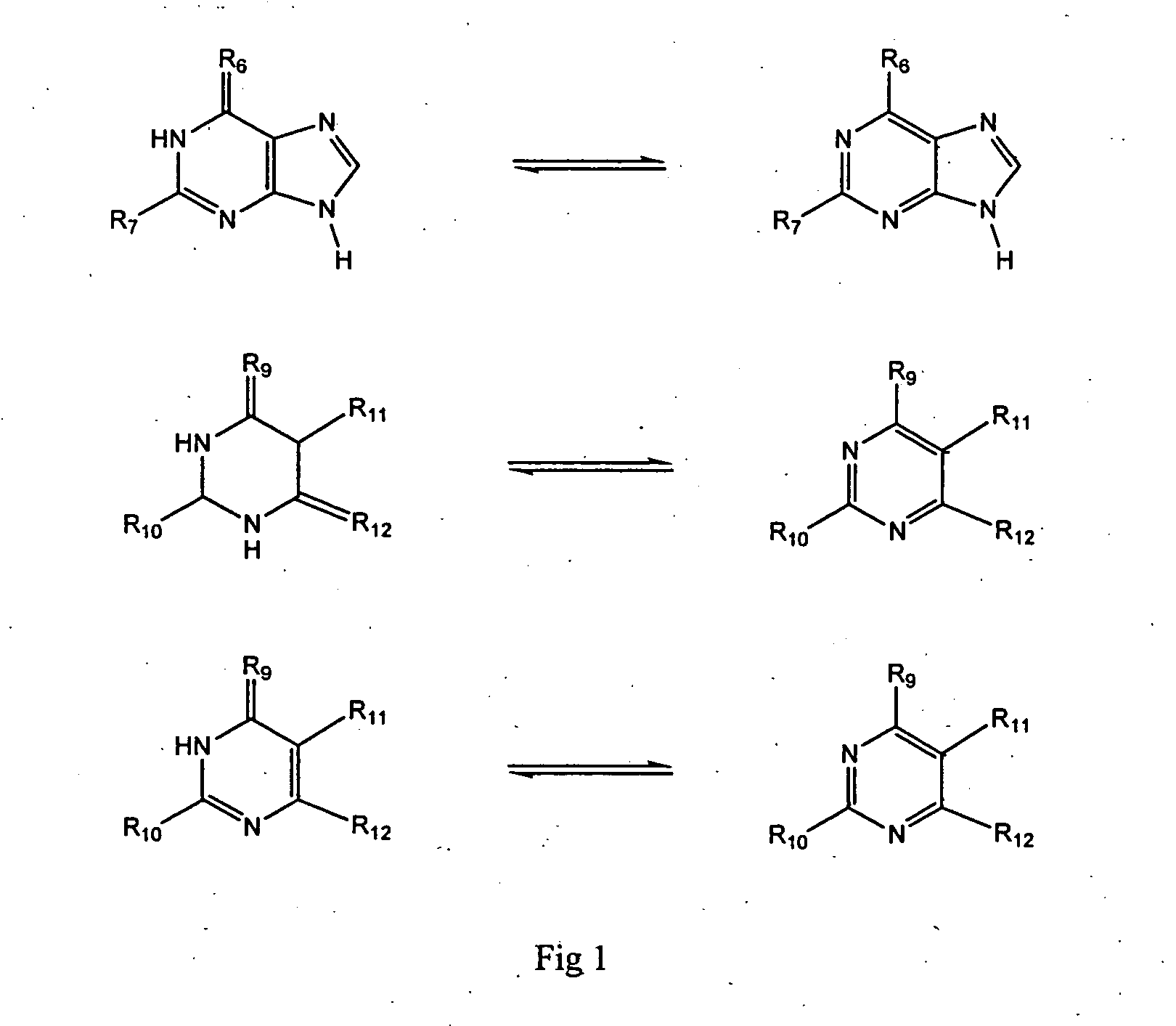
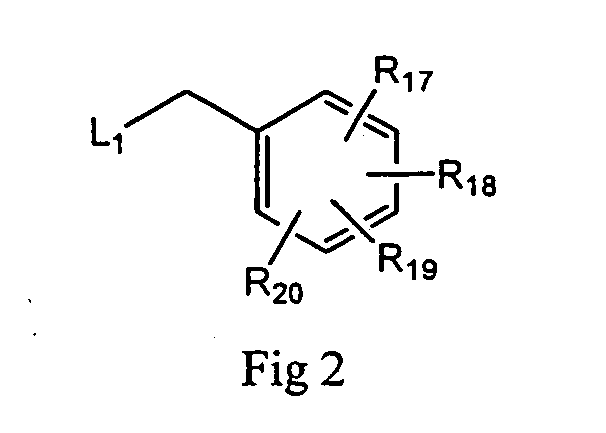
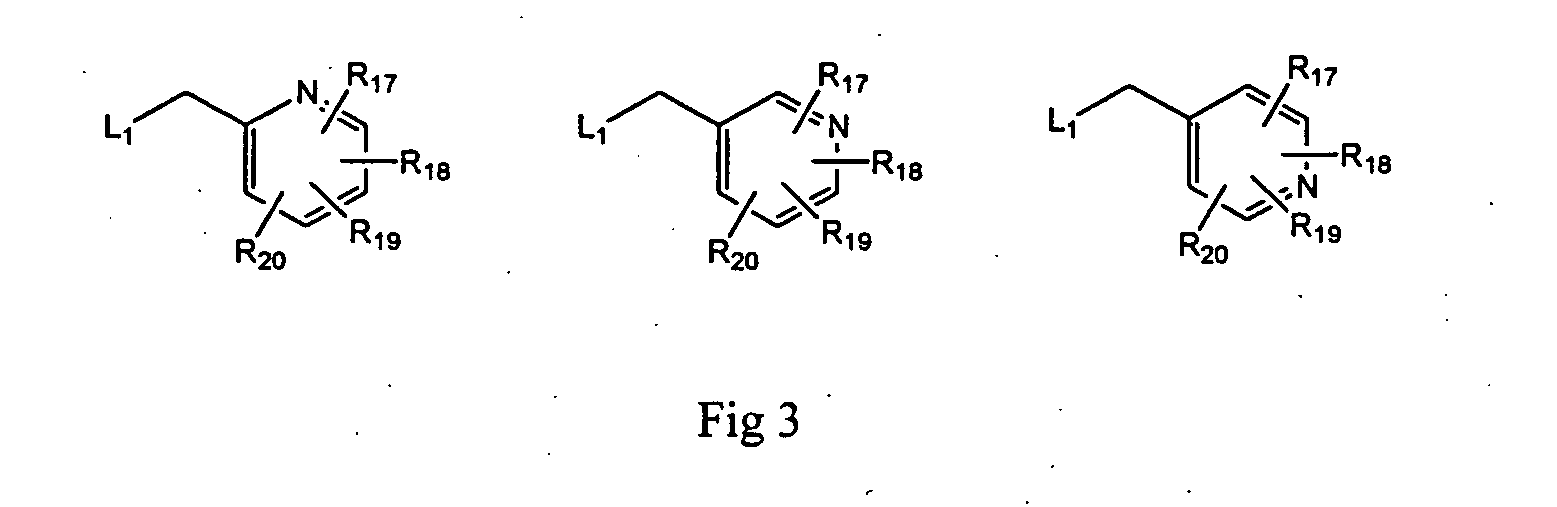
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8860results about How to "Wide range of uses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
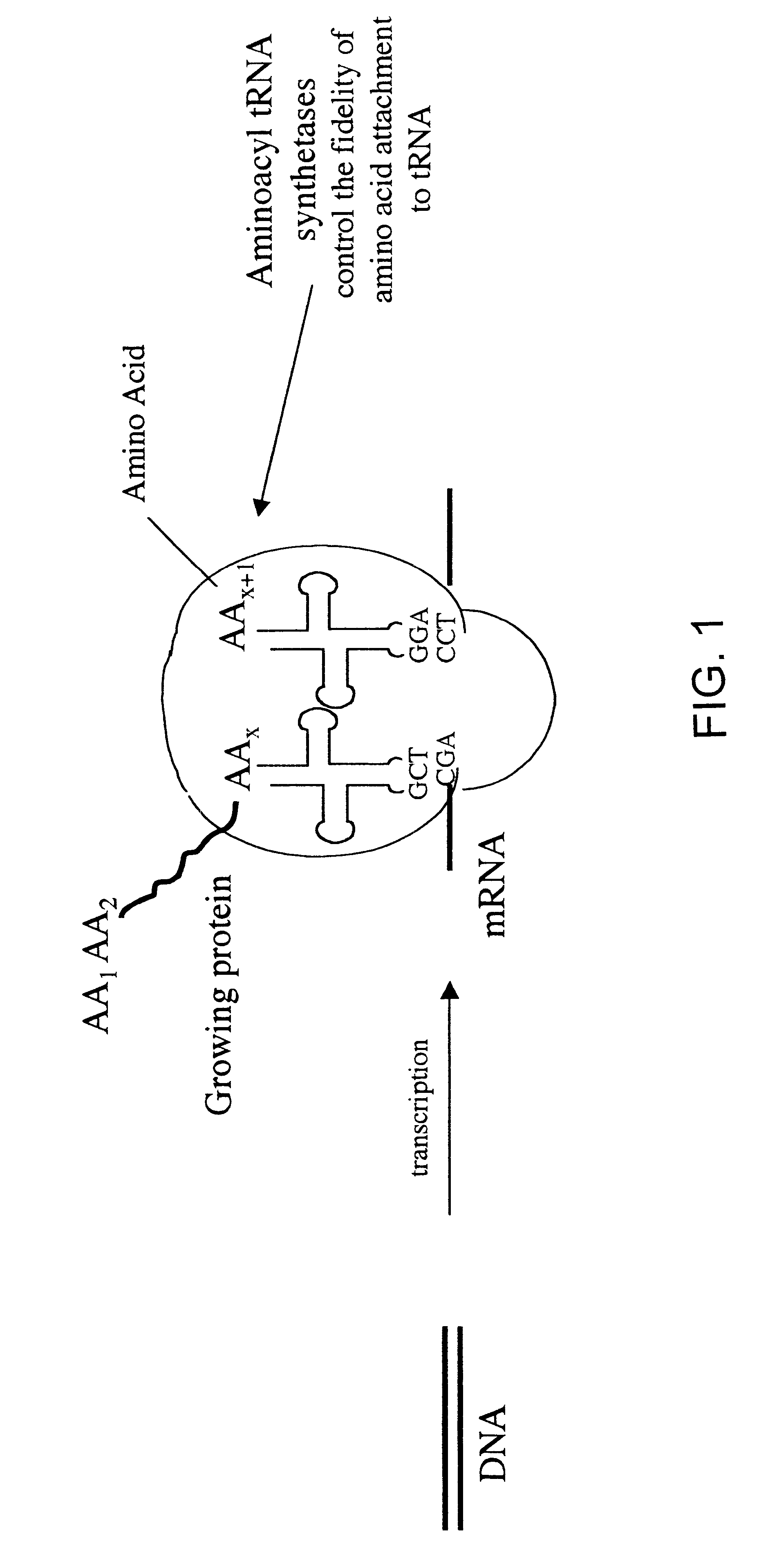
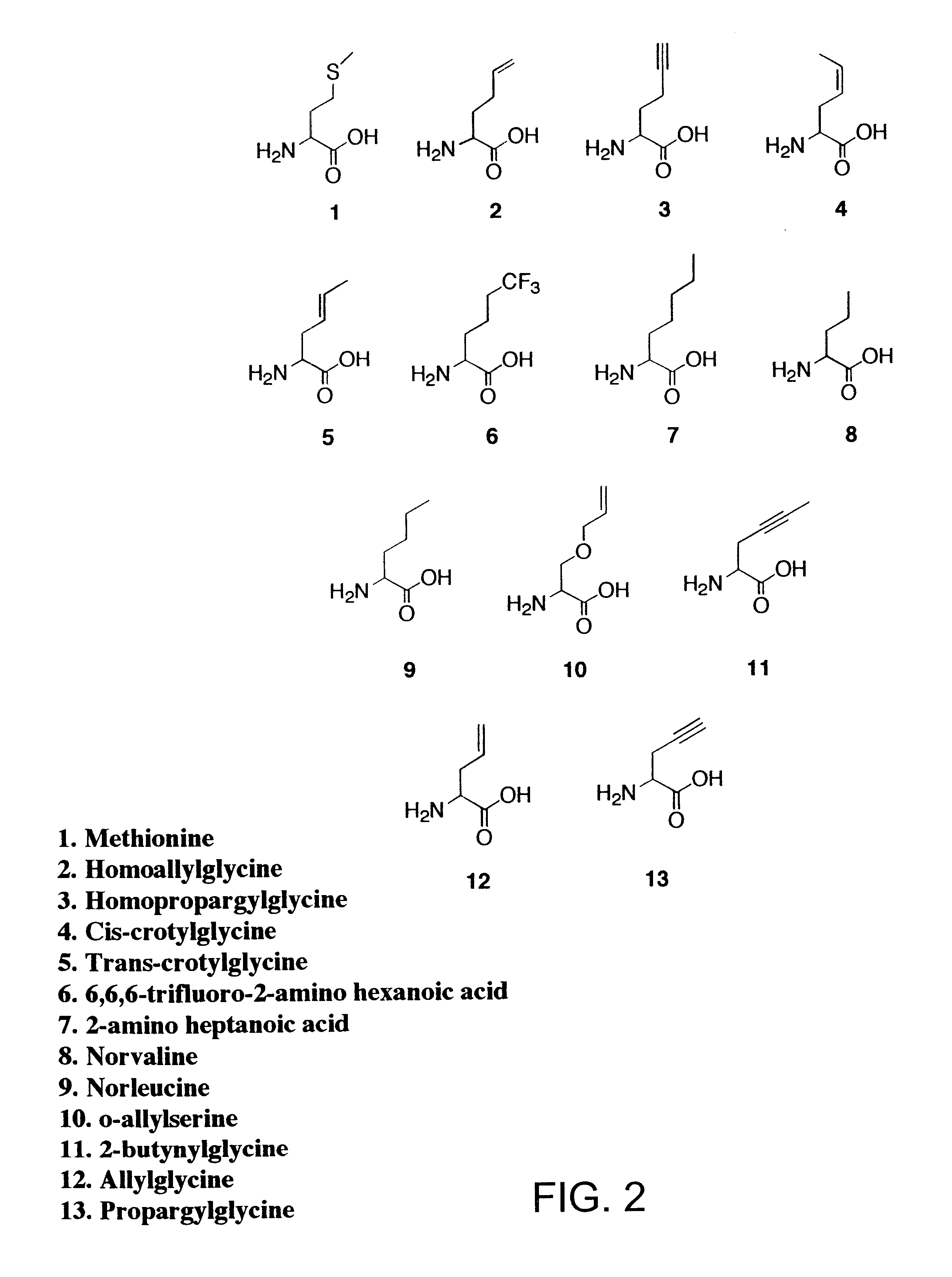
Overexpression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for efficient production of engineered proteins containing amino acid analogues
InactiveUS6586207B2High yieldRapid and predictable approachBacteriaOxidoreductasesMethionine biosynthesisDihydrofolate reductase
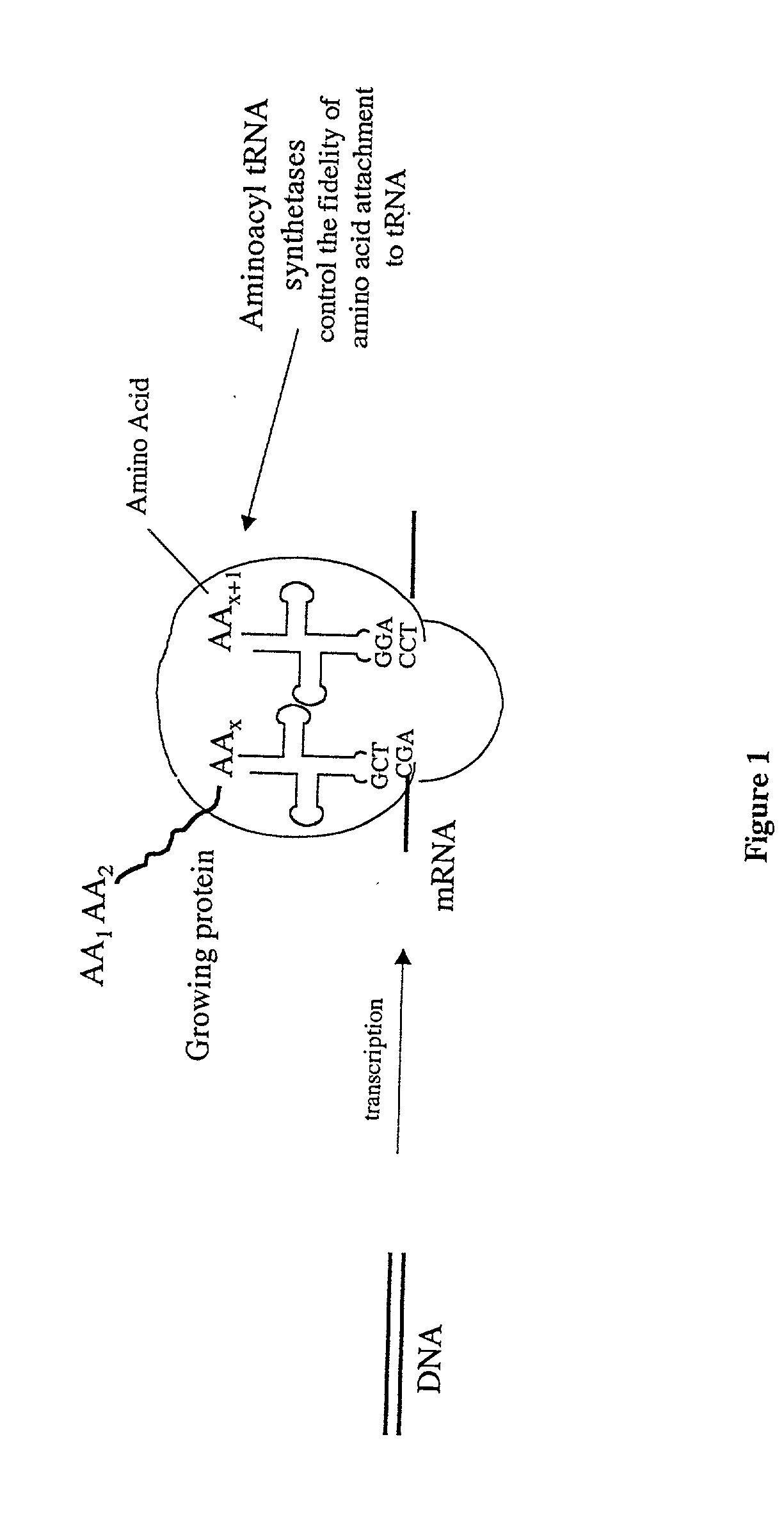
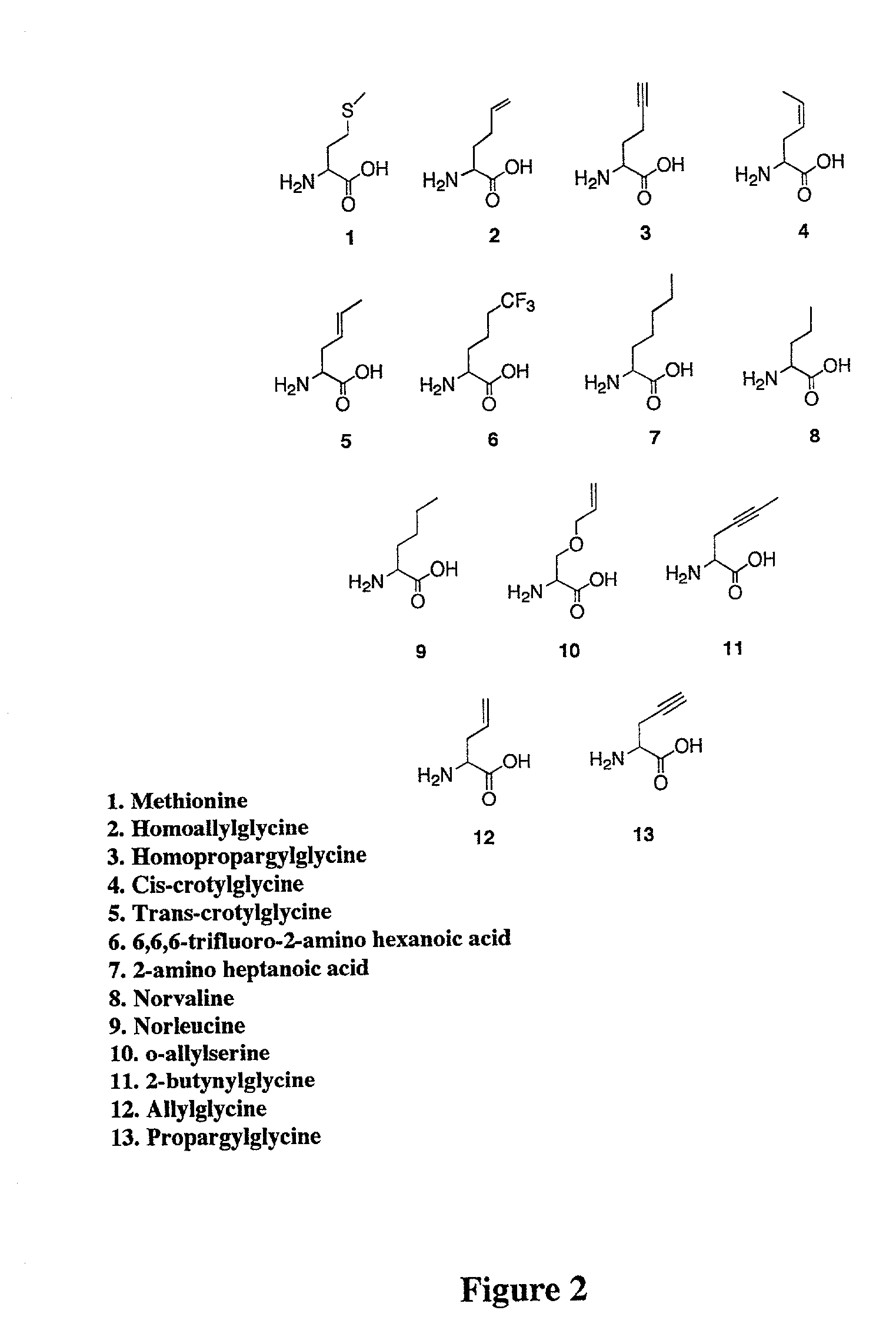
Methods for producing modified polypeptides containing amino acid analogues are disclosed. The invention further provides purified dihydrofolate reductase polypeptides, produced by the methods of the invention, in which the methionine residues have been replaced with homoallyglycine, homoproparglycine, norvaline, norleucine, cis-crotylglycine, trans-crotylglycine, 2-aminoheptanoic acid, 2-butynylglycine and allylglycine.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
RFID scanning device
ActiveUS10482292B2Minimal costMinimal effortLogisticsSensing by electromagnetic radiationInventory managementAuthorization
Owner:GARY L SHARPE
Overexpression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for efficient production of engineered proteins containing amino acid analogues
InactiveUS20020042097A1High yieldRapid and predictable approachFungiBacteriaMethionine biosynthesisDihydrofolate reductase
Methods for producing modified polypeptides containing amino acid analogues are disclosed. The invention further provides purified dihydrofolate reductase polypeptides, produced by the methods of the invention, in which the methionine residues have been replaced with homoallyglycine, homoproparglycine, norvaline, norleucine, cis-crotylglycine, trans-crotylglycine, 2-aminoheptanoic acid, 2-butynylglycine and allylglycine.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
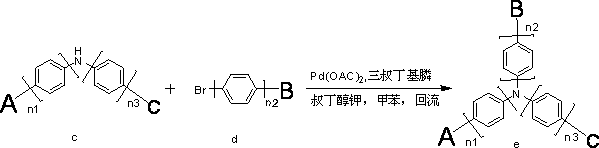
Organic electroluminescent material containing tertiary aromatic amine structure and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102702075AImprove performanceImprove luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesCarbazoleStructural formula
The invention discloses an organic electroluminescent material containing a tertiary aromatic amine structure. The organic electroluminescent material containing the tertiary aromatic amine structure is characterized in that: the structural formula is shown in the specifications; and in the structural formula, n1, n2 and n3 independently represent that the quantity of benzene ring is 0 or 1 respectively; a radical A represents a substituted carbazole radical; a radical B represents a structural radical containing substituted fluorenyl; and a structure C is a structure radical containing phenyl and substituted phenyl. The organic electroluminescent material is a fluorescent material which has high luminous efficiency; a result of the luminous efficiency in a solution can further indicate that the organic electroluminescent material which has high luminous efficiency and of which the brightness and performance can meet the industrial development can be applied to electroluminescent devices by serving as a luminous material or a luminous main body material or a transmission material. A synthesizing process has the advantages of reaction in two simple steps, easiness and convenience for operating, easiness for purifying, great increase in the industrial synthesizing yield, great reduction in cost, wide application, applicability to a plurality of materials for devices, and wide prospect. Meanwhile, a substituted radical is adjusted, so that the performance of the material further meets requirement of industrialization.
