Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94results about "Elongated resistive element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
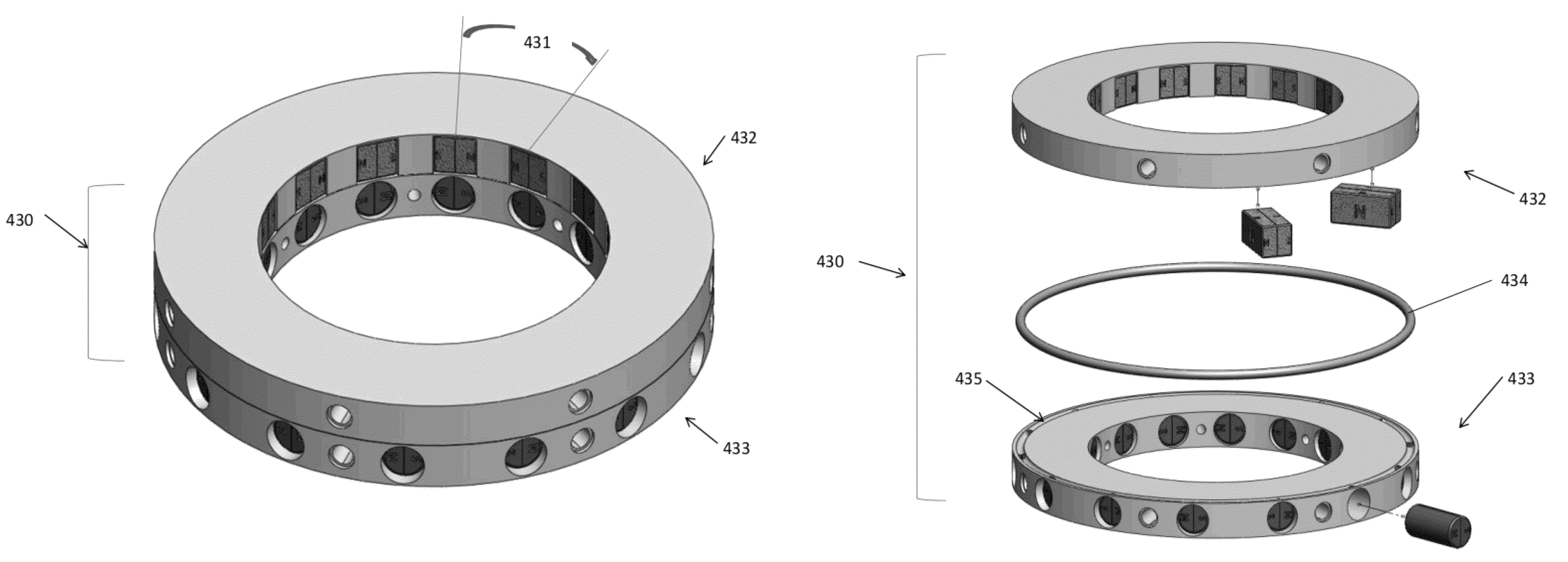
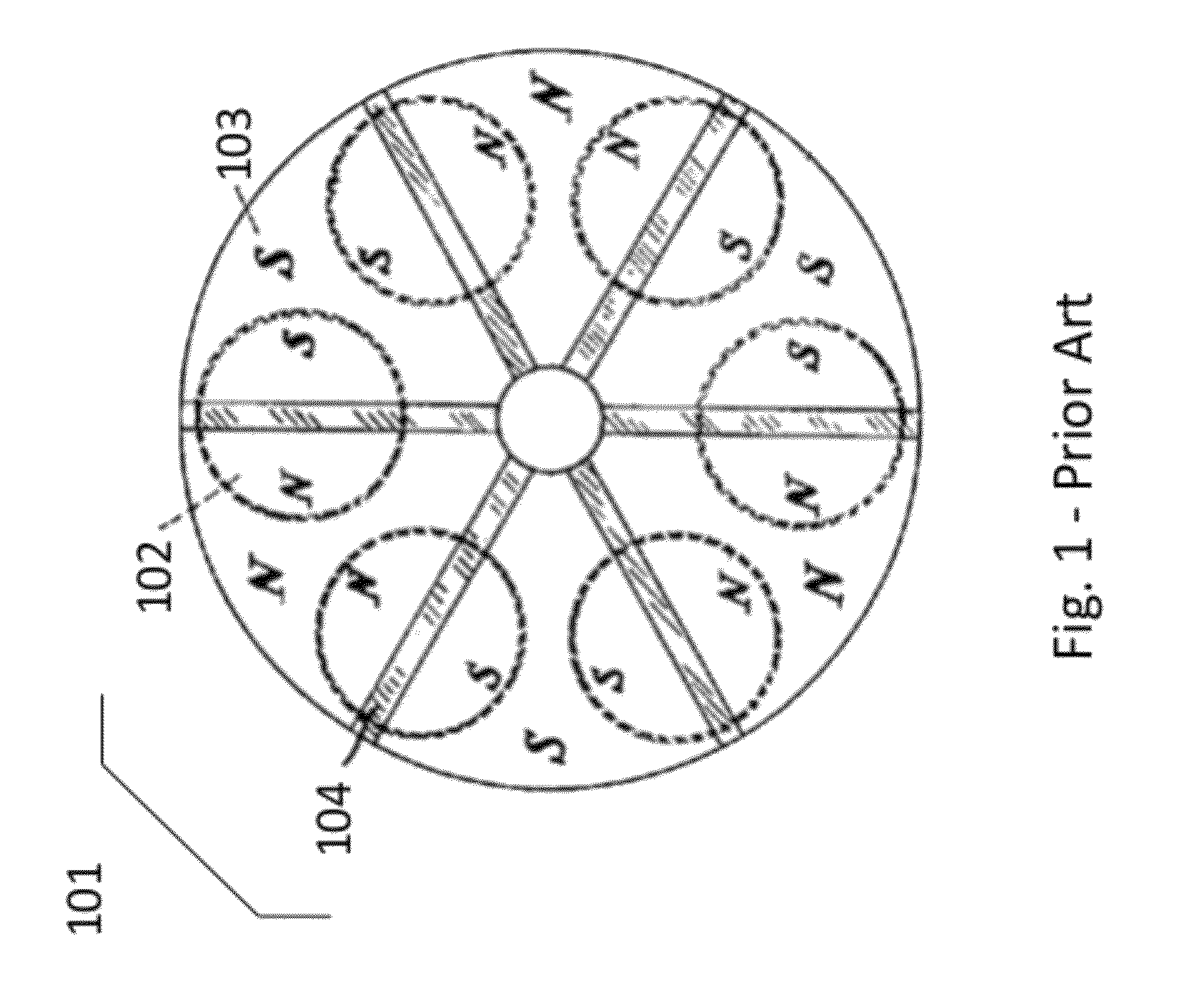
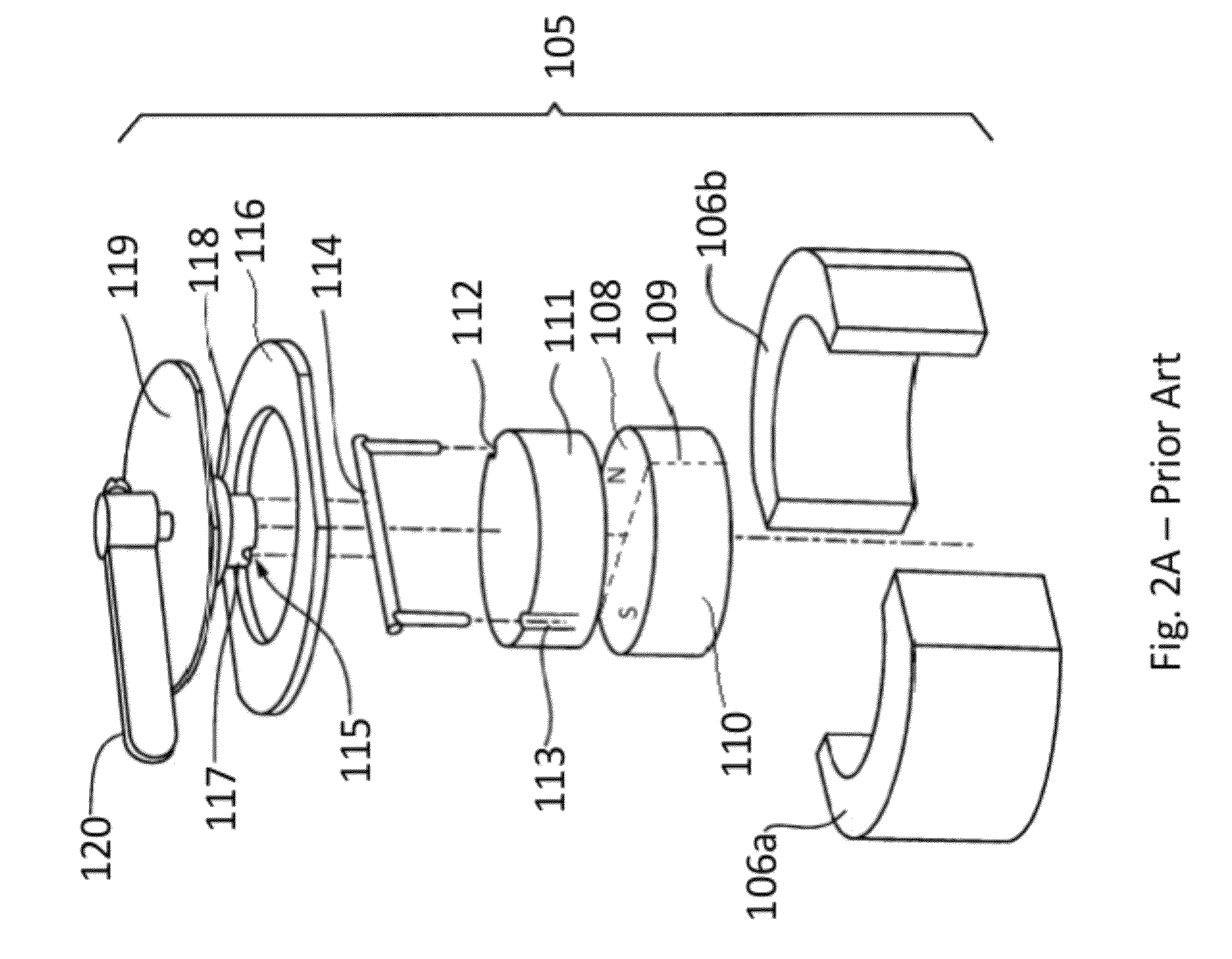
Rotary switchable multi-core element permanent magnet-based apparatus
ActiveUS8350663B1Low costRapid productionElectromagnets without armaturesElongated resistive elementEngineeringMagnet
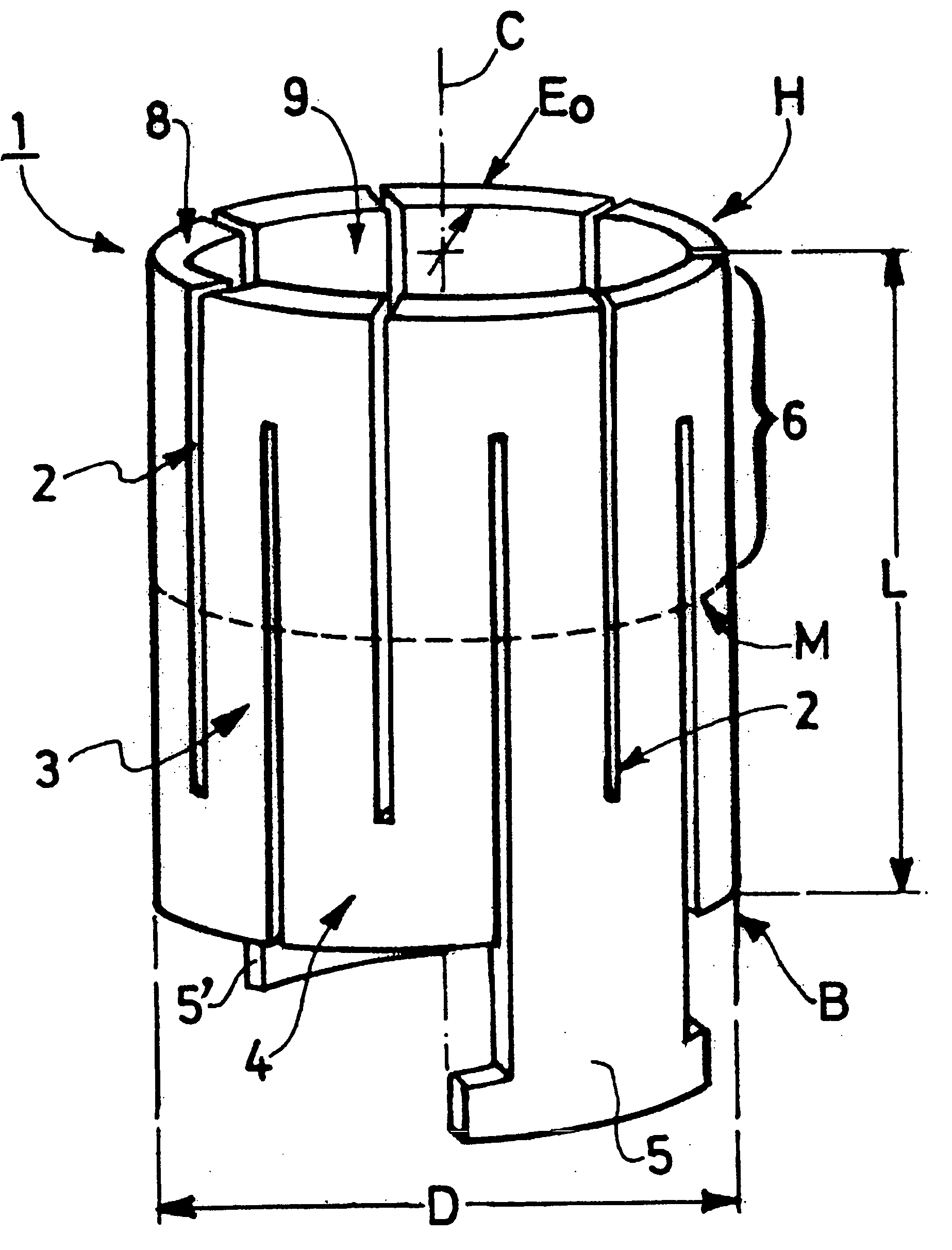
A method for creating and a device for a rotary switchable multi-core element, permanent magnet-based apparatus, for holding or lifting a target, comprised of two or more carrier platters, each containing a plurality of complementary first and second core elements. Each core element comprises permanent magnet(s) with magnetically matched soft steel pole conduits attached to the north and south poles of the magnet(s). Core elements are oriented within adjacent carrier platters such that relative rotation allows for alignment in-phase or out-of-phase of the magnetic north and south fields within the pole conduits. Aligning a first core element “in-phase” with a second core element, that is, north-north / south-south, activates that core element pair, allowing the combined magnetic fields of the pole conduits to be directed into a target. Aligning the core element pair “out-of-phase,” that is, north-south / south-north, deactivates that core element pair by containing opposing fields within the pole conduits.
Owner:CREATIVE ENG SOLUTIONS
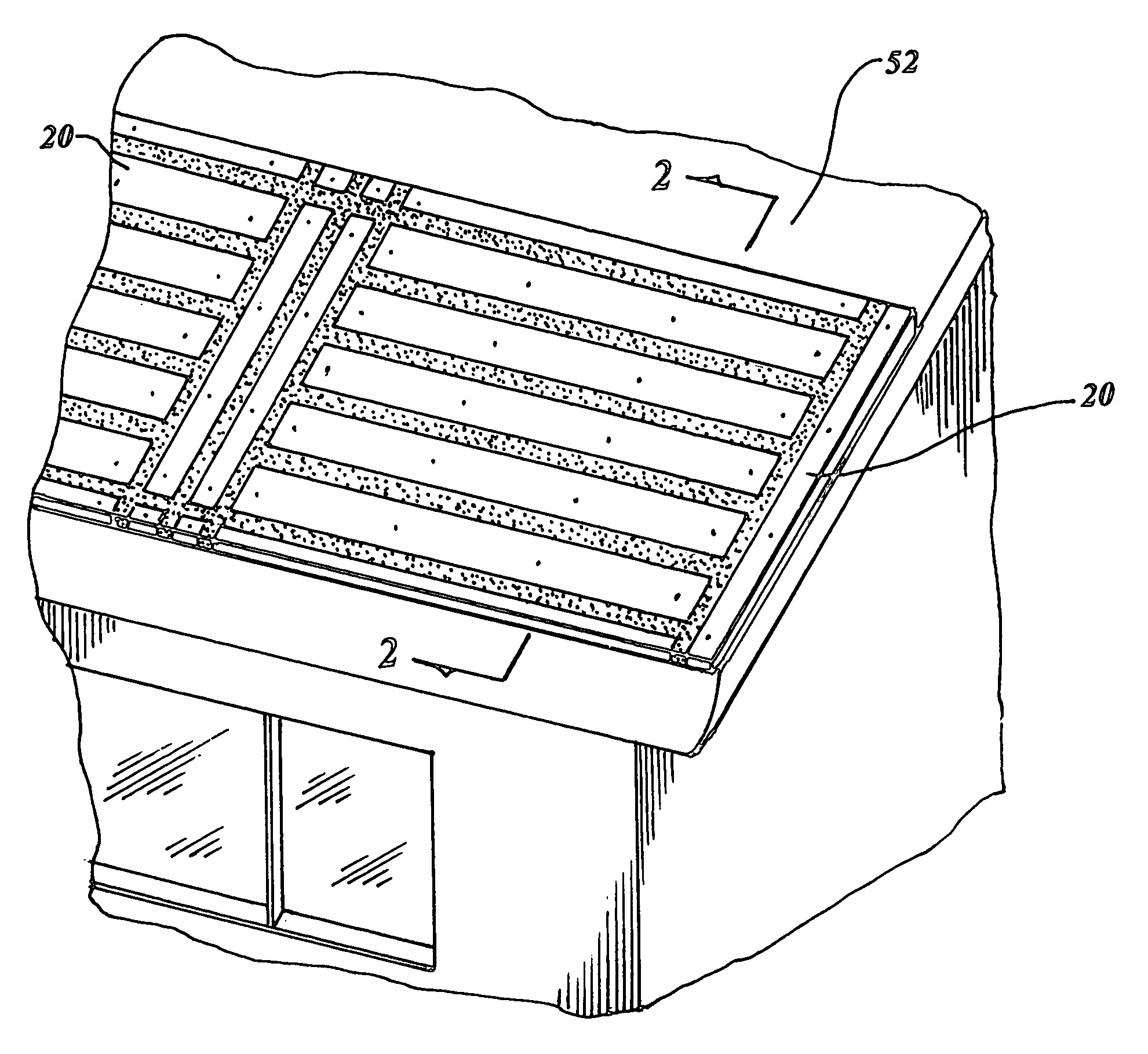
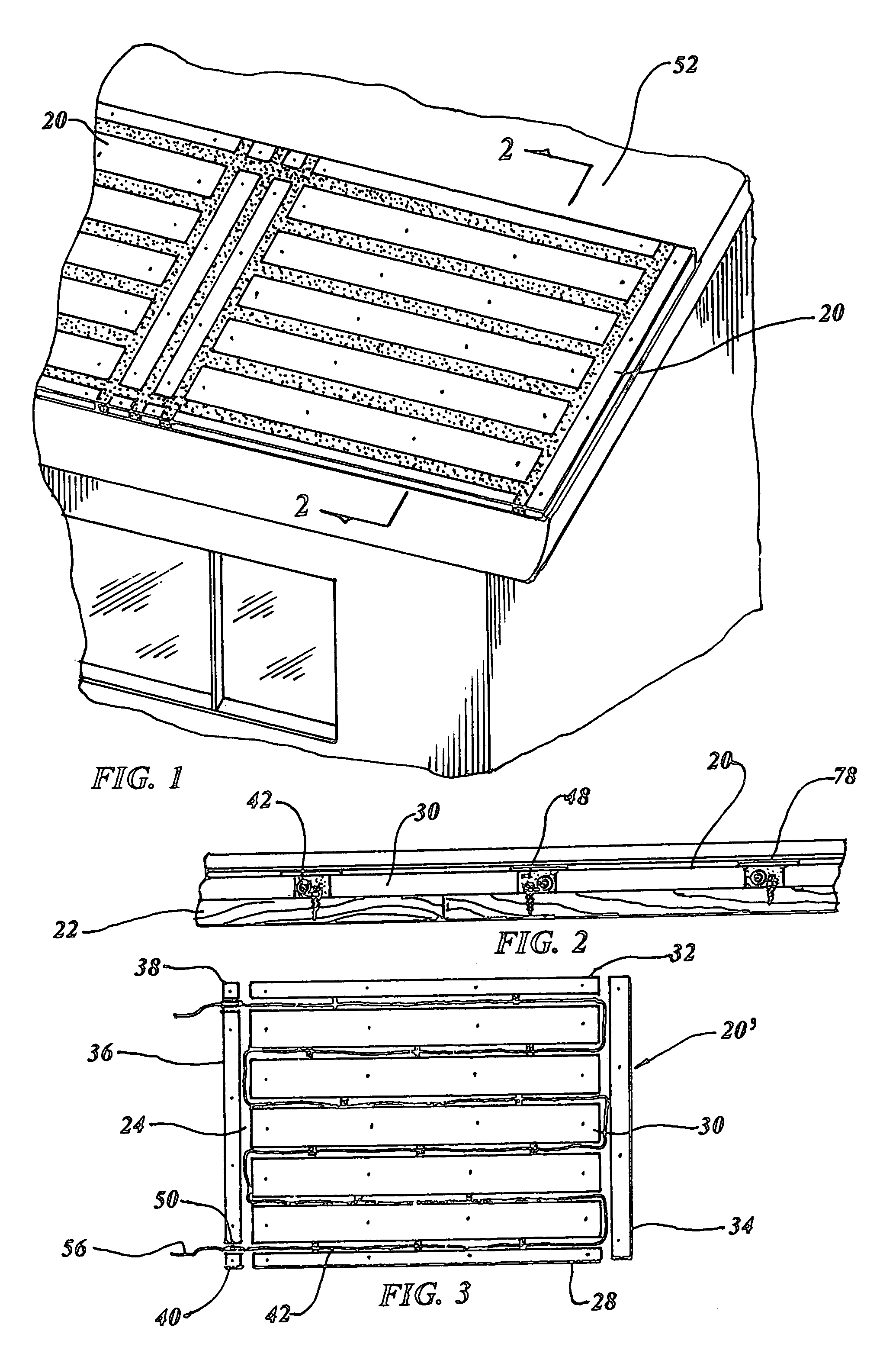
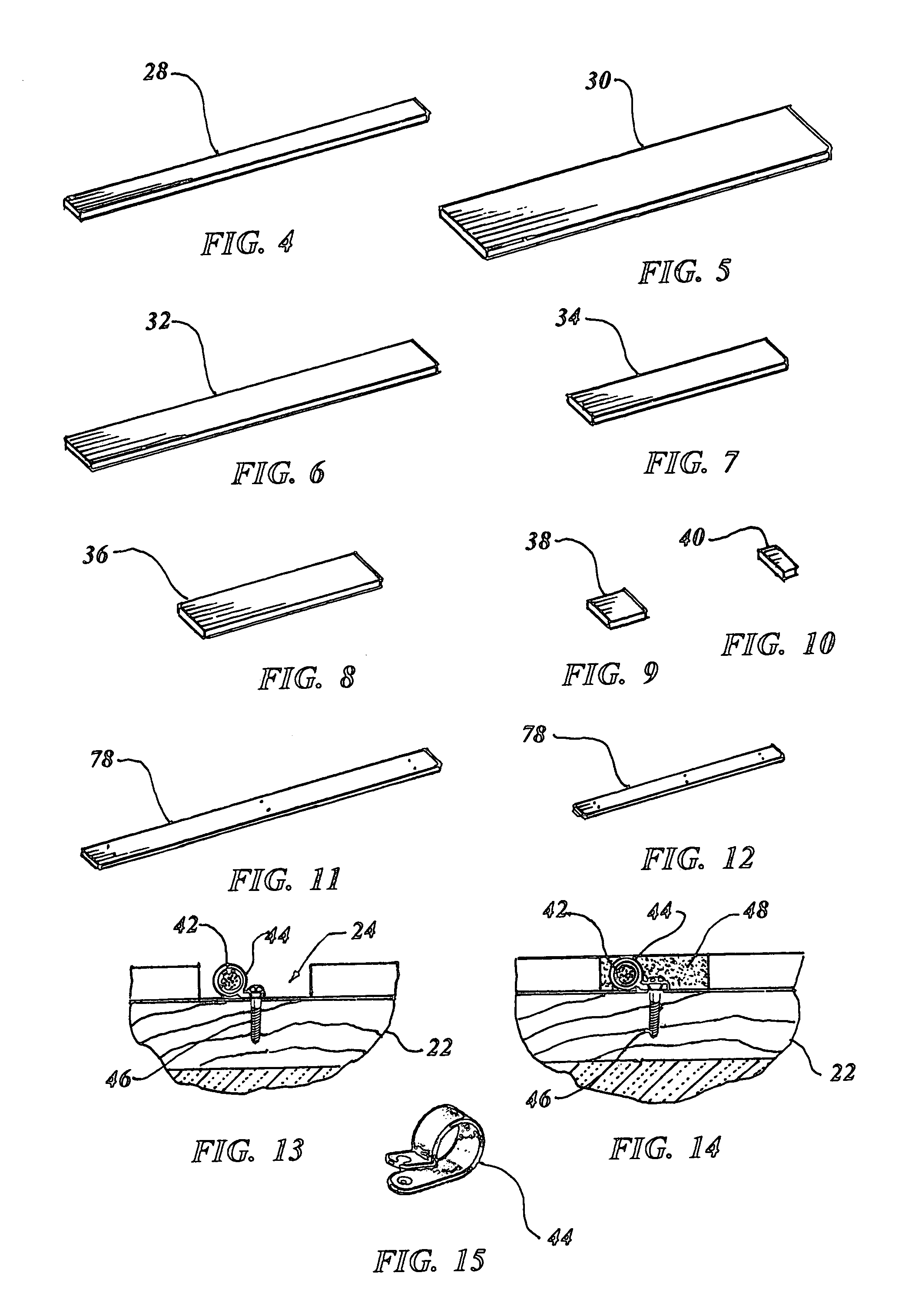
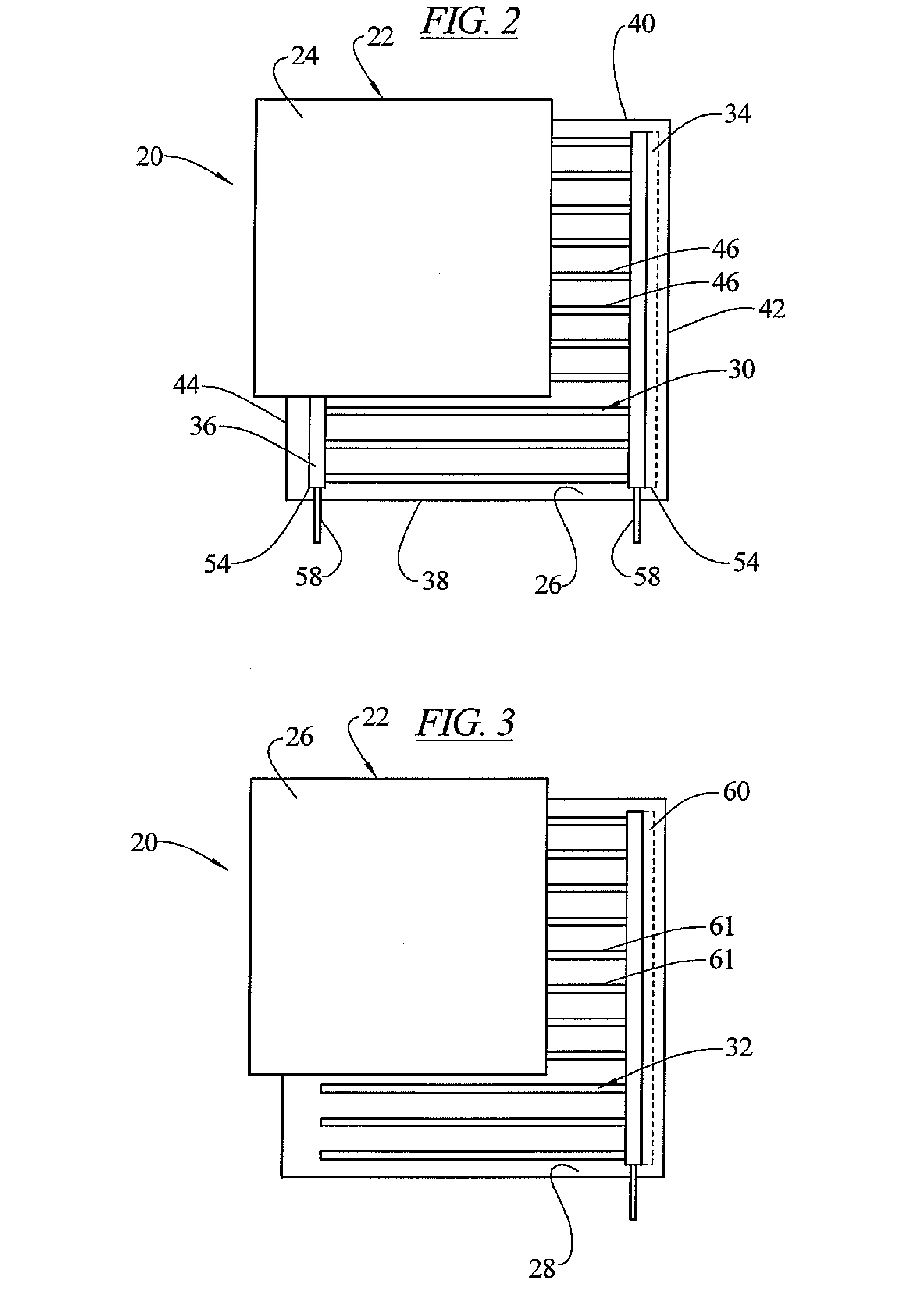
De-icing, snow melting and warming system
ActiveUS7071446B1Promote repairEasy to replaceRoof coveringElongated resistive elementTransformerLow voltage
A de-icing, snow melting and warming system is taught which utilizes a heatsink (20) consisting of a number of board strips disposed in a planer array positioned within a building structure between its exterior and interior surface. The heatsink board strips have a gap (24) therebetween in which a heating cable (42) is positioned in a continuous serpentine manner and held in place with loop clamps (44). A gap filler (48) encases the heating cable including the enclosed gap forming a homogenous closure. A low voltage power transformer (54) is attached to electrical mains providing electrical voltage reduction to the heating cable of 30 volts or less, and controls and self diagnostics regulate the power and detect anomalies within the system.
Owner:BENCH STEVEN D
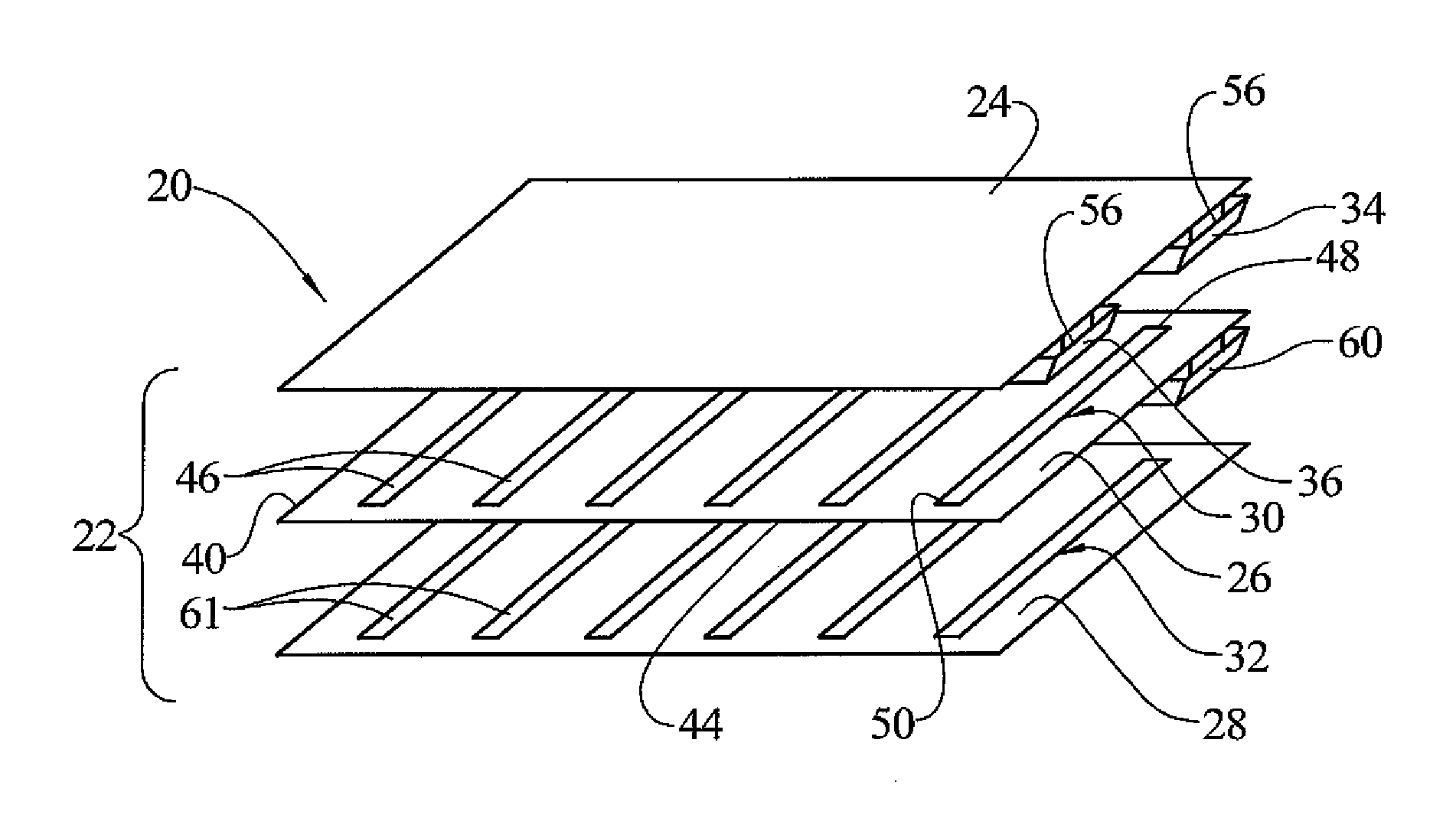
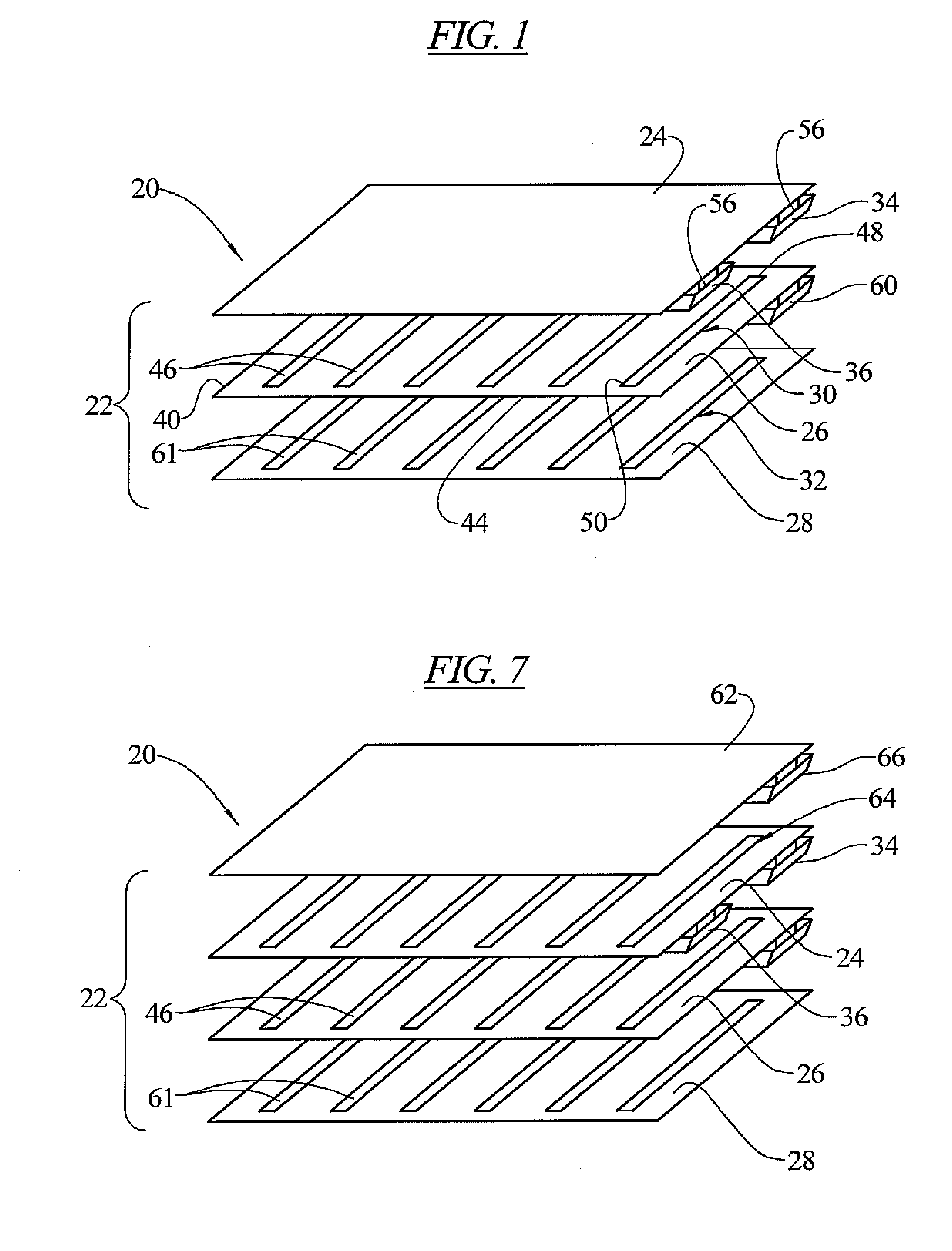
