Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Hard error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
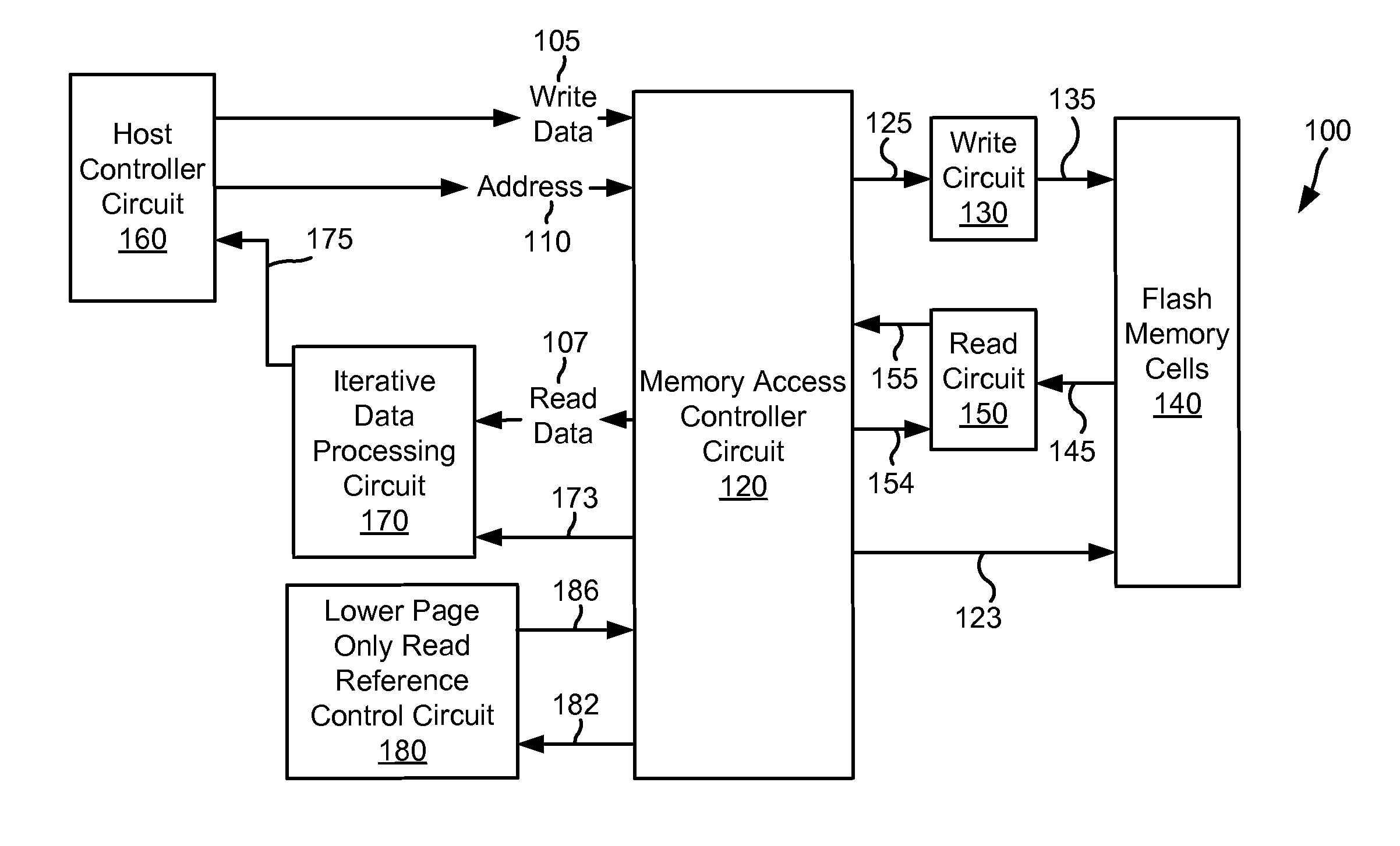
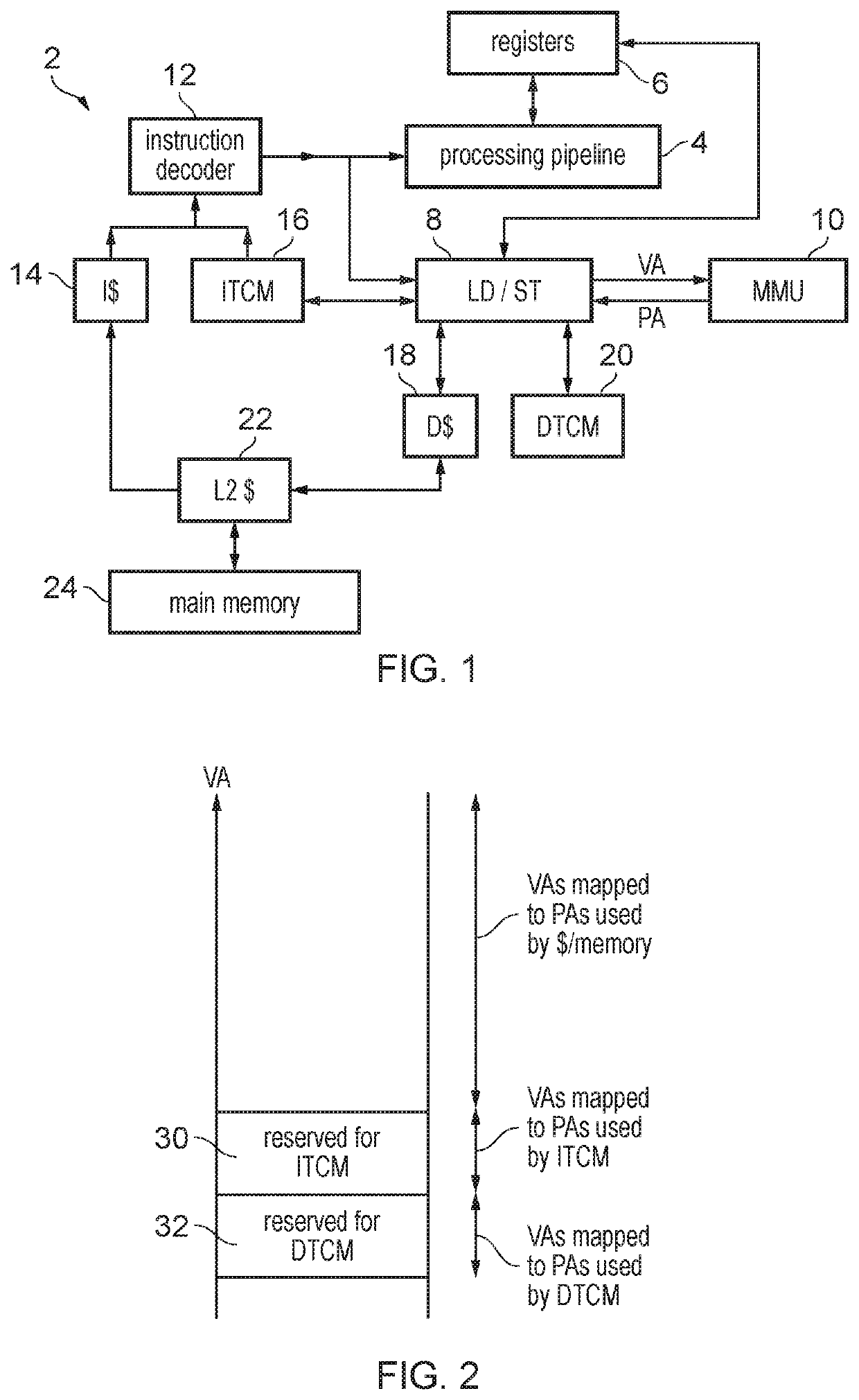
Hard error. A hard error is an issue that occurs due to malfunctioning hardware, specifically data transmission and storage devices. A hard error is usually the result of a memory chip failure in the affected hardware. Common causes are exposure to an ESD and pushing memory beyond its capabilities.
Hard/soft error detection
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Soft errors handling EEPROM devices
InactiveUS20050083726A1Used reliably and economically as a mass storageSimple and effective handling of errorRead-only memoriesDigital storageTerm memoryThreshold voltage
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method to accurately predict hard error rates resulting from encroachment
InactiveUS6975468B1Not easy to make mistakesAccurate predictionRecord information storageCarrier monitoringTransducerRandom noise
A disk drive utilizes a unique write condition for each of the transducers within the drive. Each write condition is determined based upon the specific properties of the corresponding transducer. The write condition information is preferably stored within a memory within the disk drive. When a write operation is performed, the appropriate write condition for the corresponding transducer is used to determine when to write data to the disk. A write condition will typically include one or more individual write criteria. For example, a write condition can specify a write threshold value to be used during a write operation. A write fault threshold value is selected for each transducer by determining a position error distribution corresponding to that transducer wherein the position error distribution is essentially a function of random noise associated with the disk drive, and by using that distribution to determine allowable off-track threshold value (WFL), will protect the drive from encroachments.
Owner:MAXTOR
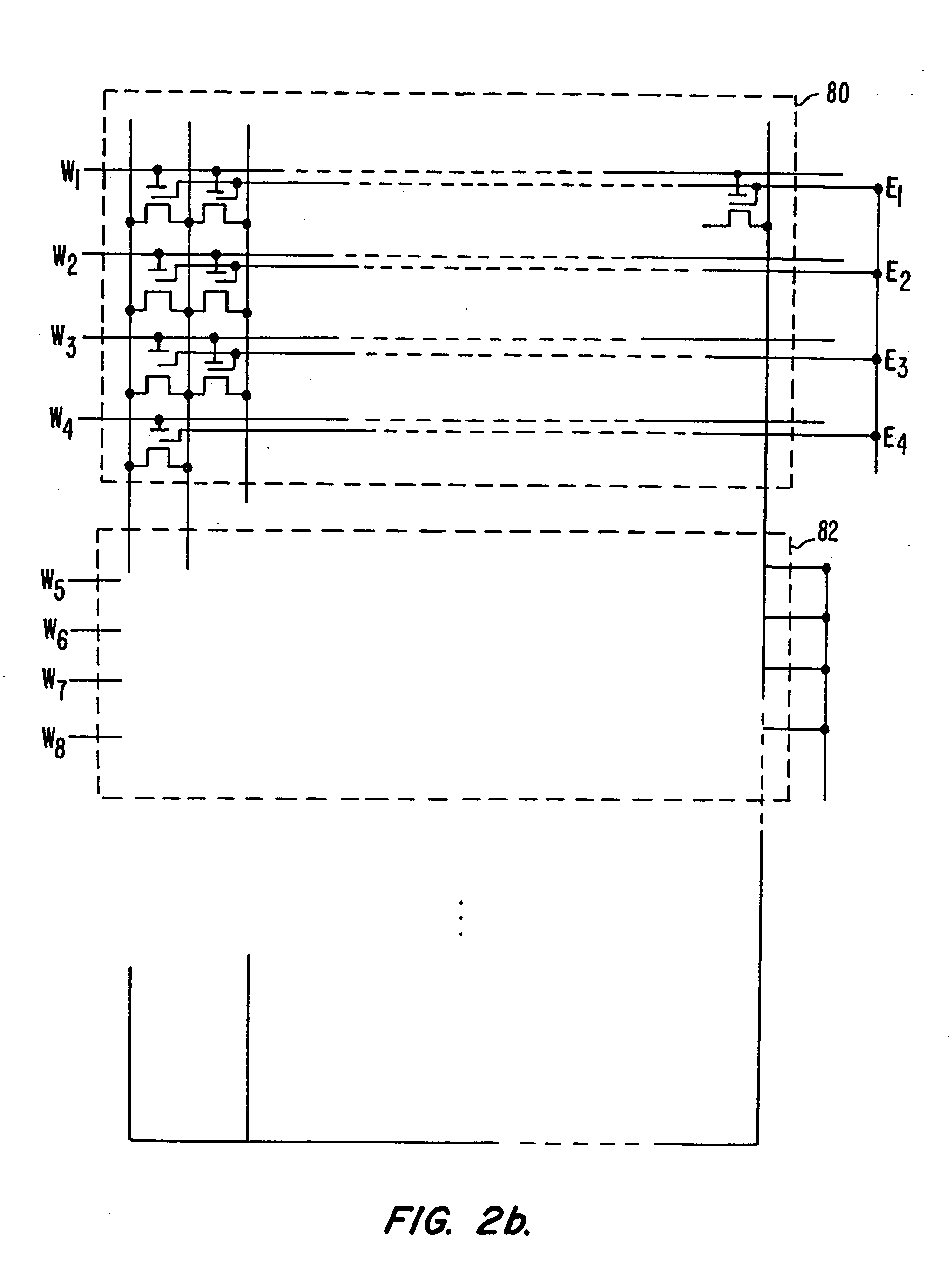
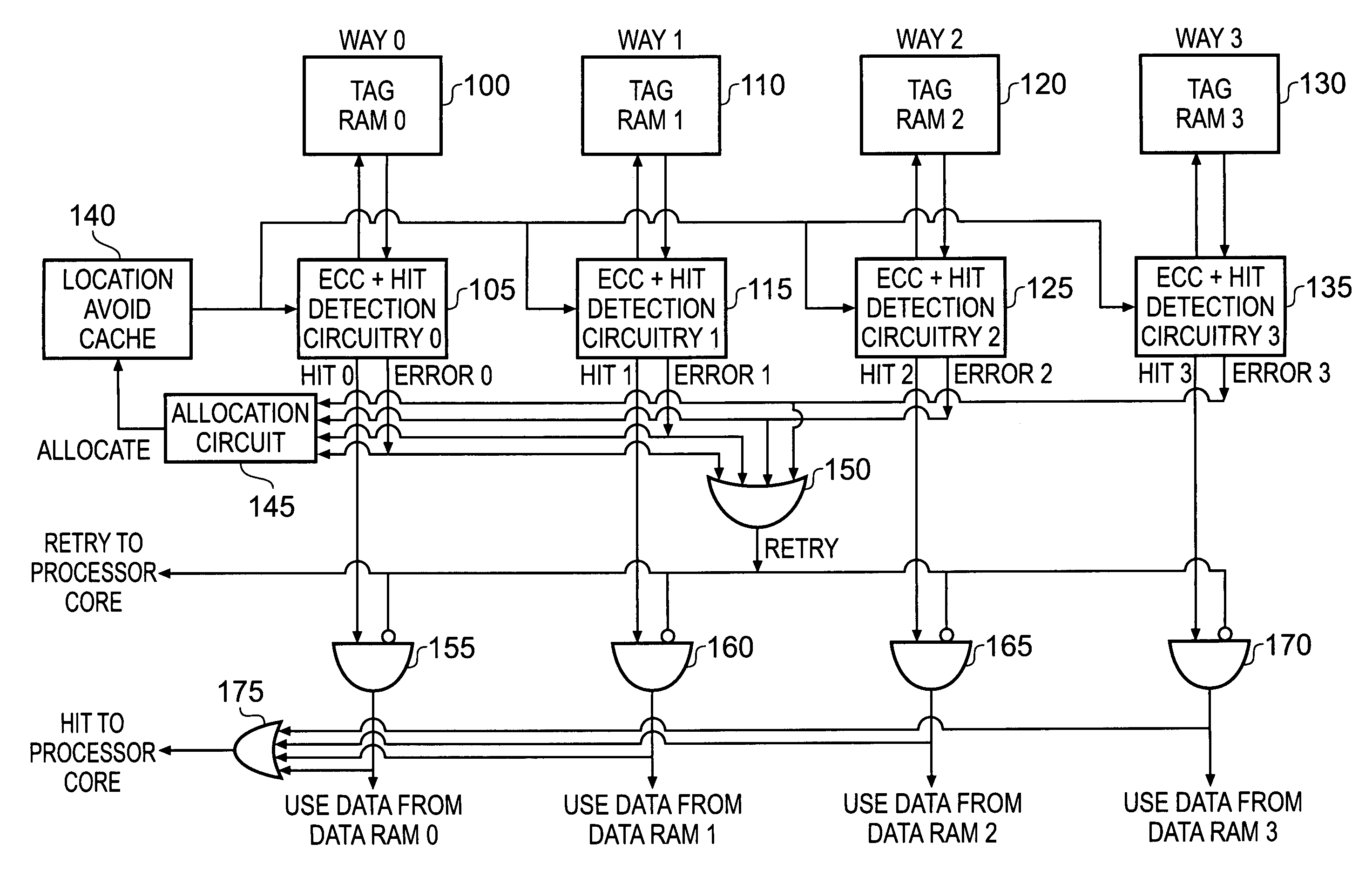
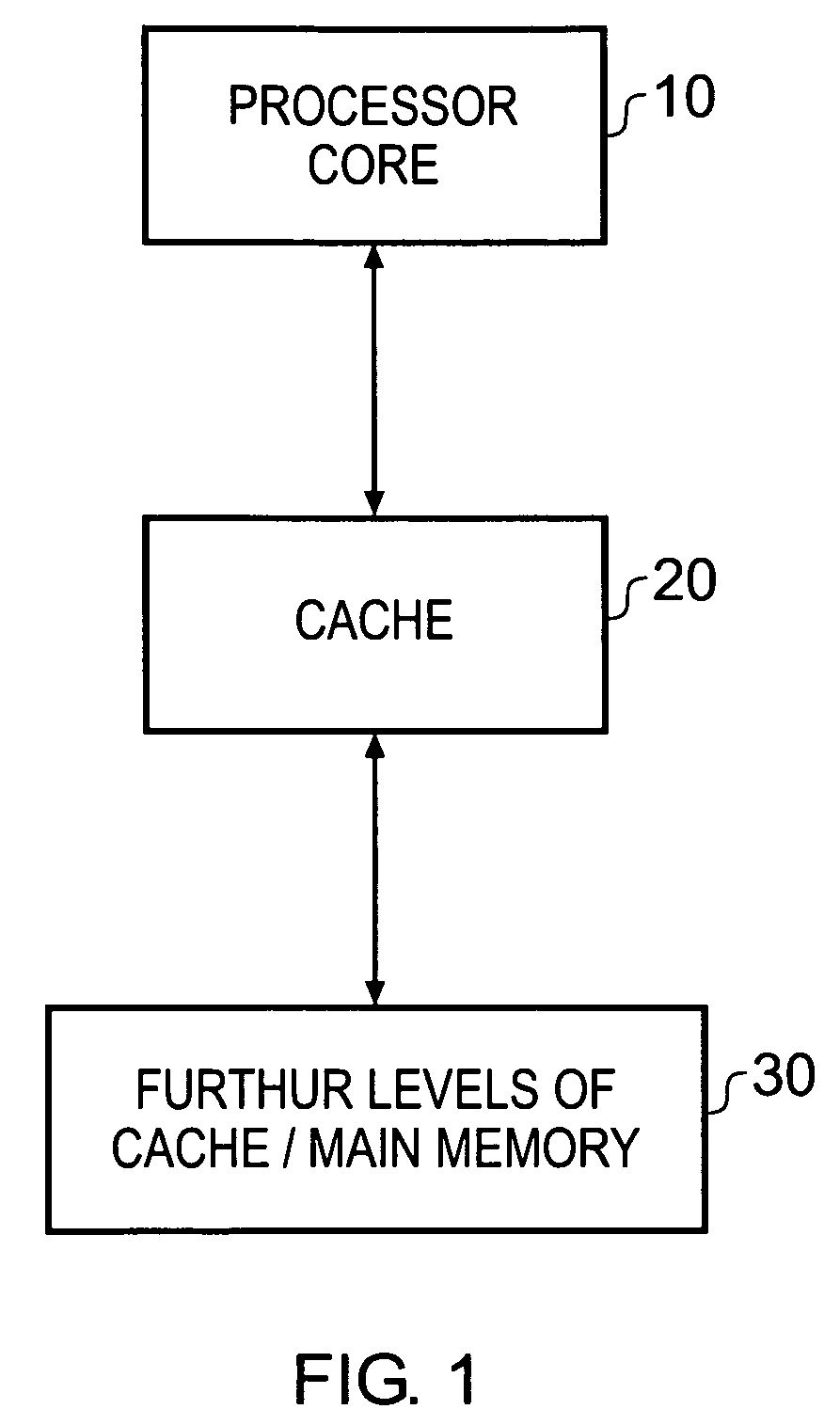
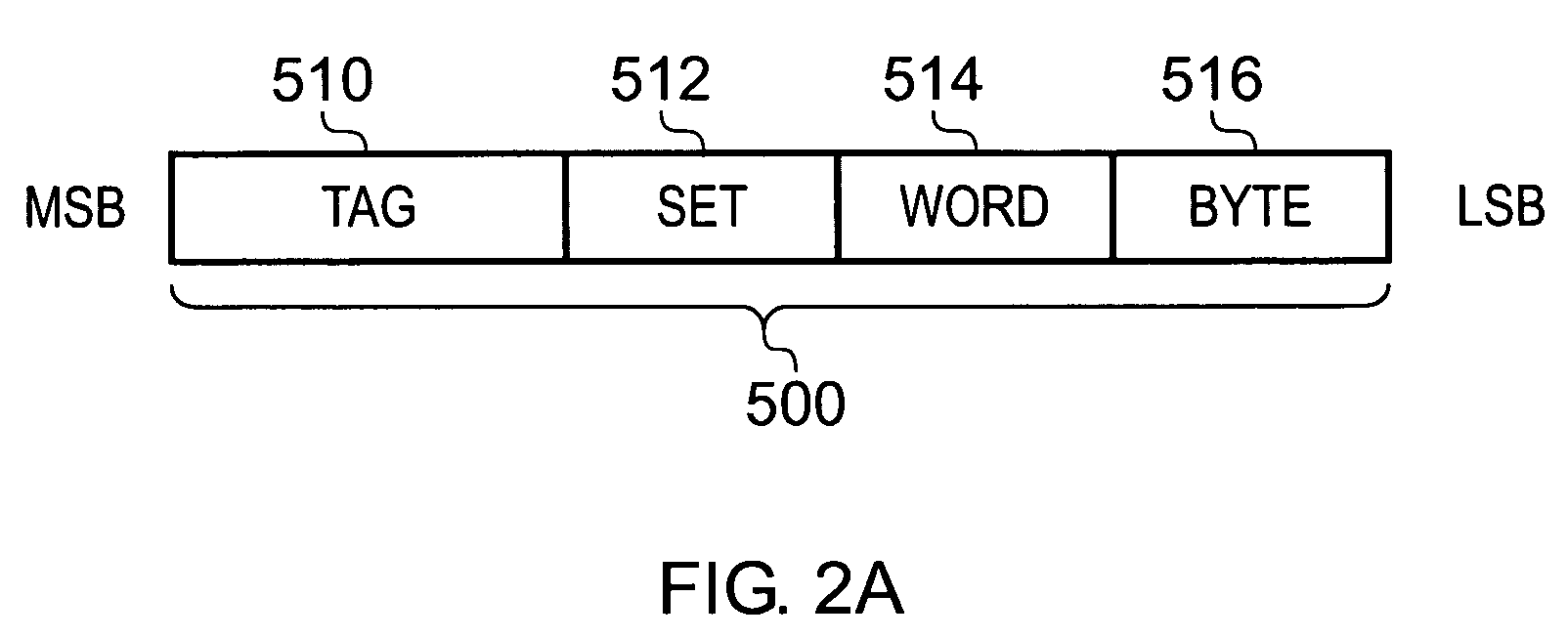
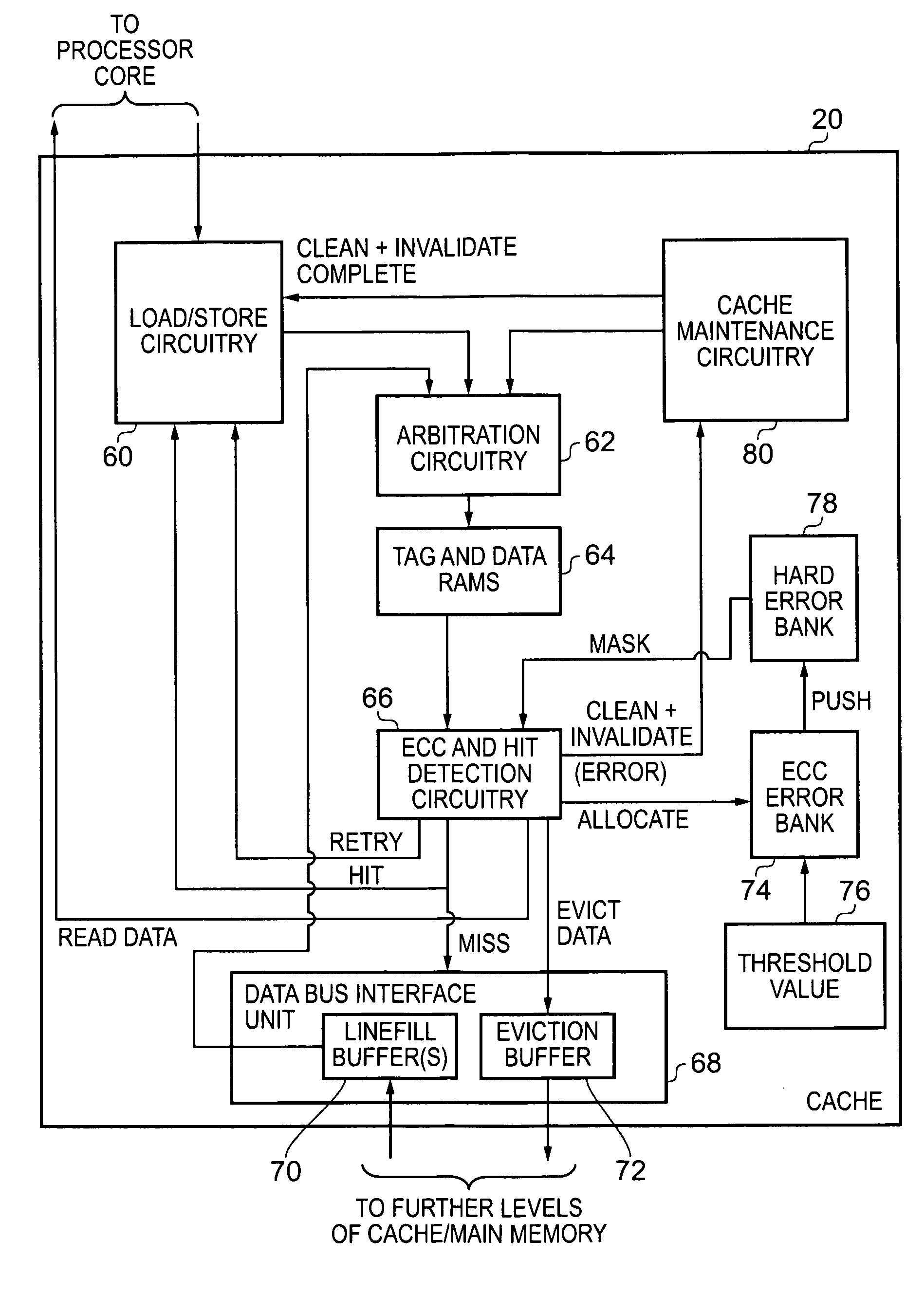
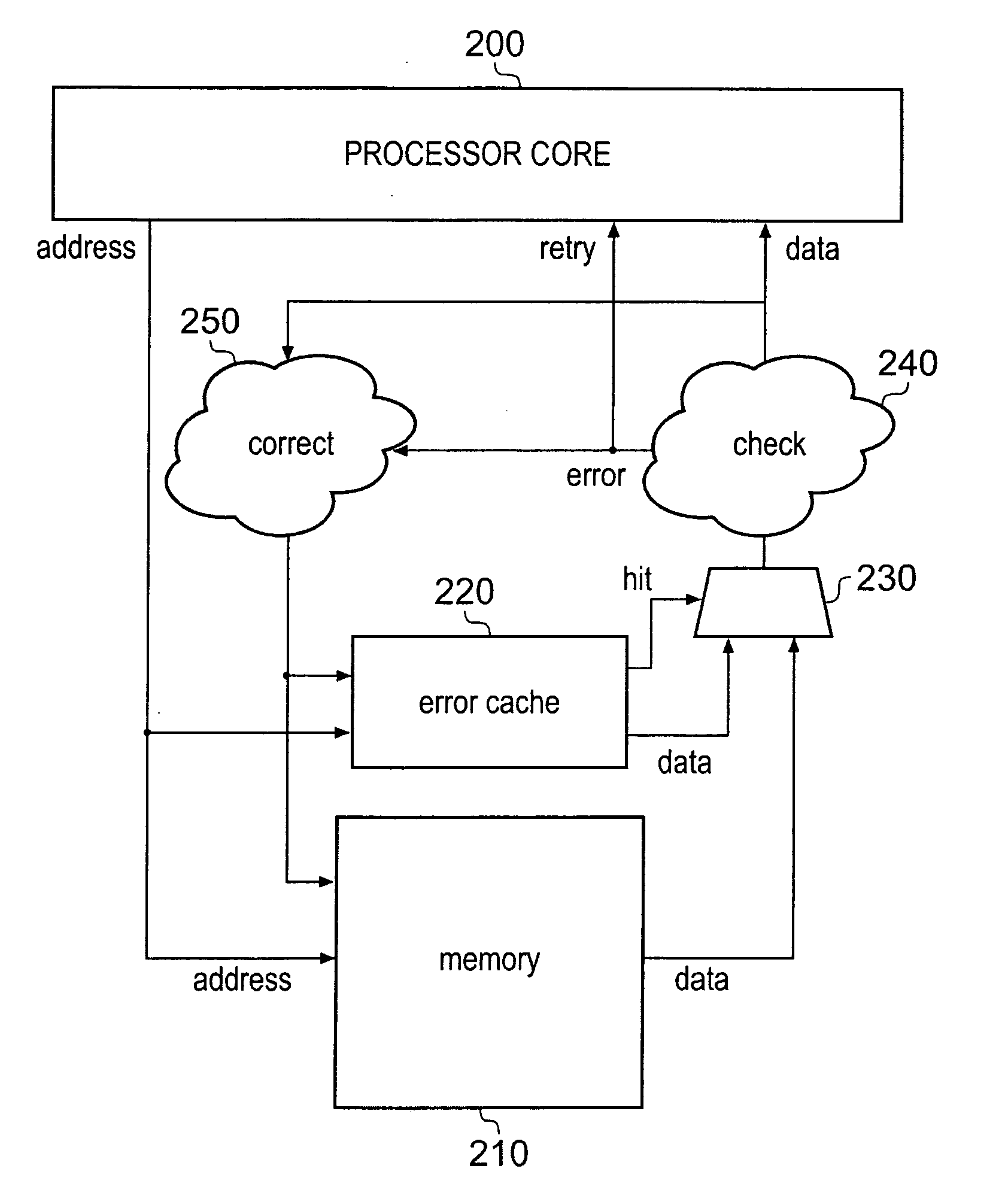
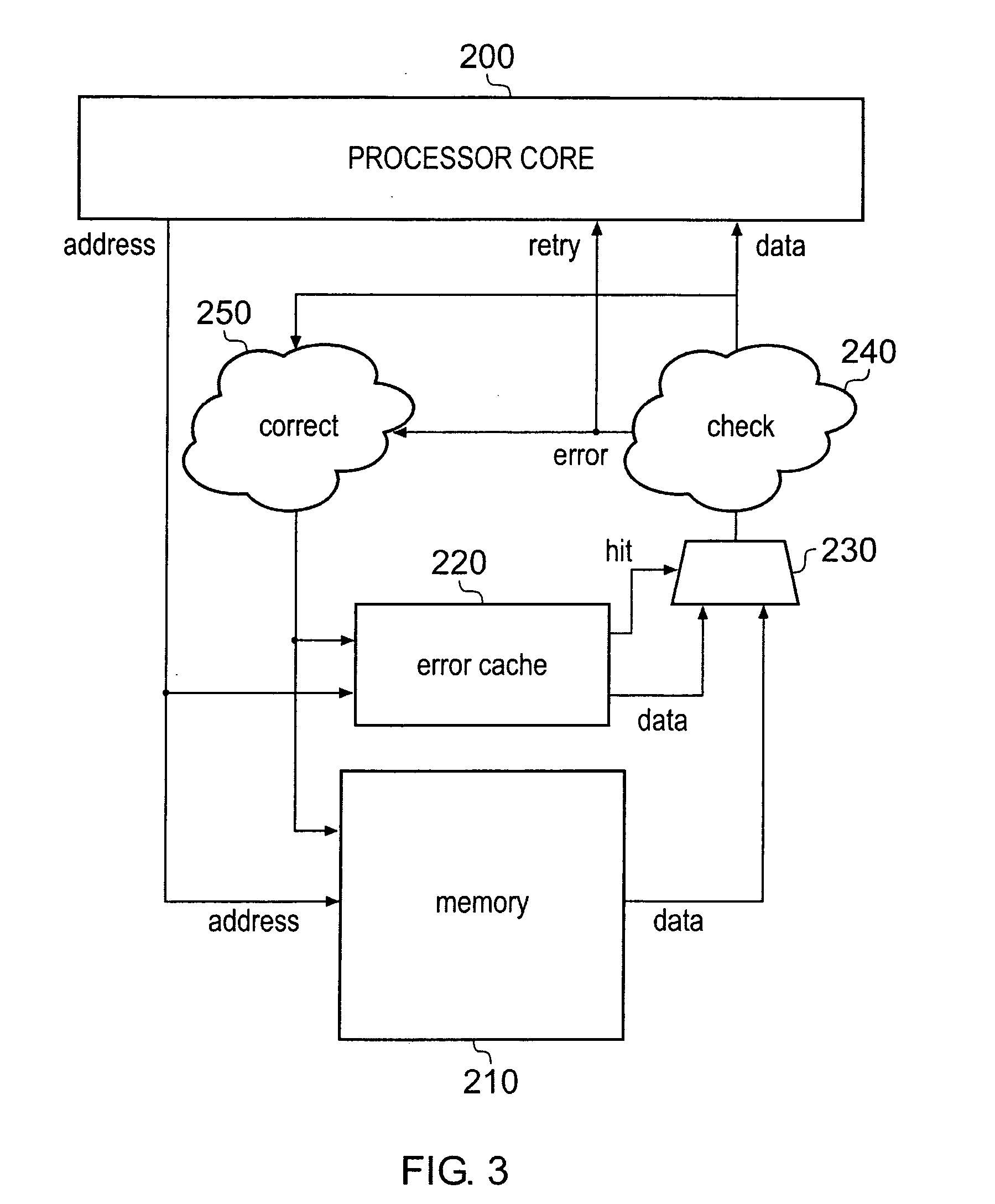
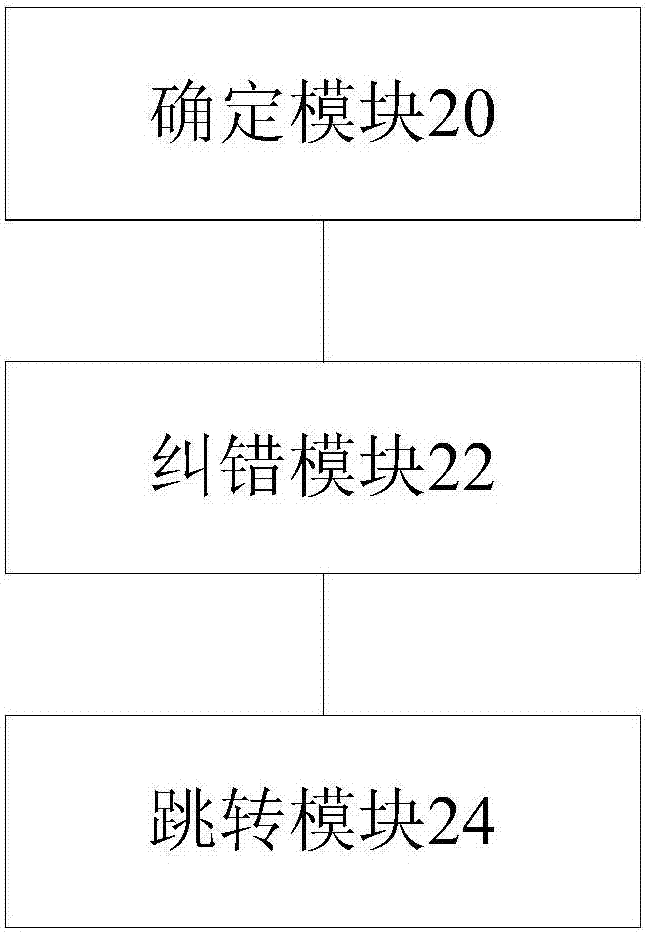
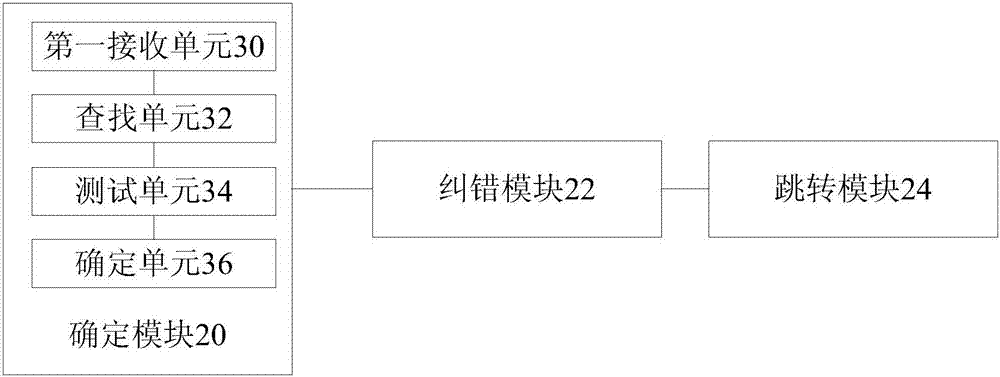