Owner:JILIN OPTICAL & ELECTRONICS MATERIALS
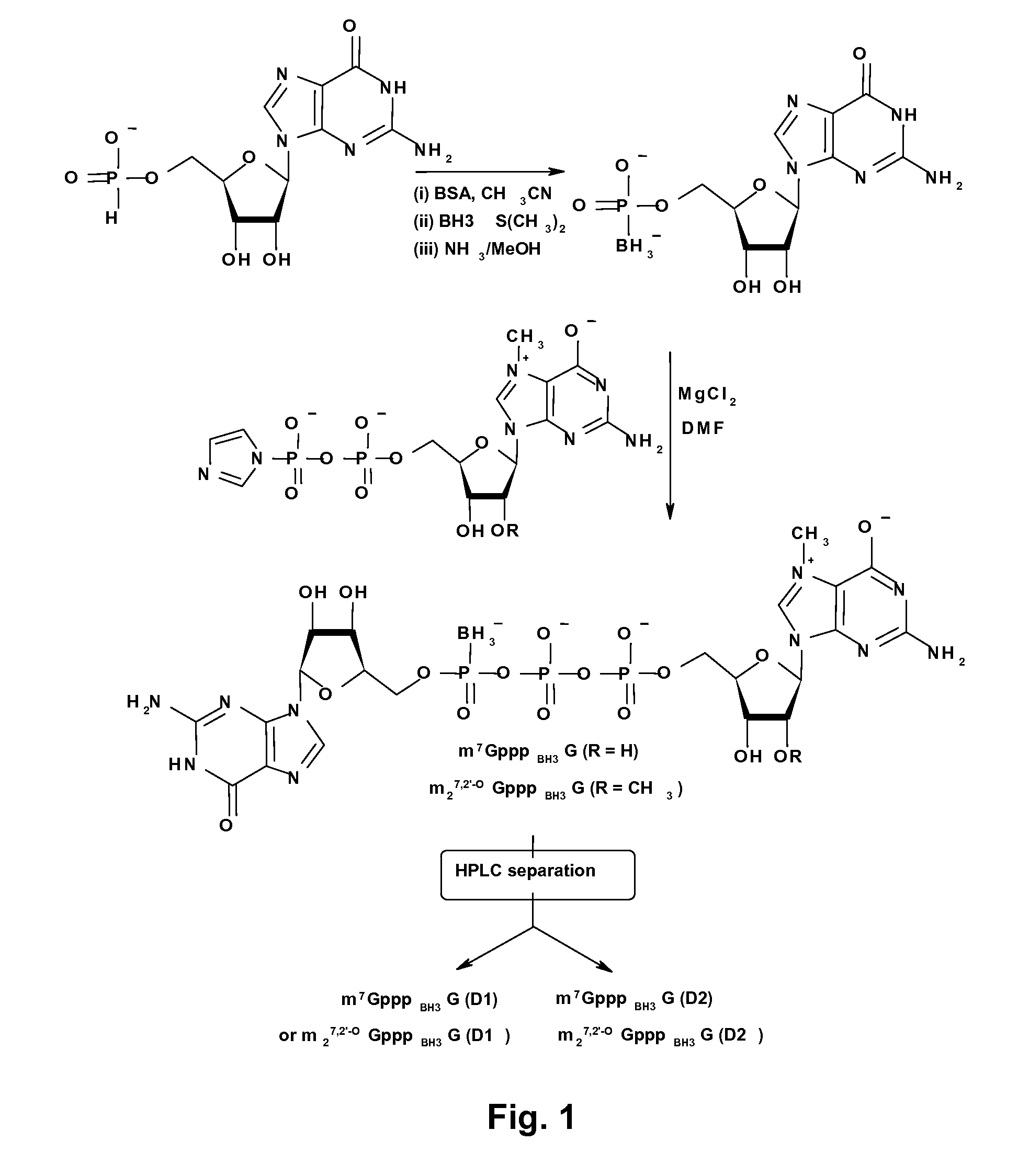
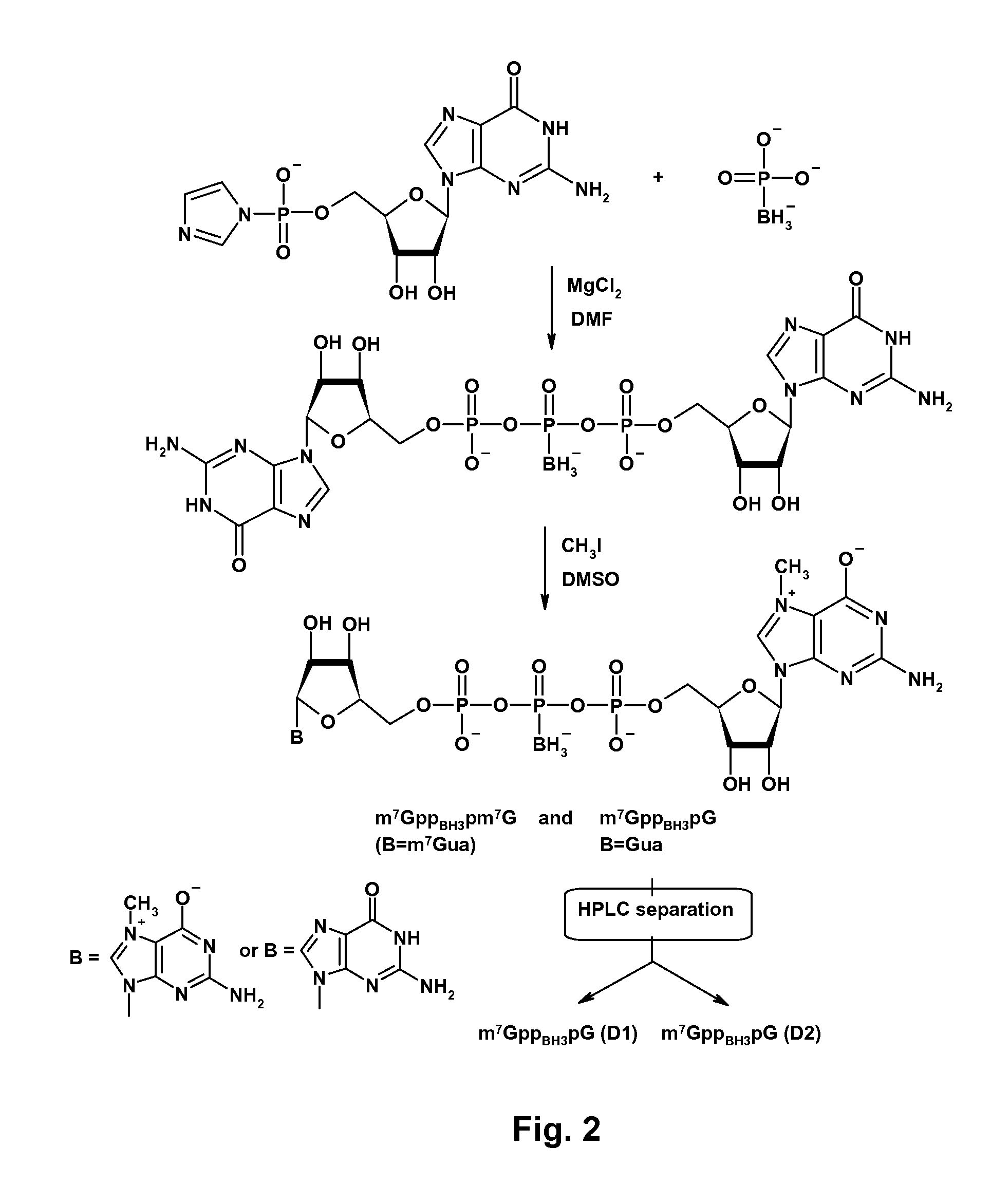
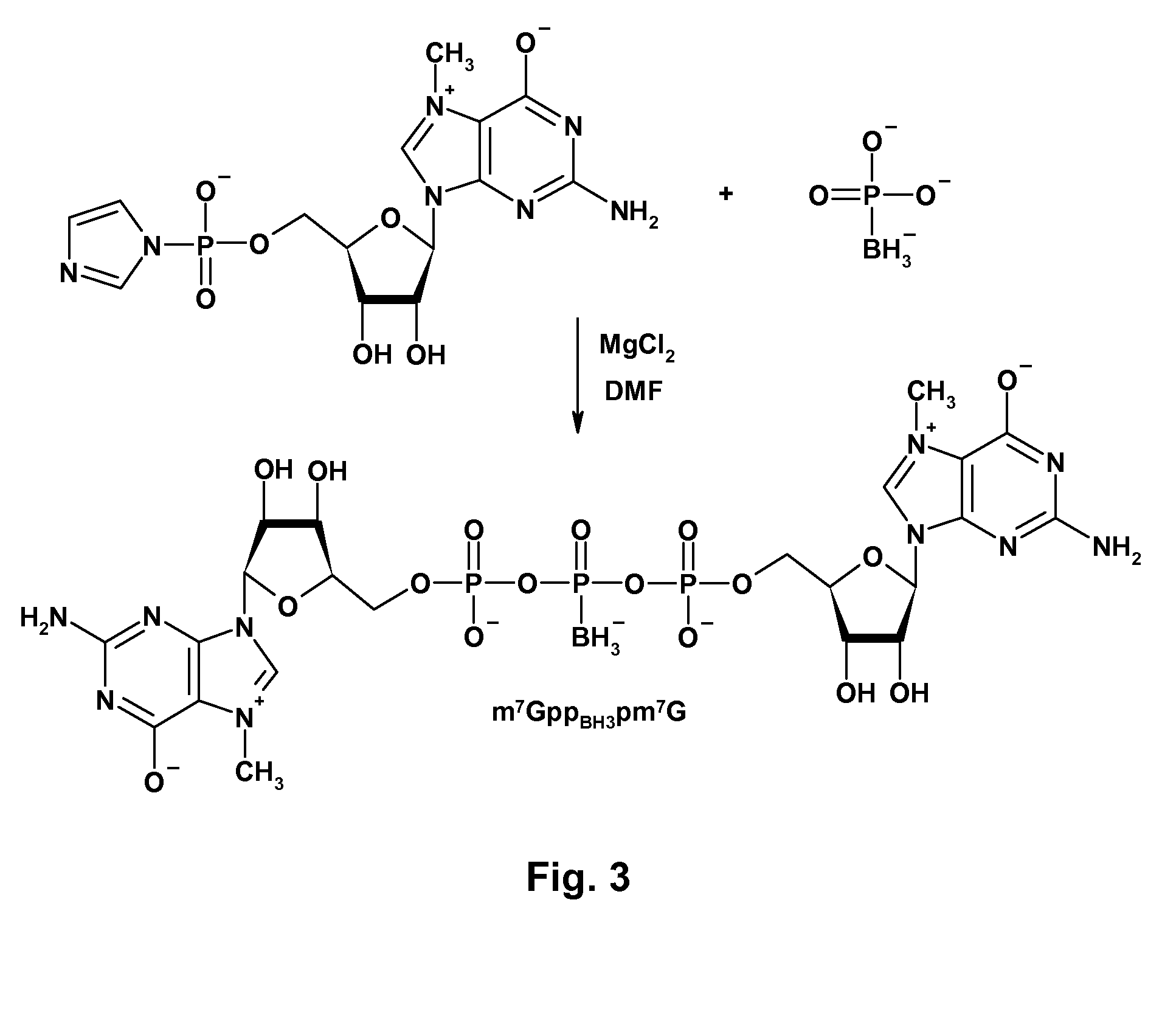
mRNA cap analogs
ActiveUS8519110B2Wide range of usesImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMetabolism disorderPhosphateIn vivo
Dinucleotide cap analogs are disclosed, modified at different phosphate positions with a boranophosphate group or a phosphoroselenoate group. The analogs are useful as reagents in the preparation of capped mRNAs and have increased stability both in vitro and in vivo. They may be used as inhibitors of cap-dependent translation. Optionally, the boranophosphate or phosphoroselenoate group has a 2′-O or 3′-O-alkyl group, preferably a methyl group, producing analogs called BH3-ARCAs or Se-ARCAs. ARCAs may be modified with α-, β-, or γ-boranophosphate or phosphoroselenoate groups.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI +1
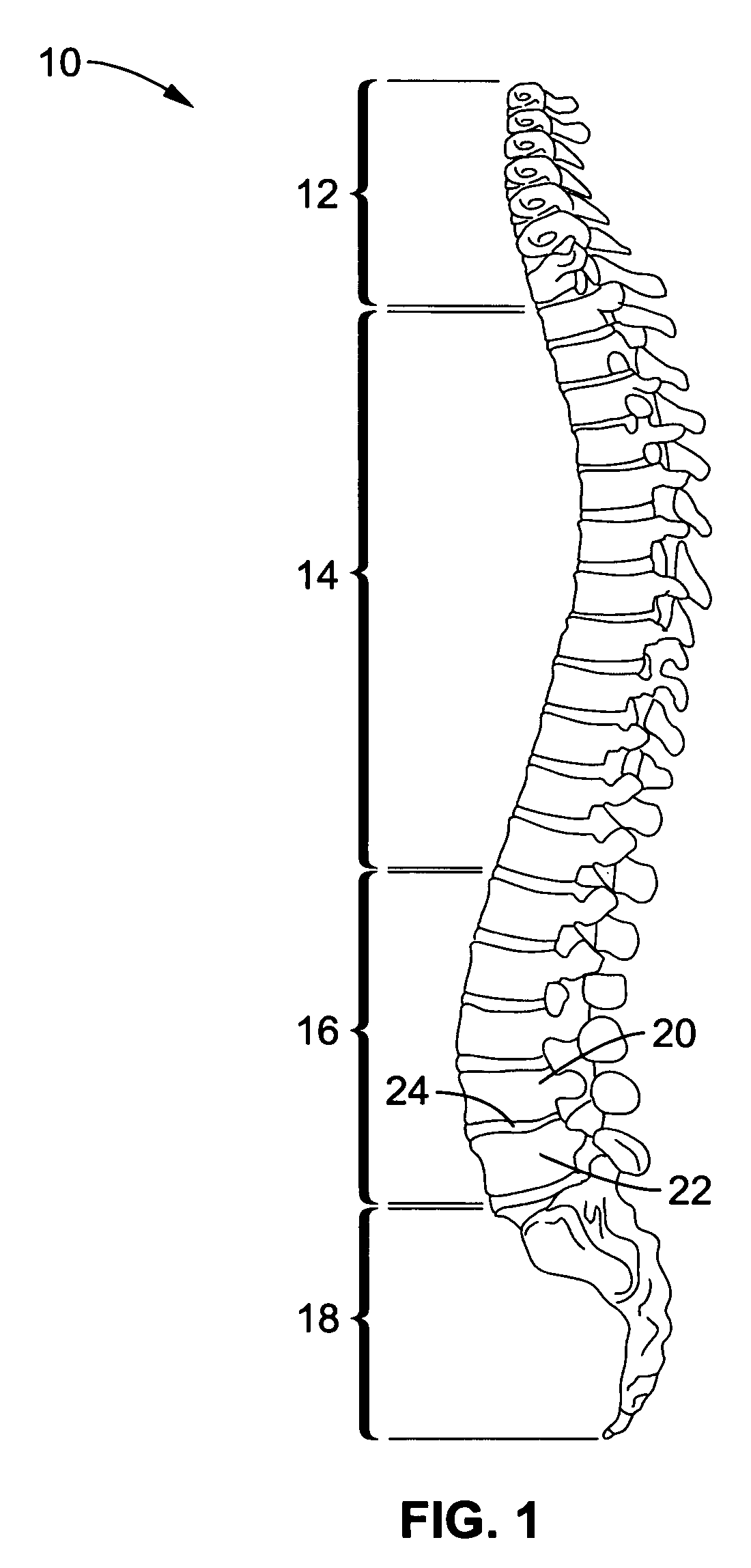
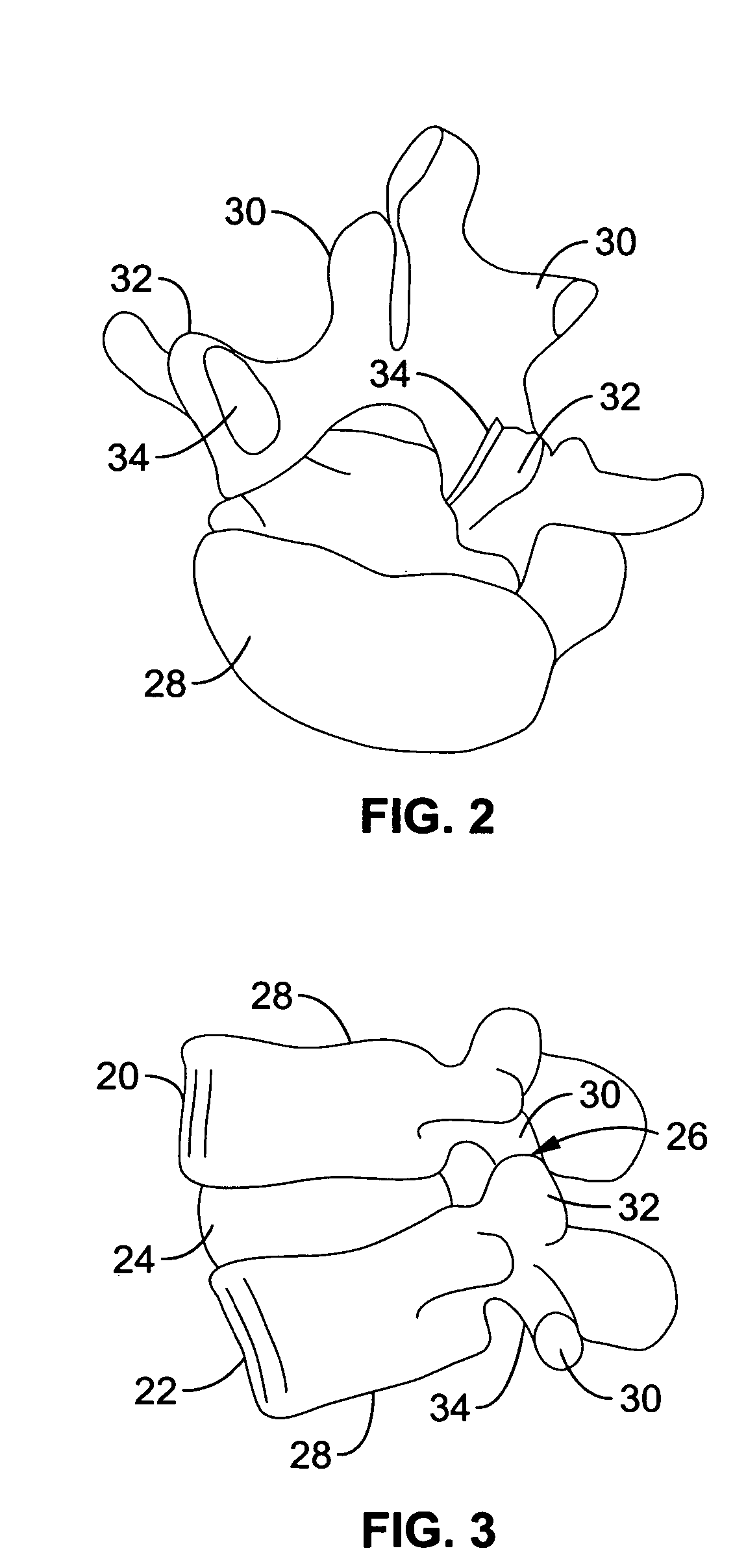
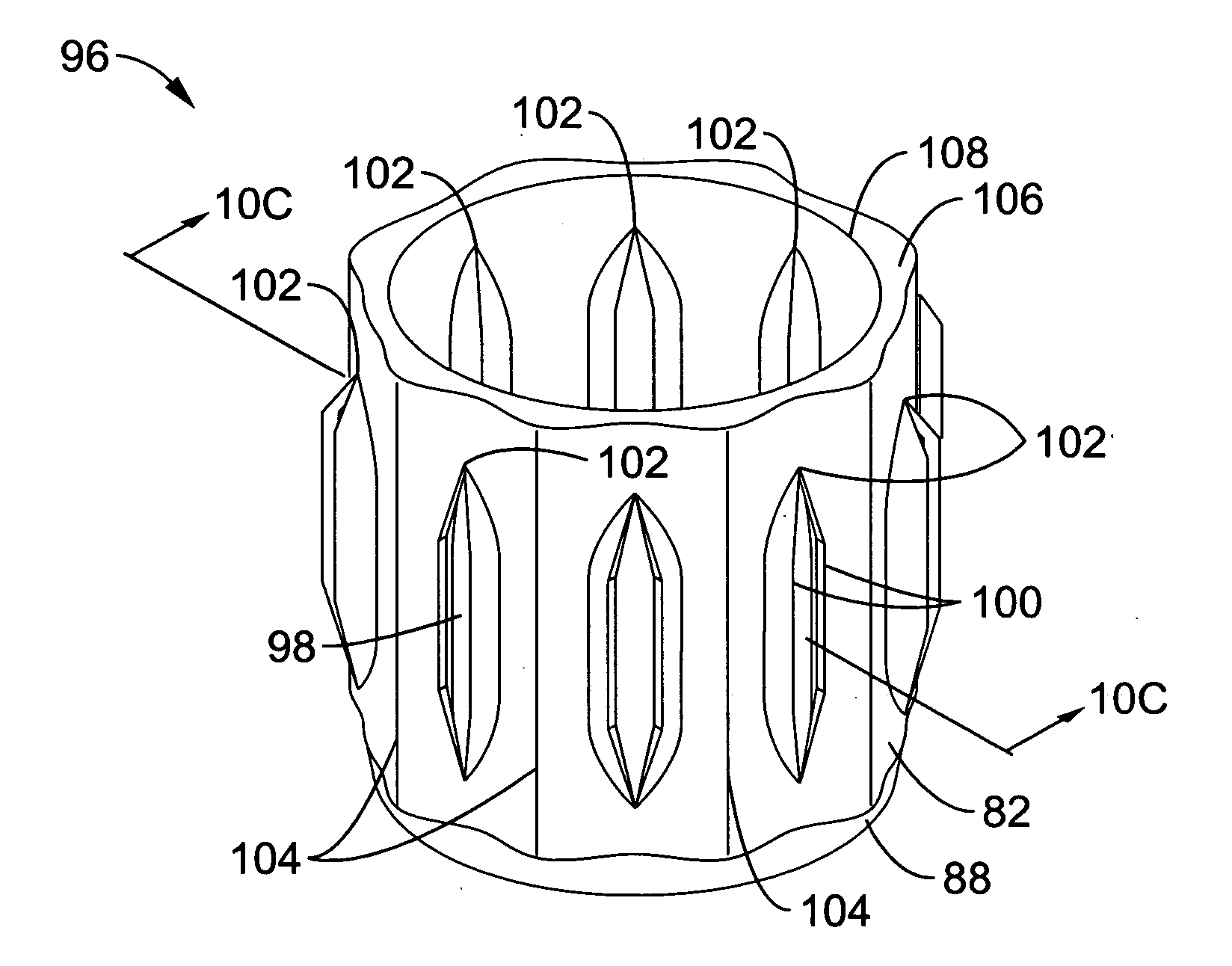
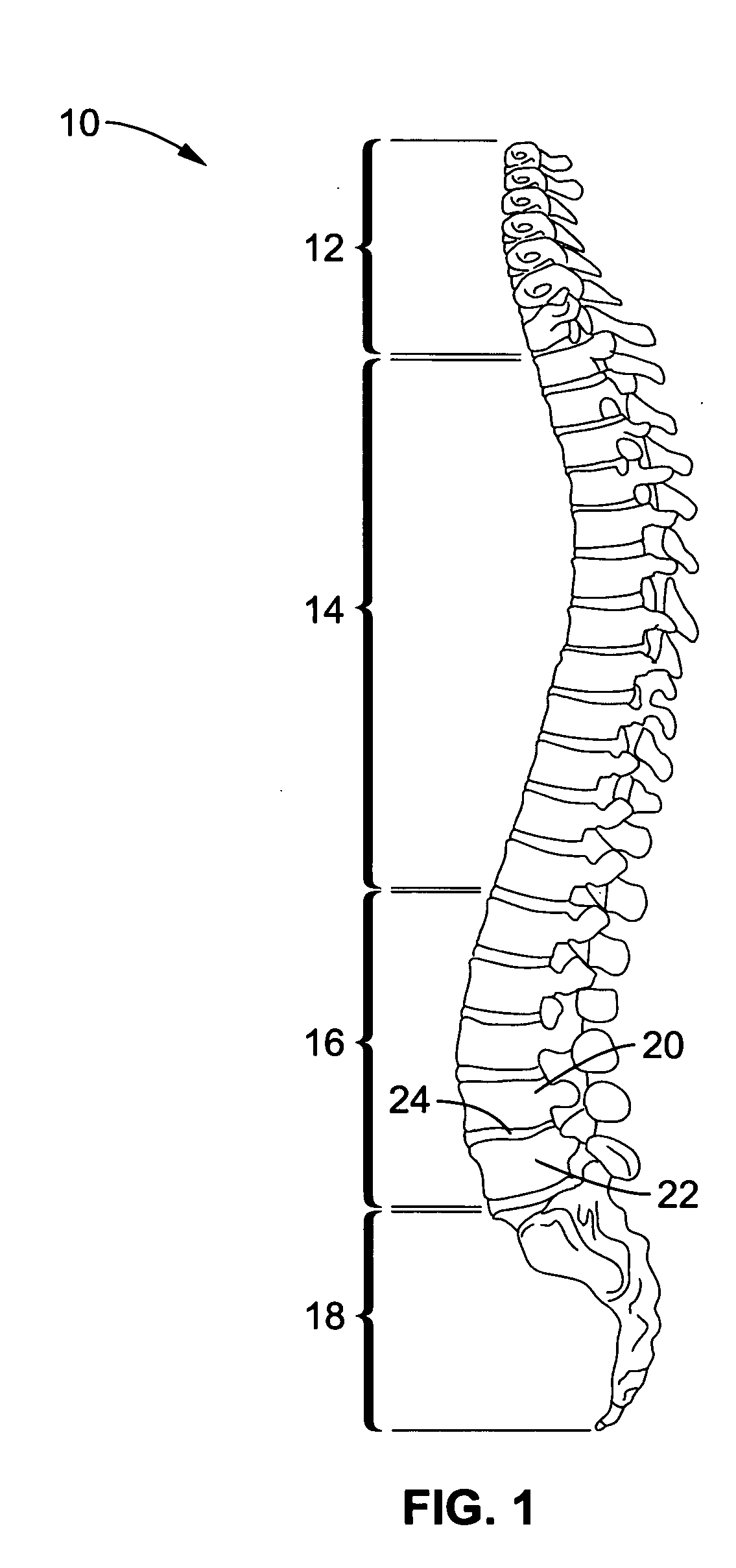
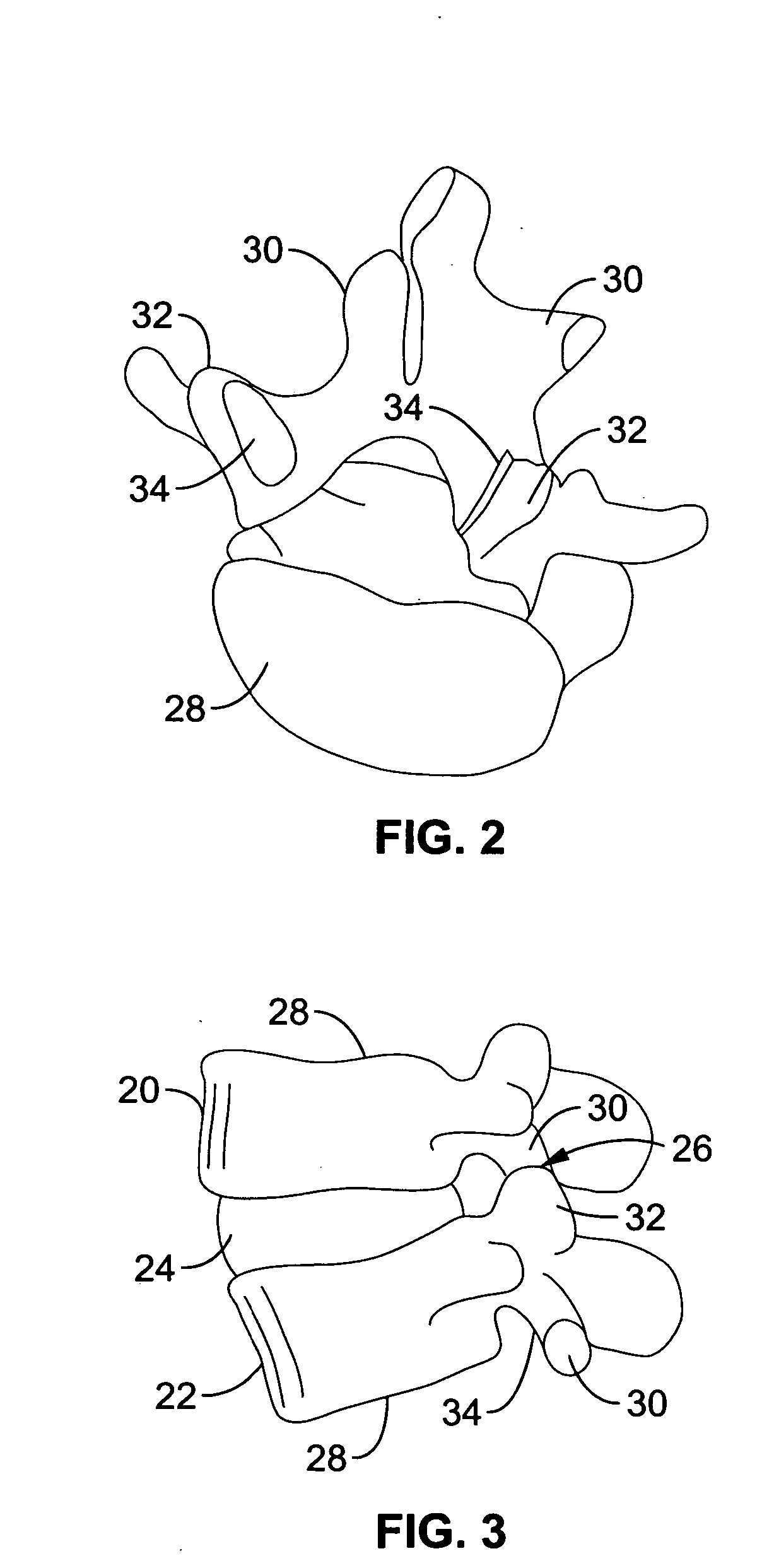
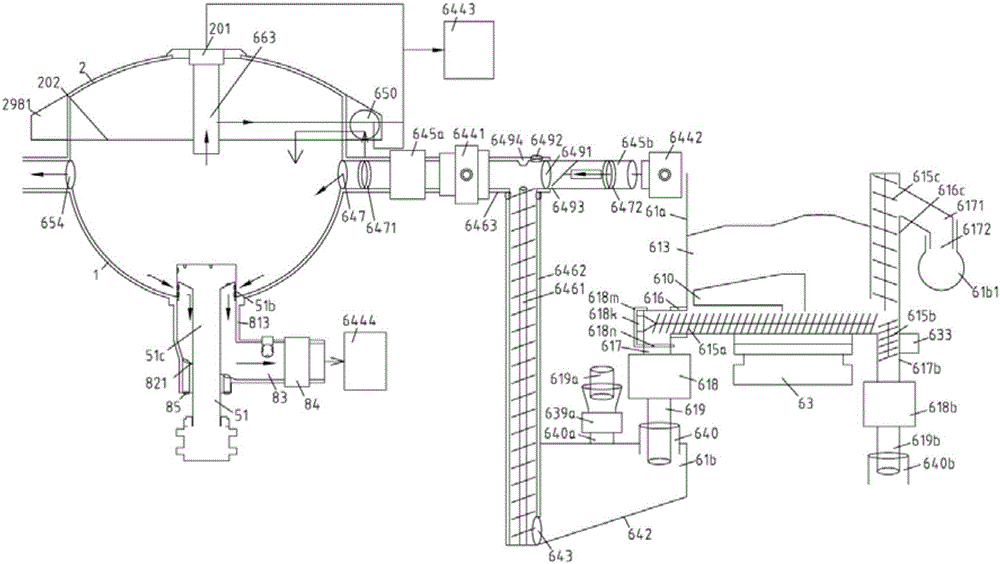
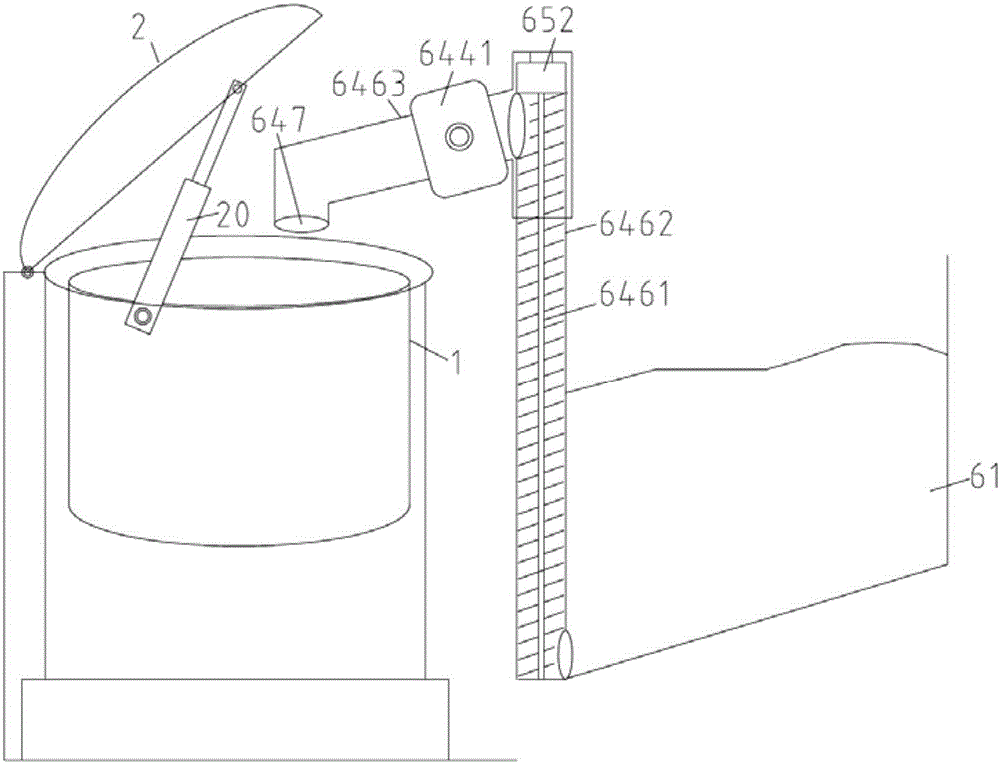
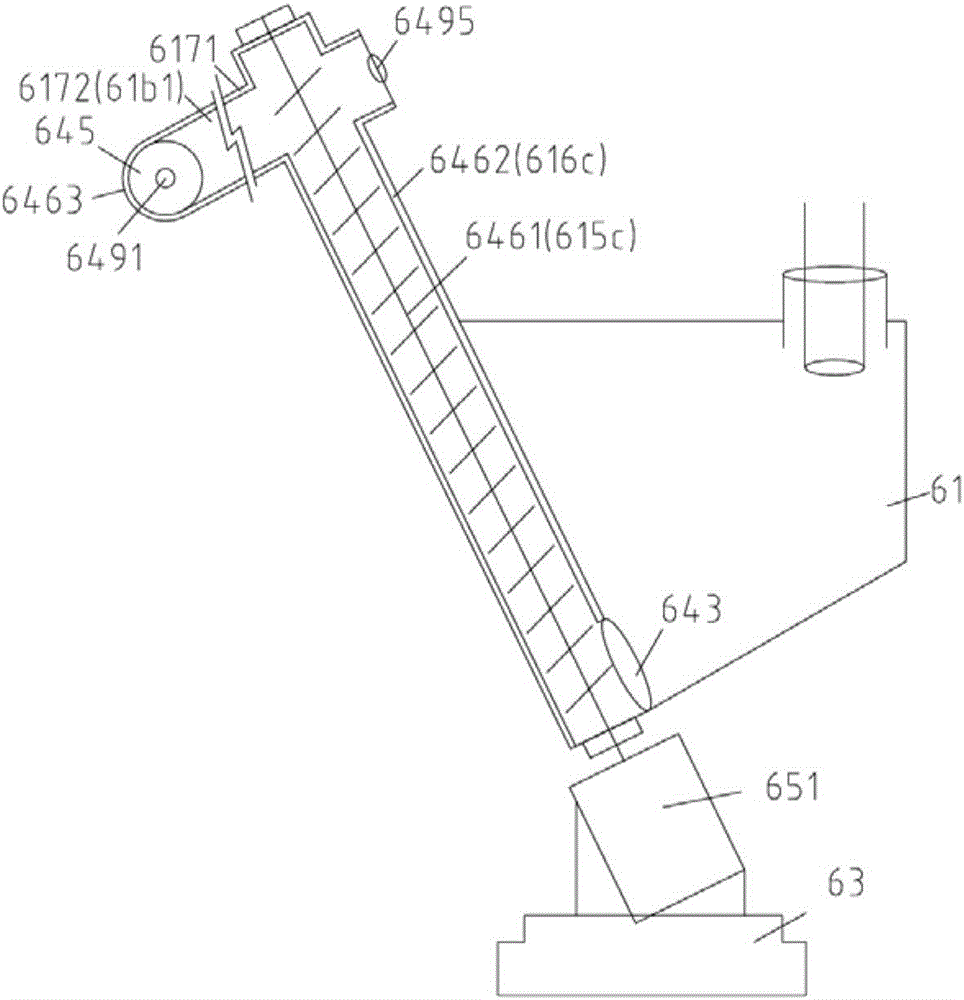
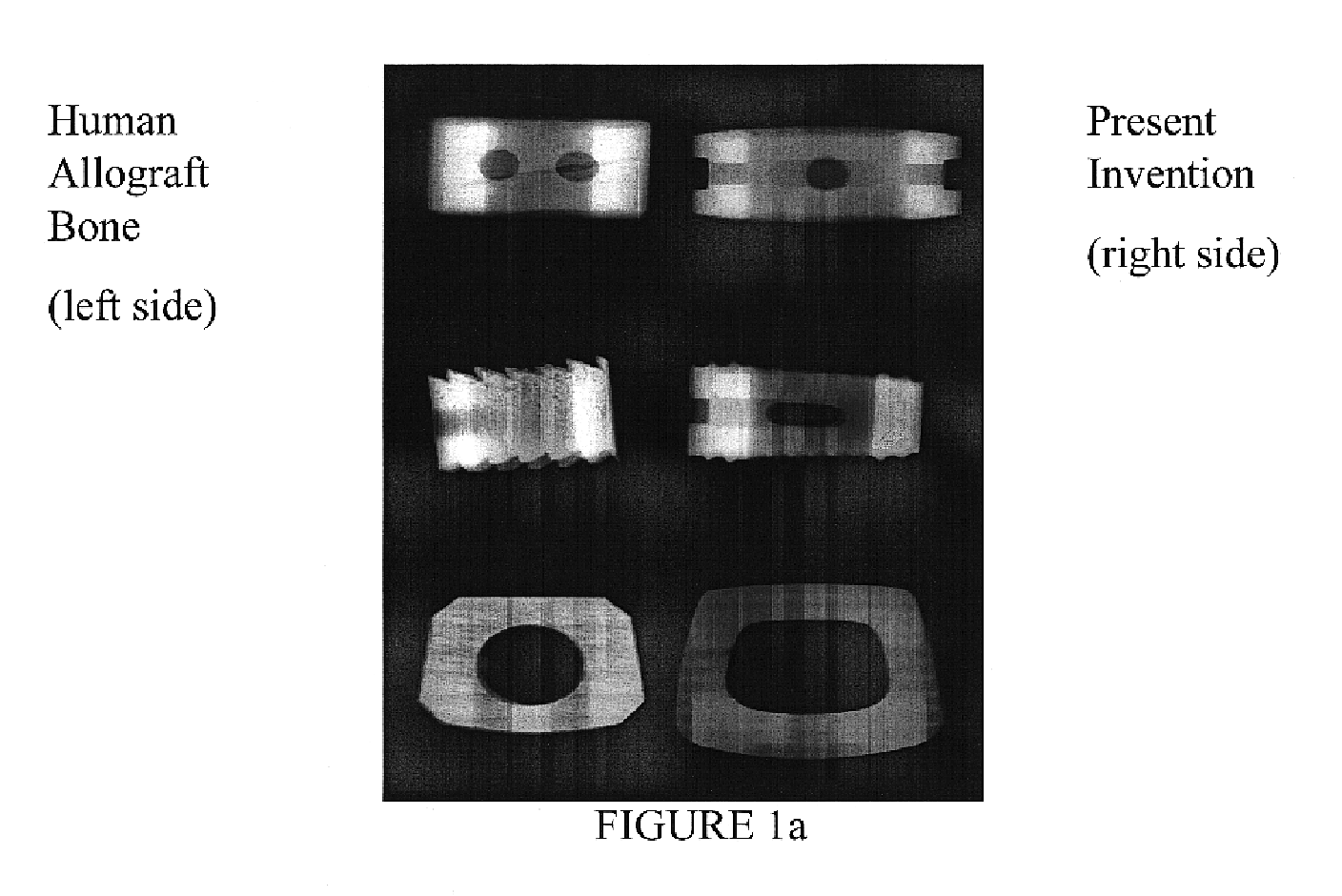
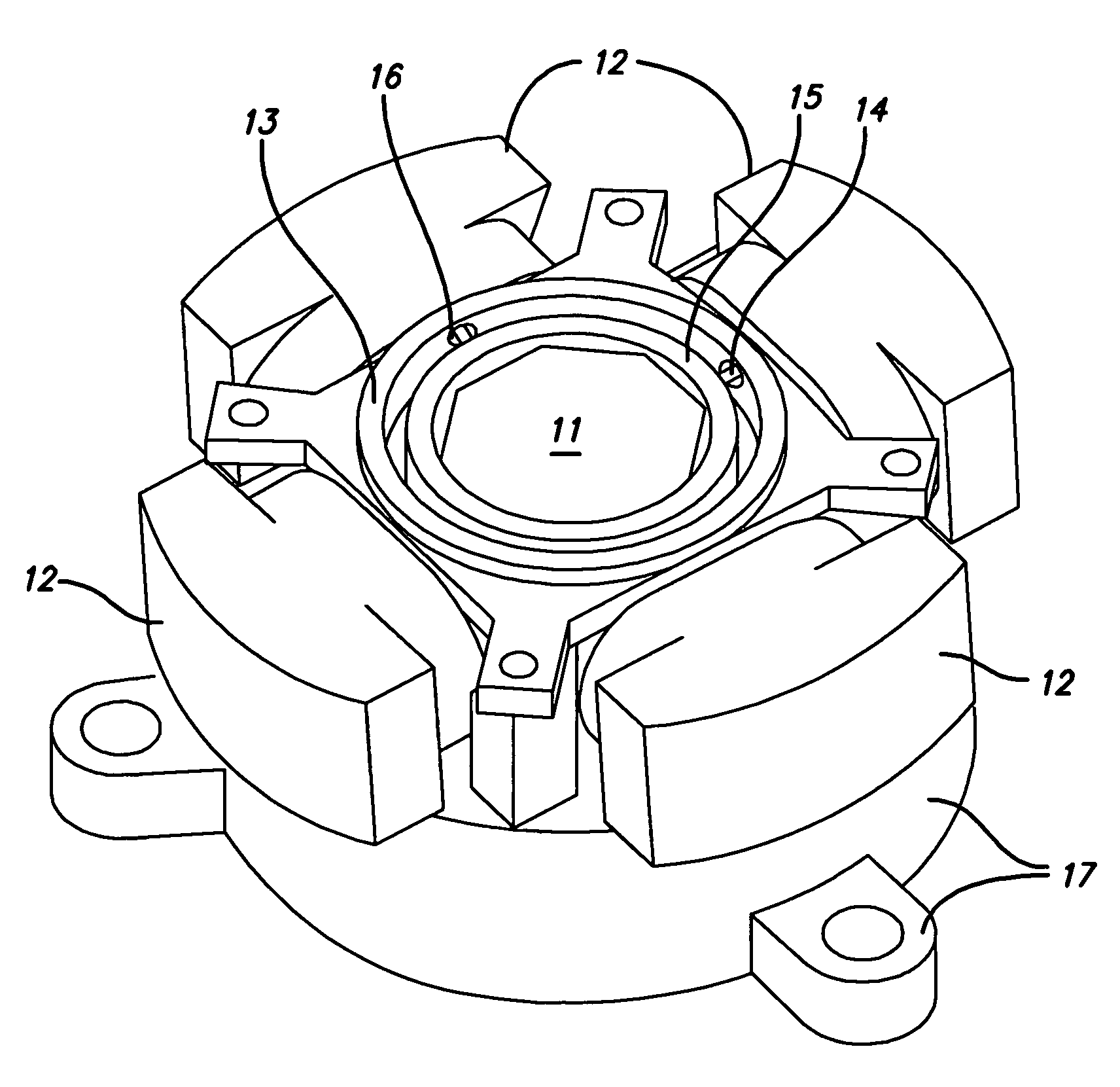
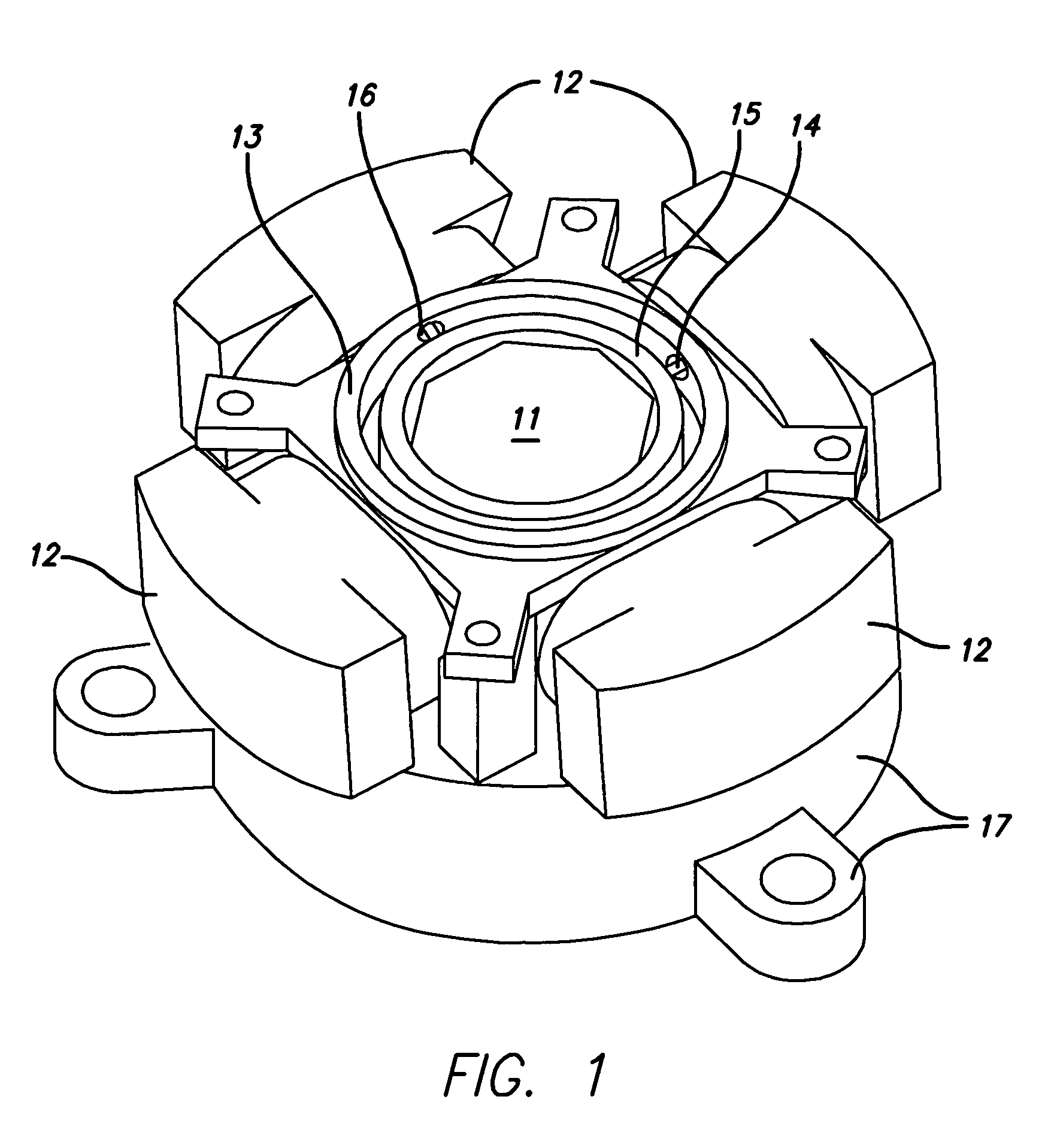
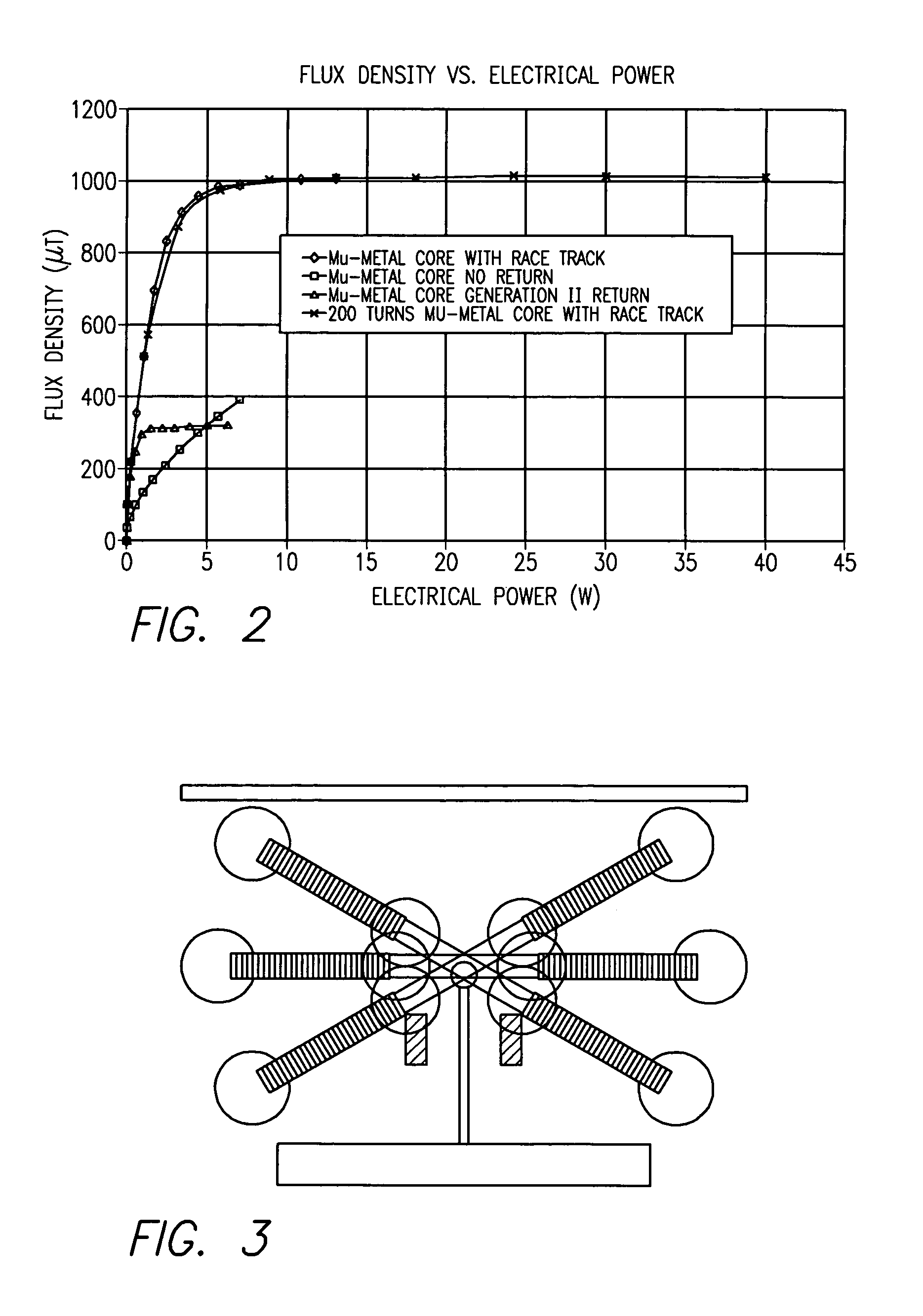
Spine microsurgery techniques, training aids and implants
InactiveUS7452369B2Improve securityWide range of usesInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresArticular facet
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
Spine microsurgery techniques, training aids and implants
InactiveUS20060085068A1Improve securityBroad utilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnArticular facet
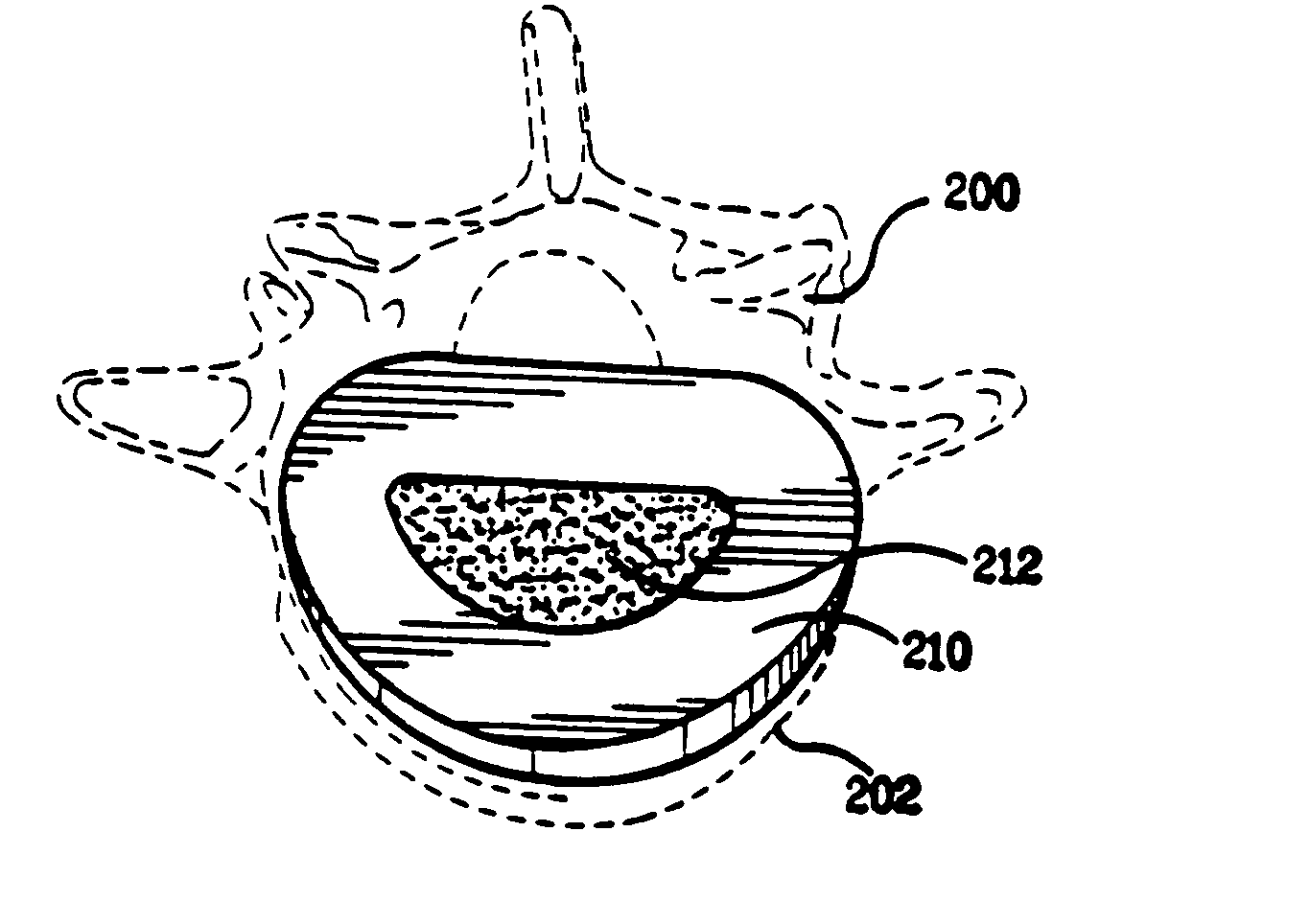
