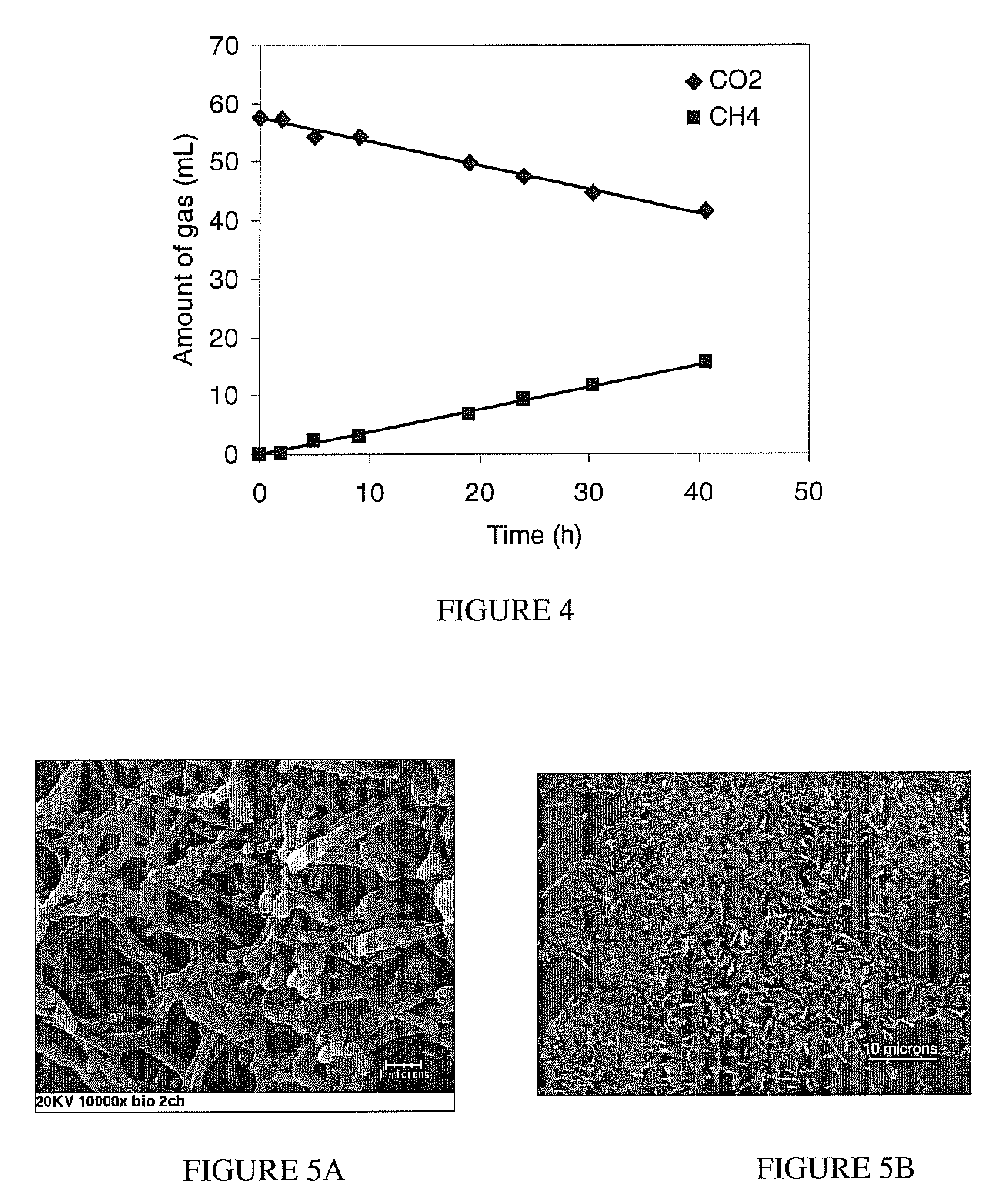
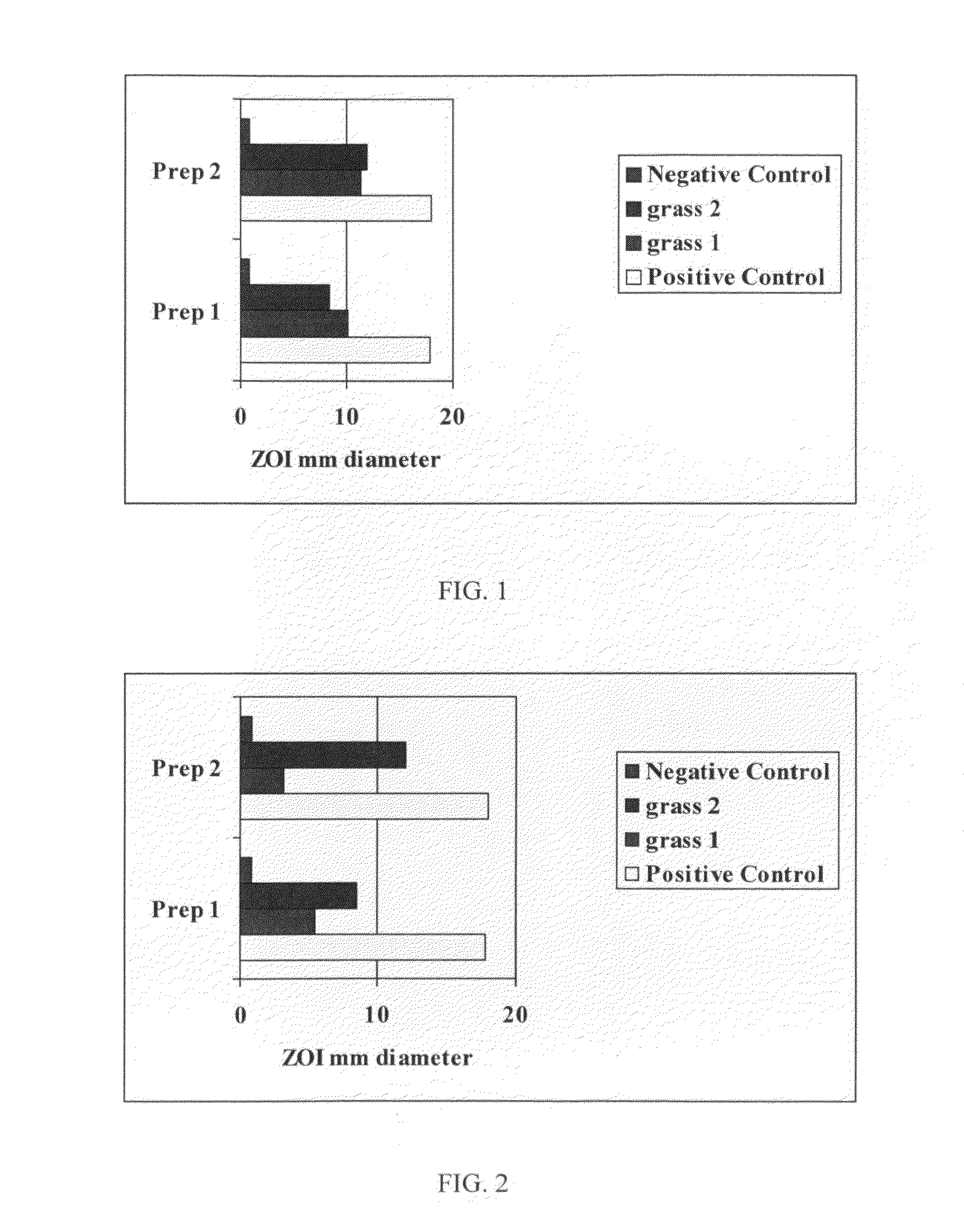
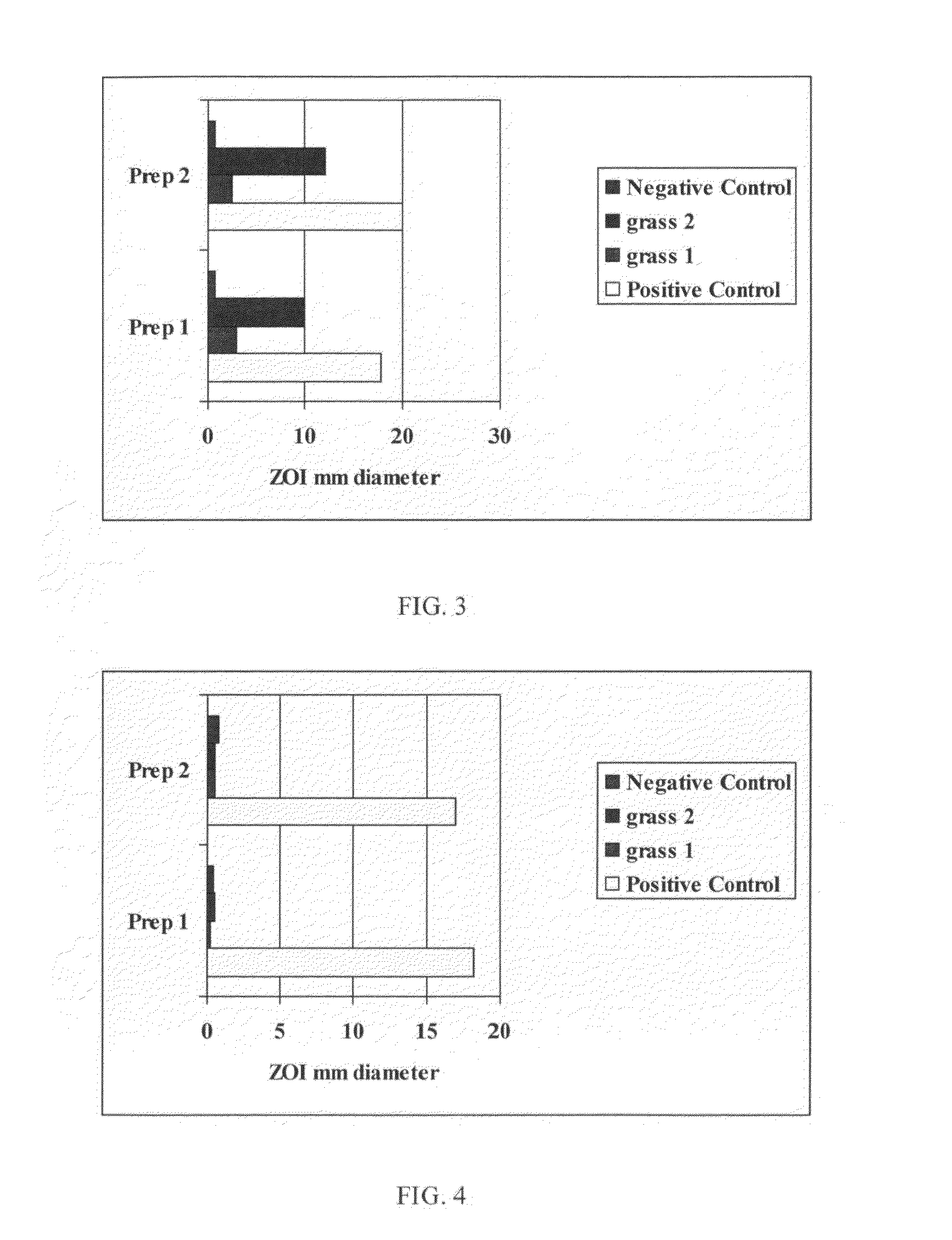
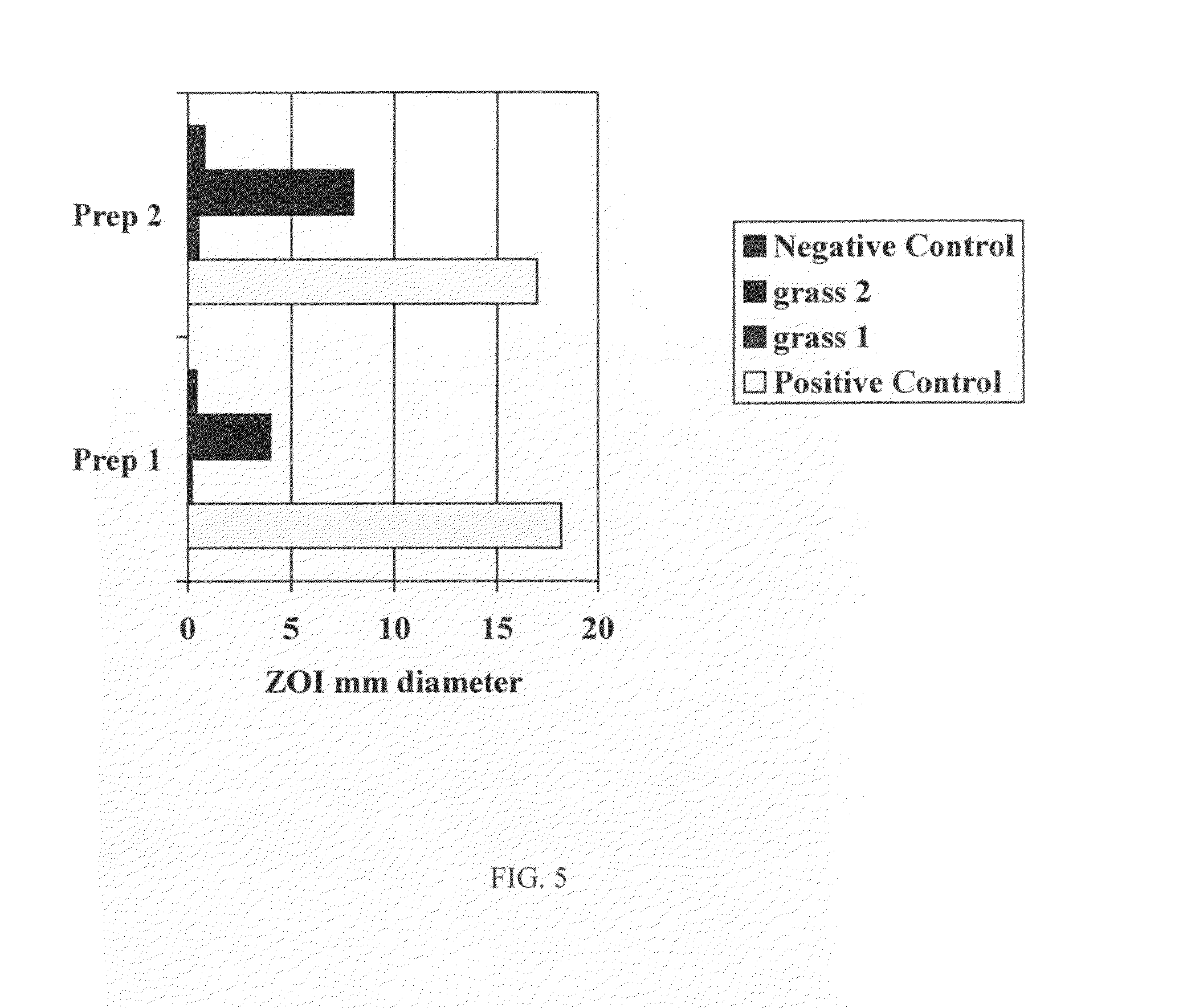
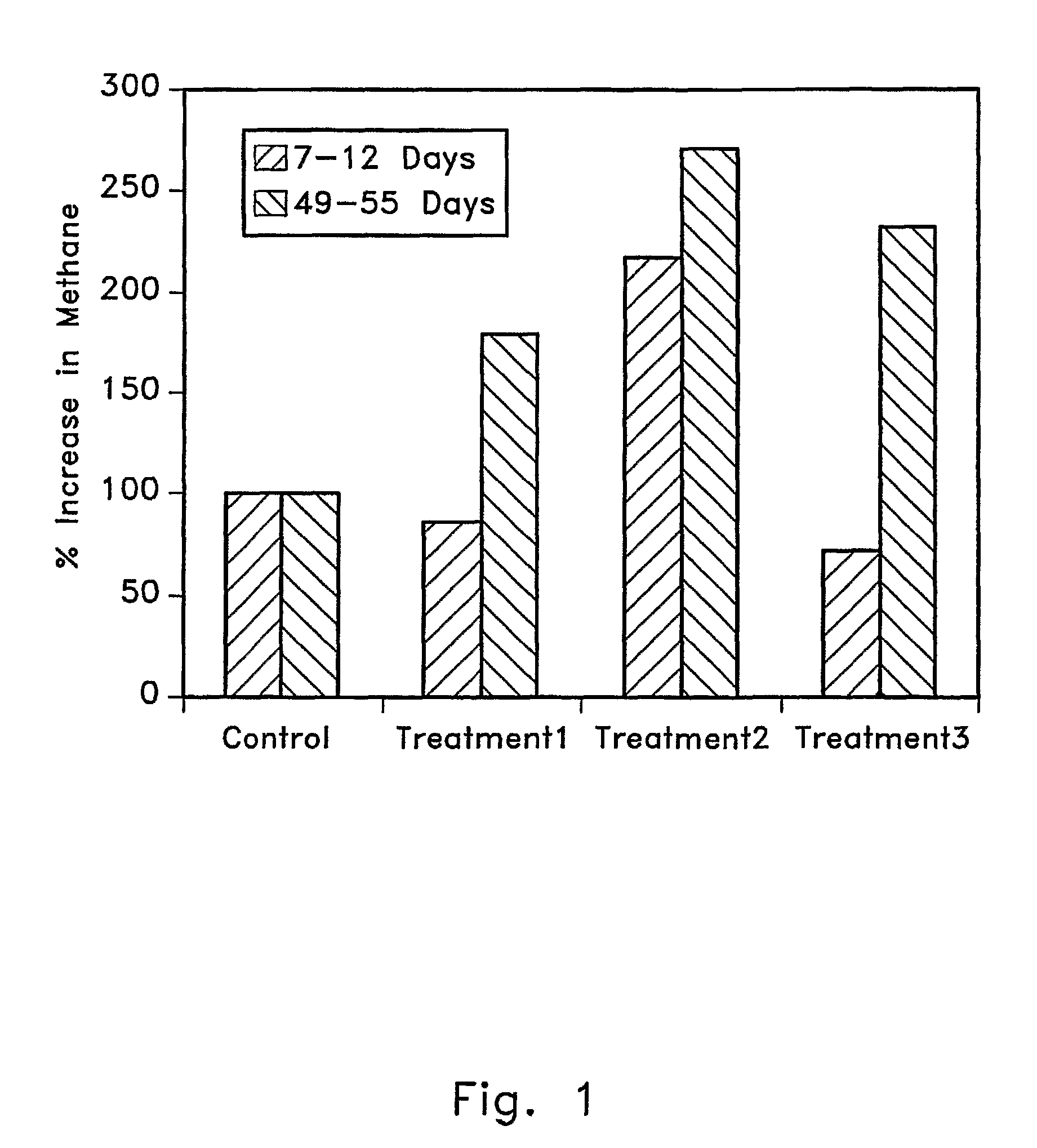
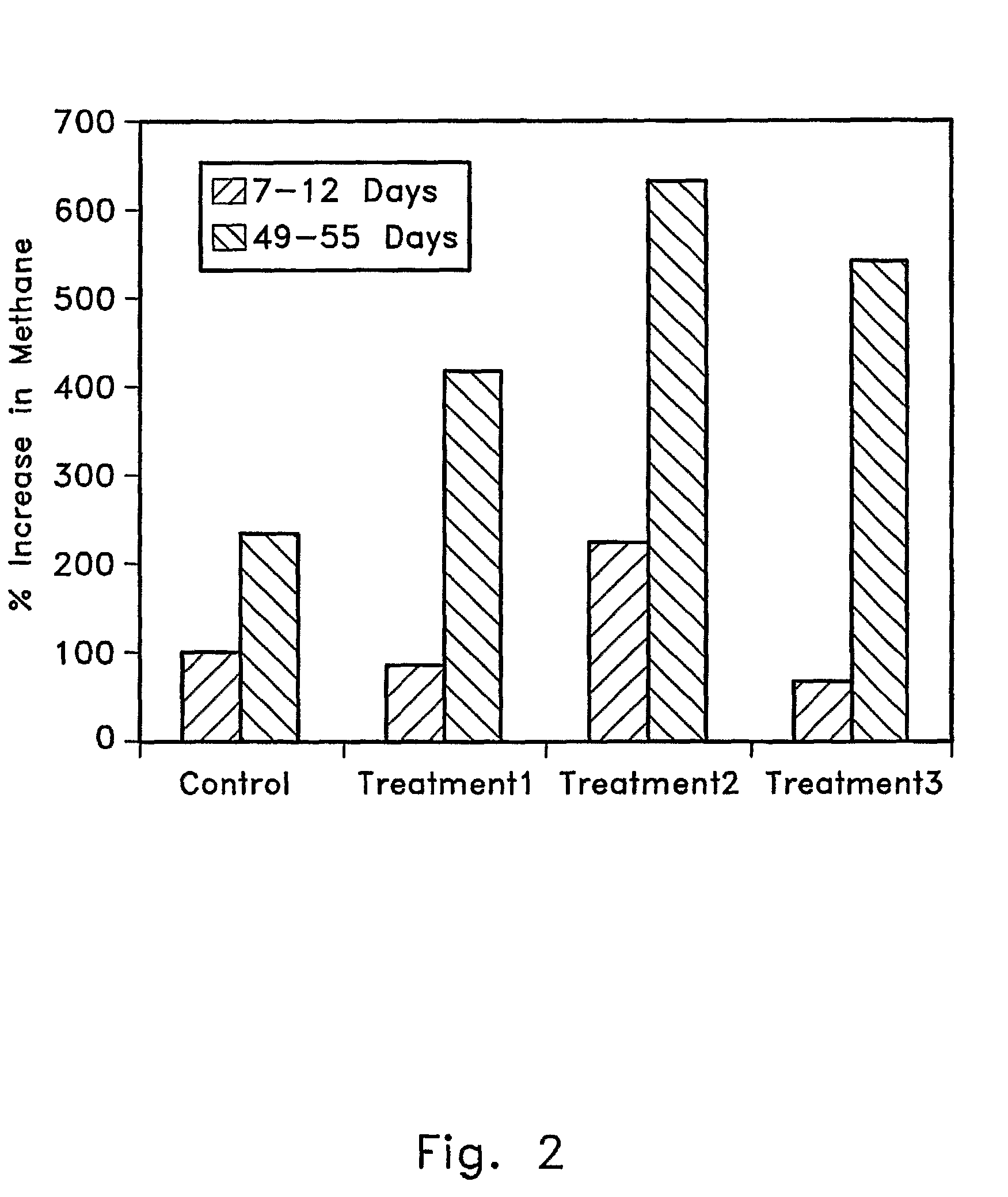
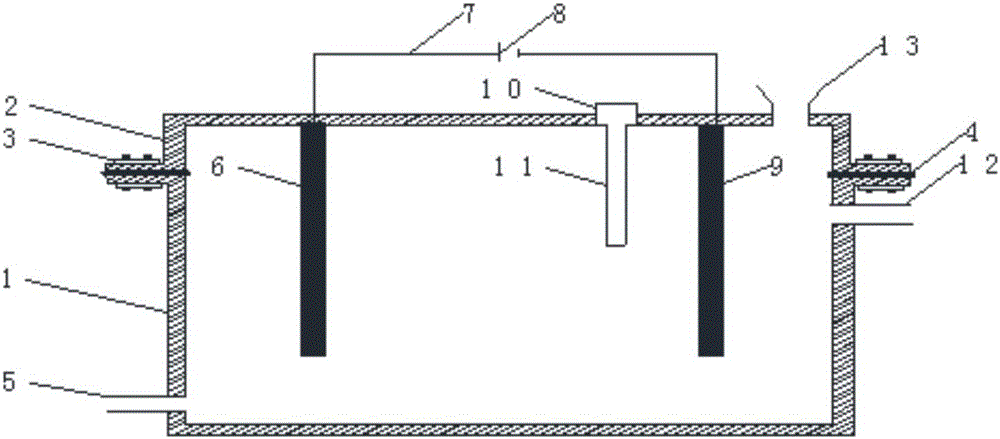
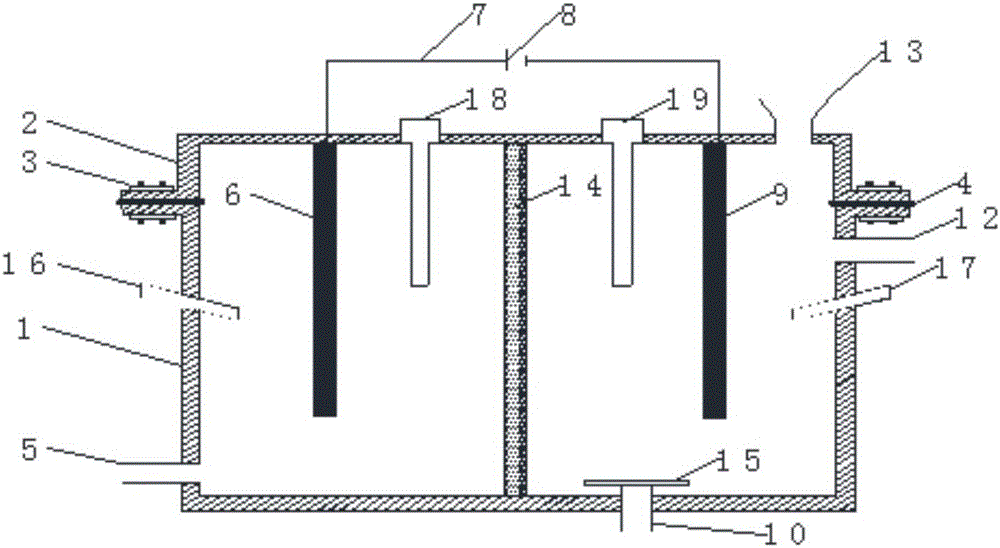
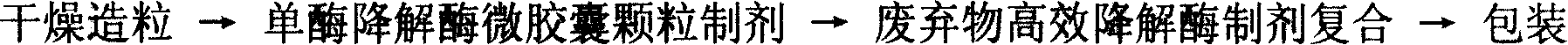Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
700 results about "Methane production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
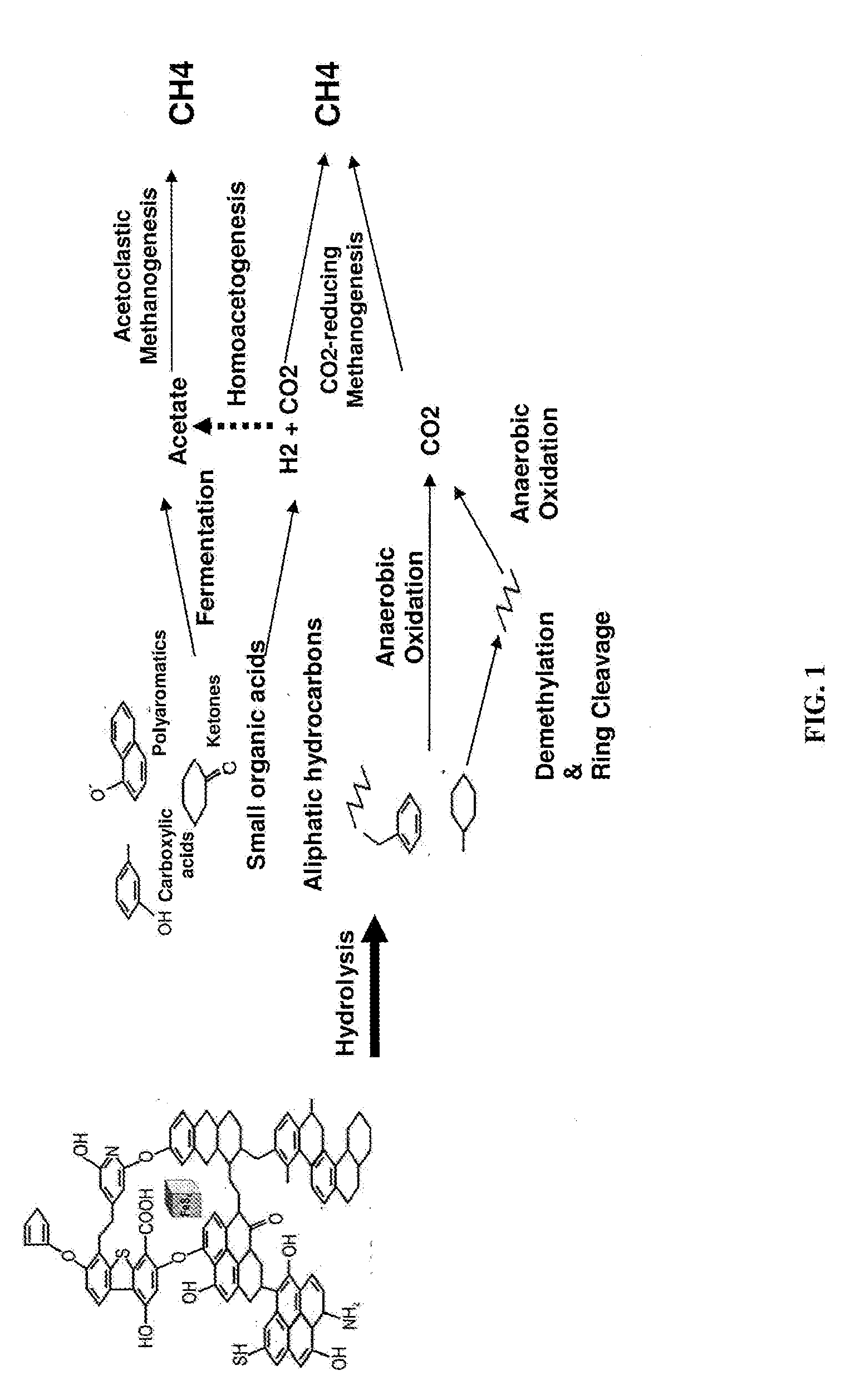
Some methane comes from human activities; landfills, rice cultivation, and ruminant farm animals (like cows) are all large methane sources. Other large methane sources, like the ocean and wetlands, are natural. Methane Production. Methane is produced in two primary ways in the ocean, thermogenically and biogenically.
