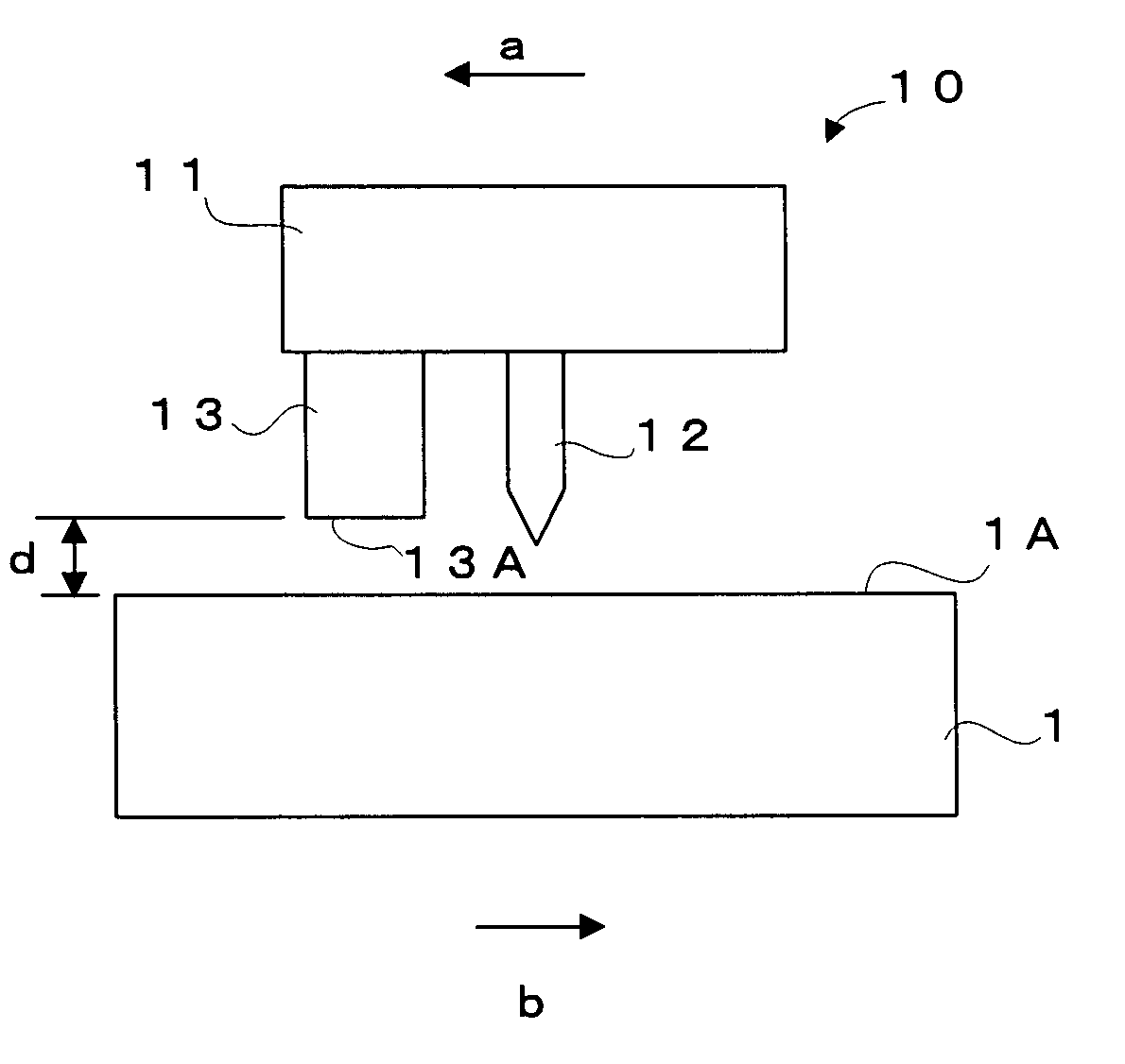
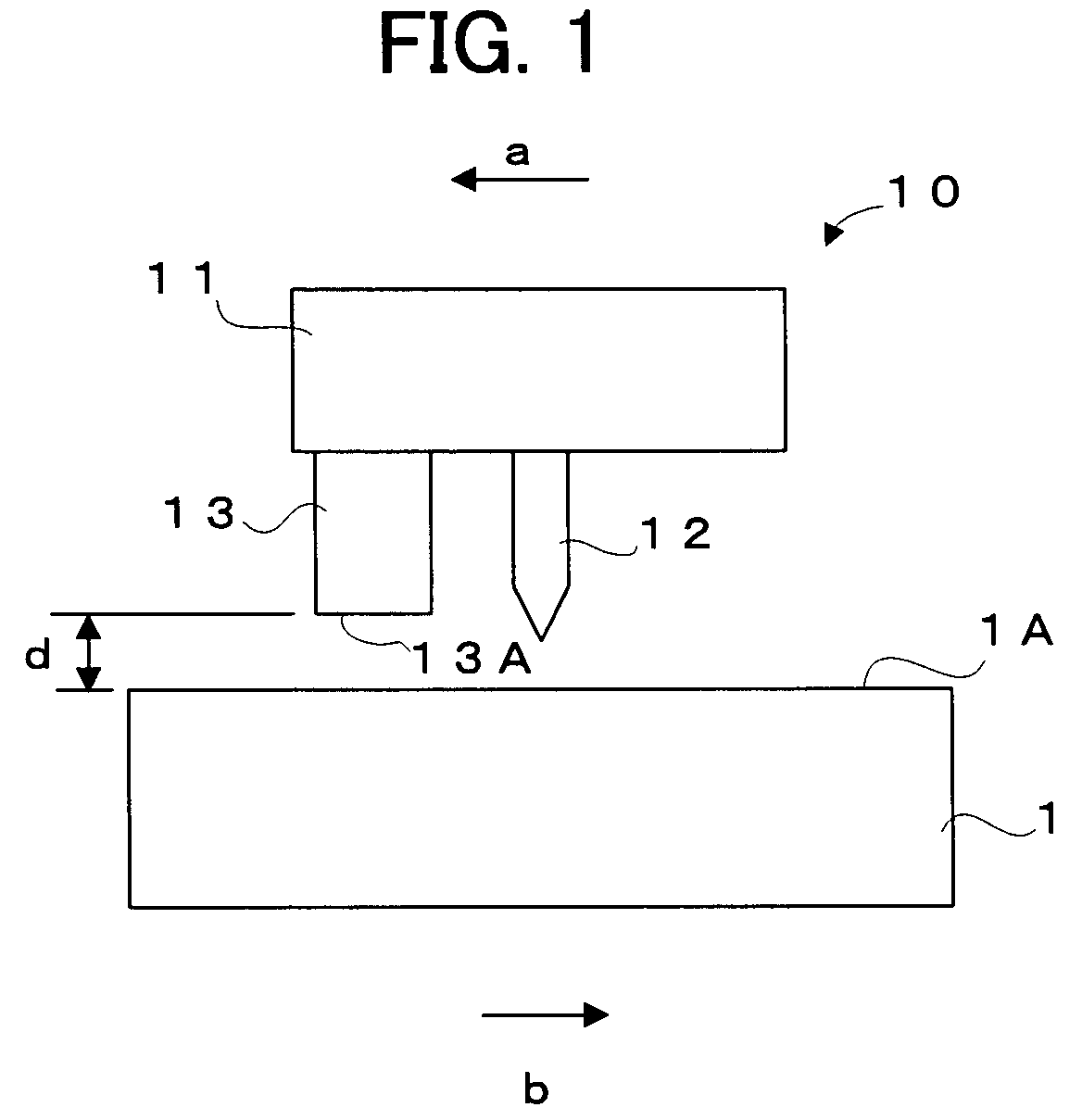
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
181results about "Electron beam carrier recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
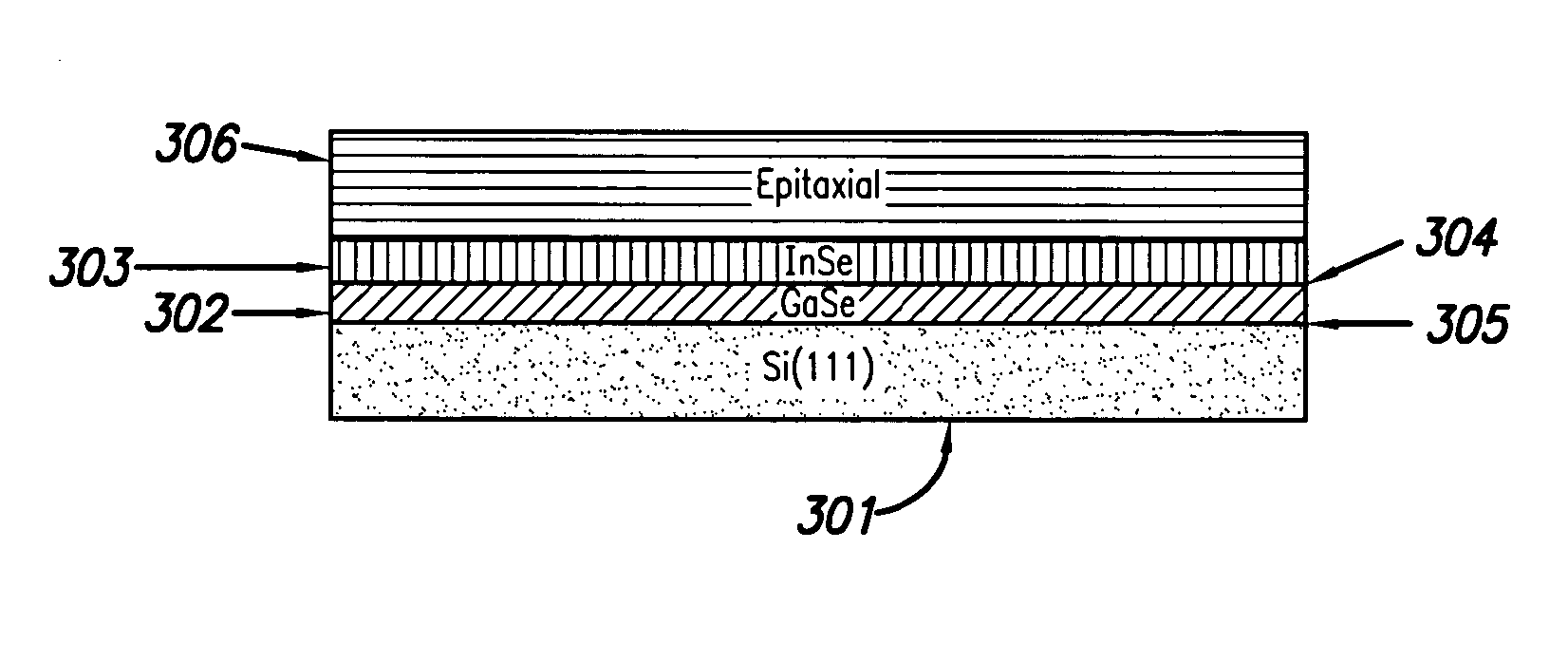
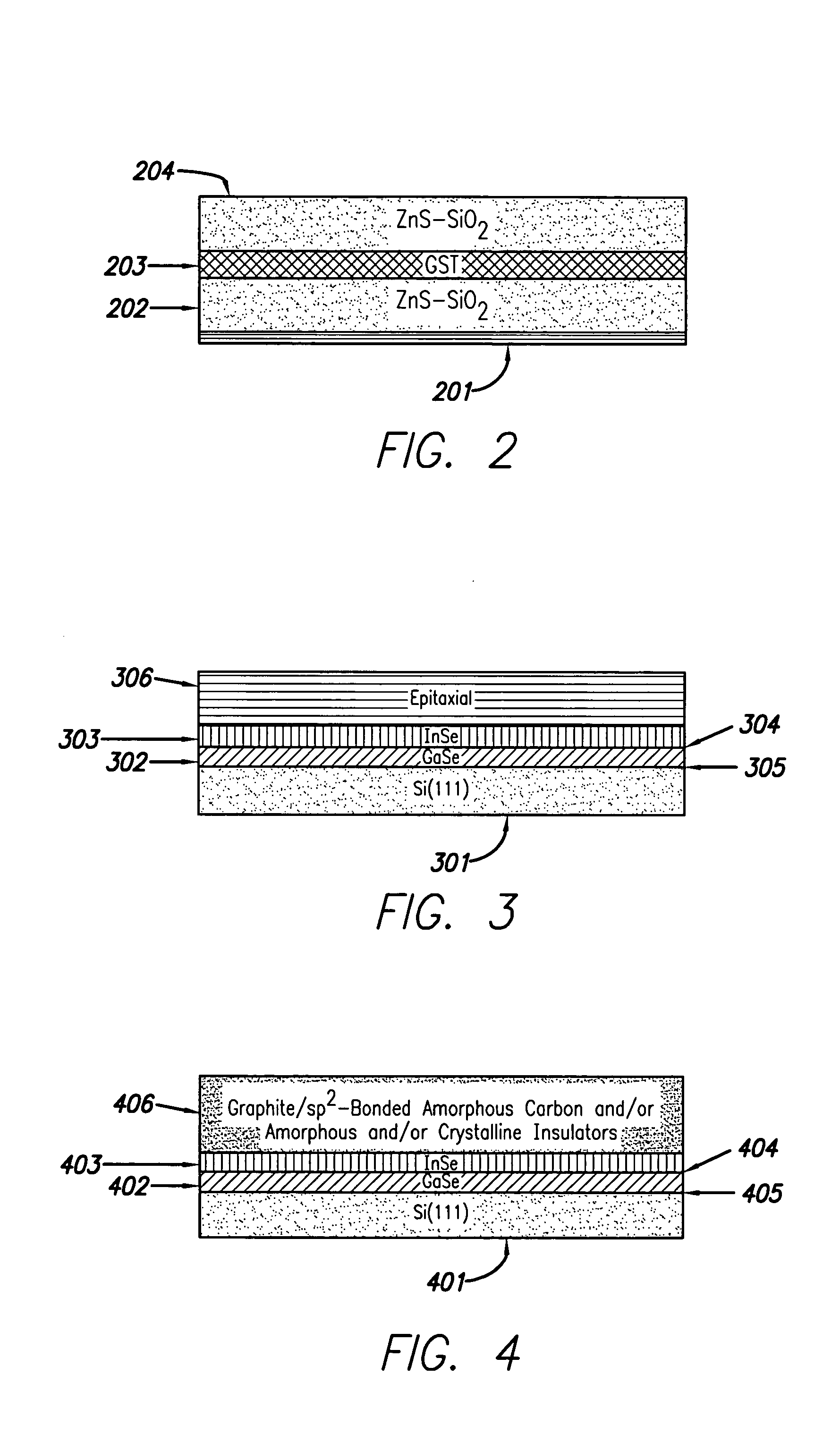
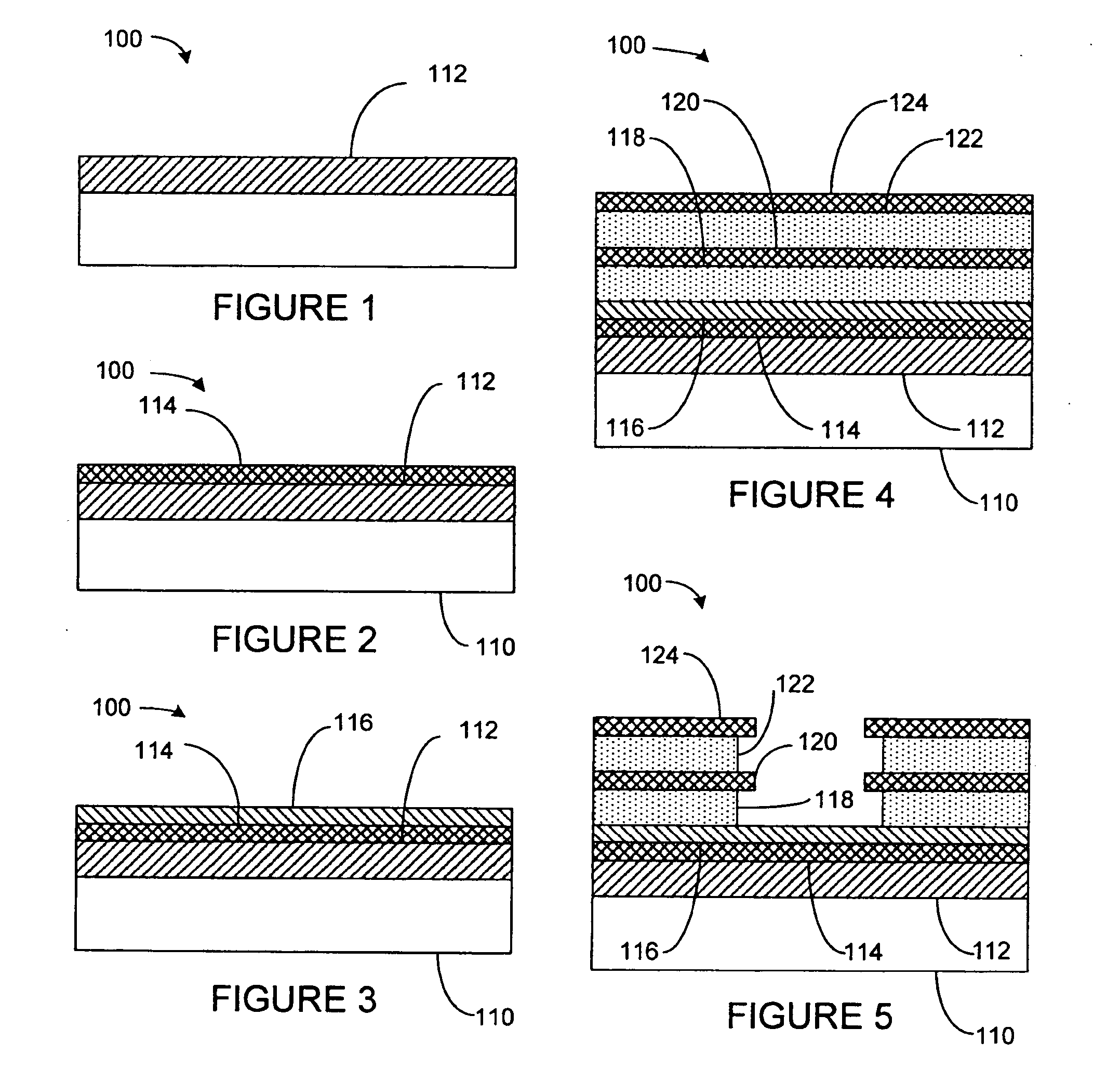
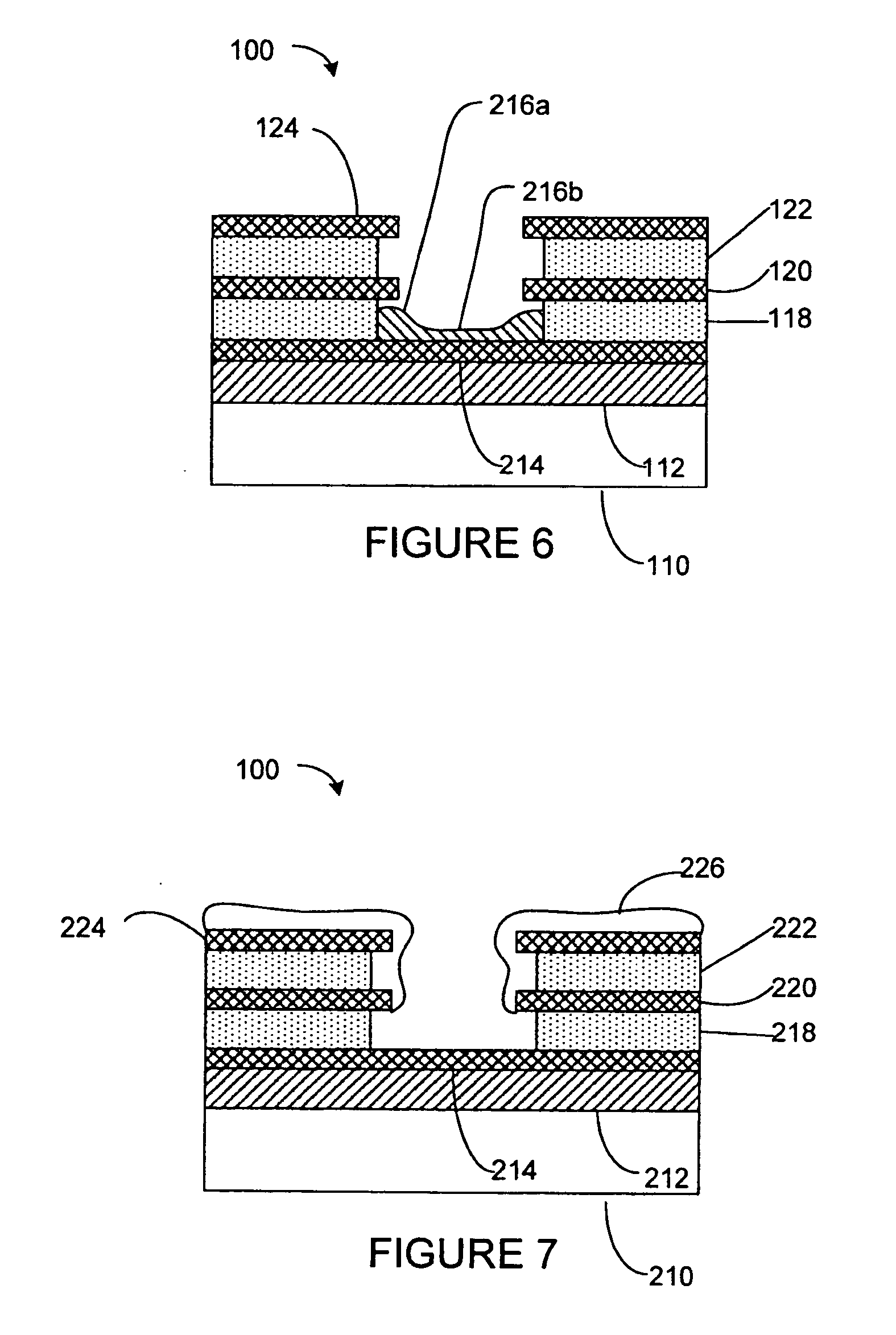
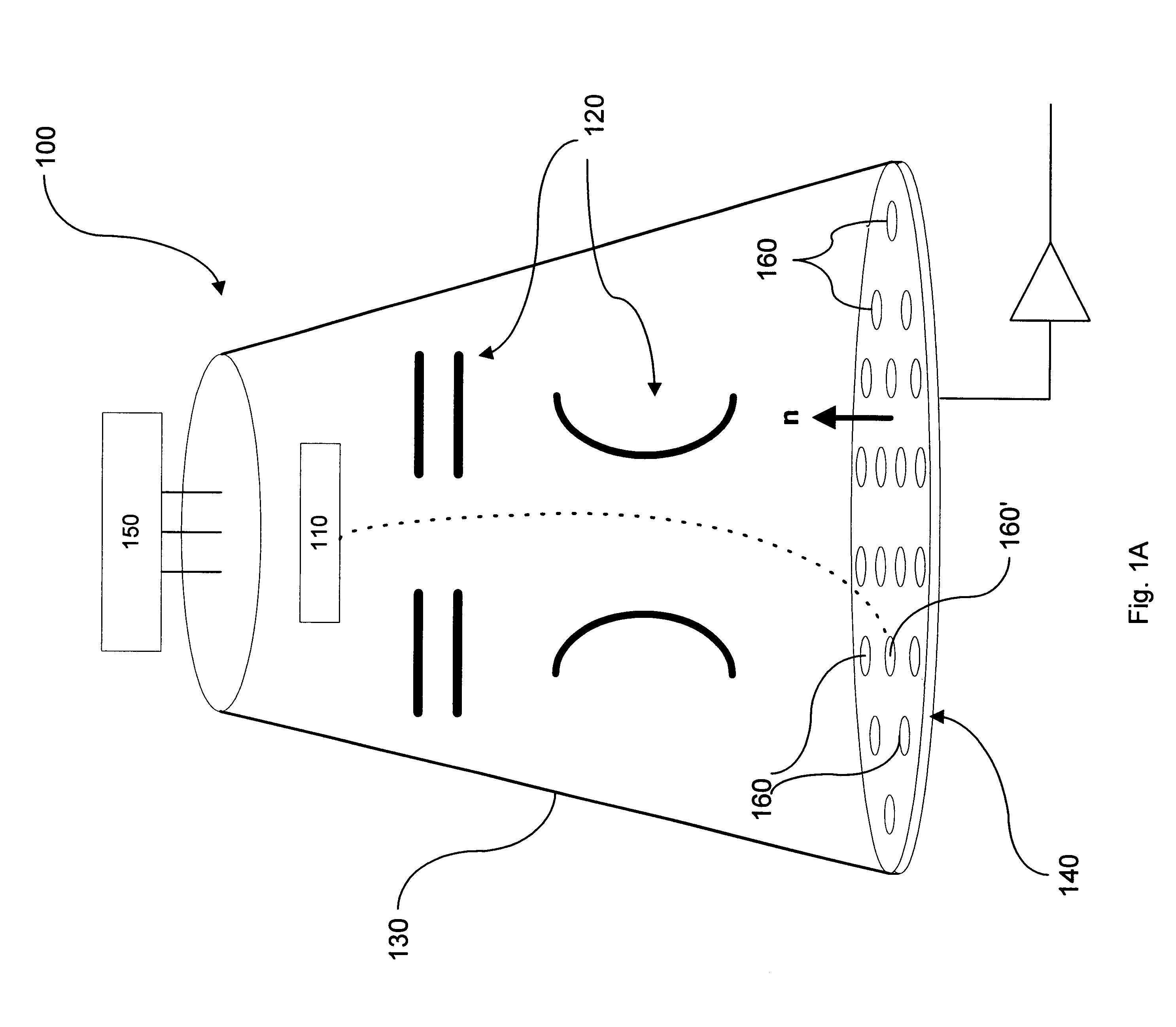
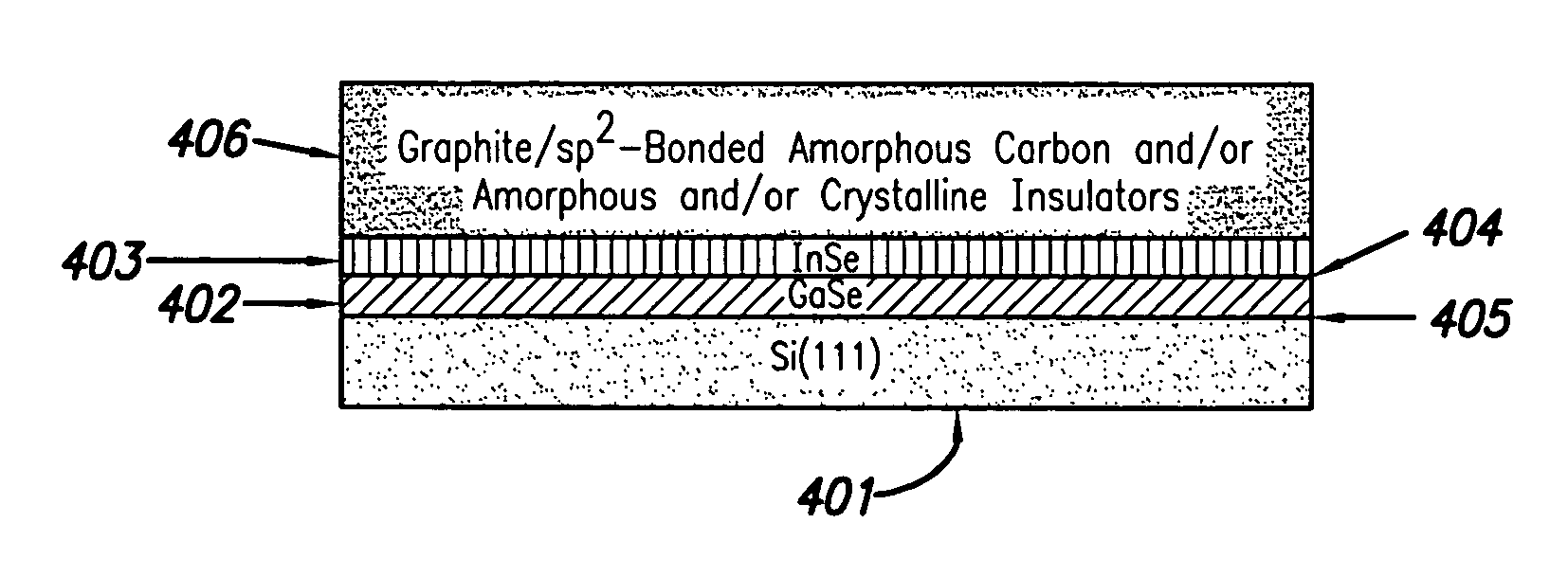
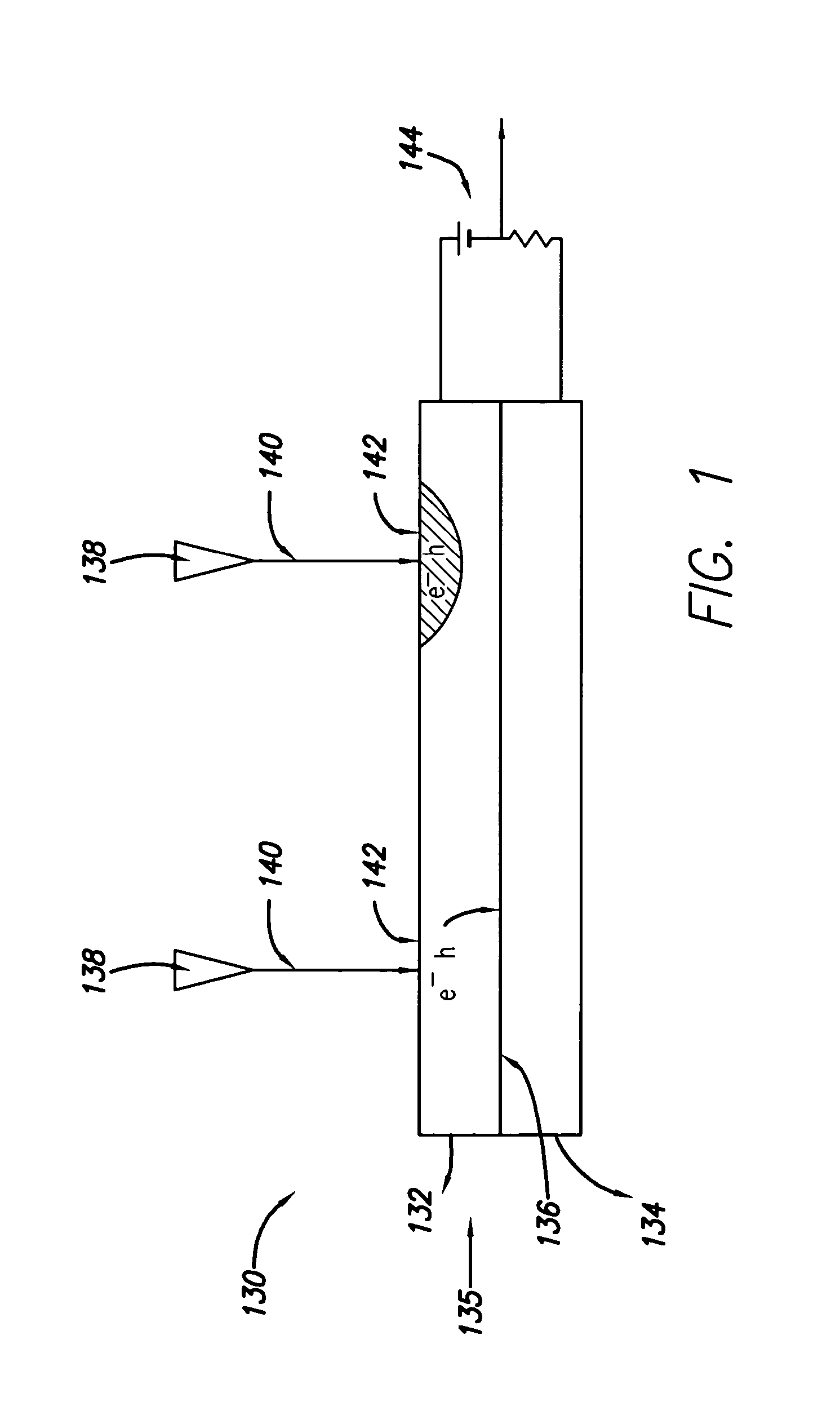
Capping layer for enhanced performance media
InactiveUS20050074576A1High materialElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingElectron beam carrier recordingEpitaxial materialConductive materials
A media storage device and method for fabricating said device is provided. The device comprises a data layer capable of storing and erasing data via application of an energy beam, such as a near field optical non diffraction limited beam or electron beam. A separate capping layer is deposited on the data layer. The separate capping layer is relatively transparent to the energy beam and may be formed from various materials, including but not limited to an epitaxial material, a conducting material, and a robust high melting point material, such as Molybdenum.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High density data storage medium
InactiveUS20050047307A1Low viscosityReduced dimensionElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsData bitsTip position
A data storage medium from which information is reproduced by scanning a surface of the medium with a probe-based tip, such as an Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) tip positioned in contact therewith. The medium comprises a substrate; and a polymer recording surface within which data bit values are determined by the topographical state at the bit location. The polymer contains thermally reversible crosslinkages. The data bit value is a function of the depth of the pit at the bit location.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head, method of manufacturing the same, and thermally-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS7042810B2Optimize timingEfficient and stable recordingElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
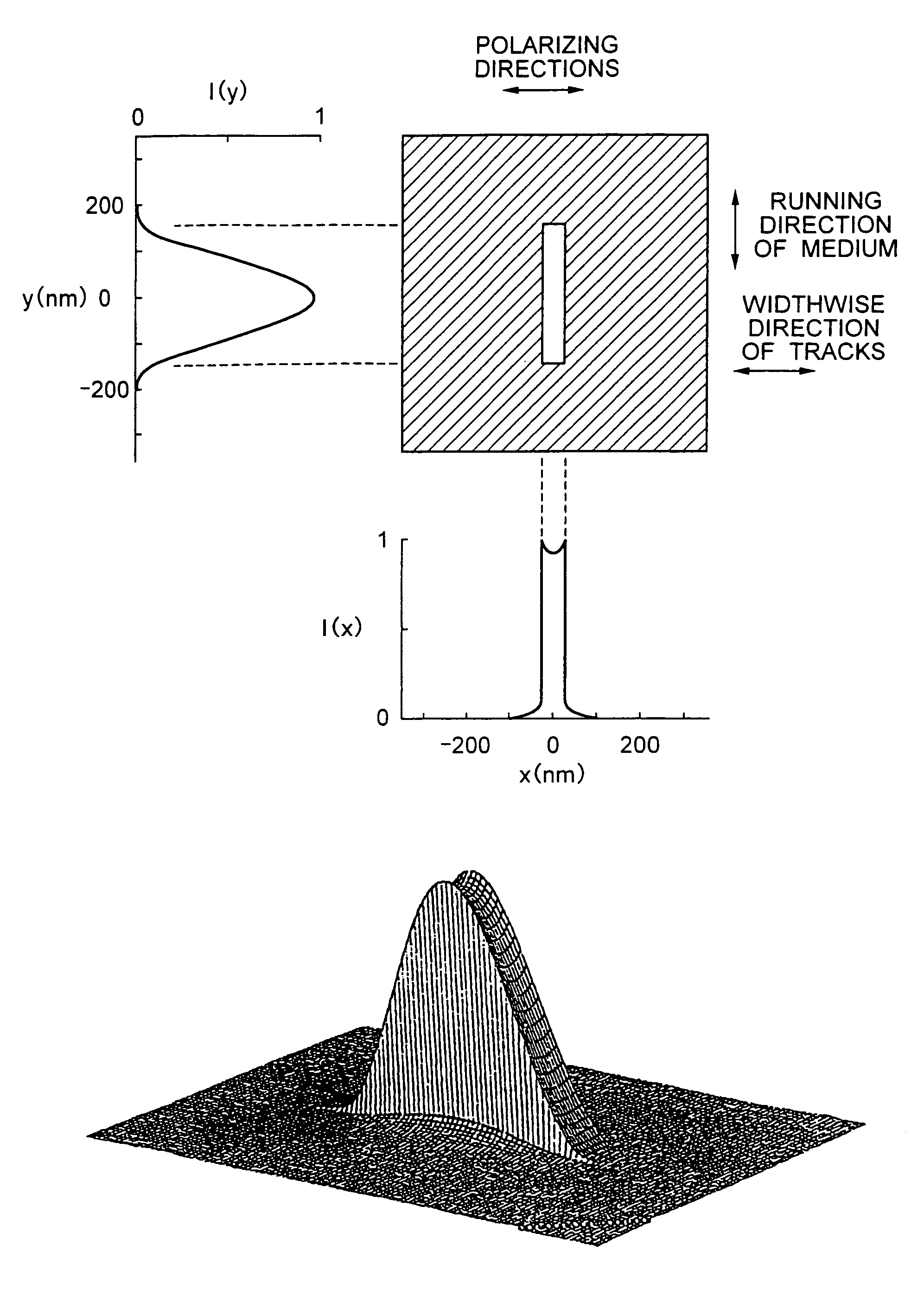
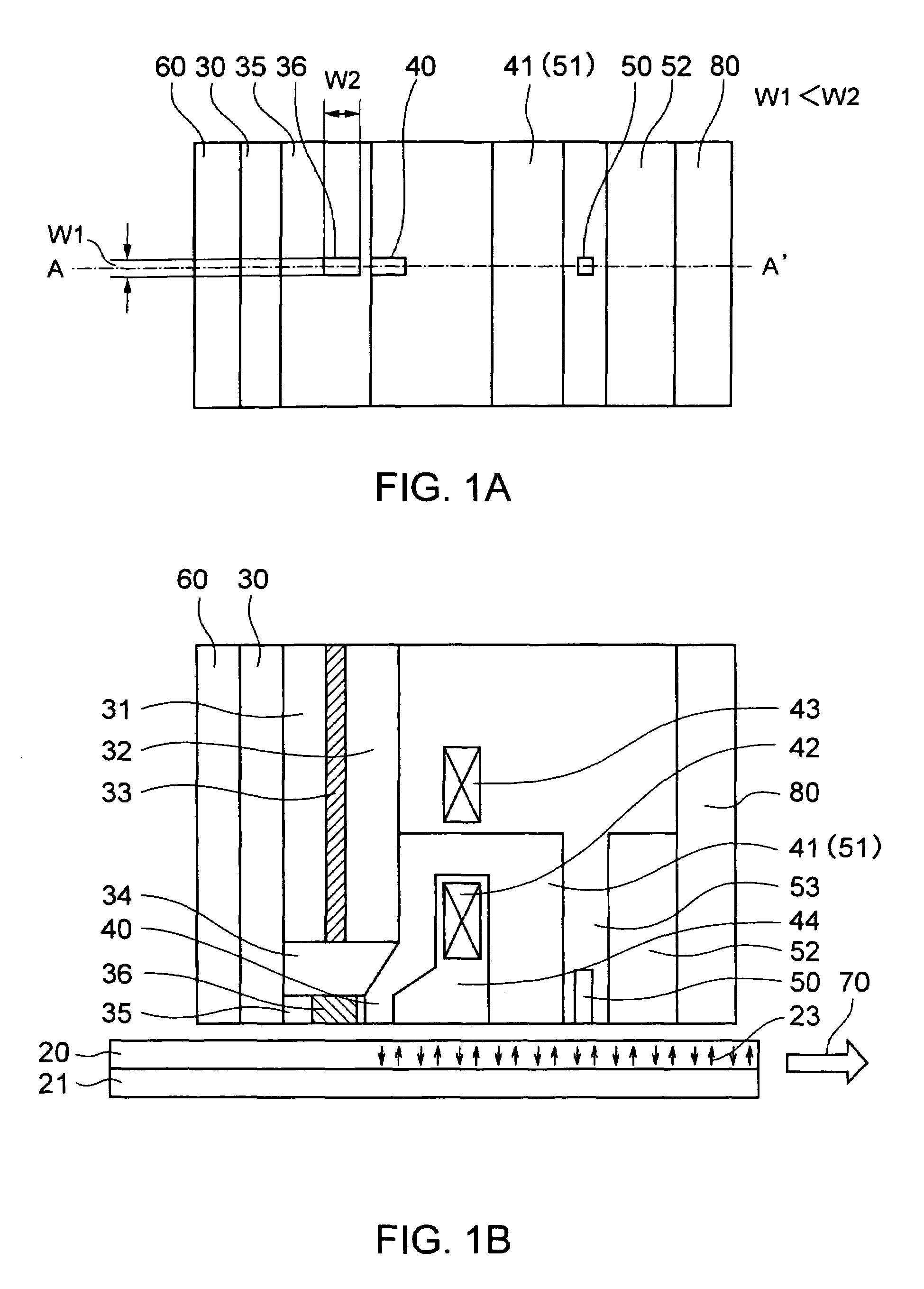
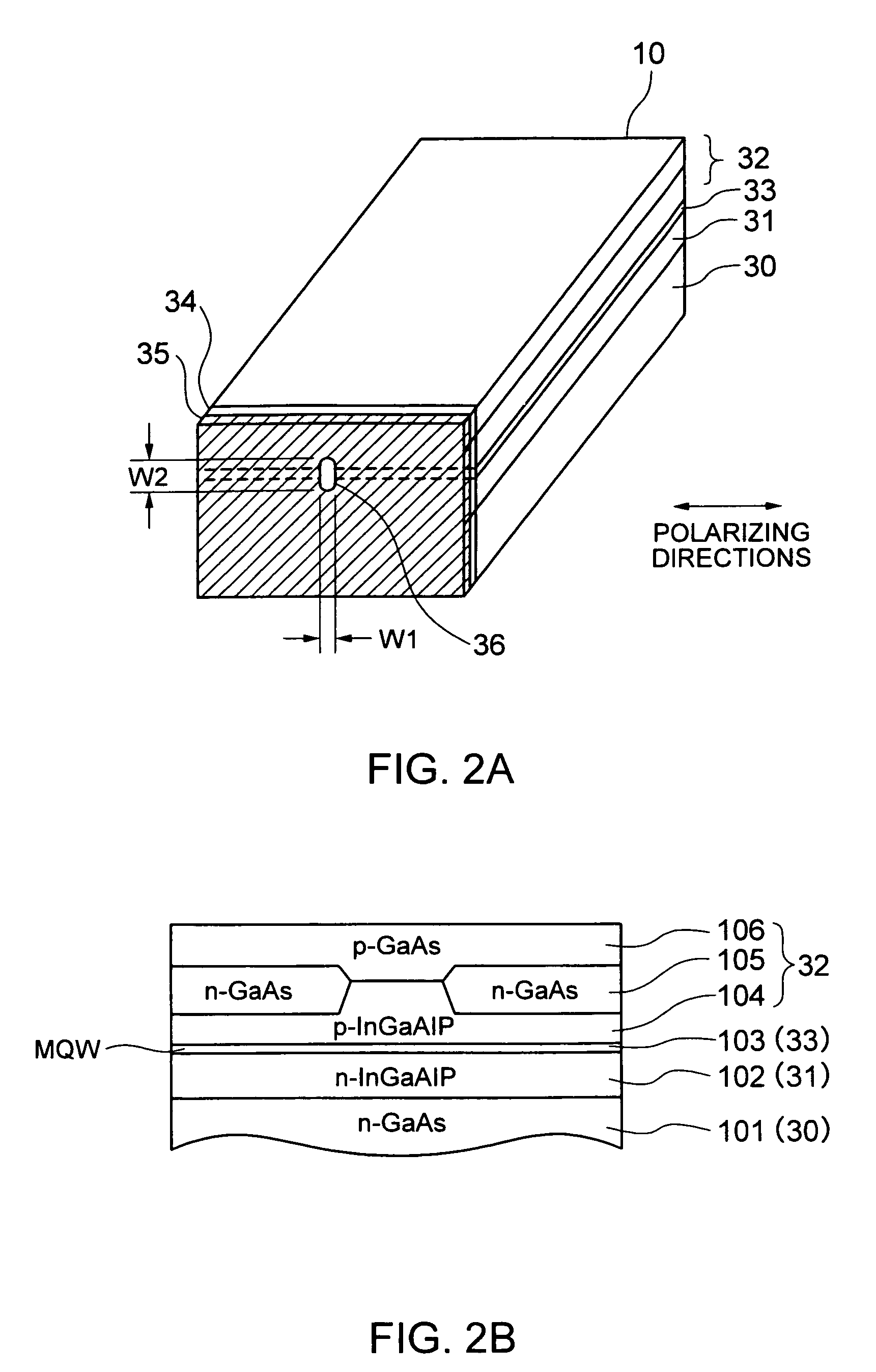
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and a magnetic recording apparatus having the magnetic recording head built in are disclosed. The magnetic recording head is capable of recording magnetic information by heating a recording unit of a recording medium and raising its temperature to reduce magnetic coercive force and then applying recording magnetic field to the recording unit having the reduced coercive force. The magnetic recording head has a light absorbing film having an aperture, a laser device emitting and directing light through the aperture to the recording medium to head the recording unit and raise its temperature, and a recording magnetic pole for applying the recording magnetic field to the recording unit. In the aperture, an aperture width W1 is along a polarizing direction of the light emitted from the laser device while an aperture width W2 is approximately perpendicular to the polarizing direction of the aperture width W1, and the aperture width W1 is shorter than the aperture width W2. The heating source such as a laser device recedes from the medium to provide a unique configuration where a tip of the recording magnetic pole protrudes ahead of the heating source, and hence, heating beam and the recording magnetic pole can be located close to each other without losing sufficient energy density to heat the medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Phase-change microhead array chip hard disk drive
