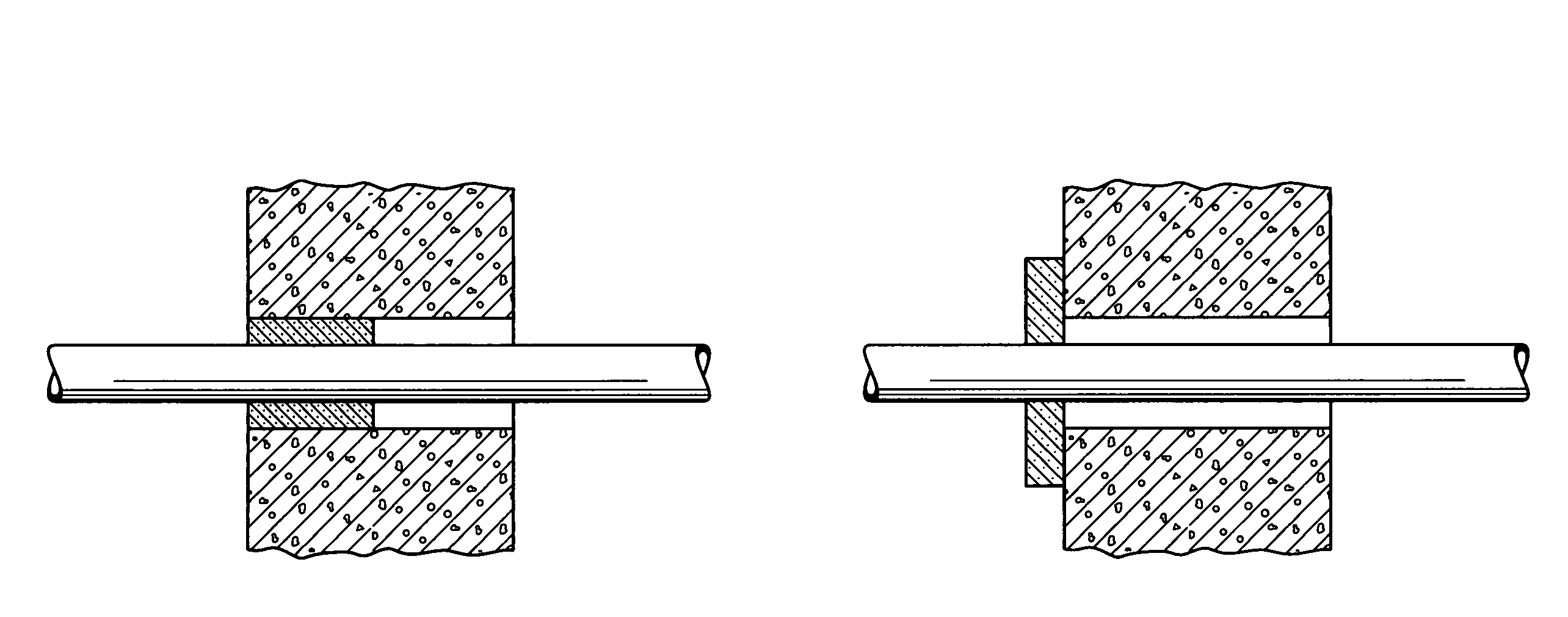
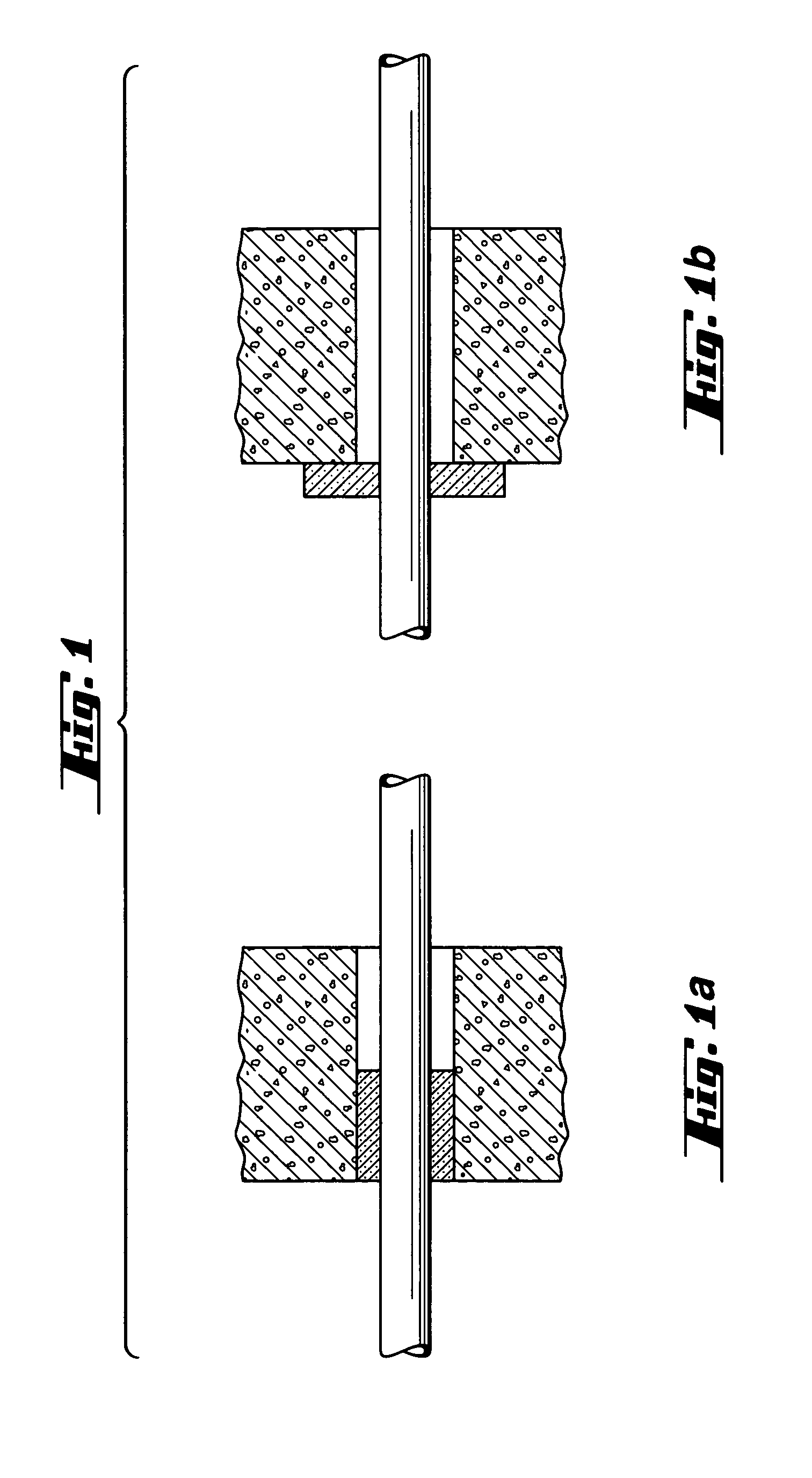
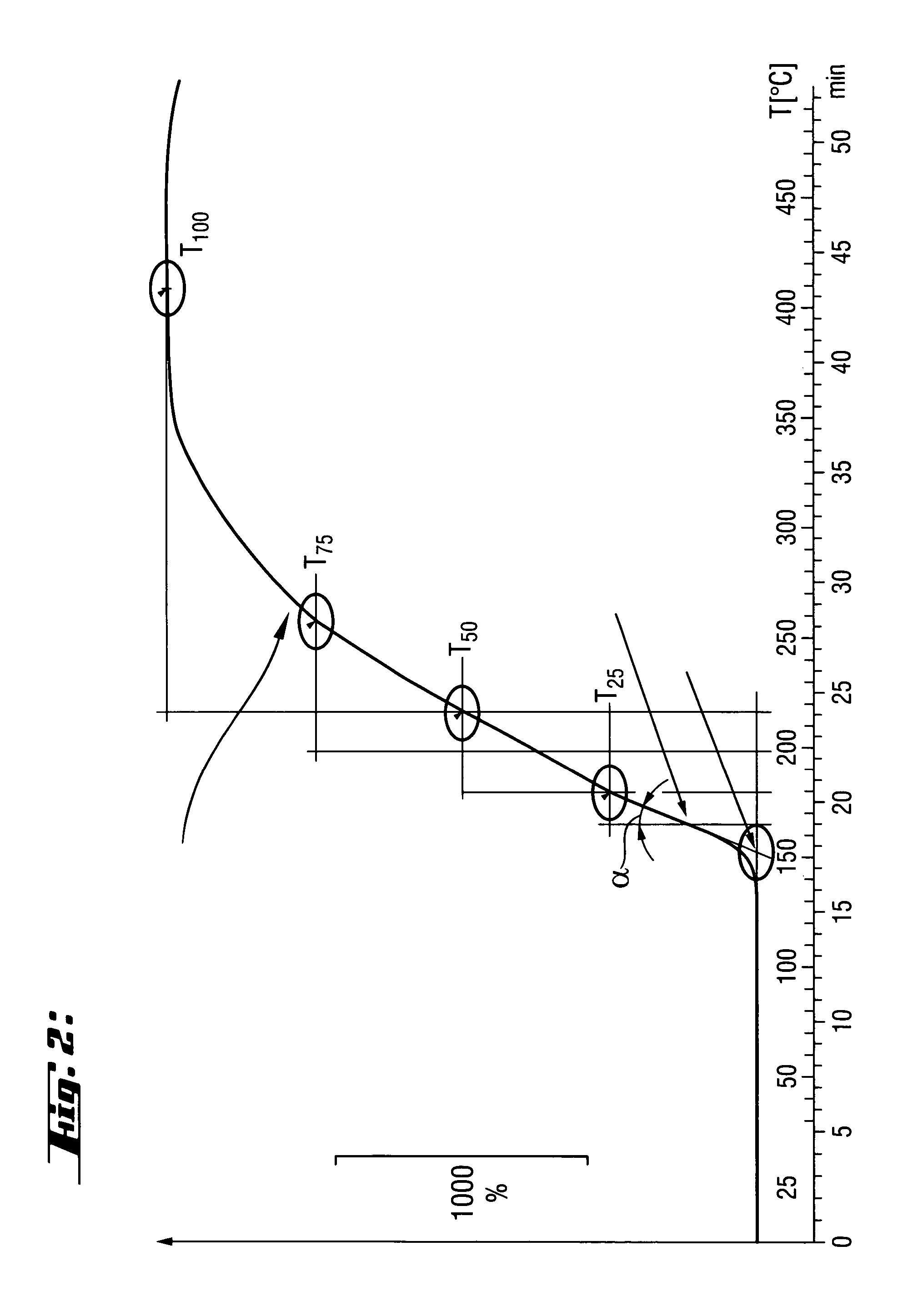
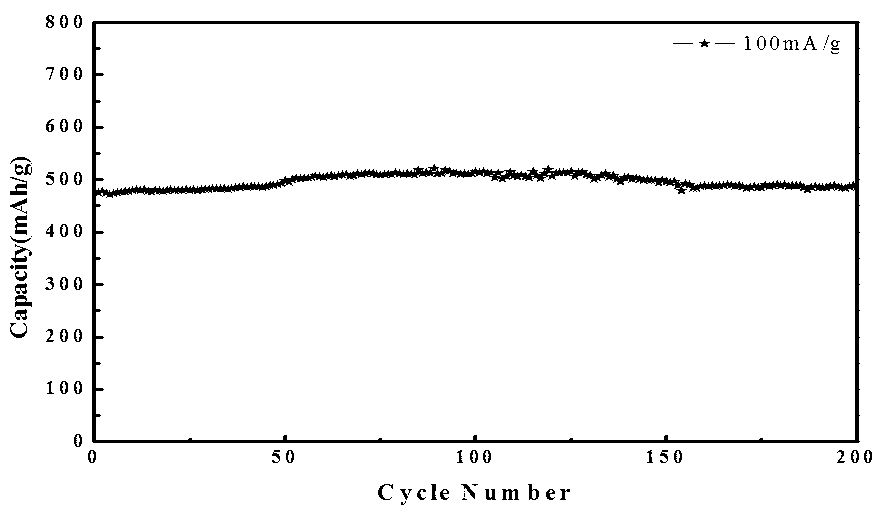
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Graphite intercalation compound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
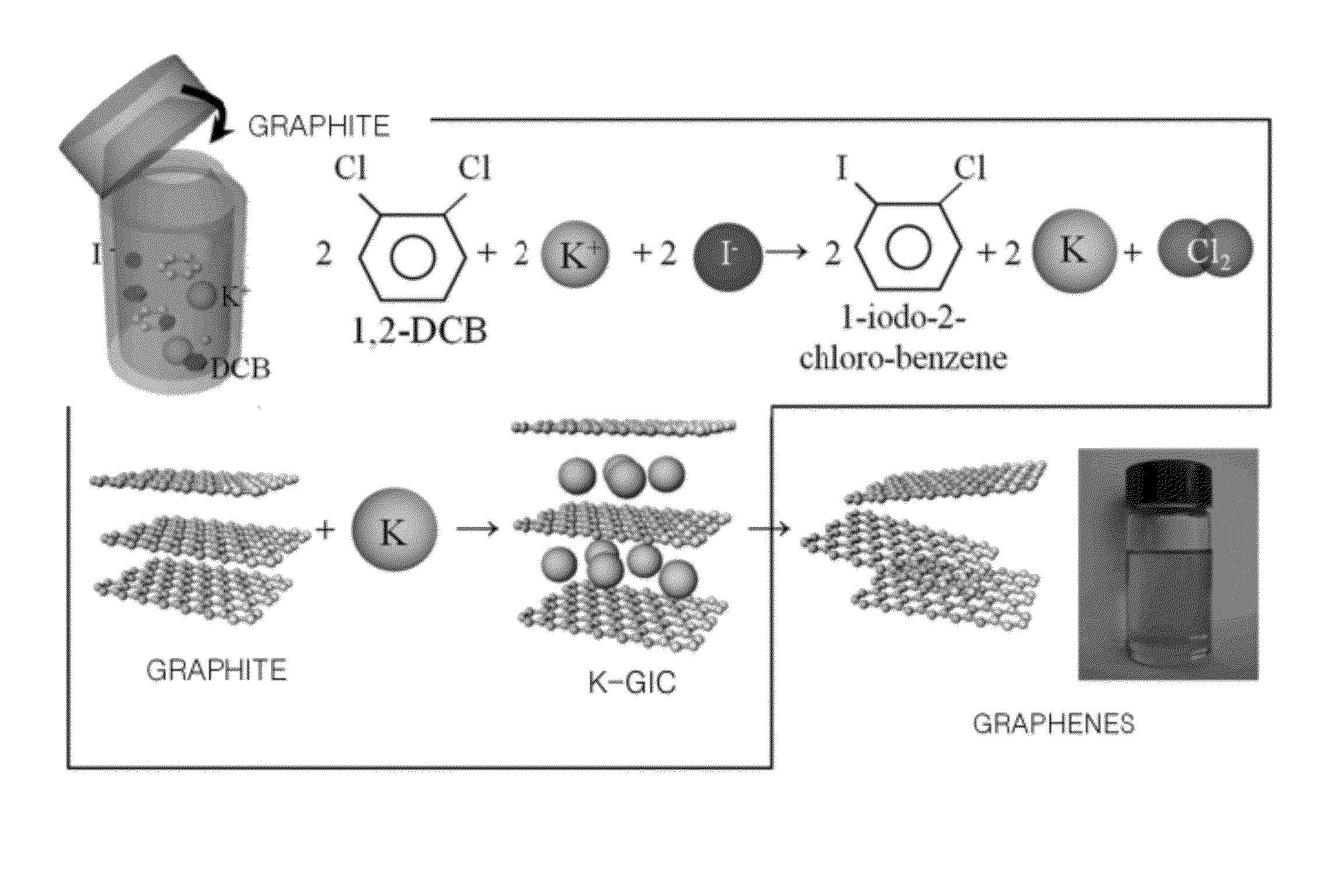
Graphite intercalation compounds (GICs) are complex materials having a formula CXₘ where the ion Xⁿ⁺ or Xⁿ⁻ is inserted (intercalated) between the oppositely charged carbon layers. Typically m is much less than 1. These materials are deeply colored solids that exhibit a range of electrical and redox properties of potential applications.
Process for producing dispersible Nano Graphene Platelets from oxidized graphite
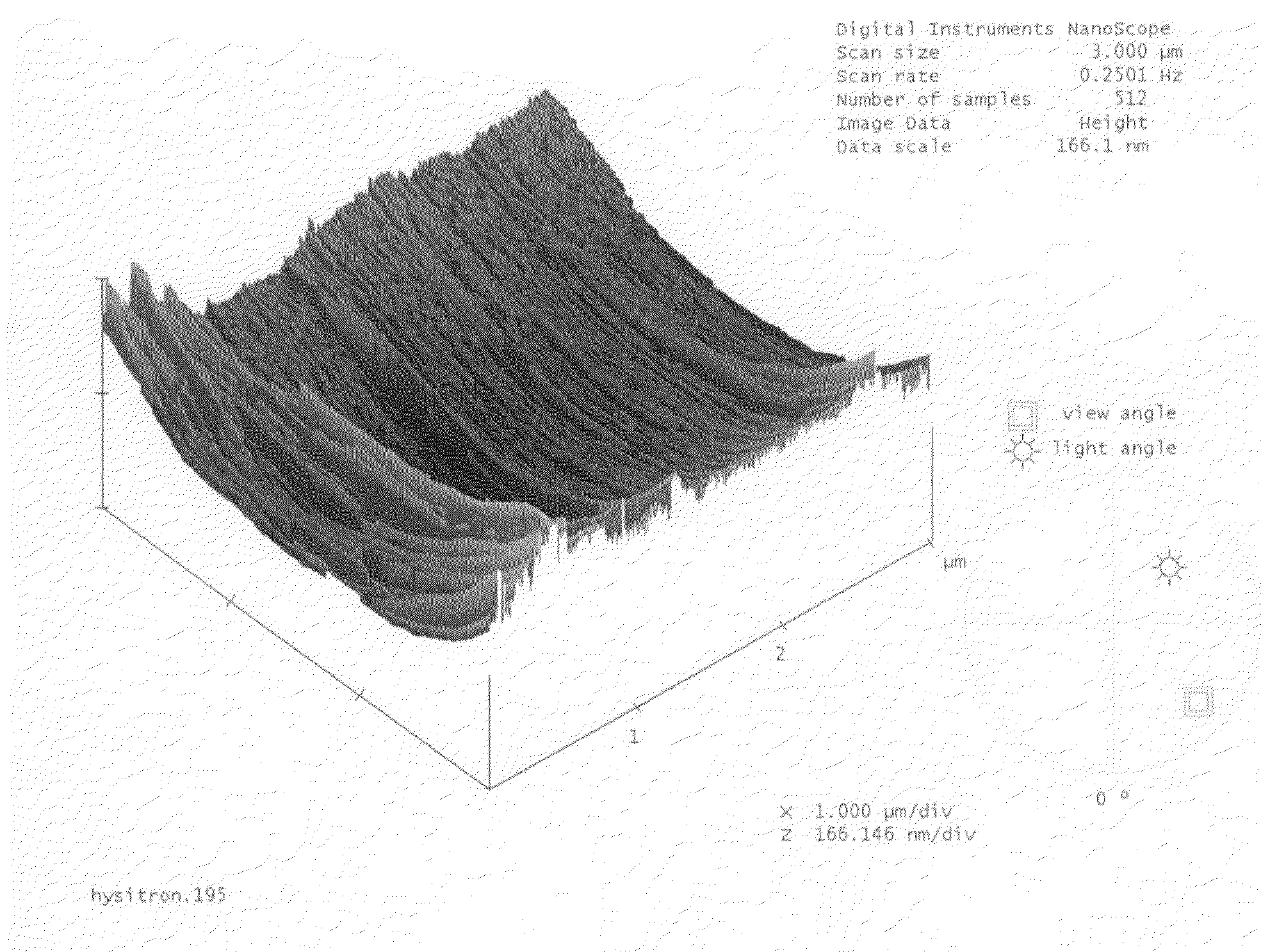
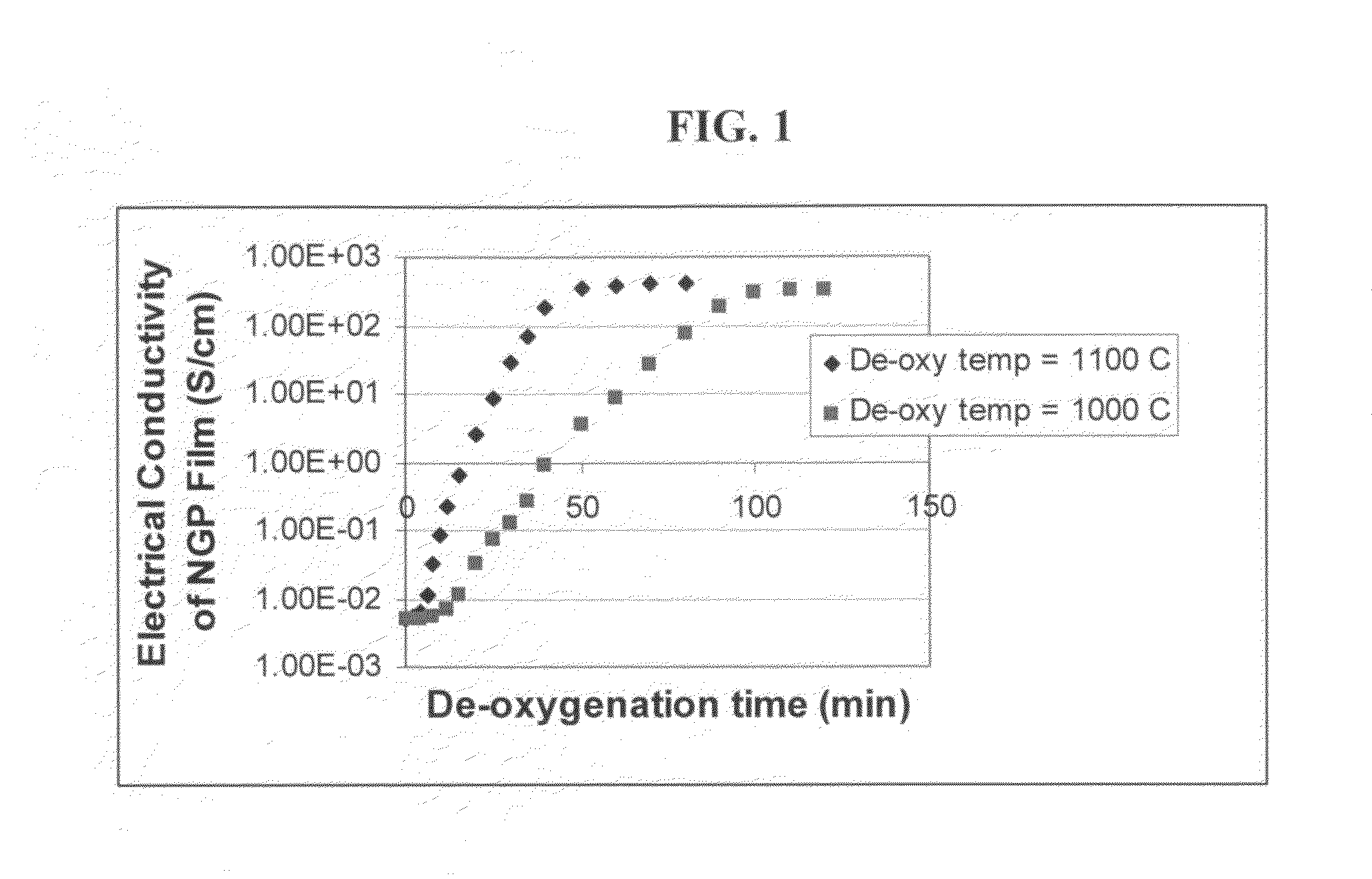
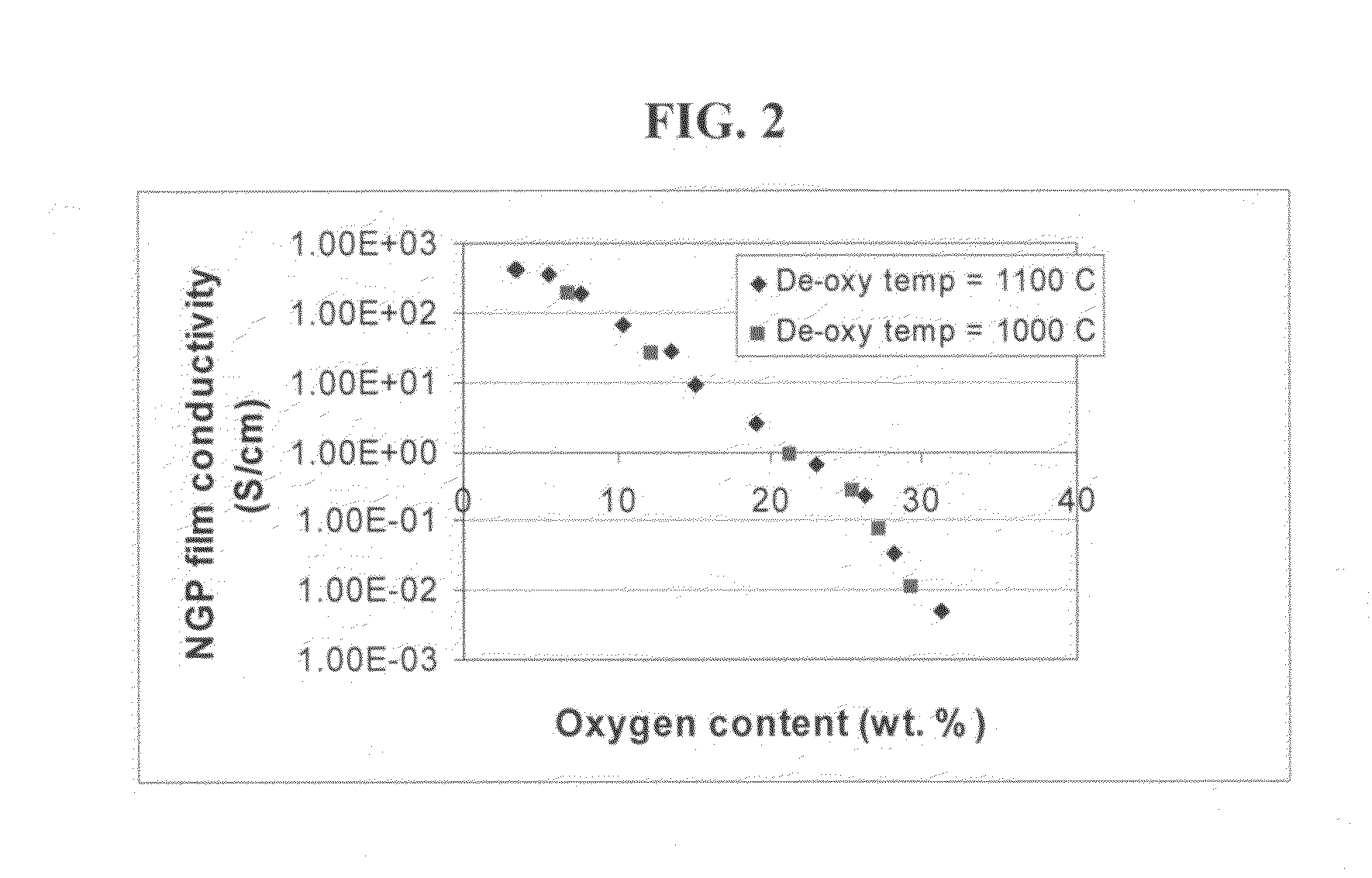
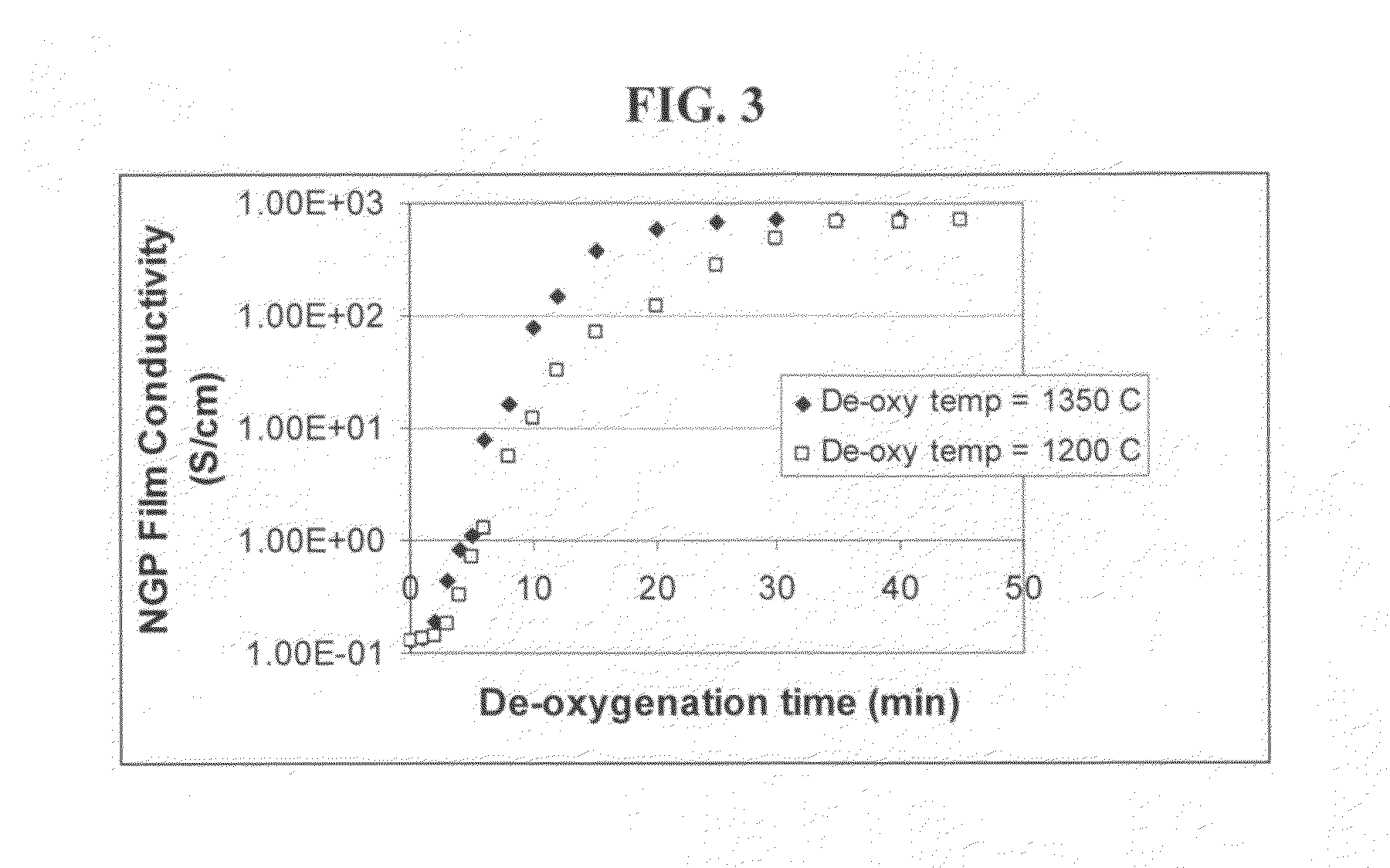
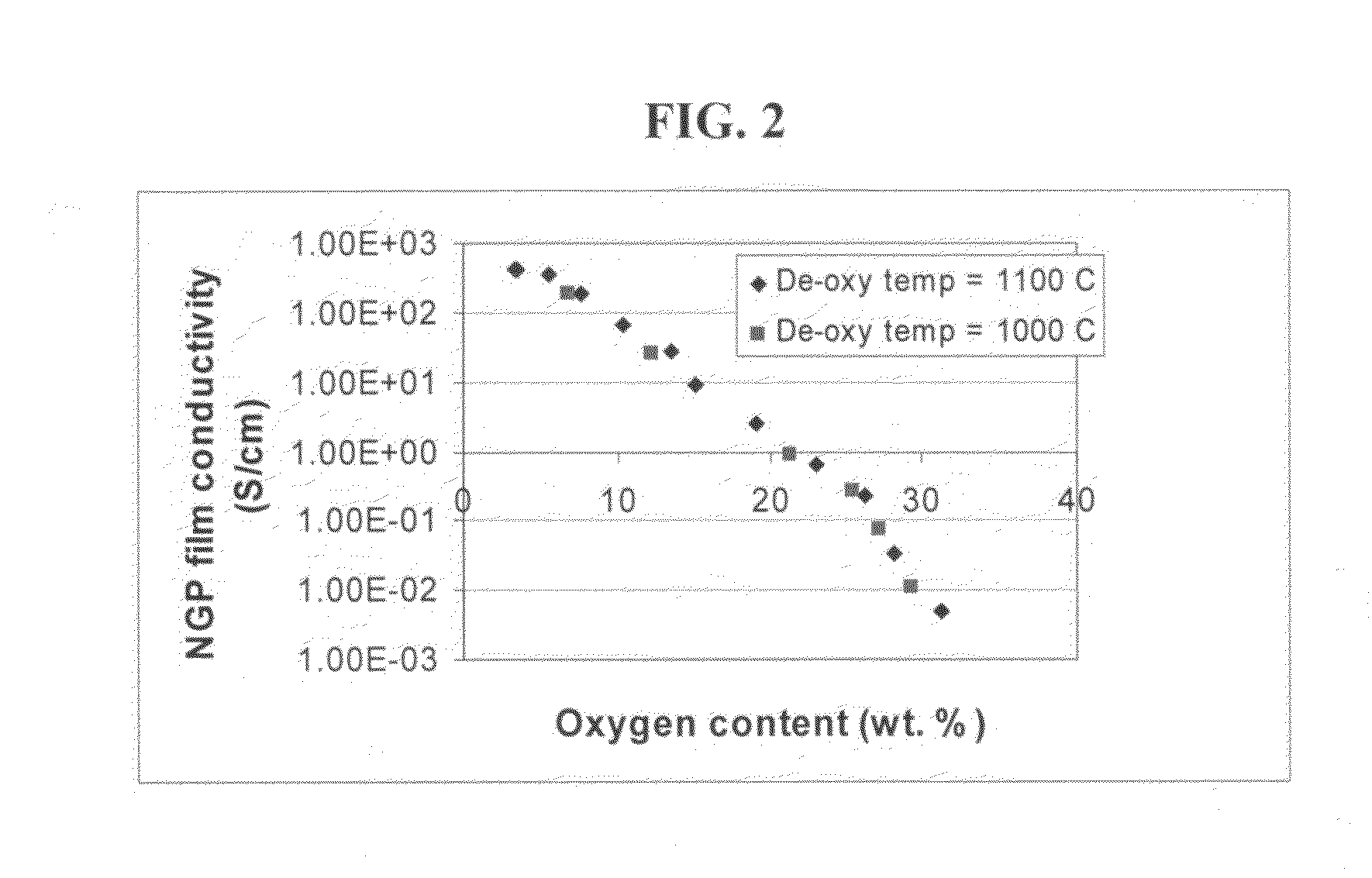
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are dispersible and conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) or graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GIC or GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time to obtain the desired dispersible nano graphene platelet with an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight, preferably below 20% by weight, further preferably between 5% and 20% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Low-temperature method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets and their nanocomposites
