Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1461 results about "Malonic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Malonic acid (IUPAC systematic name: propanedioic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH₂(COOH)₂. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (malon) meaning 'apple'.
Aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6527818B2Pigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesColloidal silicaOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
There is provided an aqueous dispersion for CMP with an excellent balance between chemical etching and mechanical polishing performance. The aqueous dispersion for CMP of the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water and a heteropolyacid. Another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water, a heteropolyacid and an organic acid. Yet another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising colloidal silica with a primary particle size of 5-100 nm, water and a heteropolyacid. Preferred for the heteropolyacid is at least one type selected from among silicomolybdic acid, phosphorotungstic acid, silicotungstic acid, phosphoromolybdic acid and silicotungstomolybdic acid. Preferred for the organic acid is at least one selected from among oxalic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, glutaric acid, adipic acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, phthalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
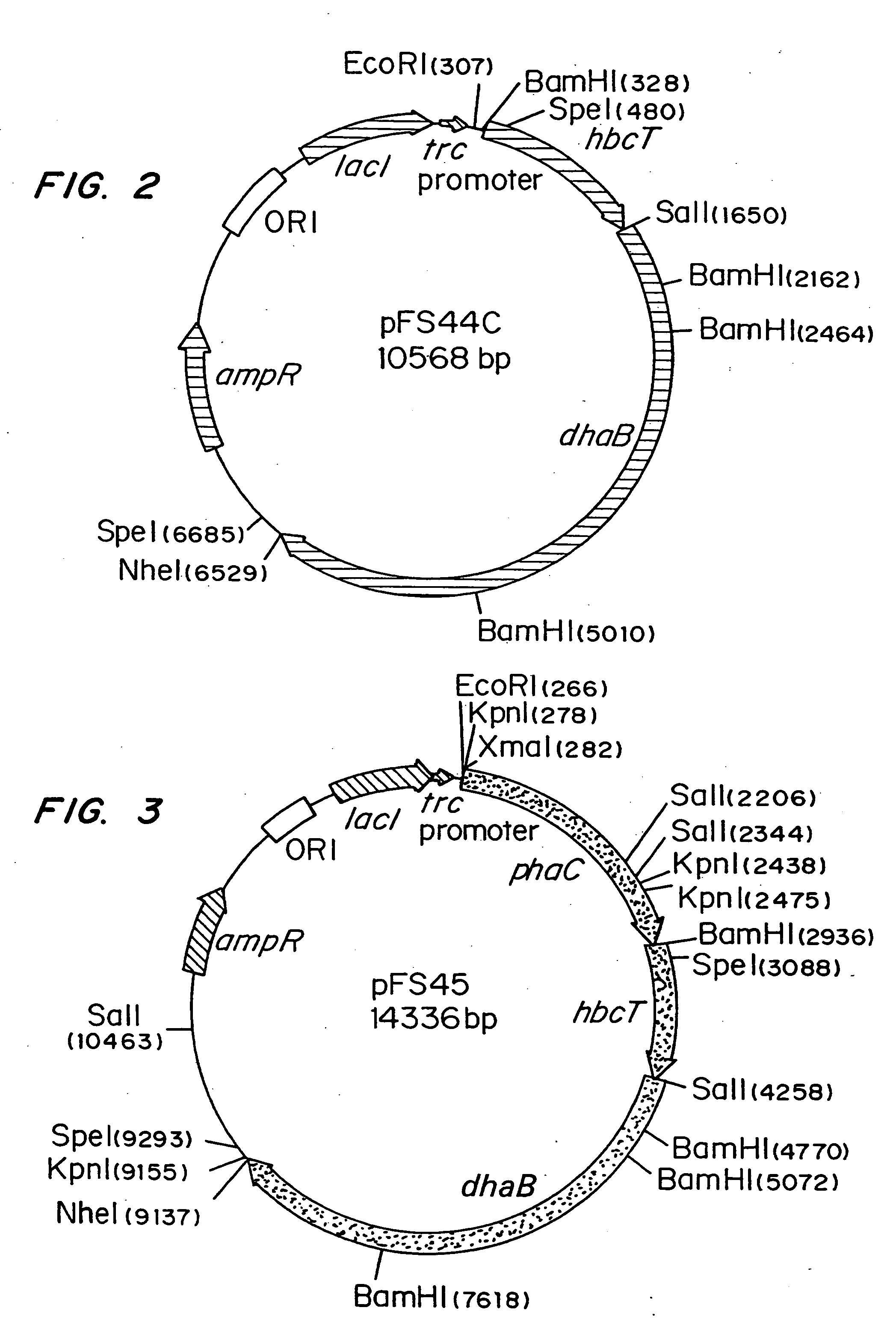
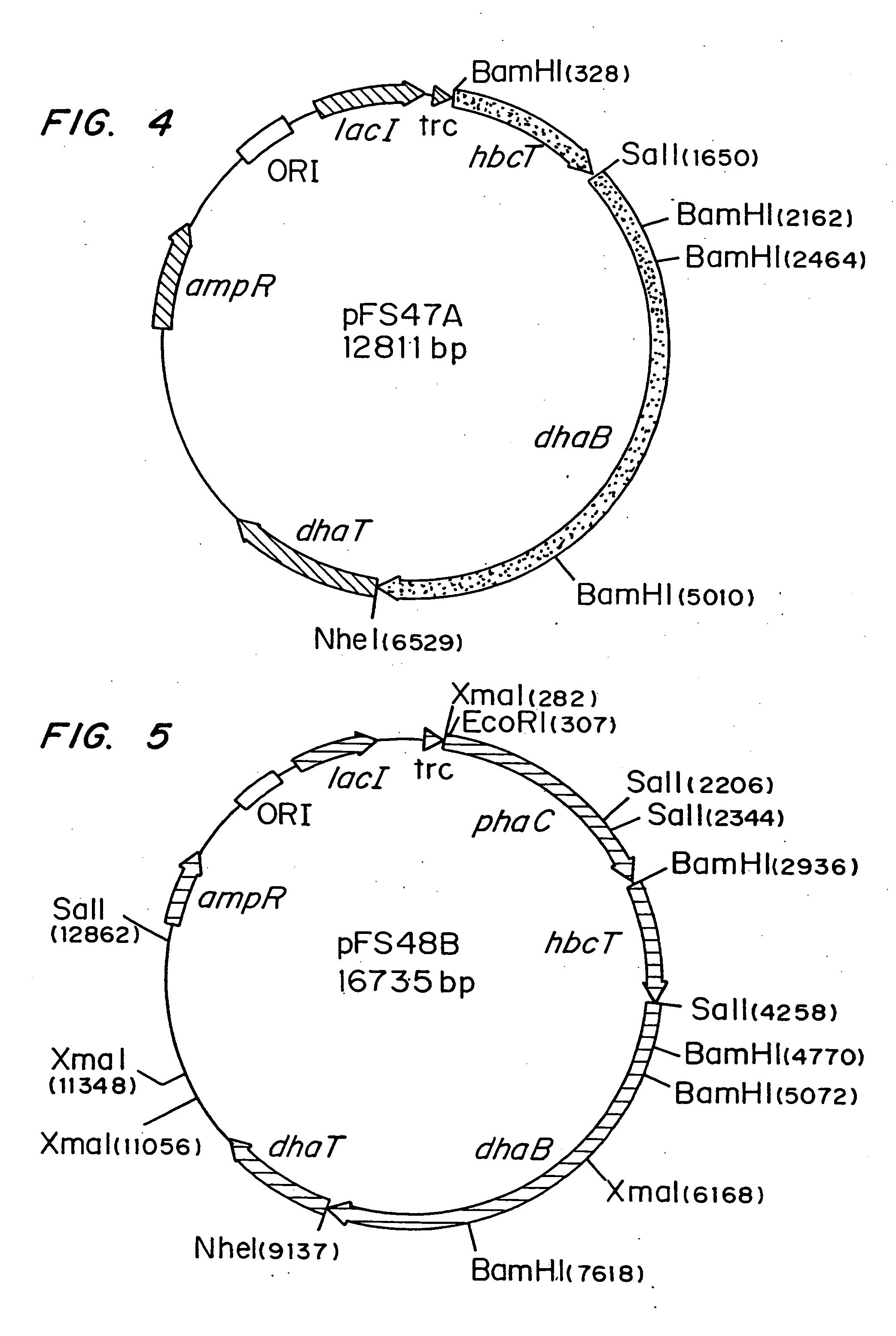
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
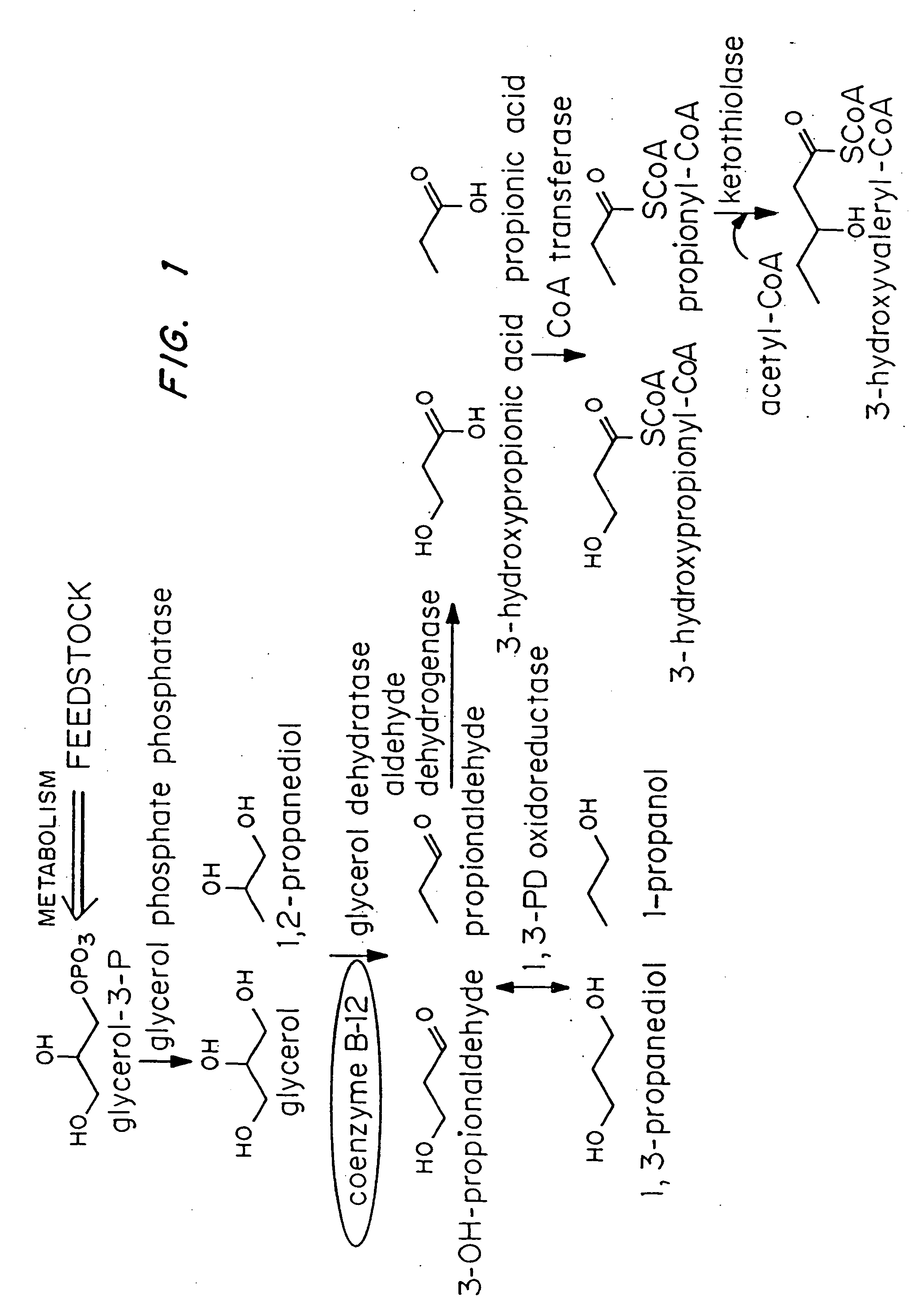
