Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Atomic resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Swallowable data recorder capsule medical device
The present invention provides a swallowable data recorder medical device. The swallowable data recorder medical device includes a capsule including a sensing module for sensing a biologic condition within a body. A recording module is provided including an atomic resolution storage device. The recording module is electrically coupled to the sensing module for recording data representative of the sensed biologic condition in the atomic resolution storage device. A power supply is coupled to the recording module.
Owner:MARSHALL DANIEL R
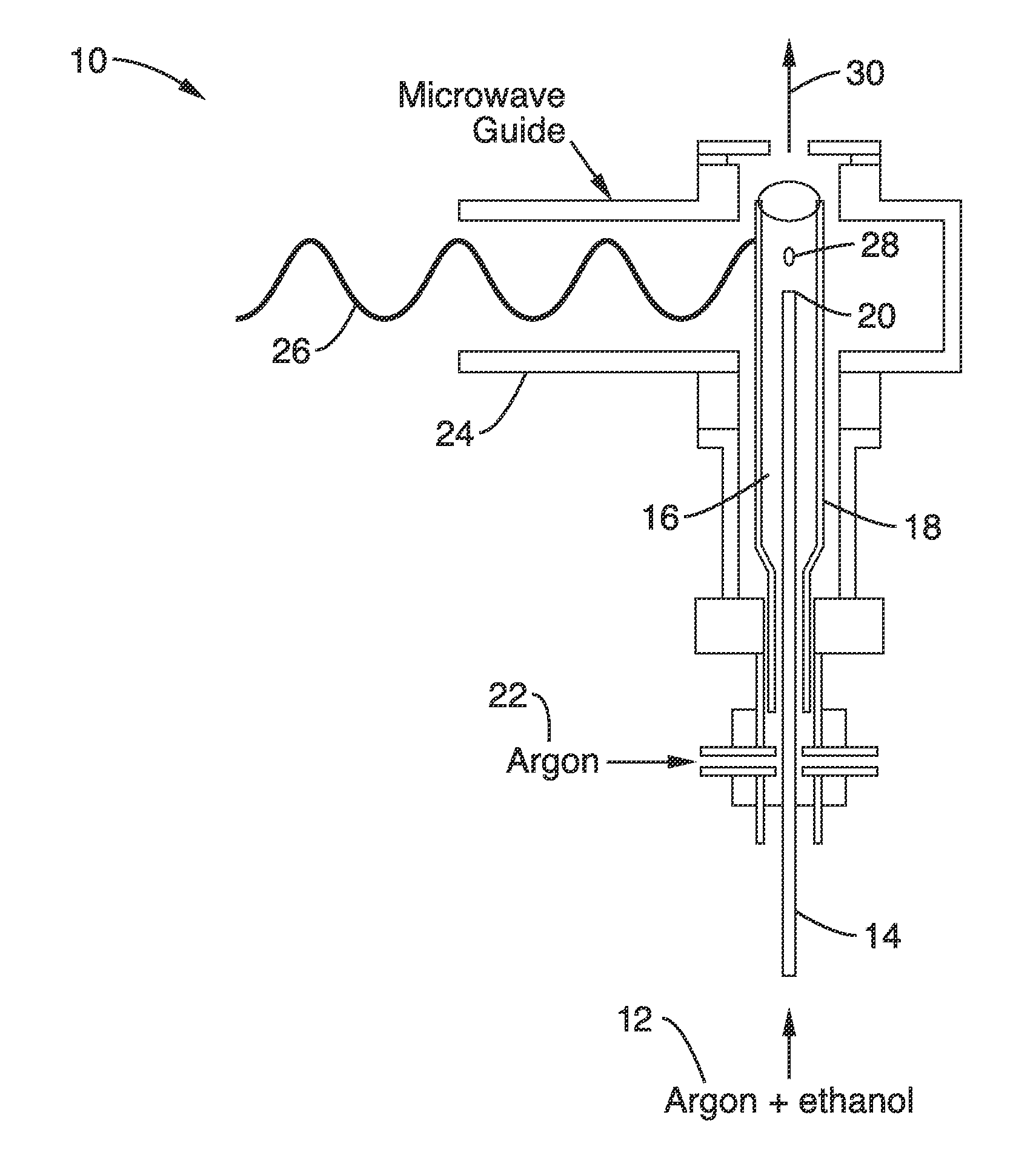
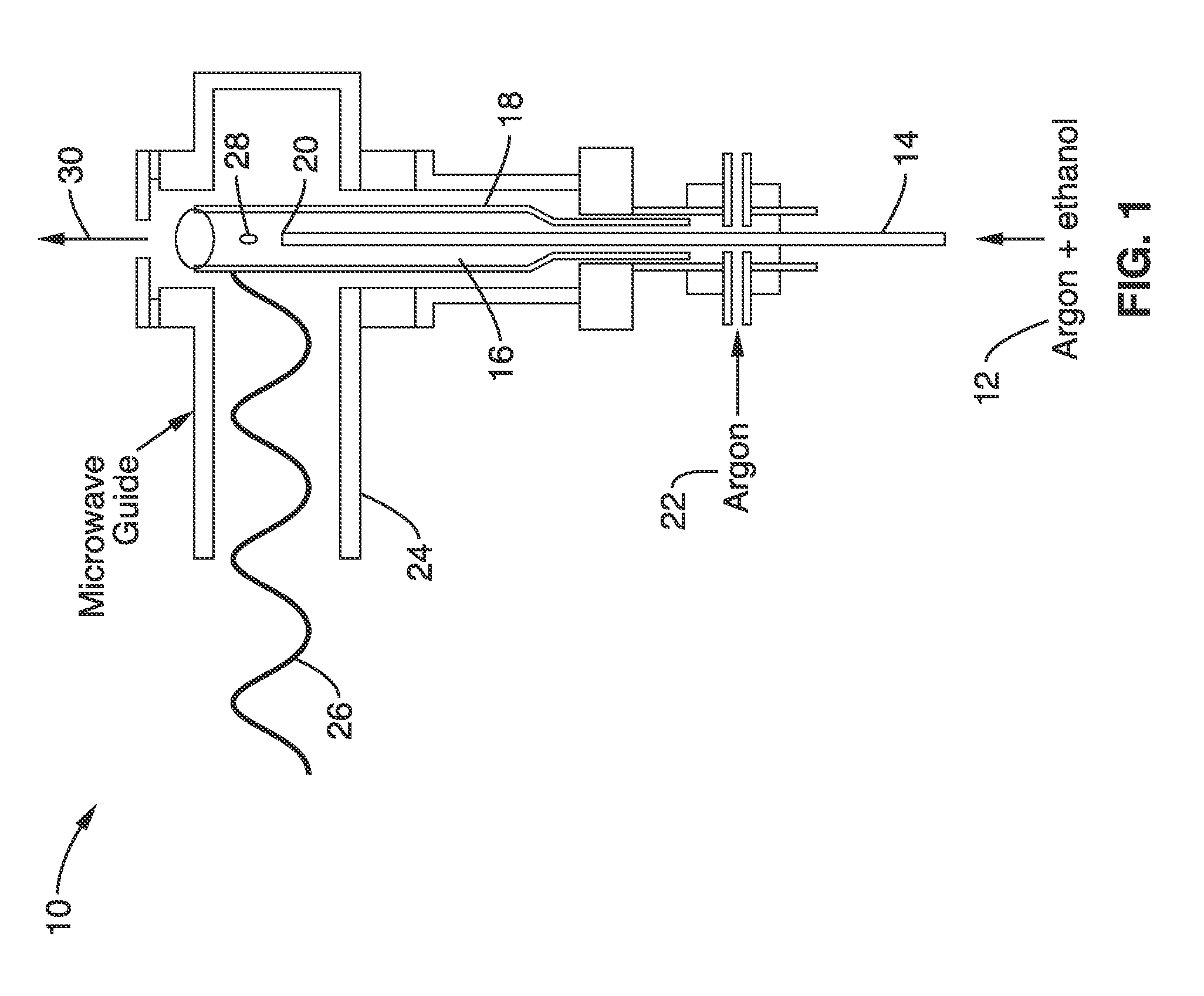
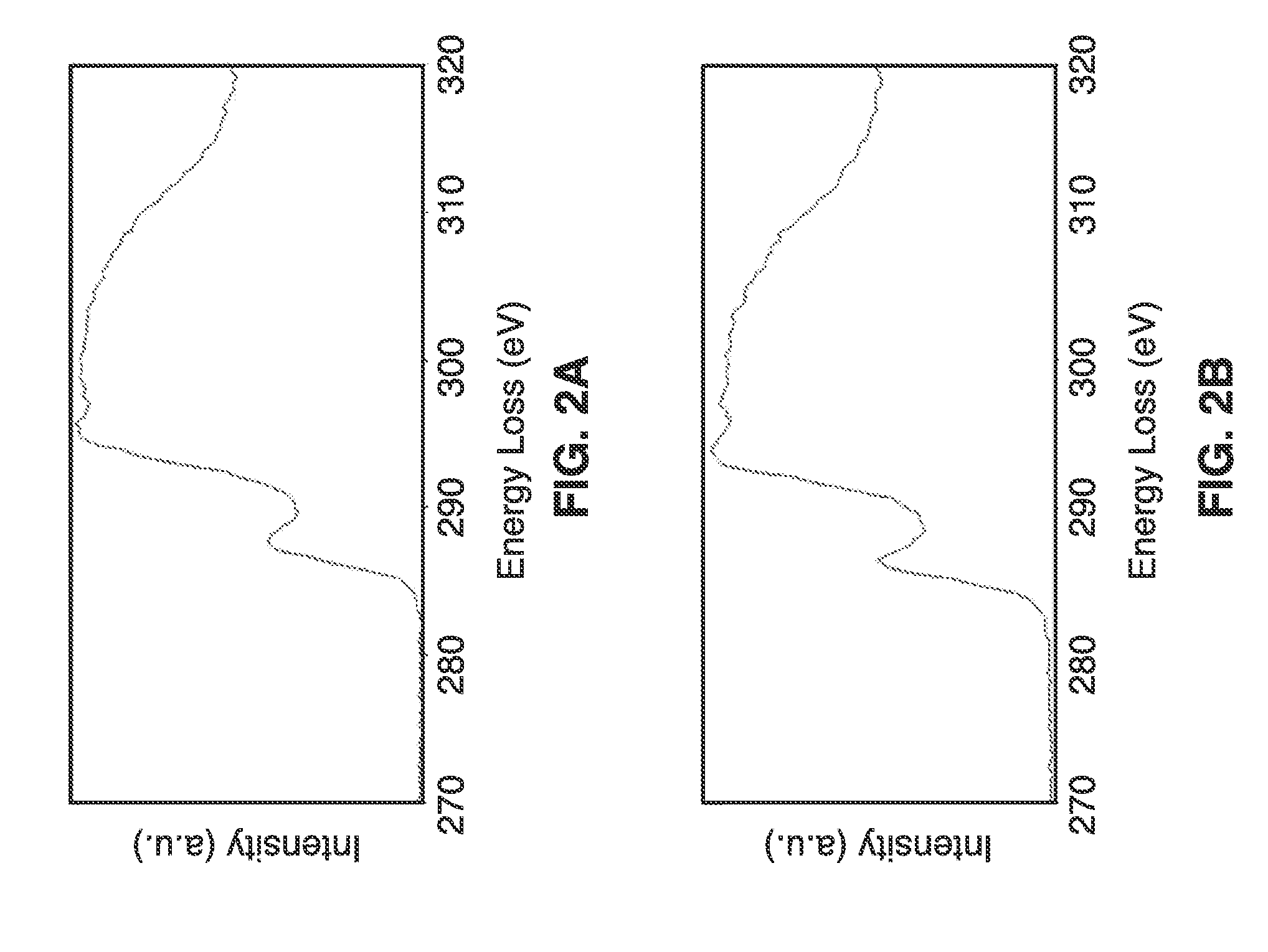
Substrate-free gas-phase synthesis of graphene sheets
InactiveUS20100301212A1Uniform and easy to produceEasy to produceMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGas phaseOxygen
A substrate-free gas-phase synthesis apparatus and method that is capable of rapidly and continuously producing graphene in ambient conditions without the use of graphite or substrates is provided. Graphene sheets are continuously synthesized in fractions of a second by sending an aerosol consisting of argon gas and liquid ethanol droplets into an atmospheric-pressure microwave-generated argon plasma field. The ethanol droplets are evaporated and dissociated in the plasma, forming graphene sheets that are collected. The apparatus can be scaled for the large-scale production of clean and highly ordered graphene and its many applications. The graphene that is produced is clean and highly ordered with few lattice imperfections and oxygen functionalities and therefore has improved characteristics over graphene produced by current methods in the art. The graphene that is produced by the apparatus and methods was shown to be particularly useful as a support substrate that enabled direct atomic resolution imaging of organic molecules and interfaces with nanoparticles at a level previously unachievable.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
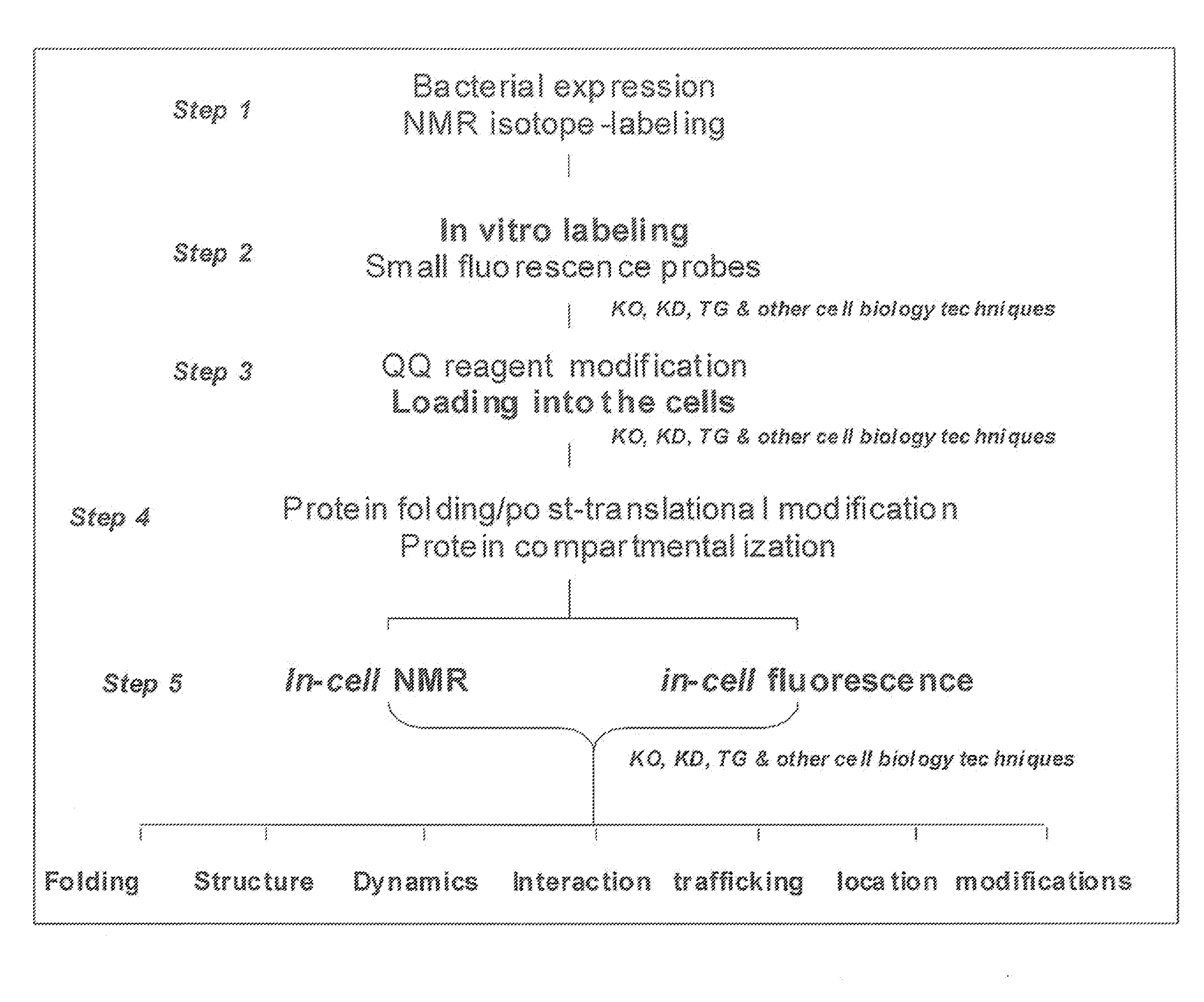
Method and composition for a protein transduction technology and its applications
ActiveUS20090298111A1Efficient deliveryBest protein transduction efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedSpectroscopyFluorophore
