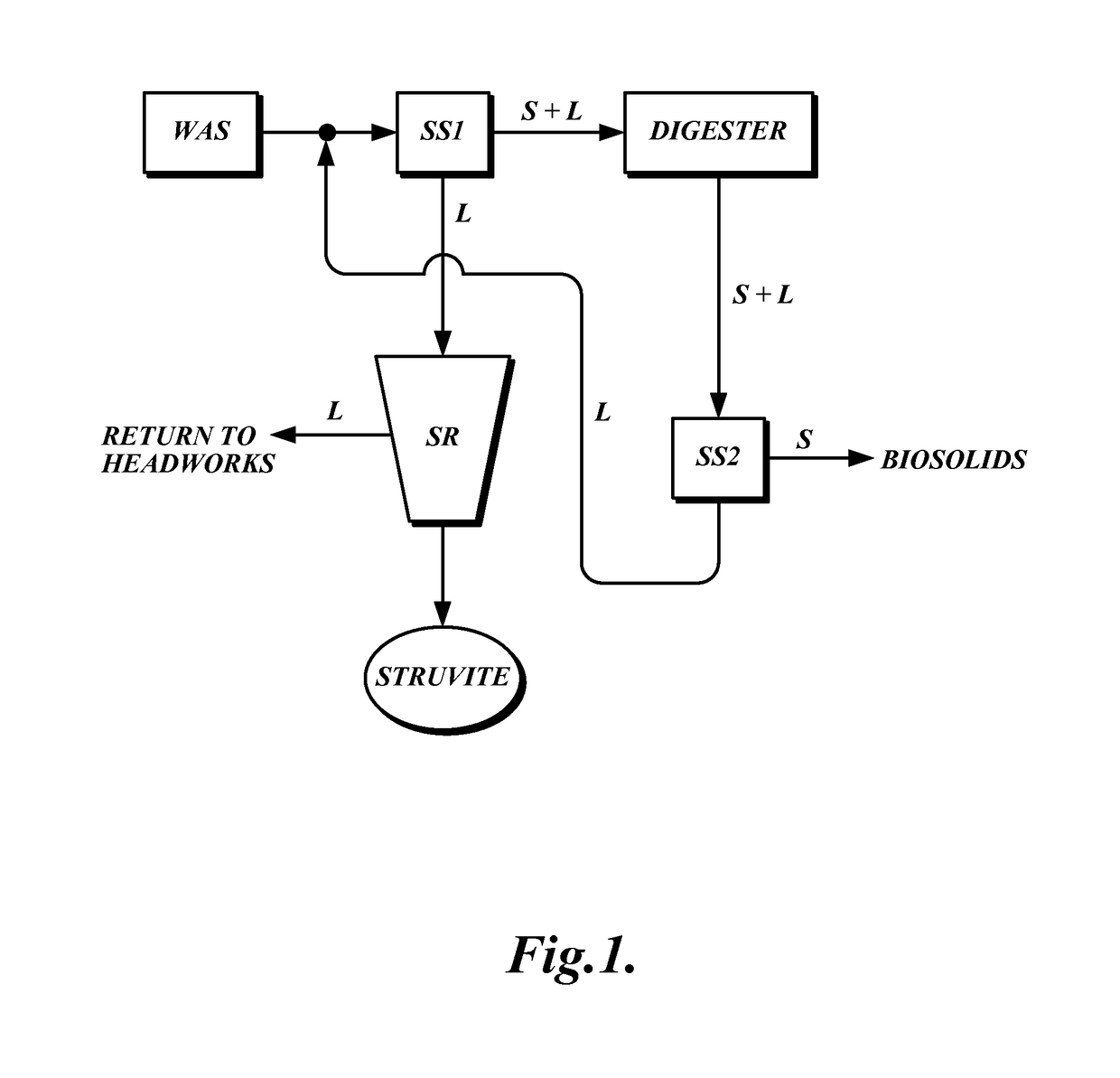
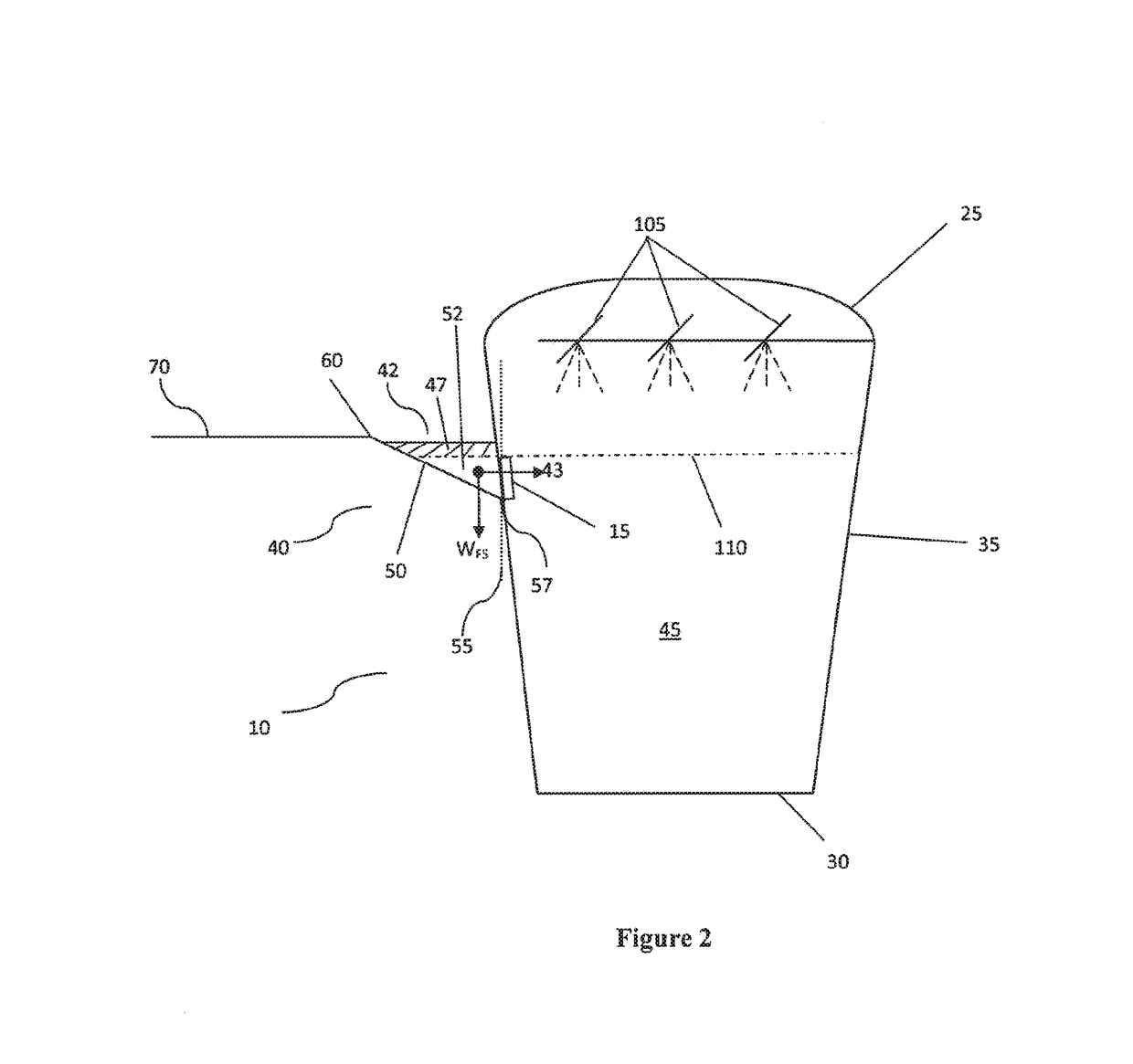
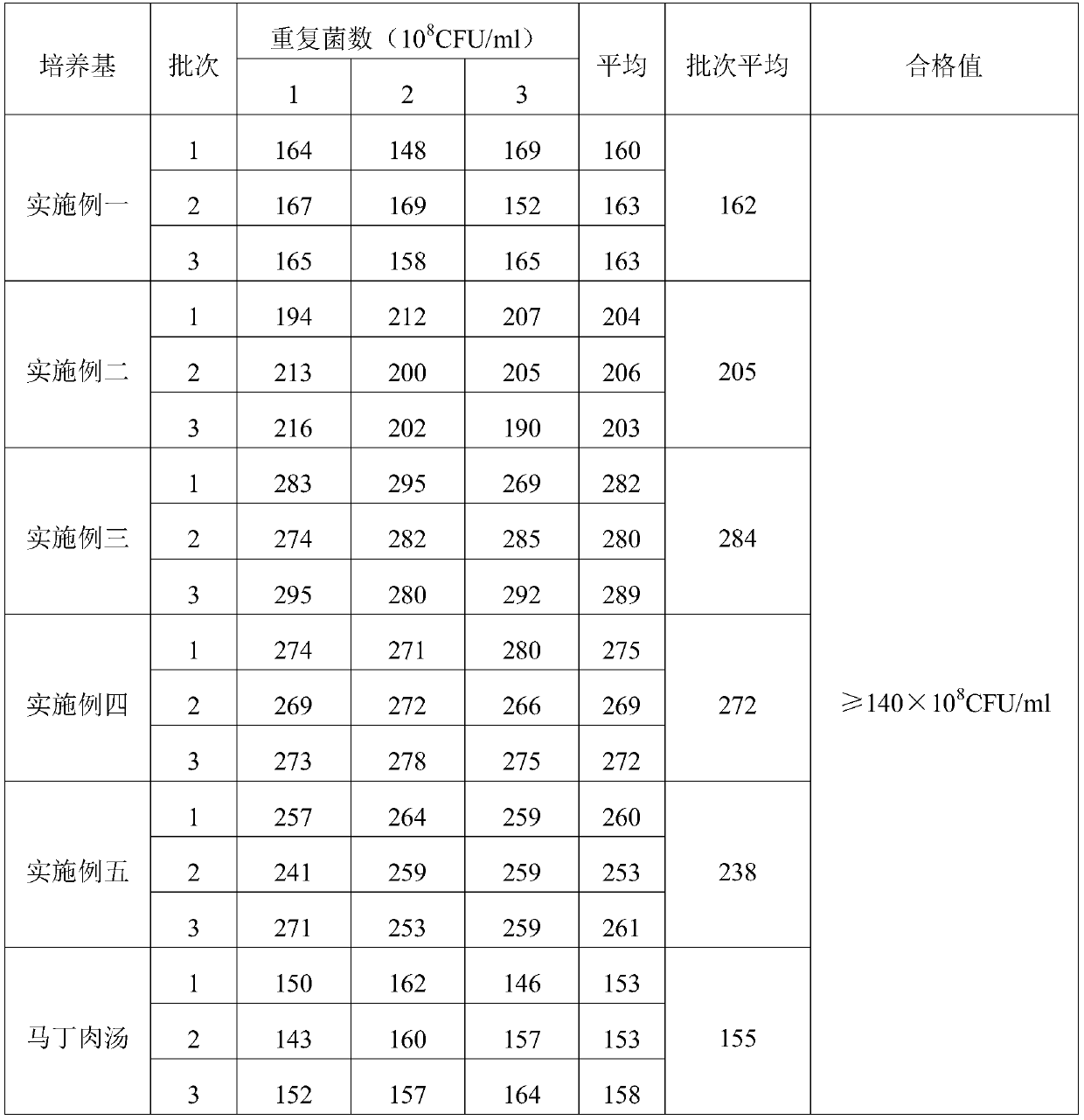
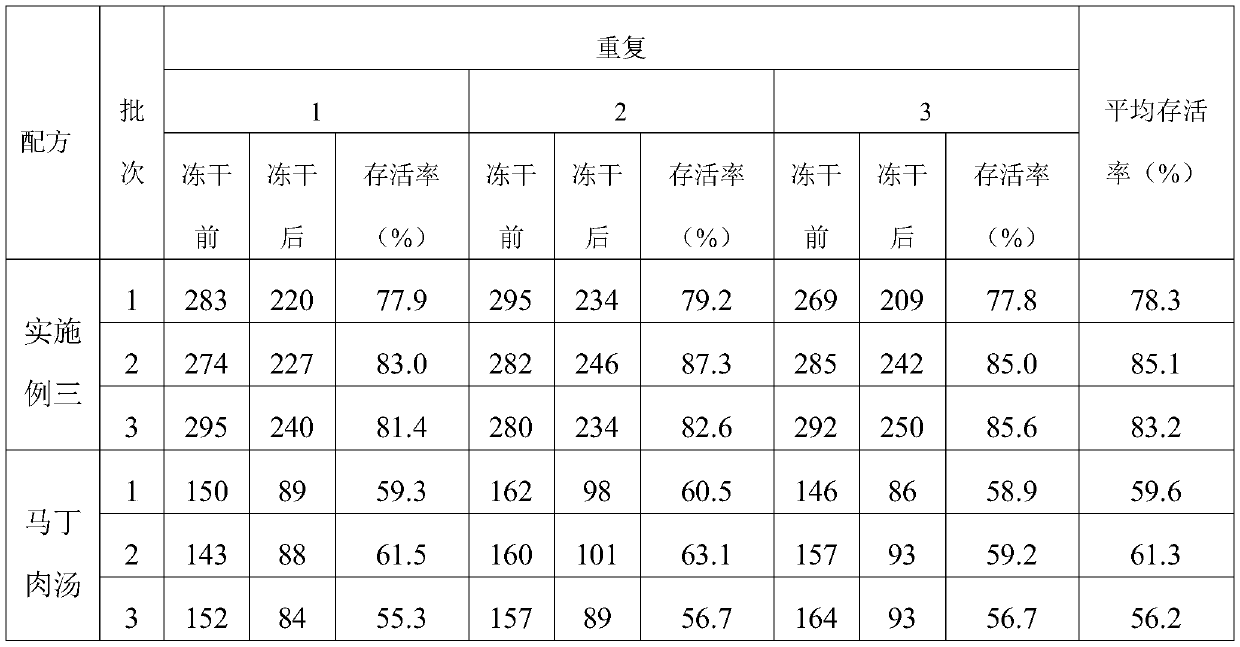
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Digestate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digestate is the material remaining after the anaerobic digestion of a biodegradable feedstock. Anaerobic digestion produces two main products: digestate and biogas. Digestate is produced both by acidogenesis and methanogenesis and each has different characteristics.