InactiveUS20050239179A1Promote recoveryProduct can be usedBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalreate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Malonic acid monoesters and process for producing the same
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Malonic acid monomethyl derivatives and production process thereof
InactiveUS7109369B2Easy to makeProduct can be usedOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrogen atomMalonic acid
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
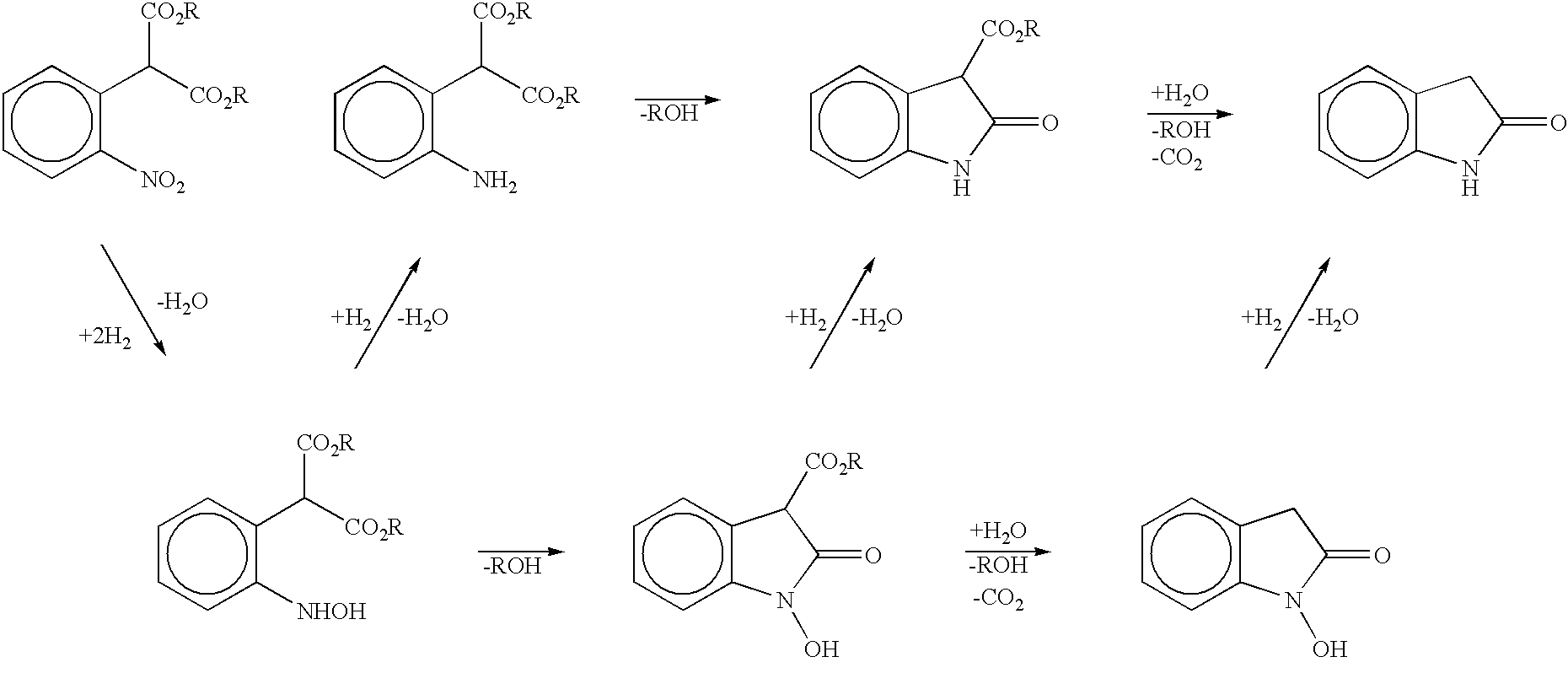
Process for preparing 2-oxindoles and N-hydroxy-2-oxindoles
InactiveUS6469181B1Avoid wastingImprove economyCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationReaction intermediateCarboxylic salt
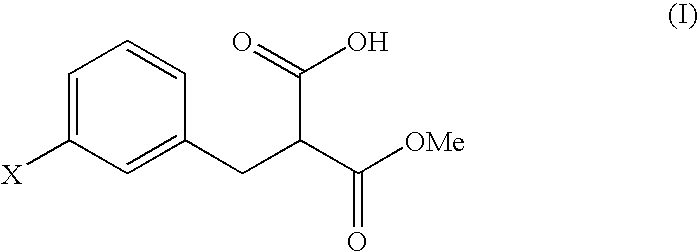
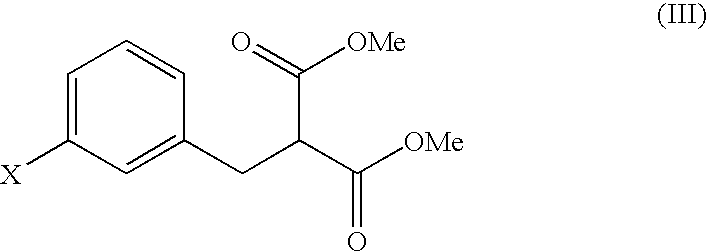
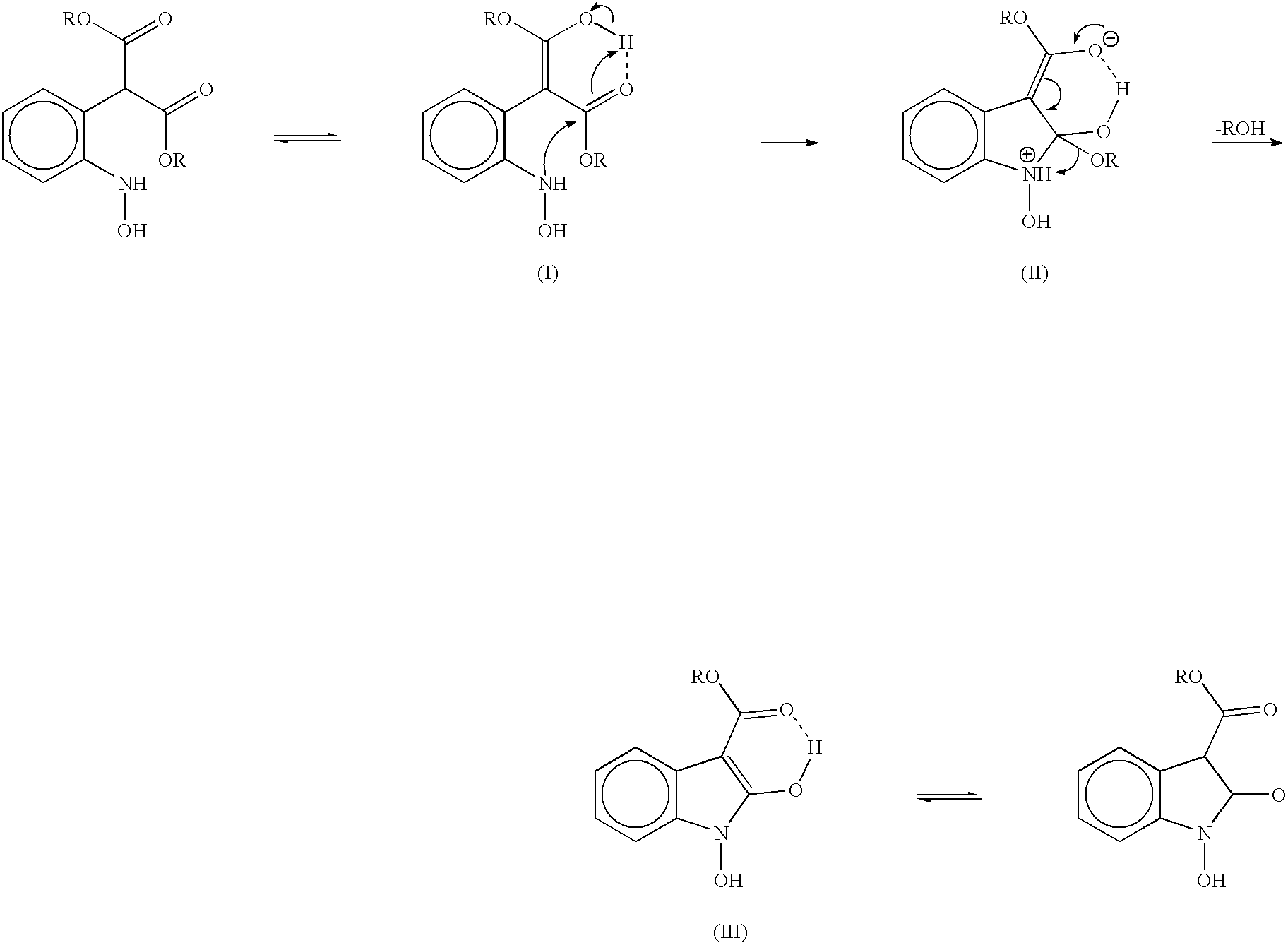
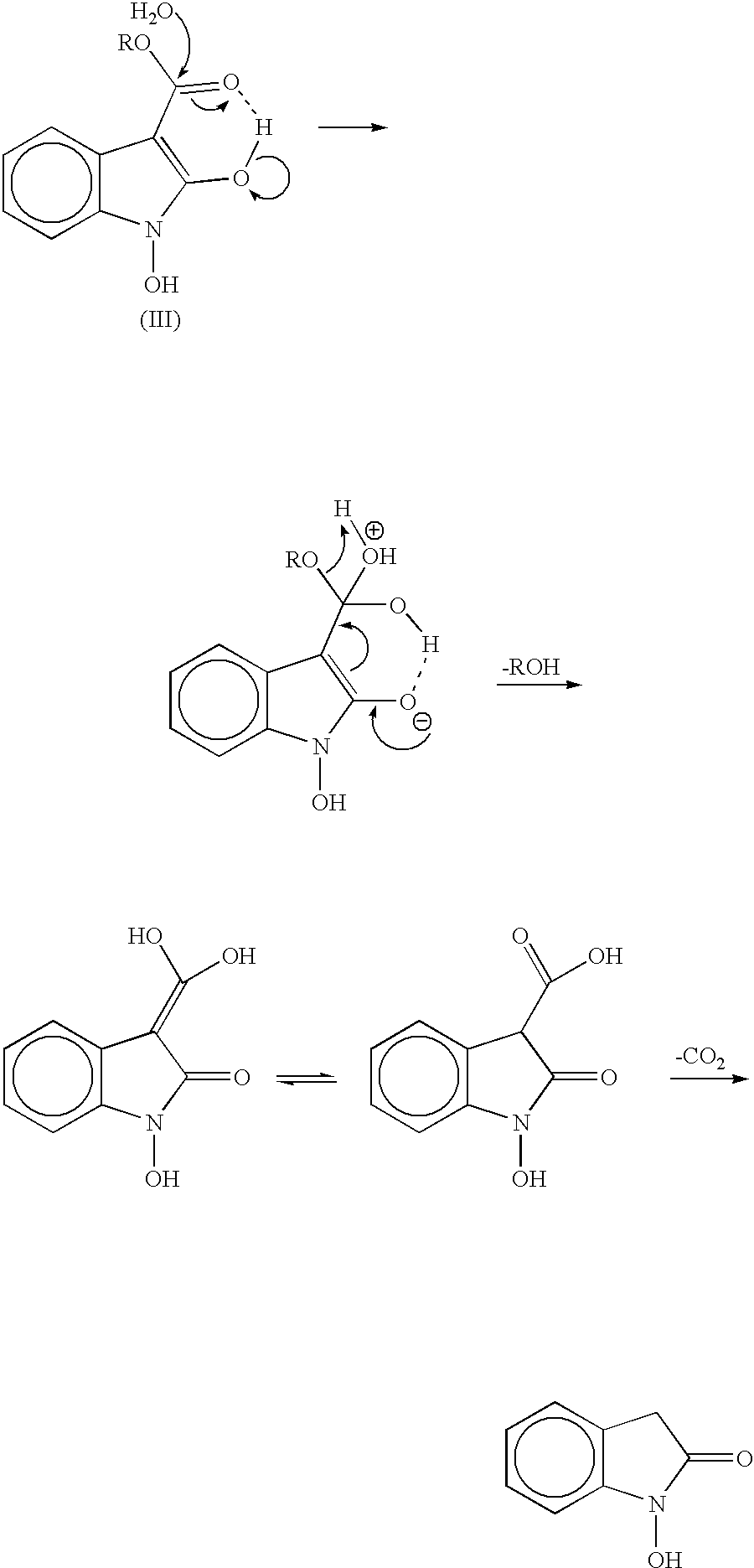
The present invention provides a processes, having practical utility, for preparing 2-oxindoles, N-hydroxy-2-oxindoles, or mixtures thereof comprising: catalytically hydrogenating a 2-nitroarylmalonate diester to produce a 2-(N-hydroxyamino)arylmalonate diester, a 2-aminoarylmalonate diester, or mixtures thereof as a first reaction intermediate; cyclizing, by intramolecular aminolysis of one ester group, the first reaction intermediate to produce a N-hydroxy-2-oxindole-3-carboxylate ester, 2-oxindole-3-carboxylate ester, or mixtures thereof as a second reaction intermediate; and hydrolyzing and decarboxylating the remaining ester group of the second reaction intermediate to produce the N-hydroxy-2-oxindole, the 2-oxindole, or mixtures thereof, wherein the cyclization reaction and the hydrolysis and decarboxylation reaction are conducted in situ with the catalytic hydrogenation reaction without isolation of said reaction intermediates.