Electrical heater with a resistive neutral plane
A heating system in the form of a multi-layer, yet relatively thin and flexible panel. The panel contains a number of layers including first, second and third electrically insulating layers. A first electrically conductive resistive layer (heater layer) is sandwiched between the first and second insulating layers. A second electrically conductive resistive layer (resistive neutral plane layer) is sandwiched between the second and third insulating layers. The heater layer has a neutral electrical connection and a live electrical connection. The neutral and live electrical connections are electrically connected to each other at the panel only by electrically resistive material of the heater layer extending between the neutral and live electrical connections. The resistive neutral plane layer has a neutral electrical connection electrically connected with the neutral connection of the heater layer. The resistive neutral plane layer is electrically isolated from the live connection of the heater layer by the second insulating layer.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Power resistor
InactiveUS7843309B2Spread heatElongated resistive elementResistor cooling/heating/ventillationMetal stripsElectrical resistance and conductance
A resistor includes first and second opposite terminations, a resistive element formed from a plurality of resistive element segments between the first and second opposite terminations, at least one segmenting conductive strip separating two of the resistive element segments, and at least one open area between the first and second opposite terminations and separating at least two resistive element segments. Separation of the plurality of resistive element segments assists in spreading heat throughout the resistor. The resistor or other electronic component may be packaged by bonding to a heat sink tab with a thermally conductive and electrically insulative material. The resistive element may be a metal strip, a foil, or film material.
Owner:VISHAY DALE ELECTRONICS INC
Wake generating solid elements for joule heating or infrared heating
ActiveUS20100132921A1Reduce dragReduce pressure dropMetal-working apparatusIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringJoule heating
An improved solid heat transfer element composed of an elongate member having a generally cylindrical surface with male vortex generating protrusions is provided. The vortex generating protrusions, which may be referred to as “turbulators,” provide improved heat transfer by convection to a flow of air transverse to the elongate members without substantially increasing the pressure drop in the flow of air passing over the