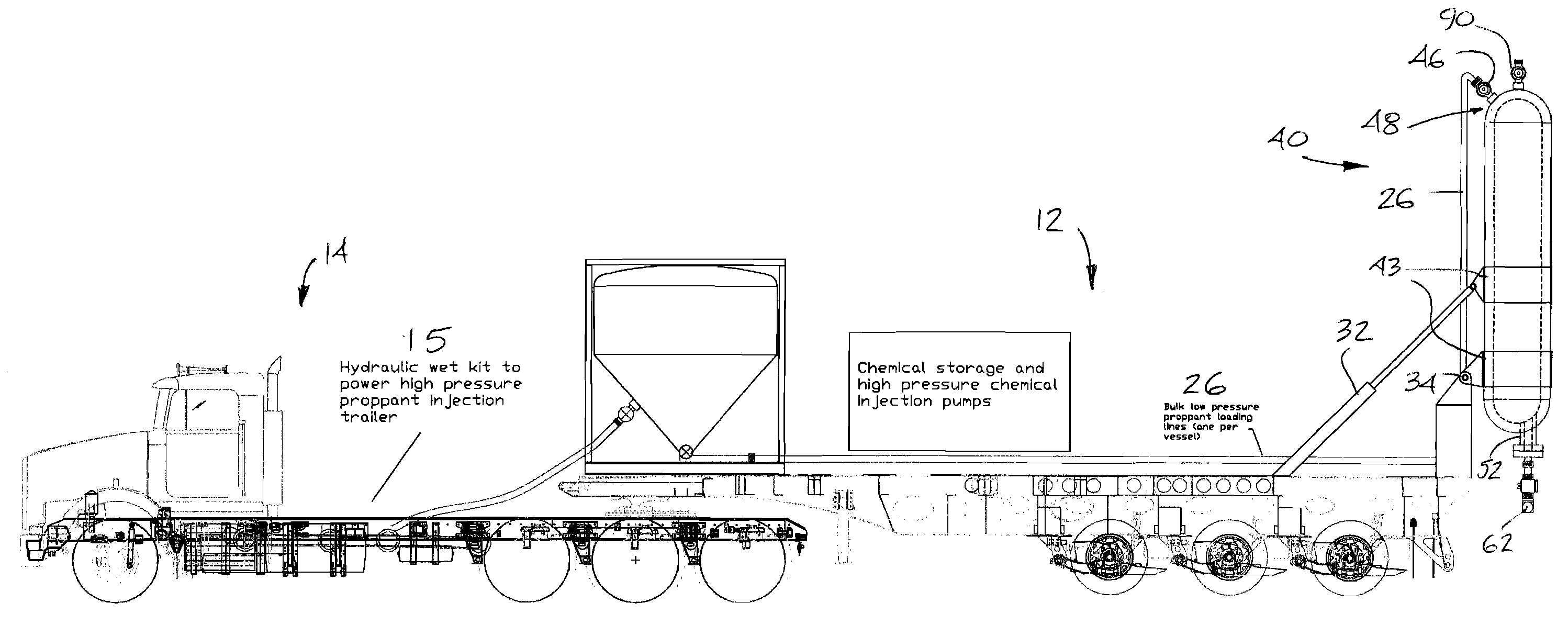
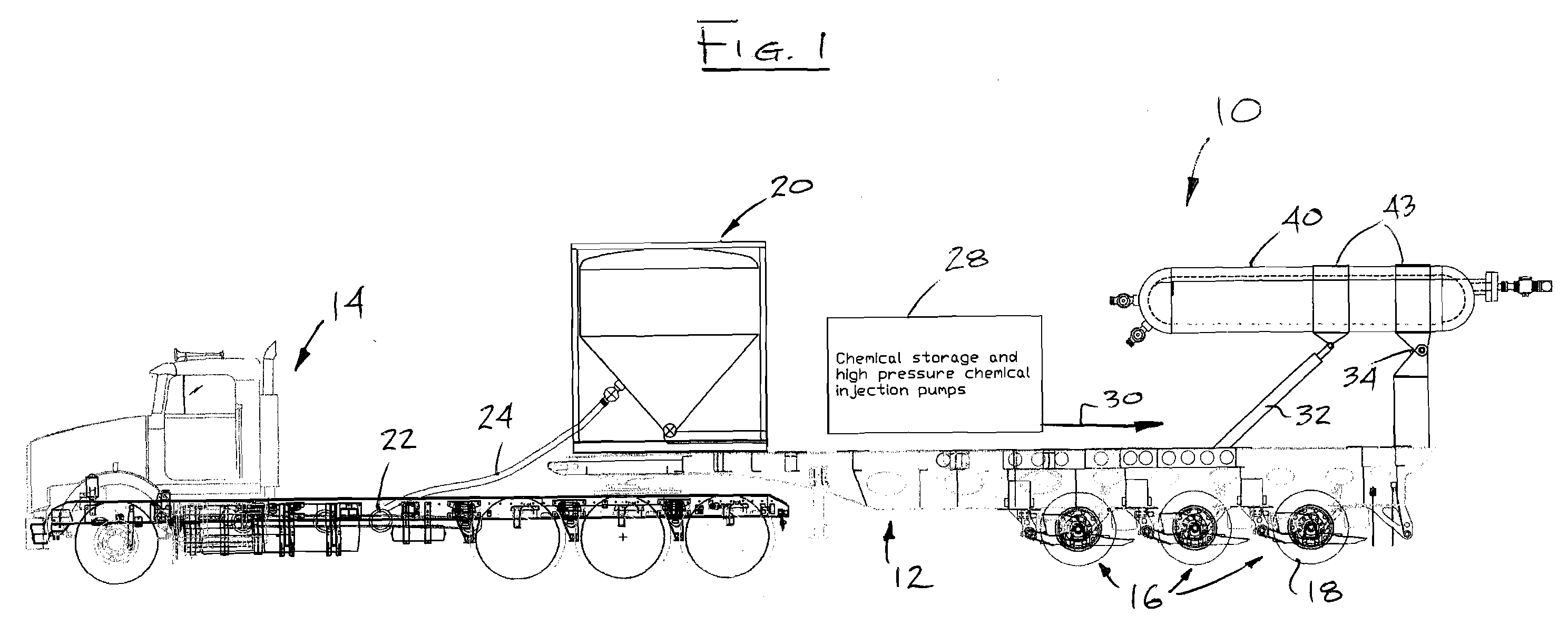
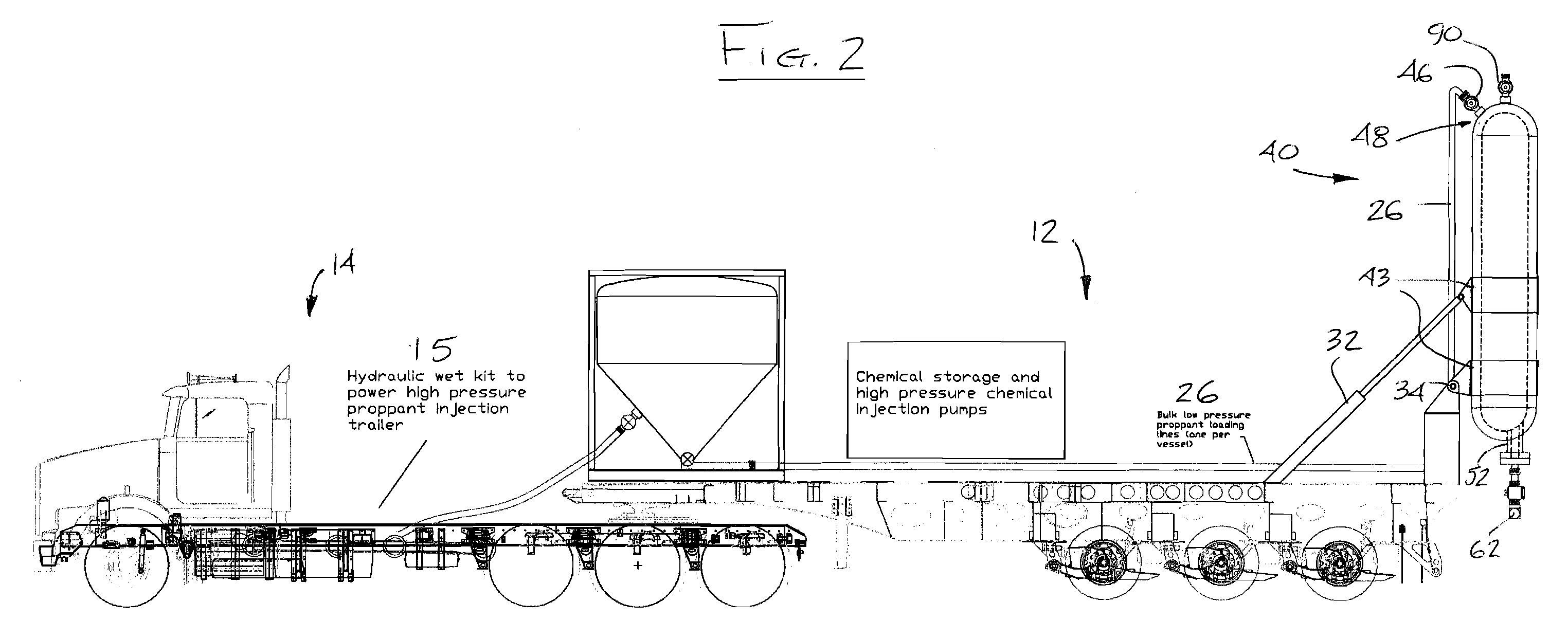
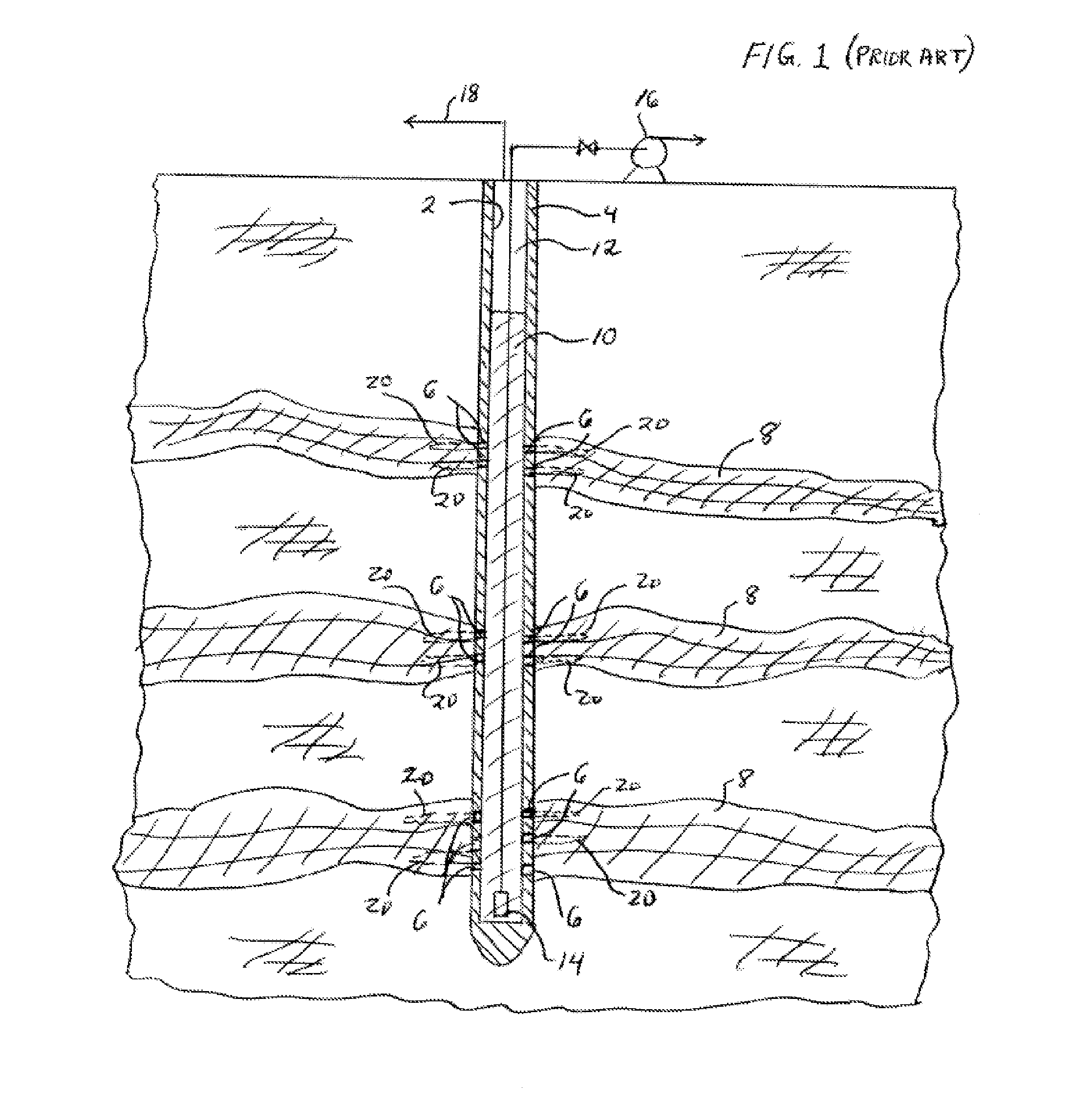
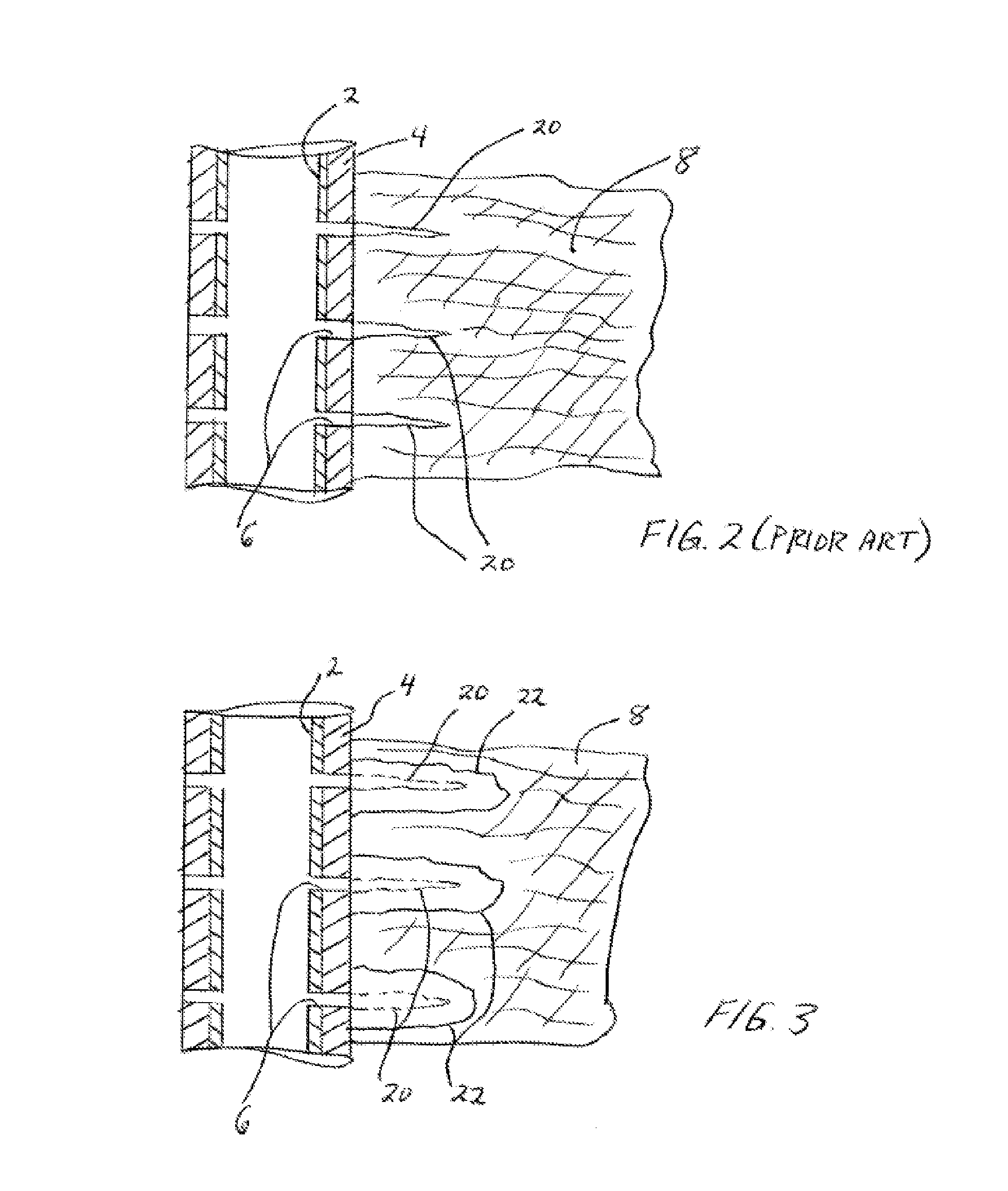
High-pressure Injection Proppant System
Owner:FRAC SOURCE
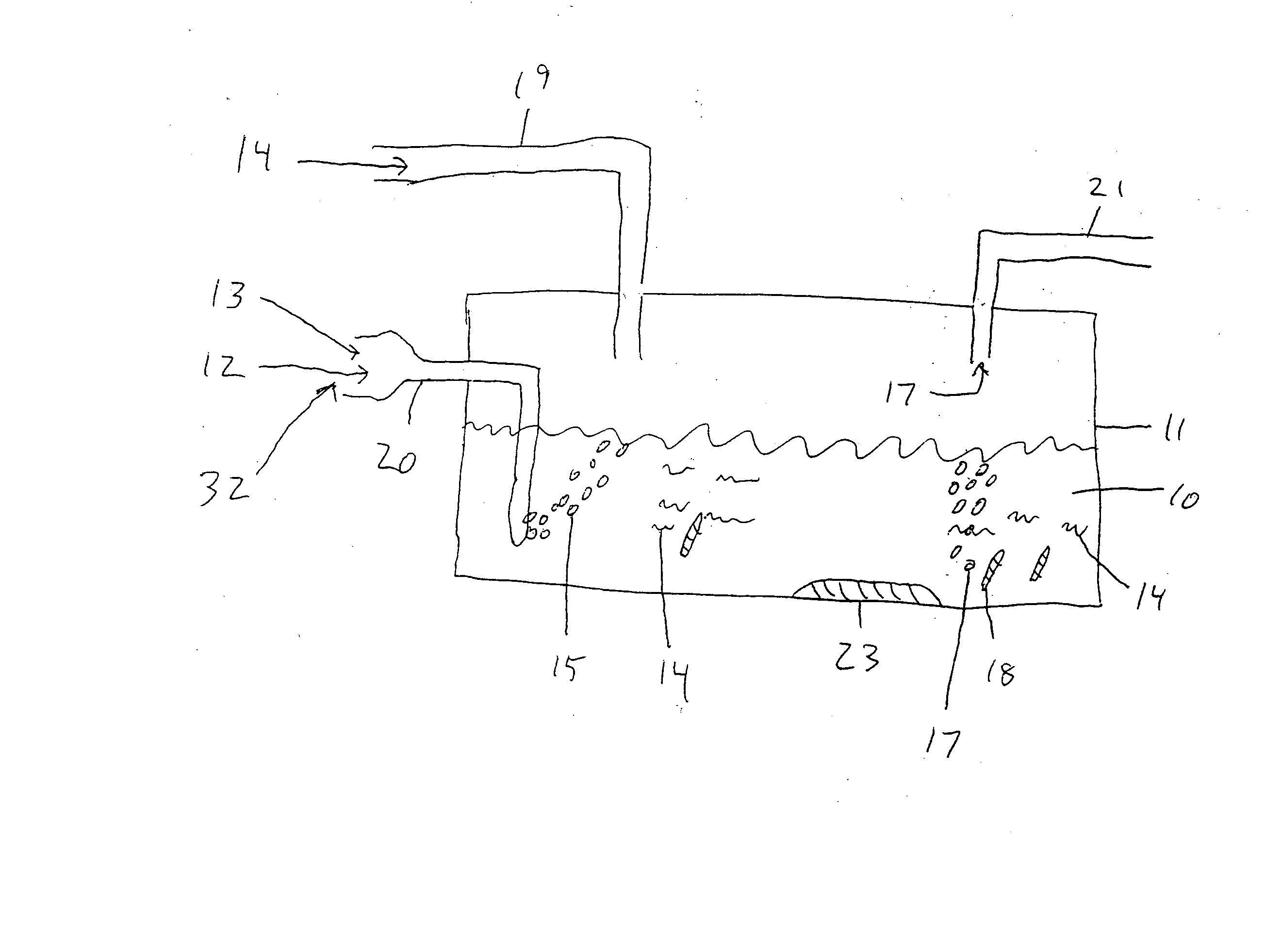
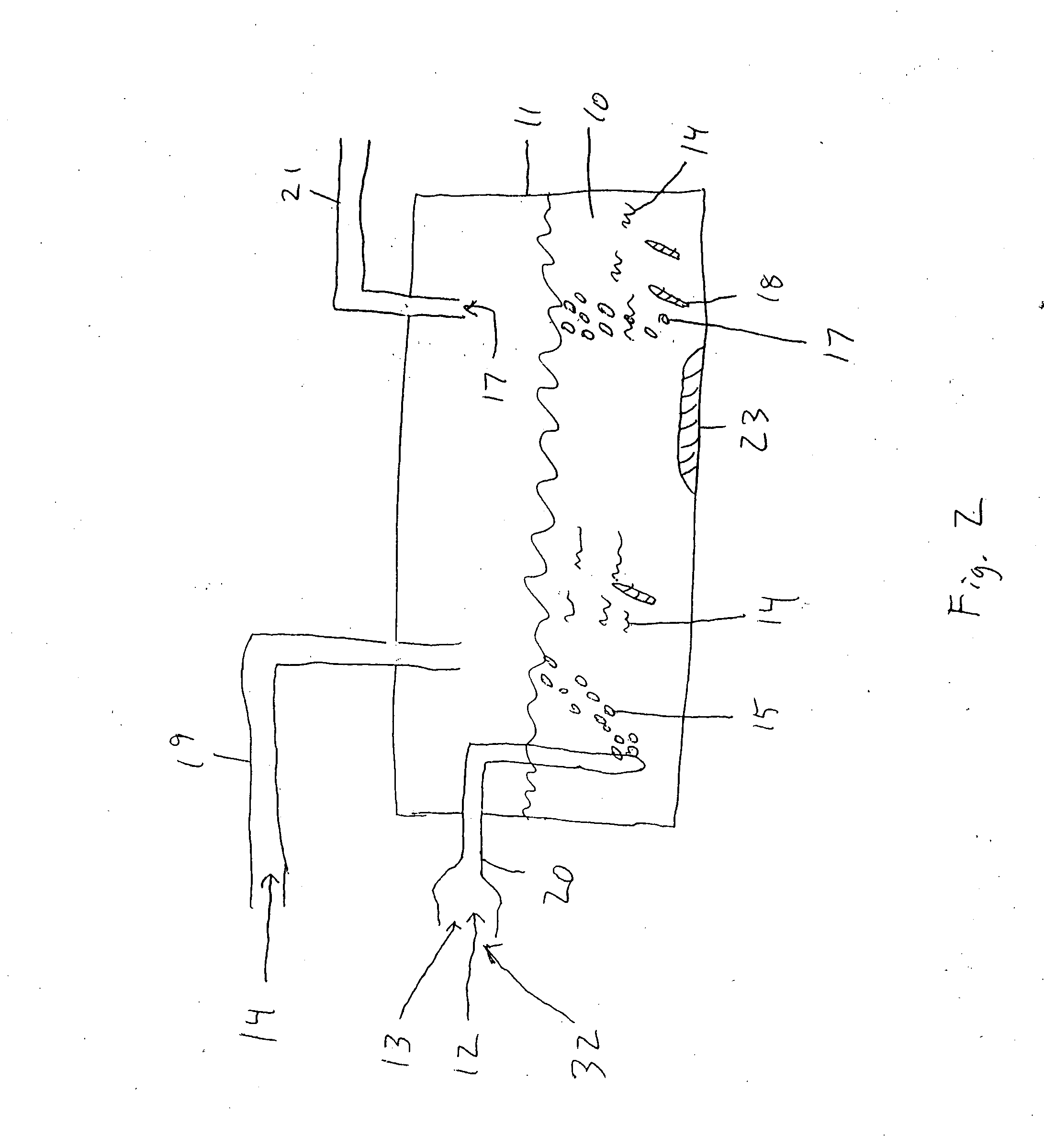
Foaming agents for use in coal seam reservoirs
InactiveUS6915854B2Increase productionGood oil wetting characteristicOther chemical processesFluid removalFoaming agentHydrogen
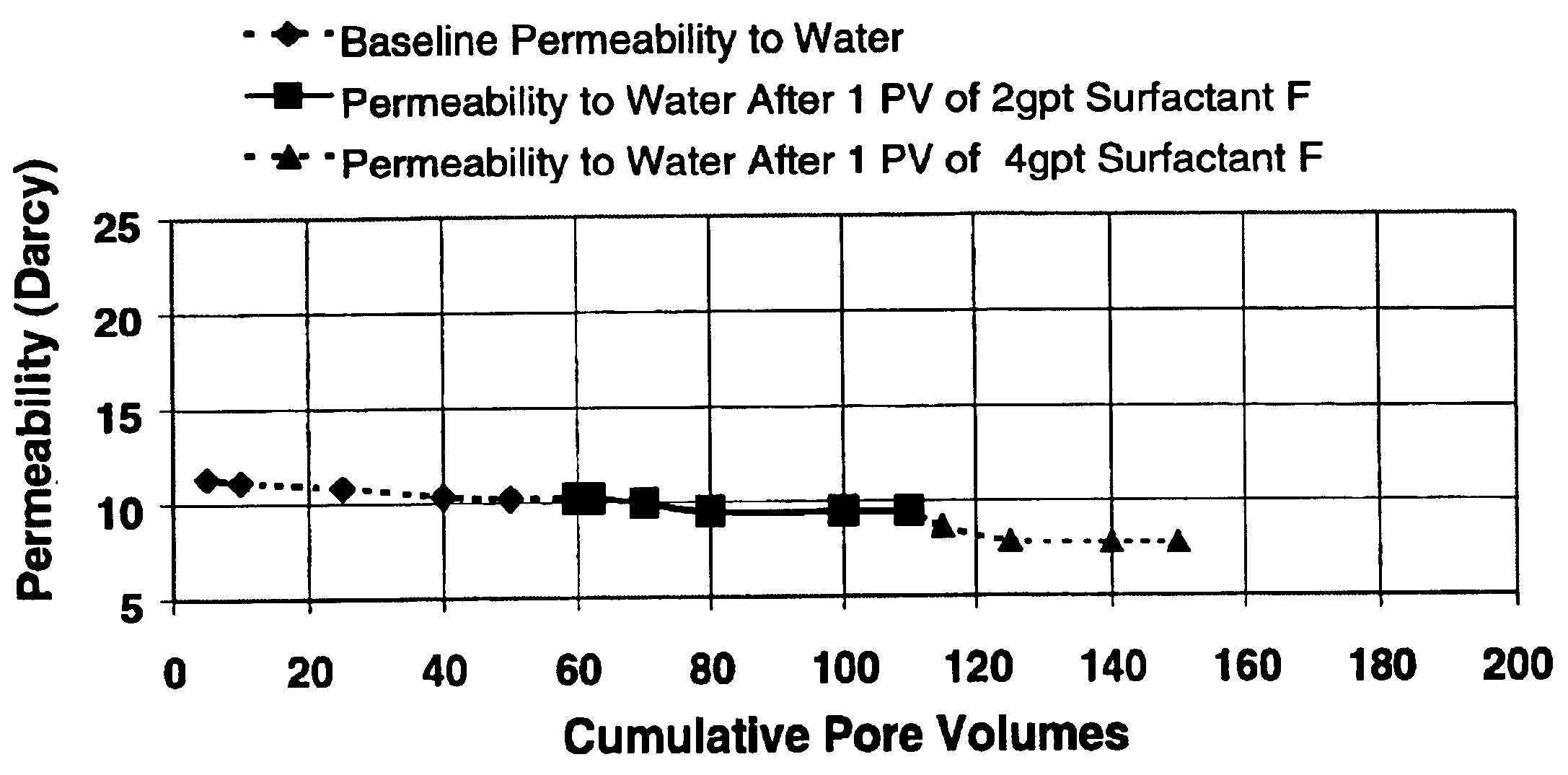
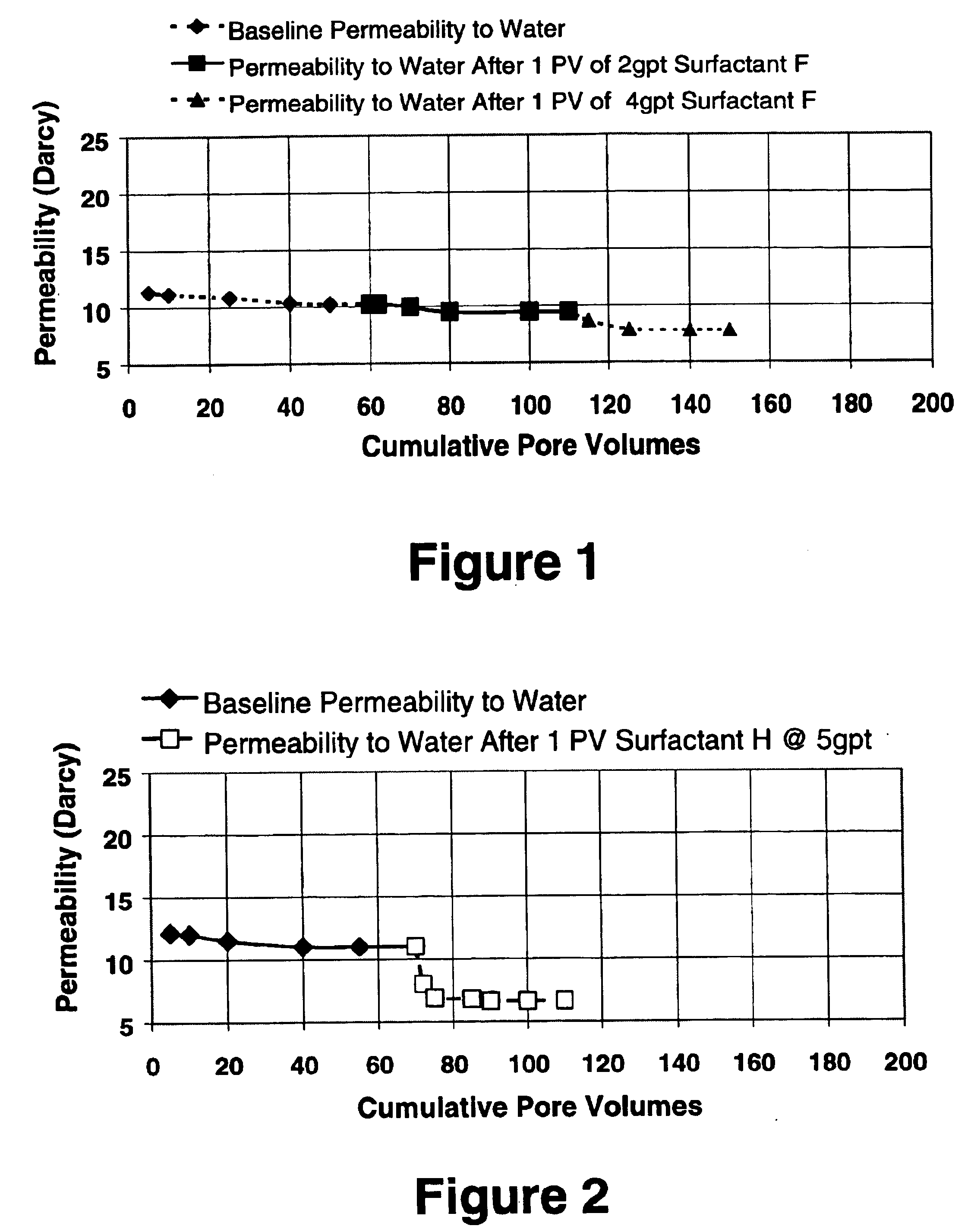
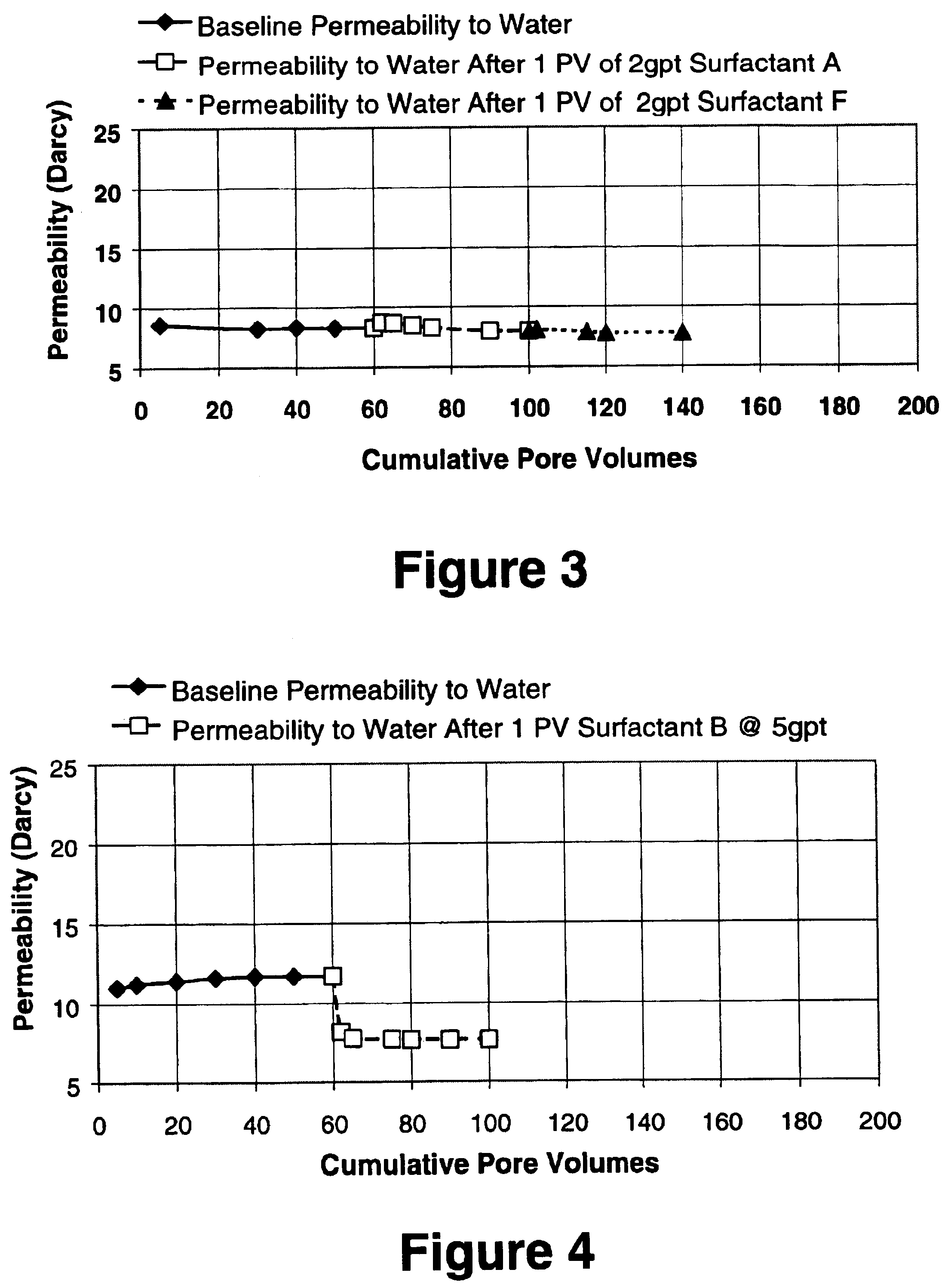
A well treatment fluid composition that comprises a carrier fluid and an amphoteric surfactant, and optionally a viscosifying agent and proppant, is well suited for use in fracturing coal beds to stimulate methane production. The composition preferably is a foam that comprises a gas such as nitrogen or air. Preferably, the surfactant has the formulaR—NH2—(CH2)n—C(O)OXwherein R is a saturated or unsaturated alkyl group having from 6-20 carbon atoms, n is from 2-6, and X is hydrogen or a salt forming cation.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Integrated processes and systems for conversion of methane to multiple higher hydrocarbon products
Integrated systems are provided for the production of higher hydrocarbon compositions, for example liquid hydrocarbon compositions, from methane using an oxidative coupling of methane system to convert methane to ethylene, followed by conversion of ethylene to selectable higher hydrocarbon products. Integrated systems and processes are provided that process methane through to these higher hydrocarbon products.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH LLC
Method and system for monitoring and reducing ruminant methane production
ActiveUS20090288606A1Low costEasy to measureMethane captureAnimal feeding devicesAgricultural scienceProximate
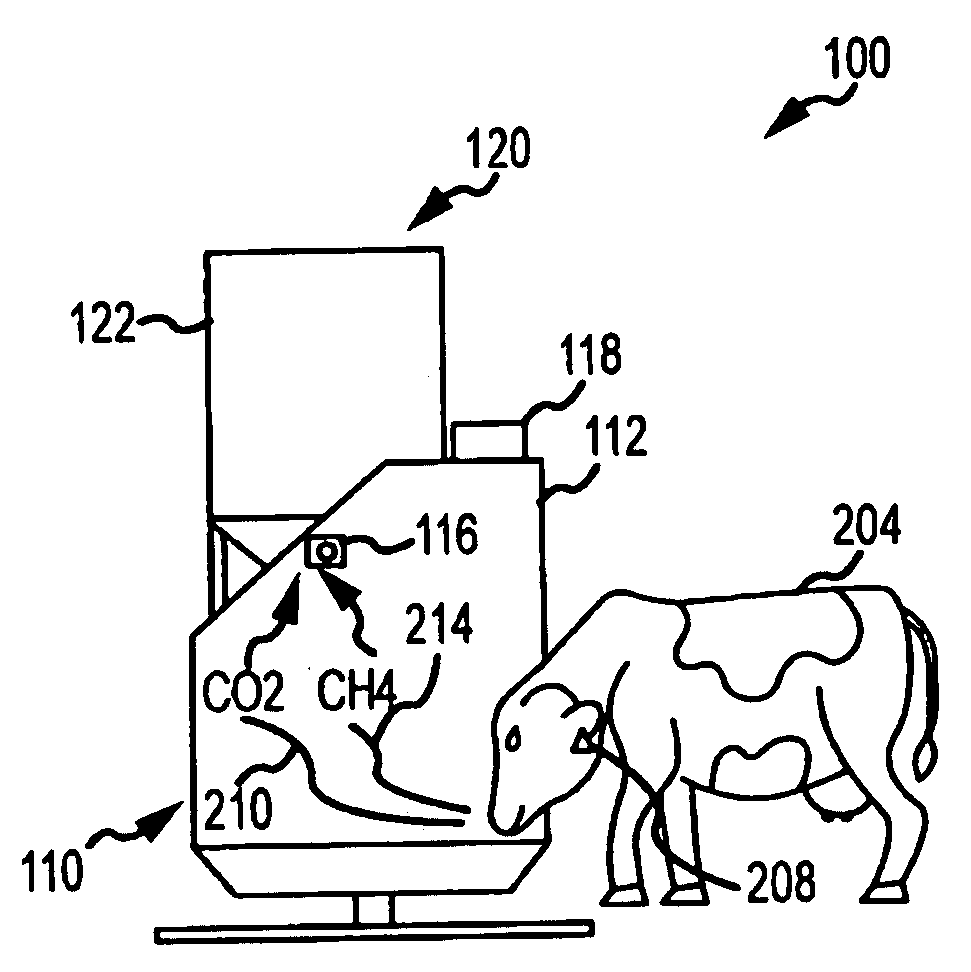
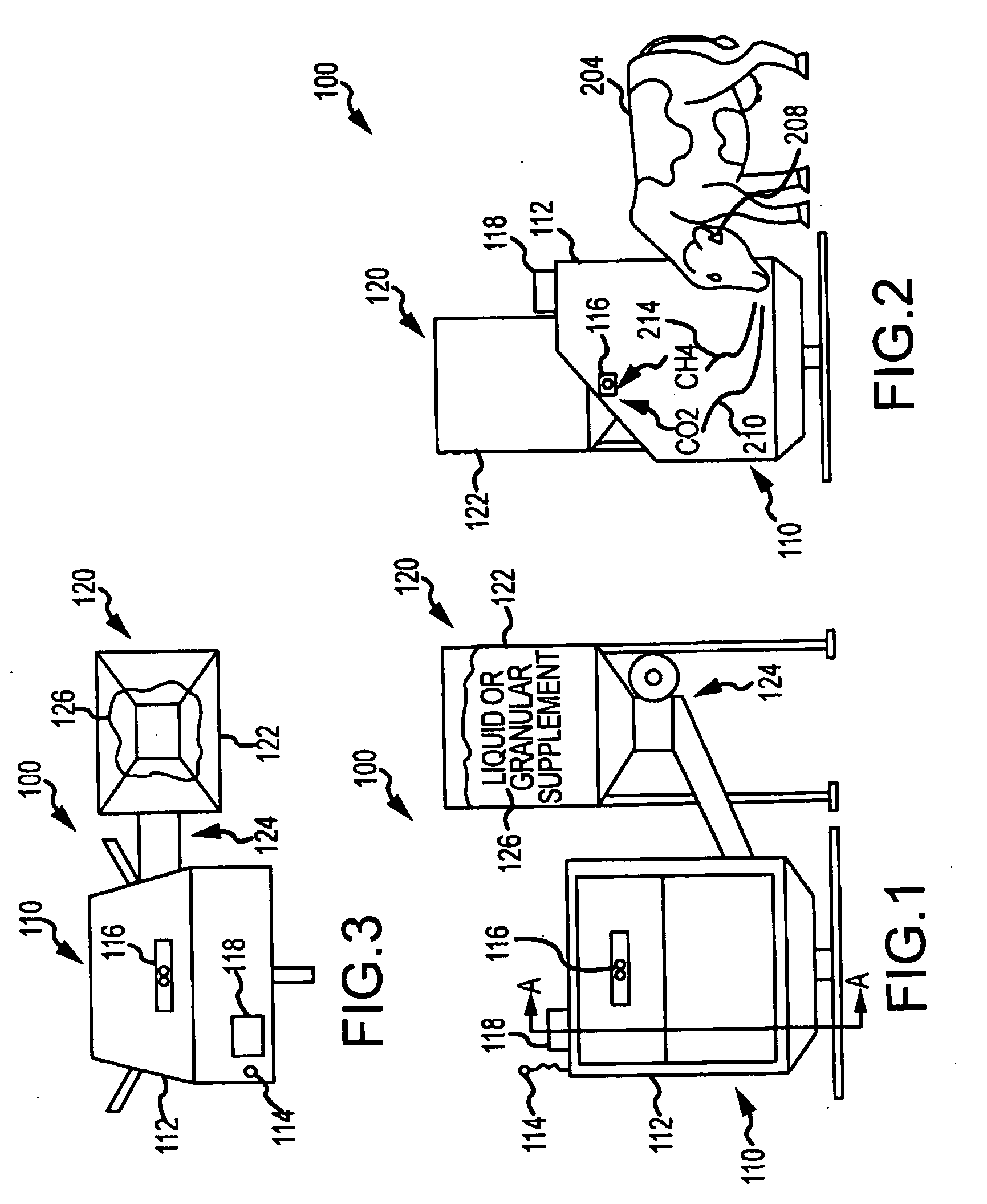
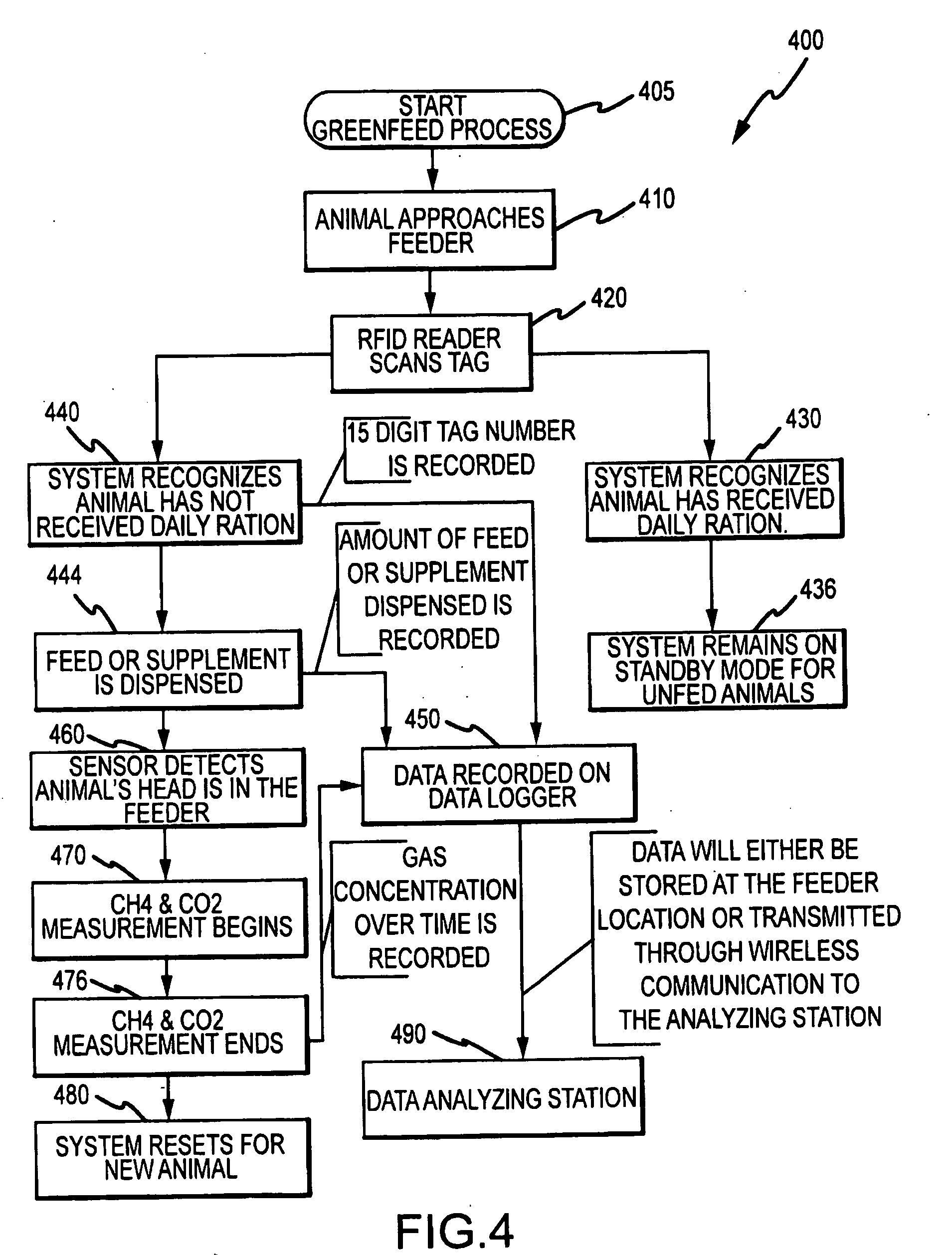
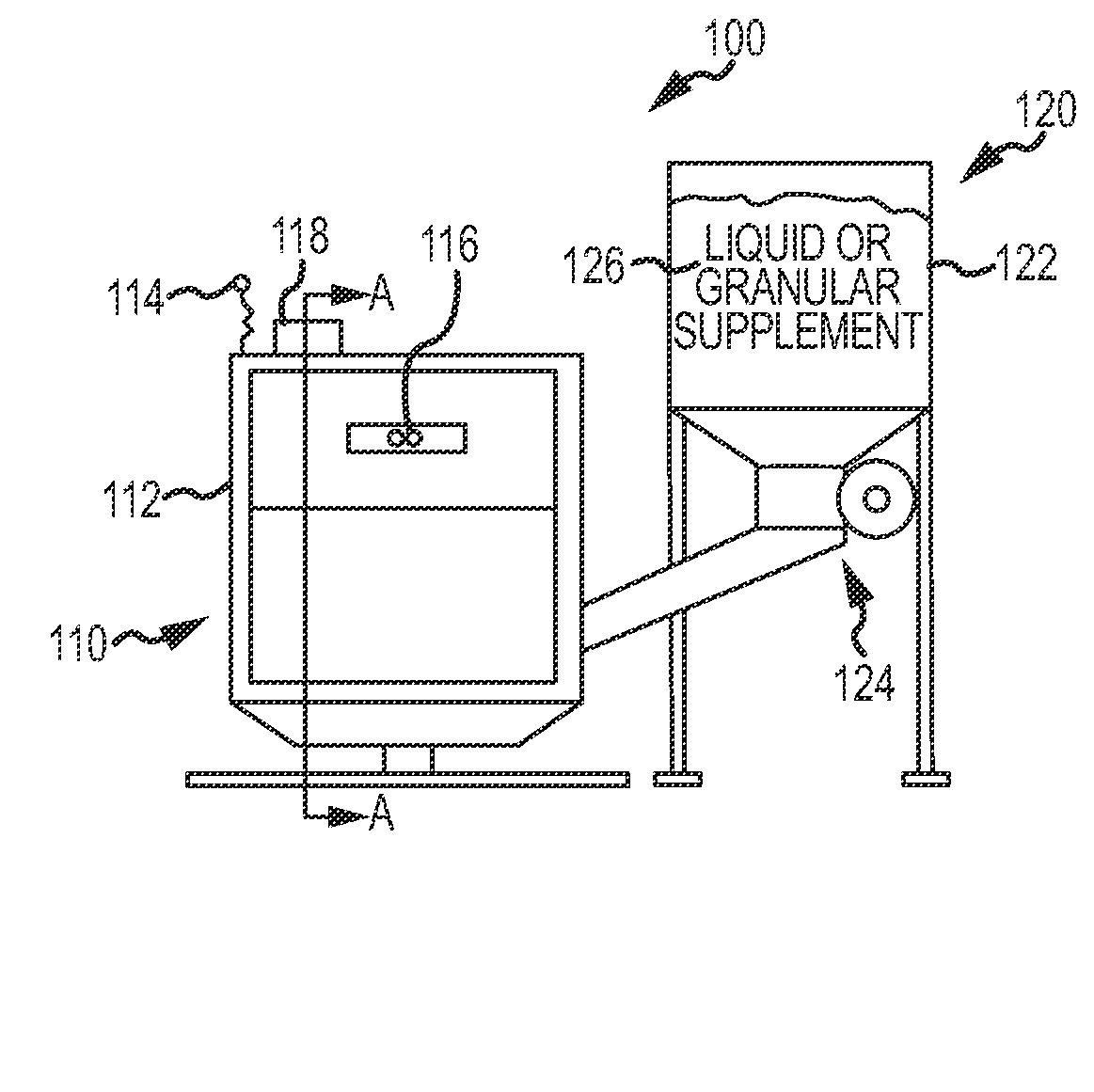
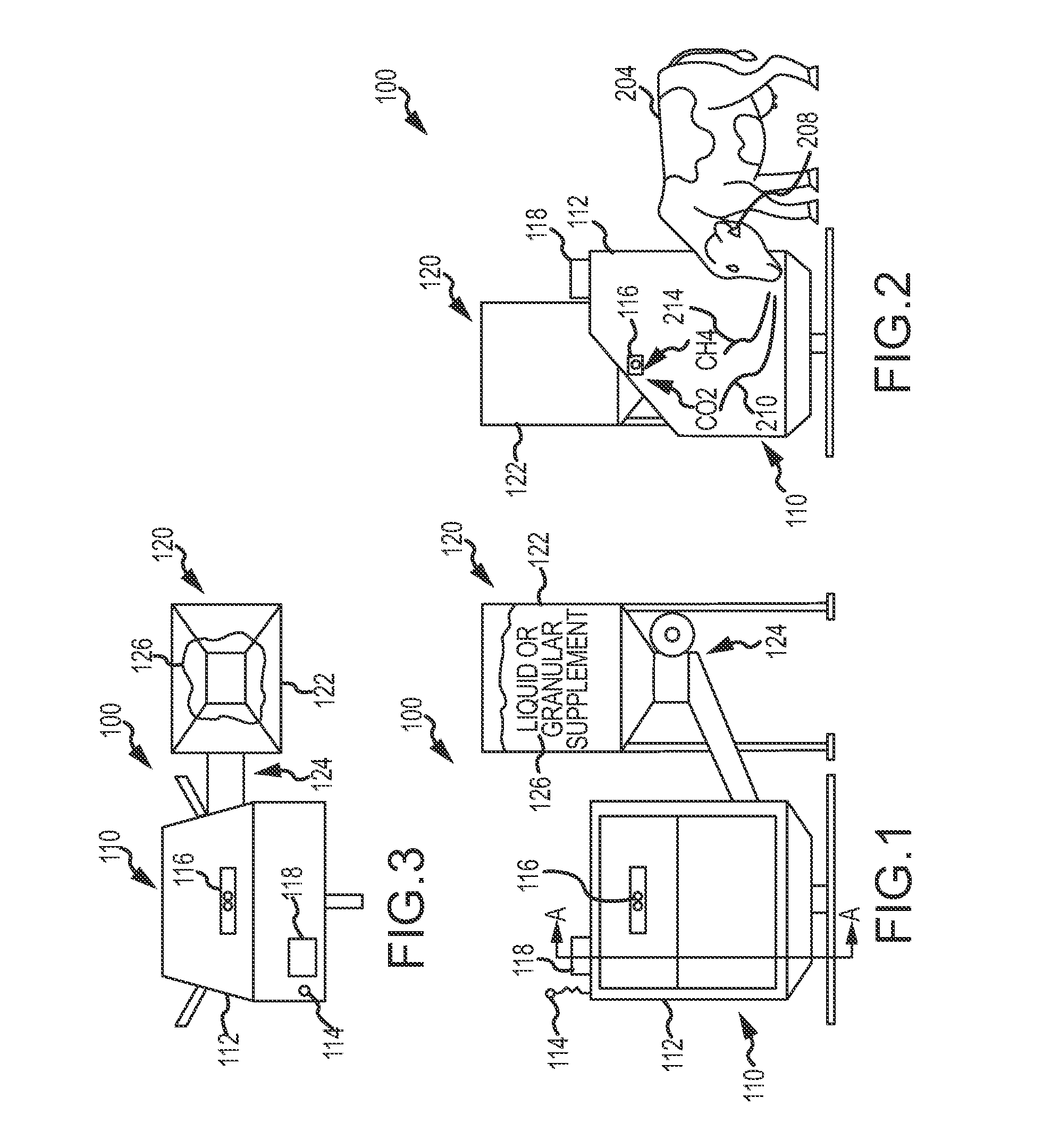
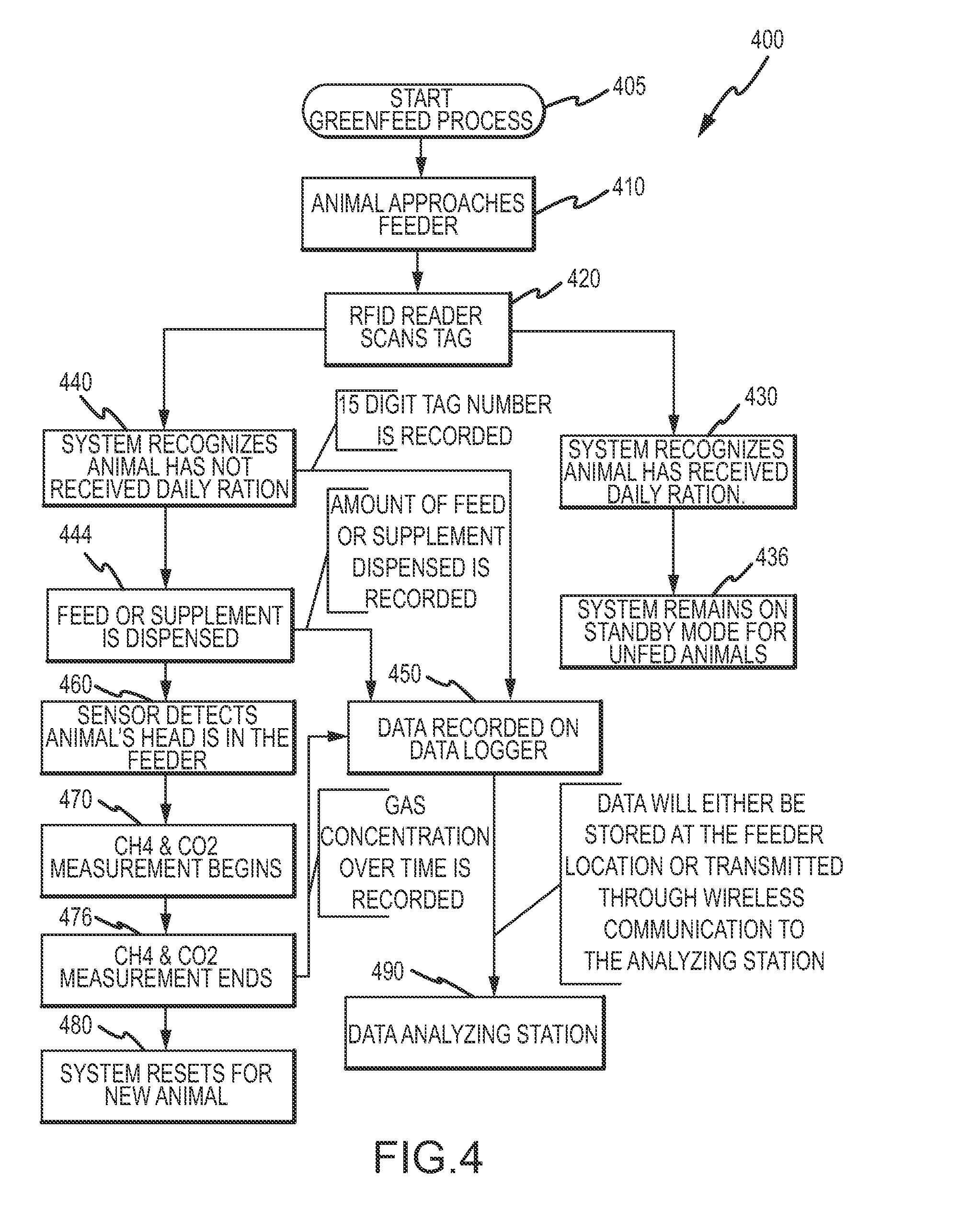
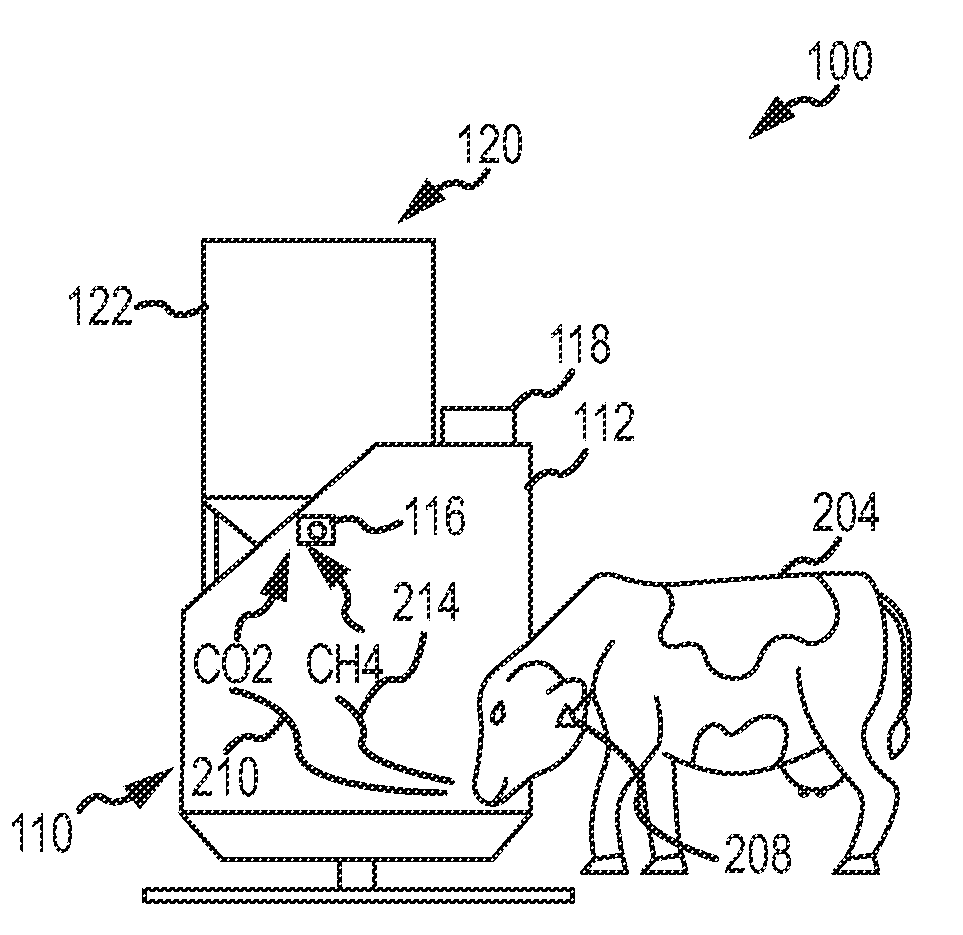
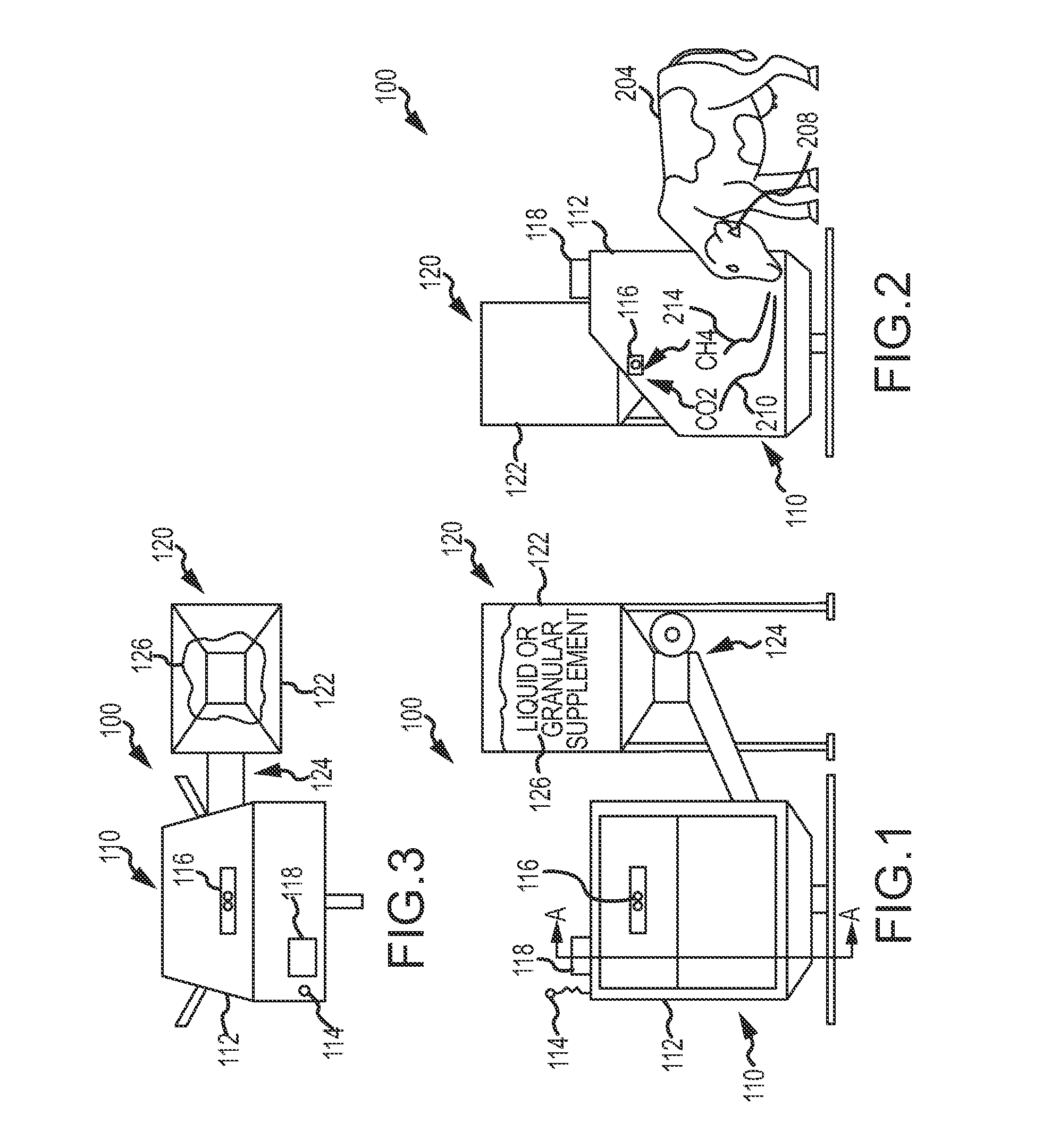
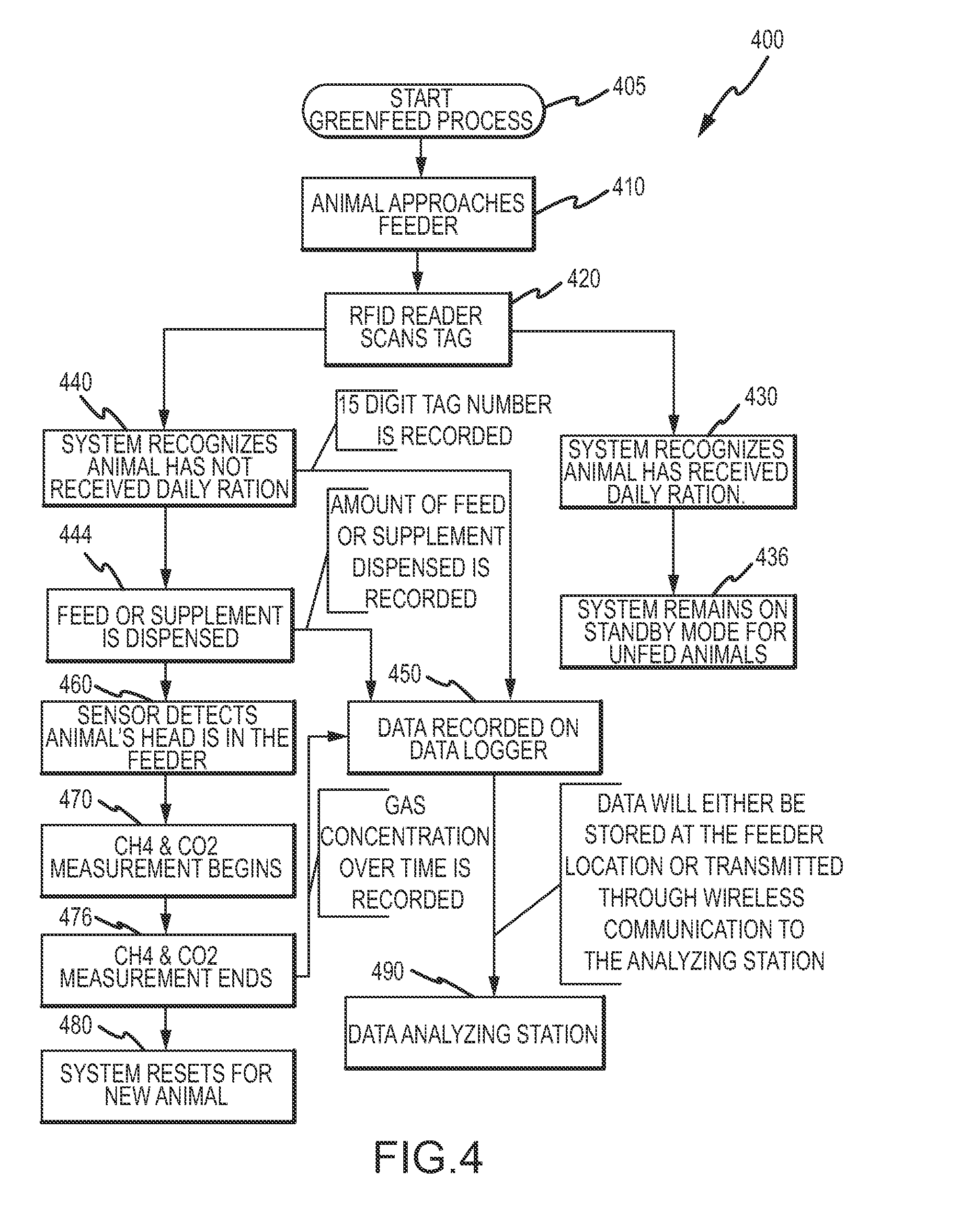
