Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
313 results about "Solid fraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
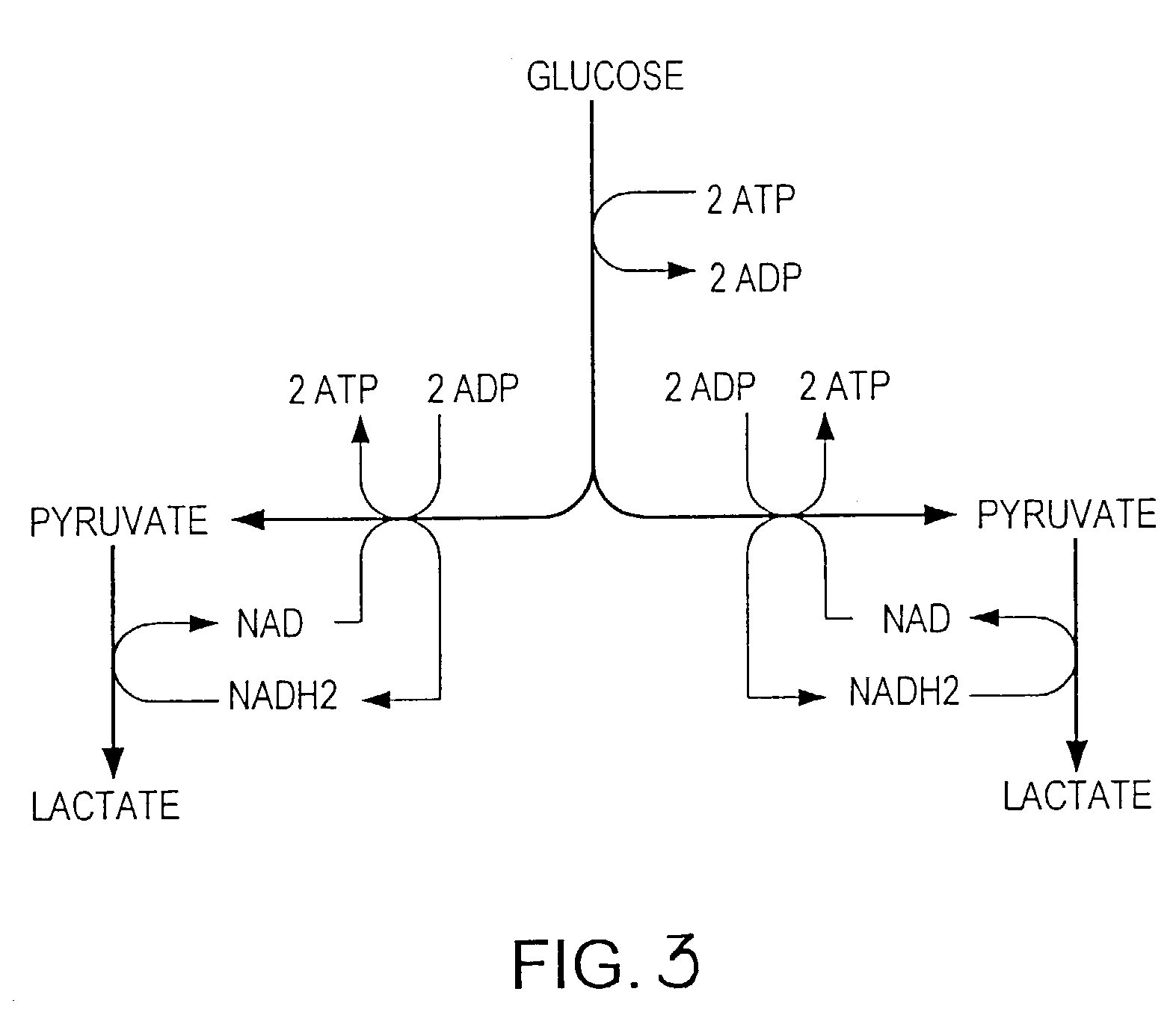
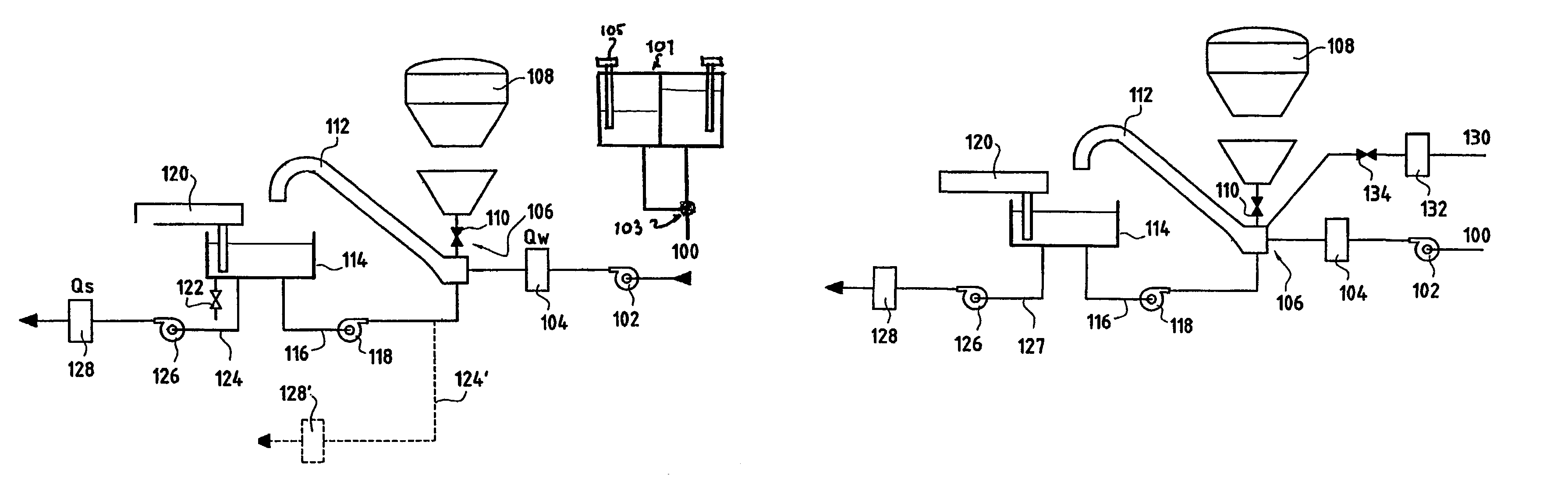
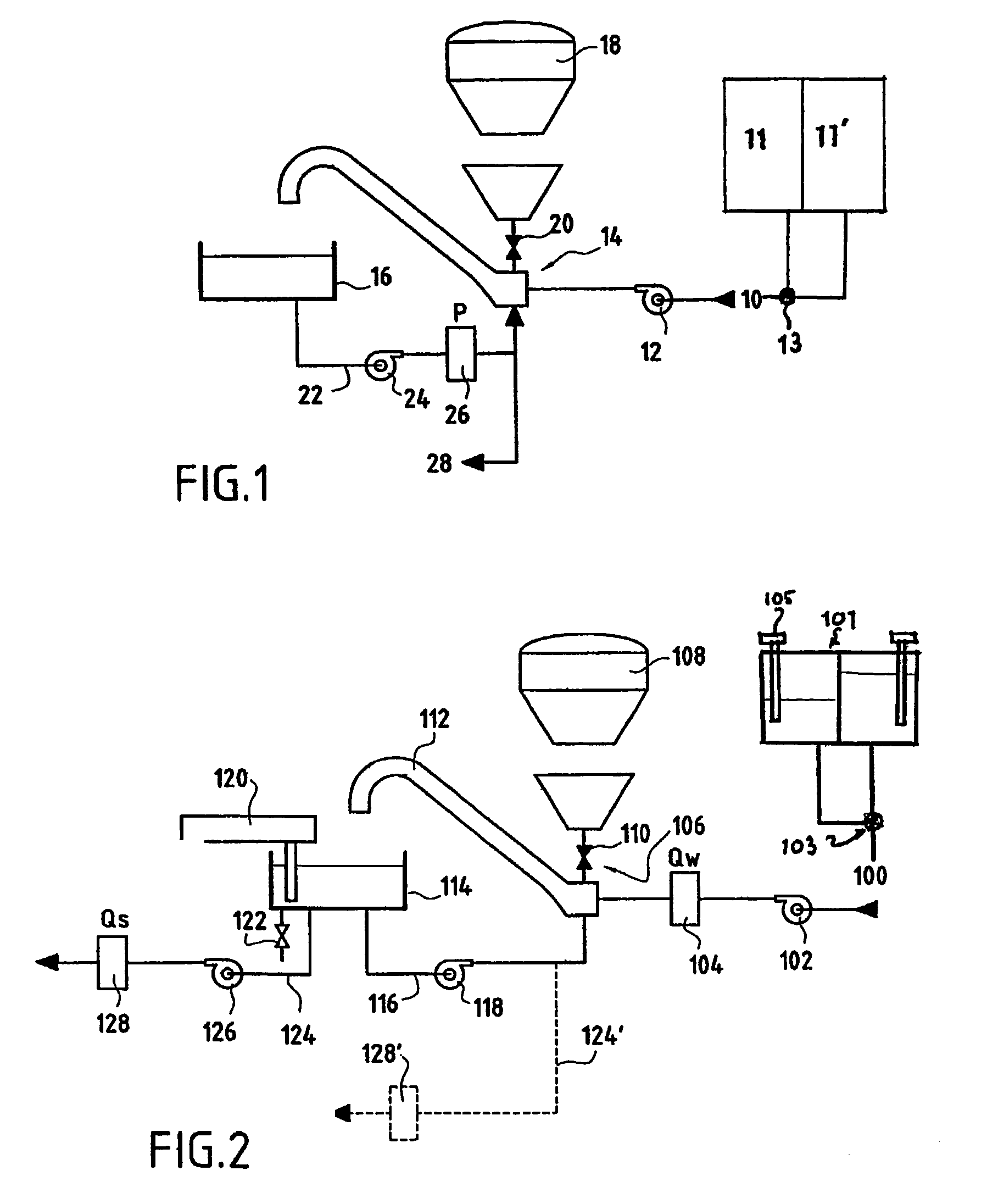
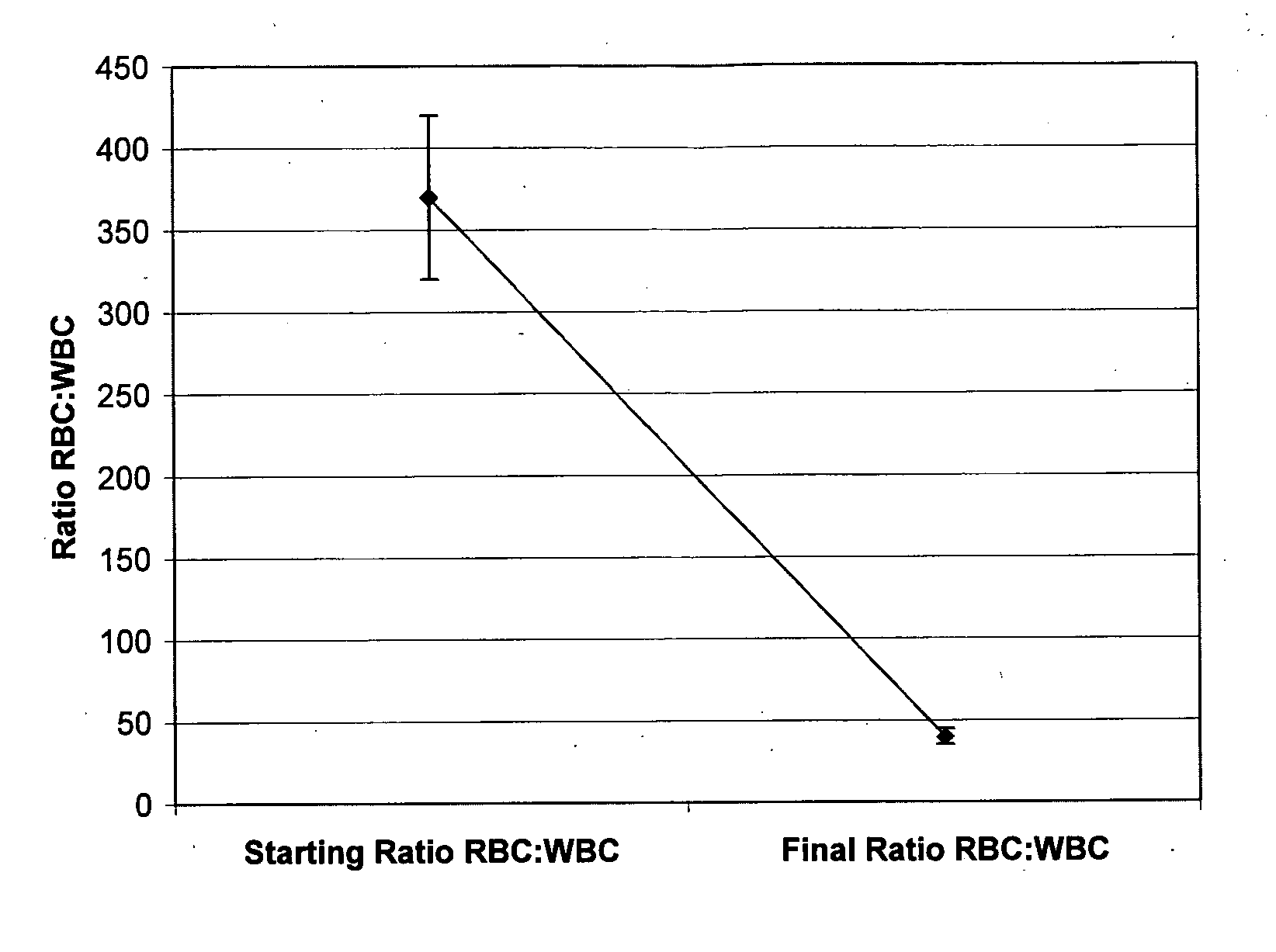
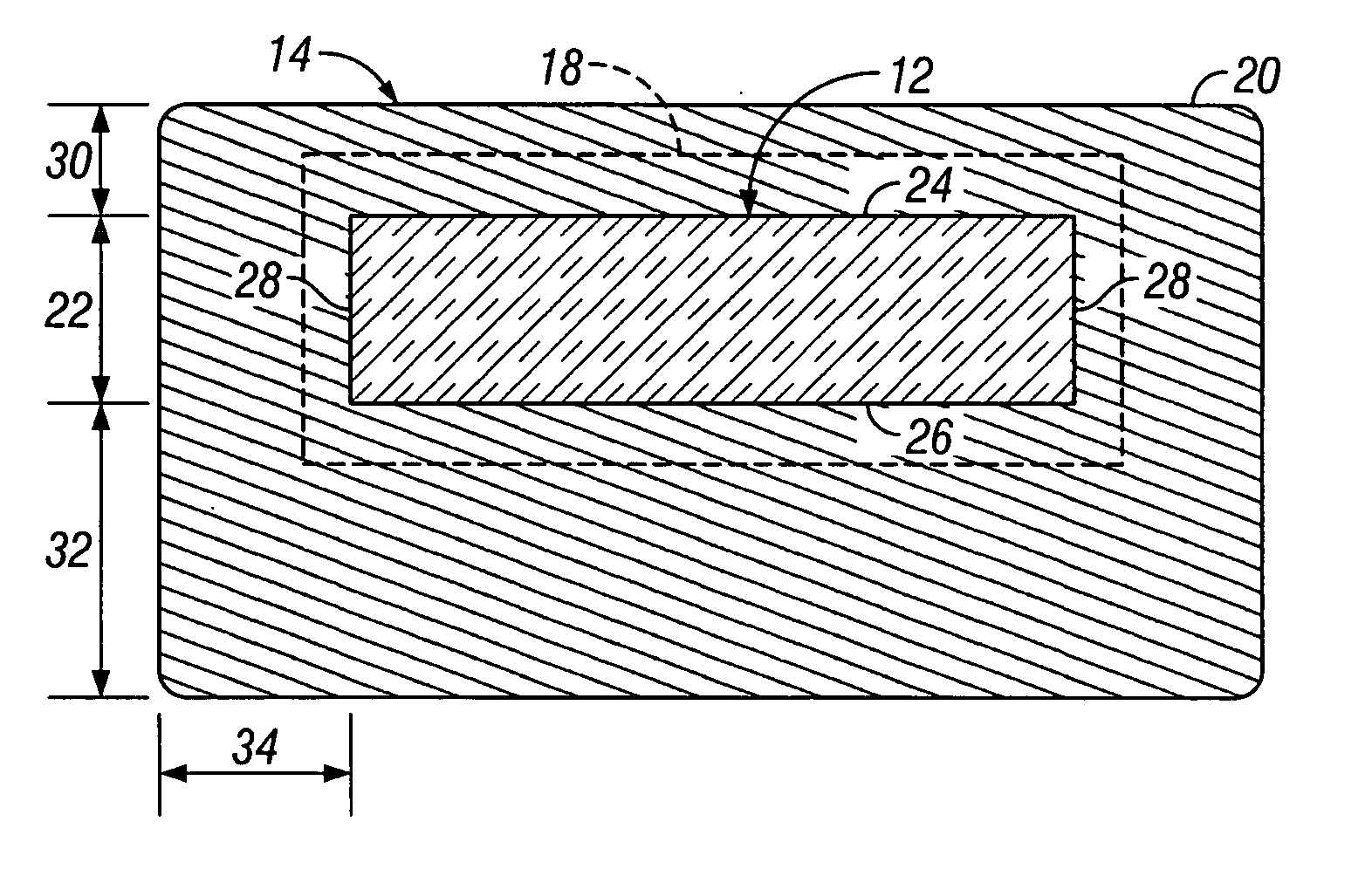
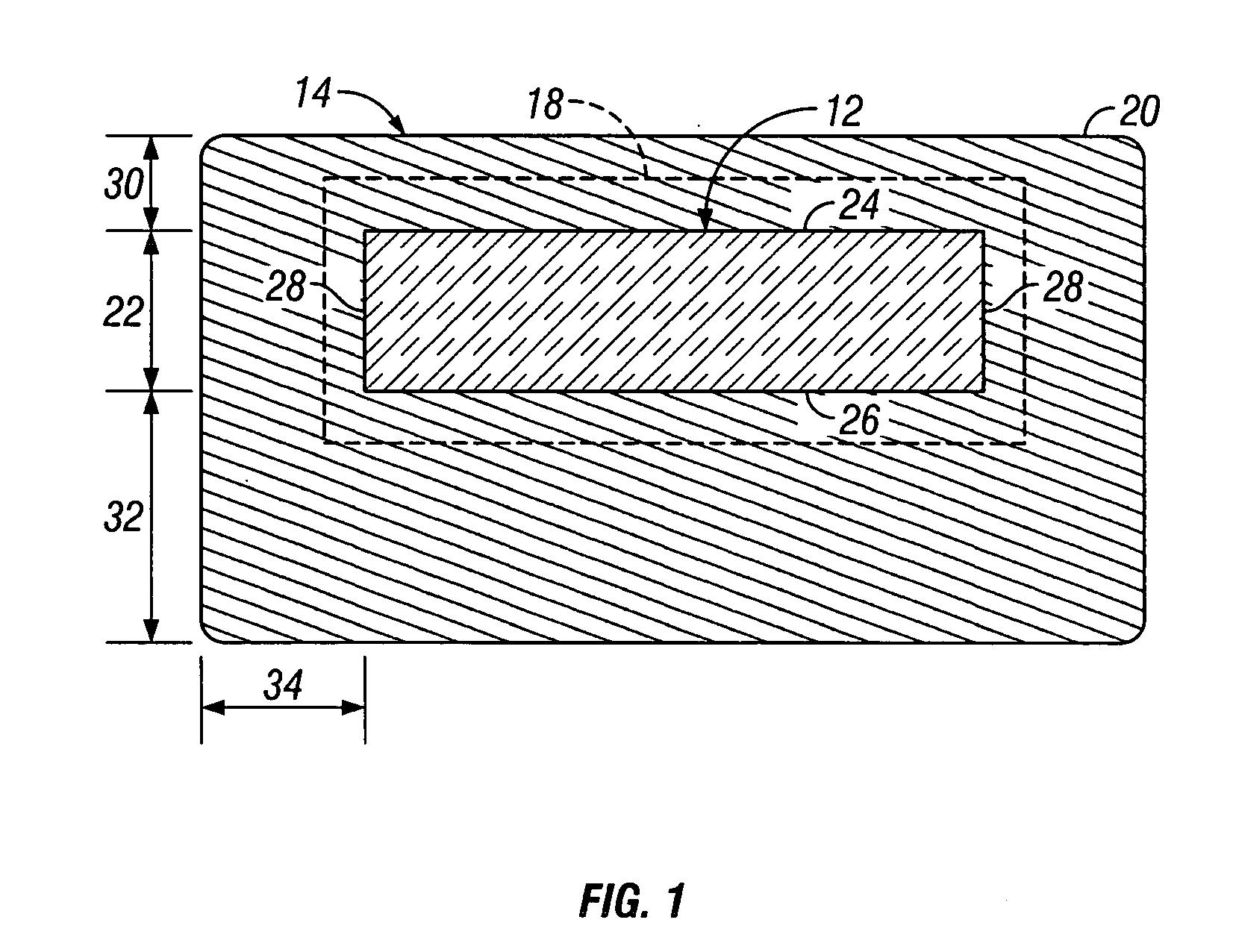
Solid fraction can then be calculated by dividing the envelope density of the ribbon by the absolute density of the granule. Tap density is obtained from filling a container with the test material and vibrating it so that the particles settle into the best packing arrangement.
