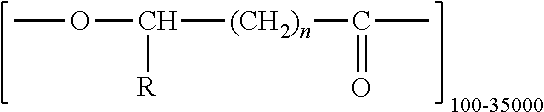Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "3-Hydroxypentanoic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
3-Hydroxypentanoic acid, or beta-hydroxypentanoate is a 5-carbon ketone body. It is made from odd carbon fatty acids in the liver and rapidly enters the brain. As opposed to 4-carbon ketone bodies, 3-hydroxypentanoic acid is anaplerotic, meaning it can refill the pool of TCA cycle intermediates. The triglyceride triheptanoin is used clinically to produce beta-hydroxypentanoate.
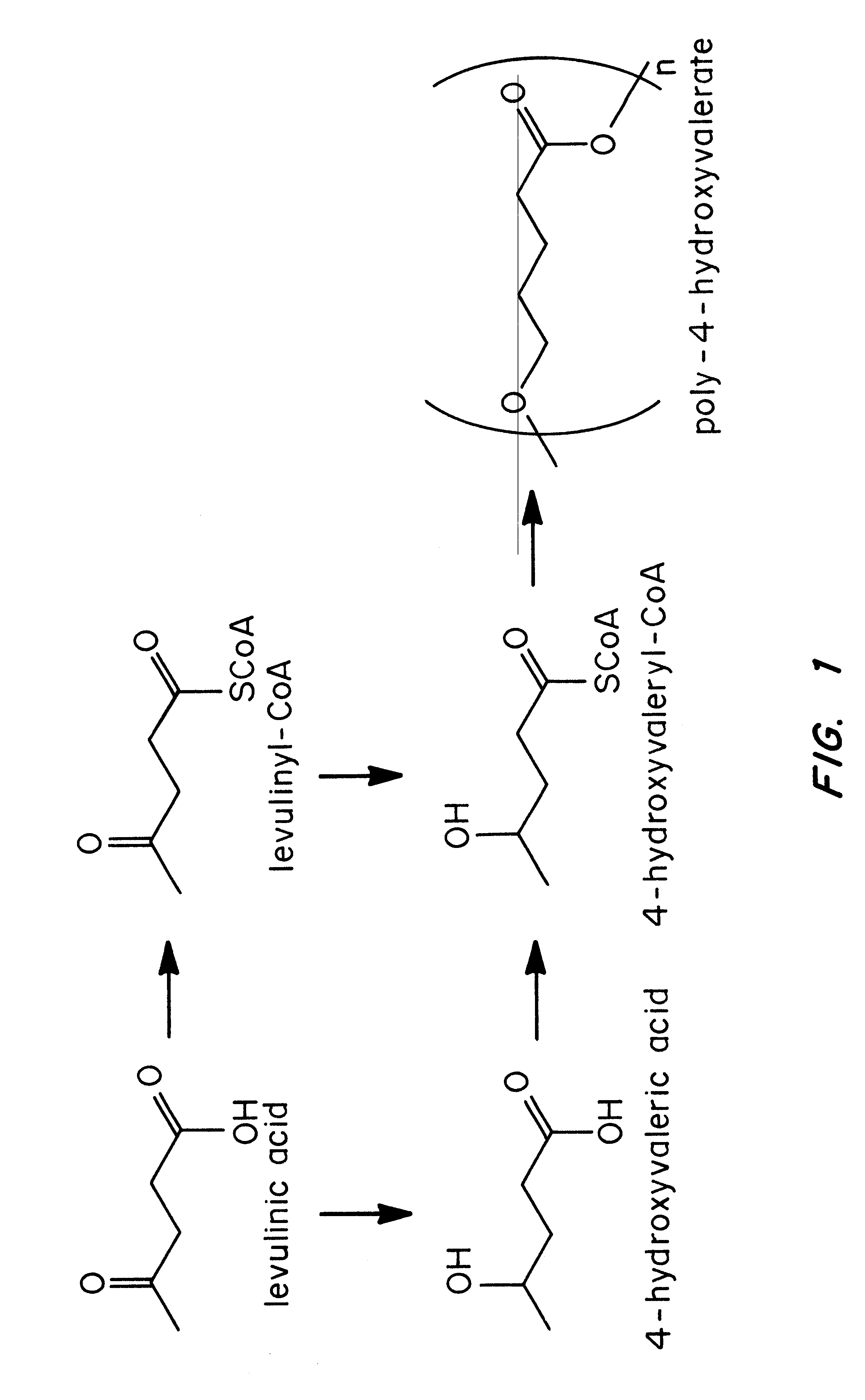
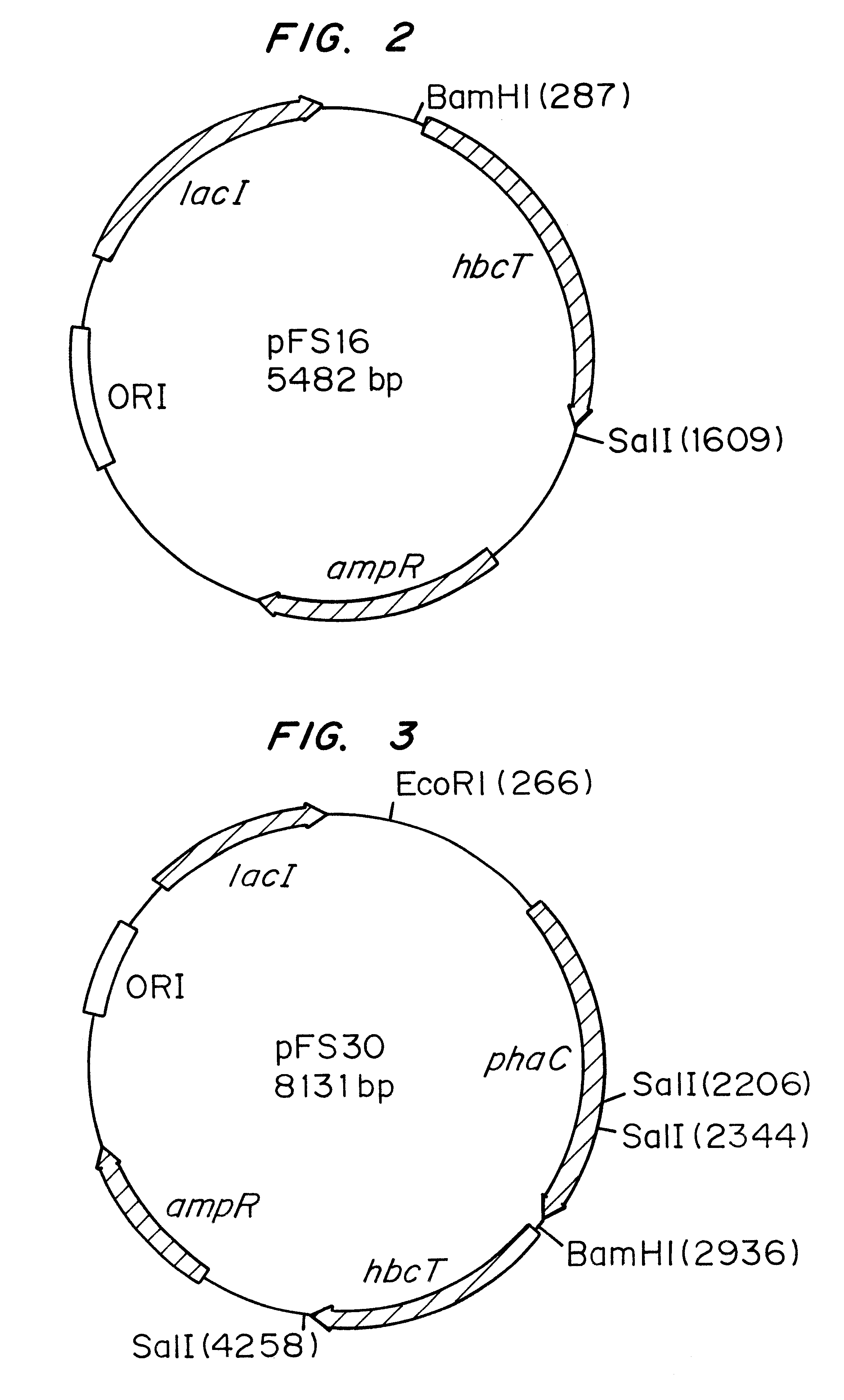
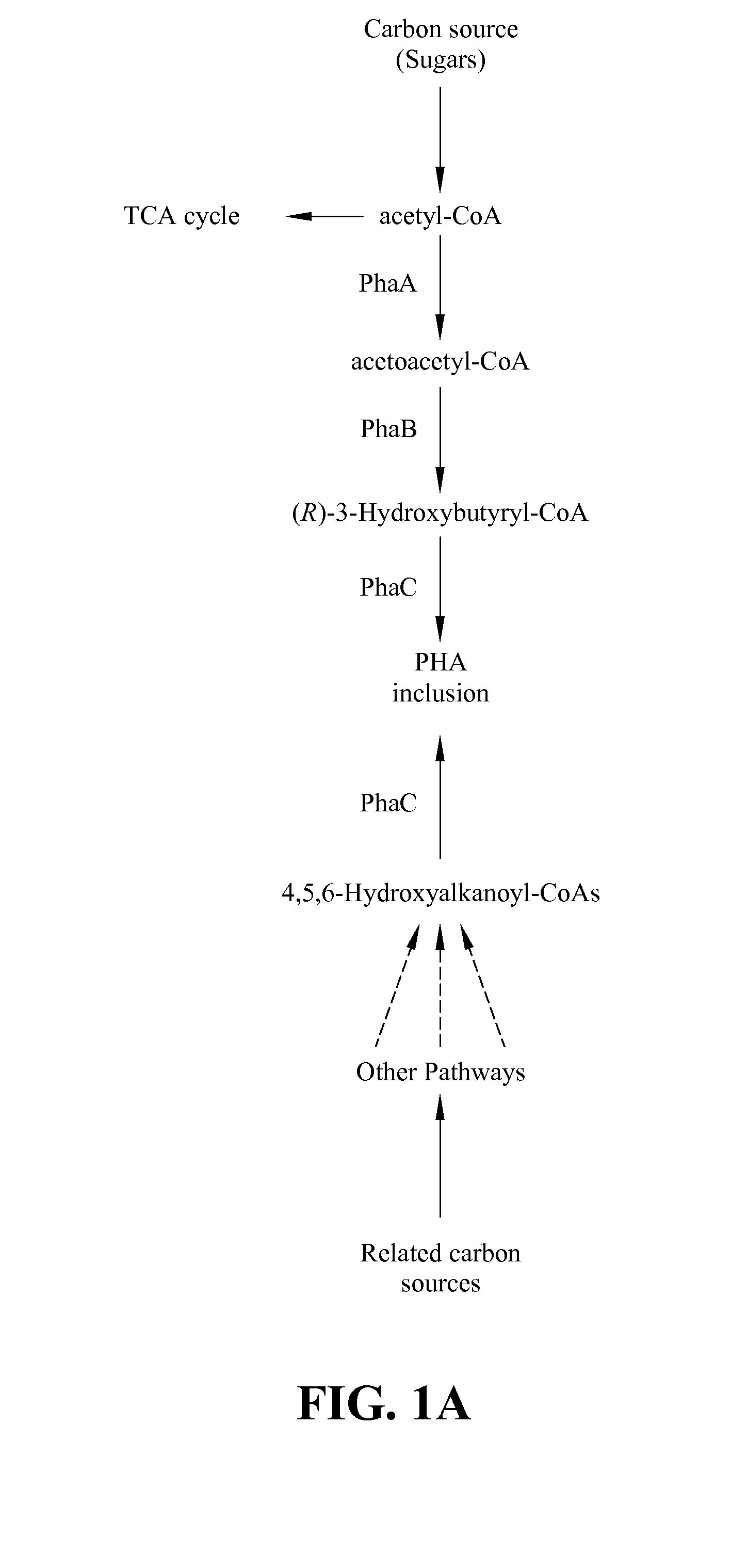
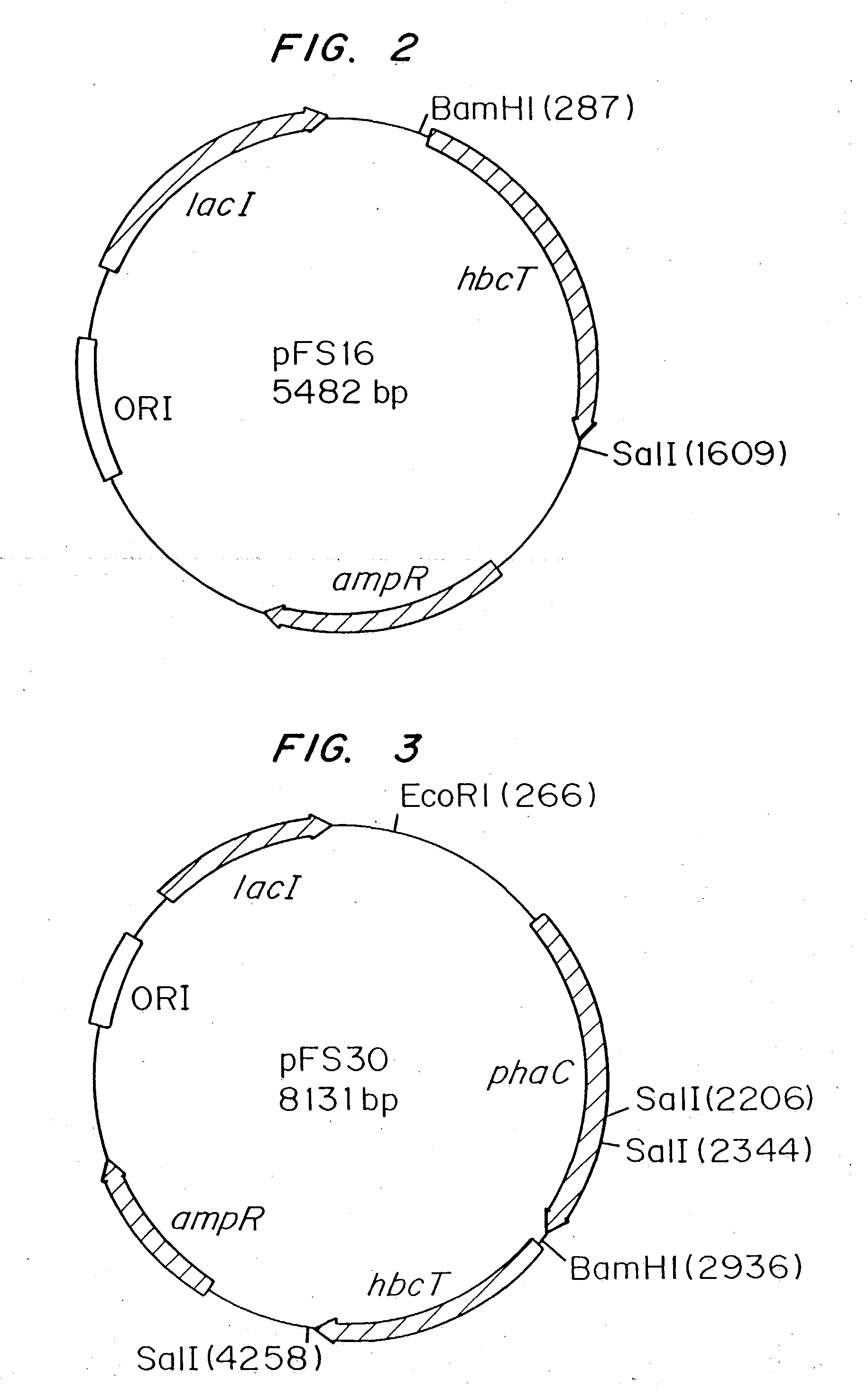
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
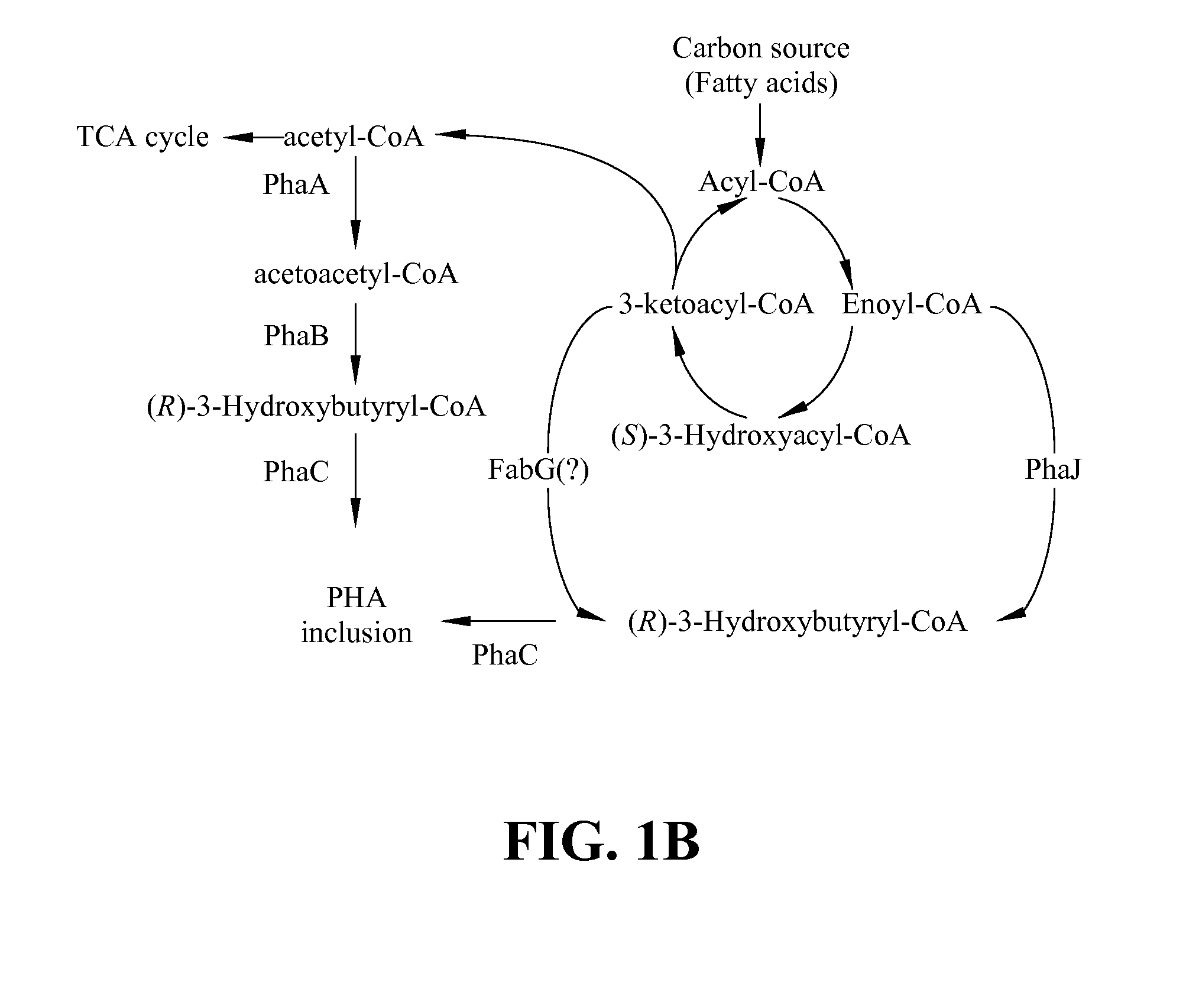
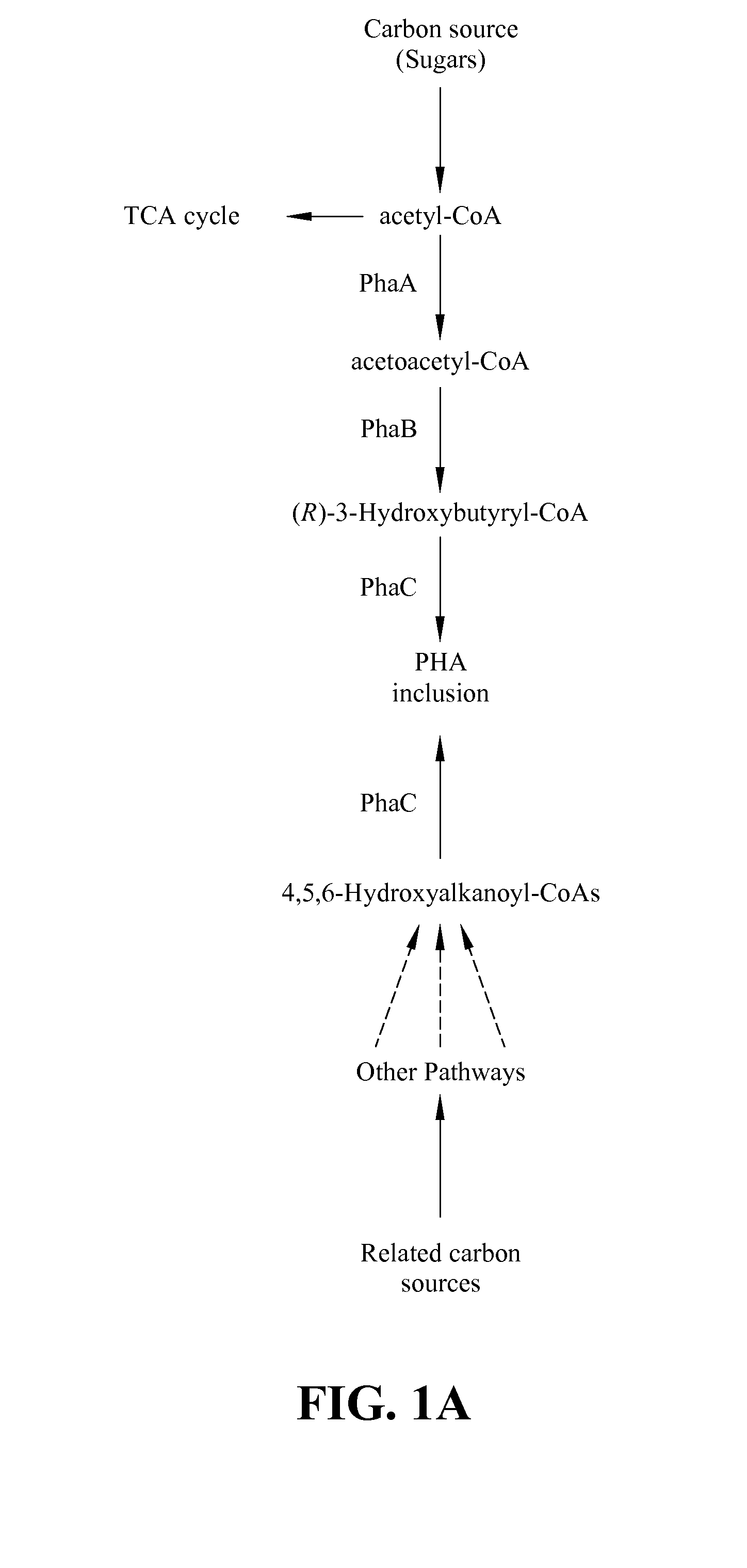
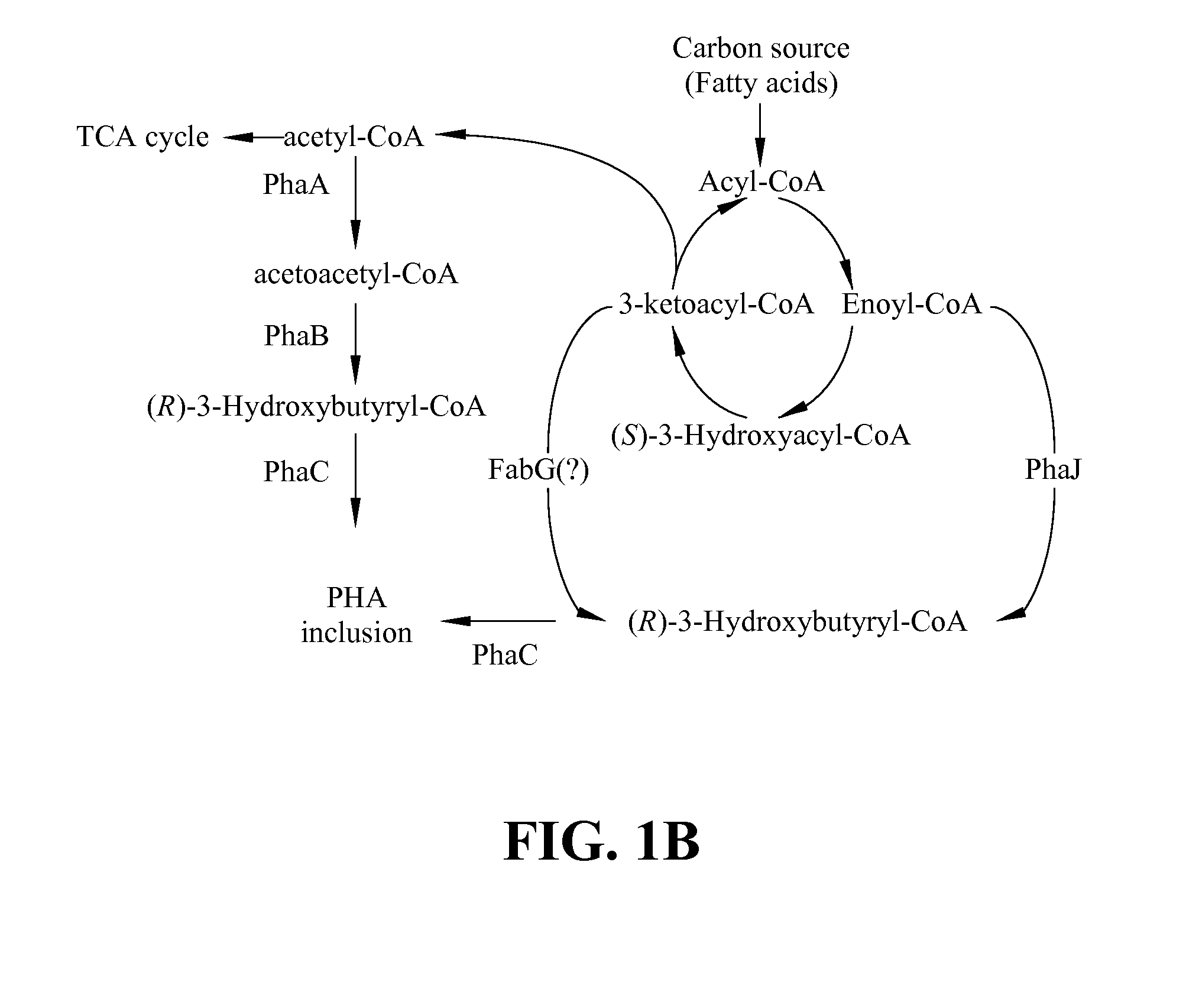
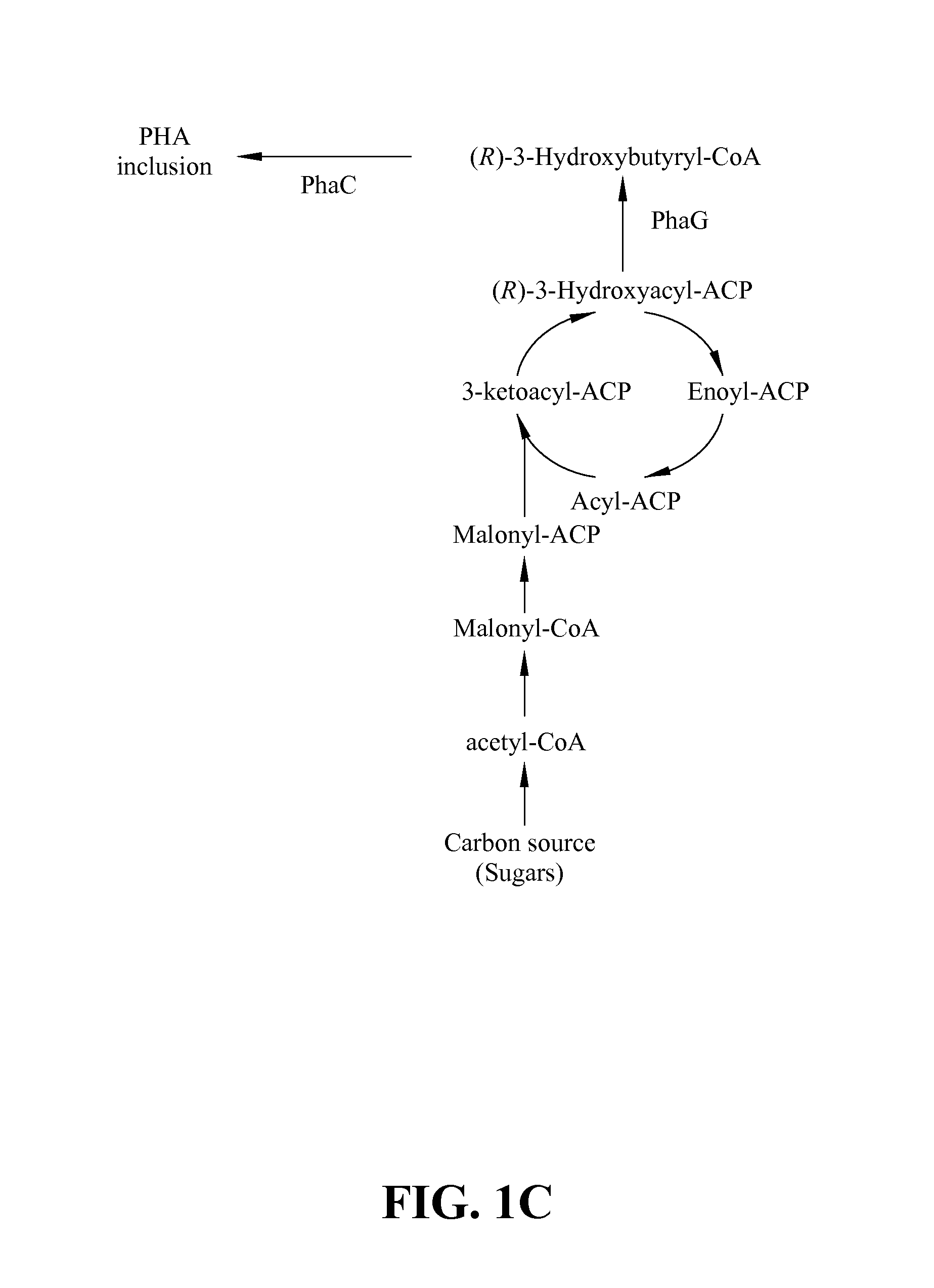
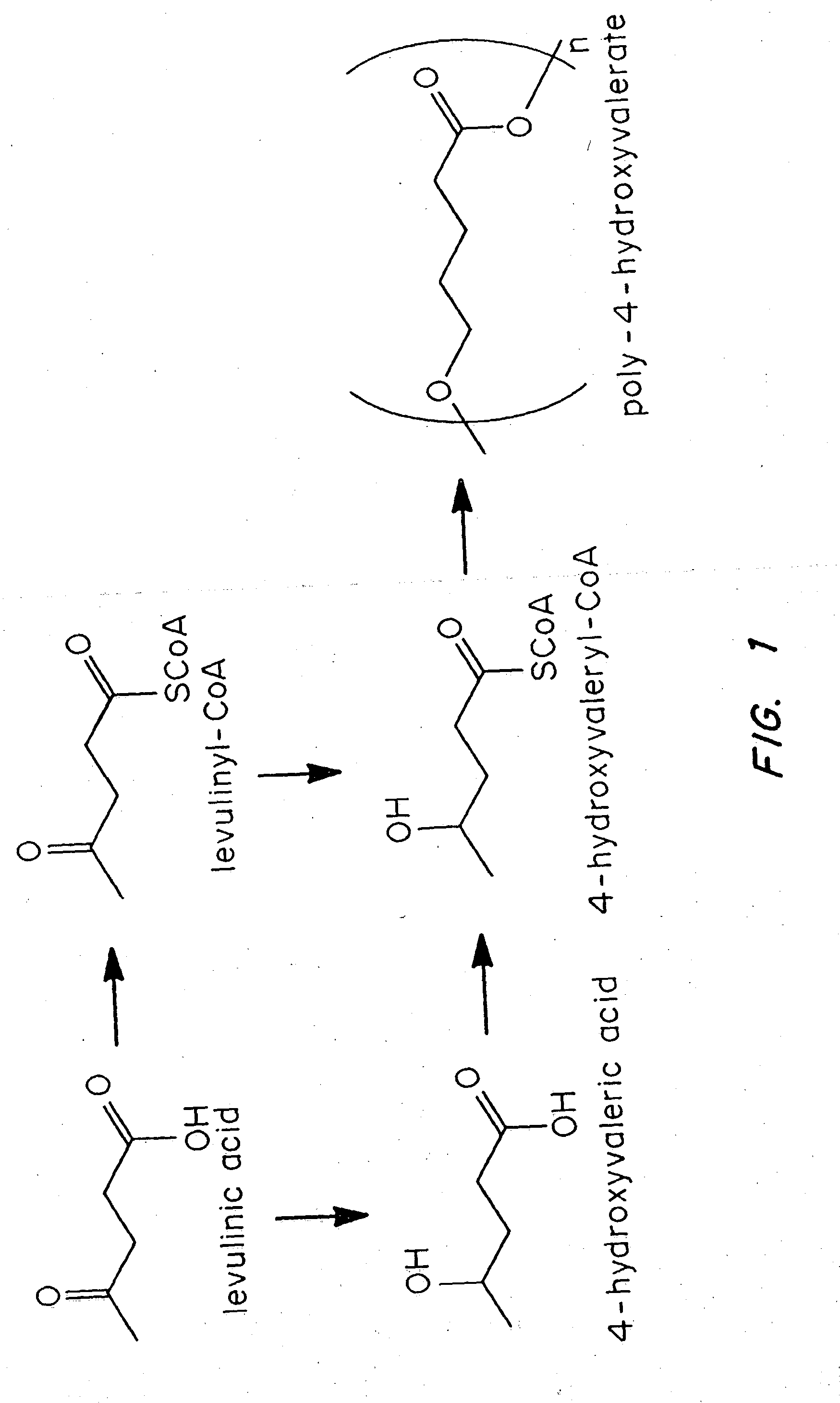
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:METABOLIX
Biodegradable card base
InactiveUS6350530B1High strengthReduce rigidityDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention provides a card base which is degradable by microbes in natural environment. The card base is excellent in properties necessary for card bases, such as tensile strength, impact strength, flex temperature, heat resistance, resistance to thermal expansion and contraction, blocking resistance and humidity resistance, and has rigidity, bending resistance and durability. The card base contains, as