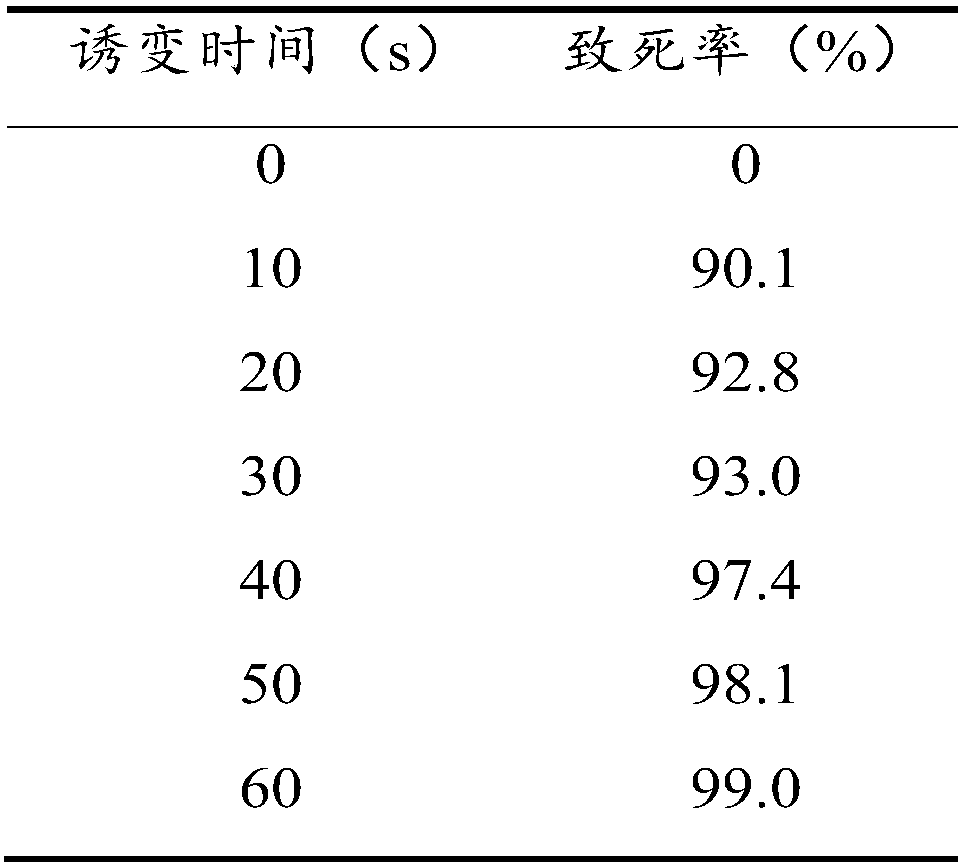
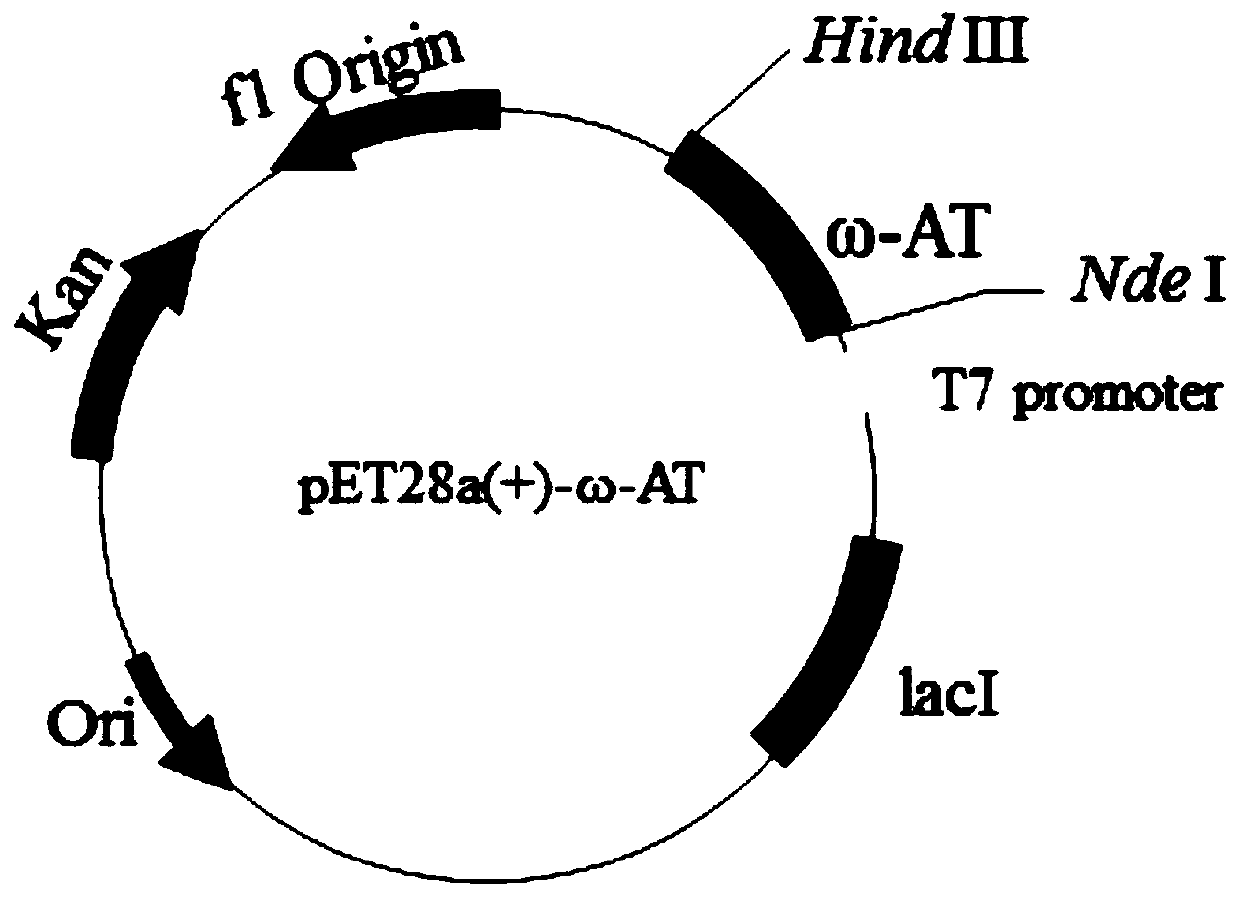
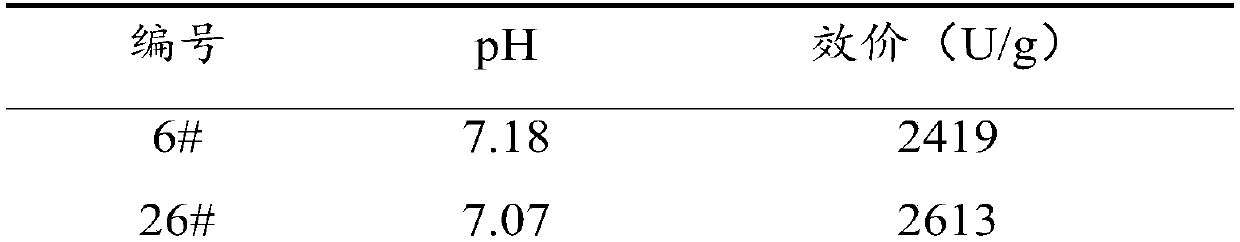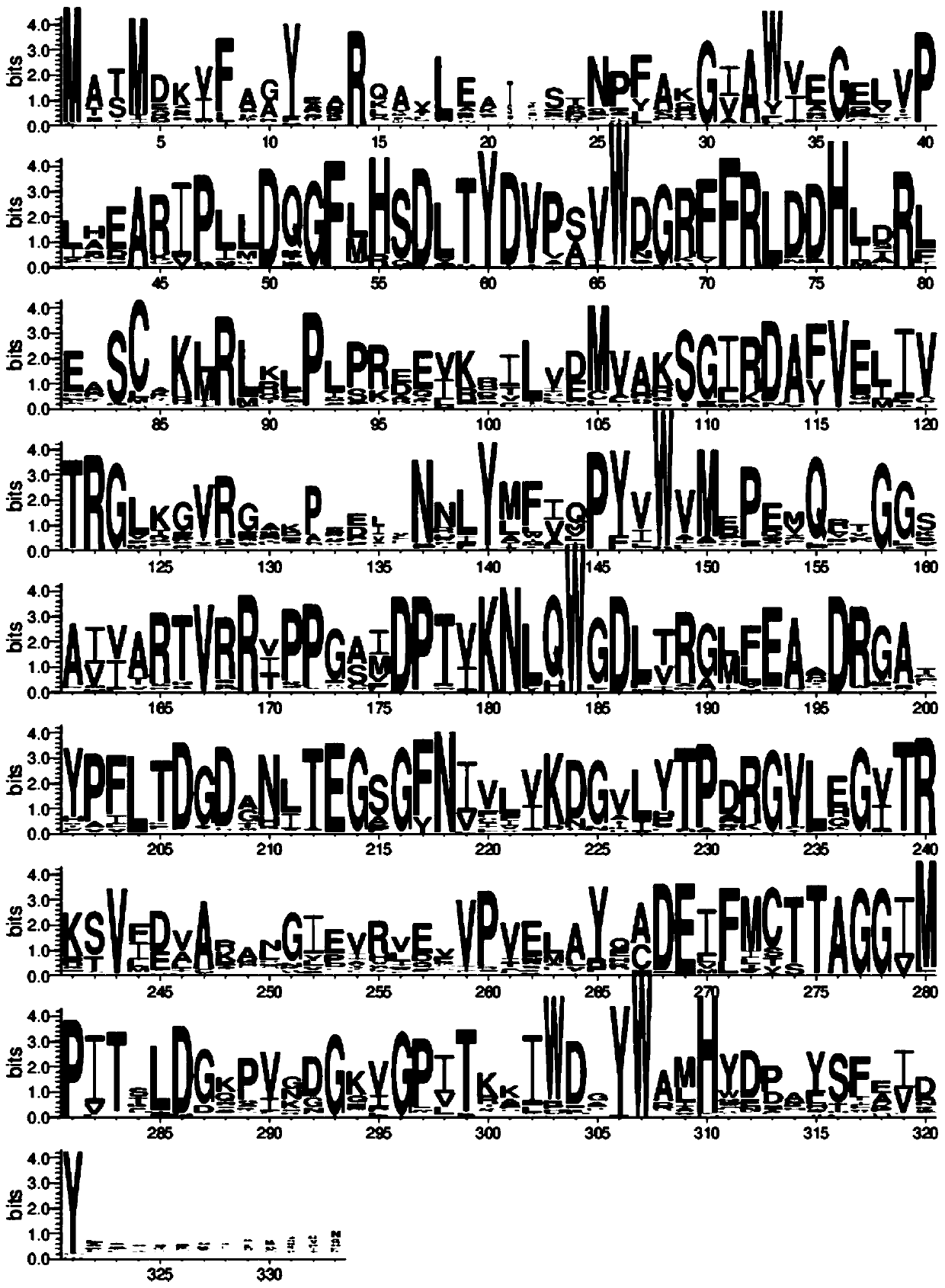Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "High positive mutation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran
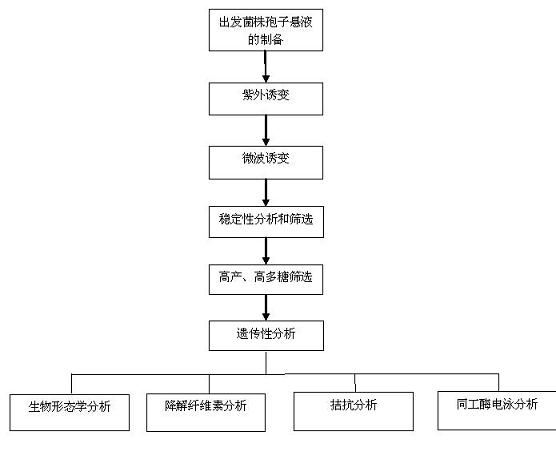
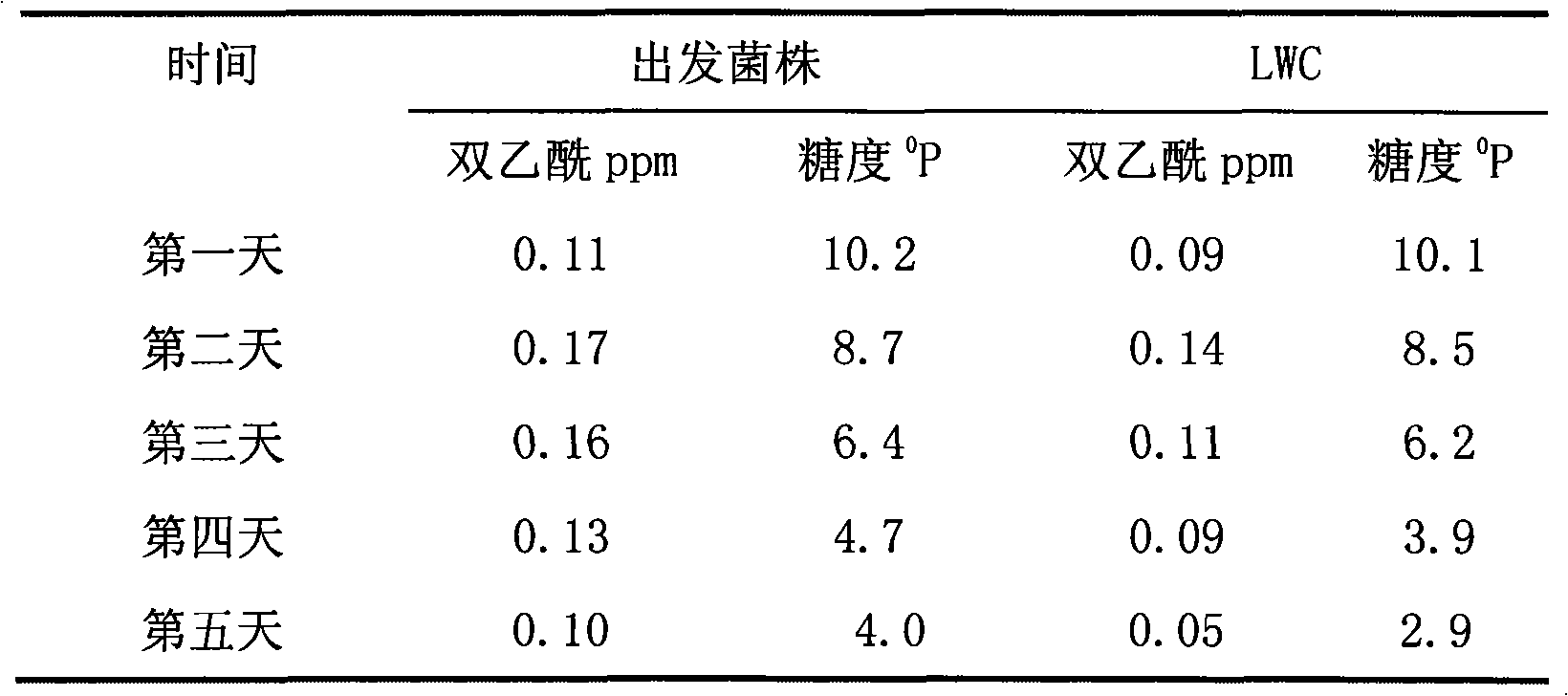
The invention discloses a Grifola frondosa strain for producing polysaccharide with a composite raw material of rice bran and wheat bran, which belongs to the technical field of microbial application technology and food biology. The Grifola frondosa strain JSU10 is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) in October 8th, 2010 with the CGMCC No. 4179 and is identified to be Grifolasp. The invention improves the positive mutation rate of the Grifola frondosa strain for rapidly growing and producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on a composite culture medium of rice bran and wheat bran by composite mutagenesis of ultraviolet rays and microwave to obtain a high-yield strain; the strain and the original strain are respectively a liquid fermentation rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium; and hypha dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutated strain are respectively improved by 39.24 percent and 42.58 percent compared with the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
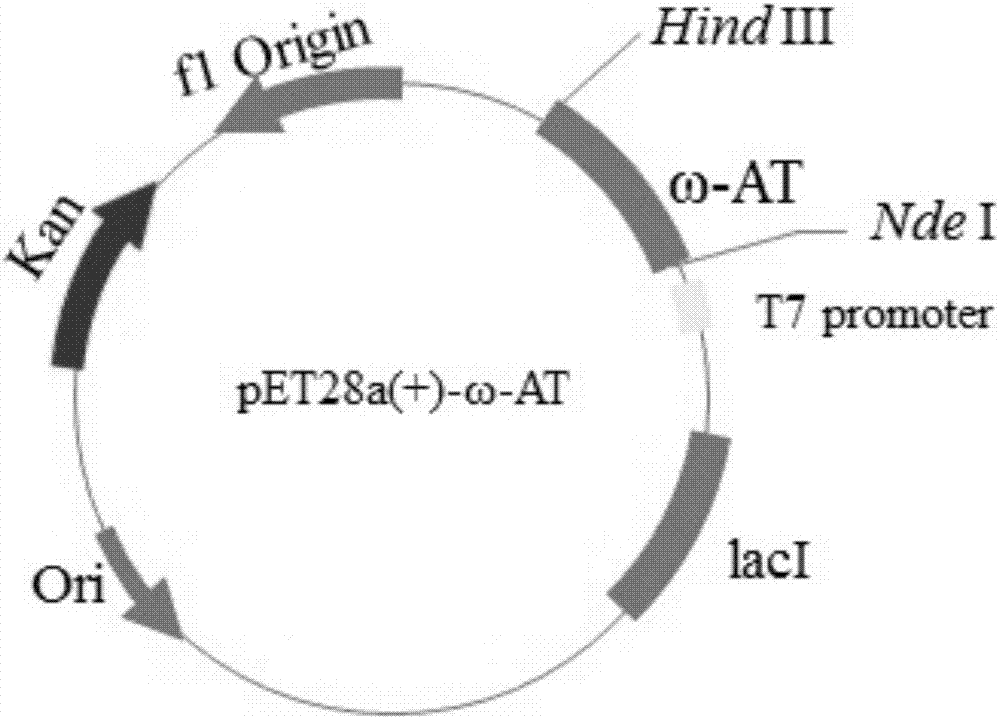
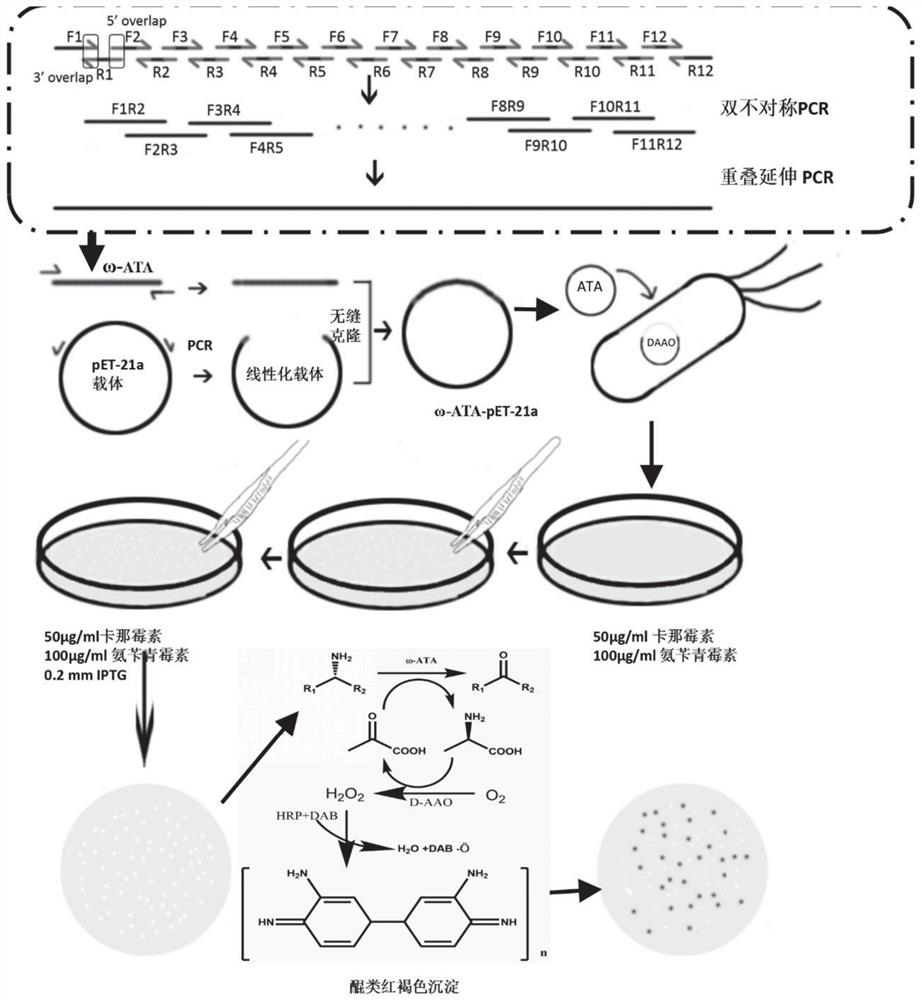
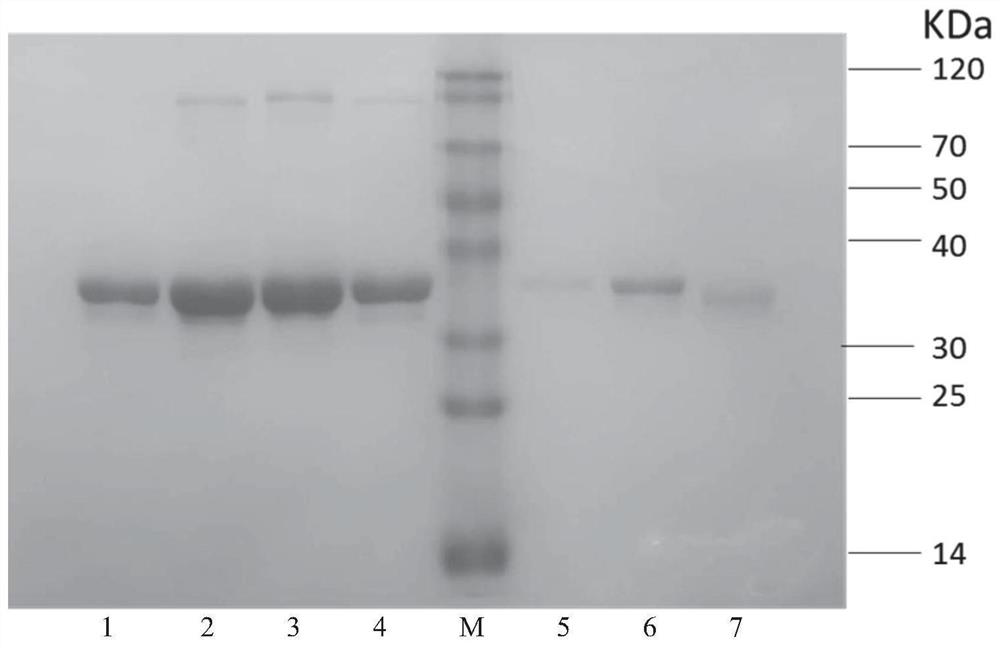
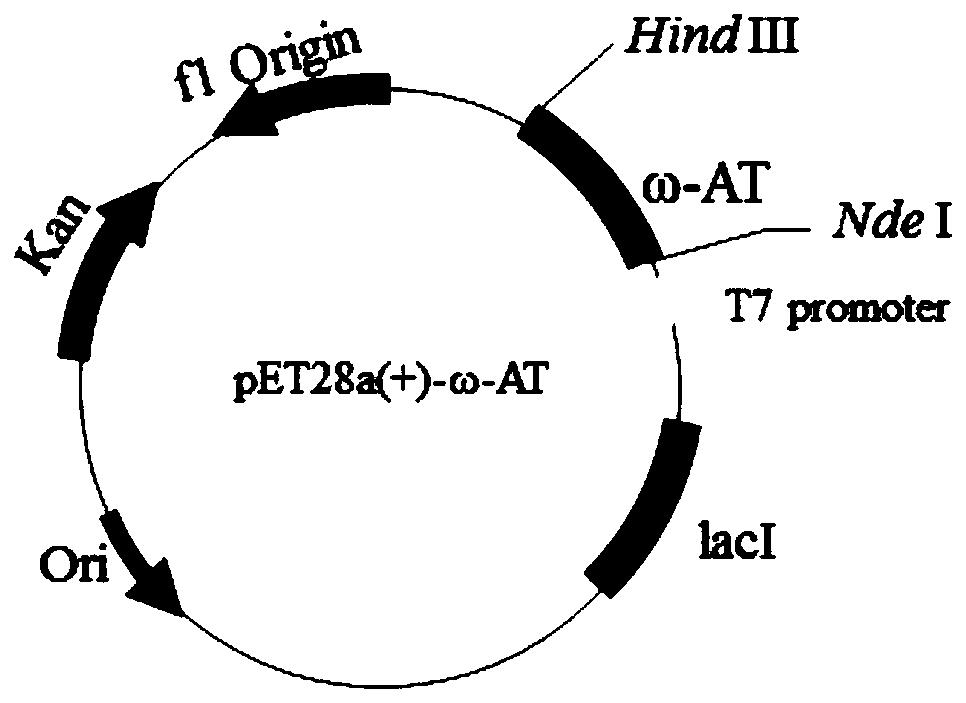
