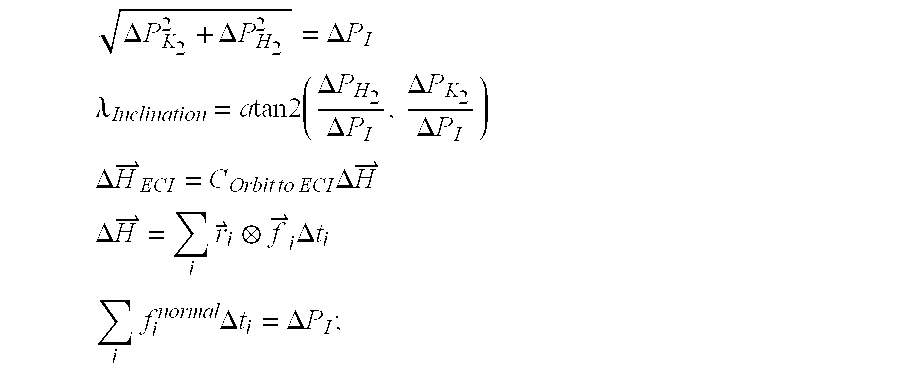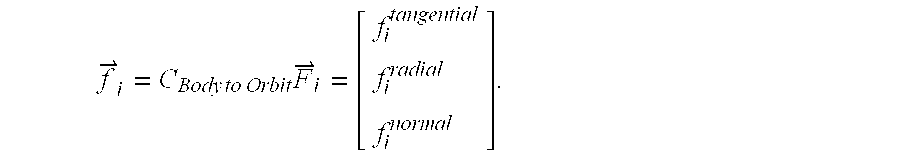Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138results about How to "Budget is reduced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
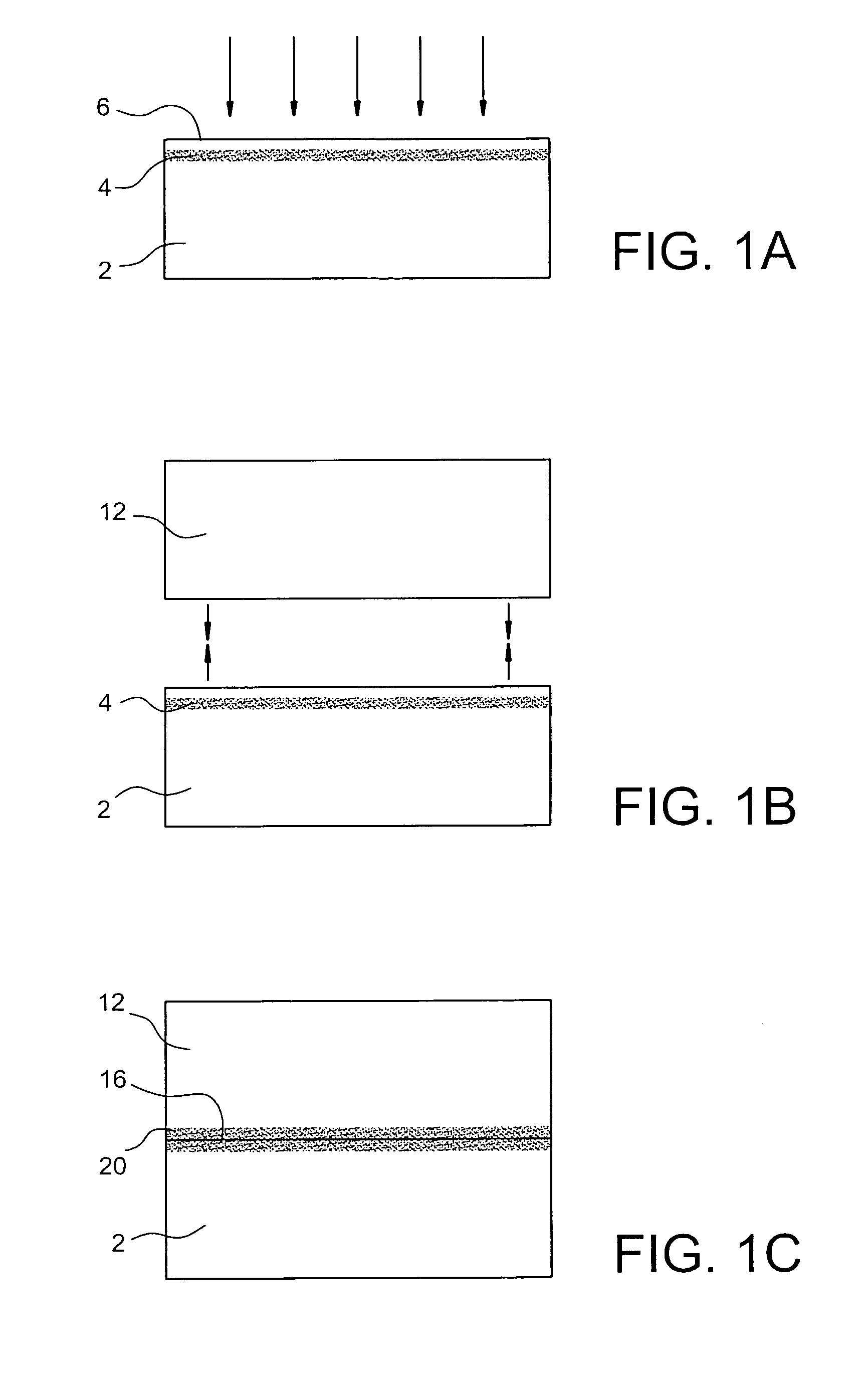
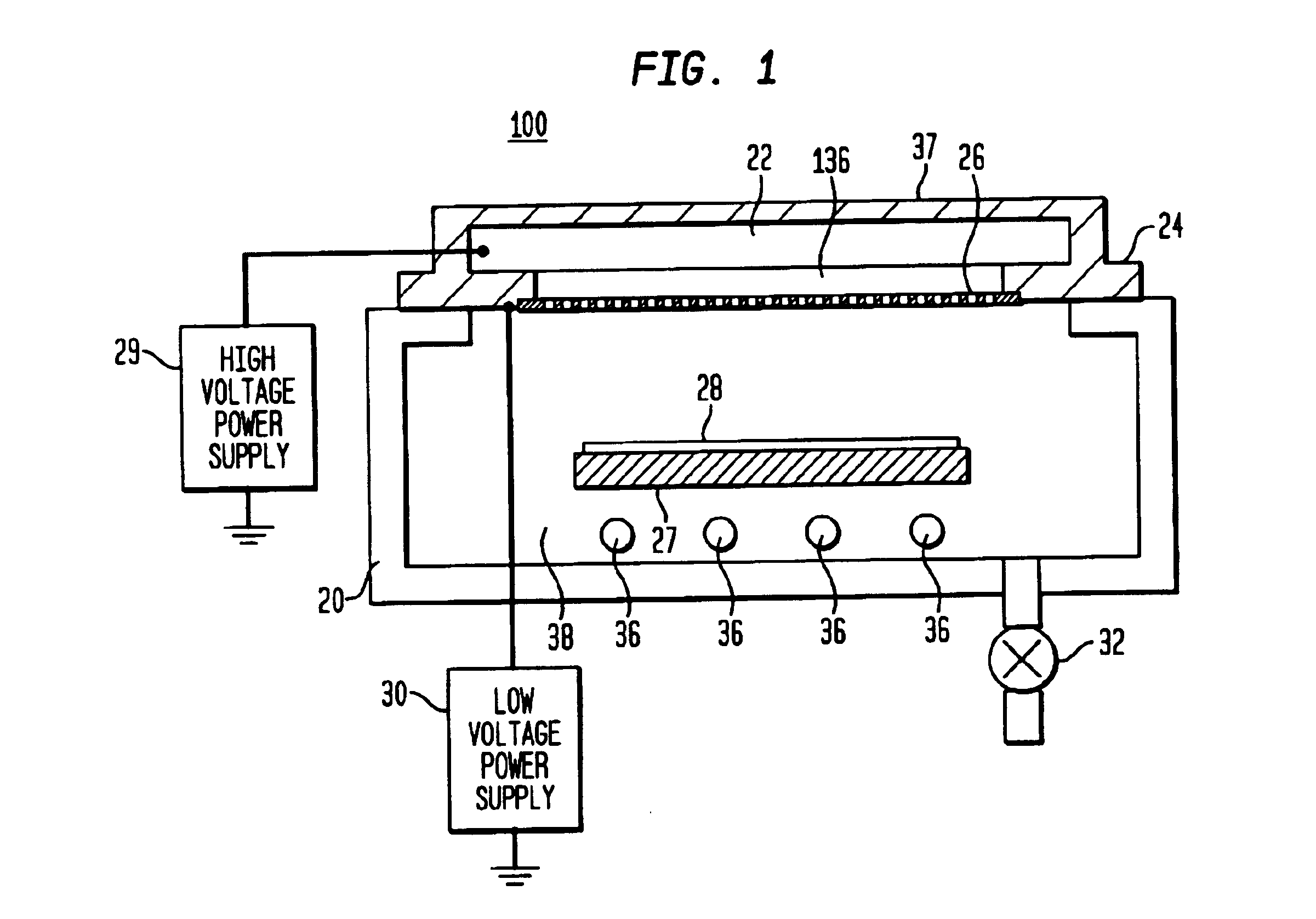
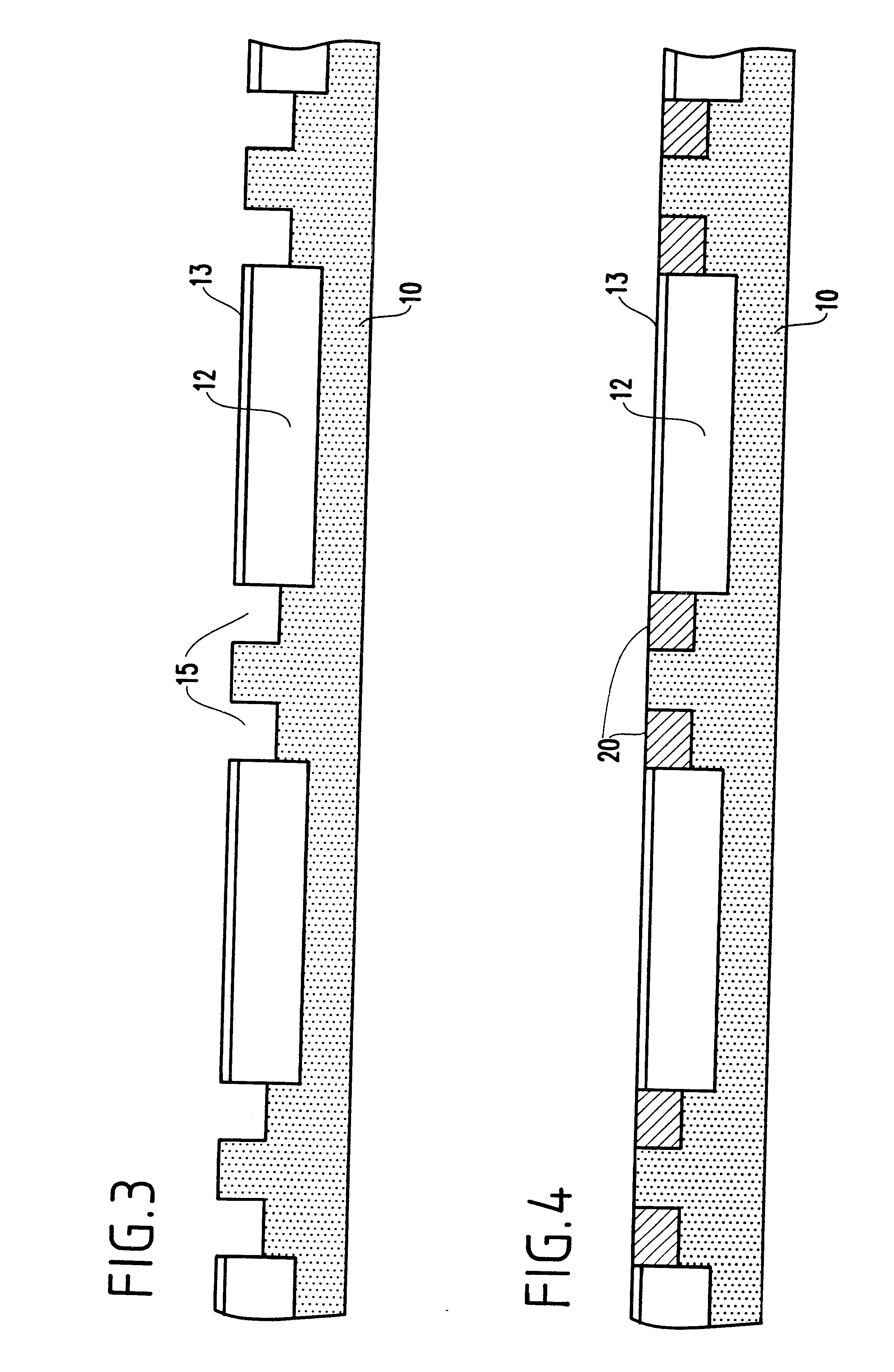
Method for transferring a thin film comprising a step of generating inclusions
InactiveUS6756286B1Reduce surface roughnessBudget is reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid massFracture plane
A process for transfer of at least one thin film of solid material delimited in an initial substrate. The process includes a step in which a layer of inclusions is formed in the initial substrate at a depth corresponding to the required thickness of the thin film. These inclusions are designed to form traps for gaseous compounds which subsequently are implanted. In a subsequent step gaseous compounds are implanted in a manner to convey the gaseous compounds into the layer of inclusions. The dose of implanted gaseous compounds is made sufficient to cause the formation of micro-cavities to form a fracture plane along which the thin film can be separated from the remainder of the substrate.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
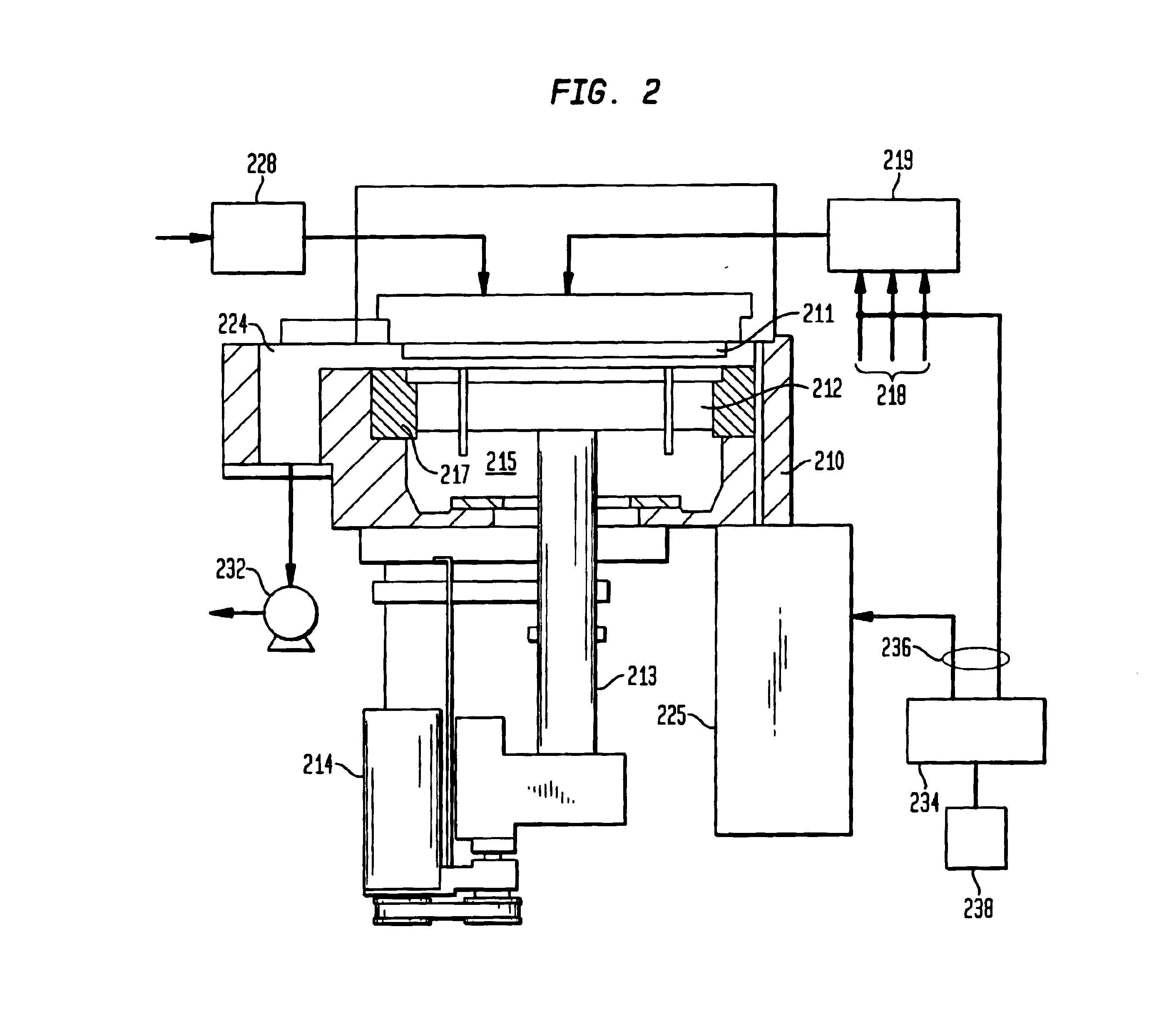
Method of sealing two plates with the formation of an ohmic contact therebetween
InactiveUS20070072391A1Reduce depthBudget is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
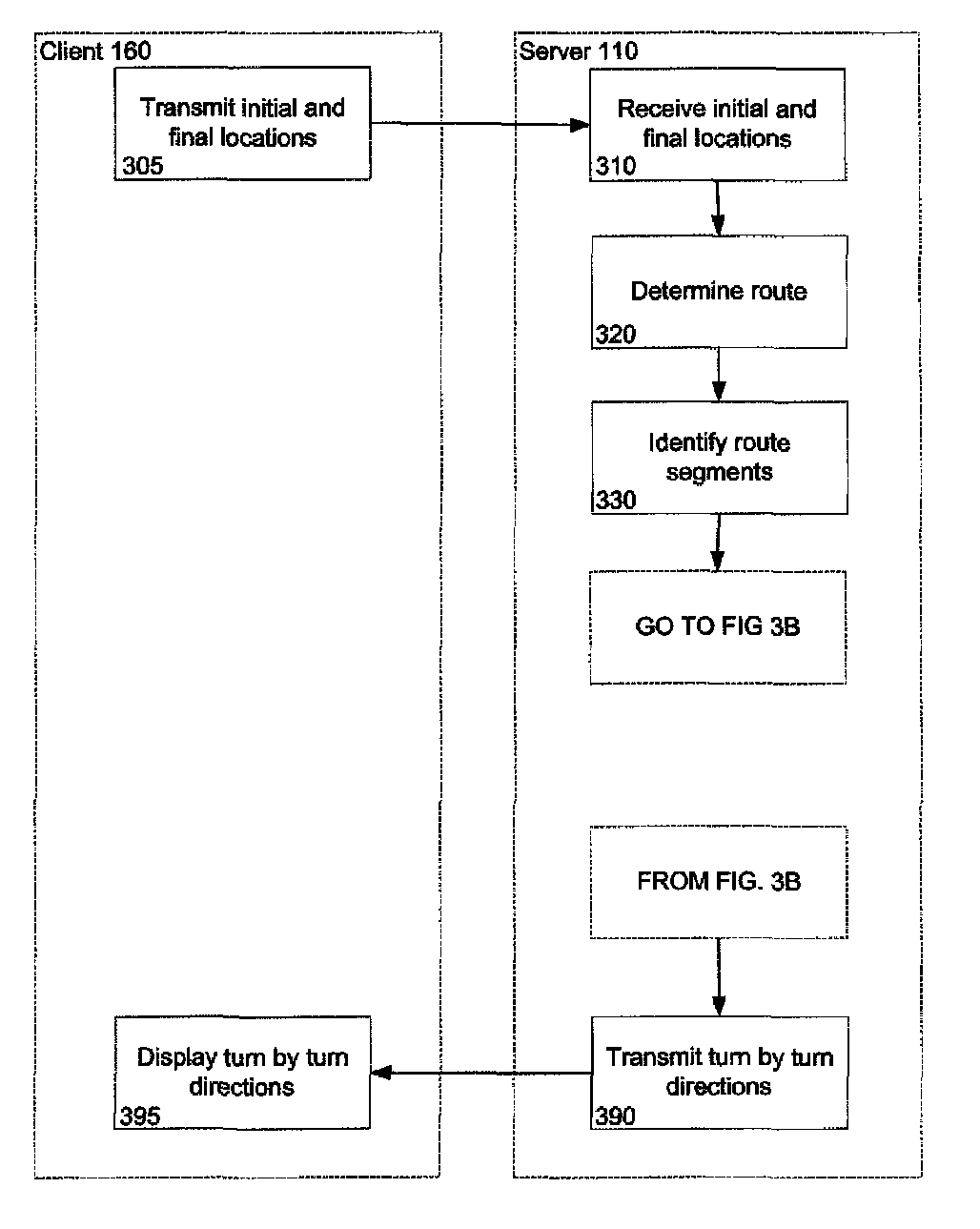
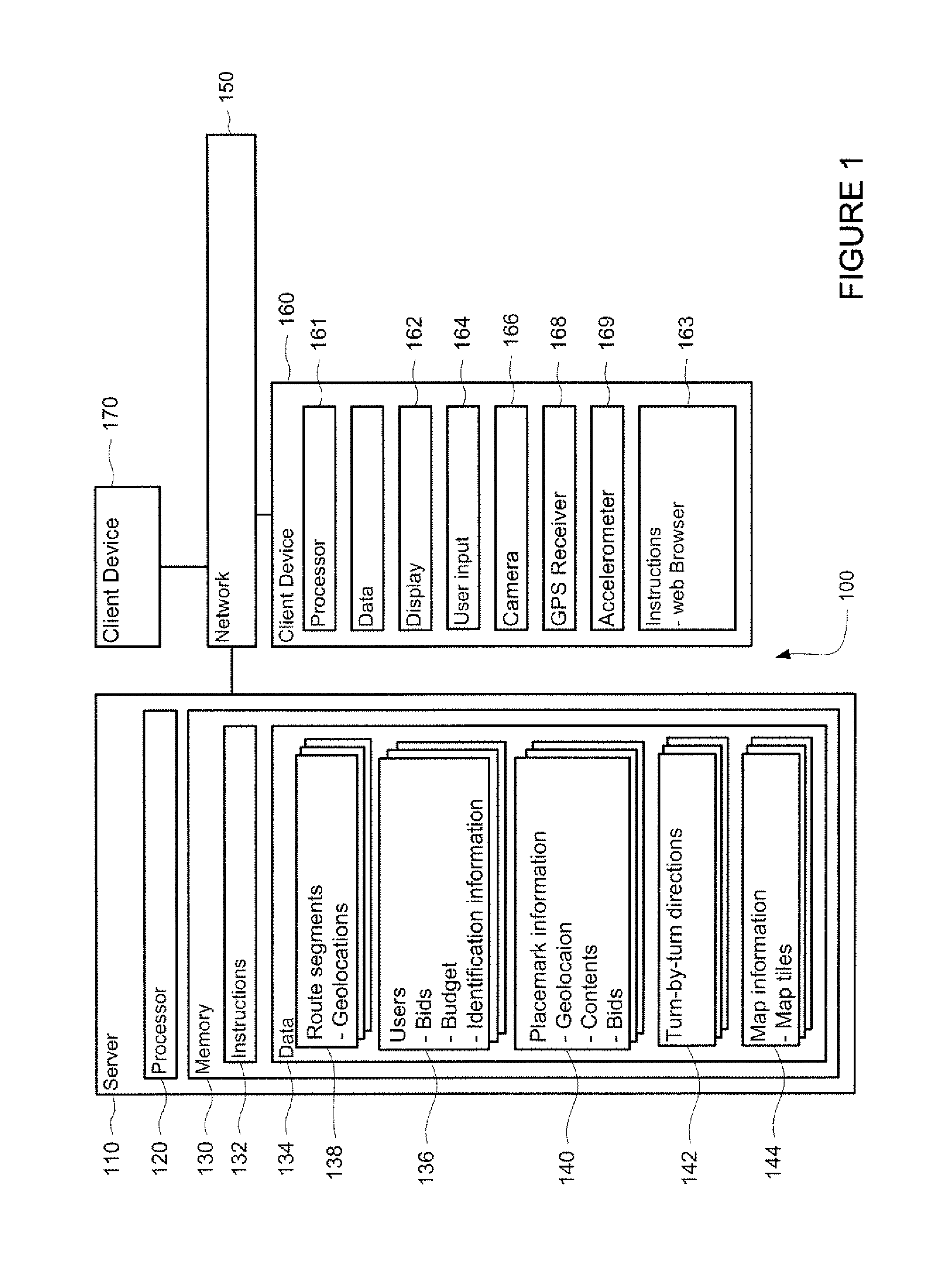
Placemarked based navigation and ad auction based on placemarks
ActiveUS8489326B1Budget is reducedInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsGeographic siteGeolocation
A system and method provides turn-by-turn directions including placemarks. Each placemark represents a geographically located object such as a business or landmark. A client device may transmit an initial and a final location. Upon receipt of the locations, a server may determine a route comprised of a plurality of route segments. For each route segment associated with one or more placemark, the server may conduct an auction to choose one of the placemarks. The server may receive a plurality of bids associated with a particular route segment. Each bid is associated with a particular placemark. The server selects the placemark by determining a highest bid or other auction criteria. The selected placemark is associated with the route segment and is used to generate a turn-by-turn direction for the route segment, where information associated with the placemark is displayed on a client device.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Transistor with dopant-bearing metal in source and drain
ActiveUS6921691B1Budget is reducedQuality improvementTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGate dielectric