Owner:CATALYTICA PHARMA
Reducing byproduction of malonates in a fermentation process
Described are methods of reducing the amount of byproduct organic acids during fermentation of an organism, based on expression of a heterologous malonyl-CoA synthetase. A polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”]-producing strain of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica was engineered to express a heterologous malonyl-CoA synthetase gene. The expression did not effect the production of PUFAs, but did result in a reduced amount of malonates when compared to the amount of malonates produced in the parental strain not expressing malonyl-CoA synthetase.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
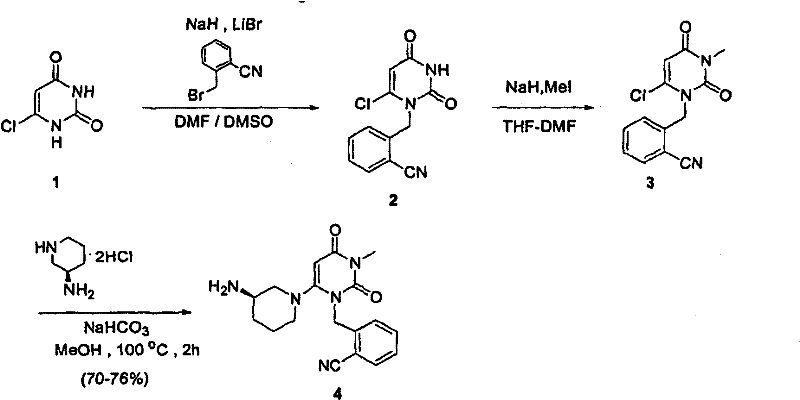
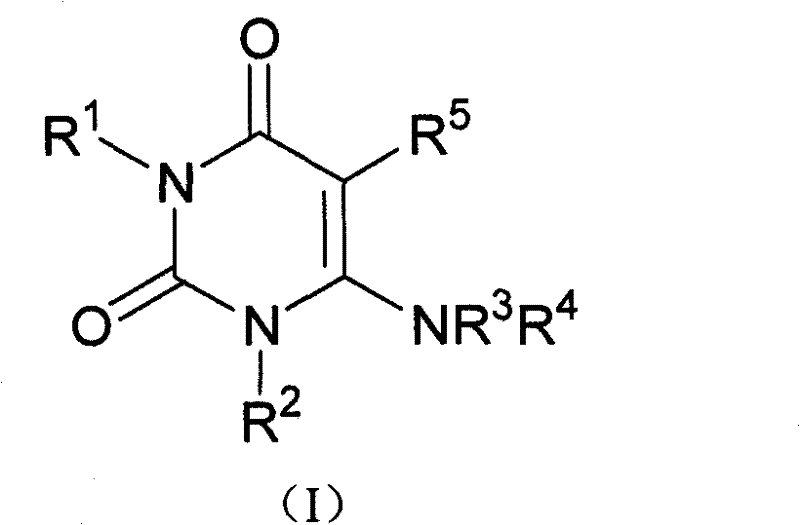
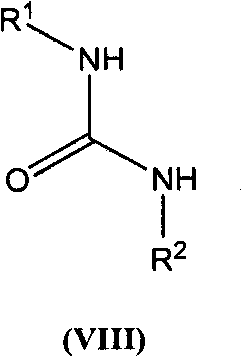
Process for the preparation of alogliptin
The present invention is based on the discovery of a process for preparing pyrimidin- dione compounds, especially alogliptin and its derivatives, which comprises the reaction of a urea derivative of formula (VIII) with a malonic acid or its derivatives to form intermediates of formulae (VII) or (VII-A), which are subsequently converted to a compound of formula (II) upon introduction of a leaving group X. Compound (II) then reacts with an amine to form compound (I), which is optionally converted to its salts of formula (IV).
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS20010039766A1Improve balanceImprove accuracyPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEColloidal silica
There is provided an aqueous dispersion for CMP with an excellent balance between chemical etching and mechanical polishing performance. The aqueous dispersion for CMP of the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water and a heteropolyacid. Another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising an abrasive, water, a heteropolyacid and an organic acid. Yet another aqueous dispersion for CMP according to the invention is characterized by comprising colloidal silica with a primary particle size of 5-100 nm, water and a heteropolyacid. Preferred for the heteropolyacid is at least one type selected from among silicomolybdic acid, phosphorotungstic acid, silicotungstic acid, phosphoromolybdic acid and silicotungstomolybdic acid. Preferred for the organic acid is at least one selected from among oxalic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, glutaric acid, adipic acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, phthalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Polycarbonate compositions
ActiveUS20090054586A1Good color retentionStrong initial fluorescence emission intensityOrganic dyesLuminescent compositionsCyanoacrylateUltraviolet
A polycarbonate composition is disclosed comprising a polycarbonate resin, a 3-hydroxychromone dye, and an ultraviolet absorber selected from the group consisting of cyanoacrylates, malonates, and oxanilides. The combination of the 3-hydroxychromone dye and ultraviolet absorber results in a composition with good color retention and strong initial fluorescent emission intensity.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
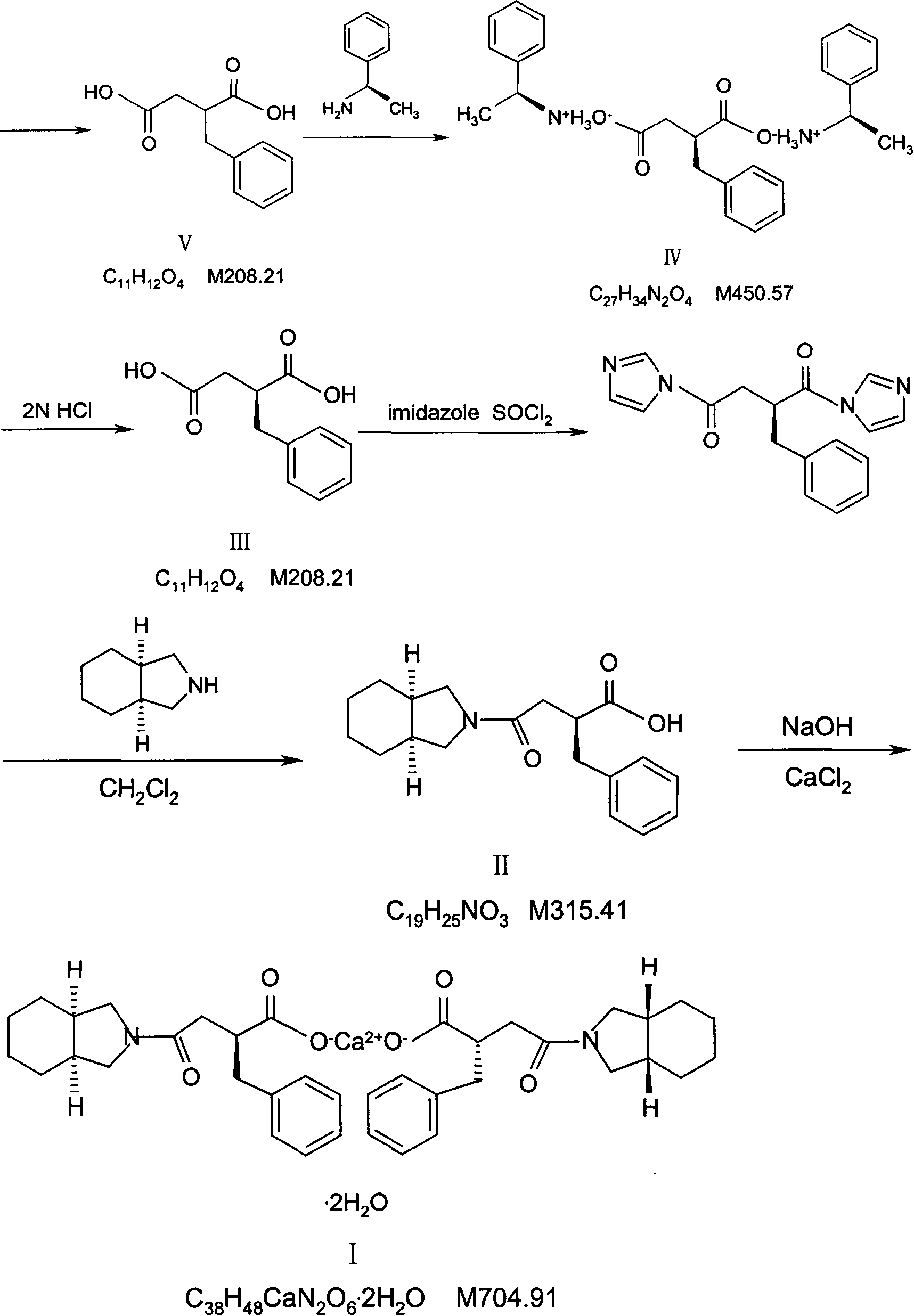
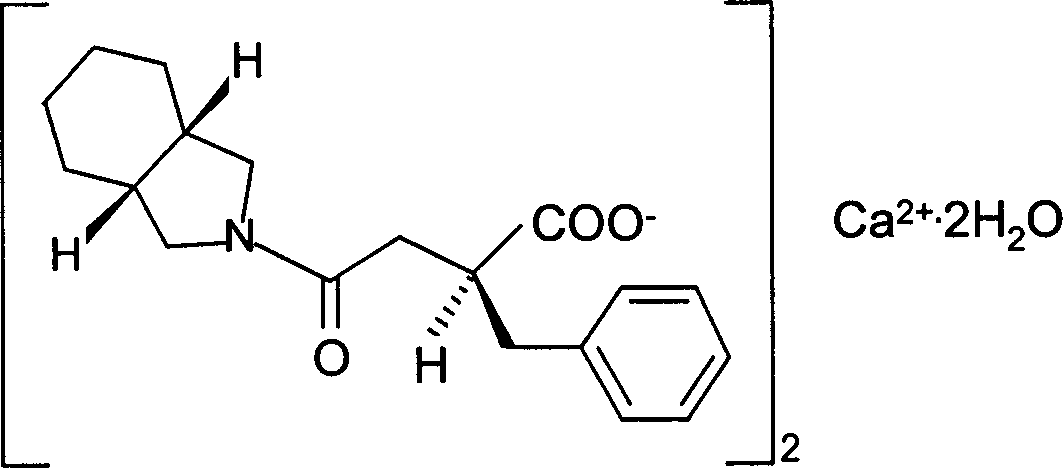
Preparation of mitiglinide calcium and its quality control method
InactiveCN1844096AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPropanoic acidMalonate
The invention relates to a preparation and quality control method of Mitiglinide Calcium comprising steps: 1,synthesis of cis- cyclohexyl-1,2-dimethylacid imide; 2,synthesis of cis-hexa-hydrogen isoindole; 3,synthesis of alpha-benzyldiethyl malonate; 4,synthesis of benzylsuccinic acid; 5,S- benzylsuccinic acid methylbenzylamine salt; 6,synthesis of s- benzylsuccinic acid; 7,synthesis of (2S)-2- benzyl-3-(cis-hexa-hydrogen isoindole-2- carbonyl) propanoic acid; 8,synthesis of Mitiglinide Calcium; 9,purity of Mitiglinide Calcium. This invention also contains the method for quality control of Mitiglinide Calcium comprising steps: watching deseription, messureing specific rotation, authenticating, checking, content messureing for Mitiglinide Calcium.
