Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3360results about How to "Reduce surface roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
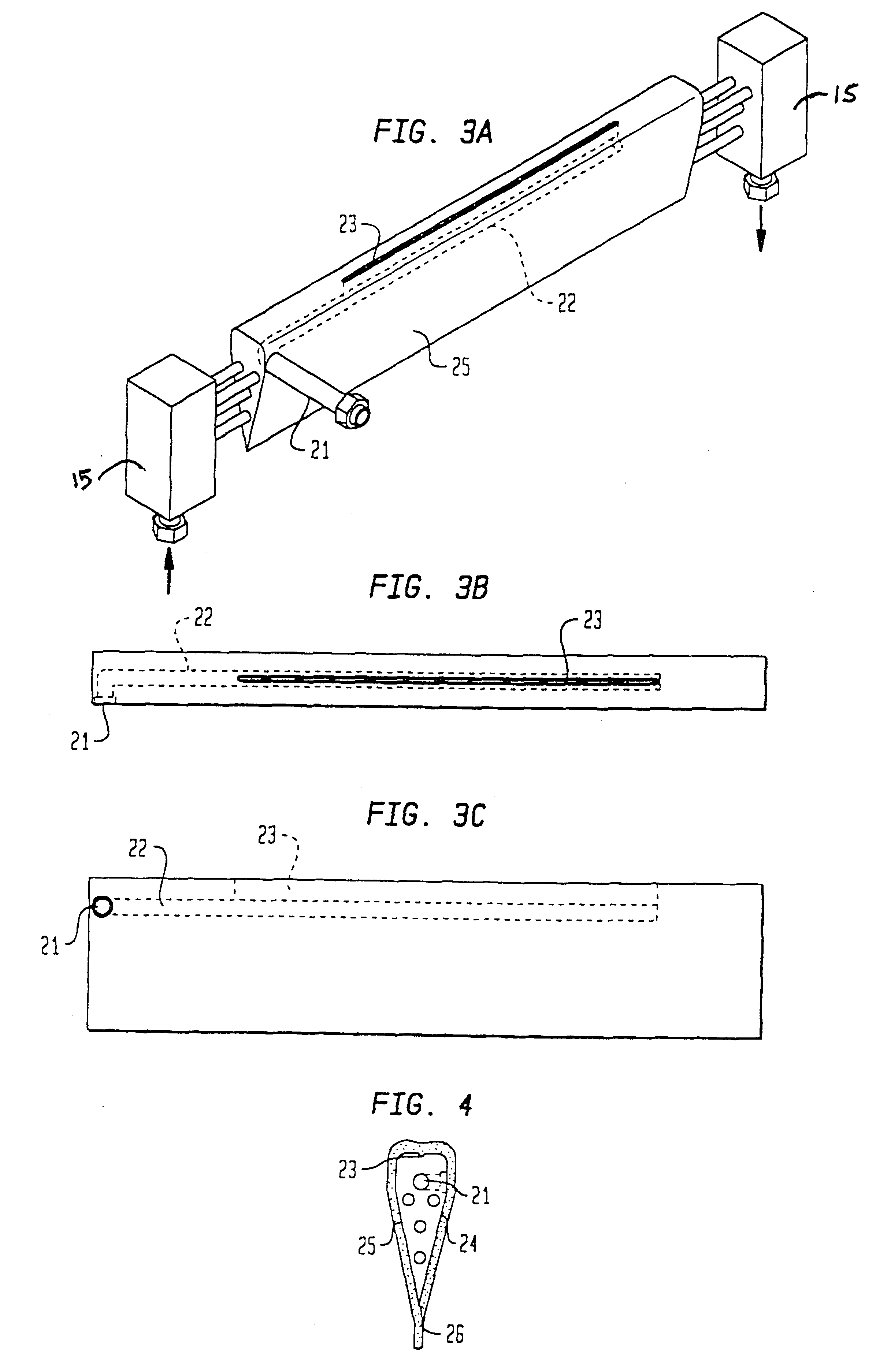
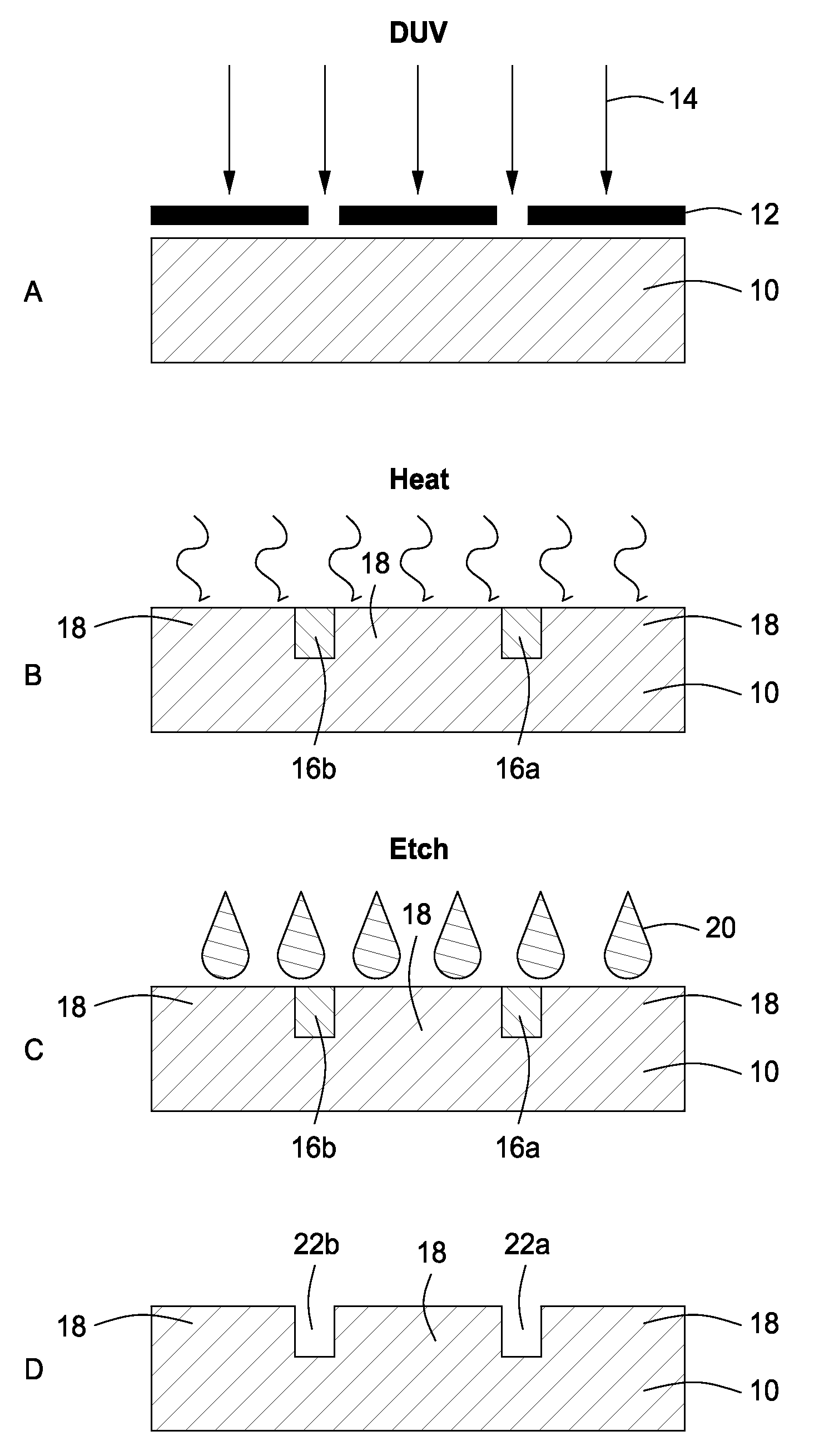
Method for transferring a thin film comprising a step of generating inclusions
InactiveUS6756286B1Reduce surface roughnessBudget is reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid massFracture plane
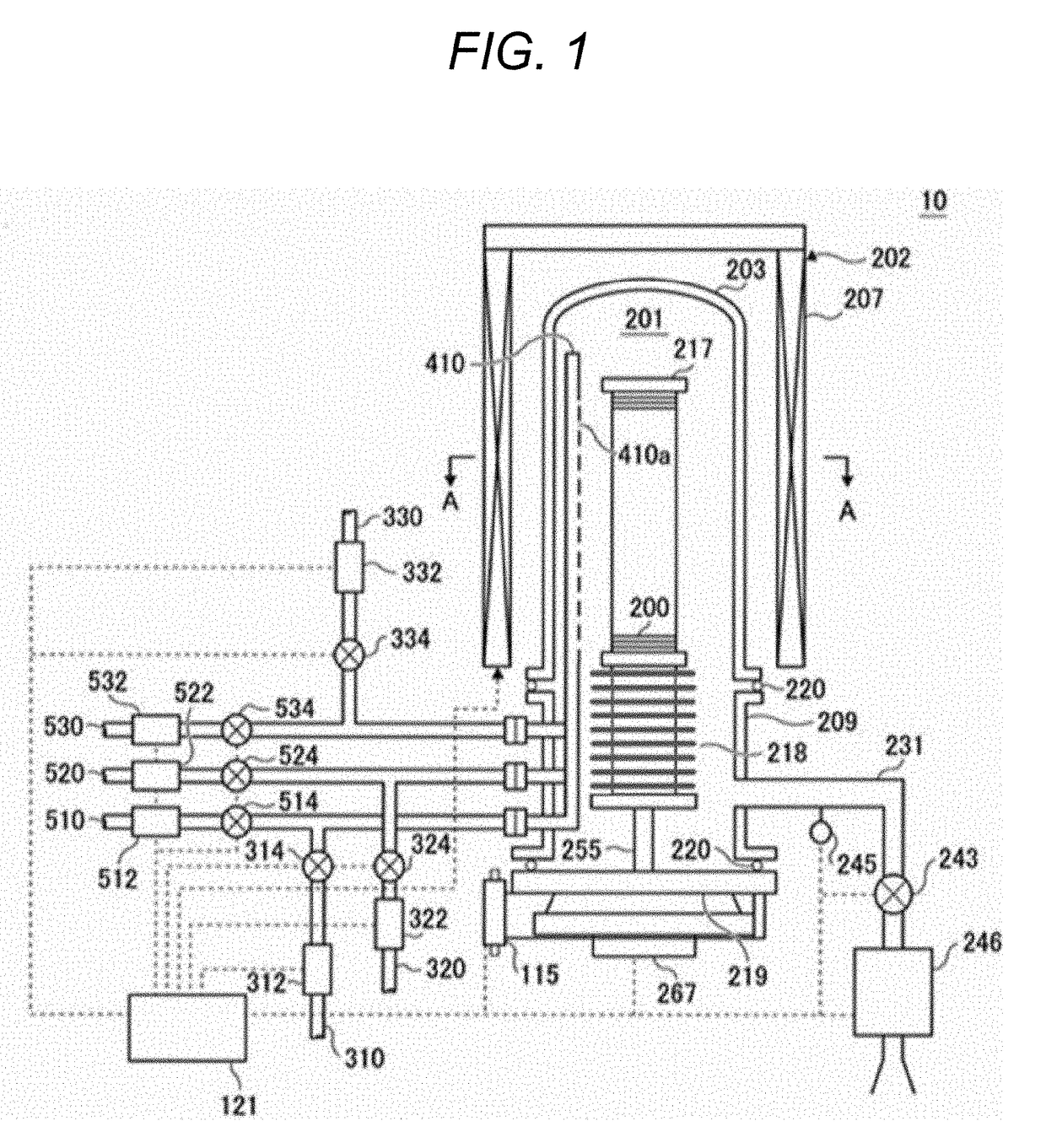
A process for transfer of at least one thin film of solid material delimited in an initial substrate. The process includes a step in which a layer of inclusions is formed in the initial substrate at a depth corresponding to the required thickness of the thin film. These inclusions are designed to form traps for gaseous compounds which subsequently are implanted. In a subsequent step gaseous compounds are implanted in a manner to convey the gaseous compounds into the layer of inclusions. The dose of implanted gaseous compounds is made sufficient to cause the formation of micro-cavities to form a fracture plane along which the thin film can be separated from the remainder of the substrate.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for depositing metal-containing film using particle-reduction step
InactiveUS20160168699A1Reduce surface roughnessSolve the lack of resistanceChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueAMINO BASENitride
A method for forming a metal oxide or nitride film on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing an amino-based metal precursor in a pulse to a reaction space where a substrate is placed, using a carrier gas; and continuously introducing a reactant gas to the reaction space; applying RF power in a pulse to the reaction space wherein the pulse of the precursor and the pulse of RF power do not overlap, wherein conducted is at least either step (a) comprising passing the carrier gas through a purifier for reducing impurities before mixing the carrier gas with the precursor, or step (b) introducing the reactant gas at a flow rate such that a partial pressure of the reactant gas relative to the total gas flow provided in the reaction space is 15% or less.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Smooth siconi etch for silicon-containing films
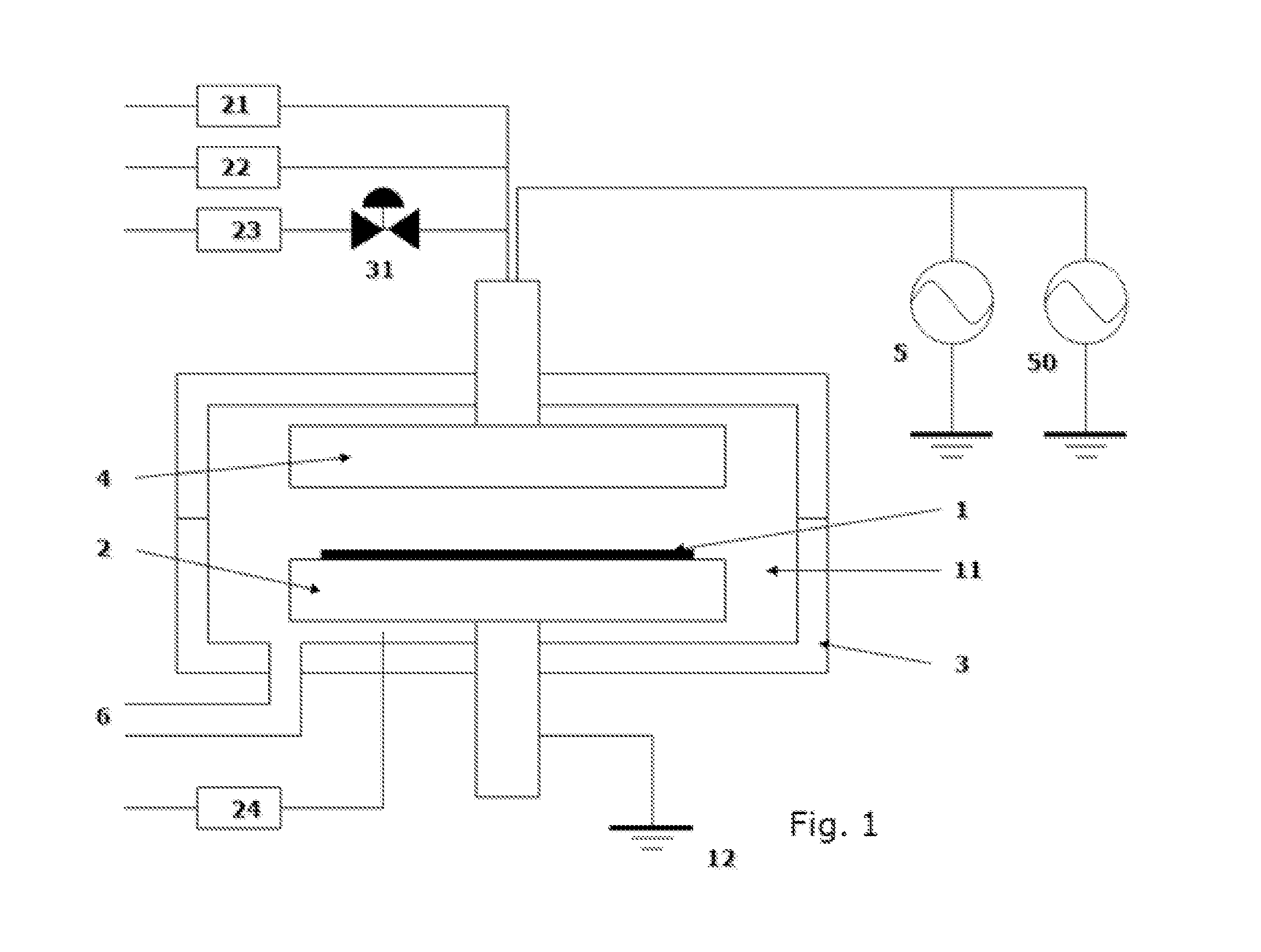
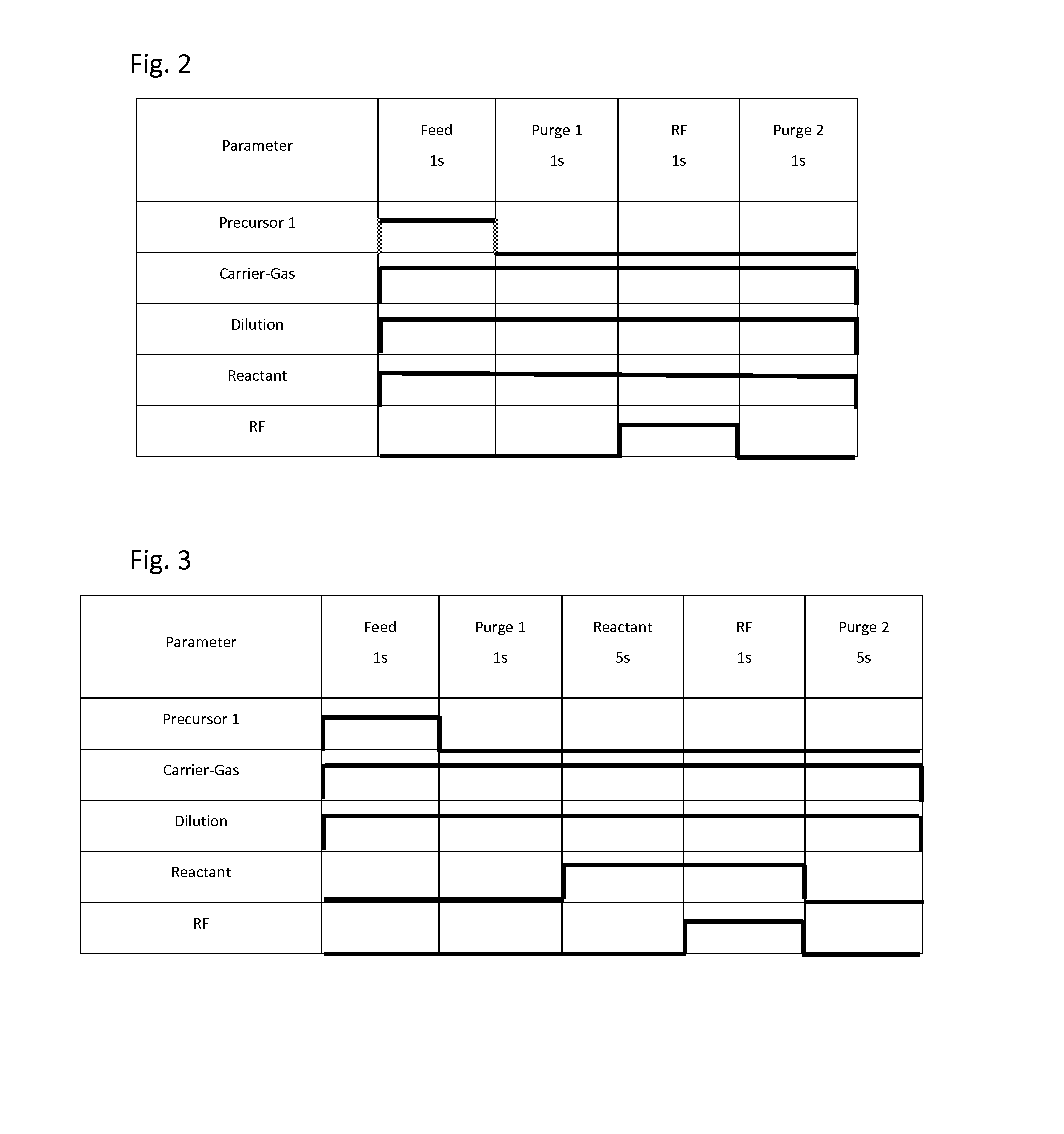
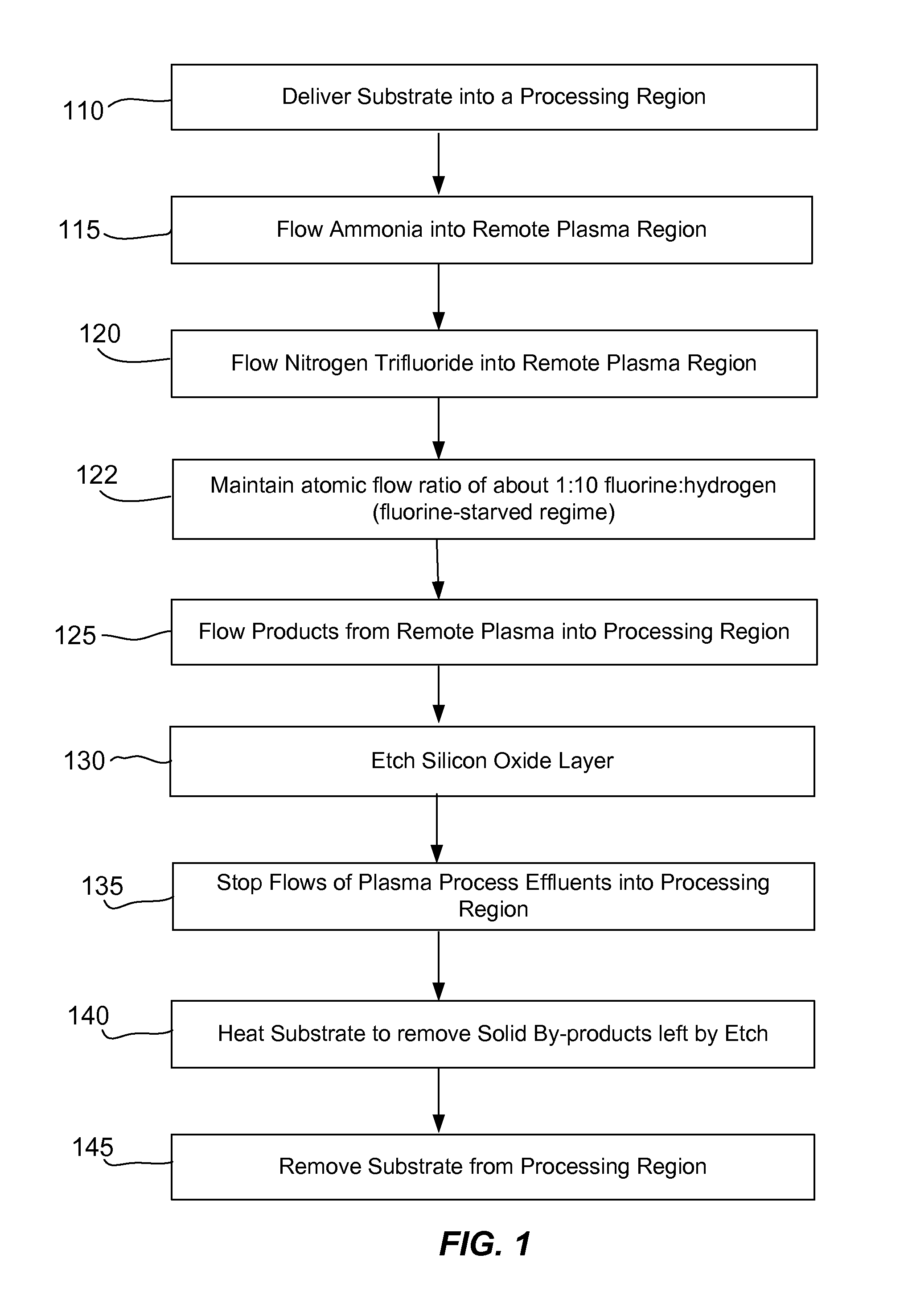
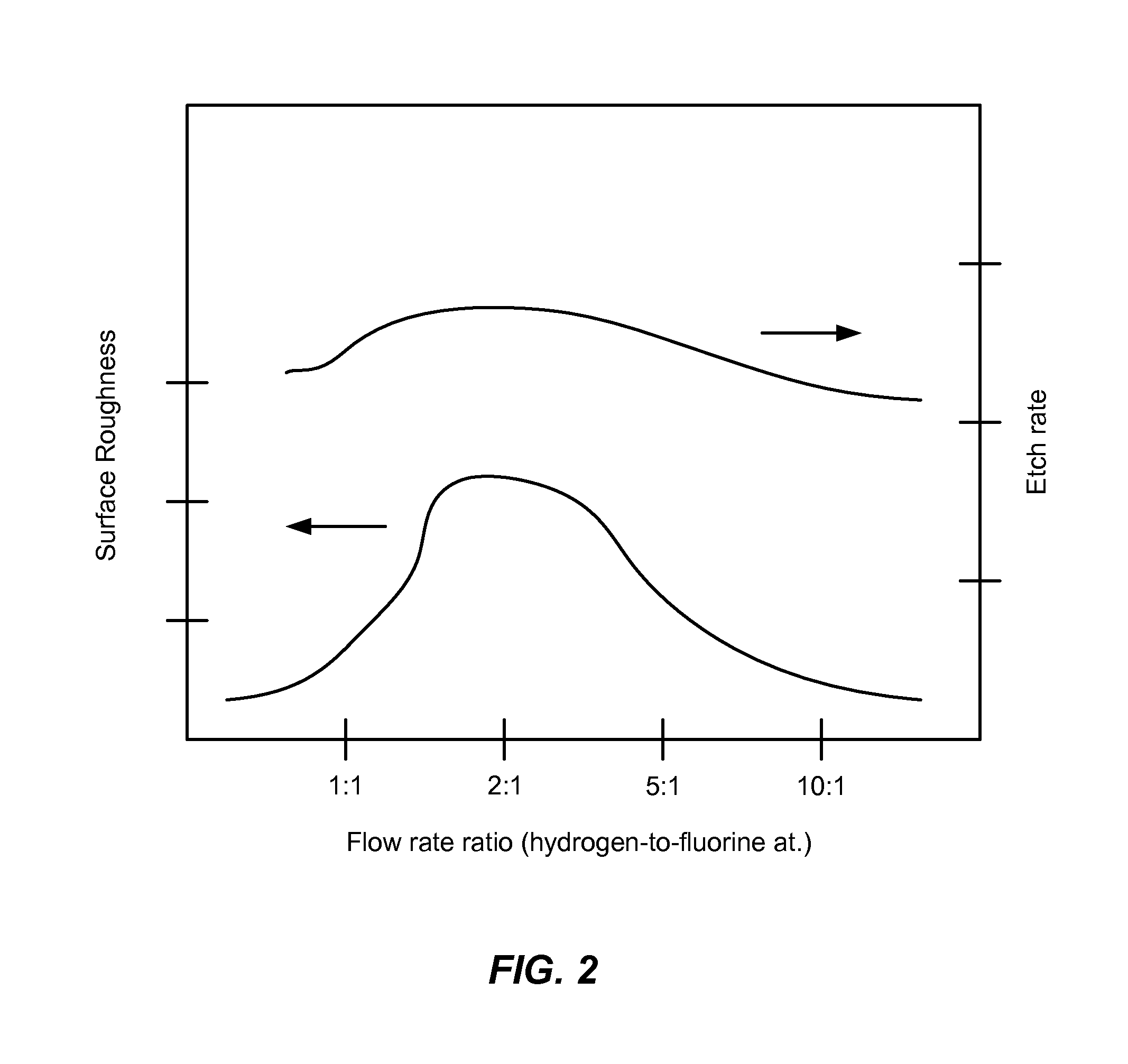
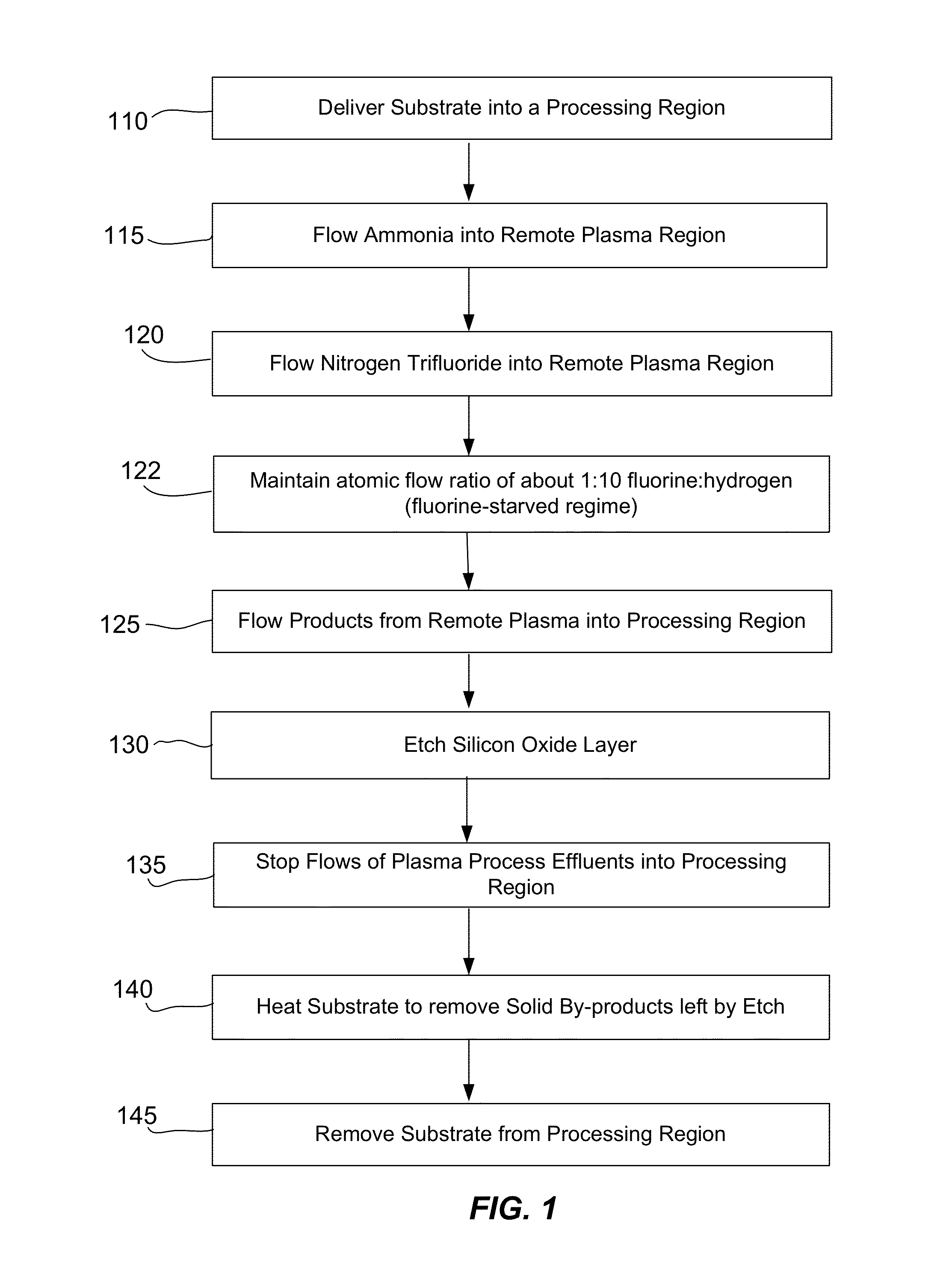
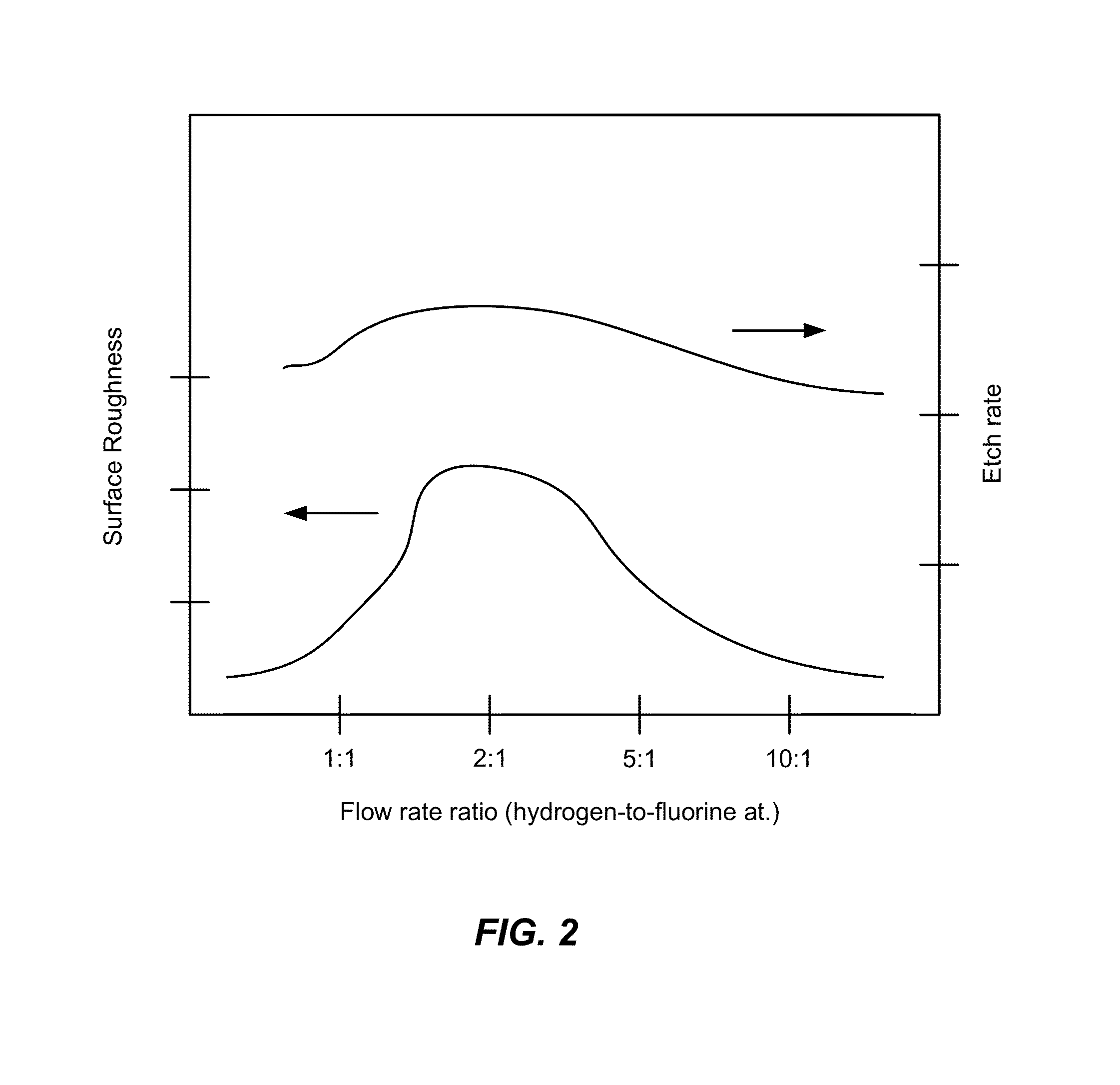
ActiveUS20110151674A1Great and less flow ratioReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSurface roughness
A method of etching silicon-containing material is described and includes a SiConi™ etch having a greater or lesser flow ratio of hydrogen compared to fluorine than that found in the prior art. Modifying the flow rate ratios in this way has been found to reduce roughness of the post-etch surface and to reduce the difference in etch-rate between densely and sparsely patterned areas. Alternative means of reducing post-etch surface roughness include pulsing the flows of the precursors and / or the plasma power, maintaining a relatively high substrate temperature and performing the SiConi™ in multiple steps. Each of these approaches, either alone or in combination, serve to reduce the roughness of the etched surface by limiting solid residue grain size.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
