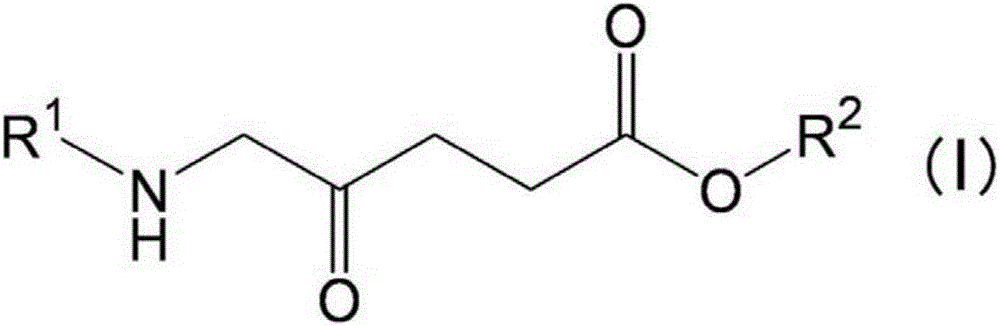
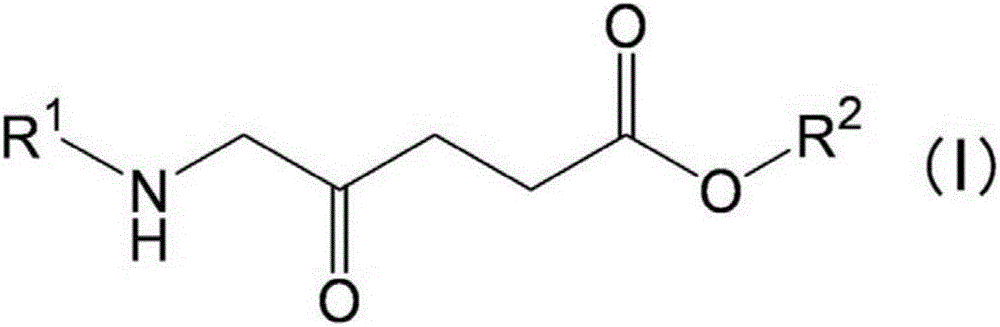
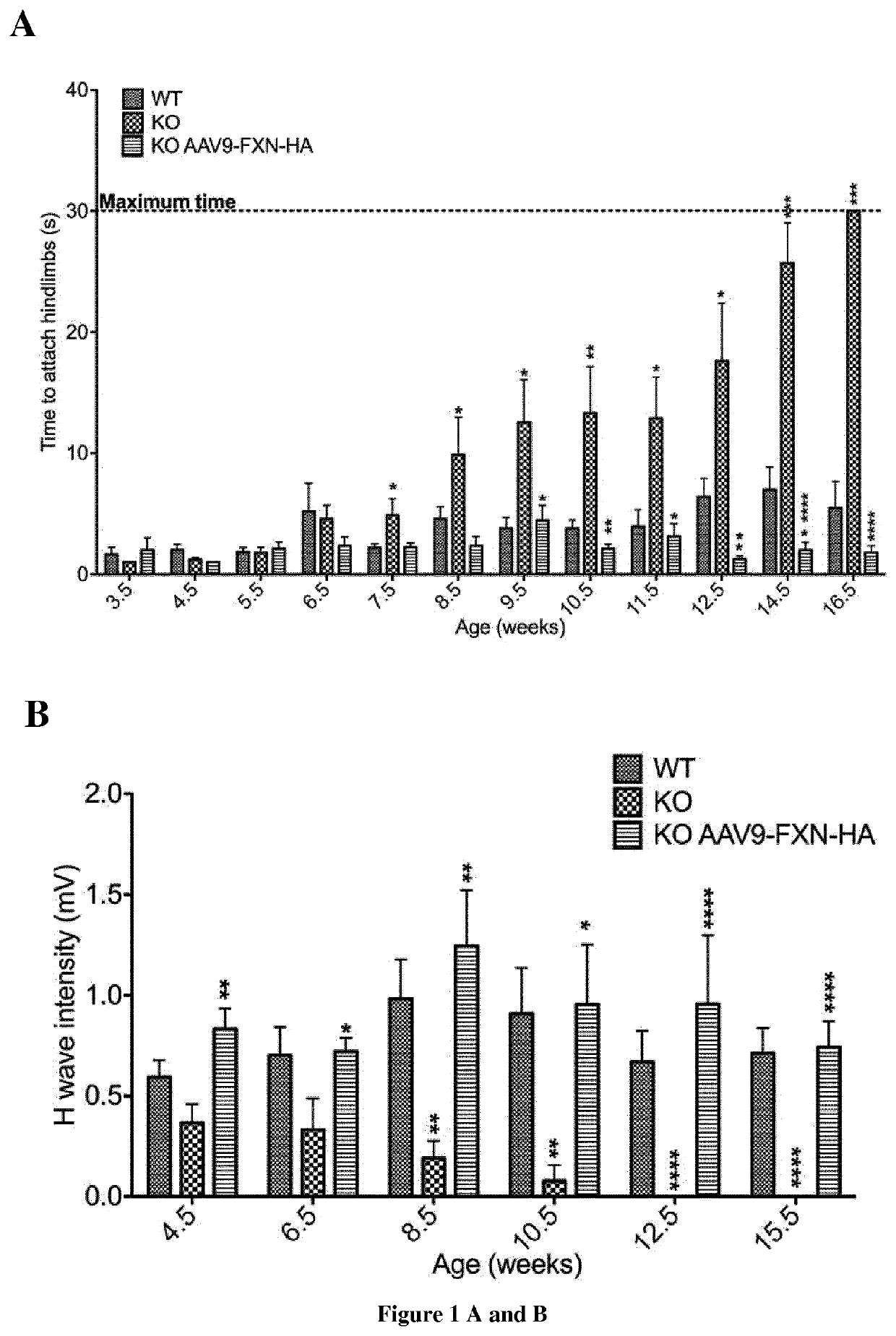
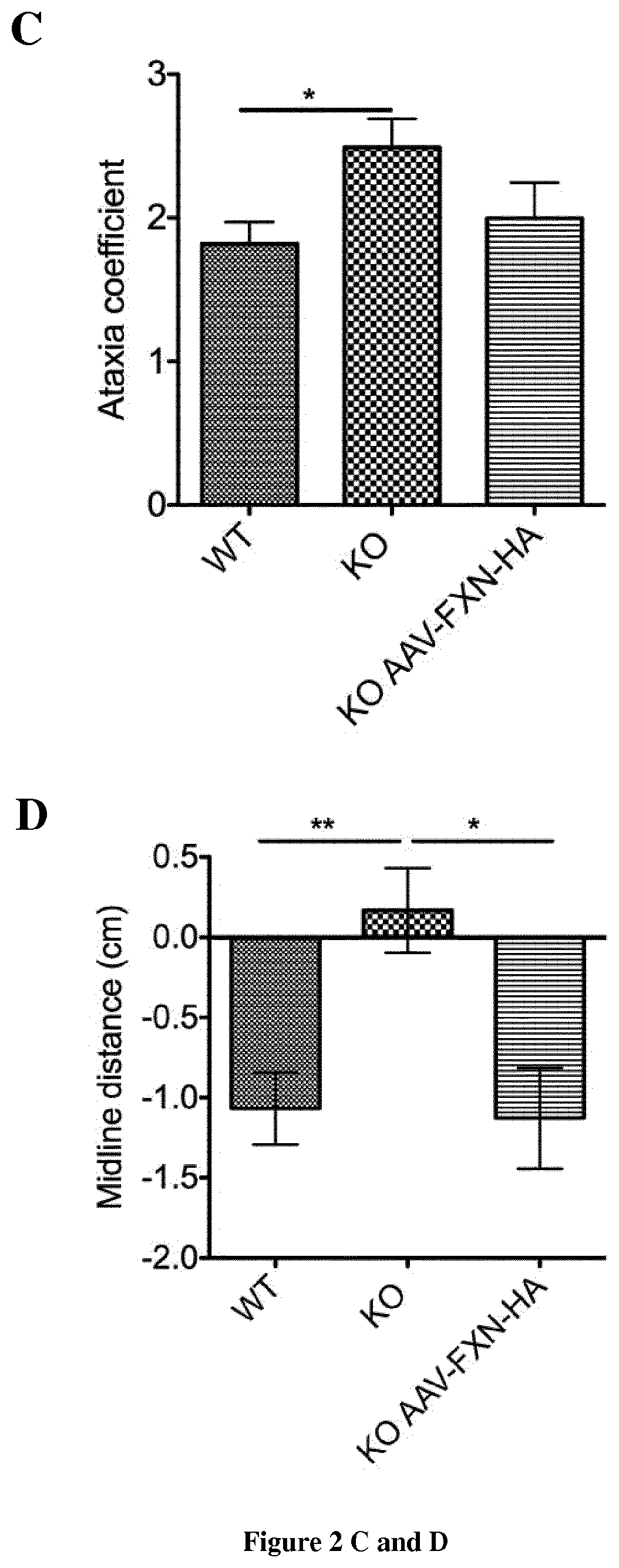
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Frataxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frataxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXN gene. It is located in the mitochondrion and Frataxin mRNA is mostly expressed in tissues with a high metabolic rate. The function of frataxin is not clear but it is involved in assembly of iron-sulfur clusters. It has been proposed to act as either an iron chaperone or an iron storage protein. Reduced expression of frataxin is the cause of Friedreich's ataxia.
Direct molecular diagnosis of Friedreich ataxia
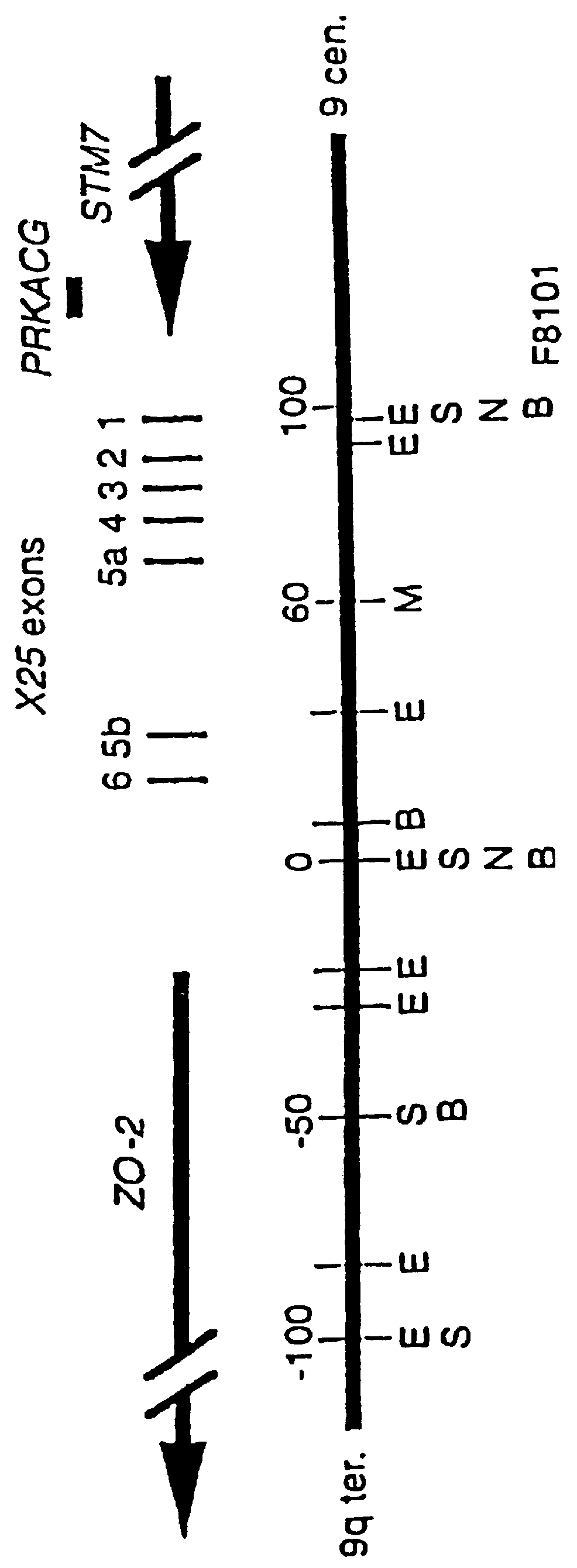
This invention relates generally to methods for the diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of Friedreich Ataxia. Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal recessive, degenerative disease that involves the central and peripheral nervous system and the heart. A gene, X25, was identified in the critical region for the FRDA locus on chromosome 9q13. The gene encodes a 210 amino acid protein, frataxin, that has homologues in distant species such as C. elegans and yeast. A few FRDA patients have been found to have point mutations in X25, but the vast majority are homozygous for a variable, unstable GAA trinucleotide expansion in the first X25 intron. Mature X25 mRNA was severely reduced in abundance in individuals with FRDA. Carriers and individuals at risk for developing FRDA can be ascertained by the methods of the present invention. Further, the methods of the present invention provide treatment to those individuals having FRDA.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Treatment of mitochondrial diseases with an erythropoietin mimetic
InactiveUS20090291092A1Stimulating erythropoiesisNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRed blood cell
Methods of treating mitochondrial disorders that are not respiratory chain disorders using compositions comprising EPO mimetic compounds or compounds capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are disclosed. Methods of treating Friedreich's ataxia, Leigh's syndrome, or other disorders by increasing the expression of frataxin with an EPO mimetic compound or a compound capable of increasing endogenous EPO levels or stimulating erythropoiesis are also disclosed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
Screening method and compounds for treating friedreich ataxia
InactiveUS20050222218A1Reducing cellular glutathione contentGood skin permeabilityBiocideCompound screeningMedicineFrataxin
The present invention relates to a method for identifying and / or validating candidate substances for the treatment of Friedreich Ataxia (FRDA). Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of selenium, Ebselen and Glutathione peroxidase (GPX) mimetics for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of FRDA. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of cells with reduced frataxin expression for identifying and / or validating candidate substances for the treatment of Friedreich Ataxia.
Owner:SANTHERA PHARMA SCHWEIZ
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of cardiomyopathy due to friedreich ataxia
ActiveUS20140221462A1Avoid developmentRecovery functionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFrataxinFriedreichs ataxia
A method for preventing or treating cardiomyopathy due to energy failure in a subject in need thereof is provided. The method comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a vector which comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding a gene that can reverse energy failure. An exemplary cardiomyopathy is that which is associated with Friedreich ataxia and an exemplary nucleic acid sequence comprises a nucleic acid that encodes frataxin (FXN).
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +5
Mitochondrial targeting and therapeutic use thereof
ActiveUS20140135275A1Enhance cell viabilityCompounds screening/testingBacteriaFrataxinMitochondrion membrane
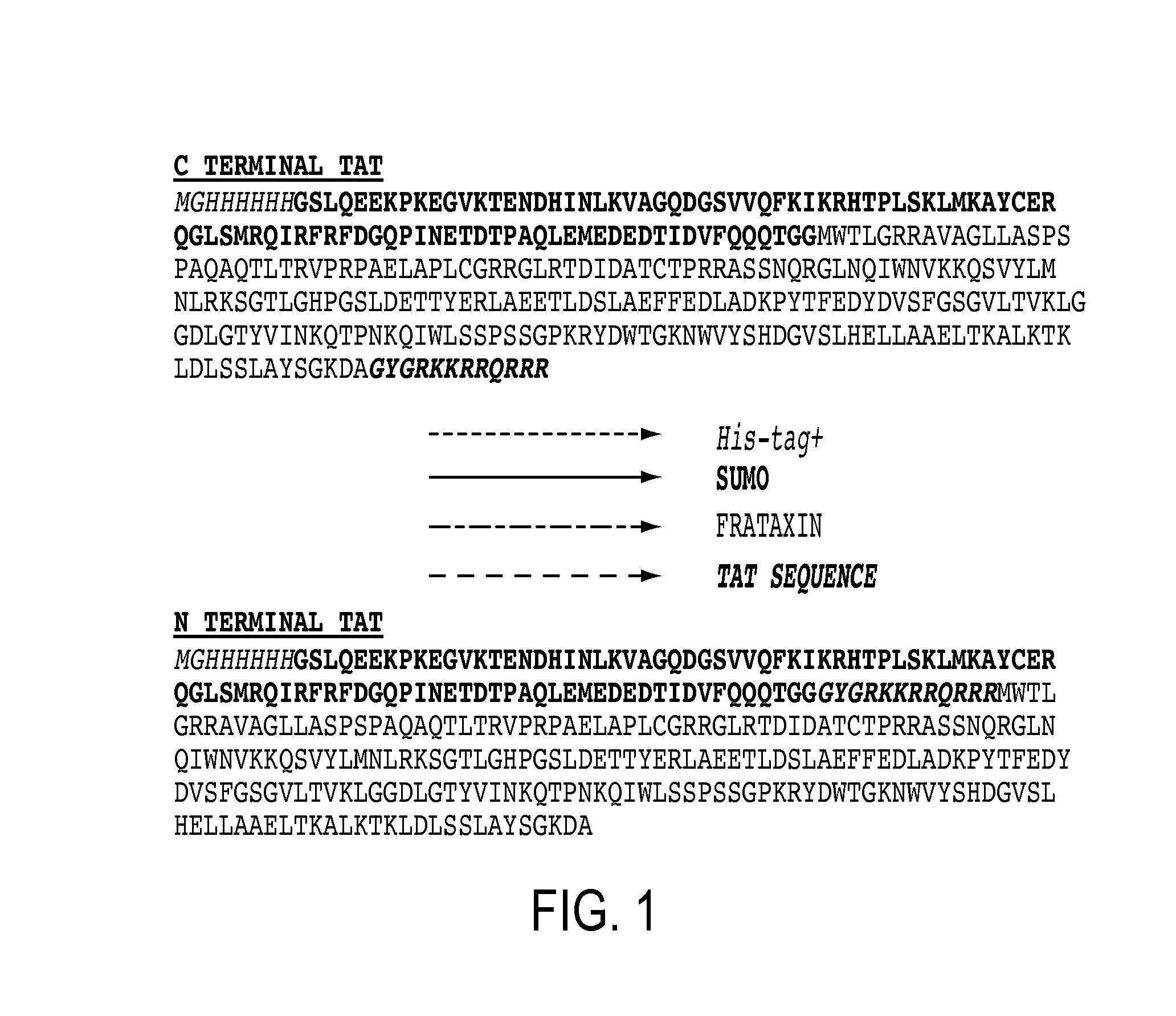
The present invention provides, among other things, compositions and methods for treatment of Friedrich's Ataxia based on effective targeting of a therapeutic moiety to mitochondria that can substitute for natural FXN protein activity or rescue one or more phenotypes or symptoms associated with frataxin-deficiency. In some embodiments, the present invention provides a targeted therapeutic comprising a therapeutic moiety, which is a polypeptide having an N-terminus and a C-terminus, a mitochondrial targeting sequence associated with the therapeutic moiety at the N-terminus, and a mitochondrial membrane-penetrating peptide associated with the therapeutic moiety at the C-terminus, wherein the therapeutic moiety is targeted to mitochondria upon cellular entry.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Epigenetic regulators of frataxin
InactiveUS20160201063A1Increasing FXN expressionLow levelSugar derivativesTissue cultureFrataxinAtaxic movements
Provided herein are methods for increasing Frataxin (FXN) expression that involve targeting or expressing regulatory factors that modulate the epigenetic state of FXN genes. Also provided herein are methods for increasing FXN expression using inhibitors of a negative epigenetic regulator of FXN. Compositions and methods for treating Friedrich's ataxia are also provided.