InactiveUS20030161245A1Electron beam carrier recordingOptical beam sourcesStationary phaseEngineering
An optical data-storage hard disk drive that uses stationary Phase-Change Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional flying-heads, rotary voice-coil actuators, or other similar types of servo-tracking mechanisms to simultaneously record and / or reproduce data to and / or from a multitude of data-tracks located across the data-surfaces of a multitude of phase-change based disc media using a multitude of microheads.
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Planar electron emitter apparatus with improved emission area and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050156500A1Electron beam carrier recordingDischarge tube luminescnet screensHigh rateOptoelectronics
The field emission planar electron emitter device is disclosed that has an emitter electrode, an extractor electrode, and a planar emitter emission layer, electrically coupled to the emitter electrode and the extractor electrode. The planar electron emitter is configured to bias electron emission in a central region of the emission layer in preference to an outer region thereof. One structural example that provides this biasing is achieved by fabricating the planar emitter emission layer so that it has an outer perimeter that is thicker in depth than at an interior portion of the planar emitter emission layer, which reduces electron beam emission at the outer perimeter when an electric field is applied between the emitter electrode and the extractor electrode. The electric field draws emission electrons from the surface of the planar emitter emission layer towards the extractor electrode at a higher rate at the interior portion than at the outer perimeter. The planar electron emitter device further includes a focusing electrode electrically coupled to the planar electron emitter.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information recording/reading head
InactiveUS20040105373A1Electrostatic charge injection carrier recordingOptical head protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP
High density data storage medium
InactiveUS7463572B2Low viscosityReduced dimensionElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsHigh densityTip position
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Information recording/reading head
InactiveUS7212484B2Improve accuracyEnhanced informationElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingOptical head protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP
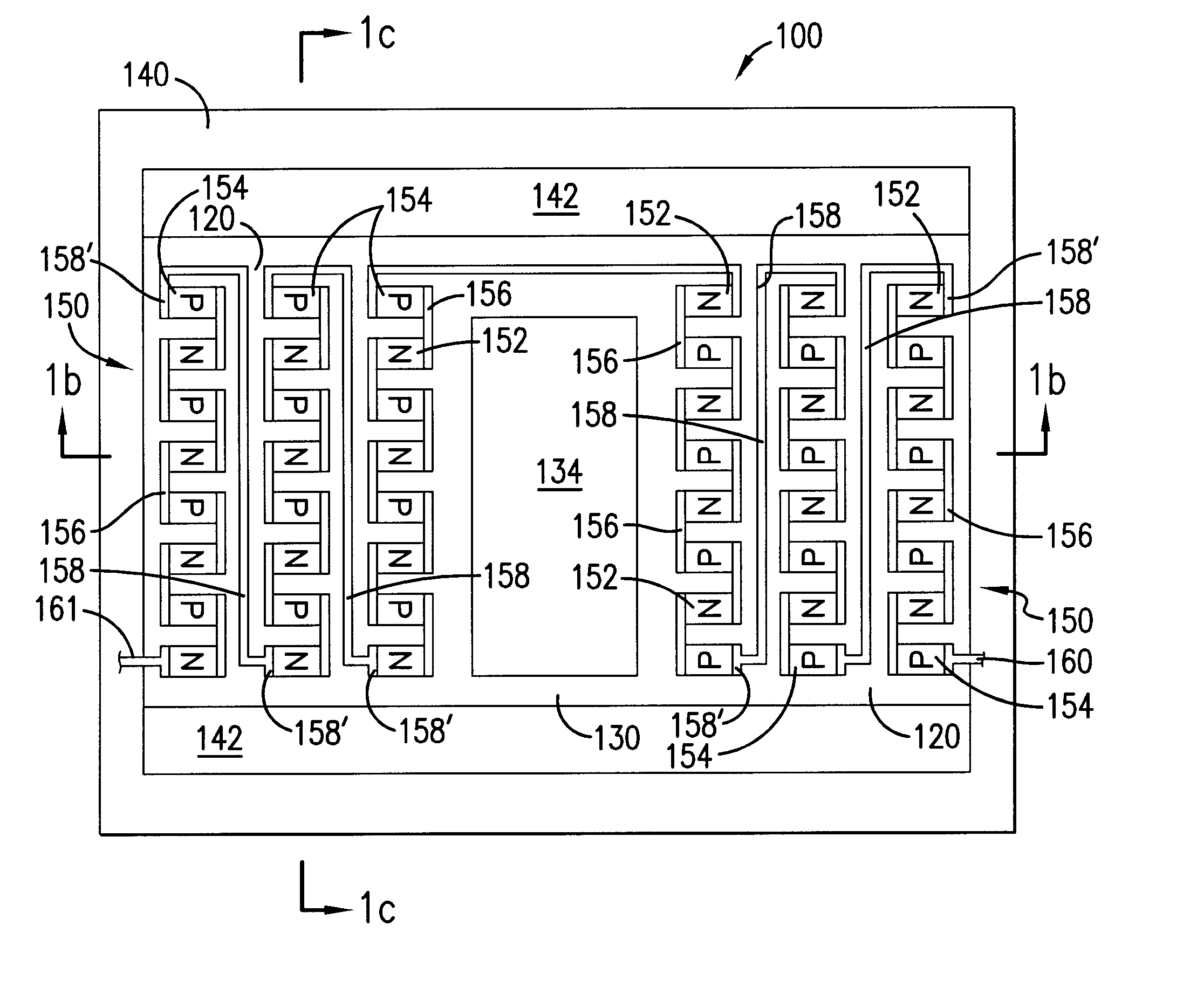
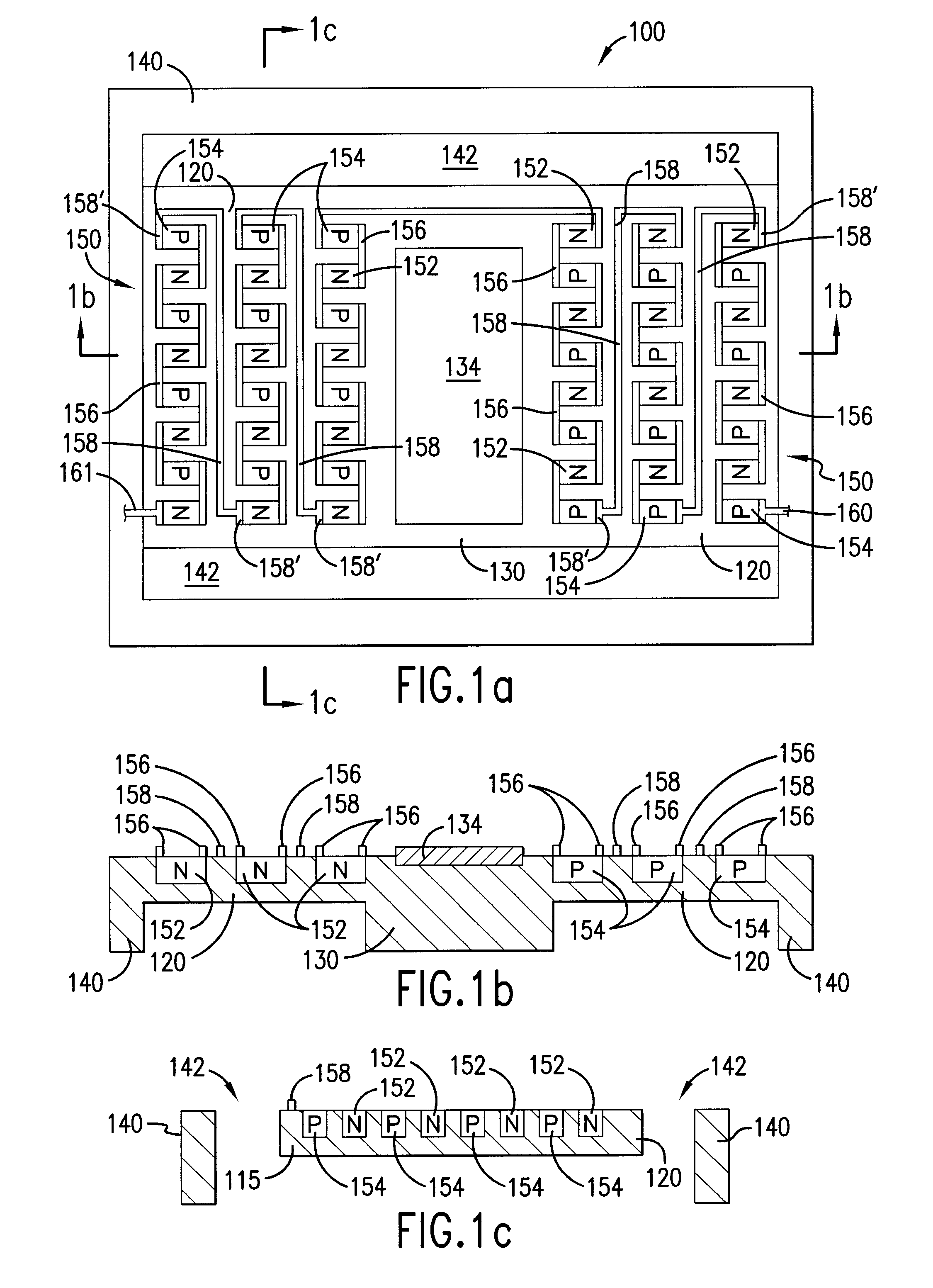
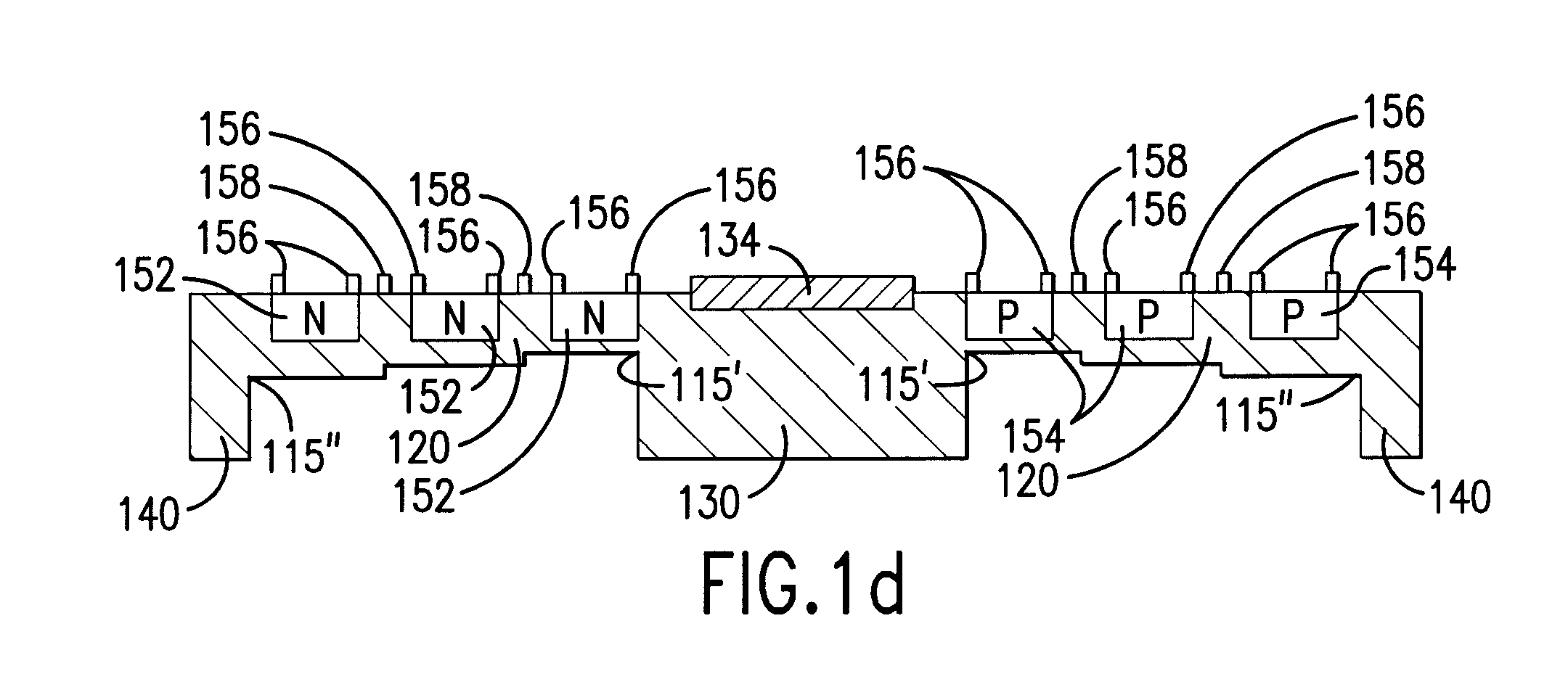
Micro-fabricated device with thermoelectric device and method of making
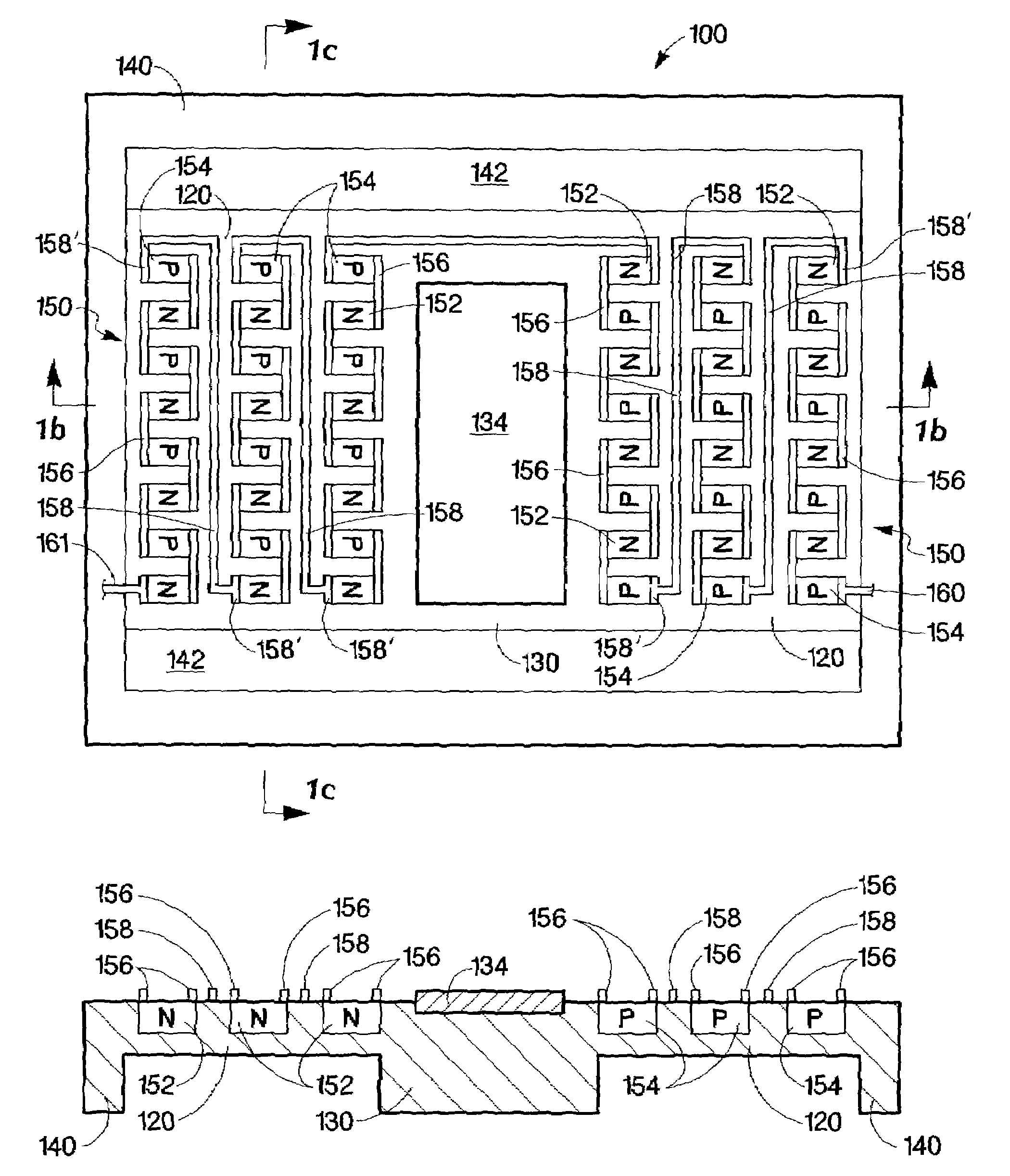
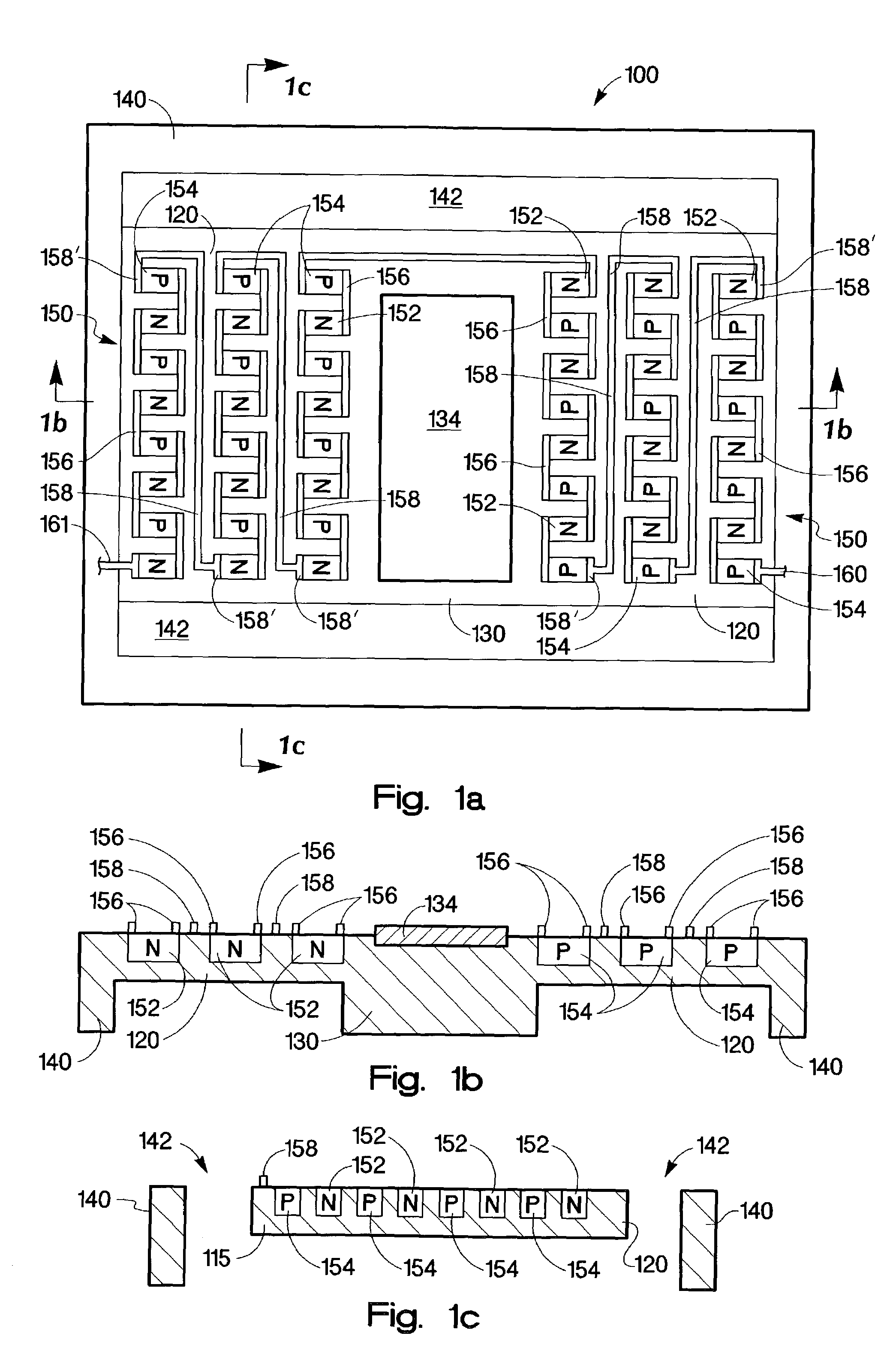
InactiveUS20070152352A1Electron beam carrier recordingThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectEngineeringElectrical interconnect
A micro-fabricated device, includes a support structure having an aperture formed therein, and a device substrate disposed within the aperture. The micro-fabricated device further includes a thermally isolating structure thermally coupling the device substrate to the support structure. The thermally isolating structure includes at least one n-doped region and at least one p-doped region formed on or in the thermally isolating structure and separated from each other. In addition, the thermally isolating structure includes an electrical interconnect connecting at least one n-doped region and at least one p-doped region, forming an integrated thermoelectric device.
