Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Track density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
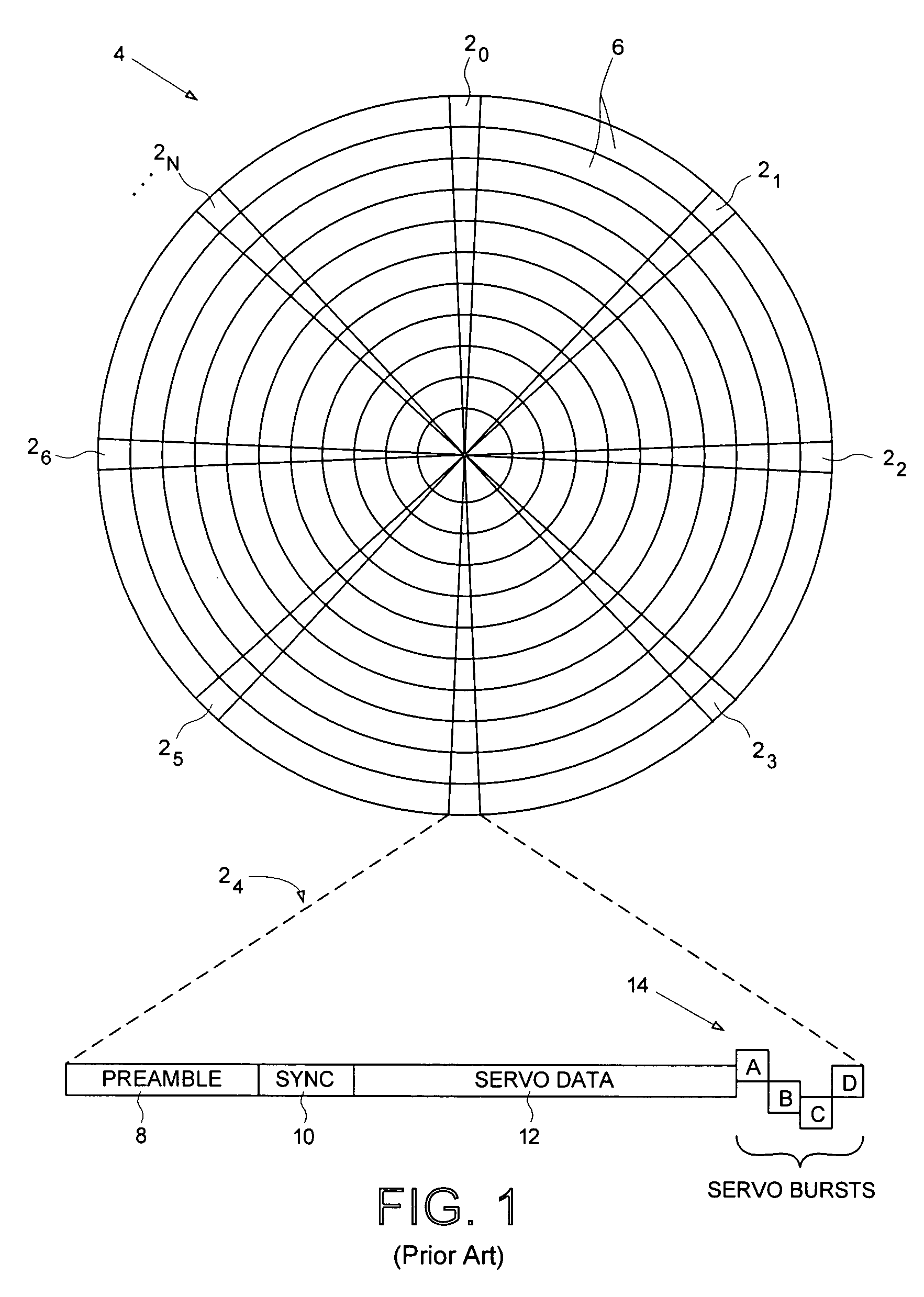
Track density - Computer Definition. The number of recording channels (tracks) per inch on a magnetic or optical surface.
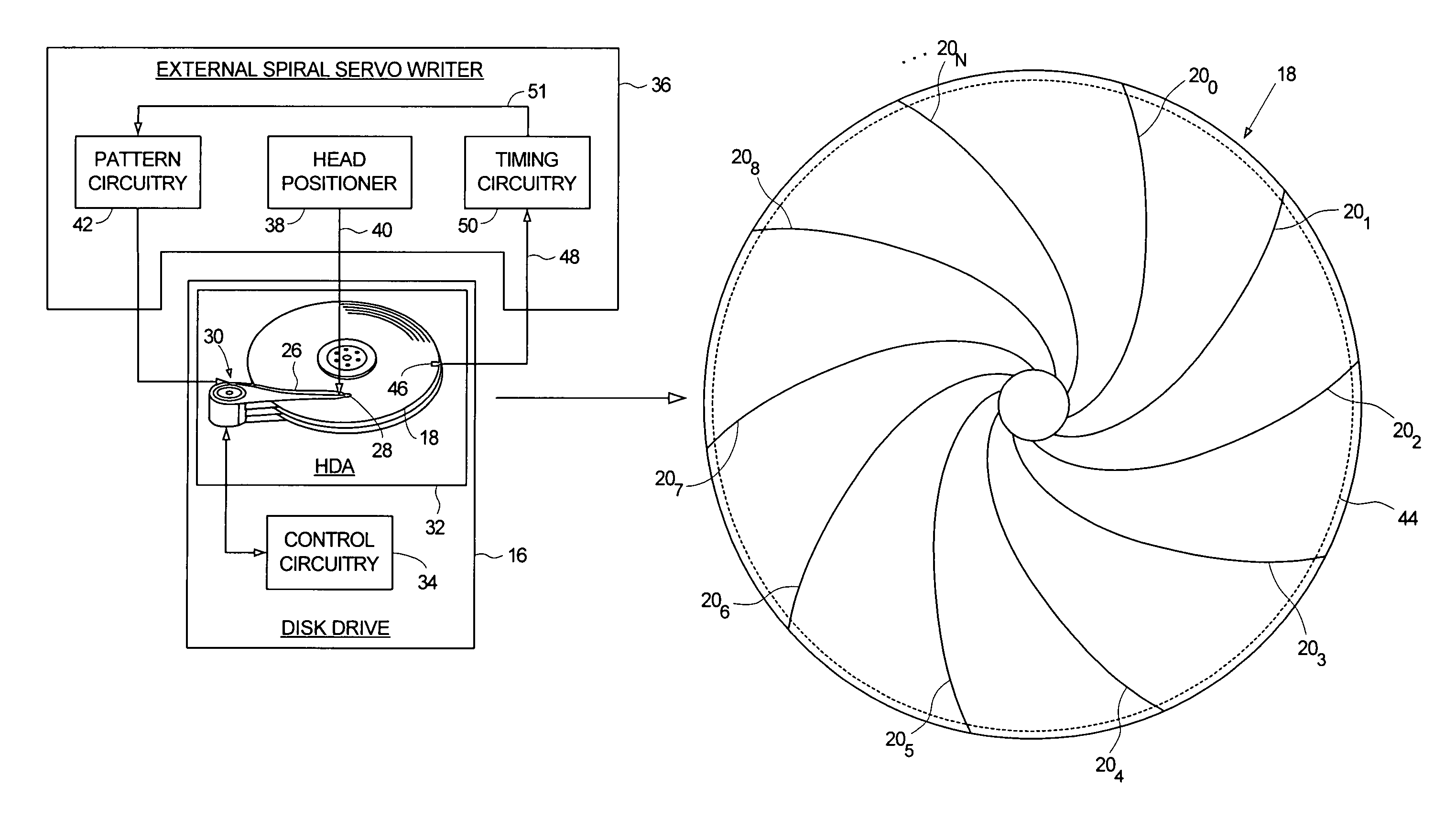
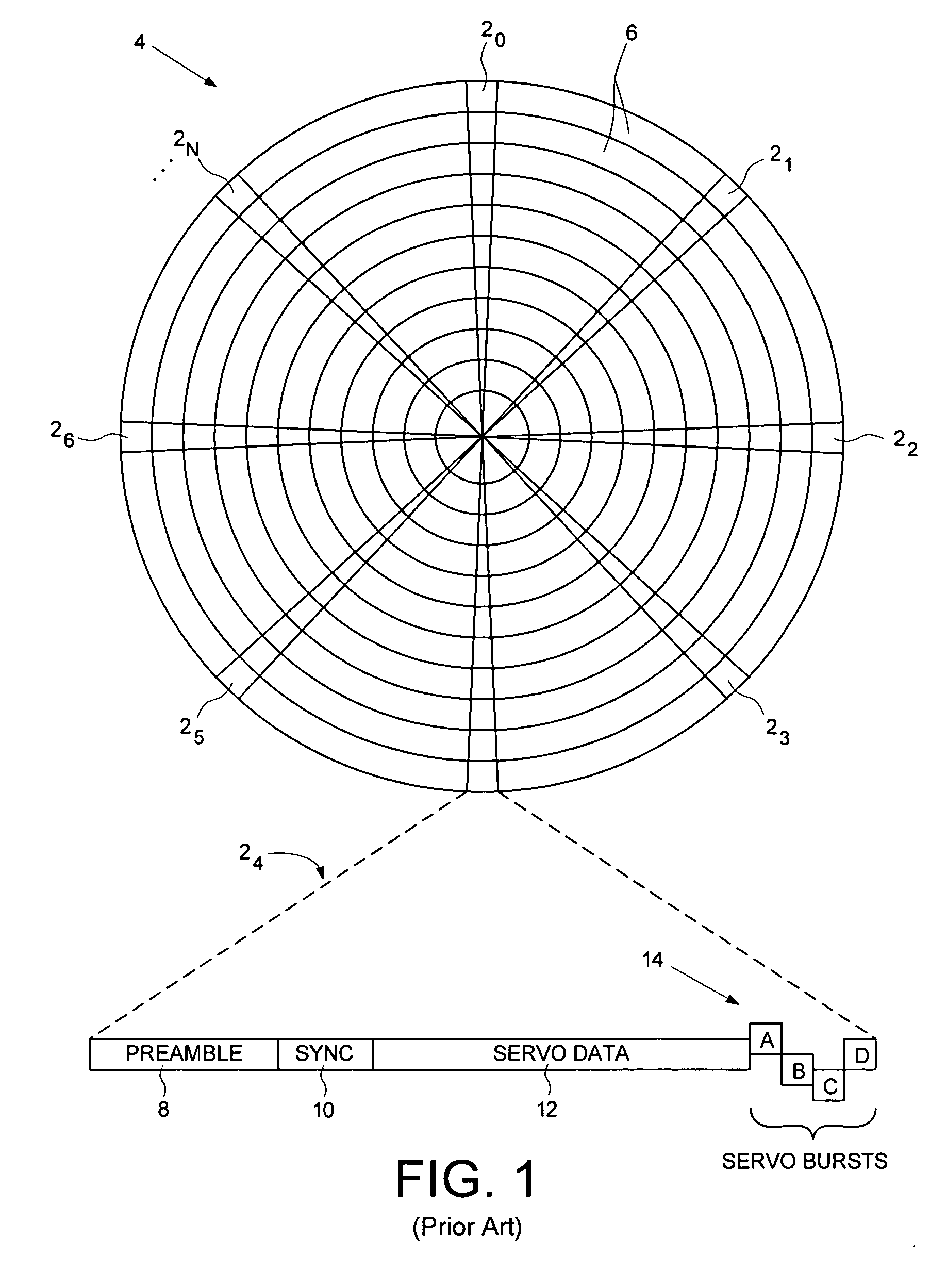
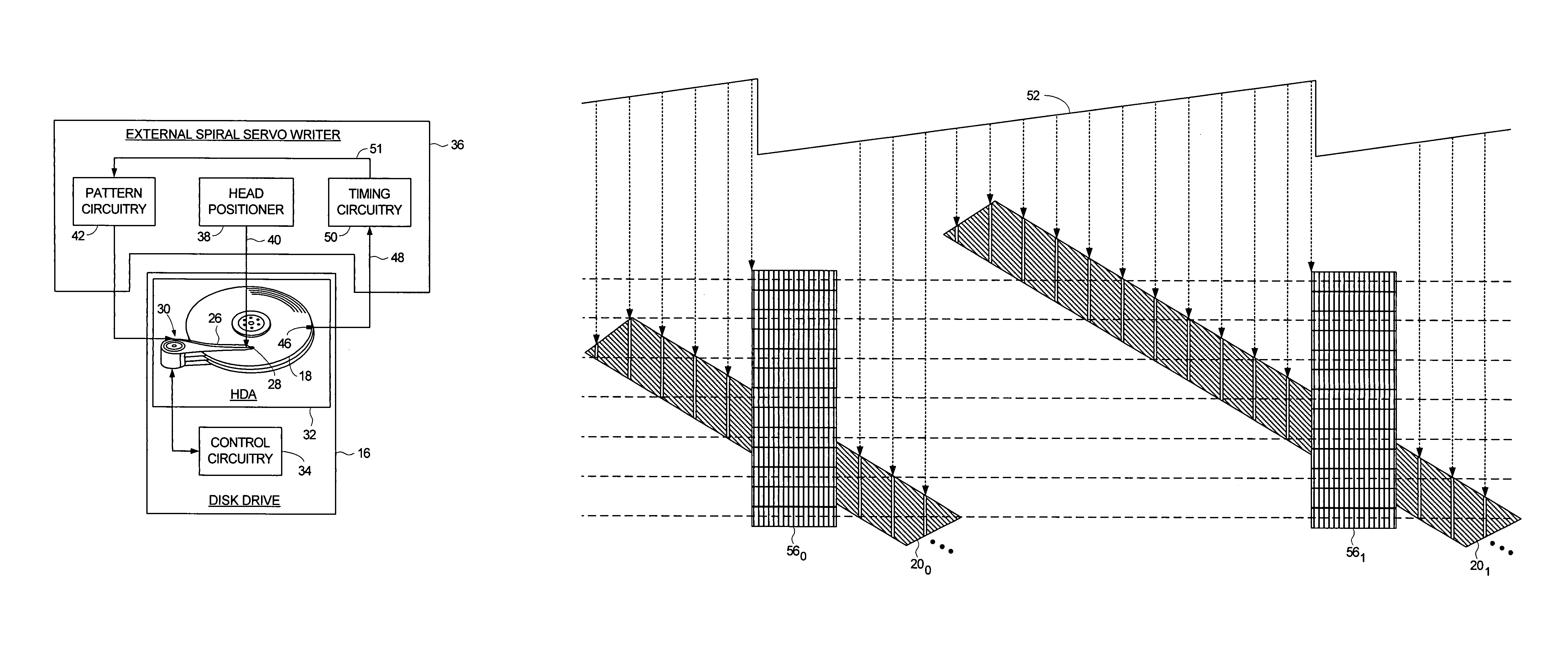
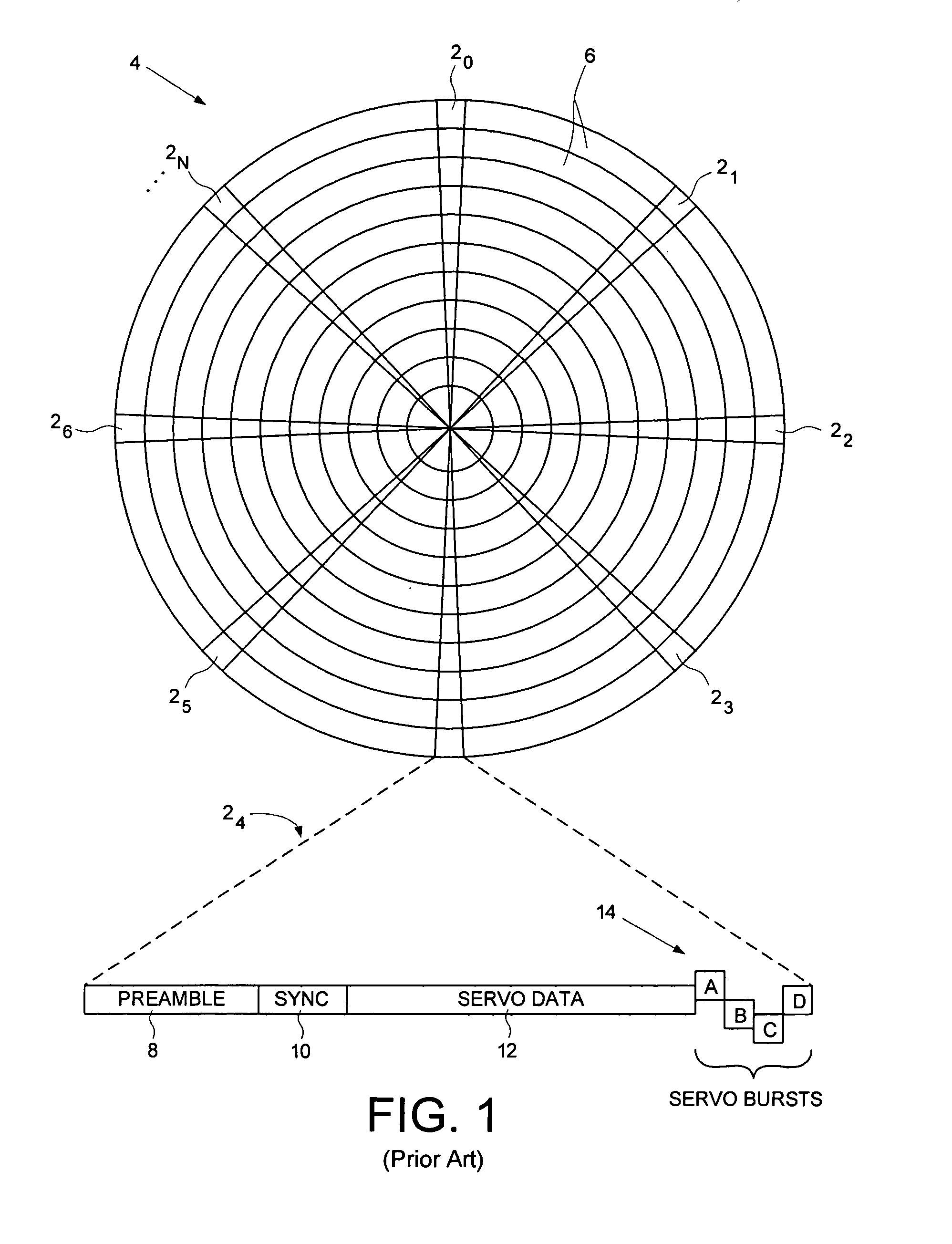
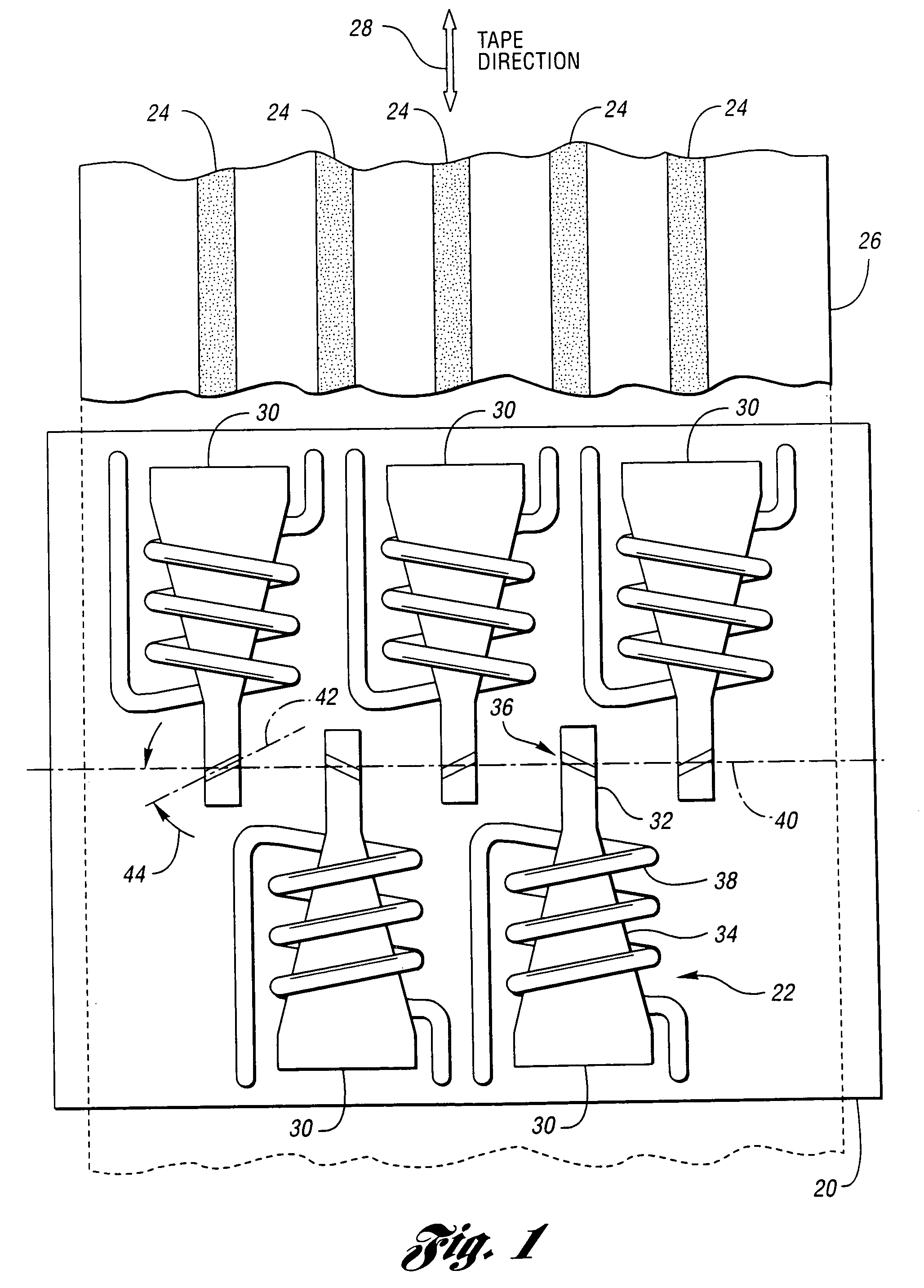
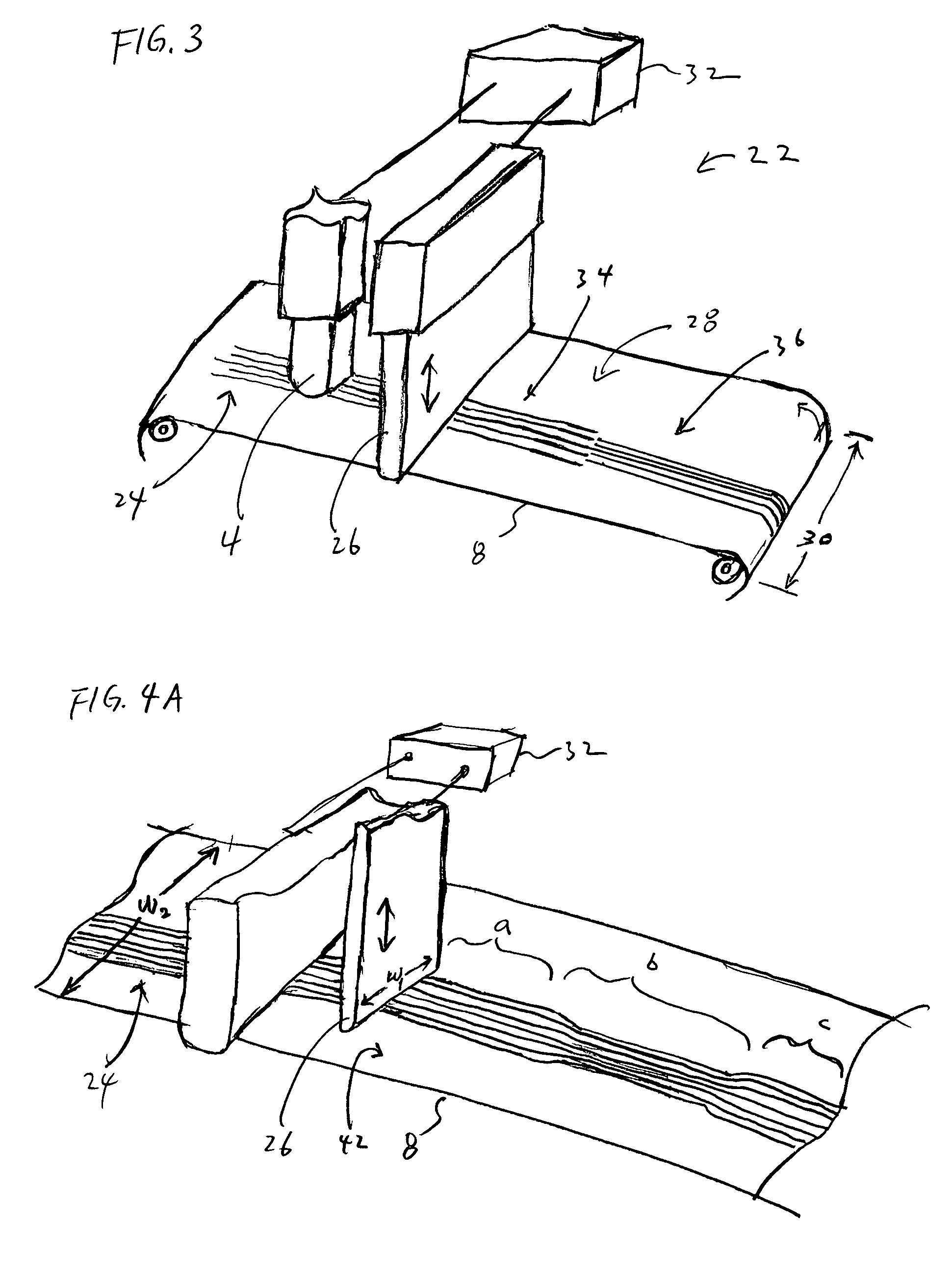
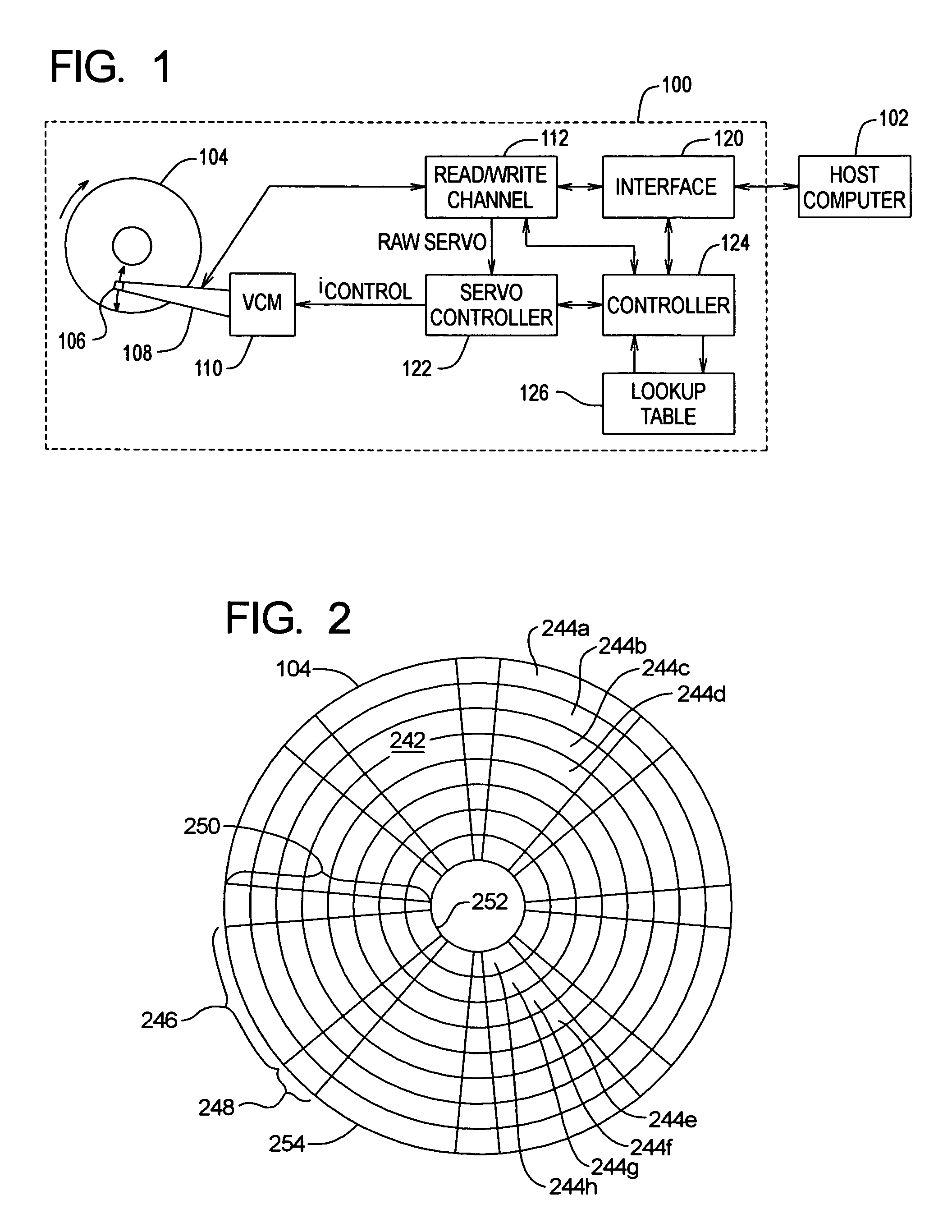
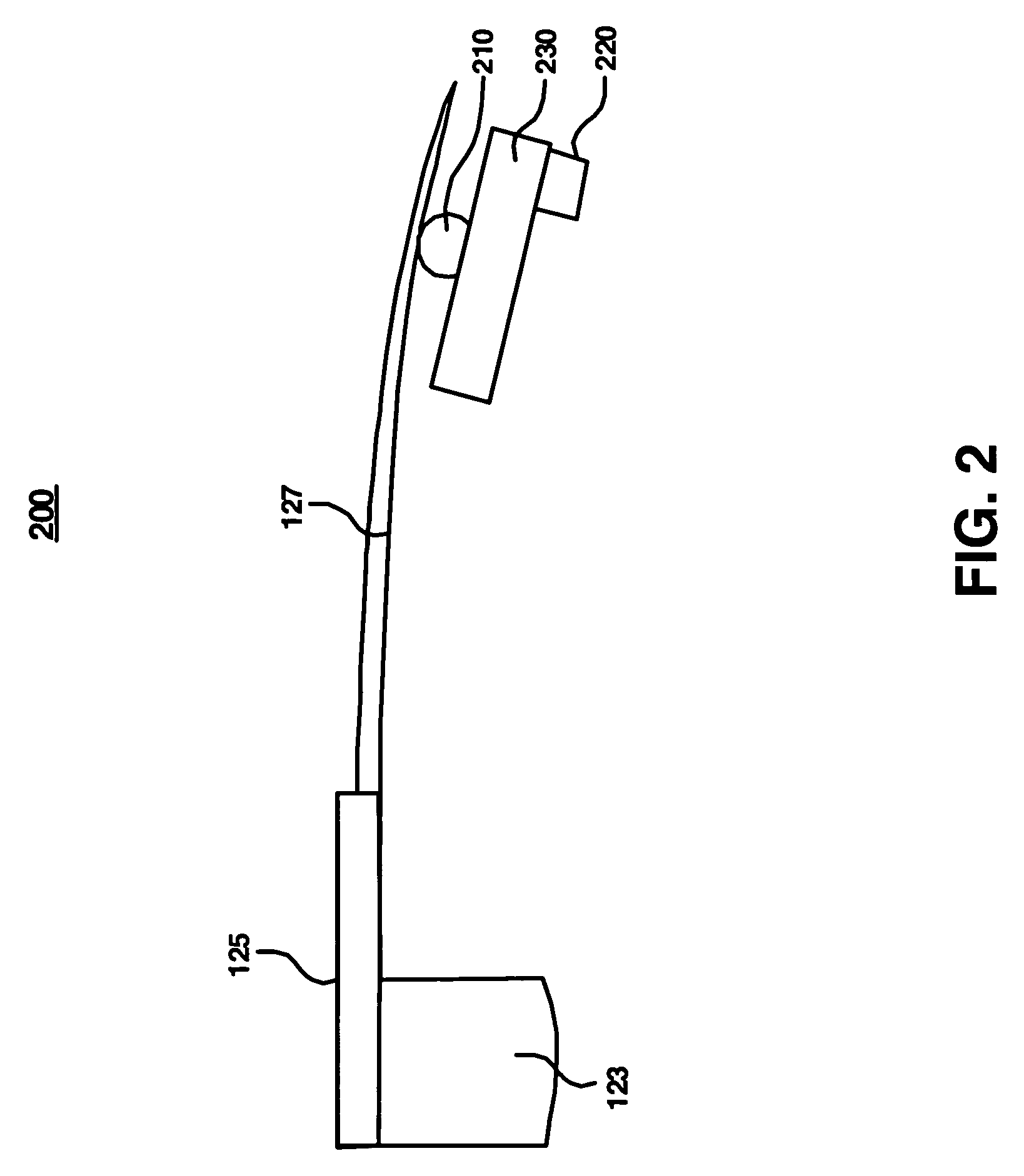
Adjusting track density by changing PES algorithm when servo writing a disk drive from spiral tracks
InactiveUS7068459B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityControl theory
A method and apparatus is disclosed for writing product servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive to define a plurality of data tracks. The disk drive comprises the disk and a head actuated over the disk. The disk comprises a plurality of spiral tracks which are read using the head to synchronize a write clock and to generate a position error signal (PES) according to a PES algorithm used to maintain the head along a first servo track while writing product servo sectors along the first servo track. The PES algorithm is adjusted to seek the head to a second servo track, and the head is used to write product servo sectors along the second servo track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
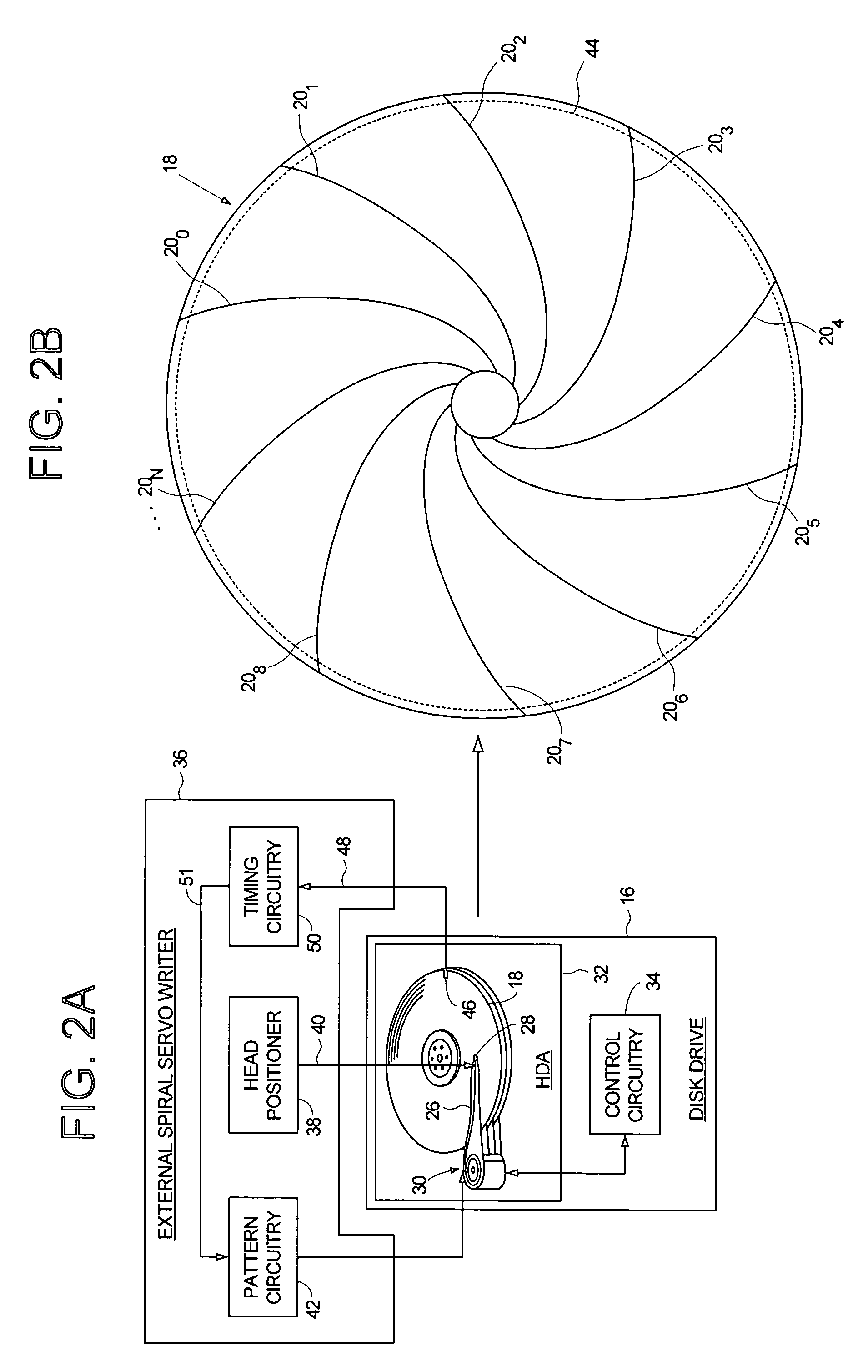
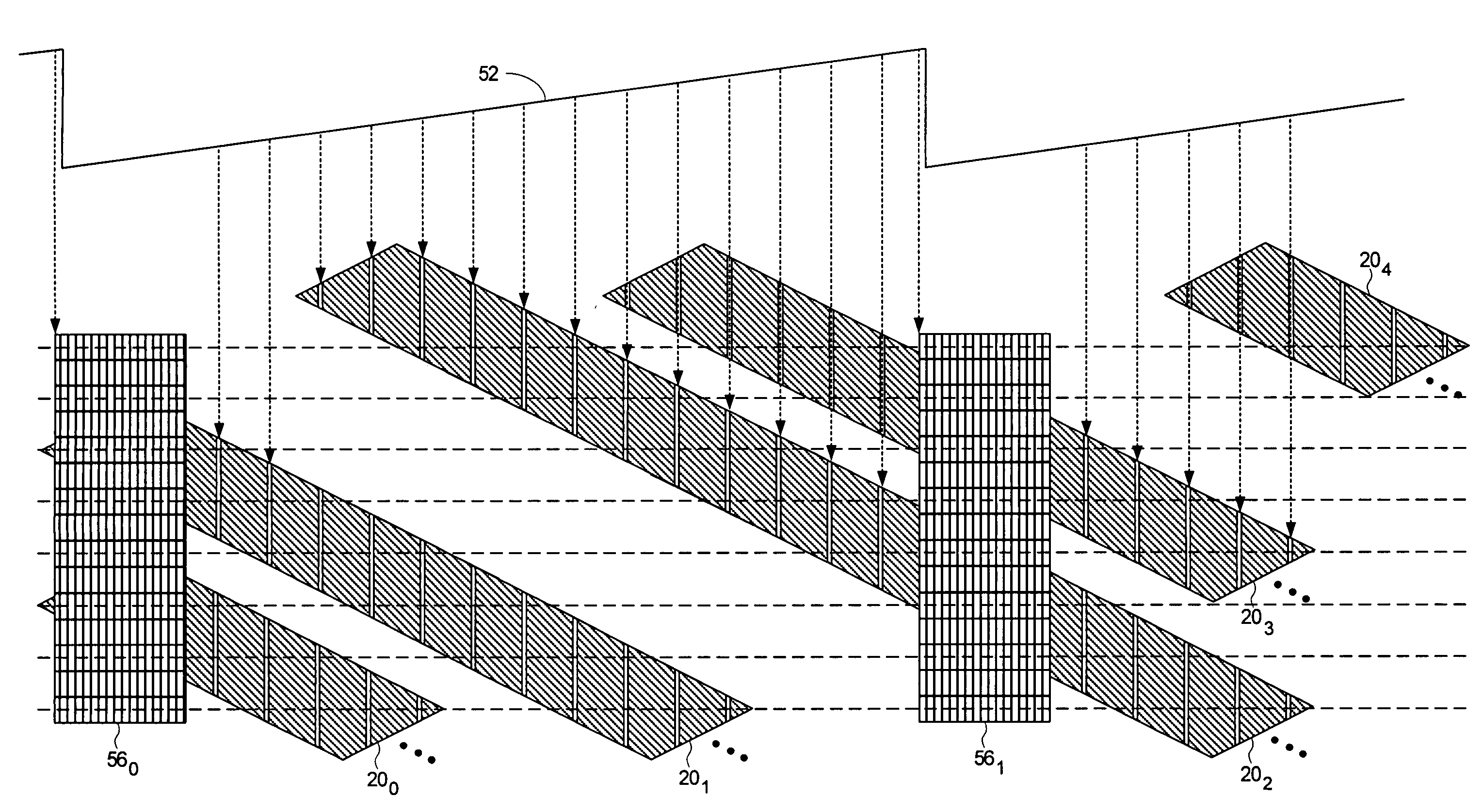
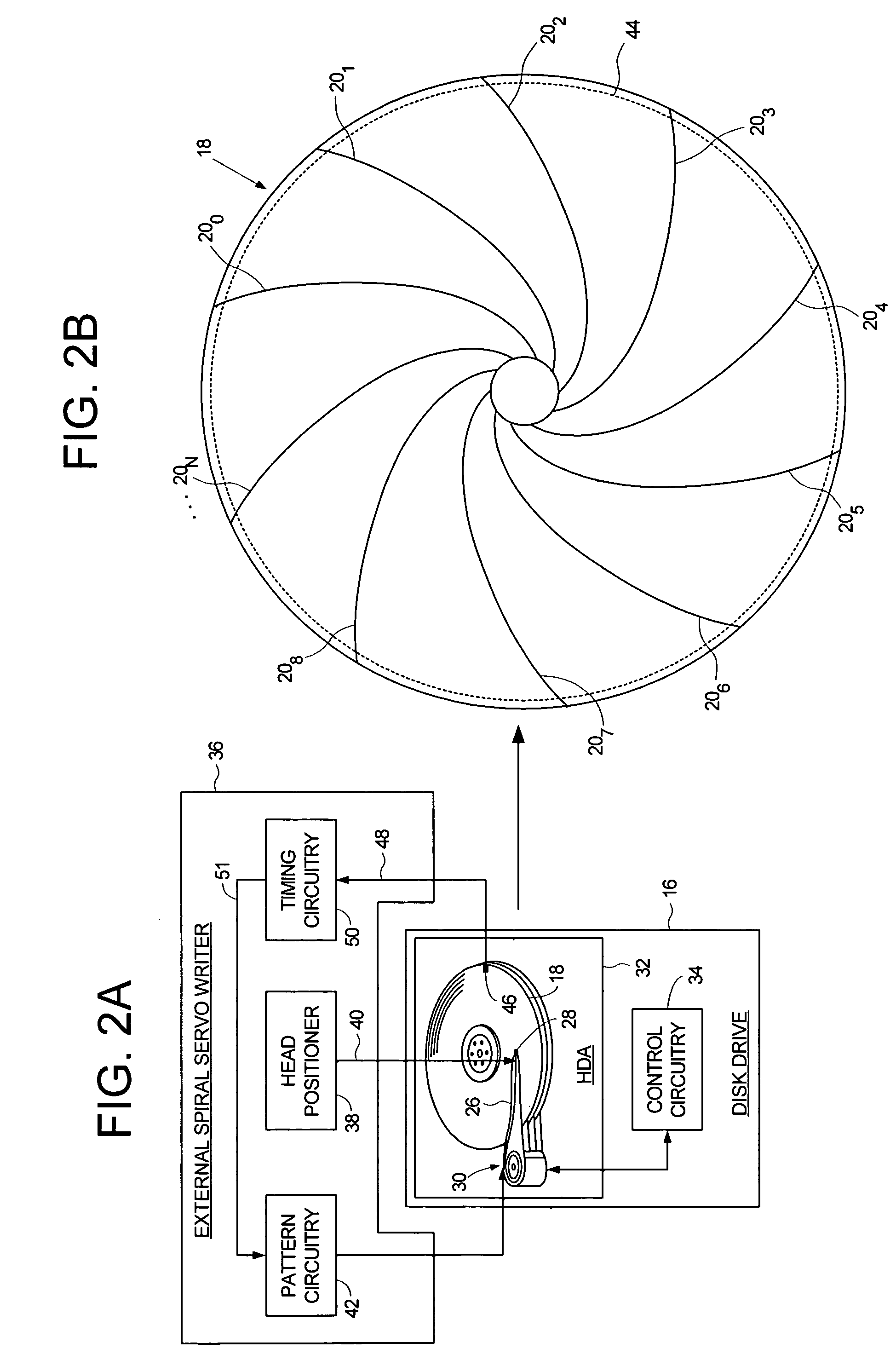
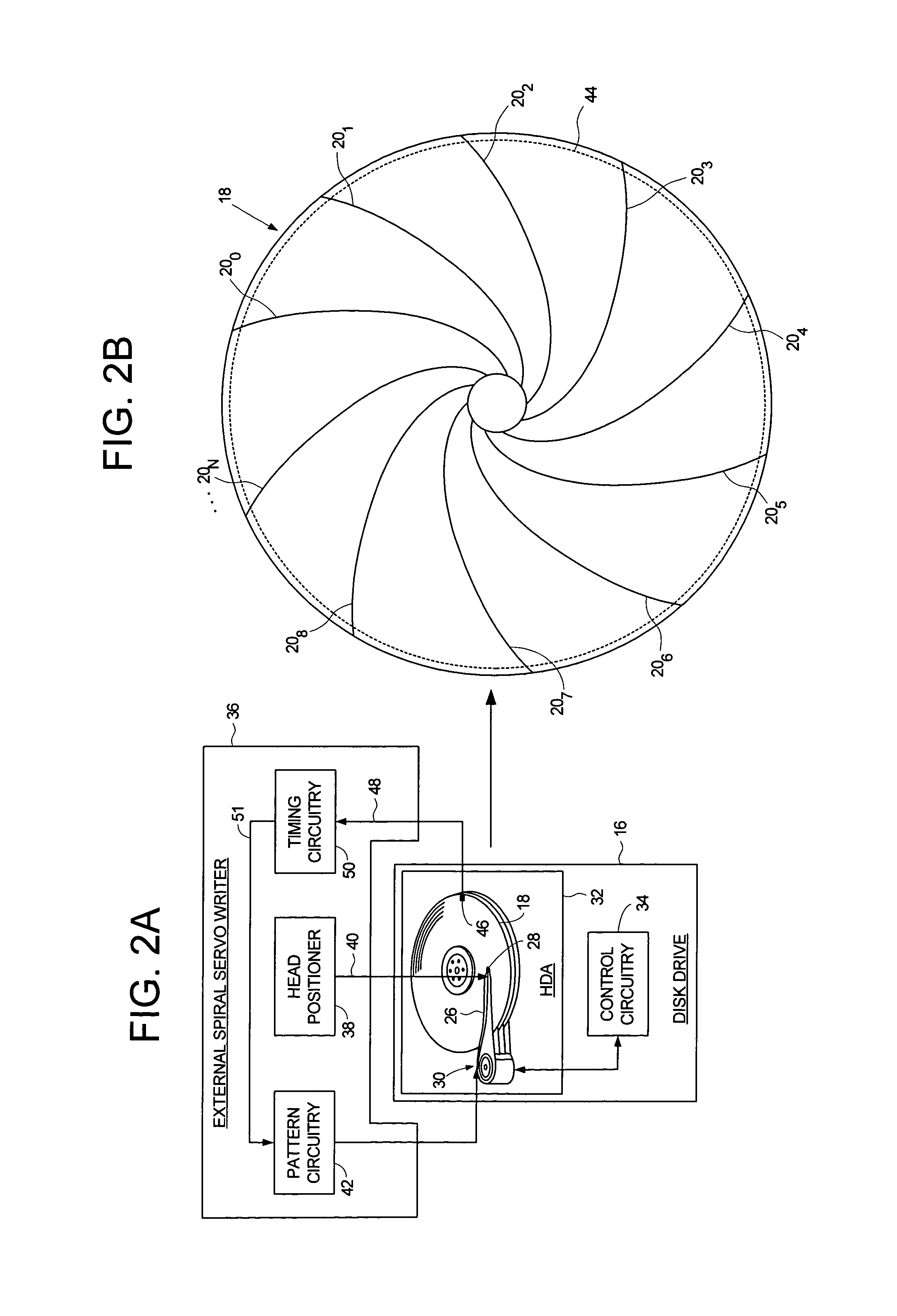
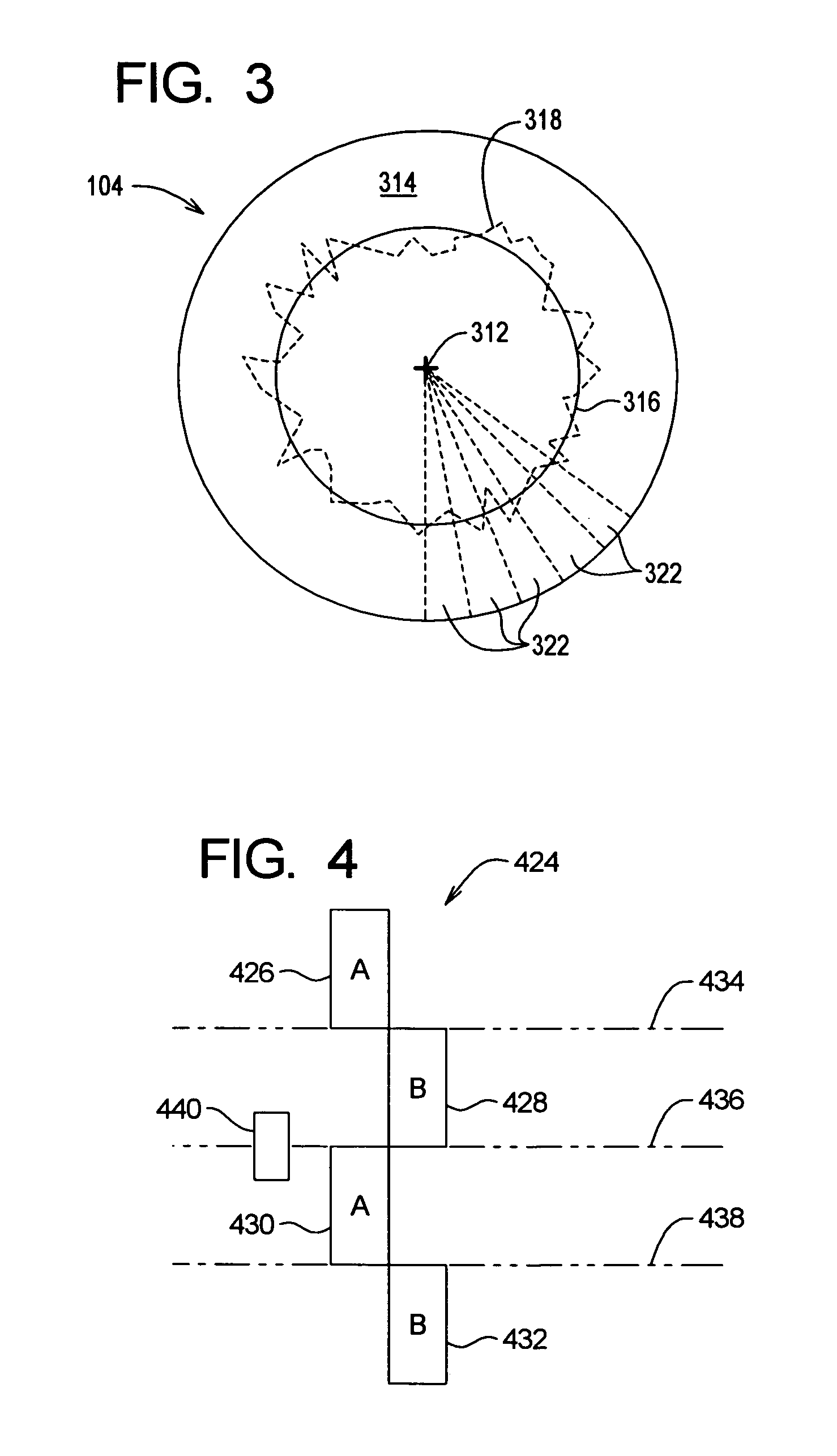
Adjusting track density over disk radius by changing slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive
InactiveUS6987636B1Steep slopeDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting the track density over the disk radius by changing the slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive. A plurality of spiral tracks are written to the disk wherein each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark. A slope of the spiral tracks over a first radial segment of the disk is substantially steeper than the slope of the spiral tracks over a second radial segment of the disk. The head internal to the disk drive is used to read the spiral tracks in order to write product servo sectors to the disk to define a plurality of data tracks. The steeper slope of the spiral tracks over the first radial segment causes a track density of the data tracks to be lower over the first radial segment compared to the track density of the data tracks over the second radial segment.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
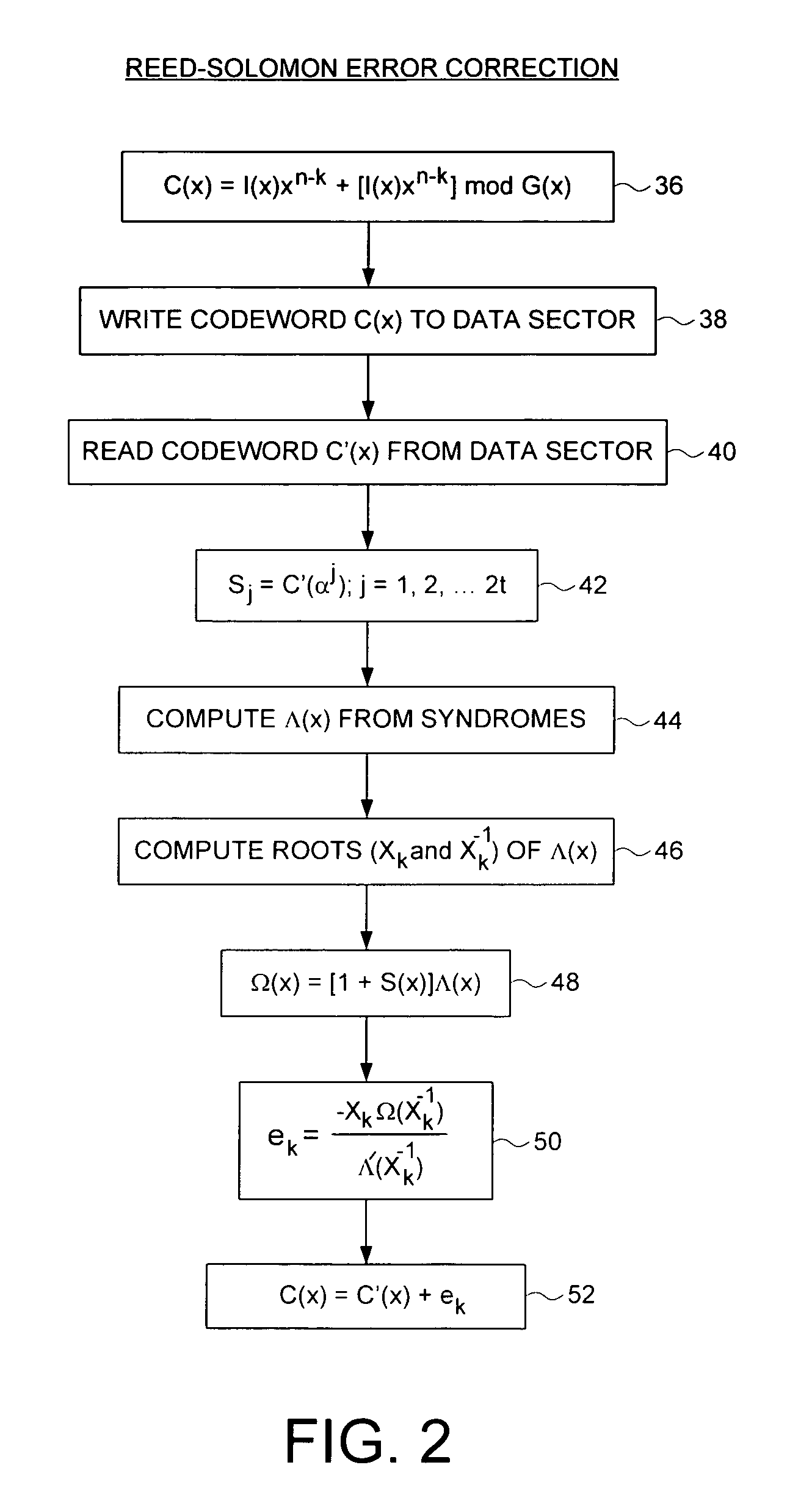
Disk drive employing error threshold counters to generate an ECC error distribution