Owner:RANA THERAPEUTICS INC
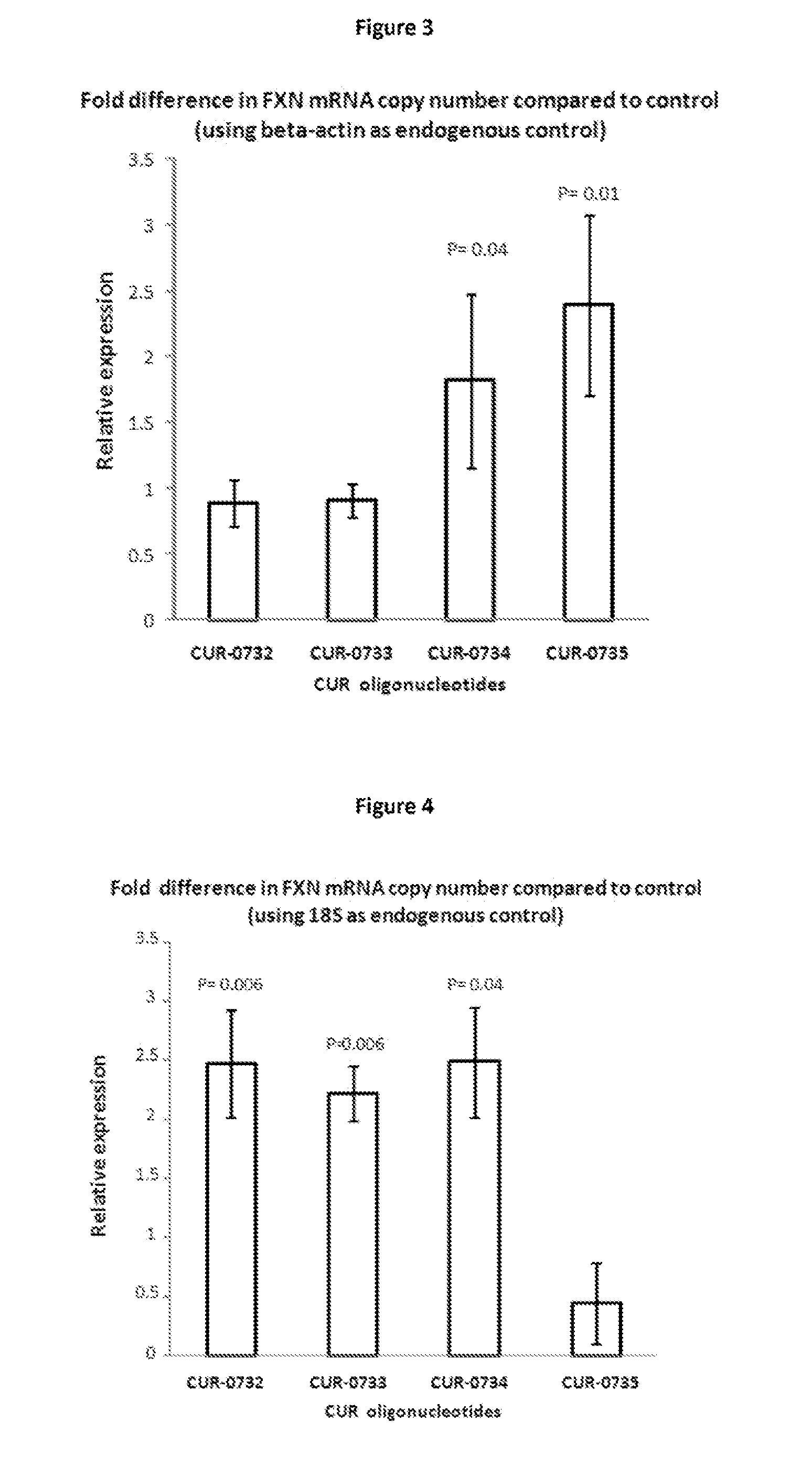
Treatment of frataxin (FXN) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to fxn
ActiveUS20140187606A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderFrataxinPolynucleotide
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Frataxin (FXN), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Frataxin (FXN). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of FXN.
Owner:CURNA INC
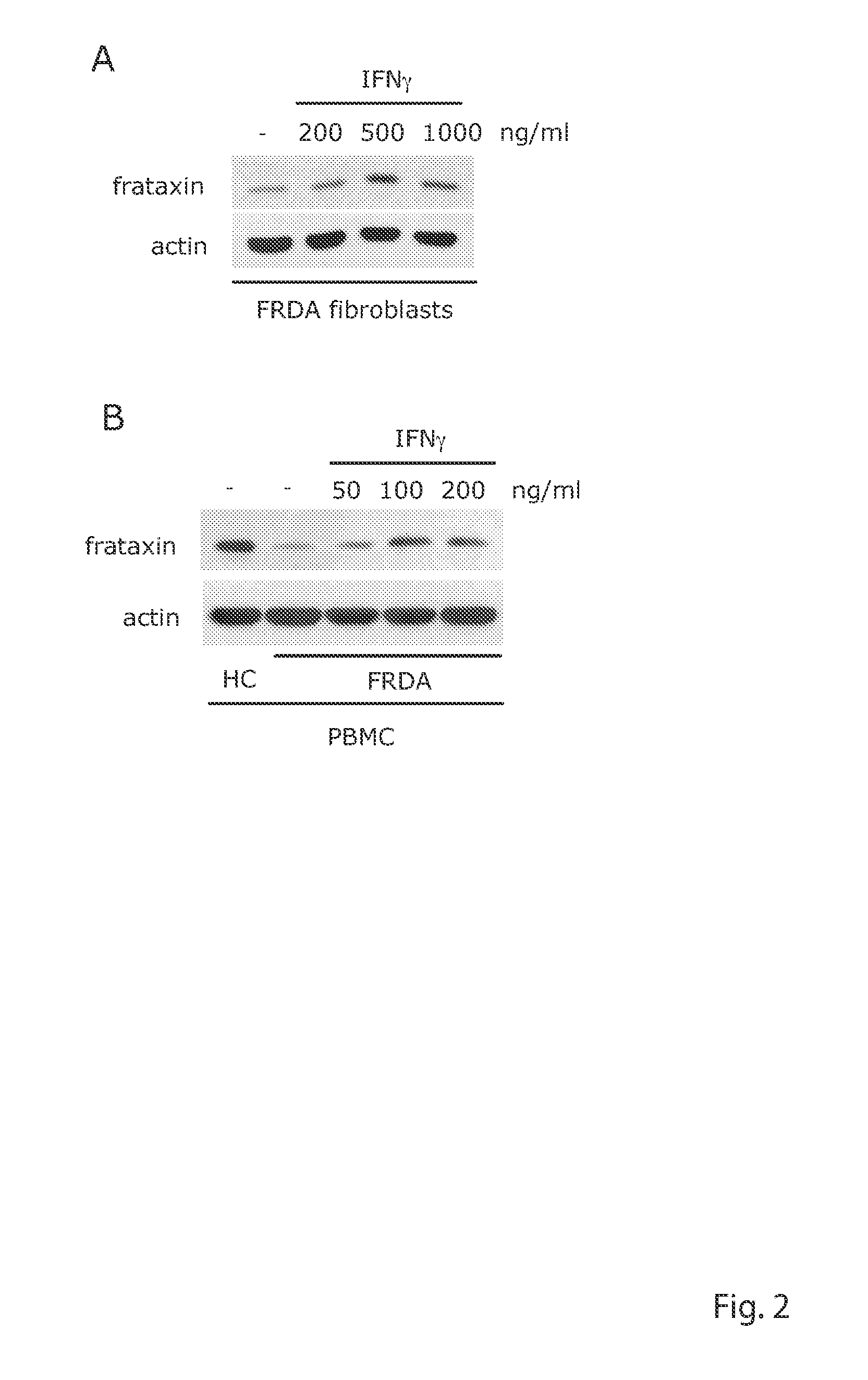
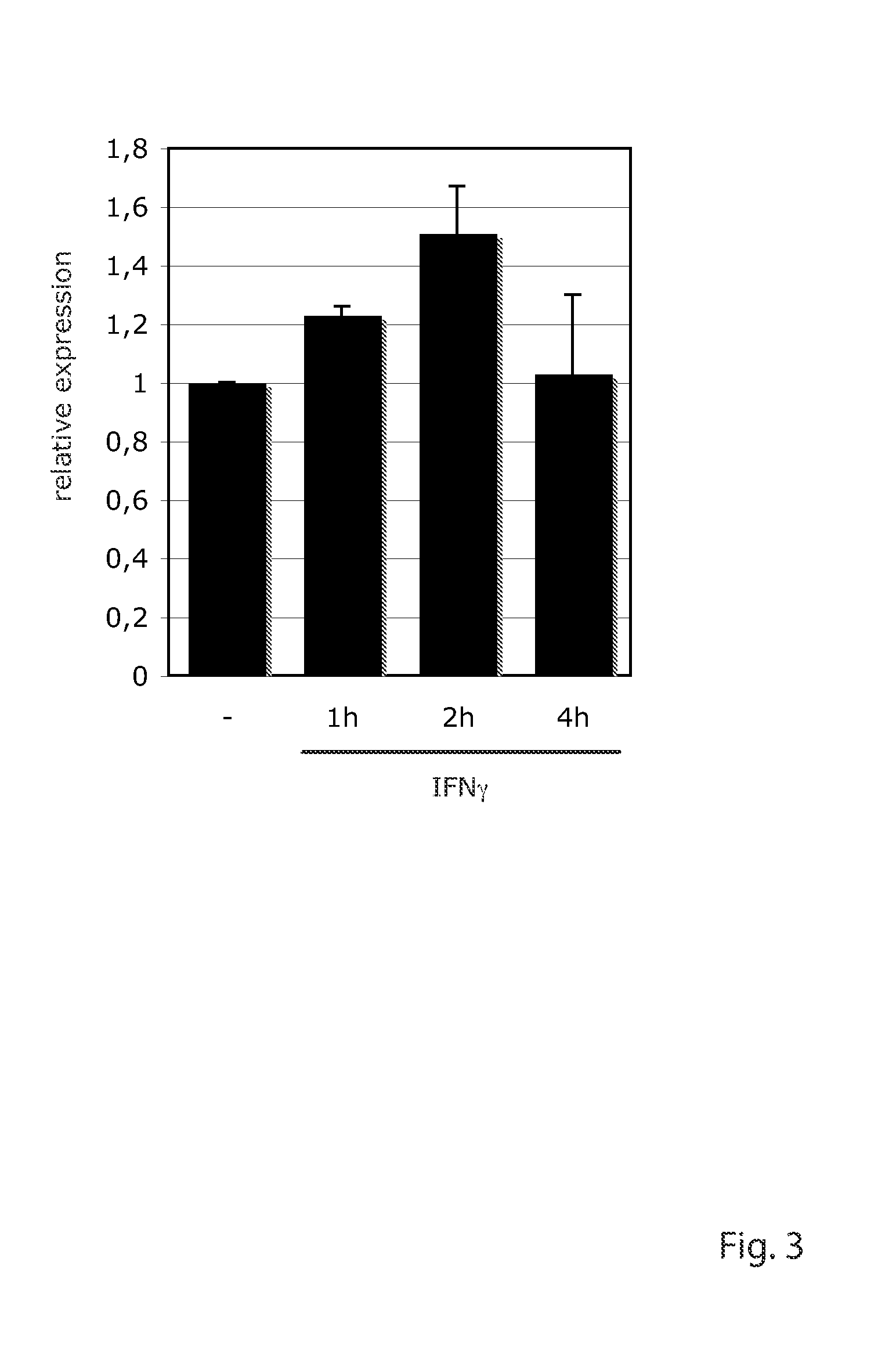
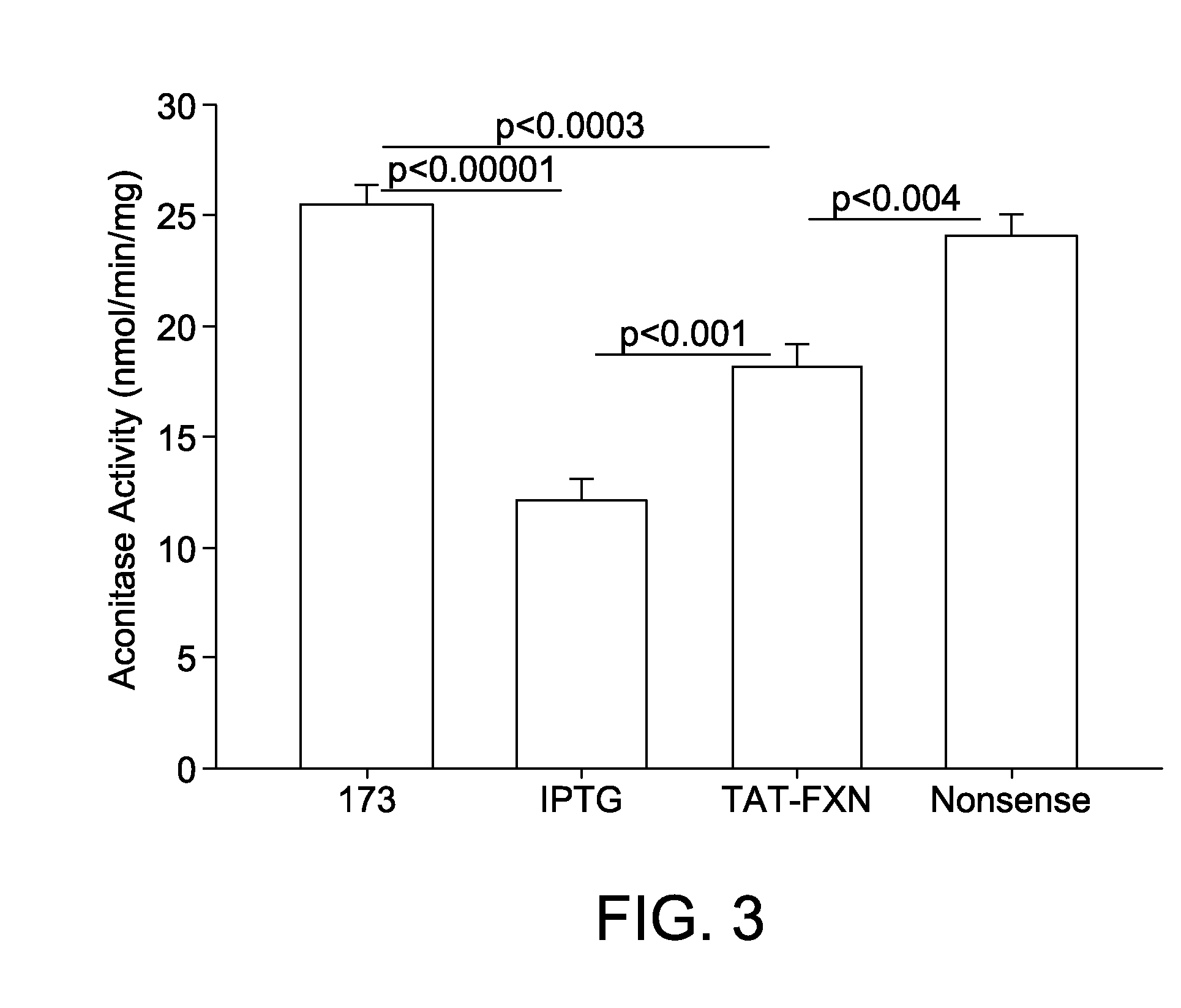
Methods for treating Friedreich's ataxia with interferon gamma
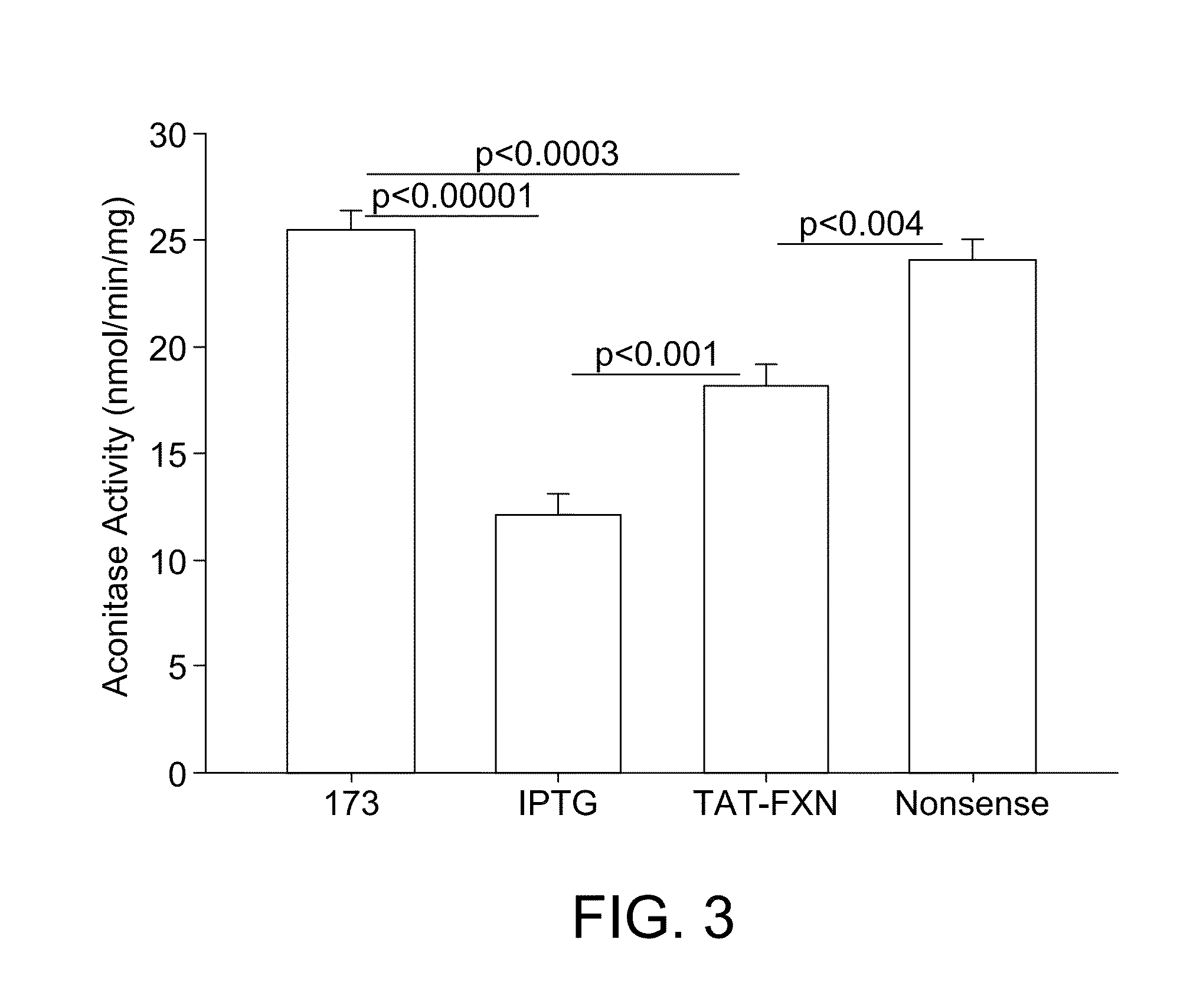
Described herein are compositions and methods for treating Friedreich's Ataxia (FRDA) with interferon gamma. In some aspects, methods for increasing expression of frataxin in cells and for treating Friedreich's Ataxia are provided. In some additional aspects, methods increasing aconitase activity in cells are provided.