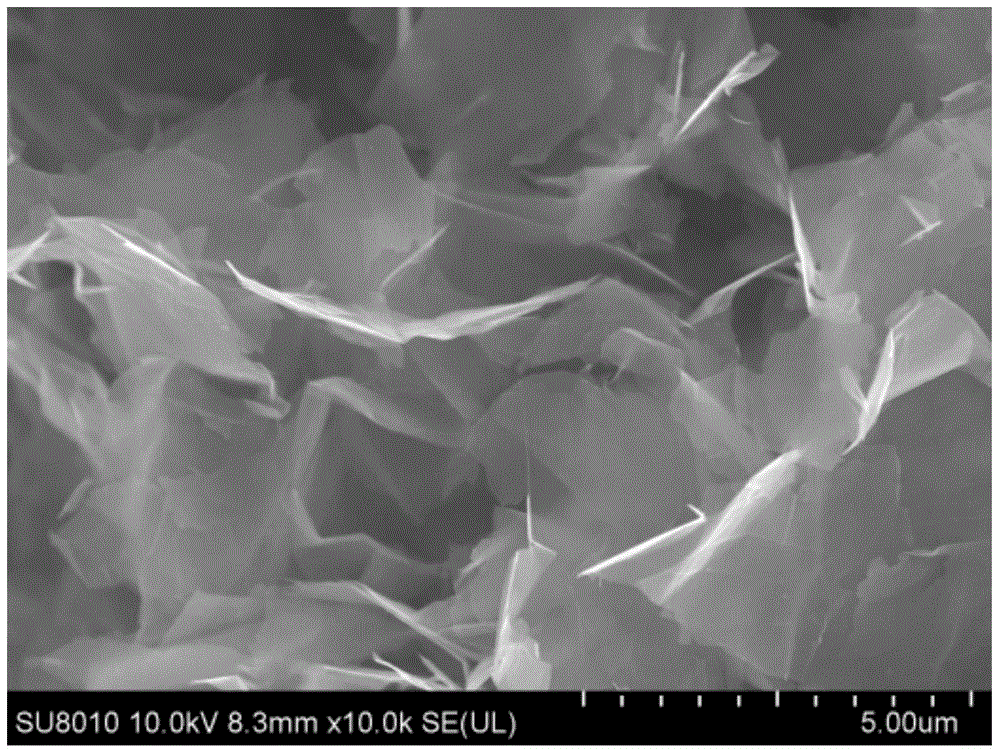
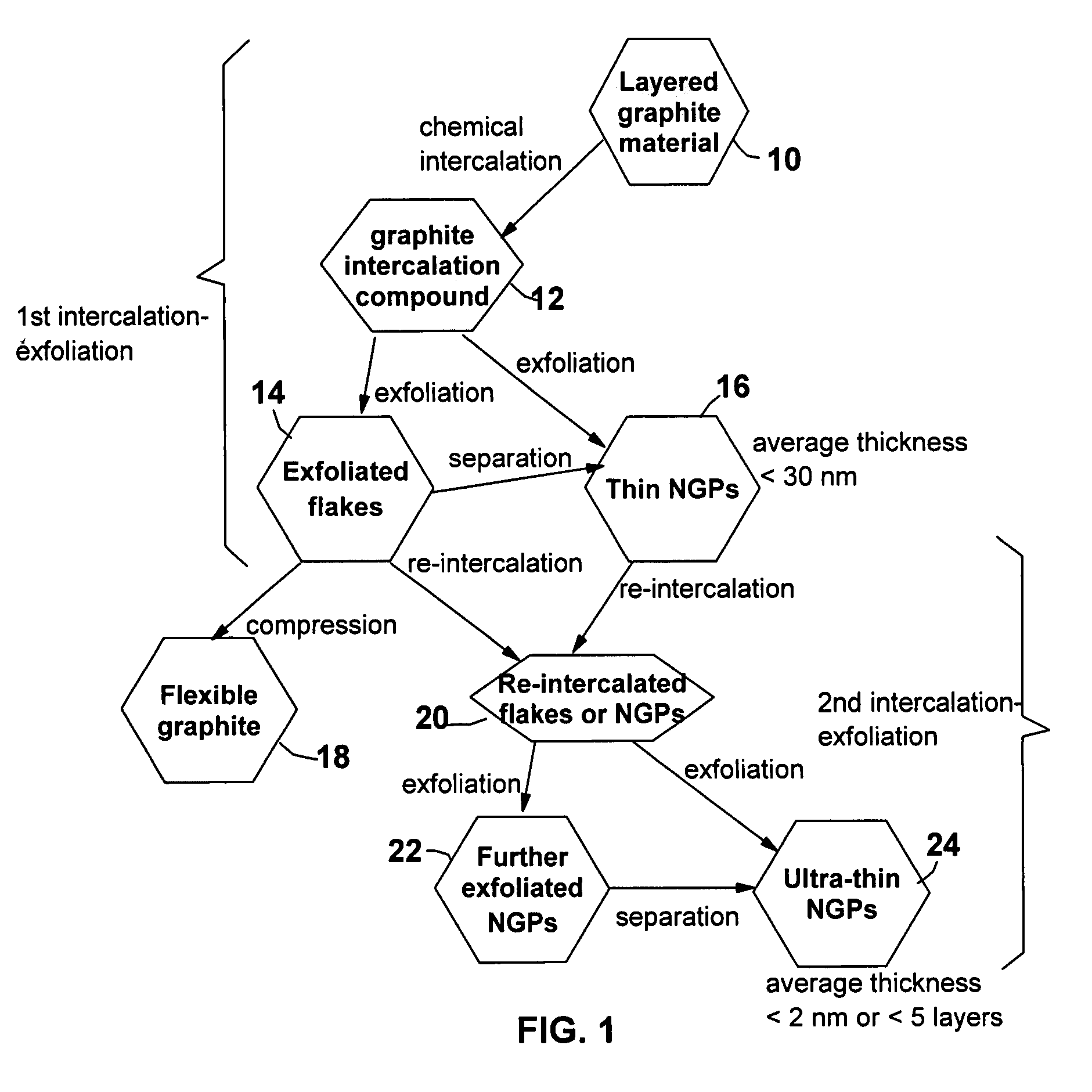
A method of exfoliating a layered material to produce separated nano-scaled platelets having a thickness smaller than 100 nm. The method comprises: (a) providing a graphite intercalation compound comprising a layered graphite containing expandable species residing in an interlayer space of the layered graphite; (b) exposing the graphite intercalation compound to an exfoliation temperature lower than 650° C. for a duration of time sufficient to at least partially exfoliate the layered graphite without incurring a significant level of oxidation; and (c) subjecting the at least partially exfoliated graphite to a mechanical shearing treatment to produce separated platelets. The method can further include a step of dispersing the platelets in a polymer or monomer solution or suspension as a precursor step to nanocomposite fabrication.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method for preparing large-size high-quality graphene with controllable number of layers