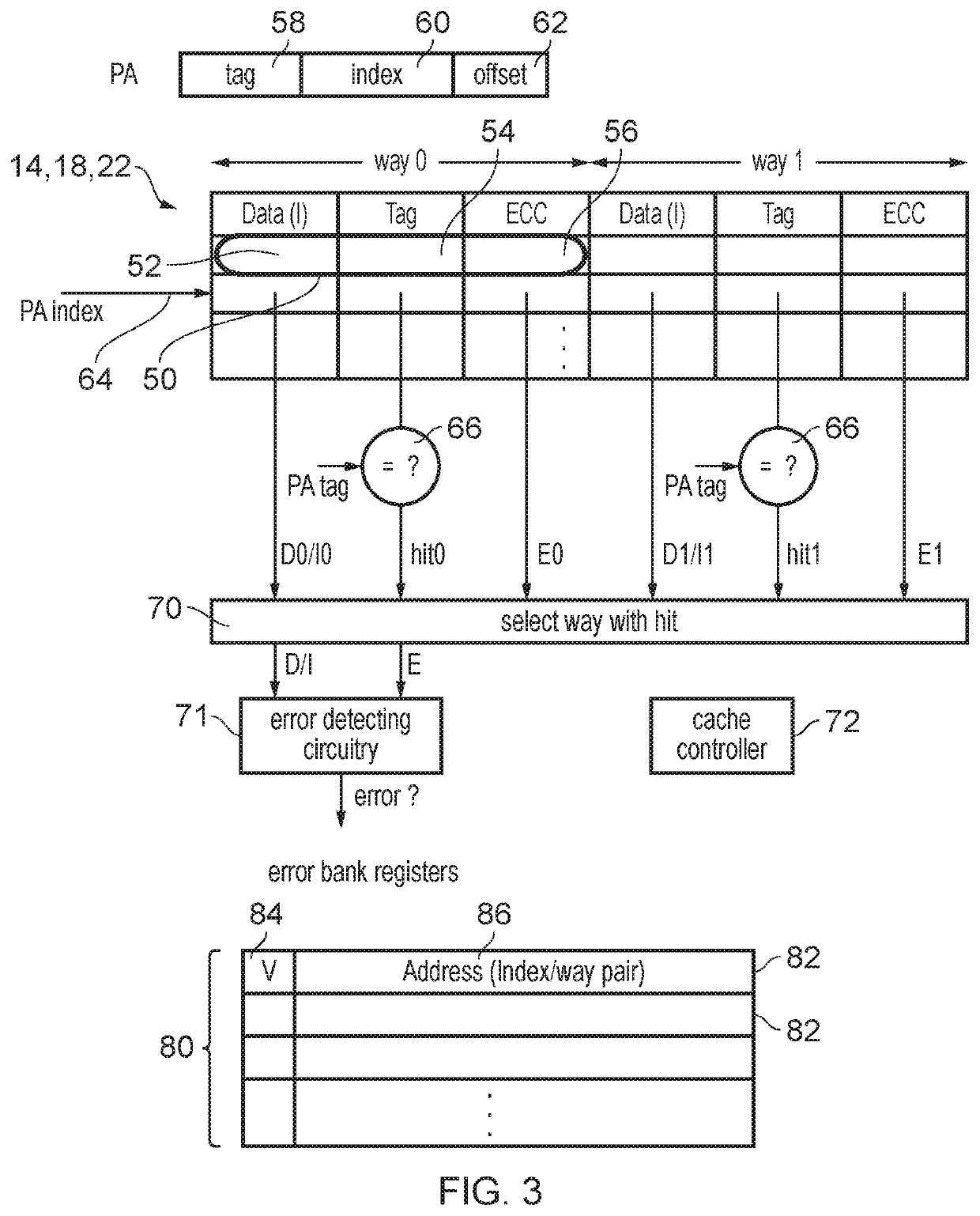
Handling of hard errors in a cache of a data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20090164727A1The process is simple and effectiveOptimization mechanismError detection/correctionDigital storageCache accessParallel computing
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for handling hard errors occurring in a cache of the data processing apparatus. The cache storage comprising data storage having a plurality of cache lines for storing data values, and address storage having a plurality of entries, with each entry identifying for an associated cache line an address indication value, and each entry having associated error data. In response to an access request, a lookup procedure is performed to determine with reference to the address indication value held in at least one entry of the address storage whether a hit condition exists in one of the cache lines. Further, error detection circuitry determines with reference to the error data associated with the at least one entry of the address storage whether an error condition exists for that entry. Additionally, cache location avoid storage is provided having at least one record, with each record being used to store a cache line identifier identifying a specific cache line. On detection of the error condition, one of the records in the cache location avoid storage is allocated to store the cache line identifier for the specific cache line associated with the entry for which the error condition was detected. Further, the error detection circuitry causes a clean and invalidate operation to be performed in respect of the specific cache line, and the access request is then re-performed. The cache access circuitry is arranged to exclude any specific cache line identified in the cache location avoid storage from the lookup procedure. This mechanism provides a very simple and effective mechanism for handling hard errors that manifest themselves within a cache during use, so as to ensure correct operation of the cache in the presence of such hard errors. Further, the technique can be employed not only in association with write through caches but also write back caches, thus providing a very flexible solution.
Owner:ARM LTD
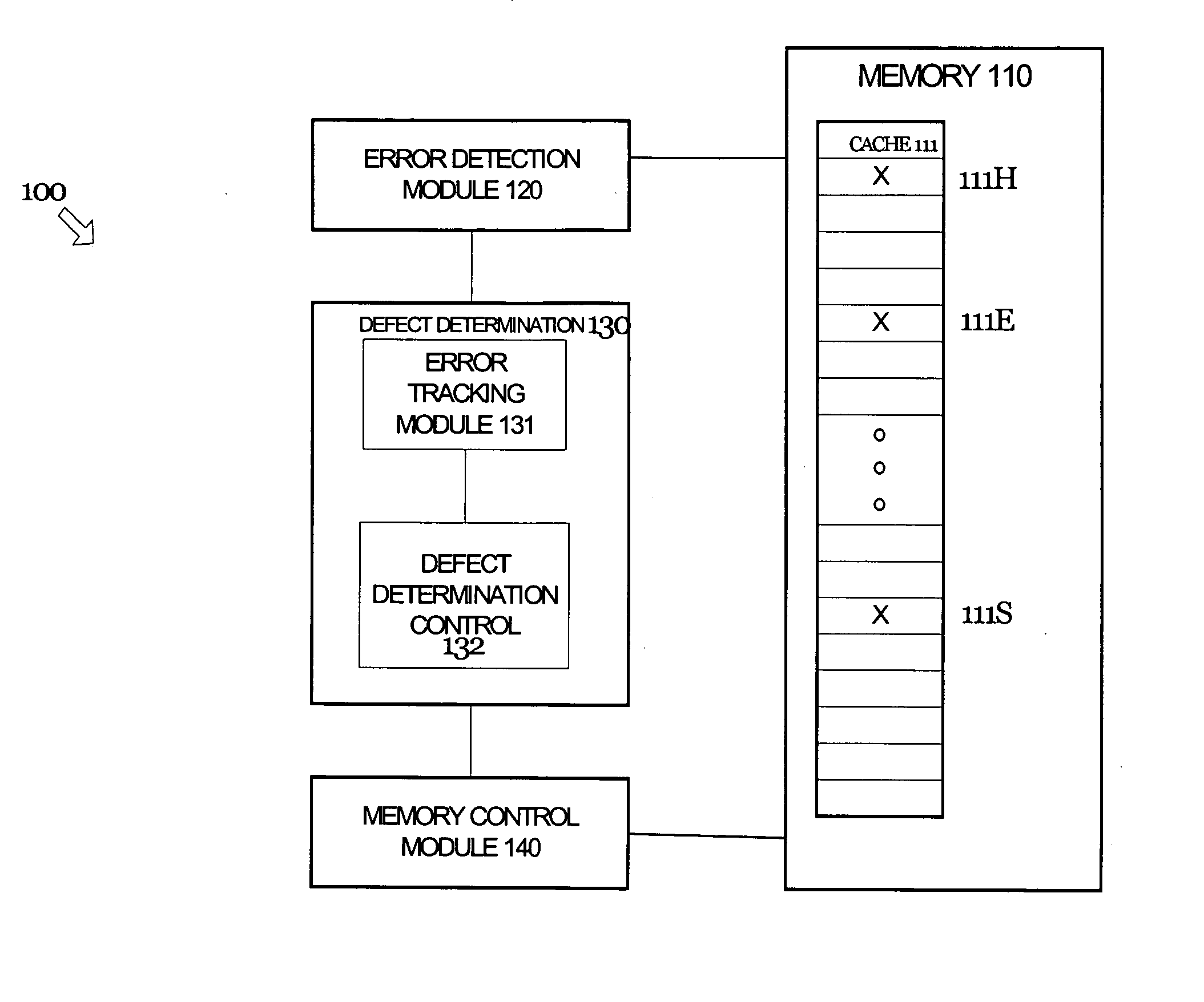
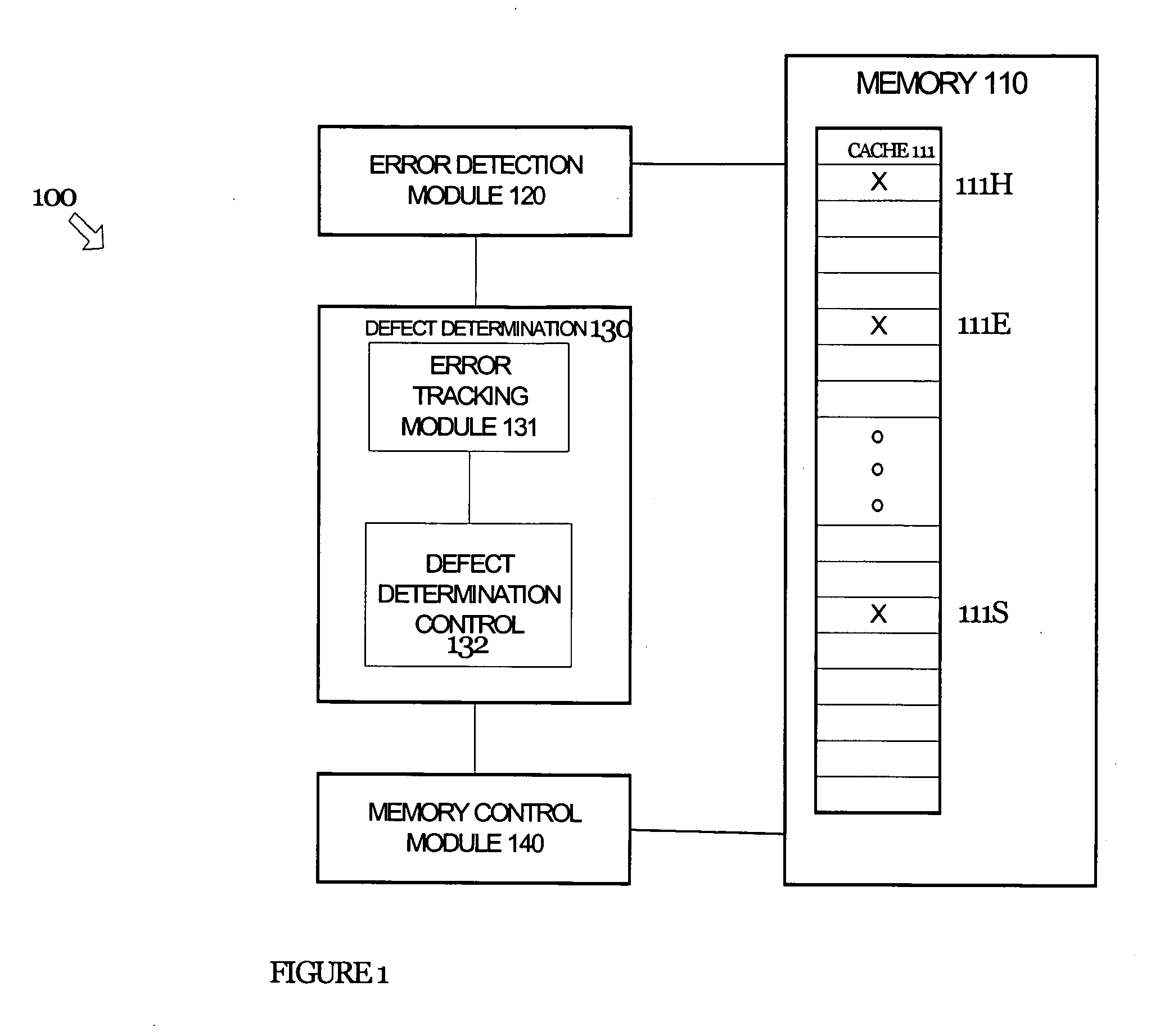
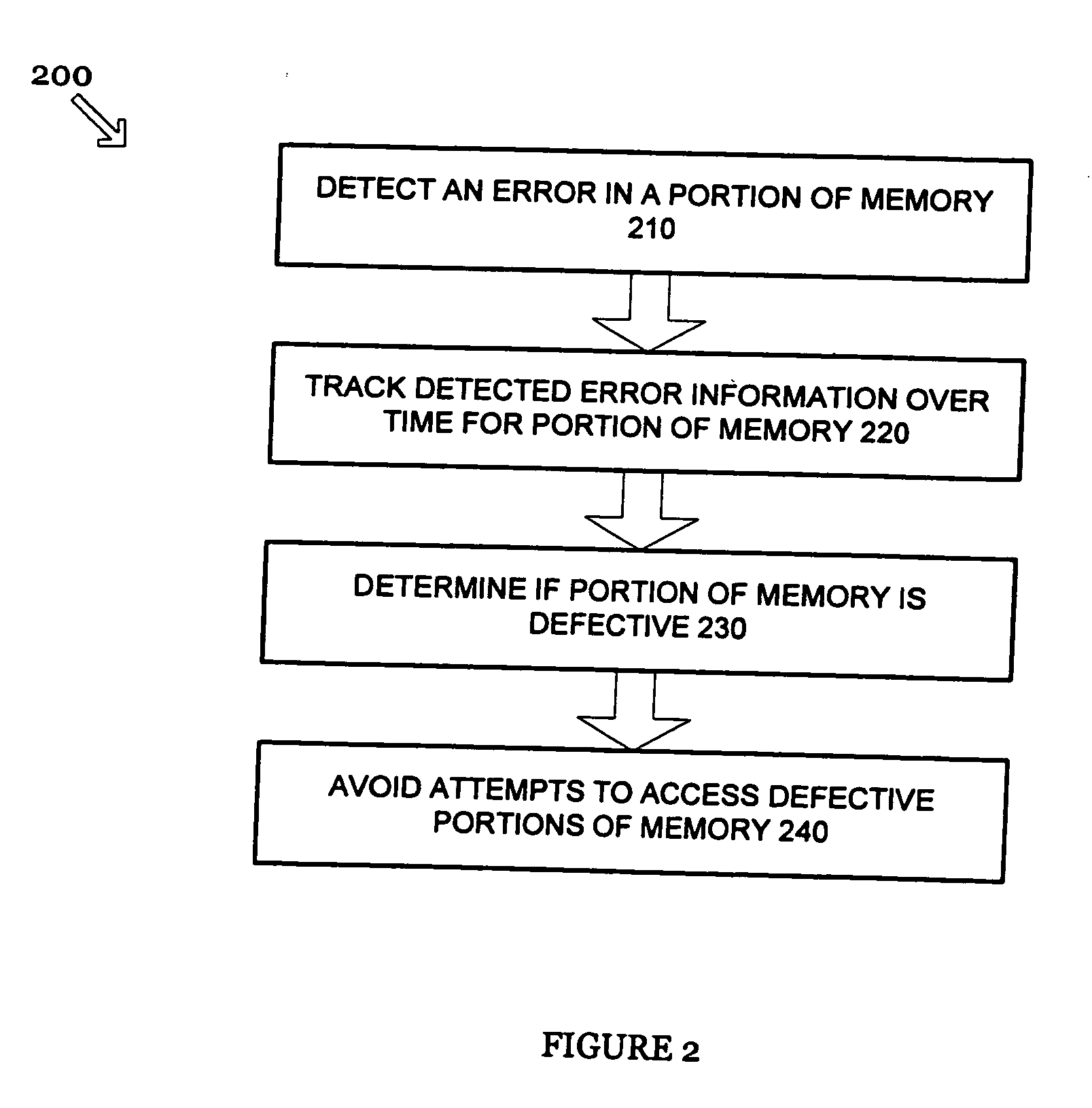
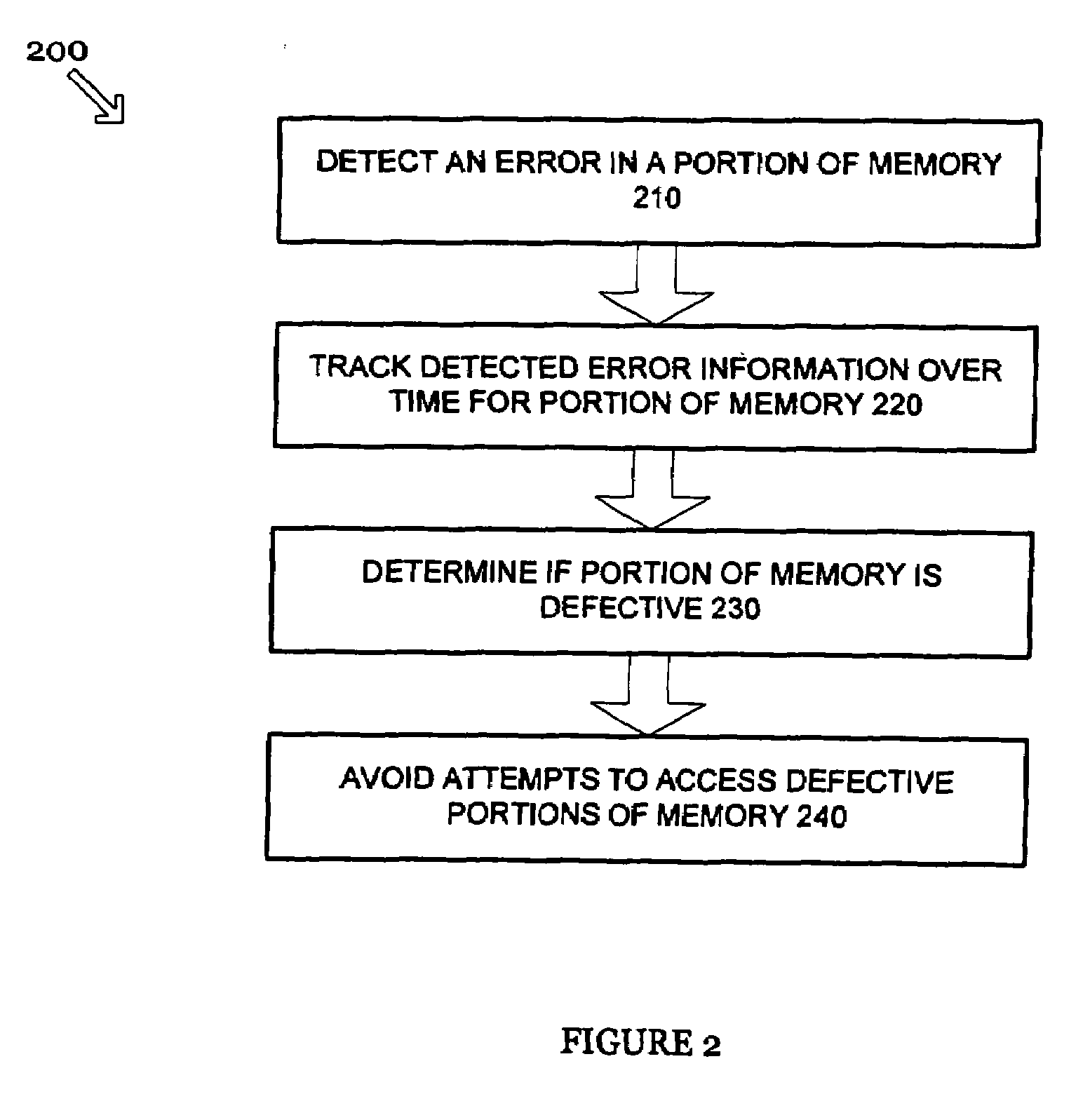