Owner:天津汉康医药生物技术有限公司
Normal temperature passivated zinc coating trivalent chromium color passivating agent
InactiveCN1858303AReduce concentrationReduce manufacturing costMetallic material coating processesMolybdateMalonic acid
The present invention discloses trivalent chromium color zinc coating passivator for passivation at normal temperature and its preparation process. The trivalent chromium color zinc coating passivator includes Cr3+ 1-7.5g / L, molybdate 1-25g / L, cobalt sulfate 5-15, ammonium bifluoride 1-8g / L, malonic acid 1-12g / L, phosphate 1-12 g / L, and silicate 0.2-6g / L. The trivalent chromium color zinc coating passivator solution has pH 1.8-2.3 regulated with sodium carbonate or nitric acid, passivating temperature of 20-35deg.c, passivating time of 30-60 sec and stoving temperature of 70-80deg.c. The present invention has the advantages of being practical and good use effect.
Owner:SUR PRECISION METAL TECH
Double layer composite collagen base guide tissue regeneration film and its preparing method
InactiveCN1586637AAchieve regenerative healingPrevent ingrownSurgeryPharmaceutical containersTissue damageMalonic acid
Collagen and hyaluronic acid or its sodium salt as main material are prepared into double layer composite material with compact layer and loose layer. The mass composition of the compact layer includes malonic acid swelling solution in 0.6-0.8 wt%; and the mass composition of the loose layer includes malonic acid swelling solution in 0.2-0.4 wt% and hyaluronic acid or its sodium salt in 5-20 wt% of dry collagen. The present invention has loose structure in one side and compact structure in the other side, and thus excellent biocompatibility capable of resisting the growth of fibroblast and other cell to the damaged part while promoting the regeneration and repairing of tissue in the damaged part. The double layer composite material has corresponding biodegrading function and may be degraded and absorbed without needing secondary operation to take out the implanted material. The present invention is suitable for repairing tissue damage.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
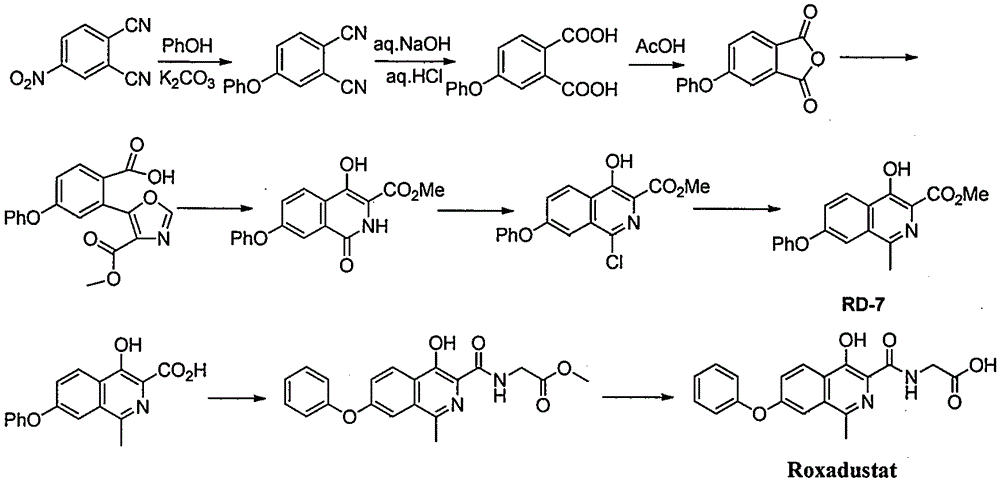
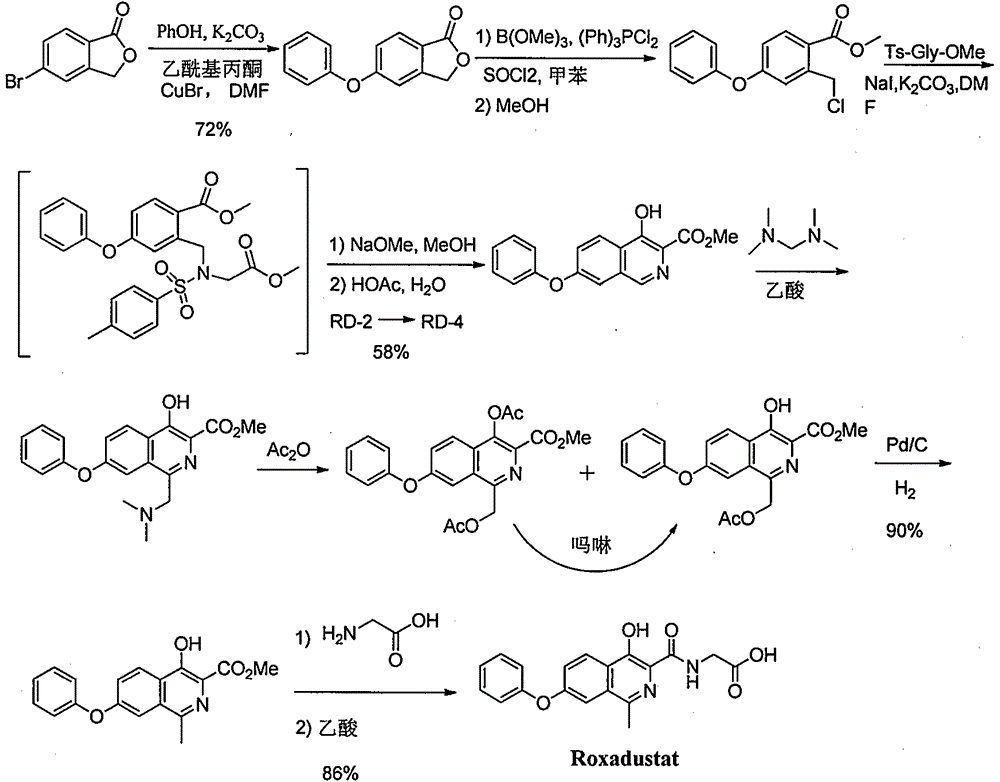
Method for preparing Roxadustat intermediate
ActiveCN106478504ARaw materials are easy to getReduce stepsImino compound preparationOrganic chemistryRoxadustat
The invention provides a preparation method of Roxadustat intermediate 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-7-phenoxy-3-isoquinolinecarboxylate (IV), comprising the step of subjecting 2-(1-(3-phenoxyphenyl)ethylimide)dimalonate (III) as a starting material to condensation and cyclization. The preparation method of the Roxadustat intermediate IV has the advantages that material is easy to obtain, operating steps are few, the process is simple, the reaction yield is high, atom utilization rate is high, and the method is easy for industrial production. The reaction general formula is shown in the specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUNHE PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Hard surface cleaning compositions
InactiveCN1636048AInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsSurface cleaningAdipic acid
An improved hard surface cleaning composition having an acidic pH having good soap scum stain removal capabilities. The composition of the present invention comprises: an acidic component comprising citric acid alone or in combination with citric acid selected from the group consisting of sorbic acid, acetic acid, boric acid, formic acid, maleic acid, adipic acid, lactic acid, hydroxysuccinic acid, malonic acid , glycolic acid, and mixtures thereof; at least one anionic surfactant; at least one thickener; at least one scrubbing agent; one or more optional components; Water; wherein, the pH value of the aqueous hard surface cleaning composition is less than or equal to 6.0.
Owner:RECKITT BENCKISER LLC
Post plasma ashing wafer cleaning formulation
InactiveUS7534752B2Increase productionImprove adhesionDetergent mixture composition preparationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfolaneInorganic compound
A semiconductor wafer cleaning formulation for use in post plasma ashing semiconductor fabrication comprising at least one organic chelating agent and at least one polar solvent, wherein the chelating agent and polar solvent are in sufficient amounts to effectively remove inorganic compound residue from a semiconductor wafer. Preferably, the chelating agent is selected from the group consisting of 2,4-Pentanedione, Malonic acid, Oxalic acid, p-Toluenesulfonic acid, and Trifluoroacetic acid; and the polar solvent is selected from the group consisting of Water, Ethylene glycol, N-Methylpyrrolidone (NMP), Gamma butyrolactone (BLO), Cyclohexylpyrrolidone (CHP), Sulfolane, 1,4-Butanediol, and Butyl carbitol.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
High anti-corrosion zinc coating trivalent chromium lue-white passivating agent and its preparing method
InactiveCN1858302AReduce concentrationReduce manufacturing costMetallic material coating processesAcetic acidMalonic acid
The present invention discloses anticorrosive trivalent chromium blue-white zinc coating passivator and its preparation process. The anticorrosive trivalent chromium blue-white zinc coating passivator includes Cr3+ 1-5 g / L, NaNO3 1-20 g / L, malonic acid 1-10 g / L, cobalt sulfate 5-20 g / L, acetic acid 1-10 g / L, phosphate 1-6 g / L, ammonium bifluoride 1-5 g / L and silicate 0.2-5 g / L. The preparation process includes dissolving the said materials in pure water successively through stirring to obtain transparent passivator. The present invention has the advantages of being practical and good use effect.