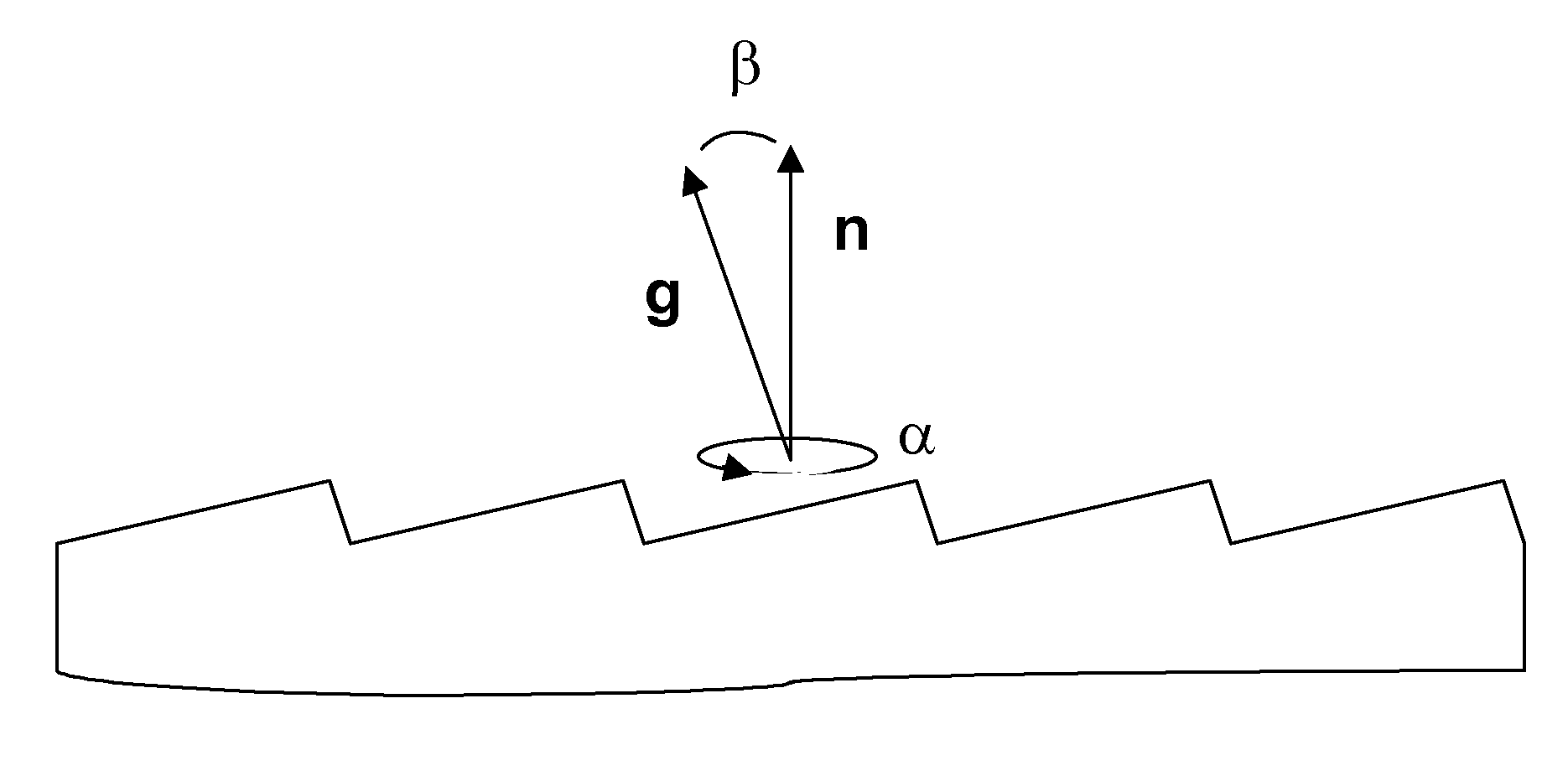
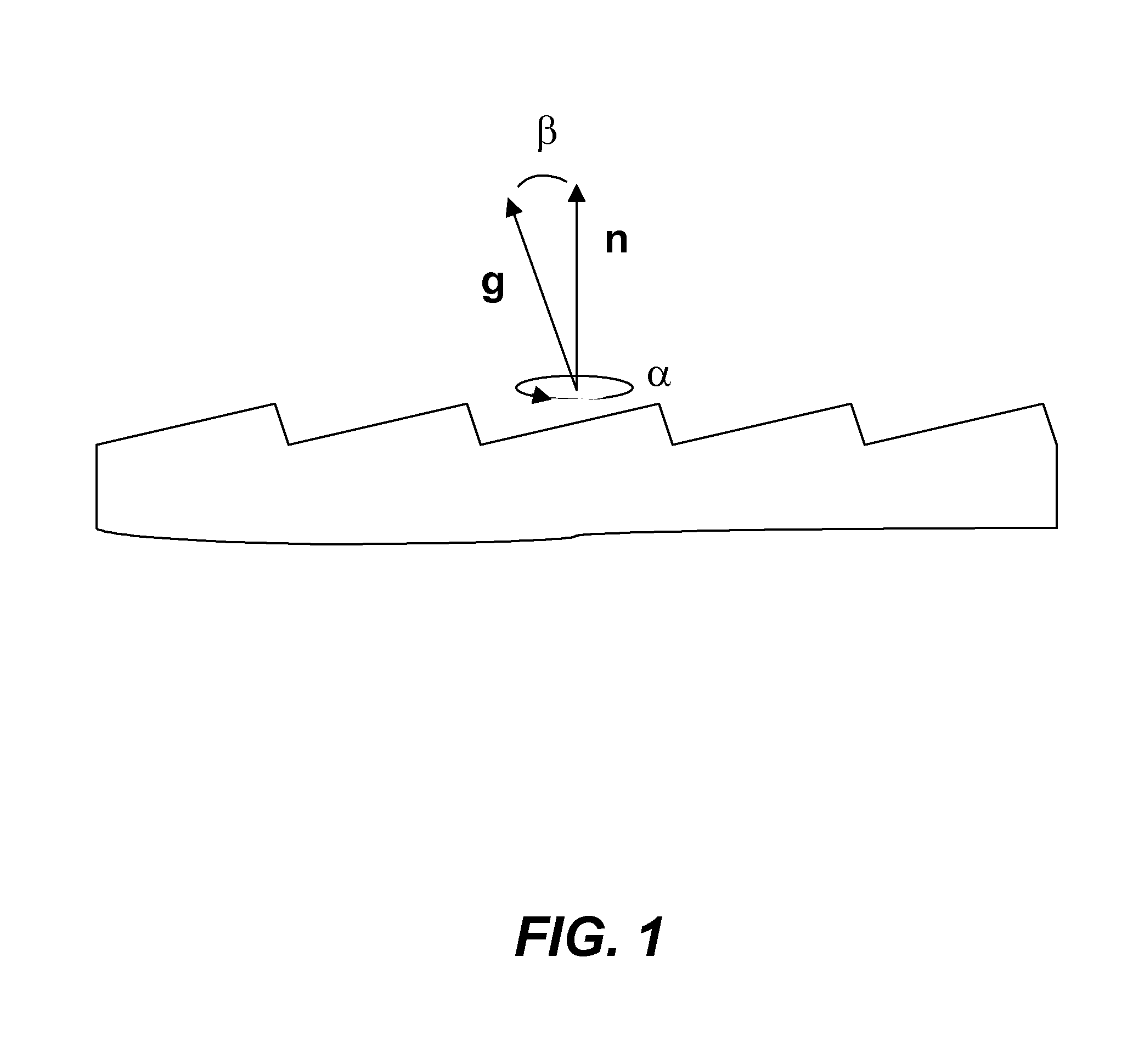
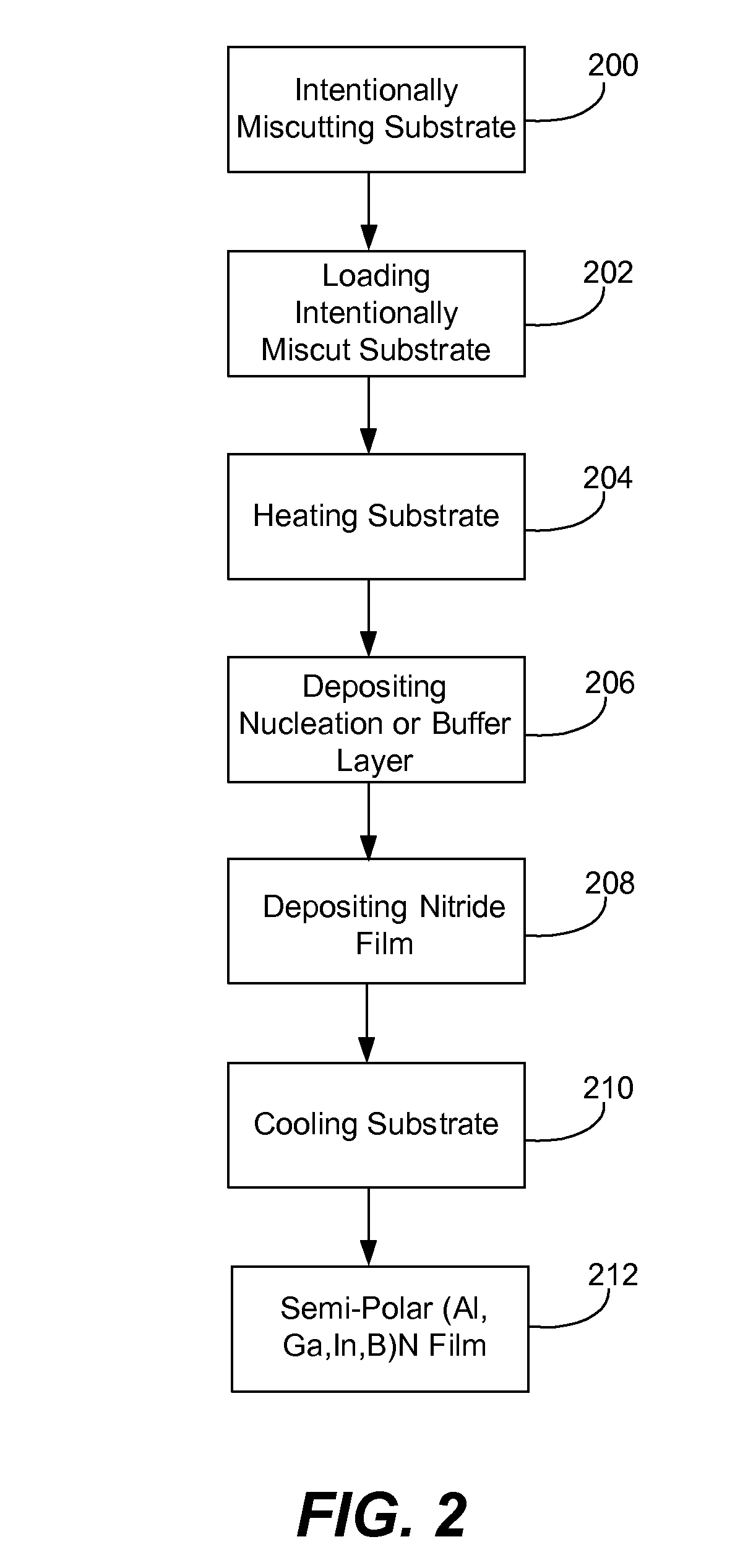
Method for improved growth of semipolar (Al,In,Ga,B)N
ActiveUS7691658B2Reduce symmetryImprove propertiesPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesHydrogenNitrogen
A method for improved growth of a semipolar (Al,In,Ga,B)N semiconductor thin film using an intentionally miscut substrate. Specifically, the method comprises intentionally miscutting a substrate, loading a substrate into a reactor, heating the substrate under a flow of nitrogen and / or hydrogen and / or ammonia, depositing an InxGa1−xN nucleation layer on the heated substrate, depositing a semipolar nitride semiconductor thin film on the InxGa1−xN nucleation layer, and cooling the substrate under a nitrogen overpressure.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
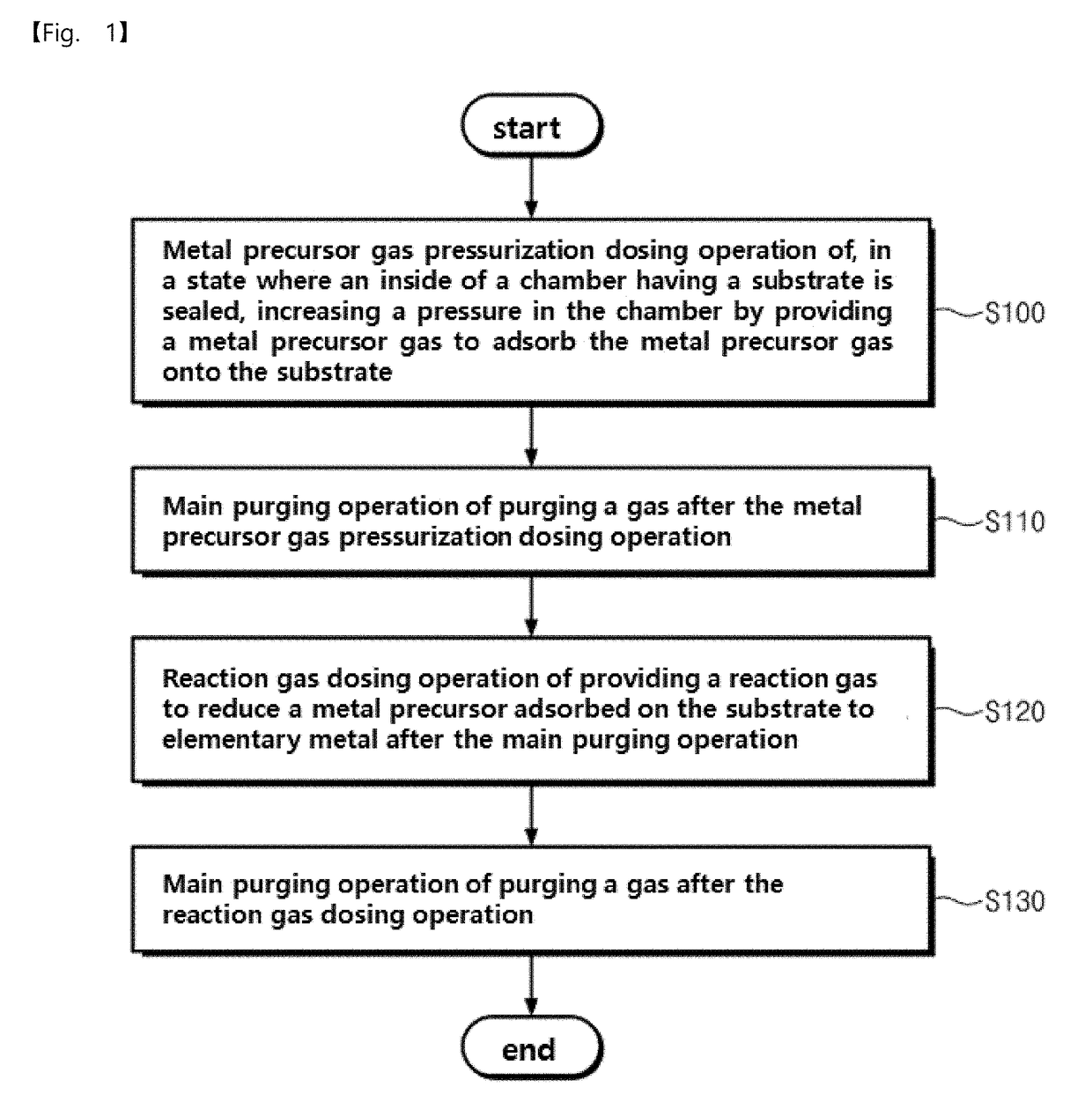
Pressurization type method for manufacturing metal monoatomic layer, metal monoatomic layer structure, and pressurization type apparatus for manufacturing metal monoatomic layer
ActiveUS20190062917A1High surface coverageReduce surface roughnessChemical vapor deposition coatingPressure/vacuum vesselsProduct gasMaterials science
A pressurization type method for manufacturing elementary metal may include a metal precursor gas pressurization dosing operation of, in a state where an outlet of a chamber having a substrate is closed, increasing a pressure in the chamber by providing a metal precursor gas consisting of metal precursors, thereby adsorbing the metal precursors onto the substrate, a main purging operation of purging a gas after the metal precursor gas pressurization dosing operation, a reaction gas dosing operation of providing a reaction gas to reduce the metal precursors adsorbed on the substrate to elementary metal, after the main purging operation, and a main purging operation of purging a gas after the reaction gas dosing operation.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Laminated semiconductor substrate process for producing the same
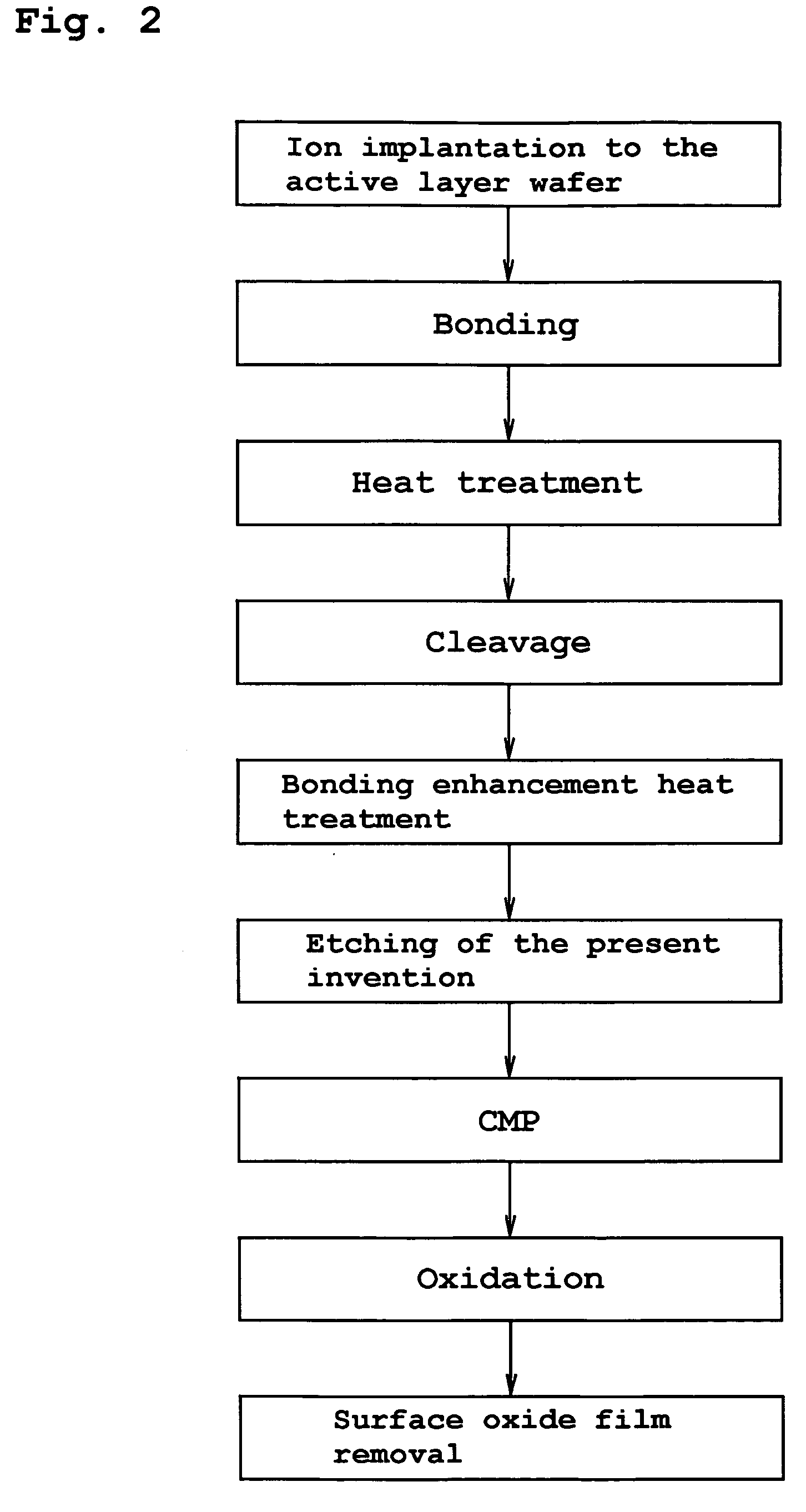
InactiveUS20060118935A1Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
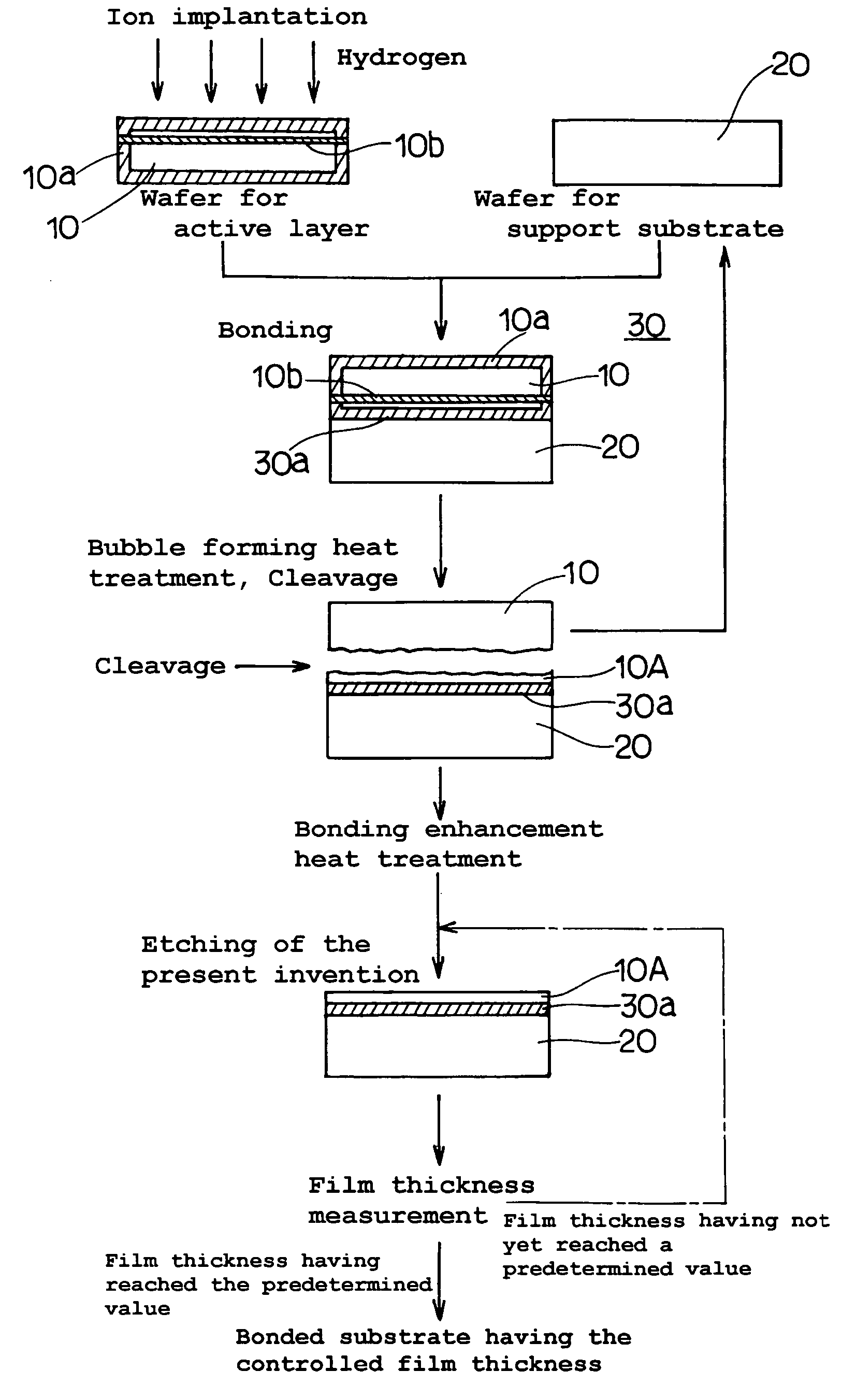
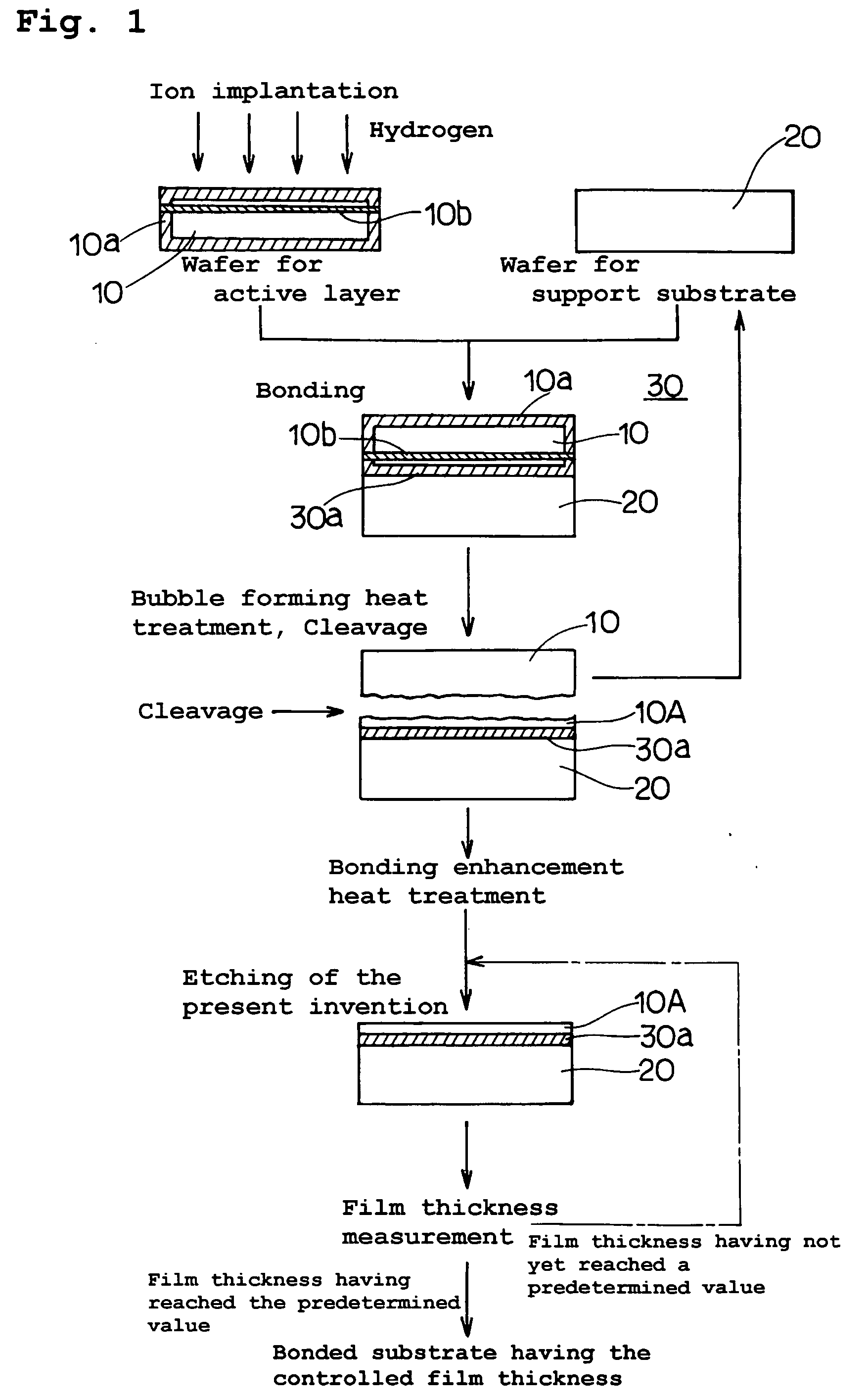
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
Smooth SiConi etch for silicon-containing films
ActiveUS8501629B2Great and less flow ratioReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSurface roughness
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
PendingUS20170309490A1Reduce roughnessLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSemiconductorAmorphous metal
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes: forming an amorphous metal film on a substrate by time-divisionally conducting a cycle a predetermined number of times, the cycle including: (a) simultaneously supplying a metal-containing gas and a first reducing gas to the substrate to form a first amorphous metal layer on the substrate, and (b) forming a second amorphous metal layer on the first amorphous metal layer by time-divisionally supplying, a predetermined number of times, the metal-containing gas and a second reducing gas to the substrate on which the first amorphous metal layer is formed; and forming a crystallized metal layer on the substrate by simultaneously supplying the metal-containing gas and the first reducing gas to the substrate on which the amorphous metal film is formed.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Stents and methods for preparing stents from wires having hydrogel coating layers thereon