A transistor and method of manufacturing thereof. A gate dielectric and gate are formed over a workpiece, and the source and drain regions of a transistor are recessed. The recesses are filled with a dopant-bearing metal, and a low-temperature anneal process is used to form doped regions within the workpiece adjacent the dopant-bearing metal regions. A transistor having a small effective oxide thickness and a well-controlled junction depth is formed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
System and method for enabling consumers to add personal charitable contributions and transfer the right to designate a beneficiary to other consumers
InactiveUS20060122856A1Powerful voice in corporate governanceDecrease and divert advertisingFundraising managementPaymentWeb site
A method for enabling registered consumers to direct matching charitable contributions donated by a plurality of program partners to a plurality of designated beneficiaries through a directed giving service provider based on consumer purchases during a predetermined purchase period. The method also enables registered consumers to donate their own funds, and to transfer their direction rights to at least one other consumer and / or consumer account. Program partners can include individual retail stores, retail store chains, credit providers and product manufacturers conducting business either at a physical location, by telephone, direct mail, or online via a web site, etc. The directing rights generated by purchases of qualified products for all registered consumers are aggregated by the directed giving service provider and individual estimates of amounts to be directed to designated beneficiaries are provided to individual consumers to enable them to allocate contribution percentages to each selected beneficiary. A directed giving service provider or charitable foundation receives funds from the program partners on a regular basis and sends those funds to the beneficiaries chosen by the consumers on a regular basis. The directed giving service provider establishes standards for beneficiary qualification and works to ensure that payments are made only to those beneficiaries meeting such standards.
Owner:THE BENEVOLINK CORP
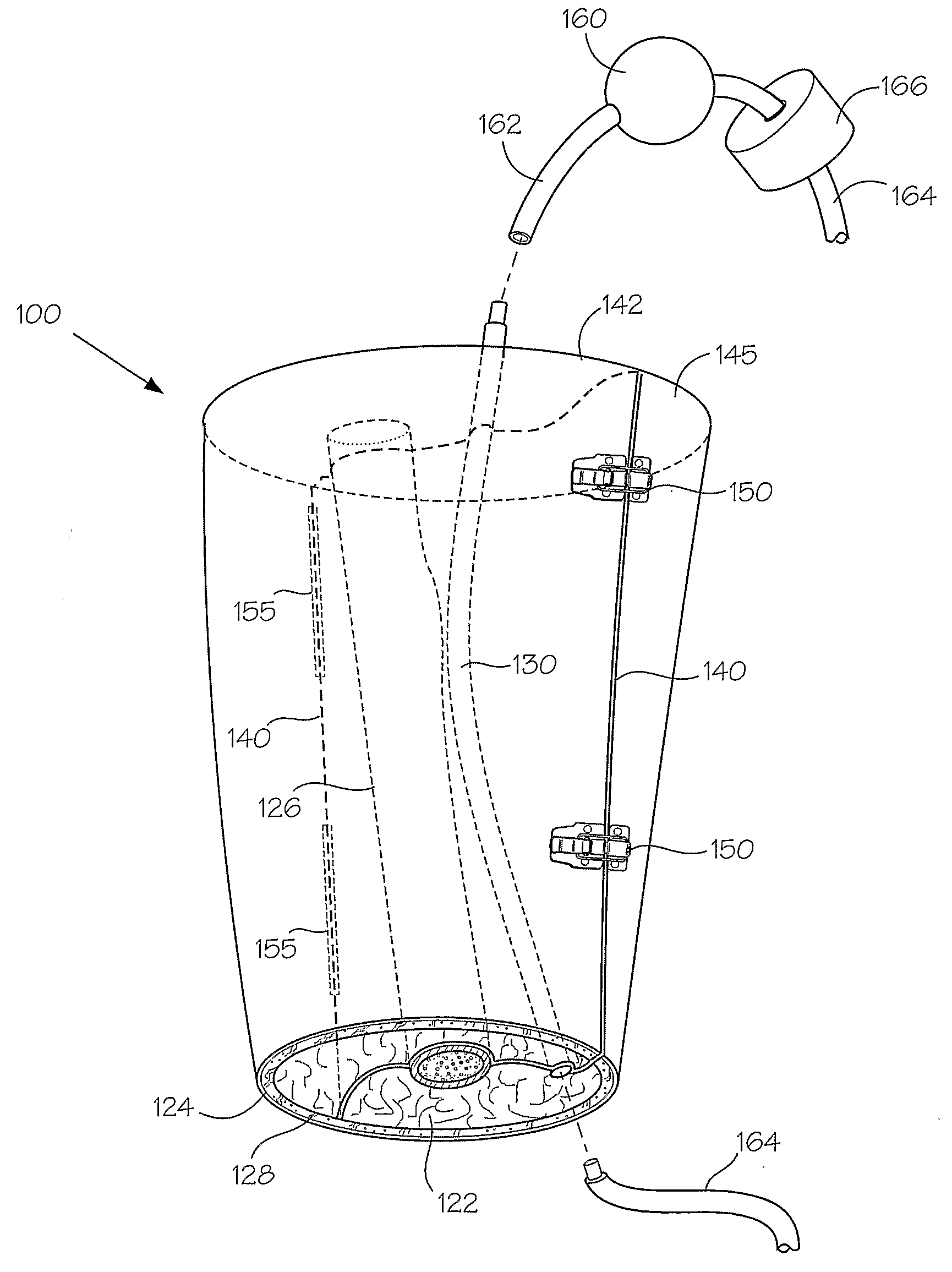
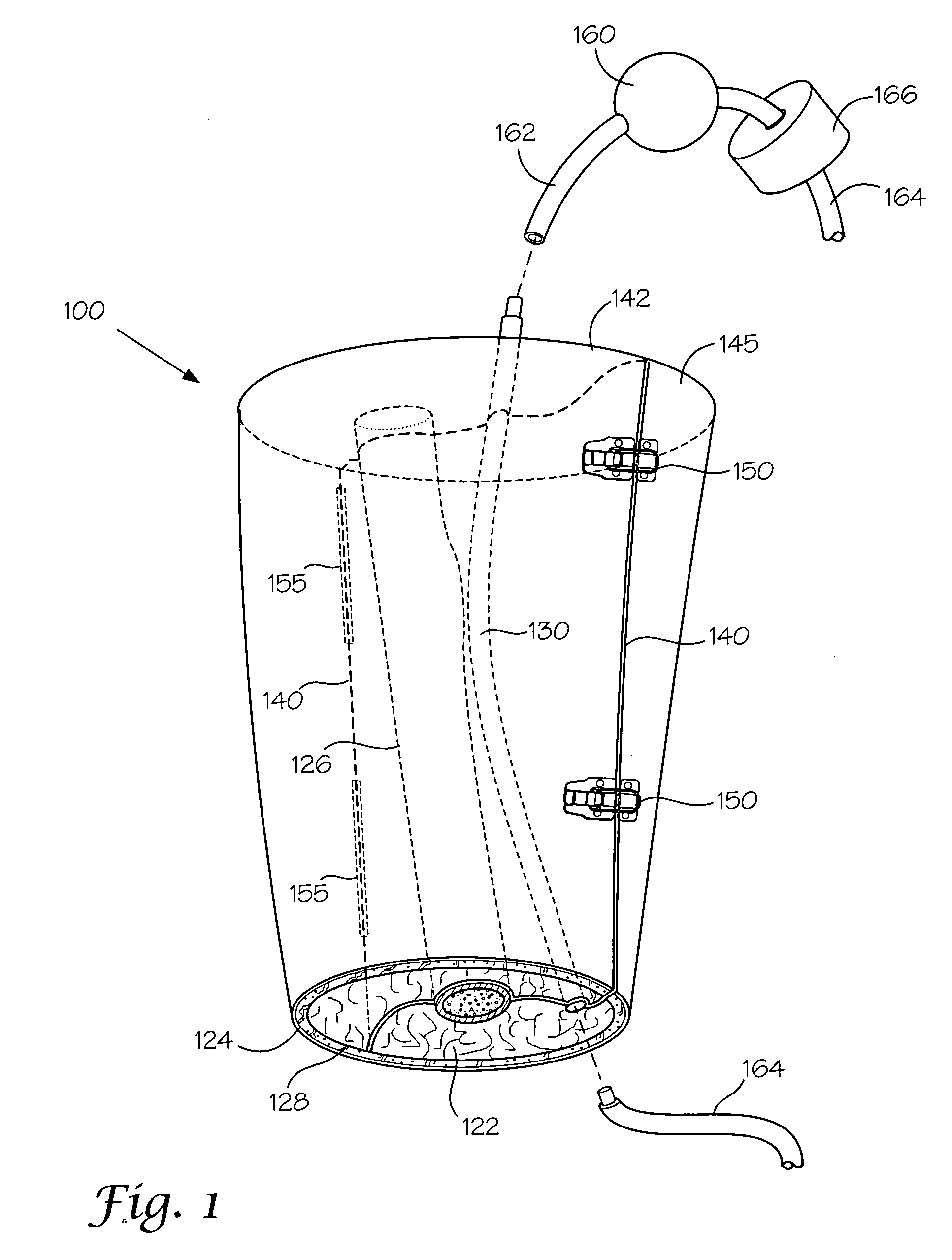
Models And Methods Of Using Same For Testing Medical Devices
ActiveUS20080187895A1Avoid product qualityIncreased development costAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsHuman bodyAnatomical structures
Disclosed herein are synthetic anatomical models that are designed to enable simulated use testing by medical device compam'es, medical device designers, individual inventors, or any other entity interested in the performance of medical devices. These models are unique in possessing a level of complexity that allows them to be substituted for either a live animal, an animal cadaver, or a human cadaver in the testing of these devices. These models are further characterized by a similarity of geometry, individual component physical properties, and component-to-component interfacial properties with the appropriate target tissue and anatomy.
