Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
21983results about "Work holders" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
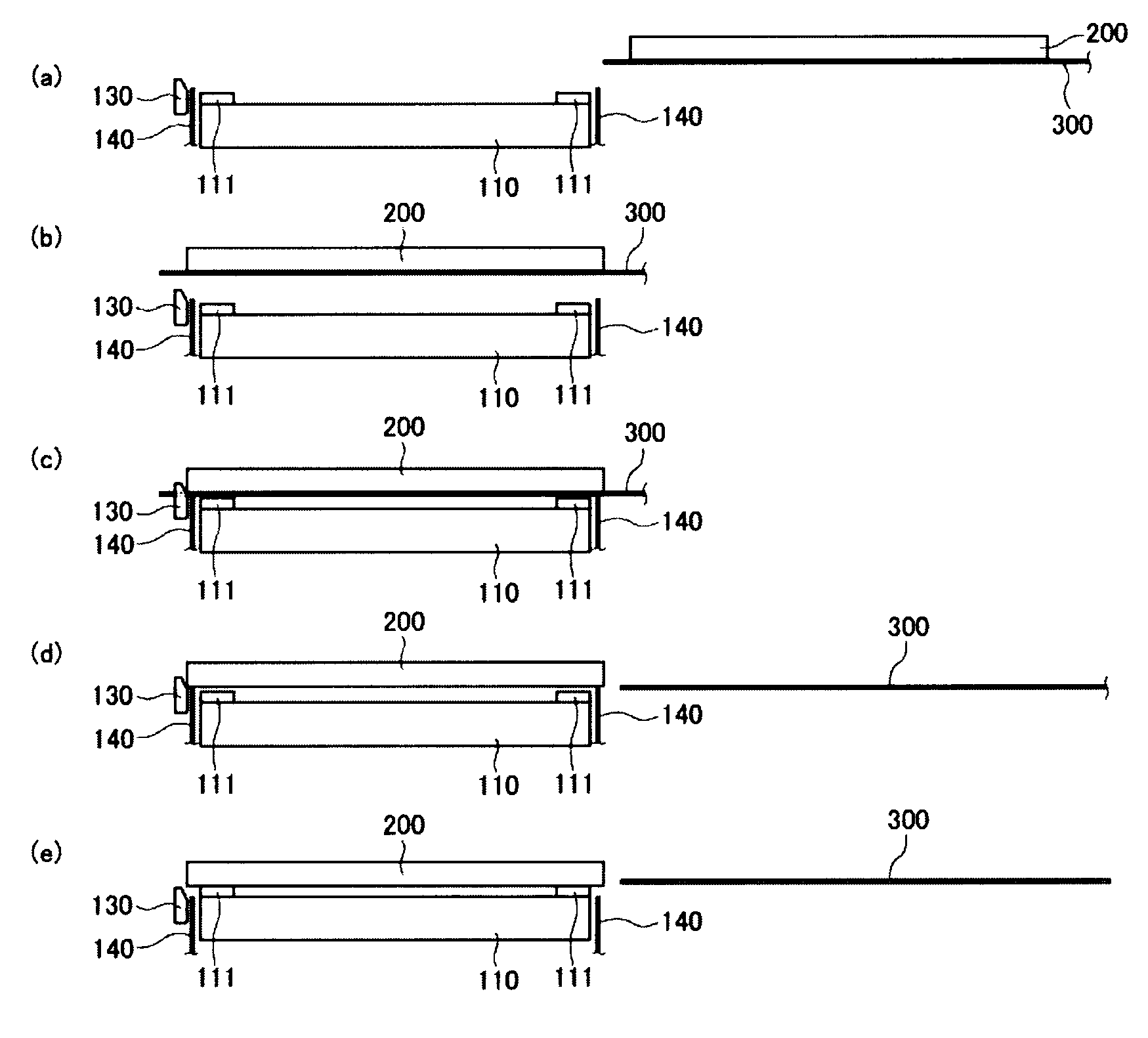
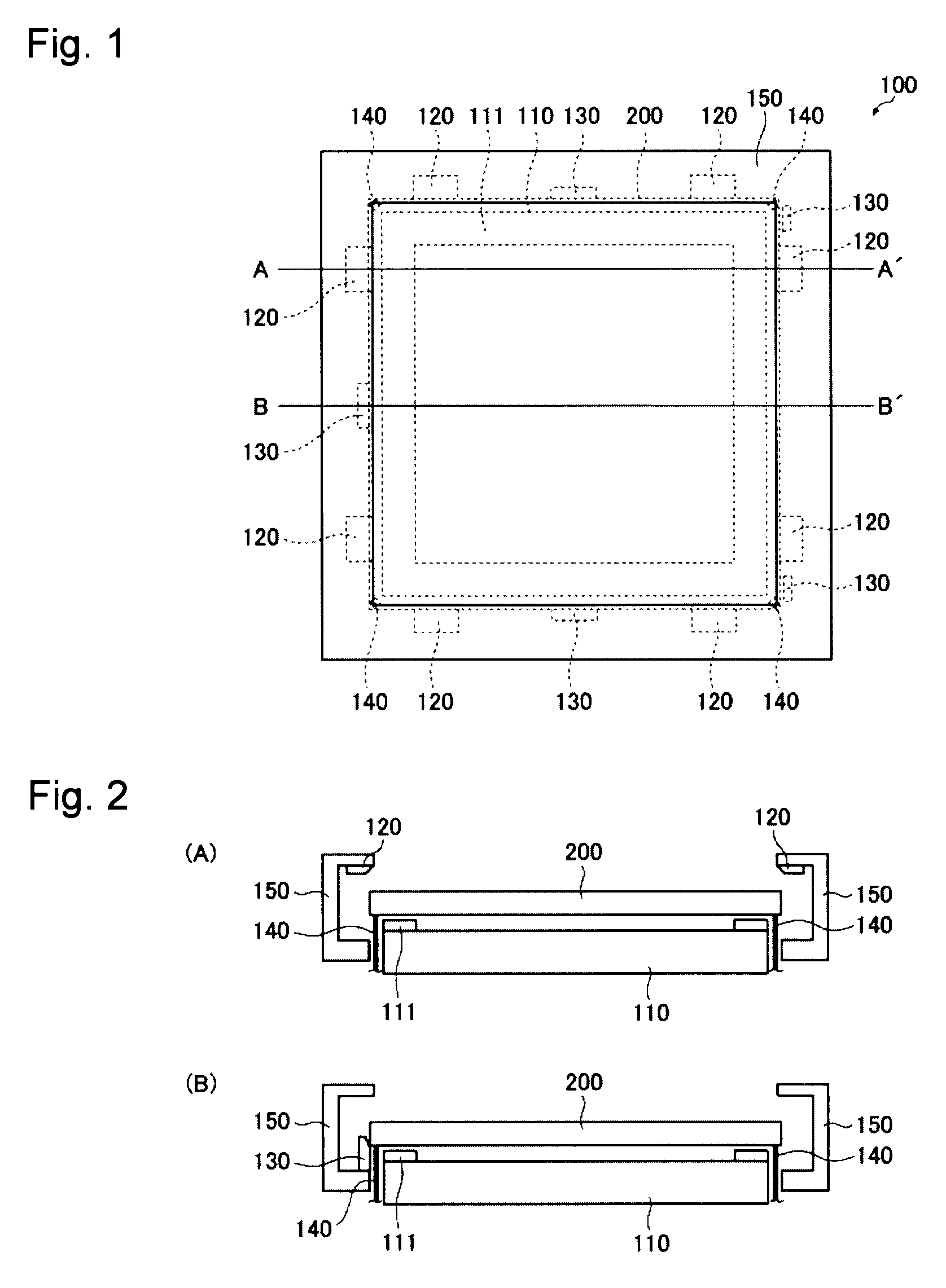
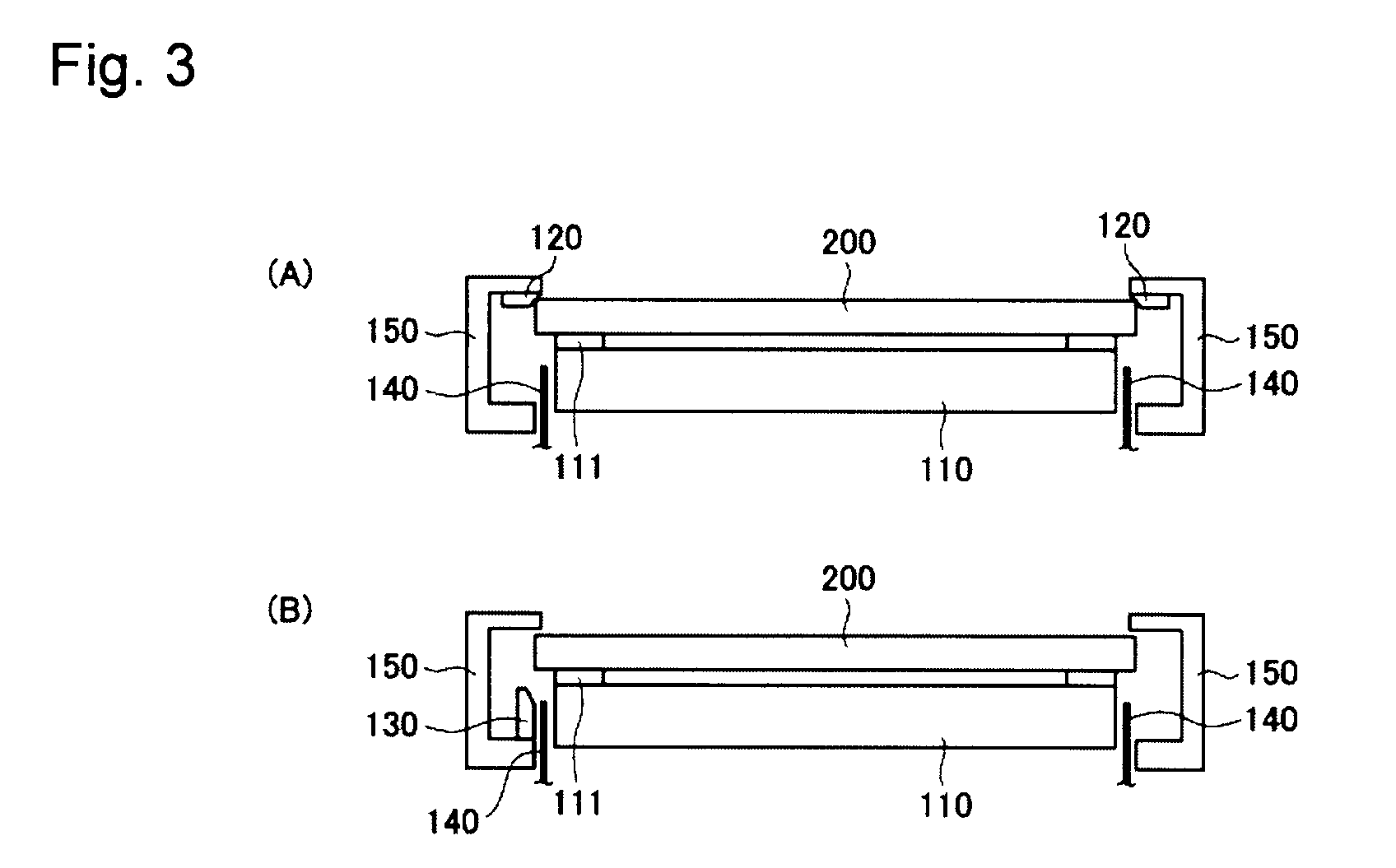
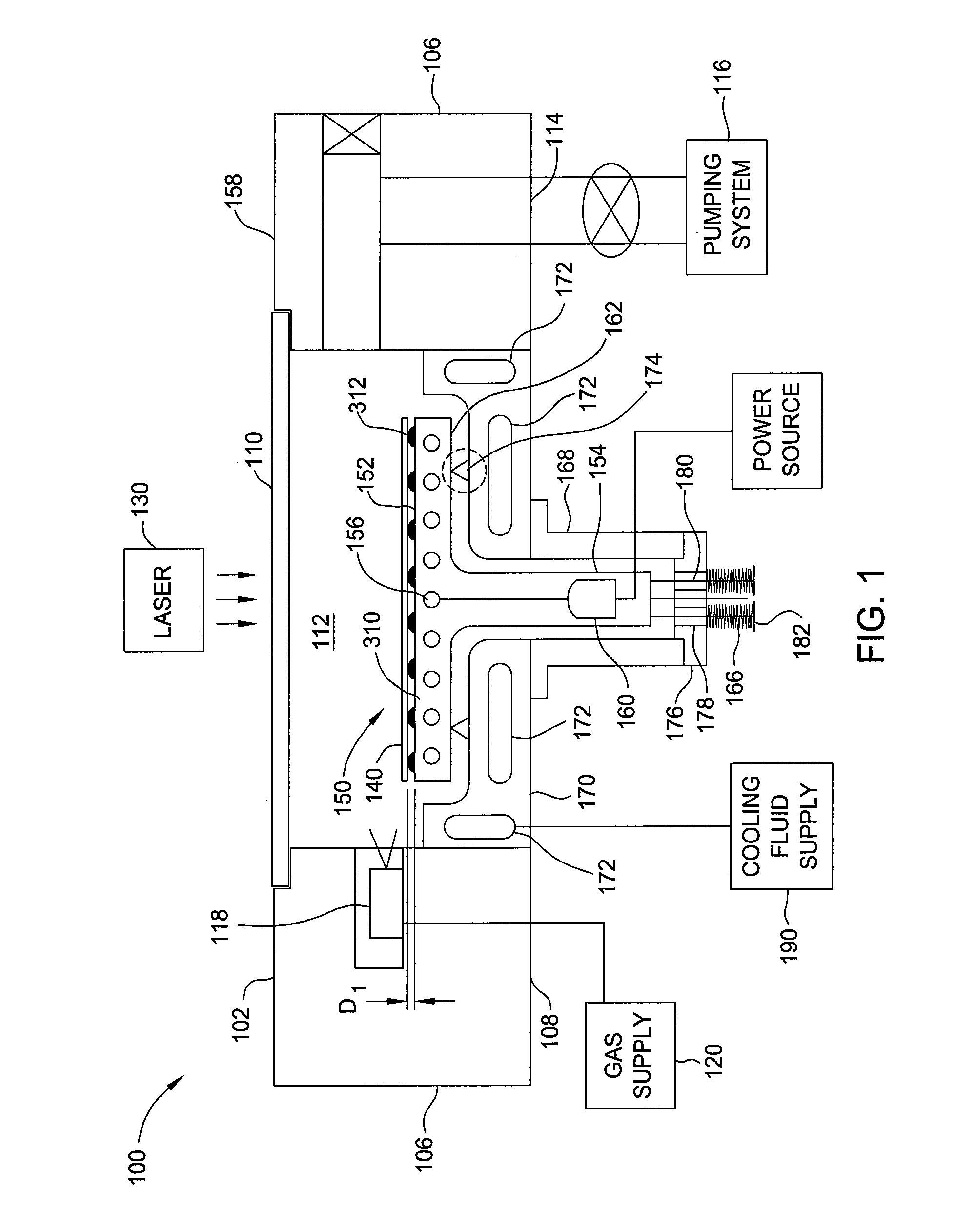
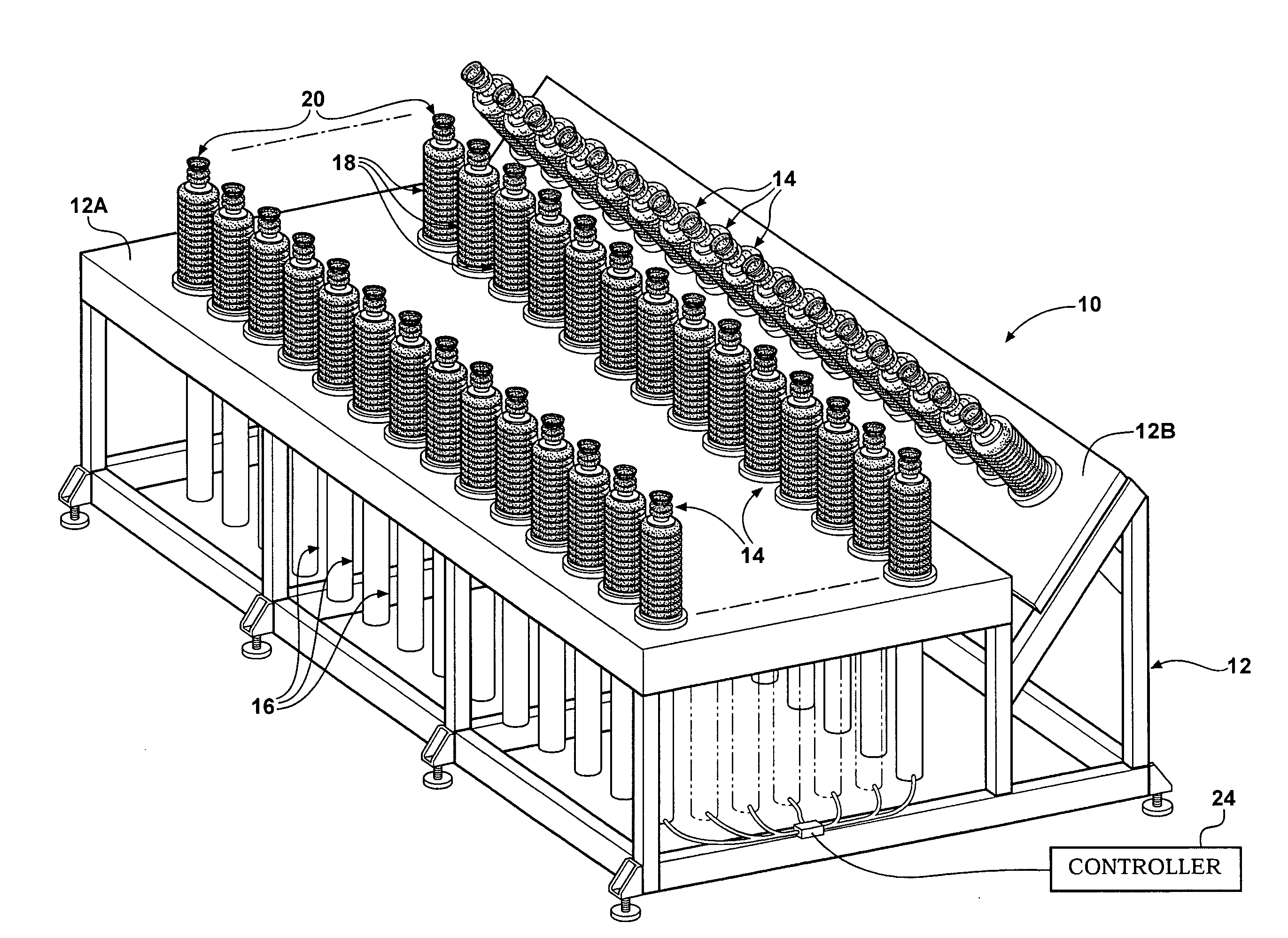
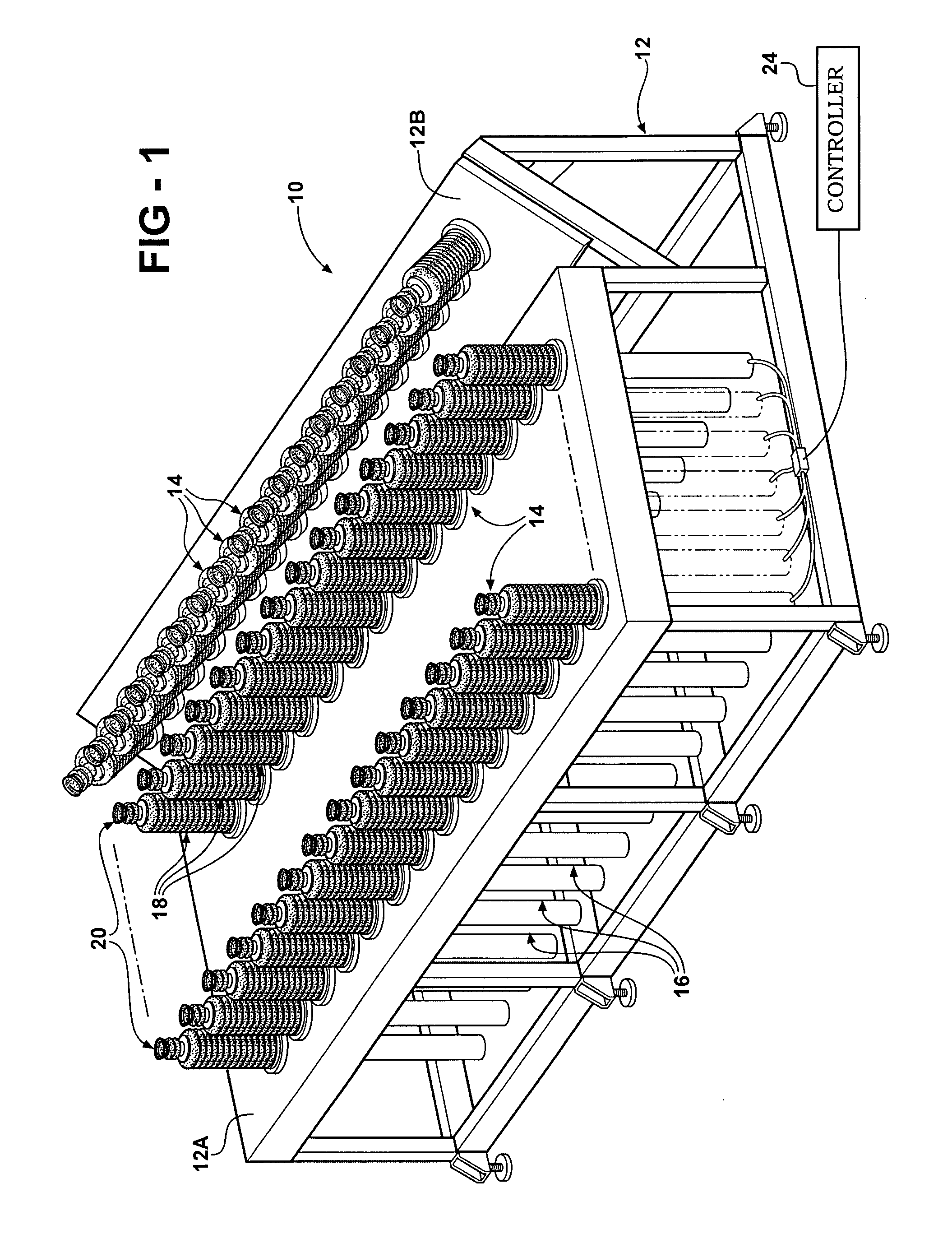
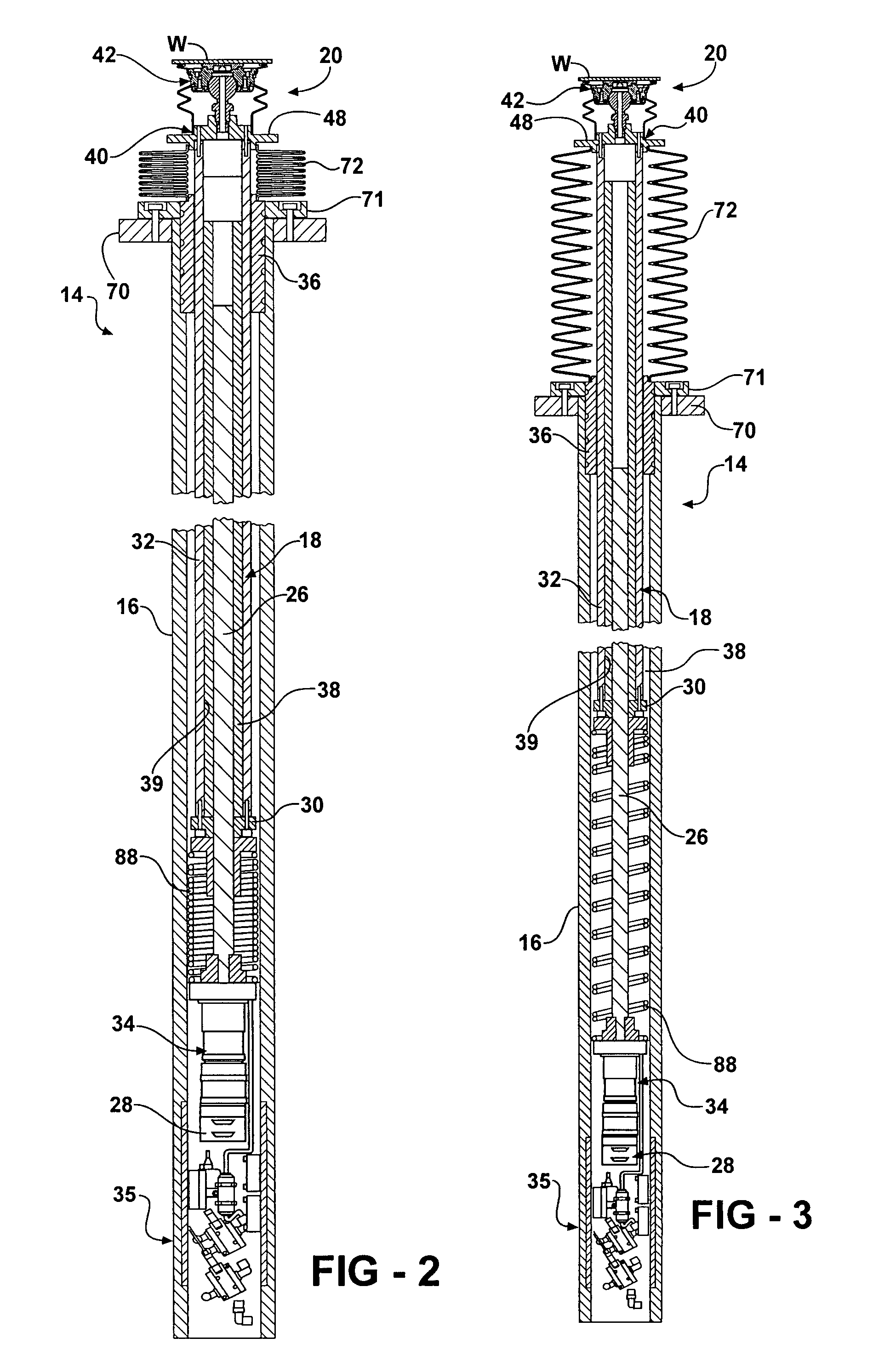
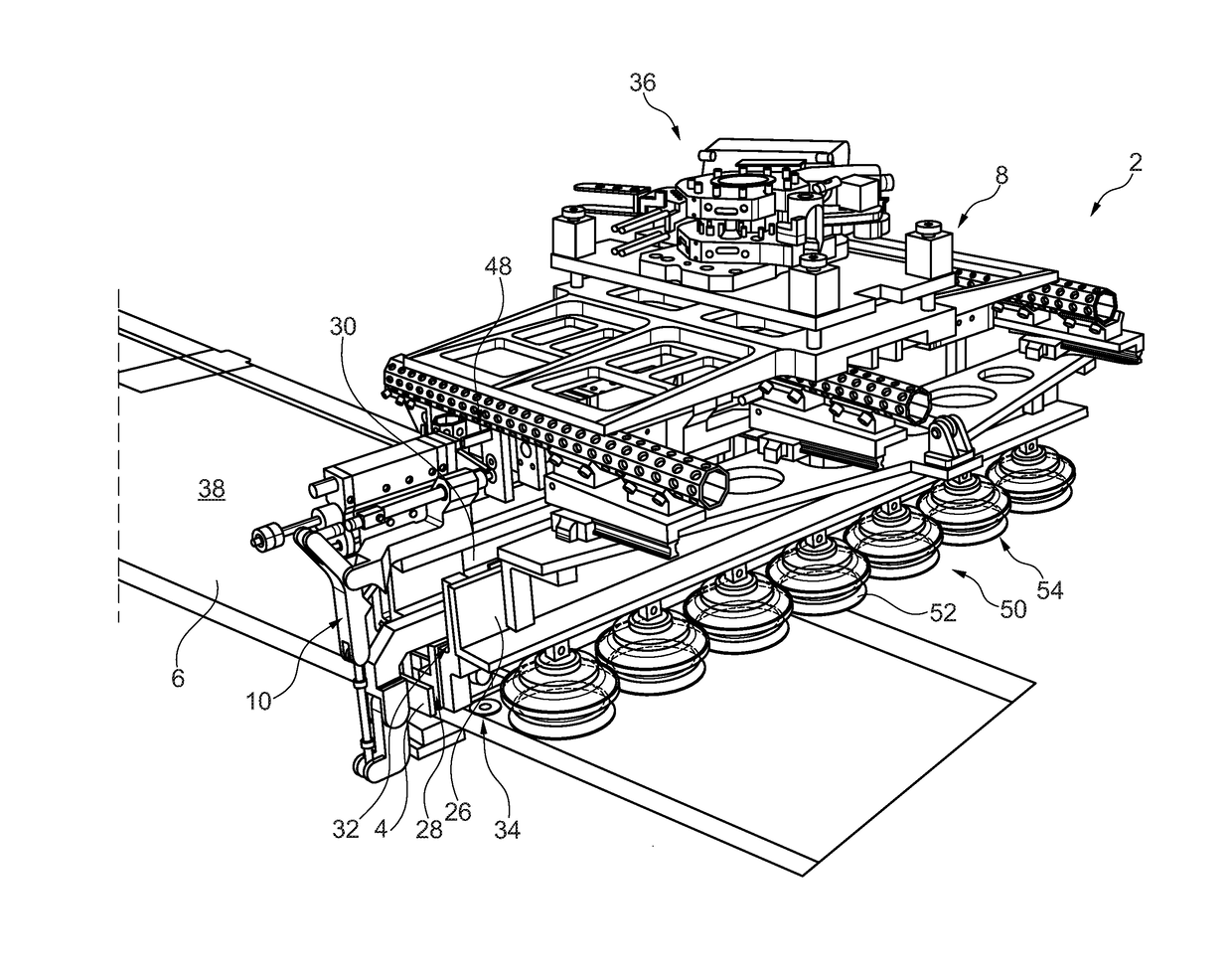
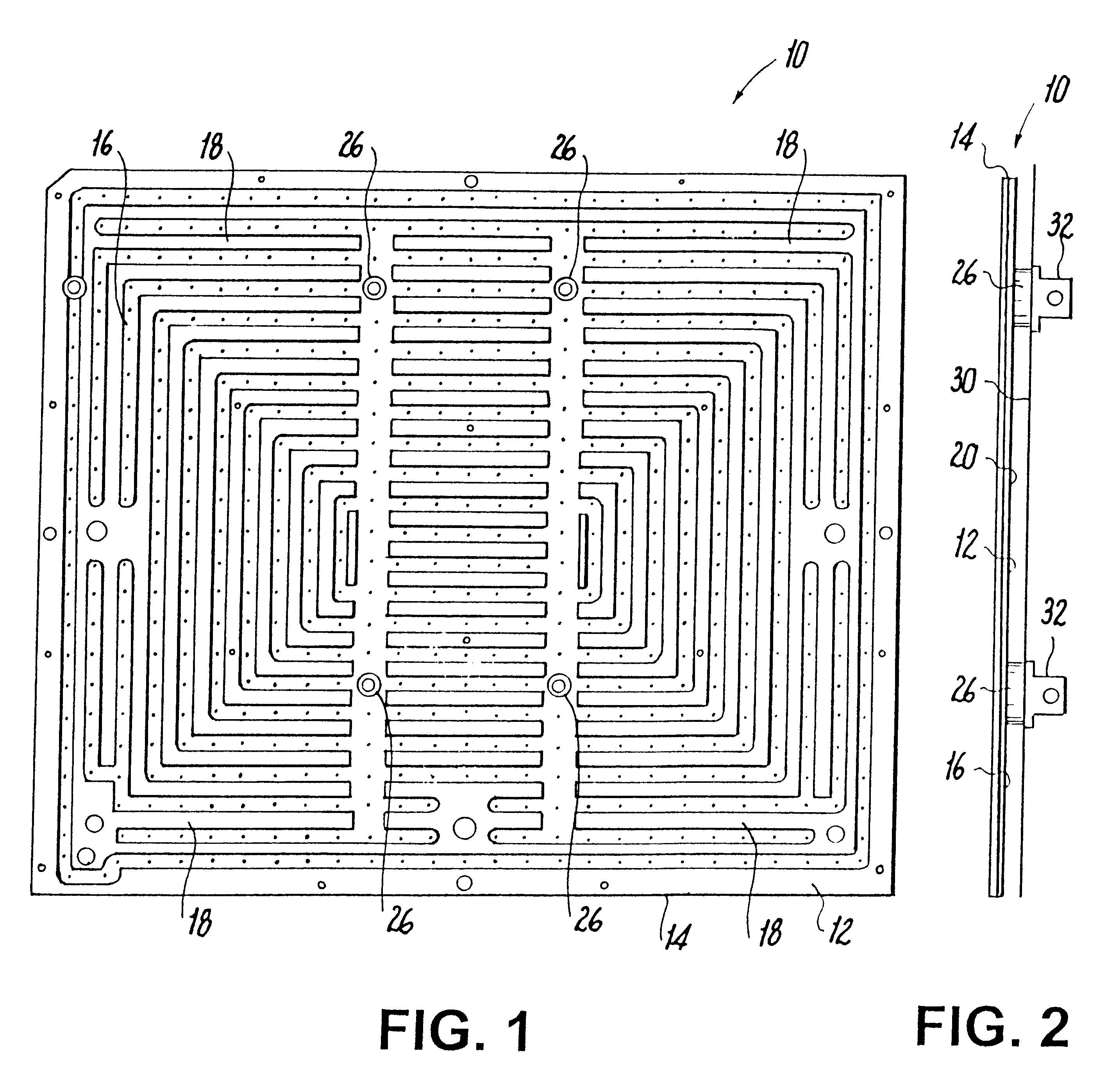
Glass substrate-holding tool and method for producing an EUV mask blank by employing the same
InactiveUS8967608B2InhibitionAccurate placementWorkpiece holdersVacuum evaporation coatingLithographic artistMaterials science
A glass substrate-holding tool employed during the production of a reflective mask blank for EUV lithography includes an electrostatic chuck and a mechanical chuck. A caught and held portion of a glass substrate caught and held by the electrostatic chuck, and pressed portions of the glass substrate pressed by the mechanical chuck are located outside a quality-guaranteed region on each of a film deposition surface and a rear surface of the glass substrate. The sum of a catching and holding force applied to the glass substrate by the electrostatic chuck and a holding force applied to the glass substrate by the mechanical chuck is at least 200 kgf. A pressing force per unit area applied to the glass substrate by the mechanical chuck is at most 25 kgf / mm2.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
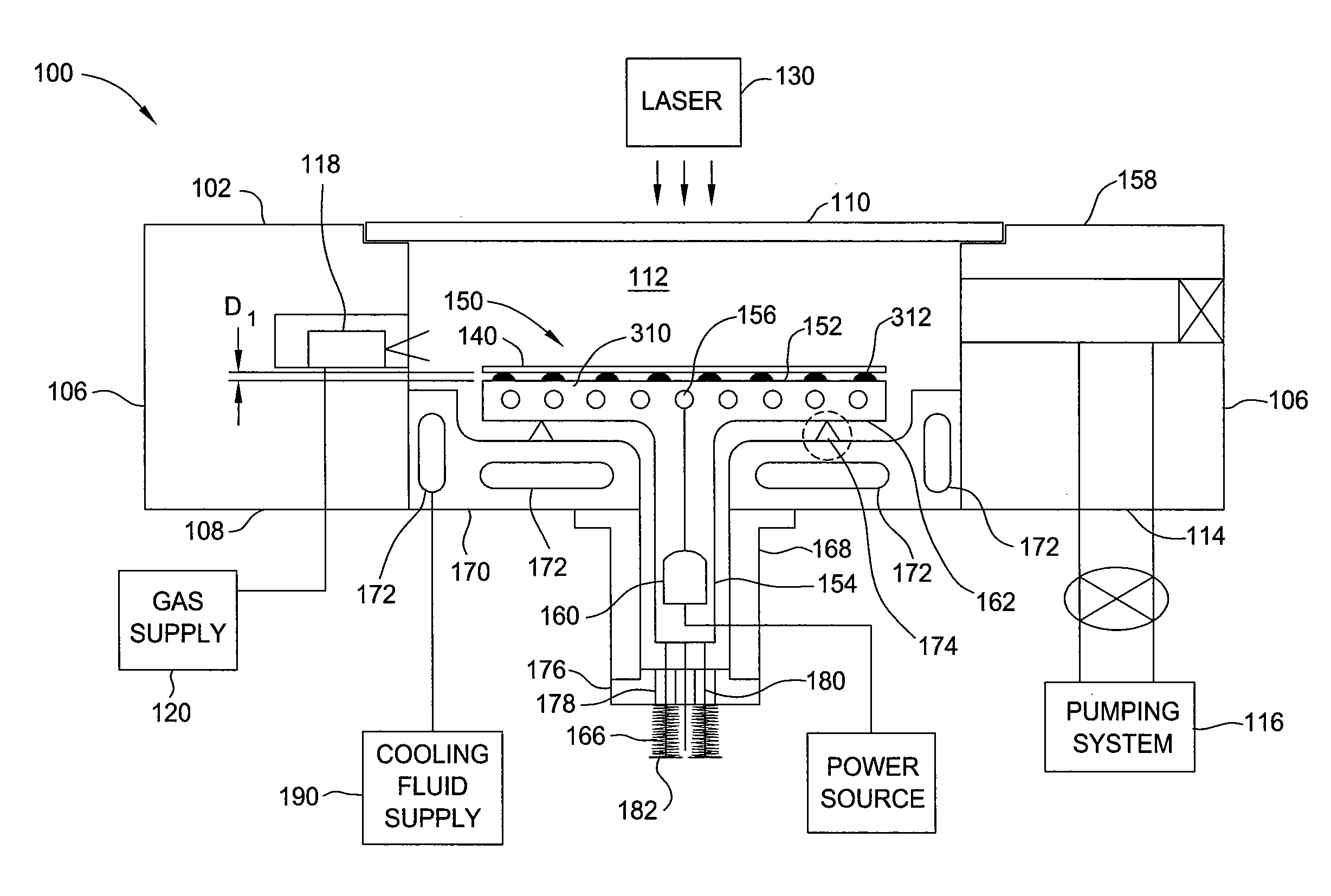
High temperature vacuum chuck assembly
ActiveUS20090179365A1Avoid overall overheatingSleeve/socket jointsMuffle furnacesEngineeringElectrical connector