Disabling portions of memory with non-deterministic errors
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for identifying and avoiding attempts to access a defective portion of memory. Various techniques are provided for detecting a defect in a portion of memory and dynamically avoiding future attempts to access the defective portion of memory. More specifically, the techniques detect and avoid both hard and erratic errors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
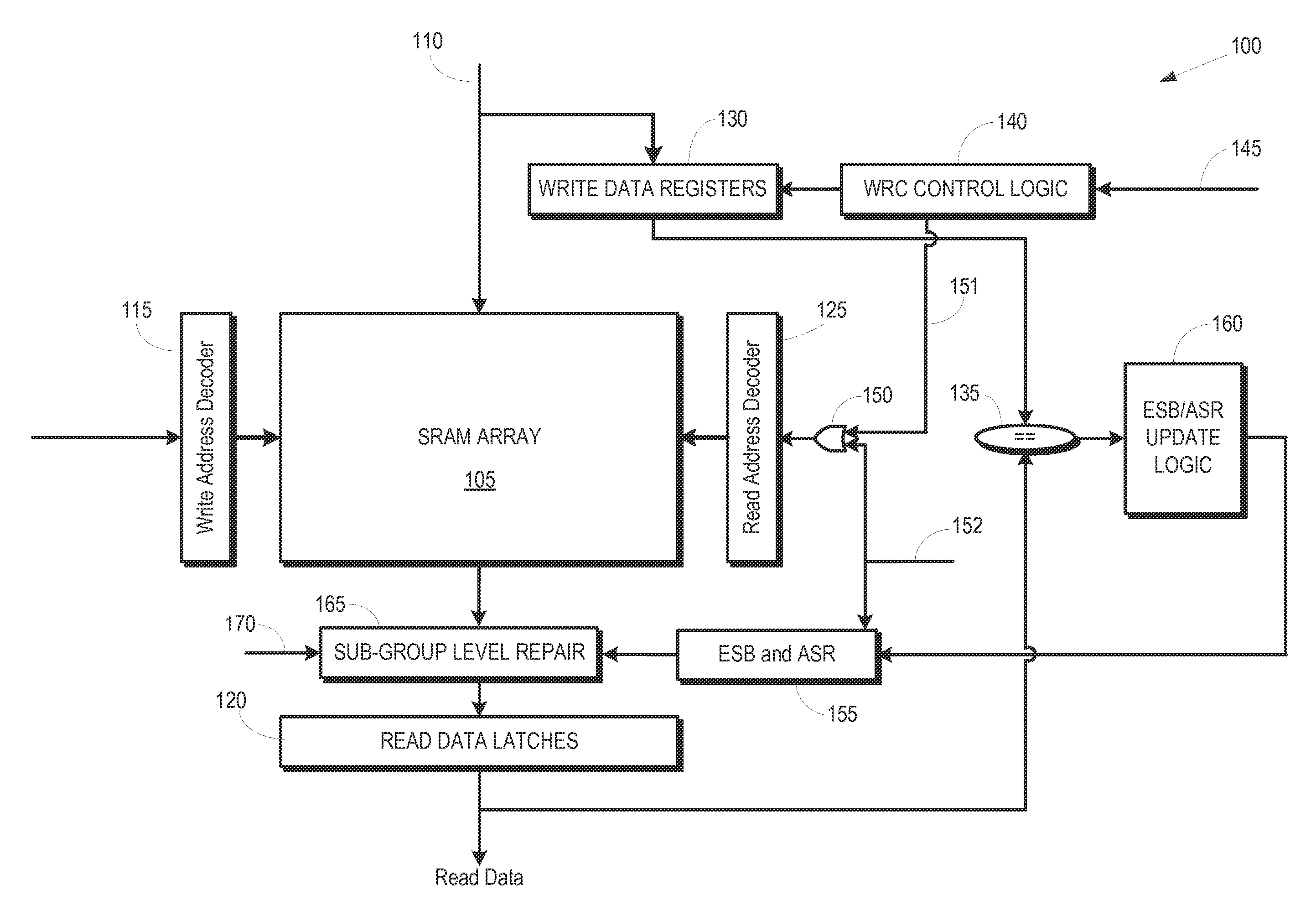
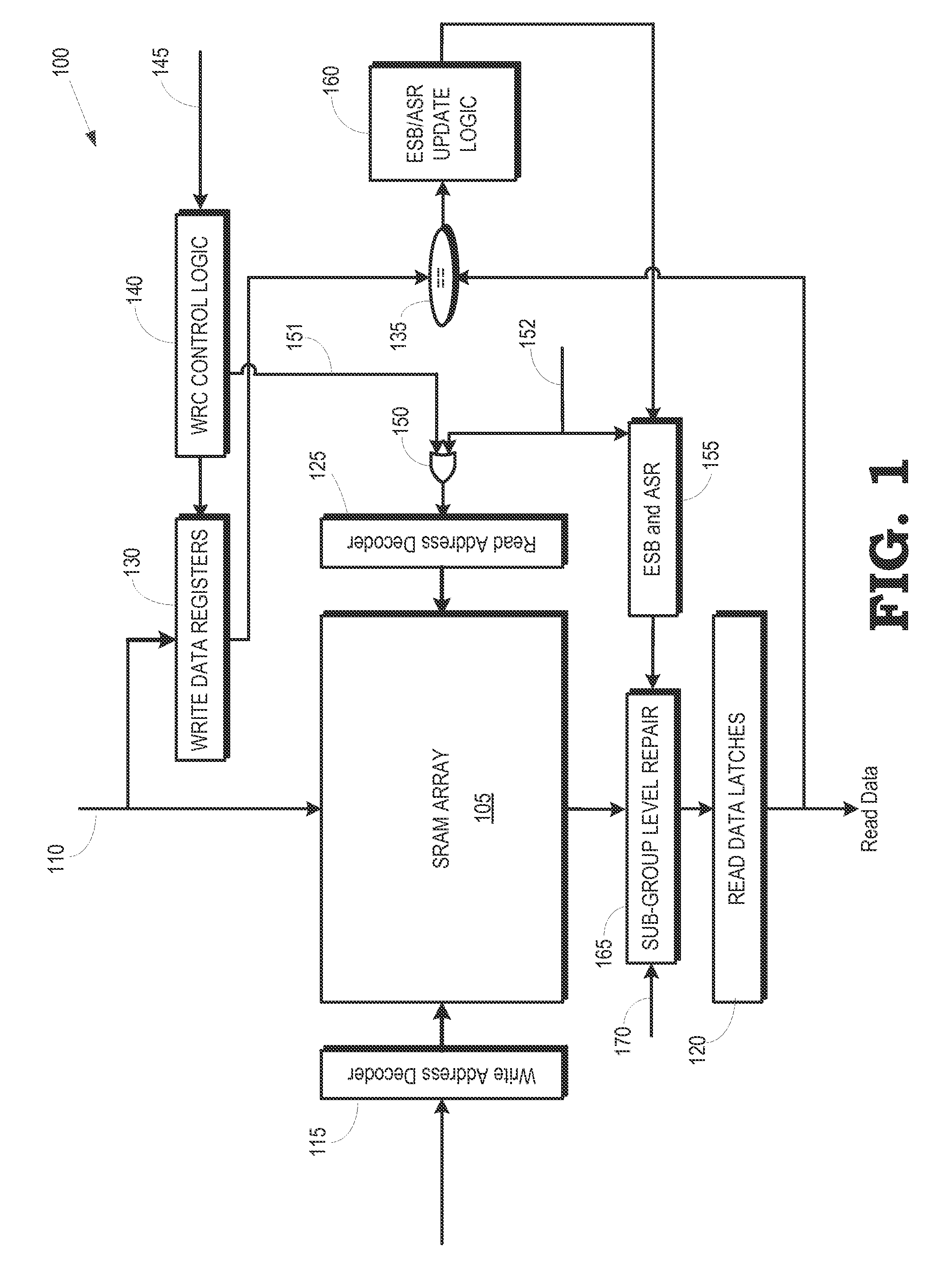
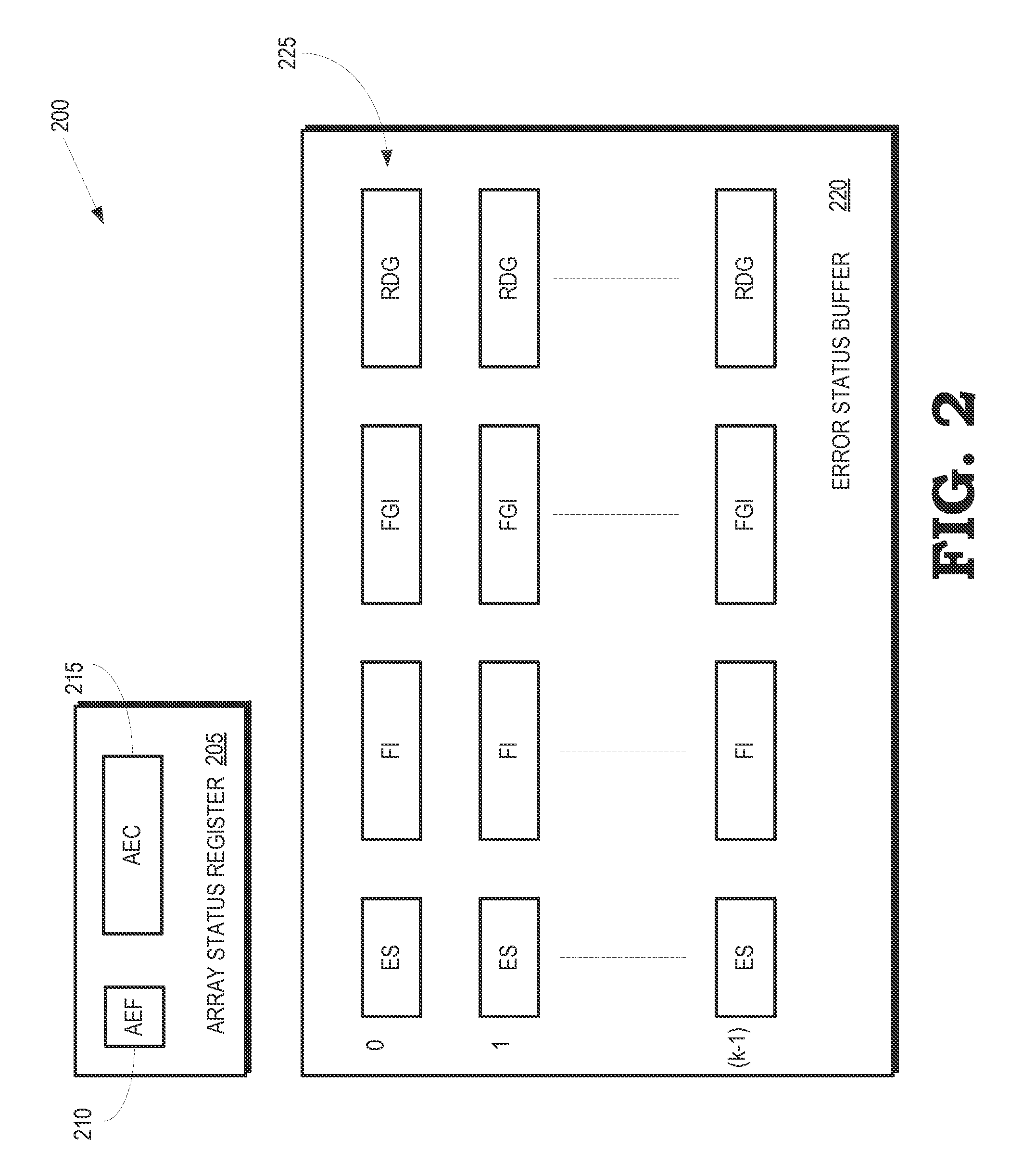
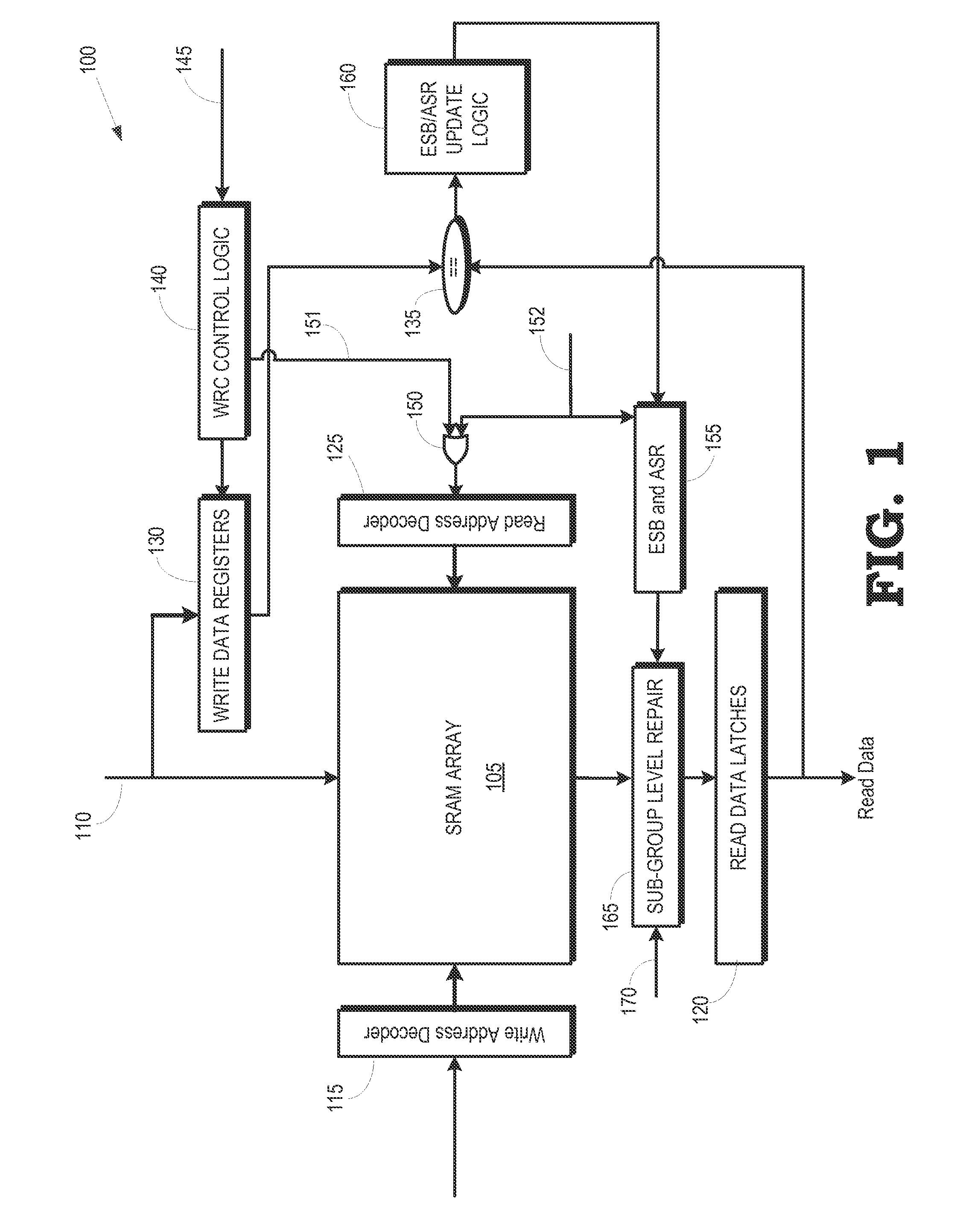
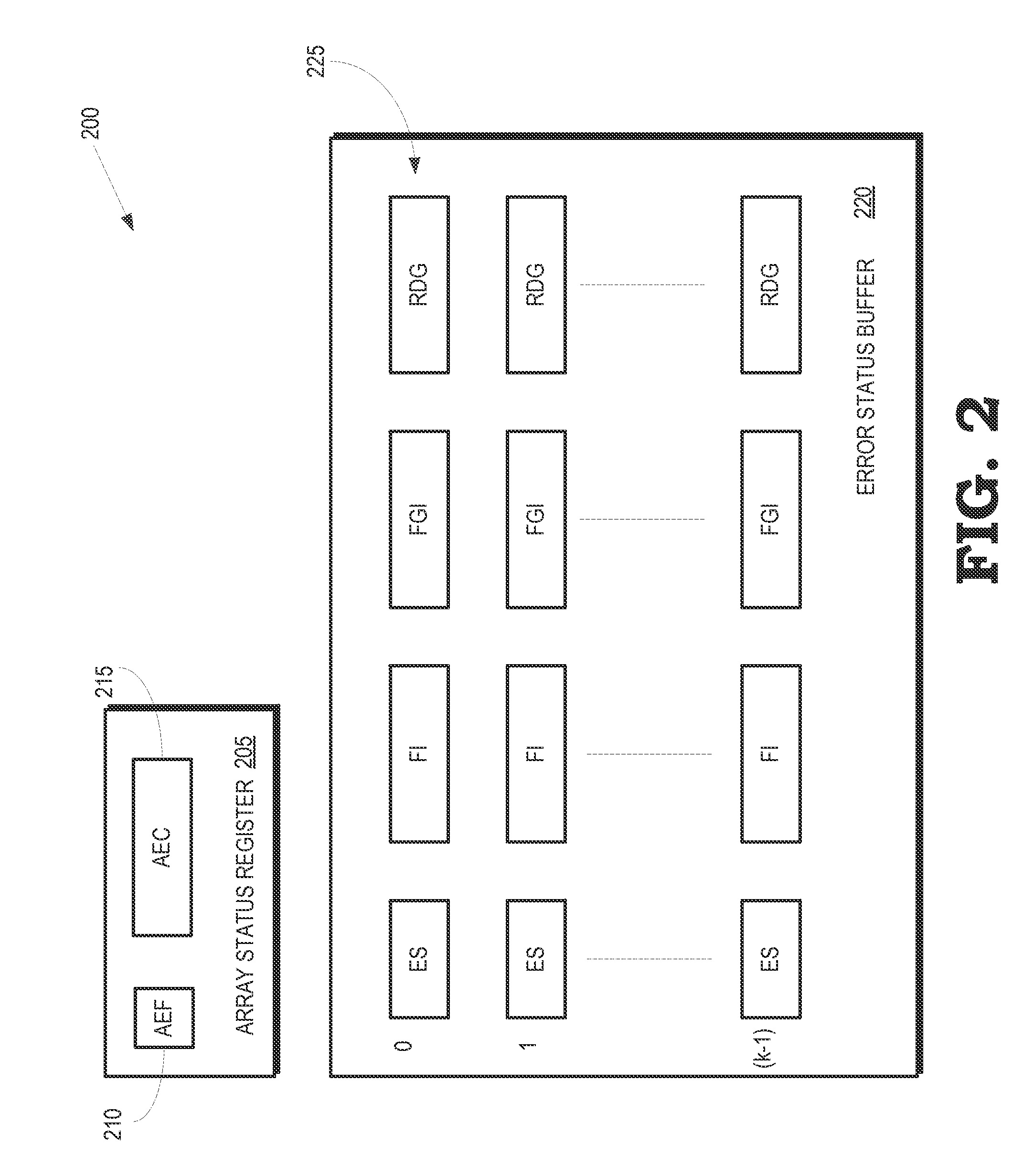
Detecting and correcting hard errors in a memory array
Hard errors in the memory array can be detected and corrected in real-time using reusable entries in an error status buffer. Data may be rewritten to a portion of a memory array and a register in response to a first error in data read from the portion of the memory array. The rewritten data may then be written from the register to an entry of an error status buffer in response to the rewritten data read from the register differing from the rewritten data read from the portion of the memory array.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and system for handling multiple bit errors to enhance system reliability
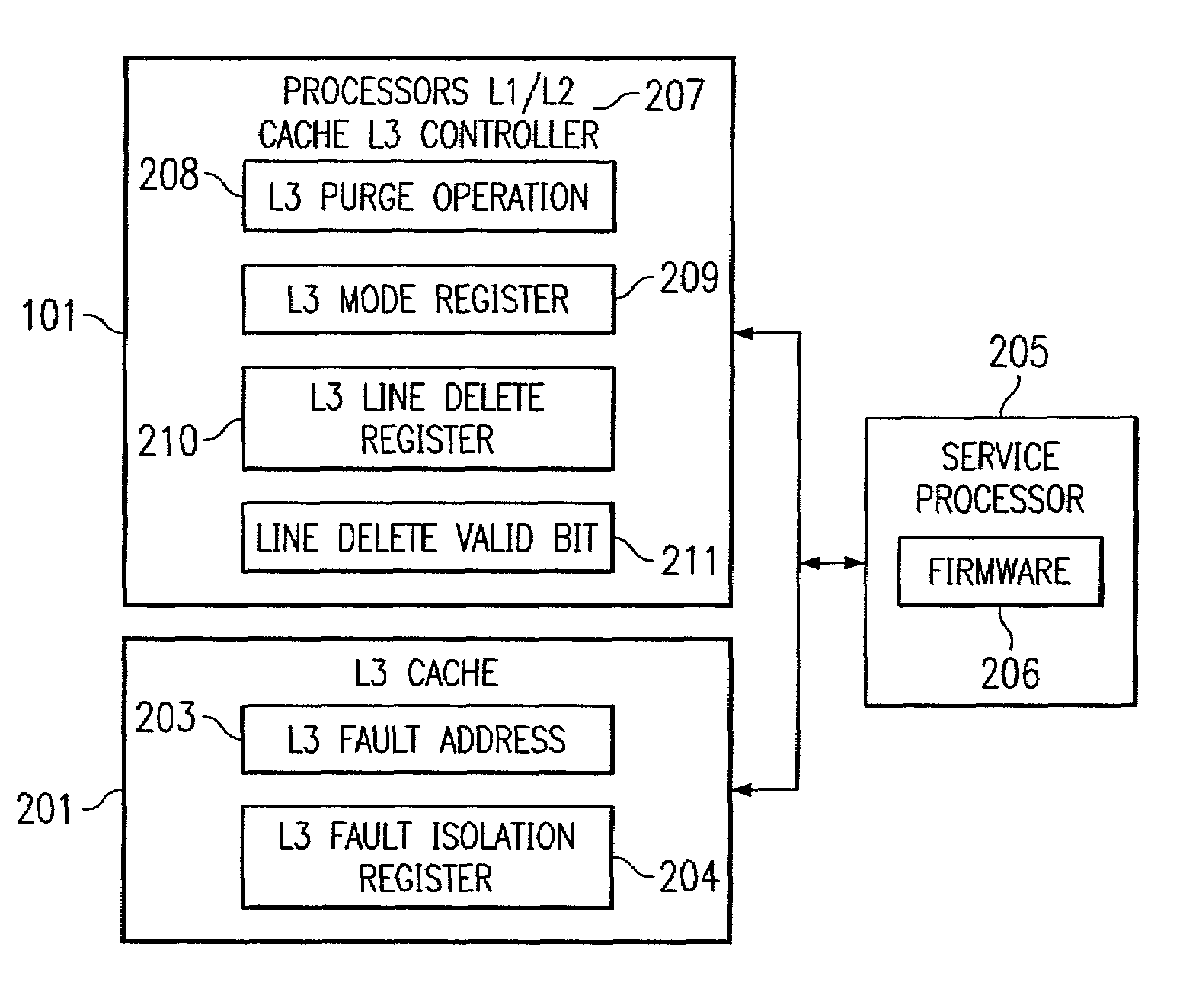
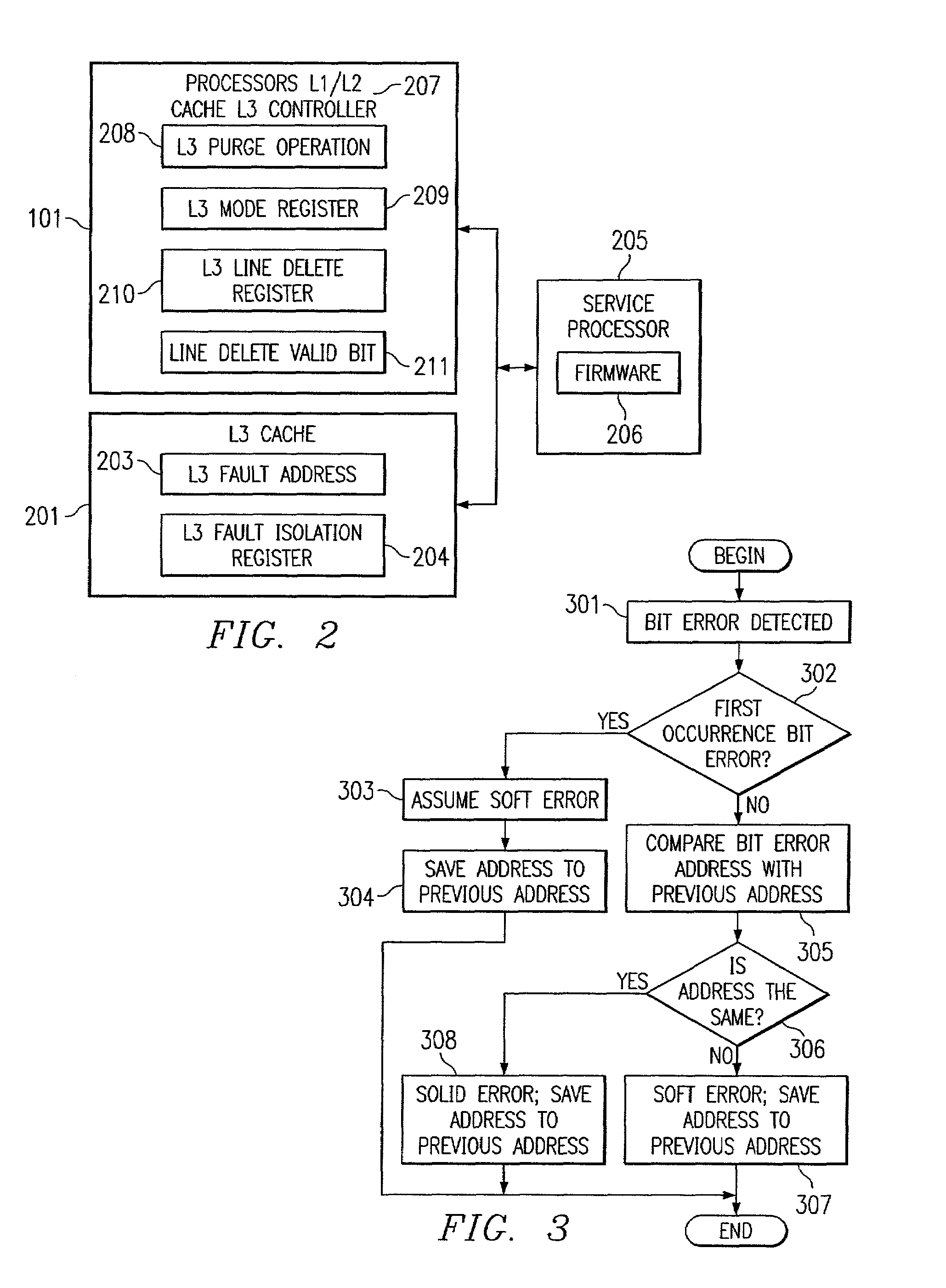
ActiveUS7007210B2Avoid downtimeNon-redundant fault processingStatic storageData processing systemParallel computing
The present invention provides an improved method, an system, and a set of computer implemented instructions for handling a cache containing multiple single-bit hard errors on multiple addresses within a data processing system. Such handles will prevent any down time by logging in the parts to be replaced by an operator when certain level of bit errors is reached. When a hard error exists on a cache address for the first time, serviceable first hard error, that cache line is deleted. Thus the damaged memory device is no longer used by the system. As a result, the system is running with “N−x” lines wherein “N” constitutes the total number of existing lines and “x” is less than “N”. An alternative method is to exchange the damaged memory device to a spare memory device. In order to provide such services, the system must first differentiate whether an error is a soft or hard error.