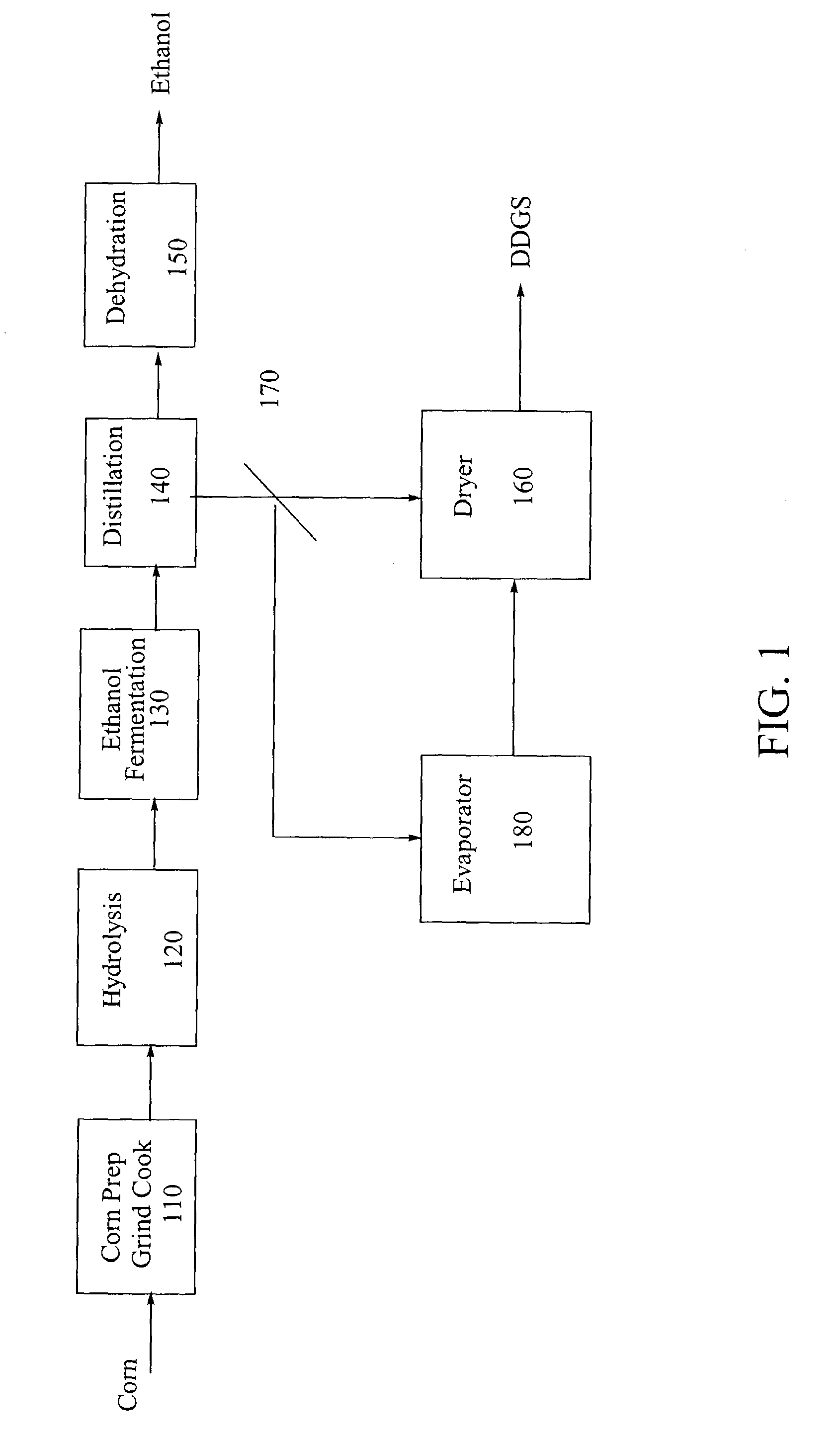
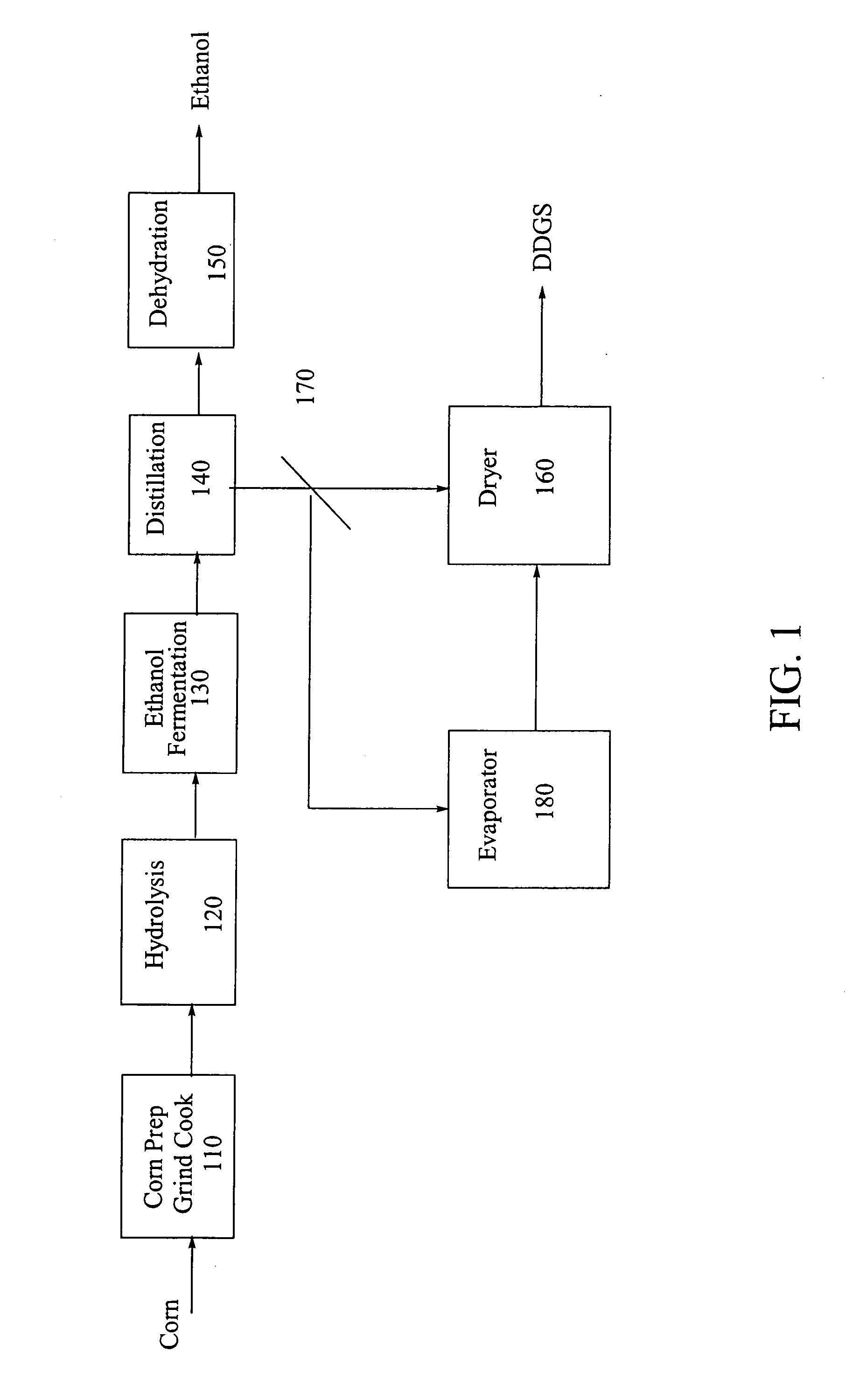
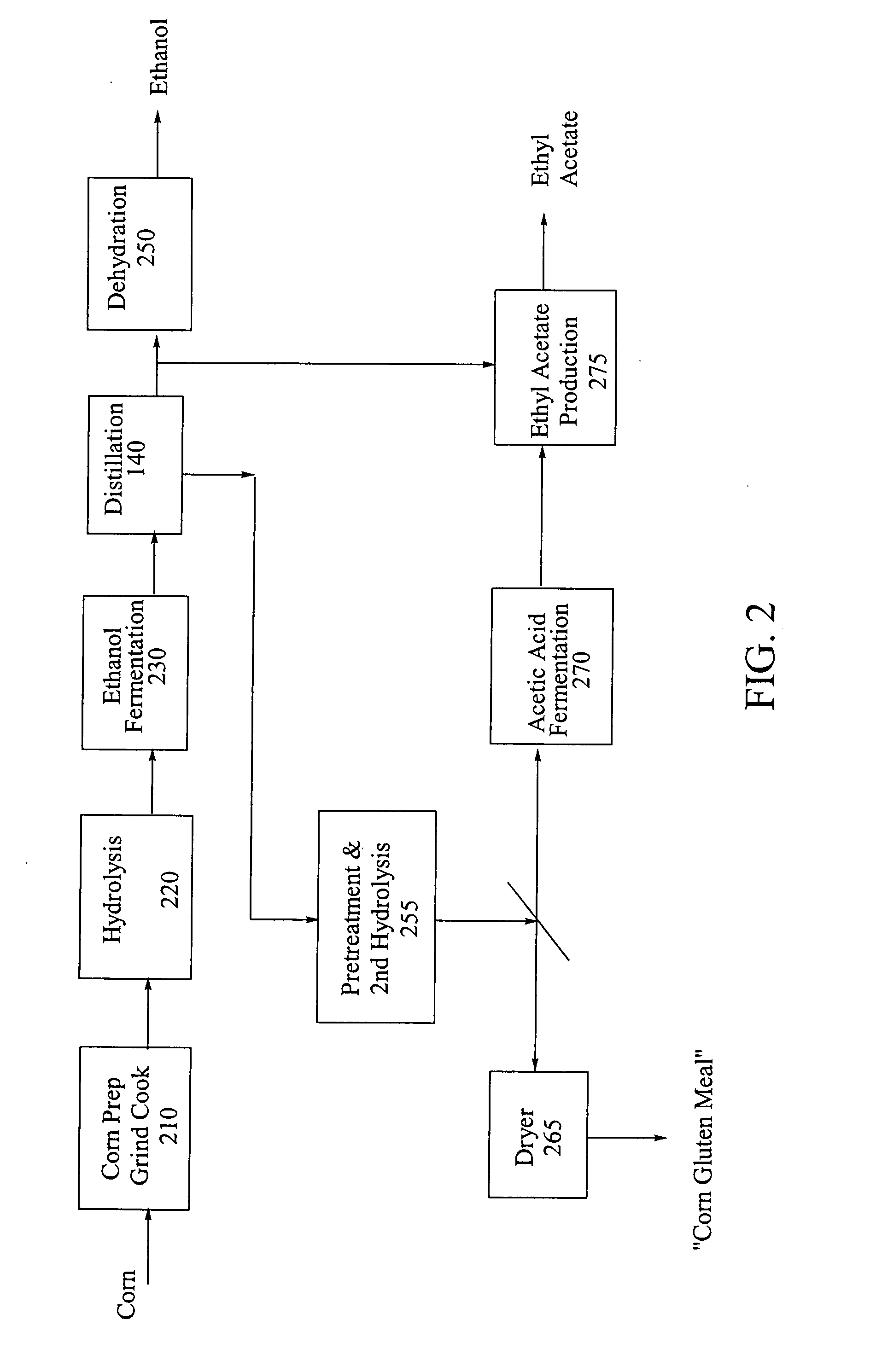
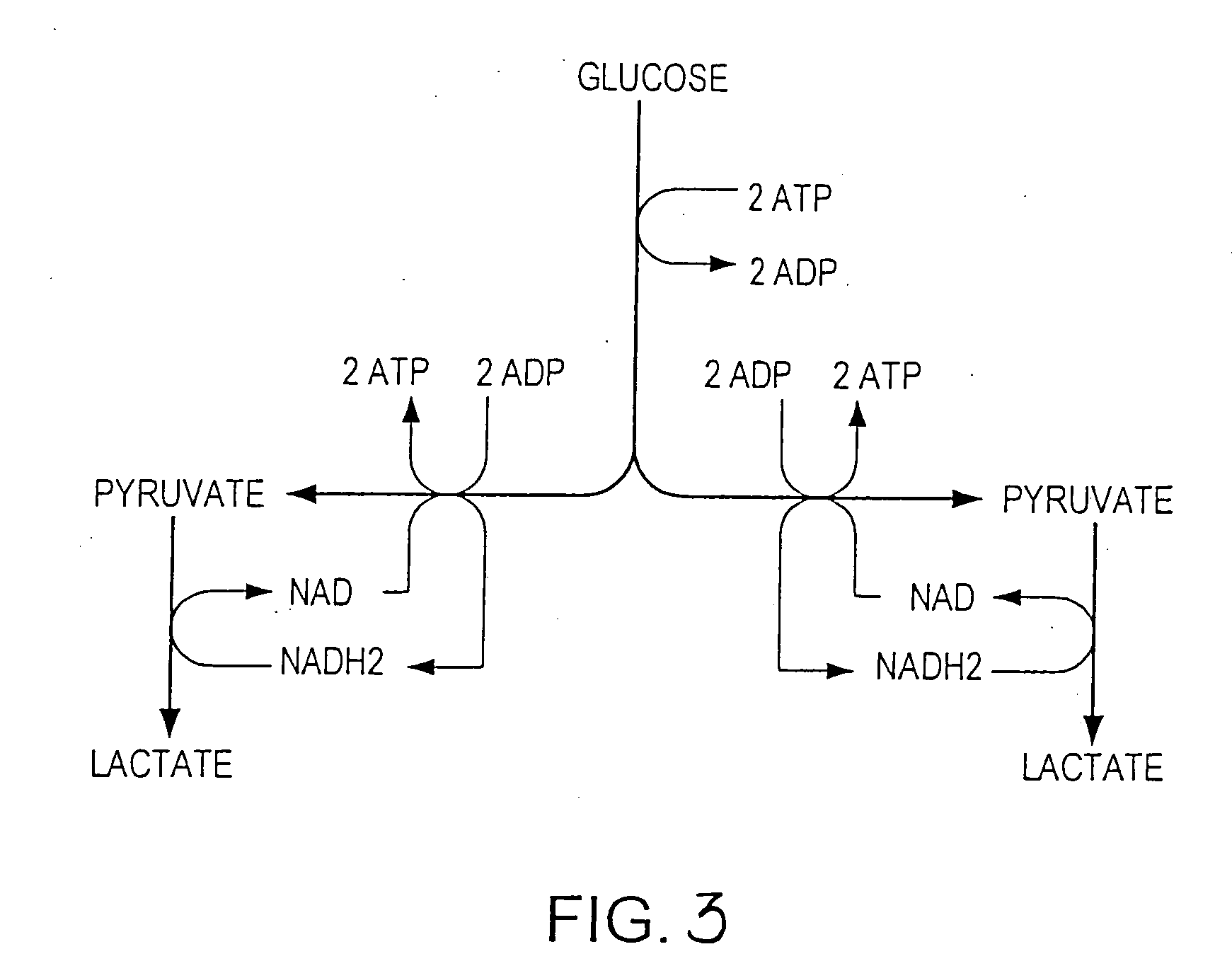
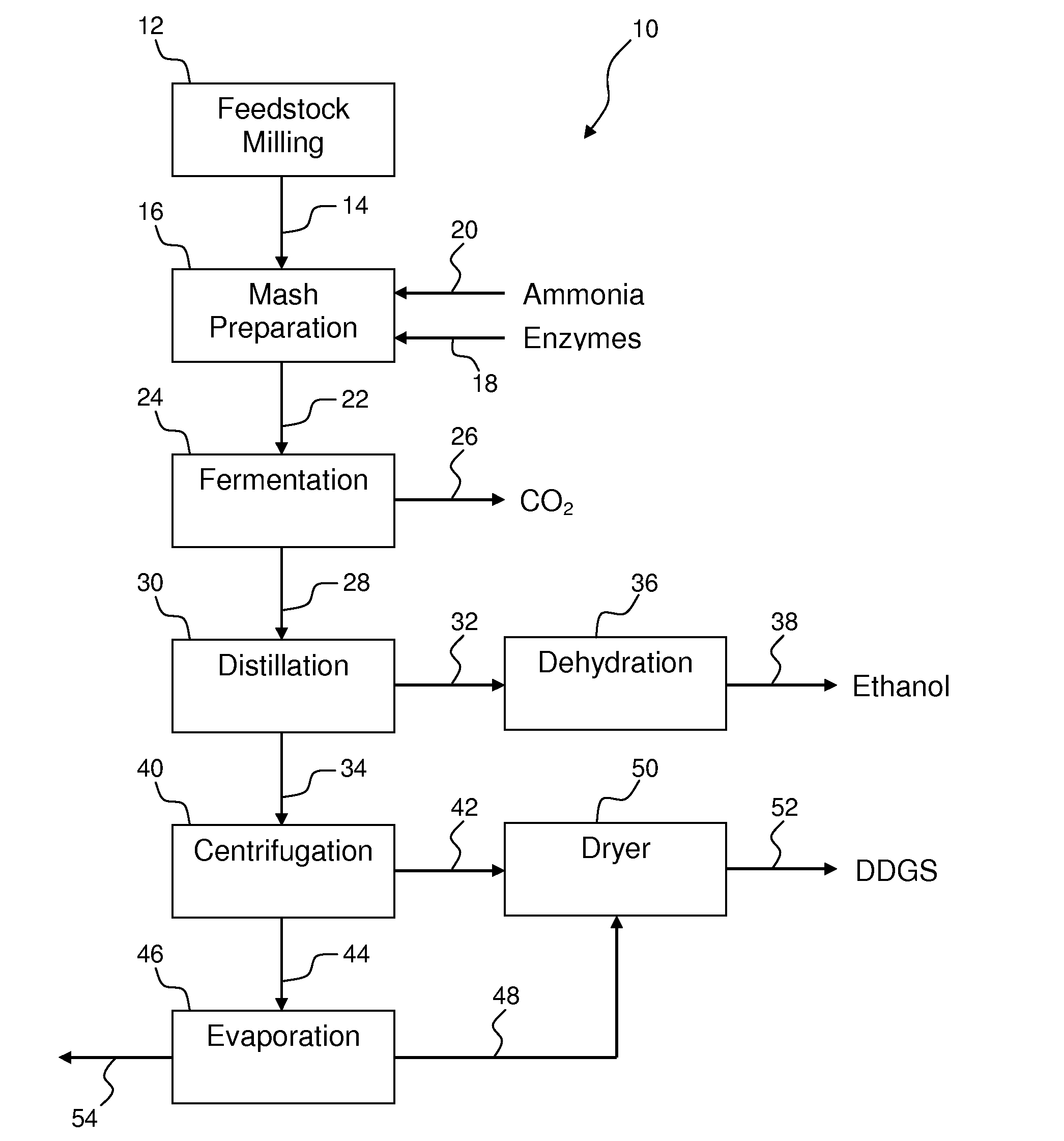
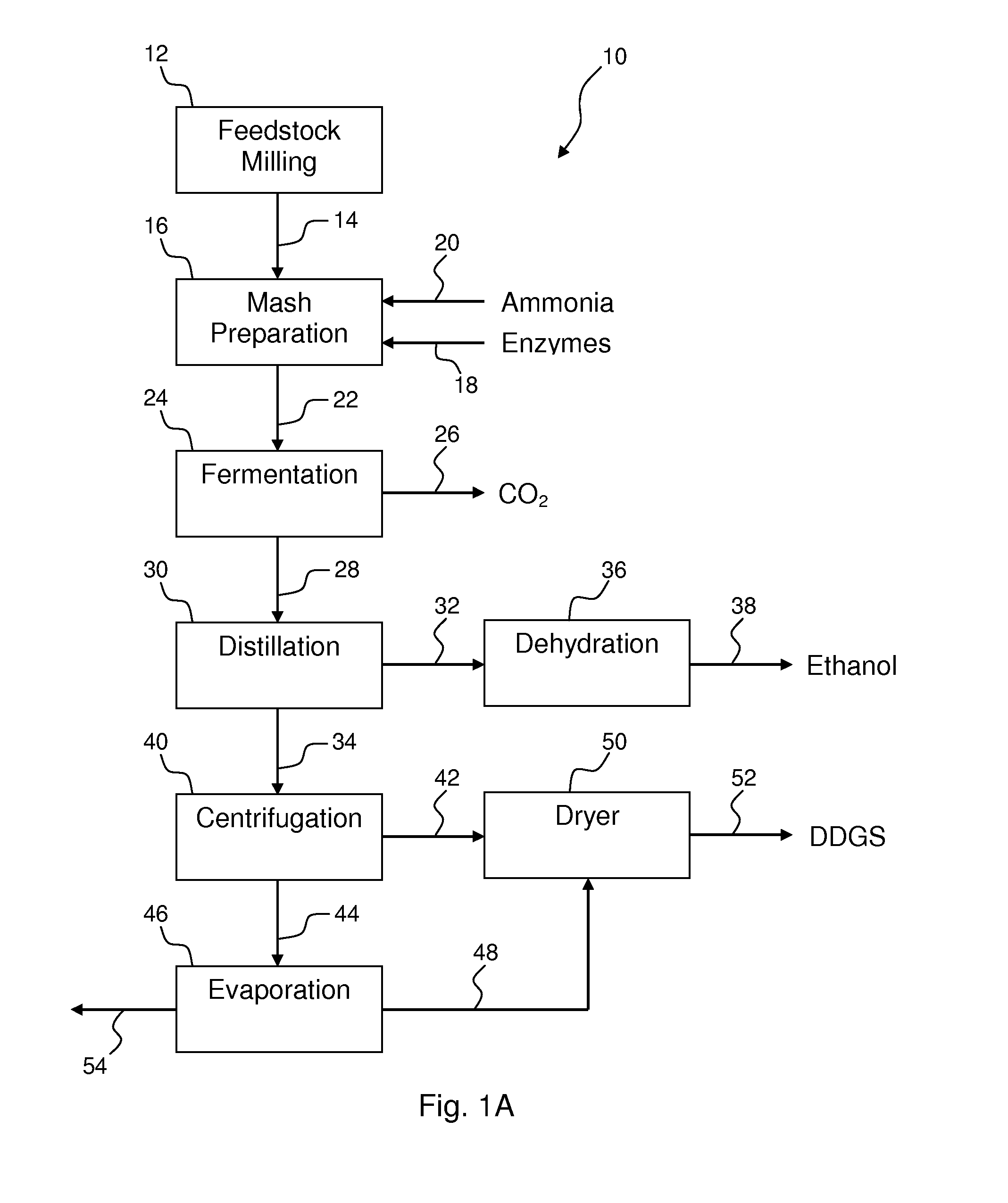
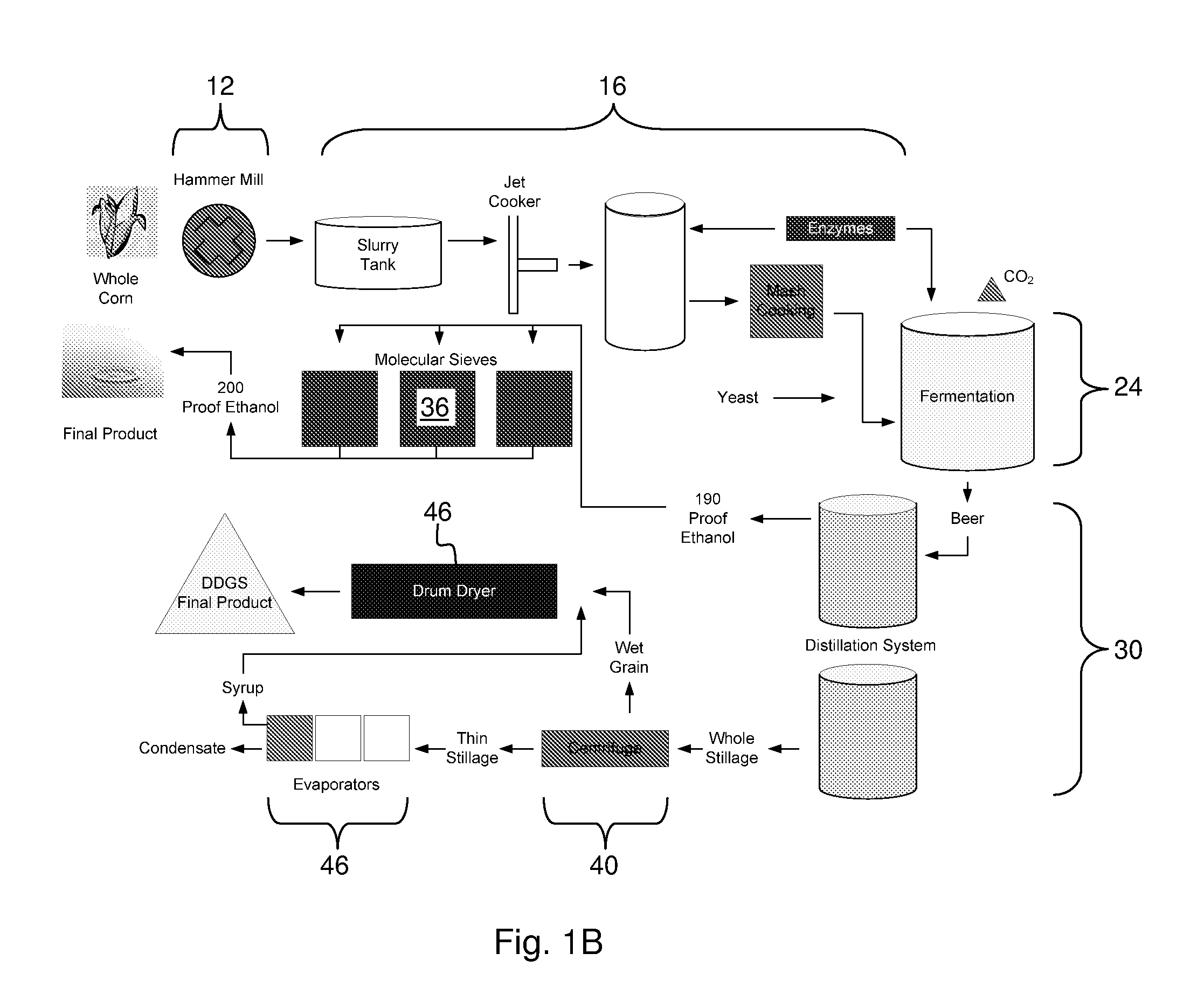
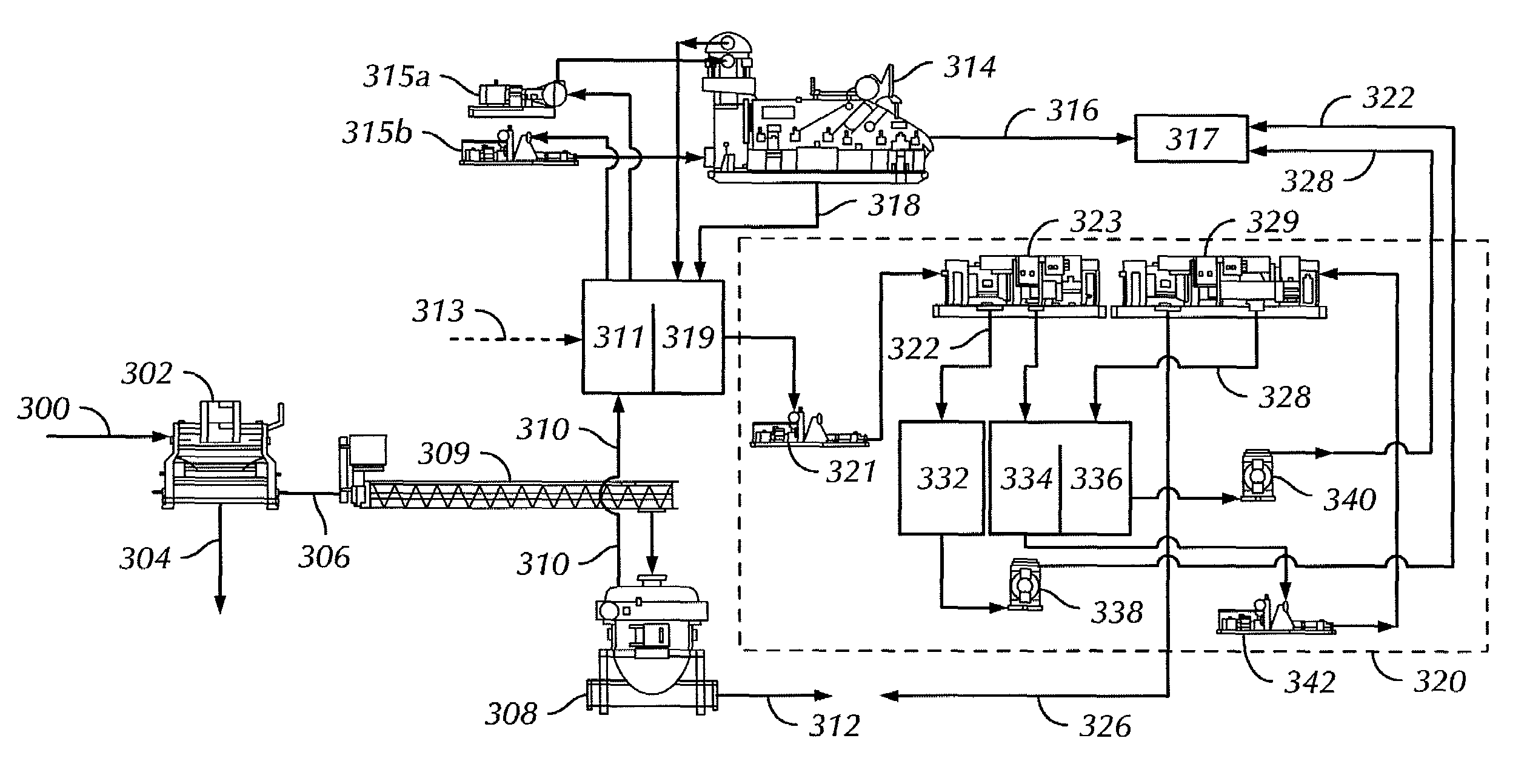
Process for producing ethanol from corn dry milling
InactiveUS7074603B2Fermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
A process for producing ethanol by the conversion of carbohydrates from a corn dry milling process in which the bottoms fraction from distillation of ethanol in a conventional yeast fermentation is used in a process including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions. The process results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from bottoms fraction, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts of the process include a high protein content solids fraction produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Procedure for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass using a new heat-tolerant yeast
InactiveUS20050069998A1Low conversion rateReduce yieldFungiBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSolid fraction
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230° C. for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of β-glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42° C.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES ENERGETICAS MEDIO AMBIENTALLES Y TECNOLOGICAS (C I E M A T)
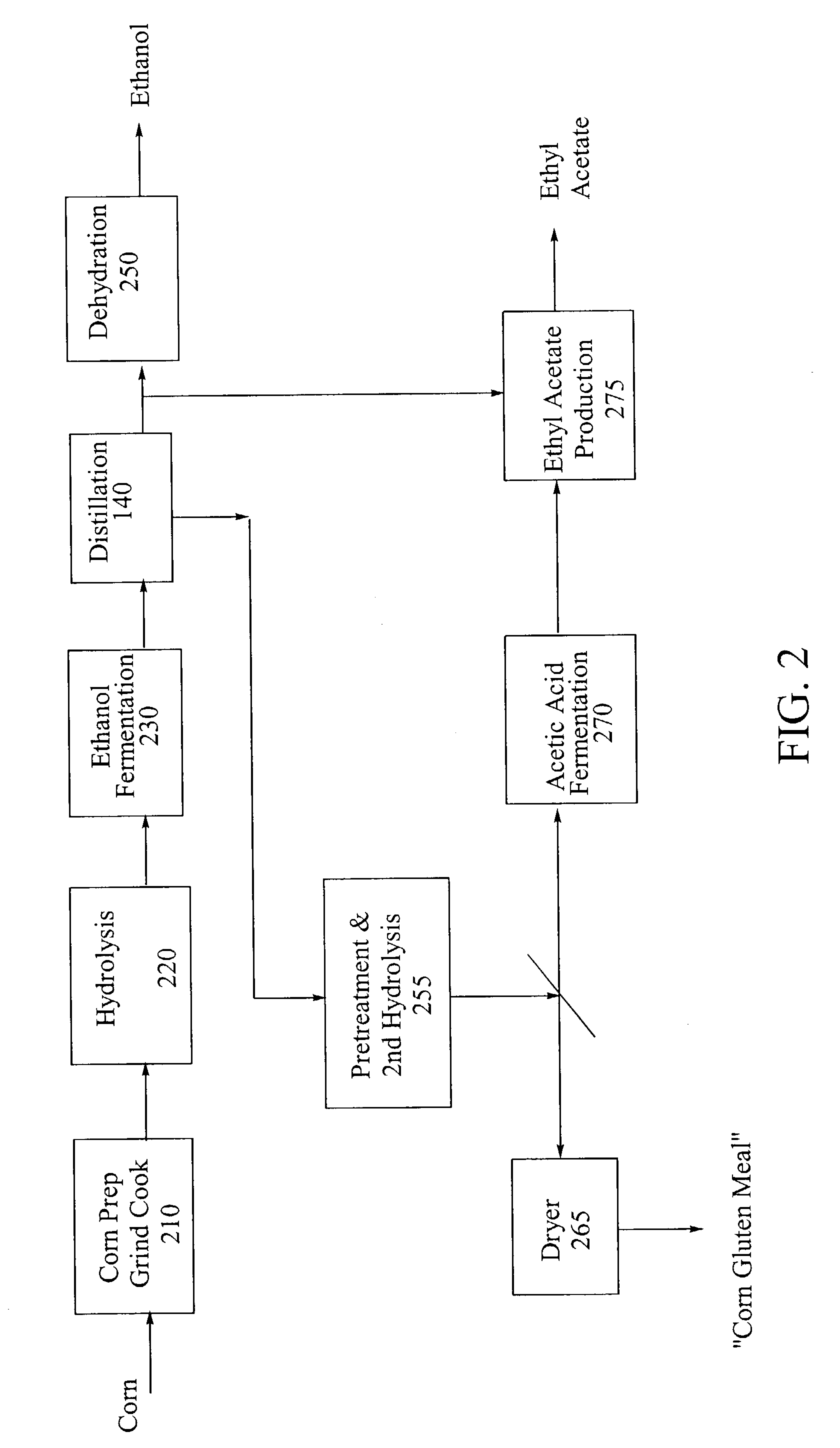
Process for producing ethanol from corn dry milling
InactiveUS20060127999A1Speed up the conversion processFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