Owner:FRATAGENE THERAPEUTICS SRL
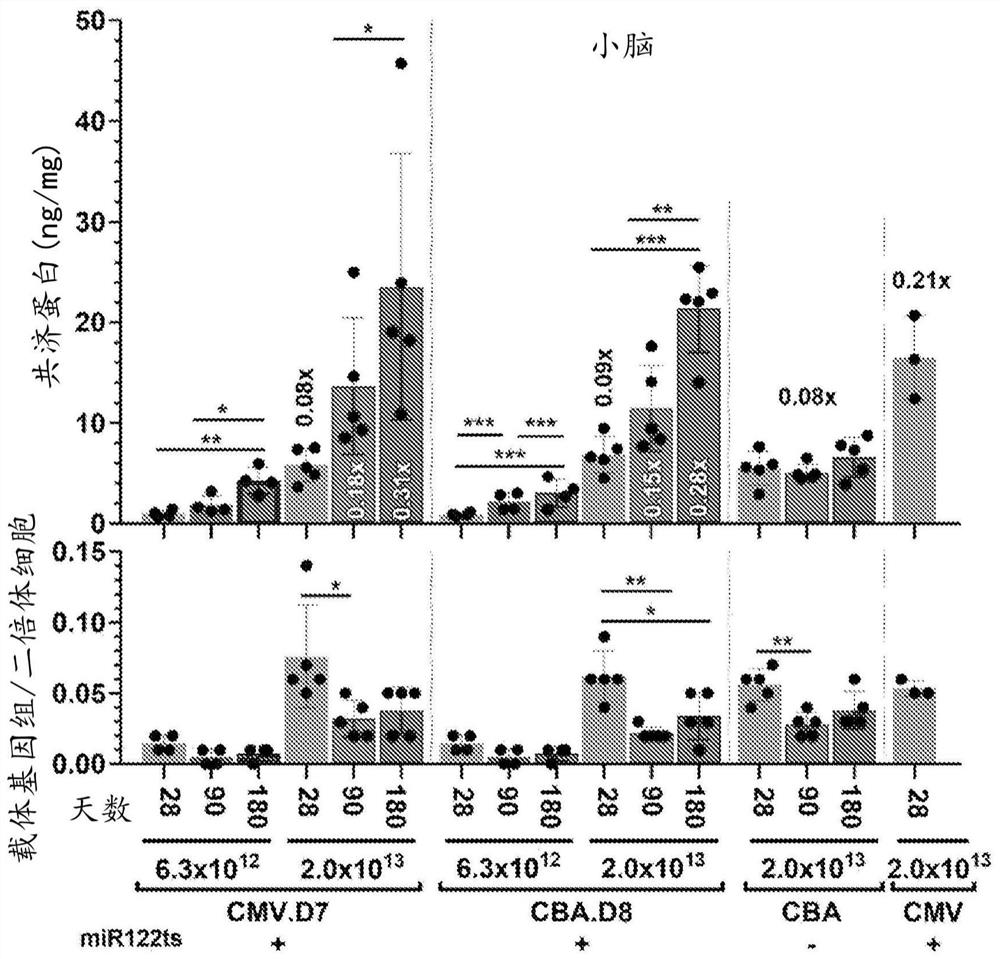
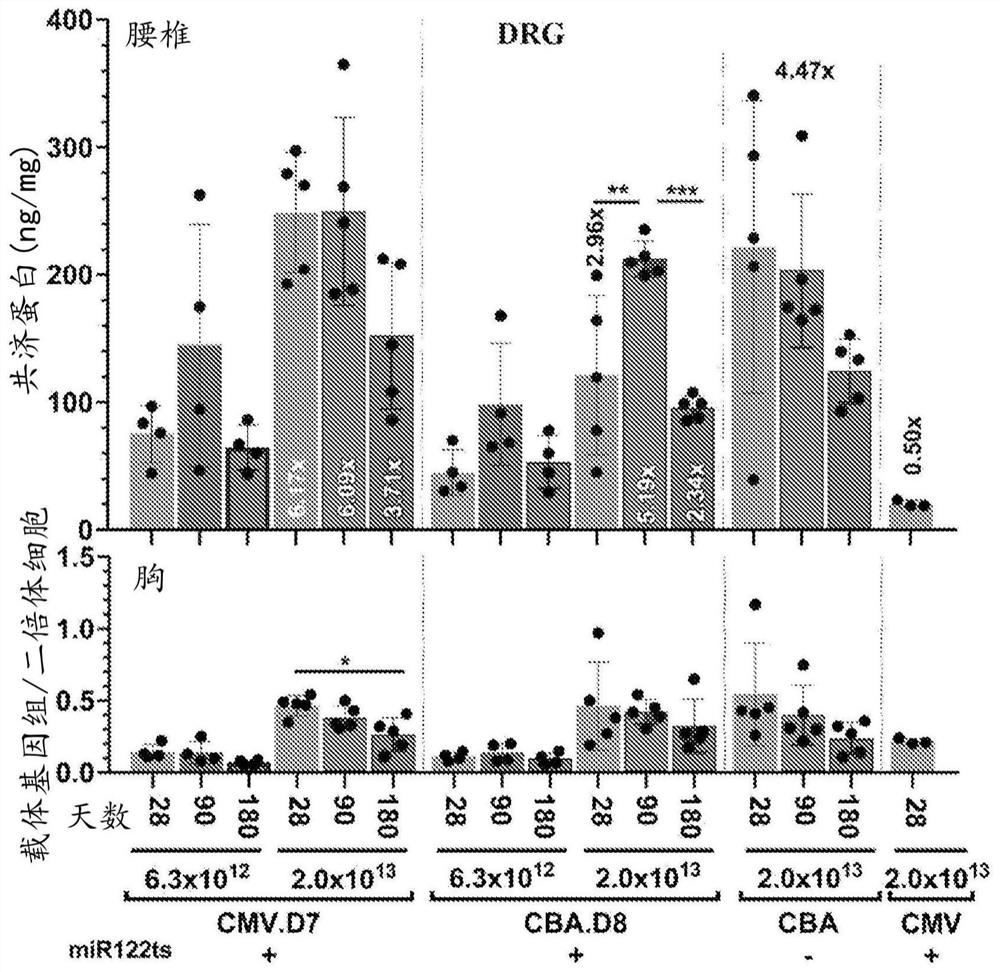
Frataxin expression constructs having engineered promoters and methods of use thereof
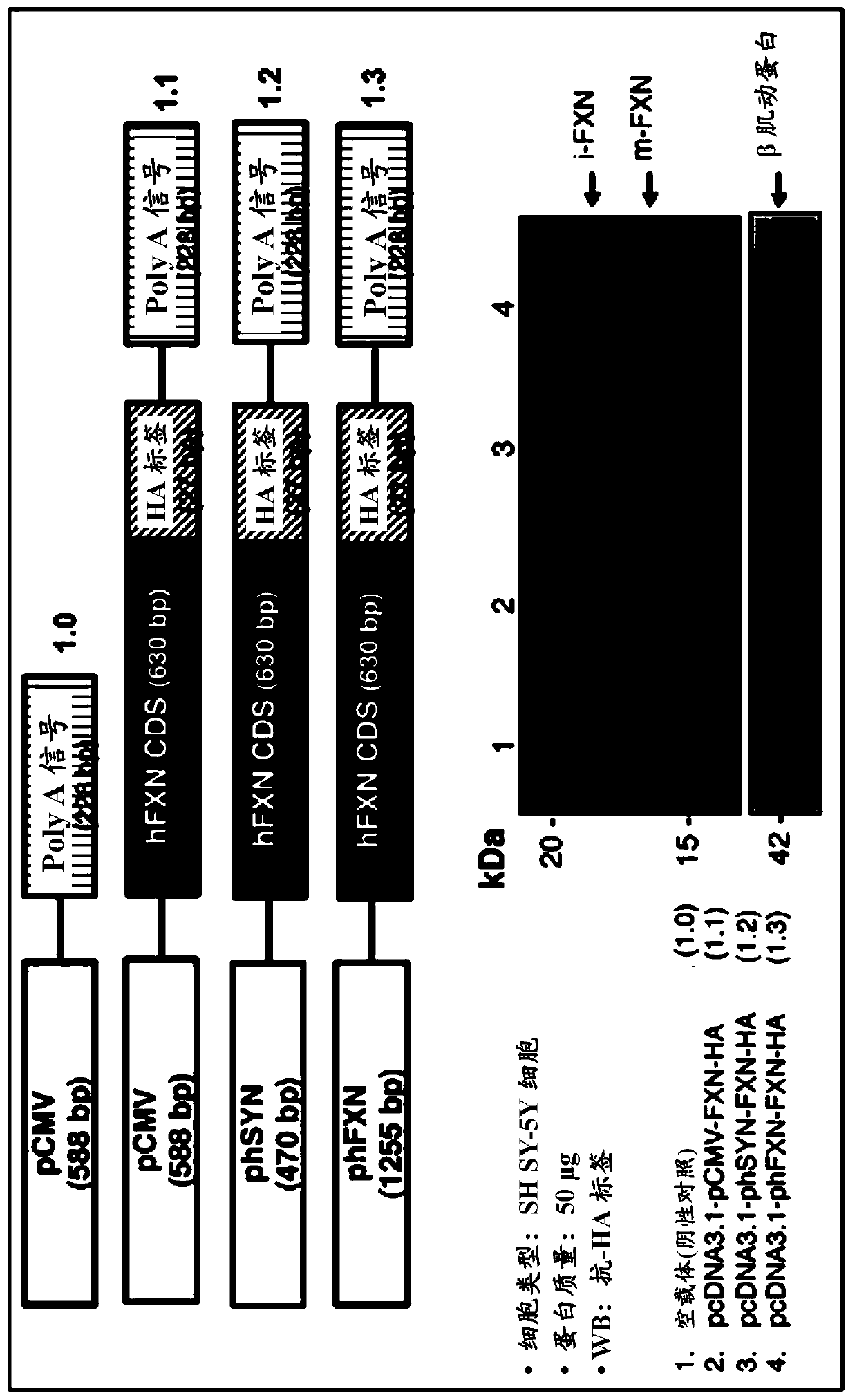
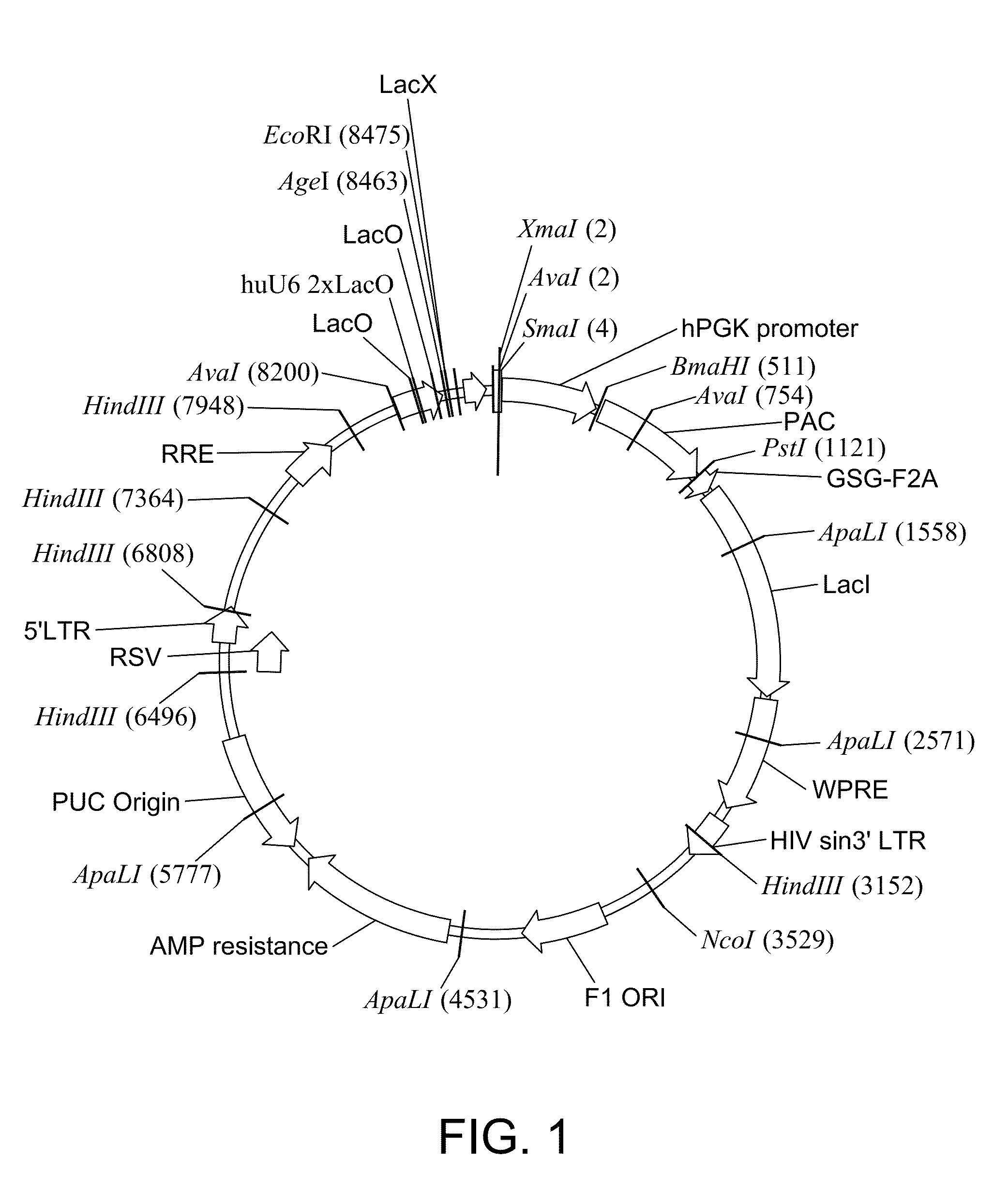
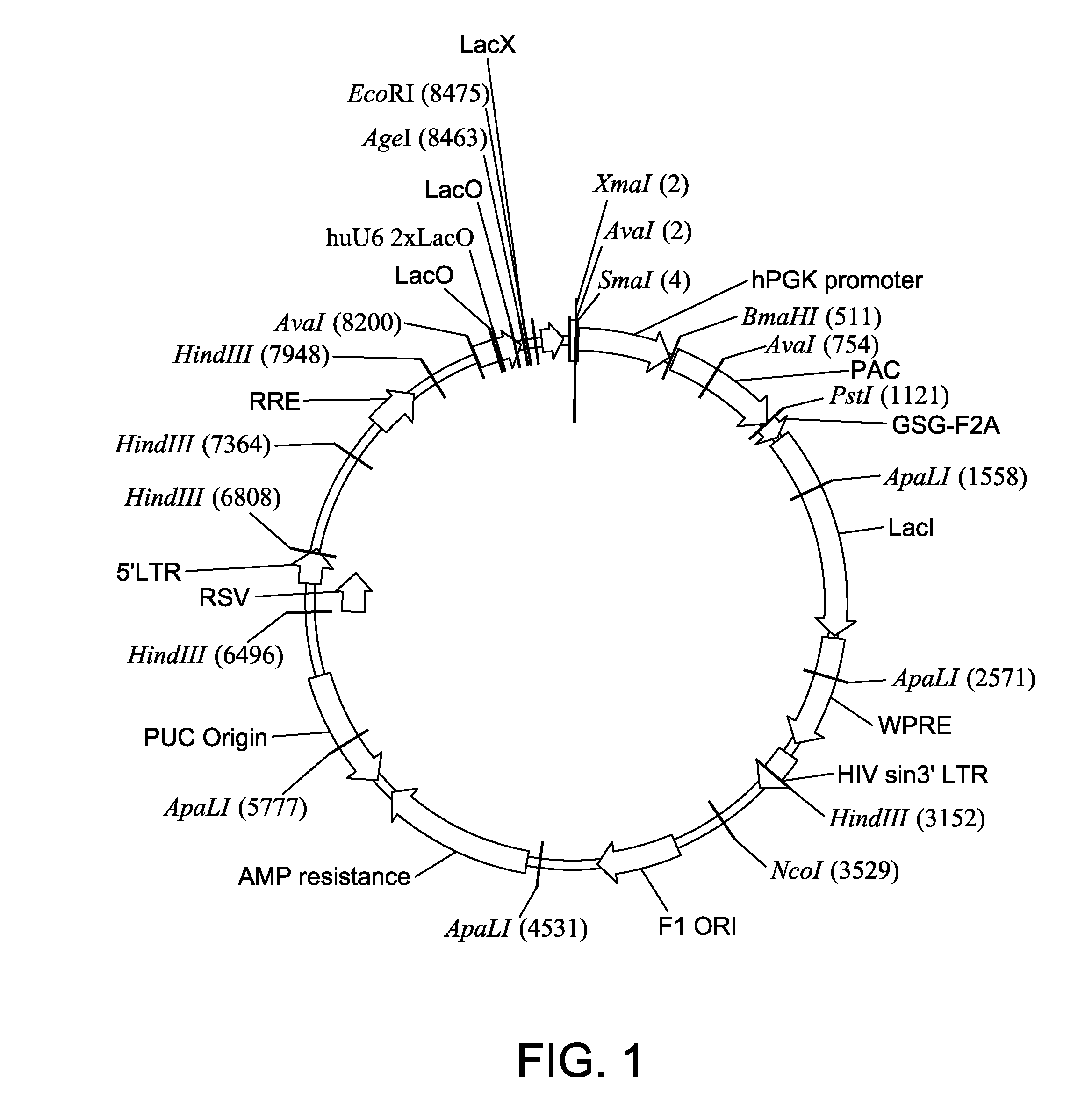
The disclosure relates to compositions and methods for altering, e.g., enhancing, the expression of frataxin (FXN), whether in vitro and / or in vivo including, but not limited to, the exploitation of engineered promoters. Such compositions include delivery via administration of an adeno-associated viral (AAV) particle. The compositions and methods of the present disclosure are useful in the treatment of subjects diagnosed with, or suspected of having Friedreich's ataxia or another neuromuscular or neurological condition resulting from a deficiency in the quantity and / or function of frataxin or associated with decreased expression or protein levels of frataxin.
