Method for producing methane by using lignocellulosic materials
A lignocellulosic raw material and biogas production technology, which is applied in biofuel, waste fuel, fermentation, etc., can solve the problem of difficult mixing of bacteria agent and lignocellulosic raw material, loss of dry matter of lignocellulosic raw material, large workload of pretreatment sites, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of facilitating decomposition and utilization, reducing the content of easily decomposable organic matter, and increasing the biotransformation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
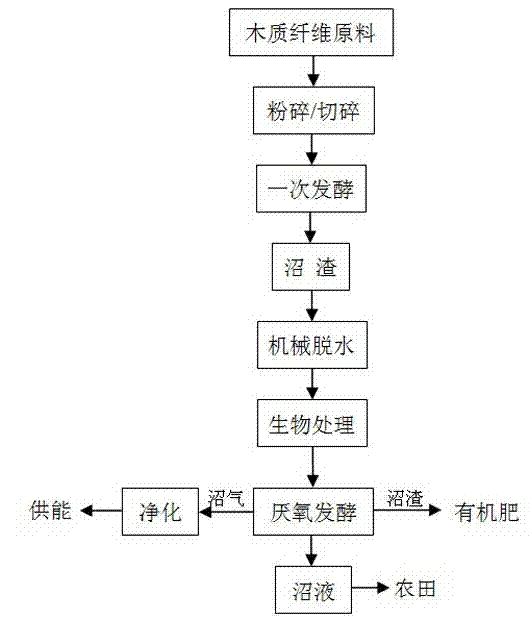
[0025] Cut the harvested lignocellulosic raw materials into small pieces no larger than 5cm by mechanical or manual methods, then put them into the anaerobic reactor, and add the inoculum (the inoculum is anaerobic digested sludge from sewage treatment plants, old biogas digesters One or a combination of sludge, spoiled river mud, and fresh cow dung, the same below), the amount of the inoculum added is 30% of the dry weight of the fermented product, and the initial dry matter concentration of the fermented product in the anaerobic reactor is reduced to Adjust to 20%, mix well. The fermentation device is closed, and the gas outlet of the fermentation device is connected to the gas storage device through a gas transmission pipe. The reaction temperature is controlled at 37±1°C, and biogas can be generated within 24 hours. The lignocellulosic raw material after primary anaerobic fermentation is taken out and dried. After one anaerobic fermentation, the lignocellulosic raw materi...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Controlled experiment:
[0033] Get two parts of the same amount of lignocellulosic raw materials as in Example 1, cut into small sections no greater than 5cm by mechanical or manual methods, one part is used as the control group 1 (traditional biological pretreatment), and the other part is used as the control group 2 (without for biological pretreatment).
[0034] Control group 1 was inoculated with microbial inoculum (the microbial inoculum was the same as in Example 1), the amount of microbial inoculum was 3% of the dry matter mass of the lignocellulosic raw material, and fermented for 7 days at 20-35°C under aerobic ventilation conditions after inoculation , forming lignocellulosic raw materials after aerobic fermentation. The spore concentration in the microbial agent (liquid) is not less than 1×10 8 pieces / ml.
[0035] Control group 2 was placed under the same conditions for 7 days without any treatment.
[0036] After 7 days, the two groups of raw materi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com