Omega-transaminase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107058256AIncrease the probability of positive mutationImprove experimental efficiency and feasibilityTransferasesFermentationSite-directed mutagenesisEnzyme
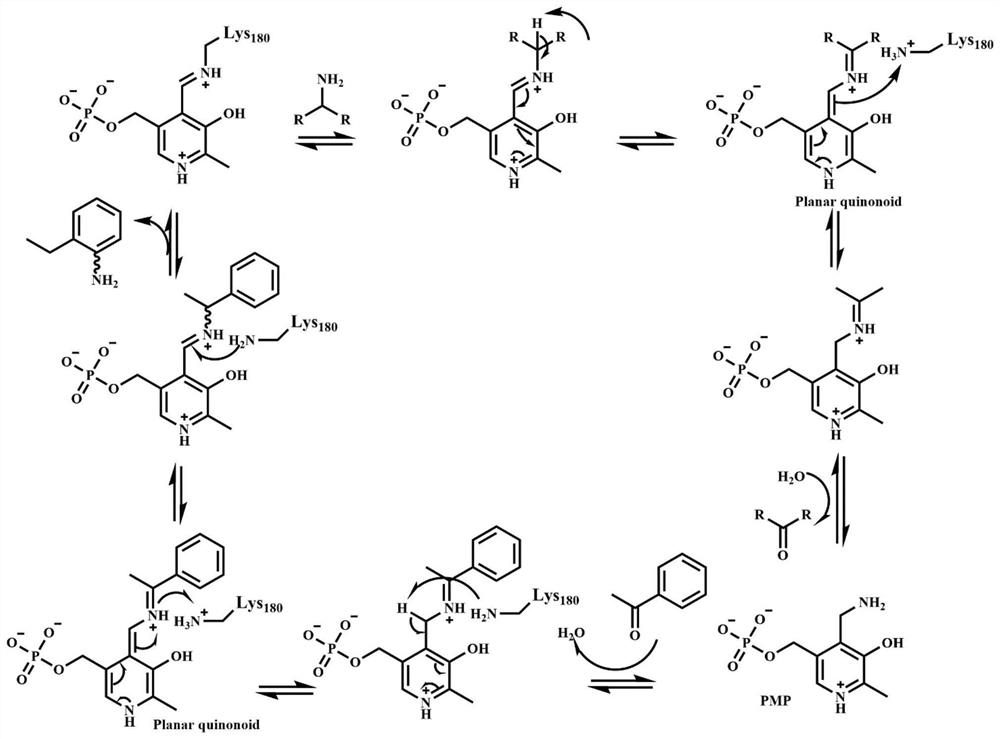
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The amino acid sequence of the omega-transaminase mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, SEQ ID No. 4, SEQ ID No. 6, SEQ ID No. 8, SEQ ID No. 10 or SEQ ID No. 12. The invention further provides the gene of the omega-transaminase mutant, an expression unit containing the gene, recombinant plasmid and a transformant. The preparation method includes: using an NCBI database and BLAST software to perform comparison screening to obtain the homologous amino acid sequence of omega-transaminase, using a Weblogo program to obtain a sequence consistency result, using the homologous amino acid sequence, the sequence consistency result and the sequence of the omega-transaminase to determine amino acid residue sites which need to be mutated, and using site-directed mutagenesis technology to perform experimental verification. The method has the advantages direct mutation probability can be increased effectively, experiment efficiency and feasibility are increased, and mutant enzymes whose thermodynamic stability is evidently better than that of wild enzymes can be screened out.
Owner:上海邦林生物科技有限公司
Penicillium citrinum strain with high nuclease P1 yield and its selective breeding process
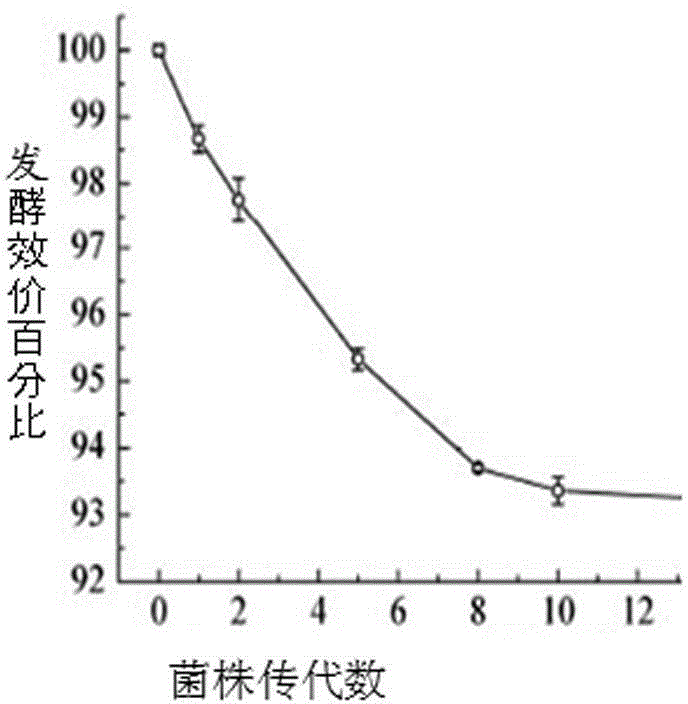
