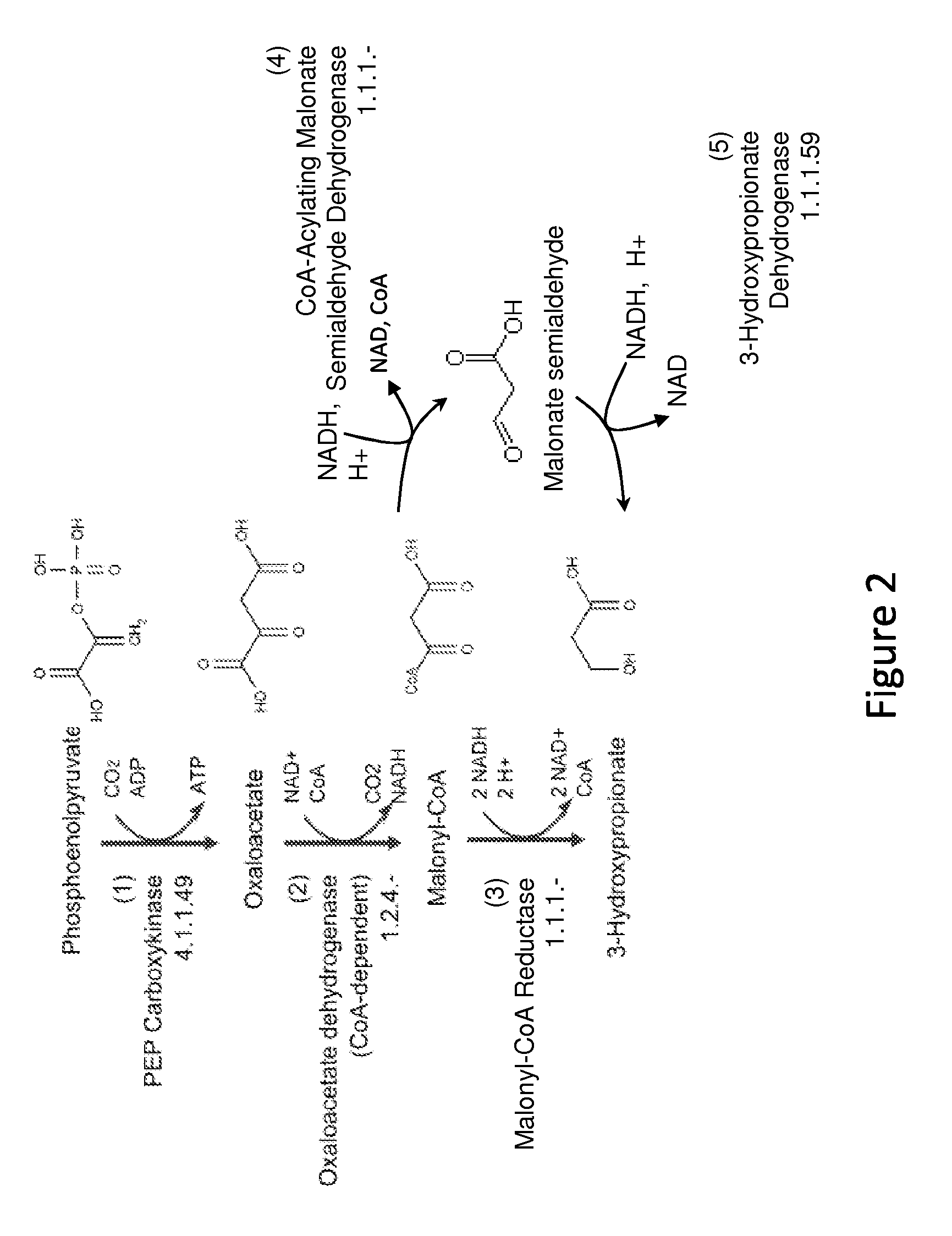
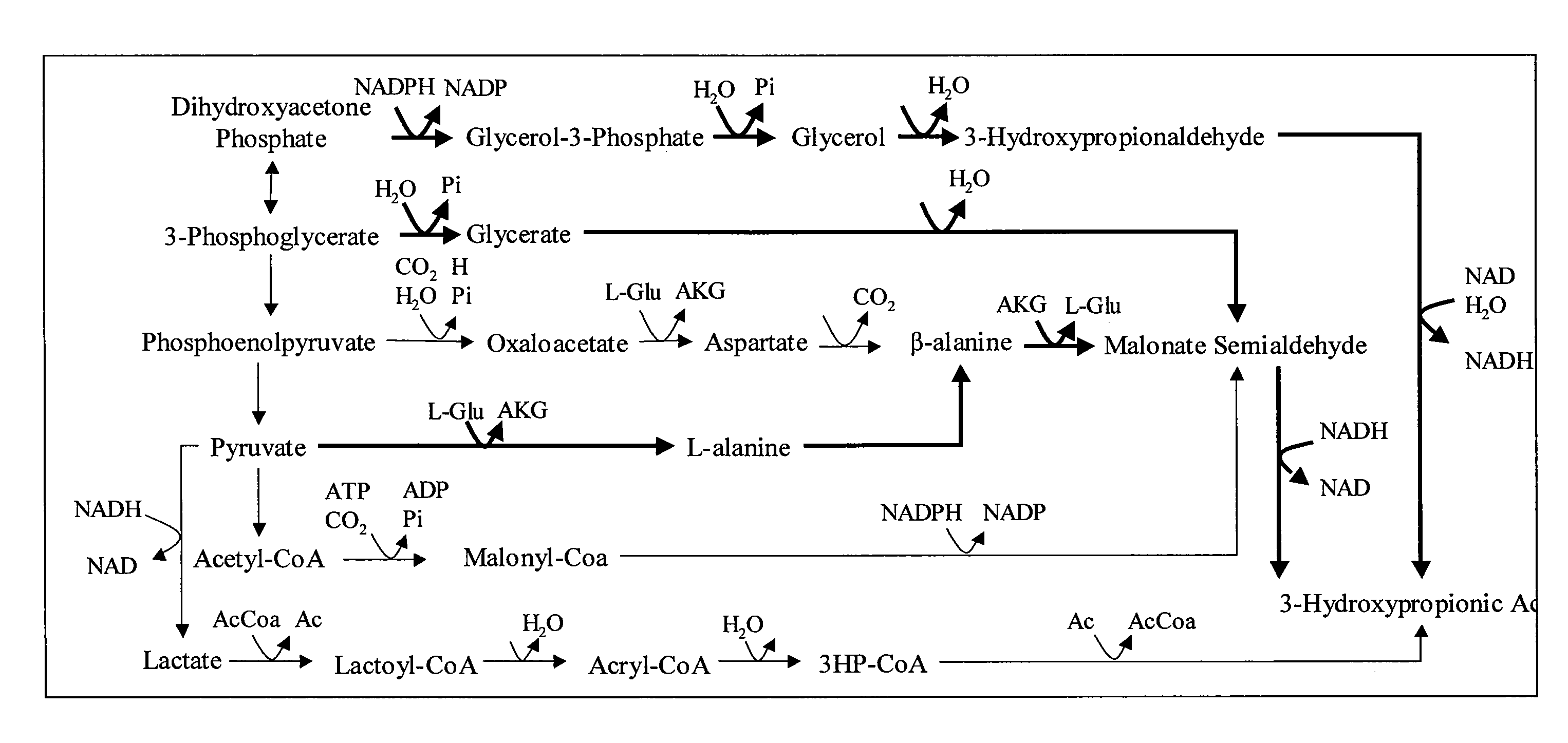
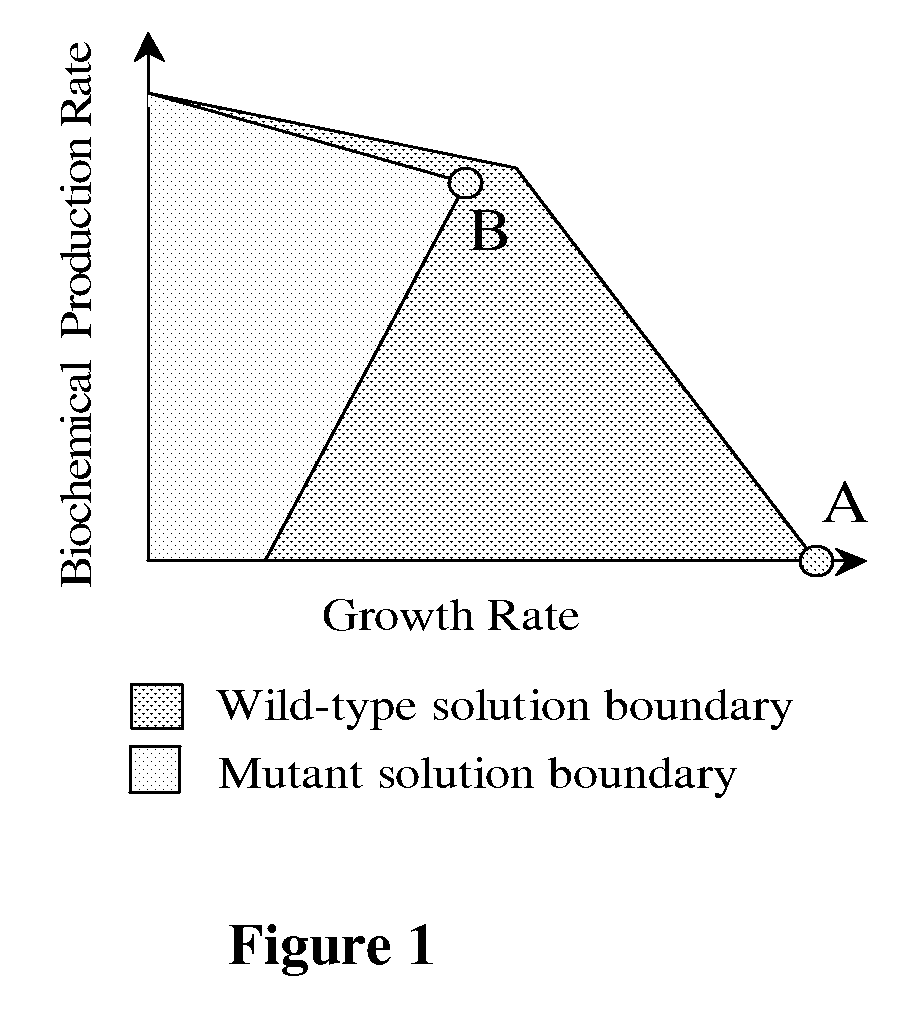
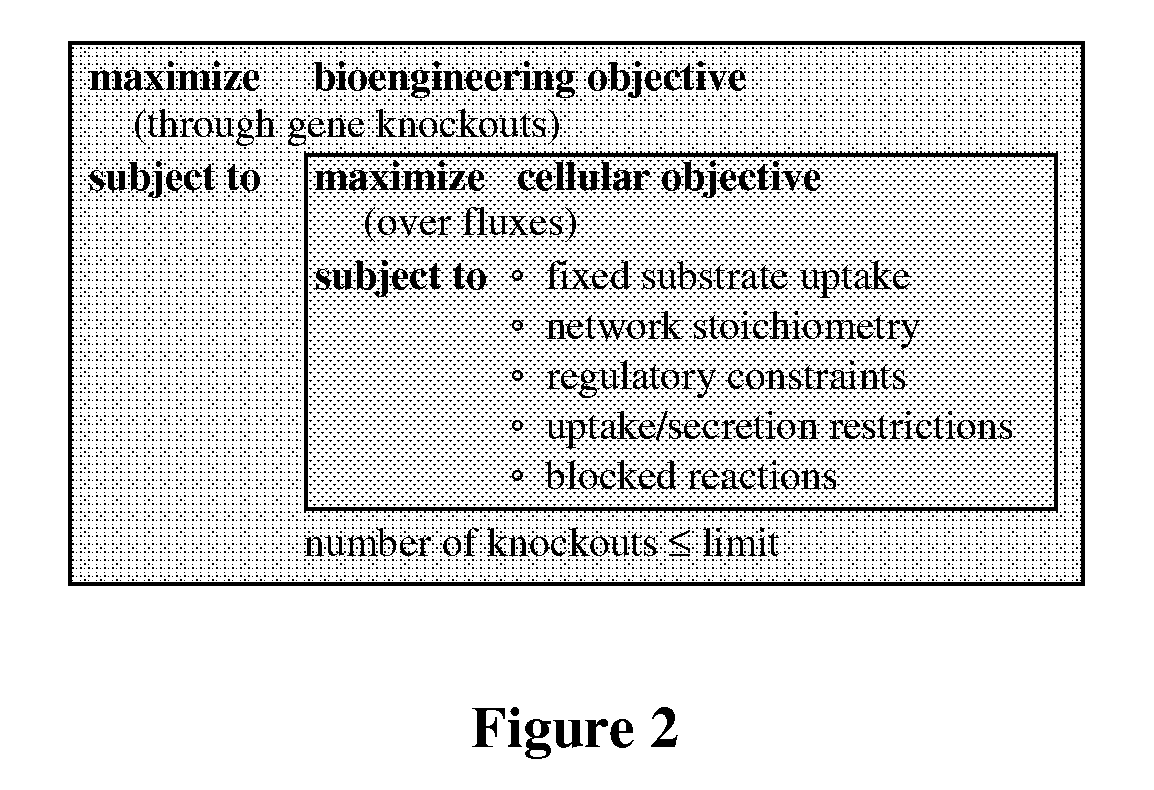
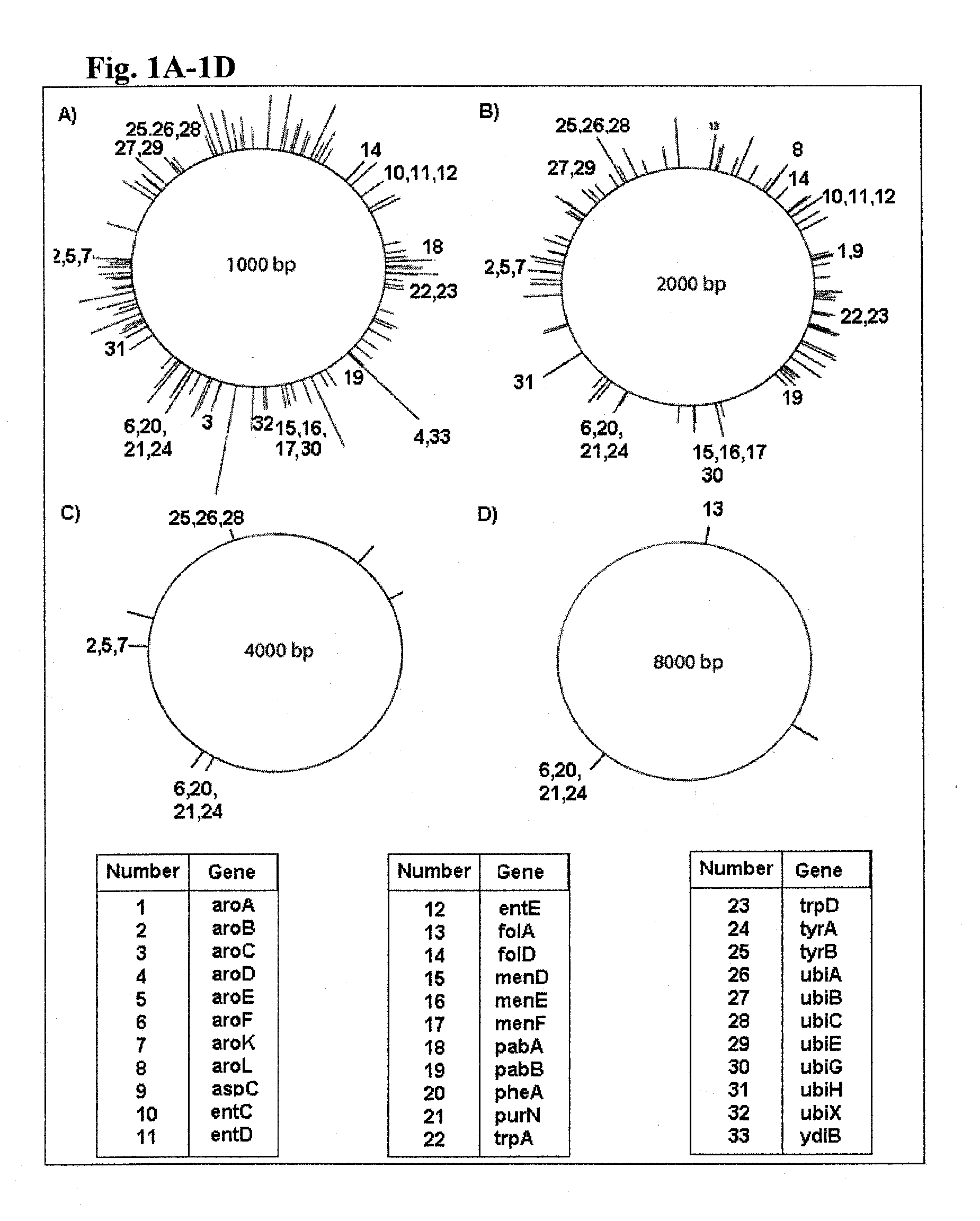
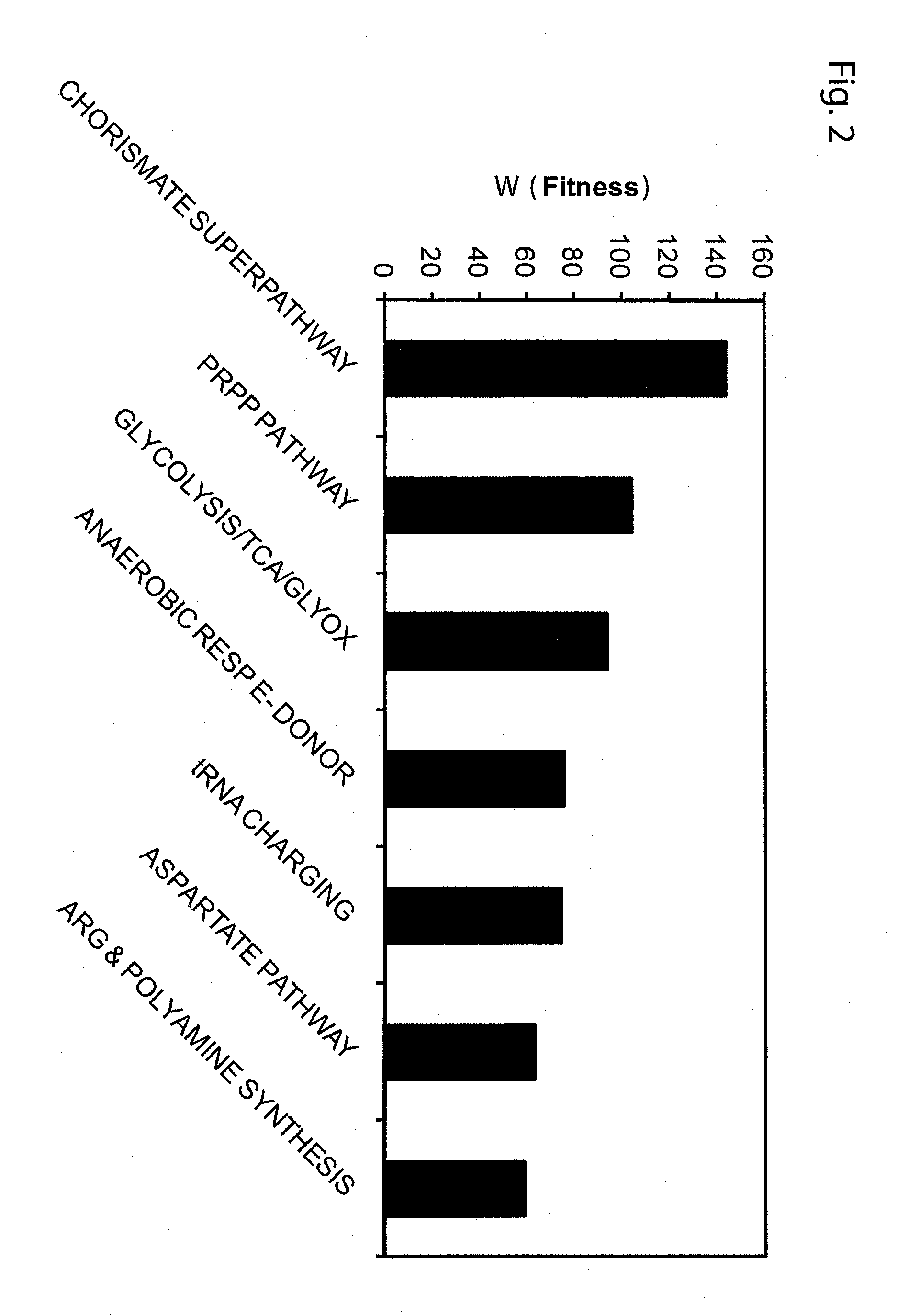
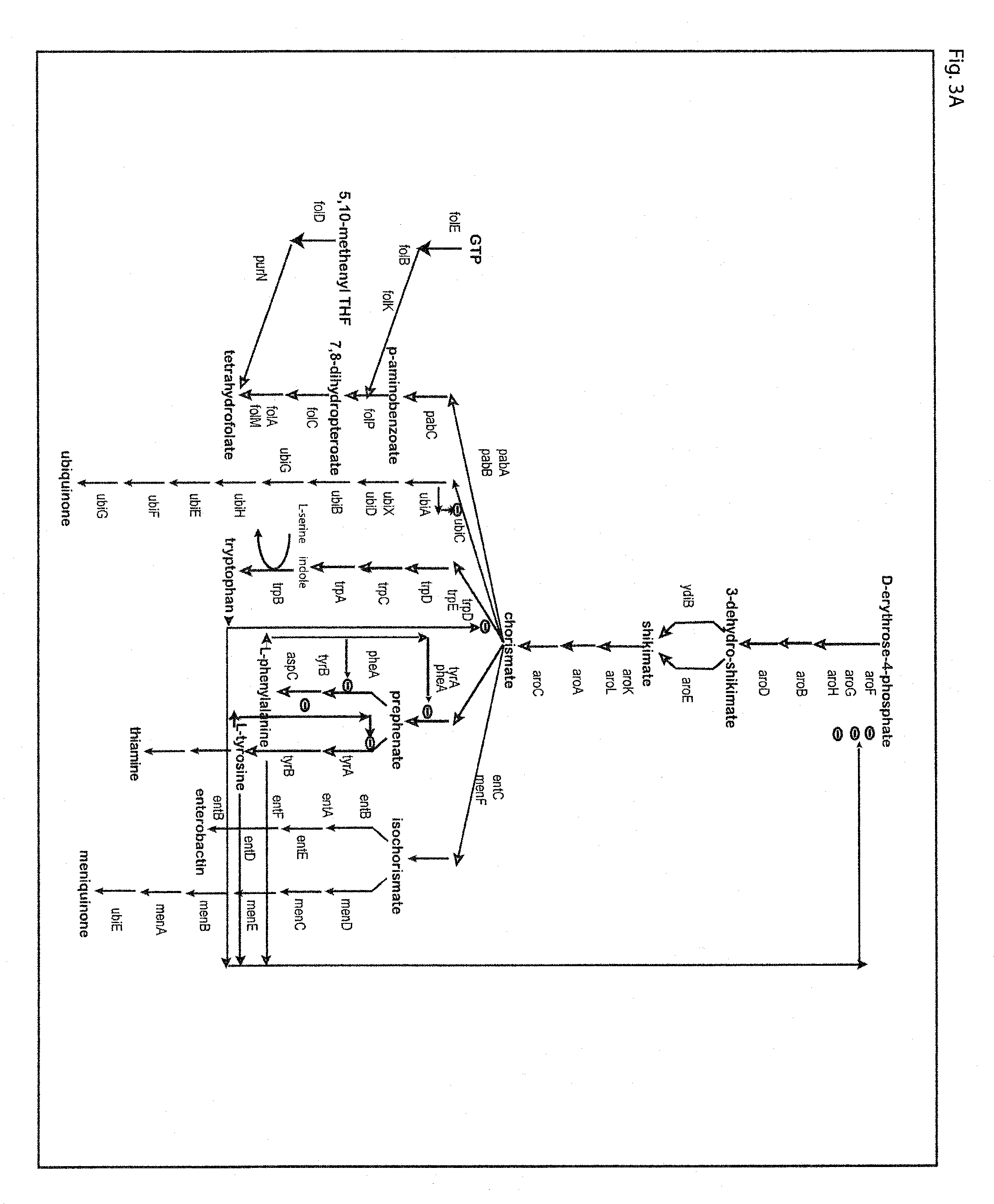
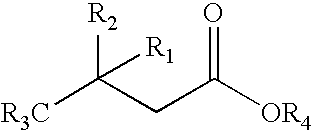
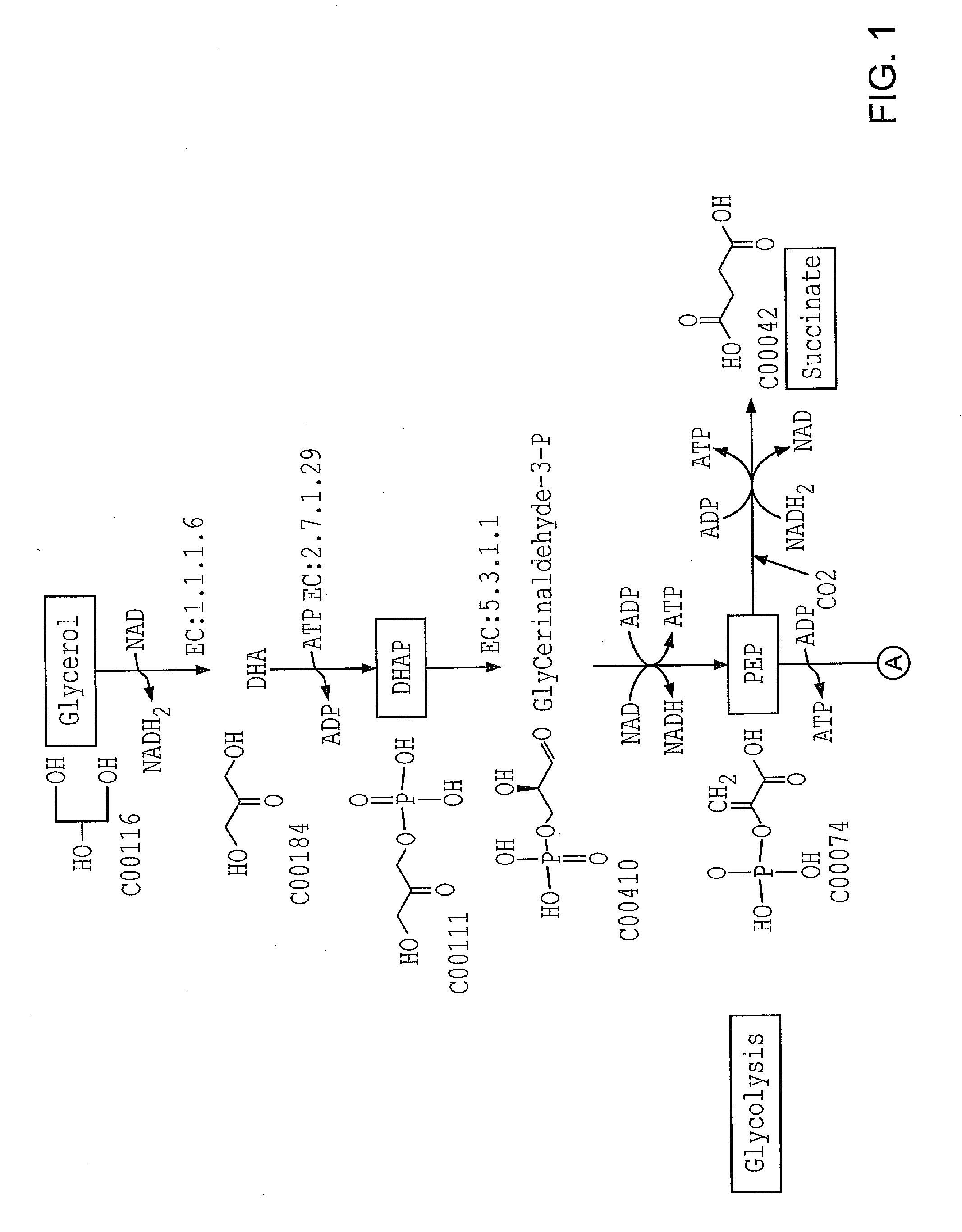
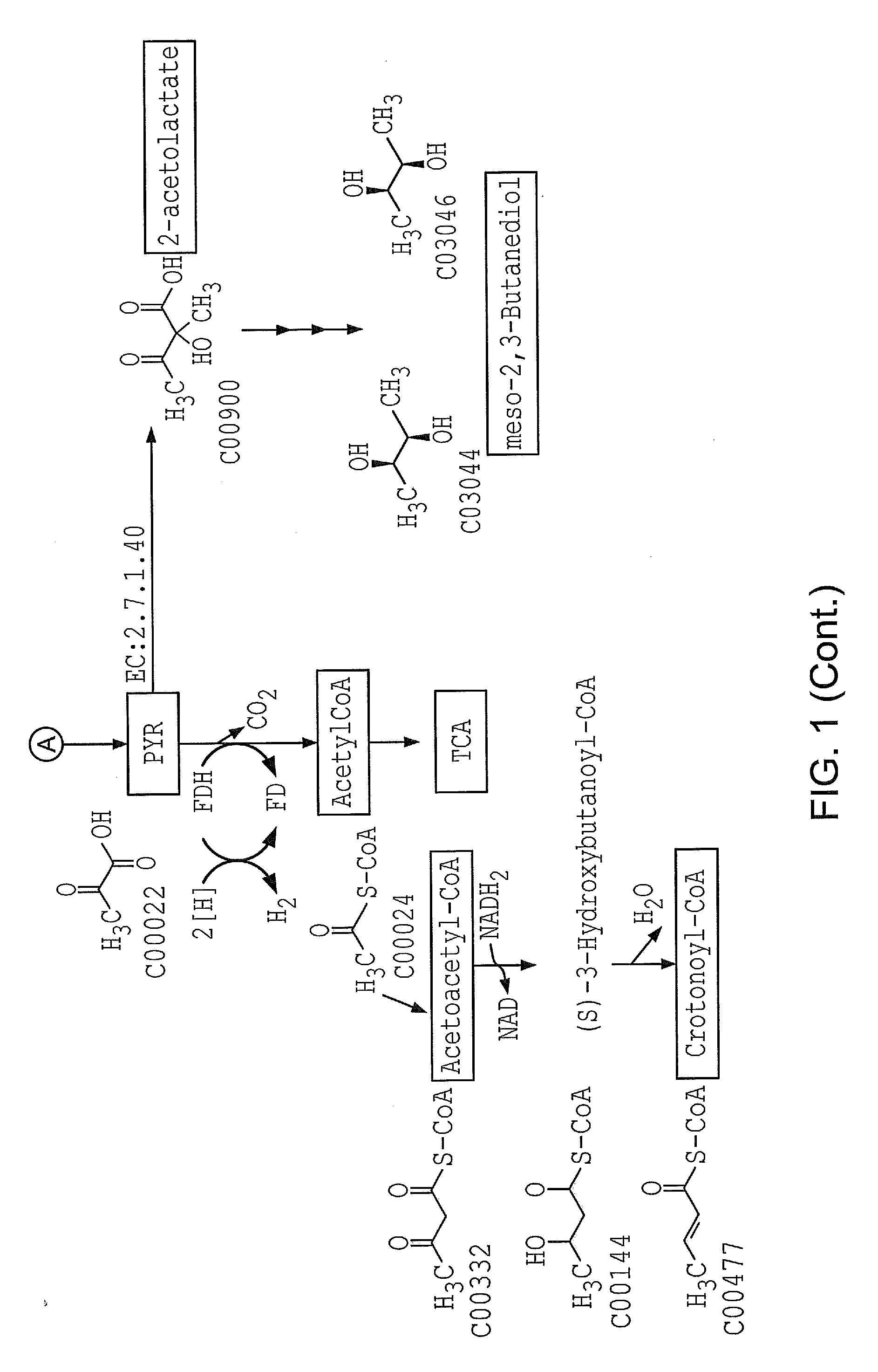
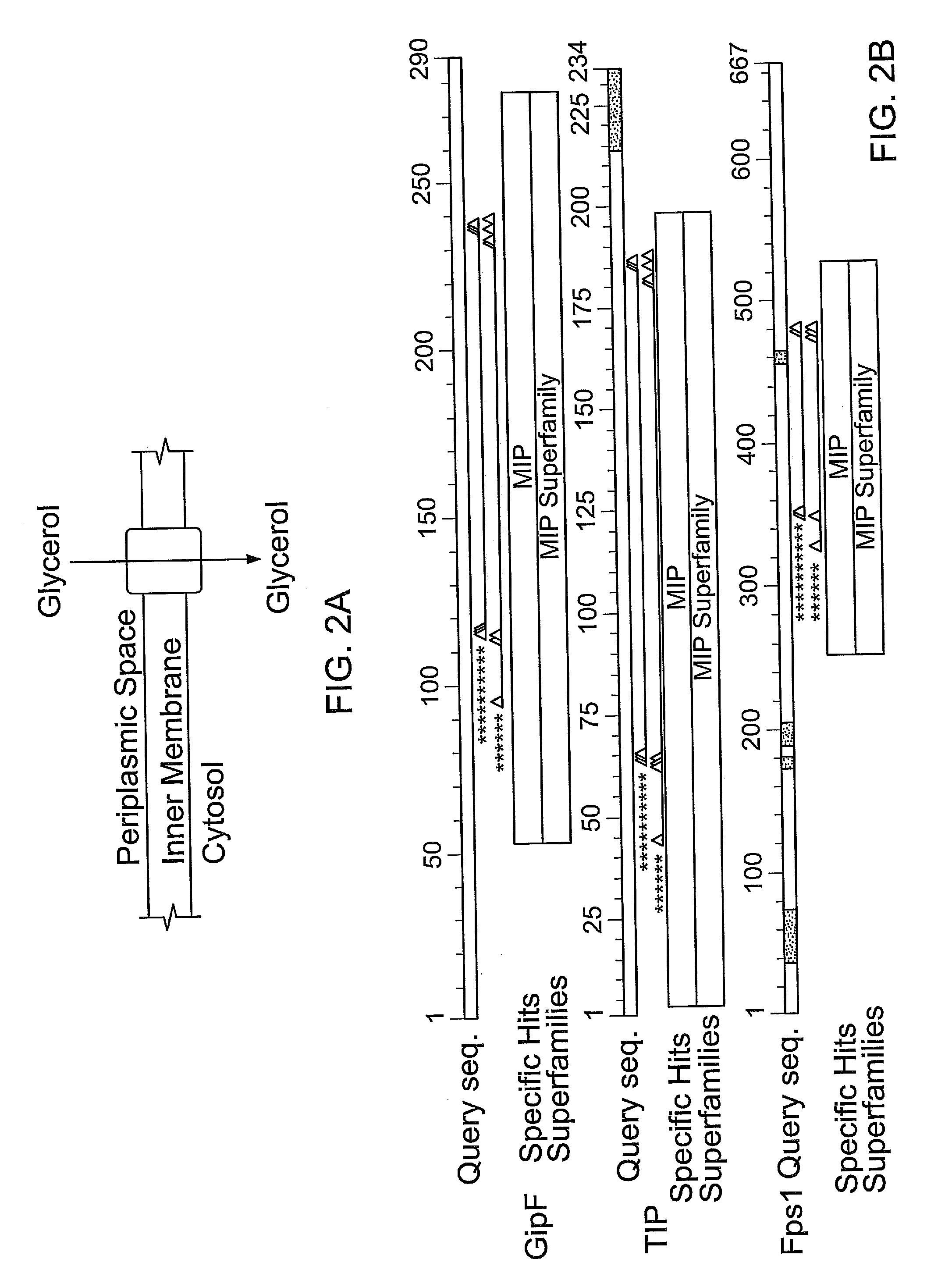
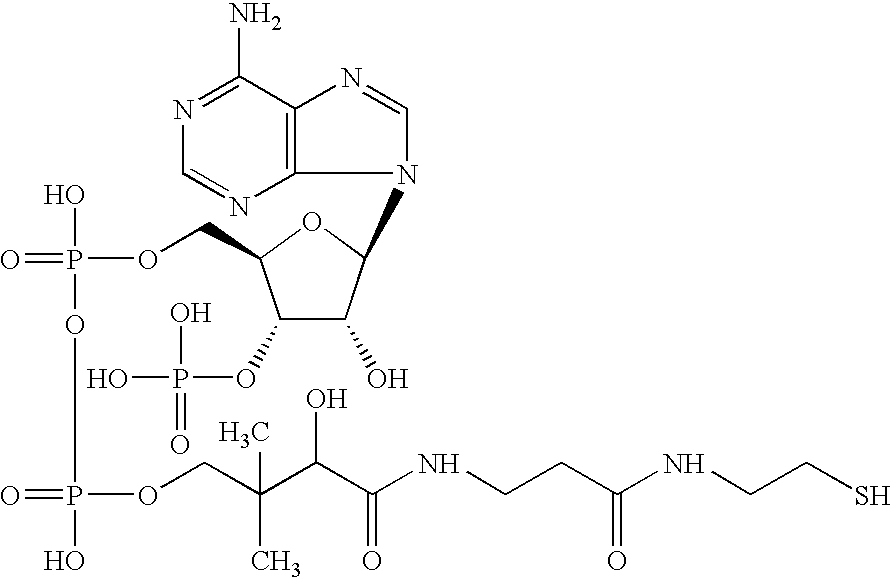
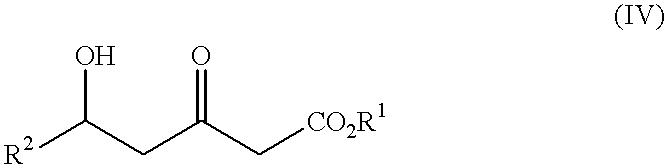
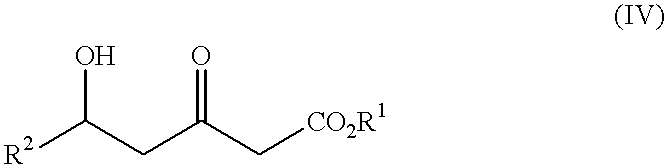
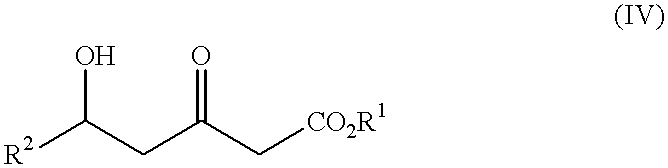
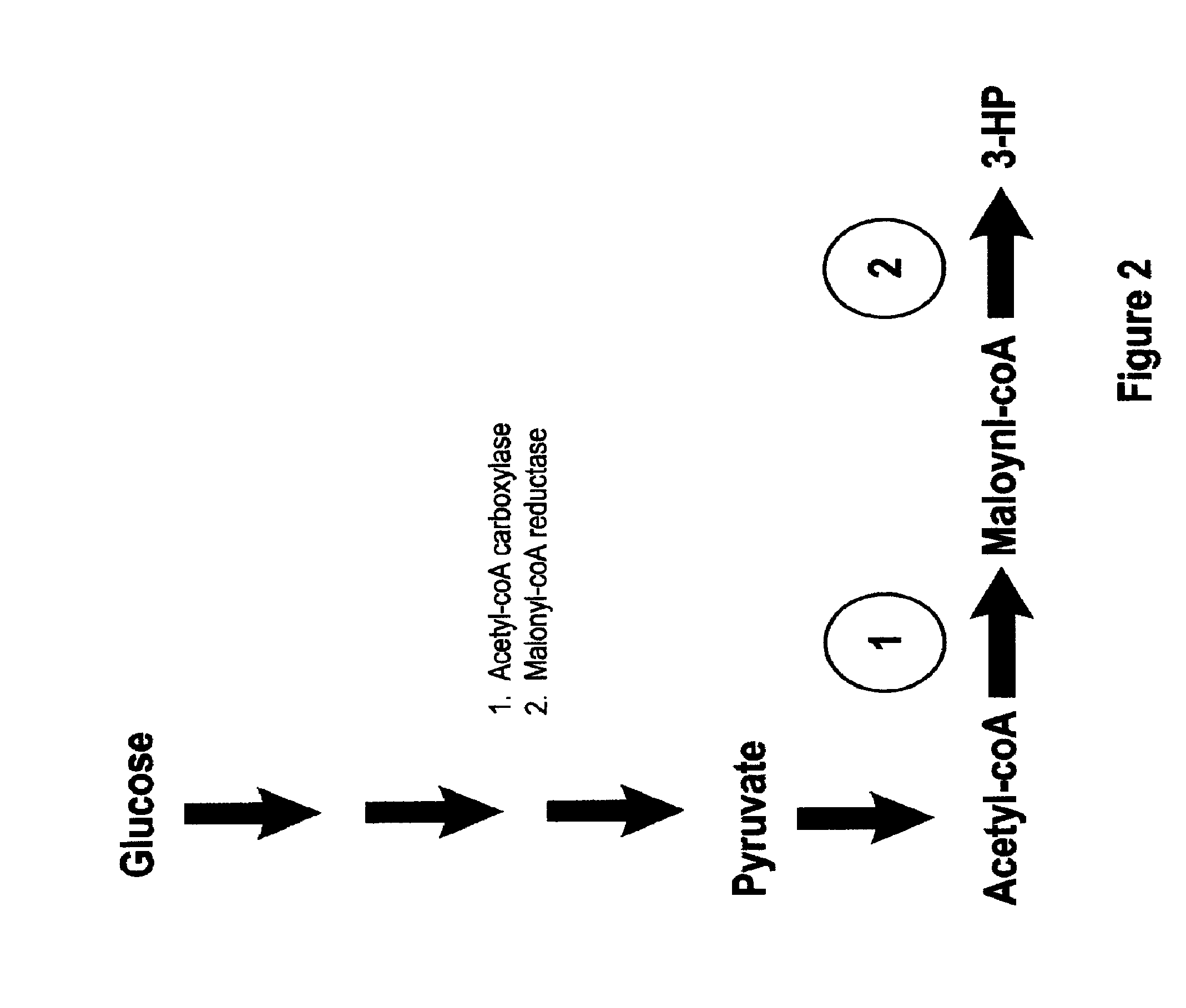
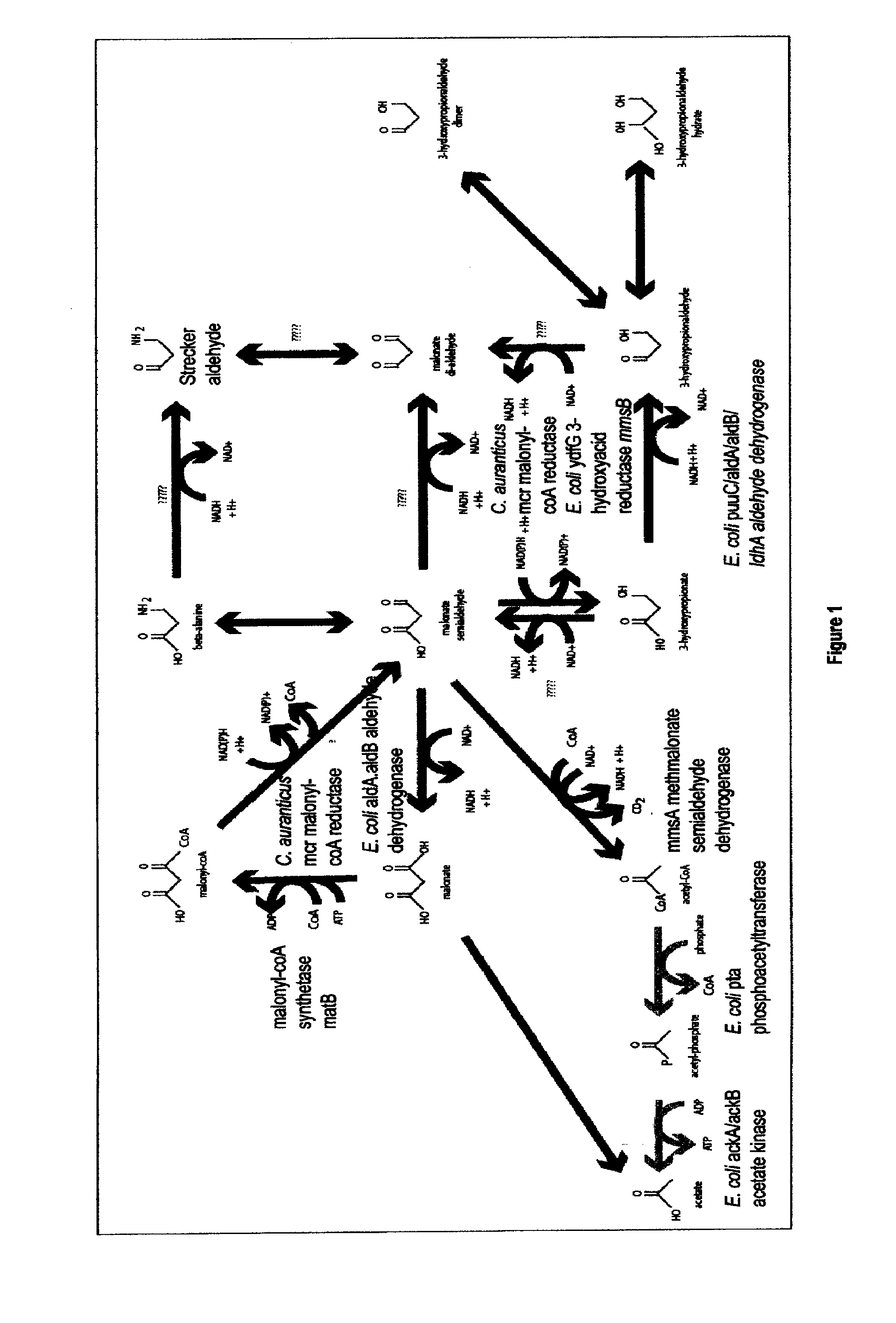
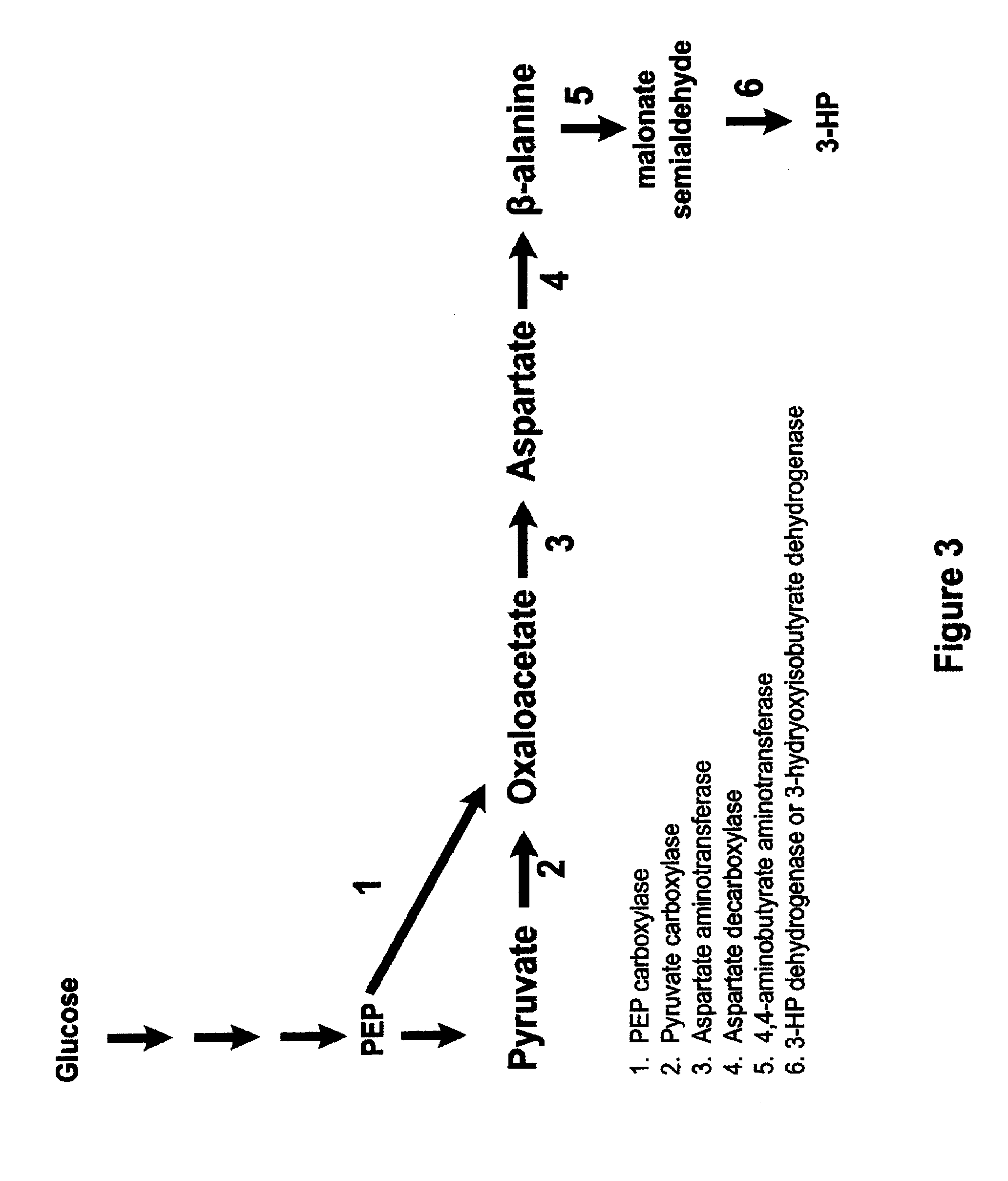
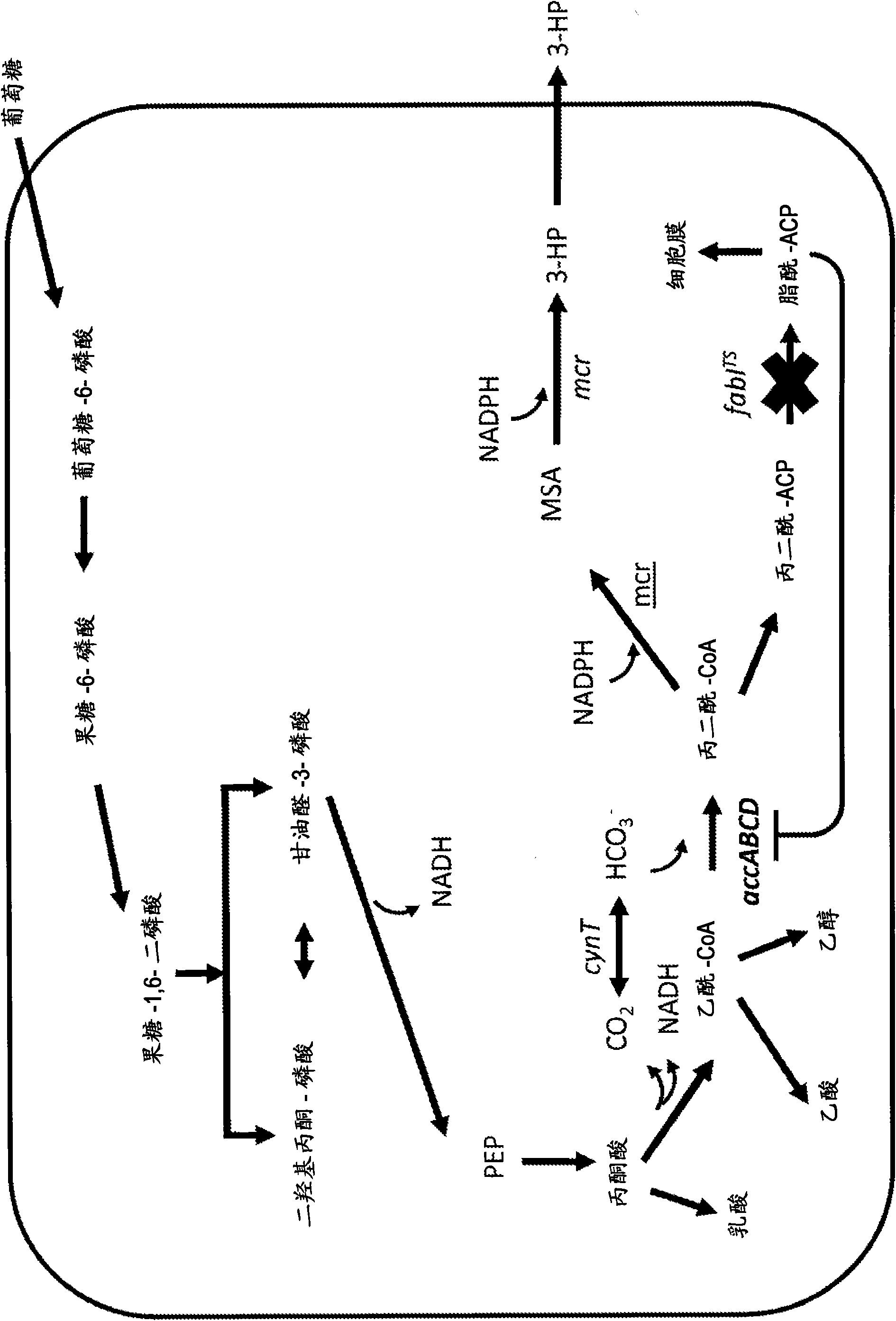
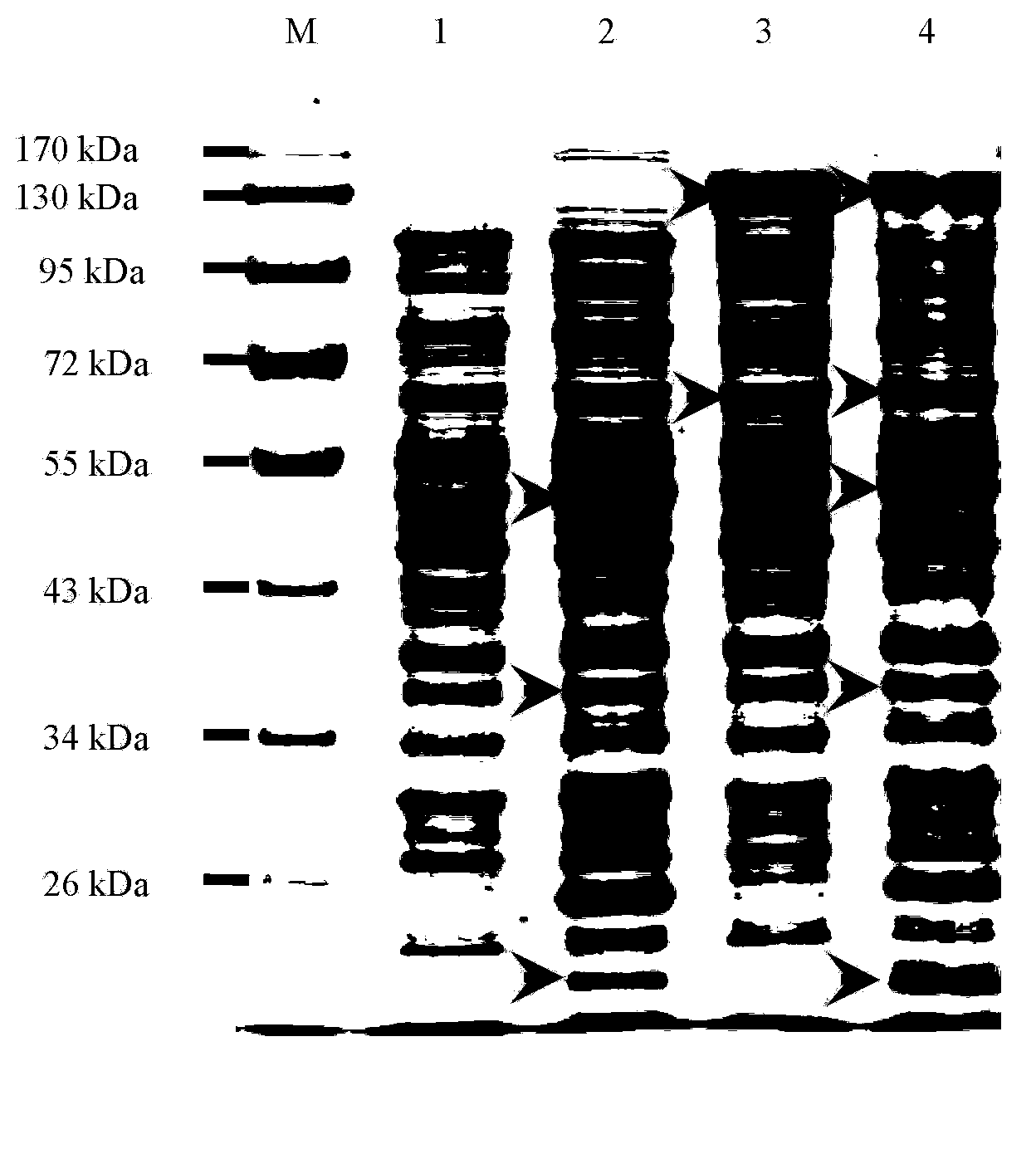
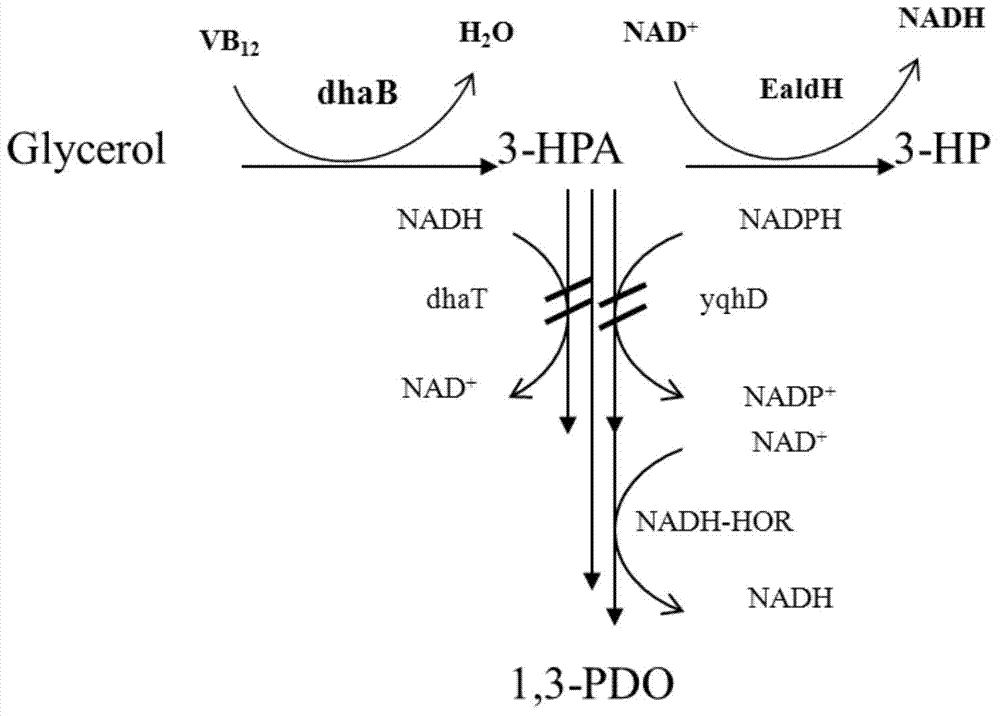
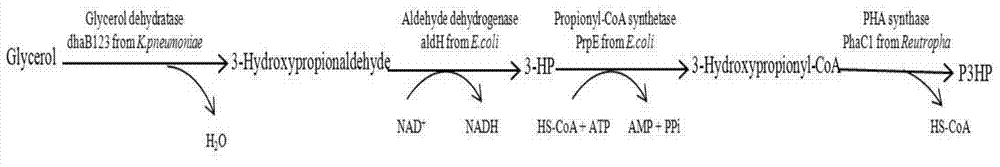
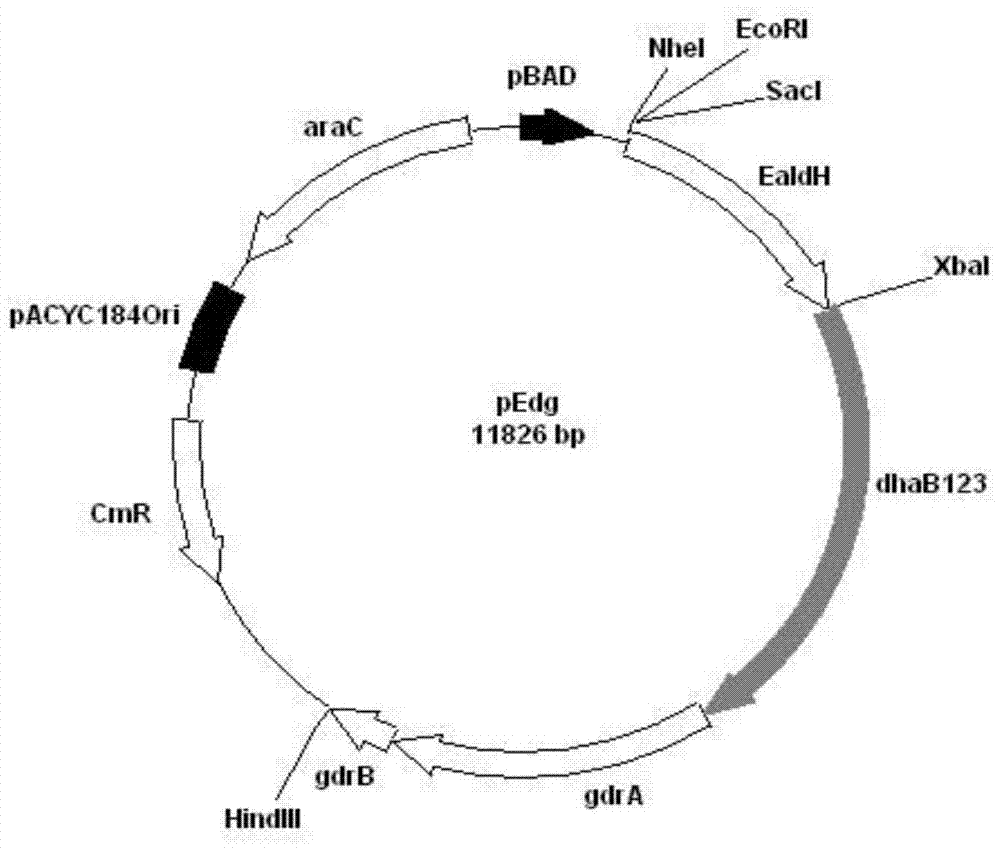
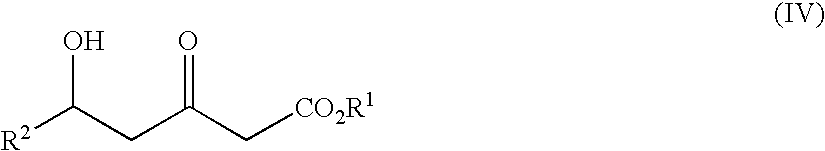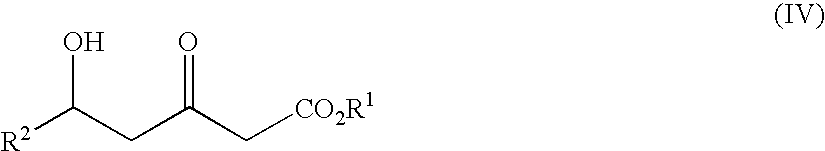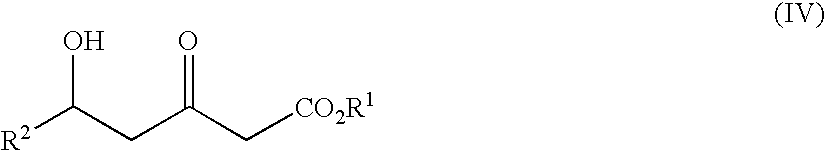Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
184 results about "3-Hydroxypropionic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
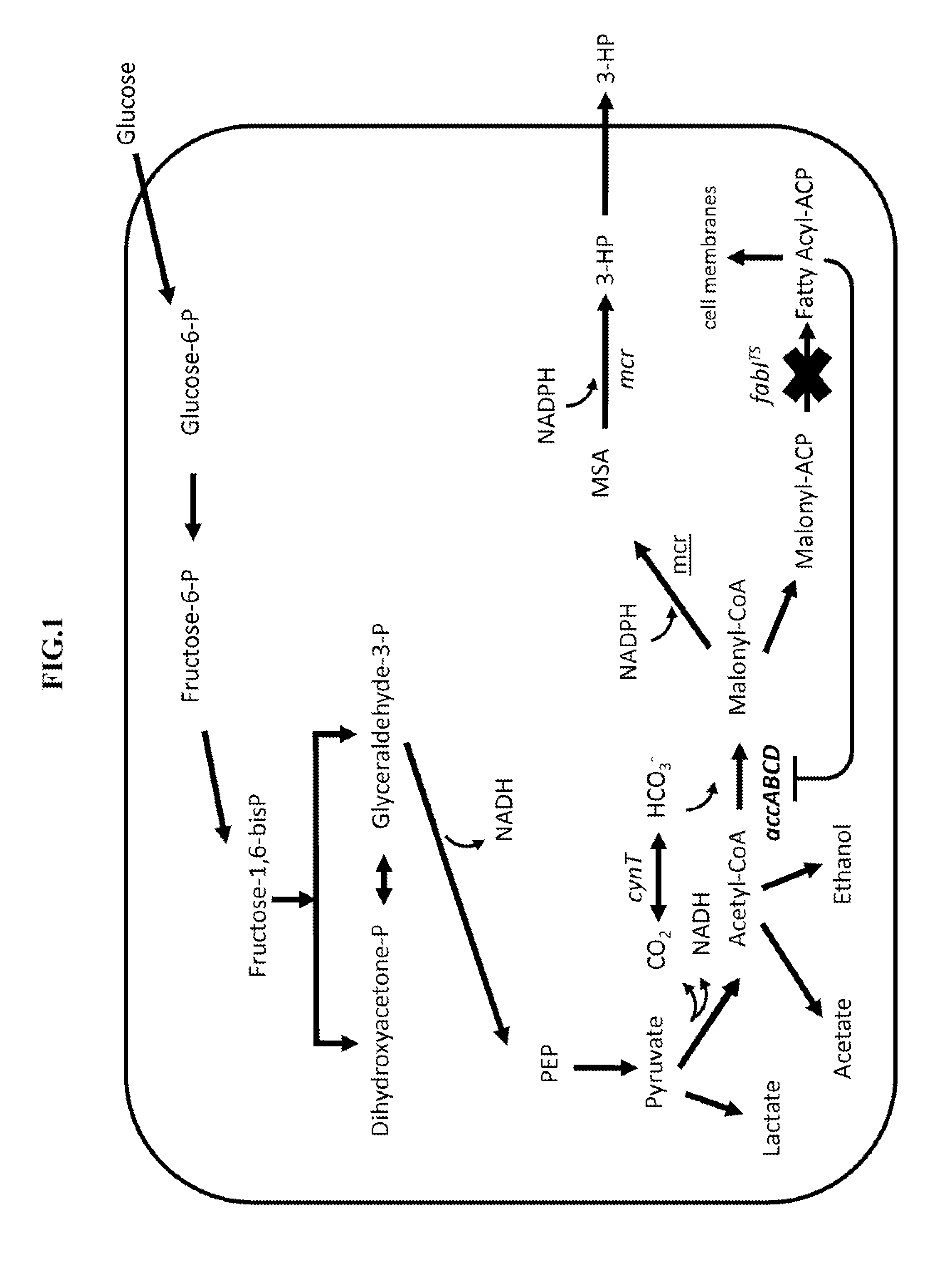
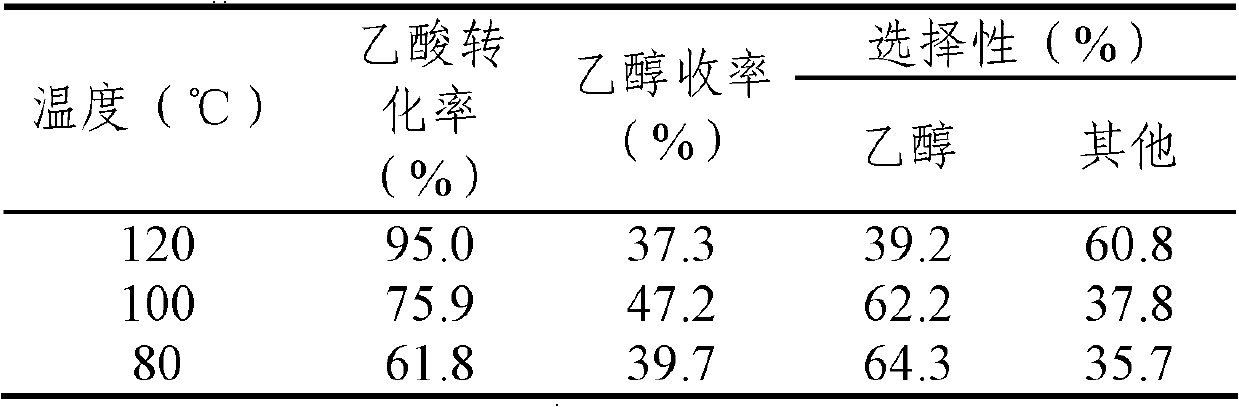
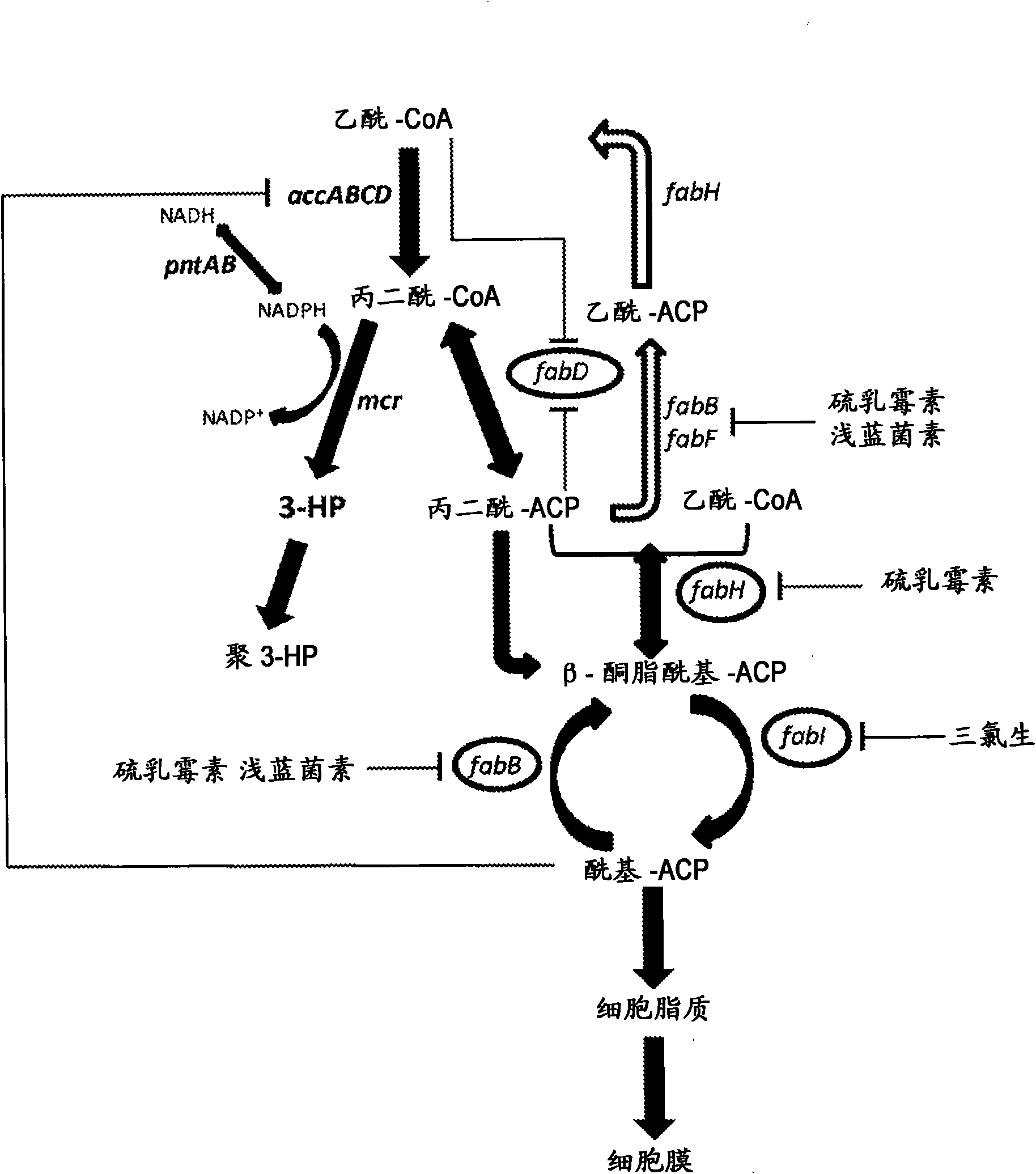
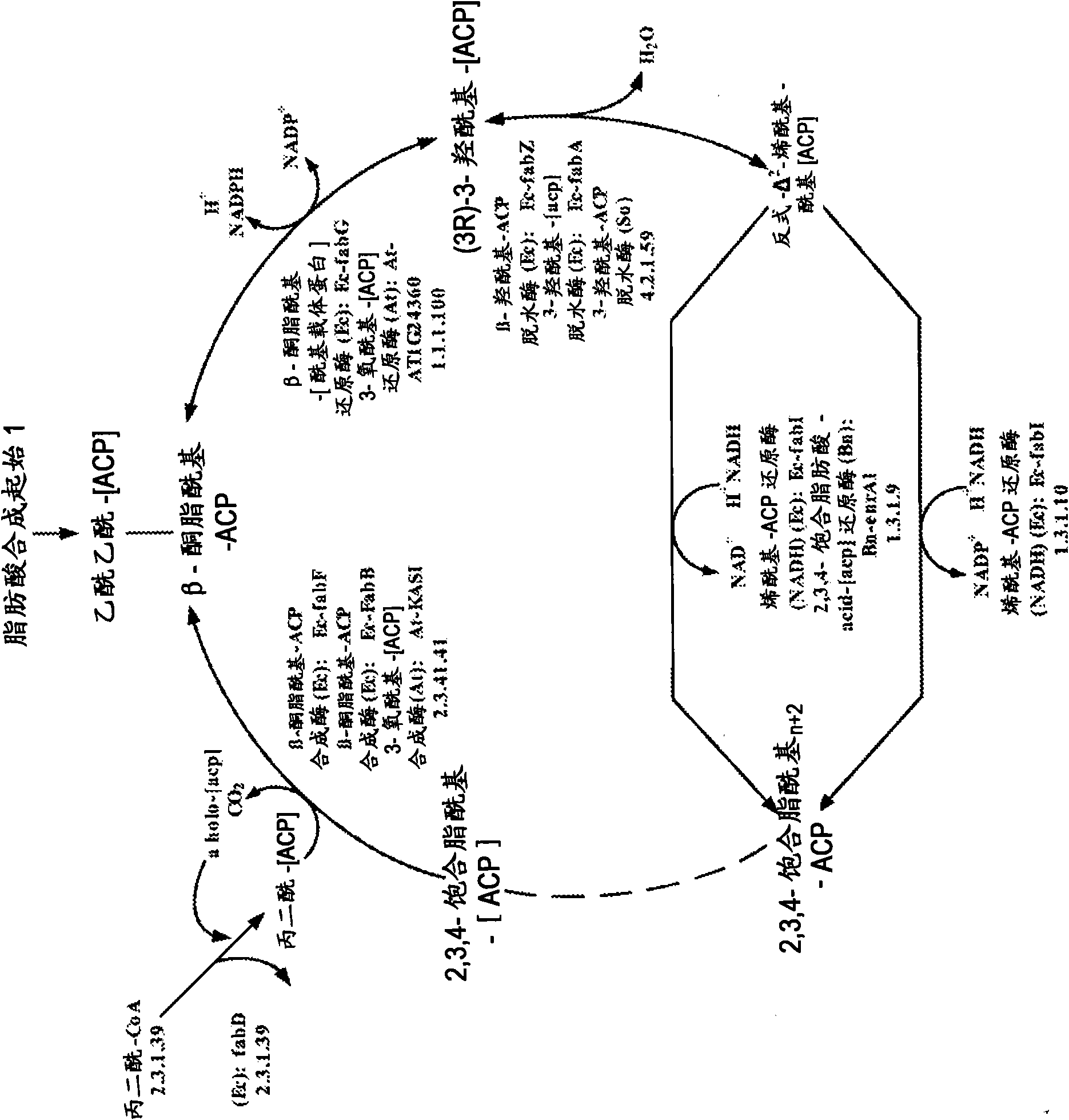
3-Hydroxypropionic acid is a carboxylic acid, specifically a beta hydroxy acid. It is an acidic viscous liquid with a pKa of 4.5. It is very soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. Upon distillation, it dehydrates to form acrylic acid.
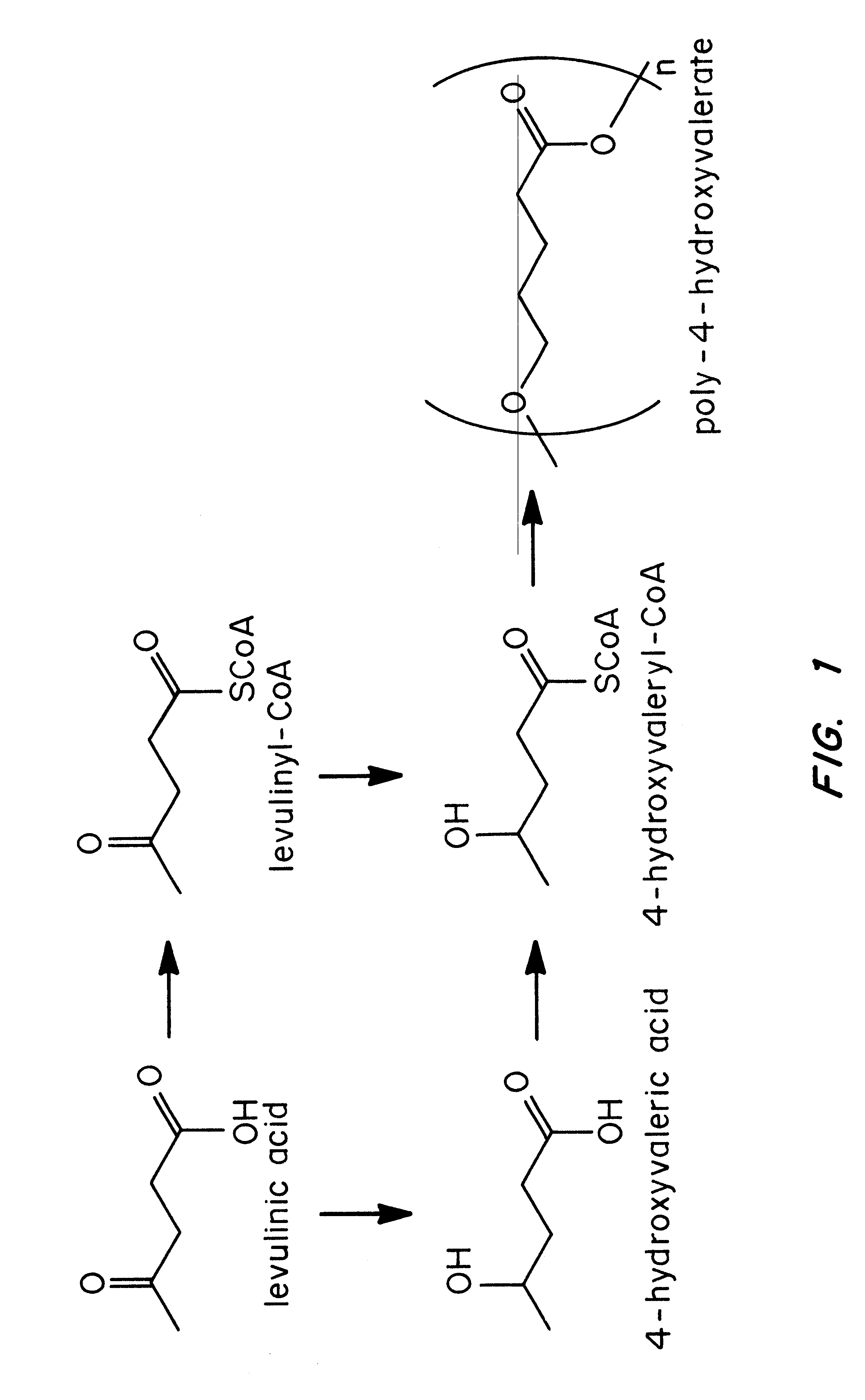
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
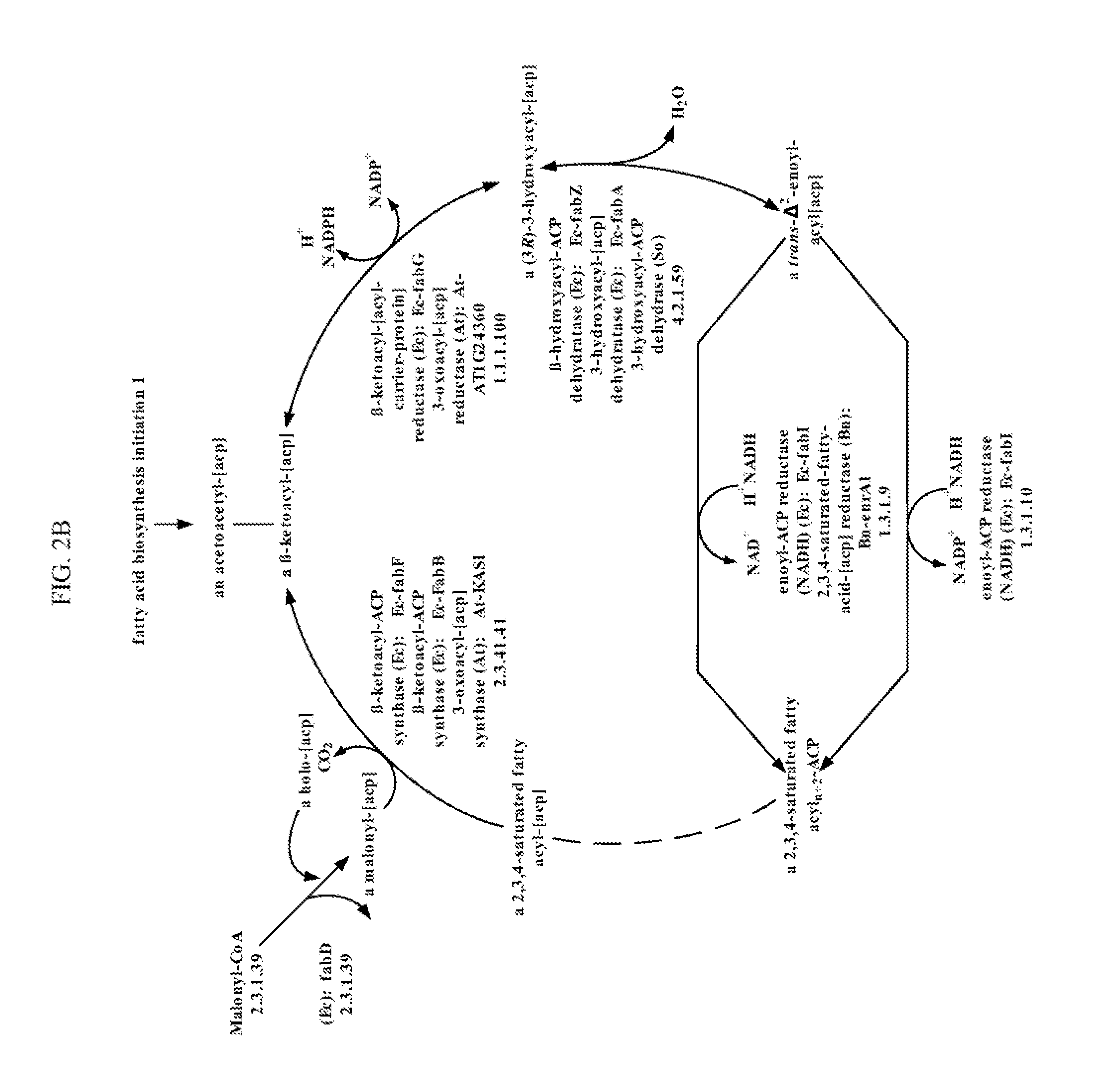
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:METABOLIX
Methods and organisms for production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
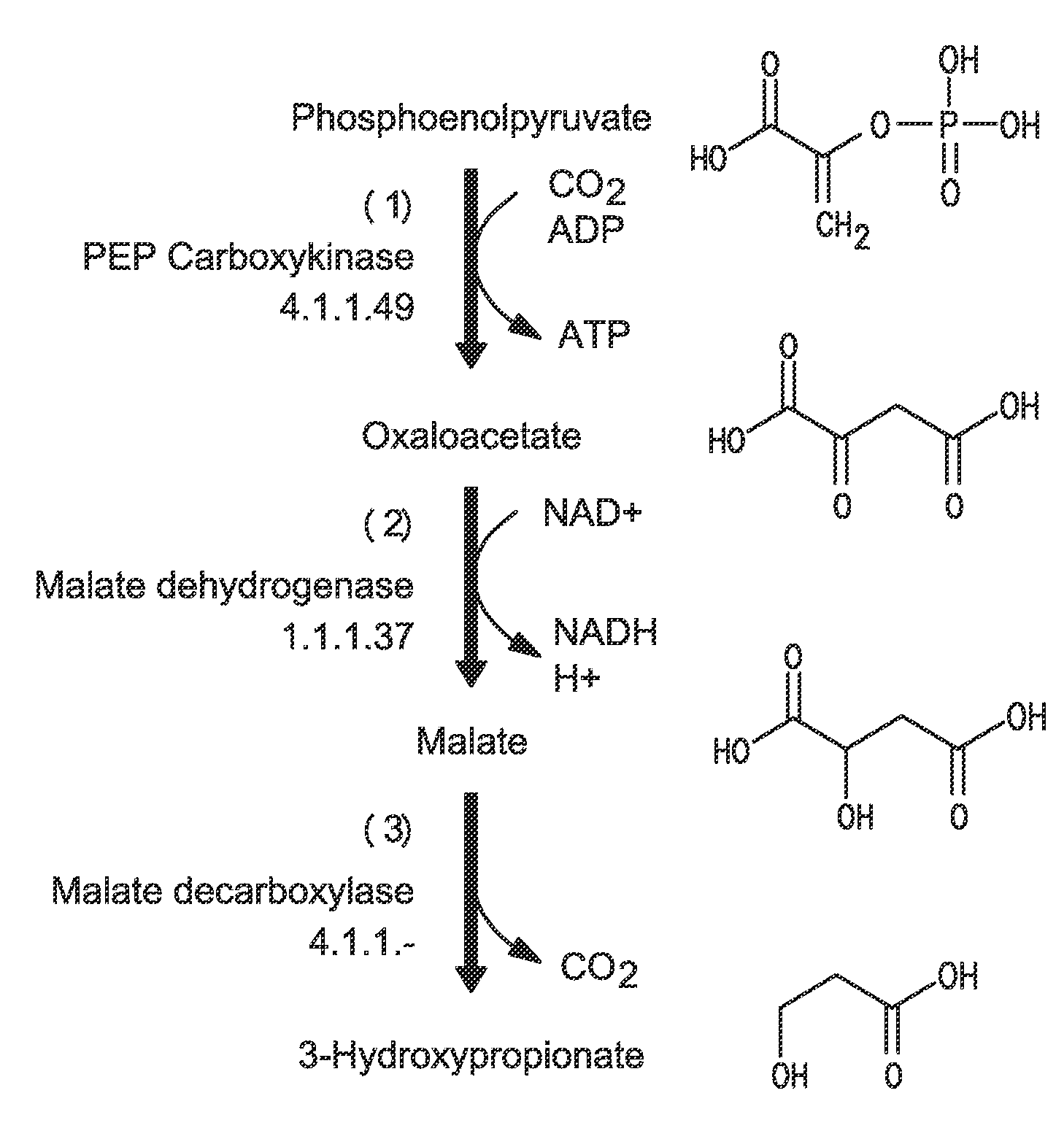
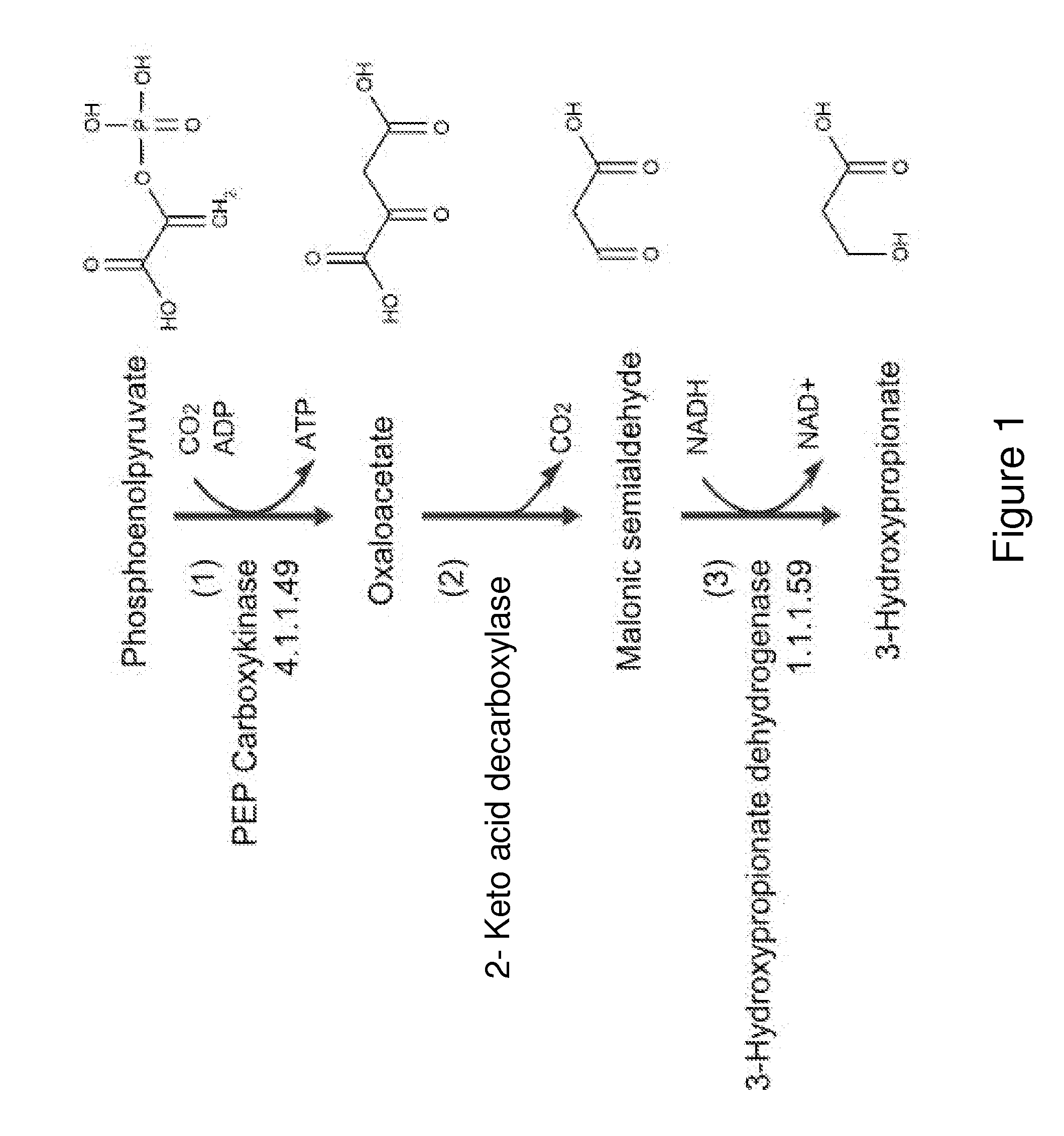
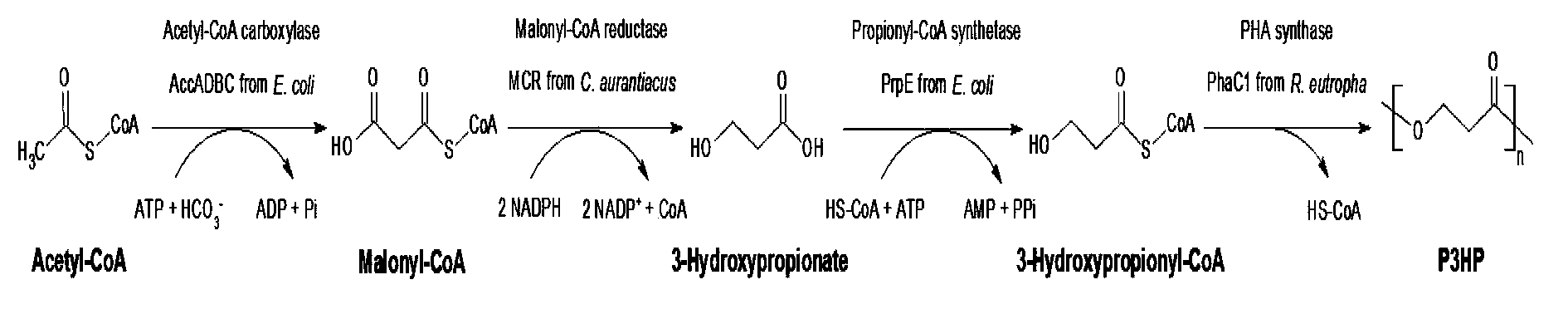
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a 3-hydroxypropanoic acid (3-HP) pathway includes at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding 3-HP pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce 3-HP. The 3-HP pathway includes a 2-keto acid decarboxylase, a CoA-dependent oxaloacetate dehydrogenase, or a malate decarboxylase. A method for producing 3-HP includes culturing a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a 3-HP pathway that includes at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a 3-HP pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce 3-HP under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce 3-HP. The 3-HP pathway includes a 2-keto acid decarboxylase, a CoA-dependent oxaloacetate dehydrogenase, or a malate decarboxylase.