members. Advantageously, a plurality of the heat transfer elements, or of straight portions of a single serpentine heat transfer element, may be arranged in an aligned or staggered array of elements or straight portions. Many advantageous profile shapes of the element and vortex generators are provided, including aerodynamic profile shapes that are symmetrical with respect to a fluid flow to provide low drag and pressure drop. Heat in the element may be generated by means of electrical resistance or absorption of radiation.
Owner:MOSKAL DANIEL
Electrical heater with a resistive neutral plane
ActiveUS8039774B2Elongated resistive elementTransparent/reflecting heating arrangementsElectricityElectrical connection
A heating system in the form of a multi-layer, yet relatively thin and flexible panel. The panel contains a number of layers including first, second and third electrically insulating layers. A first electrically conductive resistive layer (heater layer) is sandwiched between the first and second insulating layers. A second electrically conductive resistive layer (resistive neutral plane layer) is sandwiched between the second and third insulating layers. The heater layer has a neutral electrical connection and a live electrical connection. The neutral and live electrical connections are electrically connected to each other at the panel only by electrically resistive material of the heater layer extending between the neutral and live electrical connections. The resistive neutral plane layer has a neutral electrical connection electrically connected with the neutral connection of the heater layer. The resistive neutral plane layer is electrically isolated from the live connection of the heater layer by the second insulating layer.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Protective device
InactiveCN101449342ASimple structureElongated resistive elementHeating/cooling contact switchesAdhesiveShape-memory alloy
A novel protective device that has a large capacity, being capable of sensing relatively low abnormal temperatures, and that has a simple structure and a small size. The protective device comprises (1) polymer PTC element (18) provided at its both-side major surfaces with metal electrodes (14,16) and (2) shape-memory alloy lead (20), wherein the shape-memory alloy lead is connected to the polymer PTC element by means of conductive adhesive (22) containing a thermoplastic resin and a conductive filler.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS RAYCHEM BVBA
Heating resistances and heaters
ActiveUS20050173411A1Easy to adjustReduce riskElongated resistive elementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsHeat generation
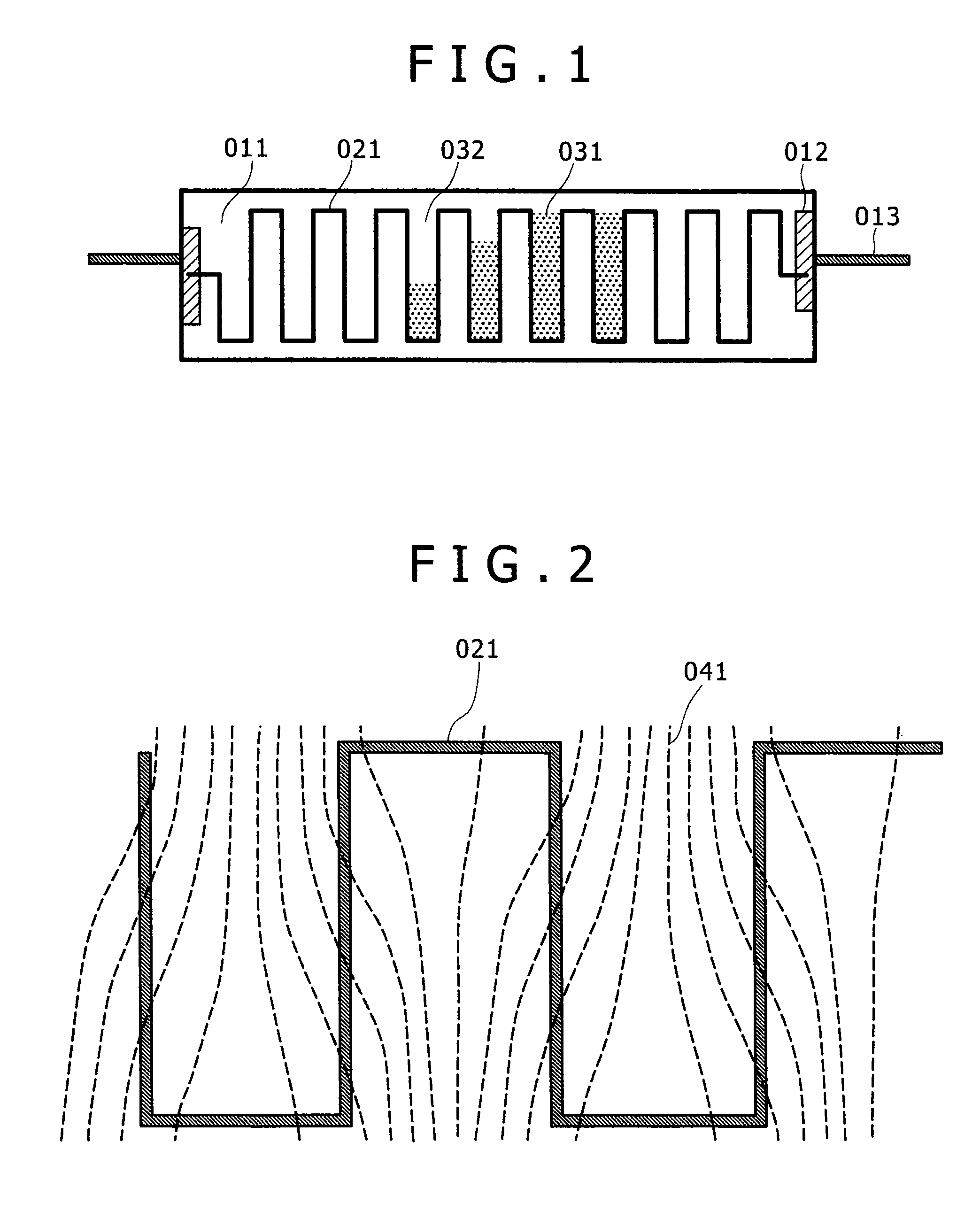