Owner:VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS
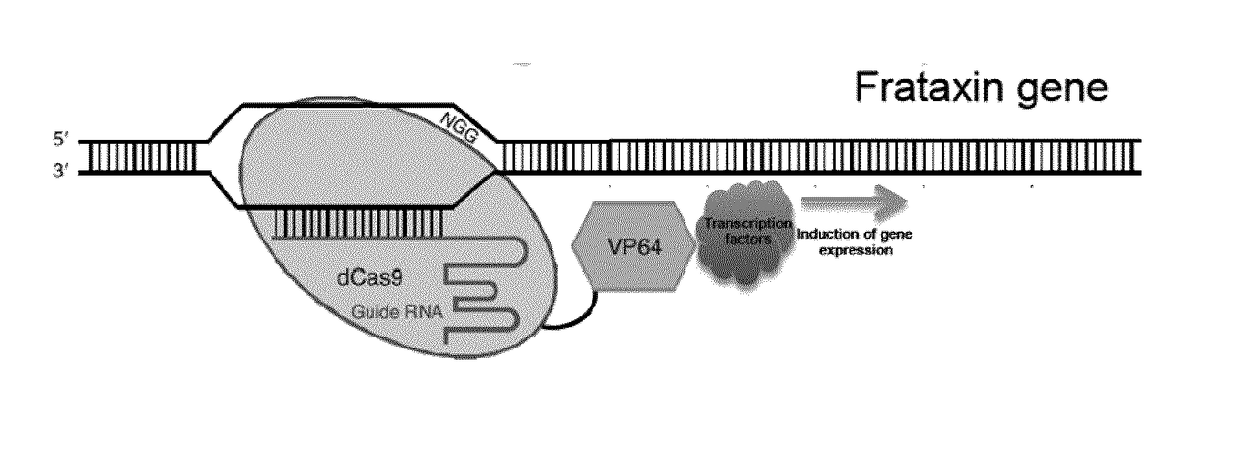
Crispr-based methods and products for increasing frataxin levels and uses thereof
Methods and products (e.g., gRNAs, recombinant fusion proteins, frataxin targeting systems, compositions and kits) are described for increasing frataxin expression / levels in a cell, as well as uses of such methods and products, for example for the treatment of Friedreich ataxia in a subject suffering therefrom.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Crispr-based treatment of friedreich ataxia
InactiveUS20200056206A1Low mutation rateIncreasing baseline levelOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNucleotideMedicine
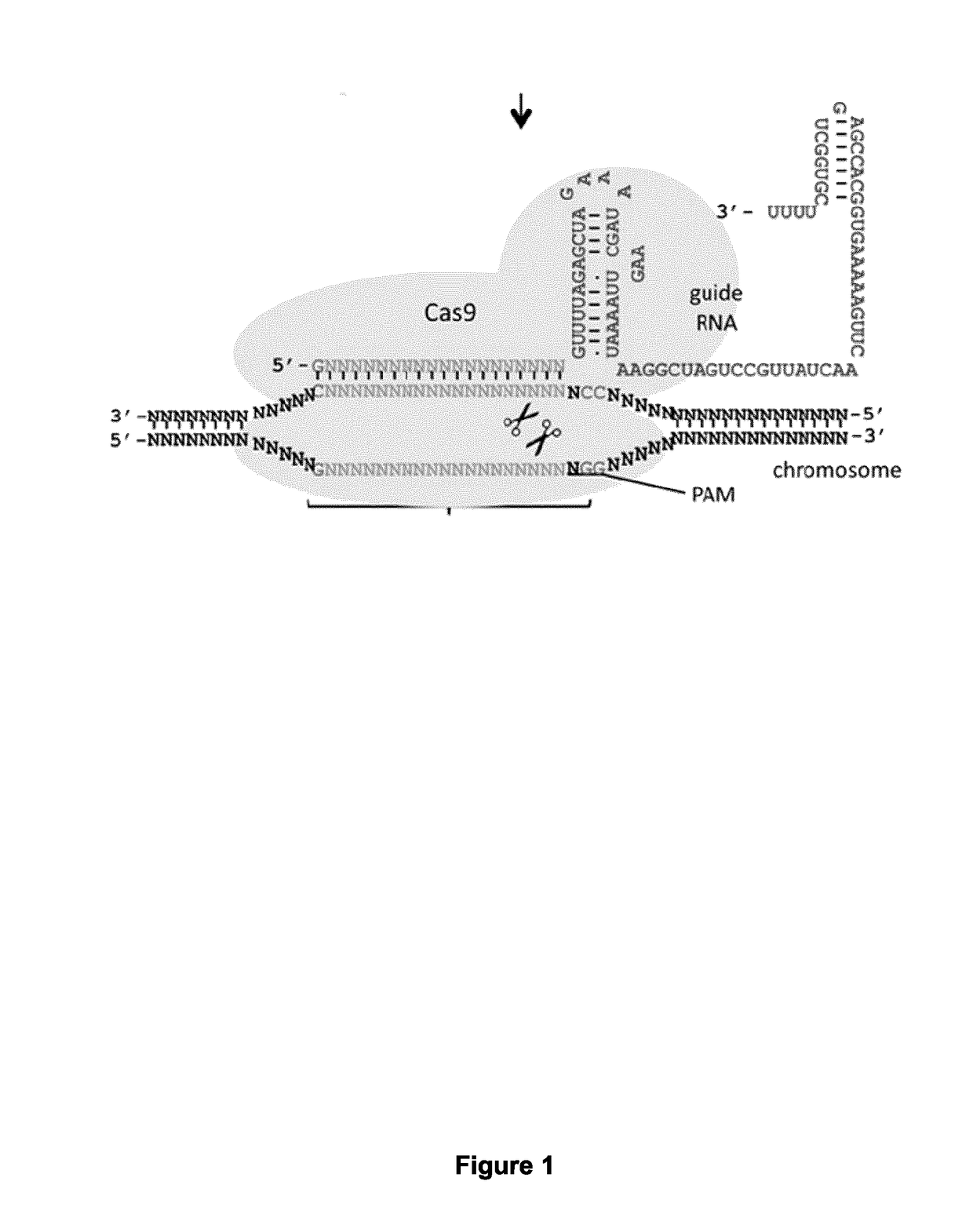
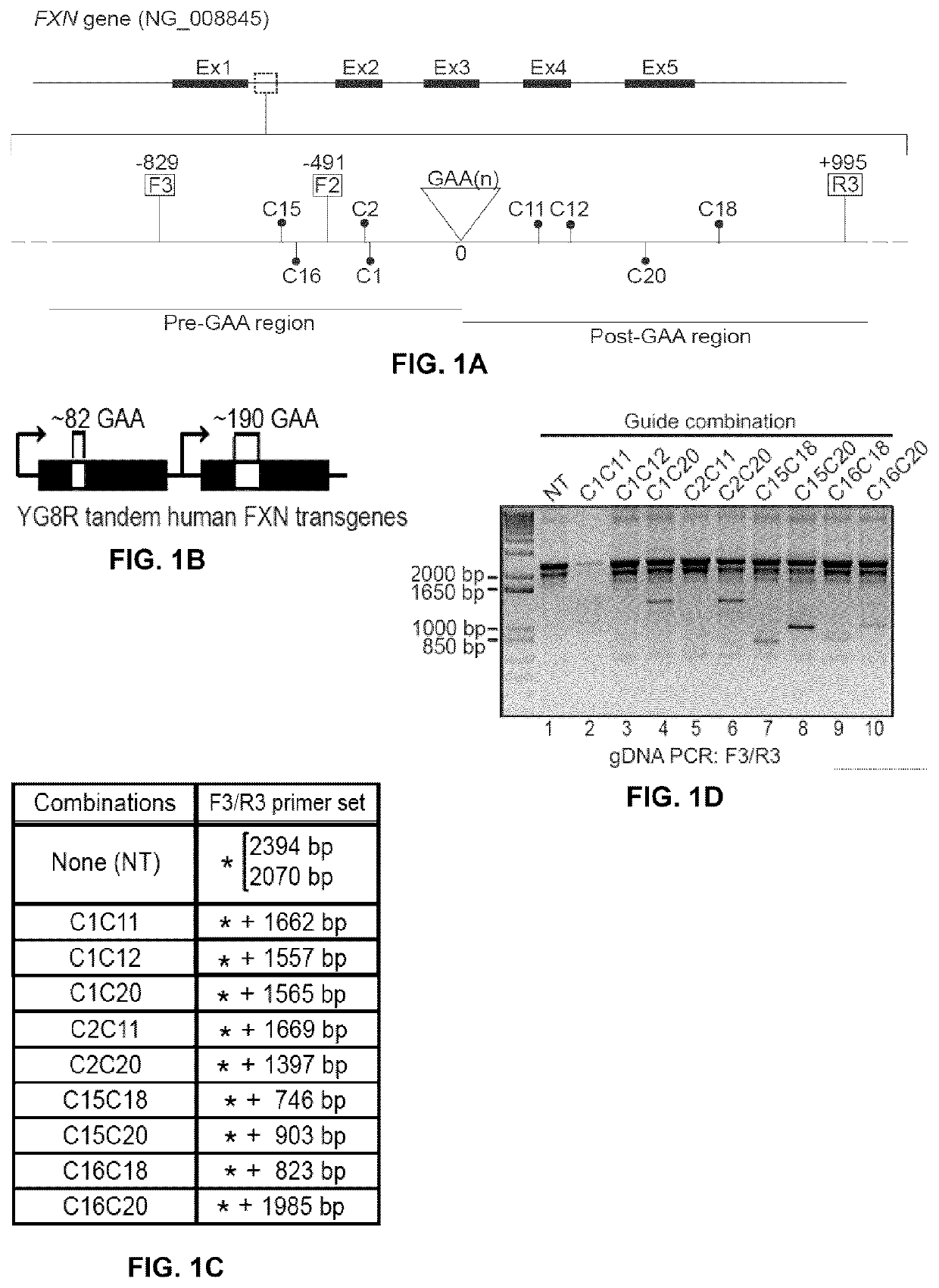
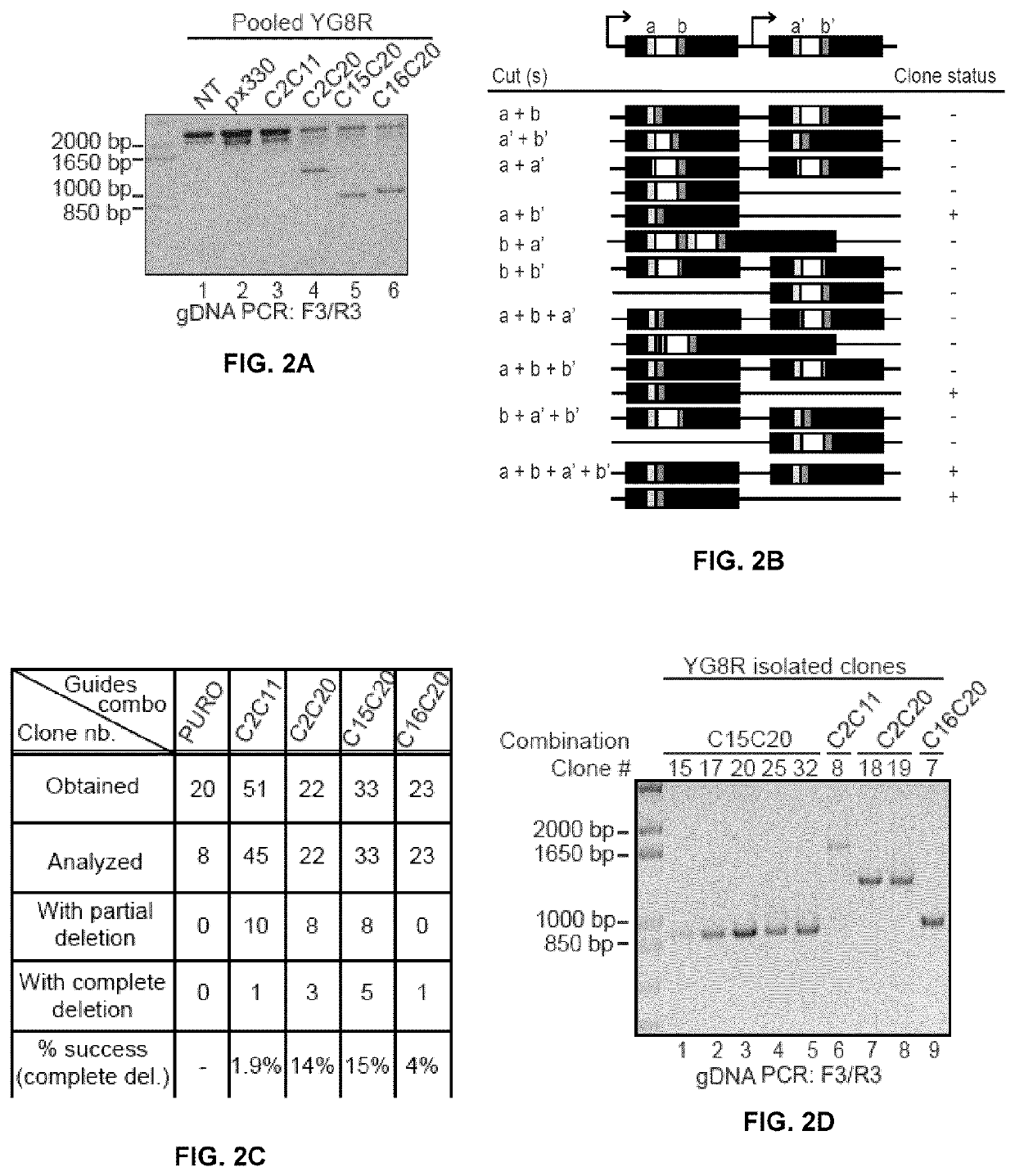
Methods of modifying a frataxin gene are disclosed, comprising removing some or all of endogenous GAA trinucleotide repeats within the frataxin gene, e.g., within an intron (e.g., intron 1) of the frataxin gene. The removal may be effected using a CRISPR / CAS nuclease system. Such modification may be used to increase frataxin expression in the cell, and also to treat a subject suffering from Friedreich ataxia. Reagents, kits and uses of the method are also disclosed, for example to modify a frataxin gene and to treat a subject suffering from Friedreich ataxia.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
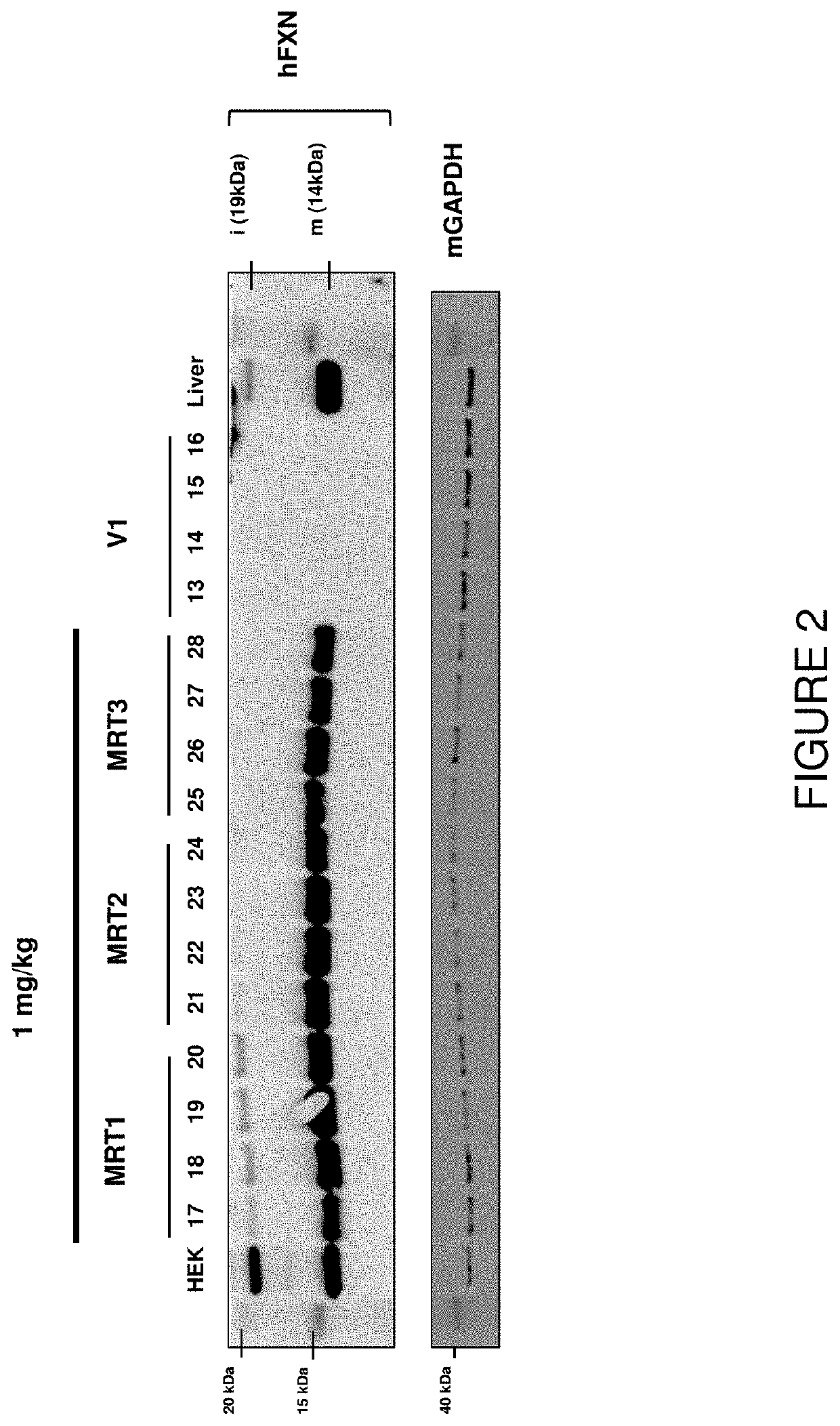