A process for producing ethanol by the conversion of carbohydrates from a corn dry milling process in which the bottoms fraction from distillation of ethanol in a conventional yeast fermentation is used in a process including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions. The process results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from bottoms fraction, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts of the process include a high protein content solids fraction produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
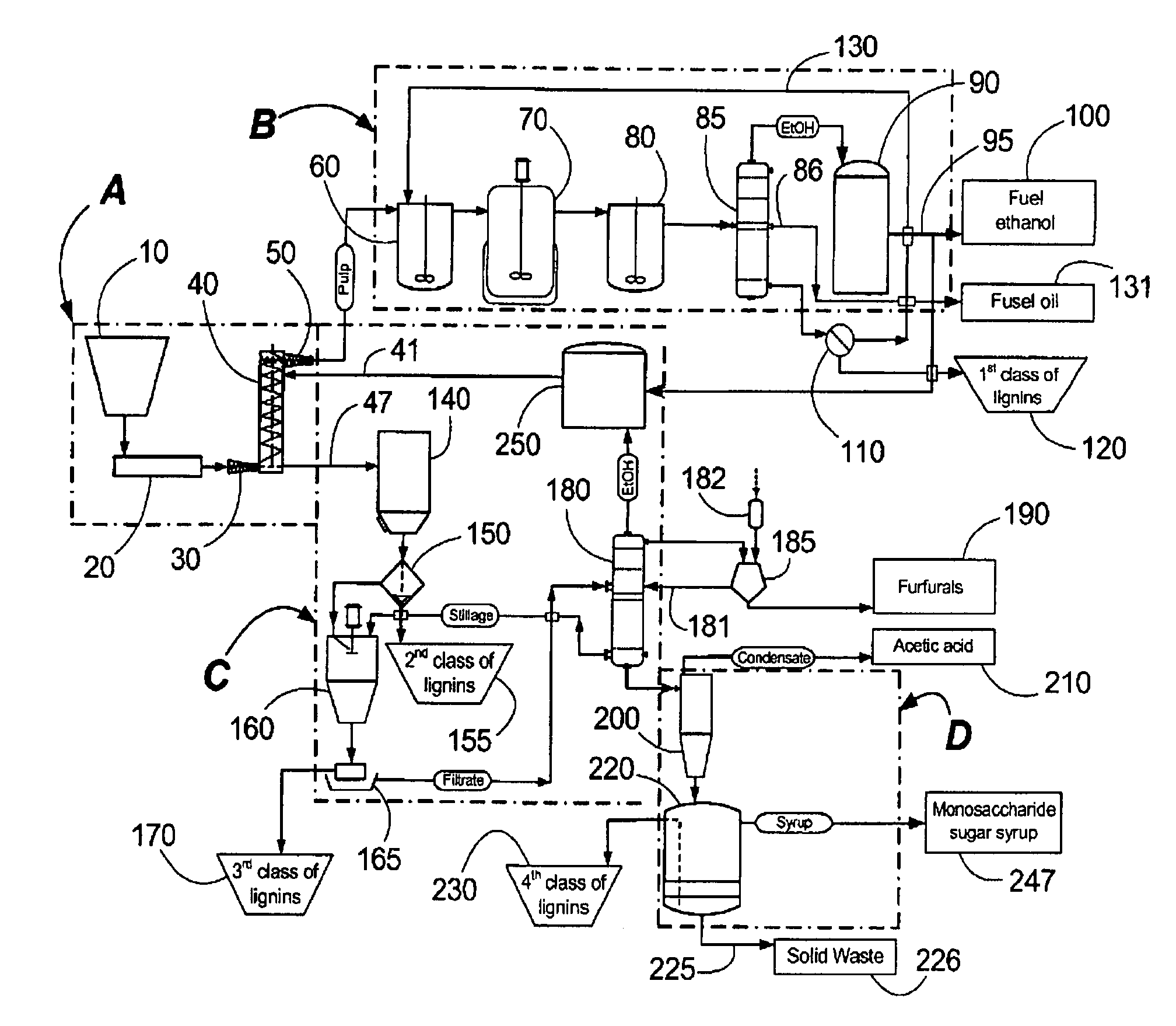
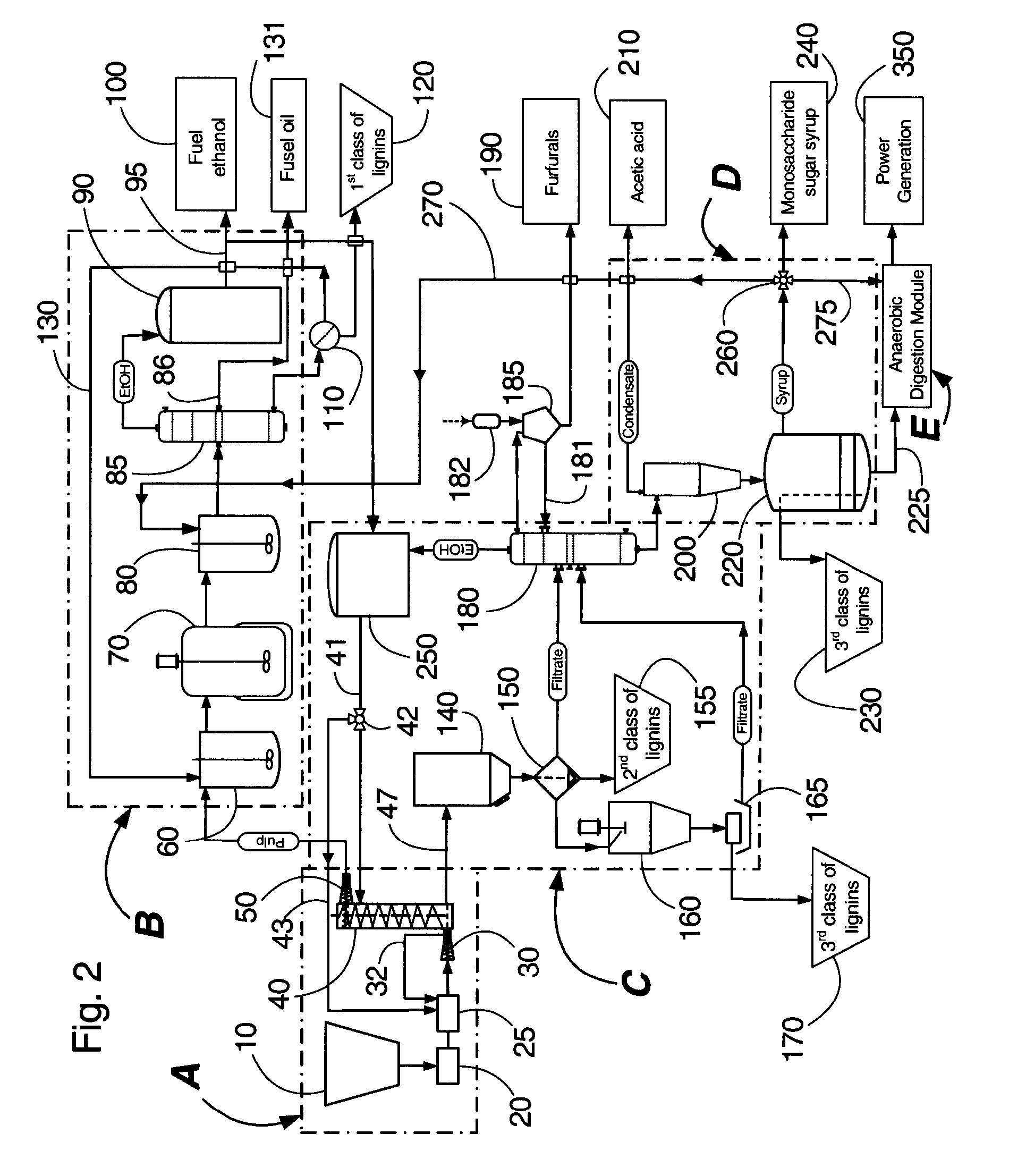
Continuous counter-current organosolv processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
InactiveUS7465791B1Low viscosityNon-fibrous pulp additionBiological substance pretreatmentsFractionationOrganosolv
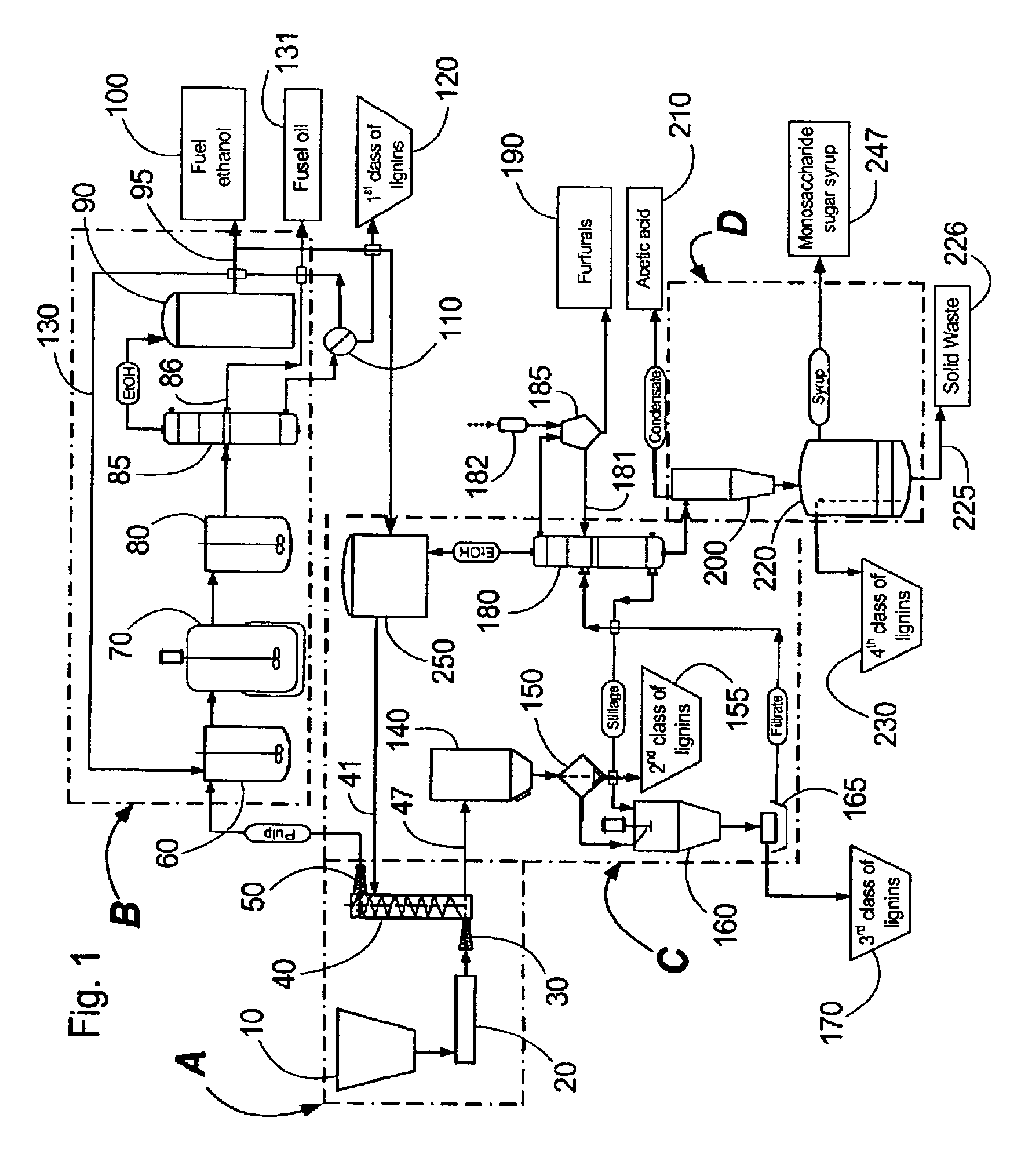
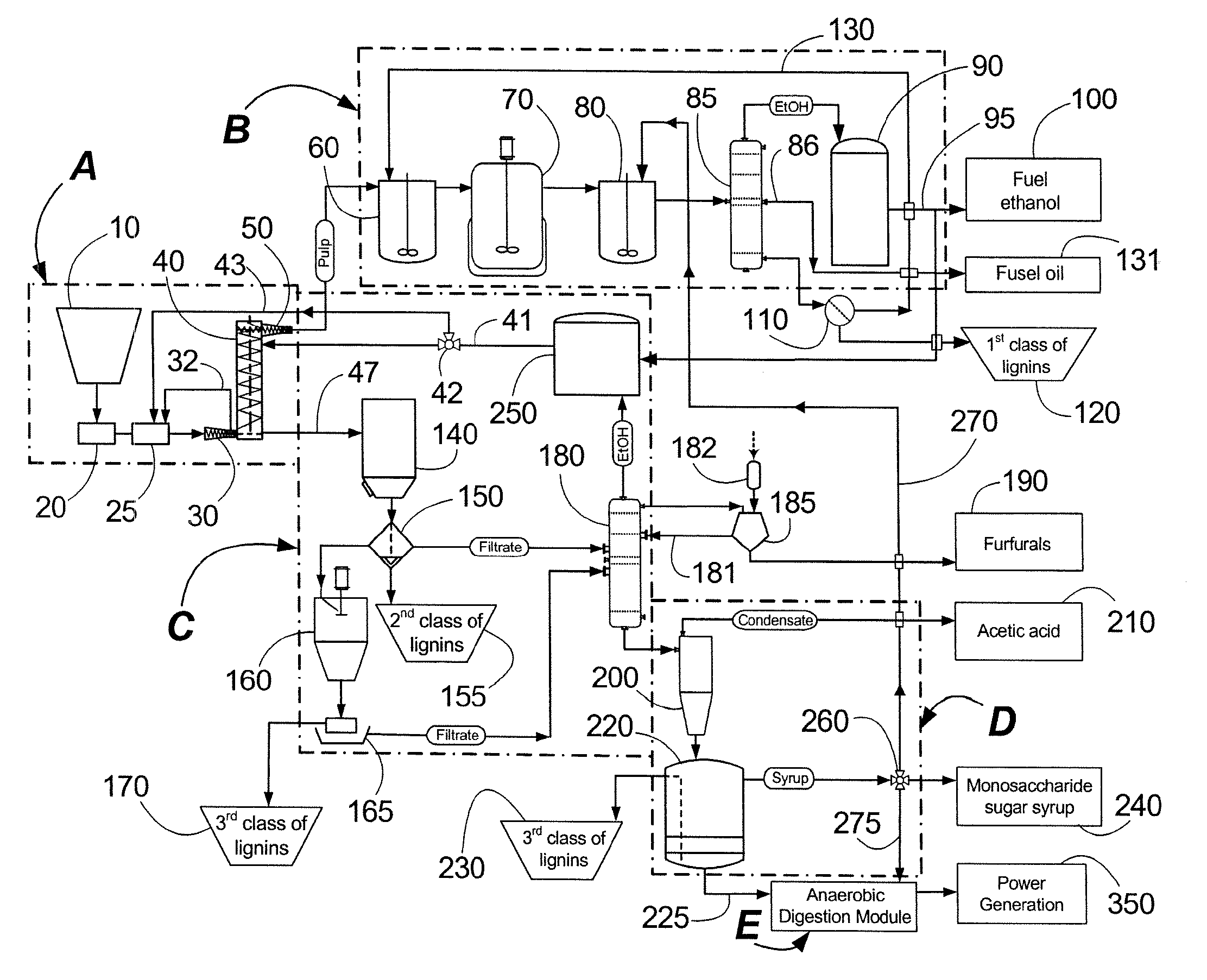
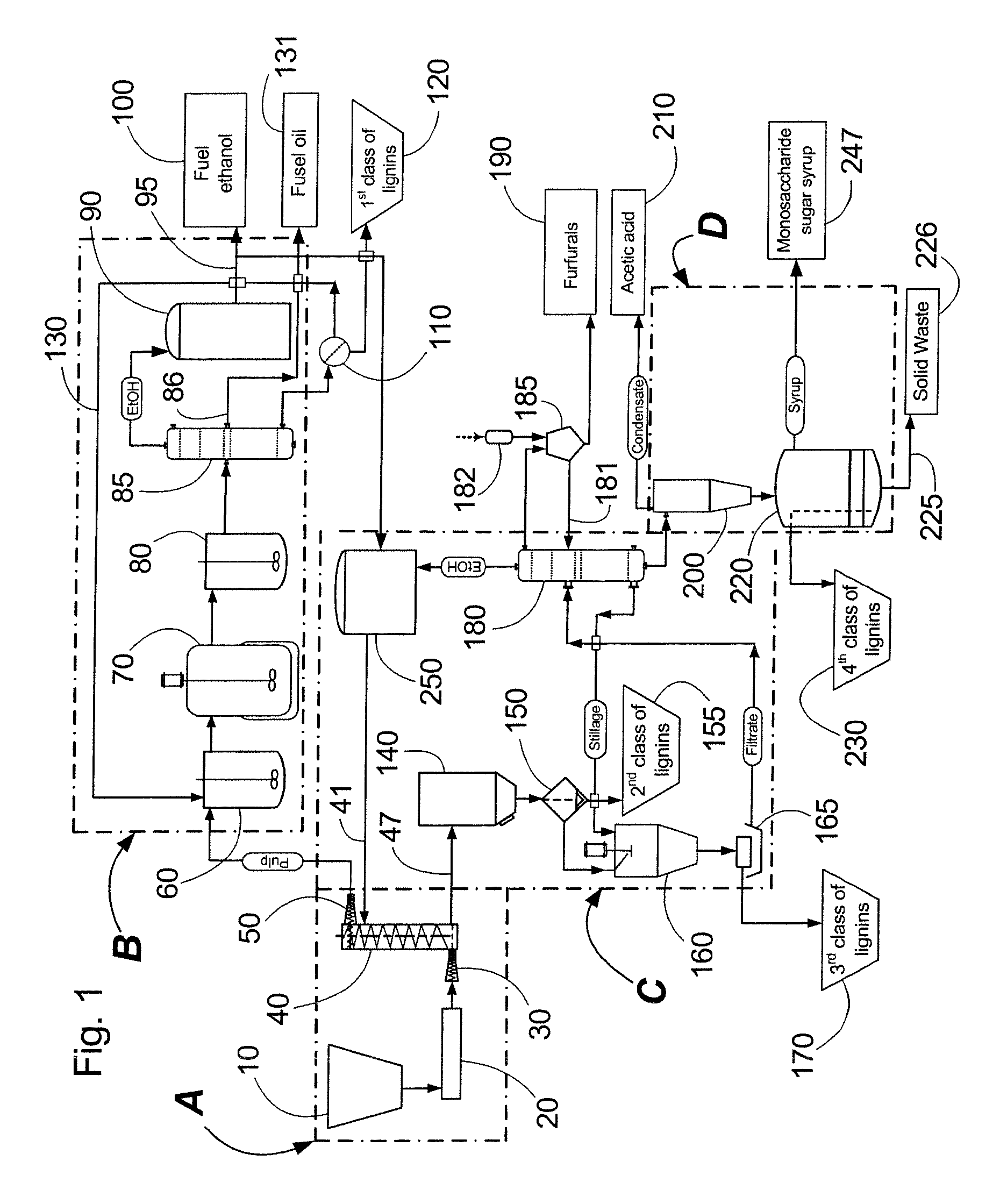
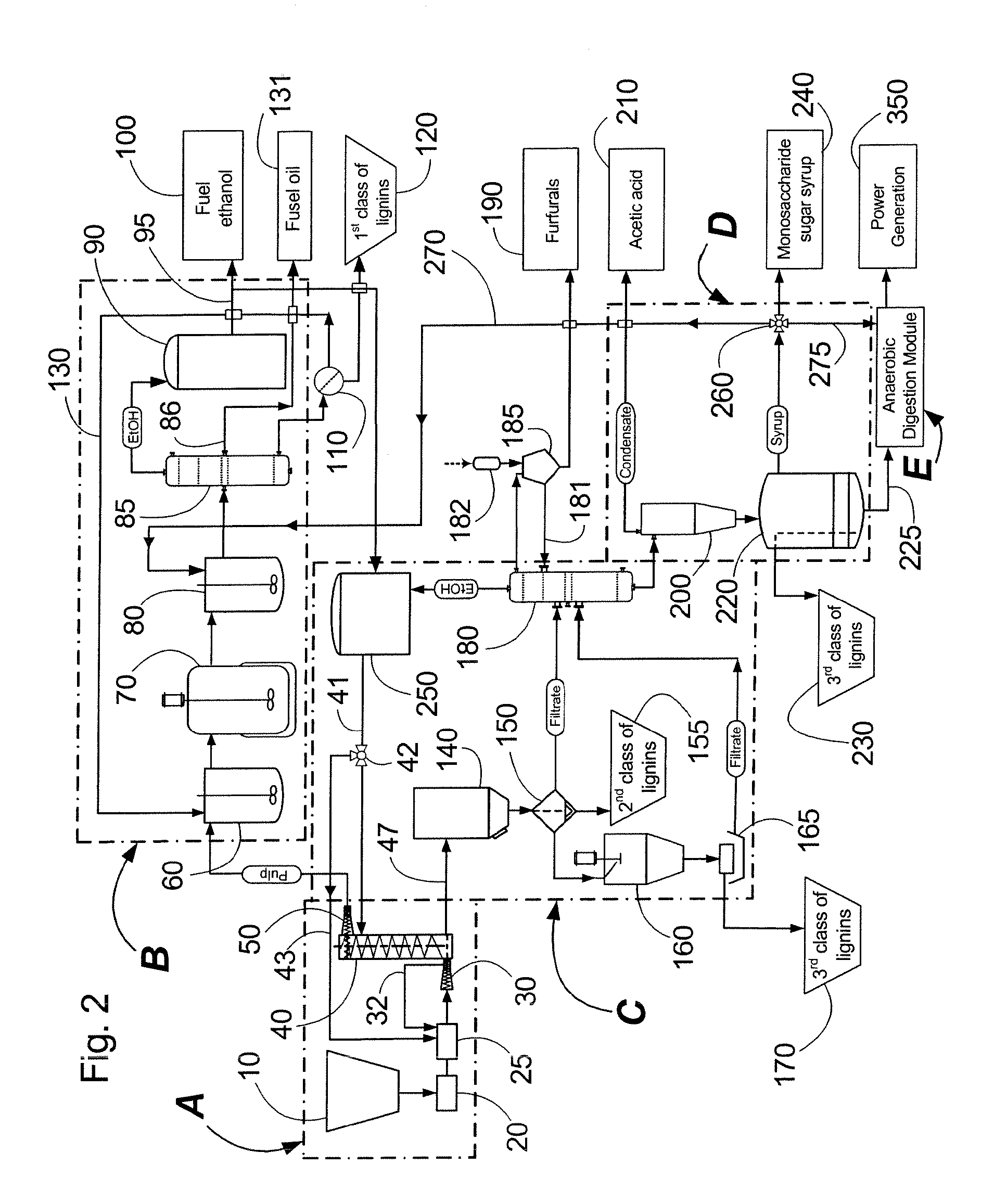
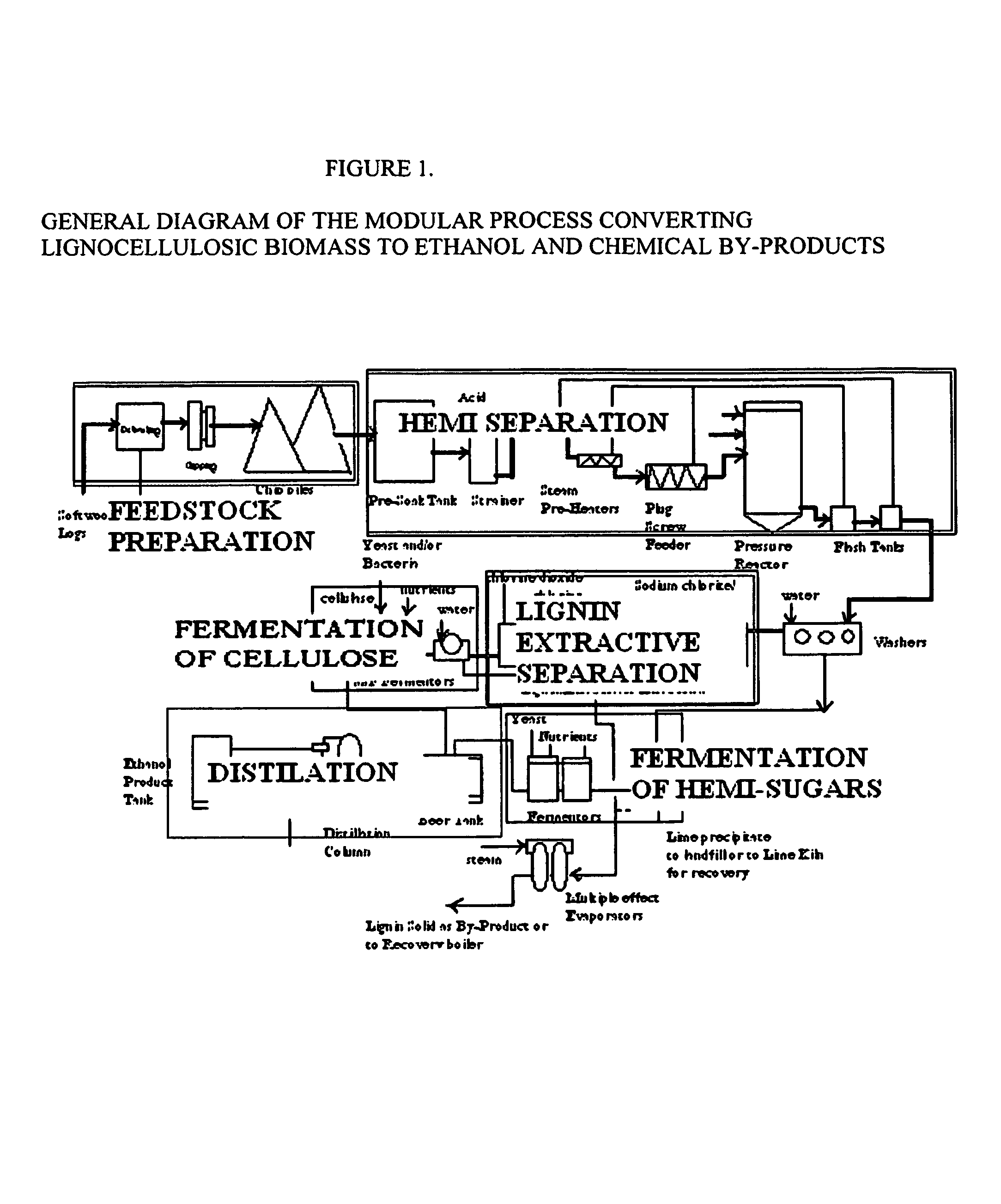
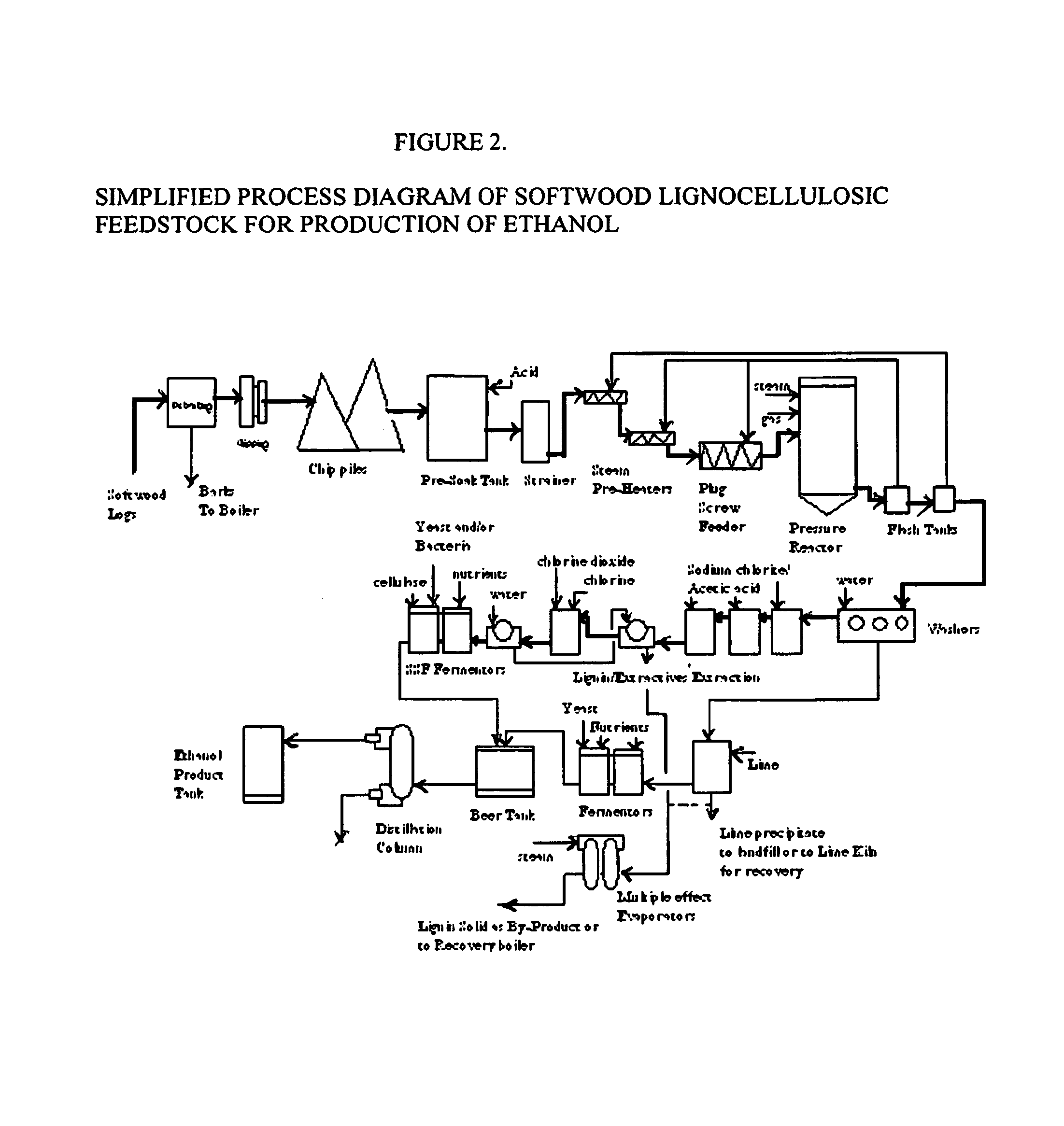
A modular process for organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic feedstocks into component parts and further processing of said component parts into at least fuel-grade ethanol and four classes of lignin derivatives. The modular process comprises a first processing module configured for physico-chemically digesting lignocellulosic feedstocks with an organic solvent thereby producing a cellulosic solids fraction and a liquid fraction, a second processing module configured for producing at least a fuel-grade ethanol and a first class of novel lignin derivatives from the cellulosic solids fraction, a third processing module configured for separating a second class and a third class of lignin derivatives from the liquid fraction and further processing the liquid fraction to produce a distillate and a stillage, a fourth processing module configured for separating a fourth class of lignin derivatives from the stillage and further processing the stillage to produce a sugar syrup.