InactiveUS20050251250A1Improved propertyReduce surface roughnessStentsSurgeryActive agentInsertion stent
Radially expandable stents having hydrogel coating layers thereon, and methods of preparing such stents are disclosed. The methods include coating a wire with a solution that includes a solvent and a water soluble polymer in the solvent, evaporating the solvent to provide a polymeric coating on the wire, and crosslinking the polymeric coating to provide a hydrogel coating layer on the wire. The coated wire can be fabricated into stents, which preferably have substantially uniform coatings with low surface roughness. Preferably the coatings have hydrophilic properties and provide a biocompatible surface. The coatings may also provide for the delivery of biologically active agents into the body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Microfluidic device and methods for construction and application
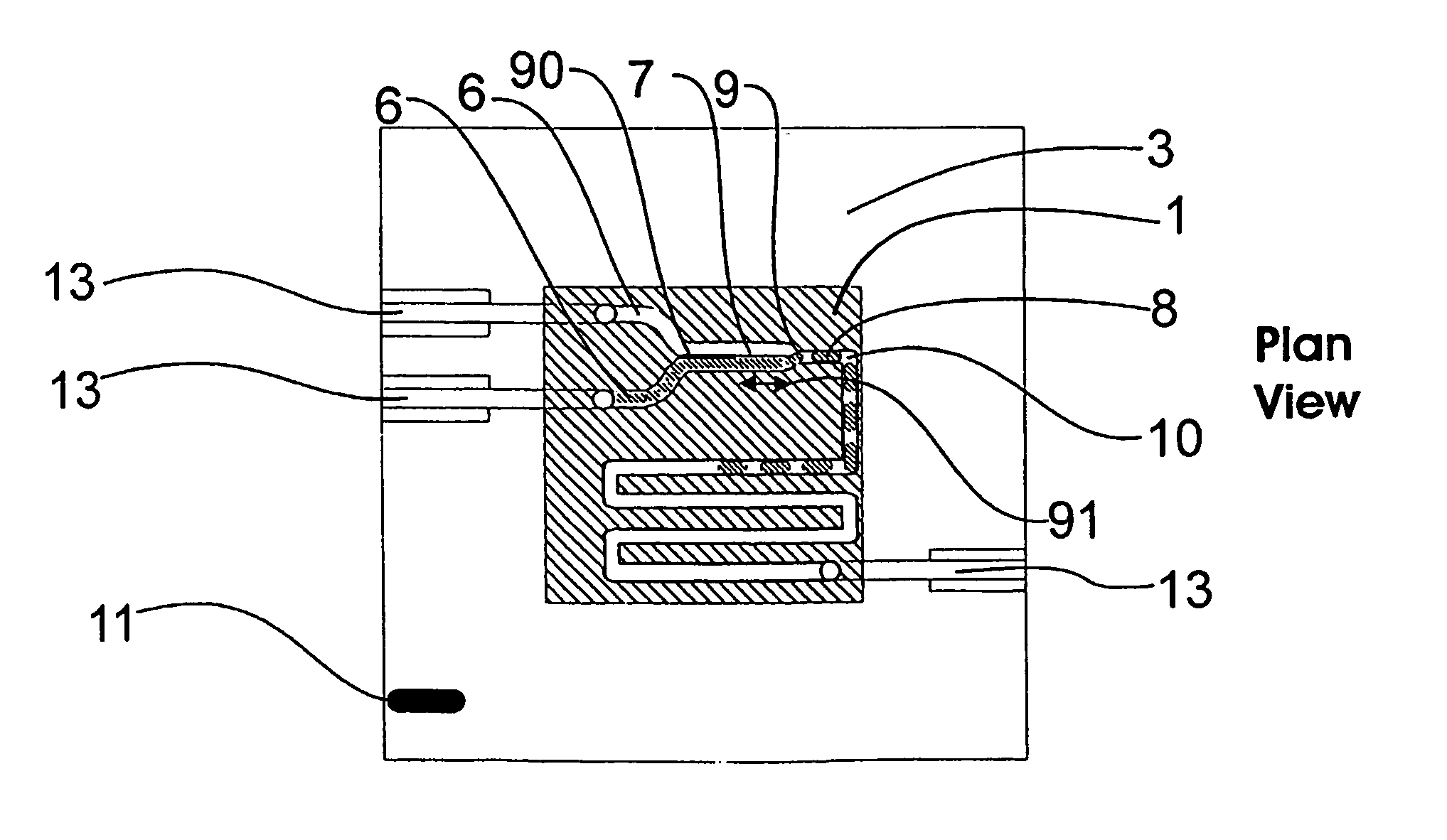
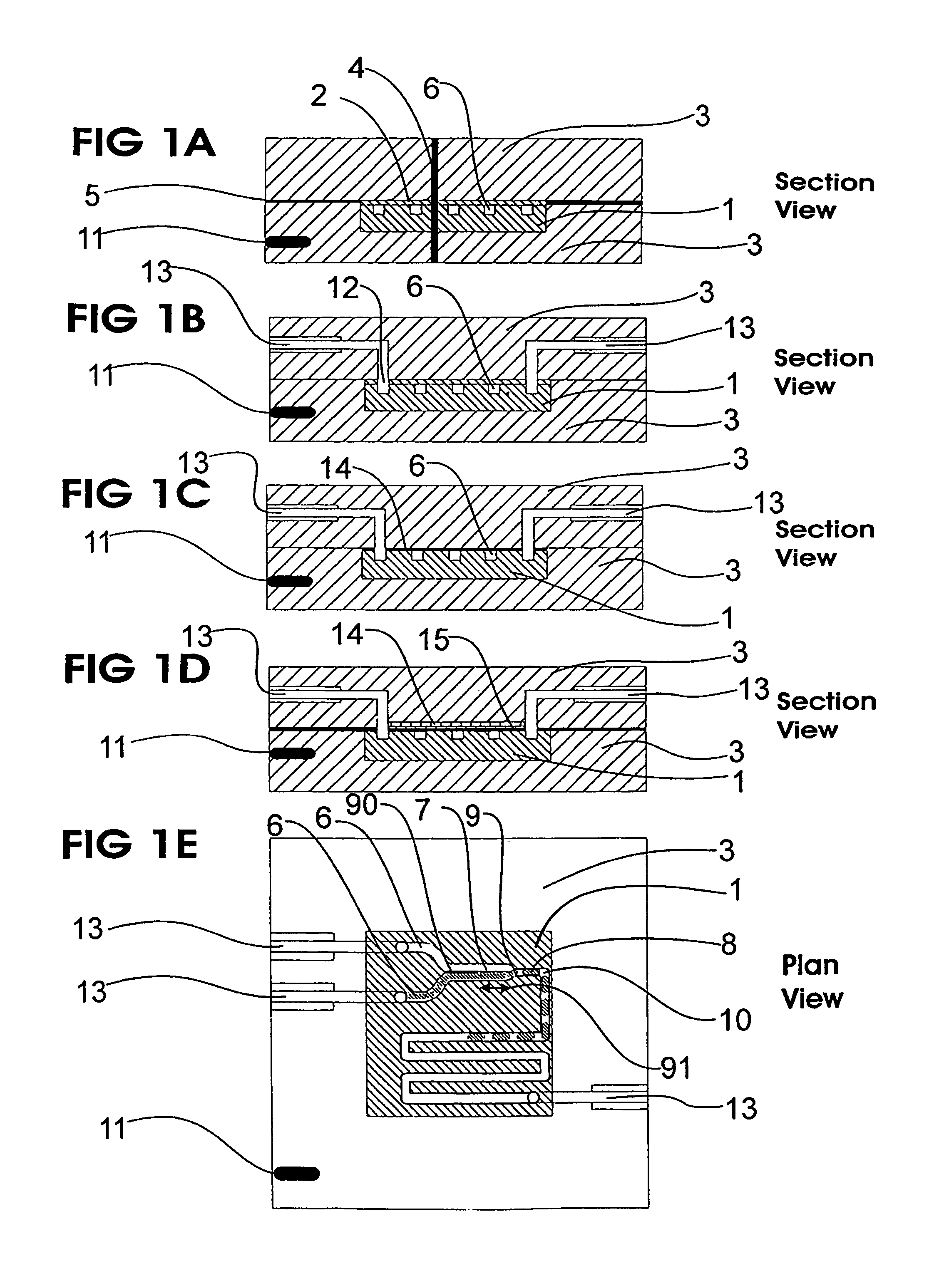
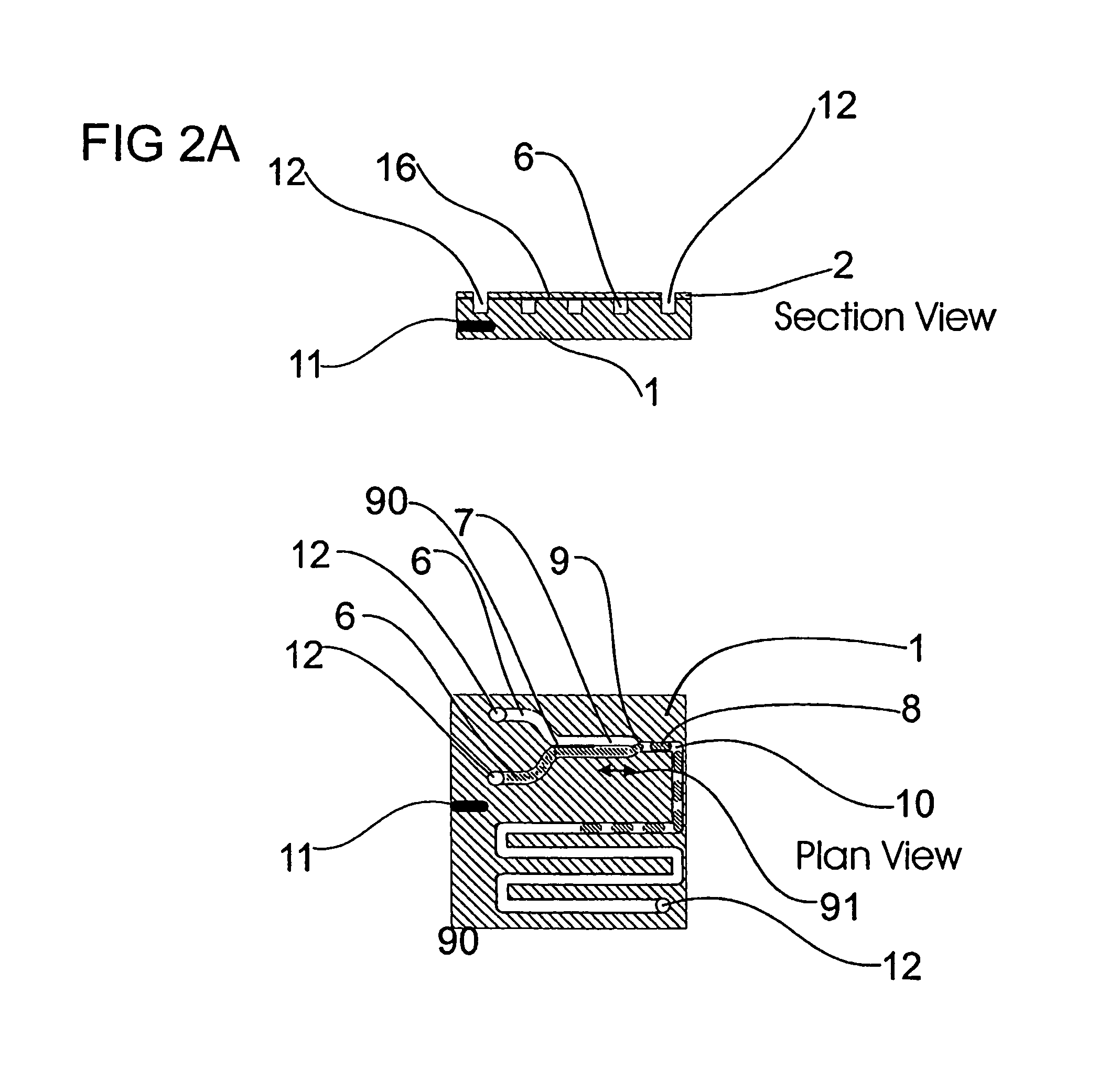
InactiveUS20060108012A1Considerable precisionEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCircuit elementsEngineeringTwo fluid
A microfluidic device comprises first and second inlet passages (13) for respective immiscible fluids, these inlet passages merging into a third passage (8) along which the two fluids flow under parallel laminar flow conditions, the third passage being formed with a constriction or other discontinuity (9) causing the two fluids to form into a flow of alternate segments.
Owner:Q CHIP
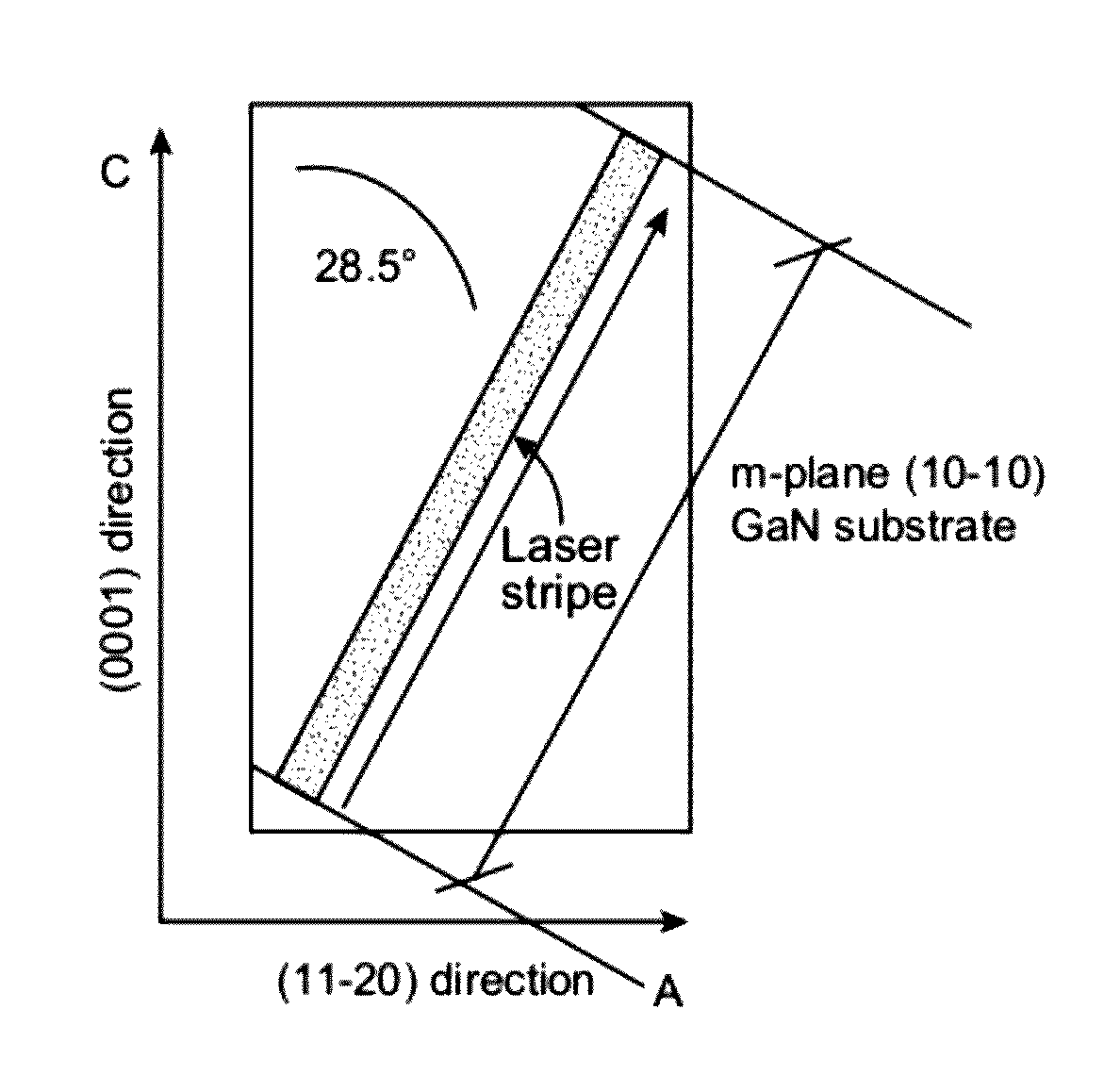
Solid state laser device using a selected crystal orientation in non-polar or semi-polar GaN containing materials and methods
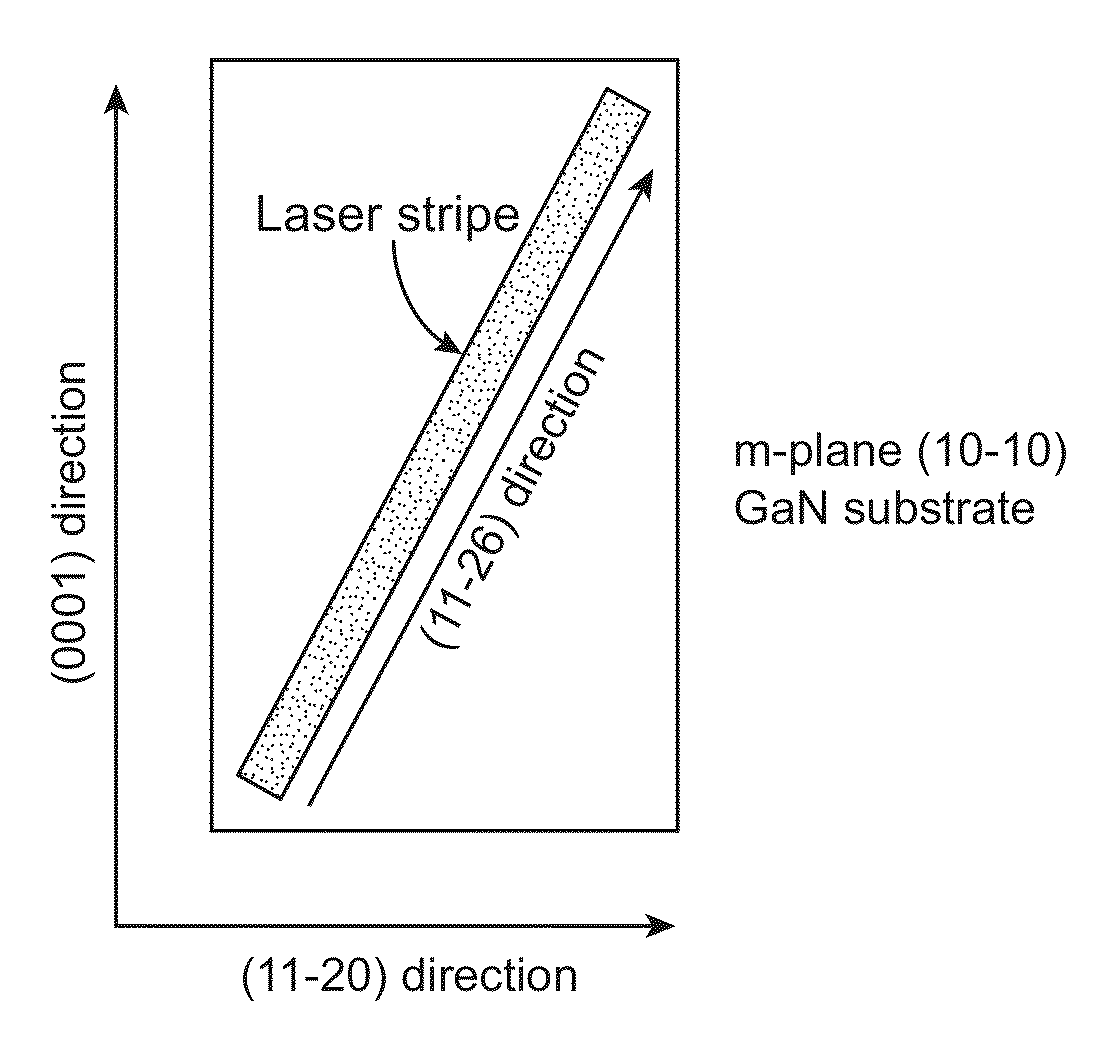
ActiveUS8284810B1Facilitates parallel facetReduce surface roughnessNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersHigh current densitySolid-state laser device
An edge emitting solid state laser and method. The laser comprises at least one AlInGaN active layer on a bulk GaN substrate with a non-polar or semi-polar orientation. The edges of the laser comprise {1 1 −2 ±6} facets. The laser has high gain, low threshold currents, capability for extended operation at high current densities, and can be manufactured with improved yield. The laser is useful for optical data storage, projection displays, and as a source for general illumination.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
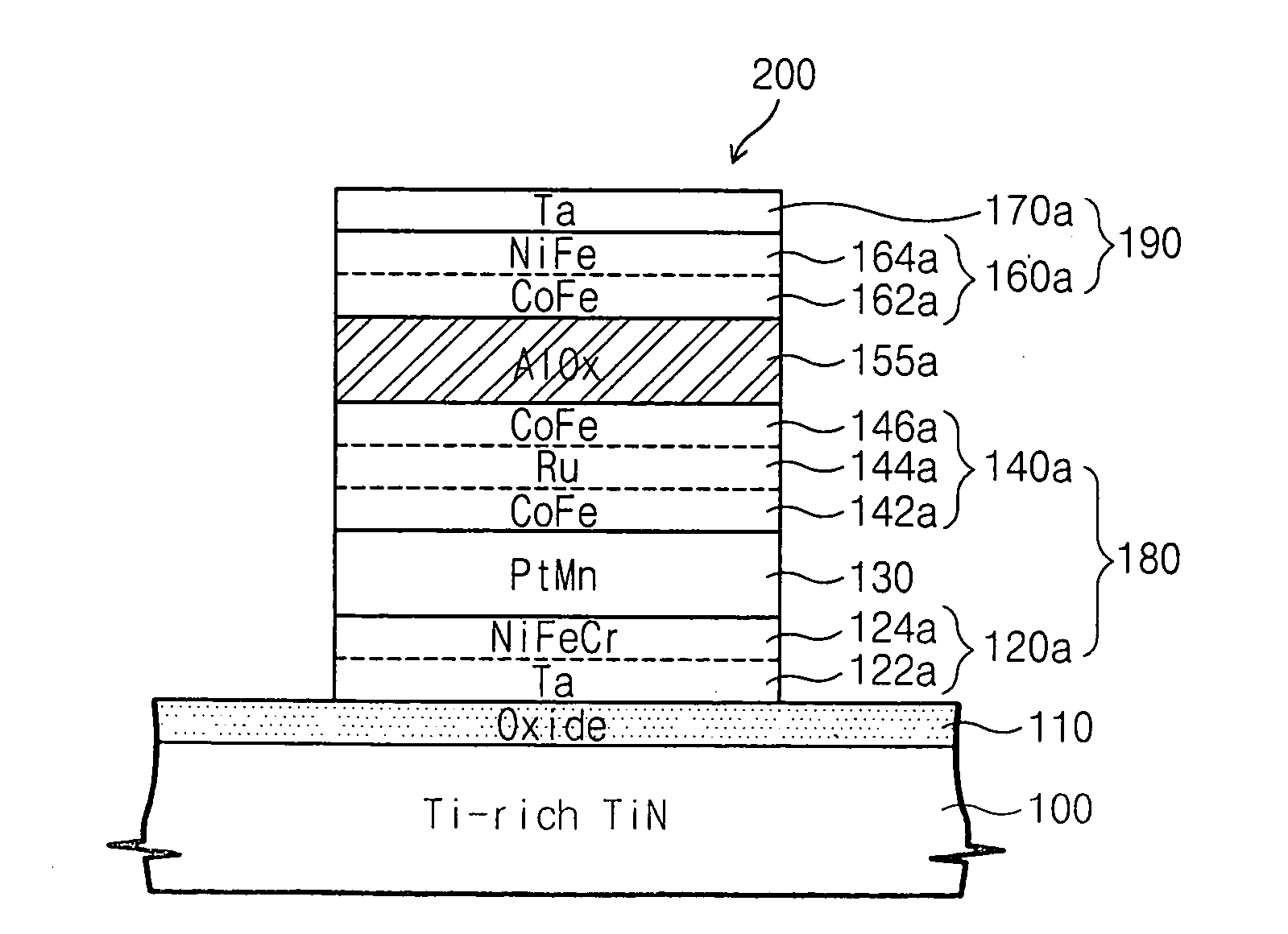
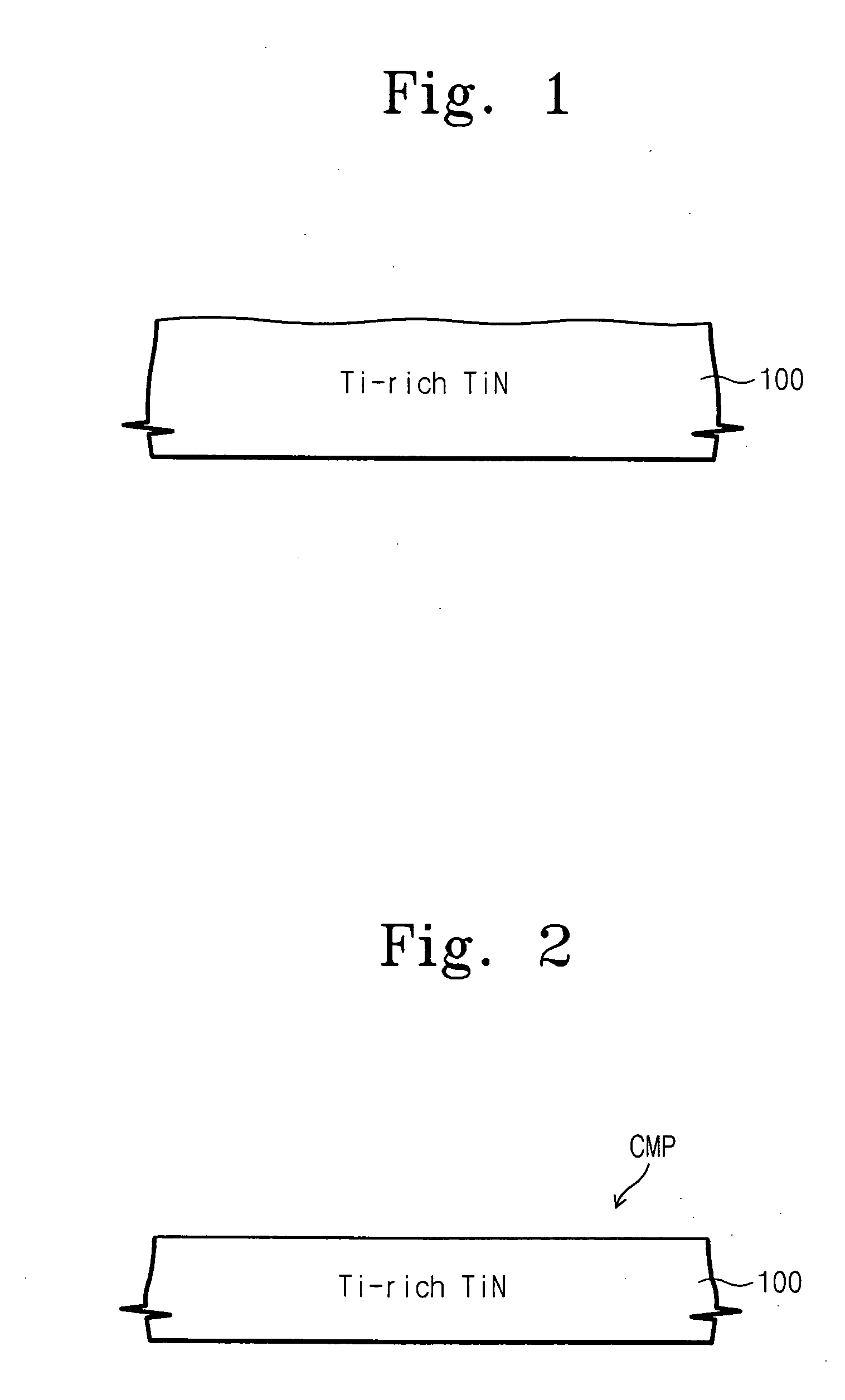
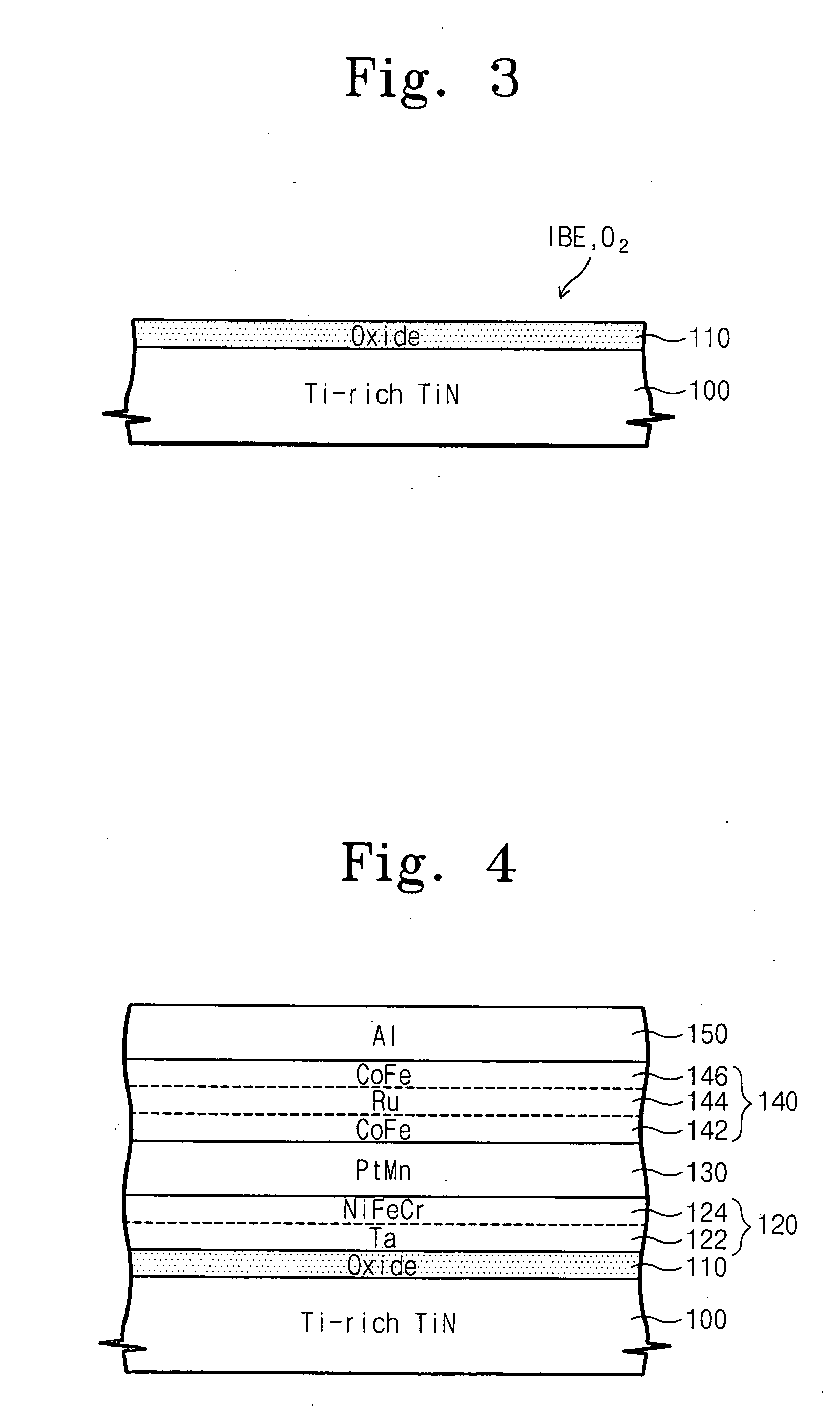
Magnetic random access memory devices having titanium-rich lower electrodes with oxide layer and oriented tunneling barrier, and methods for forming the same
ActiveUS20050006682A1Addressing Insufficient ControlLow polishing rateNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismRandom access memoryTitanium
