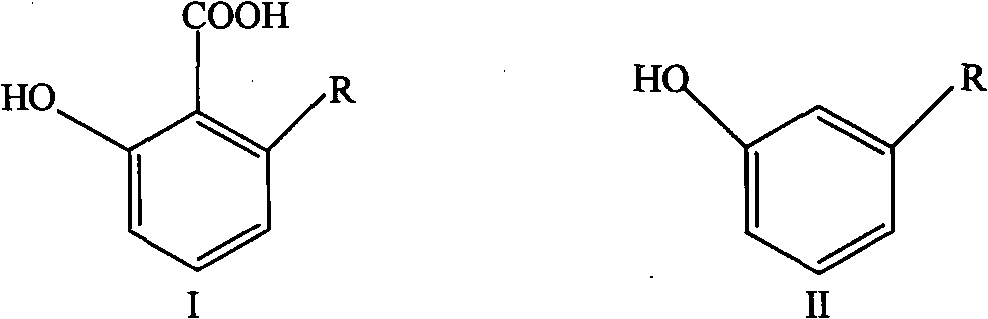Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Respiratory chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of respiratory chain. : the metabolic pathway along which electron transport occurs in cellular respiration also : the series of respiratory enzymes involved in this pathway.
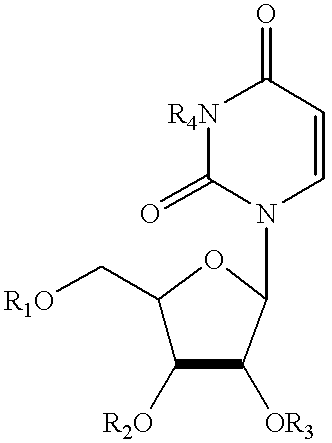
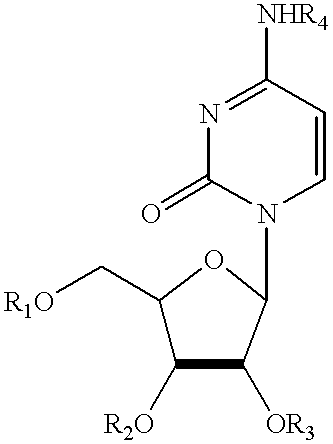
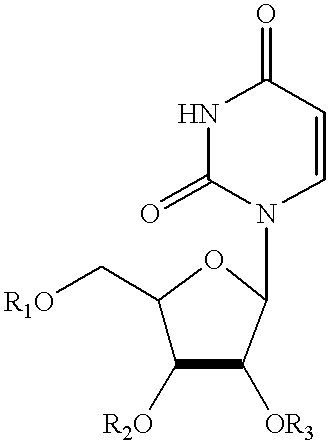
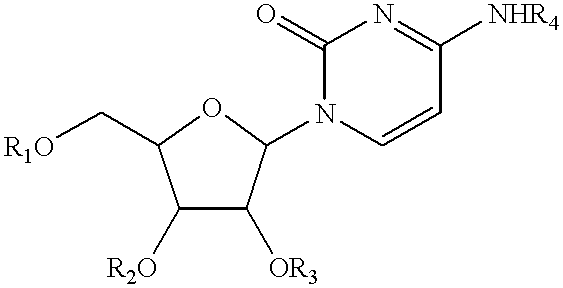
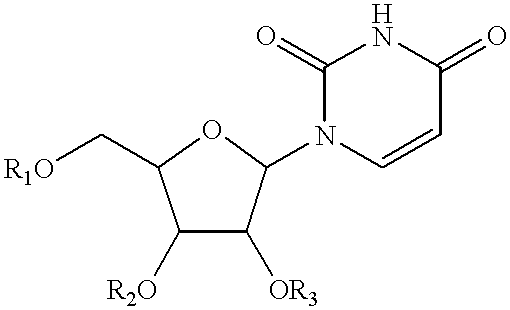
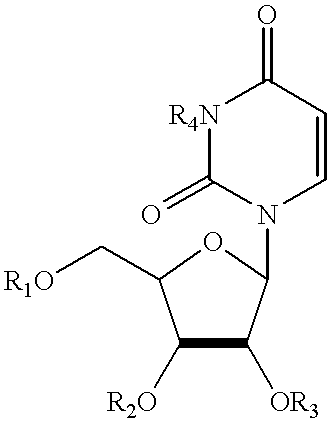
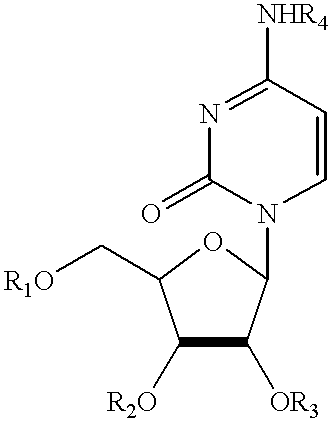
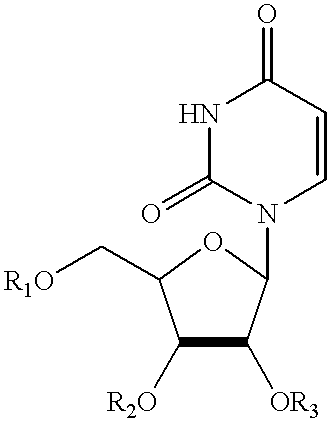
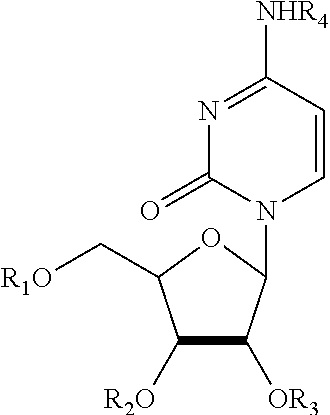
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20010005719A1Increase resistanceAvoid Cutting InjuriesBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMitochondrial disease
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Treatment of mitochondrial diseases with an erythropoietin mimetic
InactiveUS20090291092A1Stimulating erythropoiesisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRed blood cell
Methods of treating mitochondrial disorders that are not respiratory chain disorders using compositions comprising EPO mimetic compounds or compounds capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are disclosed. Methods of treating Friedreich's ataxia, Leigh's syndrome, or other disorders by increasing the expression of frataxin with an EPO mimetic compound or a compound capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are also disclosed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
Treatment of respiratory chain disorders using compounds having erythropoietin or thrombopoietin activity
Methods of treating mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders using compounds having erythropoietin activity or thrombopoietin activity are disclosed. Indicators for assessing the efficacy of treatment are discussed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
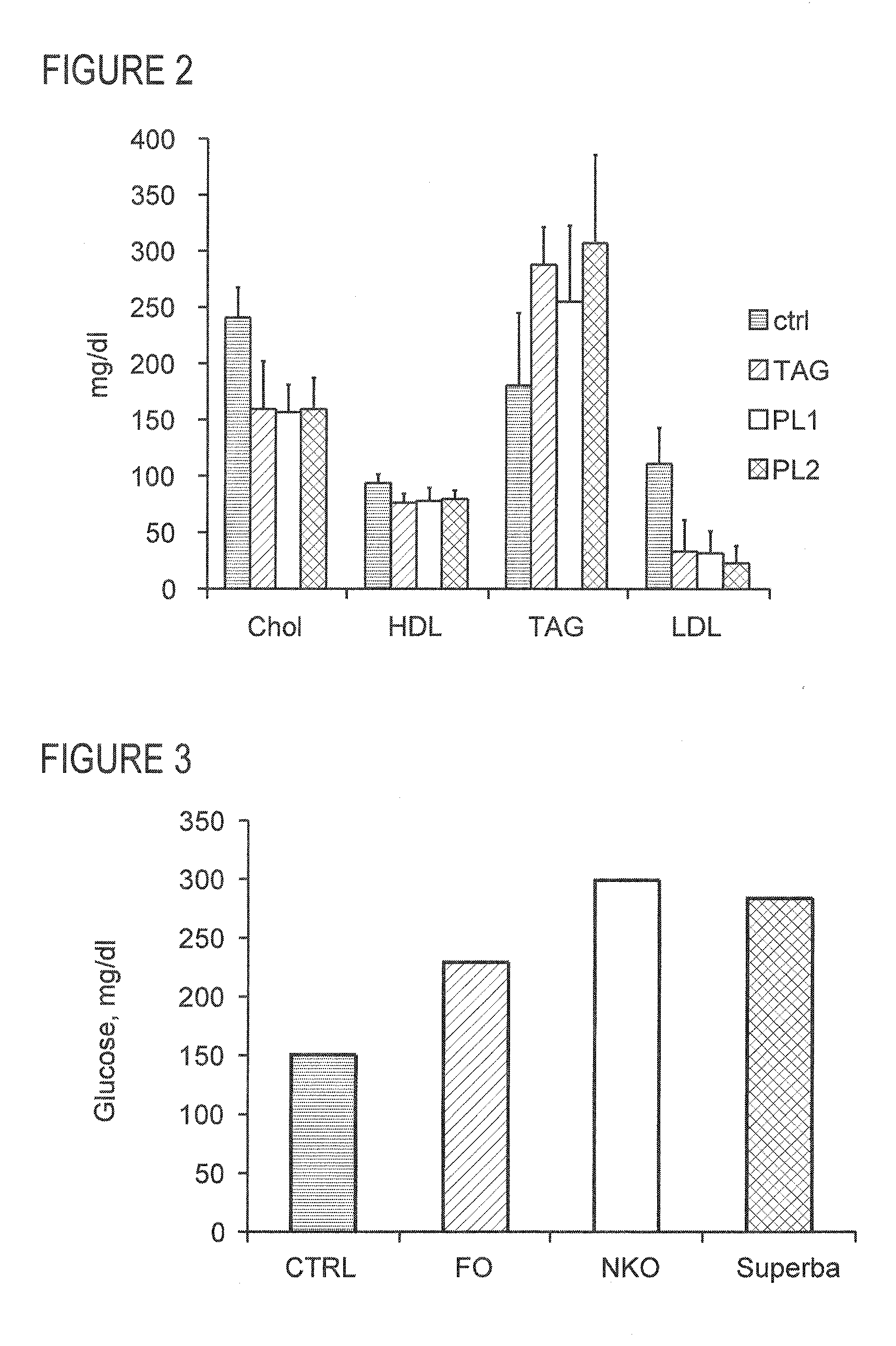
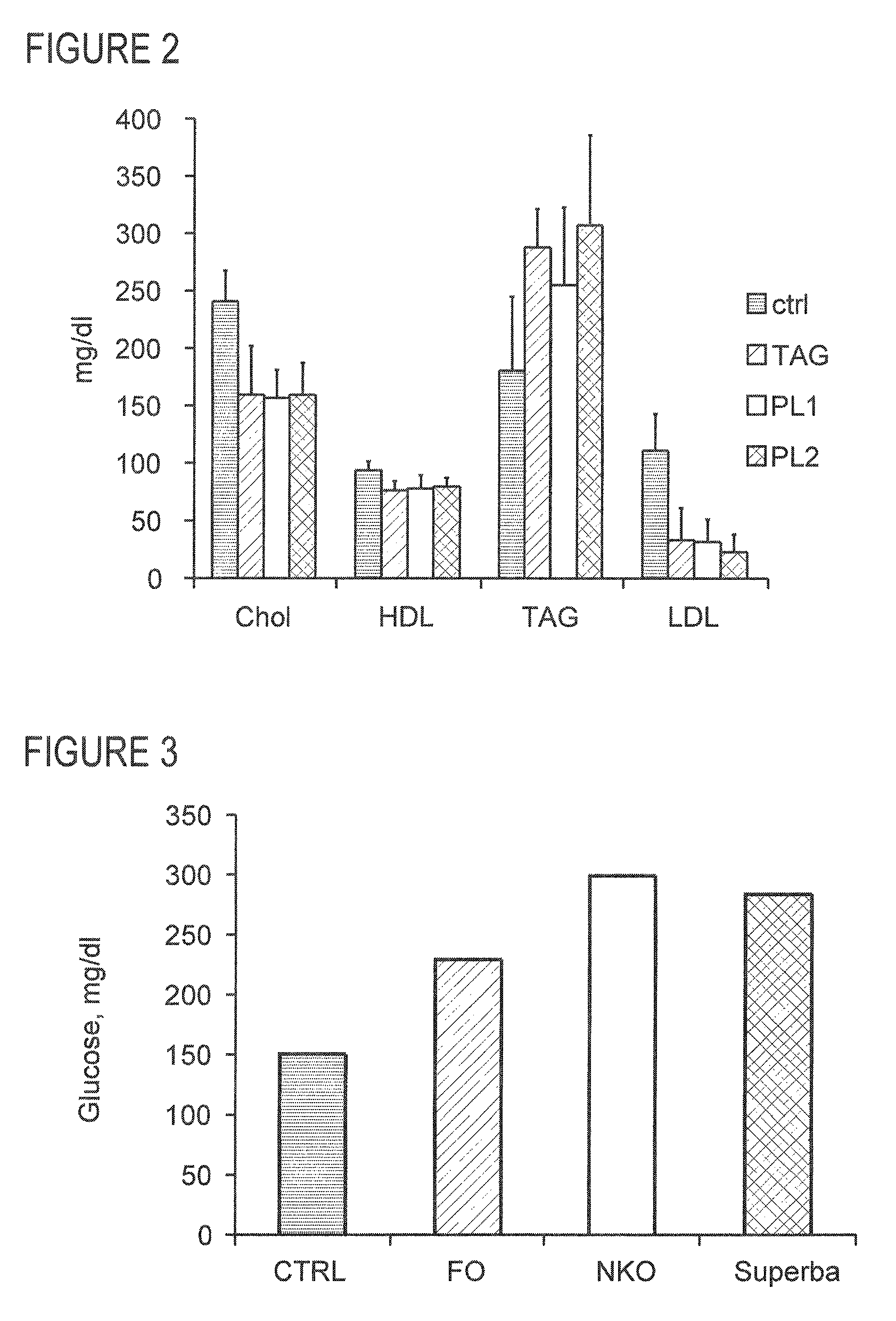
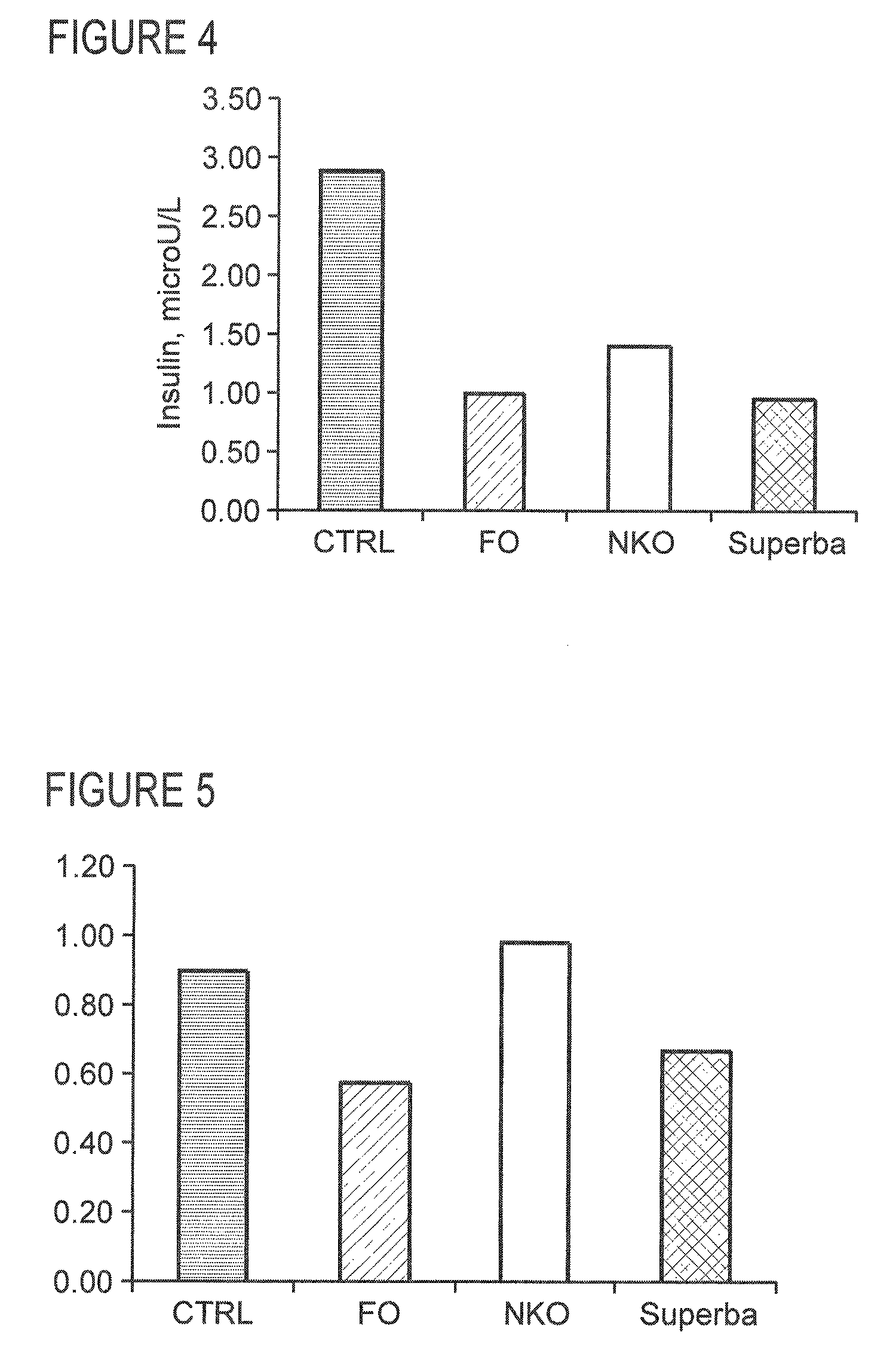
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
ActiveUS20110104297A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCvd riskOrganism
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20020049182A1Promote recoverySlow cell deathBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePyrimidine Nucleotides
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
ActiveUS8697138B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsCvd riskCholesterol biosynthesis
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
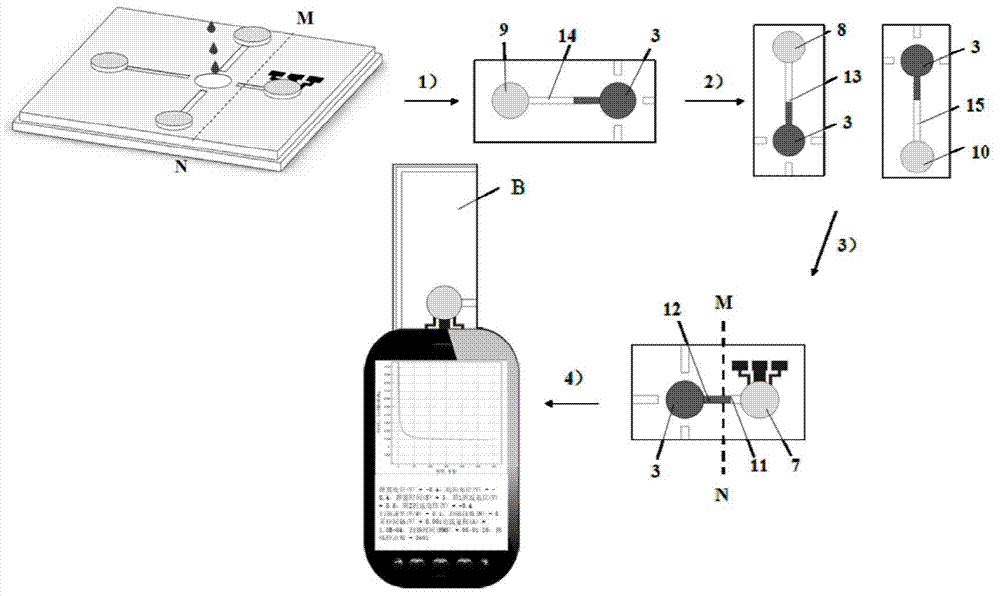
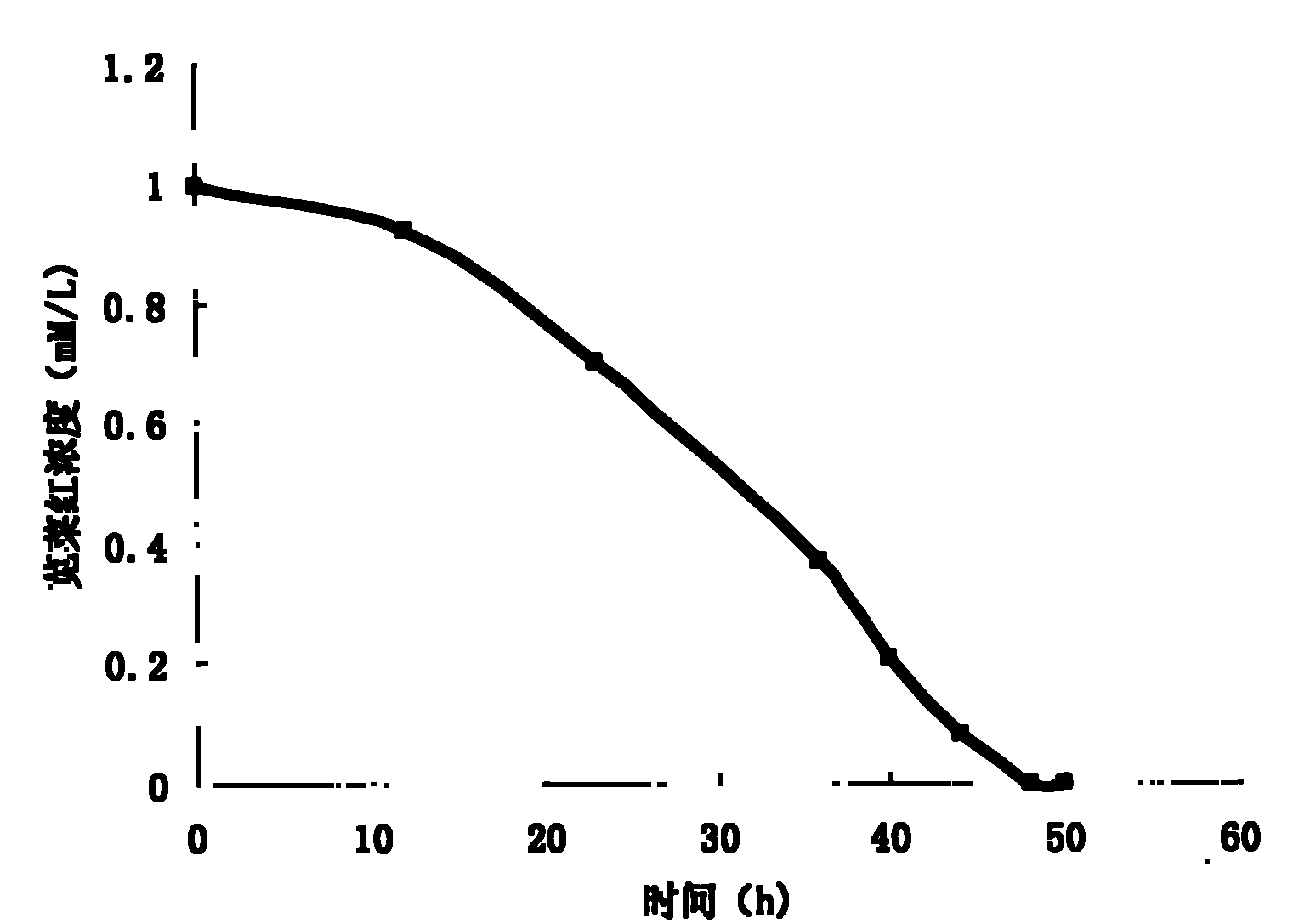
Method for detecting water pollutant biotoxicity by paper-based micro-fluidic chip anode current
InactiveCN104267073AImprove preprocessing stepSimplify preprocessing stepsMaterial electrochemical variablesCelluloseSmall sample
The invention discloses a method for detecting water pollutant biotoxicity by paper-based micro-fluidic chip anode current. The method is characterized in that a paper-based micro-fluidic chip is prepared and then water pollutant biotoxicity is determined by the paper-based micro-fluidic chip. According to a microbial respiratory chain-based BQ system electrochemical detection principle, on the paper-based micro-fluidic chip of a screen printing PDMS hydrophilic microchannel and carbon paste three-electrode system, a steam trap of the hydrophilic microchannel is dredged by a small piece of a cellulose membrane so that liquid flow release time and flowing time are controlled and separation and cleaning of a nutrient solution and cells and cell incubation by pollutants are realized and thus the interference produced by current signal detection device anode current-based quantitative determination of pollutant toxicity is reduced. The method has the advantages of light quality, carrying convenience, low cost, one-step analysis, small sample volume and fast analysis speed and is suitable for biotoxicity detection in occasions of a remote area, field on-site water pollution, soil pollution, food safety and space carrying.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Microbial fuel cell and application thereof to degradation of azo dye pollutant