Methods of treating mitochondrial disorders
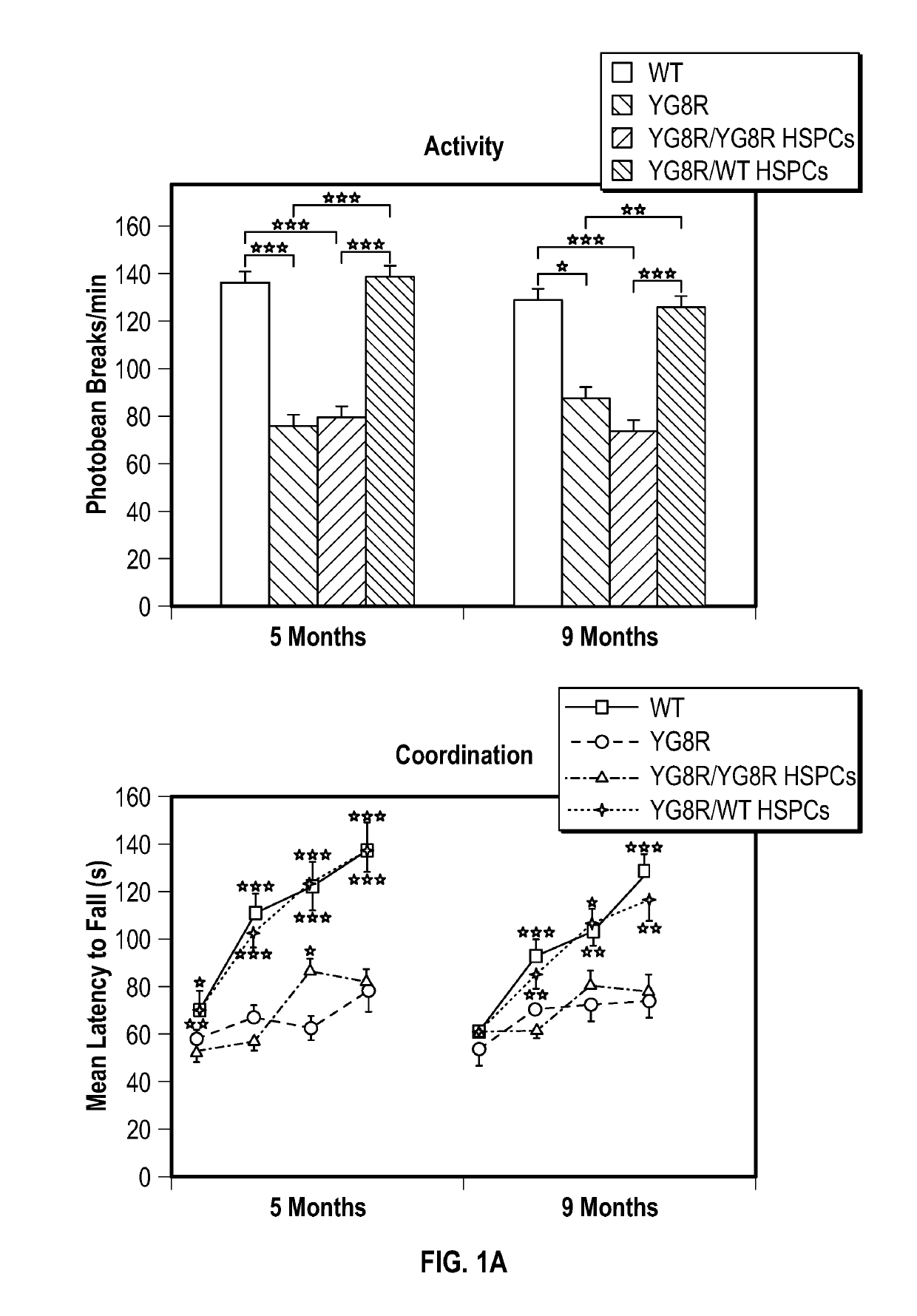
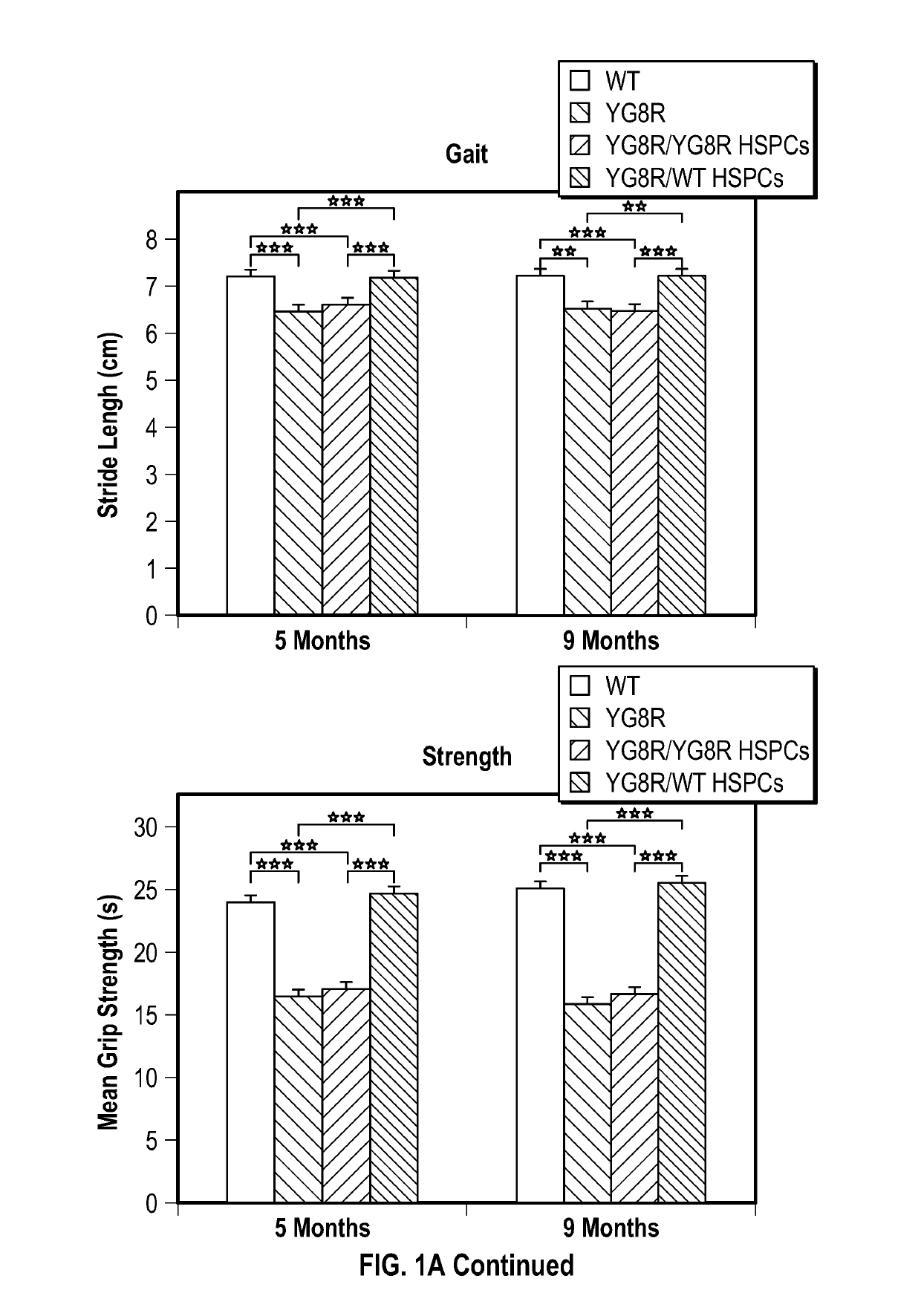
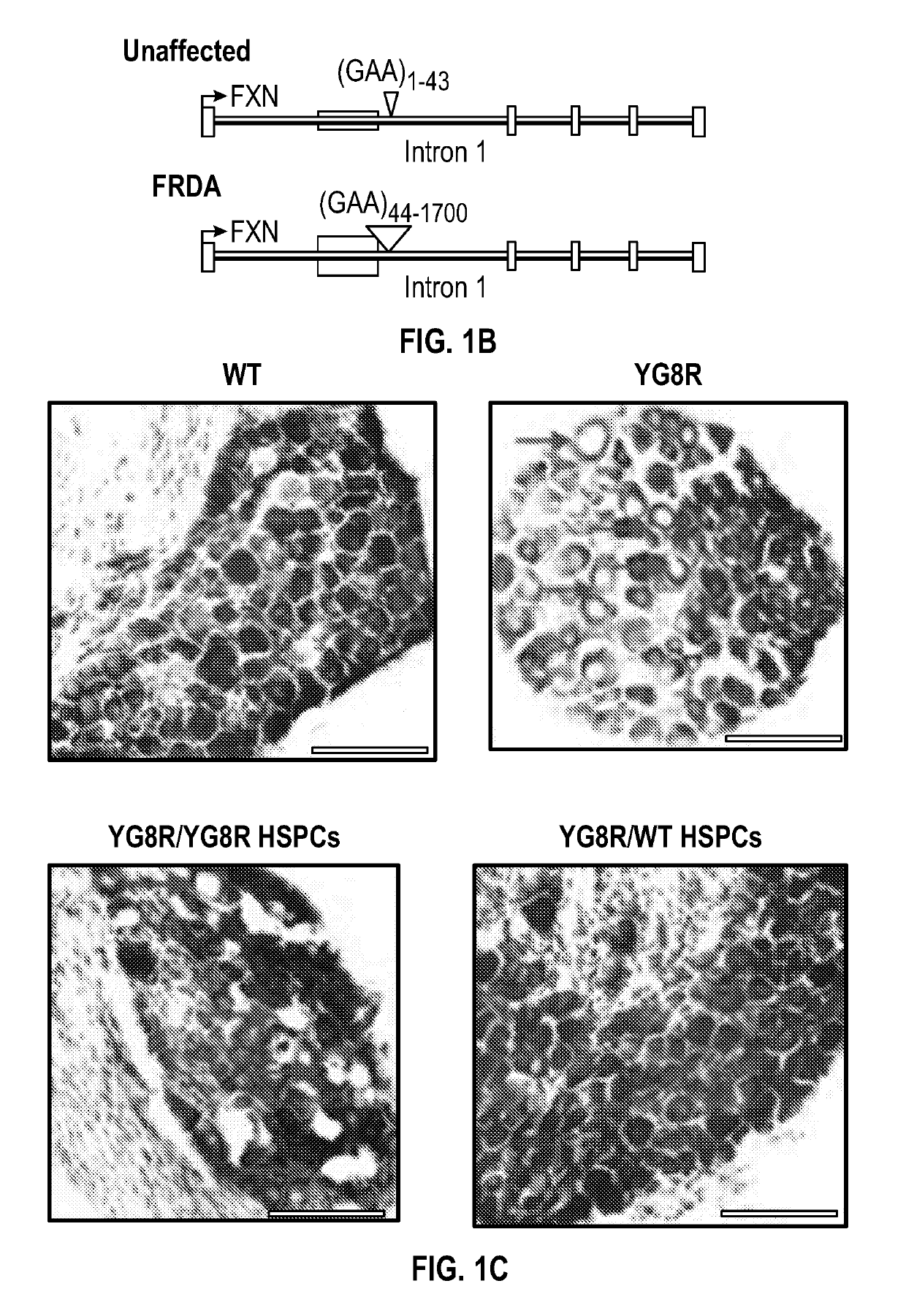
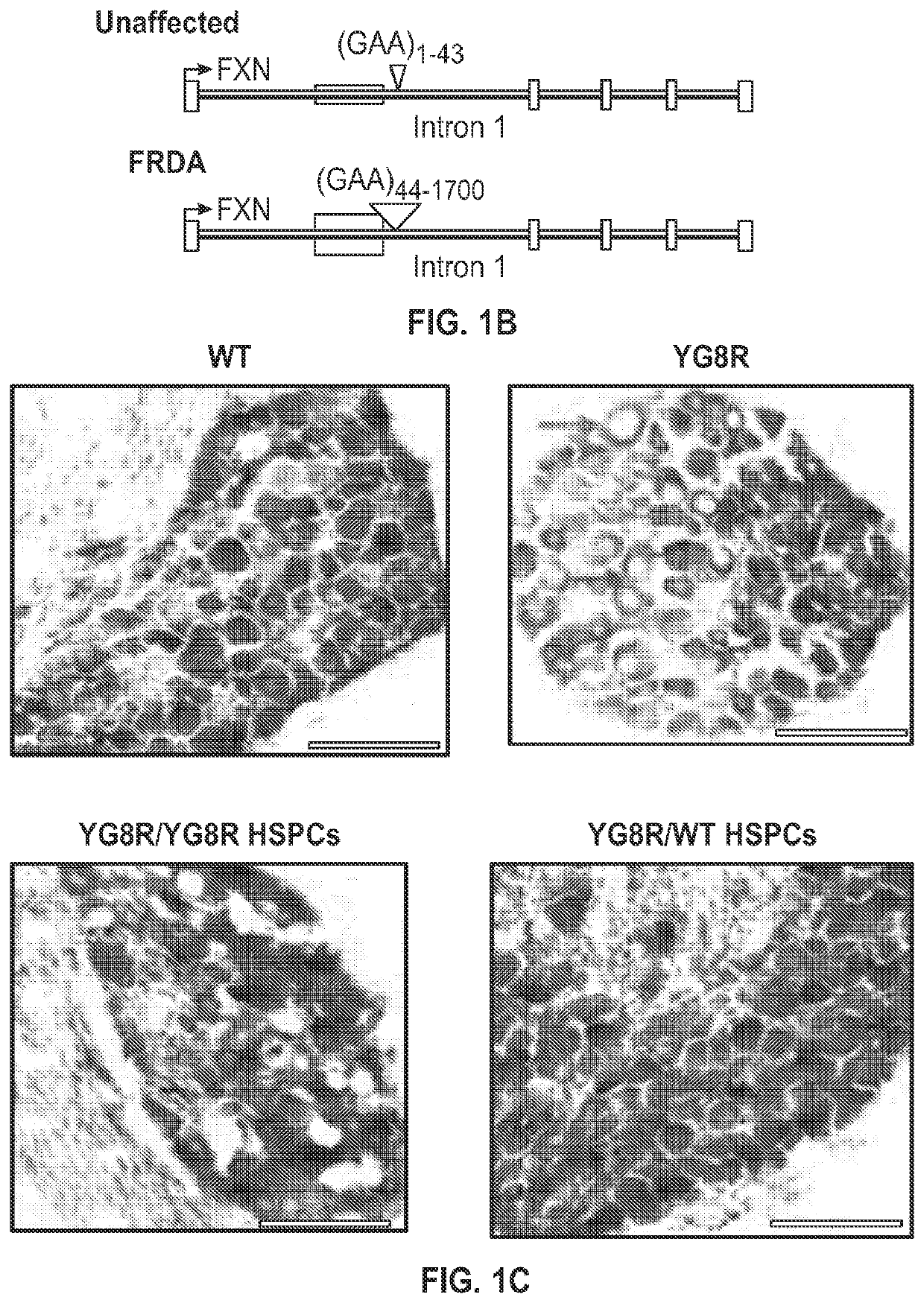
Provided herein are methods for treating a disease or disorder associated with mitochondrial dysfunction through ex vivo introduction of a nucleic acid molecule into hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) followed by transplantation of the HSPCs into a subject in need of treatment. The nucleic acid molecule may include a functional human frataxin (hFXN) or may include a gene editing system that when transfected into the cells removes a trinucleotide extension mutation of endogenous hFXN.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
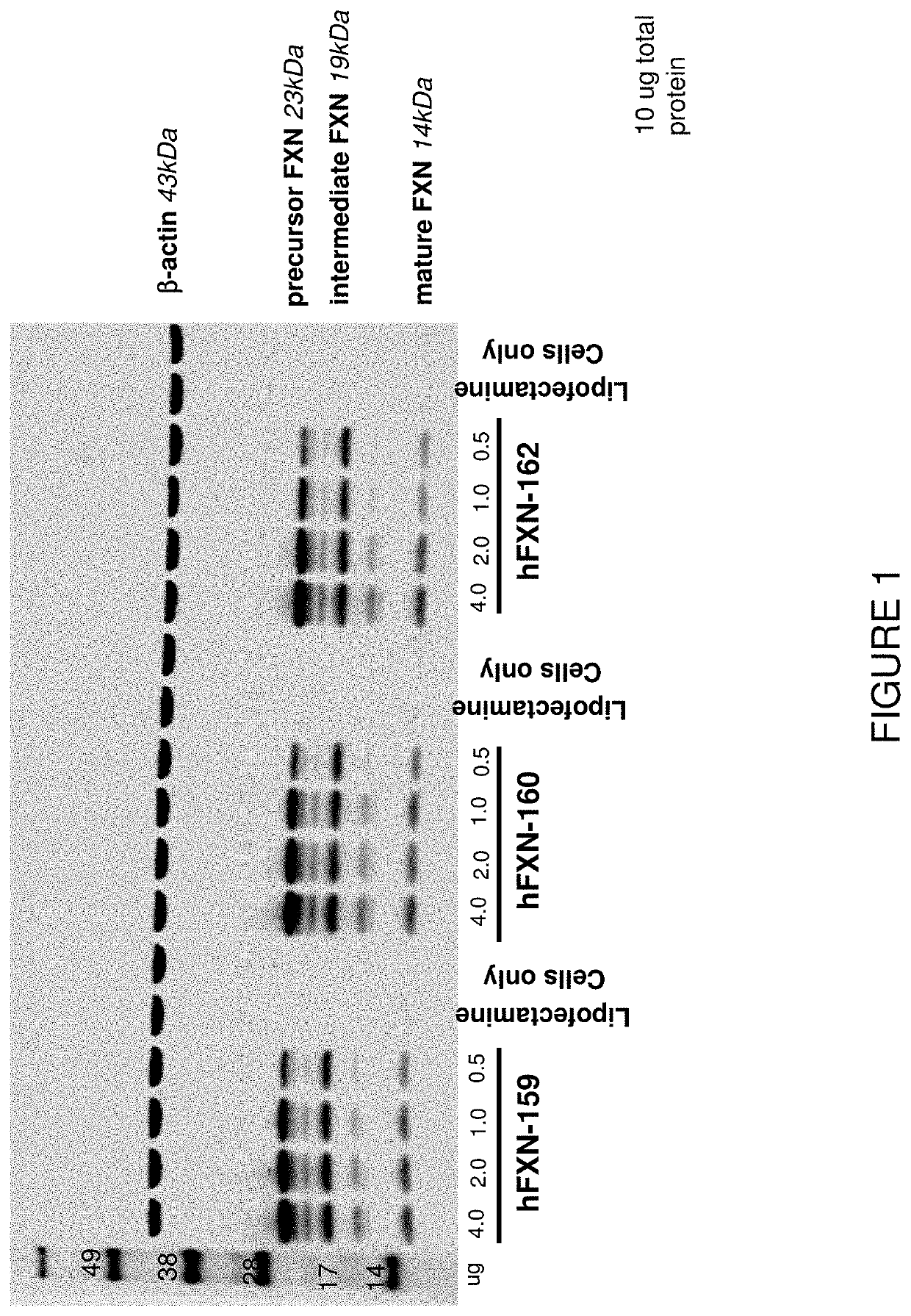
Methods for treating friedreich's ataxia with etravirine
ActiveUS20190076429A1Improve performancePrevent and alleviate vision impairmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineFrataxin
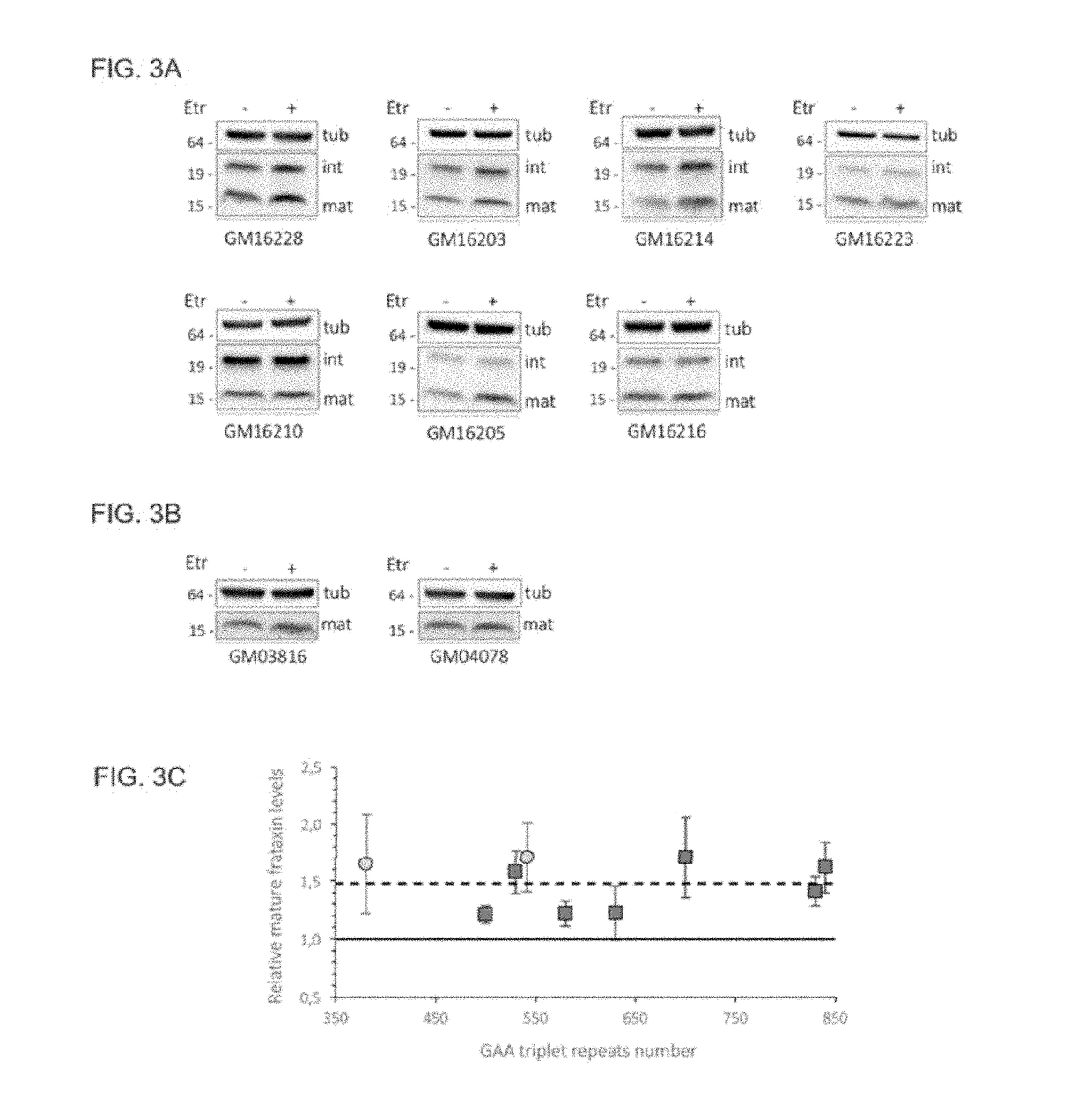
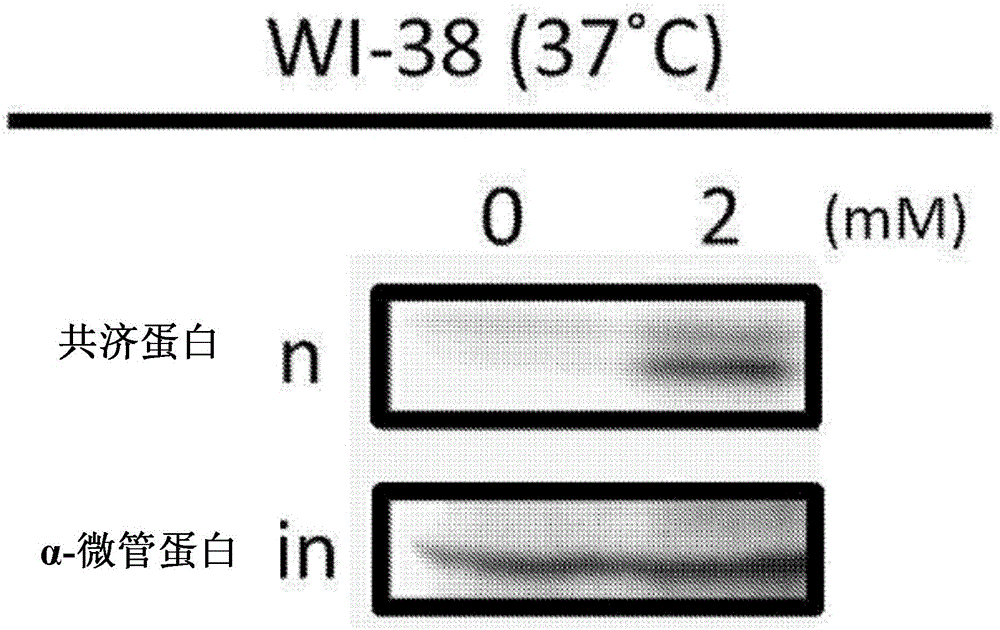
The disclosure provides methods for the treatment of Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA), an autosomal recessive ataxia caused by mutation of the FXN gene, by administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of etravirine, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Etravirine is demonstrated to increase the levels of frataxin precursor and intermediate and mature forms of frataxin.
