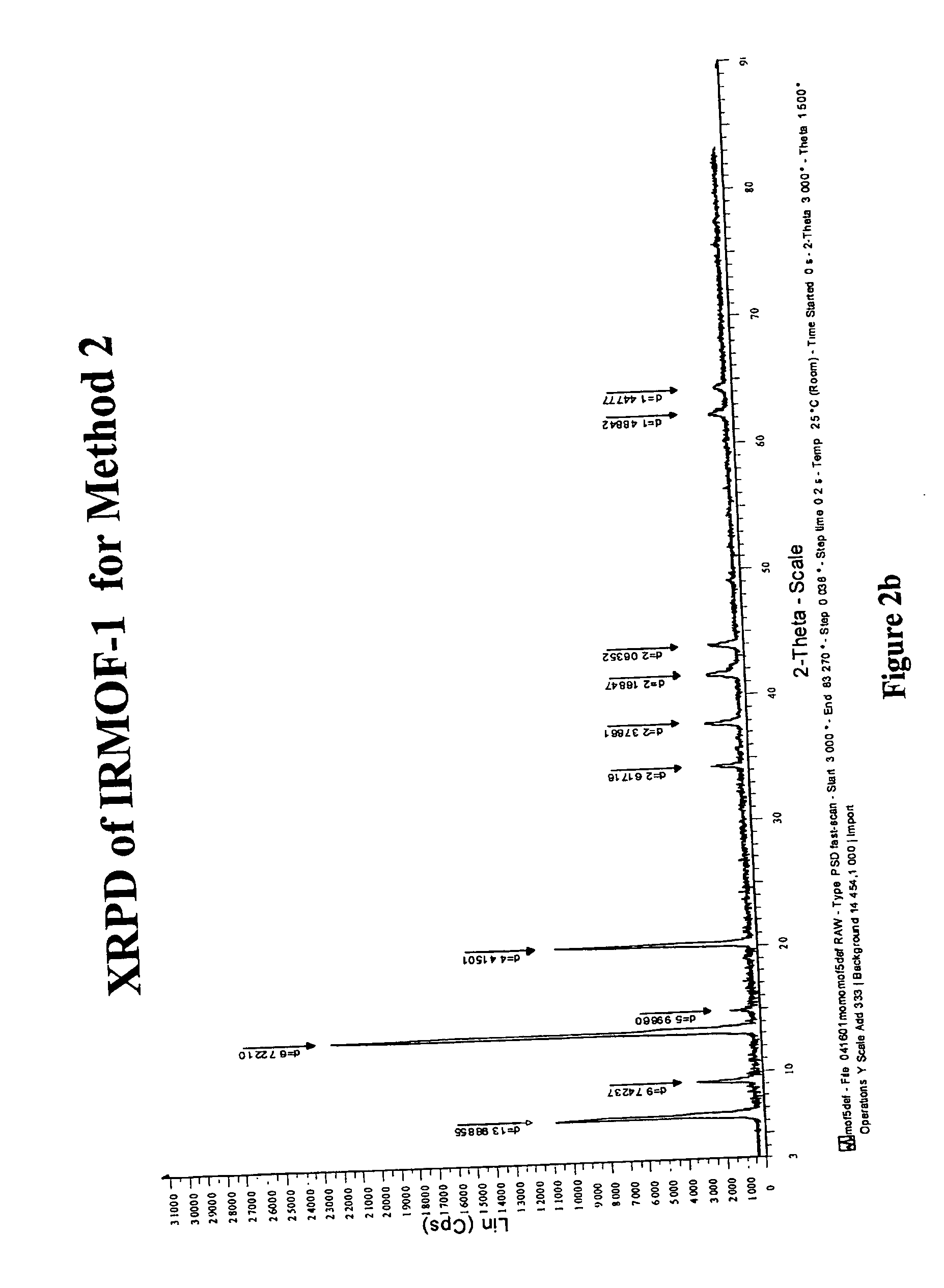
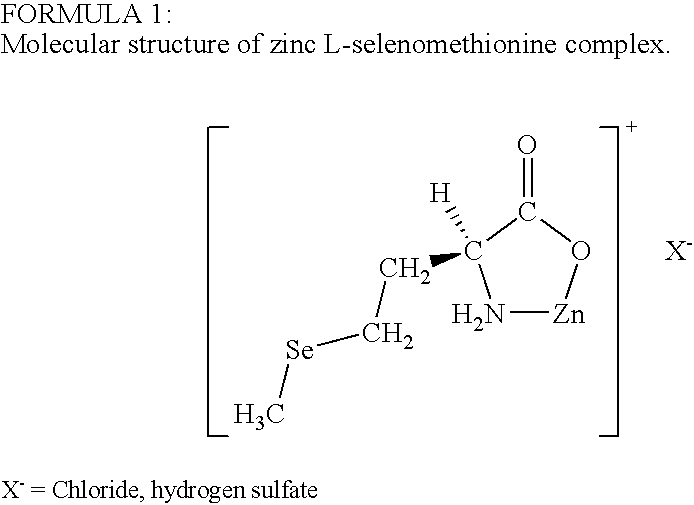Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1499results about "Zinc organic compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
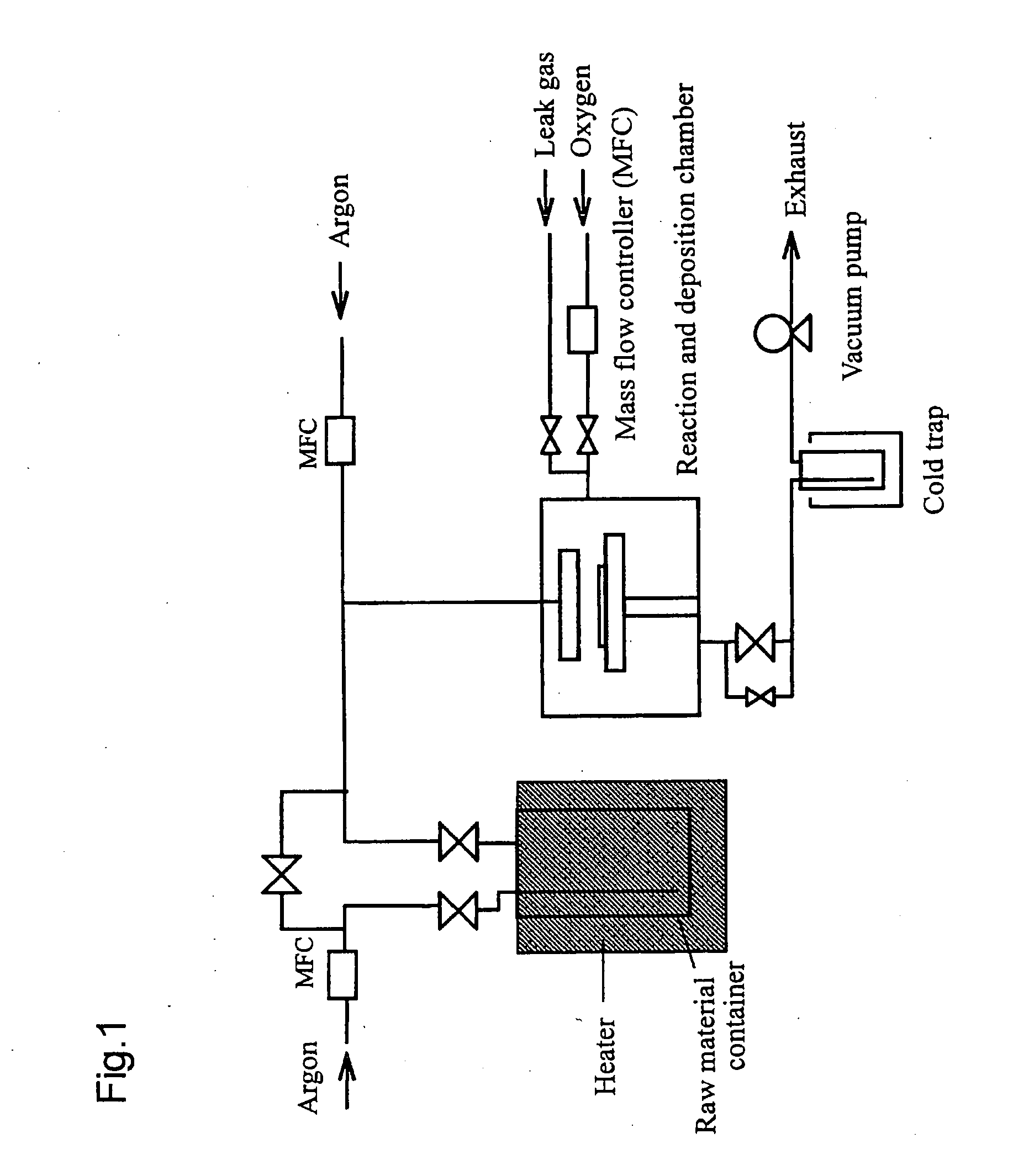
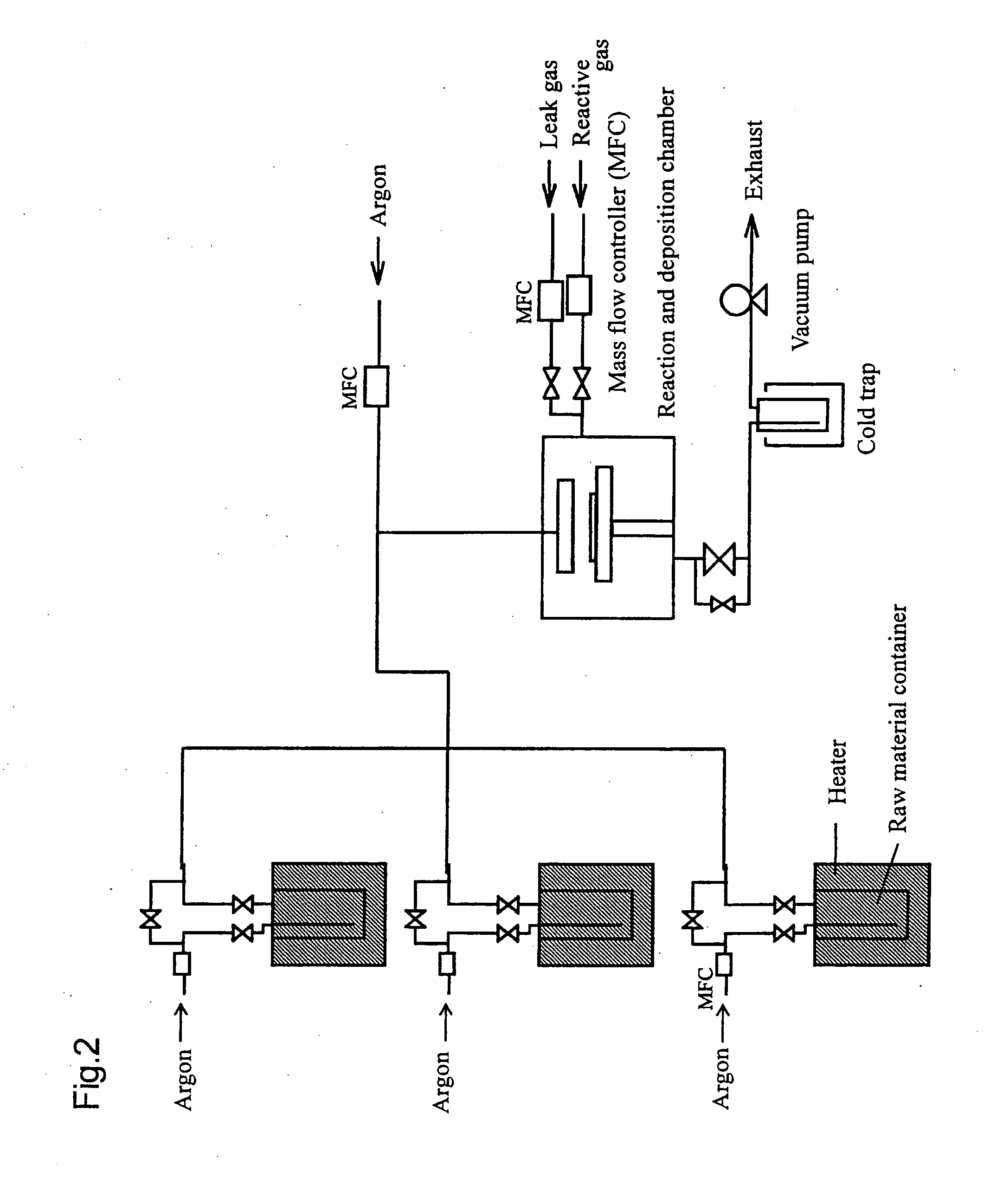
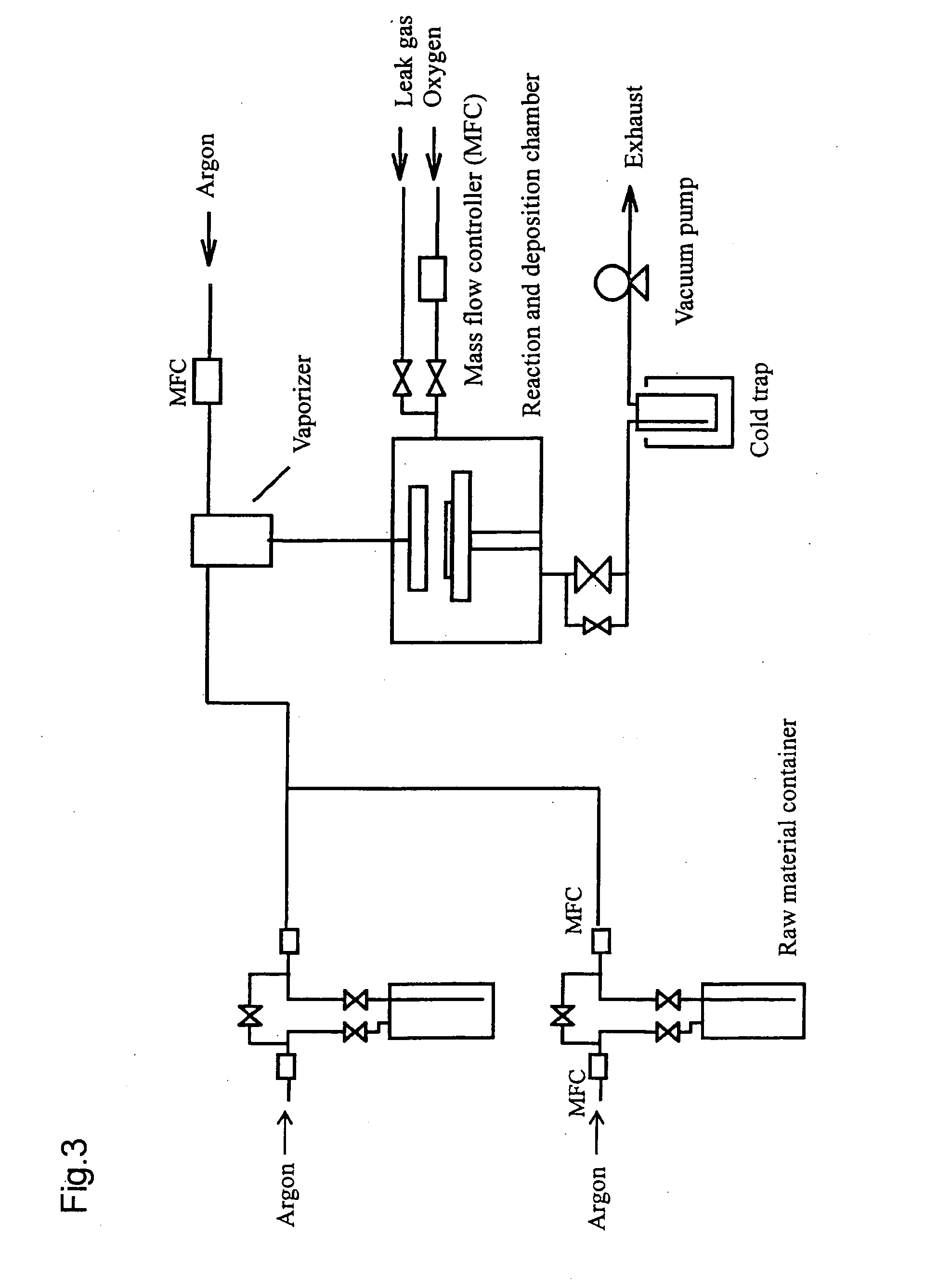
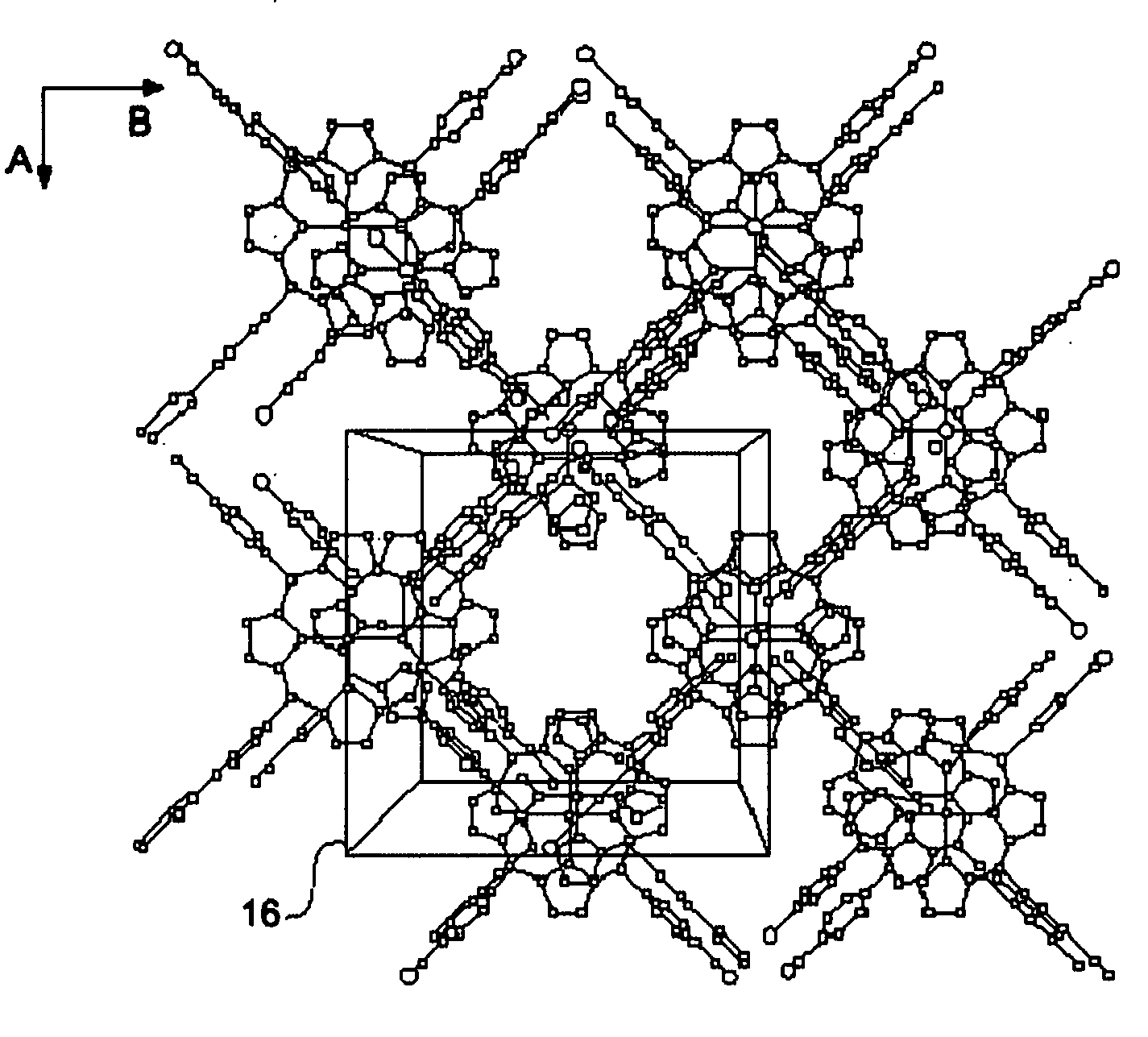
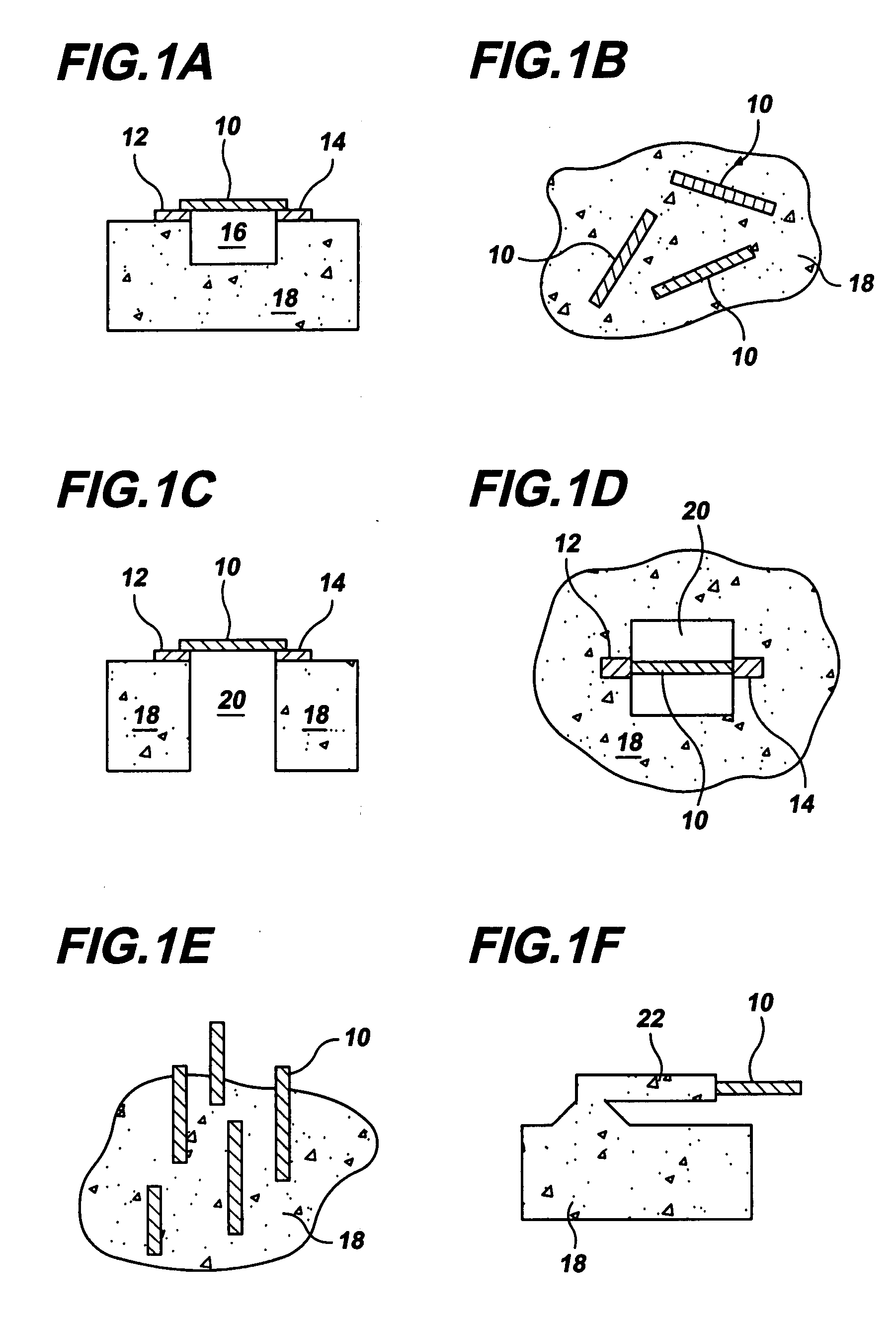
Thin film-forming material and method for producing thin film
InactiveUS20070178235A1Chemical vapor deposition coatingZinc organic compoundsZinc compoundsMaterials science
The thin film-forming material of the present invention comprises a bis(β-diketonato)zinc compound that is liquid at 25° C. and is suitable for forming a zinc-containing thin film. By using the thin film-forming material, a thin film can be produced with stable film-forming rate or stable film composition control without suffering from problems of raw material gas suppliability and in-line raw material transport. Preferred (β-diketonato)zinc compounds include, for example, bis(octane-2,4-dionato)zinc and bis(2,2-dimethyl-6-ethyldecane-3,5-dionato)zinc.