A minimally invasive, fluoroscopically guided system is disclosed for stabilizing the articular facet joints of adjacent vertebrae. Ring and dowel implants are disclosed for installation into the facet joint. The invention includes a novel spine surgical training aid used in the initial surgeon training process for refreshing the surgeon's perspective of the critical three dimensional anatomy of the vertebrae. The invention also includes a surgical kit having a range of size-specific drills, inserters, impactors and custom-length long k-wires matched to the internal diameter of the instrumentation system.
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
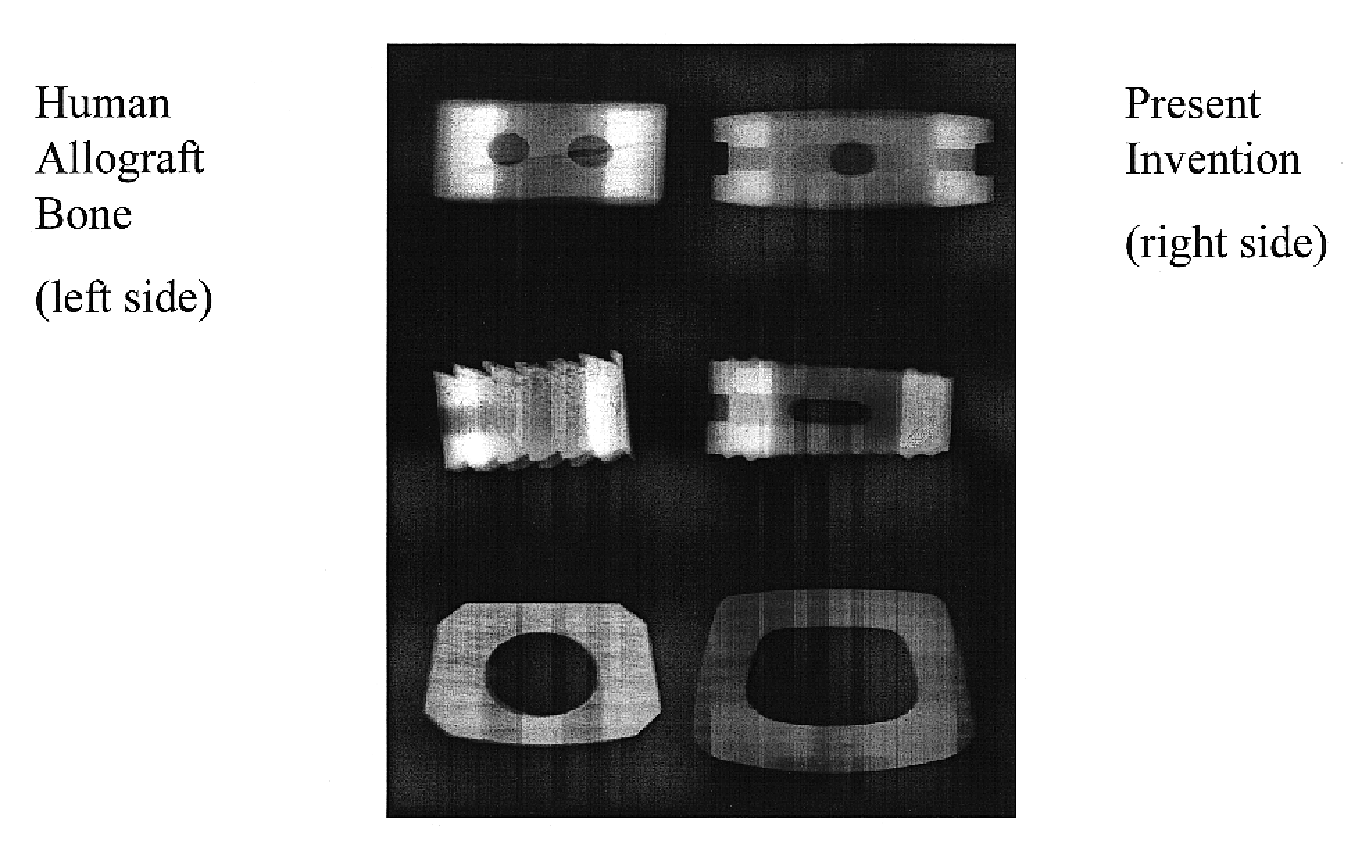
Composite shaped bodies and methods for their production and use
InactiveUS6863899B2Overcome the lack of robustnessNovel featuresCosmetic preparationsDental implantsCalcium biphosphatePlastic surgery
Shaped, composite bodies are provided. One portion of the shaped bodies comprises an RPR-derived porous inorganic material, preferably a calcium phosphate. Another portion of the composite bodies is a different solid material, preferably metal, glass, ceramic or polymeric. The shaped bodies are especially suitable for orthopaedic and other surgical use.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
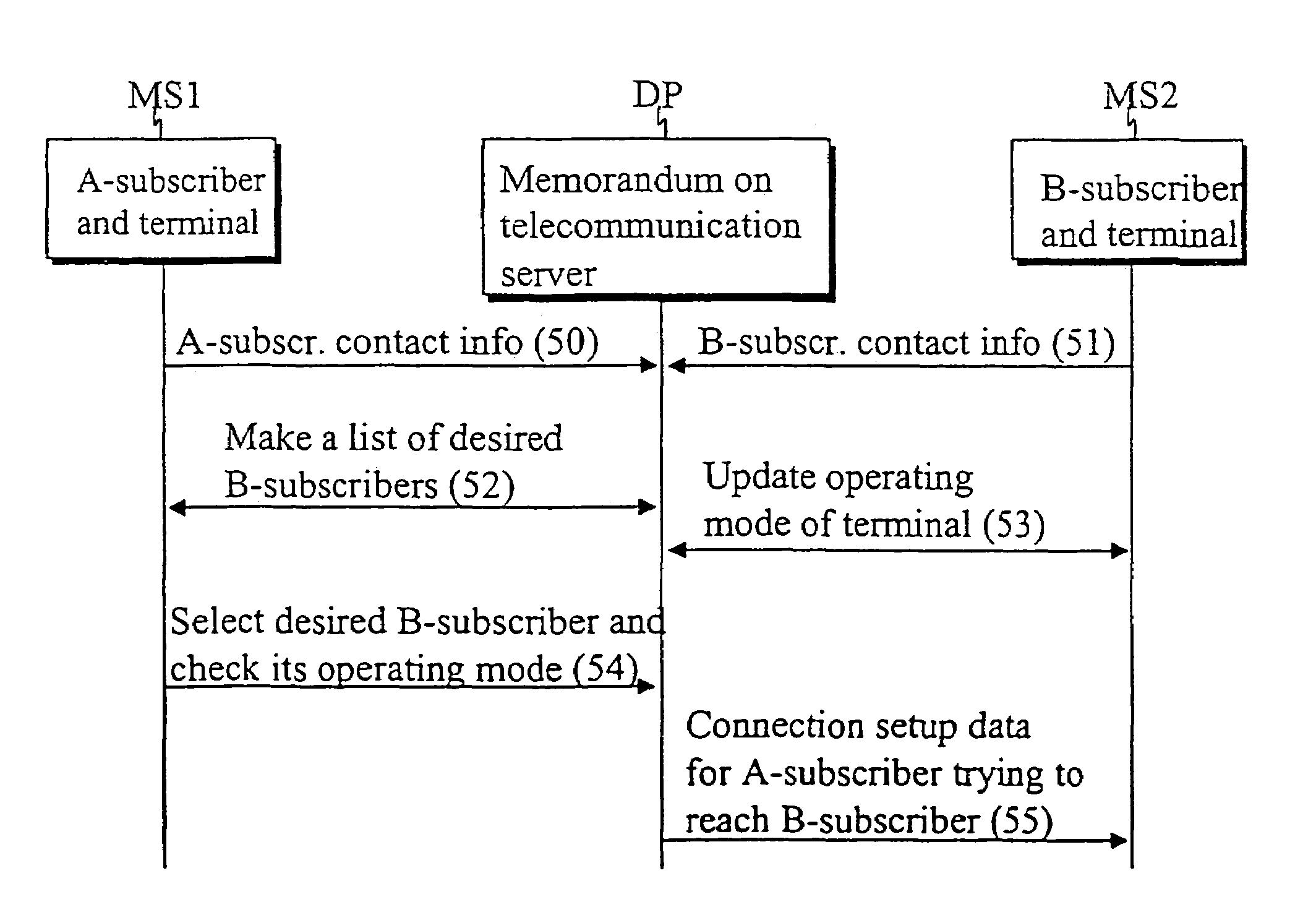
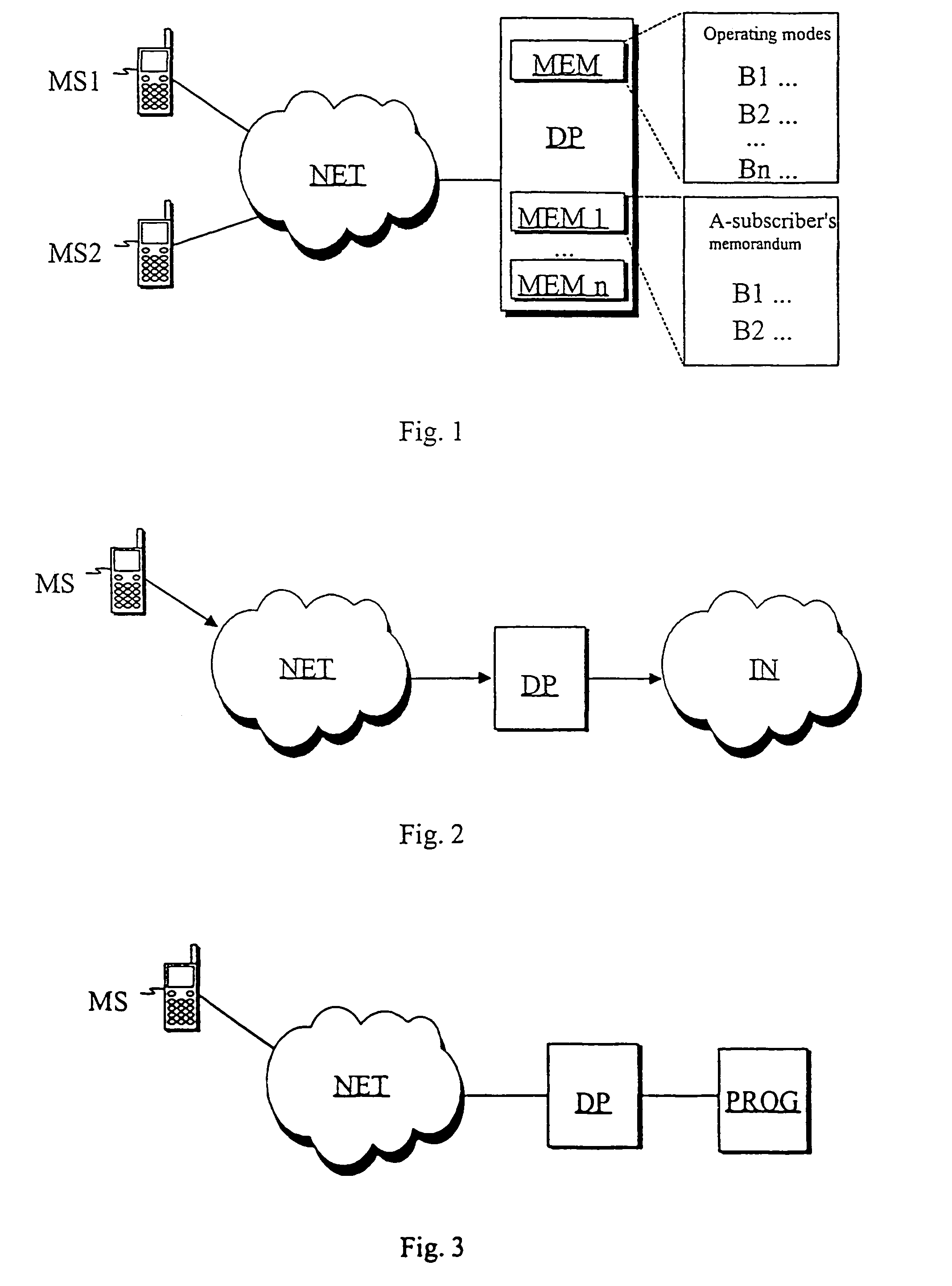
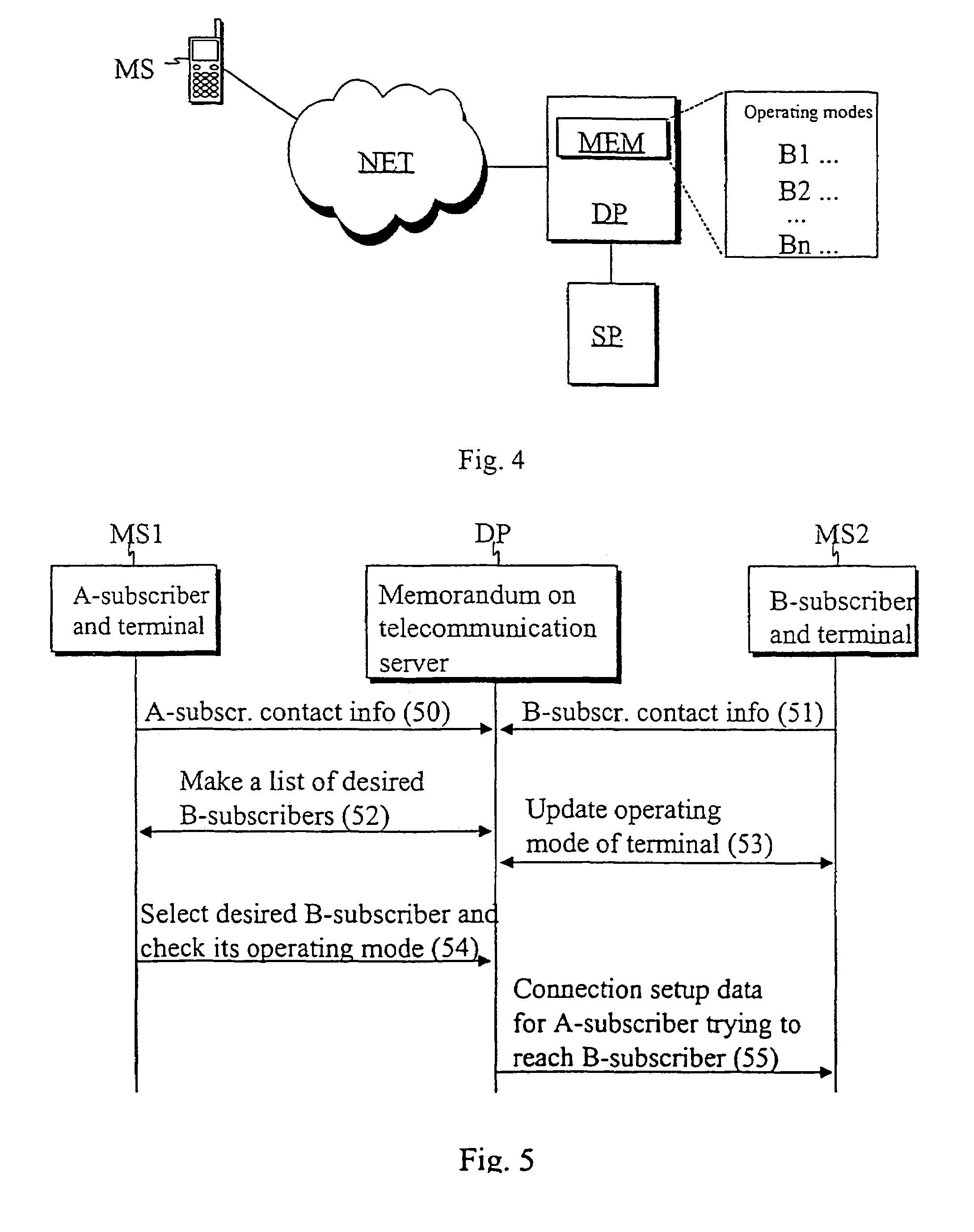
System and method for determining, storing and utilizing operating mode data of a user telecommunication terminal
InactiveUS7221959B2Wide range of usesSpecial service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunications networkOperation mode