Owner:FRATAGENE THERAPEUTICS SRL
CRISPR-based methods and products for increasing frataxin levels and uses thereof
Methods and products (e.g., gRNAs, recombinant fusion proteins, frataxin targeting systems, compositions and kits) are described for increasing frataxin expression / levels in a cell, as well as uses of such methods and products, for example for the treatment of Friedreich ataxia in a subject suffering therefrom.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Frataxin enhancer
The purpose of the invention is to provide a drug effective in the treatment and prevention of diseases and the like caused by a decrease in frataxin production. The invention provides a frataxin enhancer containing 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or a derivative thereof or a salt of these, and a therapeutic agent and / or prophylactic agent for diseases caused by a decrease in frataxin production.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE +1
Methods and pharmaceutical composition for the treatment and the prevention of neurological phenotype associated with Friedreich ataxia
ActiveUS11040113B2Preventing the onset of the sensori-motor defectAvoid problemsAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionFriedreichs ataxiaFrataxin
The present invention relates to a vector which comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding for the frataxin (FXN) gene for use in the prevention and treatment of neurological phenotype associated with Friedreich ataxia in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Vectors for treatment of friedreich's ataxia
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DINVESTIGACIO & CIENCIES DE LA SALUT GERMANS TRIAS I PUJOL +1
P38 map kinase inhibitors for treating friedreich's ataxia
The invention provides p38 MAPK inhibitors that compensate for a frataxin deficiency or mutation and methods of using the same (e.g., to treat Friedreich's ataxia).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Inducible cell-based model for the study of Friedreich's Ataxia
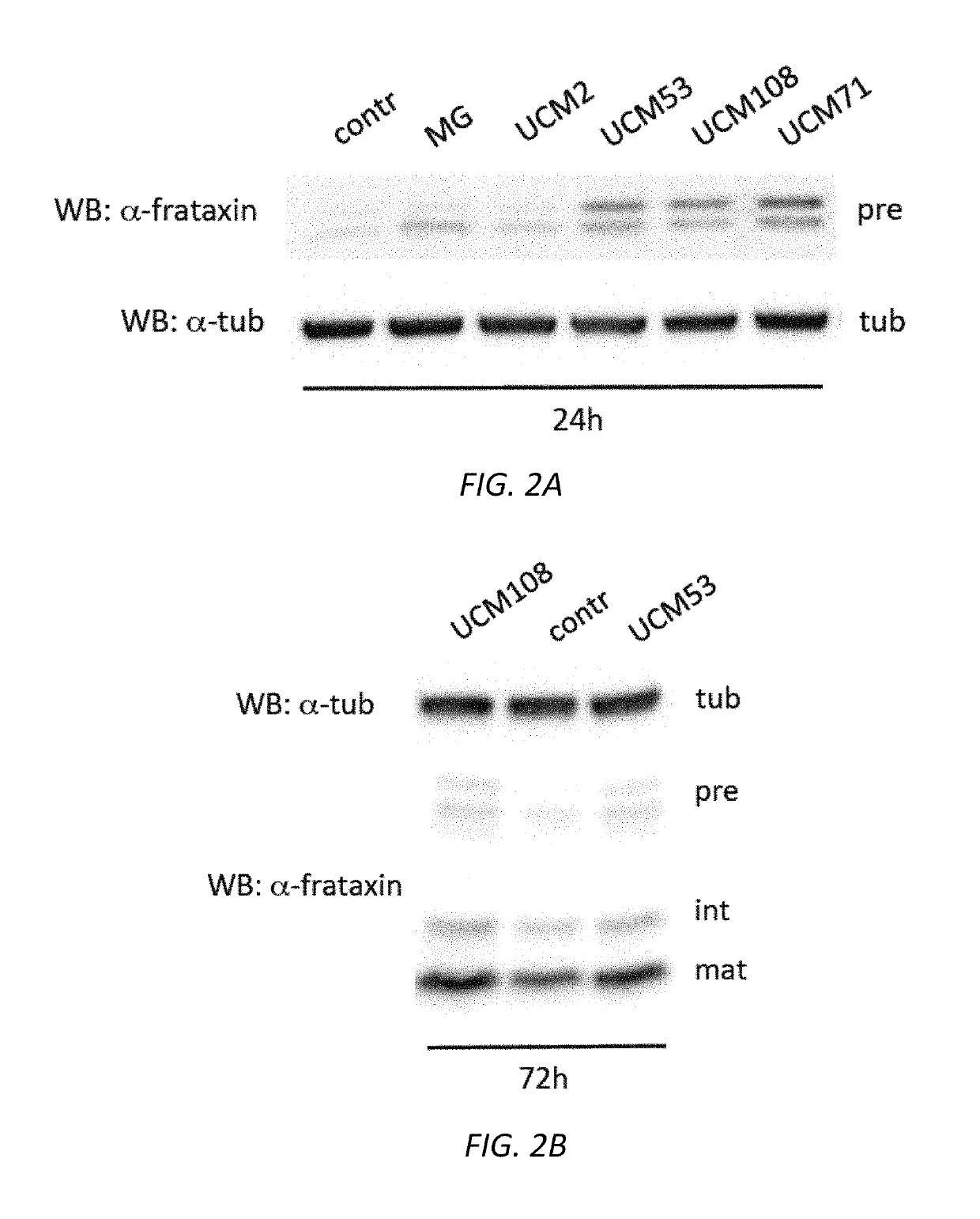
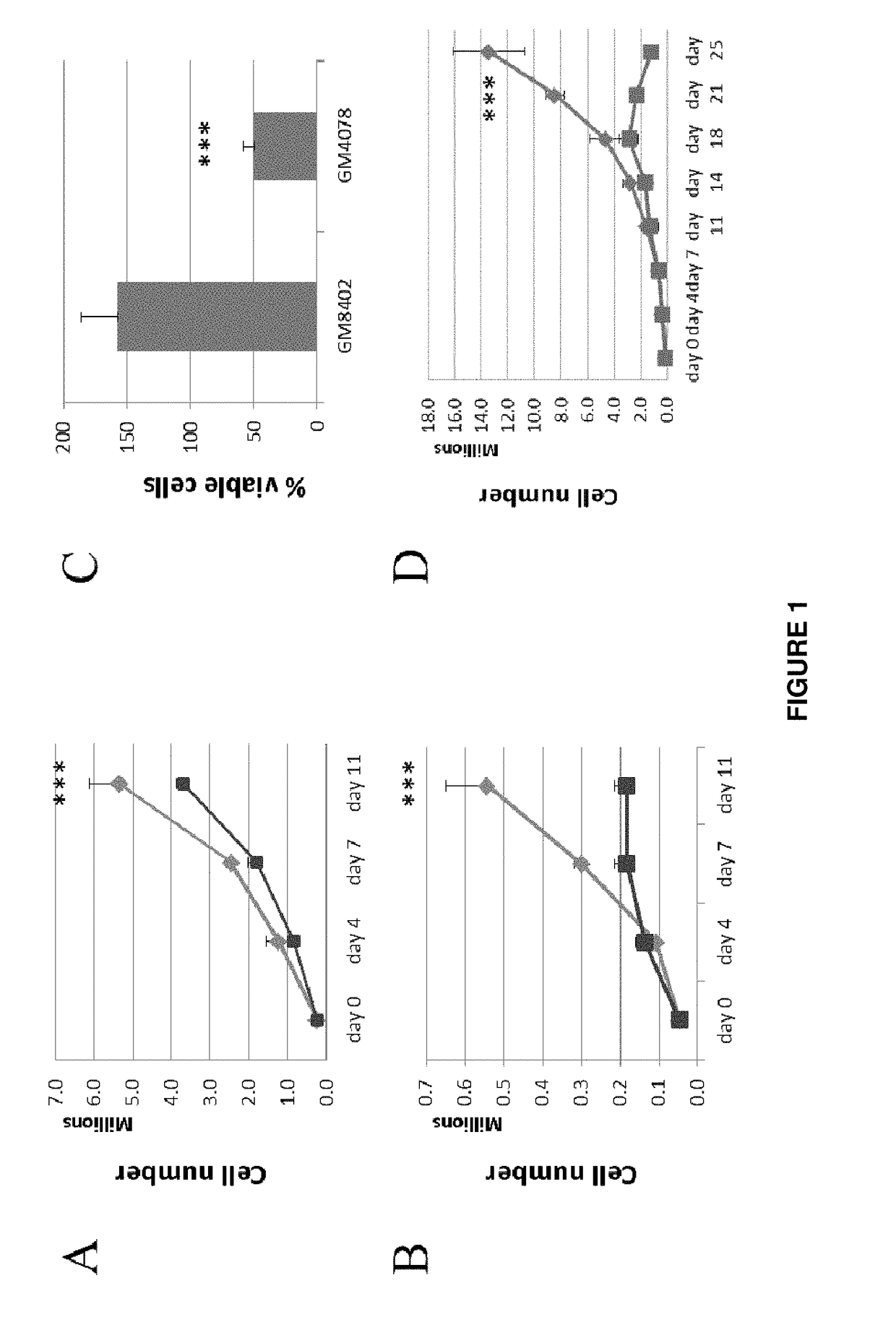
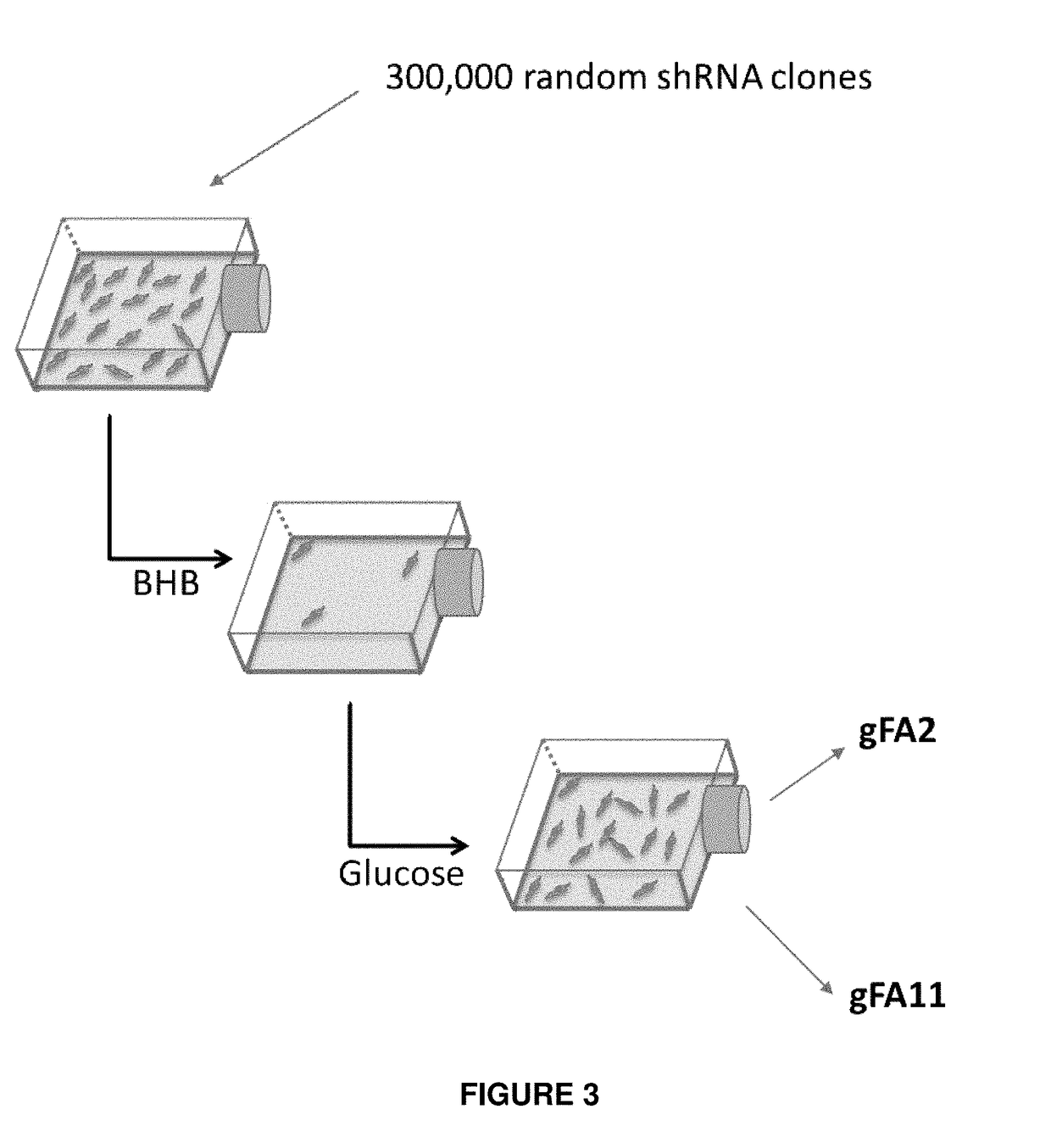
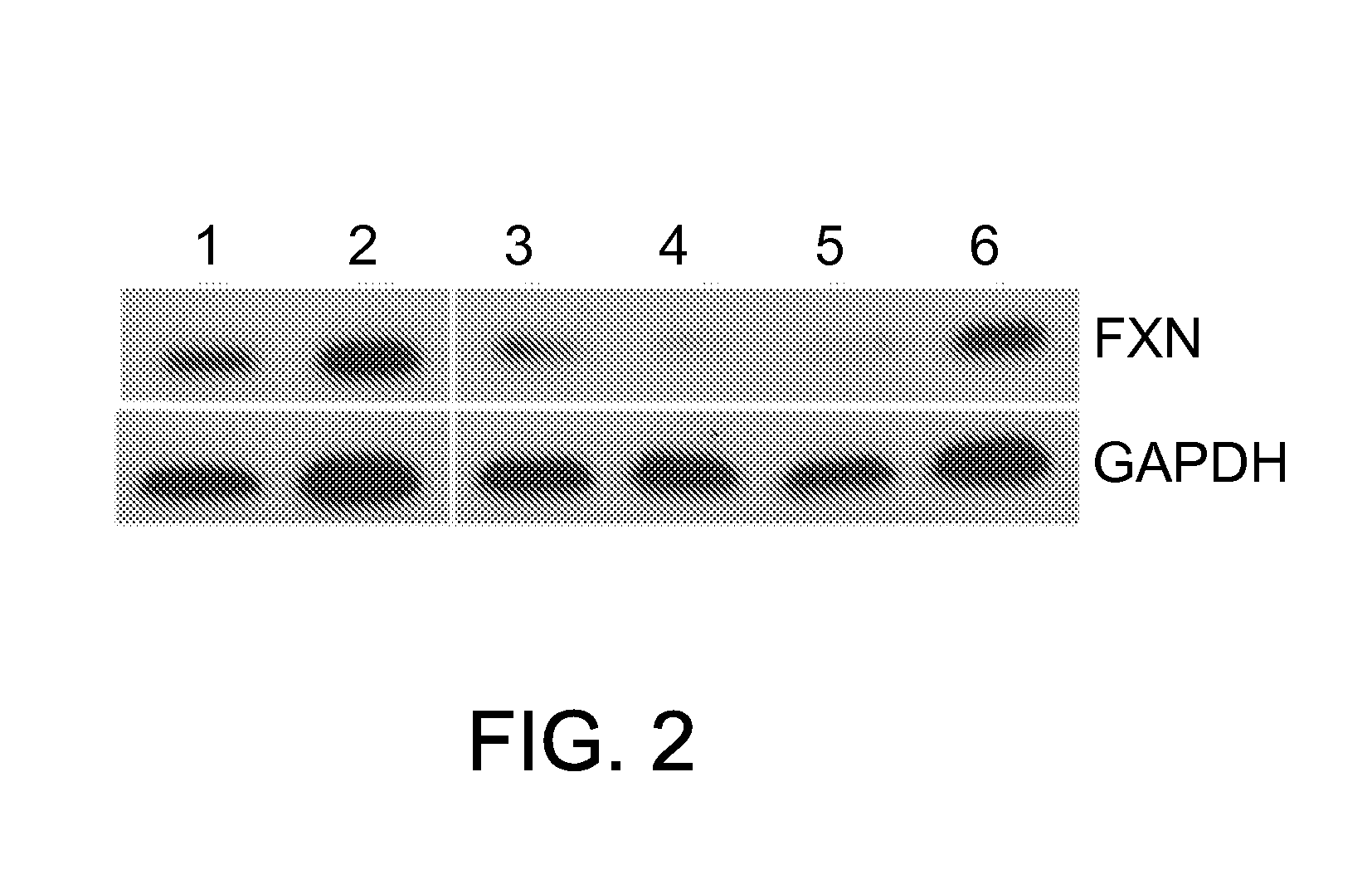
Isolated transduced cells exhibiting FRDA characteristics in an inducible fashion are disclosed. Isolated transduced cells comprise an expression vector having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an shRNA for frataxin protein knockdown and a heterologous expression control sequence. Additionally, methods of screening for a candidate therapeutic agent for treating Friedreich's Ataxia using isolated transduced cells are disclosed. Further, a recombinant nucleic acid construct for frataxin knockdown is disclosed that comprises a nucleic acid encoding an shRNA operably linked to a heterologous expression control sequence and expressing an shRNA molecule in a dose-responsive fashion.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF INDIANA UNIV
Methods of treating mitochondrial disorders
