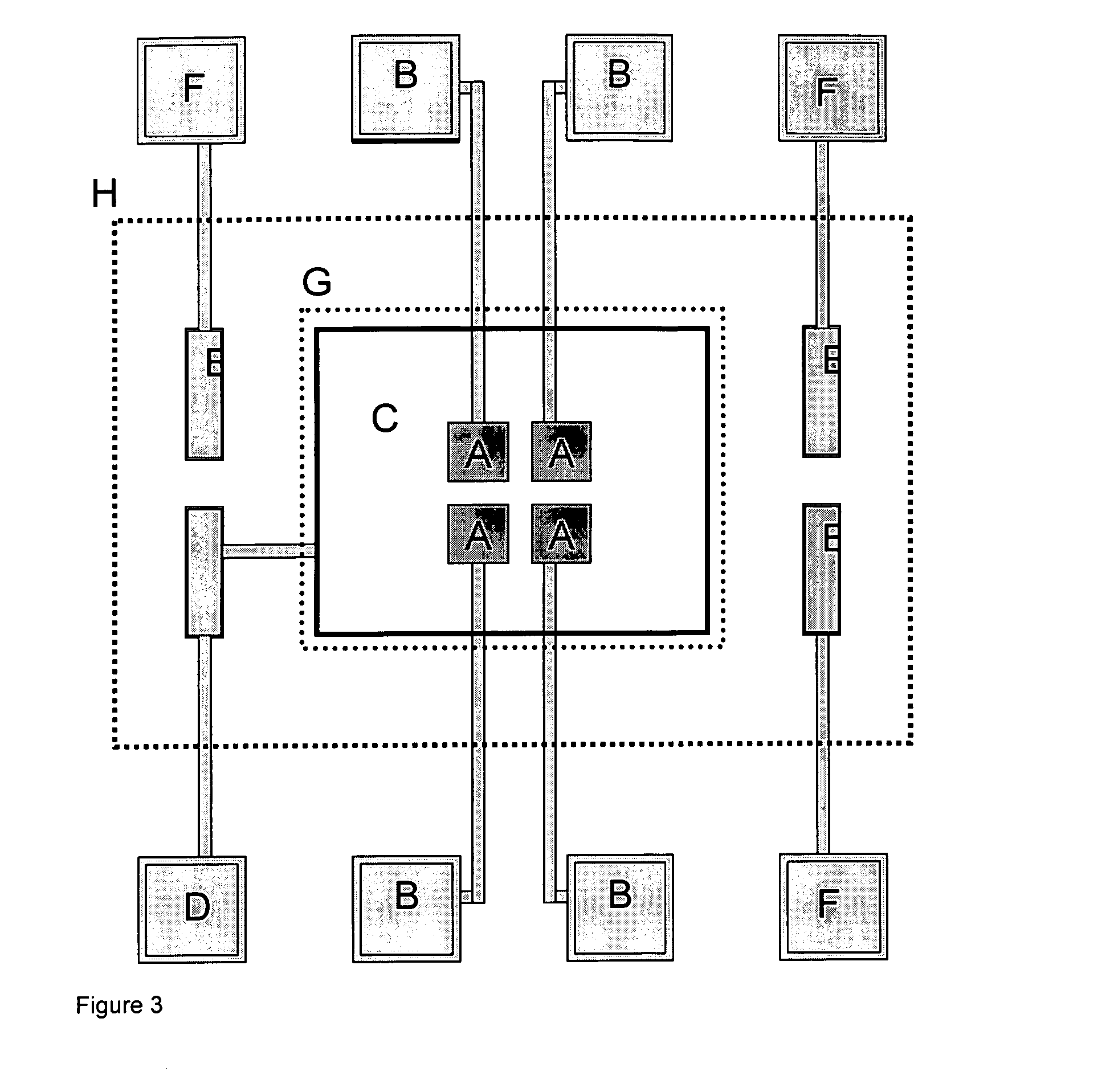
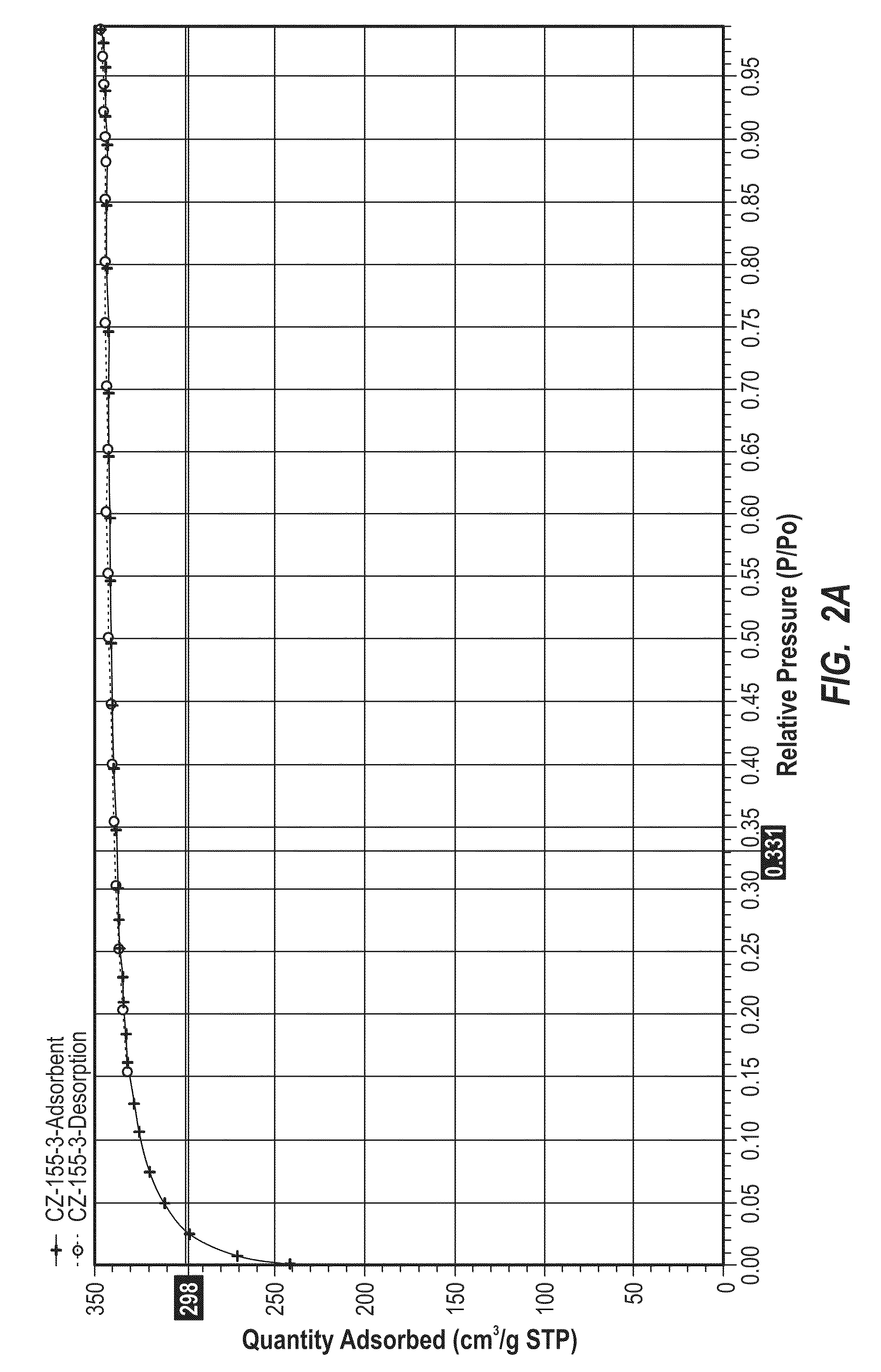
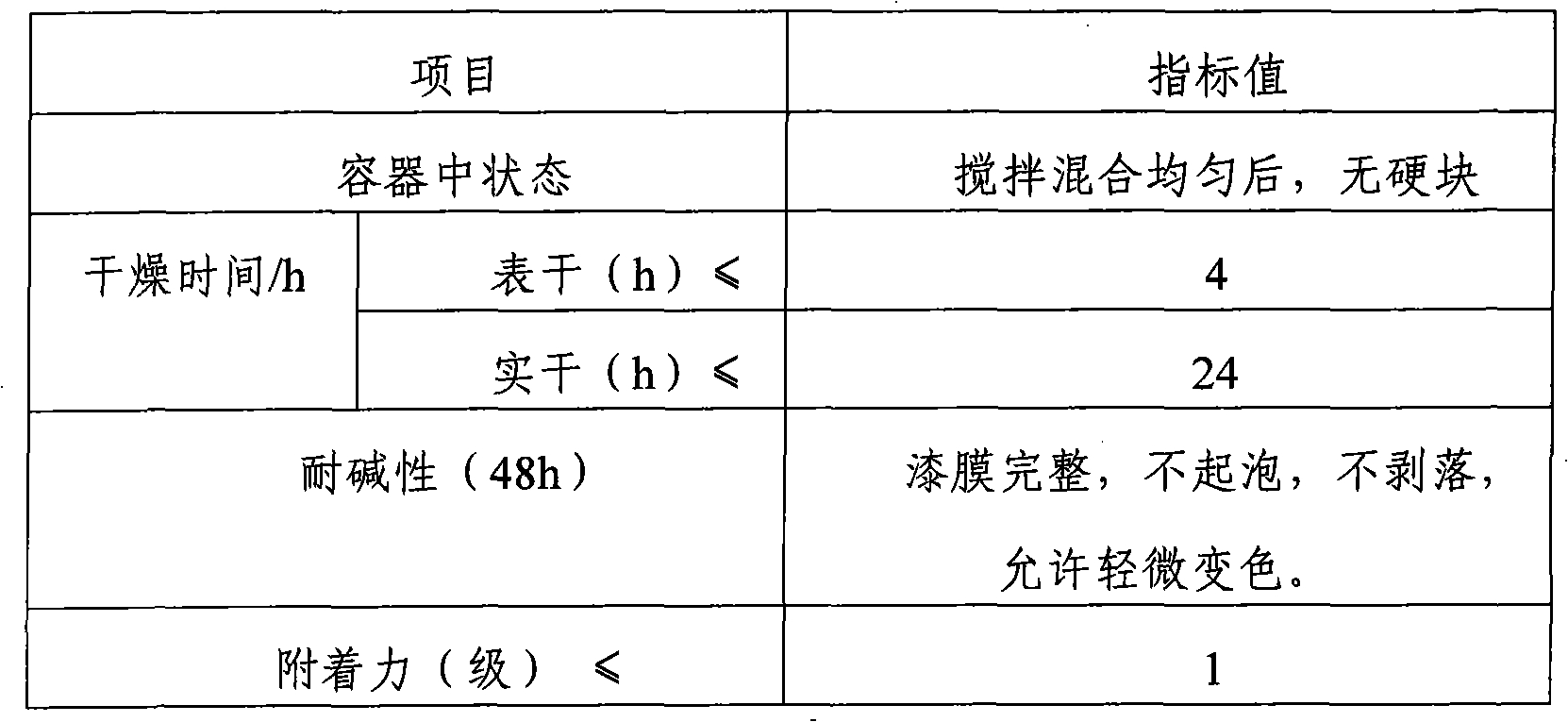
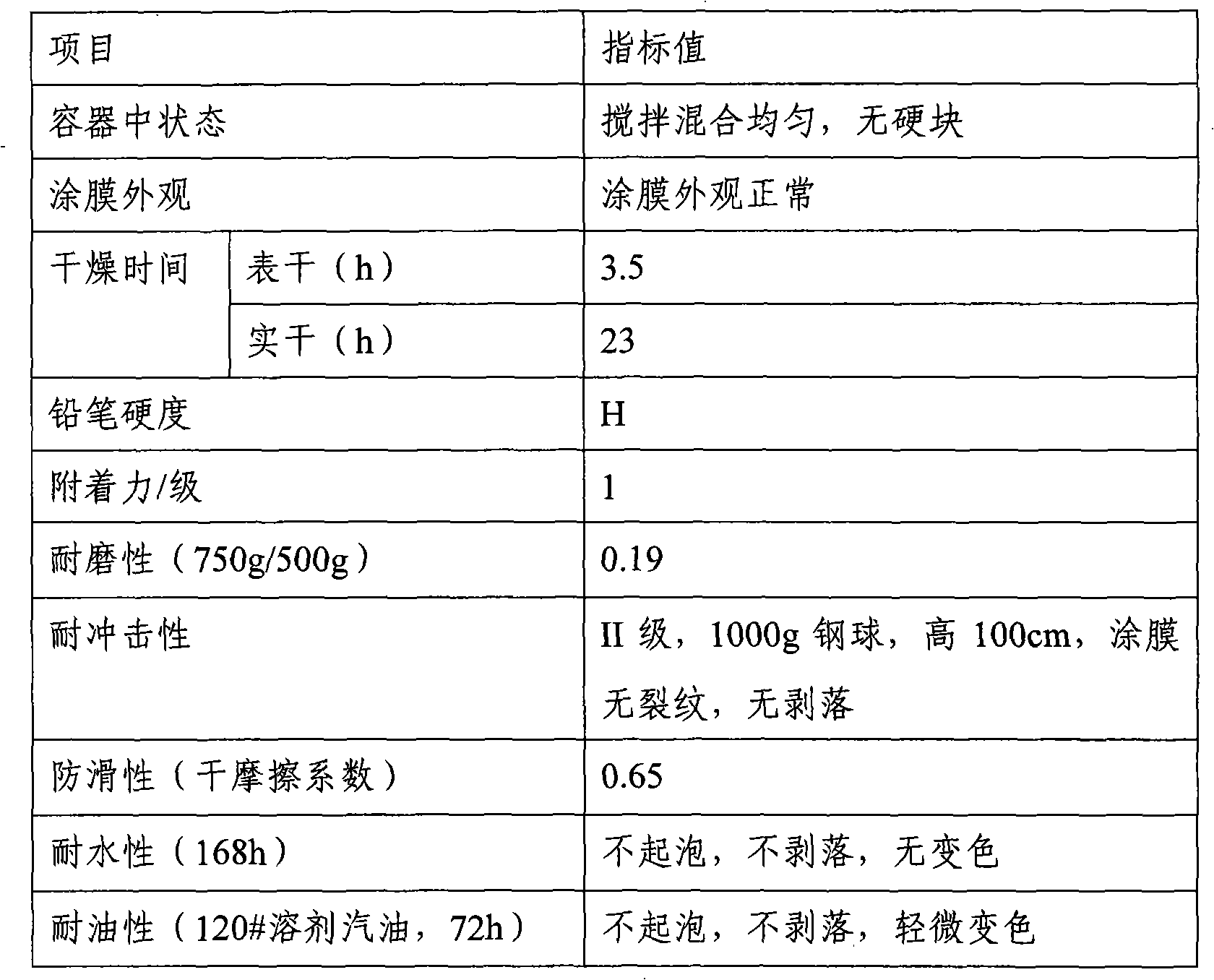
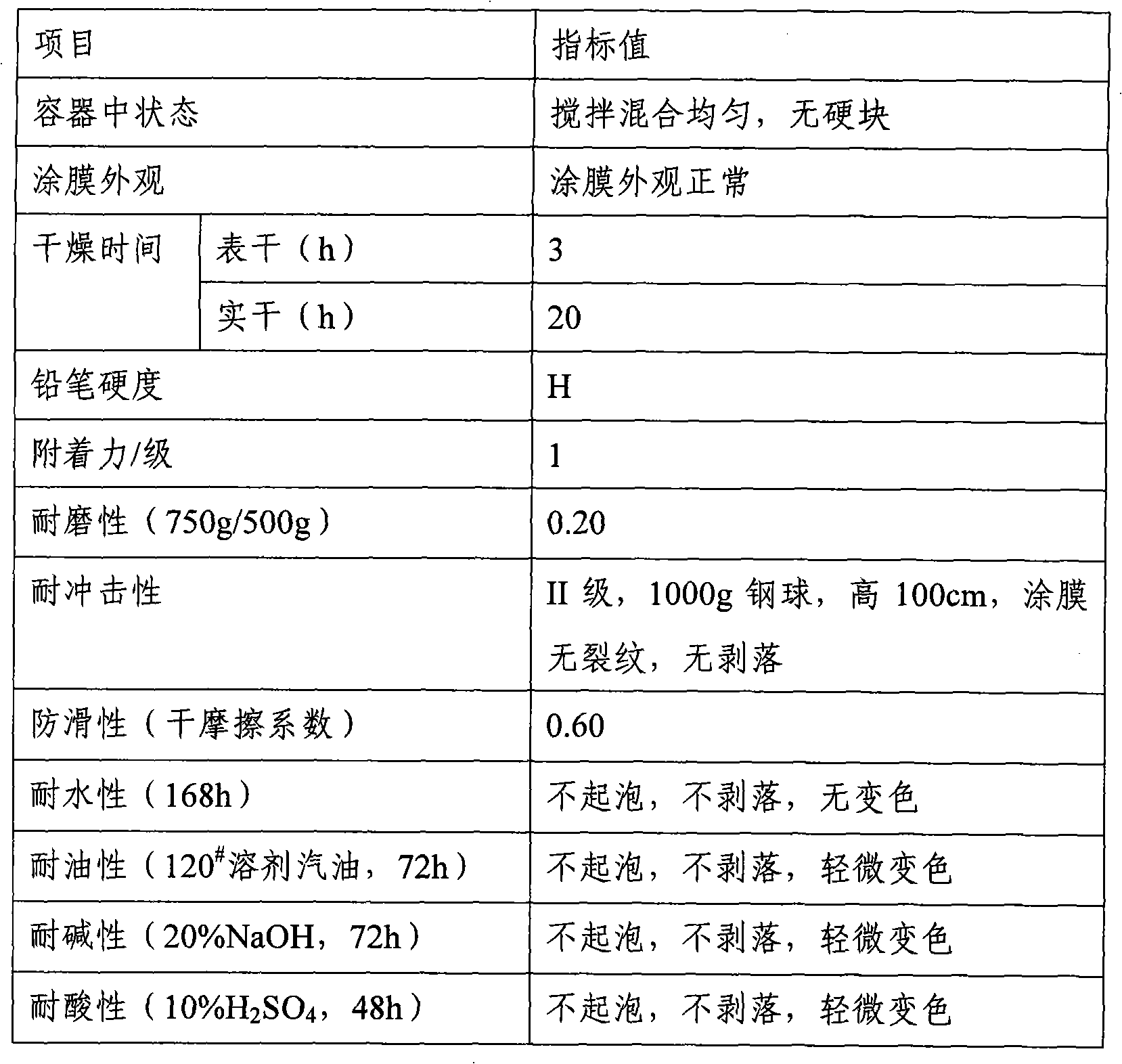
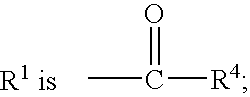
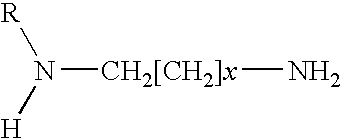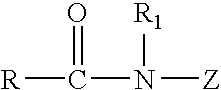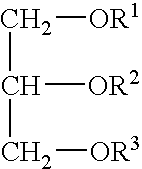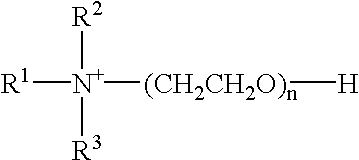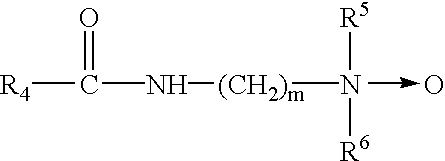Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
16542 results about "Organosolv" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
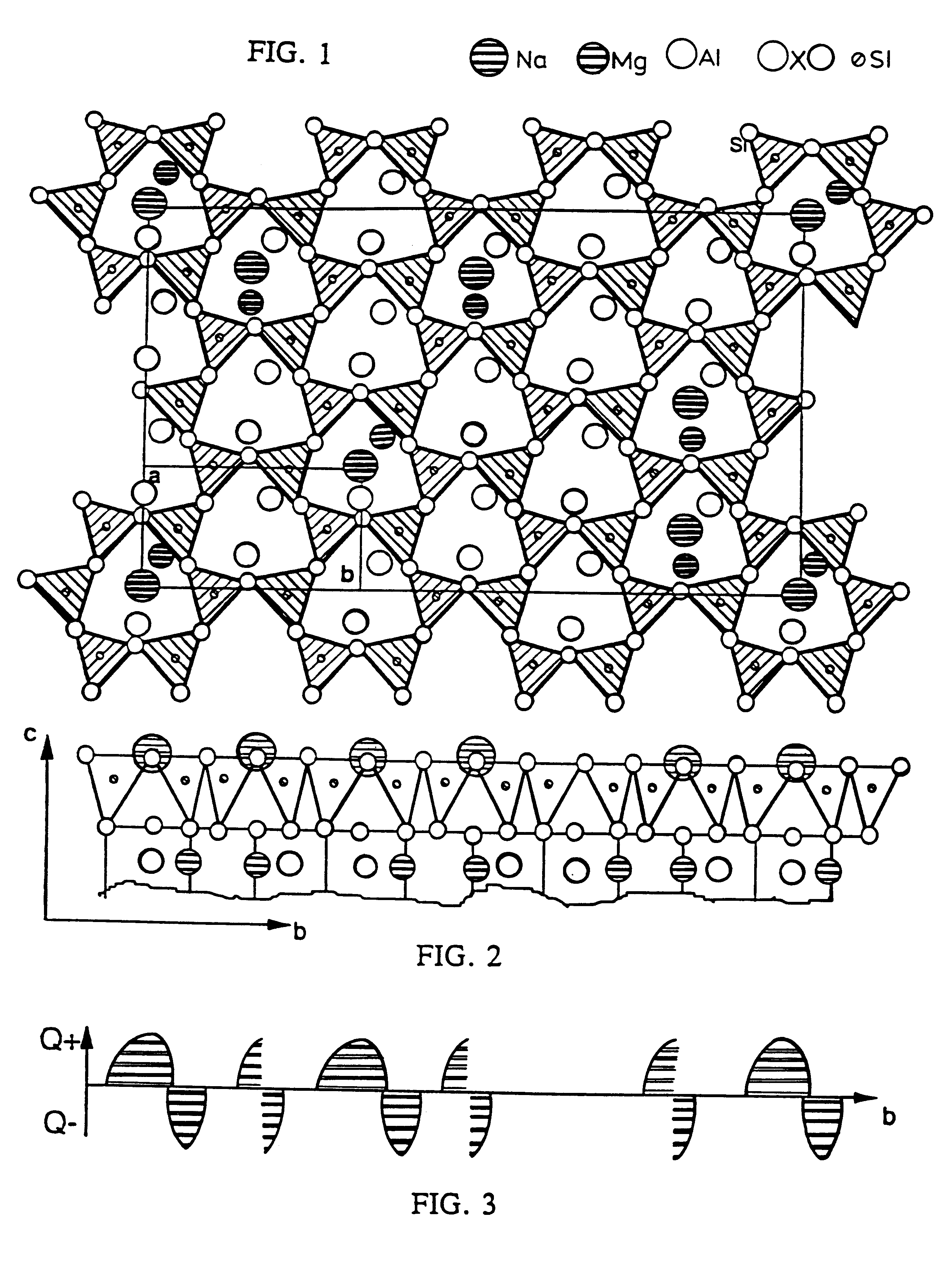
In industrial paper-making processes, organosolv is a pulping technique that uses an organic solvent to solubilise lignin and hemicellulose. It has been considered in the context of both pulp and paper manufacture and biorefining for subsequent conversion of cellulose to fuel ethanol. The process was invented by Theodor Kleinert in 1968 as an environmentally benign alternative to kraft pulping.
Carbon nanotube yarn and method for making the same