ActiveCN102315469AOvercome energy consumption,Overcome the disadvantages caused by practical difficultiesCell electrodesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesCulture fluidElectron donor
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell and application thereof to degradation of azo dye pollutants. The microbial fuel cell comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, an anode electrode, a cathode electrode, a proton permeable membrane and an external circuit. Electrochemical active microbes are inoculated in the anode chamber. Culture solution for the microbes, a carbon source and electron donors are also contained in the anode chamber. Cathode reaction liquid is contained in the cathode chamber and consists of Shewanella decolorationis and culture solution thereof. Electron acceptors of the Shewanella decolorationis are also contained in the cathode chamber. The microbial fuel cell oxidizes an organic substrate in the solution through the microbes in the anode chamber, generated electrons are transferred to the anode electrode and the electrons on the anode electrode are transferred to the cathode electrode through the external circuit. In the cathode chamber, the Shewanella decolorationis accepts the electrons on the cathode electrode, grows and metabolizes. The electrons are transferred to end electron acceptors such as the azo dye pollutants through a respiratory chain to reduce and degrade the azo dye pollutants. Therefore, the microbial fuel cell can be used for the treatment of the pollutants.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
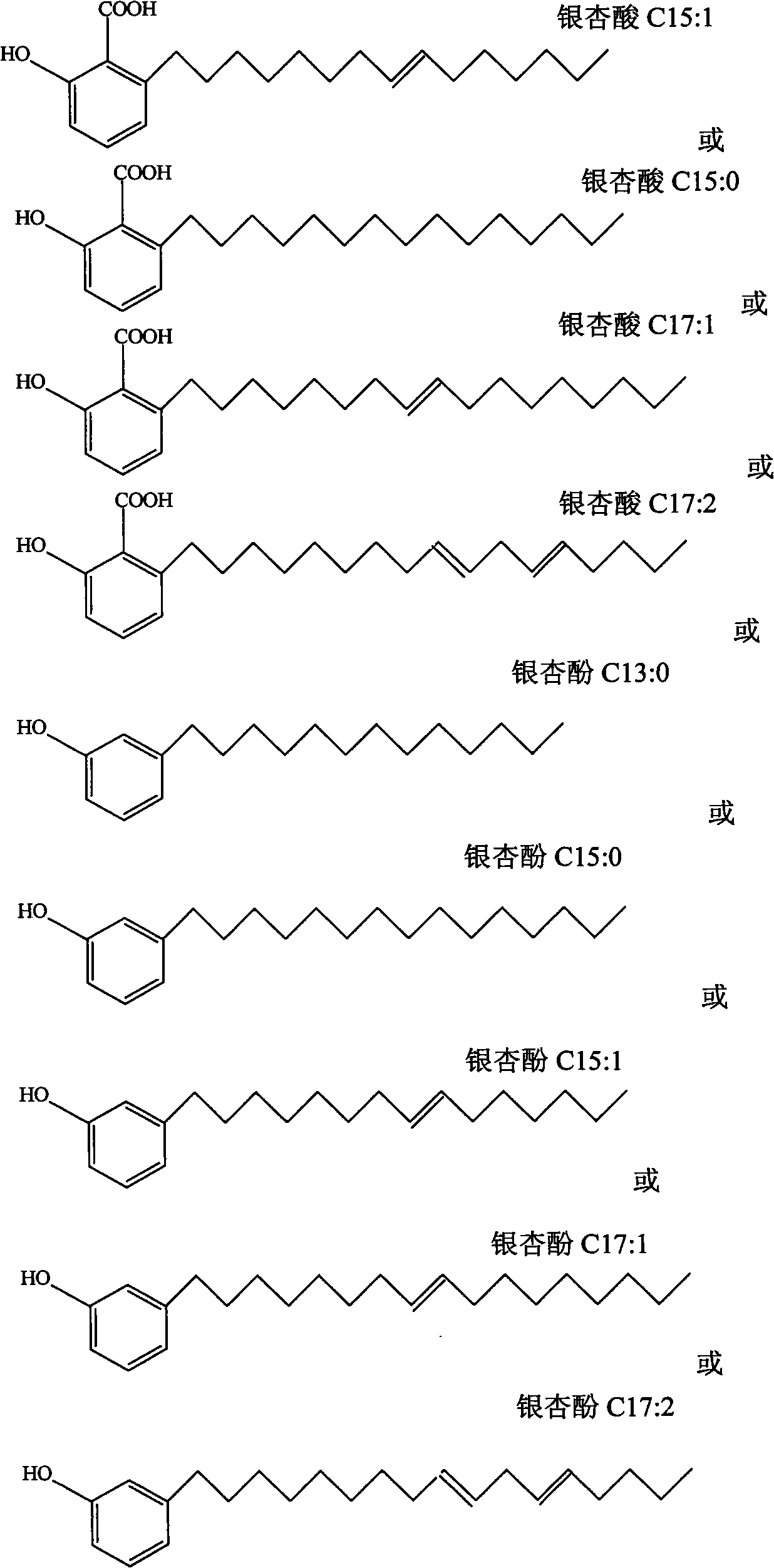
Application of ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds to killing Ampullaria gigas
InactiveCN101911938AEfficient killingPlay a role in preventing its harmBiocideMolluscicidesAcute toxicity testingRespiratory chain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biopesticides, discloses application of ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds to killing agriculturally harmful mollusks, and discloses novel application of the ginkgoic acid and ginkgol to preparation of the biopesticides. The invention shows that the ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds can effectively inhibit the synthesis of glycogen and protein inmollusk ampullaria gigas, can simultaneously inhibit the activities of ChE, SDH and MDH in the cephalopodium and the liver of the ampullaria gigas, interfere a NADH respiratory chain and cause energymetabolic dysfunction so as to cause cell energy supply deficiency and unattainability of normal synthesis and secretion functions, and promote the lack of important proteins and enzymes in the body of the ampullaria gigas so as to cause the death of the ampullaria gigas. The ginkgoic acid and the ginkgol are readily degradable in the natural environment, and have small influence on the environment; and an acute toxicity test proves that the ginkgoic acid and the ginkgol are proved to be slightly toxic pesticides, can be developed into novel biopesticides, and can be used for preventing the ampullaria gigas for rice, vegetables and fruits.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Paper base micro-fluidic chip for selecting soil active bacterium and components and application of paper base micro-fluidic chip