Owner:ADEKA CORP
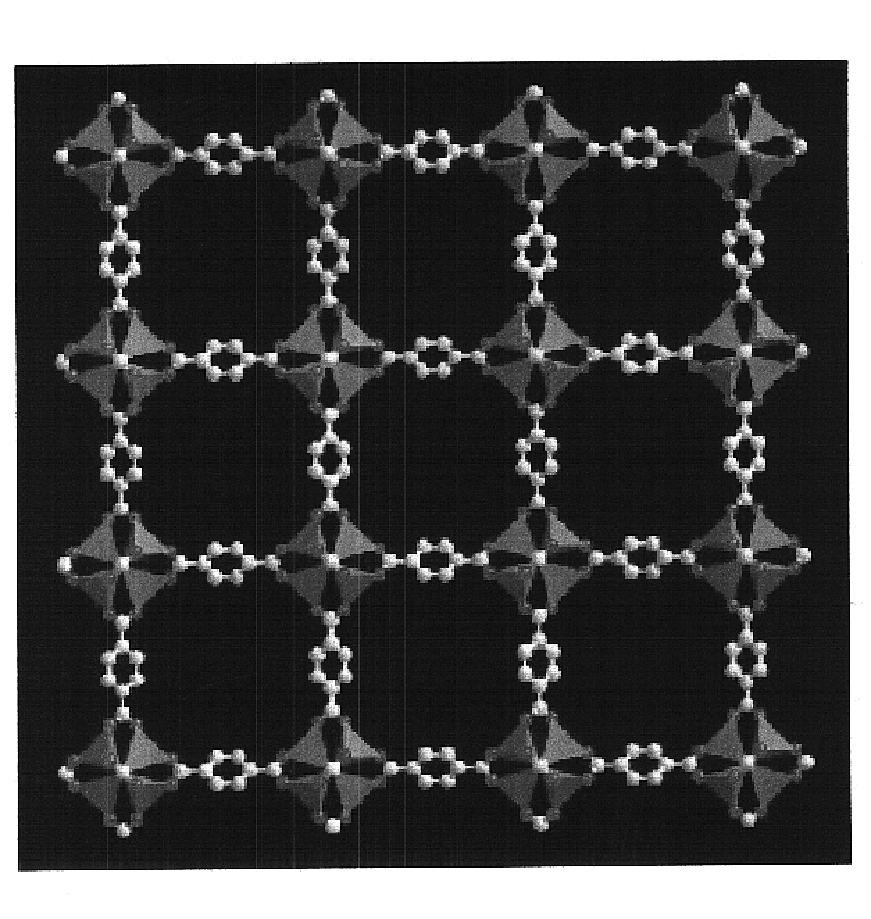
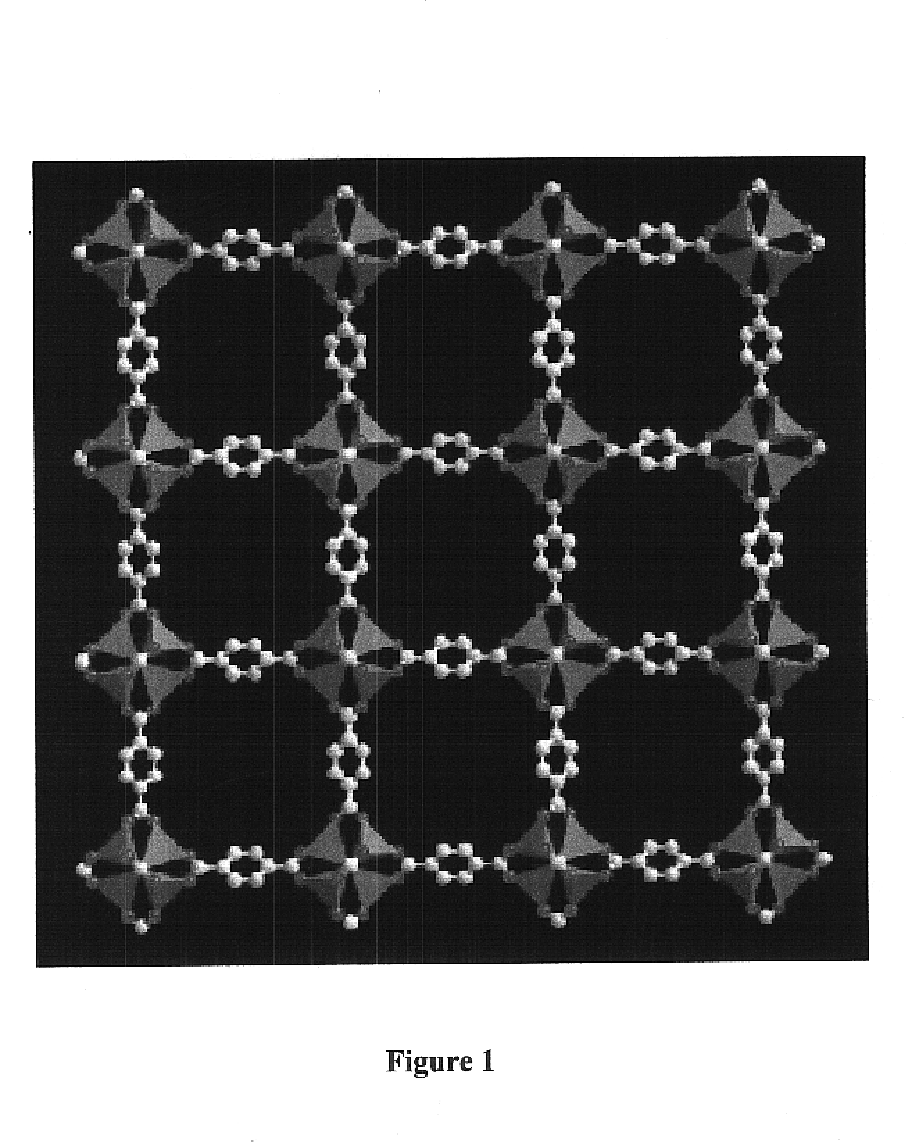
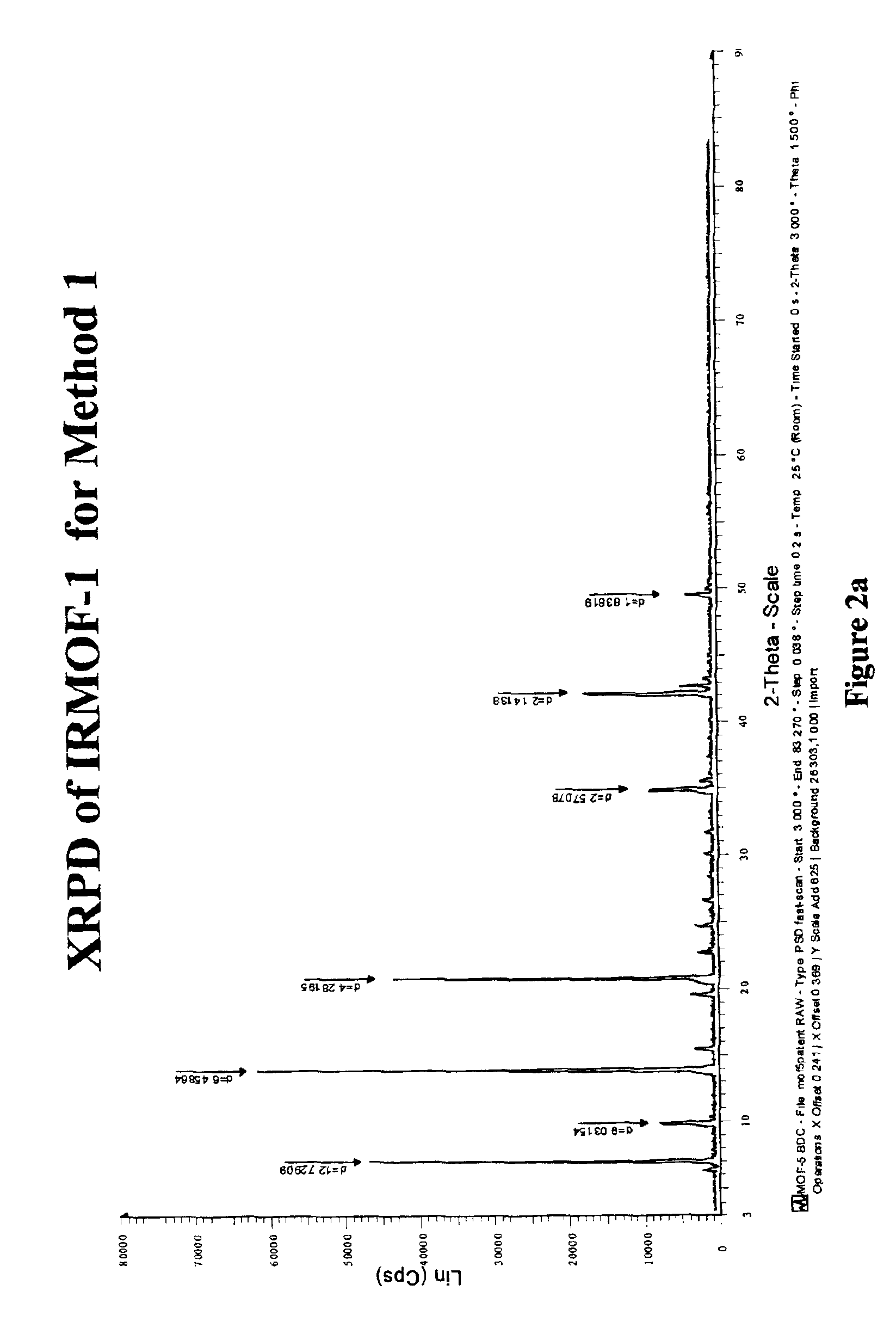
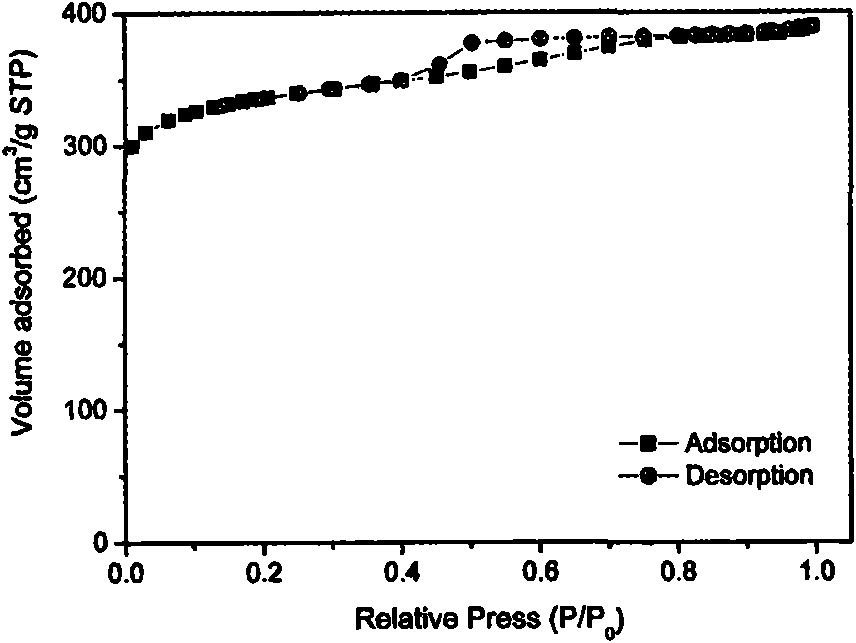
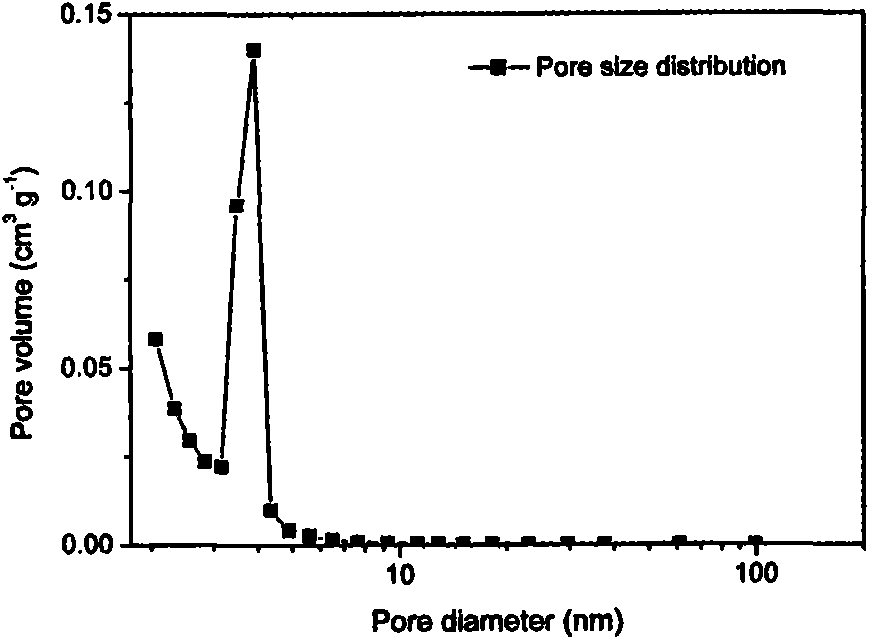
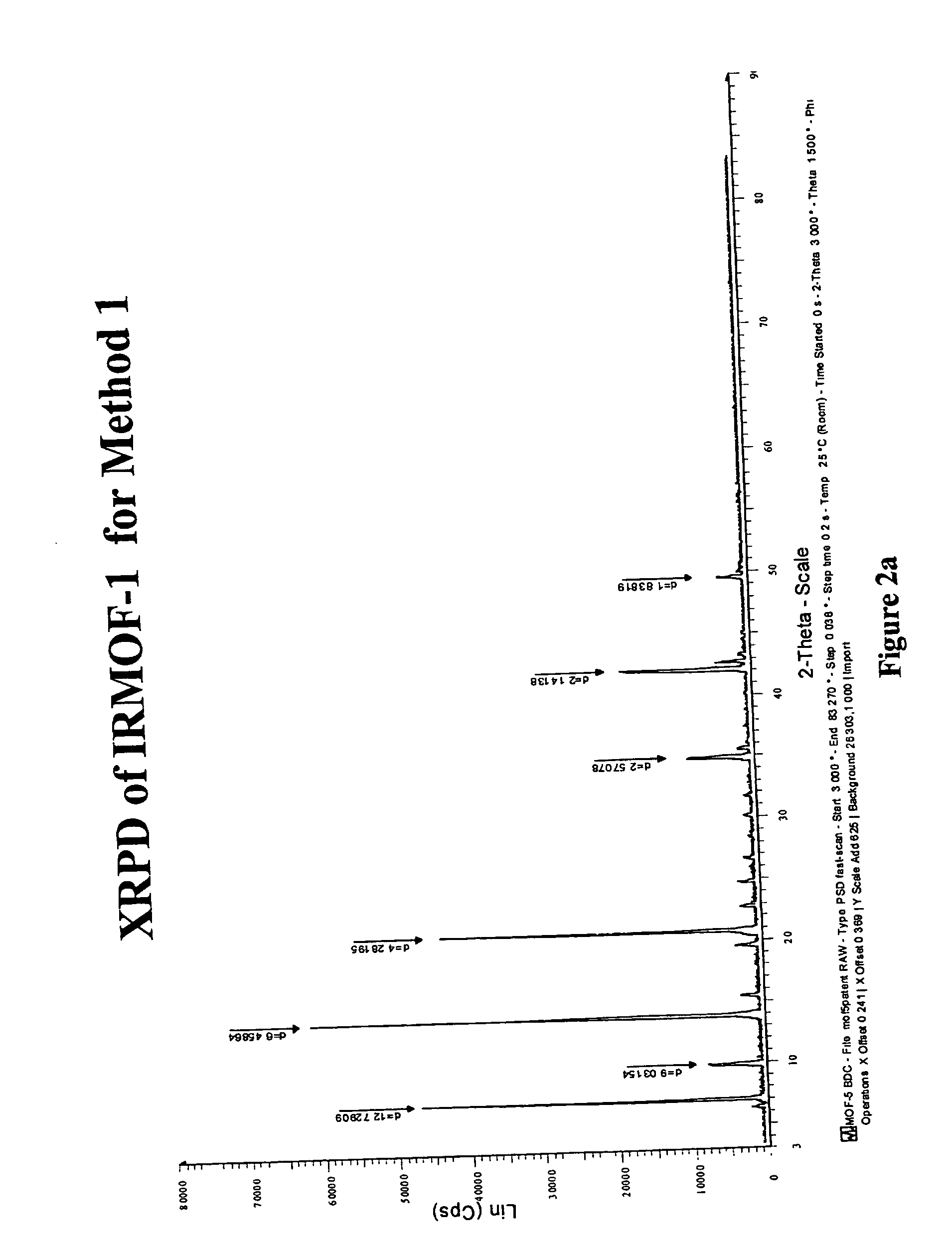
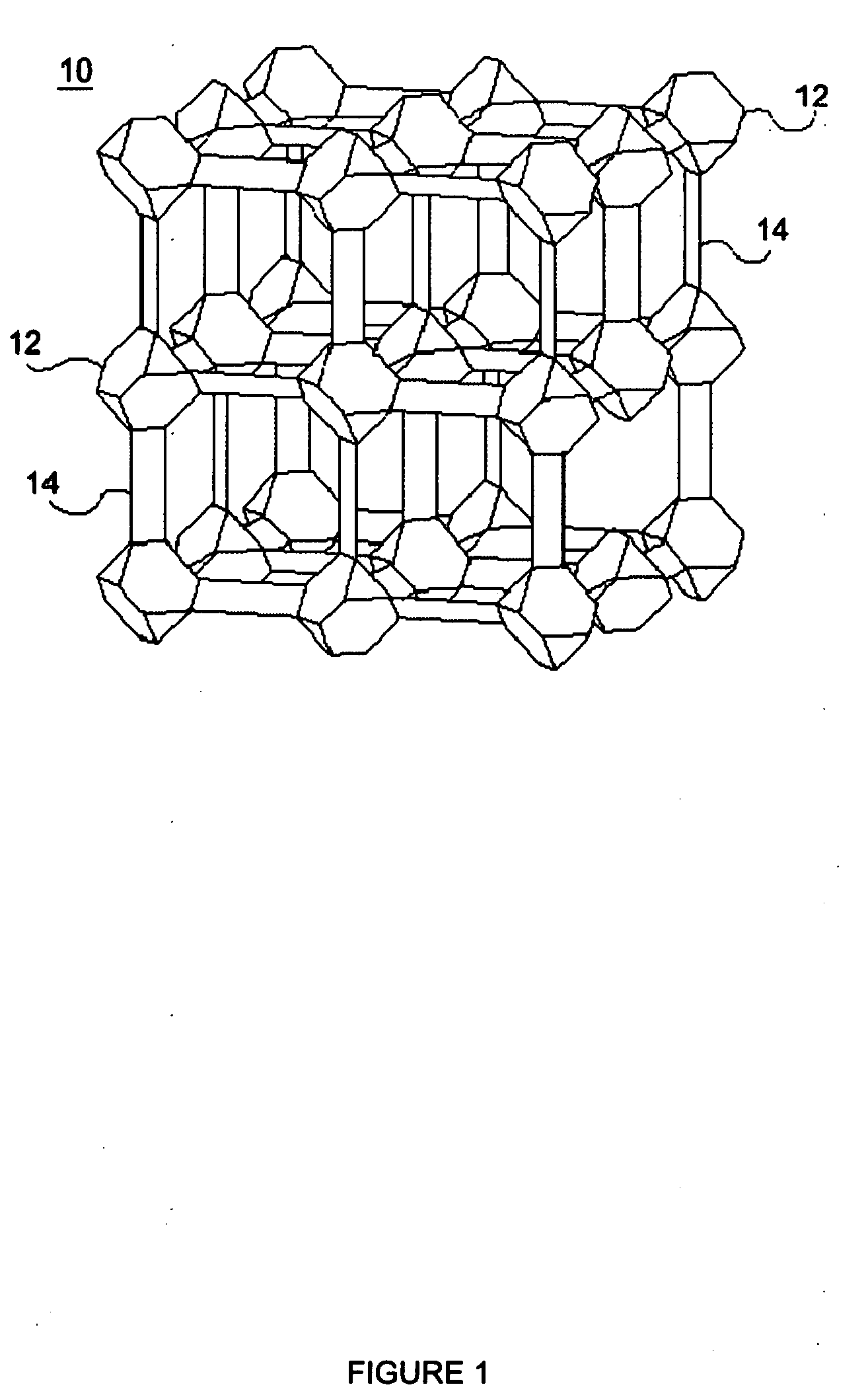
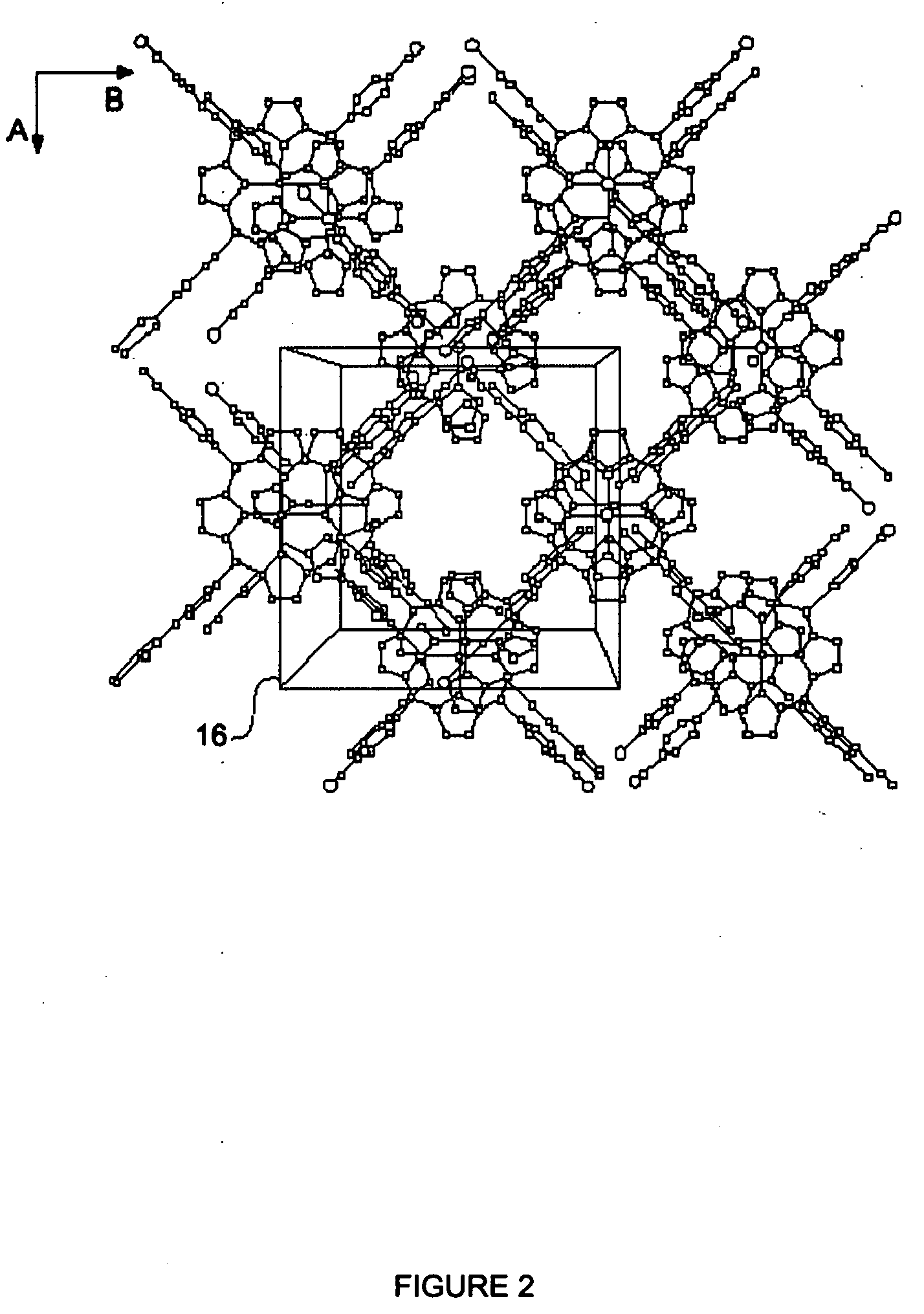
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS6930193B2High methane storage capacityIncrease storage capacityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic linkingSystems design
An isoreticular metal-organic framework (IRMOF) and method for systematically forming the same. The method comprises the steps of dissolving at least one source of metal cations and at least one organic linking compound in a solvent to form a solution; and crystallizing the solution under predetermined conditions to form a predetermined IRMOF. At least one of functionality, dimension, pore size and free volume of the IRMOF is substantially determined by the organic linking compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in single-level or multilevel pore canal structure and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in a single-level or multilevel pore canal structure as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: at least one metal salt and at least one polyfunctional group organic ligand reacts with at least one template agent in at least one solvent under the condition that no hole aid agent exists or only one hole aid agent exist, and single-level or multilevel nanometer holes or channels with the size of 0.5-100 nm exist in at least one direction in the internal space of the obtained metal-organic frame solid. The nanometer hole metal-organic frame material with large hole size and the nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in the layered multilevel pore canal structure can be obtained without the synthesis of the large-size organic ligand and have wide applications.