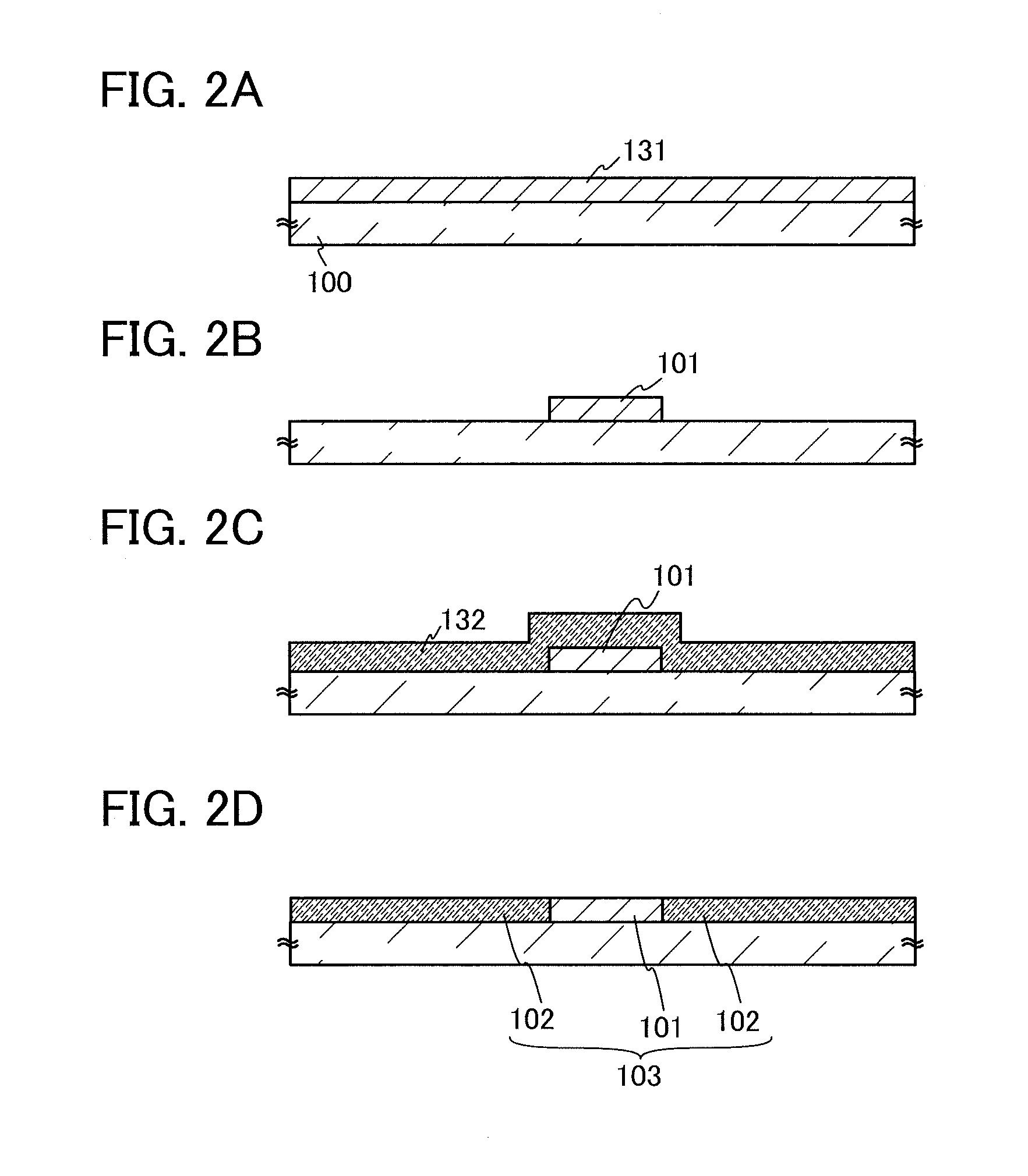
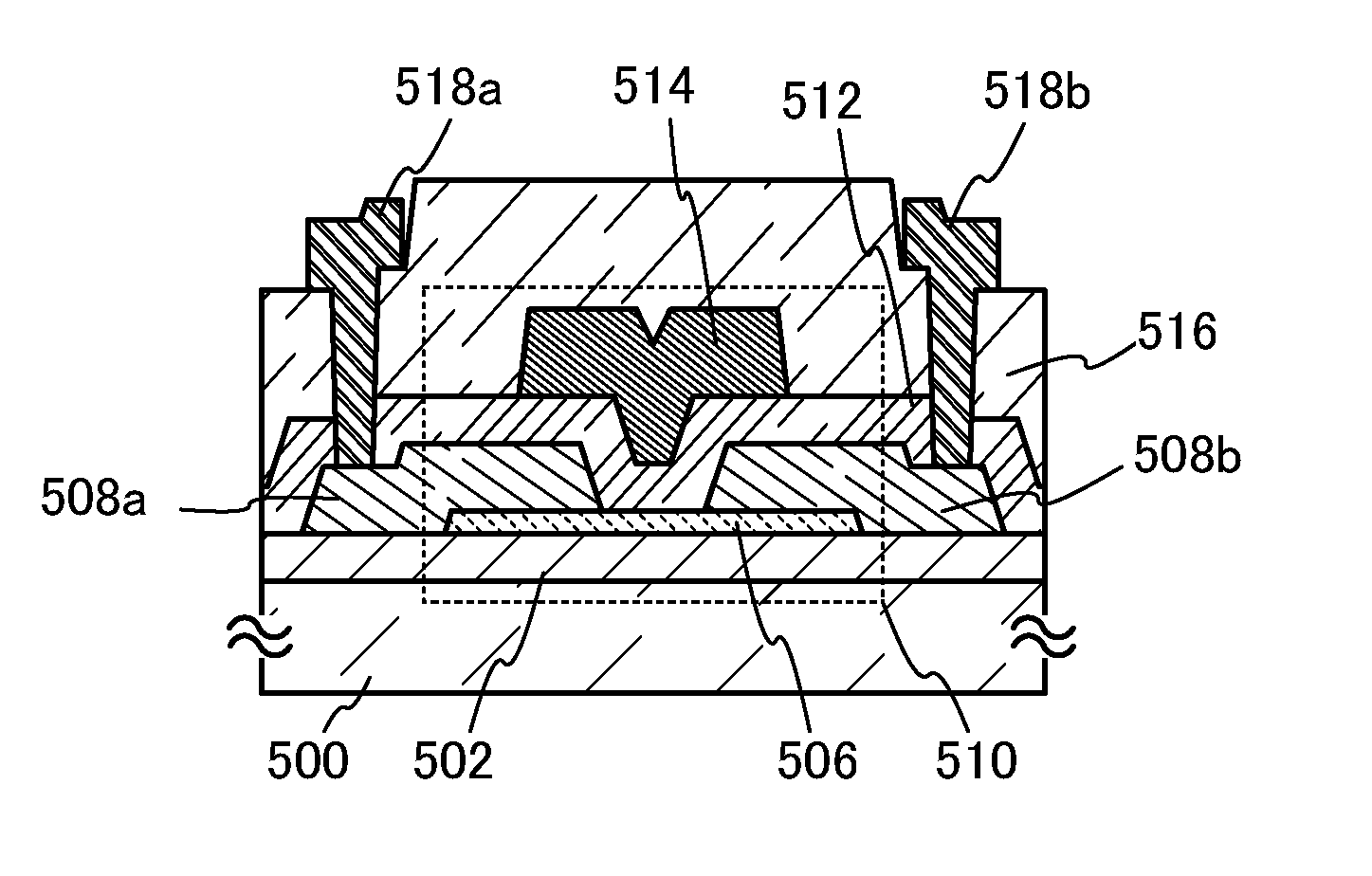
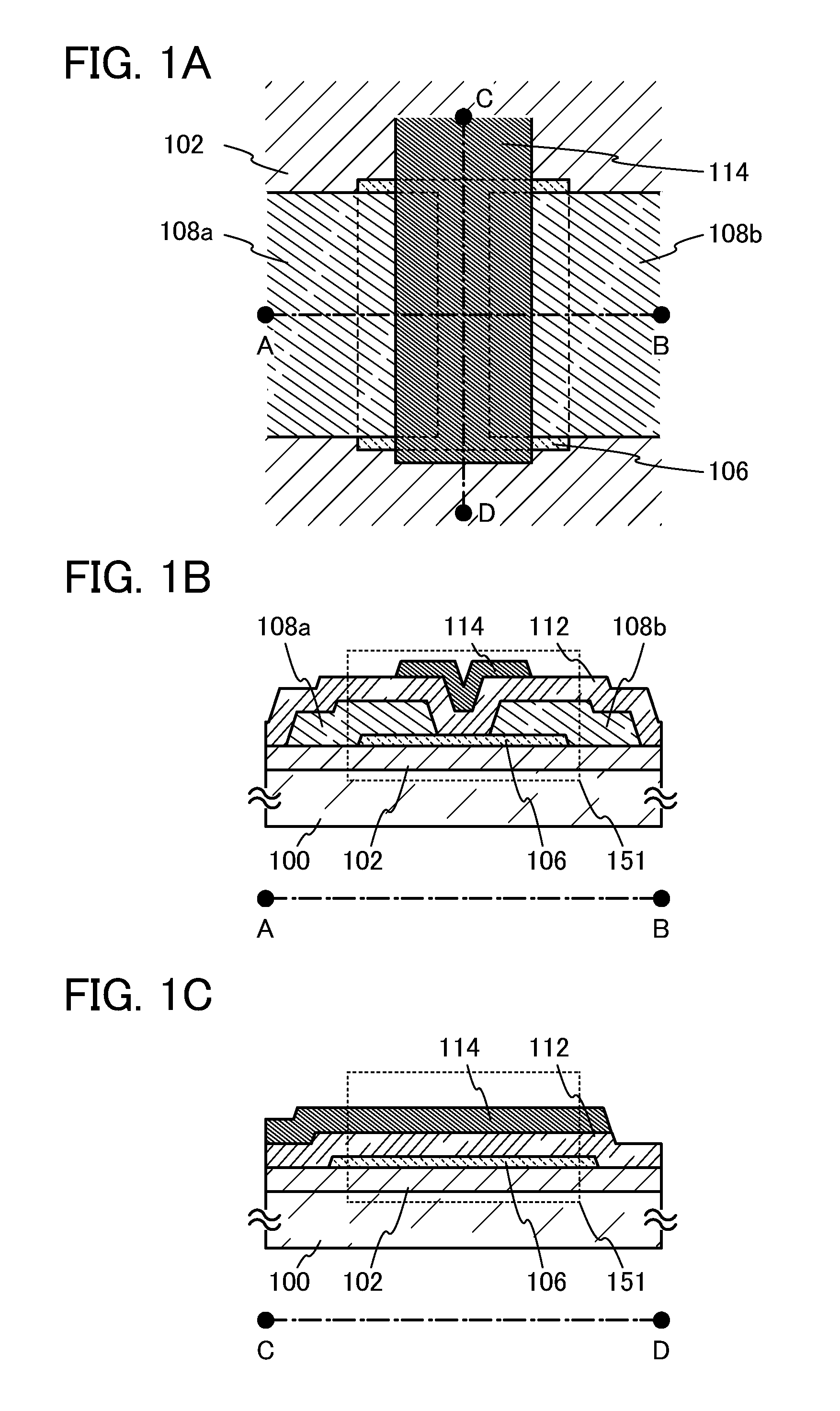
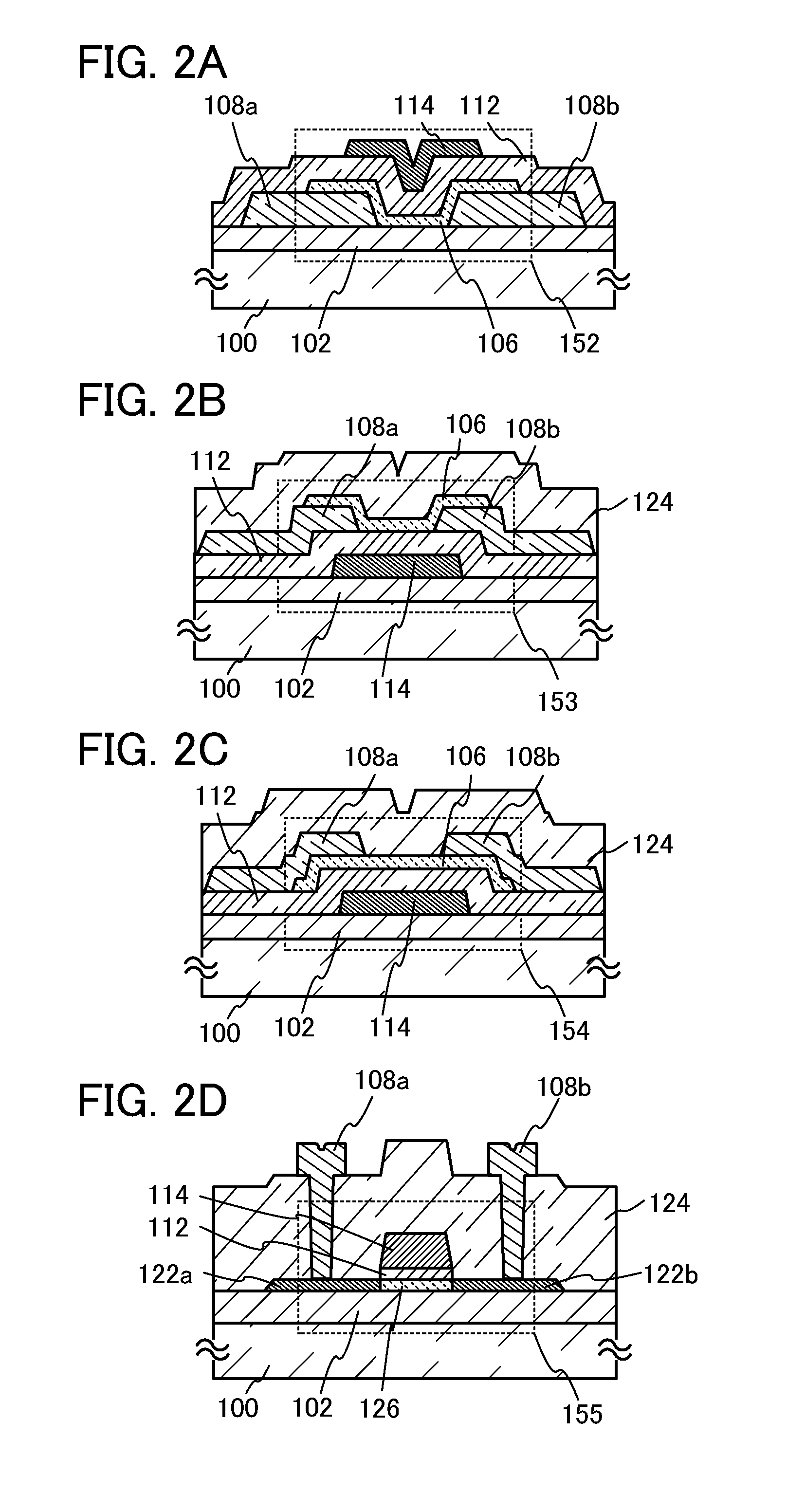
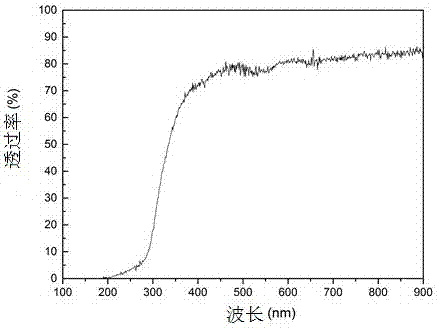
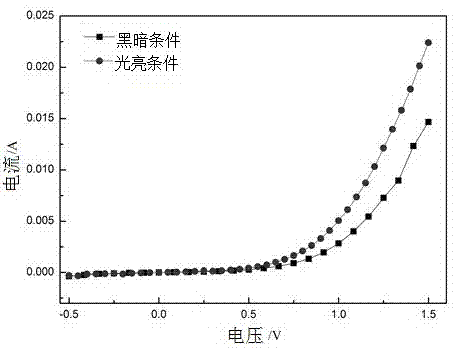
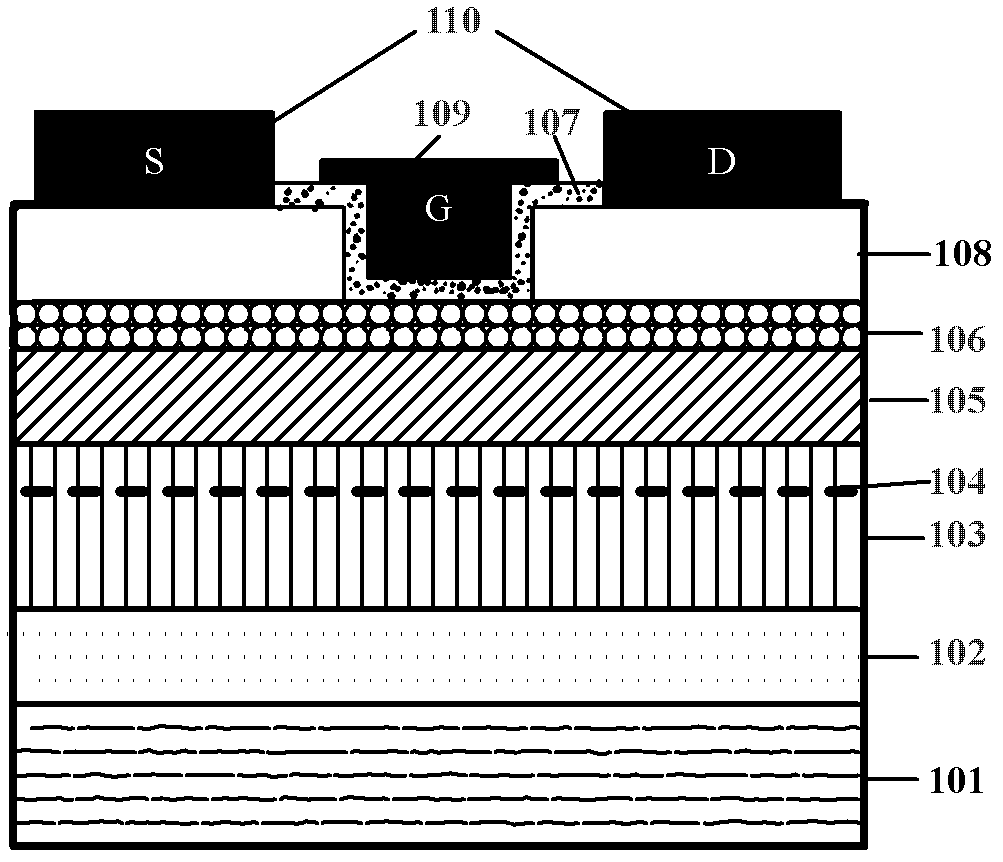
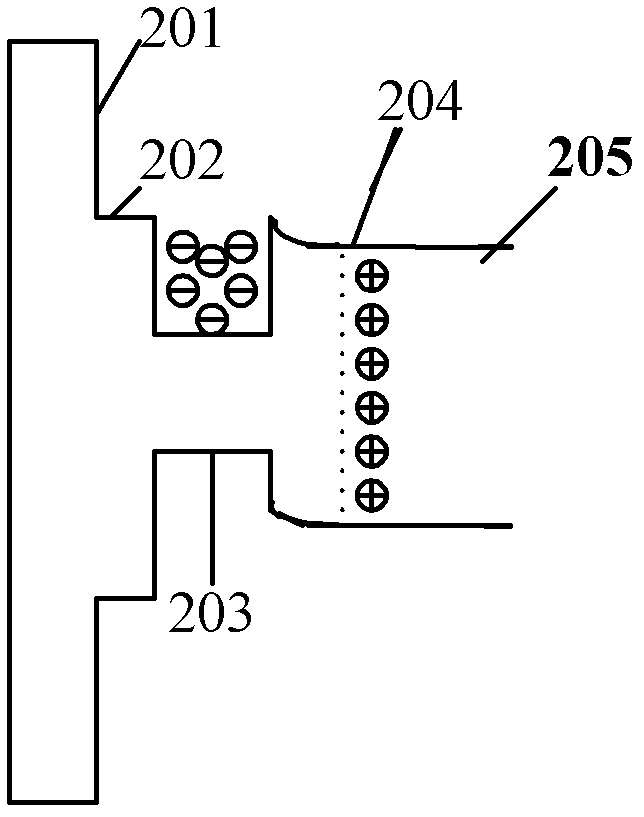
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
244 results about "State density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In 2018, the population density was approximately 92.6 residents per square mile of land area. Population density in the United States. Population density has been tracked for over two hundred years in the United States.