A carbon nanotube yarn includes a number of carbon nanotube yarn strings bound together, and each of the carbon nanotube yarn strings includes a number of carbon nanotube bundles that are joined end to end by van der Waals attractive force, and each of the carbon nanotube bundles includes a number of carbon nanotubes substantially parallel to each other. A method for making the carbon nanotube yarn includes soaking the at least one carbon nanotube yarn string drawn out from a carbon nanotube array in an organic solvent to shrink it and then collecting it.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
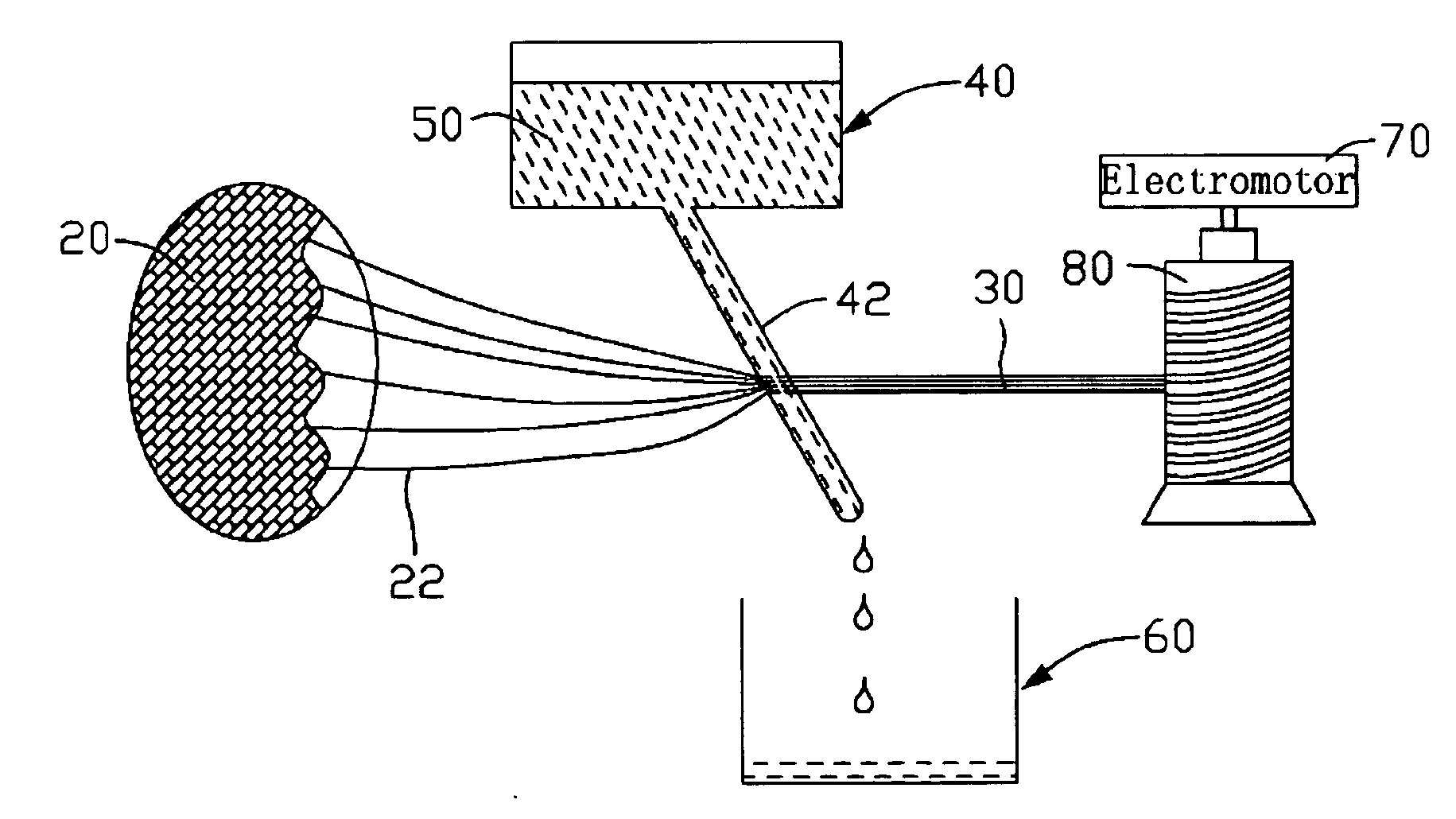
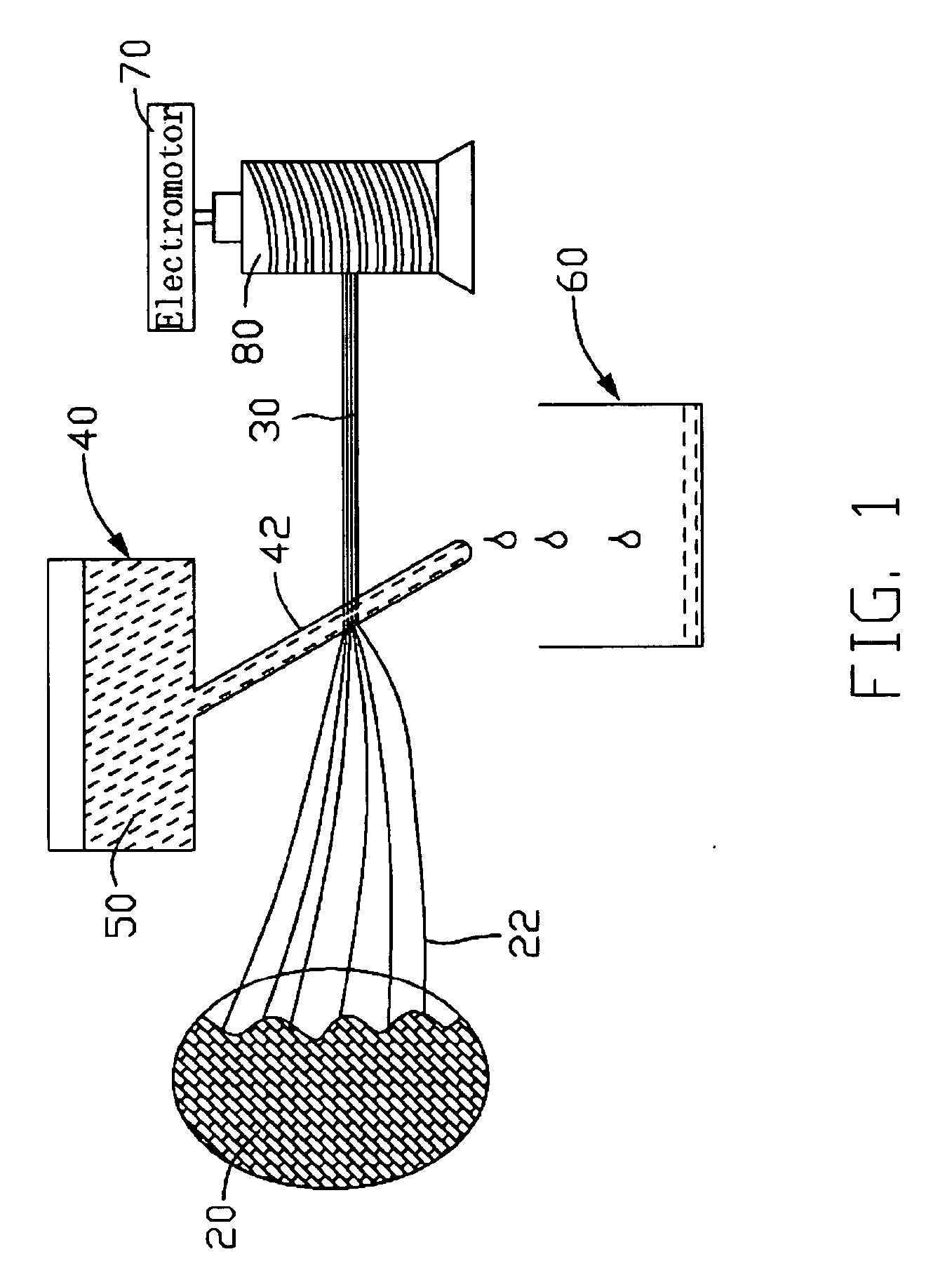
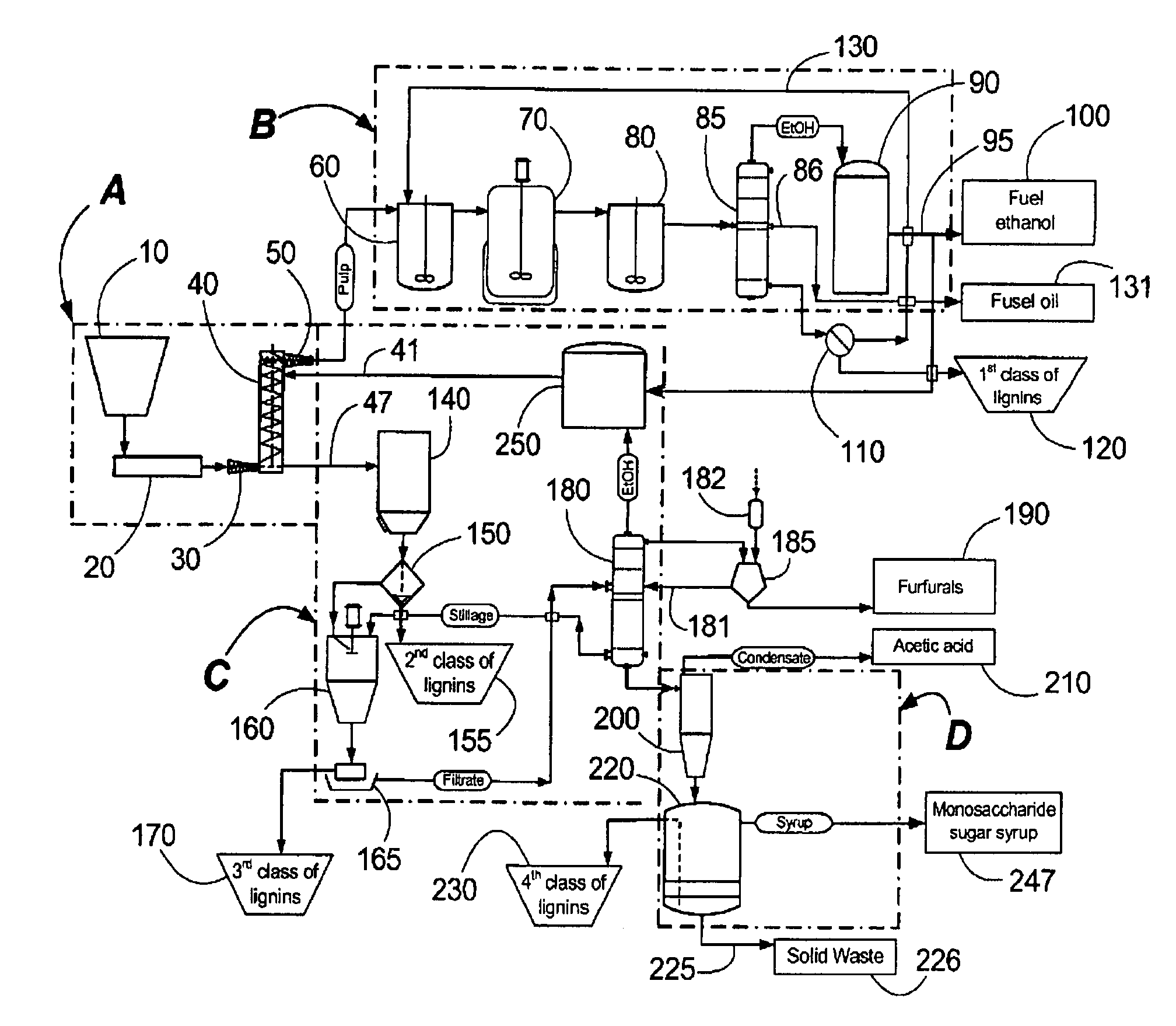
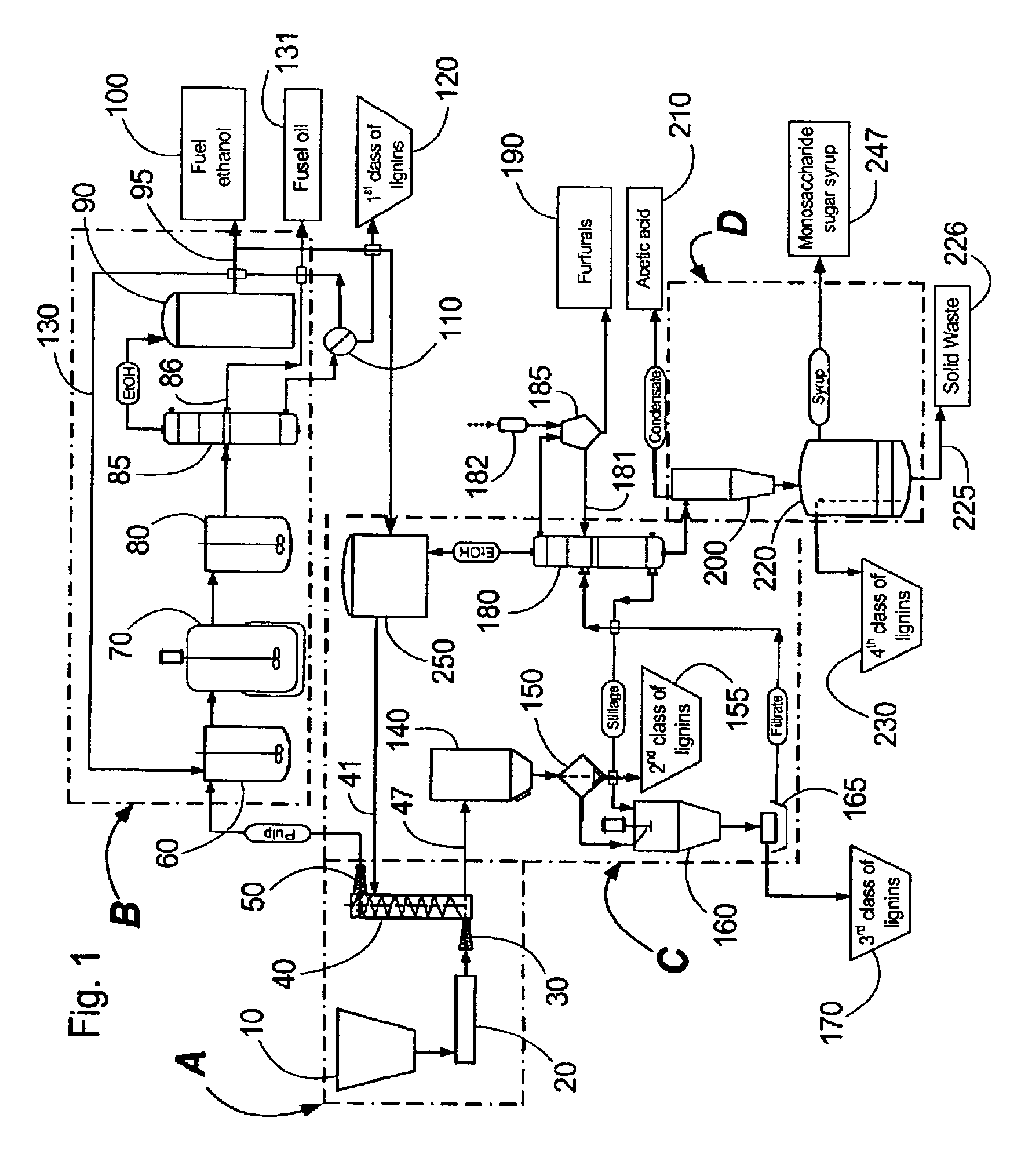
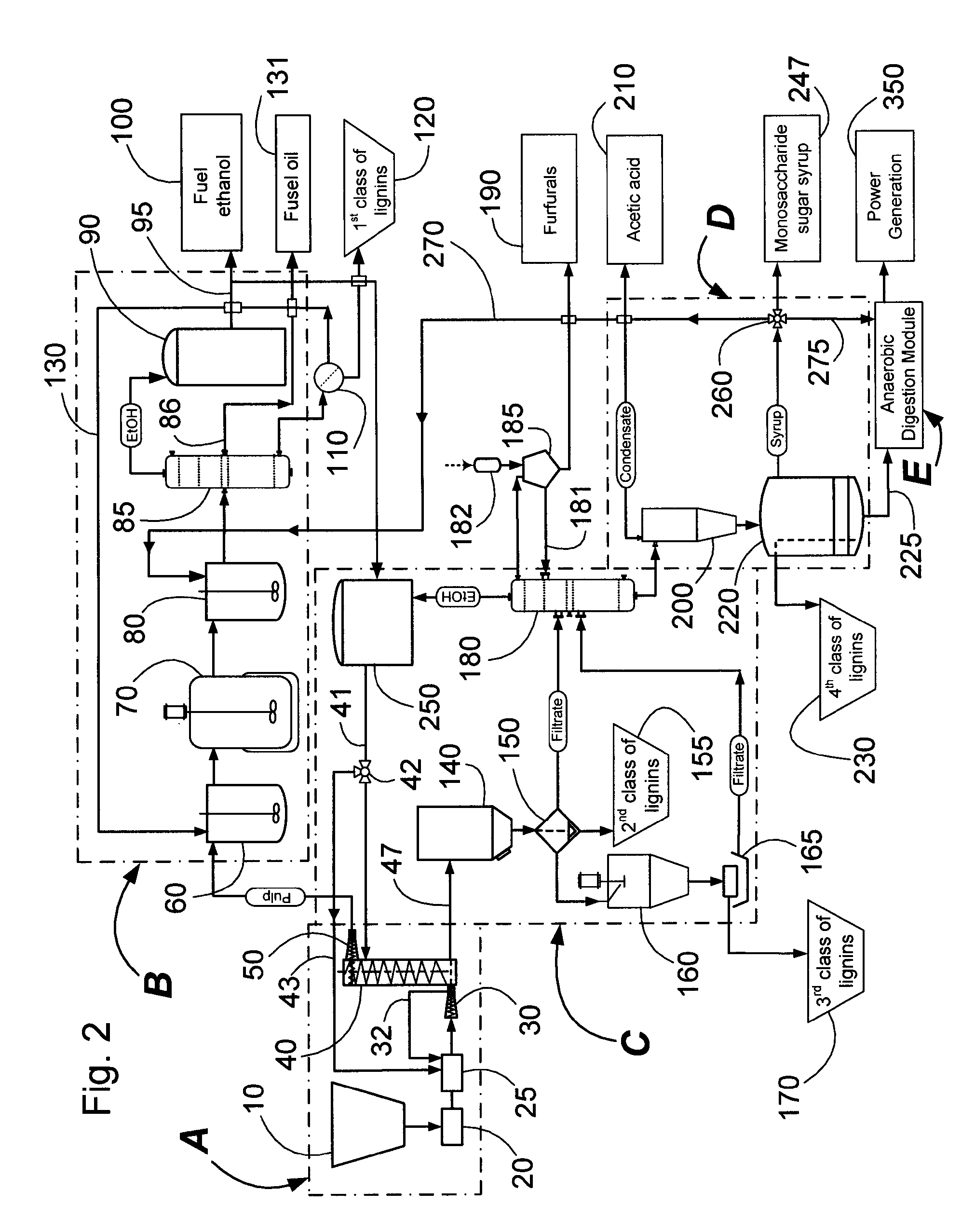
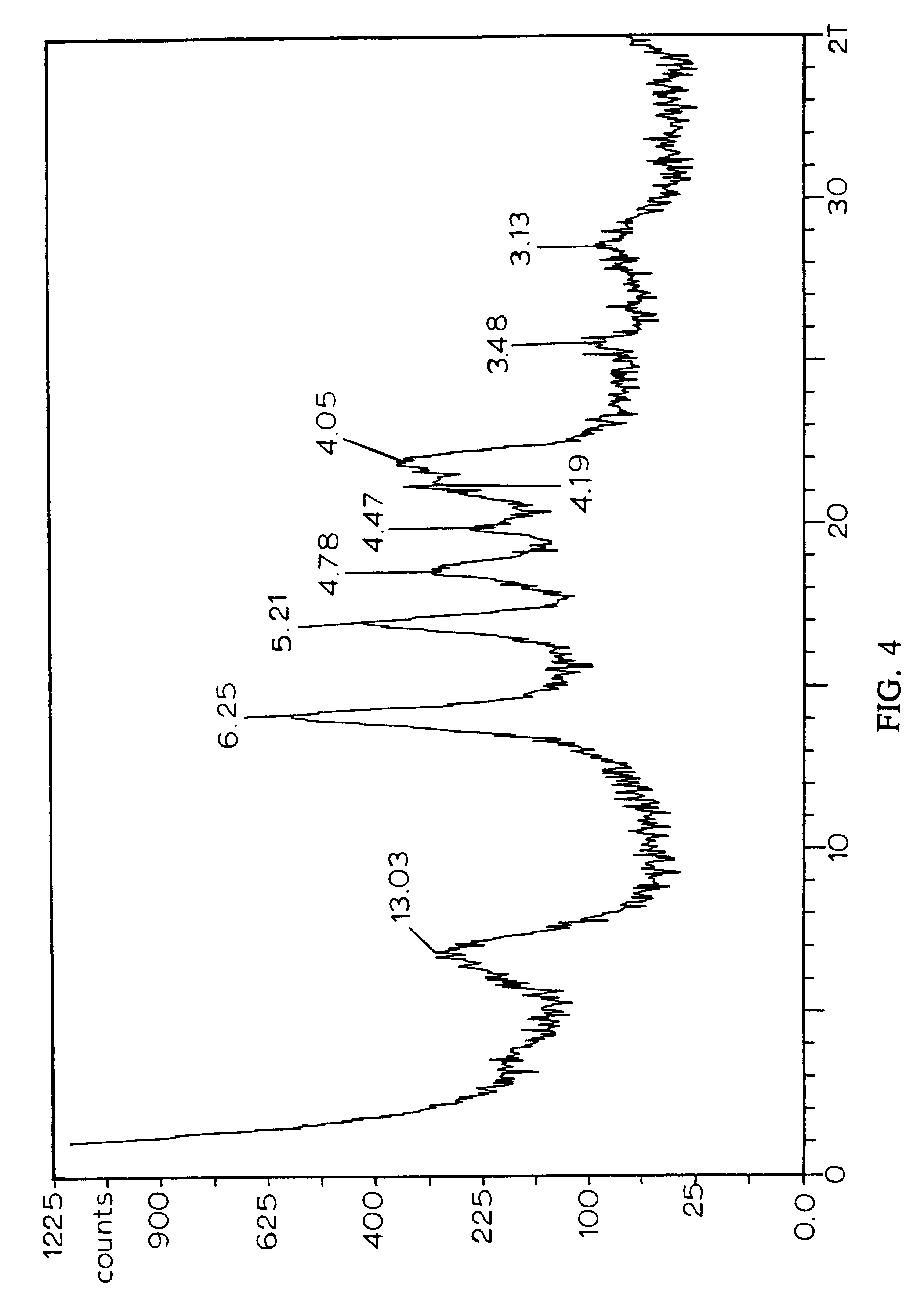
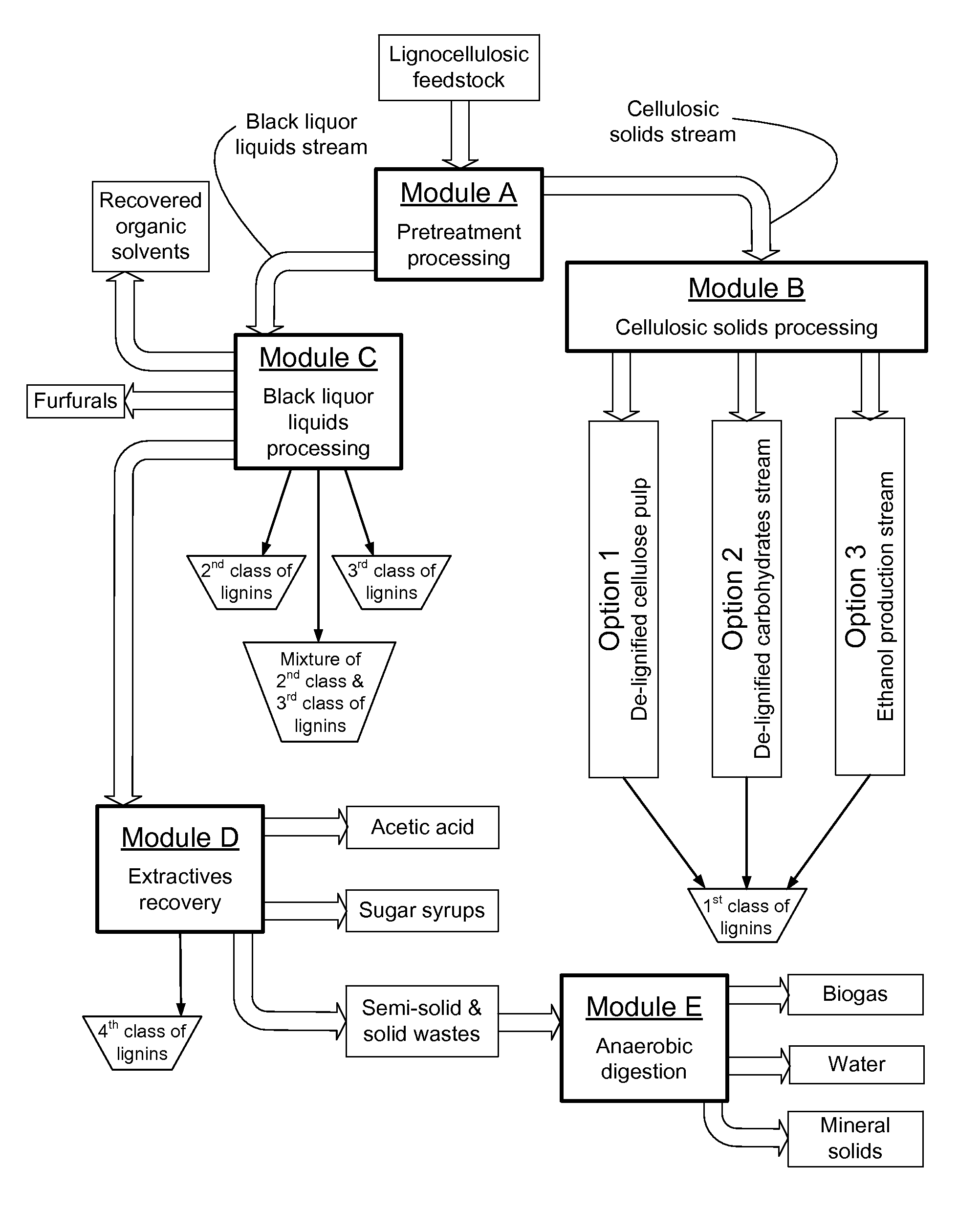
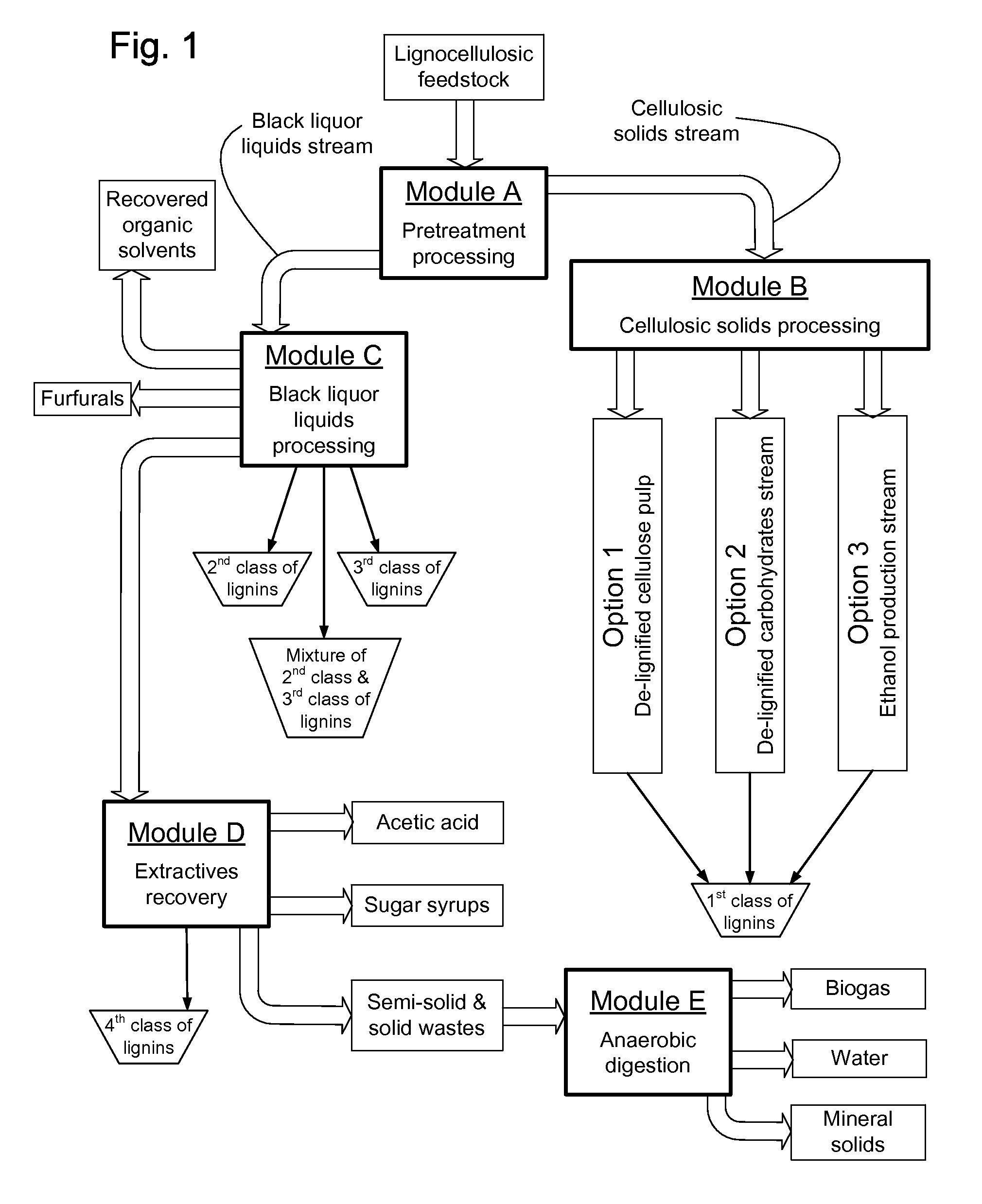
Continuous counter-current organosolv processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
InactiveUS7465791B1Low viscosityNon-fibrous pulp additionBiological substance pretreatmentsFractionationOrganosolv
A modular process for organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic feedstocks into component parts and further processing of said component parts into at least fuel-grade ethanol and four classes of lignin