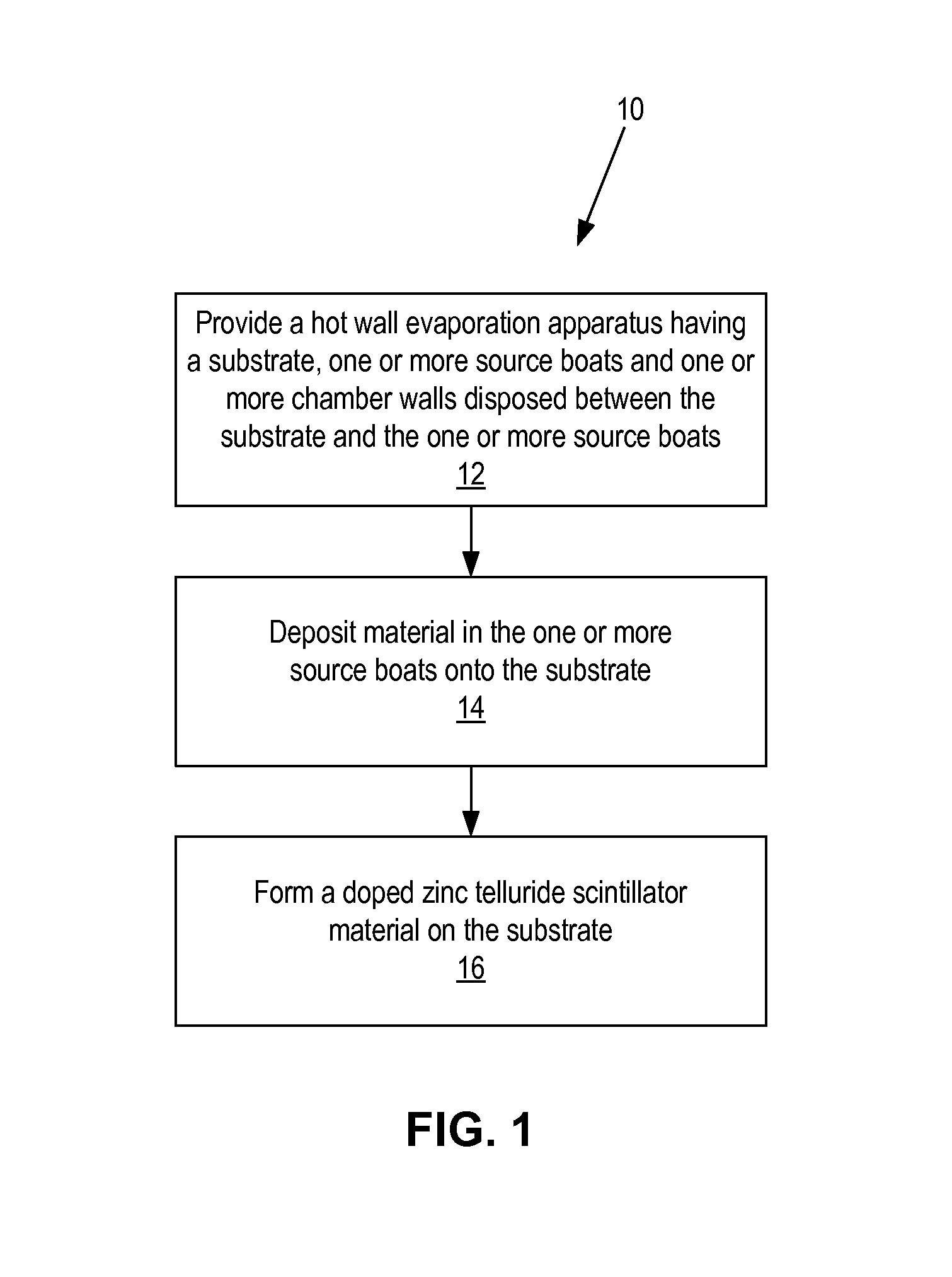
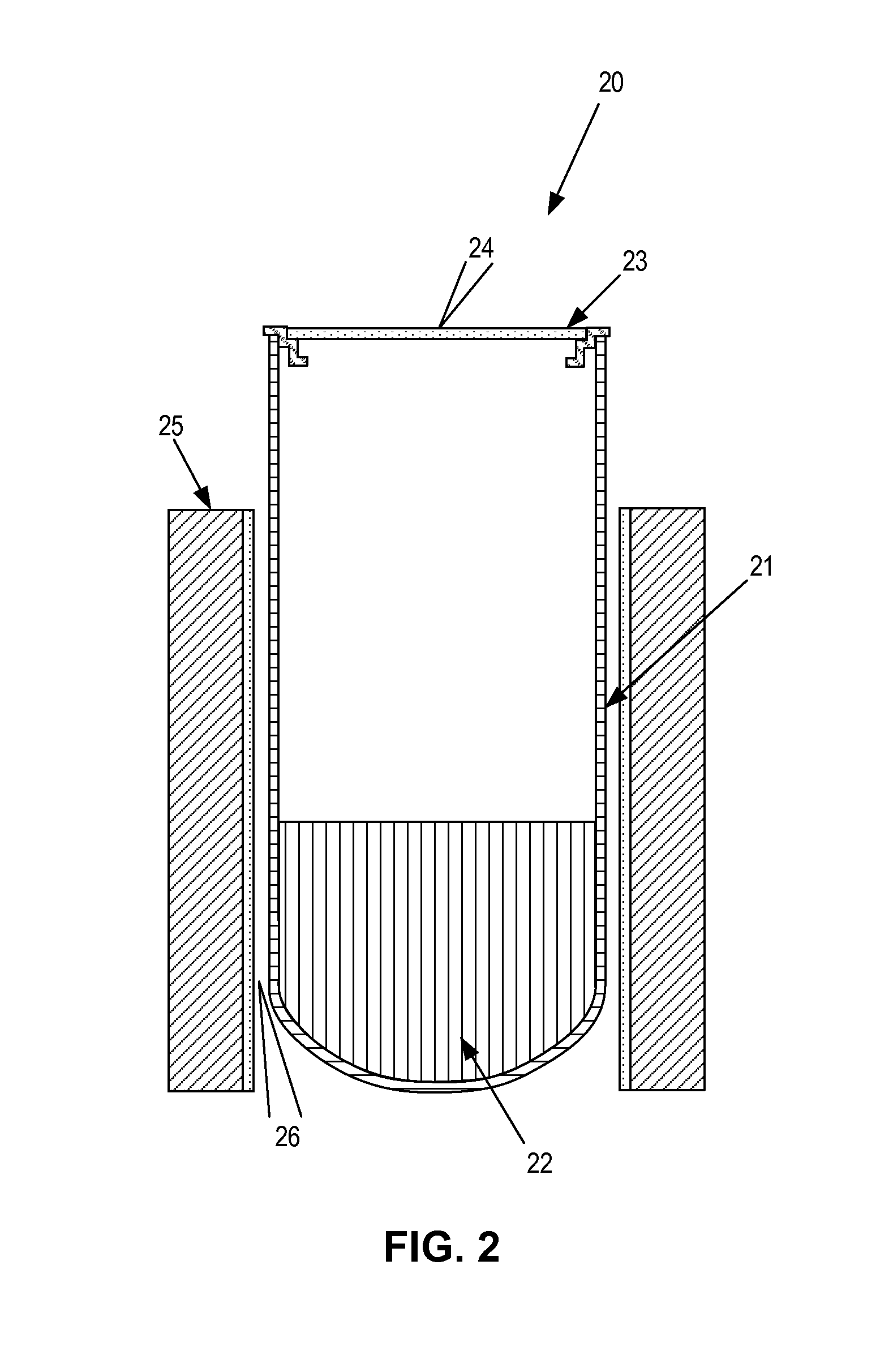
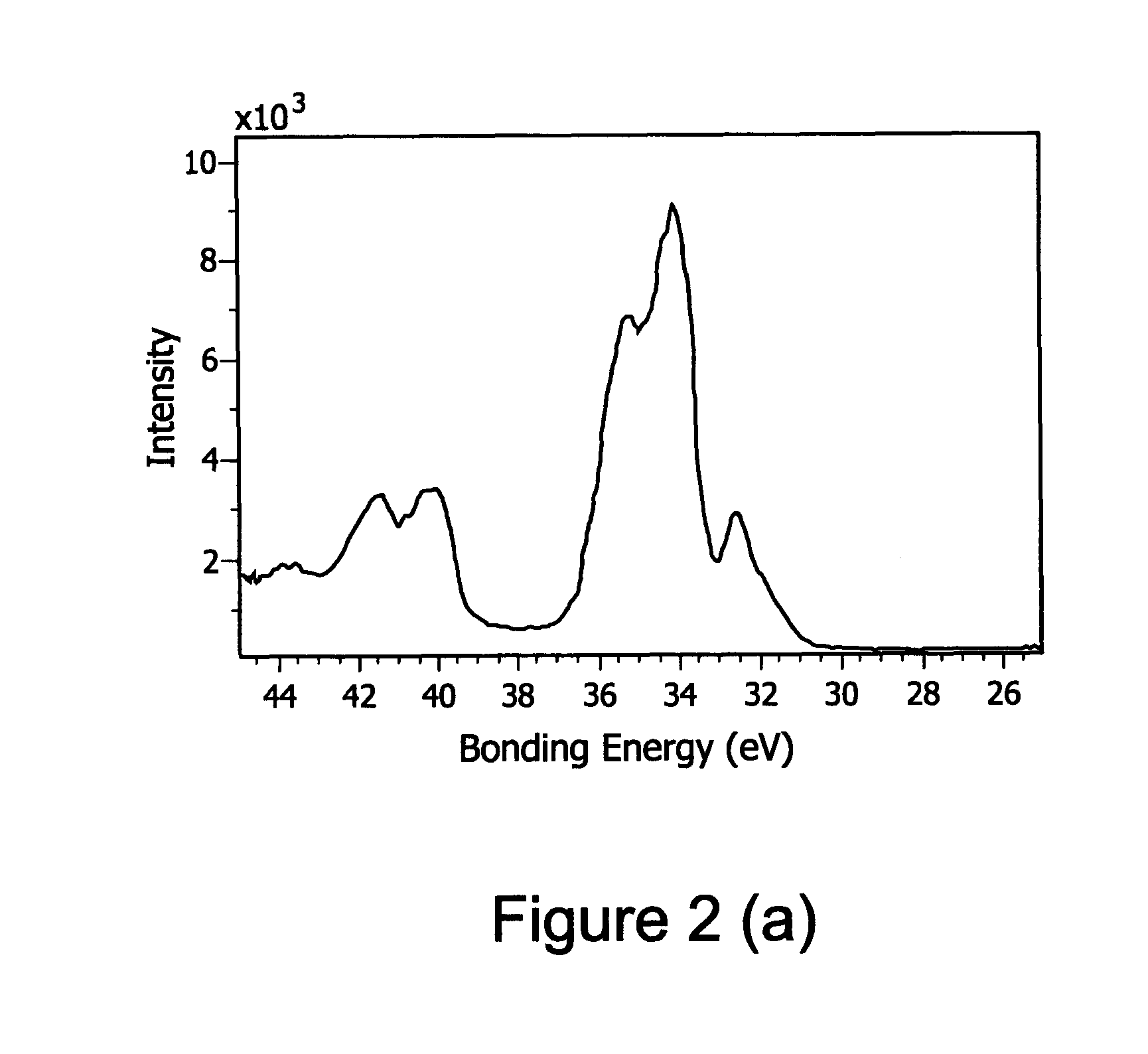
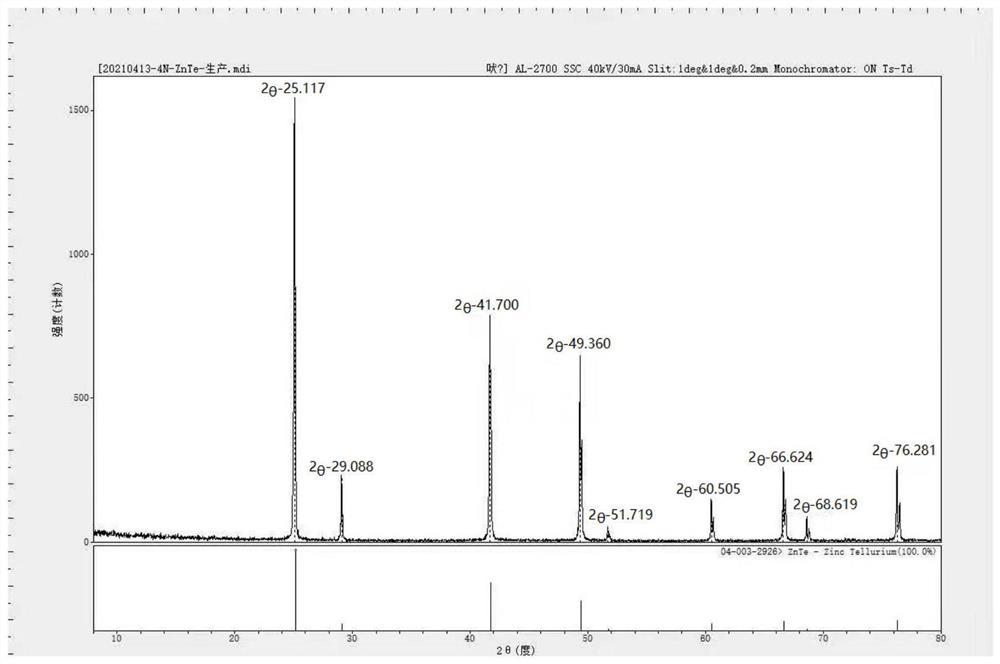
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Zinc telluride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
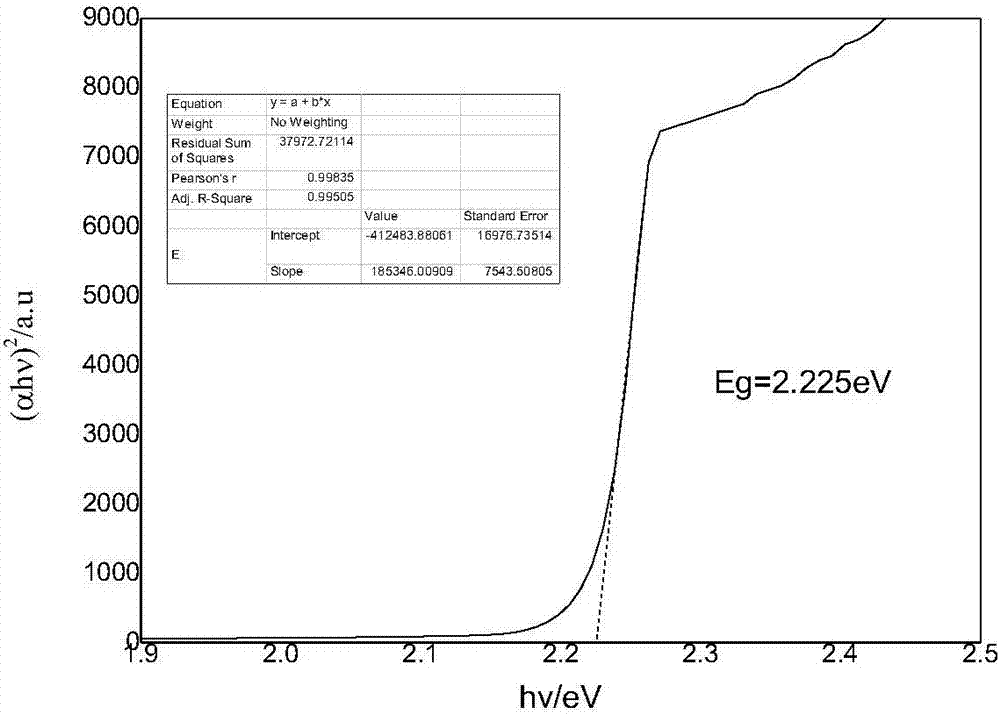
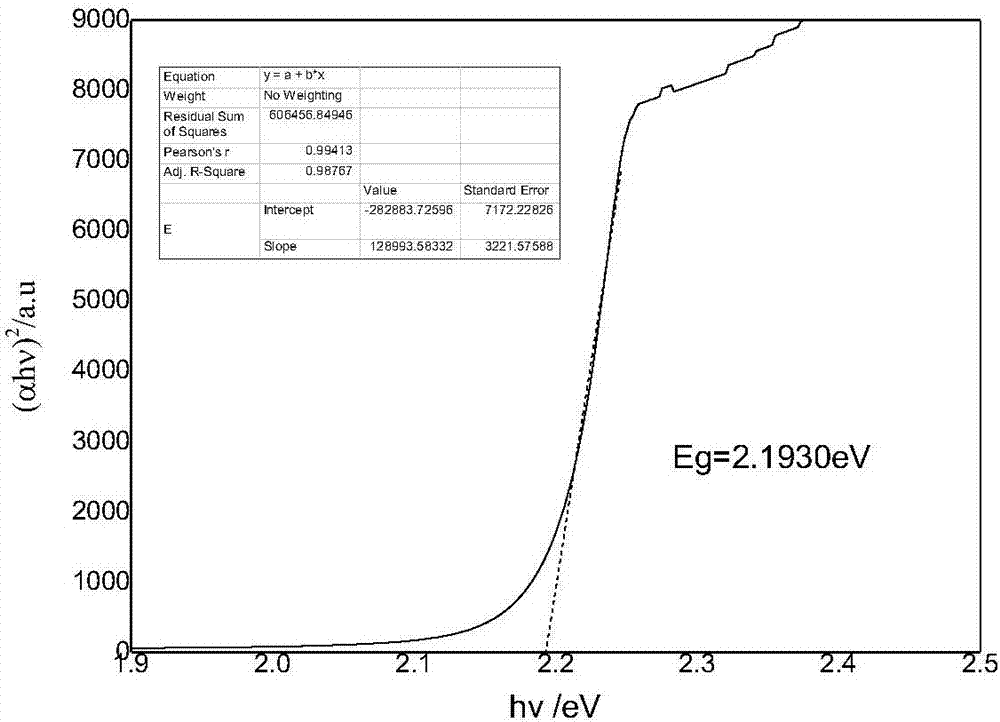
Zinc telluride is a binary chemical compound with the formula ZnTe. This solid is a semiconductor material with a direct band gap of 2.26 eV. It is usually a p-type semiconductor. Its crystal structure is cubic, like that for sphalerite and diamond.