Owner:MCKINNELL JAMES C +2
Molecular memory medium and molecular memory integrated circuit
InactiveUS7260051B1Reduce quality problemsFast accessNanoinformaticsRecord information storagePhase shiftedComputer science
A molecular memory media having a media surface and a platform with read / write heads. The platform and media are moved to allow one of addition, removal, and repositioning of atoms, electrons, and charges on a surface of the media. The media is a material capable of storing data written to it, and detectable using a vibrating tip sensor that resonates at a free space value which is phase shifted when charges or anomalies on a surface of the media are present. Other methods of reading and writing to the media are presented. The media may be enhanced by augmenting grain boundaries of the media vis deposition and removal of PMMA materials. Servo trenches and sync bits identify positions of the read / write heads and maintain alignment during memory operations.
Owner:NANOCHIP
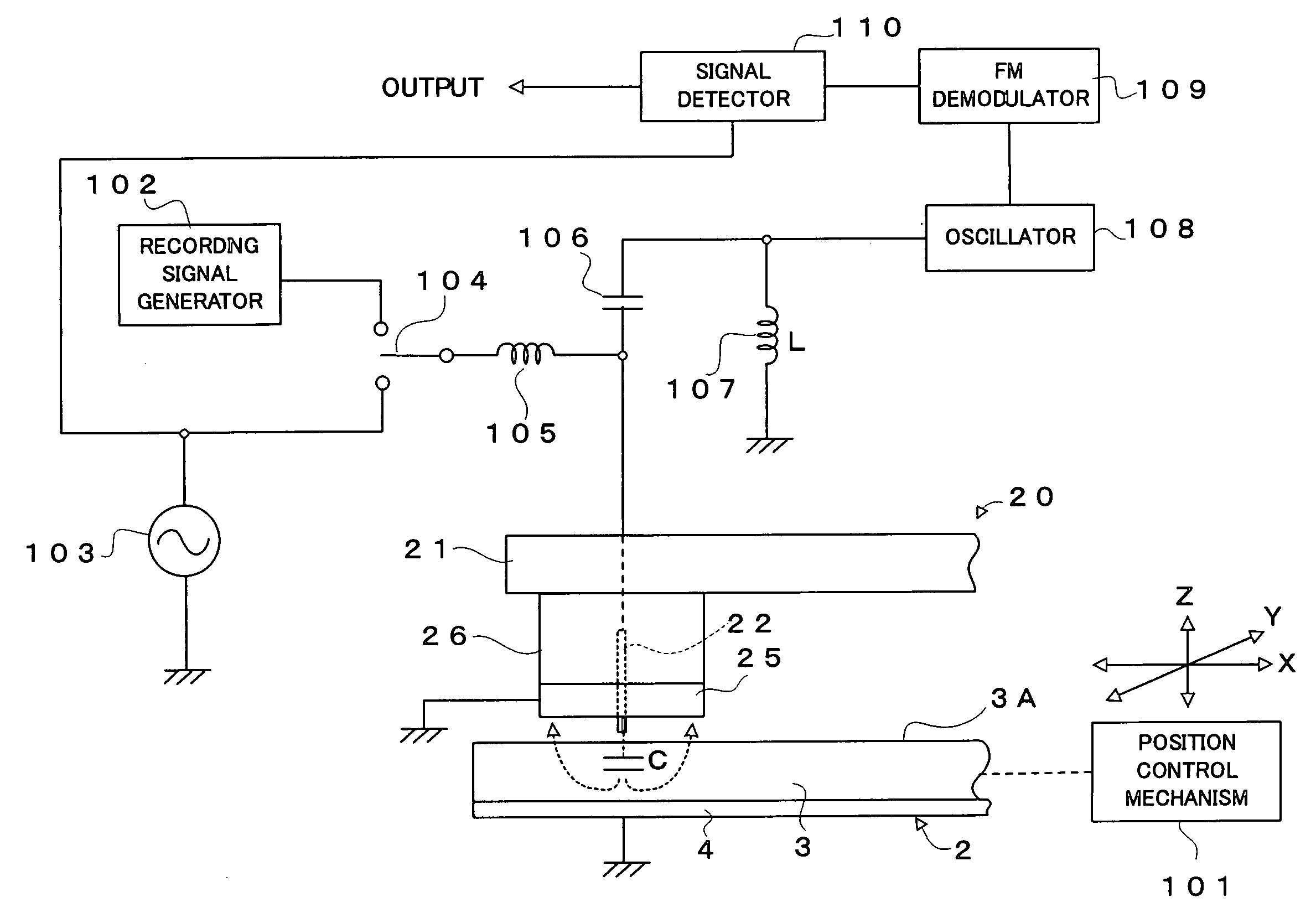
Dielectric information apparatus, tape-like medium recording/reproducing apparatus and disc-like medium recording/reproducing apparatus
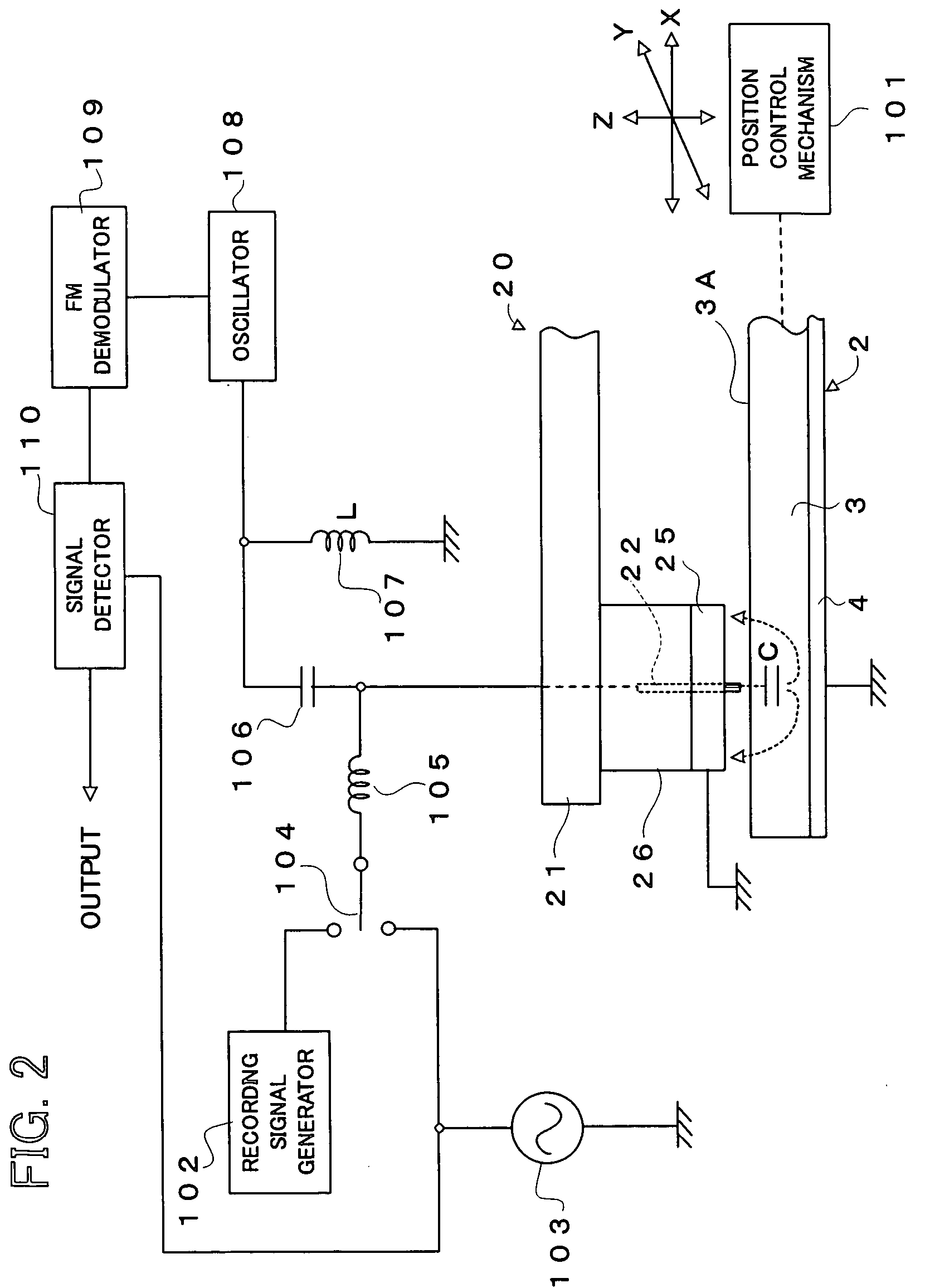
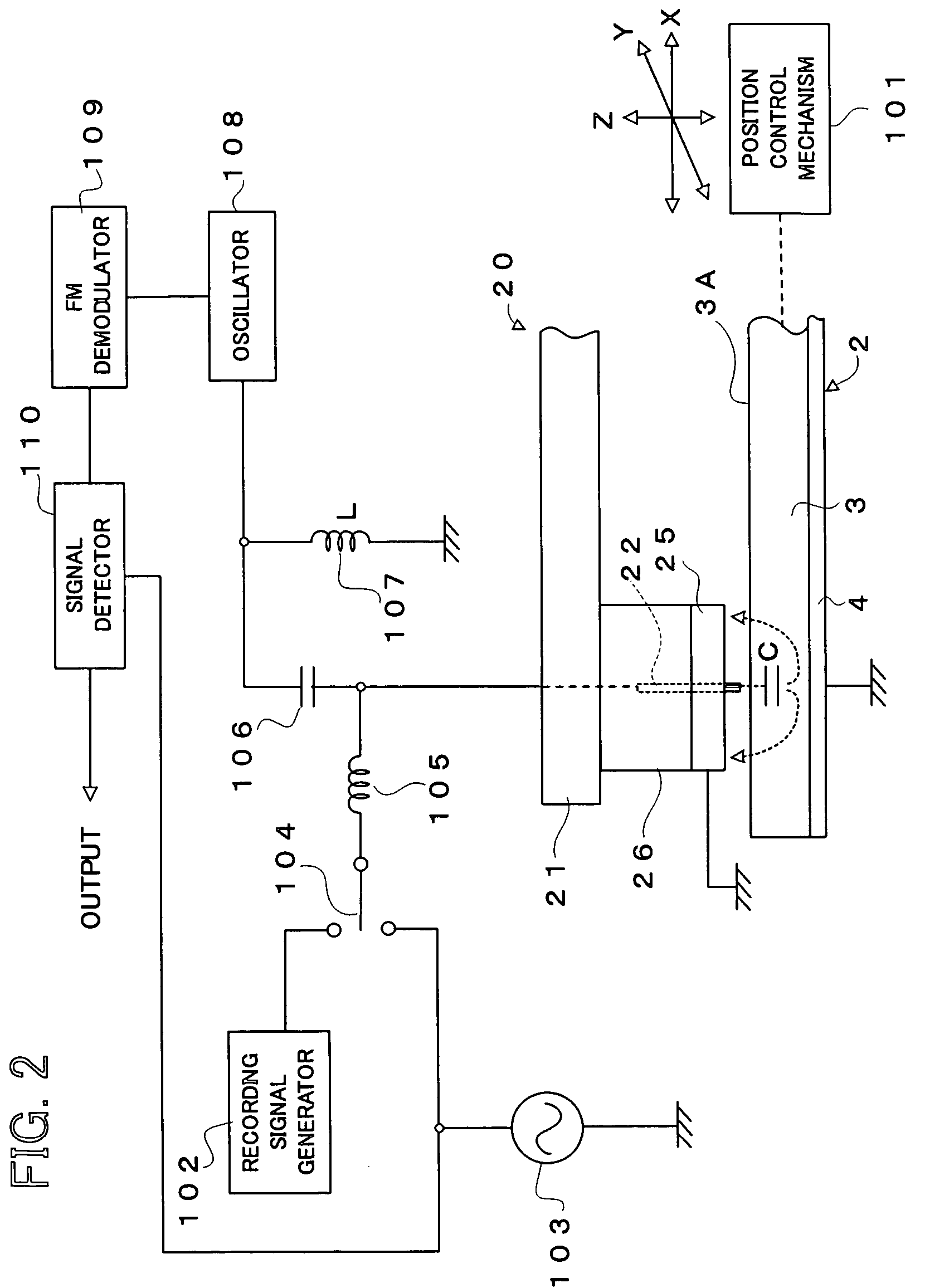
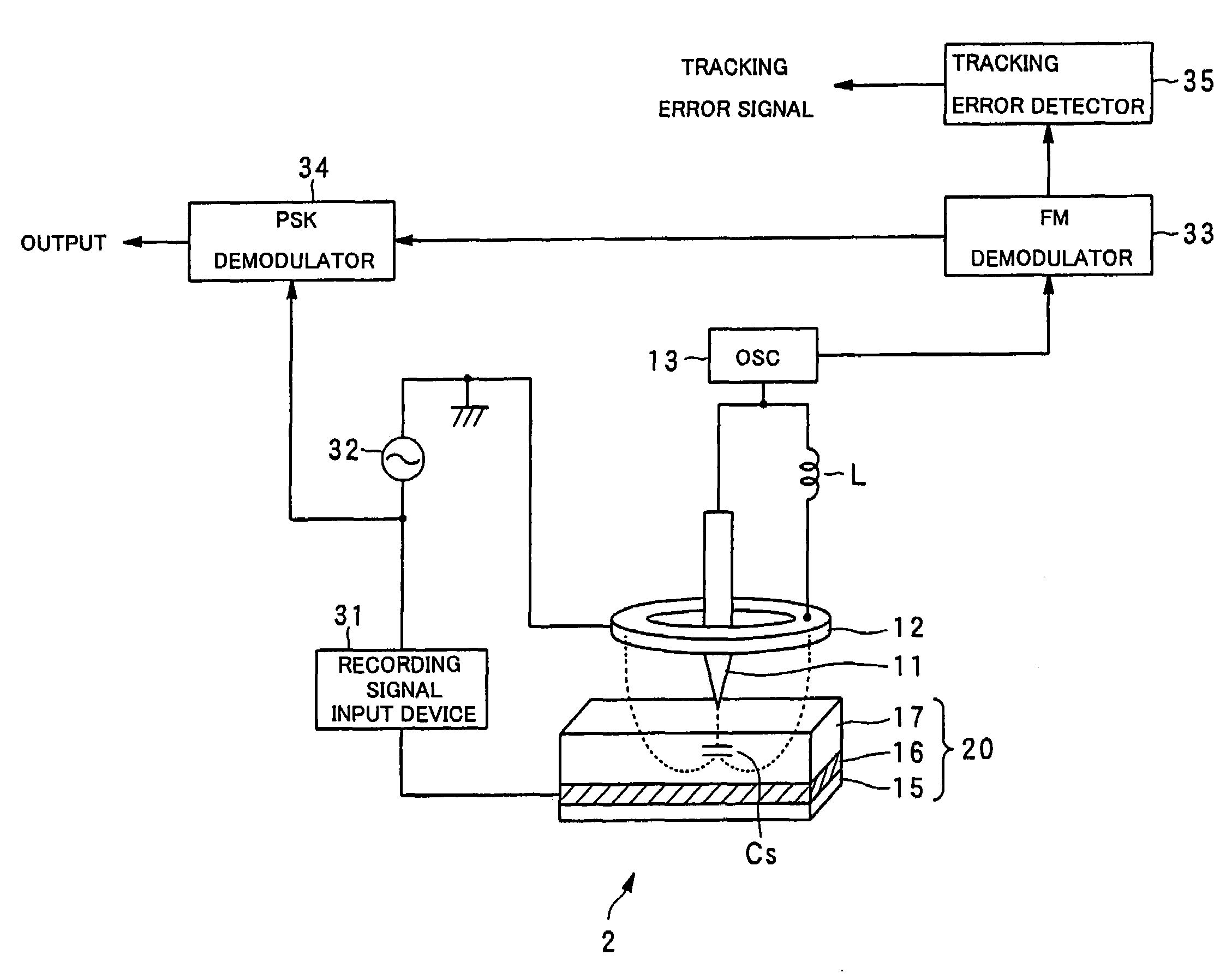
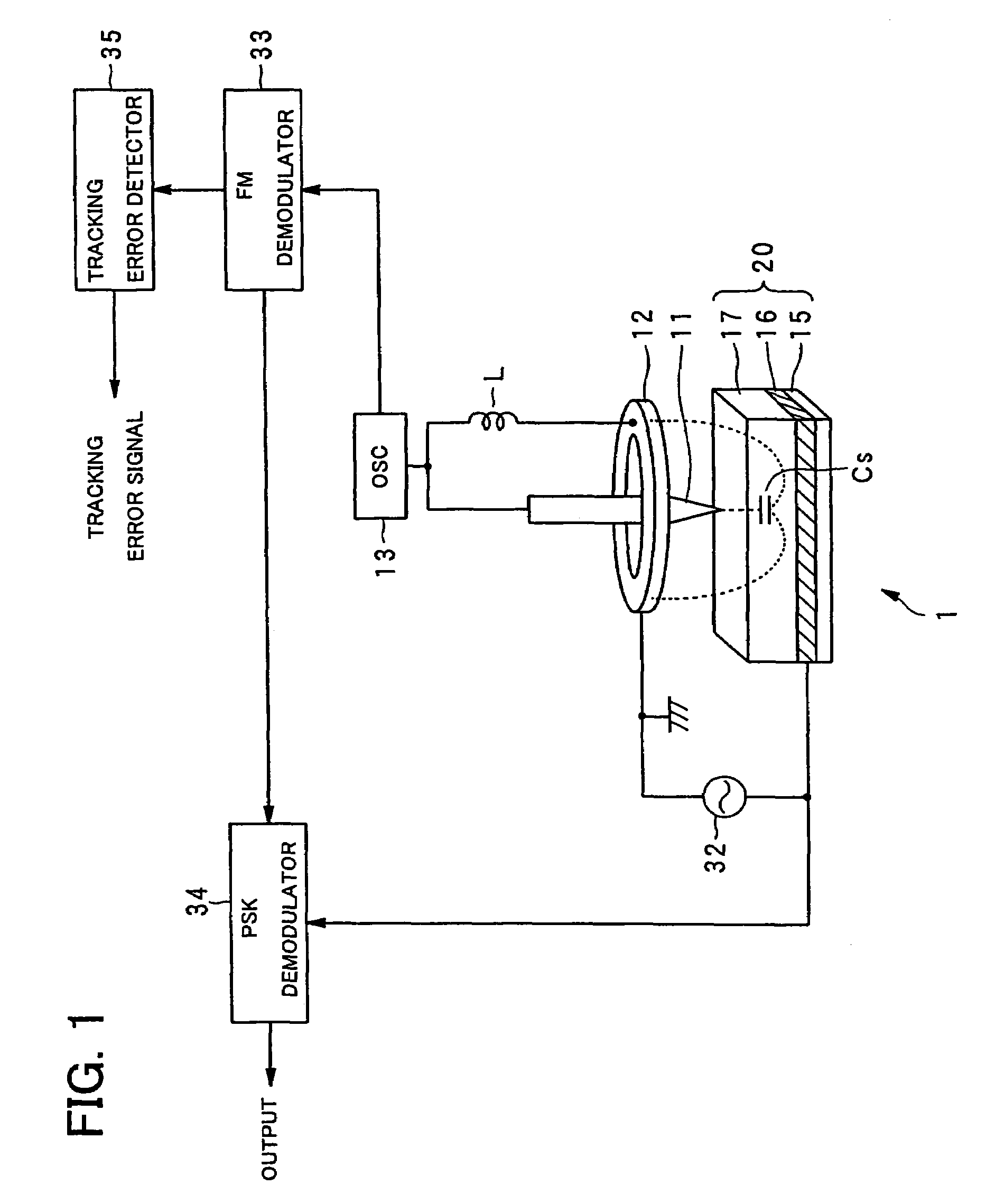
InactiveUS7242661B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioLarge circuit structureElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingElectron beam carrier recordingElectricityCapacitance
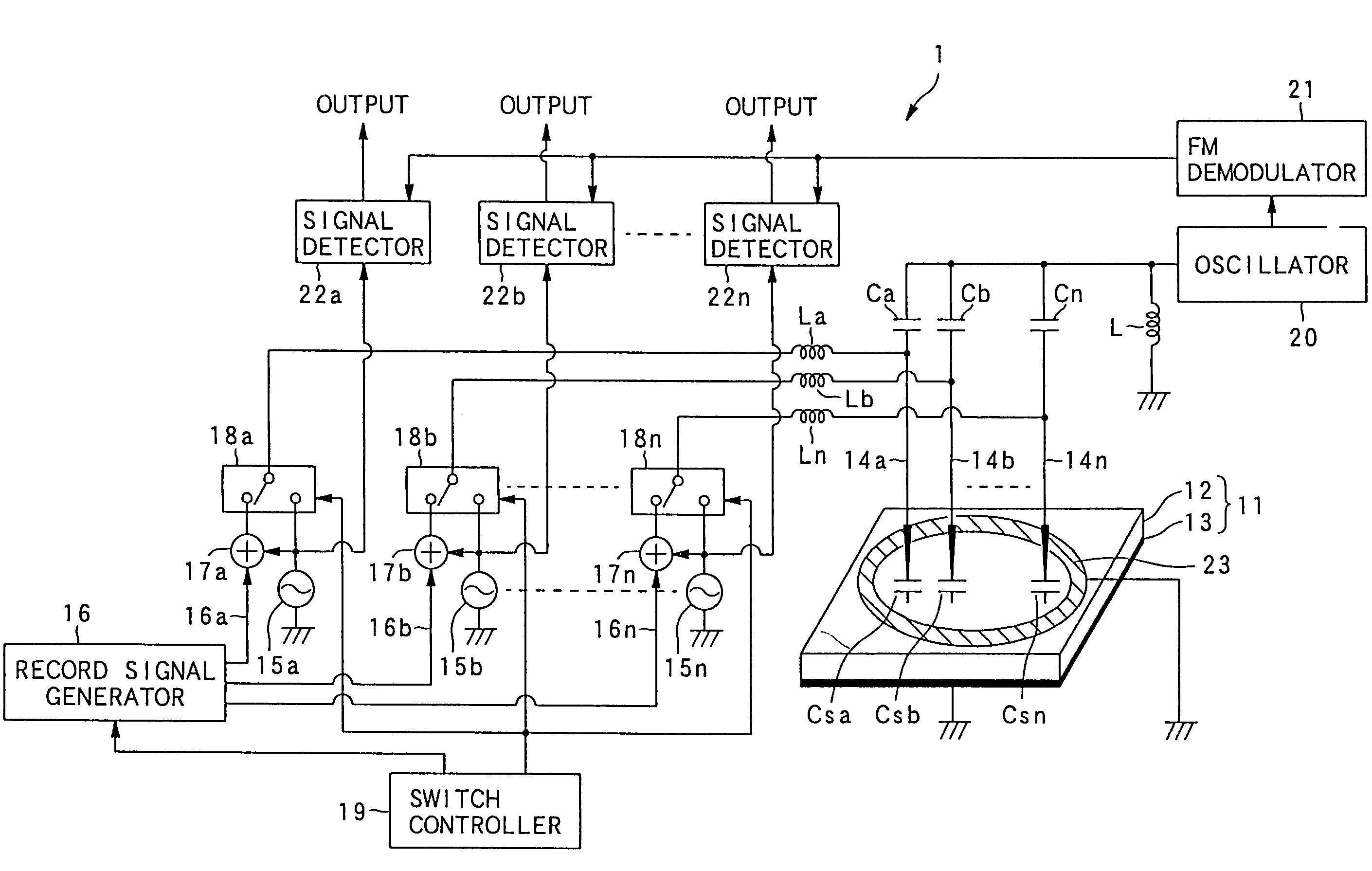
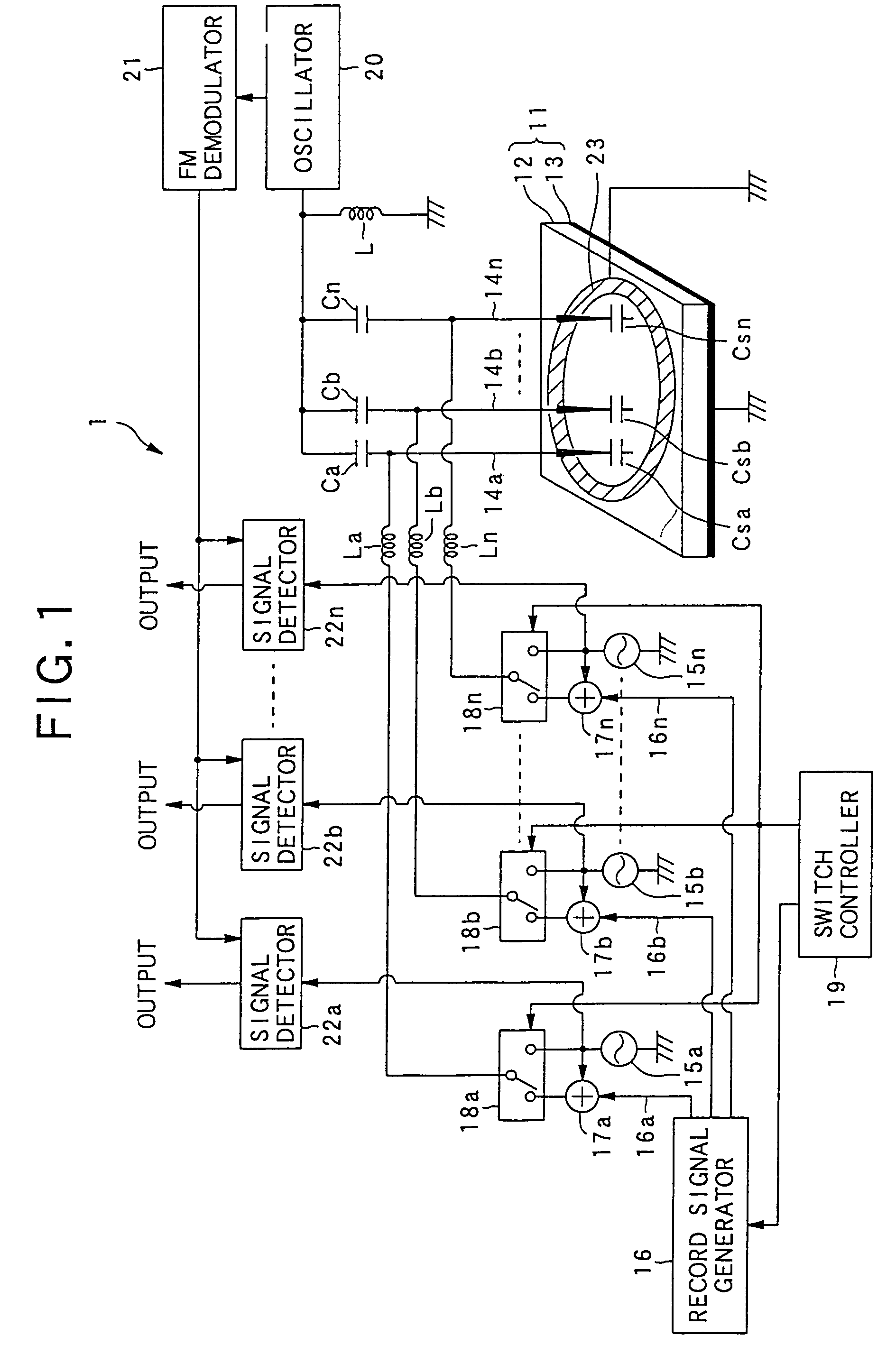
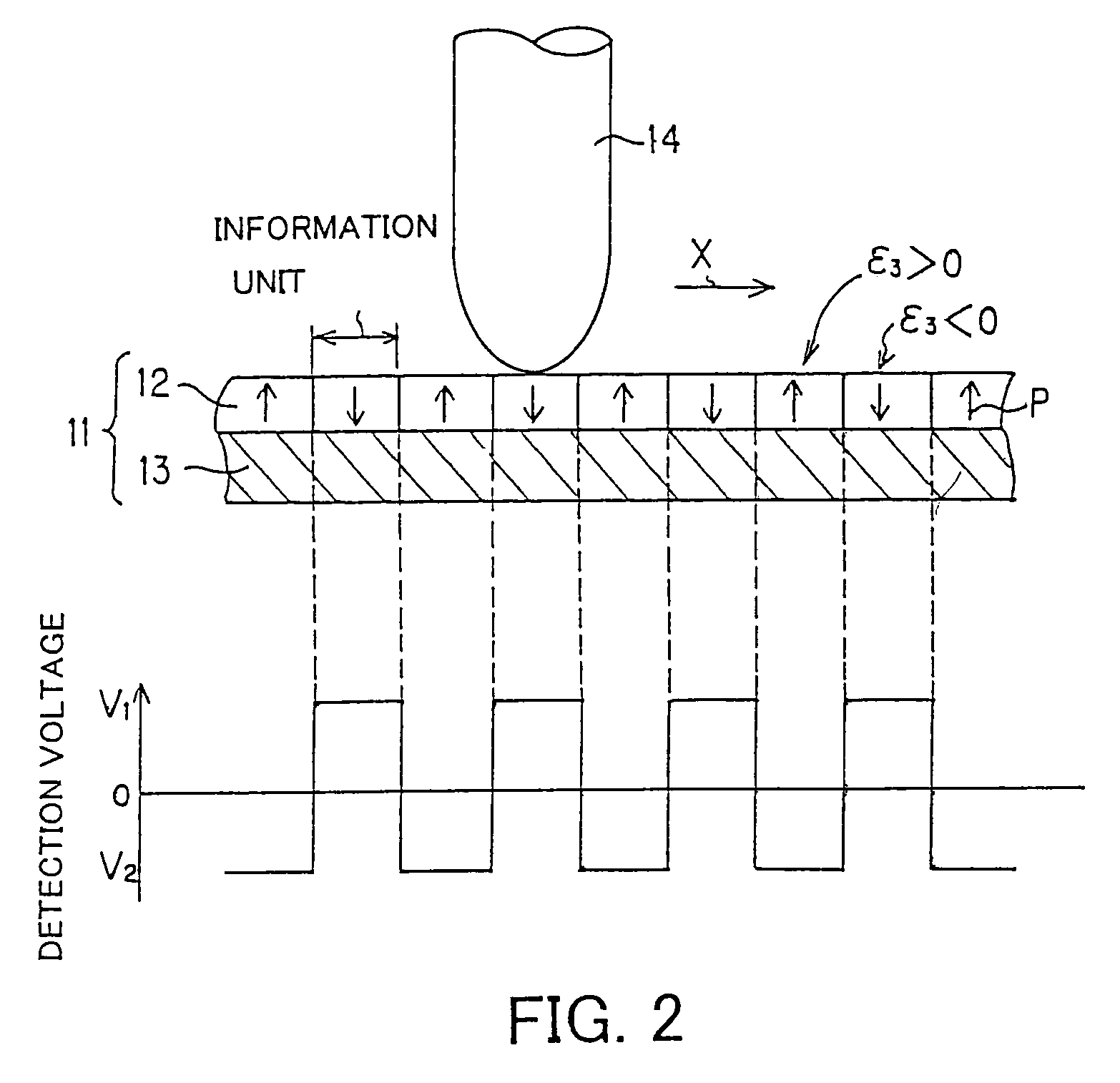
An example dielectric information apparatus is provided with a plurality of electrodes for recording information in a small area of a dielectric substance and an earthed electrode. The electrodes are placed such that the dielectric substance is sandwiched therebetween. The dielectric information apparatus reads out the information recorded in the small area of a dielectric thin film by applying alternating current signals to the first electrodes. The polarization direction of the small area and the direction of an applied electric field decide the dielectric constant of the small area, and the oscillation frequency of an oscillator is determined by a capacitance Cs corresponding to the dielectric constant. An oscillation signal of the oscillator is demodulated at an FM demodulator, and the information is detected from the demodulated signal at a signal detector. When recording, record signals are applied to the first electrodes, and the polarization direction is set to correspond to the record signals.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
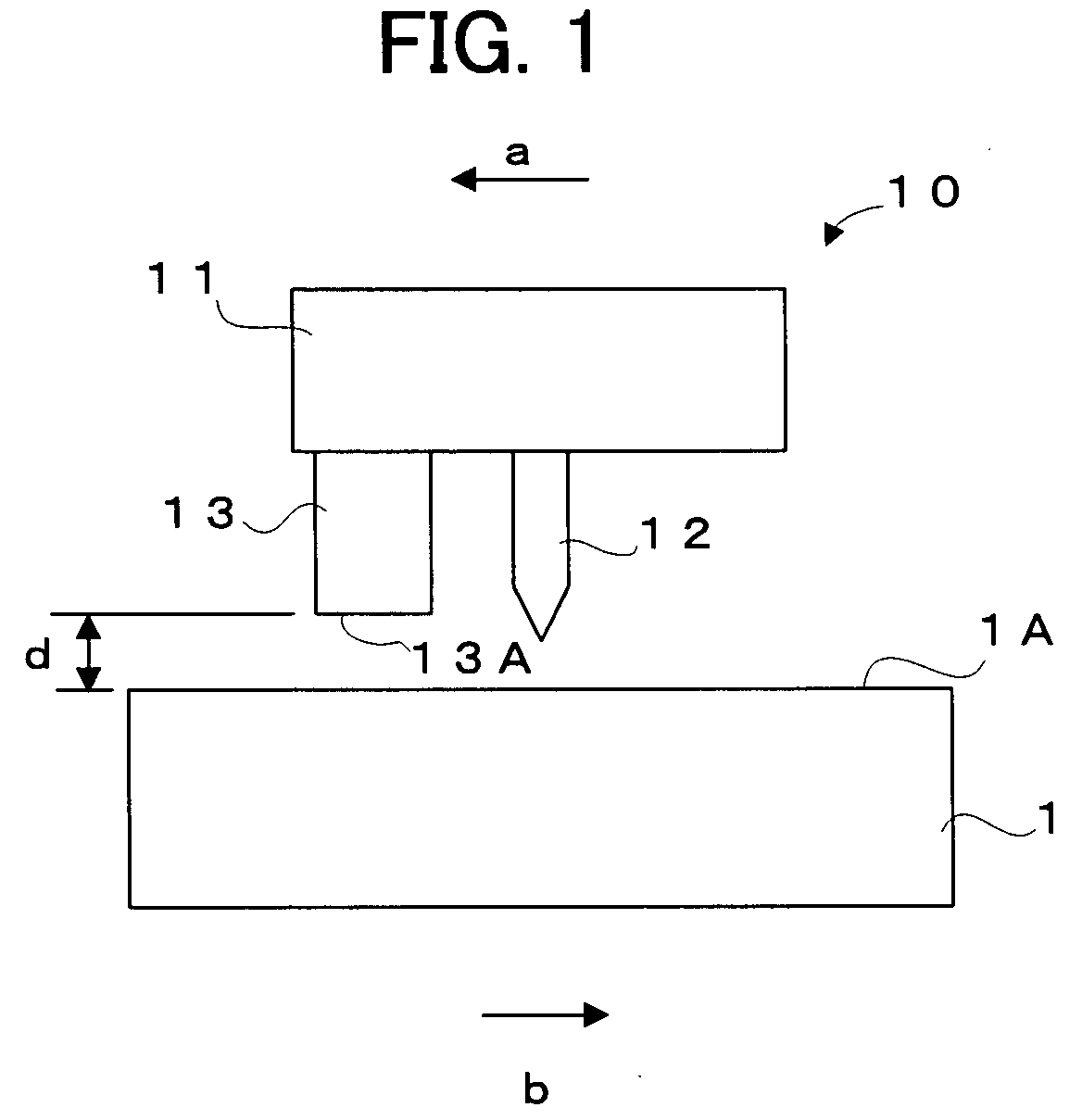
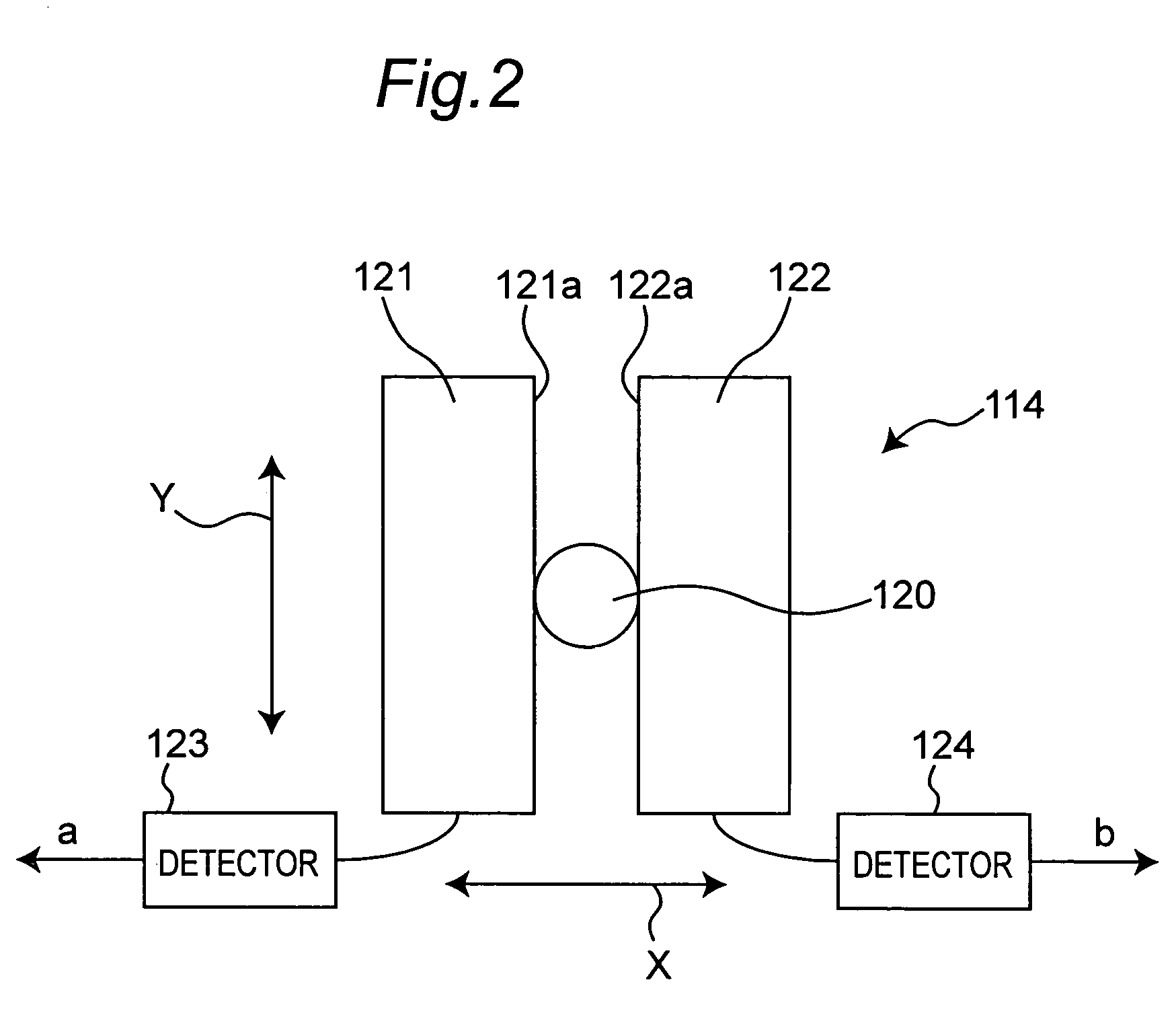
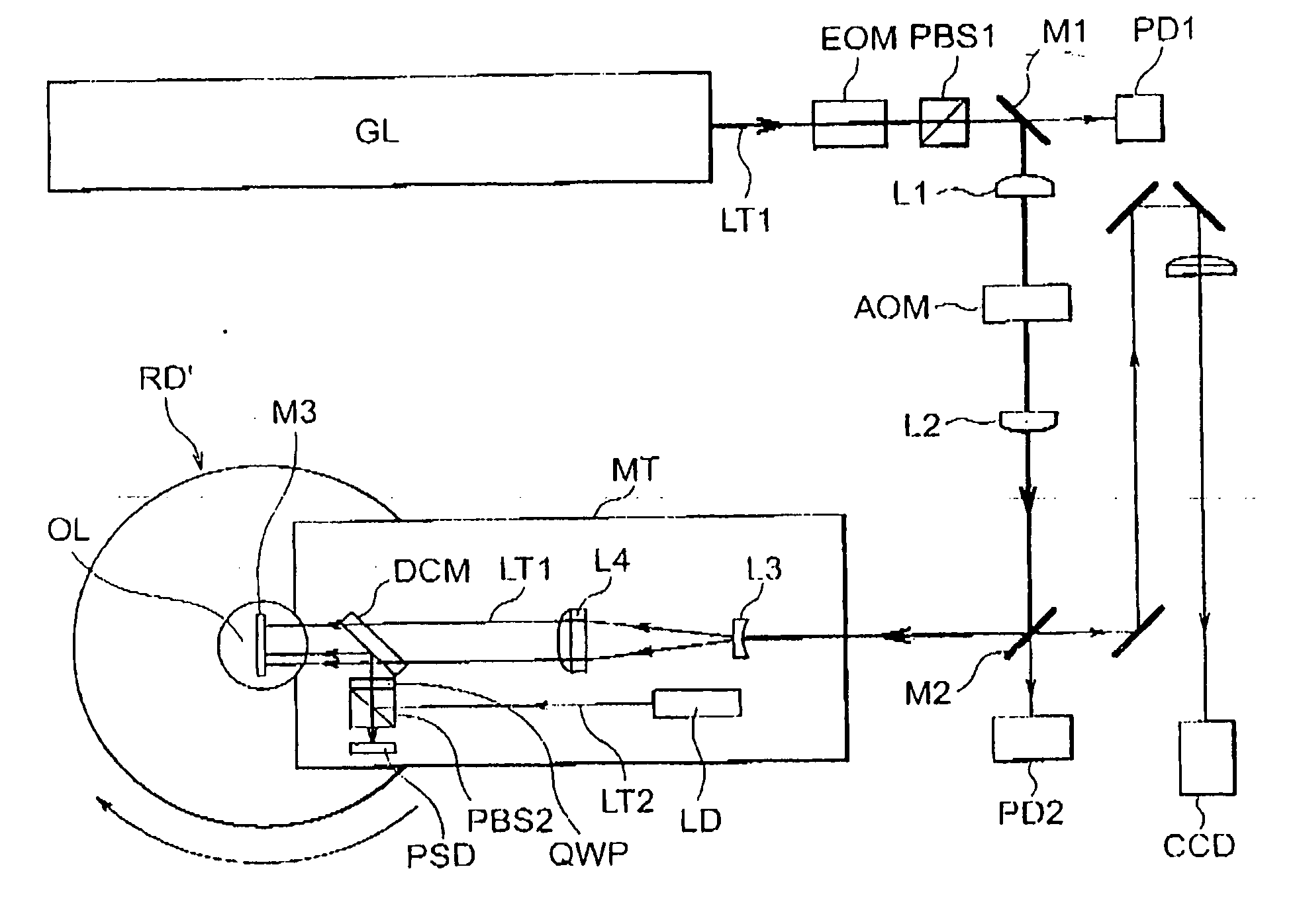
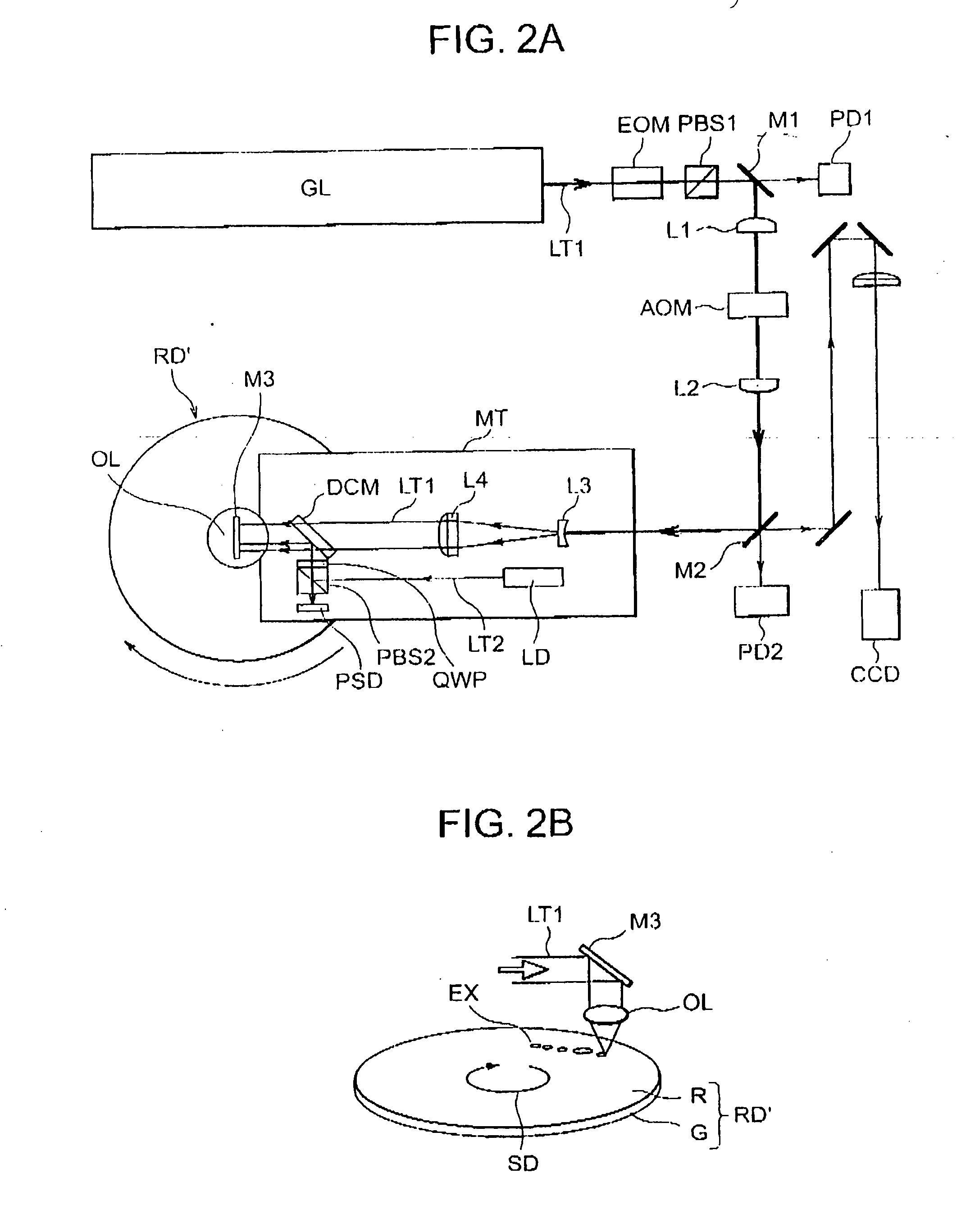
Master disc manufacturing apparatus
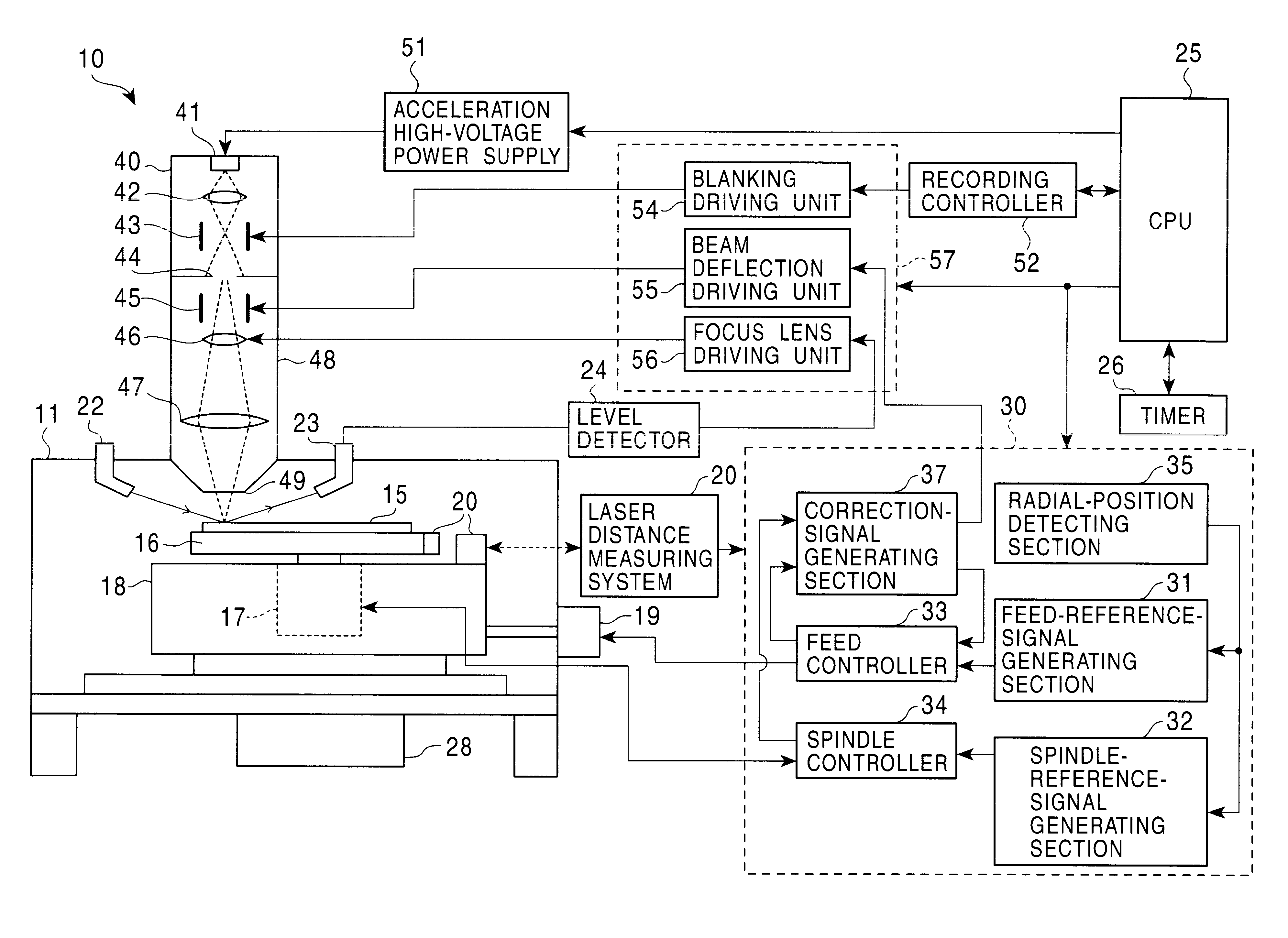
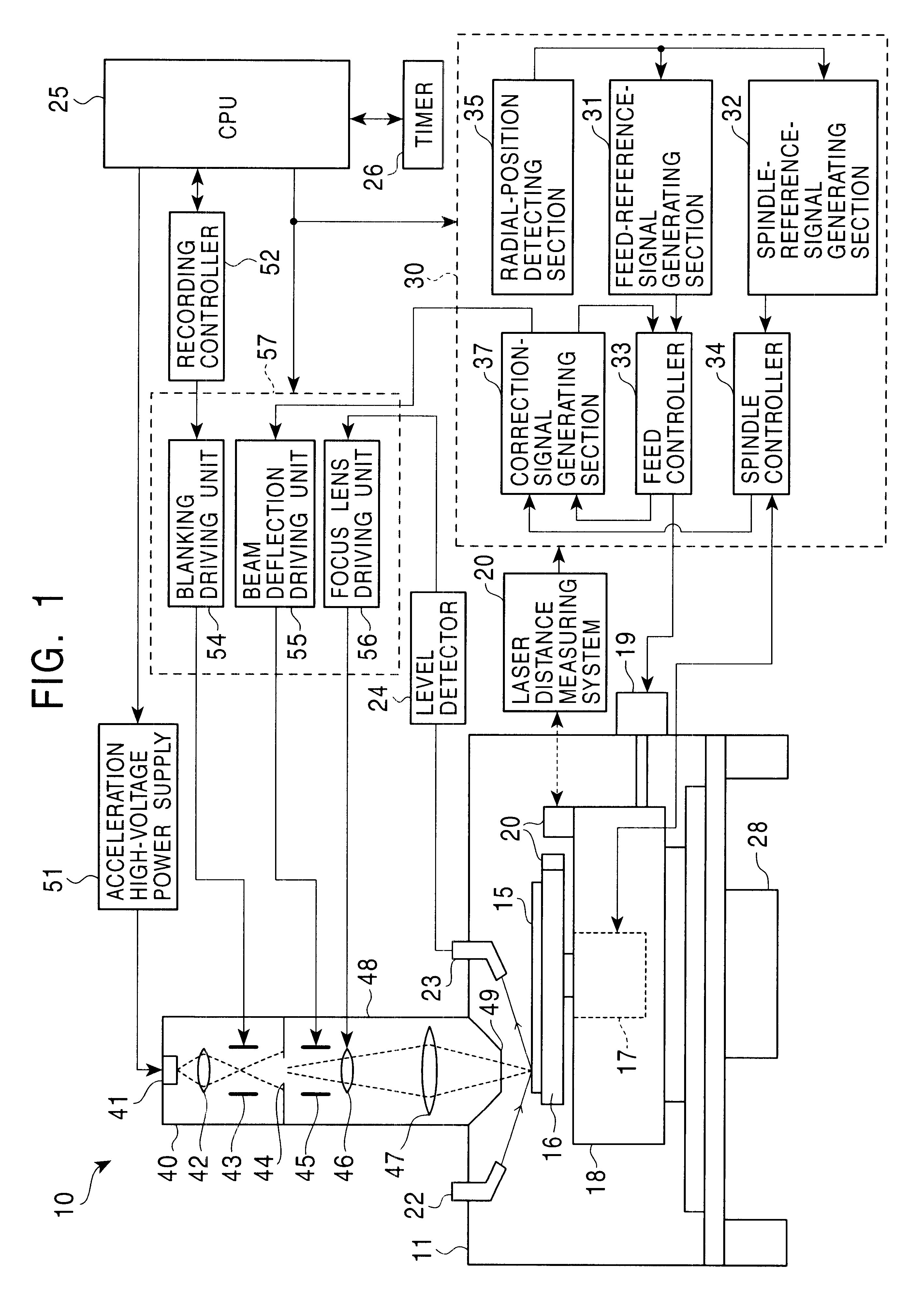
InactiveUS6650611B1Improve accuracyHigh-density discElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesEngineeringElectron
An apparatus of manufacturing a master by irradiating an electron beam on a substrate mounted on a turntable includes a rotation drive section for rotating the turntable; first and second correction-signal generating sections for respectively detecting first and second asynchronous components of rotational fluctuation of the turntable in a predetermined direction and in a direction perpendicular to the predetermined direction to generate first and second correction signals; and a deflection control section for controlling the electron beam deflection on the basis of the first and second correction signals.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Quantum magnetic memory