derivatives. The modular process comprises a first processing module configured for physico-chemically digesting lignocellulosic feedstocks with an organic solvent thereby producing a cellulosic solids fraction and a liquid fraction, a second processing module configured for producing at least a fuel-grade ethanol and a first class of novel lignin derivatives from the cellulosic solids fraction, a third processing module configured for separating a second class and a third class of lignin derivatives from the liquid fraction and further processing the liquid fraction to produce a distillate and a stillage, a fourth processing module configured for separating a fourth class of lignin derivatives from the stillage and further processing the stillage to produce a sugar syrup.
Owner:SUZANO CANADA INC
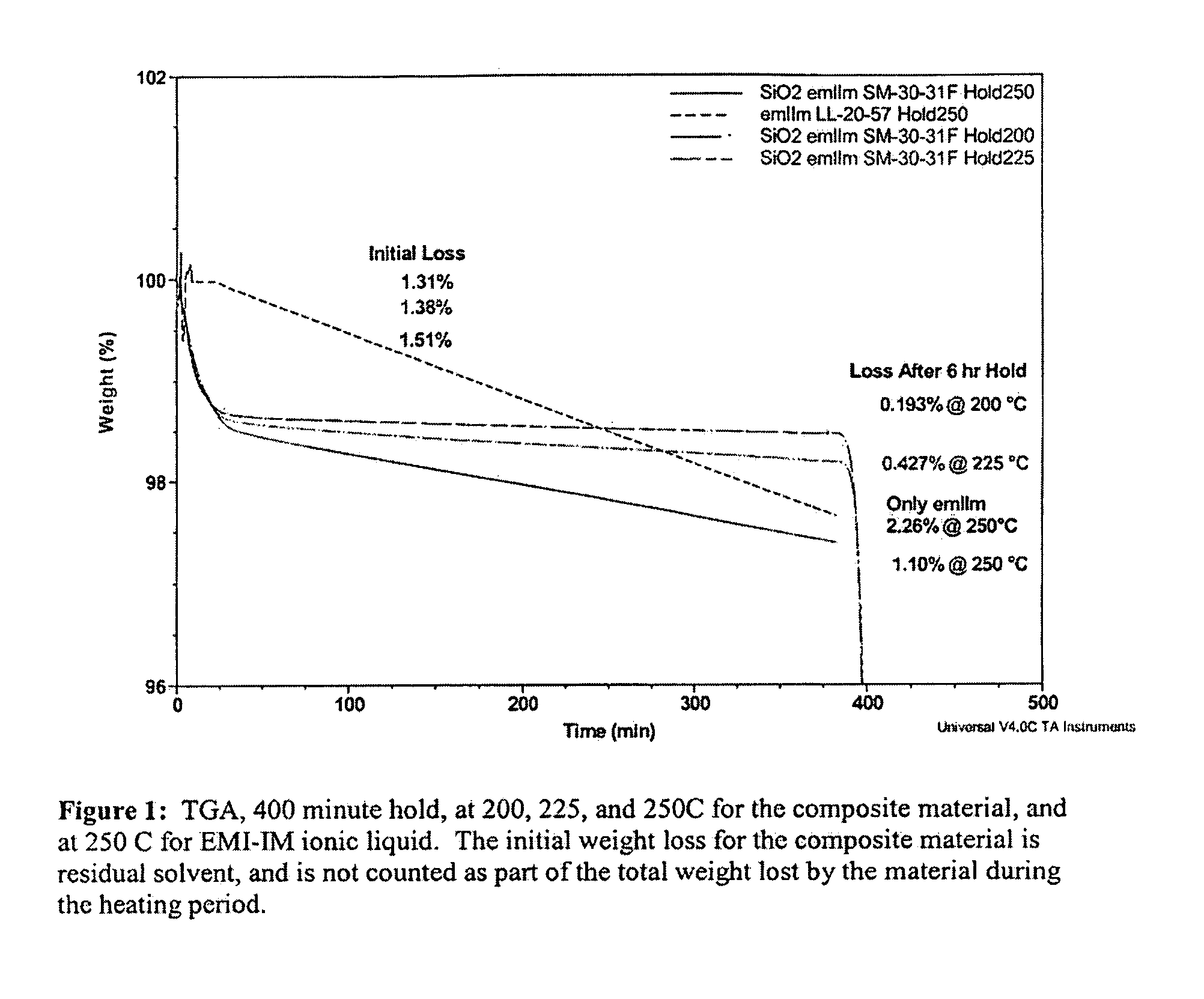
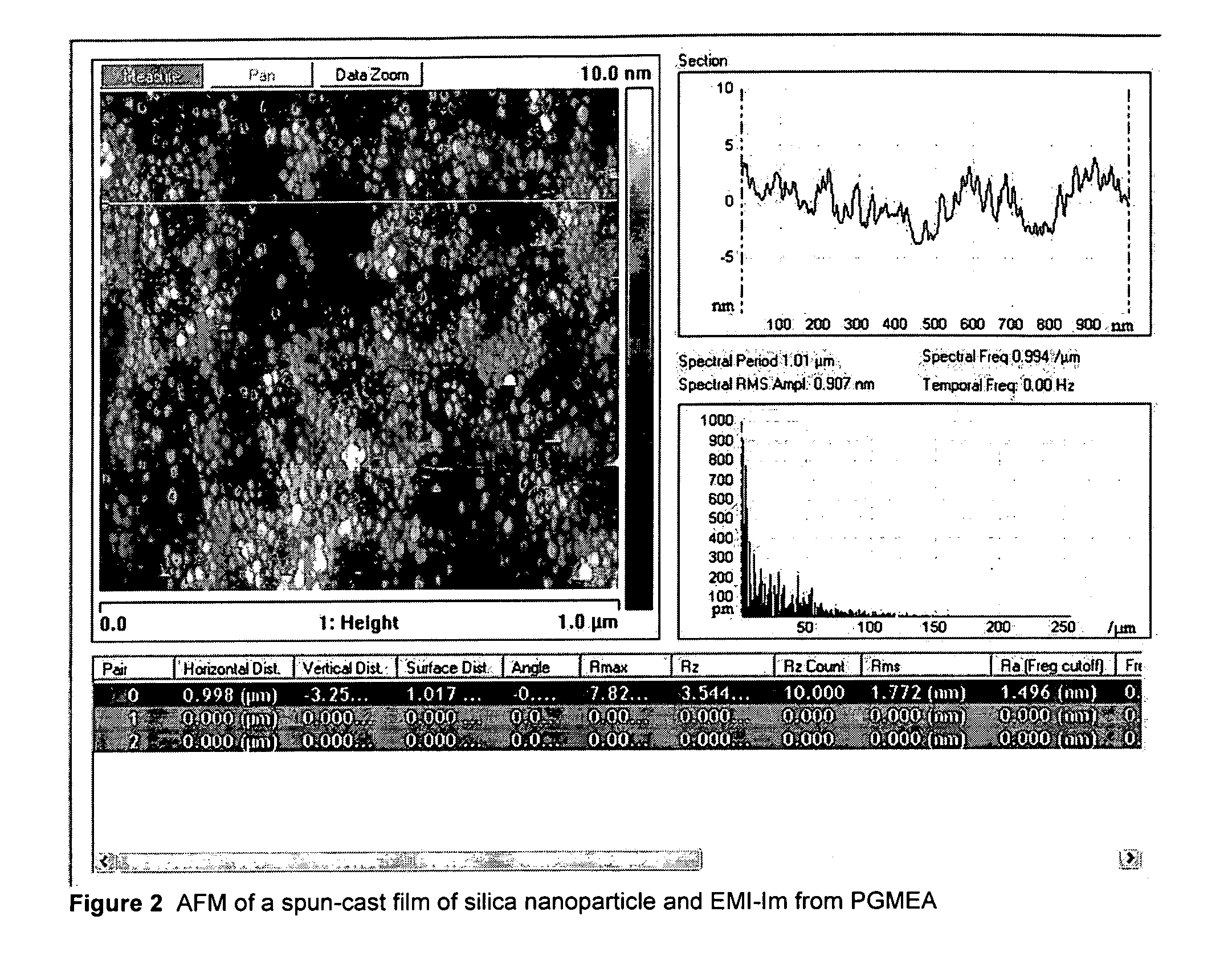
Liquid Composite Compositions Using Non-Volatile Liquids and Nanoparticles and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080209876A1Reduce CTEImprove performanceElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesOrganic solventNanoparticle
A solvent composition comprising an organic solvent; dispersed nanoparticles; and a non-volatile electrolyte.
Owner:ESIONIC
High-capacity lithium-ion electrolyte, battery and preparation method of battery
ActiveCN101771167AIncrease capacityLow costFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrolytic agentPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a high-capacity lithium-ion electrolyte, a battery and a preparation method of a battery, in particular to the high-capacity lithium-ion electrolyte and the battery using the high-capacity lithium-ion electrolyte and the preparation method of the battery. The electrolyte disclosed by the invention comprises lithium salt and non-aqueous organic solvent, and also consists of the following components in weight percent in terms of the total weight of the electrolyte: 0.5-7% of film-forming additive, 0-15% of flame-retardant additive, 2-10% of antiovefill additive, 0.01-2% of stabilizer and 0.01-1% of wetting agent; the electrolyte can enable the anode with high Ni content to work stably, and reduce the battery cost; the high-capacity lithium-ion battery can perform high ratio capacity and excellent safety and high temperature property and cyclic life fully due to the addition and synergetic functions of various functional additives.