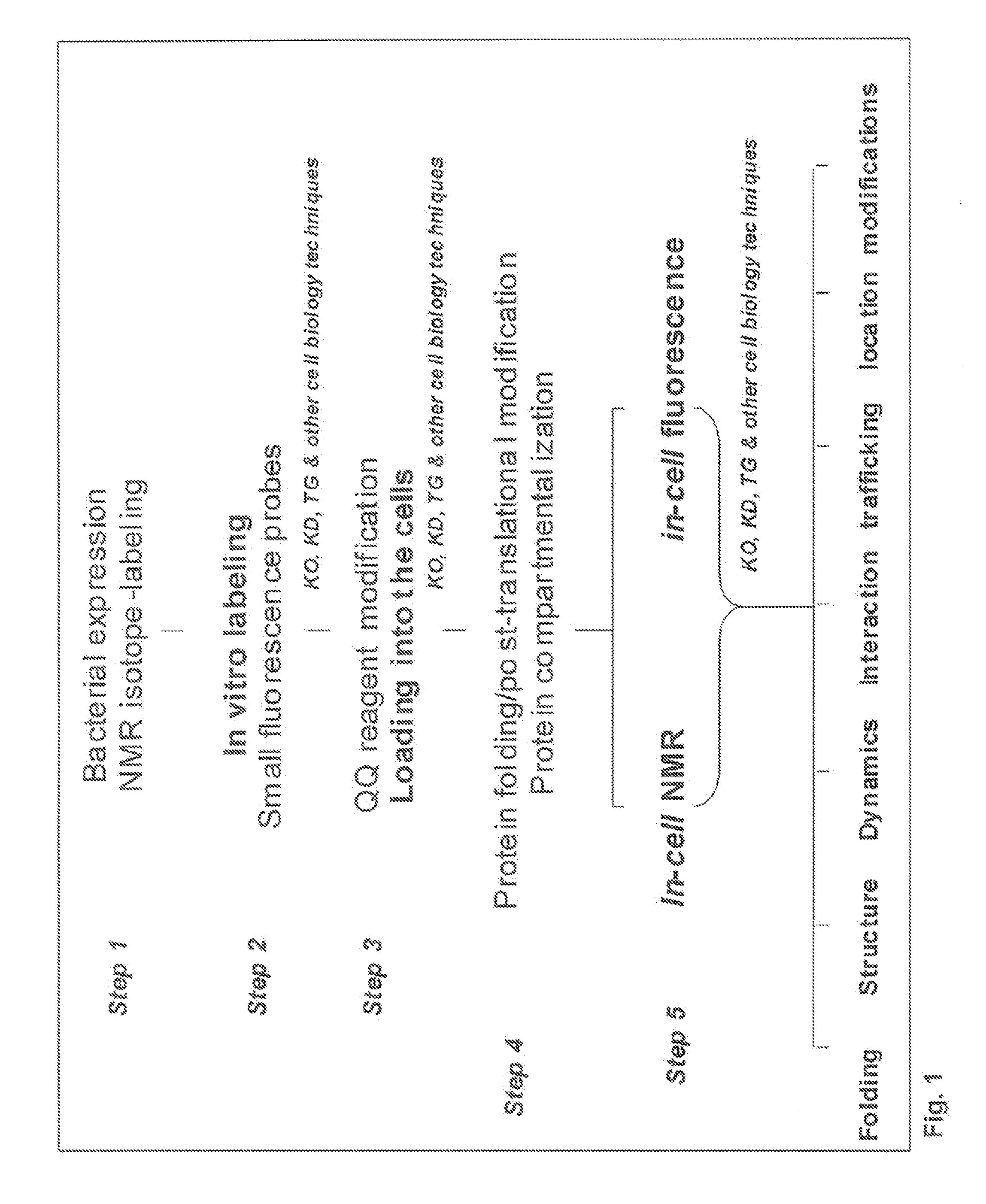
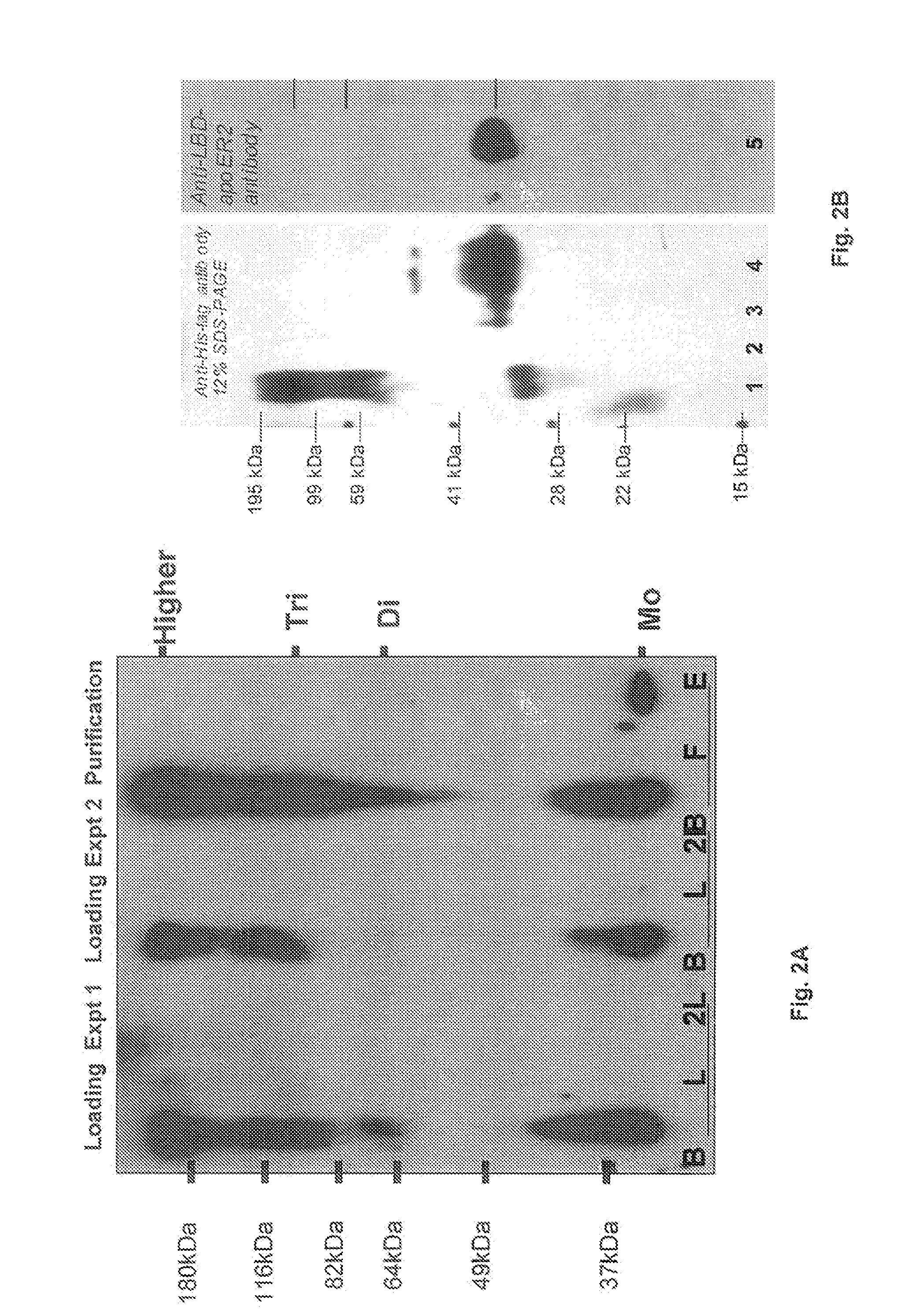
A protein transduction method for efficiently delivery of exogenous proteins into mammalian cells is invented, which has the capability of targeting different cellular compartments and protection from degradation of the delivered proteins from cellular proteases. A composition for treat proteins has cation reagents, lipids and enhancers in a carrier. The method can be used in a number of ways including: production of large quantities of properly folded, post-translationally modified proteins using mammalian cell machinery, a in-cell fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging using small molecule fluorophores and a in-cell NMR spectroscopy using living mammalian cells. The method permits cell biology at atomic resolution that is physiologically and pathological relevant and permits protein therapy to treat human diseases. The method can also be used to deliver exogenous protein inside mammalian cells, wherein the exogenous proteins follow a similar secretion pathway as that of the endogenous protein.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Contact probe storage sensor pod
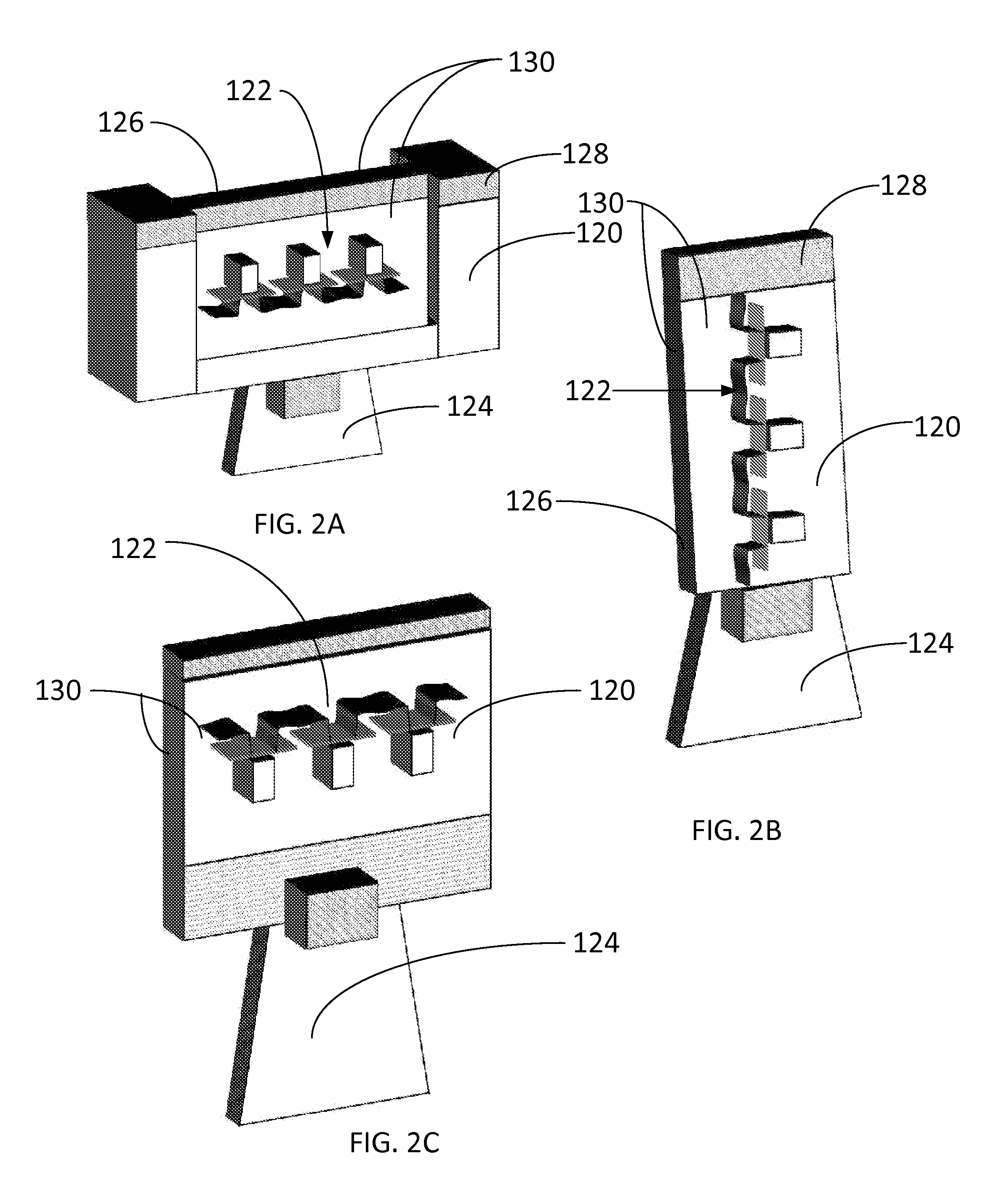
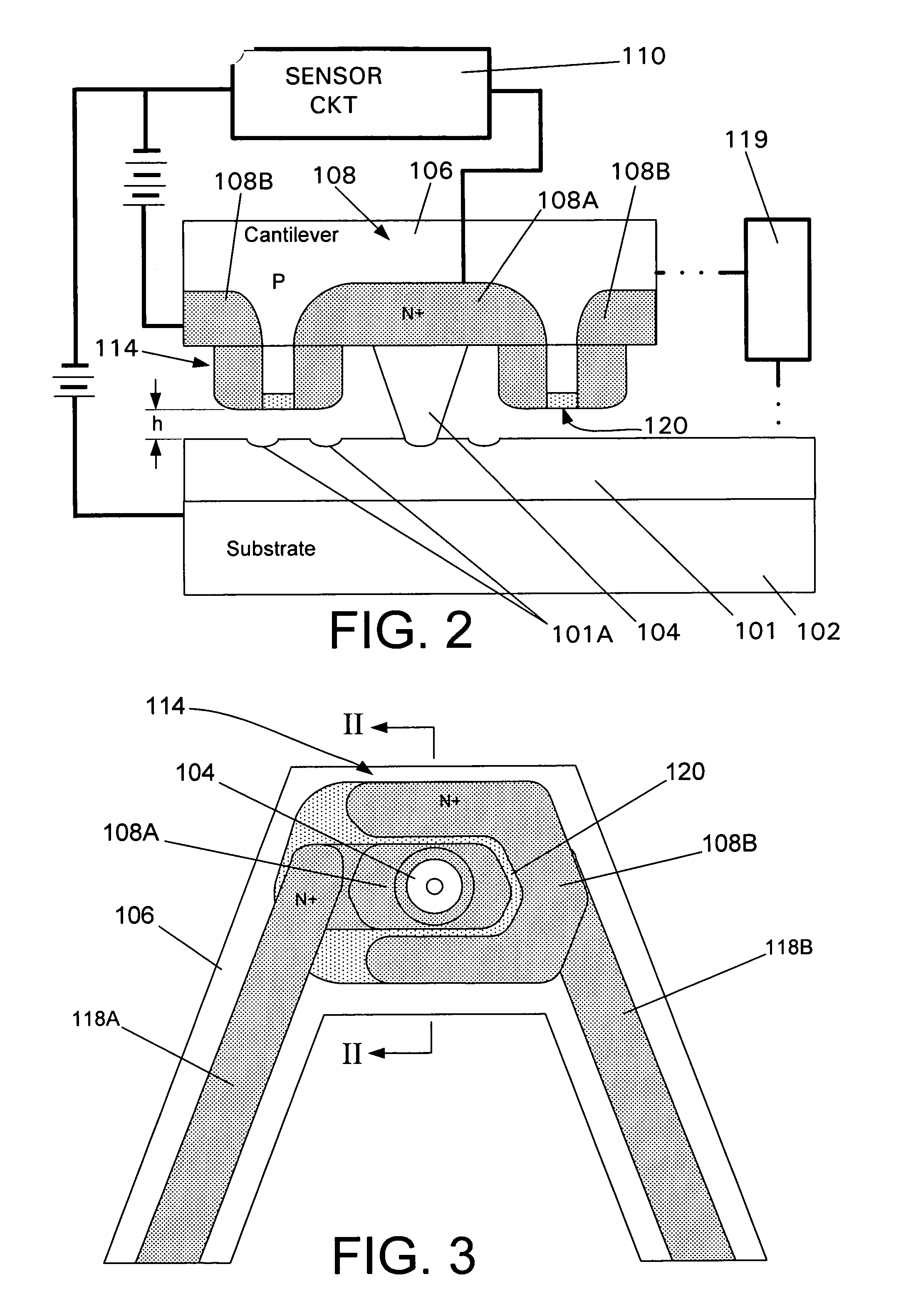
An embodiment of a read mechanism used in a contact atomic resolution storage system, has a cantilever disposed with a medium which is movable relative to the cantilever. The cantilever has a probe which extends from the cantilever and which contacts a surface of the medium. A pod is formed on a side of the cantilever facing the medium and extends toward the media. A sensor element is formed on the pod so as to juxtapose the medium.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Small molecule binding pockets in nucleic acids
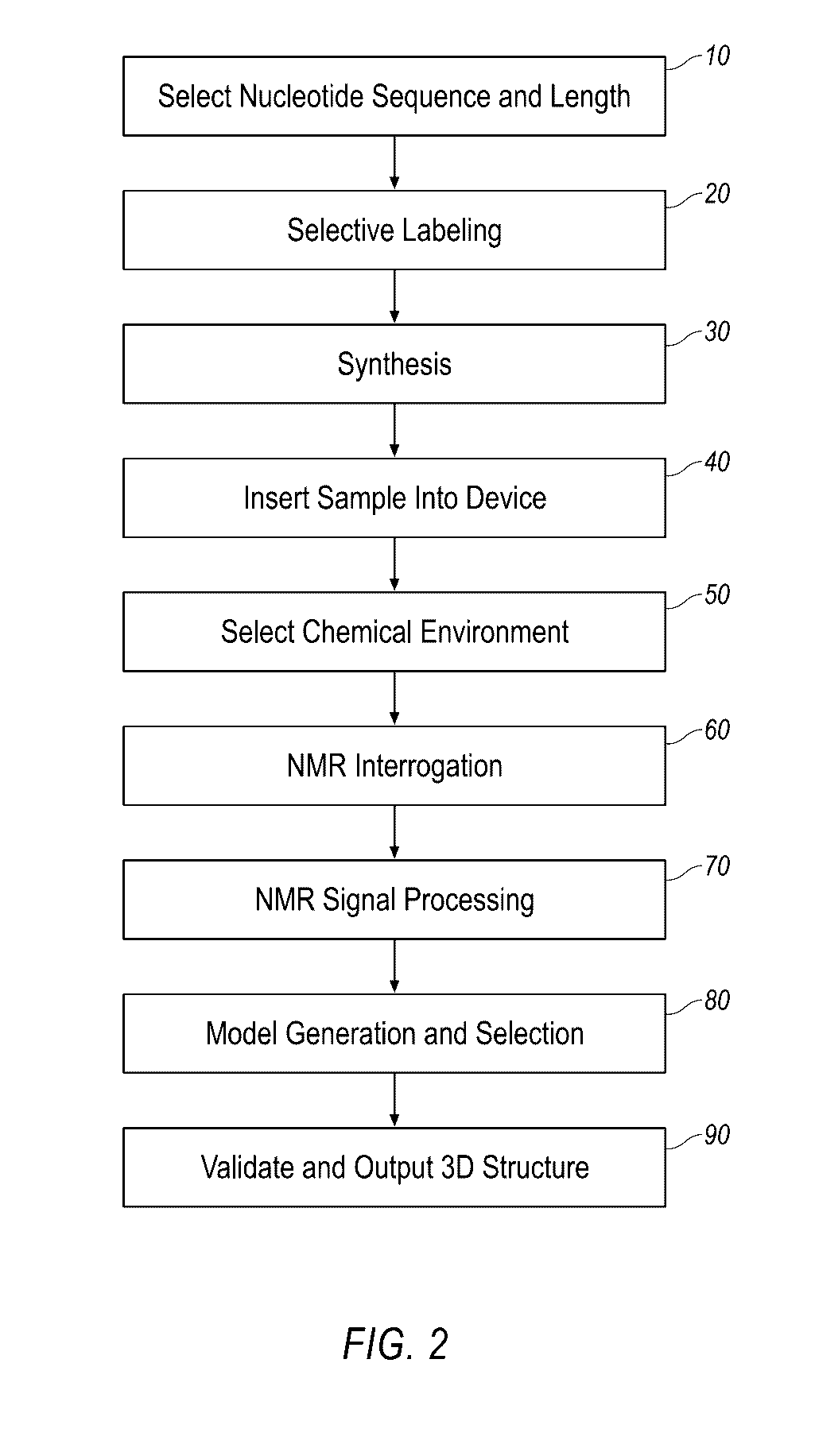
Described herein is technology for determining the 2-D or 3-D atomic resolution structure of a polynucleotide bound to and / or interacting with another molecule, for example a small molecule. In some aspects of the technology, NMR and isotopic labeling strategies are used. The technology described herein is useful for a plurality of applications including but not limited to drug discovery and chemical biology probe discovery.
Owner:NYMIRUM