Magnetic Random Access Memory (MRAM) devices include a lower electrode and a magnetic tunnel junction on the lower electrode. The magnetic tunnel junction includes a seed layer and a tunneling barrier that is oriented in a same direction as the most closely packed plane direction of the seed layer. An oxide layer may be provided between the lower electrode and the magnetic tunnel junction. The lower electrode may be a titanium-rich TiN layer having more than 50 atomic percent titanium content. Analogous fabrication methods are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
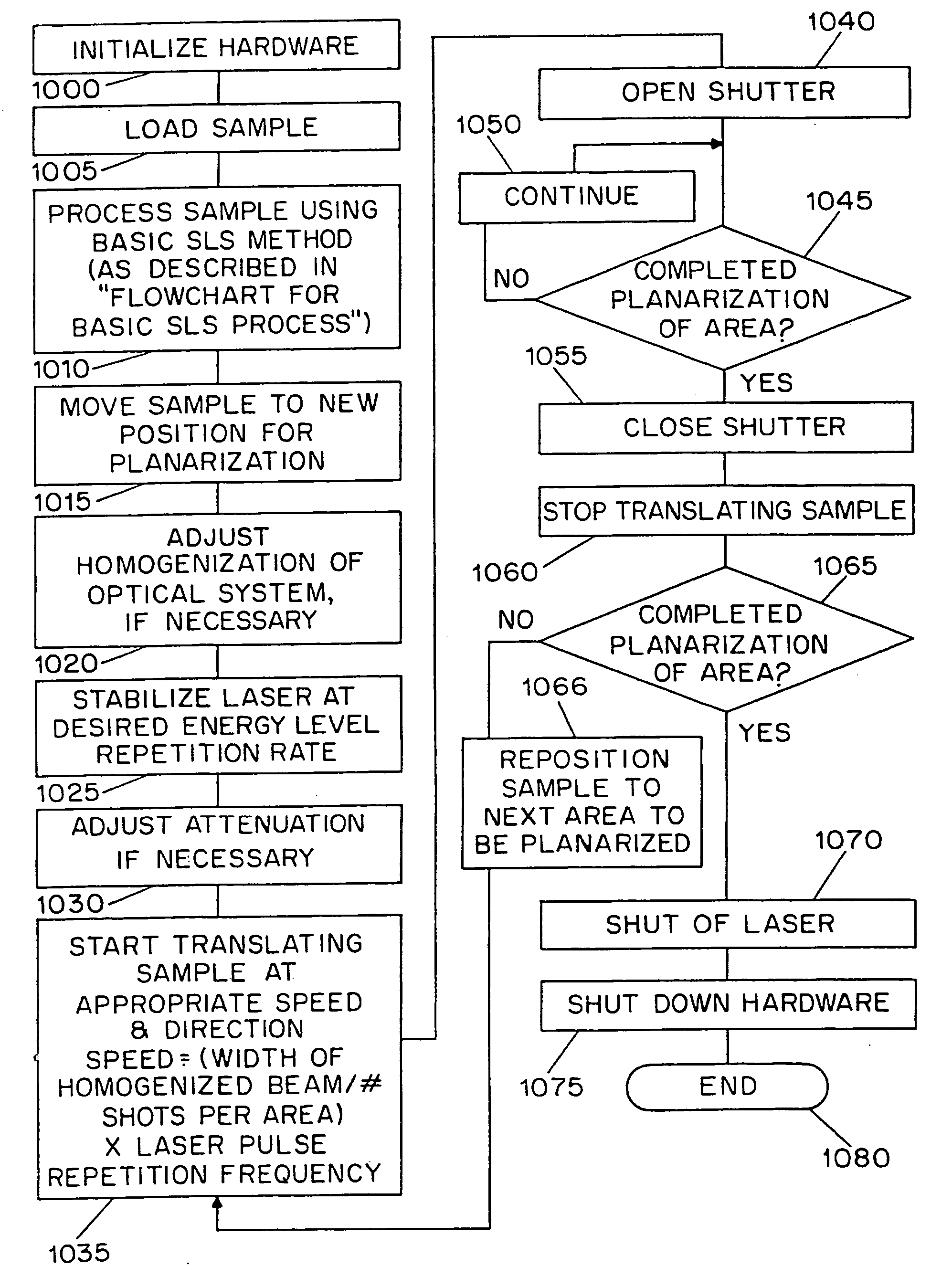
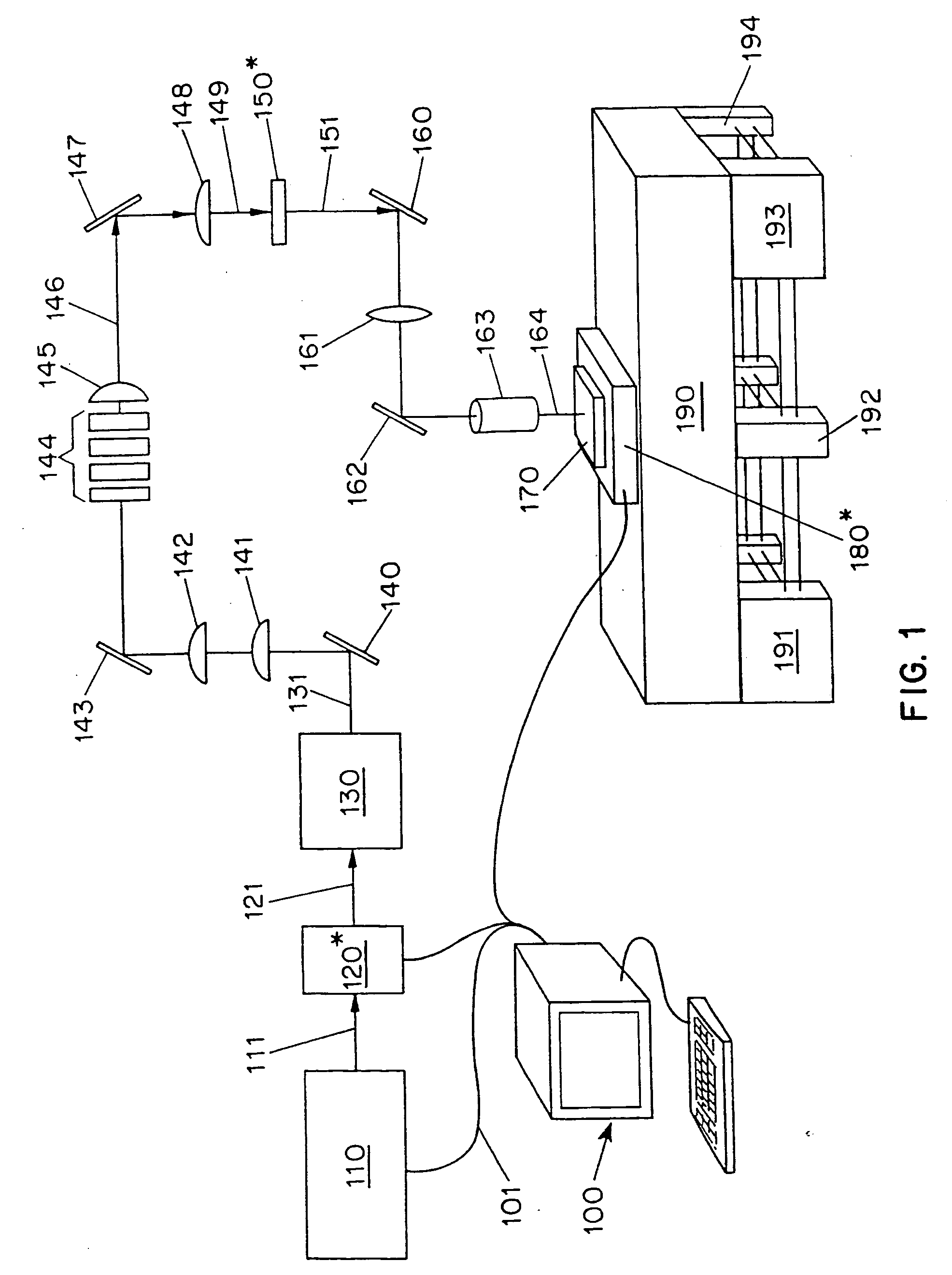
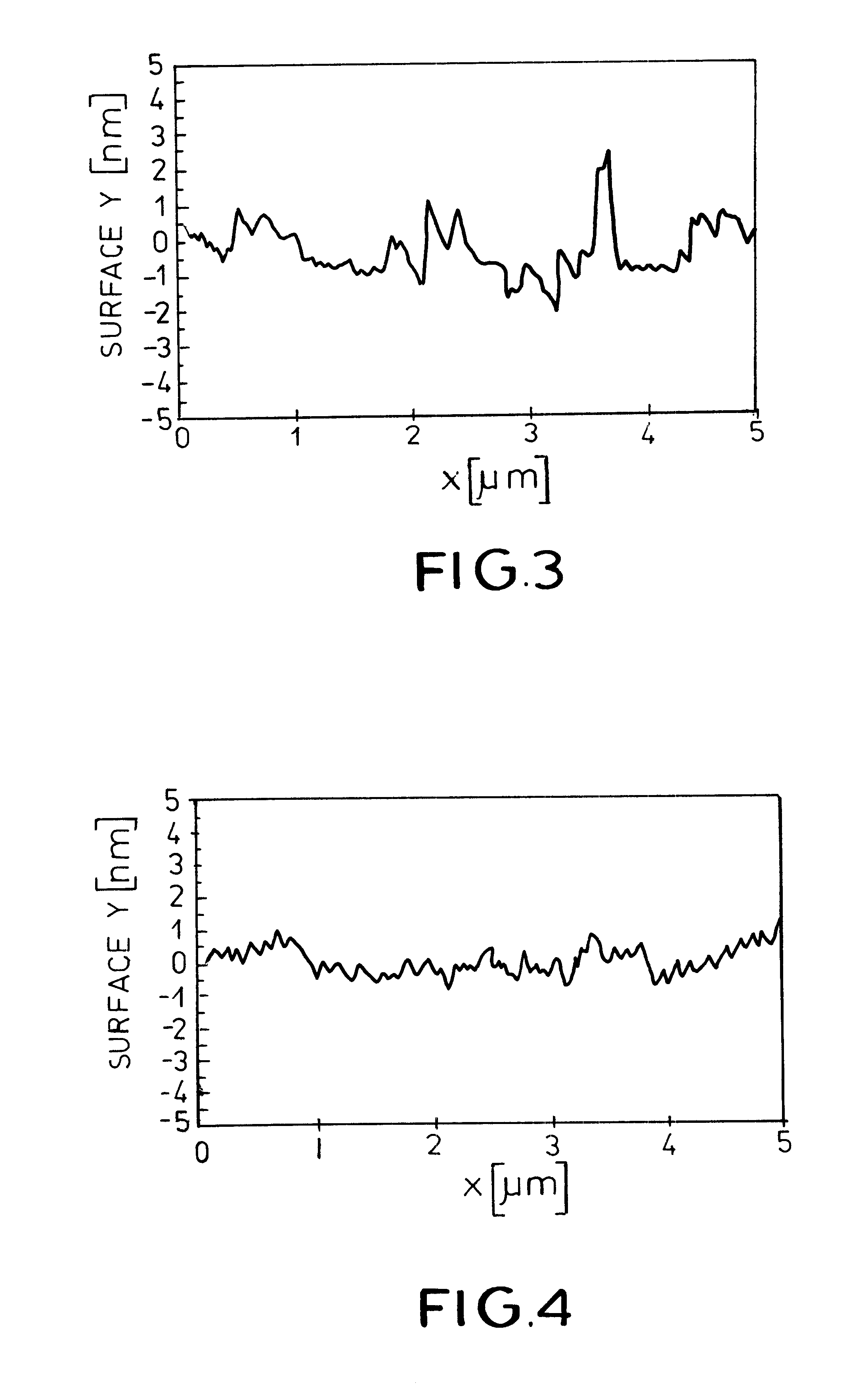
Surface planarization of thin silicon films during and after processing by the sequential lateral solidification method
InactiveUS20050032249A1Reduce surface roughnessAvoid insufficient thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusSurface roughnessLight beam
Systems and methods for reducing a surface roughness of a polycrystalline or single crystal thin film produced by the sequential lateral solidification process are disclosed. In one arrangement, the system includes an excimer laser (110) for generating a plurality of excimer laser pulses of a predetermined fluence, an energy density modulator (120) for controllably modulating the fluence of the excimer laser pulses such that the fluence is below that which is required to completely melt the thin film, a beam homoginizer (144) for homoginizing modulated laser pulses in a predetermined plane, a sample stage (170) for receiving homoginized laser pulses to effect melting of portions of the polycrystalline or single crystal thin film corresponding to the laser pulses, translating means for controllably translating a relative position of the sample stage (170) with respect to the laser pulses, and a computer (110) for coordinating the excimer pulse generation and fluence modulation with the relative positions of the sample stage (170) to thereby process the polycrystalline or single crystal thin film by sequential translation of the sample stage (170) relative to the laser pulses.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid
ActiveCN104017636ALubricity achievedImprove stabilityLubricant compositionOrganic EsterNonferrous metal
The invention discloses a water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid which belongs to the technical field of metal grinding fluids. The metal grinding fluid is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5-40wt% of an antirust agent, 1-20wt% of a cleaning agent, 0.1-10wt% of a lubricating corrosion inhibitor, 1-20wt% of a penetrant, 1-20wt% of a solubilizer, 10-40wt% of a PH adjustor, 0.5-5wt% of a defoamer and the balance of water. Based on the total weight of the water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid, the pH value of the water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid is 7-11. The lubricating corrosion inhibitor is long chain nitrogen heterocyclic ring organic ester. The water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid has excellent lubricating, rust-preventing, cleaning and cooling performances and can be widely applied to grinding of ferrous metals and nonferrous metals.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
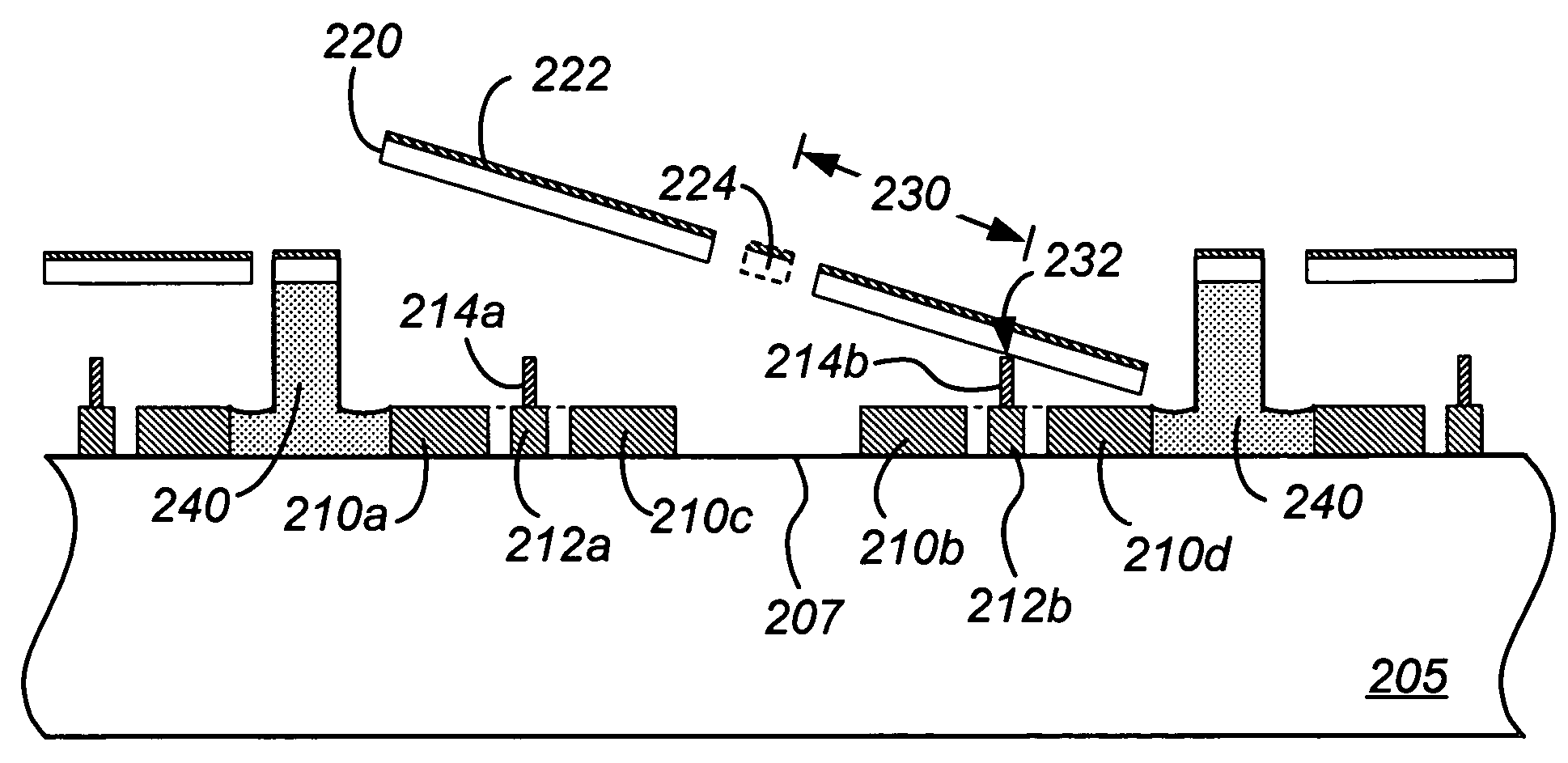