A method, and systems implementing such method, for reducing methane emissions by ruminants. The method includes providing a feed dispenser for feeding ruminants one or more nutrient supplements, and the feed dispenser includes a gas analyzer proximate to where the ruminant places its head. The method includes determining a particular ruminant has accessed the feed dispenser such as by reading an identifier from an RFID ear tag and operating the feed dispenser to provide a ration of methane-controlling nutrient supplement. The method includes using the gas analyzer to determine levels of carbon dioxide and methane and operating a data analyzing station to determine a ratio of methane to carbon dioxide and modify the type or amount of nutrient supplement for the ruminant for a next feeding to control methane production or achieve an animal production goal, such as by selectively operating a hopper with two or more supplements compartments.
Owner:CLOCK LTD
Method and system for monitoring and reducing ruminant methane production
ActiveUS20110192213A1Emission reductionEstimate dry-matter intake, digestibility, and animal efficiencyWithdrawing sample devicesAnimal feeding devicesEar tagAgricultural science
A method and system for reducing methane emissions by ruminants. The method includes providing a feed dispenser for feeding ruminants nutrient supplements, and the feed dispenser includes a gas analyzer where a ruminant places its head. The method includes determining a particular ruminant has accessed the feed dispenser such as by reading an identifier from an RFID ear tag and operating the feed dispenser to provide a ration of methane-controlling nutrient supplement. The method includes using the gas analyzer to determine levels of carbon dioxide and methane and operating a data analyzing station to determine a ratio of methane to carbon dioxide and modify the type or amount of nutrient supplement for the ruminant for a next feeding to control methane production or achieve an animal production goal, such as by operating a hopper with supplement compartments. The unit can be monitored remotely and controlled through an Internet connection.
Owner:CLOCK LTD
Electromethanogenic reactor and processes for methane production
ActiveUS20090317882A1Reduce deliveryImprove methane production efficiencyMicroorganismsGas production bioreactorsHydrogenCombustion
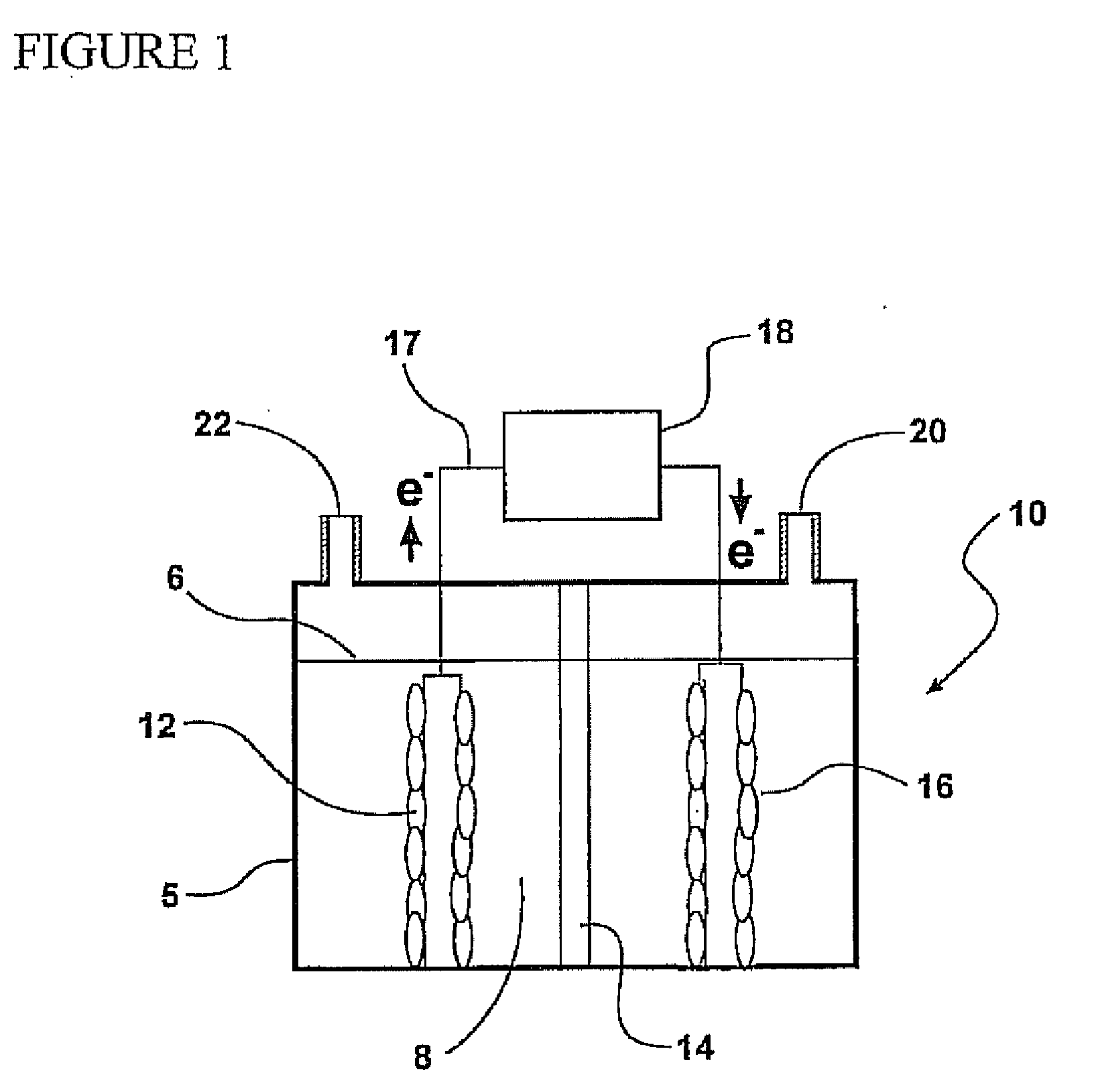
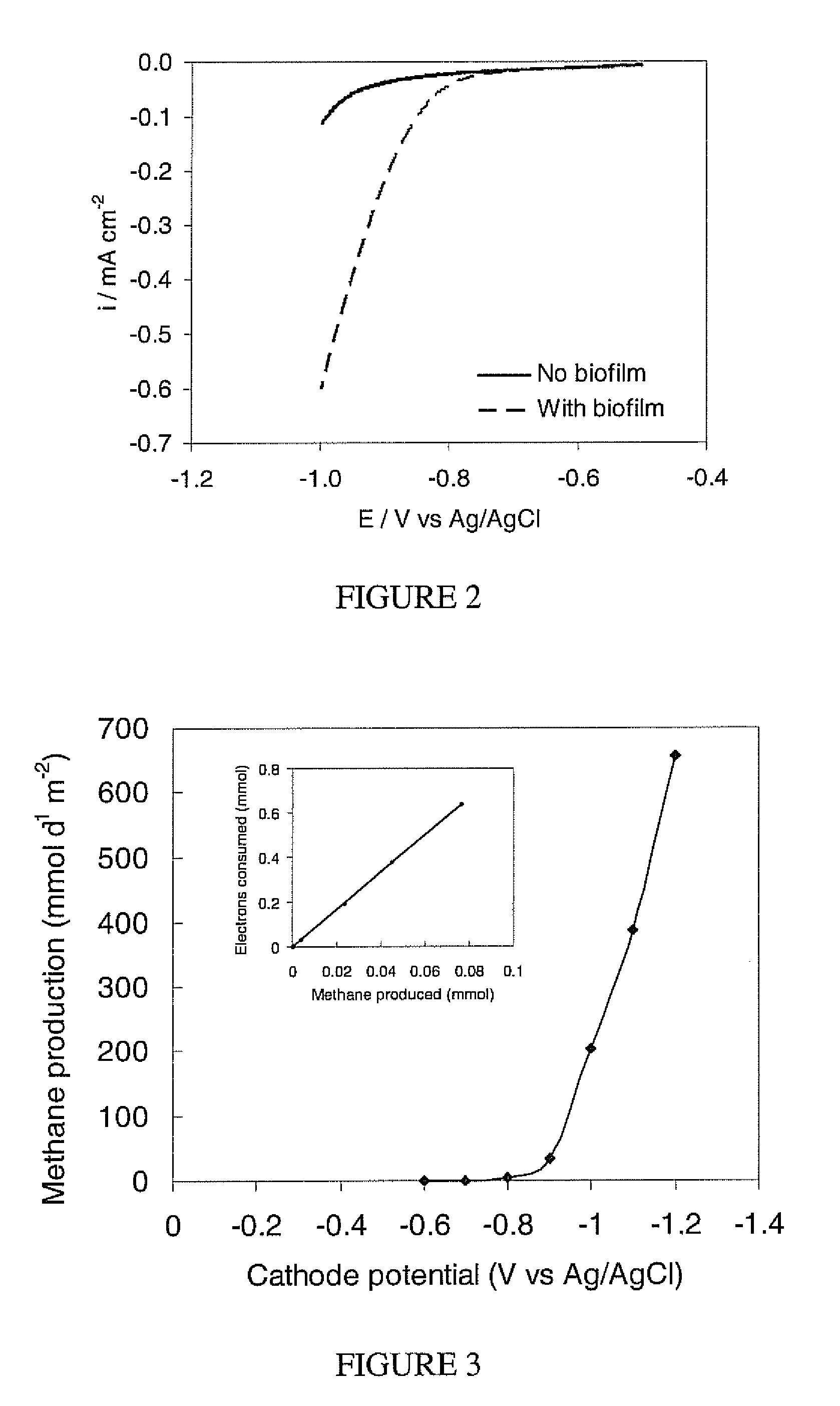