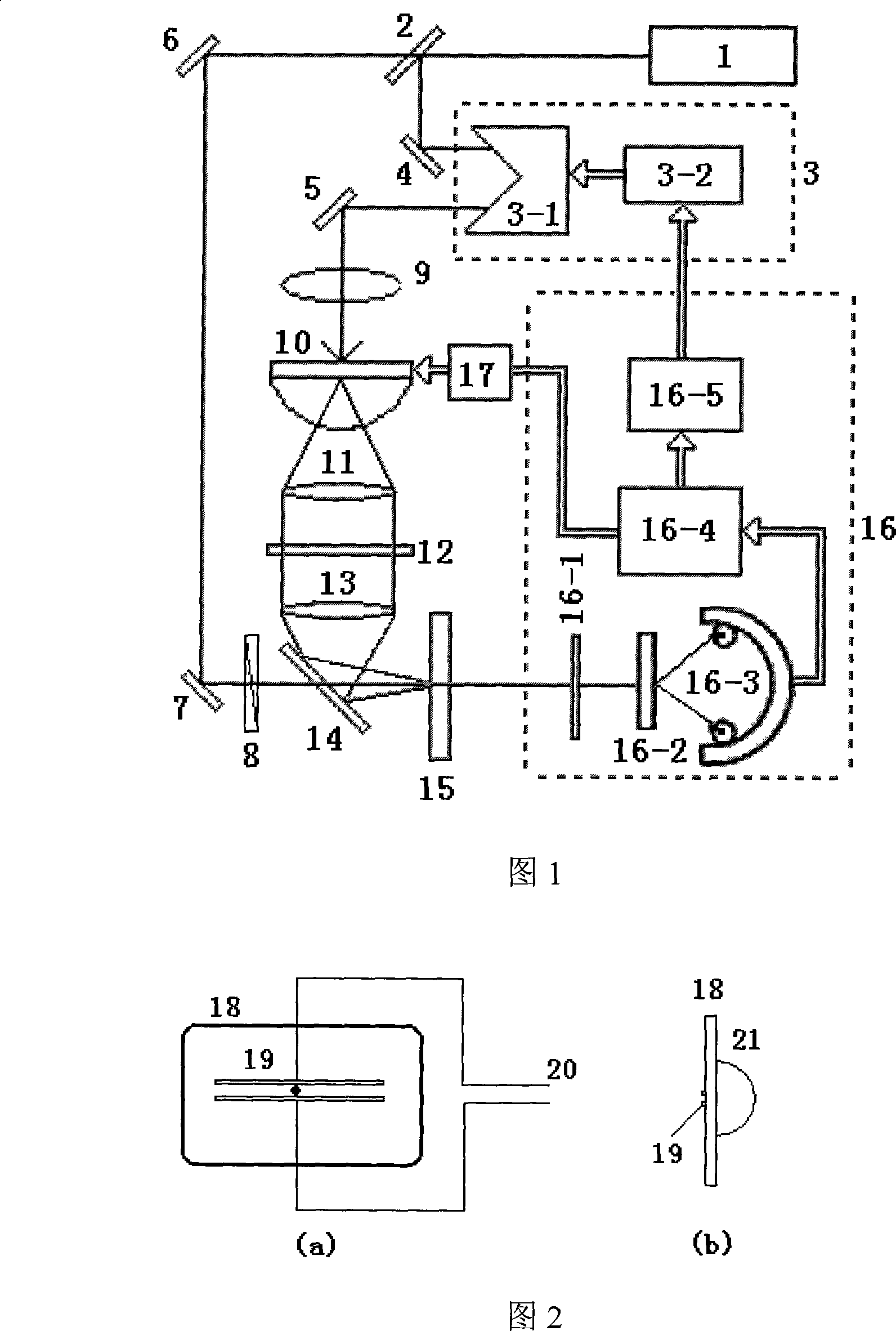
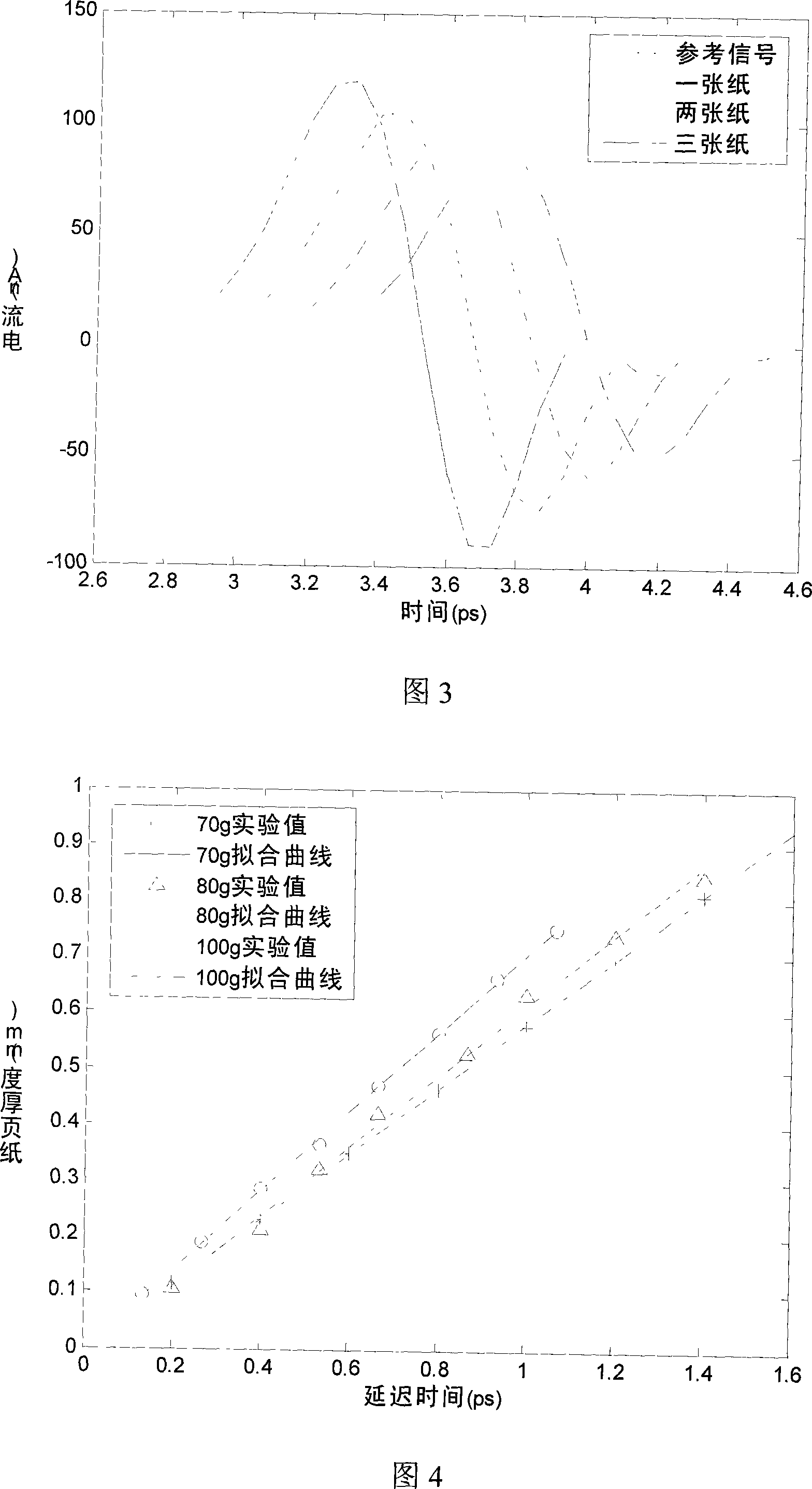
Page quantitative determination device and methods based on terahertz time-domain spectroscopic technology
InactiveCN101178355ASuitable for quantitative detectionImprove signal-to-noise ratioColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsData acquisitionPolarizer
The invention discloses a paper sheet quantitative detection device which is based on a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy technology and a method thereof. The detection device includes: a femtosecond laser, a beam splitter, an optical delay device, a reflective mirror, a focusing lens, a photoconductive antenna type terahertz transmitter, a polyethylene lens, a polarizer, a zinc telluride electro-optical crystal, a phase-locking amplifier, a high-power amplifier and a data collection and processing system. The invention makes use of the polyethylene lens for aligning the terahertz waves to the parallel light beams, and the polyethylene lens is used for focusing the terahertz waves on a terahertz detector after penetrating the paper sheet. The paper sheet quantitative detection method which is disclosed by the invention firstly establishes a paper sheet quantitative detection mathematical model, then respectively measures the time-domain signals of the terahertz waves penetrating the air and penetrating the paper sheet, extracts the delay time and applies the established mathematical model to calculate the paper sheet quantitative value. The invention has high precision of the measurement, strong anti-interference capability, small influence of multiple reflections and safe usage, so the invention can be used in the precise paper sheet quantitative detection of the field of paper making.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Photovoltaic Device Including A Back Contact And Method Of Manufacturing
ActiveUS20140284750A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseTe element
A photovoltaic device includes a substrate, a transparent conductive oxide, an n-type window layer, a p-type absorber layer and an electron reflector layer. The electron reflector layer may include zinc telluride doped with copper telluride, zinc telluride alloyed with copper telluride, or a bilayer of multiple layers containing zinc, copper, cadmium and tellurium in various compositions. A process for manufacturing a photovoltaic device includes forming a layer over a substrate by at least one of sputtering, evaporation deposition, CVD, chemical bath deposition process, and vapor transport deposition process. The process includes forming an electron reflector layer over a p-type absorber layer.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Cadmium telluride thin-film battery and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102779864AShorten the optical pathEnhanced light absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesElectrical batteryPhysics
The invention discloses a perform-optimized cadmium telluride thin-film battery and a manufacturing method for the cadmium telluride thin-film battery, wherein the cadmium telluride thin-film battery comprises a substrate and an epitaxy lamination layer; the epitaxy layer lamination sequentially consists of a conducting layer, a window layer, a light-absorbing layer, a back barrier layer and a back electrode from the bottom up; the window layer is of a textured cadmium sulfide thin-film layer; the light-absorbing layer is of a cadmium telluride thin-film layer, the back barrier layer is of a zinc telluride / copper-doped zinc telluride composite layer or a mercury telluride / copper-doped mercury telluride composite thin-film layer, and the back electrode is of one or more of graphite slurry or graphene slurry thin-film layer or copper thin-film layer, nickel thin-film layer, copper-nickel alloy thin-film layer and molybdenum thin-film layer. According to the cadmium telluride thin-film battery provided by the invention, the window area is textured and an optical path of a light-transmitting area is reduced, and thus a light-absorbing capacity is further improved and the better light-trapping effect is realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Device and method for quantitatively analyzing mine environment gas based on terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system