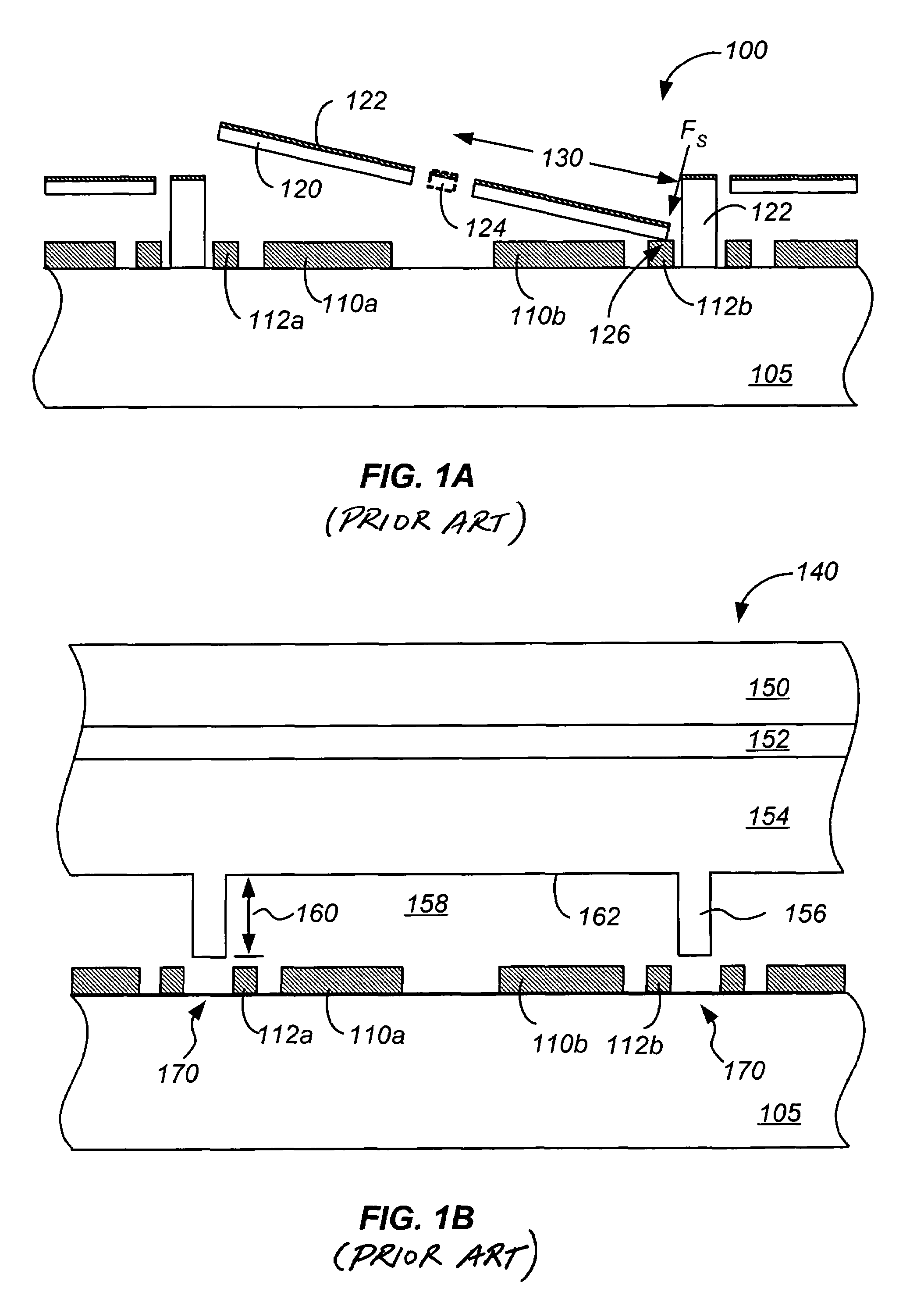
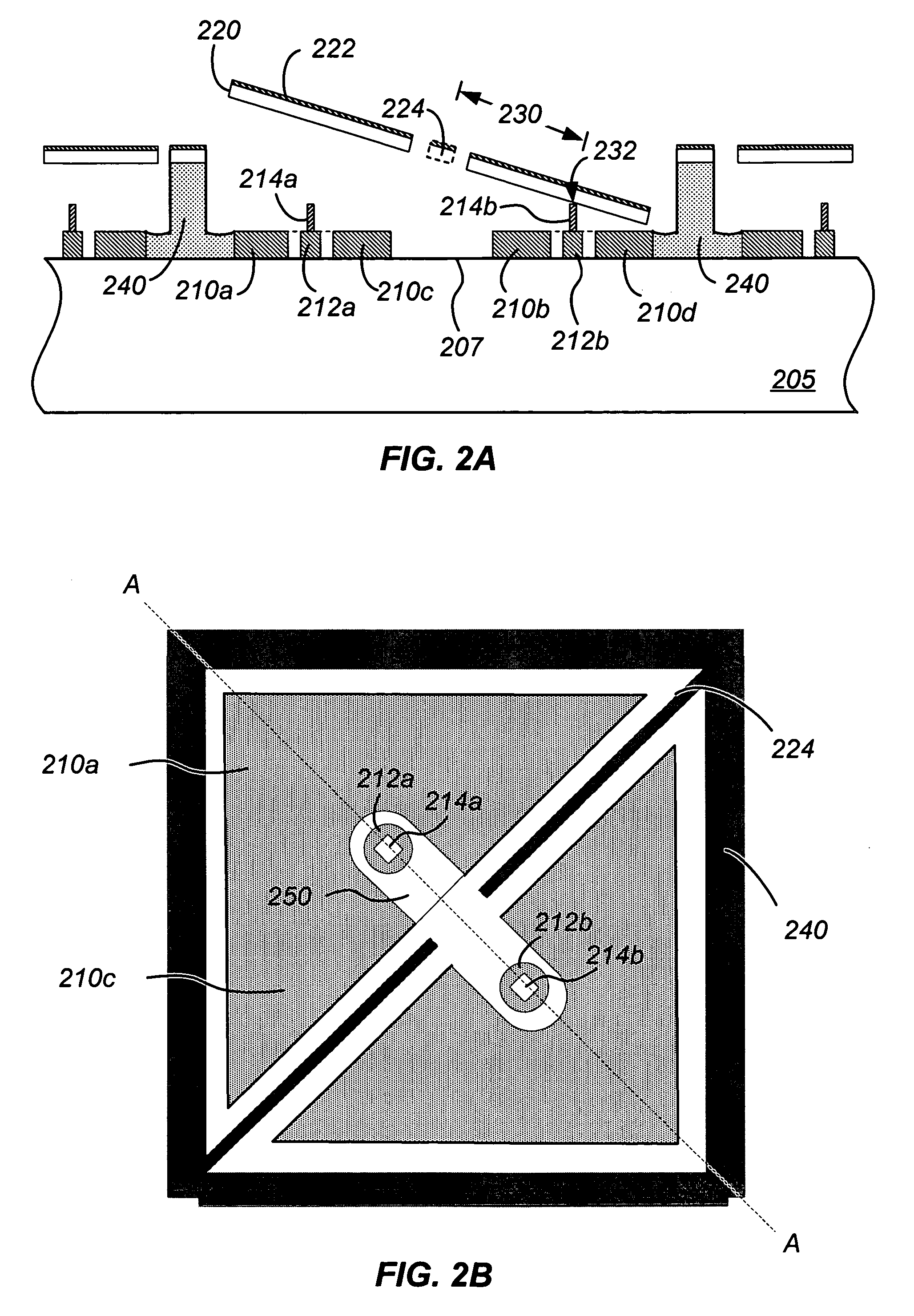
Method and structure reducing parasitic influences of deflection devices in an integrated spatial light modulator
ActiveUS7184195B2Reduce thicknessAlignment tolerances used during the substrate bonding process are greatly relaxedNon-linear opticsFlexible microstructural devicesSpatial light modulator
Owner:MIRADIA INC
Method of manufacturing three-dimensional semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170250193A1Reduce channel surface roughnessEnhance channel carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilitySurface roughness
A method of manufacturing three-dimensional semiconductor device, comprising the steps of: forming a stack structure of a plurality of a first material layers and a second material layers on a substrate in the memory cell region; etching said stack structure to form a plurality of trenches; forming channel layers in said plurality of trenches; performing annealing treatment to at least one surface of the channel layers to reduce the surface roughness and the interface state. In accordance with the three-dimensional semiconductor device manufacturing method of the present invention, the formation of interface states is depressed by introducing a dummy channel sacrificial layer for the interface treatment on the channel surface and back surface, and / or the channel surface roughness is reduced by introducing a buffer layer on the channel surface and back surface during the treatment, which can improve the channel carrier mobility, improve the channel current as well as the reliability of the memory cell.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid State Laser Device Using a Selected Crystal Orientation in Non-Polar or Semi-Polar GaN Containing Materials and Methods
ActiveUS20130064261A1Facilitates parallel facetsReduce surface roughnessLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh current densitySolid-state laser device
An edge emitting solid state laser and method. The laser comprises at least one AlInGaN active layer on a bulk GaN substrate with a non-polar or semi-polar orientation. The edges of the laser comprise {1 1−2±6} facets. The laser has high gain, low threshold currents, capability for extended operation at high current densities, and can be manufactured with improved yield. The laser is useful for optical data storage, projection displays, and as a source for general illumination.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC +1
Nanowires and nanoribbons as subwavelength optical waveguides and their use as components in photonic circuits and devices
ActiveUS20070140638A1Novel and versatileEasy constructionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsNanowireOptical integration
Nanoribbons and nanowires having diameters less than the wavelength of light are used in the formation and operation of optical circuits and devices. Such nanostructures function as subwavelength optical waveguides which form a fundamental building block for optical integration. The extraordinary length, flexibility and strength of these structures enable their manipulation on surfaces, including the precise positioning and optical linking of nanoribbon / wire waveguides and other nanoribbon / wire elements to form optical networks and devices. In addition, such structures provide for waveguiding in liquids, enabling them to further be used in other applications such as optical probes and sensors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