Owner:IBM CORP
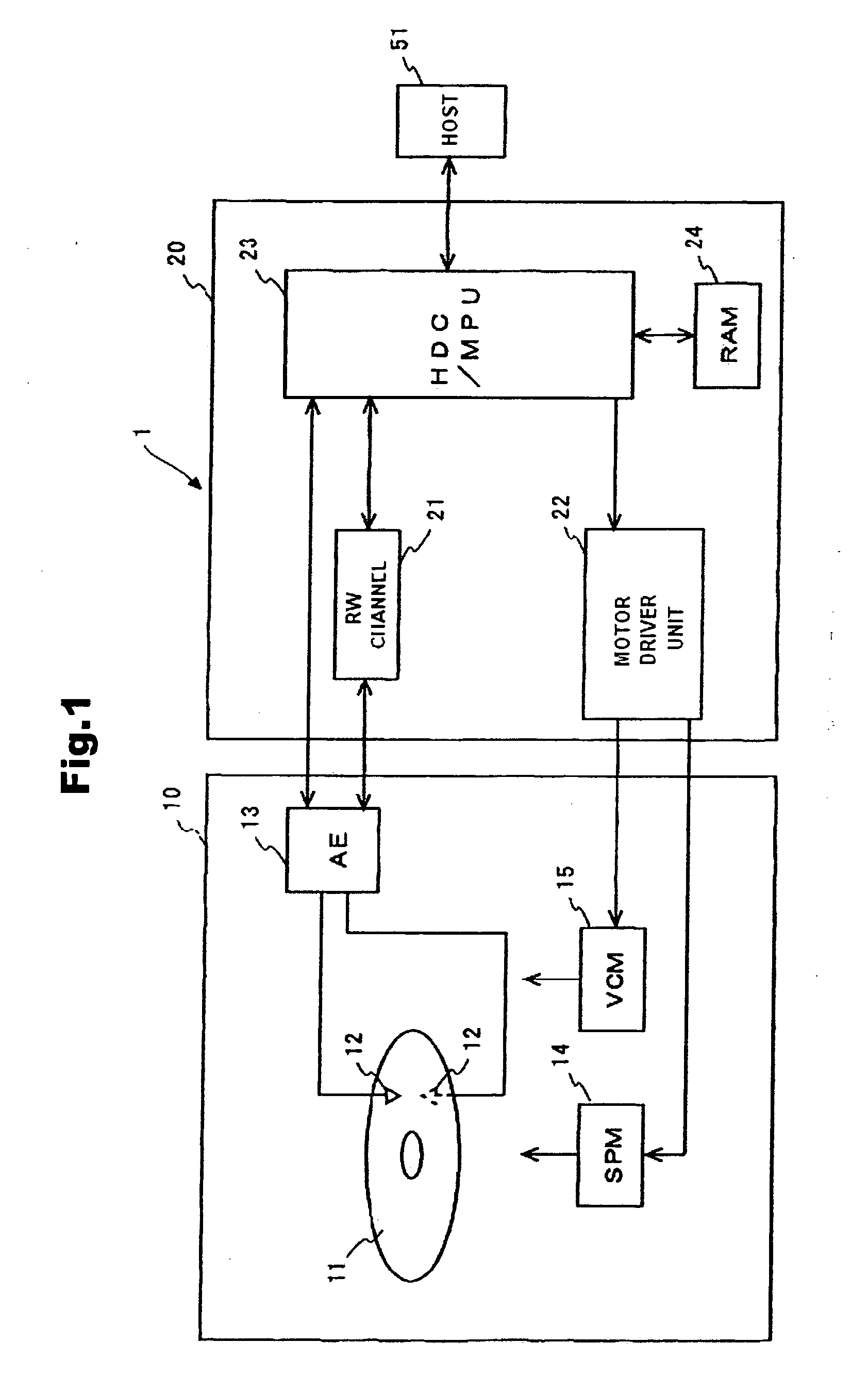
Disk drive device and data rewrite method thereof
ActiveUS20080239901A1Reduce generationCombination recordingRecord information storageHard disc driveHard error
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disabling portions of memory with defects
InactiveUS20090300413A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic storageParallel computingRemovable media
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fault isolation and availability mechanism for multi-processor system
A method and apparatus are provided for identifying a defective processor of a plurality of processors of a multi-processor system. In such method, a first command is submitted to a first processor and to a second processor within the multi-processor system. The first command is executed by each of the first and second processors. A first result of executing the first command by the first processor is compared with a second result of executing the second command by the second processor. A hard error is indicated when the first result does not match the second result. To further isolate a fault within the system, commands are submitted to different pairings of processors and the results are compared to isolate a faulty processor from among them.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7574648B2Prevent speedingReduced operating requirementsDigital storageHemt circuitsMiniaturization
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Detecting and correcting hard errors in a memory array
Hard errors in the memory array can be detected and corrected in real-time using reusable entries in an error status buffer. Data may be rewritten to a portion of a memory array and a register in response to a first error in data read from the portion of the memory array. The rewritten data may then be written from the register to an entry of an error status buffer in response to the rewritten data read from the register differing from the rewritten data read from the portion of the memory array.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
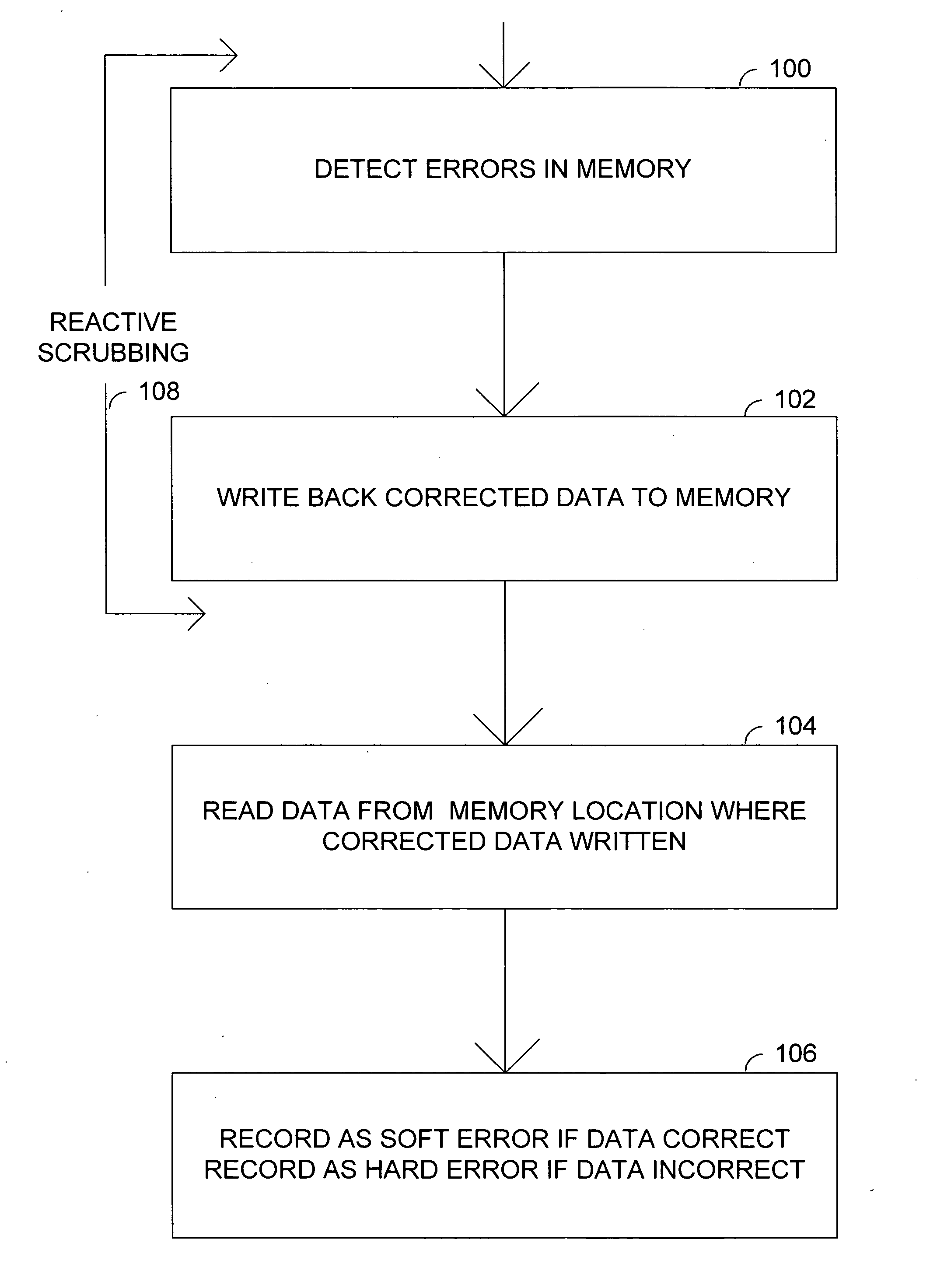
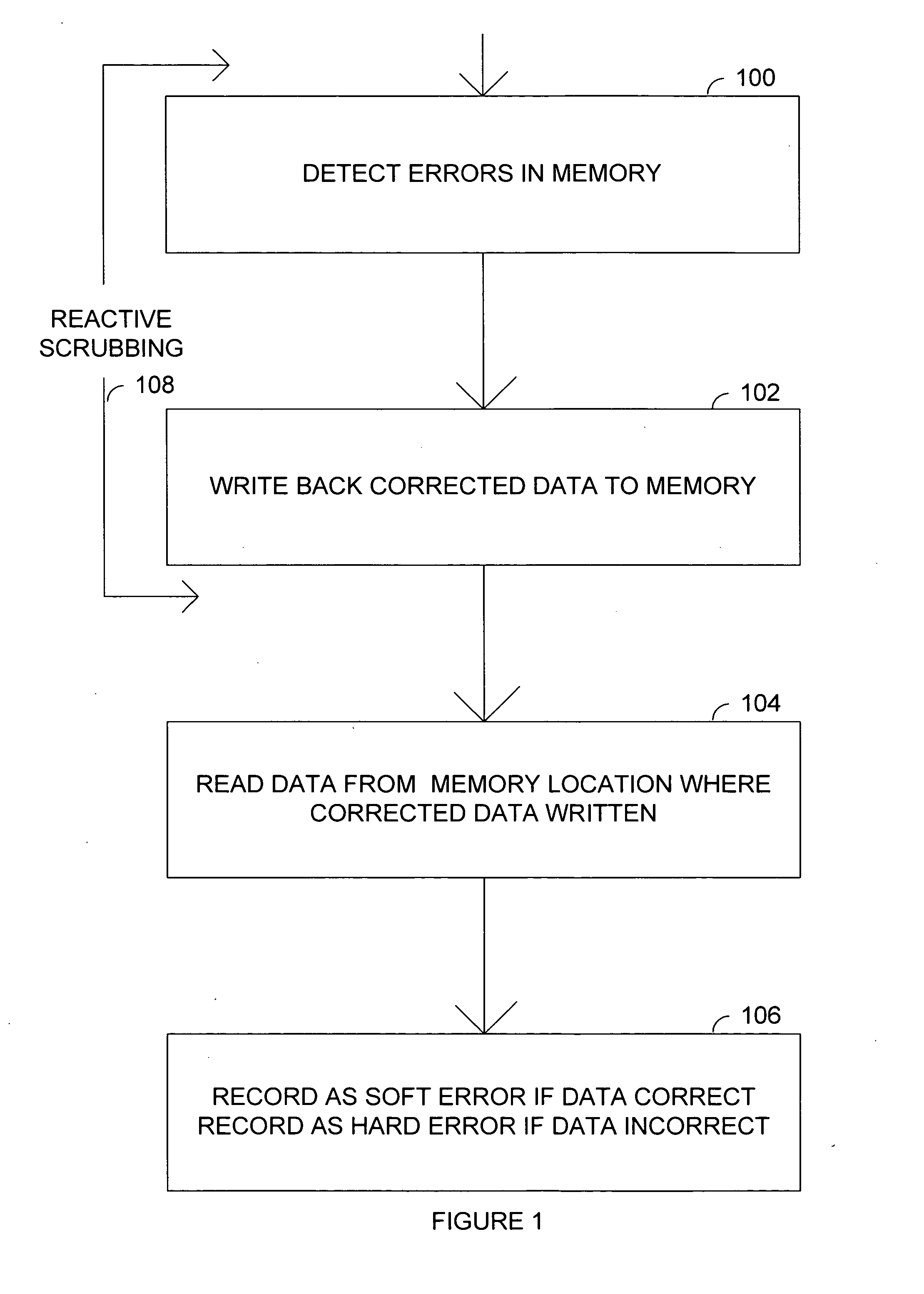
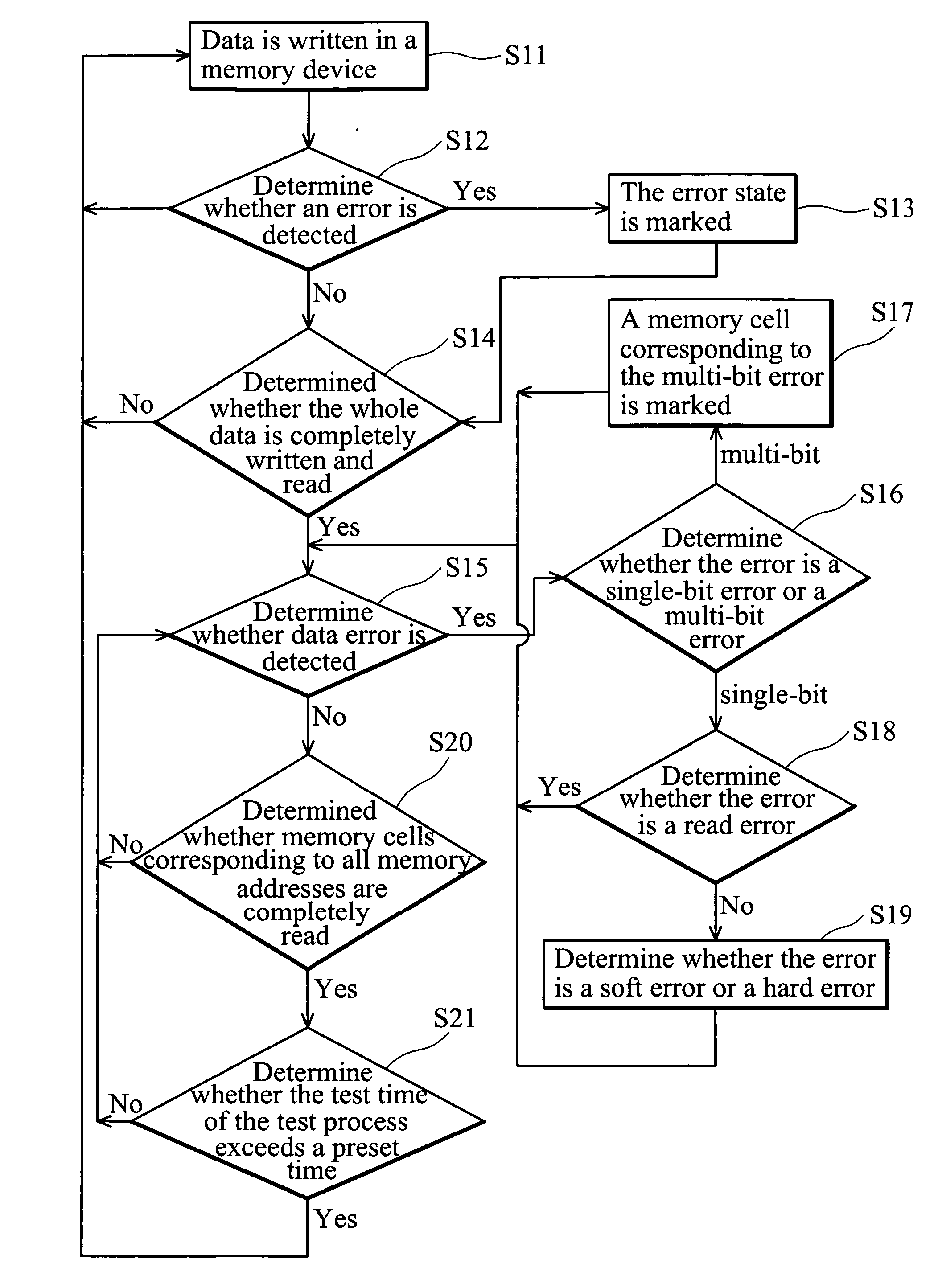
Determining hard errors vs. soft errors in memory
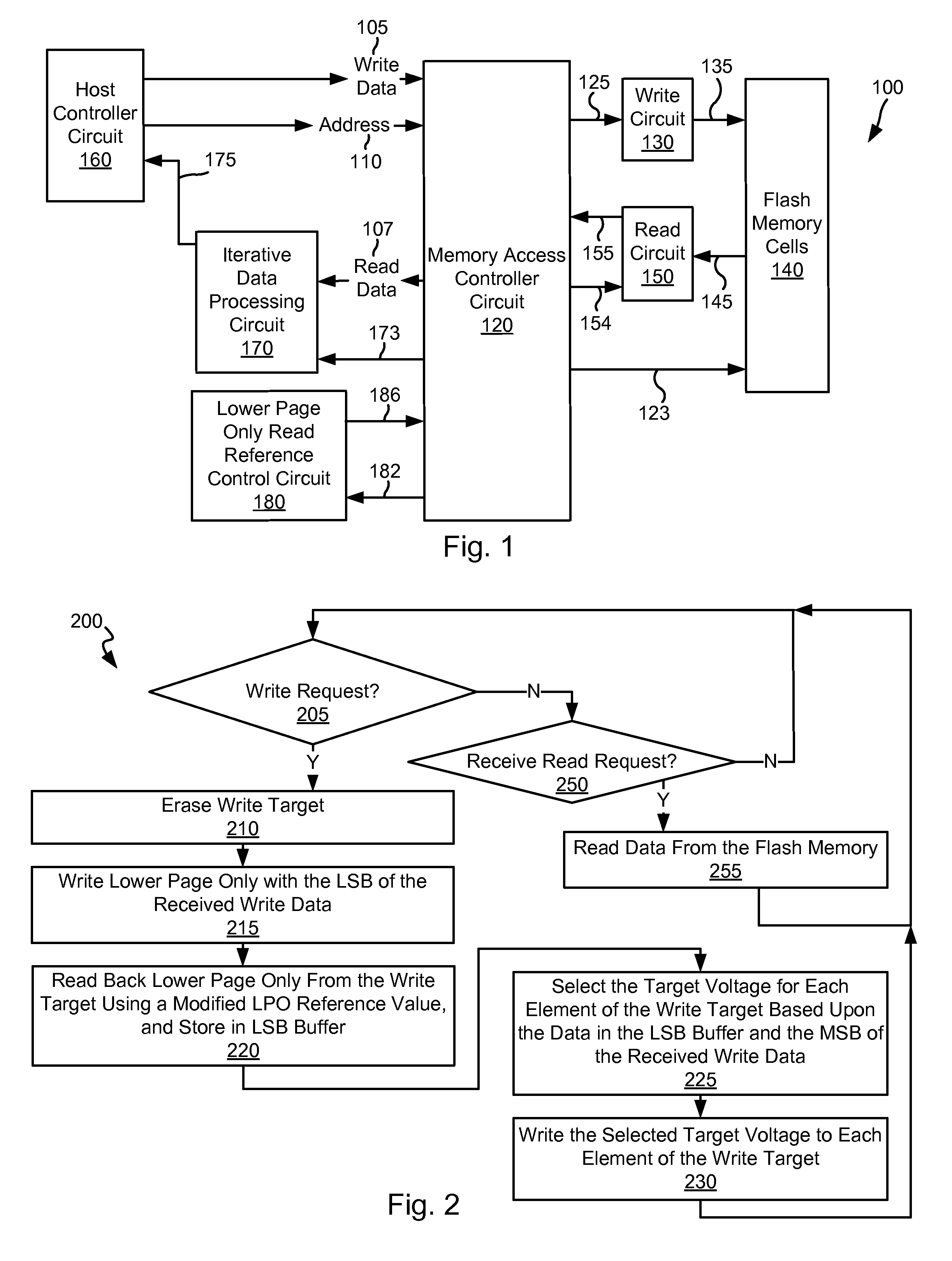
In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a method for determining soft and hard errors in memory. First one or more errors are detected in memory. Next correct data is written back to the memory locations were the error(s) were detected. Data is then read from the memory locations where the correct data was written. If the data that was read is correct, the memory locations where error(s) were detected are written to a register block indicating a soft error. If the data that was read is not correct, the memory locations where error(s) were detected are written to a register block indicating a hard error.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