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Methods and Organisms for Growth-Coupled Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism having one or more gene disruptions, the one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding an enzyme obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid onto the non-naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications having disruption of one or more genes including: (a) the set of genes selected from: (1) adhE, ldhA, pta-ackA; (2) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD; (3) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, ptsG; (4) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, pntAB; (5) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC; (6) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC, pntAB; (7) pflAB, ldhA, or (8) adhE, ldhA, pgi in a microorganism utilizing an anaerobic β-alanine 3-HP precursor pathway; (b) the set of genes selected from: (1) tpi, zwf; (2) tpi, ybhE; (3) tpi, gnd; (4) fpb, gapA; (5) pgi, edd, or (6) pgi, eda in a microorganism utilizing an aerobic glycerol 3-HP precursor pathway; (c) the set of genes selected from: (1) eno; (2) yibO; (3) eno, atpH, or other atp subunit, or (4) yibO, atpH, or other atp subunit, in a microorganism utilizing a glycerate 3-HP precursor pathway, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid is further provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
InactiveUS20050239179A1Promote recoveryProduct can be usedBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
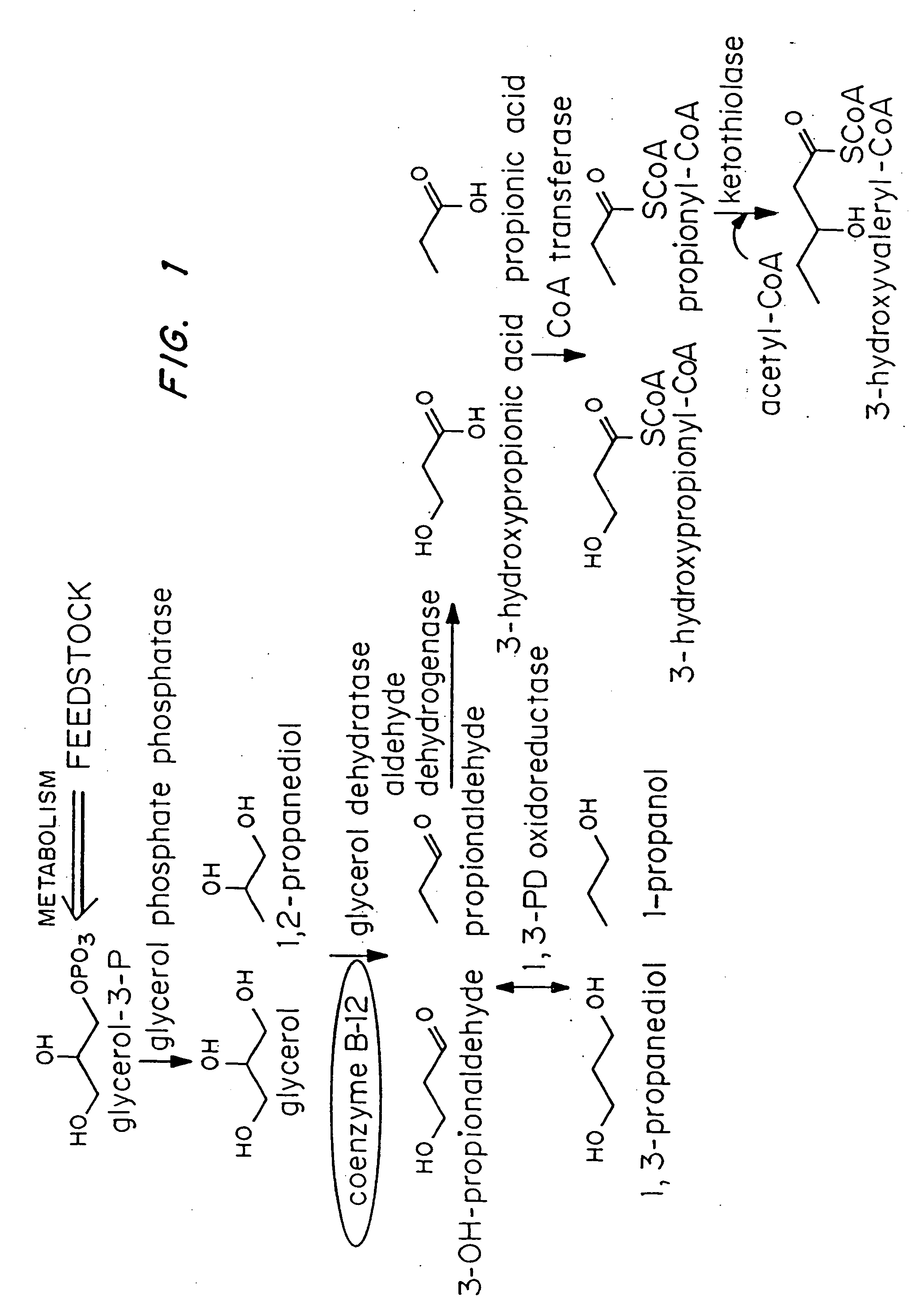
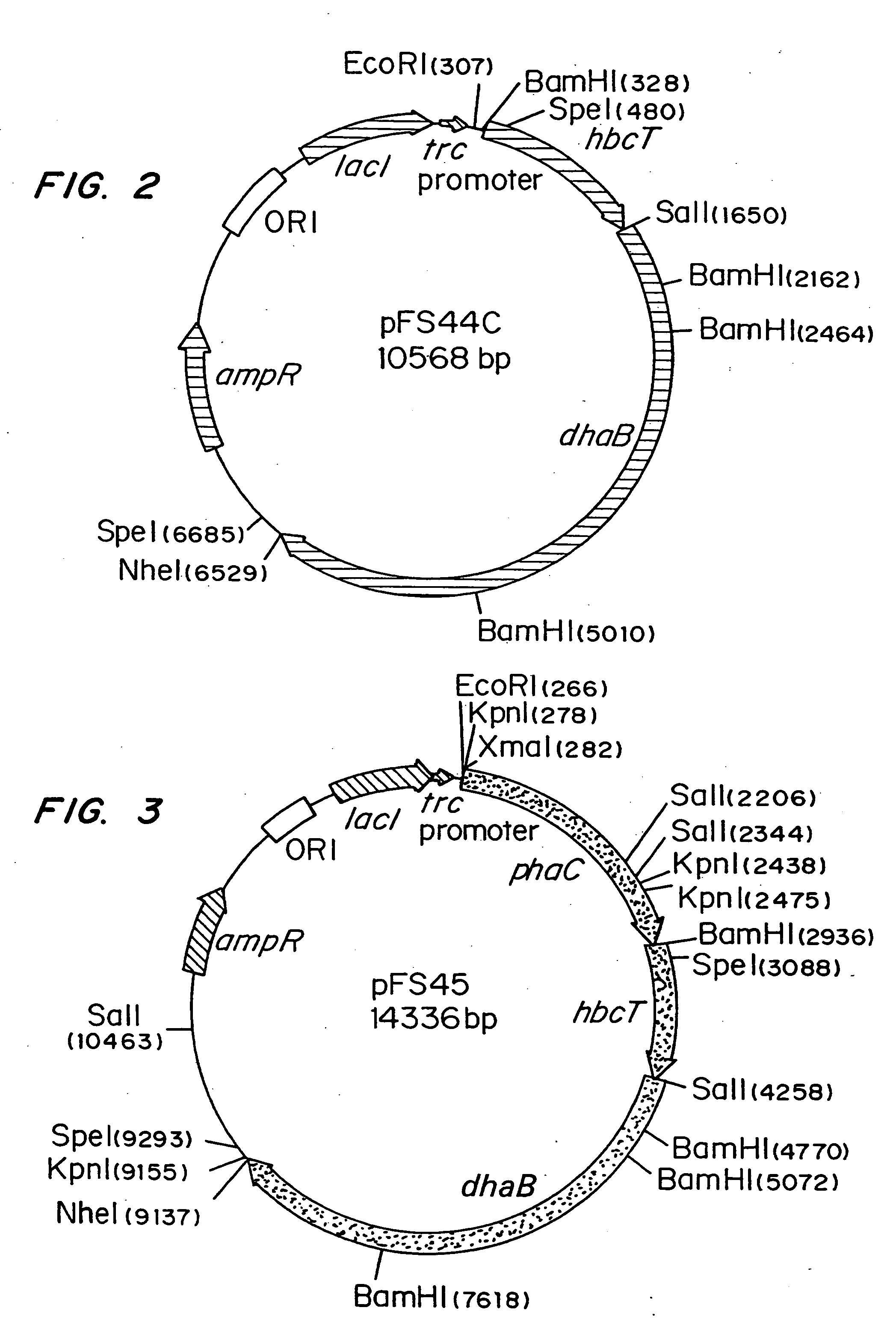
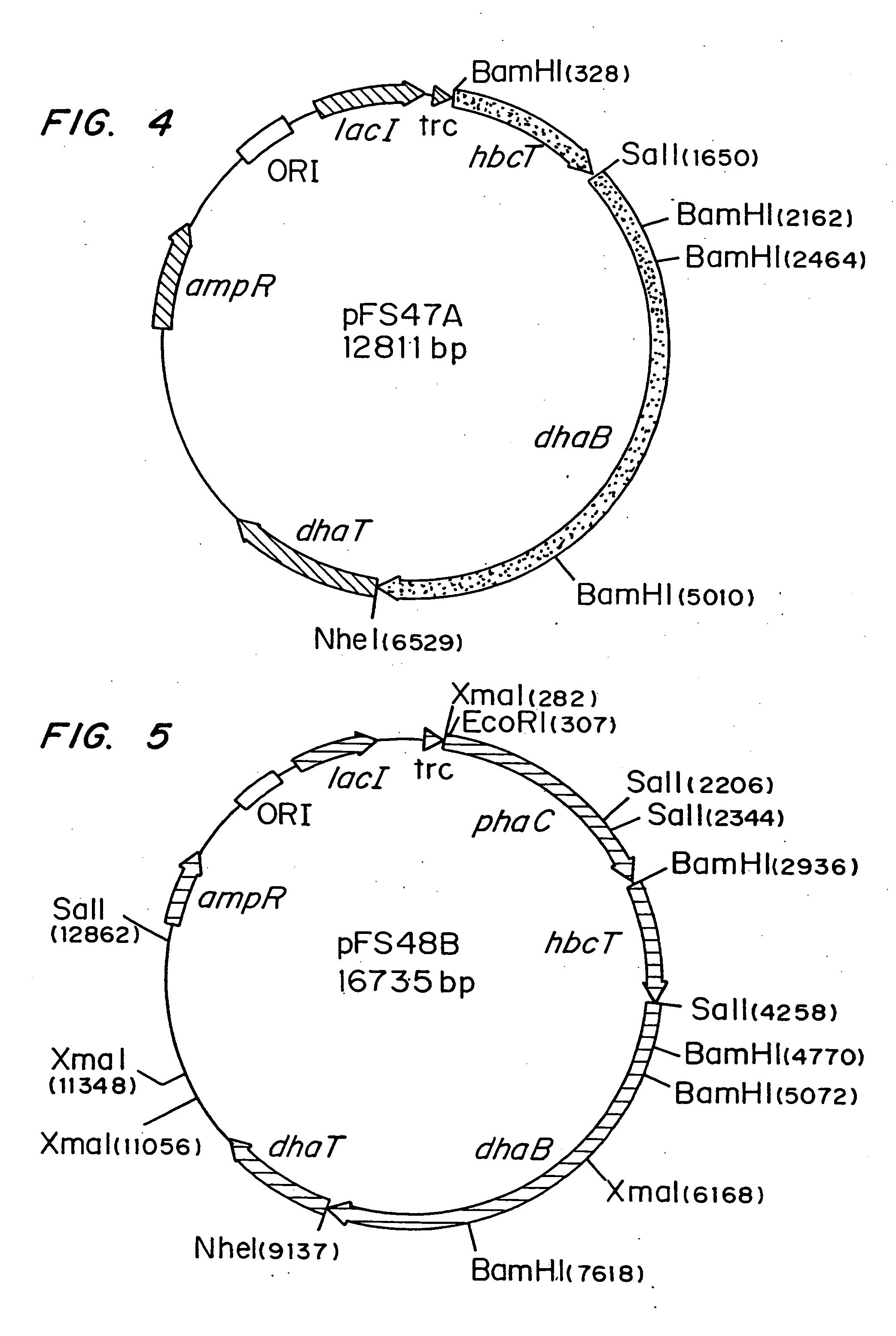
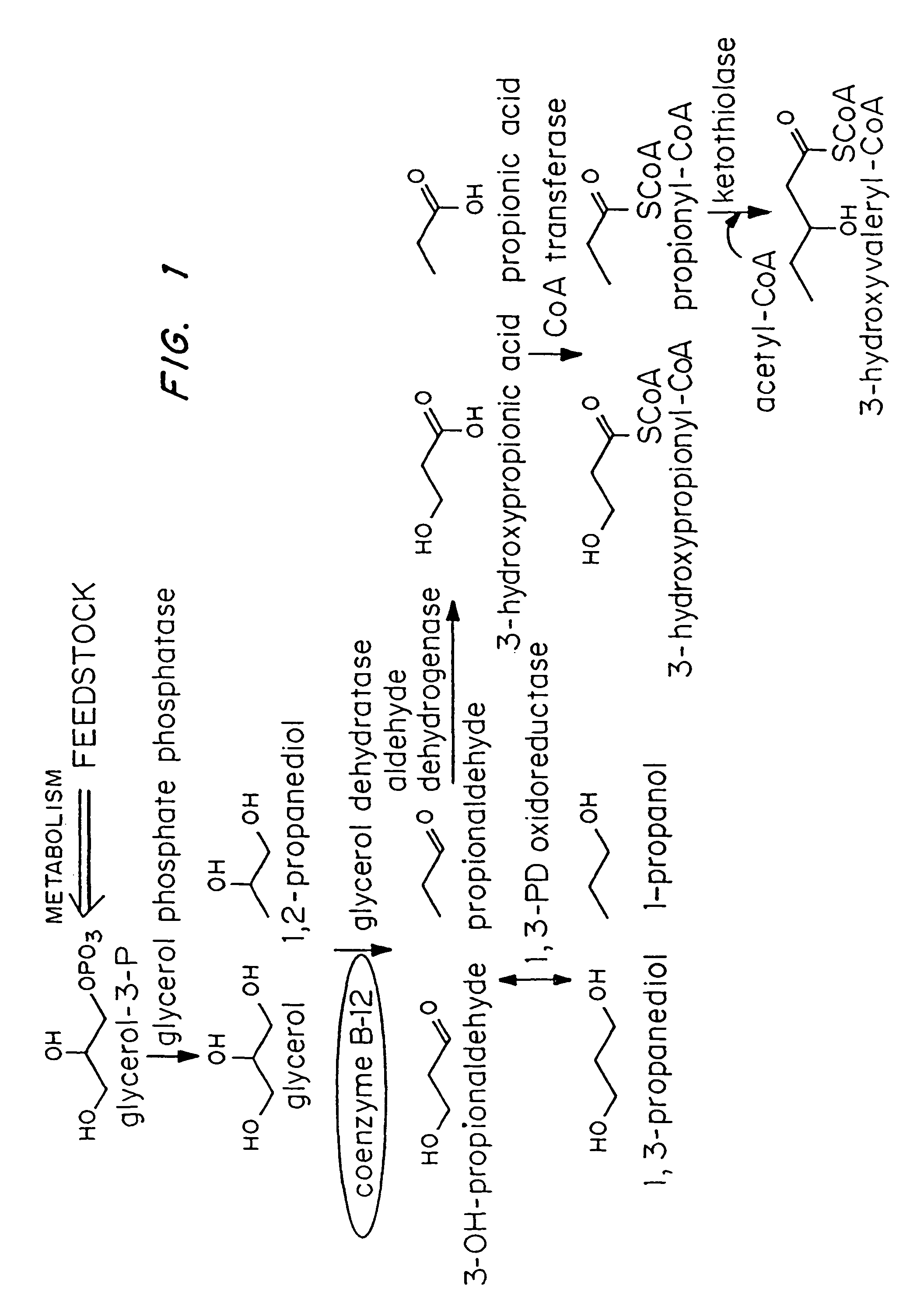
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalreate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
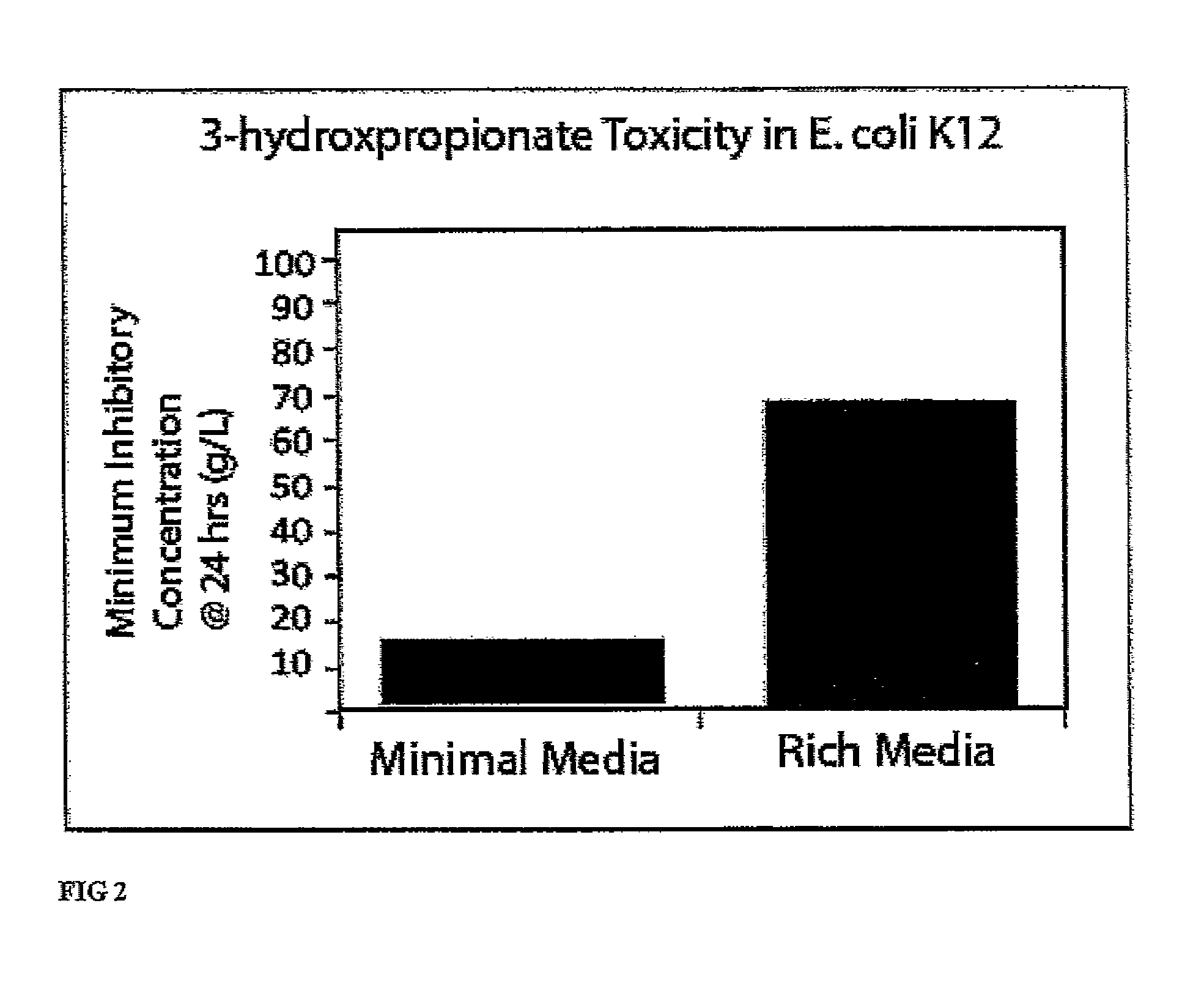
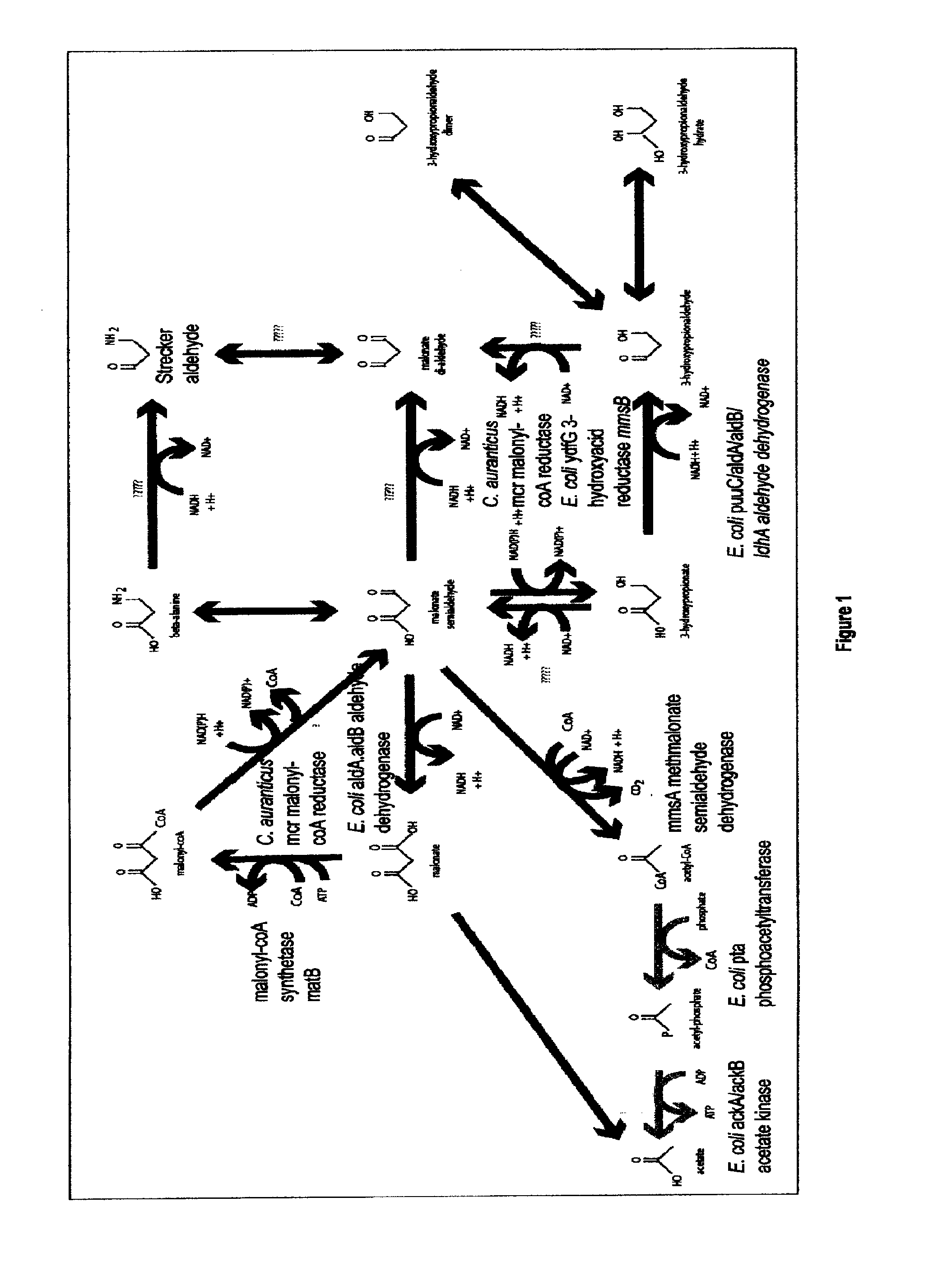
Methods, systems and compositions for increased microorganism tolerance to and production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-hp)
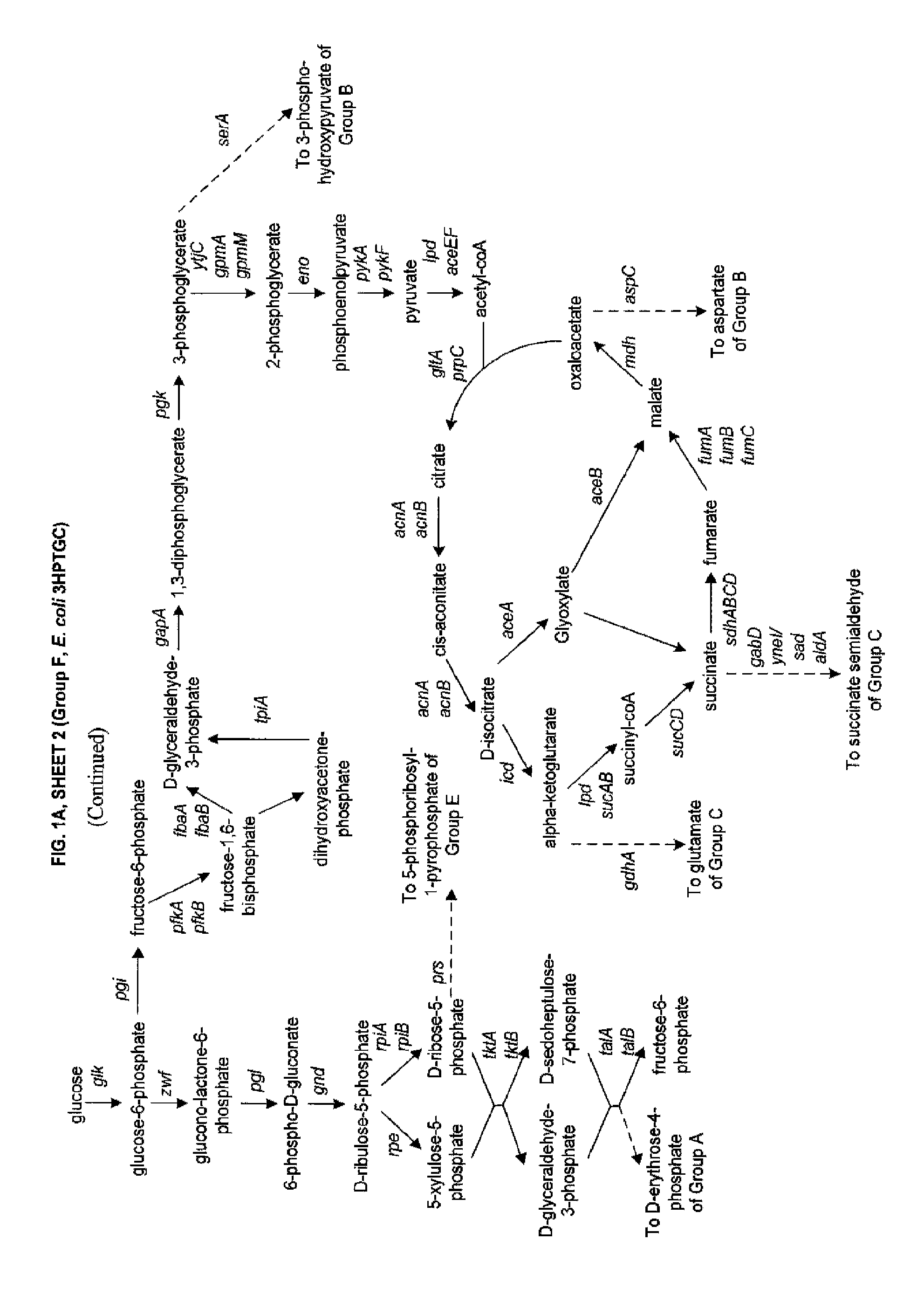
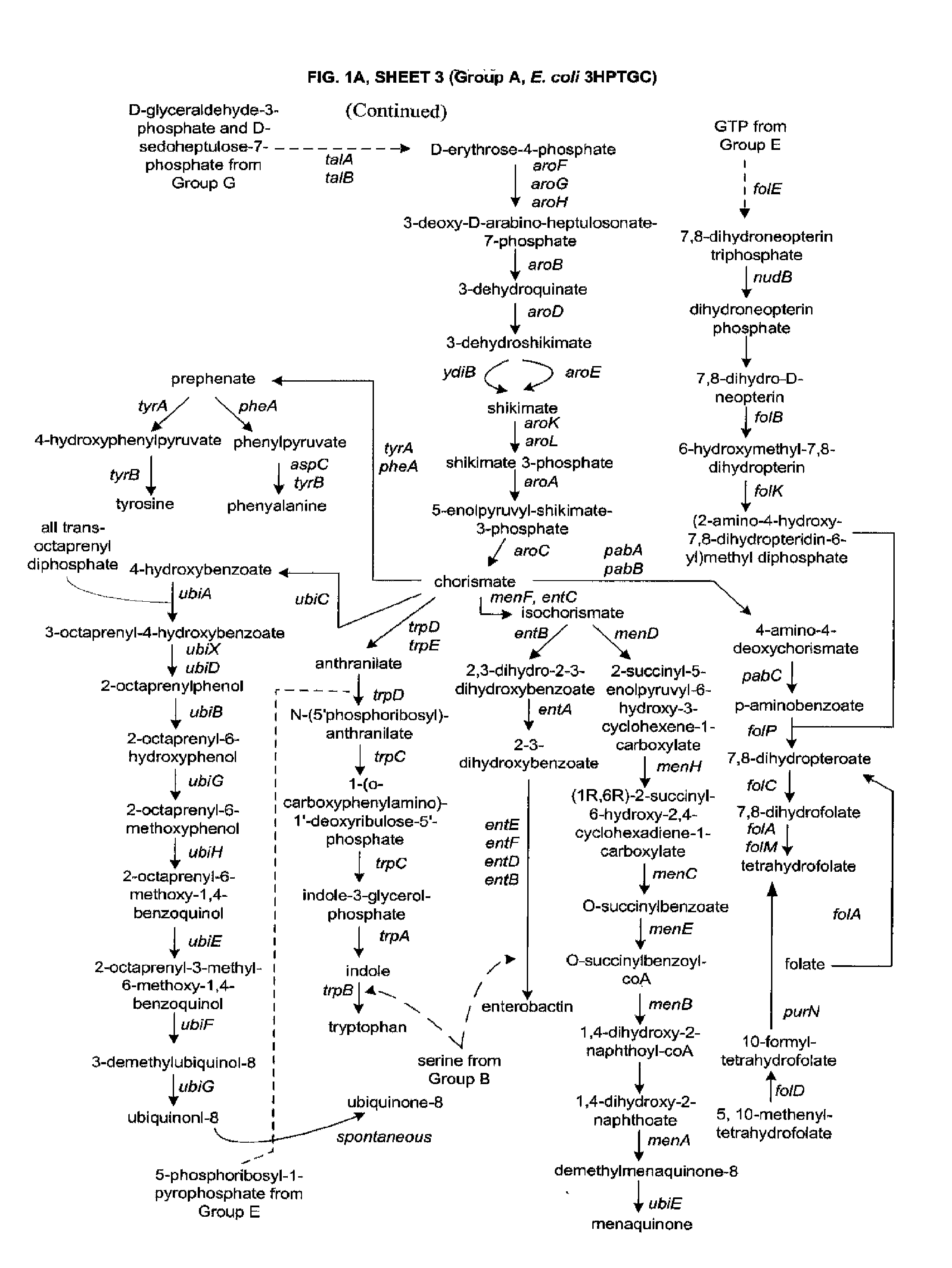
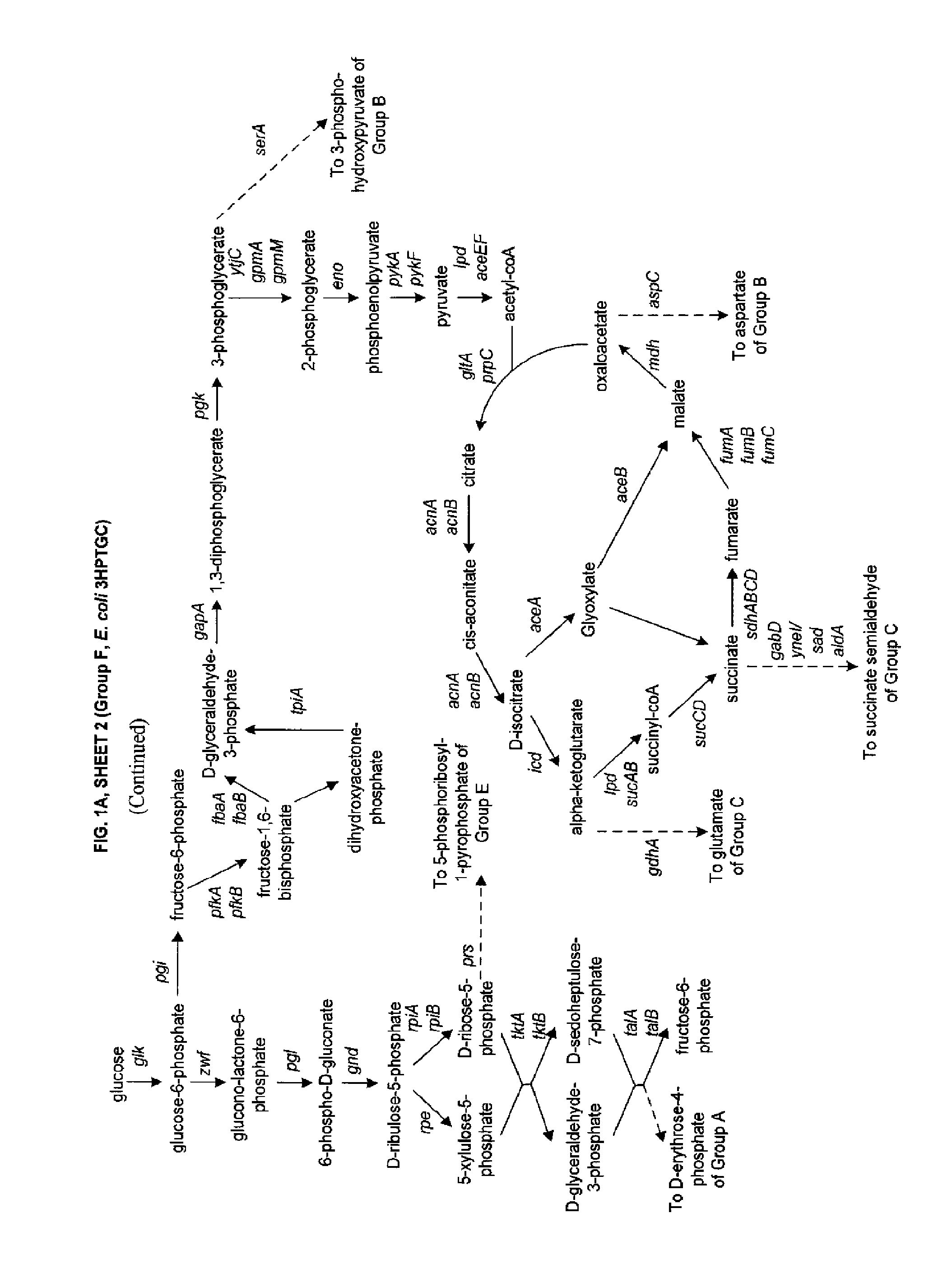
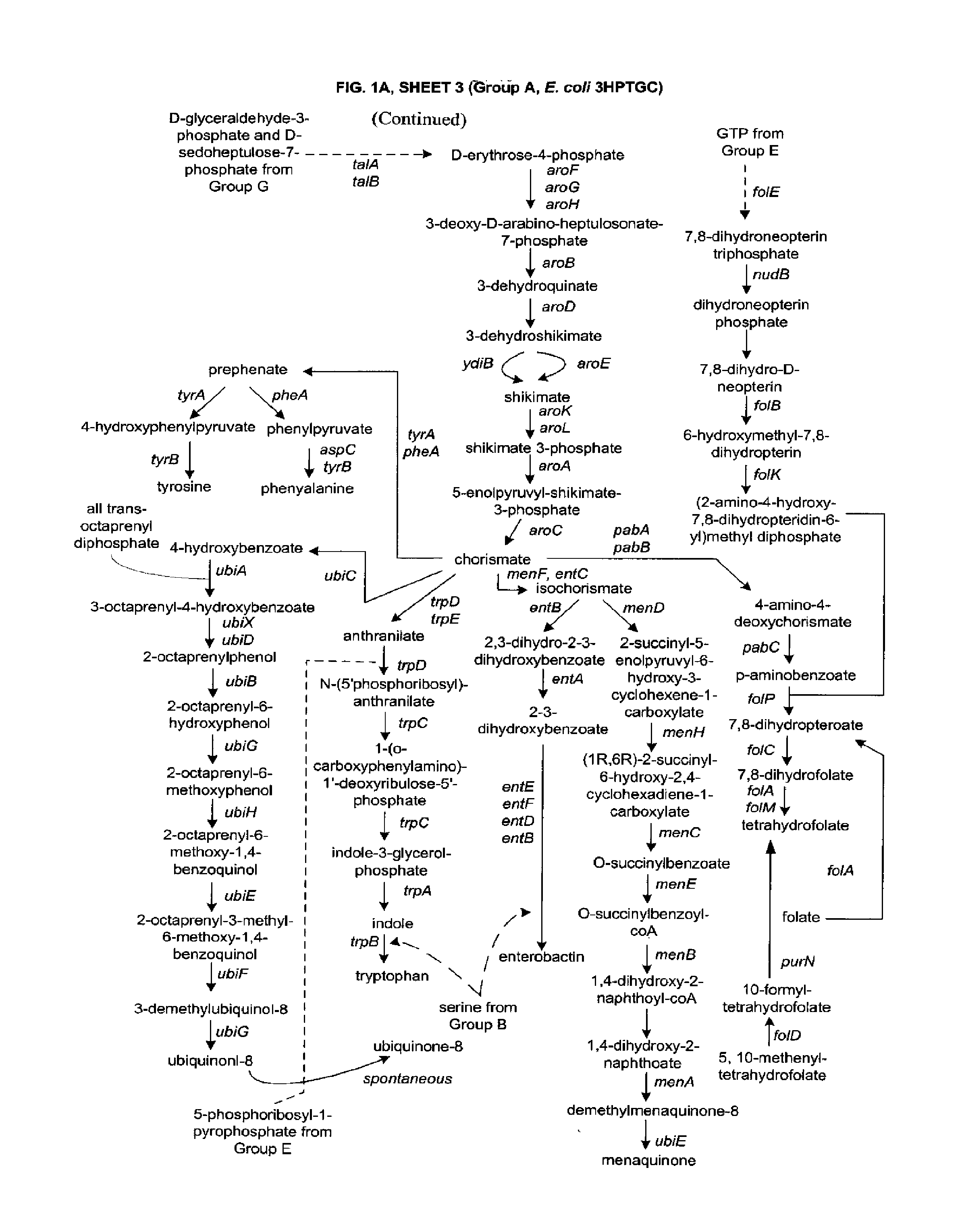
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, adapted to exhibit increased tolerance to 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP), particularly through alterations to interrelated metabolic pathways identified herein as the 3-HP toleragenic pathway complex (“3HPTGC”). In various embodiments these organisms are genetically modified so that an increased 3-HP tolerance is achieved. Also, genetic modifications may be made to provide at least one genetic modification to any of one or more 3-HP biosynthesis pathways in microorganisms comprising one or more genetic modifications of the 3HPTGC.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Methods for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid and other products
ActiveUS20130071893A1Improve enzymatic activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
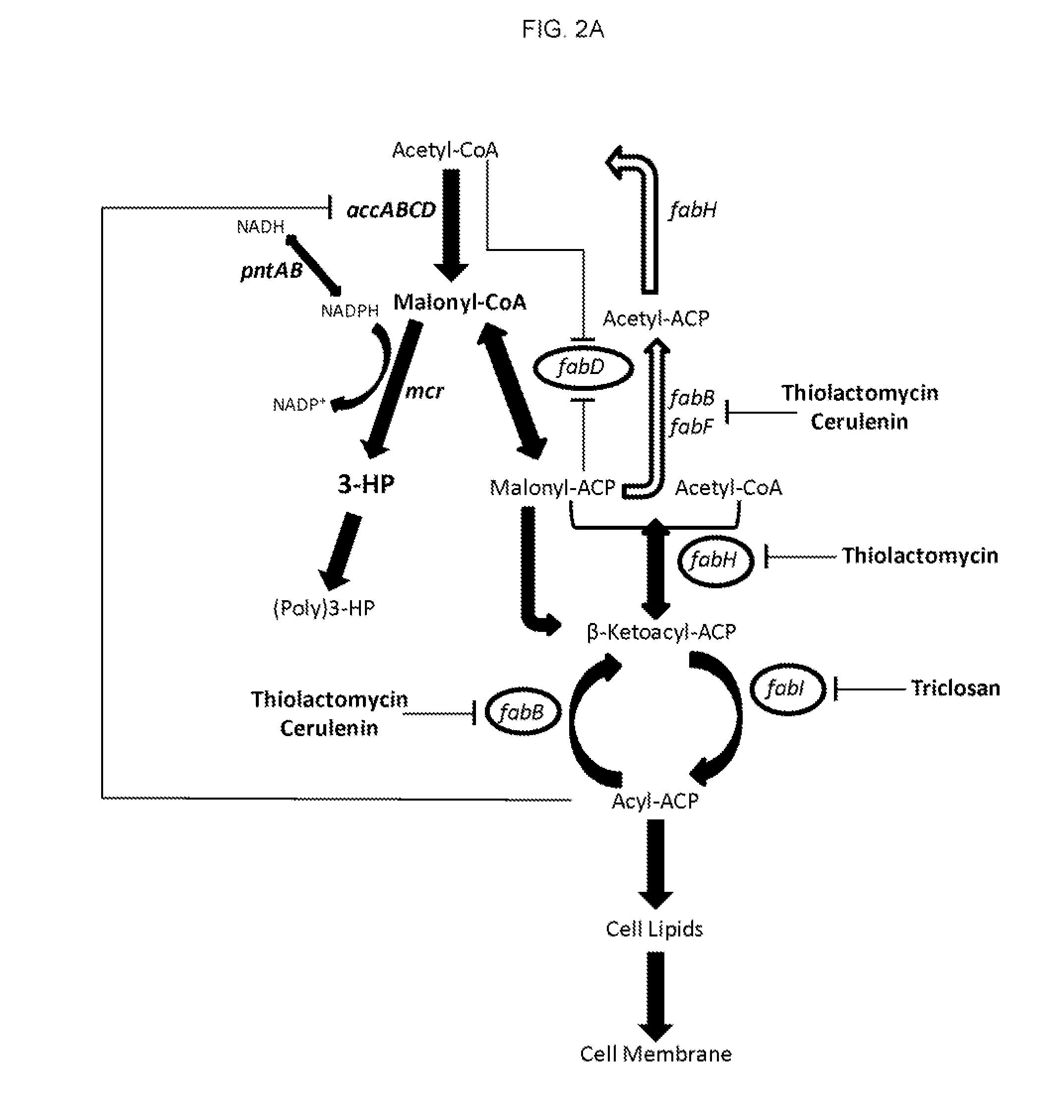
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:CARGILL INC +1