Owner:SAKEZLES CHRISTOPHER
Semiconductor-dielectric-semiconductor device structure fabricated by wafer bonding
InactiveUS20060035450A1Easy to controlEnsure qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricWafer dicing
A method of forming a gate stack for semiconductor electronic devices utilizing wafer bonding of at least one structure containing a high-k dielectric material is provided. The method of the present invention includes a step of first selecting a first and second structure having a major surface respectively. In accordance with the present invention, at least one, or both, of the first and second structures includes at least a high-k dielectric material. Next, the major surfaces of the first and second structures are bonded together to provide a bonded structure containing at least the high-k dielectric material of a gate stack.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
Method to achieve higher track density by allowing only one-sided track encroachment
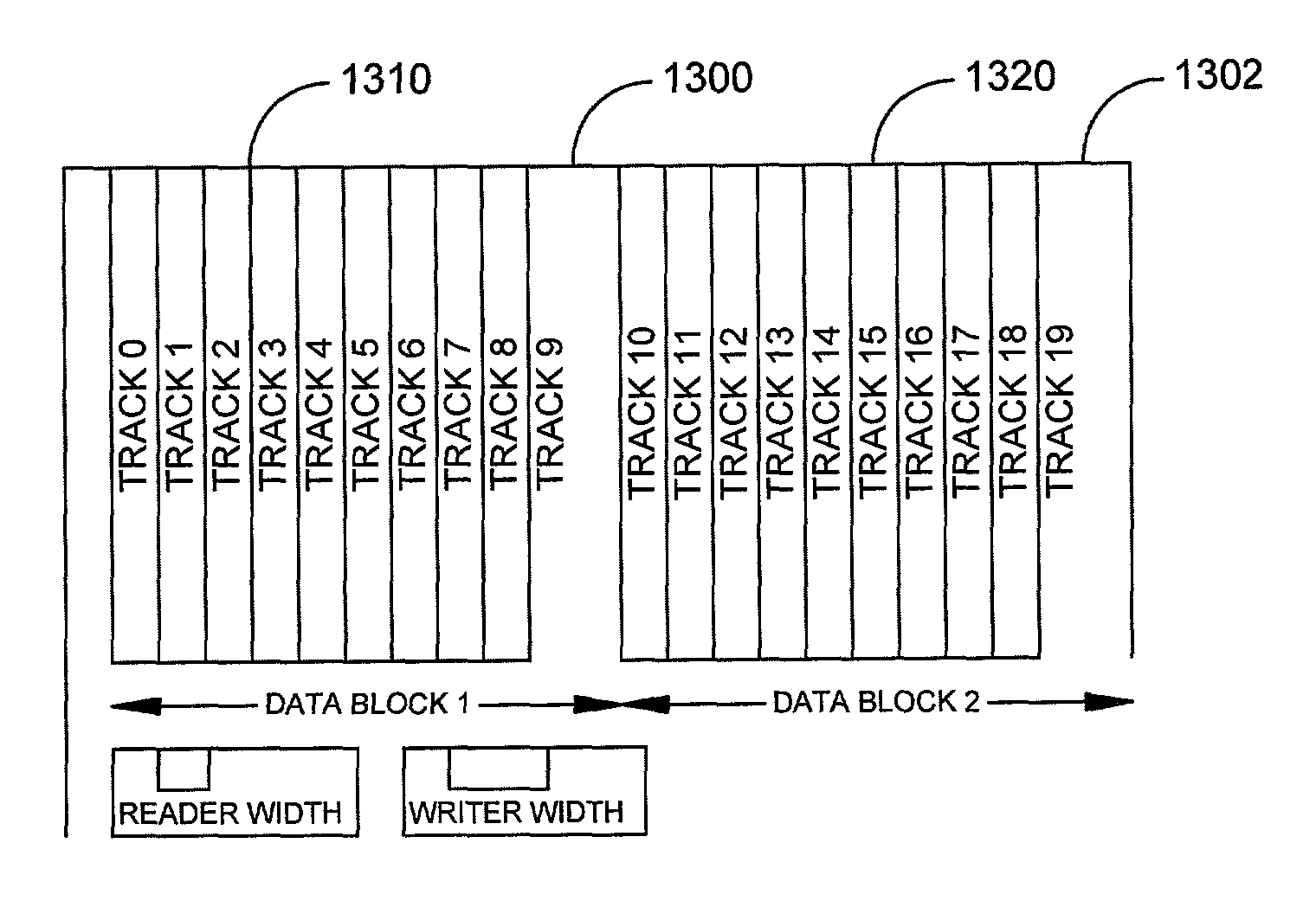
InactiveUS7082007B2Reduced and minimized amountAccurate informationFilamentary/web carriers operation controlTrack finding/aligningTrack densityTransducer
A disc drive includes a transducer having a separate element for writing information and a separate element for reading information to and from the disc. In a disc drive designated to read and write long sequential records, the track misregistration budget is reduced to account for previously written tracks not being encroached on one side. An initial track is written. Subsequent tracks are written after a seek in one direction. The subsequent track is written so that the initially written track is overwritten to one side and leaves a track having a width substantially equal to the width of the read element. Records can be written into data bands of a selected number of tracks. A guard band is left between groups of data bands so that data on tracks in subsequent data bands are not overwritten.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Methods and apparatus for E-beam treatment used to fabricate integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS6936551B2Improves property and performance of filmImprove mechanical propertiesPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTreatment use
One embodiment of the present invention is a method for fabricating a low-k dielectric film that includes steps of: (a) chemical vapor depositing a lower-k dielectric film; and (b) e-beam treating the lower-k dielectric film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
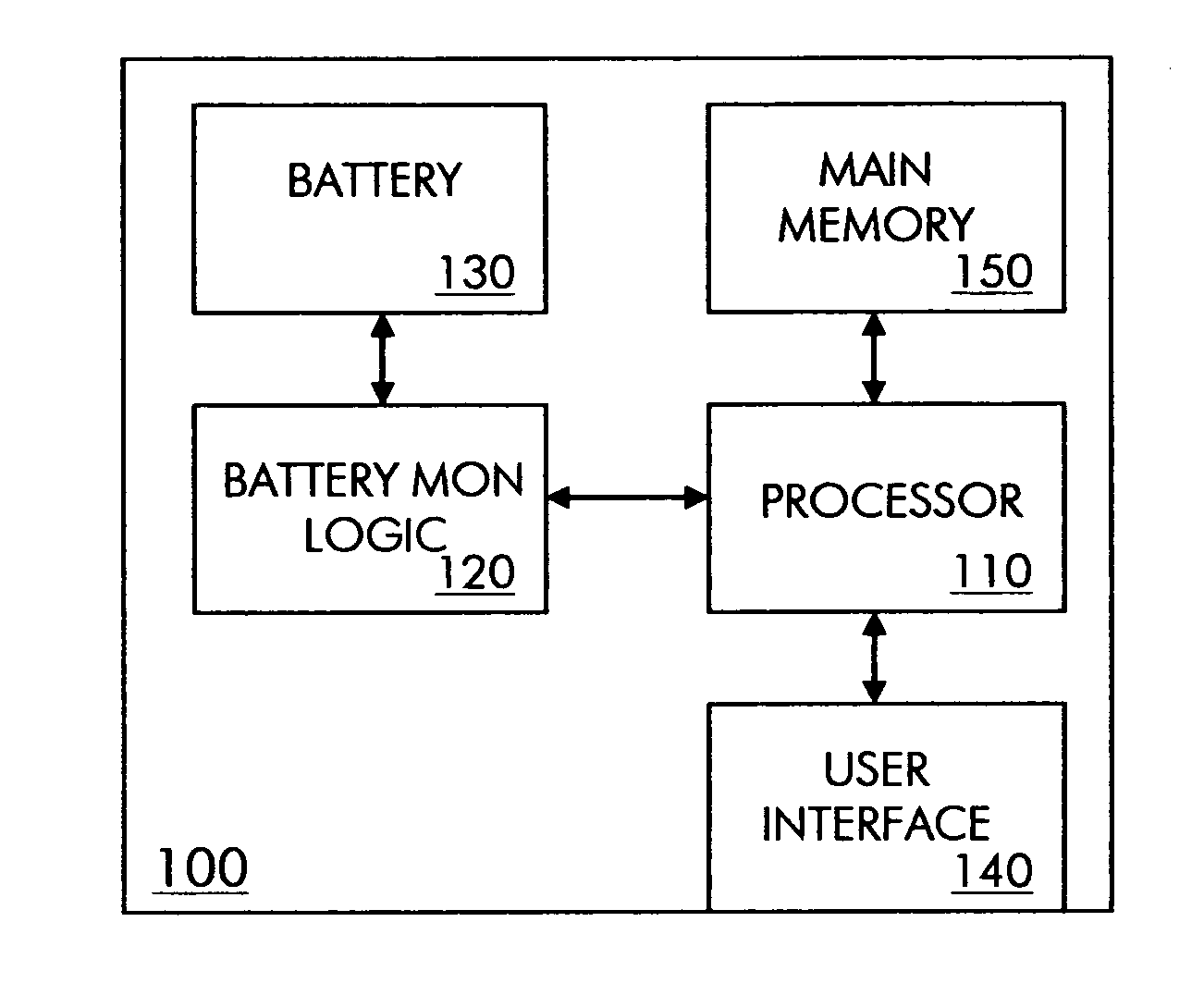
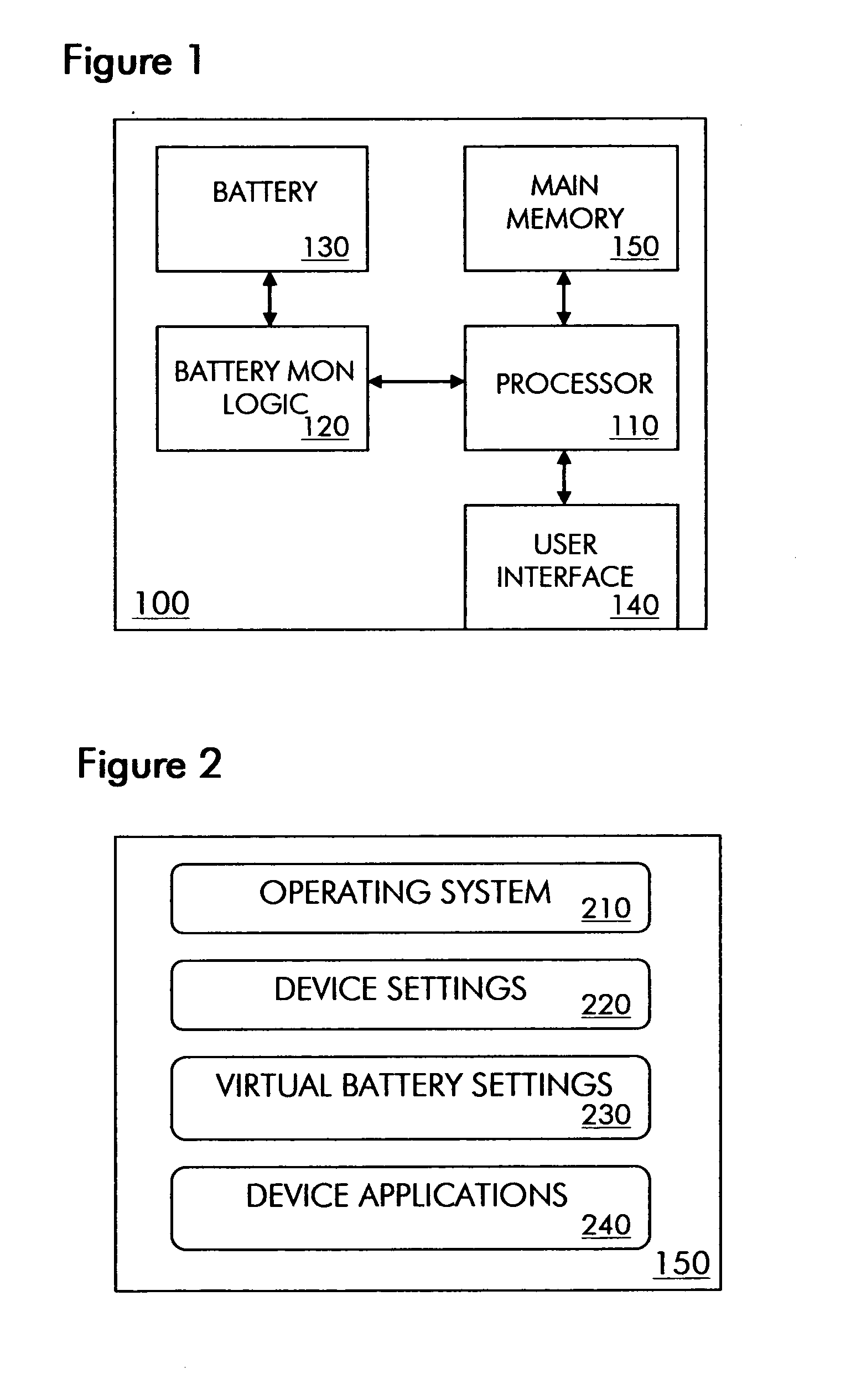
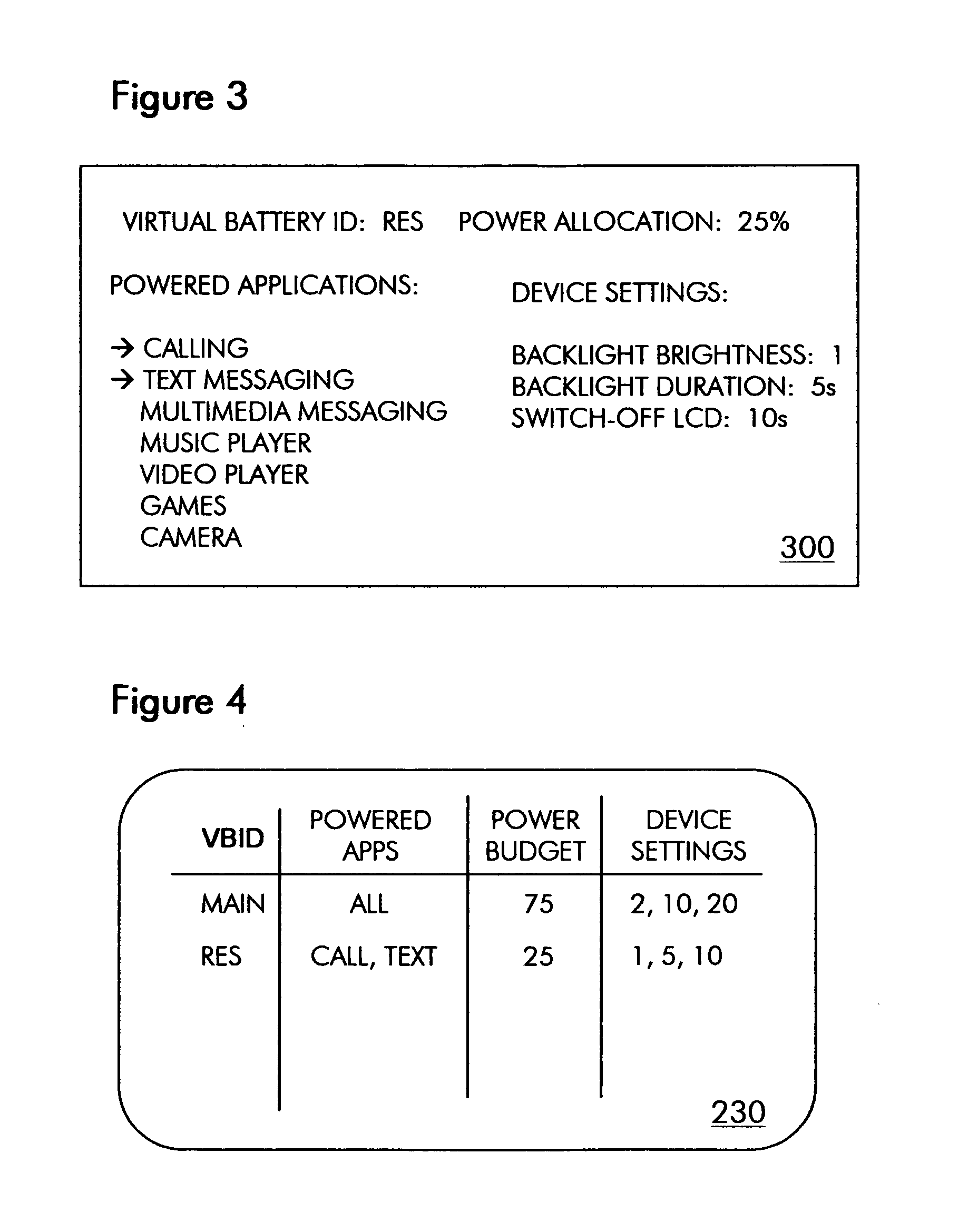