A system for storing data on a magnetic medium using spin polarized electron beams is provided. The system includes a source of spin polarized electrons and a storage medium disposed a selected distance from the source. The storage medium has a plurality of storage locations, each of which includes a layer of magnetic material sandwiched between first and second layers of a half-metallic material. The resulting sandwich structure forms a spin dependent electron trap that increases coupling between beam electrons in a first spin state and target electrons in a second spin state. An electron optics system directs the source of spin polarized electrons to one of the plurality of storage locations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Data storage device and control
InactiveUS20050281174A1High erase qualityLess mechanical wearElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsComputer scienceMicrosecond
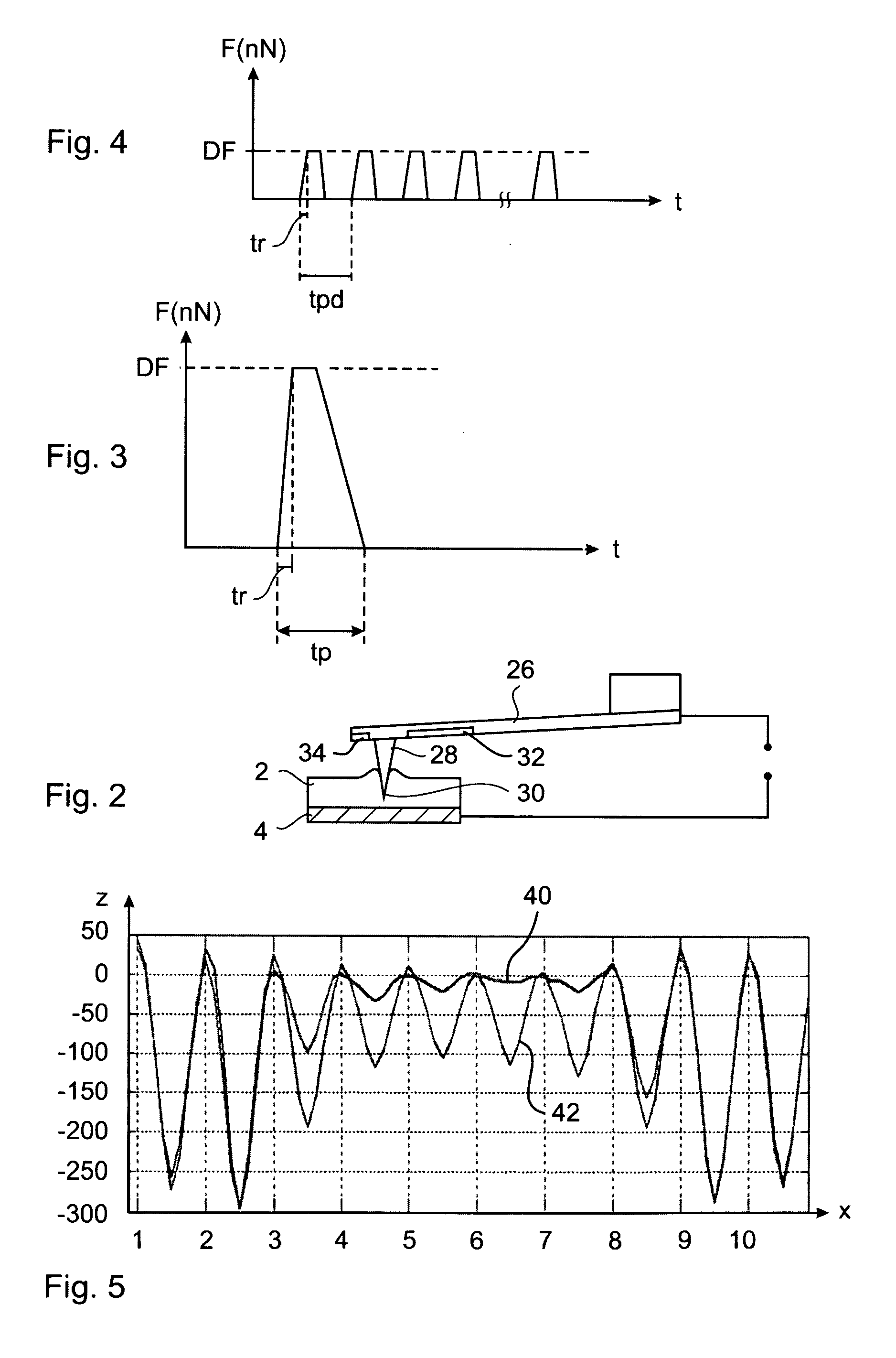
The present invention provides data storage devices, systems and methods. An example device includes: a storage medium for storing data in the form of marks; and at least one probe. The probe(s) and storage medium are operable to move relative to each other, with each probe comprising a tip facing the storage medium and having a force creating unit associated thereto. The force creating units are operable to create a force acting between the tip and said storage medium. The data storage device is operable to erase an indentation mark in the storage medium by way of controlling the force creating unit for creating at least one erase force pulse with a force rise time being less than or equal to the order of 1 microsecond.
Owner:IBM CORP
Scanning probe microscope using a surface drive actuator to position the scanning tip
InactiveUS7372025B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron beam carrier recordingScanning electron microscopeEngineering
A scanning probe microscope includes a scanning probe tip and an electrostatic surface actuator operatively coupled to the scanning probe tip. The electrostatic surface actuator includes a movable member that has a first surface with a first plurality of electrodes disposed on the first surface and a stationary member that has a second surface with a second plurality of electrodes disposed on the second surface. The first and second surfaces are disposed in a confronting relationship The movable and stationary members are resiliently coupled so that the movable member is capable of being displaced with respect to the stationary member. The first and second pluralities of electrodes are configured to generate electrostatic forces in response to voltages applied. The electrostatic forces laterally displace the movable member in the direction generally parallel to the first and second surfaces. The scanning probe tip is controllably positioned by displacement of the movable member.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Dielectric reproducing apparatus, dielectric recording apparatus, and dielectric recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS7336590B2Increase speedReduce capacitanceElectron beam carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingCapacitanceElectricity
A dielectric reproducing apparatus is provided with: a probe for applying an electric field to a dielectric material of a dielectric recording medium; a return electrode for returning the electric field applied from the probe; an inductor placed between the probe and the return electrode; an oscillator which oscillates at a resonance frequency determined from the inductor and a capacitance formed in the dielectric material just under the probe; an alternating current (AC) signal generation device for generating an AC signal which is applied to the probe; a frequency modulation (FM) demodulator for demodulating a FM modulation signal modulated by the capacitance corresponding to the polarization state owned by the dielectric material just under the probe; and a phase-shift keying (PSK) demodulator for reproducing data from the demodulated signal.