The present invention discloses one Penicillium citrinum strain with high nuclease P1 yield and its selective breeding process. The Penicillium citrinum strain is preserved in the preservation number of CGMCC No. 2014. Its selective breeding process includes low energy ion beam implantation on Penicillium citrinum spore suspension, transferring the mutagenized spore to plate culture medium for culturing, selecting single strain and transferring to malt wort and slant cultivating, liquid fermenting culturing to screen out strain with high nuclease P1 yield, and passage culturing for over 30 generations to obtain strain with stable high yield character. The Penicillium citrinum strain has high enzyme activity and stable high yield character, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN105462949AGood thermal stabilityHigh application valueFermentationGenetic engineeringGlutamate decarboxylaseMutant
The invention discloses a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and a preparation method thereof and application. An amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and a nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention further discloses an expression unit containing genes for encoding the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant, a recombinant plasmid and a transformant. According to information of comparison with a thermococcus kodakarensis glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) amino acid sequence, a method of site-directed mutagenesis is adopted to introduce proline residue at an amino acid locus corresponding to lactobacillus brevis GAD, and the thermal stability of the GAD is improved through rational design. The mutant has better thermal stability in the process of catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof to generate gamma-aminobutyric acid and is favorable for industrial production of gamma amino acid butyric acid (GABA).