Preparation method of lead titanate-strontium titanate monocrystal nanometer material with core-shell structure
ActiveCN105040090ASimple processEasy to controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsStrontium titanateSingle crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method of a perovskite phase lead titanate-strontium titanate monocrystal nanometer material with a core-shell structure. The preparation method comprises the steps of taking a monocrystal single-domain perovskite phase lead titanate nanosheet as a template and a raw material, taking tetrabutyl titanate as a titanium source, taking strontium nitrate as a strontium source, taking sodium hydroxide as a precipitant and a mineralizing agent, and preparing precursor mixed turbid liquid for a hydrothermal reaction under the condition of magnetic stirring; sealing the precursor mixed turbid liquid into a stainless steel reaction still having a teflon liner, and obtaining a core-shell structure perovskite phase lead titanate-strontium titanate monocrystal nanometer composite structure through subjecting to hydro-thermal treatment at the temperature of 160 to 220 DEG C for 4 to 24 hours. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in technical process, easy to control, free of pollution, low in cost, and easy for mass production. The prepared perovskite phase lead titanate-strontium titanate monocrystal nanometer composite structure has a clear core-shell structure, and has an interface with atomic resolution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fabrication of a Malleable Lamella for Correlative Atomic-Resolution Tomographic Analyses
ActiveUS20150253353A1Easy to analyzeHigh resolutionElectric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationImage resolutionBulk samples
A method of forming a sample and performing correlative S / TEM and APM analysis is provided wherein a sample containing a region of interest is cut from a bulk of sample material and formed into an ultra-thin lamella. The lamella is then analyzed with an S / TEM to form an image. The lamella sample and mount may then go through a cleaning process to remove any contamination. The lamella containing the ROI is then embedded within a selected material and is formed into a needle-shaped sample. The needle-shaped sample is then analyzed with the APM and the resulting data is merged and correlated with the S / TEM data.