The invention discloses a device and a method for quantitatively analyzing mine environment gas based on a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system. The device comprises a femtosecond laser, a beam splitter, an optical delay device, a reflecting mirror, a polarizer, a focusing lens, a terahertz emitter, a gas sampling tank, indium tin oxide conductive glass, a zinc telluride electro-optical crystal, a high-power amplifier, a data acquiring and processing system, a quarter-wave plate, a Wollaston prism, a balance detector, a phase-locked amplifier and a computer. The method for quantitatively analyzing the mine environment gas, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a quantitative analysis model of the mine environment gas; secondly, acquiring a terahertz spectrum of gas to be measured through the device provided by the invention; thirdly, determining the content of each component in the mine environment gas by using the established quantitative analysis model. The method has the characteristics of simple structure, operability, high analysis speed, high accuracy and the like. The method provided by the invention can be applied to mixture analysis in other fields.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Heterojunction type photoelectric detector and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102610672AFlexibleWith transparentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionZinc telluride
The invention discloses a heterojunction type photoelectric detector and a manufacturing method of the heterojunction type photoelectric detector. The heterojunction type photoelectric detector is constructed by a p-type zinc telluride nano belt and n-type graphene. The photoelectric detector is extremely sensitive to visible light, is high in responsibility and gains and quick in response, thereby providing a good foundation for the application and the integration of nano materials in a photoelectric device.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
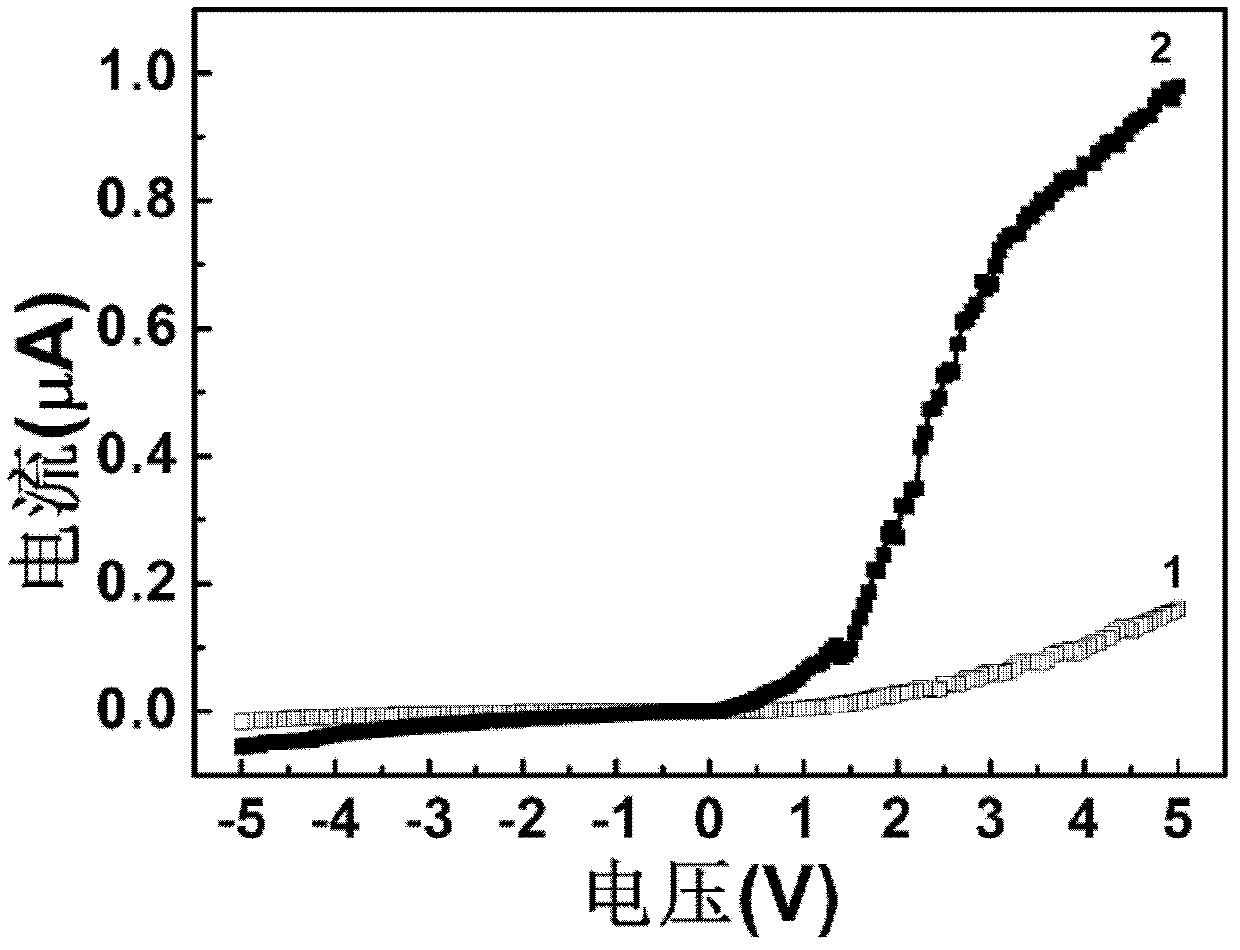
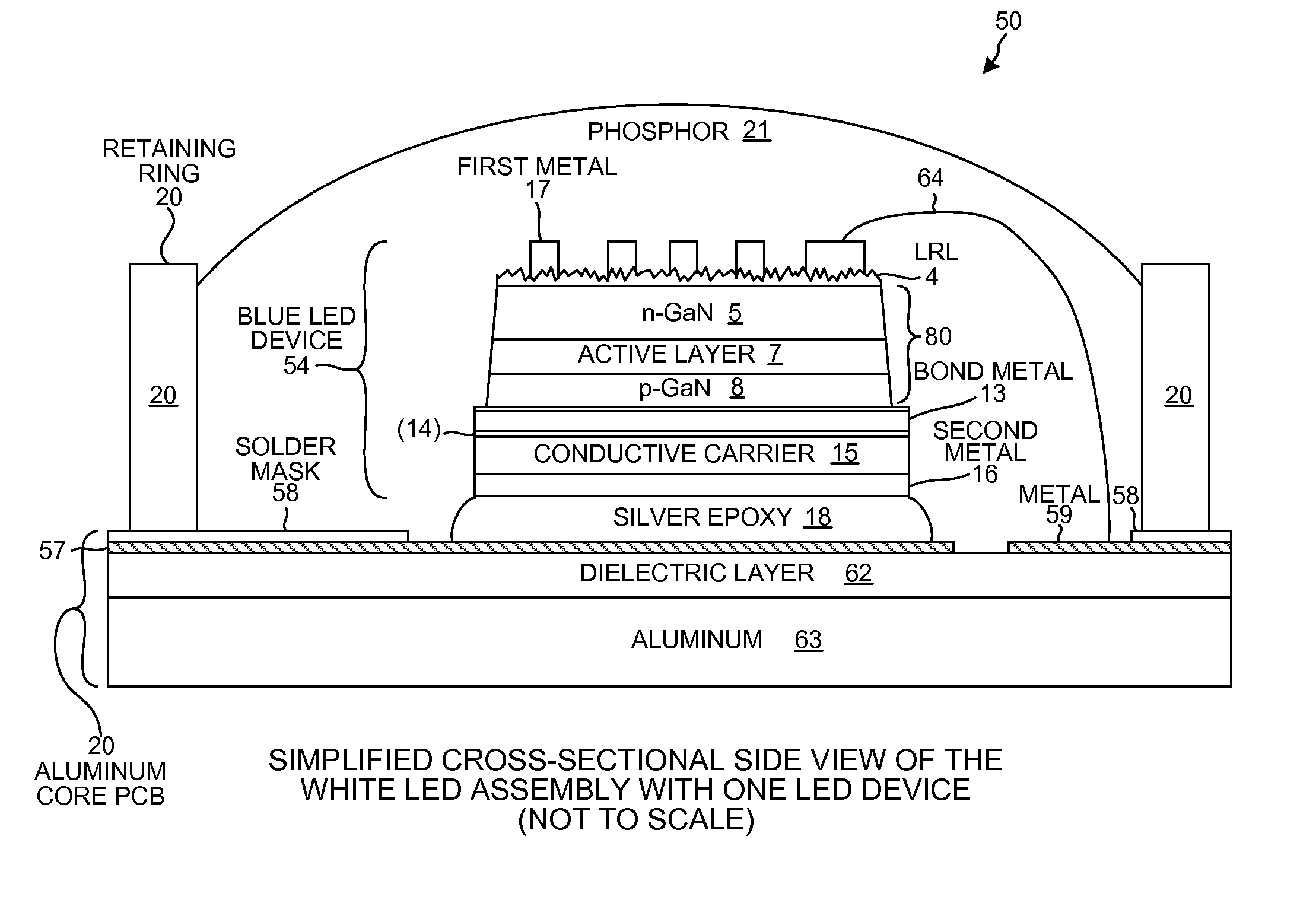
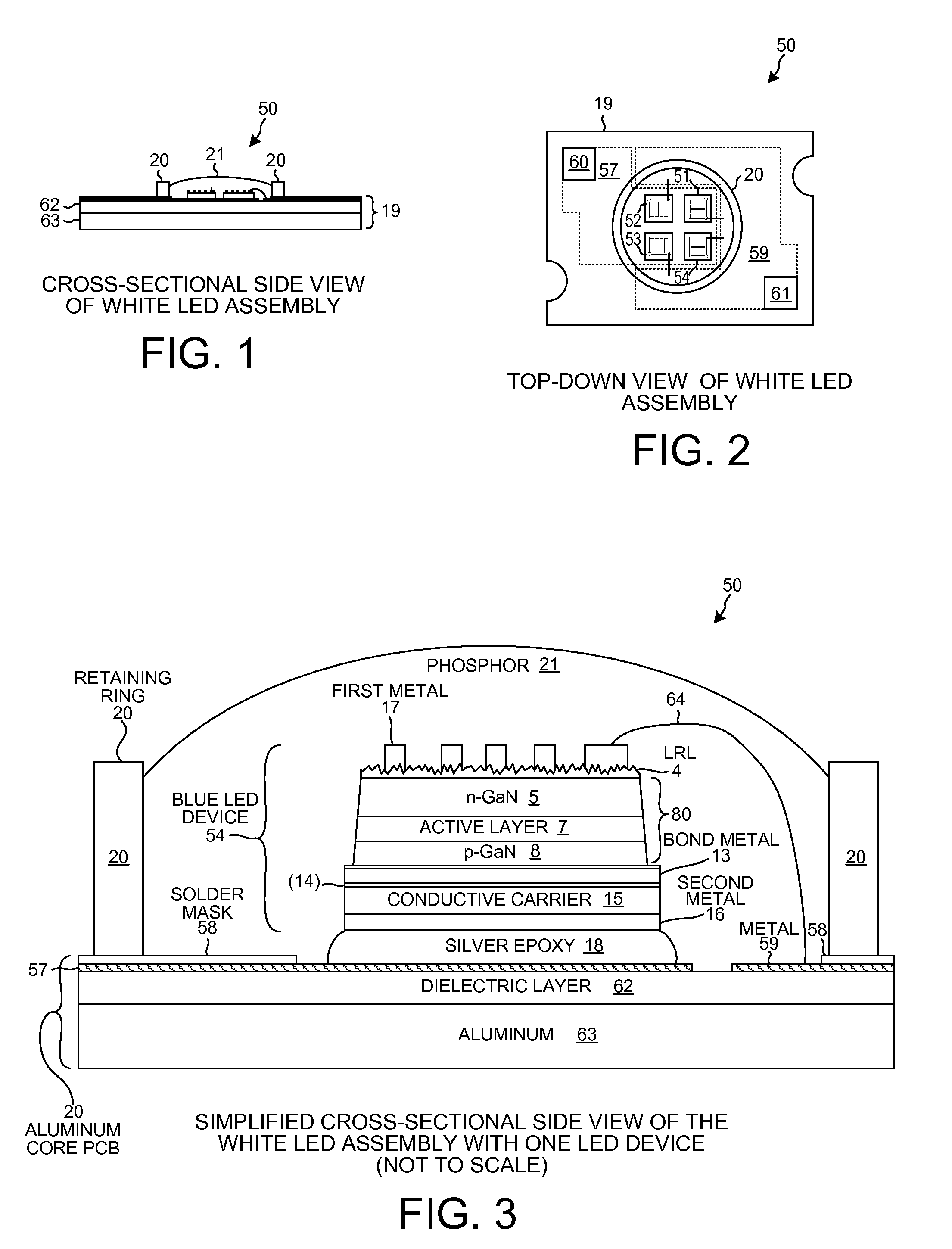
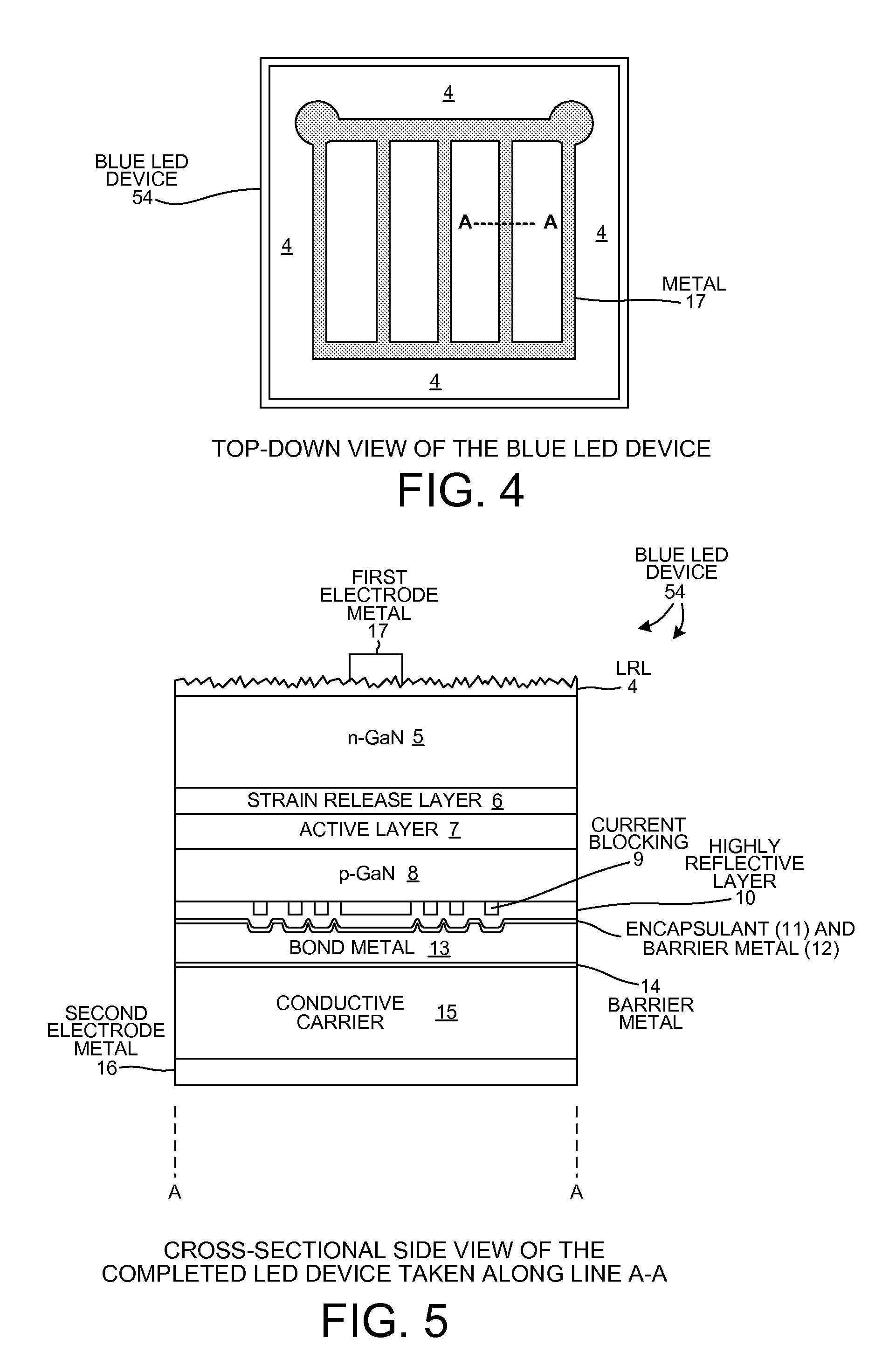
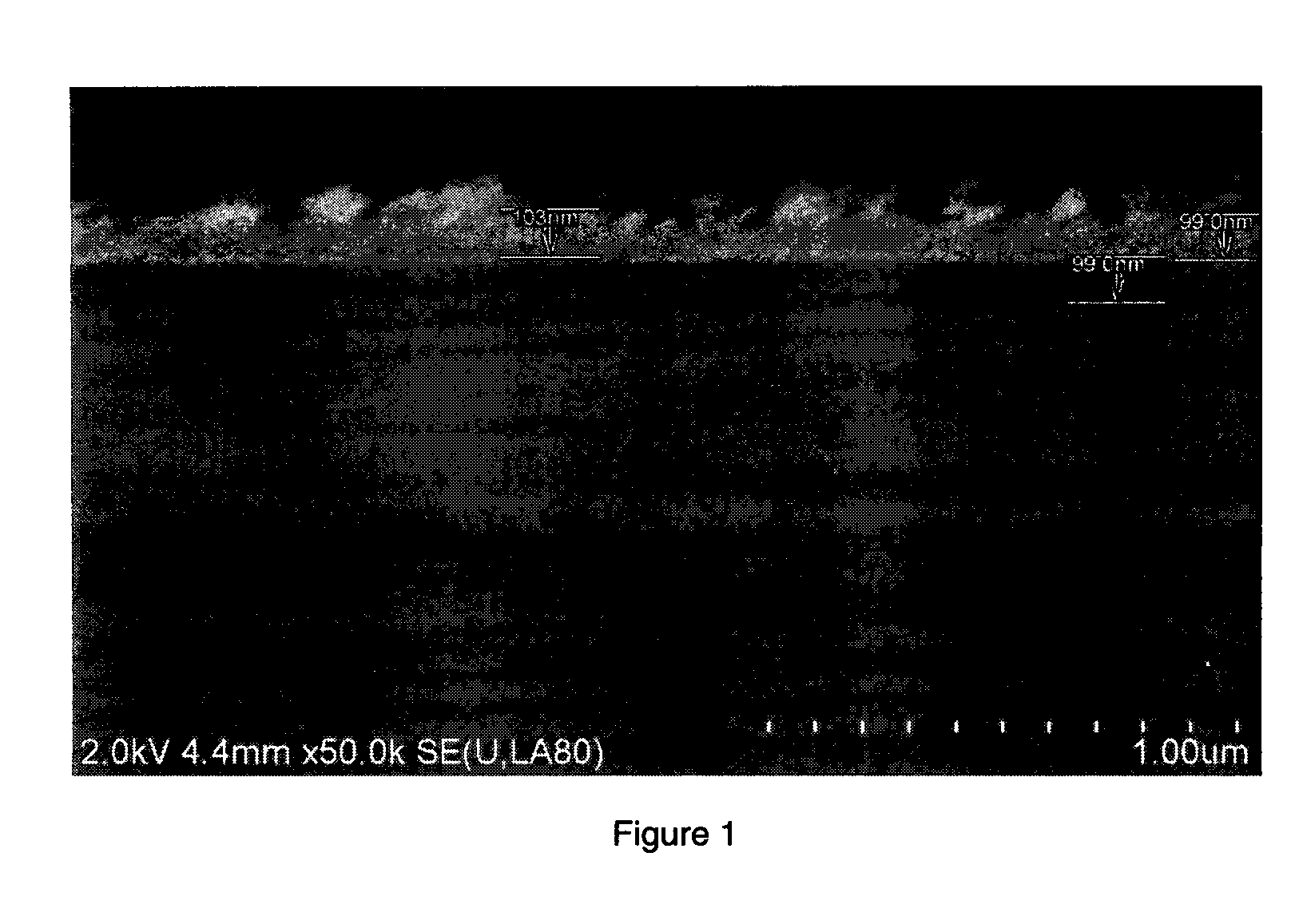
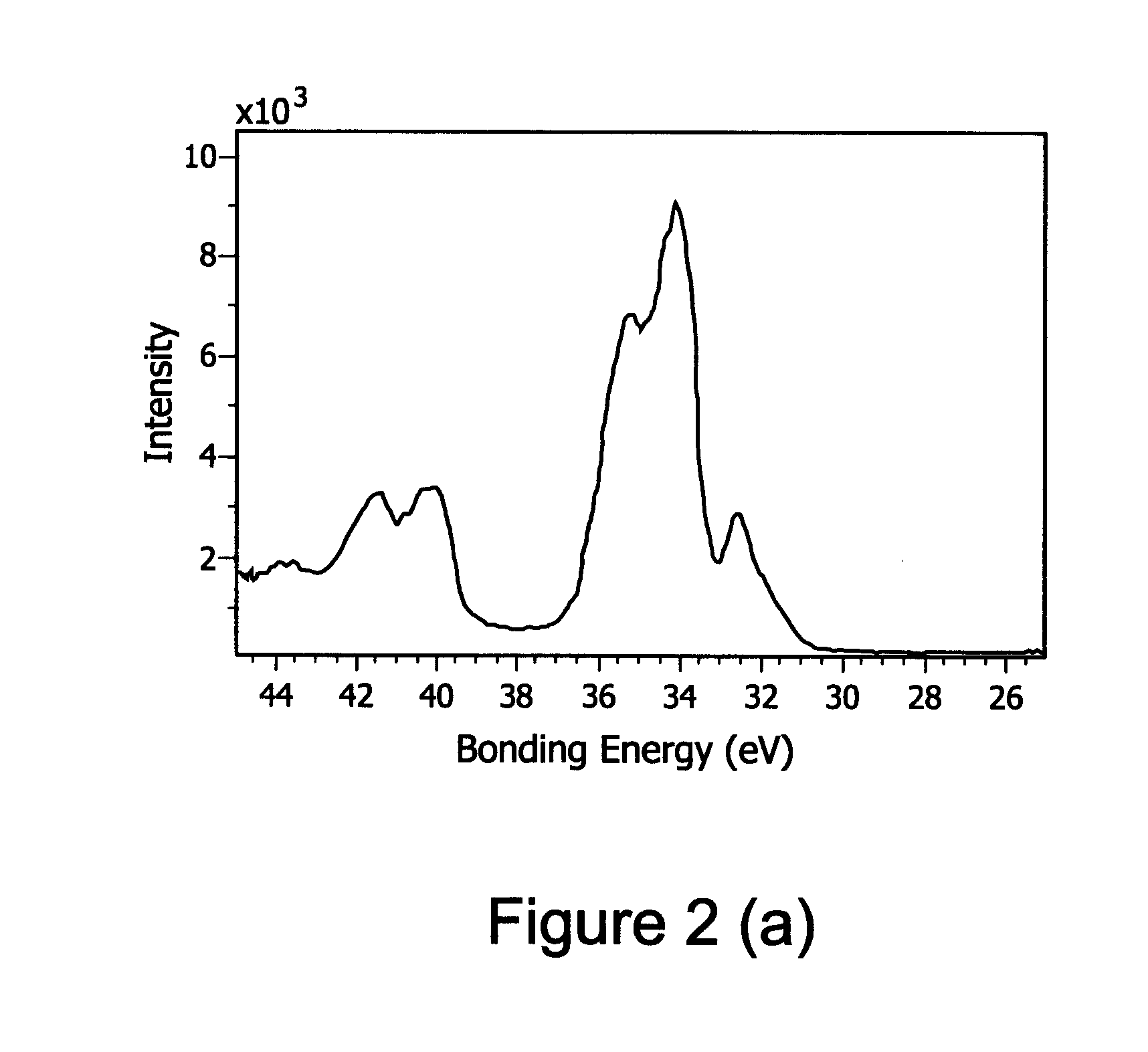
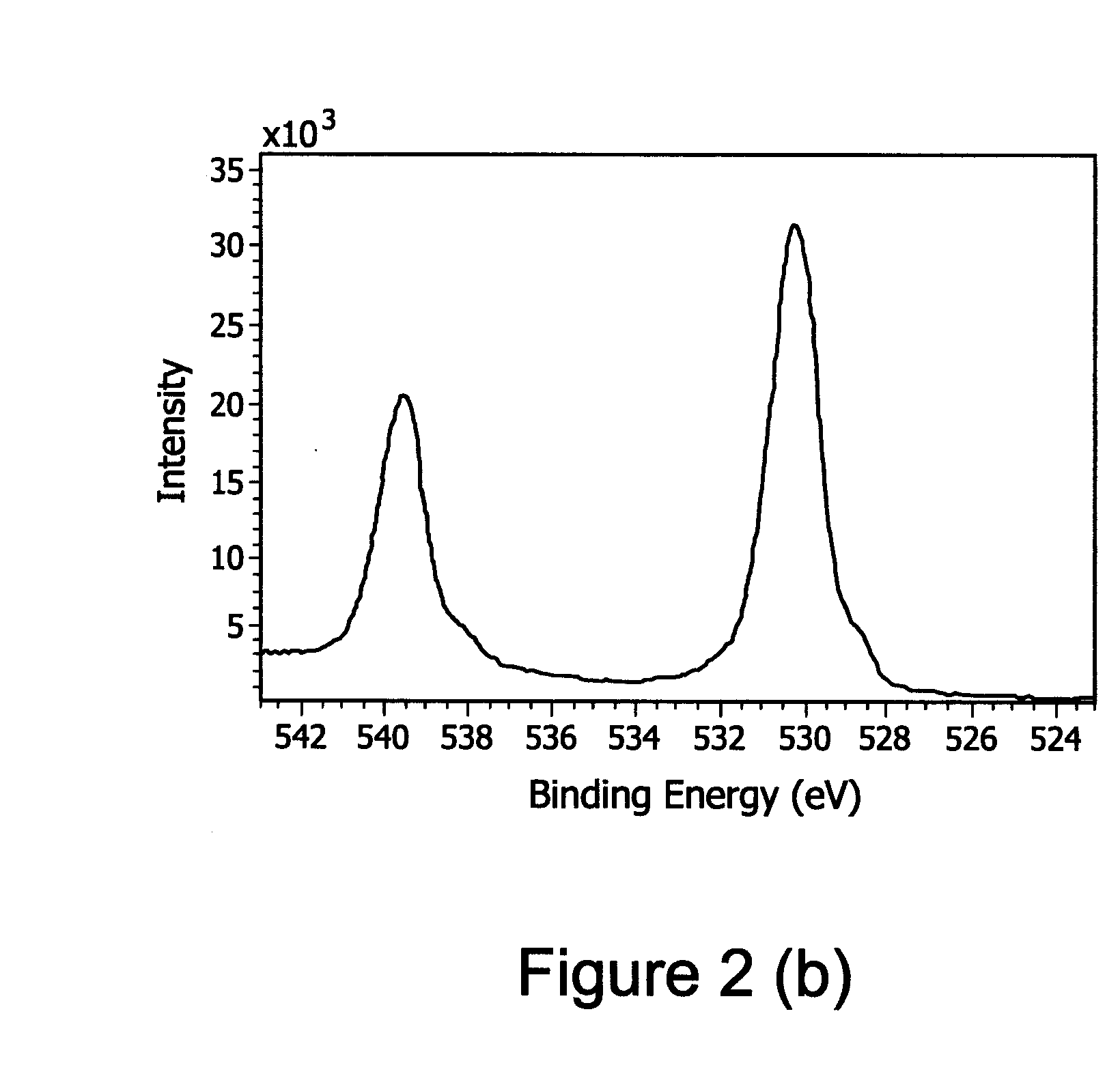
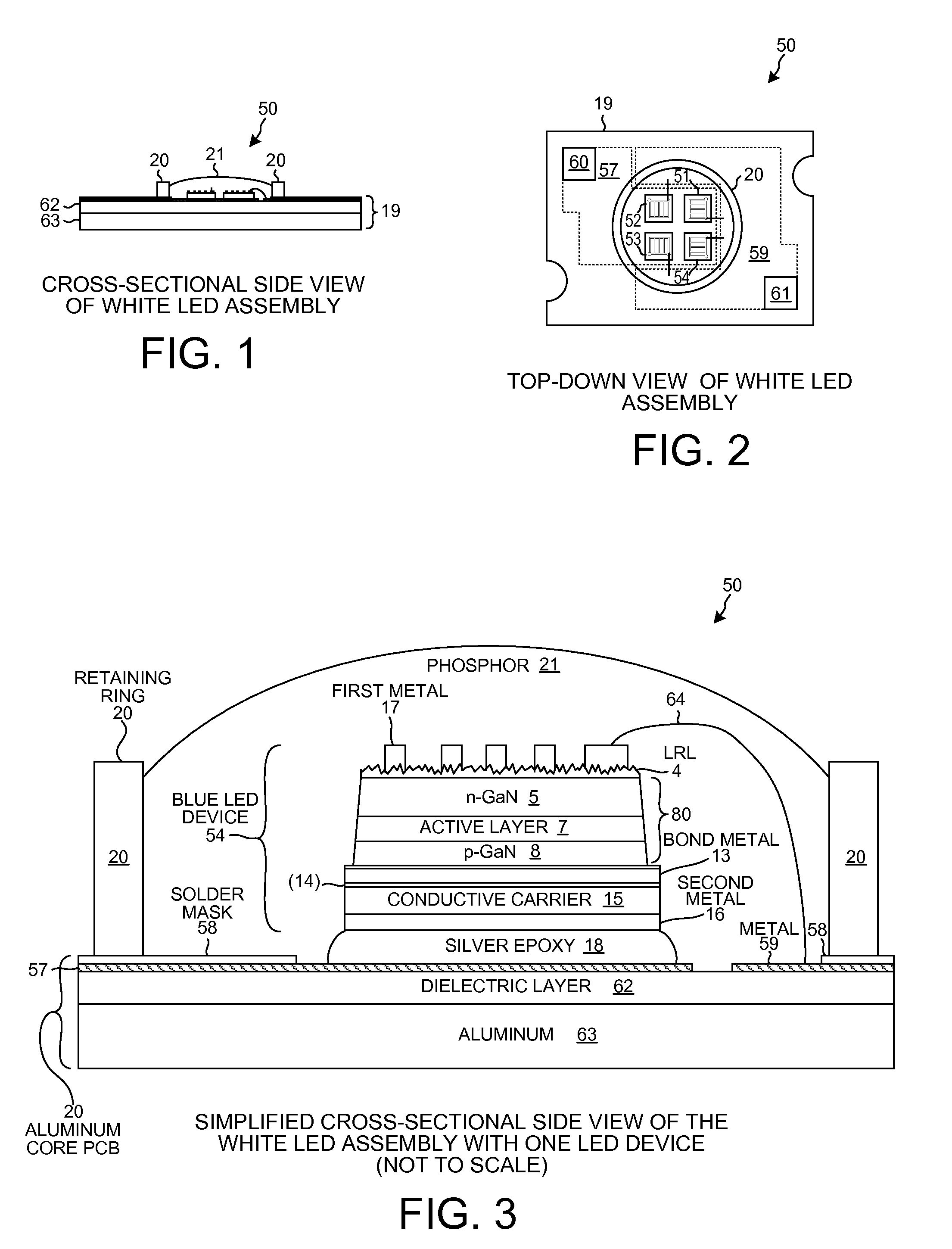
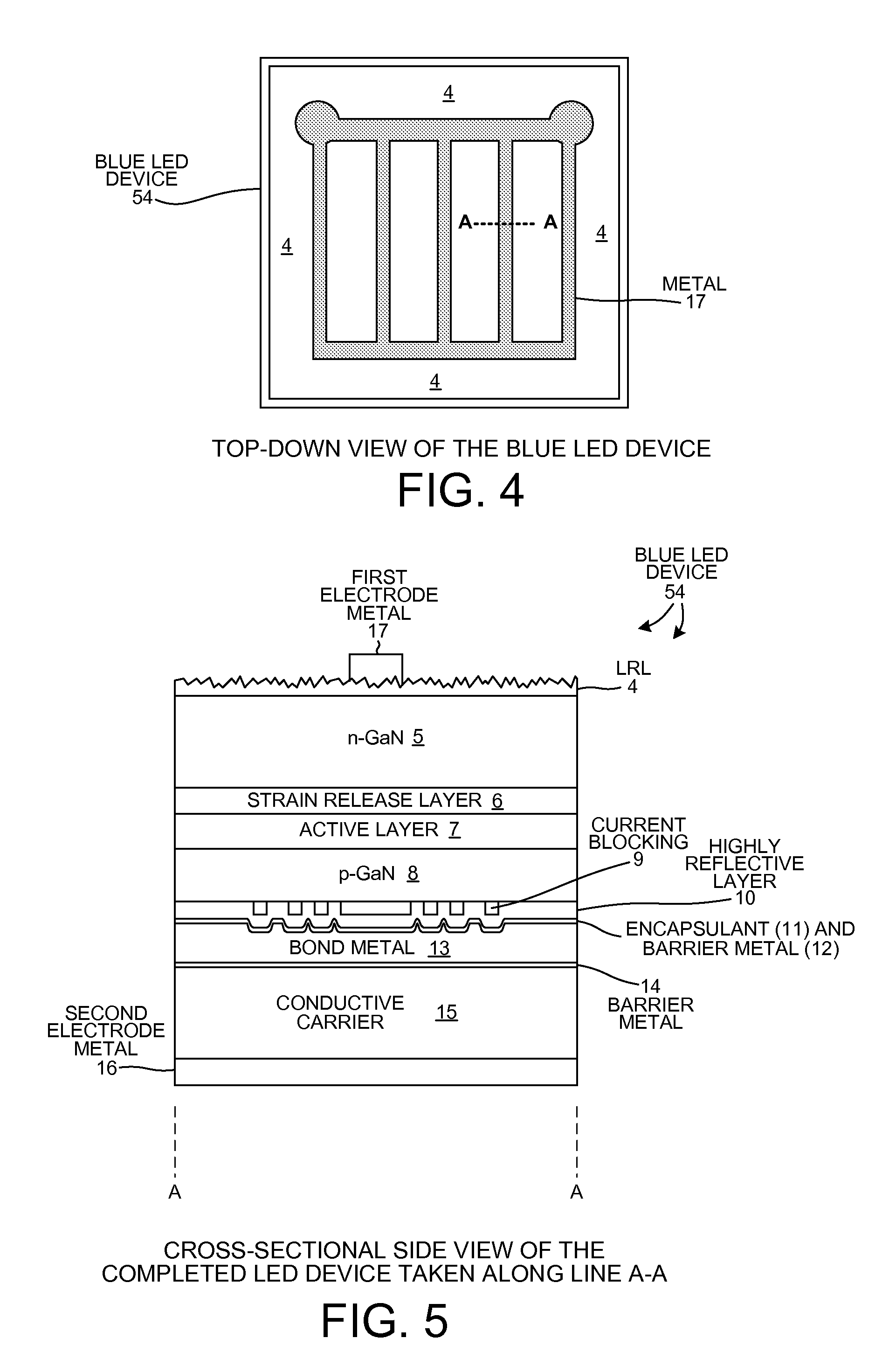
Buffer Layer for GaN-on-Si LED
InactiveUS20130056745A1Low costReduces lattice defect densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc tellurideLead structure
A buffer layer of zinc telluride (ZnTe) or titanium dioxide (TiO2) is formed directly on a silicon substrate. Optionally, a layer of AlN is then formed as a second layer of the buffer layer. A template layer of GaN is then formed over the buffer layer. An epitaxial LED structure for a GaN-based blue LED is formed over the template layer, thereby forming a first multilayer structure. A conductive carrier is then bonded to the first multilayer structure. The silicon substrate and the buffer layer are then removed, thereby forming a second multilayer structure. Electrodes are formed on the second multilayer structure, and the structure is singulated to form blue LED devices.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Growing technique of ZnTe monocrystal
InactiveCN101550586ASimple structureEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsFurnace temperatureZinc telluride
This invention relates to a bottom seed crystal growing technique of ZnTe monocrystal, comprising displacing the synthesized high-purity high-tellurium polycrystal ZnTe material into a PBN crucible with whose bottom being arranged with ZnTe seed crystal, sealing it in a quartz crucible and displacing it into a descending furnace of three-temperature region for crystal growth; controlling the furnace temperature and growing speed respectively at 1000-1250 degrees centigrade and 0.5-1 / h, wherein multiple equivalent crucible positions are arranged inside the descending furnace for the growth of multiple crystals at the same time; after the crystal growth, regulating position of crucible and controlling the furnace temperature for in-situ annealing to the crystal to obtain ZnTe monocrystal. The bottom seed crystal growing technique of ZnTe monocrystal in this invention comprises advantages of simply structured growing furnace, convenient operation, adjustable gradient temperature inside the hearth; besides, the in-situ annealing process contributes to reducing crystal disadvantage caused by heat stress. Since multiple equivalent stations are arranged inside the furnace, multiple crystals grow at the same time, thus reducing the crystal cost and being especially suitable for scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method of Making a Multicomponent Film
ActiveUS20120034767A1Consume precursor materialLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingIndiumZinc selenide
Described herein is a method and liquid-based precursor composition for depositing a multicomponent film. In one embodiment, the method and compositions described herein are used to deposit Germanium Tellurium (GeTe), Antimony Tellurium (SbTe), Antimony Germanium (SbGe), Germanium Antimony Tellurium (GST), Indium Antimony Tellurium (IST), Silver Indium Antimony Tellurium (AIST), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), Cadmium Selenide (CdSe), Zinc Telluride (ZnTe), Zinc Selenide (ZnSe), Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) films or other tellurium and selenium based metal compounds for phase change memory and photovoltaic devices.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Buffer layer for GaN-on-Si LED