The invention discloses a method for preparing large-size high-quality graphene with controllable number of layers, wherein graphite powder or flake graphite is mainly adopted as a raw material. The method specifically comprises the steps of intercalating the graphite raw material by virtue of an intercalating agent to initially weaken the intercalation interaction force and obtain different orders of graphite intercalation compounds (GICs); soaking the GICs in an appropriate expander, and then under the case that an auxiliary agent is added or not, enabling the intercalation materials to be quickly reacted with the expander to release a gases to obtain highly expanded wormlike graphene aggregate and further to cause the distances among graphene lamellar layers to be increased; and after certain processing, peeling, and then repeatedly centrifuging and dispersing to obtain a graphene dispersion with different numbers of layers. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the intercalation-expansion-peeling process is involved, raw materials are cheap, the reaction process is simple and easily controlled, and the number of layers of graphene is precisely controlled; the obtained graphene lamellar layers have the advantages of few defects, large size, high conductivity, high yield and the like, the large-scale industrial production is easily implemented, and the problems of high cost, low productivity, poor quality, small size, uncontrollable number of layers and the like in an existing graphene preparation technology are solved.
Owner:安徽百特新材料科技有限公司
Preparation method for graphene
The invention relates to a preparation method for graphene. The preparation method is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps: 1, placing graphite in a mixed solution comprising an oxidant and an intercalation agent, and carrying out treatments of impregnation, mechanical stirring or ultrasound to obtain a primary intercalation compound; 2, carrying out a treatment for the primary intercalation compound in the air, wherein the intercalation agent is rapidly decomposed, the primary separation of the graphite intercalation compound is achieved to obtain a primary stripping material; 3, adopting a secondary intercalation method or a mild oxidation method to treat the primary stripping material to obtain a secondary intercalation compound; 4, carrying out a treatment for the second intercalation compound in the air; 5, adopting a liquid phase ultrasonic treatment, solid mechanical grinding and ball milling to achieve the complete stripping of the graphite to obtain the graphene product. Compared to the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following advantages that: the prepared graphene has characteristics of less structural defects, good conductivity and high yield; the preparation process has characteristics of simple operation and low cost, and is applicable for the large-scale production.