Compositions and methods for 3-hydroxypropionate bio-production from biomass
ActiveUS8048624B1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurement3-Hydroxypropionic acidDecarboxylase activity
Methods of obtaining mutant nucleic acid sequences that demonstrate elevated oxaloacetate α-decarboxylase activity are provided. Compositions, such as genetically modified microorganisms that comprise such mutant nucleic acid sequences, are described, as are methods to obtain the same.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
Compositions and methods for enhancing tolerance for the production of organic chemicals produced by microorganisms
InactiveUS20100210017A1Quick buildEfficient methodOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Embodiments herein generally relate to methods, compositions and uses for enhancing tolerance of production of organic acids and alcohols by microorganisms. This application also relates generally to methods, compositions and uses of vectors having one or more genetic element to increase the tolerance of organic acids or alcohols by a microorganism. Certain embodiments relate to compositions and methods of enhancing the tolerance for production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) by bacteria. In some embodiments, compositions and methods relate to regulating the expression of an inhibitory molecule of an enhancing gene to increase production of organic acid by bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Corrosion inhibitor or intensifier for use in acidizing treatment fluids
The invention also provides a composition for treating a subterranean formation penetrated by a wellbore. The composition is especially useful in acidizing treatments, which when combined with a corrosive aqueous fluid, inhibits the corrosion of metal surfaces, most especially, “duplex” chrome steel surfaces. An advantageous embodiment of the invention comprises at least 0.01% by weight of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and at least 1% by weight of an acid or acid precursor that different from 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The invention also provides a method for treating a subterranean formation penetrated by a wellbore. The method comprises the steps of forming the composition and introducing the composition into the subterranean formation through the wellbore.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods of making nylon intermediates from glycerol
ActiveUS20130210090A1Reduce usageRate minimisedBacteriaHydrolases3-Hydroxypropionic acid2,3-Butanediol
Embodiments of the invention relate to the enzymatic conversion of bioderived feedstocks to commercially valuable chemicals. The enzymatic conversions of the embodiments of the invention offer the potential for lower cost routes to these value-added chemicals. Some of the chemicals that are useful include nylon intermediates such as caprolactam, adipic acid, 1,6-hexamethylene diamine; butanediols such as 1,4-butanediol, 1,3-butanediol, and 2,3-butanediol; butanols such as 1-butanol, and 2-butanol; succinic acid, butadiene, isoprene, and 3-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