InactiveUS8686430B2Reduce concentrationSheet resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc tellurideLead structure
A buffer layer of zinc telluride (ZnTe) or titanium dioxide (TiO2) is formed directly on a silicon substrate. Optionally, a layer of AlN is then formed as a second layer of the buffer layer. A template layer of GaN is then formed over the buffer layer. An epitaxial LED structure for a GaN-based blue LED is formed over the template layer, thereby forming a first multilayer structure. A conductive carrier is then bonded to the first multilayer structure. The silicon substrate and the buffer layer are then removed, thereby forming a second multilayer structure. Electrodes are formed on the second multilayer structure, and the structure is singulated to form blue LED devices.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
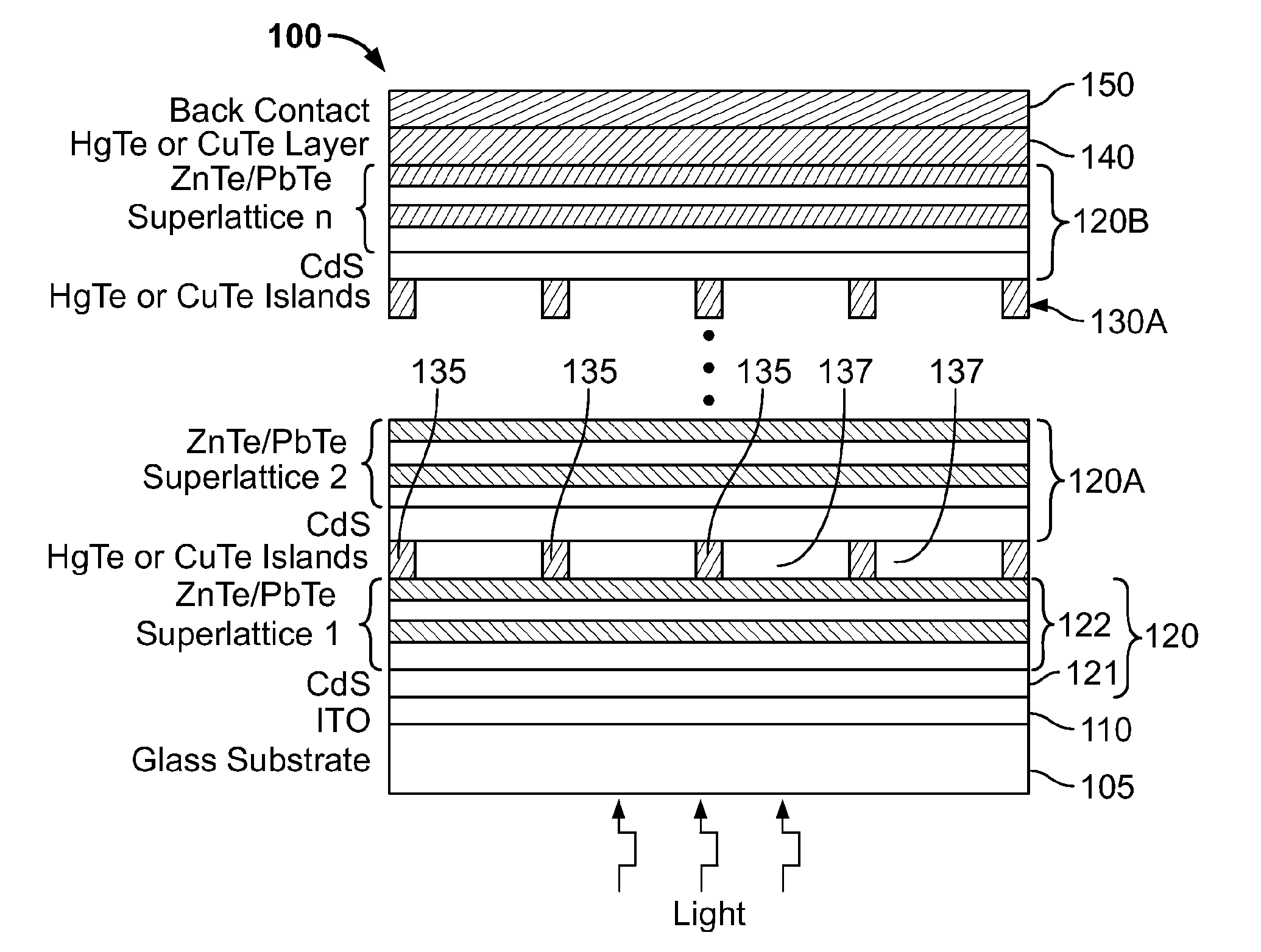
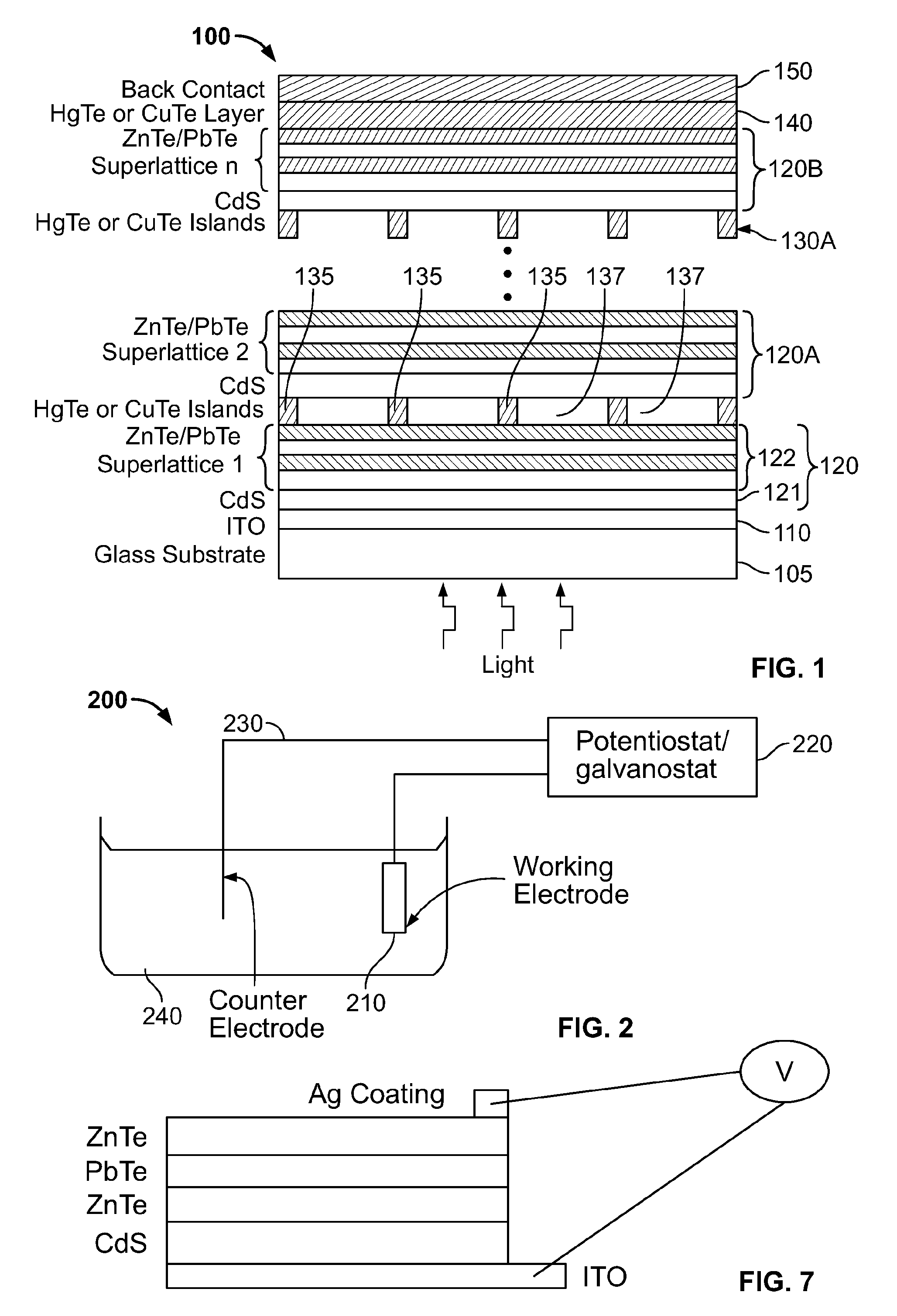
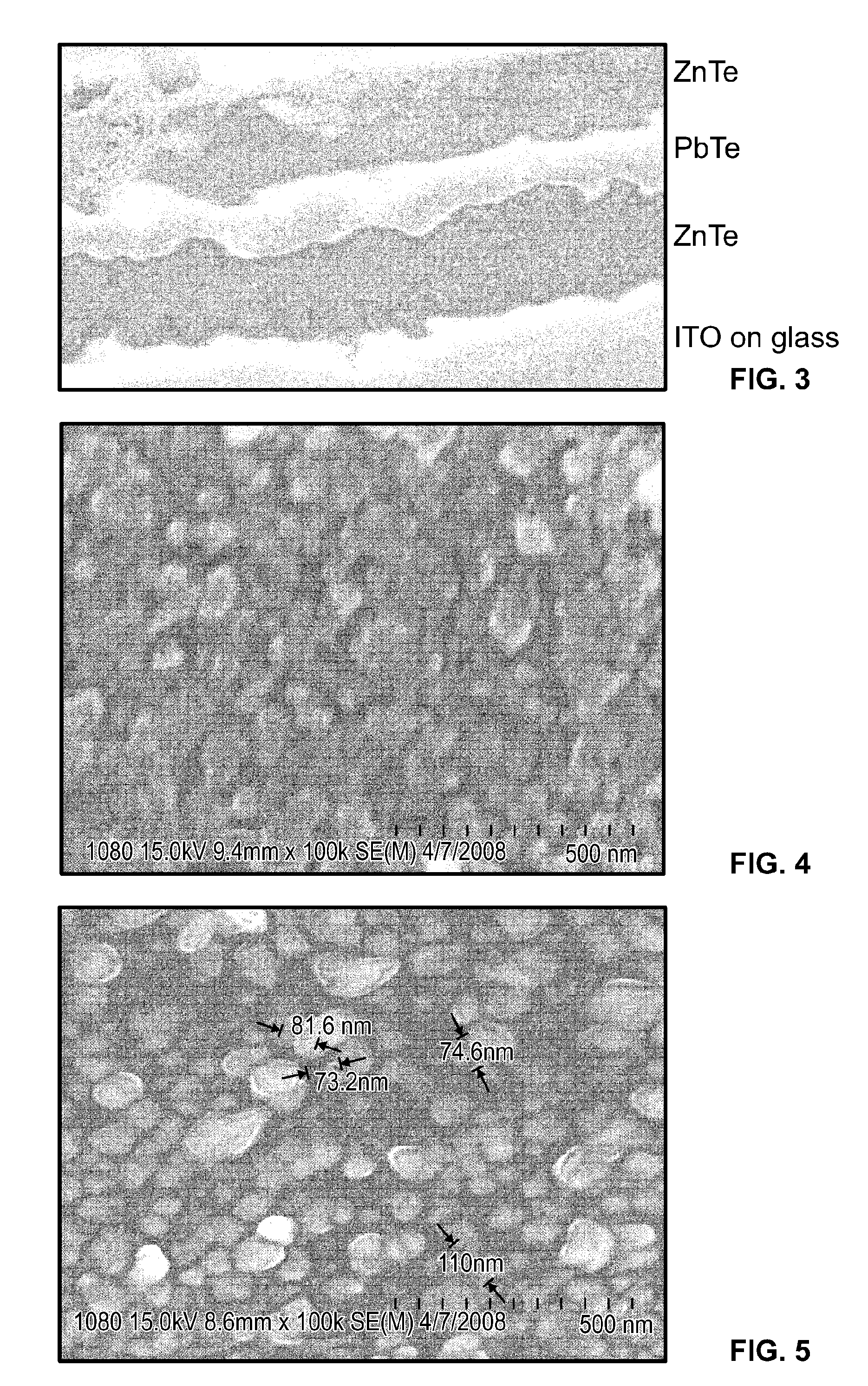
Solar cells and method of making solar cells
InactiveUS20110155207A1PV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc tellurideElectrical battery
A multi junction photovoltaic cell includes at least two P-N junctions electrically connected to each other in series. Each P-N junction includes a P-type absorber layer and a N-type emitter layer, each P-type absorber layer including a plurality of alternating thin film layers of zinc telluride and lead telluride, wherein zinc telluride and lead telluride have respective bandgaps when in bulk thickness and the effective bandgap of each P-type absorber layer is between the respective bandgaps, The effective bandgap of at least one P-type absorber layer is different from that of at least one other P-type absorber layer.
Owner:VILLANOVA UNIVERSITY
Multiple layer synthesis furnace device
InactiveCN101118111AEnsure safetyEnsure production capacityMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesZinc tellurideInsulation layer
The present invention relates to a multilayer compound synthetic furnace device, which is characterized in that an insulation layer (2), a heating wire (3), an insulation board (4) and a synthetic reaction tube (5) are arranged in a synthetic furnace (1), the furnace chamber of the synthetic furnace is divided into a plurality of synthetic chambers with the insulation board, and a plurality of synthetic reaction tubes (5) are put in each synthetic chamber, the thermal field temperature gradient of the furnace chamber is controlled in less or equal to plus or minus 5 DEG C, and each synthetic chamber being separated ensures the security during the synthetic process. The multilayer compound synthetic furnace device is applied to the synthesis of cadmium telluride, zinc telluride and lead telluride.
Owner:四川鑫龙碲业科技开发有限责任公司
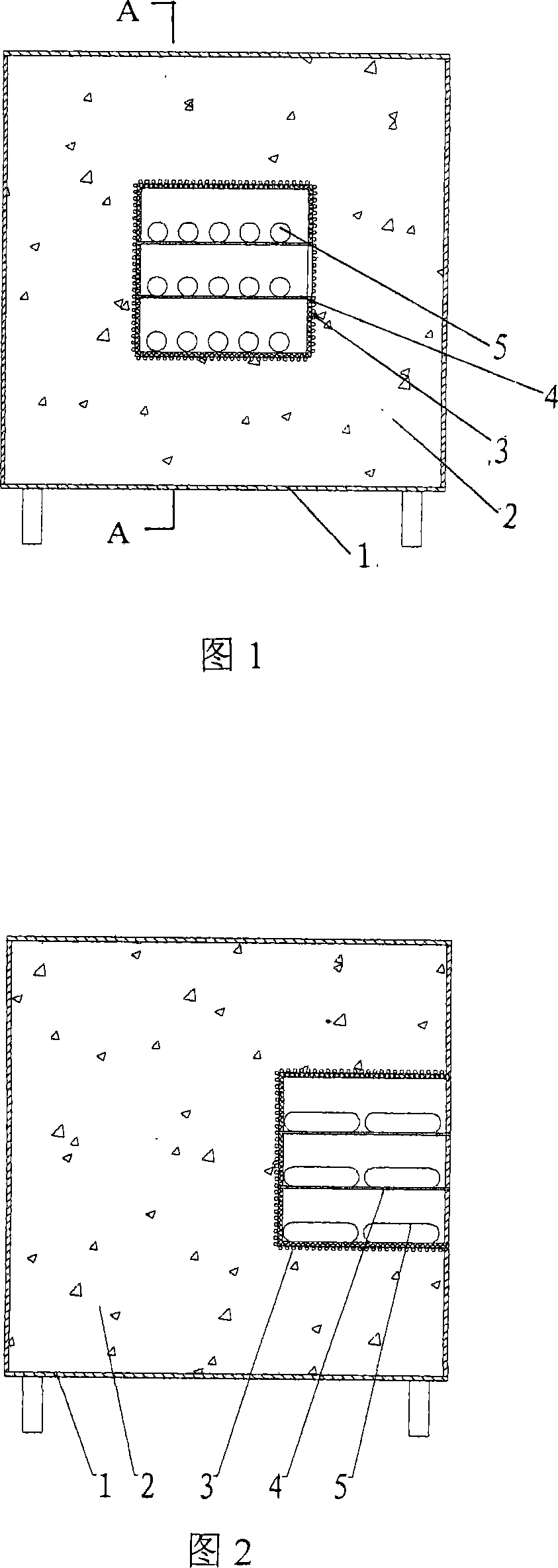
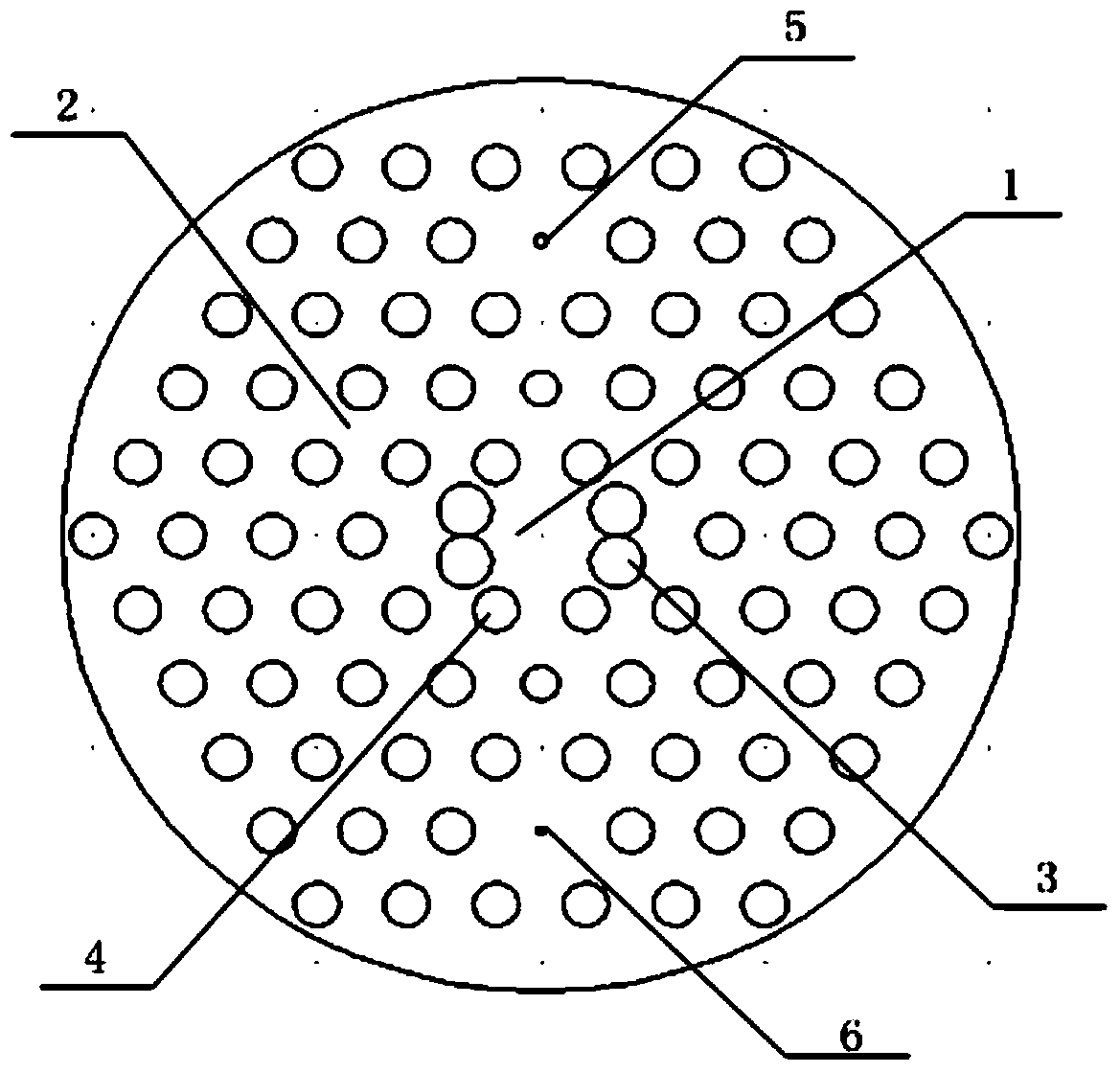
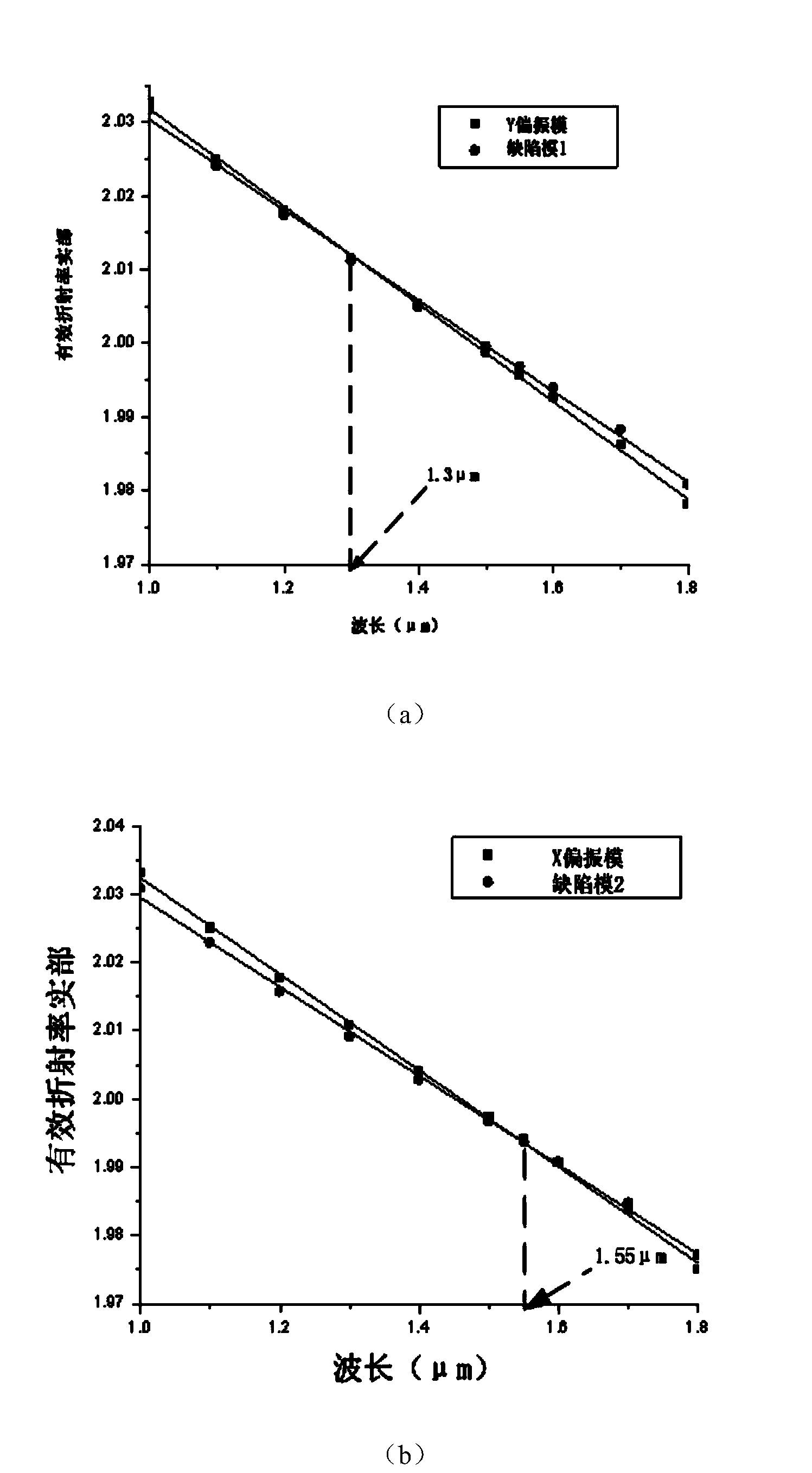
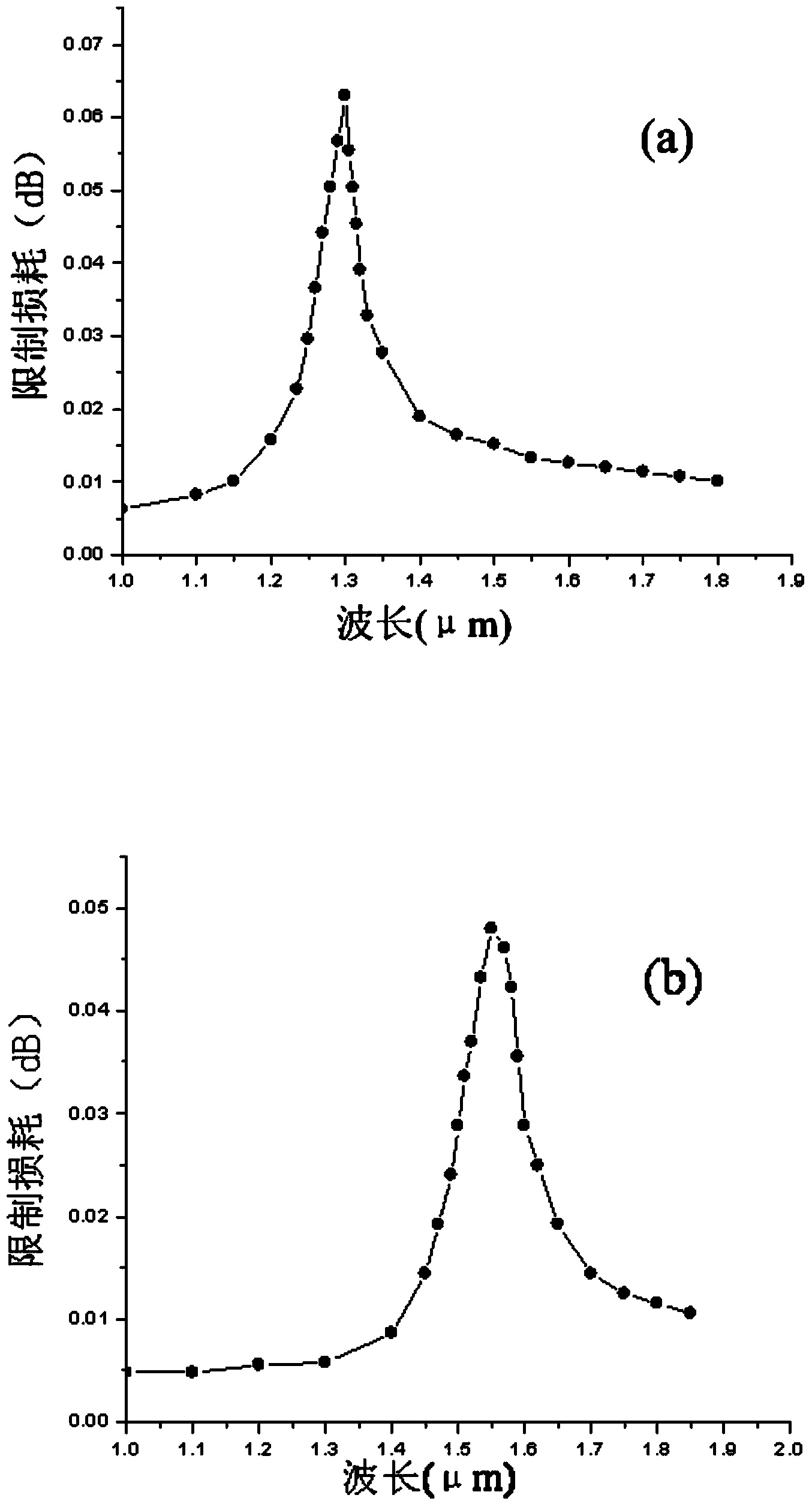
Single-core photonic crystal fiber polarization splitter
InactiveCN104297837ASimple structureImprove spectroscopic effectCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFiberTellurate
A photonic crystal fiber polarization splitter is composed of a fiber core and a wrapping layer, wherein the refractive index of the wrapping layer is smaller than that of the fiber core, the background material of the wrapping layer is tellurate, four round air holes a and four round air holes b in the center of the wrapping layer jointly form a fiber core area, the round air holes a are arranged in two rows, the two round air holes a in each row are tangential, the fiber core is encircled by the wrapping layer, the wrapping layer is formed by round air holes b which have the same diameters and are arranged periodically in a regular hexagon mode, the total number of the layers of the round air holes b which are periodically arranged is five, and a small round air hole c and a small round air hole d are formed in the outer side of the wrapping layer and located at the positions symmetrical about the fiber core. The photonic crystal fiber polarization splitter has the advantages that zinc telluride serves as the background material of the polarization splitter, the polarization splitter is simple in structure, good in beam splitting effect and easy to manufacture; the small air holes are formed in the outer side of the wrapping layer to form defects, a defect mode is generated so that the defect mode is coupled to a fiber core mode, and the purpose that light is propagated in the orthogonal direction to be split is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped carbon-coated zinc telluride nanometer wire and application thereof serving as sodium-ion battery negative electrode material