Owner:FEI CO
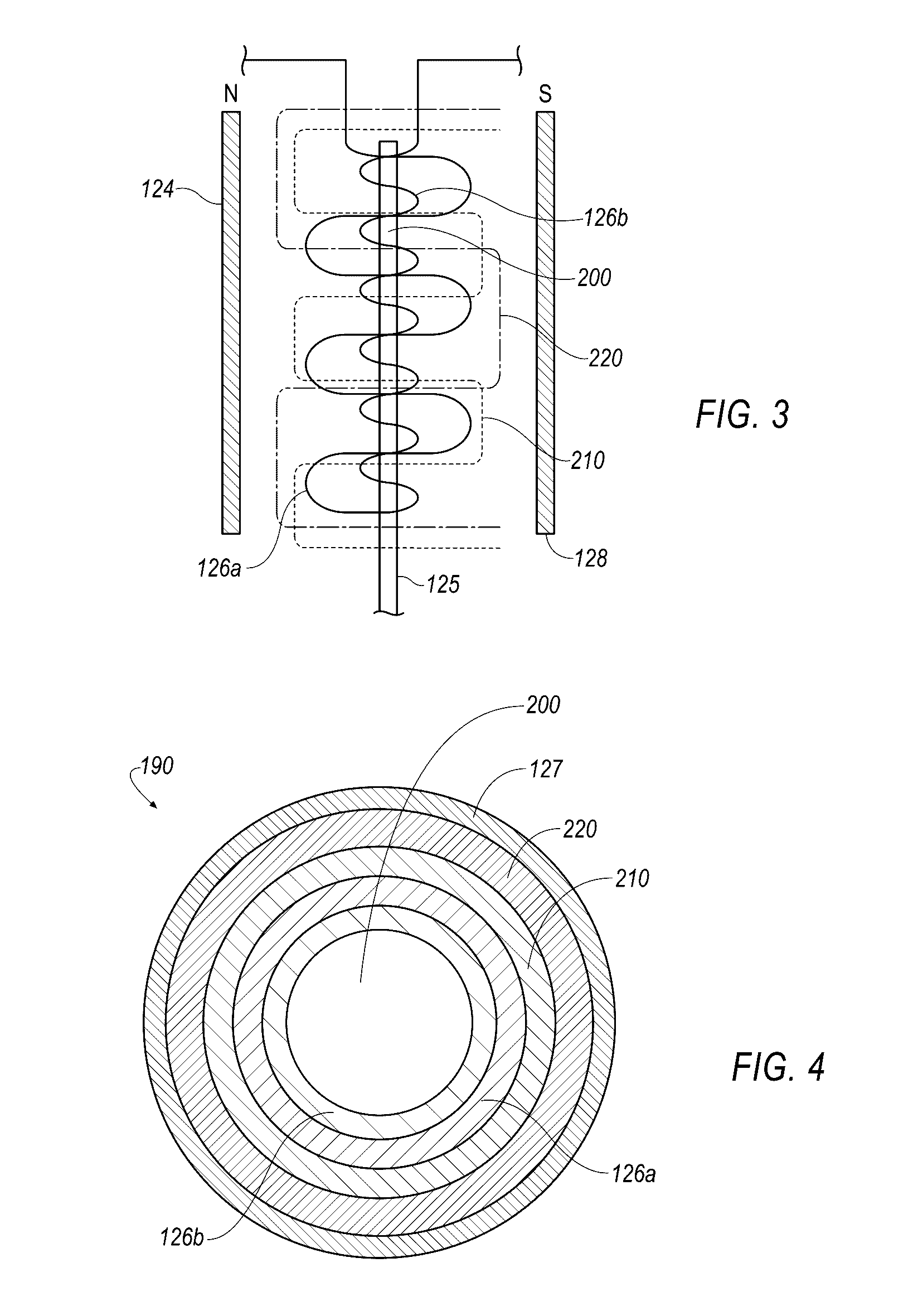
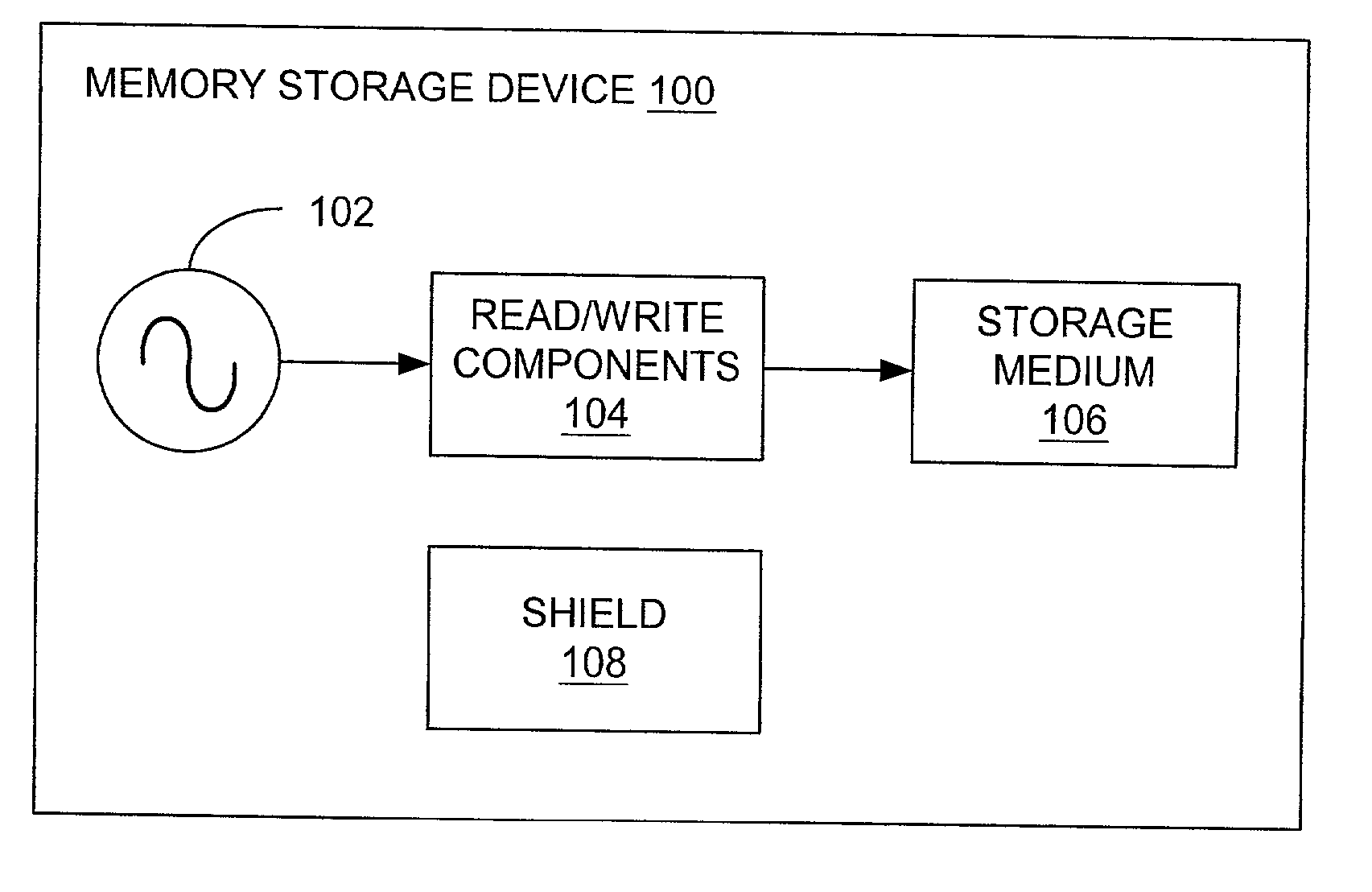
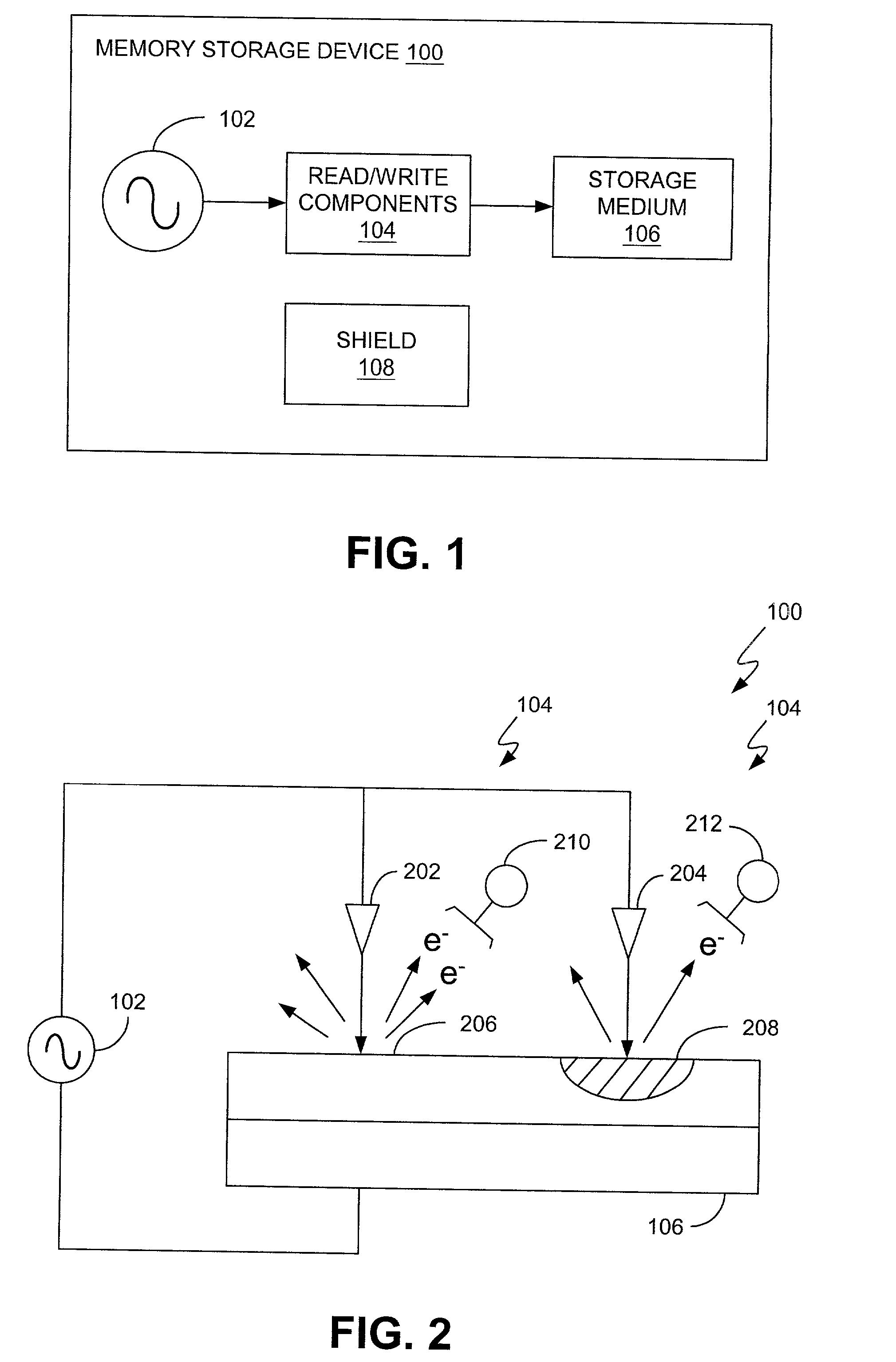
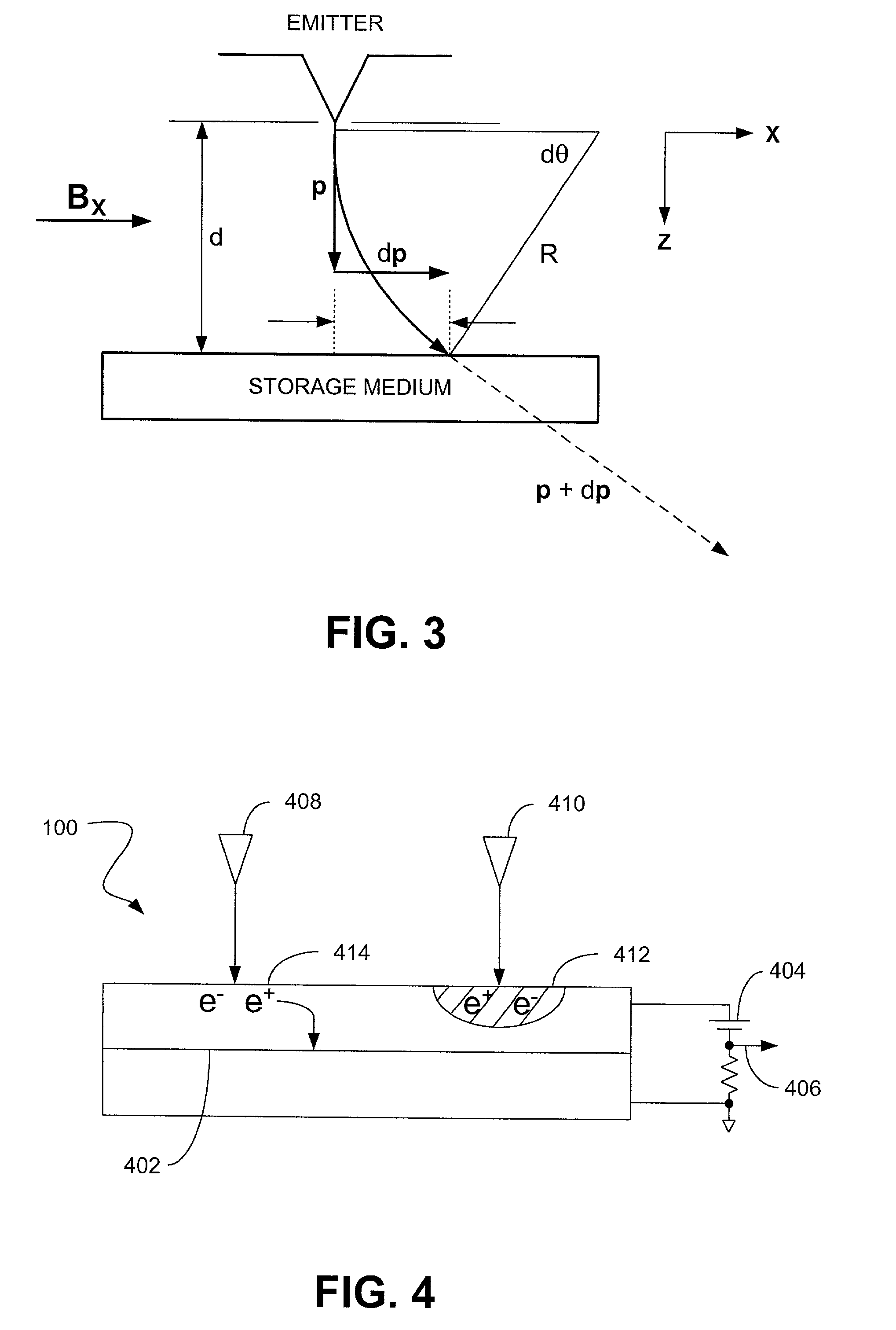
Atomic resolution storage systems with enhanced magnetic field protection
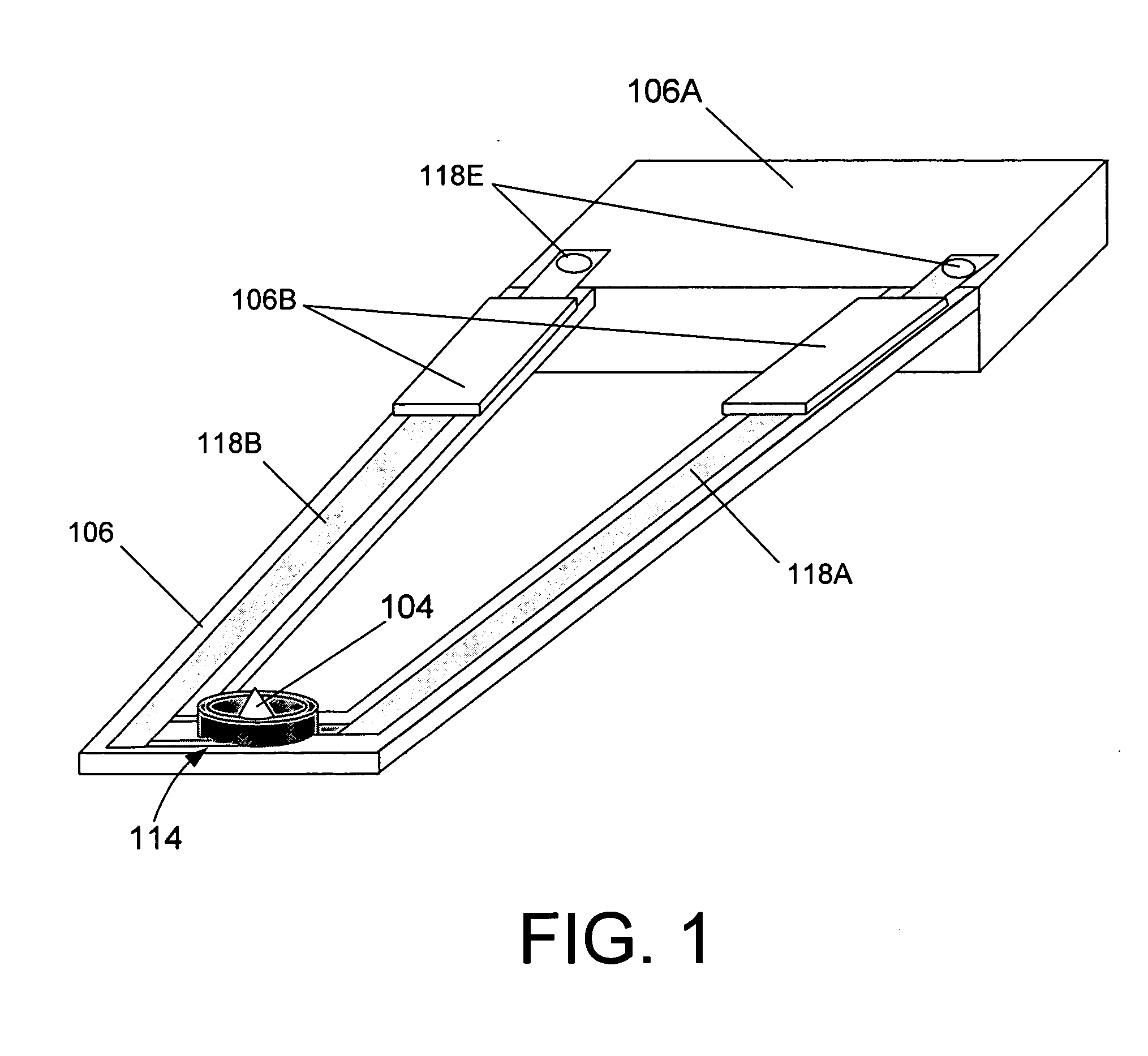
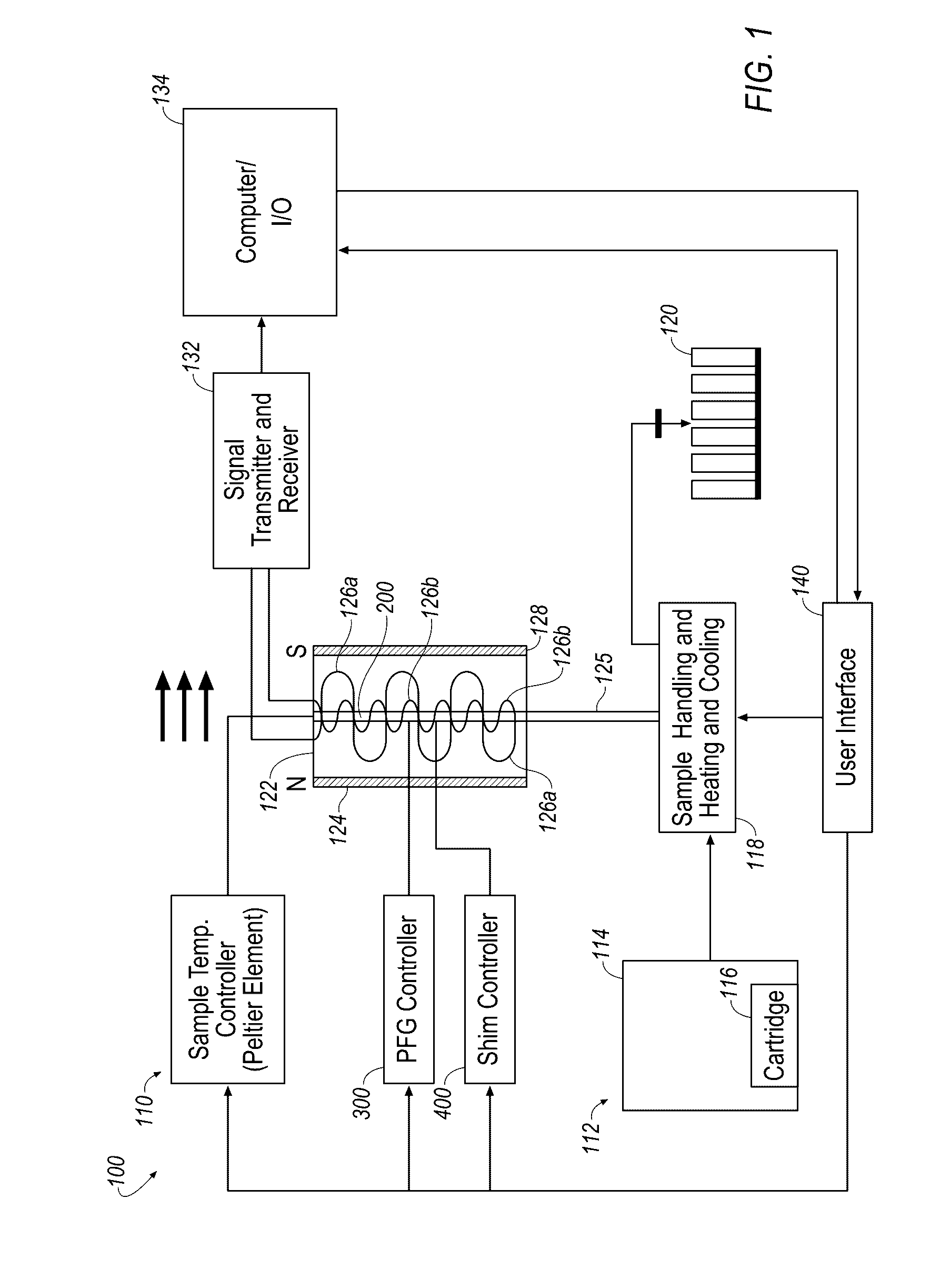
Memory storage devices that employ atomic resolution storage technology are provided. A preferred memory storage device includes a storage medium that defines one or more coverage areas. Each of the coverage areas incorporates a storage area that is configurable in one of a plurality of structural states. Typically, the structural states represent information stored in the storage area. Electron beam emitters electrically communicate with the storage medium, with the storage medium and the emitters being configured to move relative to each other. So configured, each emitter is capable of providing a beam of electrons to a respective one of the coverage areas. The memory storage device also includes a first current source that selectively electrically communicates with at least one of the emitters. Additionally, a shield is provided that is configured to reduce an influence of a magnetic field so that a tendency of an electron emitted from one of the emitters to be displaced from an intended trajectory is reduced. Methods also are provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
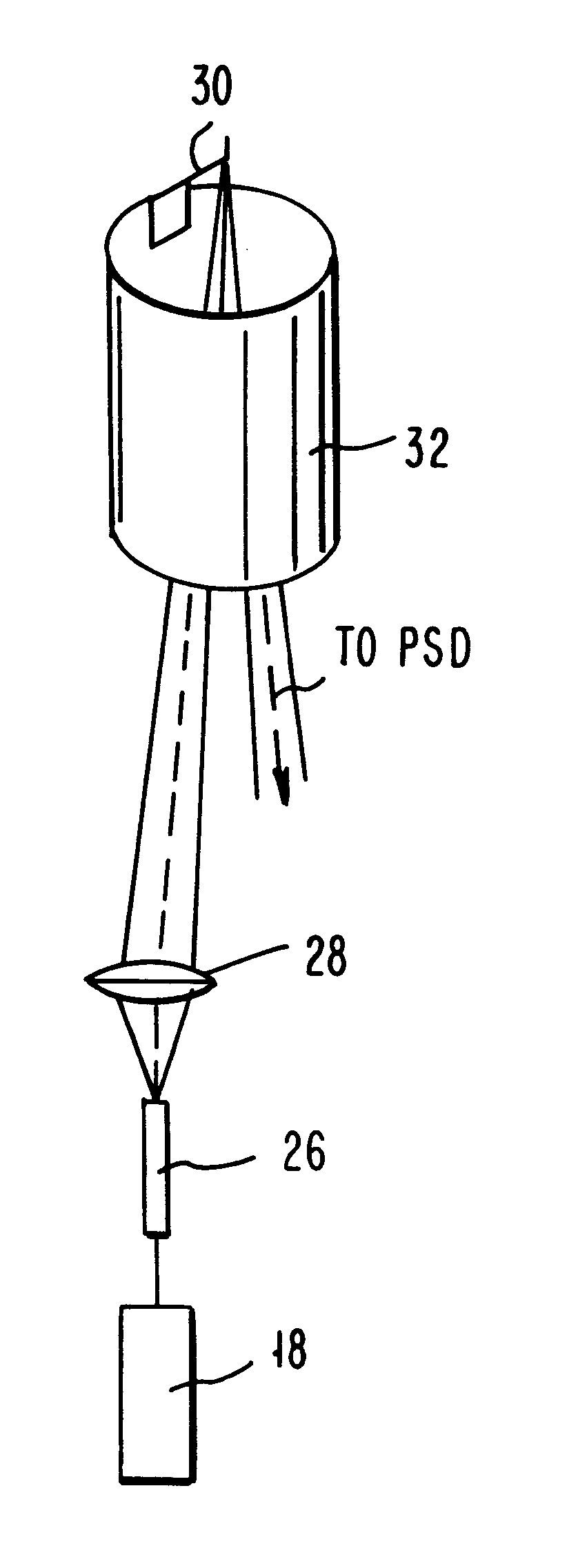
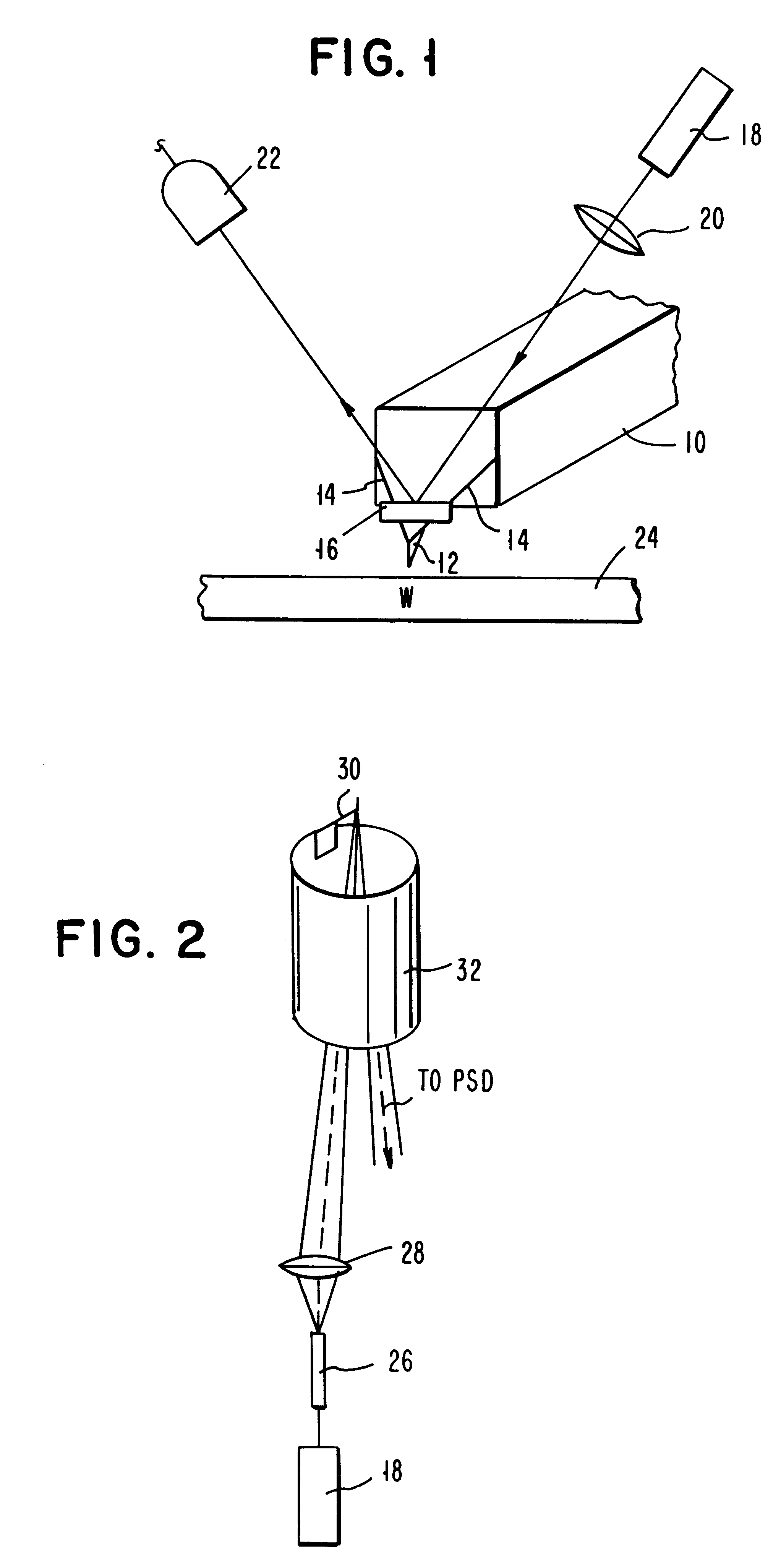
Atomic force microscopy
InactiveUSRE37299E1Convenient ArrangementMore compact designNanotechMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic force microscopyImage resolution
An atomic force microscope includes a tip mounted on a micromachined cantilever. As the tip scans a surface to be investigated, interatomic forces between the tip and the surface induce displacement of the tip. A laser beam is transmitted to and reflected from the cantilever for measuring the cantilever orientation. In a preferred embodiment the laser beam has an elliptical shape. The reflected laser beam is detected with a position-sensitive detector, preferably a bicell. The output of the bicell is provided to a computer for processing of the data for providing a topographical image of the surface with atomic resolution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electronic ink ball point pen with memory
An electronic pen for recording motion data relating to use of the pen. It includes a pen body and a ball mounted in the pen body. A sensor in the pen body, located proximate the ball, detects motion of the ball and converts the motion into corresponding electronic signals. A memory in the pen body, electronically coupled to the sensor, receives the electronic signals and stores corresponding data related to the motion. Use of a high-density memory, such as an atomic resolution storage memory, permits recording sufficient data for the motion within a memory module small enough to fit within the pen body.