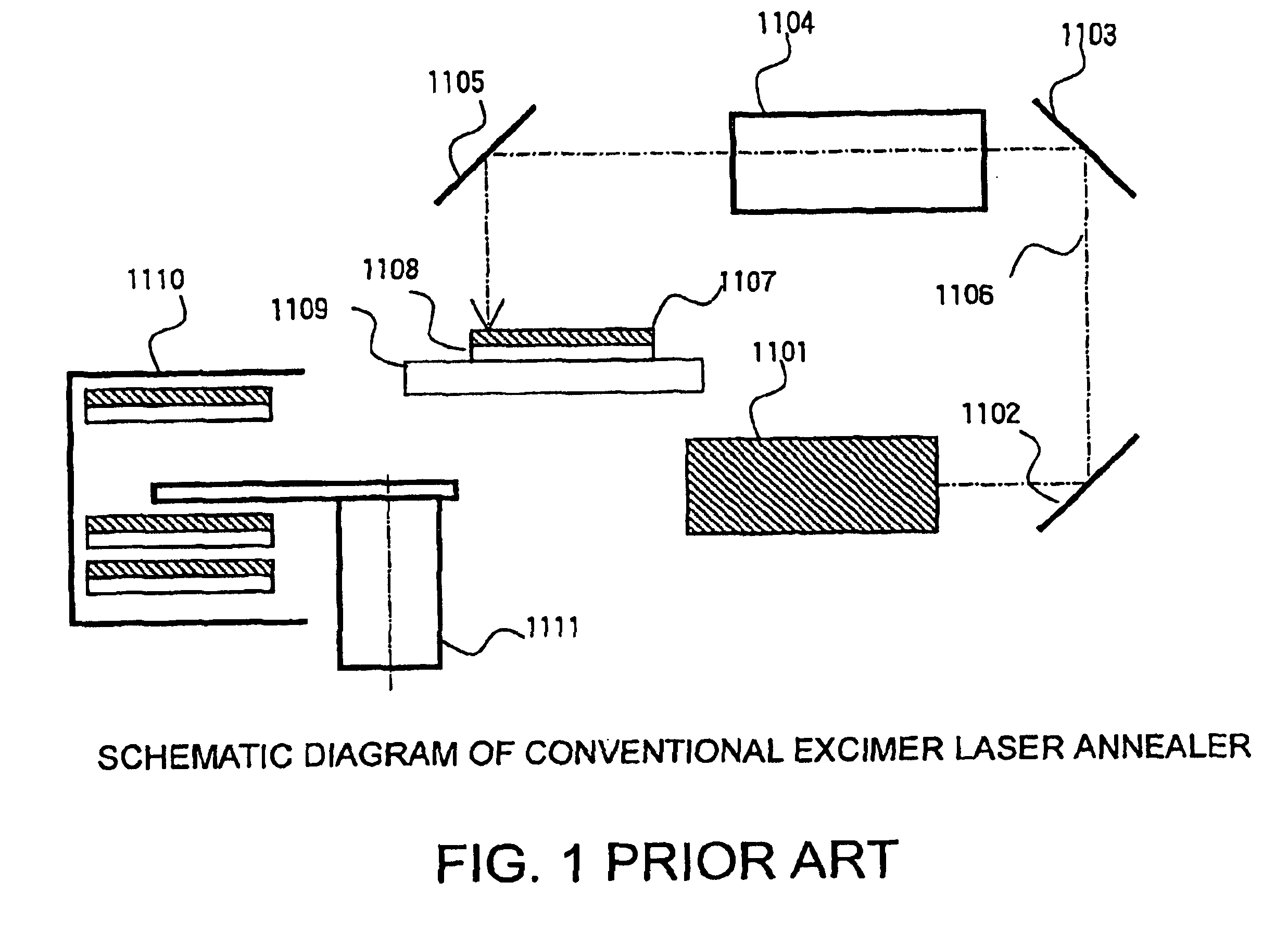
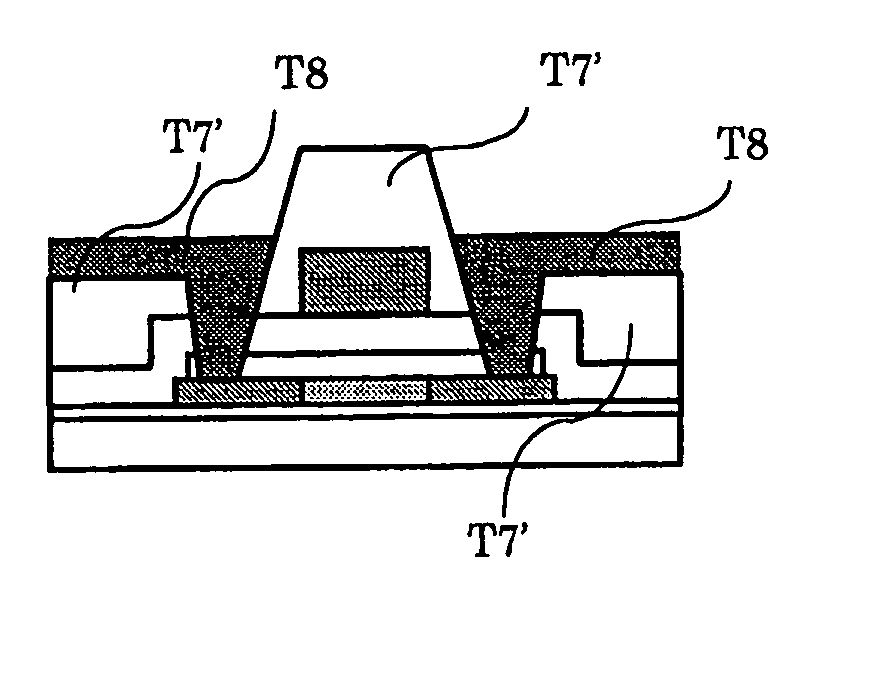
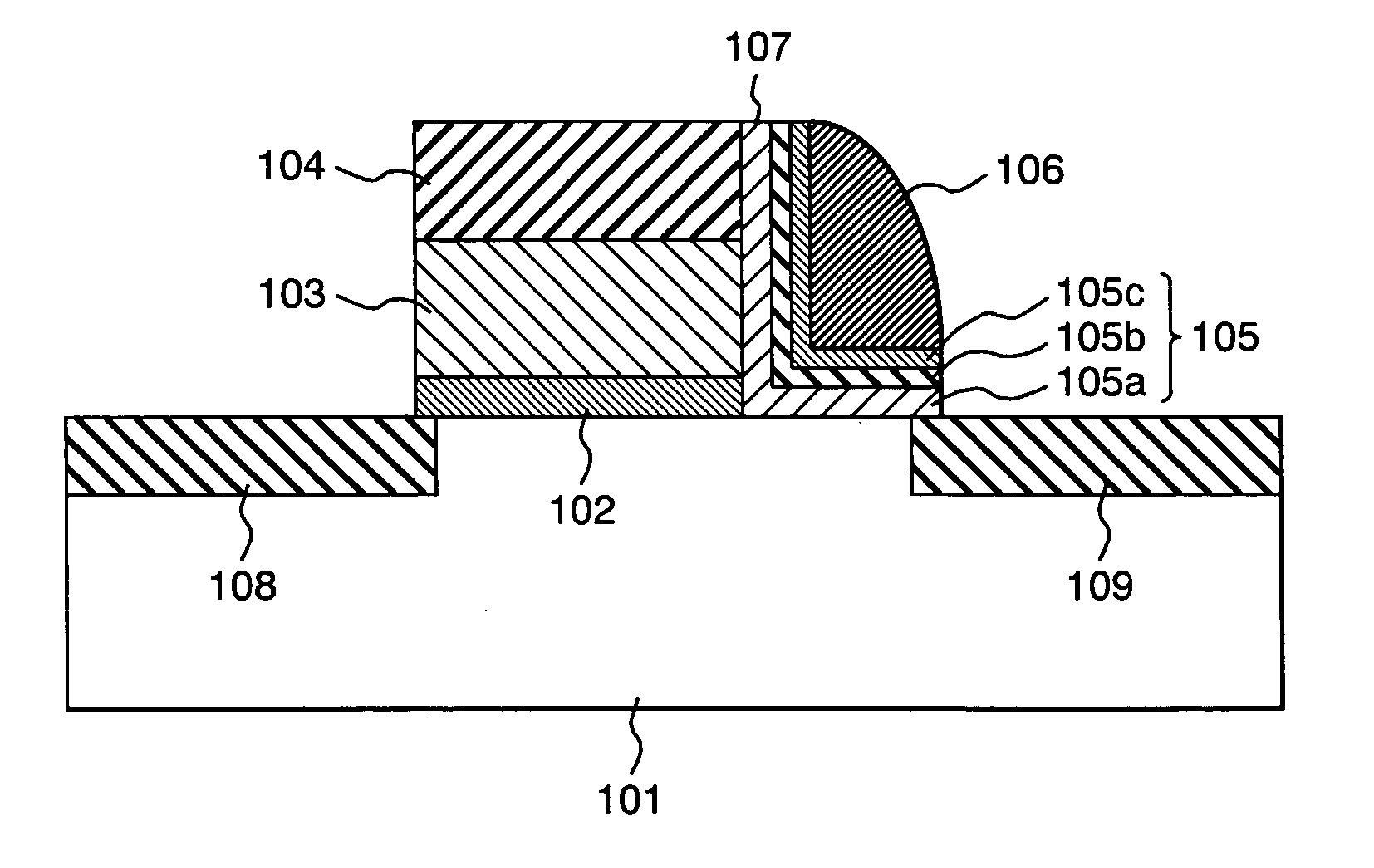
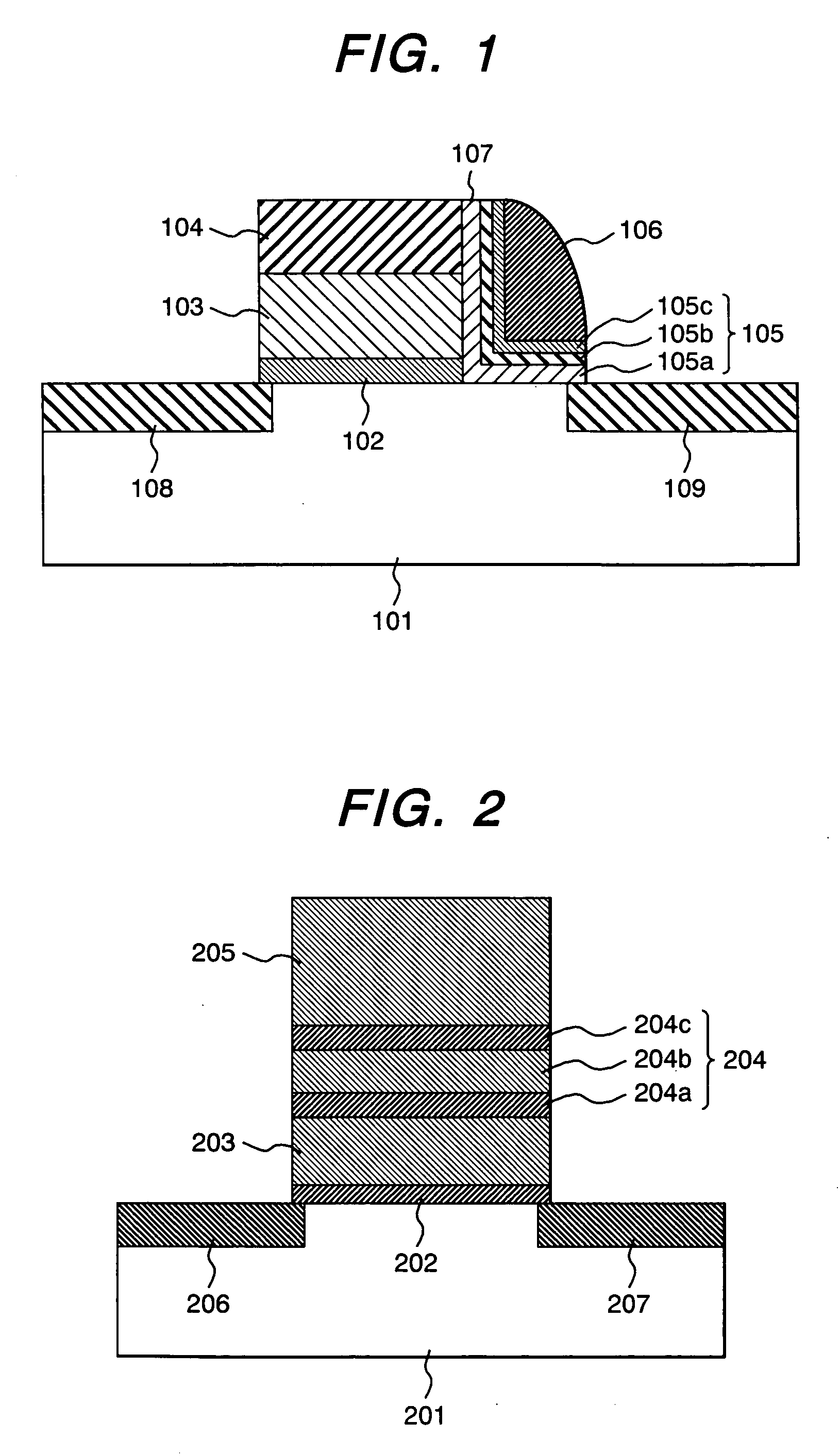
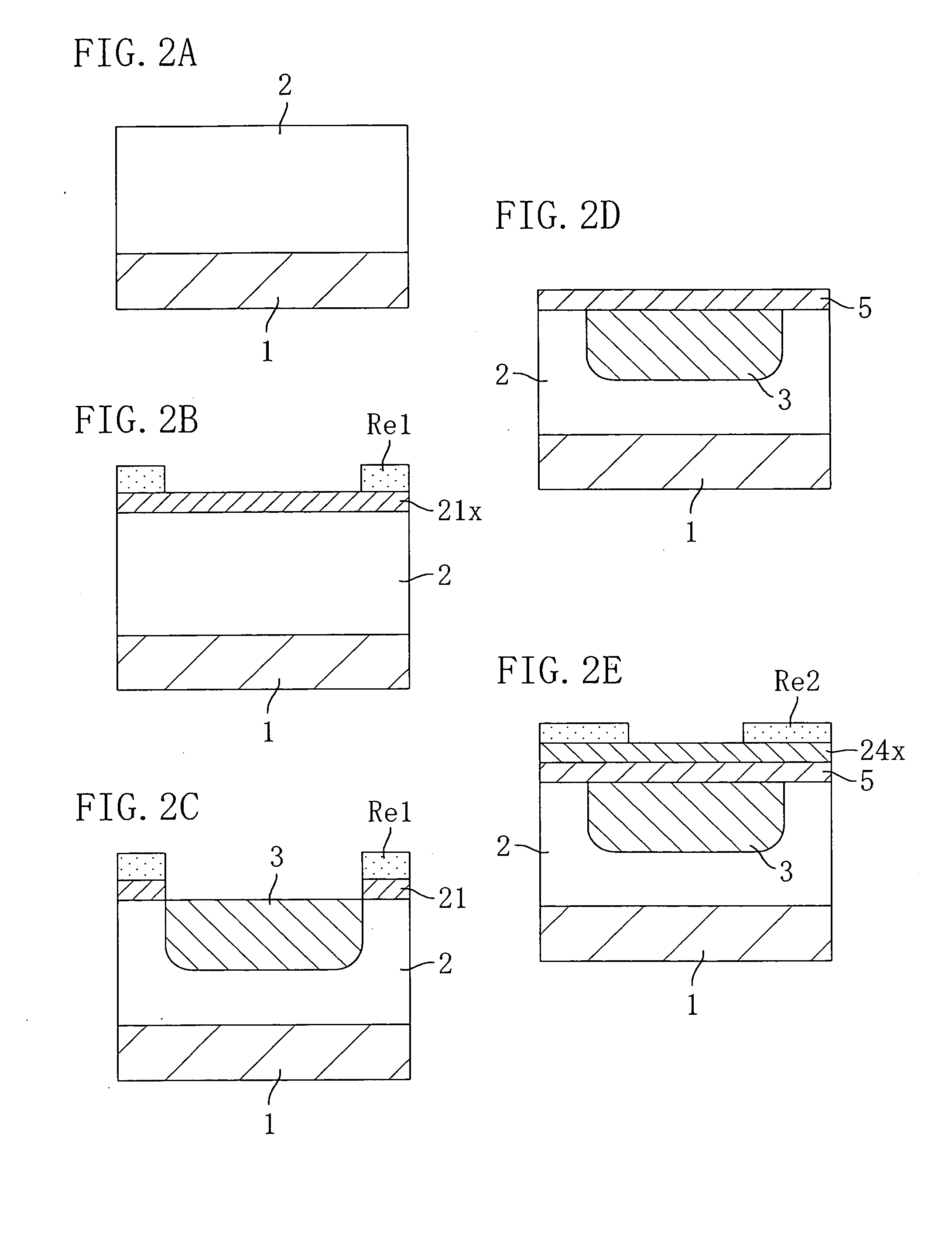
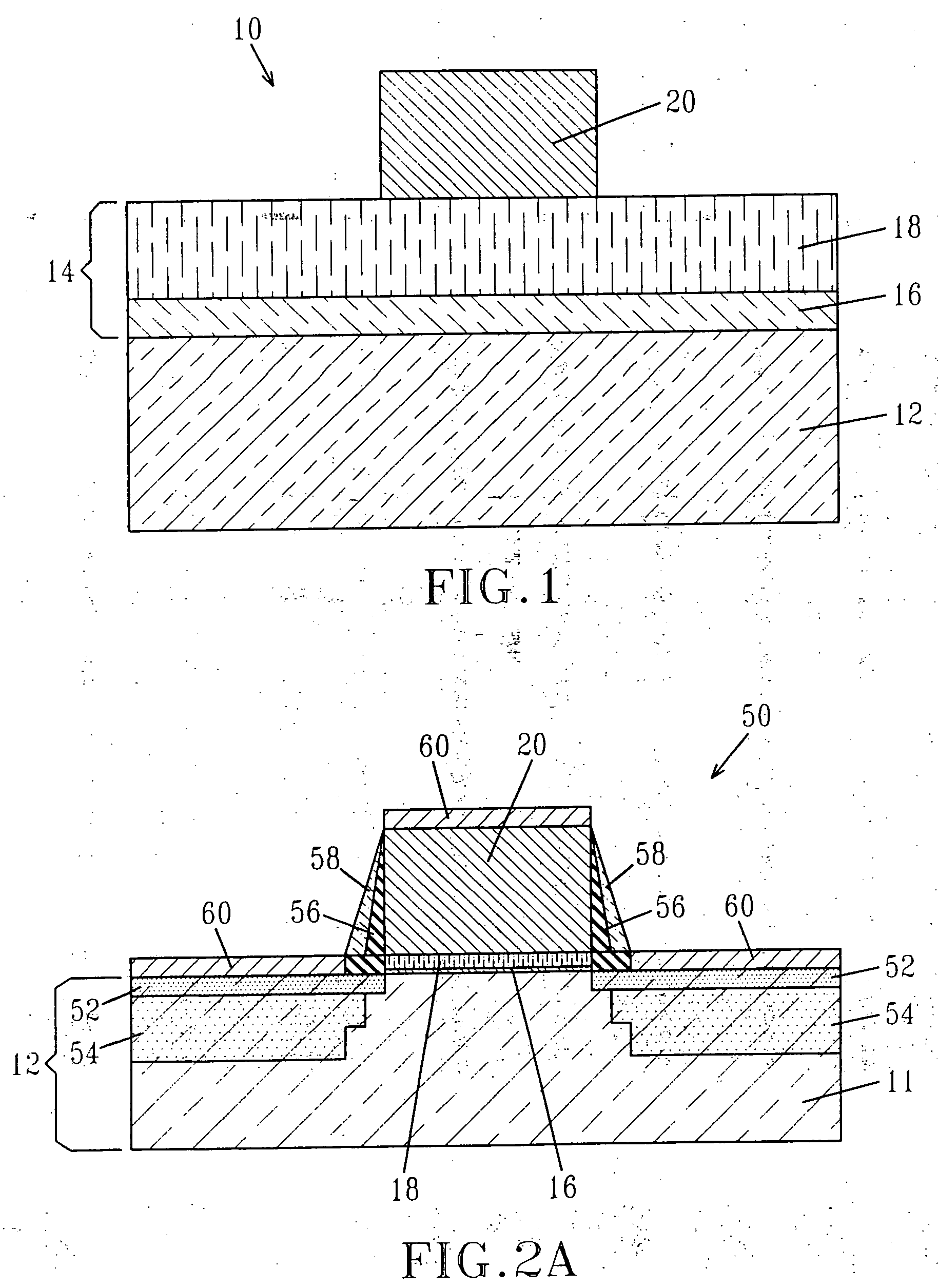
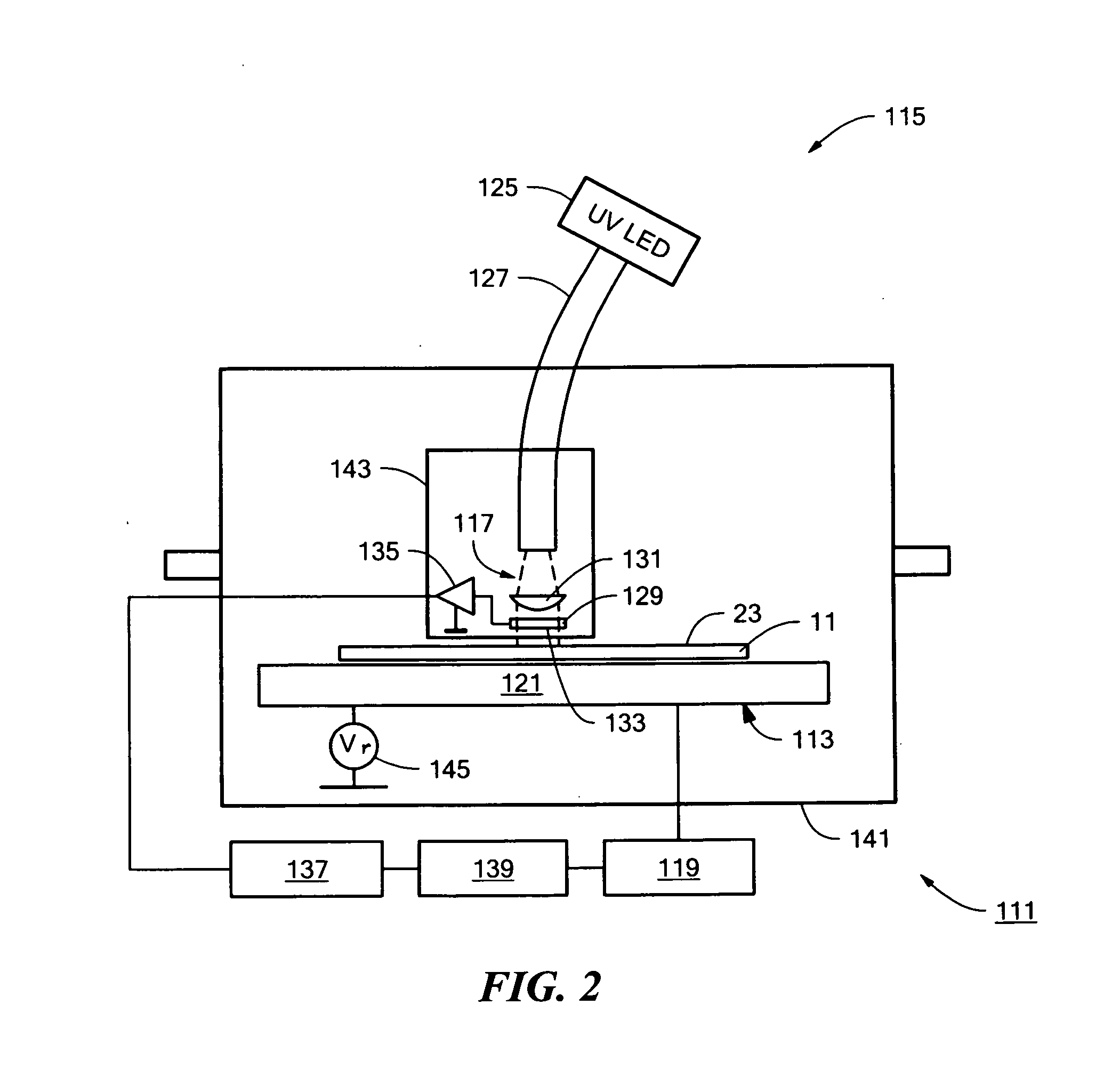
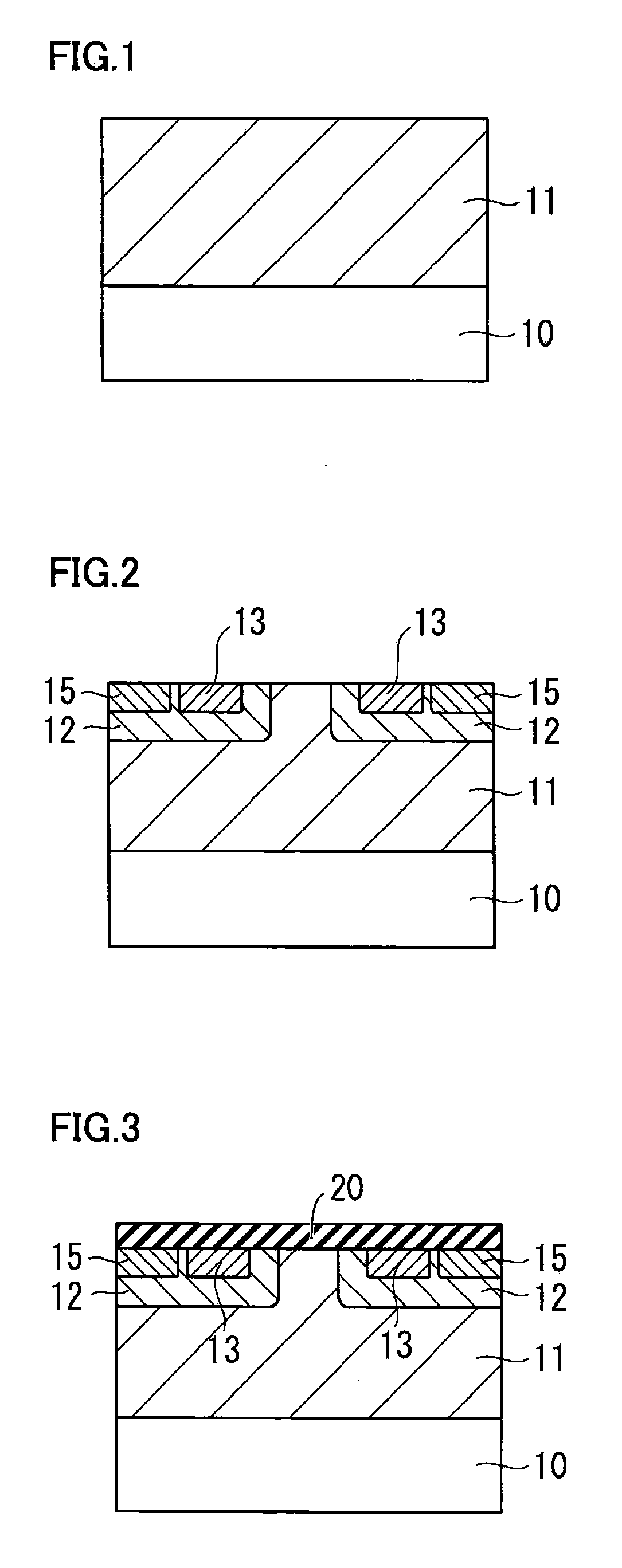
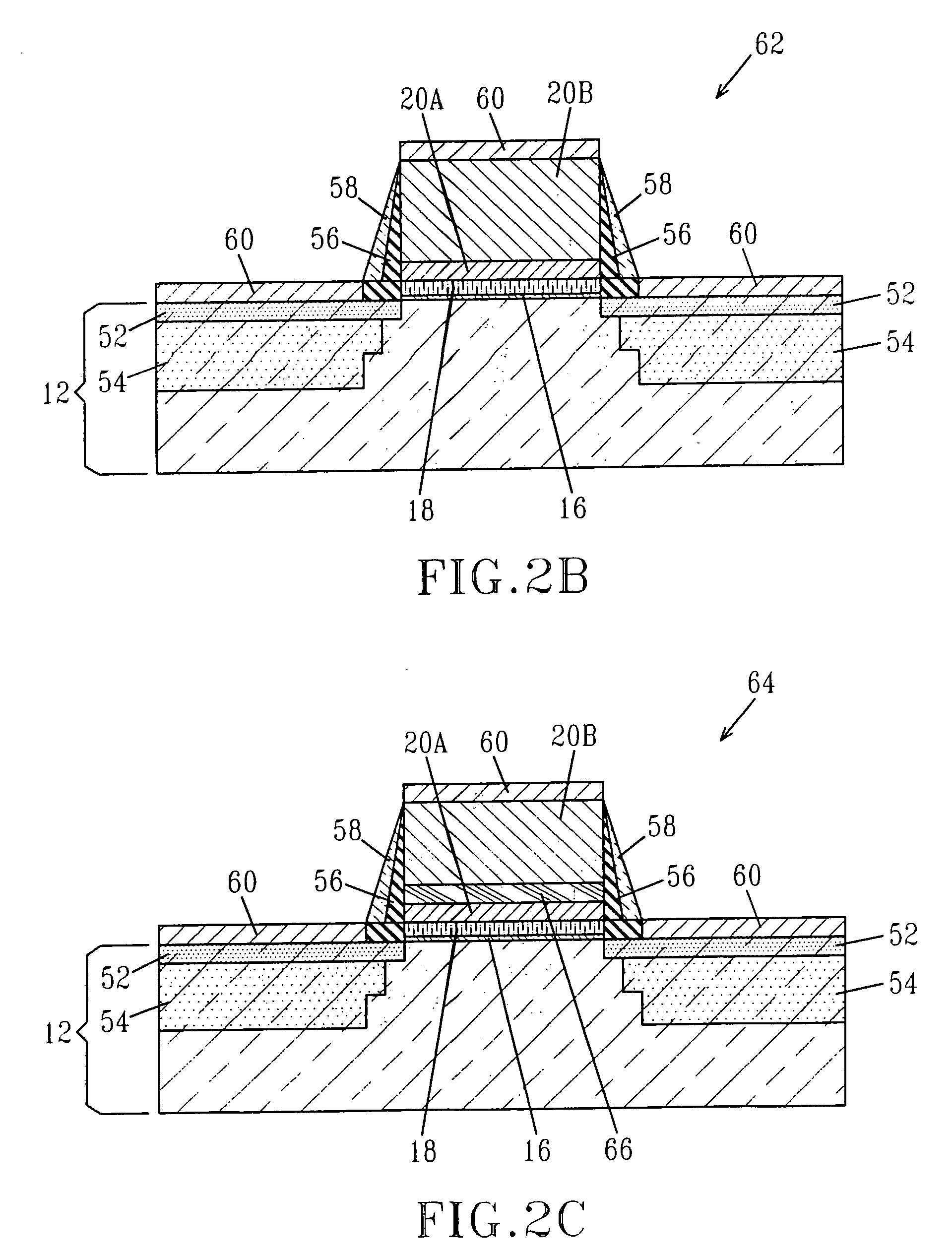
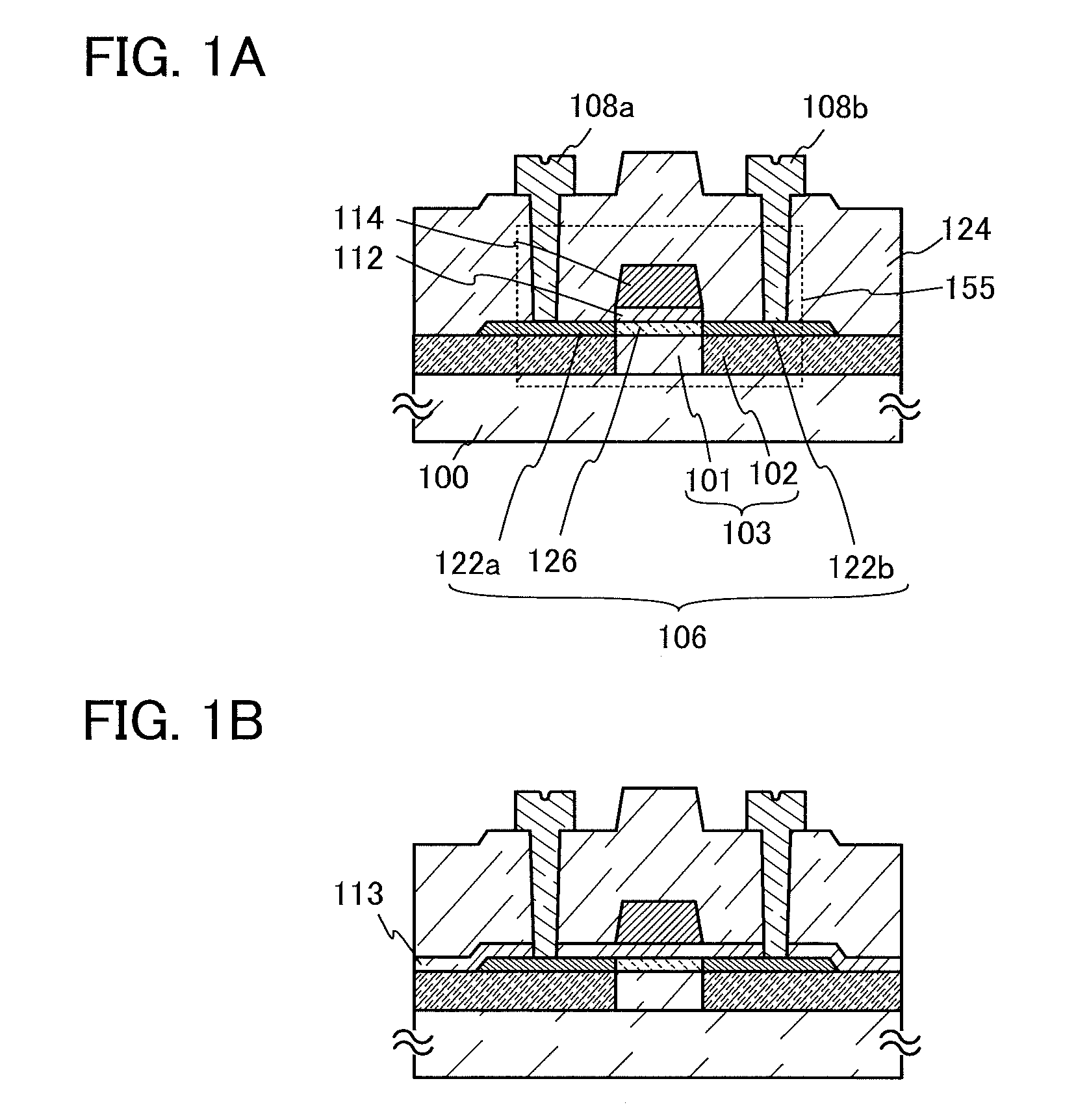
System for the formation of a silicon thin film and a semiconductor-insulating film interface
InactiveUS6861614B1Reduced trap state densityGood reproducibilityTransistorLaser detailsSilicon thin filmState density
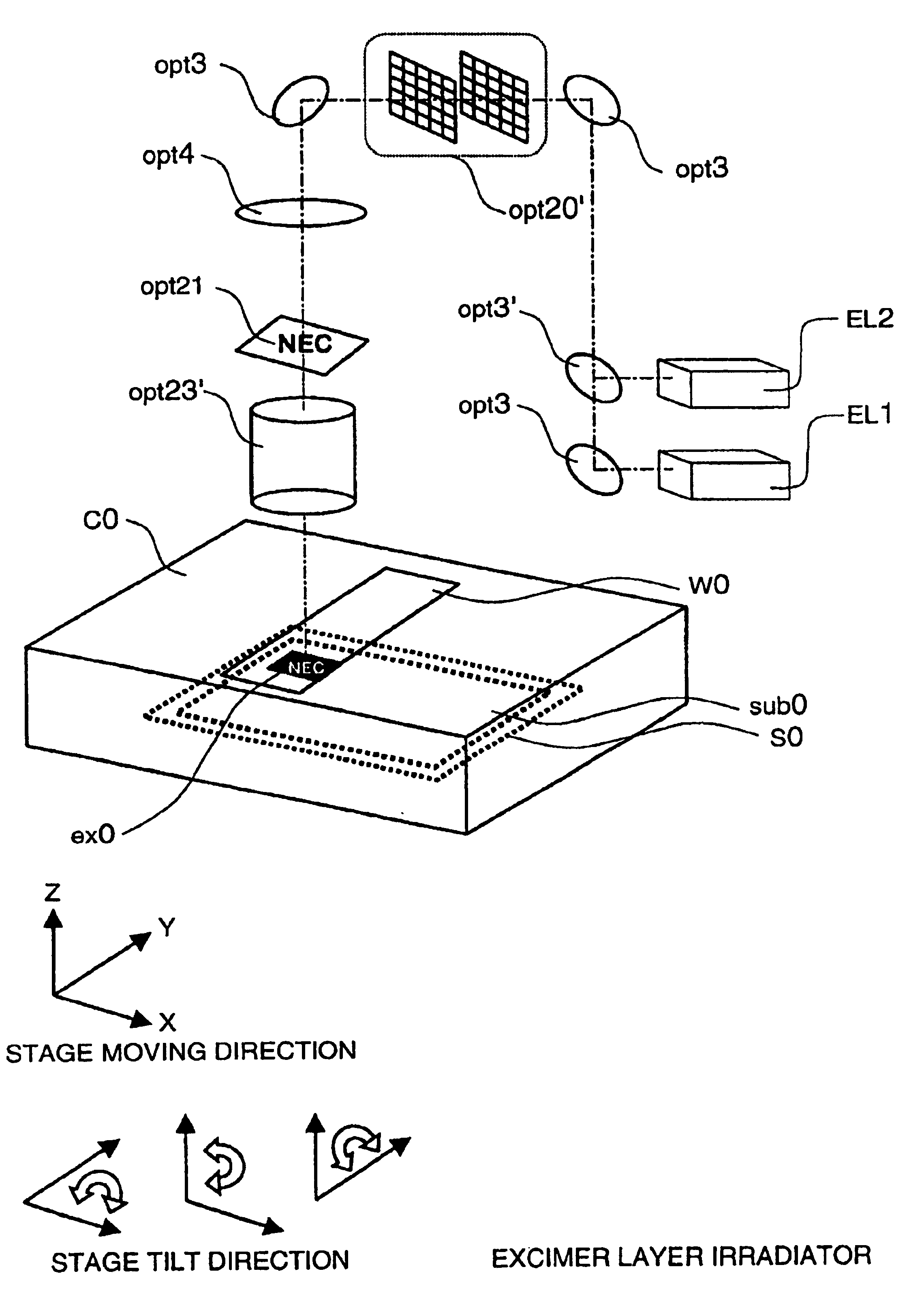
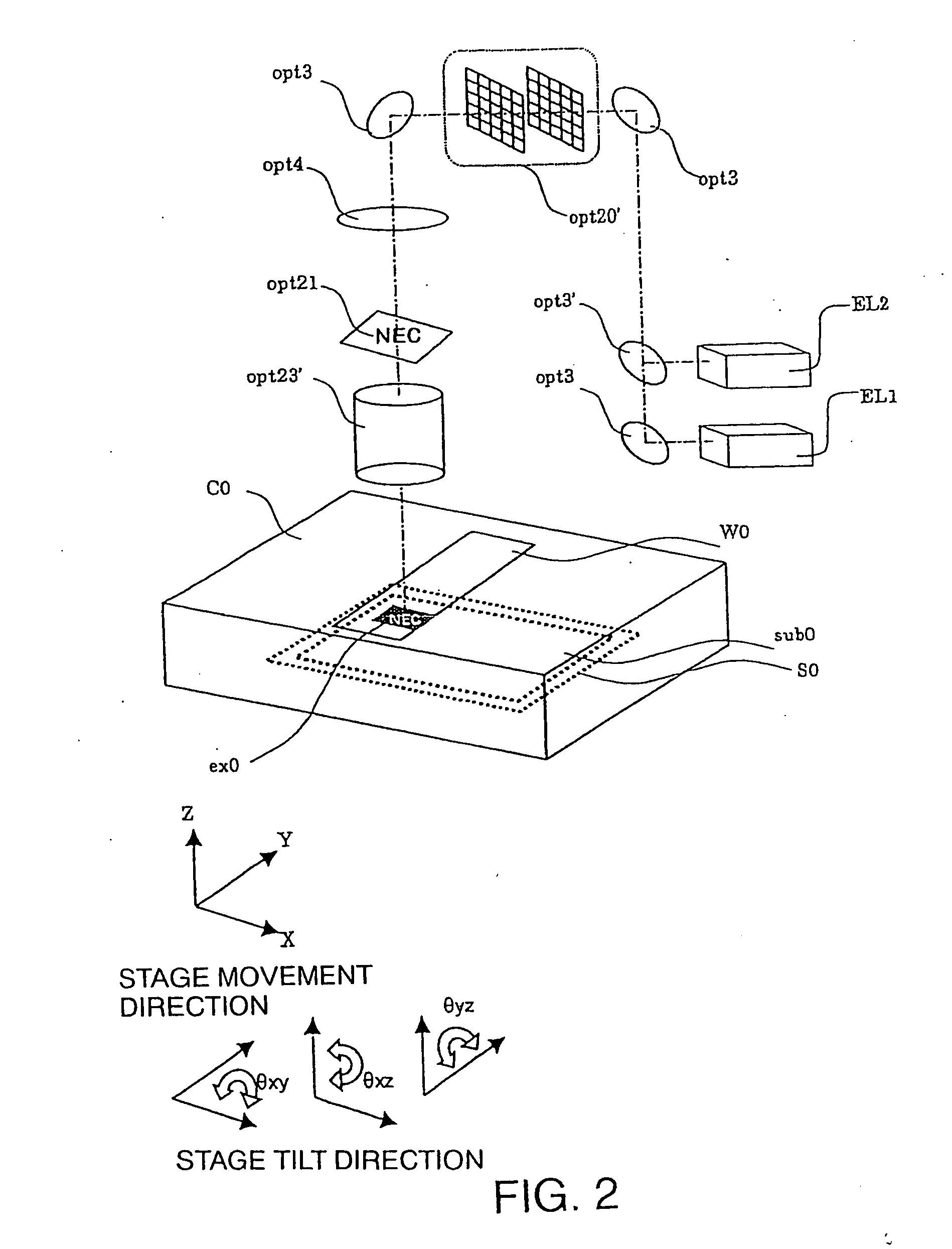
In a semiconductor thin film forming system for modifying a predetermined region of a semiconductor thin film by exposing the semiconductor thin film to a projected light patterned through a pattern formed on a photo mask, the system includes a mechanism (opt20′) for uniformizing the light for exposure in a predetermined area on the photo mask. This system can provide a crystallized silicon film having a trap state density less than 1012 cm−2 and can provide a silicon-insulating film interface exhibiting a low interface state density.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
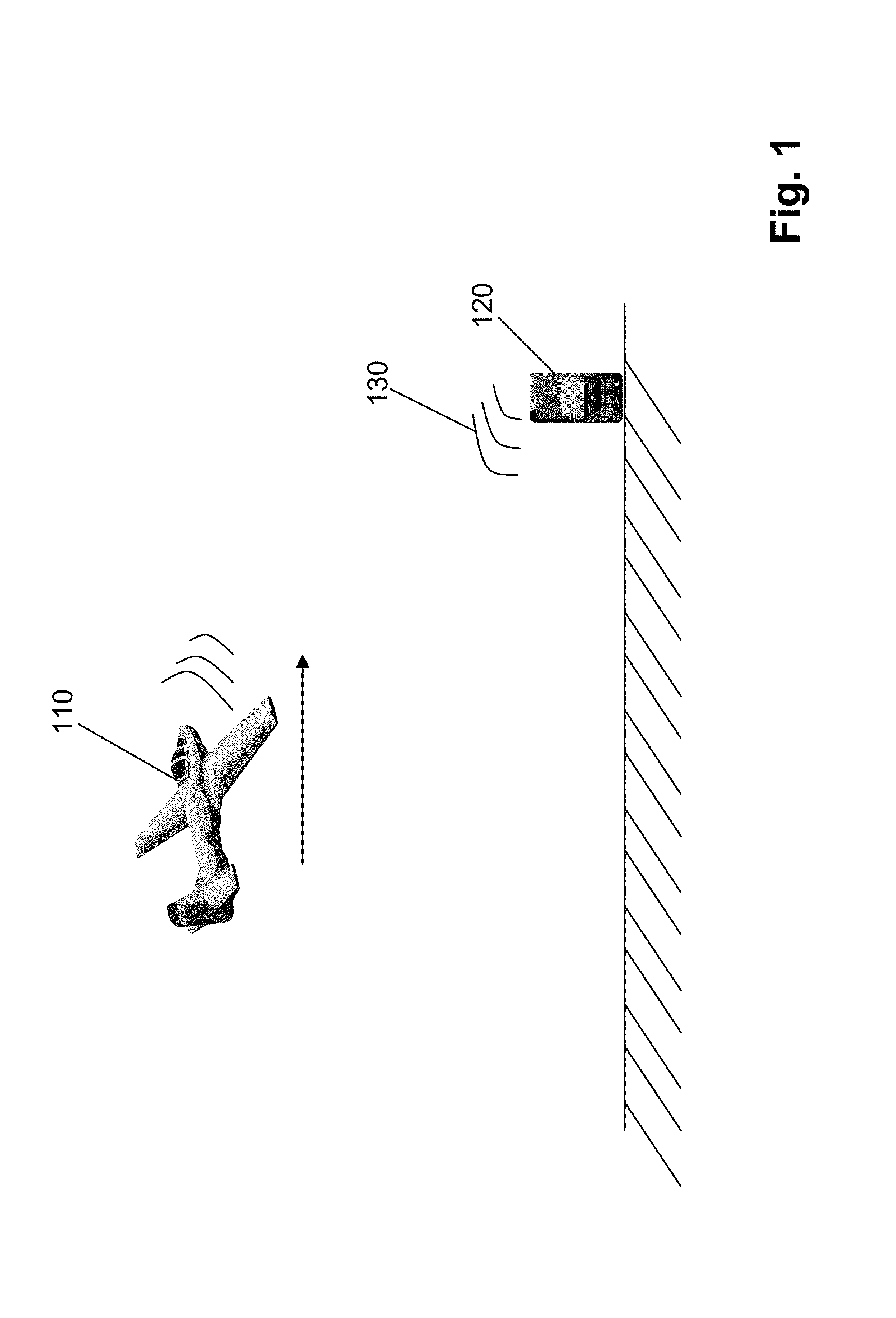
Diversified doppler for single platform geolocation
InactiveUS9007262B1Robust and accurate solutionOvercomes drawbackPosition fixationGeolocationParticle filtering algorithm
The described invention allows for rapid geolocation of one or more RF emitters using a single moving collection platform. Inaccuracies of conventional frequency of arrival (FOA) geolocation methods are overcome by solving simultaneously for emitter location and a potential emitter drift associated with an observed emitter frequency. Certain embodiments may utilize particle filtering algorithms to recursively update multimodal state densities that are typical of solutions involving both unknown emitter location and nonstationary emitter carrier drift. Moreover, certain properties of particle filters may be exploited to provide a geolocation solution given a complex multimodal state space composed of emitter location and a non-stationary emitter frequency required for FOA.
Owner:LEIDOS
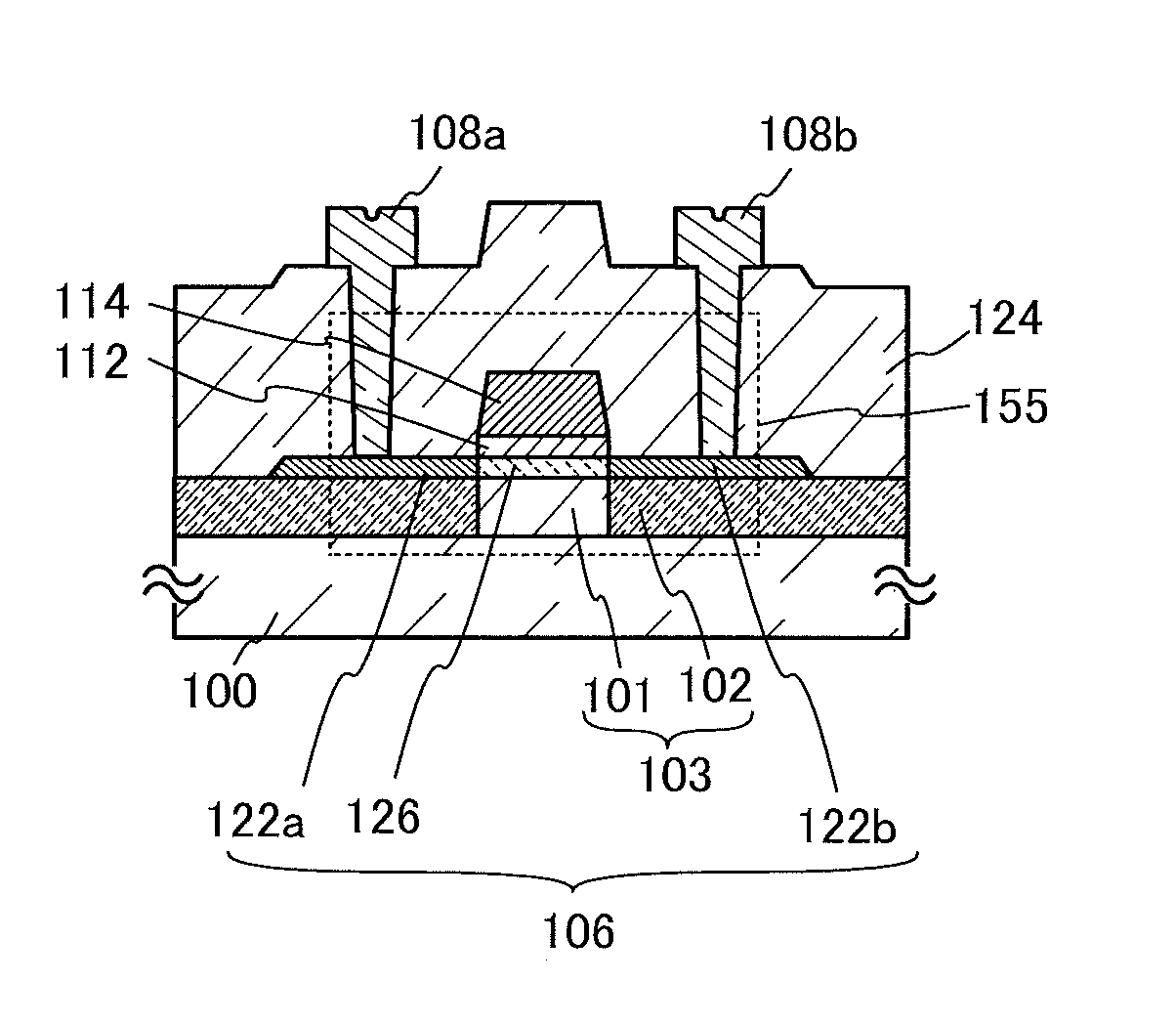
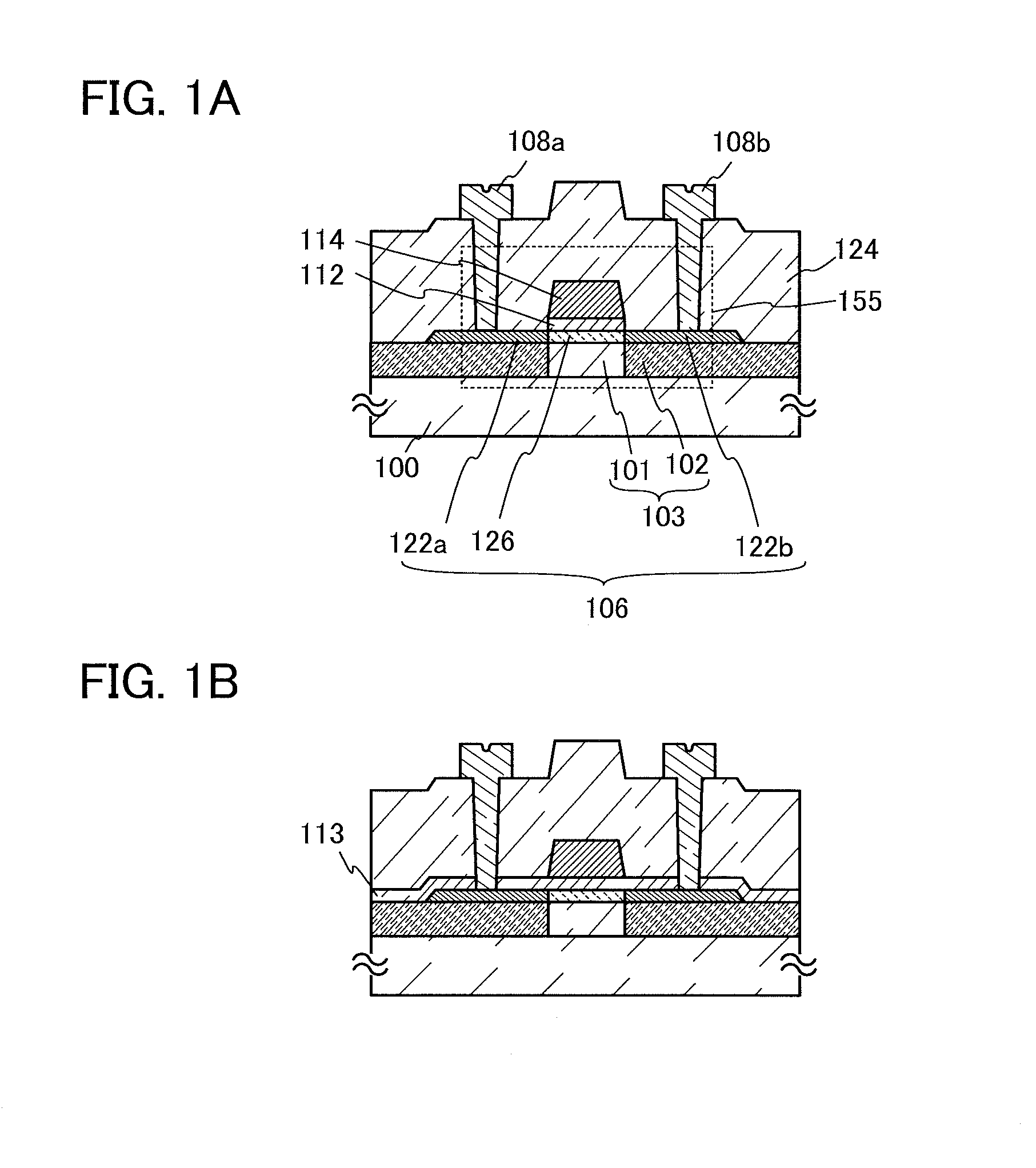
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120018727A1Stable electrical characteristicsLittle changeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceState density
An insulating layer which releases a large amount of oxygen is used as an insulating layer in contact with a channel region of an oxide semiconductor layer, and an insulating layer which releases a small amount of oxygen is used as an insulating layer in contact with a source region and a drain region of the oxide semiconductor layer. By releasing oxygen from the insulating layer which releases a large amount of oxygen, oxygen deficiency in the channel region and an interface state density between the insulating layer and the channel region can be reduced, so that a highly reliable semiconductor device having small variation in electrical characteristics can be manufactured. The source region and the drain region are provided in contact with the insulating layer which releases a small amount of oxygen, thereby suppressing the increase of the resistance of the source region and the drain region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110303913A1Stable electrical characteristicsElectrical instabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityBottom gate