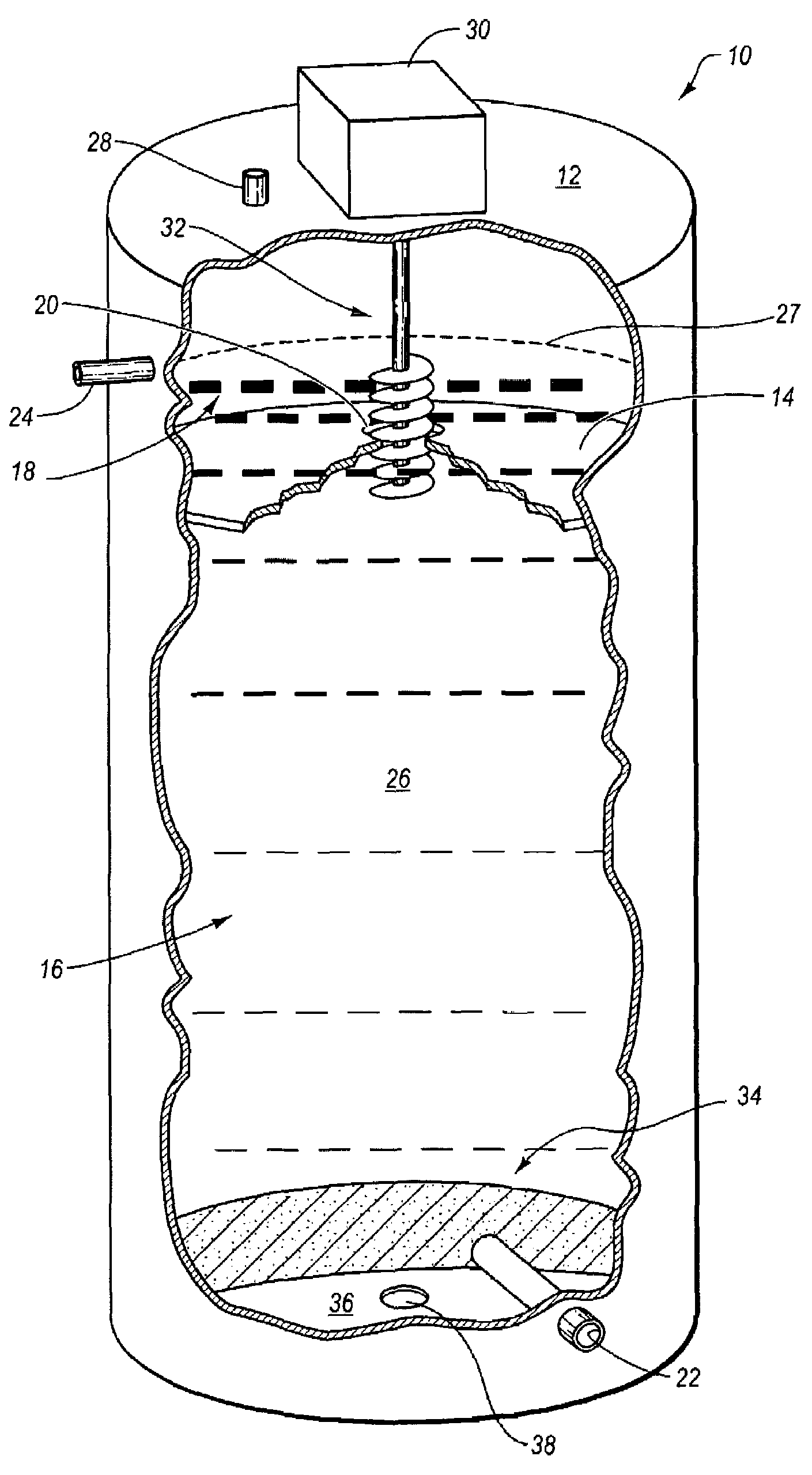
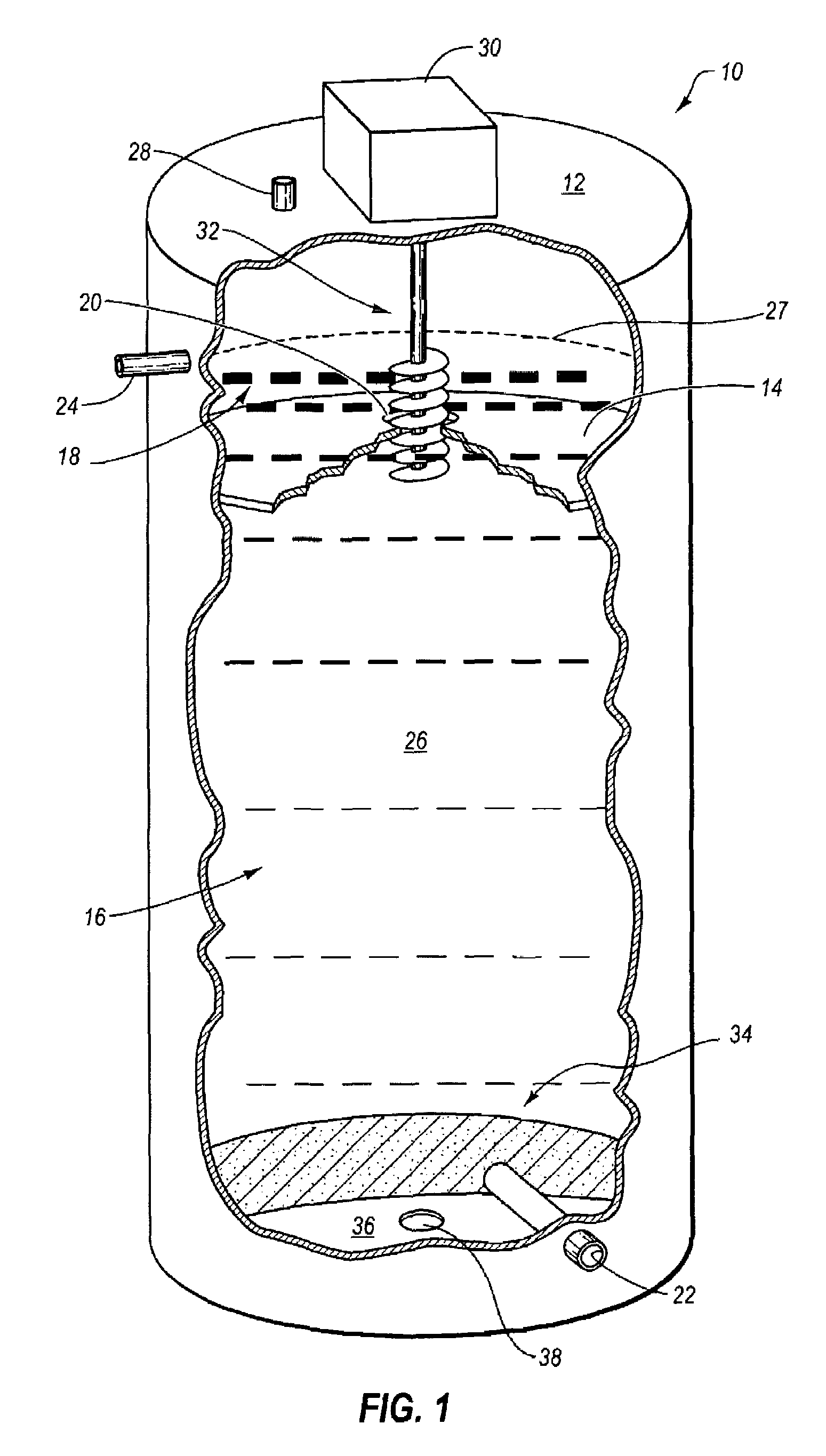
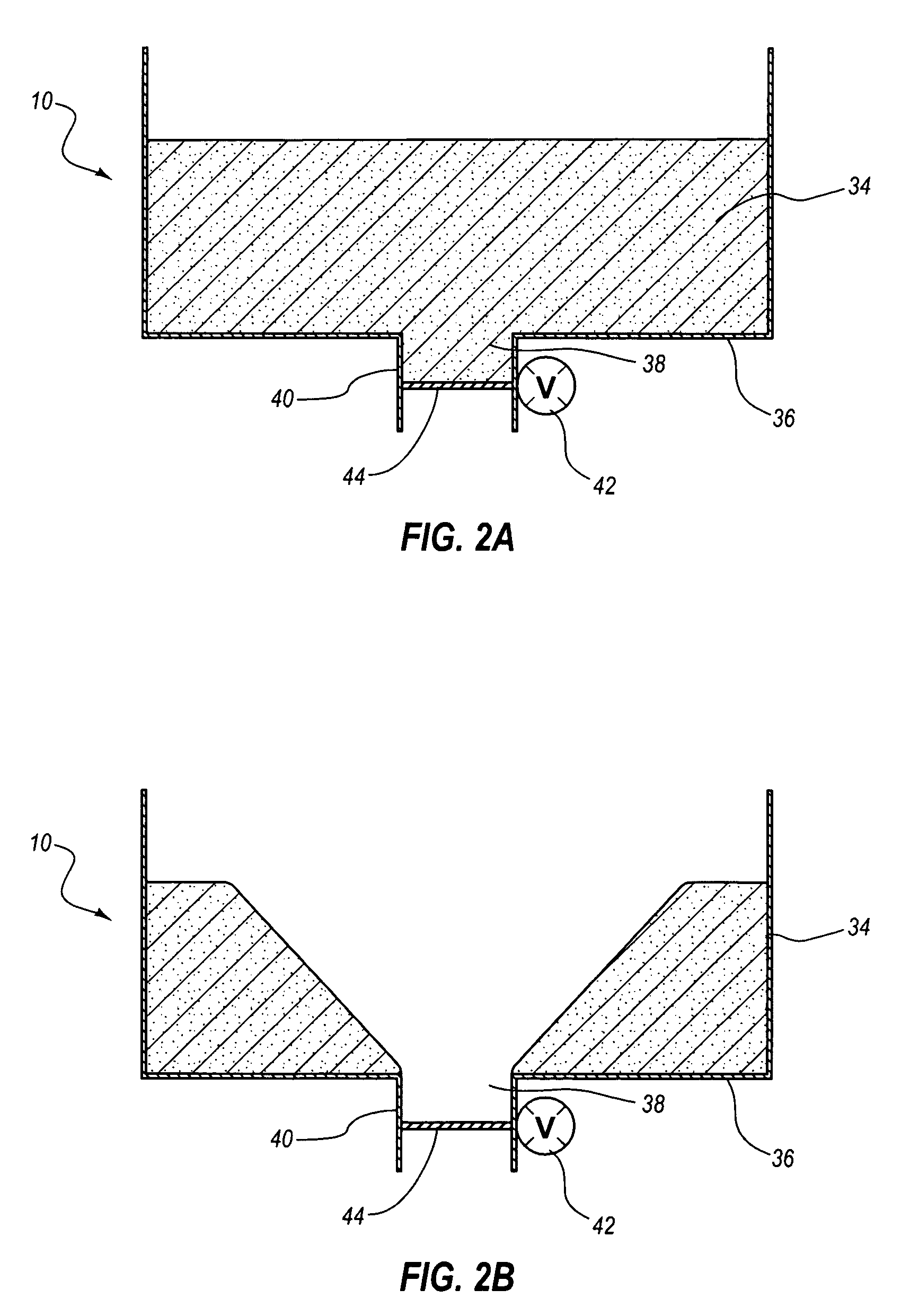
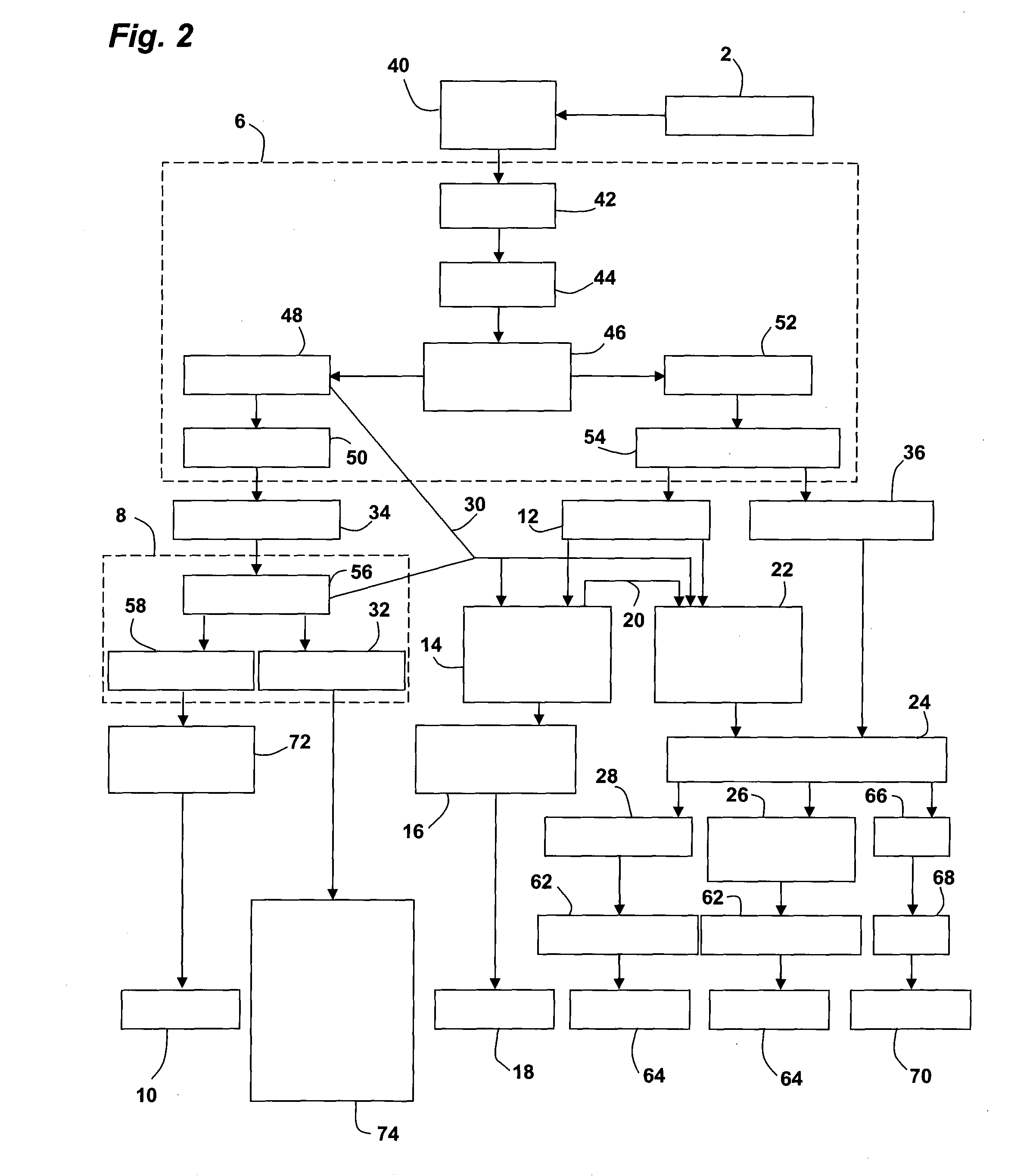
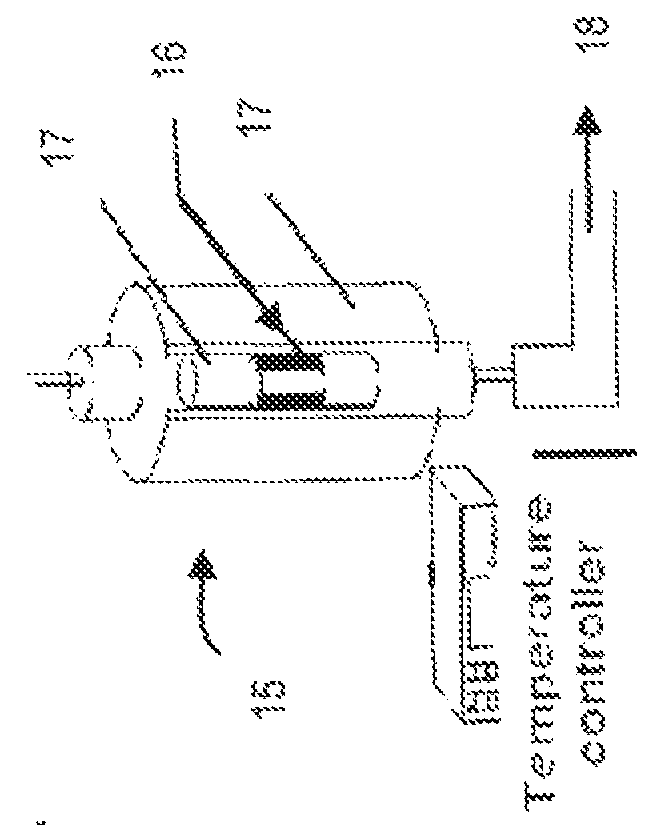
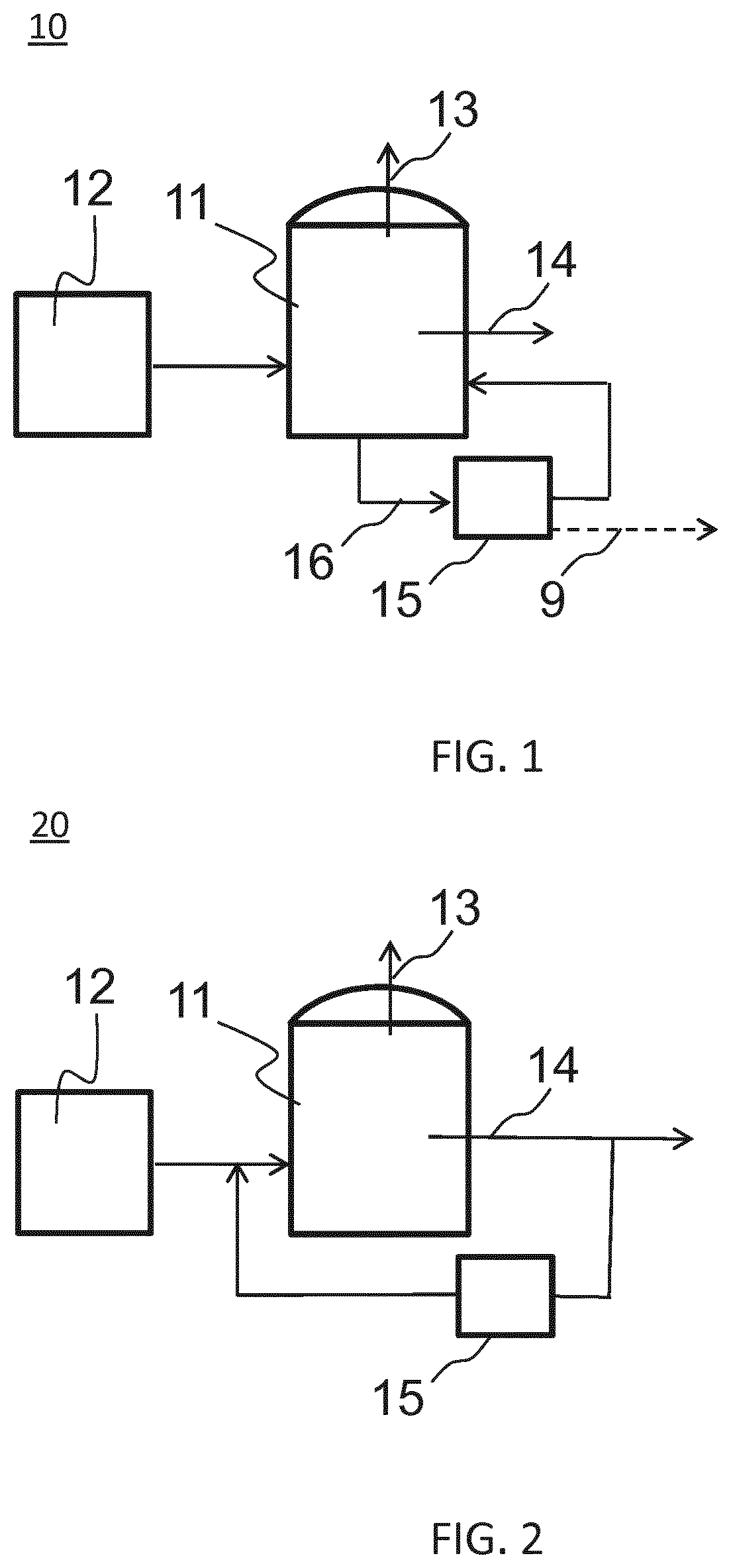
Apparatus and Process for Production of Biogas
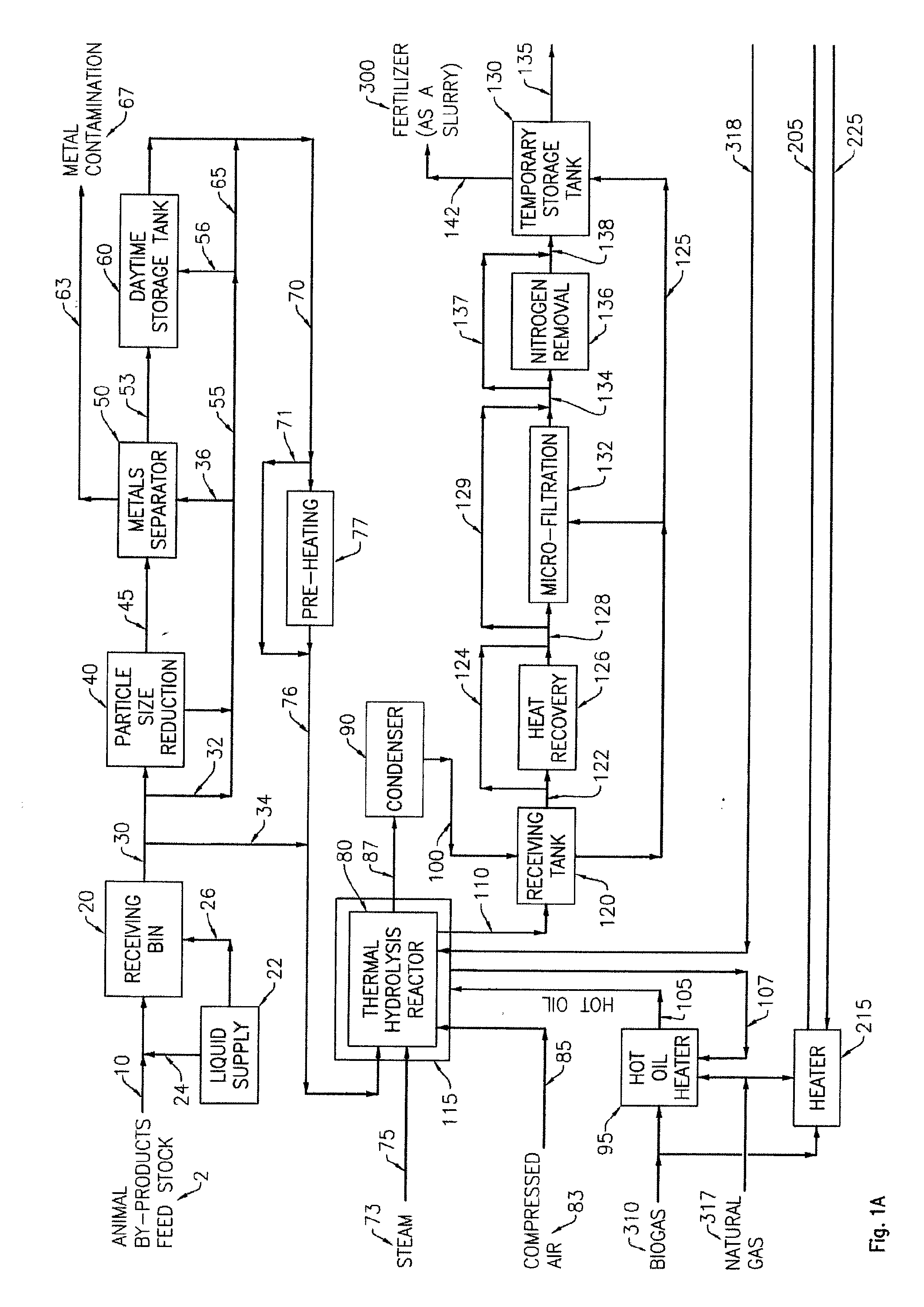
ActiveUS20100021979A1Quick conversionDigesting retention timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrolysateSolid fraction
A process and an apparatus for the manufacture of biogas and a solids fraction from an organic waste feedstock is provided. The process involves thermal hydrolysis of the organic waste feedstock at a temperature from about 100 to about 220° C., a pressure from about 5 to about 20 bars, for a period of time from about 15 minutes to 4 hours, to produce a hydrolysate. The hydrolysate undergoes anaerobic digestion at a temperature from about 25 to 60° C., for a period of time from about 1 to 35 days to produce a biogas stream and a digestate. The digestate is separated into a solids fraction and a liquid fraction, and a portion of the solids fraction is recycled for further anaerobic digestion. The biogas stream, characterized as having a methane content from between 55 to 80% by volume, and the solids fraction, are recovered. The apparatus includes a receiving bin for receiving and supplying organic waste feedstock to a thermal hydrolysis reactor. The thermal hydrolysis reactor for processing the organic waste feedstock at a temperature from about 100 to about 220° C., a pressure from about 5 to about 20 bars, for a period of time from about 15 