Owner:SUZANO CANADA INC
Cementing compositions and application of such compositions to cementing oil wells or the like
InactiveUS6874578B1Improve mechanical propertiesReduce penetrationFluid removalDrilling compositionPolymer sciencePortland cement
Method of well cementing with a foamed slurry having a very low water content. When based on ordinary cement, the solid fraction of the slurry includes (by volume) 20-35% Portland cement, 35-65% particles ranging from 200 μm to 600 μm, and 5% to 25% of fine particles in the range 0.5 μm to 5 μm and the water content is less than 50% by volume. When based on micro-cement, the solid fraction includes (by volume) 50-75% micro-cement, 15-40% fine particles in the range 0.5 μm to 5 μm, and 0-20% particles in the rang 3 nanometers to 60 nanometers and the water content is less than 72% by volume.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Process of separating components of a fermentation broth
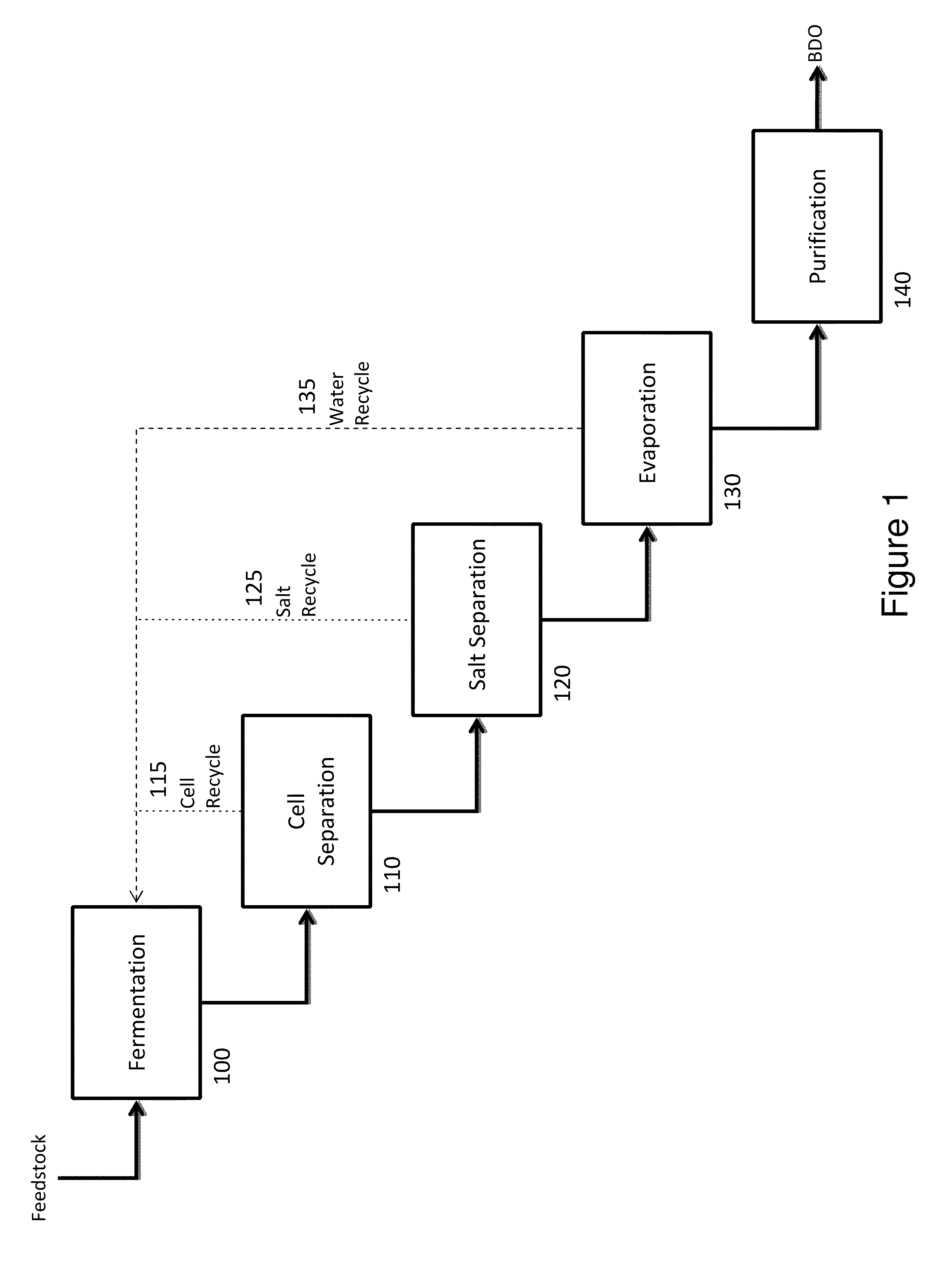
ActiveUS20110003355A1Produce lotFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparation1,4-ButanediolMicroorganism
A process of isolating 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) from a fermentation broth includes separating a liquid fraction enriched in 1,4-BDO from a solid fraction comprising cells, removing water from said liquid fraction, removing salts from said liquid fraction, and purifying 1,4-BDO. A process for producing 1,4-BDO includes culturing a 1,4-BDO-producing microorganism in a fermentor for a sufficient period of time to produce 1,4-BDO. The 1,4-BDO-producing microorganism includes a microorganism having a 1,4-BDO pathway having one or more exogenous genes encoding a 1,4-BDO pathway enzyme and / or one or more gene disruptions. The process for producing 1,4-BDO further includes isolating 1,4-BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
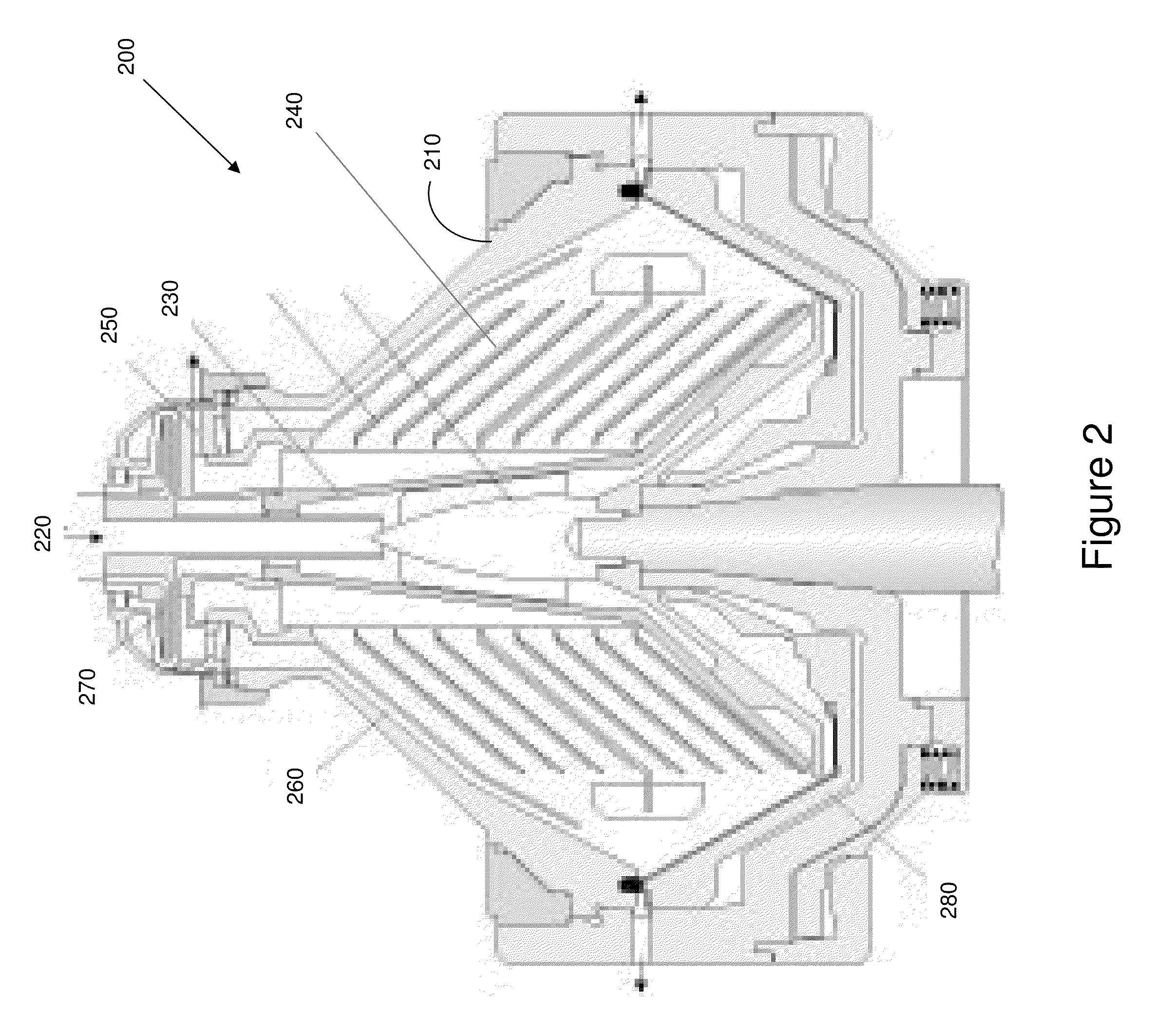
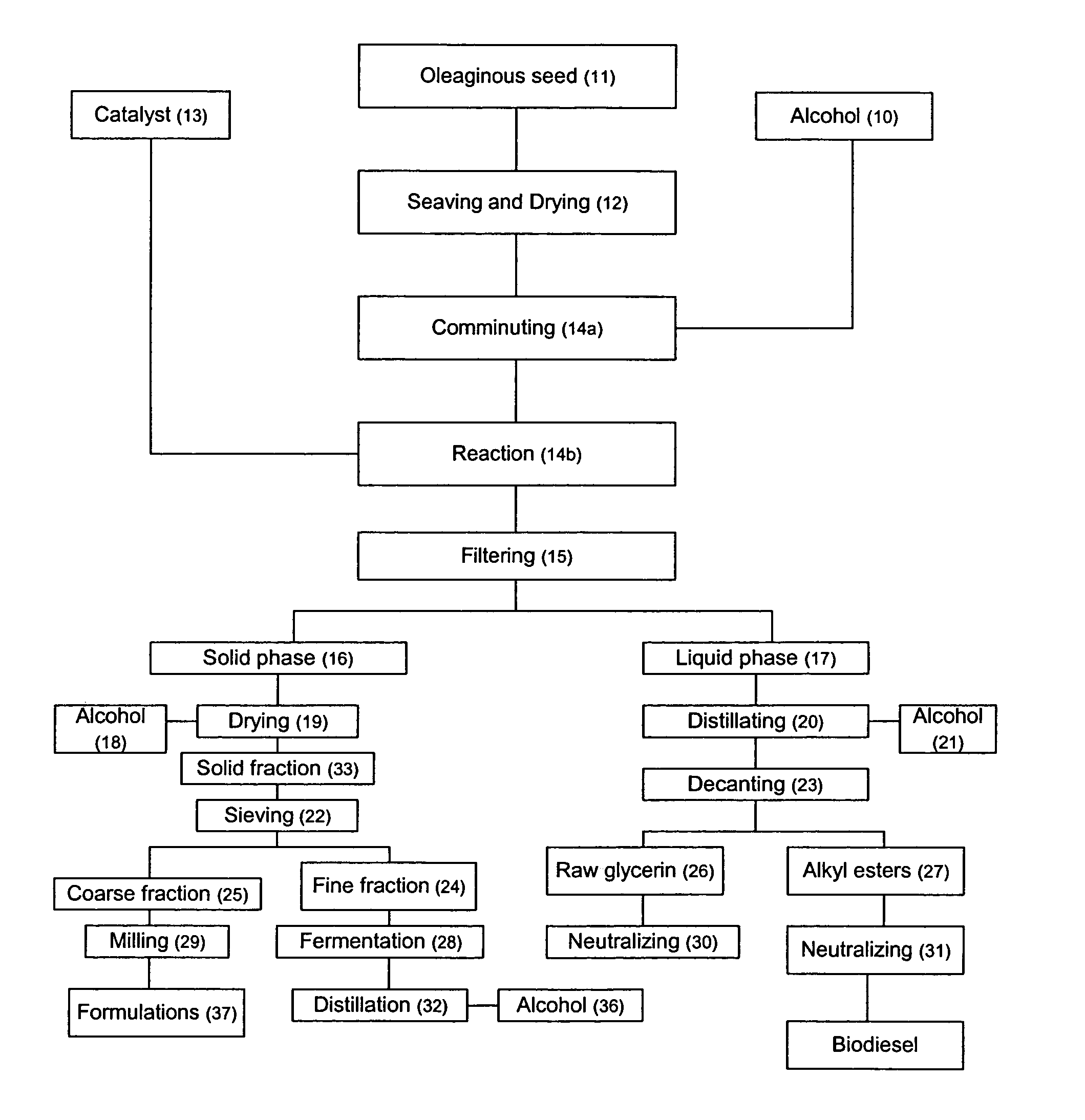
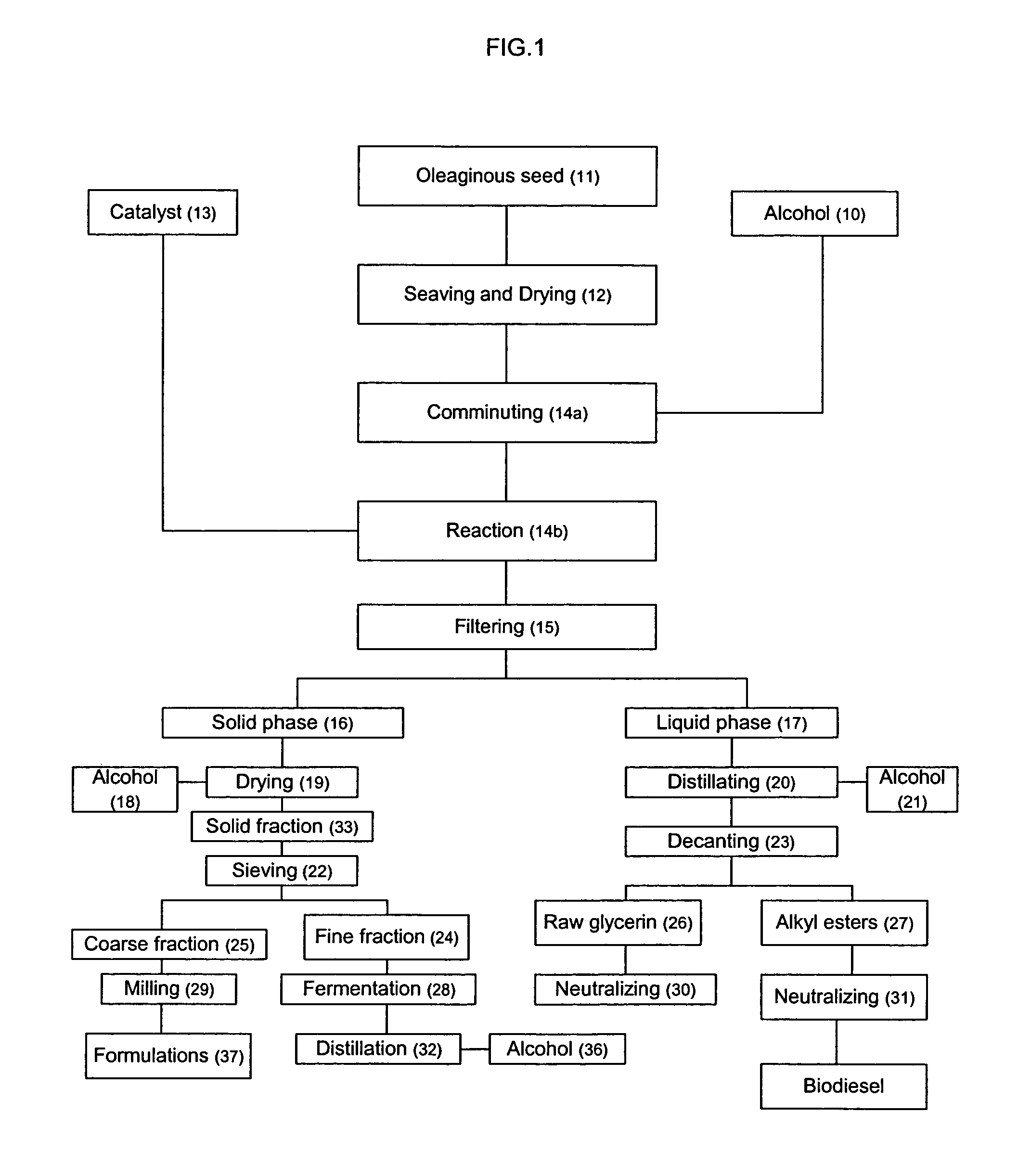
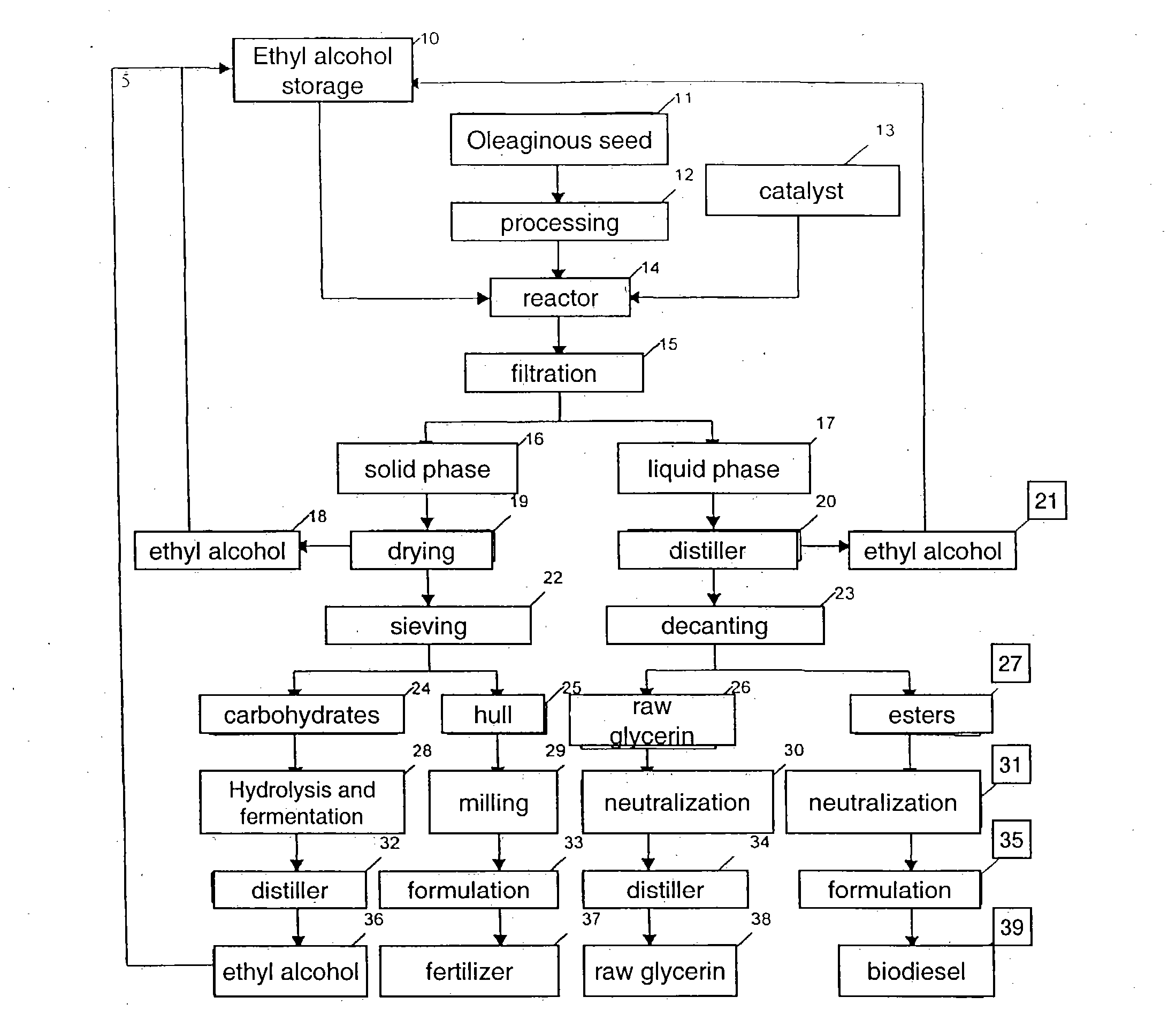
Process for producing biodiesel fuel using triglyceride-rich oleagineous seed directly in a transesterification reaction in the presence of an alkaline alkoxide catalyst
InactiveUS7112229B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationOil and greaseBiodiesel
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds. The inventive process includes a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
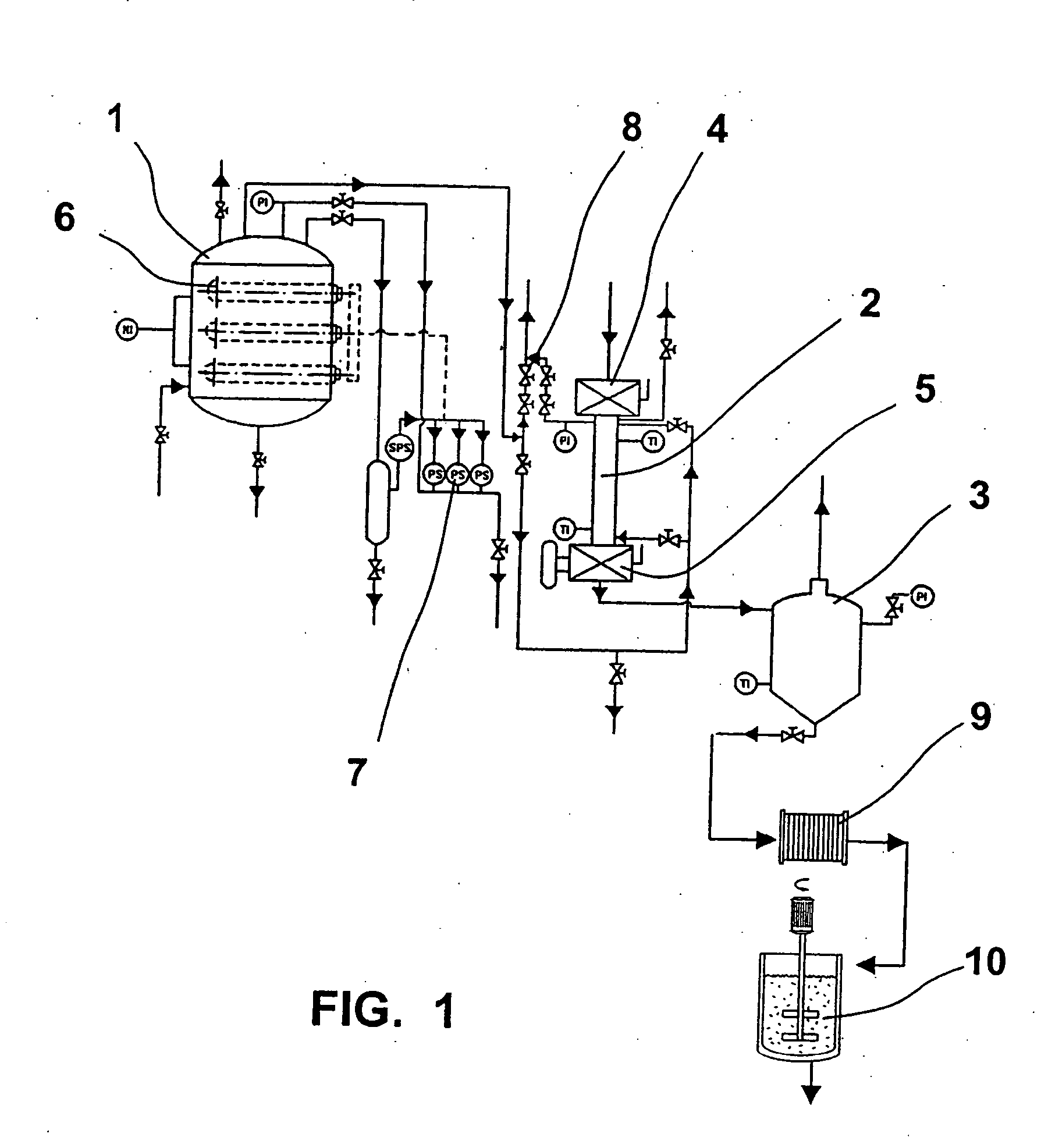
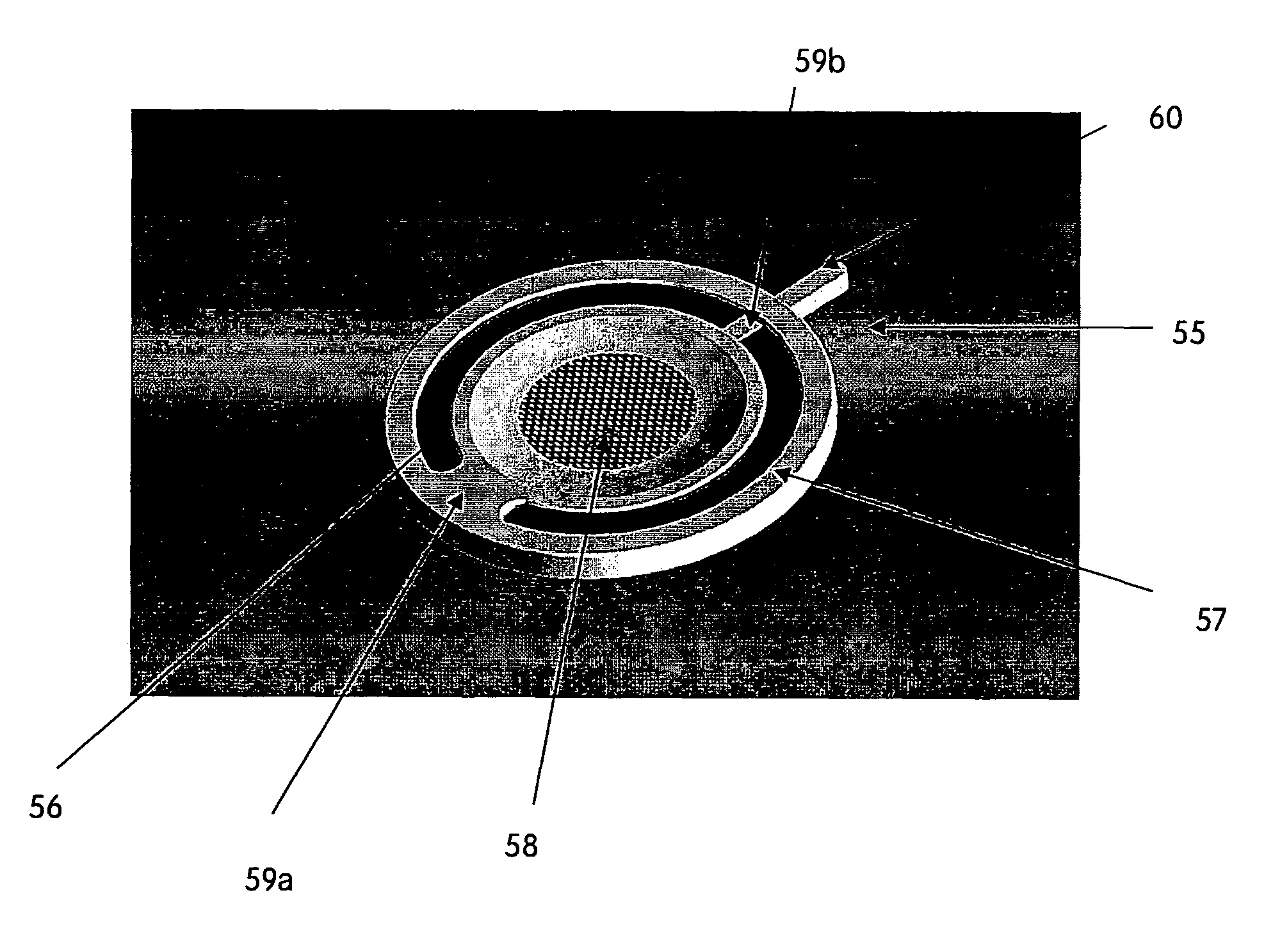
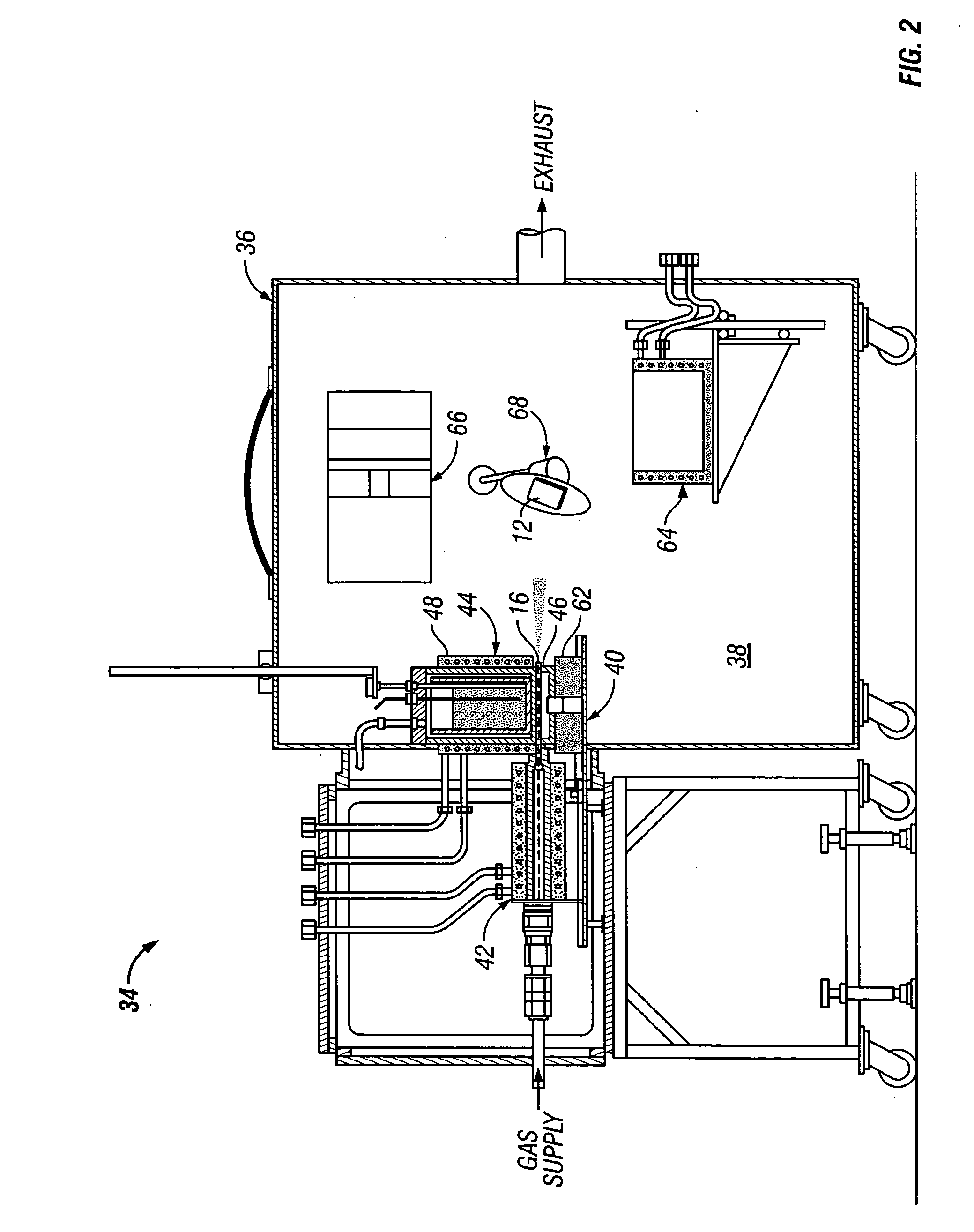
Apparatus and method for filter cleaning by ultrasound, backwashing and filter movement during the filtration of biological samples