ActiveCN108365211AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle performanceMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsIon exchangeTe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nitrogen-doped carbon-coated zinc telluride nanometer wire and application thereof serving as a sodium-ion battery negative electrode material. Firstly, a tellurium nanometer wire is synthesized by using a hydrothermal method, the tellurium nanometer wire is stirred with a silver nitrate solution at room temperature to be converted as the silver telluride nanometer wire, then silver telluride nanometer wire reacts with a zinc nitrate solution to be converted as the zinc telluride nanometer wire by using an ion exchange reaction, the zinc telluride nanometer wire is coated with dopamine hydrochloride, and the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated zinc telluride nanometer wire is obtained through high temperature calcinations under the argon or nitrogen atmosphere. The preparation method of the composite material is simple, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the obtained material has the good cycling stability and specific capacity when serving as the sodium-ion battery negative electrode, and can be taken as the excellent sodium-ion battery negative electrode material.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Charging unit based on wristwatch band
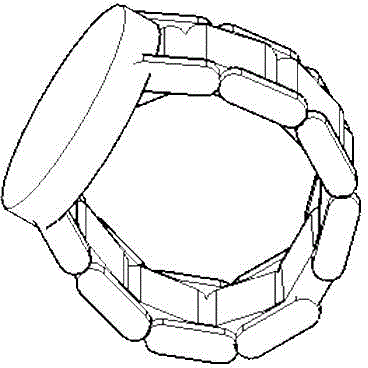
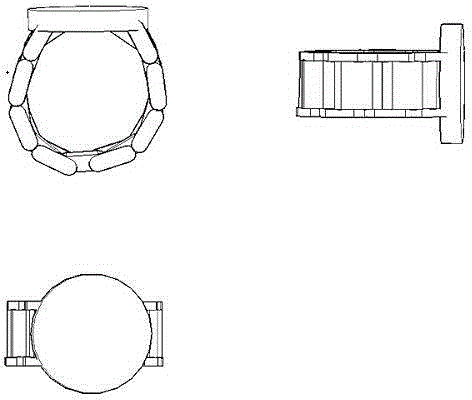
InactiveCN104617618ASuitable living environmentSuitable for wild environmentBatteries circuit arrangementsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectZinc tellurideWafering
The invention relates to a charging unit based on a wristwatch band, belonging to the technical field of environment-friendly power supplying. An assembling method of the charging unit comprises the steps: manufacturing thermoelectric power generation wafers, made from zinc telluride and alloy thereof used as subject materials, into wristwatch chains; connecting each power generation wafer by buckles and realizing the series connection of power generation modules to obtain big enough voltage. The obtained electricity is connected to a lithium battery and an external port of a dial plate by means of a stabilized voltage amplification module and a charging module; the lithium battery is connected to power consumption equipment in the dial plate. The charging unit is capable of realizing thermoelectric power generation by utilizing the temperature difference between a human skin and the surrounding, is capable of charging the lithium battery or the outside circuit at any time and is a portable and environment-friendly power supplying device for utilization of green resources. The electric energy of the thermoelectric power generation obtained by assembling is capable of permanently charging an electronic watch in the dial plate and is capable of charging an external small Bluetooth headset.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
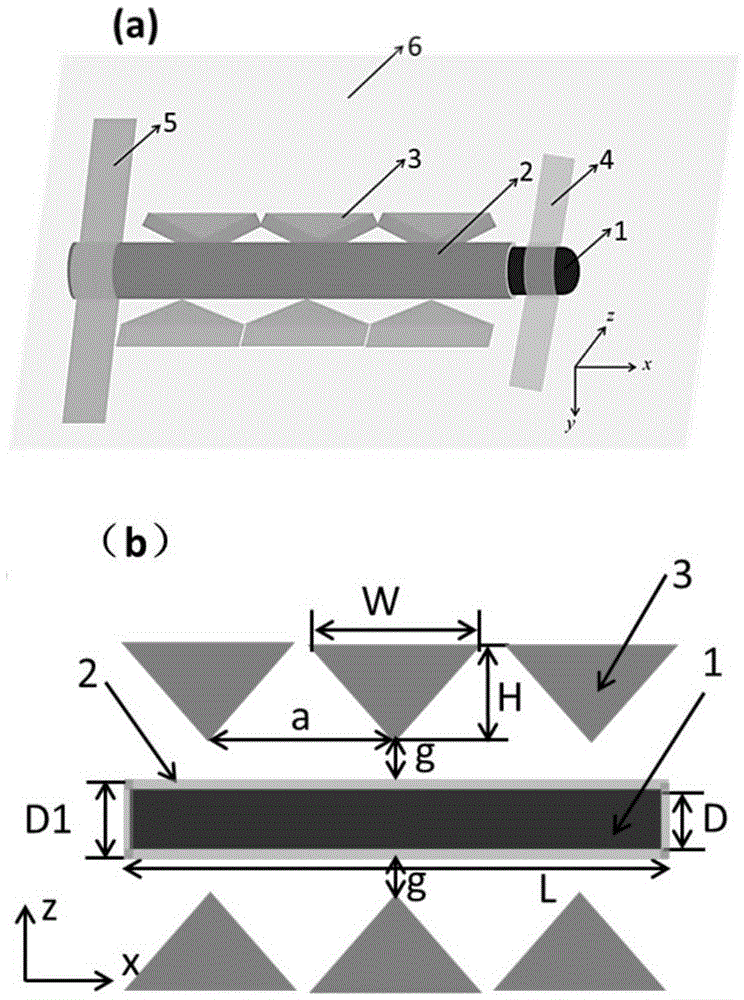
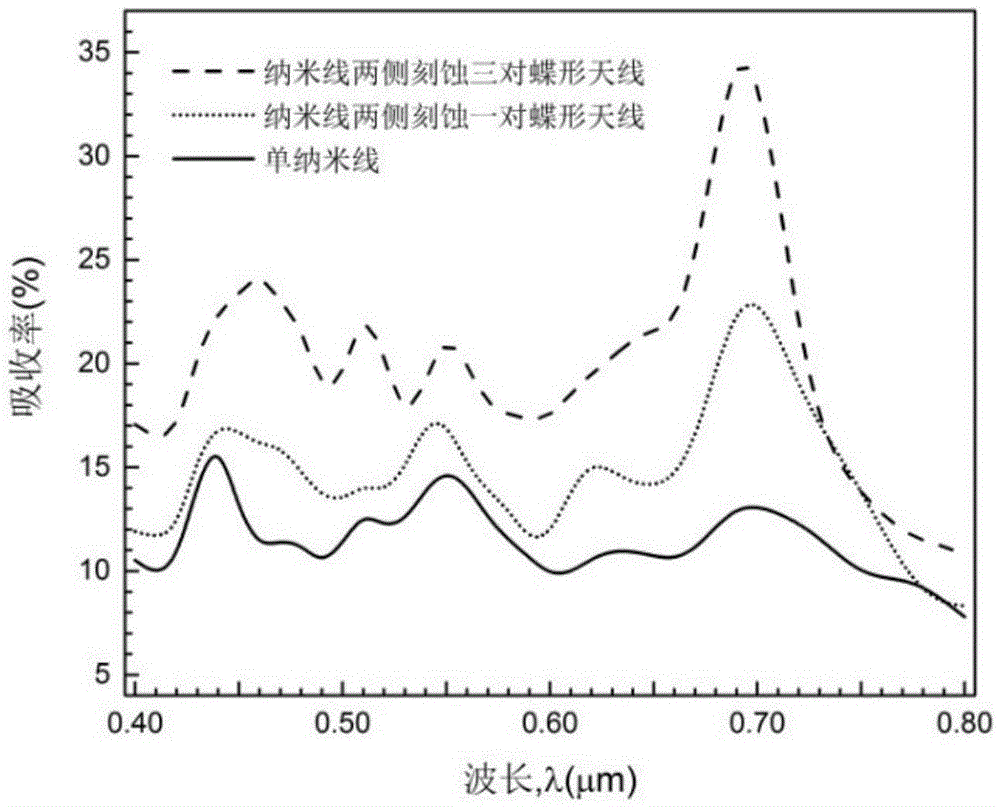
Nanowire intermediate band solar cell structure based on butterfly-shaped plasmon antenna enhancement
InactiveCN105576054AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologyPhotovoltaic energy generationNanowireOxygen
The invention discloses a nanowire intermediate band solar cell structure based on a butterfly-shaped plasmon enhancement antenna. A flat oxygen doped zinc telluride / zinc oxide core shell structure nanowire is arranged on a silicon dioxide or quartz substrate. The zinc oxide is arranged on an outer layer. A nanowire length of the oxygen doped zinc telluride / zinc oxide core shell structure is 1-10 micron. A diameter of the core shell structure nanowire is 200-400 nm. A thickness of the zinc oxide is 5-40 nm. Two sides of the core shell structure nanowire are provided with several pairs of metal-aluminum butterfly-shaped antennas. Each pair of the metal-aluminum butterfly-shaped antennas is a tip-to-tip triangular pyramid structure. In each pair of the butterfly-shaped antennas, the two tip-to-tip triangular pyramids can be centrosymmetric relative to the nanowire and can be non-centrosymmetrical. Problems that a state density of an intermediate band of an intermediate band solar cell absorption layer is small and absorption efficiency is low are mainly solved, sunlight full spectrum absorption is enhanced and overall photoelectric conversion efficiency of a device is increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Photovoltaic device including a back contact and method of manufacturing
ActiveUS9269849B2Final product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEvaporation (deposition)Materials science