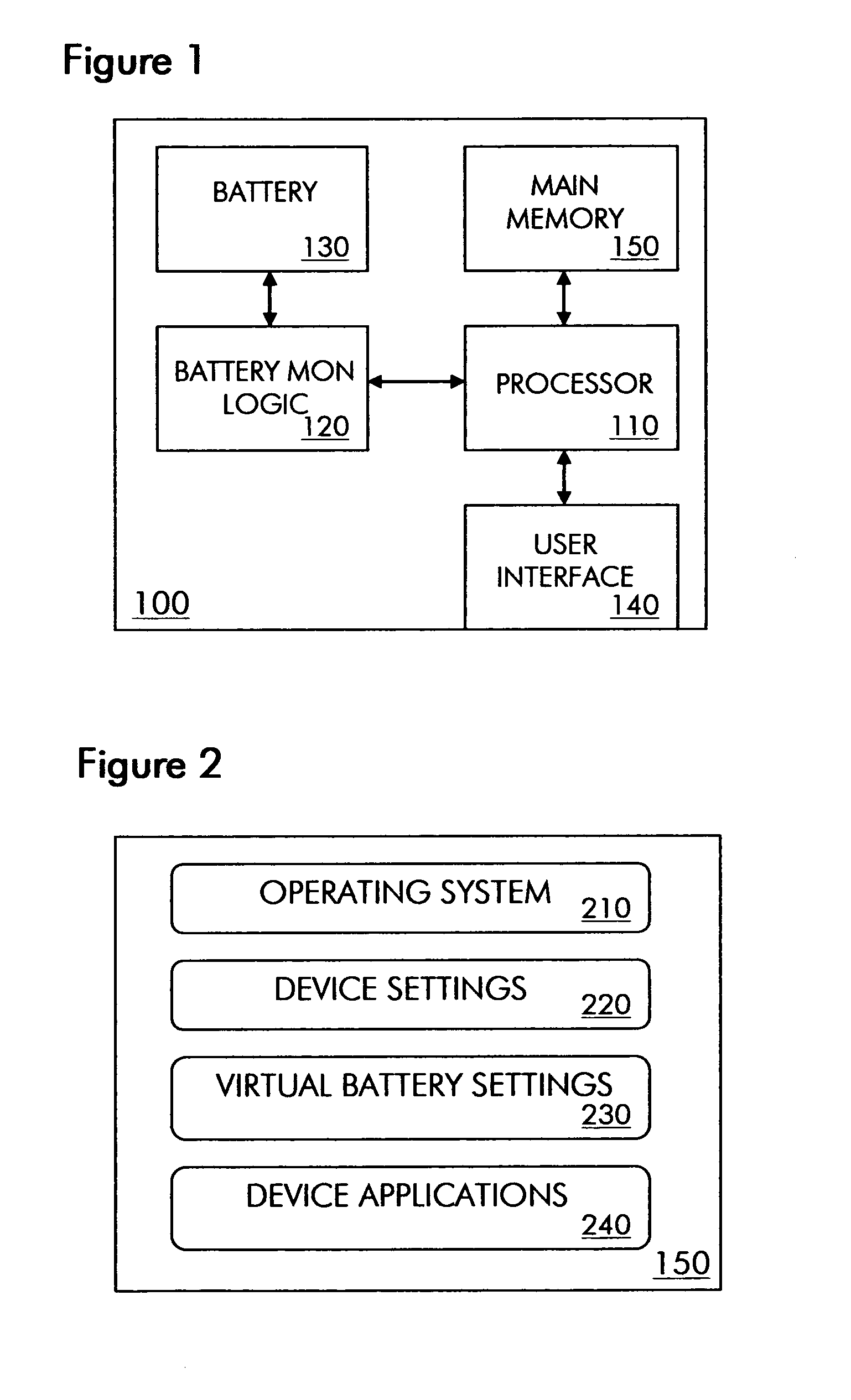
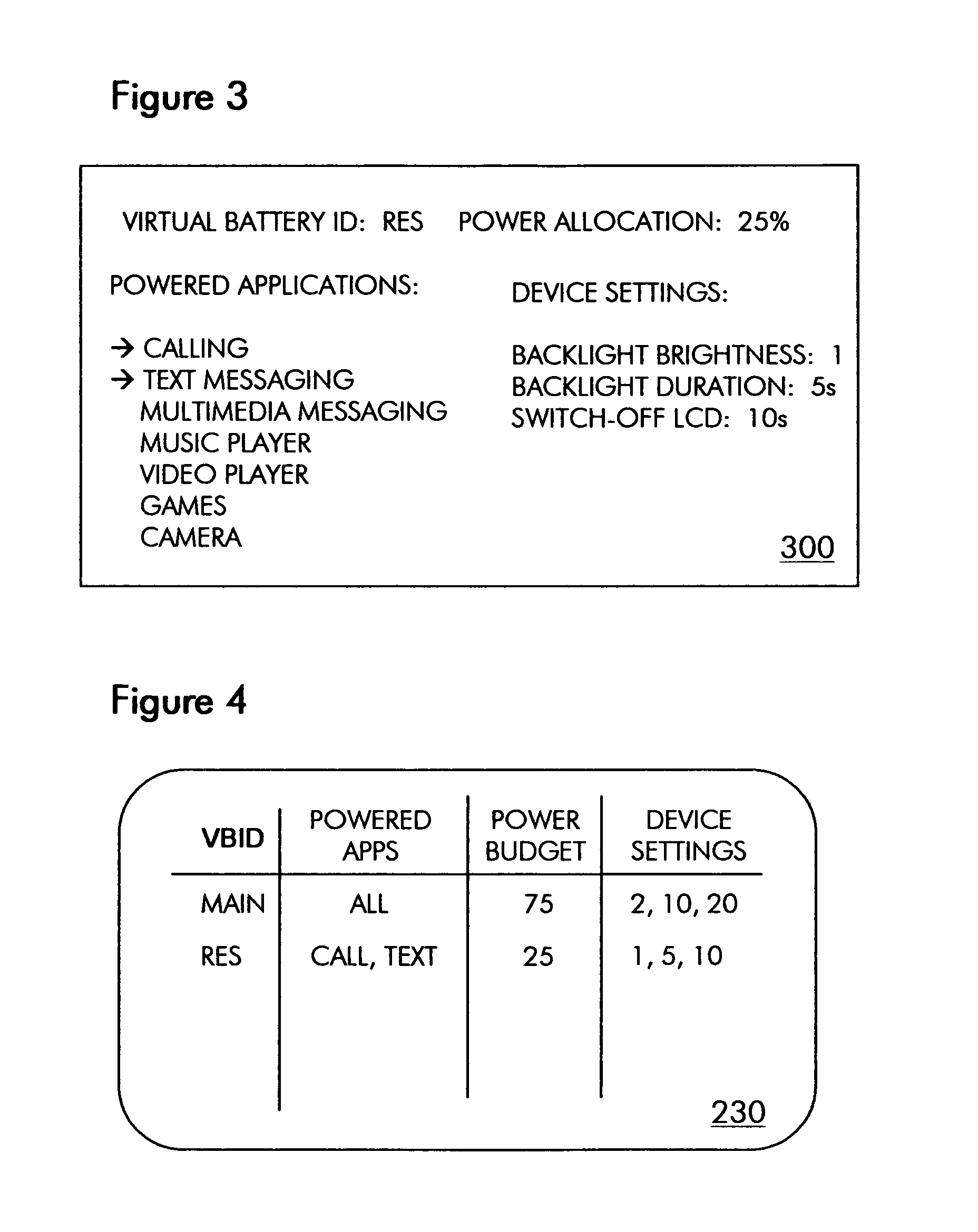
Virtual batteries for wireless communication device
ActiveUS20070243852A1Efficiently allocate powerReduce usageEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTelecommunicationsPower budget
The present invention provides virtual batteries for a wireless communication device. Generally speaking, a virtual battery is a logical construct on a wireless communication device that powers a defined set of wireless communication device applications and has a defined power budget from one or more physical batteries on the device. Through judicious assignment of wireless communication device applications and power budgets to virtual batteries, a user of a wireless communication device can efficiently allocate power among competing wireless communication device applications.
Owner:SHARP KK
Methods and apparatus for e-beam treatment used to fabricate integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS20050130404A1Improves property and performance of filmImprove mechanical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringTreatment use
One embodiment of the present invention is a method for fabricating a low-k dielectric film that included steps of: (a) chemical vapor depositing a lower-k dielectric film; and (b) e-beam treating the lower-k dielectric film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Novel semiconductor device and structure
ActiveUS20150340316A1Small footprintIncrease speedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A 3D device, including: a first layer including a first memory including a first transistor; and a second layer including a second memory including a second transistor; where the second transistor is self-aligned to the first transistor, and where the first transistor and the second transistor each being a junction-less transistor.
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
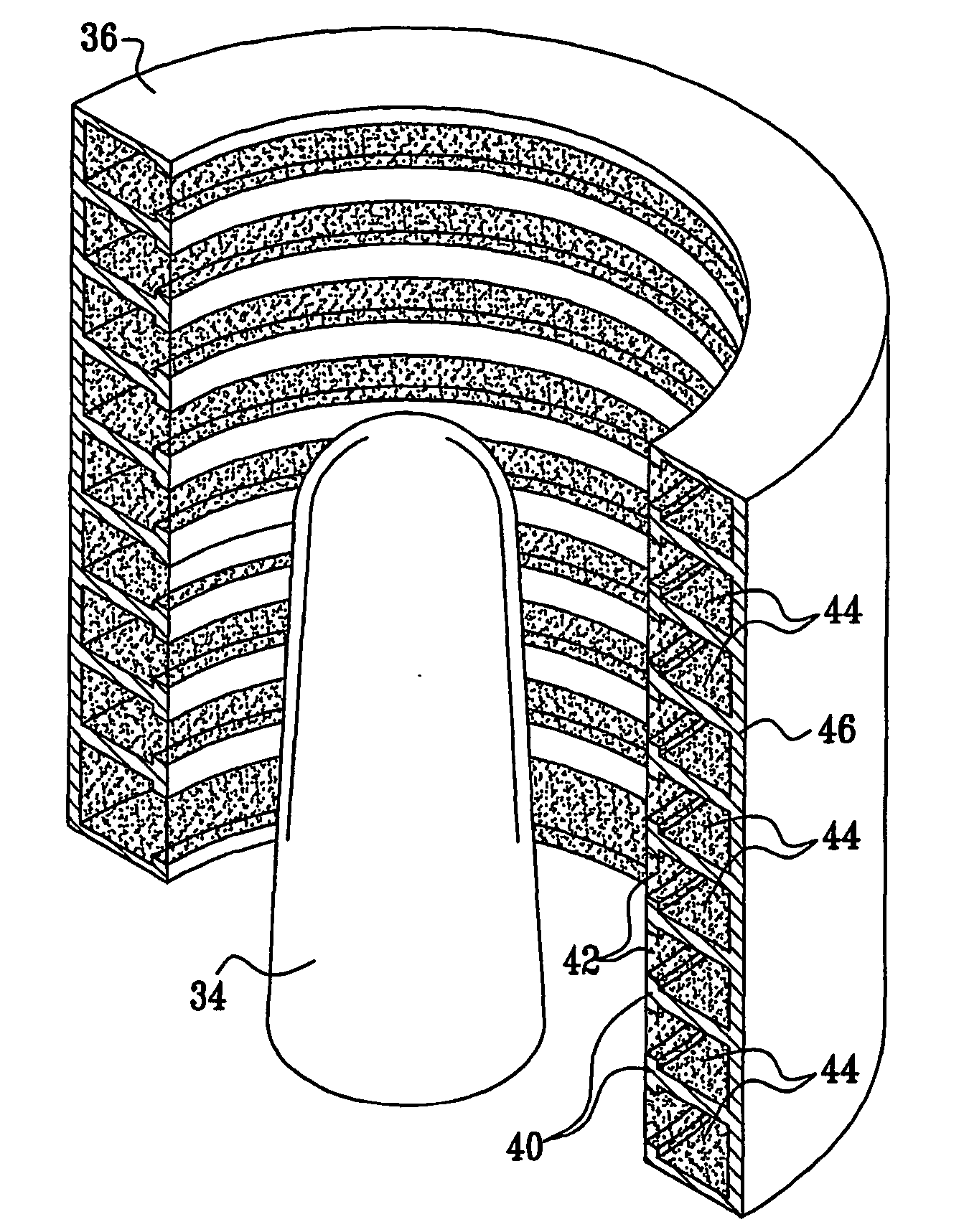
Method for producing silicon nitride films and process for fabricating semiconductor devices using said method
InactiveUS20050158983A1Reduction in thermal budgetImprove film propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogen sourceAmmonia
Silicon nitride film is formed on a silicon wafer mounted in a boat in an LPCVD tool by feeding a silicon source (SiH2Cl2, SiCl4, Si2Cl6, etc.) from an injector and feeding a mixed gas of monomethylamine (CH3NH2) and ammonia (NH3) as the nitrogen source from an injector. This addition of monomethylamine to the source substances for film production makes it possible to provide an improved film quality and improved leakage characteristics even at low temperatures (450-600° C.).
