Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Soft error detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
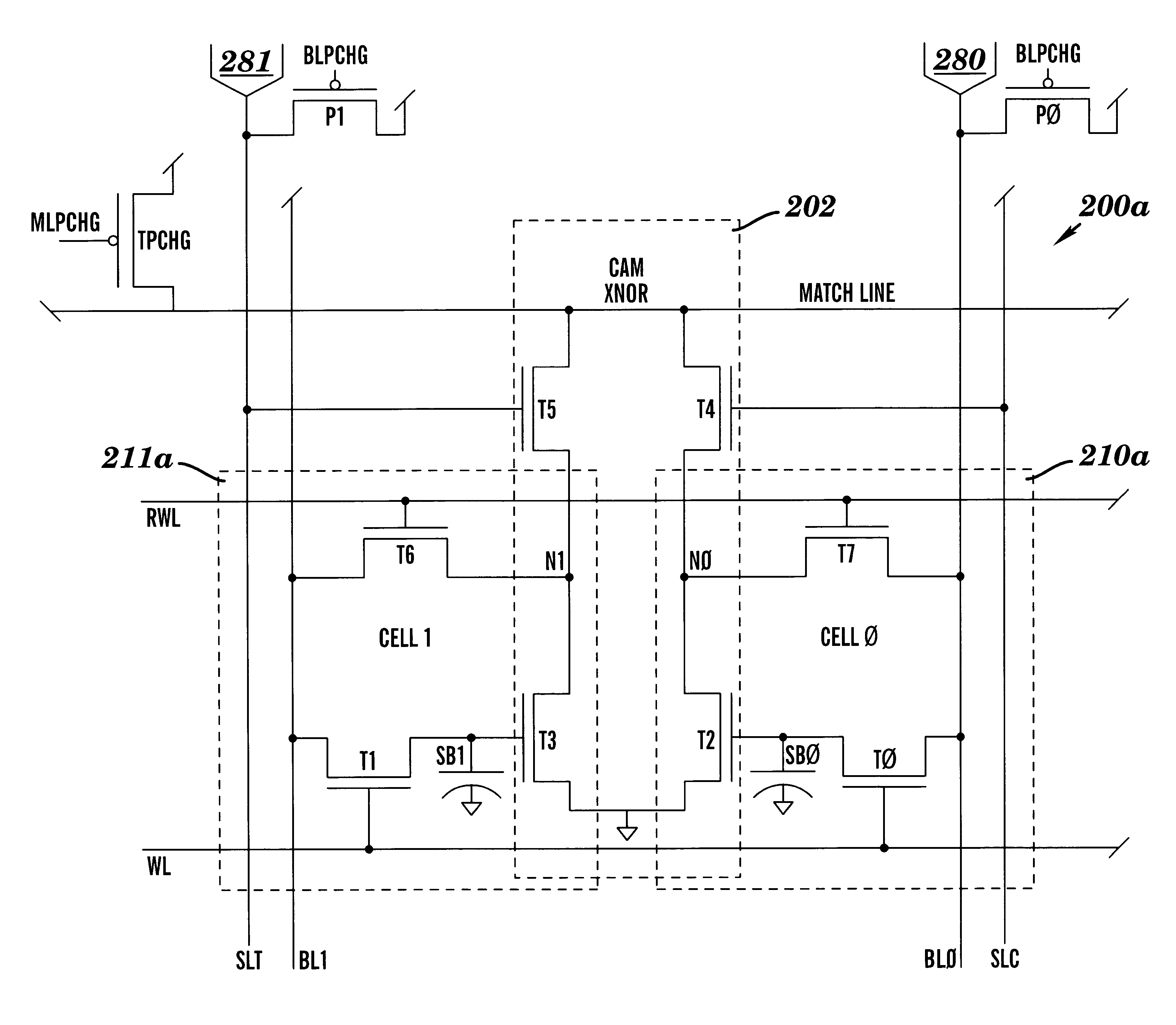
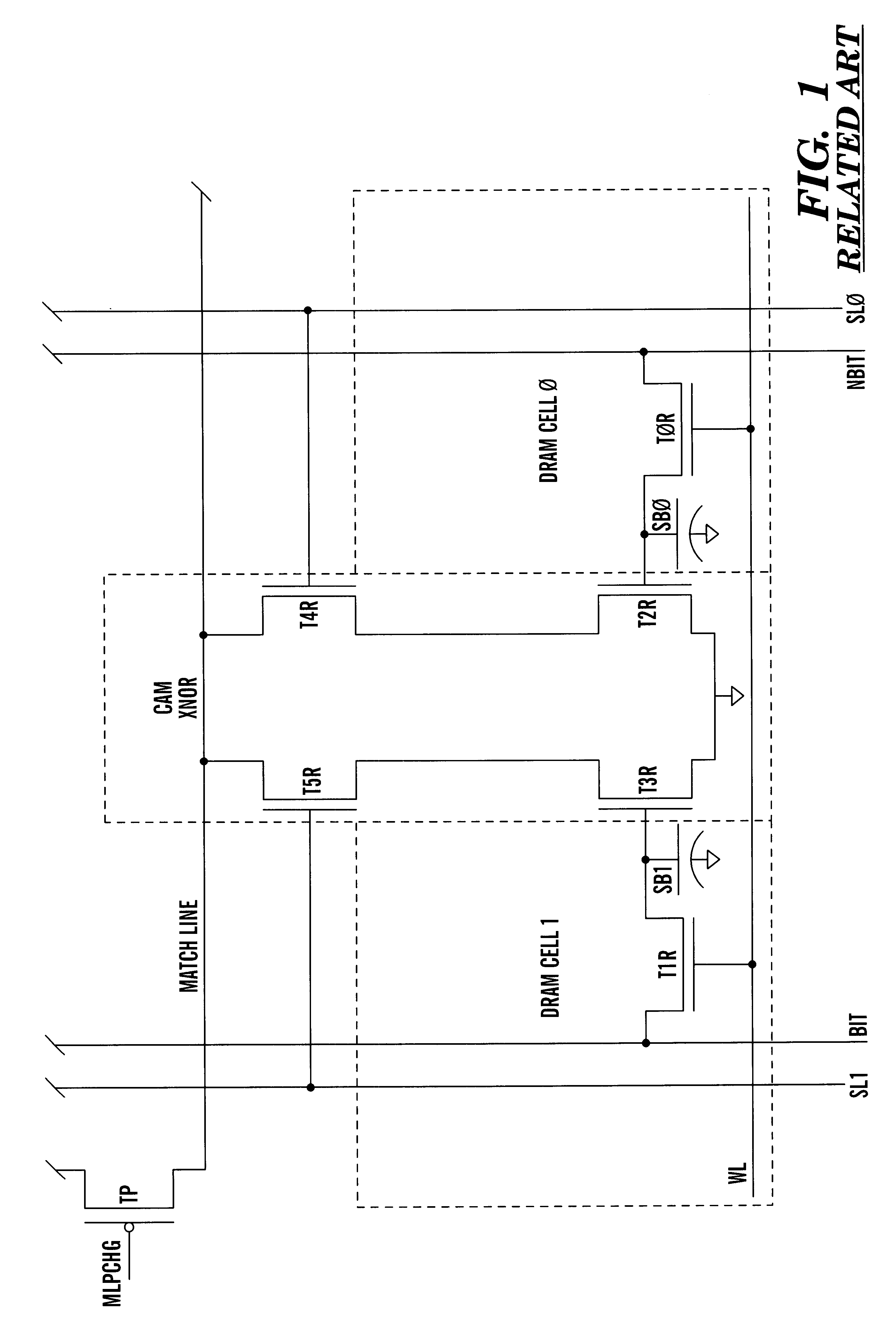
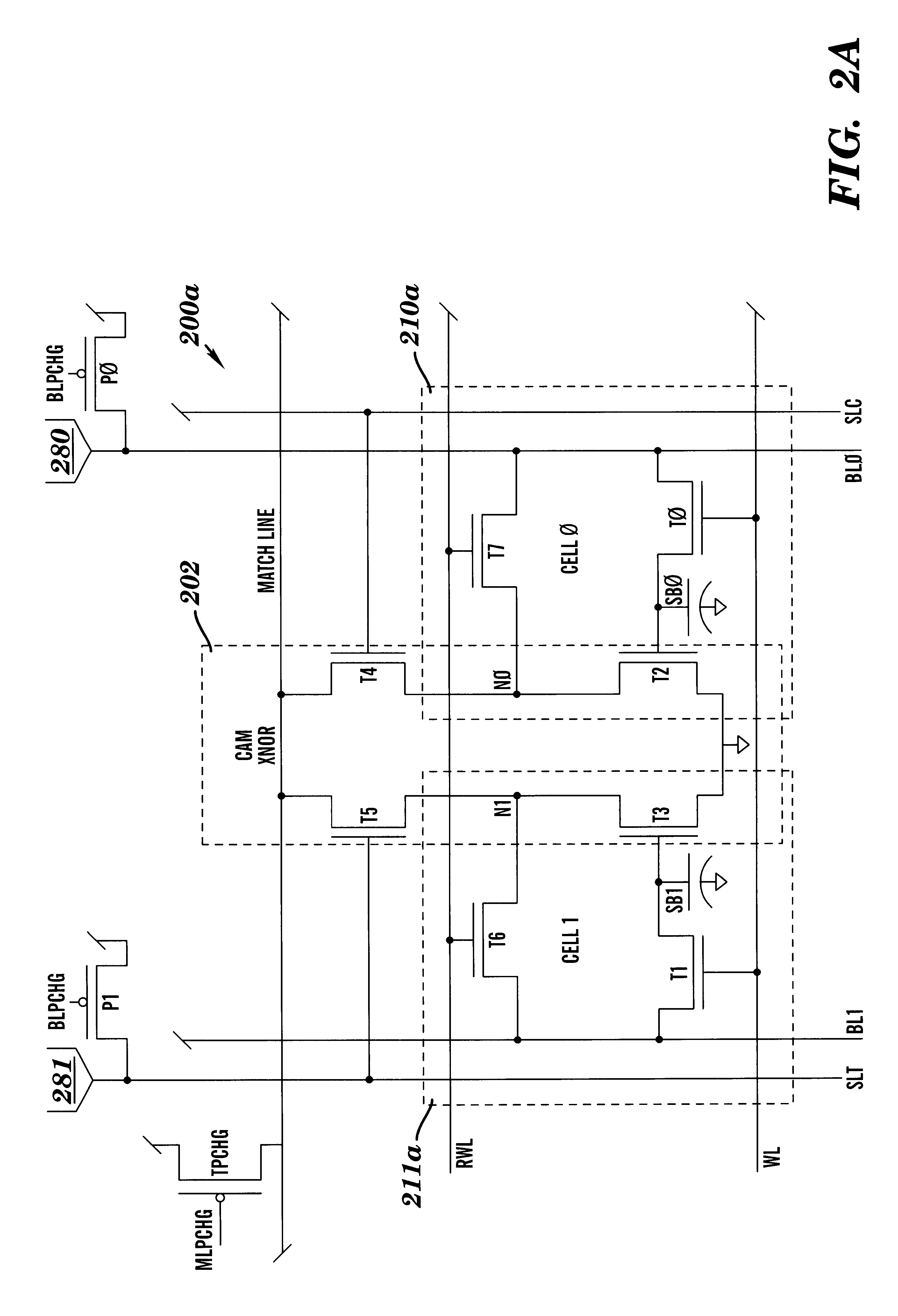
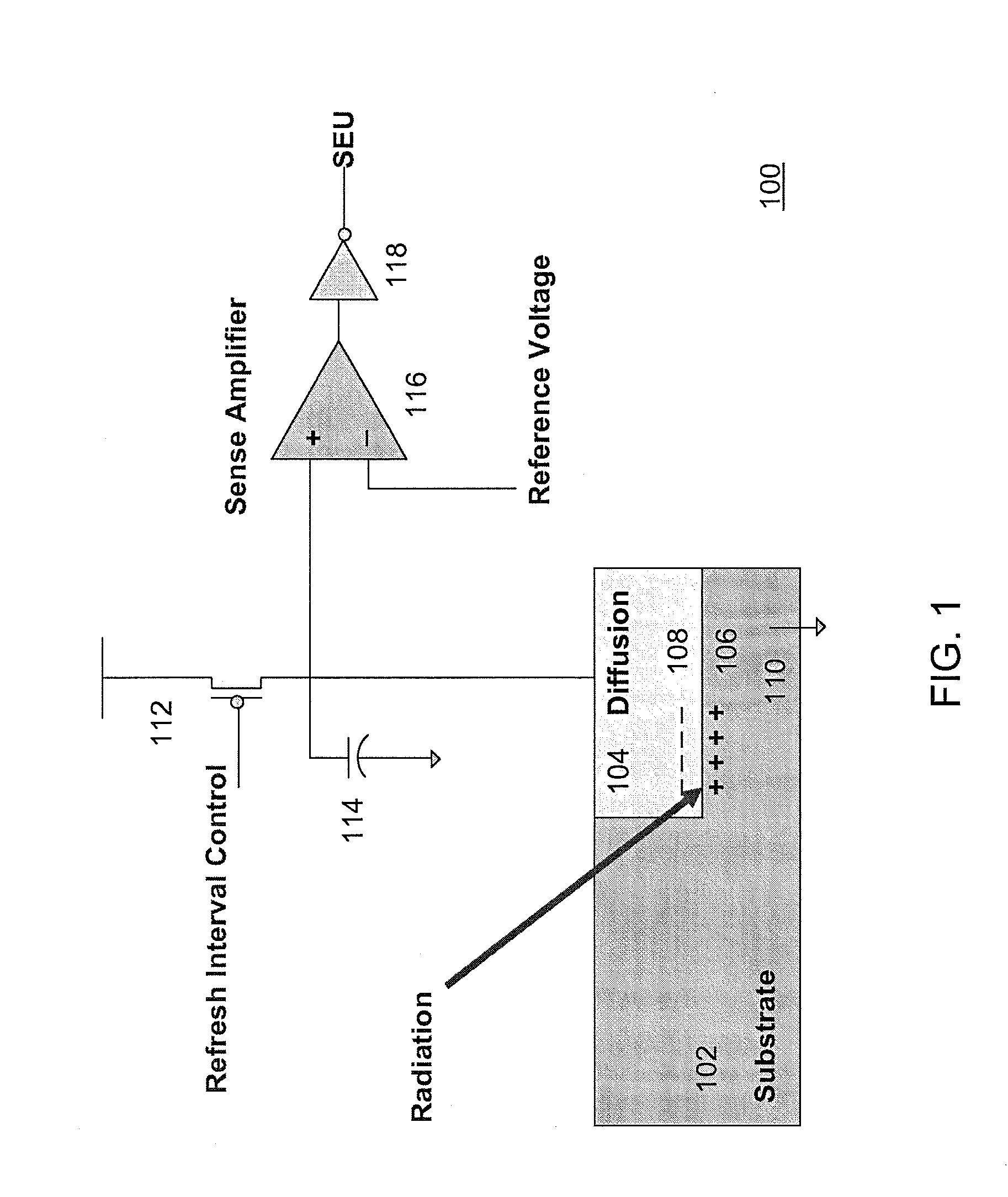
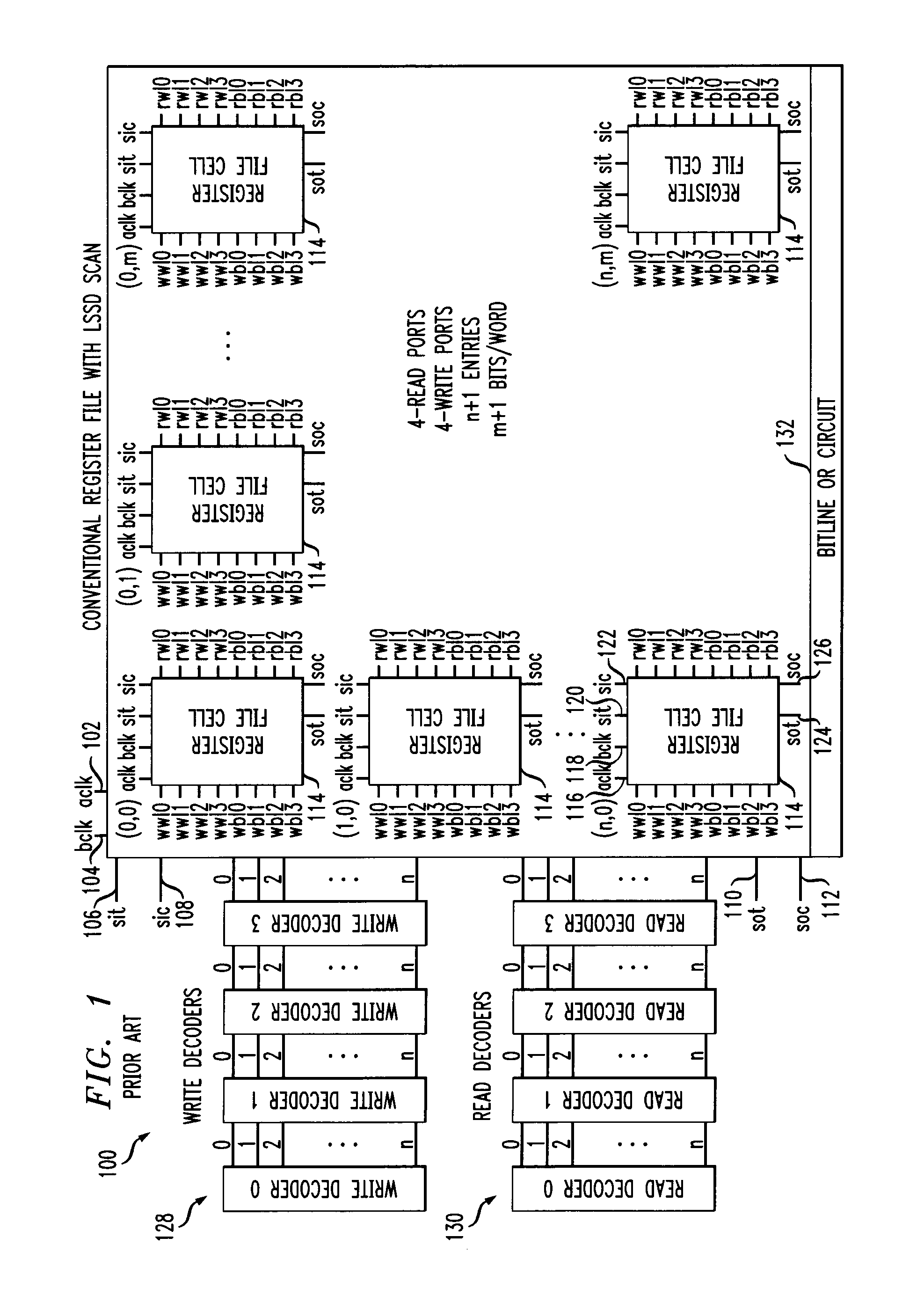
Dram CAM cell with hidden refresh
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Hard/soft error detection
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Memory ECC with Hard and Soft Error Detection and Management
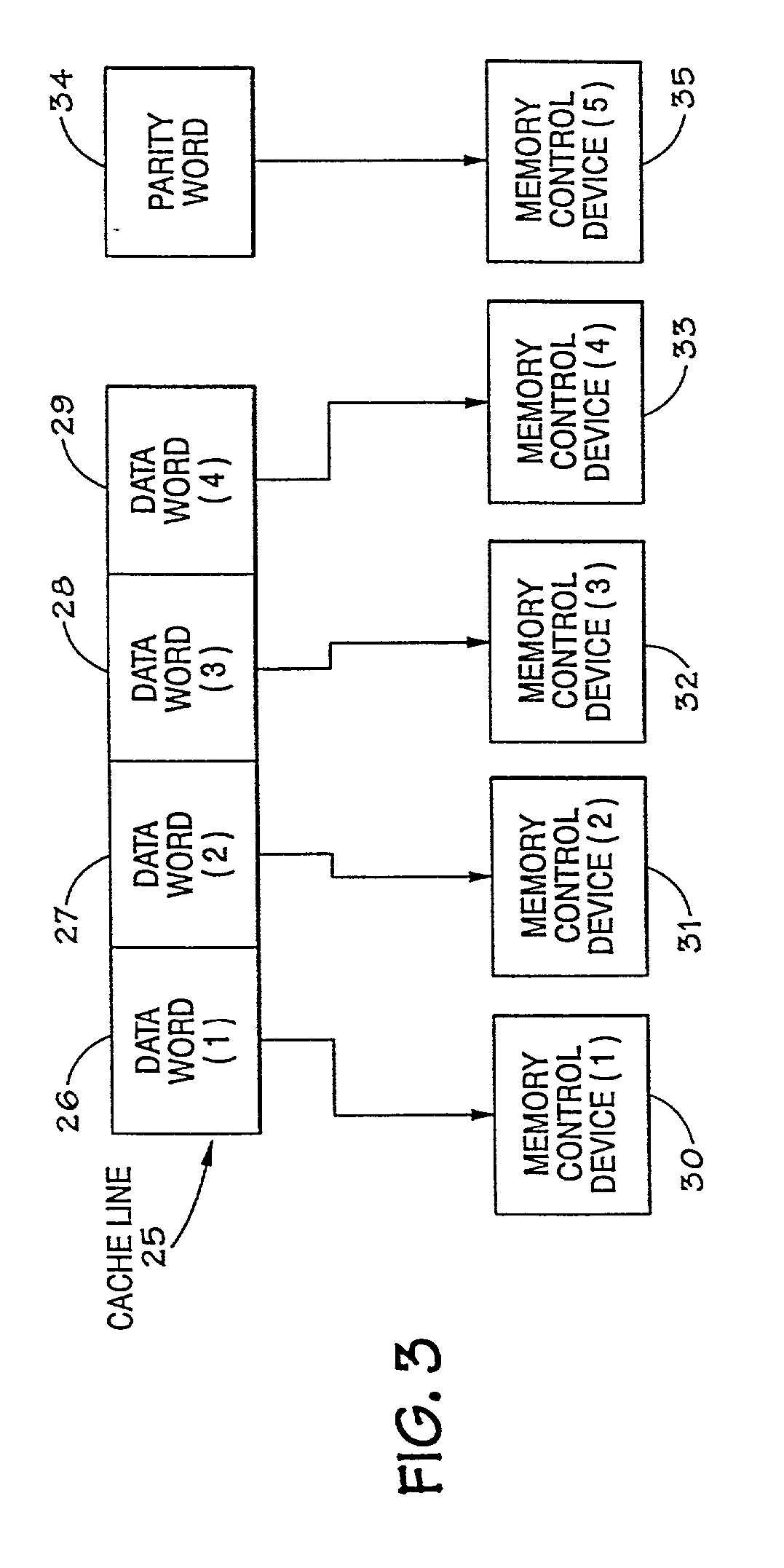
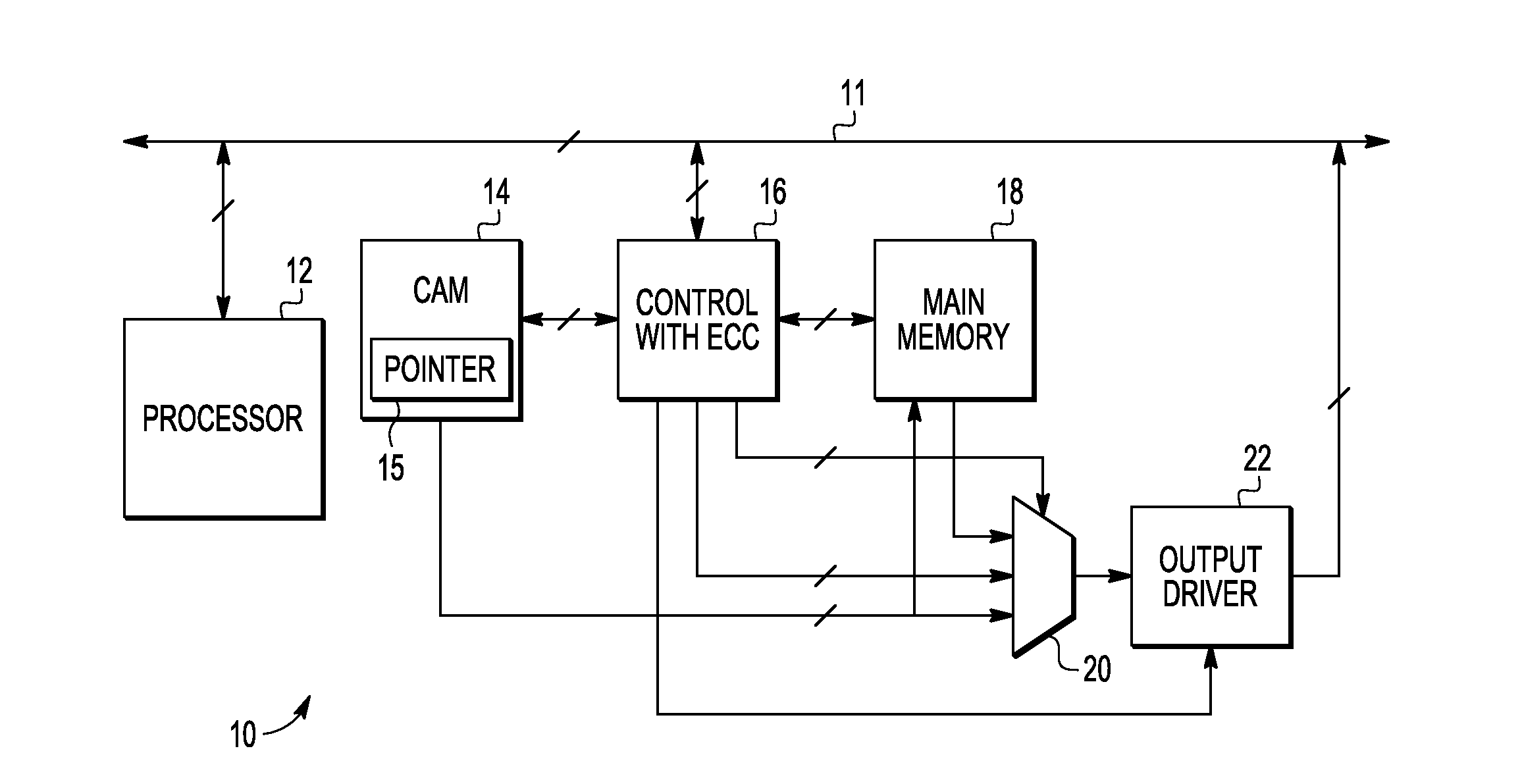
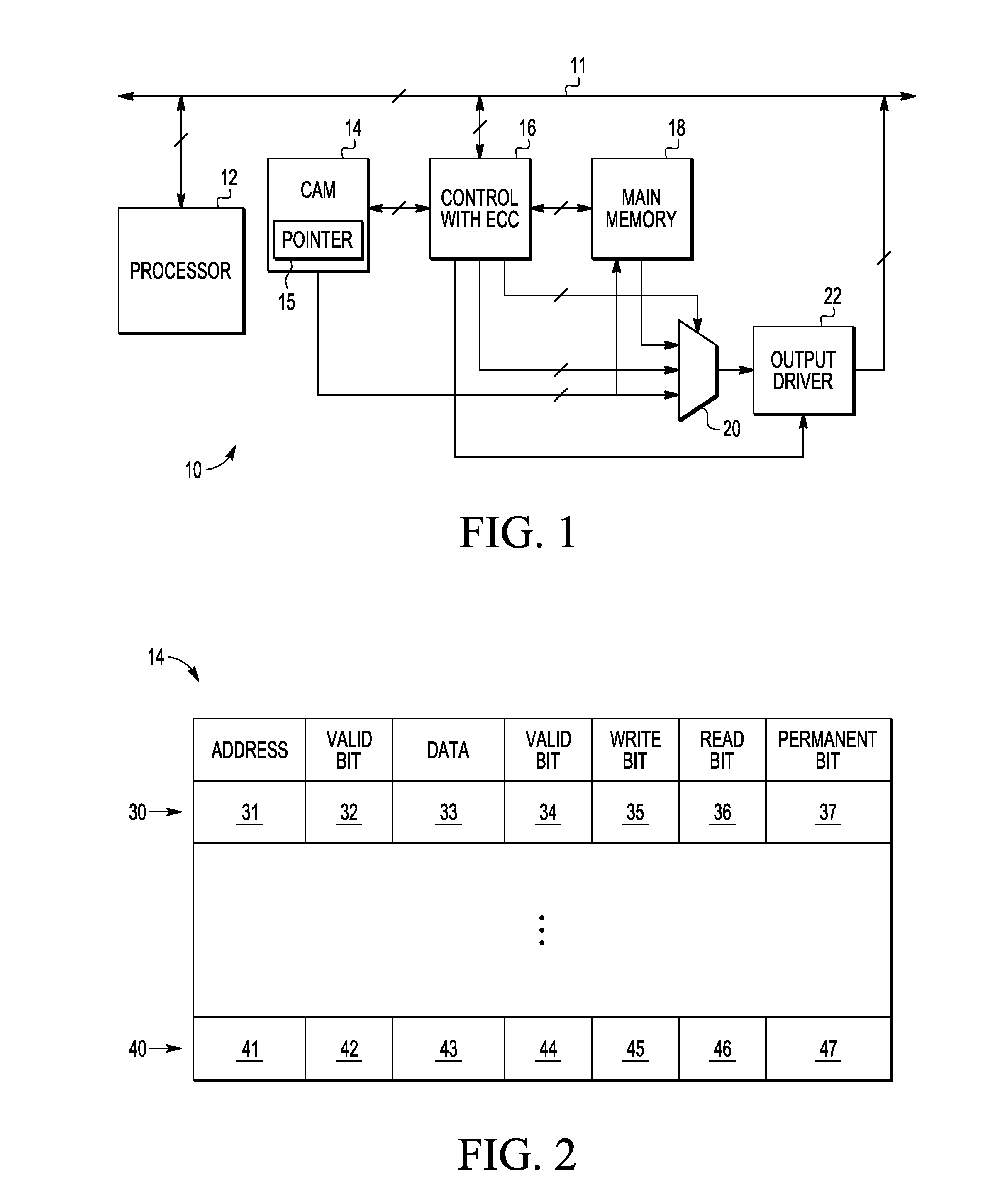
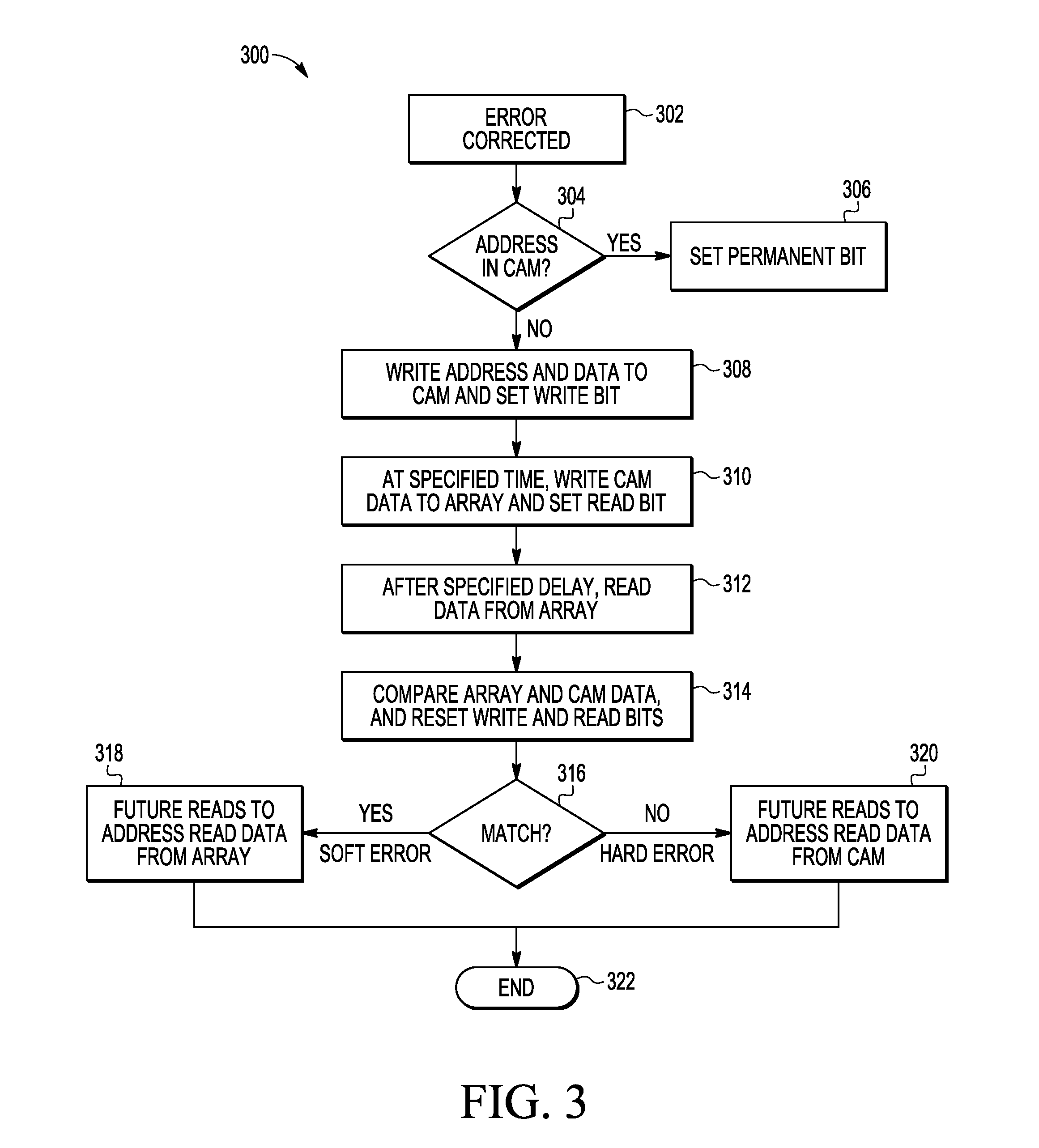
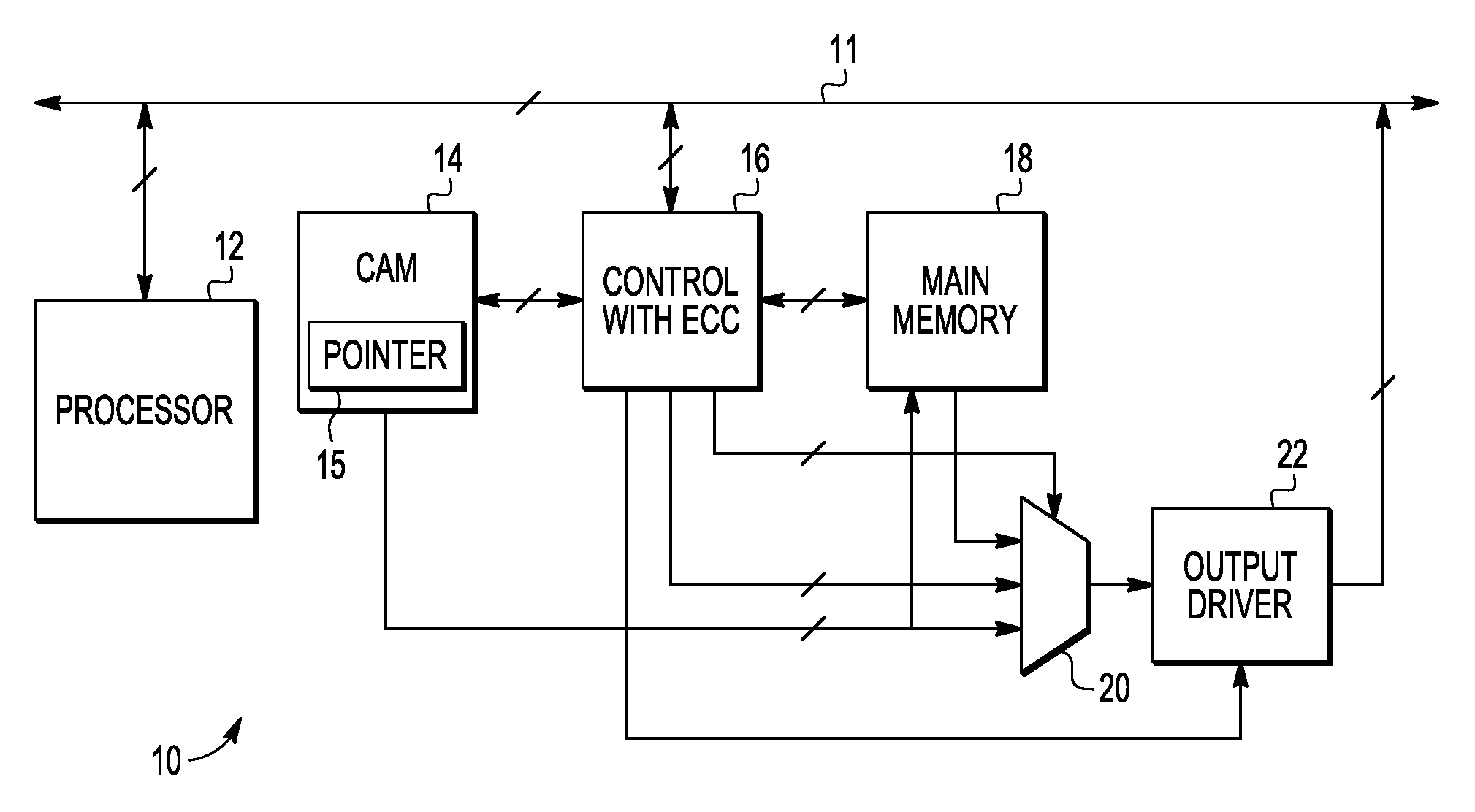
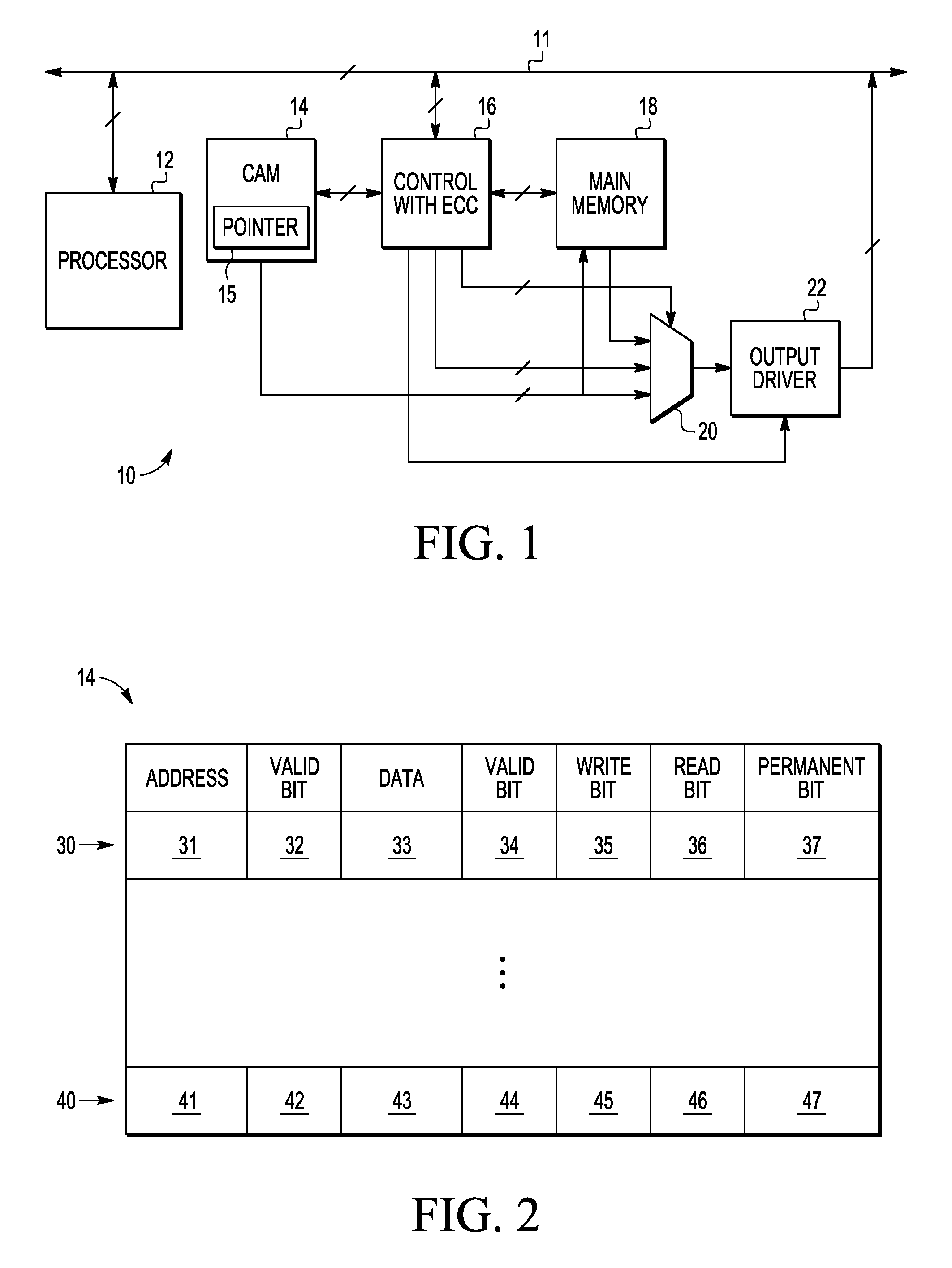
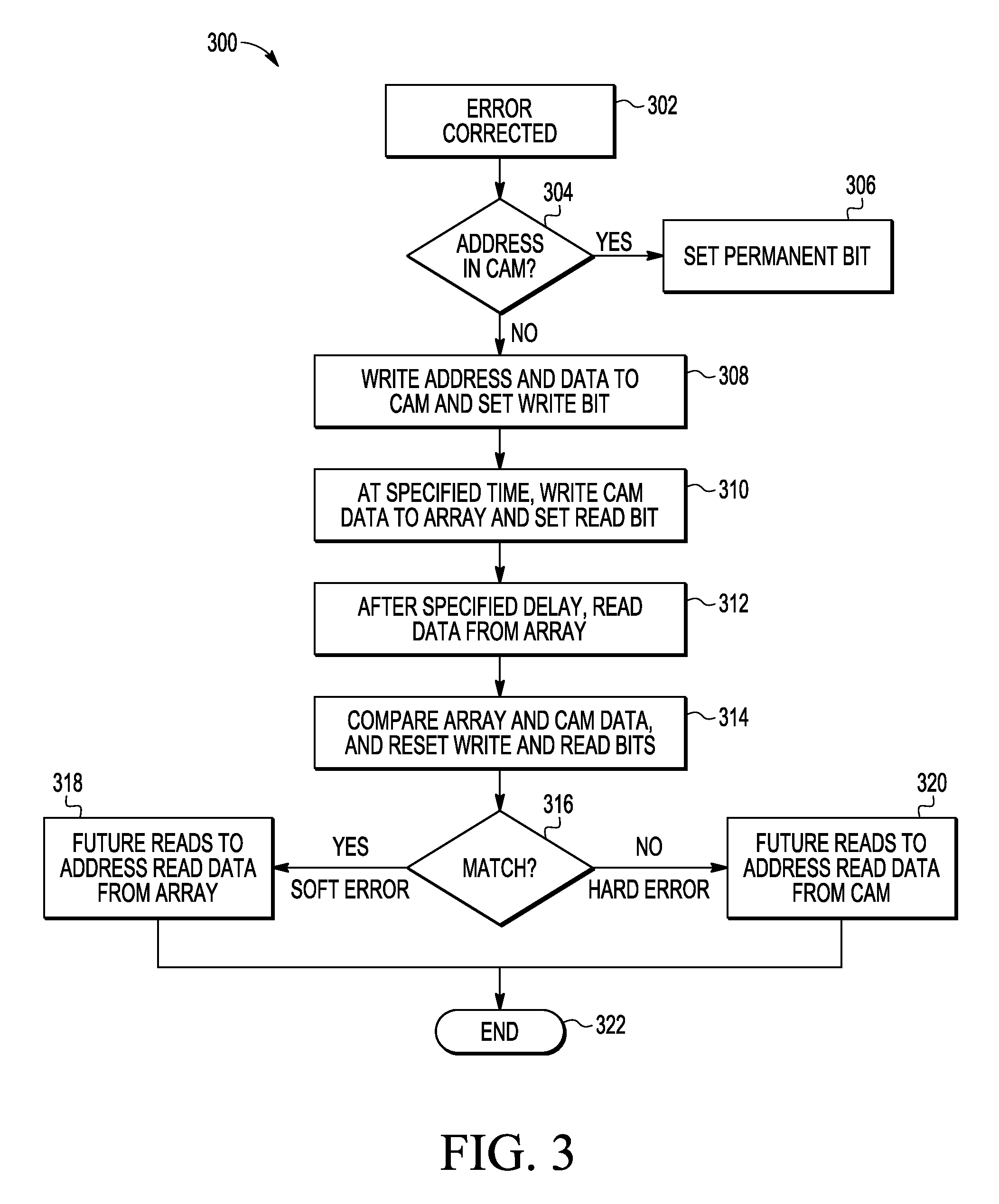
A method and apparatus are provided for error correction of a memory by using a first memory (18) and second memory (14) to perform error correction code (ECC) processing on data retrieved from the first memory and to use status control bits (35-37) in the second memory to detect and manage hard and soft errors identified by the ECC processing.
Owner:NXP USA INC
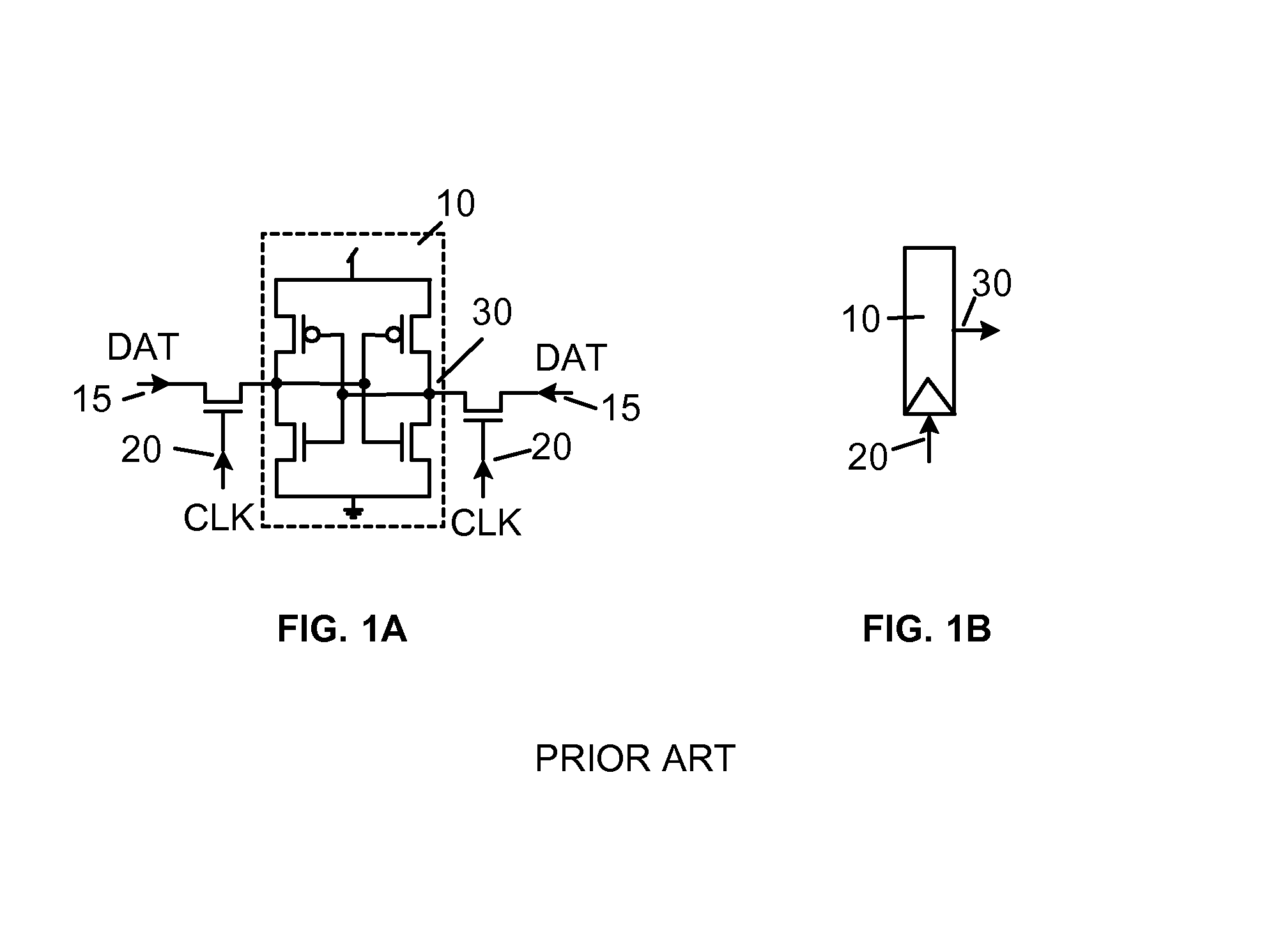
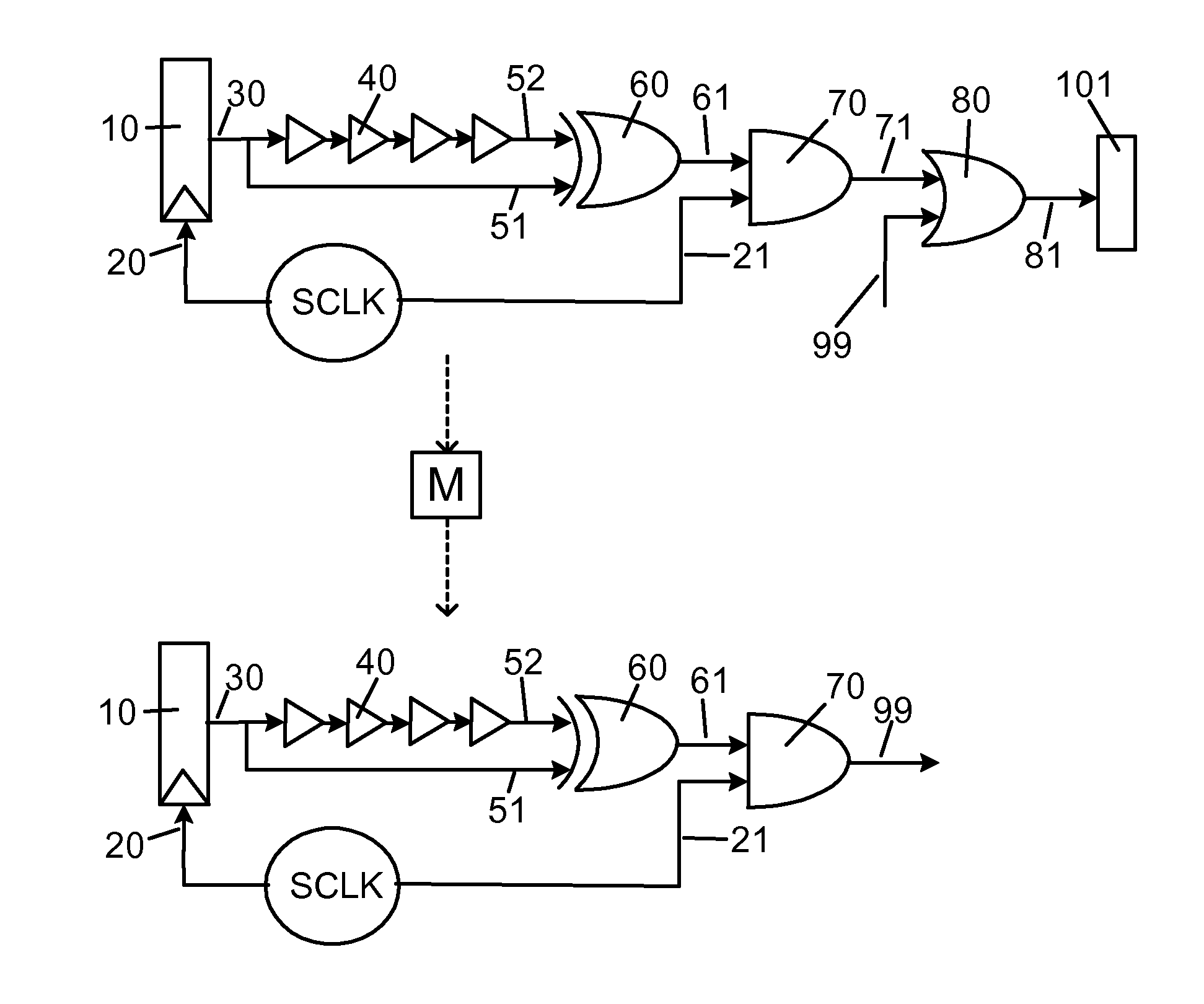
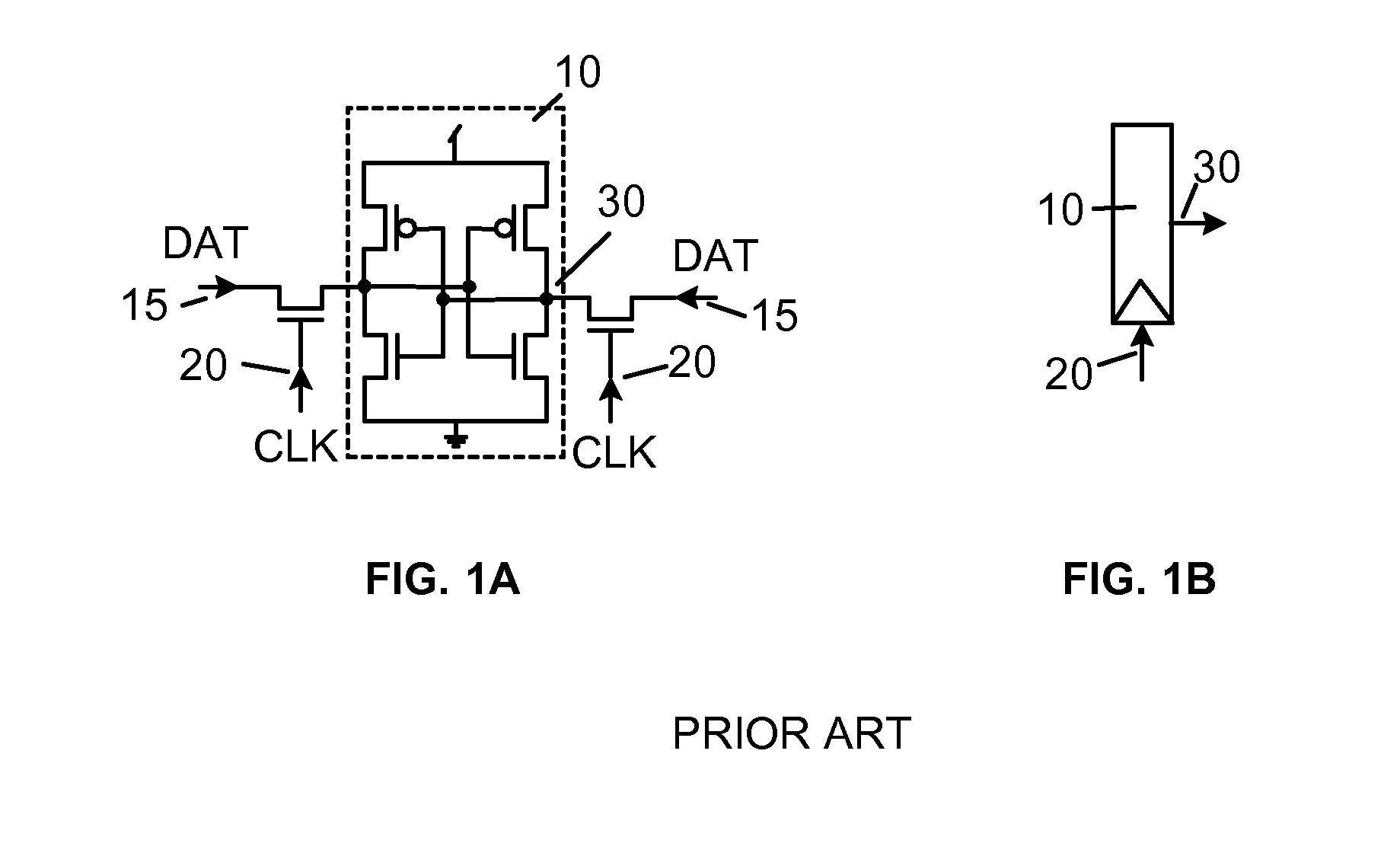
Soft error detection for latches
InactiveUS7977965B1Enabling responseReliability increasing modificationsElectric pulse generatorElectrical and Electronics engineeringSoft error detection
A system and method for soft error detection in digital ICs is disclosed. The system includes an observing circuit coupled to a latch, which circuit is capable of a response upon a state change of the latch. The system further includes synchronized clocking provided to the latch and to the observing circuit. For the latch, the clocking defines a window in time during which the latch is prevented from receiving data, and in a synchronized manner the clocking is enabling a response in the observing circuit. The clocking is synchronized in such a manner that the circuit is enabled for its response only inside the window when the latch is prevented from receiving data. The system may also have additional circuits that are respectively coupled to latches, with each the additional circuit and its respective latch receiving the synchronized clocking. Responses of a plurality of circuits may be coupled in a configuration corresponding to a logical OR.