An object of an embodiment of the present invention is to manufacture a highly-reliable semiconductor device comprising a transistor including an oxide semiconductor, in which change of electrical characteristics is small. In the transistor including an oxide semiconductor, oxygen-excess silicon oxide (SiOX (X>2)) is used for a base insulating layer of a top-gate structure or for a protective insulating layer of a bottom-gate structure. By using the oxygen-excess silicon oxide, oxygen is discharged from the insulating layer, and oxygen deficiency of an oxide semiconductor layer and the interface state density between the oxide semiconductor layer and the base insulating layer or the protective insulating layer can be reduced, so that the highly-reliable semiconductor device in which change of electrical characteristics is small can be manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
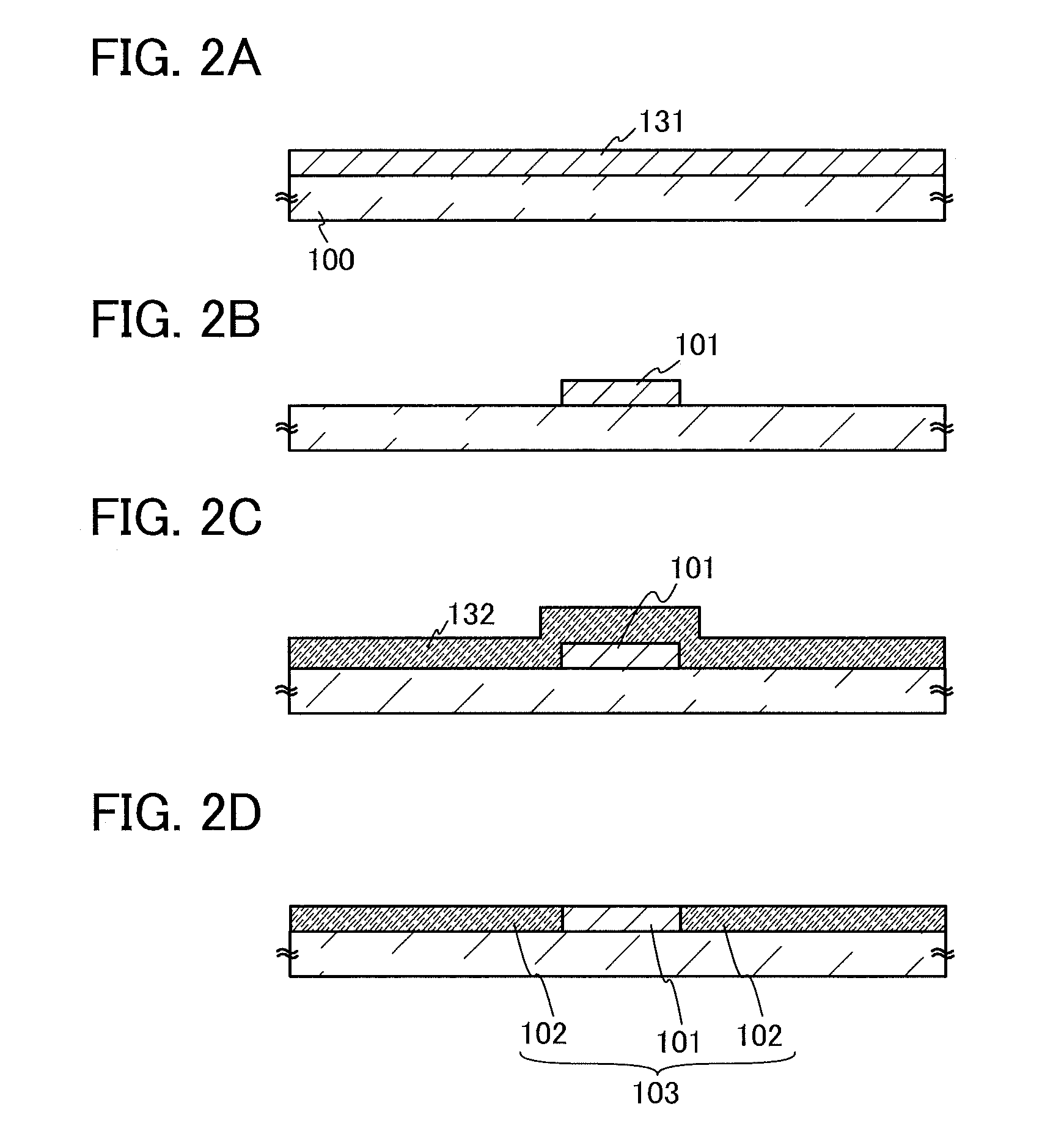
Semiconductor thin film forming system
InactiveUS20050109743A1Reduced trap state densityGood reproducibilityTransistorLaser detailsVolumetric Mass DensityState density
In a semiconductor thin film forming system for modifying a predetermined region of a semiconductor thin film by exposing the semiconductor thin film to a projected light patterned through a pattern formed on a photo mask, the system includes a mechanism (opt20′) for uniformizing the light for exposure in a predetermined area on the photo mask. This system can provide a crystallized silicon film having a trap state density less than 1012 cm−2 and can provide a silicon-insulating film interface exhibiting a low interface state density.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
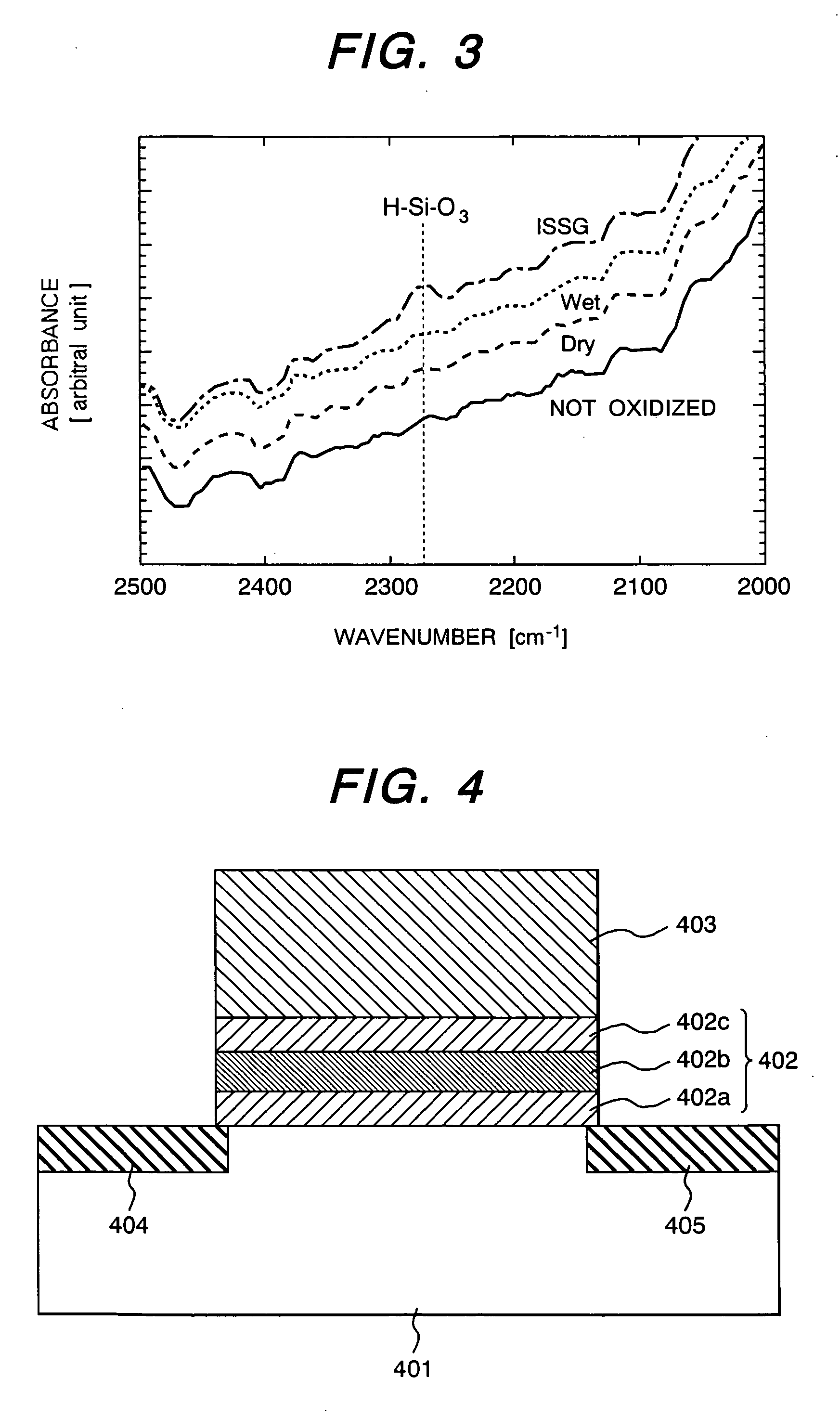
Method of manufacturing nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20050272198A1Reduce in quantityImprove attributesTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationTrapping
Conventionally, a MONOS type nonvolatile memory is fabricated by subjecting a silicon nitride film to ISSG oxidation to form a top silicon oxide film of ONO structure. If the ISSG oxidation conditions are severe, repeats of programming / erase operation cause increase of interface state density (Dit) and electron trap density. This does not provide a sufficient value of the on current, posing a problem in that the deterioration of charge trapping properties cannot be suppressed. For the solution to the problem, the silicon nitride film is oxidized by means of a high concentration ozone gas to form the top silicon oxide film.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Silicon carbide-oxide layered structure, production method thereof, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050077569A1Improve drivabilityHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricDevice material
A gate insulating film which is an oxide layer mainly made of SiO2 is formed over a silicon carbide substrate by thermal oxidation, and then, a resultant structure is annealed in an inert gas atmosphere in a chamber. Thereafter, the silicon carbide-oxide layered structure is placed in a chamber which has a vacuum pump and exposed to a reduced pressure NO gas atmosphere at a high temperature higher than 1100° C. and lower than 1250° C., whereby nitrogen is diffused in the gate insulating film. As a result, a gate insulating film which is a V-group element containing oxide layer, the lower part of which includes a high nitrogen concentration region, and the relative dielectric constant of which is 3.0 or higher, is obtained. The interface state density of an interface region between the V-group element containing oxide layer and the silicon carbide layer decreases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Thin film transistor and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7015507B2Reduce interface state densityImprove featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalEngineering
Provided is a non-single-crystal germanium thin film transistor having a gate insulating film capable of reducing the interface state density between an active layer and the gate insulating film. This thin film transistor has an active layer made of a non-single-crystal germanium film, and a gate oxide film substantially made of zirconium oxide or hafnium oxide.
