Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Mitochondrial respiratory chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
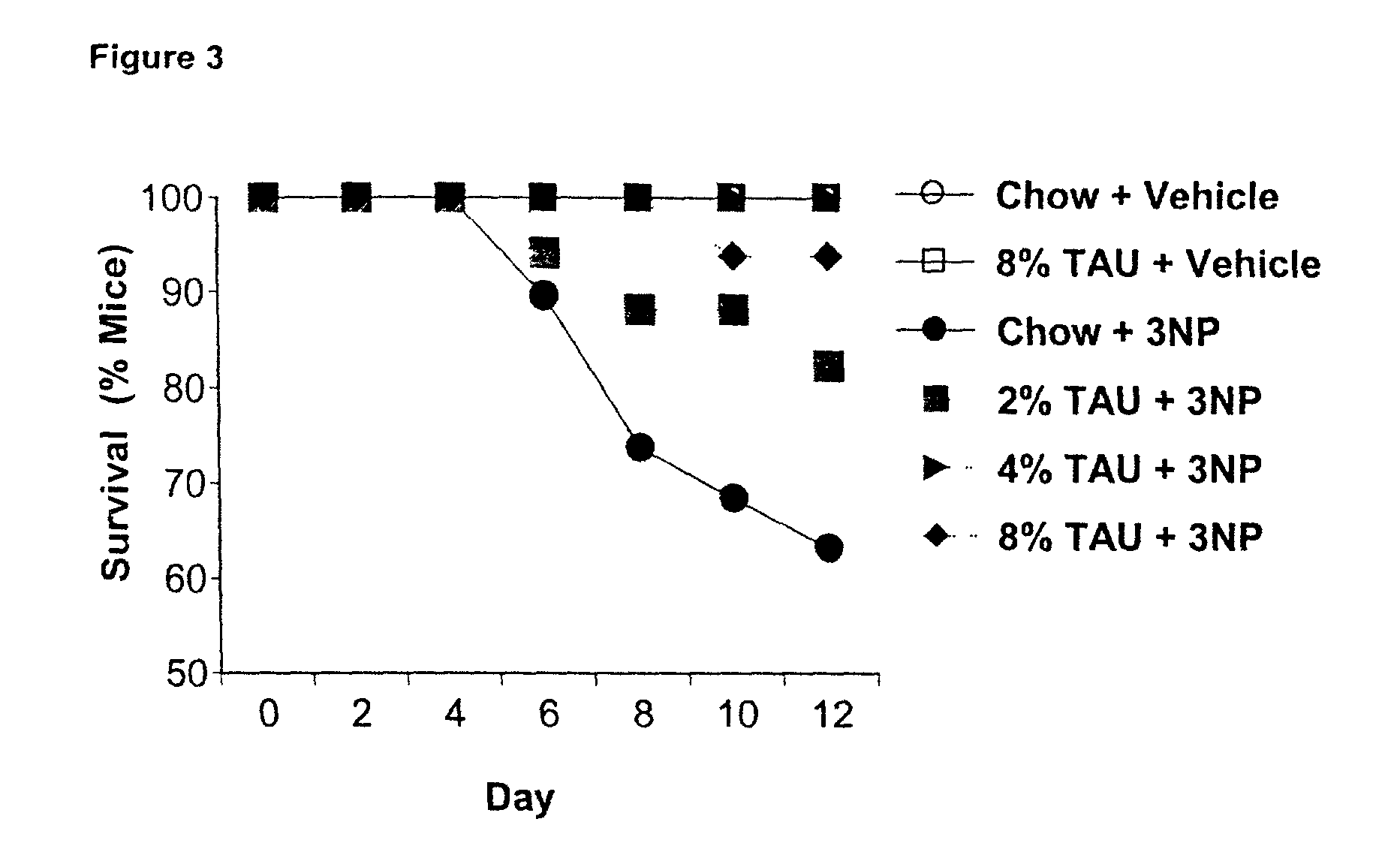
In metabolic disease: Mitochondrial disorders The mitochondrial respiratory chain consists of five multi-subunit protein complexes that produce the majority of energy driving cellular reactions. Dysfunction of the respiratory chain leads to decreased energy production and to an increase in the production of toxic reactive oxygen species.
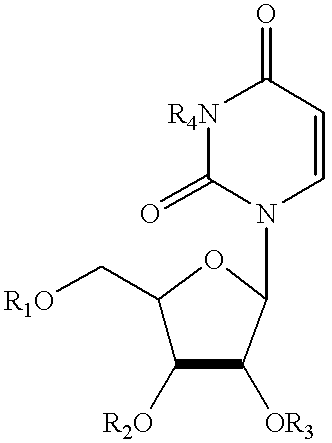
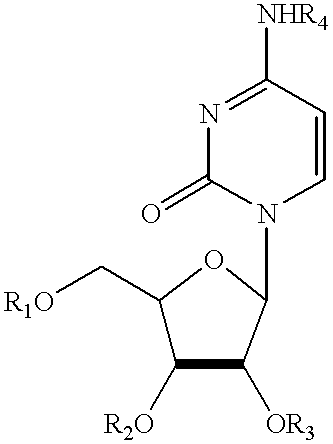
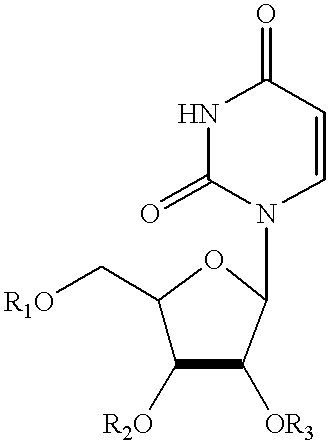
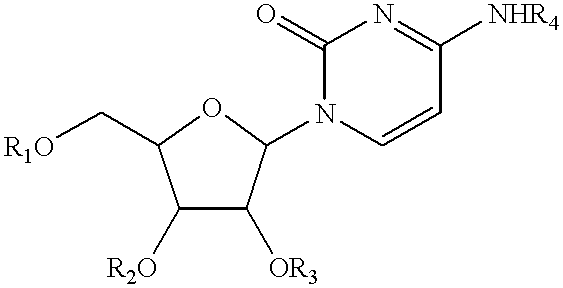
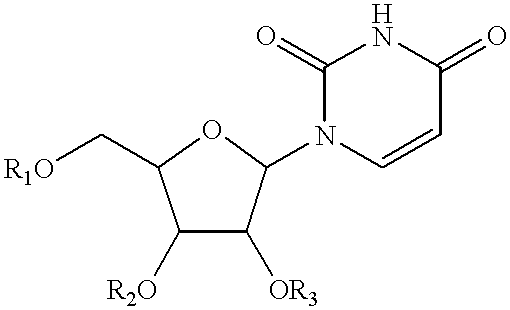
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20010005719A1Increase resistanceAvoid Cutting InjuriesBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMitochondrial disease
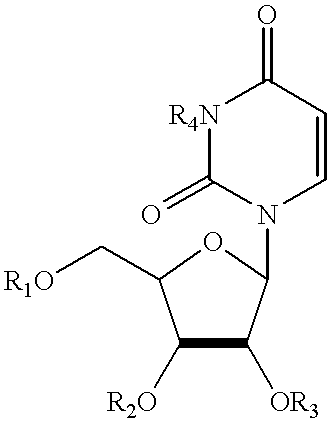
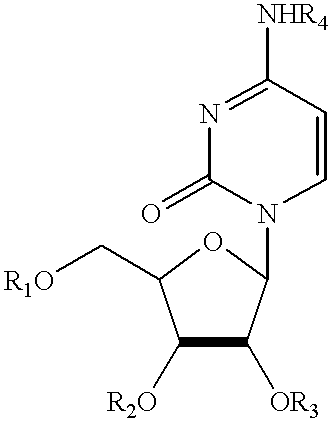
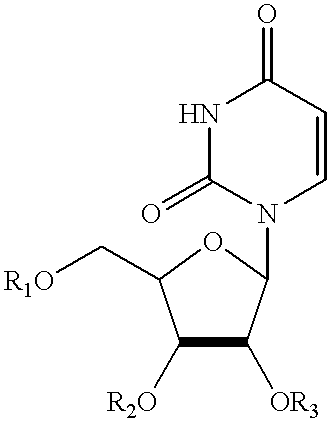
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Treatment of respiratory chain disorders using compounds having erythropoietin or thrombopoietin activity
Methods of treating mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders using compounds having erythropoietin activity or thrombopoietin activity are disclosed. Indicators for assessing the efficacy of treatment are discussed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
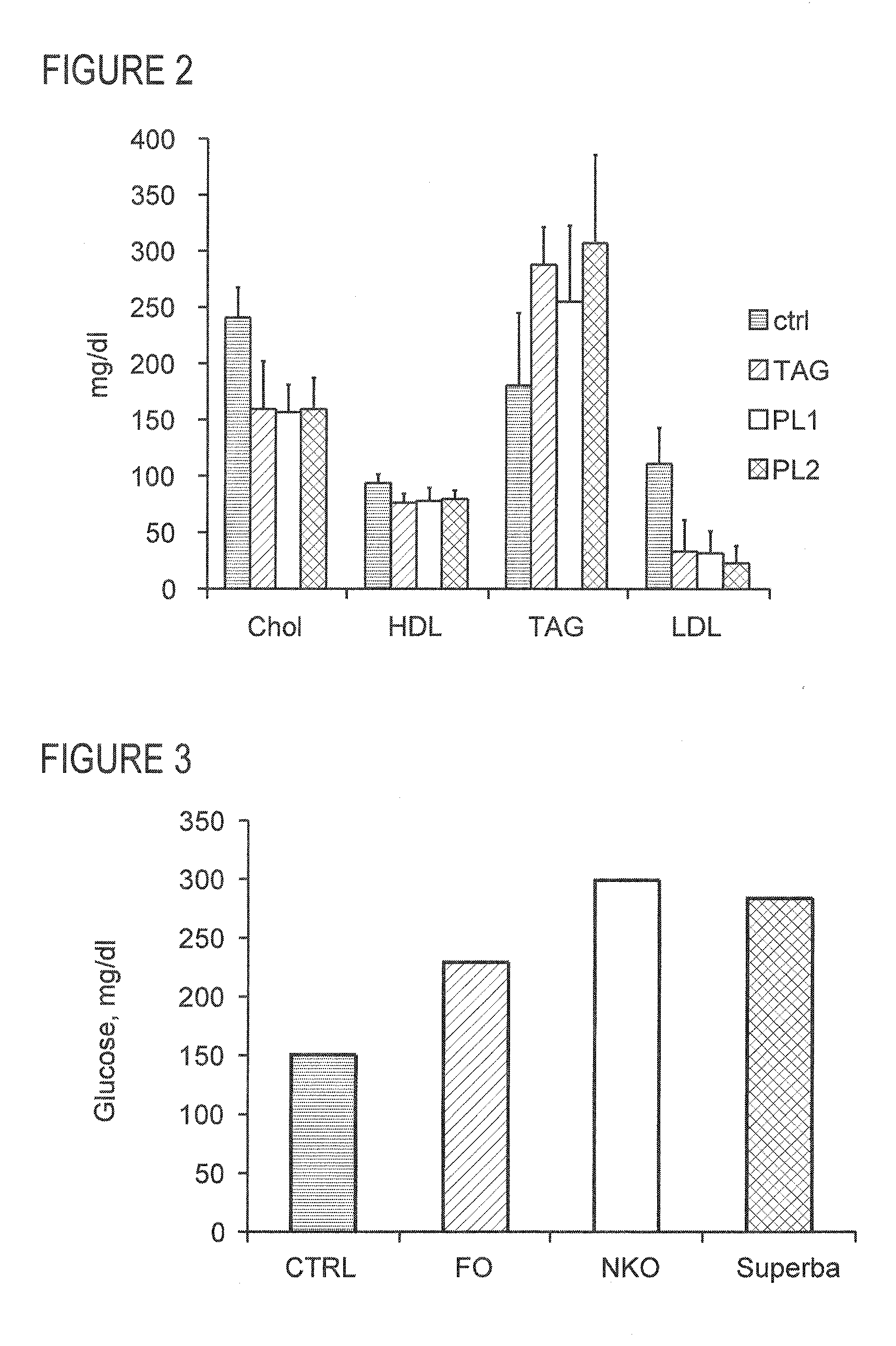
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
ActiveUS20110104297A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCvd riskOrganism
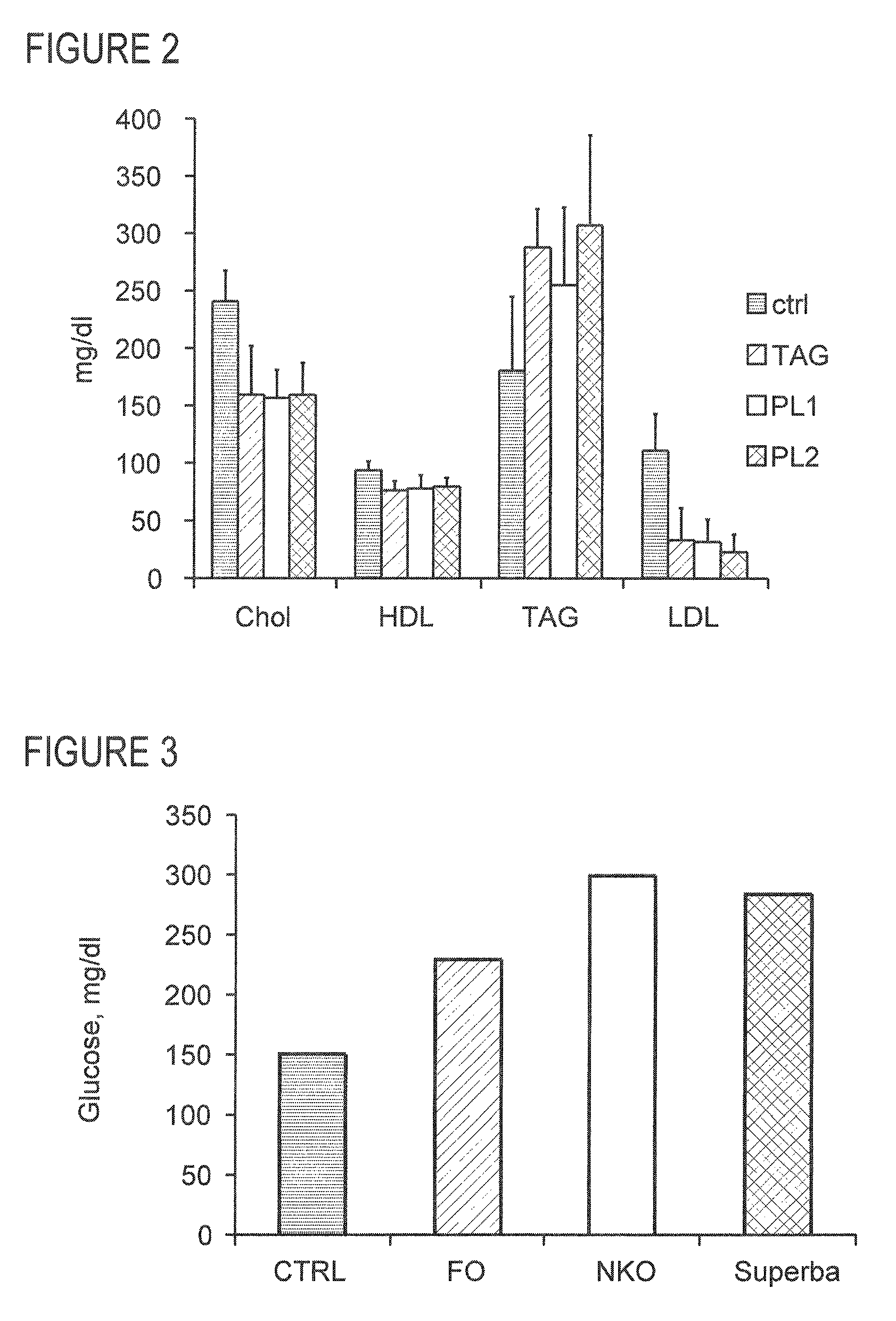
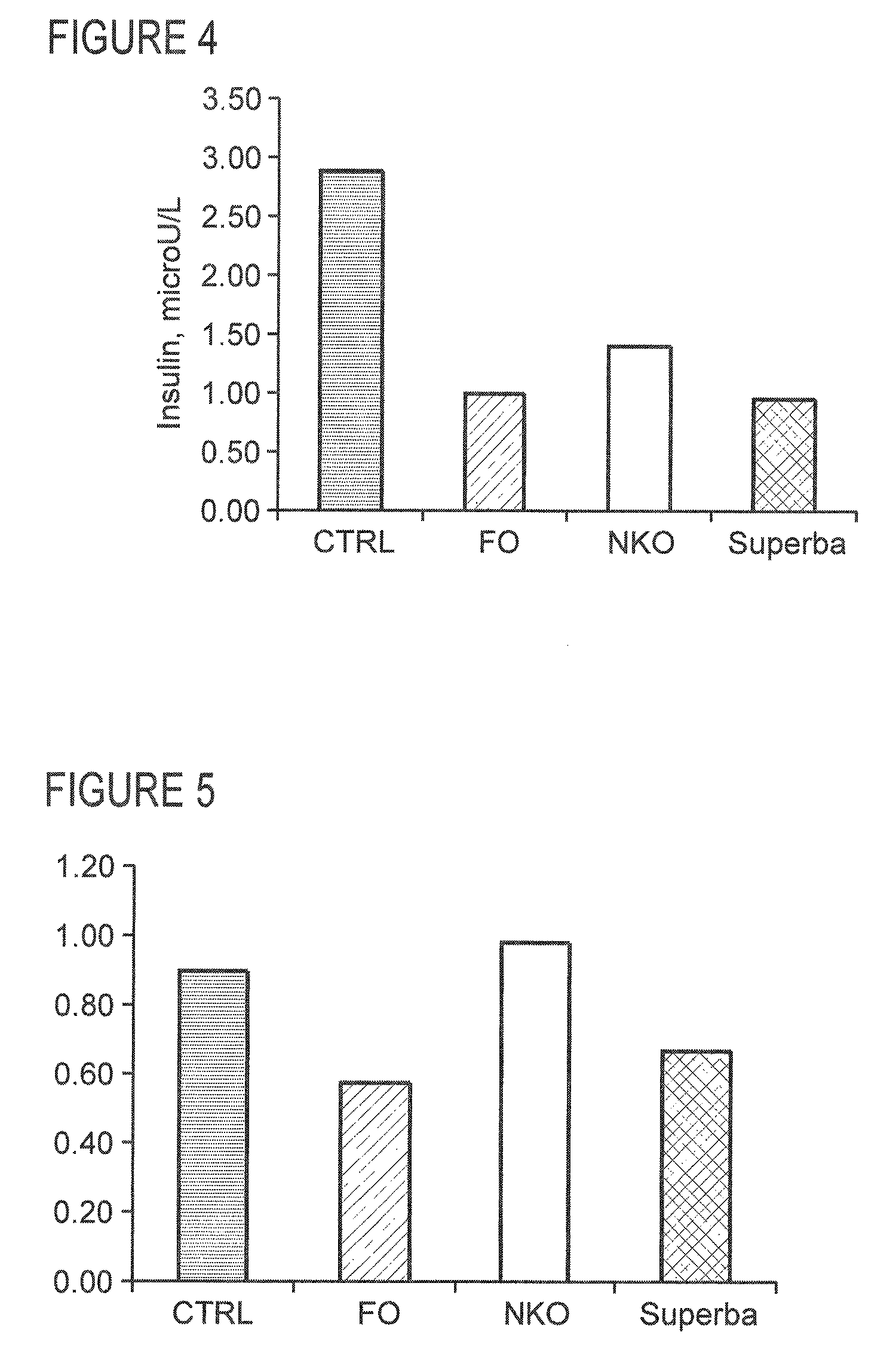
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20020049182A1Promote recoverySlow cell deathBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePyrimidine Nucleotides
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
ActiveUS8697138B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsCvd riskCholesterol biosynthesis
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Methods of using krill oil to treat risk factors for cardiovascular, metabolic, and inflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20140363517A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCvd riskMitophagy
This invention discloses methods of using krill oil and compositions comprising krill oil to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders. The present invention also relates to methods of using compositions comprising krill oil to modulate biological processes selected from the group consisting of glucose metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, cholesterol biosynthesis, and the mitochondria respiratory chain. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical and / or nutraceutical formulations made from krill oil, methods of making such formulations, and methods of administering them to treat risk factors for metabolic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20010016576A1Minimize consequencesInhibiting consequenceBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMitochondrial disease