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a head actuated over a disk. A redundancy generator generates a plurality of redundancy symbols appended to user data to form a codeword C(x) written to a selected data sector on the disk. During a read operation, a syndrome generator generates a plurality of error syndromes in response to a received codeword C′(x) generated by reading the selected data sector. An error detector, responsive to the error syndromes, detects a number of errors in the received codeword C′(x), and a plurality of counters count a number of times the number of errors falls within a predetermined plurality of ranges to thereby provide a distribution of the errors. The error distribution is used, for example, for selecting a track density or ECC depth, or for failure prediction or defect mapping.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Adjusting track density by changing slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive
InactiveUS7433143B1Steep slopeTrack density can not be increasedRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting the track density by changing the slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive. A target track density is established for a disk surface, and a plurality of spiral tracks are written to the disk surface in response to the target track density. Each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark, and a slope of the spiral tracks is selected in response to the target track density. The head internal to the disk drive is used to read the spiral tracks in order to write product servo sectors to the disk to define a plurality of data tracks, wherein the slope of the spiral tracks determines the density of the data tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
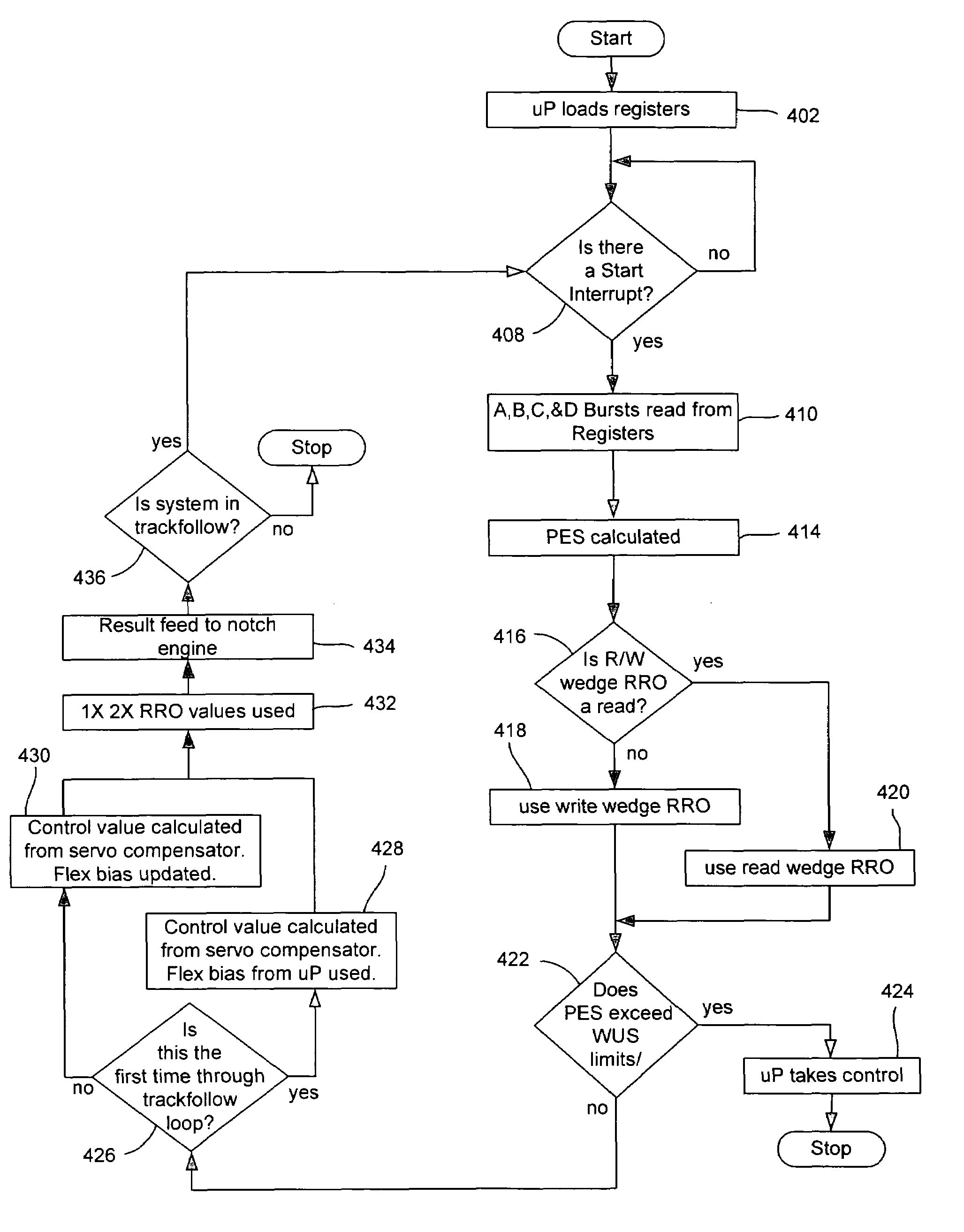
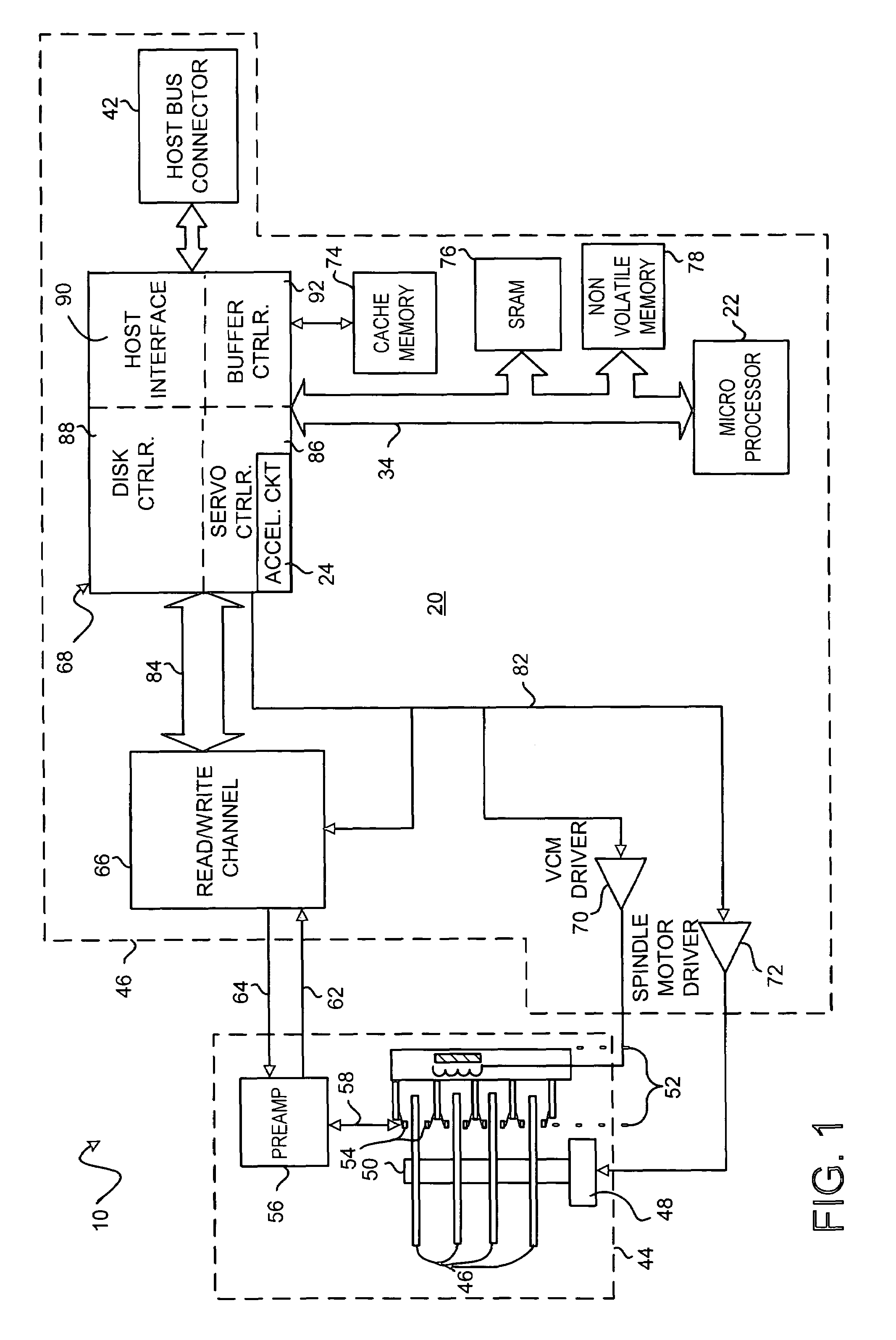
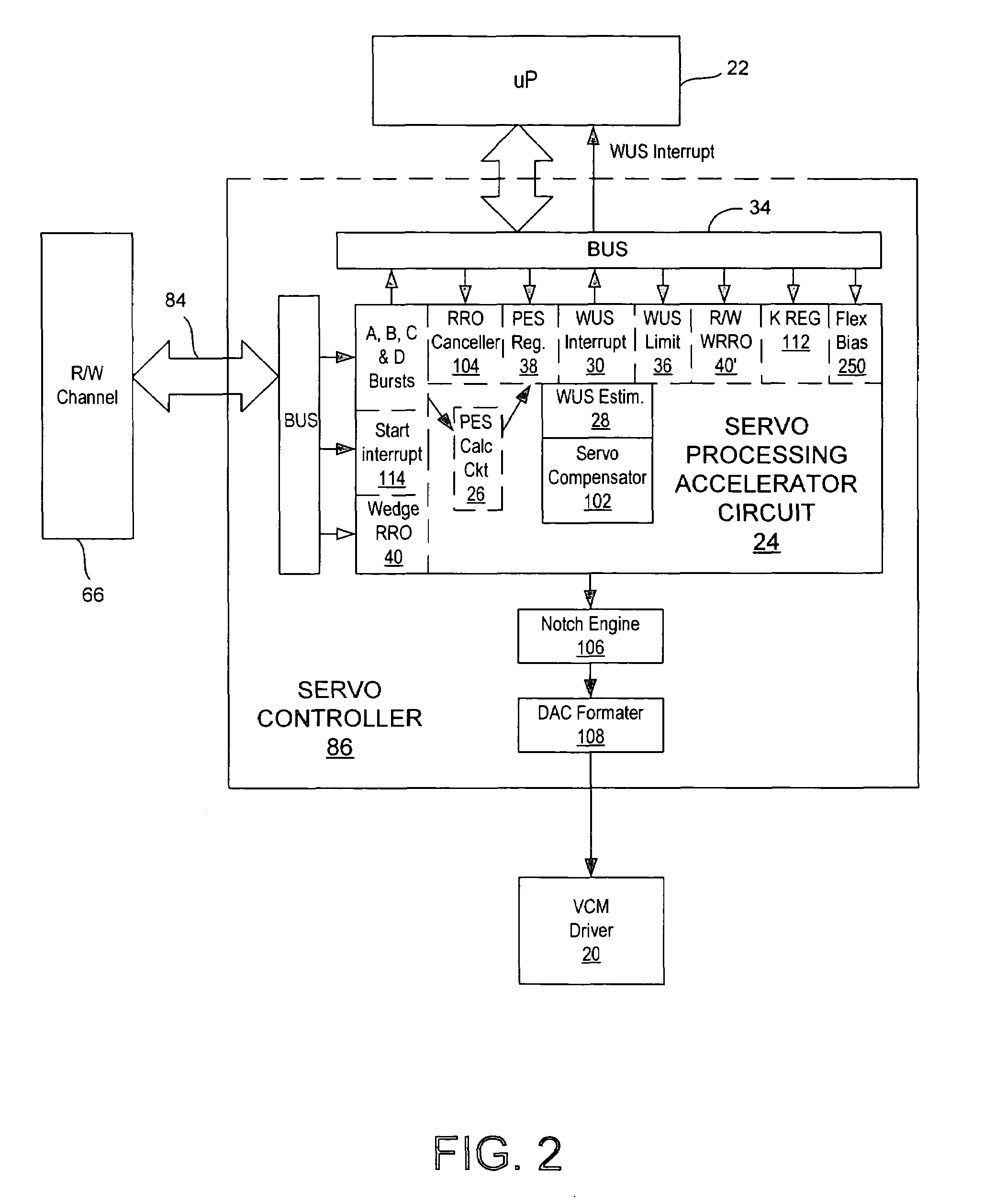
Disk drive control system having a servo processing accelerator circuit
InactiveUS6958881B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityControl system
Disclosed is a control system for processing sampled servo data in a disk drive. The control system includes a microprocessor and a servo processing accelerator circuit for performing operations on the sampled servo data while the microprocessor is executing firmware code. The accelerator circuit supports the use of a higher servo bandwidth thus allowing a higher track density resulting a greater storage capacity for the disk drive. Also, the accelerator circuit relieves the microprocessor of the ordinary servo processing function. Thus, the microprocessor's limited processing capacity to be directed to other controller and interface functions of the disk drive. Only under unusual conditions, such as a write-unsafe (WUS) limit exception, does the microprocessor need to direct processing capacity to the servo processing function. Further, the accelerator circuit may be a decreased response time after reading the servo data from the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
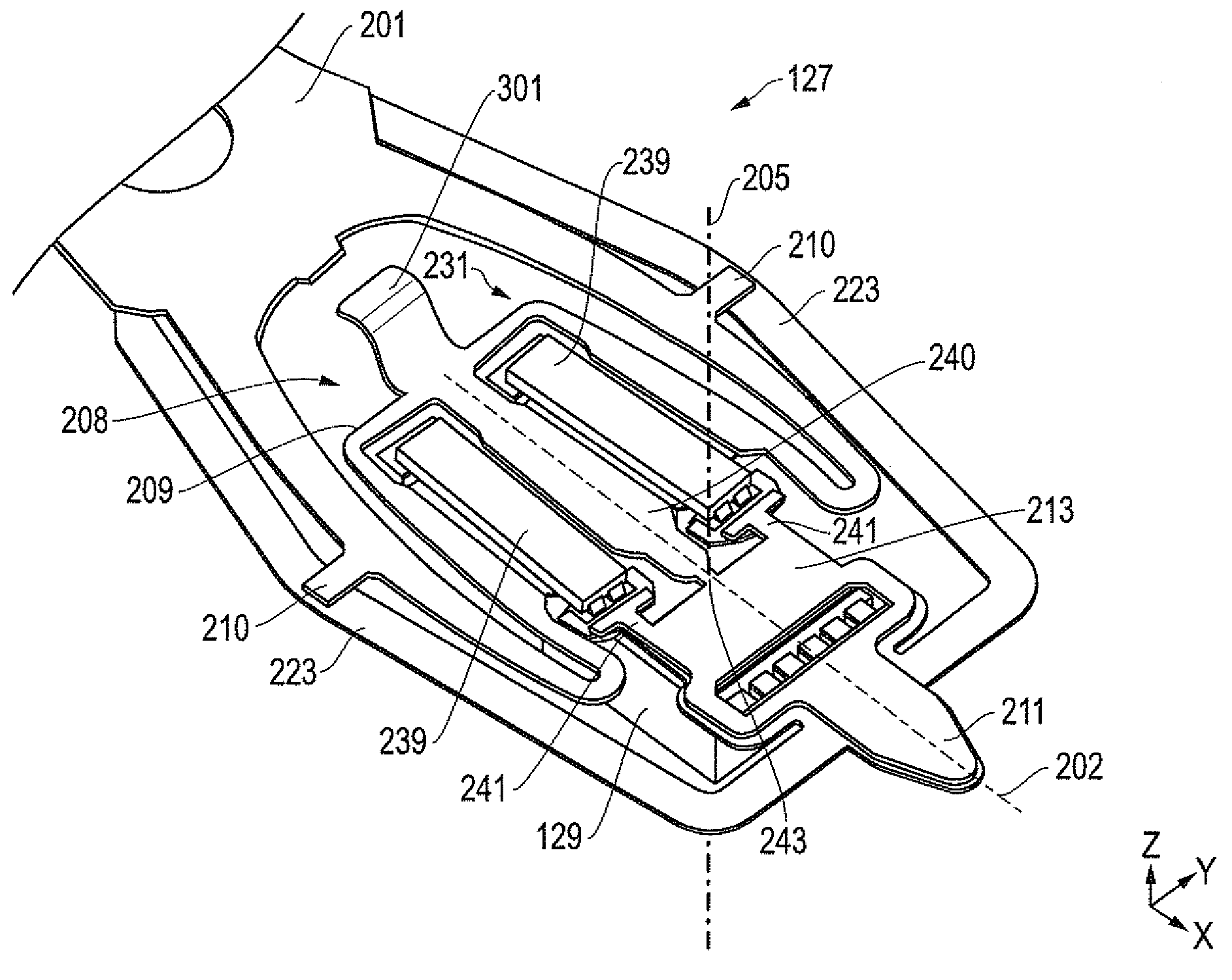
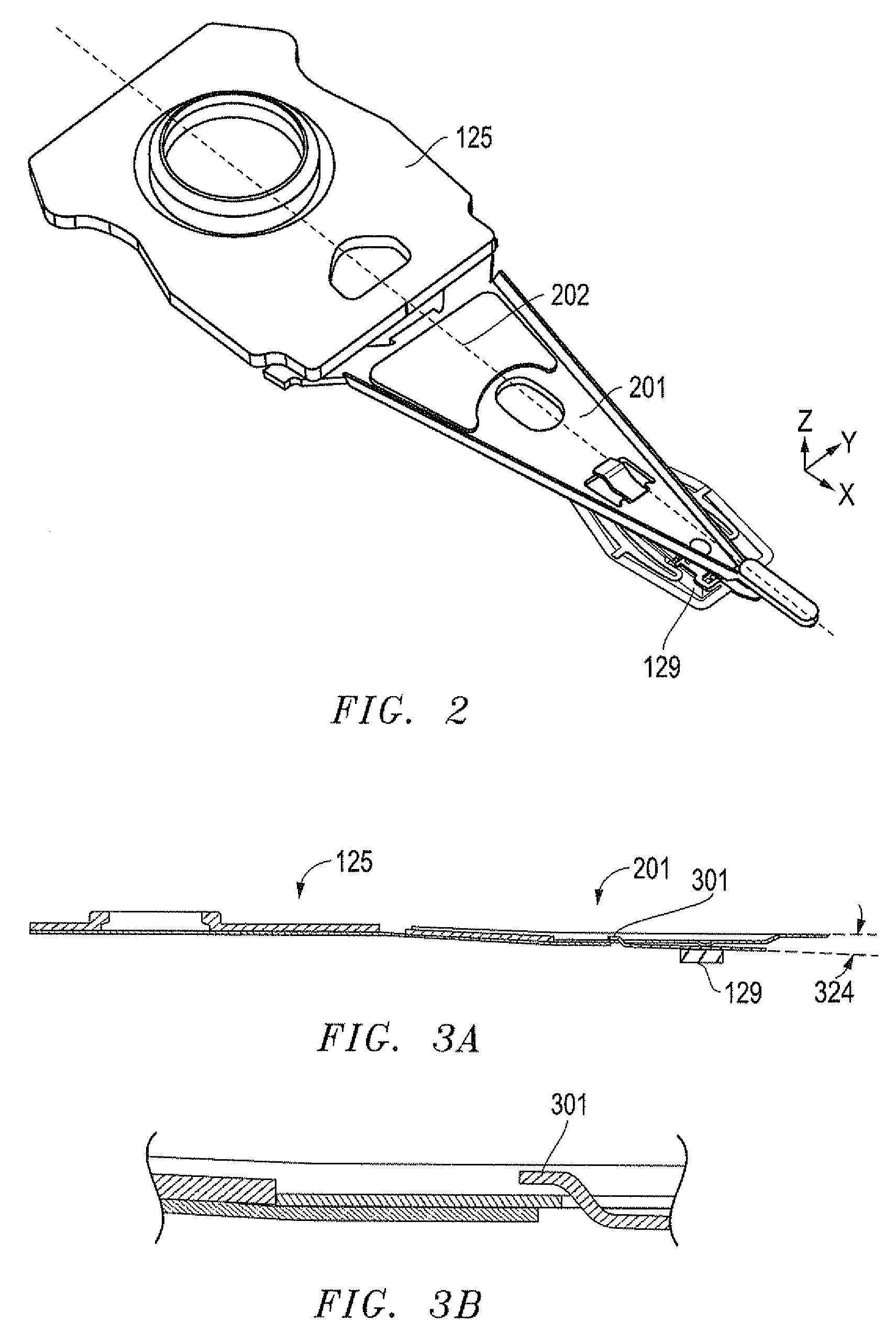
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS20090244786A1Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityHard disc drive
A piezo in-tongue microactuator includes a suspension assembly with a flexure tongue. The tongue has two slots that accept piezo actuators. The tongue also has multiple hinge flexible elements that translate the extension and / or contraction of the piezo actuators into rotary motion of the recording head. This rotary motion is then used to precisely position the recording element over the desired track on the hard disk drive and permits higher track density to be achieved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS8085508B2Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveTrack density