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
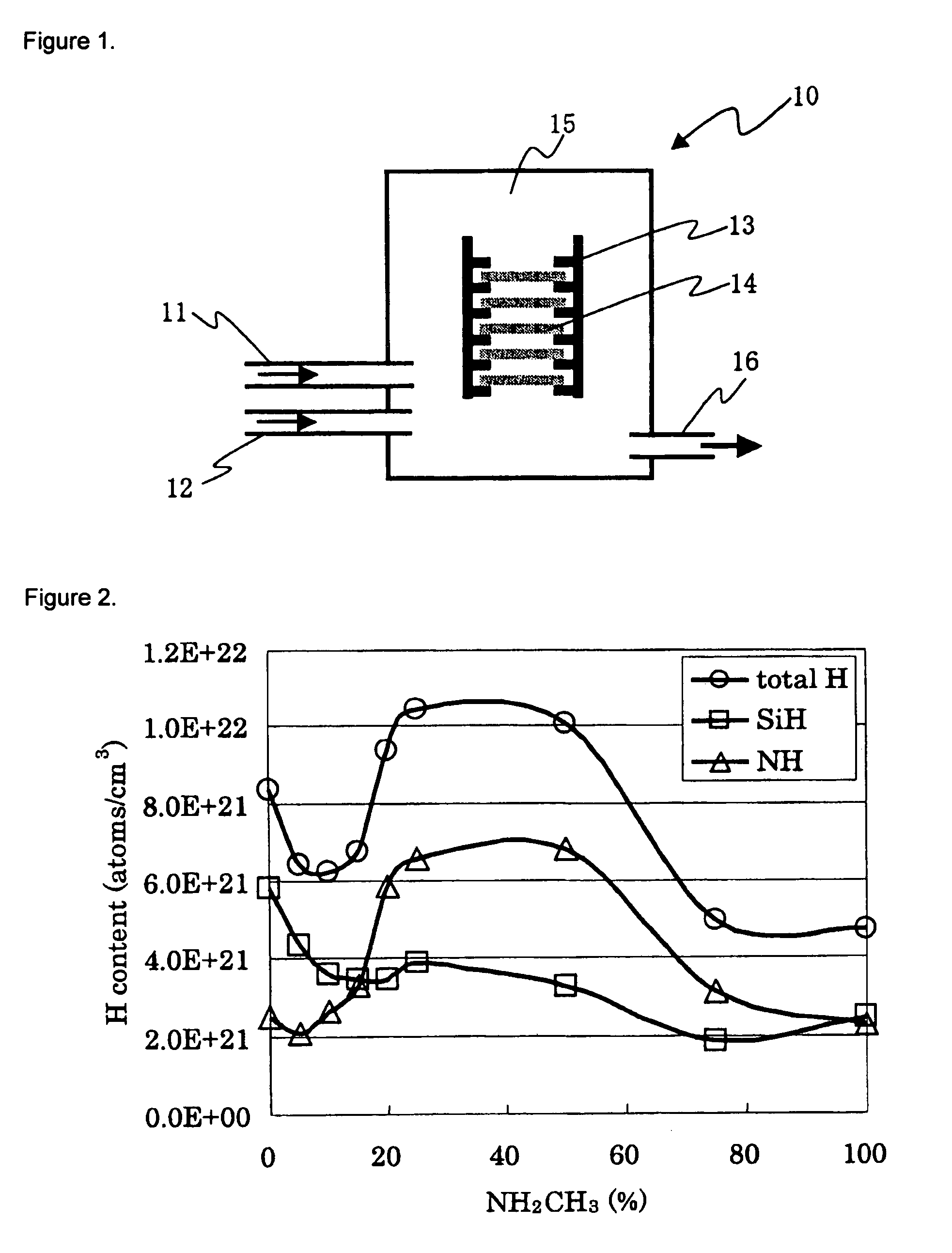
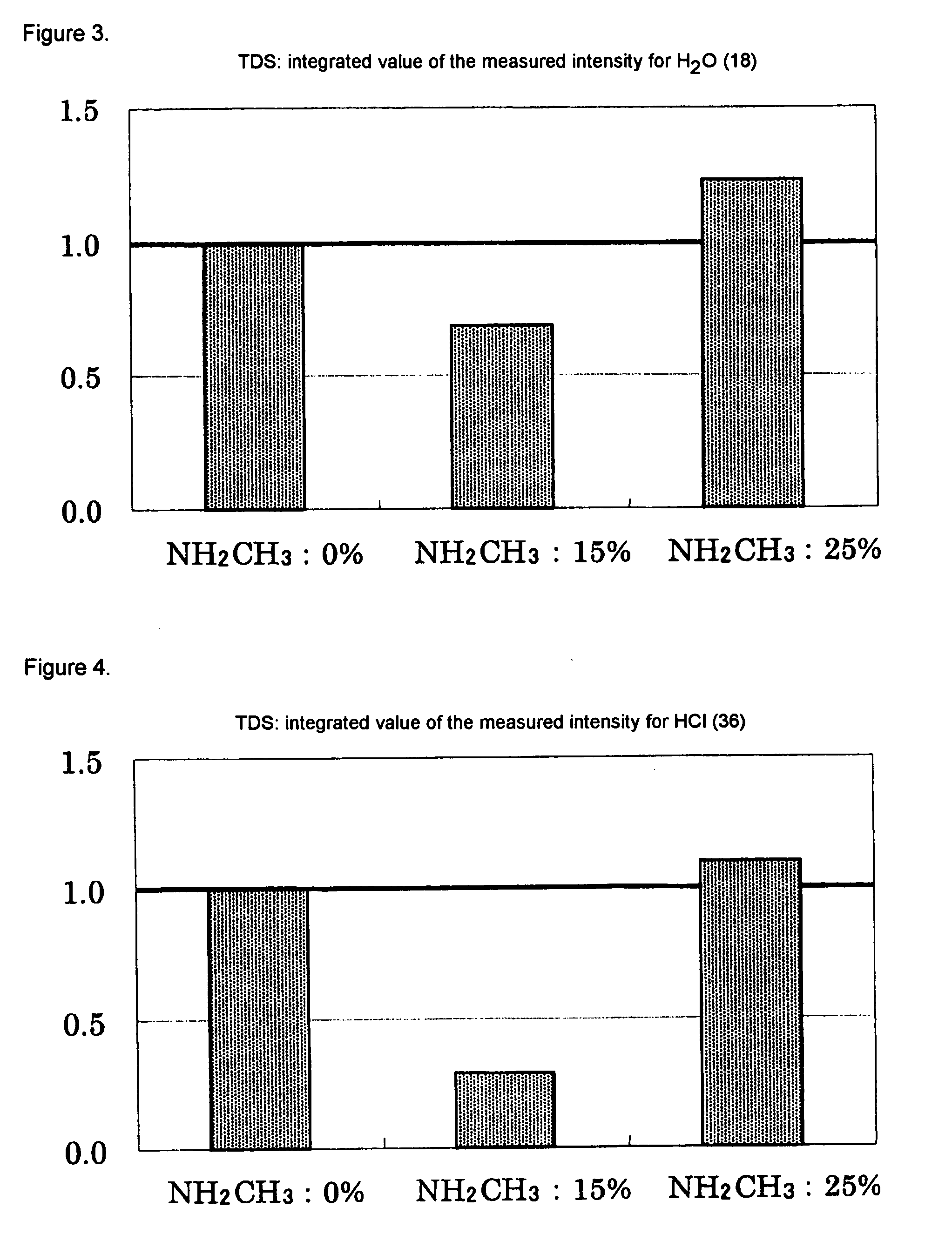
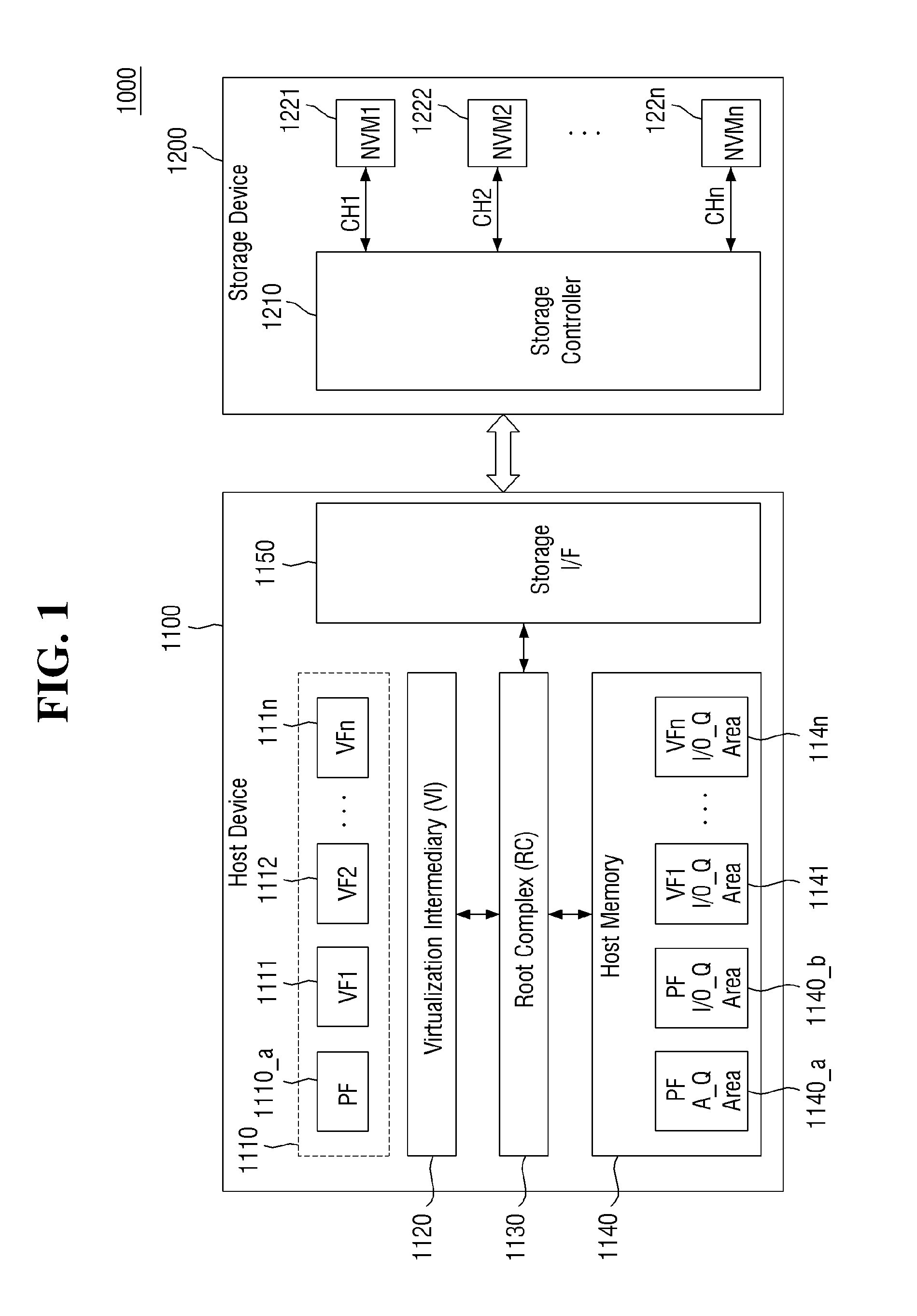
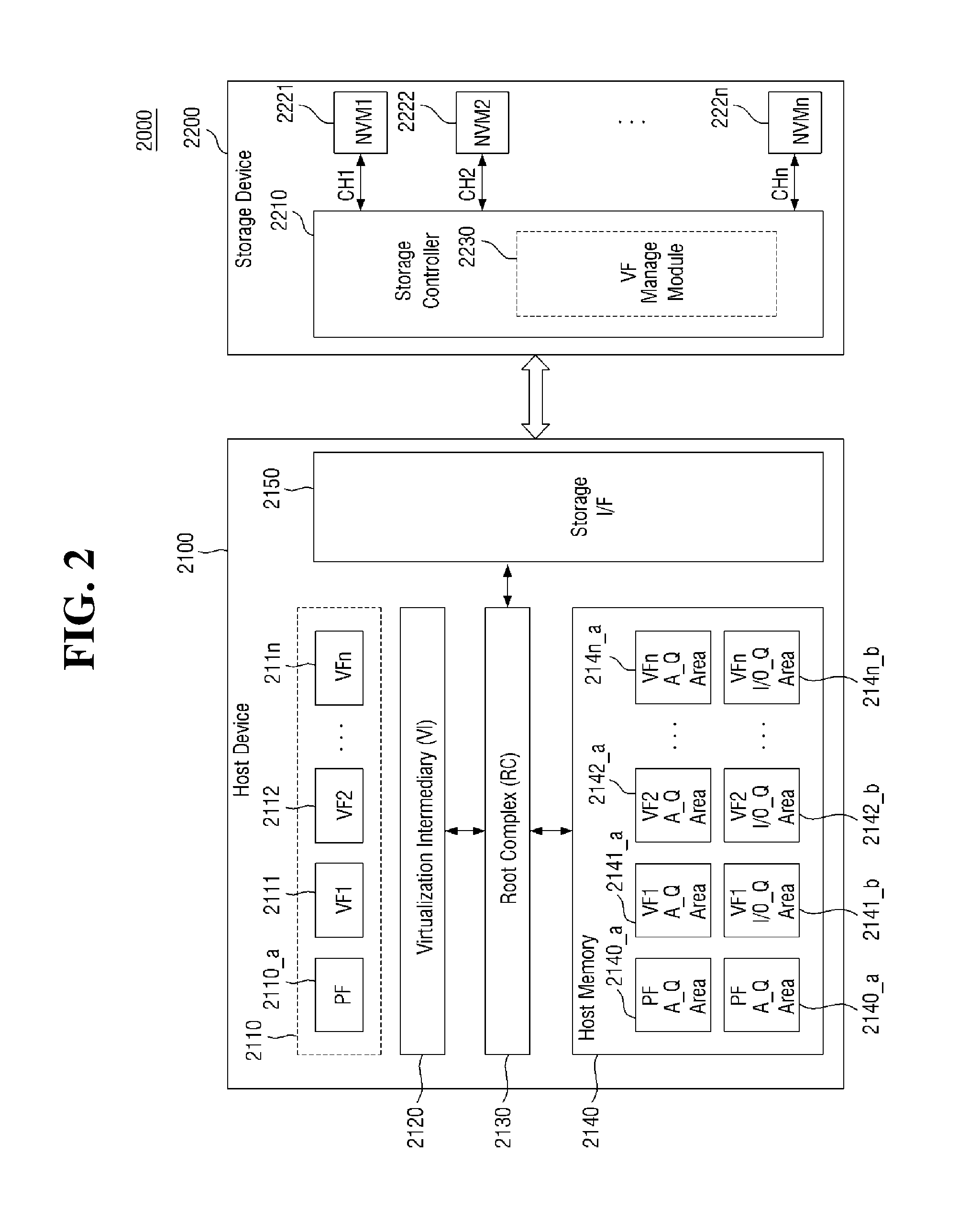
Storage device for supporting virtual machine, storage system including the storage device, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20170024132A1Exhaust fastBudget is reducedInput/output to record carriersProgram controlControl storeWorkload
A storage device includes a non-volatile memory including a plurality of blocks; and a storage controller connected to the non-volatile memory and configured to schedule a requested task of one virtual machine of a plurality of virtual machines based on a workload contribution of the one virtual machine, the workload contribution indicating a ratio between a workload generated by the one virtual machine and a plurality of workloads generated by the plurality of virtual machines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and structure
ActiveUS9117749B1Small footprintIncrease speedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSpin-transfer torque
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
Antenna with virtual magnetic wall
InactiveUS20050104782A1Enhanced near-field directional characteristicReduce SARWaveguide hornsMagnetic/electric field screeningElectromagnetic radiationMagnetic wall
A radiation shield (36) includes a virtual magnetic wall (VMW), which is adapted to be placed between a radiating antenna (34) and an object (30) so as to reflect electromagnetic radiation emitted from the antenna in a given frequency band and having an electric field with a given polarization, away from the object. The electric field of the radiation reflected by the VMW is substantially in phase with the electric field of the emitted radiation incident on the VMW.