essential components, a 3-hydroxybutylate / 3-hydroxyvalerate copolymer and a lactic acid polymer, and, where necessary, a polycaprolactone or a high-molecular aliphatic polyester. The card base has a single-layer structure, or a sandwich structure further having overlay layers comprising a composition containing, as essential components, a lactic acid polymer and either or both of a polycaprolactone and a high-molecular alphatic polyester.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Balloon catheter comprising pressure sensitive microparticles
InactiveUS20120083734A1Improve brittlenessEffective treatmentSurgeryDilatorsPolyesterPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention provides a solution to the above mentioned problem in that it provides a catheter balloon comprising a flexible coating on its outer surface wherein a plurality of microparticles are contained wherein said coating comprises a material selected from the group consisting of poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone, poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone-co-butylacrylate), poly(-vinyl pyridine), polyacrylamides, e.g. poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(amido-amines), poly(ethylene imine), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide-block-ethylene oxide), poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene), poly(hydroxystyrene-block-isobutylene-block-hydroxystyrene), polydialkylsiloxanes, polysaccharides, polyacrylates and polyalkylmethacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein said microparticles comprise a material selected from the group consisting of polyesters, e.g. poly(lactic acid), poly(lactic-co-glycol acid), poly(glycolic acid), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxyvalerate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and polycaprolactone, polyamides, polysaccharides, polyurethanes, polyalkylmethacrylates and polyacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein the microparticles comprise a pharmaceutically active compound.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Resource-renewable and biodegradable conductive fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102936761ARealize conductive functionLower percolation thresholdElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiber3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses resource-renewable and biodegradable conductive fiber and a preparation method thereof. The fiber consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-70 parts of polylactic acid (PLA), 30-70 parts of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid-co-3-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) and 0.05-8 parts of conductive filler. The preparation method of the conductive fiber comprises the following steps of: (1) proportionally pre-mixing PHBV (if PLA is not less than 50 parts) or PLA (if PLA is less than 50 parts) and the conductive filler, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA; (2) proportionally pre-mixing the PLA or PHBV and the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain composite conductive mater batches; and (3) spinning and drafting the composite conductive master batches one by one to obtain the conductive fiber. The conductive fiber disclosed by the invention can be used as the material for electrodes, static resistance, low-temperature heating, electromagnetic shielding, thermal sensitivity, gas sensitivity and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
PLA (Poly Lactic Acid) and PHBV (Poly Hydroxyl Butyrate Valerate) blending modification polyester filament and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102995160AFast degradationFeel goodFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsPolyesterState of art
The invention discloses a functional PET technology, and particularly relates to a poly 3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate and poly lactic acid blending modification polyester filament and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims at overcoming the defects in the prior art and providing a PLA (Poly Lactic Acid) and PHBV (Poly Hydroxyl Butyrate Valerate) blending modification polyester filament which is quick in degradation velocity, high in softness, good in handfeel, and easy to color and a preparation method thereof. The polyester filament consists of 20-50wt% of PLA and the balance of PHBV, can satisfy the existing pursue of people, and has the characteristics that under the condition that the quality of cloth is met, abundant colors can be selected by people, so that the more choices are provided.