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method to achieve higher track density by allowing only one-sided track encroachment
InactiveUS7082007B2Reduced and minimized amountAccurate informationFilamentary/web carriers operation controlTrack finding/aligningTrack densityTransducer
A disc drive includes a transducer having a separate element for writing information and a separate element for reading information to and from the disc. In a disc drive designated to read and write long sequential records, the track misregistration budget is reduced to account for previously written tracks not being encroached on one side. An initial track is written. Subsequent tracks are written after a seek in one direction. The subsequent track is written so that the initially written track is overwritten to one side and leaves a track having a width substantially equal to the width of the read element. Records can be written into data bands of a selected number of tracks. A guard band is left between groups of data bands so that data on tracks in subsequent data bands are not overwritten.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
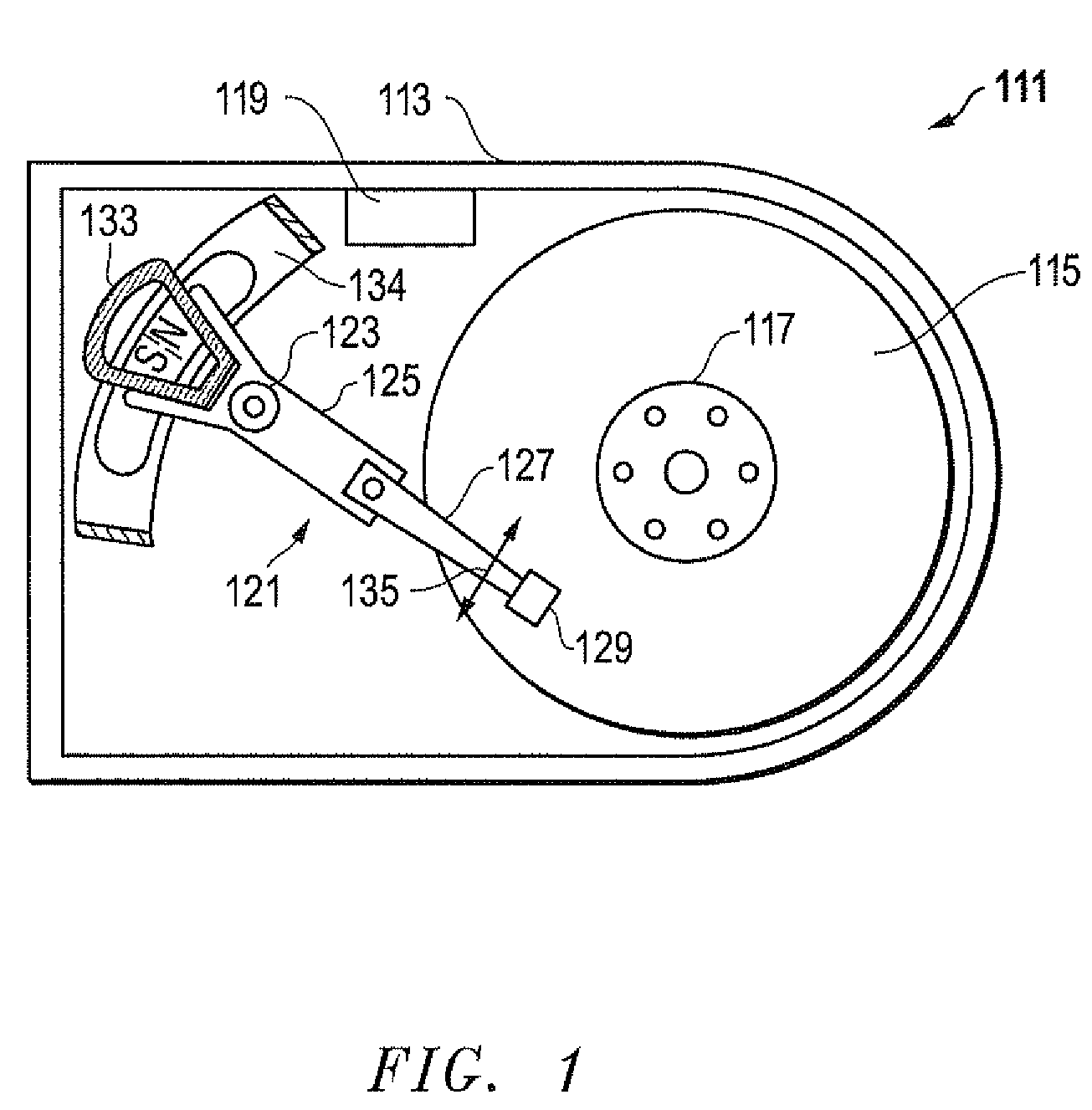
Rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor integrated into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head/gimbal assembly for improved tracking in disk drives and disk drive equipment
ActiveUS8125741B2High track densityImprove data storage capacityDriving/moving recording headsArm with actuatorsShock resistanceControl theory
A rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor is integrated with a suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) for use in disk drives and disk drive manufacturing equipment. When excited by a control voltage, the collocated, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA rotates the head enabling high frequency, high resolution track positioning of the read / write element. The motor is integrated with the head and flexure (collocation). The head rotates about a rotation axis that is ideally located at the center of mass of the head. A shear mode piezoelectric motor rotates the head. A collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA has high stiffness, high frequency response, high positioning resolution, low mass and low internal vibration for improved tracking, increased track density and greater disk drive storage capacity. Furthermore, its solid integration improves shock resistance and reduces micro-contamination.
Owner:MAGNECOMP +1
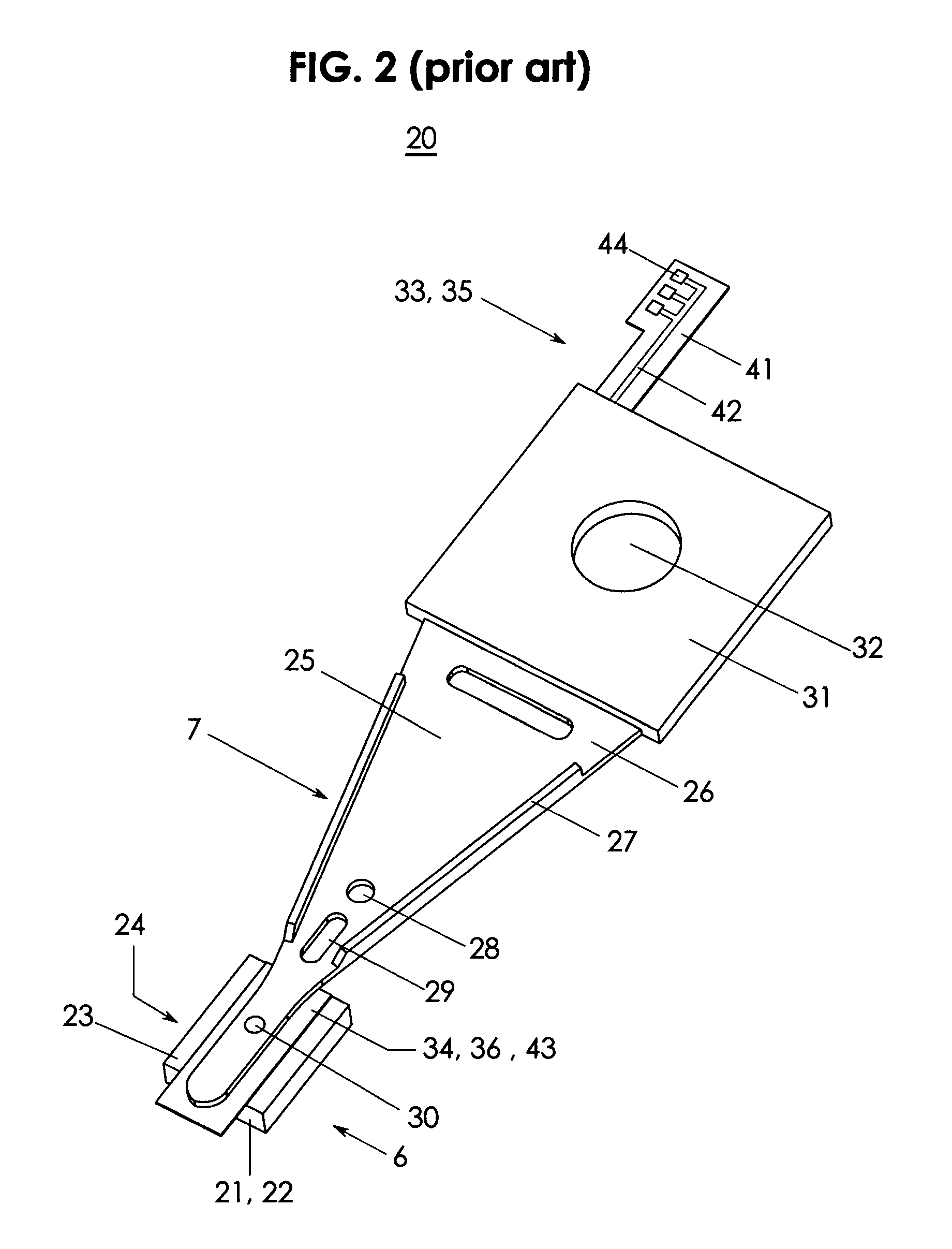
Multitrack readback and multiuser detection for disk drives
Techniques for reading data from a storage medium (150) having a high track density prone to adjacent track interference are disclosed. One or more sensing elements (120) are used to extract data stored on adjacent tracks. Multiuser detection (130) is then used to detect / decode a single track that is closely spaced to its neighboring tracks, resolve interference from adjacent tracks, or to simultaneously detect / decode multiple adjacent closely packed tracks.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
High track density magnetic recording head
ActiveUS7130152B1High track densityMade preciselyManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsTrack densityMagnetic media