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor element
InactiveUS20060220026A1Excellent electrical propertiesReduced electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCarbide
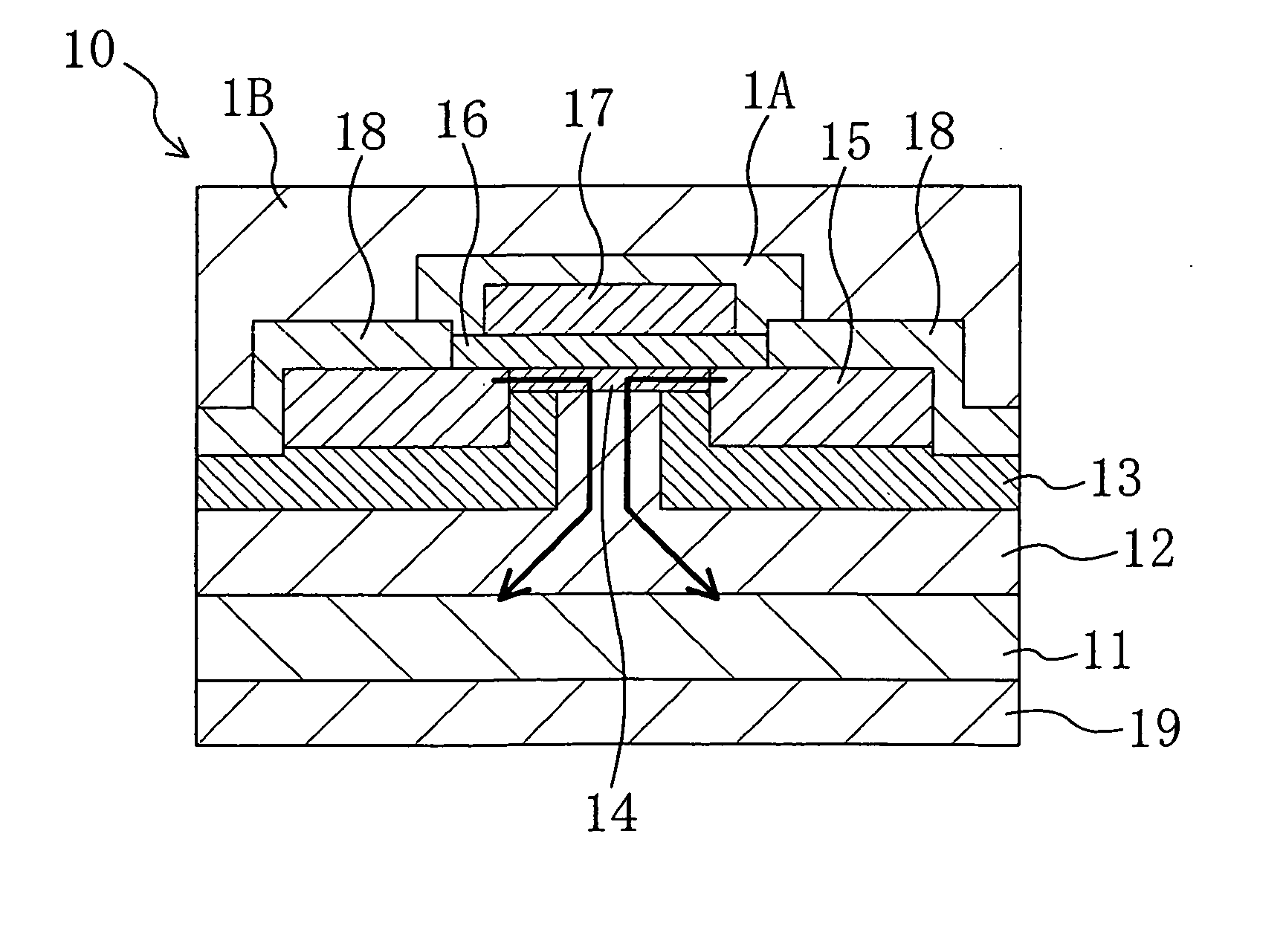
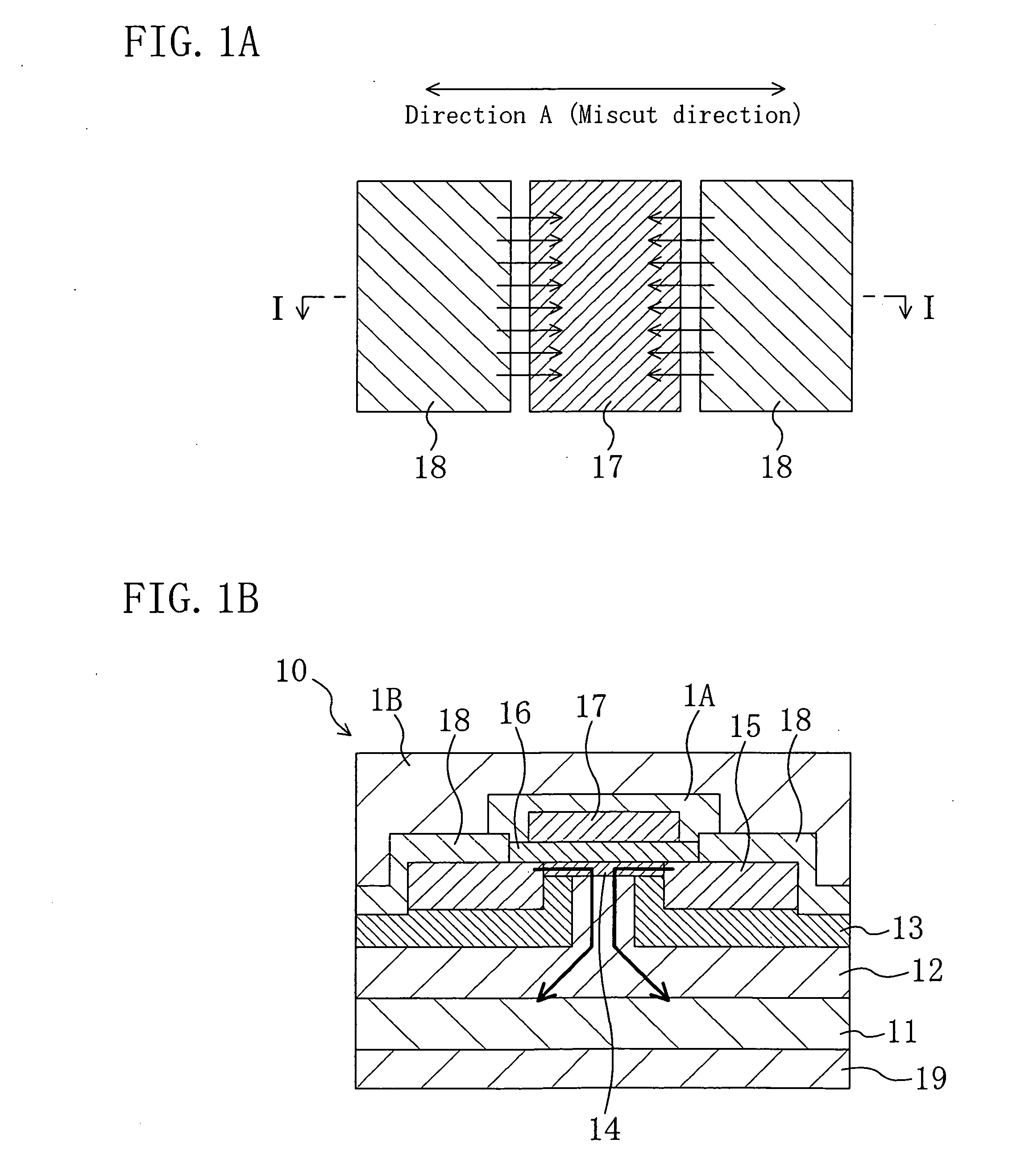
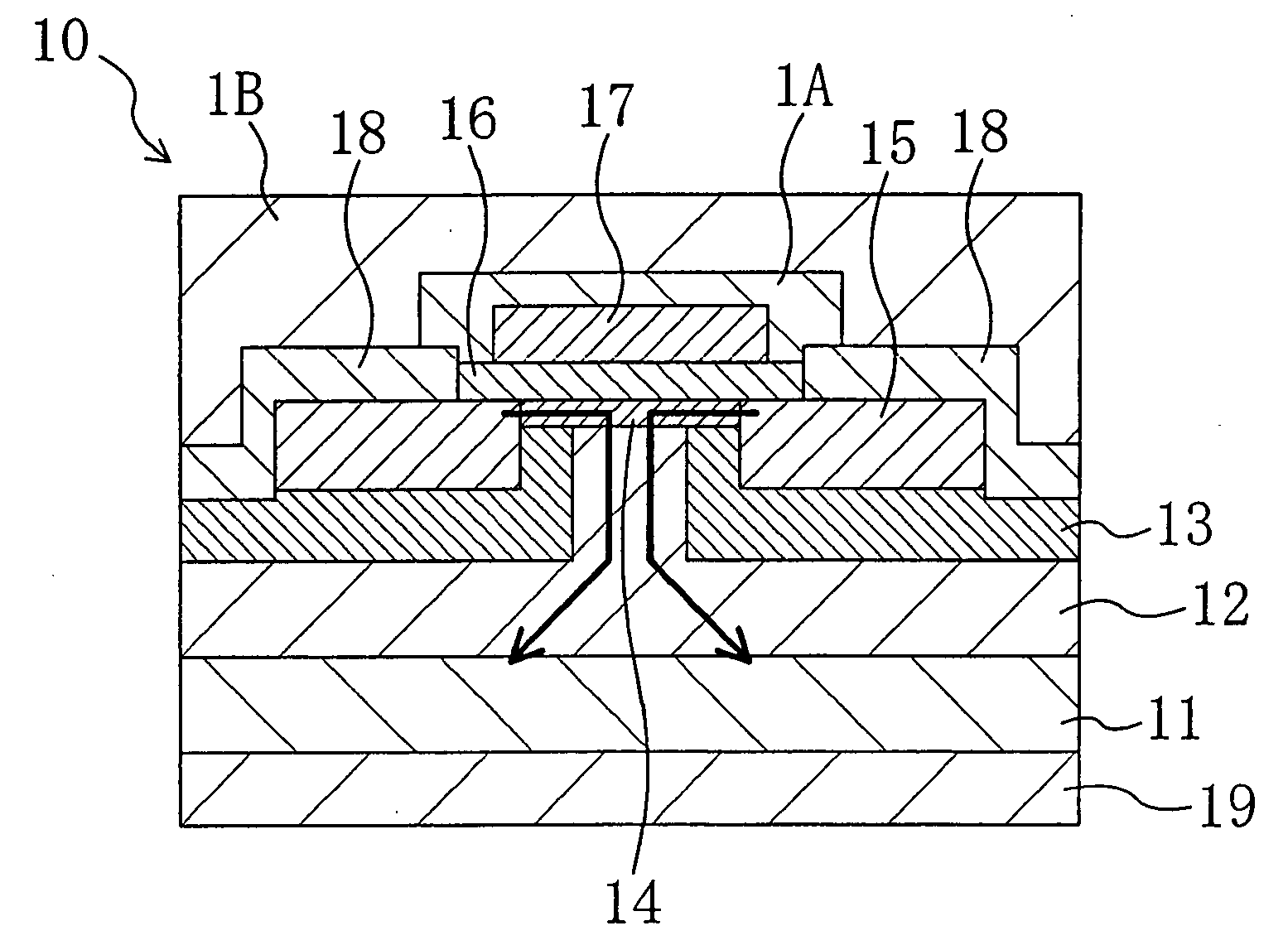
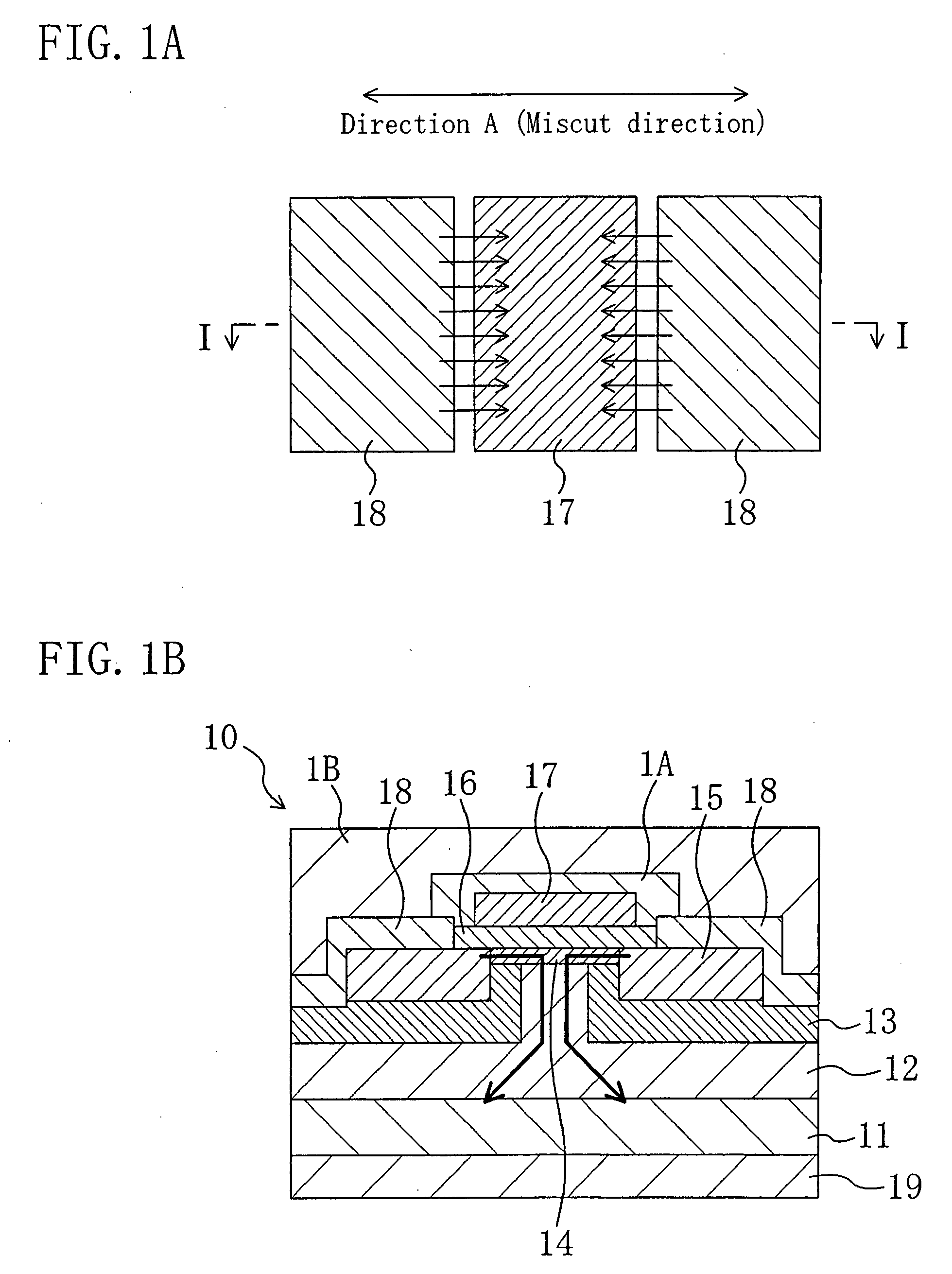
In a semiconductor device of the present invention, the top surface of an n-type silicon carbide layer formed on a silicon carbide substrate is miscut from the (0001) plane in the <11-20> direction. A gate electrode, a source electrode and other elements are arranged such that in a channel region, the dominating current flows along a miscut direction. In the present invention, a gate insulating film is formed and then heat treatment is performed in an atmosphere containing a group-V element. In this way, the interface state density at the interface between the silicon carbide layer and the gate insulating film is reduced. As a result, the electron mobility becomes higher in a miscut direction A than in the direction perpendicular to the miscut direction A.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of forming metal/high-k gate stacks with high mobility
ActiveUS20050280105A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorDevice material
The present invention provides a gate stack structure that has high mobilites and low interfacial charges as well as semiconductor devices, i.e., metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) that include the same. In the semiconductor devices, the gate stack structure of the present invention is located between the substrate and an overlaying gate conductor. The present invention also provides a method of fabricating the inventive gate stack structure in which a high temperature annealing process (on the order of about 800° C.) is employed. The high temperature anneal used in the present invention provides a gate stack structure that has an interface state density, as measured by charge pumping, of about 8×1010 charges / cm2 or less, a peak mobility of about 250 cm2 / V-s or greater and substantially no mobility degradation at about 6.0×1012 inversion charges / cm2 or greater.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
System and method for characterizing the electrical properties of a semiconductor sample
InactiveUS20110301892A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleCharge carrierLight beam
A system for characterizing the electrical properties of semiconductor wafers with high surface state densities, such as GaN wafers, includes a support subsystem for supporting the semiconductor sample, at least one light source for illuminating a spot on the sample, and a detection subsystem for measuring the photovoltage signal produced from illumination of the sample. In use, the system utilizes in-line, non-contact photovoltage techniques that exploits the presence of the high surface state density and the known components of its associated electrostatic barrier as part of its novel characterization process. Specifically, the system illuminates the sample with one or more light beams that vary in photon energy and duration in order to excite charge carriers in specific layers of the sample while either preserving or collapsing the electrostatic barrier. In this manner, the system is able to electrically characterize individual or combined layers of the sample as well as embedded junctions.
Owner:KAMIENIECKI EMIL
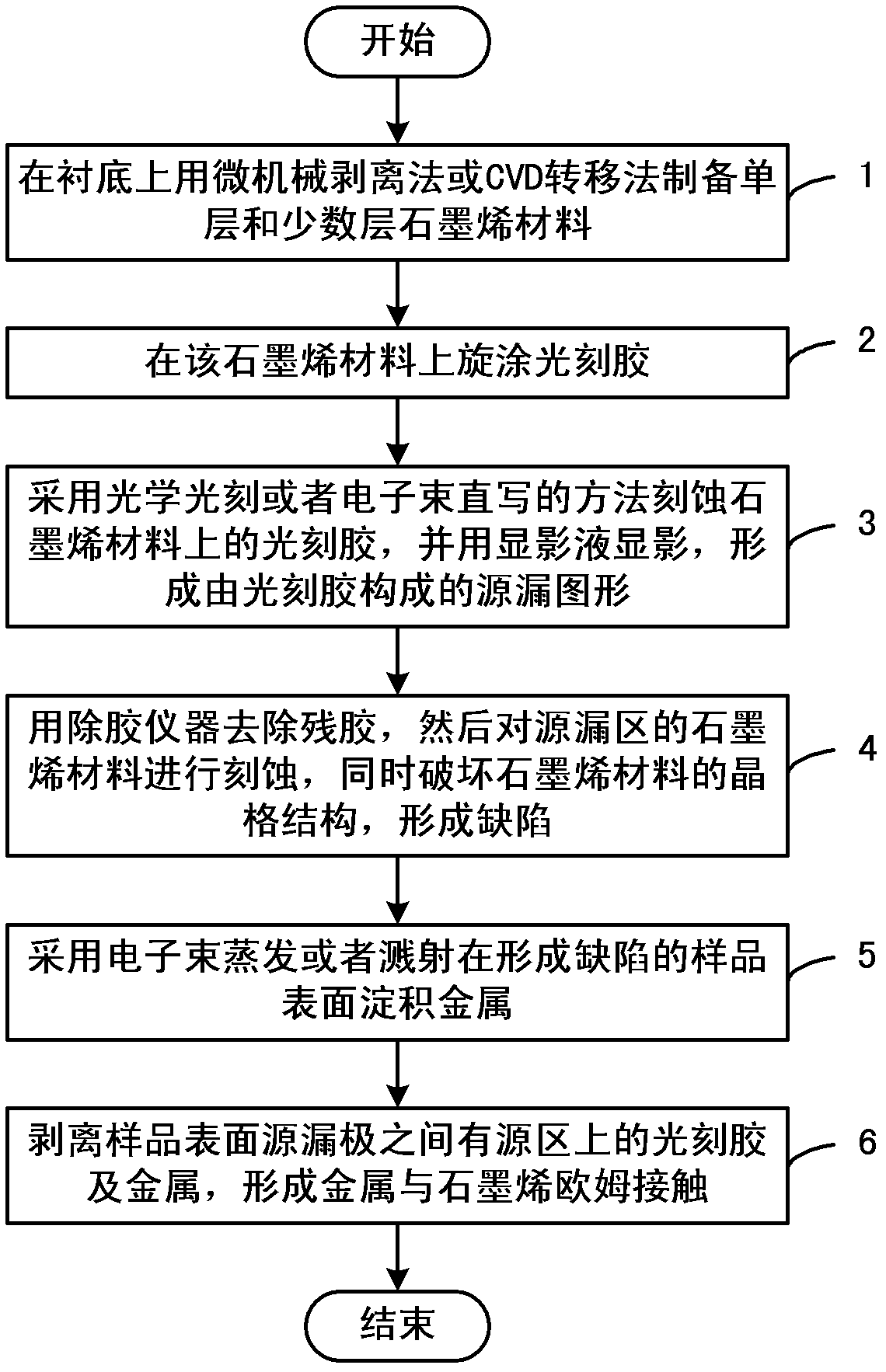
Preparation method of ohmic contact of metal with graphene
InactiveCN102623310AReduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDirect writingState density
The invention discloses a preparation method of ohmic contact of metal with graphene. The method includes preparing monolayer and a plurality of layers of graphene materials on a substrate through a micromechanical cleavage or a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) transferring method; spin-coating photoresist on the graphene materials; etching the photoresist on the graphene materials through optical lithography or an electron beam direct writing method, using a developer solution for development to form a source-drain image formed by the photoresist; removing residual gum with a degumming device, etching the graphene materials in a source-drain area, and destroying the lattice structure of the graphene materials to form defects simultaneously; using electron beam to evaporate or sputter on the sample surface where the defects form so as to deposit the metal; and stripping the photoresist and the metal on an active area and between the drain and the source on the sample surface so as to form the ohmic contact of the metal with the graphene. Compared with the existing ohmic contact of metal with graphene, the preparation method of the ohmic contact of the metal with the graphene overcomes the defect that state density of the grapheme nearby fermi level is small, and can obtain the ohmic contact of the metal with the graphene with small contact resistance.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sic semiconductor element and manufacturing method for same
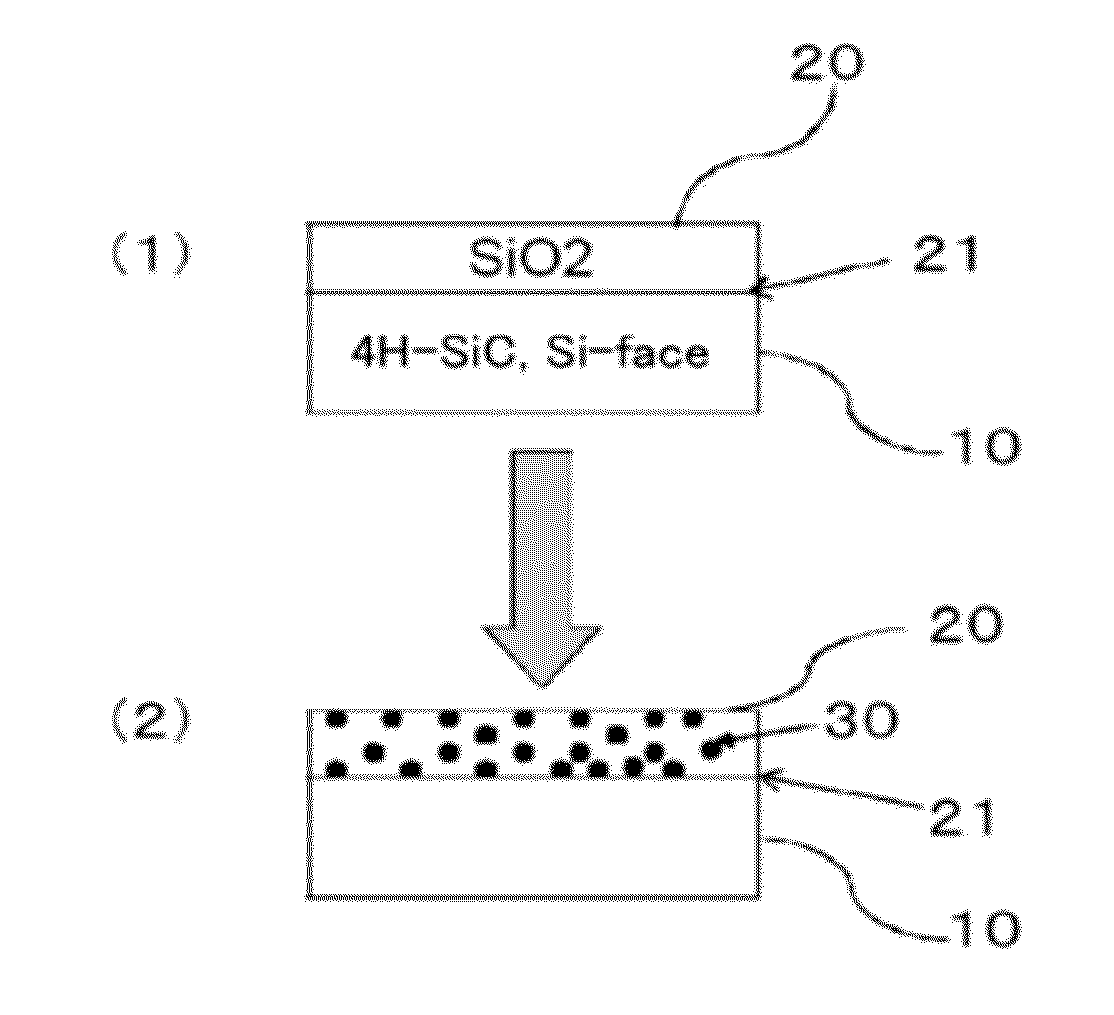
ActiveUS20120241767A1Reduce interface defectsReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesState densityThreshold voltage
Disclosed are an SiC semiconductor element and manufacturing method for an SiC semiconductor element in which the interface state density of the interface of the insulating film and the SiC is reduced, and channel mobility is improved. Phosphorus (30) is added to an insulating film (20) formed on an SiC semiconductor (10) substrate in a semiconductor element. The addition of phosphorous to the insulating film makes it possible to significantly reduce the defects (interface state density) in the interface (21) of the insulating film and the SiC, and to dramatically improve the channel mobility when compared with conventional SiC semiconductor elements. The addition of phosphorus to the insulating film is carried out by heat treatment. The use of heat treatment to add phosphorous to the insulating film makes it possible to maintain the reliability of the insulating film, and to avoid variation in channel mobility and threshold voltage.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
III-V group semiconductor MOS field effect transistor with high mobility
InactiveCN102931231AReduce scatterIncrease drive currentSemiconductor devicesControl layerLow voltage
The invention discloses a III-V group MOS (Metal-oxide Semiconductor) field effect transistor with high mobility, which comprises a single-crystal lining, a buffer layer formed on the single-crystal lining, a planar doped layer formed in the buffer layer, a high-mobility channel layer formed on the buffer layer, a doped interface control layer formed on the high-mobility channel layer, a high-doped semiconductor layer formed on the doped interface control layer, a narrow band gap ohm contact layer formed on the high-doped semiconductor layer, and a source-drain metal electrode formed on the narrow band gap ohm contact layer, wherein a grid groove etched to the doped interface control layer is located between two source drain metal electrodes; a high-K grid medium is uniformly covered on the inner surface of the grid groove structure; and a grid metal electrode is formed on the high-K grid medium. The III-V MOS device structure disclosed by the invention not only can lower MOS interface state density, and improve channel mobility, but also can improve channel two-dimensional electron (cavity) gas concentration, and satisfy the application demand of a high-speed lower voltage operation high mobility CMOS technology.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
PERC cell back side passivation technology
InactiveCN106992229AUniform thicknessInhibition thicknessFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideSolar cell
The invention belongs to the solar energy cell field and more particularly, to a PERC cell back side passivation technology, comprising: texturing, diffusing, etching and backside polishing, followed by silicon wafer baking in hot wind; turning the backside of the silicon wafer upward by 180 degrees for ozone treatment to develop the front side oxidation treatment of the SiO2 film with the backside plated by a passivation film and the front side plated by a passivation film wherein the front side oxidation treatment is annealing treatment thermal oxidation method to develop the SiO2 film. According to the PERC cell back side passivation technology proposed by the invention, a silicon oxide film is developed whose backside thickness is even and the SiO2 and Si match better, effectively reducing the interface state density of the Si surface and increasing the field passivation effect of the AI203. The probability of EL degrading is reduced while the A-grade qualified rate is increased. In addition to that, the manufacturing cost for PERC cells is reduced and the cell performance is increased, therefore, making the technology of great significance in the energy aspect.