Owner:CHO YASUO +1
Data storage devices with wafer alignment compensation
InactiveUS6987722B2Electron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsComputer hardwareCompensation methods
Methods for storing data are provided. Preferably, the method includes the steps of: providing a data storage device, and preventing an emitter associated with a first data cluster of the data storage device from writing data to another one of the data clusters. Data storage devices also are provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
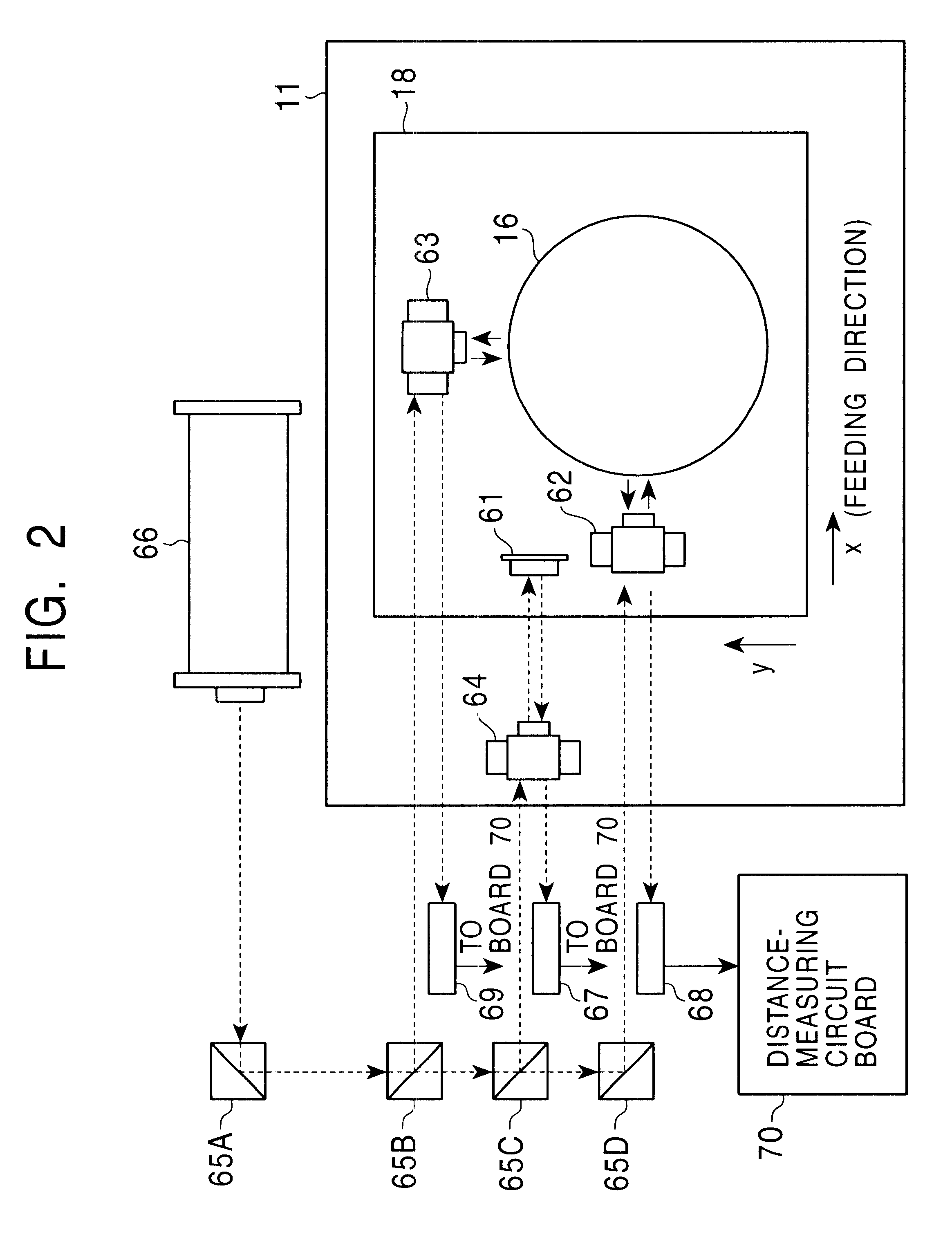
Electron beam recorder and electron beam irradiation position detecting method
InactiveUS7359305B2Improve accuracyAccuracy of a track pitchElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesLocation detectionAtomic physics
An electron beam recorder includes an electron optical system for irradiating an electron beam on a master of an information recording medium and an electron beam irradiation position detecting unit for detecting an irradiation position of the electron beam in the electron optical system while the electron beam is being irradiated on the master by the electron optical system.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
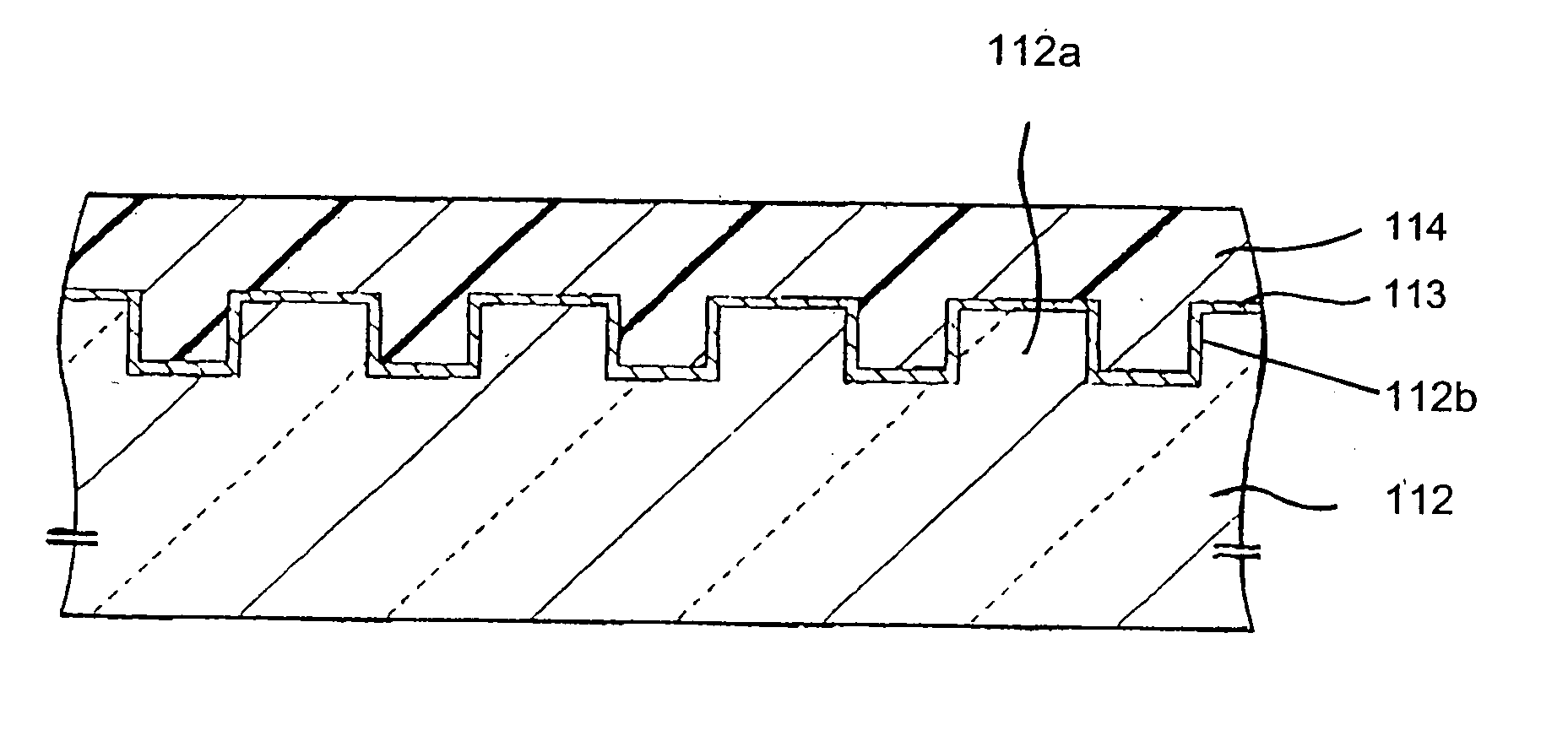
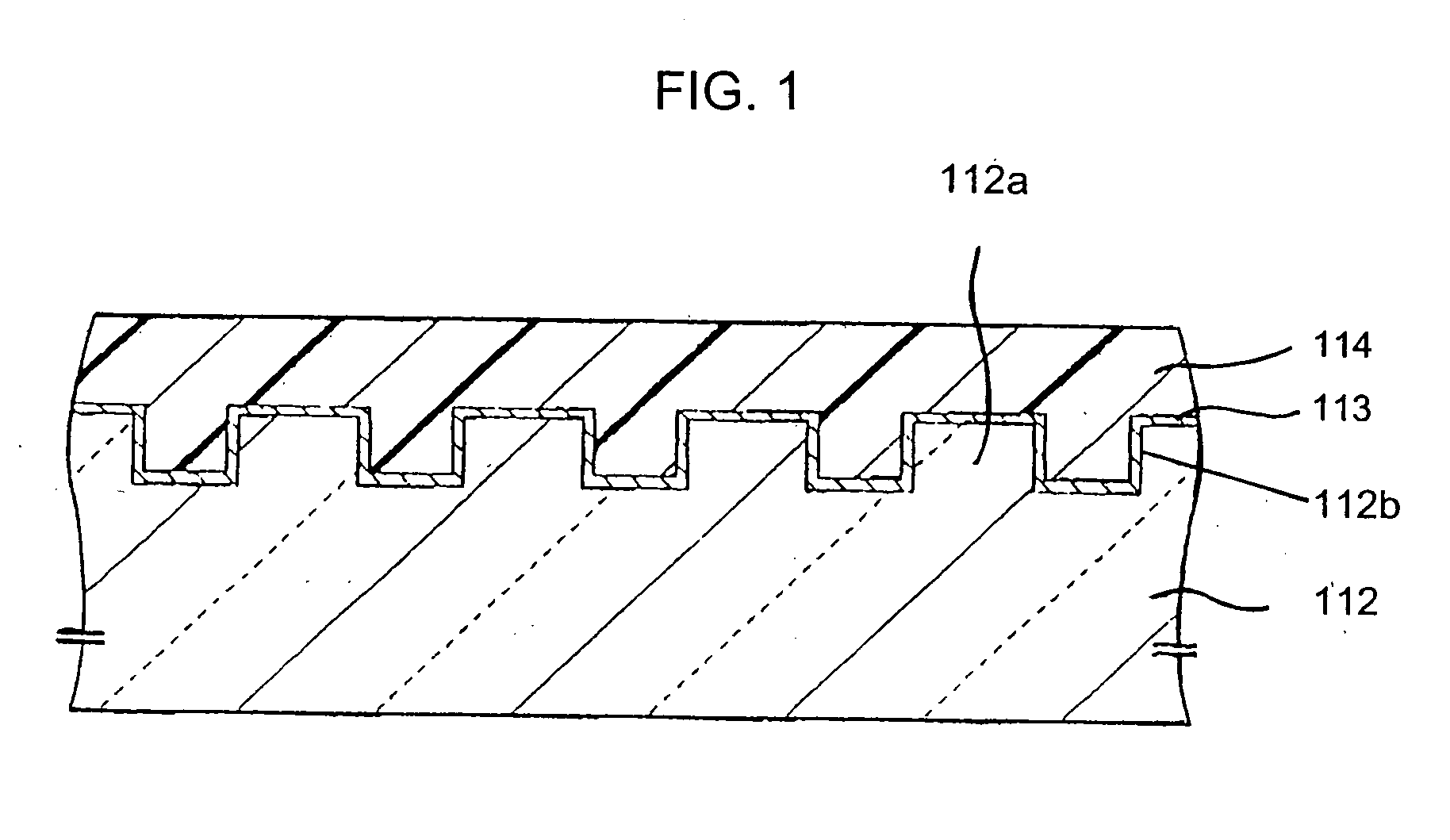
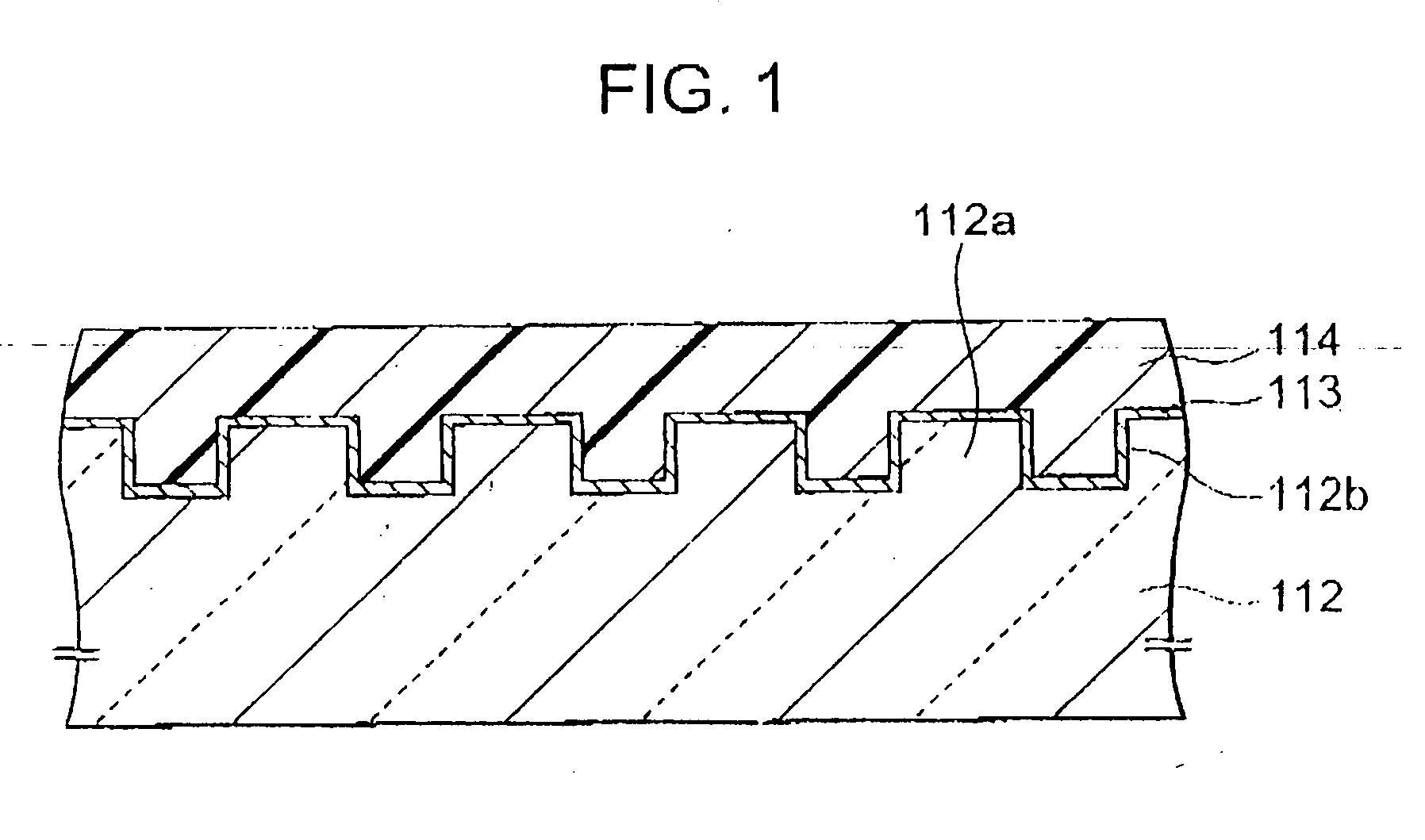
Stamper for producing optical recording medium, optical recording medium, and methods of producing the same
InactiveUS20050219992A1Reduce low frequency noiseReduce focusRecord carriersElectron beam carrier recordingResistUltraviolet
Owner:SONY CORP
Electron beam irradiation apparatus, electron beam irradiation method, and apparatus for and method of manufacturing disc-shaped object
InactiveUS20060124869A1Easy curingReduce in quantityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron beam carrier recordingUltravioletIrradiation
Disclosed are an electron beam irradiation apparatus and an electron beam irradiation method that are capable of easily curing a material that is hard to be cured by irradiation of ultraviolet rays and of reducing the number of electron beam irradiation tubes. The electron beam irradiation apparatus has a motor for rotationally driving an irradiation target object, a shield container for rotatably accommodating the irradiation target object, and an electron beam irradiation unit provided in the shield container so that the surface of the irradiation target object is irradiated with electron beams, wherein the electron beam irradiation unit and the irradiation target object are relatively moved when the electron beam irradiation unit irradiates the surface of the irradiation target object with the electron beams during a rotation of the irradiation target object.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
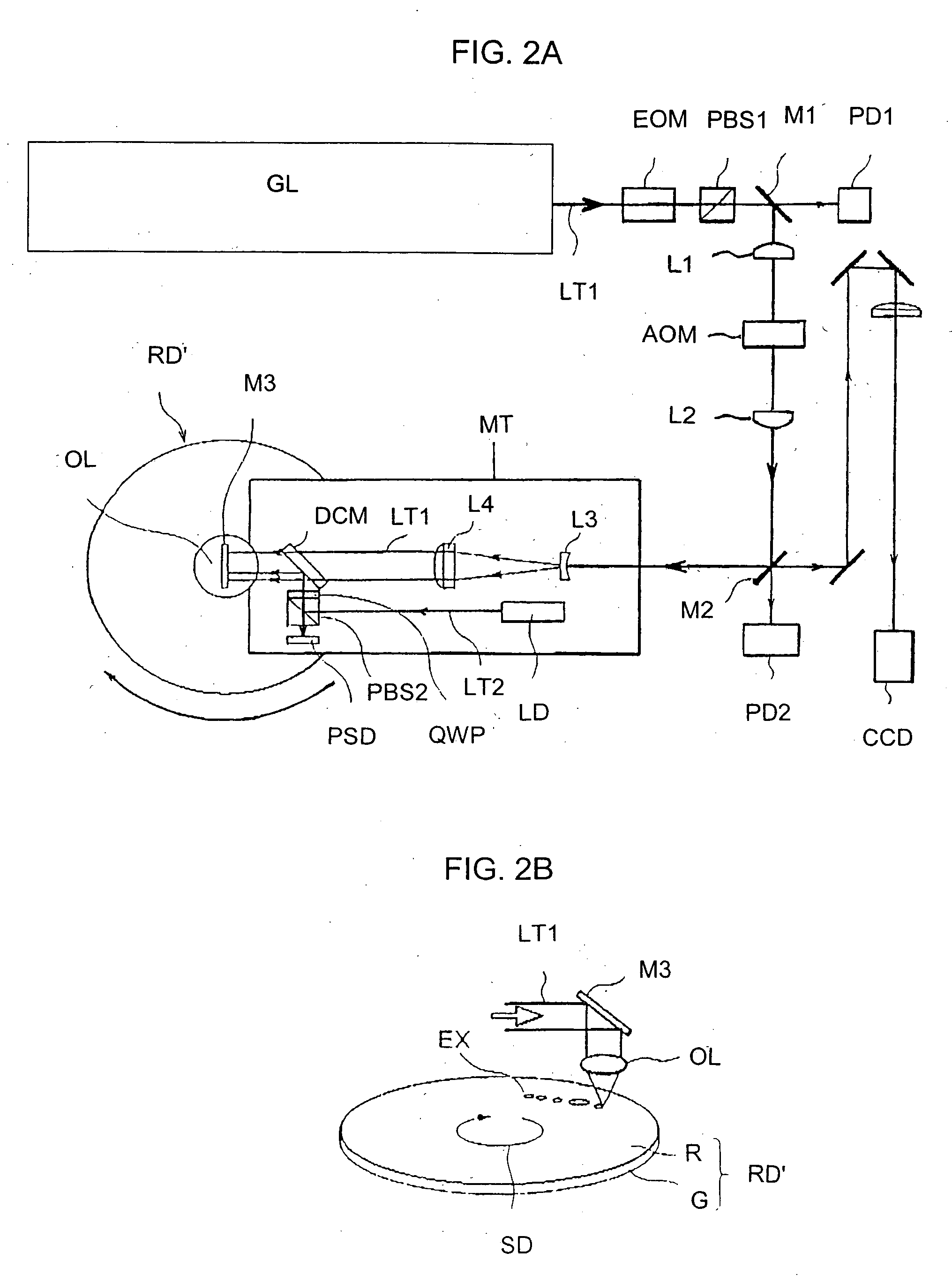
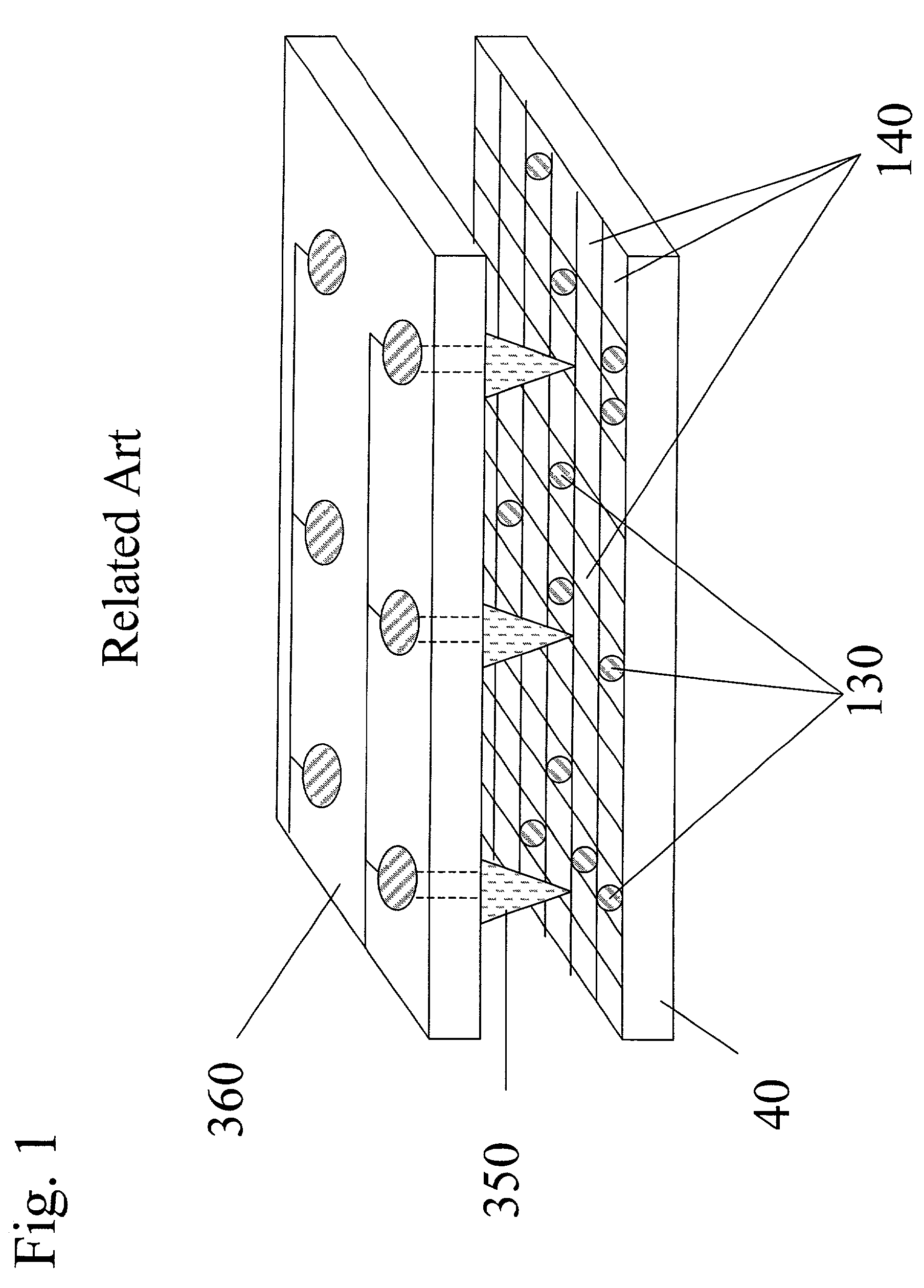
Electron beam lithography method, patterned master carrier for magnetic transfer, lithography method for patterned master carrier for magnetic transfer, and method for producing performatted magnetic recording media