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
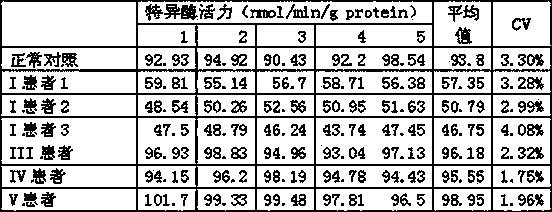
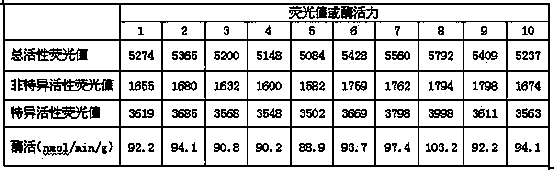
Enzyme activity detection method for mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I and reagents
The invention provides an enzyme activity analysis and detection method for mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I (NADH-Q reductase, EC1.6.5.3). The invention also provides reagents for detecting the enzyme activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I. The above method and the reagents can be used for analyzing and detecting the enzyme activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain compound I in samples to be detected, and therefore the method and the reagents can be used for analysis, examination and diagnosis of clinic diseases. Based on the method, the reagents have advantages of convenience, rapidness and high sensitivity, and are convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:北京中科非凡生物技术有限公司
Sepsis diagnosis method and reagent
InactiveCN104777109AReduced activityReduced activity levelColor/spectral properties measurementsWhite blood cellDiagnosis methods
The invention provides a method for sepsis diagnosis, severity degree monitoring, and prognosis evaluation. The enzymatic activity level of mitochondrial respiratory chain supramolecular complex: NADH-cytosome coxidoreductase, NCR in the peripheral blood leucocyte namely mitochondrial NCR enzymatic activity level is closely related with the organ dysfunction and prognosis of sepsis. The invention also provides a detection method and detection reagent for detecting the peripheral blood leucocyte mitochondrial respiratory chain supramolecular complex NCR enzymatic activity. The provided method can rapidly, specifically, and sensitively measure the mitochondrial NCR enzymatic activity of a sample, and has an important meaning on the sepsis diagnosis, severity degree monitoring, and prognosis evaluation.
Owner:AFFILIATED CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL INST OF PEDIATRICS +1
Pro-oxidant anti-cancer compounds
ActiveUS8410056B2Efficient killingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer preventionCancer cell
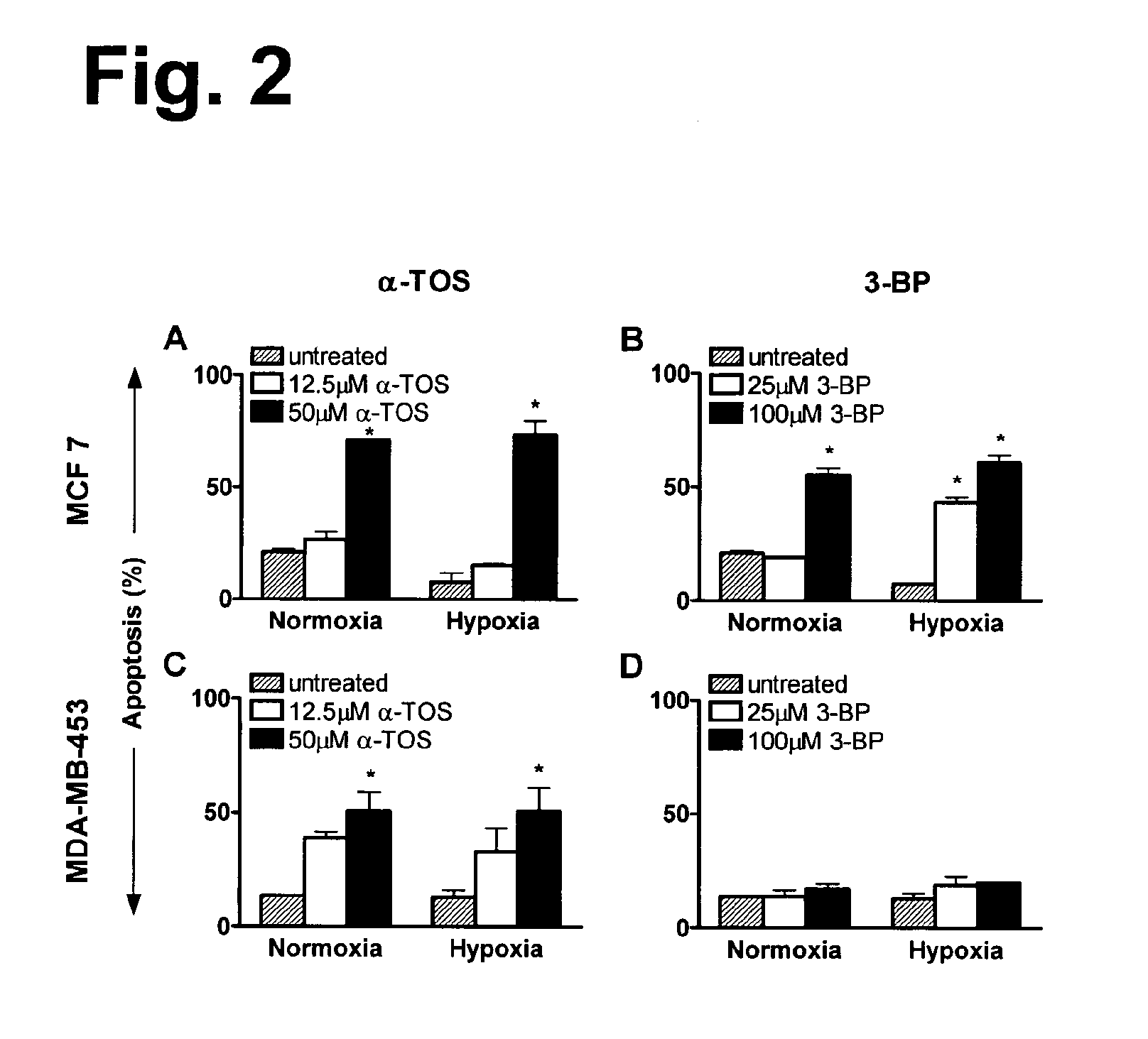
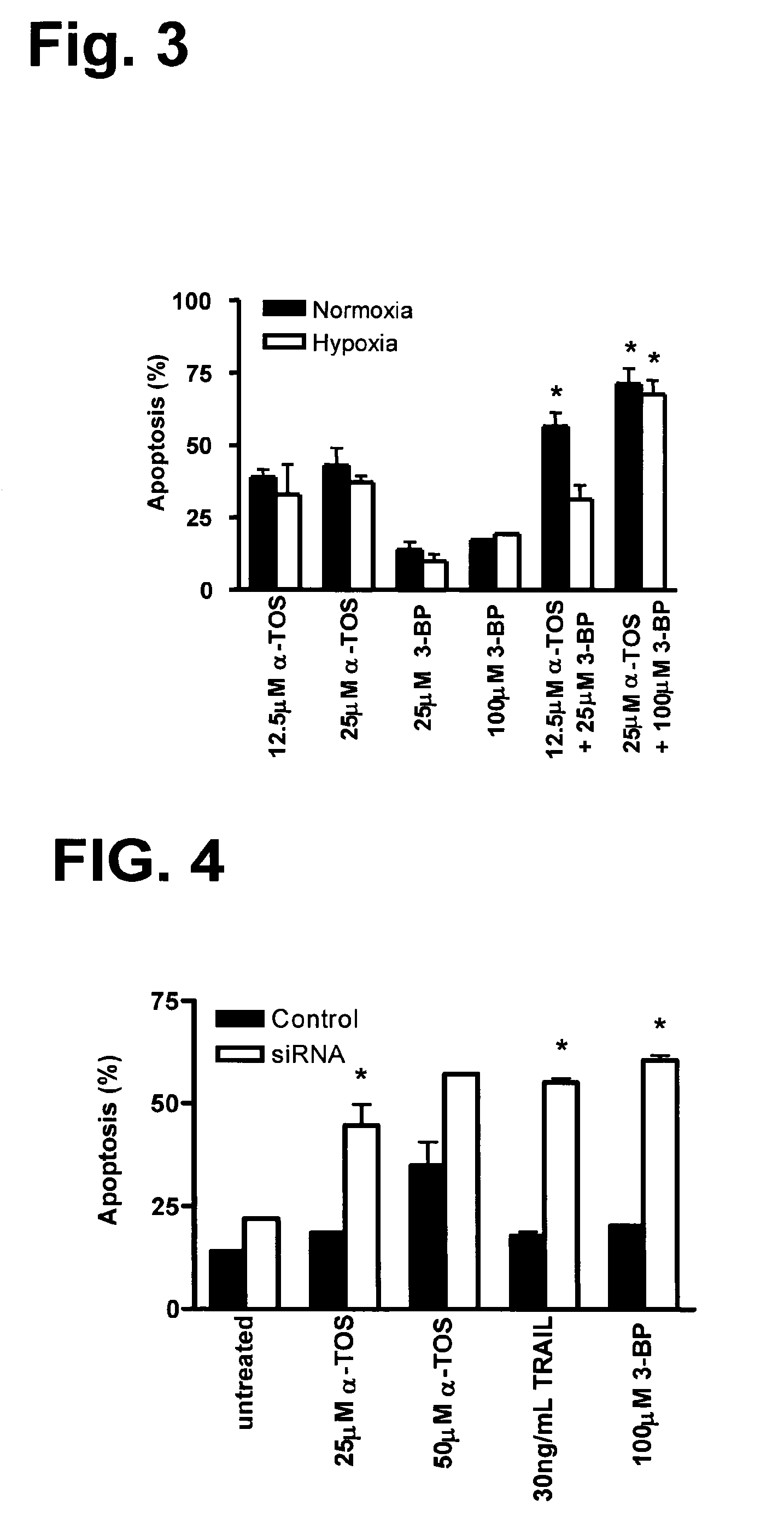
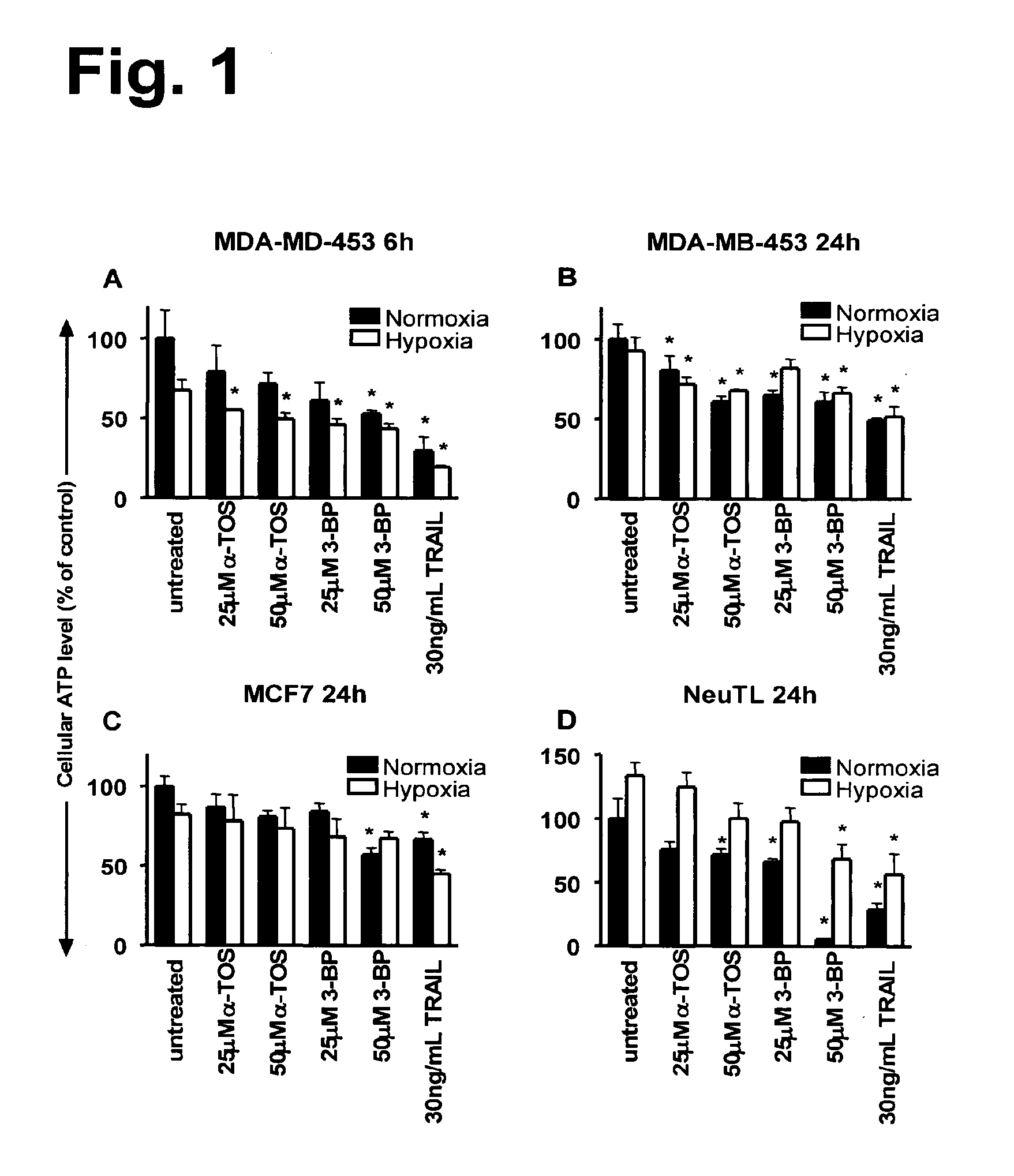
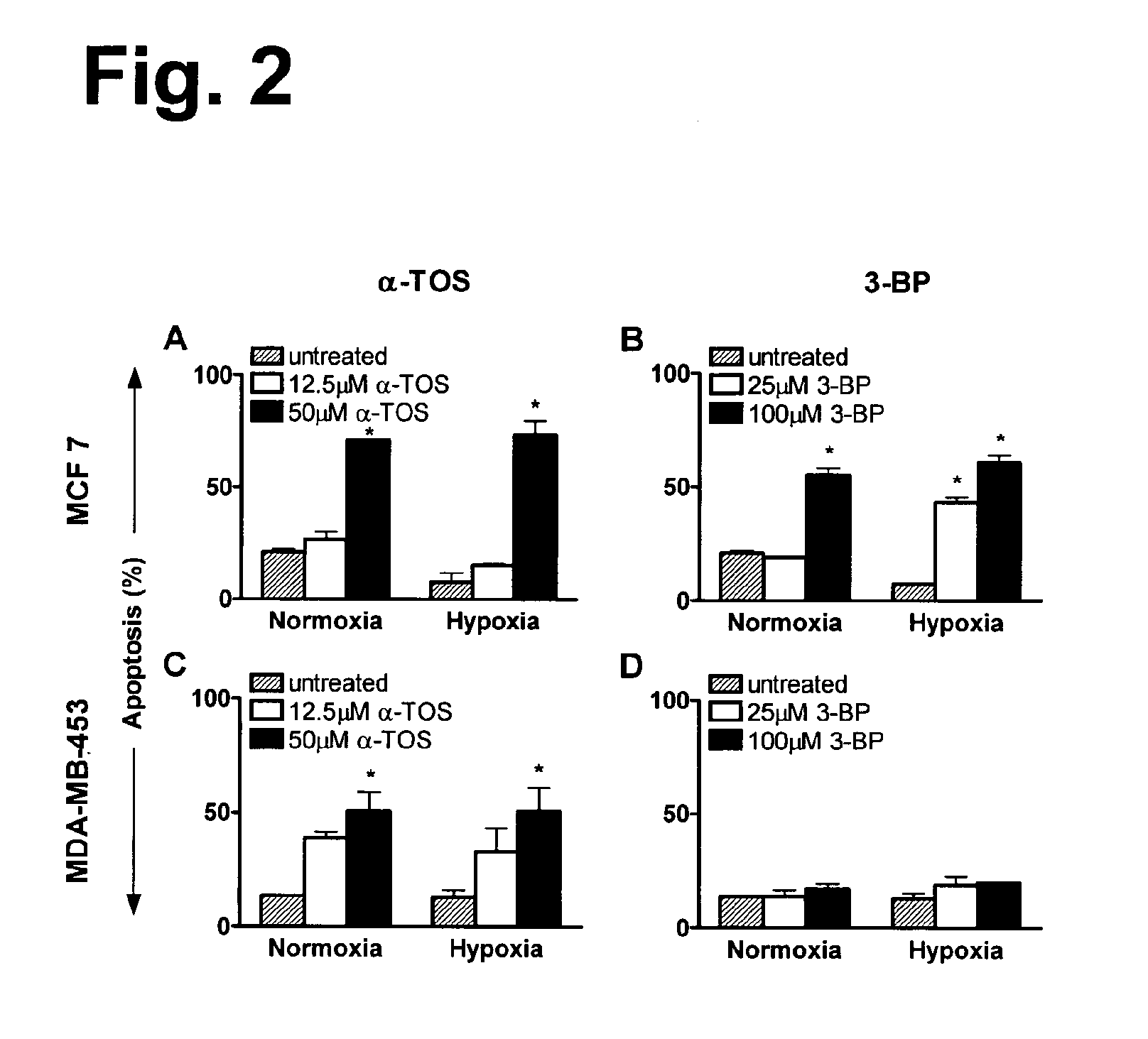
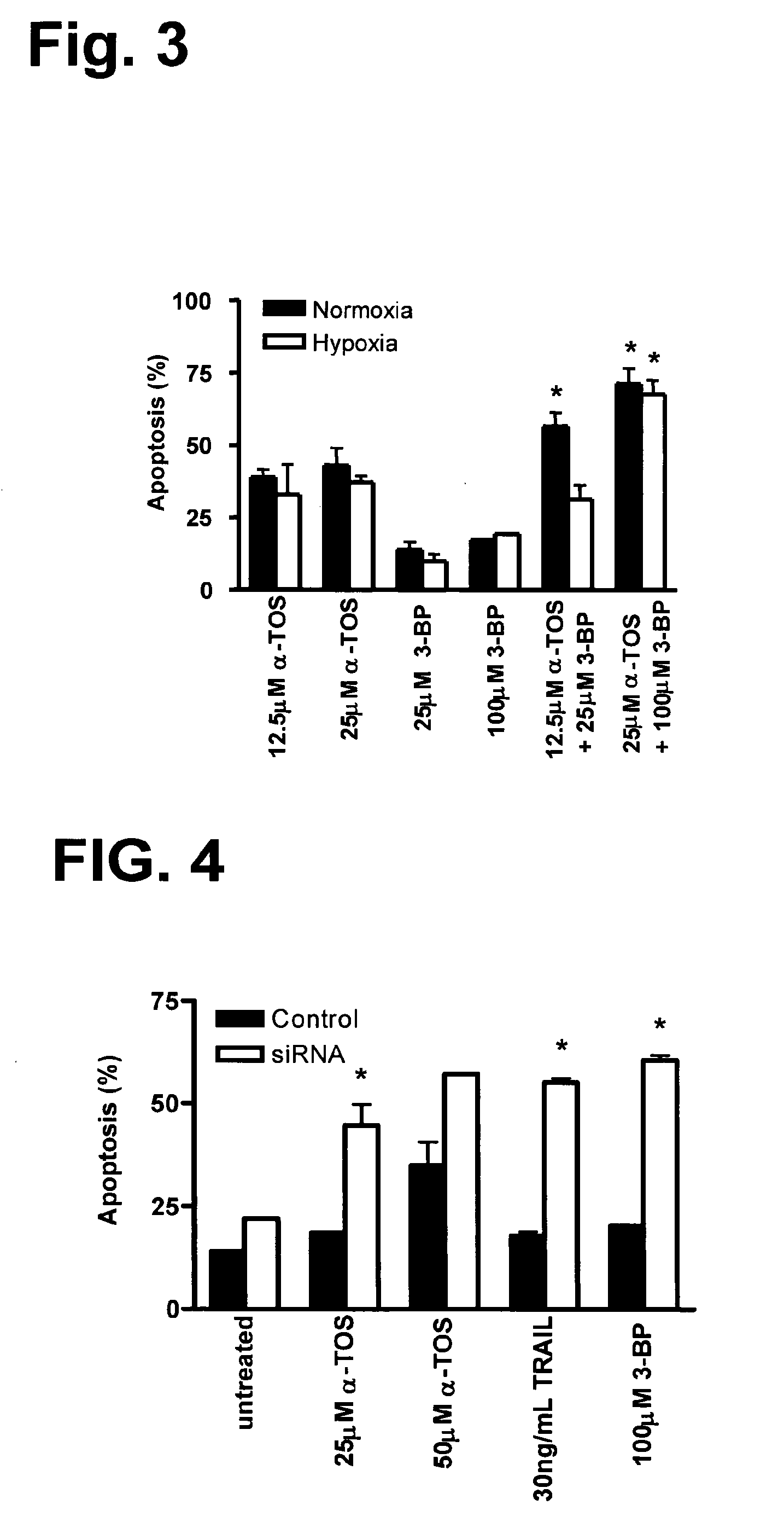
This invention relates to anti-cancer compounds and to methods for treating or preventing cancer. In particular, the invention concerns pro-oxidant anti-cancer compounds, such as pro-oxidant forms of vitamin E that selectively interact with complex II of the mitochondrial respiratory chain of cancerous cells, generate reactive oxygen species and induce apoptosis of those cells.
Owner:CANCURE LTD
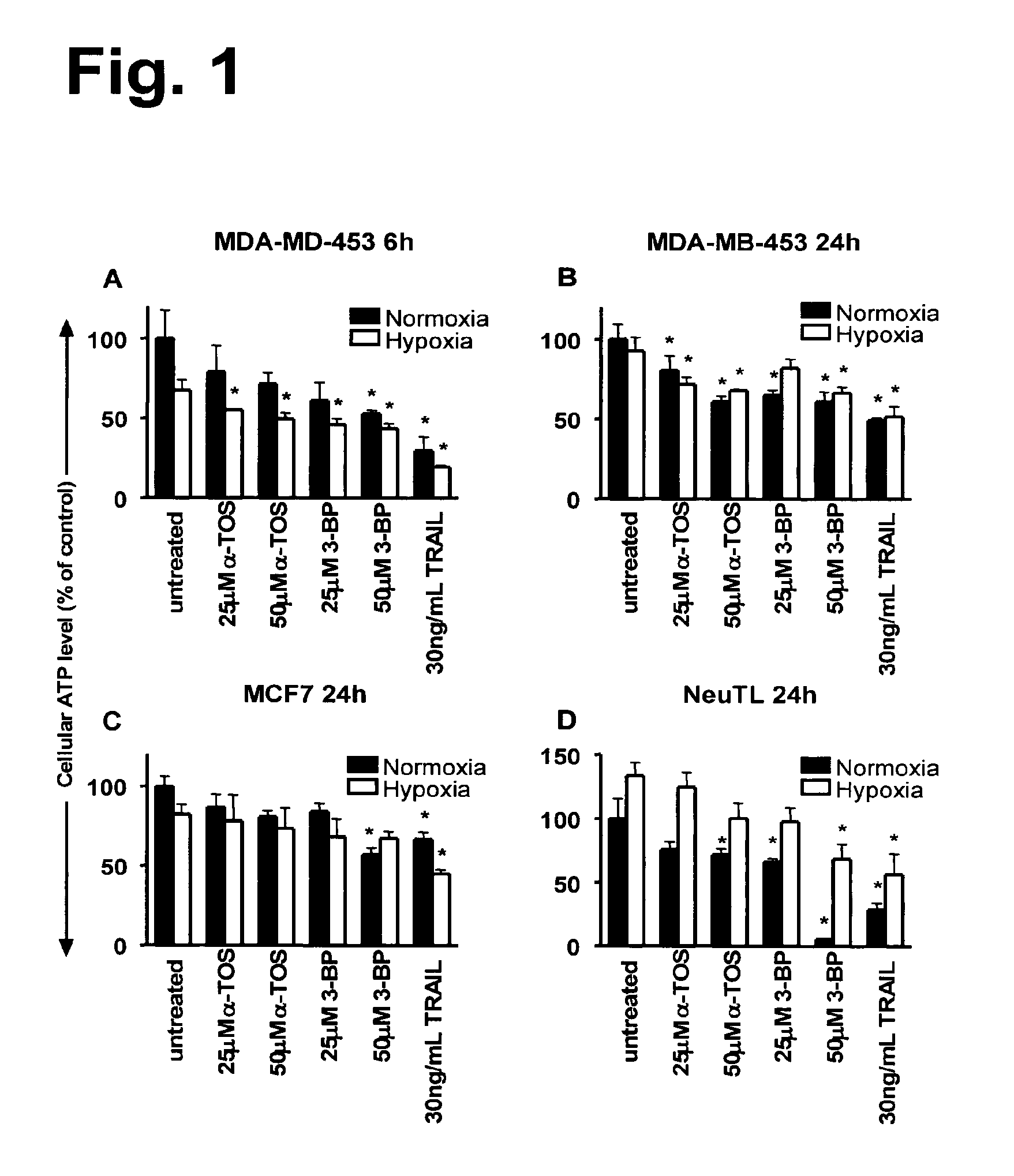
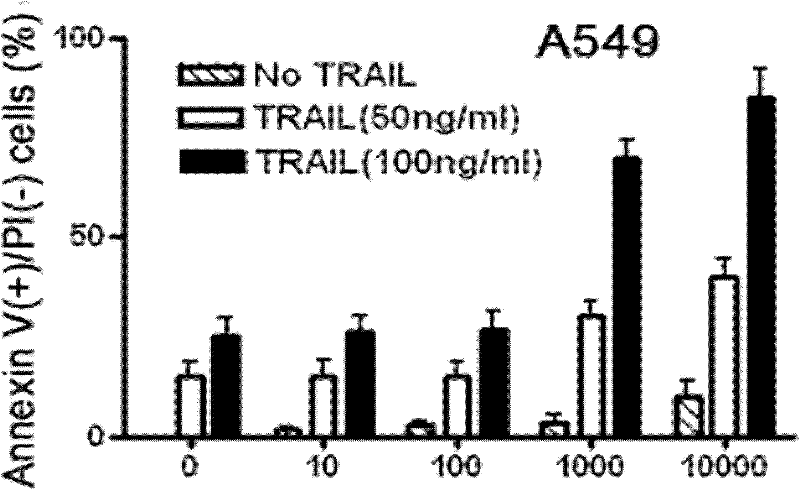
Use of rotenone as non-small cell lung cancer cell sensitizer
InactiveCN101904837ANo obvious side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectNormal cell
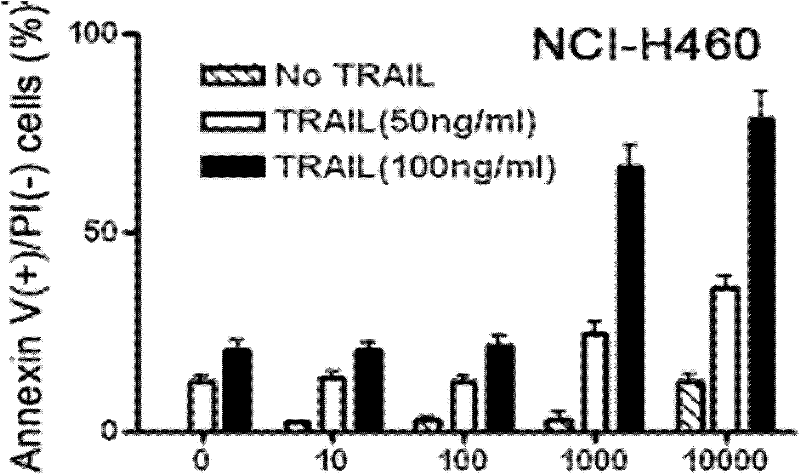
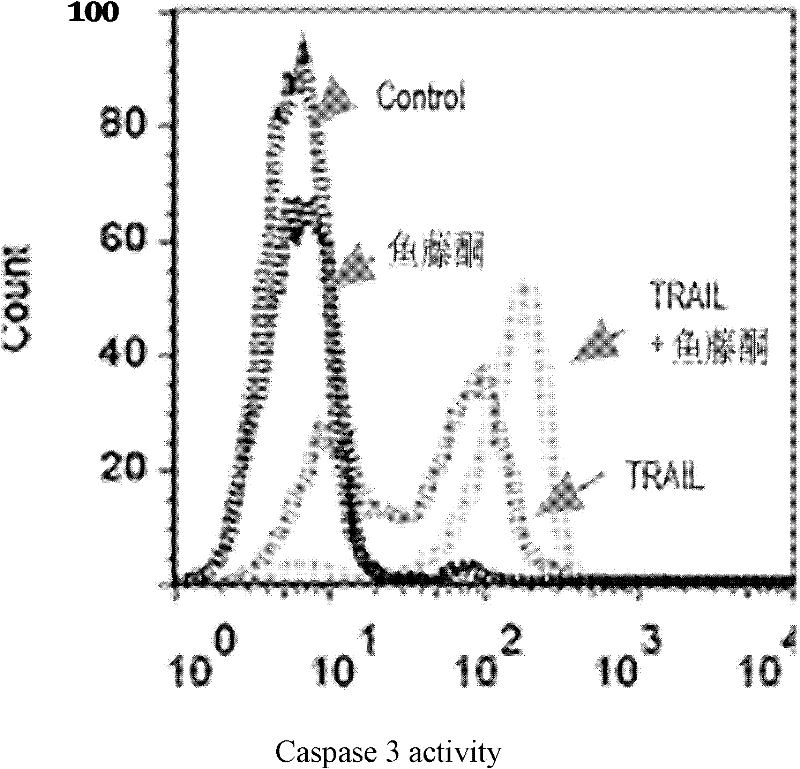