Owner:NINGBO MORSH TECH
Process for producing dispersible nano graphene platelets from oxidized graphite
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are dispersible and conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) or graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GIC or GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time to obtain the desired dispersible nano graphene platelet with an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight, preferably below 20% by weight, further preferably between 5% and 20% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Environmentally benign graphite intercalation compound composition for exfoliated graphite, flexible graphite, and nano-scaled graphene platelets
InactiveUS20090028778A1Material nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsElectrochemical responsePlatelet
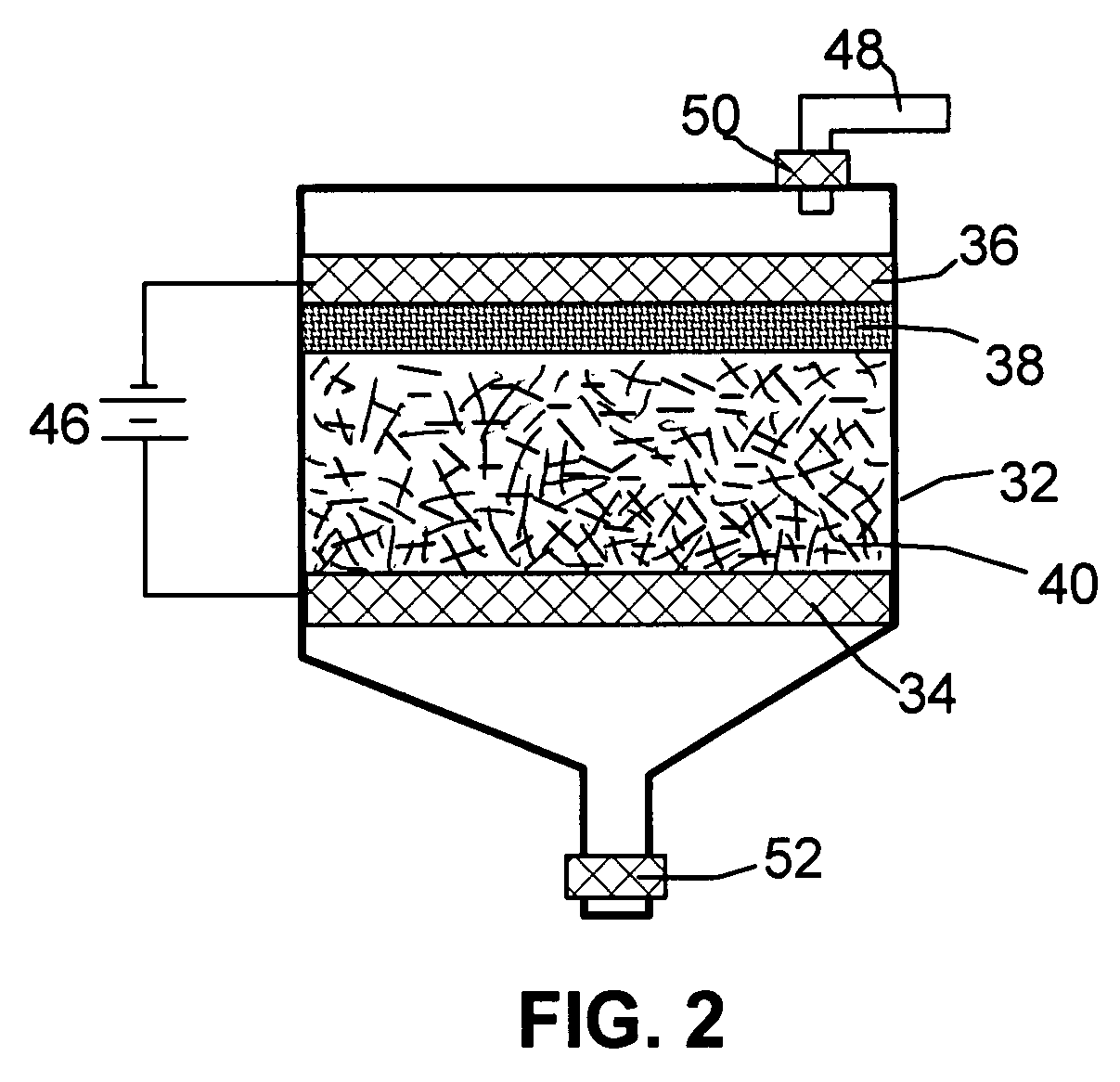
A carboxylic-intercalated graphite compound composition for the production of exfoliated graphite, flexible graphite, or nano-scaled graphene platelets. The composition comprises a layered graphite with interlayer spaces or interstices and a carboxylic acid residing in at least one of the interstices, wherein the composition is prepared by a chemical oxidation reaction which uses a combination of a carboxylic acid and hydrogen peroxide as an intercalate source. Alternatively, the composition may be prepared by an electrochemical reaction, which uses a carboxylic acid as both an electrolyte and an intercalate source. Exfoliation of the invented composition does not release undesirable chemical contaminants into air or drainage.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
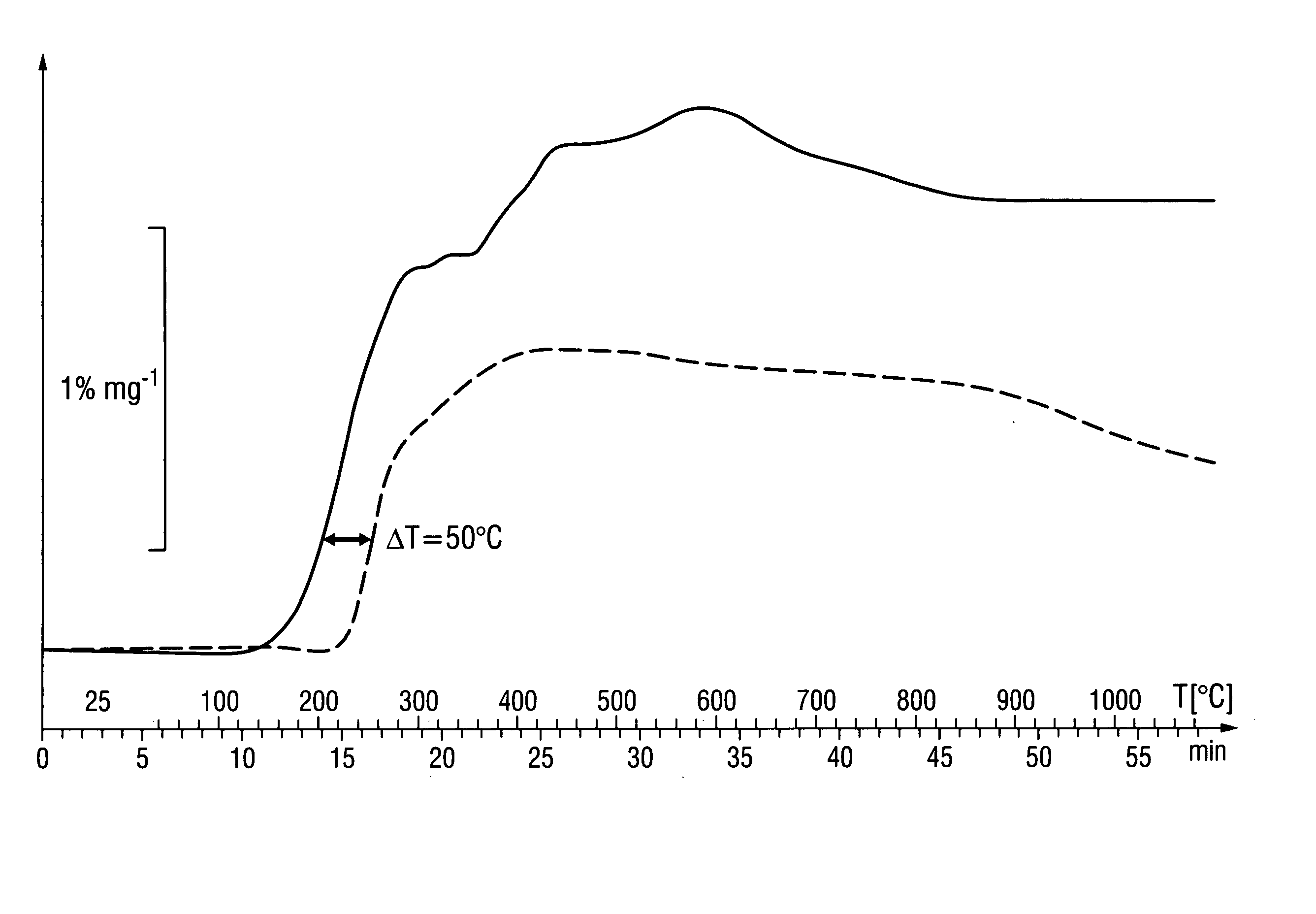
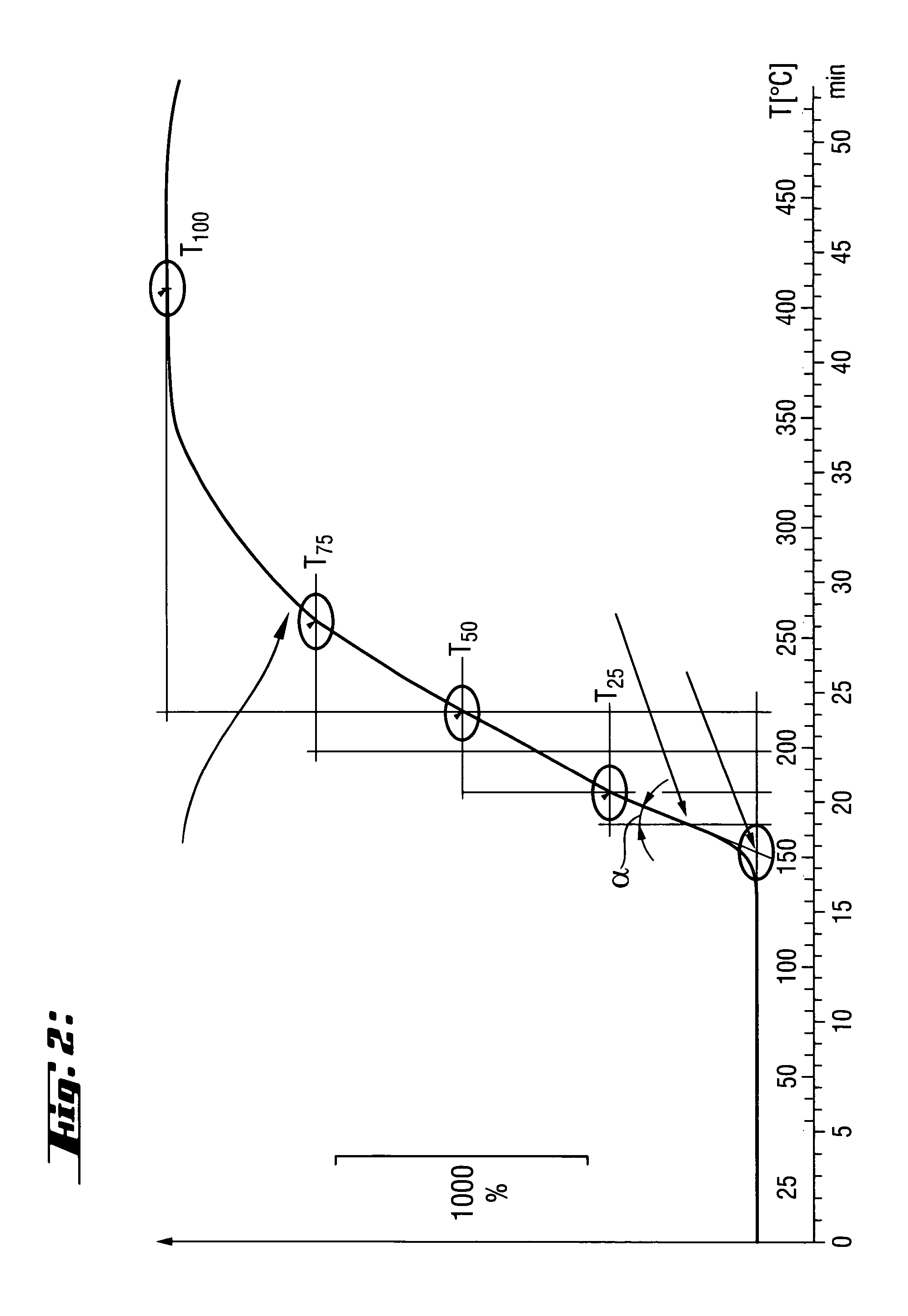
Use of thermally expandable graphite intercalation compounds for producing fire-protection seals and method for their production
The method of at least one thermally expandable graphite intercalation compound, containingA) a least one metal halide of at least one of the elements Fe, Al, Sb, Zn, Y, Cr and Ni andB) at least one nitroalkane of the general formula CH3(CH2)nNO2, in which n is a whole number from 0 to 10, as well as its structural isomers or mixtures,as intumescing, fire-protection additive in polymer matrices for producing intumescing fire-protective seals for through holes, wall bushings and other openings in walls, floors and / or ceilings of buildings, as well as a method for preparing the thermally expandable graphite-intercalation compounds used.