Increasing competition for fossil fuels, and the need to avoid release carbon dioxide from combustion of these fuels requires development of new and sustainable approaches for energy production and carbon capture. Biological processes for producing methane gas and capturing carbon from carbon dioxide are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include providing an electromethanogenic reactor having an anode, a cathode and a plurality of methanogenic microorganisms disposed on the cathode. Electrons and carbon dioxide are provided to the plurality of methanogenic microorganisms disposed on the cathode. The methanogenic microorganisms reduce the carbon dioxide to produce methane gas, even in the absence of hydrogen and / or organic carbon sources.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Feed supplement for animals for reducing methane production
InactiveUS20090285931A1Reduce enteric methane emissionImprove performanceAnimal feeding stuffAgriculture gas emission reductionAnimal scienceMethane production
A method for enhancing feed efficiency and reducing enteric methane production in livestock, comprising a formulation of natural plants and plant extracts and chemicals, including propionatic acid glycerol, that when feed to ruminants results in decreased enteric methane production and improved feed efficiency.
Owner:SHELBY NANCY J +1
Bio-recycling of carbon dioxide emitted from power plants
InactiveUS20070298478A1Enhance biogas methane productionReduce carbon dioxide emissionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationFossil fuel
The invention provides a method to decrease emission of carbon dioxide from combustion of fossil fuels or other hydrocarbons and to enhance the efficiency of methane production from anaerobic biodigesters. The invention involves feeding carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of hydrocarbon fuel combustion to an anaerobic biodigester where biomass is anaerobically fermented to produce methane. Carbon dioxide is an electron acceptor for anaerobic fermentation, and thus some of the carbon dioxide is reduced to methane, which can again be used for fuel. In this way, at least a portion of the exhaust gas CO2 is recycled to form fuel methane instead of being released into the atmosphere. Thus, the net CO2 emission from burning a given amount of fossil fuel is decreased. Adding carbon dioxide to an anaerobic fermentation also increases the efficiency and amount of methane production in the fermentation.