A vacuum chuck and a process chamber equipped with the same are provided. The vacuum chuck assembly comprises a support body, a plurality of protrusions, a plurality of channels, at least one support member supporting the support body, at least one resilient member coupled with the support member, a hollow shaft supporting the support body, at least one electrical connector disposed through the hollow shaft, and an air-cooling apparatus. The support body has a support surface for holding a substrate (such as a wafer) thereon. The protrusions are formed on and project from the support surface for creating a gap between the substrate and the support surface. The channels are formed on the support surface for generating reduced pressure in the gap. The air-cooling apparatus is used for providing air cooling in the vicinity of the electrical connector.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Stabilizing a substrate using a vacuum preload air bearing chuck
ActiveUS20080229811A1Improve rigidityAvoid deformationLinear bearingsGas cushion bearingsAir bearingEngineering
Substrate processing method and apparatus are disclosed. The substrate processing apparatus includes a non-contact air bearing chuck with a vacuum preload.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Vacuum chuck
InactiveUS6032997AEasy and less-expensive to manufactureEasy alignmentSleeve/socket jointsGripping headsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A vacuum chuck having a body portion made of moldable glass or another suitable dielectric material including a top surface and bottom surface, a series of flat lands on the top surface of the body portion for supporting a wafer, and a series of orifices and vacuum lines for drawing a vacuum to secure the wafer in place on the lands of the body portion. A method of manufacturing such a vacuum chuck. A method of aligning a wafer on such a vacuum chuck.