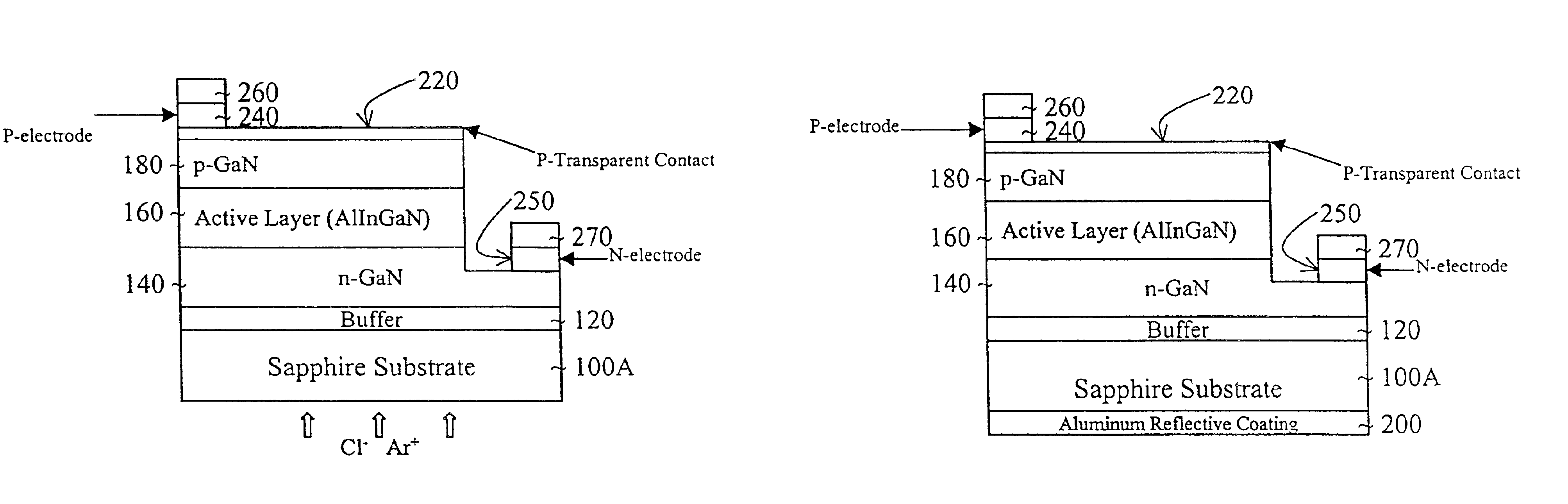
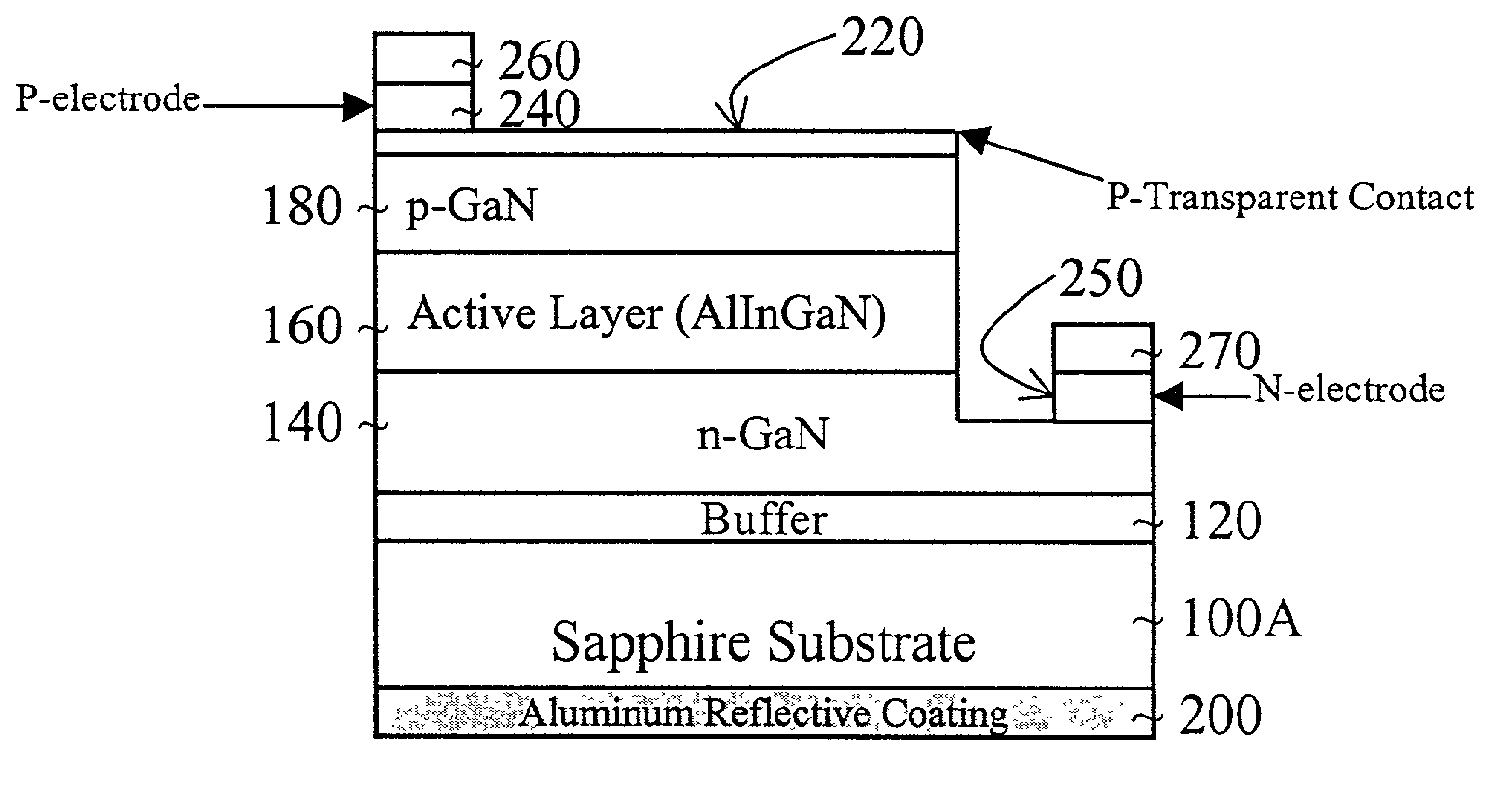
Method of making diode having reflective layer
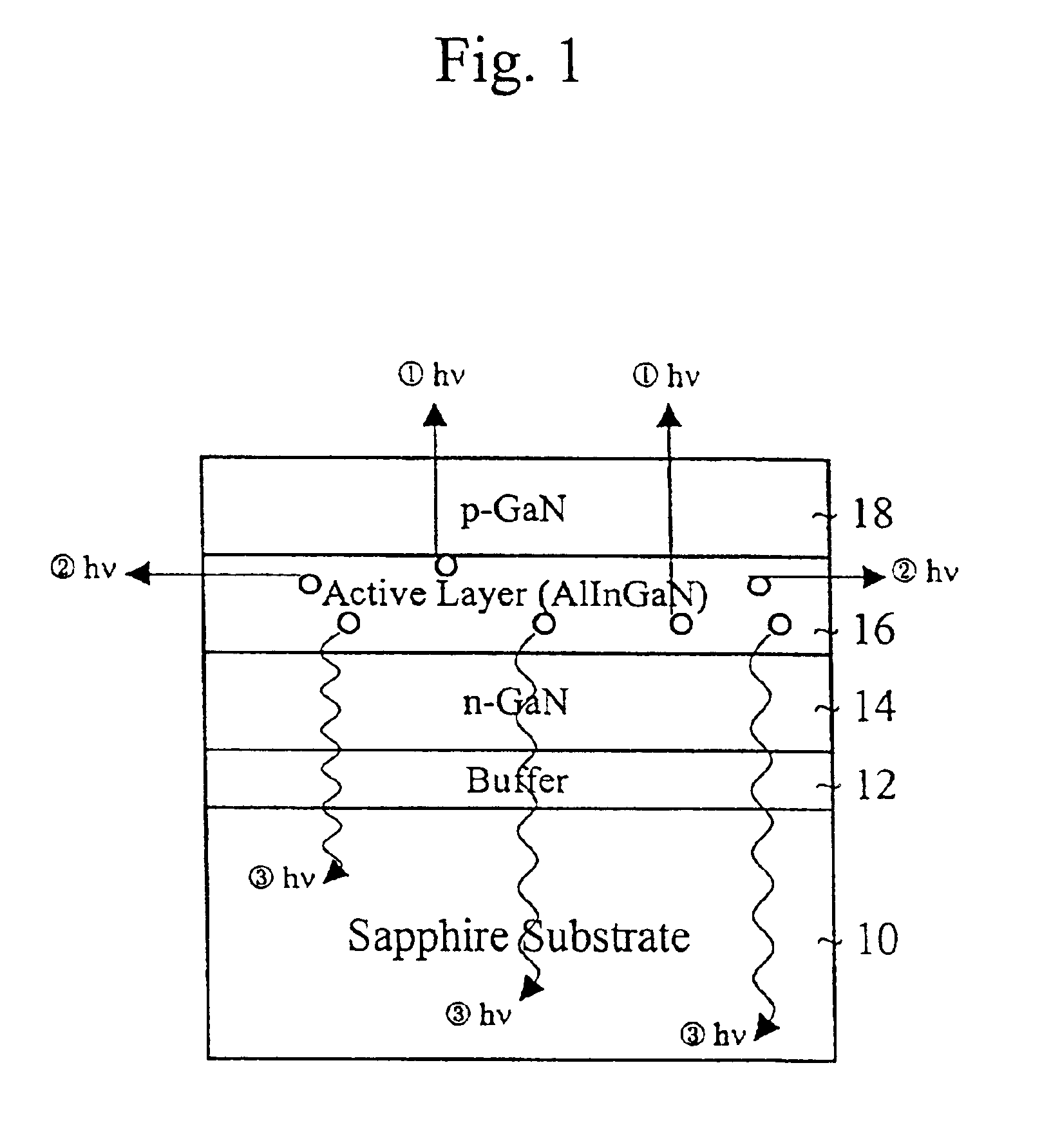
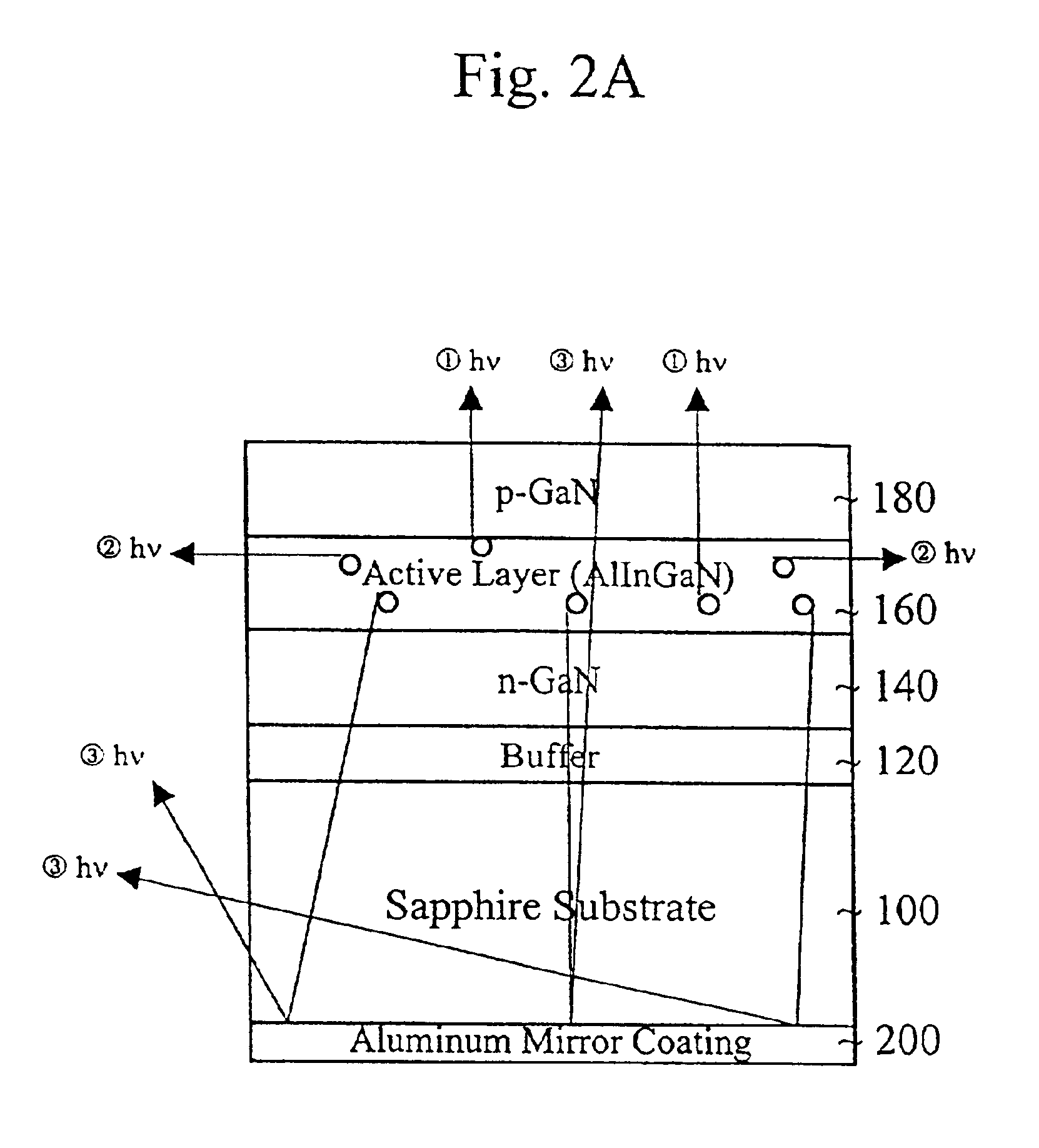
InactiveUS6949395B2Increase brightnessReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesReflective layerDiode
A method of forming a light emitting diode includes forming a transparent substrate and a GaN buffer layer on the transparent substrate. An n-GaN layer is formed on the buffer layer. An active layer is formed on the n-GaN layer. A p-GaN layer is formed on the active layer. A p-electrode is formed on the p-GaN layer and an n-electrode is formed on the n-GaN layer. A reflective layer is formed on a second side of the transparent substrate. A scribe line is formed on the substrate for separating the diodes on the substrate. Also, a cladding layer of AlGaN is between the p-GaN layer and the active layer.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
Process and apparatus for forming plastic sheet
InactiveUS6183829B1Avoid mistakesLow birefringenceRecord carriersPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
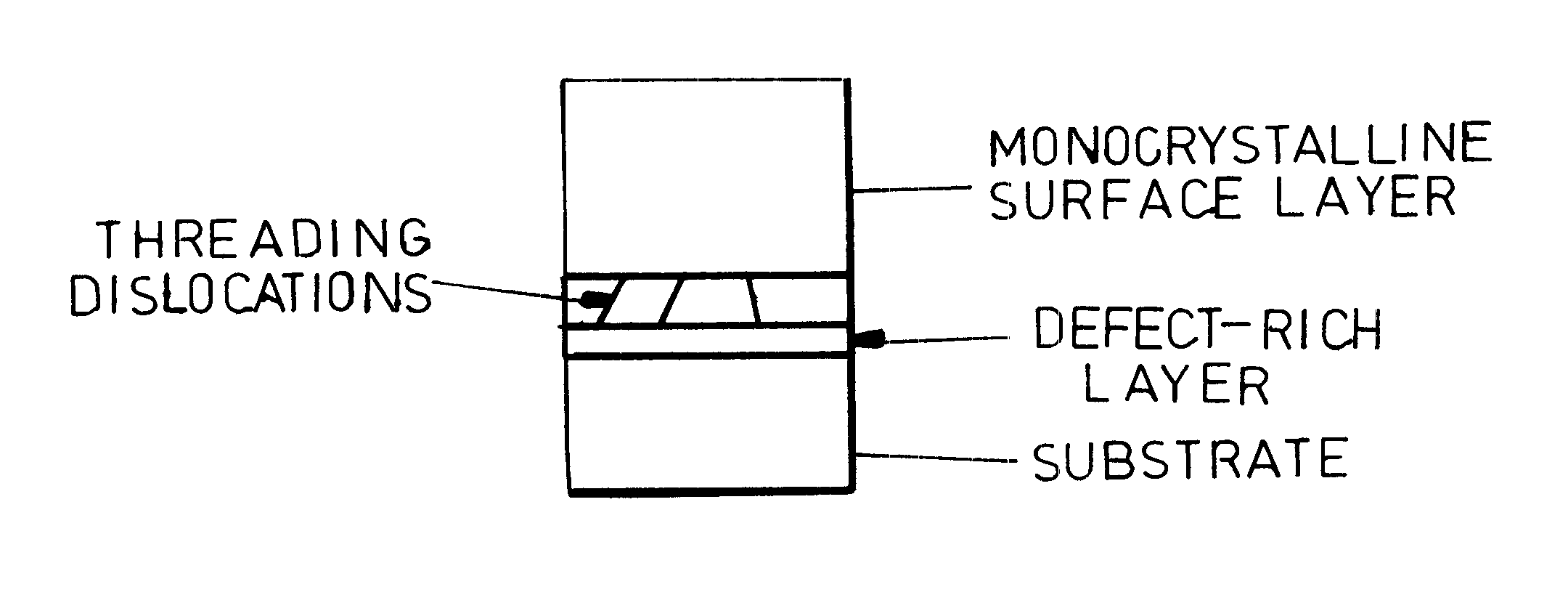
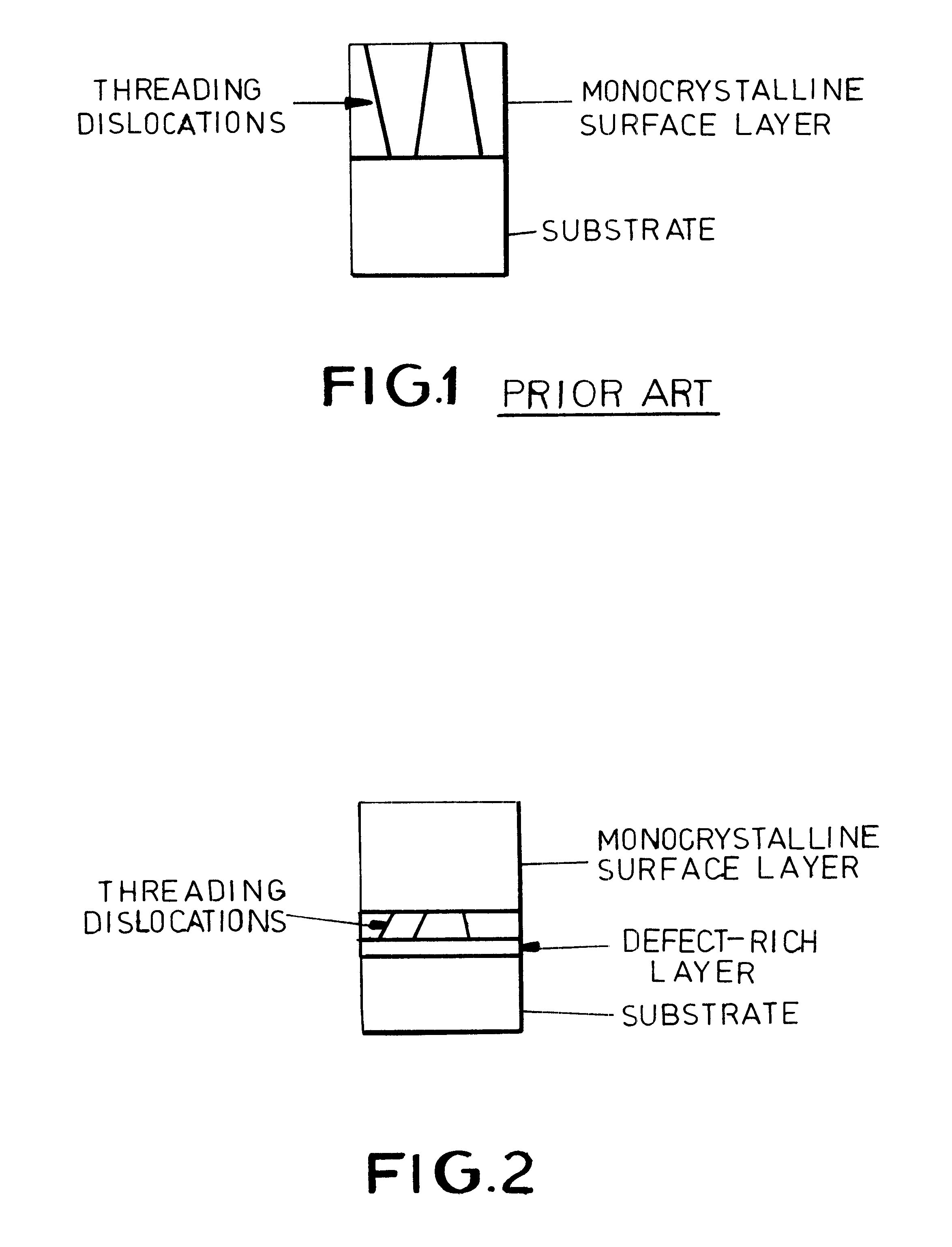
Method for the production of a monocrystalline layer on a substrate with a non-adapted lattice and component containing one or several such layers
InactiveUS6464780B1Improve featuresInhibition formationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSingle crystal substrate
The invention relates to a method for the production of a monocrystalline layer on a substrate with a non-adapted lattice. To this end, a monocrystalline substrate with a buried amply defective layer and a monocrystalline layer produce thereon are used. The buried amply defective layer can be produced by hydrogen implantation.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
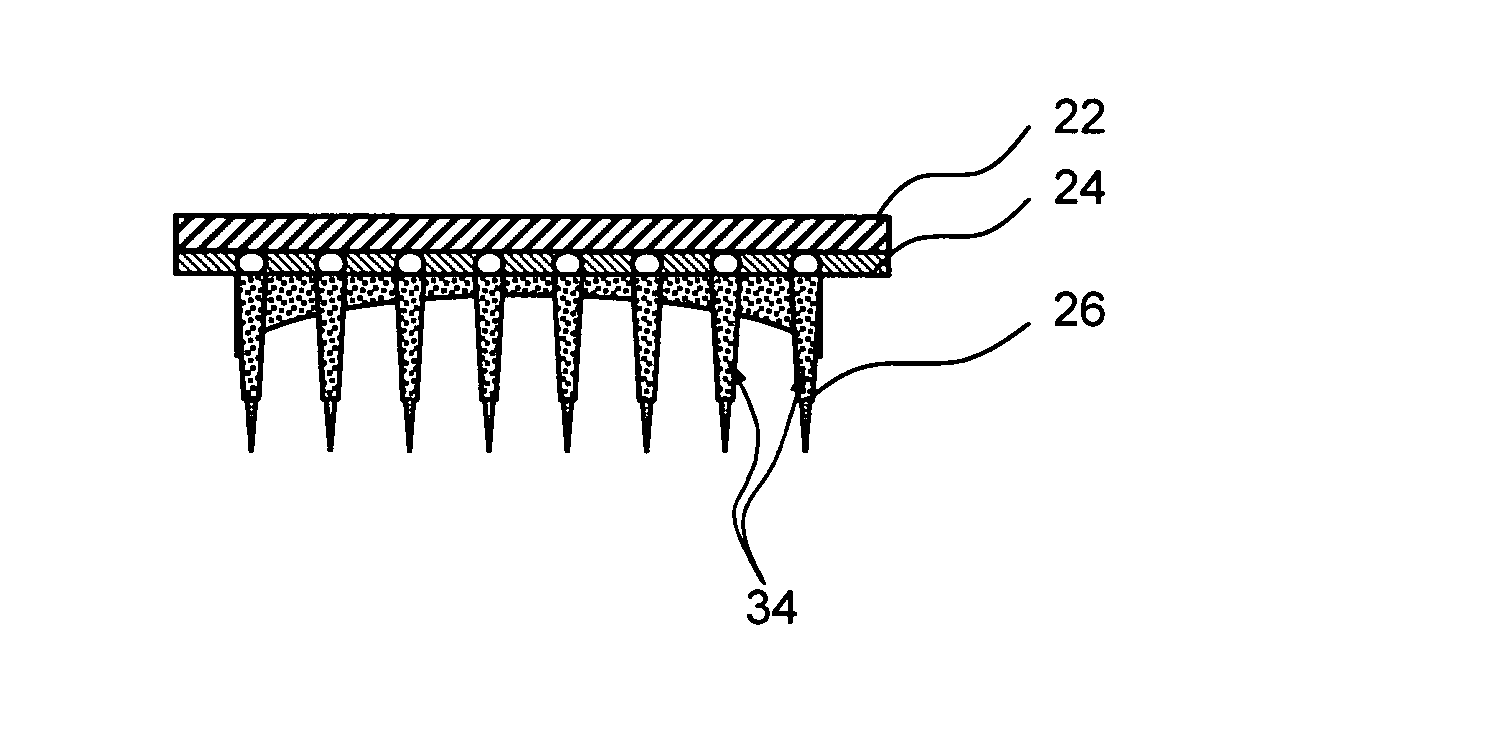
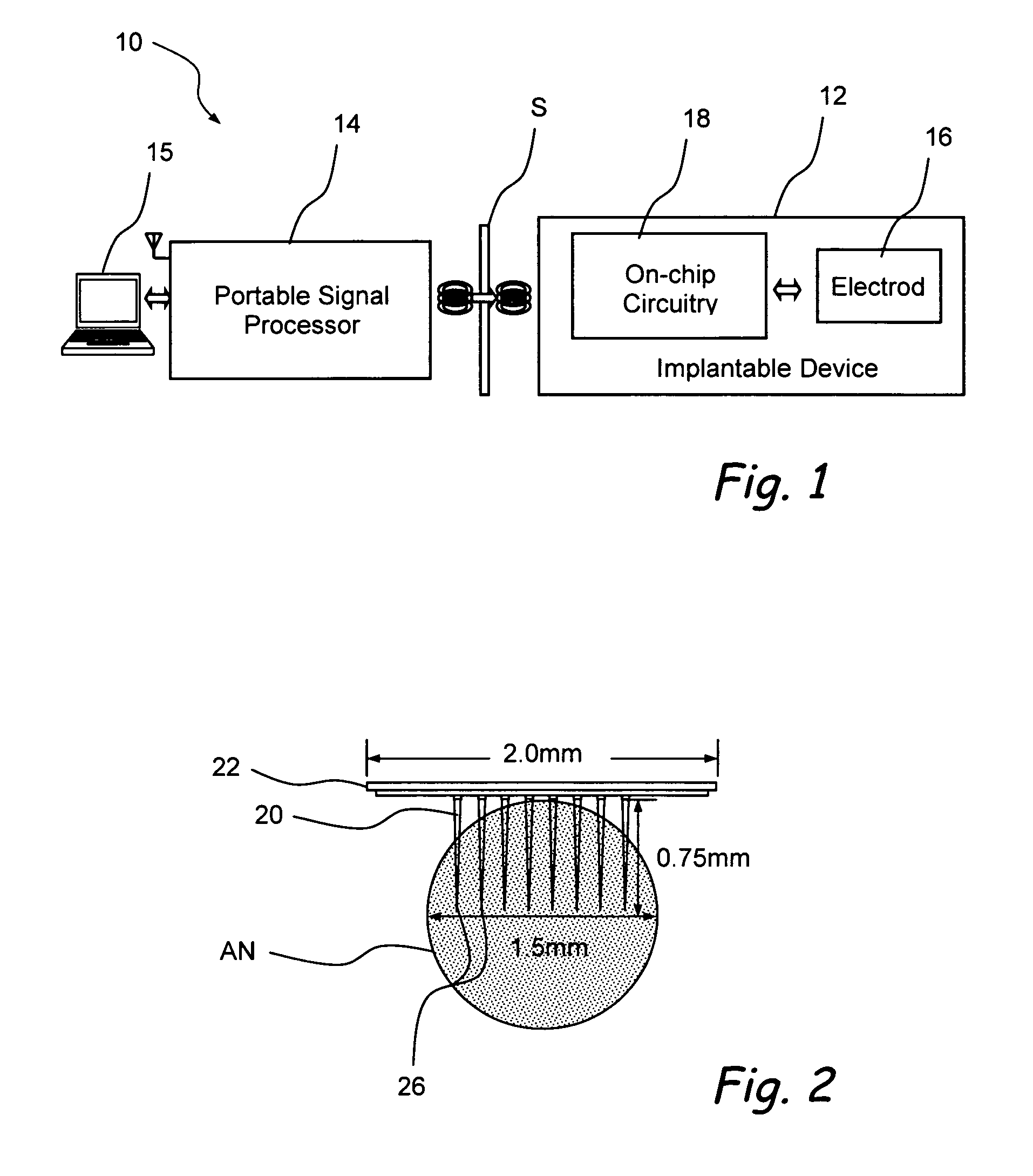
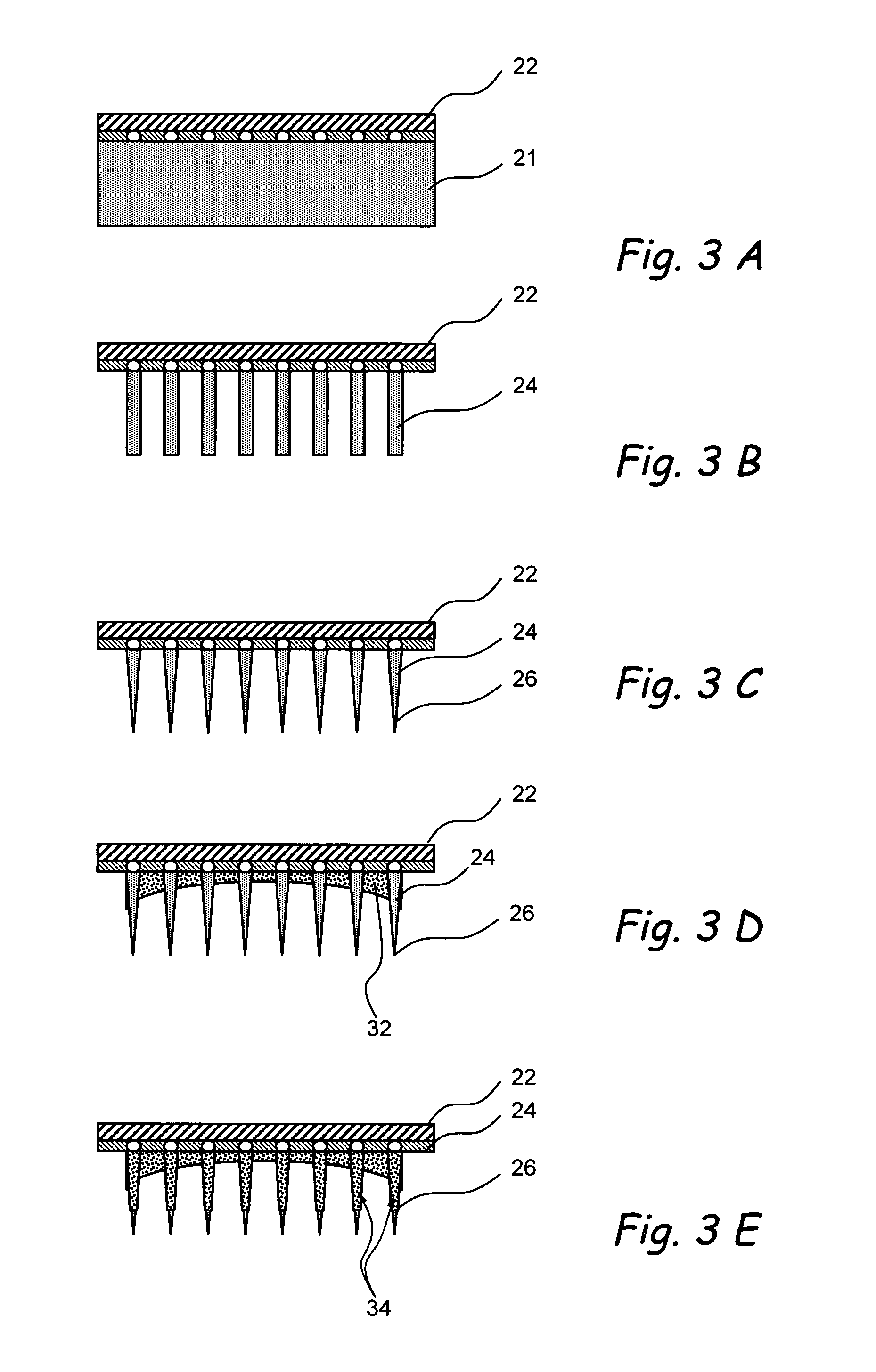
High density micromachined electrode arrays useable for auditory nerve implants and related methods
ActiveUS7991475B1Heat dissipationPrecise positioningHead electrodesSensorsImplantable ElectrodesHigh density
Devices, systems and methods that comprise or utilize implantable electrode arrays for neural stimulation and / or sensing. In some embodiments, the electrode array is implanted or inserted into the auditory nerve and is used to deliver electrical impulses to / receive data from the auditory nerve in the treatment of hearing disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
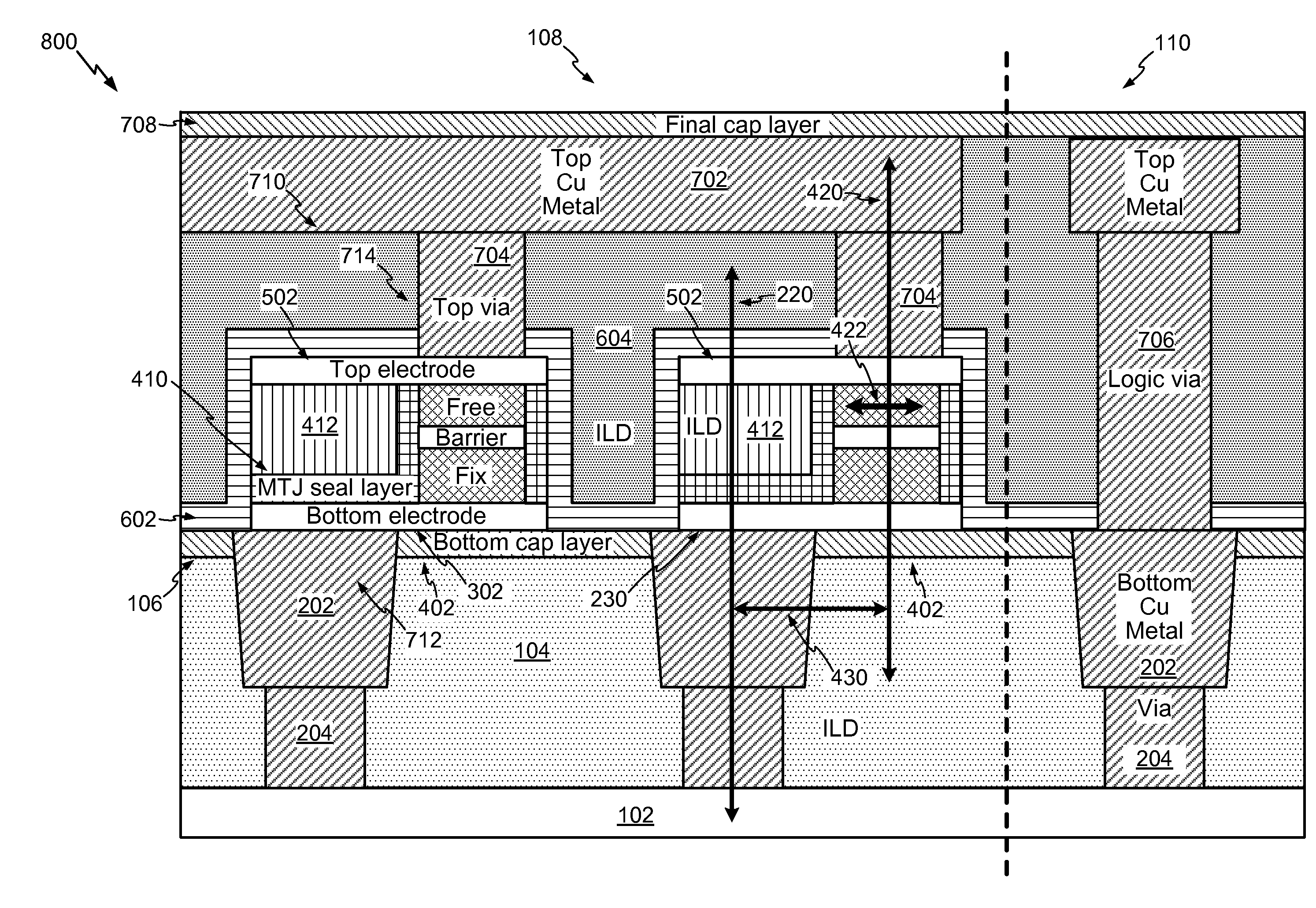
Magnetic Tunnel Junction Device and Fabrication
InactiveUS20100289098A1Eliminating surface roughness concernInhibition formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTunnel junctionCondensed matter physics