Owner:HILTI AG
Graphite intercalation compound lithium-ion battery negative electrode material, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium-ion batteries, and particularly relates to a graphite intercalation compound lithium-ion battery negative electrode material, as well as a preparation method and application of the graphite intercalation compound lithium-ion battery negative electrode material. The negative electrode material is different from the existing carbon negative electrode material of the lithium-ion battery and is a graphite intercalation compound (GICs0 adopting the graphite as an intercalation main body, wherein the graphite intercalation contains a (compound and insertion) intercalation object (such as metal salt, metal oxide, polymer or monomer) capable of storing lithium ions. The intercalation object of the graphite intercalation compound can reversibly store more lithium ions, so that the gravity and specific volume capacity are far higher than that of an ordinary carbon material; meanwhile, the main body graphite layer can provide a good electron carrier and stable structure for the object, so that the prepared graphite intercalation compound has good large-current discharging property and excellent cycling performance and is a novel negative electrode material with a good application prospect for the lithium-ion battery following the existing carbon negative electrode material.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Graphene preparation method, and graphene prepared through using method
InactiveCN102815694AWide variety of sourcesLow costGrapheneNanotechnologyCvd grapheneGraphite intercalation compound
The invention relates to a graphene preparation method, and graphene prepared through using the method. The preparation method is characterized in that a metal is intercalated into layers of graphite which is a raw material to prepare a graphite intercalation compound, and the graphite intercalation compound is peeled to prepare the graphene. The length, the width and the thickness of the graphene prepared through using the method are 5-15000nm, 5-15000nm and 0.3-15nm respectively. The method has the advantages of wide raw material source, low cost, simplicity, stable controllability of the graphene performances, and suitableness for industrialized production.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Use of thermally expandable graphite intercalation compounds for producing fire-protection seals and method for their production
InactiveUS20040256605A1Increase the amount of expansionHigh expansion ratePigmenting treatmentTin organic compoundsFire protectionNitroalkane
The method of at least one thermally expandable graphite intercalation compound, containing A) a least one metal halide of at least one of the elements Fe, Al, Sb, Zn, Y, Cr and Ni and B) at least one nitroalkane of the general formula CH3(CH2)nNO2, in which n is a whole number from 0 to 10, as well as its structural isomers or mixtures, as intumescing, fire-protection additive in polymer matrices for producing intumescing fire-protective seals for through holes, wall bushings and other openings in walls, floors and / or ceilings of buildings, as well as a method for preparing the thermally expandable graphite-intercalation compounds used.
Owner:HILTI AG
Low-temperature method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets and their nanocomposites
A method of exfoliating a layered material to produce separated nano-scaled platelets having a thickness smaller than 100 nm. The method comprises: (a) providing a graphite intercalation compound comprising a layered graphite containing expandable species residing in an interlayer space of the layered graphite; (b) exposing the graphite intercalation compound to an exfoliation temperature lower than 650° C. for a duration of time sufficient to at least partially exfoliate the layered graphite without incurring a significant level of oxidation; and (c) subjecting the at least partially exfoliated graphite to a mechanical shearing treatment to produce separated platelets. The method can further include a step of dispersing the platelets in a polymer or monomer solution or suspension as a precursor step to nanocomposite fabrication.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Preparation of low temperature expandable graphite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an expansible graphite (expansible graphite intercalation compound) which comprises the following steps: dipping a flake graphite in a solution mainly formed by oxidant and intercalation agent for intercalation reaction, replacing the intercalation compound between the graphite layers by water exchange method after filtration, drying the obtained solid formation to obtain target compounds. The invention has advantages of low energy consumption, environment friendly, and the prepared expansible graphite is capable of expansion at a low temperature.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
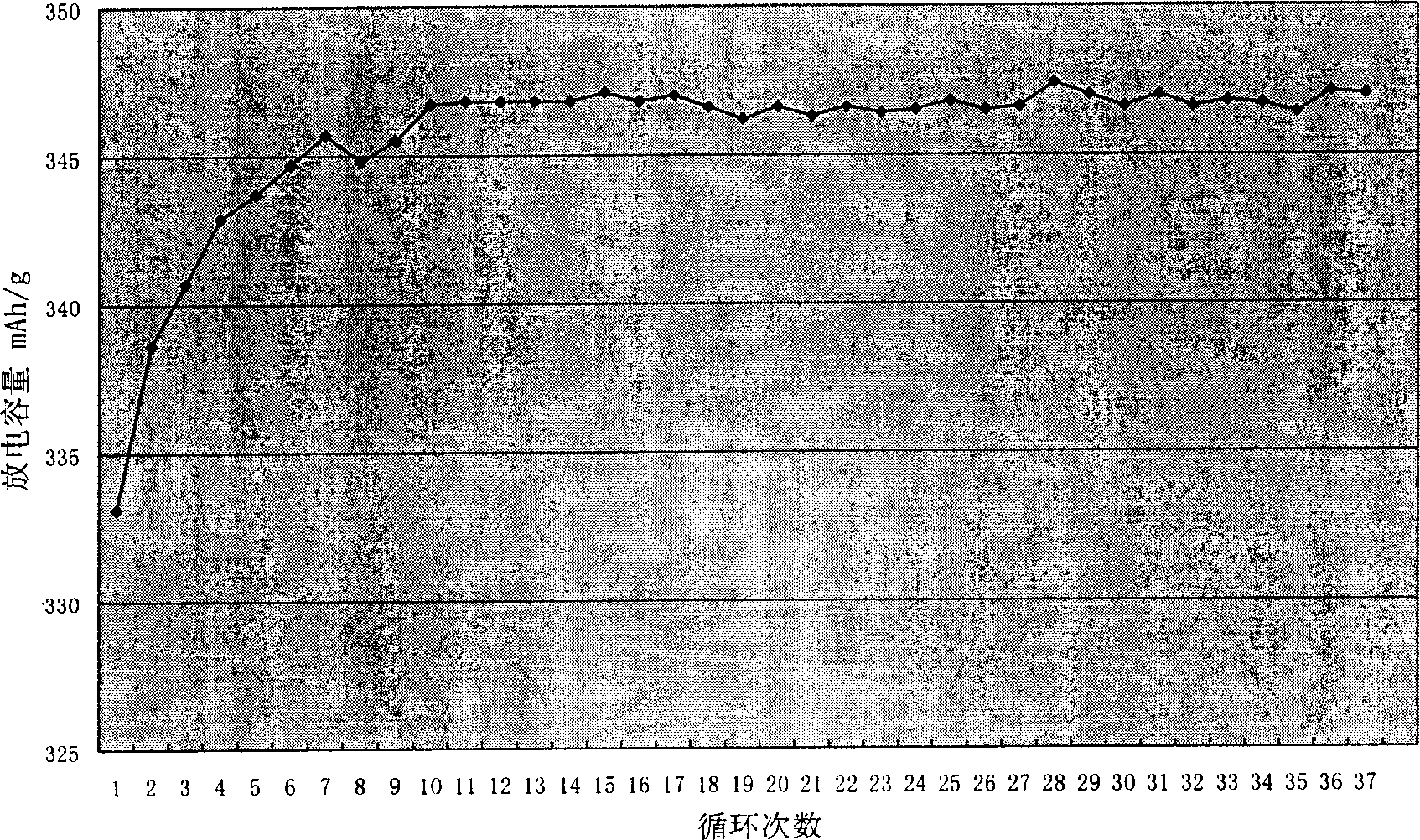
Carbonaceous lithium ion battery negative electrode material with nuclear shell structure and producing method thereof
ActiveCN1848490AIncrease capacityReduce the first irreversible capacityCell electrodesCore shellNanometre
The present invention relates to a carbonaceous lithium ion cell negative electrode material with core-shell structure and its preparation method, belonging to the field of carbon material and chemical power supply technology. The described negative electrode material is formed from core portion and shell portion. The core portion is graphite obtained after the graphite intercalation compound is disintercalated, the shell portion is amorphous carbon obtained by pyrolysis of organics. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of its preparation method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
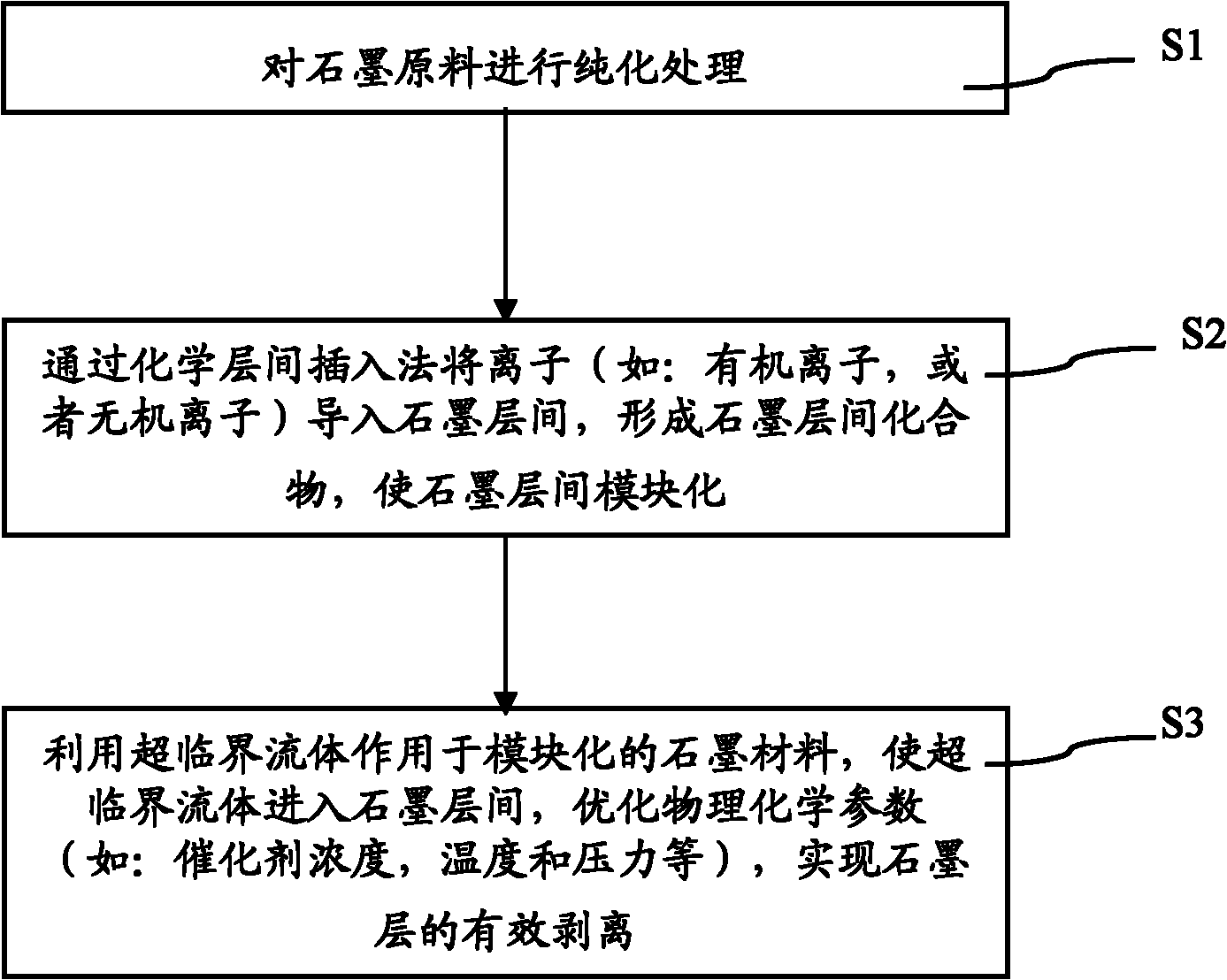
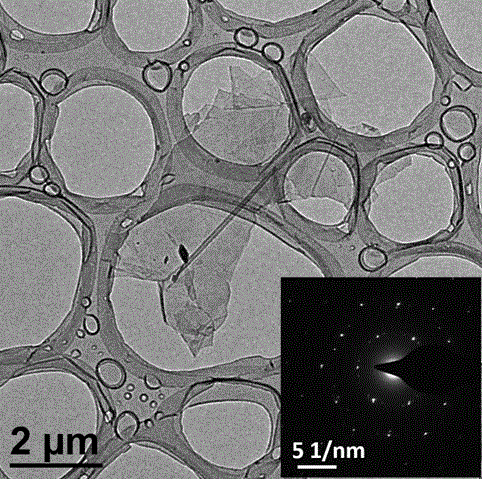
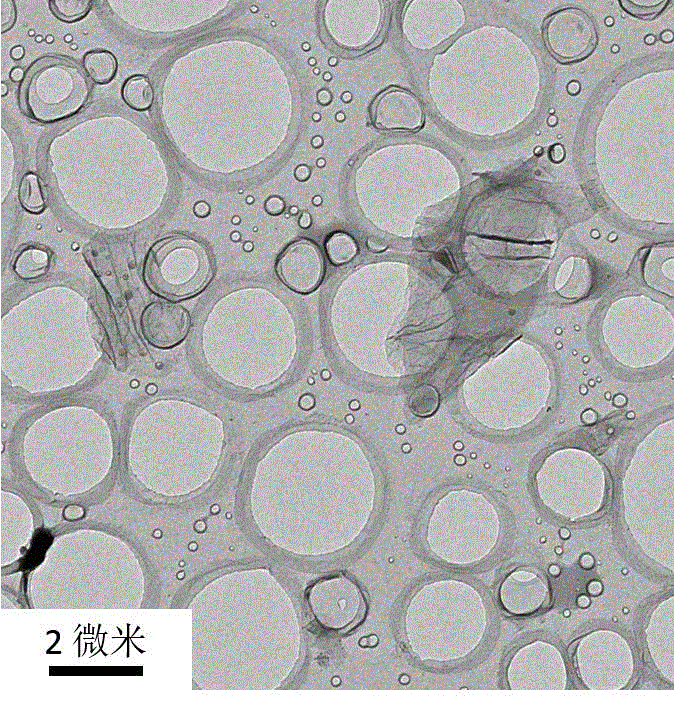
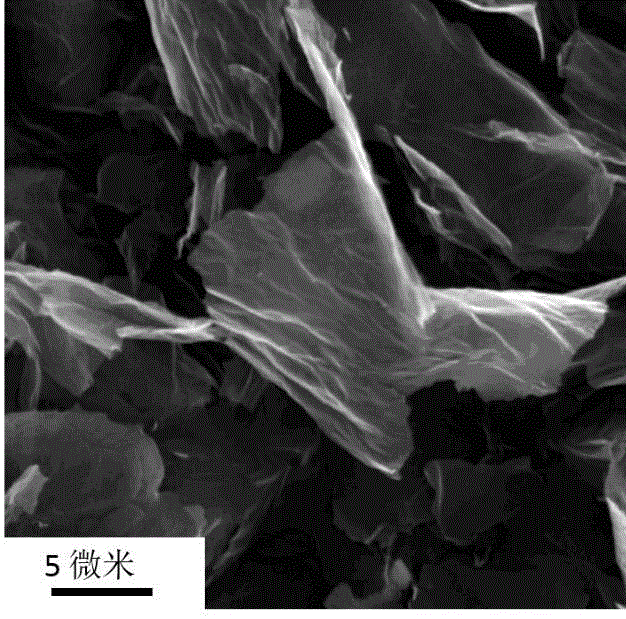
Method for preparing graphene by using modifying supercritical peeling technology
The invention provides a method for preparing graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: purifying a graphite raw material; guiding ions to a graphite intercalation by a chemical intercalation method to form a graphite intercalation compound, and performing graphite intercalation modularization; further making supercritical fluid (such as CO2, H2O, methane / ethane / propane, ethylene / propylene, methanol / ethanol, or ammonia or the like) act on the modularized graphite raw material by a modifying supercritical technology, wherein the supercritical fluid enters the graphite intercalation; and implementing effective peeling of a graphite layer by optimizing physical and chemical parameters (such as catalyst concentration, temperature, pressure and the like). According to the method, the peeling of the graphite layer is implemented by the modifying supercritical technology, and the graphene can be produced in batch.