Provided herein are methods for treating a disease or disorder associated with mitochondrial dysfunction through ex vivo introduction of a nucleic acid molecule into hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) followed by transplantation of the HSPCs into a subject in need of treatment. The nucleic acid molecule may include a functional human frataxin (hFXN) or may include a gene editing system that when transfected into the cells removes a trinucleotide extension mutation of endogenous hFXN.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
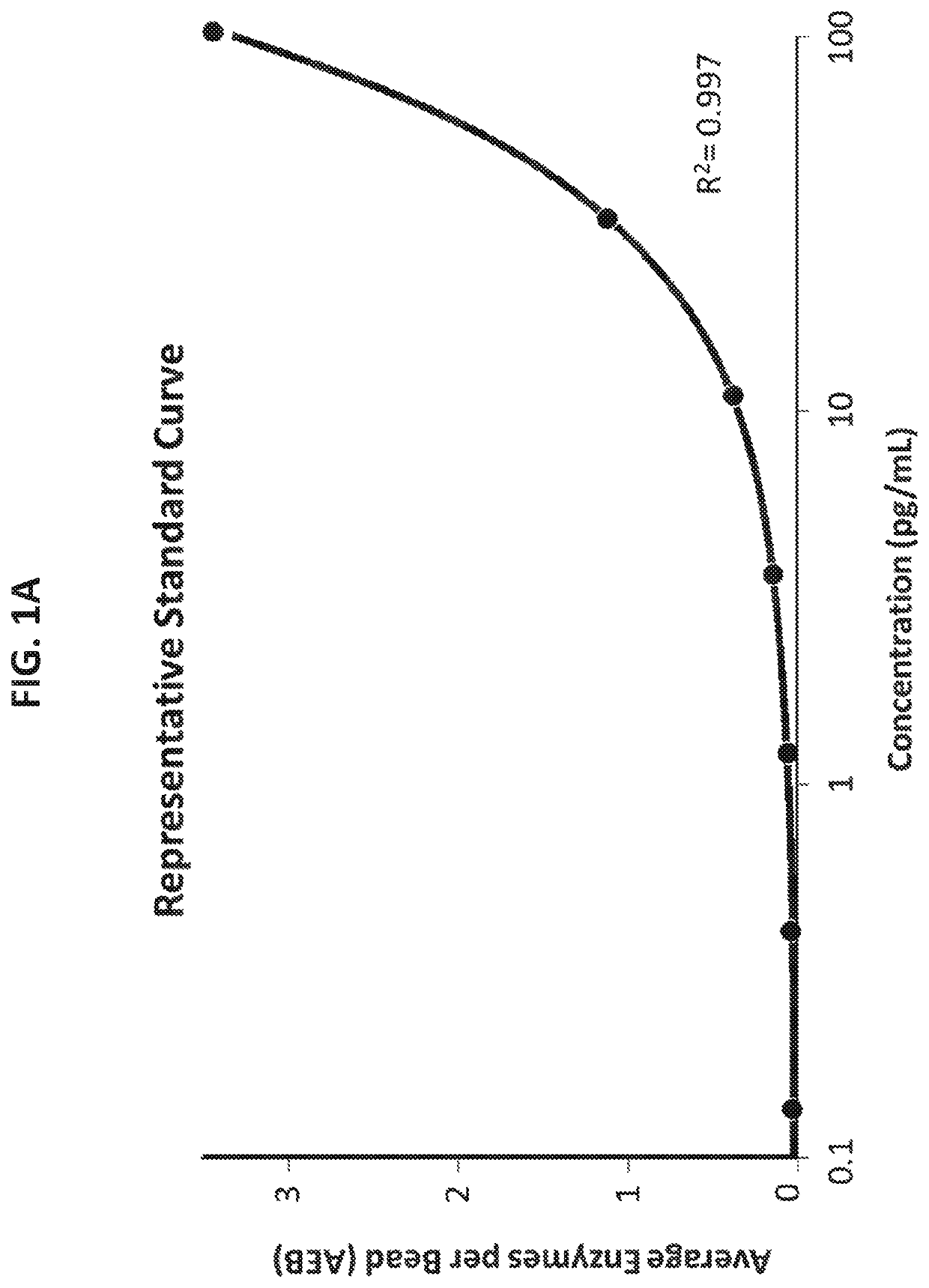
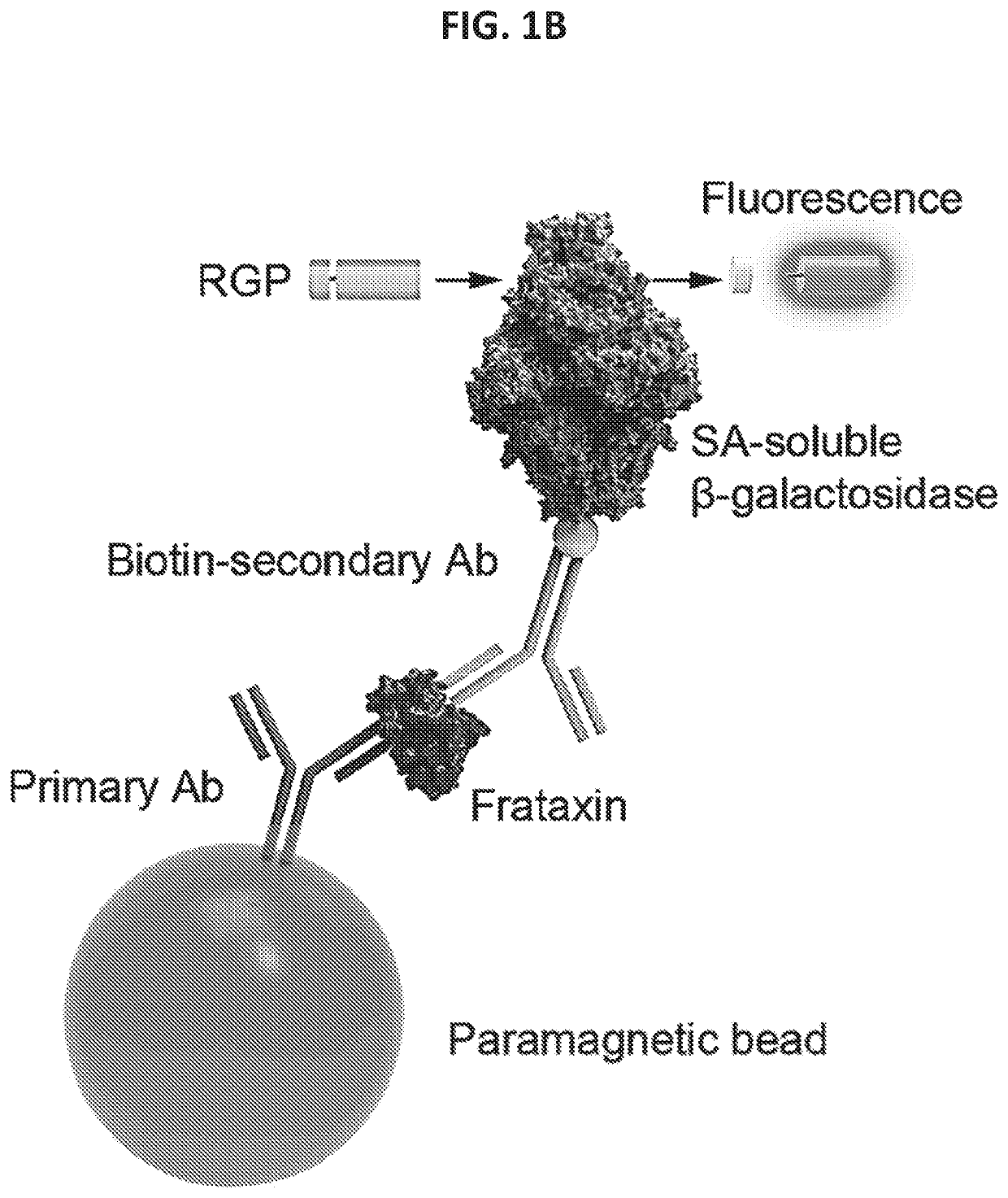
High-sensitivity immunoassay for the detection of frataxin in biofluids
PendingUS20220308072A1Reduced fractional anisotropy in white matterImprove diffusion abilityGenetic material ingredientsDisease diagnosisImmune profilingFrataxin
Disclosed herein are methods for assaying the concentration of frataxin in biofluids, and kits, reagents, and uses thereof.
Owner:VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS
Treatment and prediction of therapeutic responses in patients suffering from friedreich ataxia
PendingUS20220105073A1Nervous disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsAconitaseFriedreichs ataxia
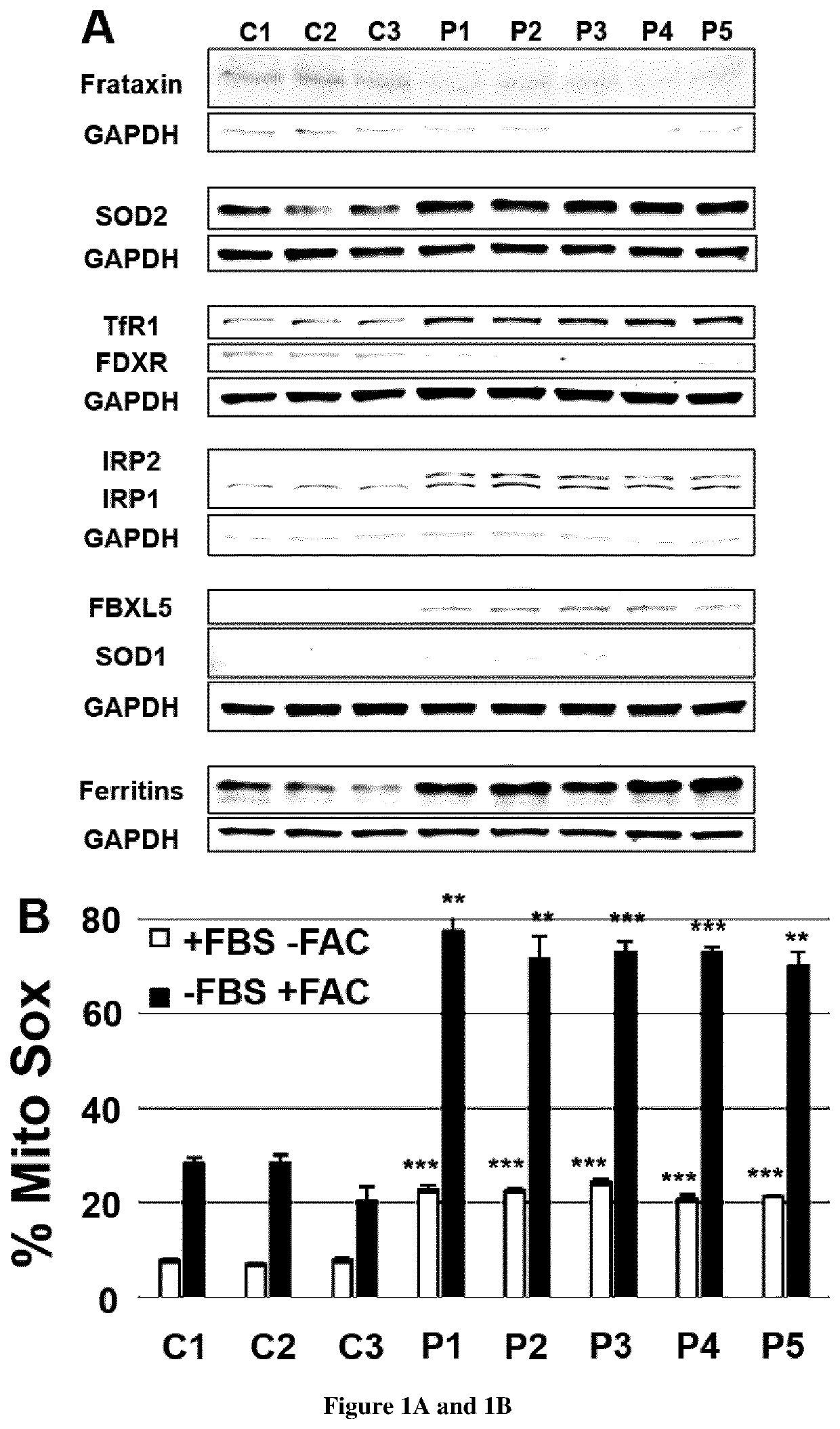
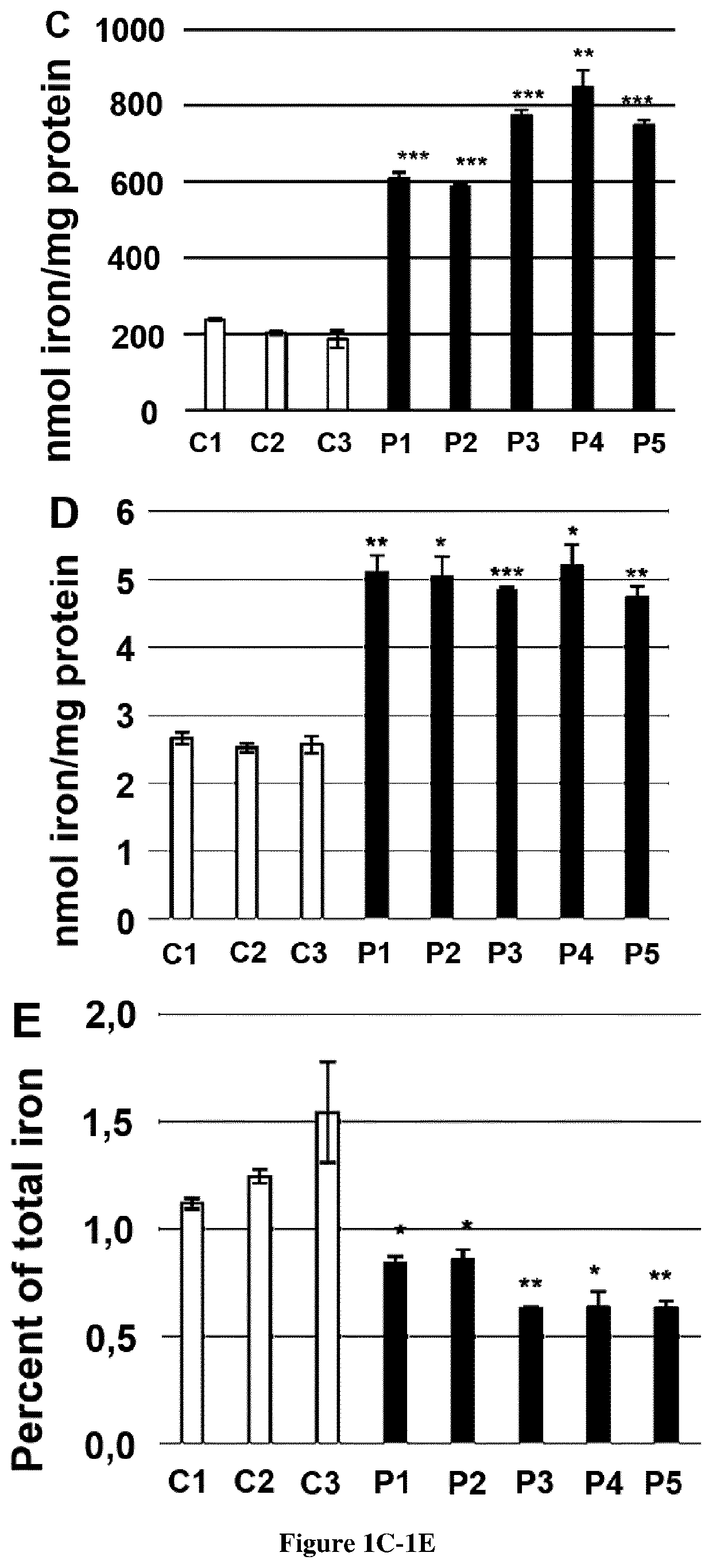
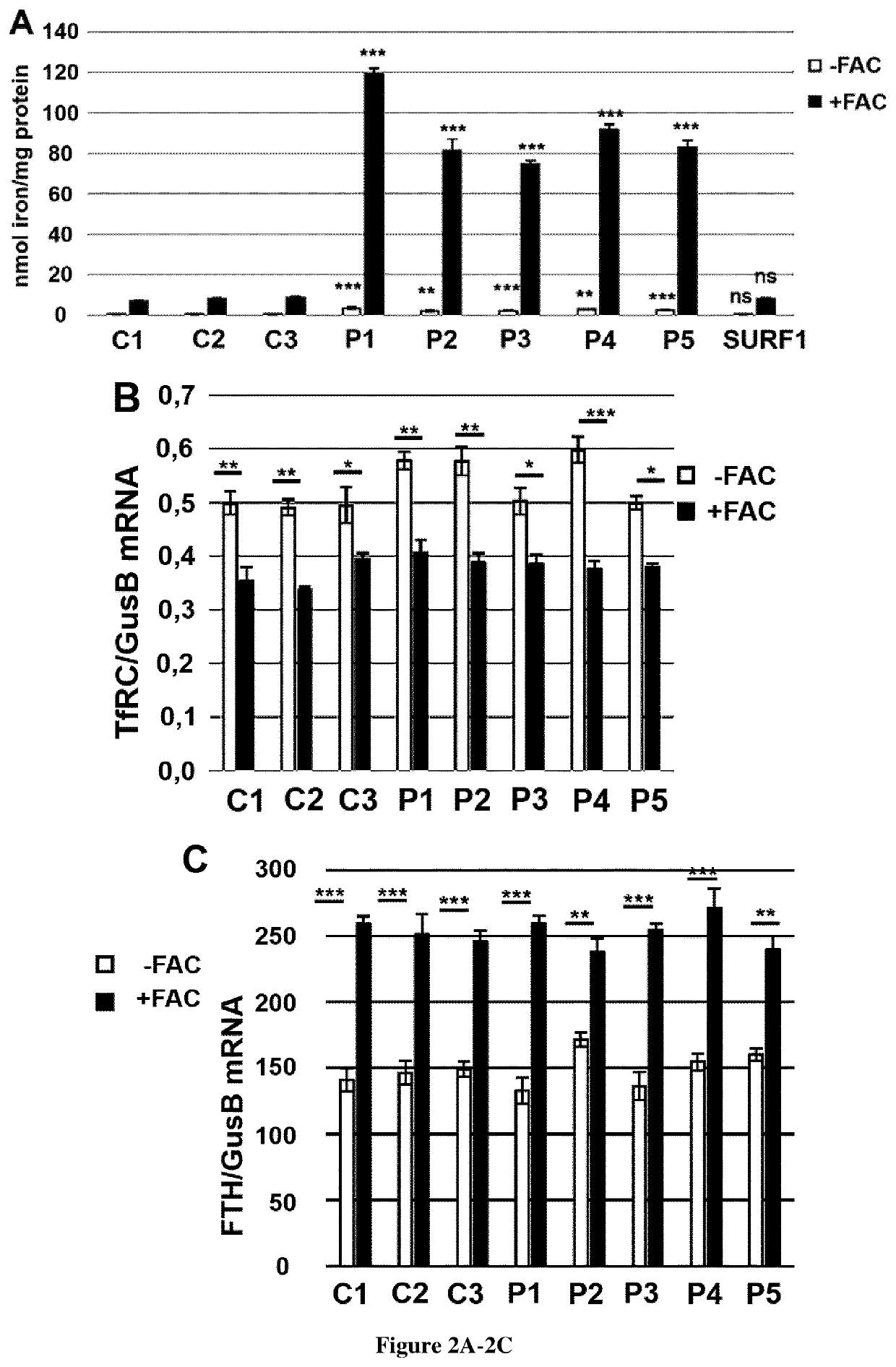
Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) is caused by a GAA repeat expansion in FXN gene that encodes a mitochondrial protein, frataxin, involved in iron sulfur complex (ISC) assembly. Frataxin deficiency results in abnormal ISC containing proteins, namely respiratory chain complex I-III and aconitases and accumulation of iron in brain and heart of patients. Here, the inventors show that FRDA fibroblasts are unable to limit iron uptake inducing a massive cytosolic iron accumulation and to a lesser extent in mitochondria. The inventors also observed increased transferrin receptor (TfR1) steady state levels and membrane TfR1 accumulation that they ascribed to impaired post-translational modification by palmitoylation as well as delayed transferrin recycling. Finally, the inventors showed that artesunate, dichloroacetate and Coenzyme-A improved TfR1 palmitoylation and thus represent candidate molecules for the treatment of patients with Friedreich ataxia. Thus the present invention relates to methods of treating Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) as well as to methods of predicting whether a patient suffering from FRDA will achieve a therapeutic response.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
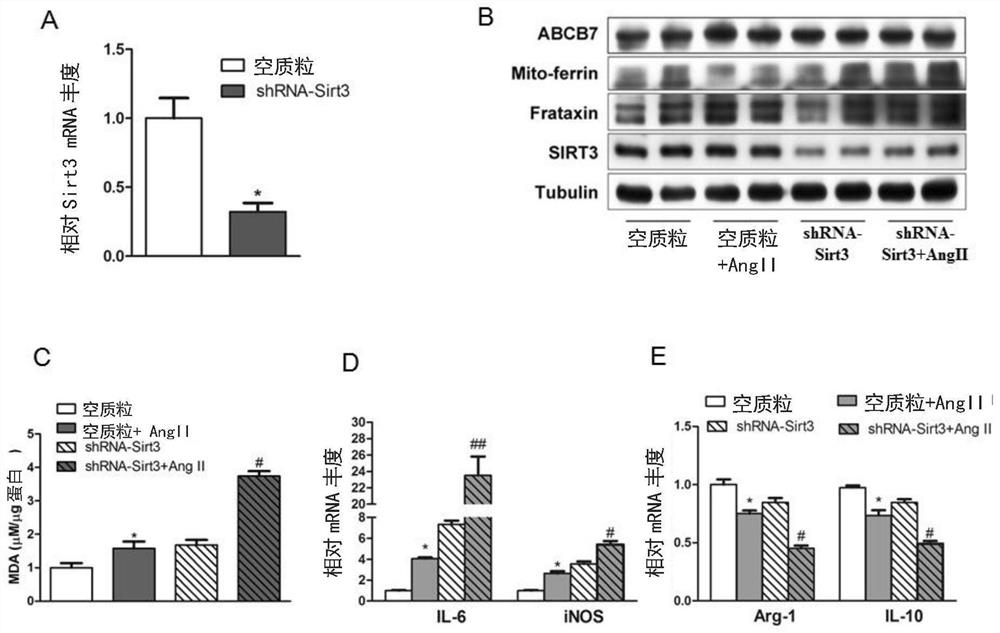
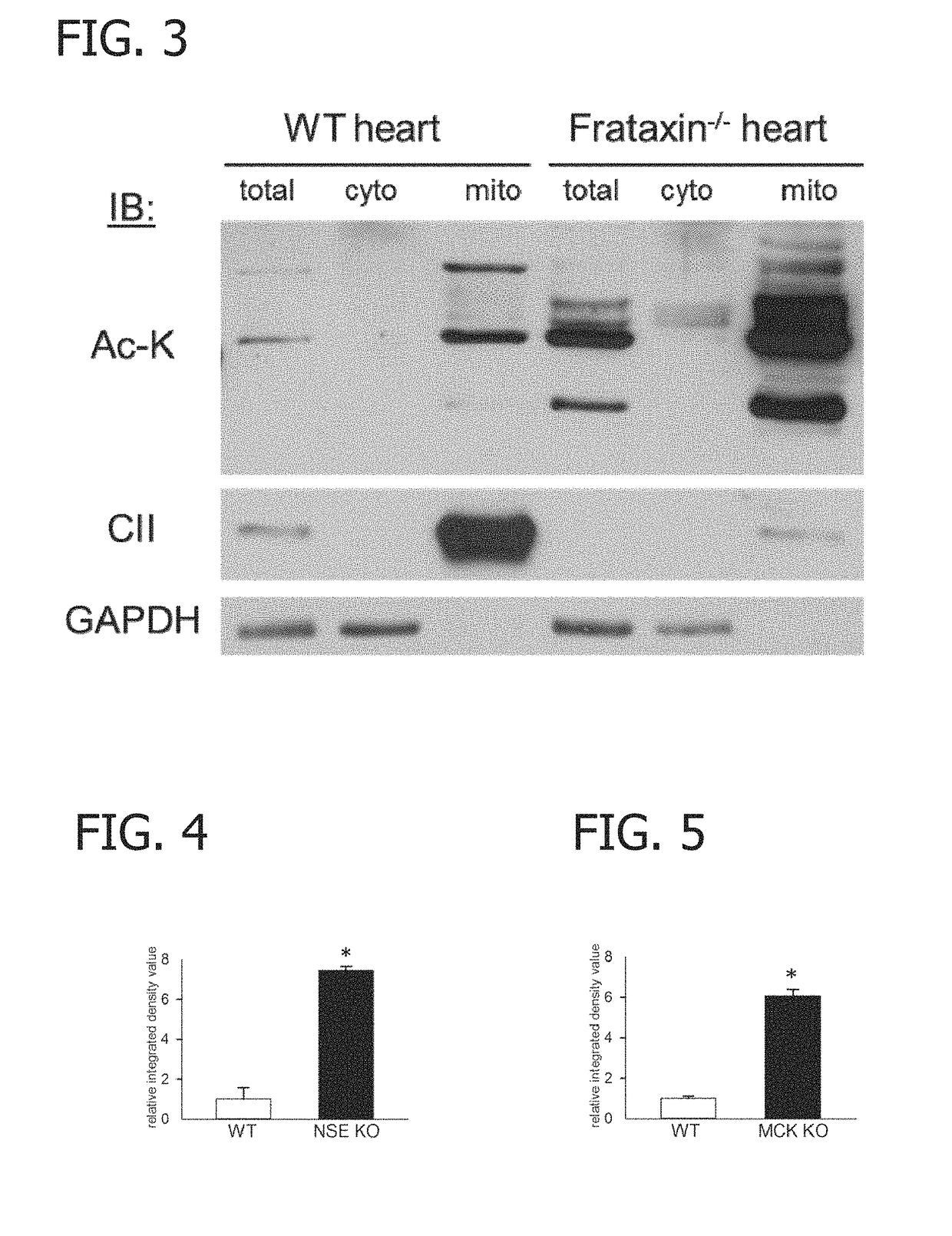
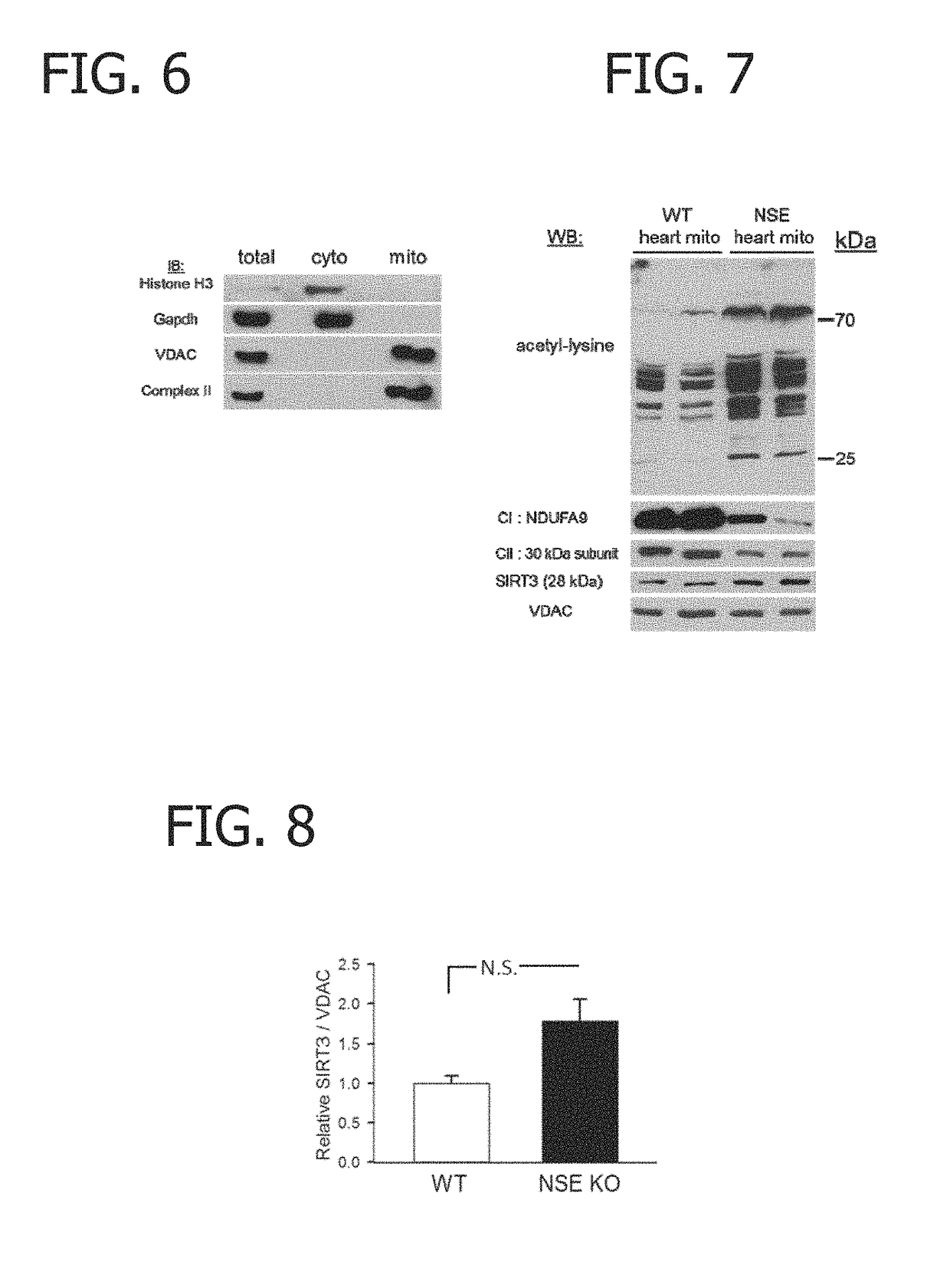
Application of SIRT3 mediated macrophage Fraxin deacetylation modification in improvement of inflammatory diseases
The invention provides an application of SIRT3 mediated macrophage Fraxin deacetylation modification in improvement of inflammatory diseases. The invention reveals that the SIRT3 and the Fraaxin can interact for the first time, and the SIRT3 can mediate the deacetylation modification of the Fraaxin, so that the polarization of the macrophage is regulated. M2-type polarization of macrophages can be adjusted by adjusting the interaction between SIRT3 and Frataxin, so that inflammation-related diseases such as hypertension can be relieved or treated. The invention has important significance for preventing and treating diseases related to mitochondrial metabolism and blood pressure disorder.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF HYPERTENSION