Owner:XELLANT
Method of improving gate activation by employing atomic oxygen enhanced oxidation
InactiveUS6566210B2Budget is reducedSmall granularityTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor
The present invention provides a method of preparing a Si-based metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) transistor which prevents the polycrystalline grains of the gate conductor from getting significantly larger by reducing the thermal budget of the sidewall oxidation process. The thermal budget of the inventive sidewall oxidation process is reduced one or two orders of magnitude over conventional prior art sidewall oxidation processes by utilizing atomic oxygen as the oxidizing ambient. The present invention also provides Si-based MIS transistors having a gate conductor having grain sizes of about 0.1, preferably 0.05, .mu.m or less.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and methods for simultaneous momentum dumping and orbit control
InactiveUS7918420B2Reduce in quantityEasy to useArtificial satellitesRocket engine plantsMomentumPresent method
The present system and methods enable simultaneous momentum dumping and orbit control of a spacecraft, such as a geostationary satellite. Control equations according to the present system and methods generate accurate station-keeping commands quickly and efficiently, reducing the number of maneuvers needed to maintain station and allowing station -keeping maneuvers to be performed with a single burn. Additional benefits include increased efficiency in propellant usage, and extension of the satellite's lifespan. The present system and methods also enable tighter orbit control, reduction in transients and number of station-keeping thrusters aboard the satellite. The present methods also eliminate the need for the thrusters to point through the center of mass of the satellite, which in turn reduces the need for dedicated station-keeping thrusters. The present methods also facilitate completely autonomous orbit control and control using Attitude Control Systems (ACS).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
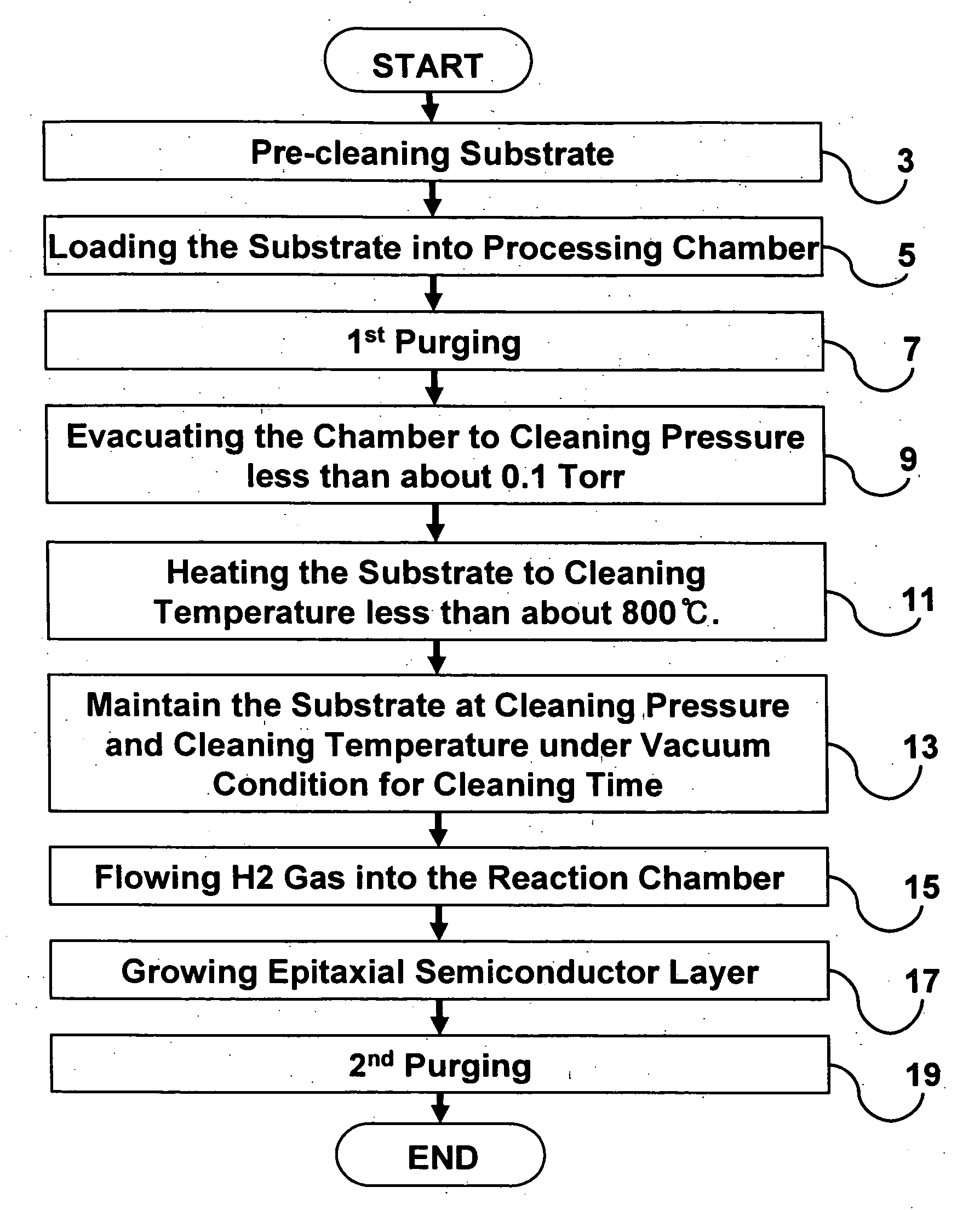
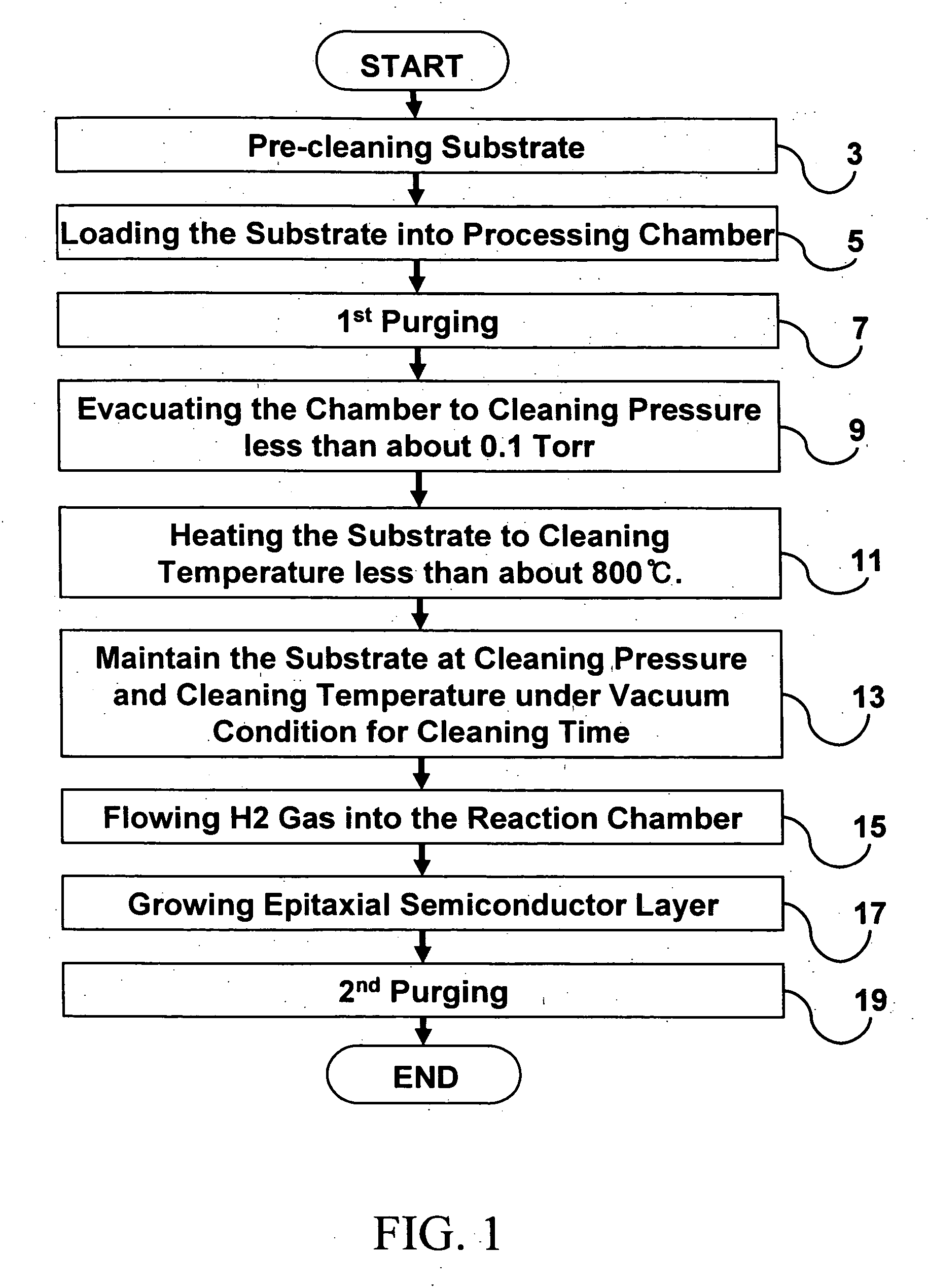
Methods for in-situ cleaning of semiconductor substrates and methods of semiconductor device fabrication employing the same
InactiveUS20060156970A1Reduce the possibilityReduce processing timePolycrystalline material growthMixing/kneading with horizontally-mounted toolsDecompositionGas composition
Provided is an in-situ precleaning method for use in conjunction with epitaxial processes that utilizes temperatures at or below those typically utilized during the subsequent epitaxial deposition under pressure and ambient conditions suitable for inducing decomposition of semiconductor oxides, such as native oxides, from exposed semiconductor surfaces. The reduced temperature and the resulting quality of the cleaned semiconductor surfaces will tend to reduce the likelihood of temperature related issues such as unwanted diffusion, autodoping, slip, and other crystalline stress problems while simultaneously reducing the overall process time. The combination of pressure, ambient gas composition and temperature maintained within the reaction chamber are sufficient to decompose semiconductor oxides present on the substrate surface. For example, the reaction chamber may be operated so that the concentration of evolved oxygen within the reaction chamber is less than about 50%, or even less than 10%, of the equilibrium vapor pressure under the cleaning conditions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High dielectric constant materials forming components of DRAM such as deep-trench capacitors and gate dielectric (insulators) for support circuits
InactiveUS6563160B2Improve performanceIncrease in gage electrode controlTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDielectric structure
A method and structure for an improved DRAM (dynamic random access memory) dielectric structure, whereby a new high-k material is implemented for both the support devices used as the gate dielectric as well as the capacitor dielectric. The method forms both deep isolated trench regions used for capacitor devices, and shallow isolated trench regions for support devices. The method also forms two different insulator layers, where one insulator layer with a uniform high-k dielectric constant is used for the deep trench regions and the support regions. The other insulator layer is used in the array regions in between the shallow trench regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Sewage treatment control device, method, and sewage treatment system
InactiveUS20080314841A1Reduce installation costsMinimize the numberWater treatment parameter controlIon-exchanger regenerationValue setControl signal
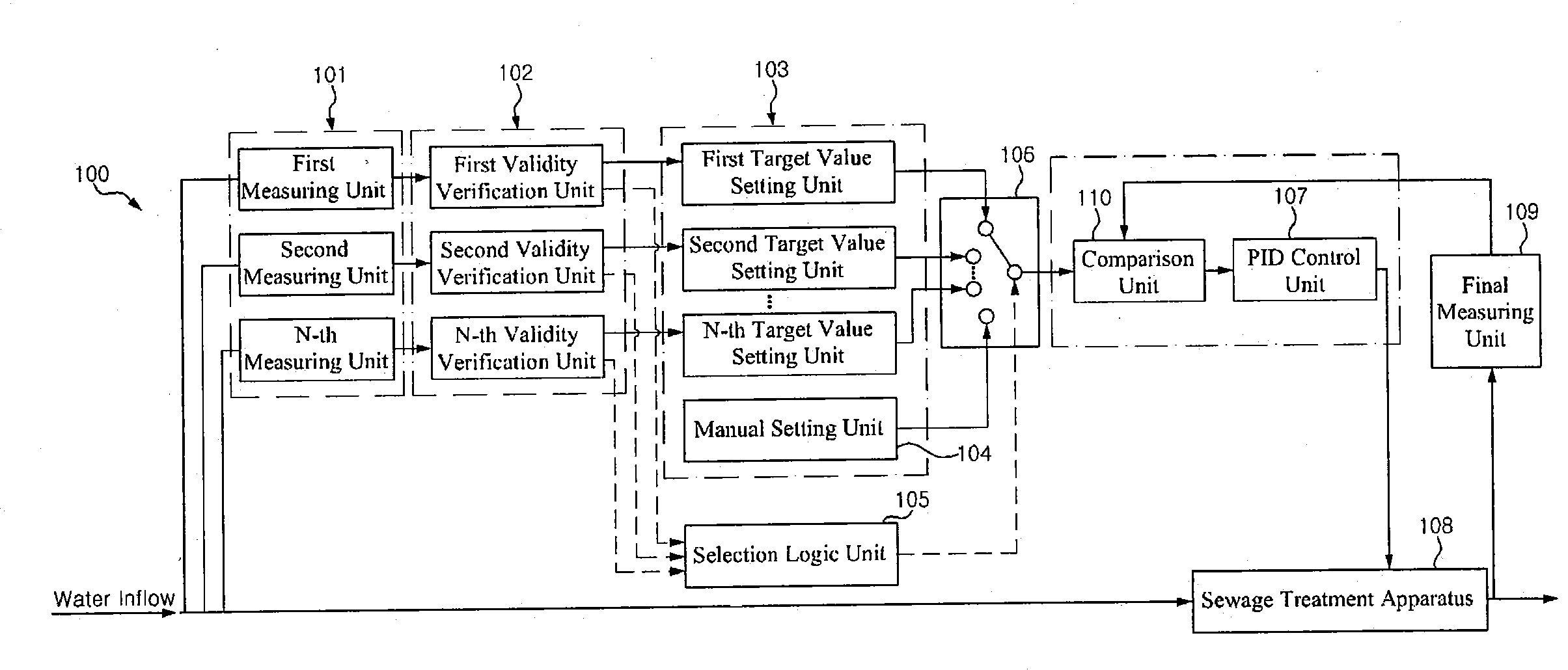
A sewage treatment control device, a method and a sewage treatment system, are disclosed. In one example, the sewage treatment control device includes measuring units having sensors for inspecting specific components in water, respectively; validity verification units connected to the measuring units to determine validities for measured component values, respectively; target value setting units connected to the validity verification units to set target values for the component values measured in the measuring units, respectively; a manual setting unit for setting a target value depending on a component value inputted by an operator; a signal selection unit for allowing either one of the respective target value setting units or the manual setting unit to be connected; a proportional-integral-derivative control unit for performing proportional, integral or derivative action for the target value inputted from the signal selection unit to convert the target value into a control signal; and a manipulation unit for manipulating a sewage treatment apparatus depending on the control signal converted in the proportional-integral-derivative control unit.