Electrostatic charge image developing toner, producing method therefor, image forming method and image forming apparatus utilizing the toner, construct and method for making the construct
InactiveUS7153622B2Uniform designExcellent in charge uniformityDiffusion transfer processesImpression caps3-Hydroxypropionic acidN-Butyric acid
A construct that comprises a base material and a polyhydroxyalkanoate, wherein at least a part of the base material is coated with the polyhydroxyalkanoate, and the polyhydroxyalkanoate comprises a 3-hydroxyalkanoic acid unit other than 3-hydroxypropionic acid unit, 3-hydroxy-n-butyric acid unit, and 3-hydroxy-n-valeric acid unit.In addition, an electrostatic charge image developing toner allows to design the toner characteristics such as chargeability, flowability, stability in time and environmental stability uniform among the toners of different colors. The toner has a small particle size enough for enabling uniform dispersion and being excellent in color saturation and transparency. The toner also shows higher contribution to the environmental security. The toner includes a coloring agent of which at least a part of the surface is covered with polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The toner is produced by dispersing the coloring agent in aqueous medium, then fixing PHA synthesizing enzyme to the coloring agent dispersed in the aqueous medium, then adding 3-hydroxyacyl CoA, and executing a PHA synthesizing reaction to cover at least a part of the surface of the coloring agent with PHA. The toner thus obtained is used for an image forming method.
Owner:CANON KK
Processes for the preparation of 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acid derivatives
InactiveUS6340767B1Increase productionGreat advantageCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acid3-Hydroxypropionic acid
This invention provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acid, a useful pharmaceutical intermediate, easily from a readily available, inexpensive starting material without using any extraordinary production equipment such as a very-low-temperature reactor.Thus, this invention provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acidwhich comprises permitting a lithium amide to act upon a mixture of an acetic acid ester and a 3-hydroxypropionic acid derivative at not below -20° C.Further, this invention also provides a process for producing a 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acidwhich comprises treating a mixture of an acetic acid ester and a 3-hydroxypropionic acid derivative with a Grignard reagent to prepare a mixture of a compound and an acetic acid ester of the above formula (I),and permitting a lithium amide to act upon the mixture at a temperature not below -20° C.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation
ActiveCN103288596AOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation. According to the method, any one of acetic acid, propionic acid, valeric acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, levulinic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid, 3-hydracrylic acid and other organic acids is taken as a reactant, and an A-B / X supported catalyst is adopted, wherein the component A is any one or more than two from Ir, Pt, Pd, Rh and Ru, the assistant B is any one or more than two from Mo, Re and W, the carrier X is any one in SiO2, activated carbon, titanium oxide, zirconium oxide, SiO2-Al2O3 (the mass content of Al2O3 accounts for 17 percent) and molecular sieves, the mass load amount of A in the catalyst is 0.5-10 percent, the molar ratio of the assistant B to A is 0.01-1.0, the reaction pressure is 2-20 MPa, and the reaction temperature is 40-180 DEG C. The catalyst has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, high reaction activity and good selectivity, and a novel effective way for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol from biomass is provided.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods, Systems and Compositions for Increased Microorganism Tolerance to and Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP)
InactiveUS20120264902A1Increase productionImprove the level ofOrganic chemistryFermentationMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, adapted to exhibit increased tolerance to 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP), particularly through alterations to interrelated metabolic pathways identified herein as the 3-HP toleragenic pathway complex (“3HPTGC”). In various embodiments these organisms are genetically modified so that an increased 3-HP tolerance is achieved. Also, genetic modifications may be made to provide at least one genetic modification to any of one or more 3-HP biosynthesis pathways in microorganisms comprising one or more genetic modifications of the 3HPTGC.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Methods, systems, and compositions for increased microorganism tolerance to and production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-hp)
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Compositions comprising 2-hydroxycarboxylic acids and related compounds, and methods for alleviating signs of dermatological aging
InactiveUS6384079B1Deepening of skin linesSkin lossBiocideCosmetic preparations3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
Uses of topical compositions comprising a 2-hydroxycarboxylic acid or related compound to alleviate or improve signs of skin, nail and hair changes associated with intrinsic or extrinsic aging are disclosed. 