Owner:青岛科孚纳米技术有限公司
Preparation method and application of graphene slurry
InactiveCN105060283AImprove cycle performanceAdd lessCell electrodesAnti-corrosive paintsPower capabilityPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to the graphene technical field, and specifically discloses a preparation method and an application of a graphene slurry. The preparation method of the graphene slurry includes the following steps of preparation of a graphite intercalated compound, preparation of a graphite expansion body and preparation of the graphene slurry, wherein an intercalator is any one of nitric acid with the mass concentration of 65%-98%, a mixture of nitric acid with the mass concentration of 65%-98% and an organic acid, and a mixture of nitric acid with the mass concentration of 65%-98% and phosphoric acid with the mass concentration of 80%-98%. The preparation of the graphene slurry has no need of concentrated sulfuric acid as a reaction medium, and the prepared graphene slurry does not contain sulfur and has less layer number. The graphene slurry can greatly increase multiplying power capability and cycle performance of lithium ion batteries when used in the lithium ion batteries, and can overcome defects of a conventional sulfur-containing graphene material in anticorrosive coatings when used in a graphene anticorrosive coating. The preparation method of the graphene slurry provides a good route for production and application of sulfur-free graphene and is suitable for realizing industrialization.
Owner:SHENZHEN SSZK NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Production of nano-structures
ActiveUS7754184B2Avoid insufficient heatingEfficient productionMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteNanostructureGraphite intercalation compound
A process for the production of nano-structures is presented, involving providing a graphite flake comprising graphene layers; intercalating the graphite flake to form a graphite intercalation compound exhibiting Stage I, II or III intercalation; and exfoliating the graphite intercalation compound under conditions such that a plurality of individual graphene layers are separated from the graphite intercalation compound.
Owner:DIRECTA PLUS
Method for preparing graphene through waste lithium batteries
InactiveCN102868006AAvoid wastingSimple methodWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingLithiumCvd graphene
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene through waste lithium batteries. The method is characterized in that graphite intercalation compounds in the waste lithium batteries are used as raw materials and stripped to obtain graphene. The method has the advantages that the raw materials are extensive, low in cost and suitable for industrial production, and recycling of resources in the waste lithium batteries is realized while the effective method for preparing graphene is found.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for green environmental-protection preparation of high-concentration ultra-clean graphene dispersion liquid
The invention relates to a method for green environmental-protection preparation of a high-concentration ultra-clean graphene dispersion liquid; graphite or a graphite intercalated compound is mainly used as a raw material and is expanded by a certain way to weaken the interaction force between graphite layers, then in an ionic liquid, stripping is achieved under a certain mechanical force by using interaction between pi-anions and pi-cations, and the high-concentration high-electric-conductivity graphene dispersion liquid is obtained. The preparation process is simple and is easy to control, and does not involve any harsh conditions such as high temperature and high pressure, has low energy consumption, and has no need for use of strong oxidizing agents, so as to avoid destruction of acute oxidization on the structure and properties of graphene. In addition, the method has the advantages of green environment protection, does not introduce any impurities, enables the used ionic liquid to be recycled and used, and is quite suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing grapheme by means of aqueous phase cutting and stripping
The invention relates to a method for preparing grapheme by means of aqueous phase cutting and stripping. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing intercalation treatment on graphite serving as a raw material to prepare a graphite intercalation compound; 2) adding a certain amount of active substances, and cutting a graphite interlamination compound under a certain condition; and 3) centrifuging or filtering mixed liquid subjected to cutting treatment to prepare a high-concentration grapheme sizing agent or a filter cake which can be dispersed again. According to the method, the cutting operation is carried out by using low-cost reagents at a room temperature; because of low energy consumption, no pollution and high efficiency, the prepared graphene nanolamellas can be widely applied to the fields of energy storage and conversion, catalysis, various types of composite materials, paintings, conductive ink and the like.
Owner:安徽百特新材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing graphene powder at large scale
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-quality graphene powder at low cost and large scale. The method comprises the following steps of: adding graphite to mixed solution containing an oxidizing agent and an intercalator, stirring evenly and then performing ultrasonic treatment, and simultaneously, continuously introducing He to form a graphite intercalation compound intercalated with the intercalator and He gas molecules; next, filtering, washing and drying, and performing thermal treatment in air to realize the first time of stripping of the graphite intercalation compound; later, dispersing the graphite intercalation compound in an organic solvent and performing ultrasonic treatment again under the condition of continuously introducing He; and then centrifuging and removing precipitate, and filtering, washing and drying the solution of the upper layer, thereby obtaining the graphene powder. The method provided by the invention is safe and environment-friendly, simple to operate and suitable for large-scale production; the prepared graphene has few defects and good electrical conductivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphene and preparation method thereof
The present invention provides a graphene preparation method, which comprises: a), mixing graphite, an acid and an oxidizing agent, and carrying out a first reaction to obtain a graphite intercalation compound, wherein the acid comprises concentrated sulfuric acid, and the oxidizing agent comprises a chlorate; b), carrying out a second reaction of the graphite intercalation compound and a peroxide to obtain an intermediate product, wherein the peroxide comprises hydrogen peroxide; and c), carrying out ultrasound stripping on the intermediate product to obtain the graphene. According to the present invention, the graphite oxidation degree through the concentrated sulfuric acid and the chlorate is weak; the concentrated sulfuric acid and the hydrogen peroxide react to release a lot of heat and gas, such that the graphite intercalation compound swells and be peeled; and the concentrated sulfuric acid and the hydrogen peroxide react to generate a lot of OH free radicals and HSO4 free radicals, and the oxygen-containing functional group on the graphite intercalation compound sheet layer can be removed through the free radicals, such that the degree of the damage on the sheet layer structure of the graphene of the present invention is low.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing graphenes through the production of a graphite intercalation compound using salts
ActiveUS20120321545A1Quality improvementReduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneAlkaline earth metalChemical compound
The present invention relates a method for producing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) and to the production of graphene using the same. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (a) obtaining alkaline metals or alkaline metal ions, or alkaline earth metals or alkaline metal ions, from alkaline metal salts or alkaline earth metal salts; (b) forming a graphite intercalation compound using the alkaline metals or alkaline metal ions, or the alkaline earth metals or alkaline earth metal ions; and (c) dispersing the graphite intercalation compound so as to obtain graphene. As the method of the present invention uses salts which are inexpensive and safe, graphite intercalation compounds can be easily produced at a low cost, and the graphene can be obtained from the thus-produced compounds, thereby reducing the costs of producing the graphene and enabling the easy mass production of the graphene.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
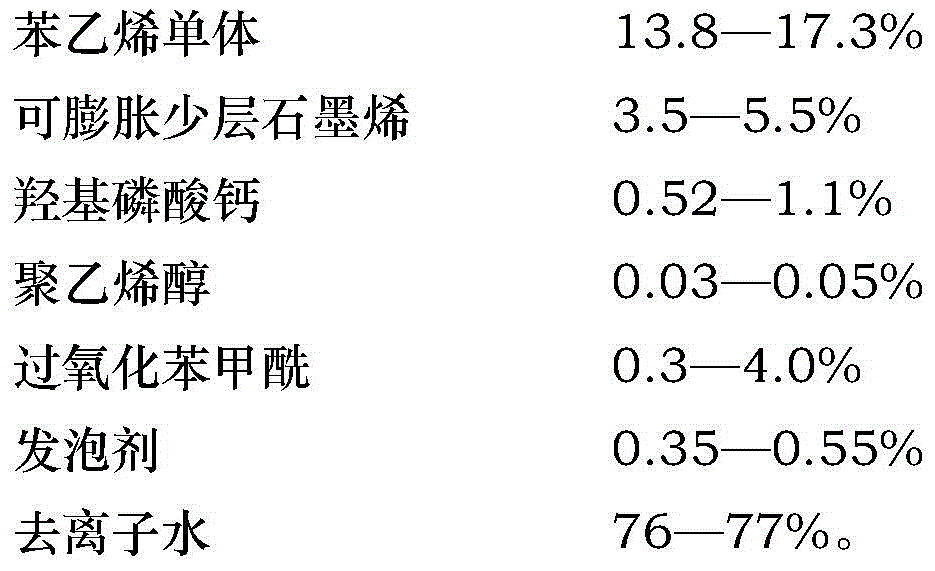
Expandable polystyrene beads prepared from expandable few-layer graphene and preparing method of expandable polystyrene beads
The invention relates to expandable polystyrene beads prepared from expandable few-layer graphene and a preparing method of the expandable polystyrene beads.Electrochemical intercalation is carried out on natural flake graphite with concentrated sulfuric acid, and a graphite interlayer compound with the interlayer space enlarged is obtained; few-layer graphene is obtained through ultrasonic concussion layer removing, the few-layer graphene is subjected to secondary intercalation with a chemical method, water washing and drying, and the expandable few-layer graphene is obtained; then, the expandable few-layer graphene and polystyrene monomers are subjected to suspension polymerization, and the expandable polystyrene beads prepared from the expandable few-layer graphene is obtained.According to the expandable polystyrene beads prepared from the expandable few-layer graphene and the preparing method of the expandable polystyrene beads, the expandable few-layer graphene is introduced into expandable polystyrene, and expandable graphene can be highly and uniformly dispersed in the expandable polystyrene beads, so that high infrared reflectivity in a cavity of expandable polystyrene is ensured, the heat insulation performance is good, and the expandable few-layer graphene can show the flame-retardant effects of smothering flames and insulating heat radiation.The flame retardant grade of a foam plate prepared from the expandable polystyrene beads reaches the B1 grade, and the heat conductivity value ranges from 0.028 W / (m.K) to 0.032 W / (m.K).