A fine pattern having first elements within track widths and second elements, which are shifted half a track pitch from the first elements, are drawn across the entire surface of a disk accurately and at high speed. A transfer pattern for a magnetic transfer master carrier is drawn by scanning an electron beam on a disk coated with resist. The first elements and the second elements, which are shifted half a track pitch such that they straddle adjacent tracks, are drawn. While the disk is rotated unidirectionally, the electron beam is deflected in the radial direction within a single track of the disk to draw the first elements. Deflection of the electron beam in the radial direction is shifted half a track, to draw the second elements that straddle adjacent tracks at the same time.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Micro-fabricated device with thermoelectric device and method of making
InactiveUS7205675B2Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentEngineeringThermoelectric effect
A micro-fabricated device, includes a support structure having an aperture formed therein, and a device substrate disposed within the aperture. The micro-fabricated device further includes a thermally isolating structure thermally coupling the device substrate to the support structure. The thermally isolating structure includes at least one n-doped region and at least one p-doped region formed on or in the thermally isolating structure and separated from each other. In addition, the thermally isolating structure includes an electrical interconnect connecting at least one n-doped region and at least one p-doped region, forming an integrated thermoelectric device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Storage device with charge trapping structure and methods
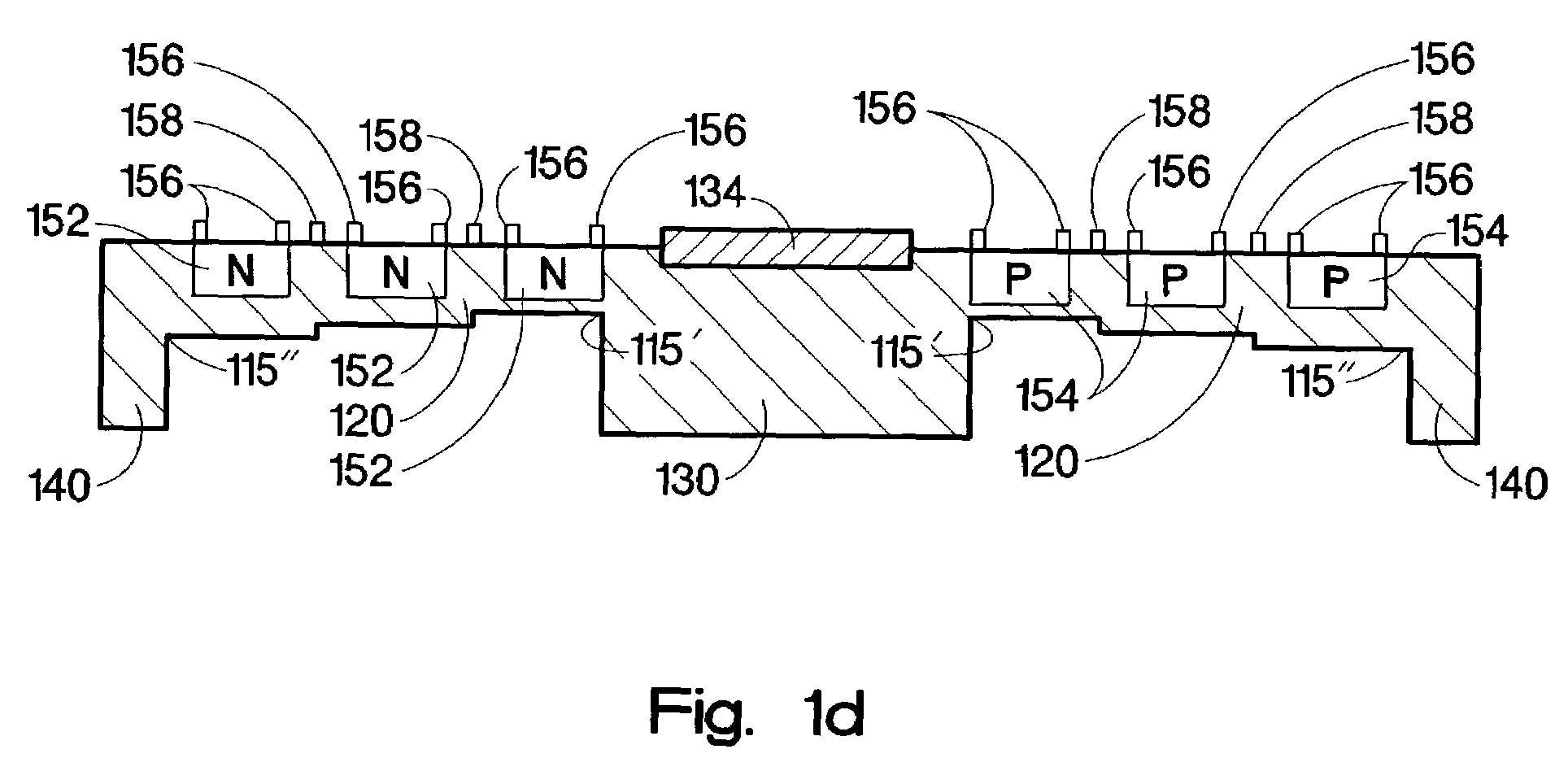
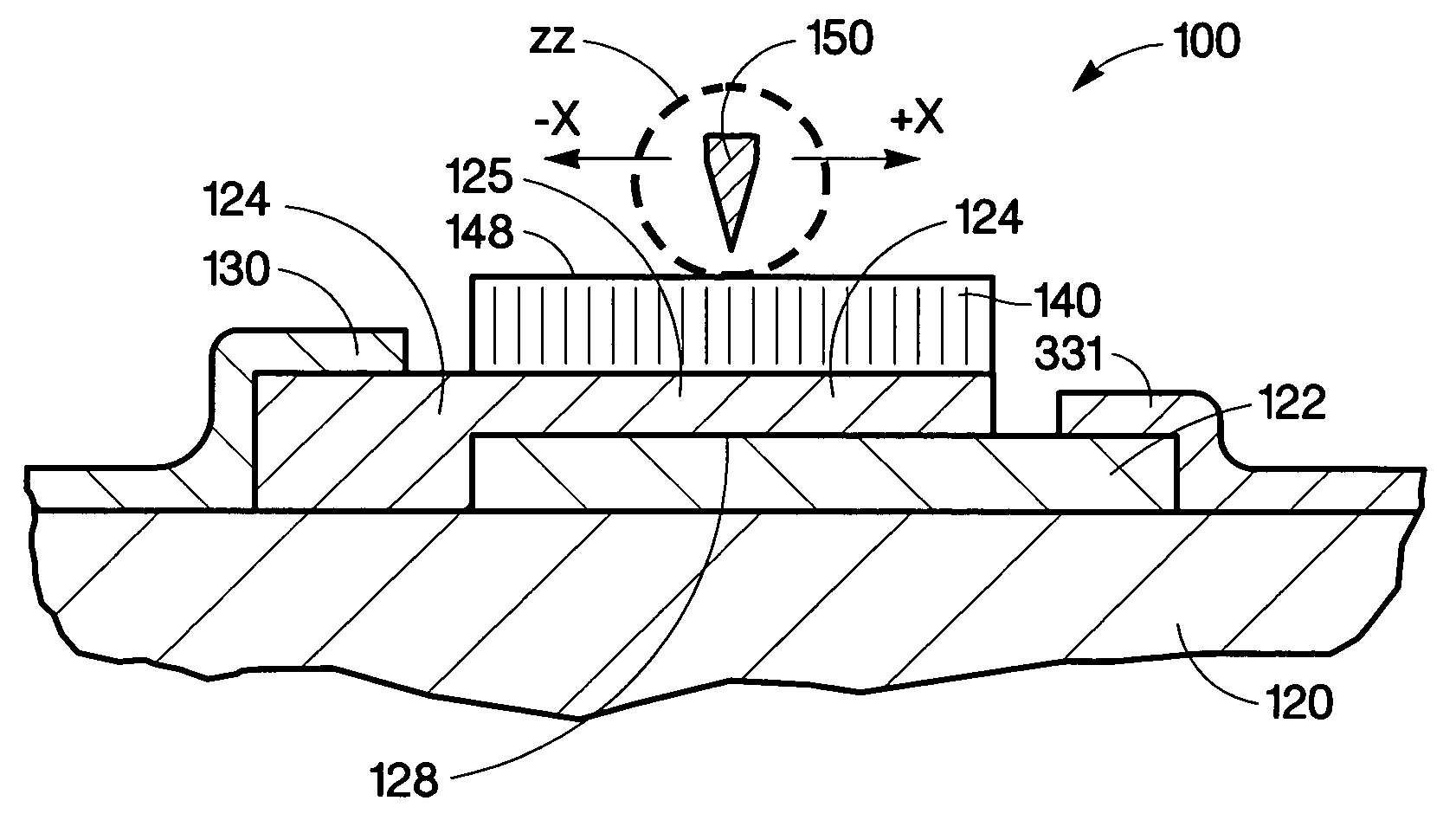
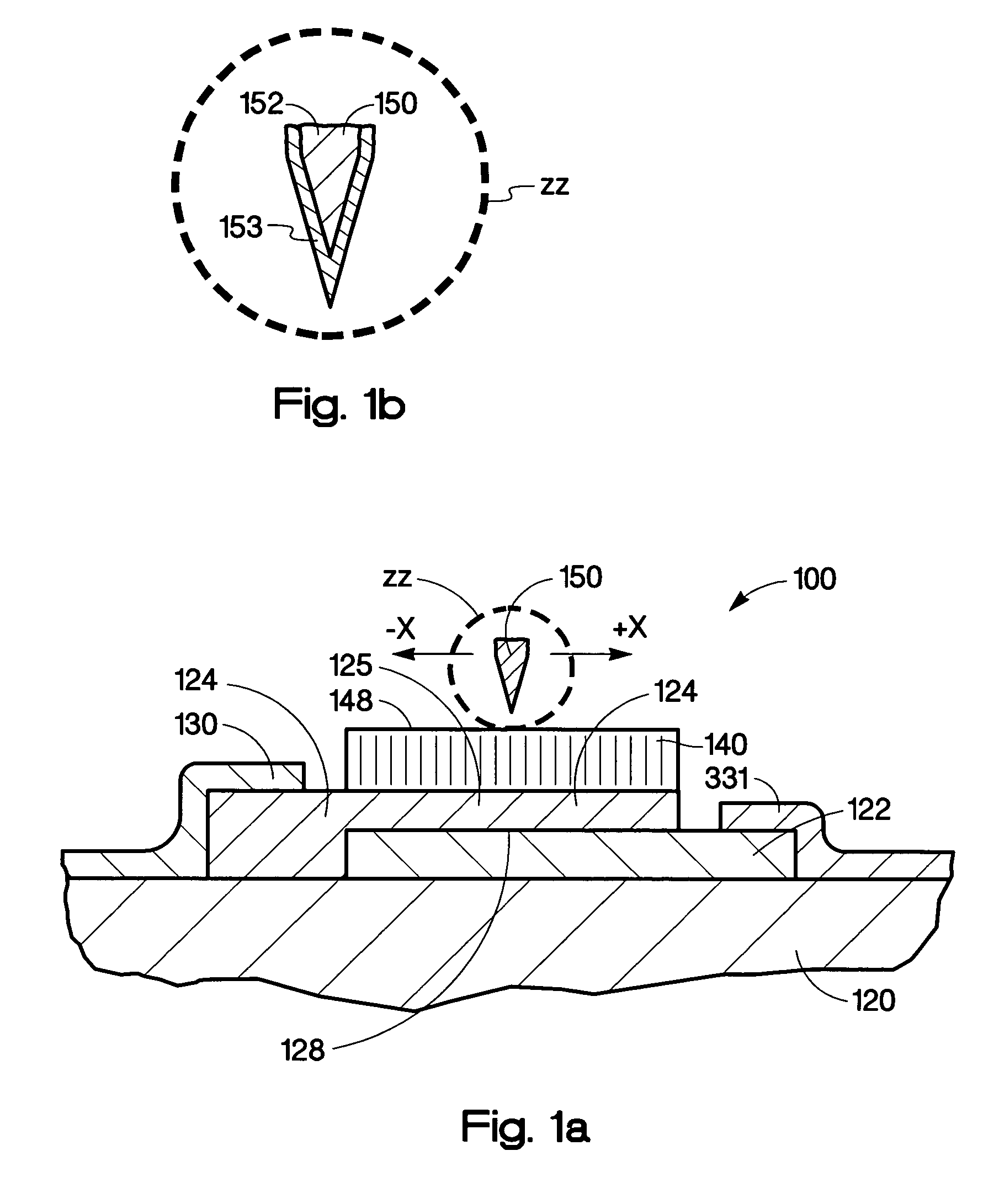
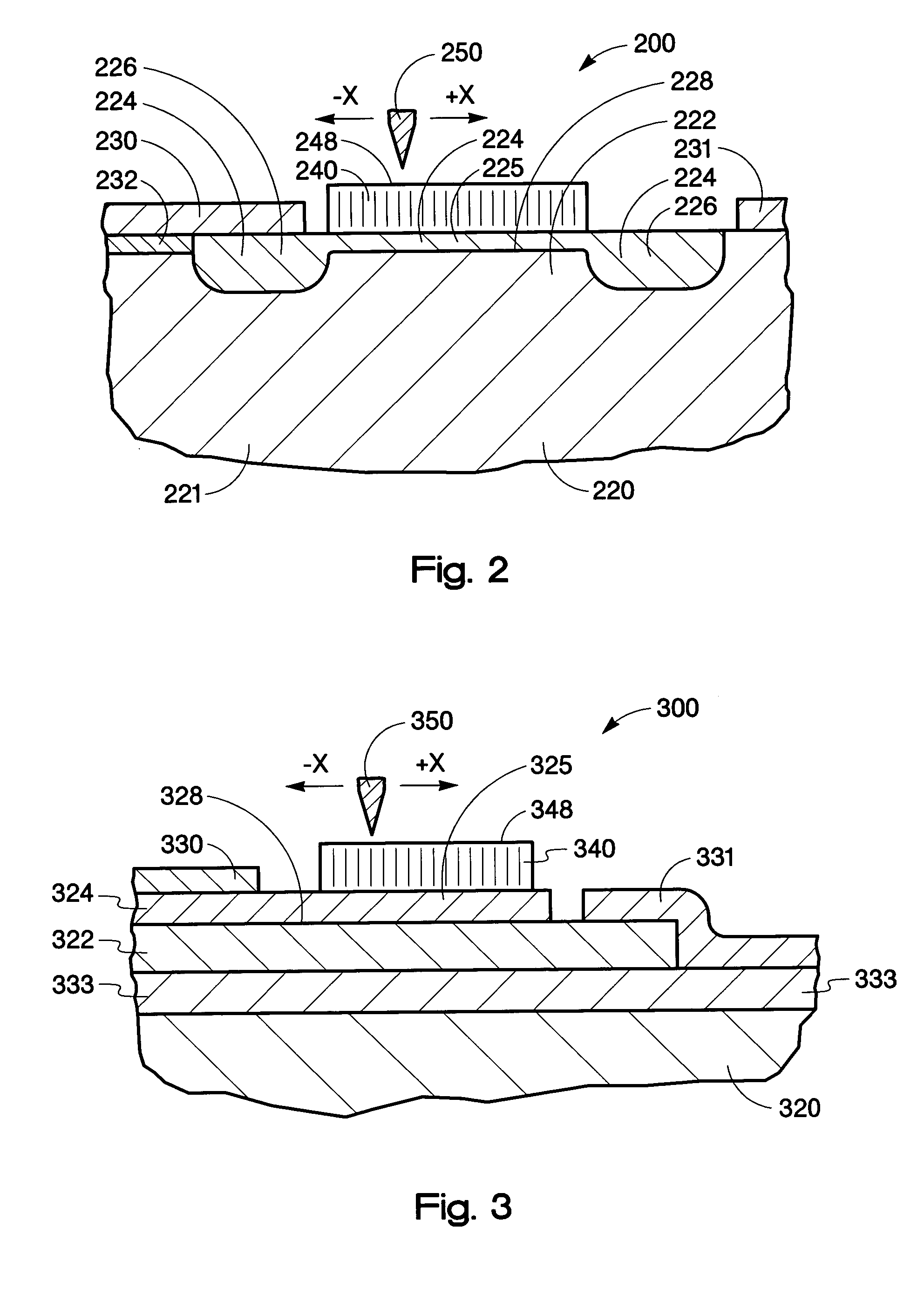
InactiveUS20050082598A1TransistorElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingDopantElectrical conductor
A storage device includes a first semiconducting layer having a p-dopant and a second semiconducting layer having an n-dopant, disposed on the first semiconducting layer forming a junction between the first and the second semiconducting layers. The storage device also includes a charge trapping structure disposed on the second semiconducting layer and a conductive gate, wherein the conductive gate and the charge trapping structure move relative to the other, wherein an electric field applied across the second semiconducting layer and the conductive gate traps charge in the charge trapping structure.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
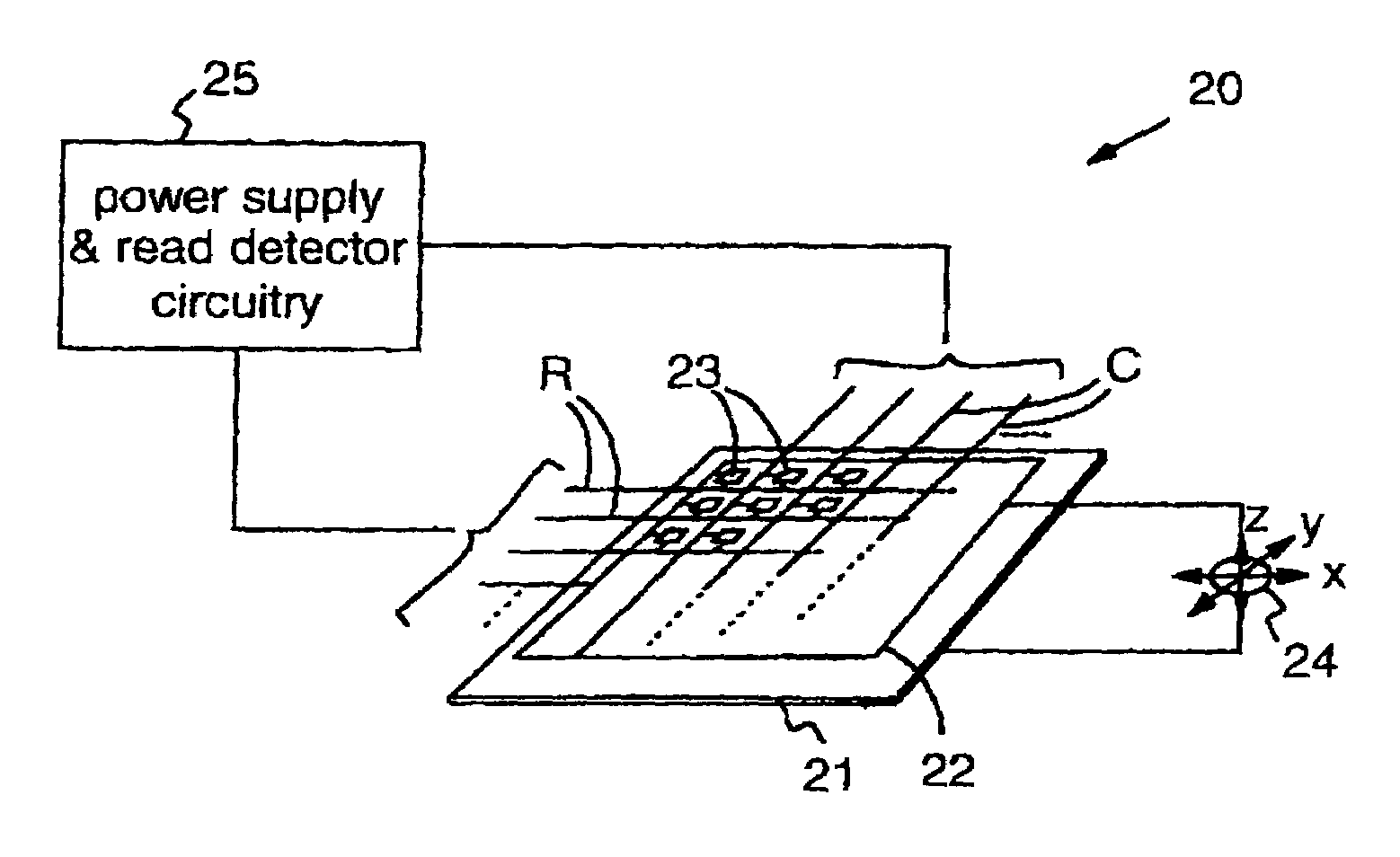
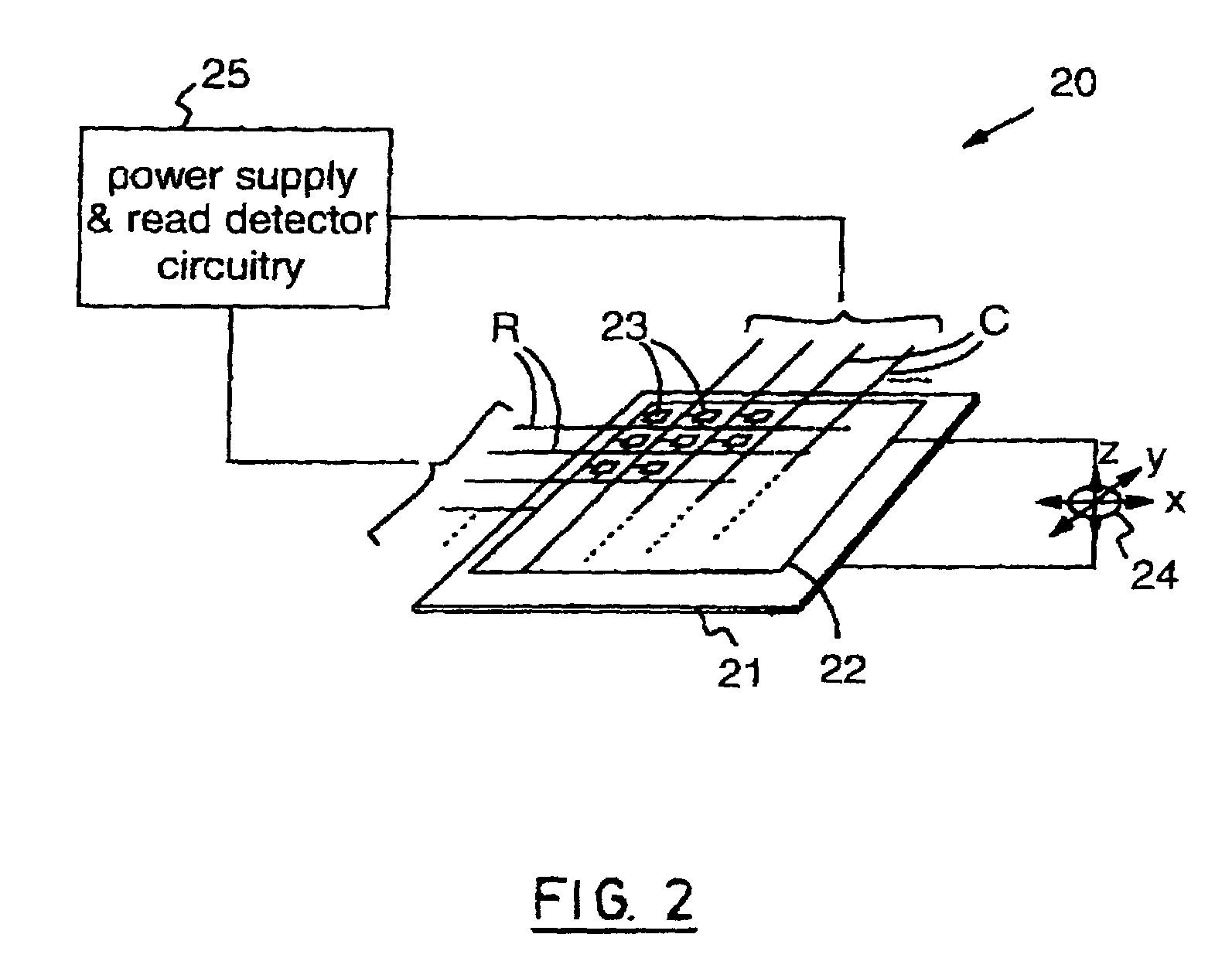
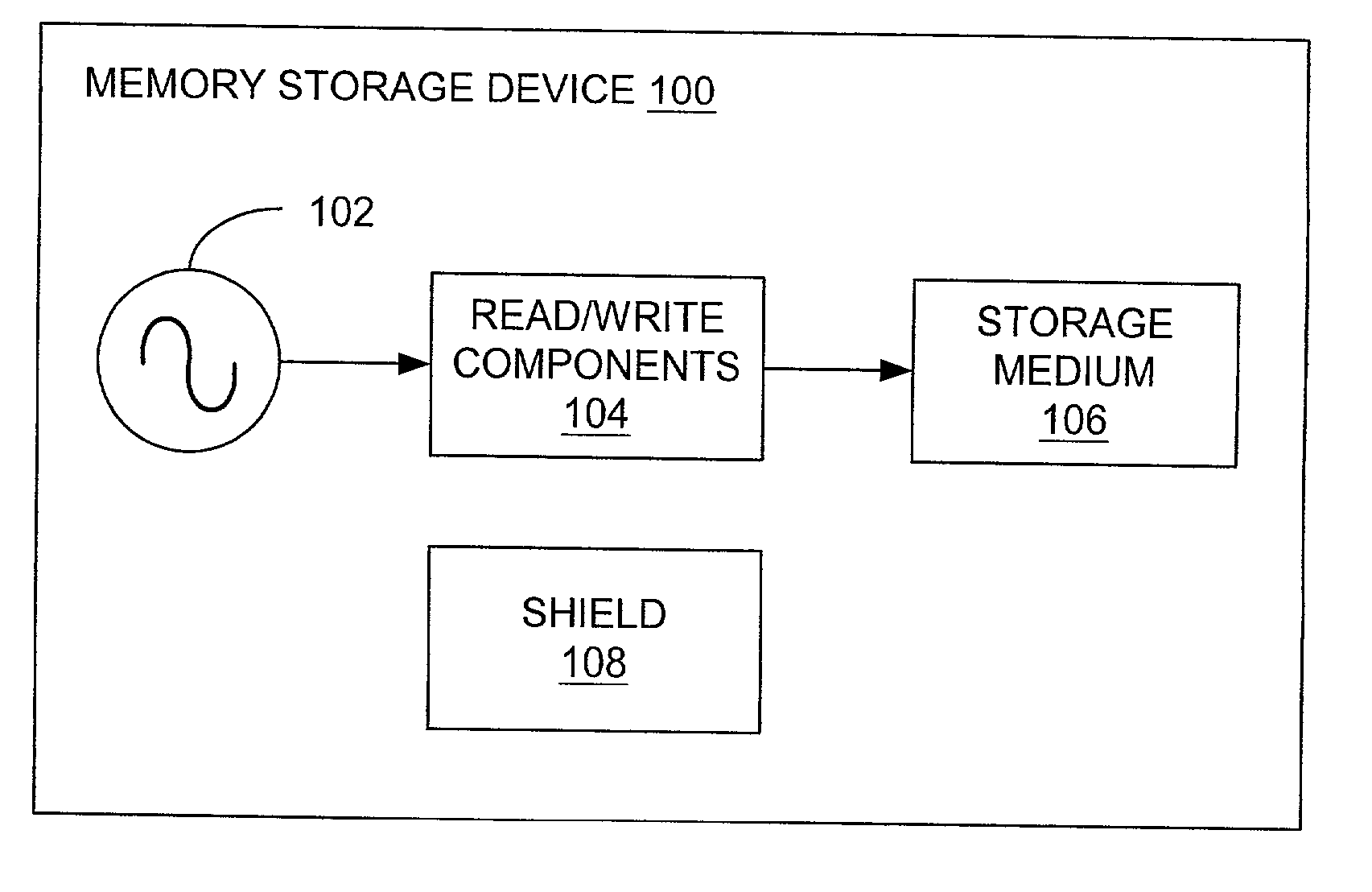
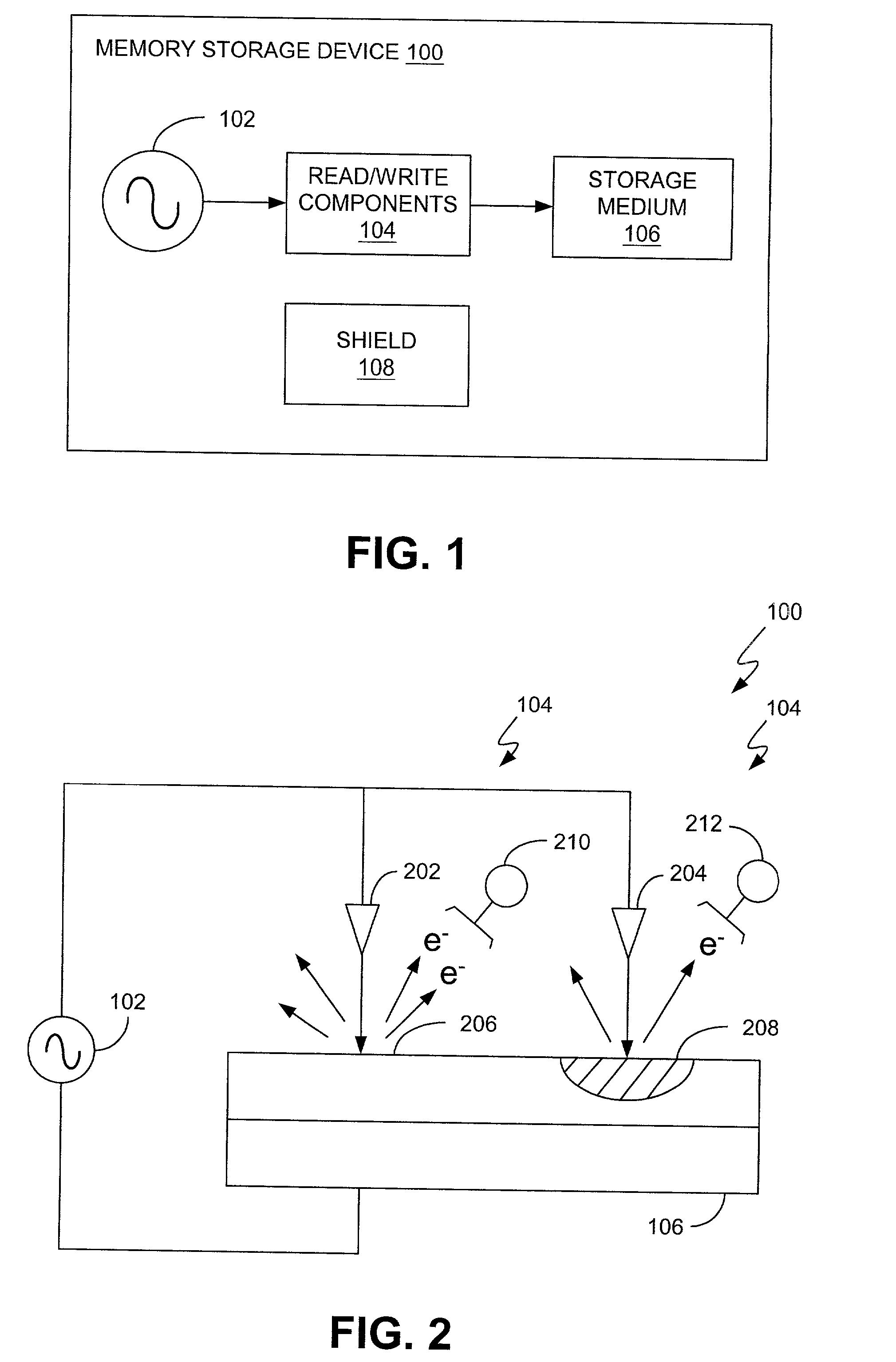
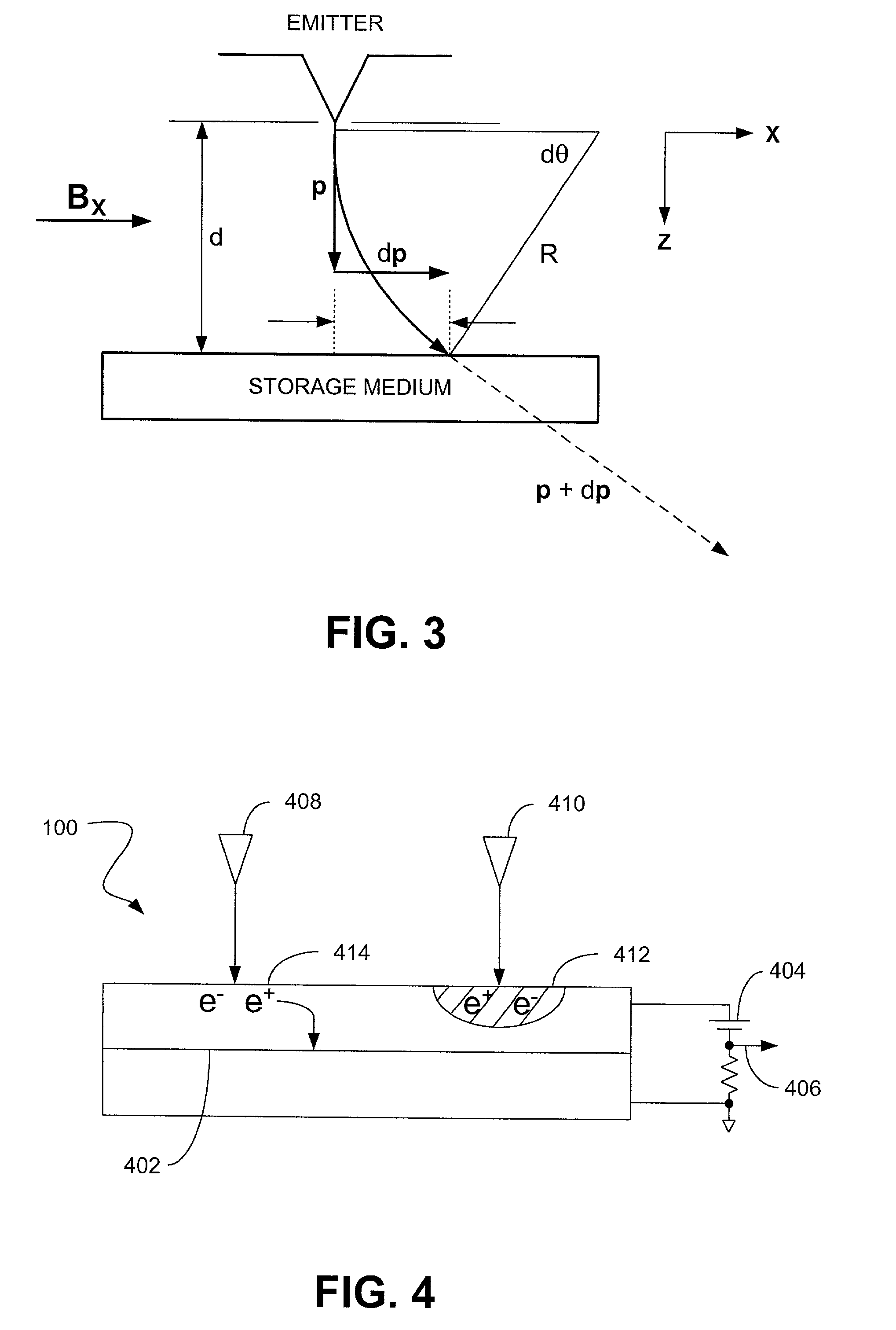
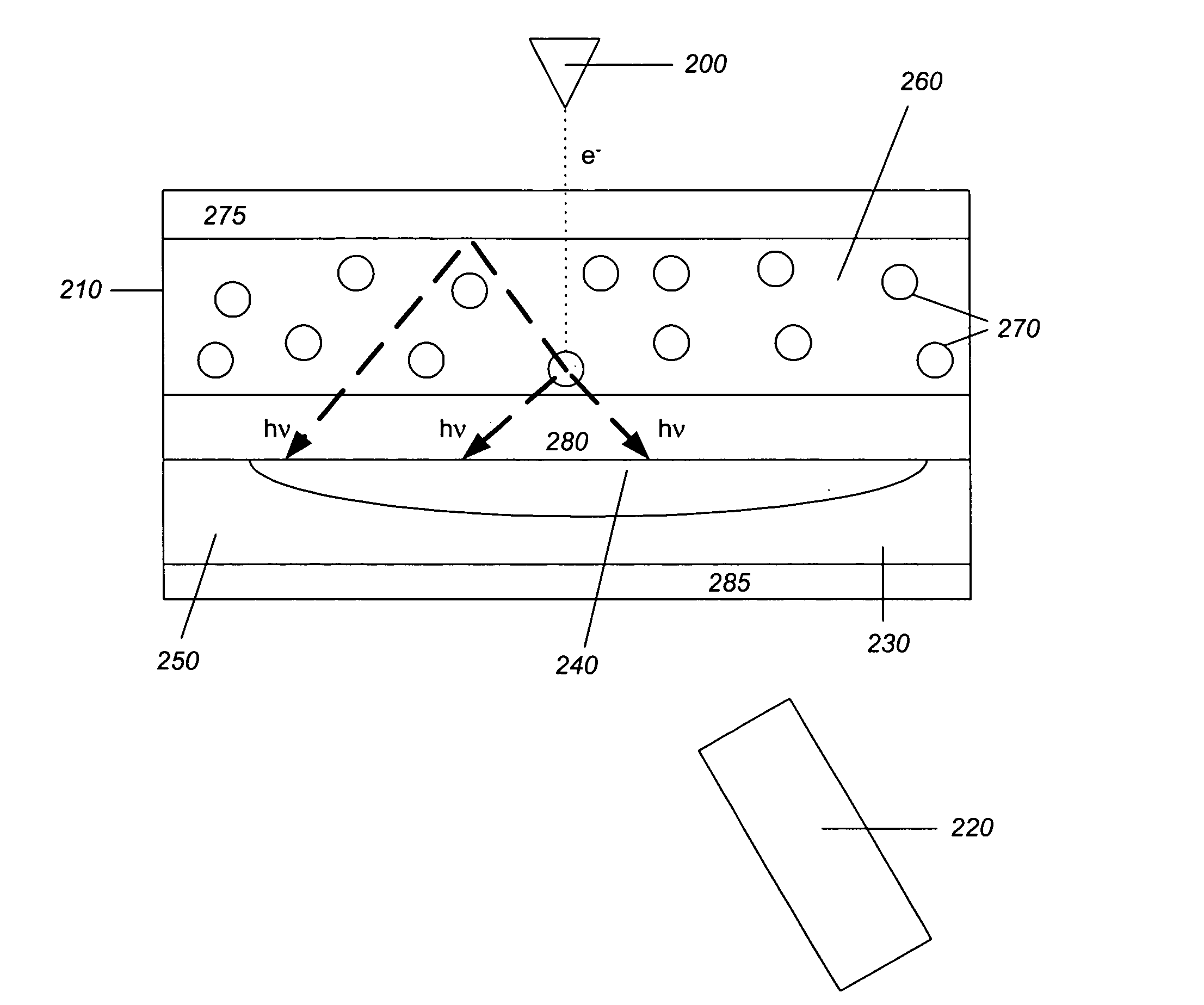
Atomic resolution storage systems with enhanced magnetic field protection
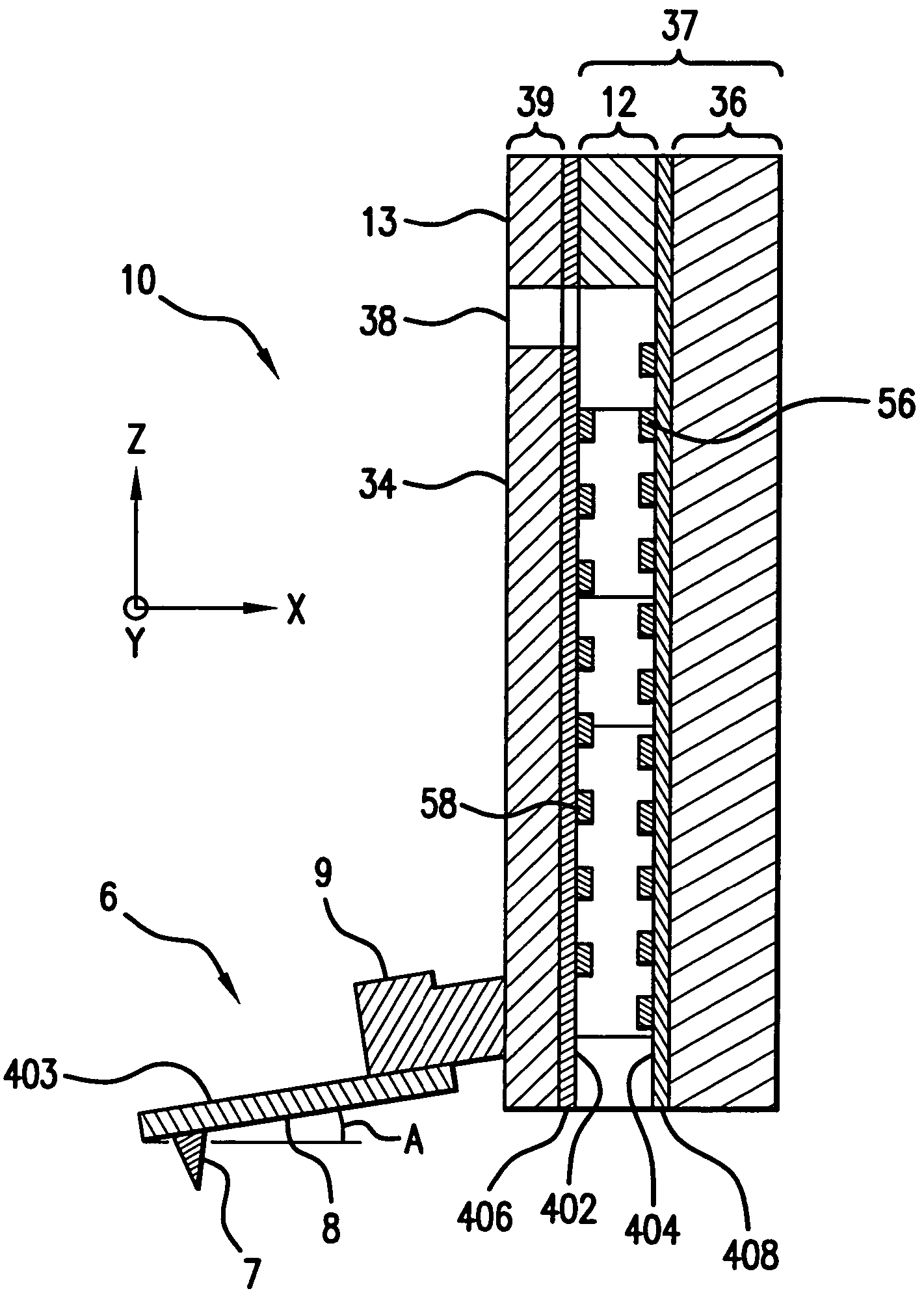
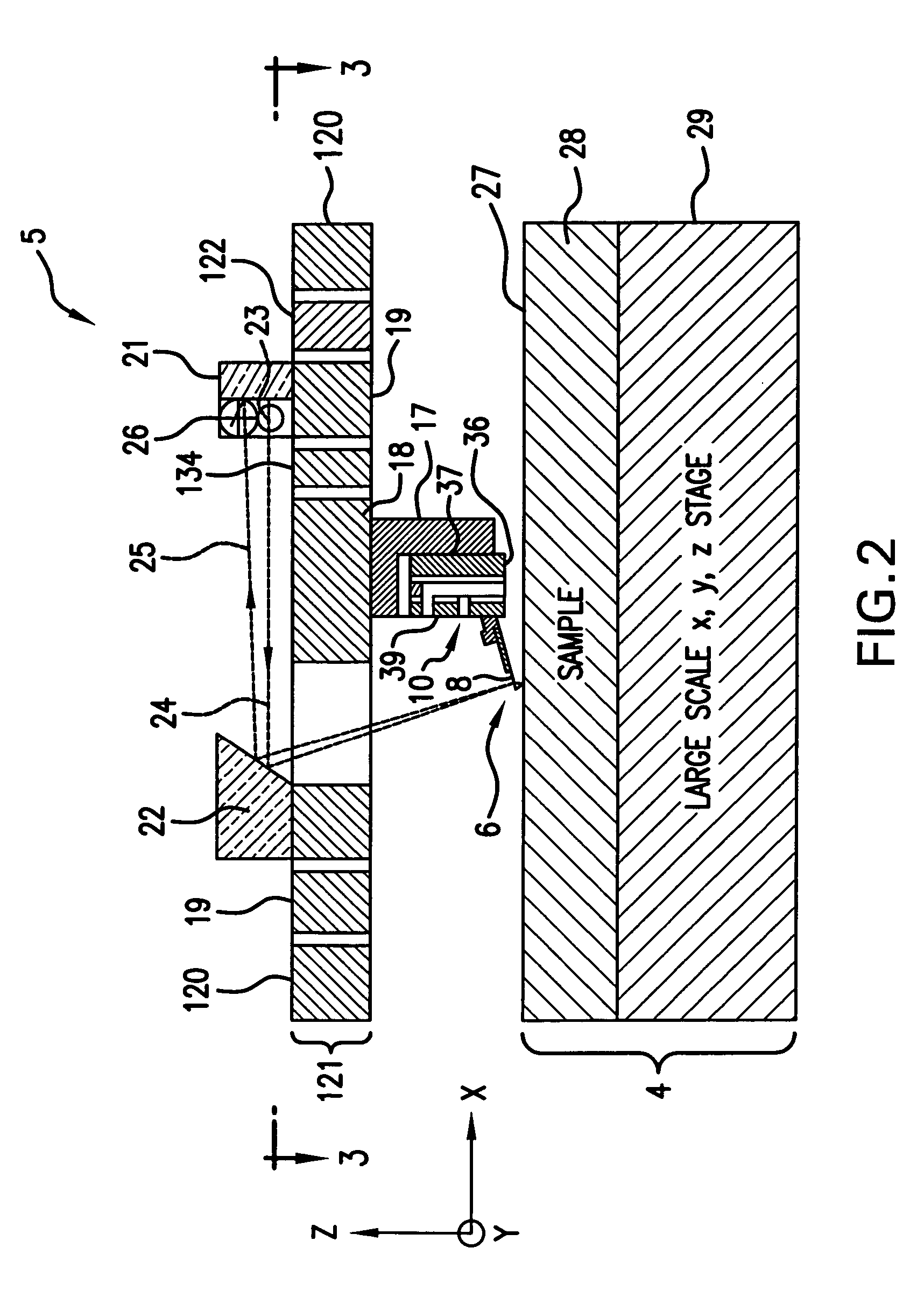