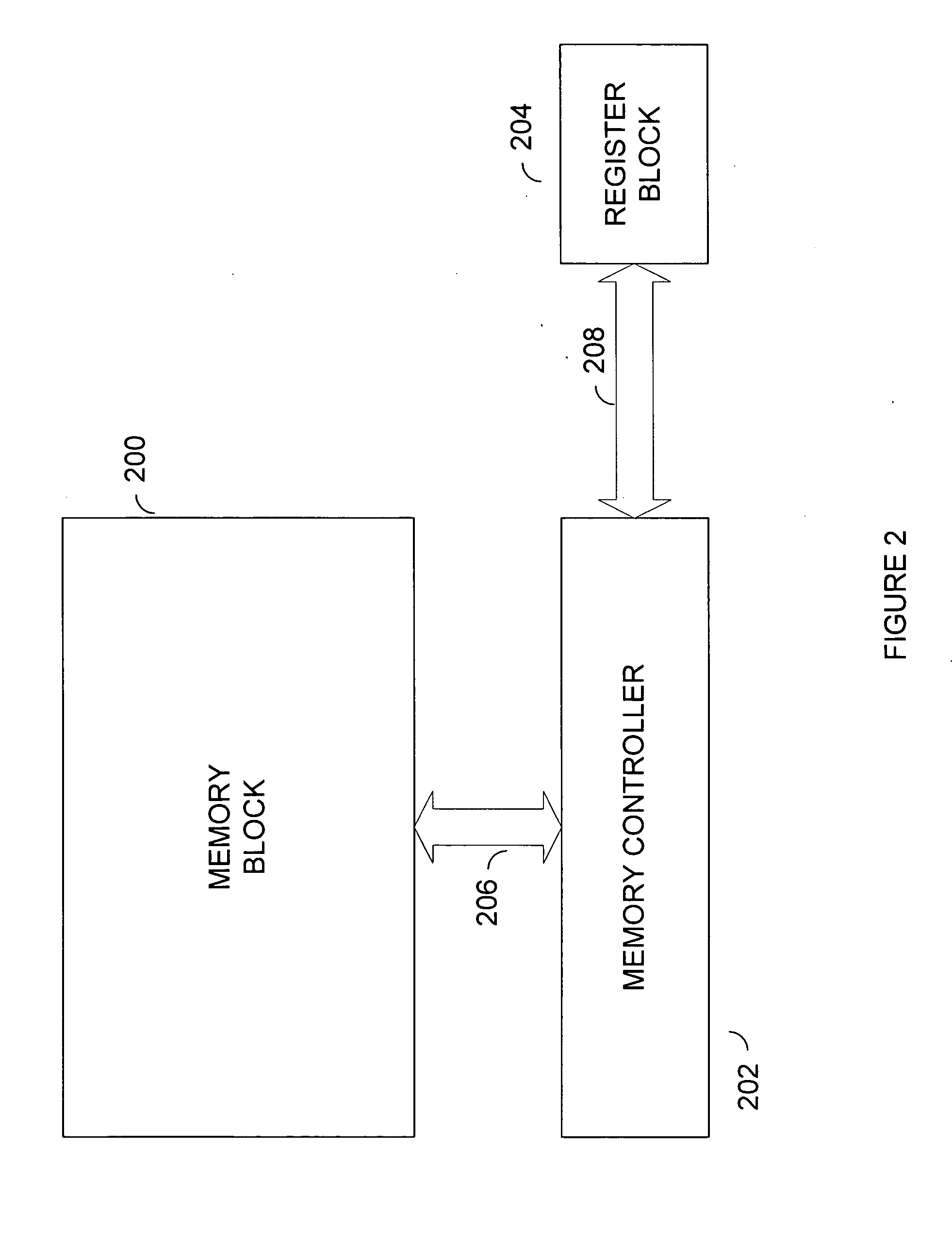
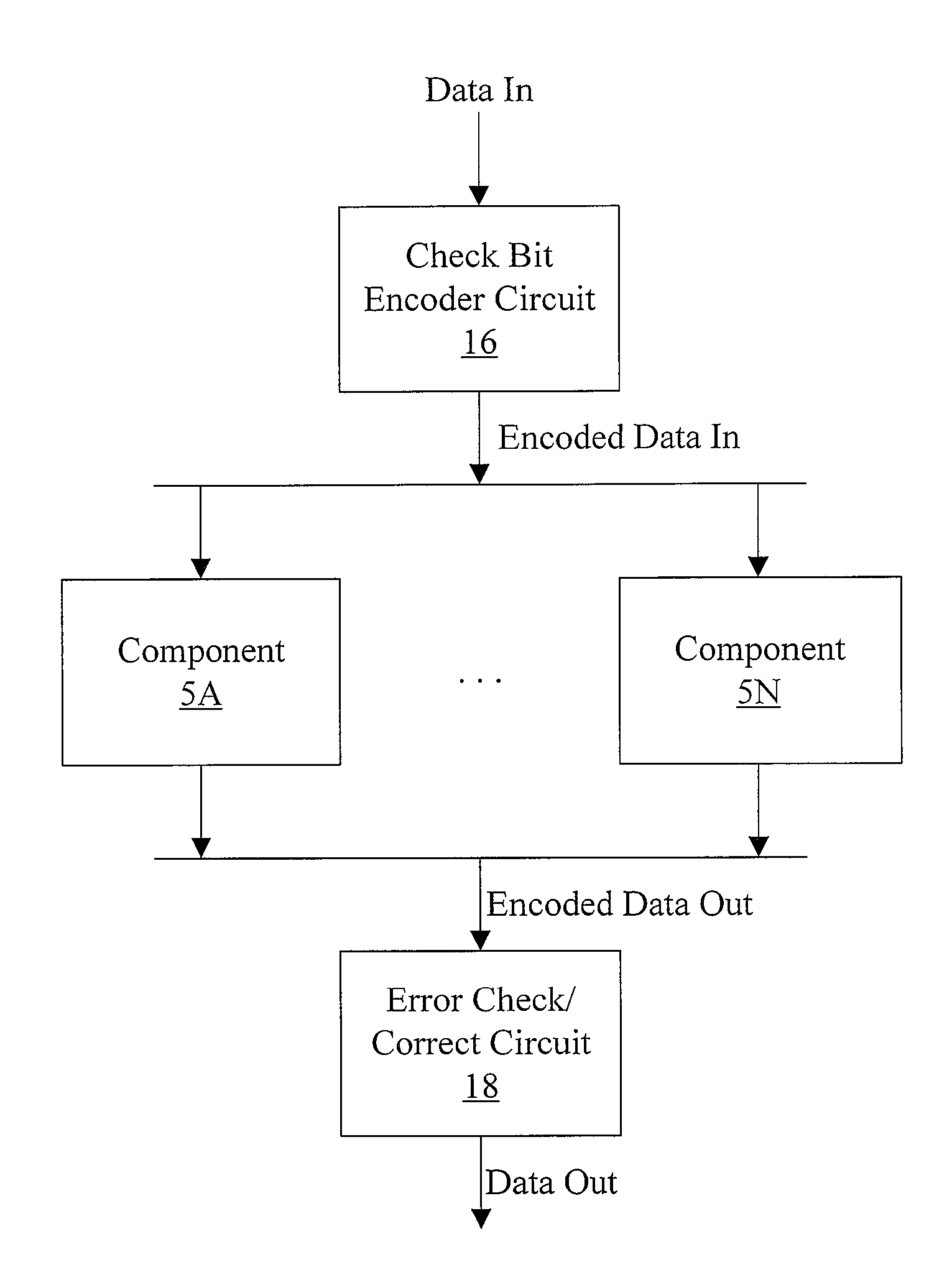
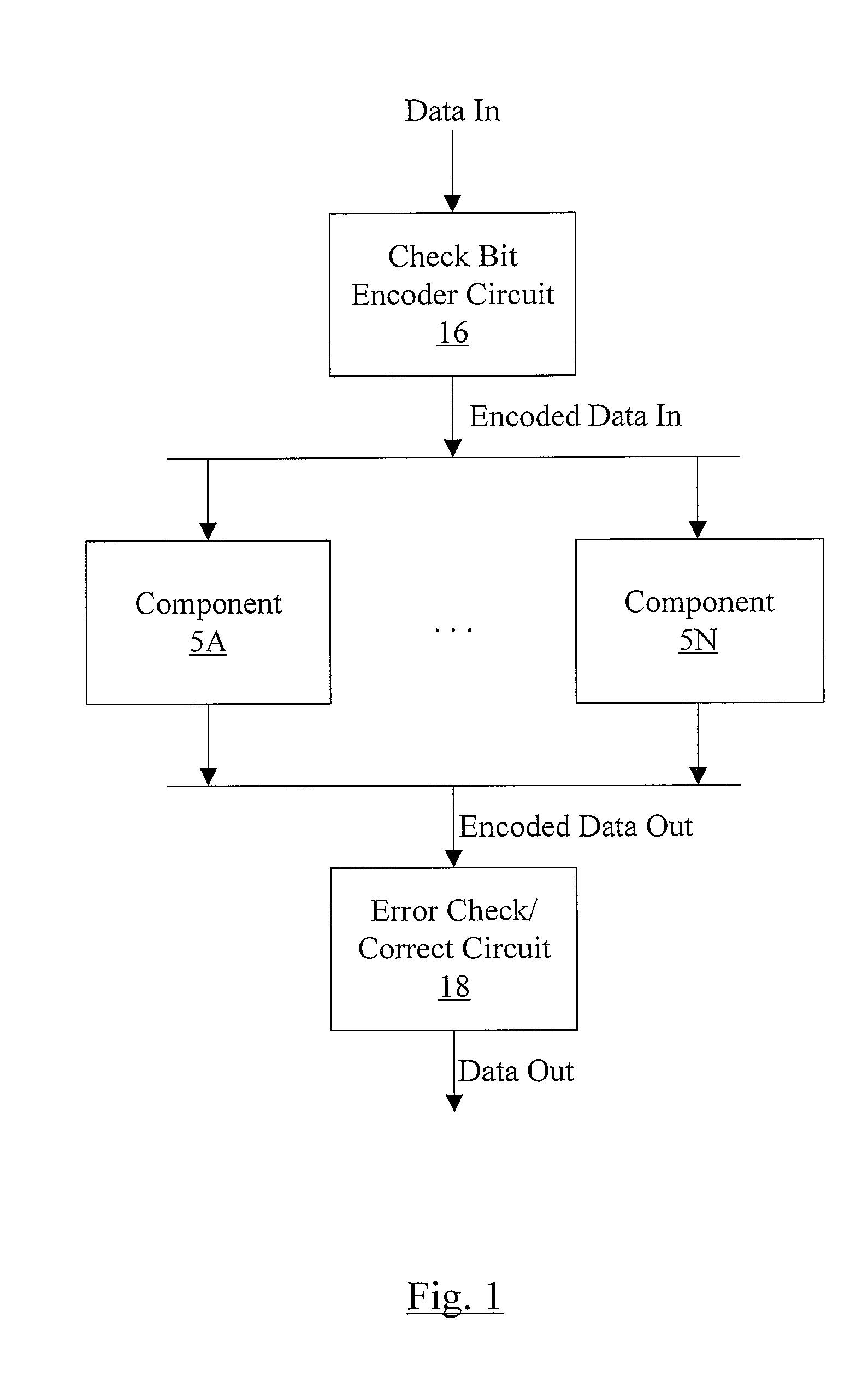
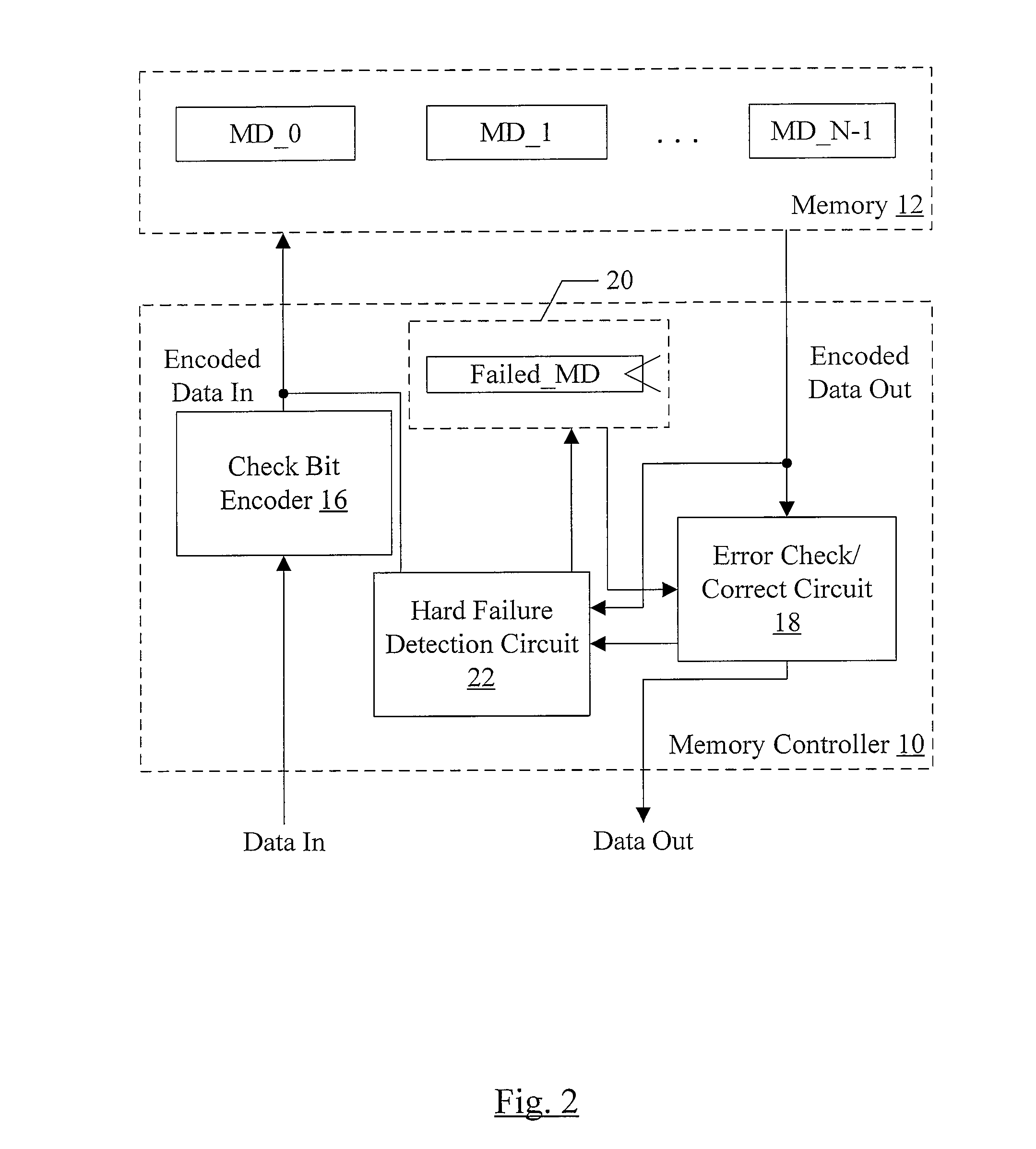
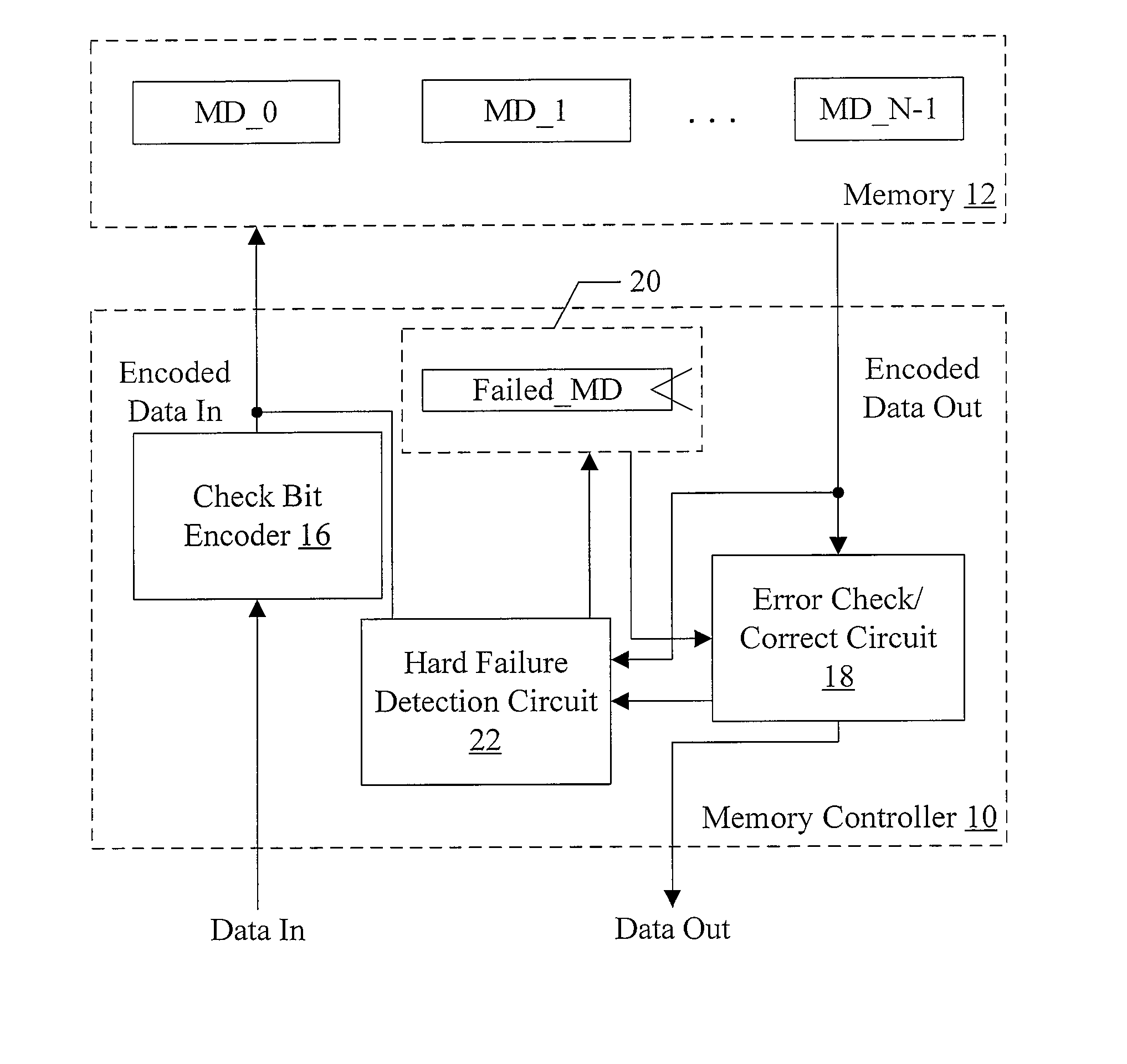
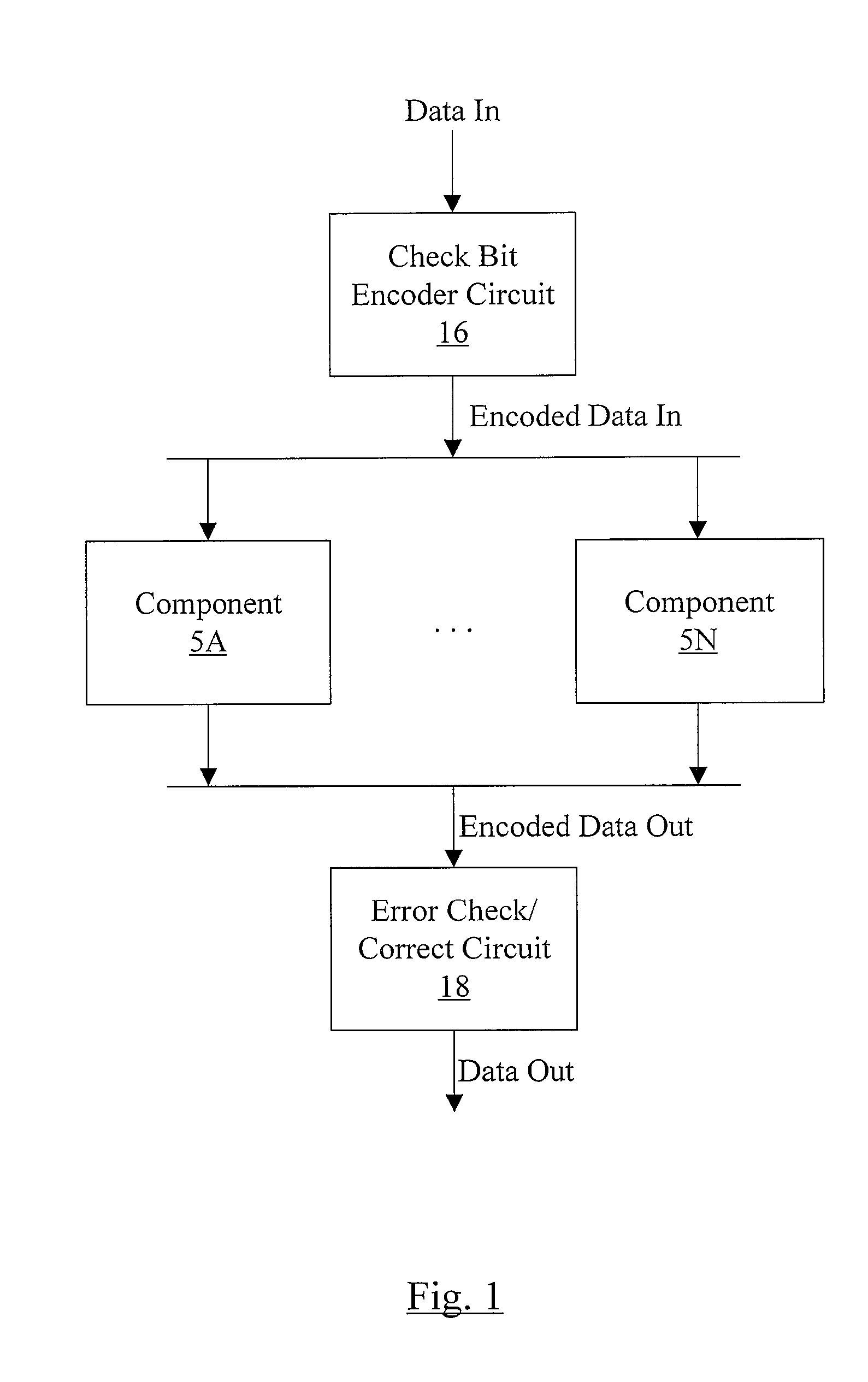
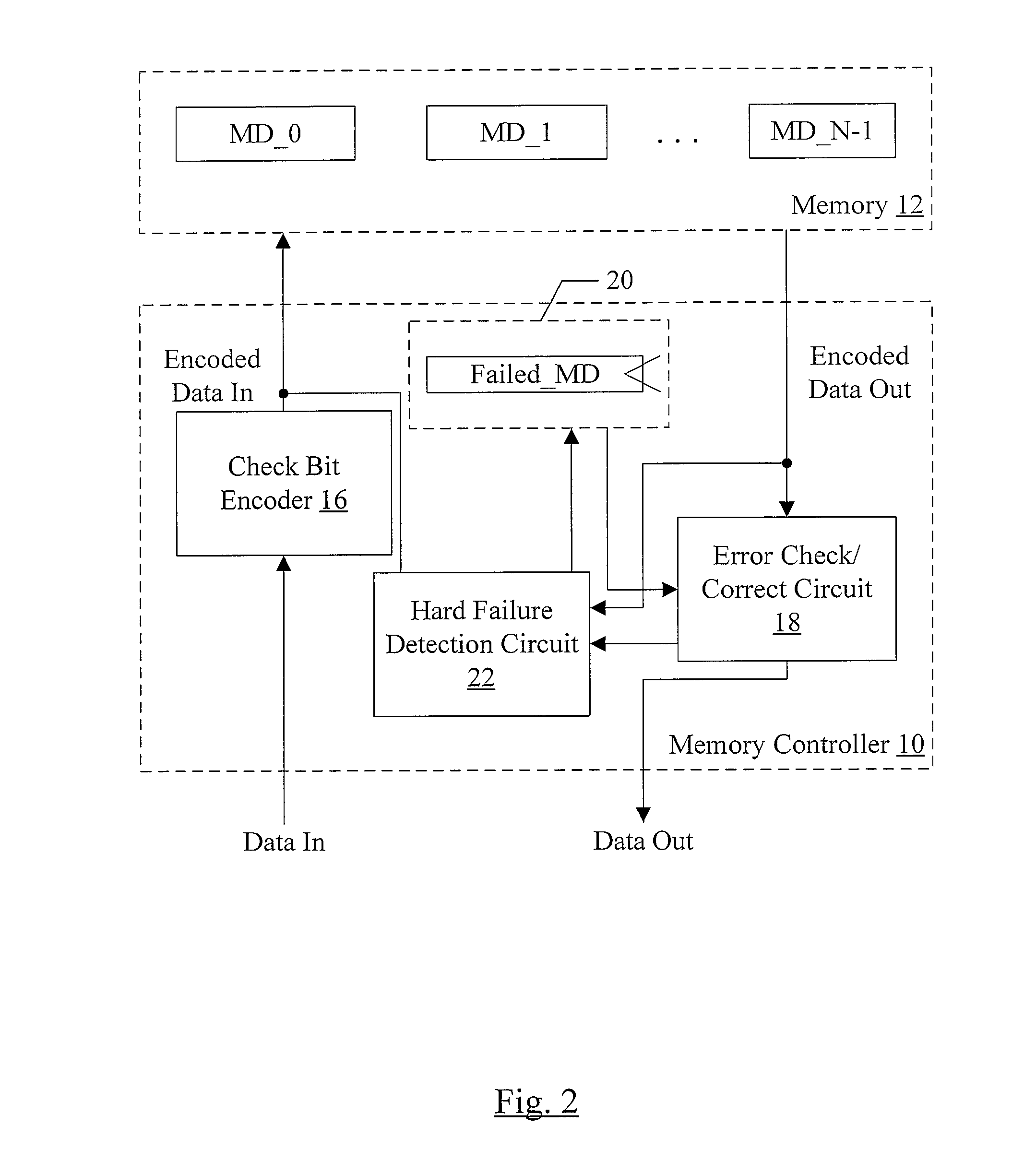
Hard Component Failure Detection and Correction
In one embodiment, a memory controller comprises a check bit encoder circuit coupled to receive a data block to be written to memory, a check / correct circuit coupled to receive an encoded data block read from the memory, and a hard failure detection circuit coupled to the check / correct circuit. The check bit encoder circuit is configured to generate a corresponding encoded data block comprising the data block, a first plurality of check bits, and a second plurality of check bits. The check / correct circuit is configured to detect an error in the encoded data block responsive to the first check bits, the second check bits, and the data block within the encoded data block, which is logically arranged as an array of R rows and N columns, wherein R and N are positive integers. Each of the first check bits covers a respective row of the array, and the check / correct circuit is configured to generate a first syndrome corresponding to the first plurality of check bits. A presence of more than one binary one in the first syndrome indicates a multi-bit error. Responsive to detecting the multi-bit error, the hard failure detection circuit is configured to perform a plurality of memory read / write operations to the memory locations in which the encoded data block is stored to identify a hard error failure in the memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
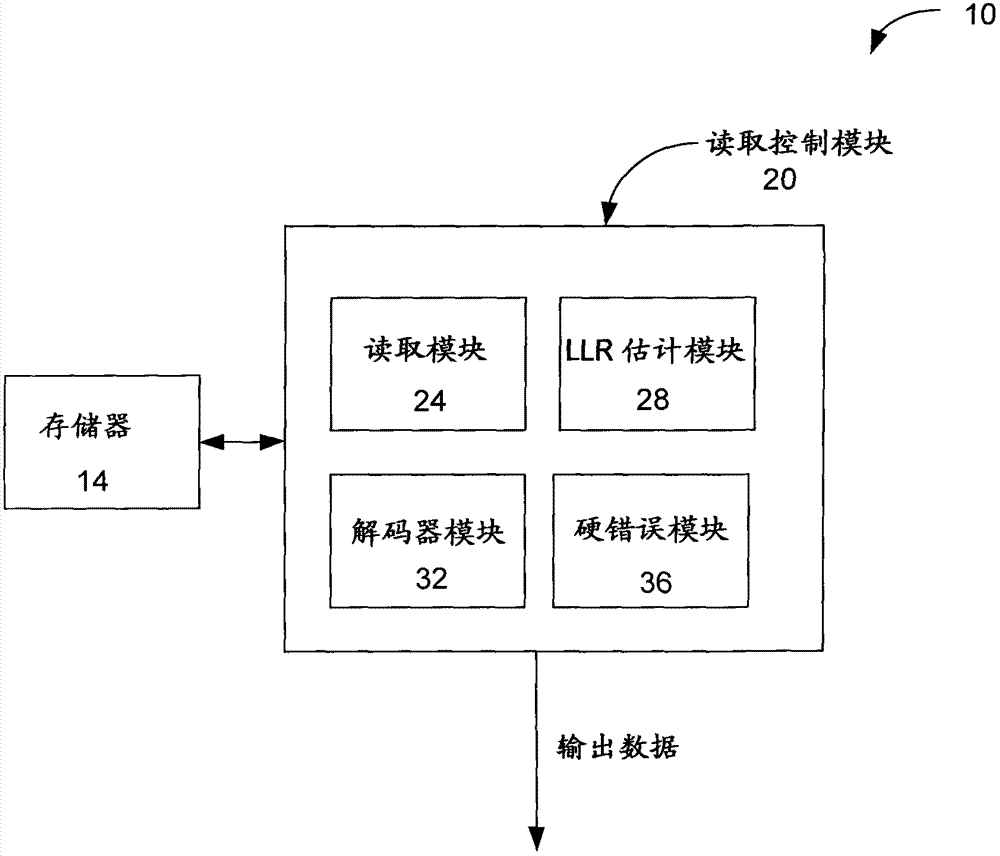
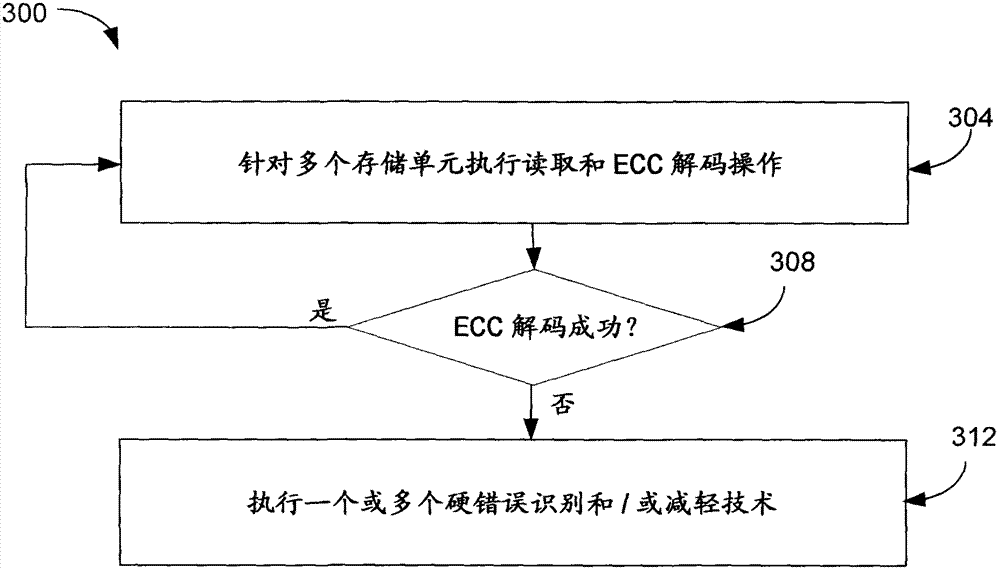
Identification and mitigation of hard errors in memory systems
InactiveCN102820064AOther decoding techniquesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareLog likelihood
The invention relates to dentification and mitigation of hard errors in memory systems. Embodiments provide a method comprising estimating a first set of log-likelihood ratio (LLR) values for a plurality of memory cells of a memory; based on the first set of LLR values, performing a first error correcting code (ECC) decoding operation; in response to determining a failure of the first ECC decoding operation, generating, by adjusting the first set of LLR values, a second set of LLR values for the plurality of memory cells; and based on the second set of LLR values, performing a second ECC decoding operation.