Owner:新凤鸣集团股份有限公司
Method for preparing high-toughness degradable material by using melt-grafting blending method
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-toughness degradable material by using a melt-grafting blending method, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out melt-grafting on polycaprolactone PCL, anhydride and an initiator, and then obtaining modified polycaprolactone by way of extrusion granulation, wherein the mass ratio of the polycaprolactone PCL to the anhydride to the initiator is 100: (1 to 10): 0.5; and (2) carrying out melt-grafting blending on poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) PHBV, the modified polycaprolactone, methyl acrylate and an initiator, and then obtaining the high-toughness PHBV-class degradable material by way of extrusion granulation, wherein the mass ratio of the poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) PHBV to the modified polycaprolactone to the methyl acrylate to the initiator is 100: (5 to 50): (0.5 to 10):0.5, the processing temperature is 100 to 170 DEG C, and the screw speed is 50-80 R.P.M. The method is simple in process, low in cost, and suitable for industrialization, and the elongation at break of the produced PHBV-class degradable material can reach 560 percent; therefore, the method of the invention has good application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
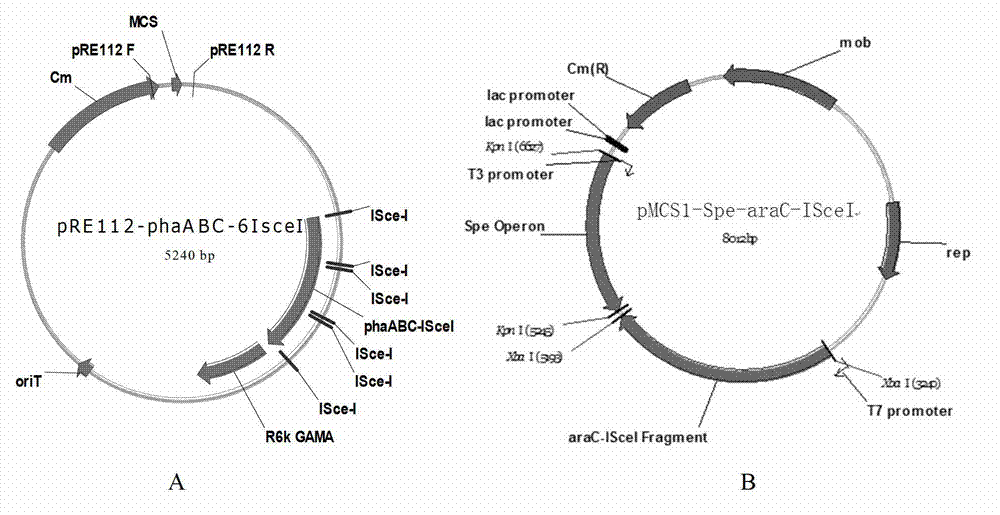
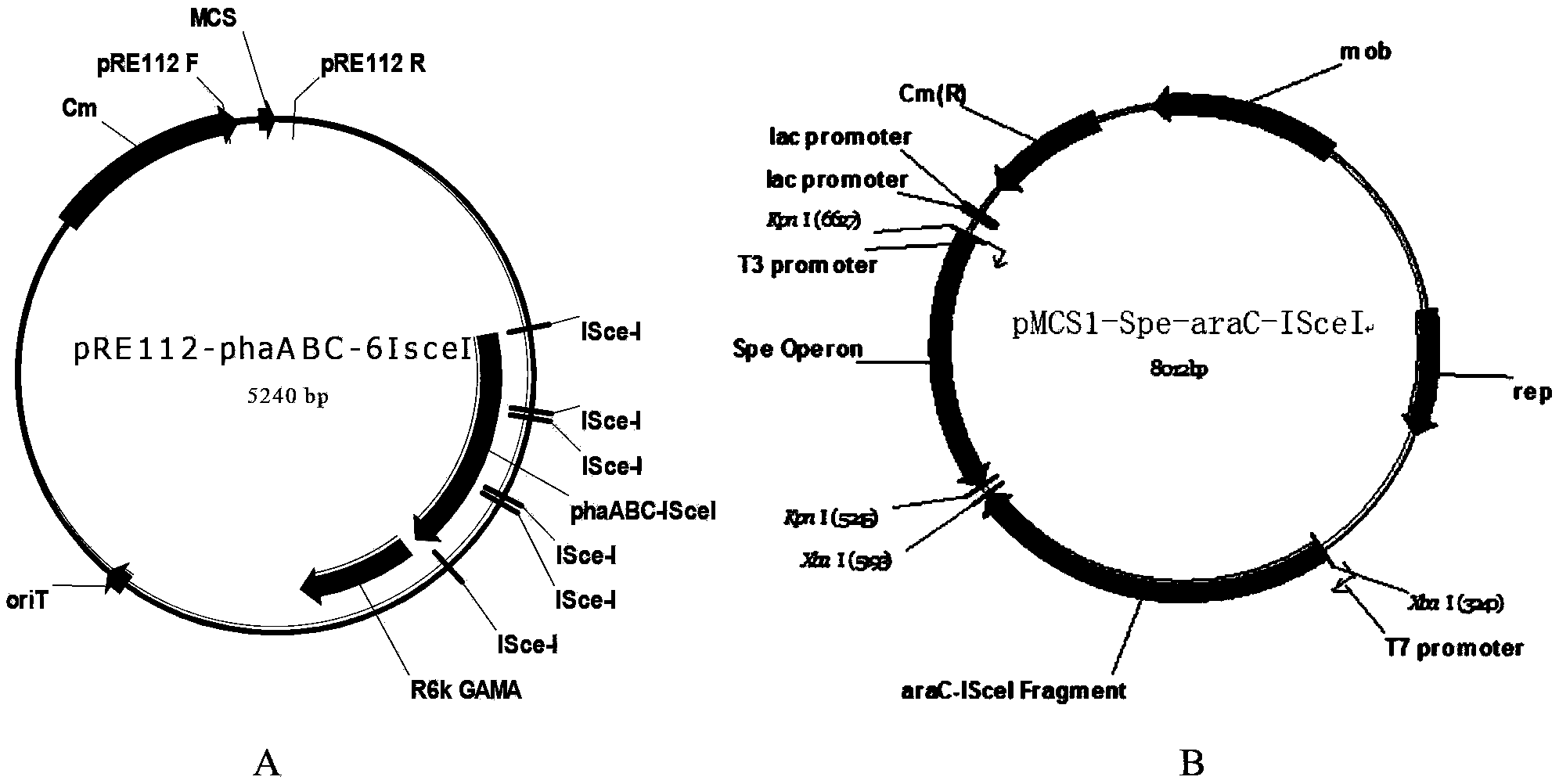
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
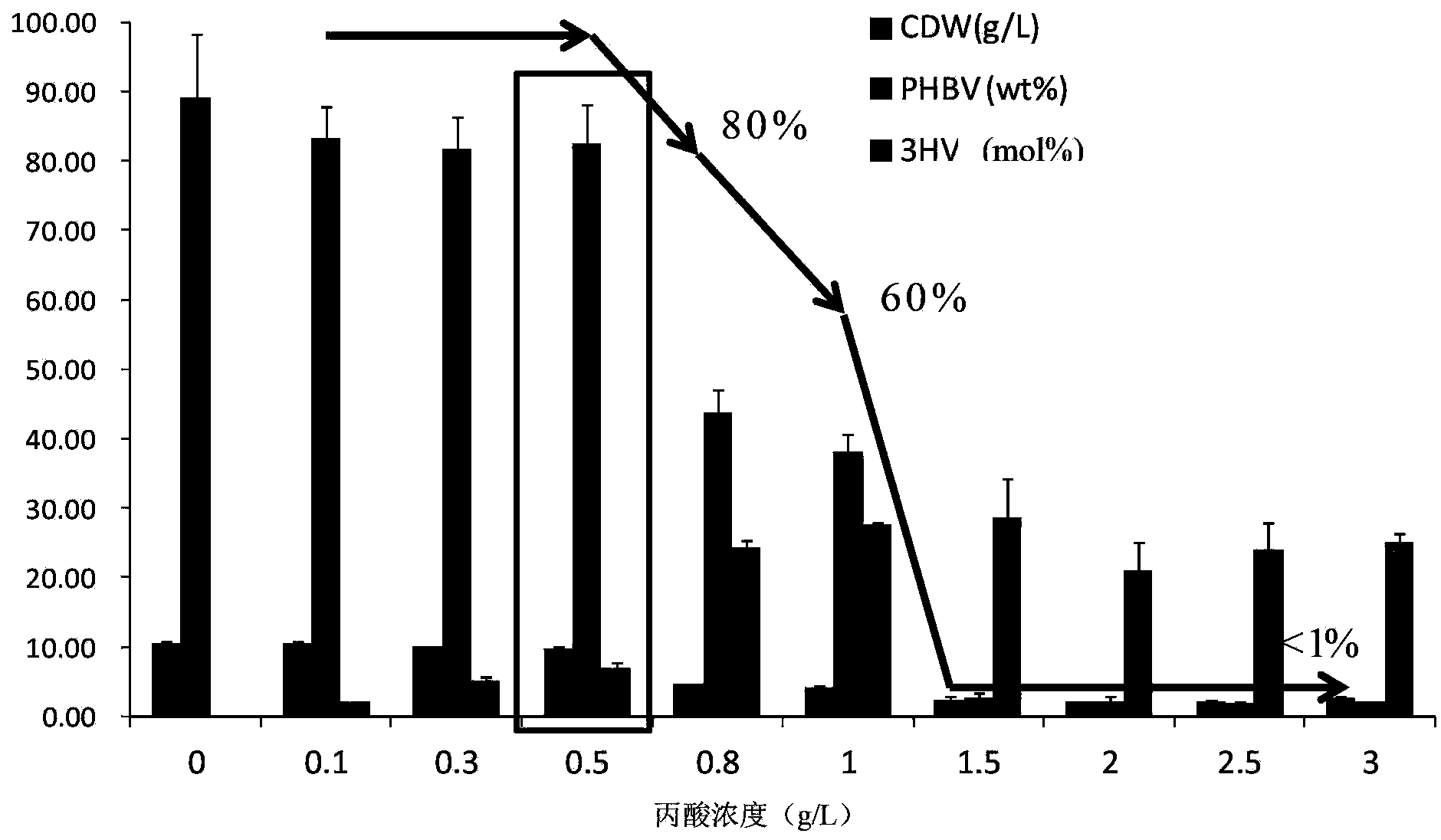
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
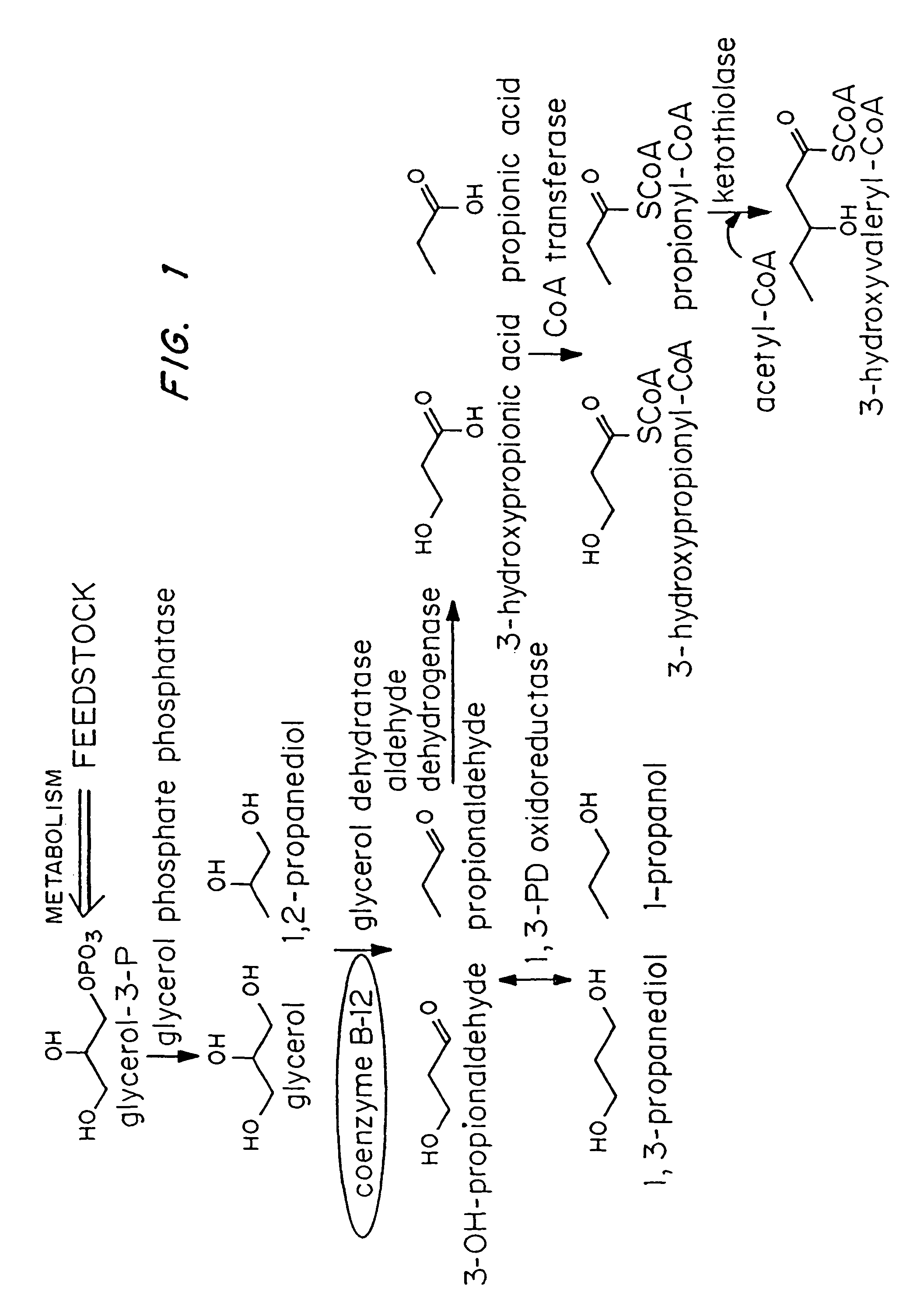
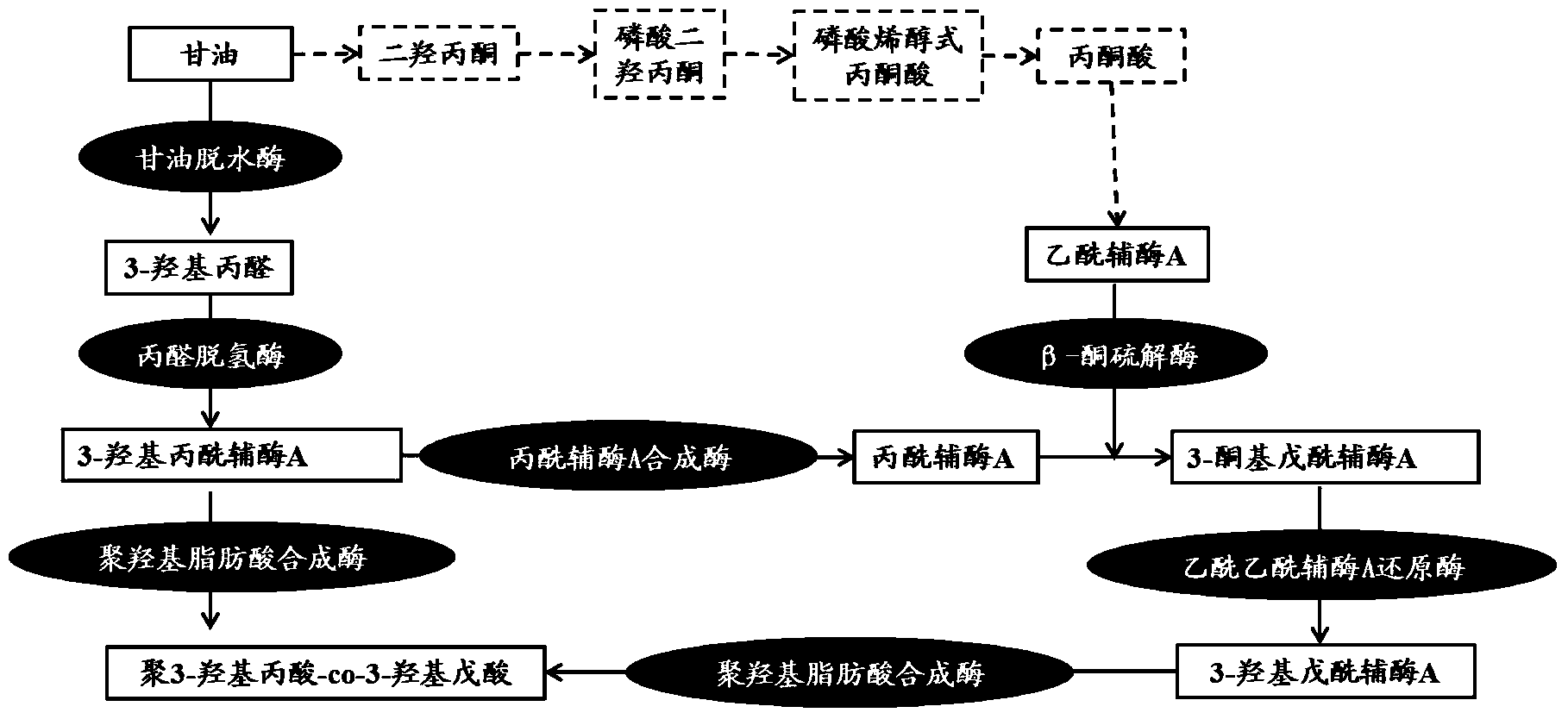
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalerate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
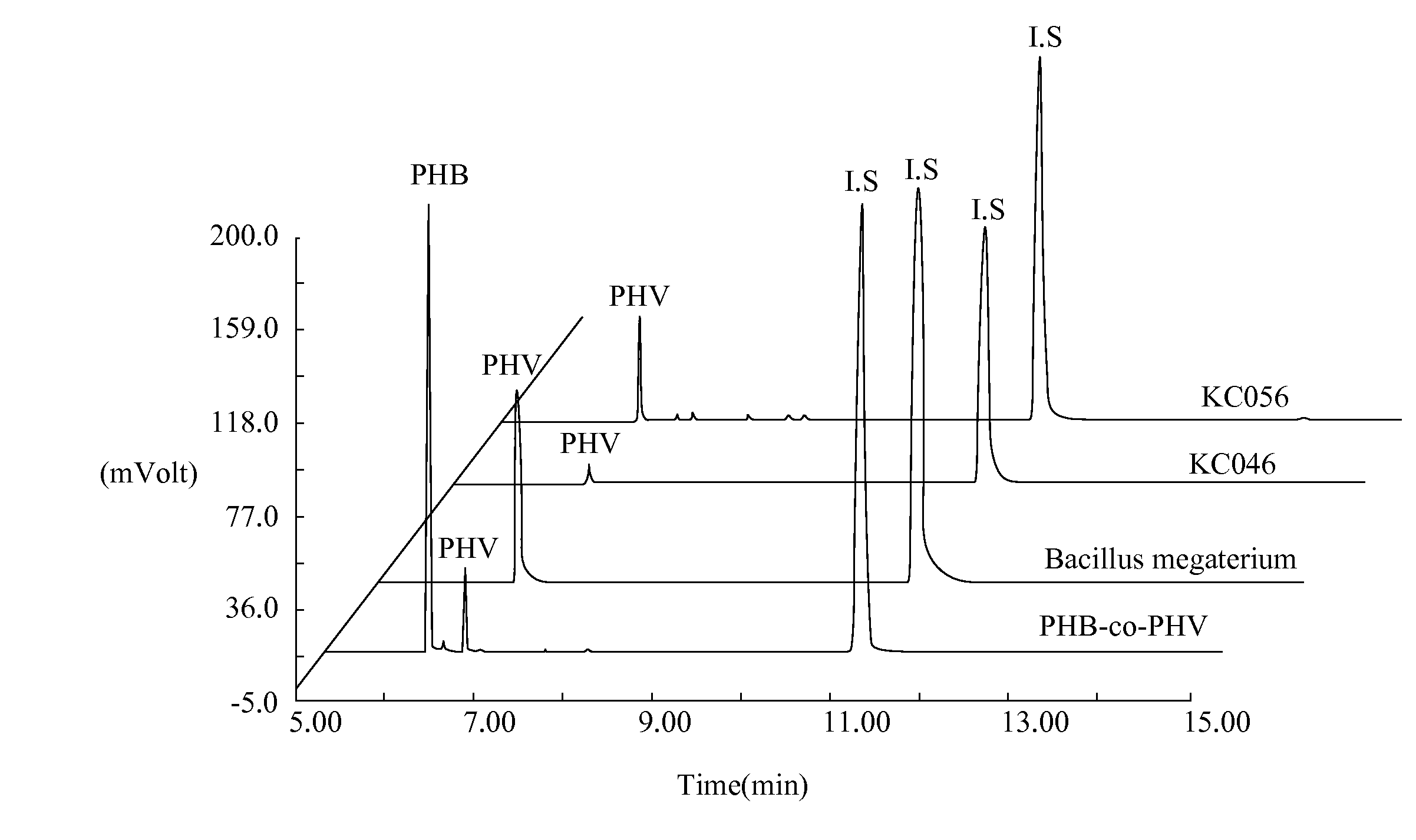
Method For Production Of High Purity Polyhydroxyalkanonate (PHAs)
The present invention relates to a method of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using Bacillus sp. with succinate as a carbon source. The PHAs comprise more than 95% of poly(3-hydroxyvalerate-co-4-hydroxyvalerate) (P3HV-co-P4HV).
Owner:FAR EASTERN NEW CENTURY COPRRATION
Method for production of high purity polyhydroxyalkanonate (PHAs)
The present invention relates to a method of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using Bacillus sp. with succinate as a carbon source. The PHAs comprise more than 95% of poly(3-hydroxyvalerate-co-4-hydroxyvalerate) (P3HV-co-P4HV).