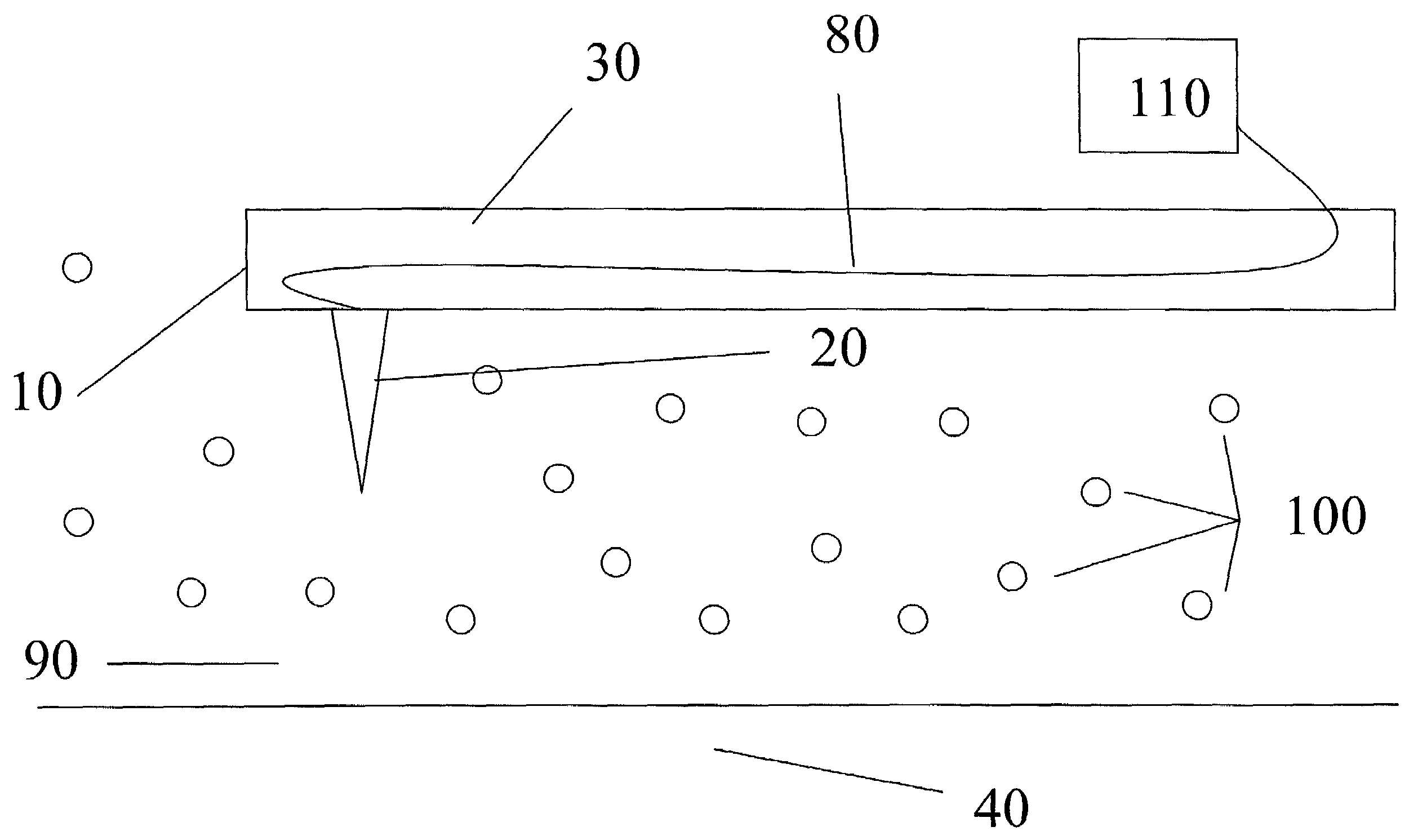
Memory storage devices that employ atomic resolution storage technology are provided. A preferred memory storage device includes a storage medium that defines one or more coverage areas. Each of the coverage areas incorporates a storage area that is configurable in one of a plurality of structural states. Typically, the structural states represent information stored in the storage area. Electron beam emitters electrically communicate with the storage medium, with the storage medium and the emitters being configured to move relative to each other. So configured, each emitter is capable of providing a beam of electrons to a respective one of the coverage areas. The memory storage device also includes a first current source that selectively electrically communicates with at least one of the emitters. Additionally, a shield is provided that is configured to reduce an influence of a magnetic field so that a tendency of an electron emitted from one of the emitters to be displaced from an intended trajectory is reduced. Methods also are provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Capping layer for enhanced performance media
InactiveUS7052757B2Electrostatic charge injection carrier recordingElectron beam carrier recordingEpitaxial materialConductive materials
A media storage device and method for fabricating said device is provided. The device comprises a data layer capable of storing and erasing data via application of an energy beam, such as a near field optical non diffraction limited beam or electron beam. A separate capping layer is deposited on the data layer. The separate capping layer is relatively transparent to the energy beam and may be formed from various materials, including but not limited to an epitaxial material, a conducting material, and a robust high melting point material, such as Molybdenum.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
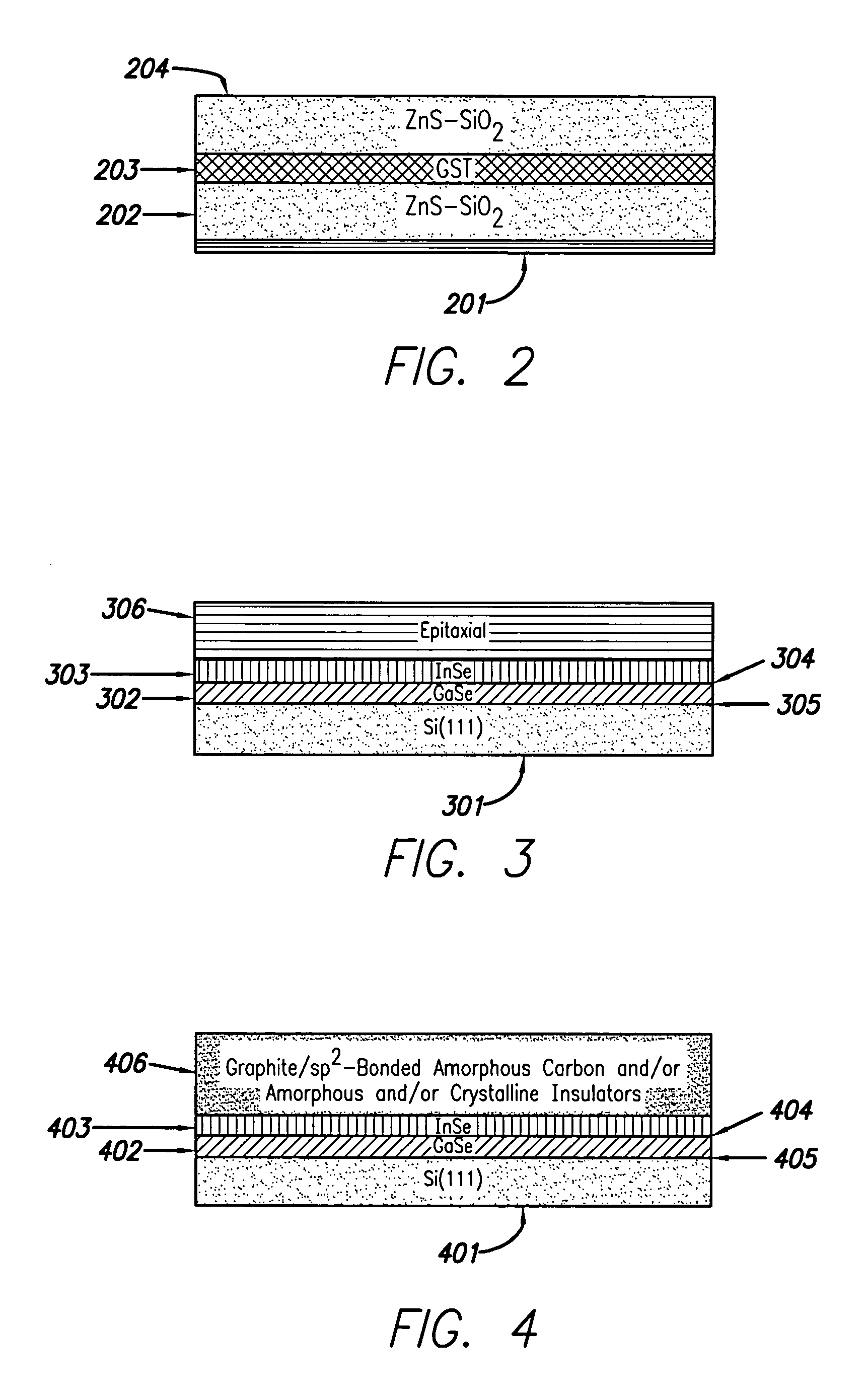
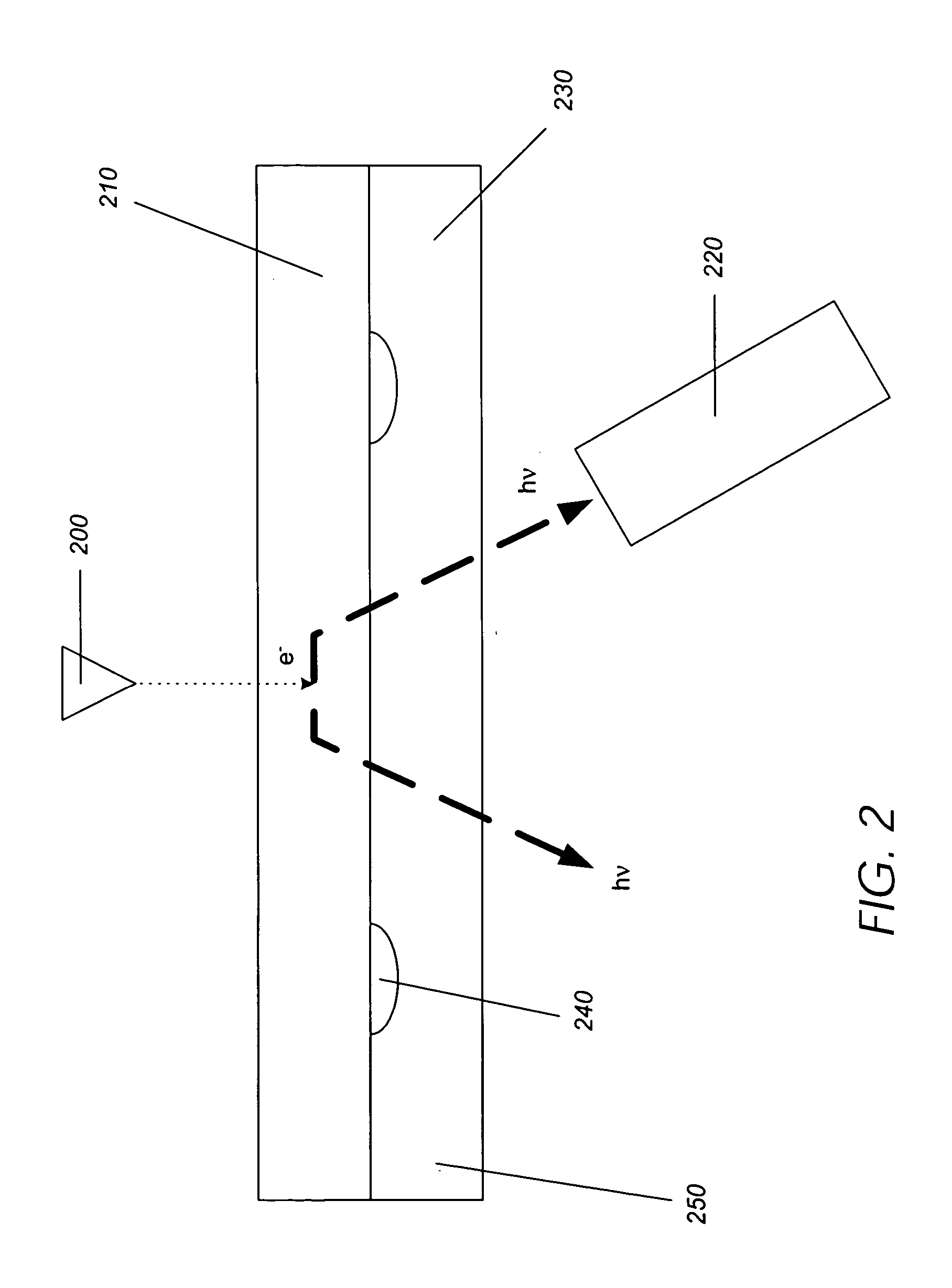
Storage device based on phase-change modulated luminescence
A media storage device is provided. The device comprises different configurations of a luminescent layer comprising a luminescent material capable of emitting light while being bombarded by a beam from a beam transmitter, a detector for detecting the light emitted from the luminescent layer, and a phase-change layer located proximate the luminescent layer. The phase-change layer is able to transform from a first phase to a second phase. Light emitted from the luminescent layer and received by the detector materially differs when the phase-change layer transforms from the first phase to the second phase.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Stamper for producing optical recording medium, optical recording medium, and methods of producing the same
InactiveUS20050167868A1Reduce low frequency noiseImproving crosstalk characteristicRecord carriersVacuum evaporation coatingResistUltraviolet