InactiveUS8273253B2Minimises fouling and clogging of filterImprove overall efficiency and accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic processVacuum pressure
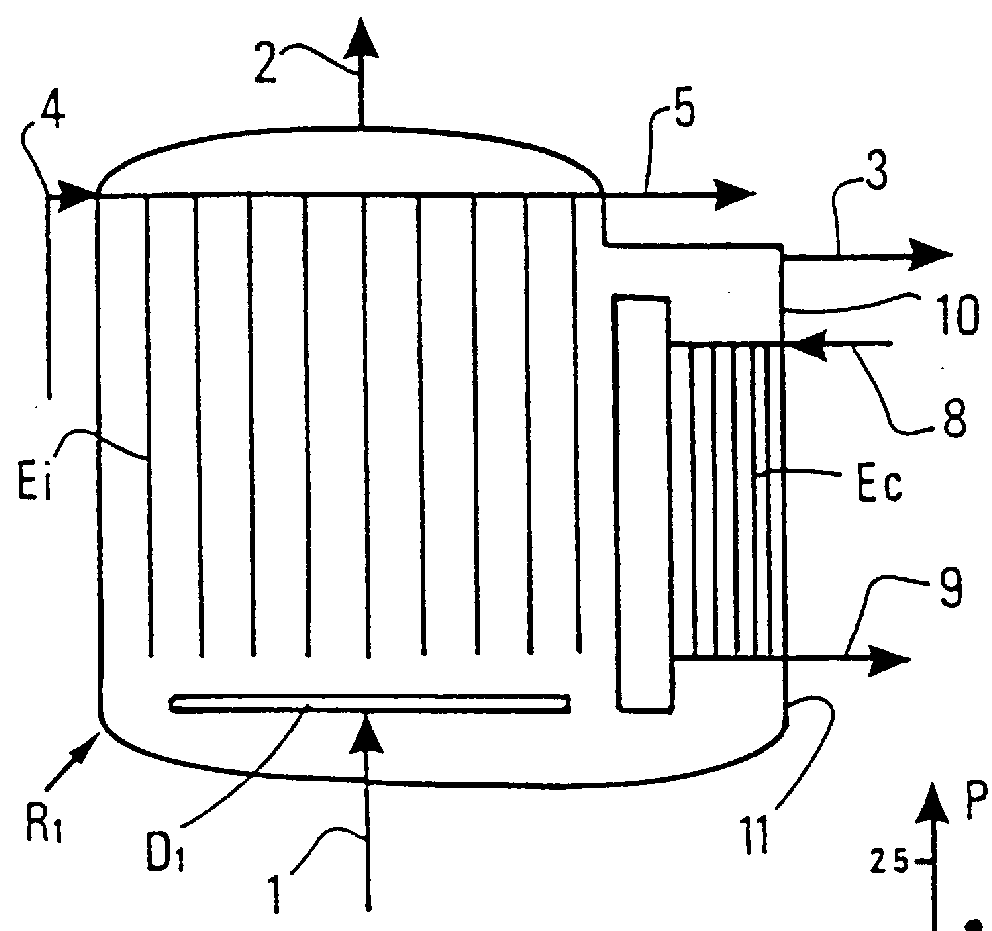
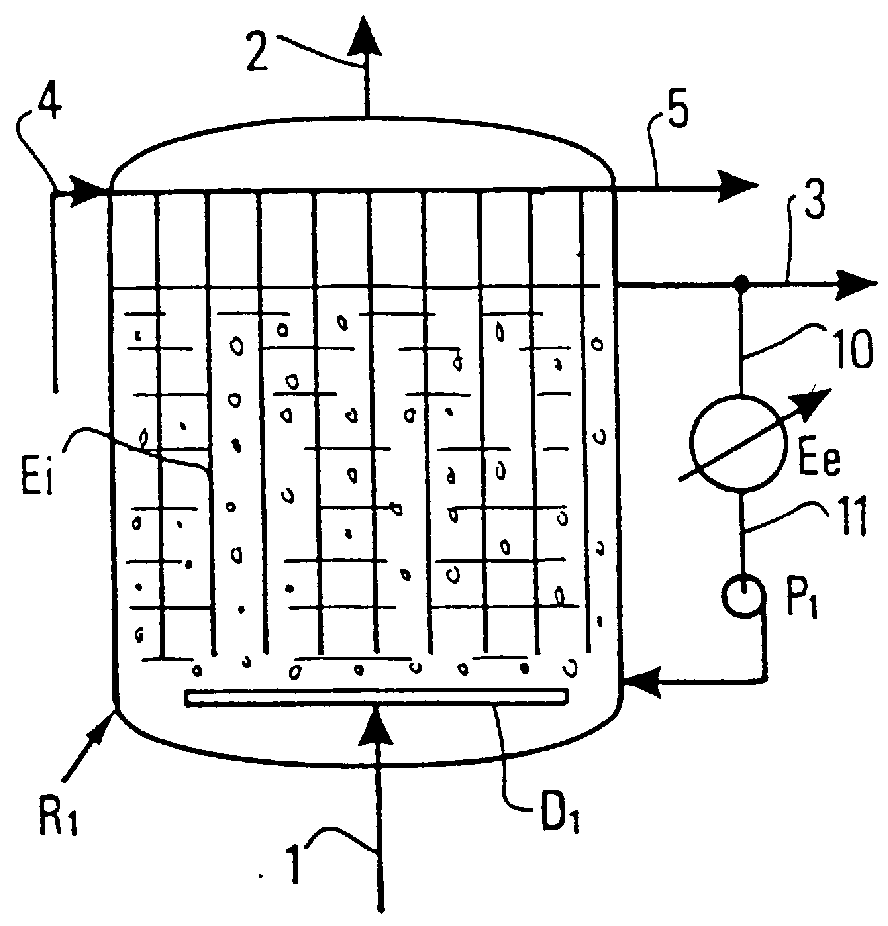
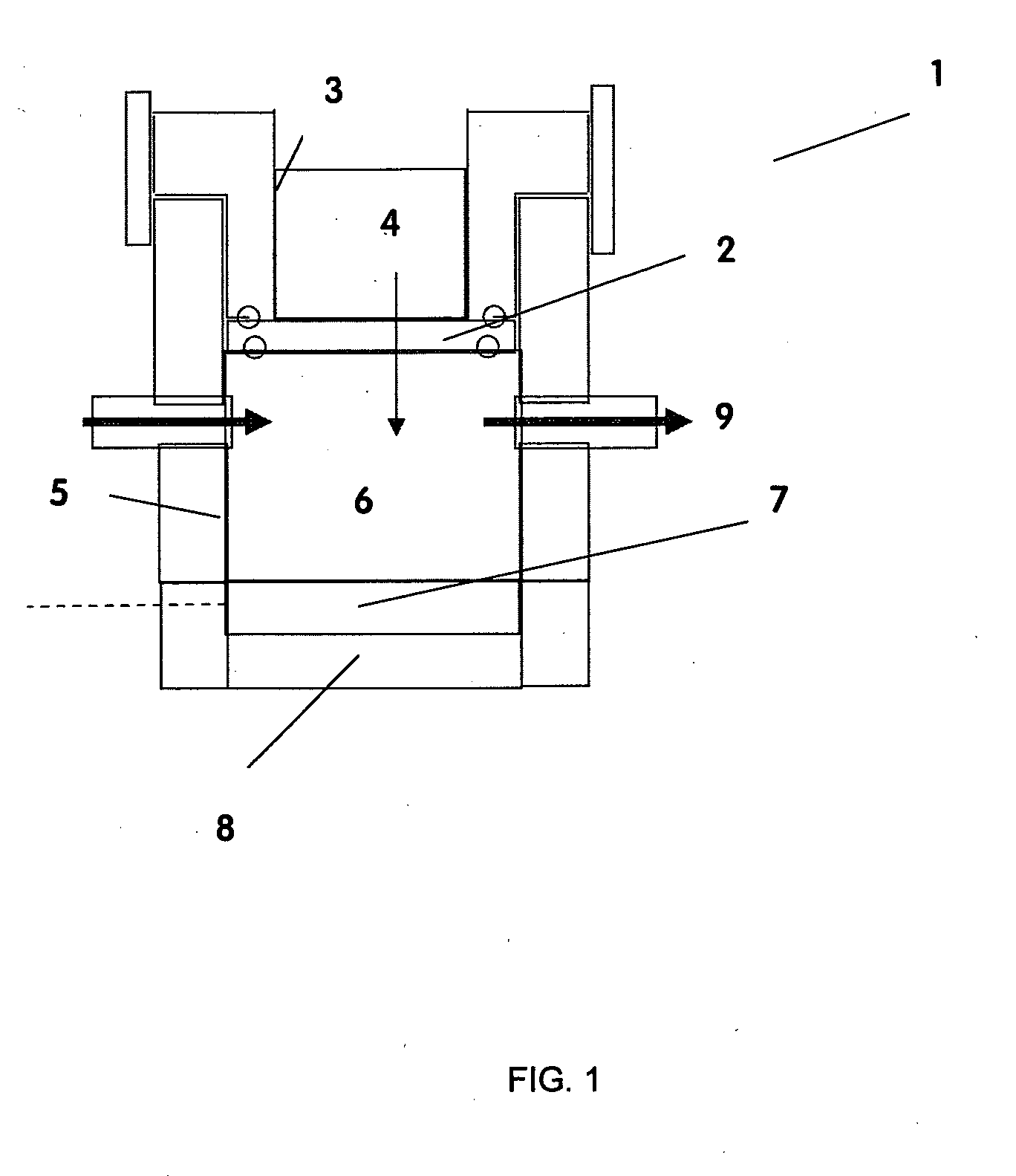
The present application is directed to the separation of—a solid fraction from a fluid sample particularly a therapeutic cellular fraction from a biological sample such as a bone marrow sample by a porous filter (2) which separates a filtration unit (1) into an upper pre-filtration chamber (3) into which a fluid sample (4) requiring cell separation is introduced and a lower post-filtration chamber (5) into which a fluid (6) capable of transmitting an acoustic standing wave is introduced. An acoustic element (8) is coupled to a substrate (7) which is located within and at the bottom of the lower chamber (5) and which resonates in response to the acoustic generating element (8) and generates a standing wave through the two fluid phases and the filter to agitate the sample (4). Simultaneously, a cyclic process of vacuum draw (9). causes movement of the sample (4) downwards through the filter (2). Vacuum pressure, fluid flow rate and frequency of vibration are controlled from a remote unit housing appropriate pumps and valves.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Sustained-release tablet composition
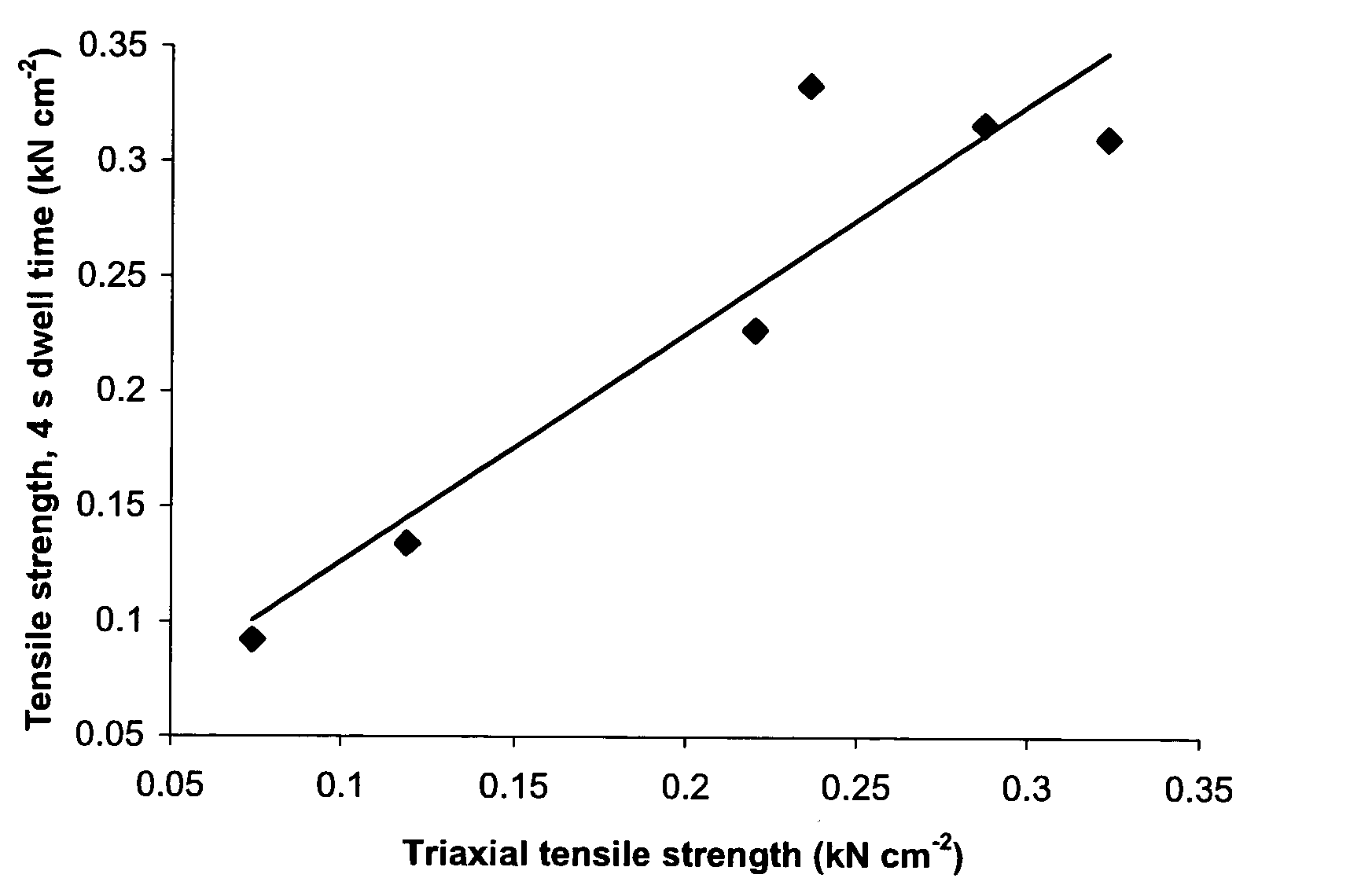
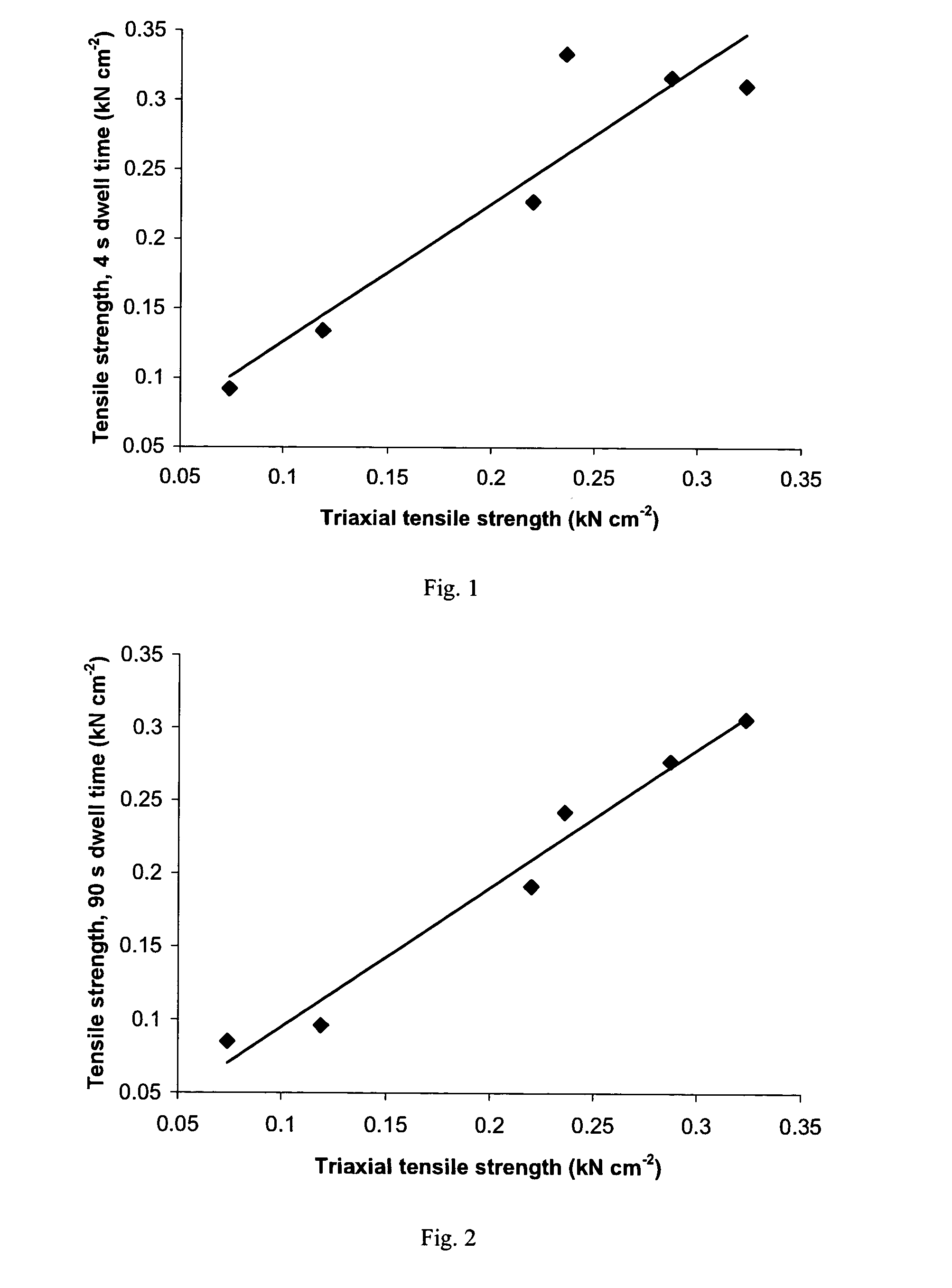
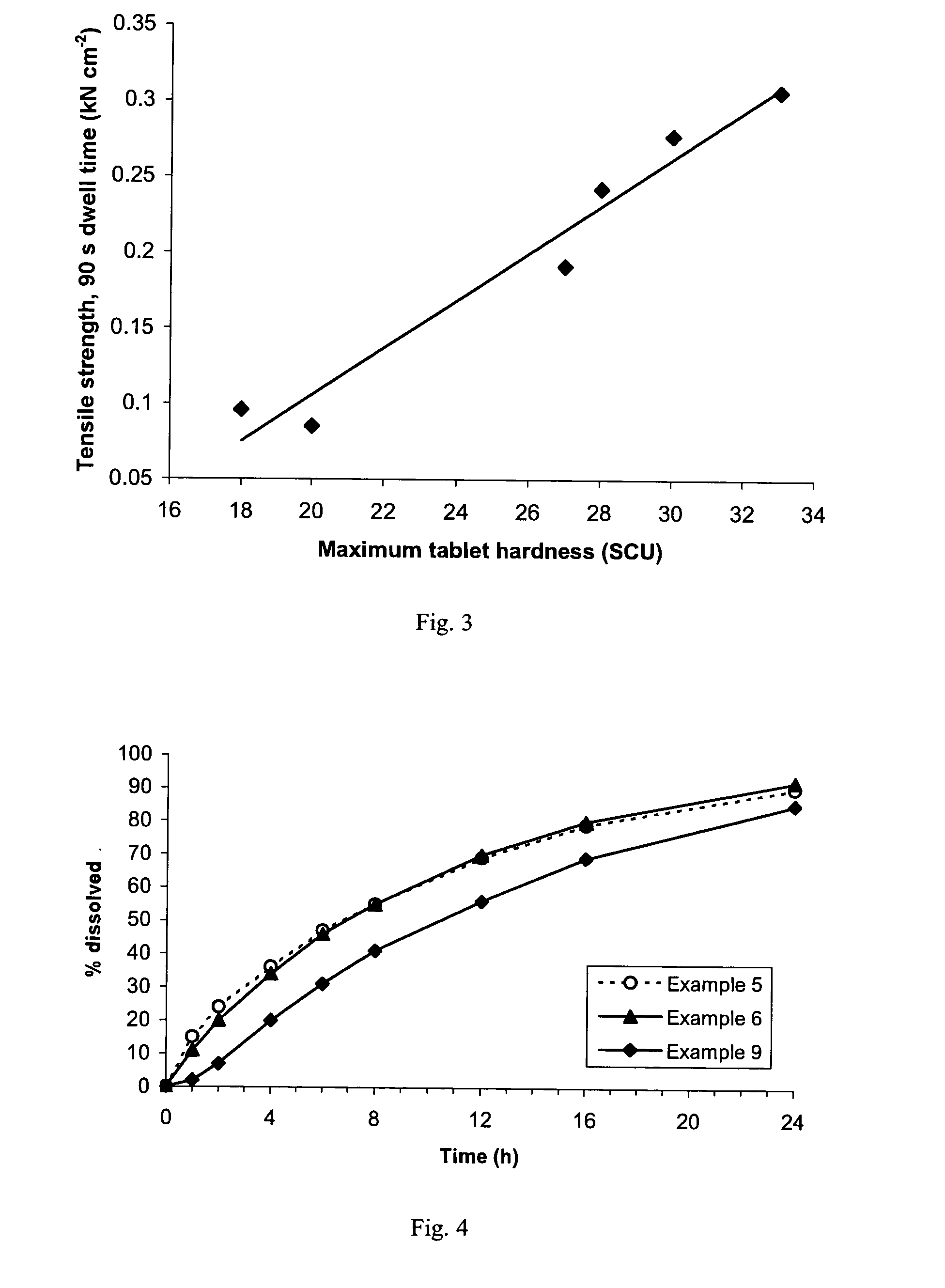
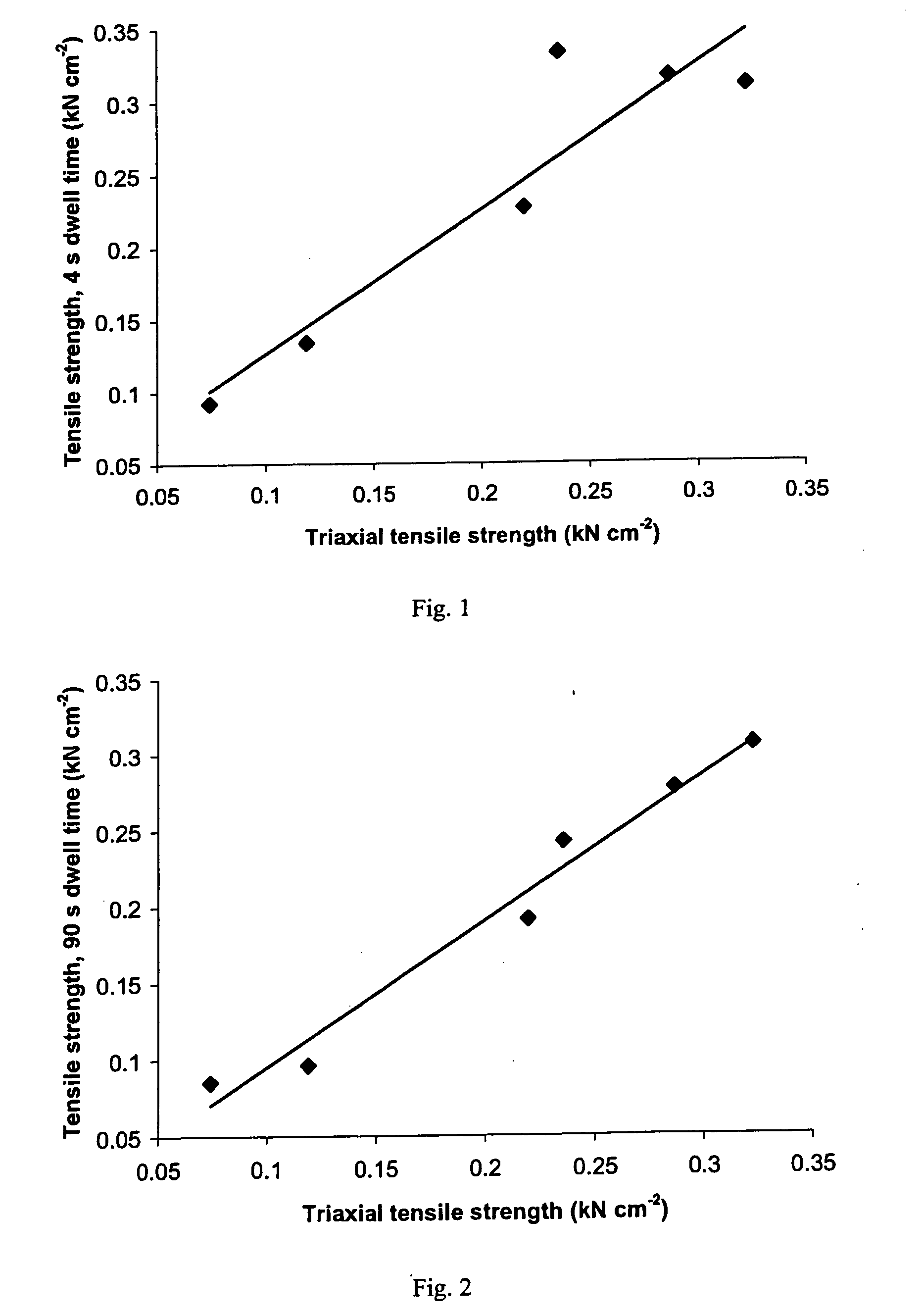
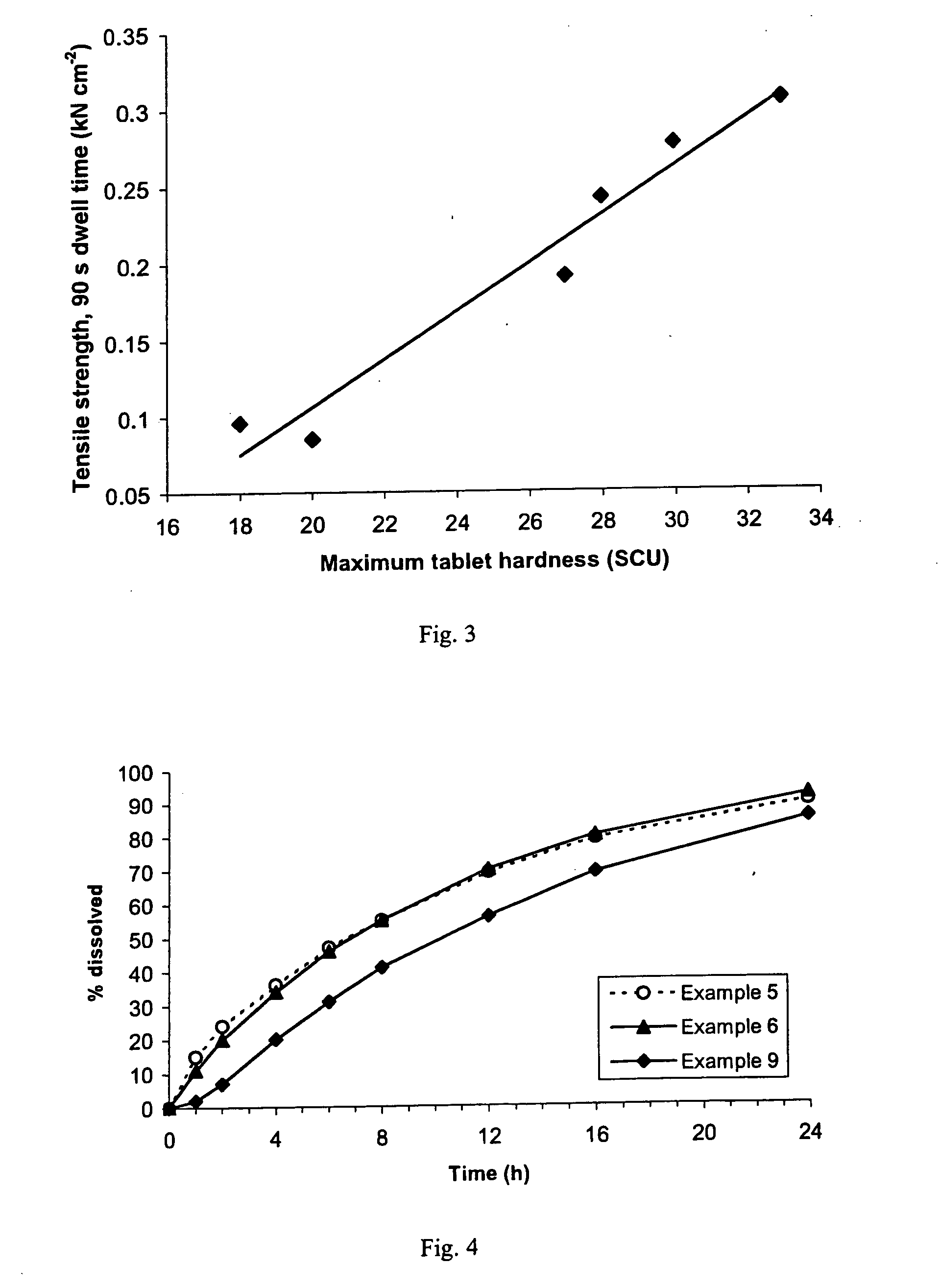
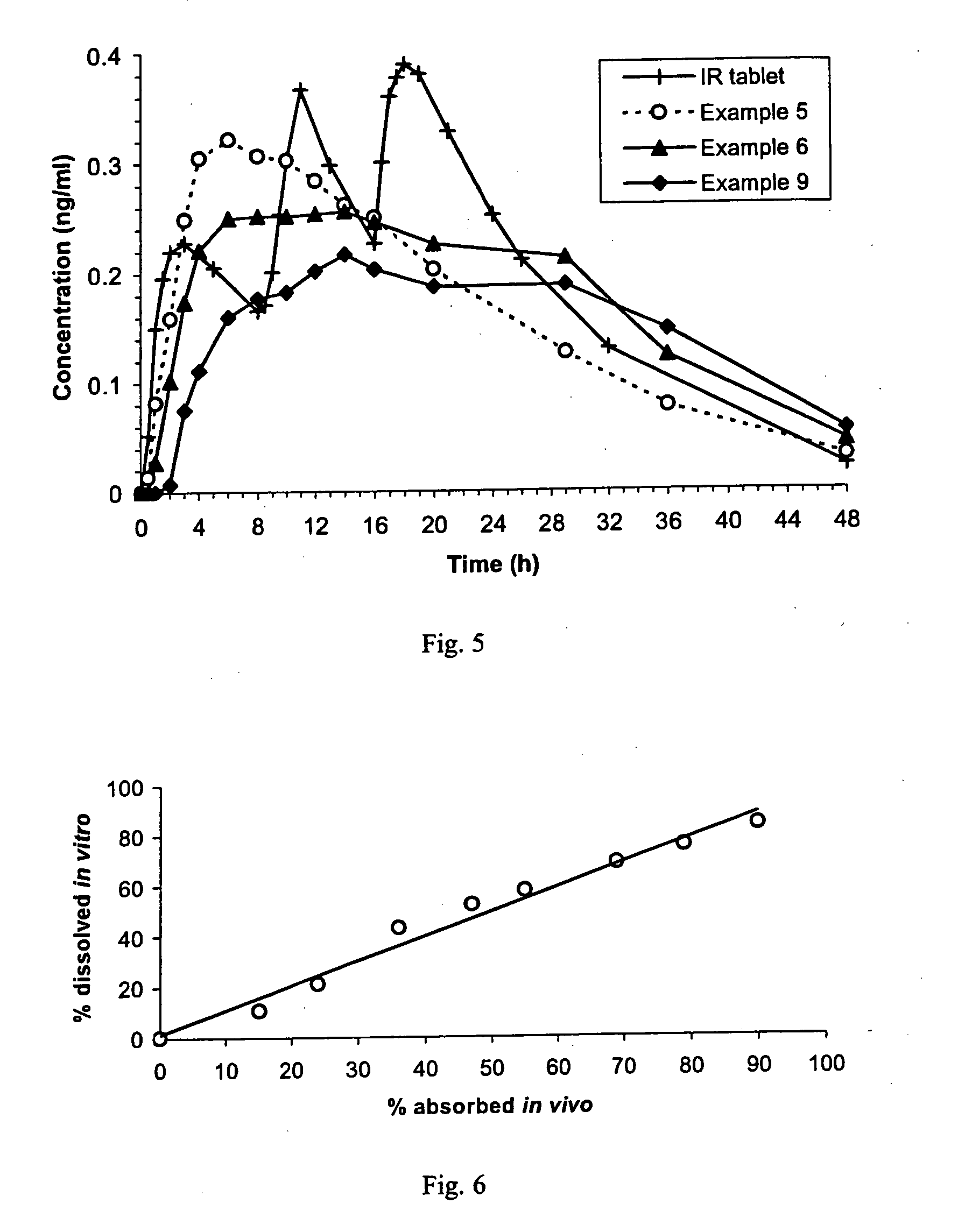
A sustained-release pharmaceutical composition in a form of an orally deliverable tablet comprises an active pharmaceutical agent having solubility not less than about 10 mg / ml, dispersed in a matrix comprising a hydrophilic polymer and a starch having a tensile strength of at least about 0.15 kN cm−2 at a solid fraction representative of the tablet.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Fractionation process
InactiveUS6552208B1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteCosmetic preparationsVegetable oilActive component
The invention refers to a process for fractionating a vegetable oil giving one or more solid fractions suitable for confectionary applications as well as a liquid fraction rich in unsaponifiable biologically active components. The liquid fractions of shea butter and rapeseed oil having a high content of phytosterols and tocoferols, respectively, are useful for cosmetical and pharmaceutical preparations.