Closer spacing of elements for writing multiple tracks onto a magnetic media increases the areal density of stored information. A thin film multiple track recording head includes recording gaps in a plane parallel with the head substrate. This configuration allows for flexible placement of the elements within the head, improved control of recording gap geometry, and alternating azimuth gap angles.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Ultra high track density adaptive head core track pitch control
ActiveUS7486464B2Filamentary/web record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesTrack densityMagnetic tape
Apparatuses and methods for adjusting the track pitches of the tracks on a data storage tape. In one variation, the method comprises adjusting the observed pitch between the tracks by applying variable amounts of pressure on the surface of the tape. In another variation, the pressure is applied to a localized region on the tape. The pressure can be modulated to induces a change in the physical characteristic of the tape in and around the area where pressure is applied. In another aspect, an apparatus is configured with a magnetic read-head for detecting written tracks on a magnetic tape, and an actuator is provided to apply pressure on the tape to control the track pitch of the written tracks.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
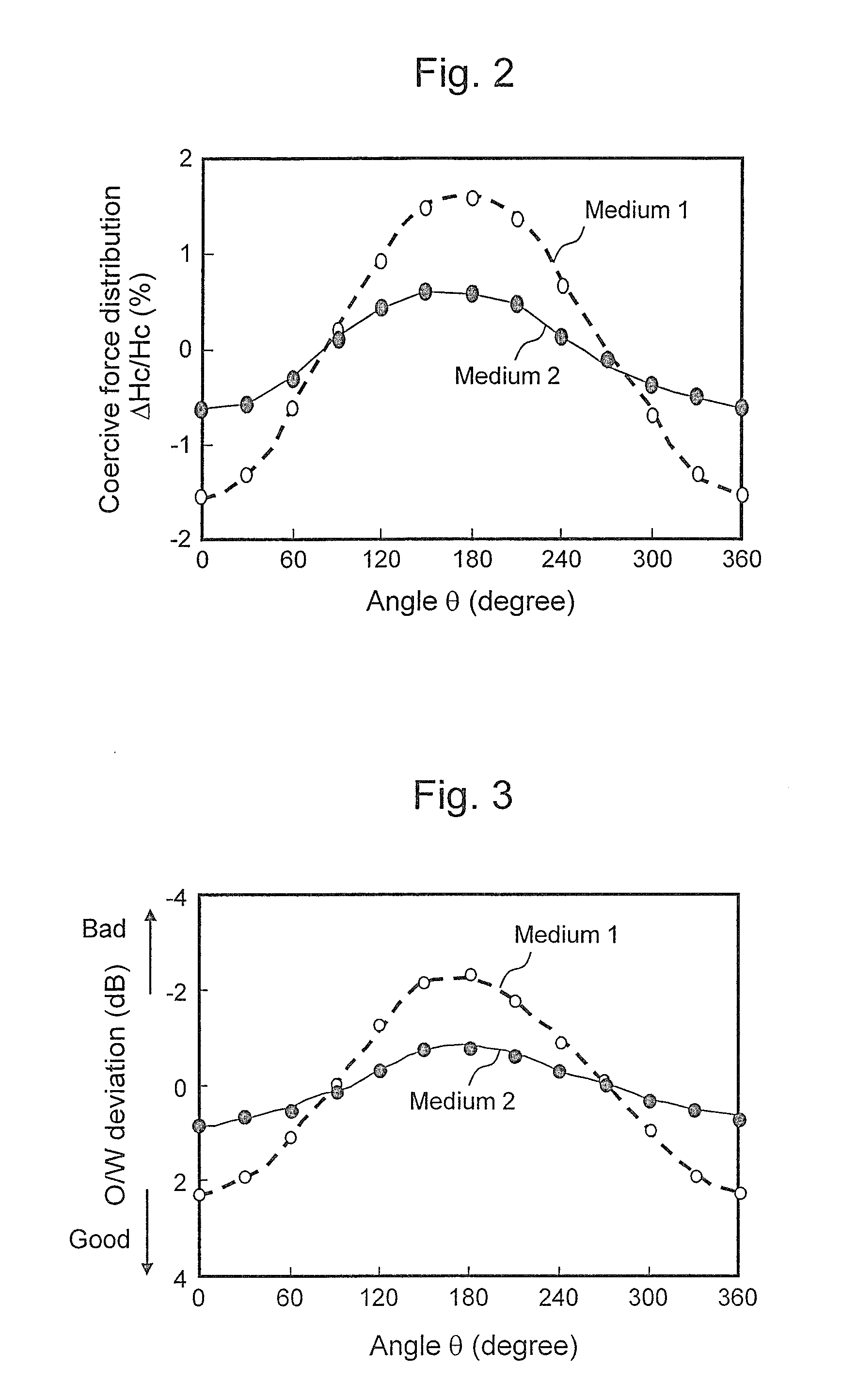
Microwave assisted magnetic recording and magnetic storage device
Disclosed is a technique of providing a large-capacity magnetic storage device at high device manufacturing yield while keeping the reliability, the magnetic storage device enabling recording on a perpendicular magnetic recording medium having distribution of characteristics in the circumferential direction as well at high track density of 500 kTPI or more that would be expected from the average characteristics of the medium. A recording condition from is selected for each sector from a parameter table that stores a set of at least two types of recording conditions by a microwave assisted magnetic recording head including a magnetic recording pole and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator in the magnetic storage device, and information is recorded for each sector based on the condition.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic tape medium
InactiveUS7474505B2Stable recording and reproducing propertyAvoid changeMagnetic materials for record carriersTape carriersTrack densityMagnetic tape
A magnetic tape medium having superior dimensional stability in the width direction and off-track resistance is provided although having a very high track width in the width direction. As a non-magnetic substrate of a magnetic tape medium in which the track density in the width direction is 50 tracks / mm or more, the off-track margin is 5 μm or less, and the maximum permissible amount of change in dimension in the width direction caused by environment factors is 0.10% or less, a laminate composed of a plastic film and films provided on two surfaces thereof is used, the films being formed of a material selected from the group including a metal, a semi-metal, an alloy, and an oxide or composite formed of the aforementioned material, having a Young's modulus of 7×103 kg / mm2 or more and a coefficient of thermal expansion of 18×10−6 / ° C. or less.