The invention relates to novel use of a mitochondrial respiratory chain inhibitor rotenone in reversing the tolerance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to targeted antineoplastic agents. The rotenone serves as a non-small cell lung cancer cell sensitizer and can reverse the tolerance of the non-small cell lung cancer cells to the targeted antineoplastic agents. The invention shows the combination of rotenone compounds and TRAIL has no obvious toxic or side effect on normal cells and is a novel medicinal composition used for treating the non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Quick extraction method of high-activity mitochondria in plant organs and special extracting solution thereof
The invention discloses a quick extraction method of high-activity mitochondria in plant organs and special extracting solution thereof. The quick extraction method comprises the following steps: mixing the plant organs, the extracting solution and grinding medium, homogenizing, collecting filtrate, carrying out differential centrifugal separation on the mitochondria in the plant organs, and thenadopting mitochondrial respiratory buffer solution for storage. The extracting solution is prepared from sucrose, sodium pyrophosphate, EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), potassium dihydrogen phosphate, BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin), cysteine, ascorbic acid and pvp-40. Proved by the experiment, the quick extraction method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages that the efficiency is high, i.e., the activity of the mitochondria is high; the applicability is wide, so that the quick extraction method can be applicable to extraction of the mitochondria of flower organs of multiple angiosperms; the storage time is long, and the activity can be maintained for 5 hours on an ice box, so that a great number of studies on the energy metabolism and the respiration of the mitochondria can be met; the operation is simple and the consumed time is short; the method provided by the invention lays a solid foundation for study on the respiratory chain and the energy metabolism of the mitochondria and has important practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Feed additive for improving sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress, preparation method and application thereof, and sea bass feed
ActiveCN109329656AImprove mitochondrial functionRegulatory targets are clearFodderClimate change adaptationChelated zincHigh fat
The invention relates to a feed additive for improving the sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress, a preparation method and application thereof, and a sea bass feed, and belongs tothe field of feeds. Each 100 parts by weight of the feed additive comprises 10-20 parts by weight of Chinese tallow bark extract, 10-20 parts by weight of ampelopsis grossedentata extract, 5-15 partsby weight of silymarin, 8-16 parts by weight of bamboo fungus polysaccharide chelated zinc, 6-12 parts by weight of methionine chelated iron, 4-8 parts by weight of biotin and the balance of carrier.The feed additive not only can improve the generation of sea bass mitochondria, promote the regeneration of mitochondria and enhance the respiratory chain activity of mitochondria, but also can improve the antioxidant capacity of liver mitochondria and reduce the oxidative damage of mitochondria, and has the effect of reducing blood fat. The preparation method is simple. The feed has good stability and good application prospect. When applied to the preparation of the sea bass feed, the feed additive can improve the sea bass liver mitochondria function under high fat stress.