Owner:EXCIMER LASER SYST
Method and arrangement for enhancing process variability and lifetime reliability through 3D integration
InactiveUS20090144669A1Improve lifetime reliabilityEnhancing process variabilitySolid-state devicesWork holdersSemiconductor chipDependability
A method of enhancing semiconductor chip process variability and lifetime reliability through a three-dimensional (3D) integration applied to electronic packaging. Also provided is an arrangement for implementing the inventive method.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thin wafer chuck
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
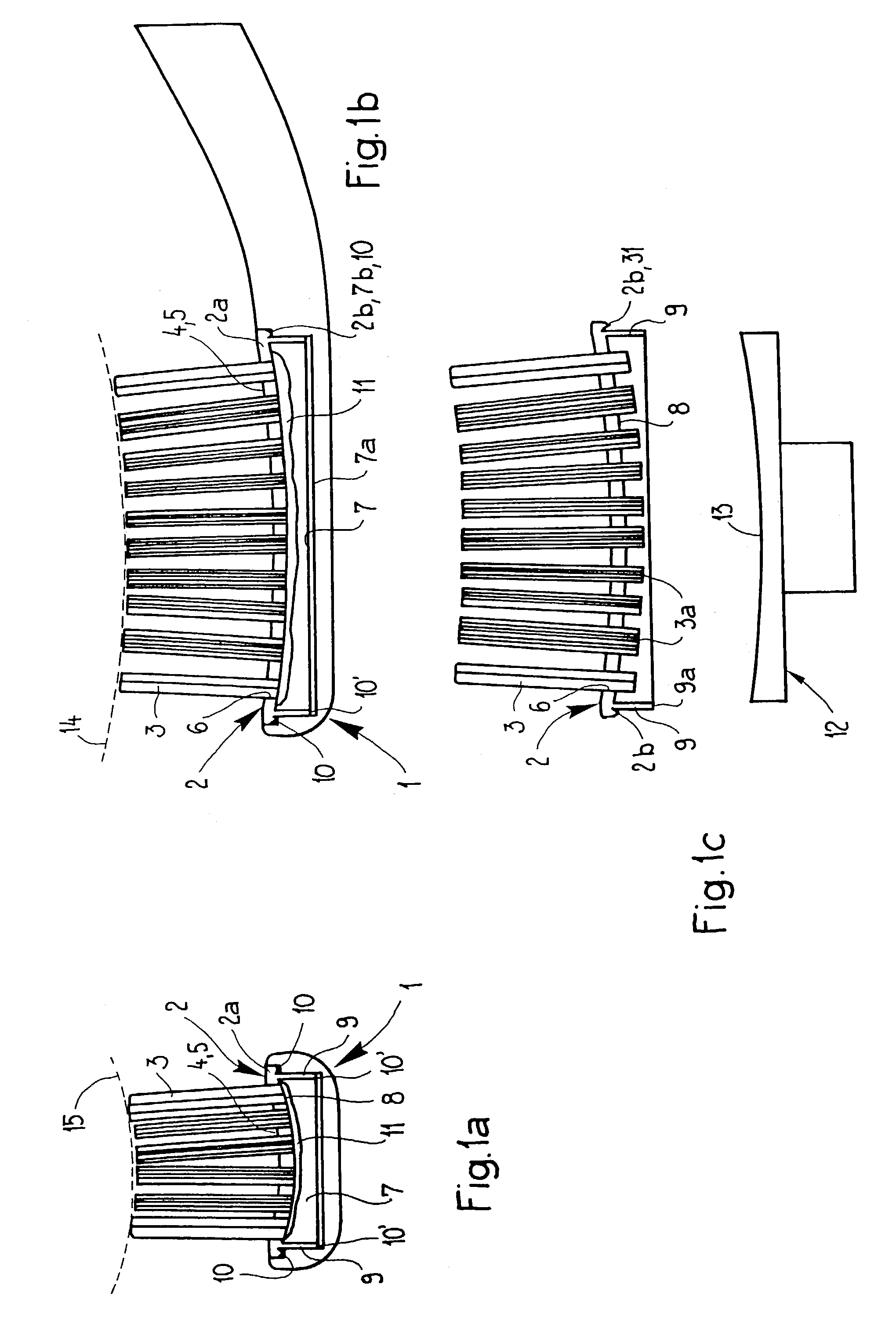
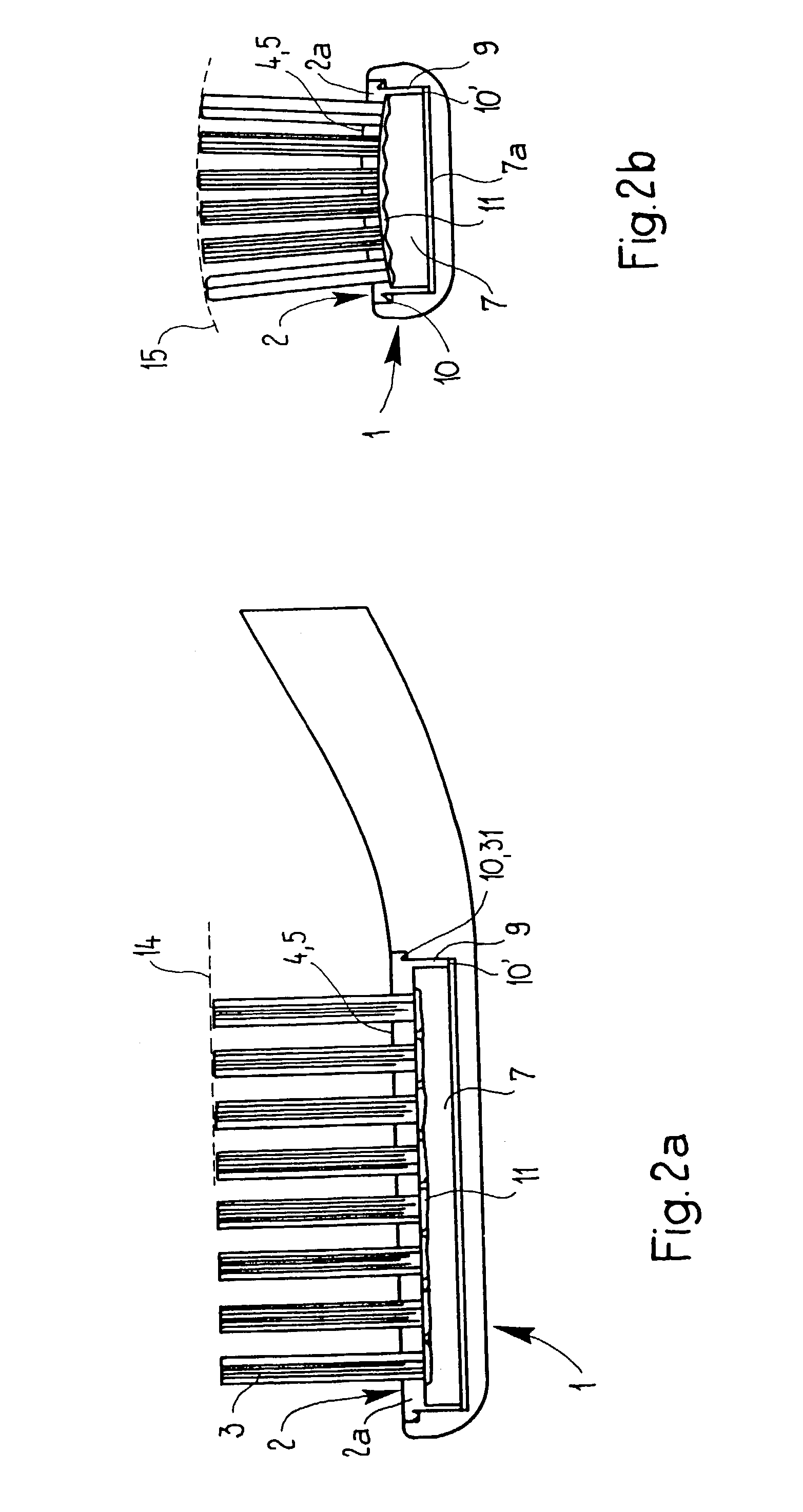
Process for producing a toothbrush
InactiveUS6988777B2Easy to cleanMultiplicityBrush bodiesBristle carriersEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a toothbrush which is produced by AFT and has a head part and at least one carrier element connected thereto, in the case of which the front surface of the head part, said front surface being formed by the top surfaces of the at least one carrier element, has a non-planar three-dimensional configuration and / or is capable of assuming such a configuration during intended use. The invention also relates to a process for producing such a toothbrush.
Owner:TRISA HLDG AG
Stabilizing a substrate using a vacuum preload air bearing chuck
ActiveUS7607647B2Improve rigidityAvoid deformationLinear bearingsGas cushion bearingsAir bearingEngineering
Substrate processing method and apparatus are disclosed. The substrate processing apparatus includes a non-contact air bearing chuck with a vacuum preload.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
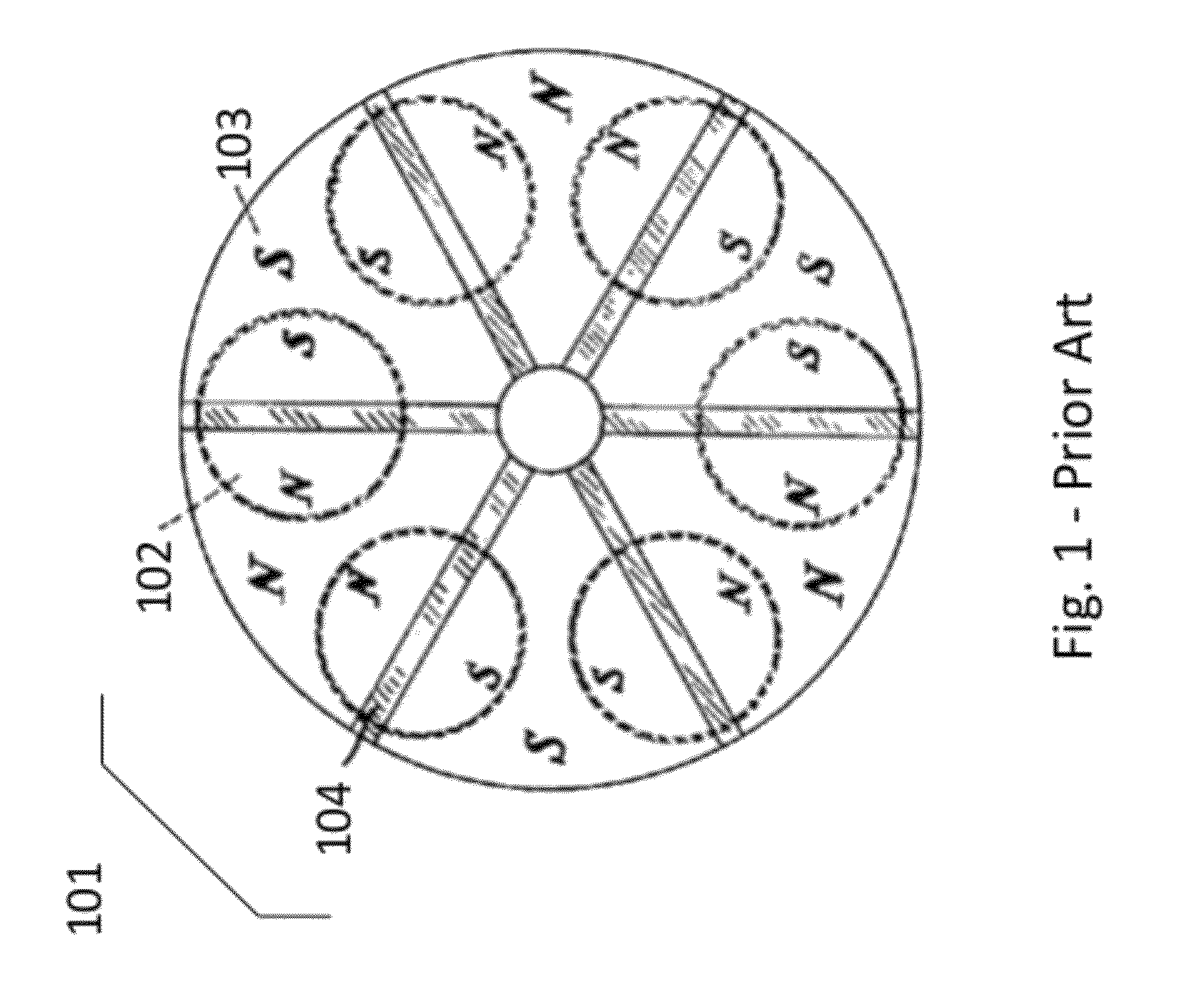
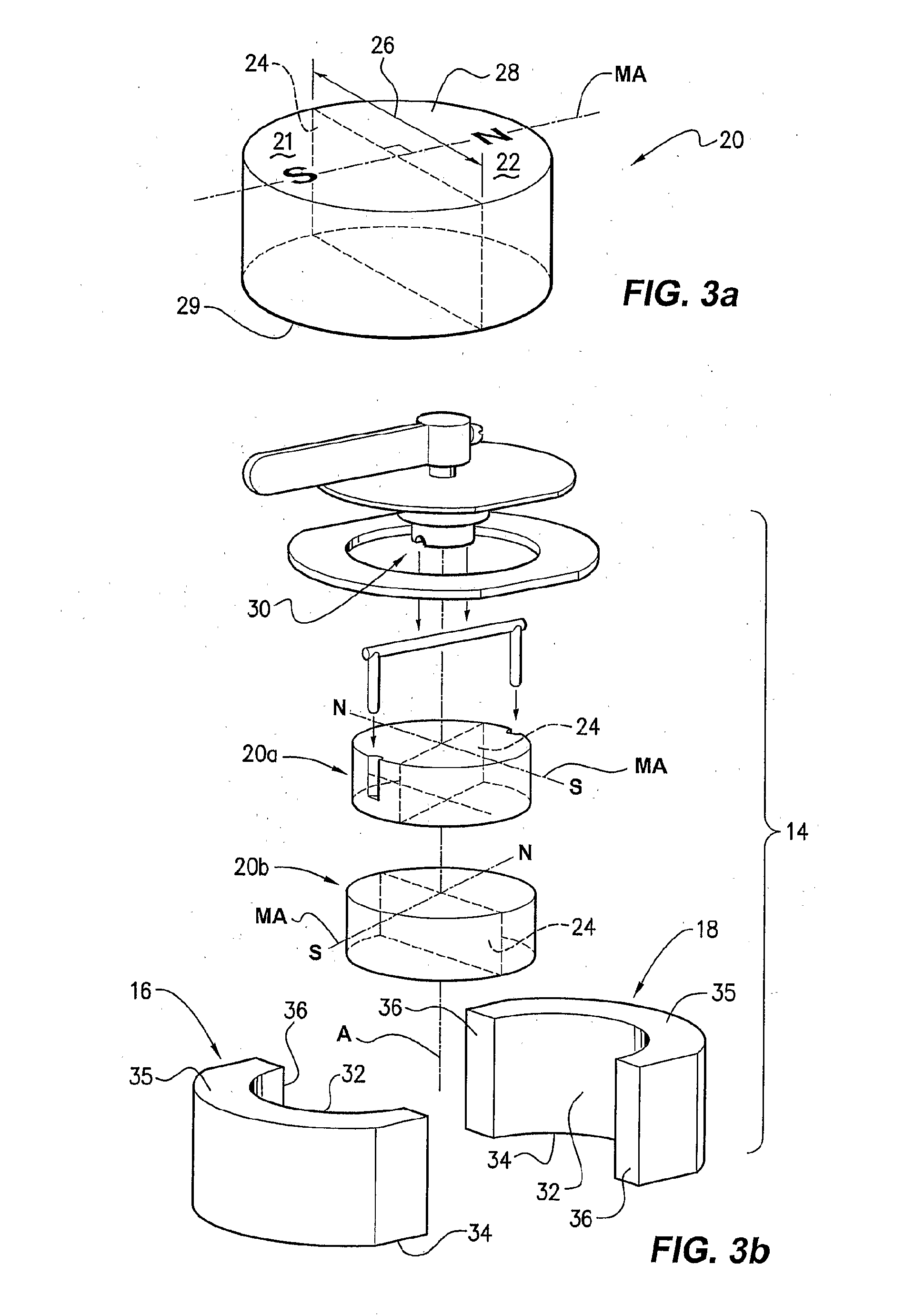
Switchable permanent magnetic device
InactiveUS7012495B2Improve propertiesMaximized strengthElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsPole pieceFerromagnetism
A switchable magnetic device includes a first magnet and a second magnet, both of which are essentially cylindrical. Magnets are housed in a housing made from pole pieces. Pole pieces are ferromagnetic. Lower magnet is fixedly mounted in the housing while upper magnet can rotate within the housing. Upper magnet is formed with notches or grooves along its vertical side walls. These notches or grooves receive downwardly depending arms of bar. Bar is received inside a groove formed on boss. Boss is connected to a short bar that, in turn, is fixedly connected to a handle or lever. By this means, rotation of handle or lever causes rotation of second magnet. When the upper magnet is positioned such that its north pole substantially overlies the south pole of lower magnet and the south pole of upper magnet substantially overlies the north pole of lower magnet, the first and second magnets act as an internal active magnetic shunt and as a result the external magnetic field strength from the device is quite low. Rotating the upper magnet 180° about its axis of rotation brings the magnets into alignment such that the respective north and south poles of the upper magnet substantially overlie respective north and south poles of lower magnet. In this alignment, the external magnet field from the device is quite strong and the device can be affixed to surfaces or objects.