A heating resistance 1 comprises a shaped body of a band made of a conductive material obtained by bending the band in a shape of a wave. The heating resistance 1 is fixed to a substrate made of an insulating material to obtain a heater. Alternatively, the heating resistance comprises a wound body of a band made of a conductive material. According to the present invention, the heating value per a unit length can be easily designed and changed, and the reliability can be improved and abnormal heat generation can be prevented at the interface where the heating value per a unit length is changed.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Device for heating shrinkable sleeves
InactiveUS20020088796A1Simple mounting attachmentIncrease contactElongated resistive elementHeater elementsHeat-shrinkable sleeveElectrical resistance and conductance
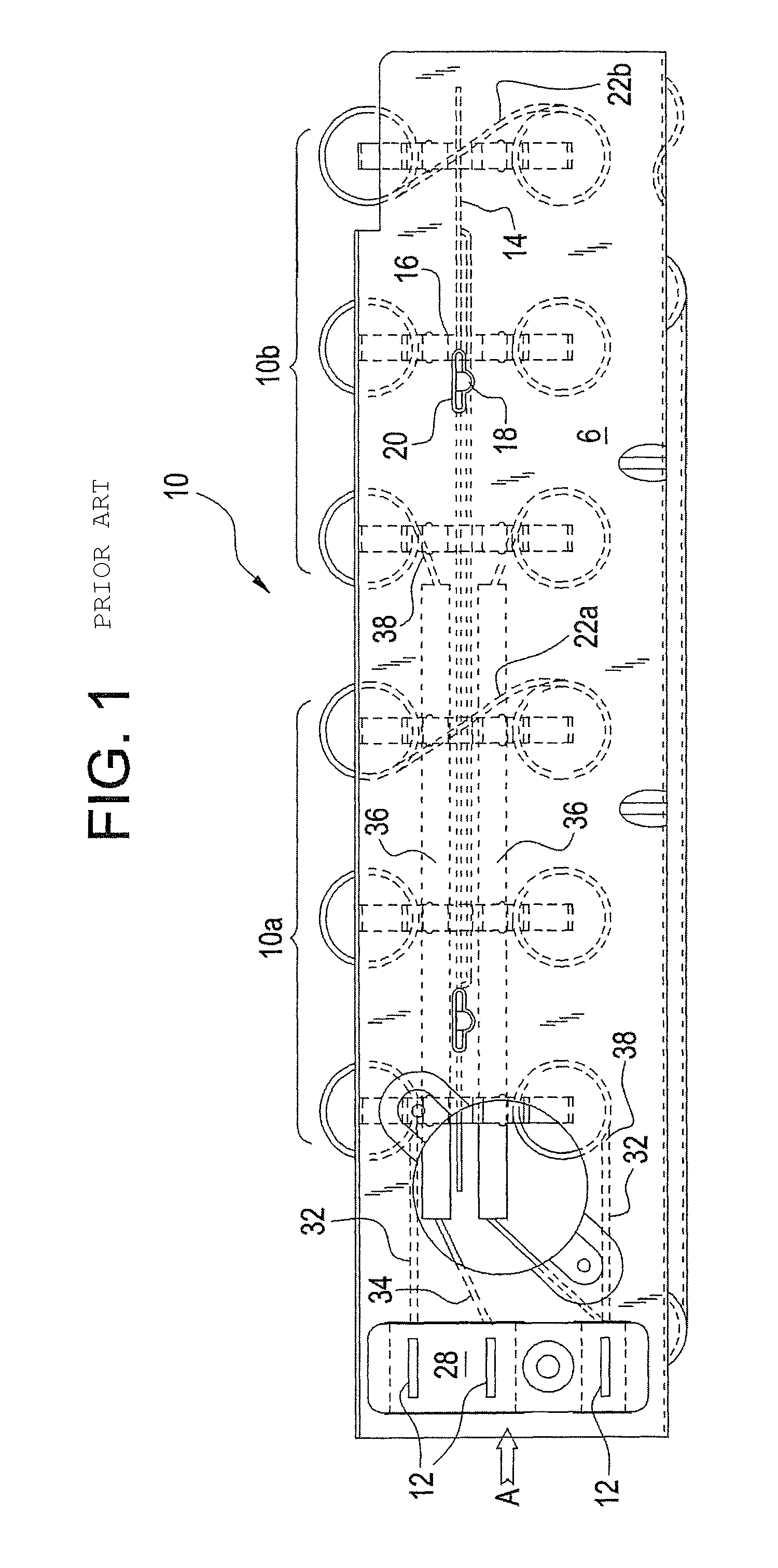
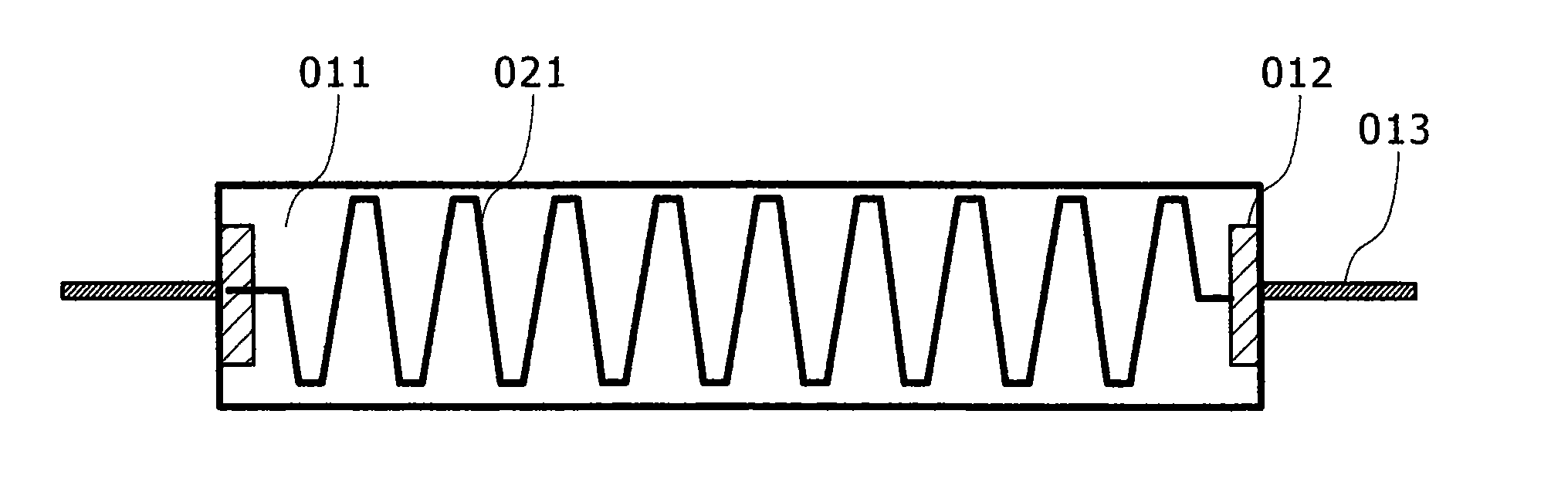
A resistance element (19) for a device for shrinking shrinkable sleeves comprises an elongate electrical conductor extending in a zigzag pattern and bent to a tunnel shape. The shrinkable sleeve including for example an optical fiber enclosed therein is placed in that region of the resistance element (19), which corresponds to approximately the geometric axis of the upper semi-cylindric portion of the tunnel shape. The resistance element (1) has attachment pins (33) and contact and attachment pins (35) at its front and rear sides respectively intended to be placed in corresponding recesses in a lid of the device. The rear contact and attachment pins (35) have portions (39) intended for contact with elastic, electrically conducting contact pins with which the resistance element (19) comes in contact, when the lid is folded down to perform the shrinking operation. The open and freely suspended design of the resistance element (19) including only small contact areas to the lid result in that the resistance element can be rapidly heated and thereafter rapidly cooled implying that a shrinking operation can be executed in a minimum of time.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Device for heating shrinkable sleeves
InactiveUS6570140B2Simple mounting attachmentIncrease contactElongated resistive elementHeater elementsHeat-shrinkable sleeveElectrical resistance and conductance