Owner:SUR PRECISION METAL TECH
High corrosion resistant trivalent chromium blue-white deactivator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101158038ASmall brightness (decorative) effectFacilitated DiffusionMetallic material coating processesCalcium hydroxideMalonic acid
The invention relates to a high corrosion resistant trivalent chromium pearl opal passivating agent and a preparation method of the high corrosion resistant trivalent chromium pearl opal passivating agent. The invention belongs to the metal surface treatment technical field. The passivating agent comprises a Cr3+ chemical compound which contains 2 to 6 g / L chromium, 5 to 8 g / L malonic acid, a Co2+ chemical compound which contains 0.5 to 1 g / L cobalt, 1 to 3 g / L ammonium acid fluoride, 1 to 2 g / L sodium hydroxide, 1.5 to 3 g / L NO3-, 0.5 to 1 g / L formic acid, a low nanometer dimension acid silicasol which contains 0.4 to 2 g / L SiO2, and the rest being water. The preparation method of the passivating agent is that the Cr3+ chemical compound, the malonic acid, the ammonium acid fluoride, and the Co2+ chemical compound are heated up and reacted under 70 DEG C to 100 DEG C. When the temperature is from 20 DEGC to 30 DEGC, the NO3- is added. The formic acid and low nanometer dimension acid silicasol are added. Adding water to constant volume, the passivating agent is obtained. The passivating agent of the invention has the advantages that no hexavalent chrome is contained, and the production process has no hexavalent chrome pollution. When passivating, the passivating agent facilitates forming a uniform and dense passivation layer. And the corrosion resistance of the passivation layer is greatly promoted.
Owner:深圳市天泽科技实业有限公司
Processing Aids and Polymer Formulations Containing the Same and Method for Producing the Same
ActiveUS20140371396A1Increase profitHigh molecular weightTransportation and packagingMixingProcedure AgentsThiol
A multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer comprising one or more functionalized ethylenically unsaturated monomer into the emulsion polymerization reactor, wherein the functionality is selected from the group consisting of β-keto esters, β-keto amides, β-diketones, cyanoacetic esters, malonates, nitroalkanes, β-nitro esters, sulfonazides, thiols, thiol-s-triazines, and amine, where the functionality is incorporated into polymers by polymerizing, ethylenically unsaturated monomers containing these functionalities or by post functionalization of a polymer with additional reactions after polymerization in one of the first or second stages. Foamable halogenated polymers comprising the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer is also provided. Also provided are methods for making the multi-stage emulsion processing aid polymer and foamable halogenated polymers.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
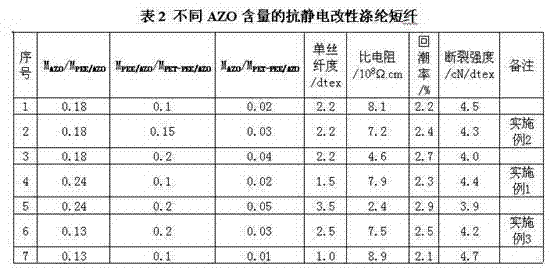
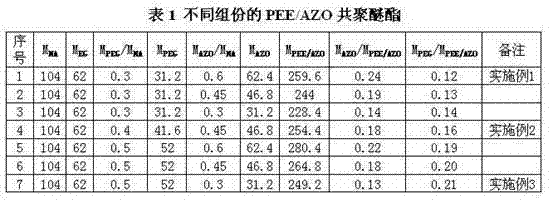
Anti-static modified polyester staple fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103361765AHas permanent antistatic propertiesImprove antistatic performanceElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureArtificial filament heat treatmentFiberPolymer science
The invention belongs to the field of processing of a high polymer material, and particularly relates to a different polyester staple fiber with an anti-static function, and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: a, preparing polyether ester fiber / aluminium-doped zinc oxide (PEE / AZO) composite polyether ester, namely adding the surface-modified aluminium-doped zinc oxide (AZO) to an ethylene glycol (EG) solution to carry out disperse treatment, esterifying together with malonic acid (MA) and polyether (PEG) to generate the PEE / AZO composite polyether ester; b, preparing PET-PEE / AZO copolyester, namely carrying out esterification on purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and EG, adding the PEE / AZO composite polyether ester to carry out copolycondensation after esterification is finished, and generating the PET-PEE / AZO copolyester with the anti-static property; and c, melting and spinning, namely preparing into the anti-static modified polyester staple fiber from the PET-PEE / AZO copolyester by melting and spinning. By adopting the preparation method, various problems caused by large static electricity in the processes of spinning, weaving and taking the polyester staple fiber are solved.
Owner:宿迁逸达新材料有限公司
Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes
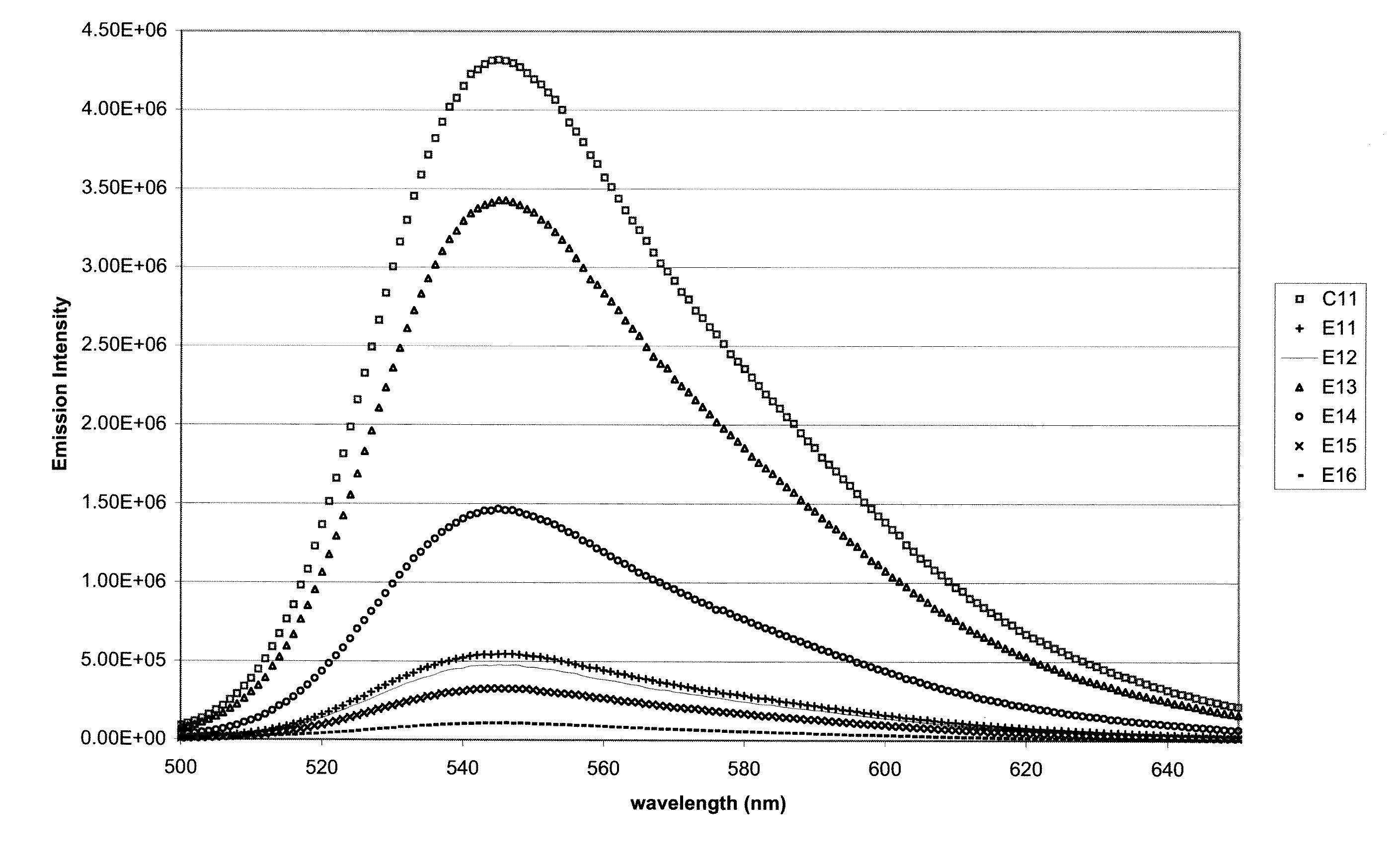
ActiveUS20050143327A1Ameliorating damage to tissues for transplantationAmeliorating spoilage of foodBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceMalonic acid
Herein are disclosed substituted fullerenes, comprising a fullerene core (Cn), wherein n is an even integer greater than or equal to 60; 3 or 5 dihydrocarbylmalonate (>C(COOR1)(COOR2)) groups bonded to the fullerene core; and 1 or 3 polar extended malonate groups (>C(COOR3)(COOR4)) bonded to the fullerene core. The substituted fullerenes can form micelles, and can be used to ameliorate oxidative stress diseases.
Owner:LUNA LABS USA LLC
Methods for Forming Back-Channel-Etch Devices with Copper-Based Electrodes
InactiveUS20140273341A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMalonic acidIndium gallium zinc oxide
Embodiments described herein provide methods for forming indium-gallium-zinc oxide (IGZO) devices. A substrate is provided. An IGZO layer is formed above the substrate. A copper-containing layer is formed above the IGZO layer. A wet etch process is performed on the copper-containing layer to form a source region and a drain region above the IGZO layer. The performing of the wet etch process on the copper-containing layer includes exposing the copper-containing layer to an etching solution including a peroxide compound and one of citric acid, formic acid, malonic acid, lactic acid, etidronic acid, phosphonic acid, or a combination thereof.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Porous carbon with high-volumetric-specific-capacitance composite graphene, preparation method thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102745666ANovel structureSimple processGrapheneCarbon preparation/purificationCapacitancePorous carbon
The invention relates to porous carbon with high-volumetric-specific-capacitance composite graphene, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof. The porous carbon comprises the raw materials of graphene oxide, hydroxyl-containing phenols and derivatives thereof (phenol, resorcinol, phloroglucin, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, or 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid), and aldehydes (formaldehyde, butyraldehyde, or terephthalaldehyde). A carboxyl-containing compound (amphoteric compound amino acid, malonic acid, or oxalic acid) is used for regulating the pH value of the system and for initiating a phenolic condensation polymerization reaction, such that a sandwich structure with nano-sheets embedded in a polymer is prepared. The structure is subjected to carbonization, and the porous carbon is prepared with a one-step method. The prepared porous carbon with the sandwich structure is advantaged in novel structure, simple preparation technology, high product purity, convenient application, and suitability for large-scale productions. The porous carbon shows a mass specific capacitance similar to that of a graphene-based material in the application in a super-capacitor. Also, the volumetric specific capacitance of the porous carbon is higher by a magnitude than that of the graphene-based material. Therefore, the porous carbon has great application potential and market prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for conversion of oil-containing algae to 1,3-propanediol
InactiveUS7777085B2Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionDocosahexaenoic acidMalonic acid
The present invention relates to a process for oxidizing renewable polyunsaturated fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to a malonic acid intermediate which is subsequently reduced to 1,3 propanediol (PDO).