Owner:VIRESCO AD LLC
Methods to stimulate biogenic methane production from hydrocarbon-bearing formations
The present invention describes methods of identifying stimulants for the biogenic production of methane in hydrocarbon-bearing formations. Methods involve the use of microbial nucleic acid sequence information for the determination of gene products that are enzymes in a variety of pathways involved in the conversion of hydrocarbons to methane. Enzymes and stimulants identified by invention methods can be used in processes for enhancing biogenic methane production, for example, by addition to coal seams and coalbed methane wells.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Integrated processes and systems for conversion of methane to multiple higher hydrocarbon products
Integrated systems are provided for the production of higher hydrocarbon compositions, for example liquid hydrocarbon compositions, from methane using an oxidative coupling of methane system to convert methane to ethylene, followed by conversion of ethylene to selectable higher hydrocarbon products. Integrated systems and processes are provided that process methane through to these higher hydrocarbon products.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH LLC
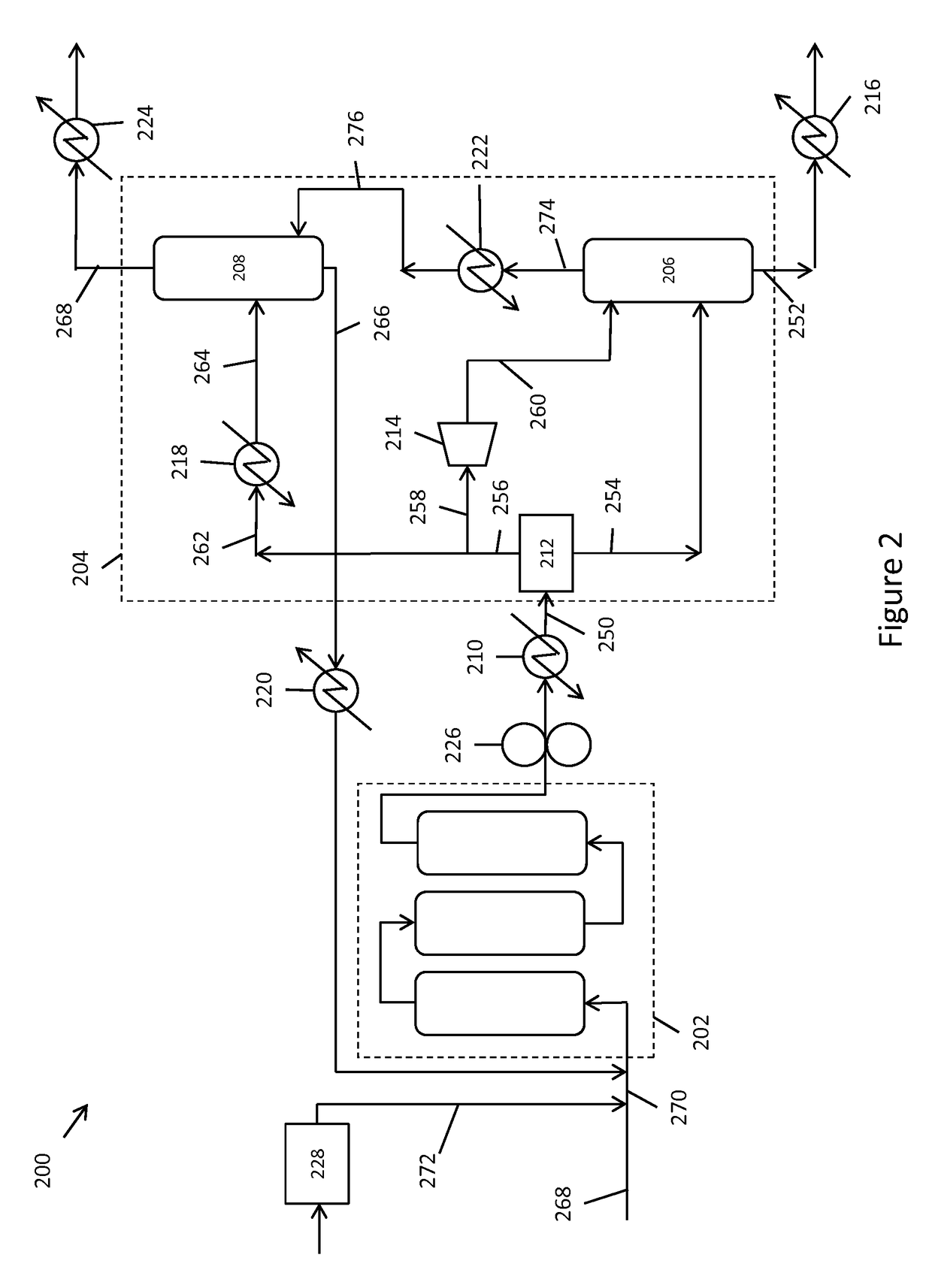
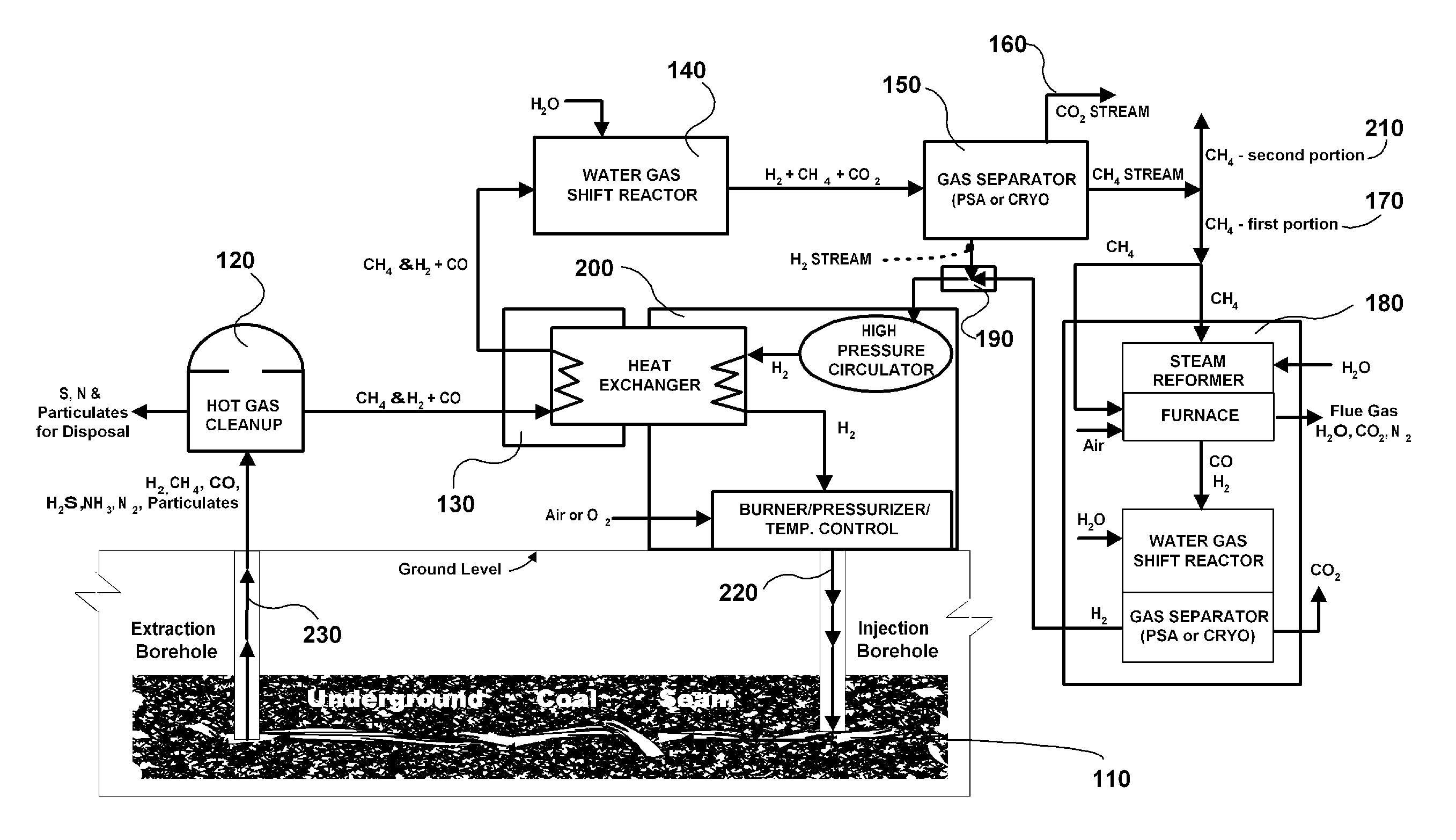
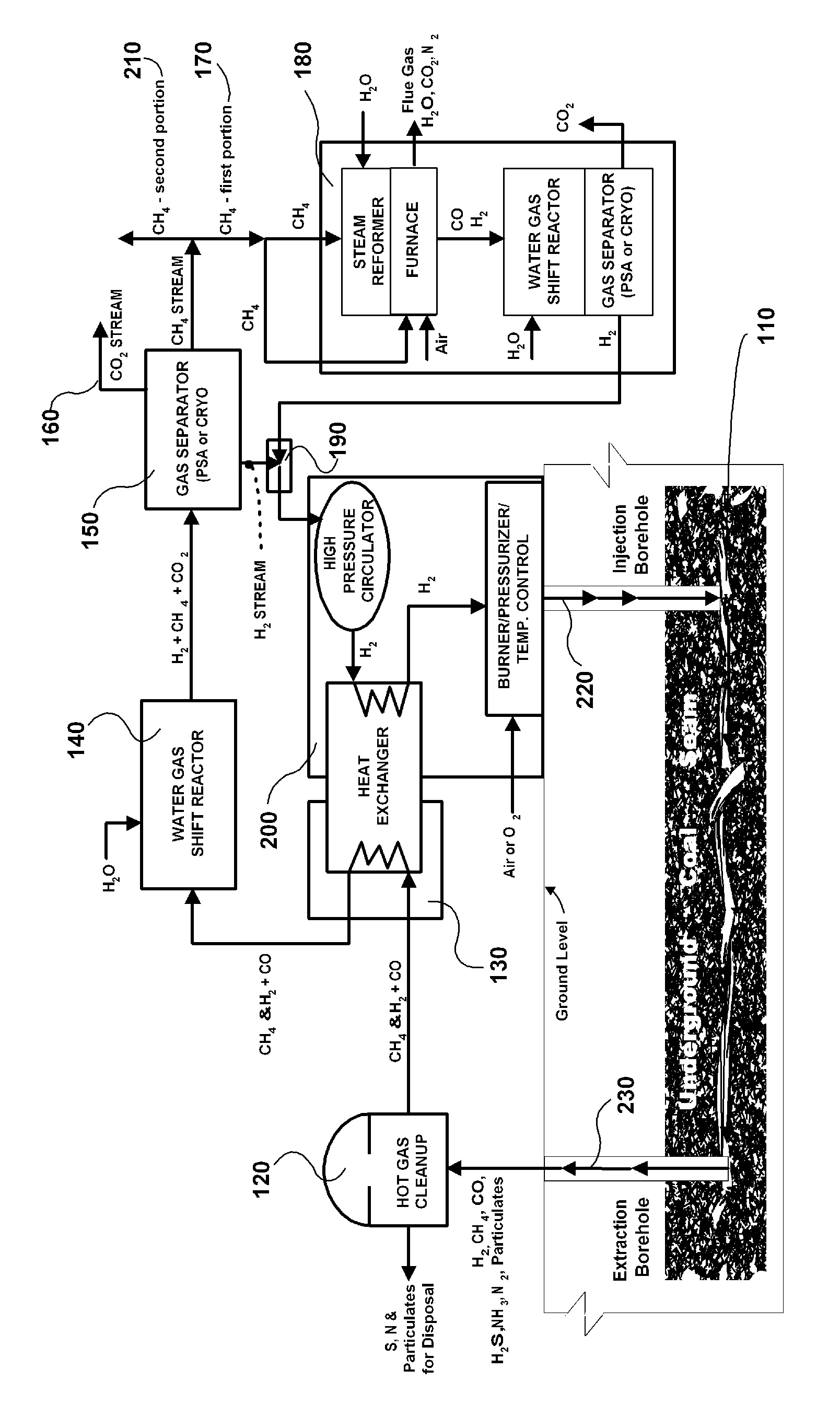
Pumped carbon mining methane production process
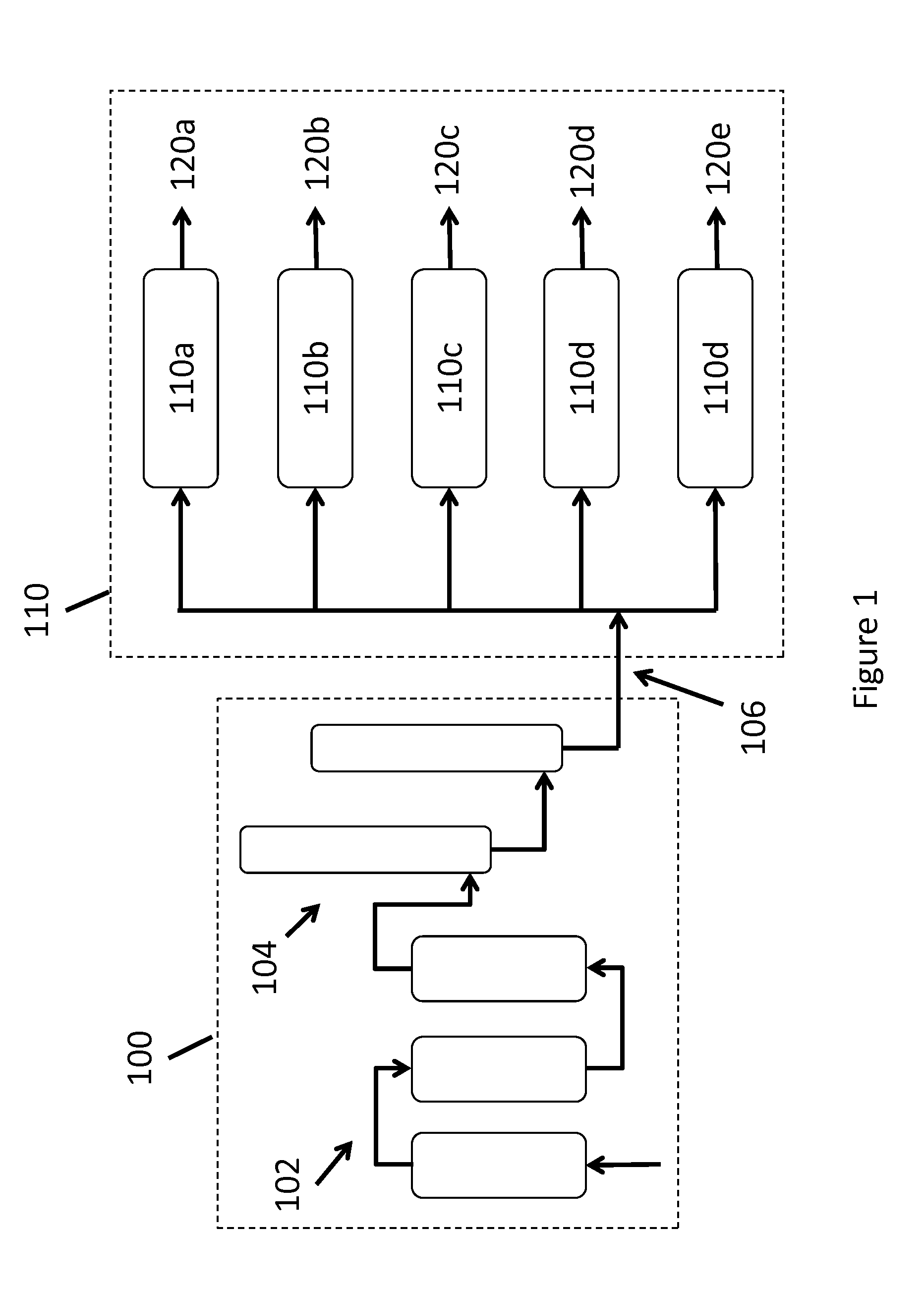
The invention is a continuous process for producing methane from an underground coal bed or an above ground carbon-containing resource using hydrogen as a recycling working fluid. For an underground coal seam, the process includes injecting (220) hydrogen into the coal seam to form a reaction effluent of methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide; extracting the reaction effluent (230) for processing above ground; cleaning the reaction effluent (120); cooling the cleaned reaction effluent (130) and processing it through a water gas shift reactor (140); separating (150) hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide into separate streams; producing the carbon dioxide stream (160) as a product gas; processing a first portion (170) of the methane stream in a steam reformer, water gas shift reactor and gas separator (180) to produce segregated flows of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, combining the segregated hydrogen flow with the separated hydrogen stream (190); heating and repressurizing (200) the combined hydrogen stream to the temperature and pressure of the hydrogen in the first step; producing a second portion (210) of said methane stream as a product gas; and injecting (220) the combined hydrogen stream into the underground coal bed to continue the process.
Owner:HCE
Sub-Surface Coalbed Methane Well Enhancement Through Rapid Oxidation
Methods of stimulating production of coalbed methane from a coal-bearing formation are described, one method involving providing a perforation charge comprising a standard charge portion and a charge additive able to produce localized temporary oxidizing environments in perforations; perforating a coal-bearing formation with the perforation charge to form initial perforations defined by carbonaceous material, the initial perforations having localized temporary oxidizing environments in them, and initiating combustion of the carbonaceous material using the oxidizing environments, thus enlarging the initial perforations. Other methods involve perforating the coal-bearing formation with a standard perforation charge, thereby creating perforations; and treating the perforations with a composition creating temporary local oxidizing environments involving an oxidant in the perforations, and initiating combustion of carbonaceous material using the excess oxidant, thus enlarging the perforations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
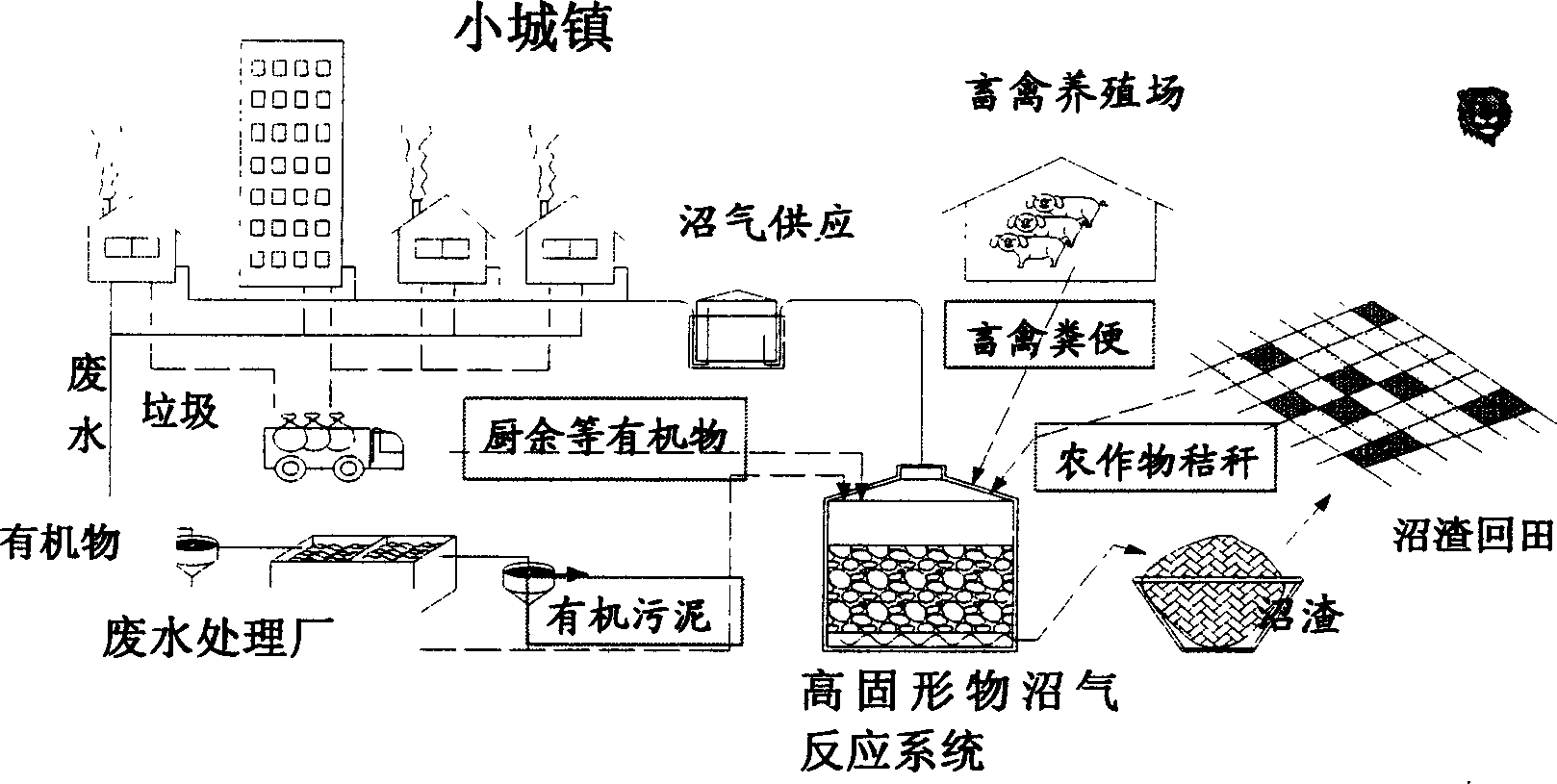
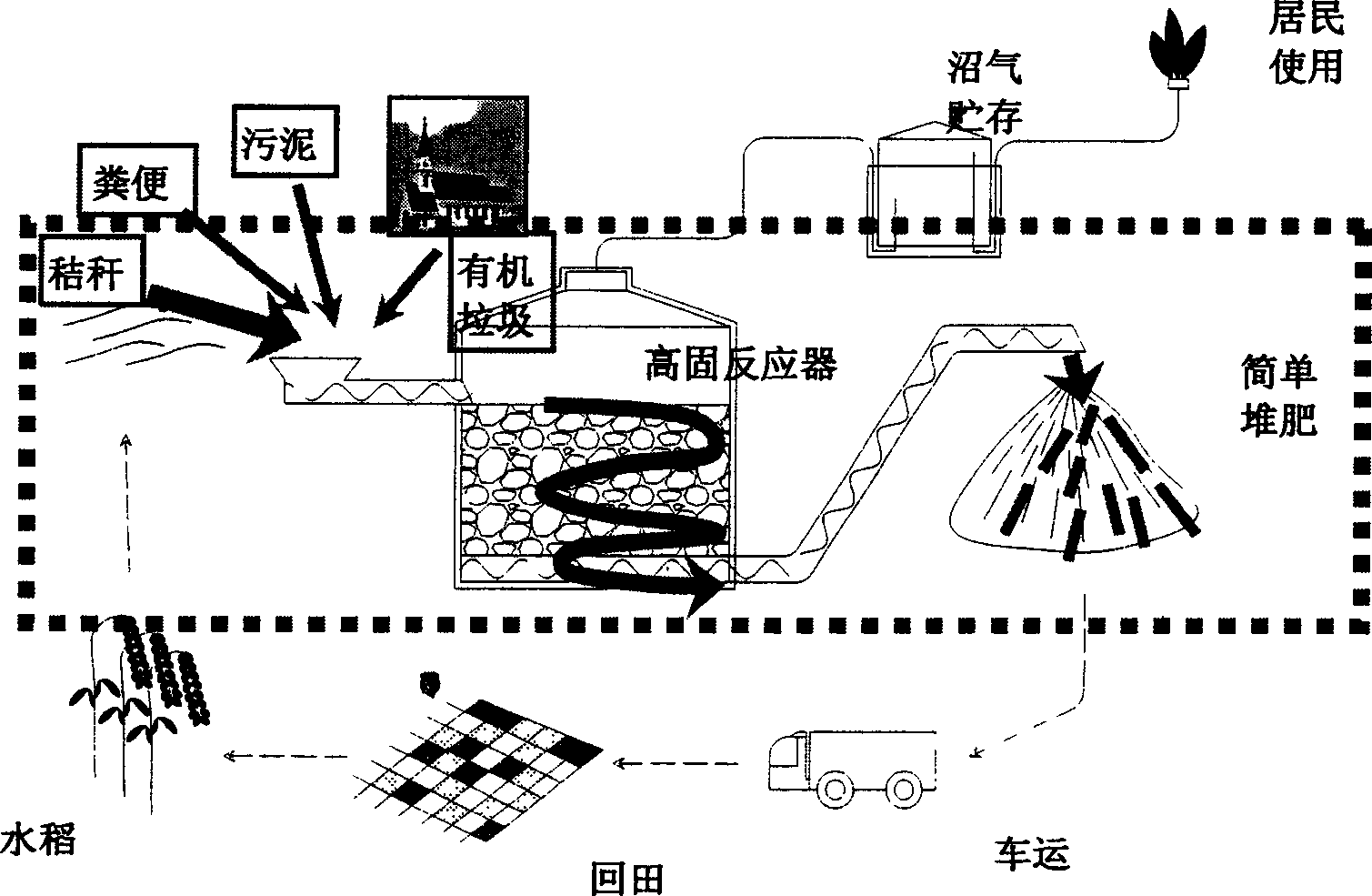
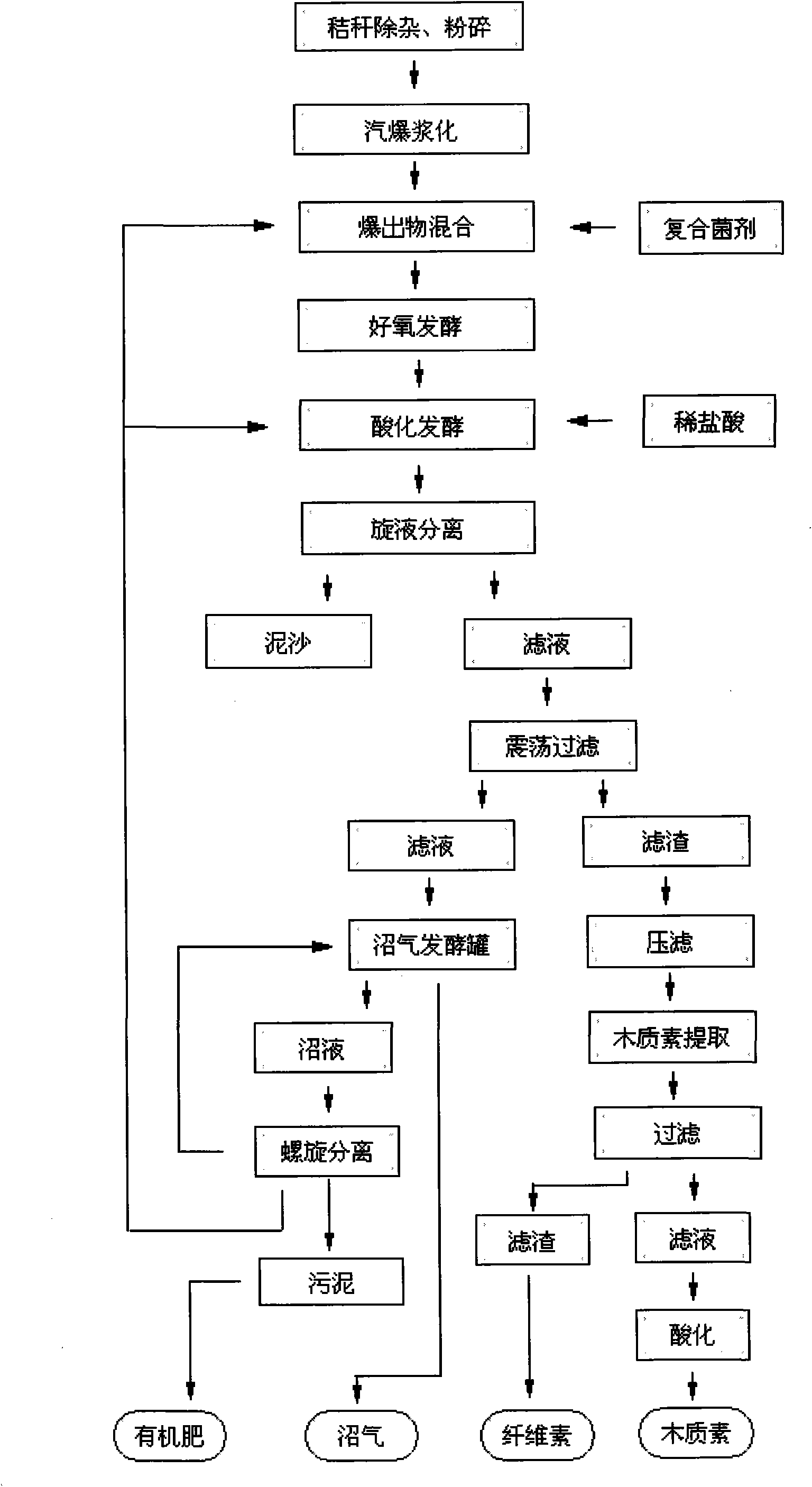
Marsh gas production technology using kitchen residue, straw, stock and fowl dejecta and active mud as material
InactiveCN1769220AReduce pretreatment costsHigh outgassing rateWaste based fuelEnergy based wastewater treatmentBiotechnologyFowl
The invention discloses a technique for producing methane with kitchen residue, straw fecal and active sludge as raw material, and relates to the key technique of methane production and a high solid methane fermentation reactor. It is characterized in: rigid anaerobic environment, adequate and good inoculum, necessary fermentation temperature, proper acid-base scale, proper fermentation concentration and carbon-hydrogen ration; the breeding speed safeguard of zymogeneous bacteria in fermentate; the killing of toxic and harmful bacterium; and the high solid reactor of stable operation. The invention is characterized in that it has significant academic meaning and practical meaning for producing methane with low investment, high stability and clean production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
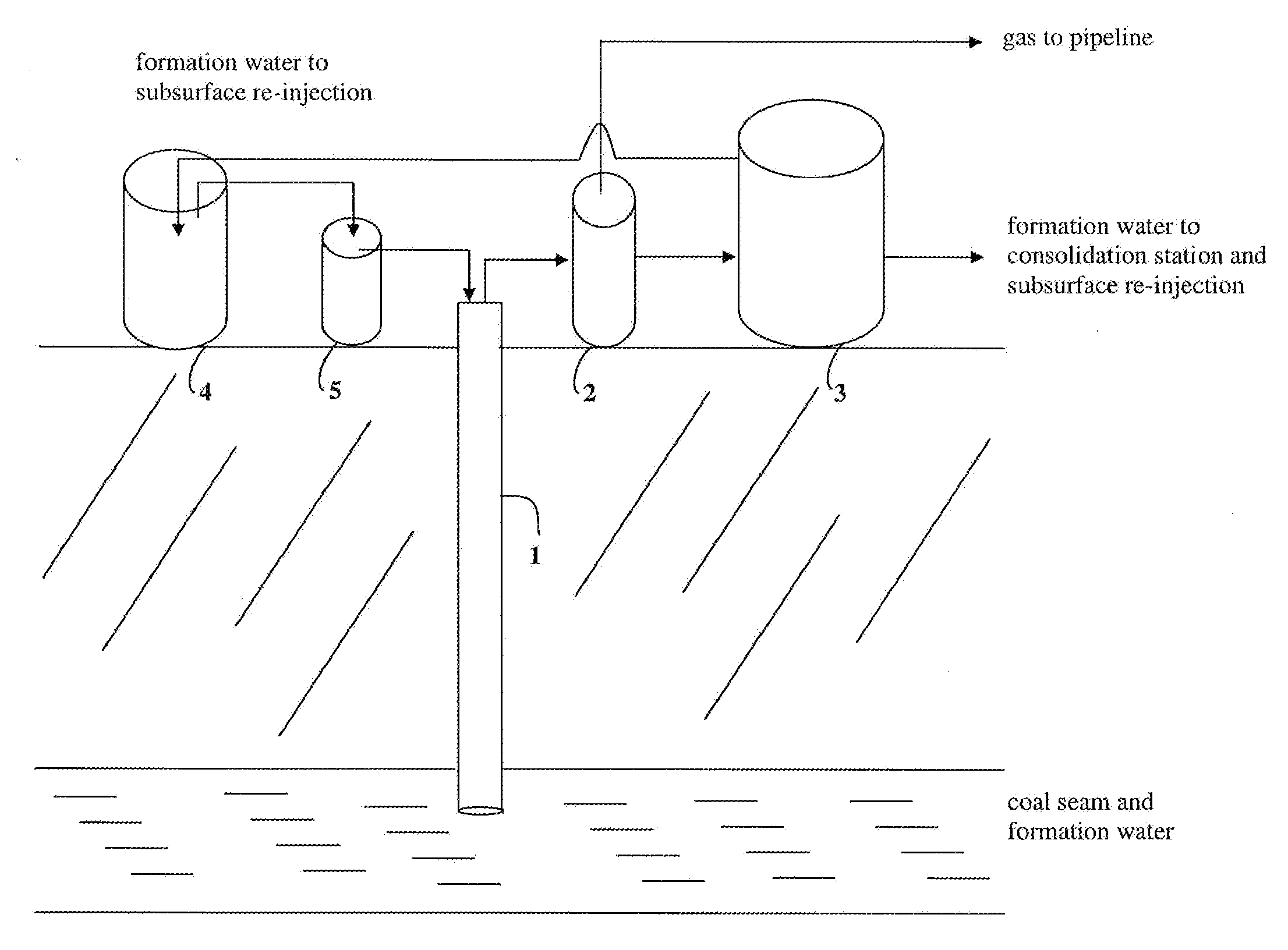
Coal bed methane wastewater treatment system
InactiveUS6929753B1Avoid pollutionEfficiently and cost-effectively treatingWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment involving filtrationWater treatment systemSodium adsorption ratio
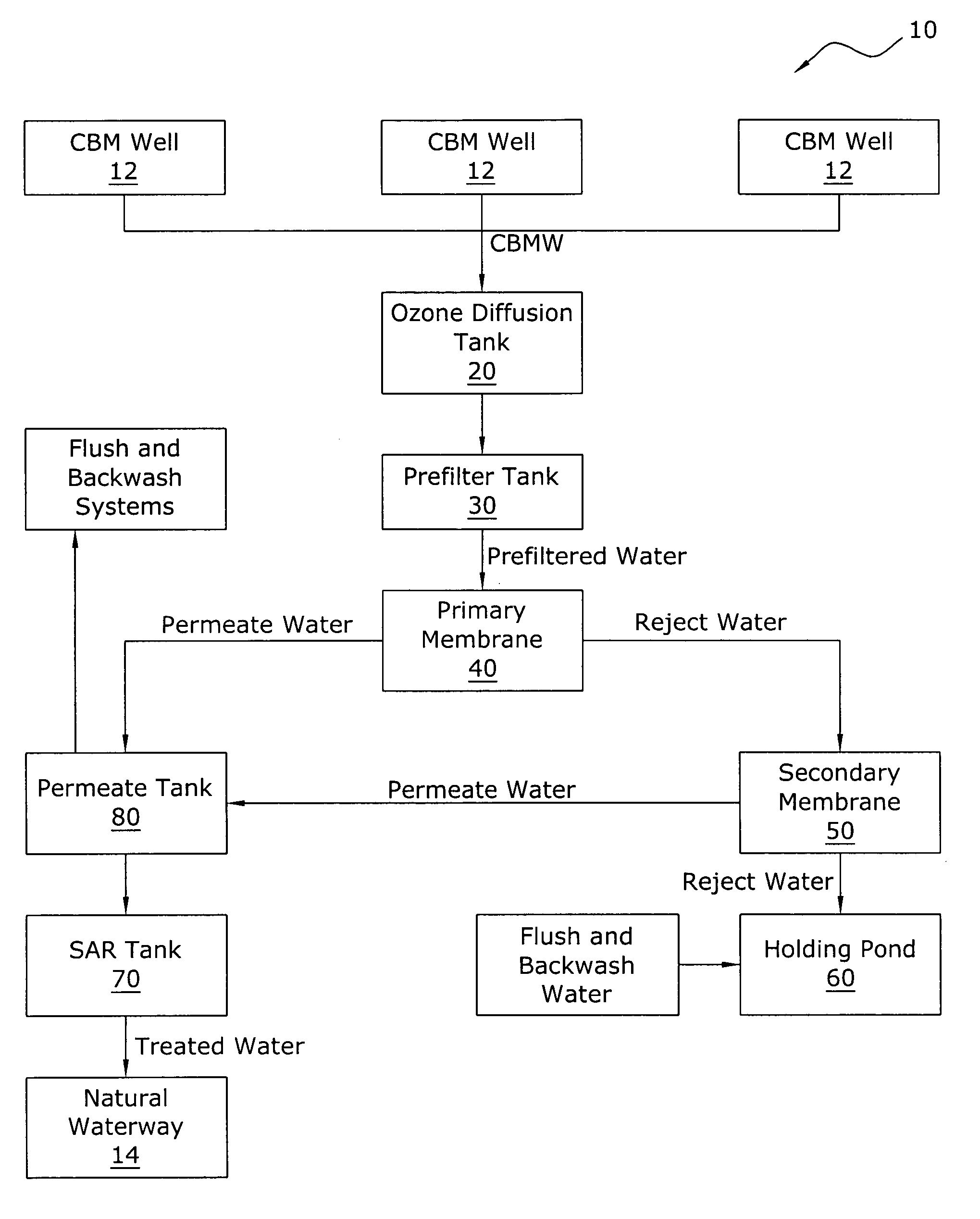
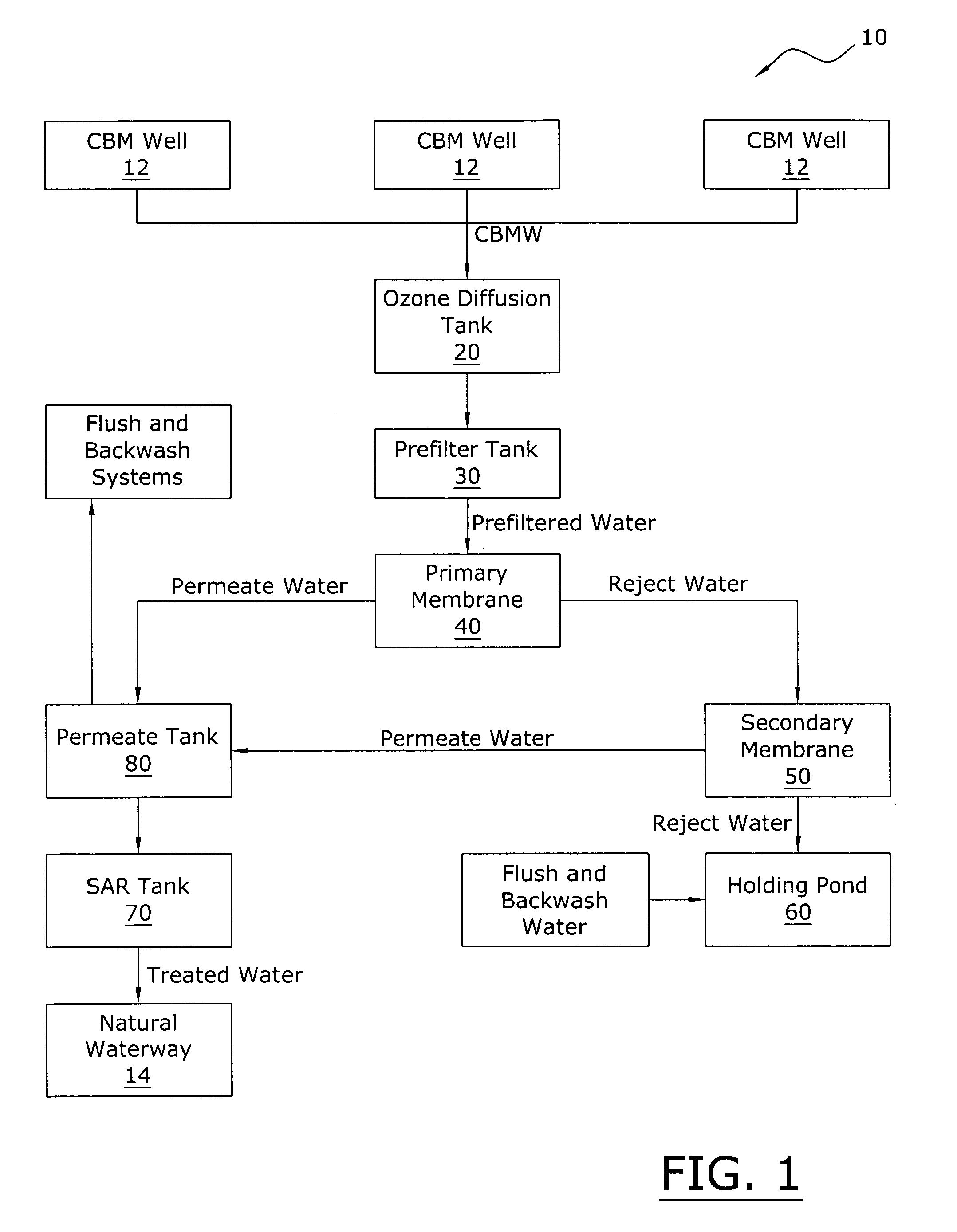
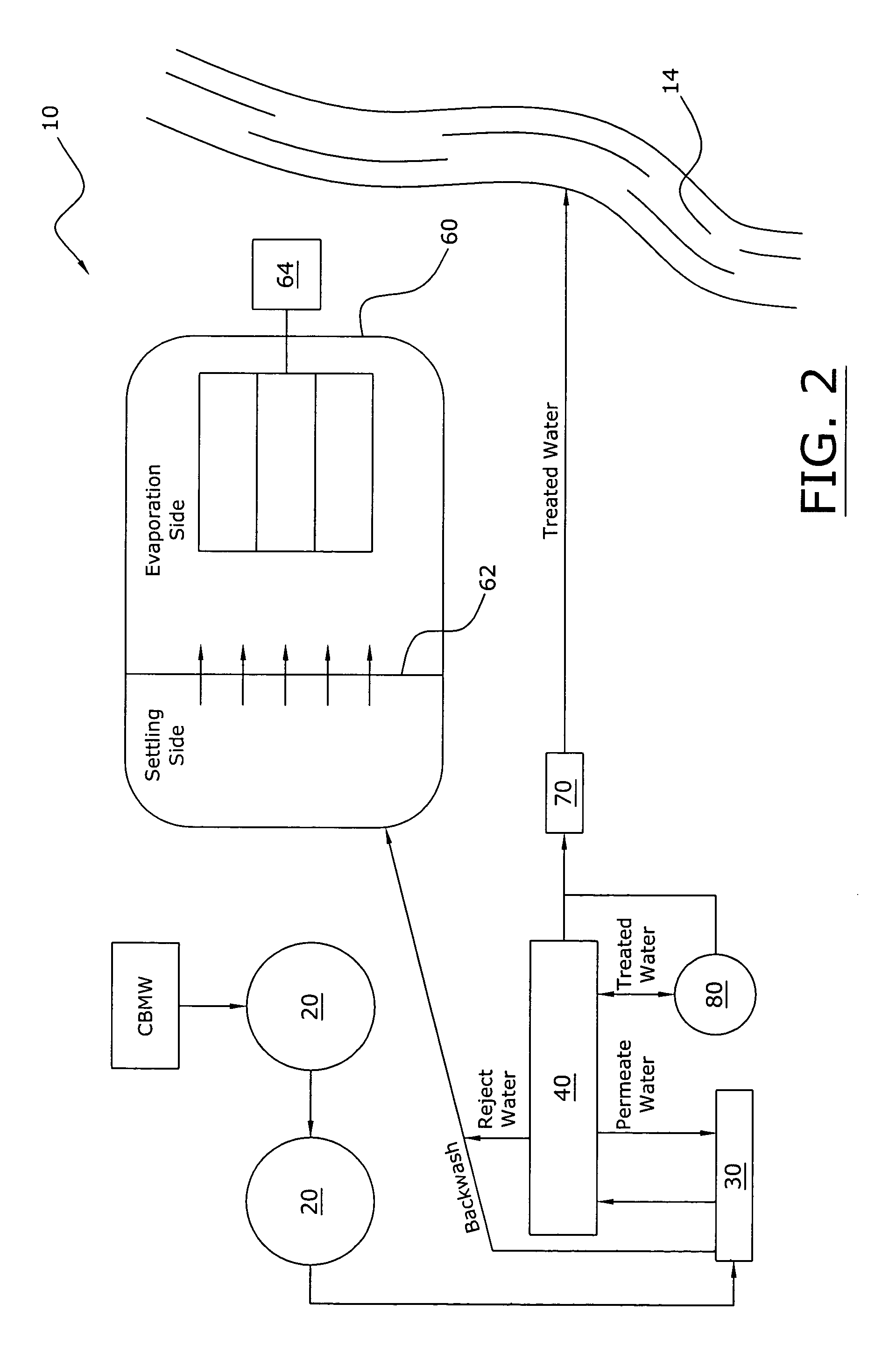
A coal bed methane wastewater treatment system for efficiently and cost effectively treating wastewater generated from coal bed methane production. The coal bed methane wastewater treatment system includes collecting wastewater into an ozone diffusion tank where ozone is injected into the wastewater, passing the wastewater through a prefilter tank and then through a primary membrane. The treated water is separated to a permeate tank and the concentrated water is passed through a secondary membrane for further separation. The concentrated water is then placed within a holding pond for evaporation thereof. The treated water may be utilized to clean the prefilter tank and the membranes. The treated water is then dispensed into a sodium adsorption ratio tank prior to being released to a natural waterway.