2-Hydroxycarboxylic acids and their related compounds include, for example, 2-hydroxyethanoic acid, hydroxypropanoic acid, 2-methyl 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, 2-phenyl 2-hydroxyethanoic acid, 2-phenyl 2-methyl 2-hydroxyethanoic acid, 2-phenyl 3-hydroxypropanoic acid, 2,2-diphenyl 2-hydroxyethanoic acid, 2-hydroxybutane-1,4-dioic acid, 2,3-hihydroxybutane-1,4-dioic acid, 2-carboxy 2-hydroxypentane-1,5-dioic acid, 2-ketopropanoic acid, methyl 2-ketopropanoate, ethyl 2-ketopropanoate, and gluconolactone. Topical application of compositions comprising 2-hydroxycarboxylic acid and / or related compounds has been found to alleviate or improve skin lines; blotches; blemishes; nodules; wrinkles; pigmented spots; atrophy; precancerous lesions; elastotic changes characterized by leathery, coarse, rough, dry and yellowish skin; and other skin changes associated with intrinsic aging or skin damages caused by extrinsic factors such as sunlight, radiations, air pollution, wind, cold, dampness, heat, chemicals, smoke and cigarette smoking. Topical applications of such compositions have also been found to improve the overall qualities of nail and hair affected by intrinsic aging or damaged by extrinsic factors.
Owner:TRISTRATA TECH
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
Owner:CARGILL INC
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxyproplonic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
InactiveUS20130189787A1Lower metabolismDecrease microbial enzymatic conversionBacteriaUnicellular algaeEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, directed to achieve decreased microbial conversion of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) to aldehydes of 3-HP. In various embodiments this is achieved by disruption of particular aldehyde dehydrogenase genes, including multiple gene deletions. Among the specific nucleic acids that are deleted whereby the desired decreased conversion is achieved are aldA, aldB, puuC), and usg of E. coli. Genetically modified microorganisms so modified are adapted to produce 3-HP, such as by approaches described herein.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
Method for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid and other products
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a chemical product, which includes 3- hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH +1
Method for preparing artificial hapten, artificial antigen and specific antibody of chlorpyrifos and its usage
InactiveCN1431213AThe pre-processing process is simpleHigh sensitivityBiocideAnimal repellants3-Hydroxypropionic acidChlorpyrifos
A process for preparing artificial antigen, artificial hapten and specific antibody of chlorpyrifos is disclosed. A hapten O,O-diethyl-O[3,5-dichloro-6(2-carboxyethyl) thio-2- pyridyl] thionophosphate (AR) is prepared through reaction between O,O-diethyl-O(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl) thionophosphate and 3-hydroxypropionic acid. A hapten O-ethyl-O-[3,5,6-trichloron-(2-pyridyl)]-O- (3-carboxypropyl)thionophosphate (PO) is prepared from trichlorothion through 4-step reaction. An artificial antigen is prepared from said hapenjs and protein by coupling. A specific antibody is generated by immunizing animal with said antigen. It can be used to detect the residue of chlorpyrifos.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalerate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Recombinant bacteria for producing glycerol and glycerol-derived products from sucrose