minutes to 4 hours to produce a hydrolysate. An anaerobic digester for processing the hydrolysate at a temperature from about 25 to 60° C., for a period of time from about 1 to 35 days to produce the biogas and a digestate, and a solids thickening tank for separating the digestate into the solid fraction, a liquid fraction and a secondary biogas fraction.
Owner:GEMINI CORP
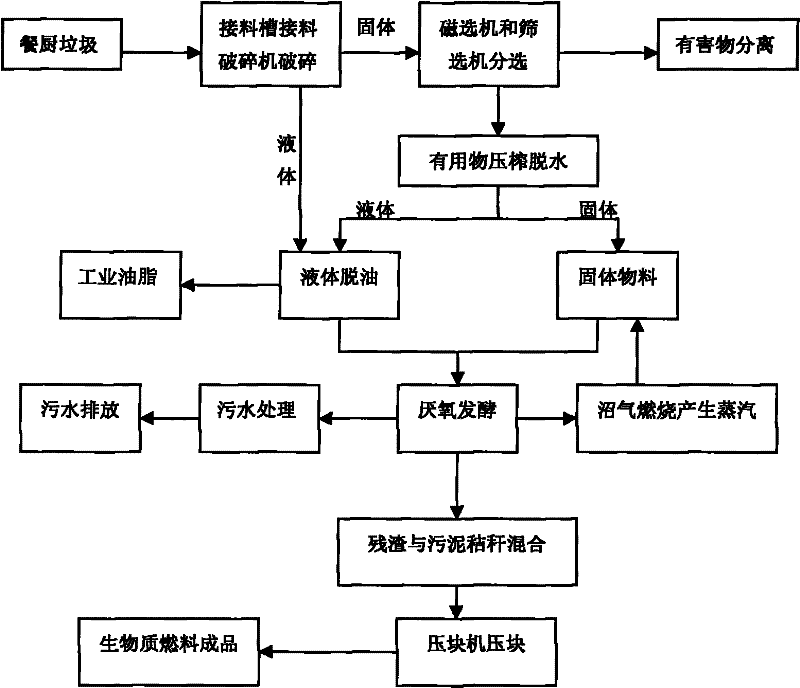
A method for preparing biomass fuel from kitchen waste
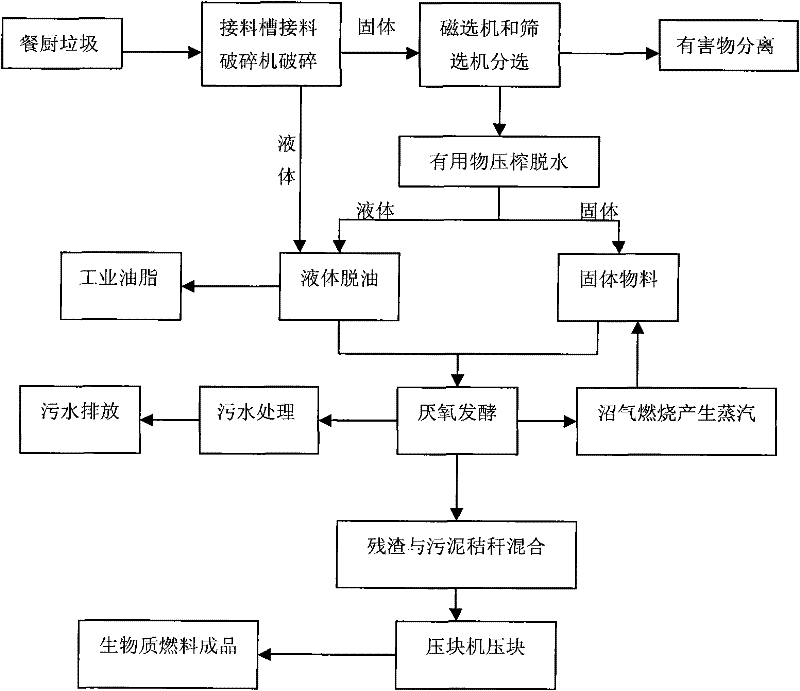
InactiveCN102268310AHarmlessAchieving processing powerFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSolid waste disposalSludgeSlurry
The invention relates to a method for recycling resources, in particular to a method for preparing biomass fuel from kitchen waste resources. The method for preparing biomass fuel from kitchen waste according to the present invention comprises sorting and crushing the kitchen waste, then dehydrating and deoiling, and anaerobically fermenting the solid materials in the kitchen waste after extracting the oil, and degrading the produced biogas Recycling, solid-liquid separation of the biogas slurry, the separated biogas residue is mixed with sludge, straw and other biomass materials, and dried and briquetted to make biomass fuel. The invention recycles kitchen waste and turns waste into treasure. It not only realizes the harmless and reduction treatment of kitchen waste, but also treats biomass waste such as sludge and straw, and the obtained products are completely burned without any waste. Secondary pollution, realize the comprehensive treatment of various wastes.