Owner:HTC CORP
Independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner
The invention discloses an independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner, and relates to a scanning structure of a scanning probe microscope. The independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner comprises an XYZ piezoelectric scanning tube, a guide rail rack, a sliding rod and a spring piece, wherein the XYZ piezoelectric scanning tube and the sliding rod are coaxial and mutually fixed at one end, the outer wall of the sliding rod is pressed on a guide rail of the guide rail rack in parallel by the spring piece, and both the two ends of the sliding rod stretch beyond the length of the guide rail of the guide rail rack. The independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner has the advantages of being simple in structure, stable in working height and extremely small in return difference. With the independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner, the scanning probe microscope which can perform scanning imaging at a low voltage by only using the small-size XYZ piezoelectric scanning tube is manufactured for the first time, and the problem that in the prior art, the two favorable conditions can not be taken into consideration is solved. Besides, by using the independent low-return-difference and high-rescanning probe microscope scanner, the scanning probe microscope which can display the same high quality atomic resolution images as well in the absence of sound insulation and vibration reduction can be manufactured.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
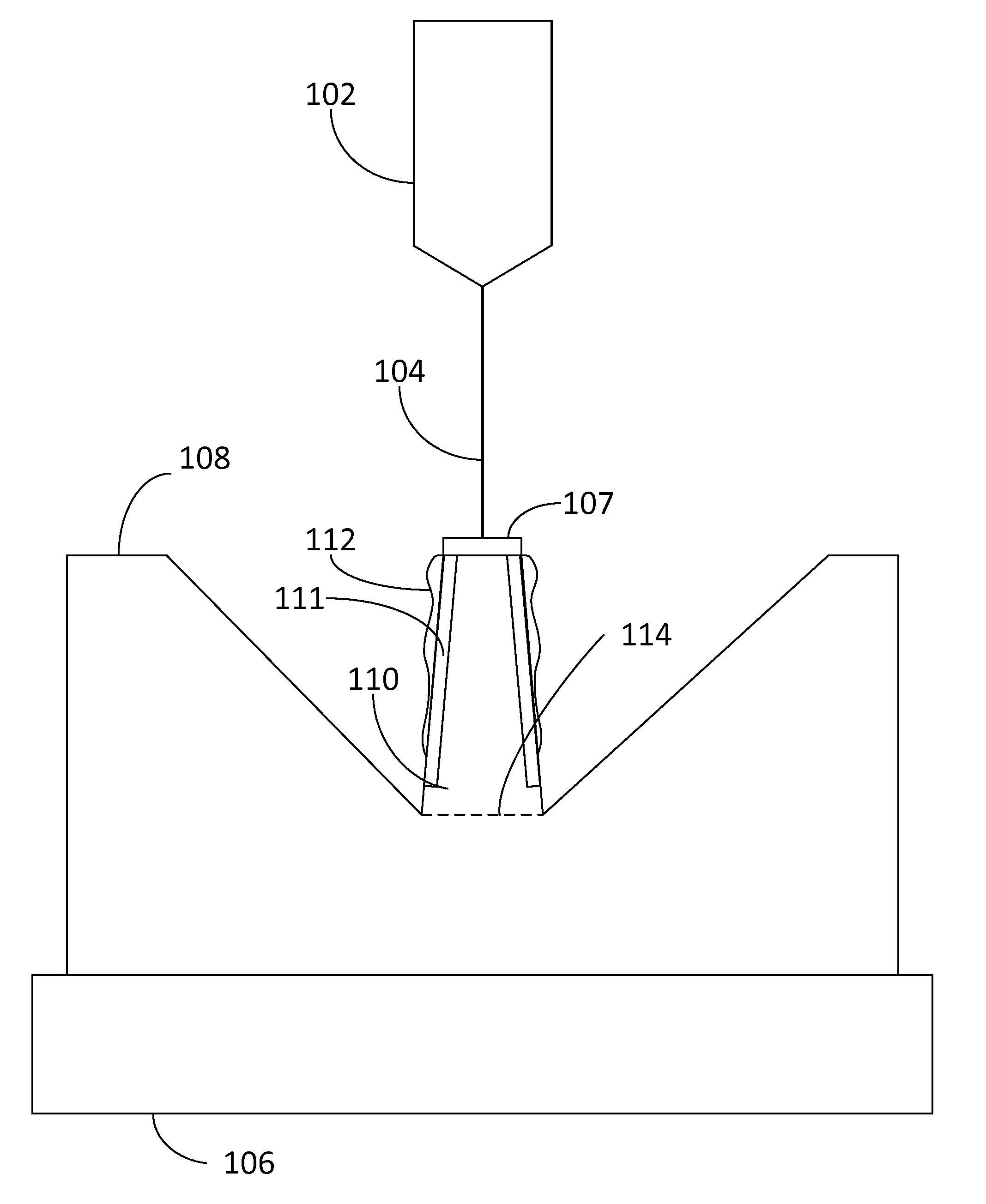
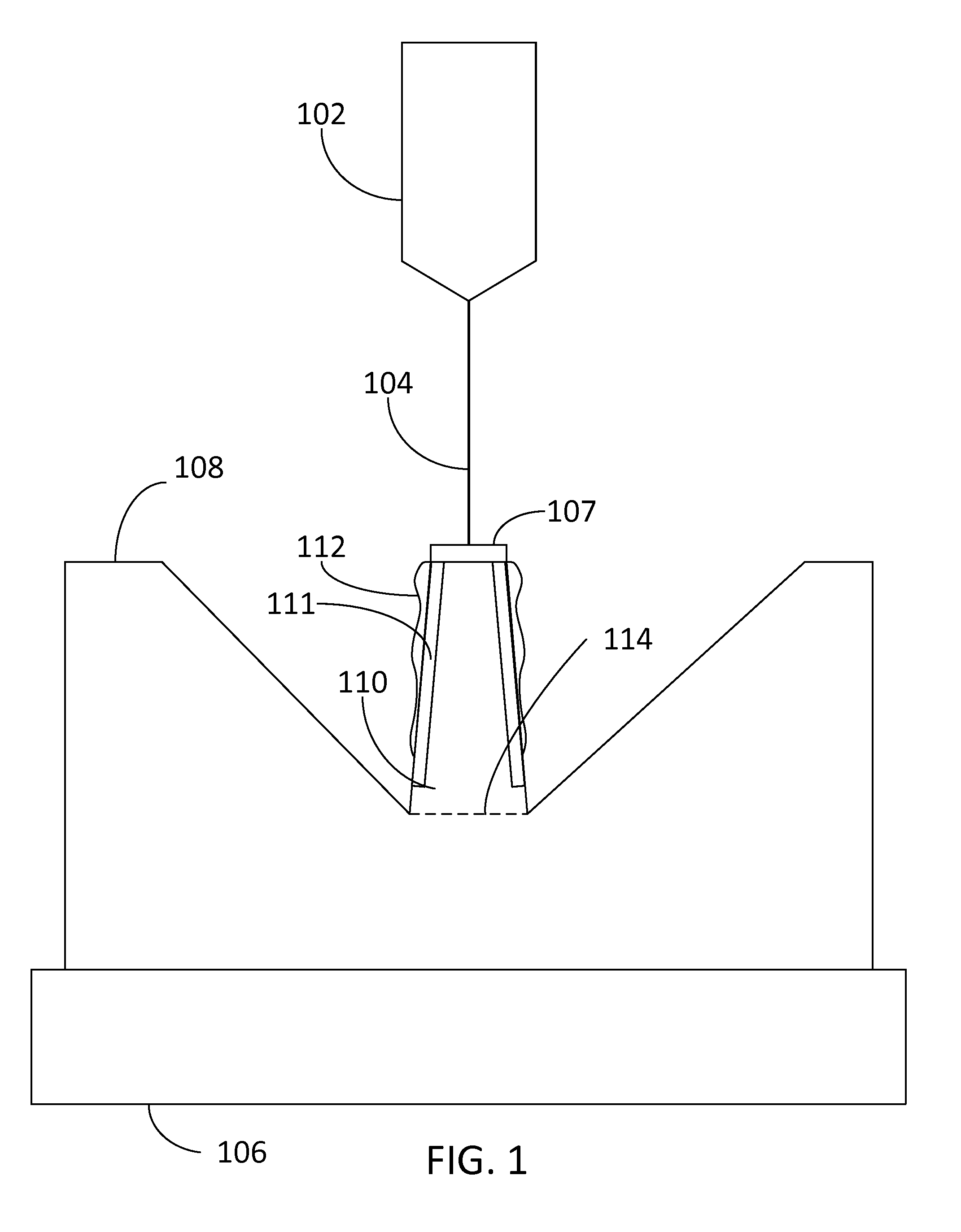
Use of standoffs to protect atomic resolution storage mover for out-of-plane motion
InactiveUS20020171326A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSnap-action arrangementsOut of plane motionImage resolution
A micro-machined actuator for use in, among other things, sensors and data storage devices. The actuator includes a stator wafer and a micro-mover positioned adjacent to the stator wafer. Between the stator wafer and the micro-mover are electrodes that are set to specified voltages and that emanate electric fields that position the micro-mover relative to the stator wafer. Also between stator wafer and the micro-mover are bumpers that prevent the electrodes from coming into contact with each other.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Double-end clamping piezoelectric motor for utilizing opposite-direction rubs to reduce friction force and control method
InactiveCN103684037ALarge thrustReduce resistancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPositive pressureTransducer
The invention discloses a double-end clamping piezoelectric motor for utilizing opposite-direction rubs to reduce friction force and a control method. The double-end clamping piezoelectric motor comprises two piezoelectric transducers, a pedestal and a slide bar, wherein the two piezoelectric transducers are arranged in parallel in the telescopic direction and fixed on the pedestal side by side; the slide bar is in sliding fit with the two piezoelectric transducers in the telescopic direction; positive pressure is applied to be perpendicular to the telescopic direction of the two piezoelectric transducers, enables the sliding bar and the free ends of the two piezoelectric transducers to be pressed with each other, and enables the sliding bar and the pedestal to be pressed with each other; the three kinds of positive pressures meet the requirements that the sum of the maximum static friction force between the free ends of the two piezoelectric transducers and the sliding bar is larger than that between the pedestal and the sliding bar, and the total dynamic friction force generated by that the free ends of the two piezoelectric transducers oppositely rub on the sliding bar to the sliding bar is smaller than the maximum static friction force between the pedestal and the sliding bar. The double-end clamping piezoelectric motor is small in size, large in thrust, strong in rigidity, easy to meet the friction force conditions, and suitable for a rough approximation motor of a high-sensitivity atom resolution scanning probe microscope and extreme conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nanomaterial in-situ photoelectric test chip of transmission electron microscope, chip fabrication method and application of chip
ActiveCN105140307AAchieve controllable lightingAdjust glow intensityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesConventional transmission electron microscopeInsulation layer
The invention discloses a nanomaterial in-situ photoelectric test chip of a transmission electron microscope, a chip fabrication method and application of the chip, belonging to the technical field of in-situ test of the performance of a nanomaterial. The chip comprises a silicon substrate, insulation layers, metal electrodes, a thin-film window and a light emitting diode, wherein the insulation layers are grown on the two surfaces of the silicon substrate; the metal electrodes are grown on the insulation layer on the front surface of the chip and can be electrically connected with a sample; and the thin-film window is arranged at the center of the chip, an electron beam transmission groove or an electron beam transmission hole is formed in a region of the thin-film window, and the light emitting diode is welded on the pair of metal electrodes in front of the thin-film window. By the chip, controllable illumination can be simultaneously carried out on the samples, an electrical effect can be applied or electrical signals of the samples are received, and thus, photoelectric in-situ measurement on the transmission electron microscope sample under the atomic resolution can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Sample holder for holding samples at pre-determined angles
The invention generally relates to atomic resolution imaging, and, more particularly, to systems and methods for calibrating an atomic resolution measurement tool. A sample holder for holding test samples used in measuring linearity of an atomic force microscope is provided. The holder includes a body having a top surface, and a plurality of inclined regions formed in the body and spaced apart along the top surface. Each of the inclined regions is structured and arranged to hold a test sample used to measure linearity of an atomic force microscope at one of a plurality of predefined angles.