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Storage system comprising logical circuit configured in accordance with information in memory on PLD
InactiveUS20070050689A1Reduce throughputElectronic circuit testingStatic storageComputer hardwareData transmission
The storage system comprises a PLD which controls data transfer between another device and a media drive; and a processor. The PLD comprises a memory for storing information input from an information source located externally to the PLD; a circuit element group comprising a plurality of circuit elements; and a logical circuit configured on the circuit element group in accordance with the information in the memory. The processor detects whether a soft error has occurred in the memory, detects whether or not an error has occurred in the logical circuit, and implements control in accordance with the results of the two detection operations.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
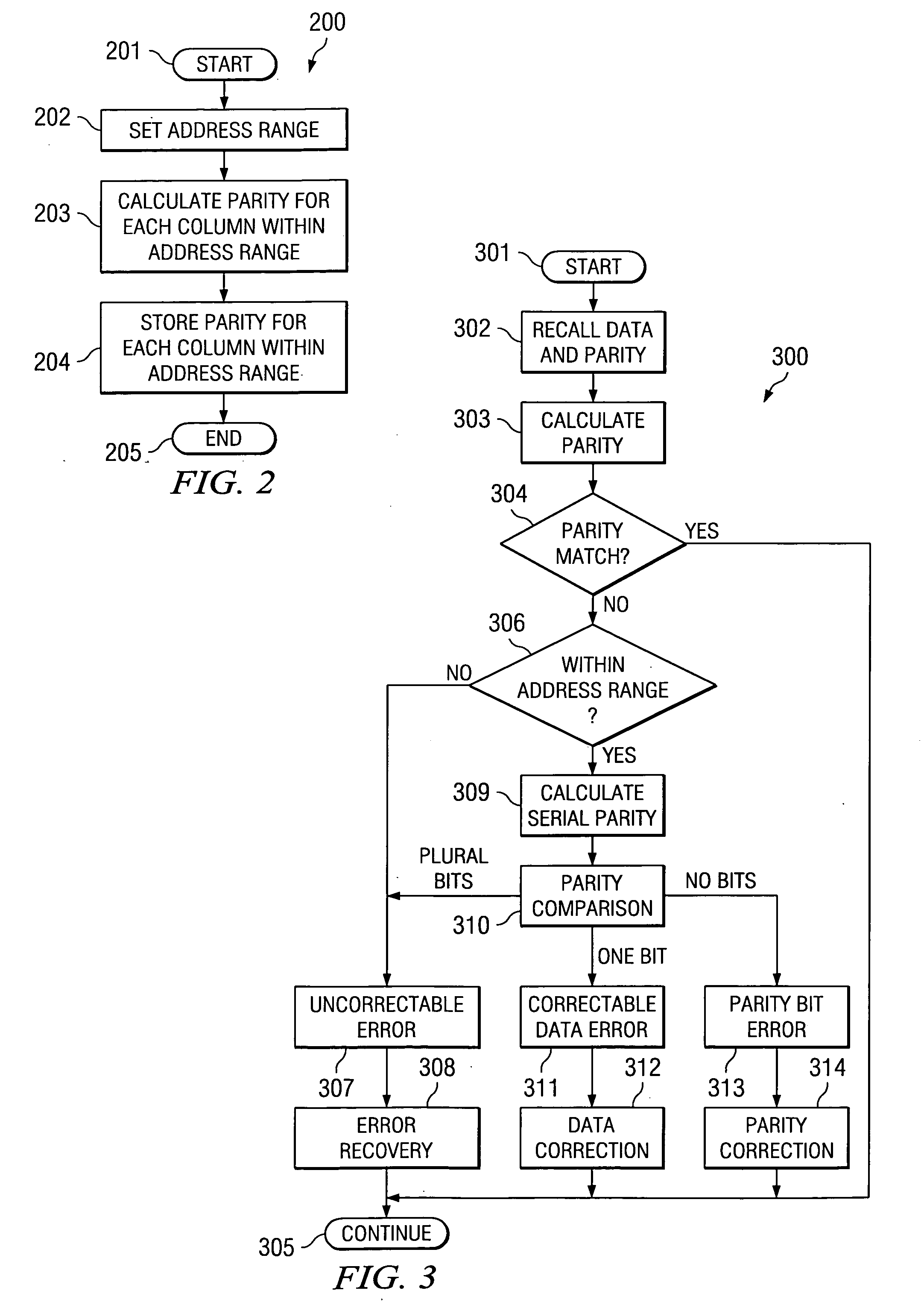
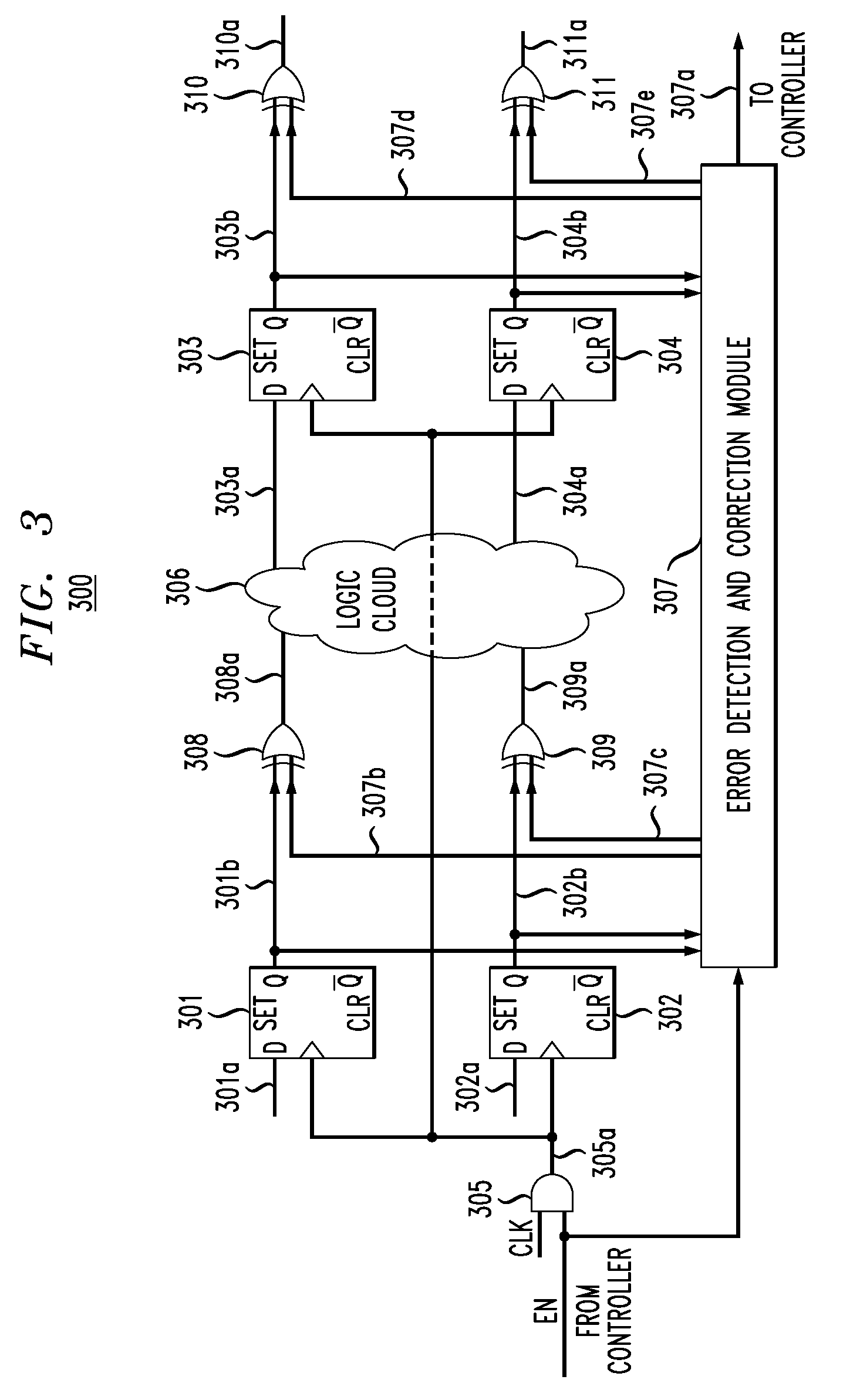
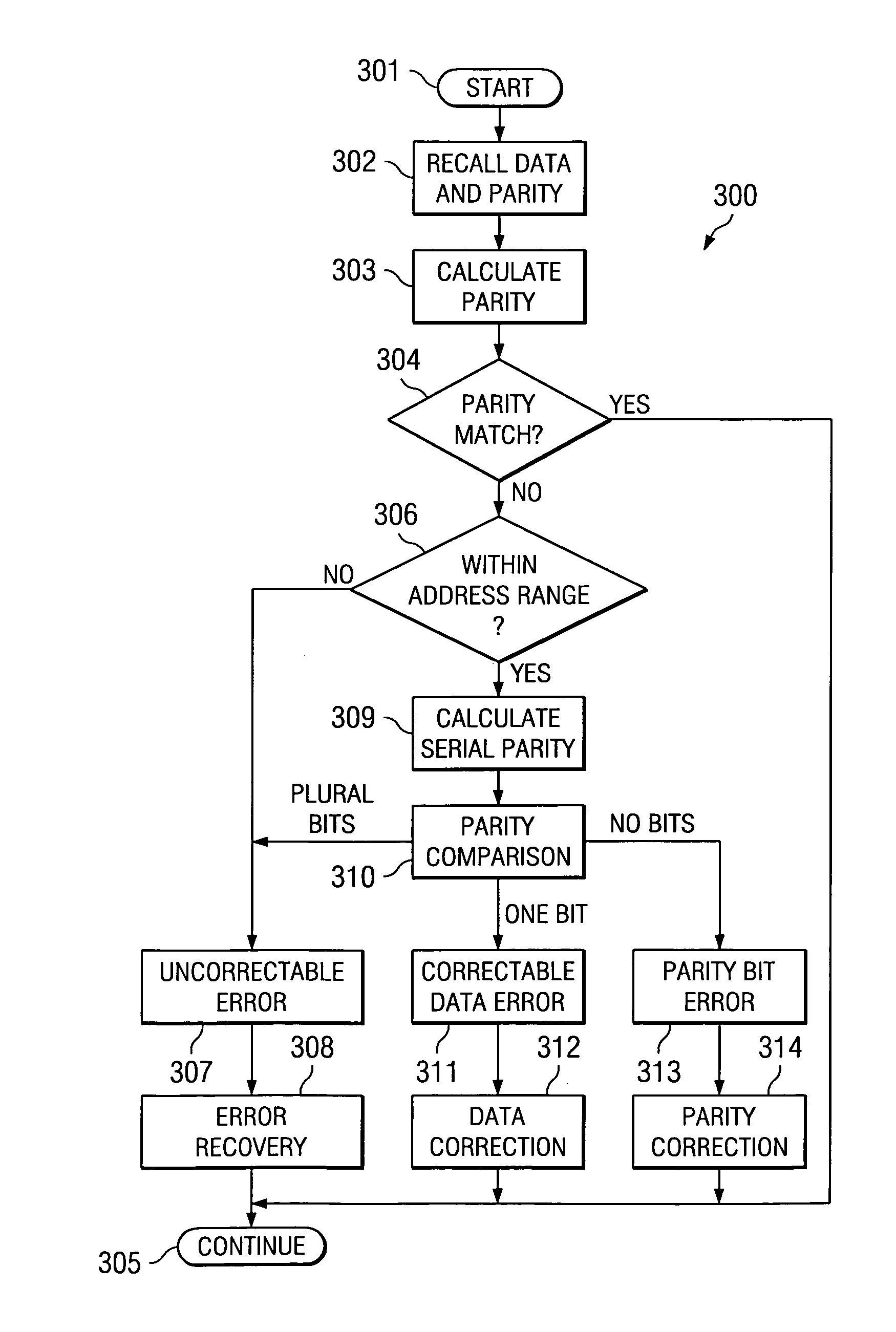
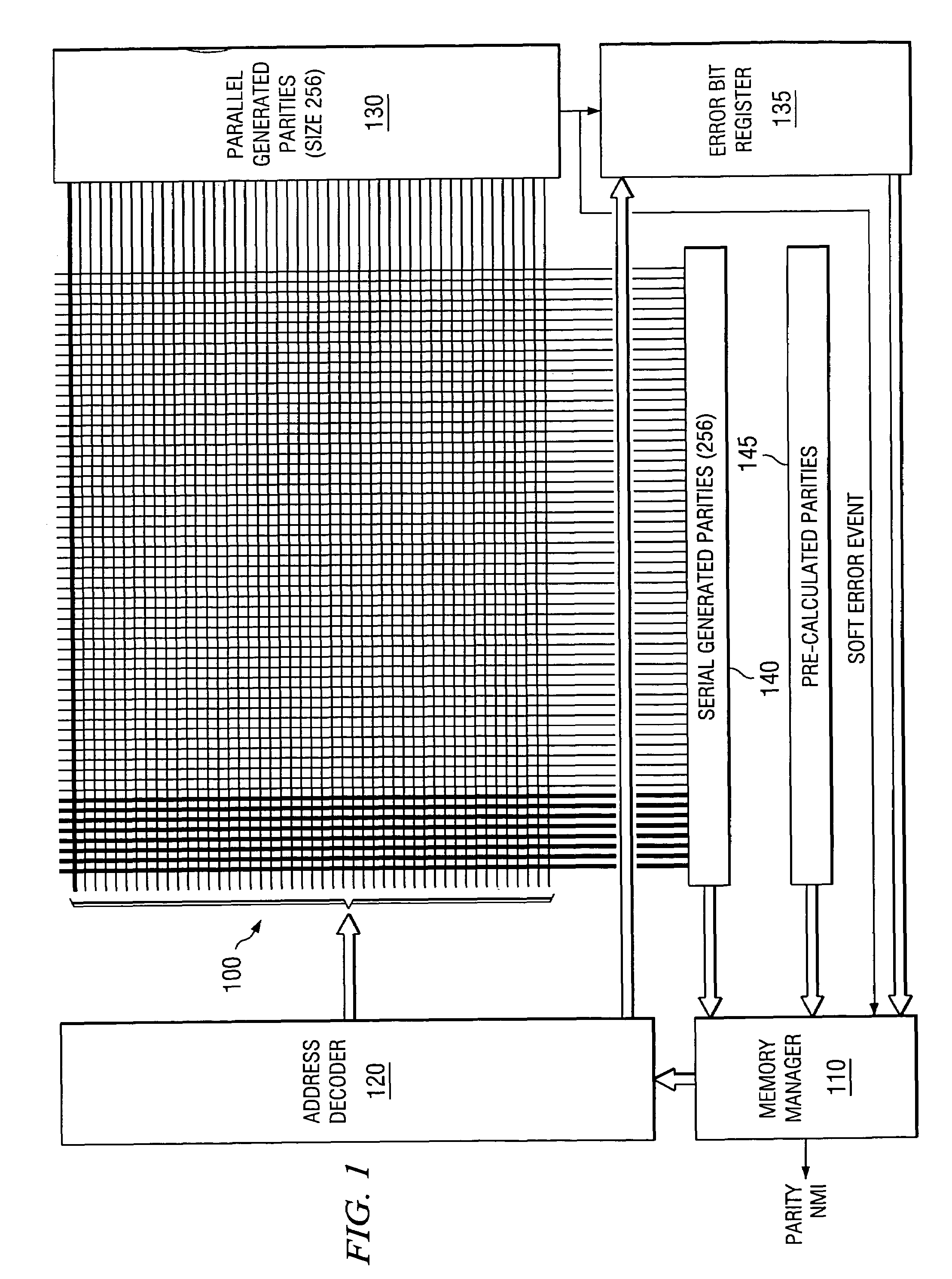
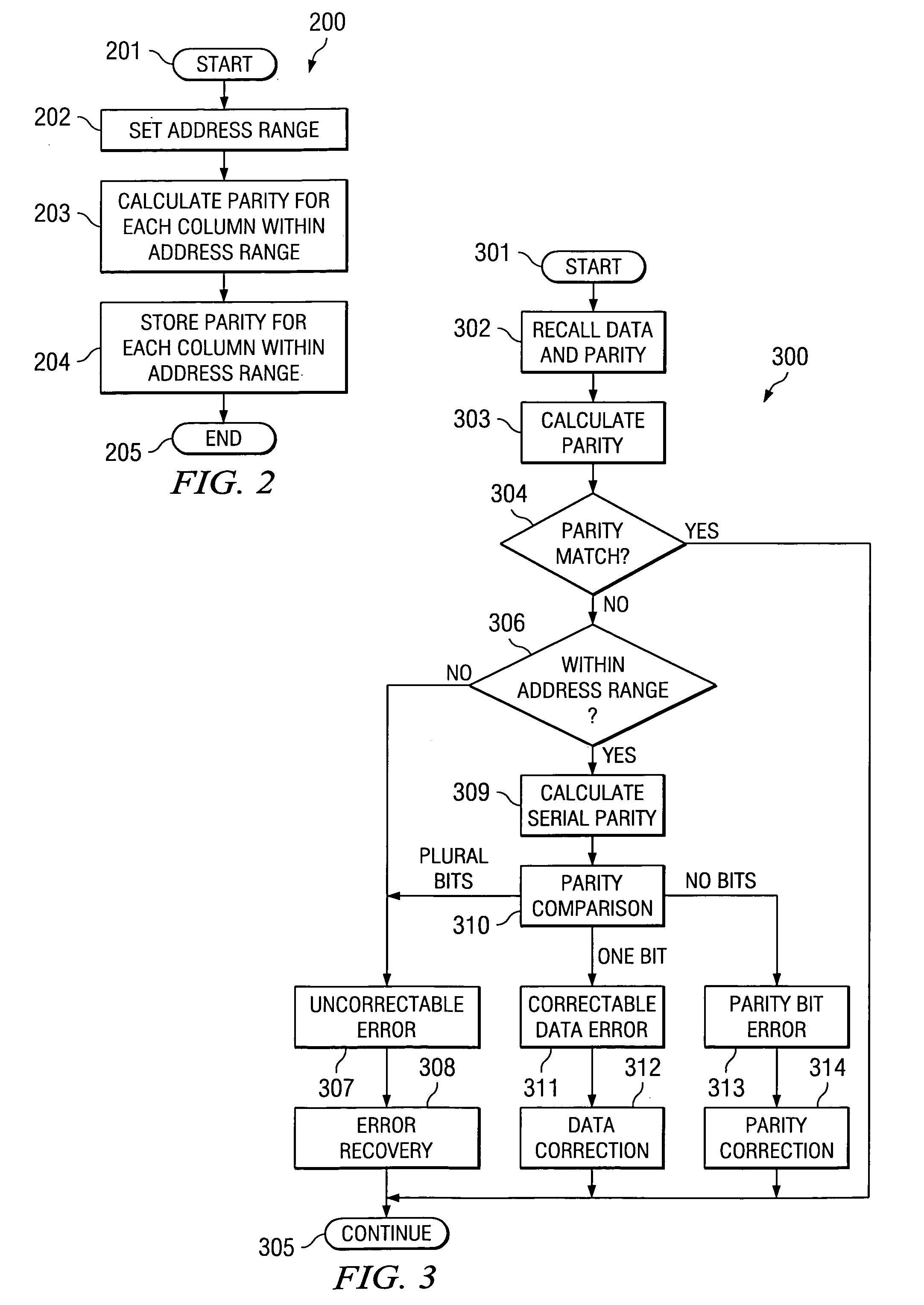
Soft error detection and correction by 2-dimensional parity
ActiveUS20050149839A1Increase in memory sizeReduce morbidityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresMemory controllerComputer science
The parity of this invention includes two arrays of parities surrounding the memory. One array is generated in parallel. The other array is generated in serial. The two dimensional parity is used to protect, locate and correct errors automatically. The second parity is provided for only a subset of the address range of the memory. The memory controller does not compare the second parities unless there is a soft error in the first parity. The second parities are calculated upon command and not upon each memory write as the first parity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