Owner:FAR EASTERN NEW CENTURY COPRRATION
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Bio-based compatilizer, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101717497AImprove interface compatibilityImprove blending effect3-Hydroxypentanoic acidDepolymerization
The invention discloses a bio-based compatilizer, a preparation method and the application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: respectively alcohol depolymerization on poly3-hydroxy-butanoic acid ester (PHB), poly3-hydroxy-butanoic acid ester-3- hydroxyvalerate (PHBV), polylactic acid (PLA) and polybutylene succinate (PBS) to obtain 4 alcohol depolymerized products; and then reactively blending more than 2 products, certain amount of isocyanate and antioxidant for reacting to obtain different bio-based compatilizers. 2-20 parts of compatilizers are added into 10 parts of bio-based resin to prepare a composite material, which obviously improves the compatibility of system interface, greatly improves the overall properties and widens the application link of the bio-based resin. The composite material can be widely applied to the production or consume fields of automobile trims, stationery products, traffic road blocks, sport products, food bags, refuge bags, disposable table cloth, outdoor flower pots, lunch boxes, knives and forks and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
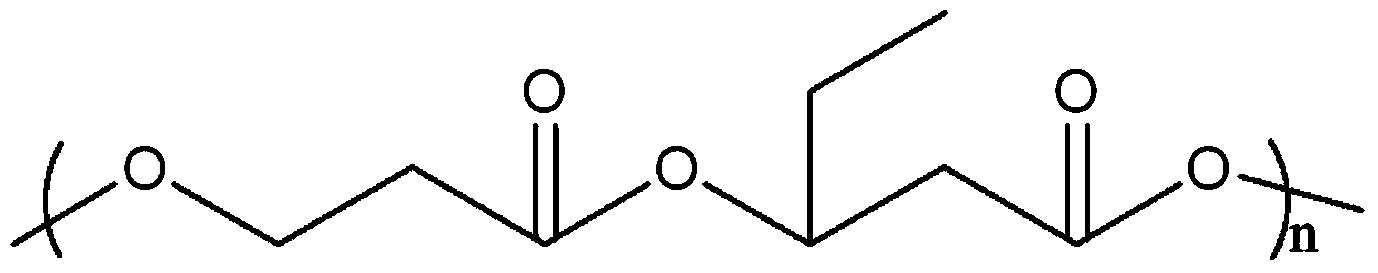
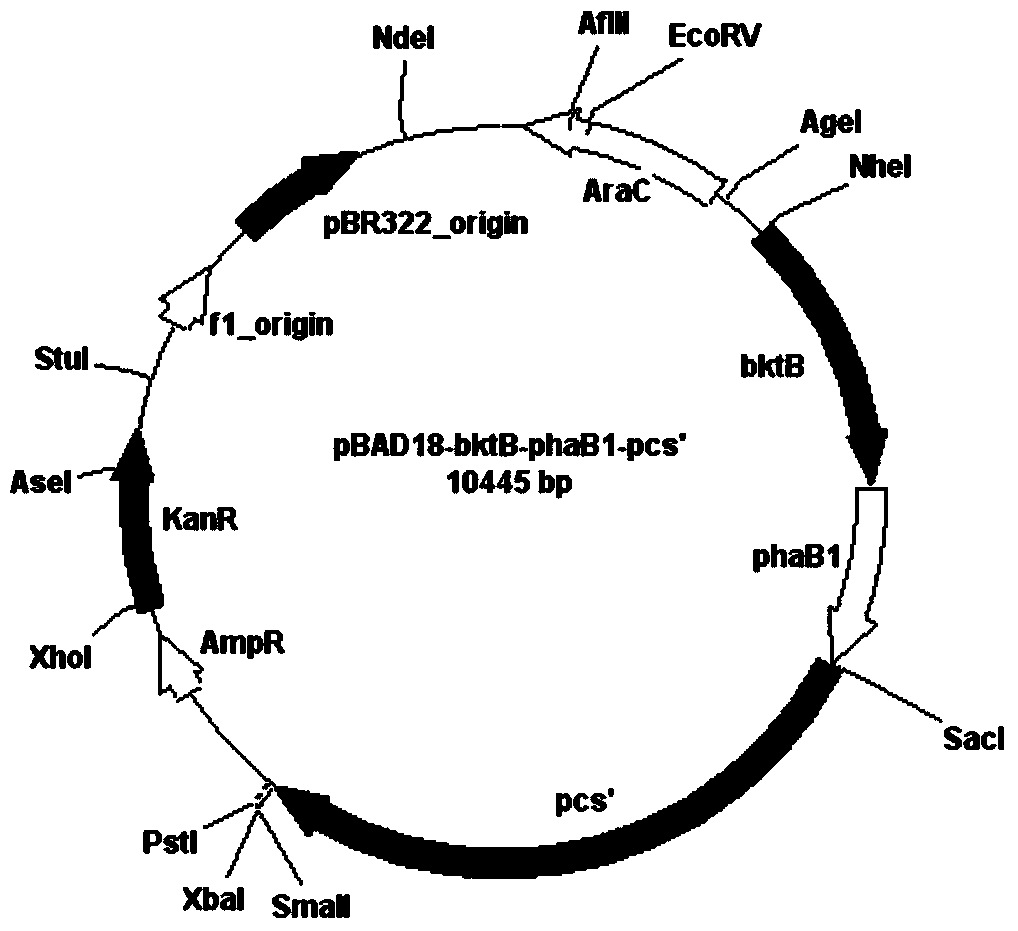
Poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and production method thereof
ActiveCN104046659AHigh melting pointReduce crystallinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, a glycerol dehydratase gene and a glycerol dehydratase re-activating enzyme gene are integrated with a host strain genome by a gene integration technology, a polyhydroxy fatty acid synthase gene, a propionaldehyde dehydrogenase gene, a beta-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase gene, an acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductase gene and a propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene are introduced, and a recombinant gene engineering strain has the ability of biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid. According to the poly-3-hydroxy propionic acid copolymer