Owner:TONGWEI SOLAR HEFEI
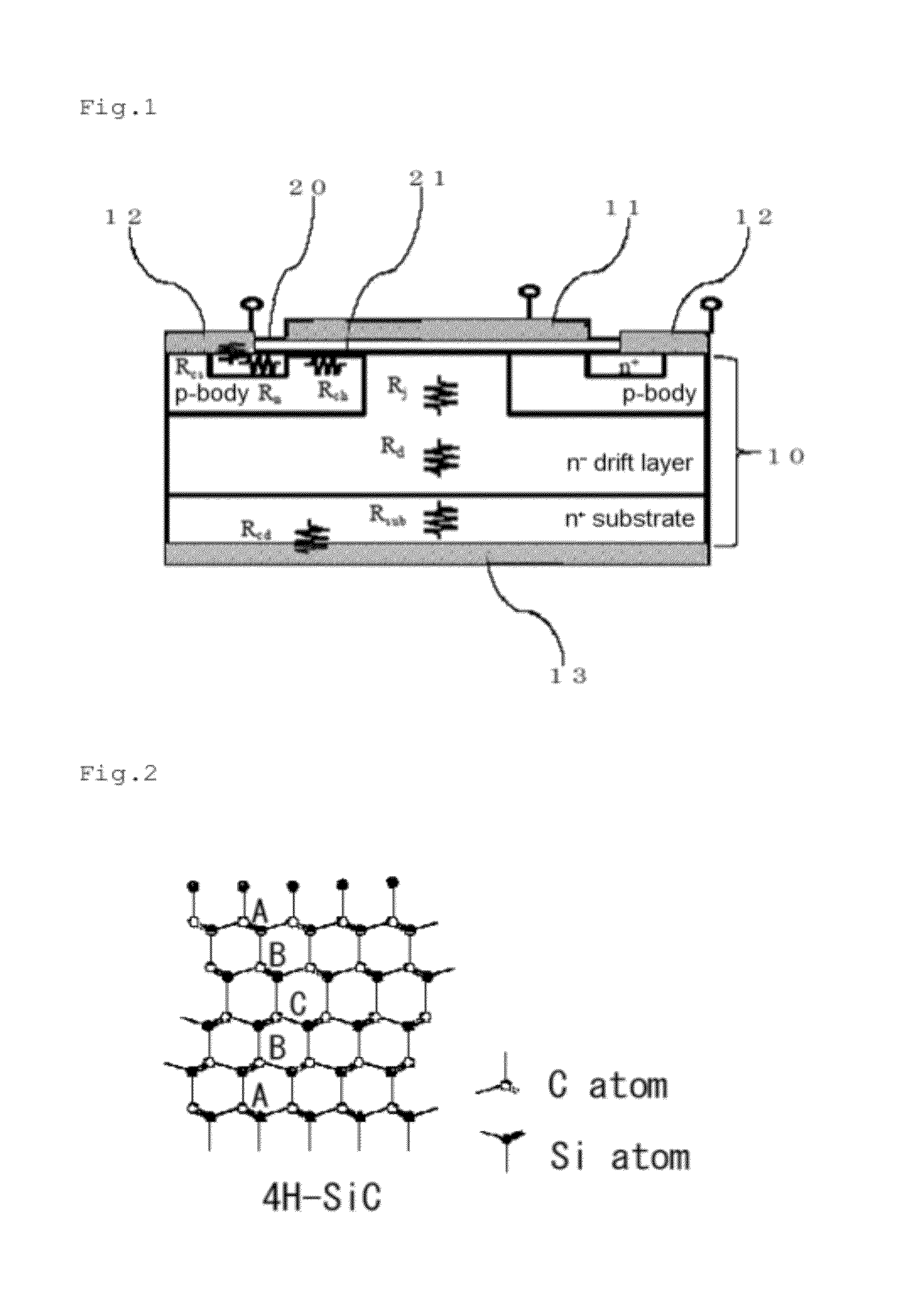
Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100221917A1Reduce interface state densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenSilicon oxide
A method of manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device having low interface state density in an interface region between a gate insulating film and a silicon carbide layer is provided. An epitaxially grown layer is grown on a 4H-SiC substrate, and thereafter ion implantation is performed to form a p well region, a source region and a p+ contact region that are ion implantation layers. Thereafter, using thermal oxidation or CVD, the gate insulating film formed by a silicon oxide film is formed on the p well region, the source region and the p+ contact region. Then, plasma is generated using a gas containing N2O, which is the gas containing at least any one of oxygen and nitrogen, so as to expose the gate insulating film to plasma.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Tin compound superlattice barrier semiconductor transistor
ActiveCN103811542AIncrease concentrationReduce dislocation densitySemiconductor devicesDriving currentPower flow
The invention discloses a tin compound superlattice barrier semiconductor transistor, comprising a superlattice barrier layer, wherein the superlattice barrier layer is formed by multi-cycle thin film layers overlapped alternatively, and the thin film layer is composed of tin compound and another doped tin compound. By using the novel compounds of tin and the doping of the tin compounds, a multi-cycle superlattice barrier layer process is formed to obtain low dislocation density, smooth profile of HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor), low chip square resistance; the multi-cycle superlattice barrier layer with high conductive performance, high driving current and low MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) interface state density is achieved, and the two-dimensional electron gas concentration or the two-dimensional hole gas concentration in a channel layer is also improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High-drive-current III-V metal oxide semiconductor device
InactiveCN102610640AIncrease drive currentReduce scatterSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricControl layer
The invention discloses a high-drive-current III-V metal oxide semiconductor device which comprises a single crystal substrate, a buffer layer, a quantum-well bottom barrier layer, a planar doped layer, a high-mobility quantum-well channel, an interface control layer, a high K gate dielectric, an elevated source / drain layer, a metal gate structure and a source / drain contact metal layer, wherein the buffer layer is formed on the upper surface of the single crystal substrate; the quantum-well bottom barrier layer is formed on the upper surface of the buffer layer; the planar doped layer is formed in the quantum-well bottom barrier layer; the high-mobility quantum-well channel is formed on the upper surface of the quantum-well bottom barrier layer; the interface control layer is formed on the upper surface of the high-mobility quantum-well channel; the high K gate dielectric and the elevated source / drain layer are formed on the upper surface of the interface control layer; the metal gate structure is formed on the high K gate dielectric; and the source / drain contact metal layer is formed on the elevated source / drain layer. According to the invention, a dangling bond on an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) interface is passivated by using an interface control layer technology, thereby realizing the low interface state density, reducing the scattering of current carriers in the channel, improving the concentration of two-dimensional electron gas or two-dimensional hole gas in a channel layer, and satisfying the requirements of a high-performance III-V CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) technology.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
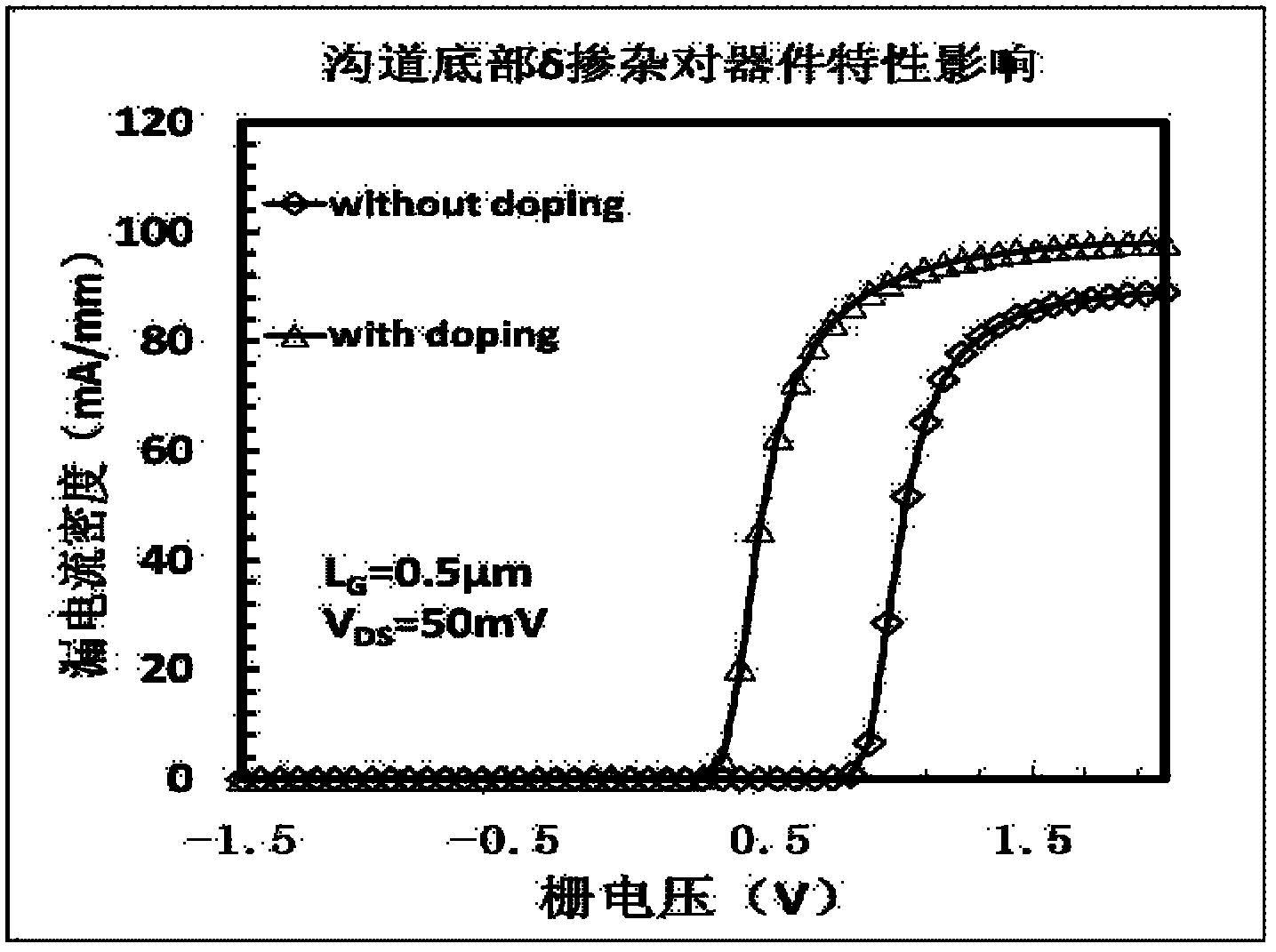
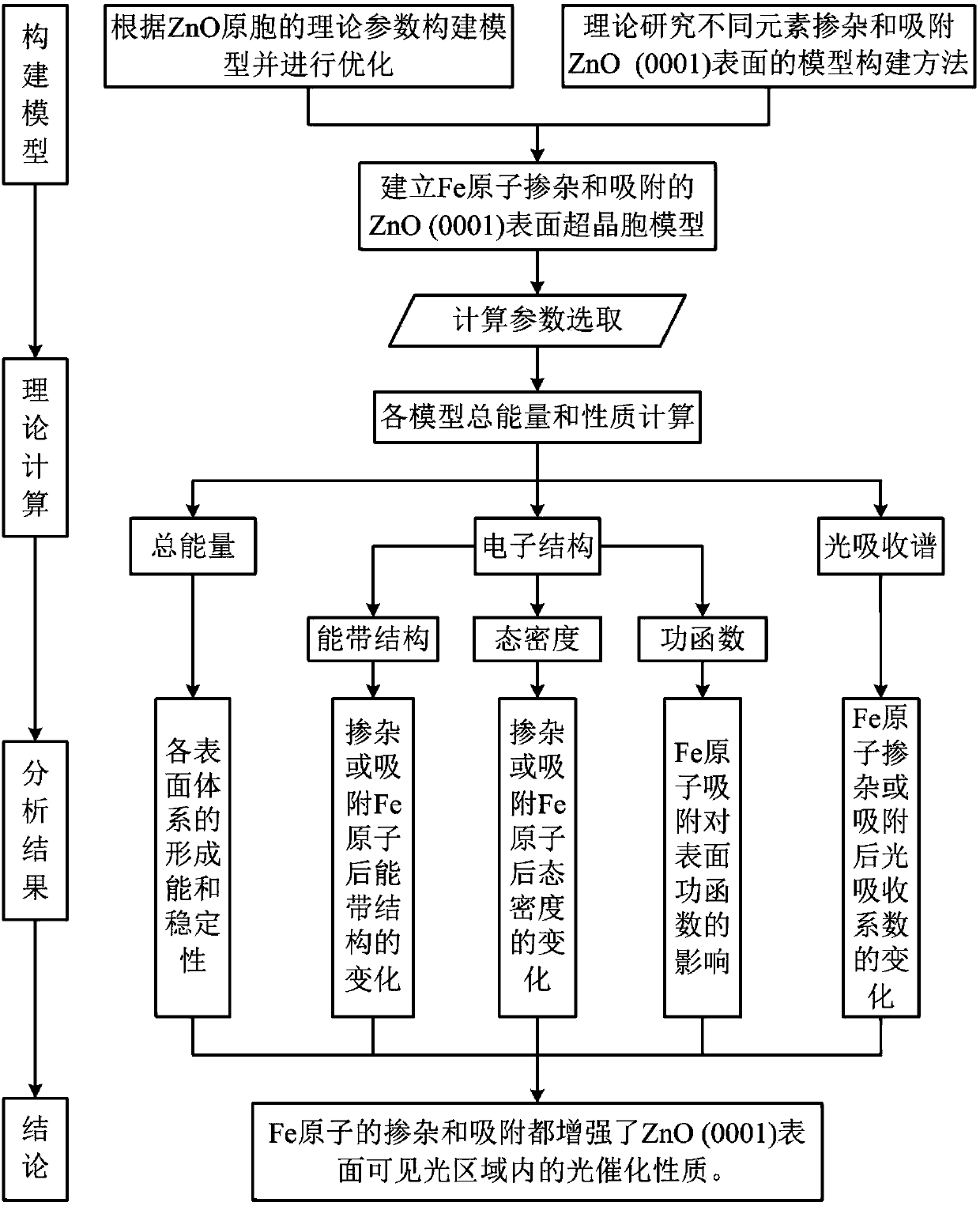
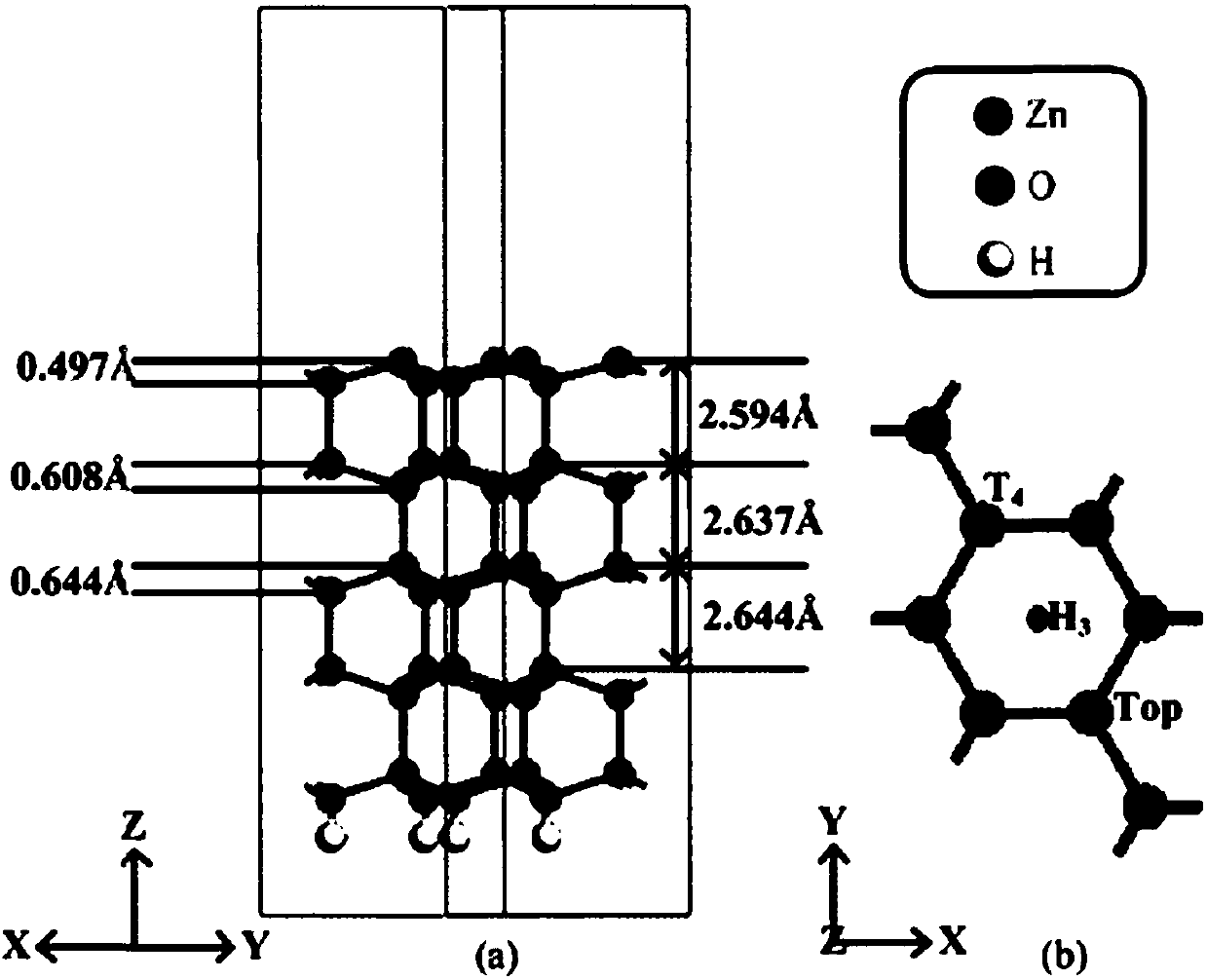
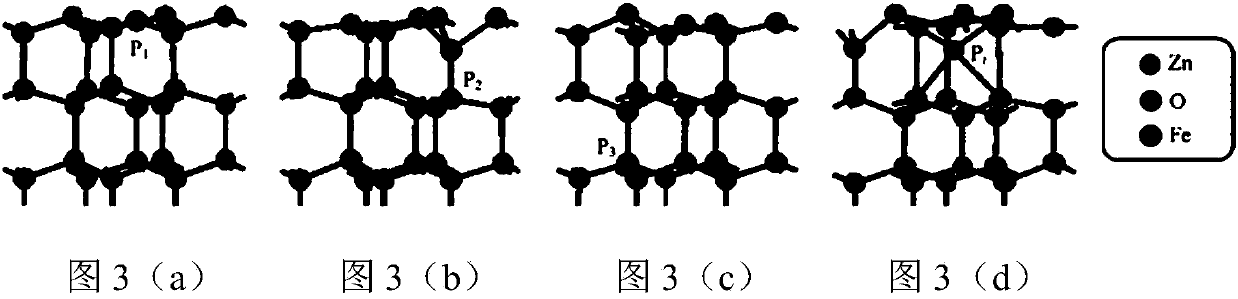
Calculation method for improving photocatalytic properties of ZnO (0001) surface through Fe atom doping and adsorption
ActiveCN108256287AImprove photocatalytic propertiesThe result is accurateChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic structureOptical property