Owner:MAGSWITCH TECH
Method for manufacturing brushes and brush manufacturing machine applying this method
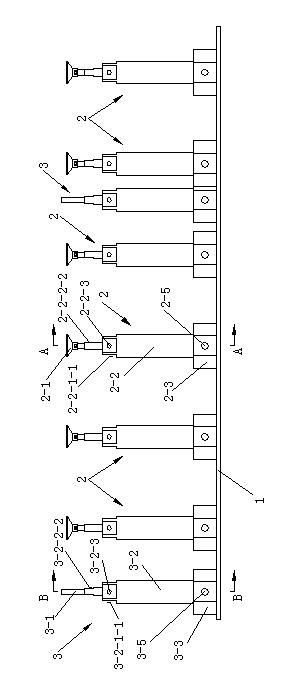
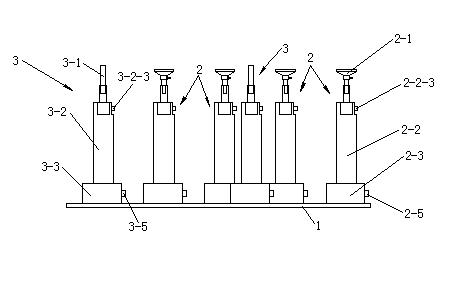
InactiveUS6290303B1Fast and easy to control systematic fillingImprove versatilityBrush bodiesBristleFiber bundleSynthetic materials
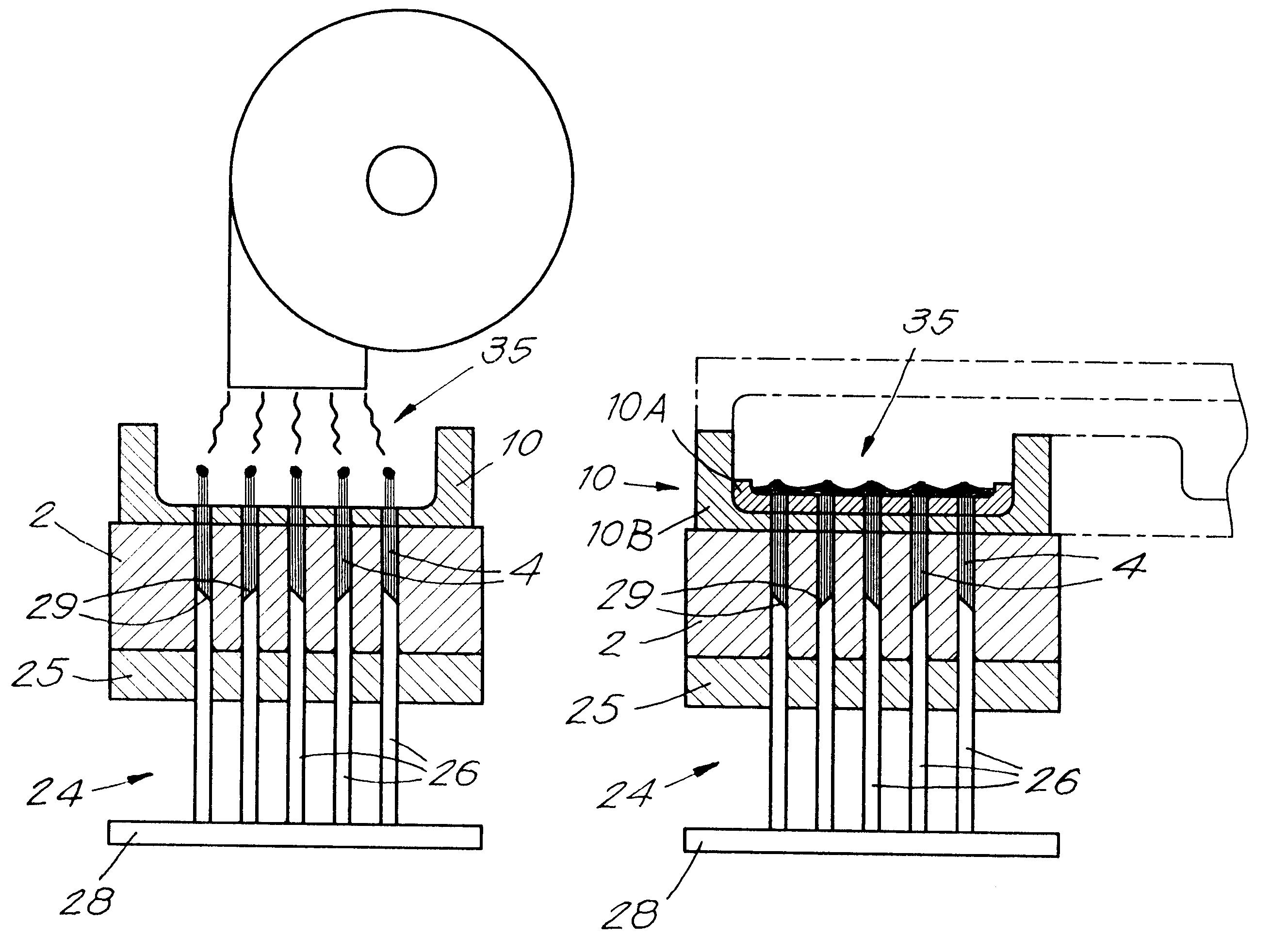
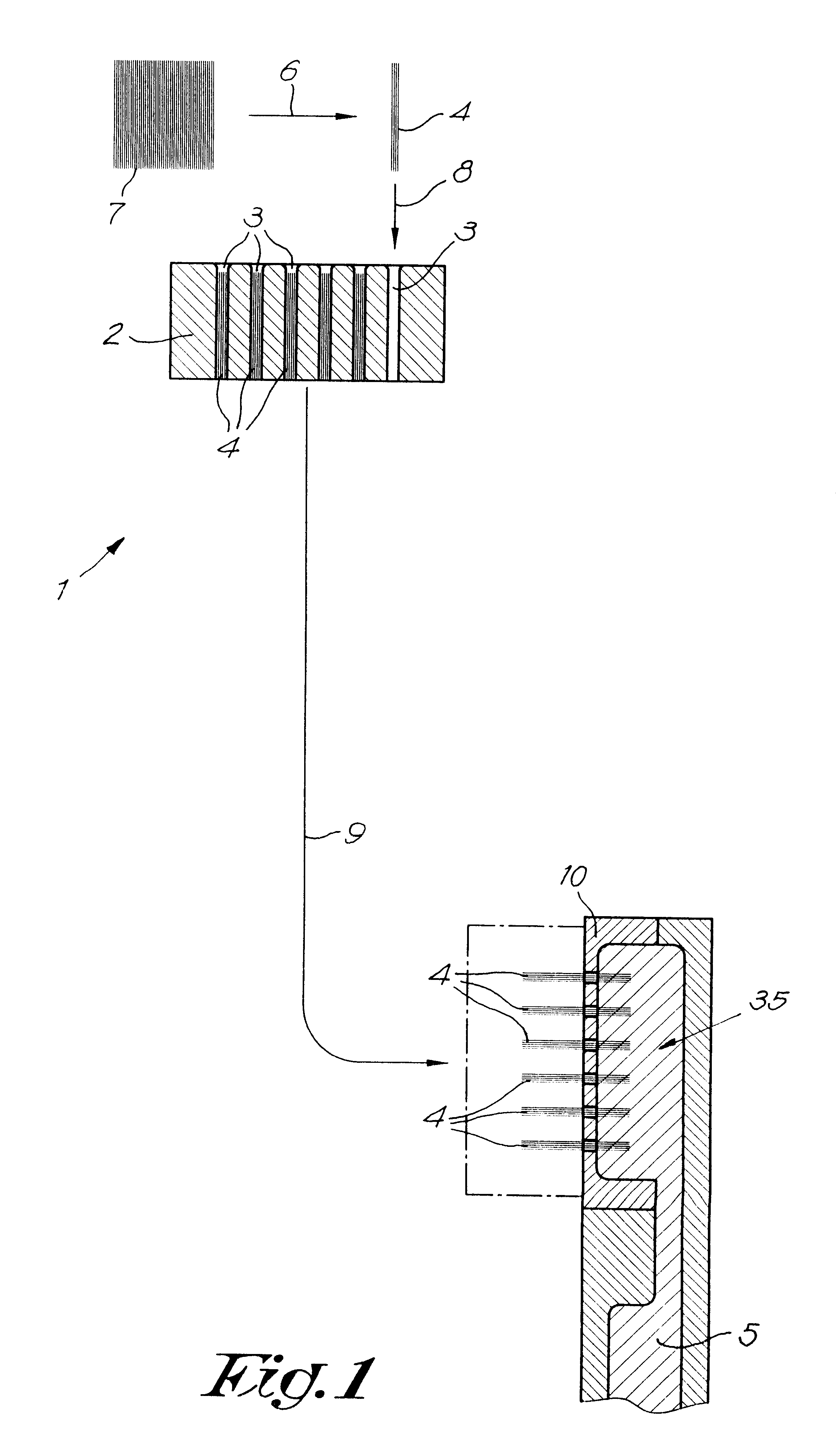
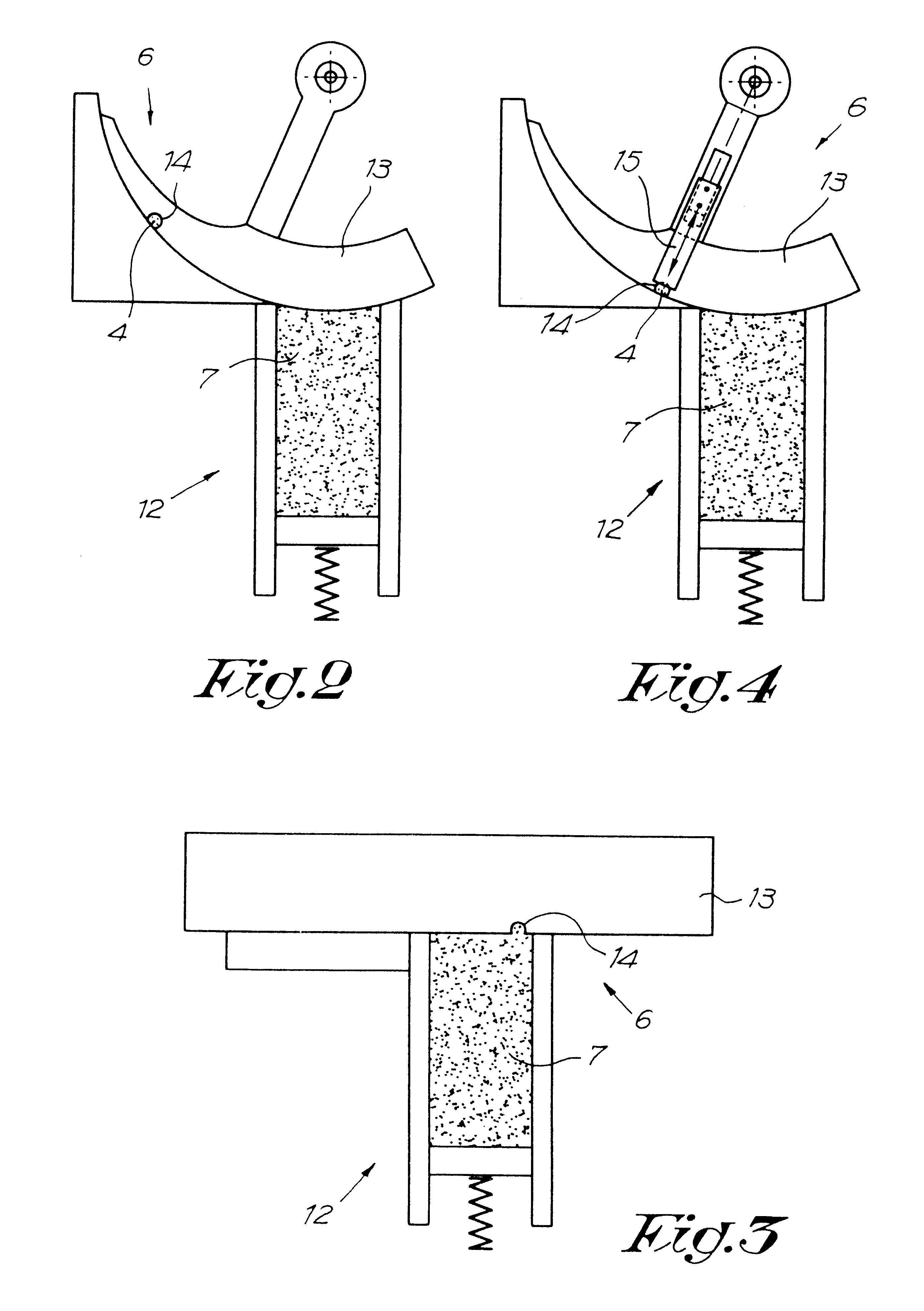
A method and device for manufacturing brushes. The device includes at least one carrier (2) with openings (3) which are mutually arranged according to a certain pattern. The fiber bundles (4) are separated laterally from at least one quantity of loose fibers (7). The fiber bundles (4) are inserted in a mechanical manner, step-by-step, in the openings (3) of the carrier (2). An extremity of the fiber bundles (4) are transferred simultaneously in a mechanical manner from the carrier (2) toward a holder (10). The fiber bundles (4) are fixed in at least a portion of a brush body (5) by positioning the extremity of the fiber bundles (4) in a mold, such that the fiber bundles (4) extend through the holder (10). A synthetic material is injected in the mold and form at least a portion of the brush body (5).
Owner:FIRMA G B BOURCHERIE NV
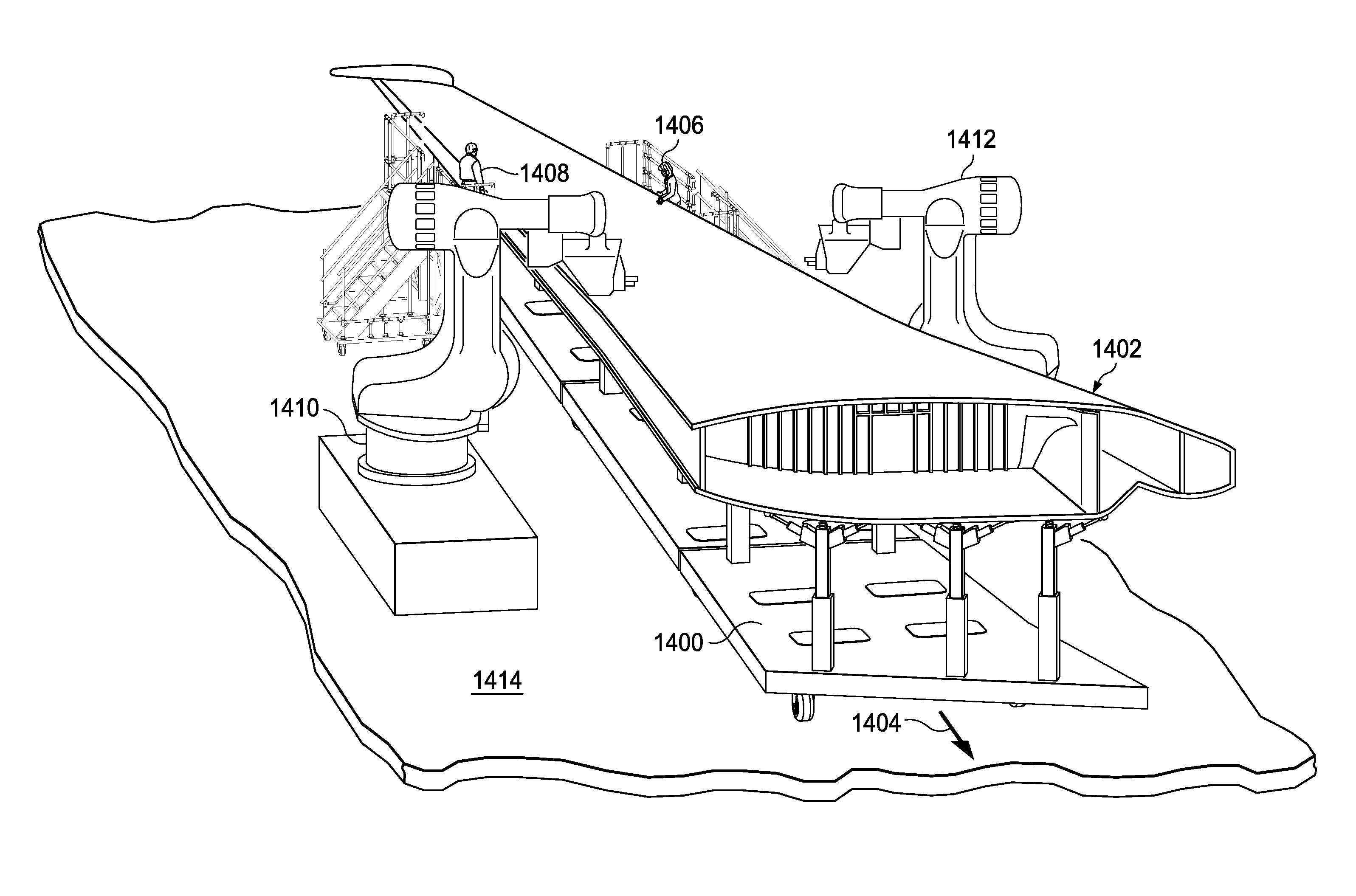
Autonomous Carrier for Continuously Moving Wing Assembly Line
ActiveUS20110054694A1Sampled-variable control systemsComputer controlSupporting systemMarine engineering
A method and apparatus for moving a structure. The structure is supported on a carrier. The carrier comprises a platform having a first side and a second side, a movement system associated with the first side and configured to move the platform on a surface, a support system associated with the second side of the platform and configured to support the structure on the platform, and a leveling system configured to substantially maintain the structure in a desired orientation during movement of the platform on the surface. The carrier is moved with the structure over the surface. At least one of the movement system and the support system is adjusted to substantially maintain the structure in the desired orientation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Vaccum support and transfer of flexible material
A transfer assembly and method for transferring a flexible sheet of material which is subject to wrinkling, folding and / or creasing. The assembly and method includes a vacuum manifold having a cavity which is connected to an evacuation source for drawing a vacuum on the cavity, and an opening on the manifold of a given size and shape and communicating with the cavity. A sheet of porous material for supporting the flexible sheet of material for transfer thereon covers the opening and has a plurality of fine pores extending therethrough. The pores are profusely and uniformly distributed entirely over an area of the sheet of porous material which area is at least substantially of the same size and shape as the flexible sheet of material which is to be transferred thereon, so that substantially the entire area of the flexible sheet of material which is to be transferred is exposed to the pores. The pores are subjected to the vacuum in the manifold cavity in the substantial absence of impairment of communication of the vacuum to the pores to uniformly pickup and hold the flexible sheet of material for transfer without folding, wrinkling or creasing of the flexible sheet of material.