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury
The invention relates to an application of caffeic acid in preparation of drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury. Through a series of observation of caffeic acid on hepatic ischemia reperfusion rats, caffeic acid is found to improve the hepatic surface blood flow quantity by the action routes: AMPK[alpha] phosphorylation and PKC[delta] membrane translocation are inhibited, NADPH subunit P41 and P47 membrane translocation is inhibited and NADPH-derived peroxides are inhibited; the activity of a hepatic ischemia reperfusion rat mitochondria respiratory chain is improved, and peroxide production caused by mitochondria injury is reduced, so as to increase the production of ATP; hepatocyte apoptosis caused by ischemia reperfusion is inhibited; and hepatic cell internal cytoskeleton injury caused by ischemia reperfusion is attenuated. The new application in preparation of the drugs for treating hepatic microcirculation disturbance and hepatic injury is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
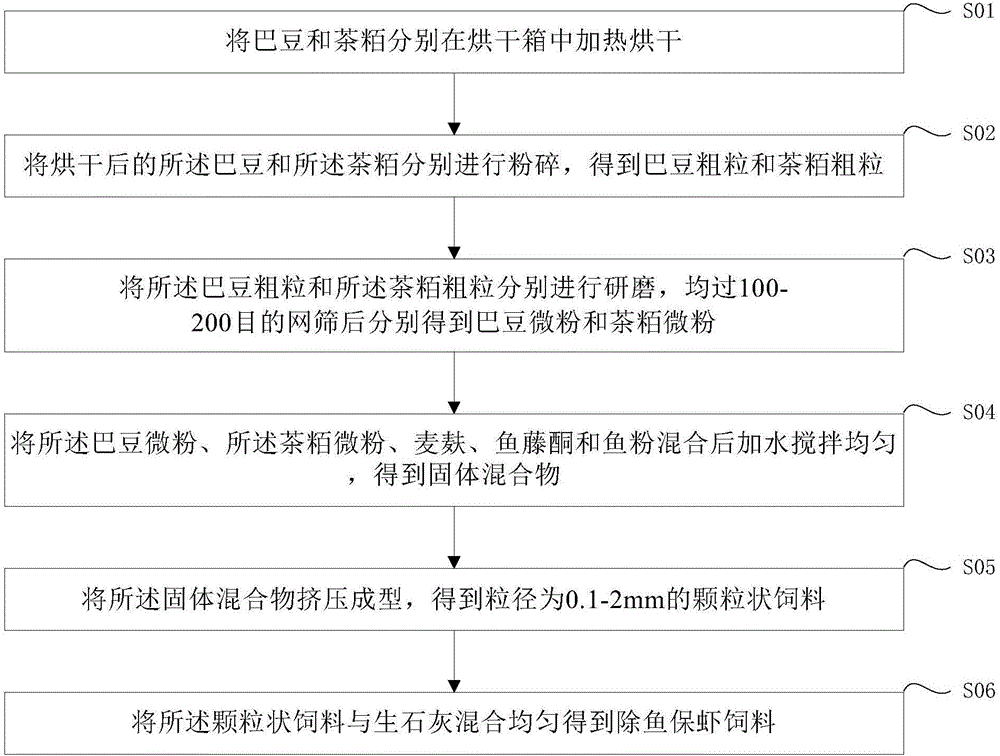
Feedstuff for killing fish and protecting crayfishes and the preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106306597AIncreased sensitivityEfficient removalFood processingClimate change adaptationRed blood cellPrawn
The invention provides a feedstuff for killing fish and protecting crayfishes. The feedstuff consists of croton, tea bran, wheat bran, fish flour, rotenone and quicklime, wherein croton can kill most fish; the tea bran contains 12-18% of tea saponin that can dissolve the red blood cells of fish, thereby killing miscellaneous fishes, loach, fresh-water snails, fresh-water mussels, tadpoles and some aquatic insects; when taken by fish, rotenone can inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and cause disorders of the respiratory system, such as dyspnea and convulsion, slackness, paralysis, and death; fish flour contains much protein and wheat bran, and can induce miscellaneous fishes, loach, and fresh-water snails who will take croton, tea bran, and rotenone, thereby killing the miscellaneous fishes, loach, fresh-water snails and other wild aquatic lives. The feedstuff for killing fish and protecting crayfishes provided in the invention is highly sensitive and can kill rough fish, fresh-water snails, etc. in the aquaculture water area of crayfishes, thereby protecting the growth environment of crayfishes.
Owner:湖南金欧农业科技有限公司
Composite feed additive capable of improving liver mitochondria function of jewfish as well as preparation method and application of composite feed additive
ActiveCN108308457AImprove mitochondrial functionNo harmful residuesOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyFeed additive