Owner:JILIN YUNTING ENERGY SAVING TECH CO LTD
Fuel cell and membrane electrode assembly
InactiveUS20050214631A1Improve conductivityIncrease productionCatalyst protectionFuel cell auxillariesConductive polymerOxygen
A fuel cell anode for oxidizing fuel, a cathode for reducing oxygen and a solid polymer electrolyte membrane sandwiched between the anode and the cathode, wherein the cathode comprises a catalyst supporter having a catalyst metal and a material having a polymer proton conductivity and a material having water-repellency, the material having water-repellency being electric conductive. The material having water-repellency is a carbonaceous material such as graphite intercalation compound, activated charcoal, carbonaceous material having water-repellent function groups. The disclosure is also related to a membrane electrode assembly comprising an anode catalyst layer, a proton conductive polymer electrolyte membrane and a cathode catalyst layer, the anode catalyst layer, the membrane and the cathode catalyst layer being laminated and united, wherein the catalyst layers contain carbon supporting metal catalyst and a water-repellent material, the water-repellent material being electrically conductive.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
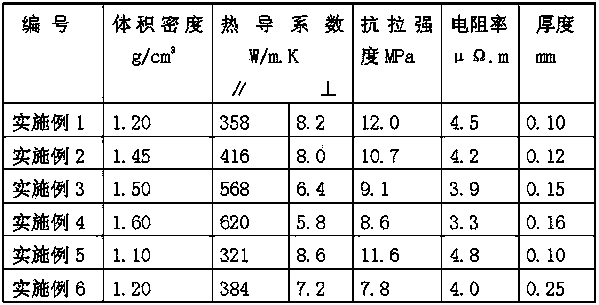
Preparation method of high thermal conductivity natural flexible graphite film
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high thermal conductivity natural flexible graphite film. The preparation method comprises the steps that HCLO4 and HNO3 are mixed together, and natural flake graphite is then added in and mixed with HCLO4 and HNO3 so as to obtain a mixture; the mixture is heated to react to obtain a perchloric acid / graphite intercalation compound; and the perchloric acid / graphite intercalation compound is washed with deionized water until the pH value is 5-7, and then drying, expanding and rolling are carried out to obtain the high thermal conductivity natural flexible graphite film. The preparation method has the advantages of no sulfur, no corrosion, high thermal conductivity and controllable thickness.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing graphene powder material and graphene powder material
ActiveCN103708445AImprove conductivityHigh thermal conductivityGrapheneHeat conductingReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene powder material and the graphene powder material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding natural flake graphite to a reaction kettle, adding 50-98% of sulfuric acid solution to evenly mix, and then adding an oxidant and controlling the temperature at 10-60 DEG C, stirring for 20-120 minutes, adding water and controlling the reaction temperature at no more than 95 DEG C, cooling to room temperature, finally separating to obtain a graphite intercalation compound; (2) puffing the dried graphite intercalation compound in a micro-wave oven, so as to obtain an expanded graphite intermediate; (3) feeding a solvent and the expanded graphite intermediate to a ball-milling or sand mill, grinding for 0.5-12 hours to obtain graphene slurry, and then drying the graphene slurry, so as to obtain the graphene powder material. The graphene powder material prepared by the method has high conductivity and thermal conductivity coefficient, and can be used as a conductive and heat-conducting additive.
Owner:深圳贝特瑞钠电新材料科技有限公司
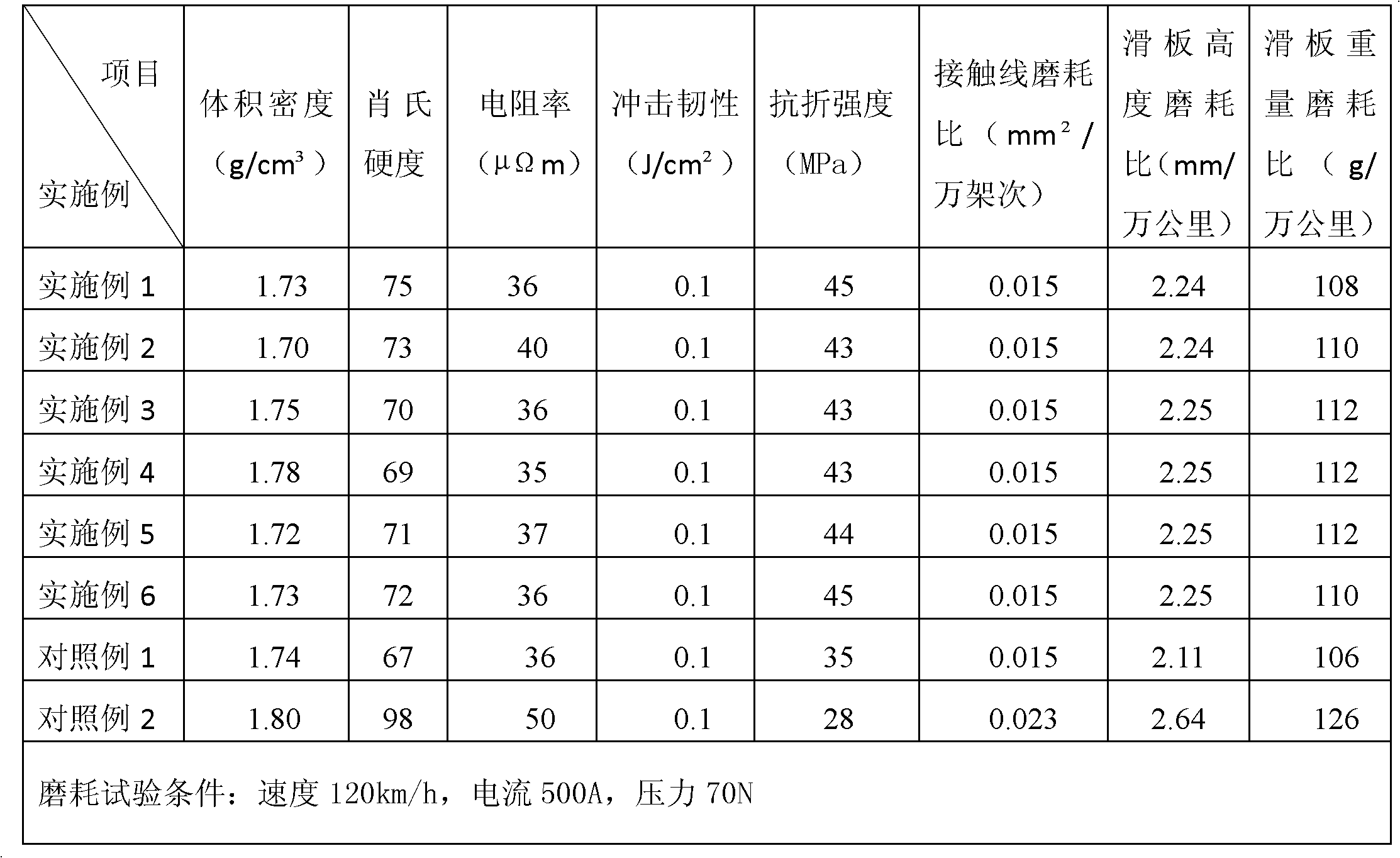
Carbon fiber reinforced pantograph carbon slide plate material and manufacturing method thereof
The present invention discloses a carbon fiber reinforced pantograph carbon slide plate material and a manufacturing method thereof. The material comprises, by mass, 30-60% of a graphite intercalation compound, 8-32% of petroleum coke, 2-16% of carbon fibers, and 15-35% of medium temperature asphalt. Compared to the carbon fiber reinforced pantograph carbon slide plate in the prior art, the carbon fiber reinforced pantograph carbon slide plate of the present invention has advantages of low resistivity, high mechanical strength and the like, and has excellent comprehensive performances such as electrical conductivity, abrasion resistance, self-lubricating and the like, wherein international advanced technology levels are met with tests. In addition, the manufacturing method is simple; the stable product performance can be achieved; and large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU DONEKA NEW MATERIALS CORP LTD
Graphite-base hydrogen storage material and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060019162A1Improve hydrogen storage performanceSimple manufacturing methodMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenCarbon layerActive point
Disclosed is a hydrogen storage material and a production method thereof. The hydrogen storage material has a carbon material having: an interlayer space for hydrogen occlusion, produced by removal at least a portion of an organic compound from a graphite intercalation compound comprising graphite and the organic compound intercalated in the graphite; and an active point at which hydrogen is adsorbed, being produced on the remaining organic compound and / or a part of the hexagonal carbon layers defining the interlayer space. It has a layered lattice structure with hexagonal carbon layers and an expanded interlayer space, and its density determined in accordance with He equilibrium pressure density measuring method changes according as pre-equilibrium He pressures and falls in a range of 0.2 to 1.2 g / cm3 at pre-equilibrium pressures of 0.2 MPa and 0.8 MPa. The hydrogen storage material is produced by; preparing an organic-graphite intercalation compound; and reducing the organic-graphite intercalation compound to remove at least a portion of the inserted organic compound from the organic-graphite intercalation compound, thereby forming an interlayer space.
Owner:HITACHI POWDERED METALS COMPANY +1
Preparation method of three-dimensional graphene structure/high-quality graphene
ActiveCN106882796AEfficient large-scale preparationSolve the key problems of large-scale preparationSingle layer grapheneCarbon nitrideMetallic sulfide
The invention provides a preparation method of three-dimensional graphene structure / high-quality graphene. The method comprises the steps of carrying out intercalation treatment on natural flake graphite or synthetic graphite to prepare a graphite intercalation compound; and carrying out expansion treatment on the obtained graphite intercalation compound in an expanding agent to obtain a three-dimensional graphene structure with high specific surface area. A high-quality single-layer or few-layer graphene dispersion liquid is obtained through ball-milling, shearing, high-speed fluid grinding or ultrasonic treatment. The obtained three-dimensional structure has the specific surface area of over 1,000m<2> / g; and the lamellar lattice structure is kept intact. The graphene lattice structure obtained through mechanical exfoliation is kept intact, and has excellent electrical properties; the volume conductivity of a thin film can reach over 1,000S / cm. The prepared graphene material can be widely applied to the fields of energy storage, a composite material, conductive ink, a conductive film and the like. The three-dimensional graphene structure can be directly used as a carbon skeleton with high specific surface area, and can be compounded with various materials such as a polymer, a metal oxide, a metal sulfide and carbon nitride to prepare a composite material with special functionality.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Production Of Nano-Structures
ActiveUS20110300056A1Avoid insufficient heatingMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesNano structuringMaterials science
A process for the production of nano-structures is presented, involving providing a graphite flake comprising graphene layers; intercalating the graphite flake to form a graphite intercalation compound exhibiting Stage I, II or III intercalation; and exfoliating the graphite intercalation compound by exposing it to a temperature between about 1600° C. and about 2400° C. such that a plurality of individual graphene layers are separated from the graphite intercalation compound.
Owner:DIRECTA PLUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com