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS7196210B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSystems designMetal-organic framework
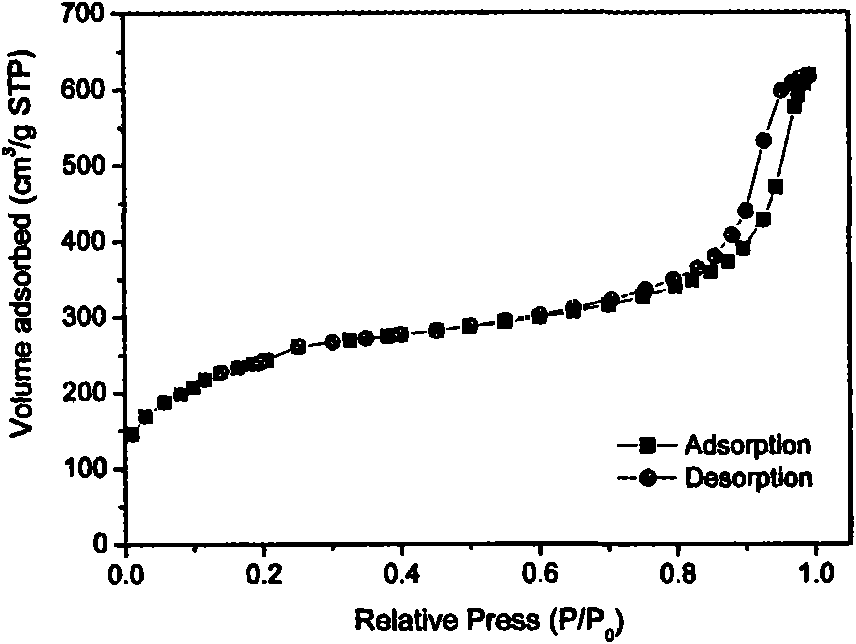
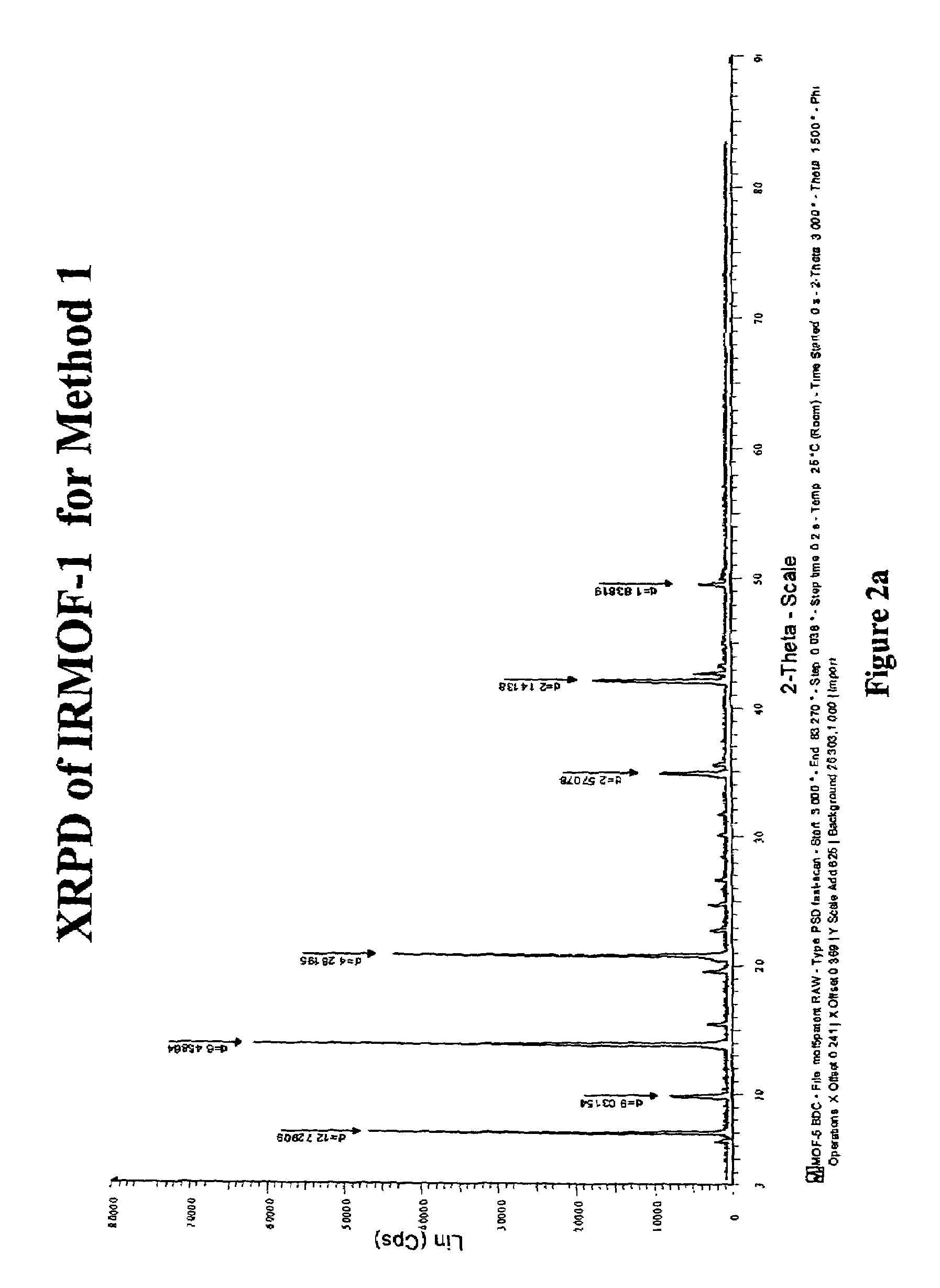
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Compound or its tautomer, metal complex compound, colored photosensitive curing composition, color filter, and production
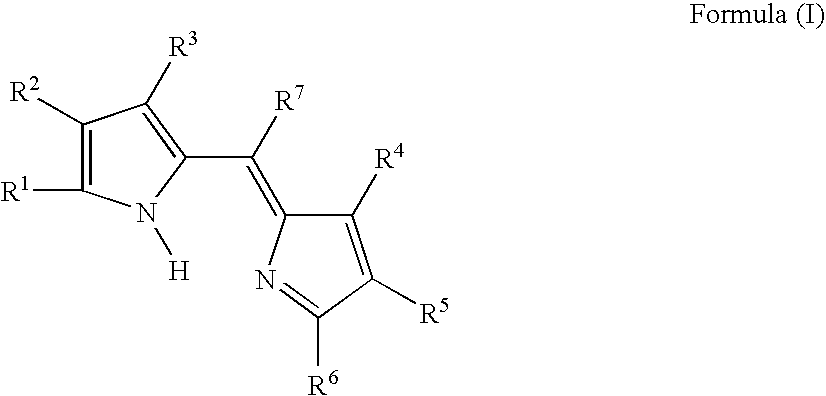
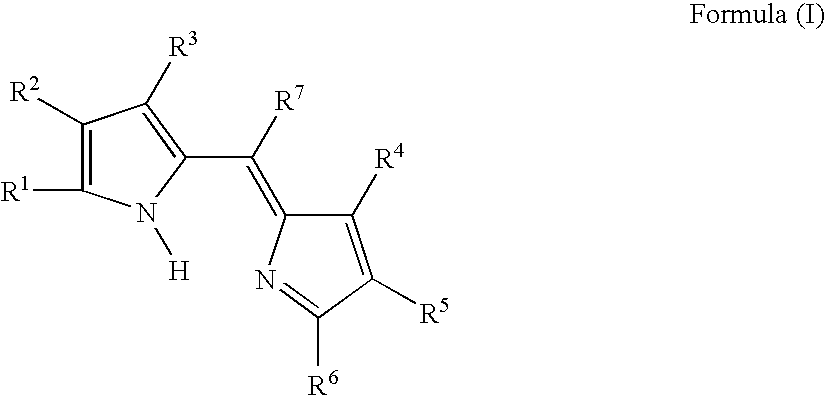
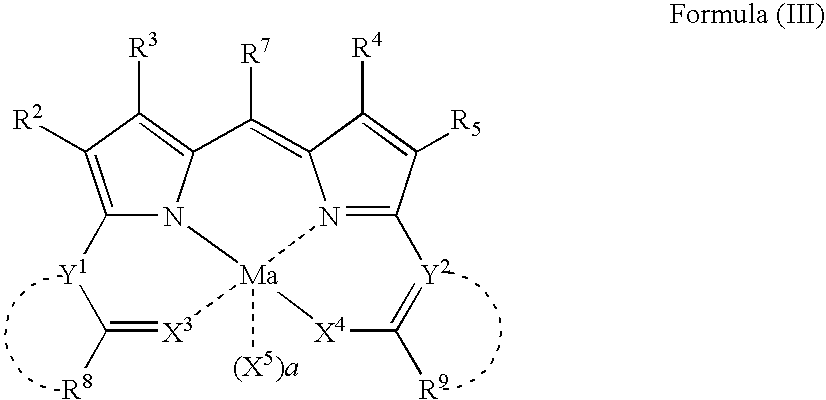
Provided is a colored photosensitive curing composition useful for color filters in primary colors, including blue, green, and red, having a high molar absorption coefficient and allowing a reduction in film thickness and superior color purity and fastness. A colored photosensitive curing composition, comprising, as its colorant, a dipyrromethene-based metal complex compound obtained from a metal or metal compound and a dipyrromethene-based compound represented by the following Formula (I): wherein in Formula (I), R1 to R6 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent group; and R7 represents a hydrogen or halogen atom, or an alkyl, aryl or heterocyclic group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Preparation method and applications of porous metal organic skeleton material