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
High-yield strain for producing L-alanine by fermentation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103602609AWide variety of sourcesLow priceBacteriaMutant preparationFiltrationUF - Ultrafiltration
The invention relates to a high-yield strain Lds.0108 for producing L-alanine by fermentation. The high-yield strain is deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection with an accession number of CCTCC M2013361. The strain is a mutant strain by using Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus (GIMI.155) as an initial strain, mutagenizing cells by utilization of a low energy ion implantation method, and screening by a reversible inhibition assay method. The growth temperature range of the strain is 35-40 DEG C. The optimum growth temperature is 37 DEG C and the optimum pH value is 7.0. A slope culture medium used is an MRS culture medium. Glucose and other carbohydrates are used as substrates for the strain. The L-alanine is produced by fermentation under anaerobic conditions. Impurities are removed by ultrafiltration membrane filtration and nanofiltration membrane filtration in a purifying process, thus guaranteeing the product quality. The strain and the preparation method are suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:淮北新旗氨基酸有限公司
Method for rapid and efficient screening of vitamin K2 (MK-7) high-yielding strain
InactiveCN106916810AGood genetic stabilityHigh positive mutation rateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesVitamin K2Biotechnology
The invention discloses a method for rapid and efficient screening of a vitamin K2 (MK-7) high-yielding strain. An original strain undergoes atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis, and plate breeding of the mutagenesis strain is carried out by the use of a vitamin K2 analogue and a respiratory chain inhibitor. After fermentation and re-screening through a 96-well culture plate, content of the high-yielding strain vitamin K2 is raised by 200%. By the above method, a batch of Bacillus natto having advantages of fast growth speed, high yield of vitamin K2, genetic stability and strong tolerance to the environment is bred.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving yield of fermentation of epsilon-polylysine
InactiveCN102154392AHigh positive mutation rateRaise the level of fermentationMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesEpsilon-PolylysineMicrowave
The invention provides a method for improving yield of fermentation of epsilon-polylysine. In the method, a microwave and dithyl sulfate combined mutation induction method is used to obviously improve the forward mutation of Streptomyces albulus CGMCC4.121 to obtain a high-yield strain for producing epsilon-polylysine by fermentation. Results show that the shake flask fermentation level of the epsilon-polylysine is improved from 0.60g / L to 0.85g / L.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Yeast strain of beer and application thereof
InactiveCN101665772AHigh positive mutation rateIncrease mutagenic effectFungiBeer fermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a yeast strain of beer and the application thereof in the aspect of beer fermentation. The strain of the beer-brewing yeast (saccharomyces cerevisiae) provided by the inventionis preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.3217. The selecting and breeding method of the strain comprises the following steps: activating the original starting strain, injecting ions for mutation, mutating by laser, primarily sieving by using wort and agar flat plate culturing medium, sieving again by using a fermentationbung, testing genetic stability, and performing a pilot-scale test. The yeast strain of beer is an excellent yeast strain of beer and has a potential suitable for large production of beer breweries.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Omega-transaminase mutant, gene and application
ActiveCN111826362AHigh positive mutation rateImprove experimental efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesGeneticsWild type
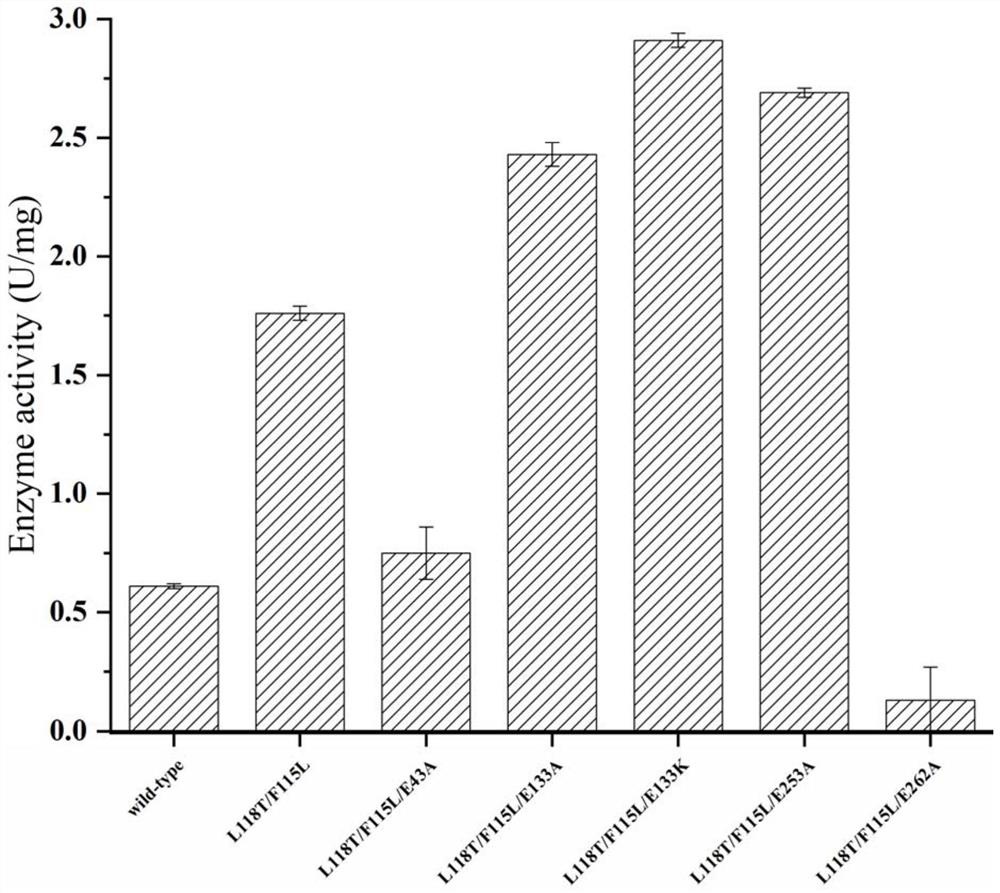
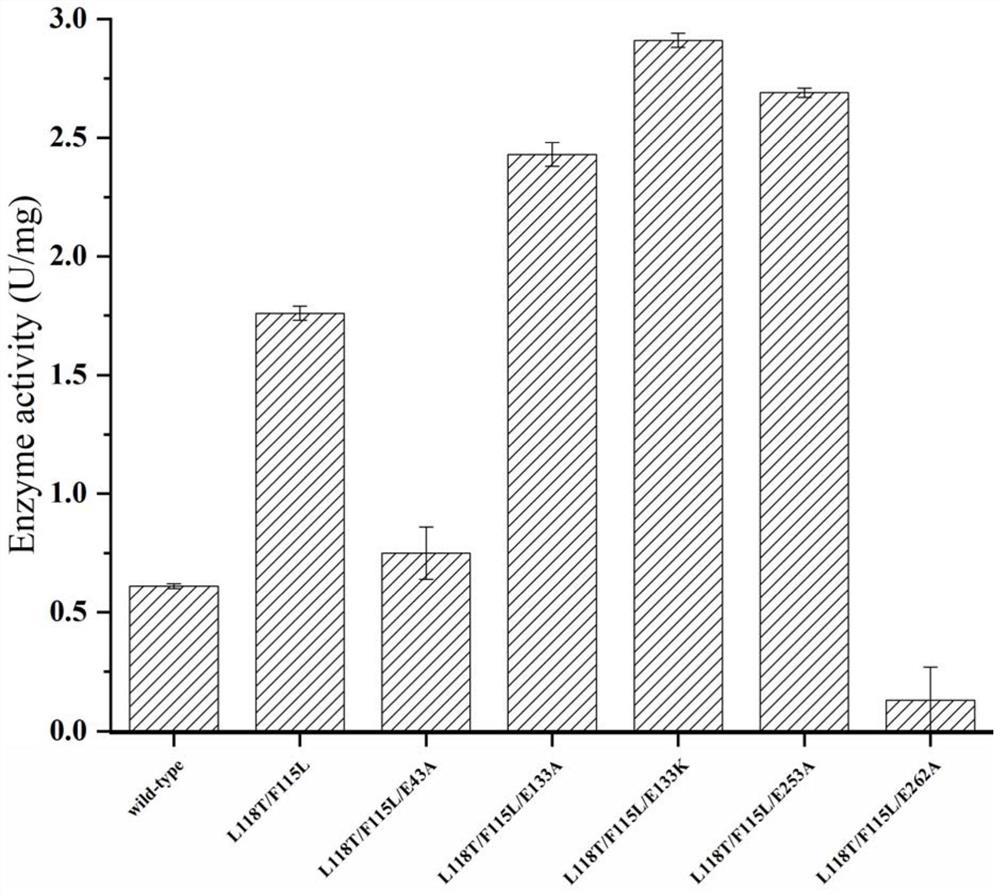
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant, a gene and an application. The amino acid sequence of the wild type omega-transaminase is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and the omega-transaminase mutantis one of the follows: (1) an L118T / F115L dual-mutation mutant, (2) an L118T / F115L / E133A three-mutation mutant, (3) an L118T / F115L / E133K three-mutation mutant, and (4) L118T / F115L / E253A three-mutationmutant. Based on a genetic algorithm mature in technique, and a TK-SA model algorithm, improvement is performed, and then an ETSS algorithm is obtained; through combination with omega-transaminase surface charge-charge interaction, an amino acid residue site needing mutation is determined, and experimental verification is performed through a fixed-point mutation technique. The method can effectively improve orthomutation probability and improve experiment efficiency and feasibility, and through screening, a mutation enzyme of which the thermodynamics stability and the enzymatic activity are obviously better than those of a wild enzyme can be obtained.
Owner:李元源 +1