Owner:JIUJIANG TINCI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for producing cross-linked hyaluronic acid-protein bio-composites
InactiveUS20060189516A1Uniform densityUniform porosityPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderCross-linkFiber
This invention is concerned with a new method for producing cross-linked hyaluronic acid—protein bio-composites in various shapes. In the present process, a polysaccharide solution and a protein solution are mixed under moderate pH values in presence of salts to form a homogenous solution, which can be processed into various shapes, such as membrane, sponge, fiber, tube or micro-granular and so on. After then, the homogenous solution is subjected to a cross-linking reaction in organic solvent containing weak acid to produce an implantable bio composite material having excellent bio-compatibility, biodegradability, prolonged enzymatic degradation time, and good physical properties.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
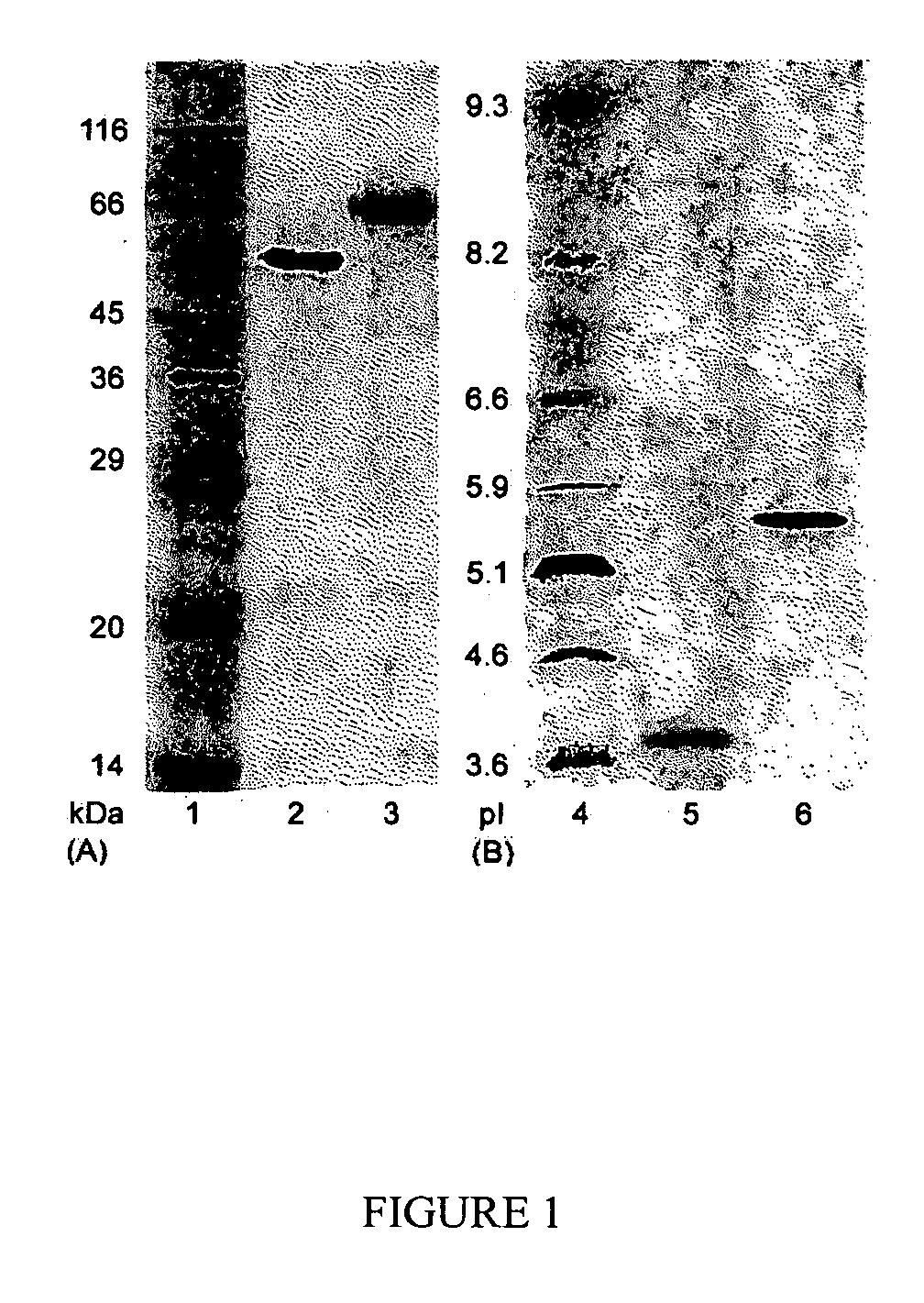
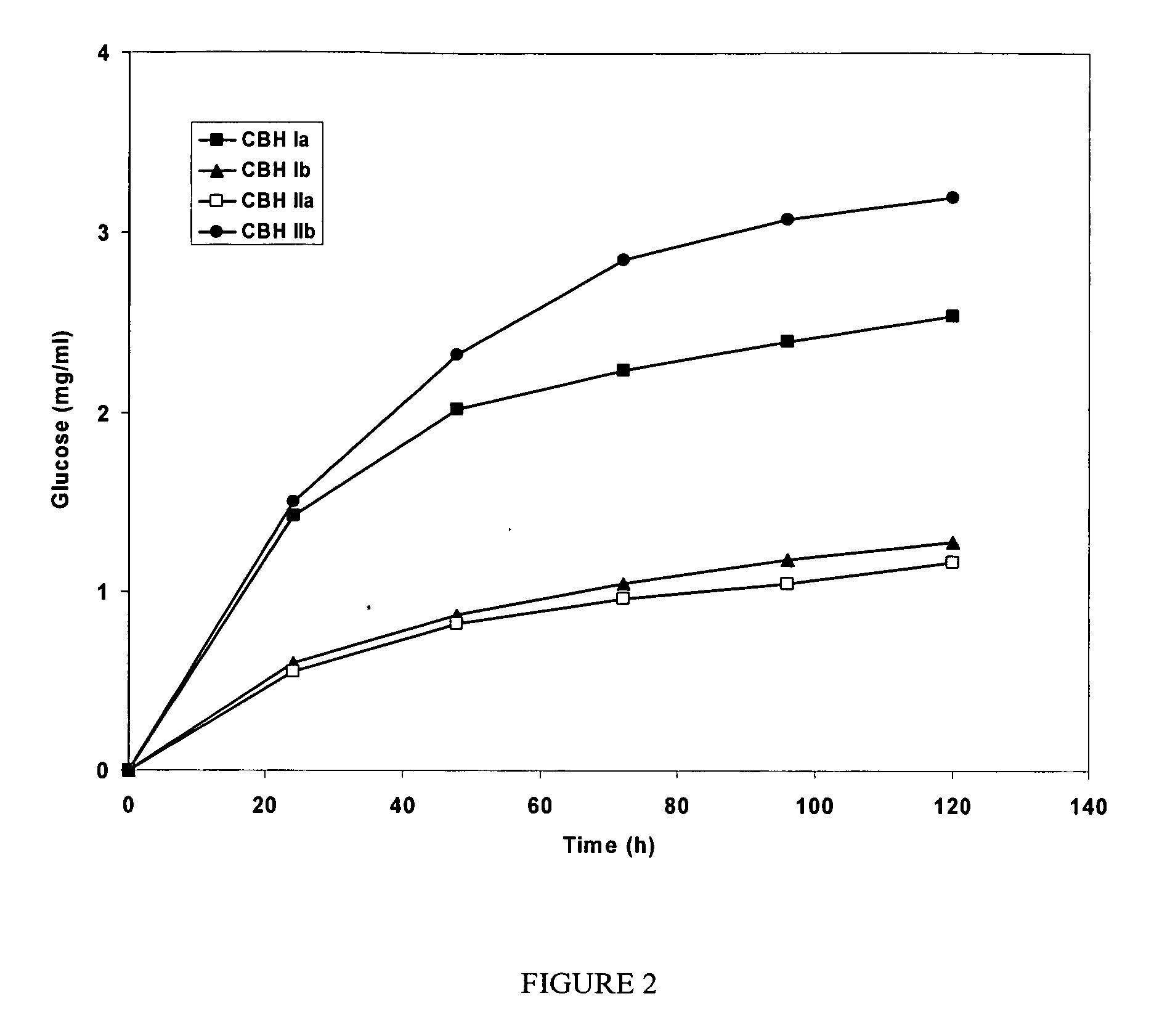
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
A kind of non-aqueous electrolytic solution for lithium secondary battery
ActiveCN102263292AGood storage stabilityImprove antioxidant capacitySecondary cellsElectrolytic agentPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a non-aqueous electrolytic solution used for lithium secondary batteries, in particular to an electrolytic solution capable of improving the high-voltage cycle performance of lithium batteries and the storage performance of the electrolytic solution. The non-aqueous electrolytic solution disclosed by the invention contains 0.01-2% by weight of antioxidant based on the total weight of the electrolytic solution, and due to the incorporation of the additives, the storage stability of the electrolytic solution is obviously improved. The non-aqueous electrolytic solution also contains lithium salt, a non-aqueous organic solvent and also contains the following components in percentage by total weight of the electrolytic solution of 0.5-7 percent of film-forming additives, 0-15 percent of flame-retardant additives, 2-10 percent of overcharge protection additives, 0.01-0.02 percent of a stabilizing agent and 0.01-1 percent of a wetting agent. According to the non-aqueous electrolytic solution provided by the invention, batteries can stably work under the high voltage of 4.3V or above, due to the synergic action of the incorporated additives with various functions, the high-capacity lithium-ion batteries can bring high specific energy into full play and have outstanding safety and high-temperature performances and cycle life.
Owner:JIUJIANG TINCI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery using the same
ActiveUS20150064578A1Excellent characteristicsImprove life characteristicsCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsOrganic solventElectrical battery
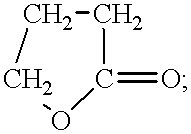
An electrolyte for a lithium secondary battery, the electrolyte including: a lithium salt; a non-aqueous organic solvent; and a piperazine derivative represented by Formula 1 having an oxidation potential lower than an oxidation potential of the non-aqueous organic solvent by about 2 V to about 4 V:wherein, in Formula 1, X, Y, and R1 to R4 are defined in the specification.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Exfoliated layered materials and nanocomposites comprising said exfoliated layered materials having water-insoluble oligomers or polymers adhered thereto
InactiveUS6228903B1Solve the lack of spaceIncreased energy requirementMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentOrganic solventOligomer
A phyllosilicate material is exfoliated by admixture of the phyllosilicate with water, and a solvent for a water-insoluble oligomer or polymer that is sorbed or electrostatically bonded to the inner surfaces of the phyllosilicate platelets after exfoliation of the phyllosilicate. Intercalation and exfoliation can be achieved via contact of the phyllosilicate with an organic solvent and water to electrostatically bond one or more polar moieties from the organic solvent to a metal cation on the platelet inner surfaces, so that after evaporation of the water used for intercalation of the organic solvent between phyllosilicate platelets, the platelets do not then collapse together, but remain exfoliated. After exfoliation of the phyllosilicate, the exfoliated platelets are contacted with a polymer / carrier composition that includes a water-insoluble polymer or water-insoluble oligomer, and a solvent for the water-insoluble polymer or oligomer. After exfoliating the phyllosilicate and prior to polymer contact, the individual phyllosilicate platelets are contacted with the polymer / carrier composition to sorb the water-insoluble polymer or water-insoluble oligomer onto one or both surfaces of the exfoliated phyllosilicate platelets and drive off the adhered solvent.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Lignin polyurethane and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing lignin polyurethane, which comprises the following steps of: using an organic solvent to dissolve the lignin which is extracted and separated from residues after producing ethanol from straws by sodium hydroxide; removing the residues, and depositing the mixture with water; separating the lignin; modifying the lignin with an epoxide; dissolving the lignin into a polylol; and finally compounding the lignin with raw materials of isocyanate and the like to obtain a polyurethane material. The lignin used in the method has high reactivity which can be further enhanced through modification so as to obtain a lignin polyurethane material; the polylol used in the method not only can be used as a solvent but also can take part in a synthetic reaction, has good dissolvability to the lignin, and ensures that undissolved lignin particles cannot appear in a polyurethane foam material; and the link for polyurethane synthesis uses no volatile organic solvents, so the production process causes no pollution to the environment, and simultaneously the cost of a polyurethane product is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Molybdenum-containing lubricant additive compositions and processes for making and using same
InactiveUS6914037B2Low costImprovement in deposit control performanceFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventSulfur
The invention relates to an improved process for producing organomolybdenum compositions with high molybdenum content that are highly useful as lubricant additives, in which the process involves reacting a fatty oil with a diamine, followed by reaction with a molybdenum source. The process of the present invention does not require a volatile organic solvent to promote molybdenum incorporation and produces an organomolybdenum composition having a high molybdenum content. In addition, the process can be conducted in the absence of sulfur and phosphorus-containing reactants.
Owner:AFTON CHEM INTANGIBLES
Additives for non-aqueous electrolyte and lithium secondary battery using the same
ActiveUS20070166609A1Improved overcharge stabilityCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsOrganic solventLithium-ion battery
Disclosed is an electrolyte for batteries, comprising: (a) an electrolyte salt; (b) an organic solvent; (c) a first compound having an oxidation initiation voltage (vs. Li / Li+) higher than the operating voltage of a cathode; and (d) a second reversible compound having an oxidation initiation voltage higher than the operating voltage of the cathode, but lower than the oxidation initiation voltage of the first compound. Also disclosed is a lithium secondary battery comprising said electrolyte. In the lithium secondary battery, two compounds having different safety improvement actions at a voltage higher than the operating voltage of the cathode are used in combination as electrolyte components. Thus, the safety of the secondary battery in an overcharged state can be ensured, and at the same time, the deterioration of the battery can be prevented from occurring when it is repeatedly cycled, continuously charged and stored at high temperature for a long time.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
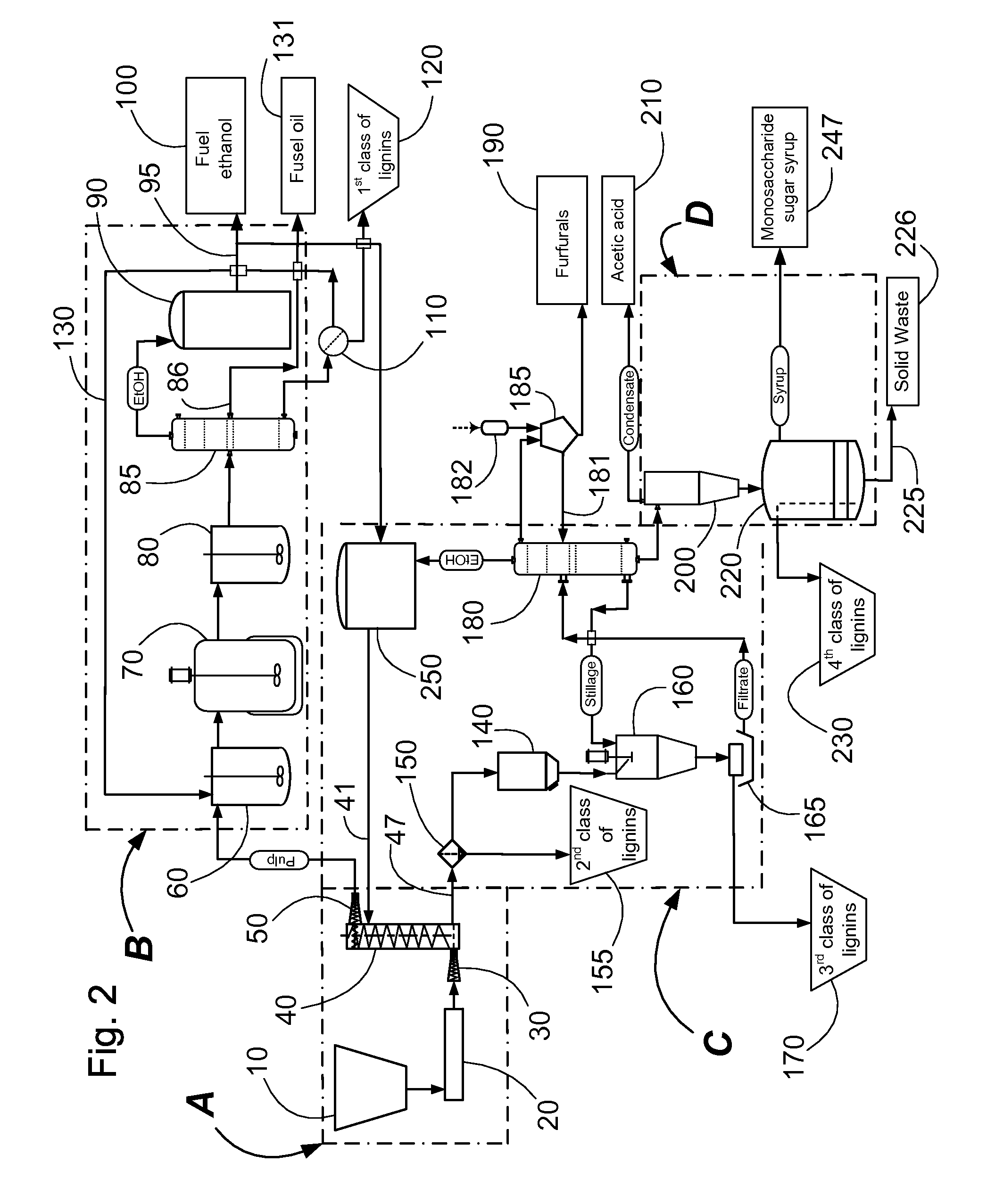
Continuous counter-current organosolv processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
A modular process for organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic feedstocks into component parts and further processing of said component parts into one or more of a de-lignified cellulose stream, a sugar stream, small-chain alcohol streams and four structurally distinct classes of lignin derivatives. The modular process comprises a first processing module configured for digesting lignocellulosic feedstocks with an organic solvent thereby producing a cellulosic solids fraction and a liquid fraction, a second processing module configured for recovering small-chain alcohols and optionally a first class of lignin derivatives from the cellulosic solids fraction, a third processing module configured for recovering from the liquid fraction at least one of a second class and a third class of lignin derivatives or mixtures thereof, and waste stream comprising a fourth class of lignin derivatives. The fourth processing module may optionally recover the fourth class of lignin derivatives.