The invention discloses a calculation method for improving the photocatalytic properties of the ZnO (0001) surface through Fe atom doping and adsorption. The method includes the steps of constructingthe primitive cells of ZnO body material in MS software, optimizing the structure, and constructing ZnO (0001) surface supercells and doping and adsorption models of Fe atoms at different loci on thepure ZnO (0001) surface; conducting structural optimization and GGA+U method calculation on the surface, selecting the energy band structure, the state density, the optical properties and the accuracycorresponding separately, and conducting calculation on each model; analyzing each model through a CASTEP module, obtaining the formation energy, optical property constant and work function of the ZnO (0001) surface doped and adsorbed by the Fe atoms, and obtaining the electronic structure and the optical property corresponding to each model. Therefore, the photocatalytic activity of the ZnO (0001) surface in the visible light range is improved, and certain reference is provided for the practical application of ZnO photocatalysis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
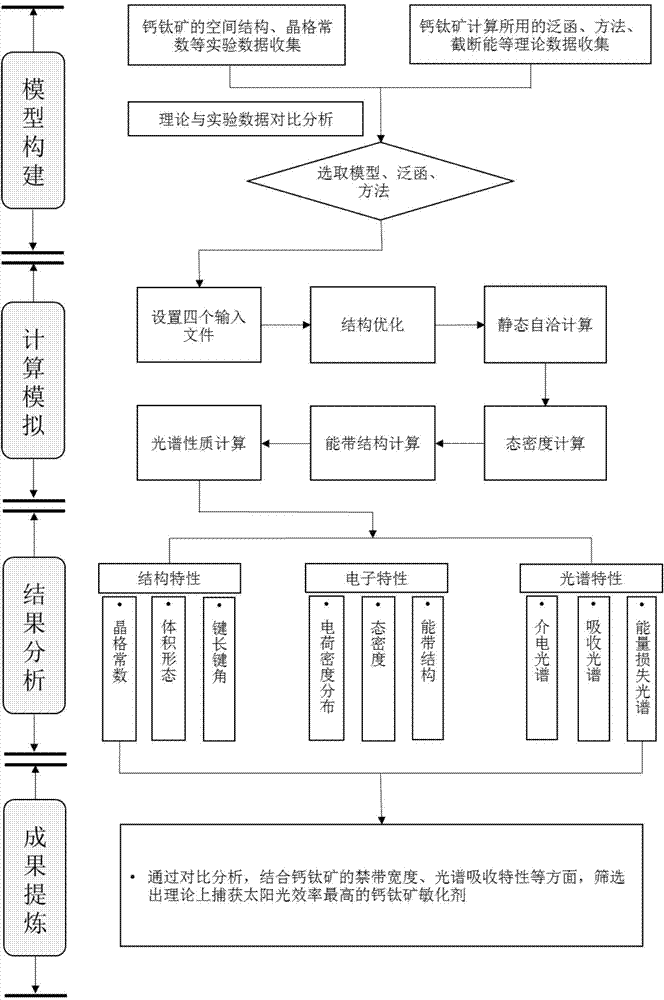
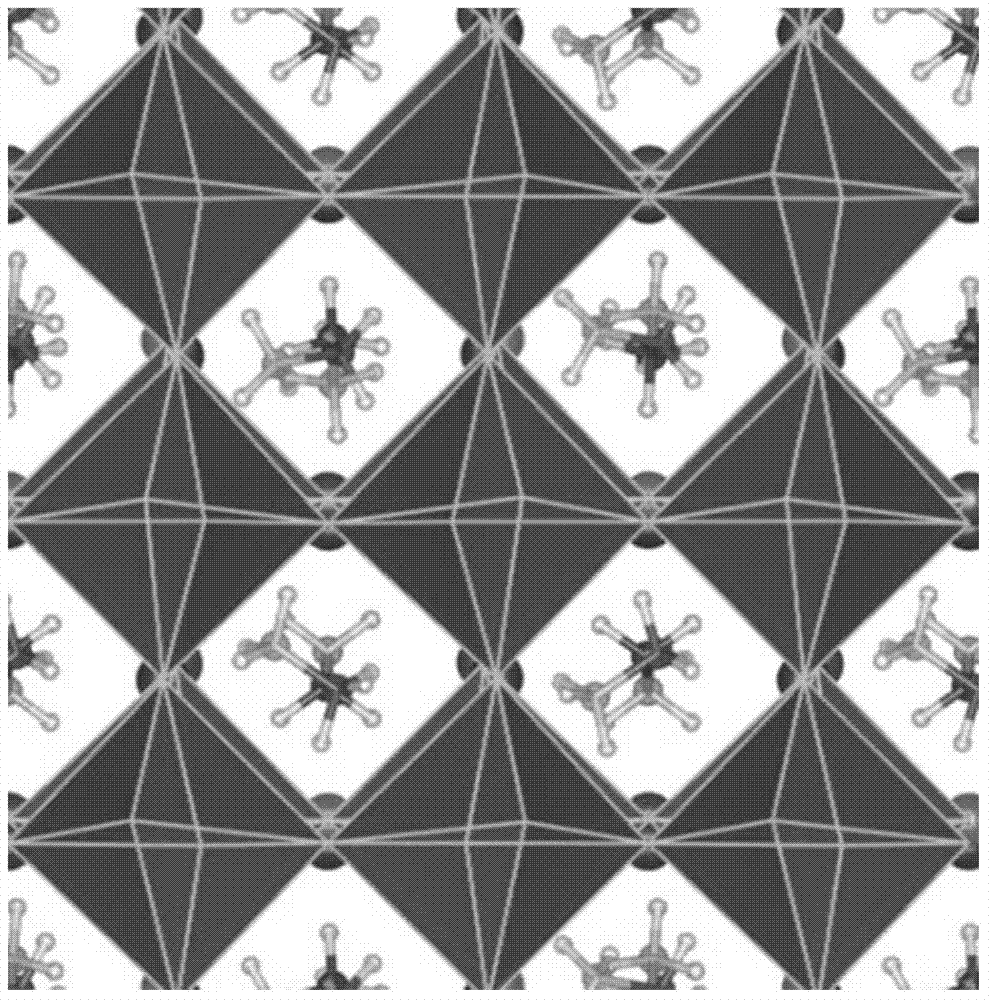
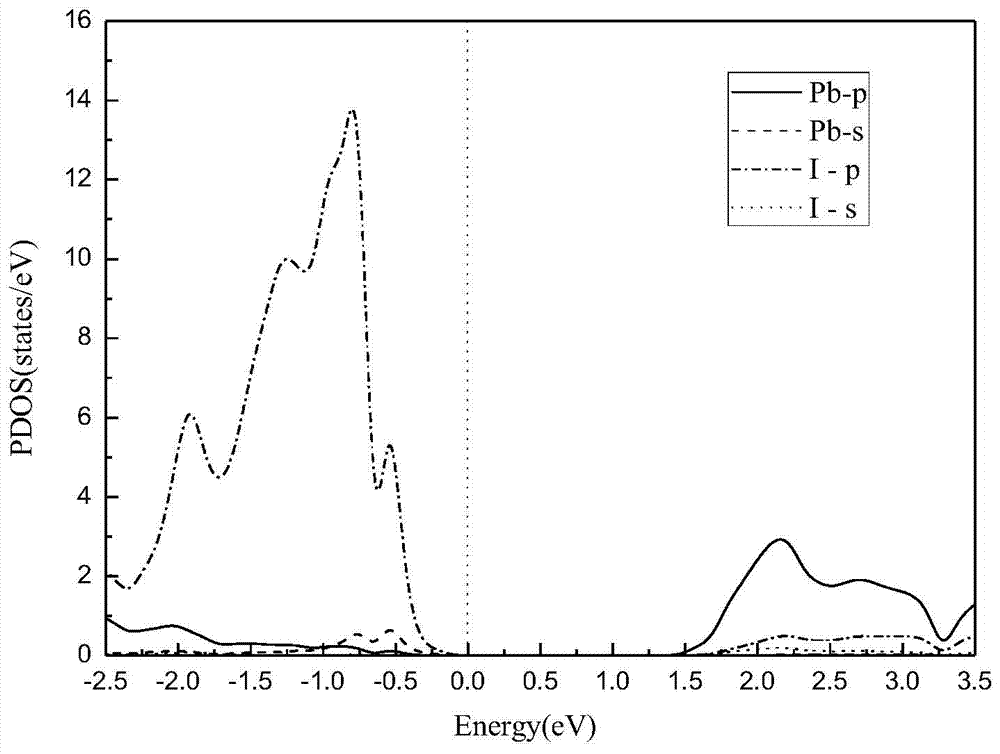
Theoretical method for screening high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer
InactiveCN104778330AImprove efficiencyQuick calculationSpecial data processing applicationsStructure chartFirst principle
The invention discloses a theoretical method for screening a high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer. The method comprises the following steps: structurally optimizing a perovskite model on the basis of a first principle, and performing electronic and spectral characteristic calculation; analyzing a stable structure to obtain a lattice constant and bond length and bond angle characteristics; performing electronic and spectral characteristic calculation on perovskite by virtue of VASP (Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package) software, drawing a charge density map, a state density map, an energy band structure chart and a spectrum chart by virtue of software such as VESTA and Origin, and analyzing the forbidden bandwidth of perovskite, an electron orbit transition rule, a crystal binding type, frontier orbit compositions and light absorption characteristics by virtue of a valence bond theory and an energy band theory; screening the high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer by comparing spectral absorption characteristics. According to the theoretical method for researching an internal mechanism of perovskite and screening the high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer, a direct theoretical guide is provided for the design of a perovskite solar cell, the research and development cycle of the cell is shortened, and research and development cost is lowered.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Enhanced high electronic mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105655395AImprove gate characteristicsImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower performanceState density
Owner:GPOWER SEMICON
Display panel and display apparatus
ActiveCN108615752AIncrease the density of statesIncreased rate of spontaneous emissionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsState density
The invention provides a display panel and a display apparatus. The display panel comprises a substrate, a thin film transistor layer, a positive electrode layer, an organic light emitting layer, a negative electrode layer, a thin film packaging layer and a particle layer. According to the display panel, the particle layer is arranged between the thin film transistor layer and the thin film packaging layer; the particle layer consists of multiple silver nanoparticles; equivalently, photon state density and exciton spontaneous radiation efficiency are improved according to an SPR effect on surfaces of the nanoparticles, so as to improve the luminous efficiency of an AMOLED display panel; and in addition, by virtue of a light reflection effect of the silver nanoparticle layer, loss of lightrays can be reduced, and the light extracting efficiency of the AMOLED is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
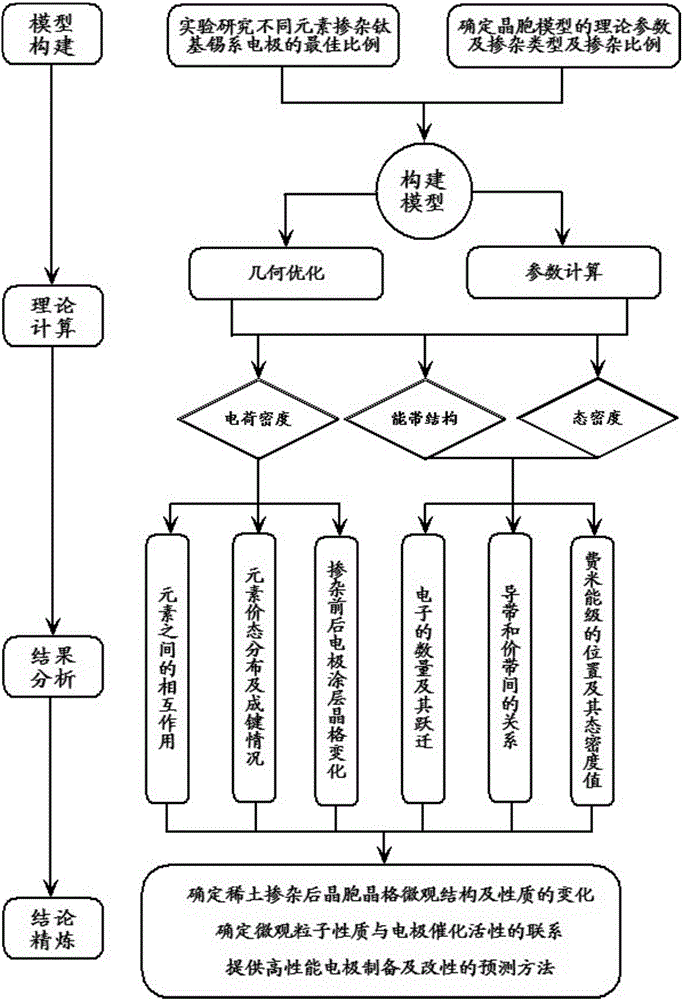
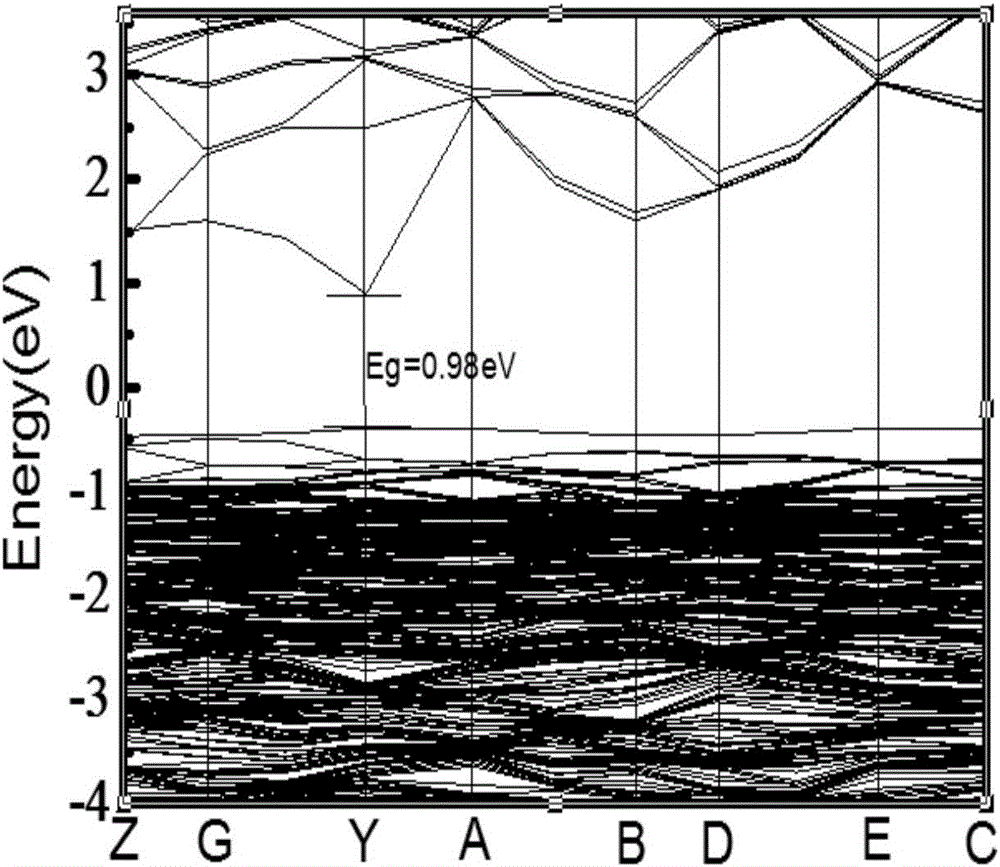
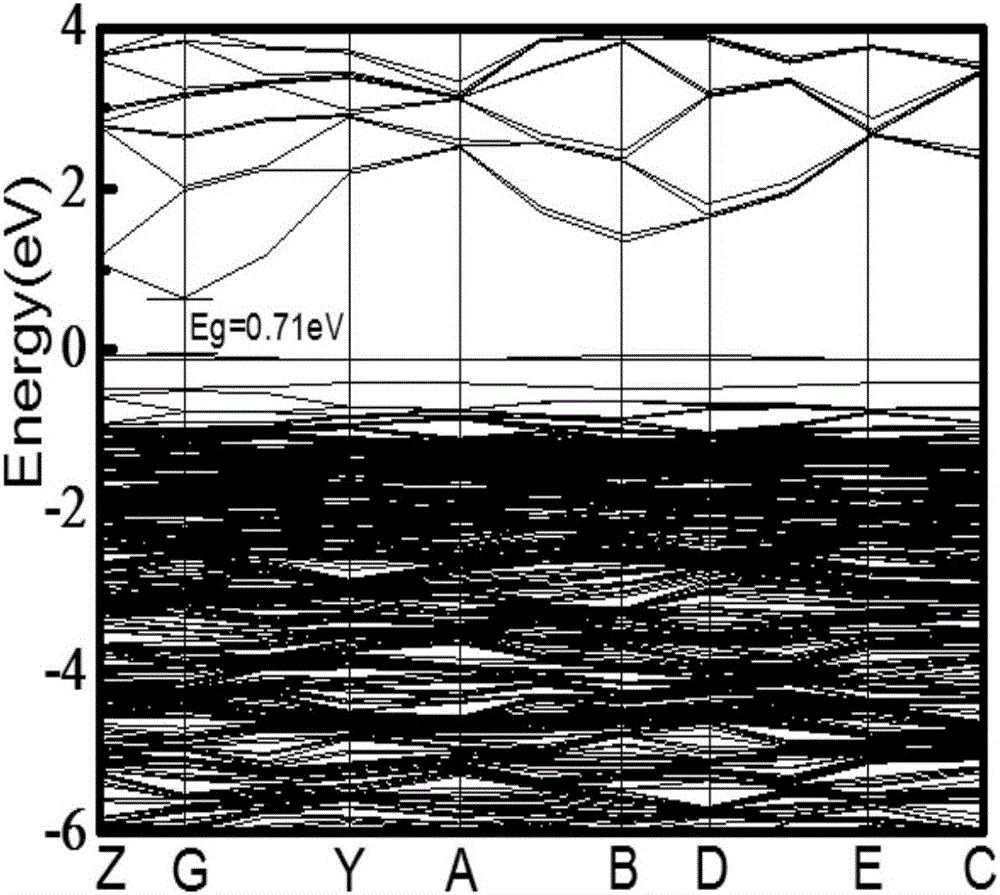
Prediction method for performance of rare-earth-doped modified titanium-based stannic oxide electrode
The invention provides a prediction method for the performance of a rare-earth-doped modified titanium-based stannic oxide electrode. The modified performance is predicted by calculating changes of stannic oxide crystal structure parameters before and after rare earth doping on the basis of a density functional theory of the first principles; the crystal geometric structures of SnO2 doped with La with the different concentrations are optimized by taking lanthanum as a doping agent, the lattice constant, the energy band structure, the state density and the formation energy of crystal cells of SnO2 with the different lanthanum doping quantities are calculated, and it shows that doped SnO2 has the higher electric conductivity and the good electro-catalytic property, energy band degeneration is intensified and the acceptor impurity energy level moves towards the direction away from the valence band maximum along with increasing of the doping concentration, the formation energy is lowest when the doping concentration is 1.39%, the electronic structure of SnO2 is most stable at the moment, and experiments verify that when the actual adding amount is 1.5%, the catalytic performance is best. According to the method, the performance of different systems of oxide electrodes doped with other rare earth or elements can be effectively predicted and analyzed according to the difference of doping elements and the different doped electrode systems.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