Owner:IBM CORP
Strong three-friction stepper driven by two piezoelectrics side by side
InactiveCN102856305AImprove sturdinessImprove rigidityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSolid-state devicesPositive pressureImage resolution
The invention provides a strong three-friction stepper driven by two piezoelectrics side by side. The stepper comprises two piezoelectrics, a base and a slide rod, wherein the two piezoelectrics are arranged in parallel in a stretching direction and fixedly stand on the base side by side to form a double-piezoelectric structure. The stepper also comprises a bridging piece, wherein the left and right ends of the bridging piece are respectively fixed to free ends of the two piezoelectrics; the slide rod is arranged to be in sliding fit with the two piezoelectrics in the stretching direction; positive pressures for pressing the slide rod to the left and right ends of the bridging piece and a positive pressure for pressing the slide rod to the base are arranged in the direction perpendicular to the stretching direction of the two piezoelectrics; and in the maximal static frictions to the slide rod generated by the three positive pressures, any maximal static friction is smaller than the sum of the other two maximal static frictions. The strong three-friction stepper driven by the two piezoelectrics side by side is simple in structure and high in rigidity, friction condition and optimal friction condition are easy to met, and the stepper can be used as coarse approximate motor in extreme conditions and of a high-sensitivity atom resolution scanning probe microscope.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reverse x-ray photoelectron holography device and its measuring method
InactiveUS20100074406A1Improve accuracyEasy to measureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayEnergy control
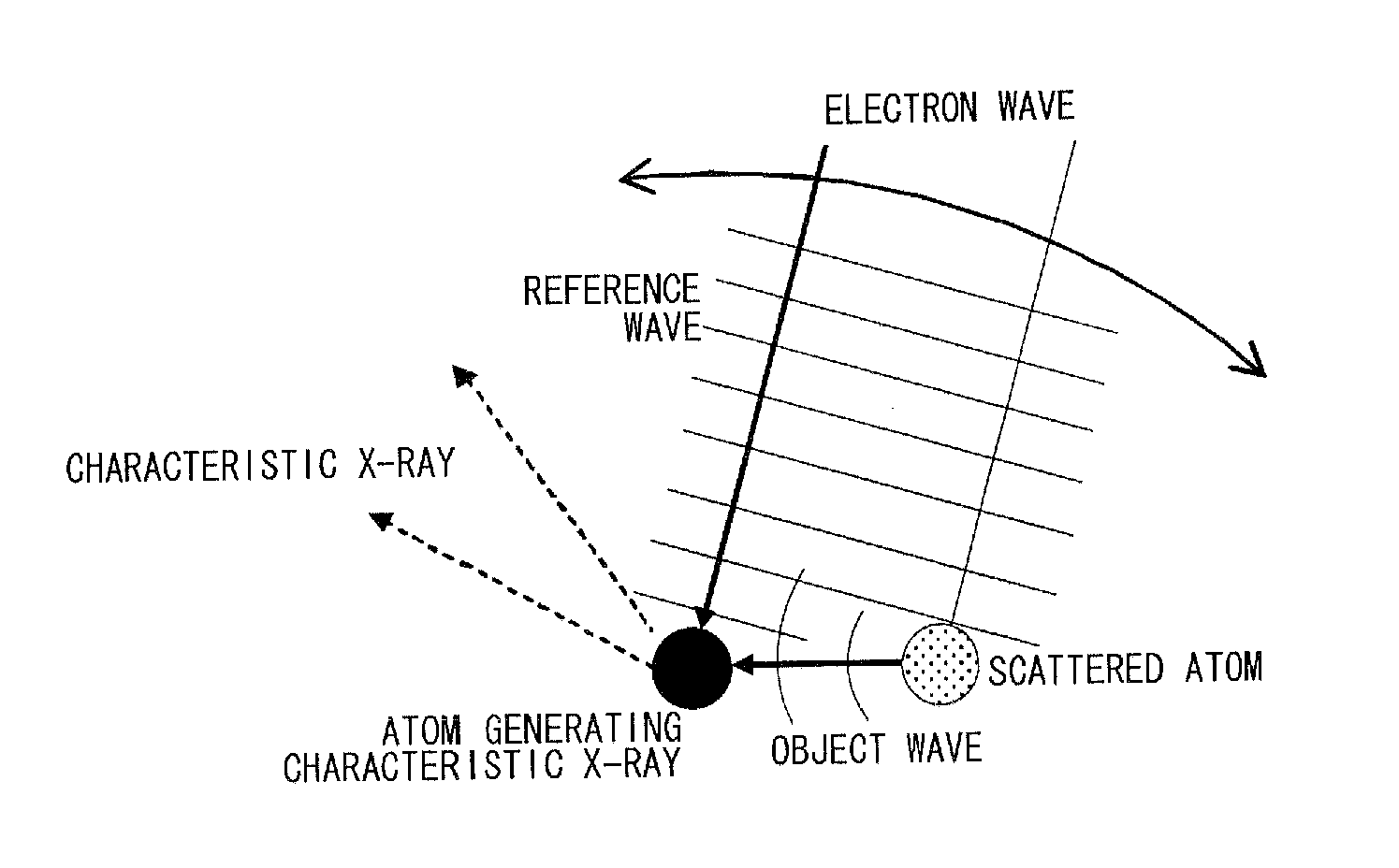
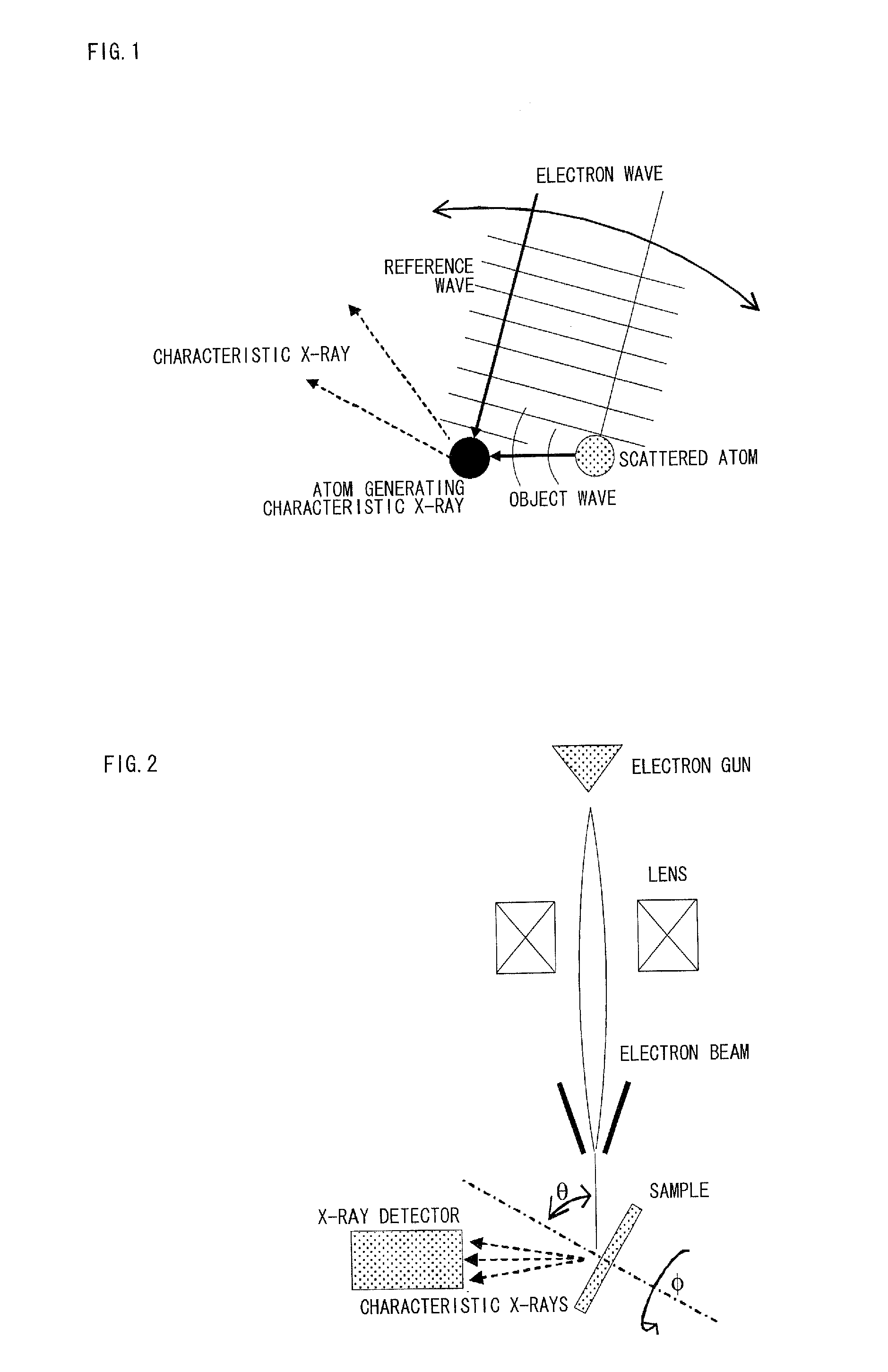
[Problems] To provide a reverse X-ray photoelectron holography device, in which energy control and convergence are facilitated and a hologram of good contrast is obtained; and to provide its measuring method.[Means for Solving Problems] A Reverse X-ray photoelectron holography measuring method where a measurement sample is irradiated with an electron beans, incident angle and rotation angle of the electron beam are varied by varying the posture of the measurement sample to the electron beam, and a variation in intensity of characteristic X-ray emitted when the measurement sample is excited is recorded as the atomic resolution hologram around the atom of a specific element, wherein, when the intensity is detected as the characteristic X-ray of the atom of the measurement sample, an object wave is generated as an electron wave scattered by the reference wave and the proximity atom in a holography where electrons incident to the measurement sample reach an atom generating specific X-ray as an electron wave, and an interference pattern is formed by compounding the reference wave with the object wave, thus monitoring the intensity of an electron beam.
Owner:JAPAN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION RES INST +1
Preparation method of large-particle powder transmission electron microscope sample
ActiveCN106645243AAvoid the problem of unclear high-resolution imagesShort sample preparation cycleMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMultiple edgesElectroscope
The invention discloses a preparation method of a large-particle powder transmission electron microscope, which belongs to the technical field of the preparation of a transmission electroscope sample. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing large-particle powder and carbon-containing conductive powder to form mixed powder, mounting the sample with a gold phase, grinding the bottom, grinding the top, fixing and washing the sample, and thinning by virtue of ion, thereby preparing the sample capable of being used for the transmission electron microscope observation. In a large-particle powder transmission electron microscope sample prepared by adopting the method, large particles with a thin area on multiple edges are difficult to find, the observation of a high-resolution image of an atomic resolution level is realized, and the unclear problem of the high-resolution image caused by the drifting or jittering of the sample can also be avoided; and the preparation method is short in sample preparation period, simple in operation, high in implementation and low in cost.