Owner:董雅清
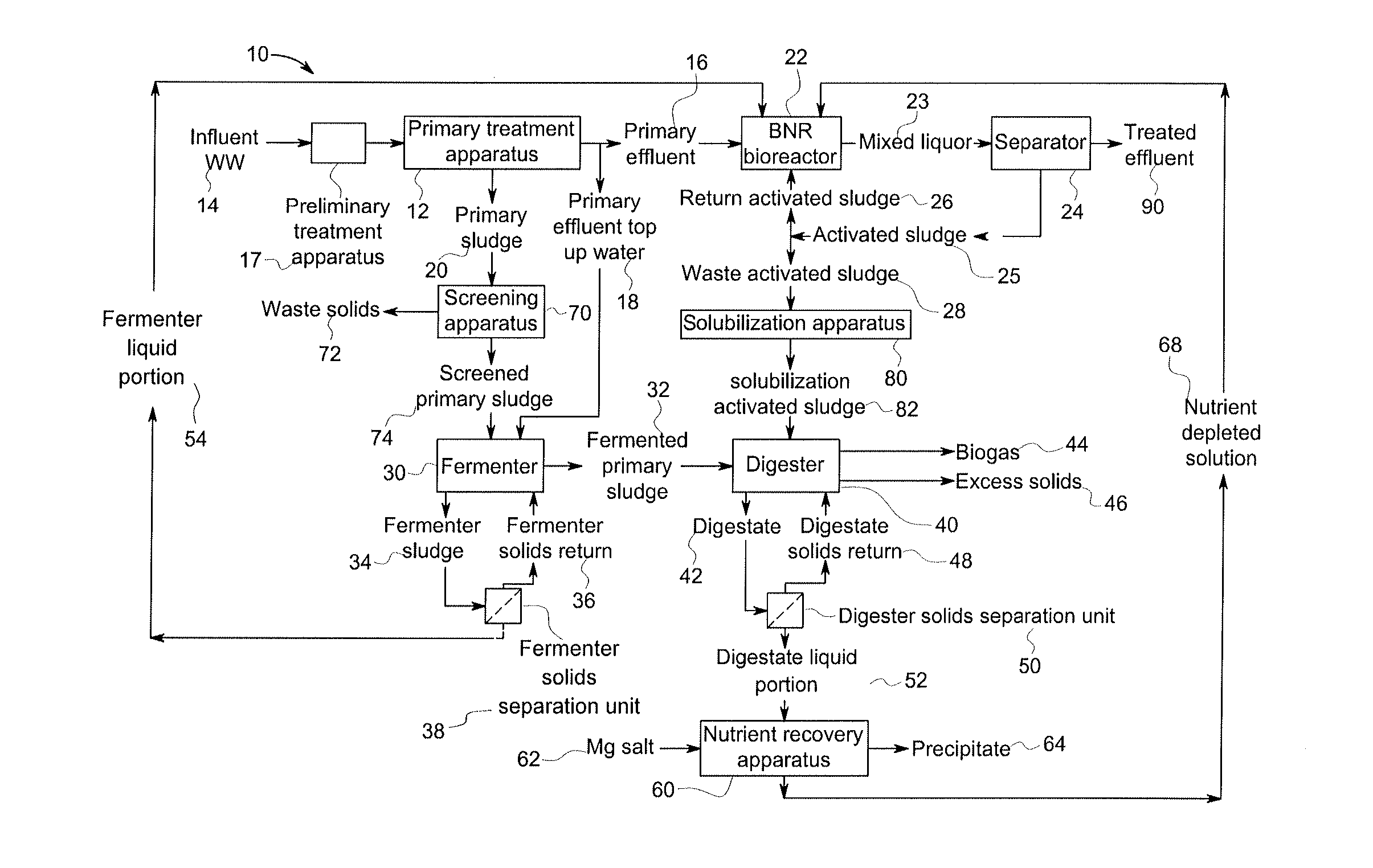
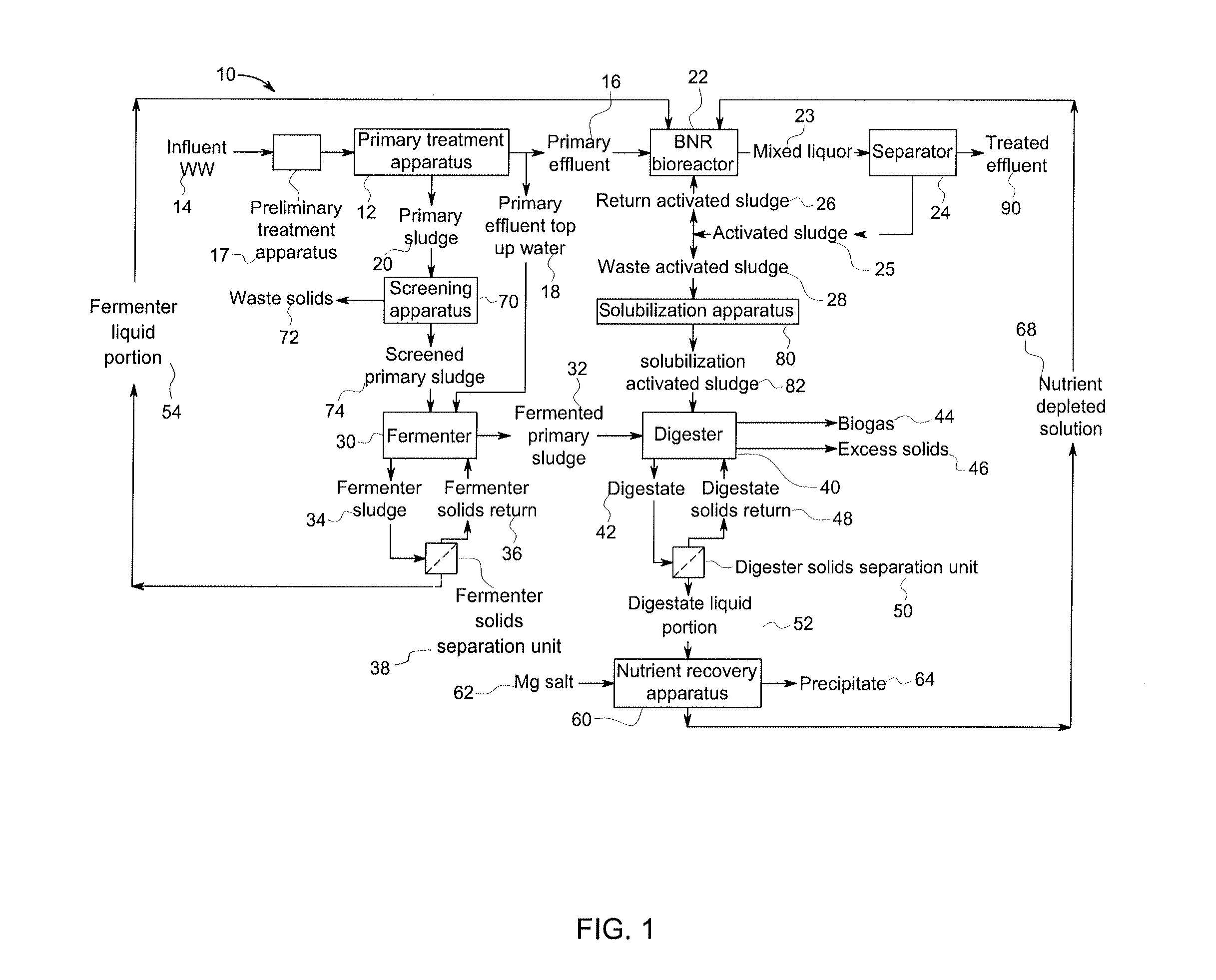
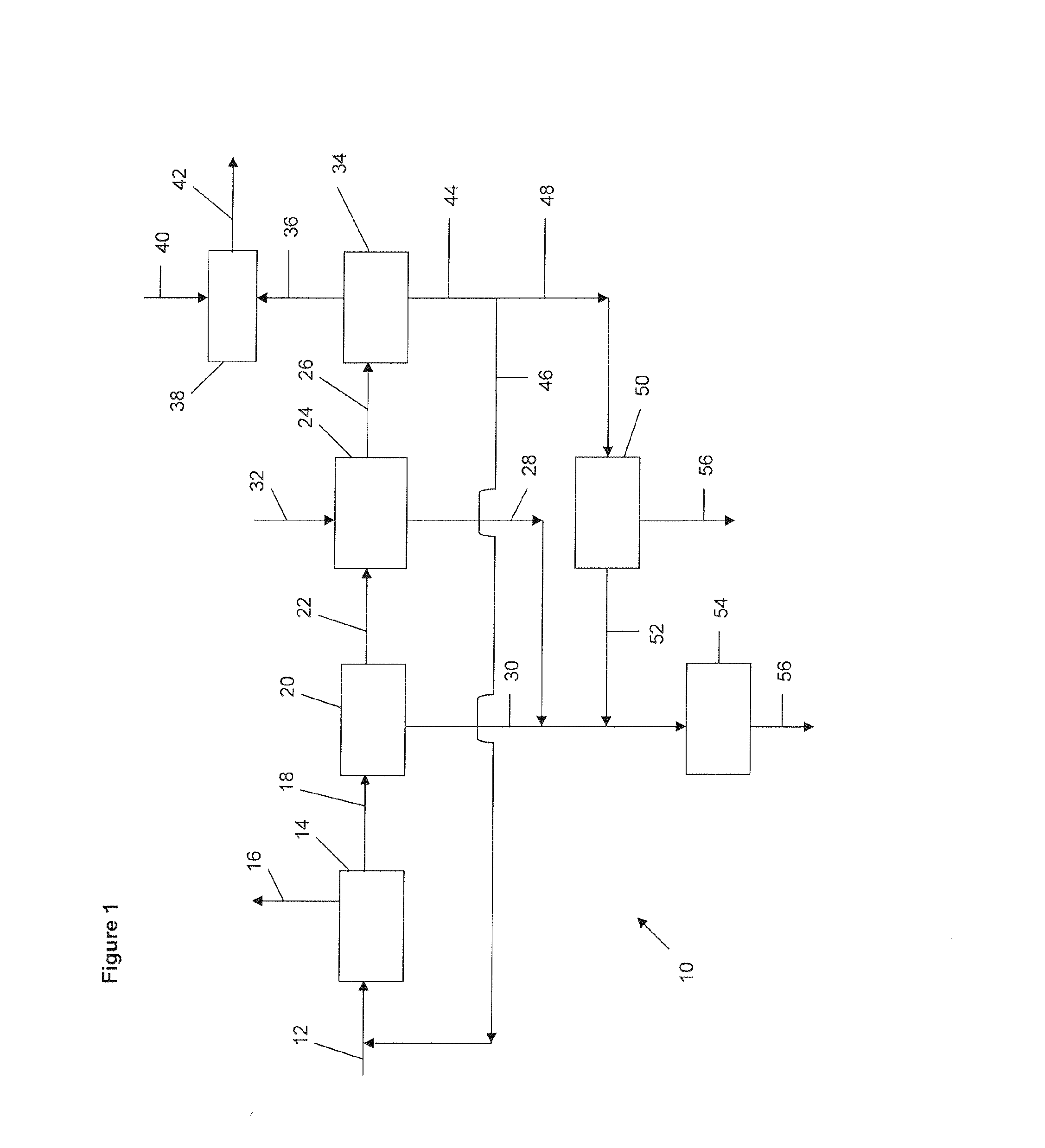
Method and system for treating wastewater
InactiveUS20130134089A1Water treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
A wastewater treatment process uses enhanced primary treatment to remove suspended solids from raw wastewater. Primary sludge is treated in a fermenter. Primary effluent is treated by biological nutrient removal (BNR) to produce a treated effluent and waste activated sludge (WAS). The WAS is treated in an anaerobic digester, which also treats sludge from the fermenter. Anaerobic digestate is separated to provide a liquid effluent. The liquid effluent is stripped of phosphorous and returned to the BNR as a source of readily biodegradable carbon. Liquid in the fermenter may also be separated to provide a liquid rich in volatile fatty acids (VFAs). This liquid is returned to the BNR when additional VFAs are required.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods for removal of non-digestible matter from an upflow anaerobic digester
ActiveUS7615155B1Preserving efficient operationBacterial population is relatively stableSolid waste disposalWaste water treatment from animal husbandryOrganic matterSteady state
Methods for steady state operation of an upflow anaerobic digester using organic matter that contains a portion of solid, non-digestible matter include (1) providing an upflow anaerobic digester, (2) providing a bacterial culture in the upflow anaerobic digester for the breakdown of organic matter, (3) introducing an influent into the upflow anaerobic digester, wherein the influent comprises a biodegradable component, a liquid component, and an amount of solid non-digestible matter, (4) operating the upflow anaerobic digester in a steady-state, (5) accumulating the solid, non-digestible matter in the upflow anaerobic digester, (6) and removing a portion of the accumulated solid, non-digestible matter from the upflow anaerobic digester through the bottom of the upflow anaerobic digester while maintaining steady-state operation of the upflow anaerobic digester. Steady-state operation of the upflow anaerobic digester is maintained by selecting a percentage of the total volume of the liquid and material that are flushed from the digester for a given period of time so as to preserve the steady-state of the bacterial culture.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Nutrient recovery process
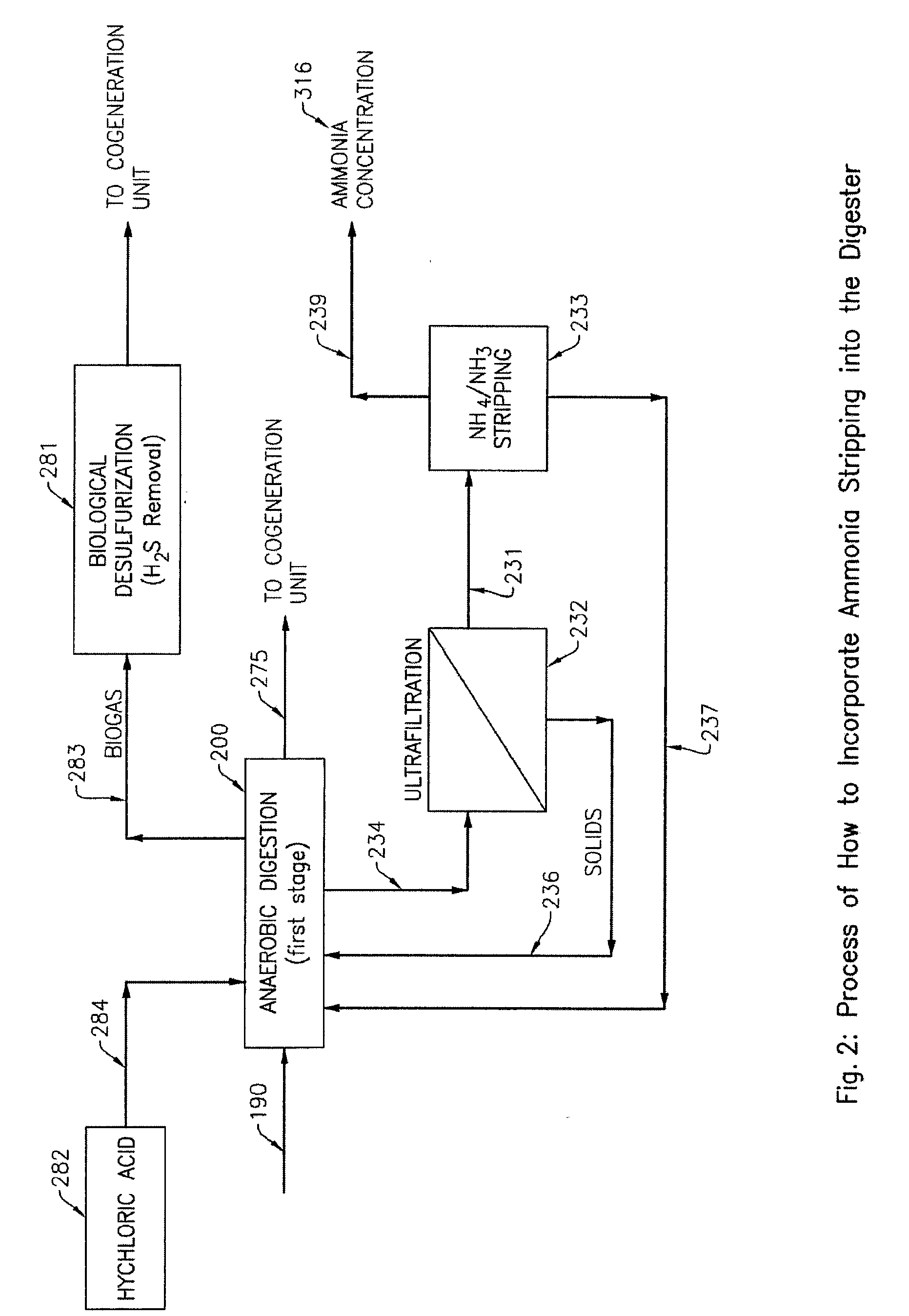
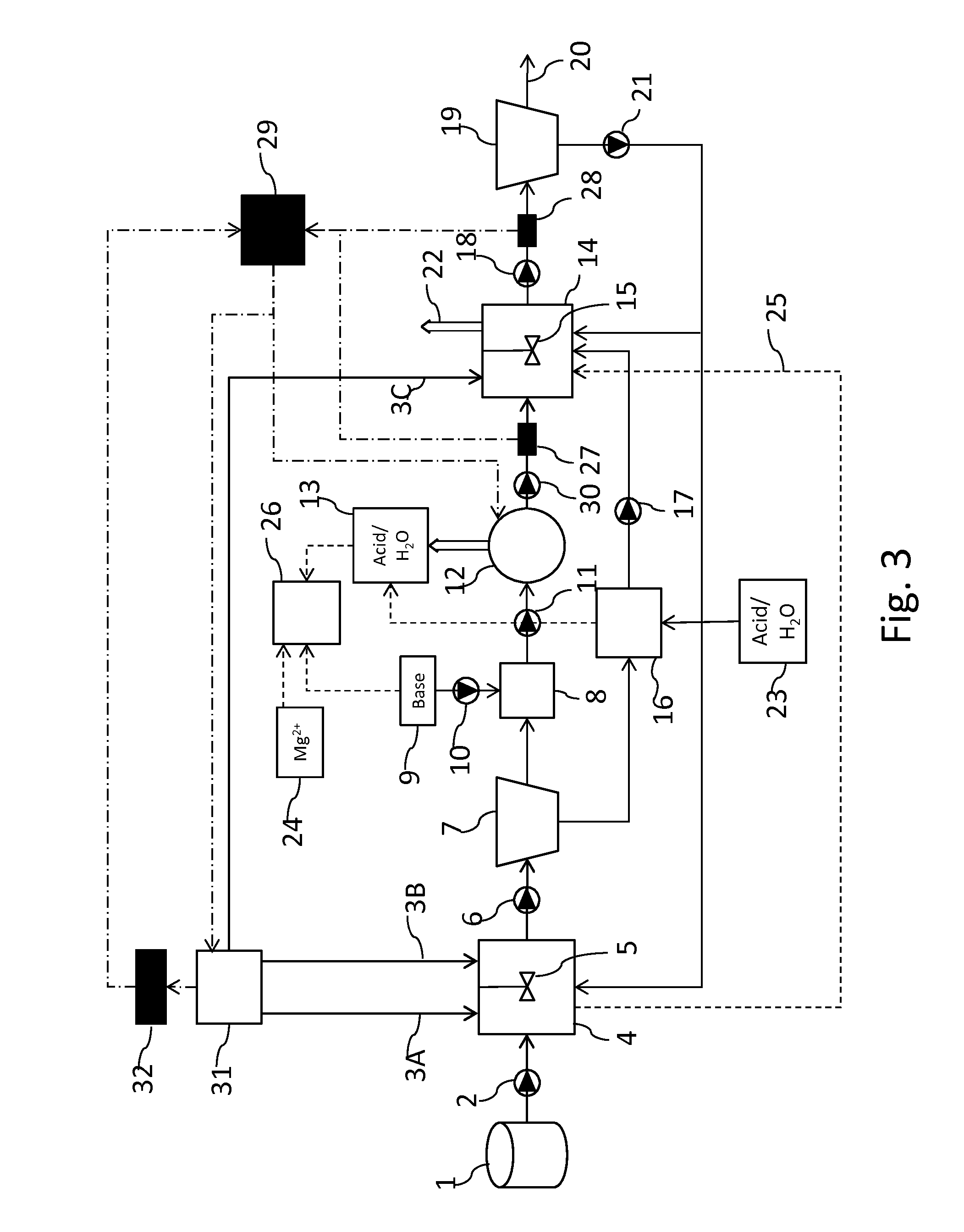
ActiveUS20150329399A1Reduce concentrationHigh pHBio-organic fraction processingSludge processingAmmoniaSalt solution
An apparatus for recovering nutrients or water from digestate comprises one or more solid-liquid separation units, an ammonia stripping device, and a gas scrubbing unit. In a process, digestate is separated into a solids portion and a liquid portion. Ammonia is stripped from the liquid portion and converted into an ammonium salt solution which may be sold or used as, or blended with, a fertilizer product. Optionally, at least part of the remaining liquid portion may be concentrated to produce brine. The brine is mixed with the solids portion. The mixture may be dried and used as, or blended with, a fertilizer product. Optionally, a least part of the remaining liquid portion may be re-used as dilution water in a digester. A solids portion of the digestate, and one or both of an ammonium salt solution and a brine, may be used as fertilizer without thermal drying.