A photovoltaic device includes a substrate, a transparent conductive oxide, an n-type window layer, a p-type absorber layer and an electron reflector layer. The electron reflector layer may include zinc telluride doped with copper telluride, zinc telluride alloyed with copper telluride, or a bilayer of multiple layers containing zinc, copper, cadmium and tellurium in various compositions. A process for manufacturing a photovoltaic device includes forming a layer over a substrate by at least one of sputtering, evaporation deposition, CVD, chemical bath deposition process, and vapor transport deposition process. The process includes forming an electron reflector layer over a p-type absorber layer.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
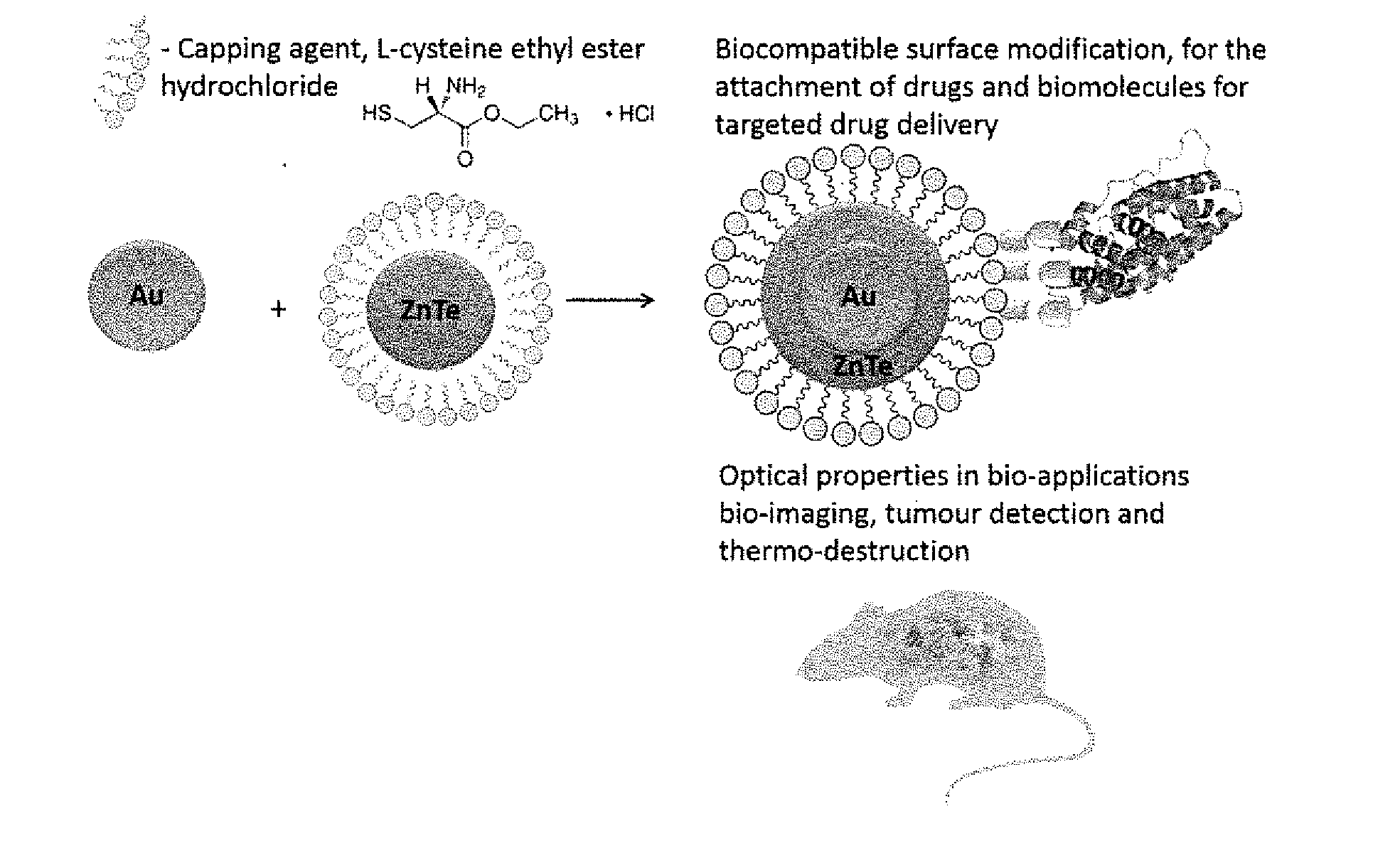
The synthesis of core-shell metal-semiconductor nanomaterials
InactiveUS20160175254A1Carefully controlledLow toxicityPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyZinc tellurideOptical property
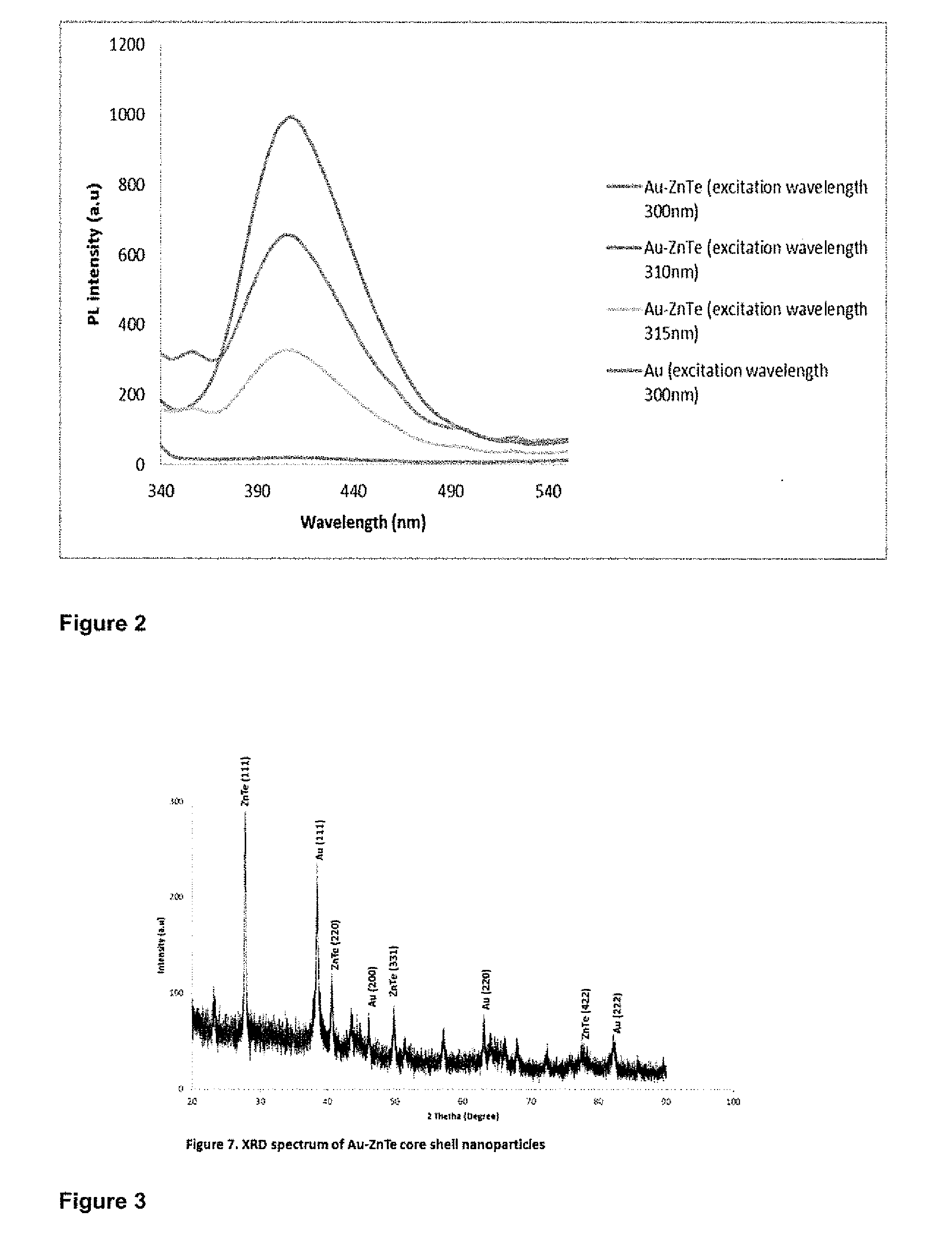
A solution-based route to biocompatible, cysteine-capped gold-zinc telluride (Au—ZnTe) core / shell nanoparticles with potential in biomedical applications is described. The optical properties of the core / shell nanoparticles show no features of the individual parent components. The tunable emission properties of the semiconductor shell render the system useful for imaging and biological labelling applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ZULULAND
Preparation method of zinc telluride
InactiveCN103950904AHigh purityAvoid touchingBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsZinc tellurideTe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of zinc telluride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: introducing an inert gas to exhaust oxygen gas after adding a material mixture of tellurium and zinc into a graphite crucible, and sealing the crucible; placing the crucible in a sealed heat-resistant container, and introducing the inert gas after exhausting the oxygen gas in the sealed heat-resistant container; regulating pressure in the heat-resistant container to 0.6-3.0 MPa, rising a temperature to 1000-1500 DEG C, and cooling after preserving the heat for 1-4 hours; exhausting gas and releasing pressure after cooling the temperature lower than 60 DEG C, taking out the material mixture to obtain the zinc telluride. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, in an inert atmosphere, the zinc telluride is synthesized by virtue of reaction of tellurium and zinc under a certain pressure; the preparation method is short in process time, less in needed equipment and low in excess coefficient, can be used for improving the product purity of the zinc telluride, lowering the production cost to a certain extent, and improving the production efficiency.
Owner:FIRST RARE MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing water phase non-toxic quantum dot zinc telluride
InactiveCN101708827AGood water solubilityNo toxicityLuminescent compositionsBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsIce waterParticle injection
The invention provides a method for preparing water-phase non-toxic quantum dot zinc telluride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, NaHTe preparation: sodium borohydride is dissolved in deionized water, tellurium powder is quickly added into the solution, and a reactor is sealed by a rubber plug which is provided with a pin hole to be communicated with the outside for releasing hydrogen generated in reaction; in the reacting process, the system is cooled by ice-water bath, after several hours, the black tellurium powder disappears, white sodium borate is generated, and upper clear NaHTe solution is light purple; b, preparation of Zn+TGA thioglycolic acid precursor: Zn(NO3)2 is added to a conical flask, a certain amount of TGA is added to the solution by a miniature pipetting gun, pH of the mixed solution of the Zn(NO3)2 and the TGA is adjusted by NaOH after sufficient stirring, the solution is kept for later use after sufficient stirring; and c, preparation of water phase ZnTe quantum dot: the mixed solution prepared in the step b is deoxidized by N2 gas, and the NaHTe in the step 1 is quantitatively taken by a particle injection needle, and is injected into the mixed solution, and the solution is continuously stirred to obtain ZnTe nanometer crystal.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnetic random access memory based on III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor
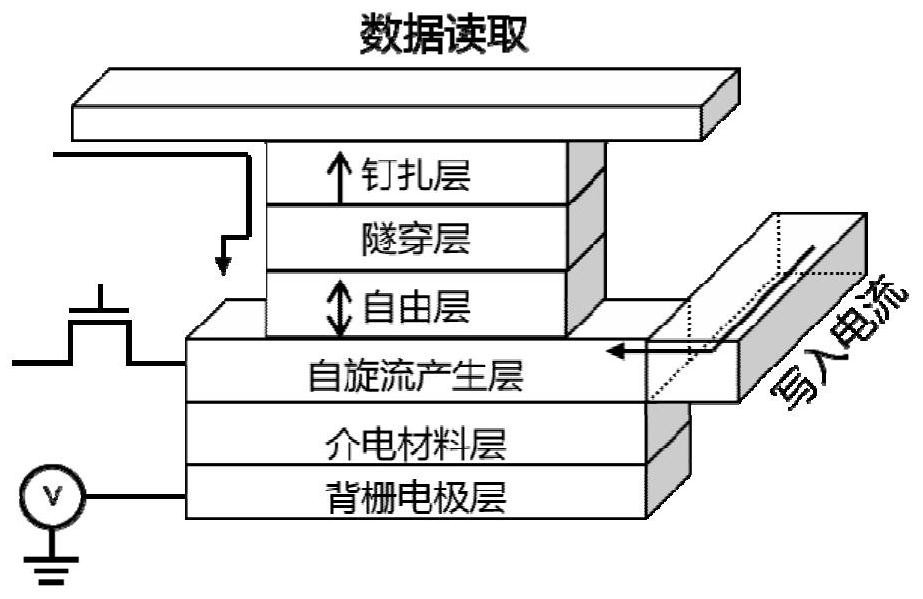
ActiveCN112054116AReduce power consumptionIncrease power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsIndium
The invention relates to a magnetic random access memory based on an III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor, the magnetic random access memory is characterized by sequentially comprising a substratewafer, a dielectric layer, a spin orbit torque acting layer and an MTJ structure layer from bottom to top, and the dielectric layer is made of a cadmium telluride CdTe or zinc telluride ZnTe material; and the spin orbit torque acting layer is made of a III-V group narrow bandgap semiconductor indium antimonide InSb or indium arsenide InAs with high mobility. The structure based on the III-V semiconductor material not only can be matched with an existing semiconductor CMOS process, but also can provide spin orbit coupling strength higher than that of a traditional heavy metal SOT material, andtherefore the problem of power consumption of device write-in current is effectively solved. In addition, the spin orbit coupling strength can be regulated and controlled by applying the back gate voltage, so that the power consumption of the device is further improved. And through electric field control, the programmable and storage integrated capability of the modified device array can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Zinc telluride scintillators
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Doping method for p-type zinc telluride single crystal thin-film material
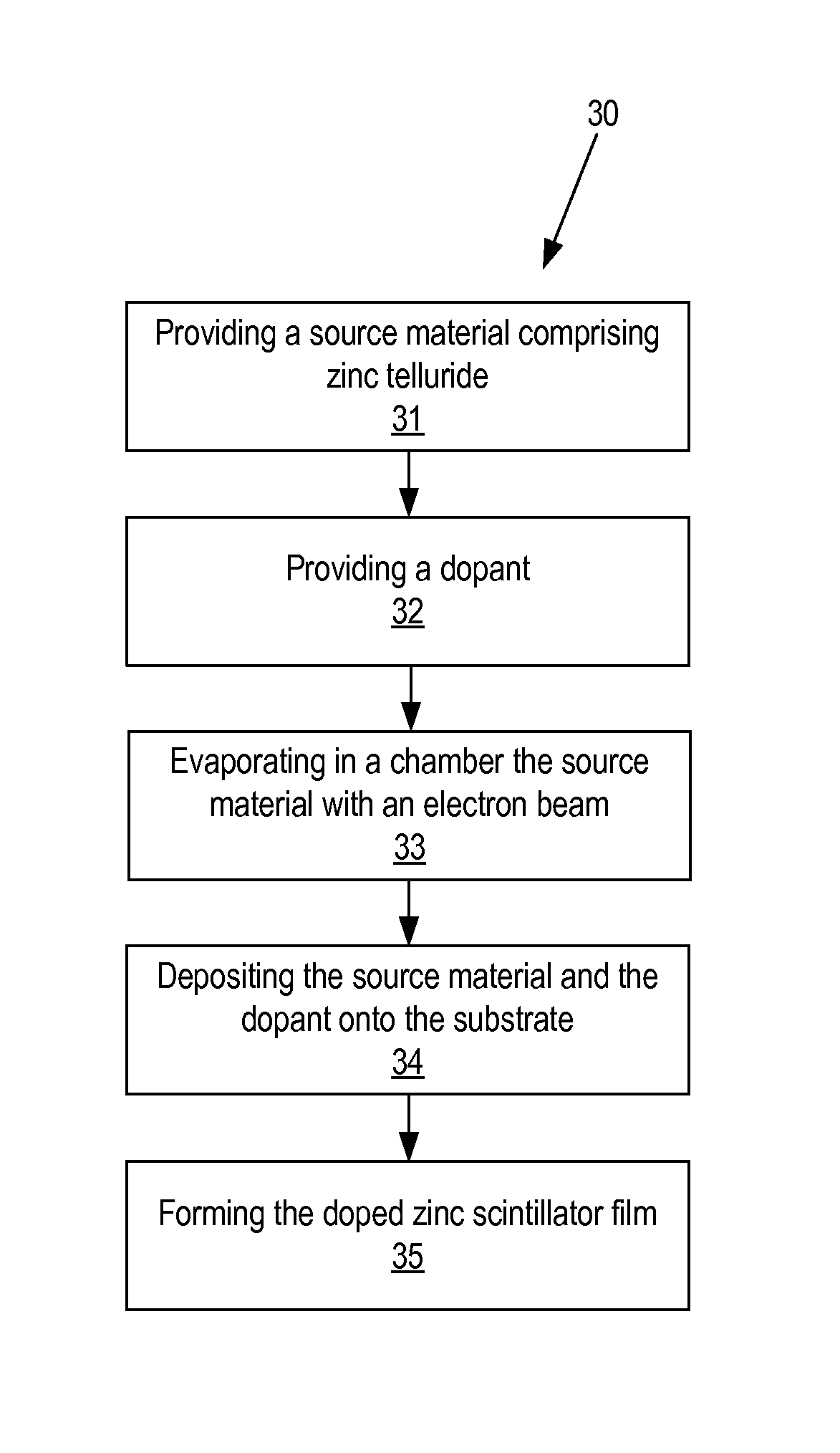
InactiveCN103474333ARealize controllable high-concentration p-type dopingInhibit the problem of volatilization of tellurium element formed by decompositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc tellurideChemical compound
Provided is a doping method for a p-type zinc telluride single crystal thin-film material. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a single crystal substrate is extracted; 2, a single crystal thin film is grown on the single crystal substrate in an epitaxial mode; 3, a layer of a SiO2 nano film is deposited on the surface of the single crystal thin film; 4, a double-energy-state nitrogen ion injection method is utilized, nitrogen is injected downwards from the surface of the SiO2 nano film, a p-type doping layer is formed on the lower face of the SiO2 nano film, and a sample is formed; 5, rapid thermal annealing processing is carried out on the sample; 6, the SiO2 nano film on the surface of the sample is removed, and preparation is achieved. The doping method is compatible with an existing microelectronic device manufacturing process and is easy to implement. In addition, the method can also be suitable for p-type doping of an intrinsic zinc telluride single crystal surface, and can provide a reference for p-type doping experiments for semiconductor thin-film materials of chemical compounds of other II-VI groups.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of making a multicomponent film
ActiveUS8193027B2Low costMaterial consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingZinc selenideIndium
Described herein is a method and liquid-based precursor composition for depositing a multicomponent film. In one embodiment, the method and compositions described herein are used to deposit Germanium Tellurium (GeTe), Antimony Tellurium (SbTe), Antimony Germanium (SbGe), Germanium Antimony Tellurium (GST), Indium Antimony Tellurium (IST), Silver Indium Antimony Tellurium (AIST), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), Cadmium Selenide (CdSe), Zinc Telluride (ZnTe), Zinc Selenide (ZnSe), Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) films or other tellurium and selenium based metal compounds for phase change memory and photovoltaic devices.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Production process of zinc telluride-doping cuprous telluride target material
The invention discloses a production process of a zinc telluride-doping cuprous telluride target material, and particularly provides a production method of a zinc telluride-doping cuprous telluride material and a production method of the target material made therefrom. The particularly include: crushing simple substances of Zn, Te and Cu into uniform chips or powders, accurately weighing the raw materials, and uniformly placing the three simple substances into a quartz tube according to theoretical amount; vacuumizing the tube, and performing sealed in-tube synthesis; and ball-milling a synthesized ZnTe(99+x)Cu2Te(1-x) at% material to obtain dried ZnTe(99+x)Cu2Te(1-x) at% powder; performing hot pressed sintering with the powder being a raw material to obtain a ZnTe(99+x)Cu2Te(1-x) at% target green body; and performing mechanical processing on the target green body to prepare the target material. By means of the sealed in-tube synthesis, the ZnTe(99+x)Cu2Te(1-x) at%, which is less in impurity phase and is uniform in component, is synthesized according to a time-temperature program researched by the company, purity of the synthetic product being higher than 99.995%. The zinc telluride-doping cuprous telluride target material, produced by the original hot pressed sintering process of our company, is high in relative density, is uniform in components and crystalline grain, is smallin size of the crystalline grain and has great film-forming property.