Omega-transaminase mutant obtained through DNA synthesis shuffling combination mutation and application
ActiveCN112481230AImprove thermal stabilityHigh positive mutation rateBacteriaTransferasesWild typeAmino acid
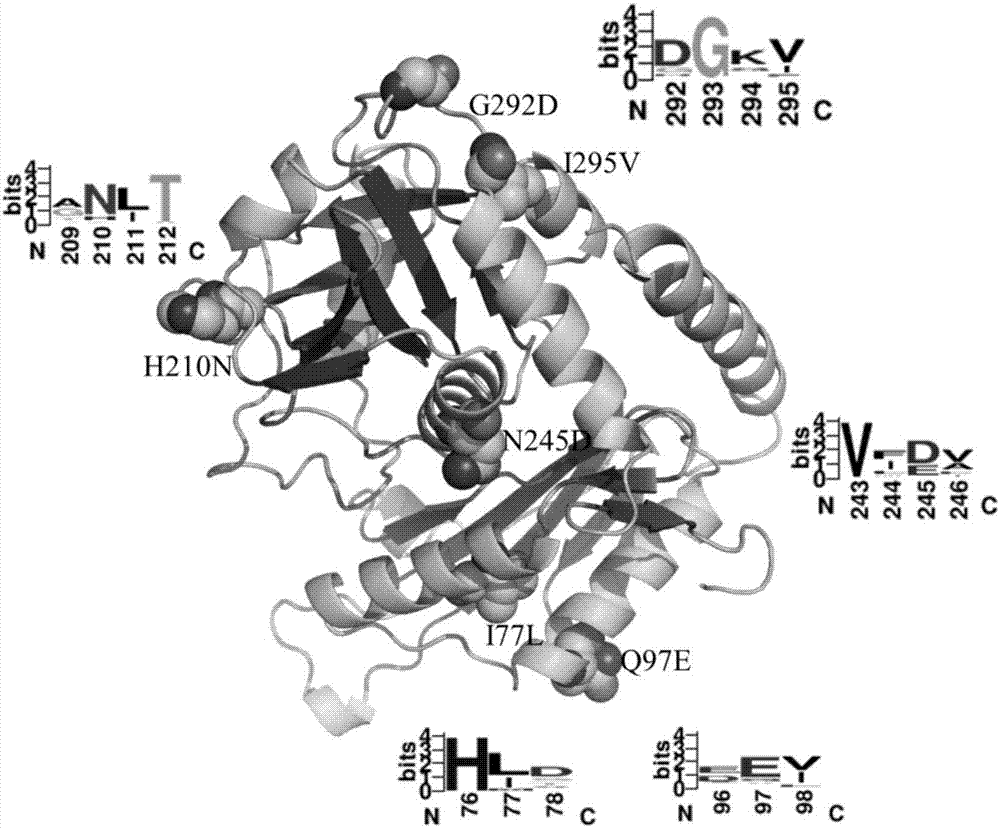
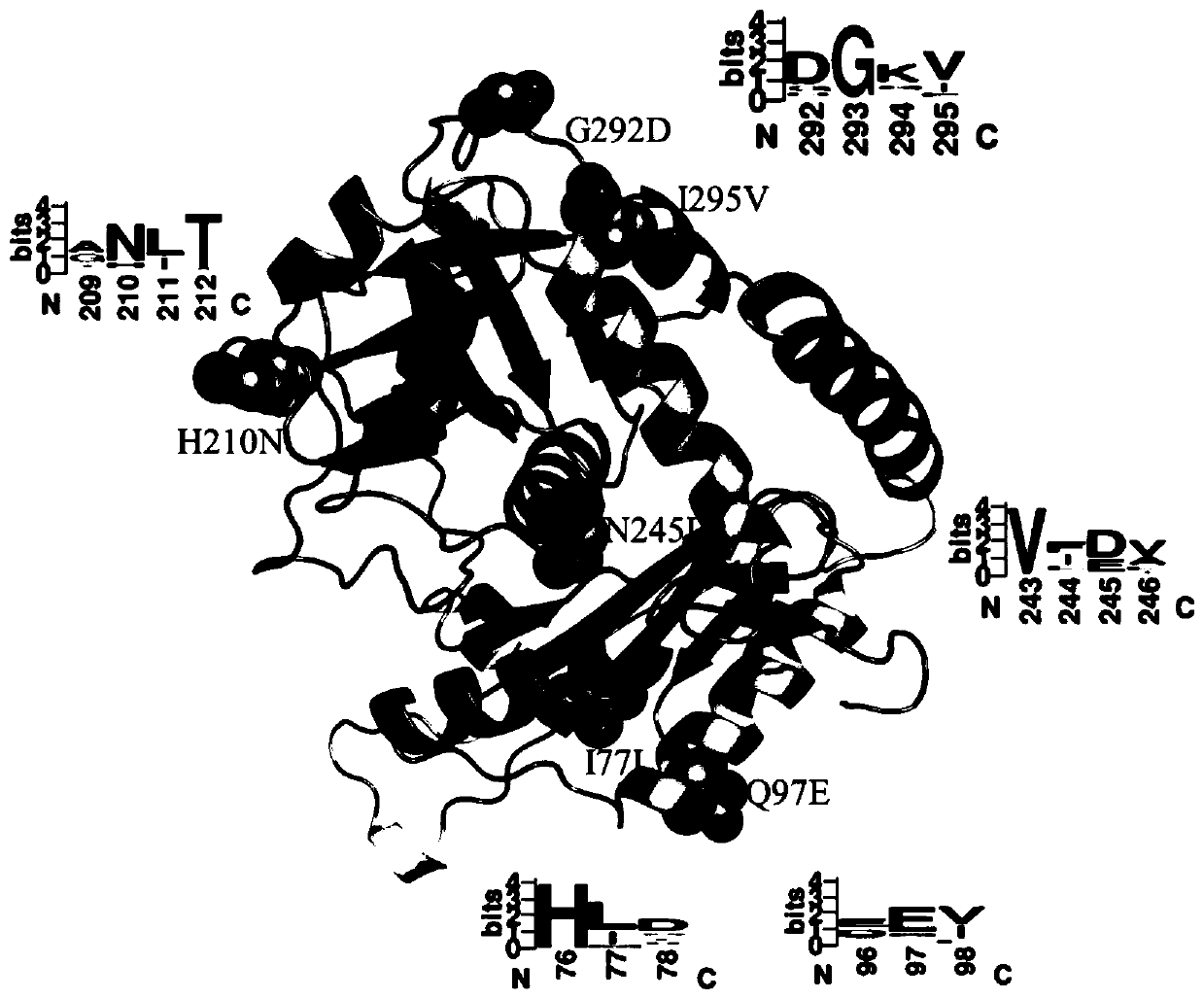
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant obtained by DNA synthesis shuffling combination mutation, the omega-transaminase mutant is obtained by point mutation of wild type omega-transaminase from Aspergillus terreus, the amino acid sequence of the wild type omega-transaminase is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the mutation site of the omega-transaminase mutant is any one of the following: (1) F115L-H210N-M150C-M280C; (2) F115L-H210N; (3) F115L-H210N-E253A-I295V; (4) I77L-F115L-E133A-H210N-N245D; (5) I77L-Q97E-F115L-L118T-E253A-G292D; (6) I77L-E133A-N245D-G292D; and (7) H210N-N245D-E253A-G292D. The forward mutation obtained in the earlier stage is randomly combined through the DNA synthesis shuffling combination mutation method, and experimental verification shows that the method caneffectively improve the forward mutation probability and improve the experimental efficiency and feasibility, and mutant enzymes with thermodynamic stability obviously superior to that of wild enzymesare obtained through screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for breeding gibberellic acid high-producing strains by performing low-energy ion induced mutation on gibberella
InactiveCN104388418AImprove fermentation titerAvoid damageMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGibberellic acid
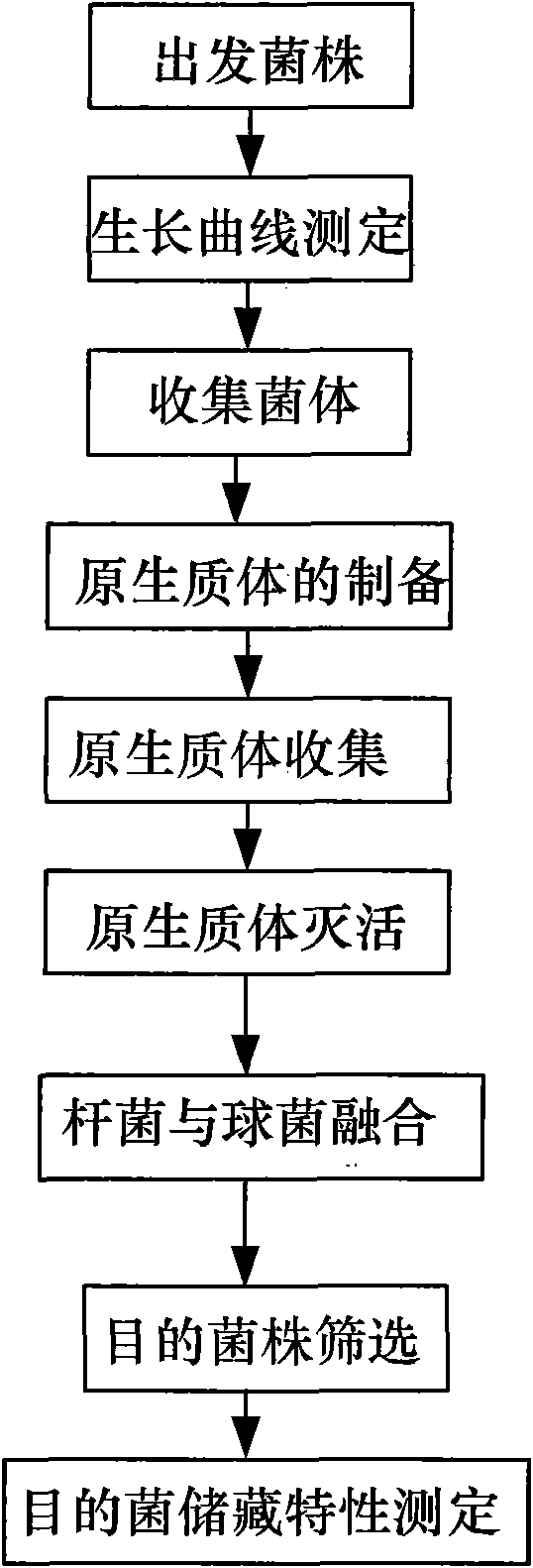
The invention discloses a method for breeding gibberellic acid high-producing strains by performing low-energy ion induced mutation on gibberella. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a protoplast suspension of 108-109 / mL by use of a gibberella strain and sterile water; applying the protoplast suspension to a culture dish for air drying; injecting a pulsed nitrogen ion beam into the air-dried protoplasts to induce the mutation of the protoplasts; adding the mutated protoplasts to sorbitol solution ice bath for suspending, and then applying the suspension to a PDAS regeneration medium plate for cultivation; performing inoculation of the well growing individual strains into a shake flask filled with a liquid fermentation culture medium for shake cultivation, thereby obtaining the gibberellic acid high-producing strains. The method for breeding the gibberellic acid high-producing strains by performing low-energy ion induced mutation on the gibberella has the advantages that the mutation of the gibberella is induced in a pulsed nitrogen ion beam injection manner and the high-producing mutant gibberella strains can be bred; according to the method, the direct mutation rate of the mutant strains can be 10%-40%, and the fermentation titer is increased by 30-90% in contrast with that of the original strain.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Screening method of lincomycin producing strain
InactiveCN101638650AScale upSpeed up the processMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationScreening methodMicrobiology
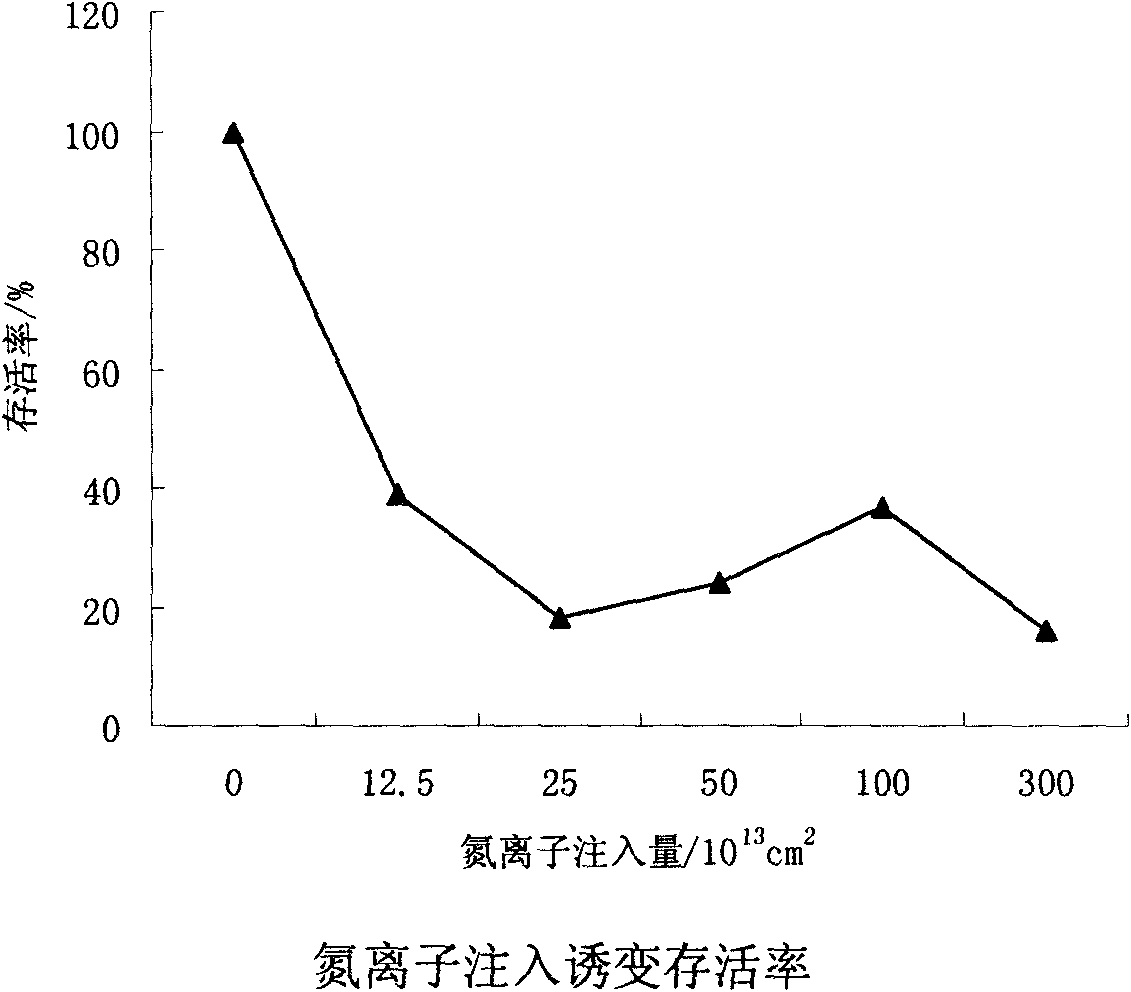
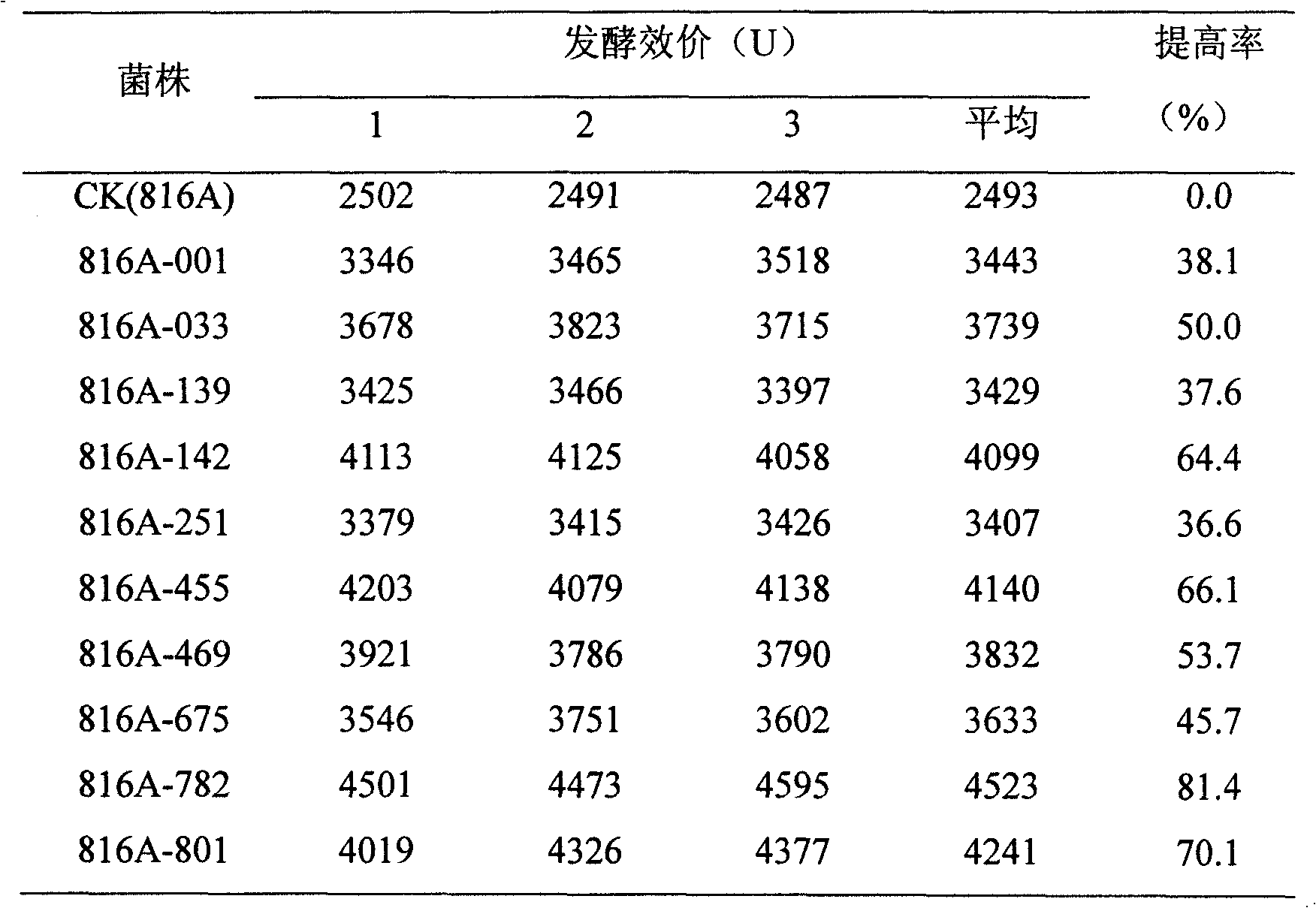
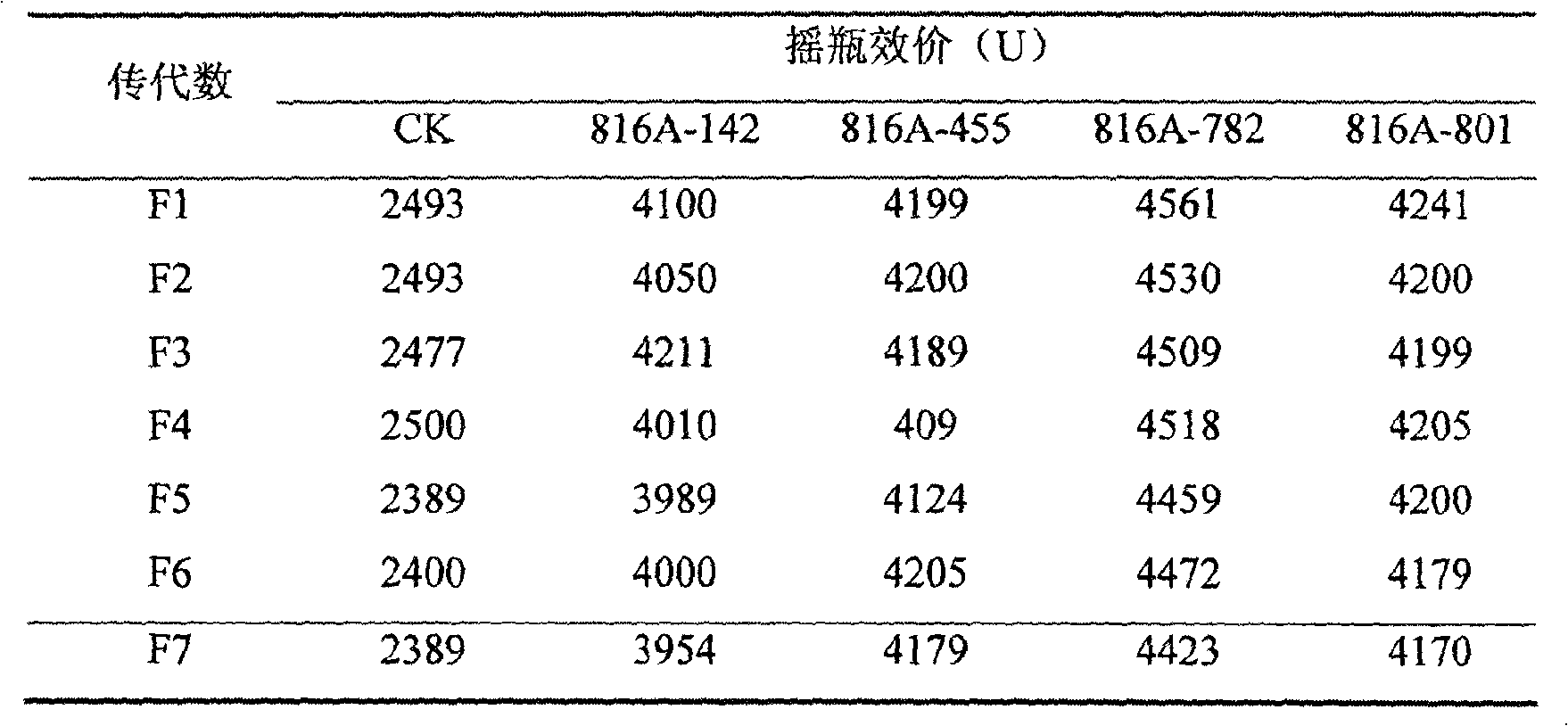
The invention discloses a screening method of lincomycin producing strain. In the screening method, composite treatment of mutagenesis and resistance screening is conducted to streptomyces lincolnensis of the lincomycin producing strain by adopting an ion implantation technology, N<+> is used as an ion source, the biological effect of N<+> implantation on the lincomycin producing strain is studied, and a lincomycin precursor which is the product of the lincomycin producing strain is used for obtaining a plurality of high-yield mutant strains with better genetic stability by the resistance screening method, so as to lead the fermentation unit of the mutant strains to be improved by 81.4% than that of original strains.
Owner:南阳普康药业有限公司
Technology of screening Prulan high yield strains from protoplast of bacillus brevis induced by laser
InactiveCN1644033AHigh sensitivityHigh positive mutation ratePlant phenotype modificationHorticulture methodsProtoplasmMutagenic Process
A process for screening the high-output pullulan strain by laser mutagenesis to the protoplasm of Aureobasidium pullulans arnaud includes such steps as inoculating Aureobasidium pullulans arnaud to the liquid culture medium, shake culturing, adding glycine solution to the fermented liquid, hyperosmotic preculturing, adding mixed enzyme liquid to remove cell walls and obtaining protoplasm, and He-Ne laser mutagenesis. Its advantages are high mutagenesis sensitivity, high positive mutation rate and high conversion rate of cane sugar.