A system and method for determining, storing and utilizing terminal operating mode data in a telecommunication system, in which the user can selectively set his terminal into two or more distinct operating modes. When the operating mode of the user's terminal is changed, information regarding the change of operating mode is sent from the user terminal to a telecommunication server using any available and / or otherwise available technique available in the telecommunication network. The user terminal operating mode change is stored on the telecommunication server for access by parties seeking to contact or communicate with the user's terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP
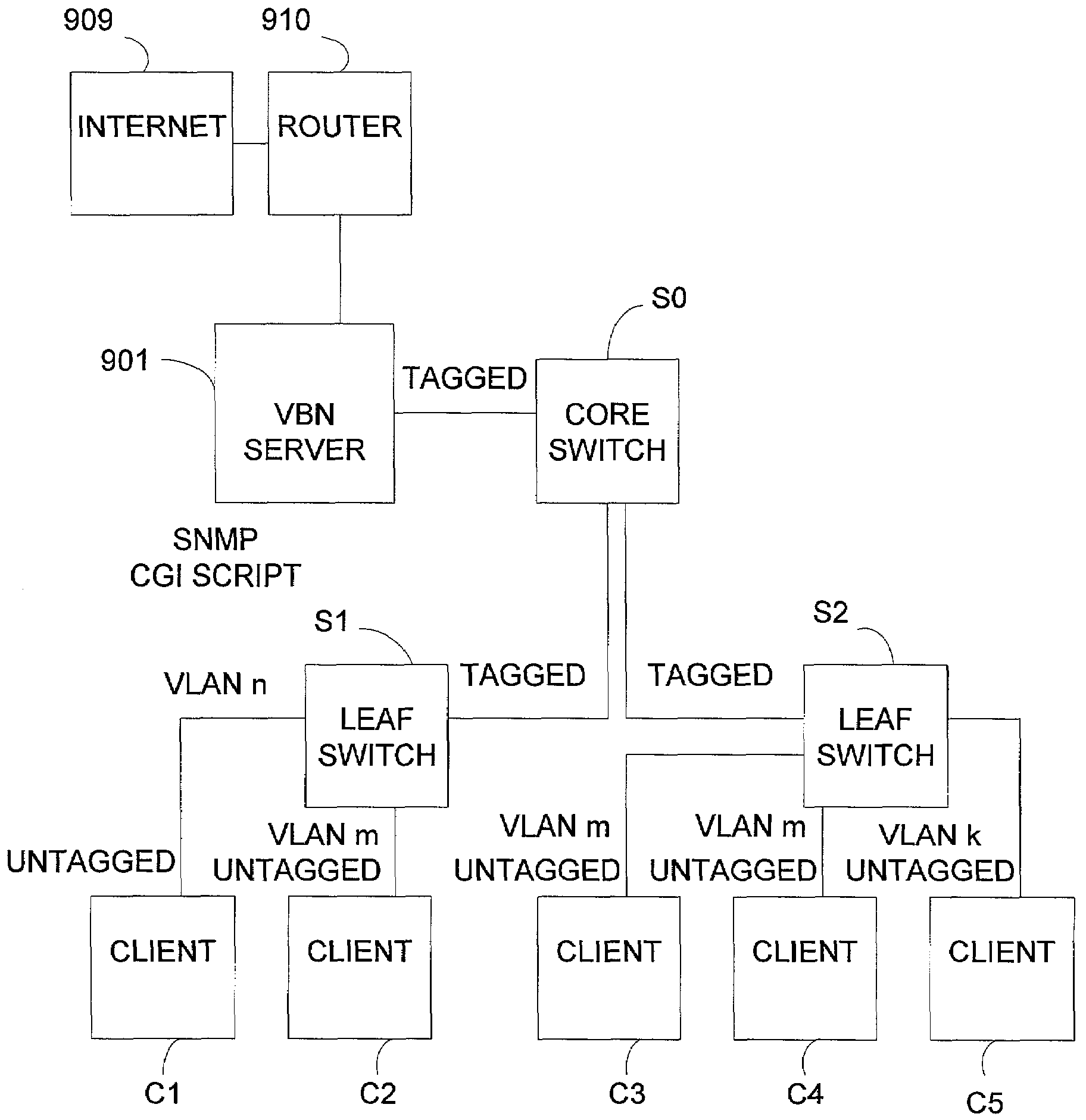
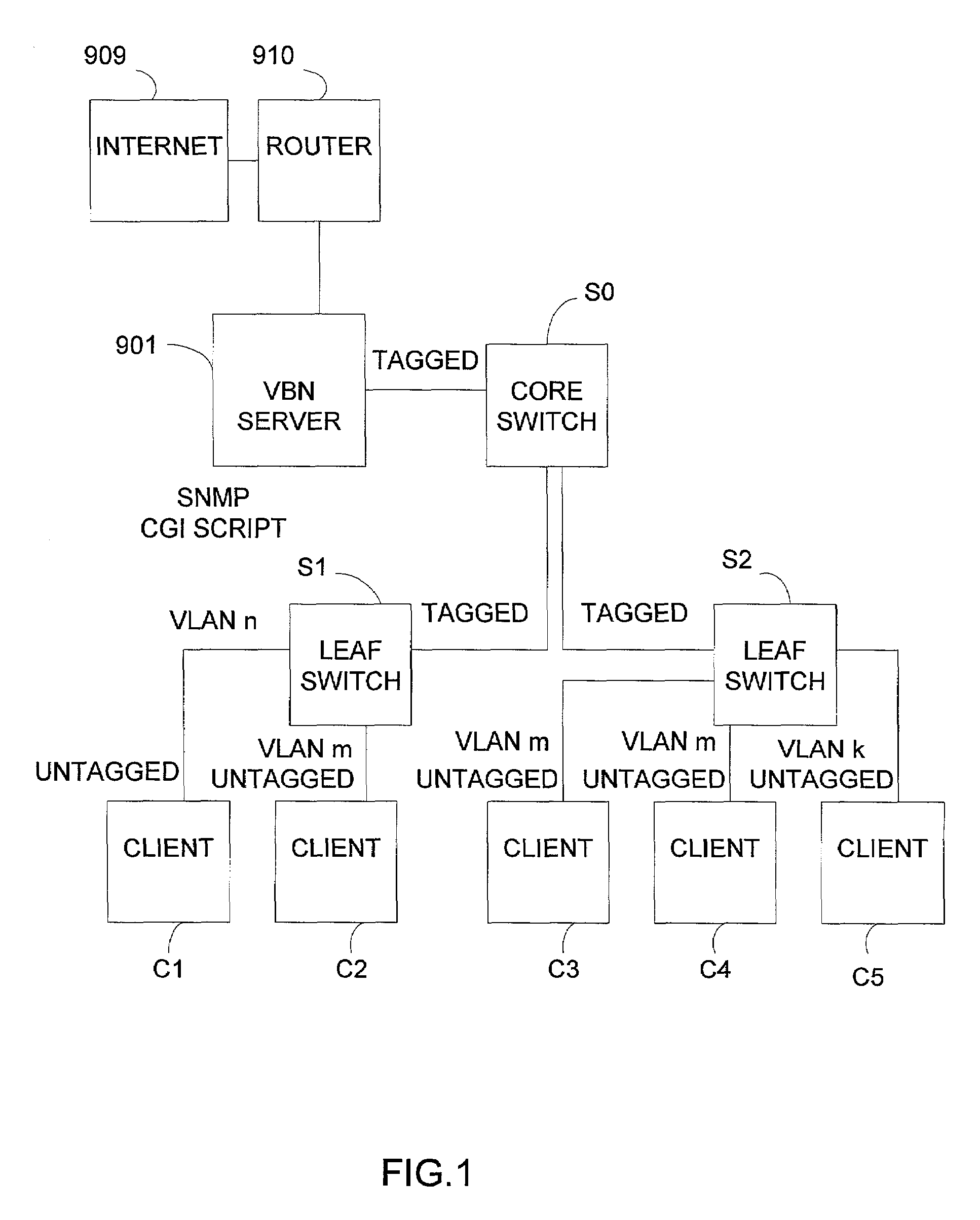
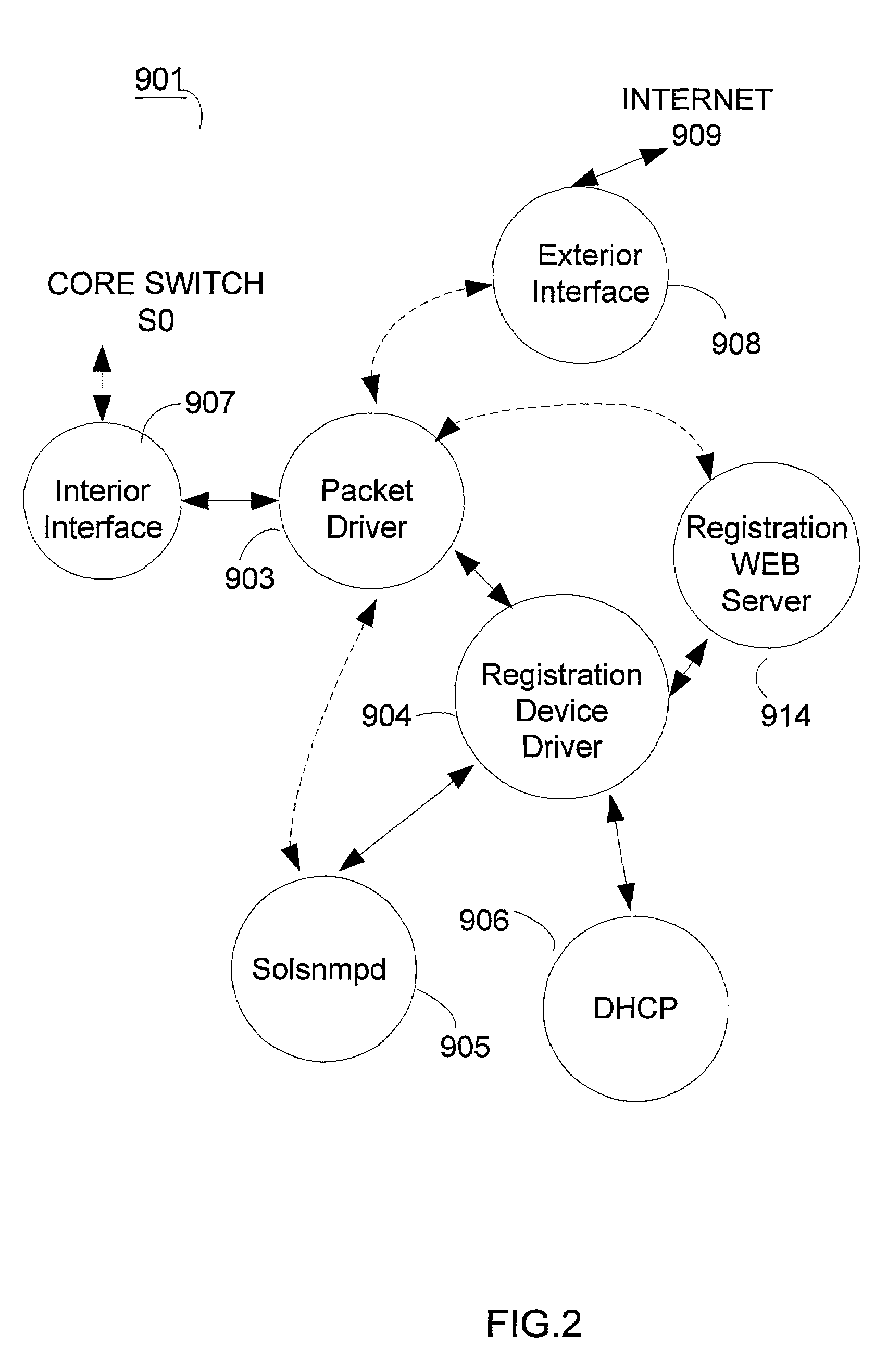
Server and method for providing specific network services
InactiveUS7356841B2Solve the shortageEasy accessMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data processing detailsIp addressRemote computer
A server and method is provided to provide a specific service to network users. The server and method automatically provide user-to-server security using VLANs. The server manages VLAN based on the request from a user for creating / deleting / joining / leaving VLANs. The server allows user to control groupings and overcomes the VLAN limit with the filtering policies on the switching infrastructure. In the second aspect of invention, the server and method provide a specific address based on requests from users. The server dynamically handles the management and facilitation of the requests. The server offers users reassignment of IP addresses from a first set of characteristics to a second set of characteristics with minimal user intervention. This allows users the ability to run a broader range of protocols. In the third aspect of invention, the server and method is provided to provide a routable IP address to a remote computer. The server allows pools of routable addresses to be maintained on one or more remote servers. The server can solve the shortage of the routable IP addresses.