Owner:江西科泰新材料有限公司
Polycrystal single-phase zinc telluride and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113307237AAny cutting and grindingUniform resistanceMetal selenides/telluridesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsZinc tellurideCrucible
The invention relates to the field of photovoltaic power generation materials, in particular to polycrystal single-phase zinc telluride and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials including zinc particles and tellurium particles, putting the mixture into a crucible, covering the crucible with a cover, and putting the crucible into a reaction kettle; vacuumizing, heating and preheating; introducing inert gas into the reaction kettle, and gradually heating and preserving heat; after cooling, taking out the crucible, carrying out ball milling on the deposited zinc telluride crystal block, putting into a mold, shaping, and then putting into a hot pressing furnace together with the mold; vacuumizing and preheating, introducing inert gas, raising the temperature, and applying pressure to the interior of the mold for heat preservation and pressure maintaining; and cooling, and vacuumizing in the cooling process to obtain zinc telluride. The high-purity zinc telluride is prepared by adopting the zinc particles and the tellurium particles which are low in cost and high in purity as raw materials, the cost is low, time is short, the yield is high, the high-purity zinc telluride is a polycrystal single-phase compound block which is combined together in a crystal form, the density is close to theoretical density, the purity is high, the resistance value is uniform, and the best semiconductor effect can be achieved in a semiconductor film layer for photovoltaic power generation.
Owner:石久光学科技发展(北京)有限公司
Preparation method for zinc telluride homoepitaxy layer
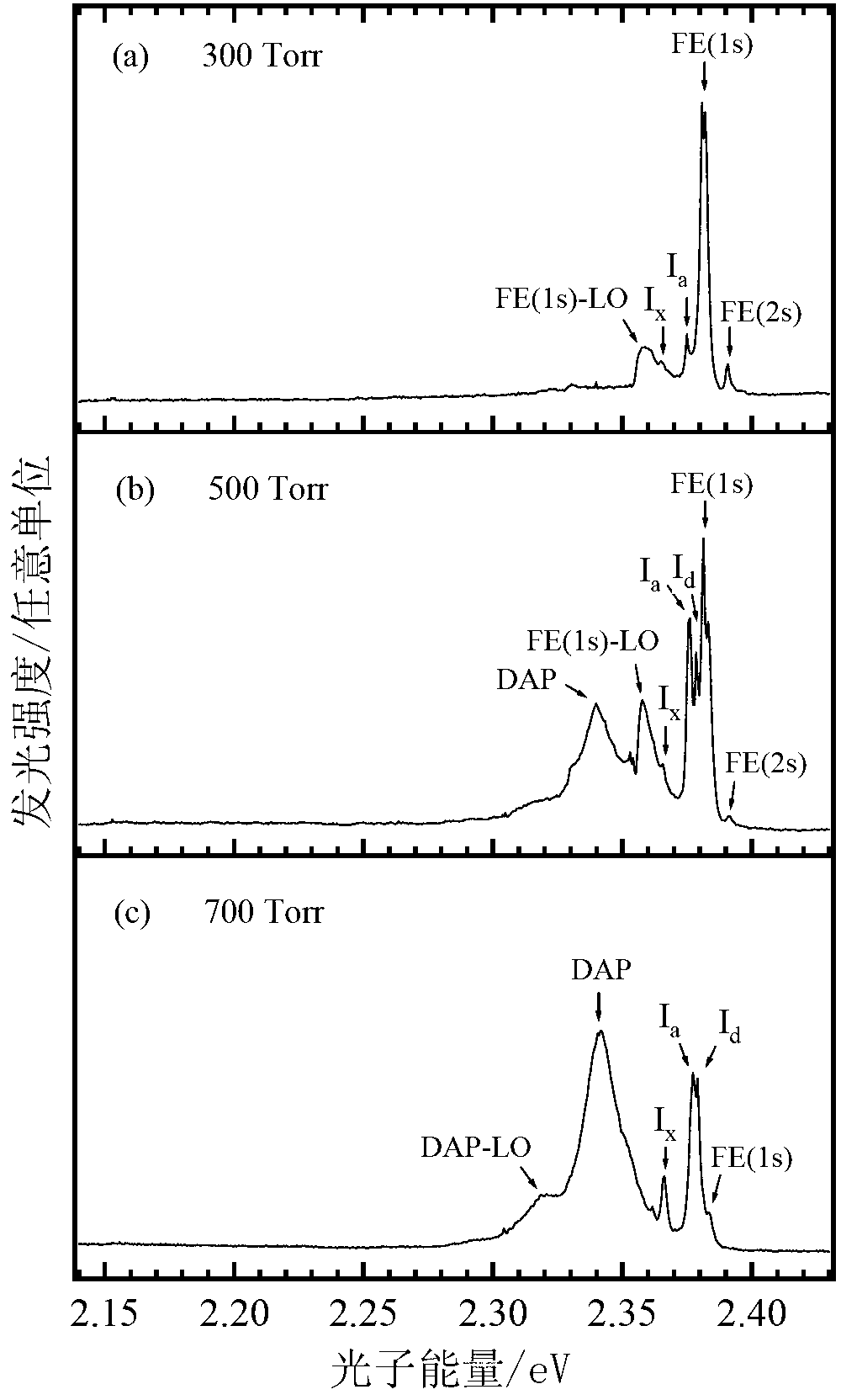
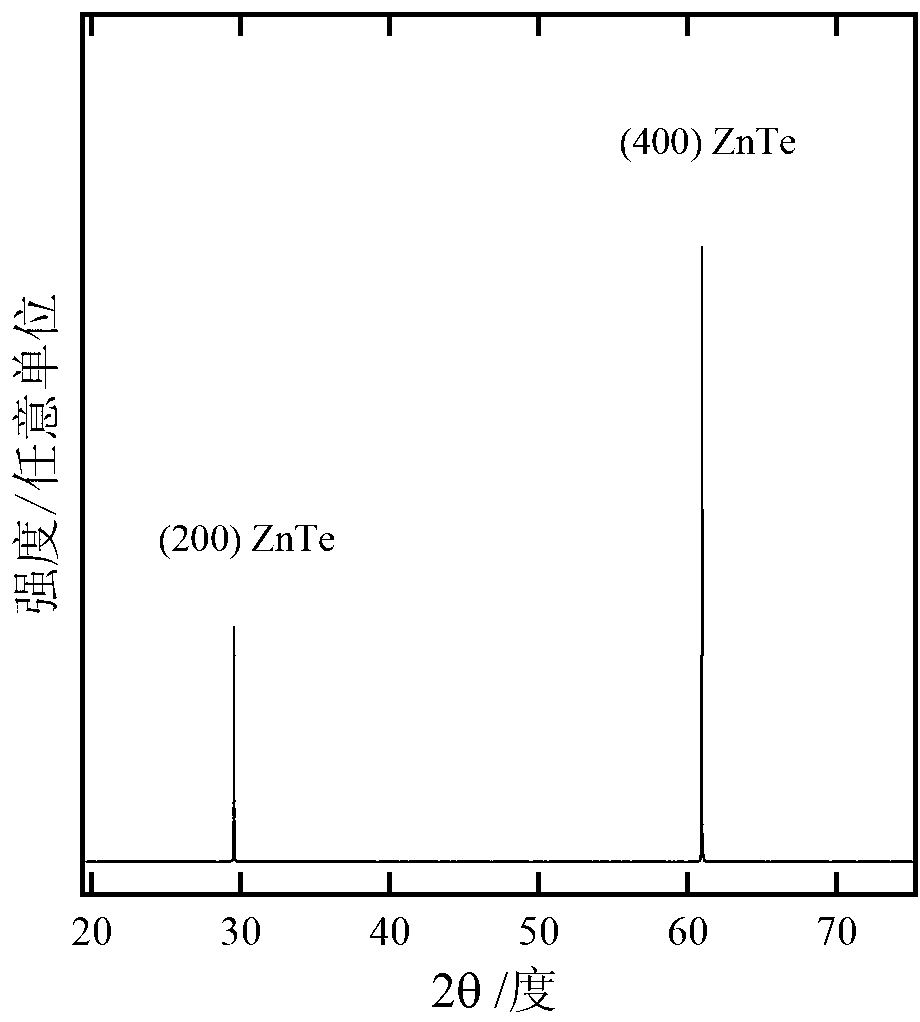
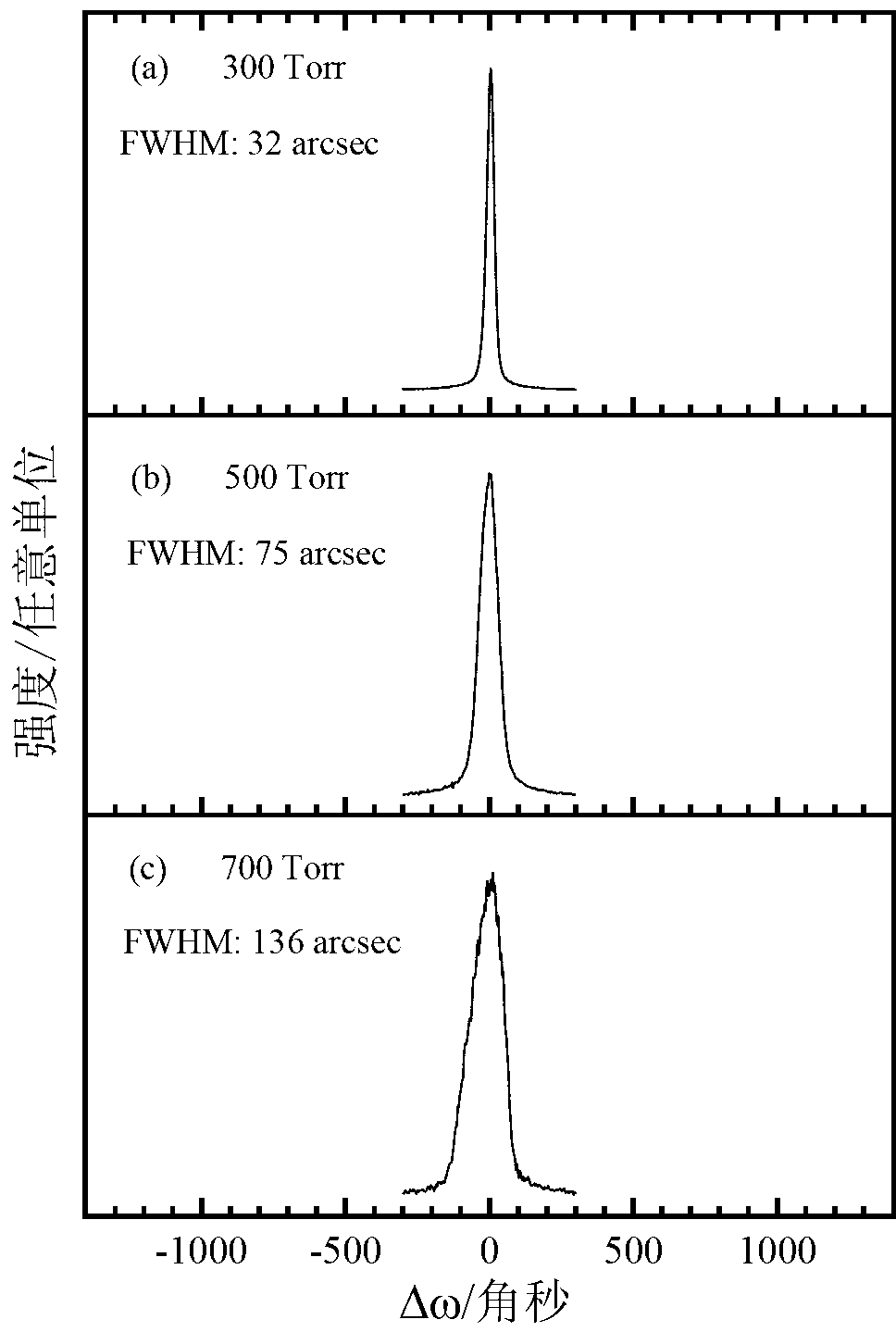
InactiveCN103074677AAvoid reducing crystallization qualityDiffusion coefficient is smallPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRocking curveSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a preparation method for a zinc telluride (ZnTe) homoepitaxy layer and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor materials. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: adopting a low-pressure metal organic chemical vapor phase epitaxy process, taking dimethyl zinc and diethyl telluride as metal organic sources and hydrogen gas as carrier gas, and growing the ZnTe homoepitaxy layer on a ZnTe (100) substrate by low-pressure metal organic chemical vapor phase epitaxy equipment. The ZnTe homoepitaxy layer prepared with the method is narrow in band edge exciton peak and XRC (X-ray diffraction rocking curve) half-width, deep energy level emission of oxygen bound excitons, dislocation-related Y rays and the like does not appear, and the results show that the epitaxial layer is very good in crystal quality. The ZnTe homoepitaxy layer prepared with the method can be used for manufacturing photoelectric devices such as green LEDs and LDs, terahertz emitters and the like, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of zinc telluride single crystal
ActiveCN107201548AEnough lengthImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsZinc tellurideTe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zinc telluride single crystal, and aims to solve the technical problem that the zinc telluride single crystal prepared through the existing method is low in quality. The technical scheme is that the preparation method comprises the following steps: putting a high-purity tellurium elementary substance and a synthesized zinc telluride polycrystal raw material into a quartz crucible for fused sealing under high vacuum; then putting the quartz crucible into an ACRT (Accelerated Crucible Rotation Technique) type five-temperature-region crystal growth furnace; firstly, heating the furnace at a certain heating rate, thus obtaining a preset temperature field, preserving the heat for a period of time, and cooling the crucible at a rate of 0.1 to 0.2 mm / h, wherein the temperature gradient for crystal growth is 10 + / - 1 DEG C / cm and the crystallizing temperature is 1,060 + / - 1 DEG C; and under a condition of keeping the temperature field in a growth process unchanged, after the crystal grows, cooling the crucible at 3 DEG C / h for 50 hours, then cooling the crucible at the rate of 5 DEG C / h for 100 hours, and finally turning off a power supply for furnace cooling. According to the preparation method, the ZnTe crystal with an enough length and high crystallizing quality is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Preparation method of cadmium zinc telluride polycrystals
ActiveCN106435738AImprove qualityNo segregationPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsZinc tellurideHigh volume manufacturing
The invention provides a preparation method of cadmium zinc telluride polycrystals. The preparation method comprises the following steps of A, uniformly mixing cadmium telluride powder and zinc telluride power to obtain mixed powder; B, under the vacuum condition, raising the temperature of the mixed powder to 600 to 750 DEG C; performing heat insulation and pressurization to obtain a first sintering body; C, performing primary temperature reduction on the first sintering body; relieving the pressure; then, performing secondary temperature reduction to obtain the cadmium zinc telluride polycrystals. By using the method, the cadmium zinc telluride polycrystals can be obtained through preparation at low temperature; safety is realized; the control is easy; the energy consumption is reduced; the cost is favorably reduced; in addition, the obtained cadmium zinc telluride polycrystals have high quality and no segregation. By using the method provided by the invention, the mass production can be favorably performed.
Owner:清远先导材料有限公司
Perovskite solar cell with zinc telluride serving as hole transporting layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103904148AGood chemical stabilityLow costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationZinc telluridePerovskite solar cell
The invention discloses a perovskite solar cell with zinc telluride serving as a hole transporting layer and a manufacturing method thereof. The perovskite solar cell is characterized in that the perovskite solar cell comprises a transparent conductive electrode, an electron transporting layer, a perovskite structure light absorbing layer, the zinc telluride hole transporting layer and a positive electrode. Due to the fact that the zinc telluride is adopted to serve as the hole transporting layer, the perovskite solar cell has the advantages that the stability of the perovskite solar cell can be improved, the service life of the perovskite solar cell can be prolonged and the manufacturing cost can be lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photovoltaically active semiconductor material and photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN101351894AAvoid lostPolycrystalline material growthPhotovoltaic energy generationZinc tellurideSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to a photovoltaically active semiconductor material and a photovoltaic cell comprising a photovoltaically active semiconductor material, wherein the photovoltaically active semiconductor material contains a crystal lattice composed of zinc telluride and, in the zinc telluride crystal lattice, ZnTe is substituted by - 0.01 to 10 mol% CoTe, - 0 to 10 mol% Cu2Te, Cu3Te or CuTe and - 0 to 30 mol% of at least one compound selected from the group MgTe and MnTe, and wherein, in the zinc telluride crystal lattice Te is substituted by - 0.1 to 30 mol% oxygen. The photovoltaic cell furthermore has a rear contact composed of a rear contact material that forms a metal telluride with tellurium.
Owner:BASF AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com