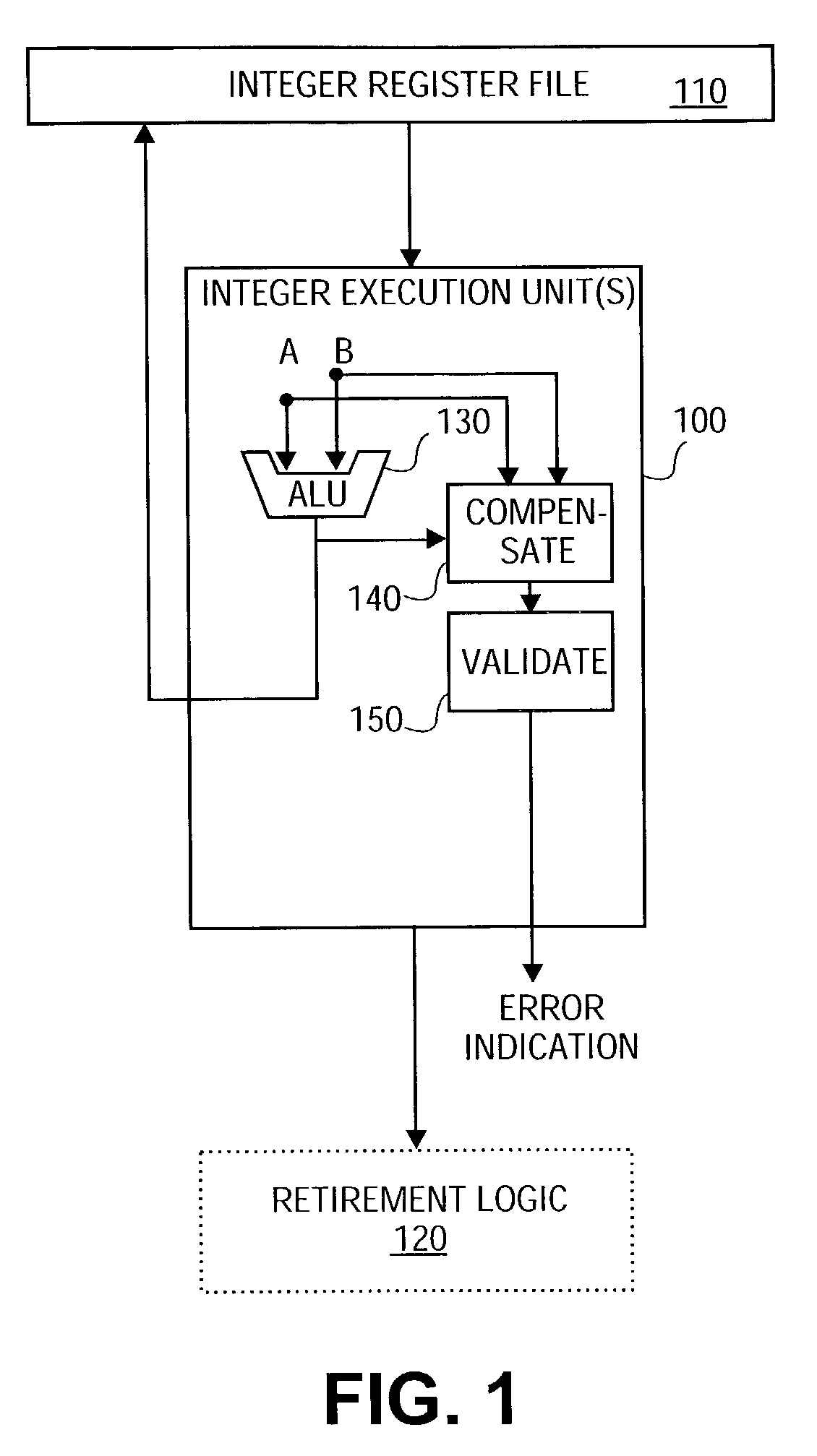
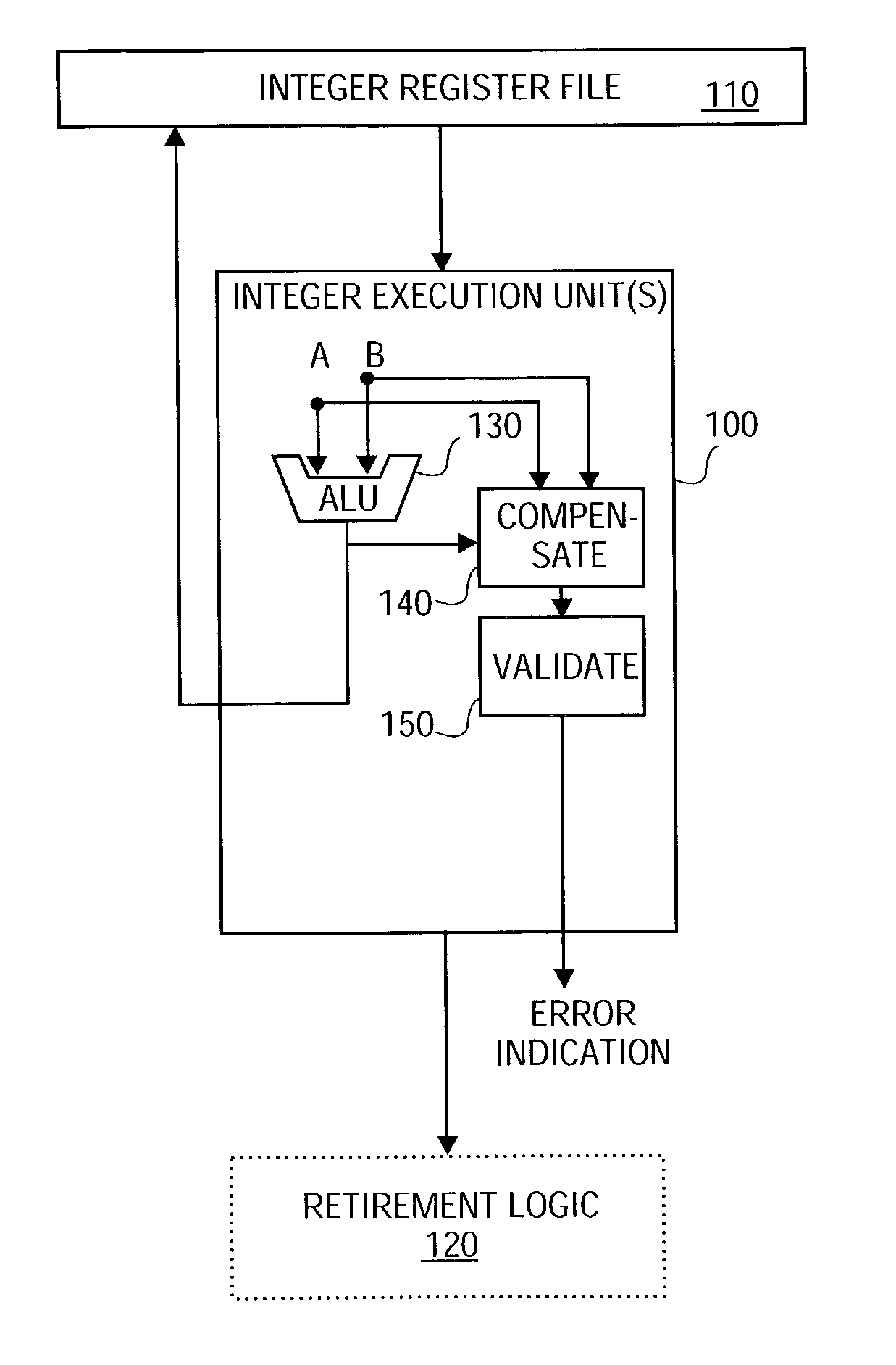
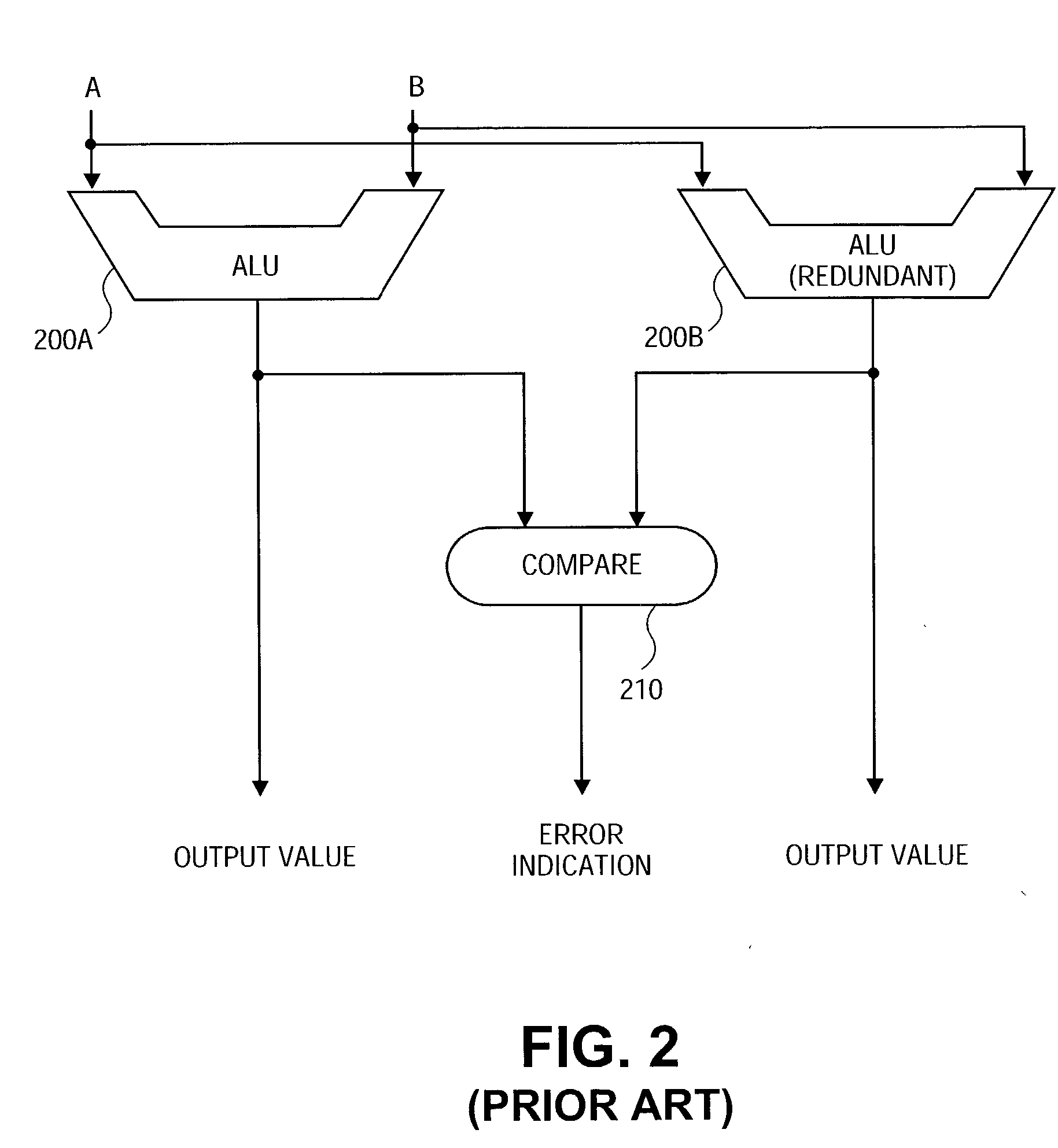
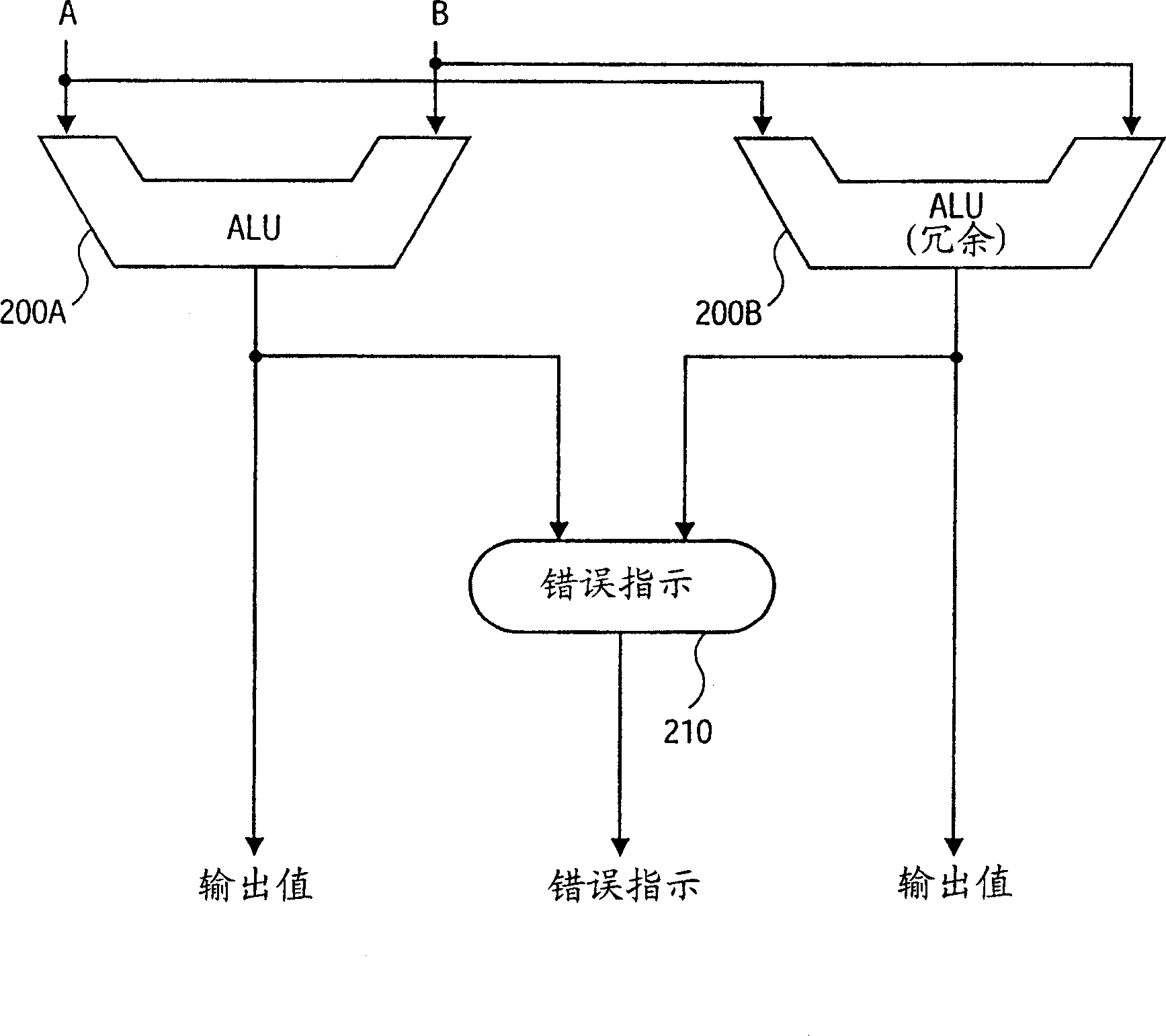
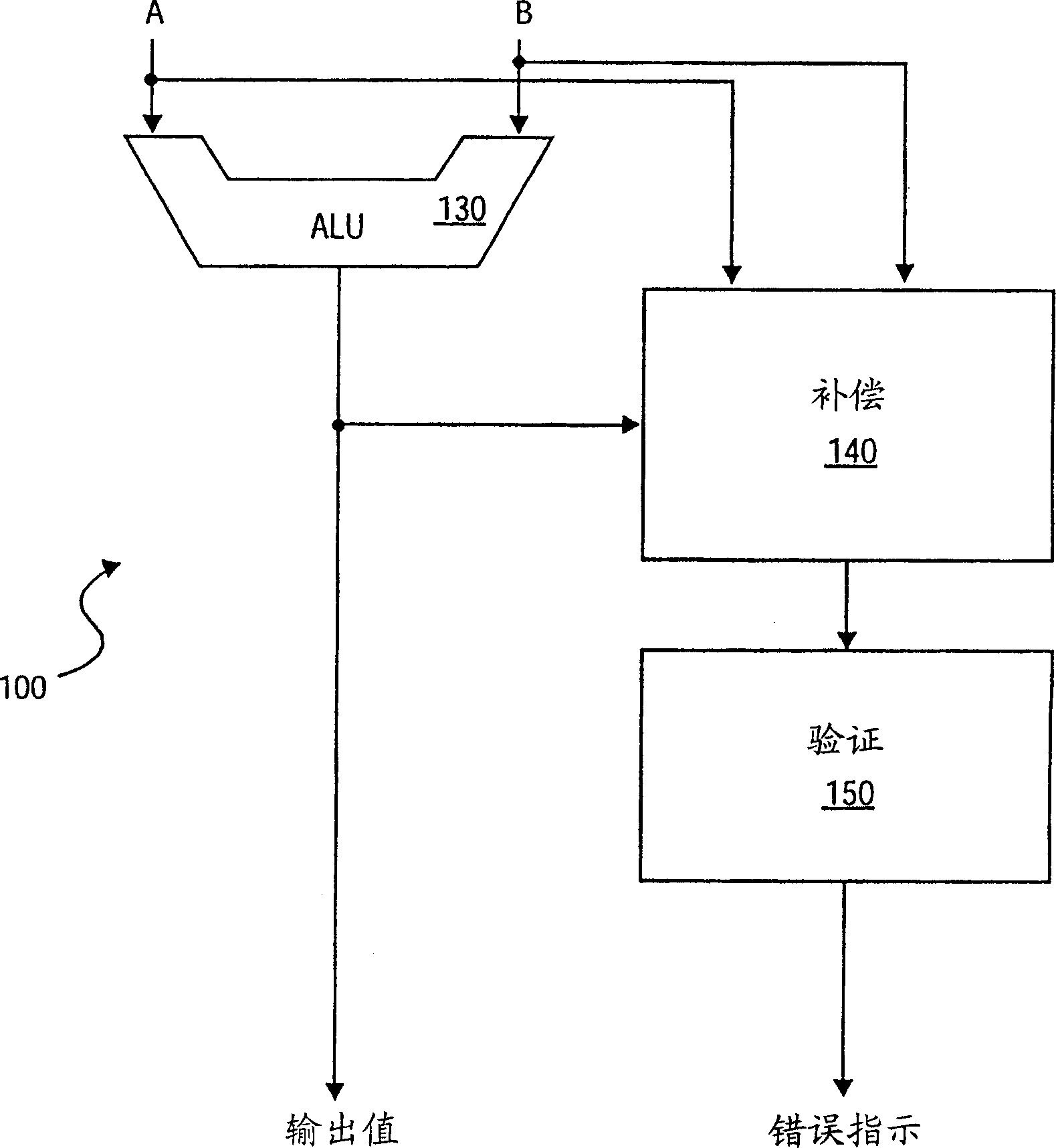
Reduced-hardware soft error detection
A method and system are provided for performing soft error detection for integer addition and subtraction operations without the use of redundant logic. For integer addition and subtraction, compensate logic produces a compensate value utilizing arithmetic logic unit (ALU) result and operands. The compensate value is validated by the validate logic against a predetermined value to determine whether a soft error has occurred. Such compensate logic and validate logic operate on the integer operands and on the result produced by the ALU without redundant carry-propagate hardware.
Owner:INTEL CORP
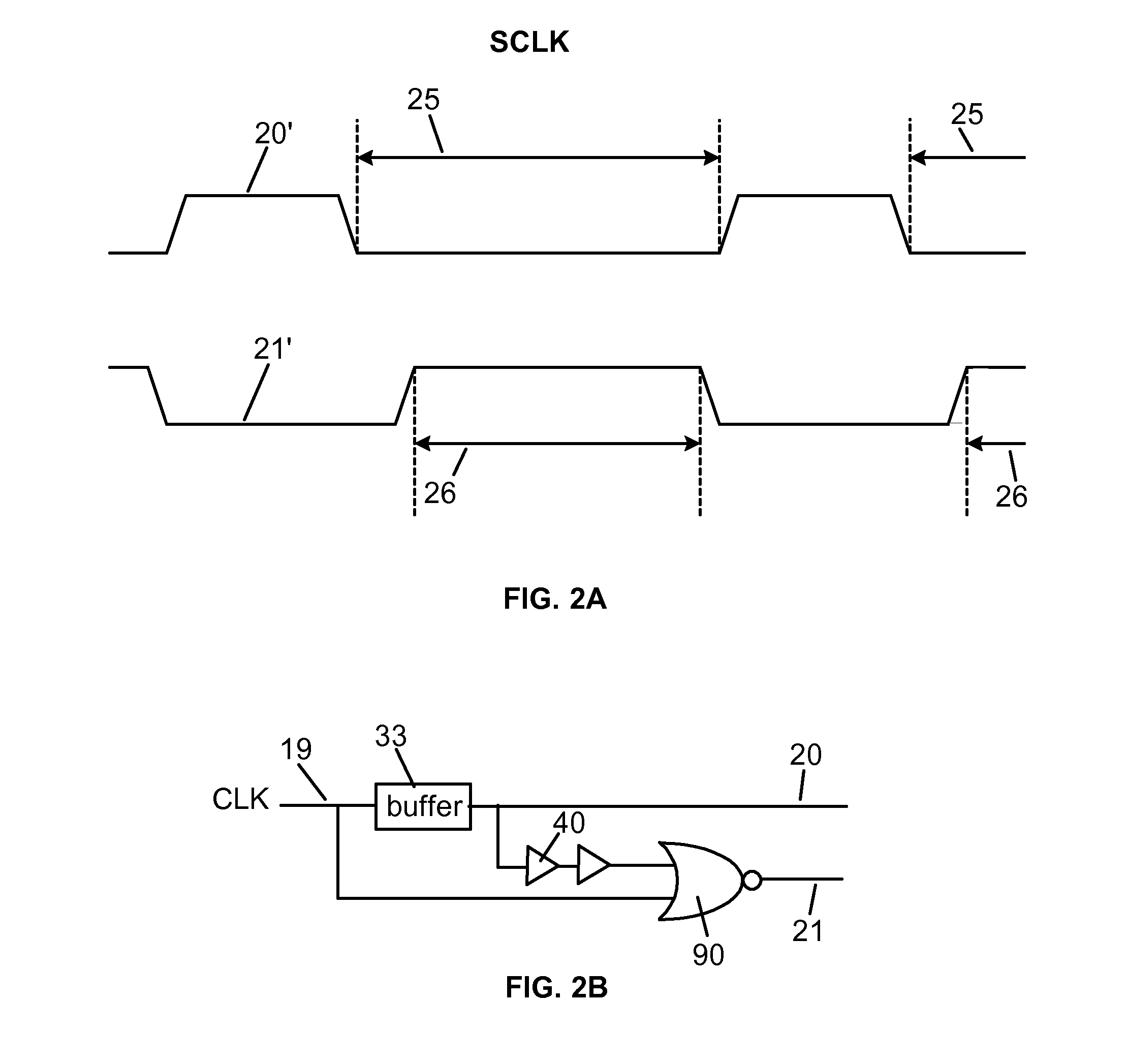
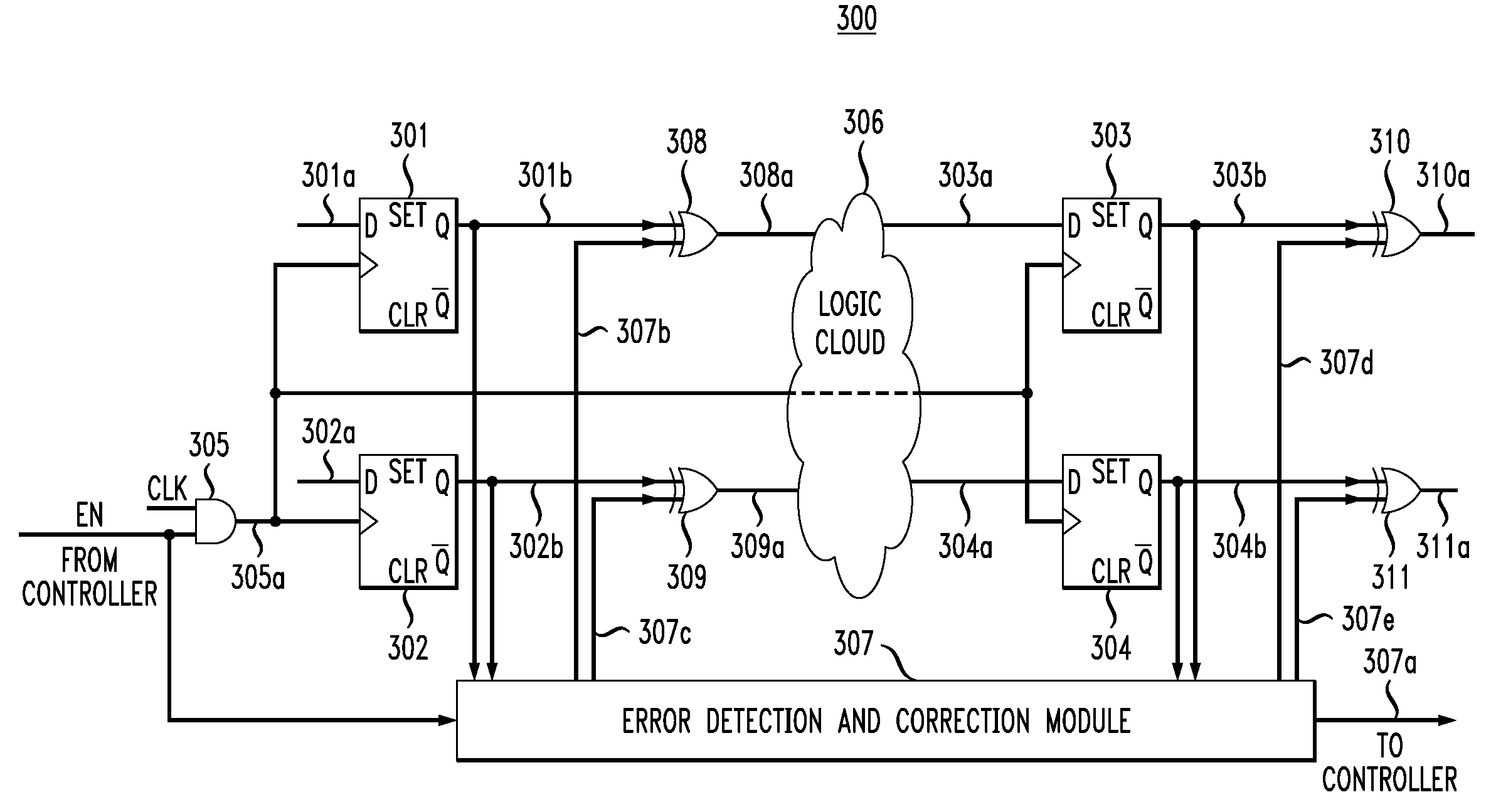
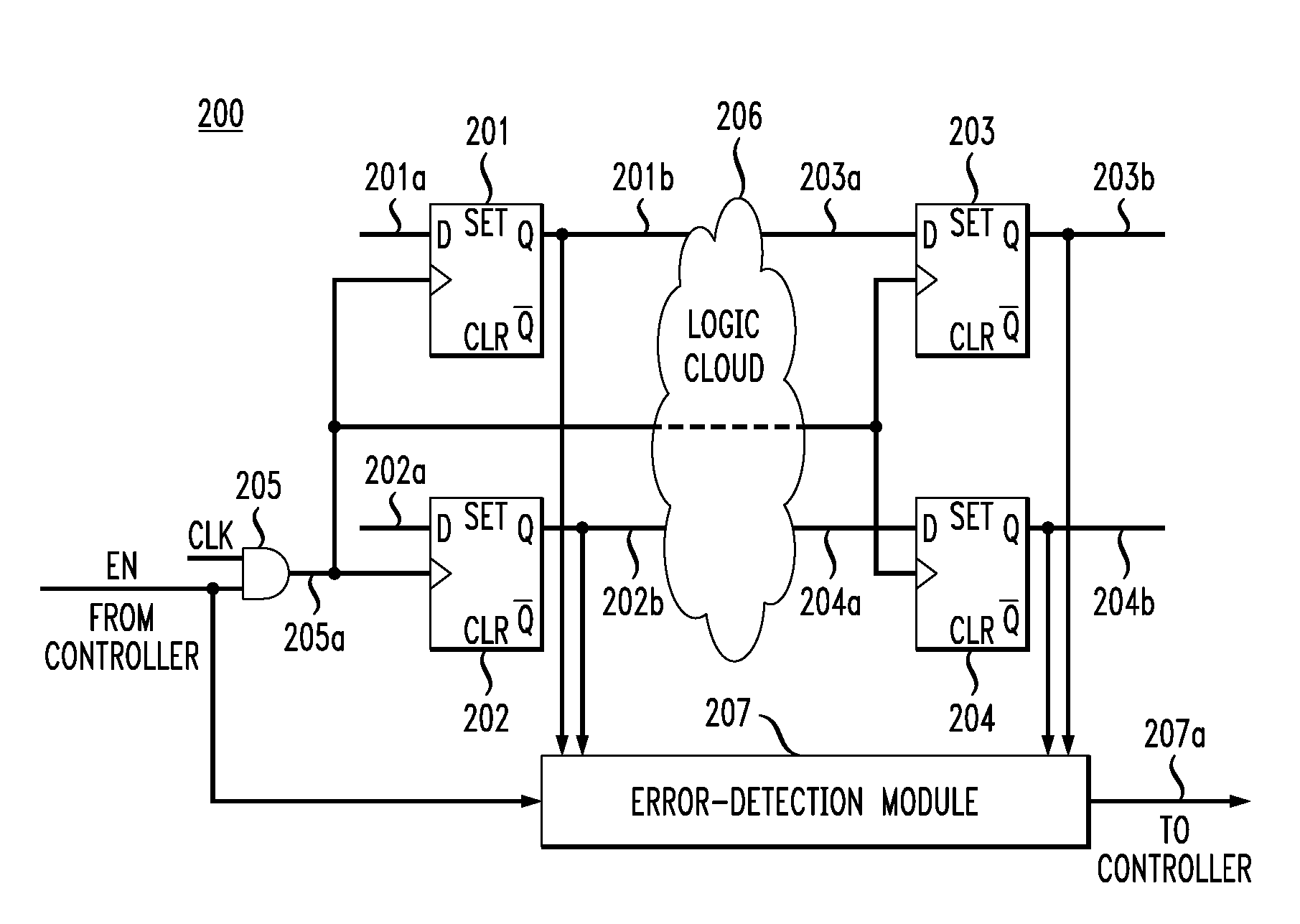
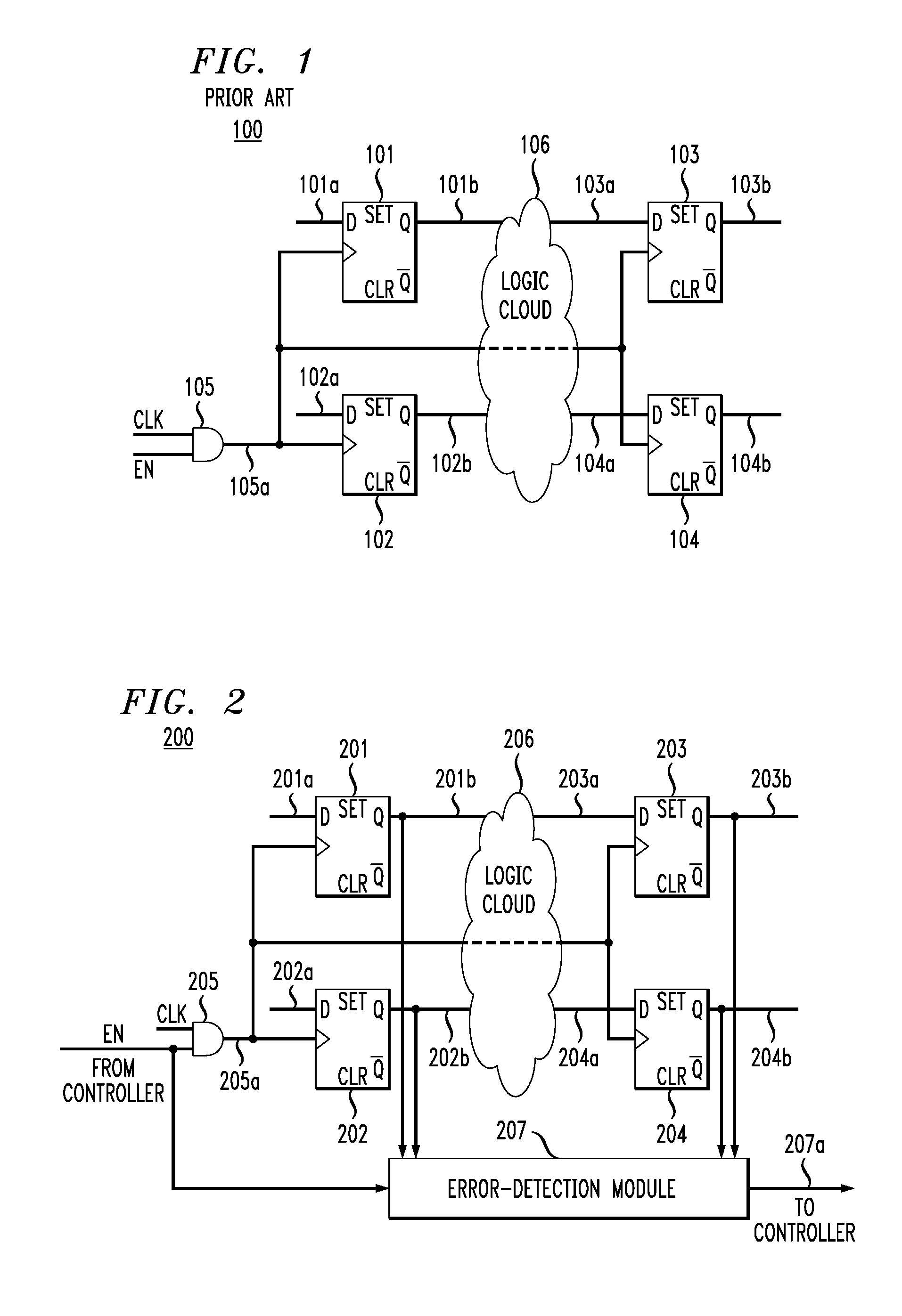
Soft-error detection for electronic-circuit registers
In one embodiment, a circuit has multiple flip-flops with gated clock inputs controlled by an enable signal, where the clock signal is gated in order to reduce power consumption by the circuit. The circuit has an error detection and correction (EDC) module that is active when the enable signal is low in order to detect and correct soft errors of the flip-flops. The EDC module generates and stores an error-correction code based on the data outputs of the flip-flops. The EDC module then compares the stored error-correction code to a presently generated error-correction code, where if they are not identical, then the EDC (a) determines (i) that a soft error has occurred and (ii) which flip-flop suffered the soft error and (b) flips a corresponding error-correction signal to provide a correct corresponding output signal while the enable signal is low.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Soft error detection and correction by 2-dimensional parity