Owner:AQUA ENVIROTECH MFG
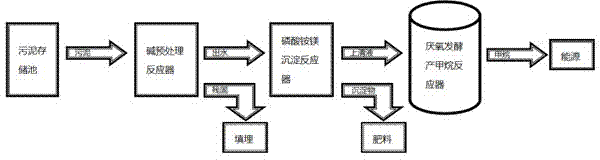
Method for processing residual sludge with integrated process of alkaline hydrolysis preprocessing, nitrogen and phosphorus recovery based on magnesium ammonium phosphate method and methane production based on anaerobic digestion
ActiveCN103693828AReduce consumptionGive full play to the role of alkaline hydrolysis pretreatmentWaste based fuelSludge processingChemical oxygen demandMagnesium salt
The invention discloses a method for processing residual sludge with an integrated process of alkaline hydrolysis preprocessing, nitrogen and phosphorus recovery based on a magnesium ammonium phosphate method and methane production based on anaerobic digestion. The method comprises the steps of: preprocessing residual sludge with a secondary alkaline hydrolysis method to obtain supernate, adding a magnesium salt solution to separate precipitates, subjecting the supernate to anaerobic processing, and drying the precipitates naturally to obtain crude magnesium ammonium phosphate; injecting the supernate into an anaerobic reactor, and inoculating with 10-60% anaerobic granular sludge, wherein the volumetric loading is controlled to be 0.30-0.75kg COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) / (m<3>.d), and the productivity of methane reaches 200-400mL CH4 / gCOD within 72h. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that nutrition elements in the residual sludge are utilized comprehensively, the process is simple and is consistent in flow with low chemical consumption and electricity consumption, methane is recovered while crude magnesium ammonium phosphate is obtained, moreover, residual alkaline solids are beneficial to subsequent processing, and the reduction, stabilization and recycling of the residual sludge are realized comprehensively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bio-recycling of carbon dioxide emitted from power plants
InactiveUS7608439B2Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove methane production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationFossil fuel
The invention provides a method to decrease emission of carbon dioxide from combustion of fossil fuels or other hydrocarbons and to enhance the efficiency of methane production from anaerobic biodigesters. The invention involves feeding carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of hydrocarbon fuel combustion to an anaerobic biodigester where biomass is anaerobically fermented to produce methane. Carbon dioxide is an electron acceptor for anaerobic fermentation, and thus some of the carbon dioxide is reduced to methane, which can again be used for fuel. In this way, at least a portion of the exhaust gas CO2 is recycled to form fuel methane instead of being released into the atmosphere. Thus, the net CO2 emission from burning a given amount of fossil fuel is decreased. Adding carbon dioxide to an anaerobic fermentation also increases the efficiency and amount of methane production in the fermentation.
Owner:VIRESCO AD LLC
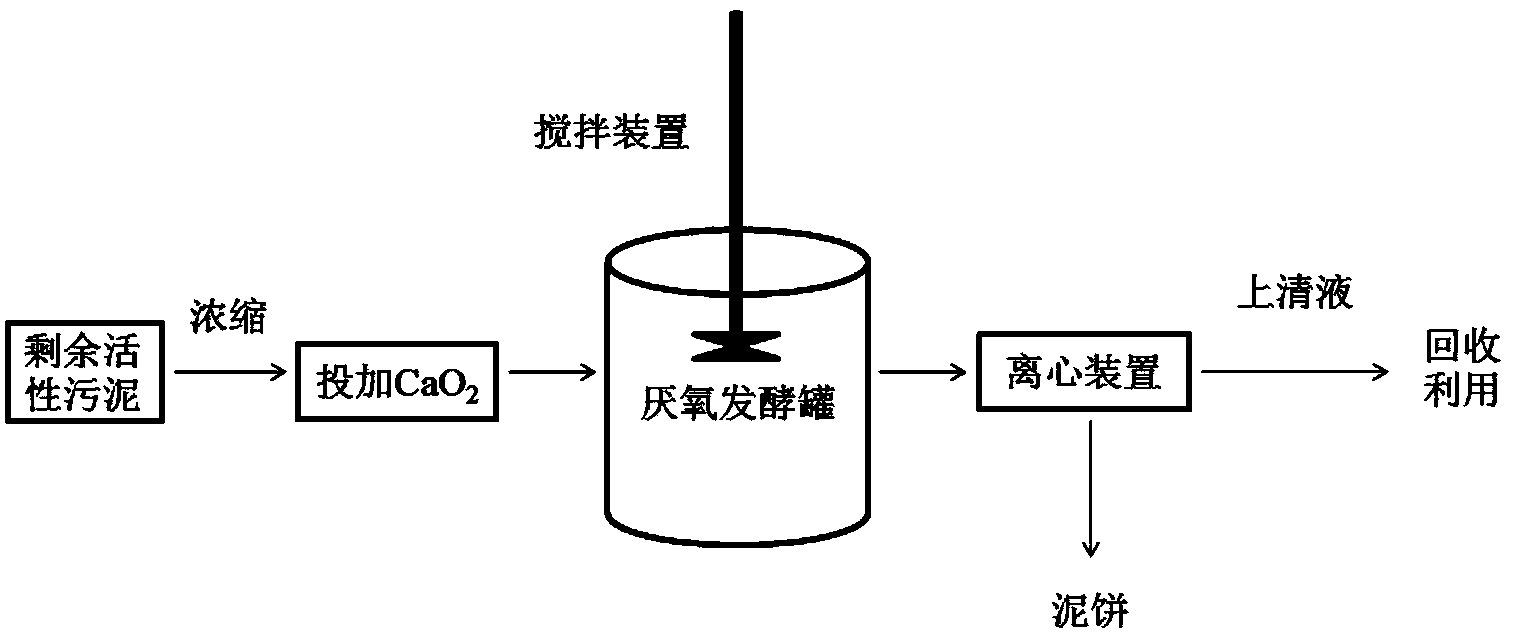
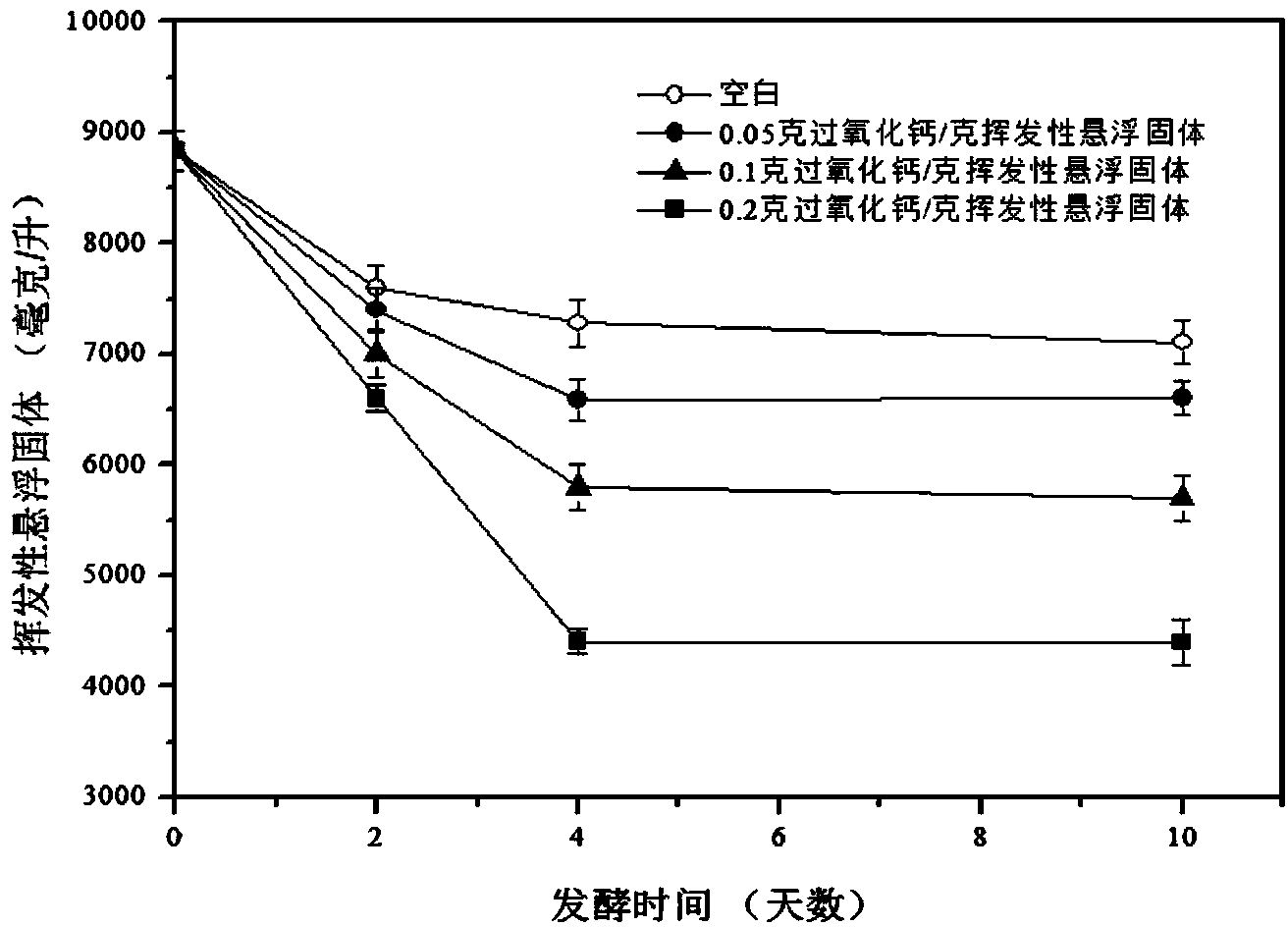
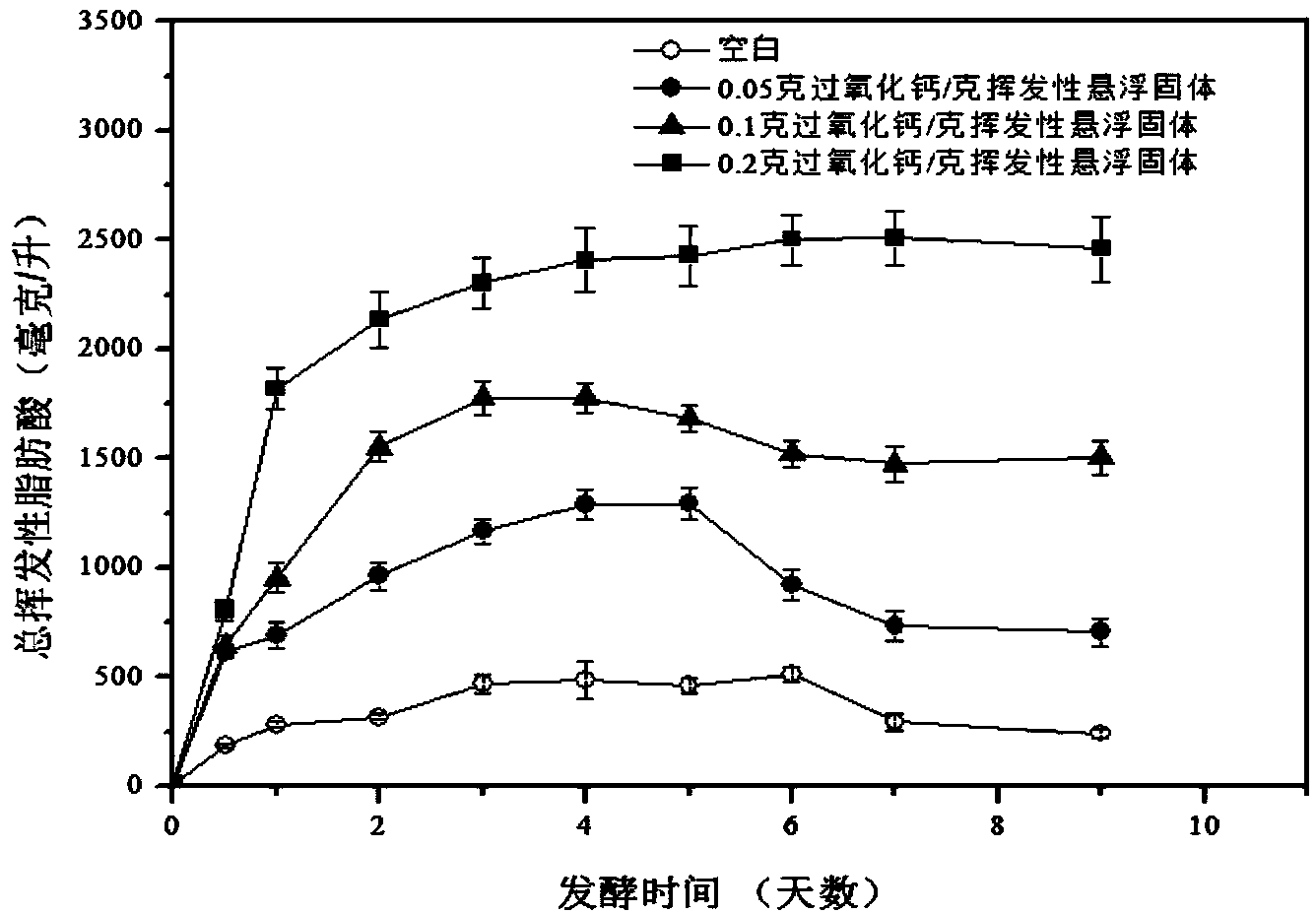
Method for improving acid production quality and acetic acid proportion in anaerobic fermentation of residue active sludge
InactiveCN104031949AImprove solubilityImprove acidificationFermentationBiological sludge treatmentSolubilityParticulates
The invention relates to a method for improving acid production quality and acetic acid proportion in anaerobic fermentation of residue active sludge. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, adding calcium peroxide into concentrated residual sludge in a wastewater treatment plant, wherein adding amount of the calcium peroxide is 5%-20% of the weight of the volatile suspended solid in the residual active sludge; then, sealing at 30-40 DEG C, carrying out anaerobic digestion in an anaerobic digestion tank with stirring speed of 100-200rpm, wherein the anaerobic digestion time is 5-10 days. The result indicates that calcium peroxide can promote dissolution of particulate organic substances, can improve acidification degree of deliquescent organic substances and can inhibit a methane production process, so that accumulation of volatile short-chain fatty acid is facilitated and transformation of other acids to acetic acid is promoted; meanwhile, a plurality of harmful organic substances in the sludge are effectively removed, so that the acid production quality in anaerobic fermentation of the residue active sludge is improved. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and gentle in reaction condition, is used for recycling and carrying out harmless disposal on the concentrated residual sludge of the sewage treatment plant, and has very good economic and social benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and system for monitoring and reducing ruminant methane production
ActiveUS8307785B2Emission reductionEstimate dry-matter intake, digestibility, and animal efficiencyAnimal feeding devicesAnimal housingAgricultural scienceEar tag
A method and system for reducing methane emissions by ruminants. The method includes providing a feed dispenser for feeding ruminants nutrient supplements, and the feed dispenser includes a gas analyzer where a ruminant places its head. The method includes determining a particular ruminant has accessed the feed dispenser such as by reading an identifier from an RFID ear tag and operating the feed dispenser to provide a ration of methane-controlling nutrient supplement. The method includes using the gas analyzer to determine levels of carbon dioxide and methane and operating a data analyzing station to determine a ratio of methane to carbon dioxide and modify the type or amount of nutrient supplement for the ruminant for a next feeding to control methane production or achieve an animal production goal, such as by operating a hopper with supplement compartments. The unit can be monitored remotely and controlled through an Internet connection.