ActiveCN104370820AGood application effectEasy to operateOther chemical processesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous metal organic skeleton material. The porous metal organic skeleton material comprises at least a metal ion and at least an organic compound that can be matched with the metal ion. The material can be prepared by dissolving metal compounds, organic ligand, and sustained-released alkali into a solvent and carrying out direct water (solvent) thermal synthesis at a certain temperature under a certain pressure so as to obtain the porous metal organic skeleton material. The operation of the provided preparation method is simple, the preparation method is suitable for massive industrial production and is suitable for the synthesis of porous metal organic skeleton membrane, and the provided porous metal organic skeleton material is used to absorb, separate, and store gas.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method
ActiveUS20060047132A1High yieldHigh purityZinc halidesGallium/indium/thallium compoundsCompound (substance)Impurity
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Bioavailable chelates of creatine and essential metals
InactiveUS6114379AImprove bioavailabilityPromote recoveryBiocideGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsMetal chelateActive transport
A chelate comprised of creatine bonded to an essential mineral selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Cu, Zn, Fe, Cr, Co, Mo, Se and Mn to form a heterocyclic ring. Preferably, the metal is Mg, but Ca, Zn, Fe, Cr and Mn are also preferred. The creatine chelates of the present invention are capable of being absorbed in the stomach or intestines via active transport without substantial metabolism of the chelate. In other words, the creatine ligand is protected by the metal from undergoing cyclization in the acidic environment of the stomach and the metal is made more bioavailable due to the presence of the creatine ligand.