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Saccharopolyspora spinosa DS190375 as well as fermentation product, microbial inoculum, fermentation and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN111849807ACause diversity damageGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses saccharopolyspora spinosa DS190375 as well as a fermentation product, a microbial inoculum, a fermentation and screening method and an application of saccharopolyspora spinosa DS190375. The preservation number of the saccharopolyspora spinosa DS190375 disclosed by the invention is CGMCC No. 18681. The fermentation method comprises the following steps: rejuvenating and screening the strain in a high-salt plate culture medium, and fermenting. The invention also provides a screening method of the saccharopolyspora spinosa with high spinosad yield, which comprises the following steps: screening to obtain the saccharopolyspora spinosa with high salt tolerance, and screening the obtained saccharopolysporaspinosa with high salt tolerance to obtain the strain with high spinosad yield. The saccharopolyspora spinosa DS190375 disclosed by the invention is resistant to high salt and high in spinosad yield.The fermentation method avoids the problem of unstable spinosad yield caused by strain performance degradation.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +2
Yeast strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101691544AHigh positive mutation rateIncrease mutagenic effectFungiBeer fermentationBiotechnologyPrimary screening
The invention discloses a beer yeast strain and an application thereof in beer fermentation. The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae Z5 with a preservation number of CGMCC No 3218. A breeding method of the yeast strain comprises the following steps: preparation of an original parent strain, activation in a test tube, ion implantation mutagenesis, laser mutagenesis, wort agar plate primary screening, fermentation bung secondary screening, passage stability test and pilot test. The yeast strain is an excellent beer yeast strain and has a potential of large-scale production of beer breweries.
Owner:山东新银麦啤酒有限公司
Method for breeding mulberry variety through colchicine mutagenesis
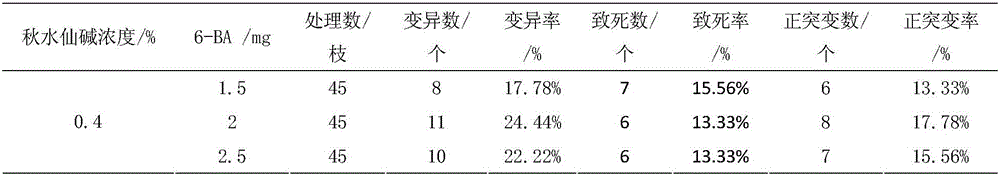
The invention relates to a method for breeding a mulberry variety through colchicine mutagenesis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing seedling cuttage, selecting new shoots of young mulberries and adult mulberries emerging after spring cutting or summer cutting, and treating terminal buds with a mutagenic agent to obtain a mutagenesis material; and (2) culturing the mutagenesis material for 15-20 days, selecting a variation strip, performing chromosome identification, determining a chromosome variation material, then breeding an induced branch, performing character direct mutation screening and genetic stability screening to obtain a new variety, grafting, and expanding propagation to establish an improved variety scion garden. According to the invention, the terminal buds of mulberries at a special period are treated by using colchicine and 6-benzylpurine as the mutagenic agent first; and in comparison with the existing conventional mutagenesis method, the direct mutation rate is obviously increased, the mutagenic lethality rate is reduced, and the breeding speed and probability of new species can be obviously be improved.
Owner:山东省蚕业研究所
Preparation method of yoghurt starter for prolonging shelf life of yoghurt
InactiveCN101874519AImprove preservationReduce manufacturing costMilk preparationMicroorganism based processesEconomic benefitsFermentation starter
The invention discloses a preparation method of a yoghurt starter for prolonging the shelf life of yoghurt, which belongs to the field of food preservation. The method comprises the following steps of: performing protoplast fusion on bacillus acidi lactici and lactic acid cocci which are separated out from homemade yoghurt lumps of Xinjiang herders; screening protoplasts after the fusion to obtain target strains; and using the strains as the yoghurt starter to prepare the yoghurt so as to prolong the shelf life of the yoghurt. The yoghurt prepared by using the starter provided by the invention has a long freshness date, and the yoghurt starter is favorable for increasing the yoghurt transport volume and reducing the cost to generate greater economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING VOCATIONAL COLLEGE OF AGRI
Quick throughput screening method of high temperature and high acid resistant citric acid high-yield strain
InactiveCN108715884AStrong acid resistanceGrow fastMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisScreening methodMicrobiology
The invention provides a quick screening method of a high temperature and high acid resistant citric acid high-yield strain. The quick screening method includes: preparing a culture medium; selectinga parent strain; preparing a fusion strain, preliminarily screening the fusion strain, screening the high temperature and high acid resistant citric acid high-yield strain, performing shake-flask fermentation re-screening and strain genetic stability testing and performing optional re-mutation breeding. The high-yield high temperature and high suspension resistant strain is obtained by applying the high-throughput quick screening method combining preliminary screening, re-screening and re-mutation, size of a selective culture medium indicating ring cultured at high temperature is taken as a preliminary screening basis for high-throughput large-scale elimination, and a HPLC measuring method is combined to accurately select the high-yield strain, so that screening efficiency is improved. Thehigh-throughput quick screening method is simple and efficient in operation, high in mutant strain directionality and important in production value.