Owner:CLOCK LTD
Acidic high sulfate organic wastewater treatment process and apparatus
ActiveCN105439374AWill not cause churnStrong resistance to shock loadsMultistage water/sewage treatmentGas phaseAnaerobic reactor
The present invention discloses an acidic high sulfate organic wastewater treatment process and apparatus. The present invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The specific process comprises the steps of: (1) neutralization and precipitation treatment: using lime milk to adjust PH of wastewater, and forming CaSO4 precipitation separated from the water; (2) first-stage anaerobic treatment, entering the first-stage anaerobic treatment after neutralization and precipitation treatment, introducing nitrogen into the bottom of an anaerobic reactor with stirring and blowing off, parsing H2S from an aqueous phase into a gas phase above a liquid level, introducing the H2S in the gas phase to a dry desulfurizer for desulfurization, and re-introducing the sulfur removed nitrogen into the first-stage anaerobic reactor for recycling through a blower; and (3) second-stage anaerobic treatment, introducing the sulfur removed wastewater into a second-stage anaerobic reactor to complete an anaerobic methane production reaction, and taking second-stage anaerobic effluent into an aerobic reaction tank for further processing. According to treatment process disclosed by the present invention, inhibition and toxic effects generated by the SO42- and S2- to the anaerobic biological treatment can be effectively reduced, and sewage treatment effects can be improved.
Owner:武汉森泰环保股份有限公司
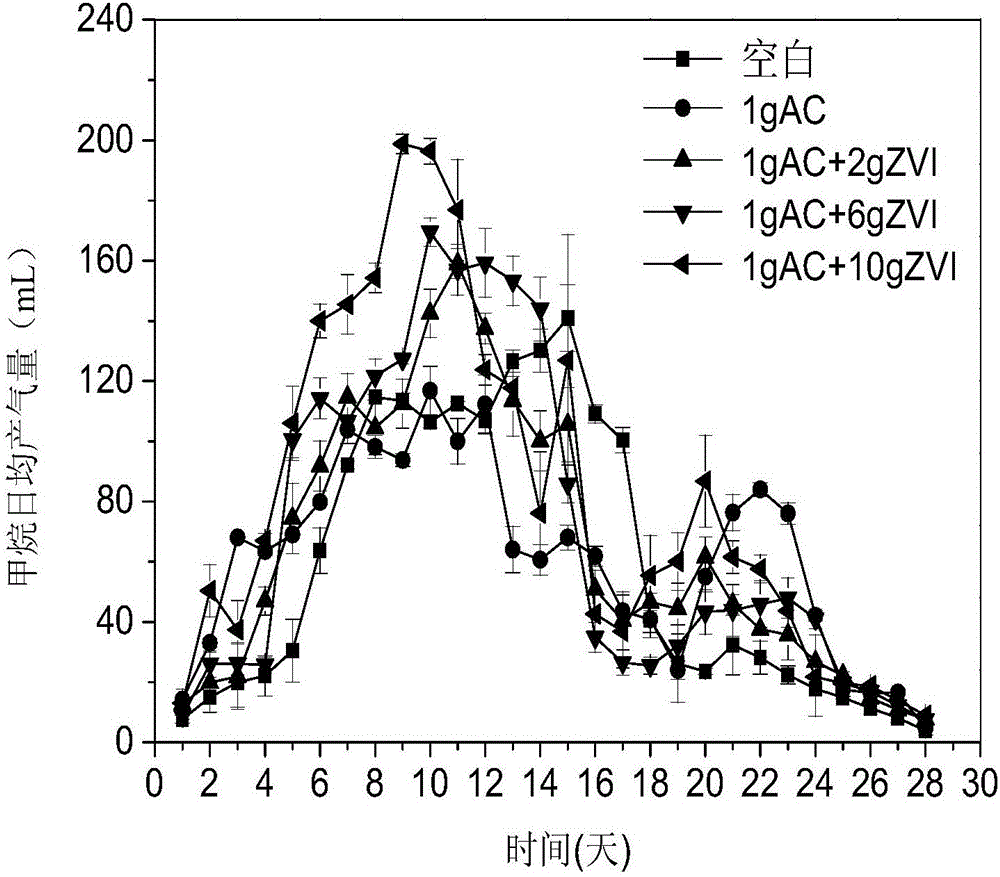
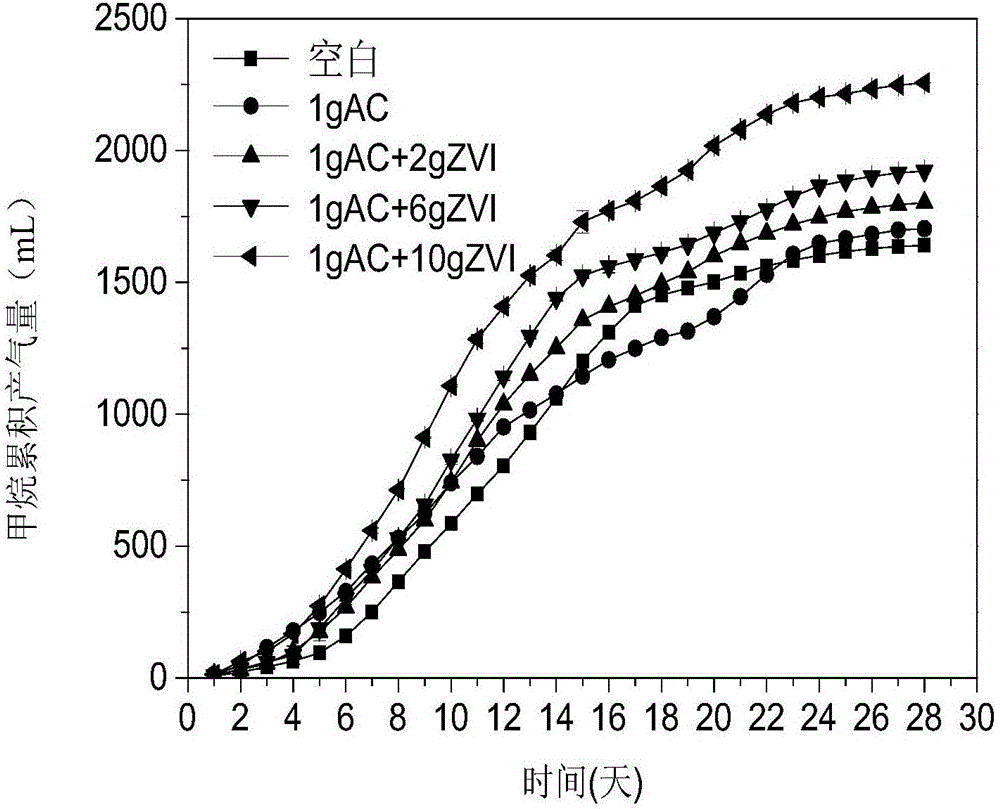
Method for enhancing anaerobic digestion and methane production of excess sludge by zero-valent iron and activated carbon
InactiveCN107522375AIncrease contactPromote decompositionWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsActivated carbonSocial benefits
The invention belongs to the technical field of sludge treatment and recycling and discloses a method for enhancing anaerobic digestion and methane production of excess sludge by zero-valent iron and activated carbon. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), the excess sludge, inoculated sludge and water are mixed, pH is regulated to 6-7.5, solid content of a mixture is enabled to be 8%-12%, and mixed sludge is obtained; (2), the mixed sludge, activated carbon and zero-valent iron are added to an anaerobic digestion device, and anaerobic digestion is implemented; (3), gas produced in the anaerobic digestion process is collected. According to the method, the anaerobic digestion is better promoted by adding activated carbon and zero-valent iron simultaneously; the method is simple, reaction conditions are mild, a gas producing effect is better than that of a traditional method, recycling, harmless and reducing treatment of the excess sludge of a sewage treatment plant is realized, and the method has good economic and social benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
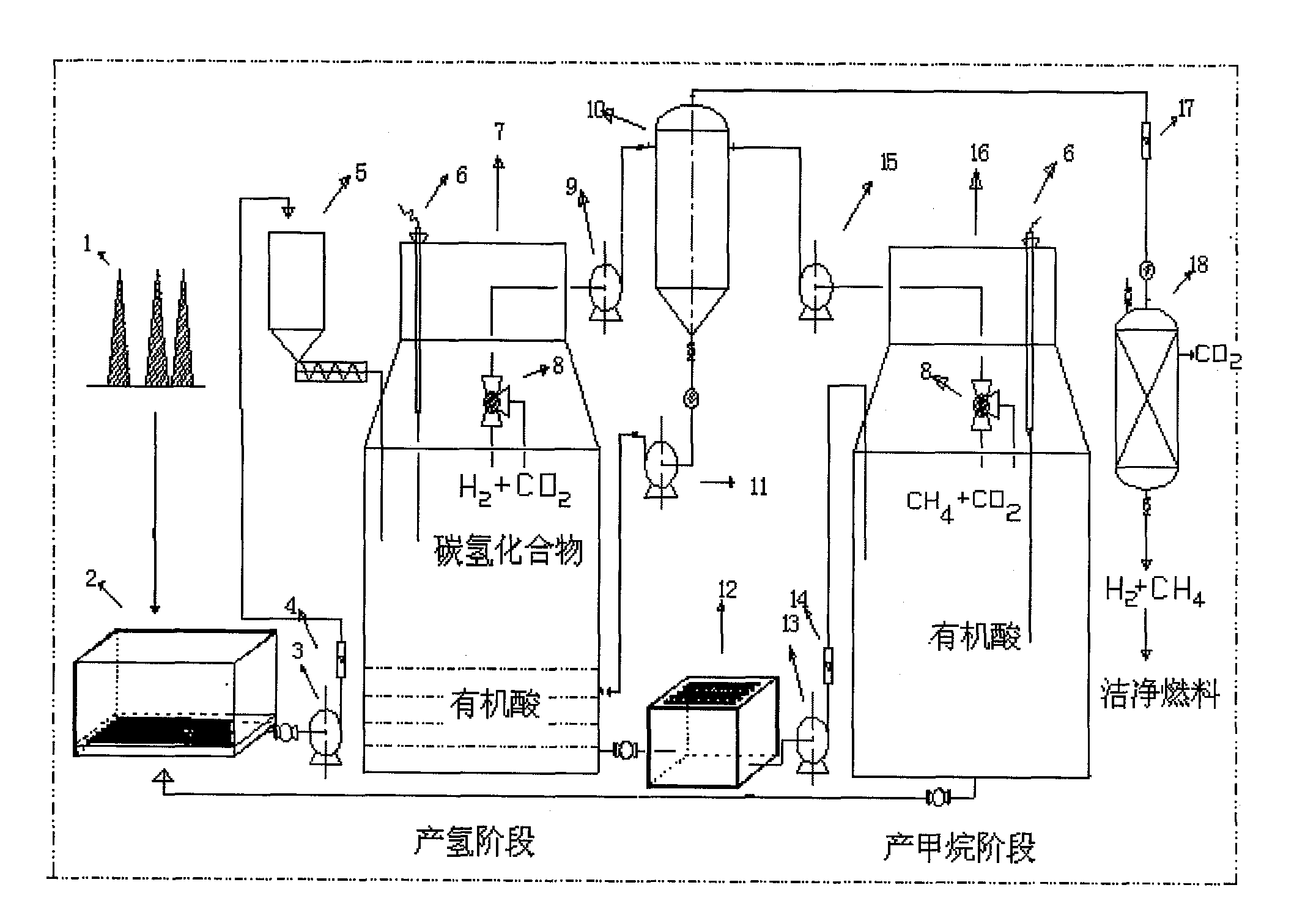
Method for co-producing hydrogen and methane by utilizing dry anaerobic fermentation of solid organic wastes
ActiveCN101638670ARealize continuous productionImprove energy efficiencyGaseous fuelsWaste based fuelMethane productionPre treatment
The invention discloses a method for continuously producing hydrogen and methane by utilizing the dry anaerobic fermentation of solid organic wastes, and relates to a method for the anaerobic digestion of urban garbage and agricultural wastes, in particular to a separation method in the stage of producing hydrogen and methane. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment process of dry anaerobic fermentation; (2) hydrogen production process of the dry anaerobic fermentation; (3) methane production process of the dry anaerobic fermentation; and (4) biogas purification. The methodavoids the problems of acid accumulation, inhibition of methanogenic activity, poor adaptability to raw materials and the like existing in the conventional methane-producing technology, and realizes the continuous production of the hydrogen and methane, thus effectively synthesizing the advantages of the pure hydrogen-producing technology and pure methane-producing technology, avoiding the respective shortcomings, improving the energy utilization efficiency of the organic wastes, and realizing the continuous production of biogases with methane as the key part simultaneously when solving environmental problems.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
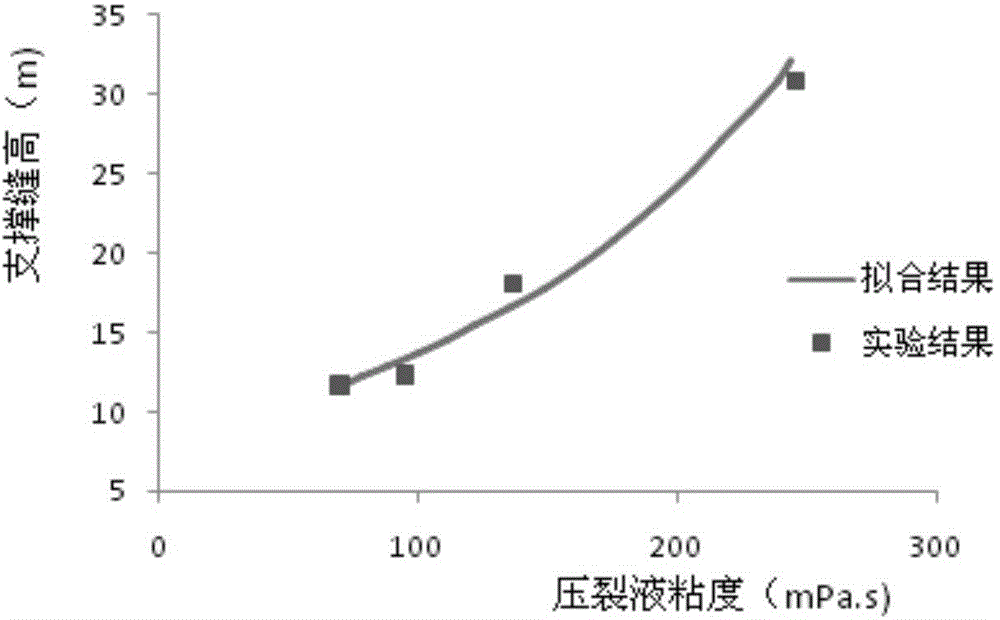
Coal bed methane hydrofracture method
ActiveCN104088616ALow viscosityLow priceFluid removalDrilling compositionFracturing fluidMethane production
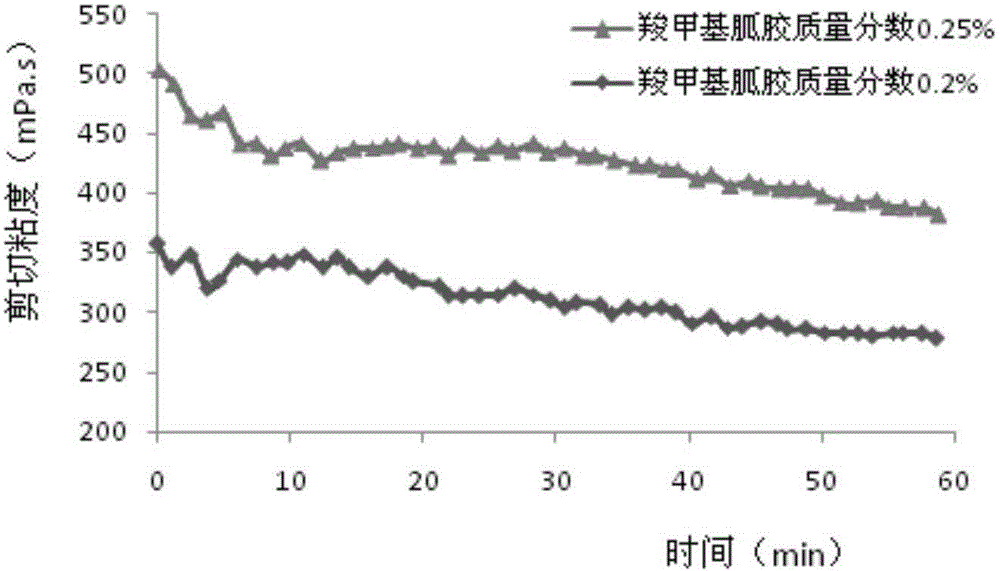
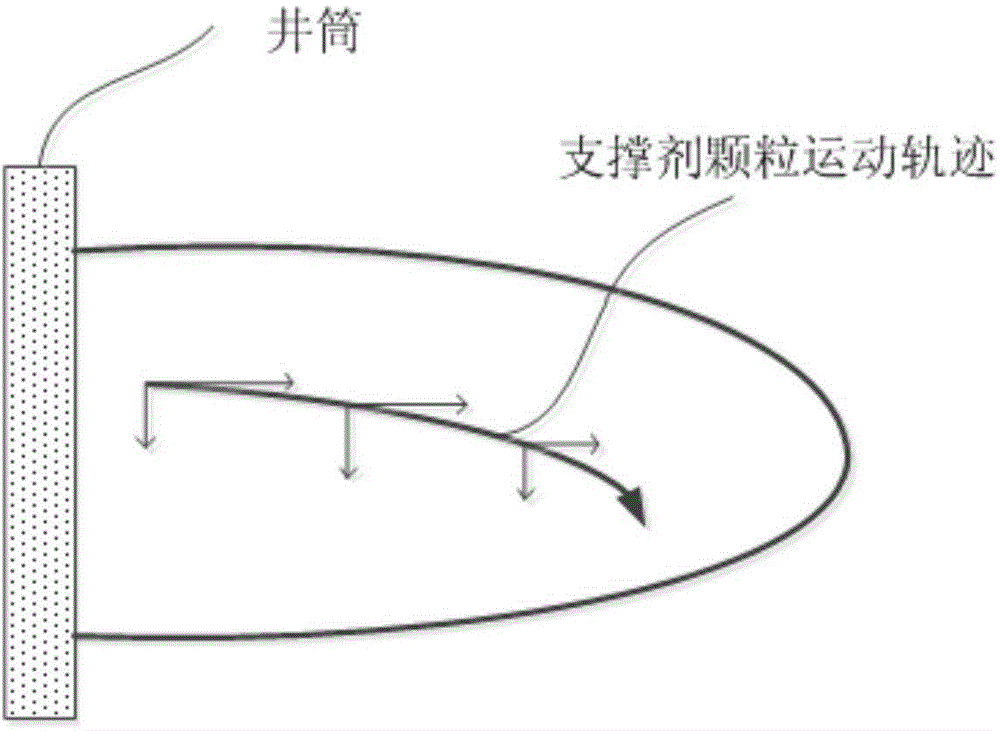
The invention relates to a coal bed methane hydrofracture method. Active water fracturing fluid is used as prepad fluid and displacing fluid, carboxymethyl guanidine gum fracturing fluid is used as sand-carrying fluid, four kinds of quartz sand different in particle size range are used as propping agents, the 100-mesh-to-70-mesh mealy sand and the 70-mesh-to-40-mesh fine sand serve as the propping agents in the prepad fluid, the 40-mesh-to-20-mesh medium sand and the 20-mesh-to-14-mesh coarse sand serve as the propping agents in the sand-carrying fluid, and the proportions of the added sand which is different in particle size and serves as the propping agents are different. The concentrations of clay stabilizers KCL in the active water fracturing fluid and the carboxymethyl guanidine gum fracturing fluid are determined according to the GR average value, represented with the API unit, of fractured objective layer section logging data. By means of the coal bed methane hydrofracture method, the coal bed methane production increasing effect is improved to a great extent, and the preparing cost of the fracturing fluid is reduced to the maximum degree while swelling is effectively prevented.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Physical simulation device and simulation method for coal bed methane production
InactiveCN101799466ARealize automatic collectionReal-time display of node pressureFuel testingGeological measurementsWater bathsMethane production
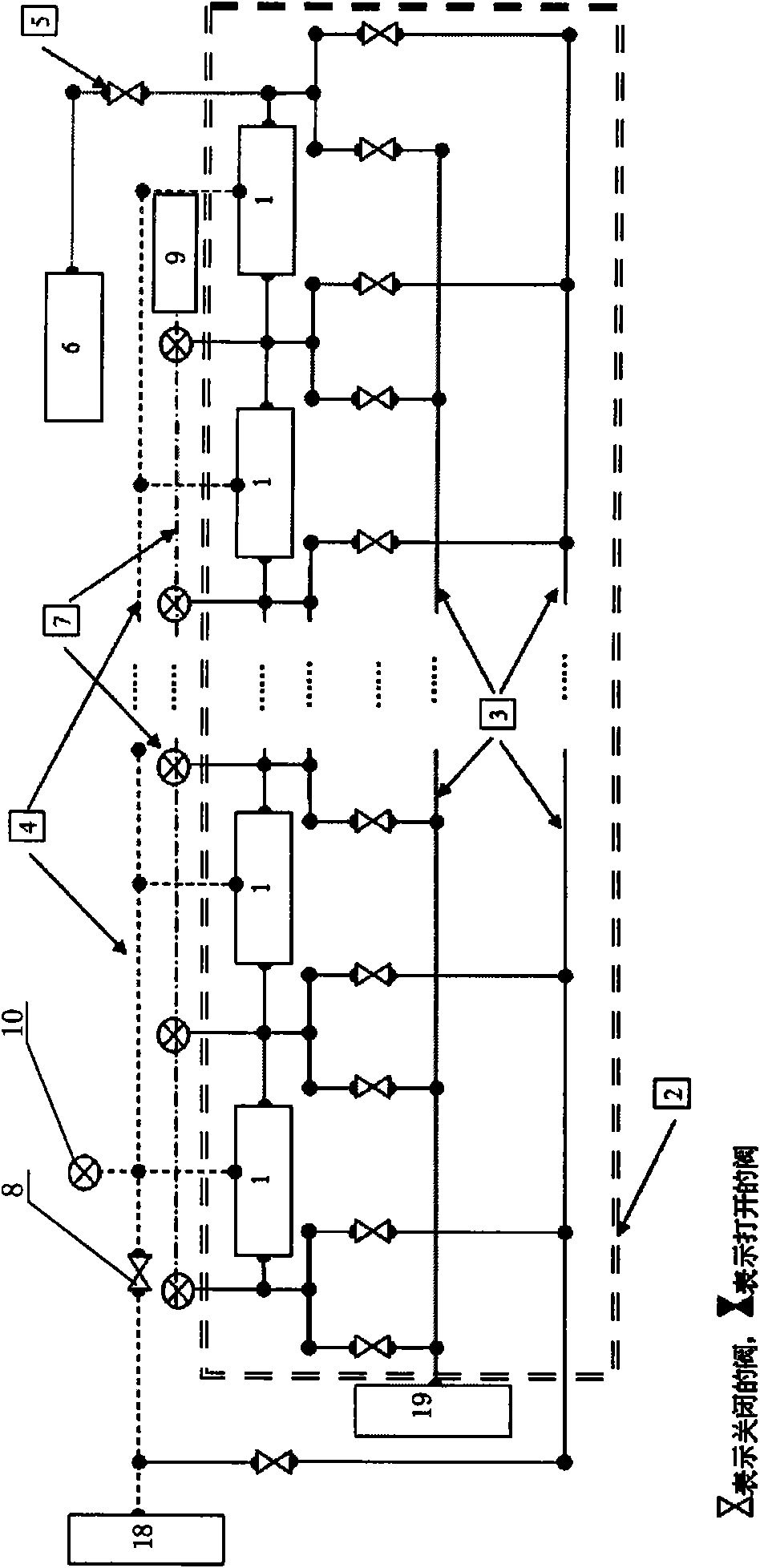
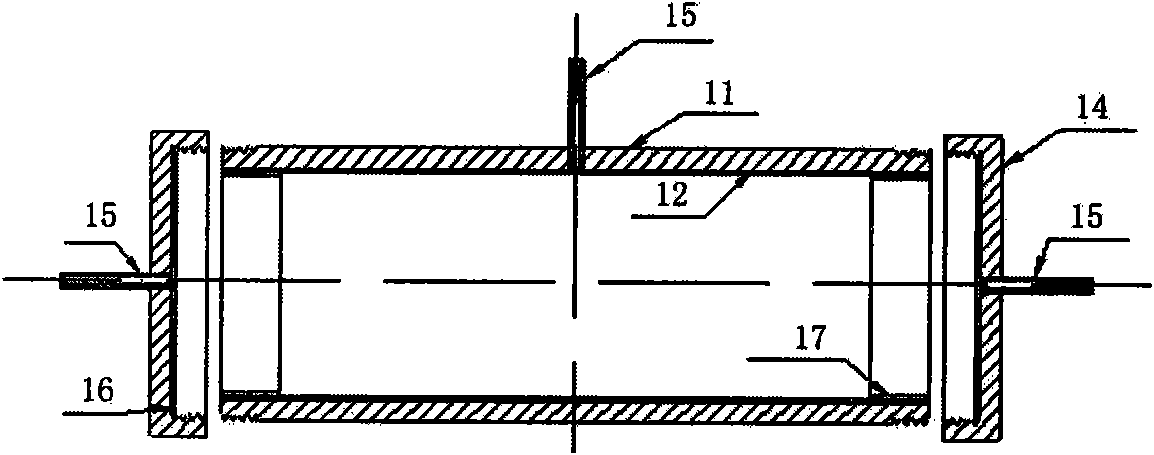
The invention relates to a physical simulation device and a simulation method for coal bed methane production. In the process of production simulation of the current production experiment well and numerical simulation, the cost is high and the accuracy of the numerical simulation can not be ensured. In the physical simulation device and the simulation method for coal bed methane production of the invention, the device comprises sample bins, a thermostatic water bath system, a gas / water metering system and a pressure monitoring system, wherein the sample bins are mutually connected through gas / water configuration production pipelines to form a simulation system; the thermostatic water bath system is arranged around the simulation system; the sample bins of the simulation system are all connected with confining pressure simulation pipelines; the pressure monitoring system is arranged on the gas / water configuration production pipelines at the ends of the sample chambers; simulation well mouths are connected with the gas / water configuration production pipelines at the tail ends of the simulation system; and the simulation well mouths are connected with the gas / water metering system. Through the device and simulation method of the invention, the gas filling, water injection and production states are simulated, thereby optimizing the gas well production working system, reducing the cost, and simultaneously ensuring safe high-efficiency exploitation of the coal bed methane.