Owner:SUZANO CANADA INC
In-situ composite silicon-based multibasic oxide oxide aerogel material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104941538AImprove your own performanceImprove catalytic performanceColloidal chemistry detailsSol-gelOrganosolv
The invention relates to an in-situ composite silicon-based multibasic oxide oxide aerogel material and its preparation method, especially to a multibasic oxide oxide aerogel material which is prepared by the following steps: using soluble glass as a silicon source, mixing metallic oxide corresponding water-soluble metal salt, adding acid or alkali to adjust pH value of the system so as to form multibasic oxide sol; mixing the multibasic oxide sol with a water-soluble organic solvent, filtering to remove produced precipitate so as to obtain salt-free multibasic oxide sol, carrying out a sol-gel method, aging, modifying and drying. By a mature silica aerogel technology, the multibasic oxide oxide aerogel material is prepared by in-situ polymerization of other oxide components which are not easy to separately prepare aerogel. In addition, the multibasic oxide oxide aerogel material has excellent properties, such as high temperature stability, high activity, magnetic property and the like, none of which are present in single-component silica aerogel. The product is widely applied in fields of high temperature insulation, sound insulation, catalysts, catalytic carriers, battery electrodes, electromagnetism, resistance, gas sensitivity, humidity sensitivity, luminescent materials and the like.
Owner:金承黎
Preparation of a carbon nanomaterial using a reverse microemulsion
InactiveUS20100092370A1Maintain good propertiesExcellent ElectricalMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon preparation/purificationSolventAmorphous carbon
Powdered, amorphous carbon nanomaterials are formed from a carbon precursor in reverse microemulsion that includes organic solvent, surfactant and water. Methods for manufacturing amorphous, powdered carbon nanomaterials generally include steps of (1) forming a reverse microemulsion including at least one non-polar solvent, at least one surfactant, and at least one polar solvent, (2) adding at least one carbon precursor substance to the reverse microemulsion, (3) reacting the at least one carbon precursor substance so as to form an intermediate carbon nanomaterial, (4) separating the intermediate amorphous carbon nanomaterial from the reverse microemulsion, and (5) heating the intermediate amorphous carbon nanomaterial for a period of time so as to yield an amorphous, powdered carbon nanomaterial. Amorphous, powdered carbon nanomaterials manufactured according to the present disclosure typically have a surface area of at least 500 m2 / g, a graphitic content of at least 25%, and a conductivity of at least 150 S / m.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION GRP
Method of separating anionic fluorochemical surfactant
InactiveUS20040010156A1Short elution timeHigh recovery rateFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic solventIon-exchange resin
Separation of an anionic fluorochemical surfactant from an aqueous solution containing the anionic fluorochemical surfactant is carried out by i) contacting the aqueous solution with a basic anion-exchange resin so that the anionic fluorochemical surfactant is adsorbed on the resin, and ii) eluting the anionic fluorochemical surfactant adsorbed on the resin with an eluent which is an alkaline solution containing water and an organic solvent.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Compound epoxy flooring coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101654583AHigh mechanical strengthImprove corrosion resistanceRosin coatingsEpoxy resin coatingsSolvent freeFirming agent
The invention relates to compound epoxy flooring coating adopting the mixture of epoxide resin and modified resin as a base material and further comprising organic solvent, dispersant, wetting agent, antifoaming agent, flatting agent, scratch resistance agent, pigment and stuffing as well as reactive diluent selected according to requirements. When in use, the coating is mixed and solidified withthe components of firming agent, accelerant, etc. By regulating the content of the components, the compound epoxy flooring coating of the invention can be used for manufacturing a solvent or solvent-free autolevelling epoxy floor. The compound epoxy flooring coating of the invention has favorable over-all properties, and not only has the characteristics of high mechanical strength, favorable anti-corrosion property, high adhesive force and good wear resistance property of the epoxide resin but also has the characteristics of good weather resistance, high decorative property and hardness and shock resistance of the modified resin; and the preparation method thereof is simple and practicable, is low-cost, and is suitable for mass preparation.
Owner:北京红狮科技发展有限公司
Laundry detergent compositions comprising amphiphilic graft polymers based on polyalkylene oxides and vinyl esters
InactiveUS20090005288A1Negatively impacting general cleaning capabilityLower surfactant levelOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent solventsOrganic solventPolybutylene
A laundry detergent composition comprising a graft copolymer of polyethylene, polypropylene or polybutylene oxide with vinyl acetate in a weight ratio of from about 1:0.2 to about 1:10; from about 0.2% to about 8% of organic solvent; and from about 2% to about 20% of a surfactant system; wherein said detergent composition is in a form selected from: liquid; gel; and combinations thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation method of graphene oxide/waterborne polyurethane nanometer composite material
InactiveCN103254400AImprove thermal performanceImprove mechanical propertiesTriethoxysilaneGraphene flake