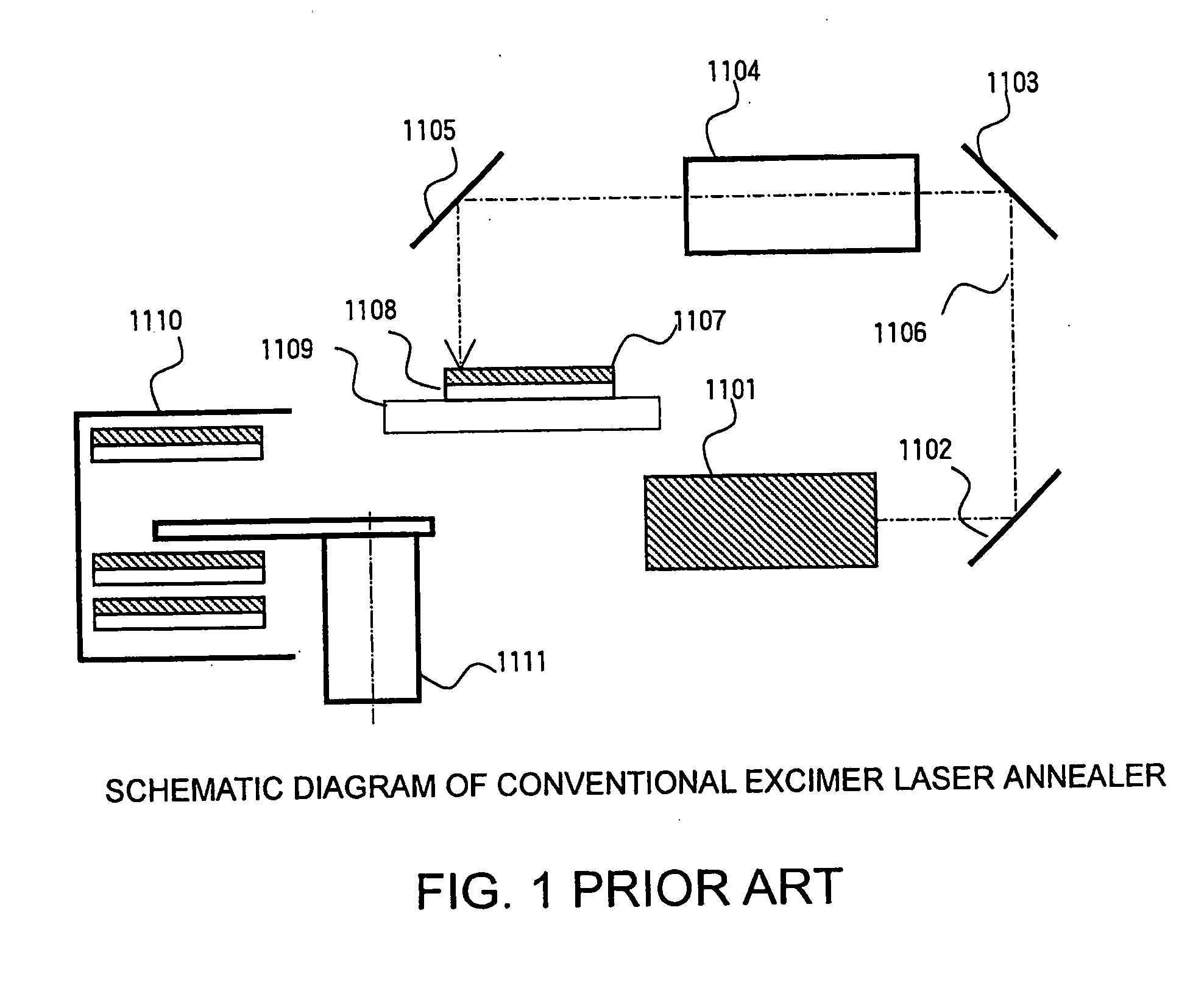
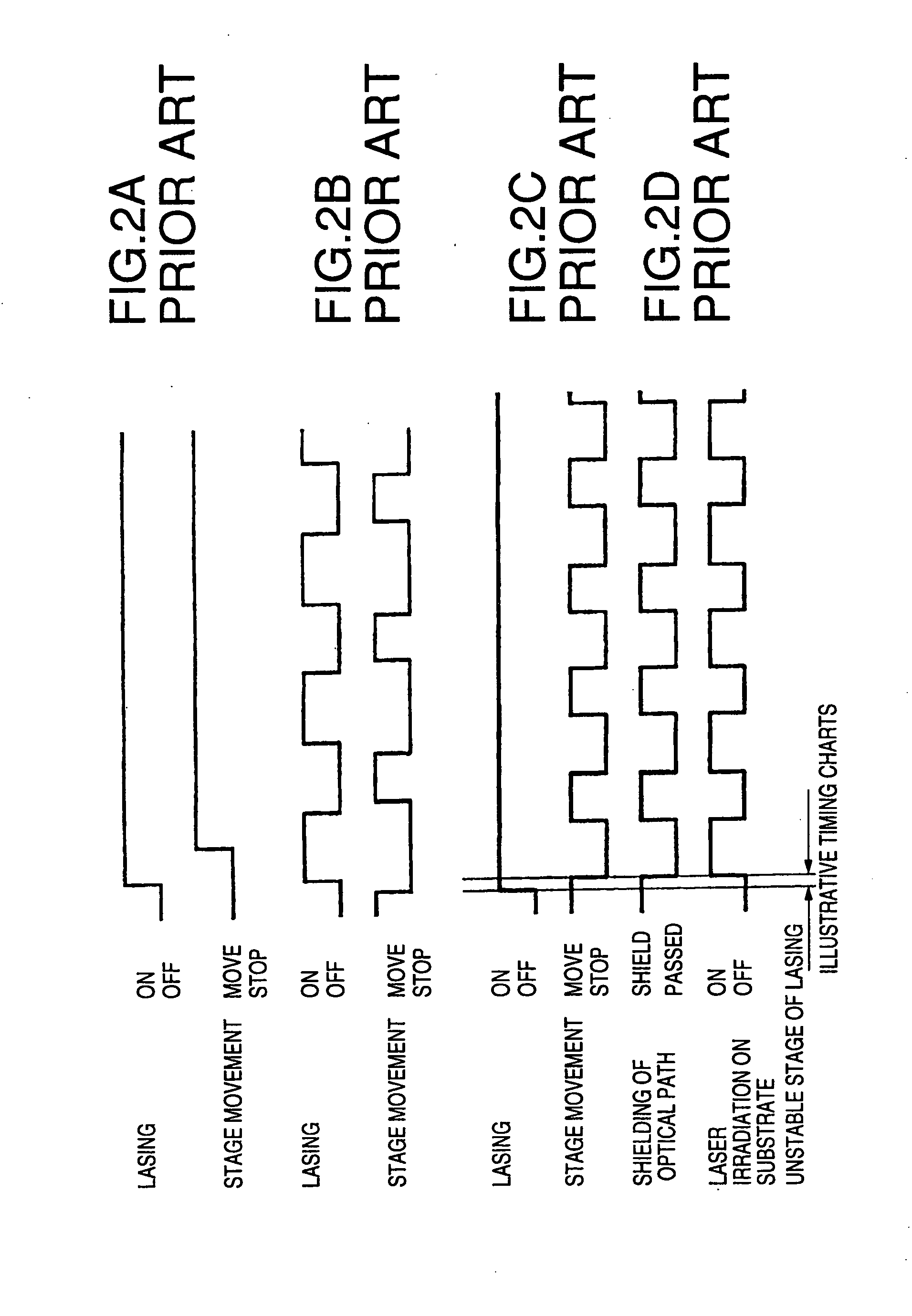
Thin film processing method and thin film processing apparatus
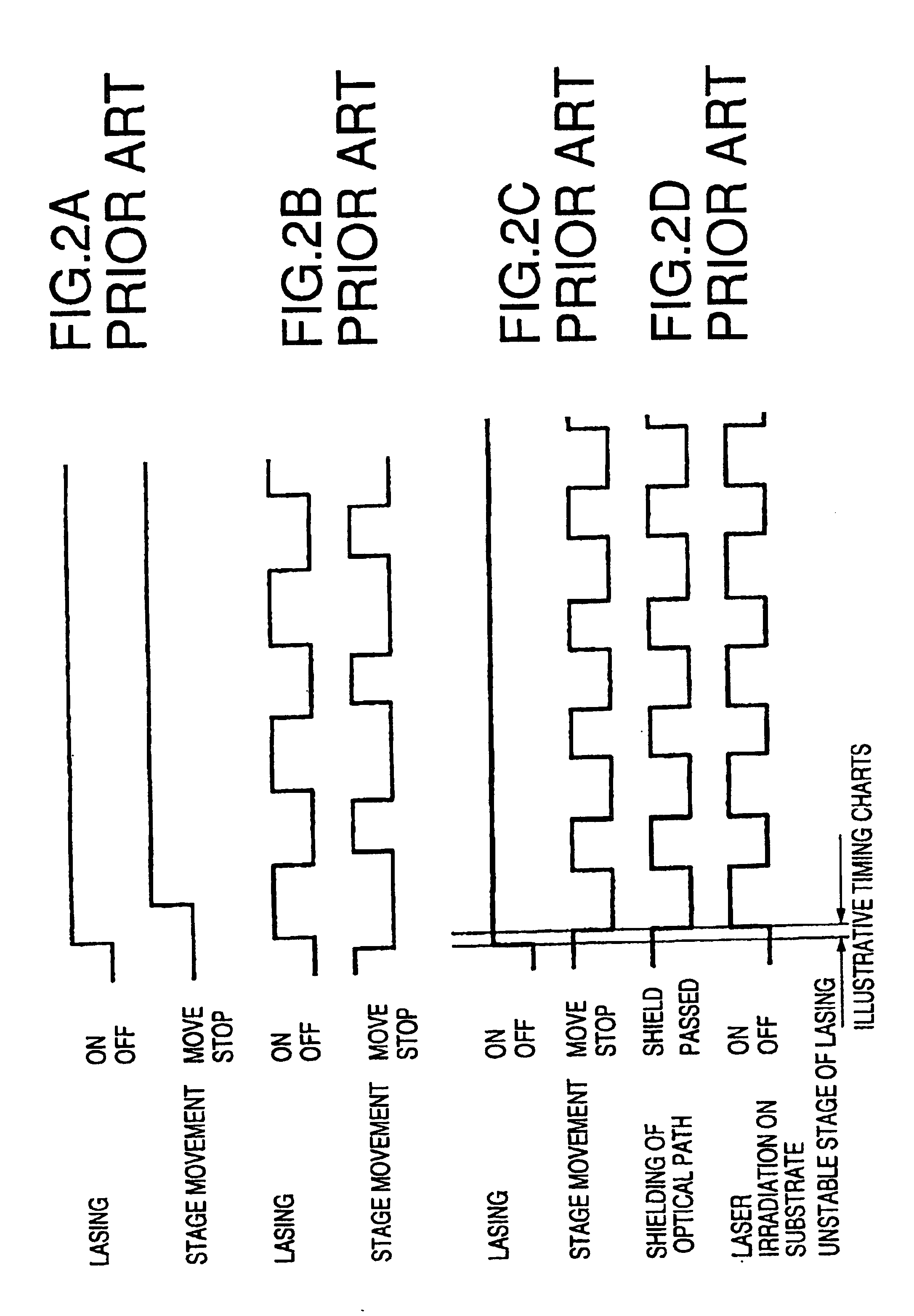
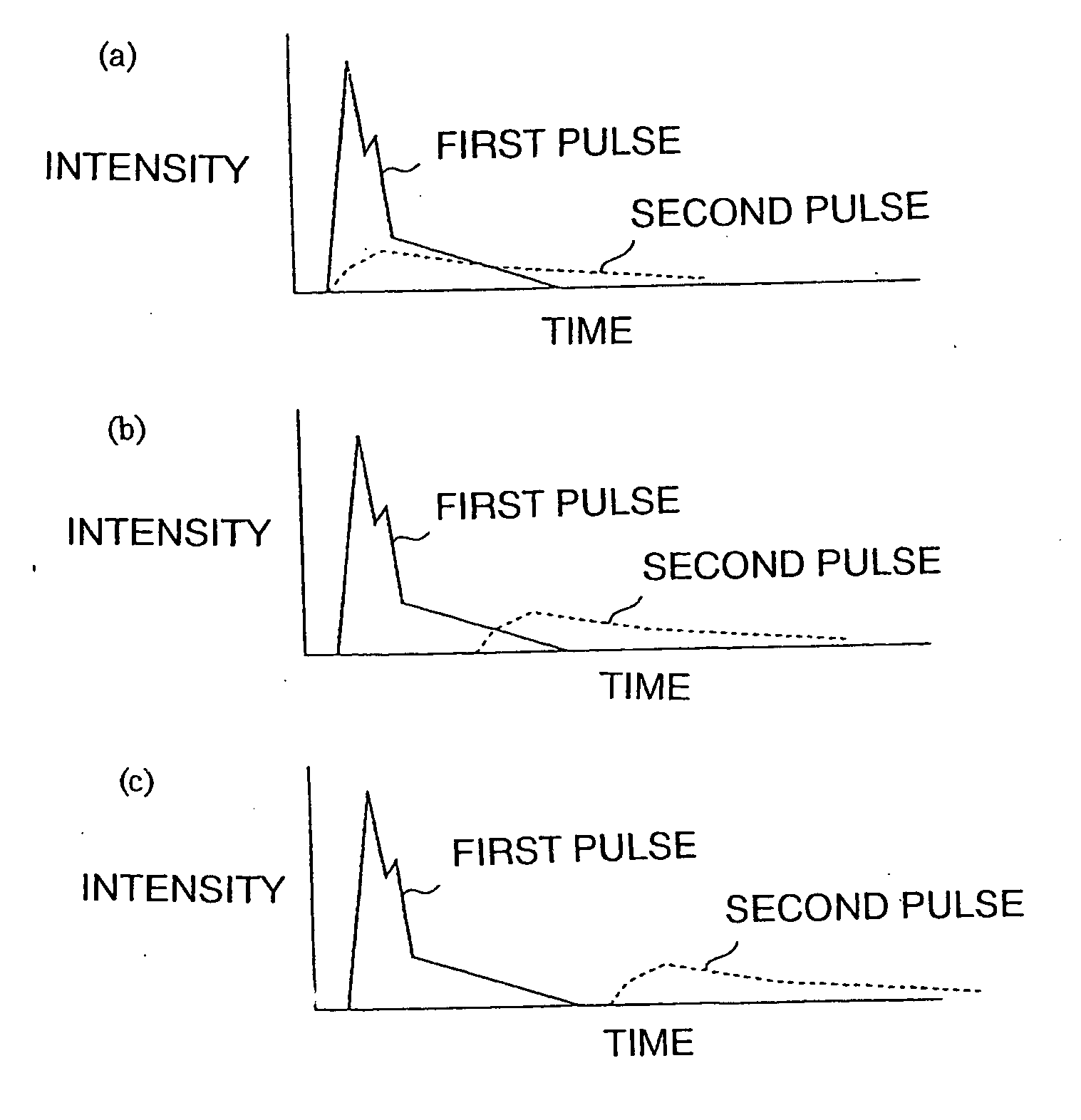
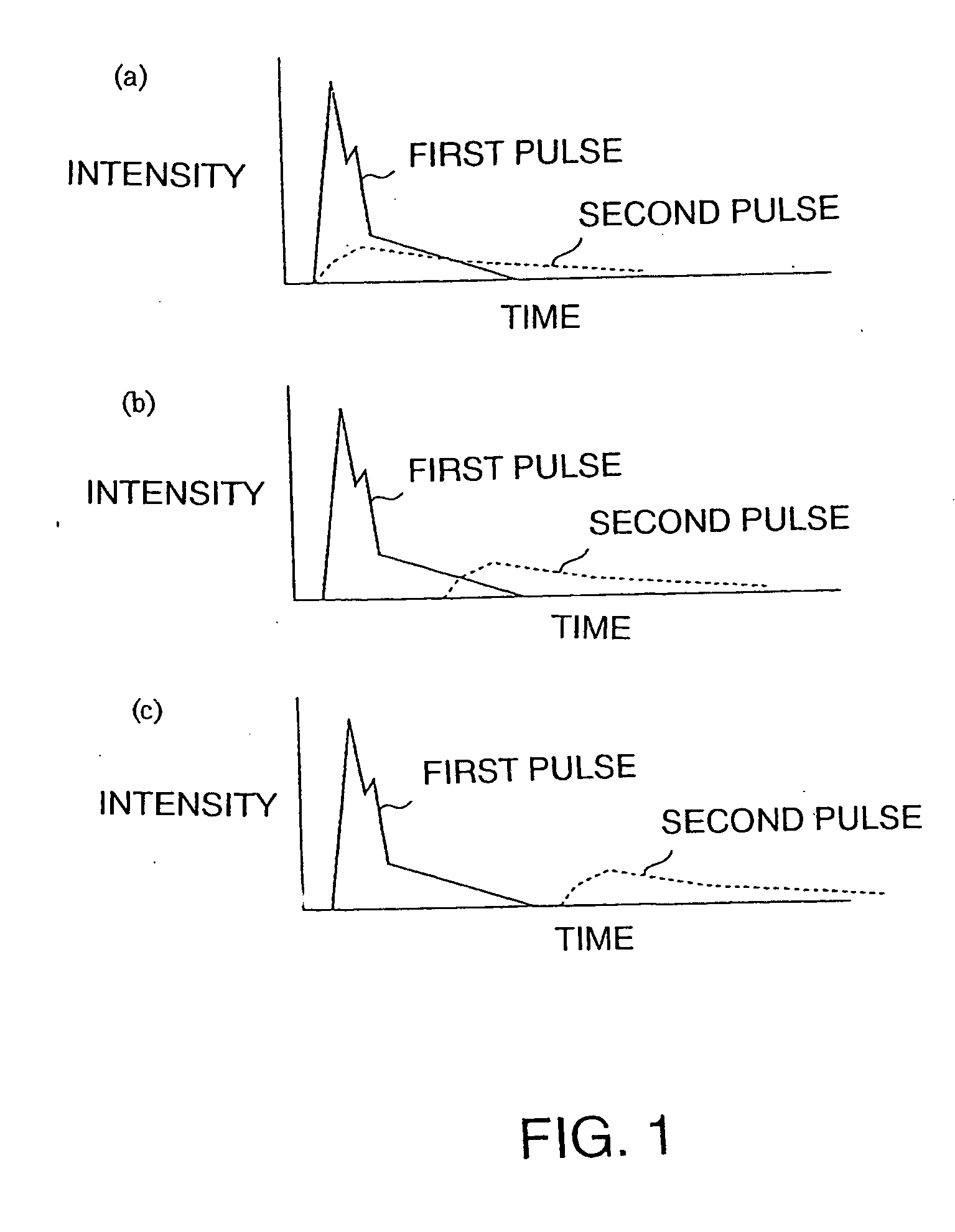
InactiveUS20060189034A1Keep energy smallRadiation to smallFrom gel stateTransistorWave shapeLight beam
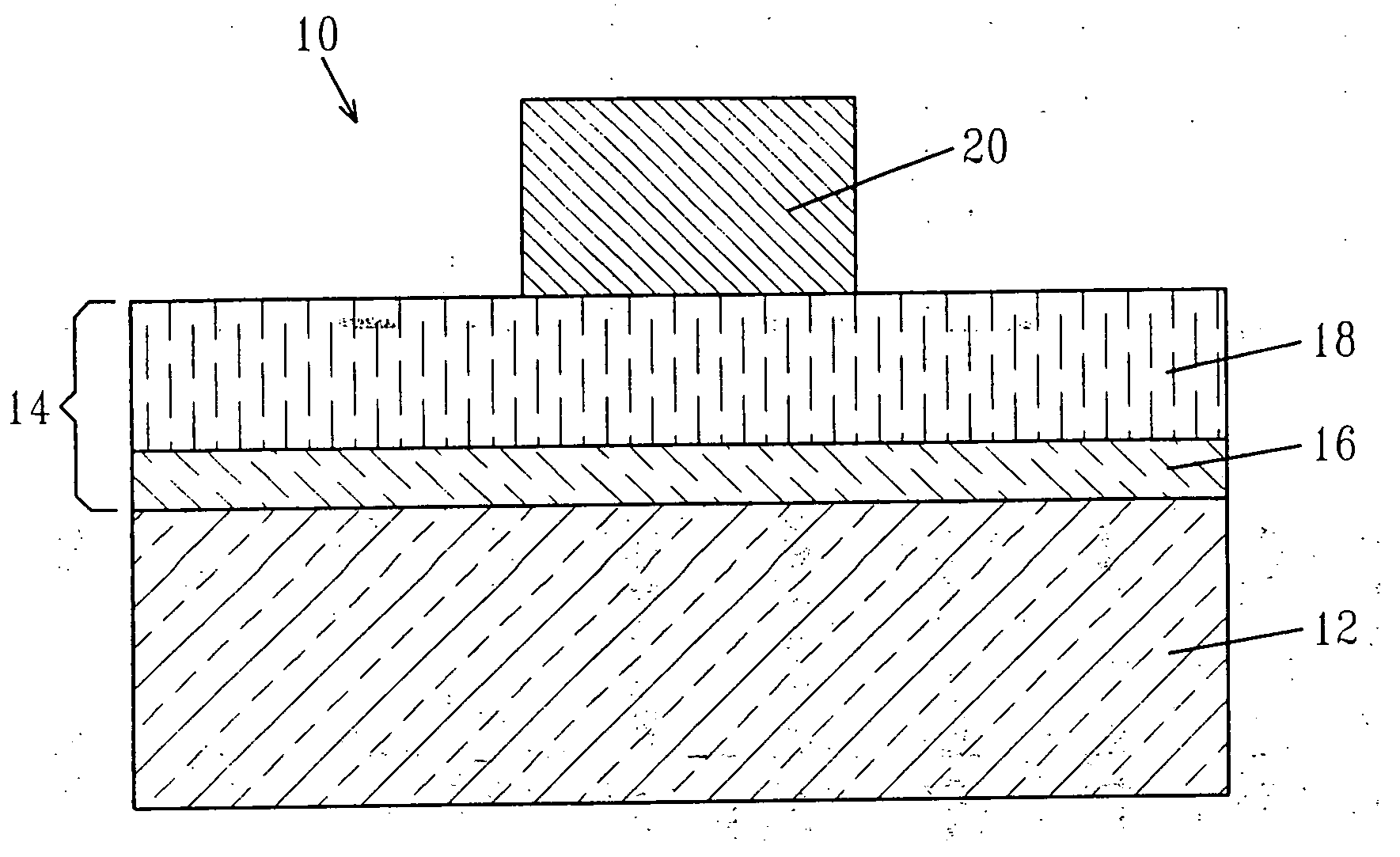
A thin film processing method for processing the thin film by irradiating an optical beam to the thin film. A unit of the irradiation of the optical beam includes a first and a second optical pulse irradiation to the thin film, and the unit of the irradiation is carried out repeatedly to process the thin film. The first and the second optical pulse have pulse waveforms different from each other. Preferably, a unit of the irradiation of the optical beam includes the a first optical pulse irradiated to the thin film and a second optical pulse irradiated to the thin film starting substantially simultaneous with the first optical pulse irradiation. In this case, the relationship between the first and the second optical pulse satisfies (the pulse width of the first optical pulse)<(the optical pulse of the second optical pulse) and (the irradiation intensity of the first optical pulse)≧(the irradiation intensity of the second optical pulse). A silicon thin film with a small trap state density can be formed by the optical irradiation.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
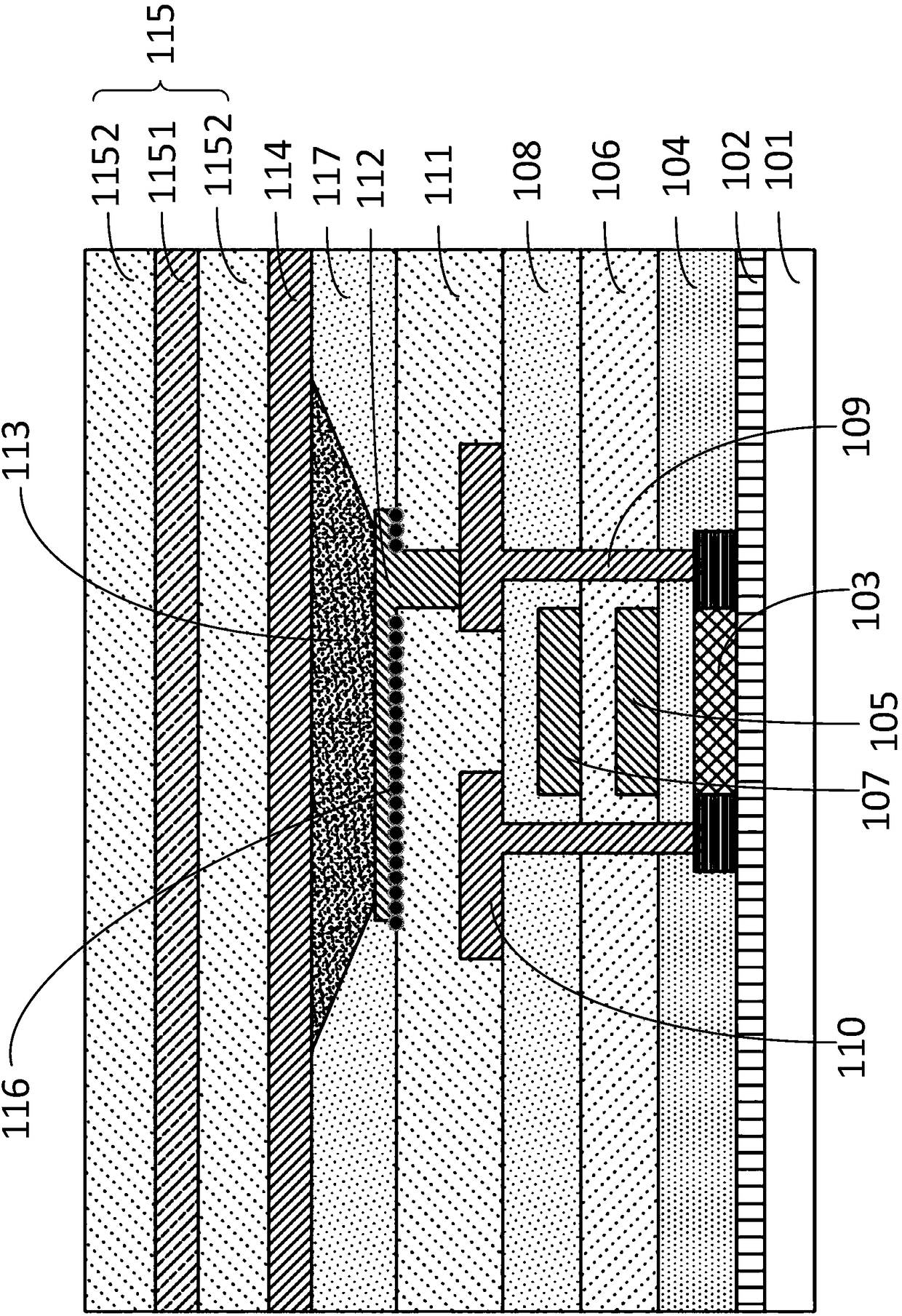
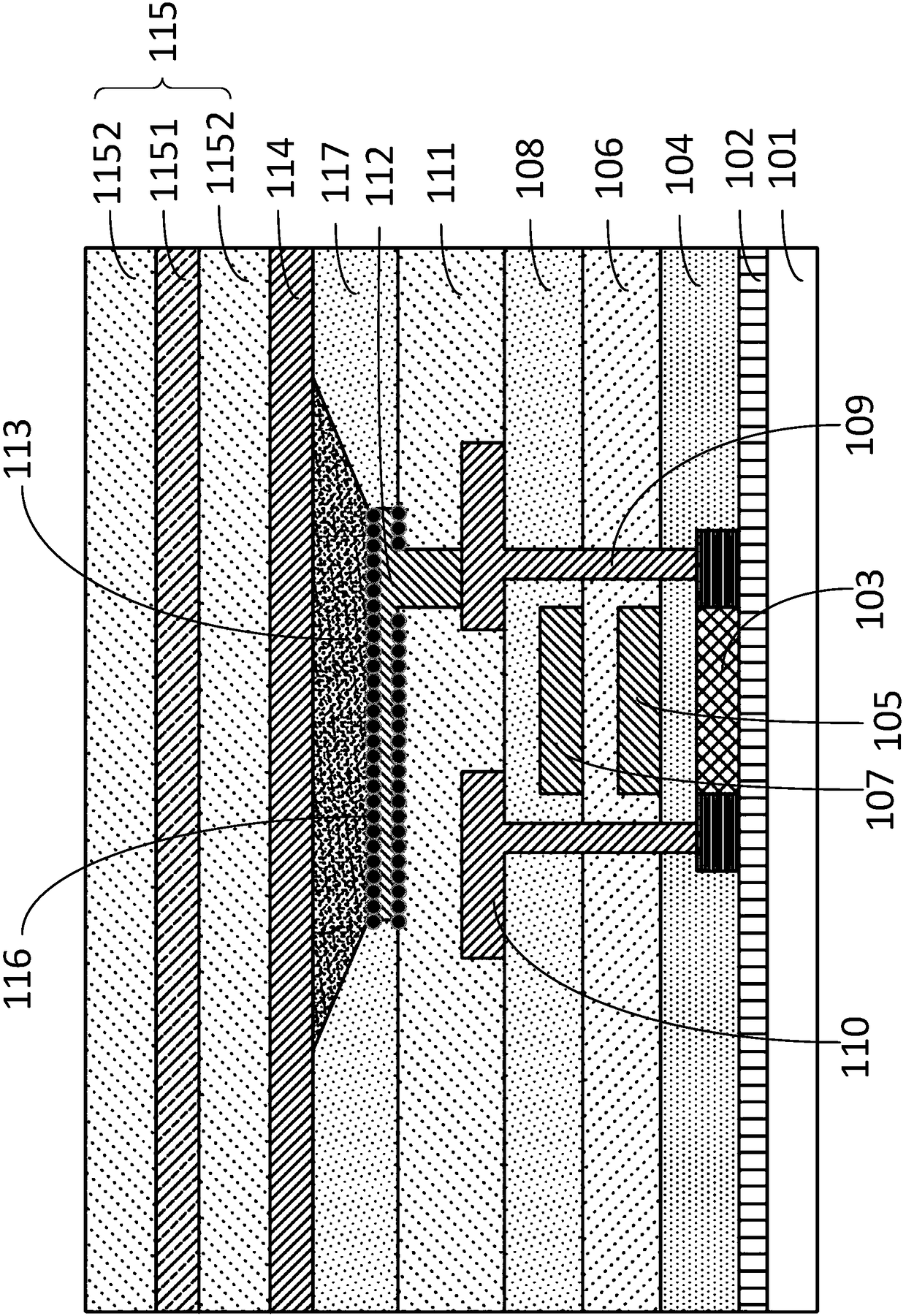
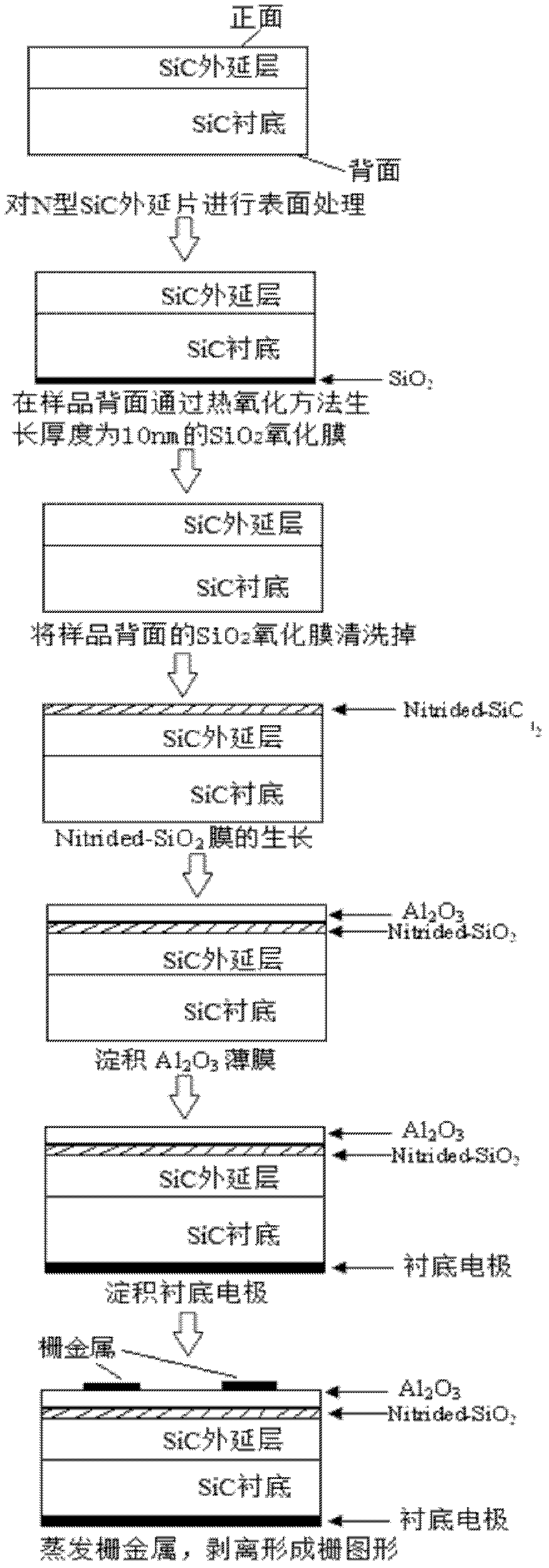
Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device
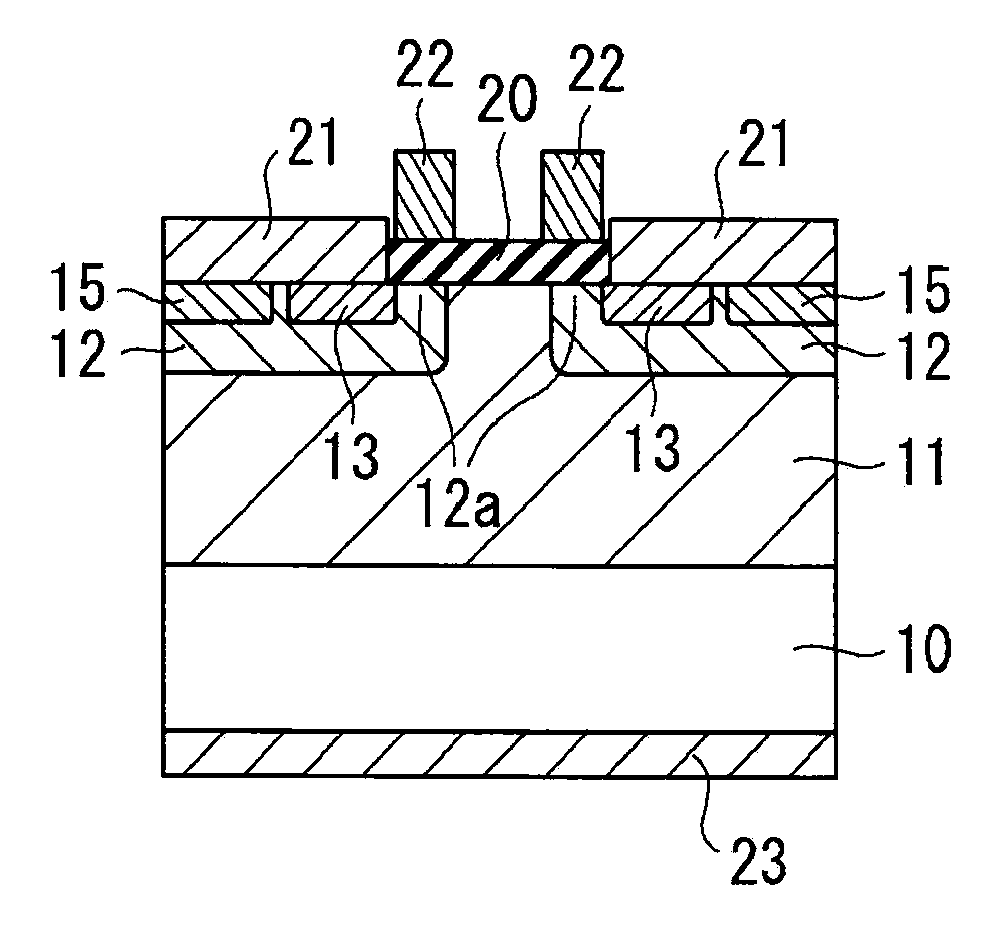
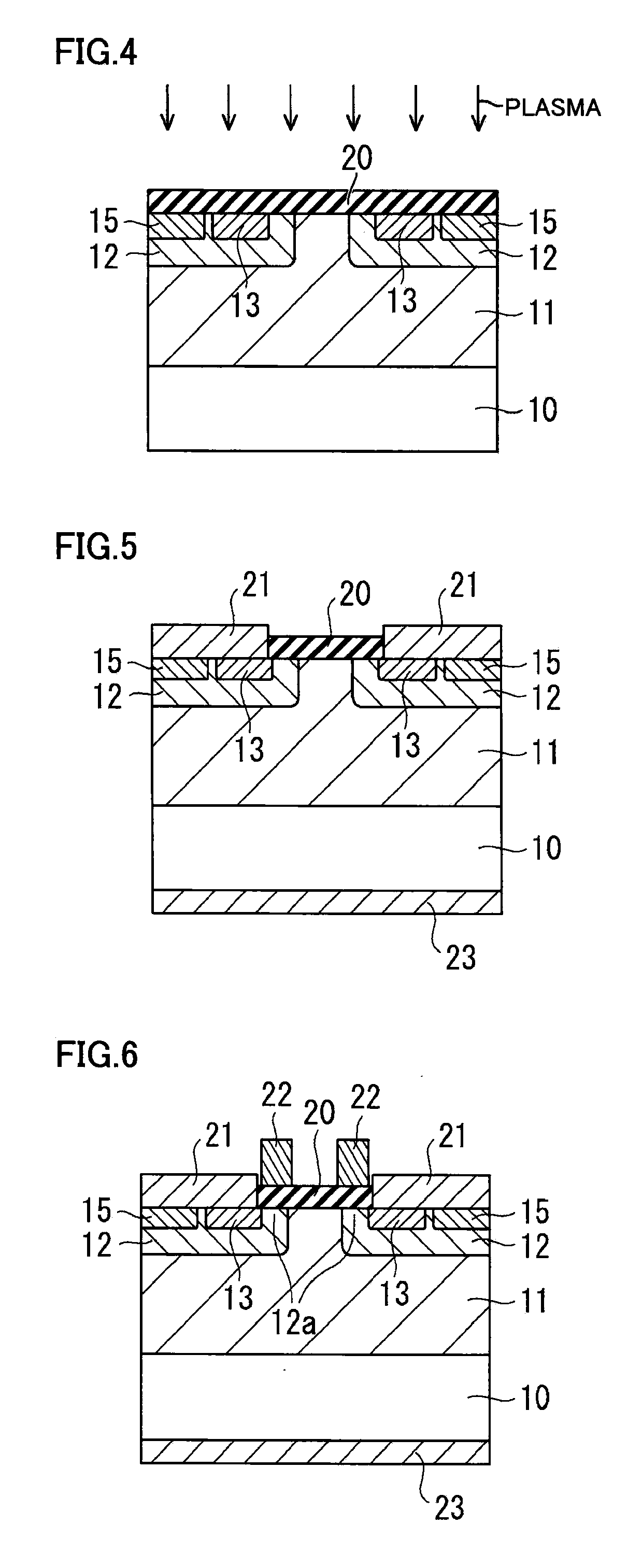
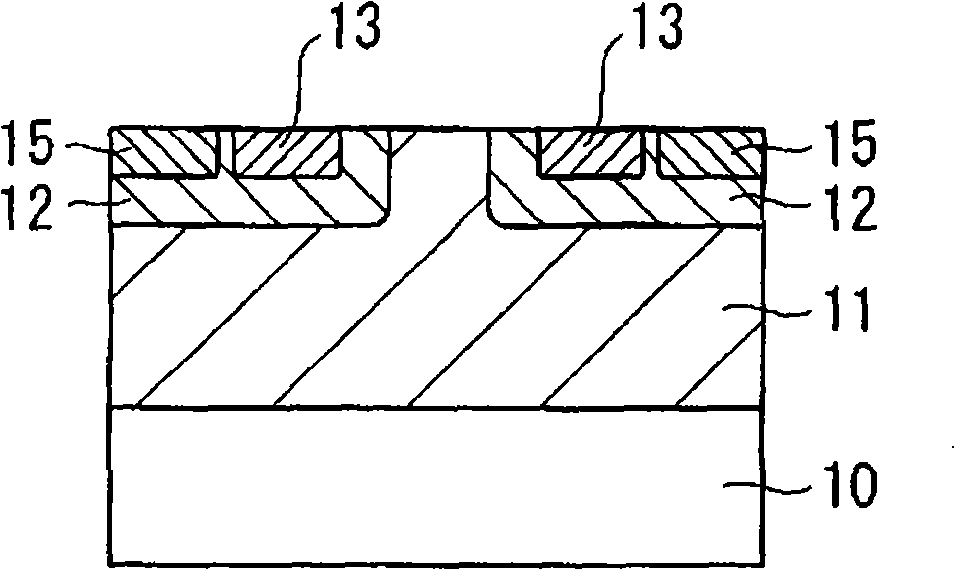
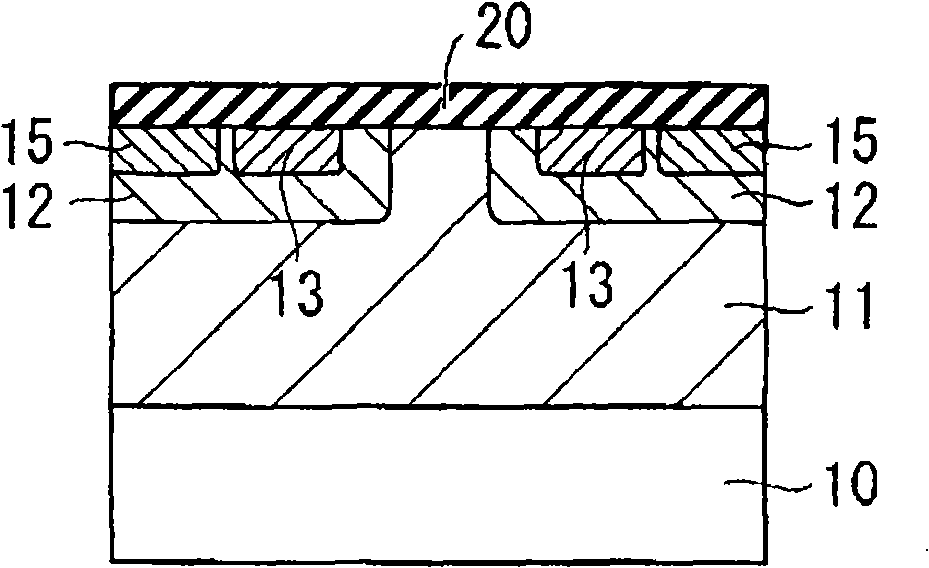
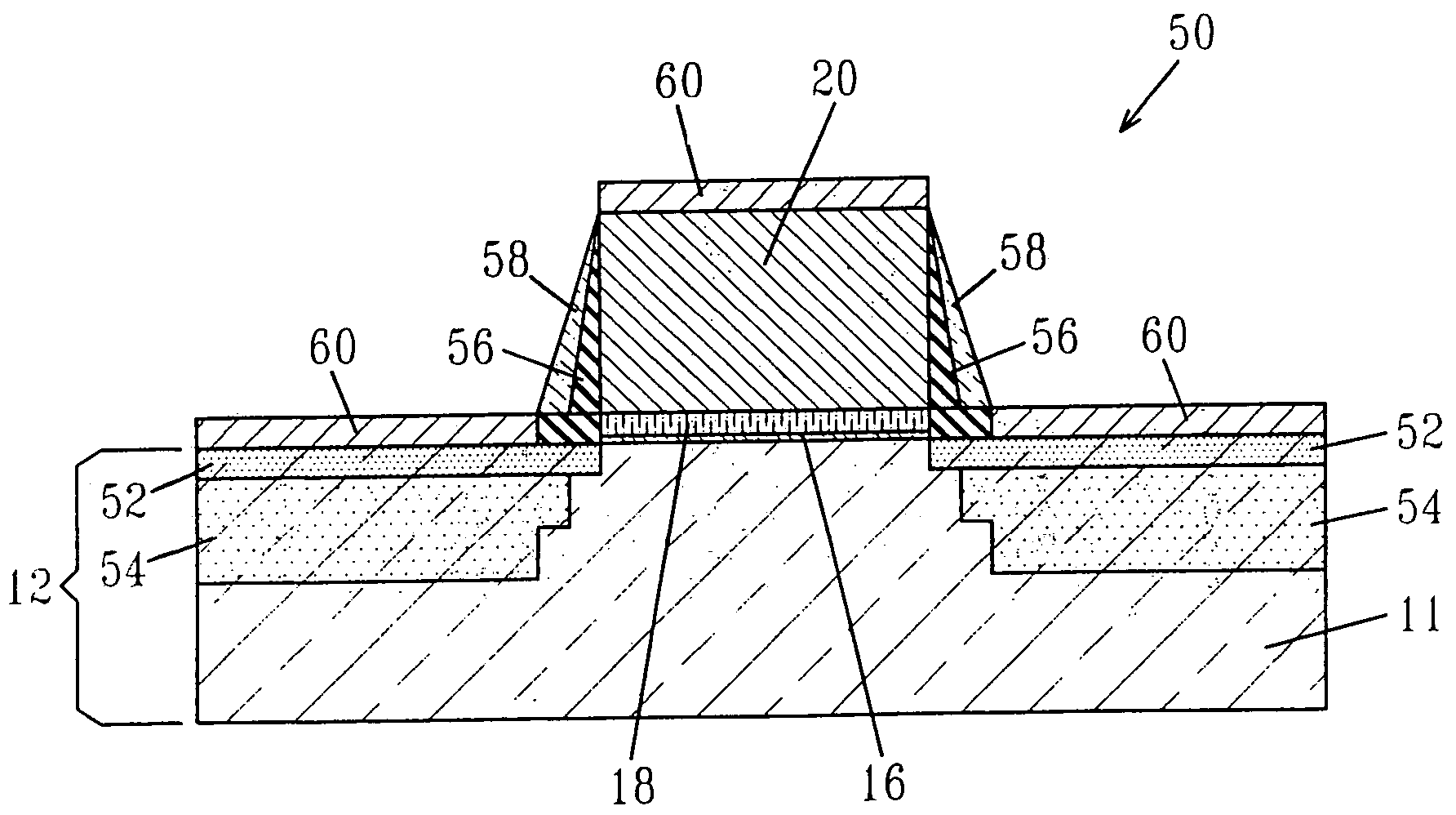
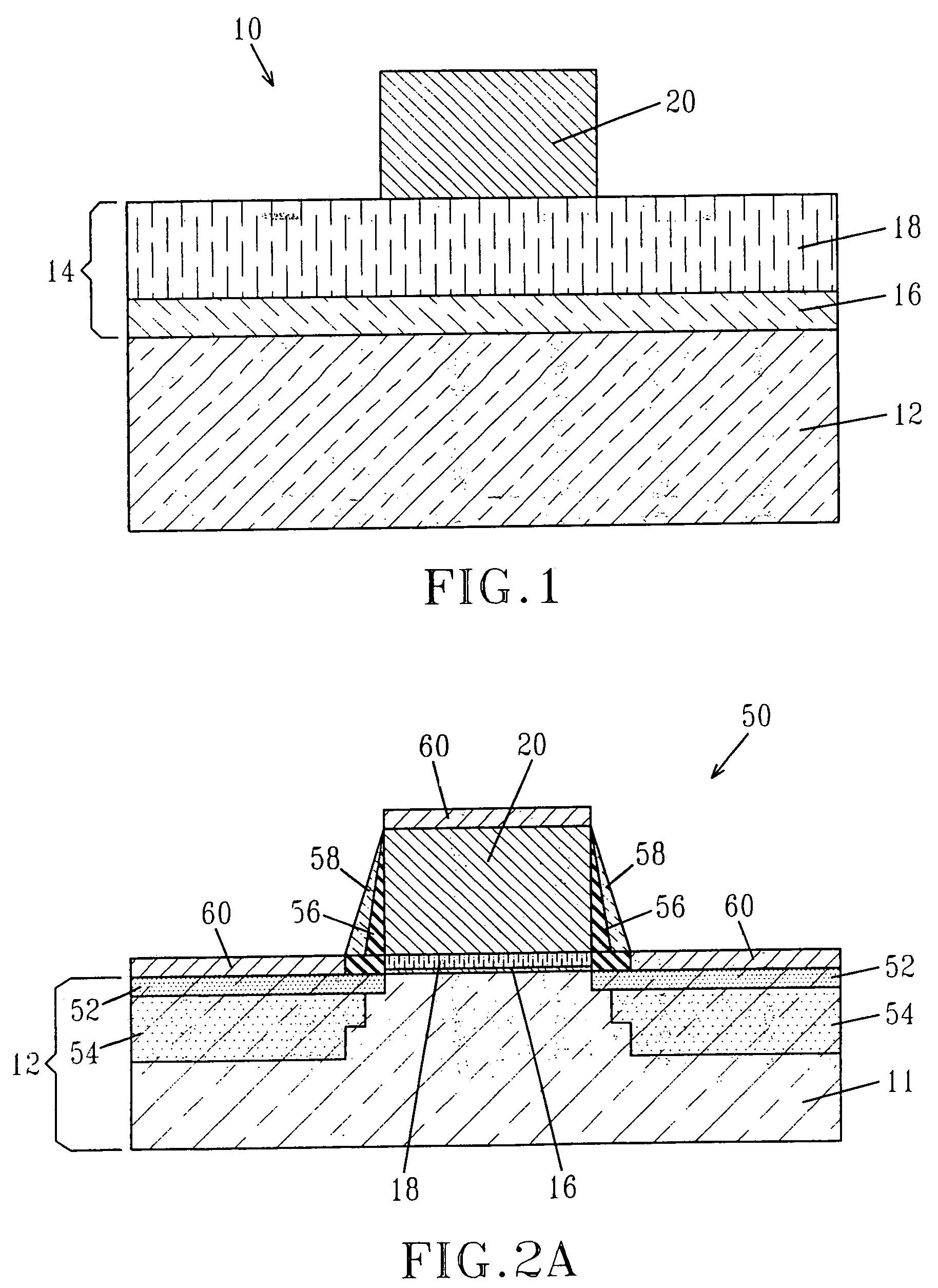
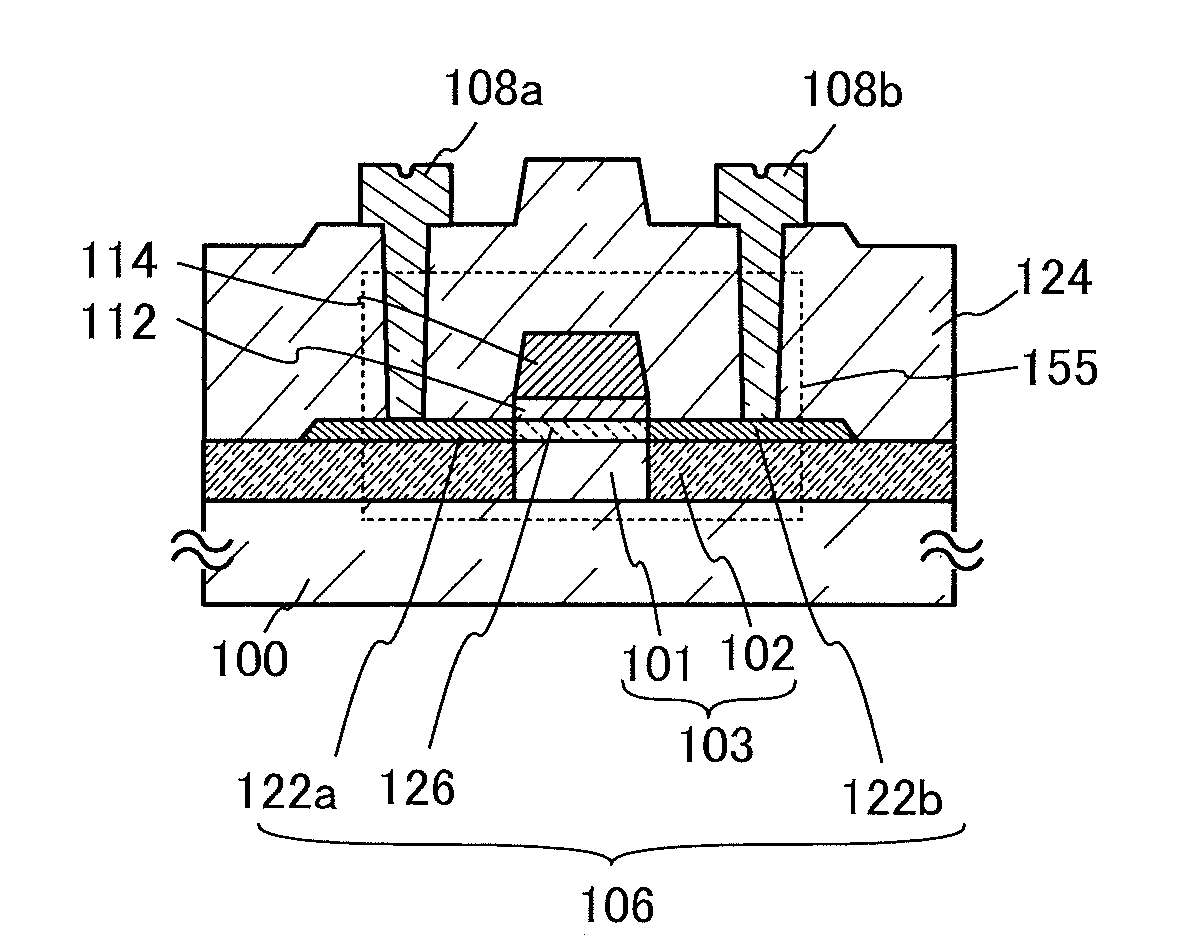
InactiveCN101336473AReduce interface state densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenSilicon oxide
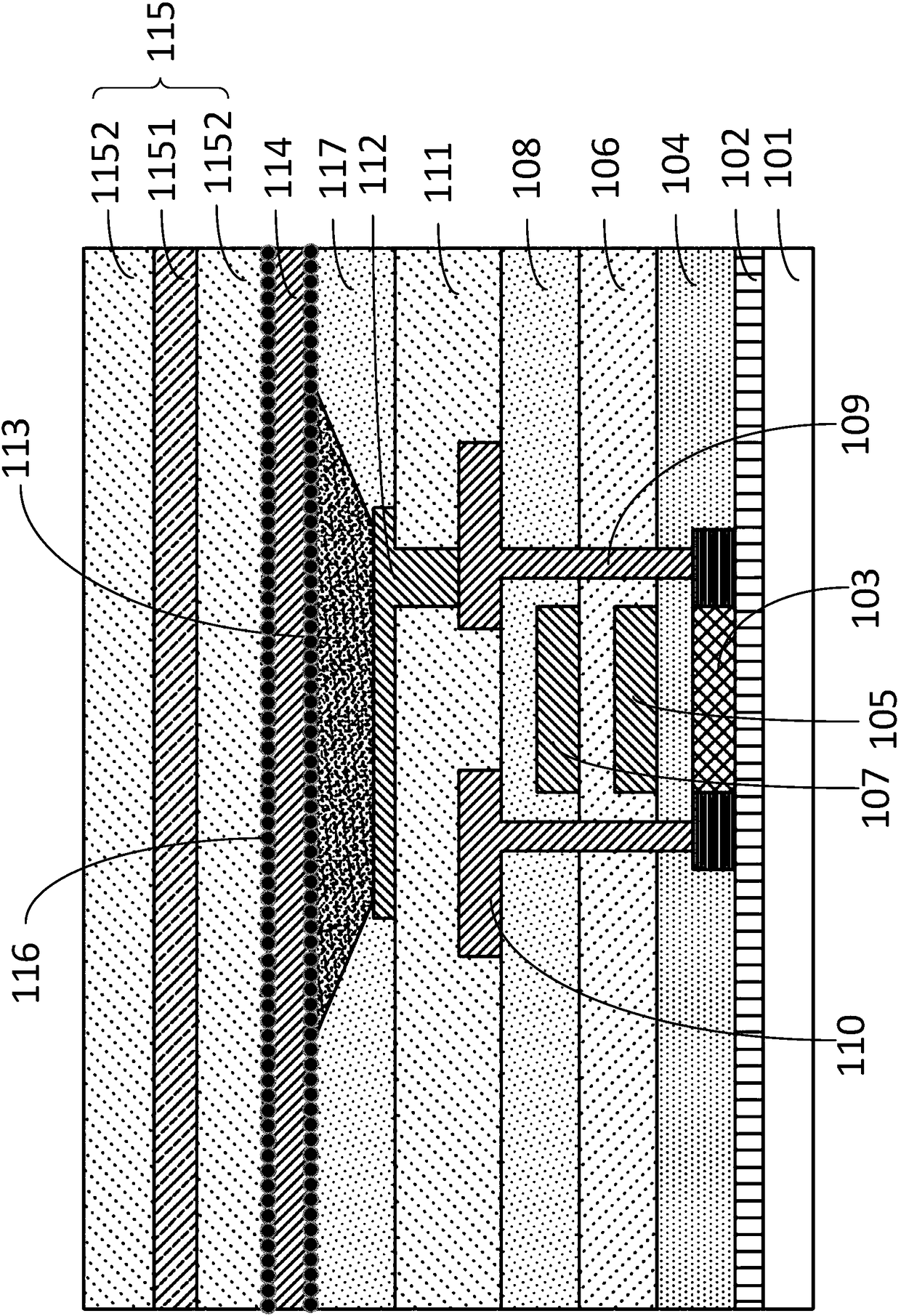
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device having a small interface state density in the interface region between a gate insulating film (20) and a silicon carbide layer (11). Specifically, an epitaxially grown layer (11) is formed on a 4H-SiC substrate (10), and after that a p well region (12), a source region (13) and a p<+> contact region (15) as ion implanted layers are formed by ion implantation. Then, a gate insulating film (20) composed of a silicon oxide film is formed on the p well region (12), the source region (13) and the p<+> contact region (15) by thermal oxidation or CVD. After that, a plasma is generated by using an N2O-containing gas, which is a gas containing at least one of oxygen and nitrogen, and the gate insulating film (20) is exposed to the plasma.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method of forming metal/high-k gate stacks with high mobility
ActiveUS7115959B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorGate stack
The present invention provides a gate stack structure that has high mobilites and low interfacial charges as well as semiconductor devices, i.e., metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) that include the same. In the semiconductor devices, the gate stack structure of the present invention is located between the substrate and an overlaying gate conductor. The present invention also provides a method of fabricating the inventive gate stack structure in which a high temperature annealing process (on the order of about 800° C.) is employed. The high temperature anneal used in the present invention provides a gate stack structure that has an interface state density, as measured by charge pumping, of about 8×1010 charges / cm2 or less, a peak mobility of about 250 cm2 / V-s or greater and substantially no mobility degradation at about 6.0×1012 inversion charges / cm2 or greater.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
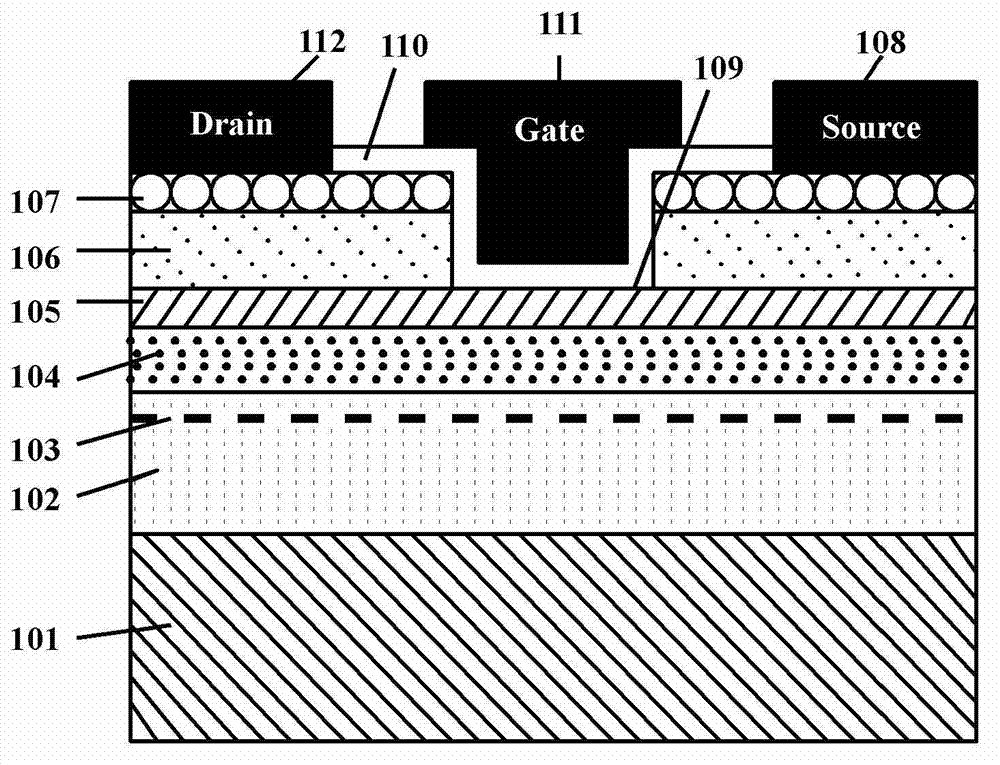
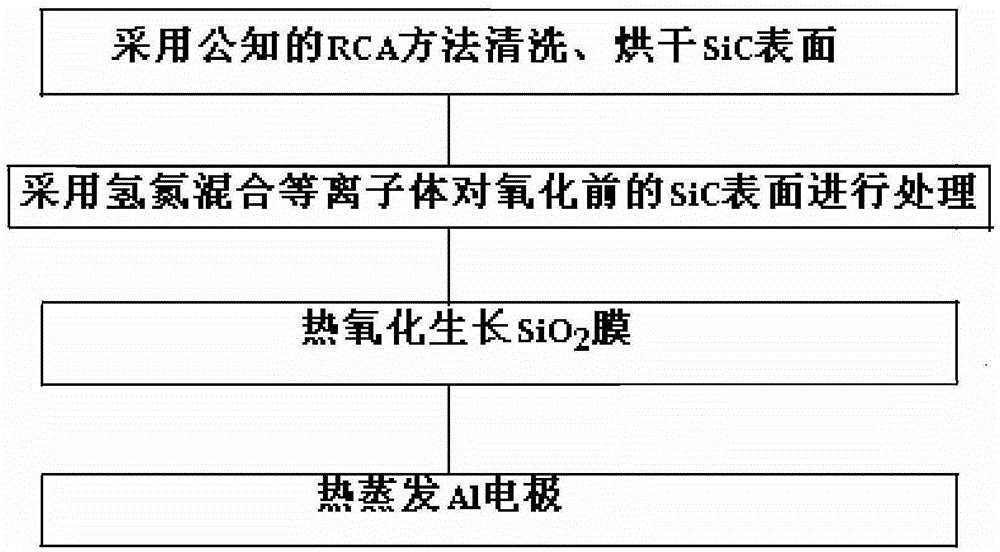
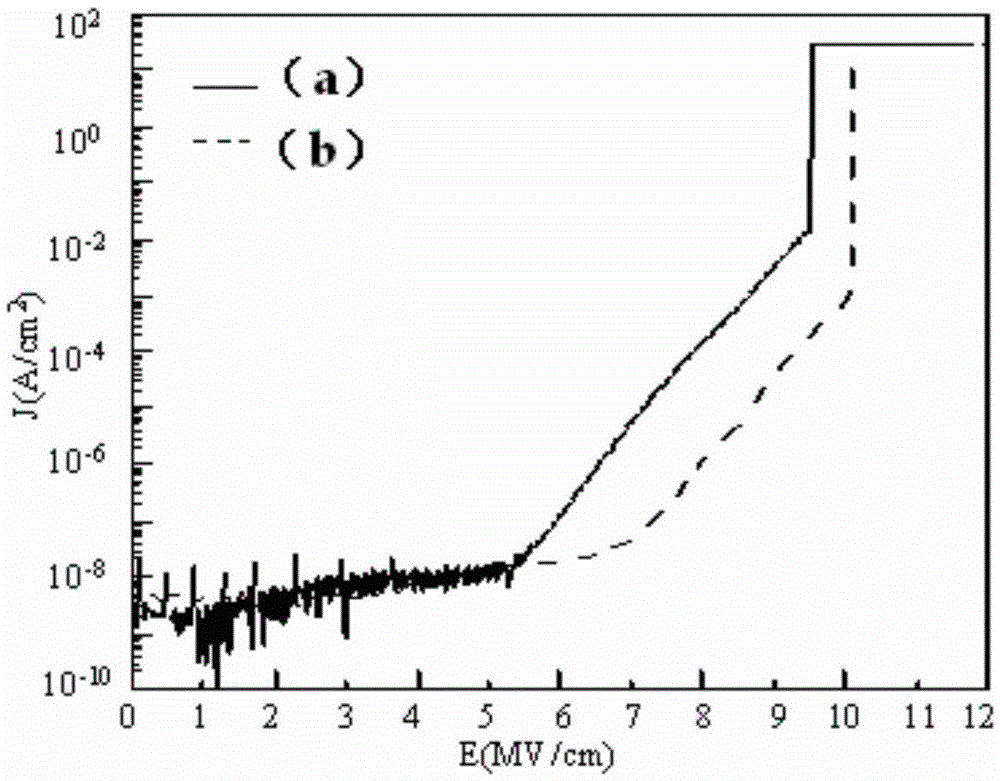
Surface pretreatment method for reducing interface state density of SiC MOS