InactiveCN104931551ALow costIncrease screening throughputMaterial electrochemical variablesSecondary metaboliteEngineering
The invention discloses a paper base micro-fluidic chip for selecting soil active bacterium and components and application of the paper base micro-fluidic chip. A plurality of micro-fluidic units, and units, such as carbon paste three-electrode arrays for bacterial respiration electrochemical measurement are printed on paper to form two types of array dual paper base micro-chamber co-culture and activity screening function units, on chromatographic paper, a carbon paste electrode, a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) passage, a PDMS micro-culture room and the like are sequentially overprinted through silk-screen printing, and furthermore, a model bacterial array unit is printed in an aseptic condition; a dual micro-chamber co-culture array unit of a sample bacterium-model bacterium and a secondary metabolite of a sample bacterium are used to inhibit adjacent model bacterium respiratory chains, and a carbon paste three-electrode printed together with a dual micro-chamber is used to find the position of some active sample bacterial colony; the secondary metabolite of the active sample bacterium is separated through paper base two-dimensional electrophoresis, and an array carbon paste three-electrode is used to find the positions of active components obtained through two-dimensional electrophoresis. The paper base micro-fluidic chip for selecting soil active bacterium is suitable for selecting the active bacterium and active complex components in multiple fields.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for producing lycopene through fermentation
ActiveCN103525871APromotes the respiratory chain systemIncreased oxygen consumption rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationSide effectBetaine
The invention provides a method for producing lycopene through fermentation. According to the invention, blakeslea trispora (+) and blakeslea trispora (-) strains are adopted, and slant culture is carried out. Culturing is carried out for 6-7 days under a temperature of 26-28 EG C in an incubator; after 36-46h of seed culturing, fermentation culture is carried out; betaine is added for a first time, and fermentation culture is carried out for 100-120h under a temperature of 26-28 DEG C and under a rotation speed of 200-250r / min; a blocking agent is added when fermentation is carried out for 42h, and betaine is added for a second time; and fermentation is continued until finished. A fermentation broth is filtered, and wet thalli are collected. Through vacuum lyophilization, dried thalli comprising lycopene are obtained. According to the invention, with the added betaine, thalli respiratory chain system can be effectively promoted, and thalli oxygen consumption rate can be improved. Also, osmotic pressure respiratory depression upon the thalli during the fermentation process can be effectively relieved, oxygen delivery rate can be accelerated, and energy consumption can be reduced. thalli growth rate and lycopene content are improved, and production cost is reduced. According to the method, the operation is simple. Betaine has no toxic or side effect, and is convenient and safe to use. The method is suitable for industrialized productions, and has high application values.
Owner:山东祥维斯生物科技股份有限公司
Method for increasing yield of itaconic acid produced by fermentation of aspergillus terreus