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
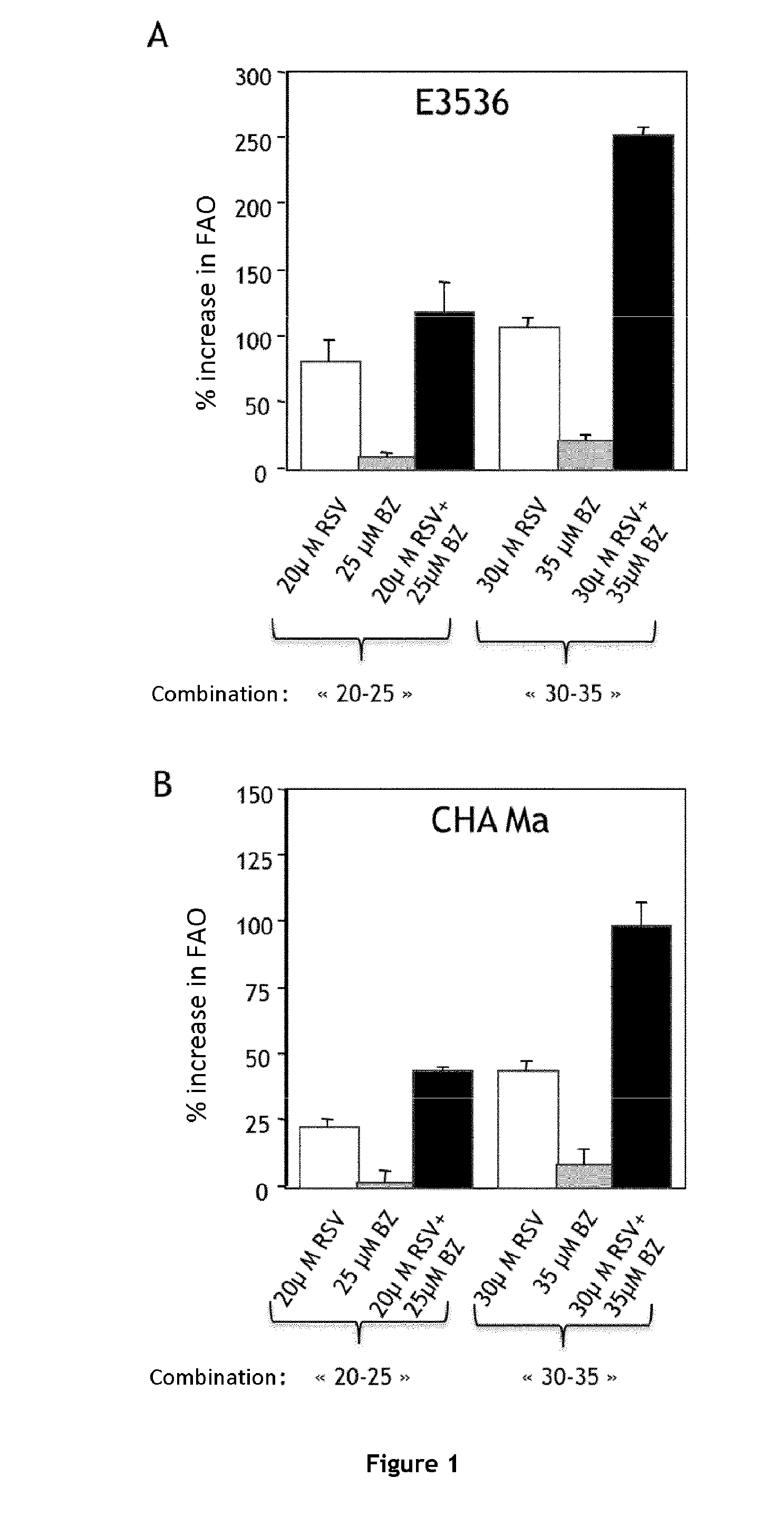
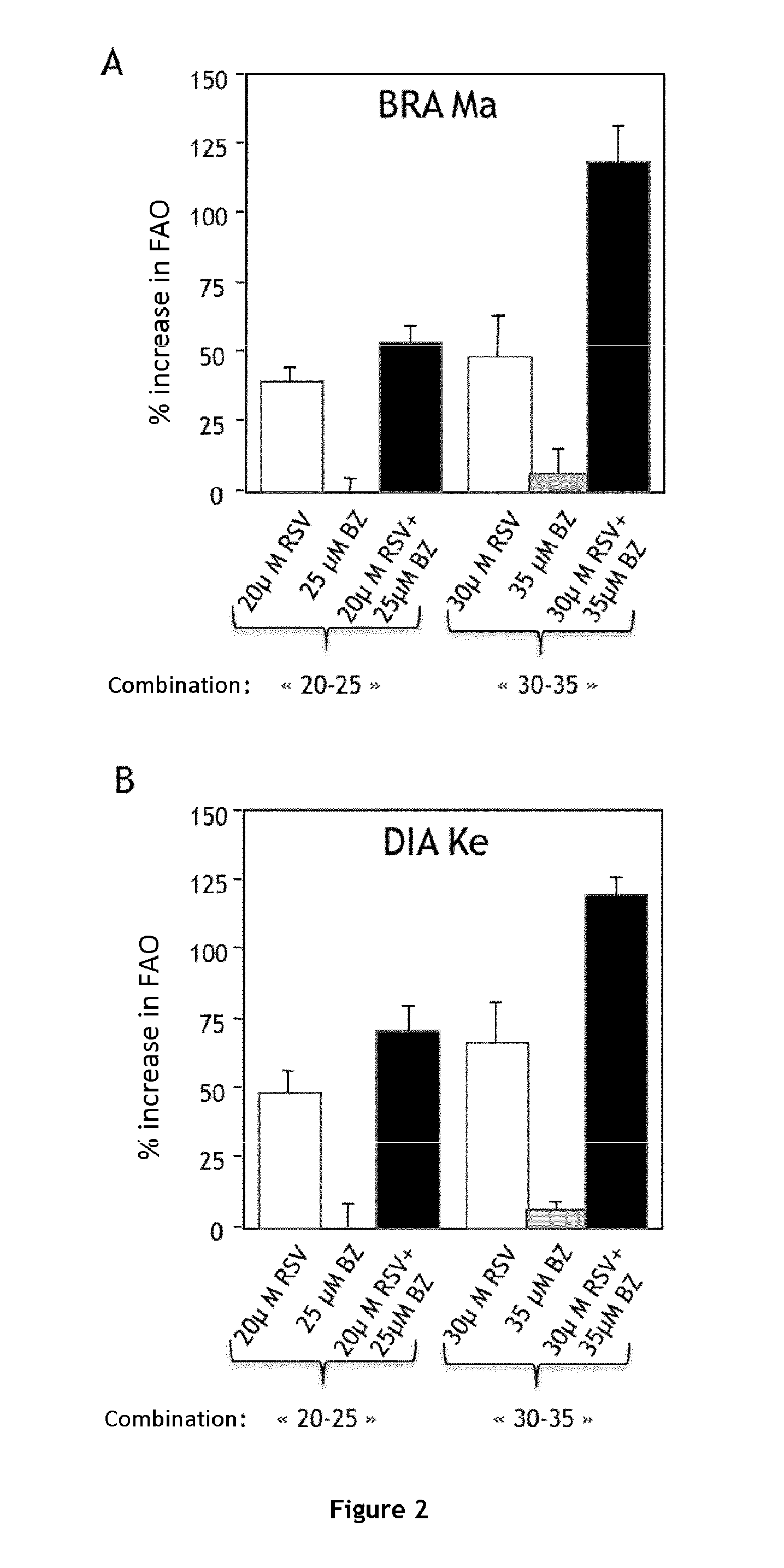
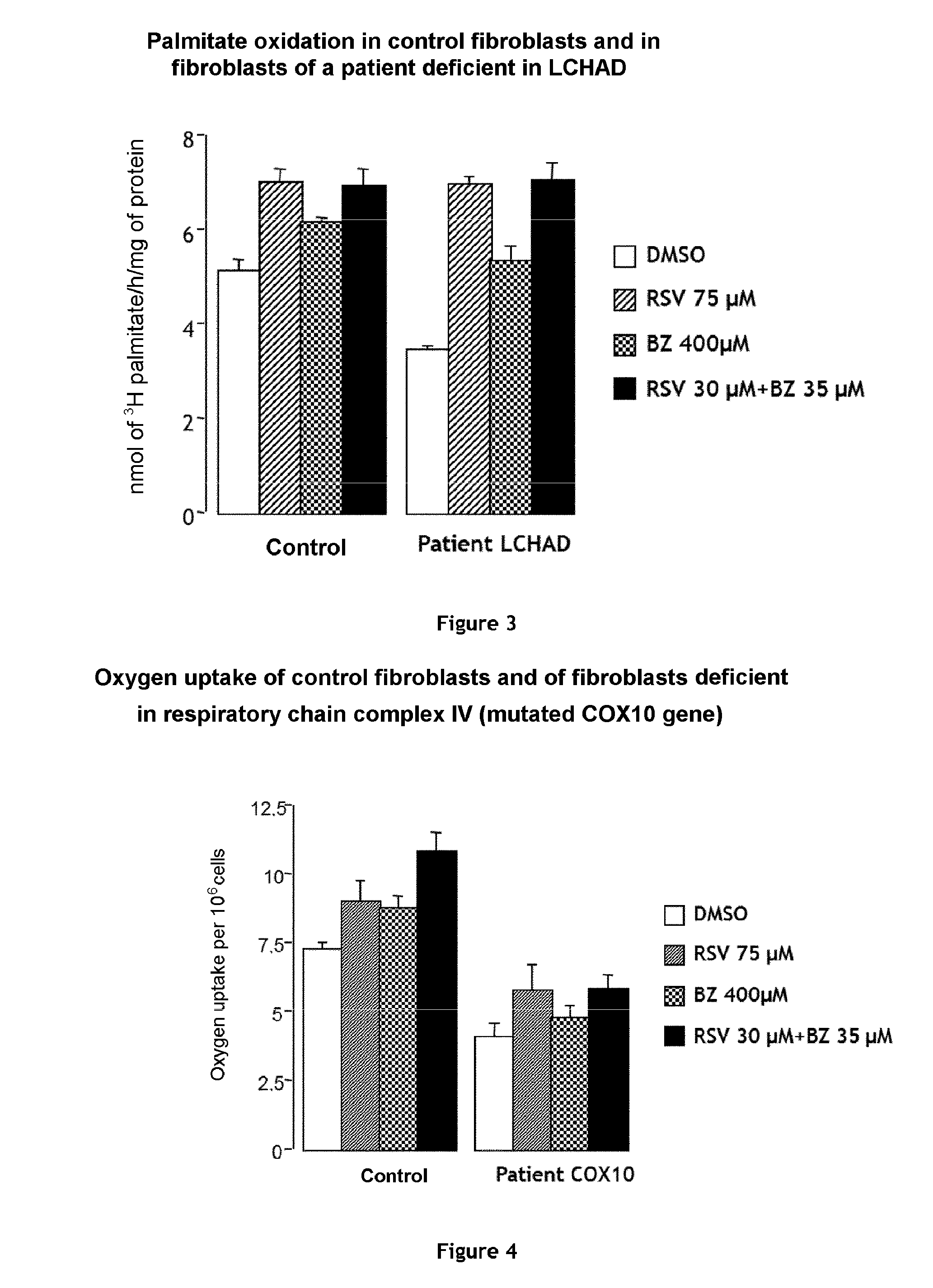
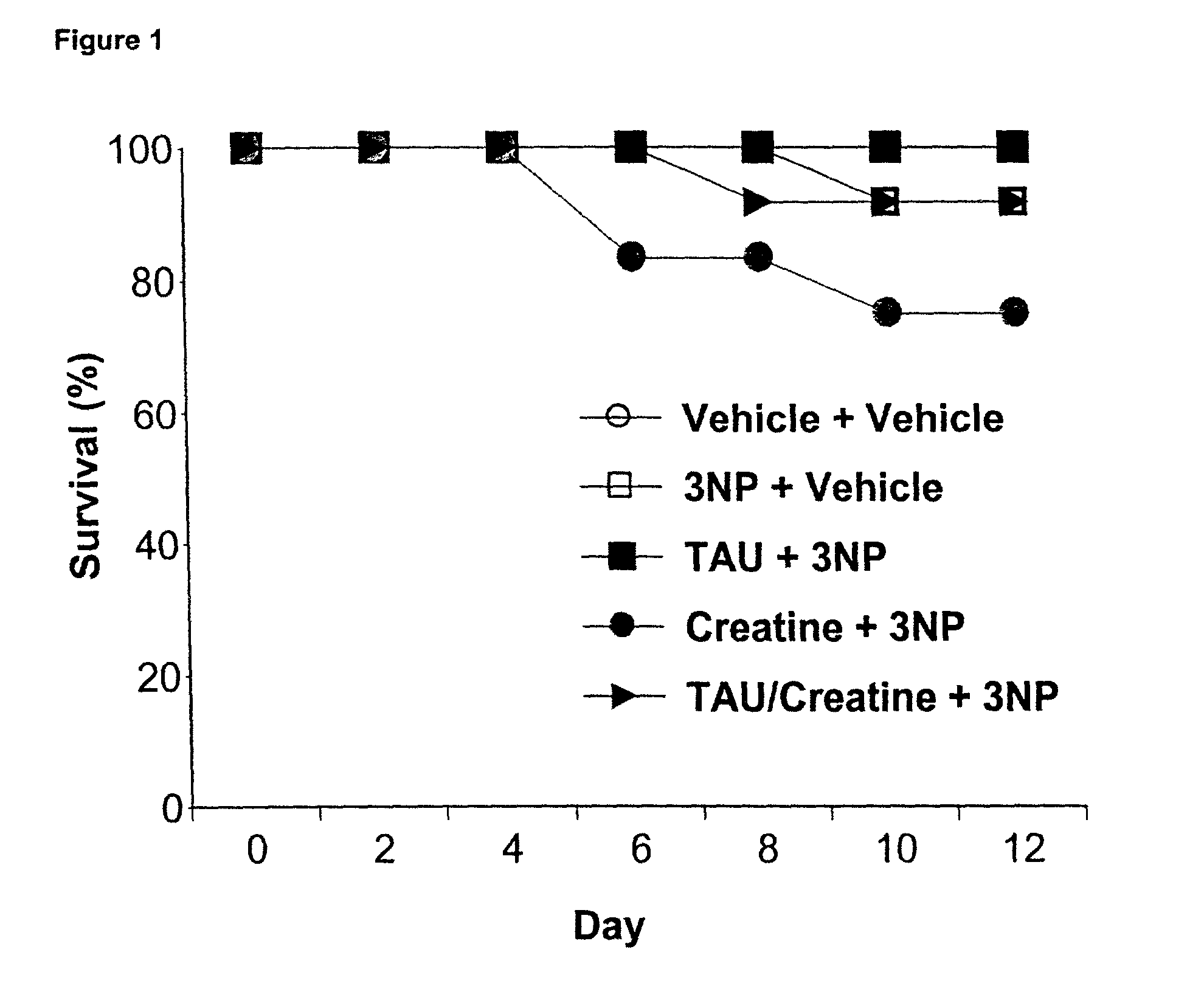
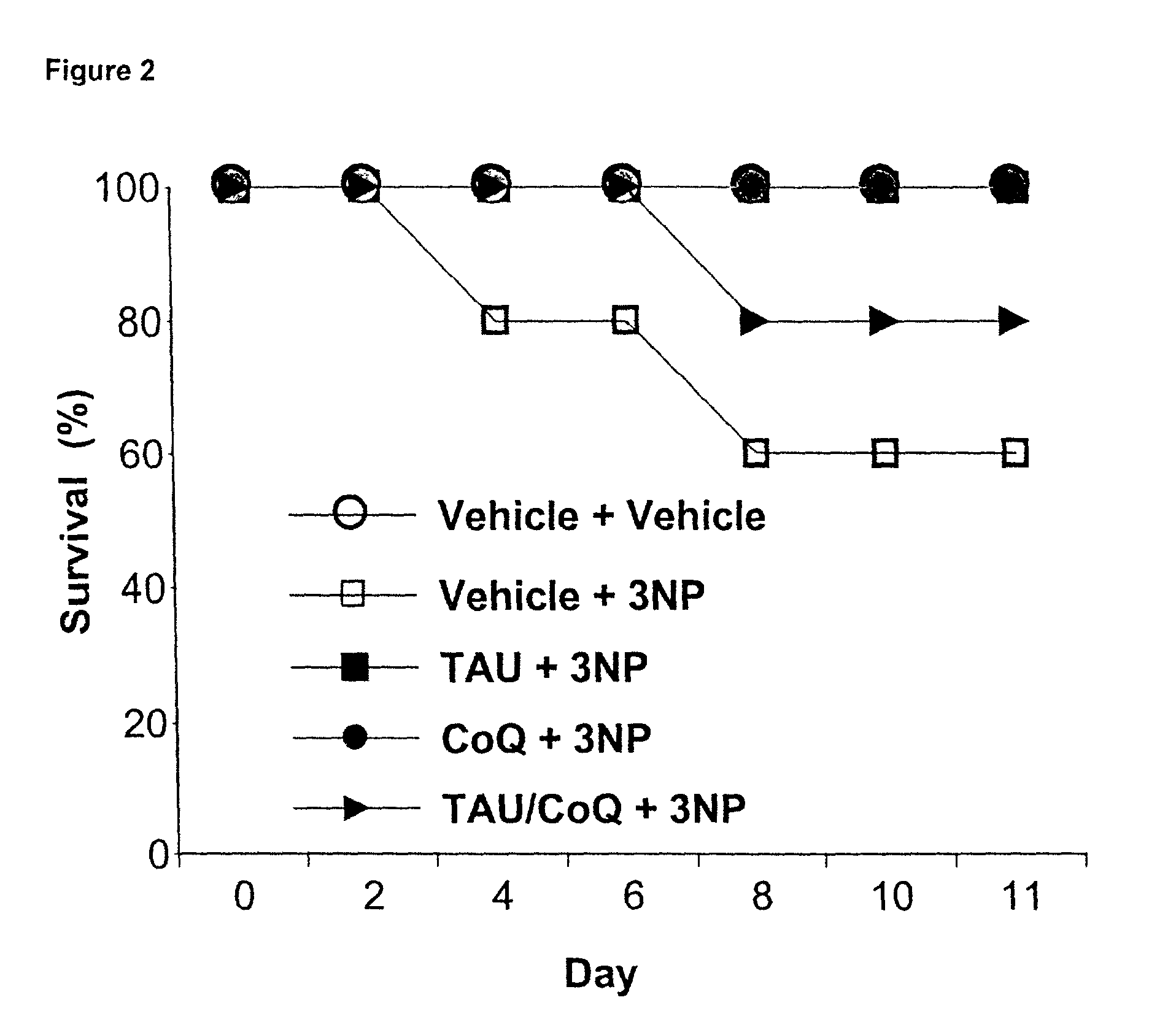
Combination of bezafibrate and of resveratrol or resveratrol derivatives for the treatment and prevention of diseases involving a mitochondrial energy dysfunction
ActiveUS20160317483A1Function increaseBetter correction of deficiencies of β-oxidationNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseBezafibrate
The present invention relates to the combined use of bezafibrate and of resveratrol or resveratrol derivatives for the treatment of diseases involving a mitochondrial energy dysfunction, and also to a pharmaceutical kit comprising both bezafibrate and resveratrol or resveratrol derivatives. The combination is more particularly used in the treatment of moderate defects of β-oxidation of long-chain fatty acids or of the respiratory chain of mitochondria.
Owner:UNIV DE PARIS +1
Compositions and methods for treatment of mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS7807654B2Increase resistancePreventing death and dysfunctionBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePyrimidine Nucleotides
Compounds, compositions, and methods are provided for treatment of disorders related to mitochondrial dysfunction. The methods comprise administering to a mammal a composition containing pyrimidine nucleotide precursors in amounts sufficient to treat symptoms resulting from mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Micro-nano hydrogel microsphere for targeted adjustment and control of mitochondrial respiratory chain as well as preparation and application of micro-nano hydrogel microsphere
ActiveCN114042147AReduce leakagePromote generationHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntipyreticCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
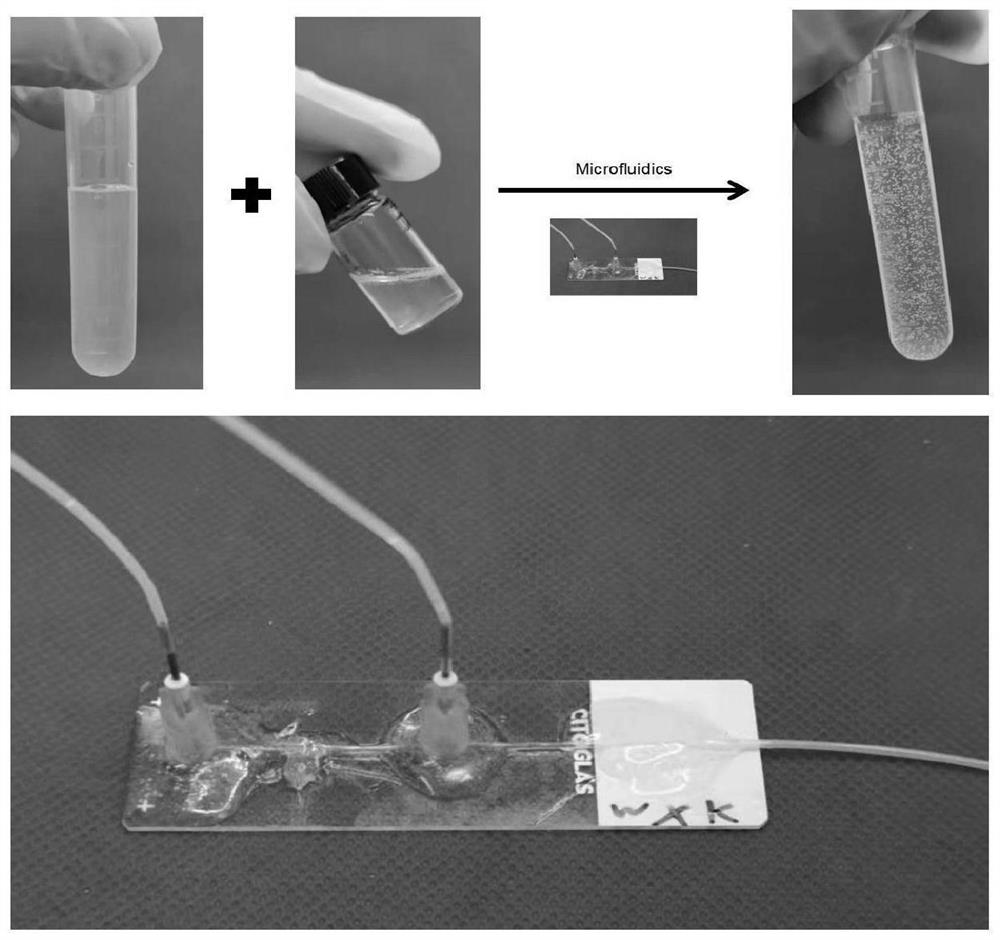
The invention provides a micro-nano hydrogel microsphere for targeted adjustment of a mitochondrial respiratory chain as well as preparation and application of the micro-nano hydrogel microsphere. According to the invention, hyaluronic acid microspheres are prepared through a microfluidic technology, and SS-31 peptide and Wyrgrl peptide modified resveratrol-loaded long-circulating liposome are connected in a microsphere nano network through a non-covalent bond, so that a micro-nano hydrogel microsphere system with a targeted cell MRC adjustment function is constructed. The system has efficient cellular uptake efficiency and mitochondrial targeting, and can significantly improve the MRC function, reduce proton leakage, protect mitochondria, down-regulate ROS expression, and promote generation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Meanwhile, the system can effectively slow down the progress of osteoarthritis in a rat osteoarthritis model. The micro-nano hydrogel microsphere system for the targeted adjustment and control of the cell MRC function, provided by the invention, has great potential in treating various degenerative diseases related to MRC dysfunction.