A resistance element (19) for a device for shrinking shrinkable sleeves comprises an elongate electrical conductor extending in a zigzag pattern and bent to a tunnel shape. The shrinkable sleeve including for example an optical fiber enclosed therein is placed in that region of the resistance element (19), which corresponds to approximately the geometric axis of the upper semi-cylindric portion of the tunnel shape. The resistance element (1) has attachment pins (33) and contact and attachment pins (35) at its front and rear sides respectively intended to be placed in corresponding recesses in a lid of the device. The rear contact and attachment pins (35) have portions (39) intended for contact with elastic, electrically conducting contact pins with which the resistance element (19) comes in contact, when the lid is folded down to perform the shrinking operation. The open and freely suspended design of the resistance element (19) including only small contact areas to the lid result in that the resistance element can be rapidly heated and thereafter rapidly cooled implying that a shrinking operation can be executed in a minimum of time.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Porous ceramic heating element and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20070003750A1High bonding strengthAccelerating formation of foamIncandescent ignitionMaintainance of heating chambersFoaming agentMetallurgy
The present invention provides a porous ceramic heating element wherein 0.08 to 1.00 wt % of a foaming agent is added in 99.00 to 99.92 wt % of a mixture of an inorganic material, a binder, a conductive material, a hardener, a bonding agent and a dispersion medium and mixed with the mixture. According to the porous ceramic heating element, the bonding strength of porous foam formed in the ceramic heating element becomes strong, thereby providing an effect that the entire structure is hardened.
Owner:KIM CHANGHEE +1
Electric heater for a clothes dryer
ActiveUS20070278211A1Increase heating powerLess fluffElongated resistive elementHeater elementsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:EICHENAUER HEIZELEMENTE
Wake generating solid elements for joule heating or infrared heating
ActiveUS8541721B2Lower overall pressure dropIndirect heat exchangersWater heatersEngineeringJoule heating
Owner:MOSKAL DANIEL
Resistor made from carbonaceous material
InactiveUS20050120547A1Elongated resistive elementFurnace componentsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A crenellated resistor made from a carbonaceous material and having the shape of a hollow cylinder for use in furnaces working at high temperature. The resistor is characterized by the thickness of the cylinder walls which follows a profile determined so as to produce an even temperature on the surface of the resistor when it is working. Thus, the wall has a radial thickness which decreases in a transition section from the peripheral edge to the internal edge. The resistor configuration allows elimination of hot spots which may appear when electricity flows through the resistor.