Owner:ALBION LAB
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS20050192175A1Catalyst protectionMolecular sieve catalystsSystems designMetal-organic framework
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Dual- or multi-headed chain shuttling agents and their use for preparation of block copolymers
ActiveUS8501885B2Silicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolyolefinOlefin polymerization
This disclosure relates to olefin polymerization catalysts and compositions, their manufacture, and the production of polyolefins using specific catalyst compositions, including the use of chain shuttling agents in the olefin polymerization process. Specifically, this disclosure provides for dual headed and multi-headed chain shuttling agents (CSAs or MSAs) and for their use in preparing blocky copolymers. By controlling the ratio of dual-headed and multi-headed CSA sites to mono-headed CSA sites, a blocky copolymer can be provided having properties such as a narrow molecular weight distribution and / or improved melt properties.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Preparation method of thermal conduction enhanced metal organic framework gas storage material
ActiveCN104624160AImprove adsorption capacityHigh thermal conductivityOther chemical processesGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesIndustrial gasSorbent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a thermal conduction enhanced metal organic framework gas storage material and belongs to the field of nanocomposites. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly selectively preparing a metal organic framework material with a large surface area and a high micropore proportion; performing synthesis post-modification on the metal organic framework material by a 'one-pot' method, regulating the polarity and contained functional groups of pores, immobilizing metal nanoparticles inside the pores to enhance the thermal conduction property of the metal organic framework material; adsorbing industrial gas by utilizing the ultra-large specific surface area and the nano duct structure of the metal organic framework material, wherein the thermal conduction enhanced adsorption material can be used for quickly transmitting the heat generated in the adsorption and desorption process of the industrial gas. The metal organic framework industrial gas adsorber prepared by the invention can be used for efficiently adsorbing and desorbing the industrial gas and effectively improving the thermal conduction property of the adsorber, and avoiding the influence of the heat effect on the adsorption quantity in the adsorption and desorption process. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of use of readily available and inexpensive raw materials, simple process, and mild reaction conditions and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Zinc amino acid chelates having ligands comprised of glycine and a sulfur-containing amino acids
InactiveUS6166071AInterfere with absorptionHigh weight percentageOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGlycineSulfur containing
A zinc amino acid chelate formulation is disclosed comprising zinc ions being chelated by an amino acid ligand mixture comprising glycine and a sulfur-containing amino acid wherein the ligand to zinc molar ratio is from about 1:1 to 2:1 and wherein the glycine to sulfur-containing amino acid molar ratio is between about 1:6 to 6:1.
Owner:ALBION LAB
Implementation of a strategy for achieving extraordinary levels of surface area and porosity in crystals
InactiveUS7652132B2Large specific surface areaIncrease the number ofGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMetal clustersPorosity
The present invention provides a metal-organic framework (“MOF”) comprising a plurality of metal clusters and a plurality of multidentate linking ligands. Each metal of the plurality of metal clusters comprises one or more metal ions. Each ligand of the plurality of multidentate linking ligands connects adjacent metal clusters. The present invention also provides a method of forming the metal-organic framework. The method of the invention comprises combining a solution comprising one or metal ions with a multidentate linking ligand having a sufficient number of accessible sites for atomic or molecular adsorption that the surface area of the resulting metal-organic framework is greater than 2,900 m2 / g.
Owner:MICHIGAN UNIV OF RGT
Metal complexes, methods, and uses thereof
Metal complexes that exhibit multiple radiative decay mechanisms, together with methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Rapid metal organic framework molecule synthesis method
InactiveUS20090131643A1Rapidly synthesizing MOF moleculesSynthesis fastGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsSynthesis methodsMetal-organic framework
A rapid, simple and versatile metal organic framework molecule (MOF) synthesis method particularly adapted to make non-linear MOFs includes heating MOF precursors, such as a metal or metal oxide and an organic ligand, in a microwave oven for a period sufficient to achieve crystallization. Microwave-assisted MOF synthesis yields high quality MOF crystals in a reaction time ranging from about 5 seconds to about 2.5 minutes, compared to hours and days required in conventional solvothermal and hydrothermal methods. In addition, microwave assisted methods provide MOF materials with uniform crystal size and well-defined shape. Further, microwave synthesis of MOFs allows the size and shape of MOF crystals to be tailored for use in a wide range applications by manipulating reaction conditions. Secondary growth processes may also be employed to grow larger crystals using seeds obtained from microwave-assisted synthesis methods.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
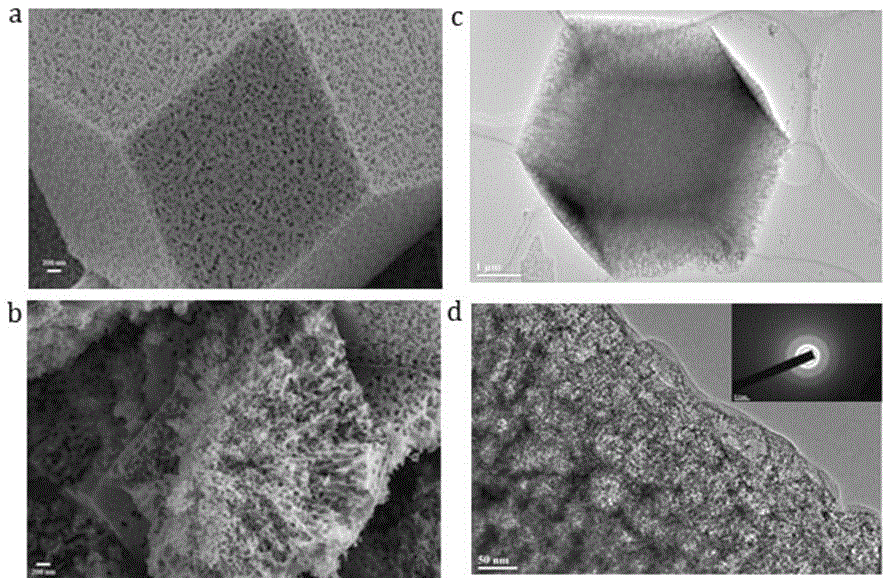
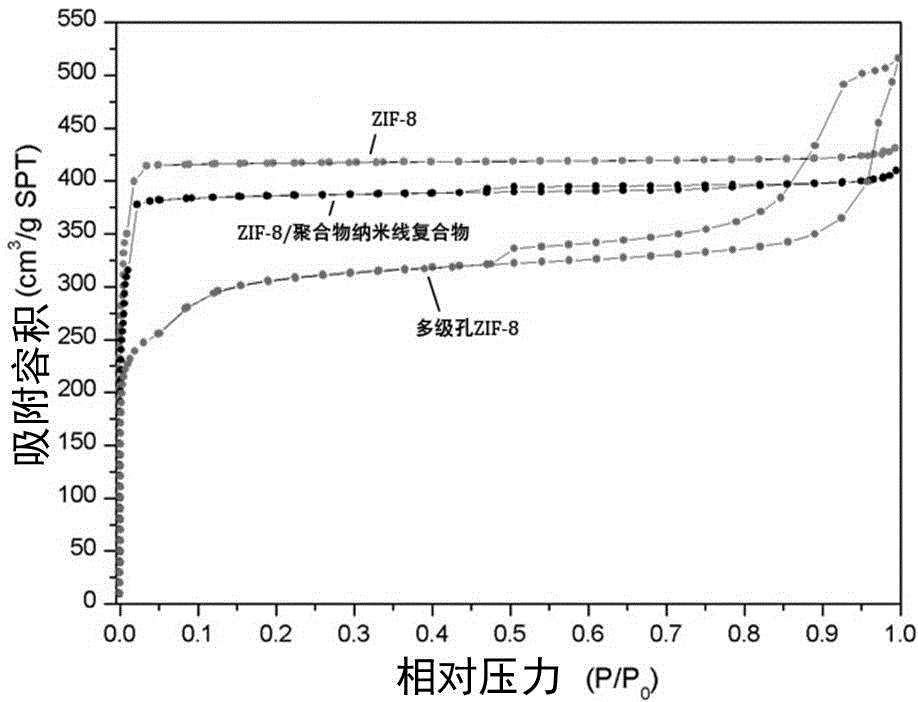
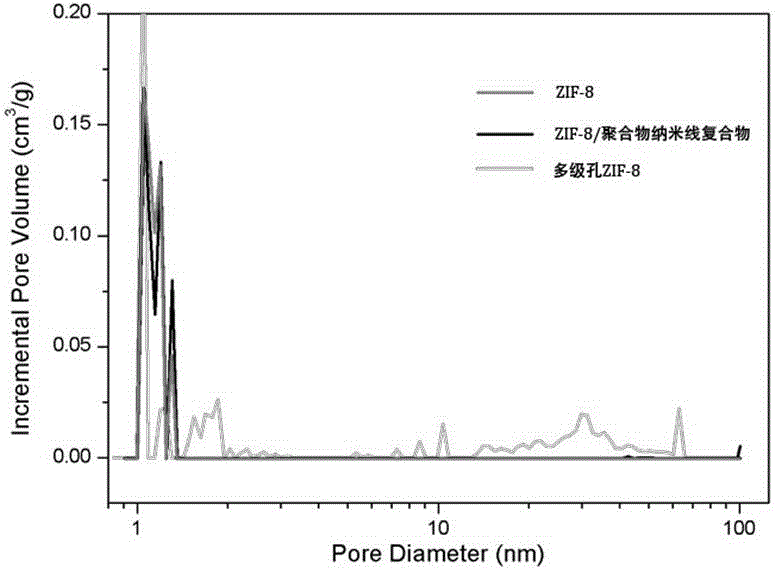
Preparation method of metal-organic framework compound with hierarchical pore structure
InactiveCN104151336AGuaranteed stabilityMaintain crystal shapeCopper organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsSolventIon
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanocomposite materials and in particular relates to a preparation method of a metal-organic framework compound with a hierarchical pore structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, self-assembling a diblock copolymer in a solvent to form a flexible polymer nanowire with a core-shell structure, and cross-linking cores to obtain a polymer nanowire with a stable solvent; adding metal ions and organic ligands into a nanowire solution to form a mixed solution; crystallizing at the room temperature to obtain a metal-organic framework / core-shell structure polymer nanowire compound; calcining to remove the polymer nanowire to obtain a hierarchical pore material with MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) micropores, small mesopores formed after calcination of a shell layer of the polymer nanowire and large mesopores formed after calcinations of a core layer. According to the MOFs material with the hierarchical pore structure, the advantages of the micropores and the micropores are combined, the mass transfer speed of the MOFs material is improved, relatively large molecules can conveniently enter the MOFs material, and the application potential of the MOFs material in the field of catalysis, adsorption and the like is improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing BTC (1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid)-based nanoscale organometallic framework material
InactiveCN102336774AAvoid pollutionAvoid wastingCopper organic compoundsNickel organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkNano devices
The invention discloses a method for rapidly synthesizing a BTC (1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid)-based nanoscale organometallic framework material at room temperature. The nanomaterial is prepared by the following steps: mixing metal acetate aqueous solution with BTC solution at room temperature, and reacting to obtain BTC-based organometallic framework nanoparticles. The method is rapid, simple and energy-saving; the yield is high; the used raw materials and solvents are inexpensive and easily available; the safety problem of commonly used nitrate is not caused; the method is favorable to the industrial production and has wide application prospects in the fields of catalysis, adsorption, drug carriers, building of nano devices and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
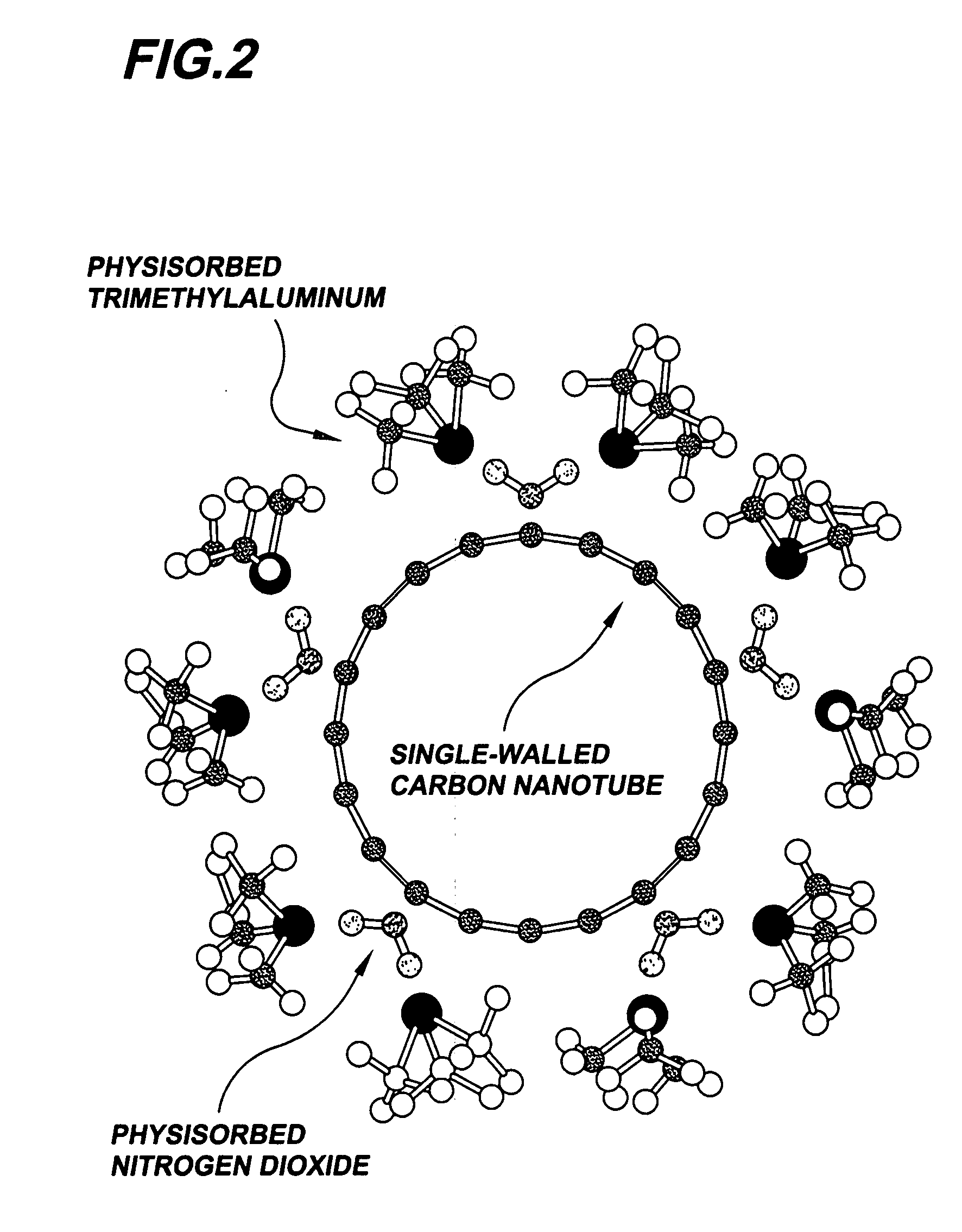
Gas-phase functionalization of carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS20080296537A1Remarkable and mechanical and optical propertyMaterial nanotechnologyAluminium compoundsGas phaseDesorption
In a method for functionalizing a carbon nanotube surface, the nanotube surface is exposed to at least one vapor including at least one functionalization species that non-covalently bonds to the nanotube surface, providing chemically functional groups at the nanotube surface, producing a functionalized nanotube surface. A functionalized nanotube surface can be exposed to at least one vapor stabilization species that reacts with the functionalization layer to form a stabilization layer that stabilizes the functionalization layer against desorption from the nanotube surface while providing chemically functional groups at the nanotube surface, producing a stabilized nanotube surface. The stabilized nanotube surface can be exposed to at least one material layer precursor species that deposits a material layer on the stabilized nanotube surface.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
High-stability metal organic skeleton hybrid material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103694260AHigh hydrothermal stabilitySimple methodOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCopper organic compoundsMass ratioHybrid material
The invention discloses a high-stability metal organic skeleton hybrid material. The metal organic skeleton hybrid material has high hydrothermal stability, and comprises metal organic skeleton and attapulgite, wherein the mass ratio of the attapulgite to the metal organic skeleton is (0.005-0.7):1.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
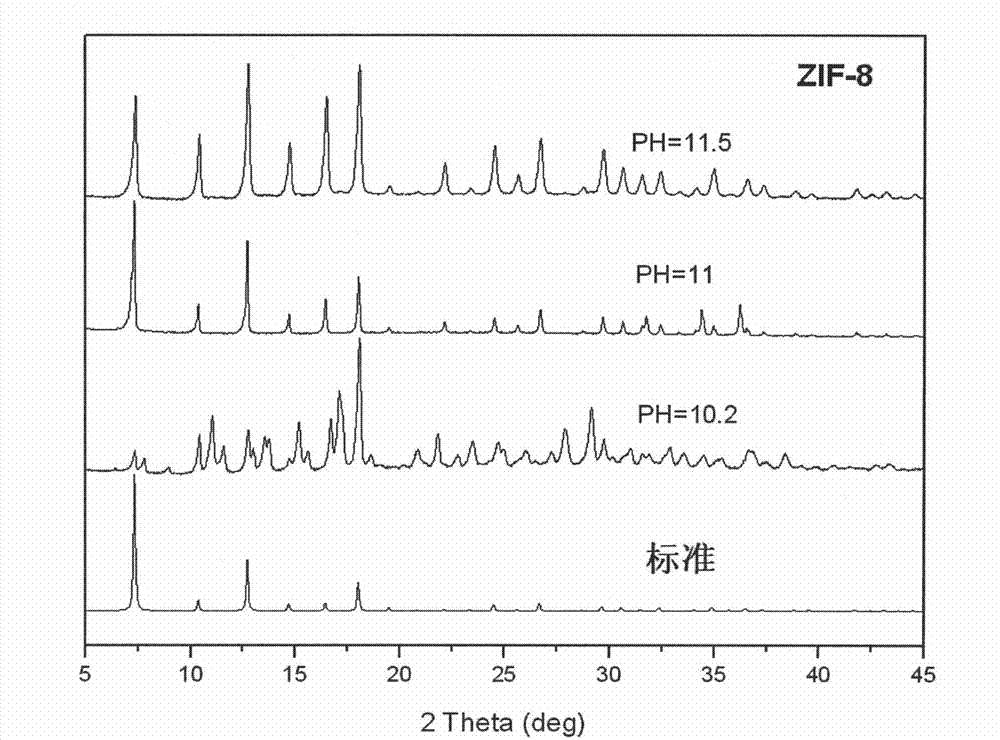
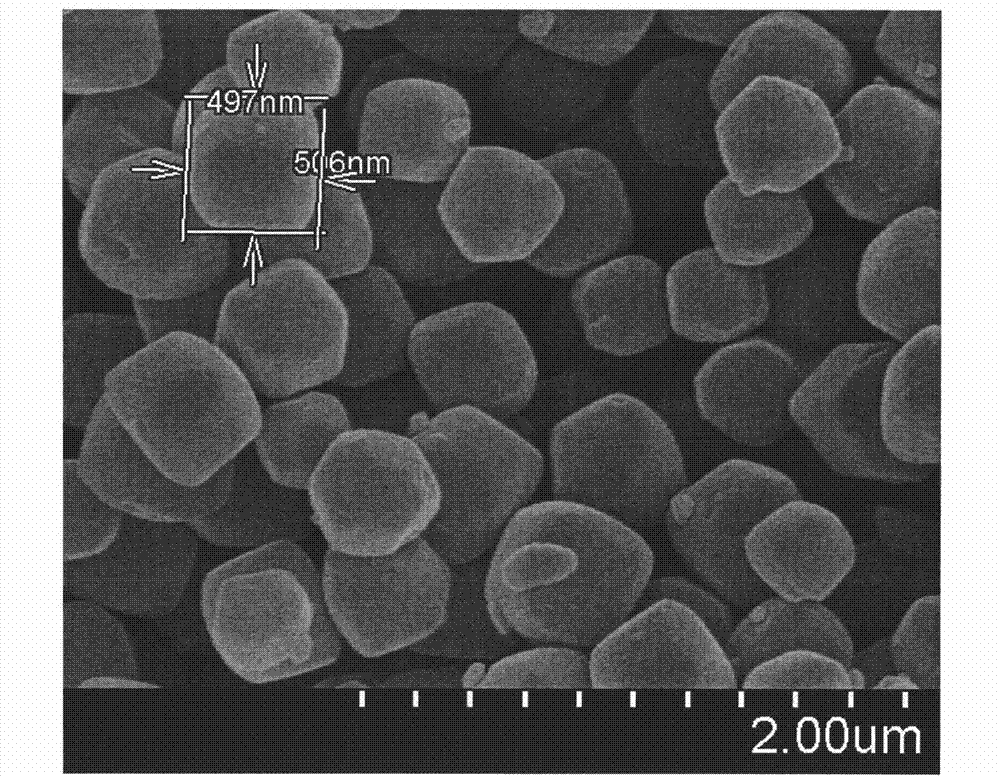
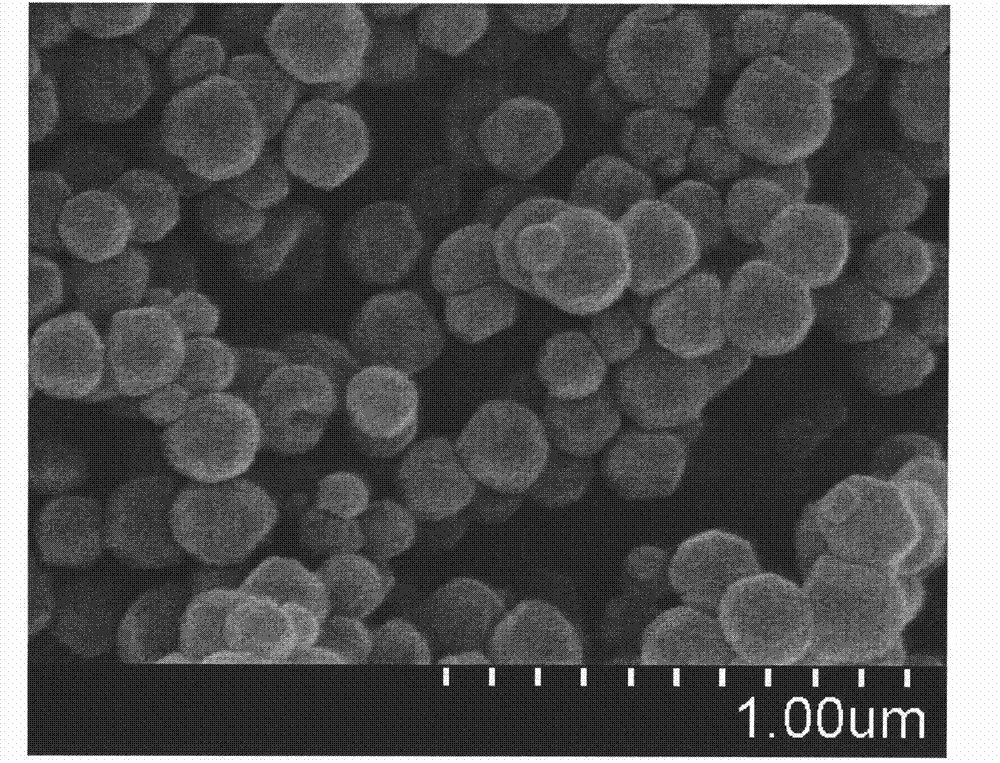
Method for regulating ZIF-8 crystal morphology by utilizing surfactant
InactiveCN107722046ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getLow costOrganic chemistry methodsGroup 2/12 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCrystal morphologyRhombic dodecahedron
The invention provides a method for regulating ZIF-8 crystal morphology by utilizing a surfactant and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of porous materials. The method disclosed by the invention is mainly characterized in that the morphology and size of the ZIF-8 crystal are controlled by adding a certain amount of a surfactant. The specific preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving a zinc salt, a surfactant and dimethyl imidazole into a certain amount of water, stirring to enable the components to be fully dissolved, and preparing a solution; mixing adimethyl imidazole solution and a surfactant solution, fully stirring, finally adding a zinc salt solution, and mixing and stirring for 10 minutes; then transferring the mixed solution into a high temperature reactor, and reacting at a constant temperature for several hours; cooling, centrifuging, washing and drying, thereby obtaining the ZIF-8 crystal. The ZIF-8 crystal prepared by the method has excellent crystallinity and has five morphologies such as rhombic dodecahedron, cube, sheet, interpenetration twin and rod. The invention provides a novel method for controlling the morphology and size of MOFs materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Metal Complexes, Methods, and Uses Thereof
Metal complexes that exhibit multiple radiative decay mechanisms, together with methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for low-temperature atmosphere-pressure hydrothermal synthesis of stephanoporate metal-organic framework
InactiveCN101429209AFully contactedQuality improvementCadmium organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkChemistry
The invention discloses a method for hydrothermally synthesizing a porous metal-organic framework under low temperature and normal pressure, which comprises the following steps: 1) bivalent transition metal salt is put into proper amount of distilled water to be dissolved; 2) a multidentate organic ligand is put into proper amount of distilled water, and ammonia (30 percent, W / W) is added into the solution until the organic ligand is dissolved; 3) solutions obtained in step 1) and step 2) are mixed, and diluted by the distilled water; 4) the solution obtained in step 3) reacts for 4 to 24h at a temperature of between 80 and 100 DEG C, and is naturally cooled to room temperature at an environmental temperature to obtain an MOF crystal product; and 5) the MOF crystal product obtained in step 4) is filtered, MOF crystals are colleted and washed by the distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol respectively, and the product is obtained after the natural drying. By performing a hydrothermal reaction in an ammonia solution, the method has mild conditions needed by the synthesis, less energy consumption and time consumption, and does not need a voltage resistant reactor. Therefore, the method is simpler and has lower cost; and a porous crystal material obtained by the synthesis has potential application value in the fields of gas separation, gas storage and heterogeneous catalysis.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Hybrid Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks: Controlling Framework Porosity and Functionality by a Mixed-Ligand Synthetic Approach
Metal-organic frameworks, in particular hybrid zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), devices having hybrid ZIFs, and methods for preparing hybrid ZIFs are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, the method includes preparing a first solution comprising a first imidazolate and a second imidazolate, preparing a second solution comprising a metal ion, and combining the first solution and the second solution to form the hybrid ZIF.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Anti-microbial metal organic framework
InactiveUS20130171228A1More cost-effectivelyQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismMetal-organic framework
The present invention relates to metal organic framework materials which possess anti-microbial properties. The present invention also provides methods of preparing such metal organic framework materials and uses of the metal organic framework materials to prevent or treat microbial infections, or provide surfaces which limit contamination by micro-organisms.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
System and method for generating and/or screening potential metal-organic frameworks
A system and method for systematically generating potential metal-organic framework (MOFs) structures given an input library of building blocks is provided herein. One or more material properties of the potential MOFs are evaluated using computational simulations. A range of material properties (surface area, pore volume, pore size distribution, powder x-ray diffraction pattern, methane adsorption capability, and the like) can be estimated, and in doing so, illuminate unidentified structure-property relationships that may only have been recognized by taking a global view of MOF structures. In addition to identifying structure-property relationships, this systematic approach to identify the MOFs of interest is used to identify one or more MOFs that may be useful for high pressure methane storage.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Preparation method of nanometer-to-micrometer scale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs)
ActiveCN102731538AGood lookingPromotes deprotonationCobalt organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsOrganic fluidSolvent
The invention which belongs to the technical field of new materials relates to a synthetic method of ZIFs, and concretely discloses a method for synthesizing nanometer / micrometer scale ZIFs based on imidazole and its derivatives at room temperature in a concise, efficient and green manner. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a single imidazole ligand or a mixture of two imidazole ligands in water or an organic liquid to form a solution, adding an alkaline substance to adjust the pH value of the solution, adding a metal salt to form a reaction system, and reacting to obtain the nanometer or micrometer scale ZIFs. The method which allows routine reactants to be utilized and the alkaline substance to be added to adjust the pH value of the system has the advantages of ligand application amount reduction, controllable product size, and high purity of the nanometer / micrometer scale ZIFs. The synthetic method has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials and solvent, and no pollution, and has important meanings to the production and the application of the ZIFs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Derivatives of seleno-amino acids with improved bioavailability and method for their preparation
InactiveUS6911550B2Improve bioavailabilityImprove stabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAcid derivativeBioavailability
Metal L-seleno-alpha-amino acids salts and their use as a bioavailable feed and water ration supplement for domesticated animals such as cattle, pigs and poultry.
Owner:ZINPRO
Bicyclic guanidinates and bridging diamides as cvd/ald precursors
InactiveUS20090275164A1Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryWafering
Precursors for use in depositing metal-containing films on substrates such as wafers or other microelectronic device substrates, as well as associated processes of making and using such precursors, and source packages of such precursors. The precursors are useful for depositing Ge2Sb2Te5 chalcogenide thin films in the manufacture of nonvolatile Phase Change Memory (PCM) devices, by deposition techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and atomic layer deposition (ALD).
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Method for making organometallic compounds
Owner:UBE IND LTD
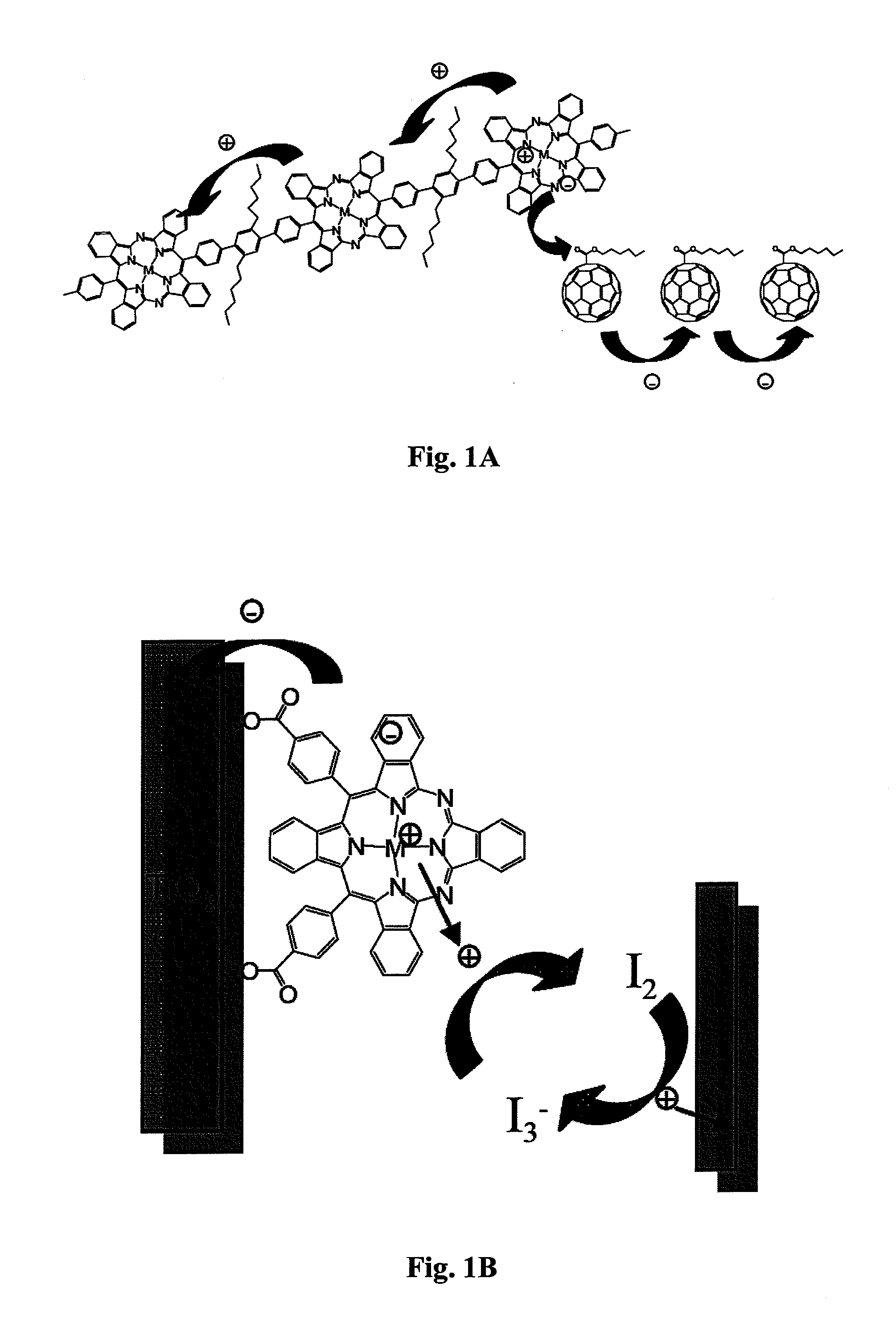
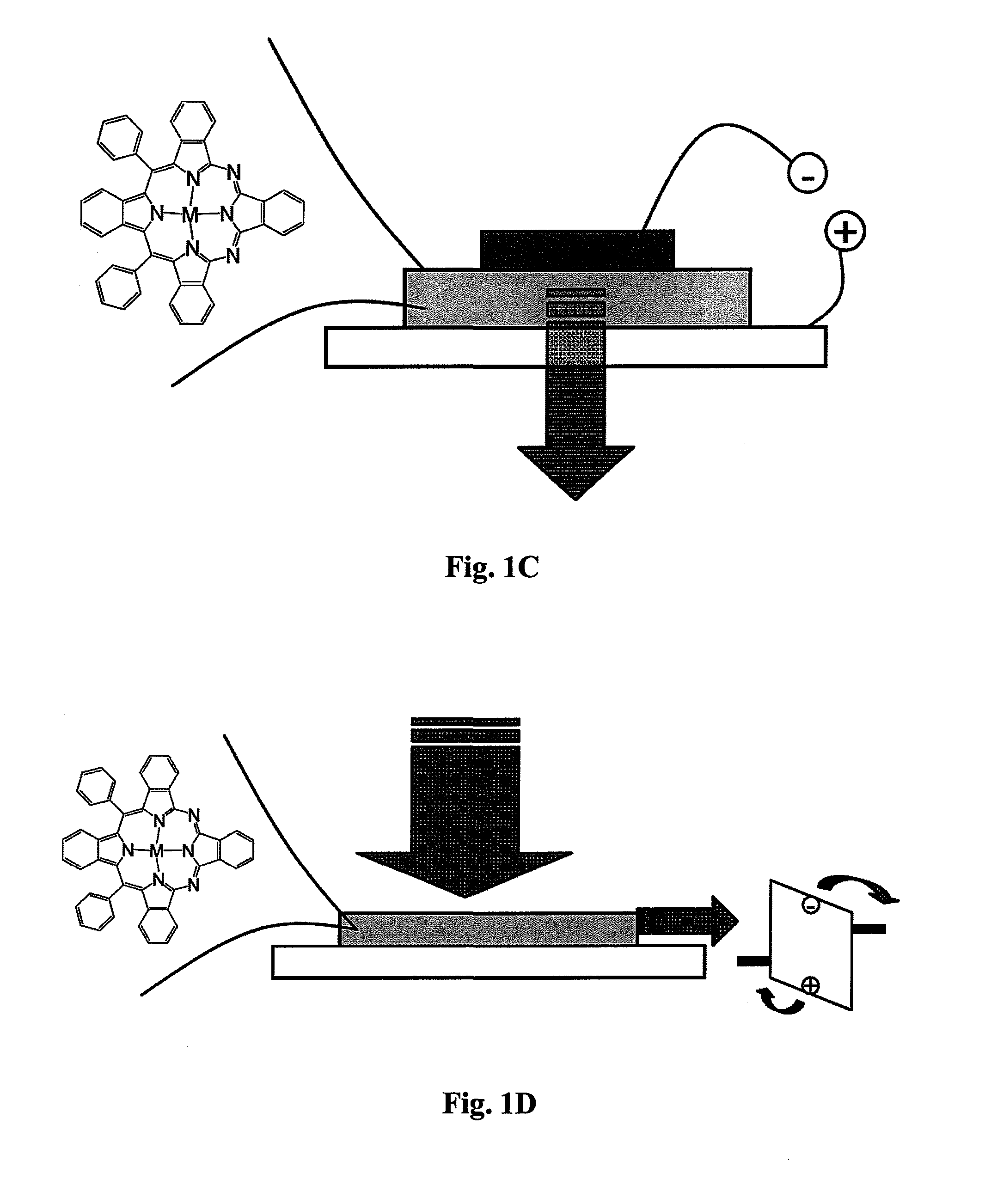
Azaporphyrins and applications thereof
InactiveUS20120108806A1Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsReactive dyesElectro-opticsChemistry
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com