Owner:川北医学院附属医院
Pro-oxidant Anti-cancer compounds
ActiveUS20110059898A1Effective compoundEfficient killingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCancer preventionCancer cell
This invention relates to anti-cancer compounds and to methods for treating or preventing cancer. In particular, the invention concerns pro-oxidant anti-cancer compounds, such as pro-oxidant forms of vitamin E, that selectively interact with complex II of the mitochondrial respiratory chain of cancerous cells, generate reactive oxygen species and induce apoptosis of those cells.
Owner:CANCURE LTD
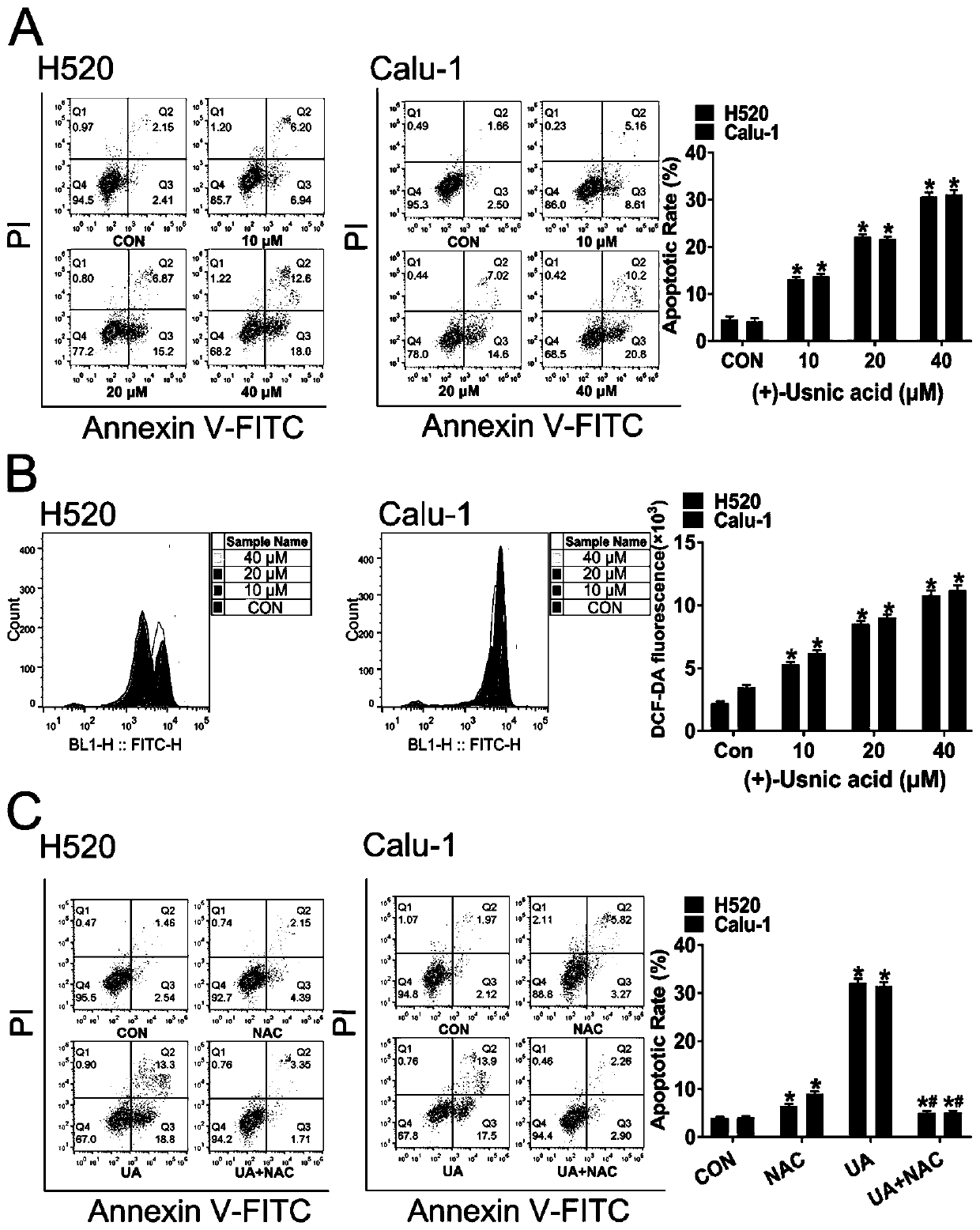
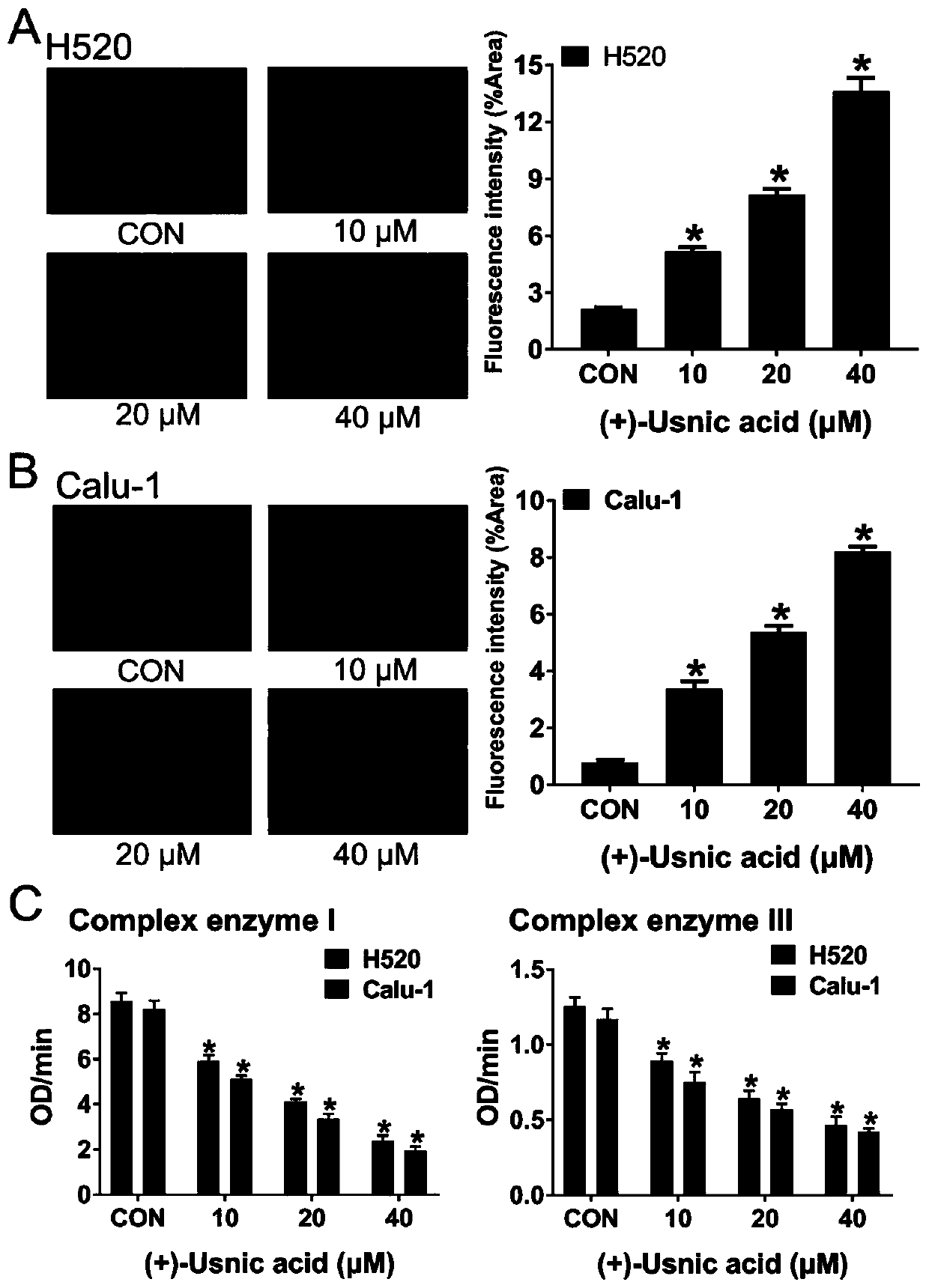
Application of d-usnic acid or combination of d-usnic acid and paclitaxel in preparing drug for treating and resisting lung squamous carcinoma
InactiveCN110840877AGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPaclitaxelMitochondrial respiratory chain
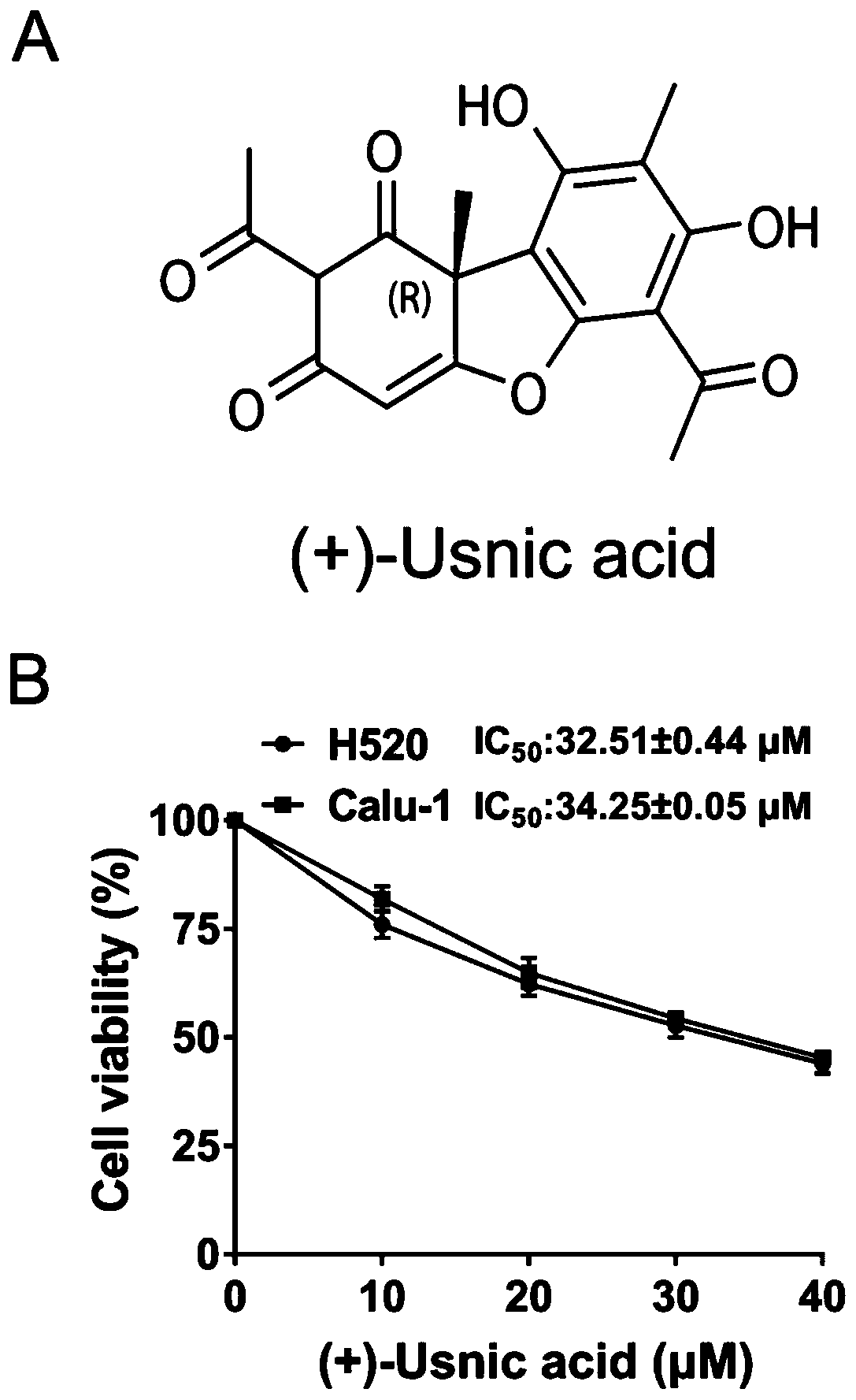
The invention discloses application of d-usnic acid in preparing drug for treating and resisting lung squamous carcinoma and application of a combination of d-usnic acid and paclitaxel in preparing drug for treating and resisting lung squamous carcinoma. Repeated experiments find that the d-usnic acid can reduce lung squamous carcinoma cell survival and can lead to explosive generation of reactiveoxygen species (ROS) by inhibiting mitochondrial respiratory chain and Nrf2 expression so as to remarkably induce lung squamous carcinoma cell apoptosis; combined application of the d-usnic acid andpaclitaxel can synergistically resist lung squamous carcinoma. Naked mouse tumor formation experiments prove effectiveness of the d-usnic acid in resisting lung squamous carcinoma in vivo and synergistic anticancer effect of the combination of the d-usnic acid and paclitaxel. An experiment basis is provided for selection of effective assistant drug for clinically resisting lung squamous carcinoma,and experimental data support to further develop the d-usnic acid which is a drug candidate for resisting lung squamous carcinoma and treatment schemes combining the d-usnic acid with paclitaxel.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 and application of rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 in resisting cell damage
ActiveCN110511933AOrganic active ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionCell damageApoptosis
The invention discloses a rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 and an application of the rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 in resisting cell damage. The sequence of the rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or has homology with more than 190% of SEQ ID NO.1; according to the invention, objective existence of the sequence is proved through PCR; a full-length transcript of the sequence can be cloned; a pcDNA 3.0-lncMSTRG10078 overexpression vector is constructed, GH3 cells are transfected, and results show that overexpression of lncMSTRG10078 can significantly regulate mitochondrial respiratory chain subunits, inflammation, apoptosis and metabolic changes so as to resist cell damage; flow results can show that overexpression of lncMSTRG10078 can significantly inhibit the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis, and further prove that the sequence can enhance the effect of cells on resisting cell damage.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
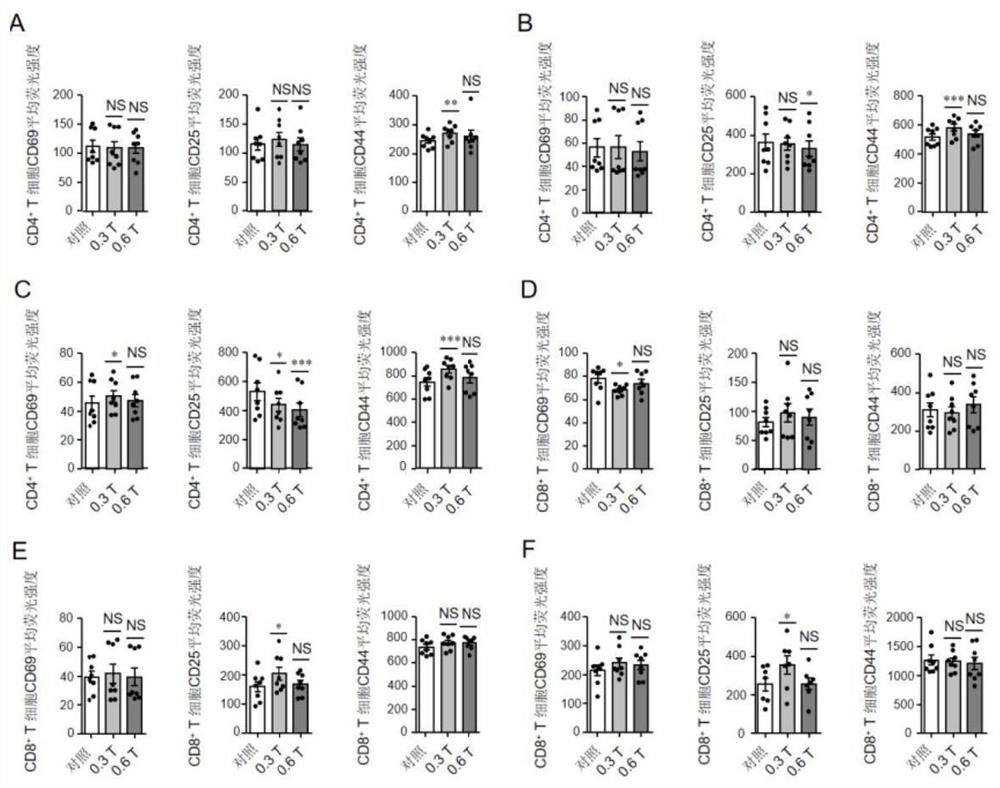
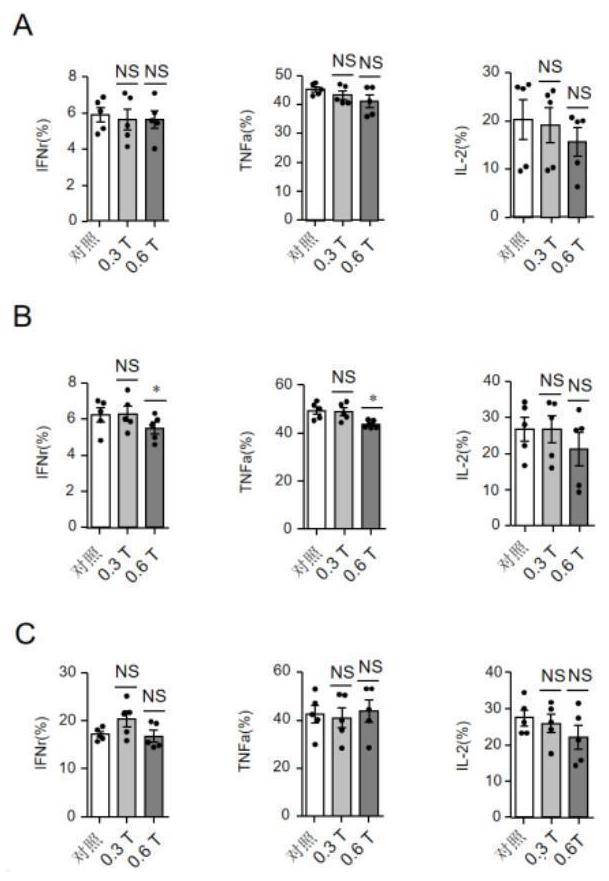
Immune cell treated by magnetic field and application thereof
ActiveCN111733154APromote secretionBoost breathing levelsCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsReceptorT cell
The invention relates to an immune cell treated by a magnetic field and application thereof. According to the invention, a medium static magnetic field with the intensity of 0.3T can promote secretionof CD8<+> T cell granzyme and cell factors of a mouse, increase the level of ATP and mitochondrial respiration and up-regulate expression of related genes Uqcrb and / or Ndefs 6 of a mitochondrial respiratory chain. In addition, magnetic receptor candidate genes Isca1 and Cry1 / Cry2 participate in regulation and control of expression of Uqcrb and / or Ndefs 6. An in-vivo experiment shows that the static magnetic field can inhibit growth and development of tumors by promoting secretion of the CD8<+>T cell granzyme and the cell factors. A killing ability test shows that static magnetic field treatment can enhance the killing ability of CD8<+> T cells, and the CD8<+> T cells treated by the magnetic field have a remarkable anti-tumor effect when being transfused back into a tumor grafted mouse.The invention not only discloses that the medium-intensity static magnetic field can enhance the killing ability of the CD8<+> T cells by promoting mitochondrial respiration, but also provides a novel method for enhancing the anti-tumor function of the CD8<+> T cells by a physical method.