Owner:CARBONE LORRAINE COMPOSANTS GENNEVILLIERS
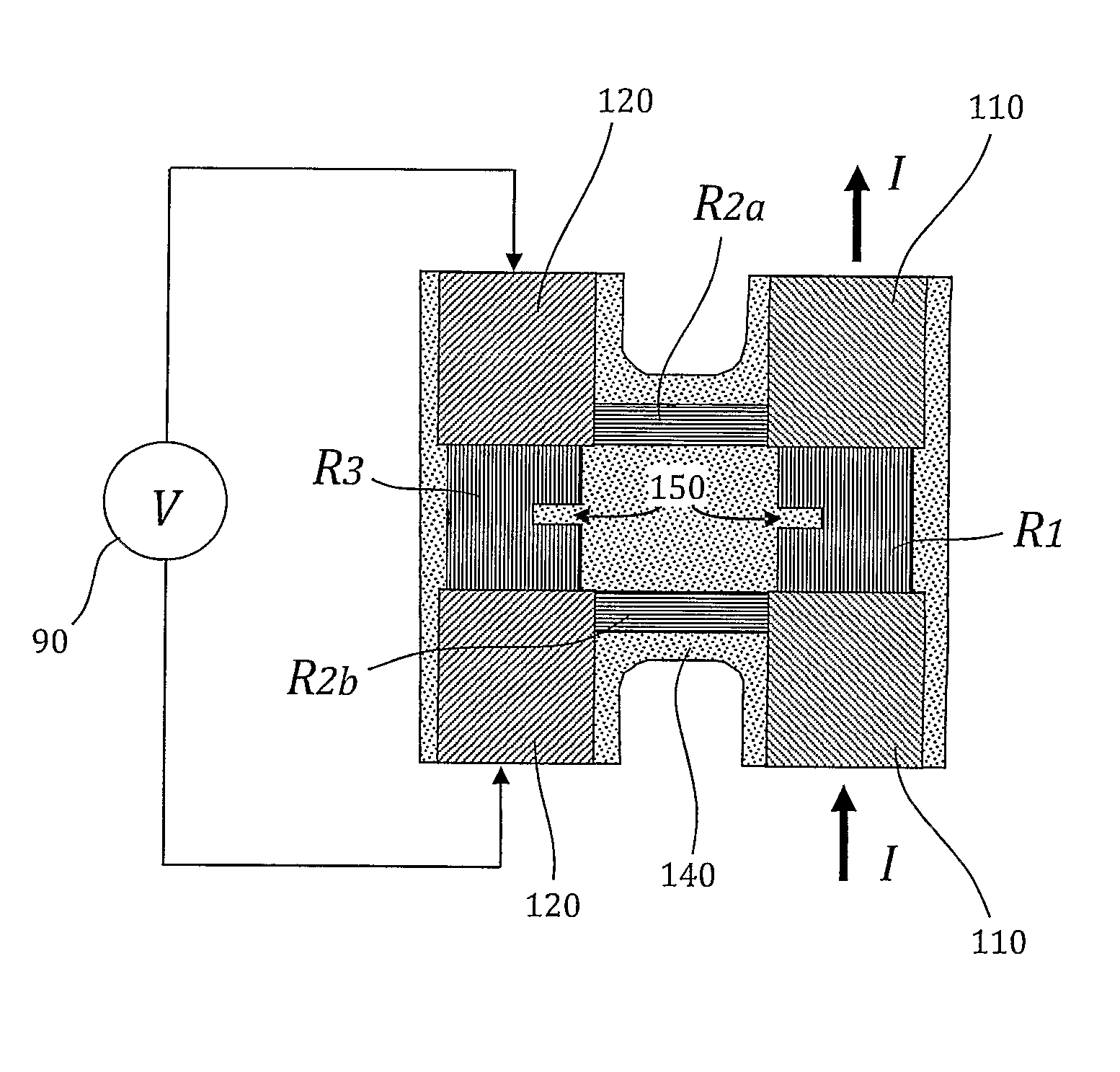
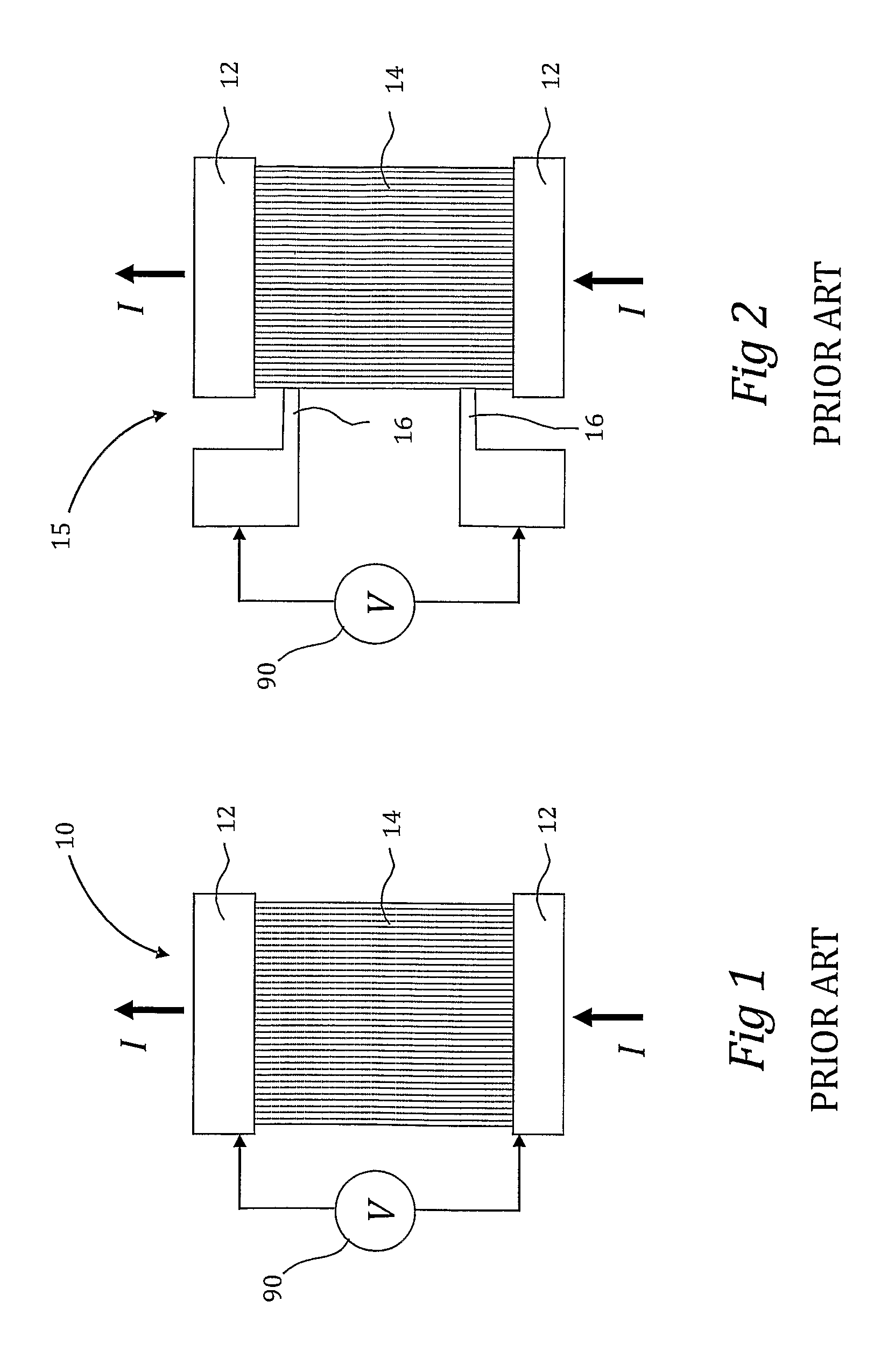
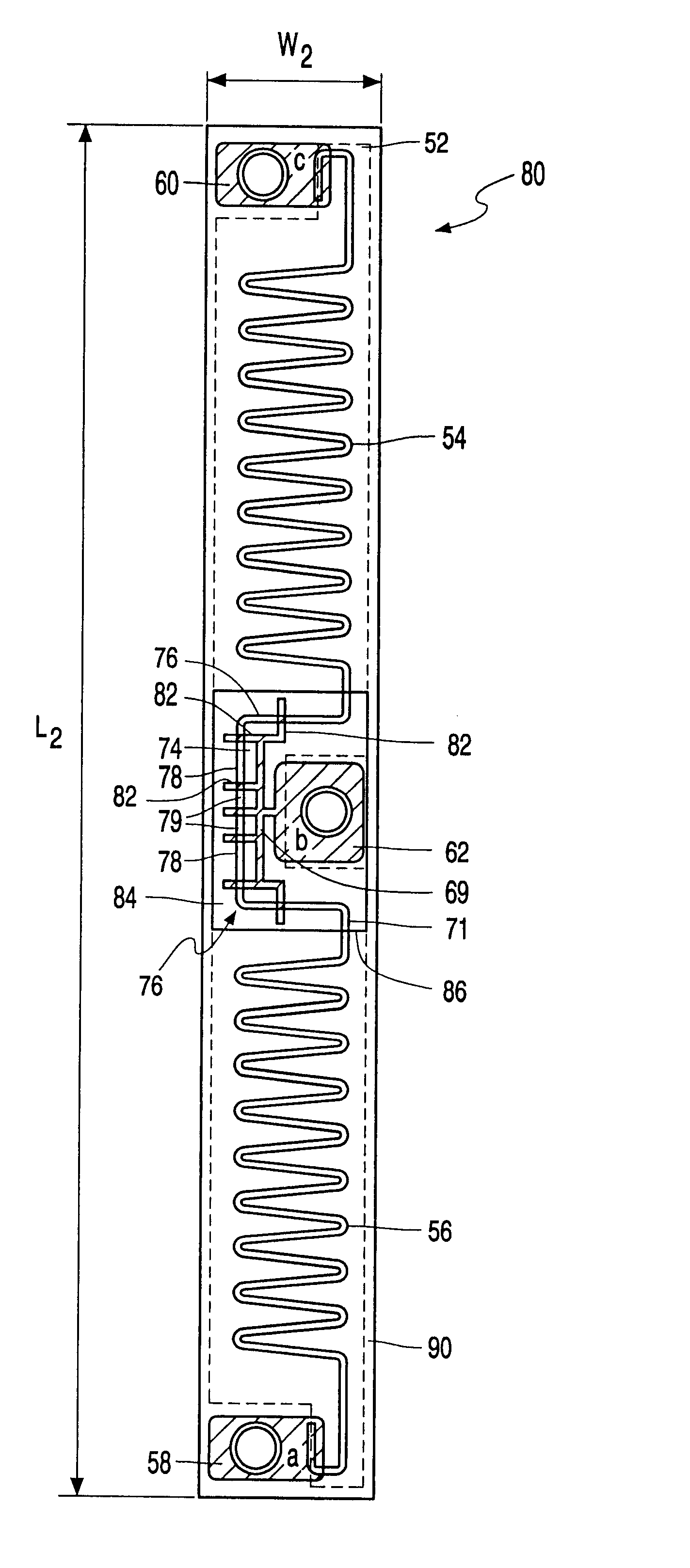
Four-terminal resistor with four resistors and adjustable temperature coefficient of resistance
Thermally stable four-terminal resistor (current sensor) is characterized by having the capacity to adjust both resistance and temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR), during manufacturing process. The four-terminal resistor includes 3 or 4 elementary resistors R1-R3 forming a closed loop. Resistor R1 is the principal low-ohmic value resistor. The terminals of resistor R1 serve as “Force” terminals of the four-terminal resistor. Resistors R2, R3 form a voltage divider intended to minimize the TCR of the four-terminal resistor and connected in parallel to resistor R1. The terminals of resistor R3 serve as “Sense” terminals of the four-terminal resistor. Resistor R2 may be split into two resistors: R2a, R2b to simplify the implementation of four-terminal resistor. Elementary resistors R1, R2 must have the same sign of TCR. Target resistance and TCR minimization in four-terminal resistor are reached by adjustment of resistance of the elementary resistors.
Owner:VISHAY DALE ELECTRONICS INC
Open coil electric resistance heater with offset coil support and method of use
ActiveUS7947932B2Better fill volumeReduce noiseElongated resistive elementHeater elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceShadowings
An open coil electrical resistance heater uses a number of offset insulators to support the coil of the heater. The offset insulators configure the run of coil in a sinusoidal shape to hold the insulators in a more secure manner and reduce vibration and noise generation during heat operation. The sinusoidal configuration of the coil also reduces the problem of shadowing of portions of the resistance wire coil.