Owner:KARLSHAMNS AB KARLSHAMN
Apparatus and Process for Production of Biogas
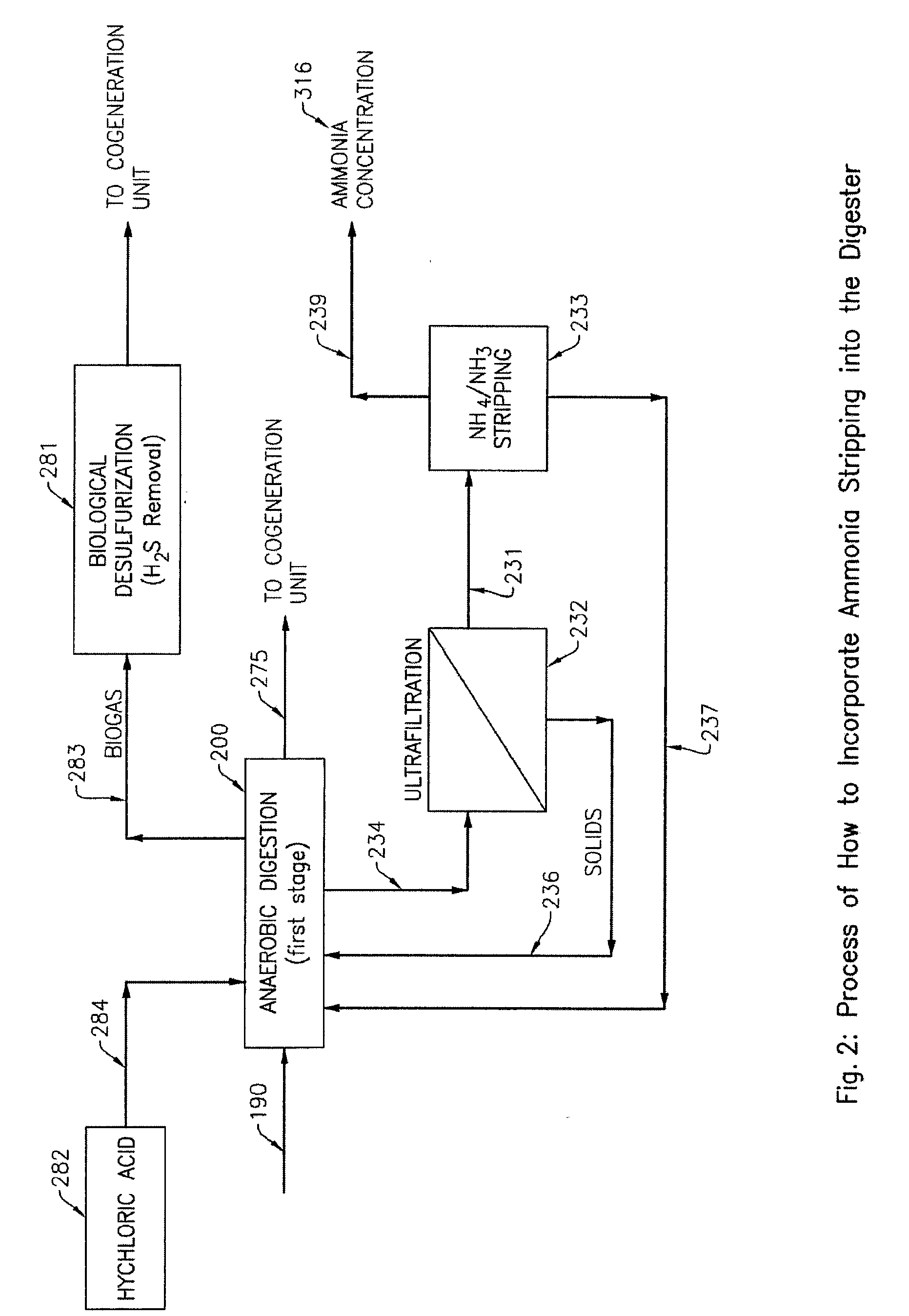
ActiveUS20100021979A1Quick conversionDigesting retention timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrolysateSolid fraction
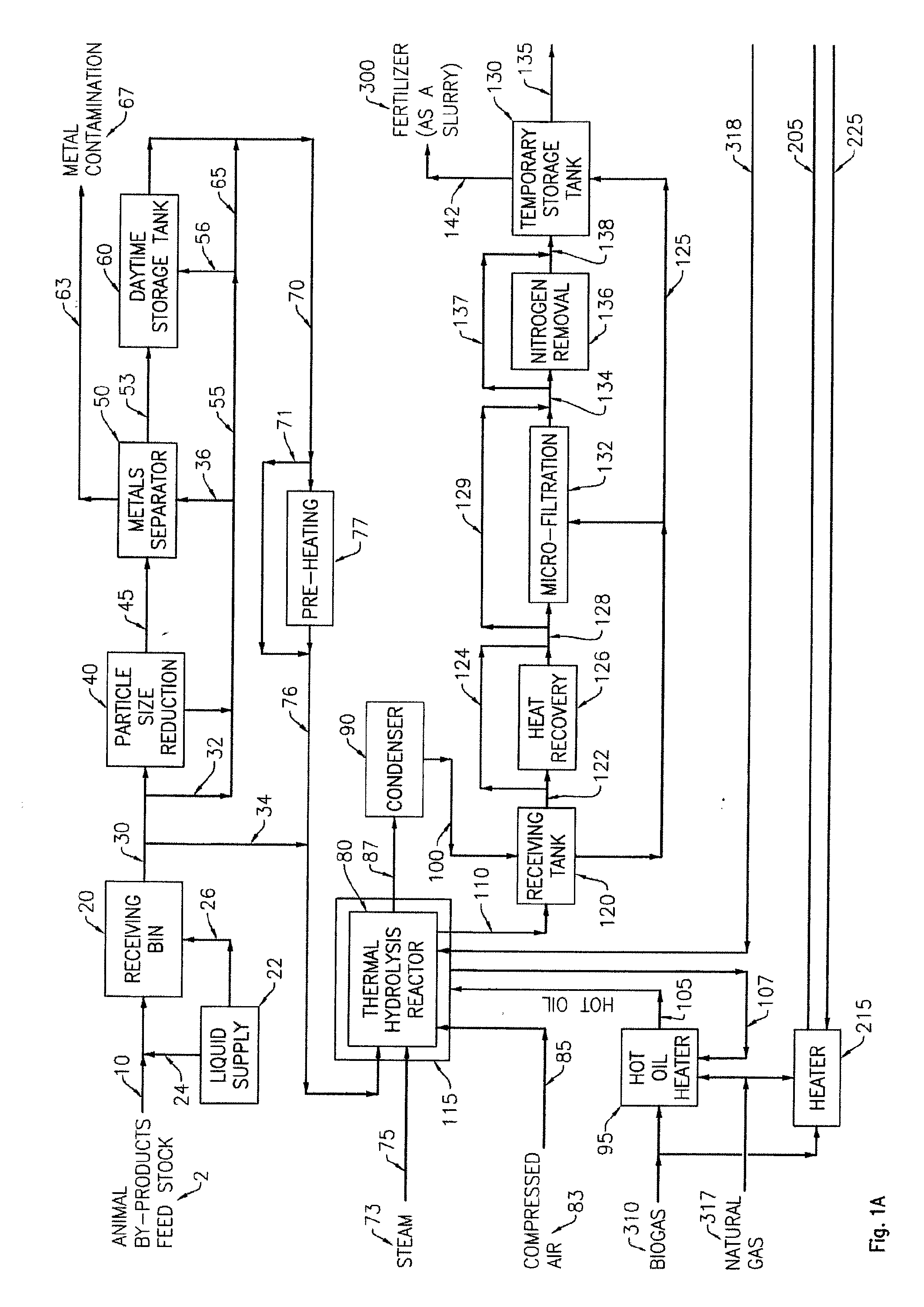
A process and an apparatus for the manufacture of biogas and a solids fraction from an organic waste feedstock is provided. The process involves thermal hydrolysis of the organic waste feedstock at a temperature from about 100 to about 220° C., a pressure from about 5 to about 20 bars, for a period of time from about 15 minutes to 4 hours, to produce a hydrolysate. The hydrolysate undergoes anaerobic digestion at a temperature from about 25 to 60° C., for a period of time from about 1 to 35 days to produce a biogas stream and a digestate. The digestate is separated into a solids fraction and a liquid fraction, and a portion of the solids fraction is recycled for further anaerobic digestion. The biogas stream, characterized as having a methane content from between 55 to 80% by volume, and the solids fraction, are recovered. The apparatus includes a receiving bin for receiving and supplying organic waste feedstock to a thermal hydrolysis reactor. The thermal hydrolysis reactor for processing the organic waste feedstock at a temperature from about 100 to about 220° C., a pressure from about 5 to about 20 bars, for a period of time from about 15 minutes to 4 hours to produce a hydrolysate. An anaerobic digester for processing the hydrolysate at a temperature from about 25 to 60° C., for a period of time from about 1 to 35 days to produce the biogas and a digestate, and a solids thickening tank for separating the digestate into the solid fraction, a liquid fraction and a secondary biogas fraction.
Owner:GEMINI CORP
Process and apparatus for operation of a slurry bubble column with application to the fischer-tropsch synthesis
InactiveUS6060524AGuaranteed uptimeAvoid small quantitiesHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationGas phaseBubble column
The invention concerns a process for optimal operation of a slurry bubble column containing a suspension of solid particles in a liquid, characterized in that a gas phase containing the reactant(s) required for the production of the desired products is injected in the form of bubbles close to the lower extremity of said reactor and at least a portion of the liquid fraction and optionally of the solid fraction of said suspension is recirculated, drawn off from close to one extremity of said reactor and reintroduced close to the other extremity of said reactor, with a liquid flow rate U1 in the reactor which is at least equal to and preferably greater than the sedimentation rate Us of the solid particles. The invention also concerns an apparatus for optimal operation of the process. Finally, the invention concerns the use of the process and apparatus in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Sustained-release tablet composition of pramipexole
InactiveUS20050226926A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderSustained Release TabletHydrophilic polymers
A sustained-release pharmaceutical composition in a form of an orally deliverable tablet comprises a water-soluble salt of pramipexole, dispersed in a matrix comprising a hydrophilic polymer and a starch having a tensile strength of at least about 0.15 kN cm−2 at a solid fraction representative of the tablet.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Process for improving the yield and efficiency of an ethanol fermentation plant
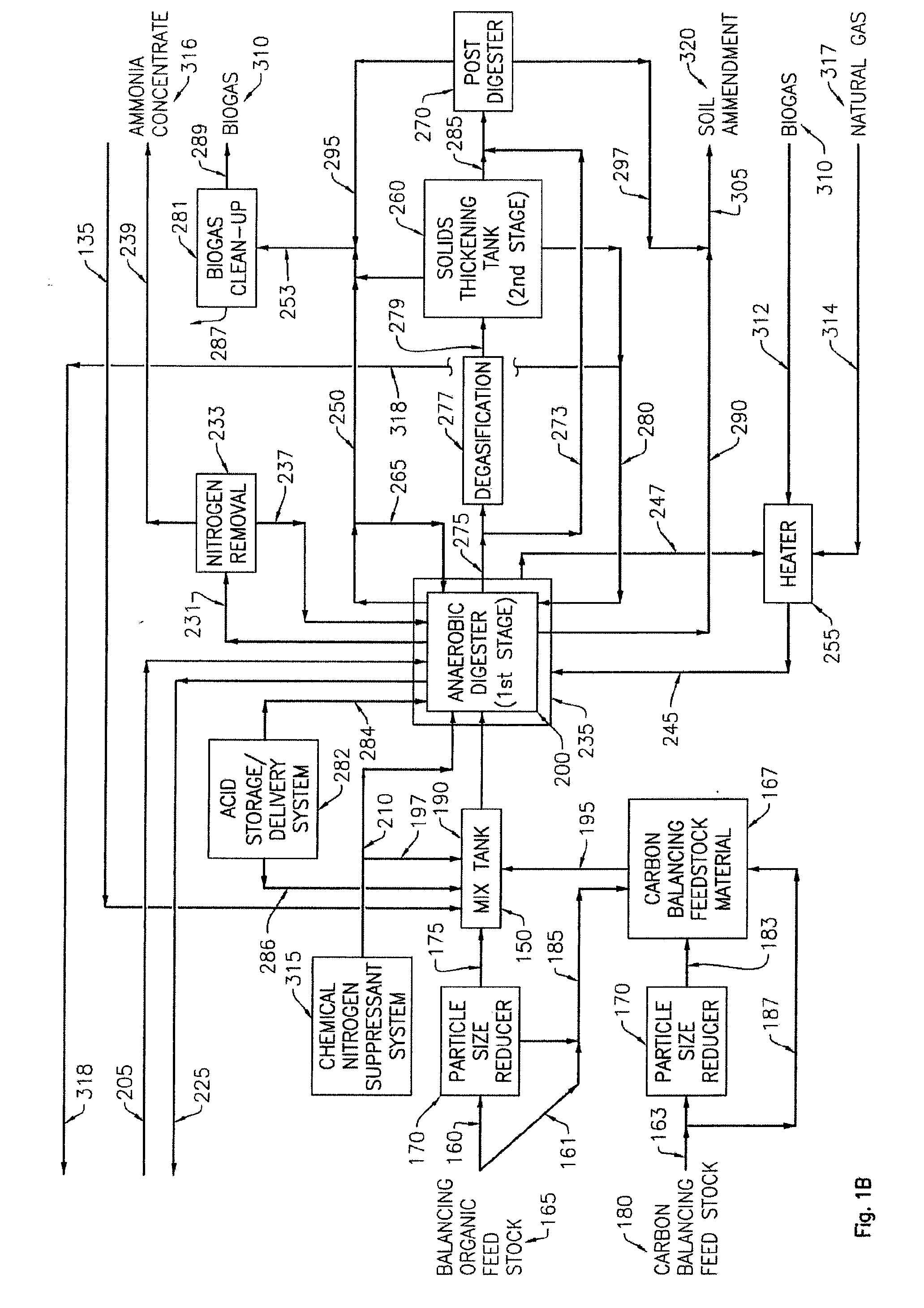
A process for improving the yield and efficiency of an ethanol fermentation plant that receives organic fermentable feedstock material, prepares the feedstock for fermentation, ferments the feedstock with yeast to produce ethanol, and produces stillage as a byproduct of ethanol fermentation. The process steps which can be operated independently or in combination, may include, but are not limited to, degrading fatty acids in the fermentable feedstock material prior to fermentation; degrading cellulose and hemicellulose present in the feedstock prior to fermentation; adding a surfactant to the fermentable feedstock; separating a liquid fraction from the stillage; recycling the liquid fraction to be combined with the fermentable feedstock; recovering a solid fraction from the stillage; and introducing at least a portion of the solid fraction to an anaerobic digester to produce methane.
Owner:WATER SOLUTIONS TECH LLC
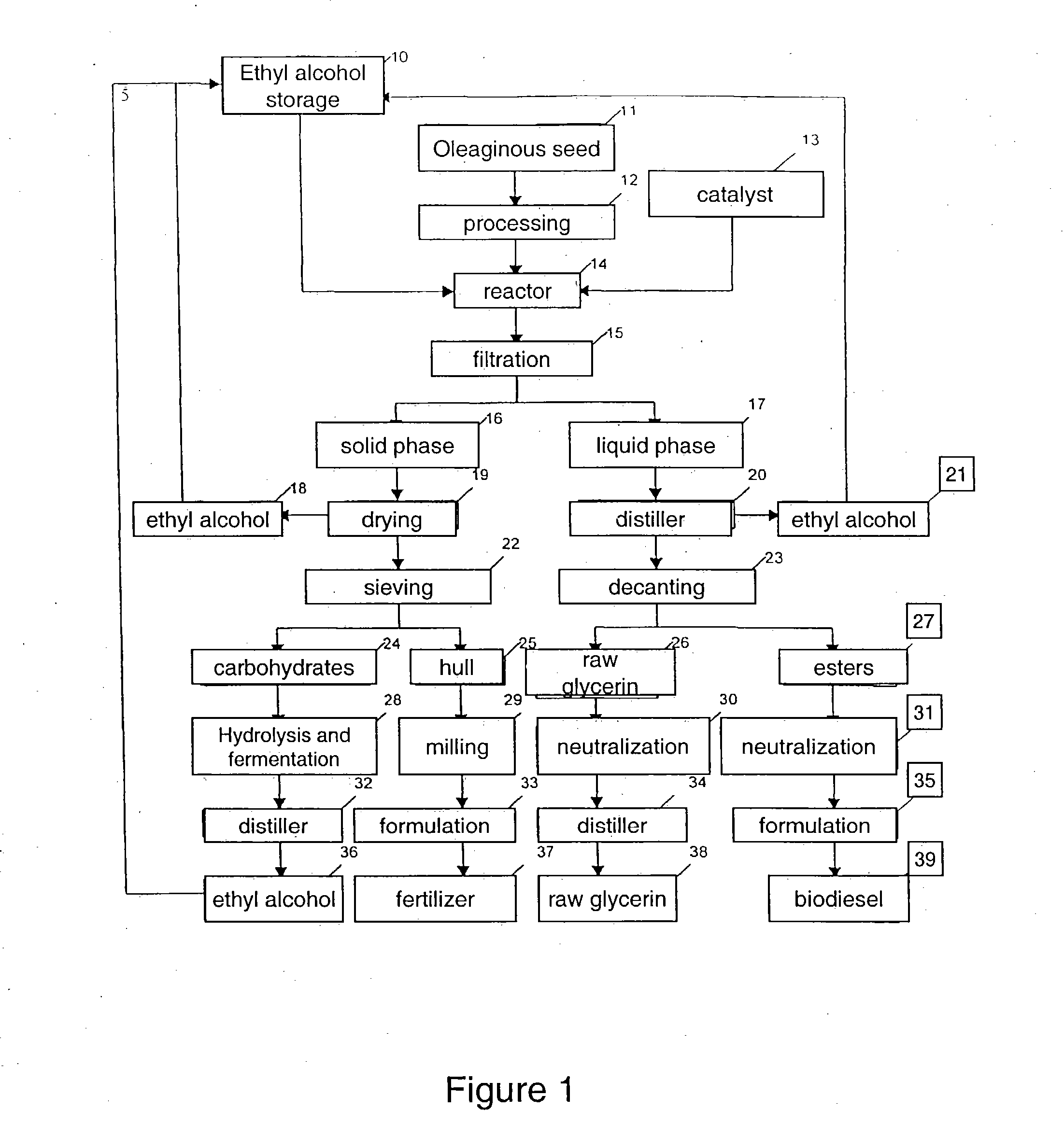
Process for producing biodiesel
InactiveUS20050011112A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselSolid fraction
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds, comprising a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Continuous counter-current organosolv processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
InactiveUS20080299628A1Facilitate and enhance of fermentation and efficiencyFacilitate and enhance rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPressurized chemical processFractionationOrganosolv
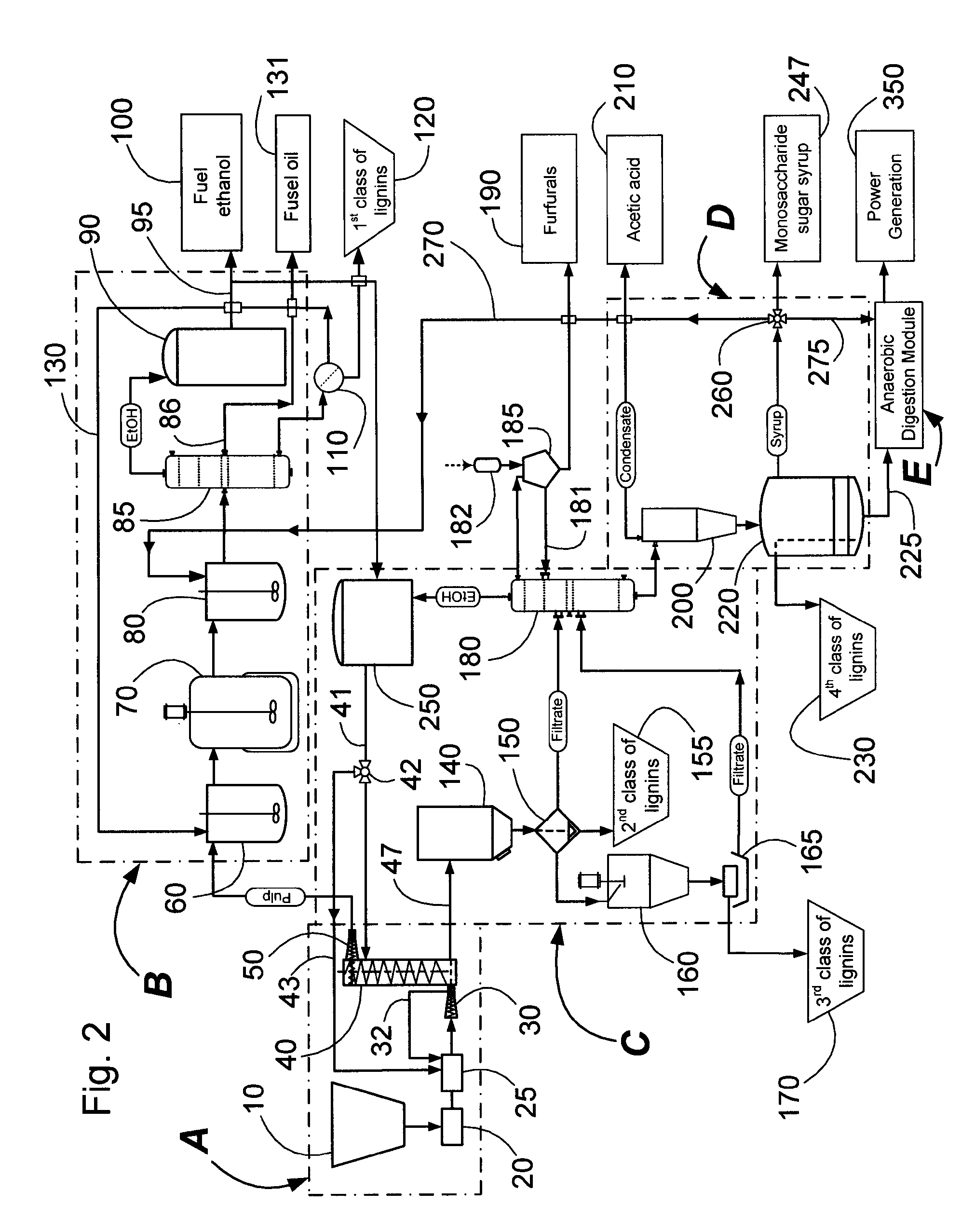
A modular process for organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic feedstocks into component parts and further processing of said component parts into at least fuel-grade ethanol and four classes of lignin derivatives. The modular process comprises a first processing module configured for physico-chemically digesting lignocellulosic feedstocks with an organic solvent thereby producing a cellulosic solids fraction and a liquid fraction, a second processing module configured for producing at least a fuel-grade ethanol and a first class of novel lignin derivatives from the cellulosic solids fraction, a third processing module configured for separating a second class and a third class of lignin derivatives from the liquid fraction and further processing the liquid fraction to produce a distillate and a stillage, a fourth processing module configured for separating a fourth class of lignin derivatives from the stillage and further processing the stillage to produce a sugar syrup.
Owner:LIGNOL INNOVATIONS
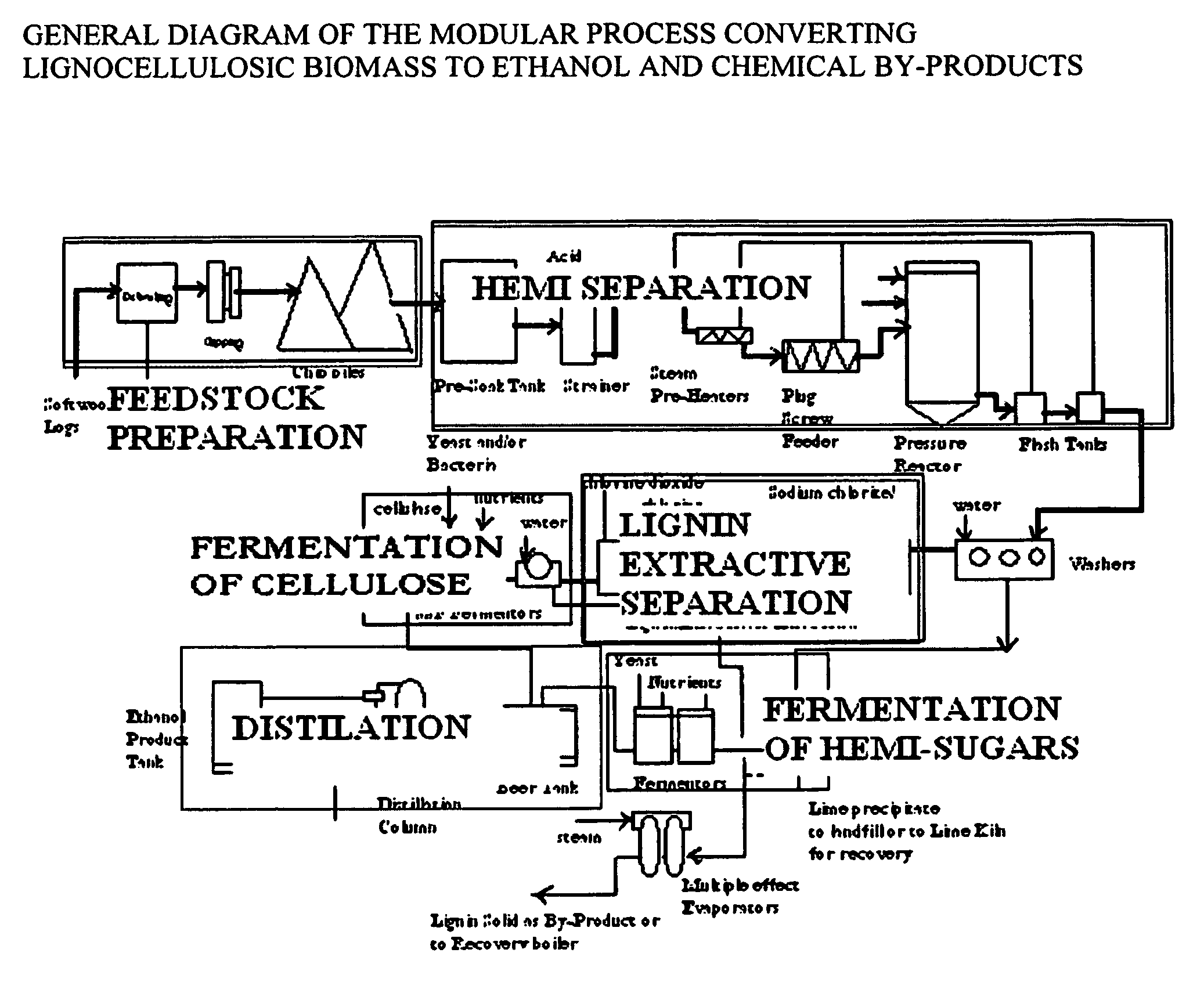
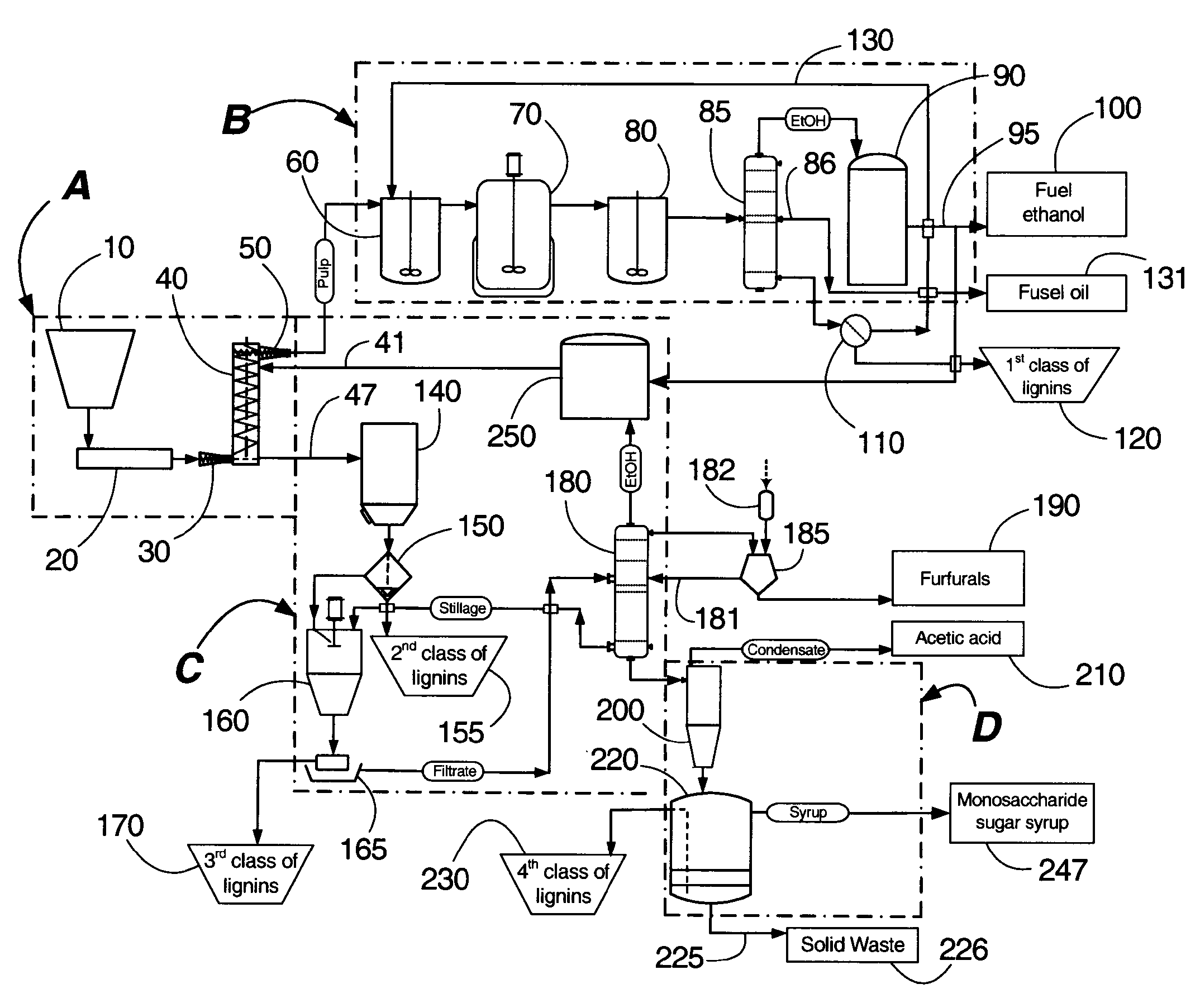
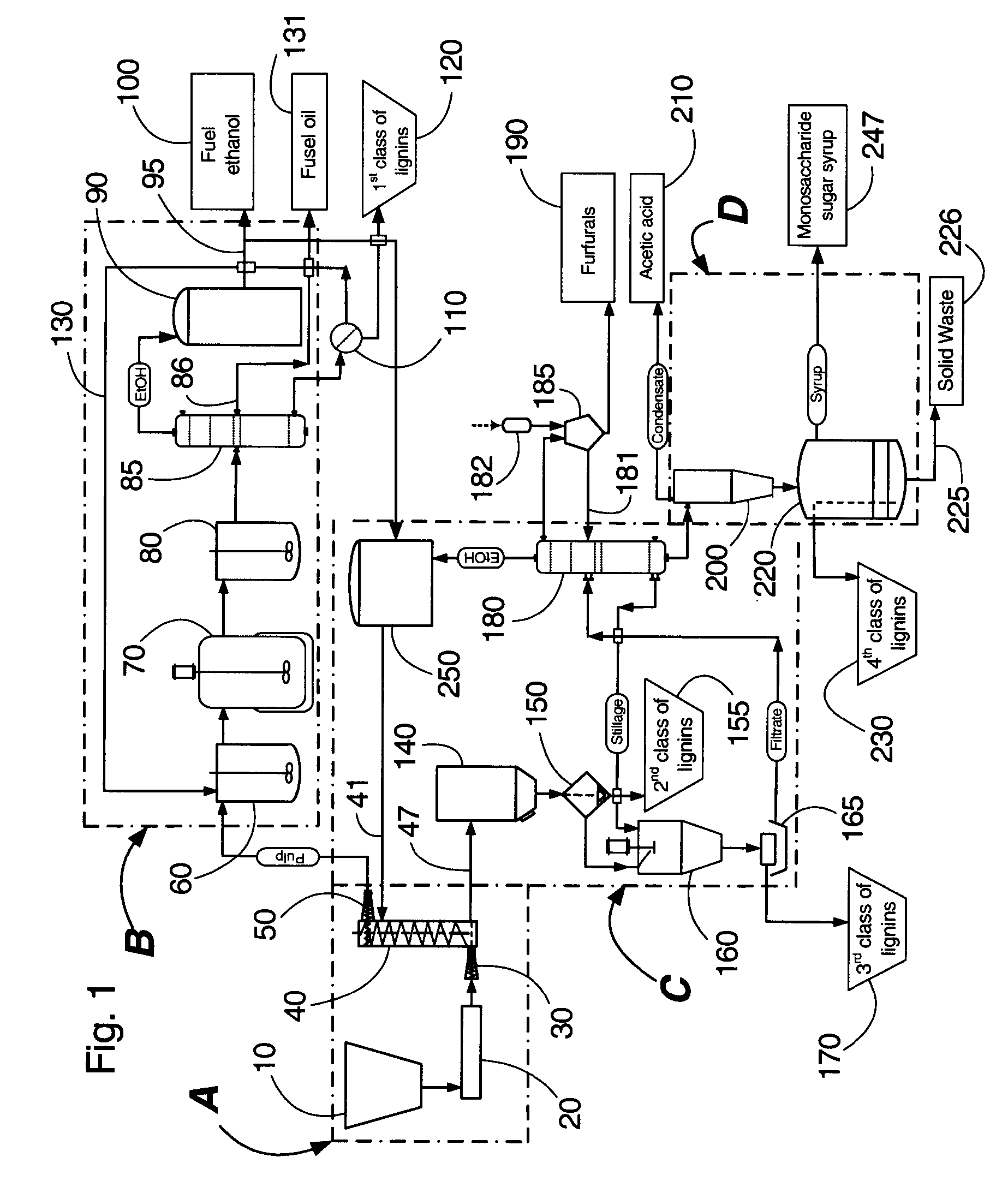
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Continuous counter-current organosolv processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
InactiveUS20080295980A1Facilitate and enhance of fermentation and efficiencyFacilitate and enhance rateNon-fibrous pulp additionBiological substance pretreatmentsFractionationOrganosolv
A modular process for organosolv fractionation of lignocellulosic feedstocks into component parts and further processing of said component parts into at least fuel-grade ethanol and four classes of lignin derivatives. The modular process comprises a first processing module configured for physico-chemically digesting lignocellulosic feedstocks with an organic solvent thereby producing a cellulosic solids fraction and a liquid fraction, a second processing module configured for producing at least a fuel-grade ethanol and a first class of novel lignin derivatives from the cellulosic solids fraction, a third processing module configured for separating a second class and a third class of lignin derivatives from the liquid fraction and further processing the liquid fraction to produce a distillate and a stillage, a fourth processing module configured for separating a fourth class of lignin derivatives from the stillage and further processing the stillage to produce a sugar syrup.