ActiveCN105274153AIncrease productionEnhanced Glycolytic PathwayFungiMicroorganism based processesItaconic acidFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and discloses a method for increasing yield of itaconic acid produced by fermentation of aspergillus terreus. By adoption of acid-induced promoters derived from aspergillus niger, lateral respiratory chain protein AOX of the aspergillus niger is introduced into the aspergillus terreus to improve supply of an intracellular NAD+ bank, and accordingly glycolytic pathway can be enhanced to realize increase of itaconic acid yield. The itaconic acid yield of recombinant aspergillus terreus strains obtained by the method is increased by about 20% to reach 60g / L. The method provides a fresh idea for itaconic acid production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20140363517A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCvd riskMitophagy
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondria respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Method for rapid and efficient screening of vitamin K2 (MK-7) high-yielding strain
InactiveCN106916810AGood genetic stabilityHigh positive mutation rateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesVitamin K2Biotechnology
The invention discloses a method for rapid and efficient screening of a vitamin K2 (MK-7) high-yielding strain. An original strain undergoes atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis, and plate breeding of the mutagenesis strain is carried out by the use of a vitamin K2 analogue and a respiratory chain inhibitor. After fermentation and re-screening through a 96-well culture plate, content of the high-yielding strain vitamin K2 is raised by 200%. By the above method, a batch of Bacillus natto having advantages of fast growth speed, high yield of vitamin K2, genetic stability and strong tolerance to the environment is bred.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20010016576A1Minimize consequencesInhibiting consequenceBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMitochondrial disease
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
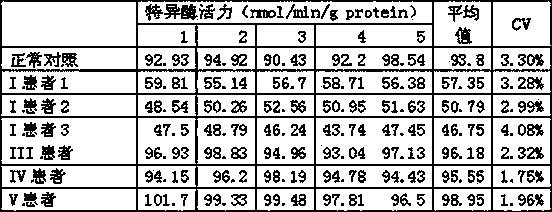
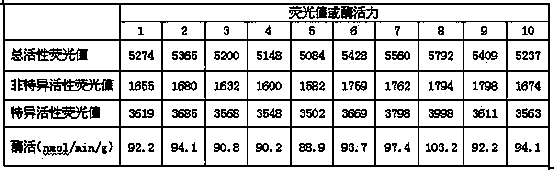
Enzyme activity detection method for mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I and reagents
The invention provides an enzyme activity analysis and detection method for mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I (NADH-Q reductase, EC1.6.5.3). The invention also provides reagents for detecting the enzyme activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I. The above method and the reagents can be used for analyzing and detecting the enzyme activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I in samples to be detected, and therefore the method and the reagents can be used for analysis, examination and diagnosis of clinic diseases. Based on the method, the reagents have advantages of convenience, rapidness and high sensitivity, and are convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:北京中科非凡生物技术有限公司
Sepsis diagnosis method and reagent
InactiveCN104777109AReduced activityReduced activity levelColor/spectral properties measurementsWhite blood cellDiagnosis methods
The invention provides a method for sepsis diagnosis, severity degree monitoring, and prognosis evaluation. The enzymatic activity level of mitochondrial respiratory chain supramolecular complex: NADH-cytosome coxidoreductase, NCR in the peripheral blood leucocyte namely mitochondrial NCR enzymatic activity level is closely related with the organ dysfunction and prognosis of sepsis. The invention also provides a detection method and detection reagent for detecting the peripheral blood leucocyte mitochondrial respiratory chain supramolecular complex NCR enzymatic activity. The provided method can rapidly, specifically, and sensitively measure the mitochondrial NCR enzymatic activity of a sample, and has an important meaning on the sepsis diagnosis, severity degree monitoring, and prognosis evaluation.