ActiveUS7380200B2Increase in sizeReduce morbidityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareArray data structure
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
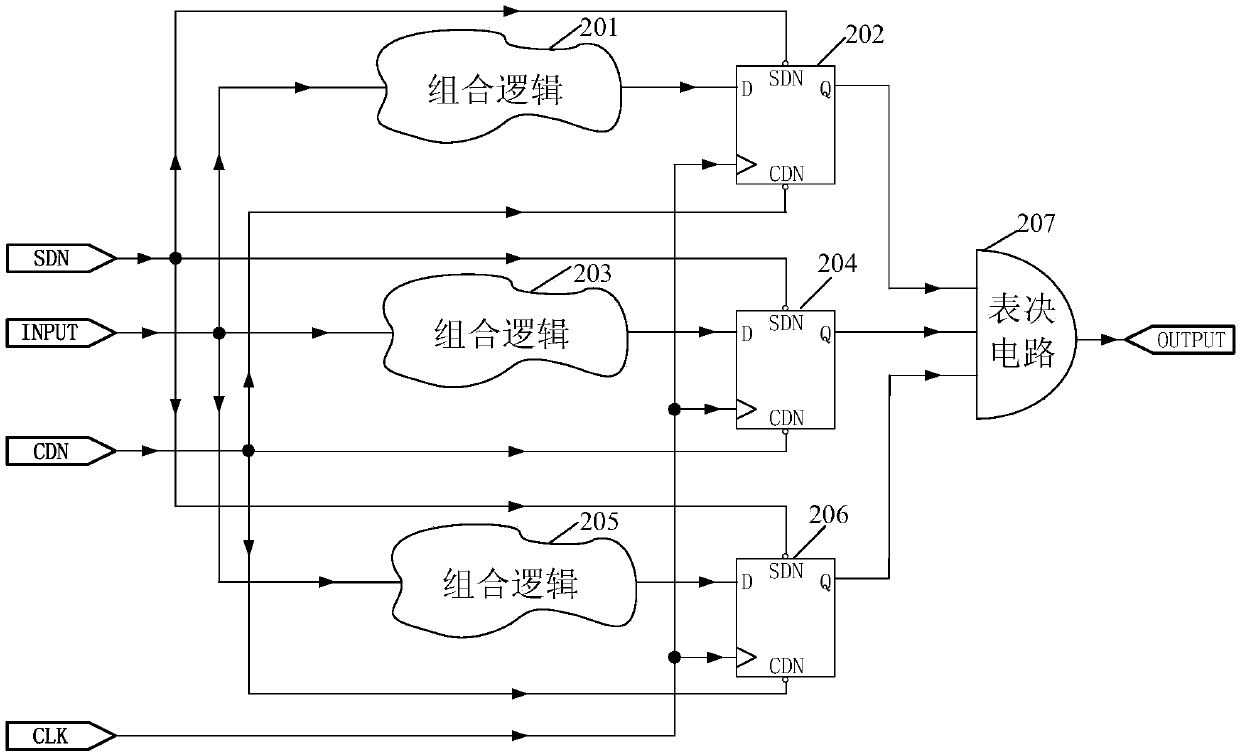
Self-restoring three-mode redundancy structure for defending single-particle soft error accumulation
ActiveCN108055031ASolve reinforcement failureReliability increasing modificationsSoft error detectionData selection
The invention discloses a self-restoring three-mode redundancy structure for defending single-particle soft error accumulation. A single-particle soft error detection circuit and a data selection circuit are added to perform optimized design on a circuit, the design based on the structure can automatically restore after single-path signal overturning in the three-mode redundancy structure, and theproblem that the three-mode redundancy structure may cause single-particle reinforcement failure due to error accumulation is effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
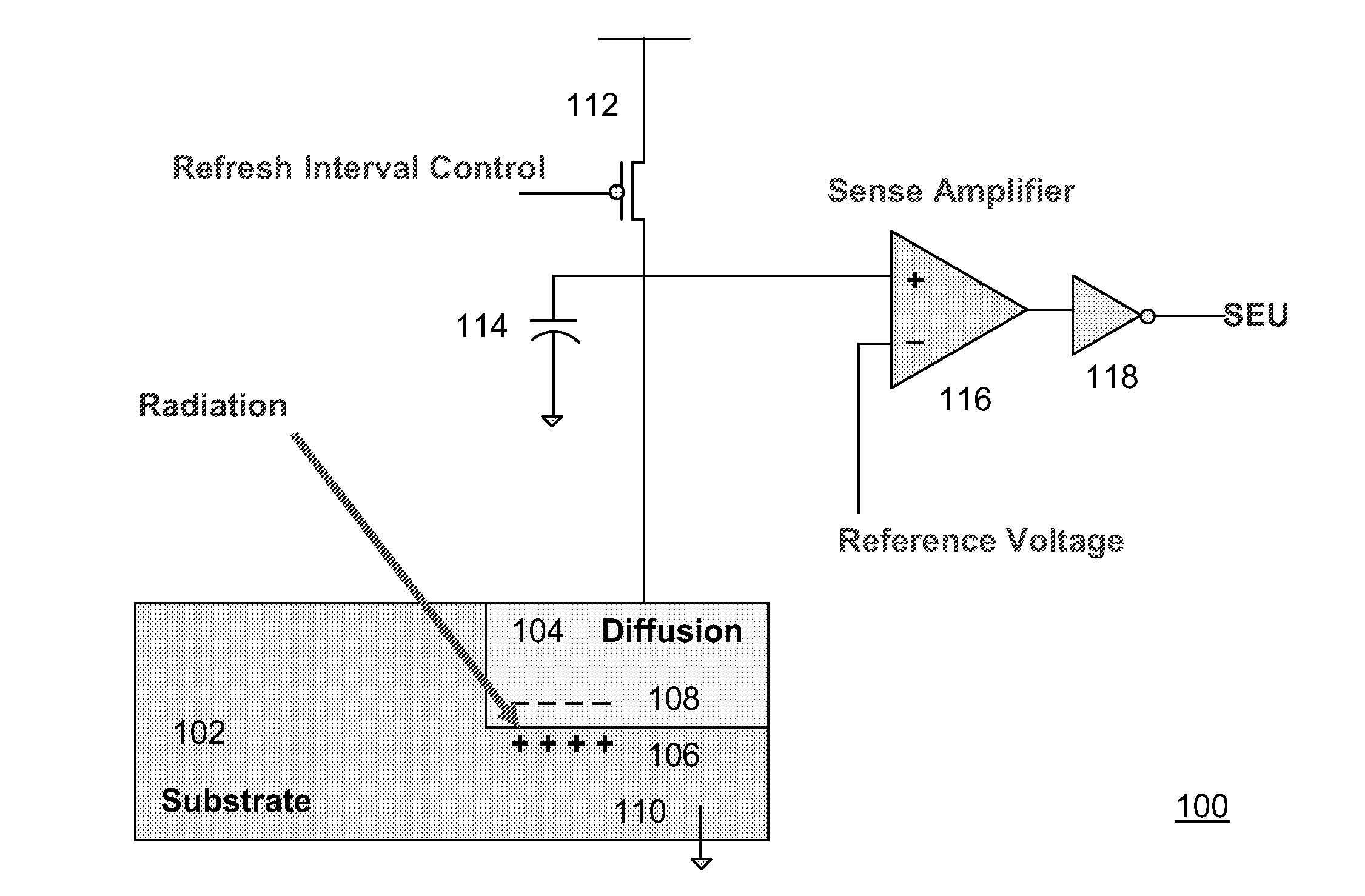
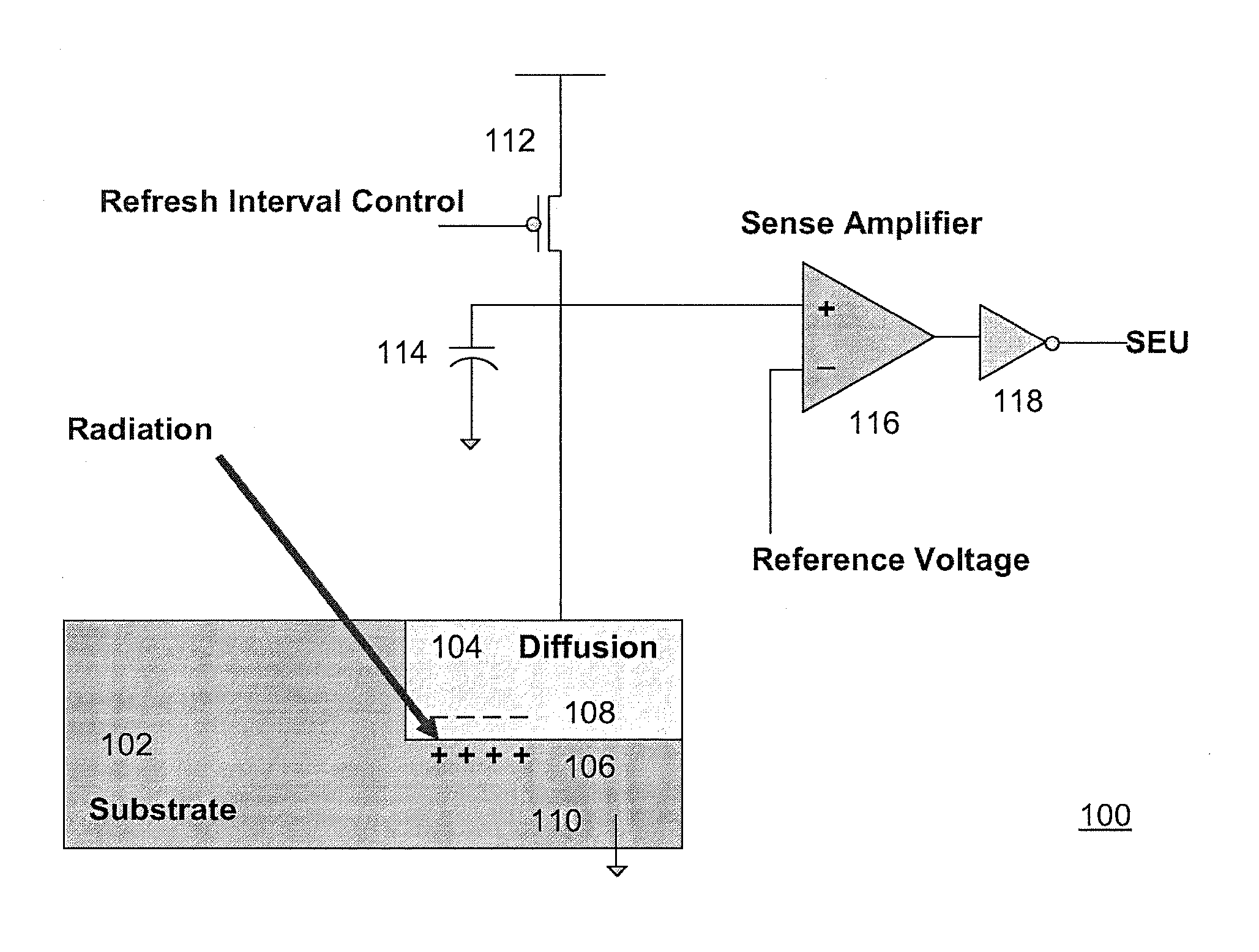
Programmable Heavy-Ion Sensing Device for Accelerated Dram Soft Error Detection
ActiveUS20080273393A1Facilitate and accelerate mappingReduce power supply voltageRead-only memoriesElectrical testingDual modeAlpha particle
Aspects of the invention relate to a programmable heavy-ion sensing device for accelerated DRAM soft error detection. Design of a DRAM-based alpha particle sensing apparatus is preferred to be used as an accelerated on-chip SER test vehicle. The sensing apparatus is provided with programmable sensing margin, refresh rate, and supply voltage to achieve various degree of SER sensitivity. In addition, a dual-mode DRAM array is proposed so that at least a portion of the array can be used to monitor high-energy particle activities during soft-error detection (SED) mode.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Programmable Heavy-Ion Sensing Device for Accelerated DRAM Soft Error Detection
ActiveUS20080266984A1Facilitate and accelerate mappingReduce power supply voltageElectrical testingDigital storageDual modeAlpha particle