and the production method thereof, the poly-3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid is obtained in a biosynthesis manner for the first time; compared with poly-3-hydracrylic acid, the obtained poly 3-hydracrylic acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid has a higher melting point and lower crystallinity, has good degradability and can serve as a packaging material, a medical implant material, a drug sustained-release material and an electrochemical material.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
PHBV (polyhydroxylbutyrate valerate) polymer, preparation method and hemostatic material manufactured by using PHBV polymer
ActiveCN104448258AImprove adsorption capacityGood coagulationMicroorganism based processesAbsorbent pads3-Hydroxypentanoic acidInternal pressure
The invention discloses a PHBV (polyhydroxylbutyrate valerate) polymer, a preparation method and a hemostatic material manufactured by using the PHBV polymer. The PHBV polymer is a copolymer of 3-hydroxybutyrate (3HB) and 3-hydroxyvalerate (3HV), and the main chain of the polymer includes at least 50 blocks of poly 3-hydroxybutyrate and at least 50 blocks of poly 3-hydroxyvalerate. The preparation method comprises: inoculating Haloferax mediterranei ES1 strains to a fermentation medium, and automatically feeding 2M hydrochloric acid solution or 2M sodium hydroxide solution under the condition that the fermentation temperature is 37 DEG C, the stirring revolution speed is 300-500r / min and the ventilatory capacity is 1.25: 1vvm to stabilize the pH value at 6.9-7.1; fermenting for 36-48h under the condition that the ventilatory capacity is 1.25: 1vvm and the inner pressure of a tank body is 1 atmosphere; and extracting the PHBV polymer from the fermentation solution.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for synthesizing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate/3-polyhydroxybutyrate from wooden carbon source domesticated sewage mixed with bacteria
InactiveCN109097429ALow costIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationActivated sludgePretreatment method