Owner:ONLINE CONNECTIVITY +1
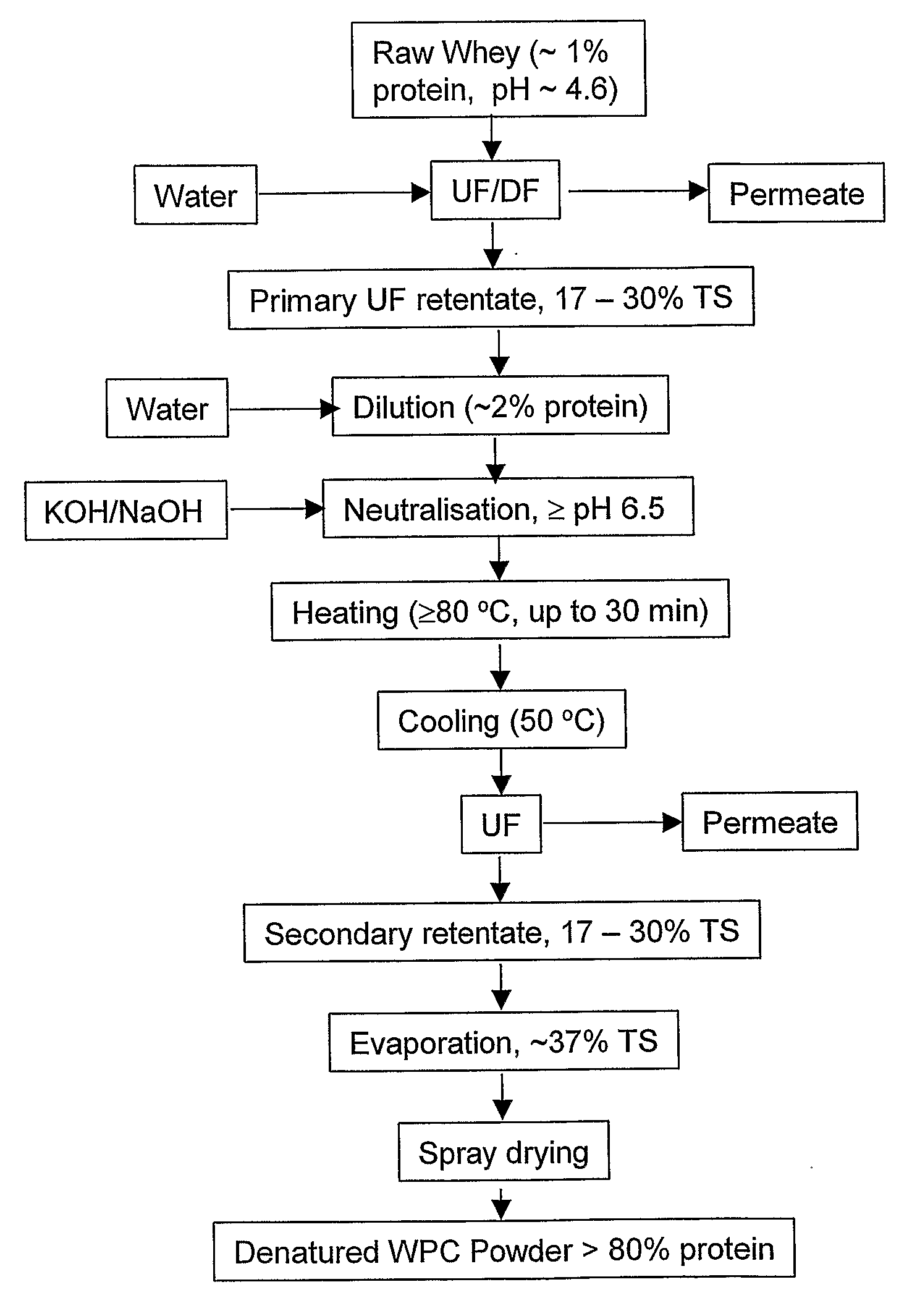
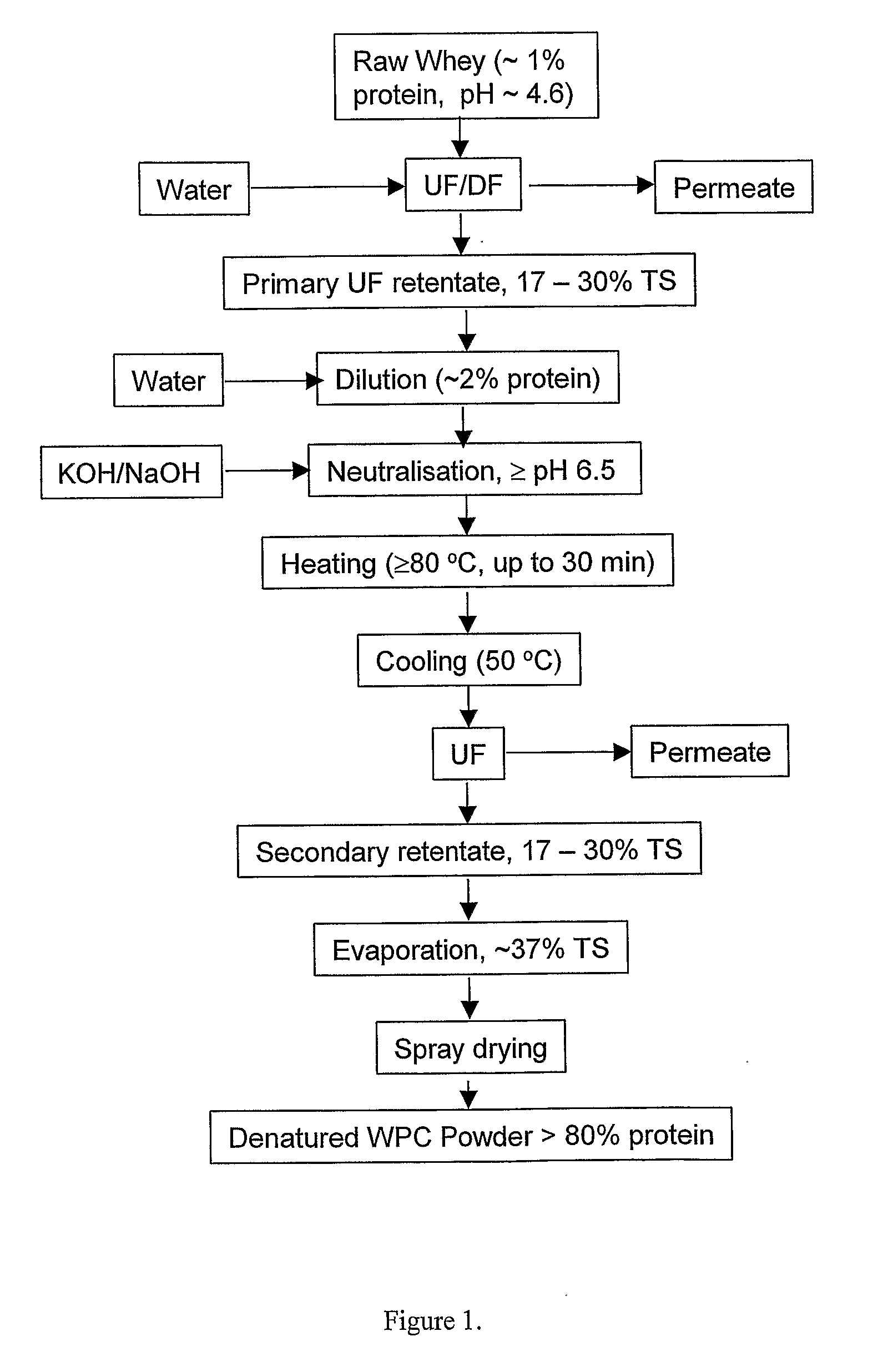
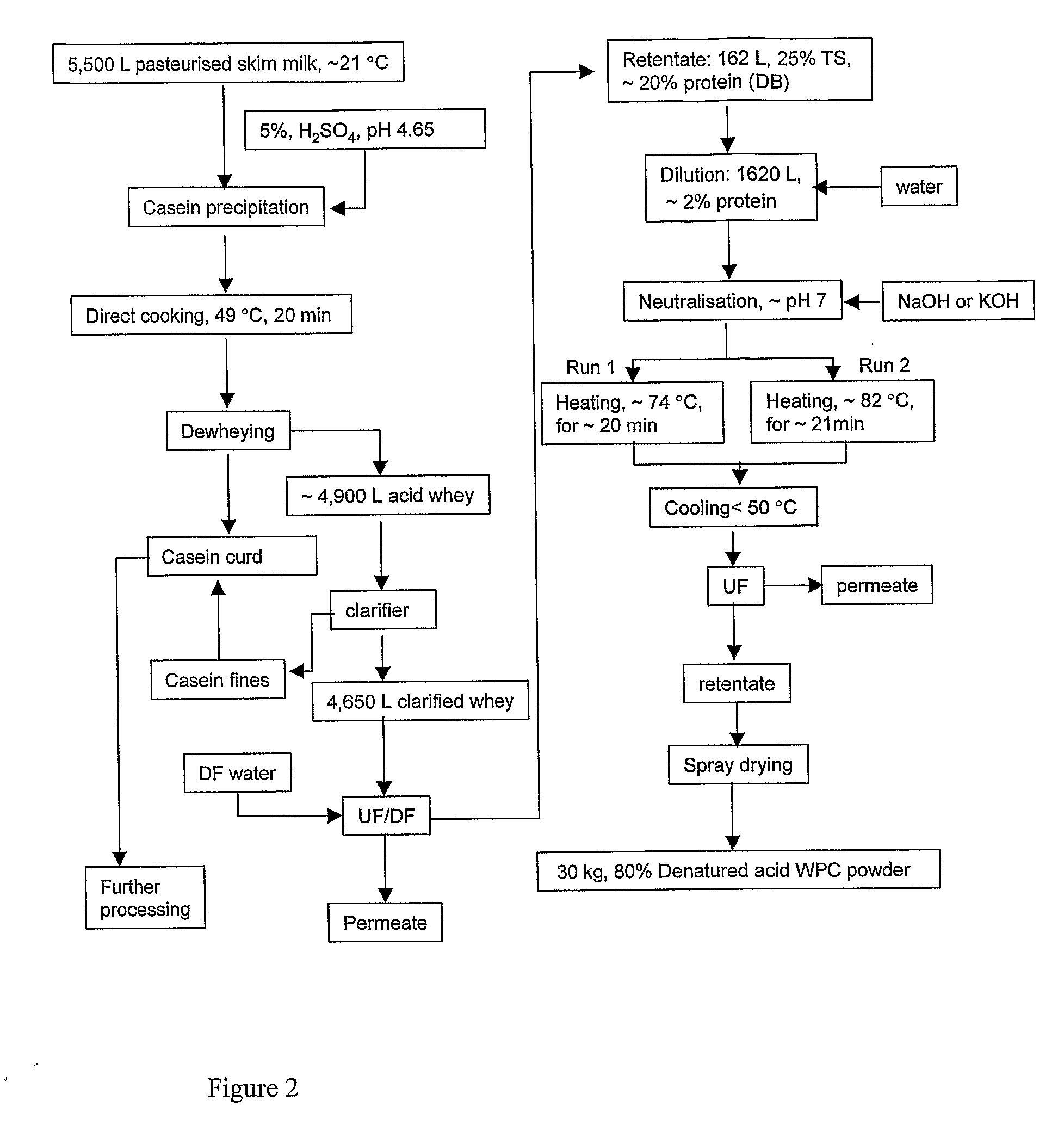
Whey Product and Process
InactiveUS20080305235A1High viscosityHigh in proteinMilk preparationFood ingredient as viscosity modification agentWhey proteinSurface heat
The invention provides a process for preparing a dried modified whey protein concentrate. A whey protein solution is used having less than 5% total solids and a combined calcium and magnesium concentration of less than 70 mmol / kg on a dry basis and a pH of 6.0-7.5. It is heated to greater than 70° C. for up to 60 minutes to denature the whey protein. The solution is then cooled to 40° C.-60° C.; and subsequently spray dried. Alternatively a higher initial concentration of total solids may be used in an embodiment where the heating is carried out on a scraped surface heat exchanger.
Owner:FONTERRA COOP GRP LTD
Water gel containing natural high molecule and its radiation preparing method
InactiveCN1944495AImprove water absorptionGood flexibilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticCross-linkWound dressing
The present invention provides one kind of water gel containing natural high molecular material and its preparation process. The water gel has cross-linking degree of 70-95 % and water absorption of 500-80000 %, and contains natural high molecular material or its derivative selected from chitin, chitin derivative, chitosan, chitosan derivative, carrageenin, etc. The water gel may have synthetic high molecular material, inorganic filler, cross-linking sensitizer, medicine and other assistant added. It is prepared through radiation cross-linking, with the radiation dosage being 10-40 kGy. The water gel of the present invention has high water absorption, high flexibility, good medicine slow releasing performance, and may be used in wound dressing, etc.