Owner:HEYE HEALTH TECH CO LTD +1
Use of rotenone as non-small cell lung cancer cell sensitizer
InactiveCN101904837BNo obvious side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectNormal cell
The invention relates to novel use of a mitochondrial respiratory chain inhibitor rotenone in reversing the tolerance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to targeted antineoplastic agents. The rotenone serves as a non-small cell lung cancer cell sensitizer and can reverse the tolerance of the non-small cell lung cancer cells to the targeted antineoplastic agents. The invention shows the combination of rotenone compounds and TRAIL has no obvious toxic or side effect on normal cells and is a novel medicinal composition used for treating the non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
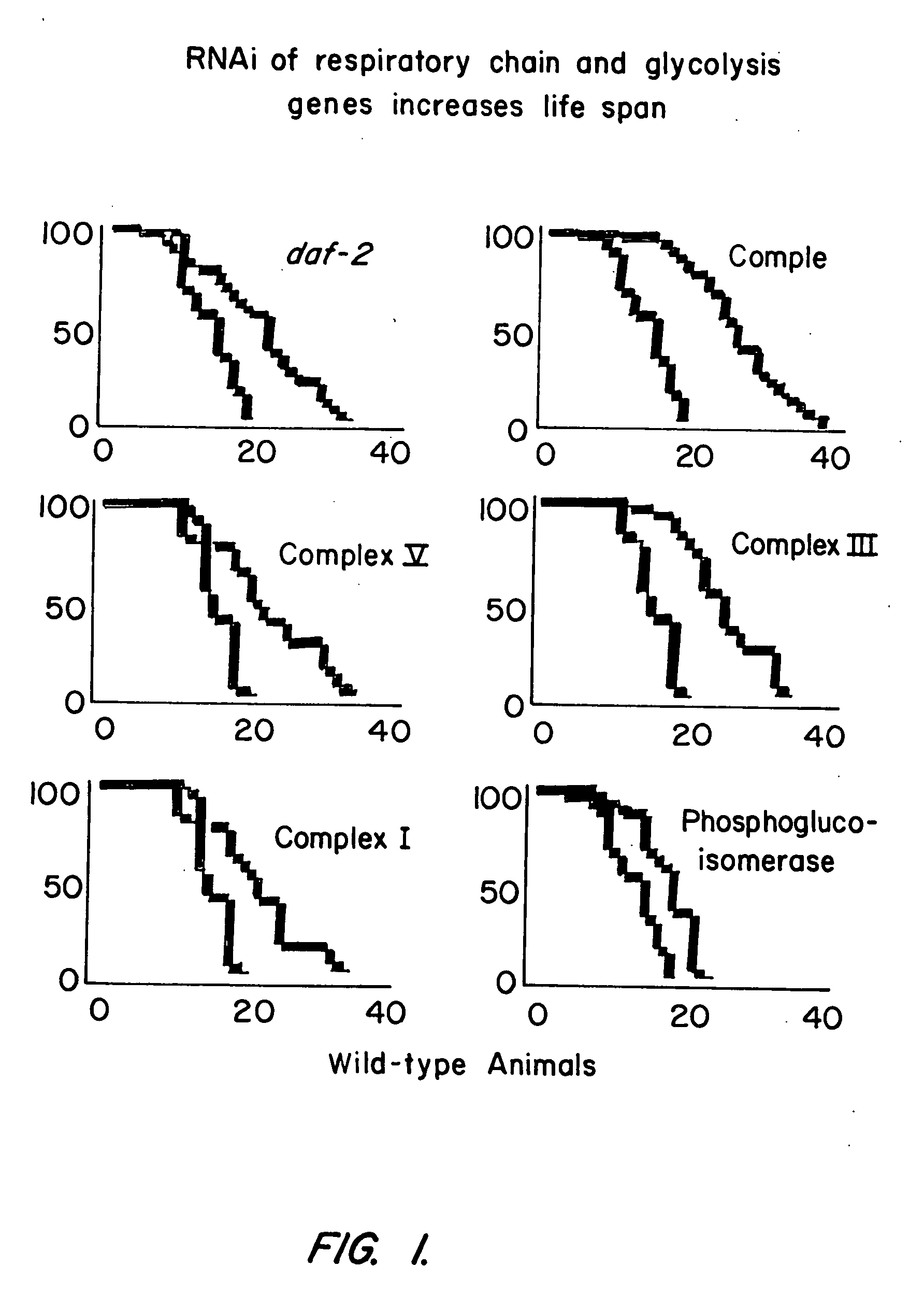
Eukaryotic genes involved in adult lifespan regulation
The present invention relates to regulation of adult lifespan in eukaryotes. More particularly, the present invention is directed to methods of assaying for genes, gene products, and genes in pathways controlled by such genes and gene products, using RNAi and microarray analysis, that regulate lifespan (e.g., extend or truncate adult lifespan) in eukaryotes such as invertebrates (e.g., C. elegans), plants, and mammals, e.g., humans. For example, the present invention is directed to genes encoding components of the mitochondrial respiratory chain and genes encoding glycolysis enzymes, which are involved in lifespan regulation, and genes and gene products in pathways controlled by such genes. Other genes and gene products identified as regulating aging and aging pathways include a gene encoding a GTPase; a transcriptional activator; novel genes: llw-1, llw-2, llw-3, and llw-4; genes encoding cytochrome P450 proteins (involved in steroid biosynthesis); a melatonin synthesis gene; genes encoding insulin and insulin-like peptides; genes encoding heat shock factors; genes encoding catalases; stress-response genes; and metabolic genes. The invention further relates to methods for identifying and using agents, including small molecule chemical compositions, antibodies, antisense nucleic acids, and ribozymes, that regulate, e.g., enhance, adult lifespan via modulation of aging associated proteins; as well as to the use of expression profiles, markers, and compositions in diagnosis and therapy related to lifespan extension, life expectancy, and aging. The present invention also relates to gene therapy involving lifespan associated genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
A compound feed additive for improving liver mitochondria function of sea bass and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108308457BNo harmful residuesSynergisticOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyFeed additive
The invention relates to a composite feed additive capable of improving liver mitochondria function of jewfish as well as a preparation method and application of the composite feed additive, and belongs to the field of feeds. Each 100 parts by weight of the composite feed additive comprises the following components in parts by weight of 6-10 parts of manganese chelate methionine, 2-6 parts of copper chelate methionine, 30-50 parts of berberine, 20-30 parts of creatine, 0.5-2 parts of red Fife yeast and the balance of a carrier. The raw materials of the composite feed additive are safe, harmless, and free from residues, and create condition for production of green feeds and aquatic products. According to the preparation method of the composite feed additive, the raw materials are mixed in compounding ratio. The preparation method is simple, good in condition controllability, and good in stability, and has favorable application prospects. The composite feed additive is applied to preparation of the feed for jewfish, so that the liver mitochondria antioxidant ability and the mitochondrial respiratory chain function of the jewfish can be improved, and the mitochondria oxidative damagecan be reduced.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, methods for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