Owner:SONY CORP
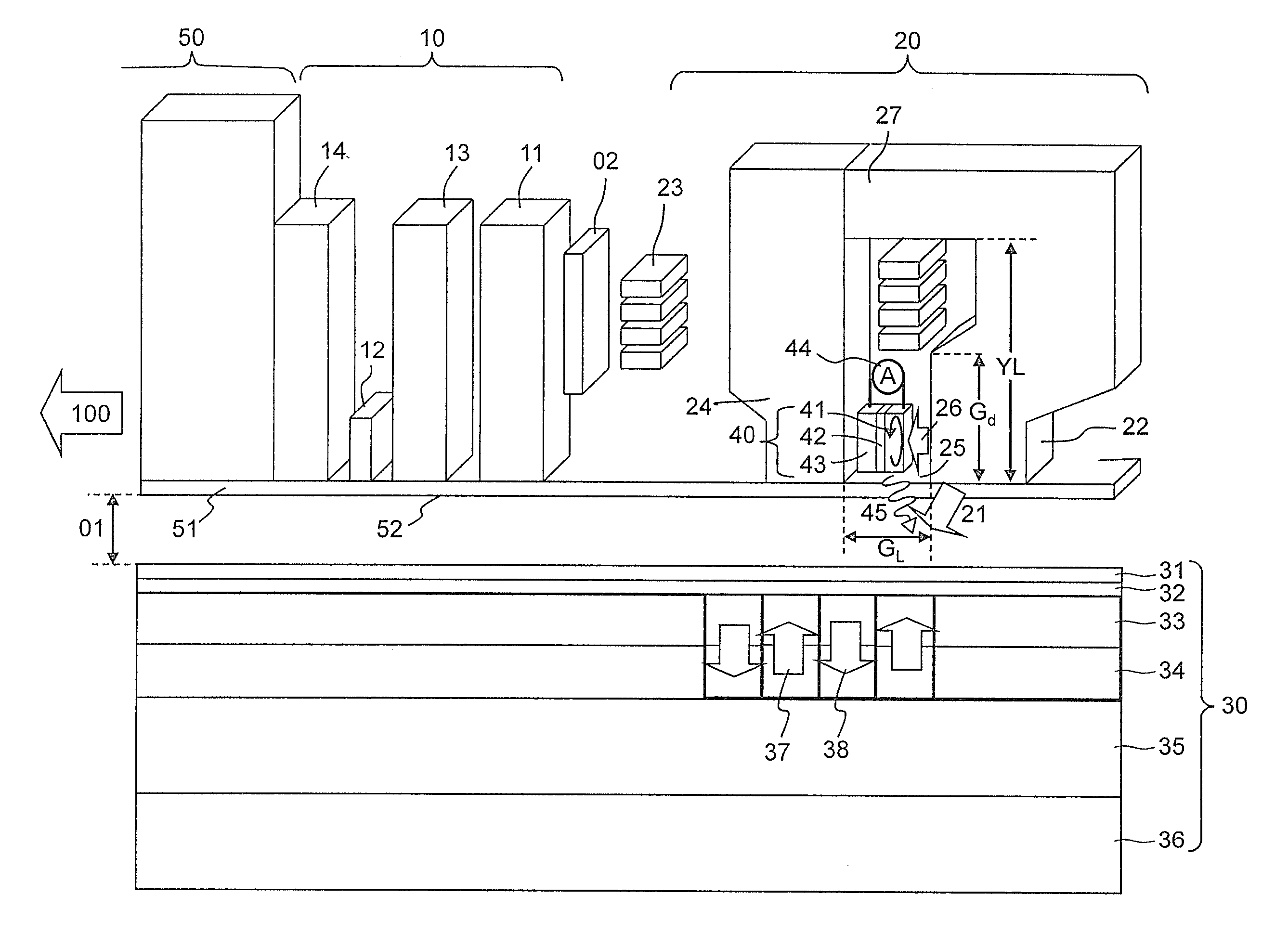
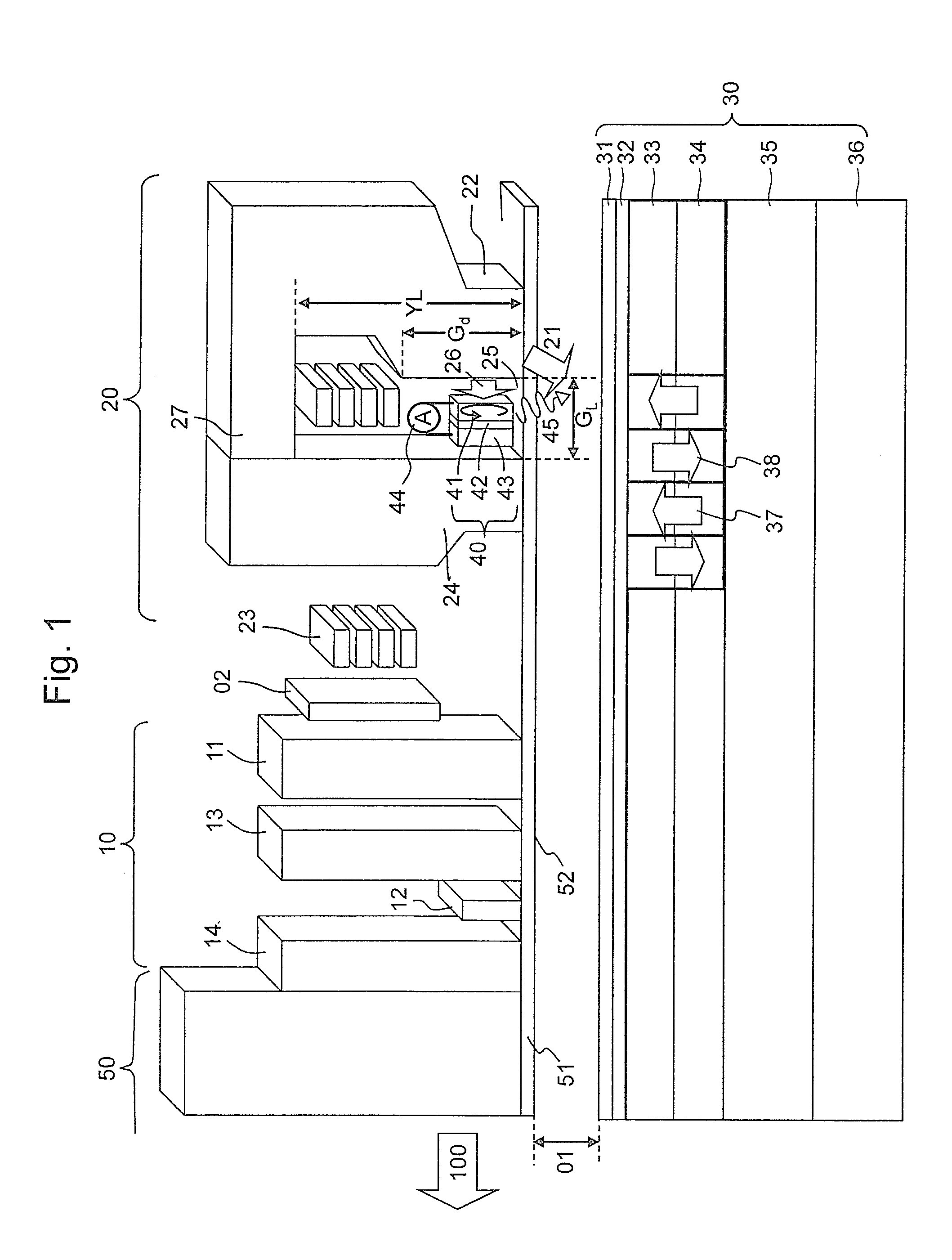
Magnetic recording drive with continuous magnetic servo system
InactiveUS6873482B1High track densityInterferenceRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityEngineering
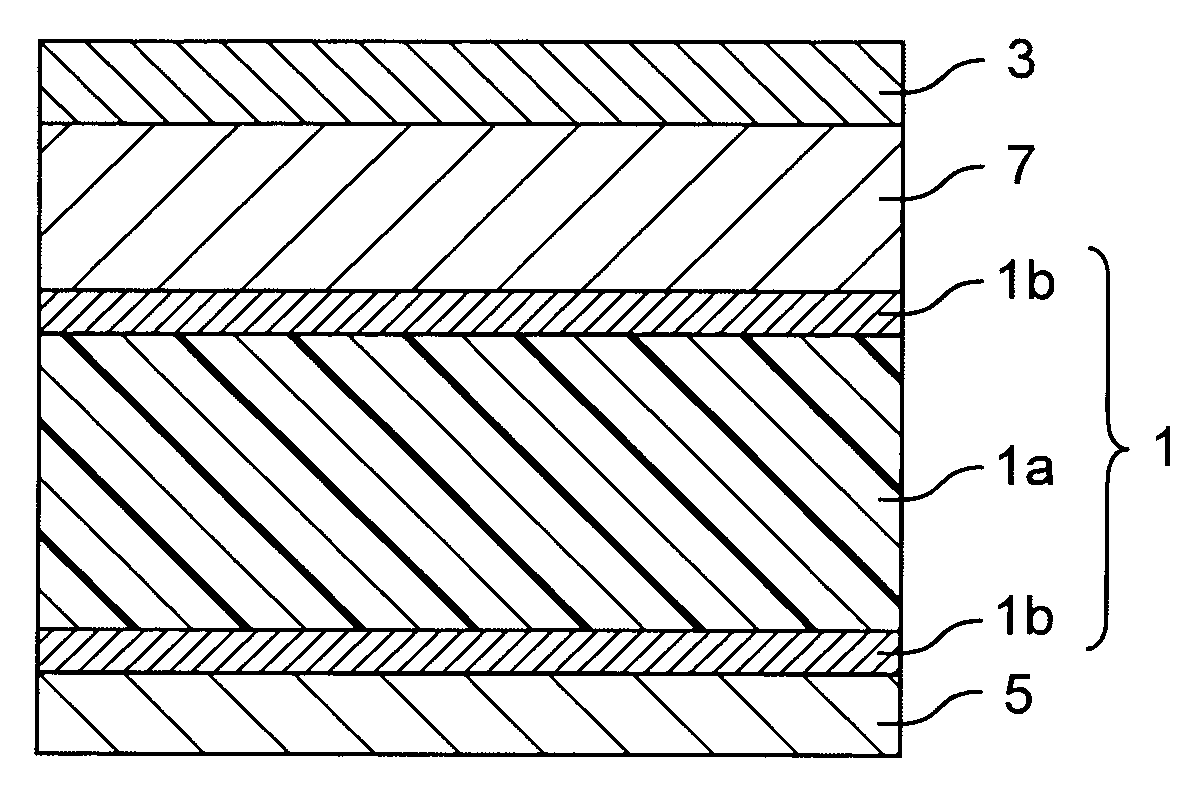
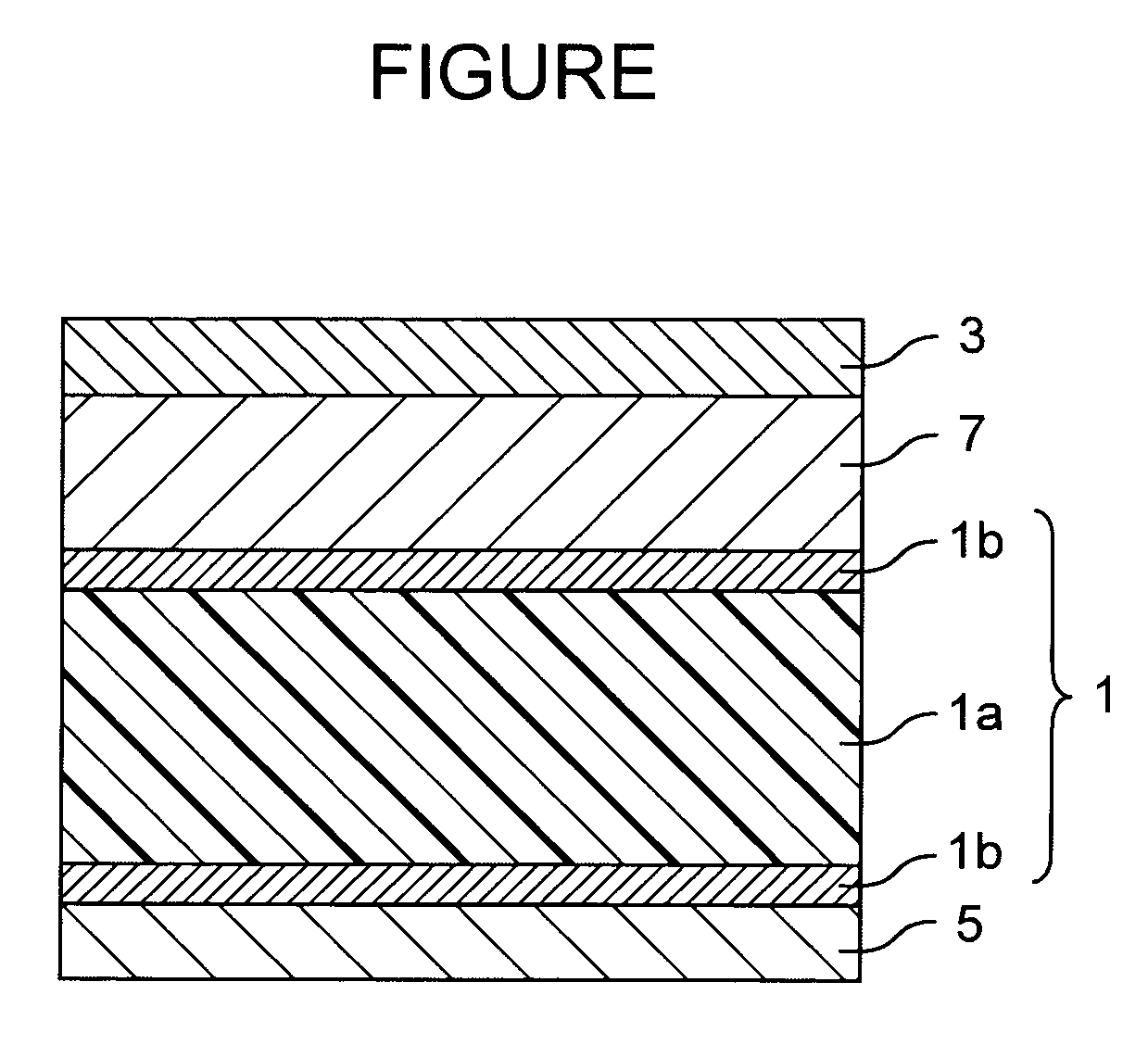
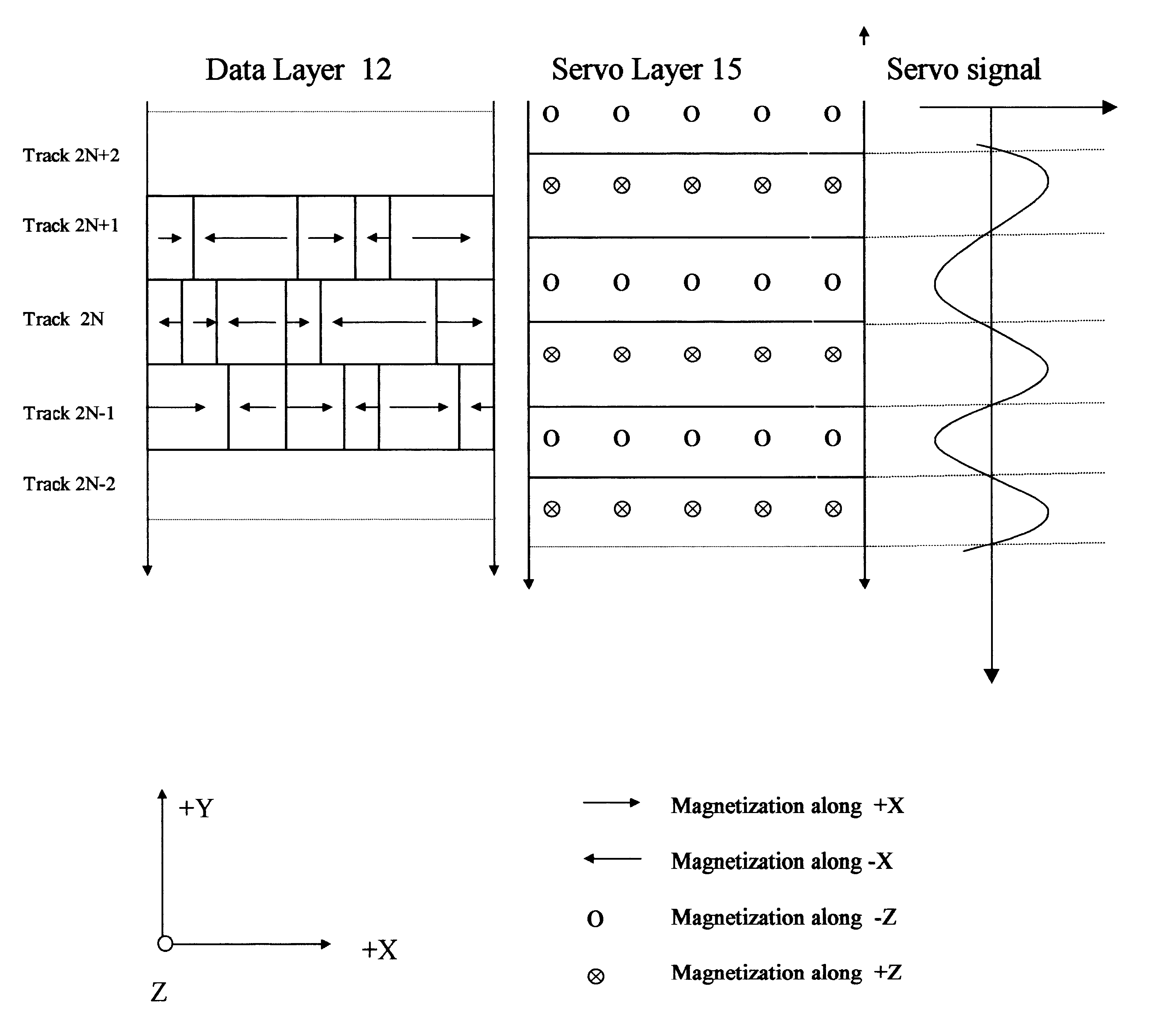
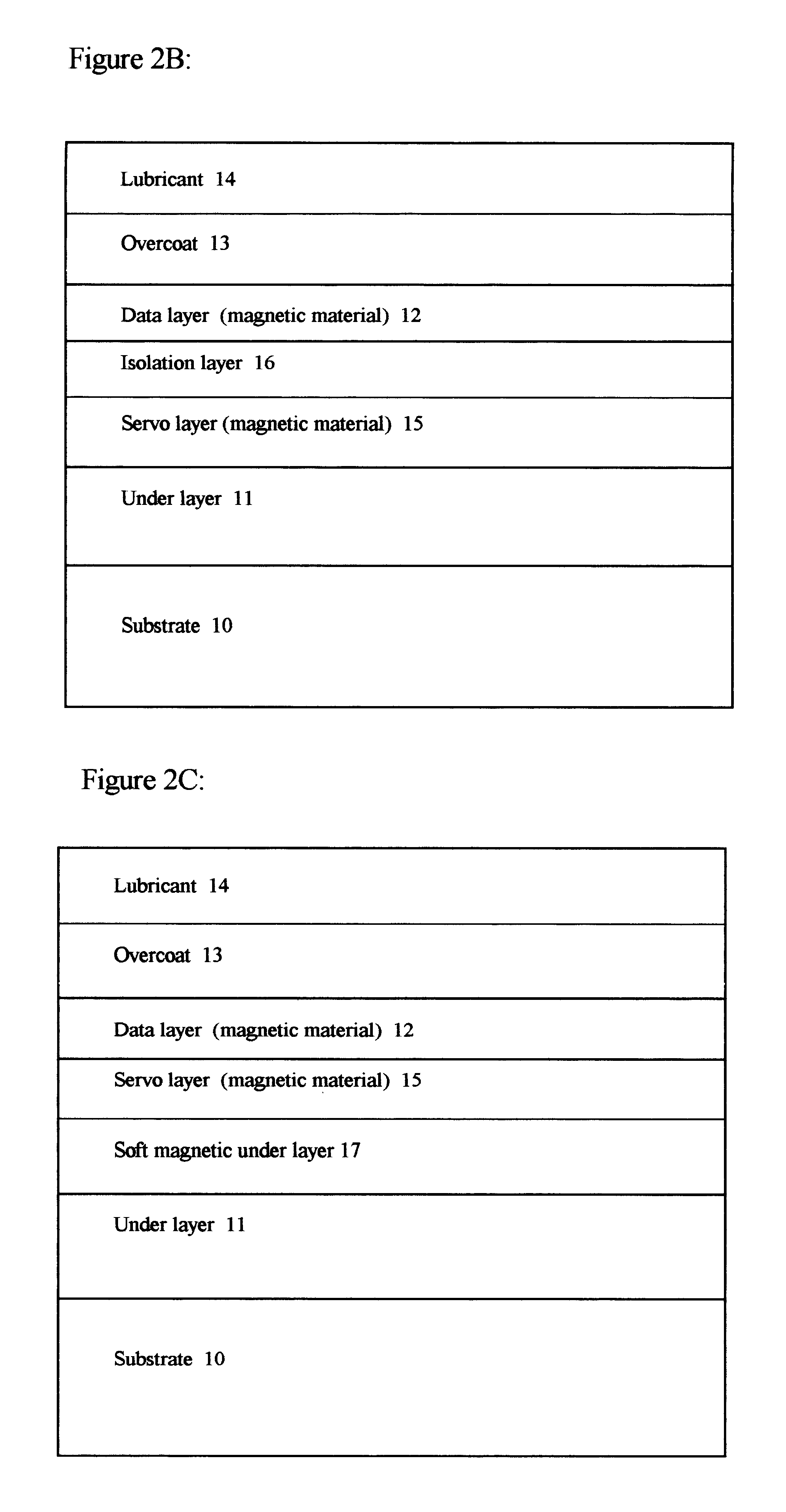
A magnetic recording system containing magnetic recording media with separate data and servo magnetic layers is disclosed. A servo magnetic layer resides usually below the data layer and has higher coercivity than that of the data layer. Interference between the data and servo signals is minimized by recording the servo patterns perpendicular or transverse direction with respect to the orientation of data bits. In addition, servo patterns are selected so that no interference with the data is generated by the servo pattern when the reader is in the middle of data tracks. Tracking error signals are approximately linear with track misregistration around the middle of data tracks. Finally, interference between the data and servo signals is further reduced by electronic processing. Continuous servo signals permit increased track densities with a single actuator and very high track densities with dual microactuator-actuator system.
Owner:HSIEH YUNG CHIEH +1
Magnetic tape medium
InactiveUS7341798B2Suppresses dimensional changesStable characteristicsMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersTrack densityMagnetic tape
A magnetic recording medium is provided that can ensure stable recording and reproducing characteristics with little off-track even when a track density in the direction of width of the tape is very high and 50 lines / mm or more, an off-track margin is 5 μm or smaller, and a variation that is permitted at maximum as a dimensional variation in the direction of width of the tape itself due to environmental factors such as the change of temperature and humidity, the change of tension, a creep, etc. is small as low as 0.10% or less. Assuming that Young's modulus in the direction of width of a non-magnetic substrate is X and Young's modulus in the direction of width of the back layer is Y, X is 850 kg / mm2 or more, or when X is less than 850 kg / mm2, X×Y is 6×105 or more, and assuming that Young's modulus in the direction of width of a layer including a magnetic layer is Z, Y / Z is not larger than 6.0.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for increasing track density by adapting write fault gate to position error signal as it varies from ID to OD
InactiveUS6940679B1Increasing capacity of diskHigh track densityRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityEngineering
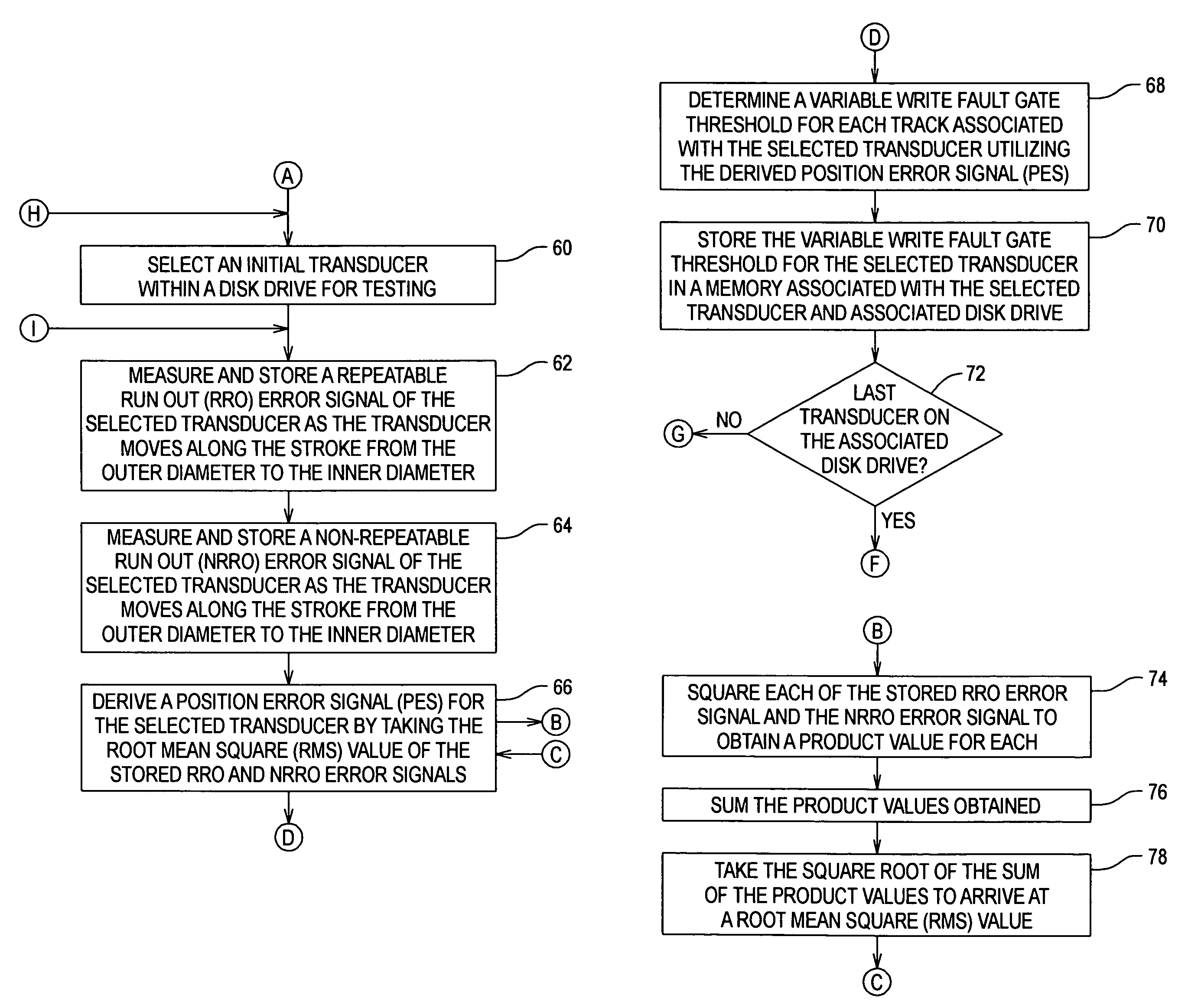
A disk drive utilizes a track dependent variable write fault gate for each of the transducers within the drive. By deriving a 3 sigma distribution across the repeatable run out (RRO) and the non-repeatable run out (NRRO), a position error signal (PES) is derived which varies in magnitude across the stroke of the transducers and which has a slope used to derive variable write fault gate thresholds for the tracks associated with each transducer. As the stroke of the transducer moves from the outer diameter (OD) to the inner diameter (ID), the magnitude of the write fault gate thresholds may be decreased relative to the PES, and track density and capacity may increase where PES and write fault gate thresholds are low. The invention thus maintains a constant hard error recovery margin across the stroke.