Owner:TROPICANA PROD INC
Magnetic clamp for welding magnetic objects
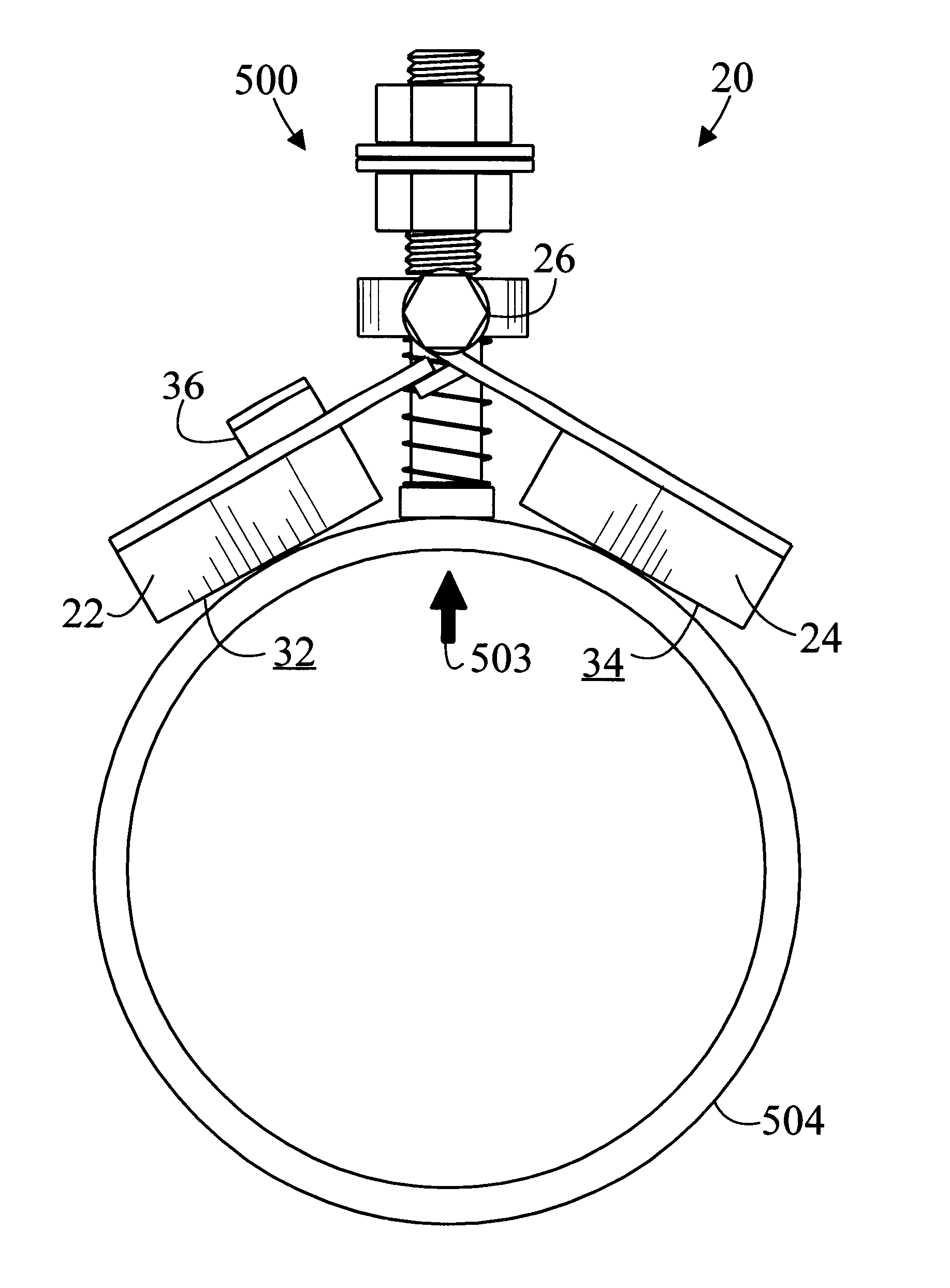
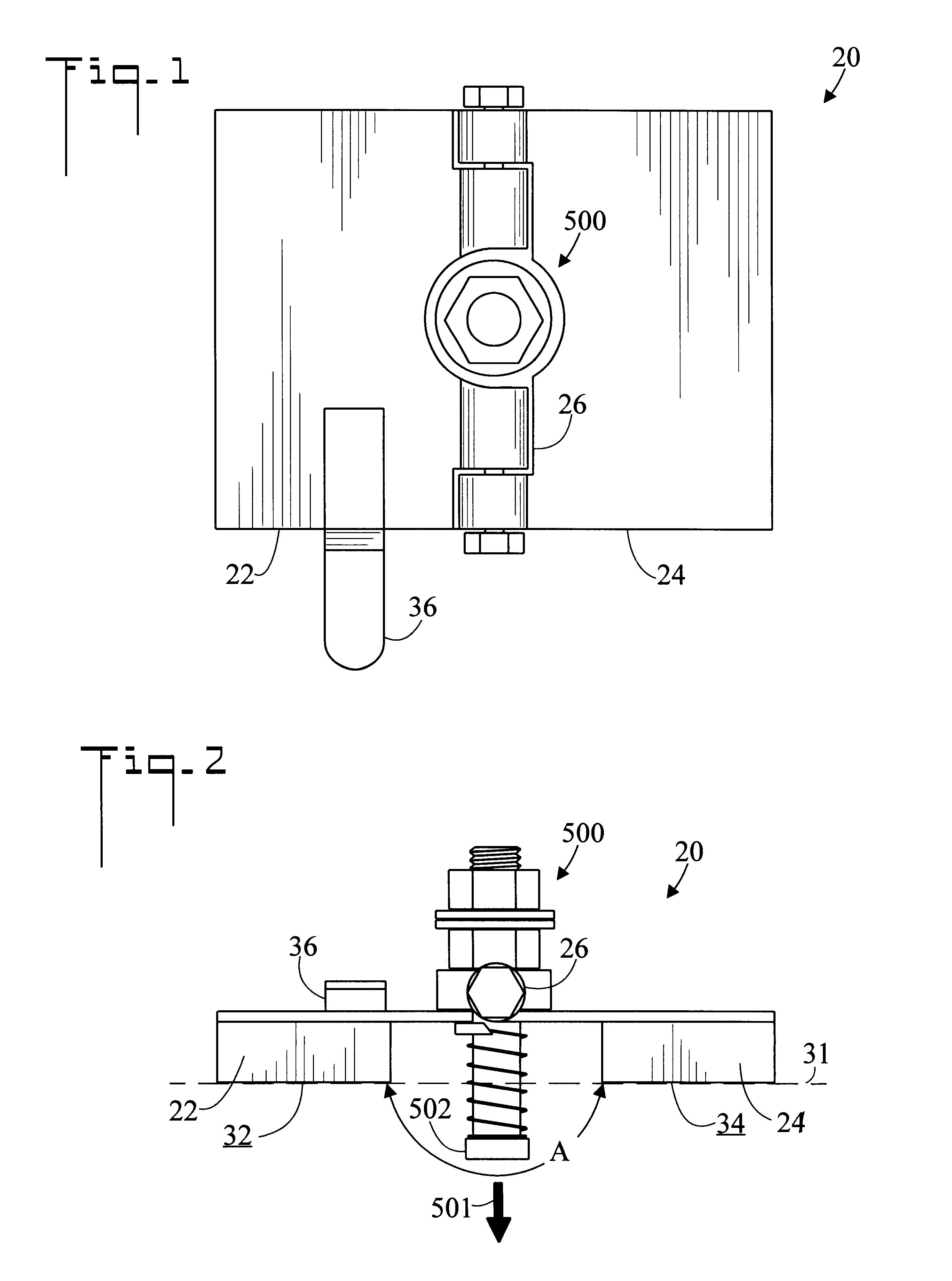
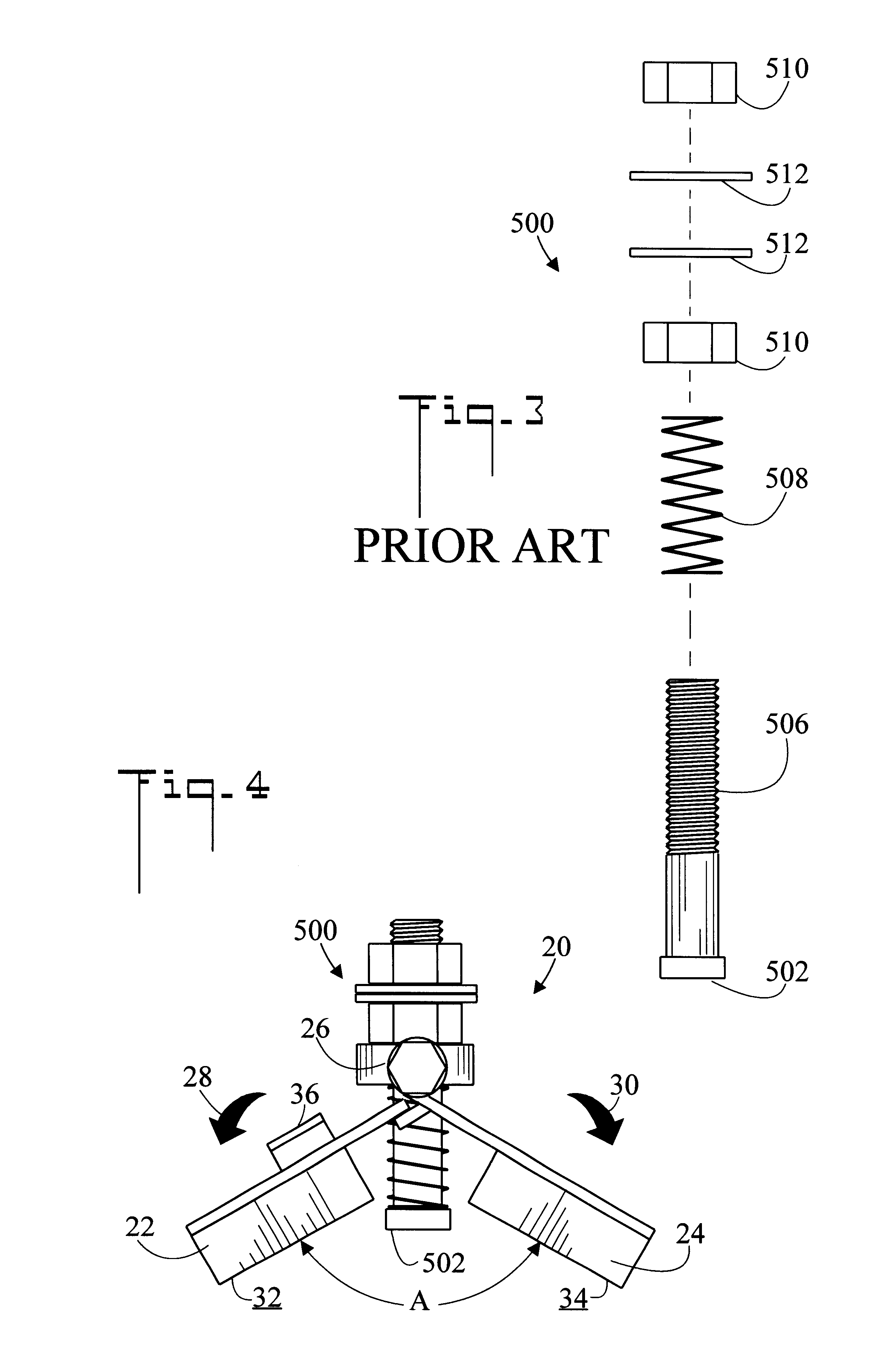
InactiveUS6279885B1Easily be twisted off of pipeImprove gripWorkpiece holdersWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringHinge angle
A magnetic clamp (20) for welding a magnetic object (504), includes a first magnetic member (22) and a second magnetic member (24). A hinge (26) connects magnetic members (22) and (24) so that an angle formed by magnetic members (22) and (24) may be changed. A spring loaded terminal (500) having a contact end (502) is disposed between first magnetic member (22) and second magnetic member (24). Magnetic clamp (20) may be attached to magnetic object (504) so that first magnetic member (22), second magnetic member (24), and contact end (502) all abut magnetic object (504). In a preferred embodiment, a removal tab (36) is connected to magnetic clamp (20) to assist in removing magnetic clamp (20) from magnetic object (504).
Owner:LEON JR RAYMOND
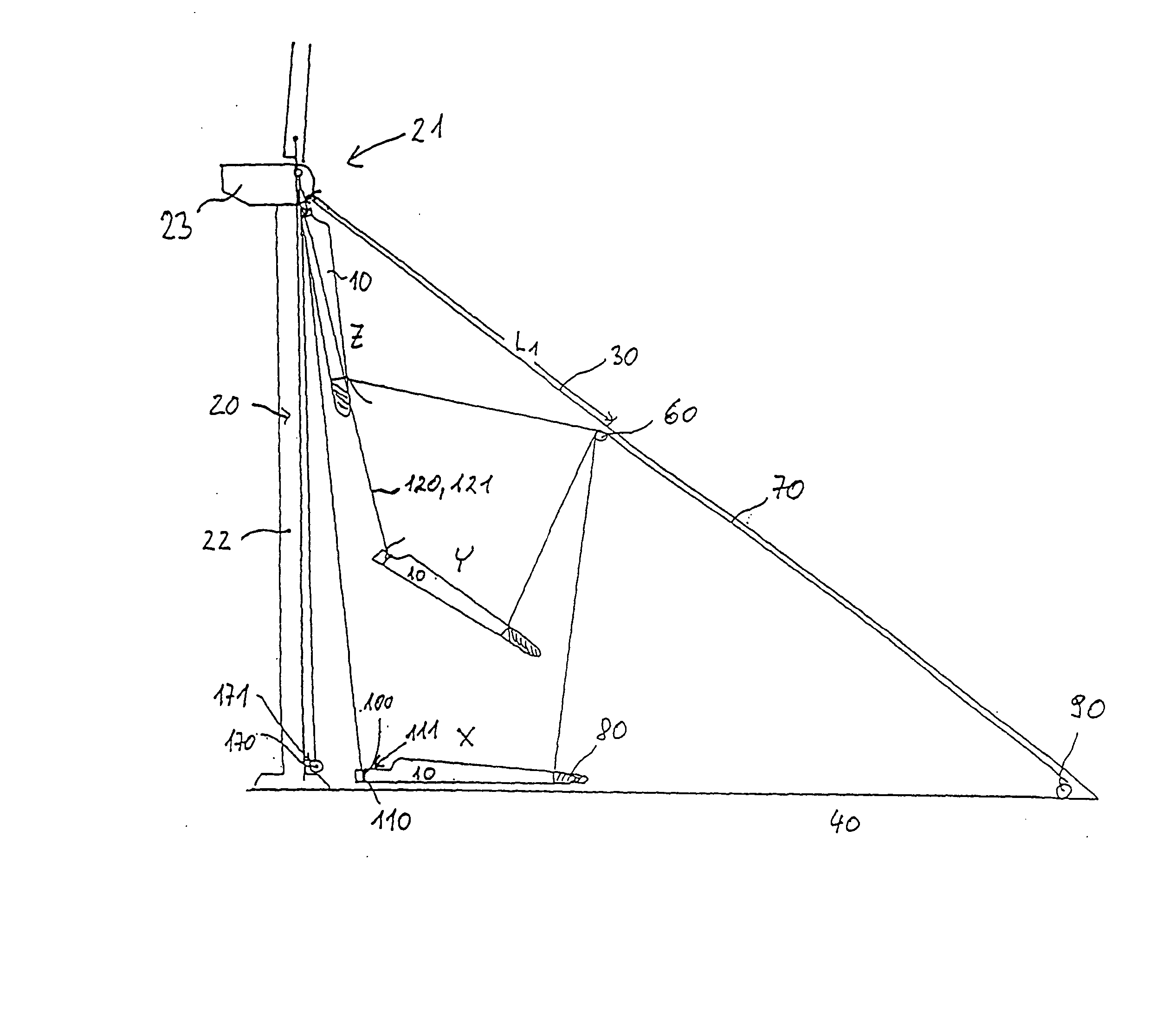
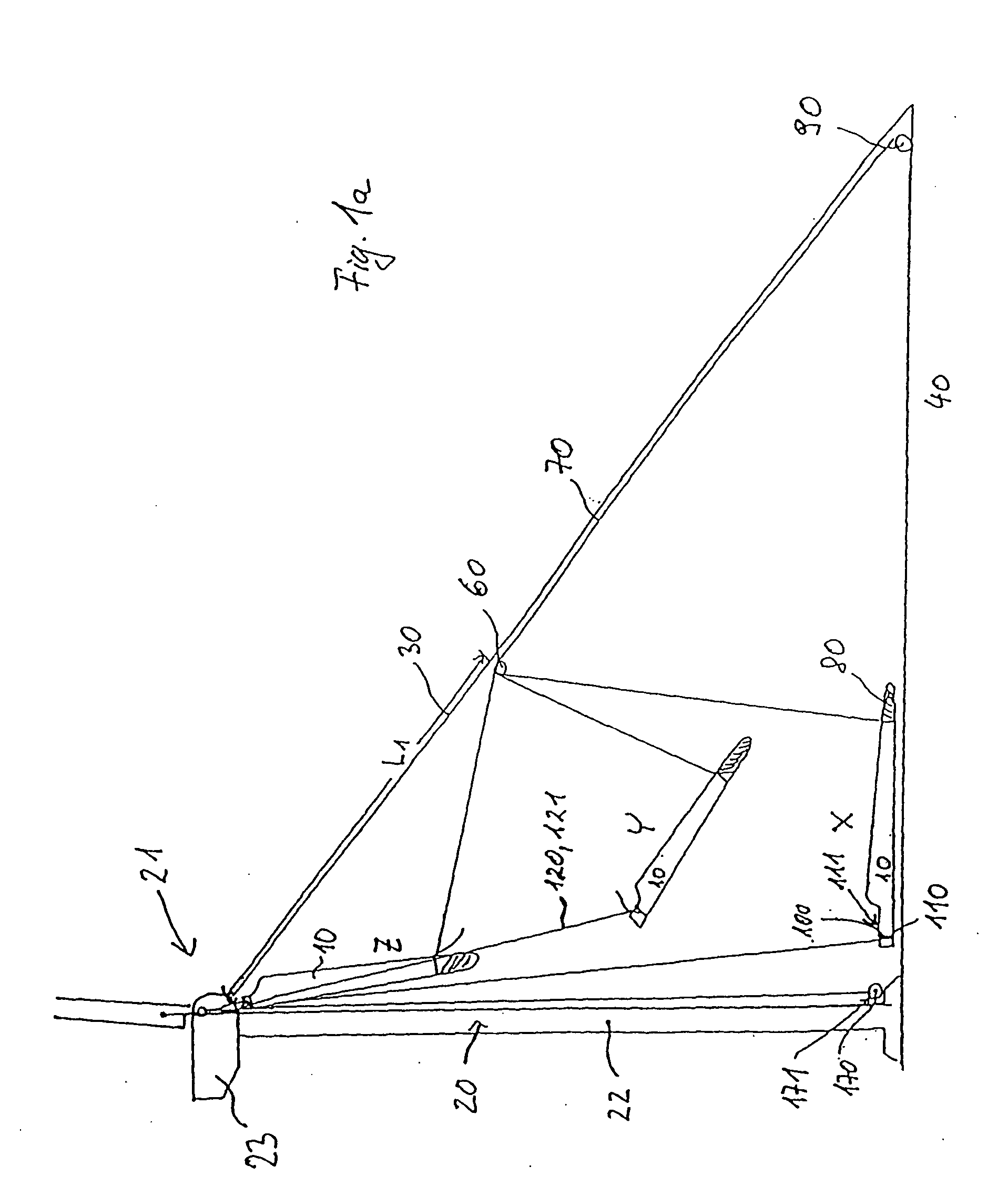
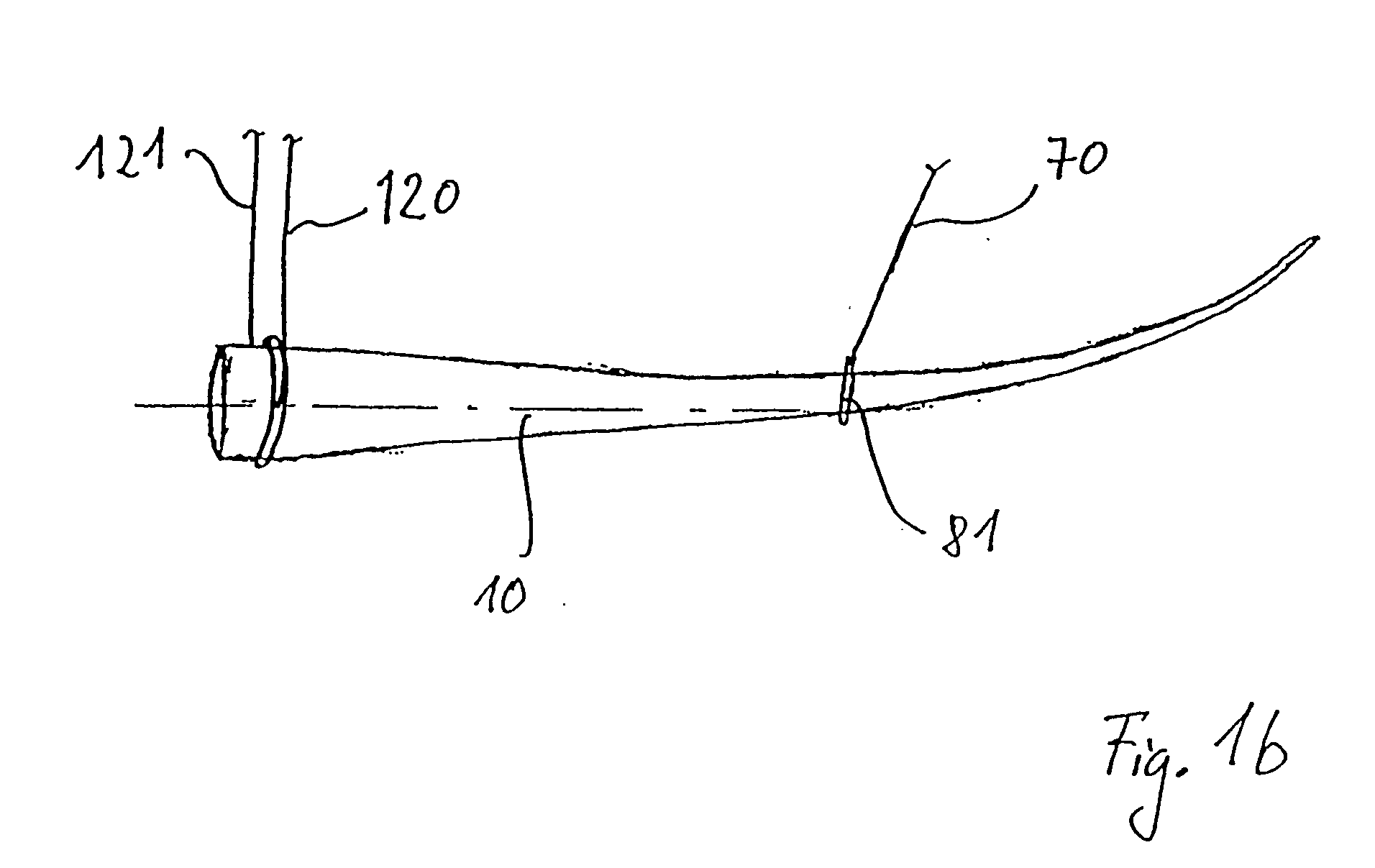
Device and Method for Mounting and Dismantling a Component of a Wind Turbine
The invention relates to a device for mounting and / or dismantling a component (10), in particular a rotor blade of a wind turbine (20) comprising a tower head (21). Said device comprises at least one guide element (30) that stretches between the tower head (21) and the ground (40) and has at least one supporting device (60) that is essentially fixed in the air, supporting at least a partial load of the weight of the component (10) during the transport of the latter (10) between the ground (40) and the wind turbine (20). At least one guy (70) leads from the supporting device (60) to the component (10), whereby the length of said guy between the supporting device (60) and the component (10) can be modified.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
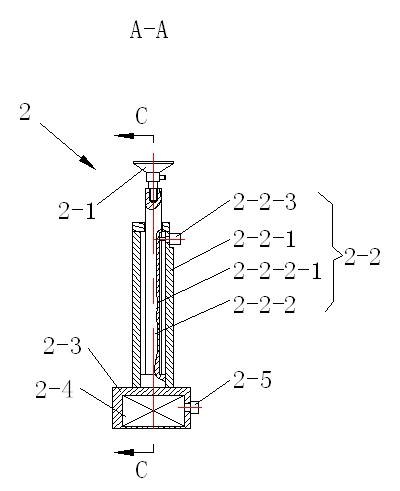
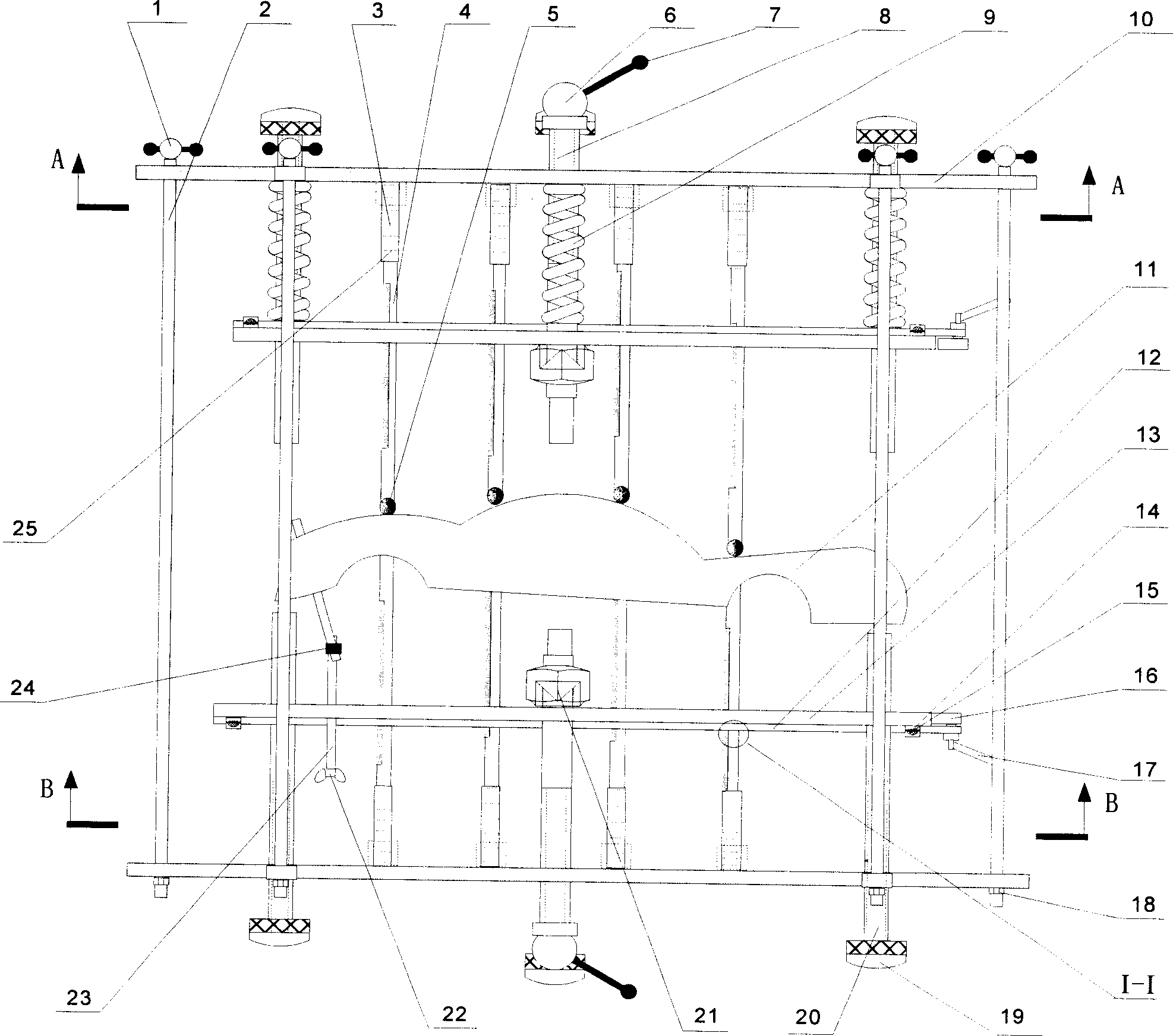
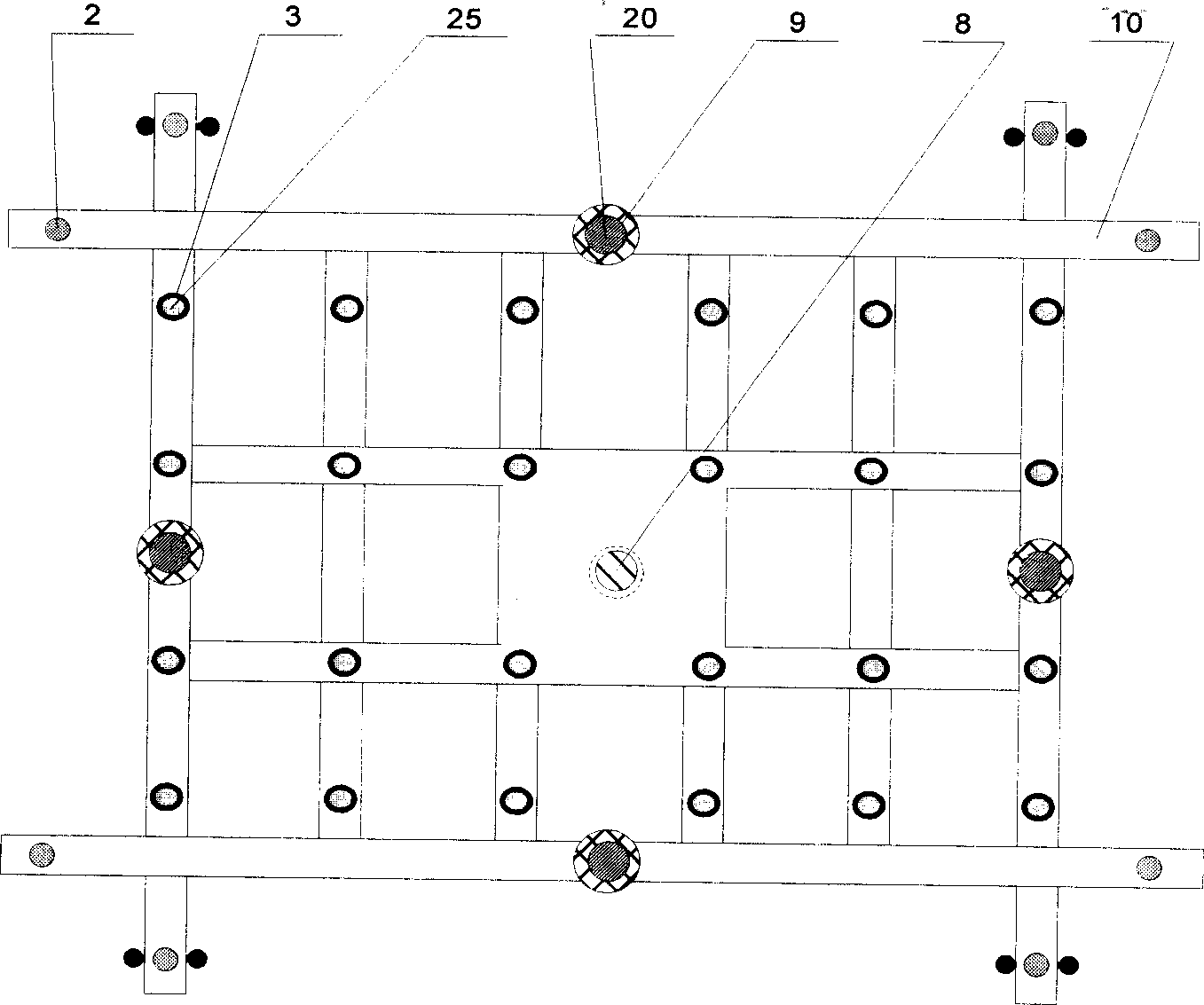
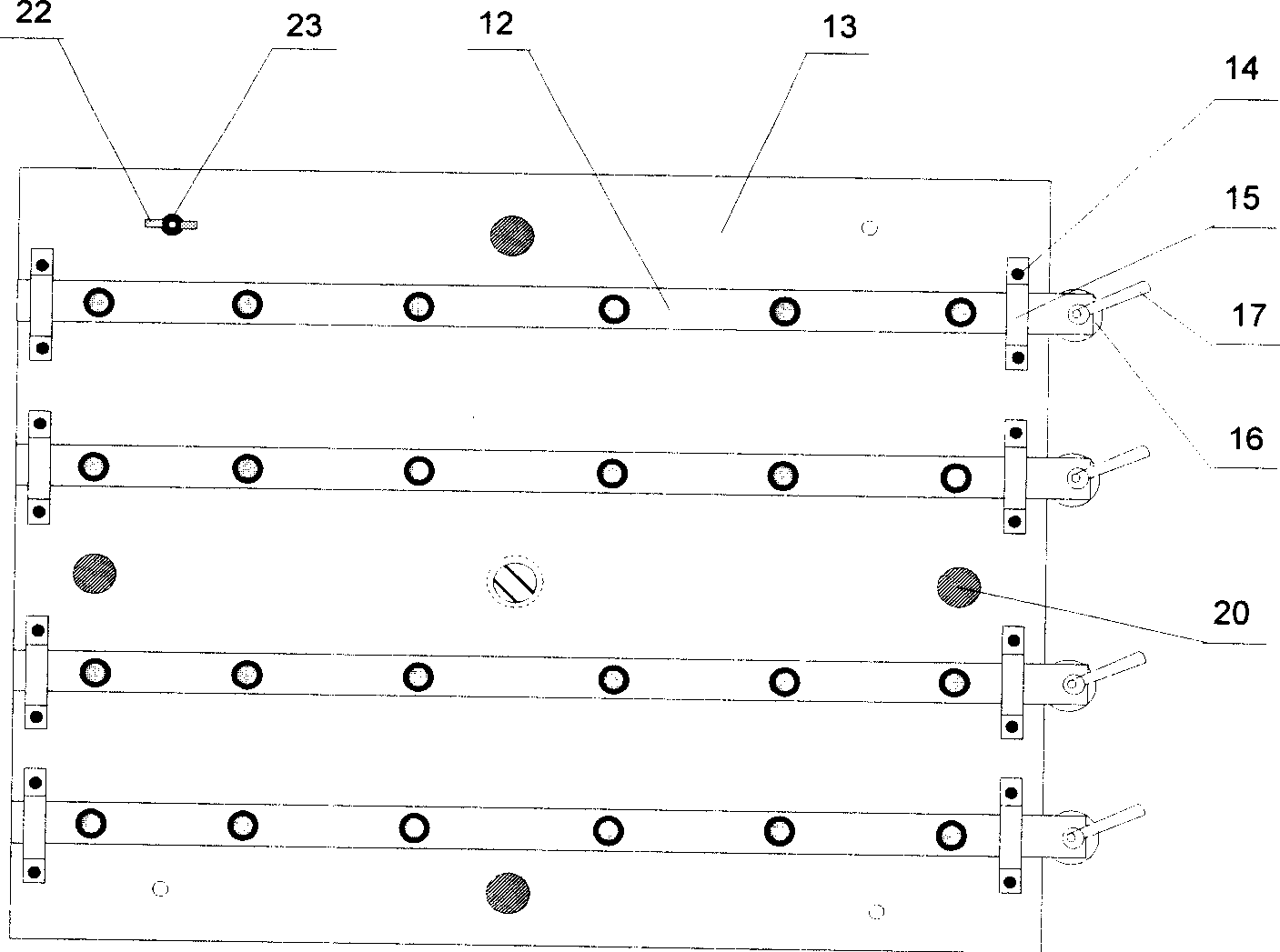
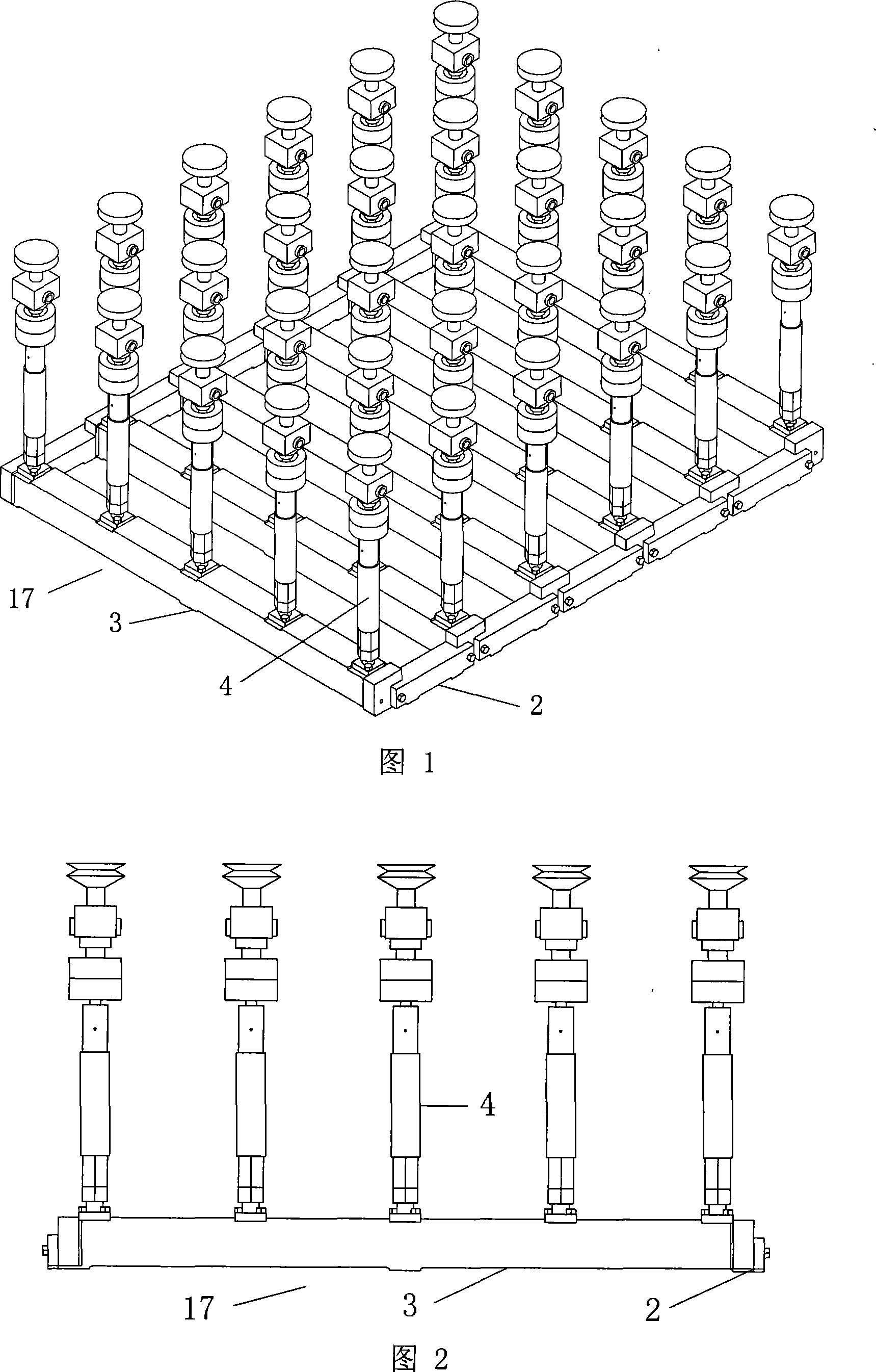
Flexible multipoint tool set for positioning and supporting thin-walled curved surface parts
The invention discloses a flexible multipoint tool set for positioning and supporting thin-walled curved surface parts, which comprises an operating platform and at least three supporting / fixing units, wherein the supporting / fixing units are all arranged on the operating platform, and each supporting / fixing unit comprises a spherical hinge side draught vacuum chuck, a first hoisting assembly and a fixed base, the spherical hinge side draught vacuum chuck is arranged at the upper part of the first hoisting assembly, and the lower part of the first hoisting assembly