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide / waterborne polyurethane nanometer composite material. Especially, the preparation method comprises the following steps of: utilizing gamma-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (KH550) to carry out surface modification (functionalization of graphene oxide) onto graphene oxide; lowering hydrophily of a graphene oxide sheet layer; improving dispersion of the graphene oxide sheet layer in an organic solvent and compatibility of the graphene oxide and the polymer; and utilizing an in-situ polymerization method to prepare the graphene oxide / waterborne polyurethane nanometer composite material. The preparation method of the graphene oxide / waterborne polyurethane nanometer composite material belongs to the preparation field of composite materials.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Multi-hole carbon fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103014921AEasy to makeLow costSemi-permeable membranesFilament/thread formingFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a multi-hole carbon fiber and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: spinning solution composed of pore former, high polymer and organic solvent is used for spinning and then carbonization to obtain the multi-hole carbon fiber. The method has the following advantages: 1, the preparation is simple, the yield is high, and the cost is low; 2, the sizes of holes of the multi-hole carbon fiber can be controlled conveniently by changing the preparation parameters; 3, the used pore former can performing pore-forming in a self sublimation manner and can be reclaimed for use, so that the preparation cost can be lowered greatly; and 4, the obtained carbon fiber has a multi-hole structure, so that the bendability is improved, and the carbon fiber can be bent and folded at will instead of being broken, and can support a finished film independently.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
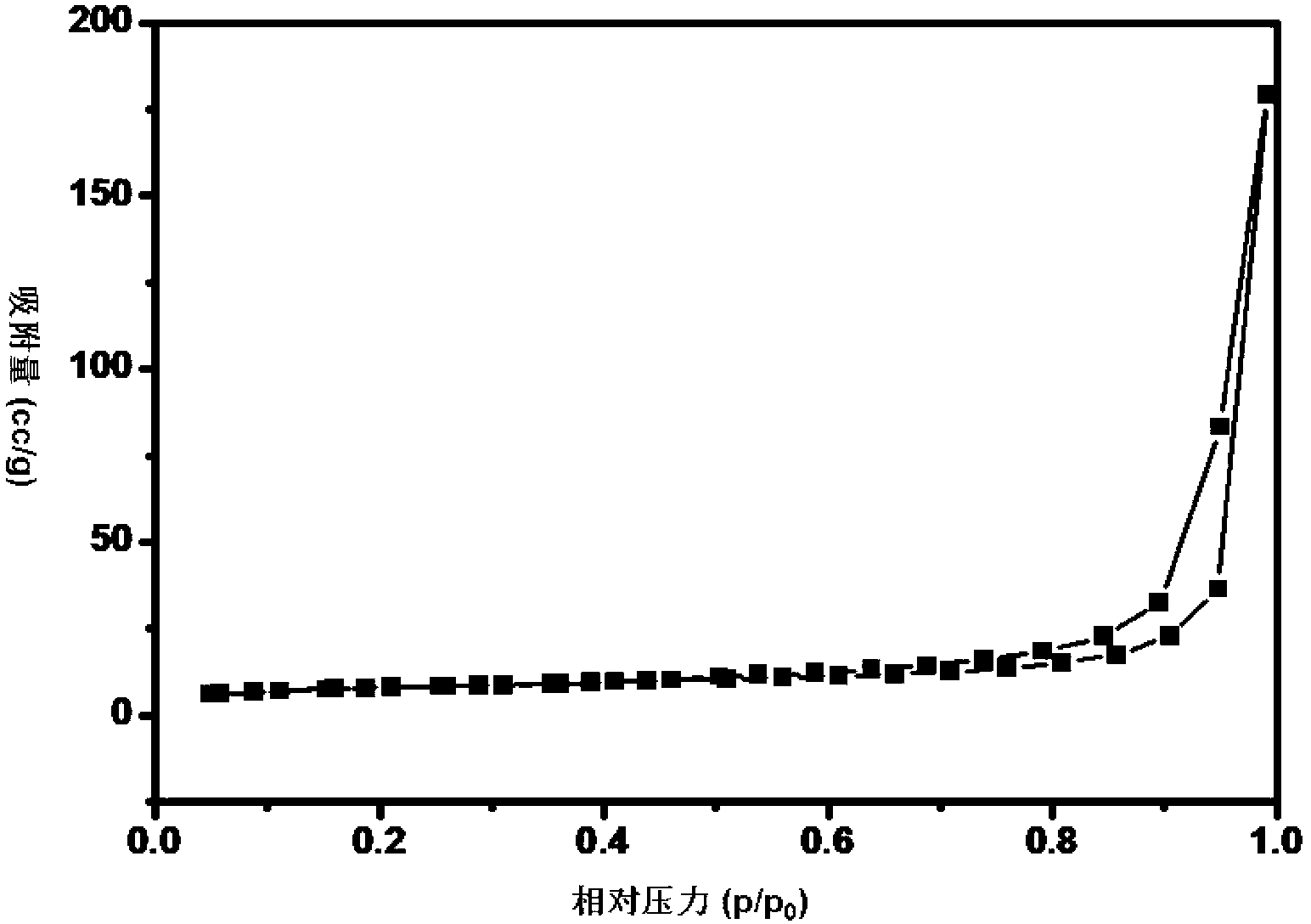
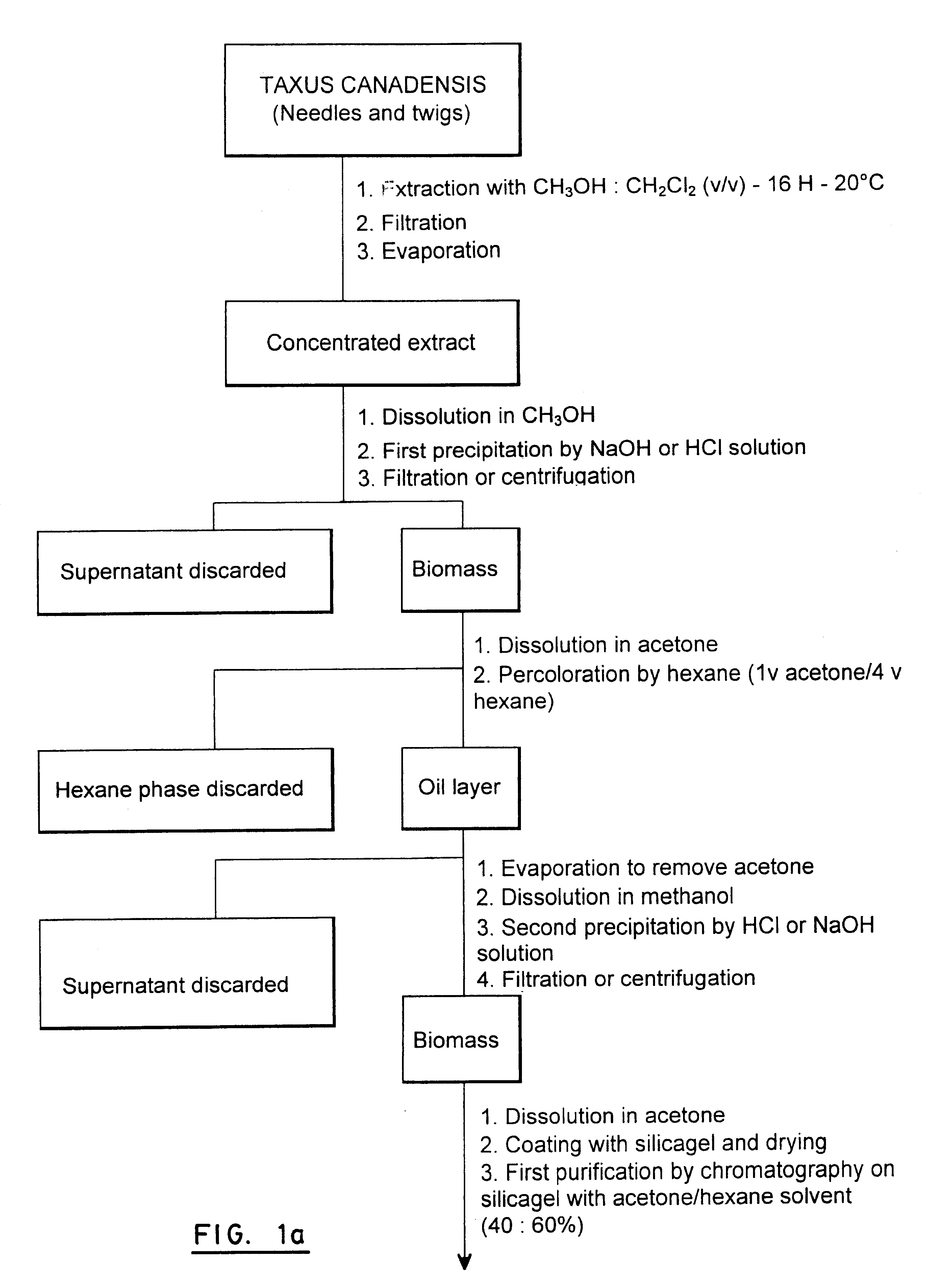
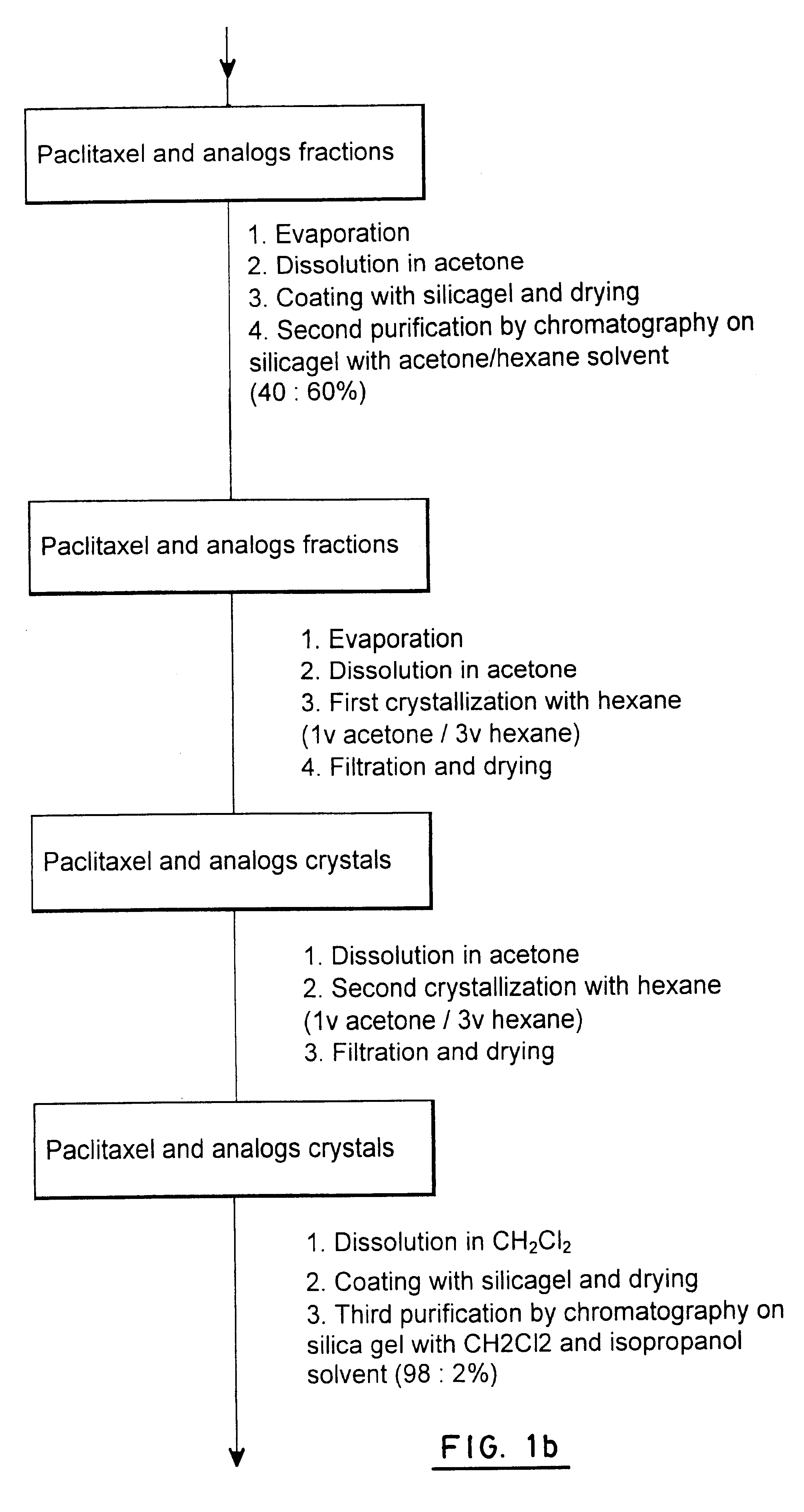
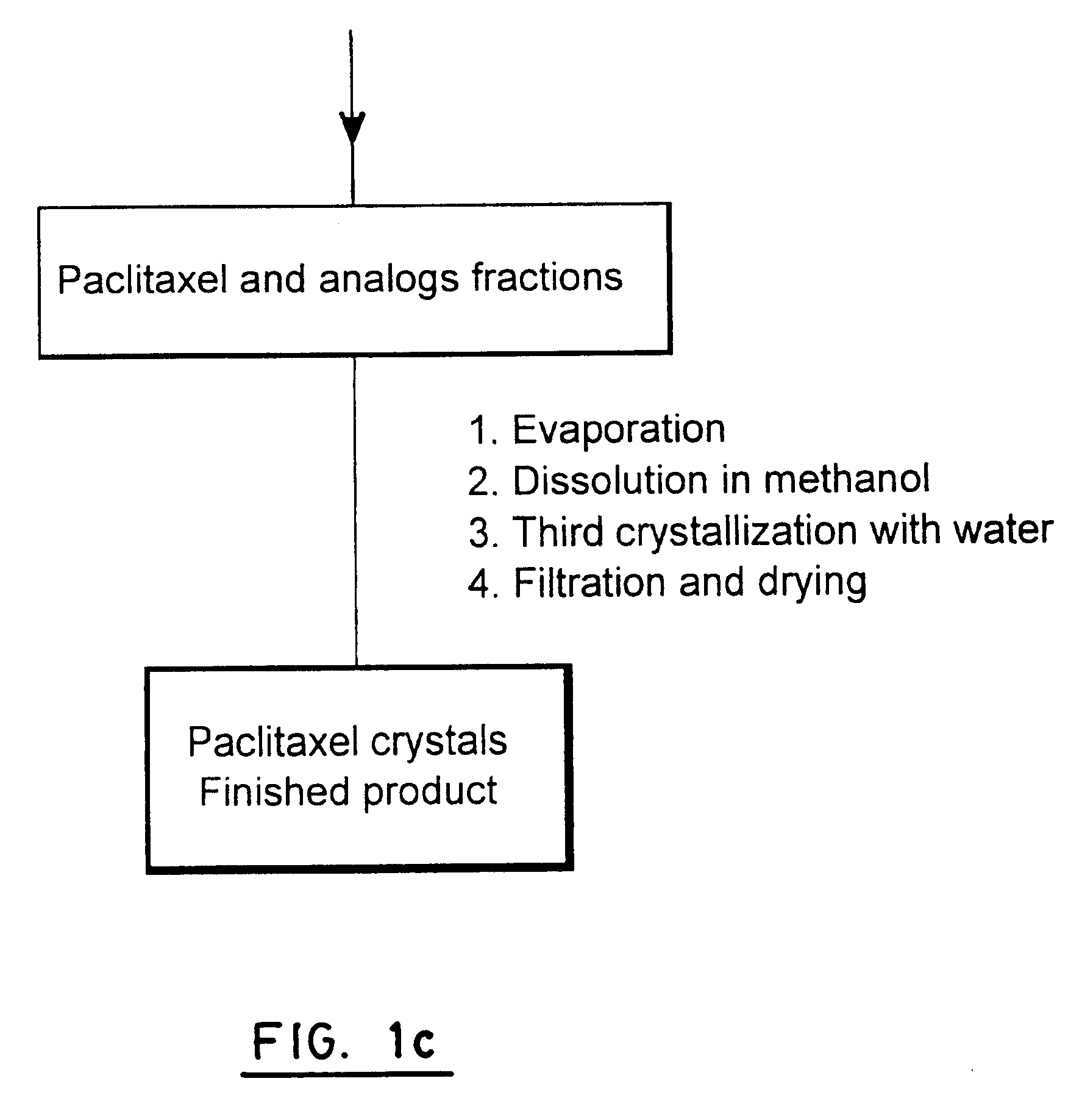
Process for extraction and purification of paclitaxel from natural sources
A process for the extraction and purification of Paclitaxel from a natural source of taxanes, comprising extracting Paclitaxel with an organic solvent from a natural source of taxanes, and treating the raw material with a base or an acid to obtain a biomass by precipitation. The biomass is isolated and dried, and resin and natural pigments are removed. The biomass is then dissolved in acetone and at least one non-polar solvent is added, until a Paclitaxel-enriched oily phase is obtained. The Paclitaxel-enriched oily phase is then treated with a base or an acid to obtain a second biomass, which is recovered by precipitation and dried. A solution of the second biomass in a volatile solvent is chromatographically purified at least once and crystallized.
Owner:CHAICHEM PHARMA INT
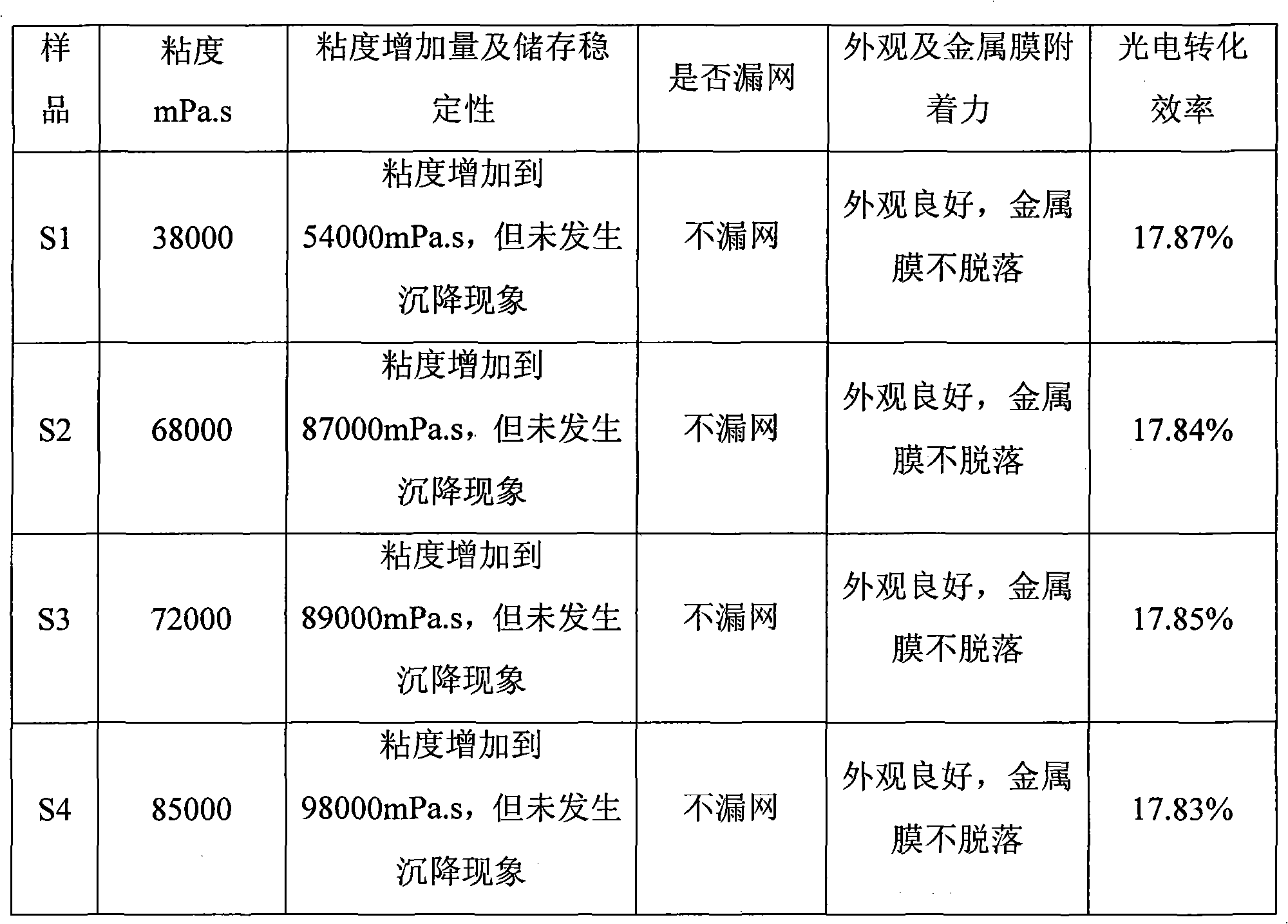
Conductive paste for solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102034877AImprove performanceNo sedimentation and caking phenomenonConductive materialInksSilicon matrixSilicon solar cell
The invention provides a conductive paste for a solar cell, comprising the following components based on the total weight: 60-85 percent by weight of conductive metal powder, 0.5-10.0 percent by weight of inorganic binder, 10.0-30.0 percent by weight of water-borne binder and 0.05-5.0 percent by weight of additive, wherein the water-borne binder is a solution formed by dissolving a water-borne polymer into the water. The conductive paste for the solar cell, provided by the invention, has no organic solvent and pollution, is environment-friendly and has low cost of materials; the mesh leakage can be avoided when the conductive paste is stood in a screen mesh; the phenomena of settling and aggregation can be avoided after the conductive paste is stored for a long time; after being subjected to the silk-screen sintering, the conductive paste has firm adhesive force to a silicon matrix and excellent electrical performance; and the average photoelectric conversion efficiency of the produced monocrystal silicon solar cell is more than 17.80 percent.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
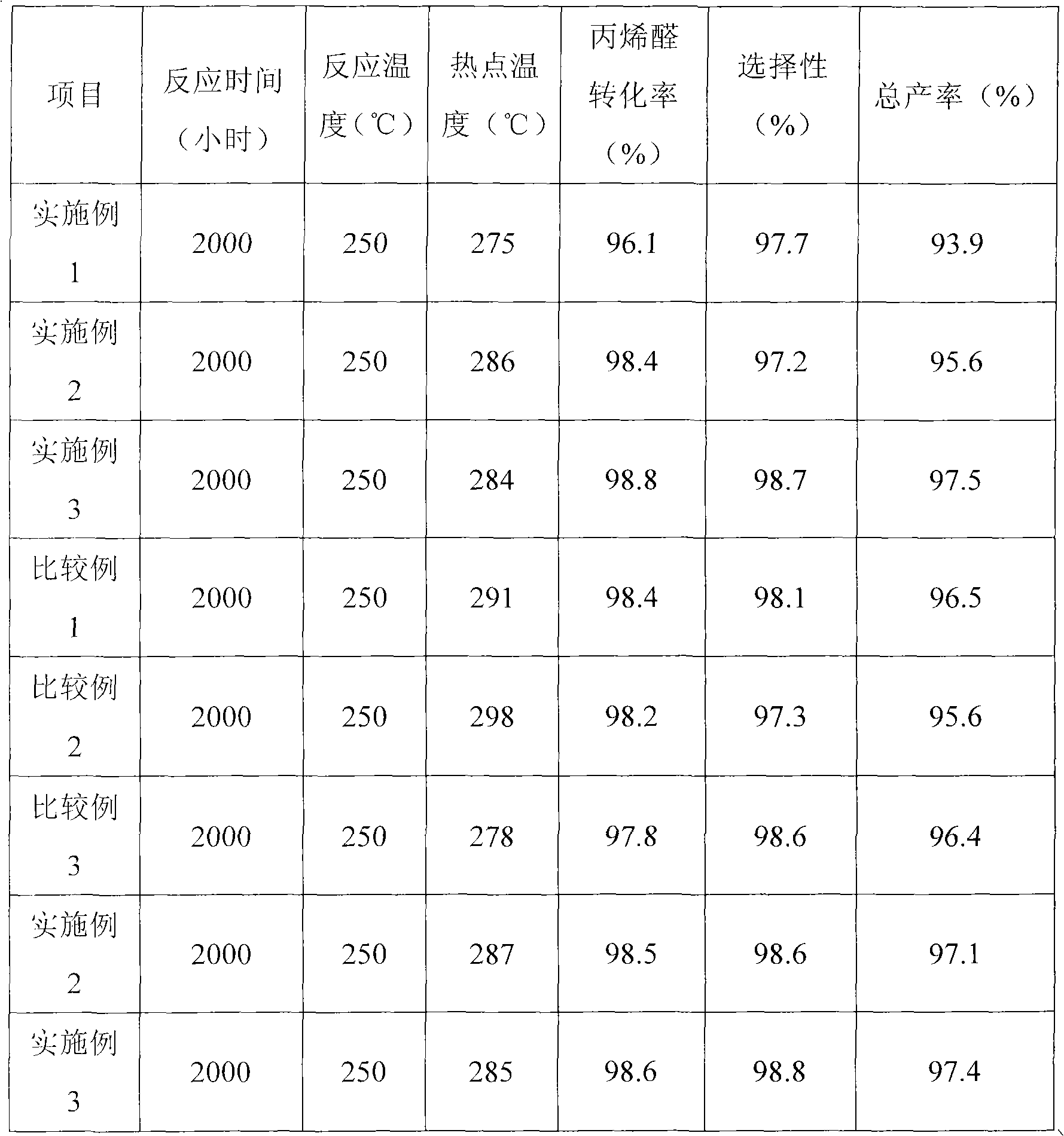
Preparation method of catalyst for acrylic acid by oxidizing acraldehyde
ActiveCN102039143ALarger than surfaceStrong loadOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationAdhesiveSlurry
The invention relates to a preparation method of a catalyst for acrylic acid by oxidizing acraldehyde, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: dispersing water soluble metal salts containing the components of Mo, V, W, Cu and Sb into a water / organic phase mixed system at the temperature of 30-100DEG C; maintaining the weight ratio of an organic solvent to water as 5-50 percent; reacting to generate composite oxide precursor serum; separating water by a distilling process under the condition of continuously supplementing organic phases at the temperature of 20-120DEG C, wherein the water content of distillate is not greater than 10 percent; then, pelleting by a spray drying process and roasting at the temperature of 200-600DEG C to prepare catalyst active components; mixing primary roasting powder, a forming additive and a strength improver; coating the active components on the surface of an inert carrier by using an adhesive, wherein the carrying capacity occupies5-70 percent of the total quantity of the catalyst; drying a formed product for 5-48 hours at room temperature; and then, roasting the formed product for 1-15 hours at the temperature of 200-600DEG Cto obtain a spherical catalyst with the active components carried on the inert carrier.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Temperature-resistant salt-resistant composite foam oil displacement agent for tertiary oil recovery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102086389ARaw materials are easy to getReduce manufacturing costDrilling compositionSulfonateActive agent