Owner:ANAERGIA
Phosphate Recovery From Acid Phase Anaerobic Digesters
A method for recovering phosphate from sewage treatment plants using multi-stage anaerobic digestion includes the treatment of organic acid digest with calcium hydroxide, calcium oxide, and similar compounds to raise pH to near neutral values and precipitate calcium phosphate compounds such as brushite and similar amorphous compounds. The method includes the formation of calcium phosphates on weak-acid ion exchange columns and membranes in contact with organic acid digest. The system includes removal of the calcium phosphate compounds formed by sedimentation, either static or against an upwelling flow, centrifugation, or filtration.
Owner:NUTRIENT RECOVERY & UPCYCLING
Apparatus and process for production of biogas
ActiveUS8470567B2Small particle sizeQuick conversionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrolysateSolid fraction
A process and an apparatus for the manufacture of biogas and a solids fraction from an organic waste feedstock is provided. The process involves thermal hydrolysis of the organic waste feedstock at a temperature from about 100 to about 220° C., a pressure from about 5 to about 20 bars, for a period of time from about 15 minutes to 4 hours, to produce a hydrolysate. The hydrolysate undergoes anaerobic digestion at a temperature from about 25 to 60° C., for a period of time from about 1 to 35 days to produce a biogas stream, characterized as having a methane content from between 55 to 75% by volume and a digestate. The digestate is separated into a solids fraction and a liquid fraction, and a portion of the solids fraction is recycled for further anaerobic digestion.
Owner:GEMINI CORP
Anaerobic treatment system and device
ActiveUS20130011896A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingWaste treatmentCollection system
An anaerobic organic substrate treatment system is provided which comprises digester tubes wherein an inner bag of the digester tube is used to collect the solids content of the waste and an outer bag of the digester tube is used to collect the liquid and gas leachate from waste slurry input into the digester tubes. The inner bag is permeable to both gas and liquid while the outer bag is impermeable to both gas and liquid and allows for collection of gas and liquid leachate in the outer bag. Collected gas and liquid leachate may then be drained and collected using a drainage and collection system. Following treatment, the outer bag may opened to retrieve the inner bag for retrieval of the treated solids substrate. The substrate may then be used as needed. In one variant, the outer bag is re-sealable and may be reused in further treatment operations. The anaerobic waste treatment system may be used to carry out such treatment operations as storage / hydrolysis, methanization, and / or digestate treatment.
Owner:CH FOUR BIOGAS
Complete pellet feed for preventing diarrhea of young rabbits as well as preparation method and application of complete pellet feed
ActiveCN103621783AImprove securityNo drug resistanceAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySodium bicarbonate
The invention discloses a complete pellet feed for preventing diarrhea of young rabbits. The complete pellet feed comprises corns, soybean meal, cottonseed meal, sunflower seed meal, wheat bran, flour, malt sprouts, rice bran meal, alfalfa, saccharose, edible salt, calcium hydrophosphate, calcium powder, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium sulfate monohydrate, L-Lysine sulphate, a complex enzyme preparation, a composite microecological agent, yellow bentonite, methionine, composite vitamins, choline chloride, a mold adsorbent and a trace element additive. The complete pellet feed for preventing the diarrhea of the young rabbits is not added with antibiotics and is high in safety; the young rabbits do not have drug resistance to the complete pellet feed, and the possibility of abnormal fermentation of hindguts is reduced; intestinal tract movement is promoted; easily digested substances can be quickly digested in the front intestinal tracts of the young rabbits, so that abnormal easy fermentation chime caused by the substances reaching the hindguts is reduced, and the diarrhea of young meat rabbits is relieved; furthermore, due to the proper processing technical parameters of the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the diarrhea occurrence rate of the young rabbits is further reduced.
Owner:武威铁骑力士饲料有限公司
Anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis system
ActiveUS20160153008A1Biological substance pretreatmentsByproduct vaporizationMethane productionSewage
An anaerobic digester is fed a feedstock, for example sludge from a municipal wastewater treatment plant, and produces a digestate. The digestate is dewatered into a cake. The cake may be dried further, for example in a thermal drier. The cake is treated in a pyrolysis system to produce a synthesis gas and biochar. The gas is sent to the same or another digester to increase its methane production. The char may be used as a soil enhancer.
Owner:ANAERGIA
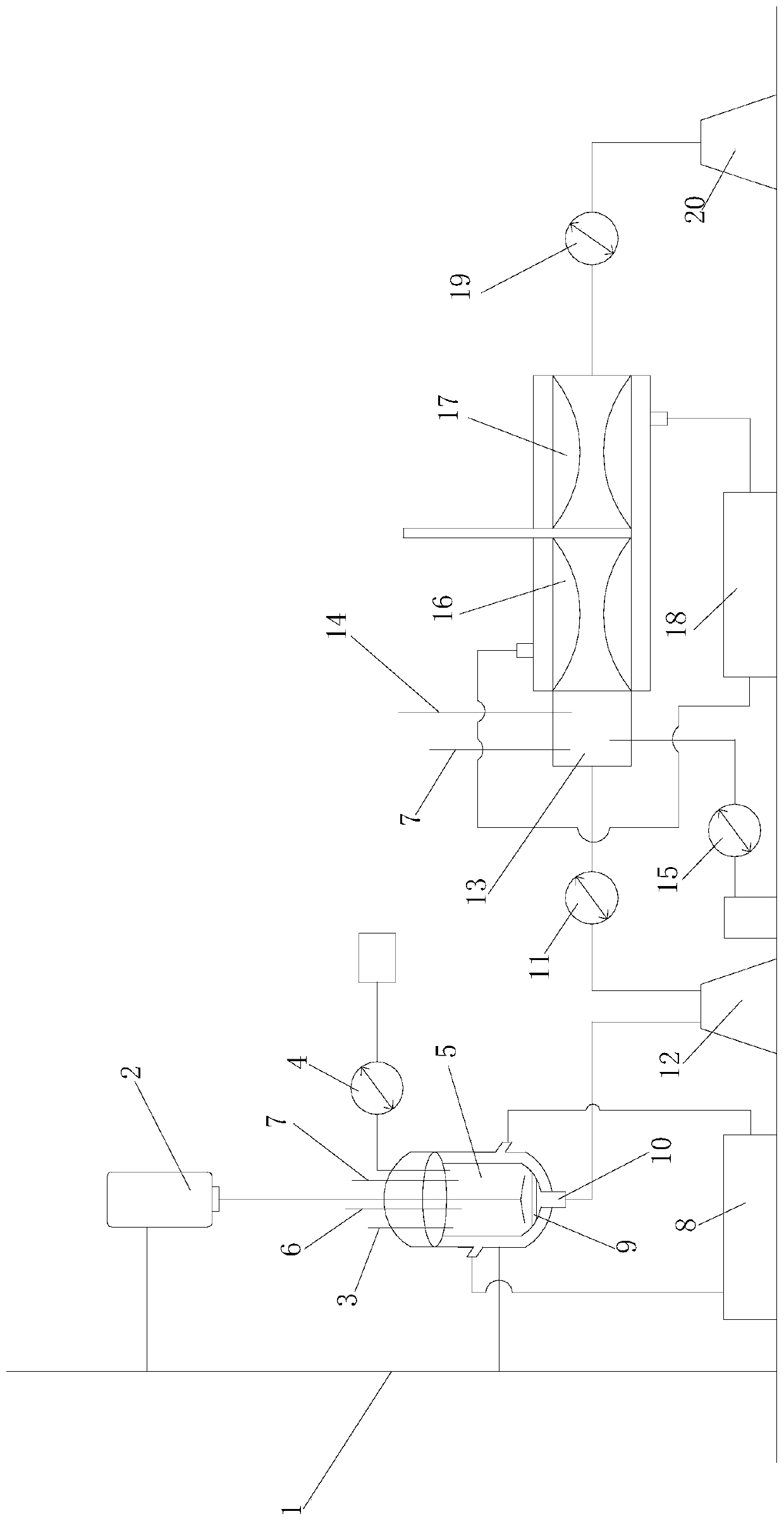
Method and device for the treatment of organic residual products of biogas systems
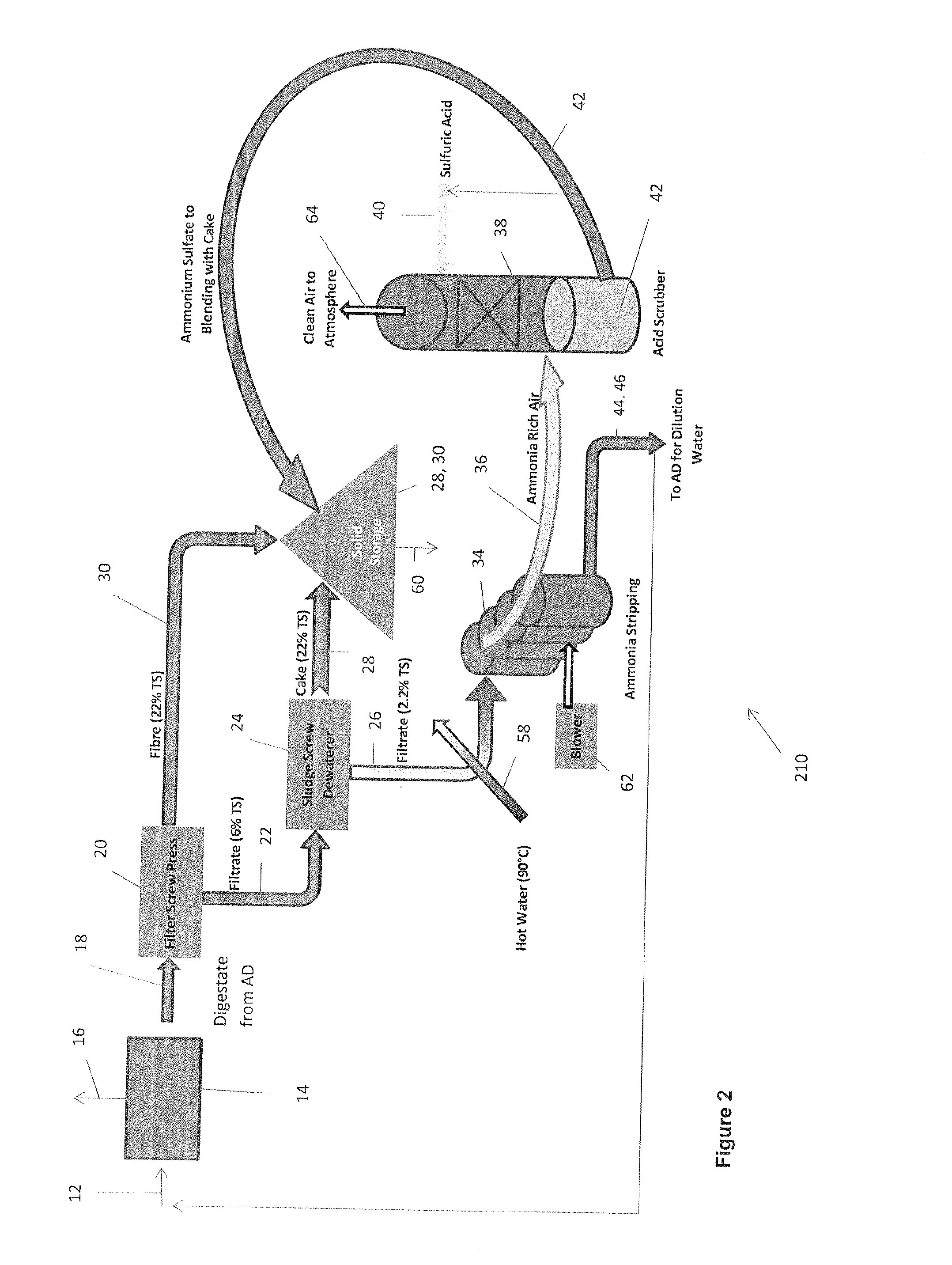
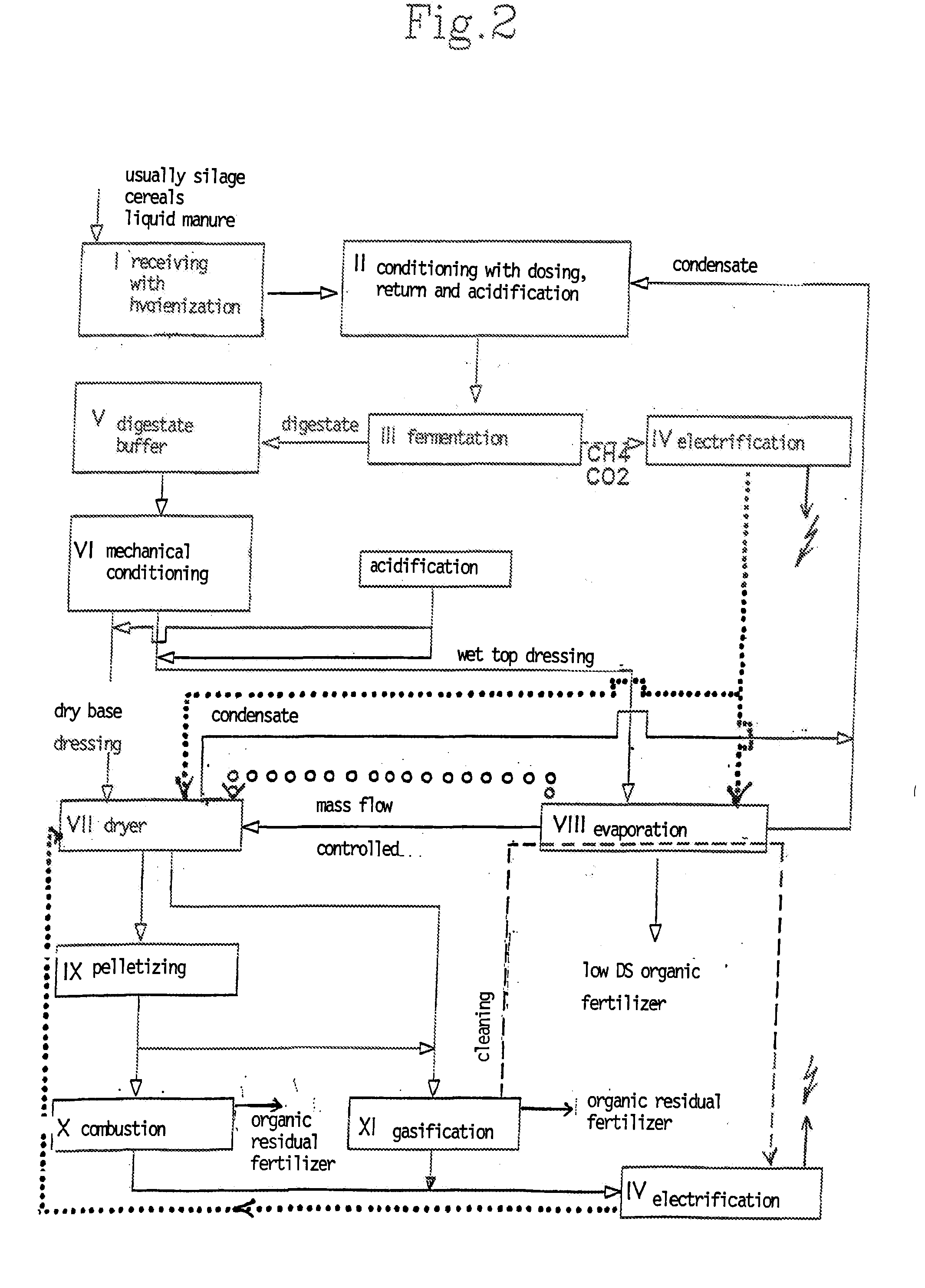
InactiveUS20100071429A1Easy to recycleHigh energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingOrganic farmingEvaporation
The invention relates to a method and a device for the conditioning of organic residuals occurring, for example, in biogas systems, wherein a digestate materializes from the organic residuals as an intermediate product during biogas regeneration in a fermenter, the digestate being subjected to mechanical conditioning comprising at least one concentration step. Subsequent to the mechanical conditioning, a first part of the liquid digestate passes through an evaporation process for the production of a top dressing, and a second part of the concentrated digestate passes through a drying process for the production of base dressing, wherein a mass flow of the top dressing concentrate is fed to the partial flow of the base dressing production such that the base dressing is enriched upgraded. Due to this enrichment, the digestate can either be gasified for energy generation, or utilized as an organic agricultural fertilizer.