Owner:TTCA
Omega-transaminase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN112359030AIncrease enzyme activityHigh positive mutation rateBacteriaTransferasesMutantEnzyme
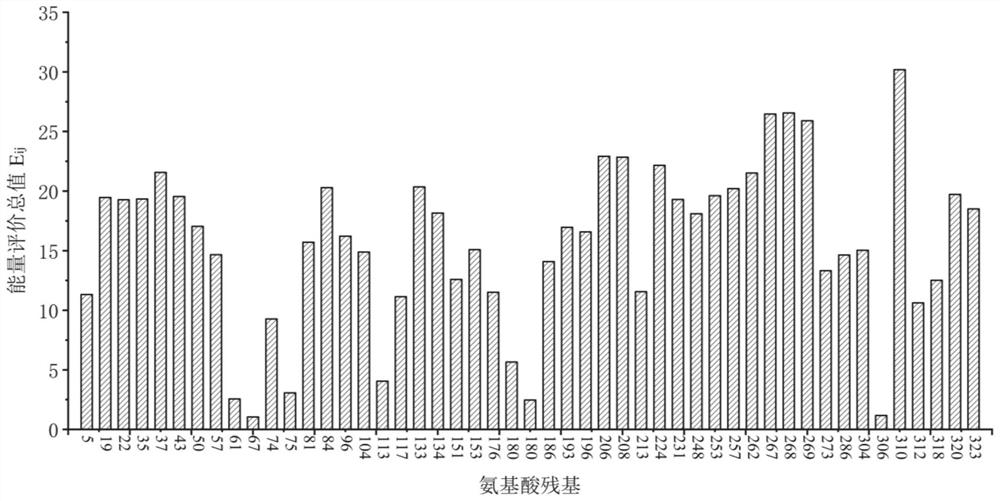
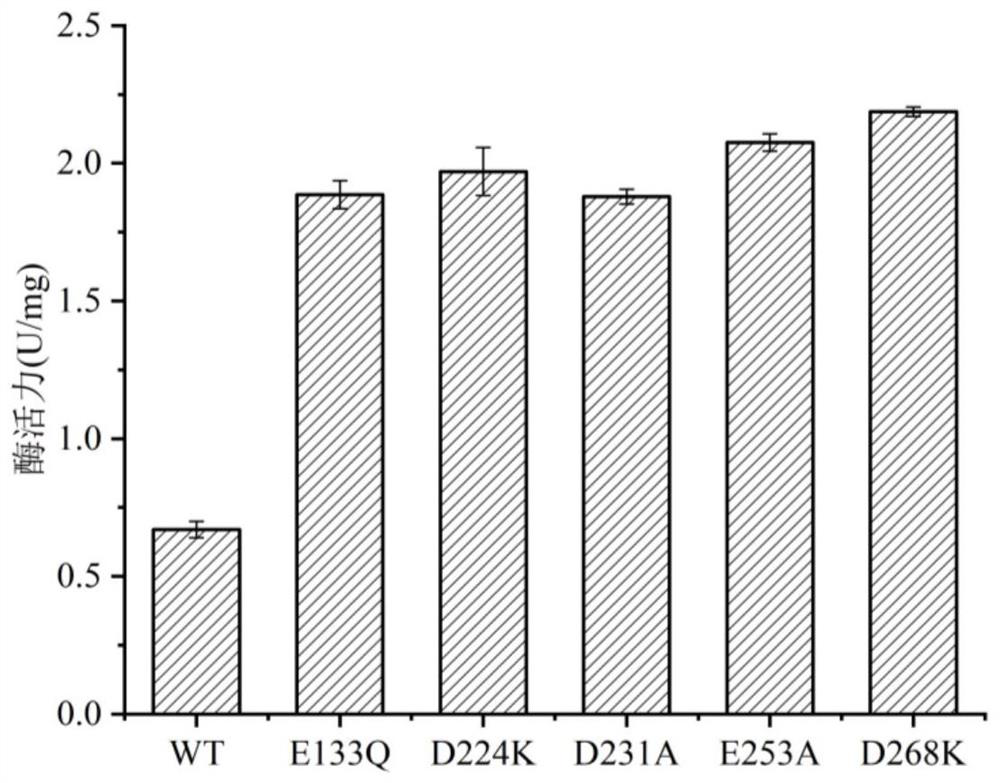
The invention discloses an omega transaminase mutant which is obtained by mutation of omega transaminase from Aspergillus terreus, the amino acid sequence of wild type omega transaminase is shown as SEQ ID No.2, and the mutation site of the omega transaminase mutant is at least one of E133Q, D224K, D231A, E253A or D268K. The omega transaminase mutant screened by the invention is obviously superiorto wild enzymes in thermodynamic stability and enzyme activity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Mutagenesis and screening method for improving yield of microalgae oil
PendingCN114317517AHigh positive mutation rateExcellent oil production performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationBiotechnologyMalonic acid
The invention relates to a mutagenesis and screening method for improving the yield of microalgae oil. The method comprises the following steps: mutagenizing microalgae by using an ARTP mutagenesis method, and culturing and screening the mutagenized microalgae in a culture medium containing malonic acid. According to the present invention, the malonic acid is added after the ARTP mutagenesis to carry out the directed resistance screening, such that the positive mutation rate of the microalgae strain can be improved so as to obtain the microalgae strain with excellent oil production performance, and the microalgae strain with the product value of the specific growth rate and the relative fluorescence intensity being 40% or more higher than the original microalgae strain is adopted as the positive mutation strain so as to provide the high screening index threshold value, the oil-producing algal strains with more excellent performance can be screened, and screening omission is avoided.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
A kind of Saccharopolyspora spinosa ds190375 and its fermentation product, bacterial agent, fermentation and screening method and application
ActiveCN111849807BCause diversity damageGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +2
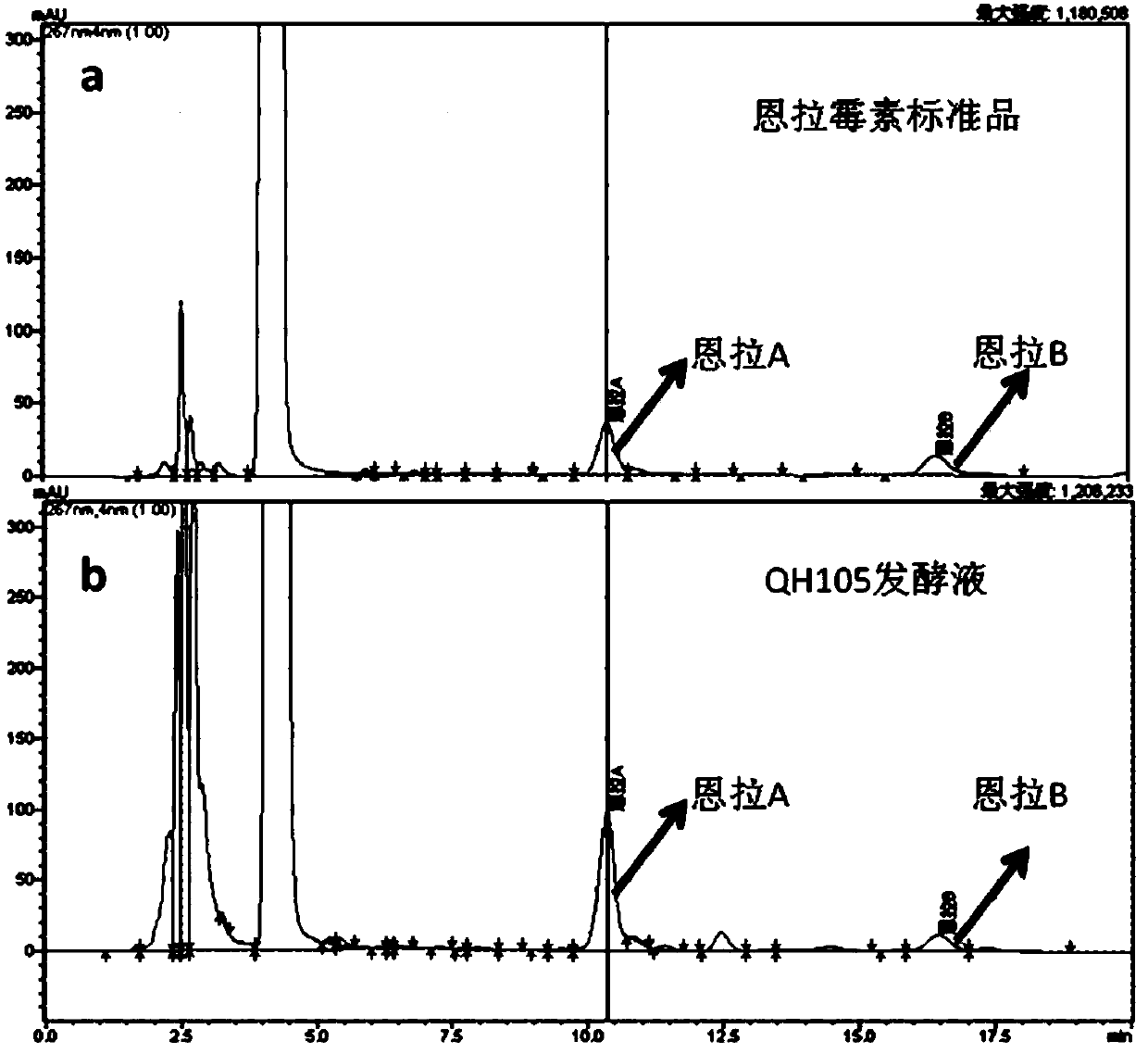
Enramycin high-yield bacterial strain and screening method thereof
InactiveCN109536485AHigh mutation rateHigh positive mutation rateBacteriaMutant preparationStreptomycesPlasma technology
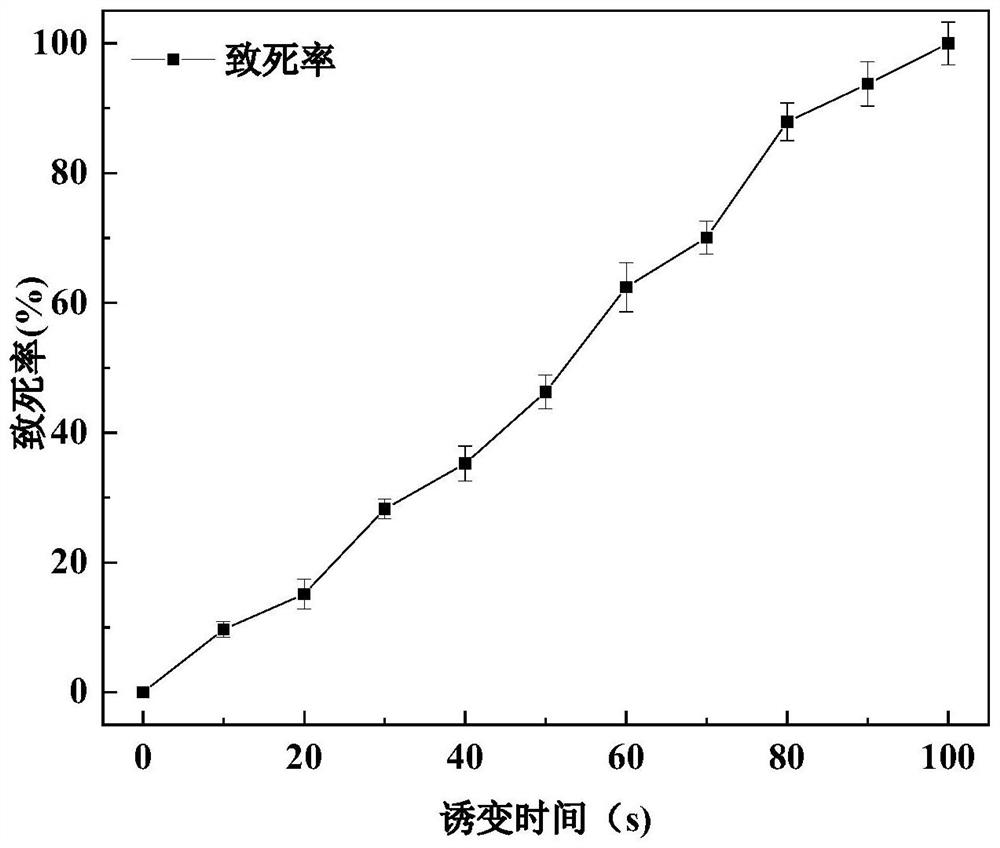
The invention relates to the field of fermenting strains, and particularly provides an enramycin high-yield bacterial strain and a screening method thereof. A breeding method of the enramycin high-yield bacterial strain comprises the steps of adopting a constant-pressure room temperature plasma method for inducing fungus-resisting streptomycete, wherein the constant-pressure room temperature plasma method comprises the steps of performing irradiation under the condition that the power is 90-110W and the gas flow is 9-11L / min for 35-45min, and finally, performing screening, so that the enramycin high-yield bacterial strain is obtained. According to the method, a constant-pressure room temperature plasma technology is used as the inducing method, and in accordance with streptomyces antifungus, design is performed, so that the test condition suitable for the streptomyces antifungus is preferably selected. Under the test condition, that the mutation rate of the streptomyces antifungus is high, and the orthomutation rate is high. The method is good in repeatability. The enramycin high-yield bacterial strain can be obtained, wherein the yield can be at least increased by three times. Theheredity stability is good. The method is simple and convenient, easy to operate, time-saving, and effortless, and the breeding cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG RONGDA BIOENG CO LTD +1
Penicillium citrinum bacteria with high nuclease P1 yield and its selective breeding process
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV +1
Omega-transaminase mutant and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107058256BHigh positive mutation rateImprove experimental efficiencyTransferasesFermentationSite-directed mutagenesisPlasmid
Owner:上海邦林生物科技有限公司
Lactobacillus plantarum with fast acid production and high acid production and application thereof
ActiveCN112410251BIncrease the rate of acid productionIncrease speedBacteriaHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyLactobacillus
The present invention provides a kind of Lactobacillus plantarum with fast acid production and high acid production and application thereof, which is Lactobacillus plantarum ( Lactobacillus plantarum ) WG03, the preservation unit is China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, the preservation number is CGMCC 20876, and the preservation date is October 12, 2020. The present invention provides a microbial inoculum comprising the above-mentioned Lactobacillus plantarum. The above-mentioned Lactobacillus plantarum or bacterial agent can be applied to the fermentation of silage. In the present invention, a strain of Lactobacillus plantarum with fast acid production and high acid production is obtained by protoplast fusion technology combined with traditional mutagenesis. Using this strain as a silage additive can well inhibit the growth of spoilage bacteria and quickly start Anaerobic fermentation process to improve the quality of silage.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
A kind of ω-transaminase mutant and its application
ActiveCN108913671BImprove thermal stabilityHigh positive mutation rateBacteriaTransferasesWild typeHistidine
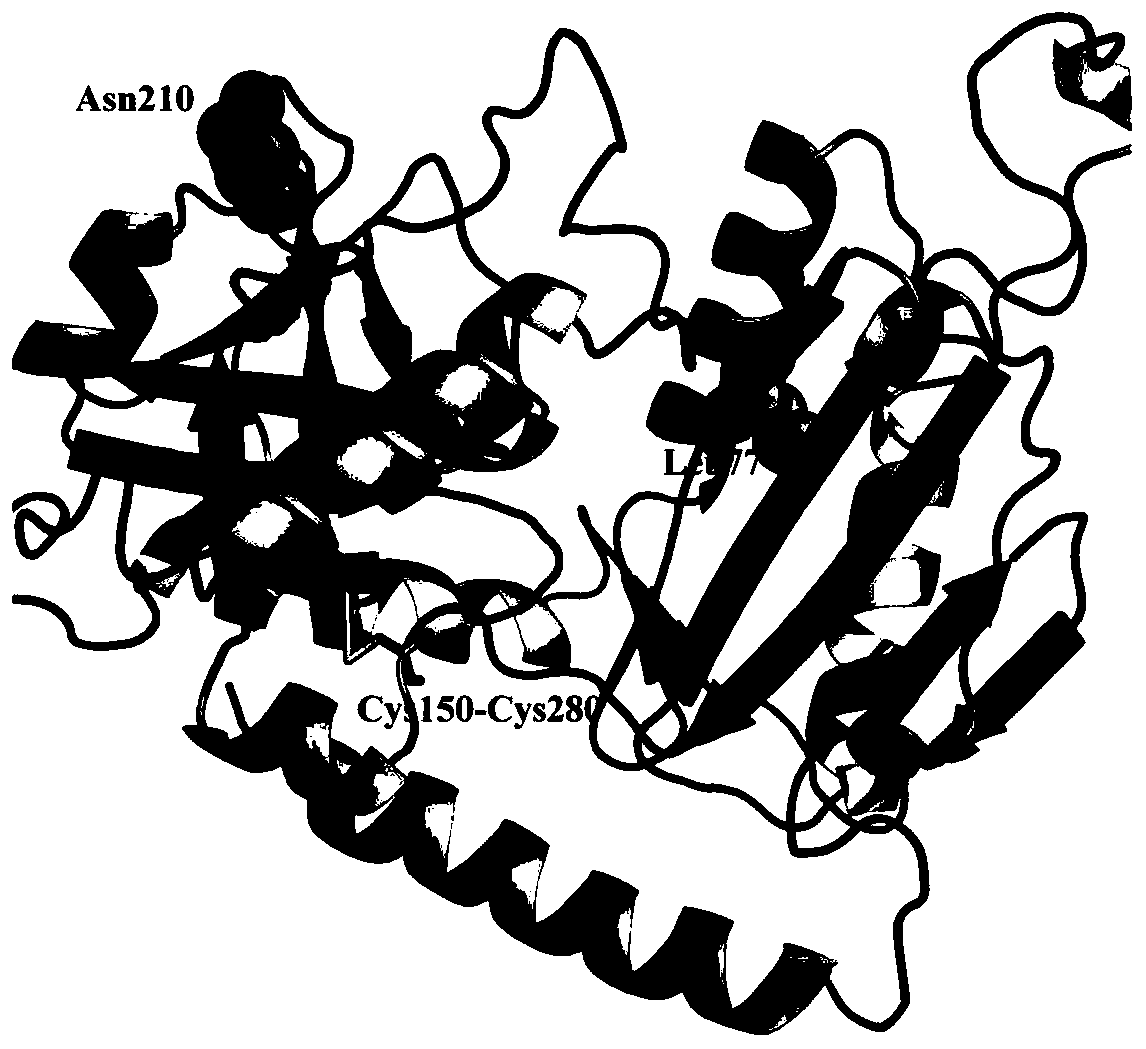