is arranged on the fixed base; the fixed base of each supporting / fixing unit is provided with a first electromagnet, and the first electromagnet is in magnetic suction with the upper surface of the operating platform; and the operating platform is also provided with at least two positioning units, each positioning unit comprises a positioning pin, a second hoisting assembly and a positioning base, the positioning pin is arranged at the upper end part of the second hoisting assembly, the lower end part of the second hoisting assembly is arranged on the positioning base, and the positioning base is connected with the operating platform. The flexible multipoint tool set disclosed by the invention not only can accurately position thin-walled curved surface parts, but also can conveniently move above the operating platform and adjust the distance between every two supporting / fixing units.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Flexible device for multipoint clamping and positioning spatial 3D thin wall part
InactiveCN1695896APrecise liftingConvenient location changeWelding/cutting auxillary devicesWork holdersCircular discMultiple point
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
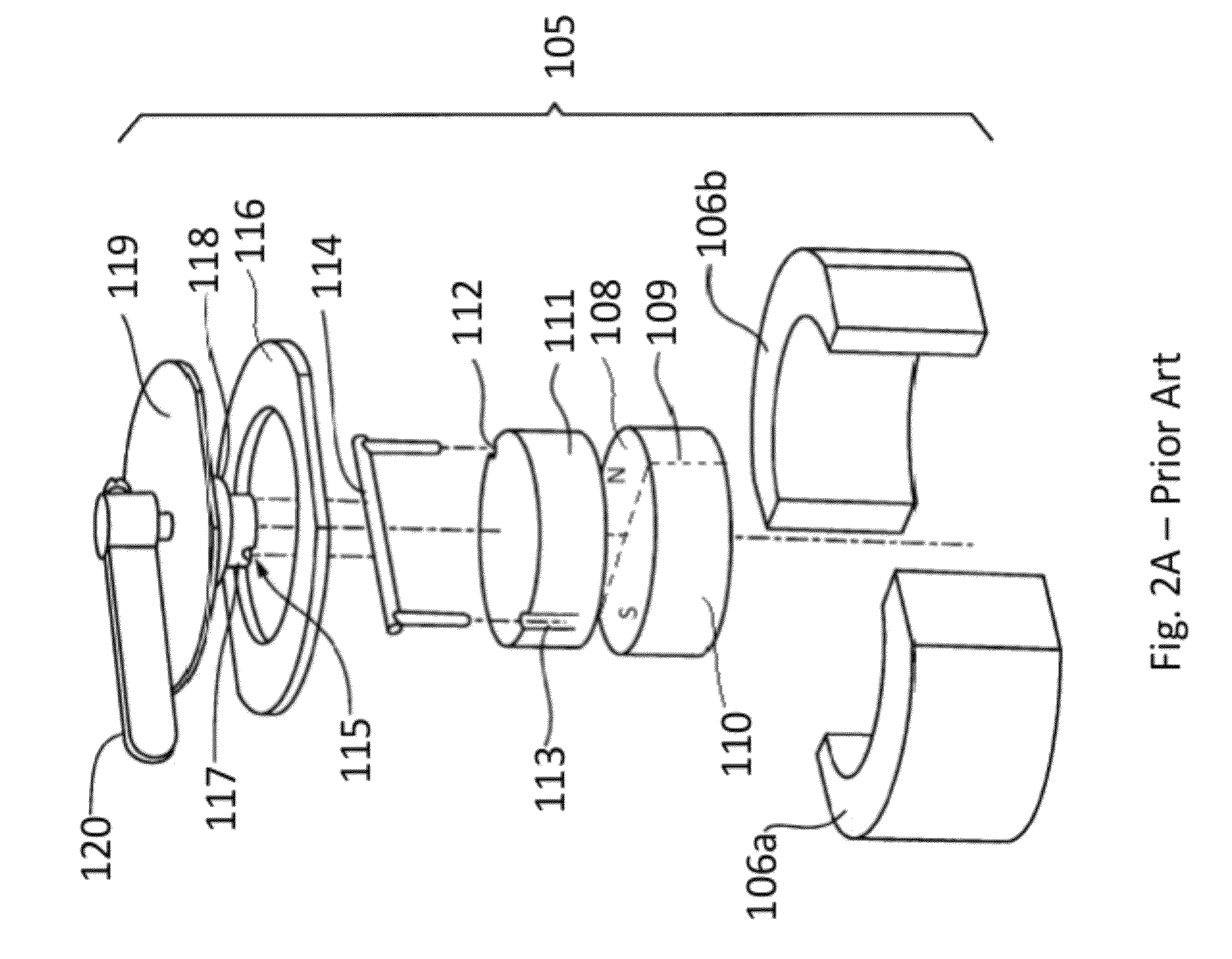
Pneumatically actuated magnetic workpiece holder
A pneumatically actuated magnetic workpiece holder comprising a housing having a contact surface for contacting a workpiece to be held, and a magnet assembly translationally disposed in the housing, the magnet assembly comprising a plurality of permanent magnets arranged so that adjacent magnets are of opposite polarities. The housing is adapted for fluid communication with a pneumatic supply. The magnet assembly is biased towards an operative position, according to which the magnet assembly is sufficiently near the contact surface to exert on a workpiece an attractive force sufficient for holding the workpiece in contact with the workpiece holder, and is translationally positionable by pneumatic pressure towards an inoperative position, according to which the magnet assembly is sufficiently distant from the contact surface so as to be unable to exert on the workpiece an attractive force sufficient for holding the workpiece in contact with the workpiece holder. The invention is adapted for replacing suction-cup workpiece holders in conventional vacuum lifting devices, and a method of utilizing the present invention in this fashion is taught to comprise providing the workpiece holder with a coupling complimentary to the coupling for such conventional suction-cup workpiece holders, so that the magnetic workpiece holder may be substituted for the conventional suction-cup holder in the vacuum lifting device. According to this method, the vacuum supply of the conventional vacuum lifting device is adapted to provide such positive air pressure for employing the magnetic workpiece holder of this invention.