Owner:MAXTOR
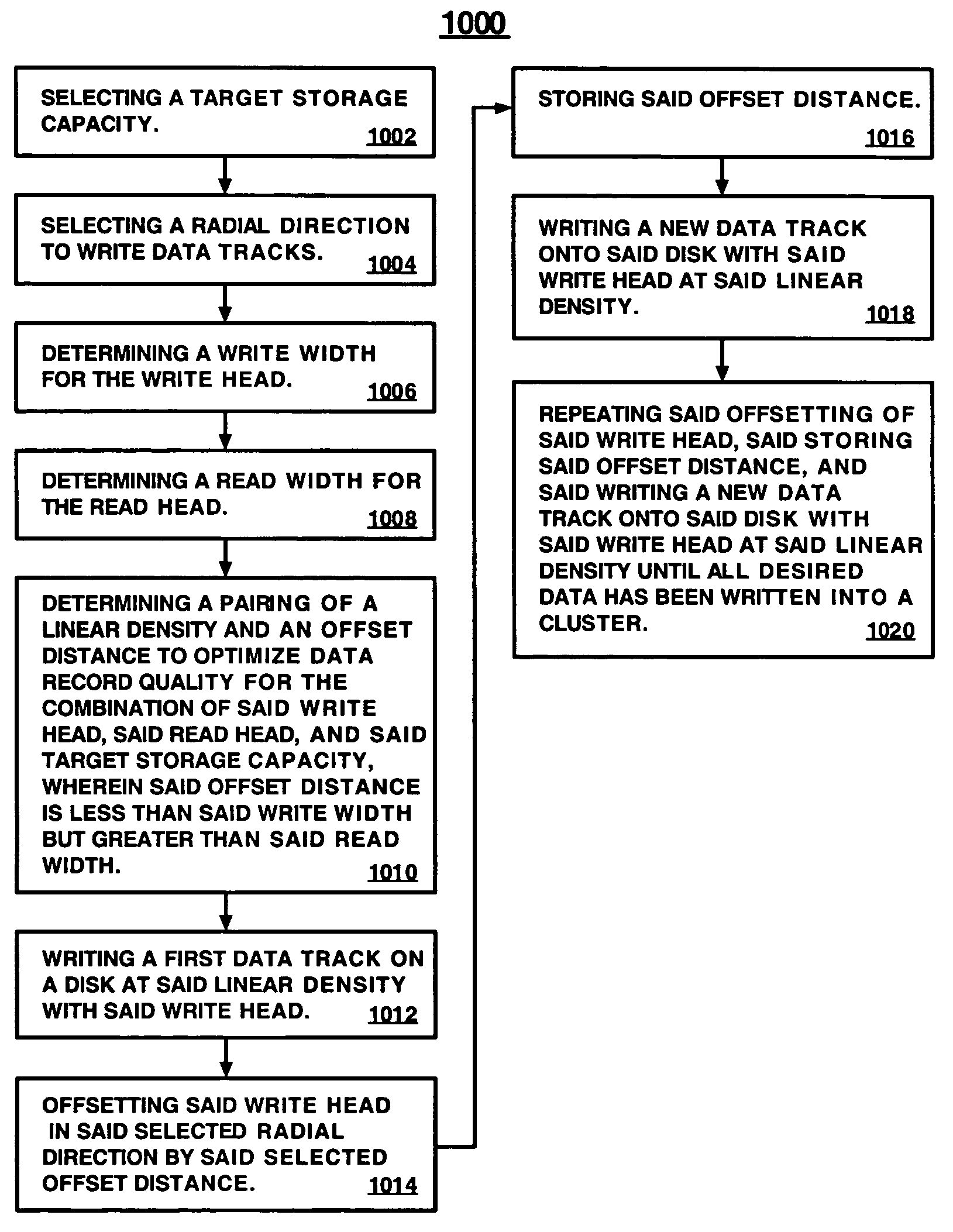
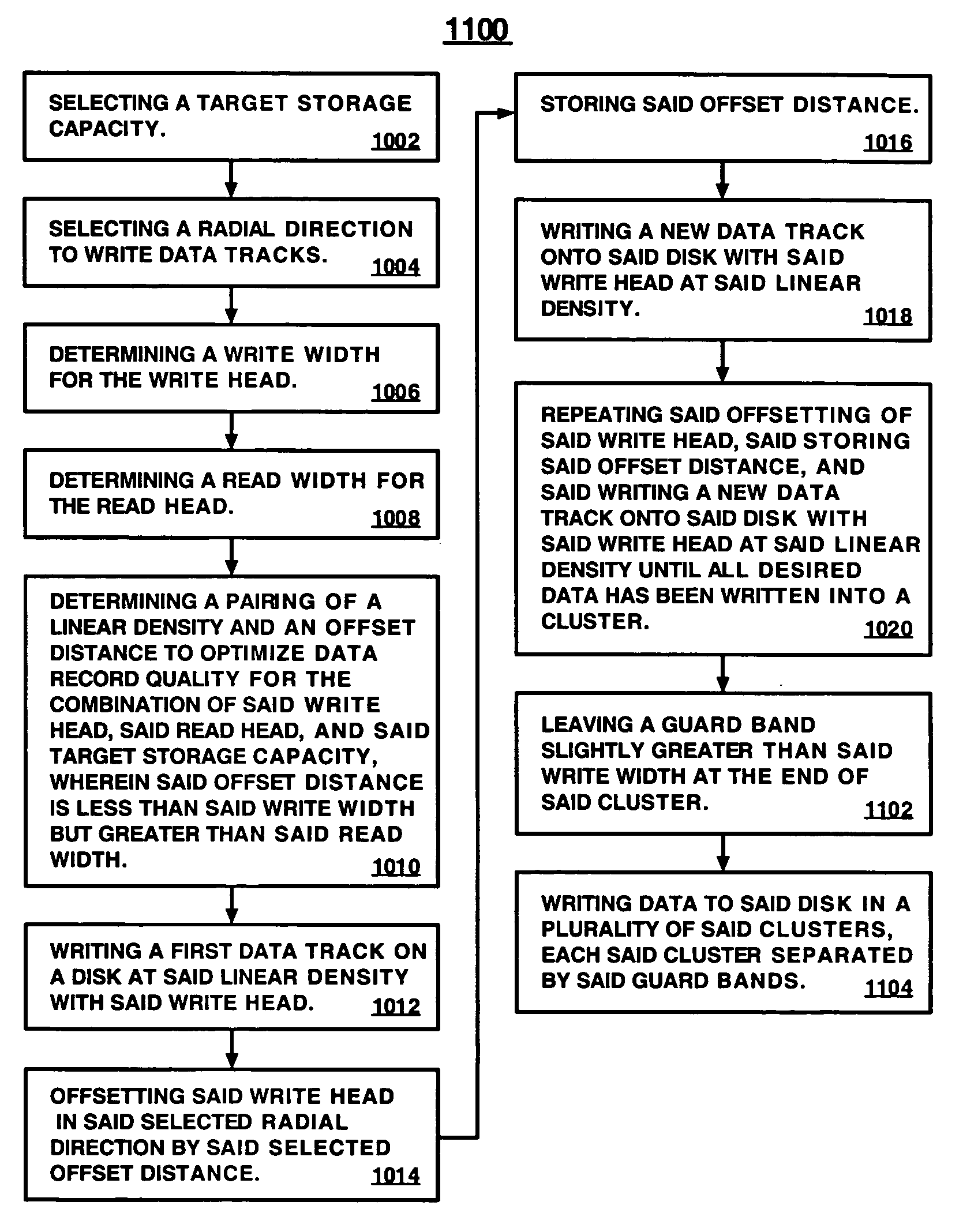
Method and apparatus for optimizing record quality with varying track and linear density by allowing overlapping data tracks
InactiveUS7133241B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityOffset distance
A method and apparatus for optimizing data record quality on a disk for a pair of read and write heads, in which the write head is bigger, by adaptively varying linear and track density of overlapping recorded tracks to achieve a target storage capacity. In the method, target storage capacity and radial writing direction are selected. Read and write widths of heads are determined. A linear density and offset distance pairing for optimizing record quality at target storage capacity is determined, wherein offset distance is less than write width but greater than read width. The write head writes a track at the linear density, is offset in the radial direction by the offset distance, and the offset distance is stored. The write head writes a new track at the linear density. Offsetting, storing offset, and writing a new track are repeated until desired data is written into a cluster.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
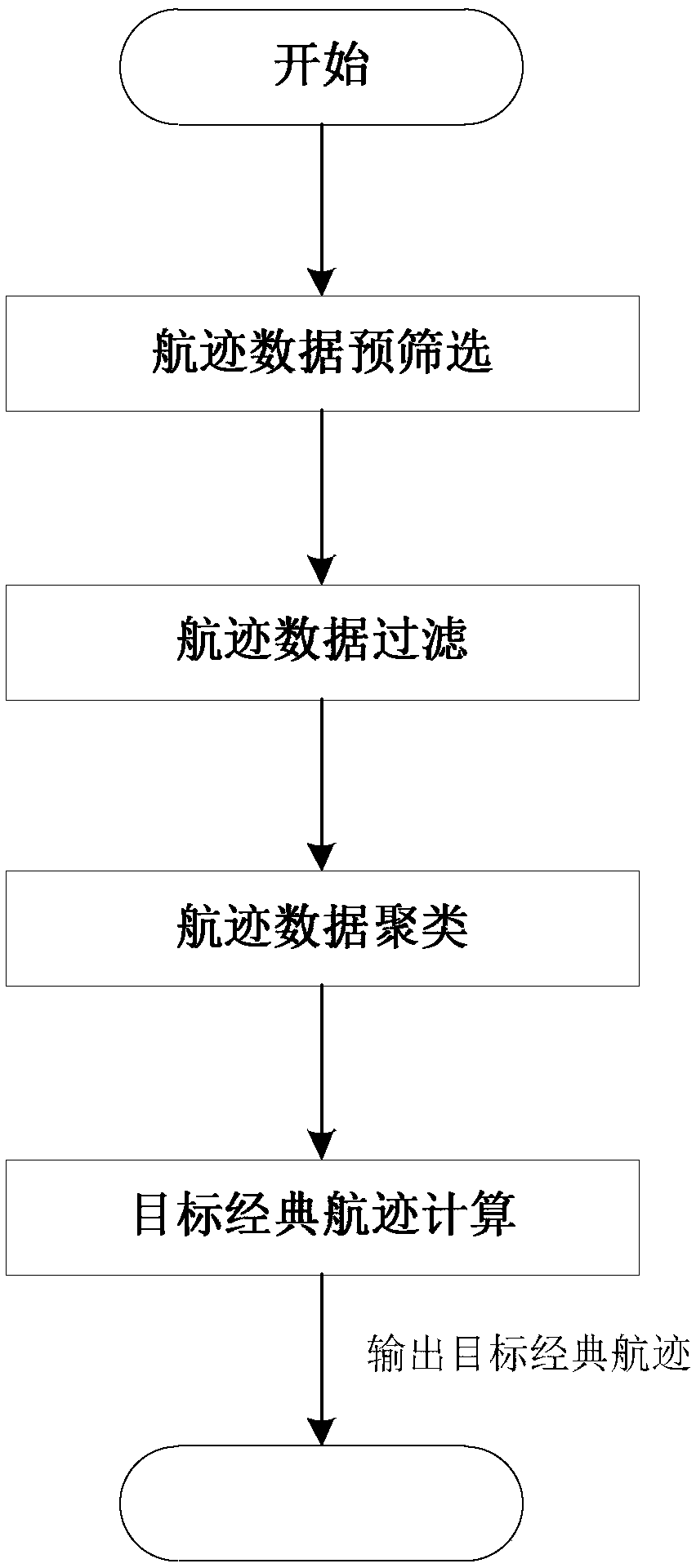
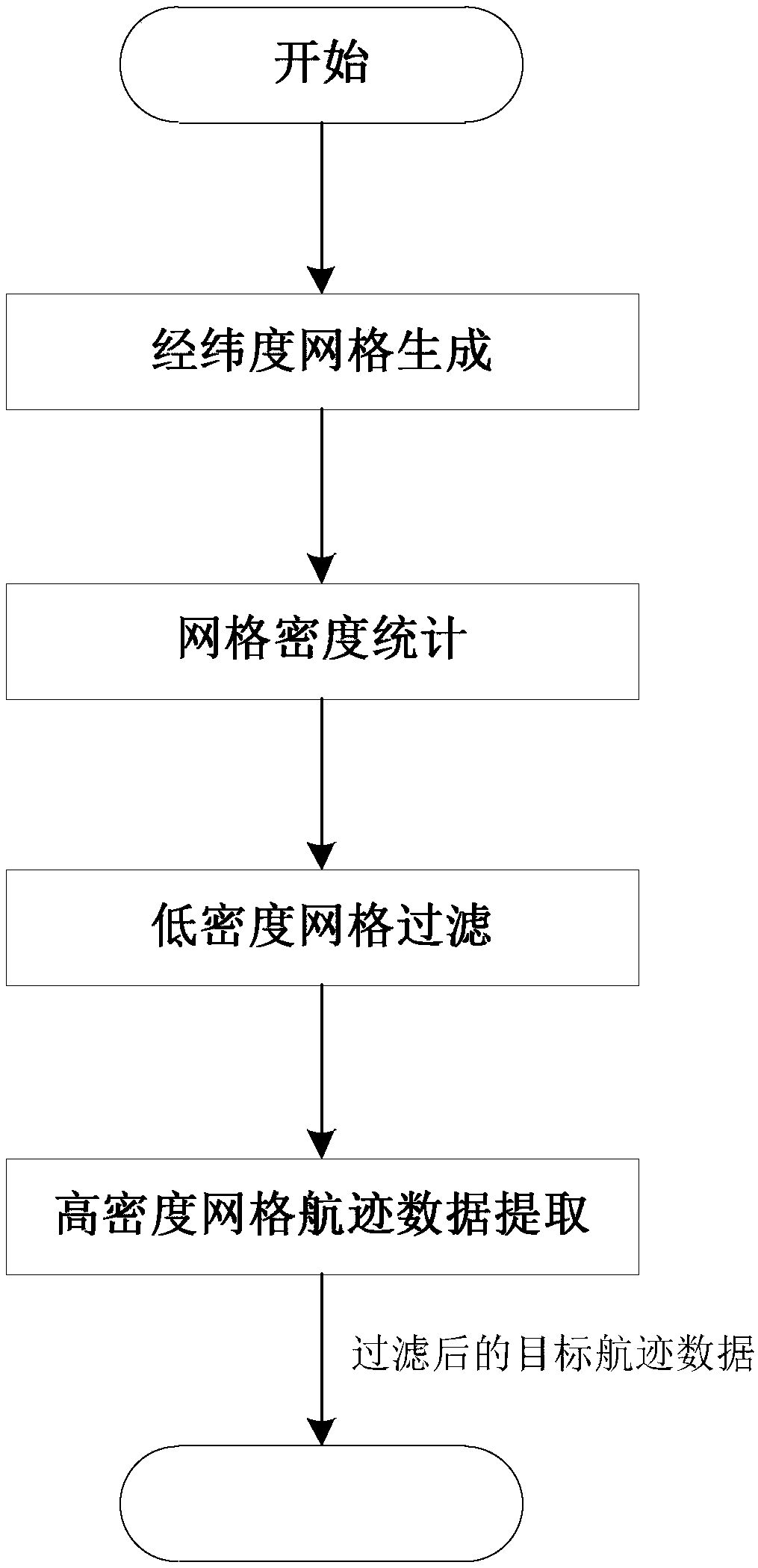
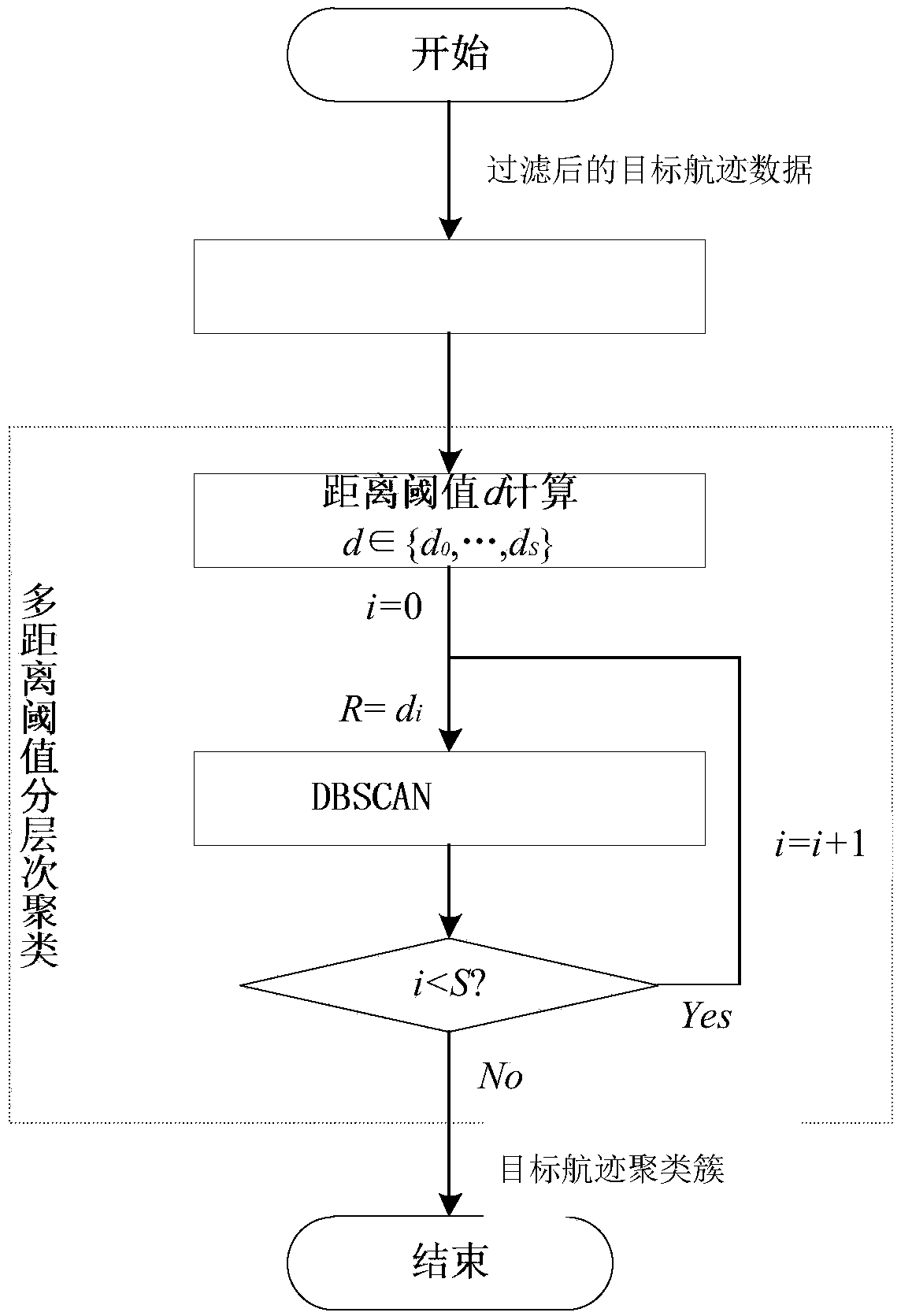
Method for extracting target classic track in complex environment
InactiveCN109000645AStrong randomnessReduce the impactNavigational calculation instrumentsCharacter and pattern recognitionTrack densityCluster algorithm
The invention provides a method for extracting a target classic track in a complex environment. The method provided by the invention can realize extraction of the target classic track under complex conditions such as strong data randomness, loud noise, different track lengths and large point track interval difference of the target track, and is realized by the following technical scheme: reading target track data, prescreening according to value range constraints with different attributes in the track data, and removing abnormal data items; rasterizing latitude-longitude grids, counting the point track density in each latitude-longitude grid, and extracting all the track data and filtering the track data with relatively high point track density; clustering the filtered track data with a multi-distance threshold DBSCAN clustering algorithm to form a plurality of track clusters; and setting a scanning line for each cluster, sequentially calculating an average value of intersection pointsof the scanning lines and the track to obtain the point tracks in the target classic track, and connecting the point tracks in order to obtain a target classic track extraction result.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
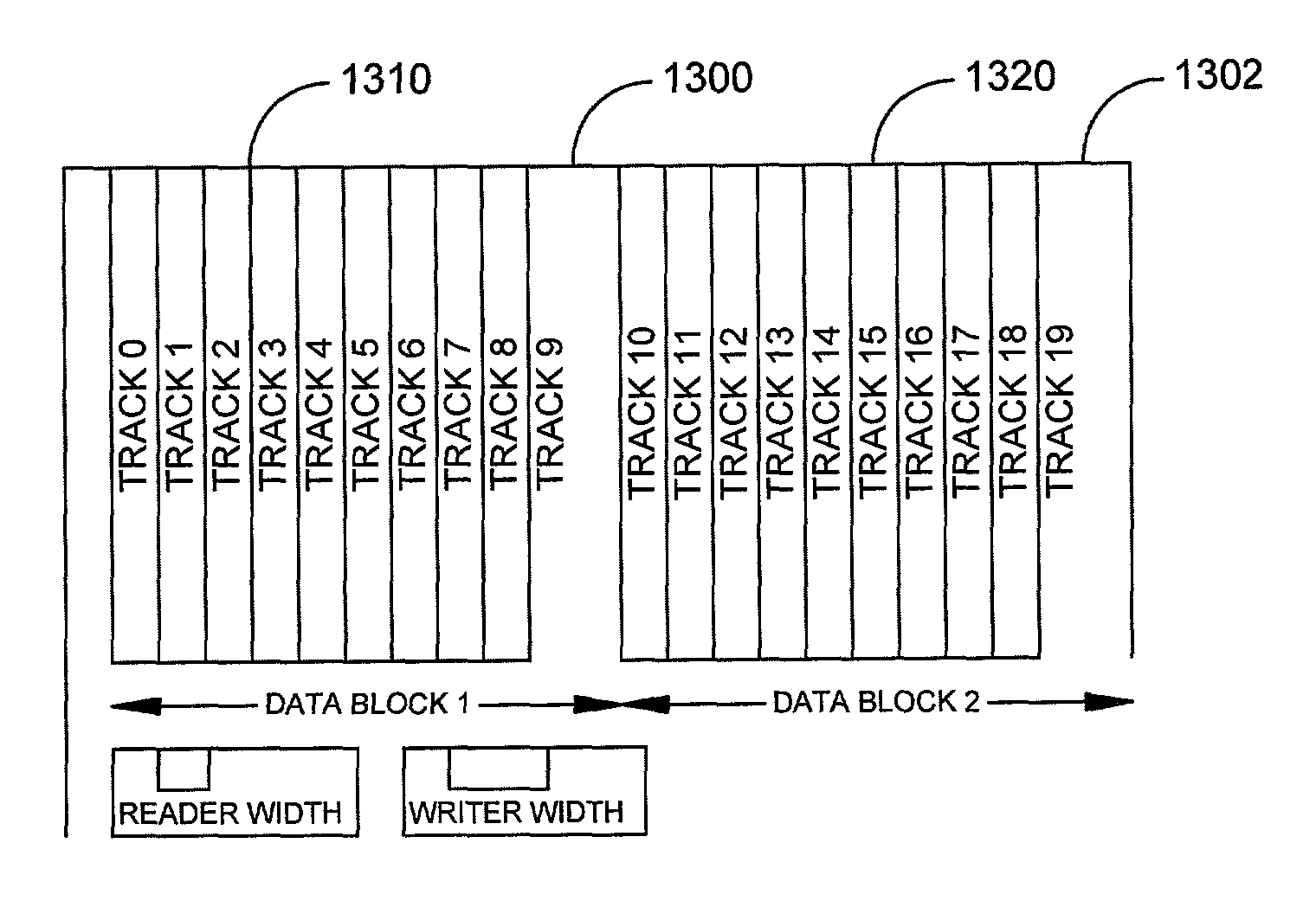
Large data block written on overlapping tracks in a hard disk drive
InactiveUS20080316639A1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityHard disc drive
A hard disk drive with a disk that includes a first group of tracks and a second group of tracks. The second group of tracks are used to write large blocks of data. For example, data in the second group may be video or audio. The second group of tracks has a higher track density than the first group of tracks. The large data block is written sequentially in the second group of tracks so that there is only one adjacent track write within the group. Using only one adjacent track write allows the tracks within the second group to be overlapped to increase track density.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor integrated into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head/gimbal assembly for improved tracking in disk drives and disk drive equipment
ActiveUS20090021857A1High track densityImproved fine track positioningDriving/moving recording headsArm with actuatorsShock resistanceControl theory
A rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor is integrated with a suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) for use in disk drives and disk drive manufacturing equipment. When excited by a control voltage, the collocated, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA rotates the head enabling high frequency, high resolution track positioning of the read / write element. The motor is integrated with the head and flexure (collocation). The head rotates about a rotation axis that is ideally located at the center of mass of the head. A shear mode piezoelectric motor rotates the head. A collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA has high stiffness, high frequency response, high positioning resolution, low mass and low internal vibration for improved tracking, increased track density and greater disk drive storage capacity. Furthermore, its solid integration improves shock resistance and reduces micro-contamination.