Owner:MARVELL WORLD TRADE LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060200727A1Highly-integratedReduced operating requirementsDigital storageDevice materialMiniaturization
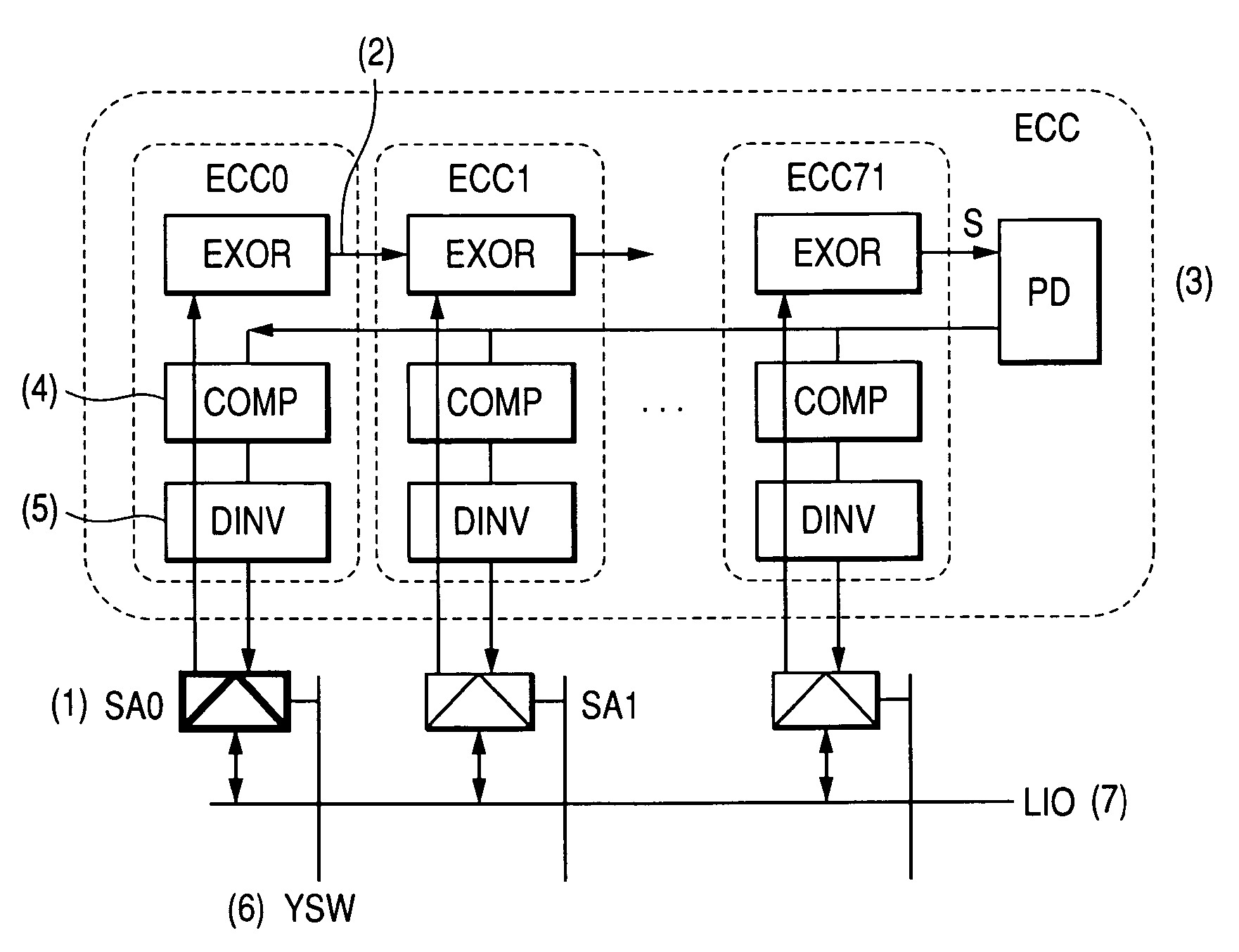
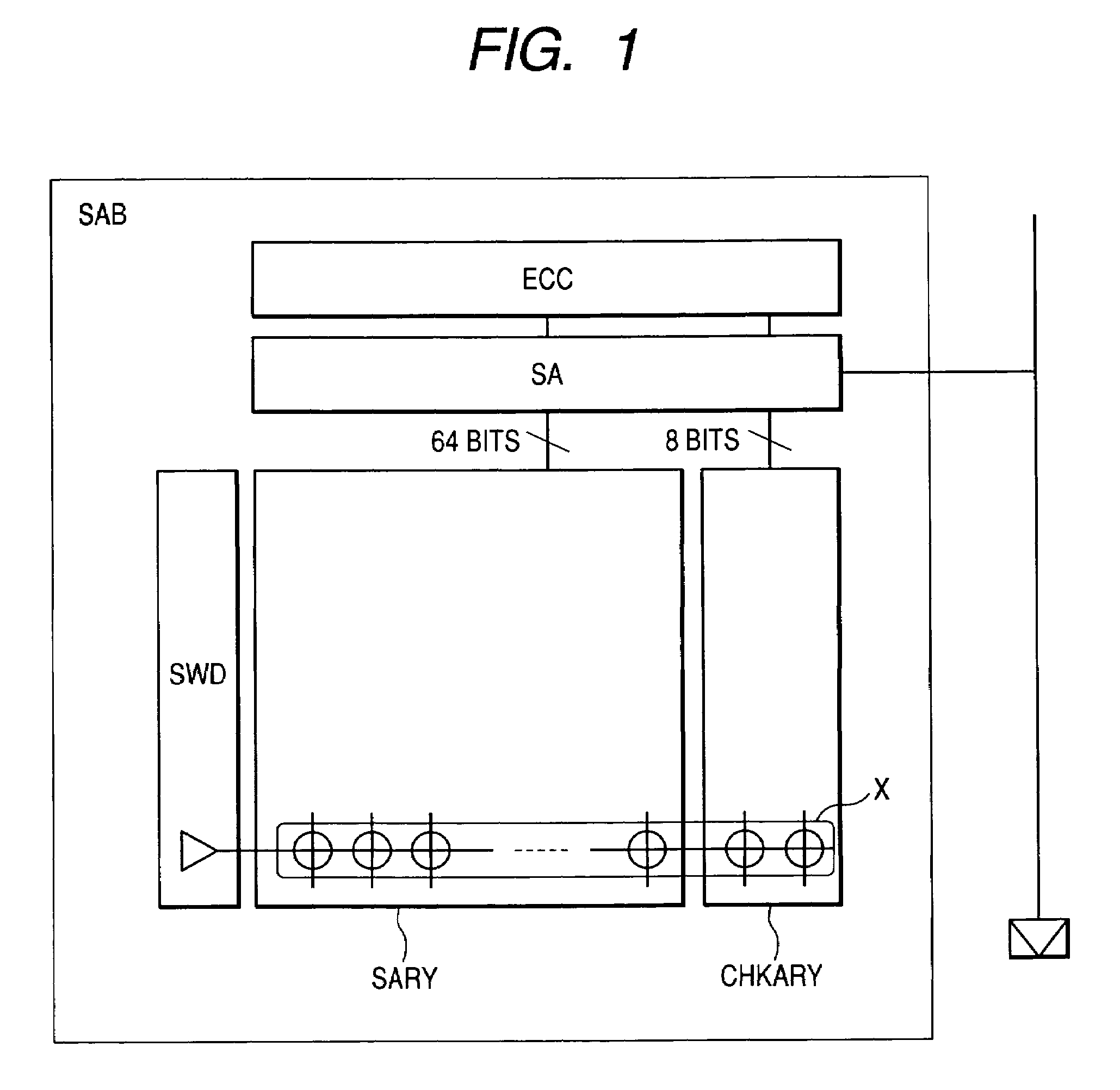
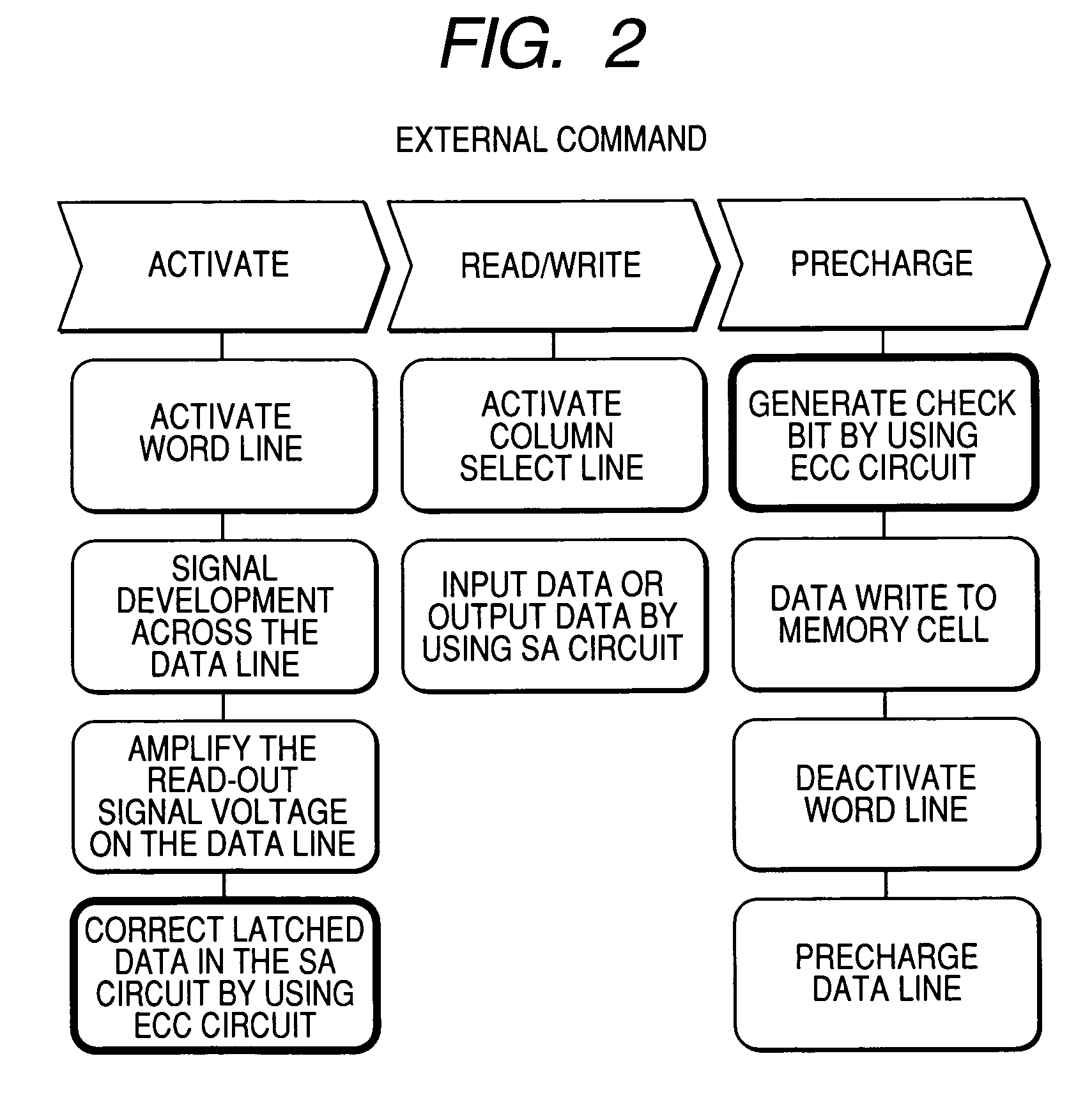
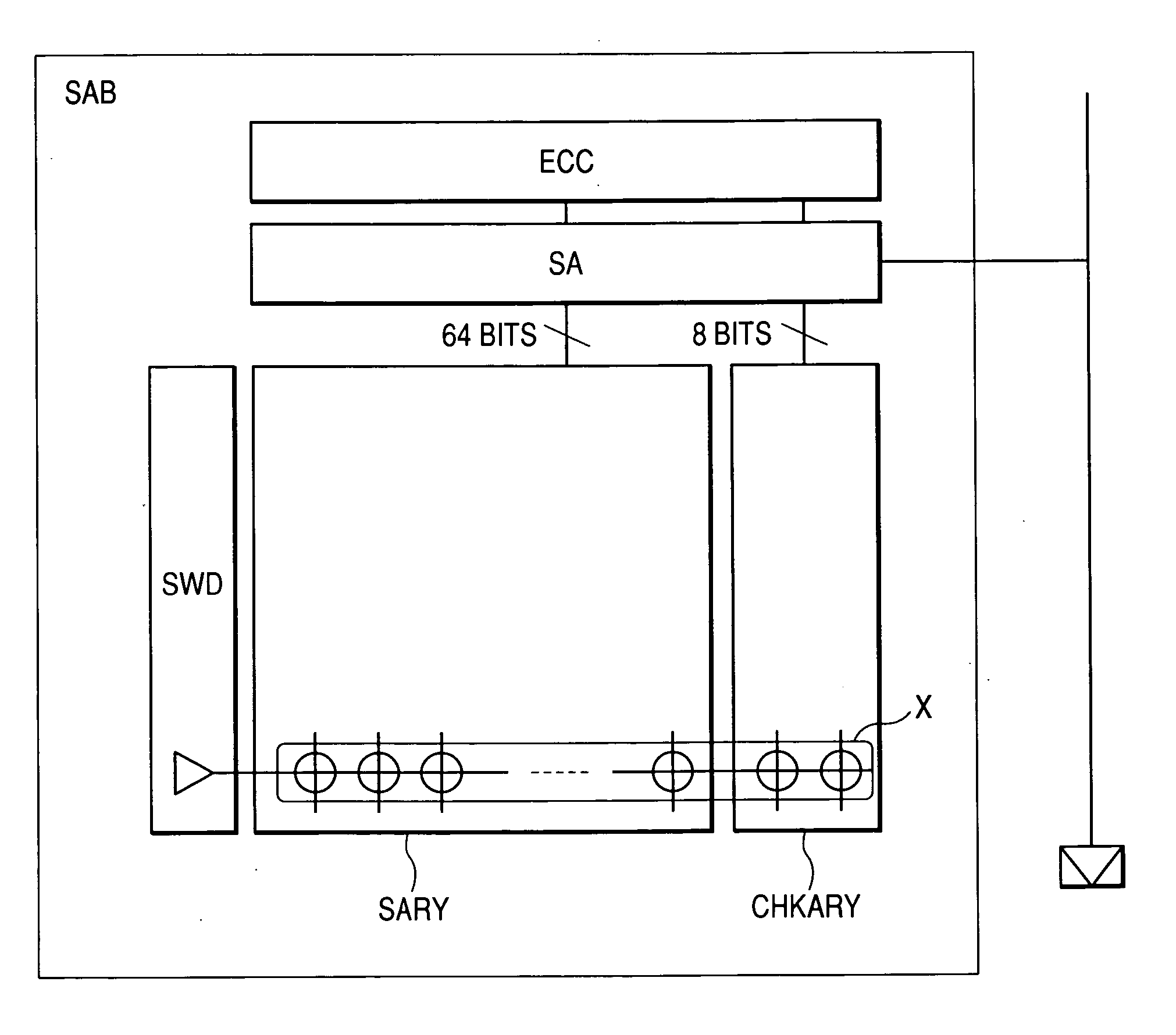
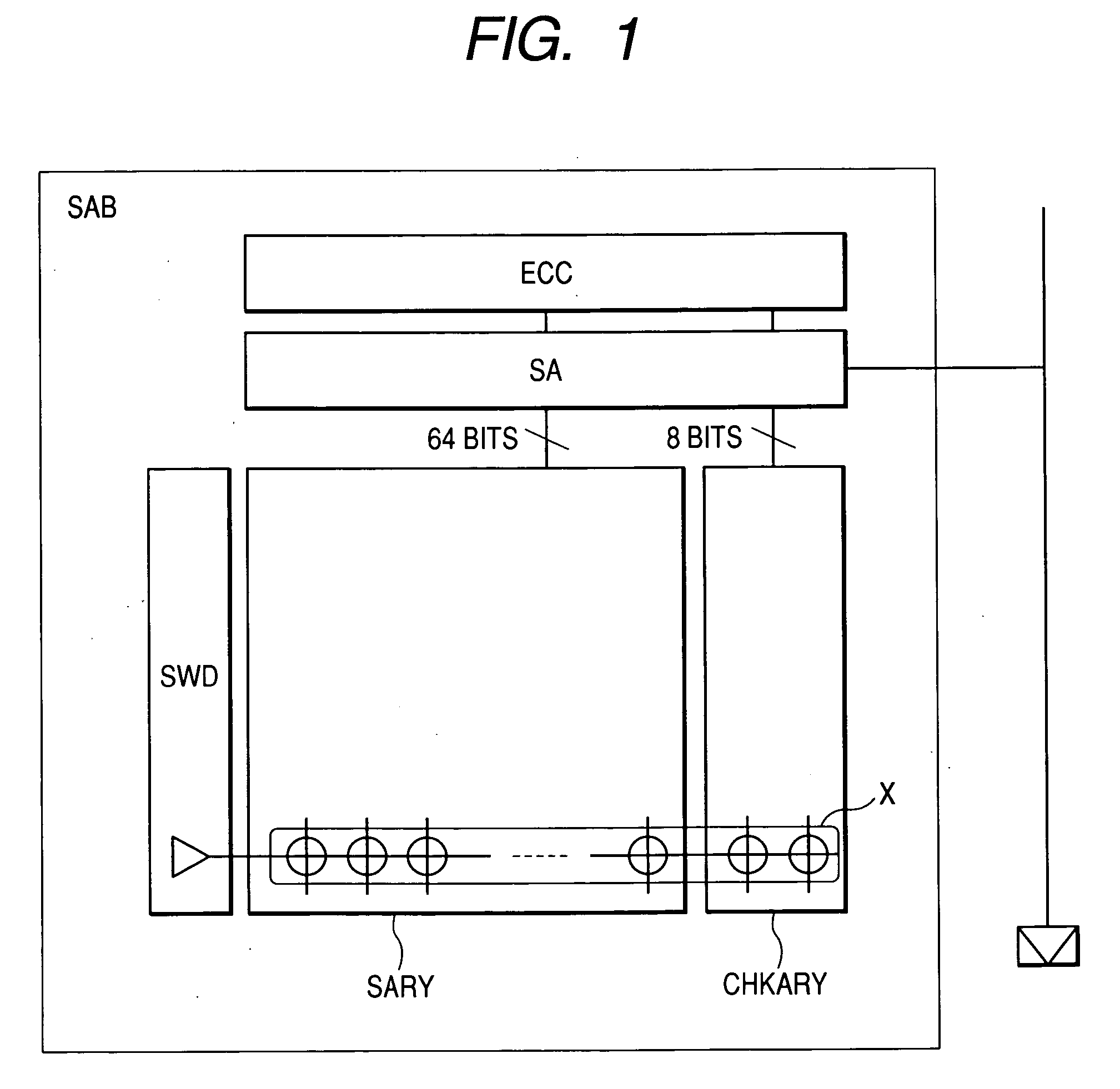
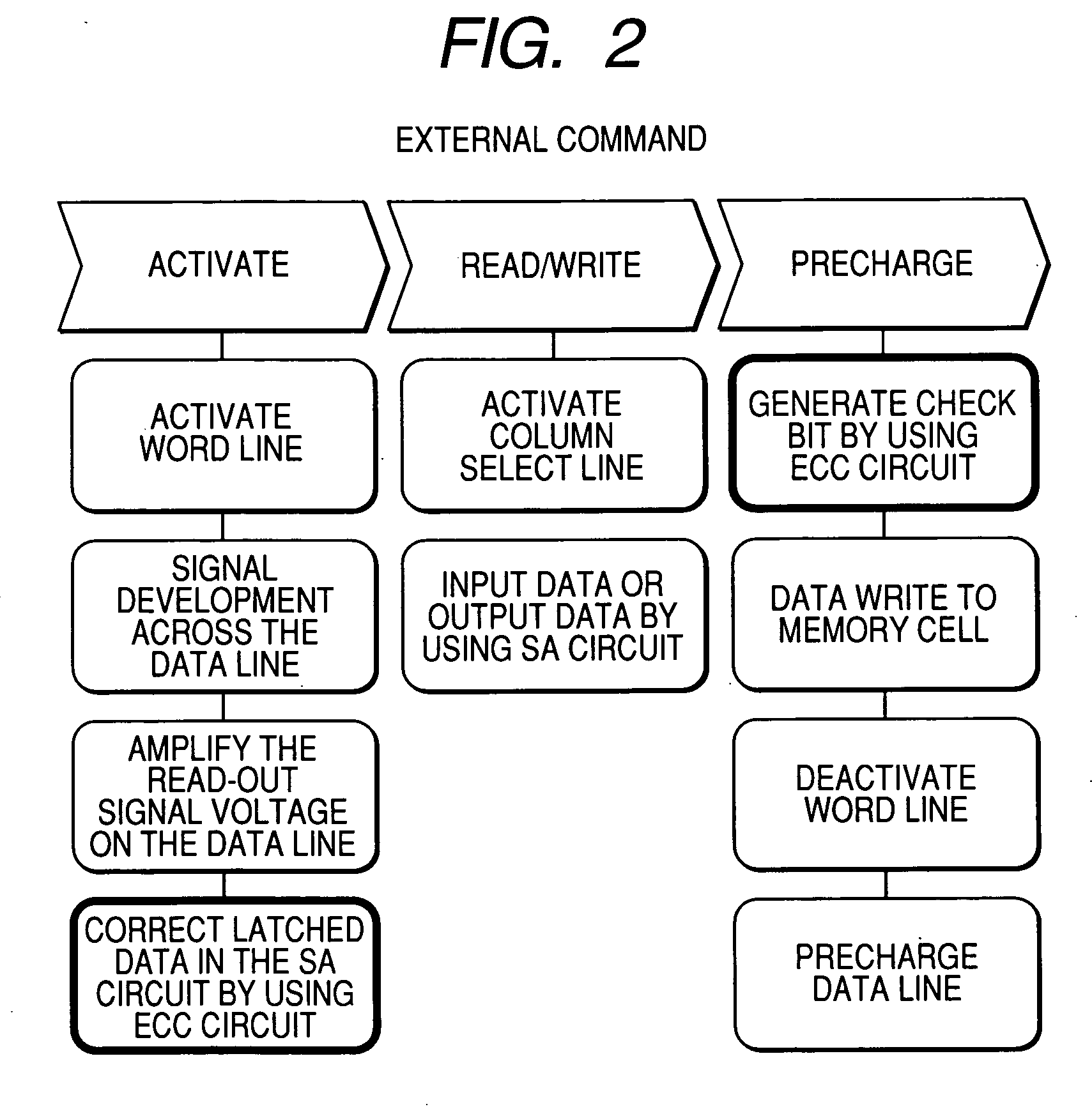
When the miniaturization of a DRAM advances, the capacity of a cell capacitor decreases, and further the voltage of a data line is lowered, the amount of read signals remarkably lowers, errors are produced during readout, and the yield of chips lowers. To solve the above problems, the present invention provides a DRAM that: has an error correcting code circuit for each sub-array; detects and corrects errors with said error correcting code circuit in both the reading and writing operations; and further has rescue circuits in addition to said error correcting code circuits and replaces a defective cell caused by hard error with a redundant bit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Single particle effect detection method and system
The present invention relates to a single particle effect detection method and system. The method comprises: reading storage information of addresses of components to be detected under irradiation of a first particle beam, generating first read information, comparing the first read information with first preset data, and generating first specific information; if it is judged, according to the first specific information, that the components to be detected are subjected to single particle flipping or a single particle hard error, reading storage information of addresses of the components to be detected under irradiation of a second particle beam, generating second read information, comparing the second read information with second preset data, and generating second specific information; and if it is judged, according to the second specific information, that the components to be detected are subjected to single particle flipping or a single particle hard error, judging that the signal particle flipping or the single particle hard error of the components to be detected is not caused by a peripheral circuit instant-state pulse. According to the present invention, correlation between the single particle effect and the peripheral circuit can be rapidly and accurately detected.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
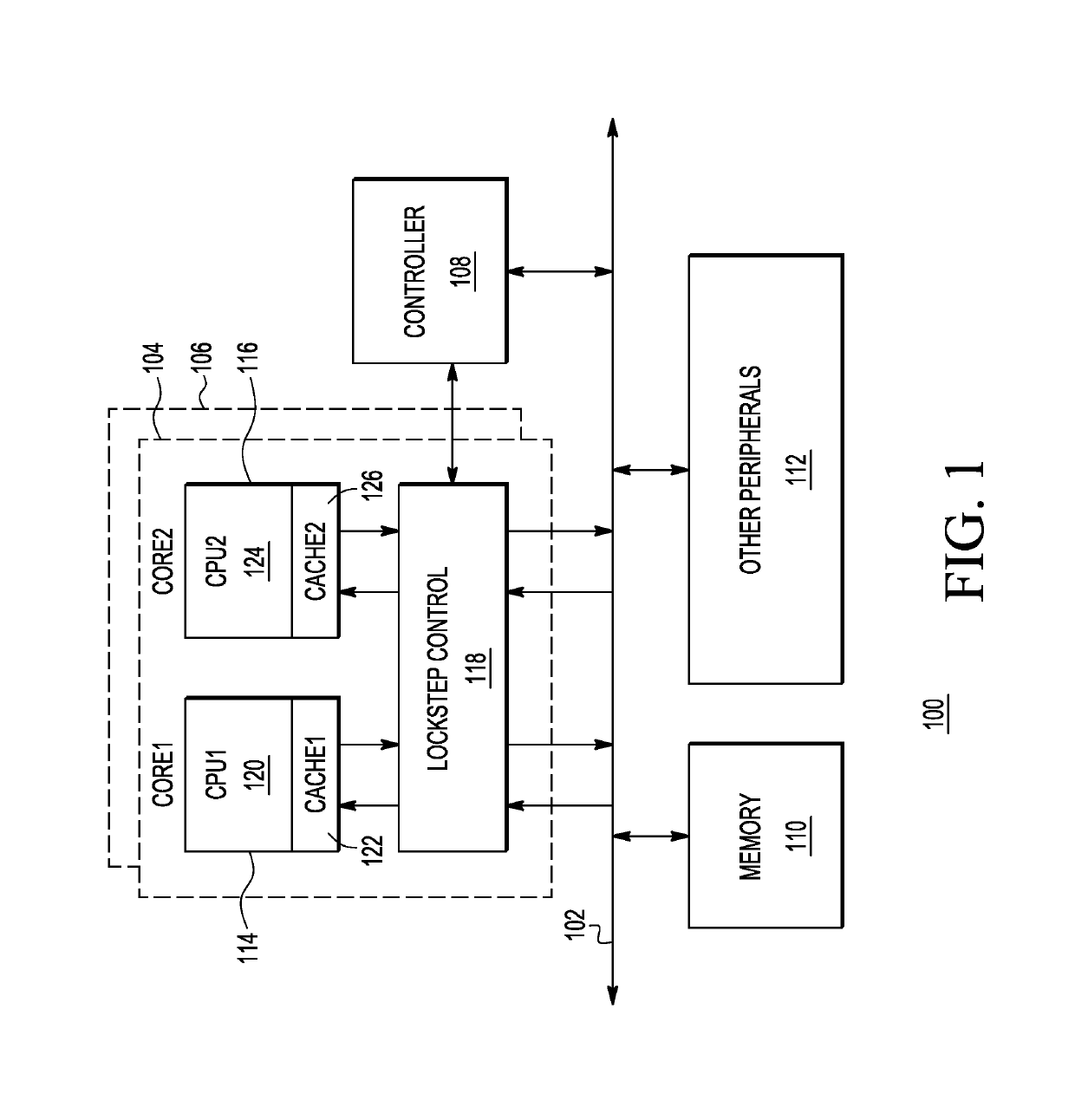
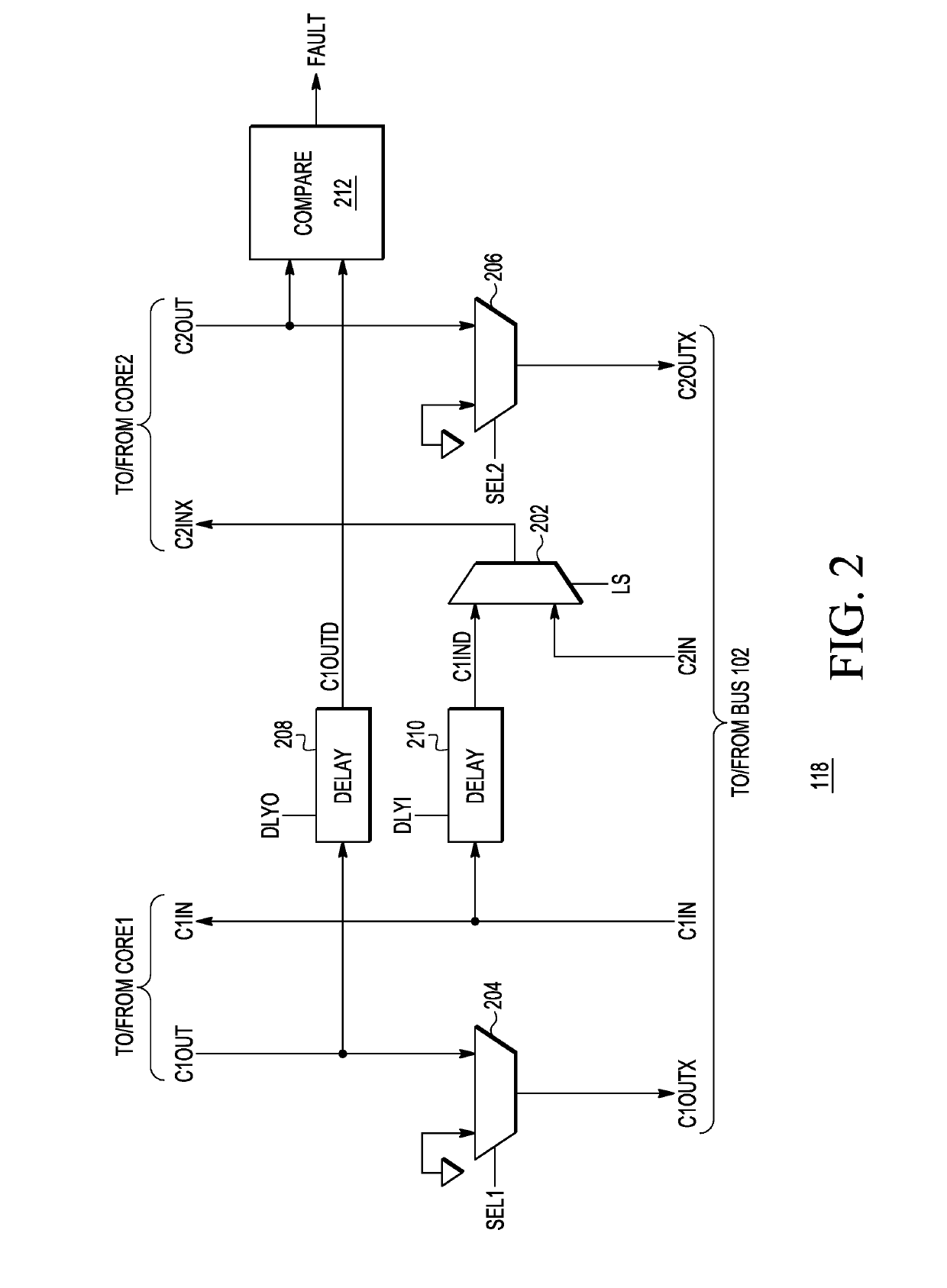
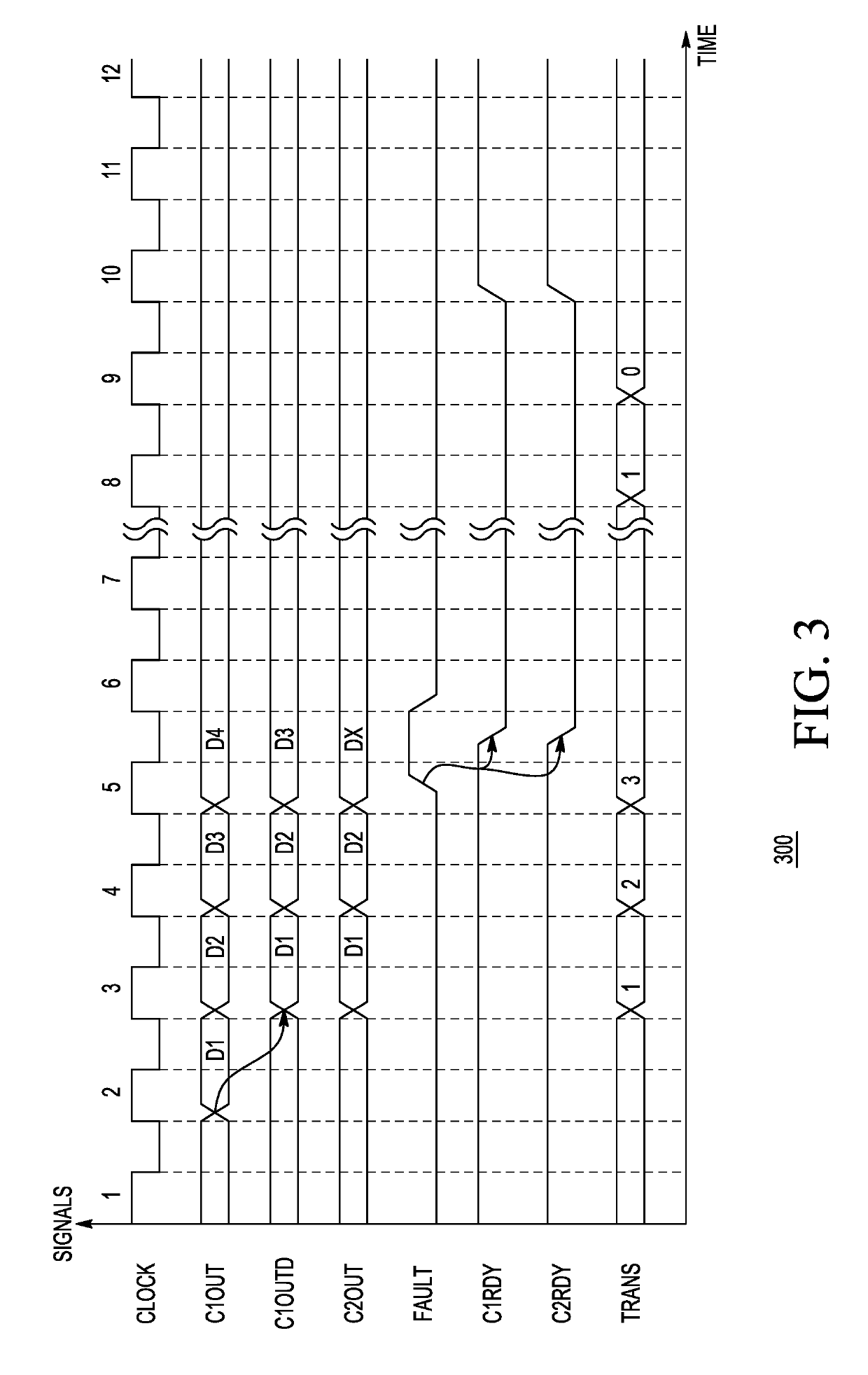
Data processing system having lockstep operation
A data processing system and methods for operating the same are disclosed. The method includes detecting a fault by comparing output signals from a first processing core and a second processing core, entering a safe mode based upon detecting the fault, completing transactions while in the safe mode, and determining whether the fault corresponds to a hard error. Based upon the fault corresponding to a hard error, one of processing cores is identified as a faulty core. The faulty core is inhibited from executing instructions and the other processing core is allowed to execute instructions.