Owner:LIGNOL INNOVATIONS
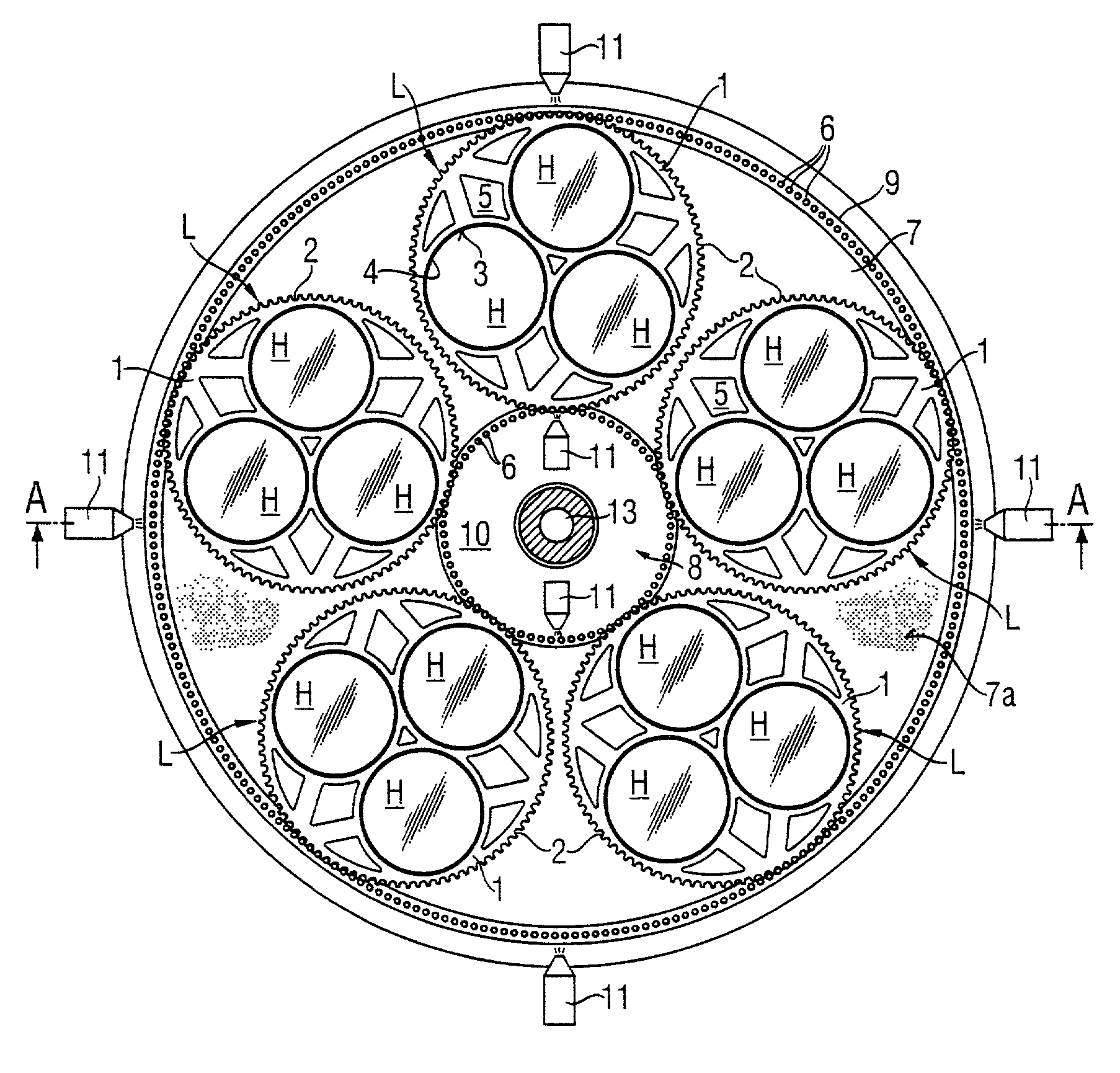
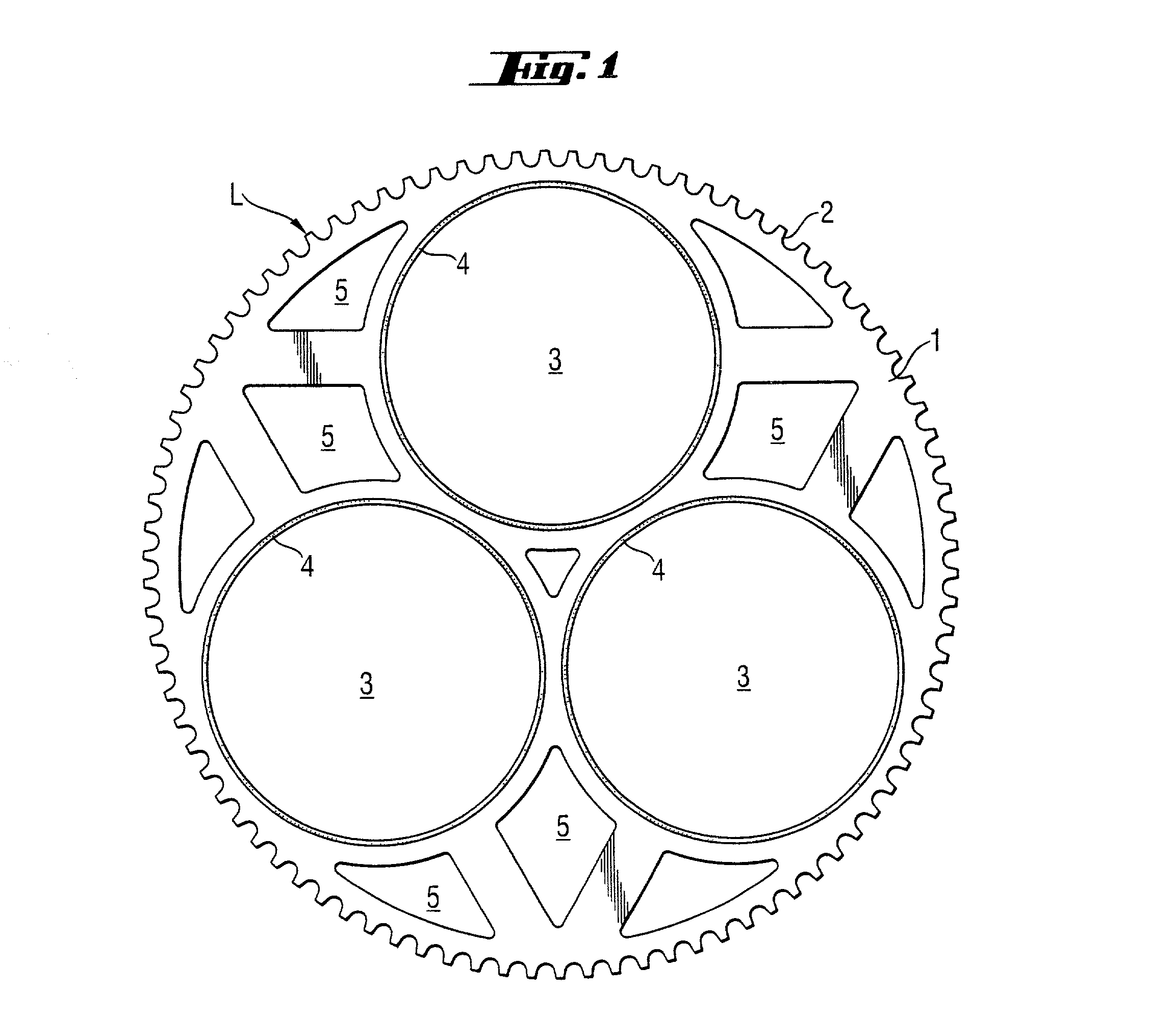
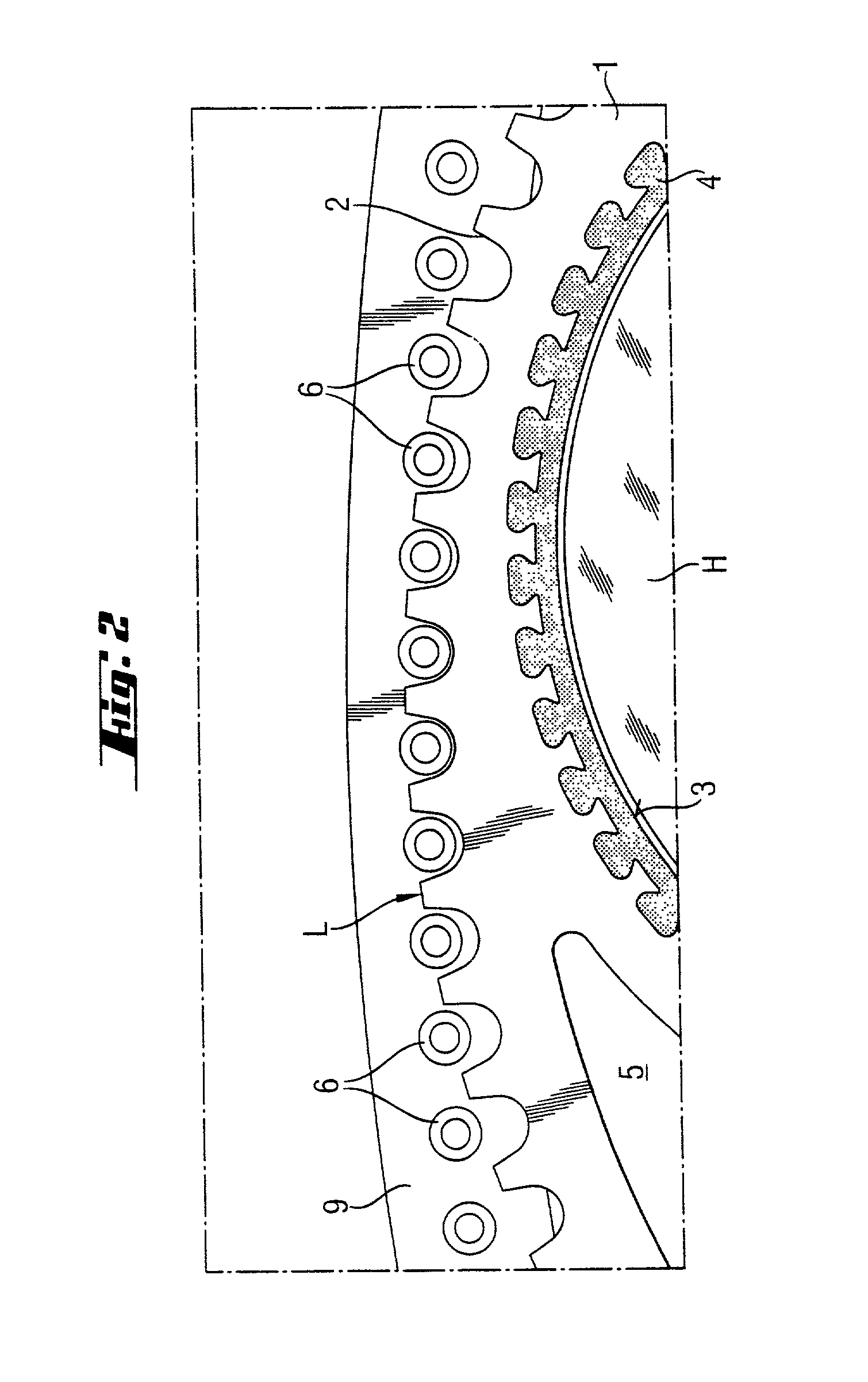
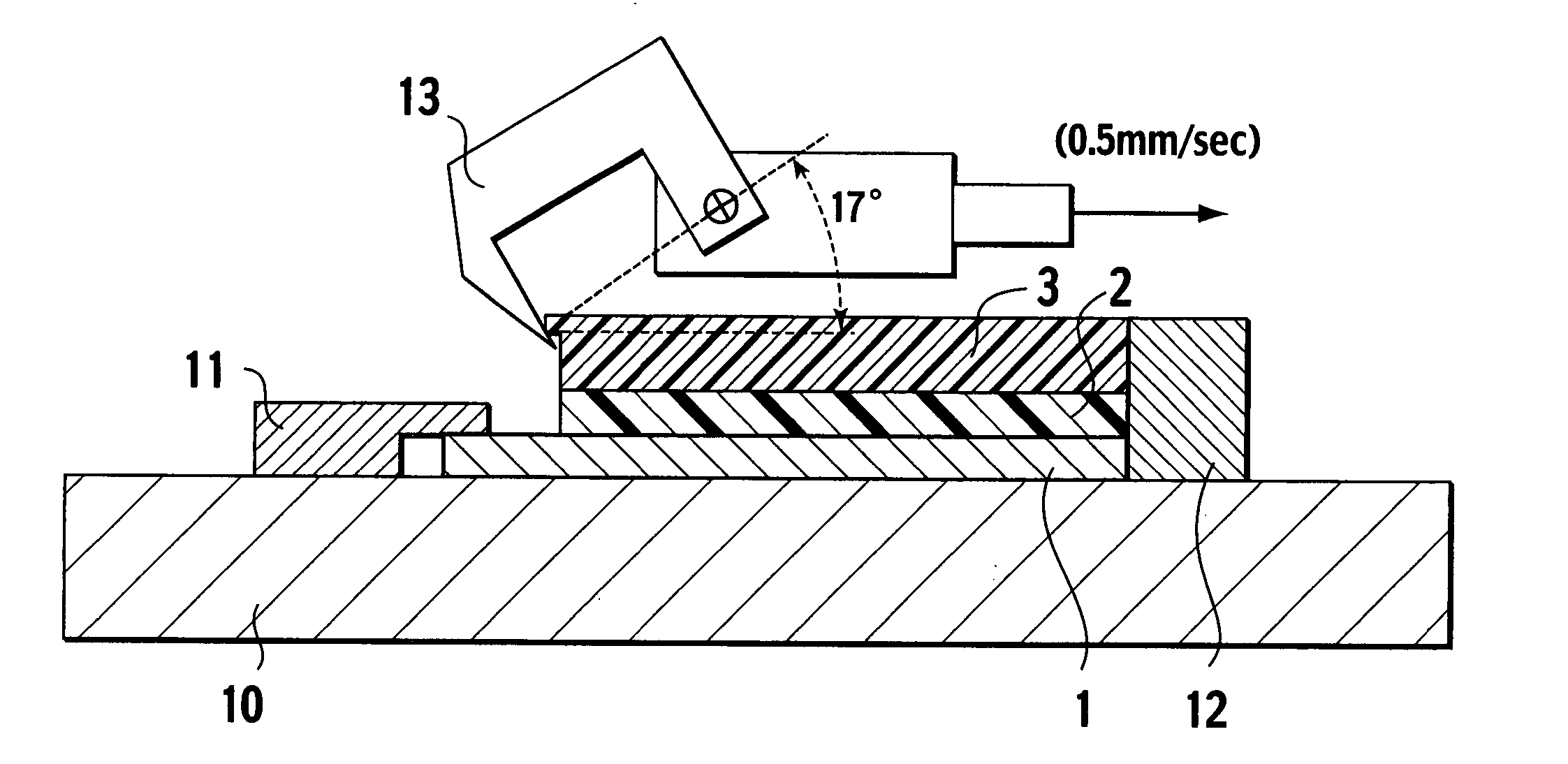
Double-side polishing process with reduced scratch rate and device for carrying out the process
InactiveUS20020115387A1Reduce probabilityAvoid scratchesPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSolid fractionColloid
A process for producing semiconductor wafers by double-sided polishing between two rotating, upper and lower polishing plates, which are covered with polishing cloth, while an alkaline polishing abrasive with colloidal solid fractions is being supplied, the semiconductor wafers being guided by carriers which have circumferential gear teeth and are set in rotation by complementary outer gear teeth and inner gear teeth of the polishing machine, which is distinguished by the following process steps: (a) at least one of the two sets of gear teeth of the polishing machine is at least from time to time sprayed with a liquid which substantially comprises water, (b) the alkaline polishing abrasive is fed continuously to the semiconductor wafers in a closed supply device. There is also a device which is suitable for carrying out the process.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Fluid mixing system
InactiveUS7056008B2Avoid problemsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow mixersHybrid systemCement slurry
A method for continuously mixing a borehole fluid such as cement includes using a measurement of the solid fraction of a cement slurry as it is being mixed to determine the ratio of the solid and liquid components to be added to the slurry. A system for mixing the includes a liquid material (water) supply including a flow meter; a solid material (cement) supply; a mixer which receives the liquid and solid materials and includes an output for delivering materials from the mixer to a delivery system; a device for measuring the amount of material in the mixer, and a flow meter in the output; wherein measurements from the flow meters and the device for measuring the amount of material in the mixer are used to control the amount of solid and / or liquid material added to the mixer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for casting ceramic sheets
A method for making a thin, free-standing ceramic sheet may include drawing a carrier film proximate a casting head and across a casting bed of a tape caster at a rate from about 2 cm / min to about 500 cm / min. Depositing a thin film of ceramic slip less than about 150 μm on the carrier film with the casting head. The ceramic slip may comprises a ceramic powder with an ultimate crystallite size of less than about 10 μm dispersed in a fluid vehicle such that the ceramic slip has a ceramic solids fraction of greater than about 20% by volume. The deposited ceramic slip may be dried on the carrier film thereby forming a green ceramic sheet on the carrier film. After the green ceramic sheet is dried, the green ceramic sheet may be sintered.