Aspects of the invention relate to a programmable heavy-ion sensing device for accelerated DRAM soft error detection. Design of a DRAM-based alpha particle sensing apparatus is preferred to be used as an accelerated on-chip SER test vehicle. The sensing apparatus is provided with programmable sensing margin, refresh rate, and supply voltage to achieve various degree of SER sensitivity. In addition, a dual-mode DRAM array is proposed so that at least a portion of the array can be used to monitor high-energy particle activities during soft-error detection (SED) mode.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Reduced-hardware soft error detection
A method and system are provided for performing soft error detection for integer addition and subtraction operations without the use of redundant logic. For integer addition and subtraction, compensate logic produces a compensate value utilizing arithmetic logic unit (ALU) result and operands. The compensate value is validated by the validate logic against a predetermined value to determine whether a soft error has occurred. Such compensate logic and validate logic operate on the integer operands and on the result produced by the ALU without redundant carry-propagate hardware.
Owner:INTEL CORP
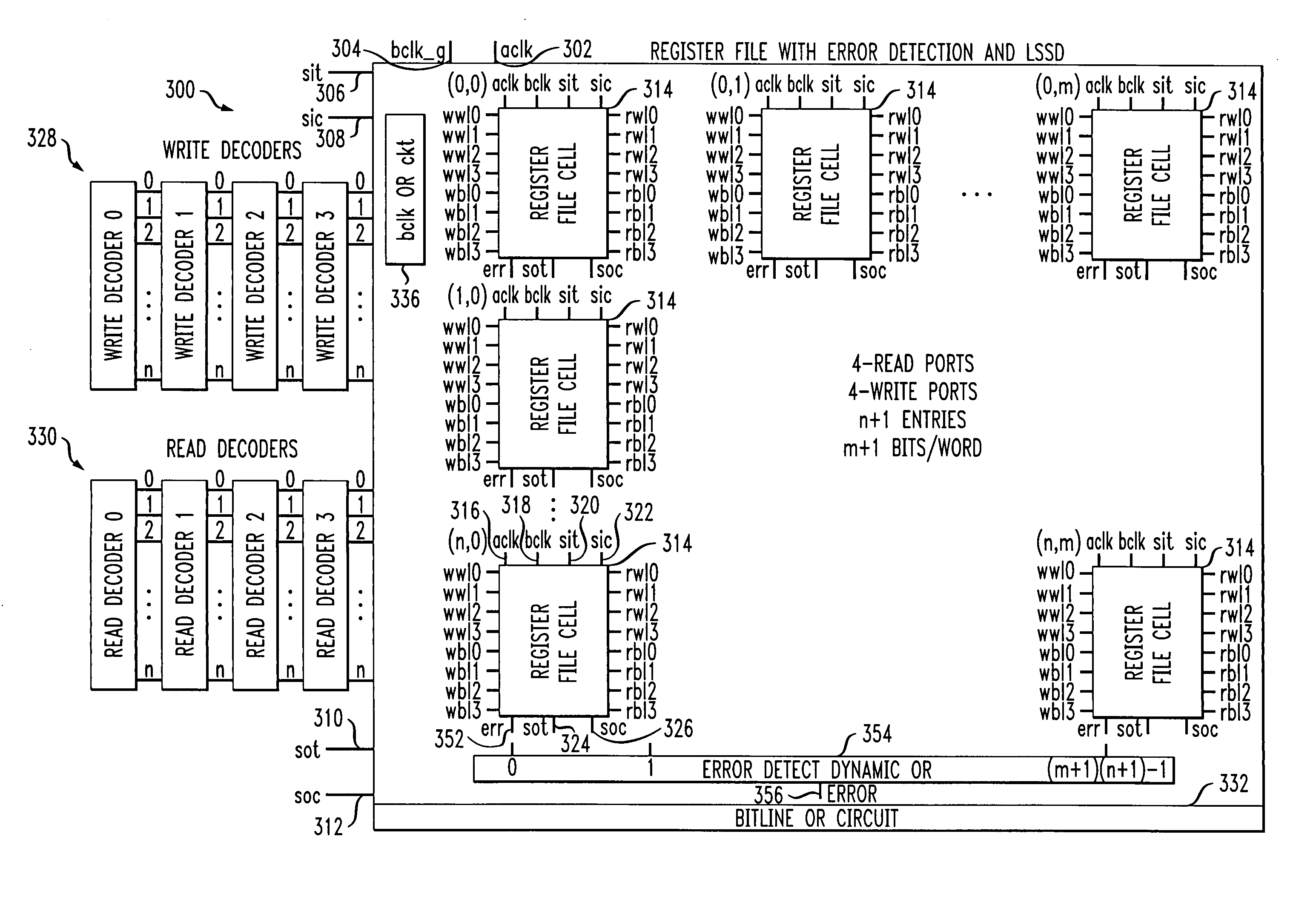
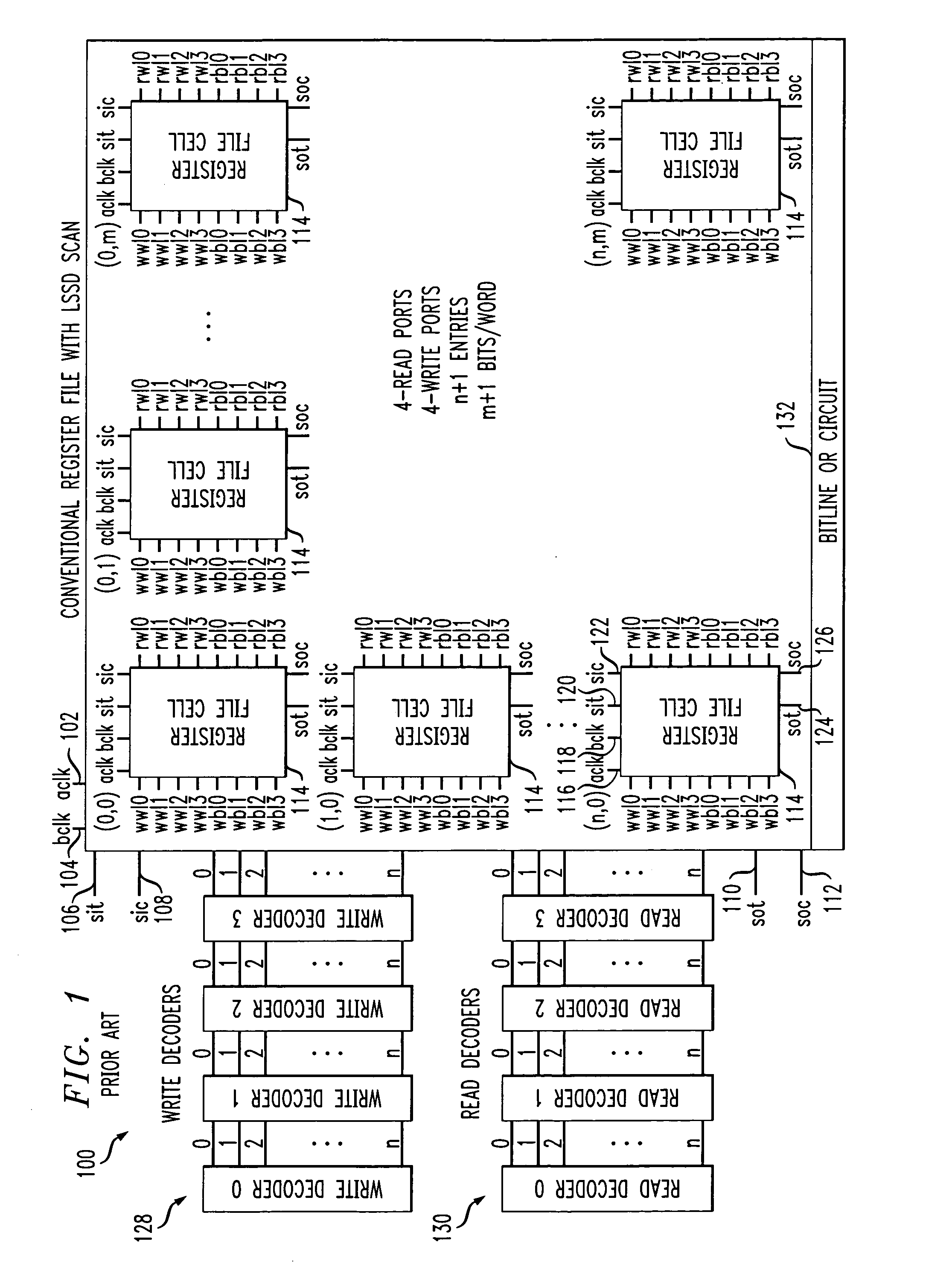
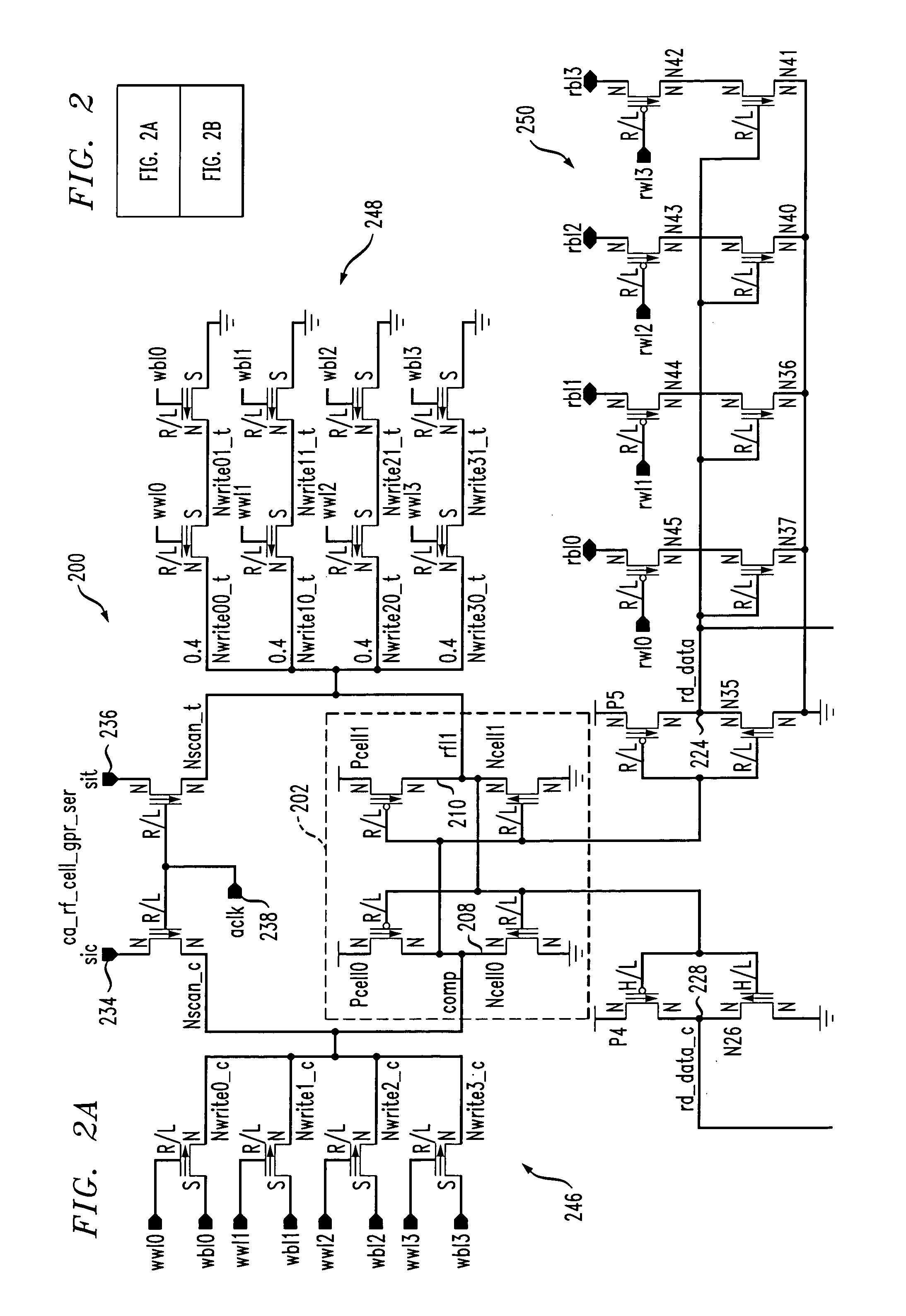
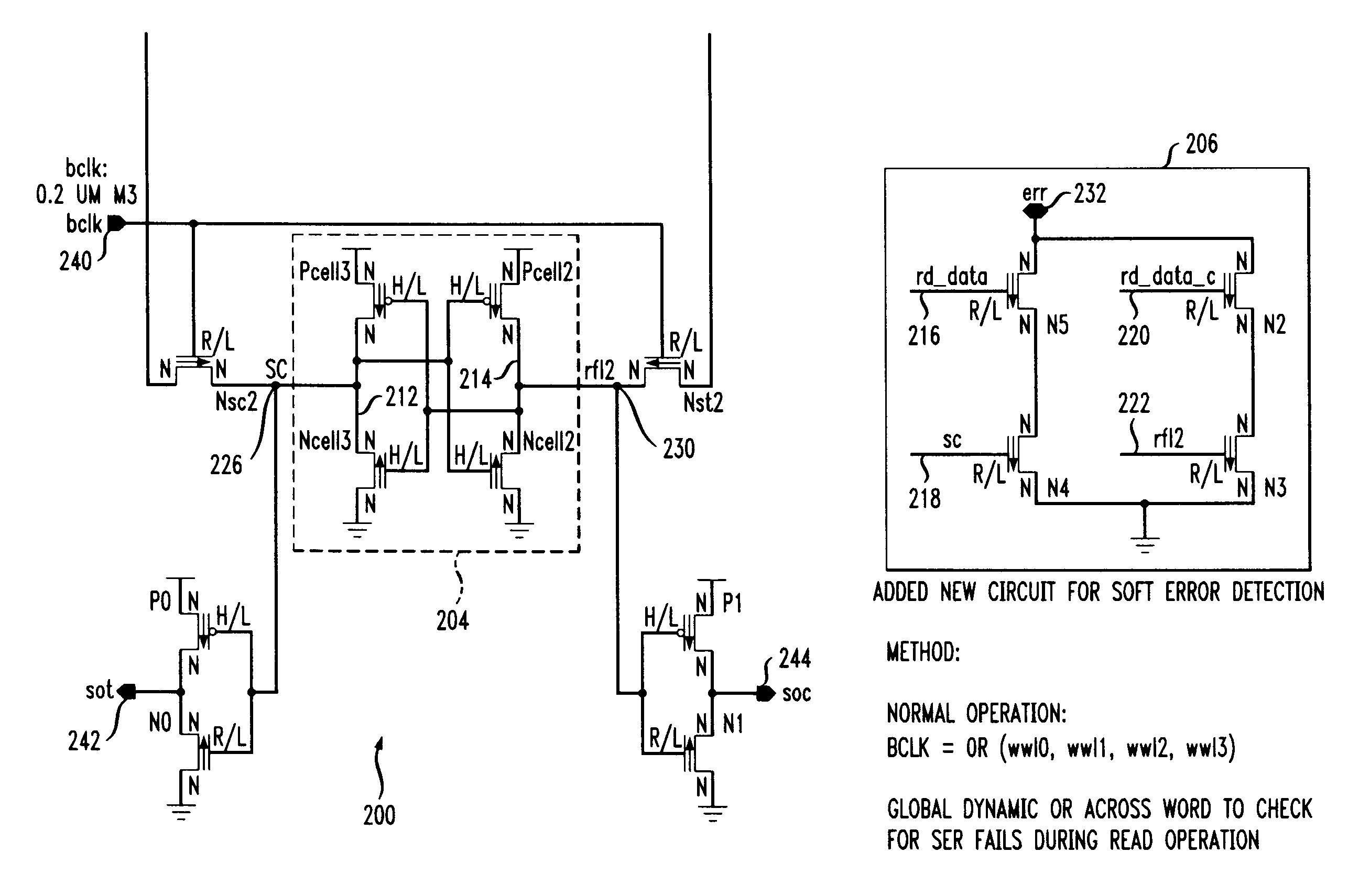
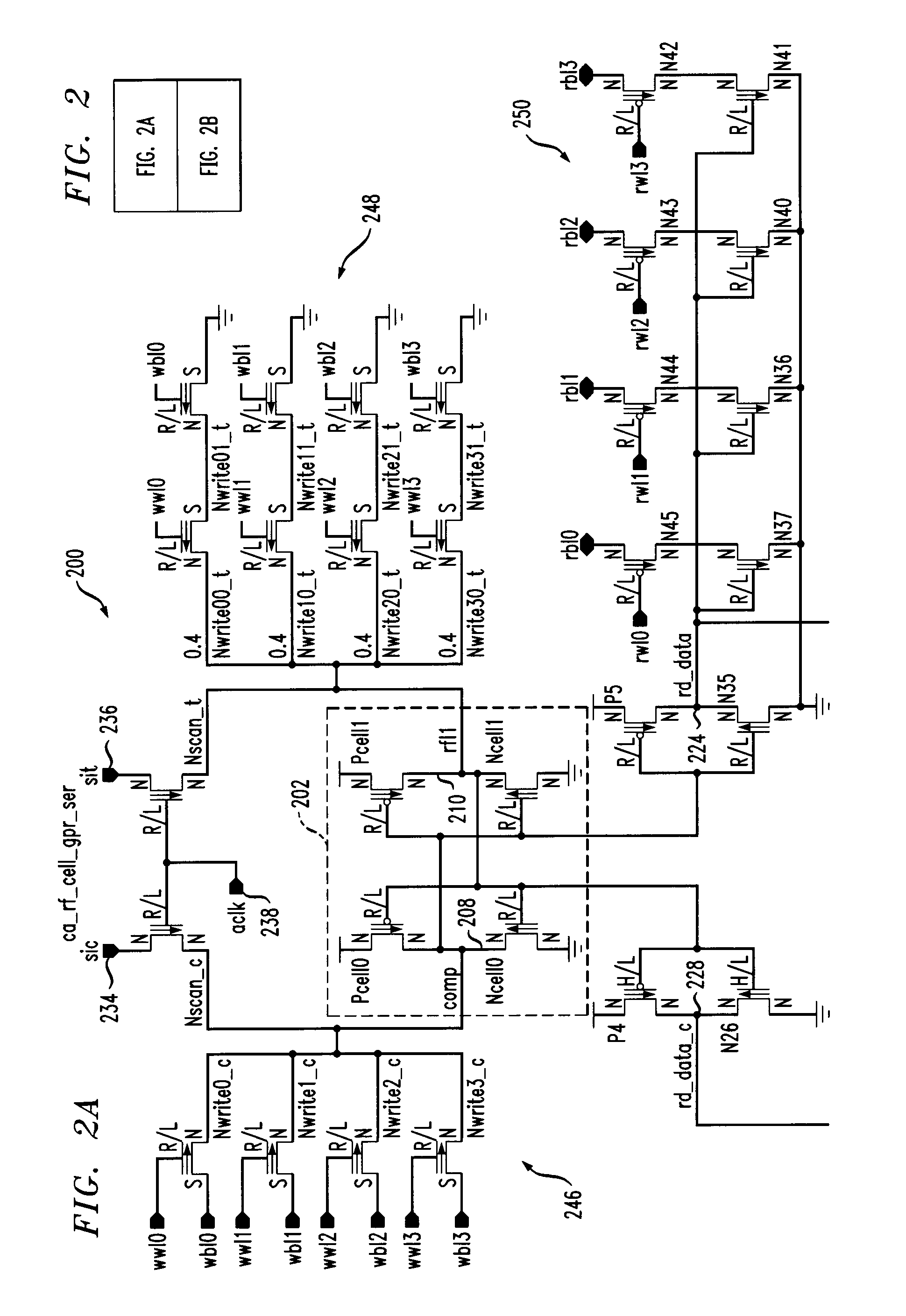
Register file cell with soft error detection and circuits and methods using the cell
Techniques are provided for a register file cell that includes a primary storage portion configured to store a first value, and a secondary storage portion that is coupled to the primary storage portion. The secondary storage portion is configured to function as a scan latch during a test operation, and is further configured to store a second value during normal operation. The second value is a duplicate of the first value. The cell further includes an error detection portion that is coupled to the primary storage portion and the secondary storage portion and is configured to indicate a difference between the first value and the second value, caused by a soft error.