Owner:厦门凝赋生物科技有限公司
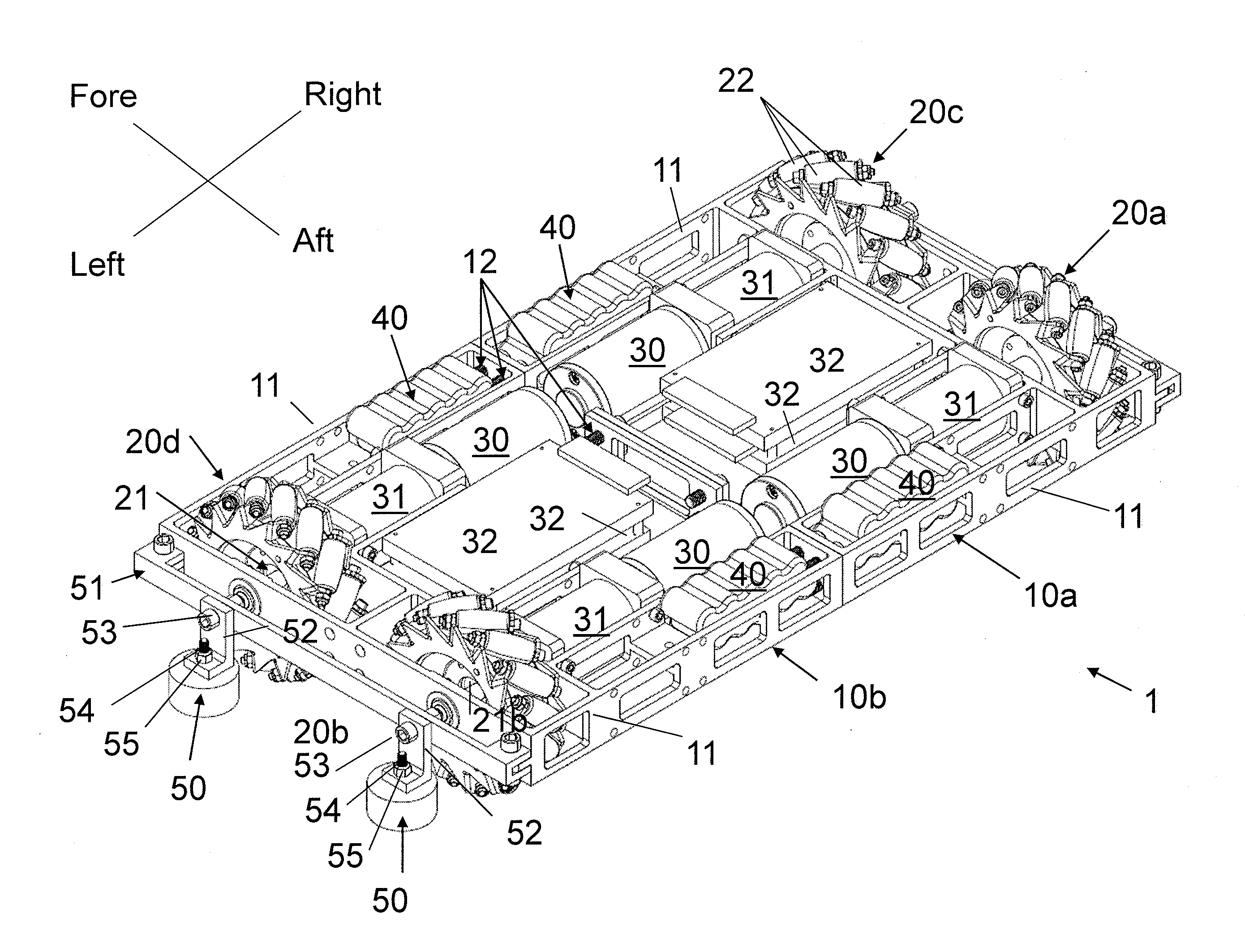
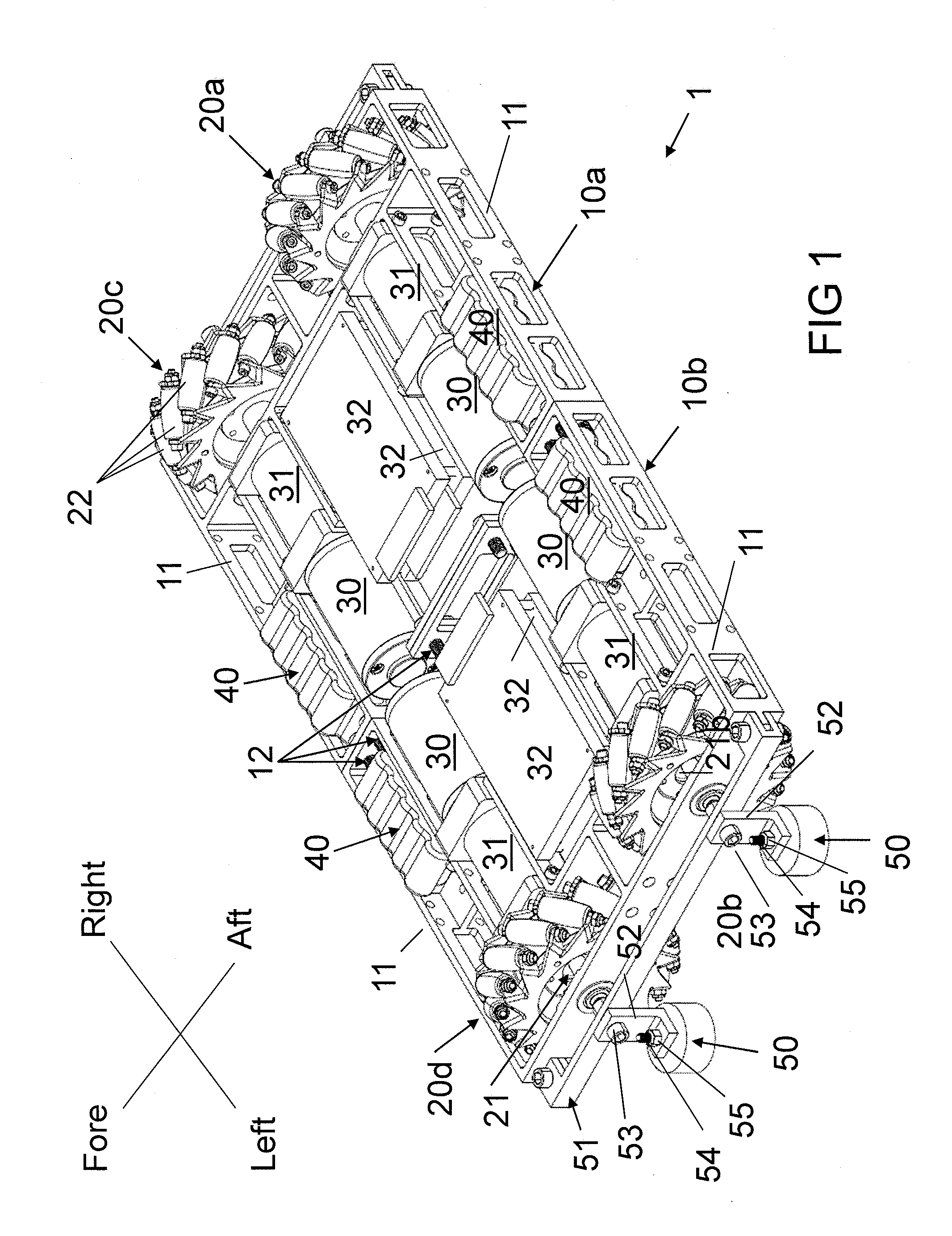
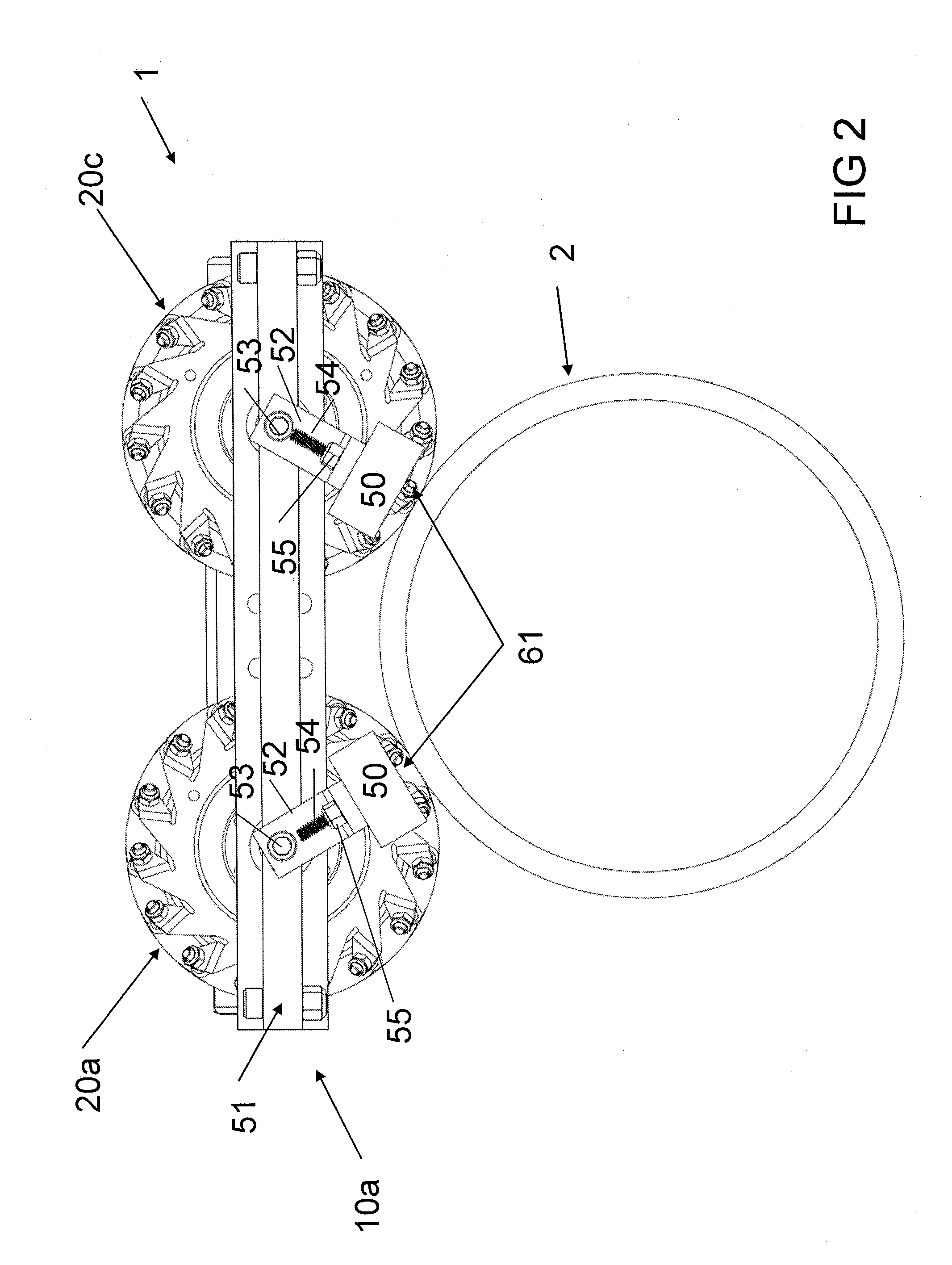
Mobile robot
ActiveUS20130140801A1Effective and efficient movementPromote sportsDeflectorsWheel adhesionCouplingControl system
A mobile robot configured to be widely versatile in its use. For example, the mobile robot can be configured for being used on a wide assortment of surfaces, regardless of the orientation and / or shape of the surfaces. Alternatively or in combination, the mobile robot can be configured for effective and efficient movement on the surfaces it traverses. In some cases, the mobile robot is configured with two or more component units. In some cases, the component units are configured with magnets and a control system for orientating the magnets. In some cases, one or more component couplings join the component units. In some cases, the mobile unit is configured with Mecanum wheels.
Owner:HELICAL ROBOTICS
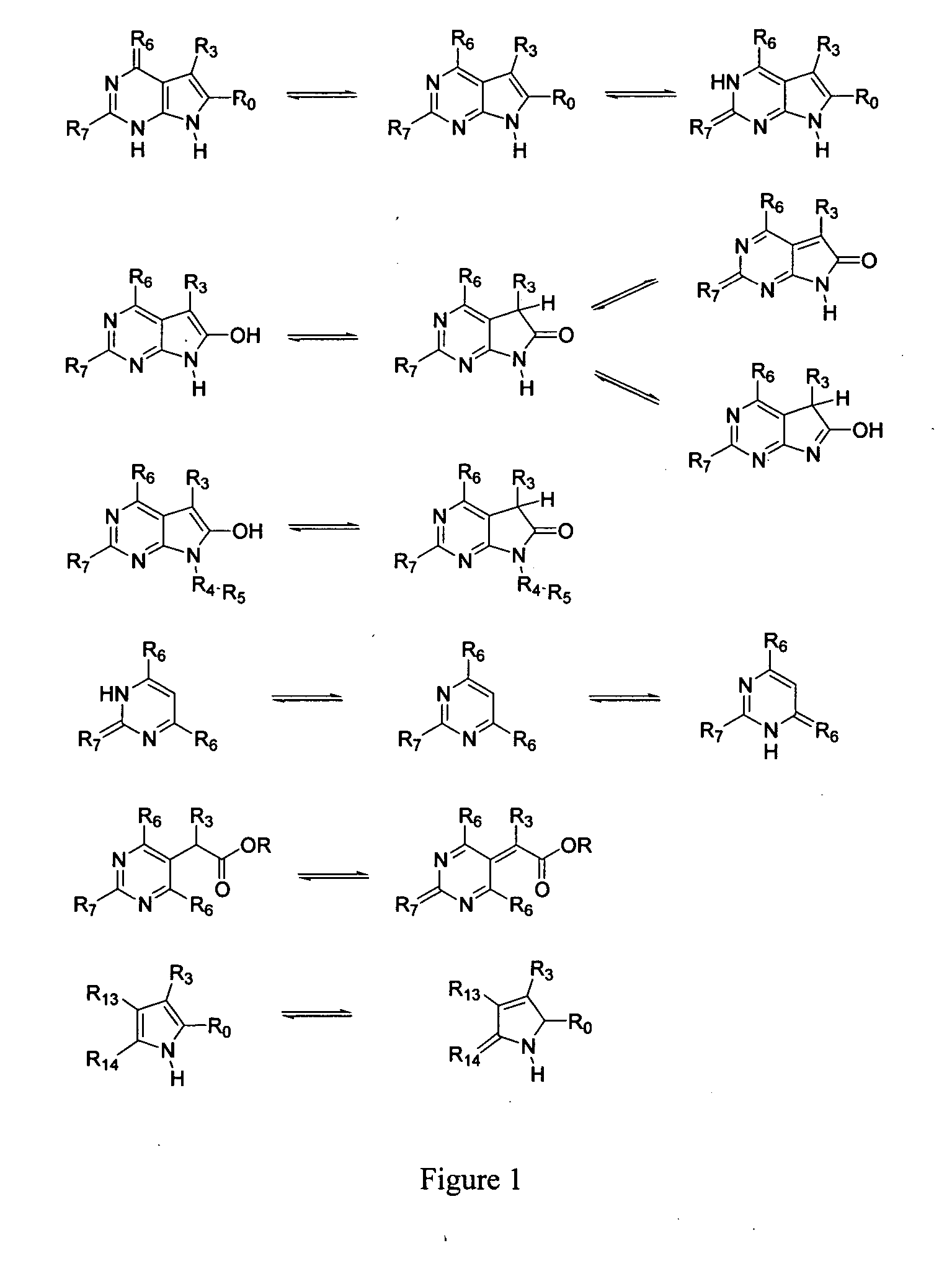
Pyrrolopyrimidines and related analogs as HSP90-inhibitors
ActiveUS20050107343A1Broad utilityWide range of usesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHsp Inhibitor
Pyrrolopyrimidines and related analogs are described and demonstrated to have utility as Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) inhibiting agents used in the treatment and prevention of various HSP90 mediated disorders, e.g., proliferative disorders. Methods of synthesis and use of such compounds are also described and claimed.
Owner:CONFORMAL THERAPEUTICS CORP (US)
Inorganic shaped bodies and methods for their production and use
InactiveUS6991803B2Overcome the lack of robustnessNovel featuresPowder deliveryDental implantsPorosityCellulose
Shaped, preferably porous, inorganic bodies are provided which are prepared from a reactive blend. In accordance with one preferred embodiment, the solution is absorbed into a porous sacrificial substrate such as a cellulose sponge. The solution-saturated substrate is heated and an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs thereby forming an inorganic solid. A shaped, inorganic body is formed in situ. Optional, but preferred additional thermal treatment of the shaped, inorganic body removes the organic substrate, leaving an inorganic body that faithfully mimics the porosity, shape, and other physical characteristics of the organic substrate. Inorganic substrates may also be used to good effect. Large varieties of shaped bodies can be prepared in accordance with other embodiments of the invention and such shapes find wide use in surgery, laboratory and industrial processes and otherwise. The invention also provides chemically and morphologically uniform powders, including those having uniformly small sizes.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
Supplying, dividing and feeding devices, cooking equipment and feeding method thereof
InactiveCN106419587ARealize feeding automationReduce labor workloadCooking-vessel lids/coversCooking vessel constructionsElectricityMating
According to the embodiment, the invention relates to the technical field of smart home, and discloses a feeding device of cooking equipment and the cooking equipment. The feeding device comprises a dividing device and a supplying device, wherein the dividing device adopts a worm or a disc provided with a charging groove; cooking raw materials in a storage box are supplied to a supplying device; and the dividing device and the supplying device are separated when the cooking raw materials are weighed. According to the supplying device, the cooking raw materials are conveyed into a pot body of the cooking equipment by virtue of a wind power device / vacuum device, or by virtue of a horizontal worm in a horizontal conduit and through self-gravity of the cooking raw materials, so that automatic feeding of the cooking equipment is achieved and workload of a user is reduced; a multipurpose mating device is provided for a plurality of intelligent home products, and a foundation is created for intelligent kitchen appliances or the smart home. The dividing device is applicable to such intelligent cooking equipment as an electric cooker, a bread maker, a frying machine, a soybean milk making machine, a bean curd machine, a stirrer, a coffee machine or a tea maker and the like.