Owner:NXP USA INC
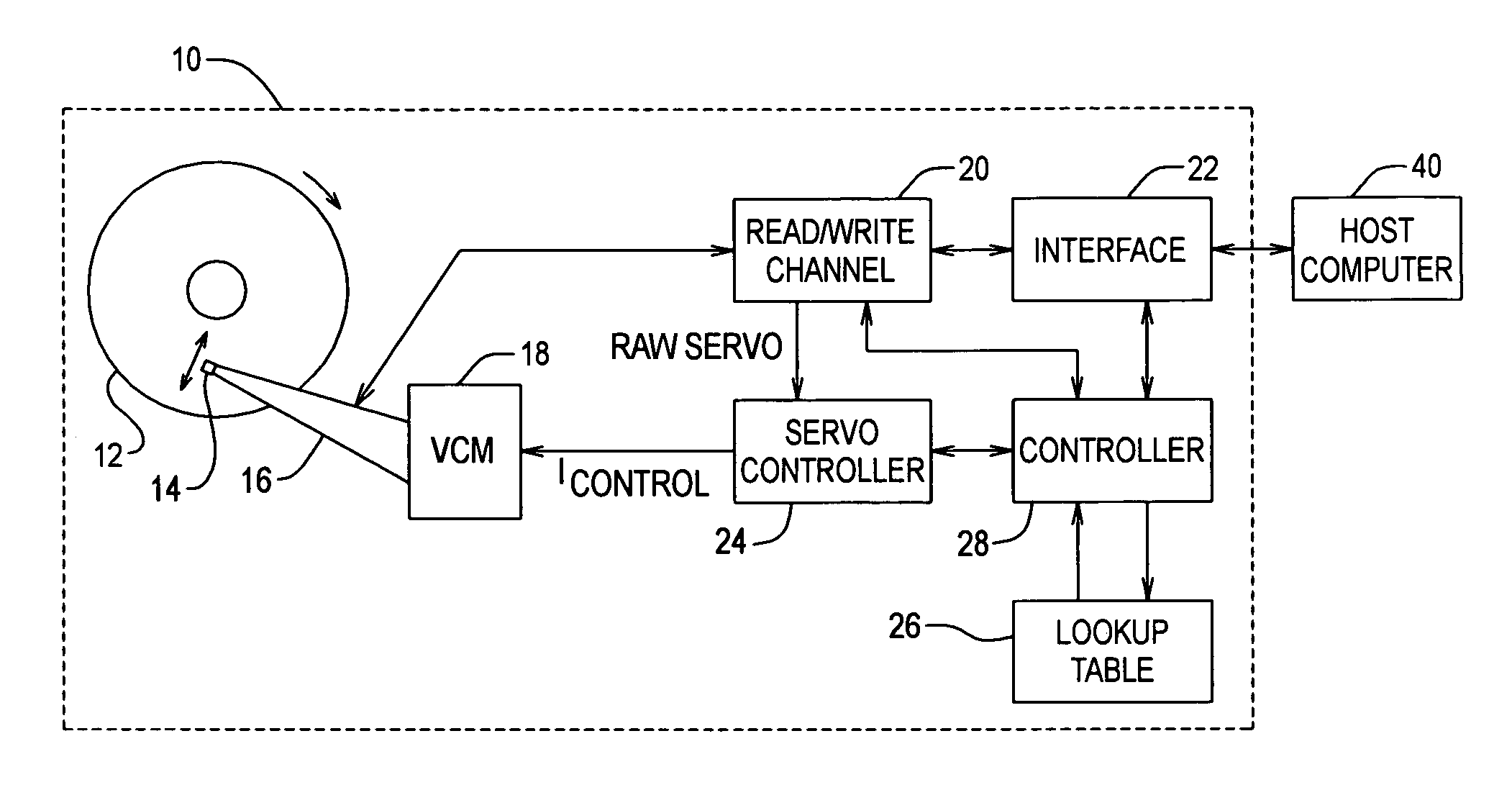
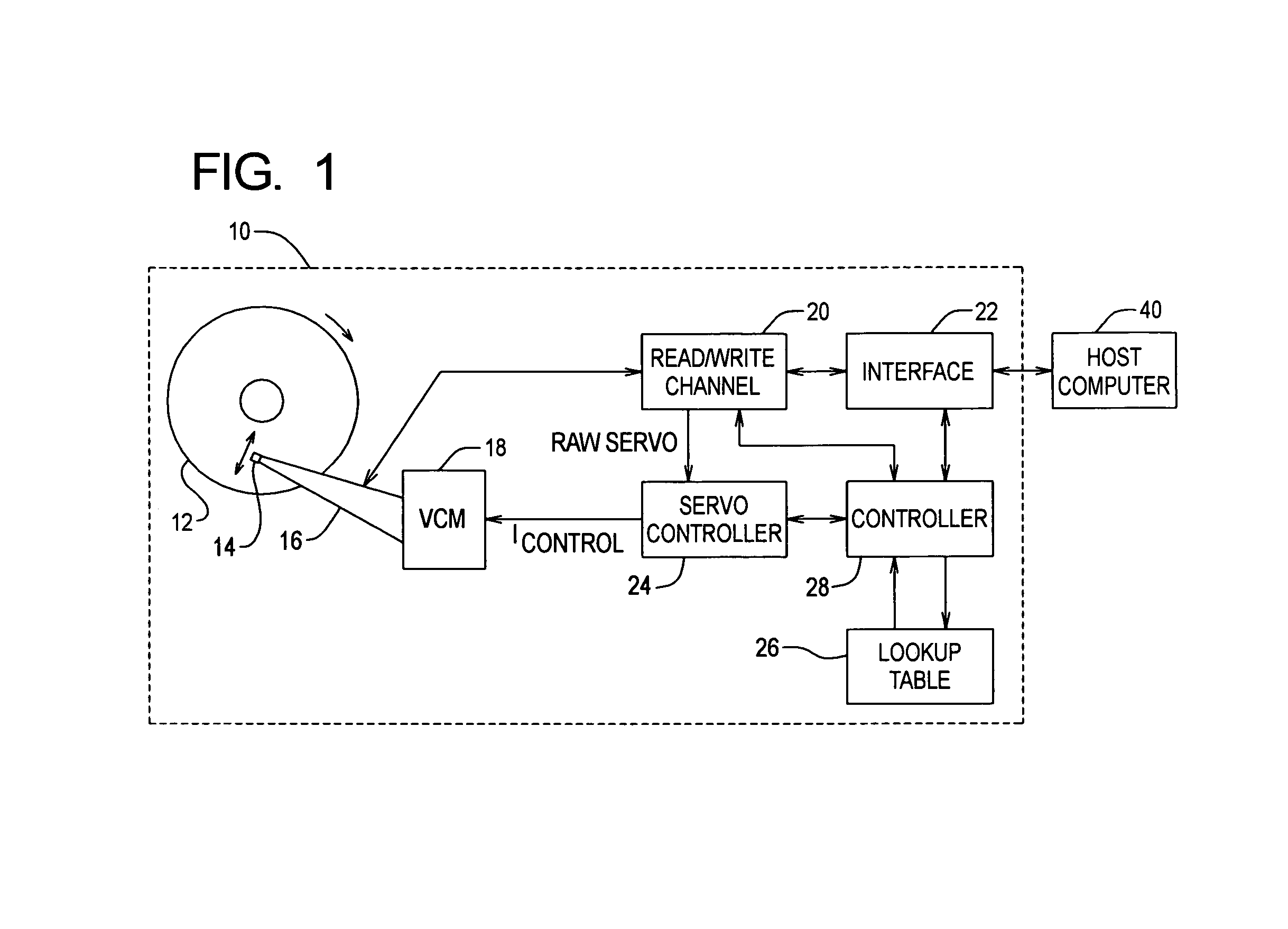
Handling of hard errors in a cache of a data processing apparatus
ActiveUS7987407B2Decreases cost and complexityReduce usageError detection/correctionStatic storageHard errorData processing
A data processor includes a cache record error storage and a hard error storage having at least one record error storage and at least one hard error record, respectively, both for keeping track of errors detected when accessing cache records. When an error is first detected, one of the error records in the cache record error storage is allocated to store a cache record identifier for that cache record, and an associated count value is set to a first value. If an error is detected when accessing a cache record, a correction operation is performed in respect of that currently accessed cache record, and access to that currently accessed cache record is then re-performed. If the count value reaches a predetermined threshold value, then the cache record identifier is moved from the cache record error storage to an error record of the hard error storage.
Owner:ARM LTD
Hard component failure detection and correction
In one embodiment, a memory controller comprises a check bit encoder circuit coupled to receive a data block to be written to memory, a check / correct circuit coupled to receive an encoded data block read from the memory, and a hard failure detection circuit coupled to the check / correct circuit. The check bit encoder circuit is configured to generate a corresponding encoded data block comprising the data block, a first plurality of check bits, and a second plurality of check bits. The check / correct circuit is configured to detect an error in the encoded data block responsive to the first check bits, the second check bits, and the data block within the encoded data block, which is logically arranged as an array of R rows and N columns, wherein R and N are positive integers. Each of the first check bits covers a respective row of the array, and the check / correct circuit is configured to generate a first syndrome corresponding to the first plurality of check bits. A presence of more than one binary one in the first syndrome indicates a multi-bit error. Responsive to detecting the multi-bit error, the hard failure detection circuit is configured to perform a plurality of memory read / write operations to the memory locations in which the encoded data block is stored to identify a hard error failure in the memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
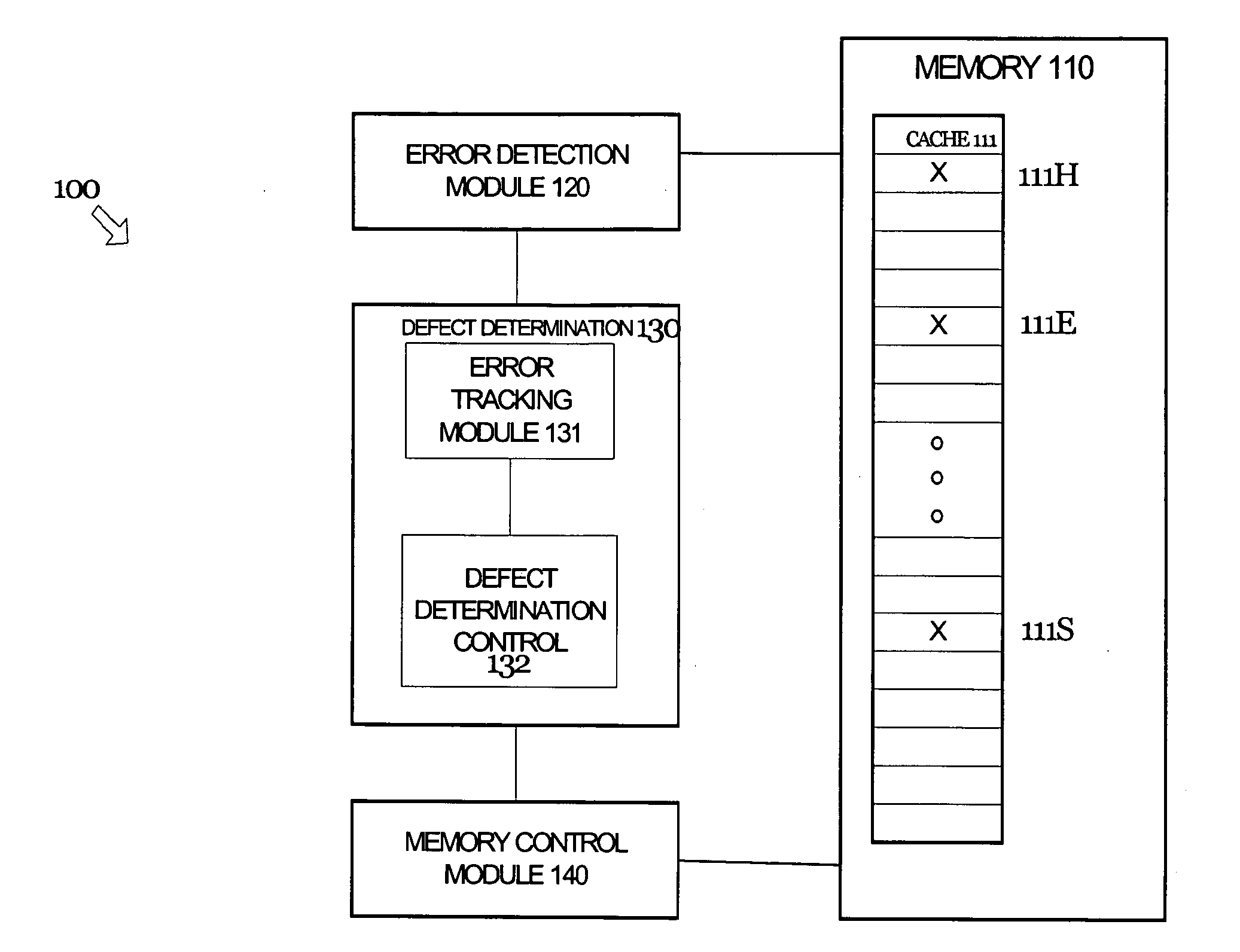
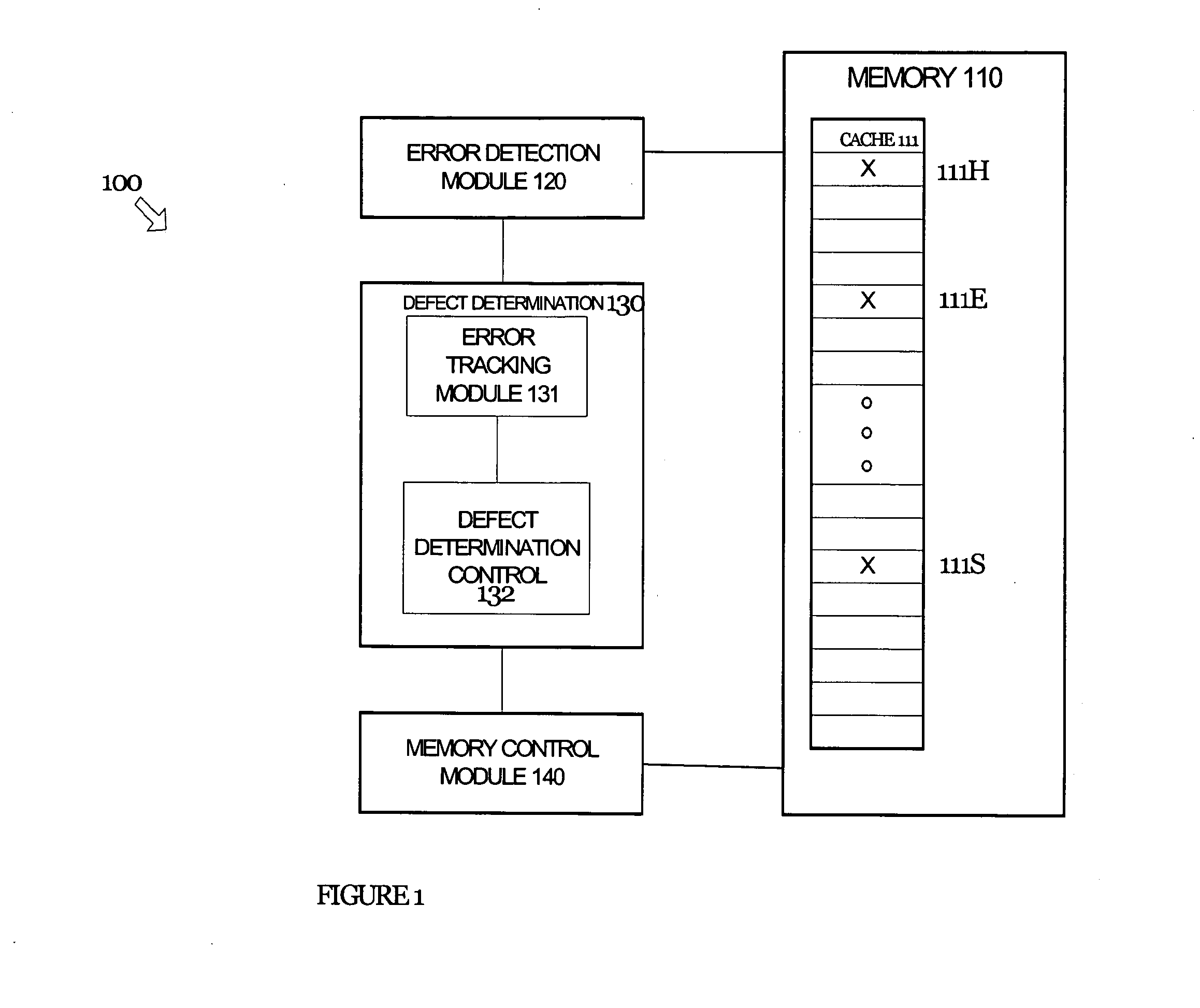
Apparatus and method for error correction of data values in a storage device
ActiveUS20090164870A1Reliable dataImprove reliabilityStatic storageRedundant hardware error correctionData valueComputer science
A data processing apparatus is provided in which a processing unit, by means of a read access request, accesses a storage device which stores data values and error data associated with those data values. When the processing unit accesses a data value in the storage device, error detection circuitry detects if an error is present in that data value and, if necessary, error correction circuitry corrects the read data value. An error cache having at least one entry stores corrected replacement data values, a corrected data value being allocated into an entry of the error cache for every corrected data value that is generated, and the read access request is re-performed. Replacement data values are read from the error cache in preference to data values stored in the storage device. This ensures that the retry mechanism will succeed irrespective of whether the error was a soft error or a hard error. Thus, if any hard errors do occur during normal operation of the storage device, they can effectively be temporarily corrected through use of the error cache to ensure that the retry mechanism proceeds correctly.
Owner:ARM LTD
Soft errors handling in eeprom devices
InactiveUS20050058008A1Improve reliabilityProlong lifeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTerm memoryThreshold voltage
Soft errors occur during normal use of a solid-state memory such as EEPROM or Flash EEPROM. A soft error results from the programmed threshold voltage of a memory cell being drifted from its originally intended level. The error is initially not readily detected during normal read until the cumulative drift becomes so severe that it develops into a hard error. Data could be lost if enough of these hard errors swamps available error correction codes in the memory. A memory device and techniques therefor are capable of detecting these drifts and substantially maintaining the threshold voltage of each memory cell to its intended level throughout the use of the memory device, thereby resisting the development of soft errors into hard errors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
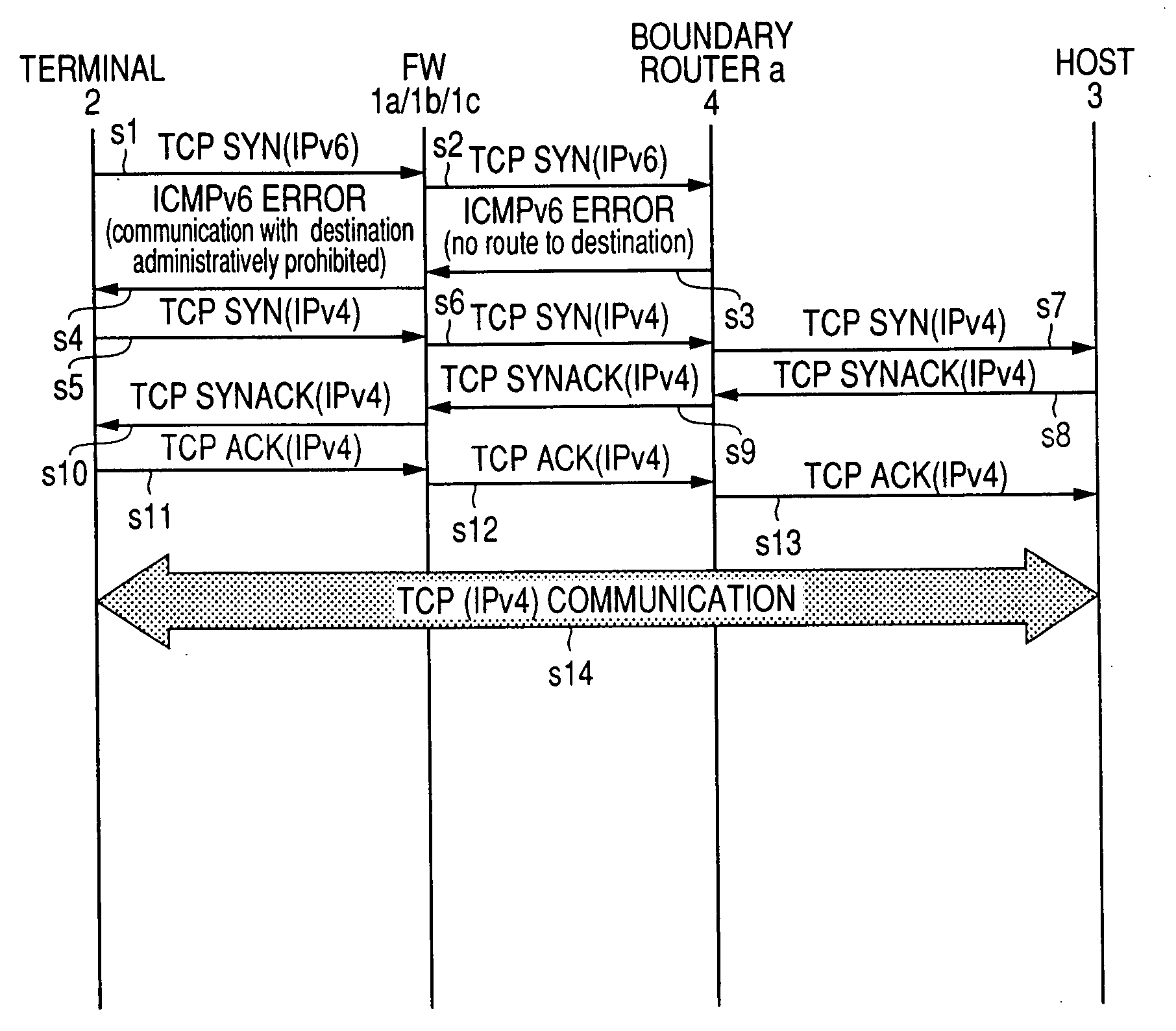
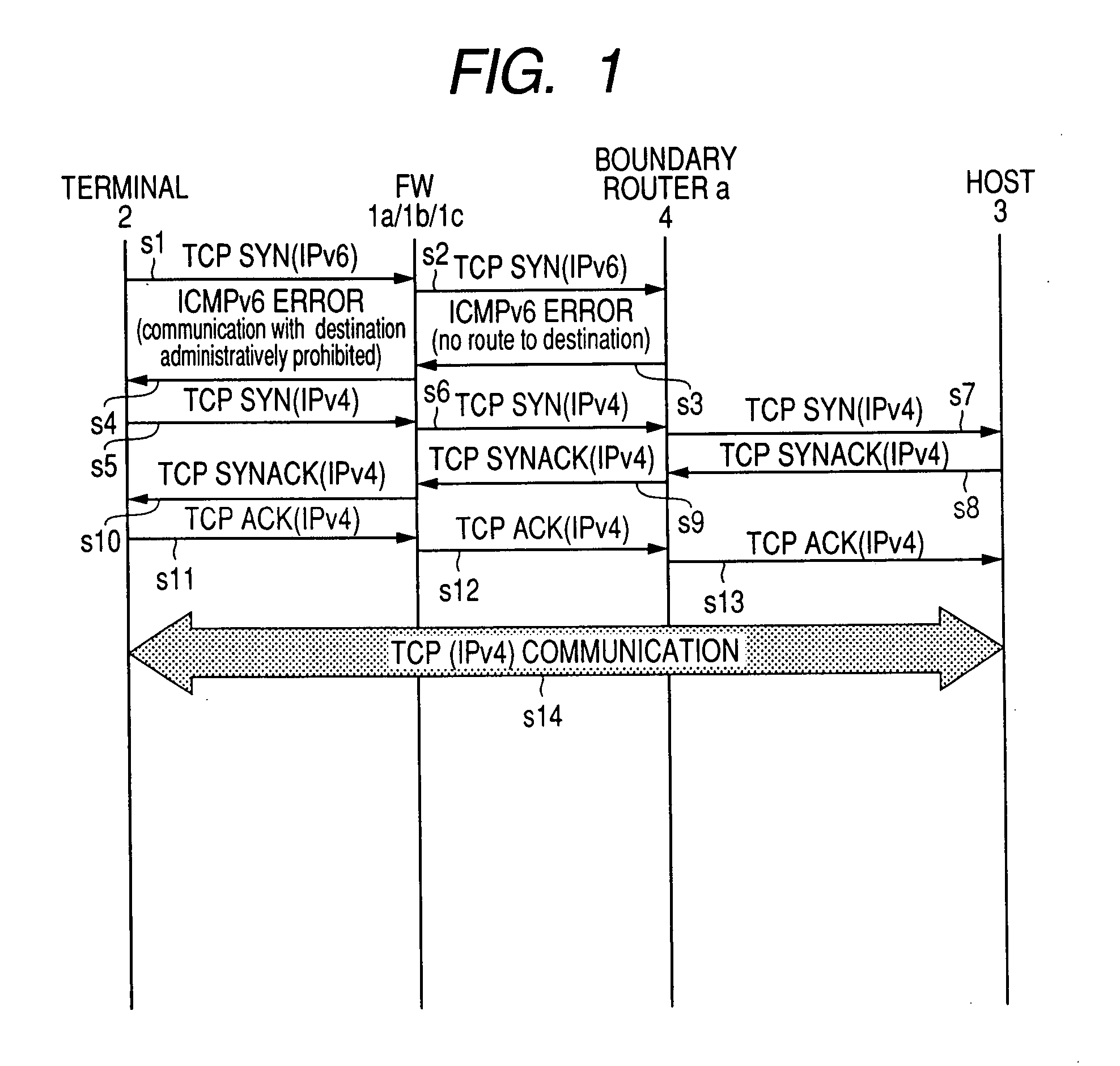
ICMP translator
InactiveUS20080212609A1Avoid delayEliminate needTime-division multiplexData switching networksReal-time computingIPv4
When an IPv4 / v6 dual stack terminal communicating via TCP on IPv6 fails to promptly switch over to IPv4 after the ICMPv6 fails due to a soft error, the problem should be resolved at the prior stage server rather than on the complicated terminal. The server at a stage prior to the terminal receives TCP packets from the terminal to find the TCP connection status on the terminal. When the terminal connection status is SYN-SENT or SYN-RECEIVED, and the server receives an unaddressed soft error such as ICMPv6 “Destination Unreachable: no route to destination (ICMP type=1: code 0)” for that terminal, the server rewrites the ICMPv6 contents as a hard error such as “Destination Unreachable: communication with destination administratively prohibited (ICMP type=1: code 1)” and sends it the terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and Methods for Hard Error Reduction in a Solid State Memory Device