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device and fabrication method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a method is disclosed that includes forming a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device on a structure that includes a bottom cap layer and a bottom metal-filled trench having a normal axis, the magnetic tunnel junction device including a bottom electrode, magnetic tunnel junction layers, a magnetic tunnel junction seal layer, a top electrode, and a logic cap layer, the magnetic tunnel junction device having an MTJ axis that is offset from the normal axis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Surface planarization of thin silicon films during and after processing by the sequential lateral solidification method
InactiveUS6830993B1Reduce surface roughnessAvoid insufficient thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom frozen solutionsLight beamSurface roughness
Systems and methods for reducing a surface roughness of a polycrystalline or single crystal thin film produced by the sequential lateral solidification process are disclosed. In one arrangement, the system includes an excimer laser (110) for generating a plurality of excimer laser pulses of a predetermined fluence, an energy density modulator (120) for controllably modulating the fluence of the excimer laser pulses such that the fluence is below that which is required to completely melt the thin film, a beam homoginizer (144) for homoginizing modulated laser pulses in a predetermined plane, a sample stage (170) for receiving homoginized laser pulses to effect melting of portions of the polycrystalline or single crystal thin film corresponding to the laser pulses, translating means for controllably translating a relative position of the sample stage (170) with respect to the laser pulses, and a computer (110) for coordinating the excimer pulse generation and fluence modulation with the relative positions of the sample stage (170) to thereby process the polycrystalline or single crystal thin film by sequential translation of the sample stage (170) relative to the laser pulses.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Planographic printing plate
InactiveUS20010041305A1High purityReduce surface roughnessPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsAnodizingSolubility
A planographic printing plate precursor comprising: an aluminum substrate which has been subjected to a roughening treatment and an anodizing treatment; and a photosensitive layer which provided on a surface of said substrate, and which contains an infrared absorbing agent and a water-insoluble and alkali aqueous solution-soluble polymer compound, and whose solubility in an alkali developing solution varies by infrared laser exposure, wherein said substrate is obtained by electrochemically roughening an aluminum alloy plate which contains a trace amount of certain elements to an aluminum alloy of high purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Compositions and methods to fabricate a photoactive substrate suitable for shaped glass structures
ActiveUS20080248250A1Decrease in overall micropost diameterHigh-precision structureLayered productsDecorative surface effectsPhotosensitive glassGlass structure
This invention provides an inexpensive and rapid method for fabricating a high-anisotropic-etch ratio, shaped glass structures using a novel photosensitive glass composition. Structures of the photosensitive glass may include micro-channels, micro-optics, microposts, or arrays of hollow micro-needles. Furthermore, such shaped glass structures can be used to form a negative mold for casting the shape in other materials.