ActiveCN105355561AControllable ratioEfficient removalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh activationPretreatment method
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor device performance improvement. A surface pretreatment method for reducing the interface state density of SiC MOS comprises the following steps: (1) using a known RCA method to clean and dry the surface of SiC; (2) using a hydrogen-nitrogen hybrid plasma to treat the surface of SiC before oxidation; (3) growing an SiO2 film through thermal oxidation; and (4) thermally evaporating an Al electrode. According to the invention, a low-energy and high-activity low-temperature hydrogen-nitrogen hybrid plasma produced by an ECR microwave plasma system is adopted to pre-treat the surface of SiC before oxidation. A low-temperature process is realized, and damage to the surface of SiC by a conventional plasma is avoided. Moreover, hydrogen and nitrogen passivation effects are combined, impurity ions and residual carbon on the surface of SiC are removed effectively, hydrogen and nitrogen on the surface inhibit the generation of defects in the oxidation process, and the interface state density of SiC MOS is reduced significantly. In addition, the system is equipped with an RHEED in-situ monitoring system, and is especially suitable for SiC surface passivation process monitoring and mechanism research.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
High-breakdown-voltage insulated gate semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070176230A1Improve featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCarbide
In a semiconductor device of the present invention, the top surface of an n-type silicon carbide layer formed on a silicon carbide substrate is miscut from the (0001) plane in the <11-20> direction. A gate electrode, a source electrode and other elements are arranged such that in a channel region, the dominating current flows along a miscut direction. In the present invention, a gate insulating film is formed and then heat treatment is performed in an atmosphere containing a group-V element. In this way, the interface state density at the interface between the silicon carbide layer and the gate insulating film is reduced. As a result, the electron mobility becomes higher in a miscut direction A than in the direction perpendicular to the miscut direction A.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing
ActiveUS8519387B2Low reliabilityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesState densityOxygen deficiency
An insulating layer which releases a large amount of oxygen is used as an insulating layer in contact with a channel region of an oxide semiconductor layer, and an insulating layer which releases a small amount of oxygen is used as an insulating layer in contact with a source region and a drain region of the oxide semiconductor layer. By releasing oxygen from the insulating layer which releases a large amount of oxygen, oxygen deficiency in the channel region and an interface state density between the insulating layer and the channel region can be reduced, so that a highly reliable semiconductor device having small variation in electrical characteristics can be manufactured. The source region and the drain region are provided in contact with the insulating layer which releases a small amount of oxygen, thereby suppressing the increase of the resistance of the source region and the drain region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
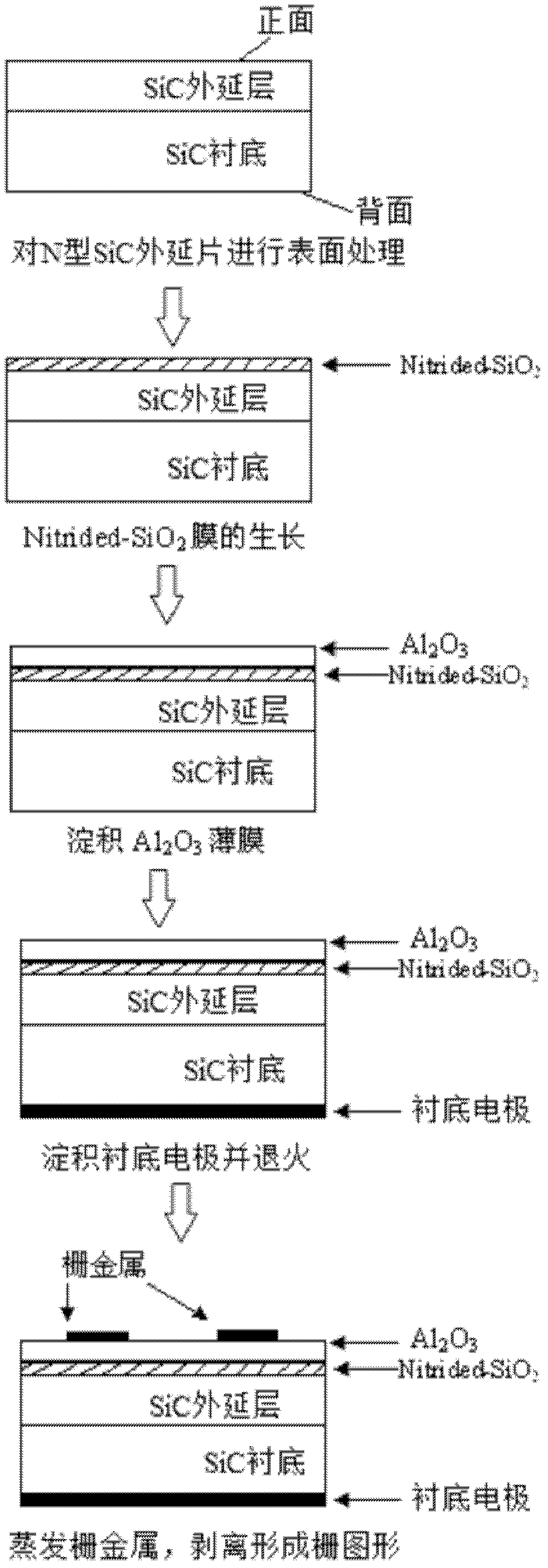
Manufacture method of stacked gate SiC-metal insulator semiconductor (MIS) capacitor
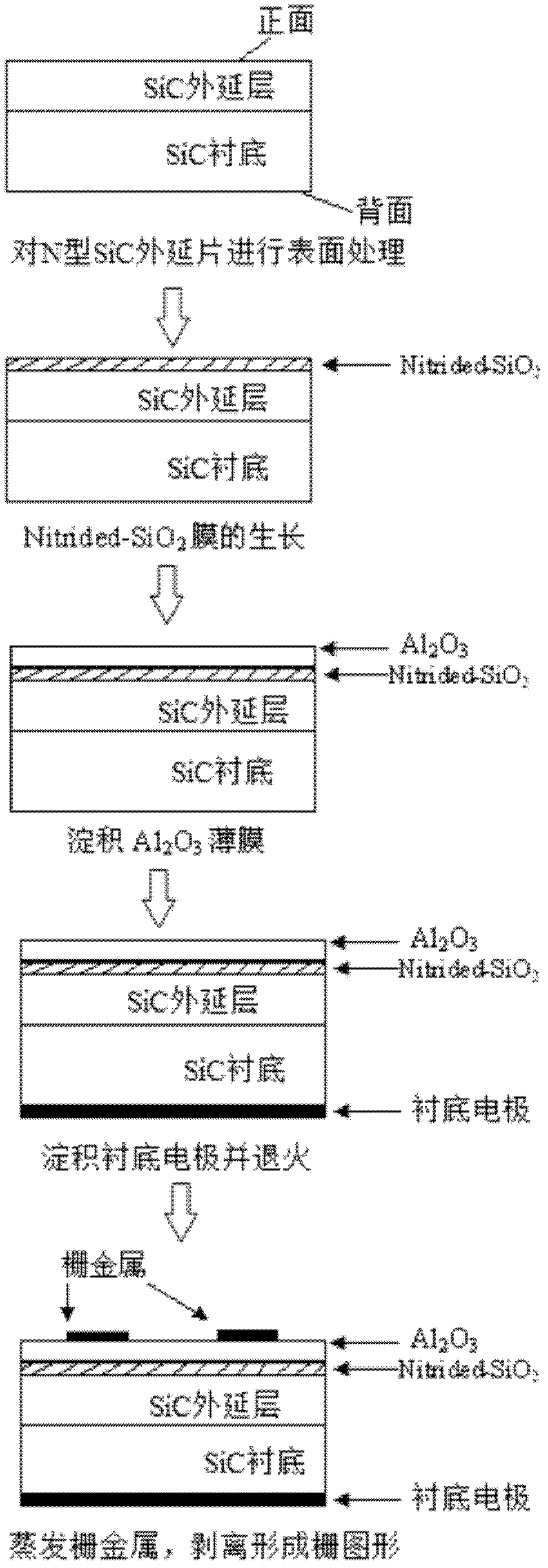
ActiveCN102629559AImprove featuresImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a stacked gate SiC-metal insulator semiconductor (MIS) capacitor and mainly solves the problem of overlarge gate leakage current, too high SiC and SiO2 interface state density and poor breakdown characteristics of a SiC power MIS device. In the manufacture process, the standard wet process cleaning is carried out on an N type SiC epitaxial wafer; a layer of SiO2 film grows by a dry-oxygen oxidation method, and bottom layer gate media are formed; the grown SiO2 film is subjected to plasma treatment in an electron cyclotron resonance plasma enhanced-metal organic chemical vapor deposition (ECR PE-MOCVD) system; an atom layer deposition (ALD) method is used for depositing Al2O3 medium films, and top layer gate media are formed; substrate metals are evaporated by electron beams to form a zero electrode; and finally, the gate metal is formed through peeling, and the device manufacture is completed. The gate medium reliability of the SiC-MIS capacitor during the high-temperature and high-power application is improved, and the manufacture method can be used for the manufacture of large-scale SiC-MIS devices and circuits.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com