Owner:TAI WHA LEASE IND
Virtual batteries for wireless communication device
ActiveUS7583951B2Efficient powerReduce usageEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTelecommunicationsPower budget
The present invention provides virtual batteries for a wireless communication device. Generally speaking, a virtual battery is a logical construct on a wireless communication device that powers a defined set of wireless communication device applications and has a defined power budget from one or more physical batteries on the device. Through judicious assignment of wireless communication device applications and power budgets to virtual batteries, a user of a wireless communication device can efficiently allocate power among competing wireless communication device applications.
Owner:SHARP KK
Workpiece support
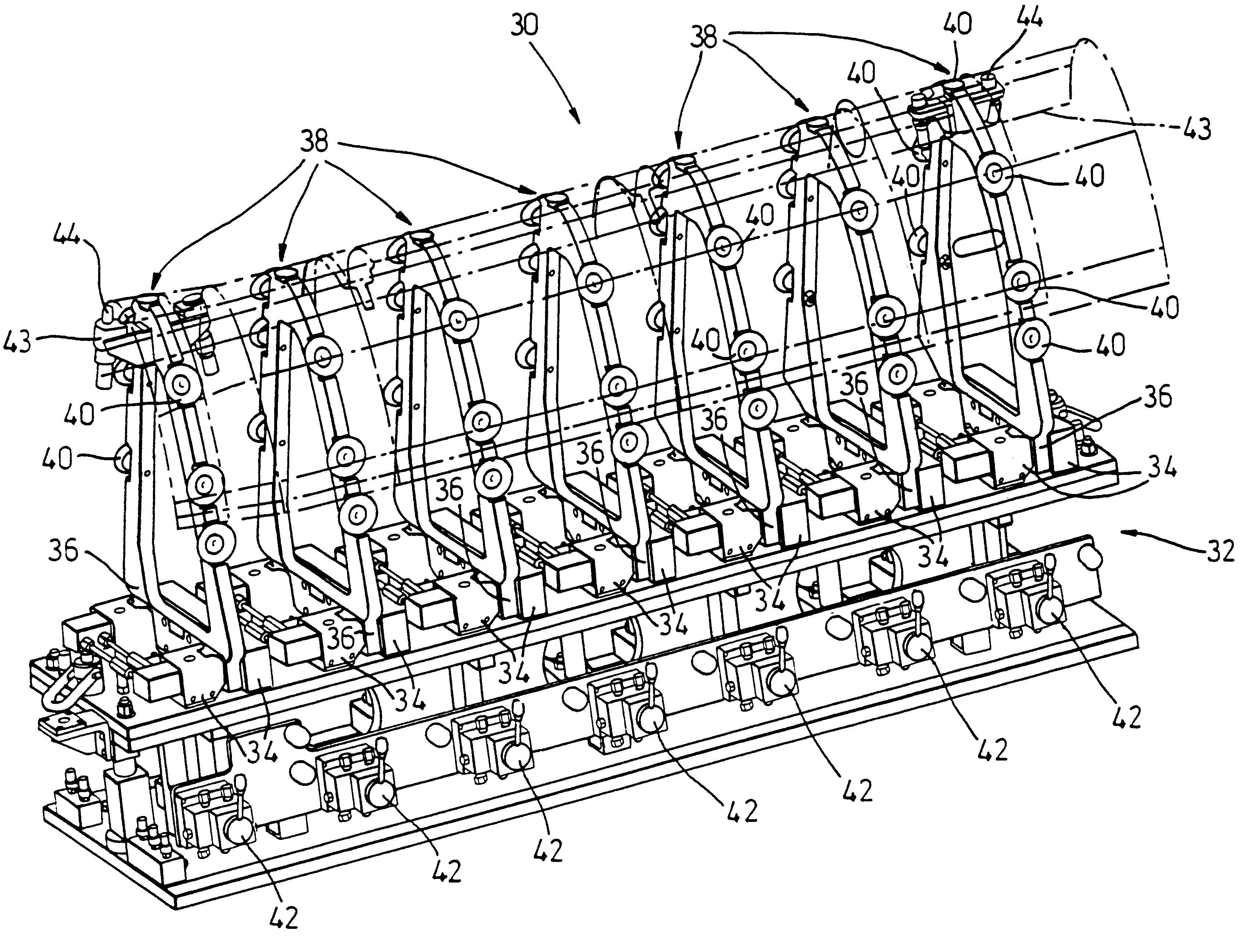
InactiveUS6598866B2Lower requirementReduce settingsWork holdersVehicle componentsLeading edgeEngineering
A modular workpiece support reconfigurable to support a number of similar, but different profiled workpieces (such as the leading edge skin sections of an aircraft wing) comprises a base 32 defining a number of stations along the component. Each station comprises a clamp block 34, and a frame element 38 of predetermined profile may be clamped in the clamp block in either of two different orientations (for hand and opposite). Each frame element includes a number of suction cups 40, the suction being controlled by a valve 42. The workpiece support may be rapidly reconfigured for a symmetric component simply by unclamping and rotating the frame element through 180°. The workpiece support may also be reconfigured for different profiles by selecting the appropriate frame elements from a library thereof.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Field effect transistor and method for fabricating it
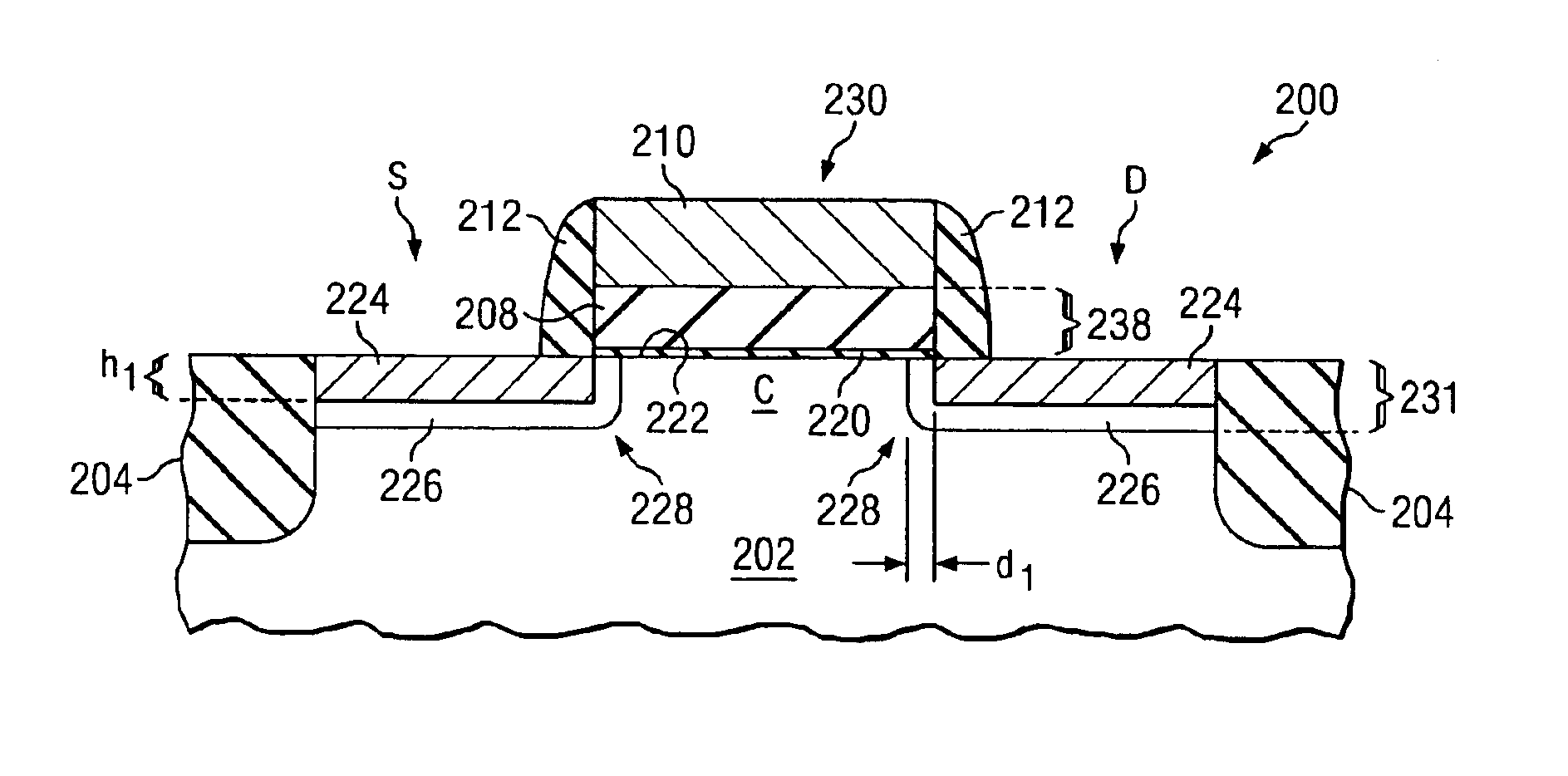
InactiveUS7119384B2Reduce spendingReduce and avoidTransistorSolid-state devicesPlanar channelReverse current
The invention relates to a field effect transistor in which the planar channel region on the upper surface of the elevation is extended in width by means of additional vertical channel regions on the lateral surfaces of the elevation. Said additional vertical channel regions connect directly to the planar channel region (vertical extended channel regions). Said field effect transistor has the advantage that a significant increase in the effective channel width for the current flow ION can be guaranteed relative to conventional transistor structures used up until the present, without having to accept a reduction in the achievable integration density. Said field effect transistor furthermore has a low reverse current IOFF. The above advantages are achieved without the thickness of the gate insulators up to the region of the charge transfer tunnels having to be reduced or a reduced stability.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
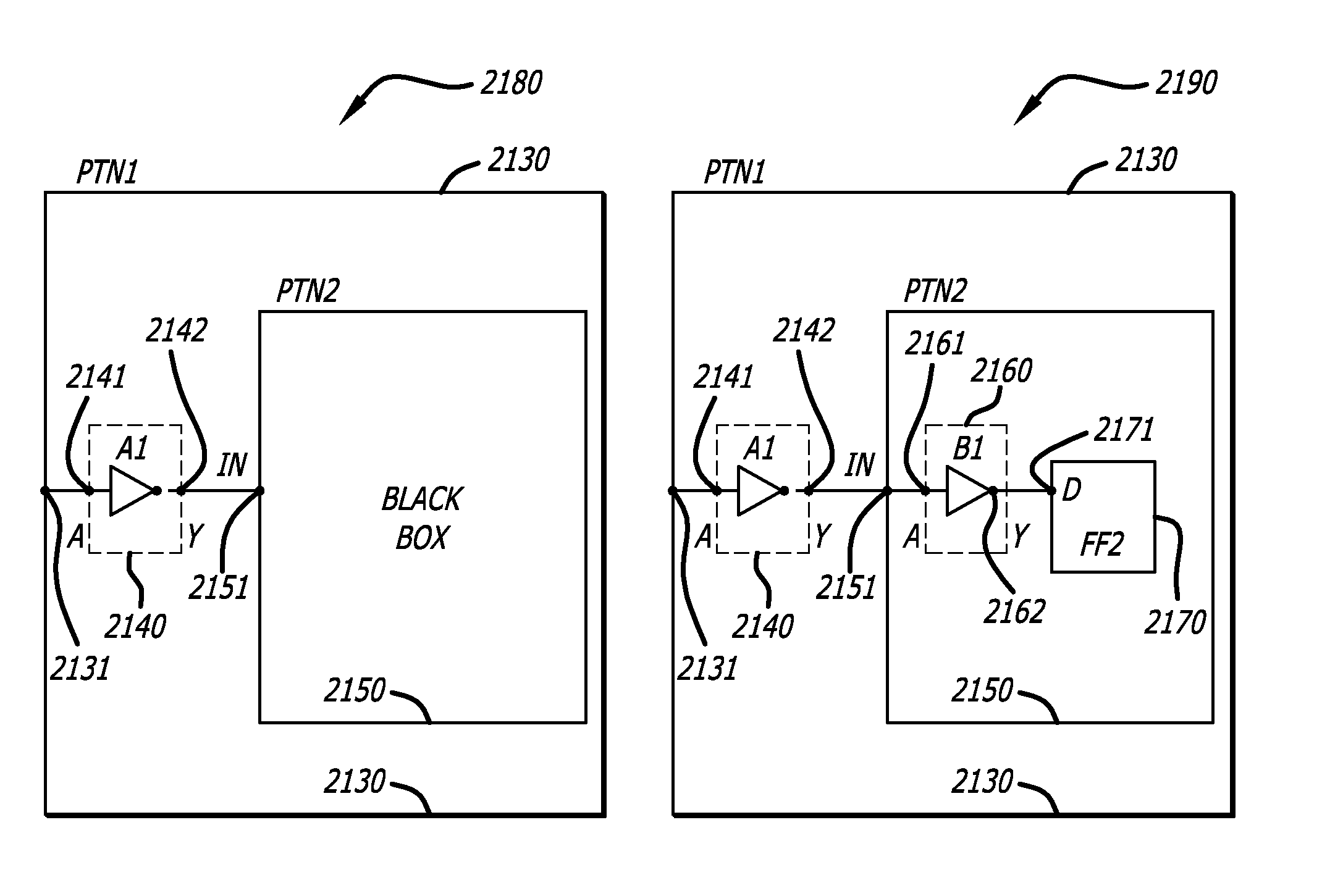
Timing budgeting of nested partitions for hierarchical integrated circuit designs
ActiveUS8977995B1Budget is reducedDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designEngineeringCircuit design
In one embodiment, a method of designing an integrated circuit is disclosed, including receiving a plurality of top level timing constraints and a description of the integrated circuit design defining a hierarchy of partitions having multiple levels with one or more nested partitions; generating timing models for each partition of the plurality of partitions in response to the description of the integrated circuit design; and concurrently generating timing budgets level by level for all partitions at each level, beginning with the lowest level to each next upper level of the hierarchy of the partitions in response to the description of the integrated circuit design, the timing models, and the plurality of top level timing constraints. Please see the detailed description and claims for other embodiments that are respectively disclosed and claimed.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
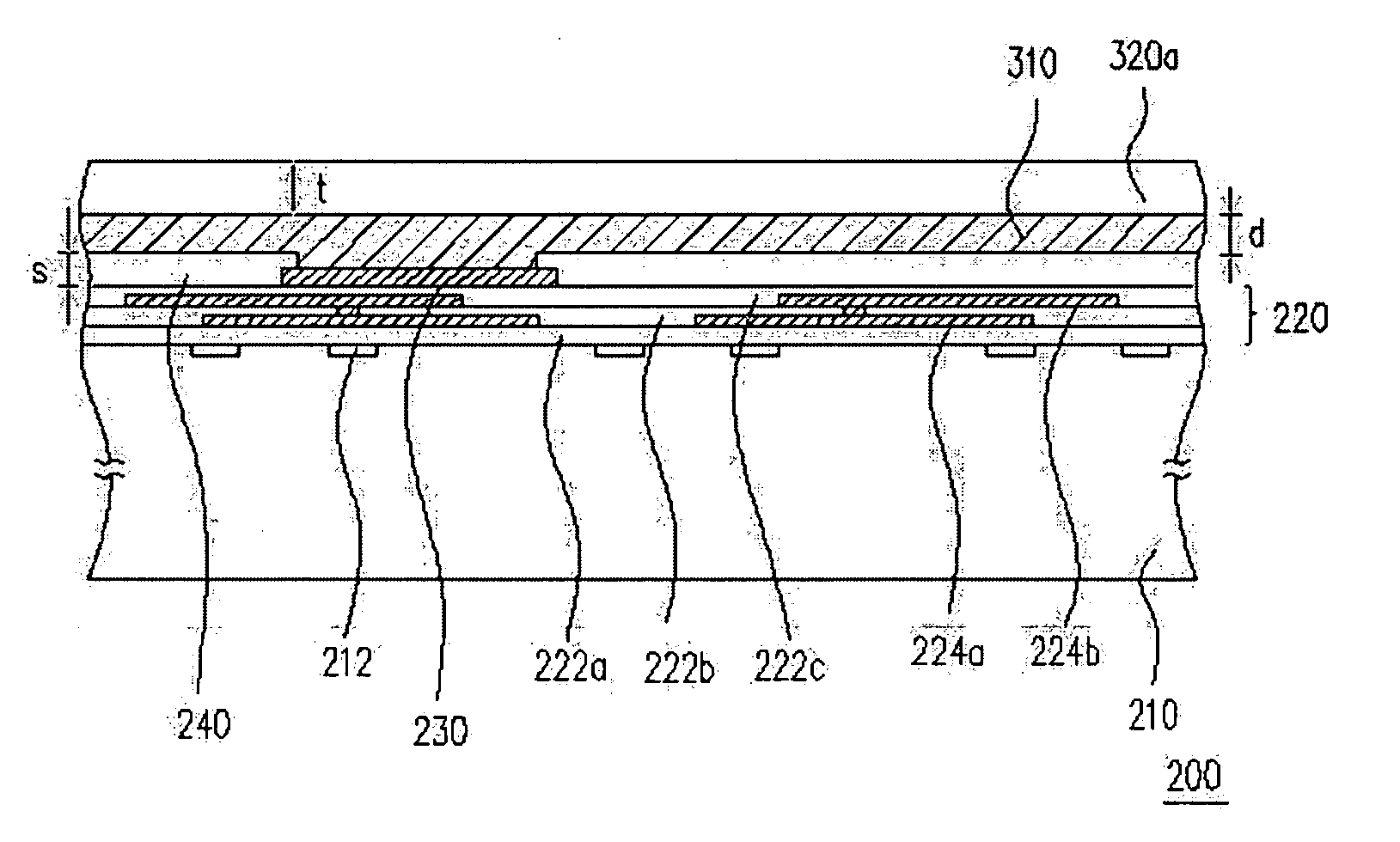
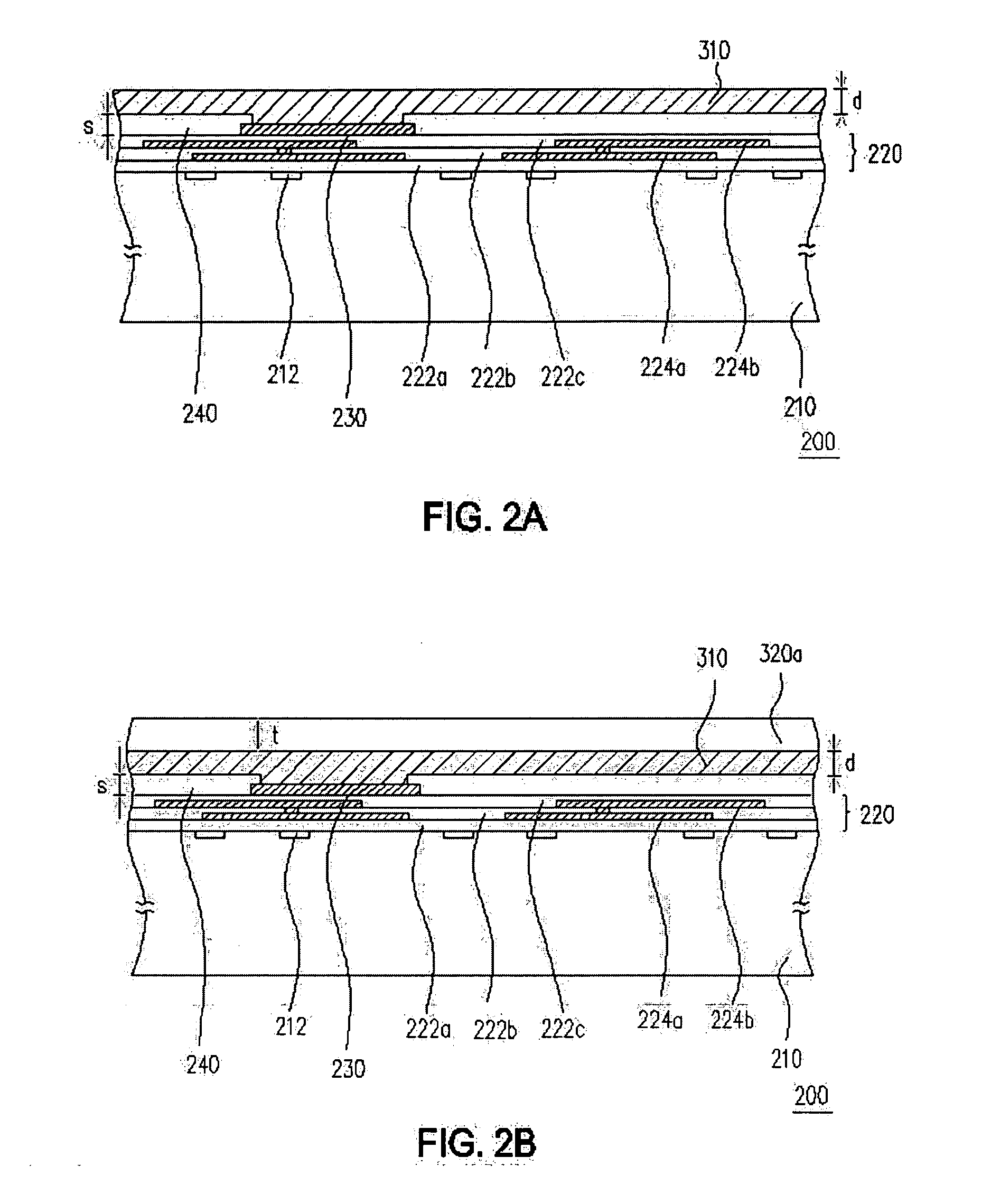
Flat panel display apparatus
ActiveUS20060138928A1Improve image display qualityReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesImage pickup tubesFlat panel displayProtection layer
A flat panel display apparatus includes a main plate, an organic light emitting element, a protecting layer and an attachable-detachable layer. The organic light emitting element includes a first electrode, a second electrode corresponding to the first electrode, and an organic light emitting layer disposed between the first and second electrodes to generate a light based on a current that flows between the first and second electrodes through the organic light emitting layer. The organic light emitting element is on the main plate. The protecting layer is on the organic light emitting element to protect the organic light emitting element. The attachable-detachable layer is on the protecting layer. Therefore, an image display quality is improved, and a manufacturing cost is decreased.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
High dielectric constant materials forming components of DRAM storage cells
InactiveUS6441421B1Increased charge storage capacityReduce processing costsTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorGate dielectric
A method and structure for simultaneously producing a dynamic random access memory device and associated transistor is disclosed. The method forms channel regions and capacitor openings in a substrate. Next, the invention deposits capacitor conductors in the capacitor openings. Then, the invention simultaneously forms a single insulator layer above the channel region and above the capacitor conductor. This single insulator layer comprises a capacitor node dielectric above the capacitor conductor and comprises a gate dielectric above the channel region.