Owner:GUOBIAO BEIJING TESTING & CERTIFICATION CO LTD
Method and composition for a protein transduction technology and its applications
ActiveUS8722348B2Efficient deliveryImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedSpectroscopyFluorophore
A protein transduction method for efficiently delivery of exogenous proteins into mammalian cells is invented, which has the capability of targeting different cellular compartments and protection from degradation of the delivered proteins from cellular proteases. A composition for treat proteins has cation reagents, lipids and enhancers in a carrier. The method can be used in a number of ways including: production of large quantities of properly folded, post-translationally modified proteins using mammalian cell machinery, a in-cell fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging using small molecule fluorophores and a in-cell NMR spectroscopy using living mammalian cells. The method permits cell biology at atomic resolution that is physiologically and pathological relevant and permits protein therapy to treat human diseases. The method can also be used to deliver exogenous protein inside mammalian cells, wherein the exogenous proteins follow a similar secretion pathway as that of the endogenous protein.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Super respiratory chain compound protein
The invention relates to a mammalian cell super respiratory chain compound protein and in particular to a super respiratory chain compound protein of a high atom resolution electron cryomicroscopy structure, and a preparation method of the protein. By adopting the protein structure, the respiratory action mechanism of mammalian animals and diseases related to respiratory action can be further studied.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Contact probe storage sensor pod
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Crystal structure of the carboxyl transferase domain of human acetyl-coa carboxylase 2 protein (acc2 ct) and uses thereof
A crystallized human ACC2 CT protein as well as a description of the X-ray diffraction pattern of the crystal are disclosed. The diffraction pattern allows the three dimensional structure of human ACC2 CT to be determined at atomic resolution so that ligand binding sites on human ACC2 CT can be identified and the interactions of ligands with human ACC2 CT amino acid residues can be modeled. Models prepared using such maps permit the design of ligands which can function as active agents which include, but are not limited to, those that function as inhibitors of human ACC2 and human ACC1 proteins.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Crystal structure of the c-fms kinase domain: applications and use of heterologous substitutions of kinase insert domains for crystallization
InactiveUS20060094081A1Increased formationGrowth inhibitionFrom normal temperature solutionsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBinding siteImage resolution
The present invention includes a crystal structure of the kinase domain of c-fms and a methodology to produce diffraction quality crystals of the c-fms kinase domain by heterologous substitution of the kinase insert domain. Also included in the invention is the structure of the c-fms kinase domain in liganded form for use in the discovery of inhibitors of c-fms for the treatment of diseases caused by inappropriate activity of c-fms. The present invention includes descriptions of the X-ray diffraction patterns of the crystals. The diffraction patterns allow the three dimensional structure of c-fms to be determined at atomic resolution so that ligand binding sites on can be identified and the interactions of ligands with amino acid residues can be modeled.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Atomic resolution storage systems with enhanced magnetic field protection
Memory storage devices that employ atomic resolution storage technology are provided. A preferred memory storage device includes a storage medium that defines one or more coverage areas. Each of the coverage areas incorporates a storage area that is configurable in one of a plurality of structural states. Typically, the structural states represent information stored in the storage area. Electron beam emitters electrically communicate with the storage medium, with the storage medium and the emitters being configured to move relative to each other. So configured, each emitter is capable of providing a beam of electrons to a respective one of the coverage areas. The memory storage device also includes a first current source that selectively electrically communicates with at least one of the emitters. Additionally, a shield is provided that is configured to reduce an influence of a magnetic field so that a tendency of an electron emitted from one of the emitters to be displaced from an intended trajectory is reduced. Methods also are provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
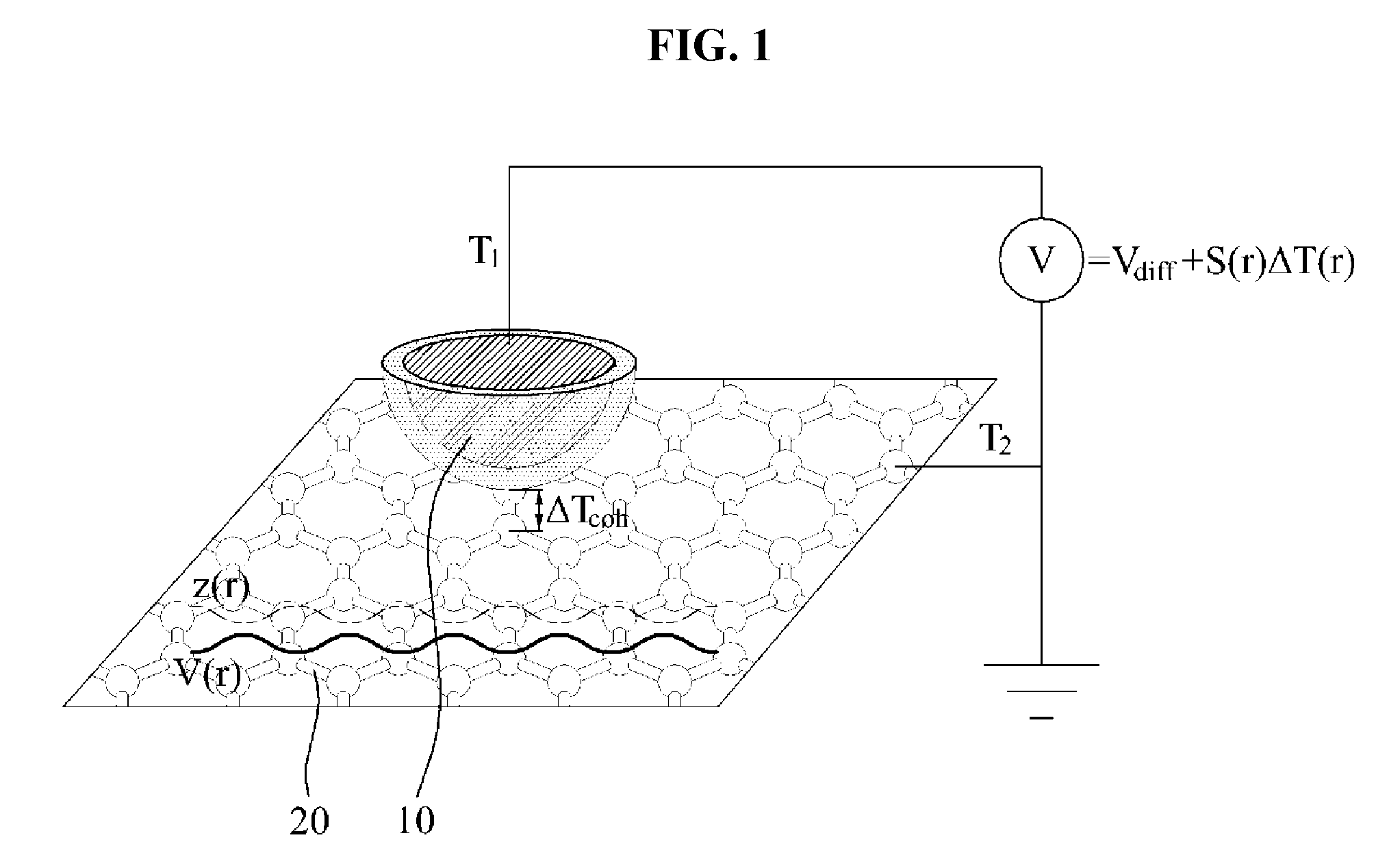
Computer-Aided Simulation Method For Atomic-Resolution Scanning Seebeck Microscope (SSM) Images
A computer-aided simulation method for an atomic-resolution scanning Seebeck microscope (SSM) image is provided. In the computer-aided simulation method, a computer may calculate a local thermoelectric voltage for a position of a voltage probe, to acquire an SSM image corresponding to the position, using the following equation:V(r)=Vdiff+Scoh(r)∫∇T(r;r′)·r′-rr′-r33r′in which V(r) denotes the local thermoelectric voltage, Vdiff denotes a thermoelectric voltage drop in a diffusive transport region in a tip and a sample, Scoh(r) denotes a position-dependent Seebeck coefficient, r denotes a distance measured from a point voltage probe, r′ denotes material internal coordinates, ∇T(r;r′) denotes a temperature gradient radially weighted by a factor of 1 / r2, and∫∇T(r;r′)·r′-rr′-r33r′denotes a volume integral of a temperature profile.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
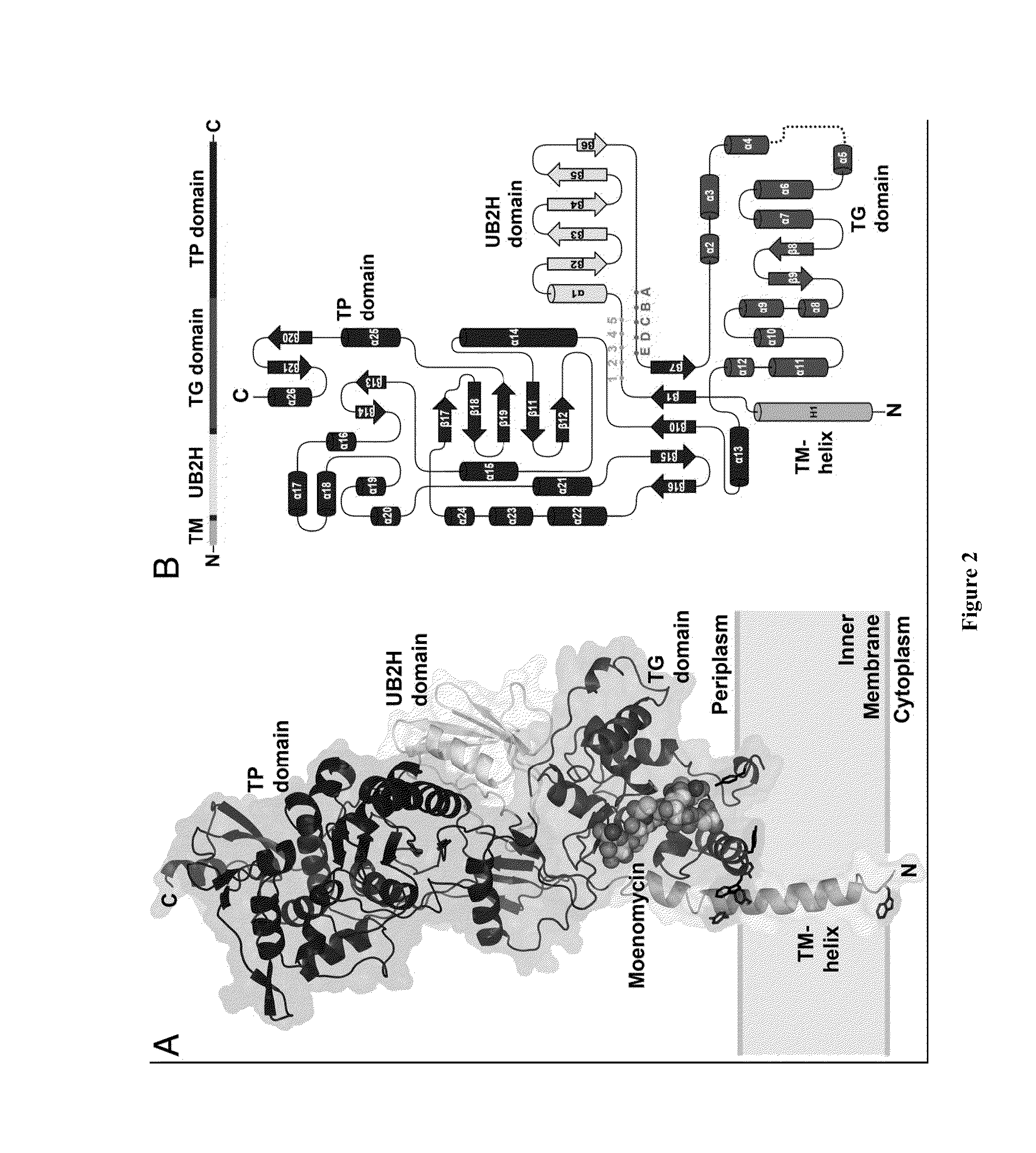
Crystal structure of bifunctional transglycosylase pbp1b from e. coli and inhibitors thereof
InactiveUS20100121107A1Growth inhibitionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEscherichia coliMoenomycins
The crystal structure at 2.16 Å resolution of the full-length bacterial bifunctional transglycosylase penicillin-binding protein 1b (PBP1b) from Escherichia coli, in complex with its inhibitor moenomycin, is provided. The atomic coordinates of the complex as well as the moenomycin binding site are provided. Three dimensional structures of amino acid residues involved in moenomycin binding and transglycosylation activity are identified. Binding site for peptidoglycan synthesis inhibitors comprising inhibitor-binding site comprises amino acid residues from at least one of transglycosylase (TG), UvrB domain 2 homolog (UB2H) and transmembrane (TM) domains of PBP1b are identified at an atomic level of resolution. Methods for rational drug design based on the atomic coordinates are provided. Methods for screening for antibiotics based on anisotropic binding assay and transglycosylase inhibitor assays are provided. Novel antibiotics based on the screening assays of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
Sphere stereoscopic recording method for X-ray hologram possessing atom resolution
InactiveCN1603787AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSurface/boundary effectHard X-raysImage resolution
It is X-ray holograph sphere solid record method with atom resolution, which comprises the following steps: to stick a hard X-ray soft pad to a hollow inner side of a semi-sphere in a dark house; to put the sample of the atom image sample to the right center of the semi-sphere with hard X-ray negative; to put a hard X-ray band filter between X-ray negative and sample; to switch synchronization radiation source and let the X-ray shoot the sample and to expose the negative; to develop and fix and wash and dry the exposed negative ; to stretch the exposed negative and to scan with black meter to get digital image data and to enter computer for digital recreation to get atom image with atom resolution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-bandwidth STM (scanning tunneling microscope) preamplifier adopting tunnel junction and resistor parallel connection method
PendingCN106849887AEliminate self-excited oscillationsHigh bandwidthAmplifiers controlled by lightScanning probe microscopyElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh bandwidth
The invention discloses a high-bandwidth STM (scanning tunneling microscope) preamplifier adopting a tunnel junction and resistor parallel connection method and belongs to the technical field of the high-bandwidth STM preamplifier circuit. According to the technical scheme, the high-bandwidth STM preamplifier adopting the tunnel junction and resistor parallel connection method comprises an STM preamplifier circuit, and resistors are connected in parallel at two ends of a tunnel junction formed by a conductive sample and a conductive probe. The resistance of the resistors is adjusted until the amplifier circuit can correctly amplify an input signal, self-excitation oscillation of the preamplifier can be eliminated on the premise that the tunnel junction information is unchanged, the bandwidth of the preamplifier is larger, and better atom resolution images can be acquired.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Computer-aided simulation method for atomic-resolution scanning seebeck microscope (SSM) images
A computer-aided simulation method for an atomic-resolution scanning Seebeck microscope (SSM) image is provided. In the computer-aided simulation method, a computer may calculate a local thermoelectric voltage for a position of a voltage probe, to acquire an SSM image corresponding to the position.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
System modules with atomic resolution storage memory
A preferred microprocessor module includes a first wafer incorporating a storage medium. The storage medium is provided with storage areas that are configurable in one of a plurality of structural states to represent information stored in the storage areas. A second wafer is arranged proximate the first wafer and includes electron beam emitters that are configured to electrically communicate with the storage medium. The storage medium and the emitters are configured to move relative to each other so that each emitter may provide a beam of electrons to at least one of the storage areas. Additionally, a third wafer is provided which includes logic circuitry configured to enable extraction of data from the storage areas of the storage medium and execution of instructions embodied within the data. Processor-based systems also are provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com