Owner:3D GLASS SOLUTIONS INC
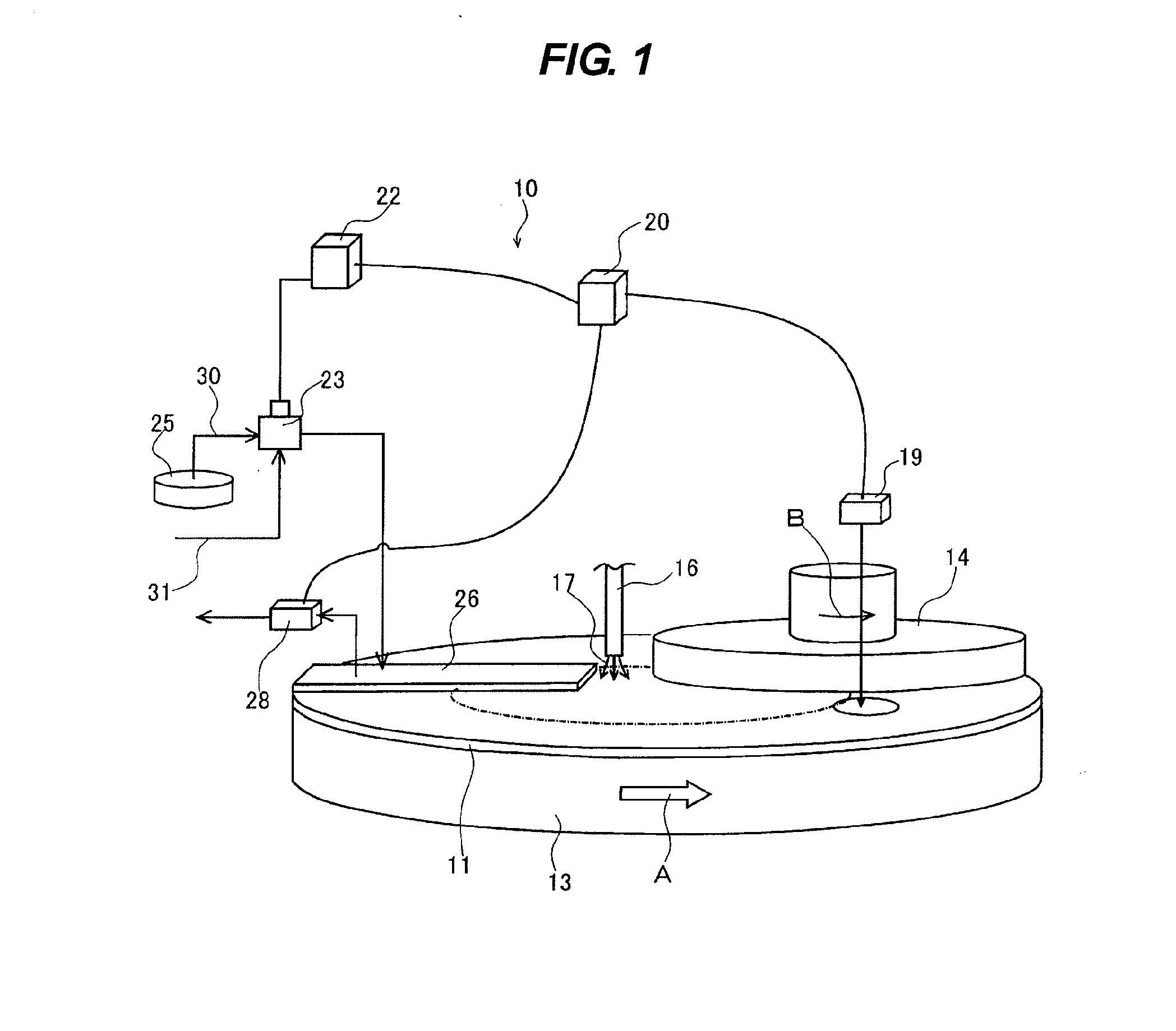
Substrate polishing apparatus, substrate polishing method, and apparatus for regulating temperature of polishing surface of polishing pad used in polishing apparatus
ActiveUS20110159782A1Polishing rate can be optimizedShorten polishing timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesTemperature controlEngineering
Owner:EBARA CORP
High density data storage medium
InactiveUS20050047307A1Low viscosityReduced dimensionElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsData bitsTip position
A data storage medium from which information is reproduced by scanning a surface of the medium with a probe-based tip, such as an Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) tip positioned in contact therewith. The medium comprises a substrate; and a polymer recording surface within which data bit values are determined by the topographical state at the bit location. The polymer contains thermally reversible crosslinkages. The data bit value is a function of the depth of the pit at the bit location.
Owner:IBM CORP
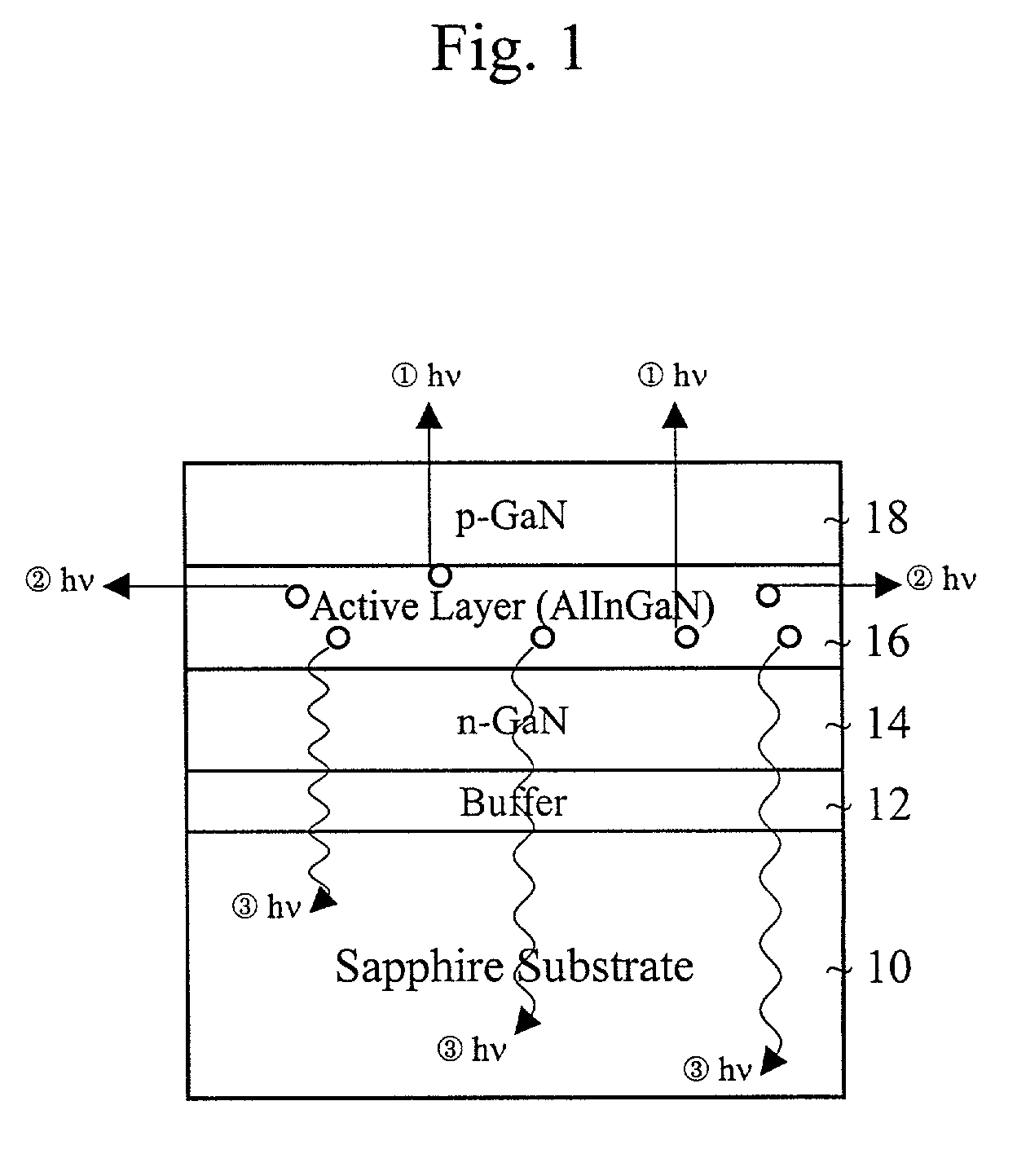
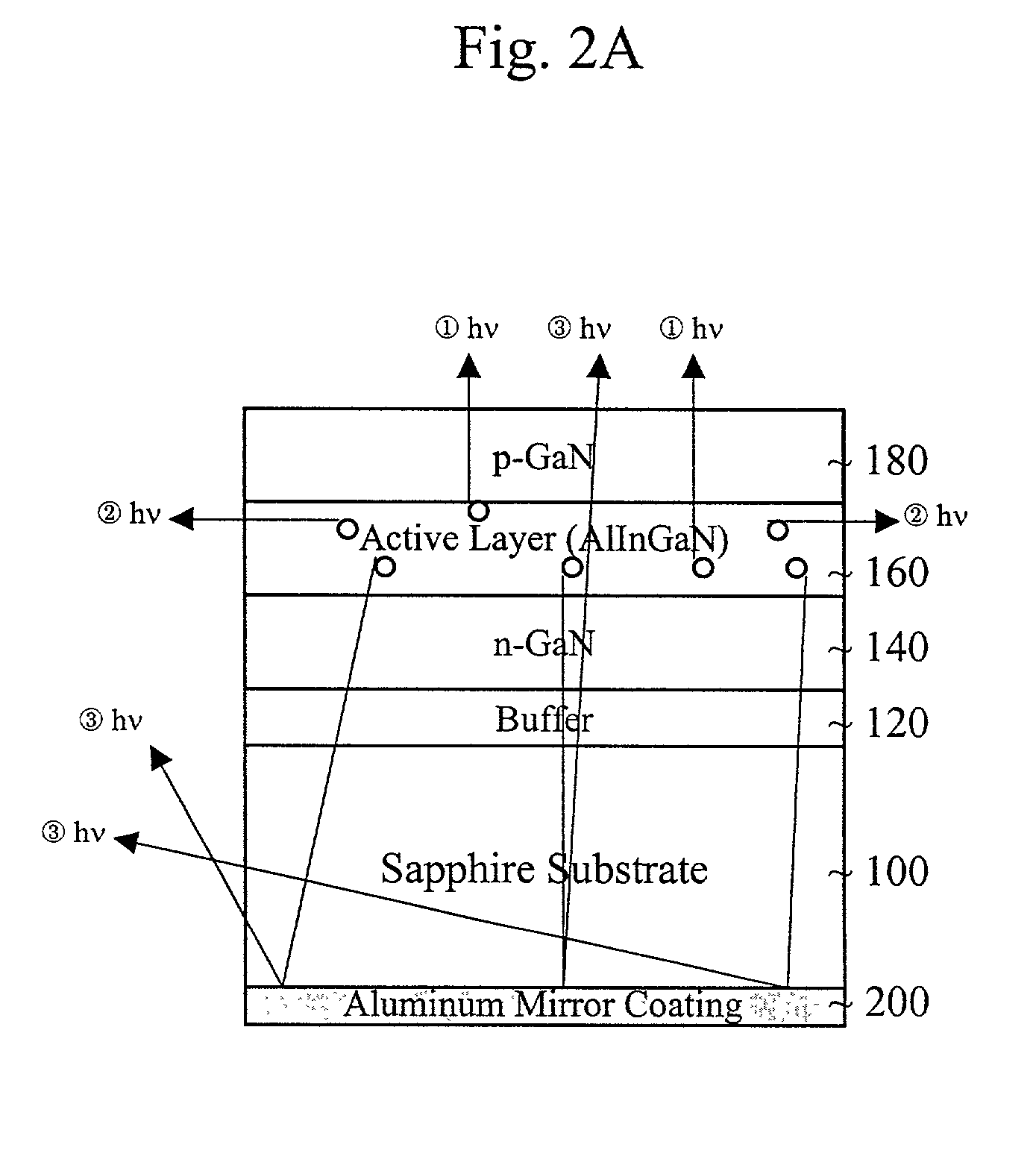
Diode having high brightness and method thereof
InactiveUS7067849B2Increase brightnessReduce thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesReflective layerActive layer
A light emitting diode includes a transparent substrate and a GaN buffer layer on the transparent substrate. An n-GaN layer is formed on the buffer layer. An active layer is formed on the n-GaN layer. A p-GaN layer is formed on the active layer. A p-electrode is formed on the p-GaN layer and an n-electrode is formed on the n-GaN layer. A reflective layer is formed on a second side of the transparent substrate. Also, a cladding layer of AlGaN is between the p-GaN layer and the active layer.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD +1
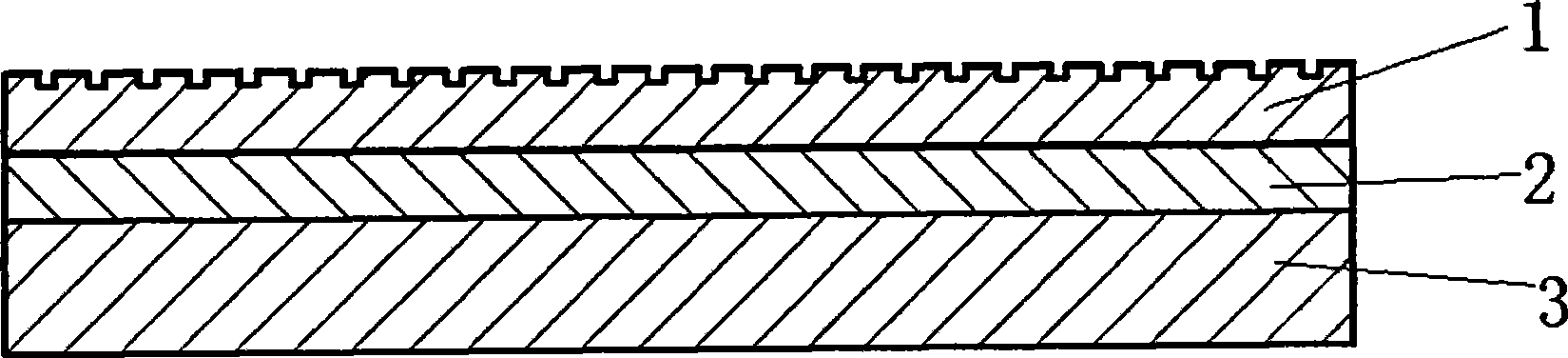
Fixed abrasive grinding polishing pad and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101428404AImprove flatnessPlay a cutting roleAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesReactive diluentEngineering
The invention provides a solidified abrading agent polishing pad and the preparation method thereof. The solidified abrading agent polishing pad comprises at least three layers, including an elastic layer (3), a rigid layer (2) and an abrading agent layer (1) sequentially arranged from the bottom layer to the top layer. The solidified abrading agent polishing pad is characterized in that the abrading agent layer (1) comprises the following components by the weight percentage: 1% to 40% of an abrading agent with the particle size being 1 nm to 40 Mum, 20% to 80% of polyacrylate prepolymer, 0.05% to 3% of free radical photoinitiator, 0% to 2% of poly-dimethylsiloxane / acrylic polymer, 0% to 20% of a performance adjusting addition agent, and 5% to 40% of esterified acrylic acid reactive diluent. The solidified abrading agent polishing pad which is prepared by the figure-transfer method has a series of advantages of stable grinding and polishing performance, high polishing efficiency, high surface texture of processed workpieces, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com