Owner:IBM CORP
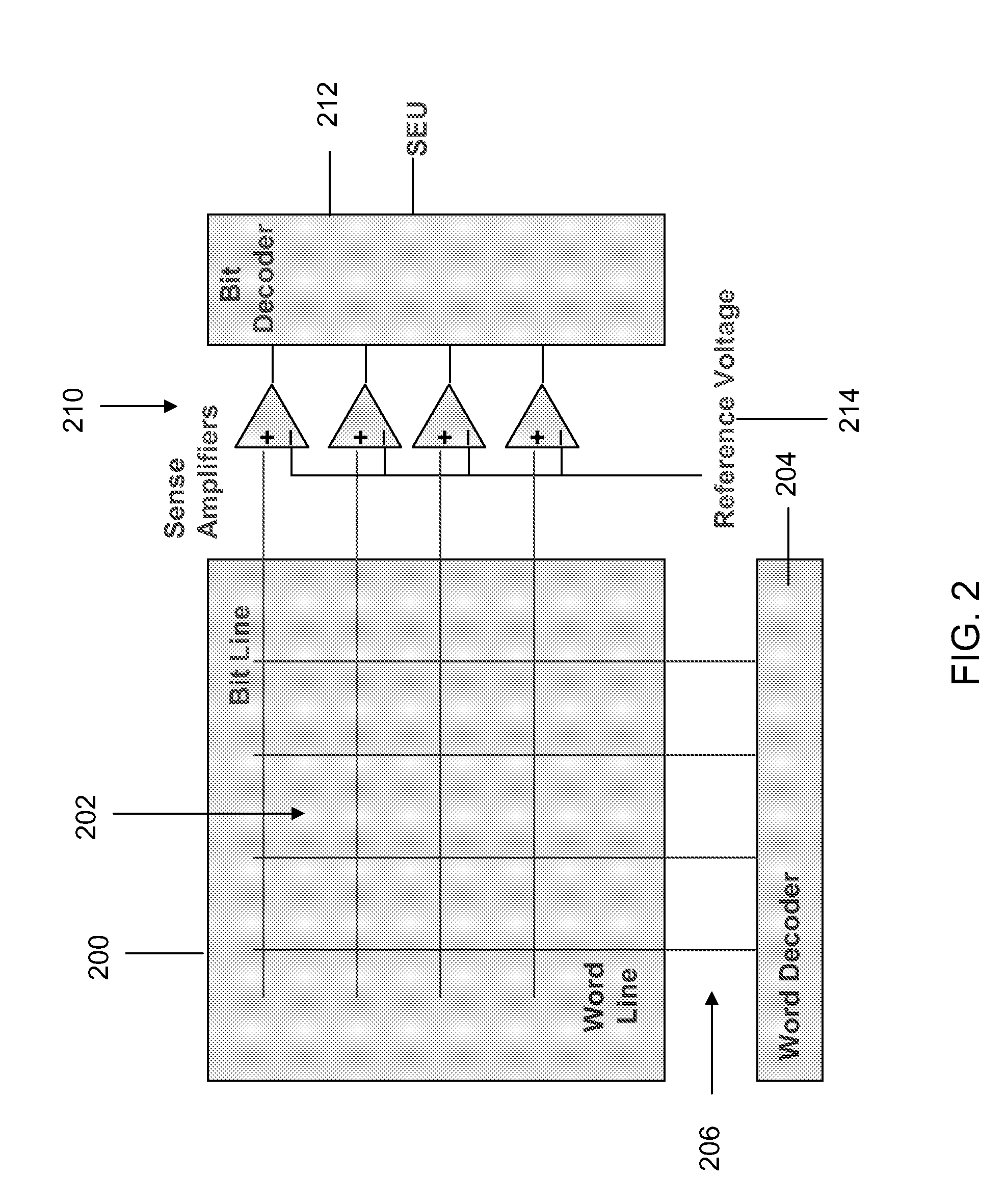
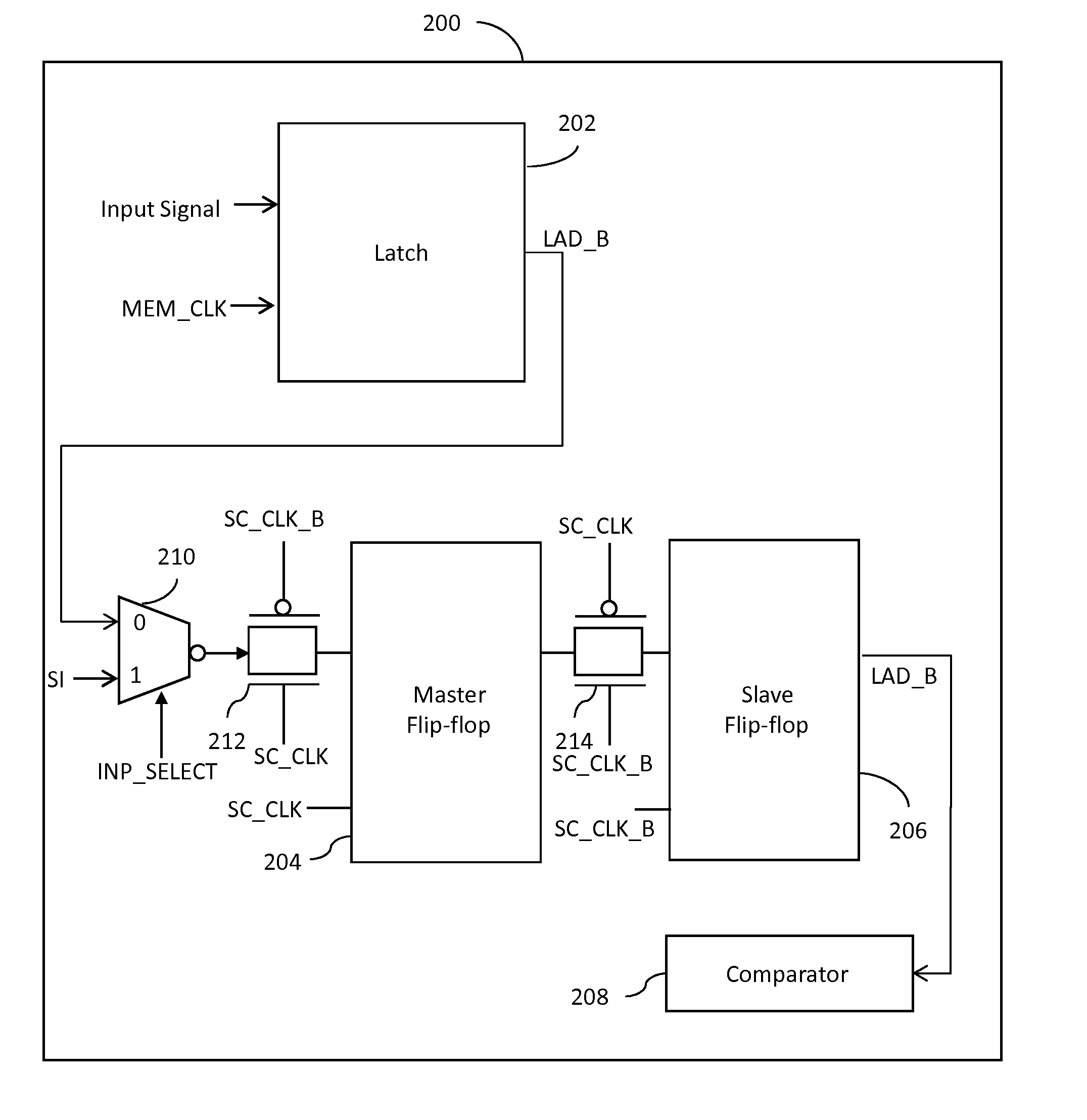
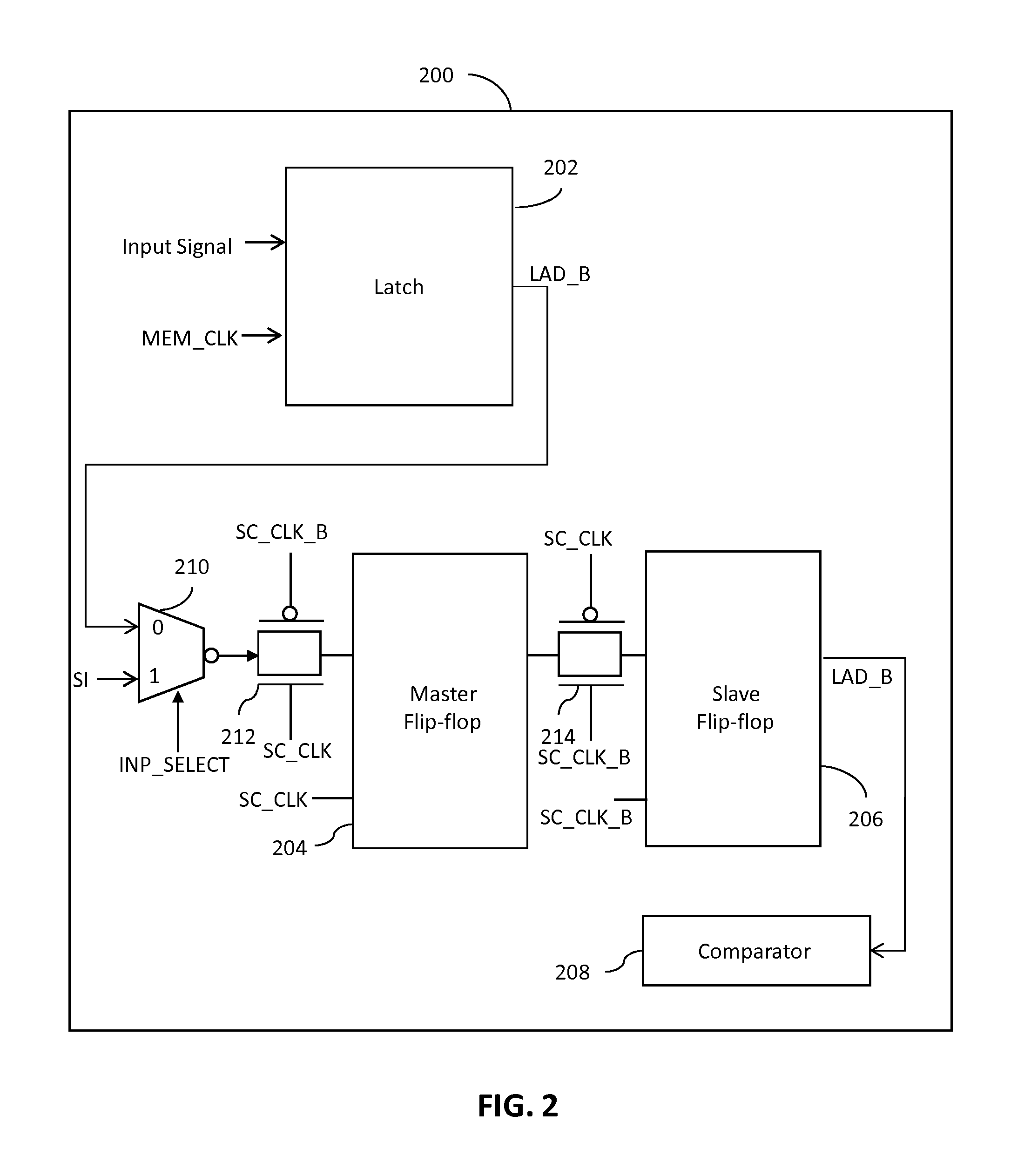
System and method for soft error detection in memory devices
A system for detecting soft errors in a memory device includes a latch, a master flip-flop and a slave flip-flop. The latch receives input data (control and / or address signals) at the beginning of a memory operation in response to a rising edge of a first clock signal. The output of the latch is provided to the master flip-flop. The master flip-flop continuously receives and stores the latch output during the memory operation based on a second clock signal. The slave flip-flop receives and stores the output of the master flip-flop at the end of the memory operation based on the second clock signal. A comparator compares the input data with the output of the slave flip-flop to detect soft errors that occur during the memory operation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Register file cell with soft error detection and circuits and methods using the cell
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
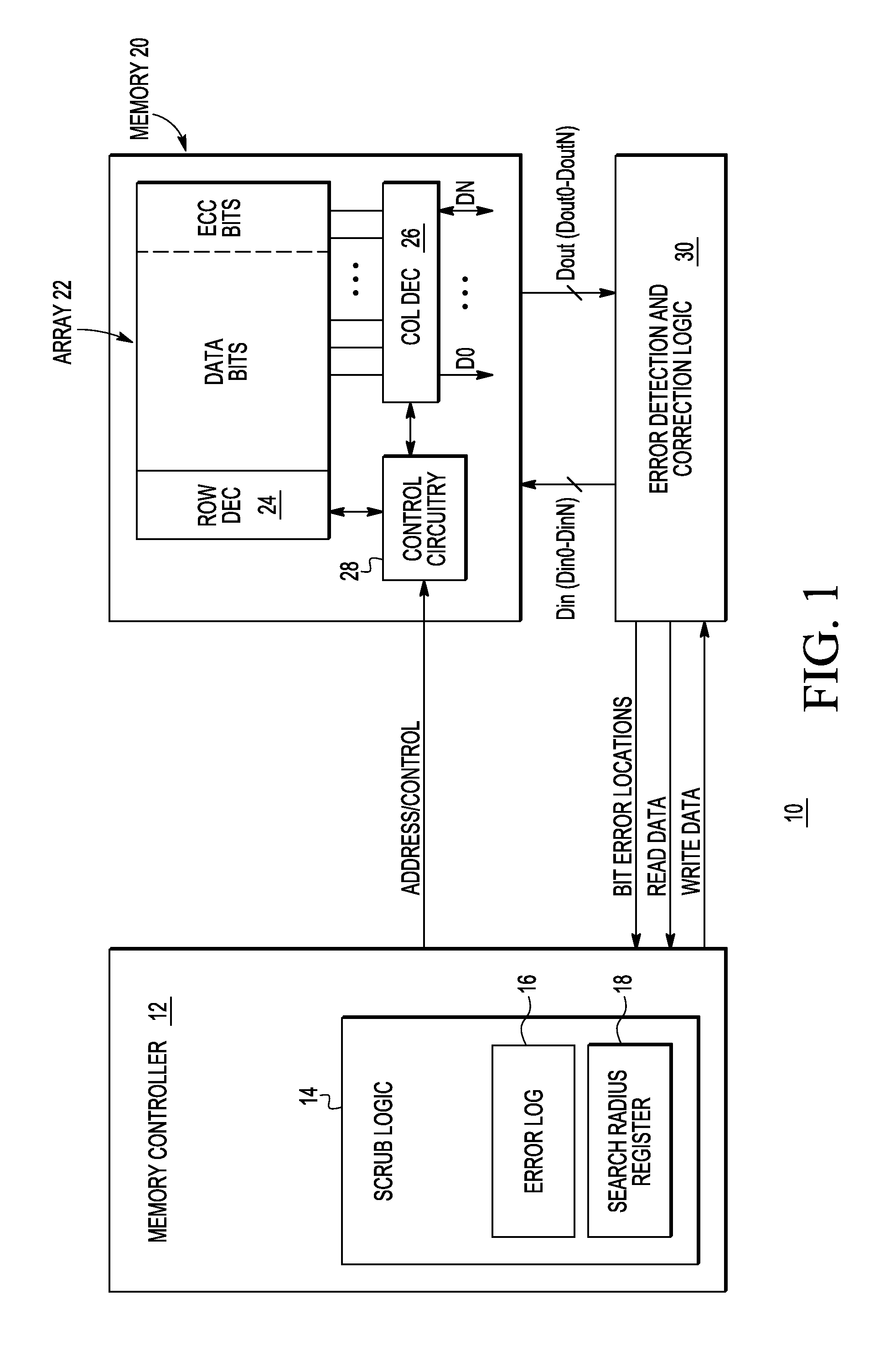
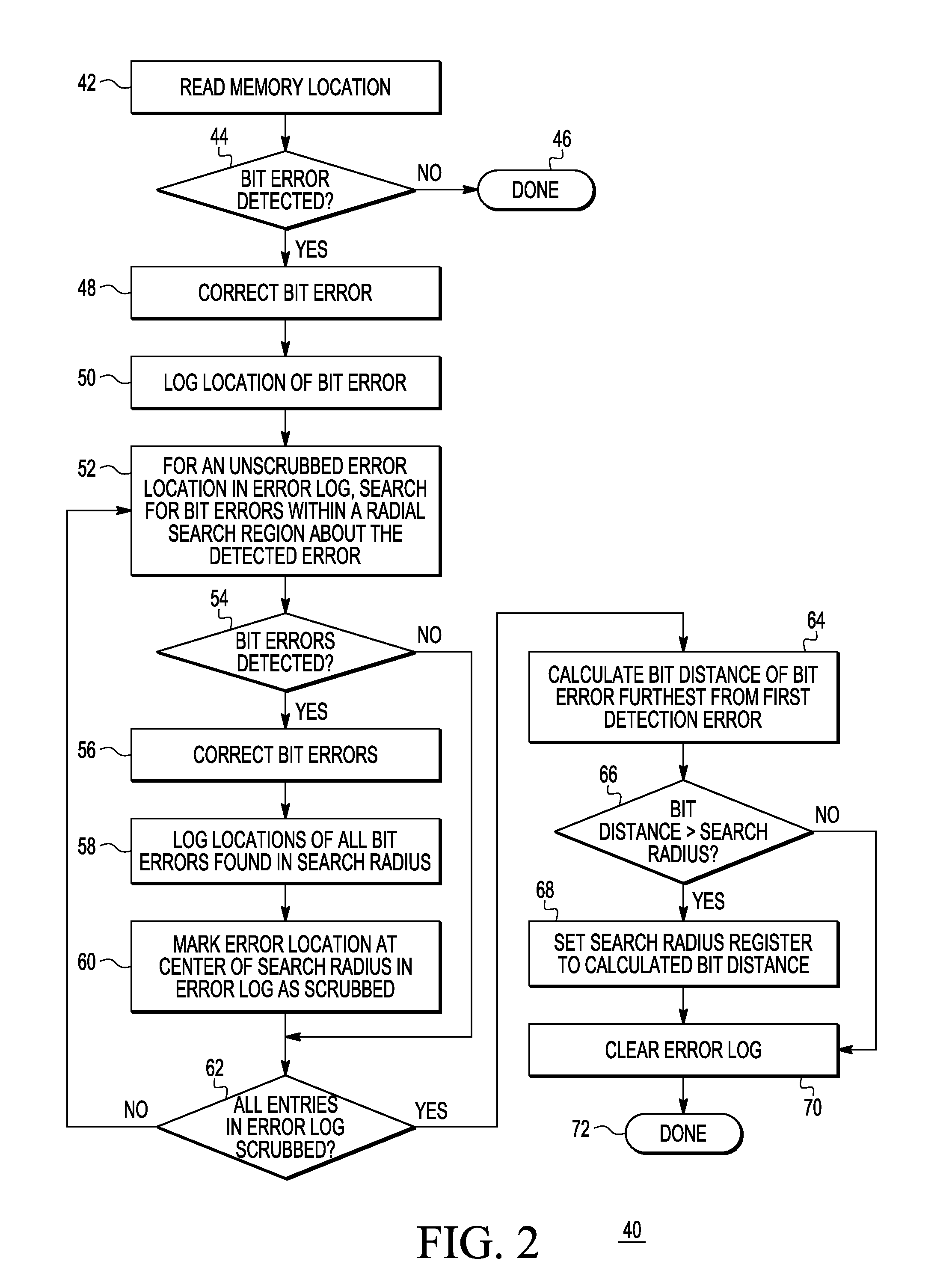
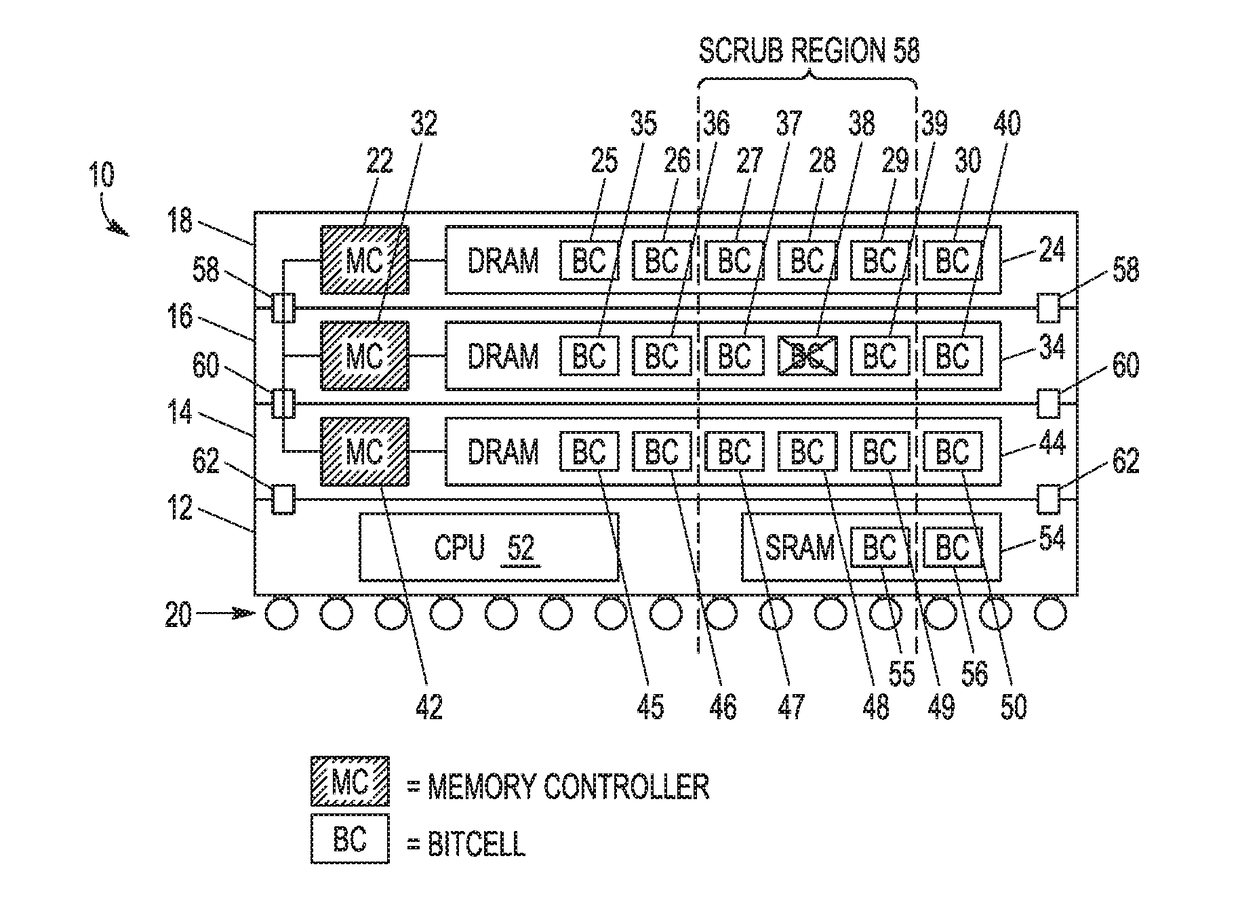
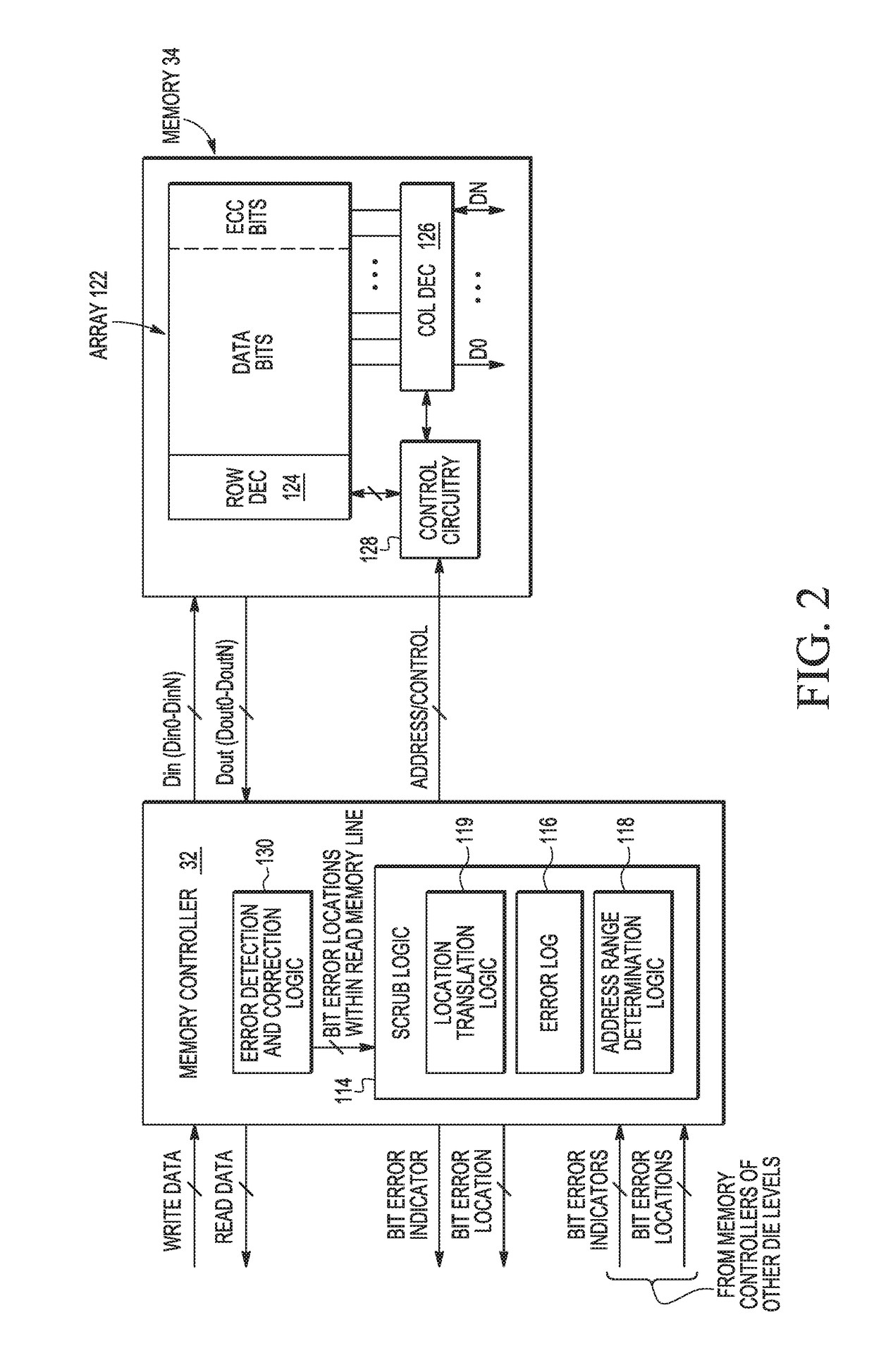
Soft error detection in a memory system
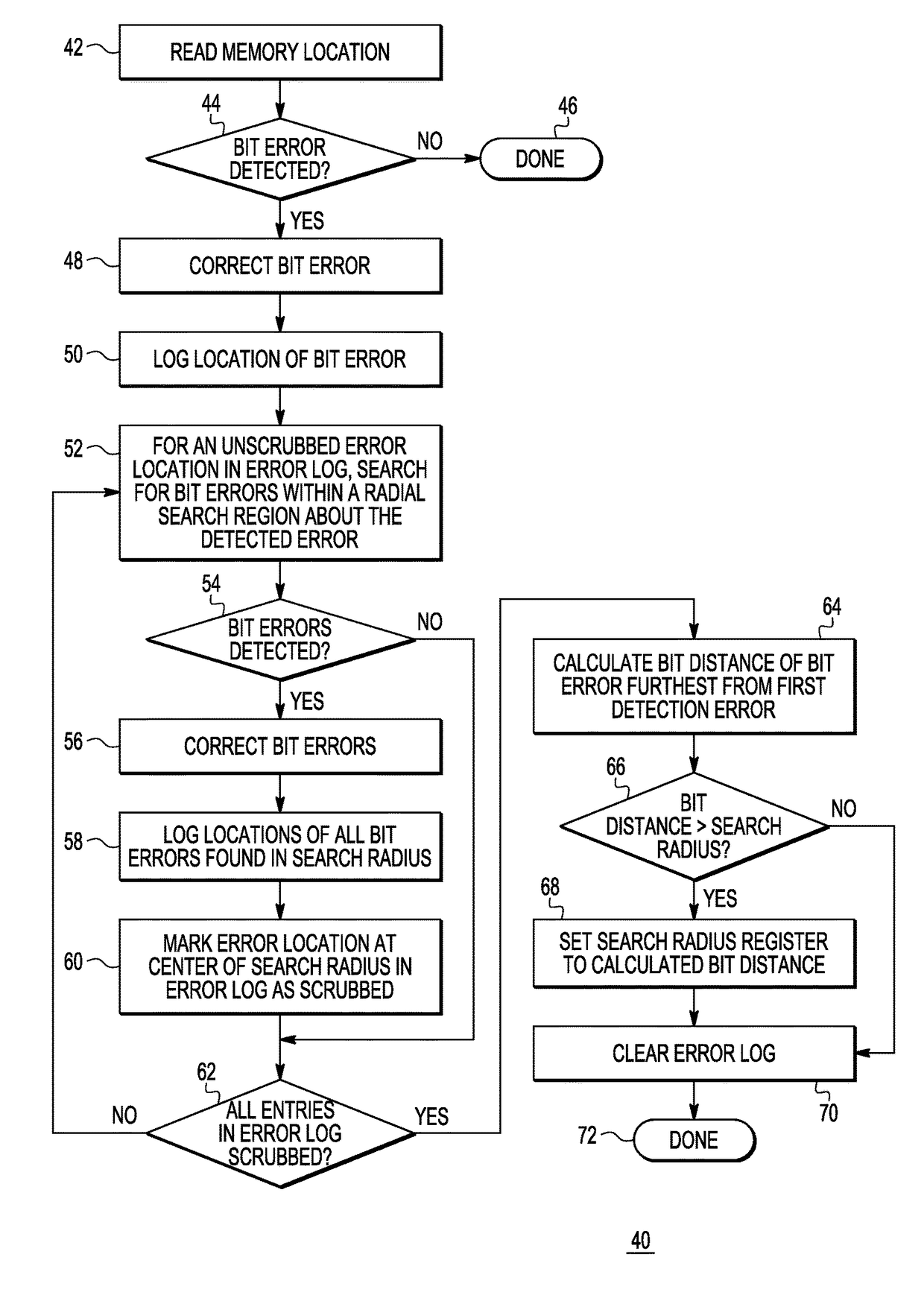
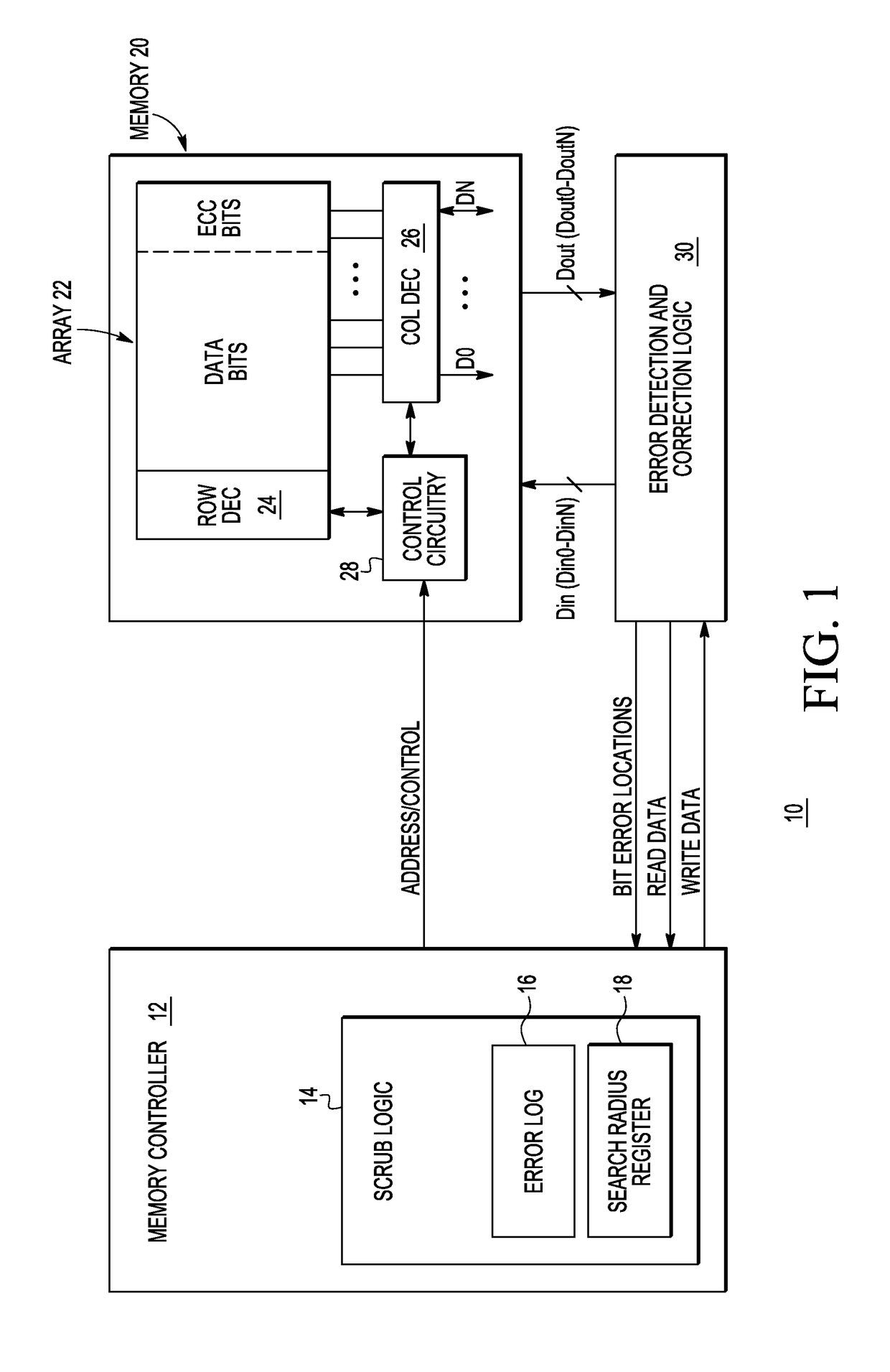
In a memory having a memory array, a method includes reading read data from the memory array, and detecting a first bit error in the read data. The method further includes checking all bitcells in a radial search region about the first bit error. The radial search region is defined by a search radius which indicates a number of concentric rings of bitcells physically surrounding the first bit error in the memory array.
Owner:NXP USA INC
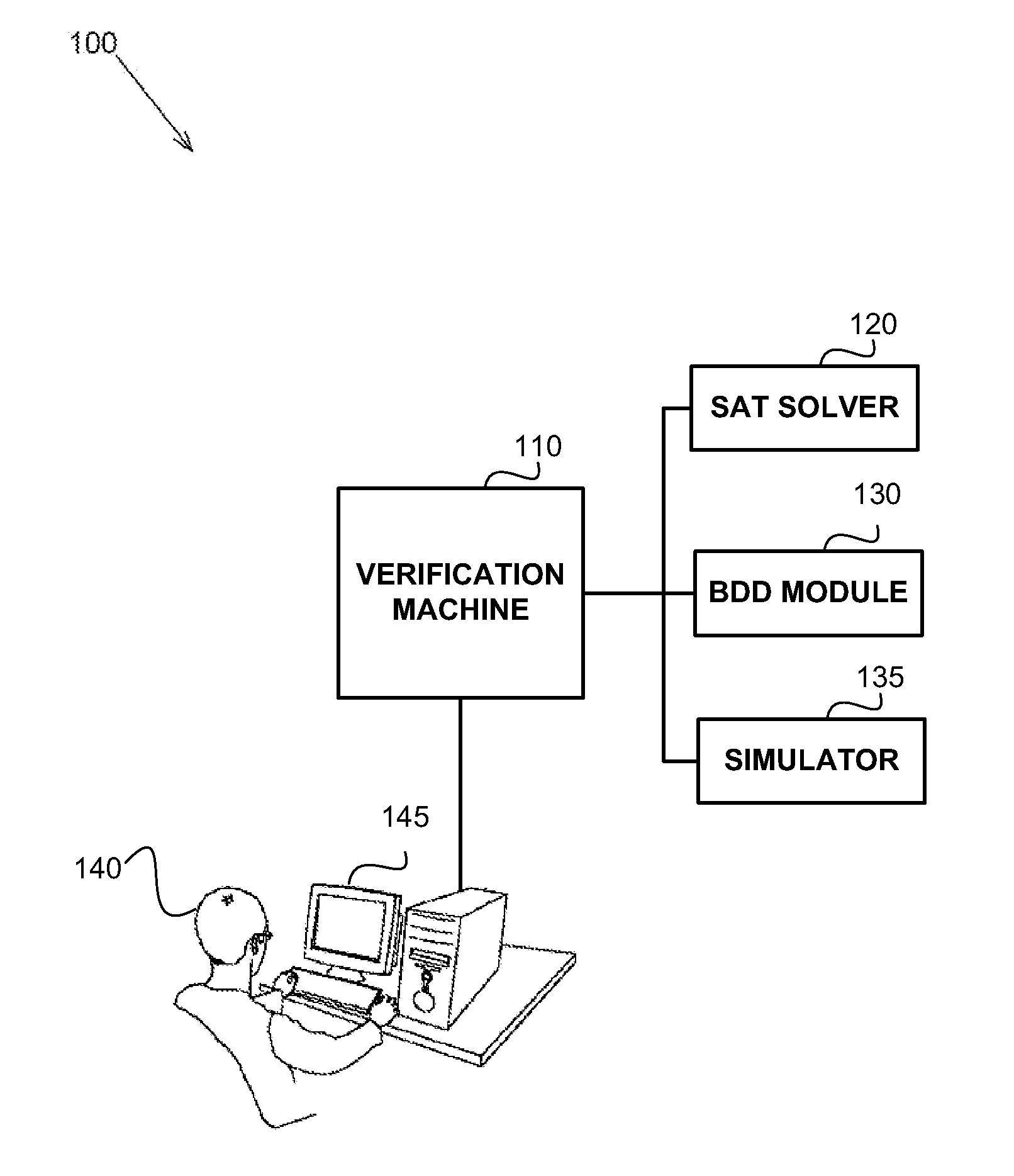
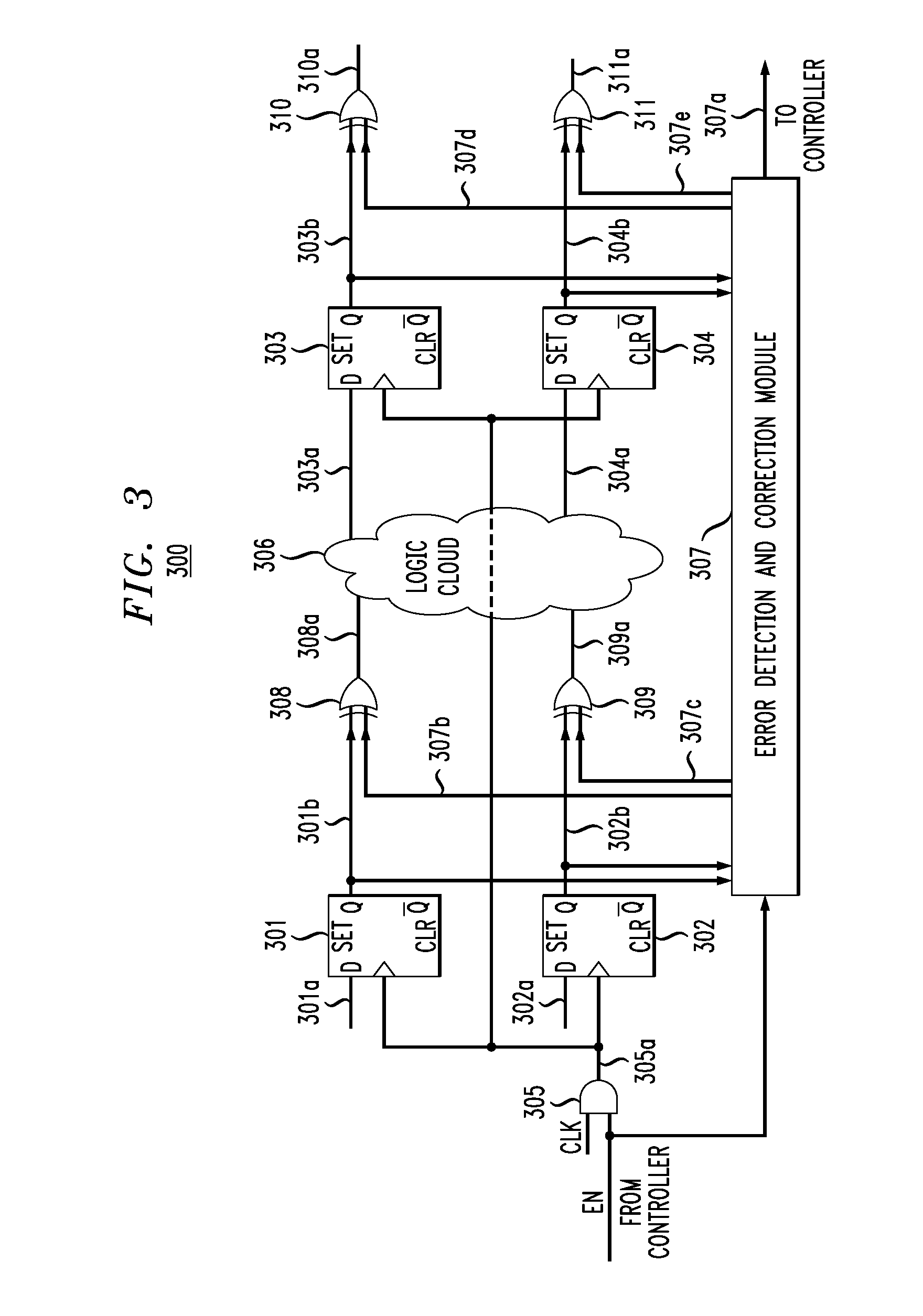
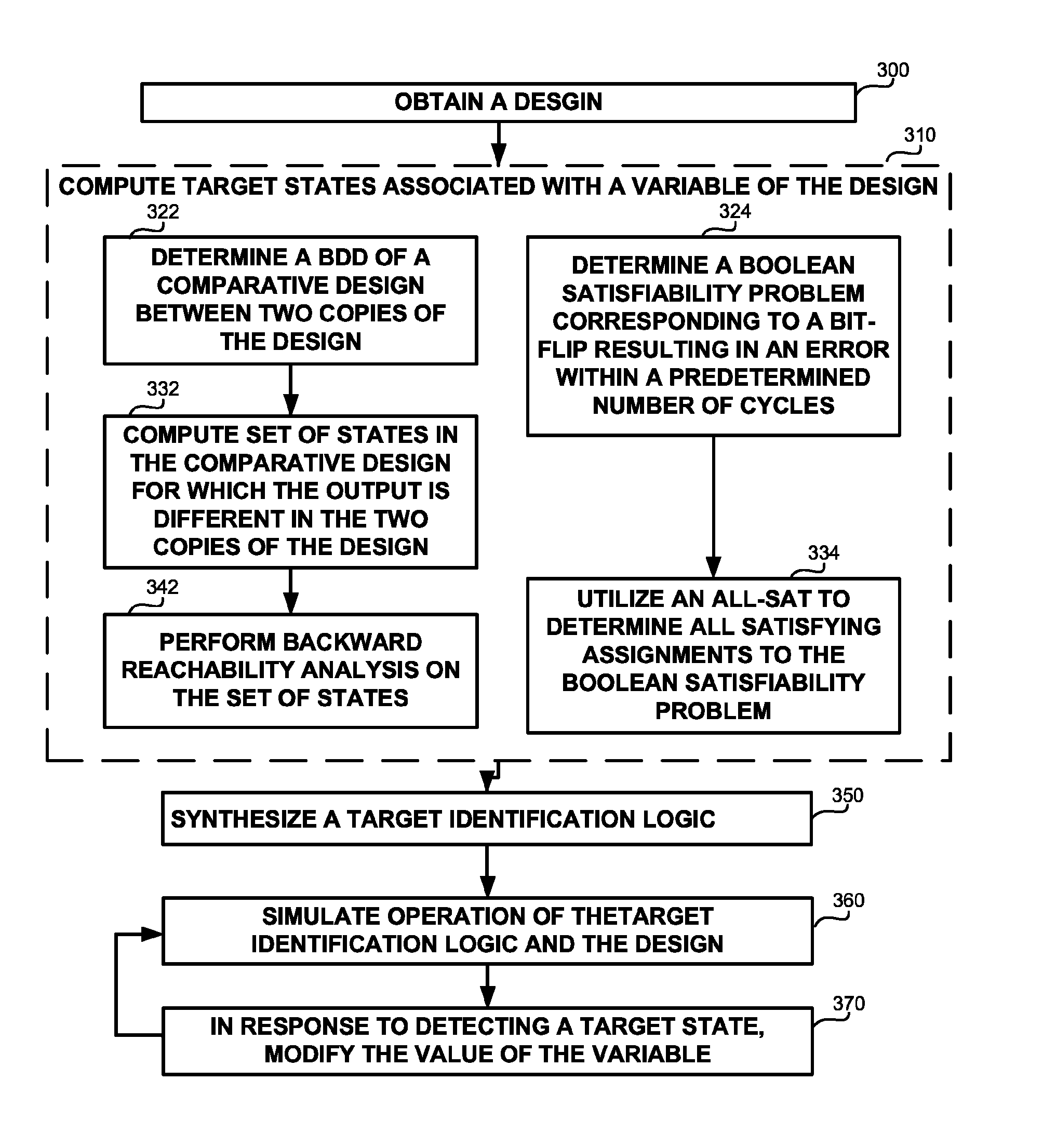
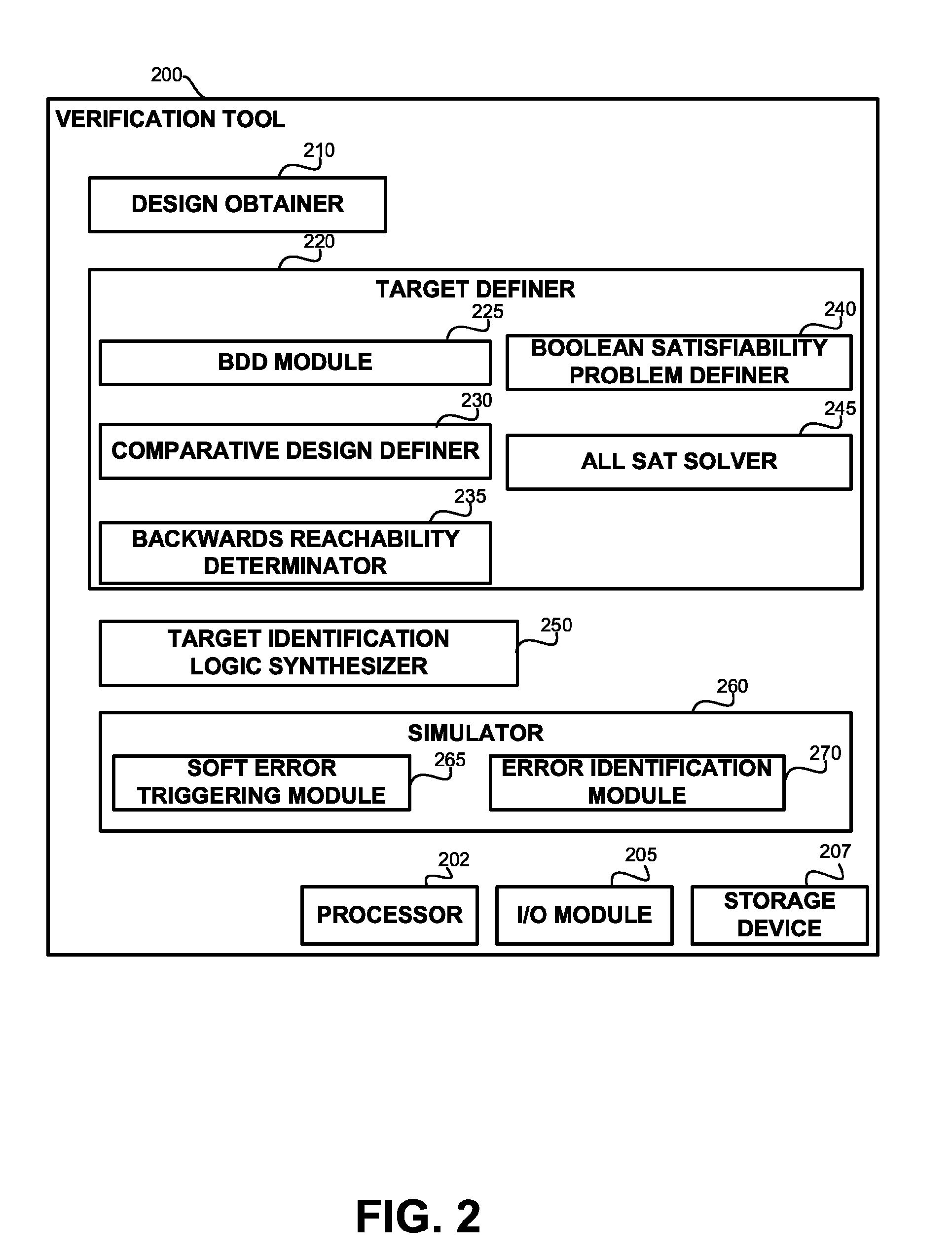
Soft error verification in hardware designs
Soft error detection is performed by computation of states based on formal methods and by simulating a synthesized target identification logic together with the design. Soft errors may be simulated in response to detecting that a simulated state of the design is comprised by the states. A BDD representation of the design may be utilized to determine the states. A Boolean satisfiability problem may be defined and solved using an all-SAT solver in order to determine the states.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System and method for soft error detection in memory devices
A system for detecting soft errors in a memory device includes a latch, a master flip-flop and a slave flip-flop. The latch receives input data (control and / or address signals) at the beginning of a memory operation in response to a rising edge of a first clock signal. The output of the latch is provided to the master flip-flop. The master flip-flop continuously receives and stores the latch output during the memory operation based on a second clock signal. The slave flip-flop receives and stores the output of the master flip-flop at the end of the memory operation based on the second clock signal. A comparator compares the input data with the output of the slave flip-flop to detect soft errors that occur during the memory operation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Soft-error detection for electronic-circuit registers