Owner:INDAL MAGNETICS
Combined type thin-gauge skin moulding surface trimming cut flexibility multi-supporting equipment
InactiveCN101229598AReduce in quantityEasy to assembleWelding/cutting auxillary devicesWork holdersEngineeringLocknut
The invention relates to a combination flexible multipoint support device with skin and trimming, which consists of a plurality of positioning plates and a plurality of adjusting components; the positioning plates is flat T-shape and a threaded hole and a matching surface are arranged on the positioning plates; the adjusting components consist of a basioccipital and a nail height adjusting unit; the adjusting components are put in parallel in an X direction and the interval between centers is fixed; the positioning plates are divided into two symmetrical rows in a Y direction; each positioning plate is connected with the same end of two adjacent adjusting components; the basioccipital shapes like a rectangular and locating holes, a threaded hole and a matching surface are arranged on the basioccipital; the locating holes are evenly distributed in a line on the basioccipital and the nail height adjusting unit is fixed in the locating holes; the nail height adjusting unit consists of a large double-screw bolt, a bolt, a locknut, a rotary nail, a replaceable nail sleeve, a joint cylinder, a universal device, a vacuum generator and a vacuum chuck. The device of the invention realizes flexible holding, reduces special clamping devices and frocks and has remarkable economic and time benefits.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Bearing press-in device and method of use thereof
ActiveCN101176967APrevent leakageAvoid misplacementWork holdersApparatus for force/torque/work measurementEngineering
Owner:广州市嘉特斯机电制造有限公司
Flexible header system for machining workpieces
A manufacturing system includes a configurable positioning apparatus and machining system for processing a workpiece retained by the positioning apparatus. The positioning apparatus has different configurations for retaining different types of workpieces, such as panels, fuselages, airfoil skins, and engine housings. The positioning apparatus includes a first support rail and a second support rail spaced apart from the first support rail. The first and second support rails support a plurality of stackable headers that cooperate to position the workpiece. The headers have adjustable heights along their lengths in order to accommodate the shape of the workpiece.
Owner:FLOW INT
Universal holding fixture
InactiveUS20090057971A1Move quickly and efficientlyReduce component countWork holdersLarge fixed membersControl theoryLinear actuator
A universal holding fixture assembly includes a plurality of linear actuators supported by the fixture and adapted to engage and support a workpiece relative to the fixture. A linear displacement member is supported by a housing and adapted to move between retracted and extended positions. An end effector assembly is operatively supported by the linear actuator and adapted to engage the workpiece when the linear displacement member is in its extended position. A sensor is operatively supported by the end effector assembly and is responsive to contact with the workpiece to establish a datum of the position of the linear actuator relative to the workpiece.
Owner:EMKO LLC
System and method for handling a component
A system for handling a first component includes: a main-device and a module-device, the module-device having a pressing section arranged to form an outer surface of the module-device, the module-device configured to releasably receive the first component, such that a connection section of the first component is attachable to the pressing section of the module-device. The module-device is releasably connected to a second component, wherein the main-device includes a grabbing unit adapted for releasably connecting the module-device, such that the pressing section is arranged to form a first outer surface section of the main-device, and wherein the main-device includes a connector for connecting to a handling-unit for arranging the main-device at the second component, such that the connection section of the first component, if attached to the pressing section of the module-device, is at least indirectly attachable to a front surface of the second component.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Workpiece holding apparatus
An apparatus for holding a workpiece having a support table, a plurality of elongated workpiece supports extendible from the support table, a plurality of a clamp assemblies, and a processing machine. Each clamp assembly is positioned about a portion of a corresponding workpiece support. The clamp assemblies are moveable between a clamping position wherein the clamp assemblies support the workpiece support in a selected vertical position and a non-clamping position wherein the workpiece supports are moveable so that the position of the workpiece support is changeable. The processing machine is in communication with the clamp assemblies for controlling the position of the clamp assemblies, and the processing machine has an end effector engageable with the workpiece supports above the support table to permit the processing machine to move the workpiece supports to selected positions when the clamp assemblies are in the non-clamping position.
Owner:KIRBY LARRY D
Systems, apparatus and methods for transporting substrates
A substrate transporting robot apparatus is disclosed which is adapted to transport a substrate to and from a chamber of an electronic device processing system. The apparatus may include an upper arm rotatable in an X-Y plane, a forearm rotatable relative to the upper arm in the X-Y plane, and a wrist member rotatable relative to the forearm in the X-Y plane, the wrist member including an end effector adapted to carry a substrate. The wrist member may be subjected to independent rotation such that various degrees of yaw may be imparted to the wrist member. In some aspects, the independent rotation is provided without a motive power device (e.g., motor) being provided on the arms or wrist member, i.e., the wrist member may be remotely driven. Systems and methods using the robot apparatus are also provided as are numerous other aspects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
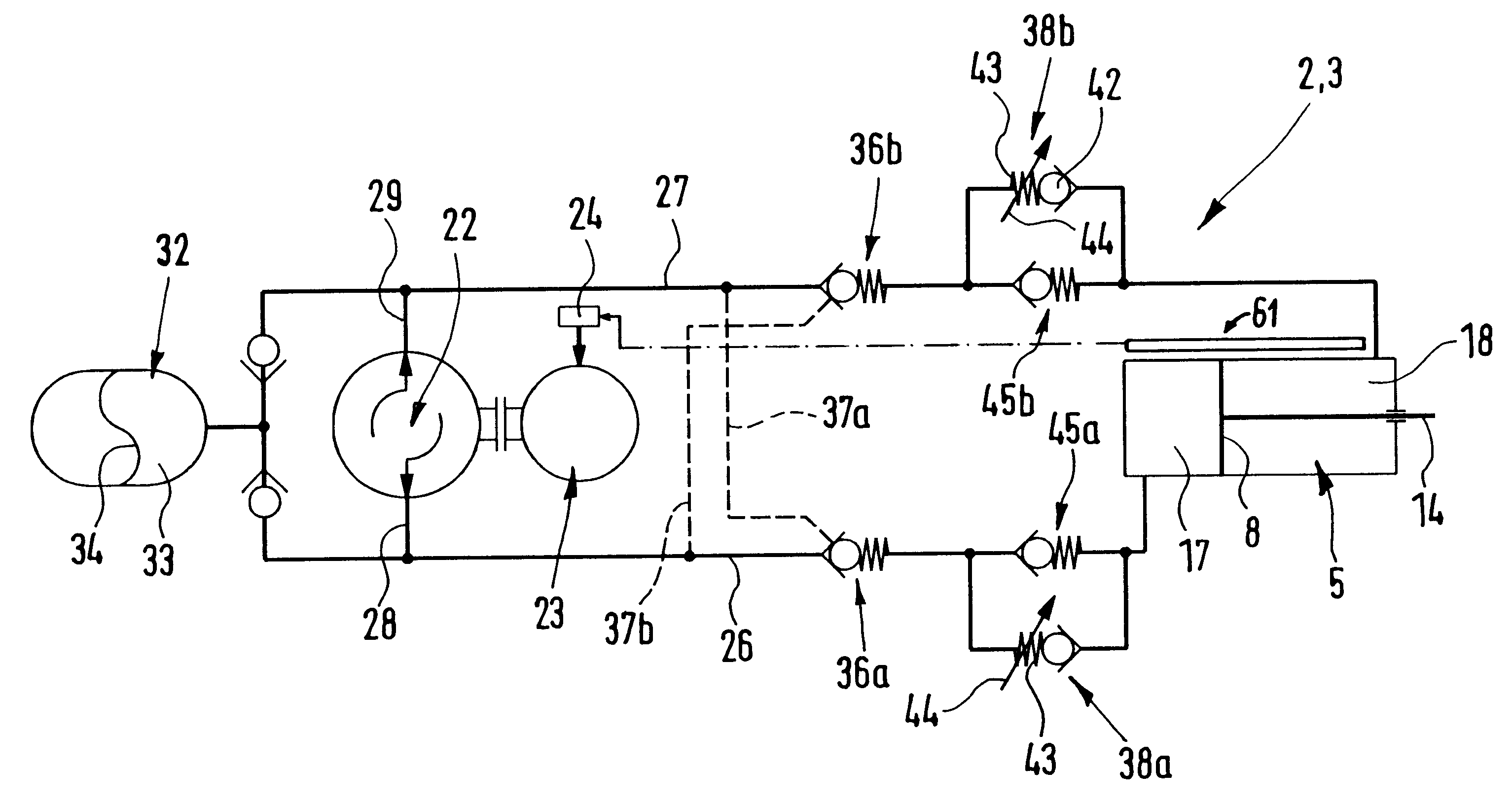
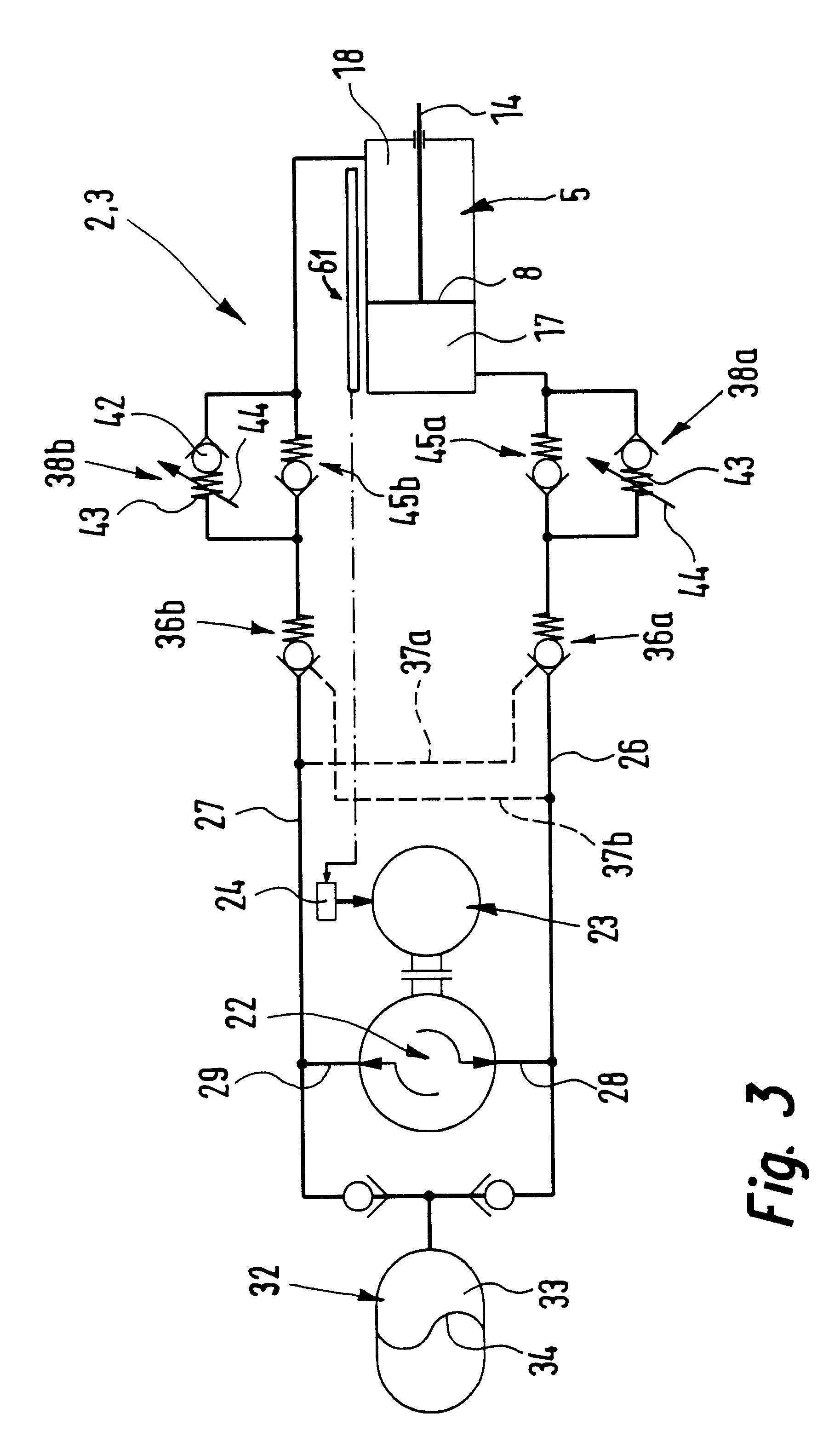
Drive device
InactiveUS6543223B2Easy to driveReduce needFluid couplingsServomotor componentsHydraulic pumpHydraulic circuit
A drive device comprising a closed hydraulic circuit which has a hydraulic drive adapted to be actuated by hydraulic medium and has a hydraulic pump responsible for the supply and removal of the hydraulic medium to and from the hydraulic drive. For the operation of the hydraulic pump an electric motor is provided. The activation of the hydraulic drive is controlled by the operational state of the hydraulic pump.
Owner:FESTO AG & CO KG
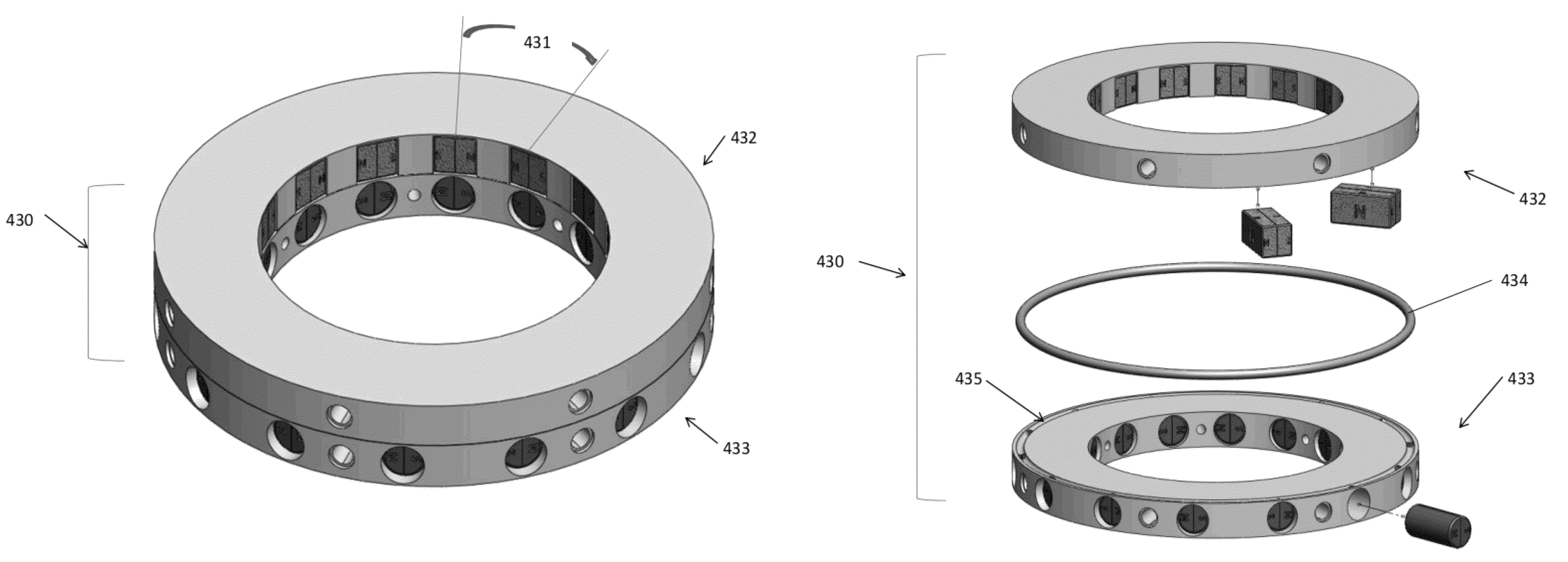
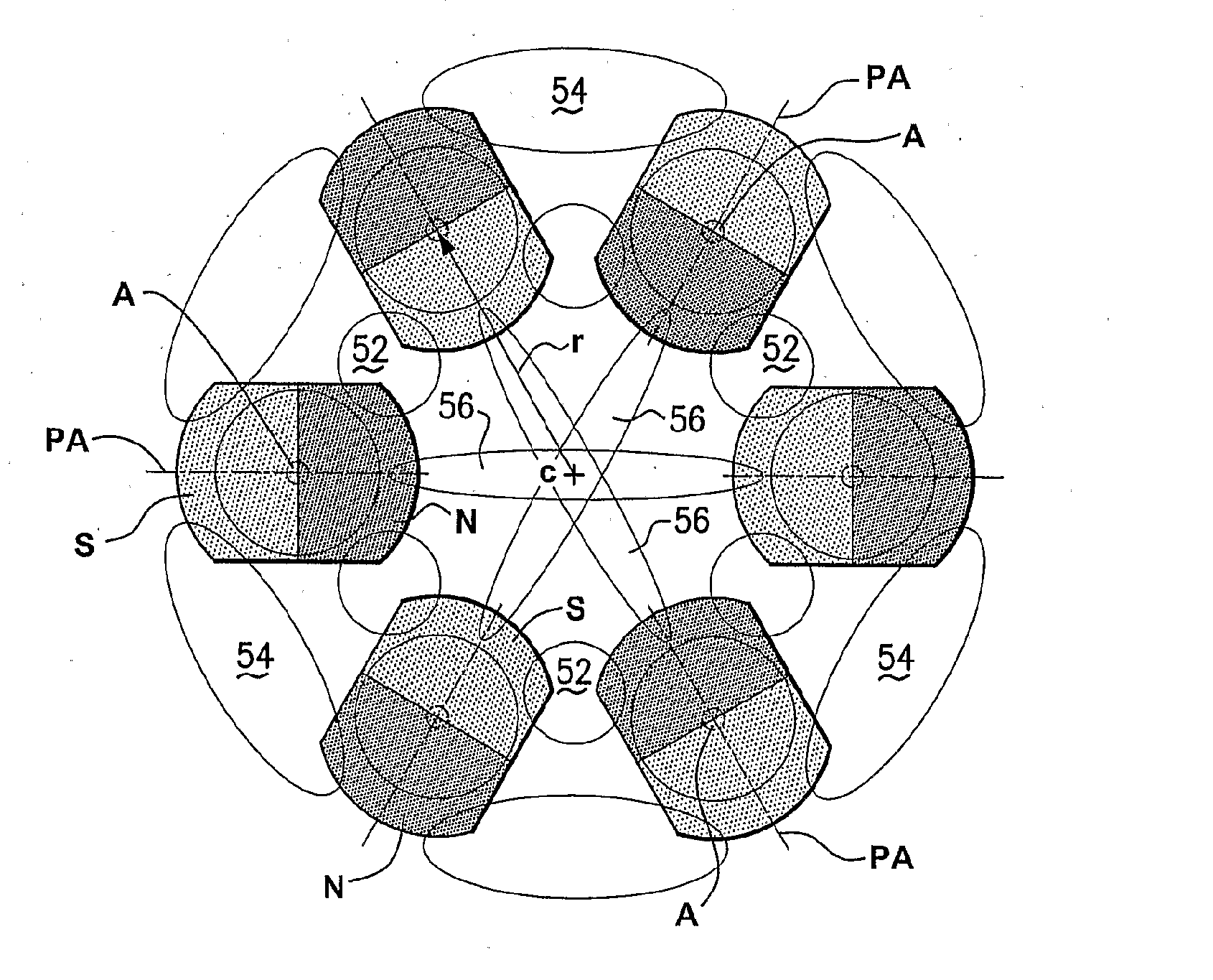
Rotary switchable multi-core element permanent magnet-based apparatus
ActiveUS8350663B1Low costRapid productionElectromagnets without armaturesElongated resistive elementEngineeringMagnet
A method for creating and a device for a rotary switchable multi-core element, permanent magnet-based apparatus, for holding or lifting a target, comprised of two or more carrier platters, each containing a plurality of complementary first and second core elements. Each core element comprises permanent magnet(s) with magnetically matched soft steel pole conduits attached to the north and south poles of the magnet(s). Core elements are oriented within adjacent carrier platters such that relative rotation allows for alignment in-phase or out-of-phase of the magnetic north and south fields within the pole conduits. Aligning a first core element “in-phase” with a second core element, that is, north-north / south-south, activates that core element pair, allowing the combined magnetic fields of the pole conduits to be directed into a target. Aligning the core element pair “out-of-phase,” that is, north-south / south-north, deactivates that core element pair by containing opposing fields within the pole conduits.