Recombinant bacteria capable of producing glycerol and glycerol-derived products from sucrose are described. The recombinant bacteria comprise in their genome or on at least one recombinant construct: a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having sucrose transporter activity; a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having fructokinase activity; and a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide having sucrose hydrolase activity. These nucleotide sequences are each operably linked to the same or a different promoter. These recombinant bacteria are capable of metabolizing sucrose to produce glycerol and / or glycerol-derived products such as 1,3-propanediol and 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
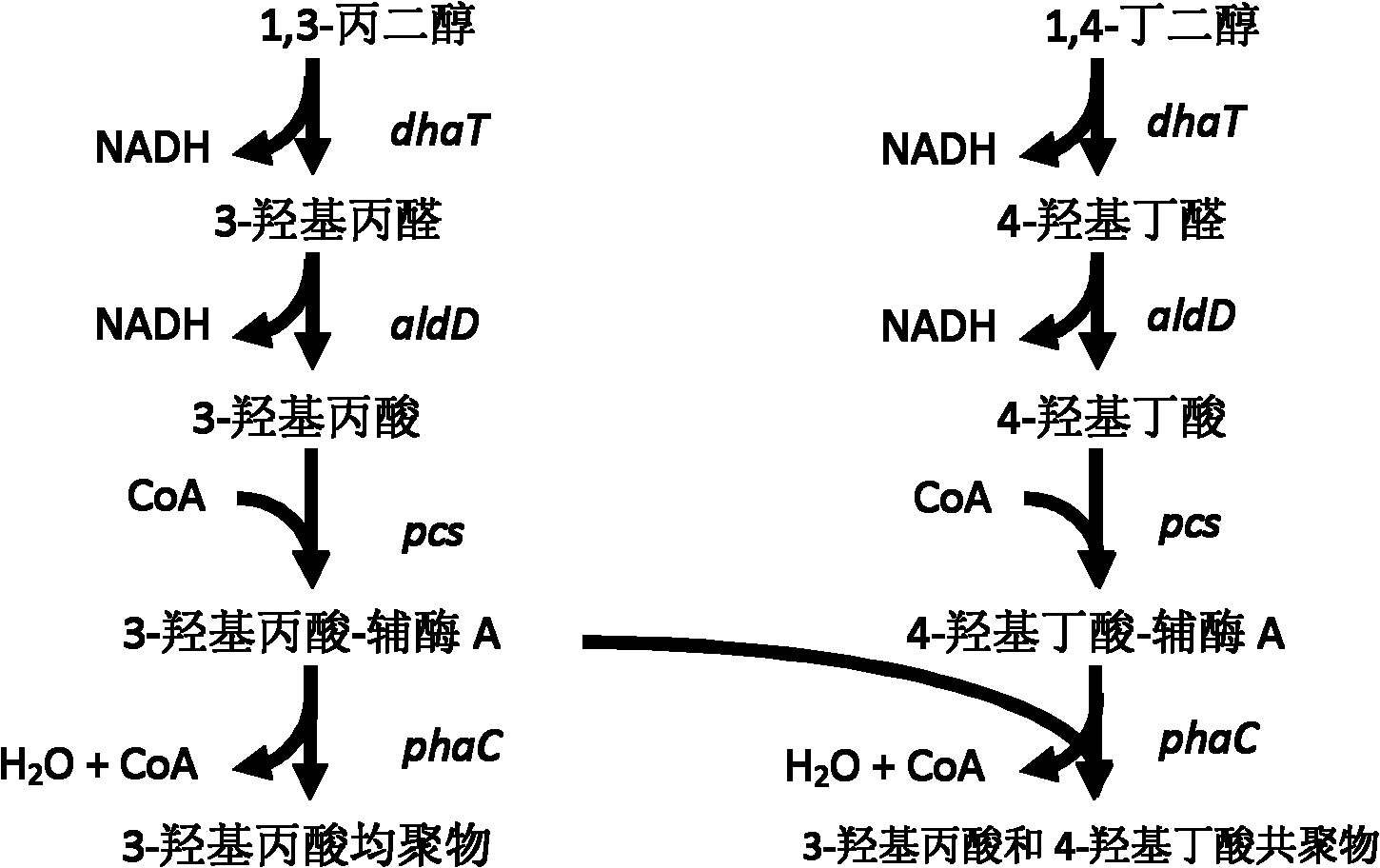
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922AReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidK pneumoniae
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for the preparation of 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanoic acid derivatives
InactiveUSRE39333E1Carboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acid3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for preparing ester by catalytic oxidization of 1,3-propanediol
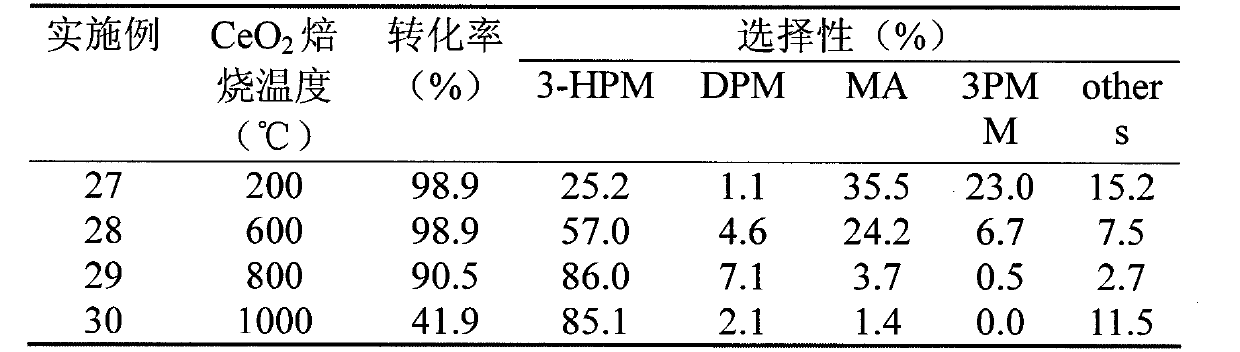
InactiveCN101906038AHigh selectivityEasy to separate and purifyMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidGas phase
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ester by catalytic oxidization of 1,3-propanediol. The catalyst adopted is a supported noble metal catalyst (gold or palladium); a carrier is made from metal oxides of different shapes and sizes or mixed oxides (such as CeO2, gamma-Al2O3, CuO, MgO, ZnO, ZSM-5, MoO3, V2O5 and the like), or a silicon dioxide-containing material or a carbon material; after the catalyst is treated by different preparation and treatment methods, the selective oxidization reaction of the 1,3-propanediol for preparing 3-methyl lactate, dimethyl malenate, 3-methoxypropionate and methyl acrylate is performed under a mild liquid-phase or liquid- and gas-phase reaction condition. The highest yield of the produced 3-methyl lactate is 81.5 percent (the conversion rate is 97.0 percent and the selectivity is 84.0 percent); the highest yield of the produced dimethyl malenate is 58.2 percent ( the conversion rate is 99.6 percent and the selectivity is 58.4 percent); and the highest yield of produced 3-methoxypropionate is 53.0 percent (the conversion rate is 97.0 percent and the selectivity is 58.4 percent) and the highest yield of produced methyl acrylate is 38.4 percent (the conversion rate is 92.2 percent and the selectivity is 41.6 percent).