Owner:AFFILIATED CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL INST OF PEDIATRICS +1
Alternative oxidase and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080103088A1Anti agingExtend your lifeNervous disorderVirusesWhole OrganismPhosphorylation
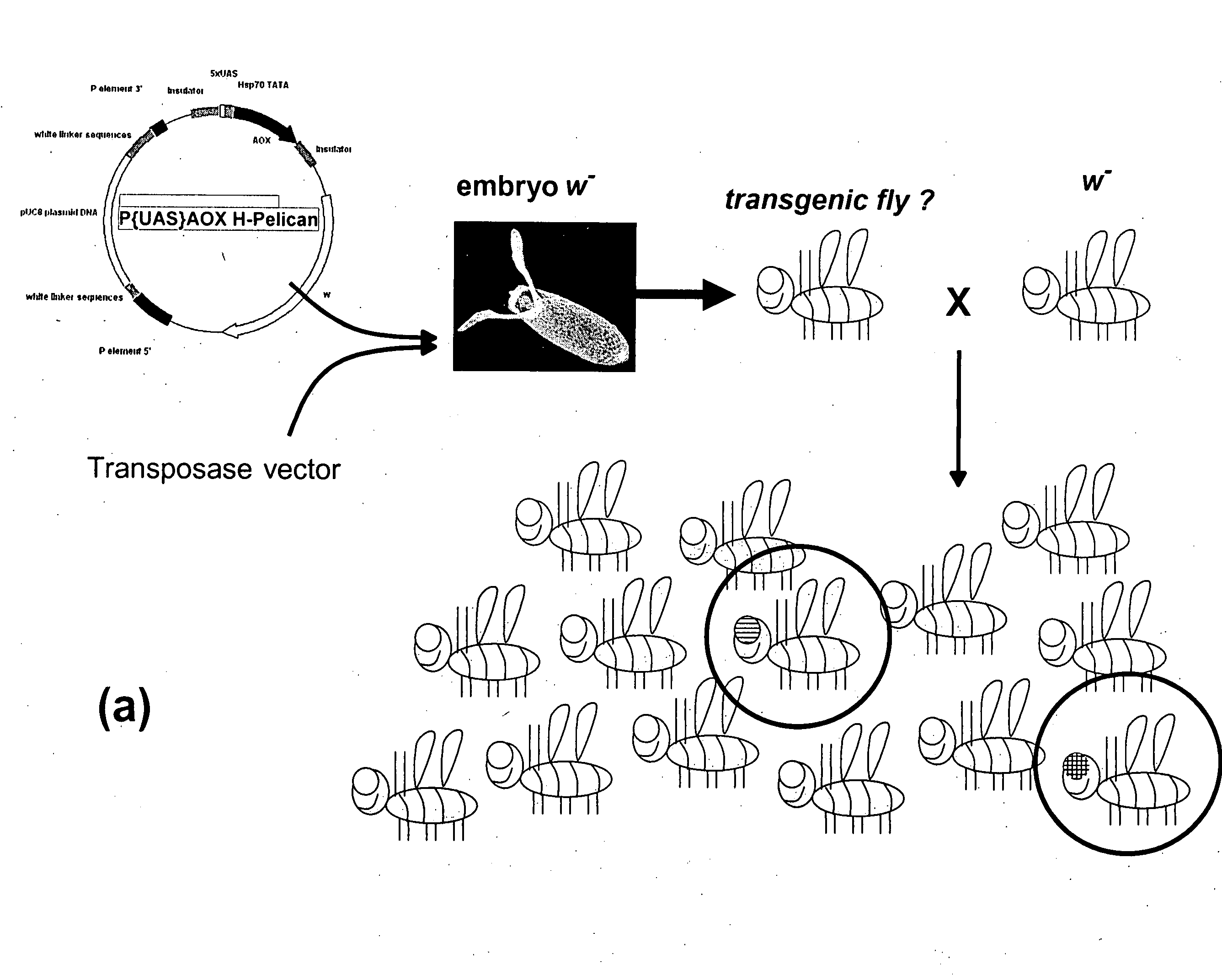
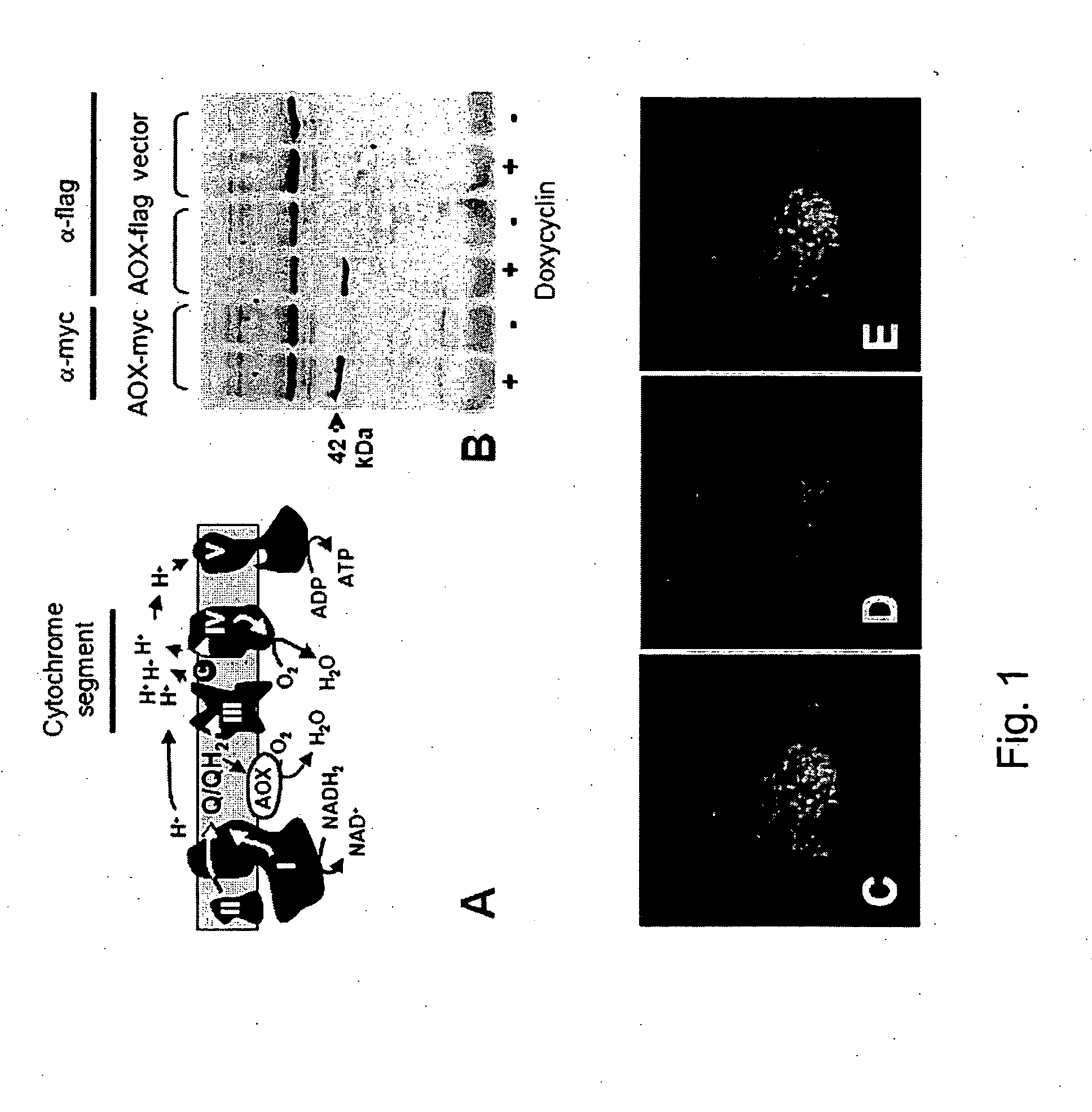
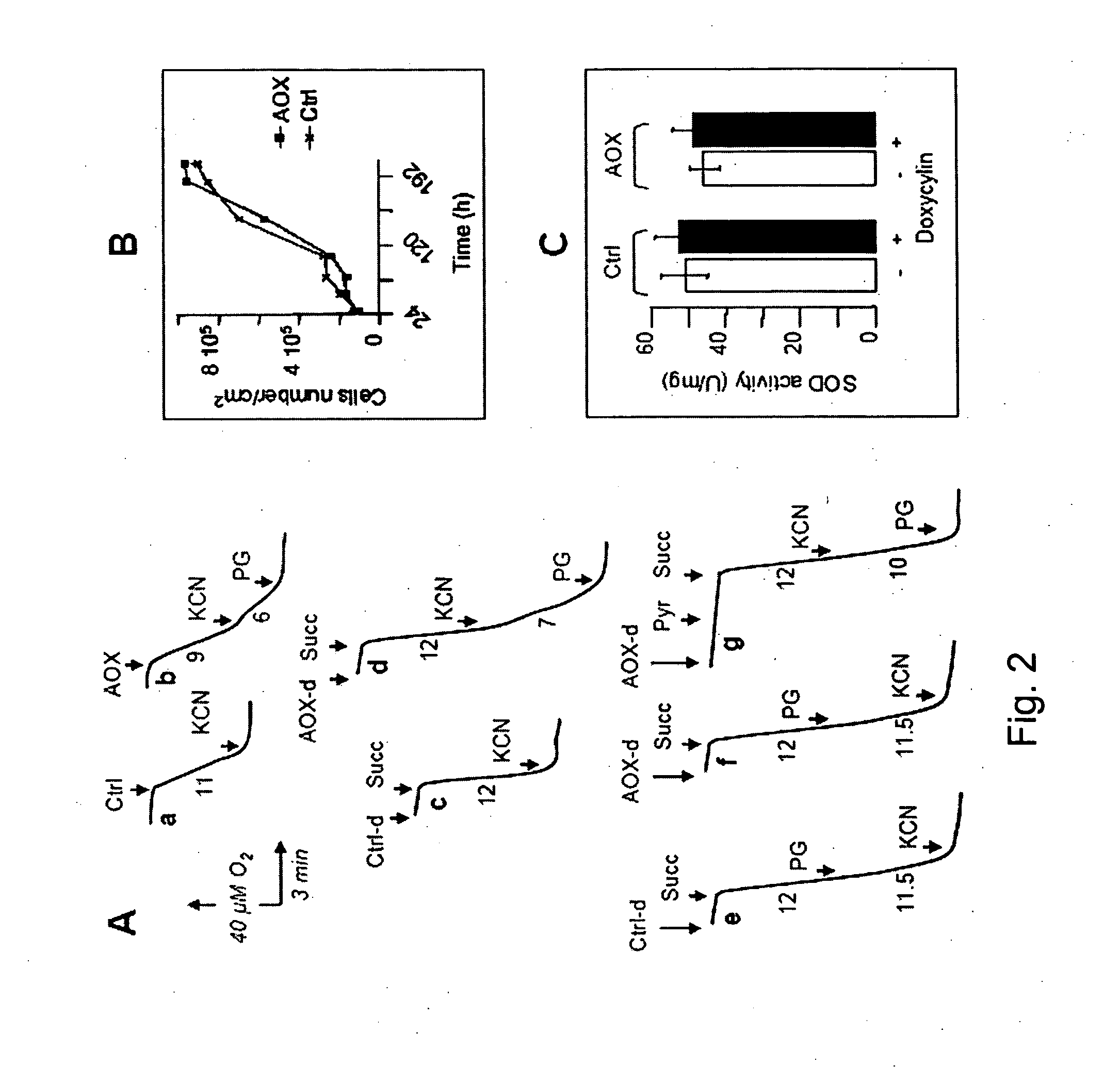
The invention relates to a method for combating disorders affecting the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system by allotopic expression of the cyanide-insensitive alternative oxidase (AOX) in human cells. The successful expression of AOX in human cells and in Drosophila has been shown to confer spectacular cyanide-resistance to mitochondrial substrate oxidation, alleviate oxidative stress, apoptosis susceptibility and metabolic acidosis. AOX is well tolerated when expressed ubiquitously in the whole organism. AOX expression is a valuable tool to limit the deleterious consequences of respiratory chain deficiency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TAMPERE
Treatment of mitochondria-related diseases and improvement of age-related metabolic deficits
InactiveUS20130108709A1High expressionMitigate mitochondrial swellingHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideOxidative stressCvd risk
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of subjects, including humans, who have or are at risk for various disease, disorders and conditions, including, mitochondria-associated diseases, disorders, and conditions, including respiratory chain disorders, and diseases, disorders and conditions associated with or characterized at least in part by mitochondria swelling, mitochondria dysfunction, mitochondria leaking, oxidative stress, increased mitochondria number, increased mitochondria and mitochondria-related protein mass, and increased mitochondria and related-related proteins expression.
Owner:PHILERA NEW ZEALAND
Super respiratory chain compound protein
The invention relates to a mammalian cell super respiratory chain compound protein and in particular to a super respiratory chain compound protein of a high atom resolution electron cryomicroscopy structure, and a preparation method of the protein. By adopting the protein structure, the respiratory action mechanism of mammalian animals and diseases related to respiratory action can be further studied.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
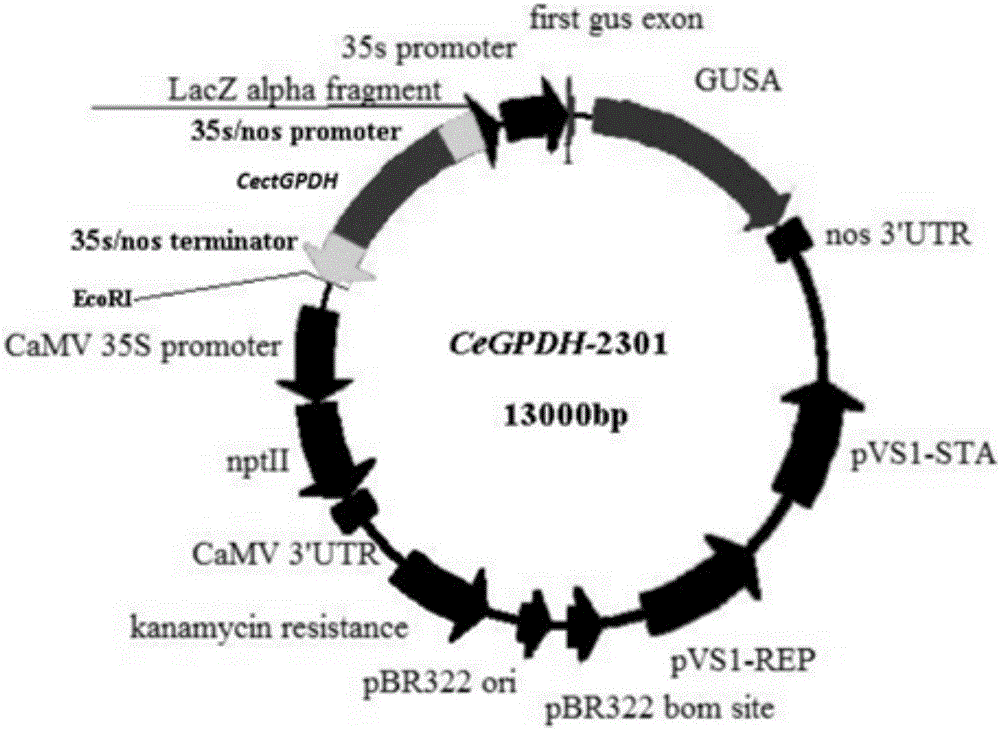
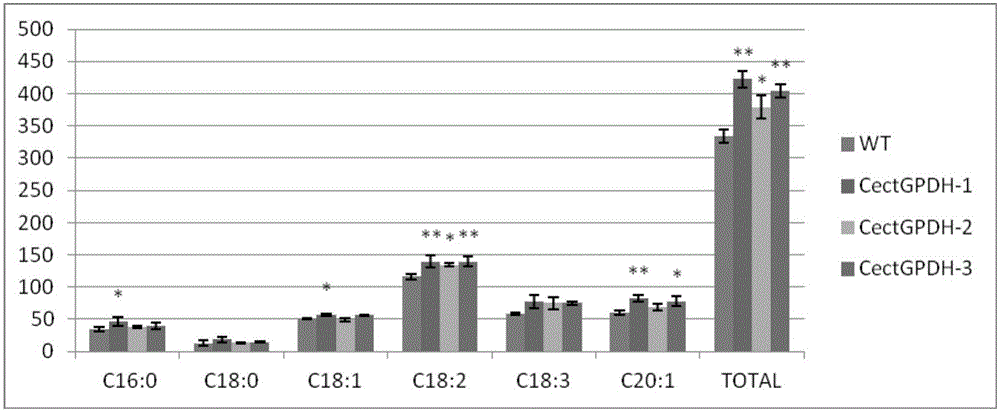
CectGPDH2 (cytosolic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a CectGPDH2 gene and an application thereof in increase of fatty acid content. The nucleotide sequence of the CectGPDH2 gene is shown as SEQ NO.1. The gene comes from Chlorella ellipsoidea and encodes GPDH, wherein the GPDH participates in shuttle of the mitochondrion G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate), provides electrons for respiratory chains, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of the key enzymes for connecting glucose metabolism with lipid metabolism and plays an important role in lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants. The total fatty acid content of seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana and rape genetically modified with the gene can be increased obviously, and the gene can be used for increasing the oil content of plant cells and the content of linoleic acid (C18:2) and eicosenoic acid (C20:1) in the plants and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS7915233B1Treating and preventing ovarian dysfunctionEliminate side effectsBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseNucleotide
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidien nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
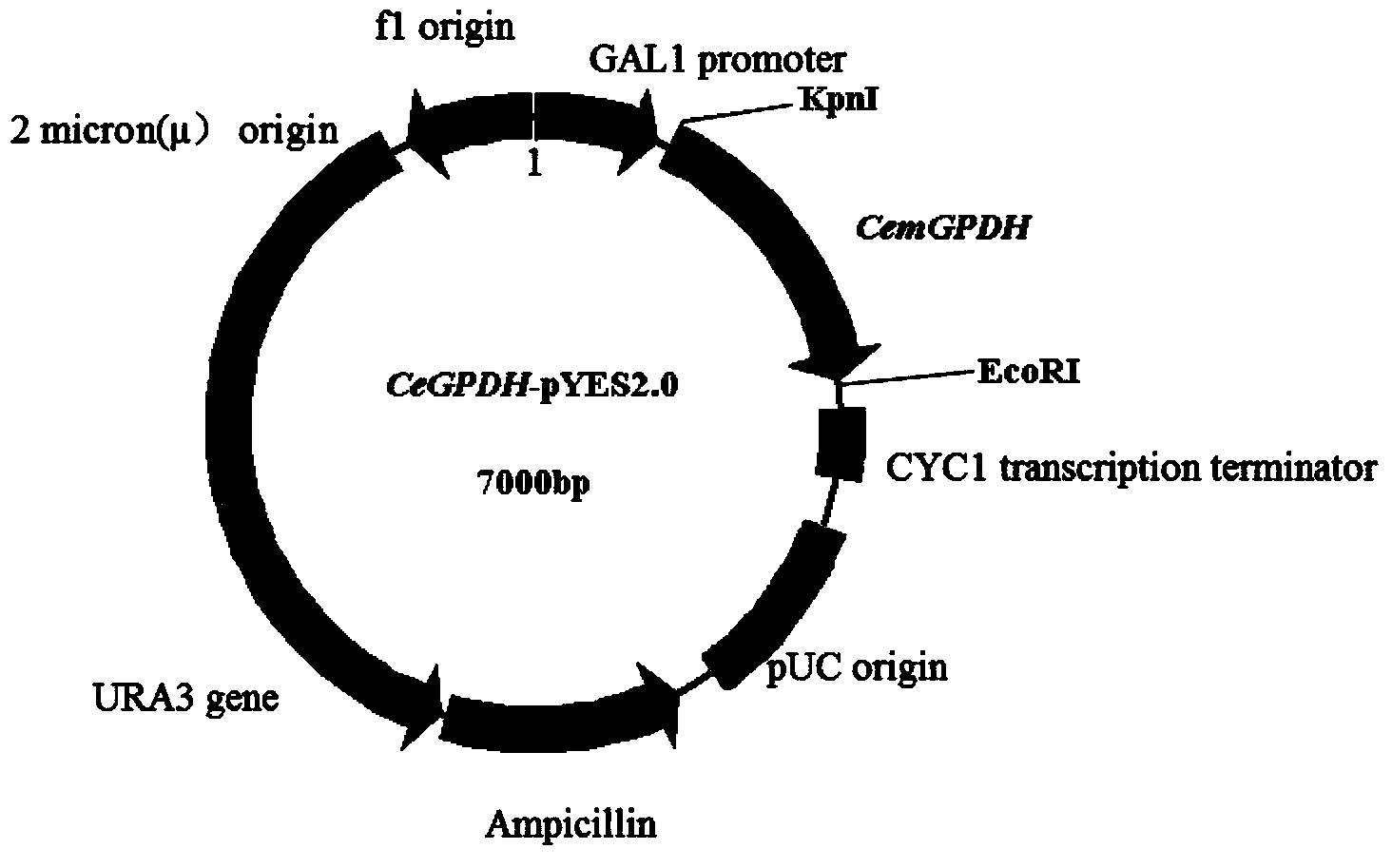
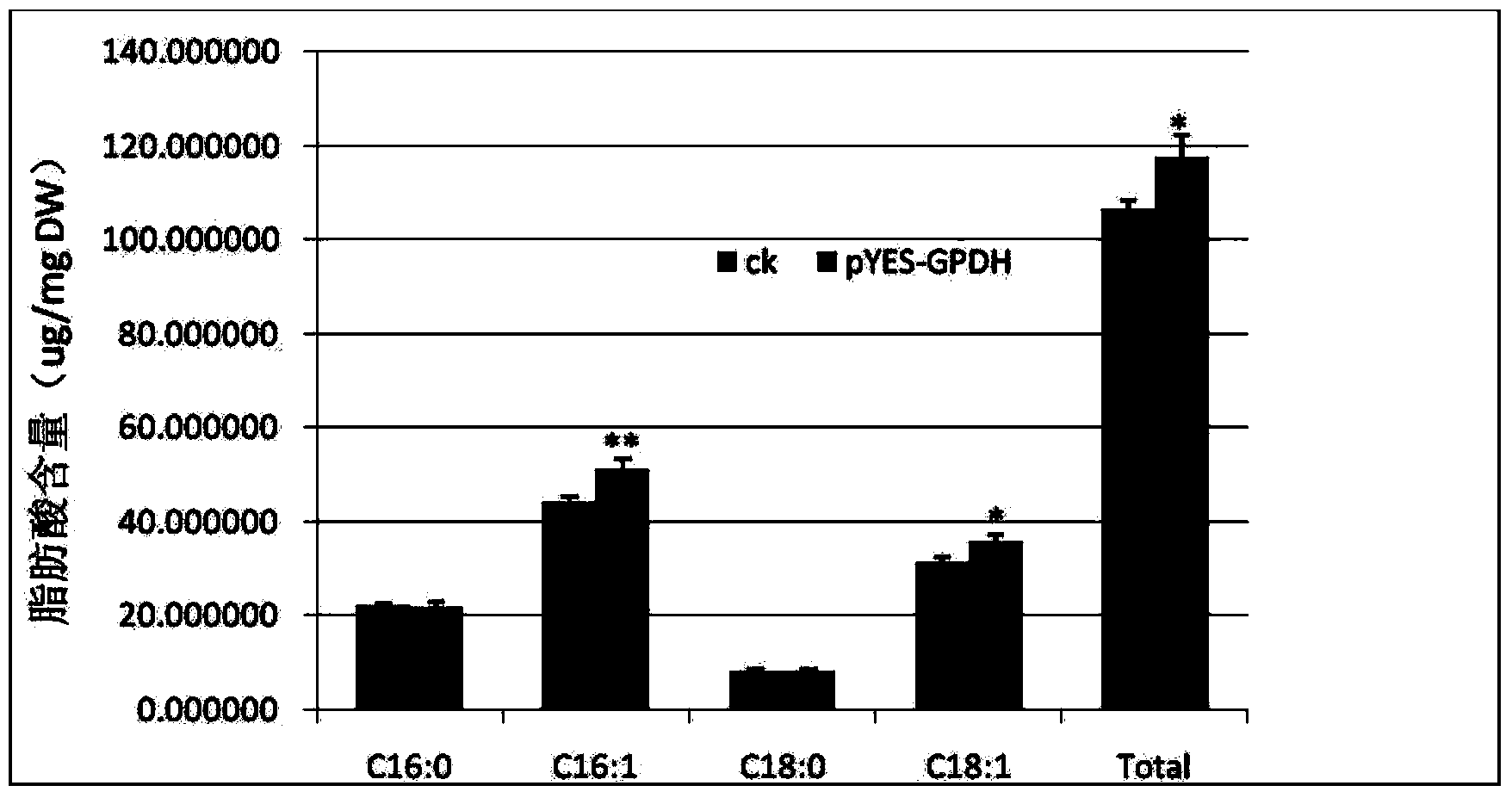
Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and an application of the Cem GPDH gene in the aspect of increase of cellular fatty acid content. A nucleotide sequence of the Cem GPDH gene is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is derived from Chlorella ellipsoidea, and GPDH is coded. G3P (Glycerol-3-phosphate) synthesized through catalysis by GPDH is an important raw material for synthesis of TAG (triacylglycerol), the enzyme participates in mitochondria G3P shuttle, provides electrons for a respiratory chain, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of key enzymes for connecting glycometabolism and lipid metabolism and has an important effect on lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants; and besides, the gene can remarkably increase the total fatty acid content of cells when utilized to convert yeast cells, plant cells and microalgae cells.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing coenzyme Q10 by microbial transformation under condition of supercritical CO2
InactiveCN101591685AImprove solubilityEasy to synthesizeFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityMicrobial transformation
The invention discloses a method for preparing coenzyme Q10. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: switching-in schizosaccharomyces pombe to culture medium containing solanesol, carrying out fermentation in the supercritical CO2 environment with temperature ranging from 25 DEG C to 35 DEG C and pressure ranging from 5MPa to 20 MPa, thus obtaining the coenzyme Q10.The method of the invention makes full use of dissolution characteristics of the supercritical CO2 to increase solubility of the solanesol, thus effectively reducing product inhibiting effect in the process of conversion, providing a high anaerobic environment for yeast, changing respiratory chain oxygen supply mode of microorganism, and promoting synthesis of the coenzyme Q10; in addition, in the method of the invention, the solanesol is added as substrate of the coenzyme Q10, thus improving speed and output of the synthesis of the coenzyme Q10.Experiments indicate that the output of the coenzyme Q10 prepared by the method of the invention is increased by 60-162% compared with the output thereof prepared by ordinary fermentation methods.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease diagnosis marker and application thereof in preparing diagnosis or prognosis tool
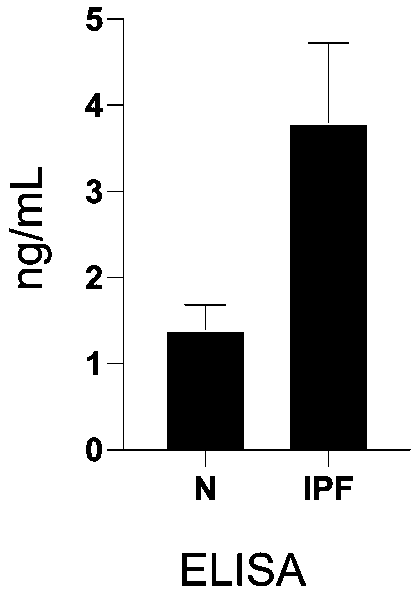
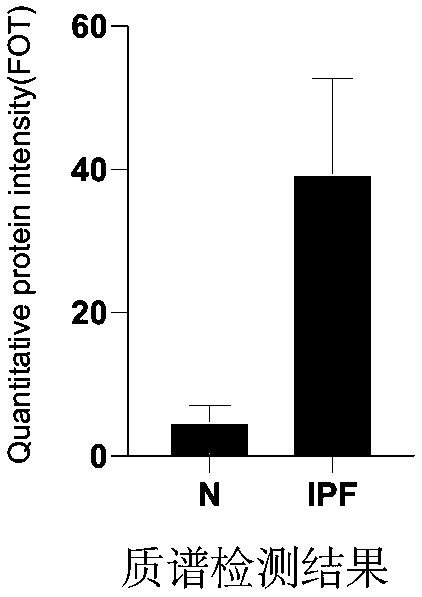