A stamper suppressed in surface roughness, uneven thickness, and deviation of circularity in inner circumference, a method of producing the same, an optical recording medium produced by molding using the stamper, and a method of producing the same, wherein a base member having a mirror polished main surface and comprising silicon or glass is formed with a resist film; the resist film is exposed by a focused electron beam, an ultraviolet ray laser, etc. and developed so as to form a resist film of a pattern corresponding to relief shapes; the mirror surface of the base member is processed to relief shapes (projecting regions and recessed regions) by dry etching etc. using the obtained resist film as a mask so as to obtain a stamper; the obtained stamper is used for injection molding to form a medium substrate; and an optical recording multilayer film and a protective layer are formed to thereby produce an optical recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
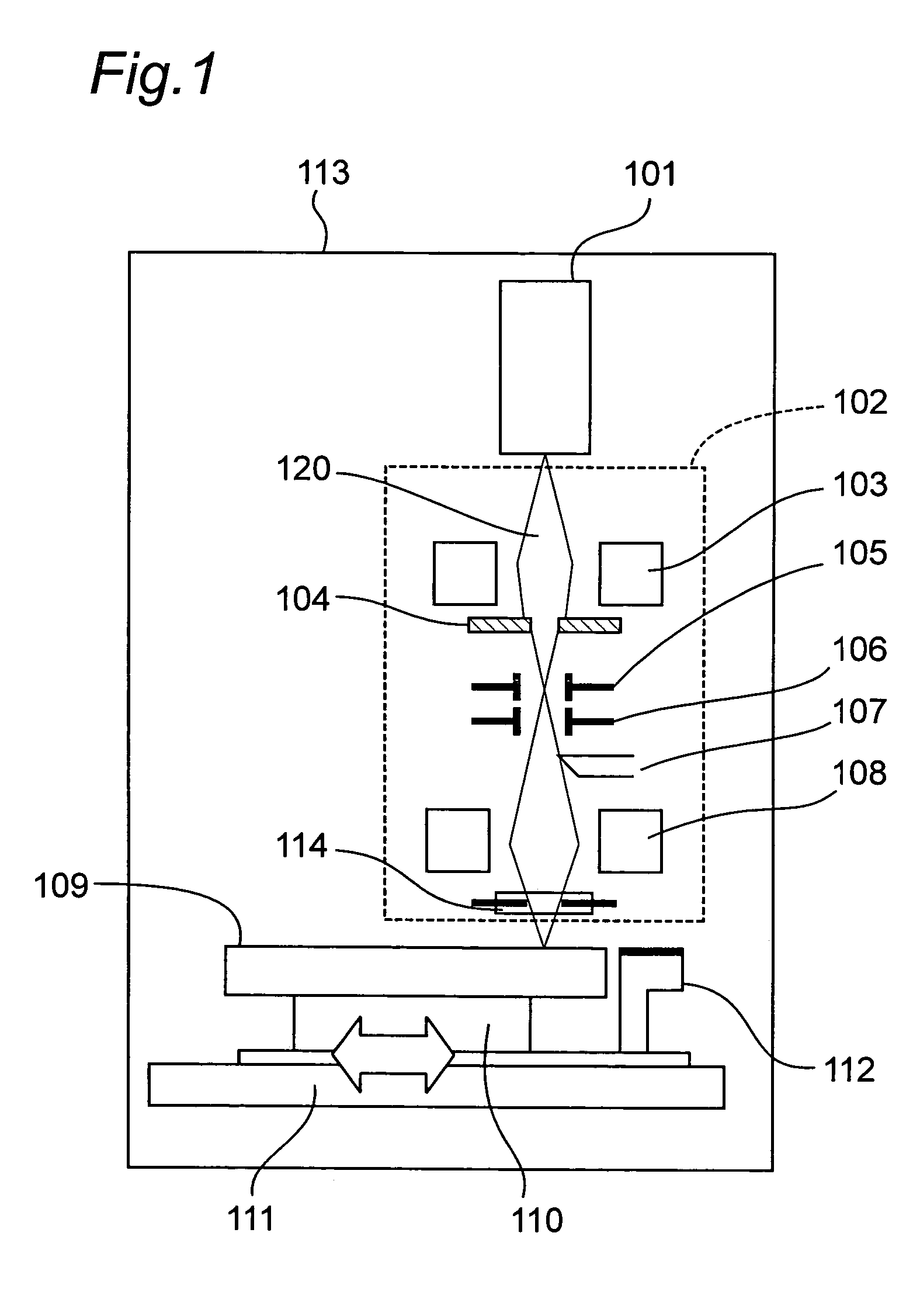
Electron beam applying apparatus and drawing apparatus
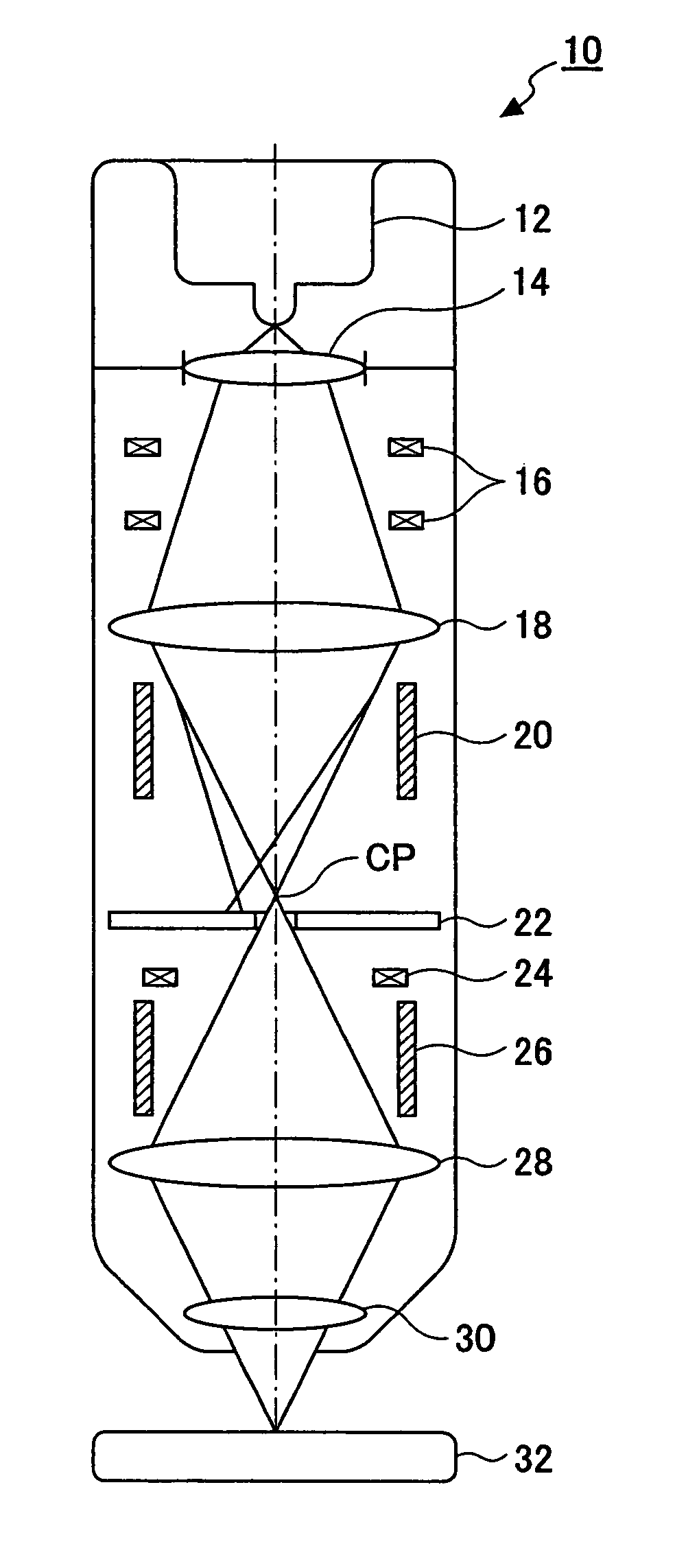
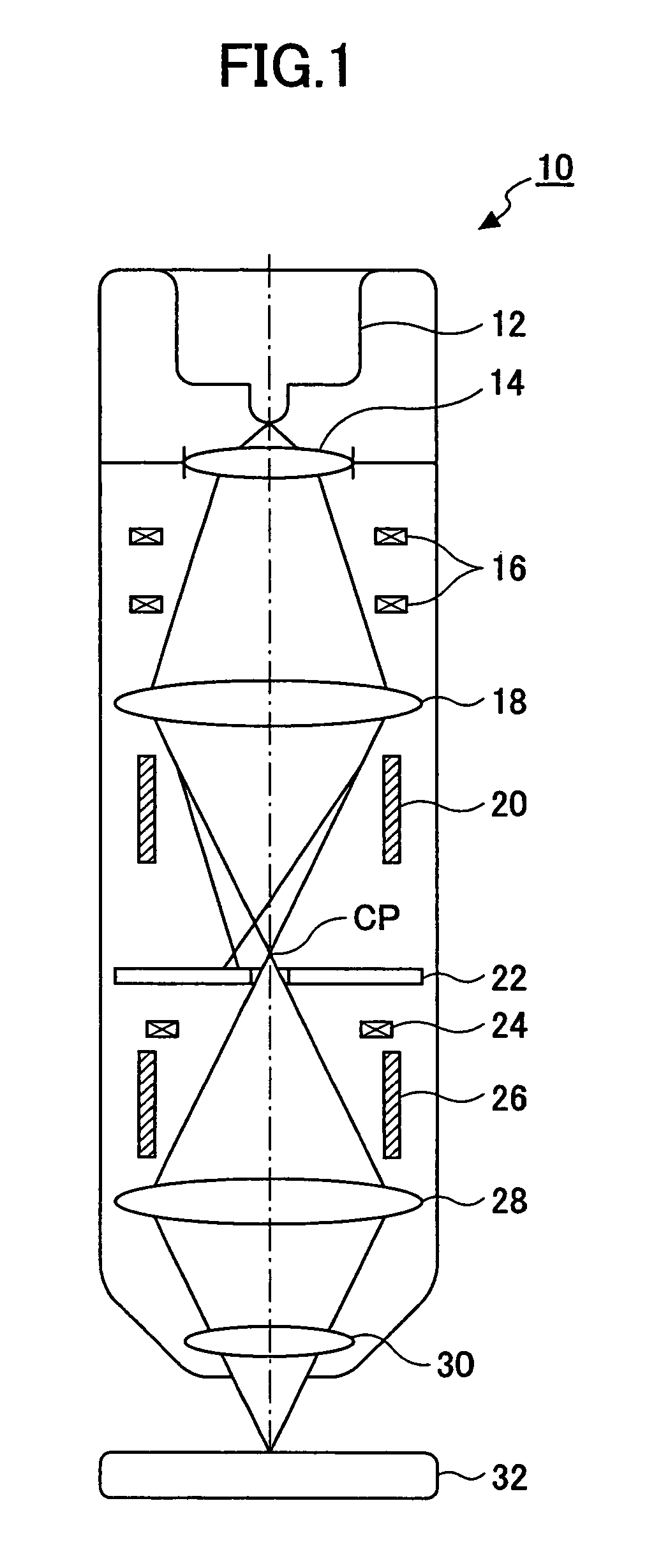
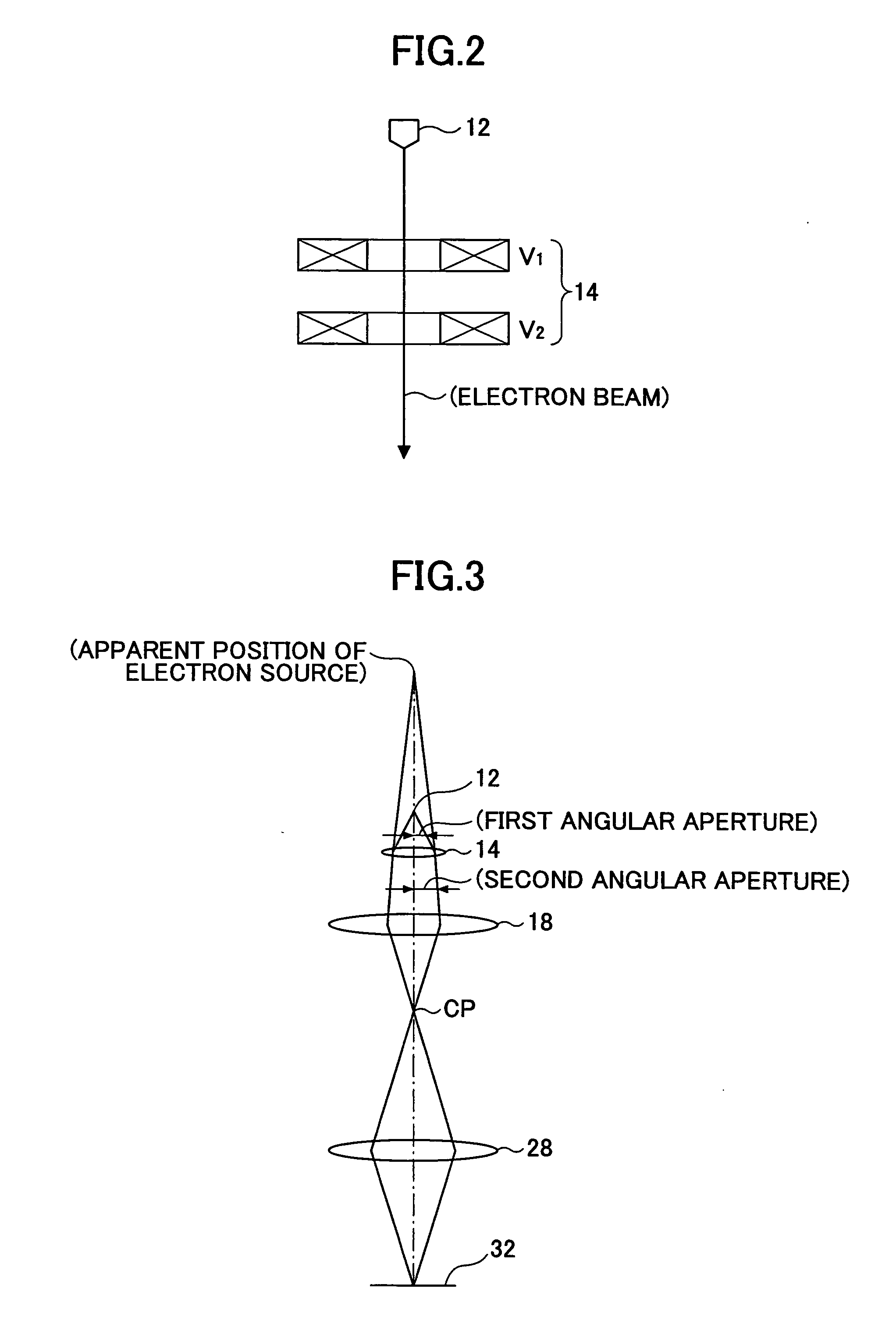
InactiveUS20070085003A1Minimal beam diameterLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron beam carrier recordingElectron sourceAtomic physics
An electron beam applying apparatus includes: a thermal field emission type electron source emitting an electron beam; an electrostatic lens disposed immediately below the electron source and acting as a condensing electrode for condensing the electron beam in a first angular aperture emitted by the electron source in a second angular aperture smaller than the first angular aperture; a condenser lens disposed on a downstream side of the electrostatic lens and condensing the electron beam condensed in the second aperture angel by the electrostatic lens in a crossover point; and an objective lens disposed on a downstream side of the condenser lens and condensing the electron beam condensed in the crossover point by the condenser lens on the surface of the material.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
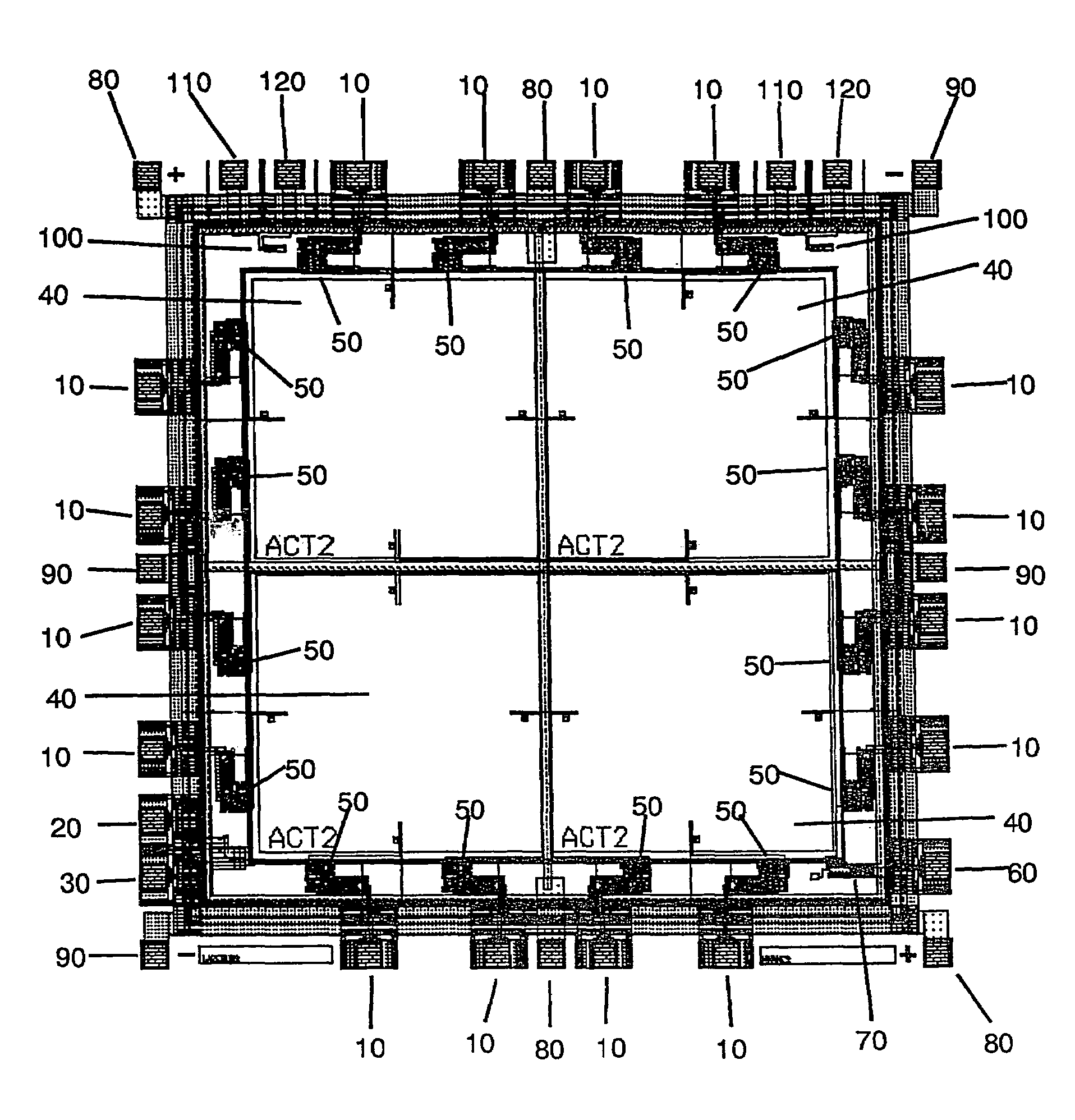
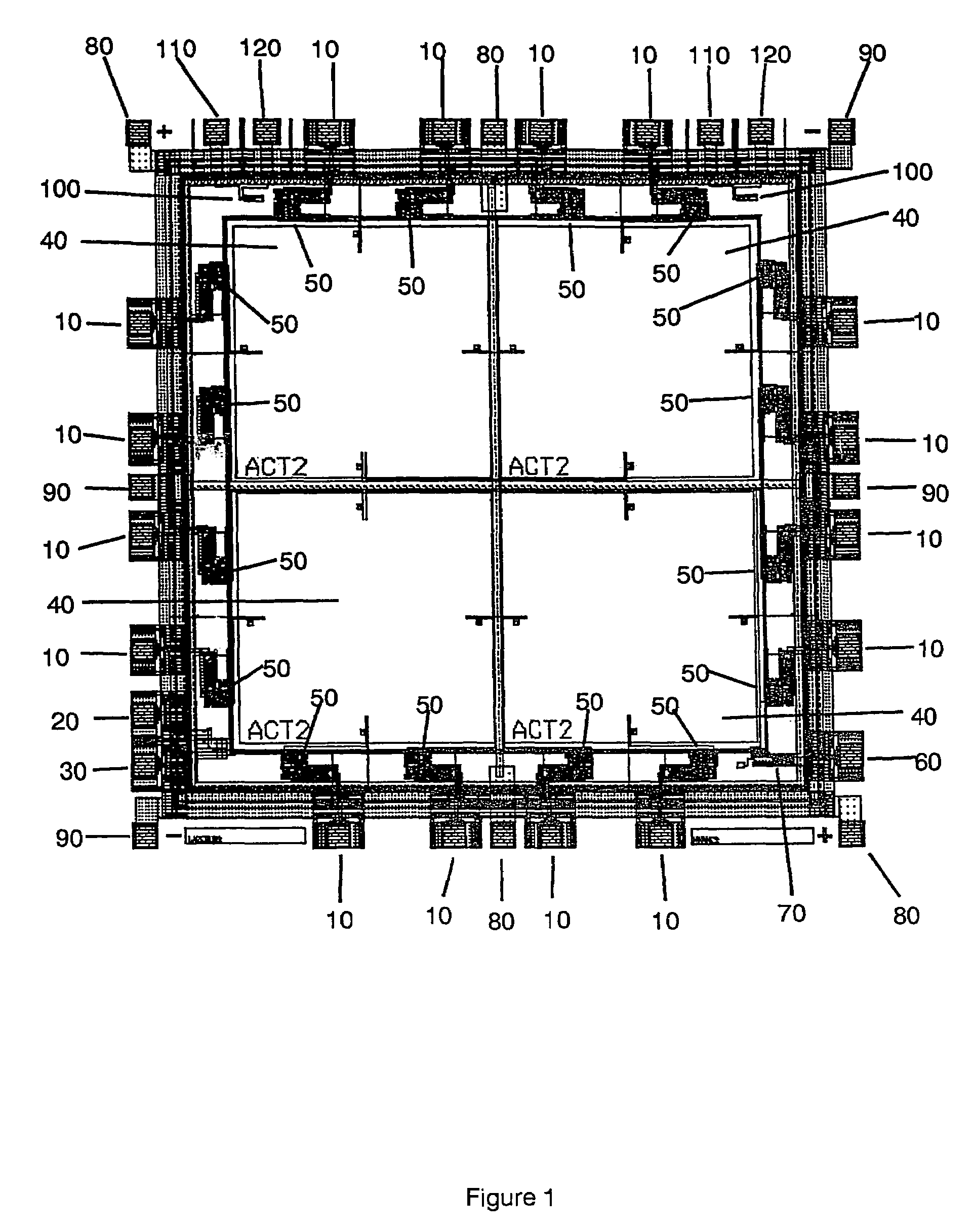
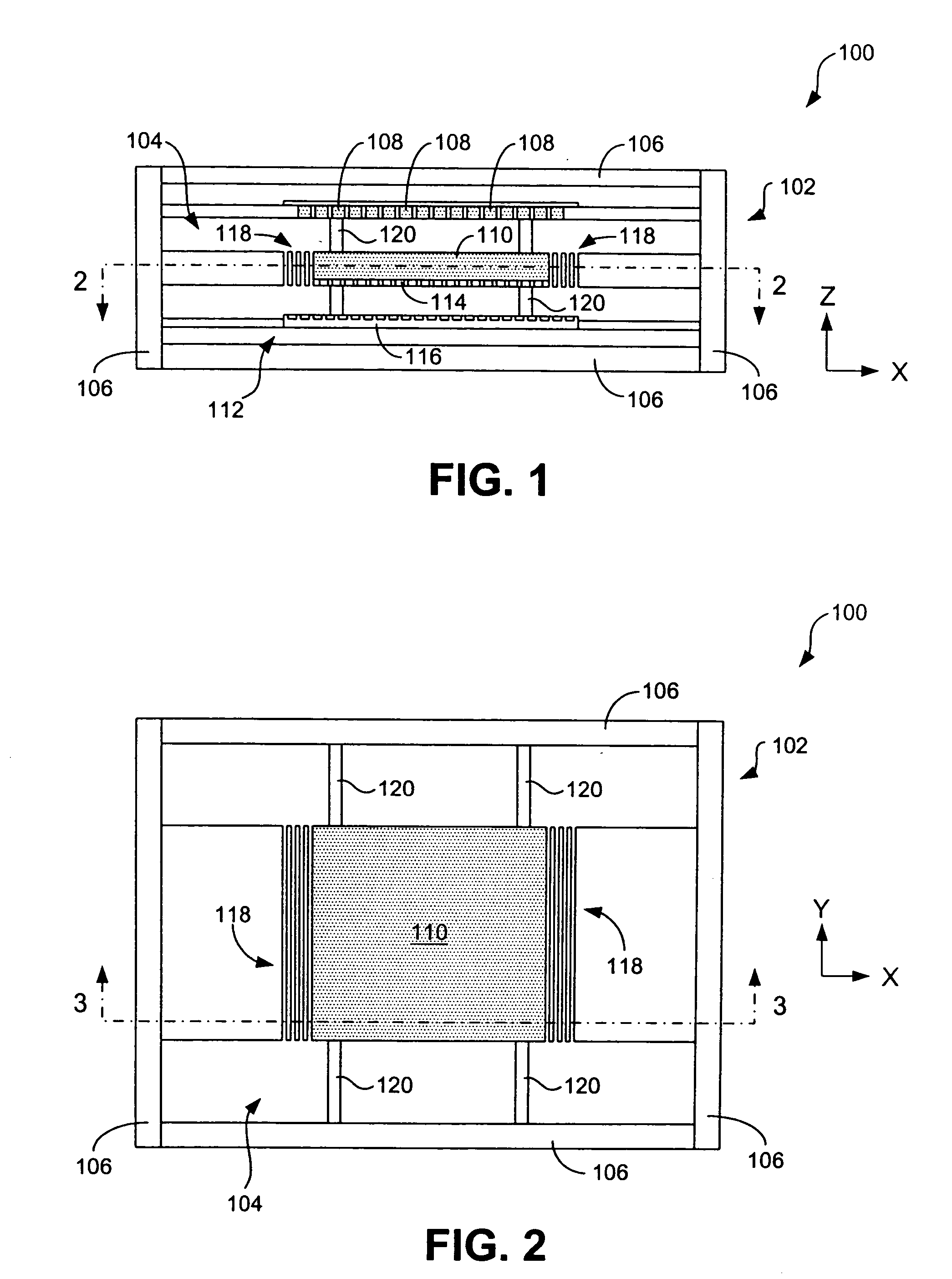
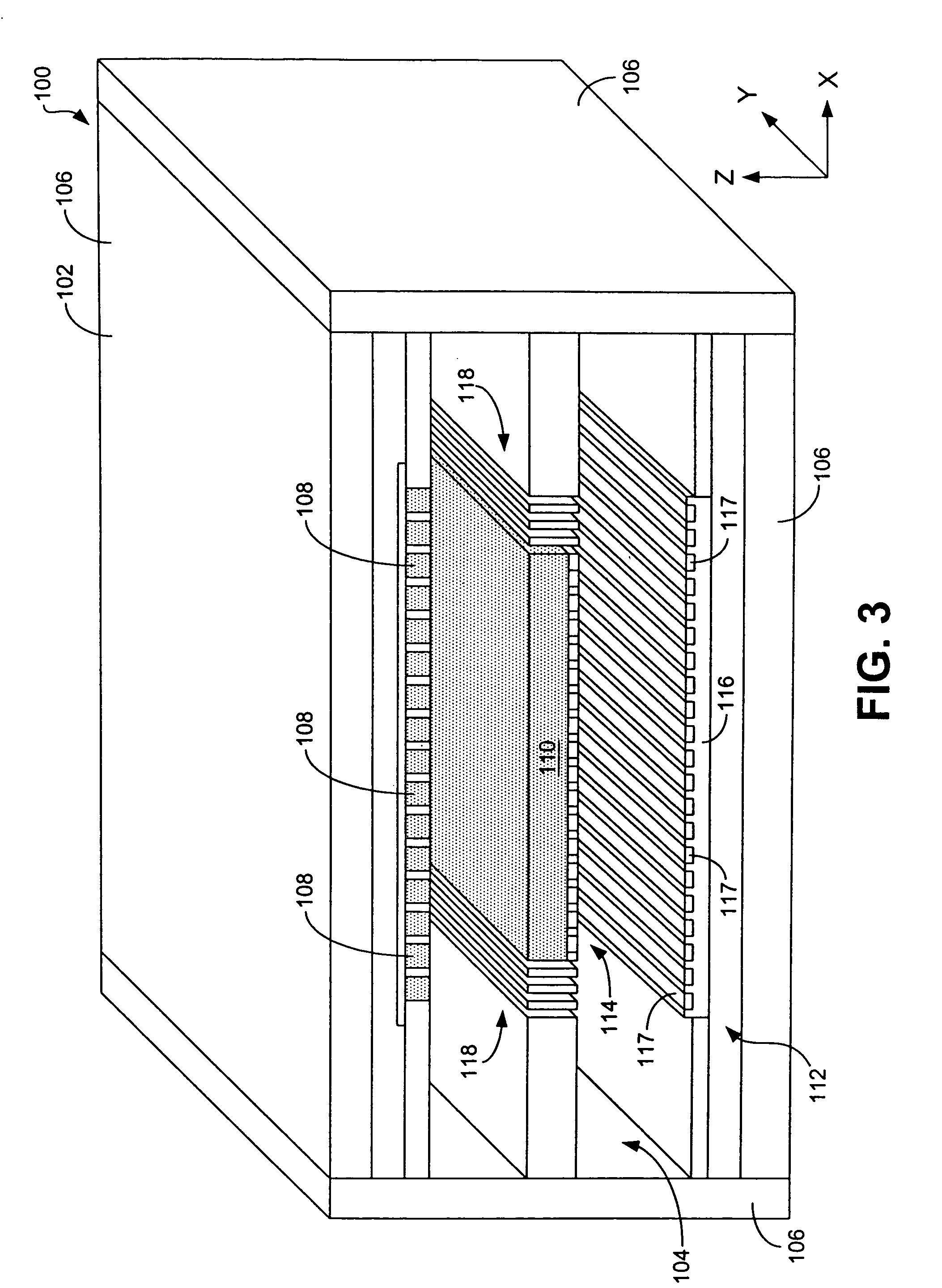
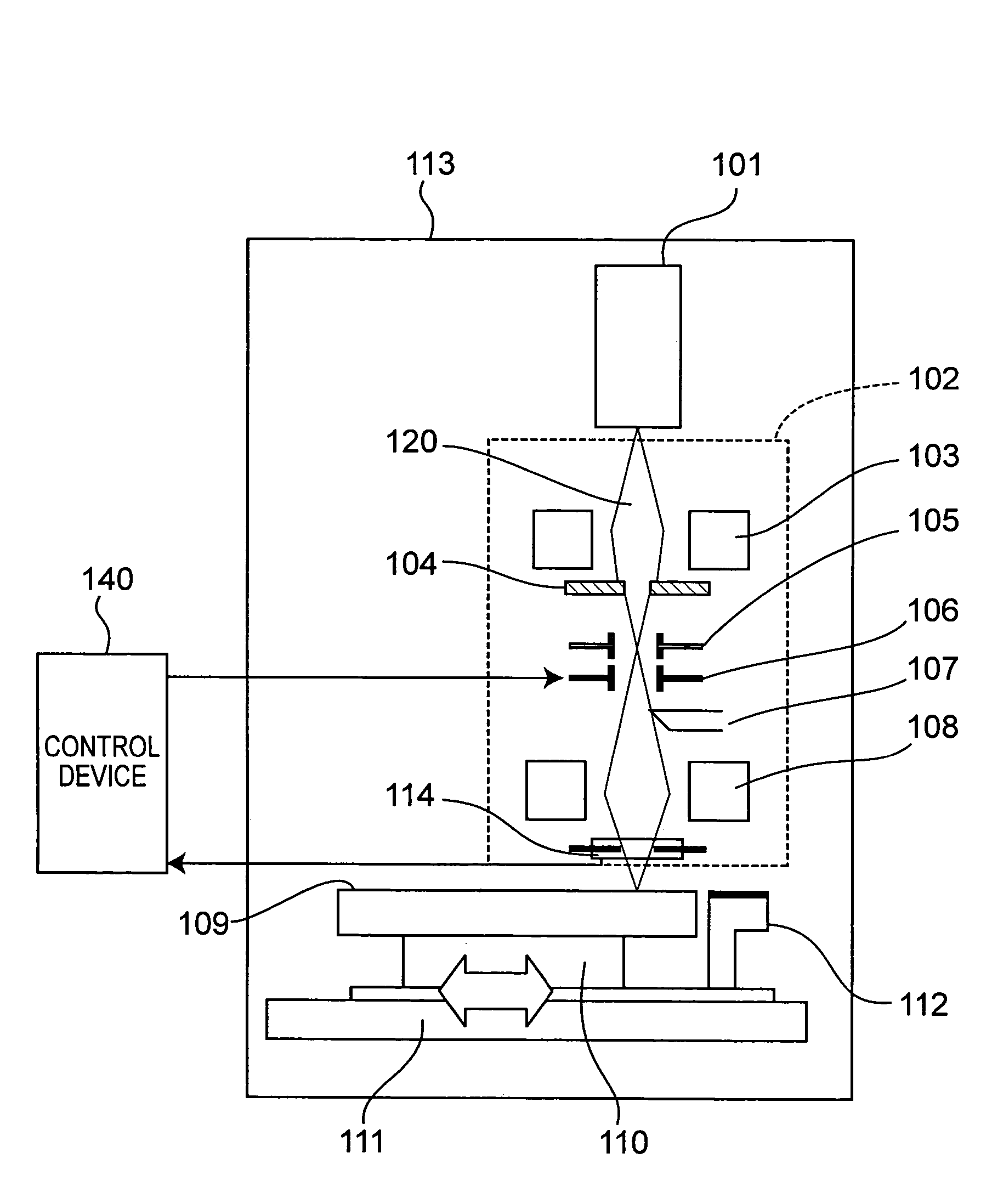
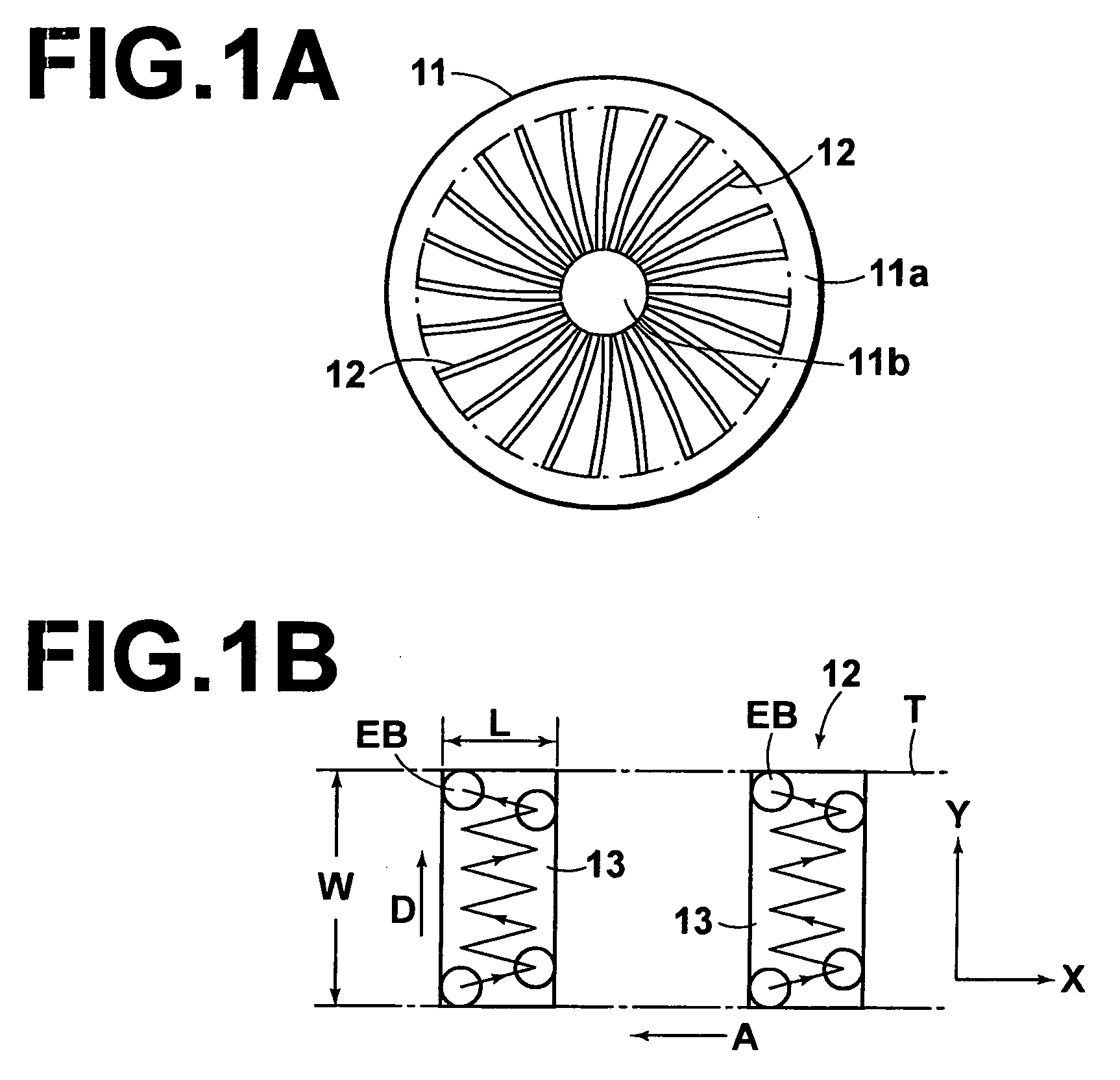
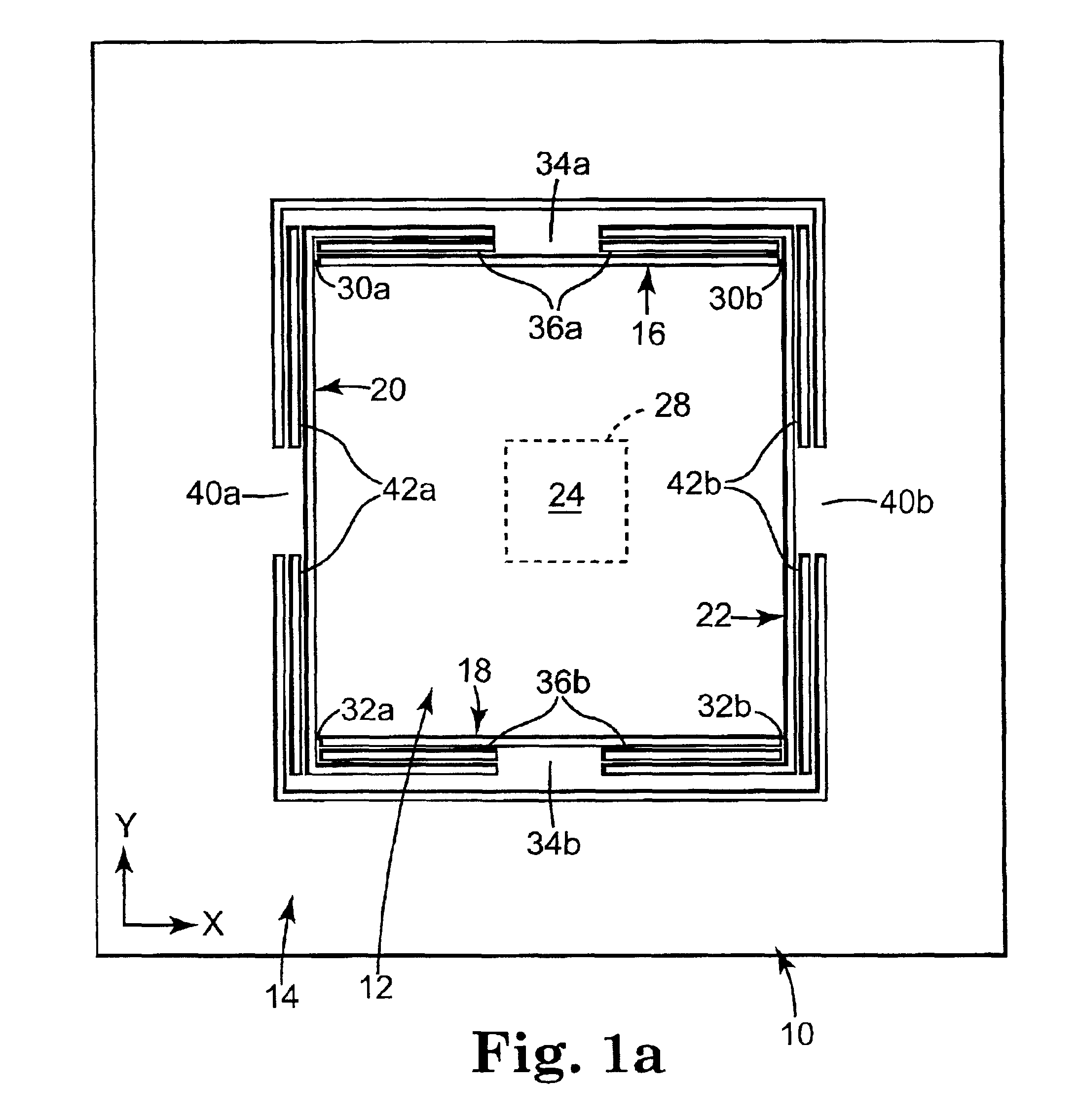
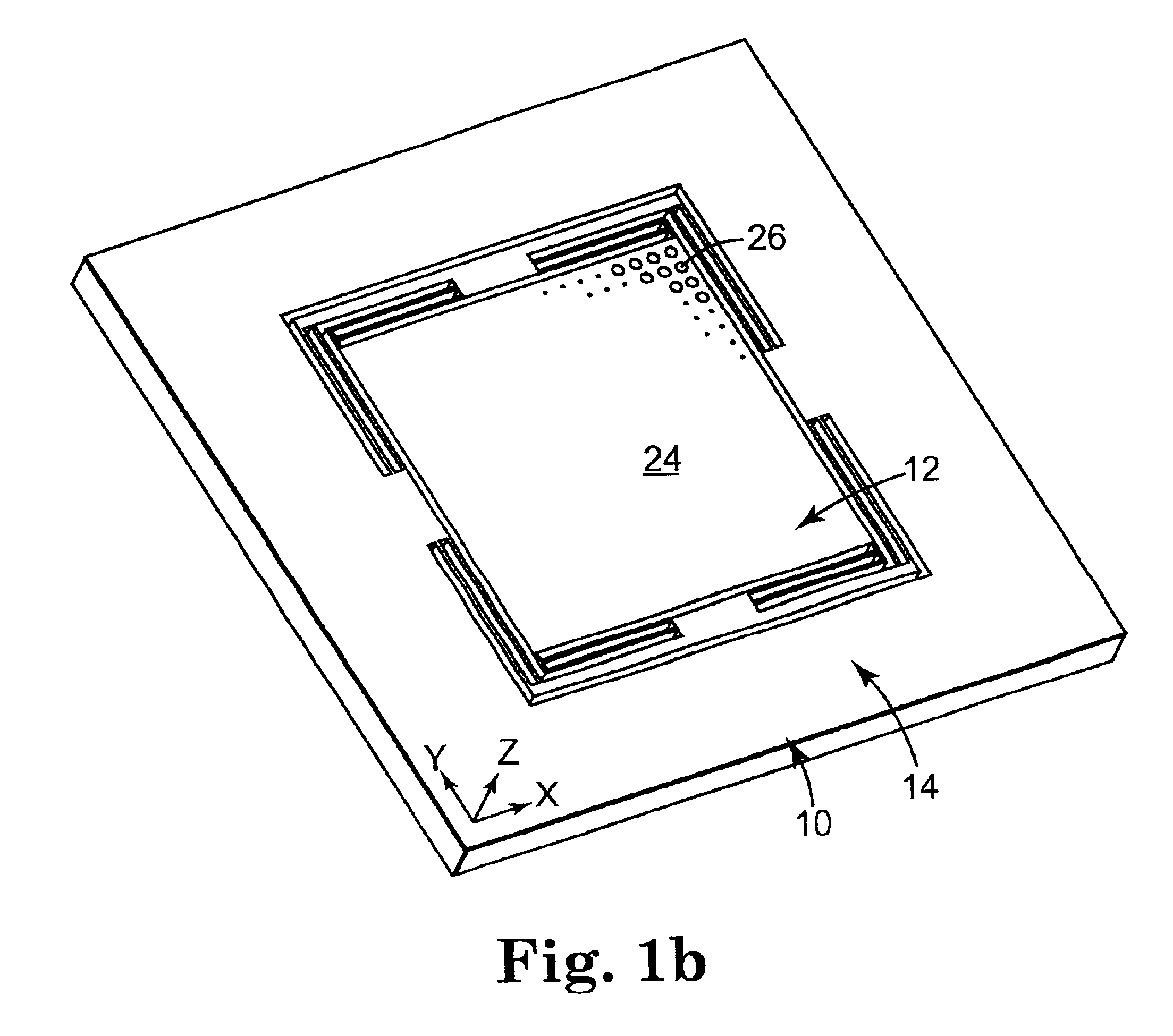
High density data storage module
A data storage module for a high density data storage device. The storage module includes a planar rotor having top, bottom, left and right edges. The rotor is suspended within a frame surrounding the top, bottom, left and right edges of the rotor. The rotor is suspended by a plurality of flexures, wherein the flexures adjacent to the top edge are aligned with the top edge, the flexures adjacent to the bottom edge are aligned with the bottom edge, the flexures adjacent the left edge are aligned with the left edge, and the flexures adjacent to the right edge are aligned with the right edge.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods for conducting current between a scanned-probe and storage medium
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com