Owner:煤炭科学研究总院有限公司西安研究院
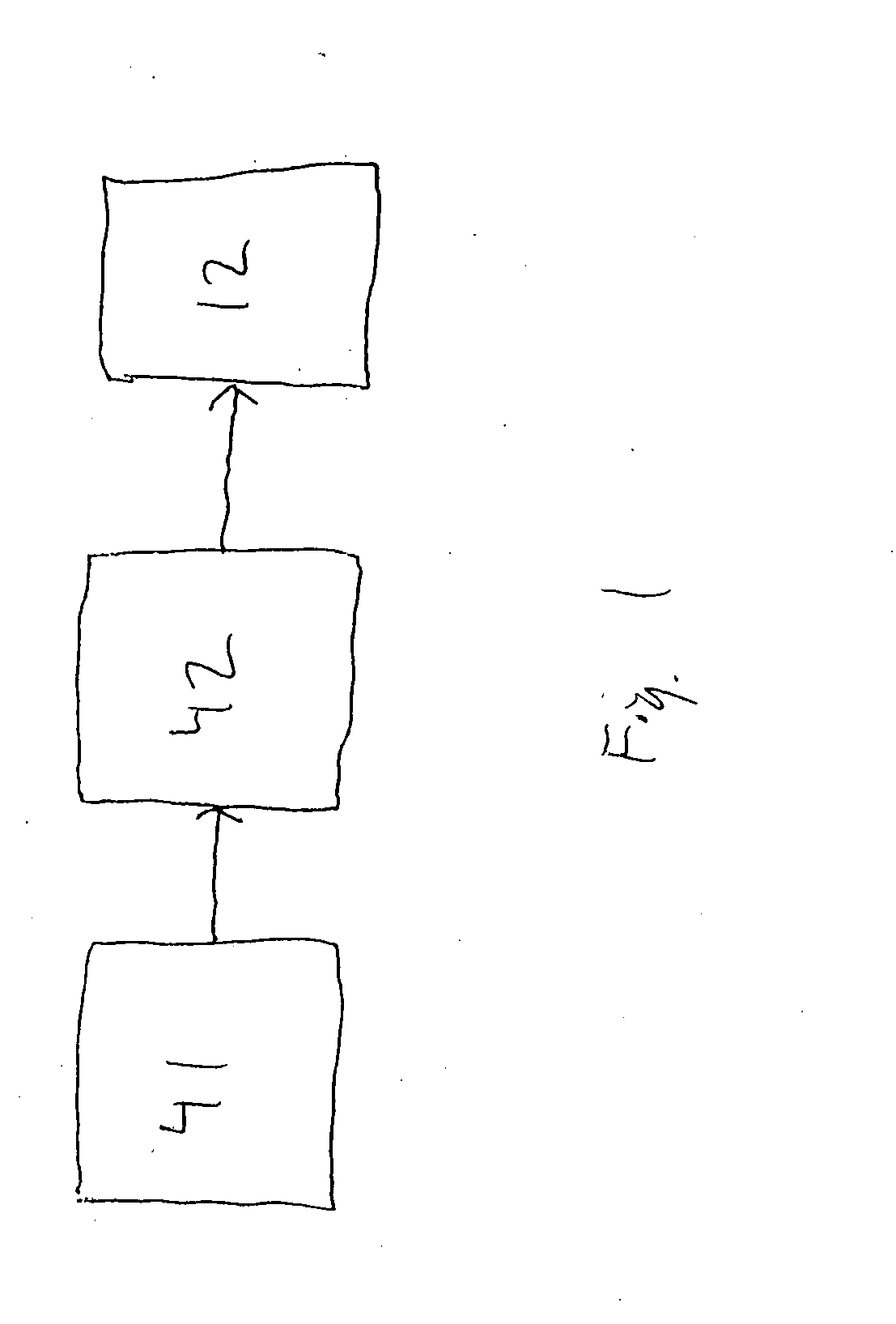
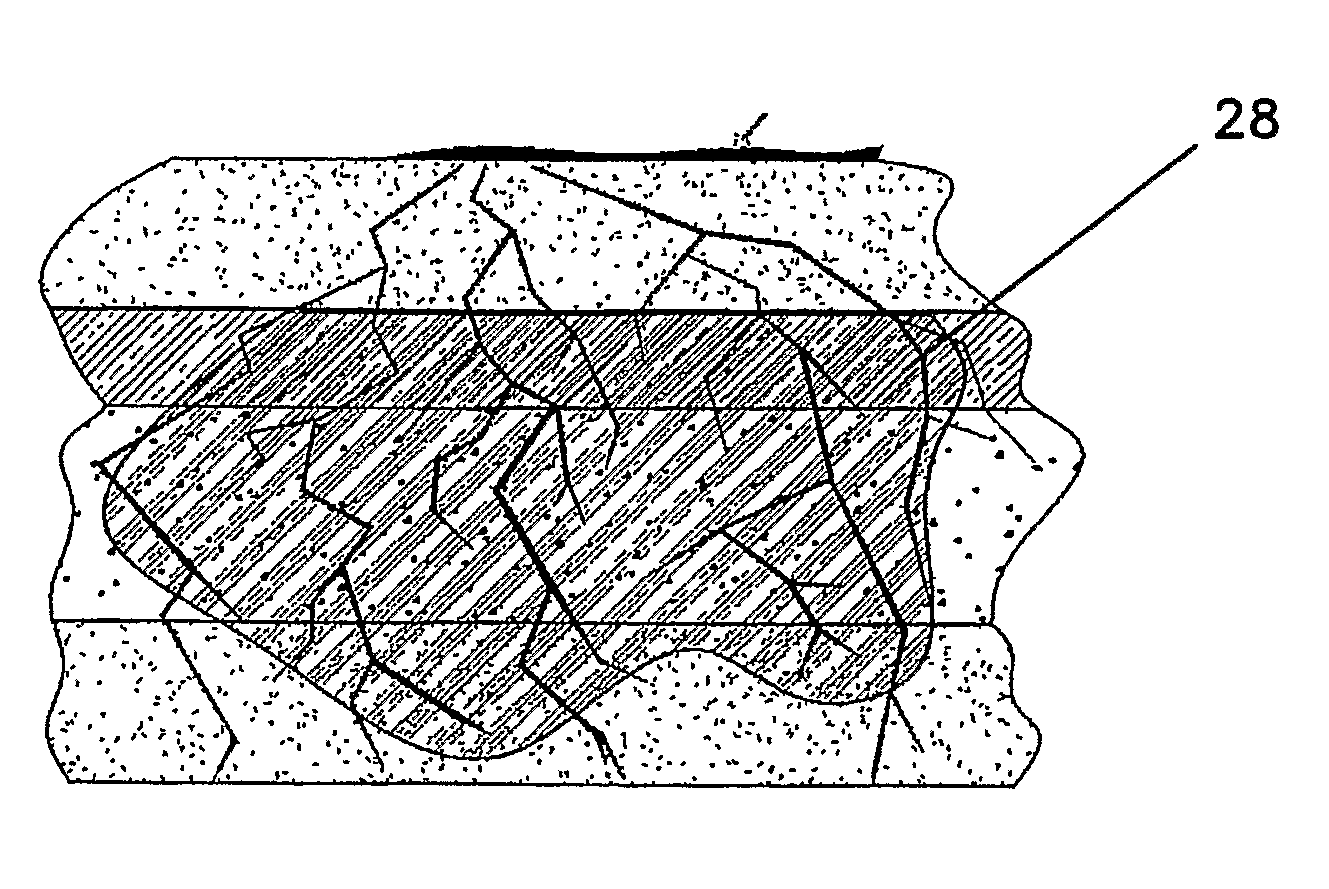
Biogenic Methane Production Enhancement Systems
InactiveUS20090246849A1Increase methane productionReduce competitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSulfateMethane production
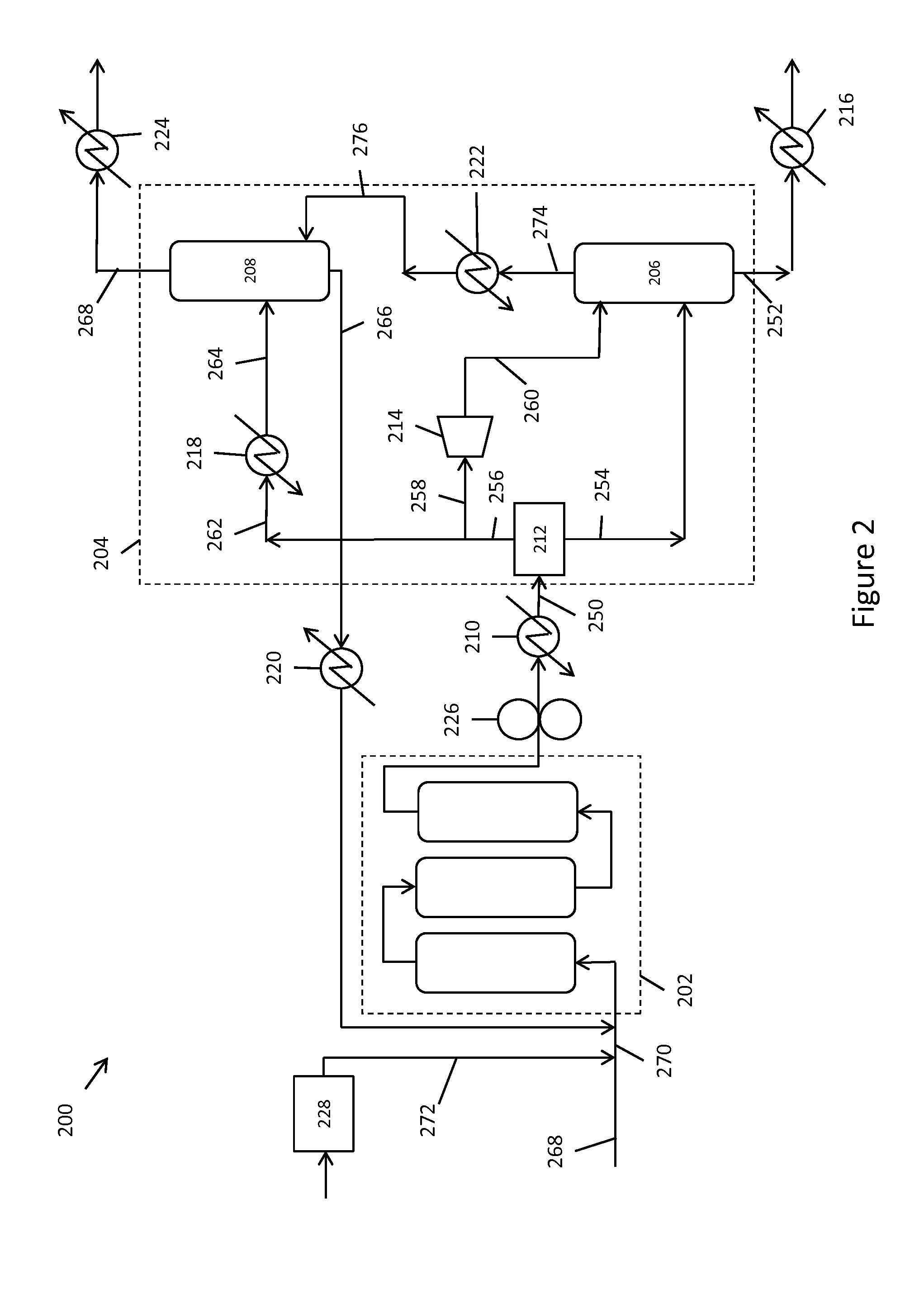
Systems for enhanced in-situ or perhaps even ex-situ biogenic methane production from hydrocarbon-bearing formations (1) including coal seam, oil shale, coal, coal derivates and the like are presented in embodiments such as but not limited to: increasing and perhaps even selection of microbial populations (2), amending CBM water and other microbe-containing media, diminishing sulfate reduction competition, enhancing organic matter concentrations and generation of biogenic methane (10), universally treating hydrocarbon-bearing formations, and introducing amendments (3) to hydrocarbon-bearing formations.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
Soybean straw industrialization methane production and method for extracting cellulose and lignin
InactiveCN101629188ASoft inner structureLoose internal structureTreatment using aerobic processesBioloigcal waste fertilisersChemical industryCellulose
The invention provides a technical method which uses soybean straw as main raw material to industrially produce methane in large scale, and simultaneously extracts cellulose and lignin from waste residue from fermented and decomposed organisms so that soybean straw is fully utilized, the economic benefit is increased and the industrialization production benefit is obvious. The produced methane can be directly used for generating electricity, resident gas and the like; the methane also can be compressed so that carbon dioxide gas is liquefied and separated and the content of the methane in the methane reaches more than 85%; the methane is stored in high pressure and used for environmental protection material of automobiles. The extracted cellulose and lignin are used for papermaking and chemical industry raw materials.
Owner:陈福库
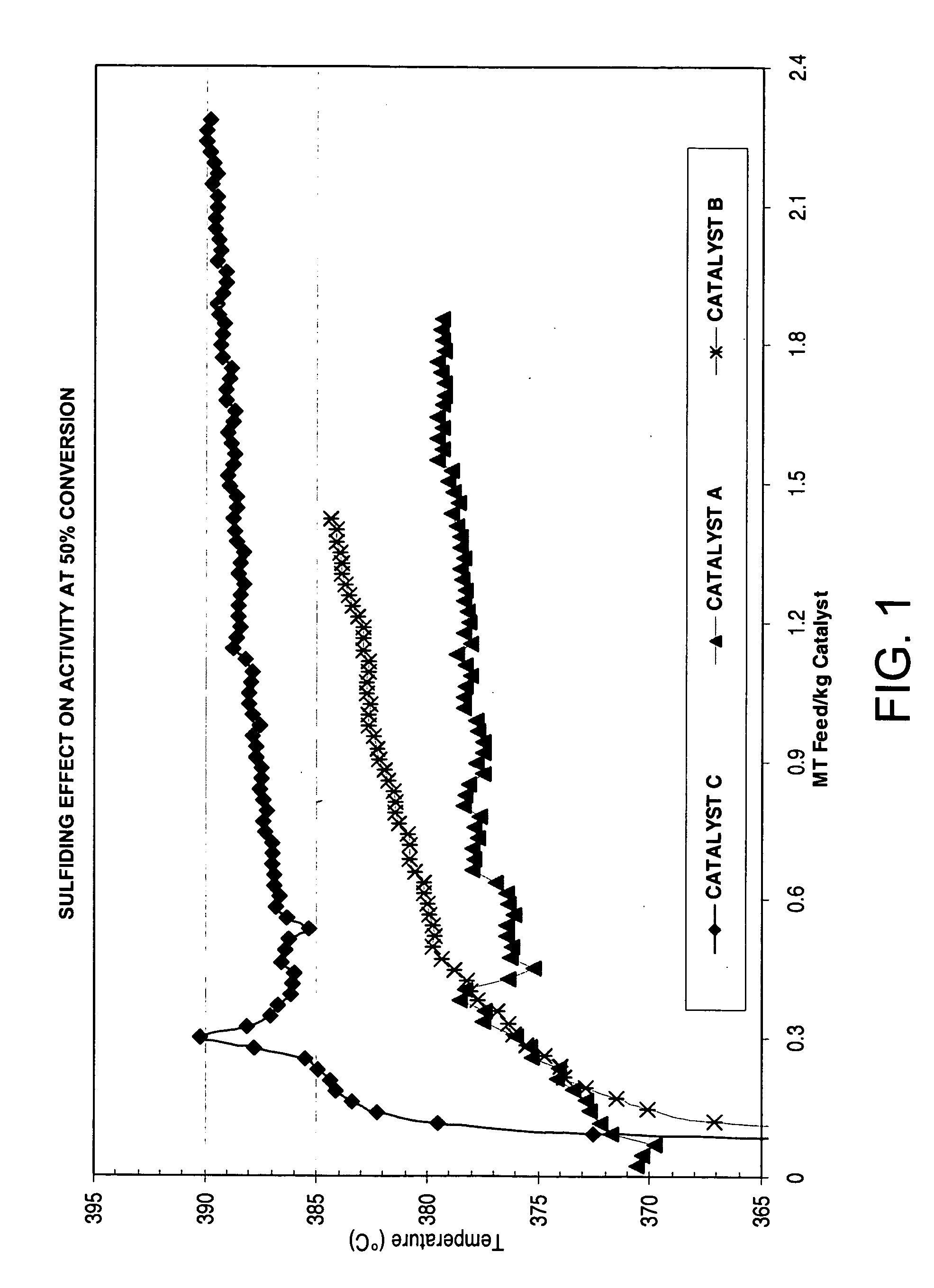
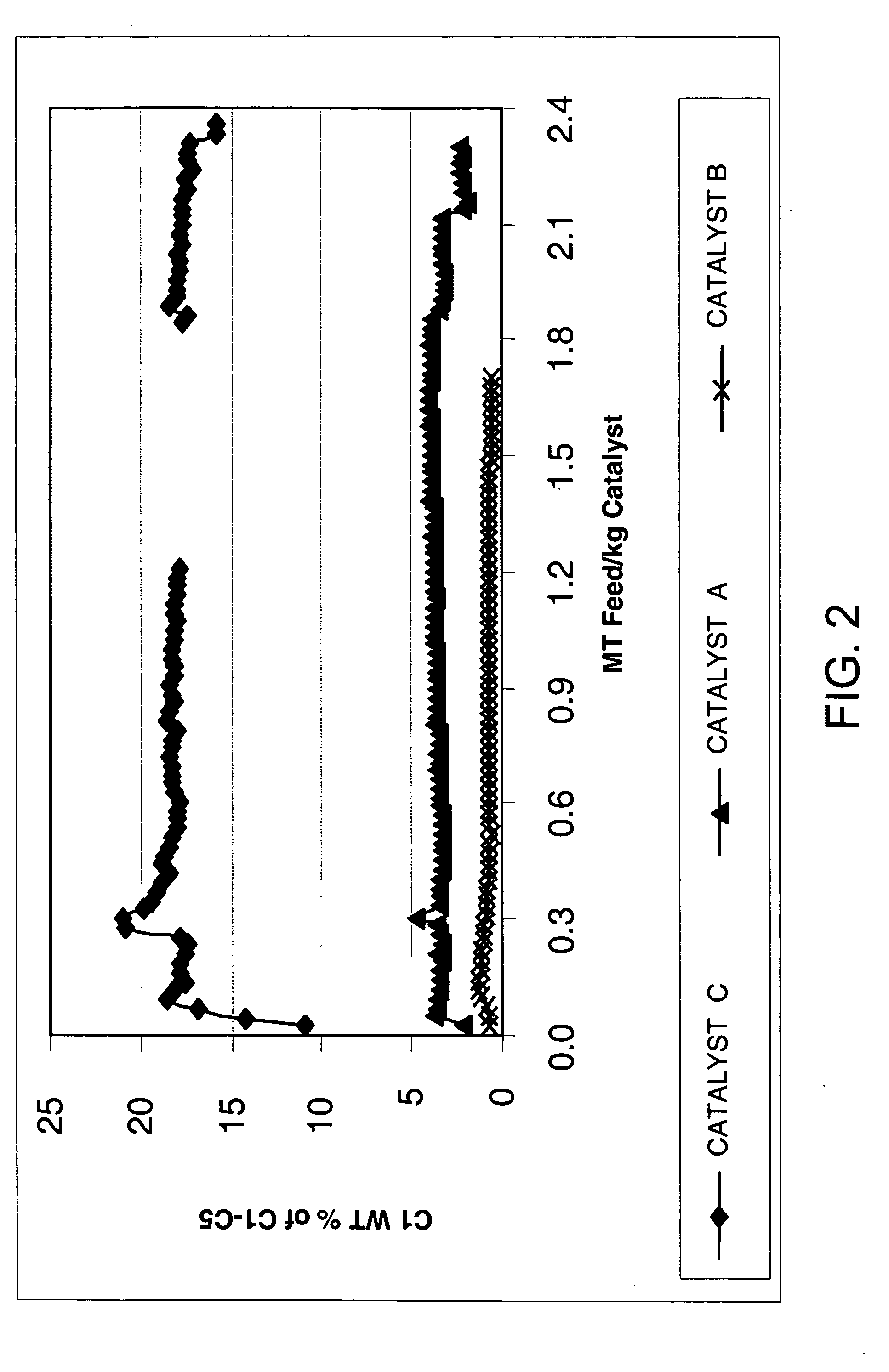
Catalyst treatment useful for aromatics conversion process
A process for preparing a transalkylation catalyst, the catalyst itself, and a transalkylation process for using the catalyst are herein disclosed. The catalyst comprises rhenium metal on a solid-acid support such as mordenite, which has been treated with a sulfur-based agent. Such treatment reduces the amount of methane produced by metal hydrogenolysis in a transalkylation process wherein heavy aromatics like A9+ are reacted with toluene to produce xylenes. Reduced methane production relative to total light ends gas production results in lower hydrogen consumption and lower reactor exotherms.
Owner:UOP LLC
Biogenic methane production enhancement systems
InactiveUS7832475B2Increase methane productionReduce competitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSulfateMethane production
Systems for enhanced in-situ or perhaps even ex-situ biogenic methane production from hydrocarbon-bearing formations (1) including coal seam, oil shale, coal, coal derivates and the like are presented in embodiments such as but not limited to: increasing and perhaps even selection of microbial populations (2), amending CBM water and other microbe-containing media, diminishing sulfate reduction competition, enhancing organic matter concentrations and generation of biogenic methane (10), universally treating hydrocarbon-bearing formations, and introducing amendments (3) to hydrocarbon-bearing formations.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
Electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system
ActiveCN105906051AEfficient couplingAccelerate reaction mass transfer efficiencyTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsSmall footprintElectrochemistry
The invention discloses an electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system. The system comprises a microorganism electrolytic tank shell, a sealed cover, a microorganism positive electrode, a microorganism negative electrode and a power supply, wherein the sealed cover covers the microorganism electrolytic tank shell to form a closed space; the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode are connected with a negative electrode and a positive electrode of the power supply respectively, a short-distance nitrification microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism positive electrode, and denitrification methane anaerobic oxidation microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism negative electrode; the side, close to the microorganism positive electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water inlet, and the side, close to the microorganism negative electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water outlet. An inorganic carbon source put-in opening is formed in the position, close to the microorganism negative electrode, between the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode. By means of one electrolytic tank, short-distance nitrification, electrochemical methane production and methane anaerobic oxidation are effectively coupled, reaction mass transfer efficiency is accelerated, occupied area is small, and capital construction investment is small.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
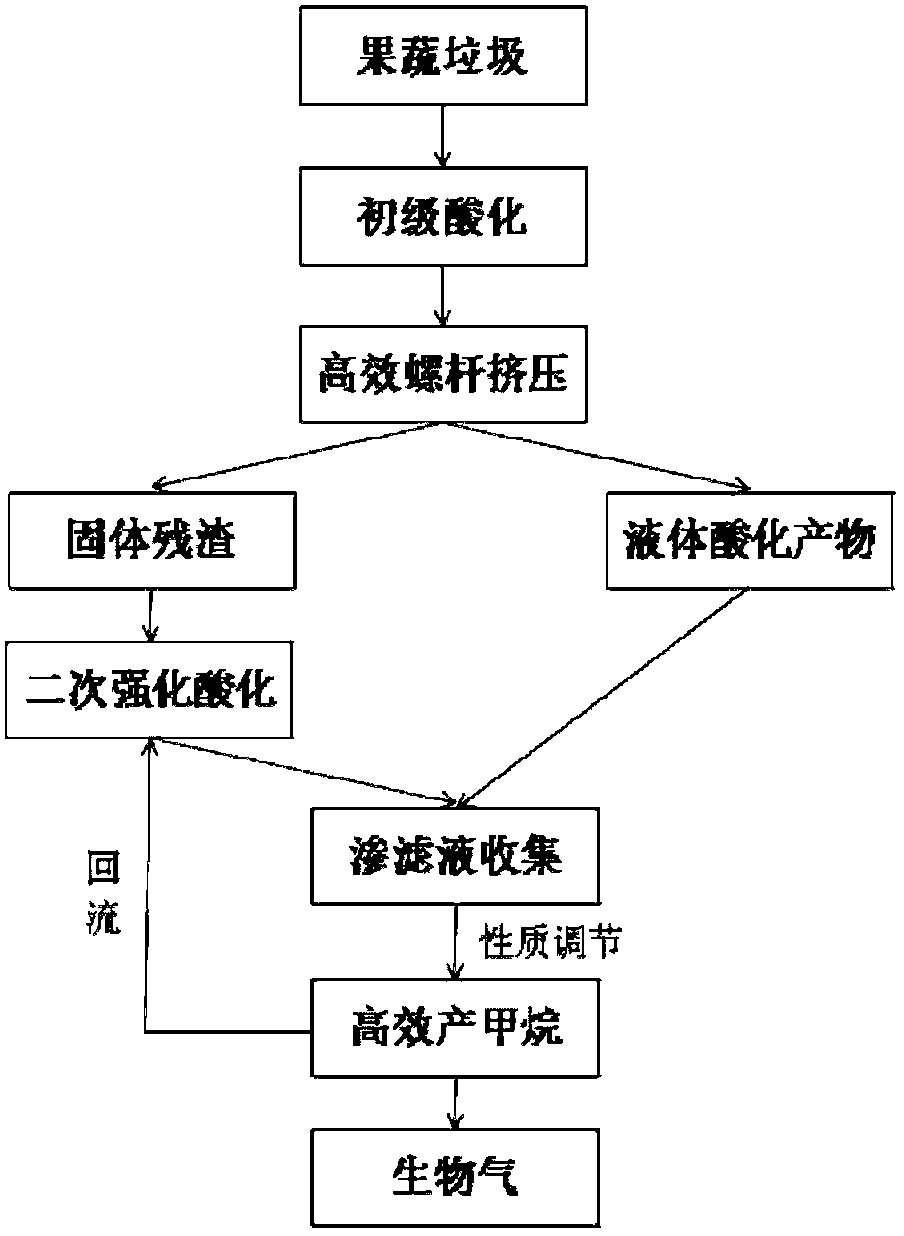
Method for producing biogas through anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable waste
ActiveCN102703515AHigh efficiency of hydrolysis and acidificationReduce consumptionWaste based fuelFermentationMethanationAerobic digestion
The invention discloses a method for producing biogas through anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable waste, and belongs to the field of high-efficiency recycling of organic solid waste. The fruit and vegetable waste is firstly subjected to acidification as well as a high-efficiency extrusion process to realize solid-liquid separation, and then a solid-state product and a liquid-state product are treated respectively. Solid-state residue is subjected to secondary reinforcing acidification to enter a high-efficiency anaerobic digestion methane production reactor together with a liquid-state acidification product; and meanwhile, effluent water of the methanator is used as reflux liquid to be circulated in a solid-state residue secondary reinforcing hydrolytic acidification reactor to speed up the hydrolytic acidification reaction. According to the method, high-efficiency transformation of the waste is realized, and the effluent water in the methanator is pumped into the secondary reinforcing acidification reactor for recycling. The method has the advantages of high treatment rate, high gas production rate, short period, capability of realizing continuous stable gas production, no wastewater discharge and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
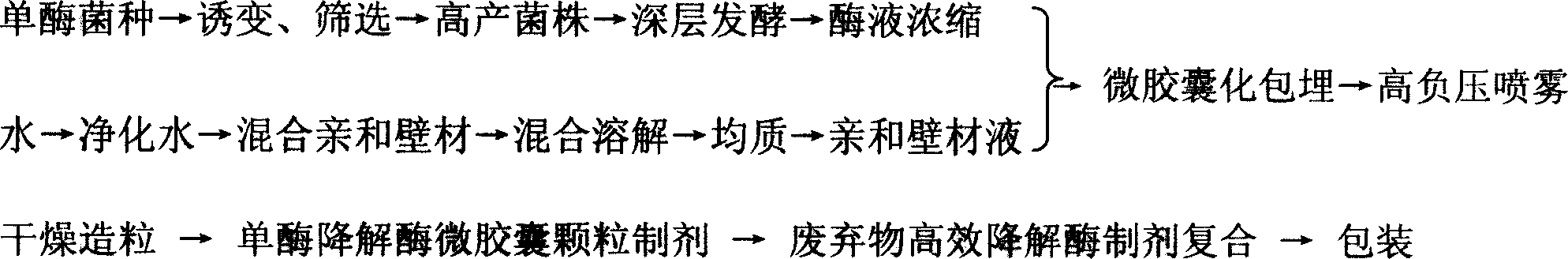
Composite enzyme prepn for degrading agricultural waste effectively and its prepn process
InactiveCN101045919AHigh potencyImprove digestion and absorption rateHydrolasesHeat recovery systemsProteinase activityMethane production
The present invention relates to enzyme preparation, and is especially one kind of composite enzyme preparation for degrading agricultural waste effectively and its preparation process. The composite enzyme preparation includes xylanase with enzyme activity not lower than 100 KU / g, beta-dextranase with enzyme activity not lower than 80 KU / g, cellulose with enzyme activity not lower than 28 KU / g, acid protease with enzyme activity not lower than 56 KU / g, lipase with enzyme activity not lower than 15 KU / g, pectase with enzyme activity not lower than 6 KU / g, and alpha-amylase with enzyme activity not lower than 12 KU / g. Its preparation process includes the steps of spawn preparation, enzyme preparation production, compounding, etc. The present invention may be used in feed production, methane production and other fields.
Owner:唐东升 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com