The invention discloses an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease diagnosis marker and application thereof in preparing a diagnosis or prognosis tool. The invention relates to novel discovery of a cytochrome C oxidase subunit 5B (COX5B) as an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patient serum marker. COX5B is one of constitution components of respiratory chain composites III on a mitochondrial innermembrane, the content of COX5B in IPF patient serum is increased, it means that mitochondria of an IPF patient is seriously damaged, COX5B is released into the serum, in addition, the content of COX5B in the serum of the IPF patient is in negative correlation with Oversall Survival, and the content of COX5B in serum of an IPF patient in poor survival is high. Research results disclosed by the invention provide a noninvasive method for clinical diagnosis on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis diseases and are applicable to clinical popularization.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Quick extraction method of high-activity mitochondria in plant organs and special extracting solution thereof
The invention discloses a quick extraction method of high-activity mitochondria in plant organs and special extracting solution thereof. The quick extraction method comprises the following steps: mixing the plant organs, the extracting solution and grinding medium, homogenizing, collecting filtrate, carrying out differential centrifugal separation on the mitochondria in the plant organs, and thenadopting mitochondrial respiratory buffer solution for storage. The extracting solution is prepared from sucrose, sodium pyrophosphate, EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), potassium dihydrogen phosphate, BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin), cysteine, ascorbic acid and pvp-40. Proved by the experiment, the quick extraction method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages that the efficiency is high, i.e., the activity of the mitochondria is high; the applicability is wide, so that the quick extraction method can be applicable to extraction of the mitochondria of flower organs of multiple angiosperms; the storage time is long, and the activity can be maintained for 5 hours on an ice box, so that a great number of studies on the energy metabolism and the respiration of the mitochondria can be met; the operation is simple and the consumed time is short; the method provided by the invention lays a solid foundation for study on the respiratory chain and the energy metabolism of the mitochondria and has important practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Feed additive for improving sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress, preparation method and application thereof, and sea bass feed
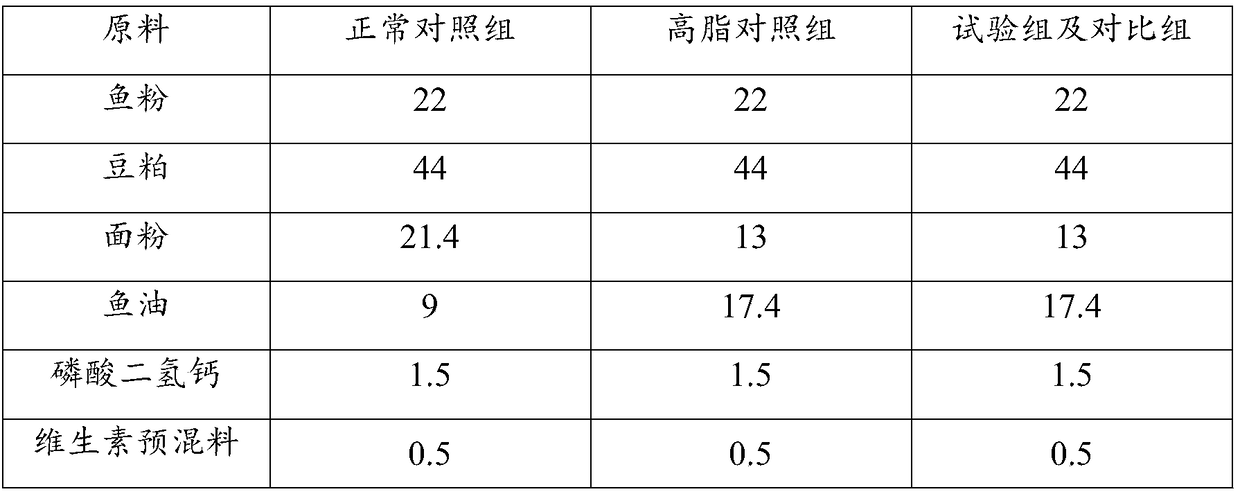
ActiveCN109329656AImprove mitochondrial functionRegulatory targets are clearFodderClimate change adaptationChelated zincHigh fat
The invention relates to a feed additive for improving the sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress, a preparation method and application thereof, and a sea bass feed, and belongs tothe field of feeds. Each 100 parts by weight of the feed additive comprises 10-20 parts by weight of Chinese tallow bark extract, 10-20 parts by weight of ampelopsis grossedentata extract, 5-15 partsby weight of silymarin, 8-16 parts by weight of bamboo fungus polysaccharide chelated zinc, 6-12 parts by weight of methionine chelated iron, 4-8 parts by weight of biotin and the balance of