Frataxin enhancer
InactiveUS20160271090A1Practical use is extremely highOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmino-Levulinic AcidDisease
The object of the present invention to provide an agent effective for treating and preventing e.g. a disease caused by reduction in frataxin production. The present invention provides a frataxin enhancer comprising 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or a derivative thereof or salts thereof, as well as a therapeutic and / or prophylactic agent for a disease caused by reduction in frataxin production.
Owner:SBI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Messenger RNA therapy for the treatment of Friedreich's ataxia
ActiveUS10780183B2Efficient productionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMessenger RNAFrataxin
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
Inducible cell-based model for the study of friedreich's ataxia
Isolated transduced cells exhibiting FRDA characteristics in an inducible fashion are disclosed. Isolated transduced cells comprise an expression vector having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an shRNA for frataxin protein knockdown and a heterologous expression control sequence. Additionally, methods of screening for a candidate therapeutic agent for treating Friedreich's Ataxia using isolated transduced cells are disclosed. Further, a recombinant nucleic acid construct for frataxin knockdown is disclosed that comprises a nucleic acid encoding an shRNA operably linked to a heterologous expression control sequence and expressing an shRNA molecule in a dose-responsive fashion.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF INDIANA UNIV
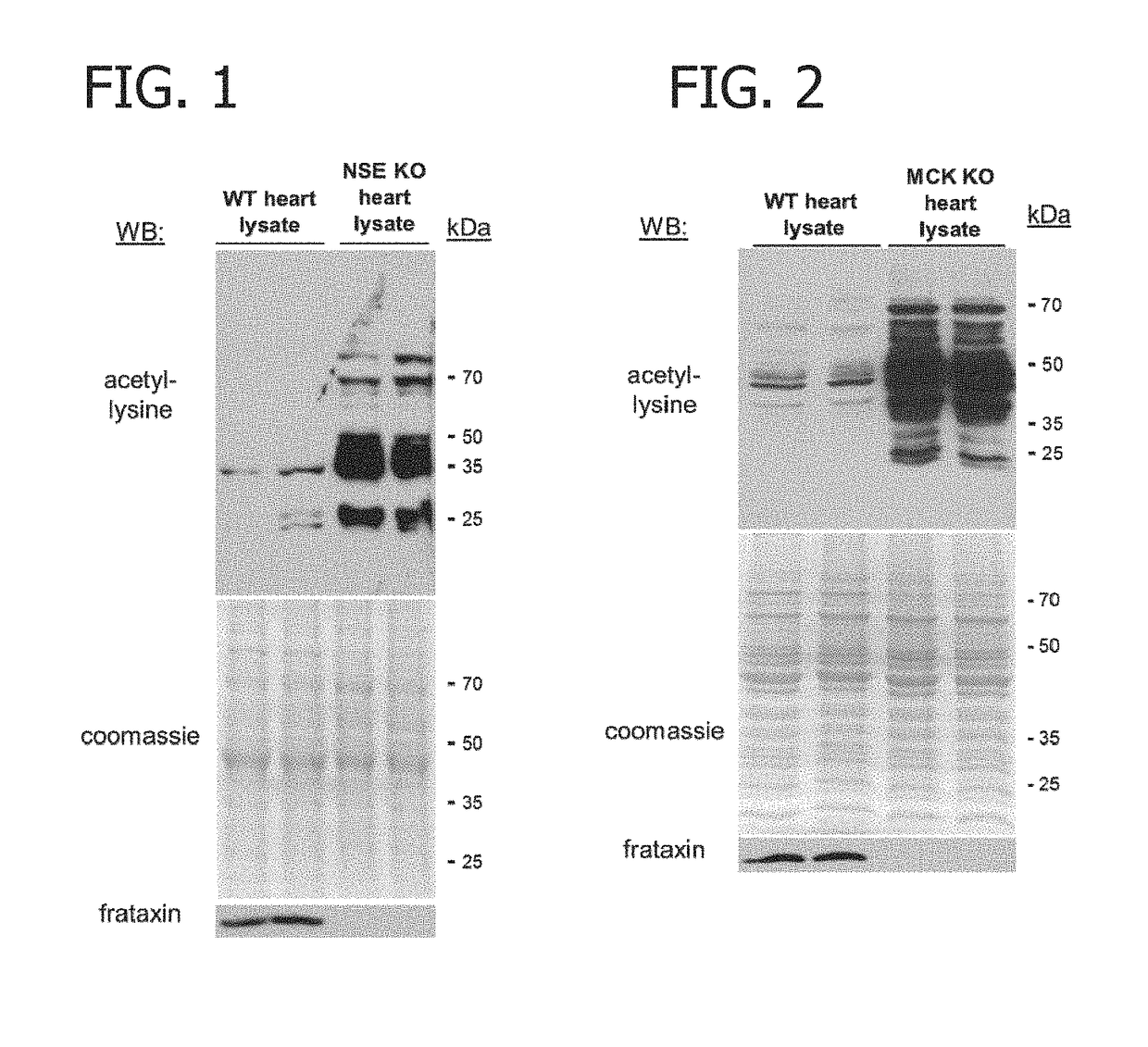
Biomarker for determining mitochondrial damage in friedreich's ataxia
Compositions and methods for screening for a disease or a disorder associated with a deficiency in frataxin in a subject using biomarkers for diseases or disorders associated with a deficiency in frataxin are disclosed. The compositions and methods include determining the acetylation status of mitochondrial proteins. Also disclosed are methods of detecting progression of a disease or a disorder associated with a deficiency in frataxin in a subject and methods of monitoring effectiveness of a therapy for diseases or disorders associated with a deficiency in frataxin.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF INDIANA UNIV
Tataxin-sensitive markers for determining efficacy of ataxin replacement therapy
The present disclosure is based, at least in part, on providing a set of markers, also referred to herein as FXN-sensitive genomic markers (or FSGMs), each expression level of which exhibits a positive or negative correlation with an ataxin (FXN) level in a cell. Thus, these FSGMs may be used to determine, assess, and / or monitor the efficacy of FXN replacement therapy in a subject.
Owner:라리마테라퓨틱스인코포레이티드
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com