Owner:VON NORDENSKJOLD REINHART
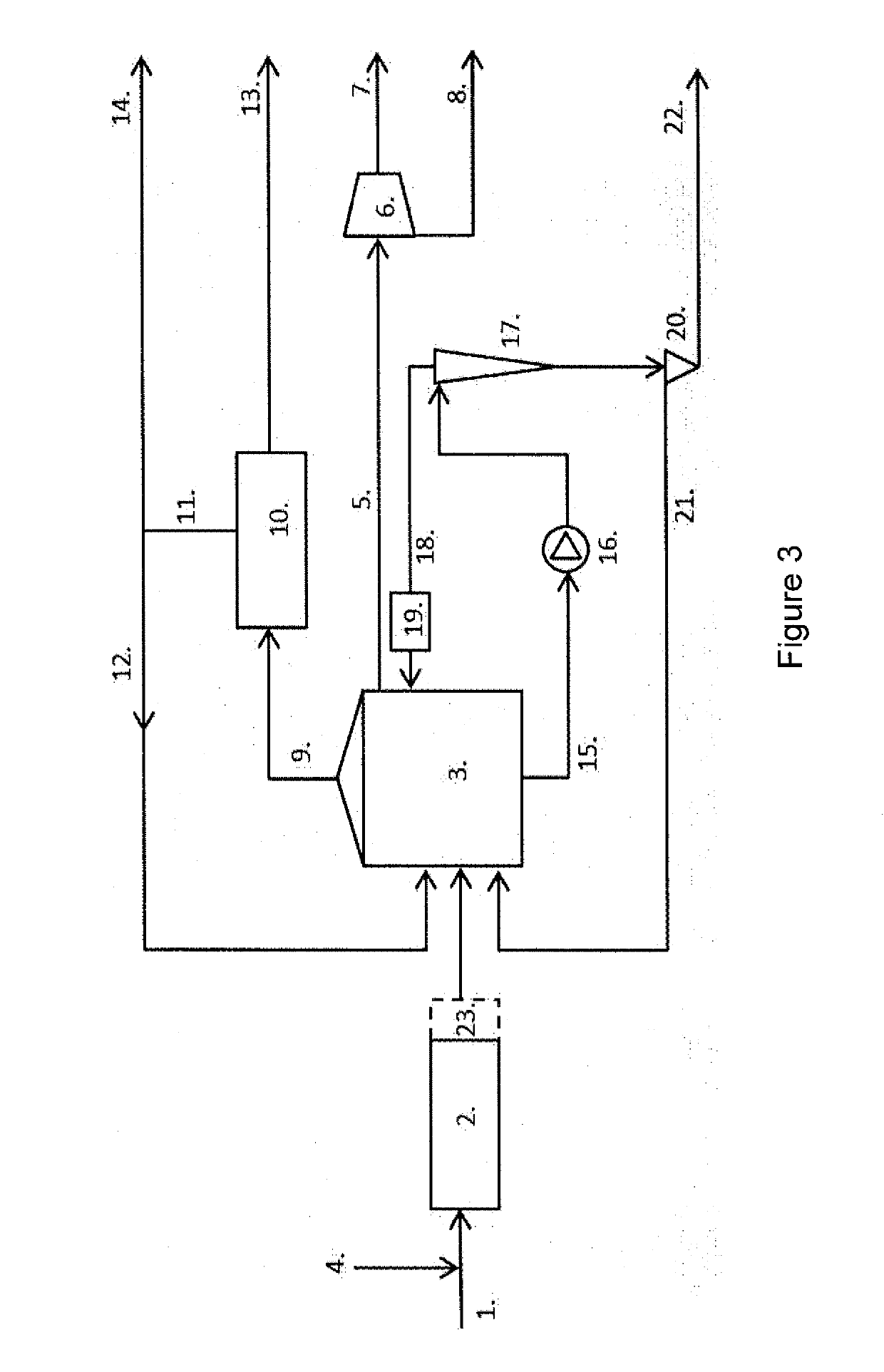
Biogas process with nutrient recovery
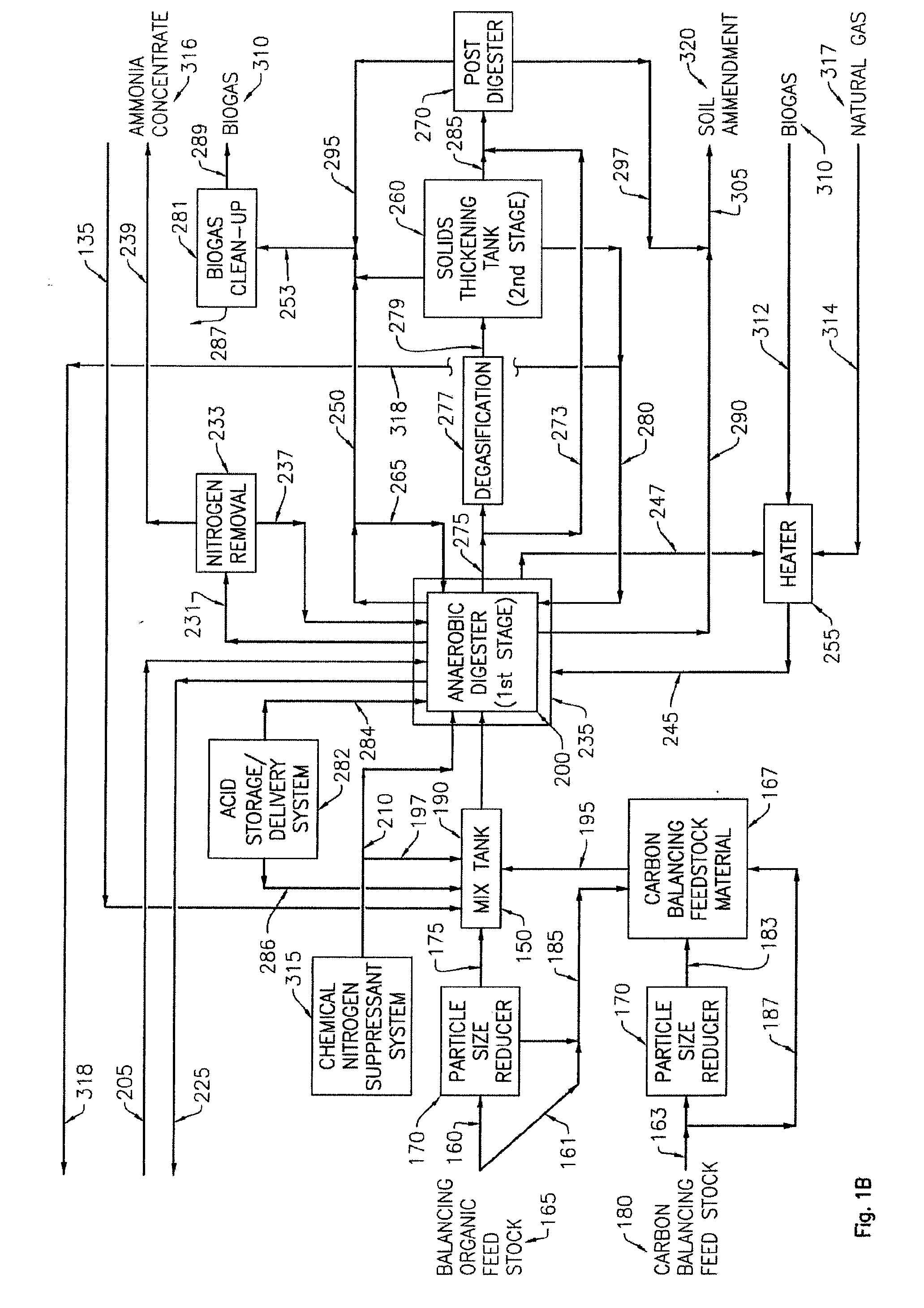
ActiveUS20150275234A1Increase biogas productionImprove concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmmoniacal nitrogenMicroorganism
The invention is a method of two-phase anaerobic digestion where monitoring and adjusting the nitrogen status (carbon to nitrogen molar ratio, i.e. C / N molar ratio or total or ammoniacal nitrogen content) enables maintaining optimum conditions during the process. The method improves the use of a variety of feedstock materials or facilitates monodigestion of one feedstock. Especially the introduction of nitrogen rich feedstock materials in the process is amended. A community of hydrolyzing and acidogenic microorganisms in the first phase digester performs ammonification i.e. release of organic nitrogen as ammonia. Nitrogen and phosphorus are removed and recovered from the digestate which then undergoes biogasification in the second phase of the process. Reject water from biogasification can be recycled within the process.
Owner:DUCTOR
Phosphate recovery from acid phase anaerobic digesters
A method for recovering phosphate from sewage treatment plants using multi-stage anaerobic digestion includes the treatment of organic acid digest with calcium hydroxide, calcium oxide, and similar compounds to raise pH to near neutral values and precipitate calcium phosphate compounds such as brushite and similar amorphous compounds. The method includes the formation of calcium phosphates on weak-acid ion exchange columns and membranes in contact with organic acid digest. The system includes removal of the calcium phosphate compounds formed by sedimentation, either static or against an upwelling flow, centrifugation, or filtration.
Owner:NUTRIENT RECOVERY & UPCYCLING
Facility for treating and recycling animal waste comprising methanisation, cultivation of microalgae and macrophytes, and vermiculture
ActiveUS20160264484A1No wasteAvoid disadvantagesFlowers cultivationBio-organic fraction processingElectricitySludge
A facility for treating and recycling animal waste (2), including a unit (6) for methanizing the waste including treatment of the obtained biogases, a cogeneration unit (8) delivering electricity and heat (32) from the biogases, and a unit for hydroponically cultivating microalgae (14) in photo-bioreactors supplied by the liquid phase (12) of the organic residues from the methanization. The facility further includes a unit for cultivating macrophytes (22) supplied with water (20) leaving the unit for cultivating microalgae, and a vermiculture unit (24) fed by harvesting the macrophytes (22) and by the sludge (36) coming from the raw digestate from the methanization.
Owner:SKYWORLD INT OVERSEAS
Experimental device for automatic simulation of gastrointestinal continuous digestion and application method
PendingCN110231437AStable pHReal-time monitoring of particle size changesMaterial analysisPylorusPh regulation
The invention provides a device capable of realizing automatic simulation of gastrointestinal continuous digestion and an application method of the device. The device comprises a stomach reactor, a stirrer, a constant-temperature water circulation system, a gastrointestinal fluid conveying system, a gastric emptying control device, an automatic pH titration device, a small intestine reactor and asample receiving device. According to the application method, to-be-digested food is conveyed into a stomach digester, stomach digestive fluid is input at a constant speed, the stirrer simulates stomach peristalsis, a micropore glass plate at the bottom of the stomach reactor simulates a pylorus to realize stomach "sieving emptying", the to-be-digested food is conveyed into a pH regulation chamberfor automatic pH regulation, small intestine digestion is simulated in the small intestine reactor provided with an internally-arranged latex sleeve, and the pressure-changing water circulation system is adopted to realize regular vibration of the latex sleeve so as to simulate the stomach peristalsis. Through the device and the application method, the whole reaction process can be continuous andautomatic under the situation that parameters are set; and moreover, the device is simple in structure, free of a complicated control system and easy to assemble and can be used to realize a digestion simulation experiment in a scientific research experiment.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Two stage pyrolysis of organic waste
InactiveUS20190002323A1Sludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningTransportation and packagingSoil conditionerDigestate
Organic waste is treated by pyrolysis or by anaerobic digestion followed by pyrolysis of the digestate. The pyrolysis is performed in two staged reactors. The second stage reactor treats char produced in the first stage. The temperature of the first stage reactor is preferably 450 degrees C. or less. The temperature of the second stage reactor is higher than the temperature of the first stage, for example by 50 degrees C. or more. Optionally, there may be a char cooler, a water sprayer, or both downstream of the char outlet of the second reactor. In an exemplary system, a digestate outlet is connected to the inlet of the first pyrolysis reactor. A pyrolysis liquid outlet of the first pyrolysis reactor is connected to the digester. Char produced in the second pyrolysis reactor may be used as a soil amendment.