Owner:TUTCO
Compensation of field effect on polycrystalline resistors
ActiveUS20090085657A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElongated resistive elementResistive circuitsEngineering
A resistive circuit includes a first terminal and a second terminal and polycrystalline first and second resistive segments coupled between the first and second terminals. A third terminal A is coupled to the first resistive segment, and a third terminal B is coupled to the second resistive segment. The third terminal A has a first voltage with respect to the first terminal, and the third terminal B has a second voltage with respect to the second terminal. With this arrangement, the non-linearity of resistance of the first resistive segment at least partially compensates for non-linearity of resistance of the second resistive segment.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Power resistor
InactiveUS20090085715A1Spread heatElongated resistive elementEnvelope/housing resistor manufactureElectrical resistance and conductanceMetal strips
A resistor includes first and second opposite terminations, a resistive element formed from a plurality of resistive element segments between the first and second opposite terminations, at least one segmenting conductive strip separating two of the resistive element segments, and at least one open area between the first and second opposite terminations and separating at least two resistive element segments. Separation of the plurality of resistive element segments assists in spreading heat throughout the resistor. The resistor or other electronic component may be packaged by bonding to a heat sink tab with a thermally conductive and electrically insulative material. The resistive element may be a metal strip, a foil, or film material.
Owner:VISHAY DALE ELECTRONICS INC
Protection Device
InactiveUS20100013591A1Large capacityFunction increaseProtective switch detailsElongated resistive elementShape-memory alloyAlloy
It is provided a new protection device with a large current capacity, which can sense a relatively low abnormal temperature, and further has a simple construction and is not large in size. The protection device comprises (1) a polymer PTC device (18) having metal electrodes (14, 16) on the both main surfaces, and (2) a shape memory alloy lead (20), wherein the shape memory alloy lead is connected to the polymer PTC device by an electrically conductive adhesive (22) containing a thermoplastic resin and an electrically conductive filler.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS RAYCHEM KK
Chip resistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7286039B2Increase the lengthImprove anti-surge performanceElongated resistive elementAlarmsElectrical and Electronics engineeringYield rate
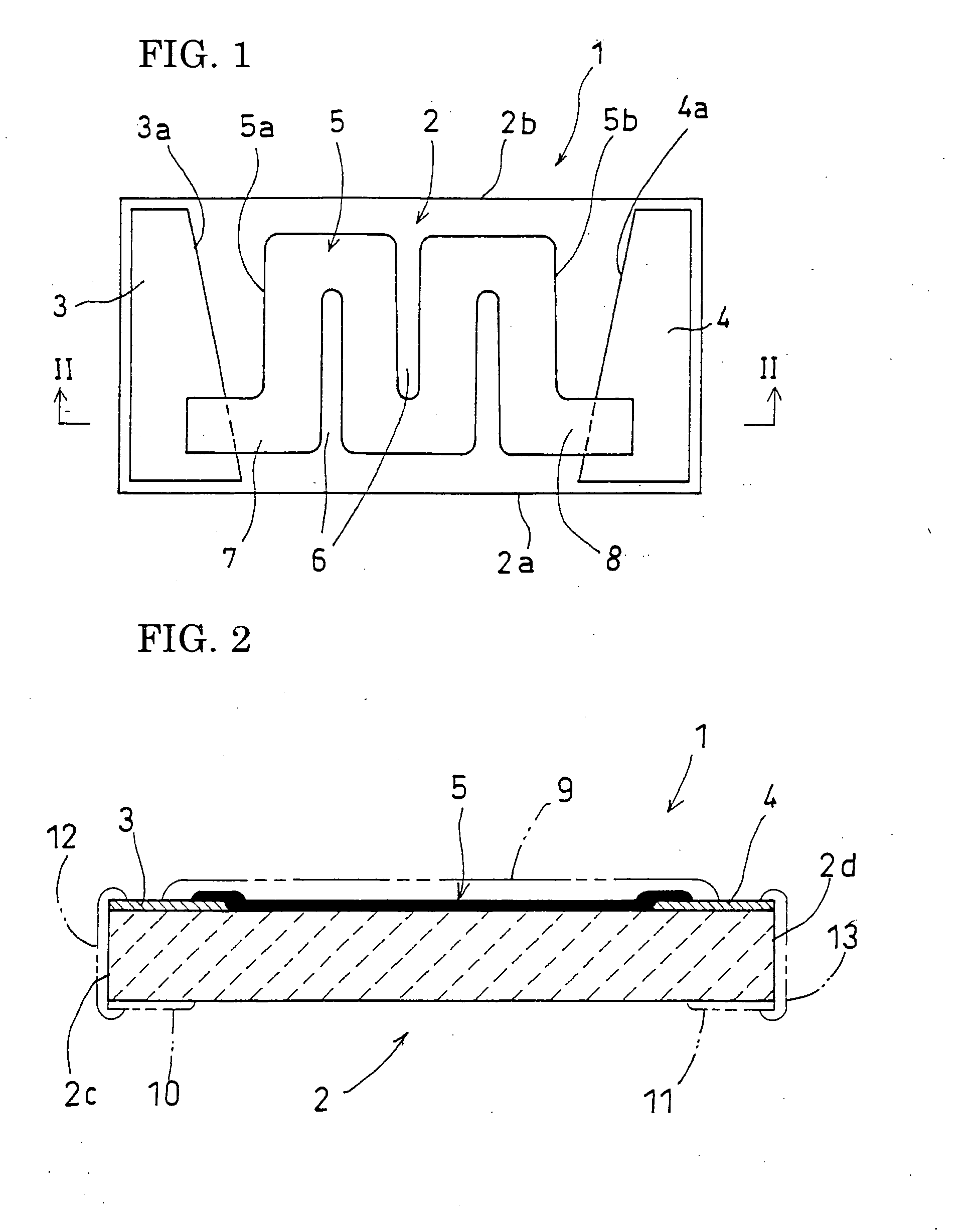
A chip resistor is provided which includes a resistor film 5 formed between a pair of terminal electrodes 2 and 3 on an upper surface of an insulating substrate 2. The resistor film is formed with two inward grooves 7, 8 and two trimming grooves 9, 10 which are alternately provided for causing the current path in the resistor film to have a winding shape. The two inward grooves 7 and 8 are provided approximately at the midpoint between one end edge 5a and the other end edge 5b of the resistor film 5. The trimming groove 9 is provided between the inward groove 8 and the end edge 5a of the resistor film, whereas the other trimming groove 10 is provided between the inward groove 7 and the end edge 5b of the resistor film, whereby the time required for the trimming adjustment to adjust the resistance to a predetermined value is shortened, and the yield rate is reduced to reduce the cost.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Resistor circuit and oscillation circuit
InactiveUS7825768B2Other resistor networksElongated resistive elementResistive circuitsElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Thick film resistor
InactiveUS20090174523A1Improve stabilityImprove noise characteristicsElongated resistive elementCoil/loop resistive elementsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
In a flat plate type thick film resistor, an insulation performance is improved by excluding the nonuniformity of potential distribution on a wiring plane, which is generated when electric current flows in a resistance wire. Simultaneously, generation of noise depending on potential distribution and variation of stray capacitance around a resistor is suppressed. When the resistance wire having a constant thickness and uniform resistivity, which is formed on an insulating substrate, is connected to a pair electrode conductors that face to each other, in the way that the resistance wire is repetitively bent to the alternate side in zigzags, a potential gradient on the wiring plane, which is generated when electric current flows in the resistance wire, is constant by properly selecting the line width, the bending angle, and the spacing between bending vertexes of a resistance wire.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
Meander resistor
ActiveUS20110241820A1Reliable and reliableMitigating ESD damageElongated resistive elementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceMeander
The present invention relates in general to the field of integrated circuits, and more specifically to a meander resistor. Basically, a meander resistor can be considered as a bar resistor with the exception of the corner squares (right-angle bends). The Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) sensitivities of on-chip resistors can be a problem for both electronic manufactures and electronic component users. As others components, passive devices are known to be susceptible to ESD events. The context of this invention is to improve the reliability of the resistors during an ESD event. An ESD stress means that high current and high voltage levels are applied to the device. The device has to be able to dissipate this energy without failure.
Owner:NEXPERIA BV
Chip resistor and its manufacturing process
ActiveUS20090237200A1Resistor chip manufactureElongated resistive elementElectrical and Electronics engineeringElectrode
A chip resistor (1) includes a chip substrate (2) a mutually separated terminal electrodes (3, 4) formed on the upper surface of the substrate (2), and a meandering resistor film (5) formed between the two terminal electrodes (3, 4). Each of the terminal electrodes (3, 4) includes an inner edge (3a, 4a) extending diagonally from one side surface (2a) toward the other side surface (2b) of the chip substrate (2). Each of the inner edges (3a, 4a) has a portion closer to the resistor film (5) that is electrically connected to a narrow portion (7, 8) formed integral with the resistor film (5). The narrow portion extends outward from an end (5a, 5b) of the resistor film (5).
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Resistor assembly and cathode ray tube
InactiveUS6593697B1Shorten the timeShorten the lengthElongated resistive elementElectrode and associated part arrangementsAnode voltageEngineering
The invention relates to a resistor assembly for dividing an applied voltage into an intermediate voltage being below the applied anode voltage in a cathode ray tube. The resistor assembly comprises an insulating substrate and a resistive voltage divider including a first and a second resistive layer provided on the insulating substrate, and an additional resistive network with a first network terminal and a second network terminal. The additional resistive network is coupled in series with the first resistive layer. Furthermore, the additional resistive network comprises first and second resistive portions which are releasably coupled to the network terminals via bridge connections. According to the invention, the first and second resistive portions have substantially different resistance values for selecting a predetermined resistance value from a range of resistance values of the additional resistive network.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Resistive structure and resistive voltage divider arrangement
ActiveUS20130342227A1Elongated resistive elementResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringVoltage divider
A resistive structure has an improved electric field profile deposited on the surface of a cylindrical insulating substrate. At least one resistive path or trace is provided with a helix-looking shape and is directly printed on the surface of the insulating substrate. A resistive voltage divider includes first and second resistors electrically connected in series, where each resistor is made of one or more traces of electrically resistive film material applied onto a cylindrical insulating substrate. At least one of the traces is shaped like a helix and is applied onto the substrate by direct printing.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Stamped resistive element for use in electrical equipment, manufacturing process of stamped resistive element and apparatus equipped with stamped resistive element
InactiveUS20170268801A1Maximize contact areaElongated resistive elementHeater elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceBiochemical engineering
A stamped resistive element for use in electrical equipment, manufacturing process of stamped resistive element and apparatus equipped with stamped resistive element are provided. The stamped resistive element is produced from a stamping process and is intended to be used in replacement of conventional helical electrical resistances, whether in hair dryers and similar equipment or in other types of heating equipment. The stamped resistive element is produced as a blank from a metal sheet presenting a known resistive coefficient.