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
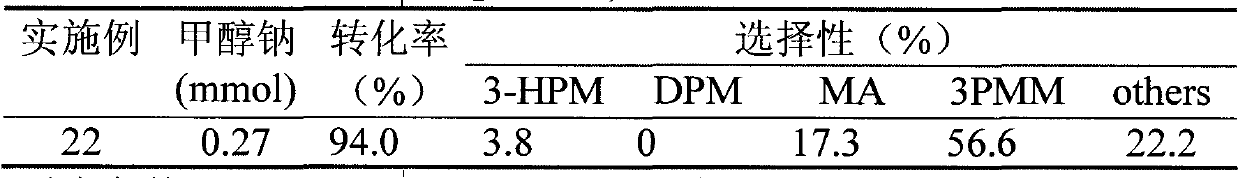
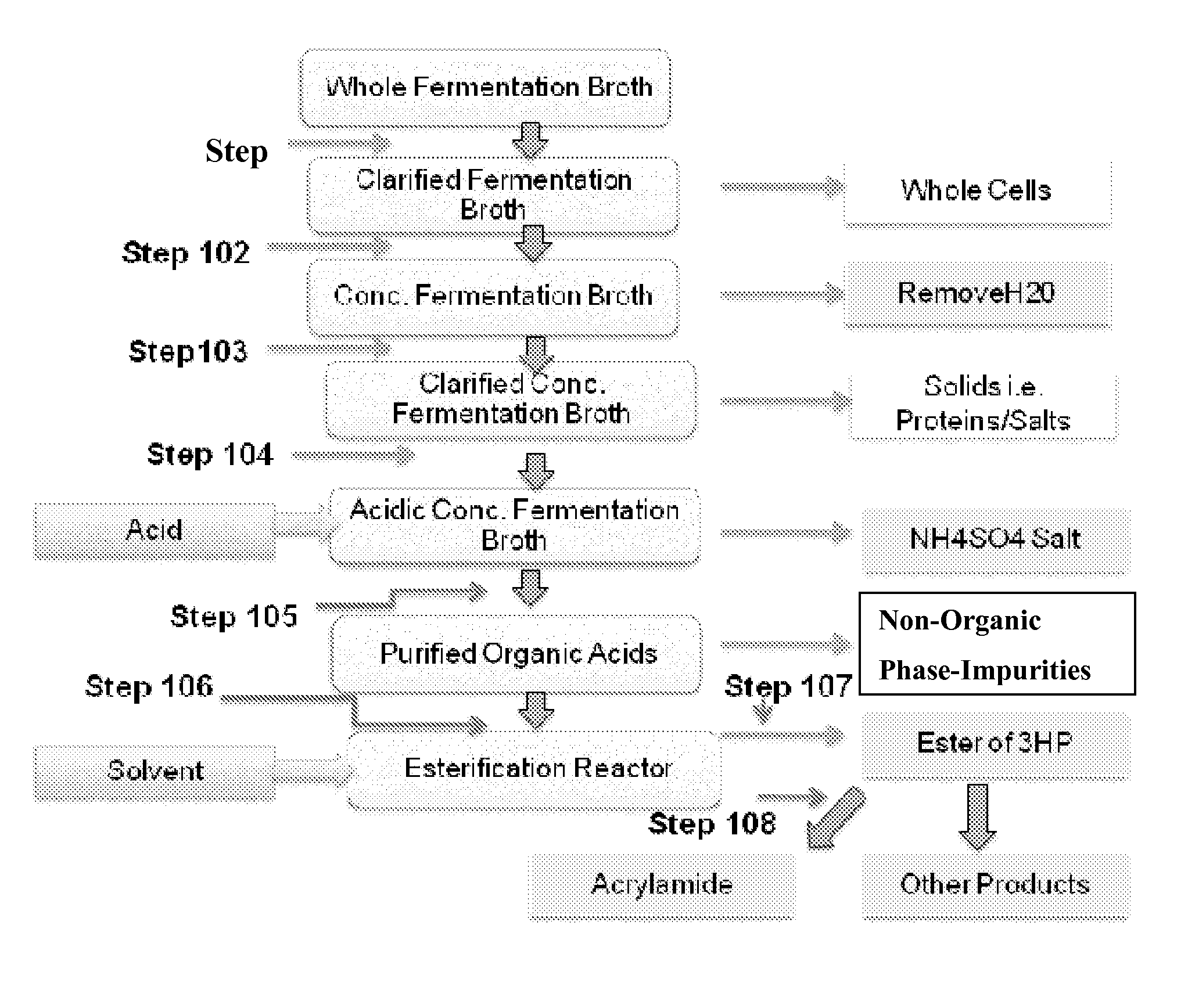
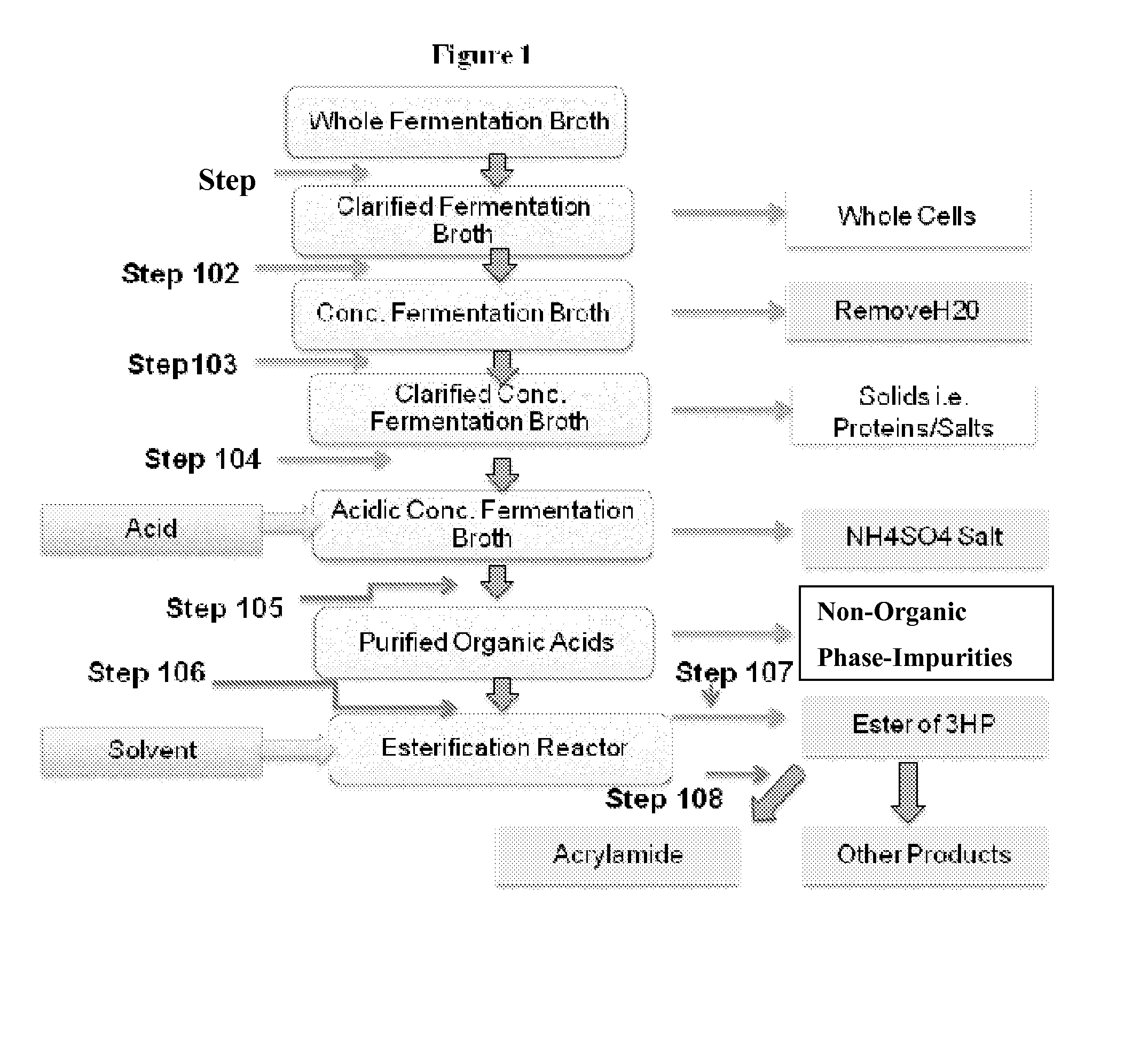
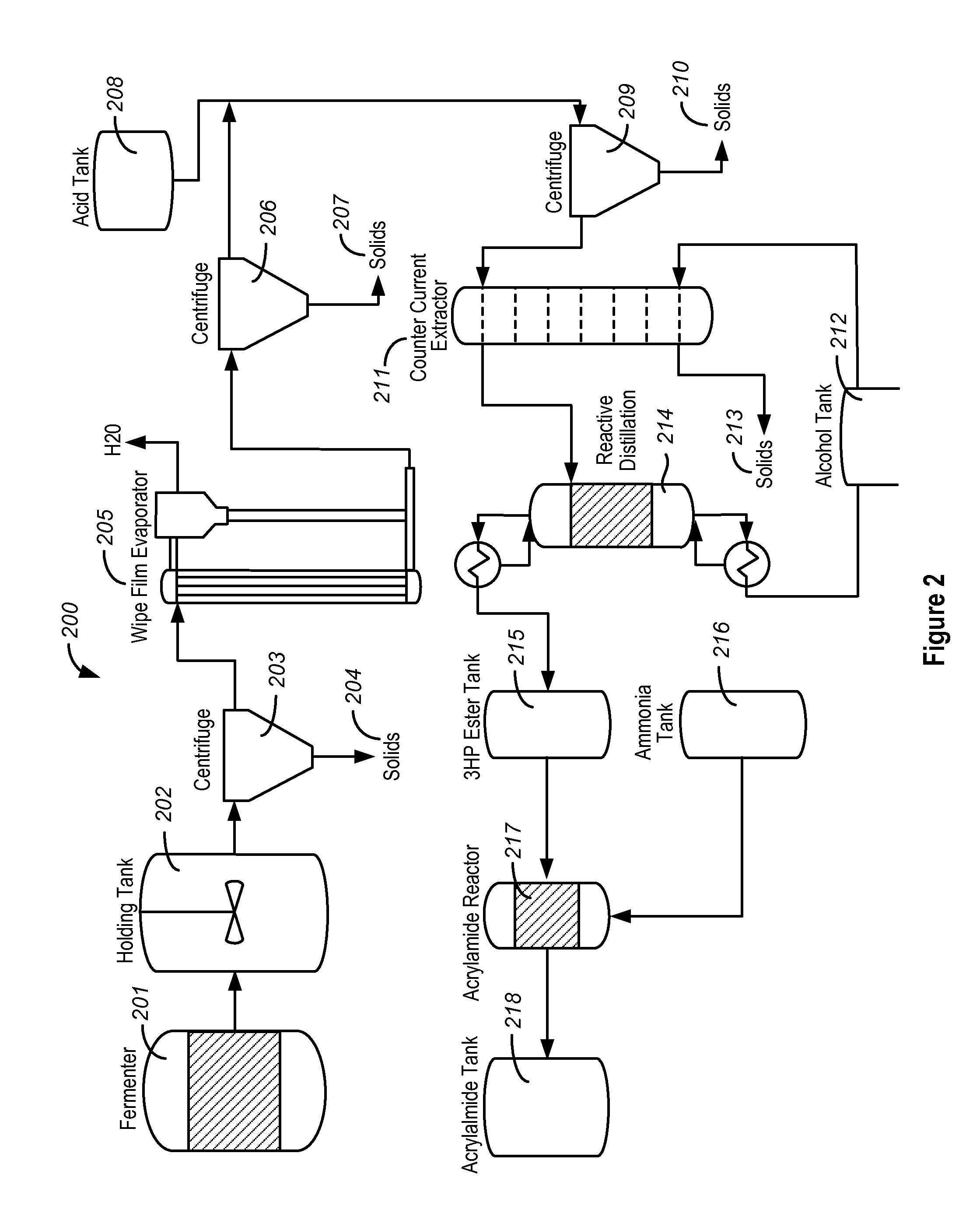
Purification of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from crude cell broth and production of acrylamide
InactiveUS20140309451A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidWaste stream
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
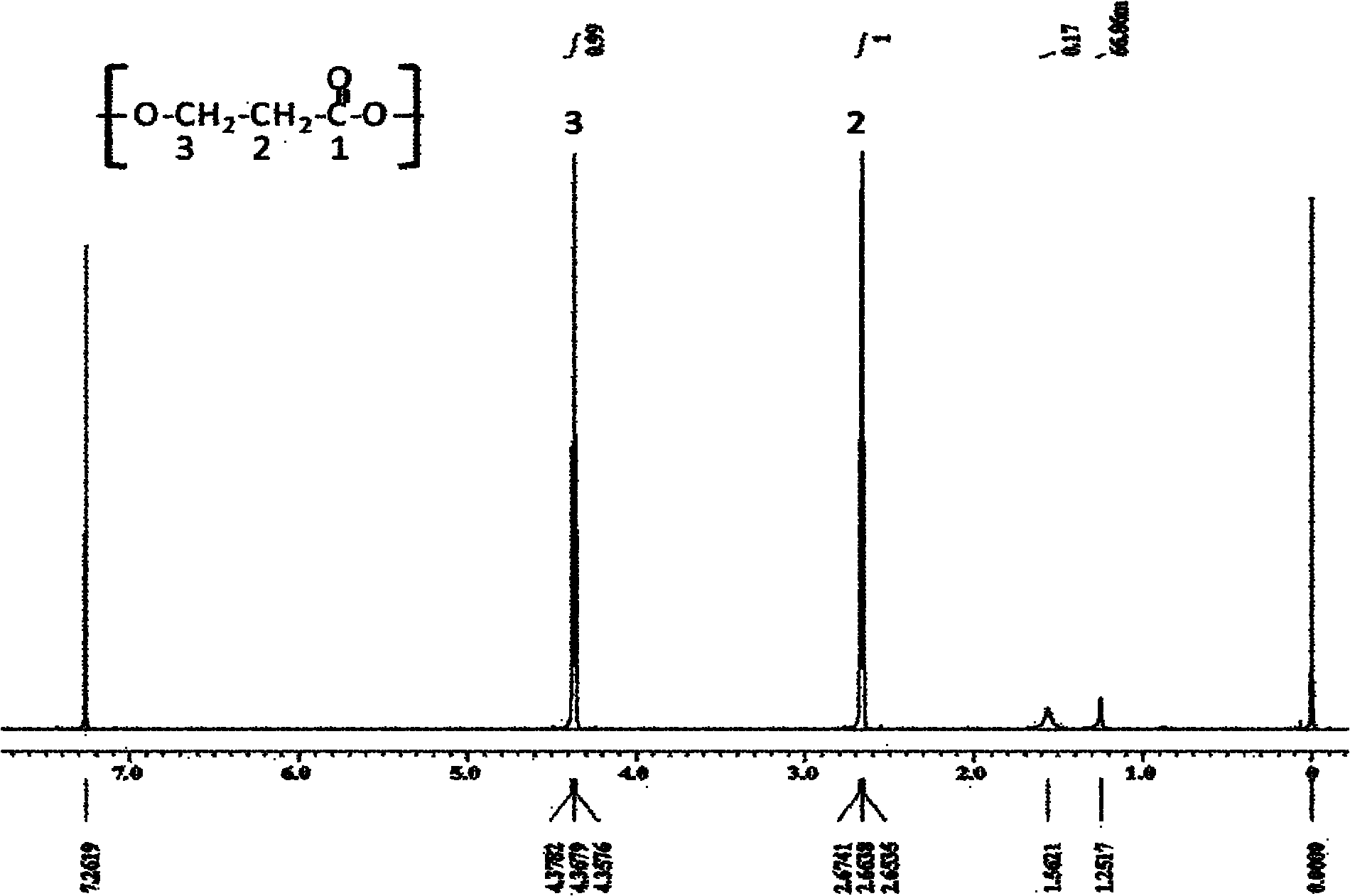
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPolymerase L
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant Escherichia coli and application of recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid
ActiveCN105567622AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
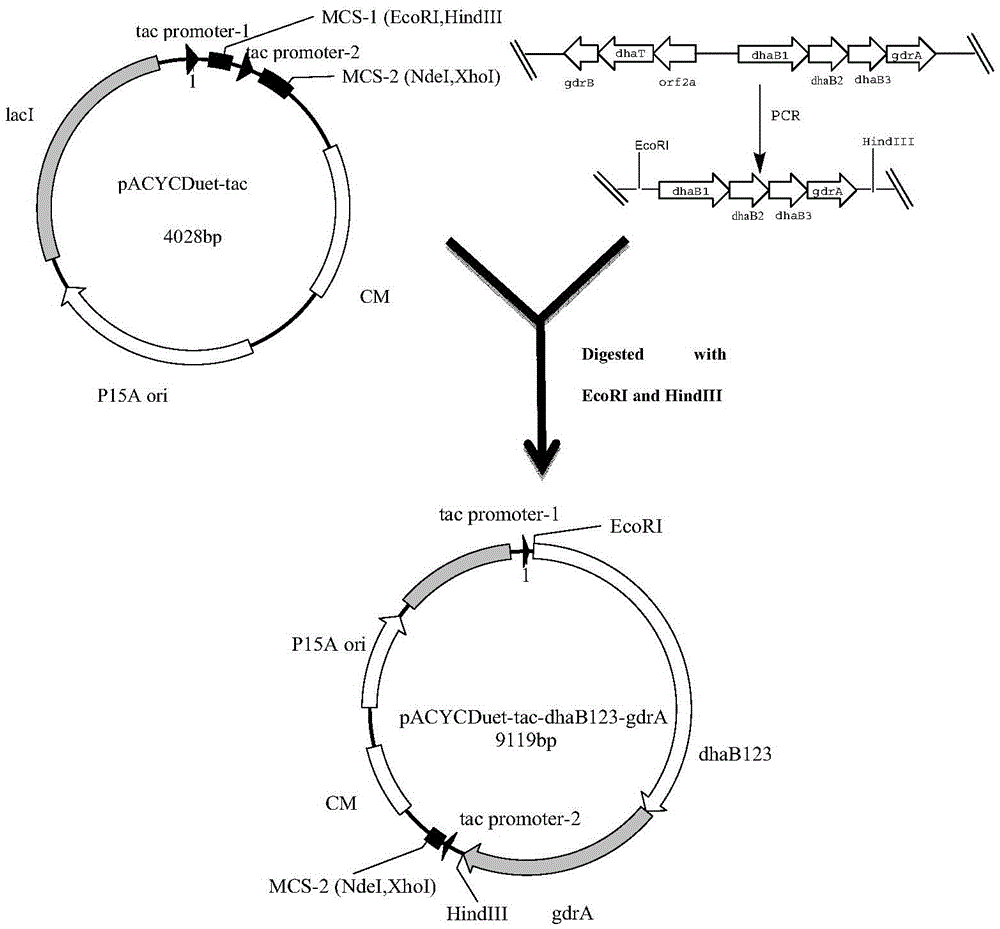
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli and application of the recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The recombinant Escherichia coli is formed by glycerol dehydratase genes dhaB123, glycerol dehydratase reactivating factor genes gdrA, alpha-oxoglutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase mutant coding genes TUkgsadh and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase coding genes gpdl which are guided into host bacteria. By means of the gene knockout technique, the yield of byproduct 1,3-propylene glycol is reduced, and meanwhile, cofactors NAD+ of aldehyde dehydrogenase are regenerated. Thus, the yield of the 3-hydroxypropionic acid is improved by 1.5 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com