Owner:李亚锐
Bioactive spinal implant material and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6987136B2High strengthGreat advantageImpression capsSurgical adhesivesMedicineSpinal implant
Bioactive spinal implant materials having optimized radiopacity, stiffness, and bioactivity properties for formulation of shaped bodies capable of withstanding large dynamic, compressive loads are provided. The invention also provides methods of making the optimized implant materials.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
Optical system
ActiveUS8203702B1Reduce frictionEnormous difference potential speedAngle measurementAdditive manufacturing apparatusBeam divergencePiston
Method / system locate external articles using source, detector (PSD), entrance aperture, and magnifying / reducing afocal element—expanding FOR>90°, or refining precision. Between (1) source or detector and (2) aperture, at least one plural-axis-rotatable mirror addresses source / detector throughout FOR. ½- to 15-centimeter mirror enables ˜25 to ˜45 μradian beam divergence. Aperture, afocal element, and mirror(s) define source-detector path. Mirror(s) rotate in refractory- (or air / magnetic-) bearing mount; or mirror array. Auxiliary optics illuminate mirror back, monitoring return to measure (null-balance feedback) angle. To optimize imaging, auxiliary radiation propagates via splitters toward array (paralleling measurement paths), then focusing on imaging detector. Focal quality is developed as a PSF, optimized vs. angle; stored results later recover optima. Mirror drive uses magnet(s) on mirror(s). “Piston” motion yields in-phase wavefronts, so array dimensions set diffraction limit. Also: destructive reply; scaling optimizes acceleration vs. thickness; passive systems.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Apparatus and method for releasing a measured amount of content from a container
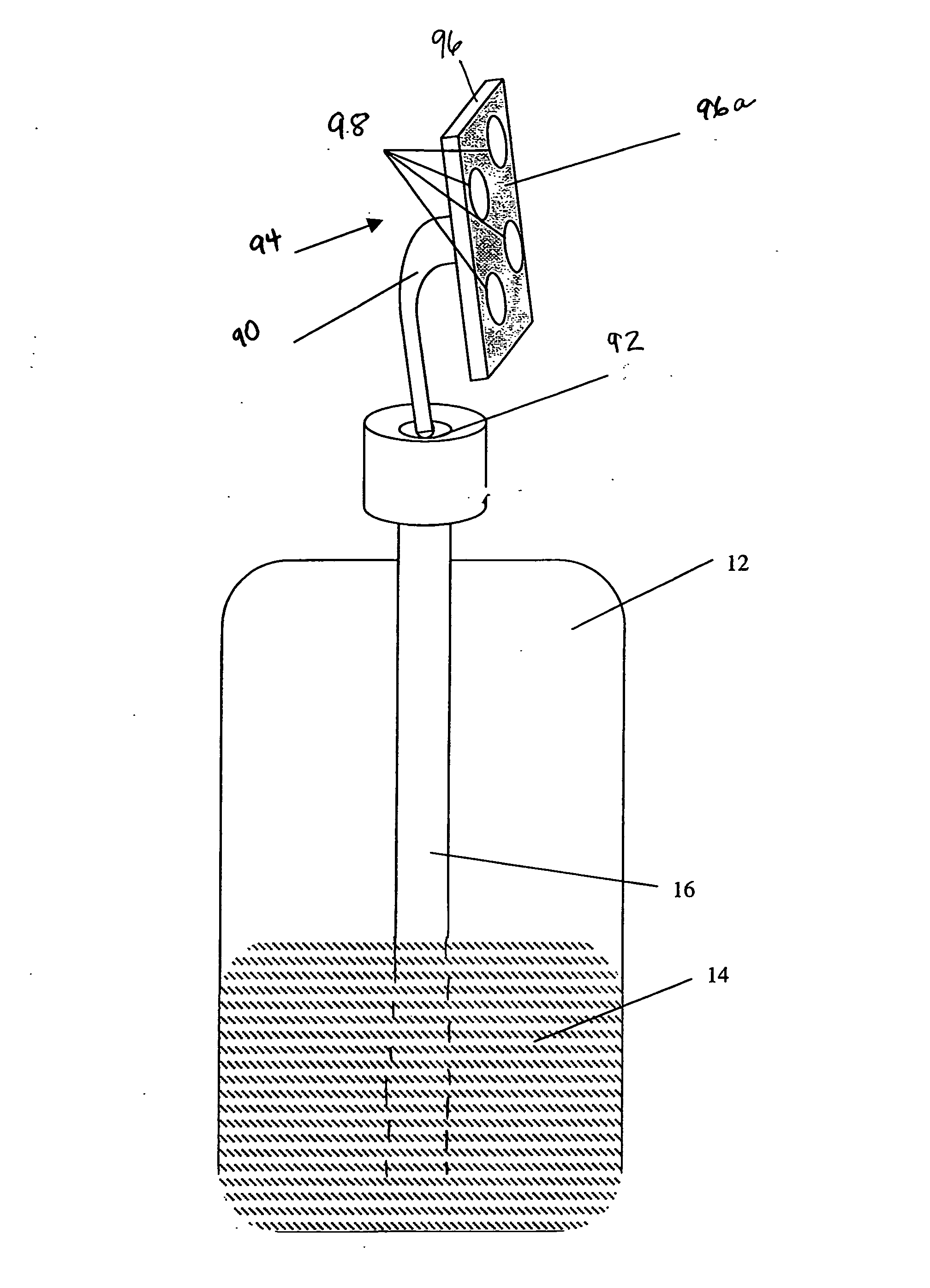
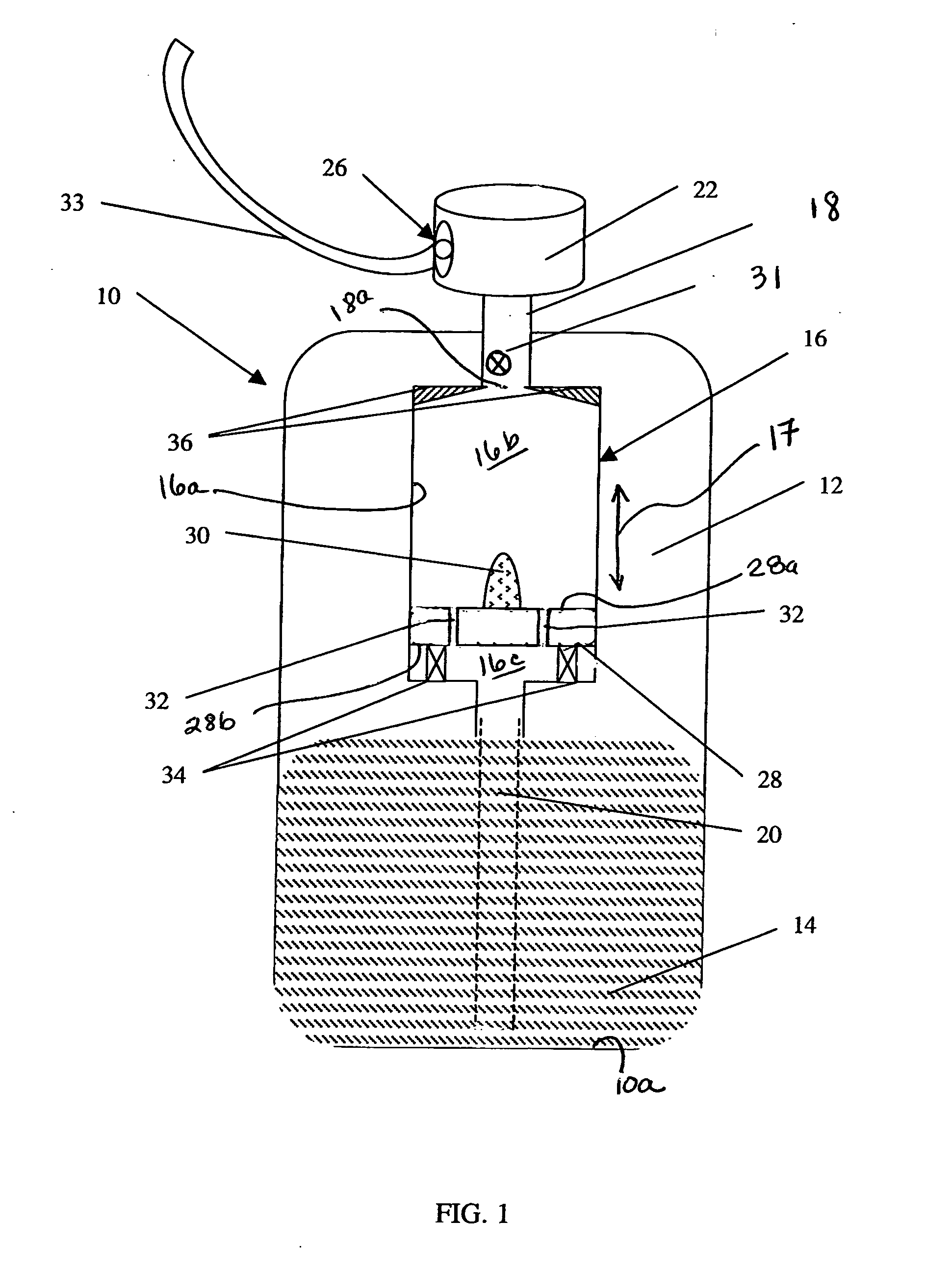
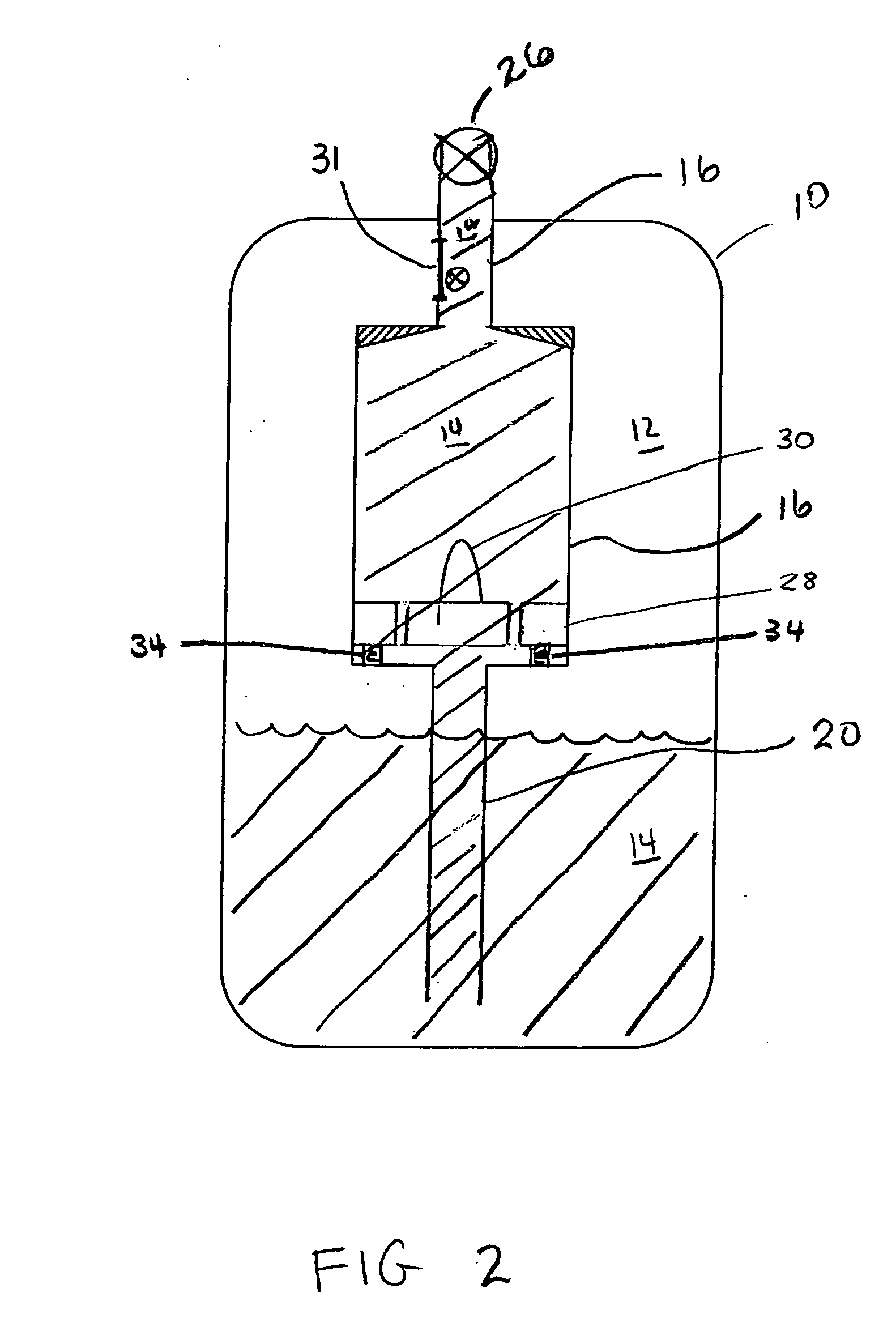
InactiveUS20060285912A1Easy to adaptVersatile in useBrushesPackaging toiletriesRest positionEngineering
Owner:FOAMIX PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Composite shaped bodies and methods for their production and use
InactiveUS20050042288A1Increase productionLow process temperatureDental implantsPowder deliveryCalcium biphosphatePlastic surgery
Shaped, composite bodies are provided. One portion of the shaped bodies comprises an RPR-derived porous inorganic material, preferably a calcium phosphate. Another portion of the composite bodies is a different solid material, preferably metal, glass, ceramic or polymeric. The shaped bodies are especially suitable for orthopaedic and other surgical use.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
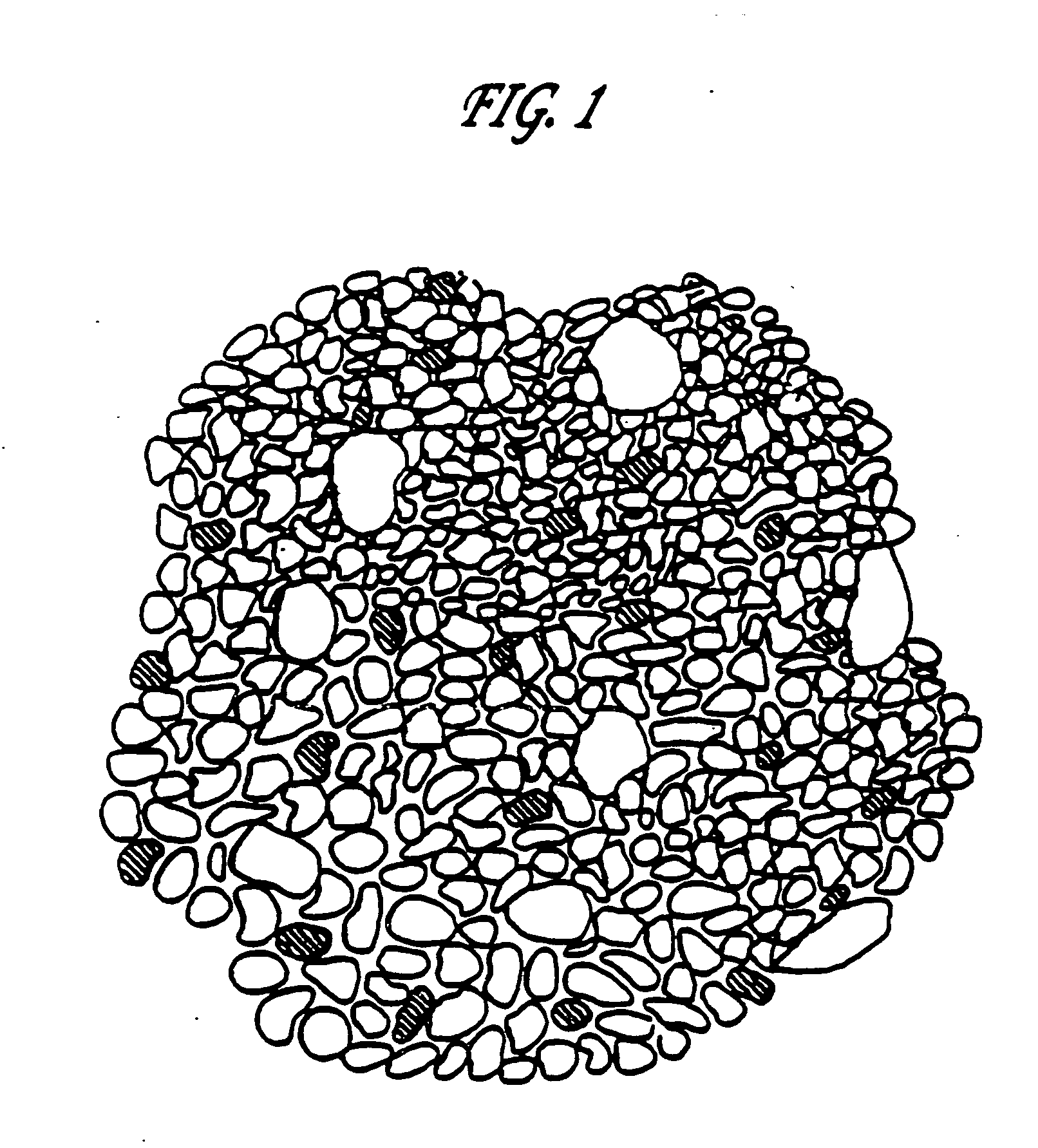
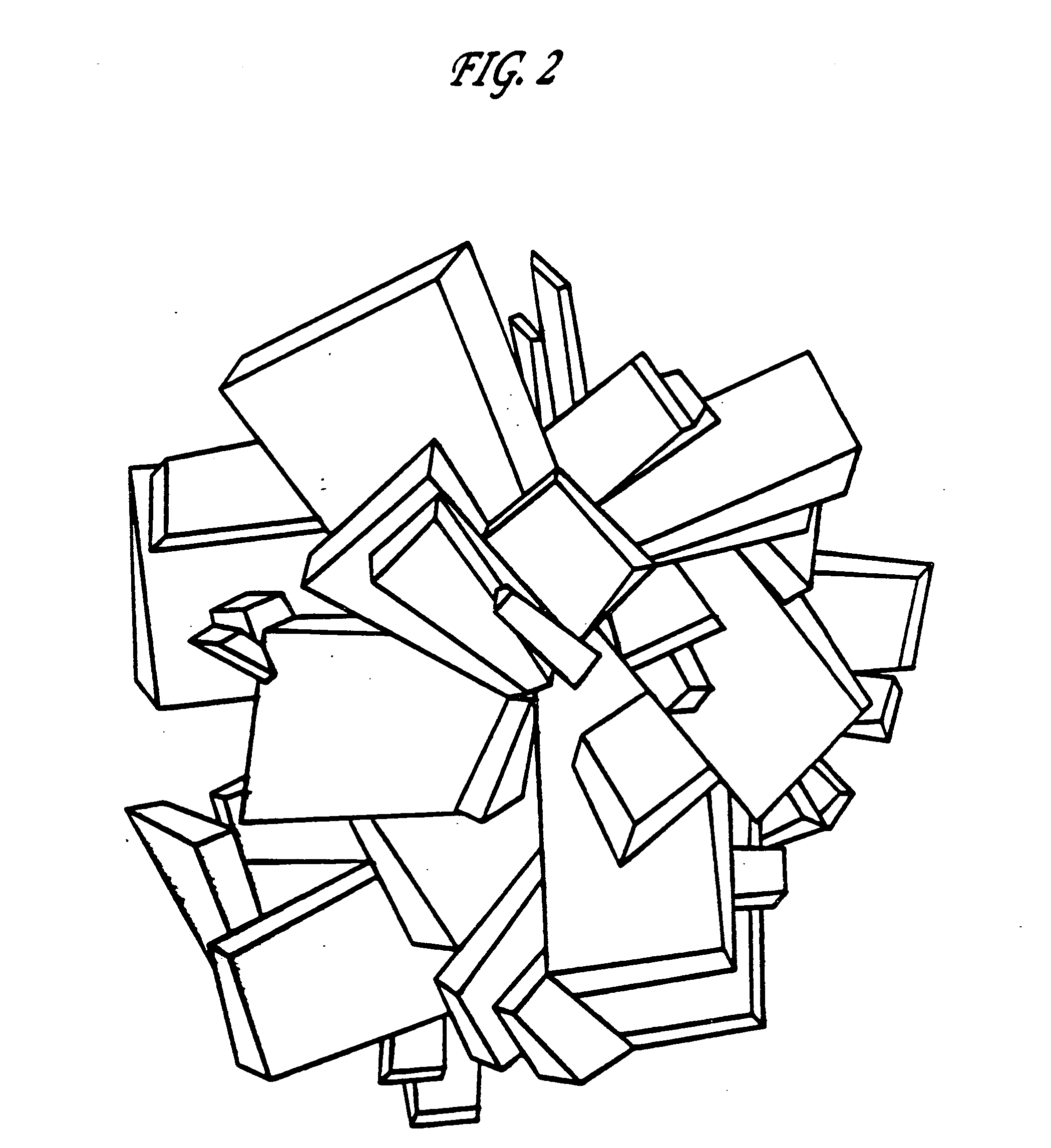
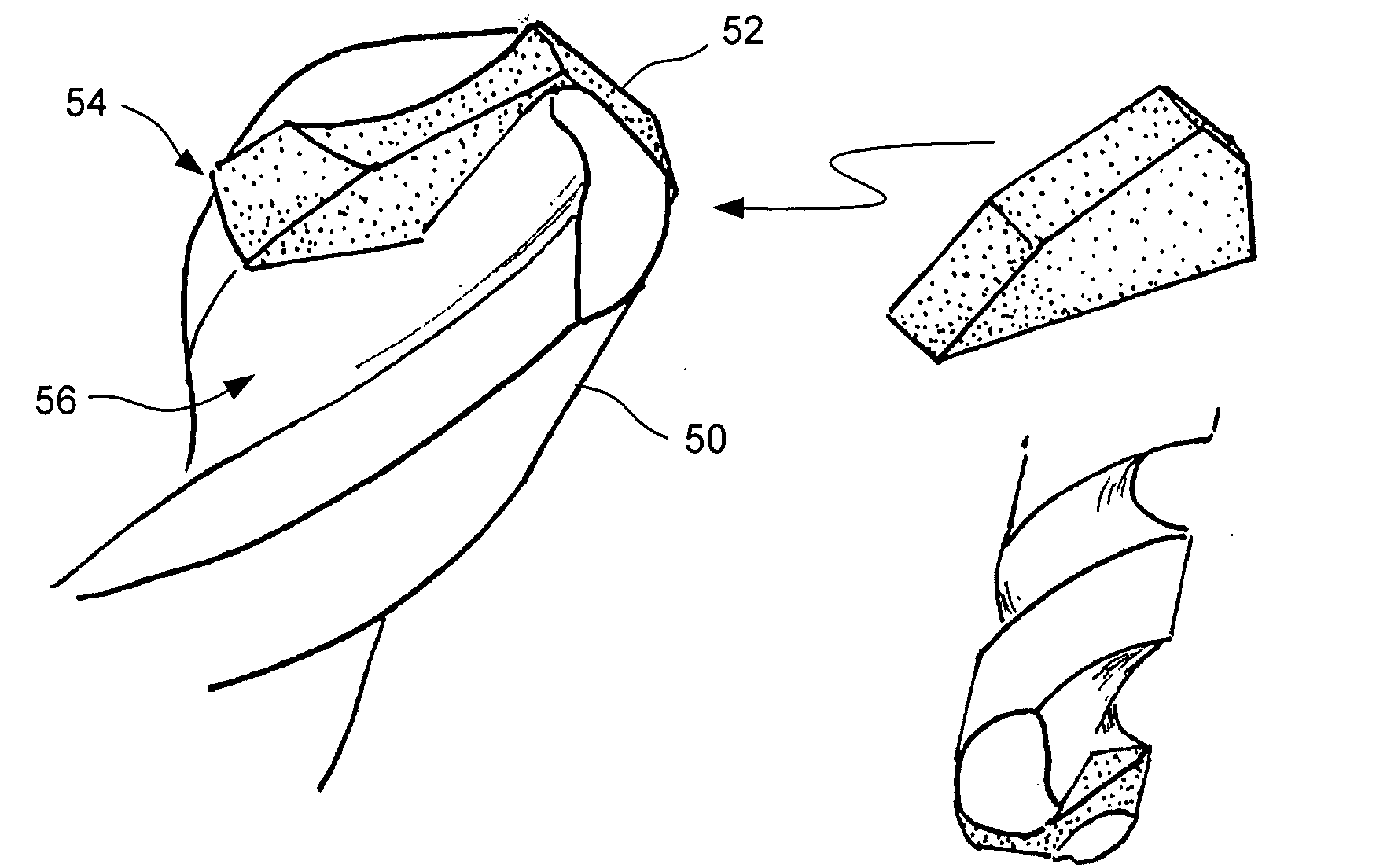
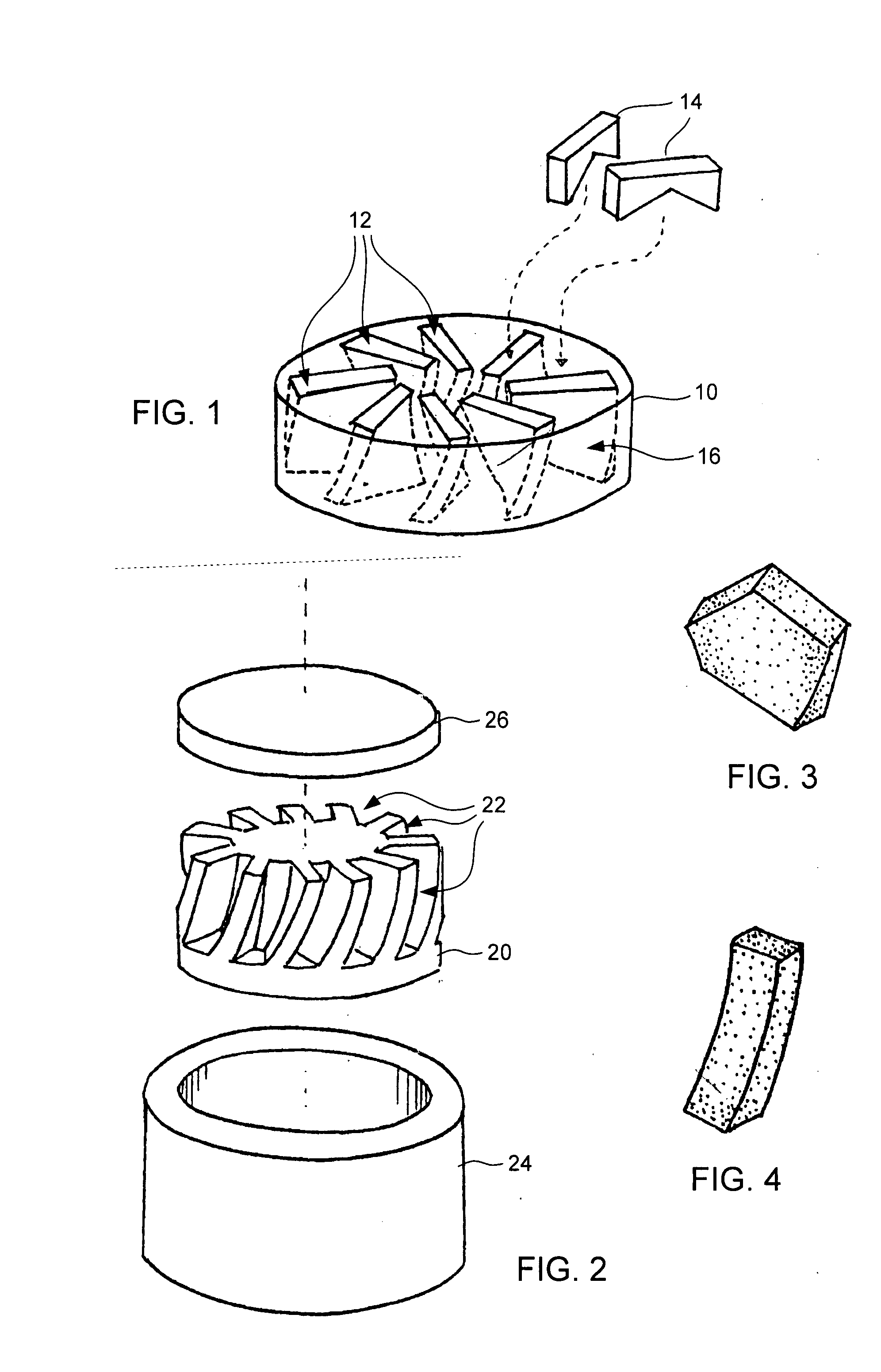
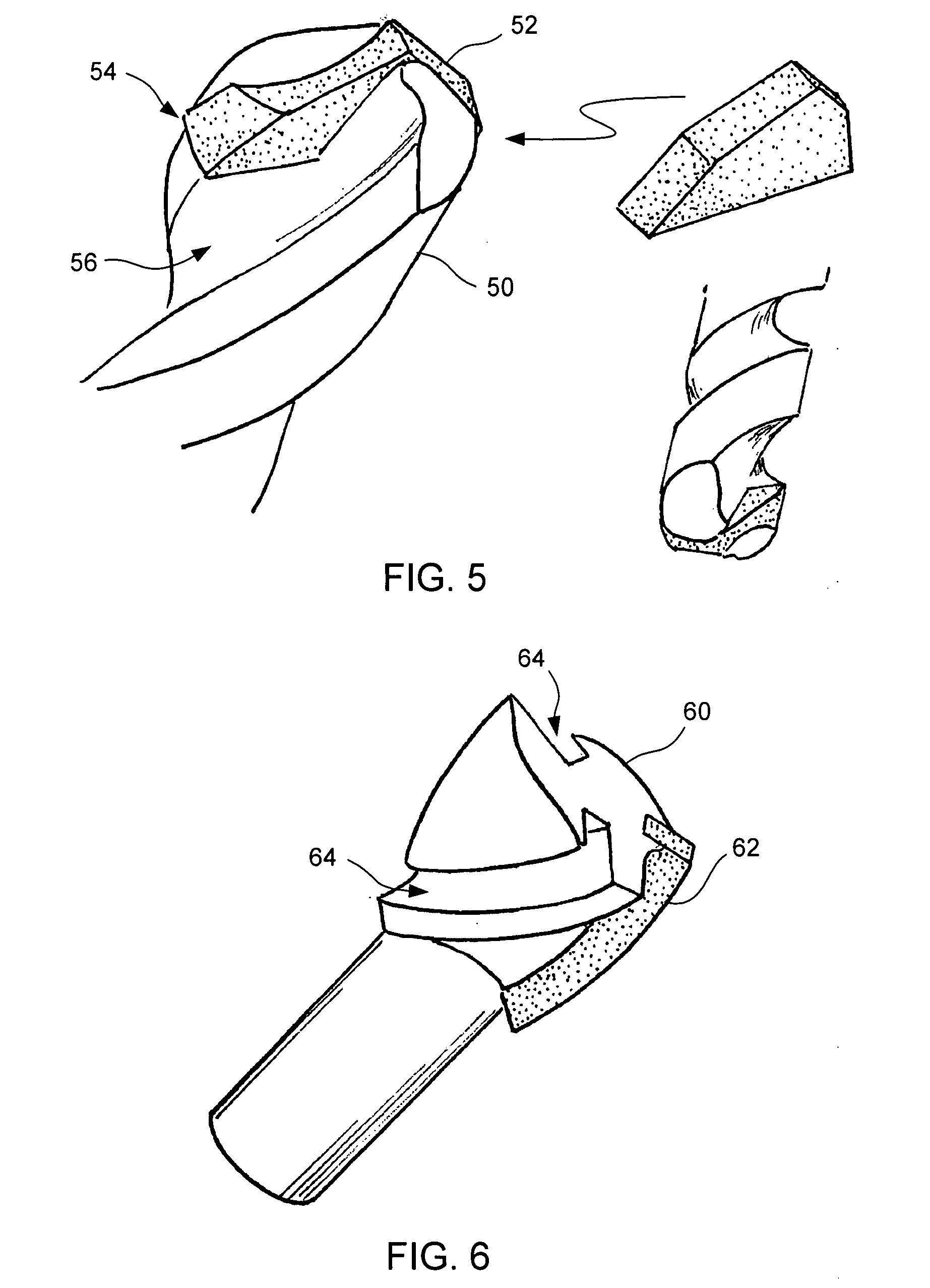
Contoured PCD and PCBN for twist drill tips and end mills and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20080247899A1Easy to provideLess grinding timePigmenting treatmentAdditive manufacturing apparatusMilling cutterMaterials science
Contoured solid polycrystalline superabrasive material such as twist drill tips and endmill flank segments can be formed by preparing a precursor mold having a plurality of shaped openings each corresponding to a predetermined shape. A specially prepared charge feed can be placed into the shaped openings to form a charged precursor. The charge feed can include a substantially homogeneous mixture of superabrasive source particulates, sintering binder, and optional inorganic bonding medium. A loaded reaction cup-assembly including the charged precursor can be subjected to a pressure, temperature and time sufficient for sintering and formation of the contoured polycrystalline superabrasive material. Reduced finishing steps and increased tailorability of grade and quality of final polycrystalline products can be readily achieved.