Owner:ANAERGIA
Method for recovery of phosphate
ActiveUS20190144320A1Reduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRecovery methodSemi solid
The present invention provides a method for recovery of phosphate, in the form of magnesium ammonium phosphate (MAP), from a process for treating a biomass material which process comprises a digestion step performed in a digestion tank and includes a pre-treatment step employing a thermal hydrolysis, characterised in that a magnesium source is added to the material in the process flow before said flow enters the digestion tank, and phosphate is recovered as MAP as an integral part of a solid or semi-solid digestate product from the digestion tank.
Owner:CAMBI TECH AS
Production of biochar absorbent from anaerobic digestate
ActiveUS9381493B2Avoid environmental impactHigh activityBio-organic fraction processingMethane captureActivated carbonSource material
A novel carbon absorption material is described which is formed from anaerobic digestate. The material has a hollow tubular structure and is particularly advantageous in converting hydrogen sulfide in biogas and in absorbing the converted sulfur and sulfur compounds from biogas into its structure. The material after use as a hydrogen sulfide absorbent has value as a horticultural or agricultural product or as a sulfur impregnated activated carbon. The process for producing this novel carbon absorption material is described. In an embodiment, the process described uses in particular, a humidified inert gas over a temperature range of between about 500° C. to 900° C. to convert anaerobic digestate to an active carbon absorbent. The thermal treatment is relatively mild and retains the fibrous structure of the source material while removing cellulosic and hemicellulosic components from the anaerobic digestate.
Owner:CHAR TECH INC
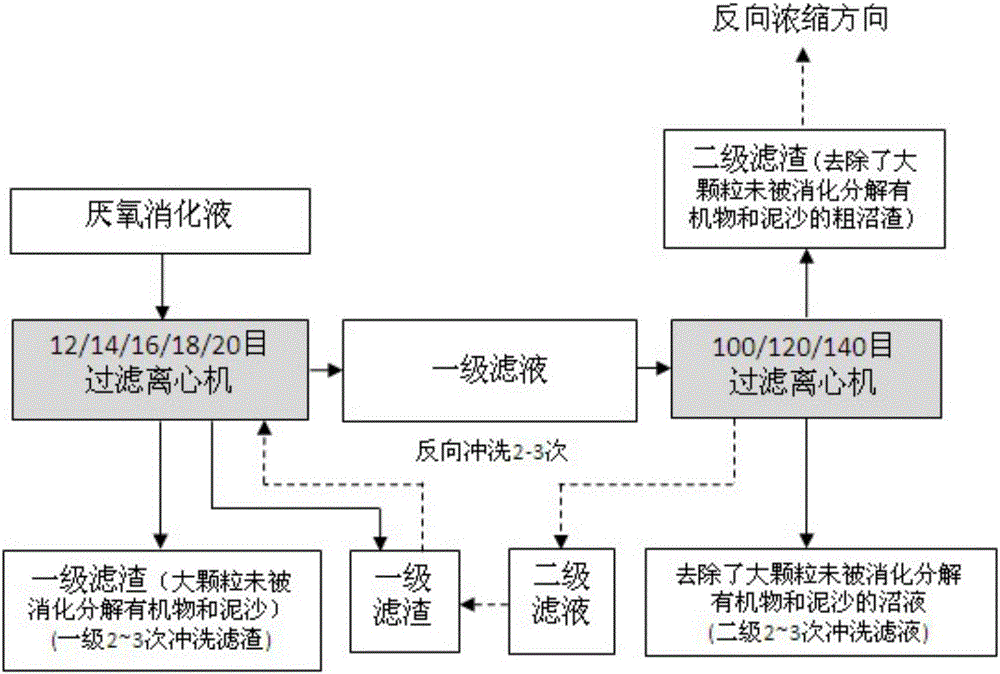
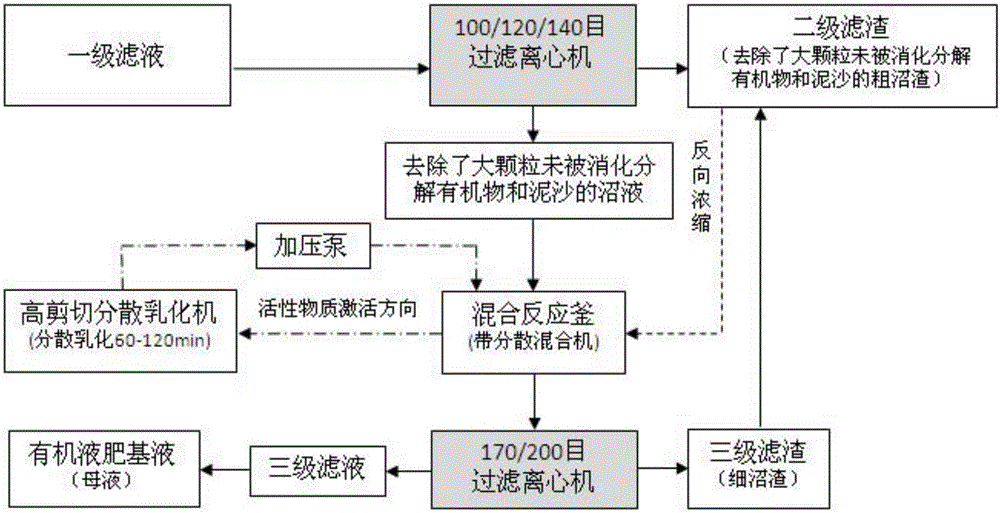
Method for removing undigested matter in anaerobic digestive liquid and preparing organic liquid fertilizer base fluid
ActiveCN105776611AAvoid bringing outIncrease concentrationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationBio-organic fraction processingFiberSlurry
The invention discloses a method for removing large-particle undigested and undecomposed organic matter and sand in anaerobic digestive liquid stage by stage and a method for preparing organic liquid fertilizer base fluid with the anaerobic digestive liquid without large-particle undigested and undecomposed organic matter and sand as the raw material.Plant fibers and other large-particle undigested and undecomposed organic matter separated after staged treatment, sand and other inorganic matter are used as initial raw materials of solid biogas manure or soil conditioner, and anaerobic digestive liquid biogas residues and biogas slurry which are obtained through staged treatment are used as initial raw materials of the organic liquid fertilizer base fluid.By means of the method, the plant fibers and other large-particle undigested and undecomposed organic matter, sand and other inorganic matter can be removed from the anaerobic digestive liquid, an organic liquid fertilizer base fluid product is prepared by means of the anaerobic digestive liquid with the large-particle undigested and undecomposed organic matter, sand and inorganic matter removed, and accordingly the bottleneck problem about resource reuse of the anaerobic digestive liquid is solved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods and systems for recovering phosphorus from wastewater including digestate recycle
ActiveUS20140178281A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWastewaterCoordination complex
Methods and systems for removal and recovery of phosphorus from wastewater and producing inorganic phosphorus complexes including digestate recycle.
Owner:MULTIFORM HARVEST
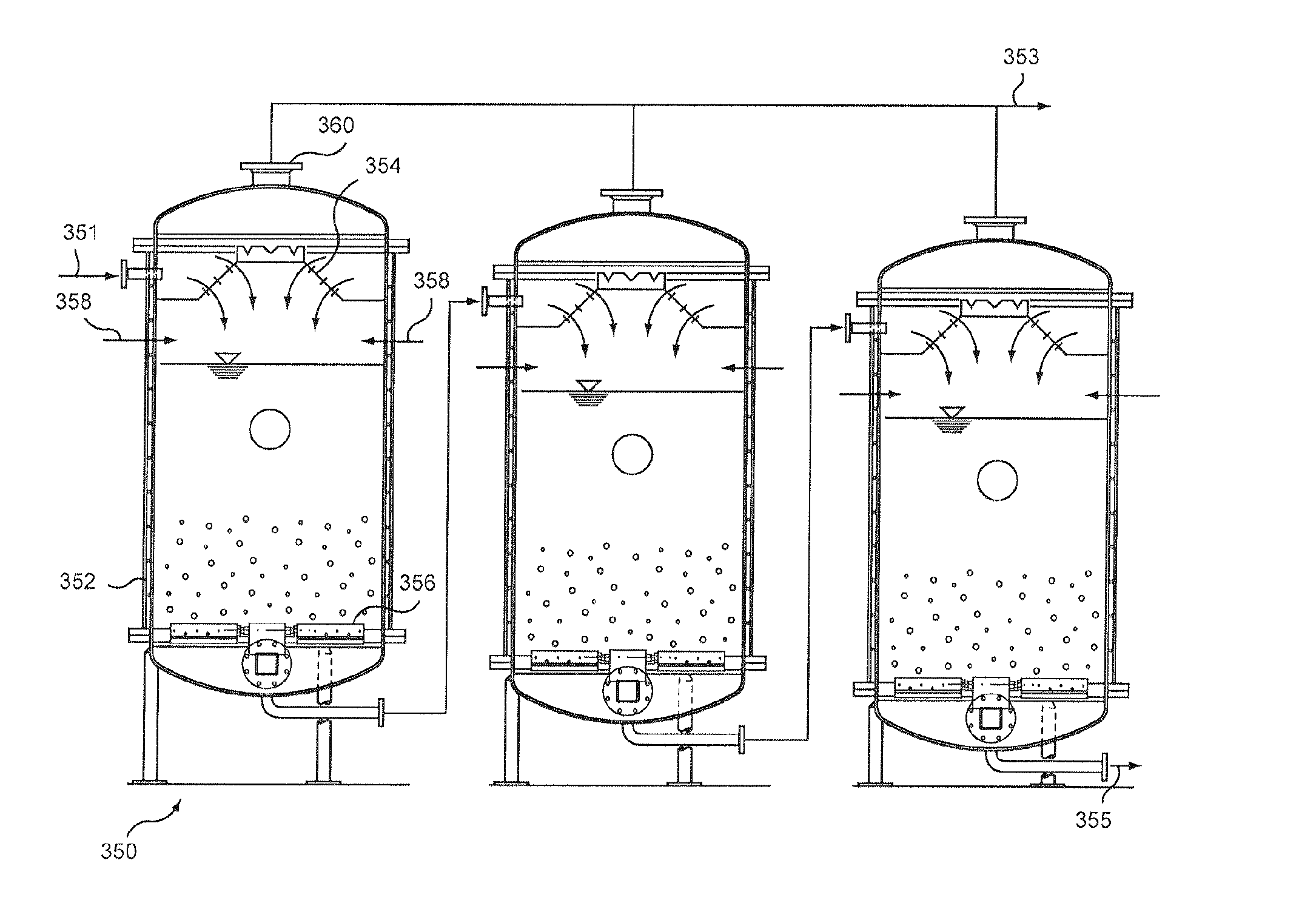
Multiple tank high solids anaerobic digester
A multi-stage anaerobic digester is designed to treat a high solids, stackable feedstock. The system may also receive a pumpable feedstock such as a slurry or sludge. In a first stage, the digestate circulates in one direction around a raceway such that the digestate may pass a feed inlet multiple times before leaving the first tank. An optional side stream loop withdraws fibrous material from near the top of the reaceway and return digestate with chopped fibers, preferably lower and further along the raceway. An outlet from the raceway located near, but upstream of the feed inlet discharges partially digested substrate to a second stage, which is operated as a stirred tank reactor. The two stages may be provided in a single tank with an internal wall separating a ring shaped outer portion from a cylindrical inner portion. The digester may be operated in a thermophilic temperature range.
Owner:ANAERGIA
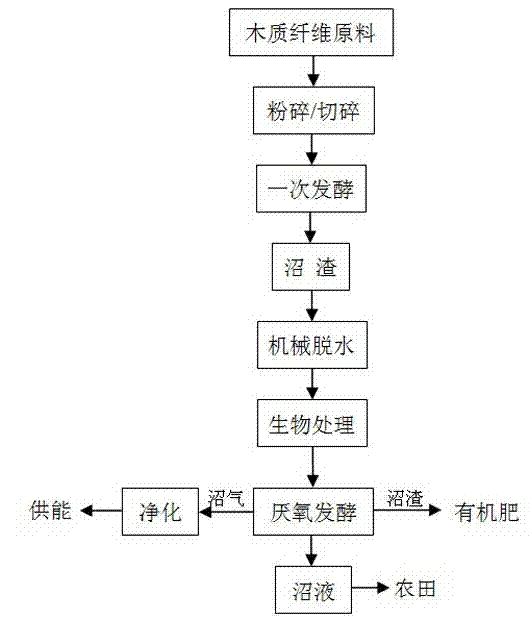
Method for producing methane by using lignocellulosic materials
The invention discloses a method for producing methane by using lignocellulosic materials. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing the lignocellulosic materials, adding the crushed lignocellulosic materials into an anaerobic reactor, inoculating an inoculum for carrying out primary fermentation to produce methane; after a methane producing peak, taking digestate out, mechanically dewatering until the water content is 60-75 percent, carrying out biological treatment, inoculating a microbial agent containing one or more of white rot fungi, monilinia fructicola and peurotoid fungi, under the conditions of inoculum size being 1-3 percent, water content being 55-75 percent and temperature being 20-35 DEG C, carrying out aerobic fermentation for 2-7 days; and then inoculating the inoculum for carrying out secondary anaerobic digestion to produce methane. Compared with a technology for producing the methane through pretreatment of the lignocellulosic materials through microorganism inoculating, the method has the advantages that the methane producing rate of the lignocellulosic materials can be increased by 27.64-47.89 percent, the consumption of the microbial agent is reduced by about 50 percent, the loss of readily decomposable organic matters in the lignocellulosic materials in a biotreatment process is greatly reduced, and the accumulated methane production yield of the lignocellulosic materials is increased by 21.77-41-32 percent compared with that in the biological pretreatment.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
In-vitro semi-dynamic simulation digestion method and device for aquatic products
InactiveCN112034114AChoose scientifically and comprehensivelyMeticulous designComponent separationTesting foodAquatic productDigestion
The invention discloses an in-vitro semi-dynamic simulation digestion method and device for aquatic products, and belongs to the technical field of in-vitro simulation digestion. The method comprisesthe following steps of: oral cavity simulation, specifically, adding an oral cavity simulation digestive juice and a CaCl2 (H2O) 2 solution into an aquatic product, and incubating to obtain an oral cavity simulation digested product; stomach simulation, specifically, adding a stomach simulation digestive juice into an oral cavity simulation digested product, and adding a hydrochloric acid solutionin batches until the pH value is 2.0-1.2, supplementing 20mL of the system with water, adding a CaCl2 (H2O)2 solution for incubation to obtain a stomach simulated digested product; and intestine simulation, specifically, adding intestine simulation digestive juice into the stomach simulation digested product, adjusting the pH value to 6.9-7.4 by adopting sodium hydroxide, adding water to supplement the system to 40 mL, and adding a CaCl2 (H2O) 2 solution for incubation to obtain an intestine simulation digested product. The simulated digestive juices are more scientific and comprehensive in formula, the pH value of the digestion condition is finer, the simulated digestion stage is not unchanged. Therefore, the method and device can better fit the digestion condition of a human body.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for producing a fertilisation product
InactiveUS20170088478A1Reduce riskSimple materialBio-organic fraction processingProductsFiltrationFertilisation
A method of treating a digestate material, comprising the steps of obtaining an anaerobically produced digestate exerting pressure on the digestate to remove water from the digestate to form a low-water digestate and including the further step of filtering the low-water digestate filtered through a filtration means.
Owner:SUGGITT SARAH ELIZABETH +1
Methods and systems for recovering phosphorus from wastewater including digestate recycle
ActiveUS10189711B2Treatment with anaerobic digestion processesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWastewaterInorganic phosphorus
Methods and systems for removal and recovery of phosphorus from wastewater and producing inorganic phosphorus complexes including digestate recycle.