InactiveUS20120064091A1High expressionImprove concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineRespiratory chain dysfunction
The invention relates to a method, of assessing whether a subject is affected with or at risk for developing a dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, the method comprising determining the concentration of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in a biological sample from the subject, and comparing it to the concentration of FGF21 in a biological sample from at least one normal control, wherein an increase in the concentration of FGF21 in the biological sample from the subject when compared to the concentration of FGF21 in the biological sample from at least one normal control is indicative of occurrence of the dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in said subject, or of risk for developing said dysfunction. The invention also relates to a method for follow-up of a dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in a subject diagnosed with but not being treated for said dysfunction, to a method for treating a subject having a dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, to a method for determining whether a dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in a subject diagnosed with and being treated for said dysfunction is responding to the treatment, and for selecting patients for clinical trials.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI
A rat long non-coding lncRNA-lncmstrg10078 and its application against cell damage
ActiveCN110511933BOrganic active ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionCell damageApoptosis
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
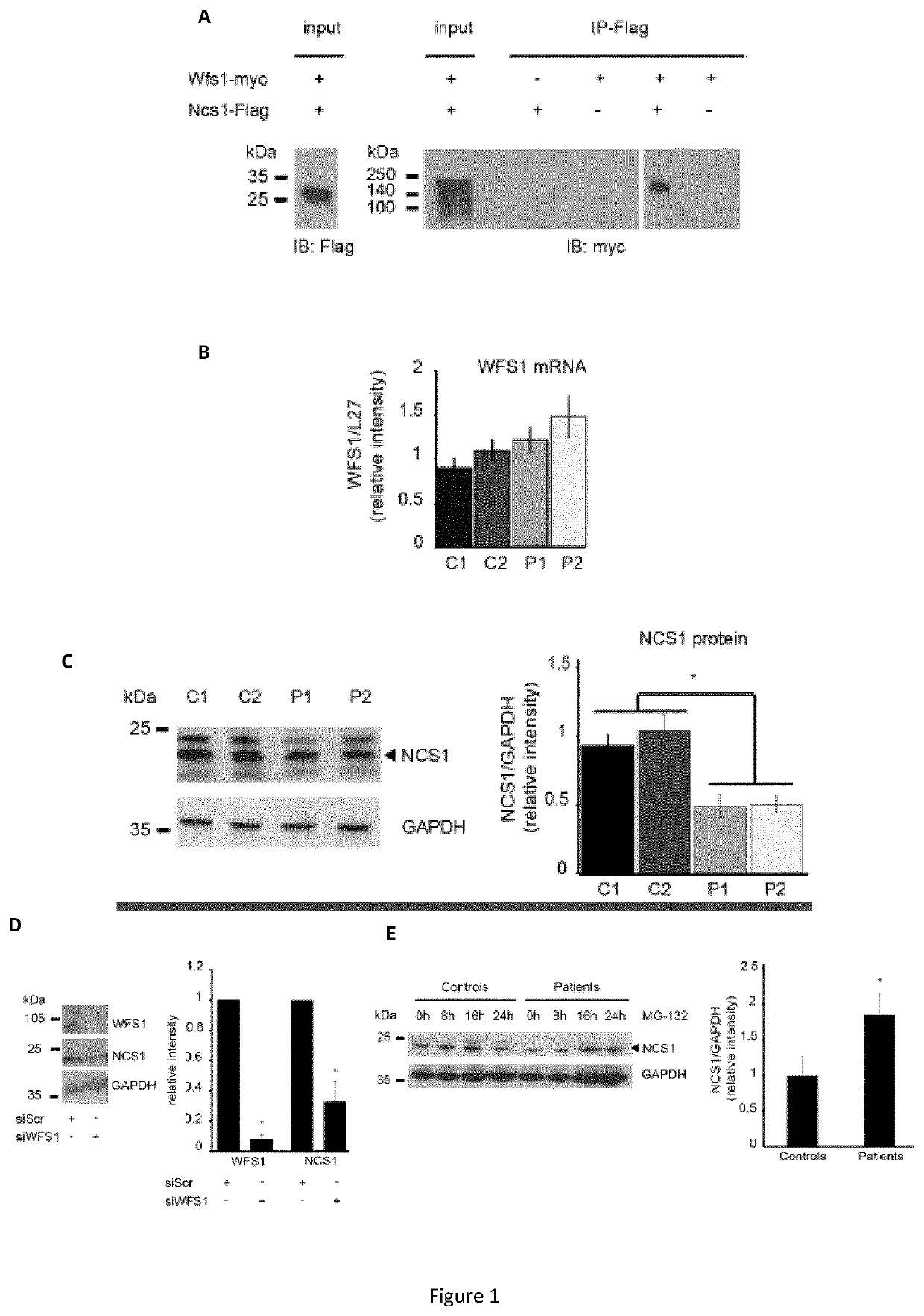
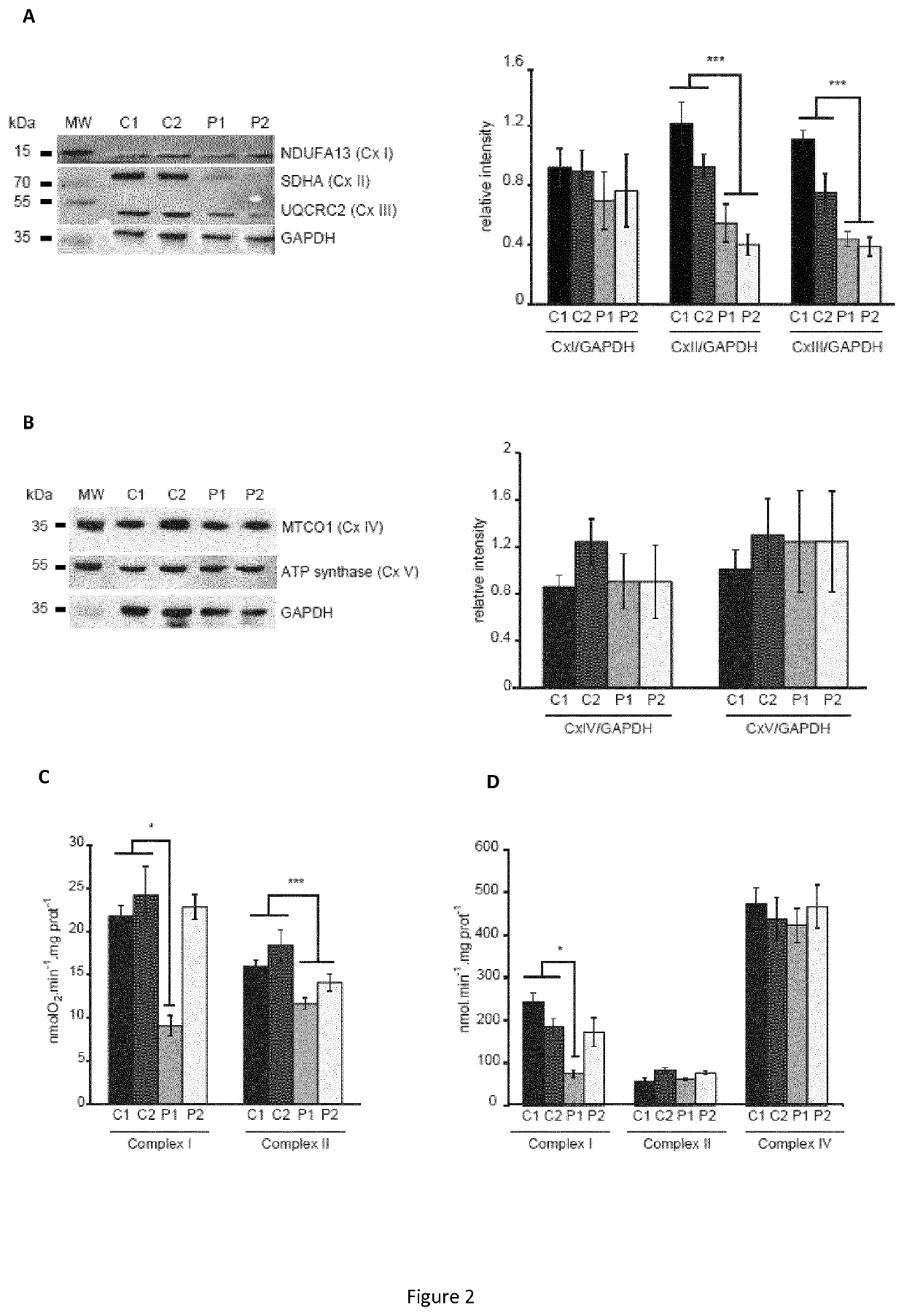
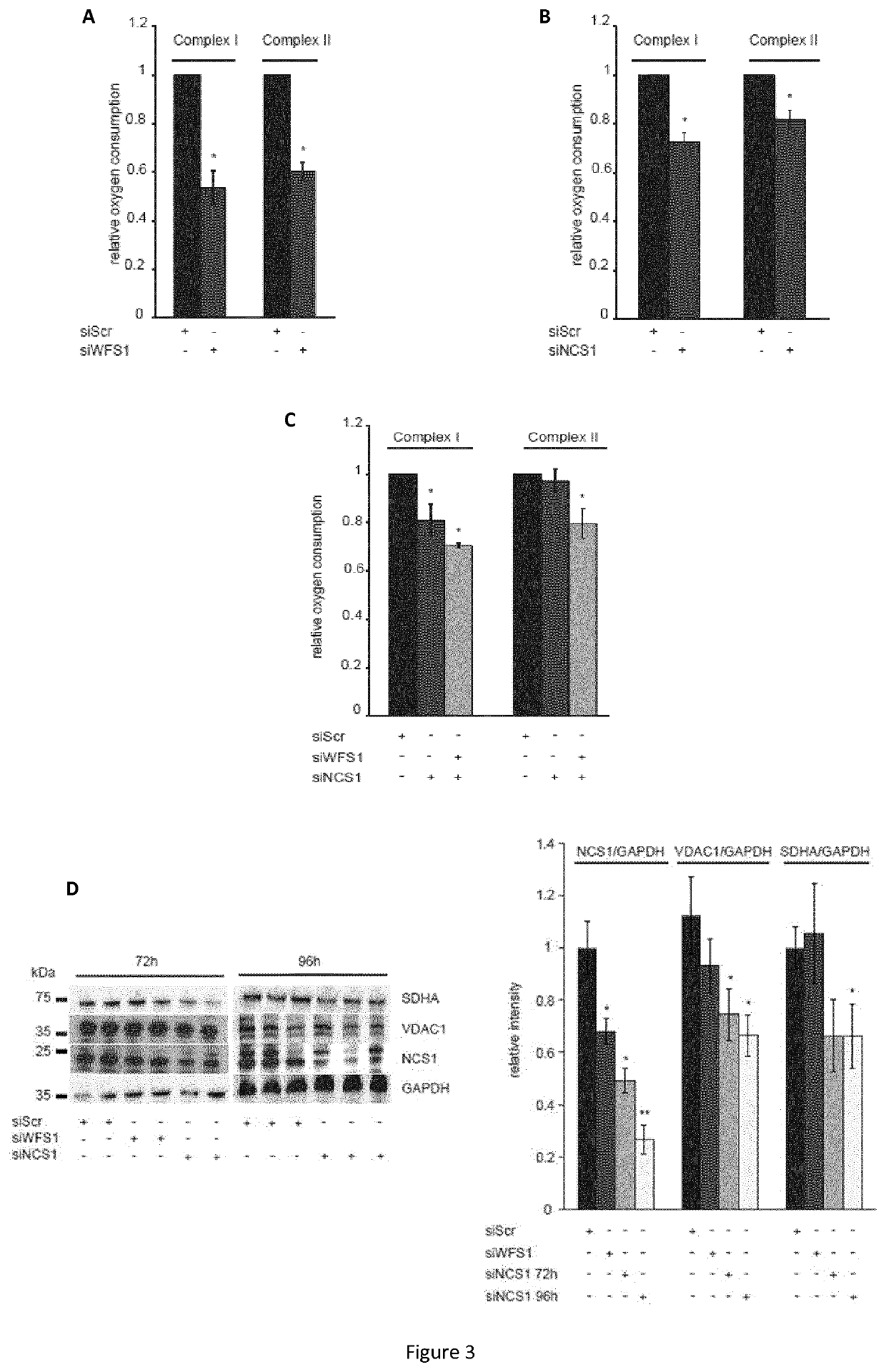
Targeting the neuronal calcium sensor 1 for treating wolfram syndrome
ActiveUS10639384B2Prevent degradationEasy transferOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderProteasome degradationMedicine
The present invention relates to novel therapeutic ways for treating Wolfram Syndrome (WS) by targeting the neuronal calcium sensor 1 (NCS1). The present inventors have demonstrated that WFS1, which loss of function is responsible of the Wolfram Syndrome, forms a complex with the neuronal calcium sensor 1 (NCS1). The inventors have further demonstrated that WFS1 associates with NCS1 to prevent its degradation by the proteasome and that NCS1 regulates VDAC expression and mitochondrial respiratory chain. Thus, present invention provides an agonist of NCS1 for use in the treatment of WS. Such an agonist is e.g. a NCS1-encoding polynucleotide, an inhibitor of the proteasome or of calpains. The inventors have further shown that overexpression of NCS1 in WS cells allows increasing complex II driven respiration. The present invention further relates to a method for predicting the severity of WS by measuring the NCS1 level in a sample obtained from a patient.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
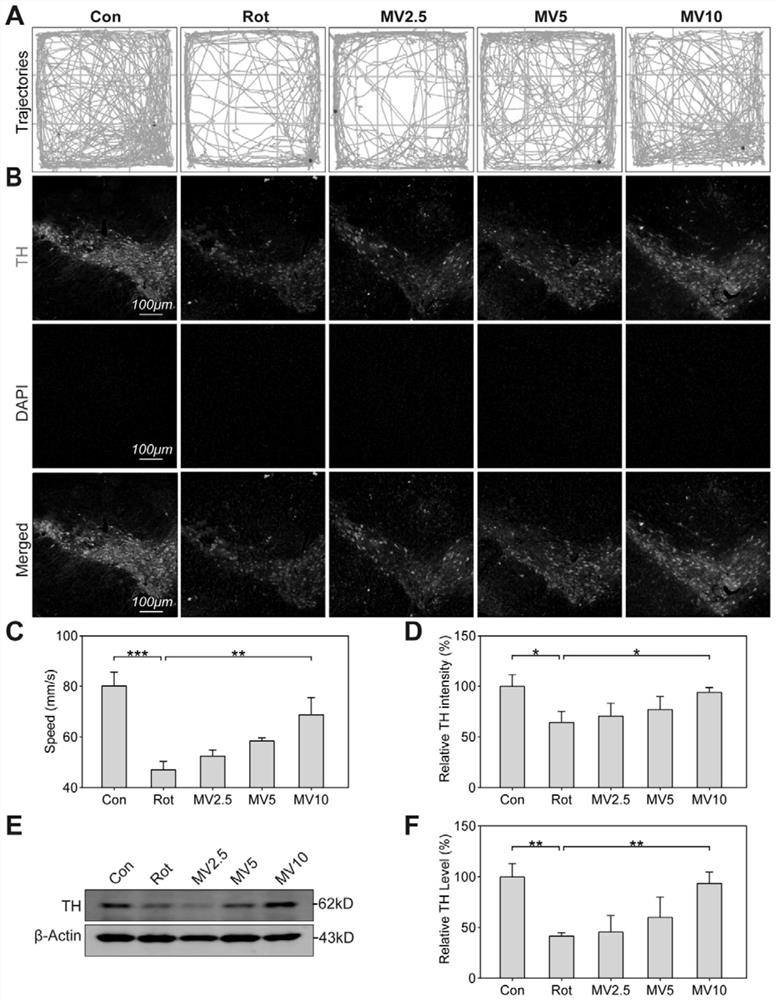
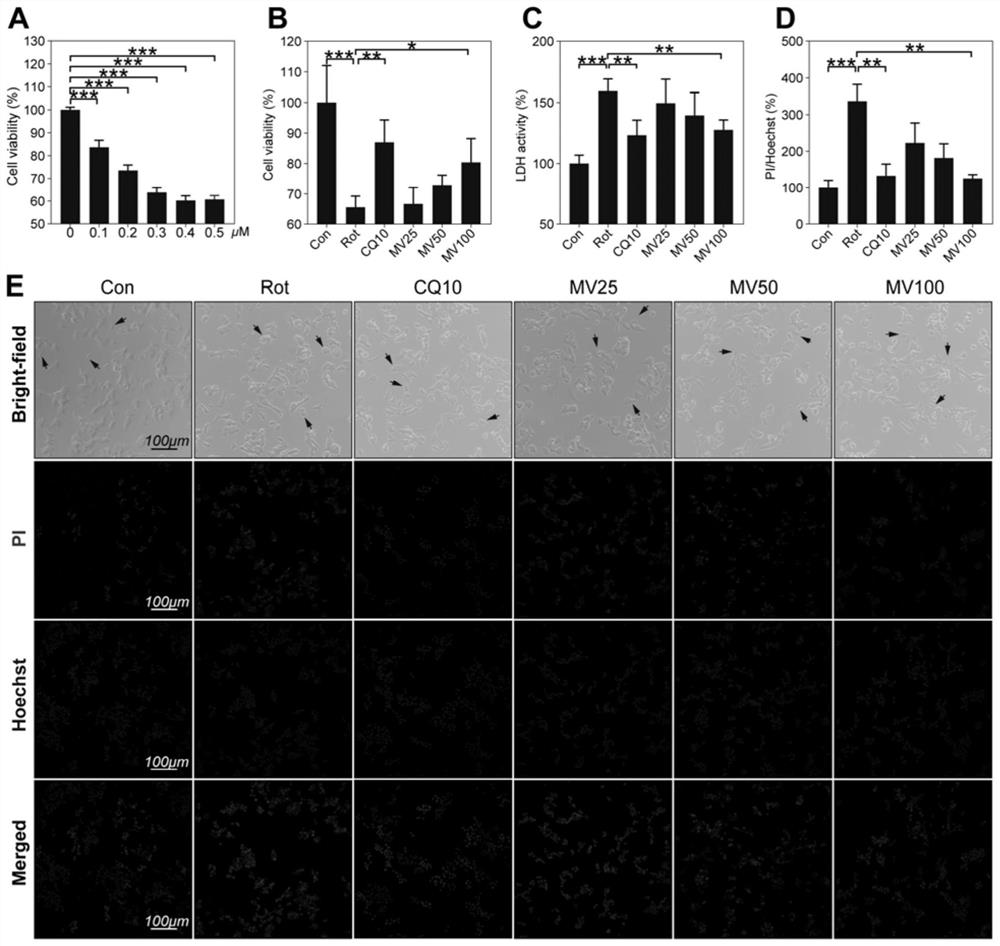
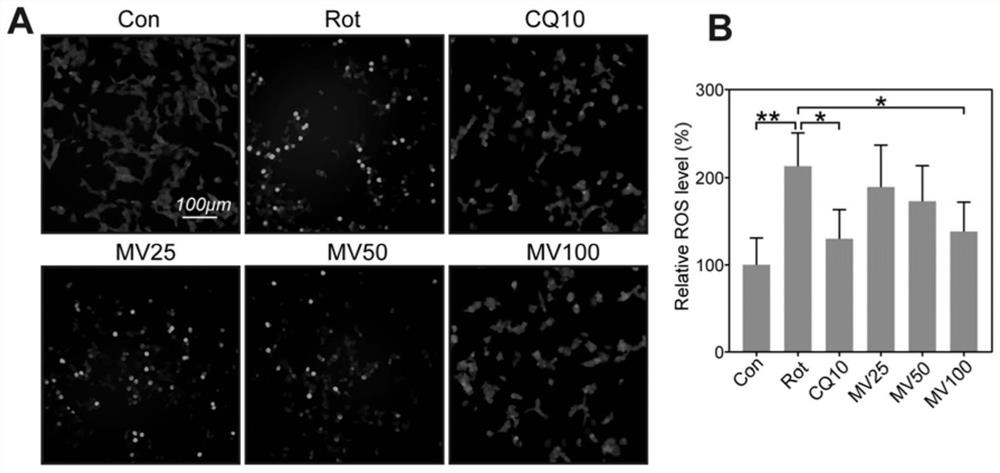
Application of mogroside V (MV) in preparation of medicine with protection effect on neuronal injury caused by Parkinson's disease (PD)
PendingCN114042078AReduced dysfunctionDiscuss the mechanism of actionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMogroside VSIRT3
The invention discloses application of MV in preparation of a medicine with protection effect on neuronal injury caused by PD. The protection effect of the MV on neurotoxicity induced by Rotenone (Rot) is researched; in-vivo and in-vitro models of PD are established; then behavioristics and nerve injury, cell viability, ROS (reactive oxygen species) level, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), mitochondrial respiratory chain function, early apoptosis and ATP (adenosine triphosphate) level of model mice are detected; and finally, by up-regulating Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3), the action mechanism of the MV in the neuroprotection of PD is discussed.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUILIN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com