In one embodiment, a circuit has multiple flip-flops with gated clock inputs controlled by an enable signal, where the clock signal is gated in order to reduce power consumption by the circuit. The circuit has an error detection and correction (EDC) module that is active when the enable signal is low in order to detect and correct soft errors of the flip-flops. The EDC module generates and stores an error-correction code based on the data outputs of the flip-flops. The EDC module then compares the stored error-correction code to a presently generated error-correction code, where if they are not identical, then the EDC (a) determines (i) that a soft error has occurred and (ii) which flip-flop suffered the soft error and (b) flips a corresponding error-correction signal to provide a correct corresponding output signal while the enable signal is low.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Soft error verification in hardware designs
Soft error detection is performed by computation of states based on formal methods and by simulating a synthesized target identification logic together with the design. Soft errors may be simulated in response to detecting that a simulated state of the design is comprised by the states. A BDD representation of the design may be utilized to determine the states. A Boolean satisfiability problem may be defined and solved using an all-SAT solver in order to determine the states.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Memory ECC with hard and soft error detection and management
A method and apparatus are provided for error correction of a memory by using a first memory (18) and second memory (14) to perform error correction code (ECC) processing on data retrieved from the first memory and to use status control bits (35-37) in the second memory to detect and manage hard and soft errors identified by the ECC processing.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Detection for reducing soft error of hardware
The soft error detection method and system for integral number addition and subtraction operation without adopting redundance logic is provided. For integral number addition and subtraction, the compensation logic generates the compensation value with the ALU result and operand. The compensation value is verified with the verification logic corresponding to the preset value to judge whether to have soft error. Under the hardware condition of carry transfer and no redundance, the compensation logic and the verification logic operate on the integral operand and the result ALU generates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Soft error detection in a memory system
An integrated circuit (IC) device including a first memory device, a second memory device stacked with the first memory device, and one or more memory controllers configured to detect a first error in data stored in the first memory device at a first physical location in the IC device, and upon detecting the first error, determine whether there is a second error in data stored in the second memory device in a second physical location in the IC device near the first physical location.