Owner:INVENTURE RENEWABLES INC
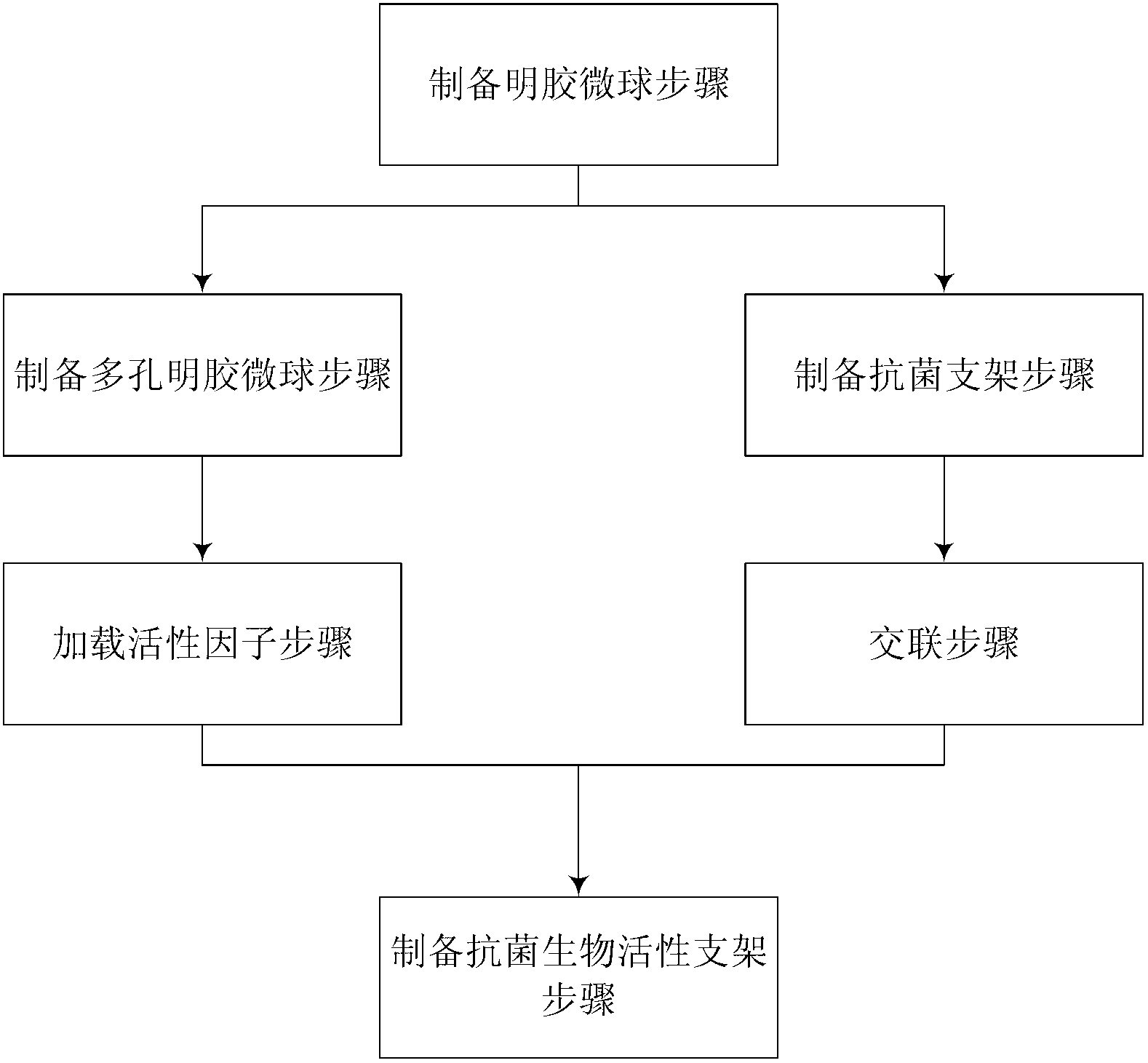
Antibacterial biological activity stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103007345AFully biologically activeImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisUltra Low Temperature FreezerCambium
The invention relates to an antibacterial biological activity stent and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps that gelatin microspheres are prepared; porous gelatin microspheres are prepared; gelatin microspheres carried with active factors are obtained; an antibacterial stent is prepared, wherein the preparation of the antibacterial stent comprises the steps that at least one of collagen, chitosan and silk fibroin and nano-silver grains are added to acetic acid or malonic acid to prepare a mixed solution, the mixed solution is poured into a die which is horizontally paved with the solid gelatin microspheres, the die is rapidly placed in an ultra cold refrigerator for freezing treatment, and the die is frozen and dried to obtain the antibacterial stent; and the antibacterial biological activity stent is prepared by the steps that the gelatin microspheres carried with the active factors are placed into normal saline to prepare a suspension liquid, and the suspension liquid is poured into the antibacterial stent to obtain the antibacterial biological activity stent after dried at the room temperature. According to the antibacterial biological activity stent and the preparation method thereof, pure natural polymers are taken as raw materials, the nano-silver grains and the bioactive factors are compounded to prepare the stent, so that the stent has the biological activity and antibacterial capacity, can effectively promote vascularization of cambium and can be used for skin injury healing.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
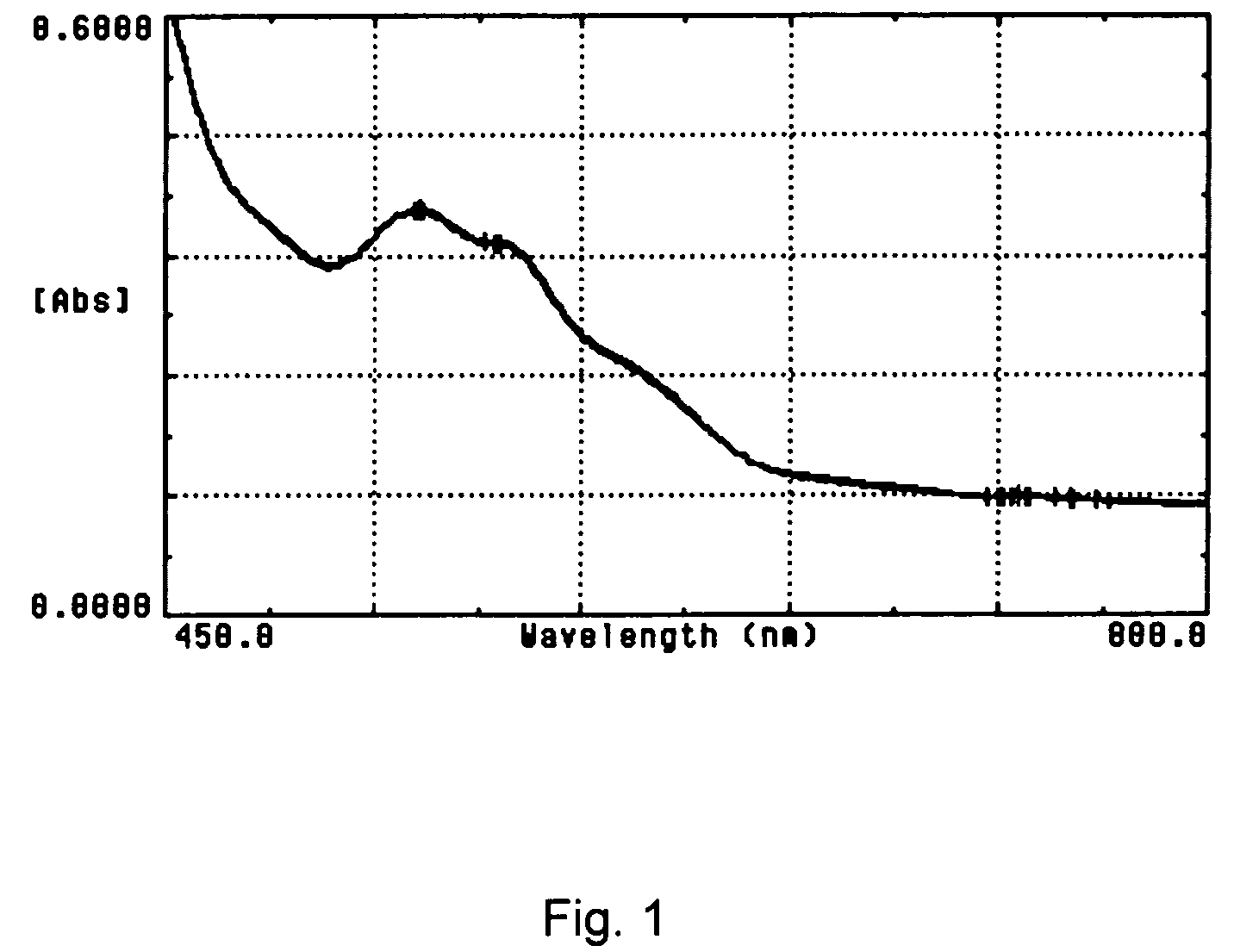
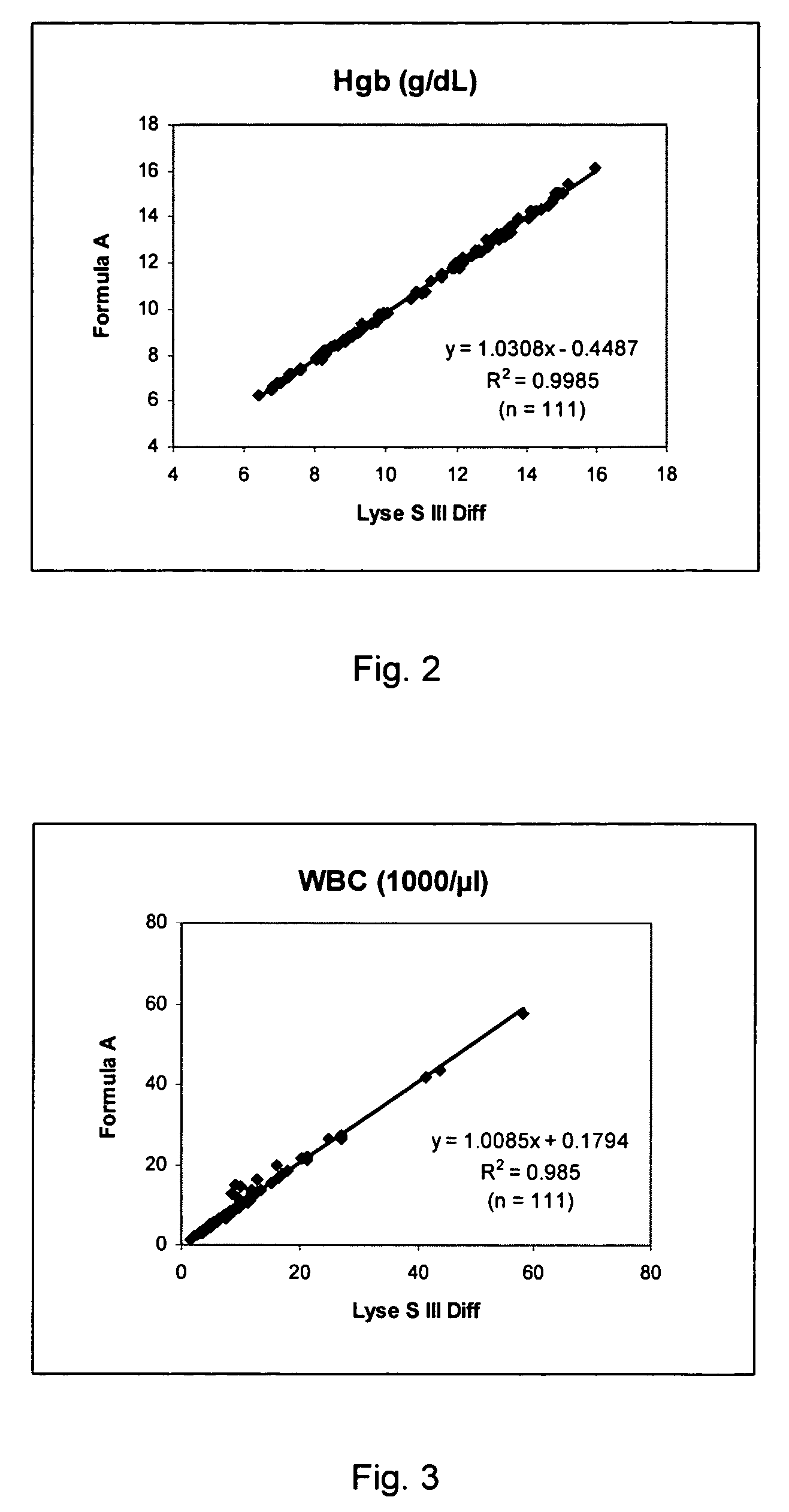
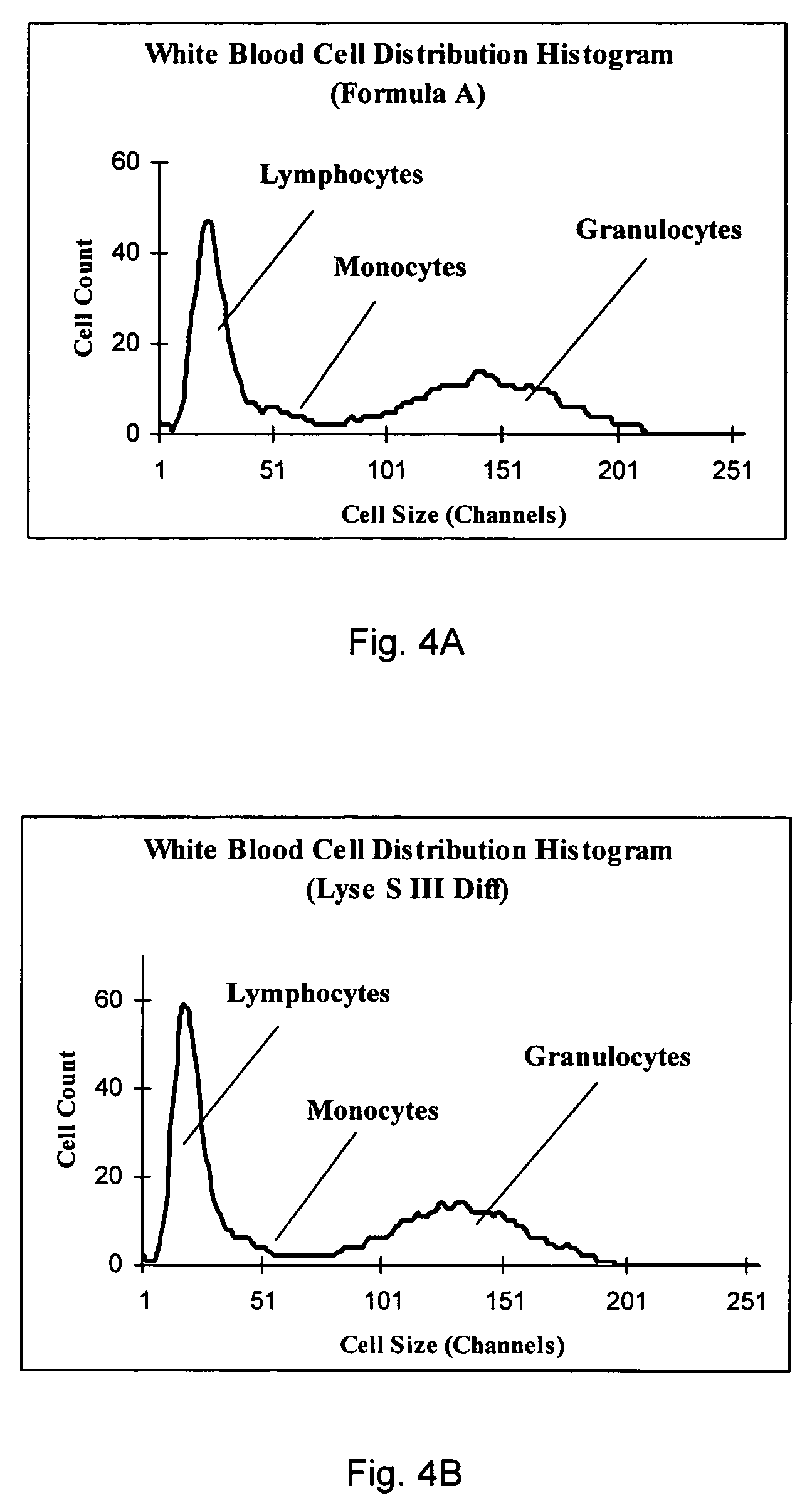
Cyanide-free lytic reagent composition and method of use for hemoglobin and white blood cell measurement
A cyanide-free lytic reagent composition and method of use for measuring the total hemoglobin concentration and white blood cells in a blood sample are disclosed. The lytic reagent composition includes a quaternary ammonium surfactant to lyse red blood cells and release hemoglobin and a ligand to form a stable chromogen with the hemoglobin. The lytic reagent composition has a pH in a range of 3 to 10. The lytic reagent composition can also include a second quaternary ammonium surfactant. The ligand can be malic acid, malonic acid, ethylene diamine, N,N-diethylethylene diamine, N,N′-diethylethylene diamine, diethylene triamine, tetraethylene pentamine, 1,6-hexanediamine, 1,3-pentanediamine, 2-methylpentamethylenediamine, 1,2-diaminocyclohexane, 4-aminoacetophenone, bis-hexamethylenetriamine, pyridazine, or 3,6-dihyroxypyridazine.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Polishing composition and polishing method