Owner:CORNING INC
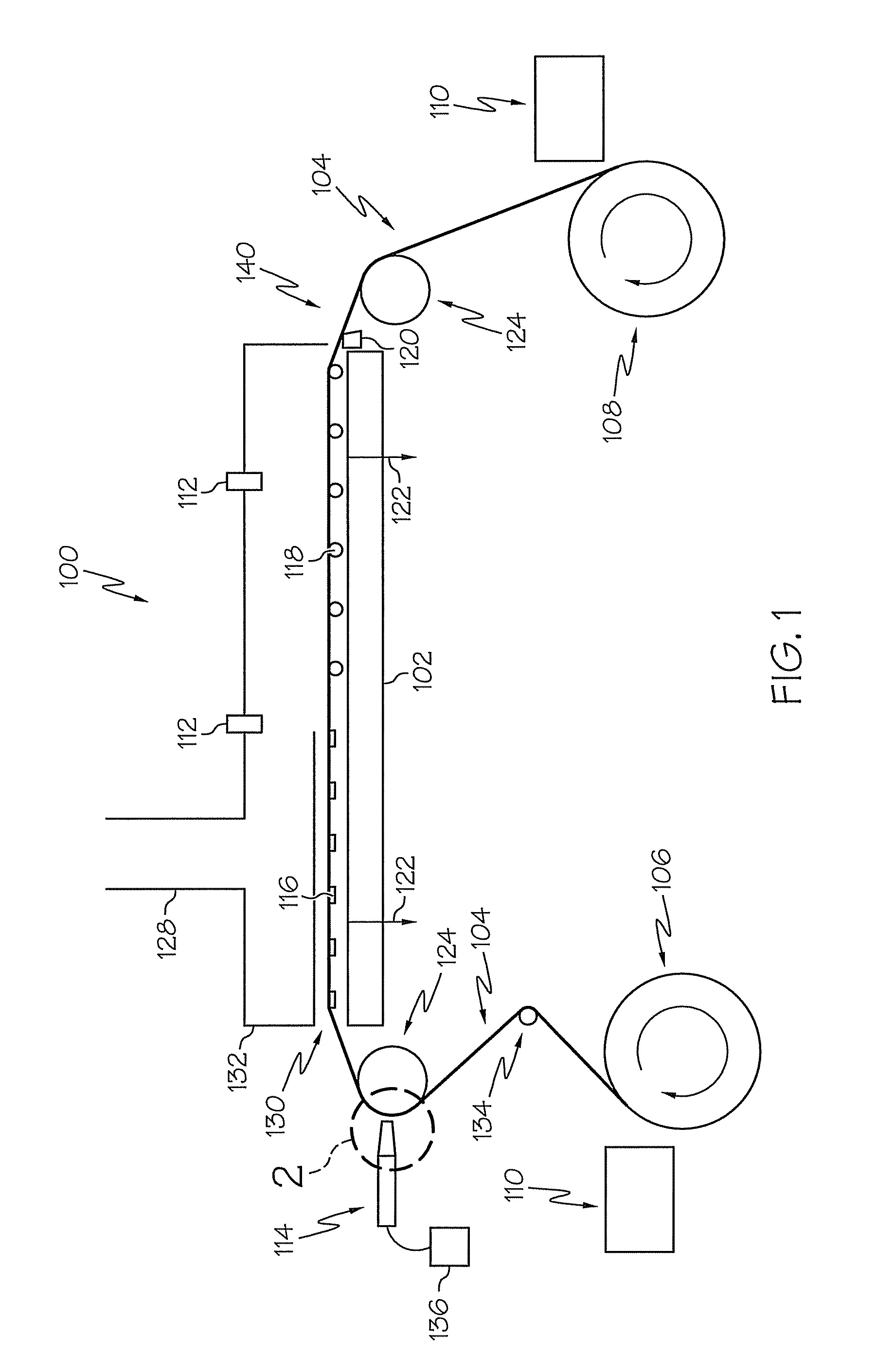
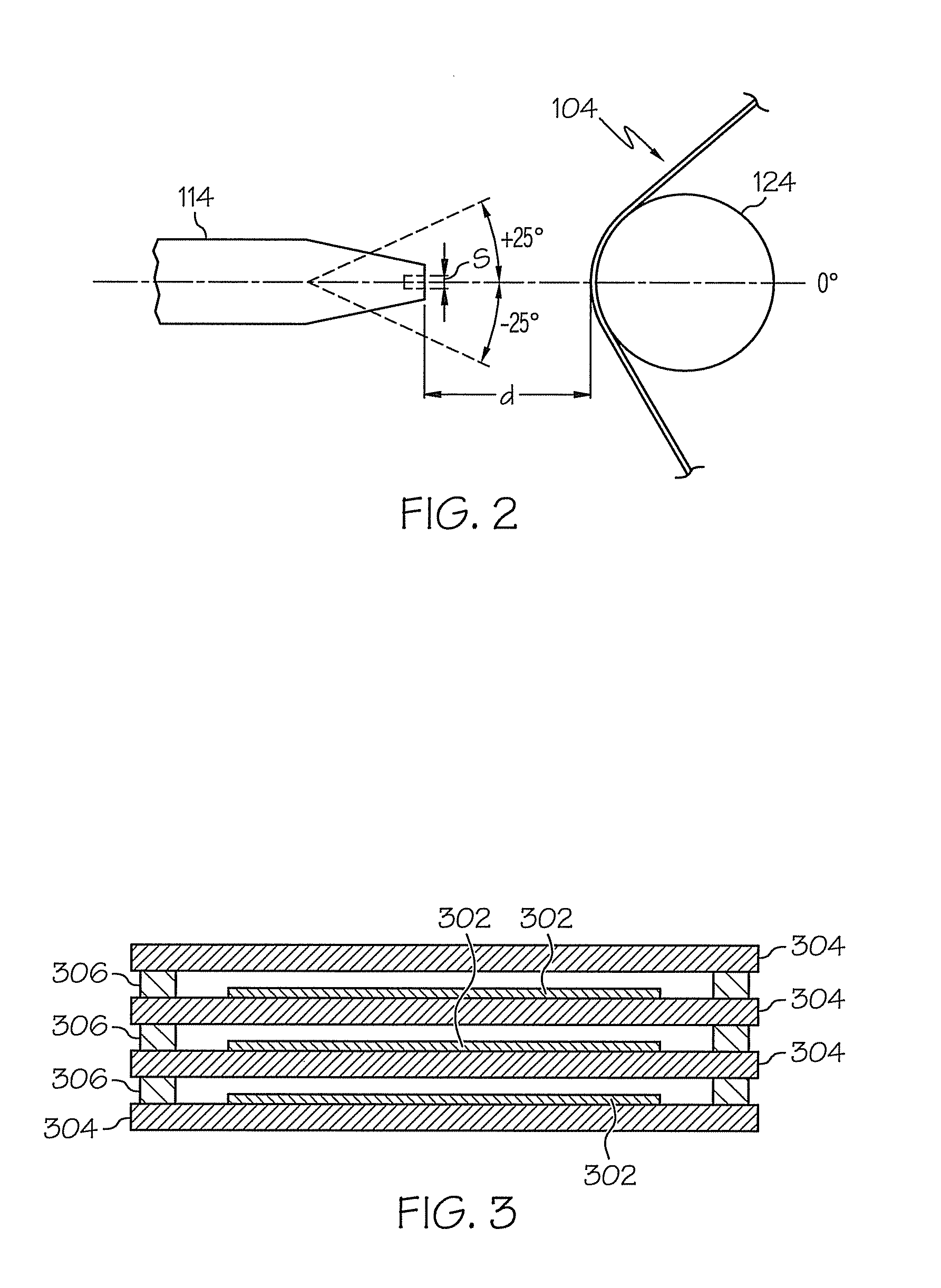
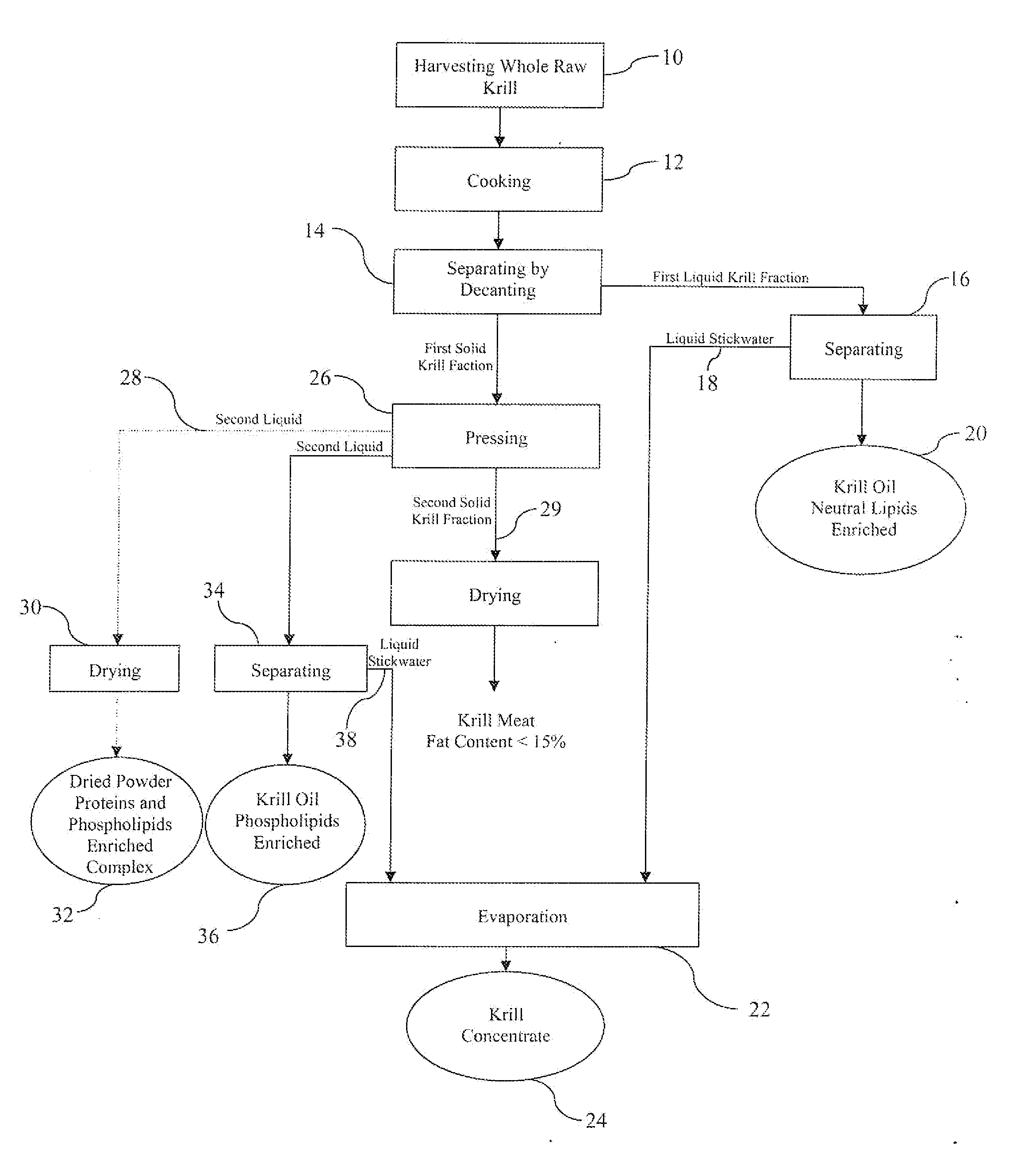
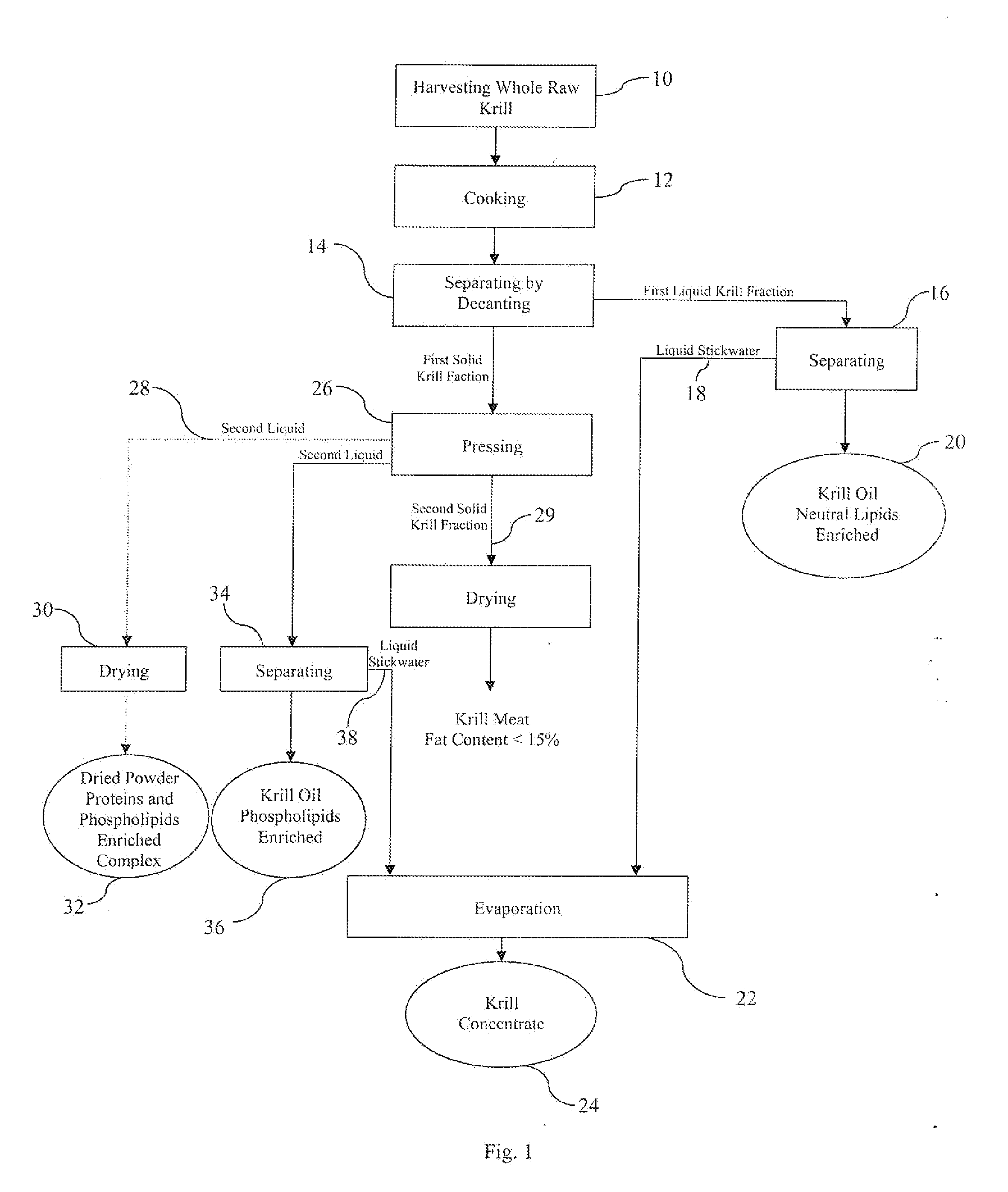
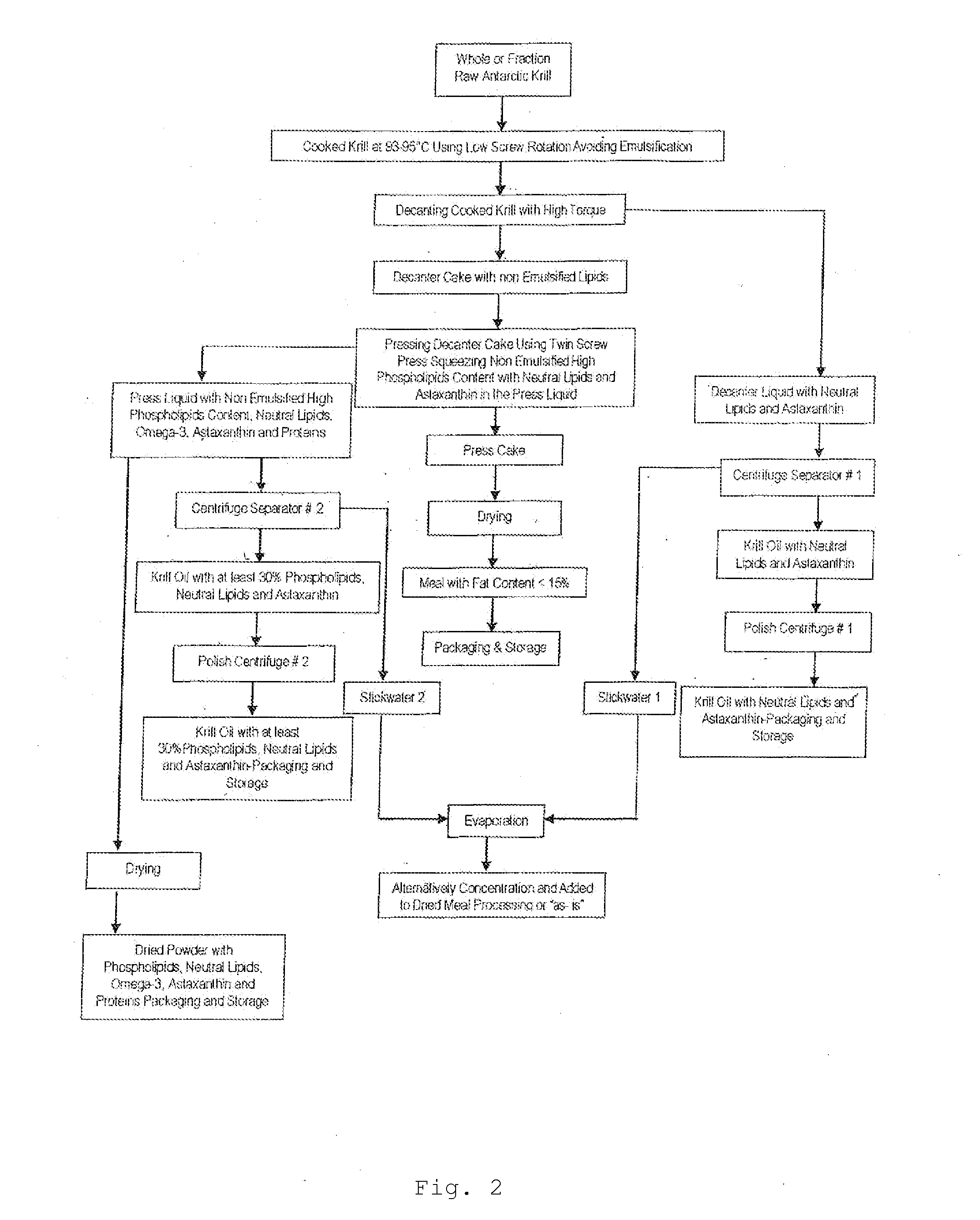
Solvent-free process for obtaining phospholipids and neutral enriched krill oils
ActiveUS20110224450A1Prevent freezingCost for structure can be reducedFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteCosmetic preparationsOrganic solventSolvent free
Organic solvent-free processes for obtaining krill oil compositions are disclosed. The processes include a) cooking krill in a cooker vessel for a time and at a temperature sufficient to denature the protein content of the krill and cause a first solid krill fraction and a first liquid krill fraction to be formed while substantially avoiding emulsification of the first solid and first liquid hill fractions; b) removing the first solid and first liquid krill fractions from the cooker vessel at a temperature of at least about 90° C.; c) separating the first solid fraction and the first liquid fraction; and d) obtaining krill oil with neutral enriched from the first liquid fraction, and e) by pressing of first solid fraction to obtain press liquid or a second liquid krill fraction for obtaining hill oil with phospholipids enriched krill oil, the separating and the obtaining steps being carried out without the use of organic solvents. Krill oil compositions made by the process are also disclosed.
Owner:THAROS +1
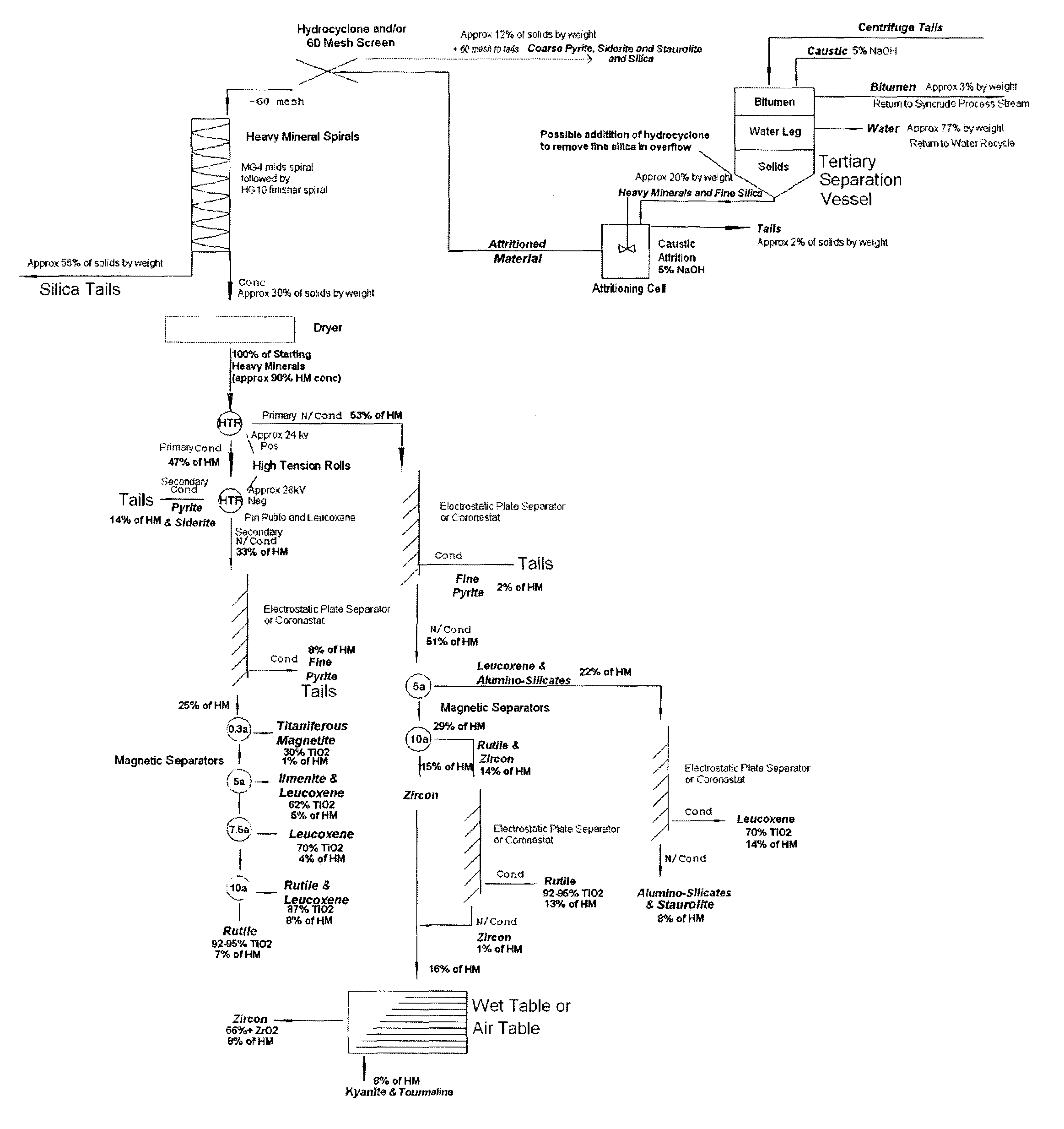
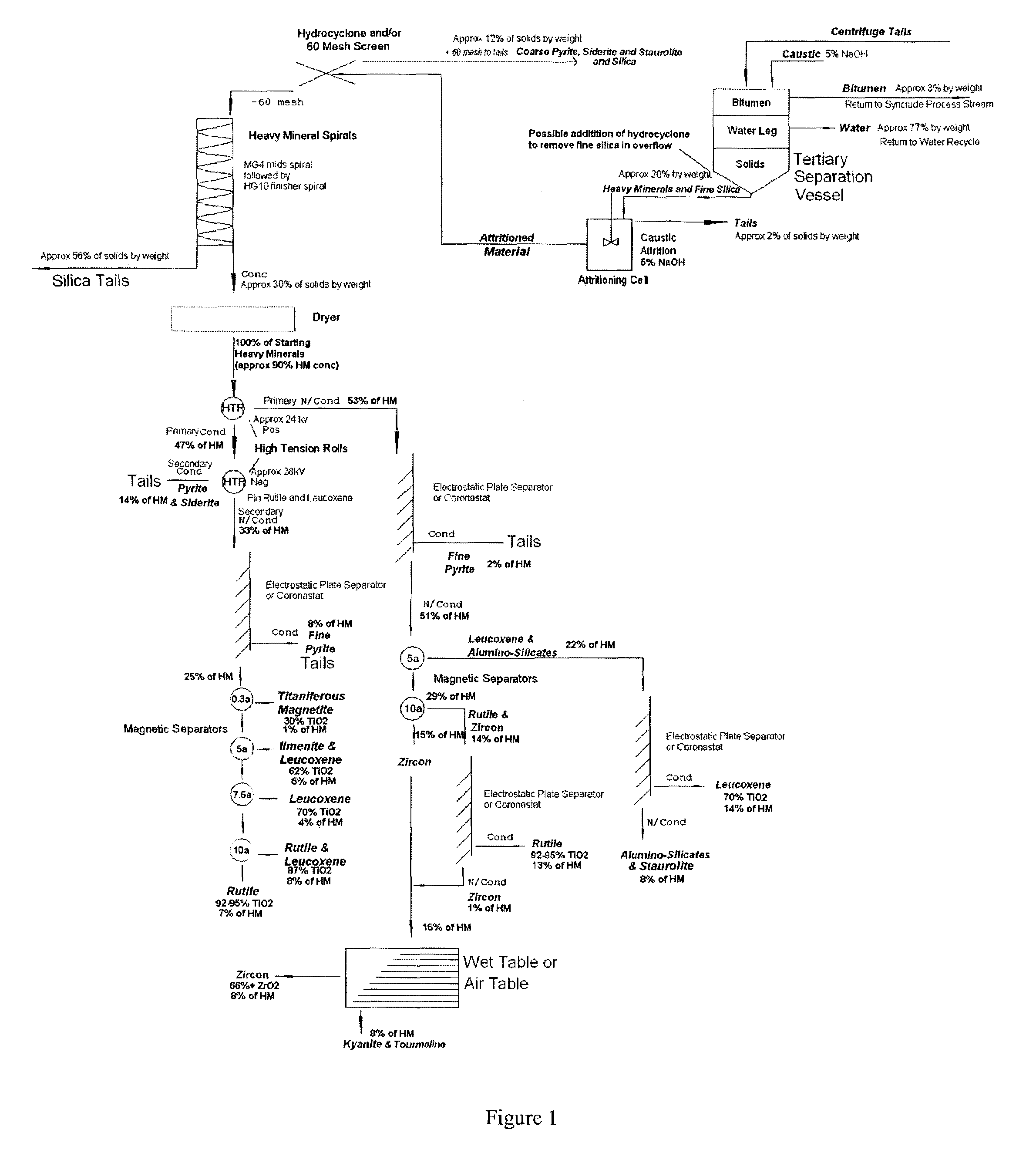
Recovery of heavy minerals from a tar sand
A process for recovering heavy minerals (e.g., titanium minerals such as TiO2) from a feedstock comprising tar sands or a tar sands-derived solids fraction. The feedstock comprises bitumen and heavy minerals. The process comprises the steps of: (i) contacting the solids fraction with water at a temperature of at least about 100° F. to cause production a bituminous phase and a heavy minerals phase; and (ii) separating the heavy minerals phase from the bituminous phase. Optionally, these steps may be preceded by one or more steps used to produce a tar-sands derived solids fraction from a tar sands feedstock.
Owner:TITANIUM CORP
Method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose biomaterial by use of neu-heat-resistant enzyme
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230 DEG C for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of beta -glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42 DEG C.
Owner:RES CENT OF ENERGY SOURCE ENVIRONMENT & TECH
Recovery system
A process for the recovery of drilling fluid additives, including industrial carbon, calcium carbonate, natural and synthetic fibers, and other materials from a mixture. The mixture may include drilling fluids, drilled solids, and drilling fluid additives from a mud system. The process may include: separating at least a portion of the drilled solids from the mixture to form a first effluent and a drilled solids fraction; separating at least a portion of the drilling fluid additives from the first effluent to form a second effluent and a recovered additives fraction; and recycling at least a portion of the recovered additives fraction to the mud system. The drilling fluid additives may have a specific gravity greater than 1.4, and may include particles having an average size greater than 2 microns.
Owner:MI
Process for the production of furfural and levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20140018555A1Enough timeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCelluloseOrganic solvent
A process for producing furfural and levulinic acid from lignocellulose-comprising biomass is disclosed. The biomass is slurried using water and optionally an acid, subjected to hydrolysis, and then subjected to a solid / liquid separation to yield at least an aqueous fraction comprising C5 and C6 sugars and a solid fraction comprising cellulose and lignin. Furfural is obtained by adding an organic solvent to the aqueous fraction, heating at 120-220° C. for a sufficient time to form furfural, cooling, and separating an organic phase comprising at least part of the furfural from an aqueous phase. Levulinic acid is obtained by suspending the solid fraction in water and optionally an acid, heating the suspension to 140-220° C., and separating an aqueous fraction comprising the levulinic acid from a solid fraction.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Resin Paste For Die Bonding And Its Use
InactiveUS20070290369A1Broaden applicationIncrease supplySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEthylene Homopolymers
Disclosed is a resin paste for die bonding comprising a butadiene homopolymer or copolymer (A) having a carboxylic acid terminal group, a thermosetting resin (B), a filler (C), and a printing solvent (D), wherein the elastic modulus of the resin paste following drying and curing is within a range from 1 to 300 MPa (25° C.). The solid fraction is preferably from 40 to 90% by weight, the thixotropic index is preferably from 1.5 to 8.0, and the viscosity (25° C.) is preferably from 5 to 1,000 Pa·s. Using this resin paste, a semiconductor device is produced by a method comprising (1) applying a predetermined quantity of the resin paste to a substrate, (2) drying the resin paste to effect B-staging of the resin, (3) mounting a semiconductor chip on the B-staged resin, and (4) conducting post-curing of the resin.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
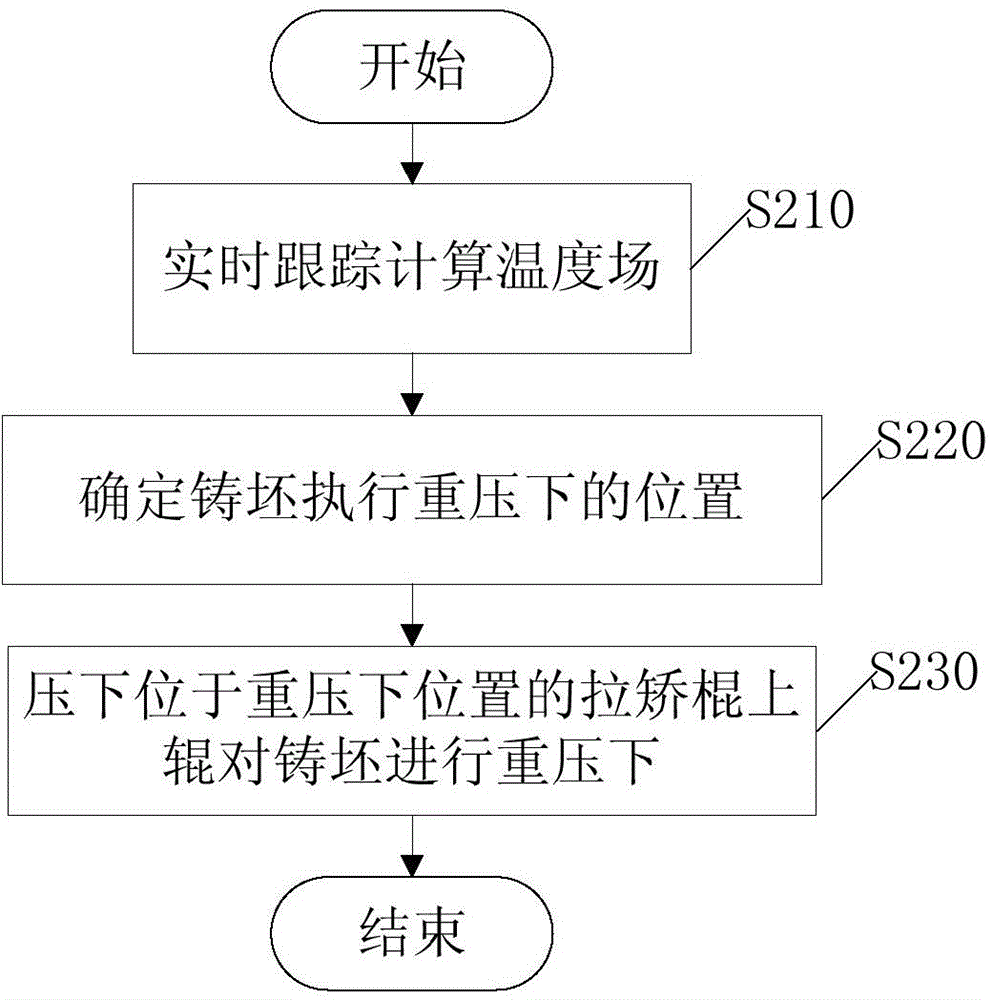
Control method and device under continuous casting weight
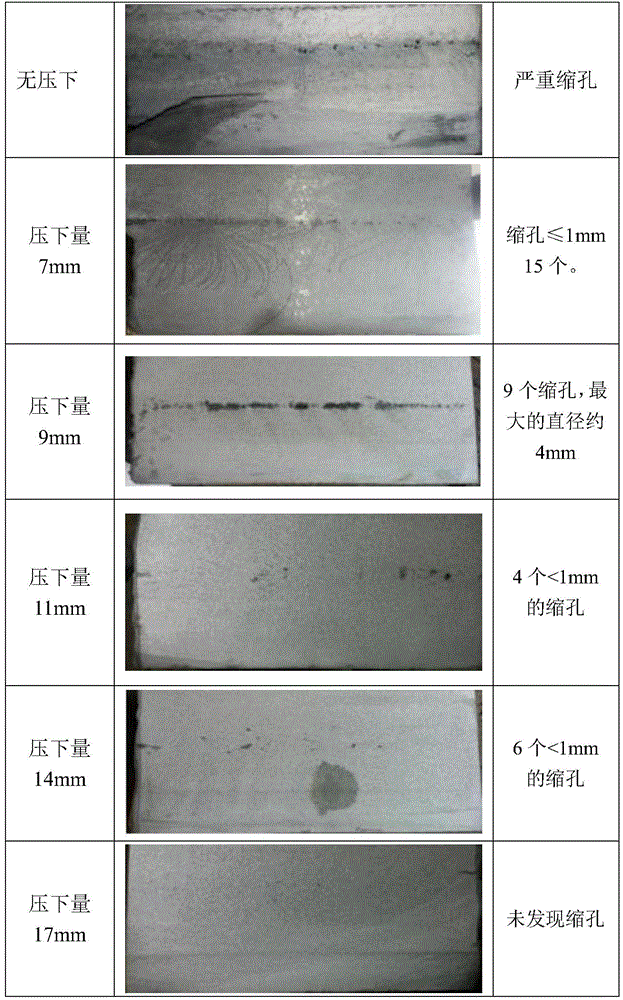
The invention provides a control method and a control device under continuous casting weight. The method comprises the steps of performing real-time tracking to calculate a casting blank temperature field, so as to obtain a center solid fraction of a casting blank; determining the position of the casting blank when the weight is performed, wherein the position is in the scope of between 0.6 of the center solid fraction of the casting blank and 1.5m behind a solidification position; and pressing an upper roller of a withdrawal and straightening roller at a weighting position so as to weight the casting blank. The device comprises a tracking unit, a determining unit and a roll gap control unit, wherein the tracking unit is used for performing real-time tracking to calculate a casting blank temperature field, so as to obtain the center solid fraction of the casting blank, the determining unit is used for determining the position where the casting blanks performs weighting, and the position is in the scope of between 0.6 of the center solid fraction of the casting blank and 1.5m behind the solidification position, and the roll gap control unit is used for pressing the upper roller of the withdrawal and straightening roller at the weighting position so as to weight the casting blank. According to the control method and the control device under continuous casting weight provided by the invention, microstructures and metallographic structures in the center of the casting blank can be improved, the center segregation and looseness of a continuous casting blank can be effectively reduced, the shrinkage cavity can be eliminated, the pressing efficiency can be improved, and the pressing effect can be stabilized.
Owner:CONTINUOUS CASTING TECH ENG OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for filter cleaning by ultrasound, backwashing and filter movement during the filtration of biological samples
InactiveUS20100143879A1Minimises fouling and clogging of filterImprove overall efficiency and accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic processVacuum pressure
The present application is directed to the separation of—a solid fraction from a fluid sample particularly a therapeutic cellular fraction from a biological sample such as a bone marrow sample by a porous filter (2) which separates a filtration unit (1) into an upper pre-filtration chamber (3) into which a fluid sample (4) requiring cell separation is introduced and a lower post-filtration chamber (5) into which a fluid (6) capable of transmitting an acoustic standing wave is introduced. An acoustic element (8) is coupled to a substrate (7) which is located within and at the bottom of the lower chamber (5) and which resonates in response to the acoustic generating element (8) and generates a standing wave through the two fluid phases and the filter to agitate the sample (4). Simultaneously, a cyclic process of vacuum draw (9). causes movement of the sample (4) downwards through the filter (2). Vacuum pressure, fluid flow rate and frequency of vibration are controlled from a remote unit housing appropriate pumps and valves.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Coated armor system and process for making the same
An armor system and method involves providing a core material and a stream of atomized coating material that comprises a liquid fraction and a solid fraction. An initial layer is deposited on the core material by positioning the core material in the stream of atomized coating material wherein the solid fraction of the stream of atomized coating material is less than the liquid fraction of the stream of atomized coating material on a weight basis. An outer layer is then deposited on the initial layer by positioning the core material in the stream of atomized coating material wherein the solid fraction of the stream of atomized coating material is greater than the liquid fraction of the stream of atomized coating material on a weight basis.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com