carrier.The feed additive not only can improve the generation of sea bass mitochondria, promote the regeneration of mitochondria and enhance the respiratory chain activity of mitochondria, but also can improve the antioxidant capacity of liver mitochondria and reduce the oxidative damage of mitochondria, and has the effect of reducing blood fat. The preparation method is simple. The feed has good stability and good application prospect. When applied to the preparation of the sea bass feed, the feed additive can improve the sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury
The invention relates to an application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury. Through a series of observation of caffeic acid on hepatic ischemia reperfusion rats, caffeic acid is found to improve the hepatic surface blood flow quantity by the action routes: AMPK[alpha] phosphorylation and PKC[delta] membrane translocation are inhibited, NADPH subunit P41 and P47 membrane translocation is inhibited and NADPH-derived peroxides are inhibited; the activity of a hepatic ischemia reperfusion rat mitochondria respiratory chain is improved, and peroxide production caused by mitochondria injury is reduced, so as to increase the production of ATP; hepatocyte apoptosis caused by ischemia reperfusion is inhibited; and hepatic cell internal cytoskeleton injury caused by ischemia reperfusion is attenuated. The new application in preparation of the drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Composite feed additive capable of improving liver mitochondria function of jewfish as well as preparation method and application of composite feed additive
ActiveCN108308457AImprove mitochondrial functionNo harmful residuesOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyFeed additive
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for obtaining medicament with mitochondrial uncoupling effect
InactiveCN108398549ACell-specificImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseSide effect
The invention belongs to the fields of biology and medicine and discloses a method for generating mitochondria uncoupling and activating adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK). The method is characterized in that horizontal reversed electron transfer of a mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I is caused by oxidation of a sulfur-containing compound through SQR, cross-mitochondrial inner membrane potential is reduced, and thereby mitochondrial uncoupling is generated; by the mitochondrial uncoupling, the synthesis level of ATP in cells can be reduced and further the AMPK is activated. The invention also discloses a method for obtaining a mitochondria uncoupling agent and an AMPK activator based on the SQR. The experiment verifies that the method disclosed by the inventionhas the advantages that firstly, oxidation of the sulfur-containing compound by the SQR is a novel method for generating the mitochondria uncoupling or activating the AMPK; secondly, a novel mitochondria uncoupling agent or the AMPK activator can be obtained on the basis of the SQR; thirdly, an obtained compound has the mitochondria uncoupling of cell specificity or AMPK activating effect as wellas low toxic and side effects, and can be used for treating related diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com