Owner:CREATIVE ENG SOLUTIONS
Magnet Arrays
InactiveUS20090027149A1Expand the field of viewDoubling numberElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetic reluctancePole piece
Method and device for self-regulated flux transfer from a source of magnetic energy into one or more ferromagnetic work pieces, wherein a plurality of magnets, each having at least one N-S pole pair defining a magnetization axis, are disposed in a medium having a first relative permeability, the magnets being arranged in an array in which gaps of predetermined distance are maintained between neighboring magnets in the array and in which the magnetization axes of the magnets are oriented such that immediately neighboring magnets face one another with opposite polarities, such arrangement representing a magnetic tank circuit in which internal flux paths through the medium exist between neighboring magnets and magnetic flux access portals are defined between oppositely polarized pole pieces of such neighboring magnets, and wherein at least one working circuit is created which has a reluctance that is lower than that of the magnetic tank circuit by bringing one or more of the magnetic flux access portals into close vicinity to or contact with a surface of a ferromagnetic body having a second relative permeability that is higher than the first relative permeability, whereby a limit of effective flux transfer from the magnetic tank circuit into the working circuit will be reached when the work piece approaches magnetic saturation and the reluctance of the work circuit substantially equals the reluctance of the tank circuit.
Owner:MAGSWITCH TECH WORLDWIDE PTY LTD
Method for assembling faucet valve core and fully automatic assembly machine
InactiveCN101590595ASmall footprintIncrease productivityAssembly machinesWork holdersEngineeringFully automatic
The invention discloses a method for assembling a faucet valve core and a fully automatic assembly machine. Before the assembly of the valve core, all parts are first sorted by a specially arranged vibration disk, then conveyed to specific positions through conveying pipes, and finally assembled into a whole through the action of a mechanical clamp and the positioning of a worktable. The middle of the fully automatic assembly machine is a working turntable; the periphery of the working turntable is provided with part vibration sorters; and the sorted parts are conveyed to the locking end of the turntable to assemble the core. The fully automatic assembly machine is provided with secondary pressure supplementing and product quality inspecting equipment. The fully automatic assembly machine adopts a circular production turntable to complete the assembly of the valve core, thereby having the advantage of small space occupation; and the working turntable cooperate with mechanical hands at the ends of the part conveying pipes to rotate a certain angle to complete a next assembly step, so the production efficiency is high.
Owner:苏锦波
Clamping and positing device capable of automatically aligning center and using method thereof
The invention provides a clamping and positing device capable of automatically aligning center and a using method thereof, relating to a tooling clamp capable of automatically aligning center and being used in a plurality of fields of mechanical manufacture, printing, surface coating, electronic assembly and the like. The device comprises a driving mechanism, a clamping mechanism, a guiding mechanism and a supporting mechanism, wherein, the driving mechanism comprises a driving device and a driving force transmission device; the clamping mechanism comprises a positioning board (5); the supporting mechanism comprises a base (7) and a fixed seat (10); the driving mechanism, the clamping mechanism and the guiding mechanism are supported by the supporting mechanism; the driving mechanism drives the positioning board (5); the guiding mechanism ensures that the positioning board (5) moves according to a guided movement route; thus, the positioning board (5) can clamp a piece (13) to be processed, and the central reference position of the piece (13) to be processed is automatically positioned on the station for positioning a centre (central line or central point). The device can automatically align center and eliminate central line / point position offset.
Owner:李梓鸿 +1
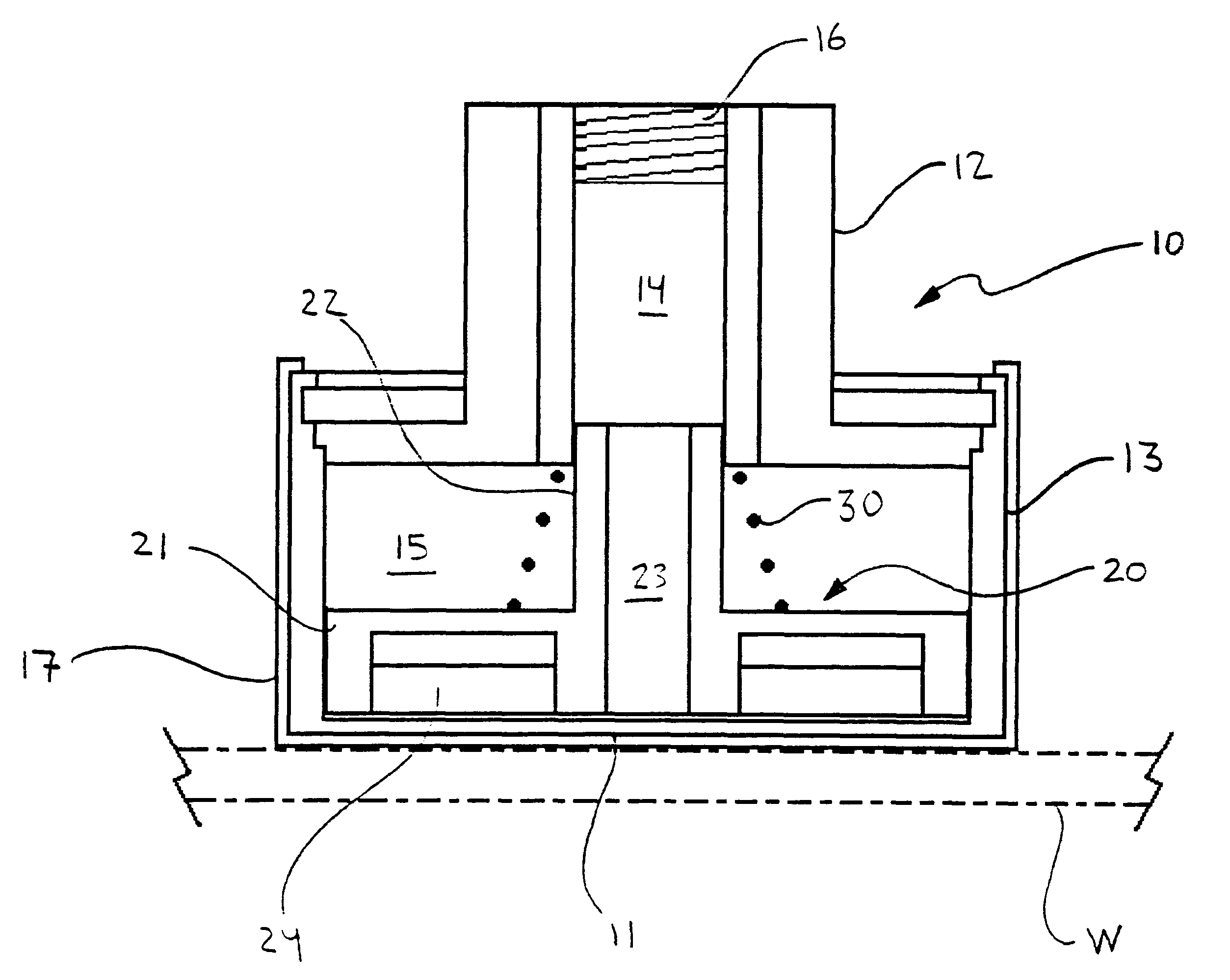
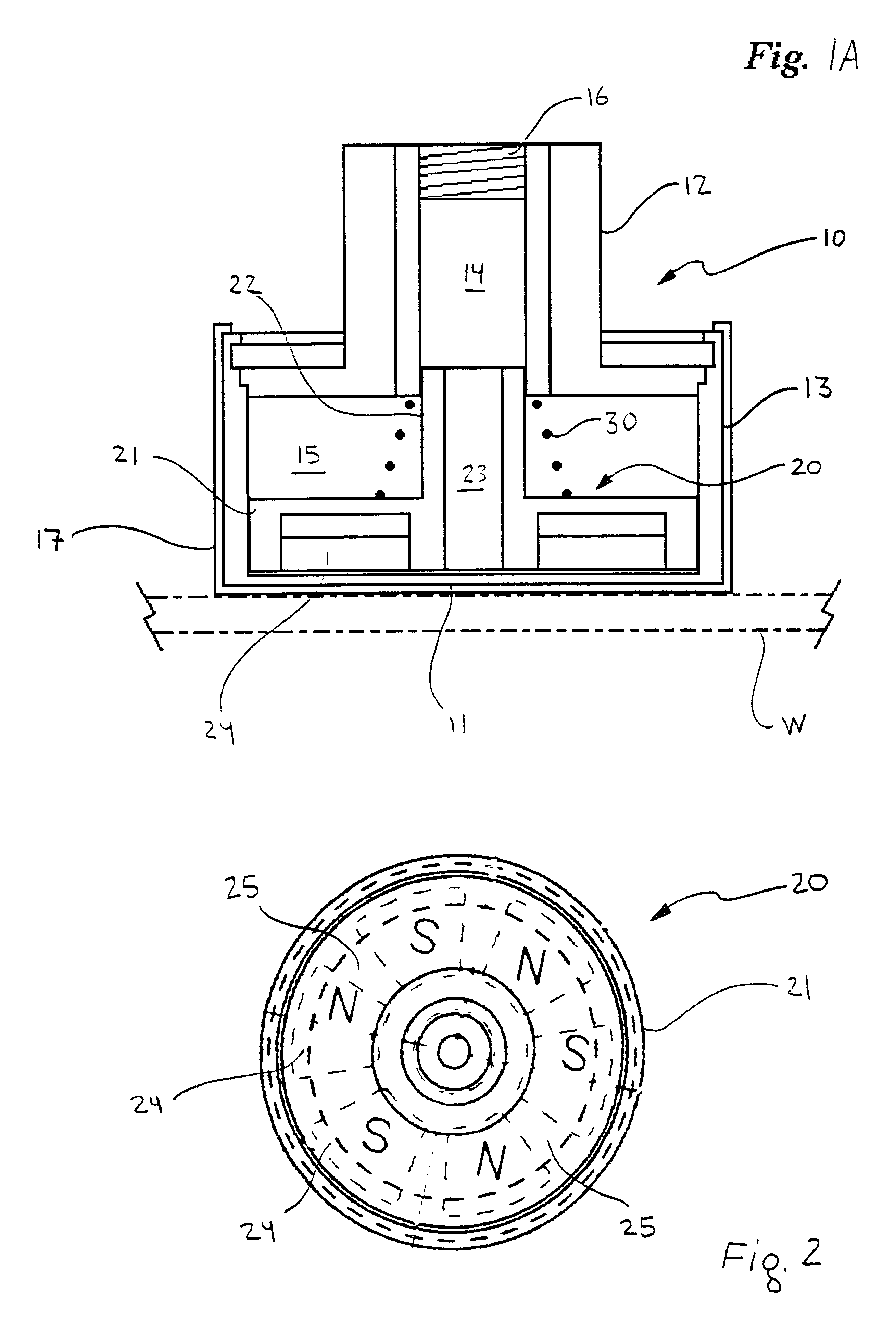
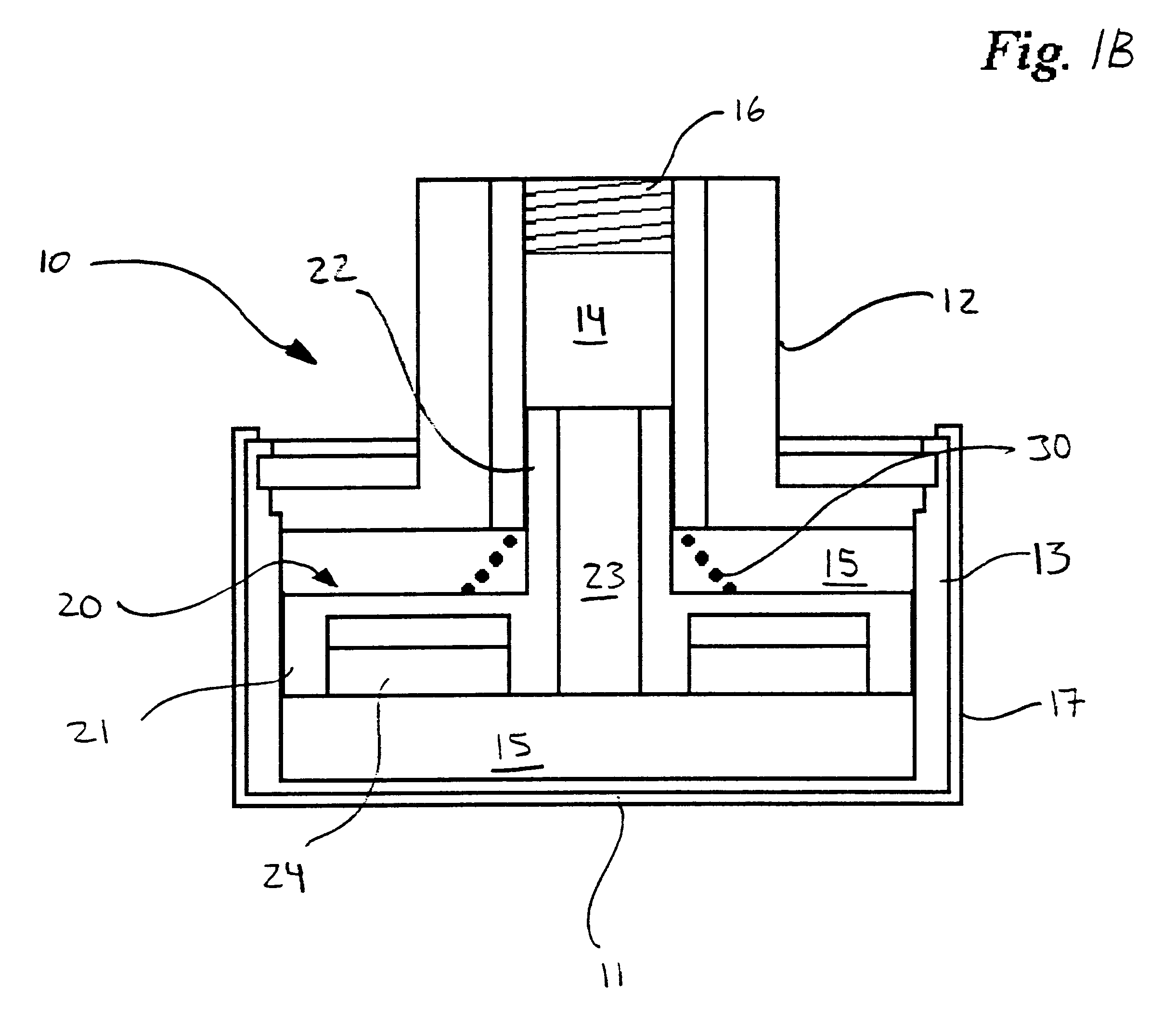
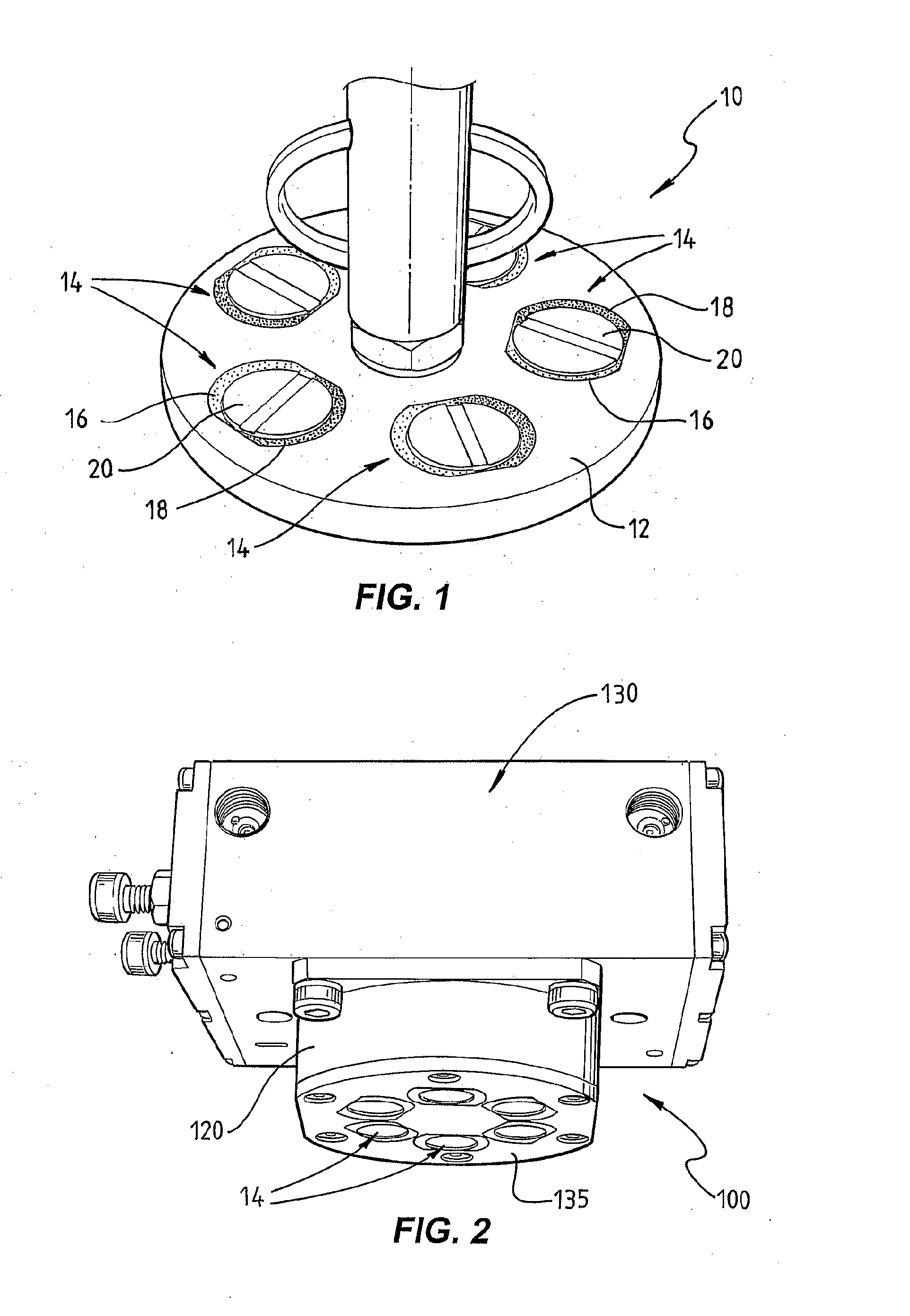
Apparatus and method for holding a flexible product in a flat and secure position
An apparatus for retaining a product, preferably such as a flexible product in a flat and secure position on a generally planar surface. More specifically, the apparatus consists of a self-contained multi-zone vacuum chuck fixture which is adapted to enable the selectively controlled securing and holding of flexible products possessing various sizes and configurations on a flat work surface. The apparatus may be transparent so as to be also utilized as a light table.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com