A polishing composition includes fumed alumina, alumina other than fumed alumina, colloidal silica, a first organic acid, a second organic acid, an oxidizing agent, and water. When the second organic acid is citric acid, the first organic acid is preferably malic acid, while when the second organic acid is malic acid, the first organic acid is preferably citric acid. When the second organic acid is succinic acid, iminodiacetic acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid, malonic acid, crotonic acid, gluconic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, or mandelic acid, the first organic acid is preferably either citric acid or malic acid. The polishing composition can be suitably used for polishing the surface of a substrate for a magnetic disk.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Etchant composition
An etchant composition for silver or silver alloys which comprises at least one polycarboxylic acid, phosphoric acid, nitric acid, and water. The polycarboxylic acid preferably is at least one member selected from the group consisting of oxalic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, glutaric acid, aconitic acid, ketoglutaric acid, maleic acid, citraconic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, and citric acid.
Owner:NAGASE CHEMTEX CORPORATION
700V high-voltage aluminum electrolytic capacitor electrolyte
InactiveCN106252079AHigh molecular weightLow mobilityLiquid electrolytic capacitorsSalicylic acidGluconic acid
Disclosed is a 700V high-voltage aluminum electrolytic capacitor electrolyte. The electrolyte comprises 50-80% of main solvent, 20-50% of auxiliary solvent, 5-20% of main solute, 2-10% of auxiliary solute, 0.1-1% of auxiliary additive and 5-15% of spark additive, wherein the main solute comprises one or more of azelaic acid, ammonium hydrogen azelate, ammonium sebacate, decane dicarboxylic acid, 7, 9-dimethyl-7, 9-dimethoxy carbonyl-1, 11-dodecane dicarboxylic acid, and 7, 8-dimethyl-7, 8-dimethoxy carbonyl-1, 14 tetradecane dicarboxylic acid; and the auxiliary solvent comprises one or more of ammonium salicylate, salicylic acid, oxalic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, ammonium benzoate, ammonium maleate, ammonium hydrogen maleate, ammonium adipate and hexanedioic acid. The spark voltage of the electrolyte is greater than 700V; and in addition, the electrolyte is simple to prepare, stable in performance and excellent in related parameters.
Owner:HUNAN AIHUA GRP
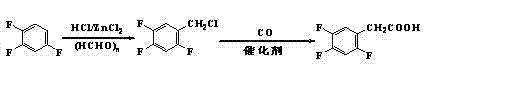
Preparation method 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid
ActiveCN103012111AFew synthetic stepsMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationPhenylacetic acidNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a preparation method 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid. The method is characterized by consisting of four reaction steps of: A, reaction of 2,4,5-trifluoronitrobenzene (I) and diethyl malonate which are condensed to prepare 2,5-difloro-4-nitrobenzophenone diethyl malonate; B, hydrolysis, acidification and decarboxylic reaction of dibasic ester; C, reduction reaction of nitryl; and D, diazotization fluoridation of amino. The four reaction steps can be sequentially carried out according to A, B, C and D, or A, C, B and D, or A, C, D and B. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, condensation of 2,4,5-trifluoronitrobenzene (I) and diethyl malonate is easy to realize by means of high substituting activity of nitryl p-fluorine, and the raw material 2,4,5-trifluoronitrobenzene (I) is low in cost and easy to obtain and can be easily prepared by nitration and fluorination of 2,4-dichlor fluorbenzene. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method provided by the invention has the characteristics of low-cost and easily obtained raw materials, mild reaction condition, high total yield, low production cost and the like, and is comparatively suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:江苏中丽新材料有限公司
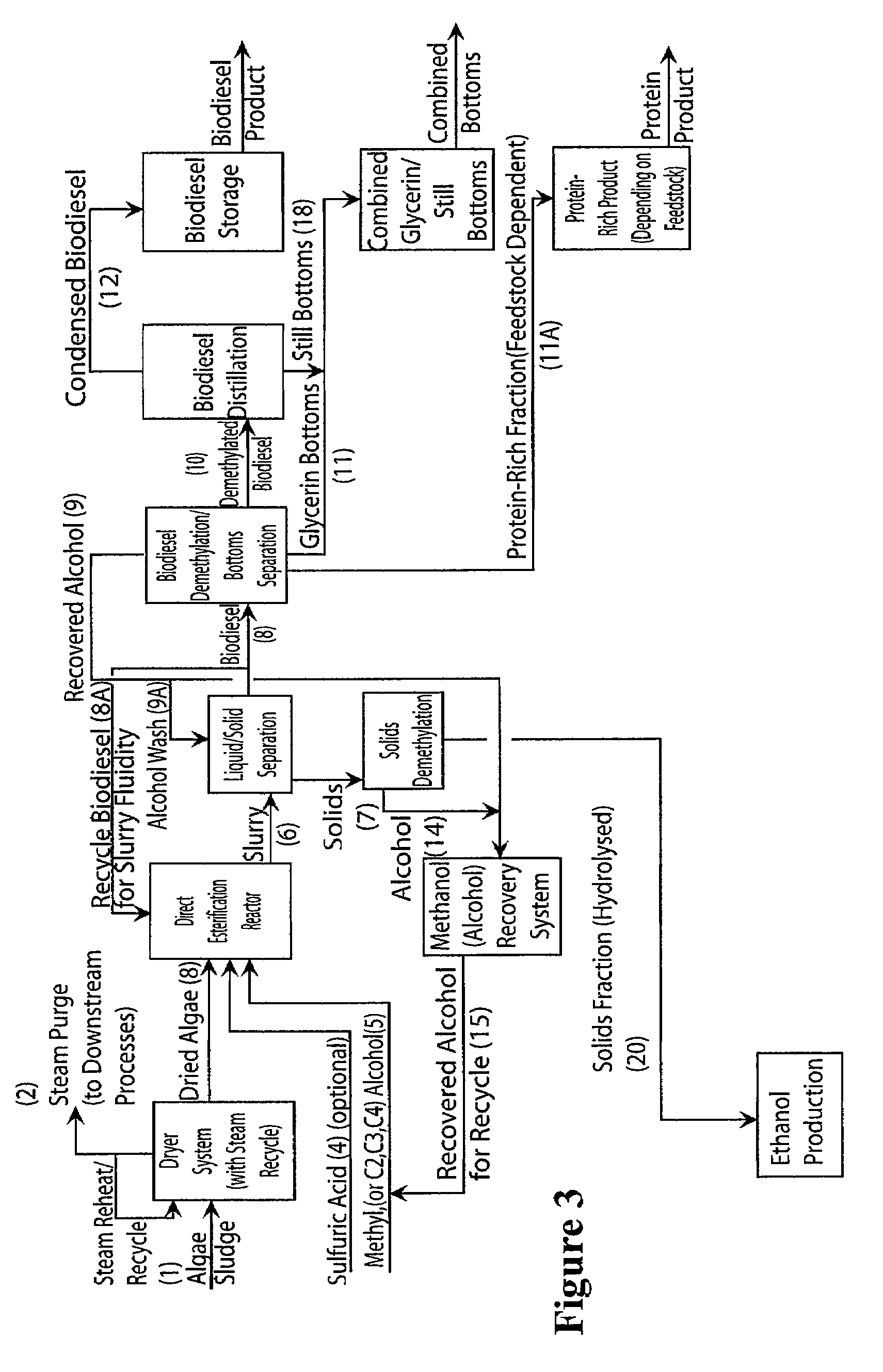
Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives
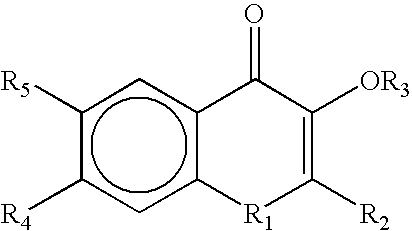
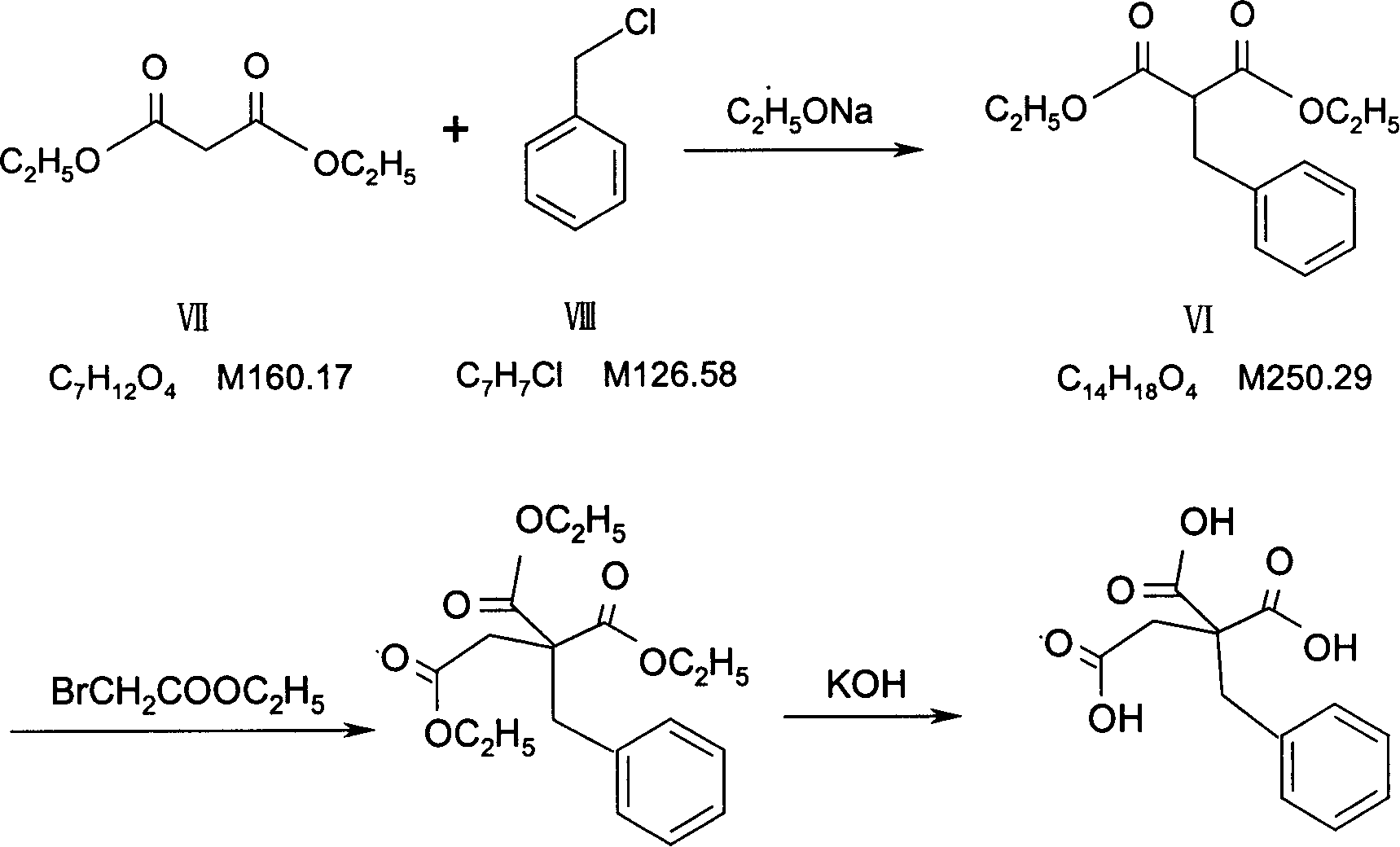
This invention involves a synthesis method for dextrorotatory alpha- [2-(naphthoxy) ethyl] toluidine derivatives, including: make benzaldehyde react with malonic acid and ammonium acetate, then split it with dextrorotatory anhydrous tartaric to get dextrorotatory beta-aminophenylpropionic acid, after alkyl substitution and deoxidizing to alcohol, react with alpha-bromonaphthalene. This invention has saved the raw materials consumption that every step reacts afterwards, the castoff is reduced greatly, thus reduced the cost.
Owner:曹丽 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


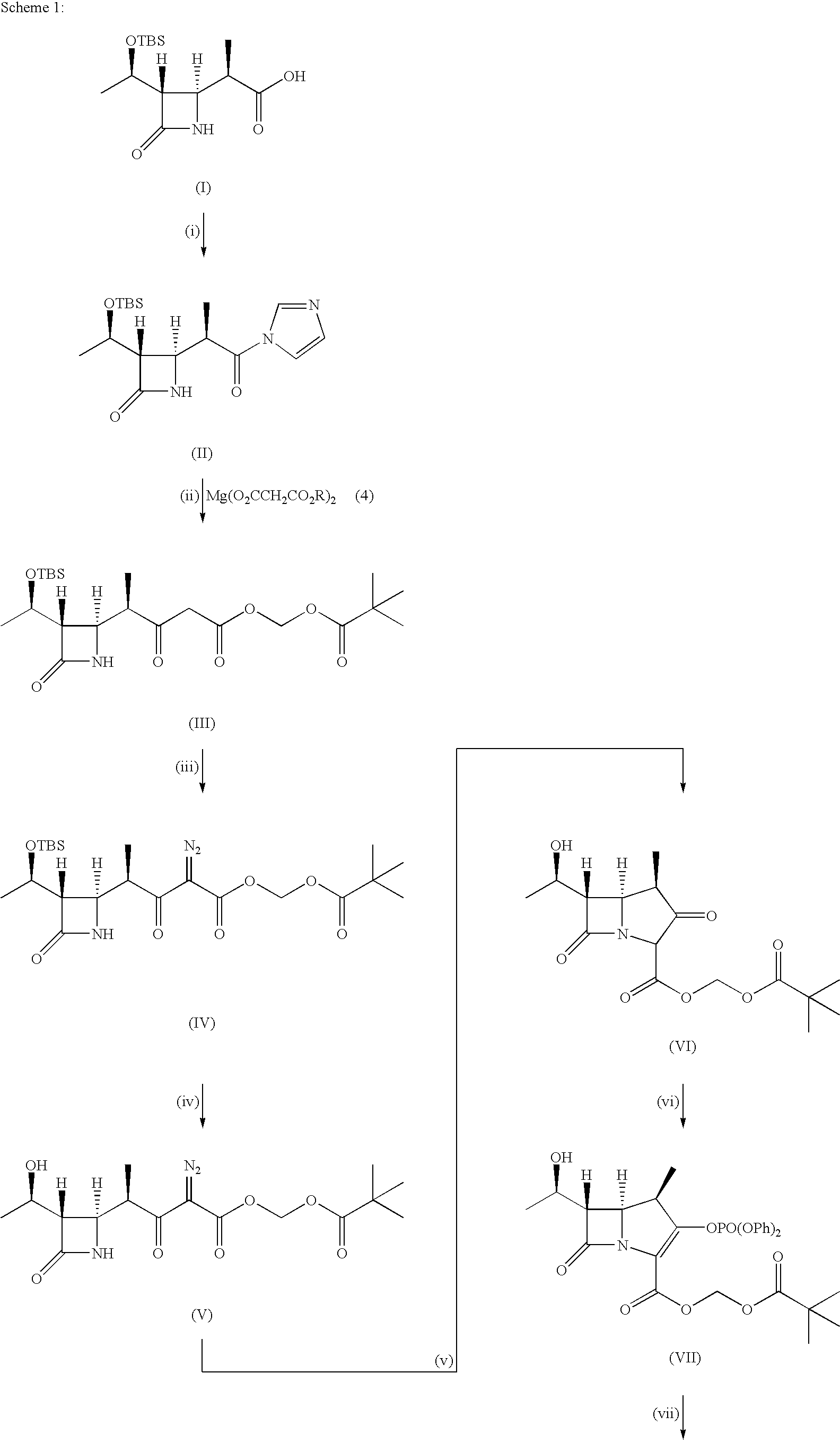







![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00001.png)
![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00002.png)
![Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes Amphiphilic [5:1]- and [3:3]- hexakisadducts of fullerenes](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1a2f6665-a551-442d-a298-41ccefc1f89a/US20050143327A1-20050630-D00003.png)



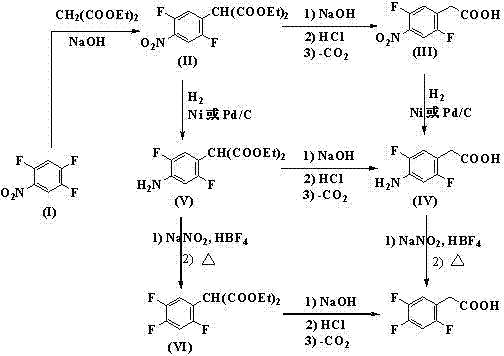
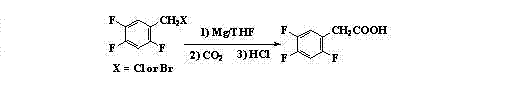
![Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cdb83058-ee4b-4005-87cf-84c861b90c95/A2005100126240002C1.PNG)
![Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cdb83058-ee4b-4005-87cf-84c861b90c95/A2005100126240002C2.PNG)
![Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives Method for preparing dextroa-[2-(naphthoxy, ethyl] phenyl methylamine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/cdb83058-ee4b-4005-87cf-84c861b90c95/A2005100126240002C3.PNG)