Owner:NXP USA INC
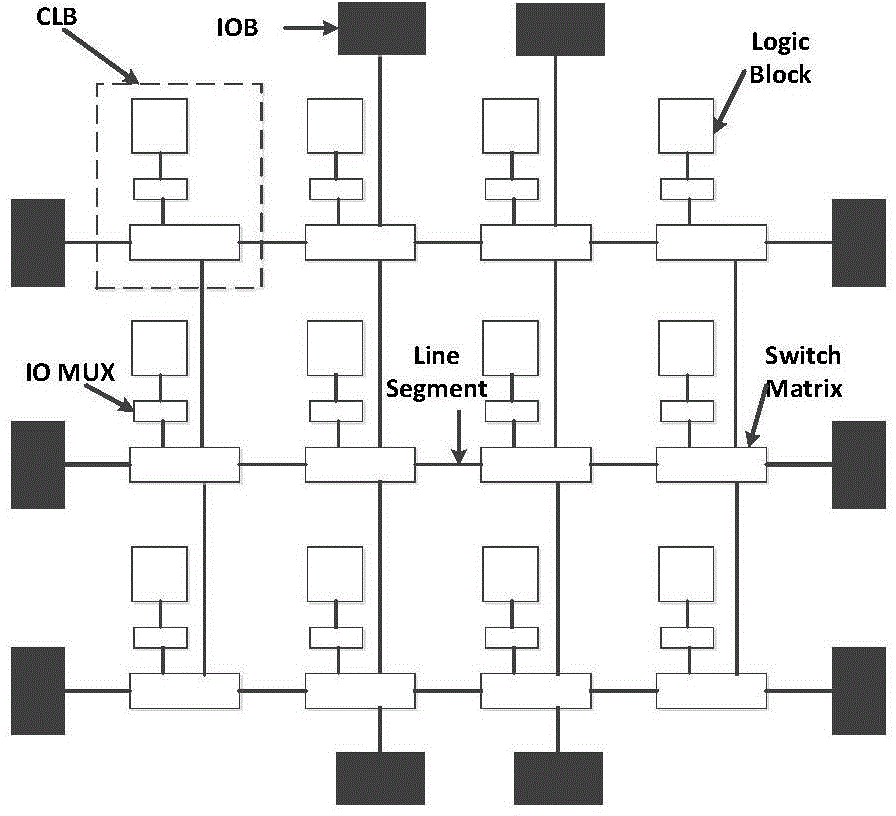
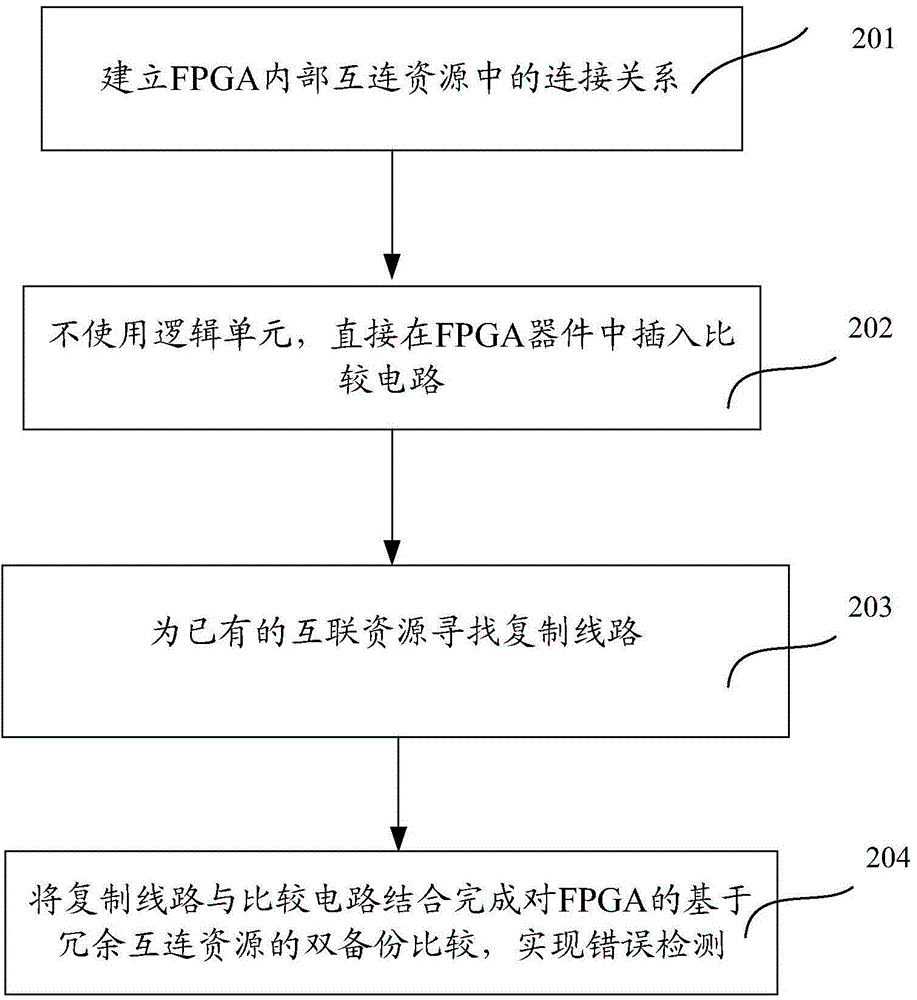
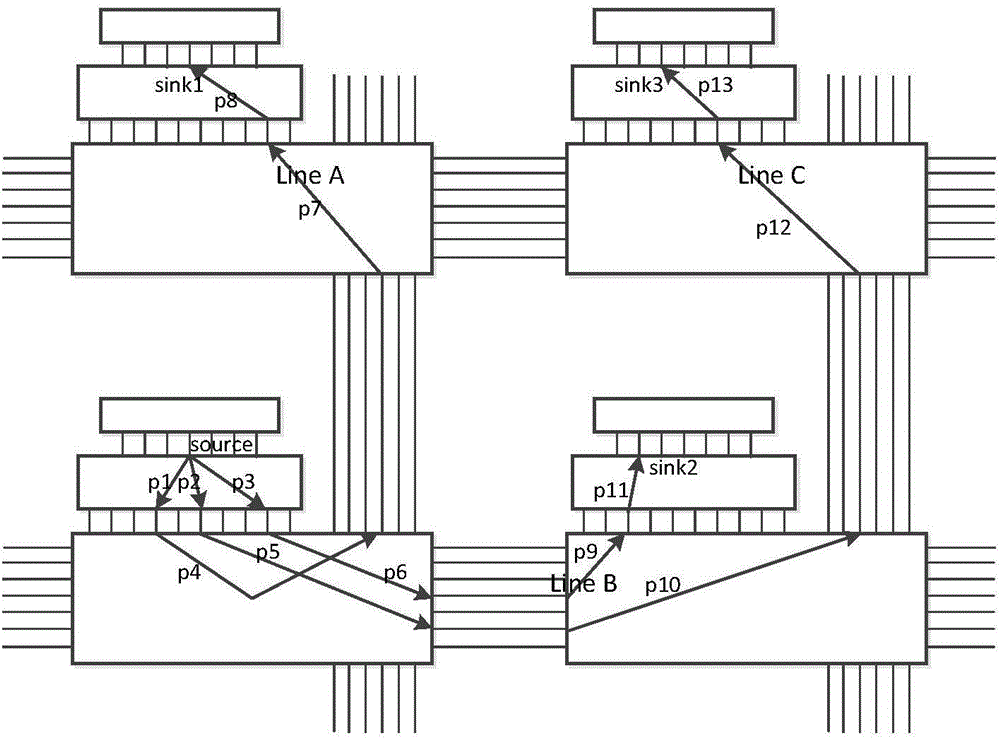
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) single-particle overturning soft error detection method based on redundancy interconnection resources
ActiveCN104699571AEfficient online detectionRedundant hardware error correctionLogic cellInterconnection
The invention discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) single-particle overturning soft error detection method based on redundancy interconnection resources. The FPGA single-particle overturning soft error detection method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a connection relation in interconnection resources in an FPGA; step 2, not using a logic unit and directly inserting a comparing circuit into an FPGA device; step 3, finding a copying line for the existing interconnection resources; and step 4, combining the copying line and the comparing circuit to carry out dual backup comparison on the FPGA based on the redundancy interconnection resources so as to realize error detection. By the aid of the FPGA single-particle overturning soft error detection method, a phenomenon that more redundancy exists in the interconnection resources of the design is sufficiently designed, and an efficient redundancy interconnection resource search algorithm is explored; an FPGA structure is simply modified so that the efficient online detection on single-particle overturning soft errors is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Soft error detection for latches
InactiveUS20110221473A1Reliability increasing modificationsElectric pulse generatorEngineeringClock control
A system and method for soft error detection in digital ICs is disclosed. The system includes an observing circuit coupled to a latch, which circuit is capable of a response upon a state change of the latch. The system further includes synchronized clocking provided to the latch and to the observing circuit. For the latch, the clocking defines a window in time during which the latch is prevented from receiving data, and in a synchronized manner the clocking is enabling a response in the observing circuit. The clocking is synchronized in such a manner that the circuit is enabled for its response only inside the window when the latch is prevented from receiving data. The system may also have additional circuits that are respectively coupled to latches, with each the additional circuit and its respective latch receiving the synchronized clocking Responses of a plurality of circuits may be coupled in a configuration corresponding to a logical OR.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Robust Hamming Code Implementation for Soft Error Detection, Correction, and Reporting in a Multi-Level Cache System Using Dual Banking Memory Scheme
ActiveUS20120192027A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTHamming codeMemory bank
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Soft error detection in a memory system
Owner:NXP USA INC
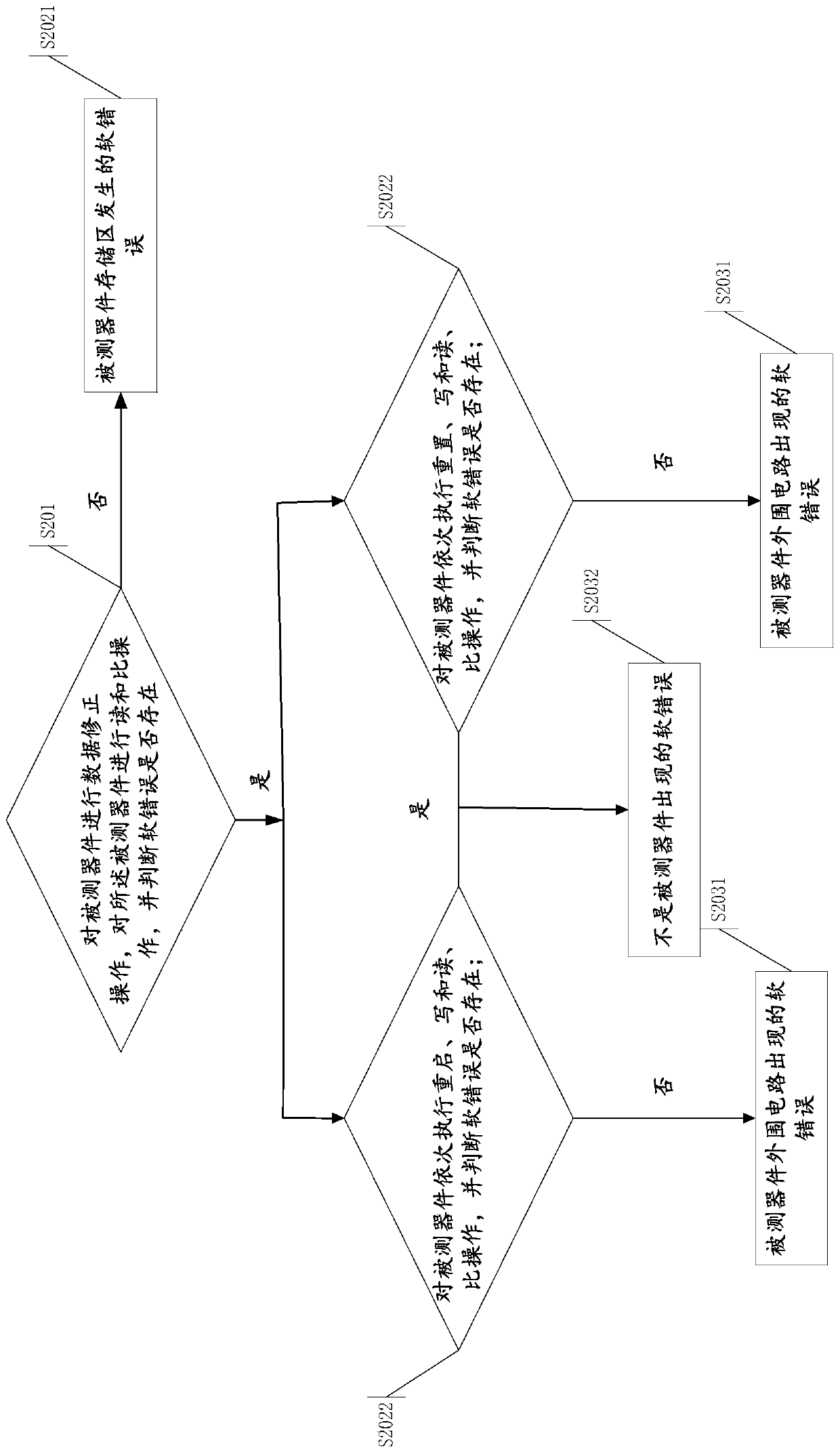
Method and device for discriminating soft errors of tested device and computer equipment
InactiveCN110221143AImprove practicalityEnvironmental/reliability testsSoftware errorComputer engineering
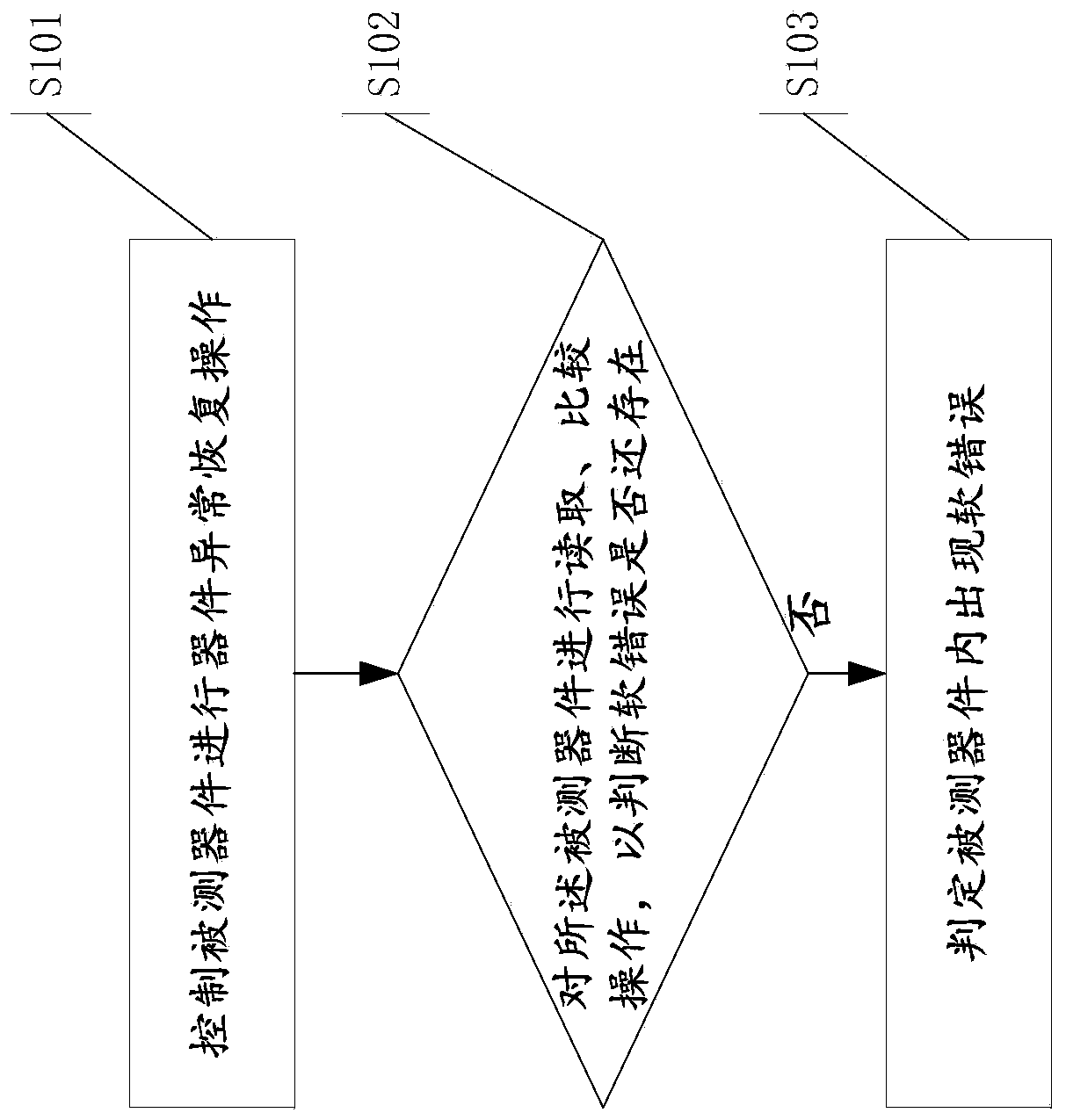
The invention provides a method and device for discriminating software errors of a tested device and computer equipment. Under the condition of the occurrence of the soft error, according to the method, device abnormal recovery operation is carried out on the tested device, soft error detection is carried out again, and whether the soft error comes from the tested device is determined according toa detection result, thereby distinguishing the radiation effect generated in the tested device and other equipment and obtaining the soft error rate of the tested device. The method for discriminating software errors of the tested device is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS PROD RELIABILITY & ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING RES INST
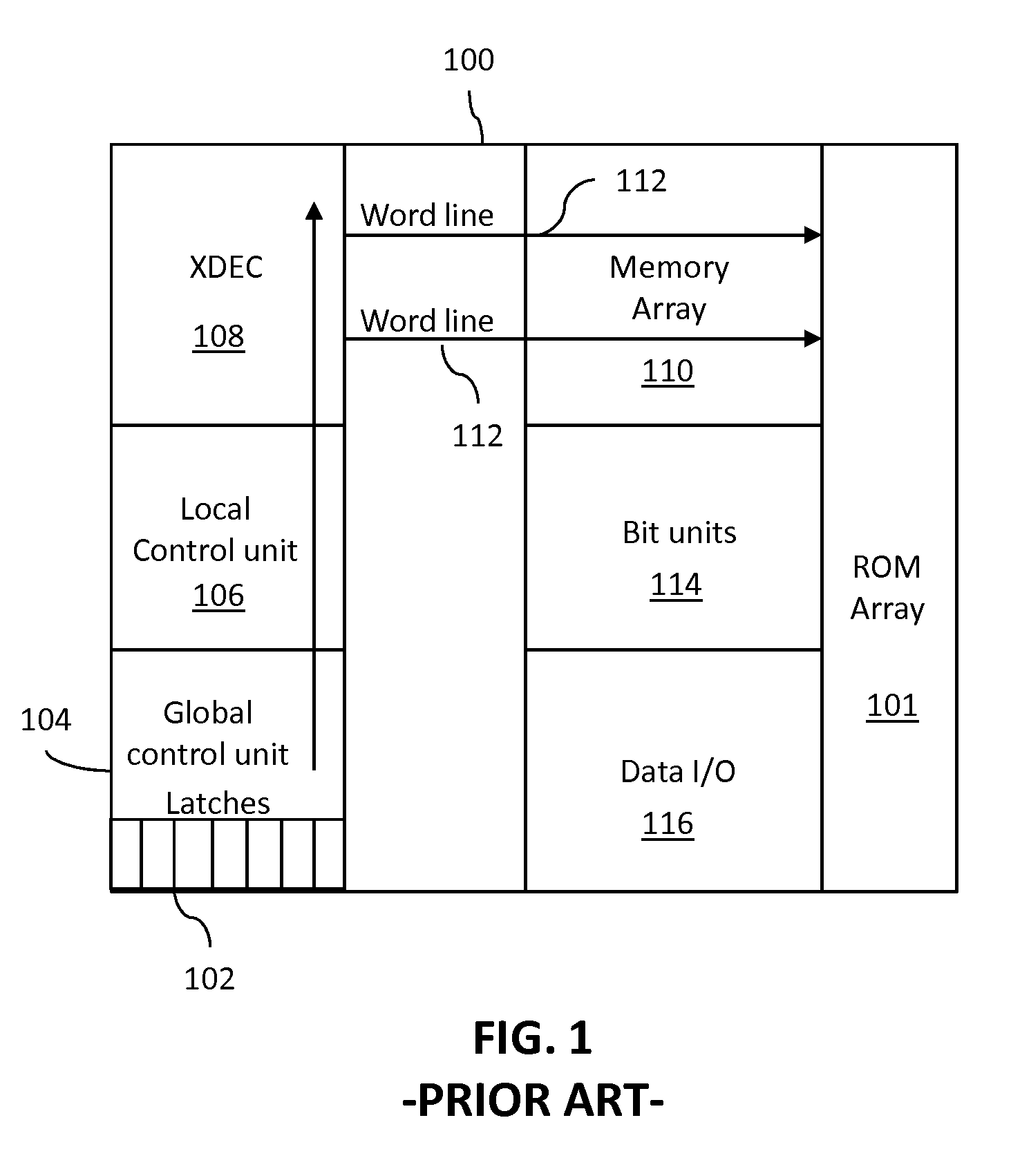
Testing of soft error detection logic for programmable logic devices
ActiveUS8370691B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionProgrammable logic deviceLogic state
In one embodiment, a programmable logic device (PLD) with configuration memory includes at least one configuration memory cell and soft error detection (SED) logic for checking for errors in data stored by the configuration memory. The SED logic calculates a present data value for the configuration memory for comparison with a pre-calculated data value. A fuse within the PLD is configurable in a first logic state to enable the SED logic to read from the configuration memory cell in calculating the present data value and configurable in a second logic state to prevent the SED logic from reading from the configuration memory cell in calculating the present data value. The SED logic may be tested for correct operation by writing data representing a soft error into the configuration memory cell and enabling the SED logic to read from the configuration memory cell in calculating the present data value.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com