ActiveUS20150220388A1Reduce bit error rateRead-only memoriesDigital storageSolid state memoryHard error
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Synchronous replication error detection and handling
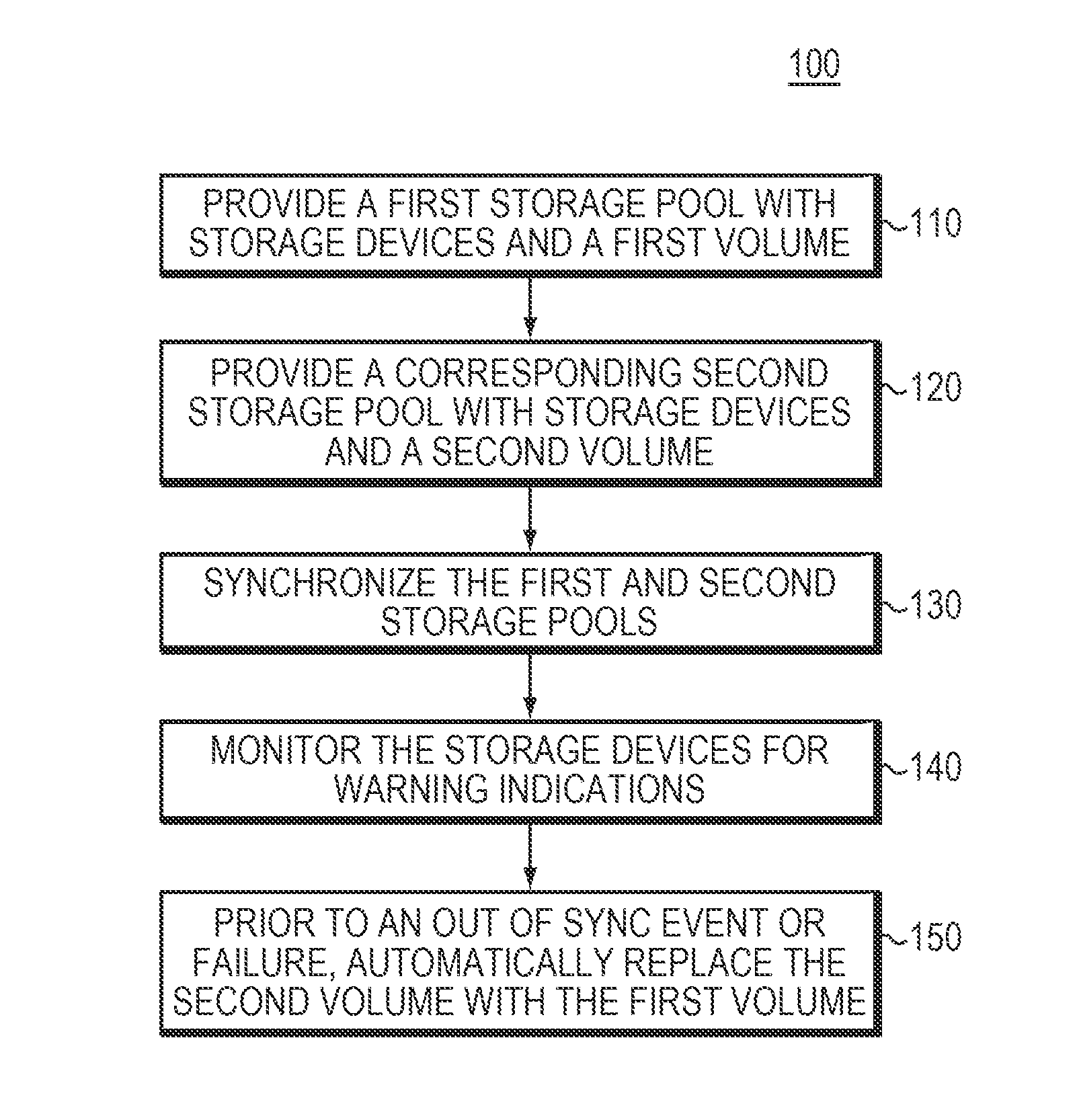
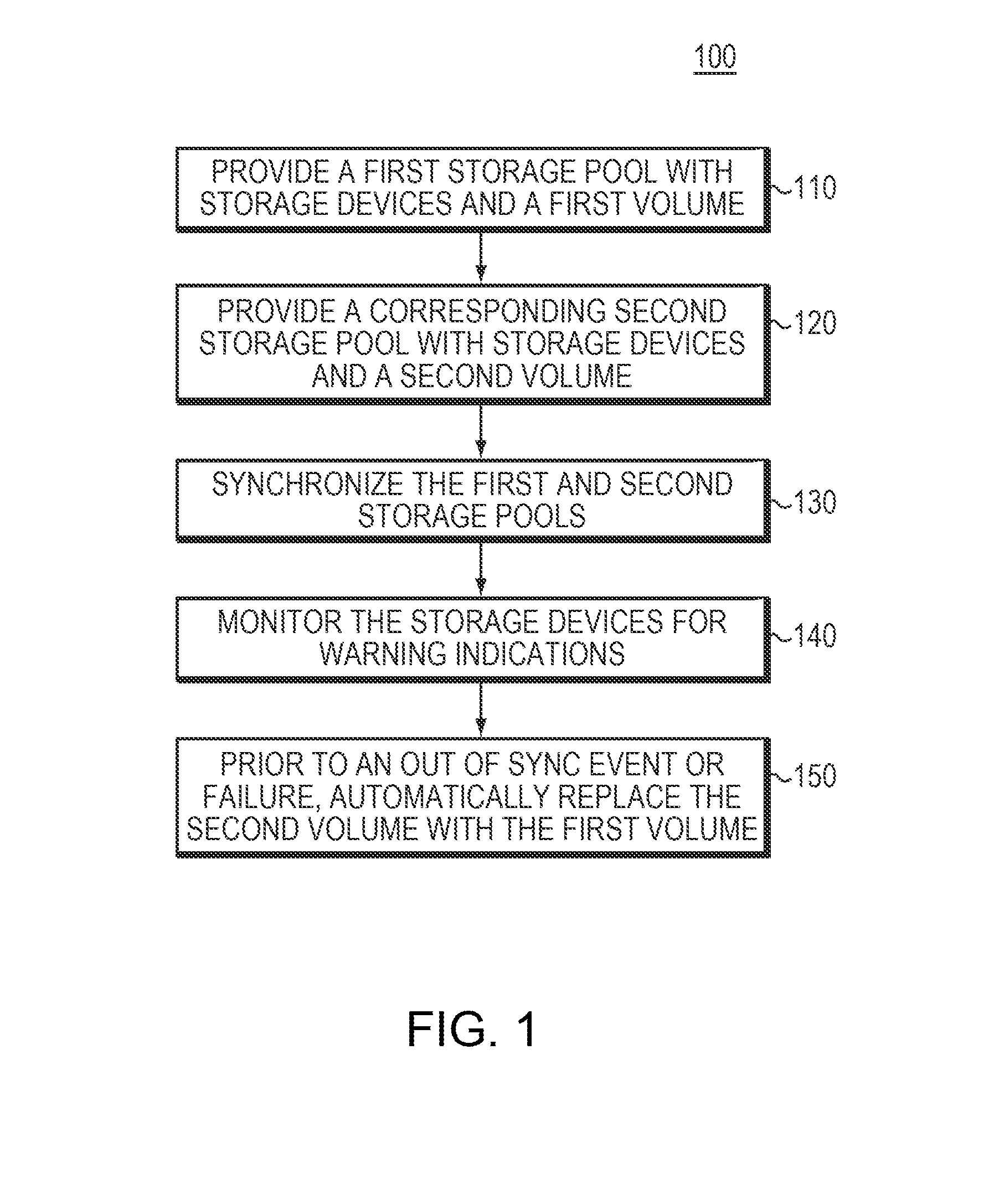
ActiveUS20160224441A1Efficient and reliableHardware monitoringRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareStorage pool
Some embodiments are directed to a method, corresponding system, and corresponding apparatus that may store data and may monitor, detect, and handle one or more warning or error indications within one or more synchronized replication volumes. Some embodiments may provide first and second storage pools of storage devices with respective volumes. In some embodiments, the first and second storage pools may not share the same controller. Some embodiments may synchronize the first and second storage pools by a storage device of the first storage pool. Some embodiments may monitor for failures, including but not limited to warnings, soft errors, and / or hard errors, at a storage device of the first storage pool. In some embodiments, the one or more failures may be invisible or inaccessible to a user. Prior to an out of sync event or failure, some embodiments may automatically replace the second volume with the first volume.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
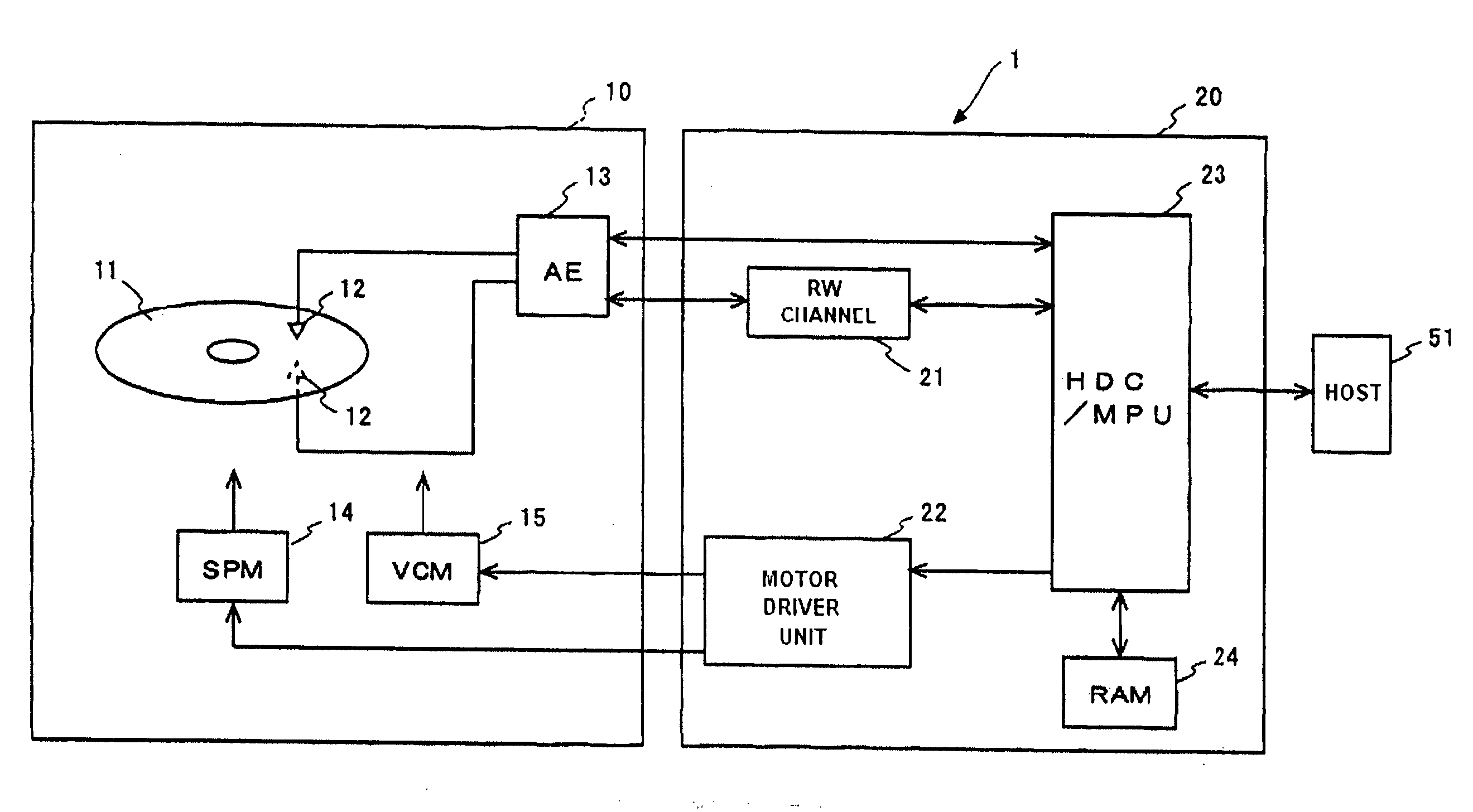
Method and structure for improving performance and storage density in a data storage device
ActiveUS20140055883A1Easy to optimizeReduce average track-to-track spacingRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksComputer hardwareData store
A data storage device with improved data storage densities, coupled with lower hard error and write-inhibit events is described. A feed-forward write inhibit (FFWI) method enables data tracks to be written more densely. Alternatively, the FFWI method may reduce the hard error and write inhibit events to improve data storage performance. A concept of virtual tracks enables the FFWI method to be applied to the writing of circular data tracks with non-circular servo tracks, or to the writing of non-circular data tracks with PES data from circular servo tracks—in both cases, improvements to performance and / or storage densities are enabled. The FFWI method may also be applied to the case of both non-circular servo and data tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
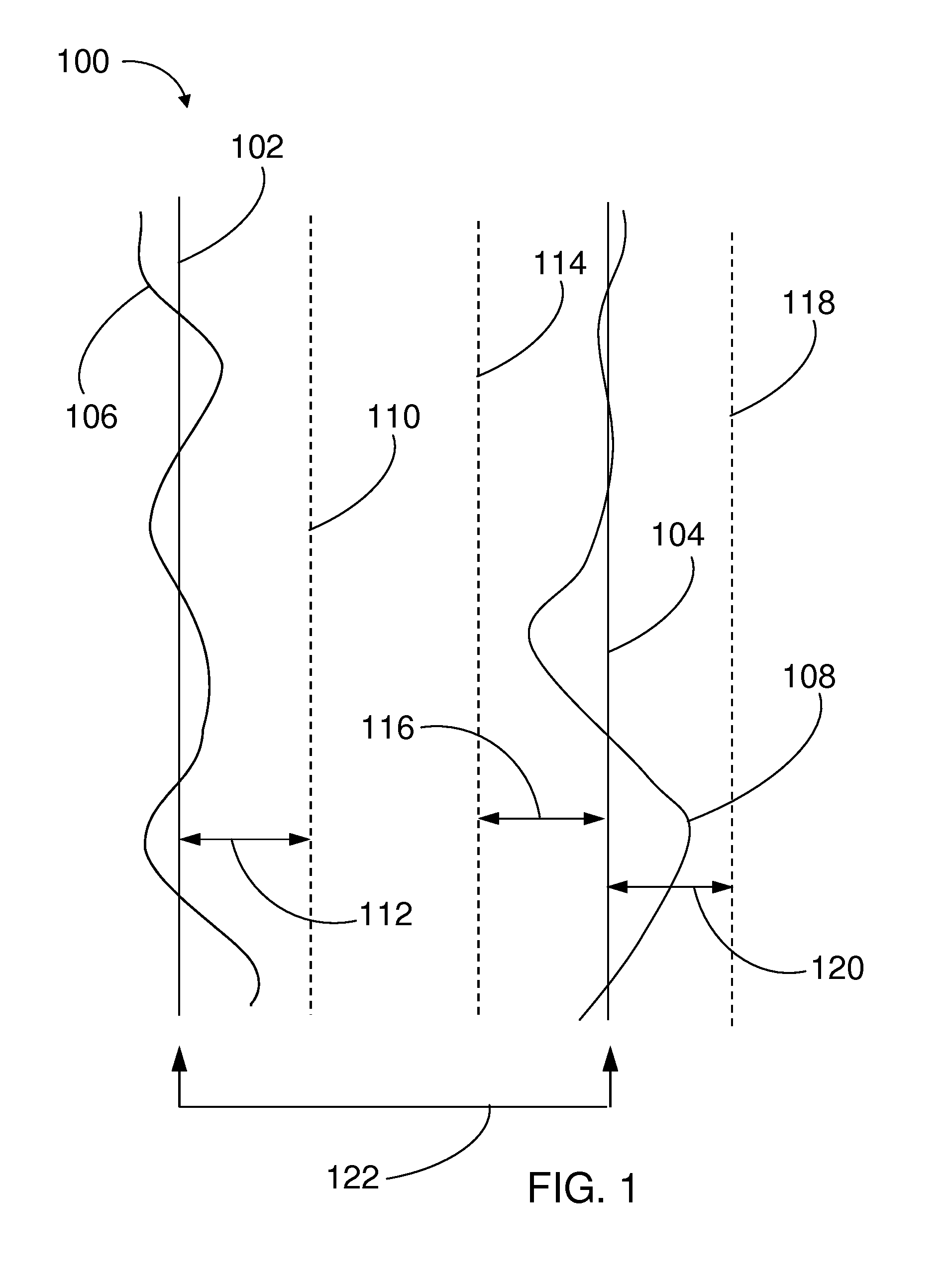
Sample screening method for system soft error rate evaluation
A sample screening method for system soft error rate evaluation. Memory cells of a memory device are written and read according to a first test condition to locate hard errors. The memory cells of the memory device are read according to a second test condition to locate functional errors. The memory cells of the memory device are read according to a third test condition to locate soft errors.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Method and system for error recovery of a hardware device
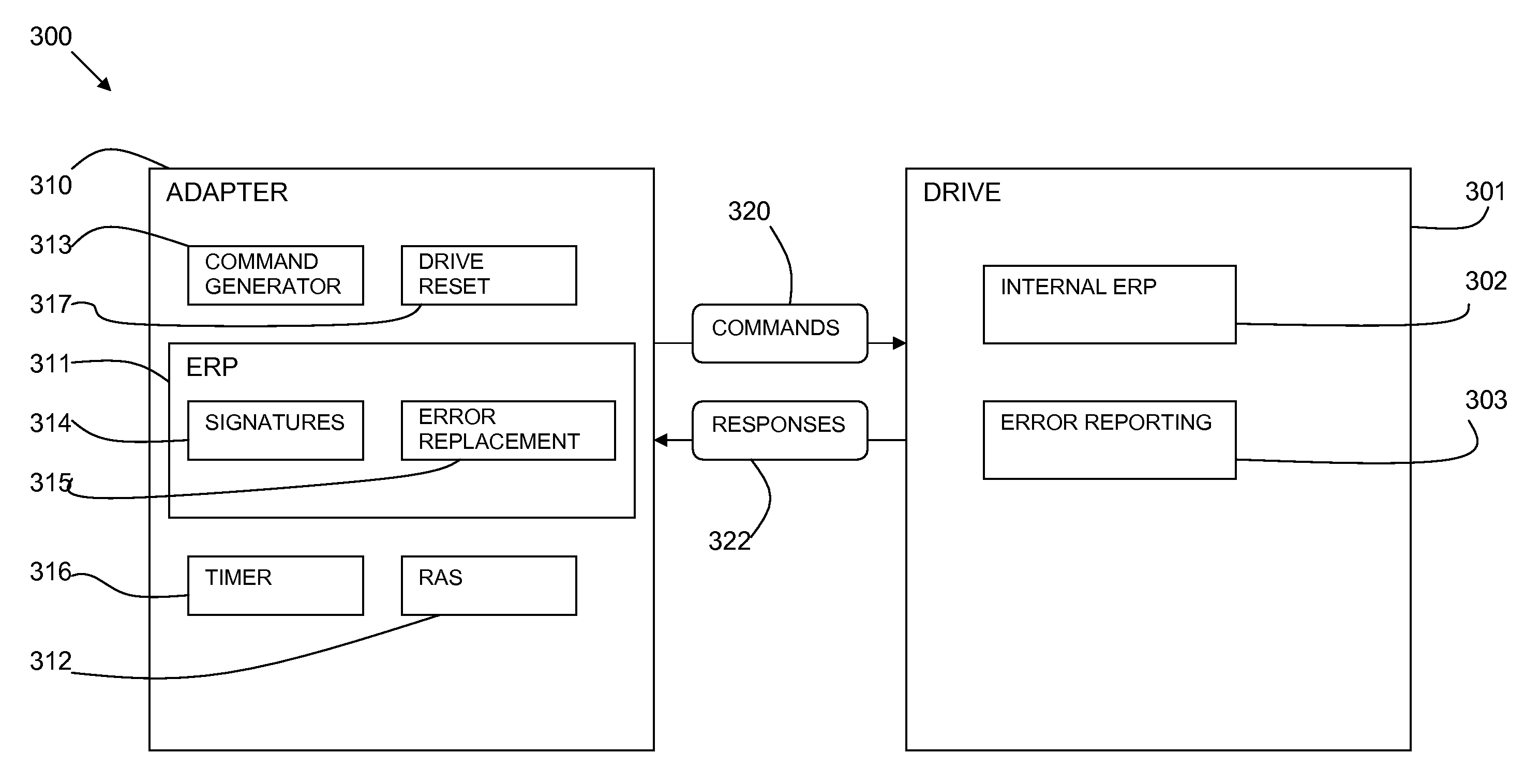
A method and system for error recovery of a hardware device is provided. The method includes detecting a target hard error indication from the hardware device by comparing the hard error indication to signatures of hard error indications which indicate a temporary failing and modifying the reported error to a stalling indication. The hardware device is allowed to recover in a predefined time period or by issuing one or more resets, or both. A hard error indication usually instigates an external error recovery of the hardware device and the method temporarily stalls such external error recovery.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for processing hard memory error
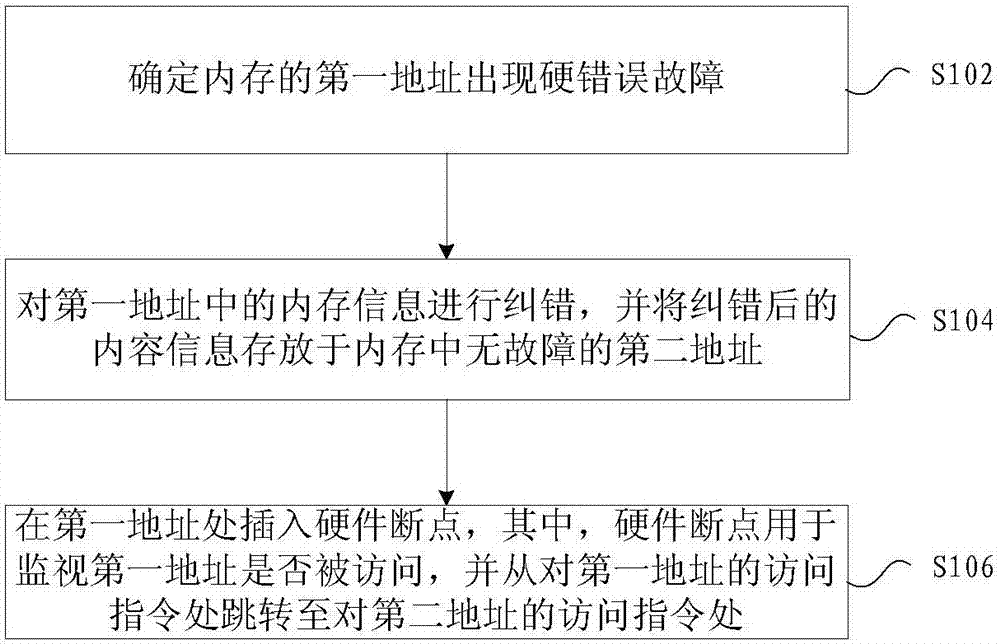
InactiveCN107516547ATroubleshoot hard errors for error correctionAvoid serious consequences such as crashesStatic storageRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareBreakpoint
The invention provides a method and apparatus for processing a hard memory error. The method comprises determining if a hard error fault occurs in a first address of a memory, performing error correction on memory information in the first address, storing the memory information subjected to error correction in a second address of the memory, and inserting a hardware breakpoint into the first address, wherein the hardware breakpoint is used for monitoring whether the first address is accessed and switching from the access instruction to the first address into the access instruction to the second address. The method and apparatus solve the problem that the prior art cannot carry out correction on the hard memory error without interrupting the service.
Owner:ZTE CORP
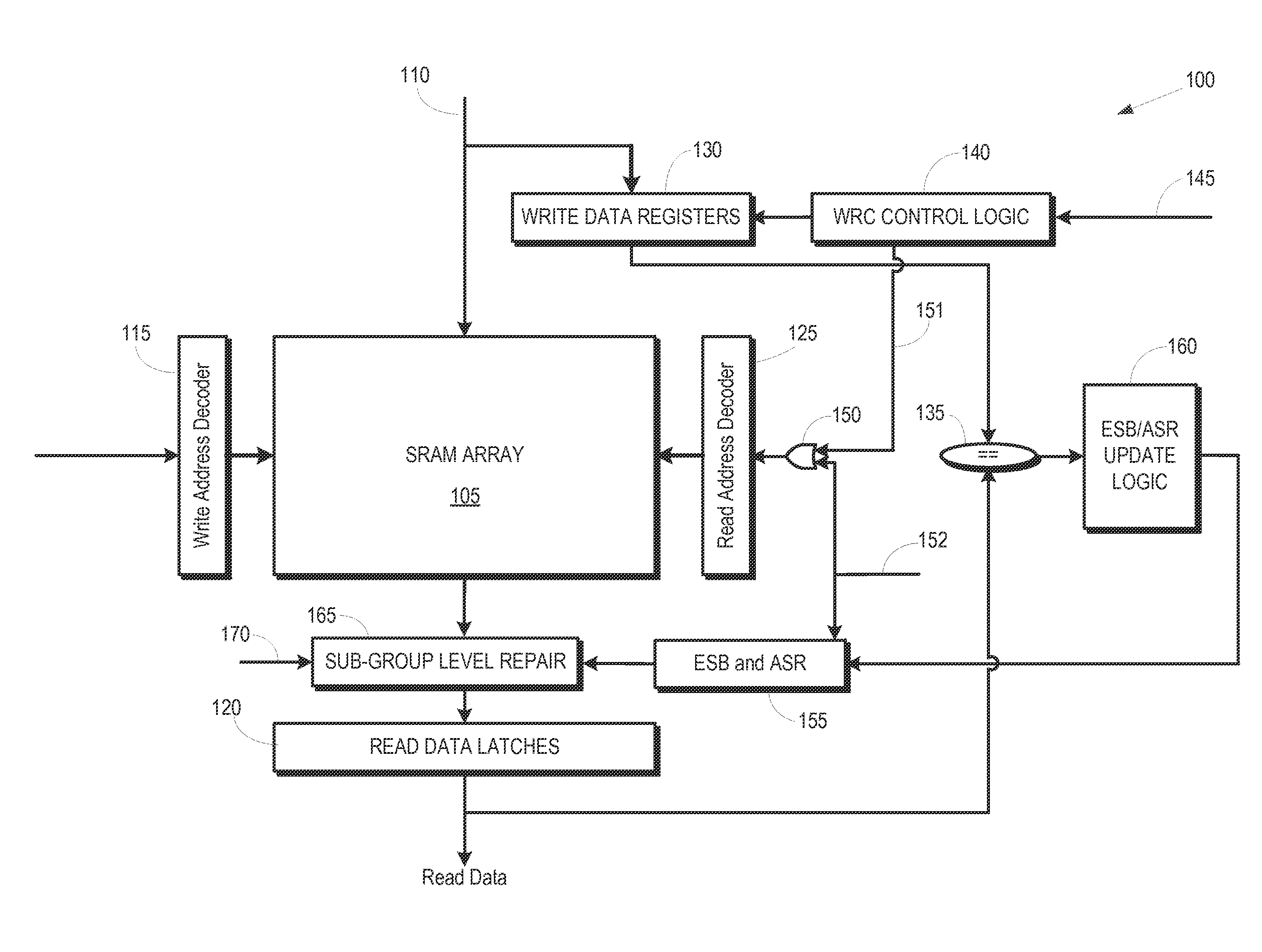
Error recovery storage for non-associative memory
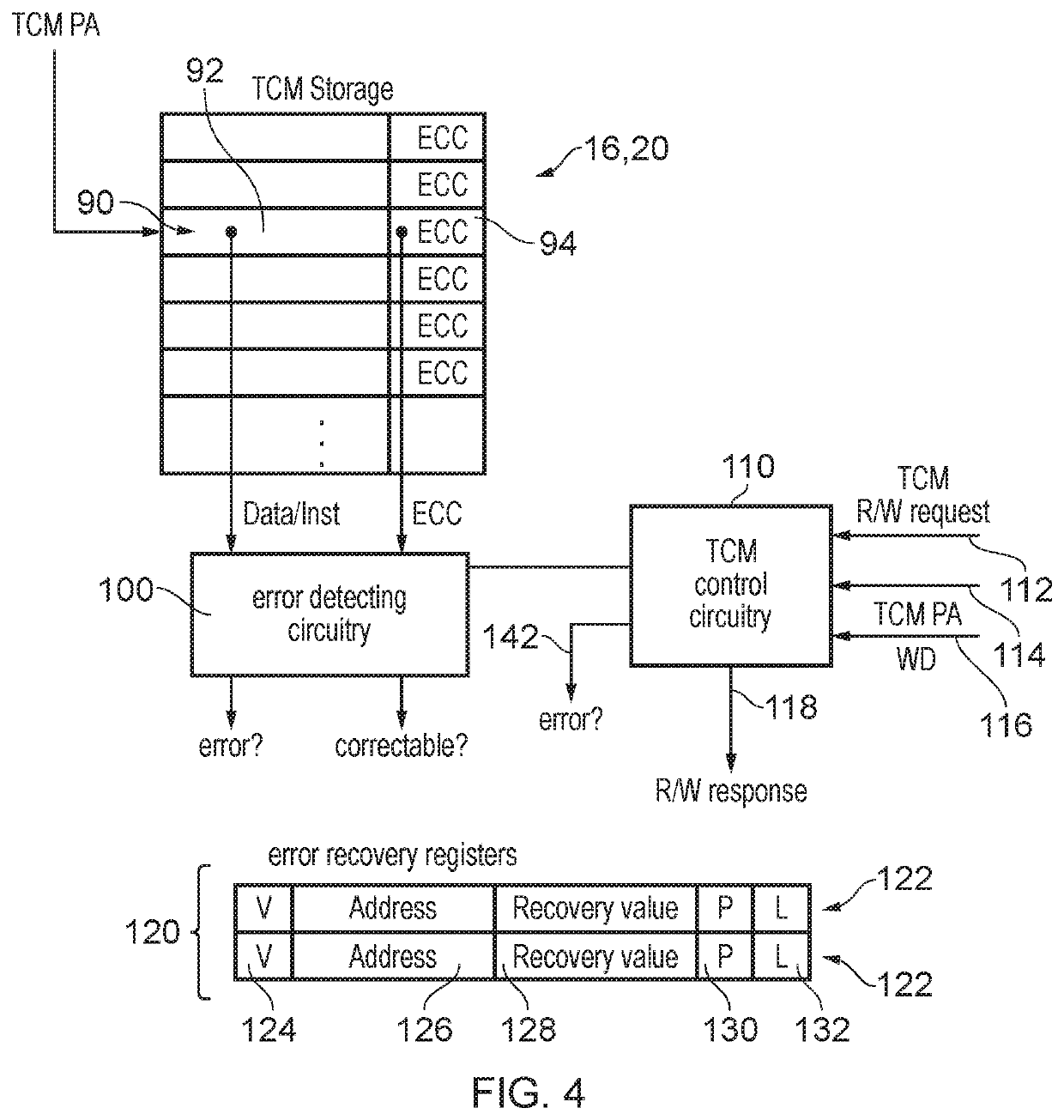
ActiveUS20200285550A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant operation error correctionComputer hardwareEngineering
An apparatus comprises a non-associative memory comprising a plurality of storage locations, and error recovery storage to store at least one error recovery entry providing a recovery value for a corresponding storage location of the non-associative memory. Control circuitry is responsive to a non-associative memory read request specifying a target address of a storage location of the non-associative memory, when the error recovery storage includes a valid matching error recovery entry for which the corresponding storage location is the storage location identified by the target address, to return the recovery value stored in the valid matching error recovery entry as a response to the non-associative memory read request, instead of information stored in the storage location identified by the target address. This enables the apparatus to continue to function even if hard errors occur in a storage location of the non-associative memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com