Owner:IBM CORP
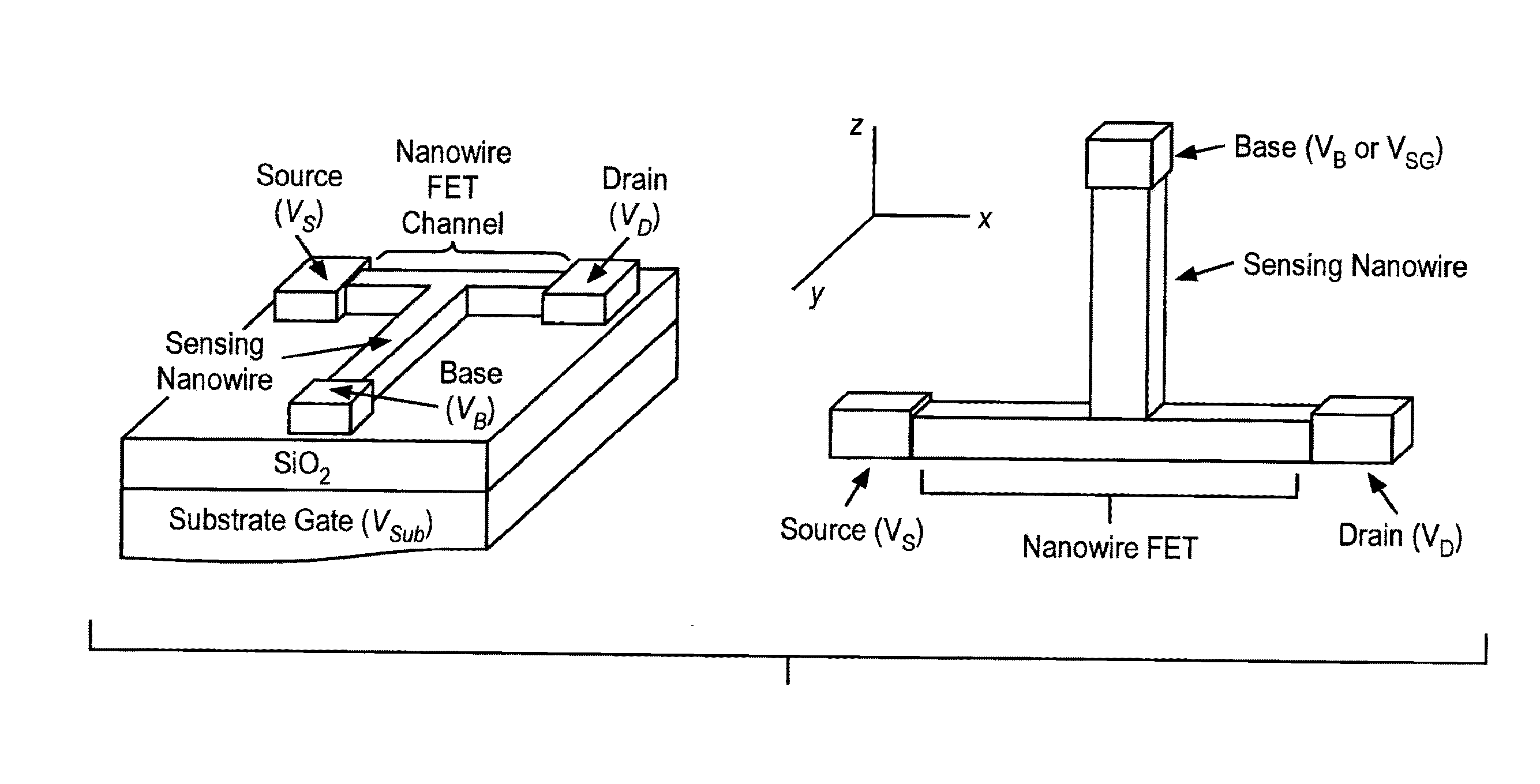
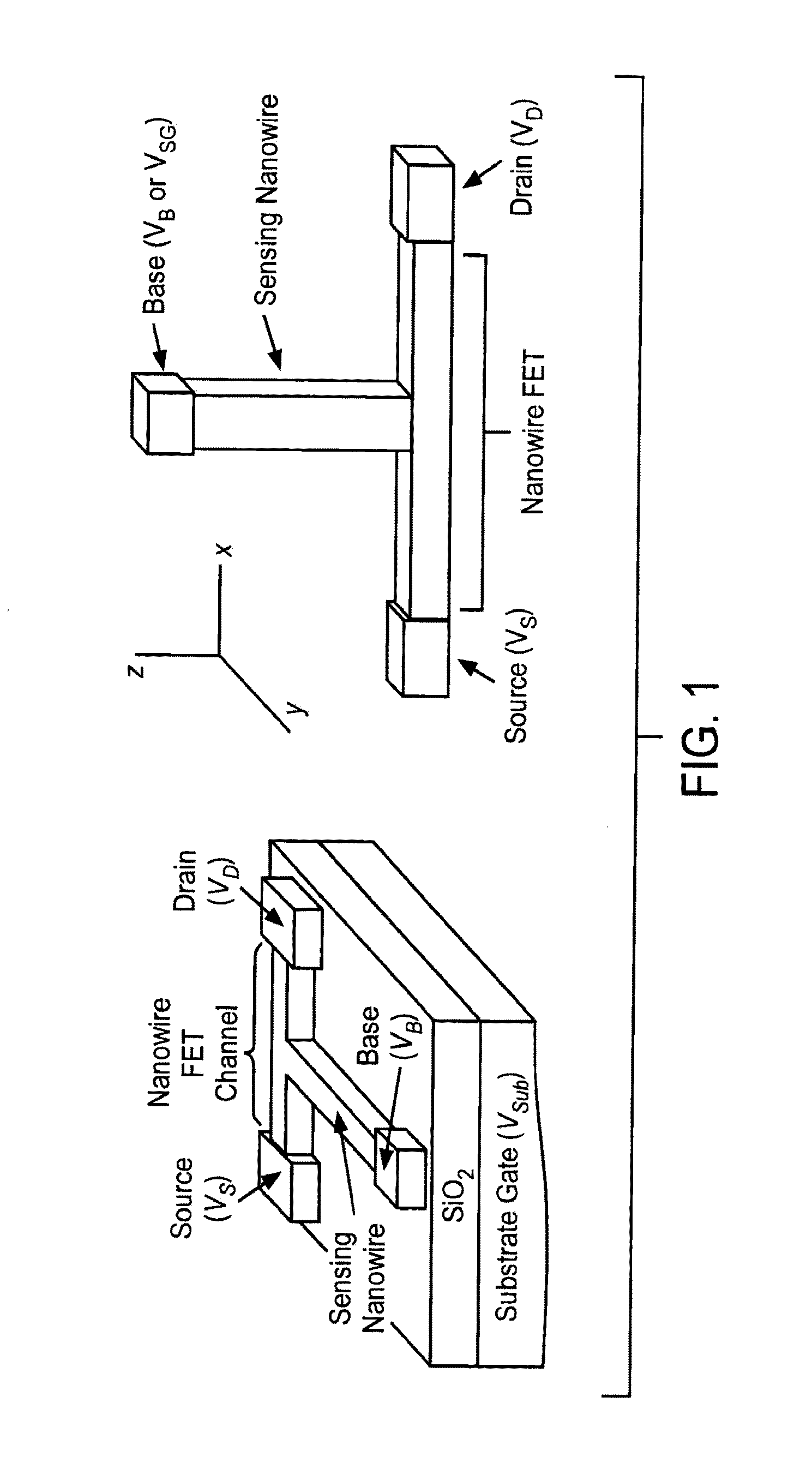
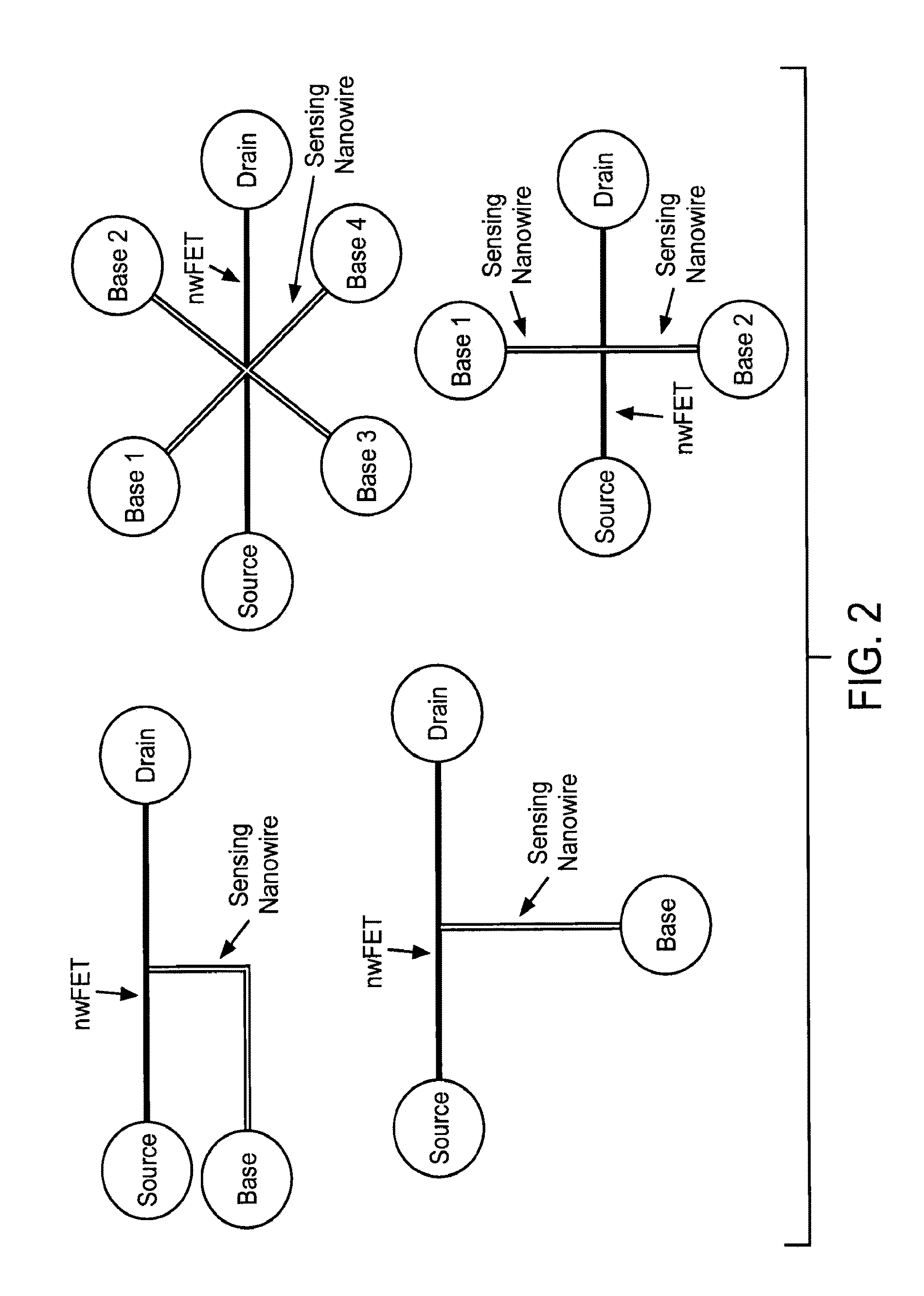
Nanowire field-effect transistor biosensor with improved sensitivity
ActiveUS20130337567A1Alters chargeChange electrical propertiesMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanowireField-effect transistor
The present invention is directed to a multiwire nanowire field effect transistor (nwFET) device for the measurement. The device includes a sensing nanowire having a first end and a second end and a nanowire FET having a first end and a second end, wherein the first end of the sensing nanowire is connected to the nanowire FET to form a node. Additionally, the first end of the nanowire FET is connected to a source electrode, the second end of the nanowire FET is connected to a drain electrode, and the second end of the sensing nanowire is connected to a base electrode. The sensing nanowire is derivatized with a plurality of immobilized capture probes that are specific for a target(s) of interest. The device is used to detect biomolecules or to detect the change in the ionic environment of a sample. In a further embodiment, the sensing nanowire is derivatized with amino, carboxyl or hydroxyl groups. Upon a change in ionic environment, or binding of a molecule to the sensing nanowire, the sensing nanowire current (IB) fluctuates. This fluctuation is amplified and readout as the nanowire FET drain current (ID). Accordingly, the present invention provides for label-free detection of biomolecules and may find use as a point-of-care diagnostic device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Over-passivation process of forming polymer layer over IC chip
InactiveUS20050250255A1Reduce generationBudget is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDegree CelsiusSemiconductor chip
A method for forming a semiconductor chip or wafer includes following steps. A semiconductor substrate is provided, and then a polymer layer is deposited over the semiconductor substrate, wherein the polymer layer comprises polyimide. The polymer layer with a temperature profile having a peak temperature between 200 and 320 degrees Celsius. Alternatively, the temperature profile may comprises a period of time with a temperature higher than 320 degree Celsius, wherein the period of time is shorter than 45 minutes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
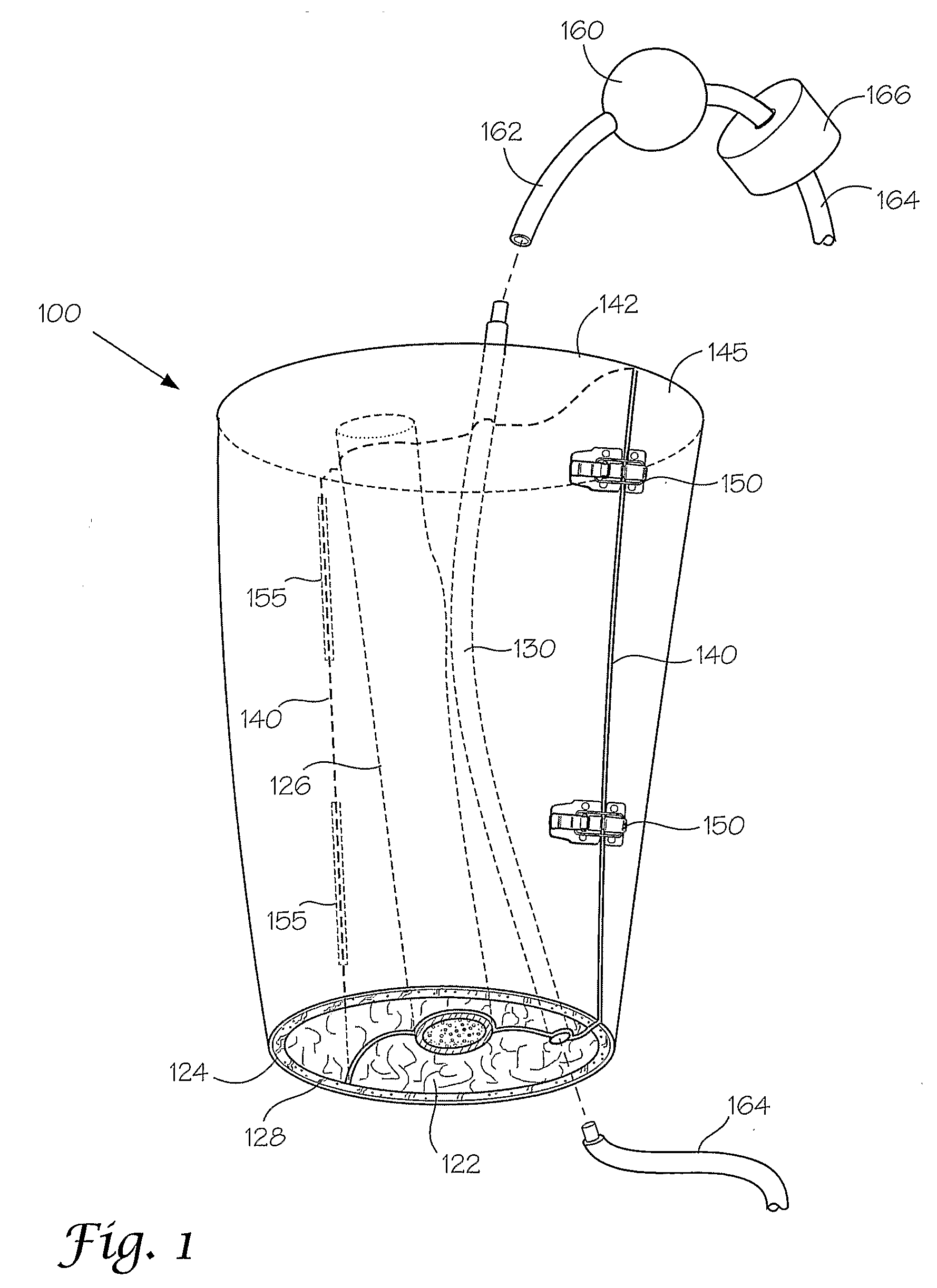
Models and methods of using same for testing medical devices
ActiveUS20060184005A1Avoid product qualityIncreased development costAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresLiving body
Disclosed herein are synthetic anatomical models that are designed to enable simulated use testing by medical device companies, medical device designers, individual inventors, or any other entity interested in the performance of medical devices. These models are unique in possessing a level of complexity that allows them to be substituted for either a live animal, an animal cadaver, or a human cadaver in the testing of these devices. These models are further characterized by a similarity of geometry, individual component physical properties, and component-to-component interfacial properties with the appropriate target tissue and anatomy.
Owner:SAKEZLES CHRISTOPHER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com