The invention discloses a Omega-transaminase mutant and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the Omega-transaminase mutant is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The Omega-transaminase mutant disclosed by the invention is acquired by respectively mutating isoleucine on locus 77, methionine on locus 150, histidine on locus 210 and methionine on locus 280 of aspergillus terreus Omega-transaminase into leucine, cysteine, asparaginate and cysteine. Semi-inactivation temperature (T5010) of the Omega-transaminase mutant is at 50.3 plus or minus 0.5 DEG C and is 11.8 DEG C higher than that of wild type; the half-life period (t1 / 2) at 40 DEG C is 114.6 plus or minus 2.8 min and is 16.6 times of that of wild type; heat stability is obviously promoted.
Owner:杭州快格科技有限公司
Lactobacillus plantarum with fast acid production and high acid yield and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN112410251AIncrease the rate of acid productionIncrease speedBacteriaHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides lactobacillus plantarum with fast acid production and high acid yield and an application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum is lactobacillus plantarum WG03, the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC 20876, and the preservation date is October 12, 2020. The invention provides a microbial agent containing the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum or the microbial inoculum can be applied to silage fermentation. The lactobacillus plantarum with rapid acid production and high acid yield is obtained by combining a protoplast fusion technology with a traditional mutagenesis method, and the lactobacillus plantarum is used as a silage additive, so that the growth of spoilage bacteria can be well inhibited, the anaerobic fermentation process is quickly started, and the quality of silage is improved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Compound induction mutation method for high-producing strain capable of producing epsilon-poly-L-lysine at high yield
InactiveCN106520605AIncrease damageIncrease productionBacteriaMutant preparationCobalt-60Microbiology
The invention belongs to the field of fermentation engineering and particularly relates to a compound induction mutation method for a high-producing strain capable of producing epsilon-poly-L-lysine at a high yield. The method comprises the following steps: performing initial screening based on fatality rate, separation, purification and diluting times, single colony site condition, developing and transparent ring size on a resistant plate by irradiation of cobalt 60 rays with different radiant quantities; then coating the plate when the accumulated radiant quantity is 80 thousand rad, the fatality rate is 90-95%, and the diluting concentration is 10<-4>-10<-5>; selecting single colonies which are big in colony size, develop color and obviously relatively big in transparent ring on the resistant plate for bottle shake, and performing culturing in a 10L fermenting tank for screening; and finally obtaining the high-producing strain, the output of which reaches 12g / L. Compared with that (9g / L) of an original strain, the output is increased by 33% or above. A passage stability test verifies that the strain is good in passage stability. By virtue of an ARTP induction mutation method, the high-producing strain, the output of which reaches 17g / L is finally obtained, and the strain is good in passage stability.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF FOOD & FERMENTATION INDS
Method for screening rifamycin SV high-yielding strain through oxygen stress mutagenesis
InactiveCN111979169AImprove filtration efficiencyHigh positive mutation rateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySulfite salt
The present invention discloses a method for screening a rifamycin SV high-yielding strain through oxygen stress mutagenesis. The method is an efficient breeding method of the rifamycin SV hypoxia-tolerant high-yielding strain based on combination of an oxygen limitation model and low-temperature plasma mutagenesis. The method comprises the following steps: during a process of breeding the rifamycin SV production strain of nocardia mediterranean, oxygen limitation model plates are used to screen the strain that can grow rapidly and has dark brown moss under hypoxia; 0.8-1.2 g / L of anhydrous sodium sulfite is added in a screening culture medium to prepare screening plates, a bacterial suspension with a low-temperature plasma mutagenesis treatment time of 22-28 seconds is diluted and spreadon an oxygen limitation plate culture medium and cultured at 28 DEG C for 6-7 days, the strain with faster growth and darker color is picked, and positive mutation rate of screening can be significantly increased. The method can screen the high-efficiency rifamycin production strain capable of rapid growth and product synthesis under the hypoxic conditions, and the strain is well adapted to the oxygen-limitation environment of the production process and also exhibits good fermentation production capacity.
Owner:HEBEI XINGANG PHARMA +1
A kind of ω-transaminase mutant, gene and application
ActiveCN111826362BHigh positive mutation rateImprove experimental efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesGenetics algorithmsSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention discloses an ω-transaminase mutant, gene and application. The amino acid sequence of the wild-type ω-transaminase is shown in SEQ ID No.2, and the ω-transaminase mutant is one of the following: (1) L118T / F115L double mutant mutant; (2) L118T / F115L / E133A three Mutated mutants; (3) L118T / F115L / E133K triple-mutated mutants; (4) L118T / F115L / E253A triple-mutated mutants. The present invention is based on a technically mature genetic algorithm and a TK-SA model algorithm, on which the ETSS algorithm is improved, combined with the surface charge-charge interaction of ω-transaminase, to determine the amino acid residue site that needs to be mutated, and through the site-directed mutation technique Experiments were conducted to verify that this method can effectively increase the probability of positive mutations, improve experimental efficiency and feasibility, and screen out mutant enzymes with thermodynamic stability and enzyme activity that are significantly better than wild enzymes.
Owner:李元源 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com