Owner:ACTION TECH IND E COMERCIO DE ELETROELECTRONICSOS LTDA
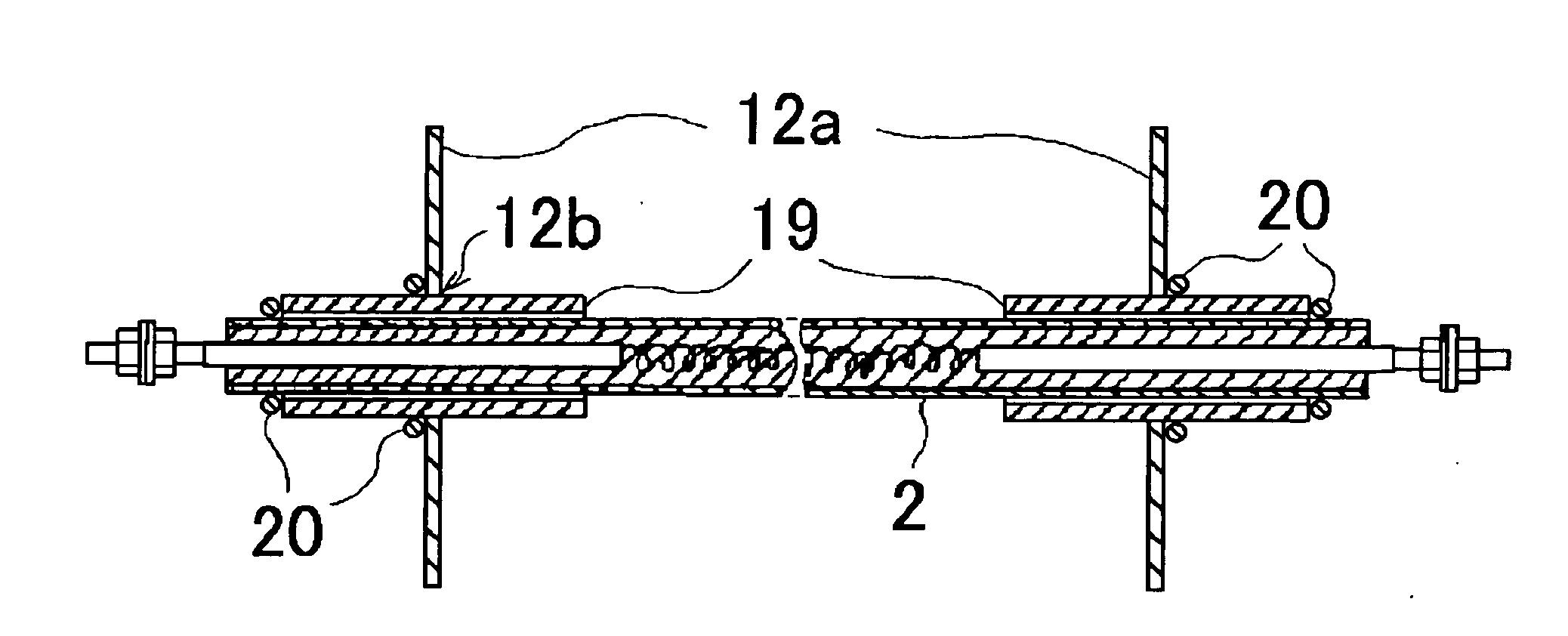
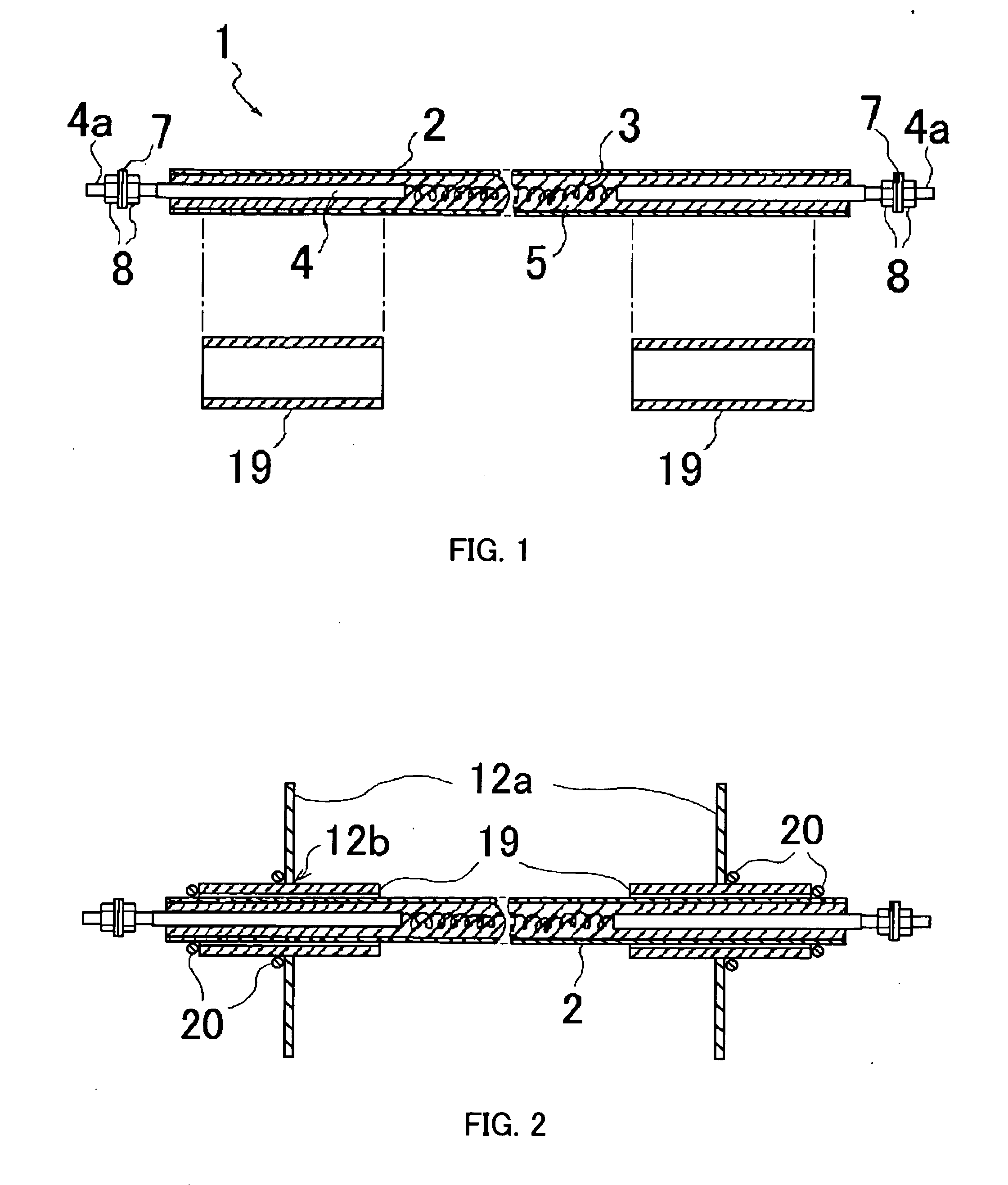
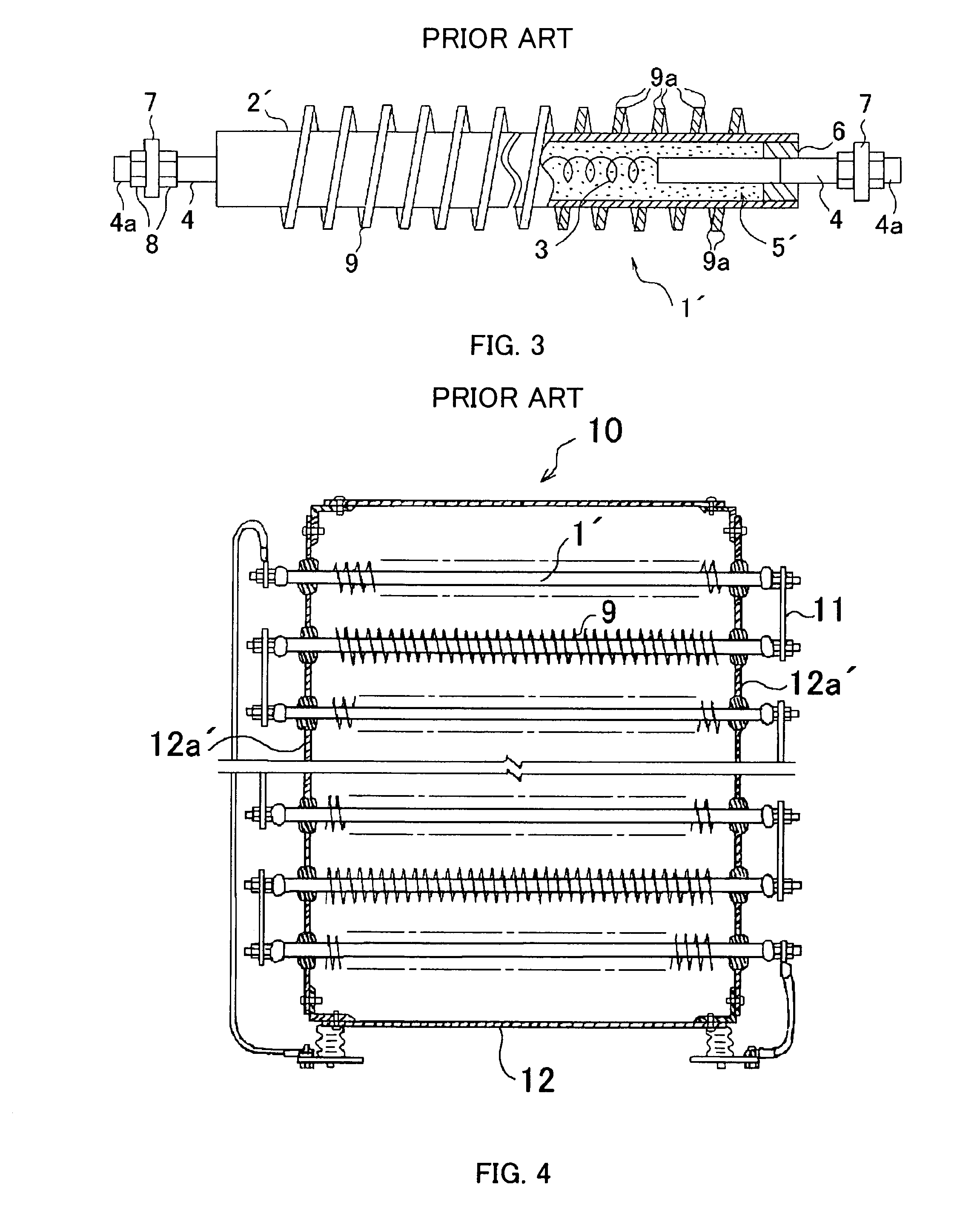
High pressure resistance body element
ActiveUS20060097840A1Reduce vibrationHazard reductionElongated resistive elementResistor electrostatic/electromagnetic shieldingElectrical resistance and conductanceHeat resistance
A high-voltage resistor element which is superior to heat resistance, dielectric breakdown strength, vibration resistance and durability performance, and is advantageous to maintenance, inspection, adjustment, replacement and repair, is made up of: a cylindrical outer tube made of metal; a resistive heat-generating wire in a coiled shape tensionally extending between inner ends of electrode rods inserted respectively from both ends of the outer tube; an insulating material filing up a space between the resistive heat-generating wire with the electrode rods and the internal surface of the outer tube and fired; and insulating sleeves extractably encasing and anchored in the portions adjacent to the both ends of the outer tube penetratingly bridging between arrangement boards.
Owner:KOUKEN CO LTD
High pressure resistance body element
ActiveUS7218201B2Reduce vibrationHazard reductionElongated resistive elementBase element modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceHeat resistance
A high-voltage resistor element which is superior to heat resistance, dielectric breakdown strength, vibration resistance and durability performance, and is advantageous to maintenance, inspection, adjustment, replacement and repair, is made up of: a cylindrical outer tube made of metal; a resistive heat-generating wire in a coiled shape tensionally extending between inner ends of electrode rods inserted respectively from both ends of the outer tube; an insulating material filing up a space between the resistive heat-generating wire with the electrode rods and the internal surface of the outer tube and fired; and insulating sleeves extractably encasing and anchored in the portions adjacent to the both ends of the outer tube penetratingly bridging between arrangement boards.
Owner:KOUKEN CO LTD
Open coil electric resistance heater with offset coil support and method of use
ActiveUS20090139984A1Better fill volumeReduce noiseElongated resistive elementHeater elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceShadowings
An open coil electrical resistance heater uses a number of offset insulators to support the coil of the heater. The offset insulators configure the run of coil in a sinusoidal shape to hold the insulators in a more secure manner and reduce vibration and noise generation during heat operation. The sinusoidal configuration of the coil also reduces the problem of shadowing of portions of the resistance wire coil.
Owner:TUTCO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com