Owner:CHO H SAM +4
Specimen-container rack for automated clinical instrument
ActiveUS20050194333A1Easy to transportWide range of usesBottle cupboardsMaterial analysisTransport systemClassical mechanics
A magnetically-attractive specimen-container rack for use with a magnetic transport system for transporting racks of specimen-containers to or within an automated clinical instrument for analysis and / or processing. The specimen-container rack comprises a pair of U-shaped magnetically-attractive members mounted in the base section of the rack housing so that the distal ends of such members extend towards the base of the rack and terminate in a plane slightly short of the plane in which the rack is supported for movement atop a rack-supporting surface. Such members are adapted to cooperate with similarly-shaped permanent magnets carried by an X / Y-movable truck that underlies a non-magnetic rack-supporting plate. Other features of the rack include a pair of side-pockets formed in one side of the rack in the vicinity of the end walls of the rack housing, such pockets serving to receive a movably-mounted member associated with a linear drive mechanism by which the rack can be physically advanced edgewise along a linear path; and notch structure by which the rack can be releasably engaged by a movably-mounted plate which serves to lift and invert the rack to effect mixing of contained specimens.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
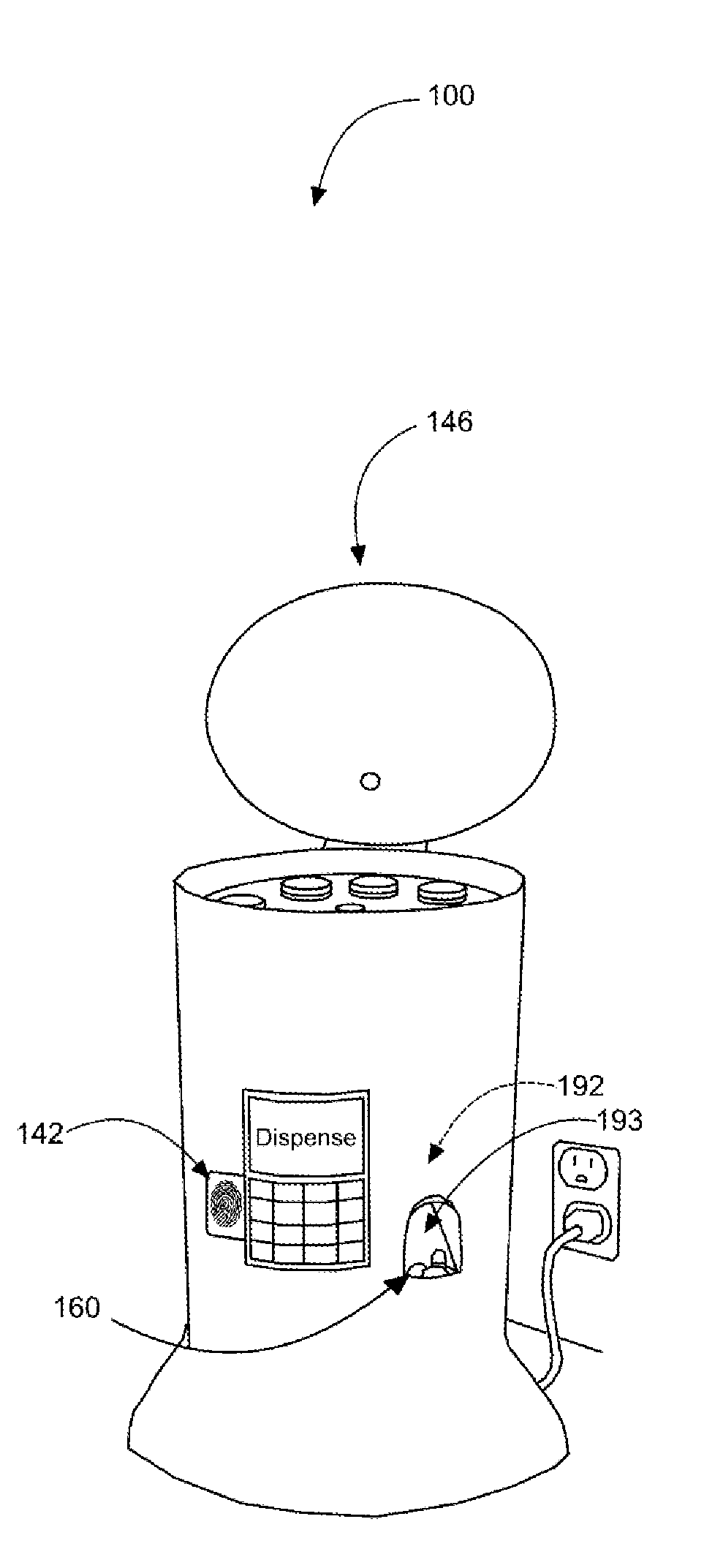
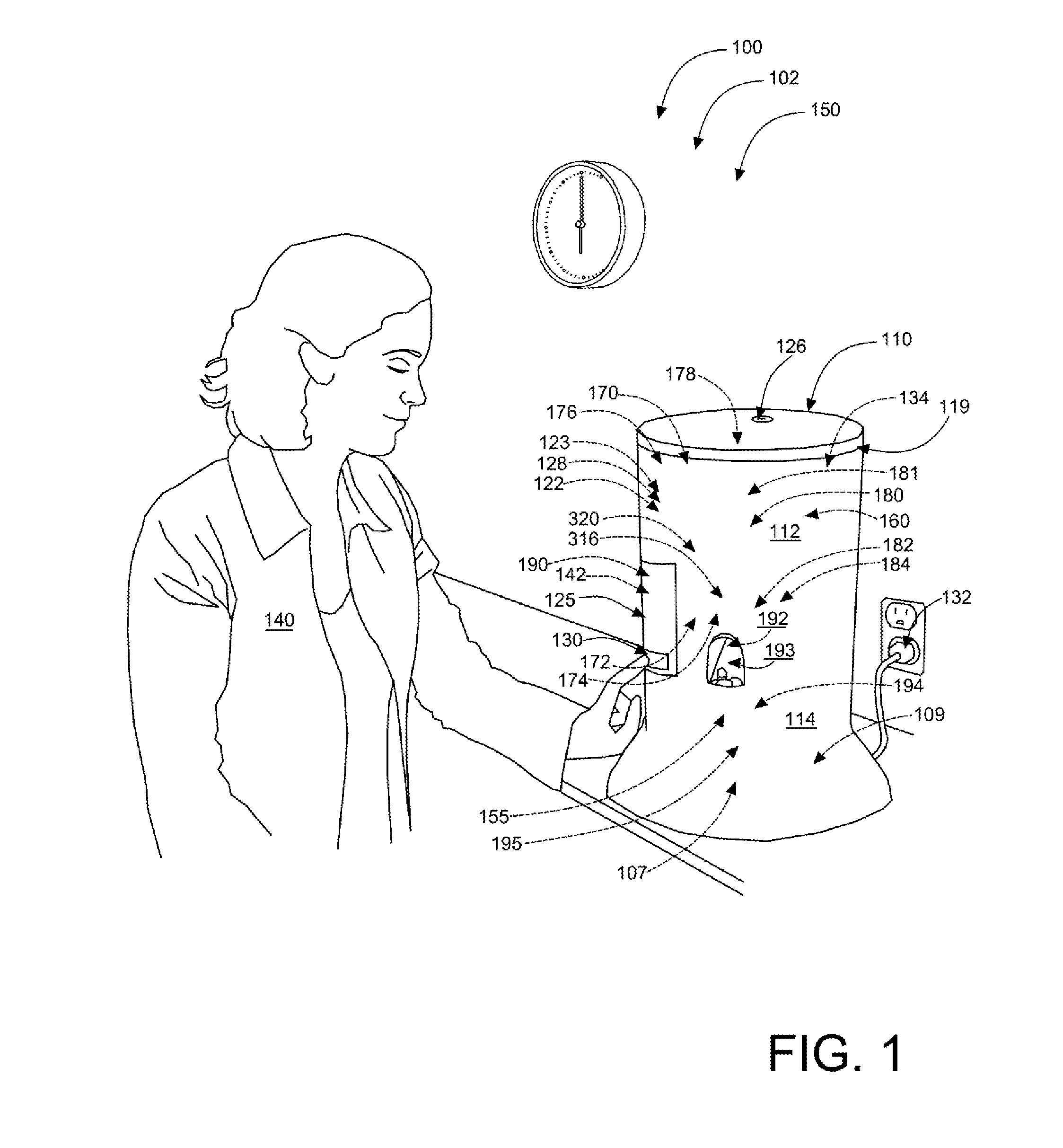
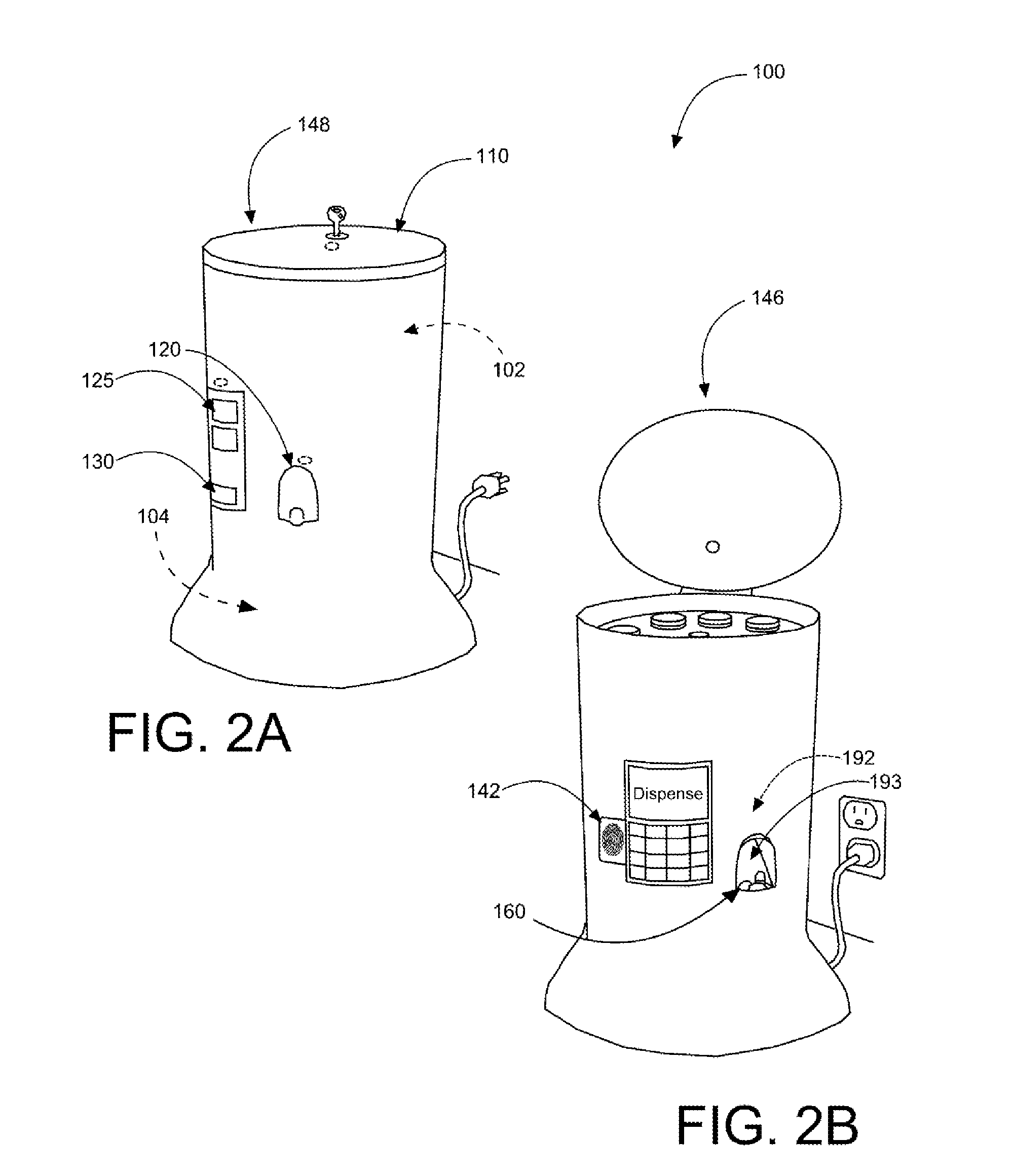
Prescription medication security and dispensing systems
InactiveUS20160158107A1Avoid misuseEfficient use ofSmall article dispensingCoin-freed apparatus detailsDispensing medicationsMedication Prescriber
A prescription drug monitoring / dispensing device ensures prescription medication housed within is taken only as directed, and not abused or sold on the streets. The device serves as an intricately guarded casing that may only dispense the preprogrammed dosage amounts at preset times, as directed by a prescribing physician. The device may include a housing having a biometric finger scanner and a display screen in communication therewith, a loading tube capable of holding a pill therein, a rotating hub in communication with the loading tube, a rotating disc in communication with the loading tube, and an exit port capable of dispensing the pill out from the housing.
Owner:DVORAK SHERI +1
Method for preparing environment-friendly type organosilicon modified acrylic ester binding agent
InactiveCN101423735APromote environmental protectionImprove stabilityFibre treatmentEster polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The invention relates to a method for preparing an environment-friendly silicone-modified acrylate adhesive. Raw materials of the preparation method comprise a basic monomer, a modified monomer and an auxiliary agent, wherein the basic monomer comprises a hard monomer, a soft monomer and a crosslinking monomer; the modified monomer comprises a silane monomer, a coupling agent and inorganic nano-powder; the crosslinking monomer is glycidyl acrylate or glycidyl methacrylate; and the grain diameter of the inorganic nano-powder is less than 80 nanometers. In the preparation method, the crosslinking monomer adopts the glycidyl acrylate or the glycidyl methacrylate so as to be environment-friendly. The product prepared by the method is a nanometer / silicone double-modified molecular composite polymer material. The molecular composite material is combined with the advantages of two polymer materials, namely silicone and polyacrylic ester and an inorganic nanometer material, and has better performance and broad application.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Ferment making black garlic method
InactiveCN101120783ASolve the smellSolve the discomfortFood preparationSocial benefitsNutritive values
The present invention relates to a black garlic manufacturing method through fermentation, which can effectively solve the problem of peculiar smell or discomfort of garlic. The technical proposal is as following. Firstly, far infrared heating device is used to produce anion. Secondly, garlic is marinated in the garlic fermentation inducing medium. Thirdly, after the garlic is fished out, the garlic is put into the far infrared heating device. Fourthly, the garlic is heated and fermented step by step. And lastly, the black garlic is made. The garlic fermentation inducing medium is made by the following components based on weight-volume percent: salt 8.6 percent, ethanol 4.1 percent, amino acids 3.1 percent, protein 0.6 percent, sugar 12.4 percent, ash content 7.9 percent, lipid 0.02 percent and water for the rest. The present invention has simple method, good garlic processing effect. After procession, the garlic has no peculiar smell, is convenient to eat, has high nutritive value, is used widely, and has great economic and social benefits.
Owner:北村清彦 +1
2-Aminopurine analogs having HSP90-inhibiting activity
2-Aminopurine analogs are described and demonstrated or predicted to have utility as Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) inhibiting agents in the treatment and prevention of various HSP90 mediated disorders, e.g., proliferative disorders. Method of synthesis and use of such compounds are also described and claimed.
Owner:CONFORMAL THERAPEUTICS CORP (US)
Polymerized thylene carbonate urethane elastomer and its preparation method
ActiveCN1865311AMolecular chain softRoom temperature and good flexibilityCross-linkMedical equipment
The invention discloses a polyethylene carbonate polyurethane elastomer and making method, which produces polycarbonate polyhydric alcohol through carbon dioxide and oxirane with 20-60 percent diisocyanate, 0.05-2 percent polymerization inhibitor, 2.4-17 percent chain-extending agent and or cross linking agent and 0-0.4 percent catalyst. The method possesses better mechanic property, plasticity, anti-oxidizing property and water weakened-durability, which can be applied in the liner, screen, sealing ring and medical equipments.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGKE JINLONG CHEM
Water system chargeable sodium-ion battery
InactiveCN103022577AIncrease energy densityImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
The invention discloses a water system chargeable sodium-ion battery system. The system uses a concept of a 'rocking chair battery' of a lithium ion battery; and the entire battery system is formed by using sodium-based prussian blue matter as an embedded anode, titanium sodium phosphate as an embedded cathode, and sodium-contained inorganic salt solution as electrolyte. The system has the advantages of high discharge voltage, large specific capacity, good rate capability, long cycle life and the like, and further has the characteristics of green and environmental friendliness, and high security and no pollution. The system very hopefully becomes an electrochemical stored energy system with low price and environmental friendliness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Identity certifying system based on intelligent card and dynamic coding
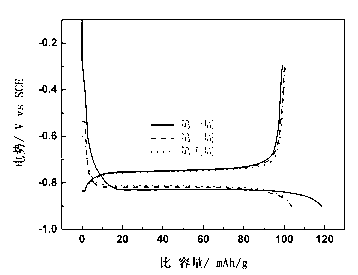
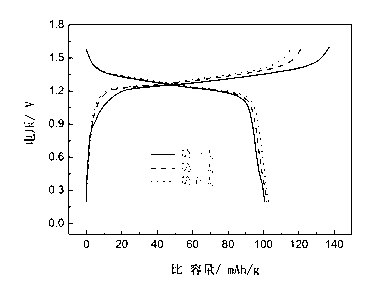
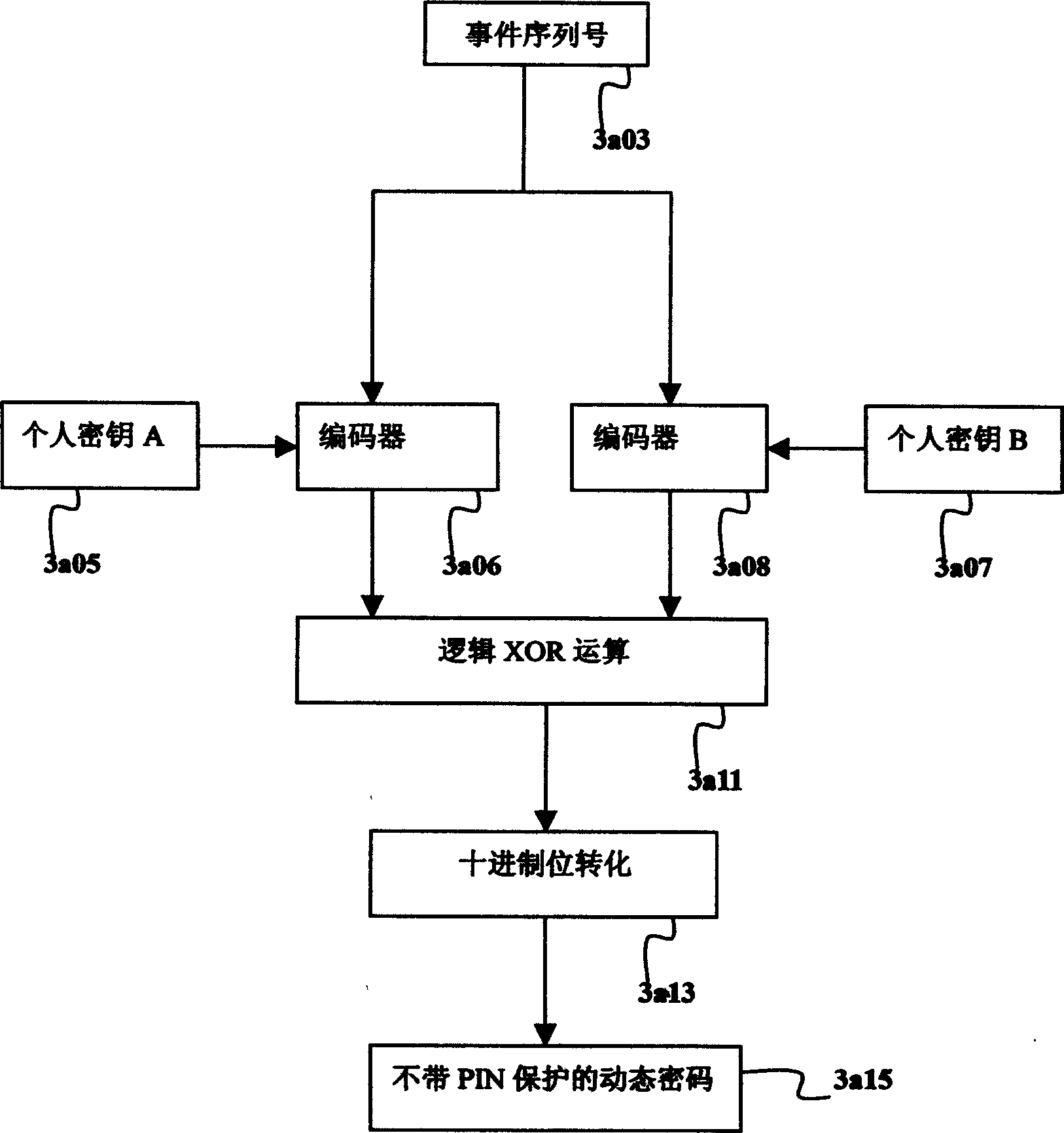
InactiveCN1614924AImprove securityLow costMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationFault toleranceSmart card
The system consists of smart card for generating one time password (OTP), device for creating OTP, authentication server, windows fault-tolerance authentication and synchronization method. The personal ID information and OTP are transmitted to authentication system through network. The authentication system selects one or more possible examining passwords from a large group of examining passwords to build up a smaller group of examining password. The received OTP is compared with the smaller group of examining password; if the OTP is in the smaller group the authentication of the use is passed.
Owner:王小矿
Stereotactic access devices and methods
ActiveUS20130053867A1Wide range of usesAccelerated trainingDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxisMedical device
This invention is directed to devices and methods for stereotactic access, and particularly to a frameless stereotactic access device for accessing a body cavity and methods therefor. In general, a stereotactic device may include portions or features for fixing the device to a portion of a patient's body, such as, for example, a skull, such that the device may be generally spatially fixed in relation to the patient's body or part thereof. The stereotactic device may also generally include portions or features for guiding a medical device or other device at a particular trajectory in relation to the patient's body or part thereof.
Owner:VISUALASE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com