Owner:MAGNECOMP +1
Composite shield structure of PMR writer for high track density
InactiveUS7804666B2High gradientSufficient magnitudeRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsTrack densityMechanical engineering
Improved writability and a substantial reduction in adjacent track erasure are achieved by incorporating a composite shield structure in a PMR writer. There is a trailing shield formed a certain distance above the top surface of a write pole, a leading shield formed a certain distance below the bottom surface of the write pole, and a partial side shield having a section formed on each side of the write pole. The partial side shield thickness is less than that of the write pole. Each partial side shield section has a side that is parallel to the nearest write pole side and a top surface that is offset from the write pole top surface by 0 to 0.15 microns. A plurality of magnetic connections between two or more shield elements is employed to ensure correct magnetic potential. The large write pole has a flare angle of 45 to 75 degrees.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Areal density capability improvement with spin-orbit torque based structures surrounding main pole tip
ActiveUS10157632B1High track densityImproves write-abilityHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageTrack densityMagnetic media
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a heavy metal structure surrounding at least a portion of the main pole at a media facing surface (MFS), and two magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure. Spin-orbit torque (SOT) is generated from the heavy metal structure, inducing magnetization switching (or precession) in the magnetic structures. The SOT reduces the magnetic flux shunting from the main pole to the trailing shield, and the magnetization switching sharpens the write field profile in the cross-track direction. The SOT based head with the magnetic structures sandwiching the heavy metal structure increases both track density (tracks per inch) and linear density (bit per inch), which in turn increases the areal density capability (ADC), which is the product of tracks per inch and bit per inch.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
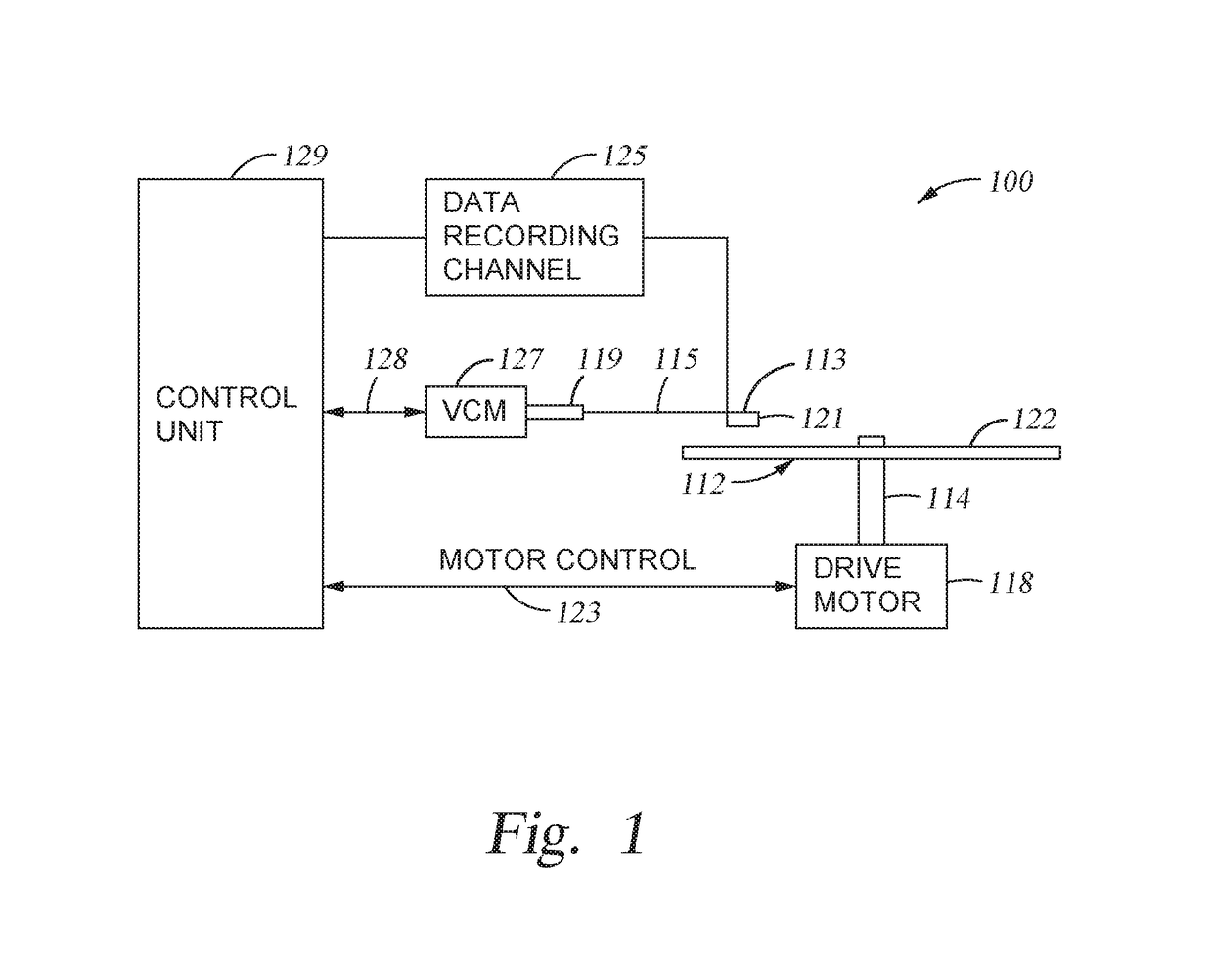
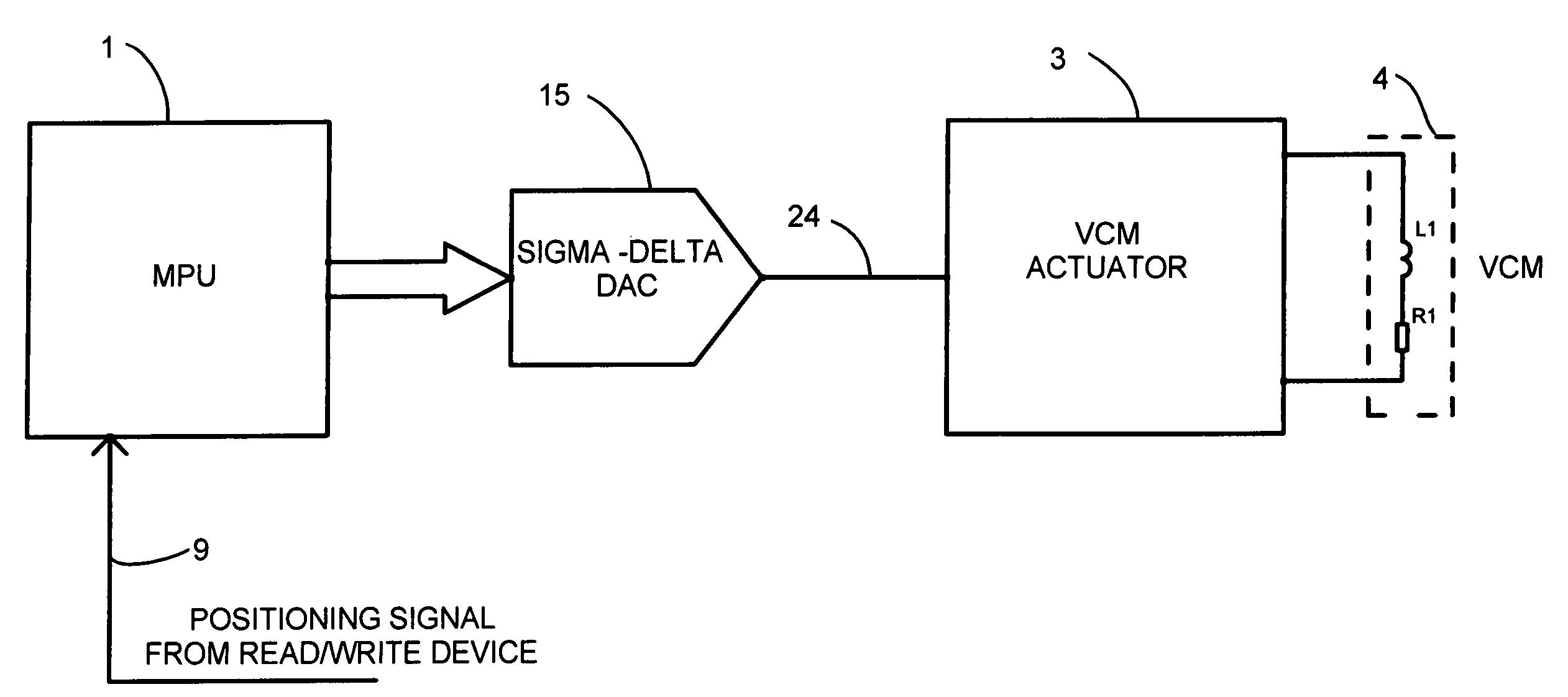
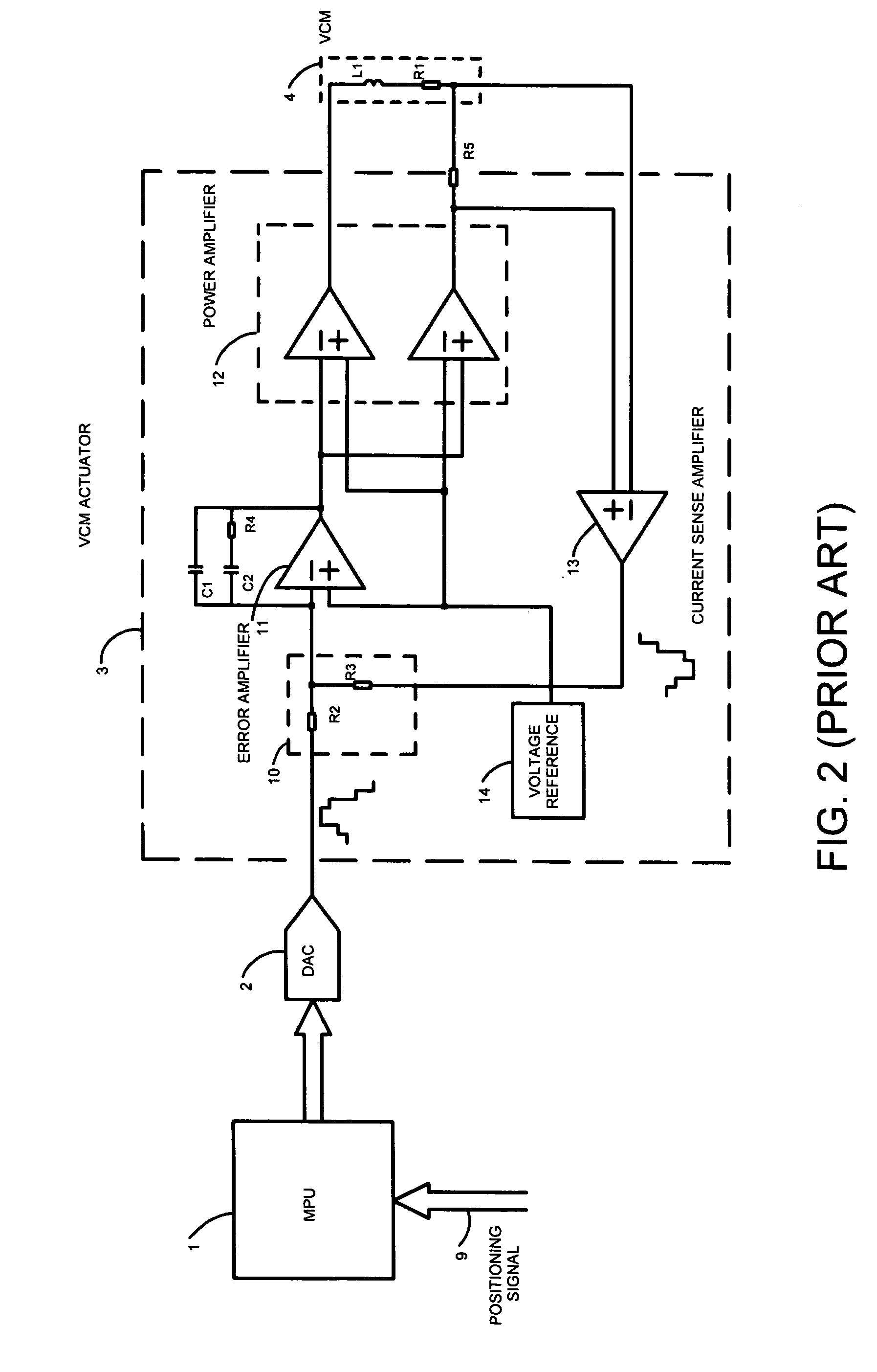
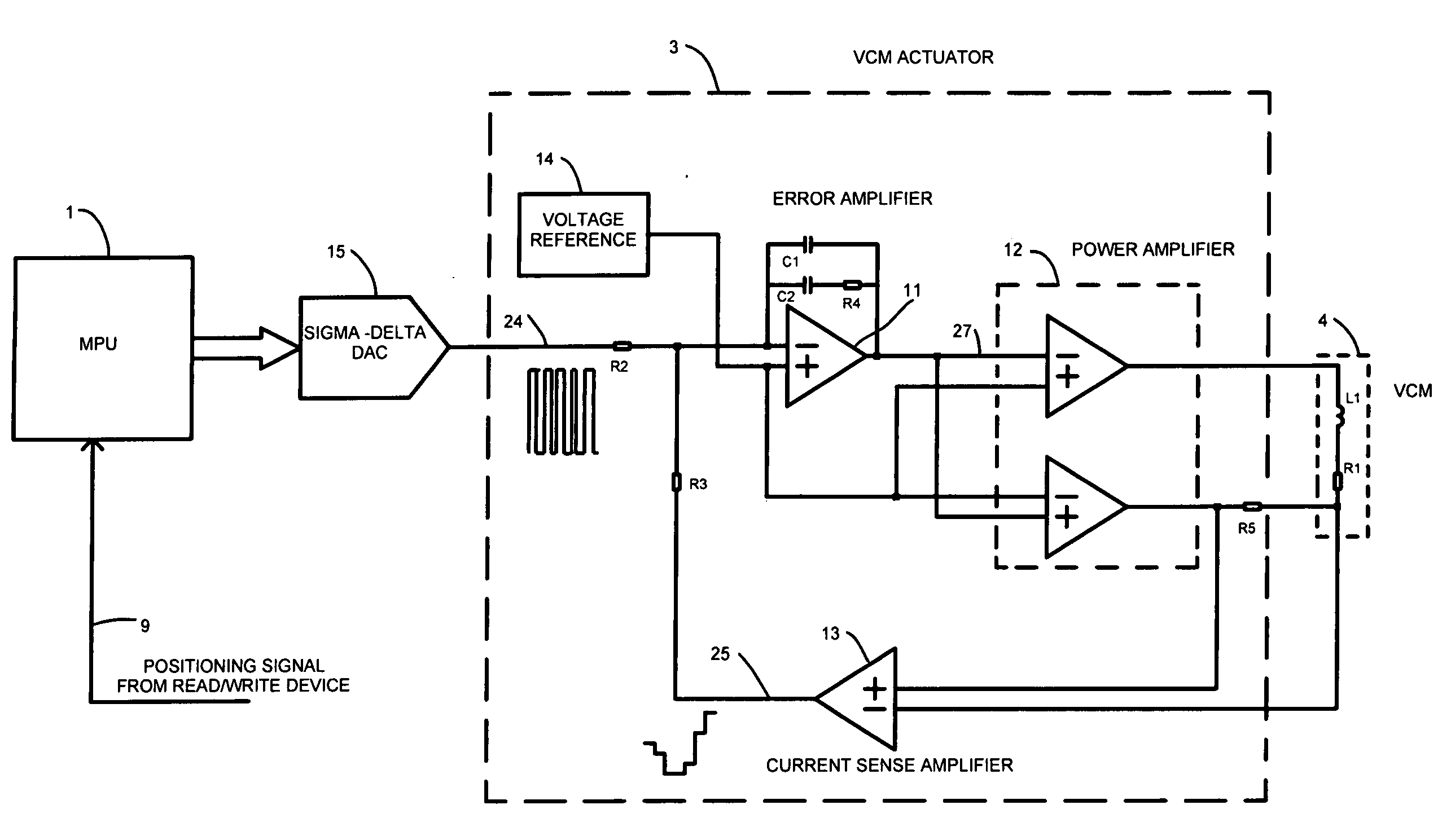
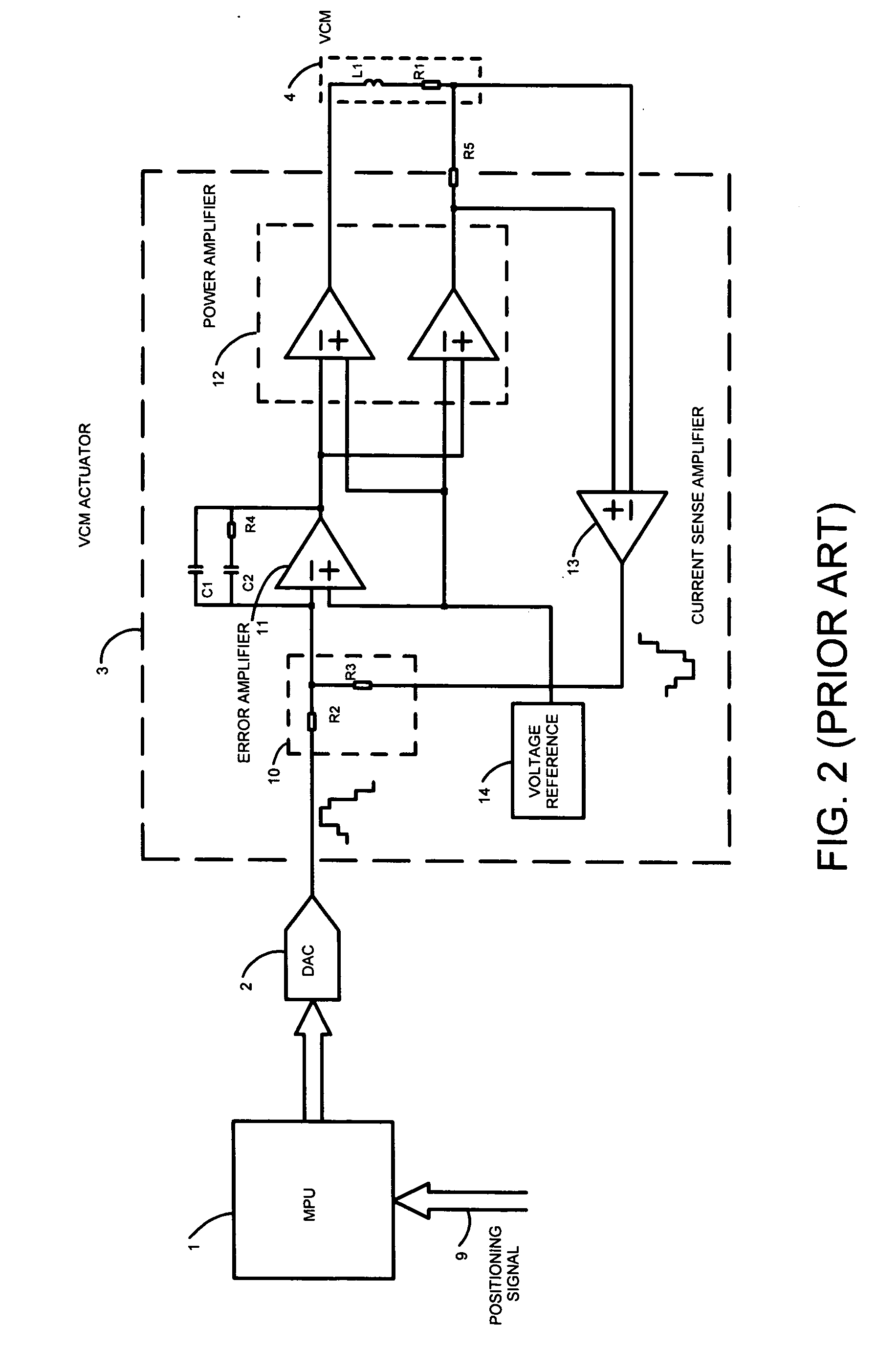
Motor positioning servo loop using oversampling bitstream DAC
InactiveUS7034490B2Improve accuracyImprove resolutionComputer controlSimulator controlLow noiseEngineering
A Hard Disk Drive VCM positioning servo loop comprises an oversampling bitstream Digital to Analog converter. The oversampling DAC is a sigma-delta converter which yields higher resolution and lower noise than Nyquist-rate DACs. This allows driving the VCM with finer level of current control for higher track density. This approach can be implemented in the VCM driver chip (“combo chip”) or in the microprocessor device either in hardware or in software, reducing significantly the development and manufacturing cost. Furthermore this approach can be utilized in combination with a VCM actuation method known as “voltage mode drive” wherein the output of the sigma-delta converter represents the voltage to be applied directly to the VCM actuator. Furthermore this approach can be utilized for optical data storage motor positioning servo loops or any other motor positioning servo loops where high dynamic and resolution is needed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
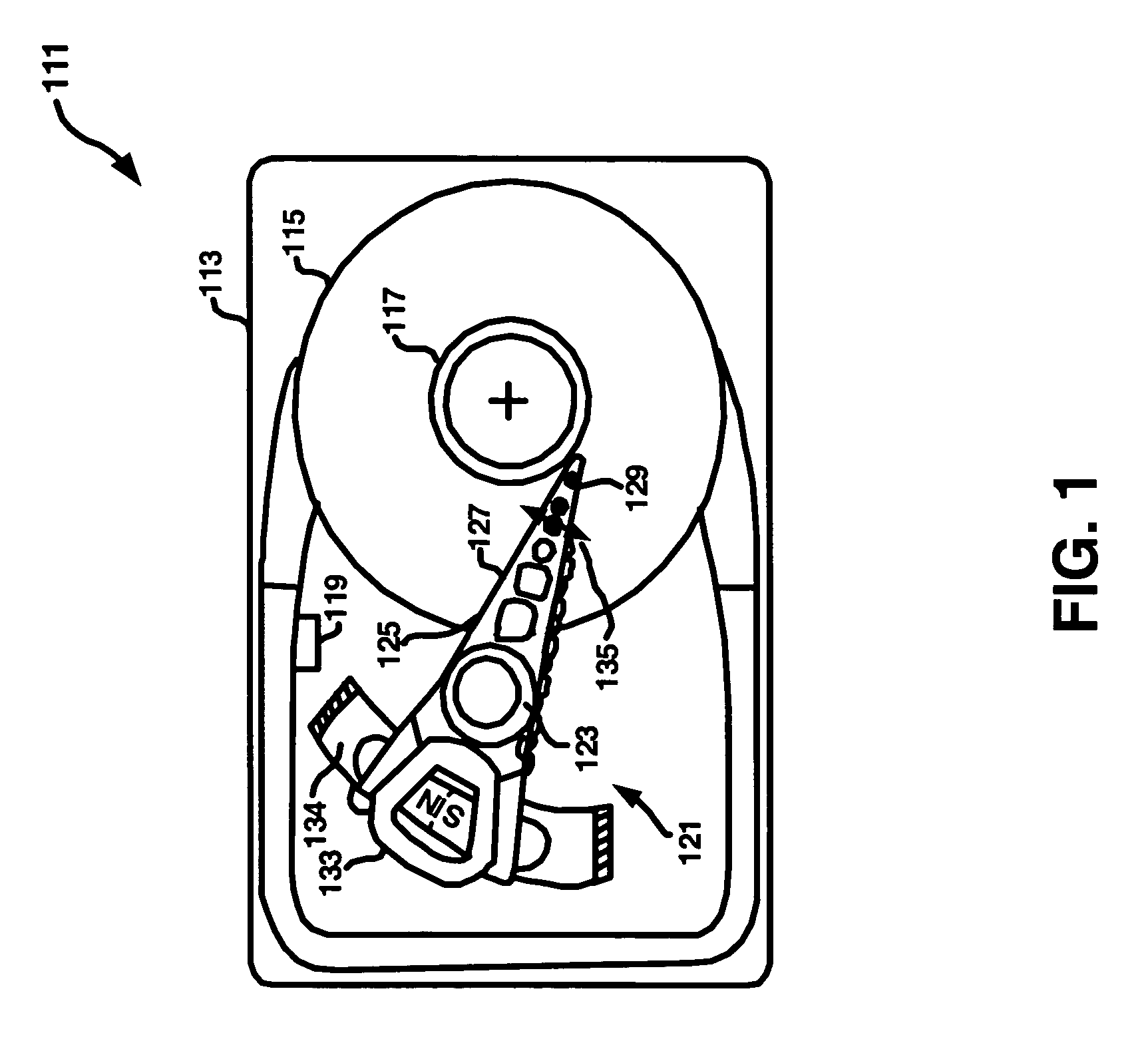
Method and apparatus reducing off-track head motion due to disk vibration in a disk drive through flexure mounting and/or non-symmetric hinging within the head gimbal assembly
InactiveUS6920018B2Easy to buildLow costRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsTrack densityHard disc drive
Improved head gimbal assemblies reducing TMR (Track Mis-Registration) in a hard disk drive are provided. These head gimbal assemblies are as mechanically simple as contemporary head gimbal assemblies, support parallel flying sliders over flat disk surfaces, and reduce TMR' induced by disk vibration. They are easier to build, more reliable, and cost less to make, than other known approaches at comparable track densities and rotational rates. The improved head gimbal assemblies include three sets of mechanisms moving the slider parallel the disk surface, when the disk surface is flat, and radially moving the slider toward the track, when the disk surface is bent. The first and third mechanisms as well as the second and third mechanisms can be used together in a head gimbal assembly.An improved and distinctive servo-controller scheme resulting in an overall improvement in PES performance, particularly when applied to hard disk drives employing the invention's TMR reduction mechanisms. The servo-controllers trade off gain in the disk vibration frequency range, in favor of, increased rejection of low frequency disturbances. This leads to the lowest PES statistics, when applied to hard disk drives with the TMR reduction mechanisms of the invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic tape medium
InactiveUS20060087767A1Stable recording and reproducing propertyAvoid changeMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageTrack densityMagnetic tape
A magnetic tape medium having superior dimensional stability in the width direction and off-track resistance is provided although having a very high track width in the width direction. As a non-magnetic substrate of a magnetic tape medium in which the track density in the width direction is 50 tracks / mm or more, the off-track margin is 5 μm or less, and the maximum permissible amount of change in dimension in the width direction caused by environment factors is 0.10% or less, a laminate composed of a plastic film and films provided on two surfaces thereof is used, the films being formed of a material selected from the group including a metal, a semi-metal, an alloy, and an oxide or composite formed of the aforementioned material, having a Young's modulus of 7×10 kg / mm2 or more and a coefficient of thermal expansion of 18×10−6 / ° C. or less.