Owner:MULTIFORM HARVEST
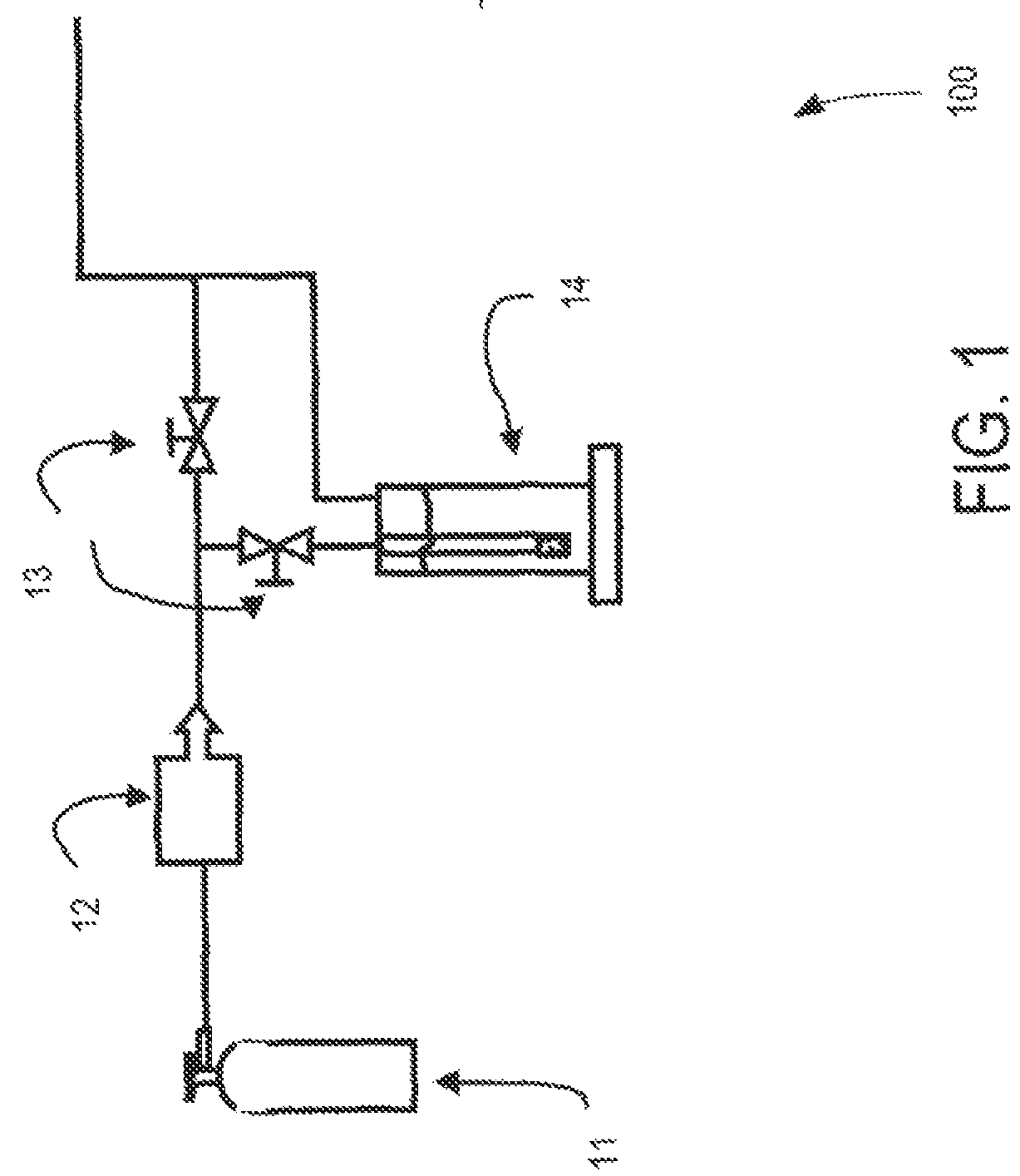
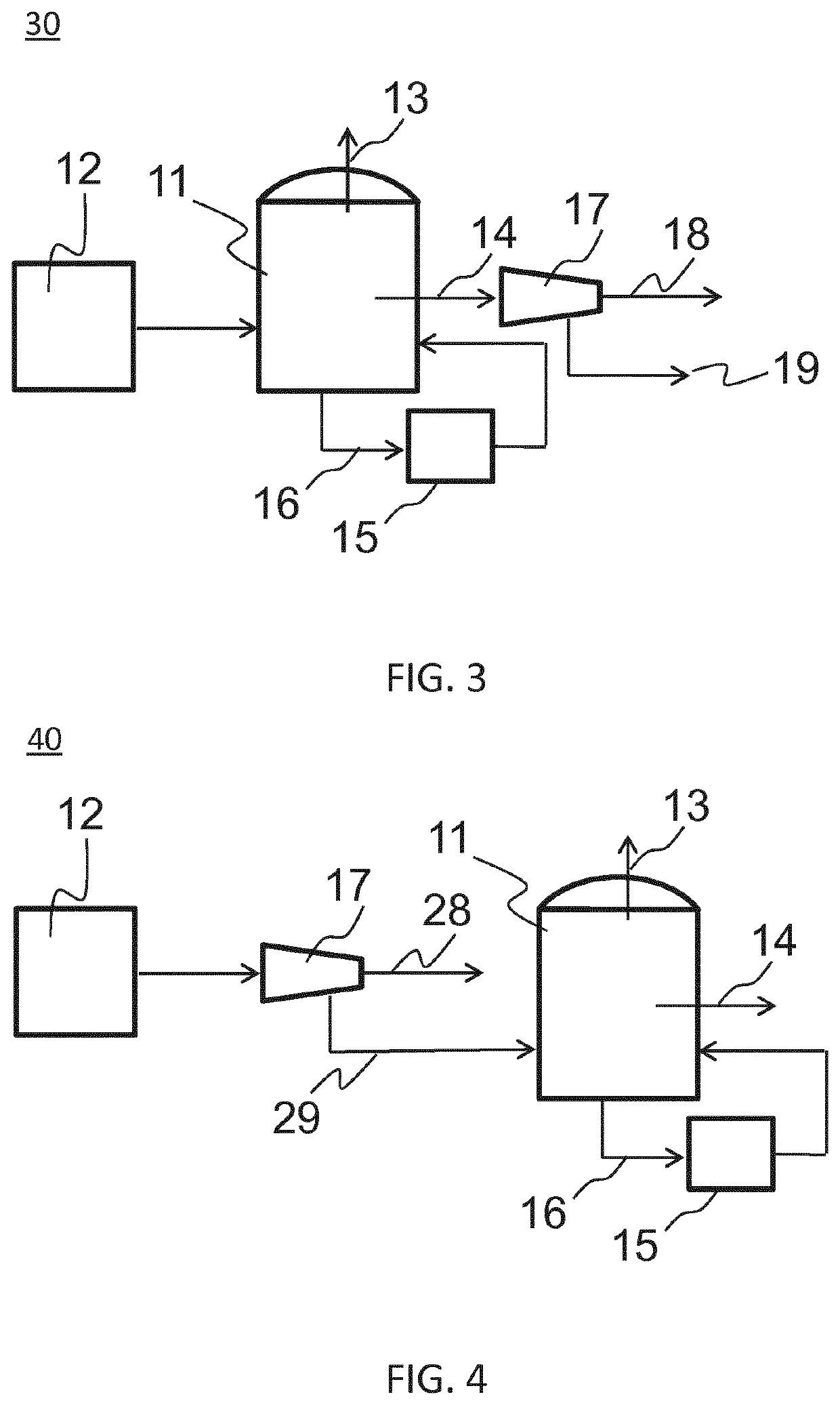
Improved biogas production system and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20180079997A1Reduce downtimeReduce equipmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiogas productionEngineering
The present invention provides a biogas production system comprising: at least one digester for generating biogas and digestate, each digester comprising: a first end portion, a second end portion, and a peripheral side-wall there-between; one or more inlets, wherein at least one inlet is arranged to receive organic substrates; one or more outlets, wherein at least one outlet is arranged to release biogas; and a feed system comprising a pit arranged to receive and supply said organic substrates to the digester, said inlet positioned adjacent to a lower portion of said pit, the pit arranged such that a weight of the organic substrates within the pit bias the organic substrates into the digester.
Owner:KRU ENERGY ASIA PTE LTD
Swine pasteurellosis vaccine enrichment medium
PendingCN111040971APromote growth and reproductionRich in nutrientsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyVaccine Production
The invention provides a swine pasteurellosis vaccine enrichment medium, and relates to the field of biology. The swine pasteurellosis vaccine enrichment medium is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 20.0g of meat liver and stomach membrane digestive juice powder, 8.0g of bovine pancreas digestive juice, 10.0g of peptone, 5.0g of NaCl, 1.0g of a growth promoting factor, and purified water added to 1000ml. A preparation method of the swine pasteurellosis vaccine enrichment medium comprises the following steps: adding all the raw materials for preparing the swine pasteurellosisvaccine enrichment medium into purified water, fully dissolving the raw materials, and carrying out sterilization at 121 DEG C for 15 minutes for later use. The invention relates to an application ofa synthetic dry powder culture medium in swine pasteurellosis vaccine production. The synthetic dry powder culture medium has the beneficial effects that commercial raw materials can be selected, theculture medium is clear, the number of cultured bacteria is high, and the freeze-drying survival rate of the bacteria is increased.
Owner:青岛高科技工业园海博生物技术有限公司
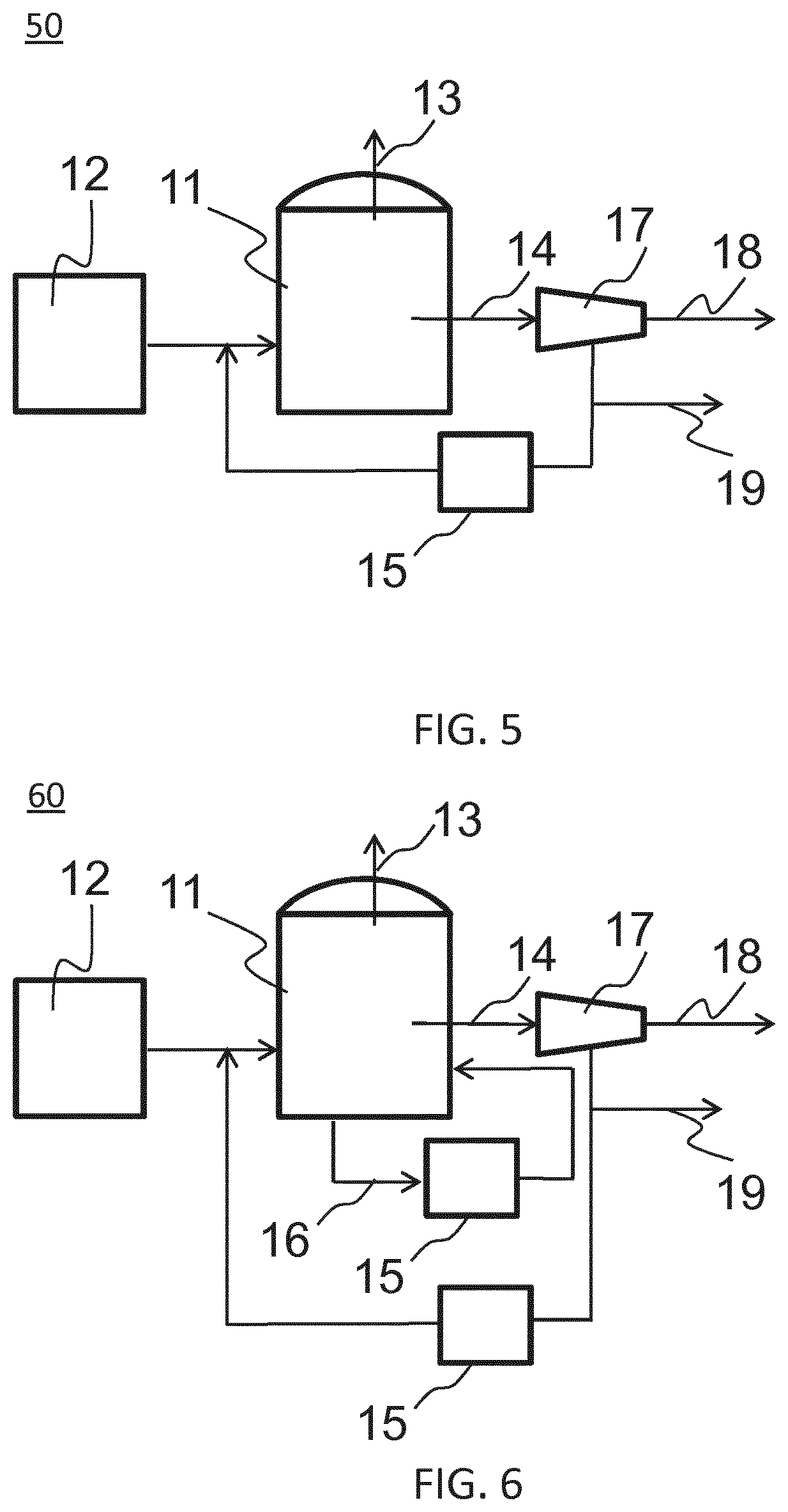
Apparatus and method for refractory organics conversion into biogas
ActiveUS20200165553A1Increase biogas productionLower requirementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysical chemistryDigestate
An apparatus for refractory organics conversion into biogas includes an anaerobic digester configured to be fed with organic material comprising refractory organics and to generate biogas and a digestate comprising at least a part of the refractory organics, wherein the apparatus comprises a device for a controlled partial oxidation of the refractory organics comprising an inlet configured to be fed with refractory organics and means configured to control the residence time of the refractory organics within the device for a controlled partial oxidation, so as to partially degrade refractory organics. A method for refractory organics conversion into biogas carried out using such an apparatus is also provided.
Owner:SUEZ INT
Spray dryer exhaust treatment and anaerobic digester
InactiveUS20150000156A1Drying solid materials with heatWaste based fuelCombustion chamberExhaust fumes
A spray dryer exhaust gas treatment system and process recovers waste heat, removes odors from the exhaust gas, or both. The spray dryer may be used to dry digestate from an anaerobic digester. Spray dryer exhaust is at least partially recirculated to the spray dryer, or condensable vapors are removed from the spray dryer exhaust, or both. Optionally, a bleed from a recirculating exhaust stream may pass through a combustion chamber. Preferably, waste heat is added to the recirculating exhaust stream or used to evaporate water upstream of the spray dryer. In a case where the spray dryer is used to treat digestate, a biogas burner may provide the combustion chamber and a source of waste heat. The system and method reduce odors from spray dryer exhaust by condensing odorous compounds, by combustion, or both while using waste heat and spray dryer exhaust gas recirculation to reduce energy consumption.
Owner:ANAERGIA
High porosity cellulosic sponge
PendingCN111494332AEliminate absorptionNo change in uptakePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCapsule deliveryCelluloseChemical compound
The present invention provides compositions, devices, and methods for affecting, among other things, weight loss and / or weight control, by sequestering nutrients or other compounds such as toxins fromabsorption in the digestive tract. The compositions, devices, and methods employ one or more members made of a compressible, absorbent matrix material. In various embodiments, the matrix material issuitable for the routine use. The compressible absorbent matrix material has a size, shape and / or geometry configured for efficient packing into a small space, and / or configured to absorb and substantially retain digested material in the stomach. The devices and the compositions may further comprise one or more hydrogel(s), soluble or insoluble fibers, waxes, and / or gums to provide the desired mechanical properties and / or absorptive or shielding properties.
Owner:SLENDINE AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com