The invention relates to a temperature-resistant salt-resistant composite foam oil displacement agent for tertiary oil recovery and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of chemical oil displacement for increasing the crude oil recovery ratio of the oil field. The oil displacement agent is compounded by 0.5-1% of alpha-alkene sulfonate as a main surfactant and other auxiliary agents and comprises the following components in percentage by mass:0.1-1.5% of anionic surfactant, 0.2-0.8% of zwitterionic surfactant, 2-10% of organic solvent, 5-12% of stabilizing agent and the balance of a salt solution added to be 100%. Compounds related to the oil displacement agent are industrially produced fine chemical products, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the production cost is low, and the preparation is simple; the oil displacement agent has performances of temperature resistance, salt resistance, ultralow interfacial tension and the like; the persistence of the foam is strong, and the half-life period can be more than 120min at 85 DEG C; the oil displacement age has excellent compatibility with other surfactants, and the comprehensive recovery ratio of the crude oil can be increased by about 10-15%.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Thermal-insulating external-wall coating of nano-composite water and its production
InactiveCN101029206AImprove insulation performanceGood weather resistanceFireproof paintsEmulsion paintsRefractive indexSlurry
A water nan-composite thermal-insulating coating for external wall and its production are disclosed. The coating consists of water, polymer emulsion, high-refractive index pigment, filler, nano-tin-antimony oxide slurry, nano-SiO2, wet dispersant, filming accessory, pH adjuster, thickener, de-foaming agent, anti-freezing agent and mildew-proof bactericide. It's cheap and simple, has excellent wash and weather resistances, better thermal-insulating performance, safe storage and no environmental pollution. It can be used for apparatus surface and architecture external wall.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Antimicrobial hard surface cleaner
InactiveUS20030064910A1Improving cleaning performance and aesthetic quality of cleanerIncrease residueInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCationic surface-active compoundsQuaternary ammonium surfactantChemistry
The invention provides an improved, non- or minimized streaking / filming antimicrobial formulation, the cleaner containing: a. an akoxylated quaternary ammonium surfactant, present in a cleaning-effective amount; b. an alkoxylated short chain nonionic surfactant, also present in a cleaning-effective amount; c. alkanolamine as an alkalinity source, present in an amount effective to enhance soil removal in said cleaner; d. a quaternary ammonium compound in an amount present for antimicrobial efficacy; e. at least one water-soluble or dispersible organic solvent having a vapor pressure of at least 0.001 mm Hg at 25° C., said at least one organic solvent present in a solubilizing-or dispersion-effective amount; and f. the remainder, water.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Method for preparing microspheres and microspheres produced thereby
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND +1
Catalyst For The Selective Hydrogenation Of Acetylenic Hydrocarbons And Method For Producing Said Catalyst
InactiveUS20100217052A1Narrow particle size distributionReduced tendency to form by-productOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationOrganic solventAcetylenic Compounds
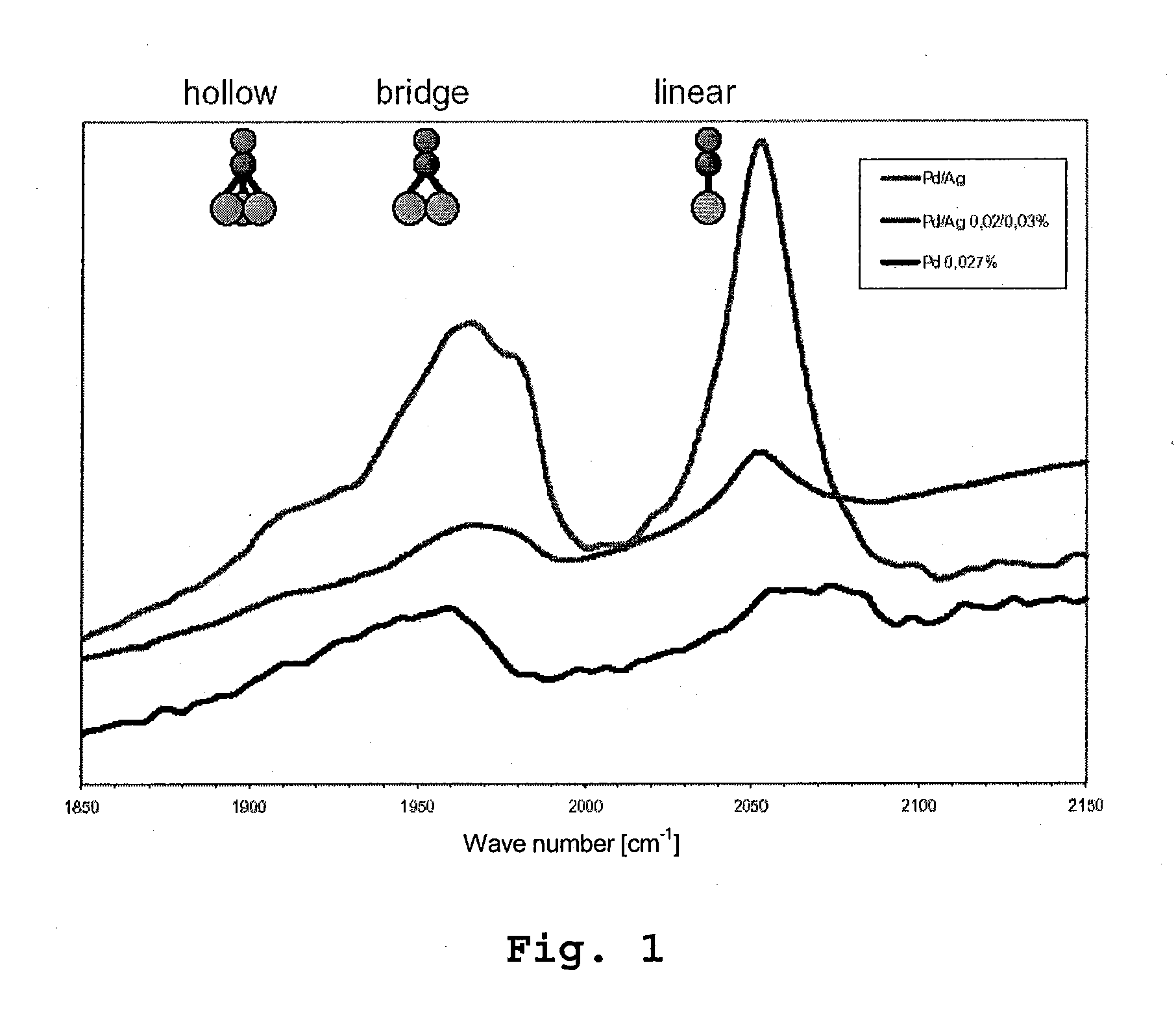
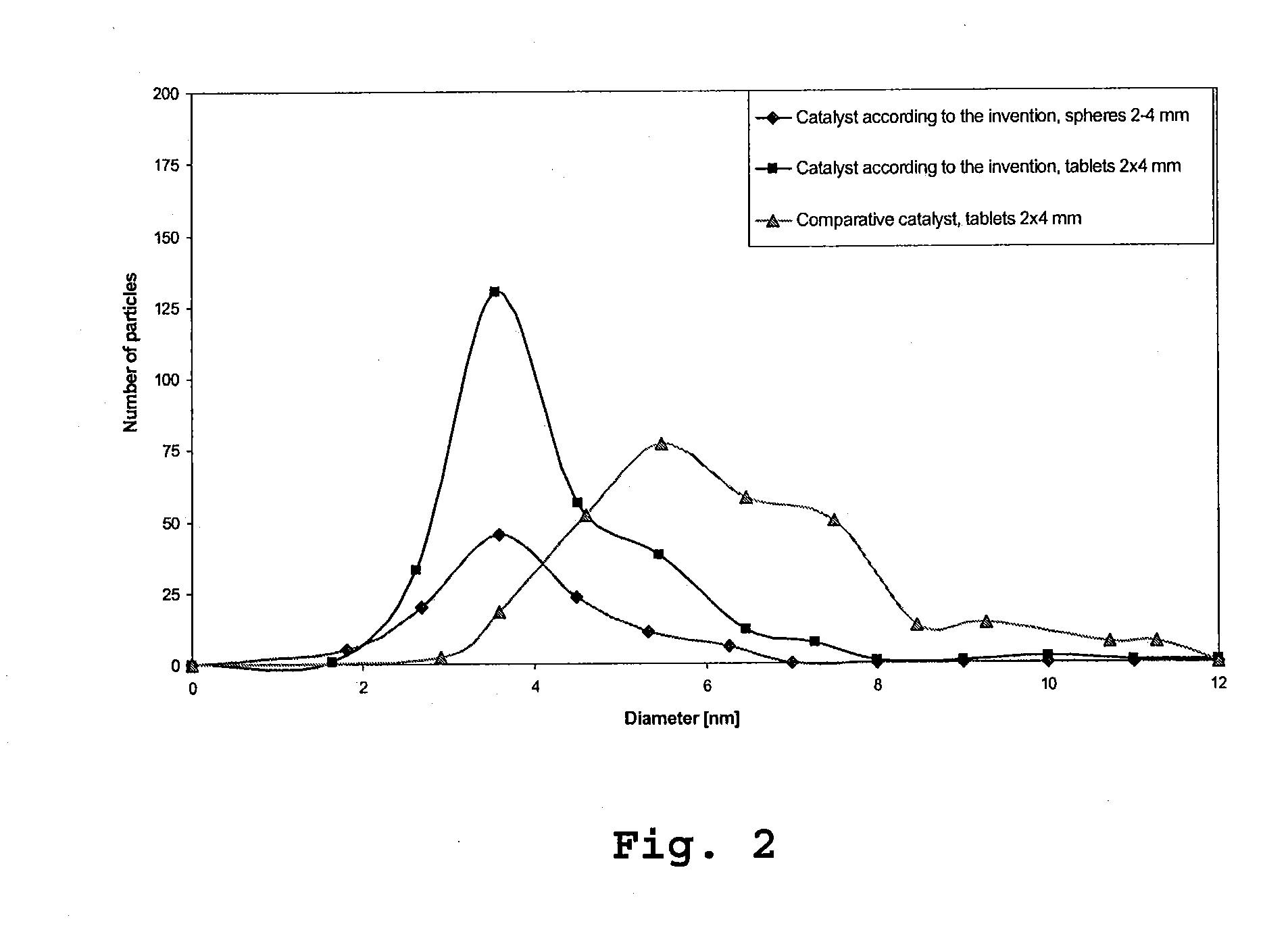
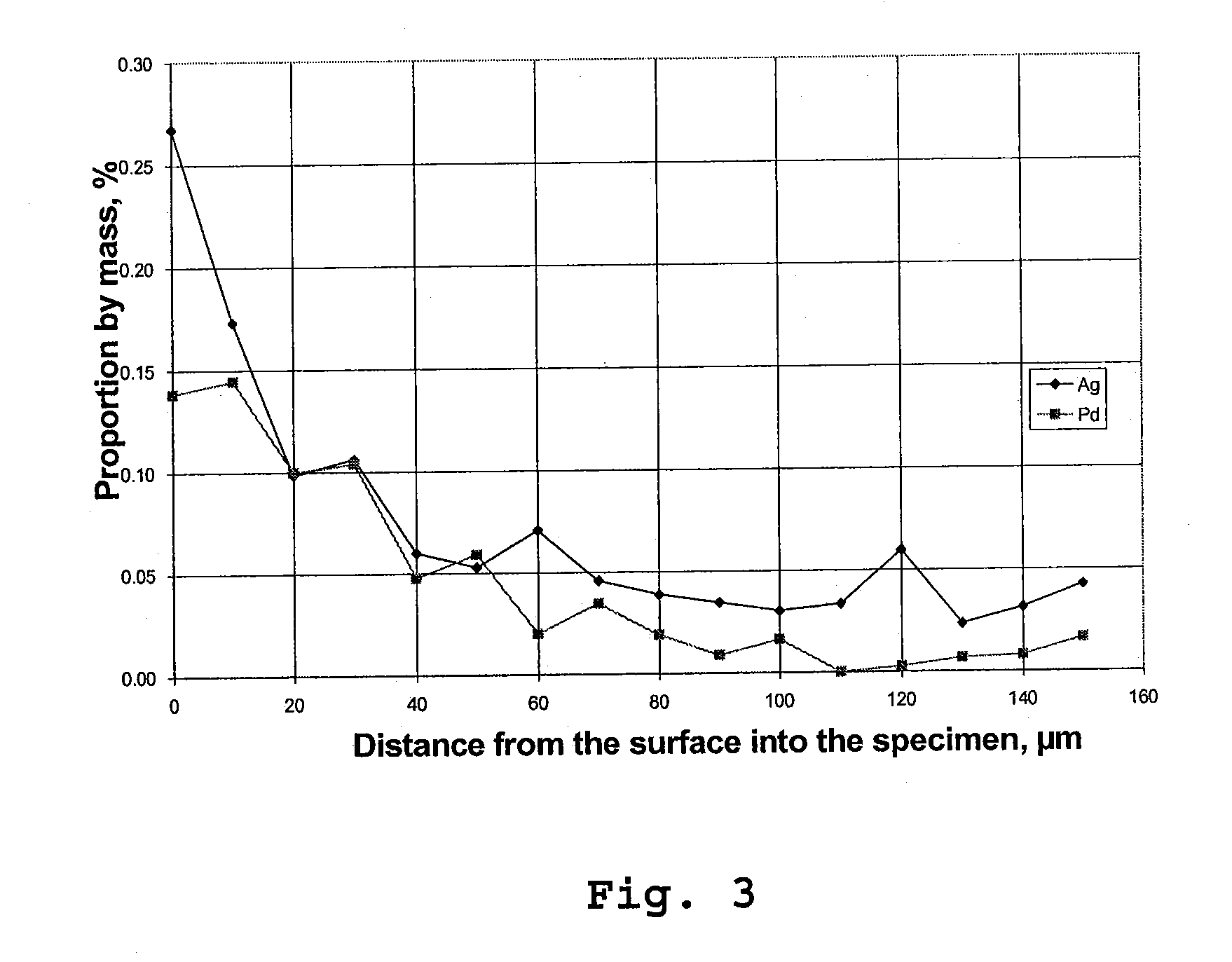
A method for producing a catalyst, in particular for the selective reduction of acetylenic compounds in hydrocarbon streams. An impregnation solution is provided, which contains a mixture of water and at least one water-miscible organic solvent as solvent in which at least one active metal compound and also preferably at least one promoter metal compound is dissolved. A support is provided, the support is impregnated with the impregnation solution, and the impregnated support is calcined. Palladium is preferably used as active metal and silver is preferably used as promoter metal. Also, a catalyst as is obtained by the method and also its preferred use for the selective hydrogenation of acetylenic compounds.
Owner:SUED CHEM IP GMBH & CO KG
Method for preparing furfural compounds from biomass
The invention relates to a method for preparing furfural compounds from biomass. The method specifically comprises the preparation of a solid acid catalyst and a reaction process of the solid acid catalyst. The method disclosed by the invention can also be applied to biomass derivatives. The method comprises the steps of adding biomass or biomass derivatives and the solid acid catalyst to a reactor, filling with protective gas, and adopting an organic solvent / saturated inorganic salt aqueous-solution two-phase reaction system, thereby obtaining furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in a high yield manner under mild conditions. The method has the advantages that after the reaction is completed, the produced furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural are efficiently extracted into an upper-layer organic phase, the solid acid catalyst and an unreacted substrate are retained in a bottom-layer water phase, the furfural, the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural or a mixture of the furfural and the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural can be obtained through simple separation, and fine chemicals and liquid fuels can be prepared in a manner that the furfural, the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural or the mixture of the furfural and the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural serves as a reaction intermediate; and the used catalyst is pollution-free and can be recovered and reused, so that the method has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of noble metal nano-particle array
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com