Owner:SONY CORP
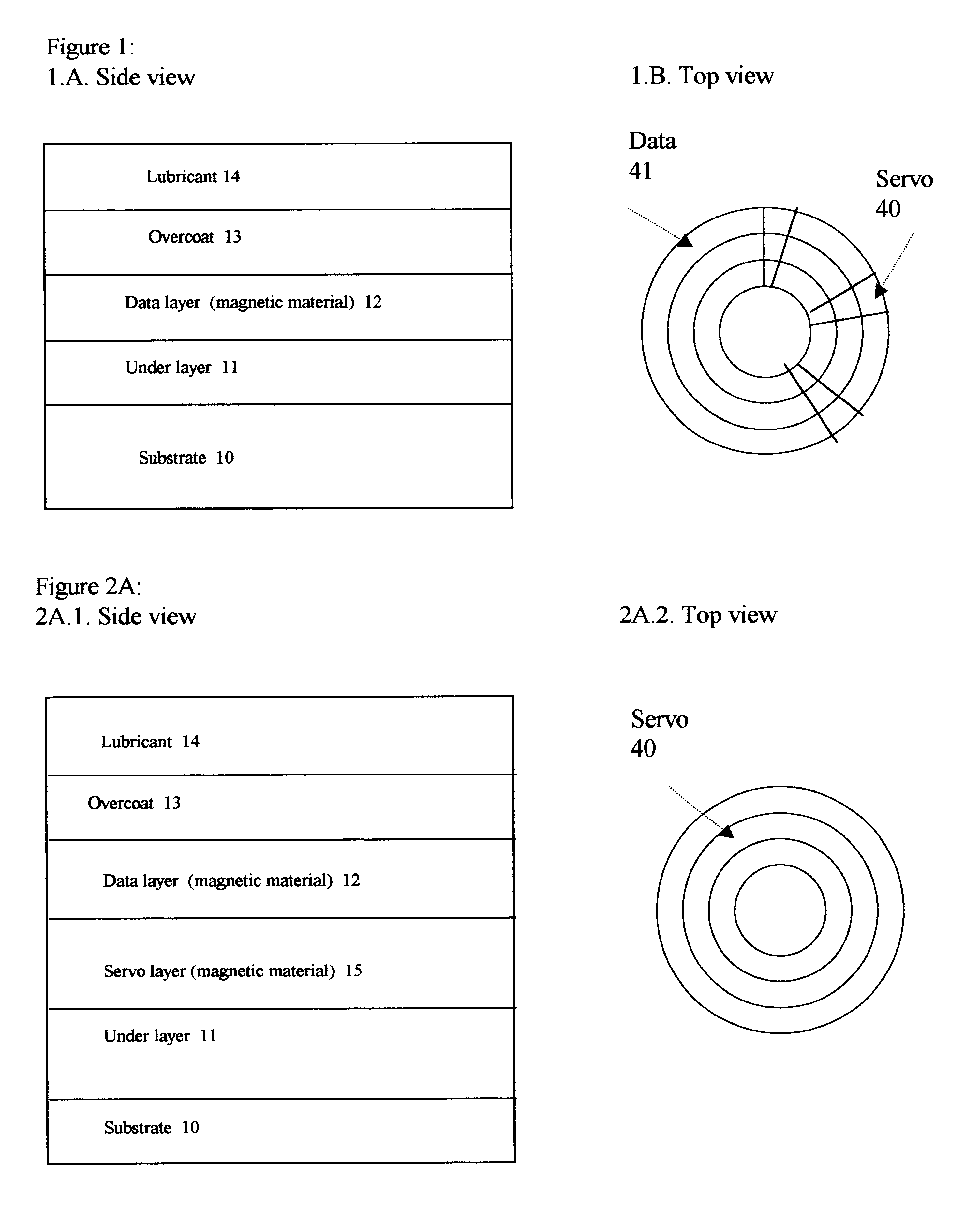
Information storage apparatus, and control method and program for the same
InactiveUS20060082918A1Improve signal qualityIncrease recording capacityDisc-shaped record carriersDriving/moving recording headsTrack densityRecording density
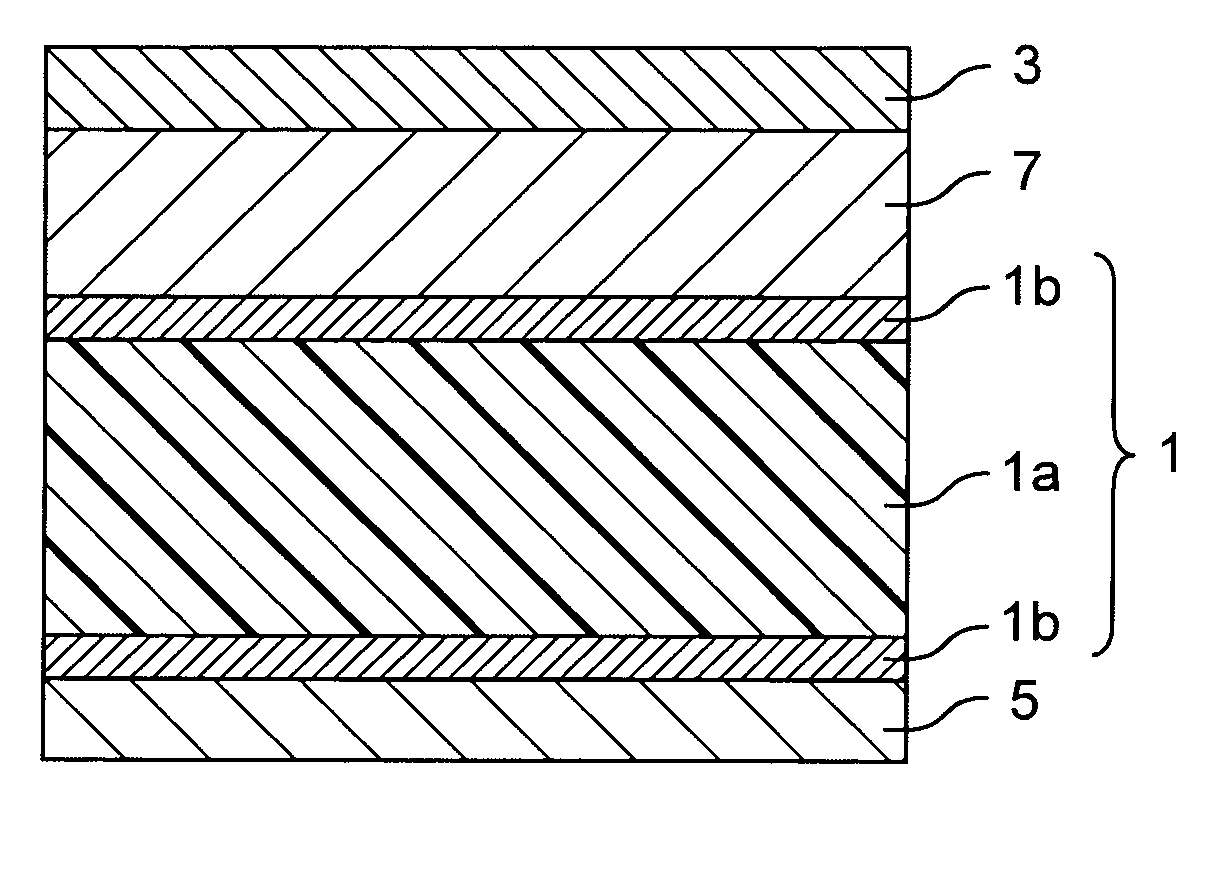
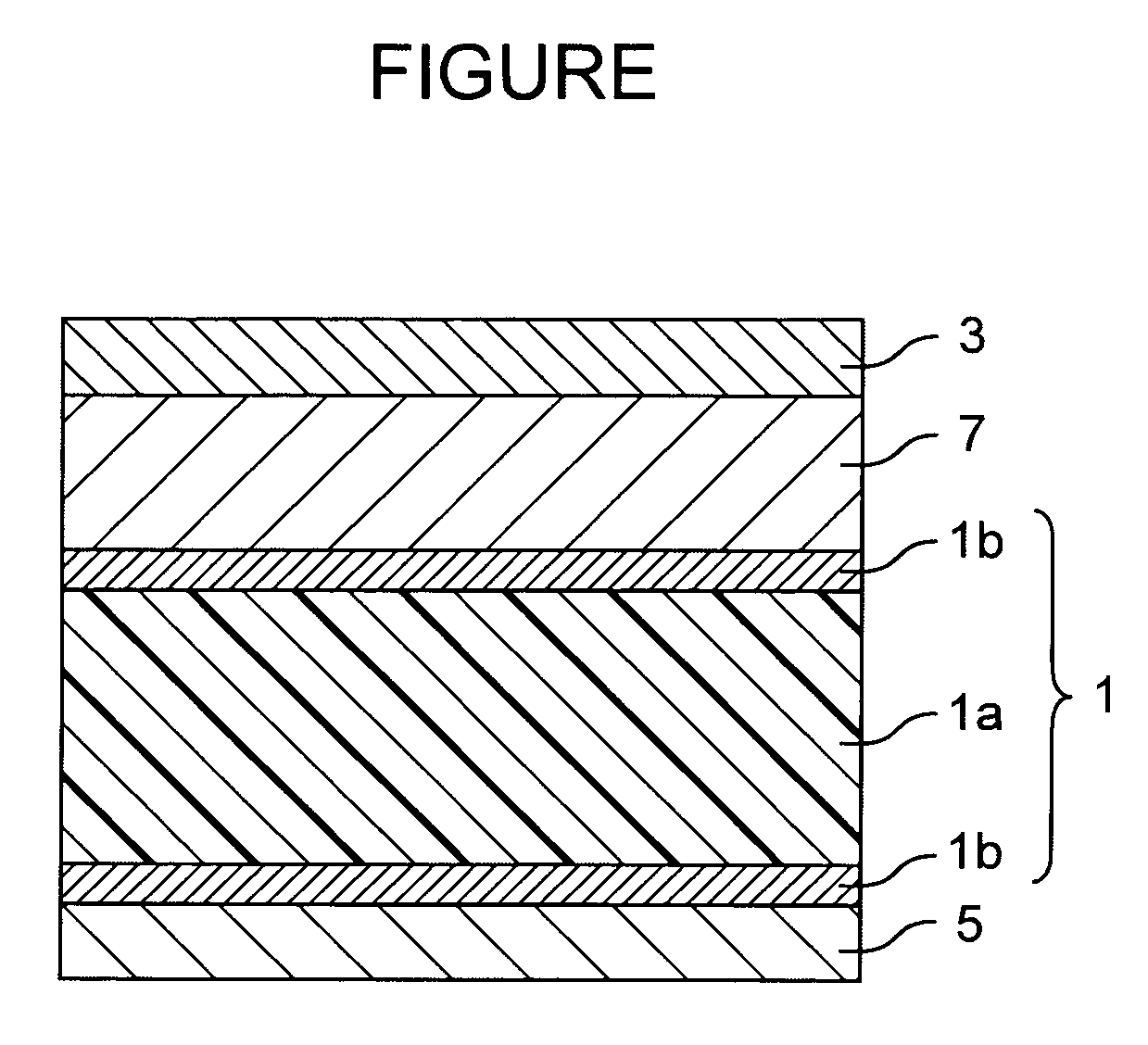
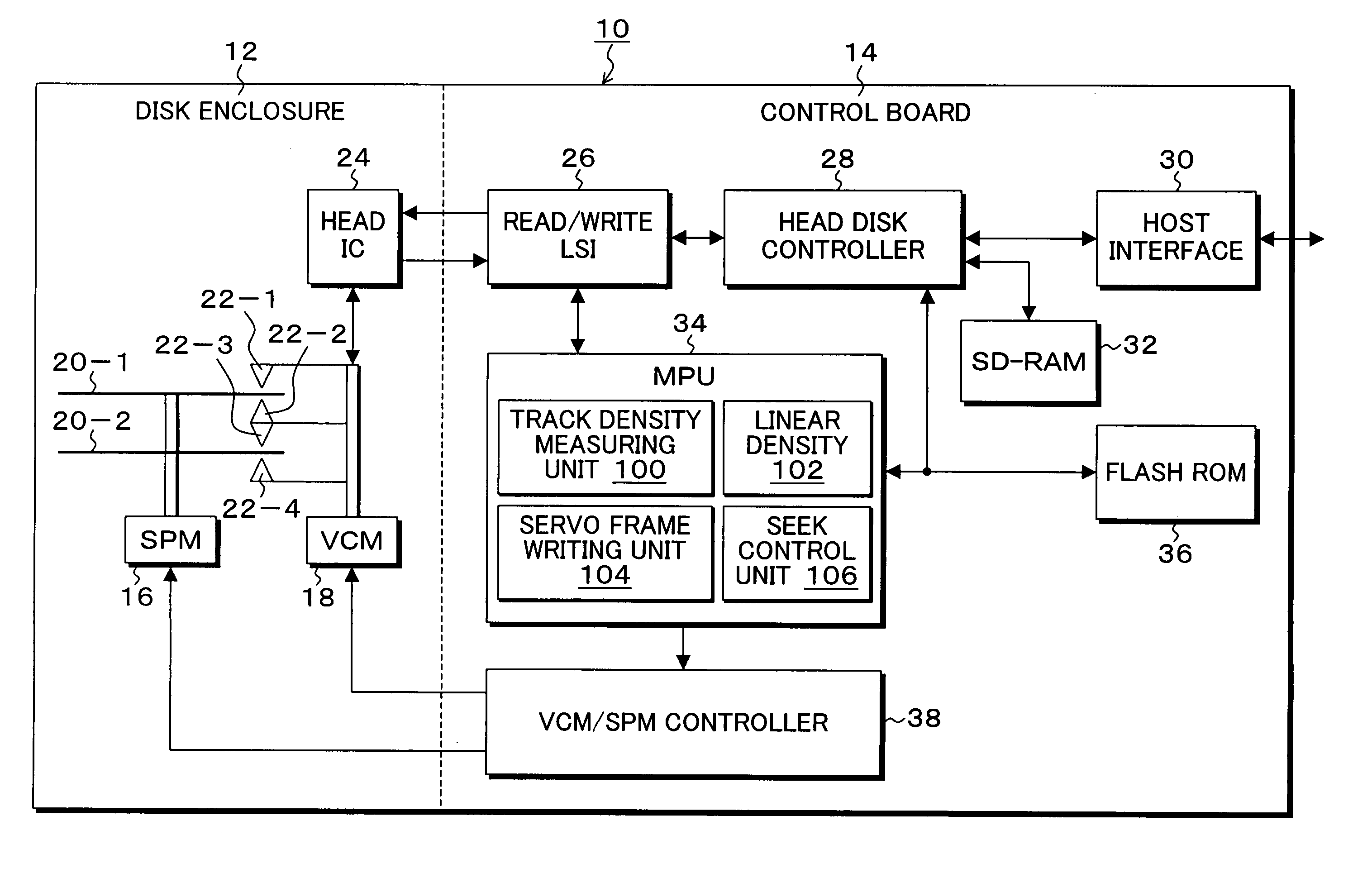
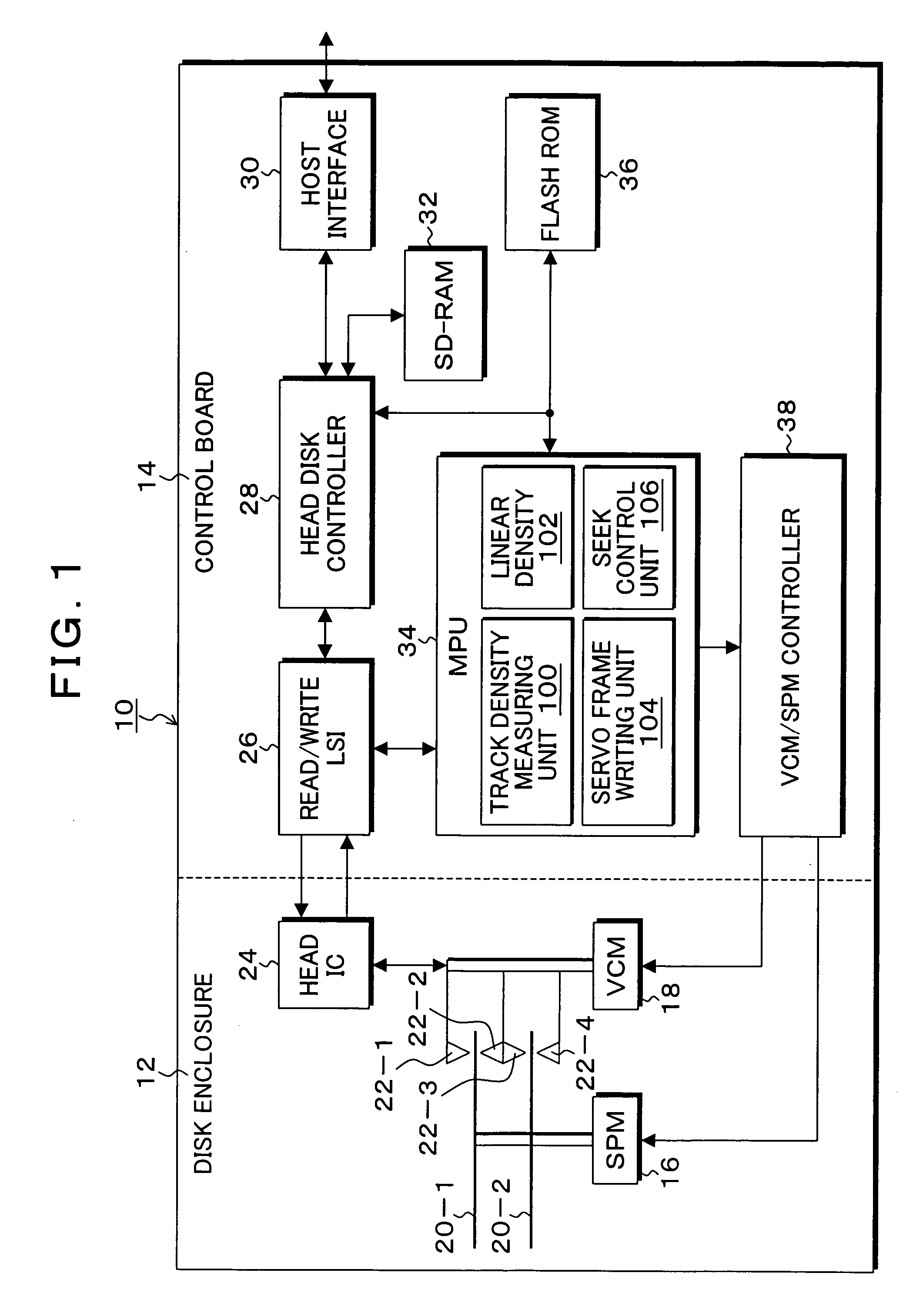
An information storage apparatus that records servo information and user data on a recording face of a recording medium wherein a track density measuring unit measures the optimal track density for a recording face corresponding to each head targeting a storage medium on which the servo information has not yet been recorded and a recording density measuring unit measures the optimal linear density for each recording face. A servo frame writing unit writes the servo information varying a track pitch to a track pitch corresponding to the optimal track density measured by the track density measuring unit and a recording frequency to a recording frequency corresponding to the optimal linear density measured by the linear density measuring unit, for each head.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for optimizing record quality with varying track and linear density by allowing overlapping data tracks
InactiveUS20060227449A1Quality improvementImprove recording qualityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityOffset distance
A method and apparatus for optimizing data record quality on a disk for a pair of read and write heads, in which the write head is bigger, by adaptively varying linear and track density of overlapping recorded tracks to achieve a target storage capacity. In the method, target storage capacity and radial writing direction are selected. Read and write widths of heads are determined. A linear density and offset distance pairing for optimizing record quality at target storage capacity is determined, wherein offset distance is less than write width but greater than read width. The write head writes a track at the linear density, is offset in the radial direction by the offset distance, and the offset distance is stored. The write head writes a new track at the linear density. Offsetting, storing offset, and writing a new track are repeated until desired data is written into a cluster.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Vertical track zoning for disk drives
InactiveUS20060018051A9Improve yield/performanceImprove performanceFilamentary/web carriers operation controlDriving/moving recording headsComputer hardwareTrack density
A method of defining storage format in a data storage device having a plurality of storage media and a plurality of corresponding data transducer heads, each transducer head for recording on and playback of information from a corresponding storage medium. A storage format is defined in at least one region on each storage medium, wherein each region includes a plurality of concentric tracks for recording on and playback of information. The method includes: moving each storage medium with respect to the corresponding transducer head and reading data from each storage medium with the corresponding transducer head; measuring a record / playback performance capability of each transducer head; selecting a group of track densities, one track density for each region on a storage medium, based on the measured record / playback performance capability of the corresponding transducer head.
Owner:MAXTOR
Motor positioning servo loop using oversampling bitstream DAC
A Hard Disk Drive VCM positioning servo loop comprises an oversampling bitstream Digital to Analog converter. The oversampling DAC is a sigma-delta converter which yields higher resolution and lower noise than Nyquist-rate DACs. This allows driving the VCM with finer level of current control for higher track density. This approach can be implemented in the VCM driver chip ("combo chip") or in the microprocessor device either in hardware or in software, reducing significantly the development and manufacturing cost. Furthermore this approach can be utilized in combination with a VCM actuation method known as "voltage mode drive" wherein the output of the sigma-delta converter represents the voltage to be applied directly to the VCM actuator. Furthermore this approach can be utilized for optical data storage motor positioning servo loops or any other motor positioning servo loops where high dynamic and resolution is needed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com