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate / 3-polyhydroxybutyrate (PHBV) from wooden carbon source domesticated sewage mixed with bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out hydrolysis and enzymolysis on a wooden biological resource by using a hydrothermal pretreatment method; (2) by taking the hydrolysis and enzymolysis product as a carbon source, domesticating sewage with activated sludge by using an aerobiotic dynamic material supply method, and enriching bacteria capable of synthesizing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA); (3) accumulating PHAby controlling an unbalanced nutrition environment, and increasing the yield of PHA, thereby finally confirming that the accumulated PHA is PHBV. With the comparison between dry cell weights of different experiment groups and data of PHBV yields, optimal culture conditions can be acquired. After 9 accumulation cycles of the domesticated activated sludge, 303.7-1084.4 mg / of PHBV can be produced, PHB accounts for 40.45-69.14%, and PHV accounts for 30.86-59.55%; finally, at a pH value of 7 and a total sugar concentration of 1700 mg / , the yield of the PHBV meets the maximum value under a condition of sufficient inorganic salt components and oxygen.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
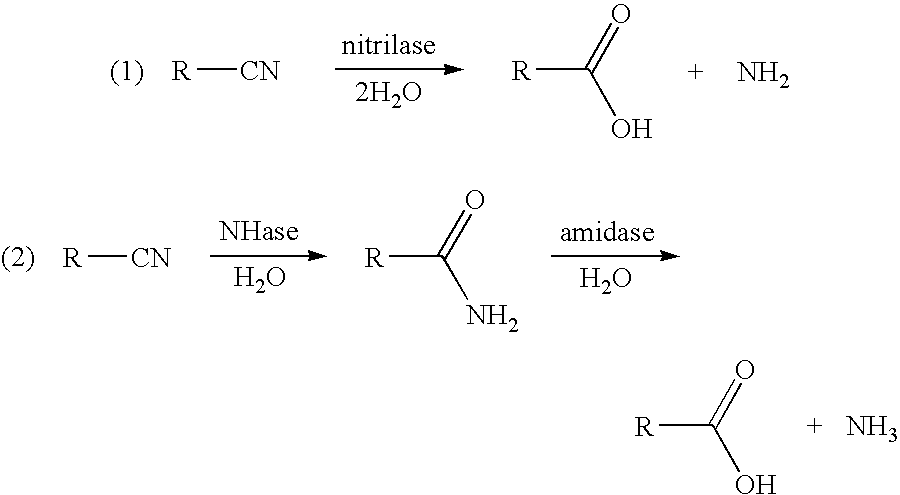
3-hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
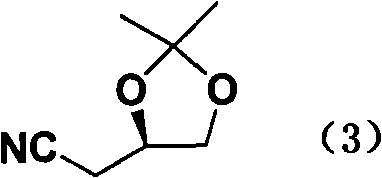
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of a 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid from a 3-hydroxynitrile. More specifically, 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile is converted to 3-hydroxyvaleric acid in high yield at up to 100% conversion, using as an enzyme catalyst 1) nitrile hydratase activity and amidase activity or 2) nitrilase activity of a microbial cell. 3-Hydroxyvaleric acid is used as a substitute for ε-caprolactone in the preparation of highly branched copolyester.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
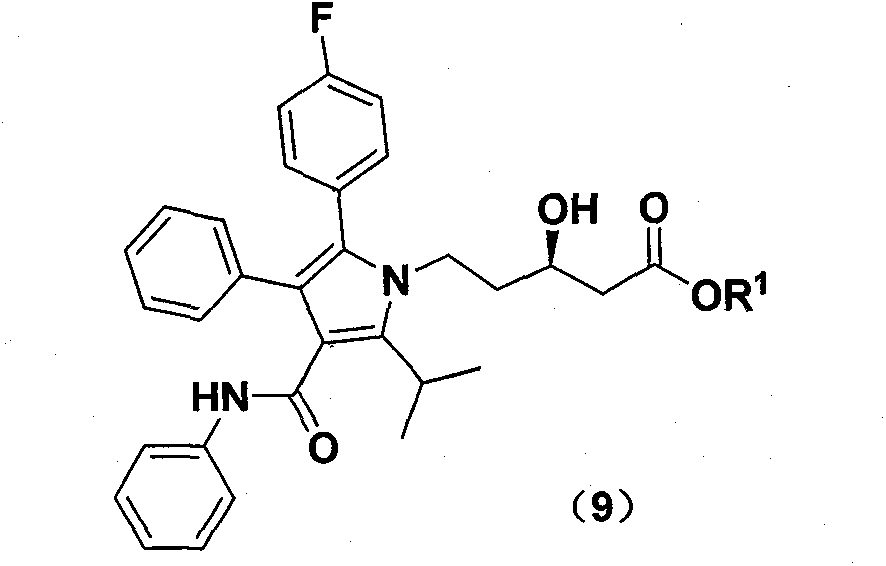
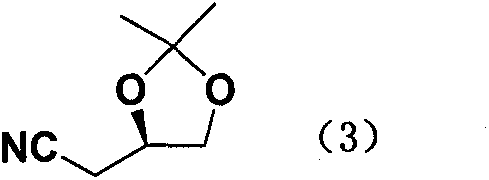
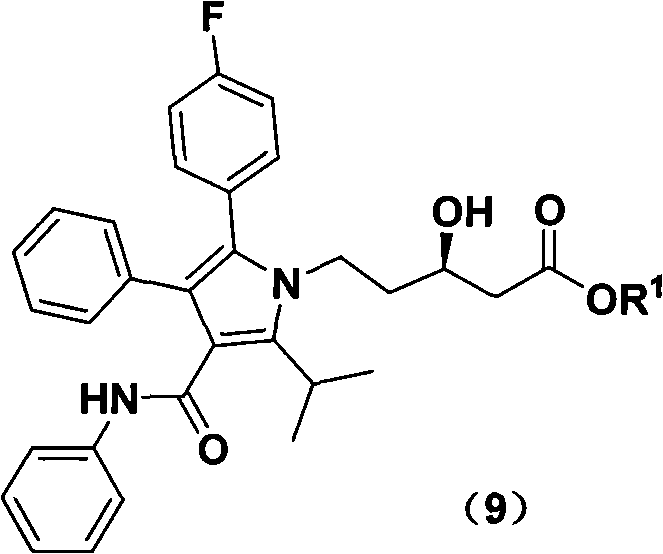
New preparation method of atorvastatin calcium 1H-pyrrole derivatives
The invention relates to a synthetic route and a method for preparing (R)-5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylamino formyl-1H-pyrrole-1-ethyl)-3-hydroxyvalerate. The (R)-5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylamino formyl-1H-pyrrole-1-ethyl)-3-hydroxyvalerate is obtained through seven steps by using (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-chloropropane as raw material. The method provided bythe invention has low cost, simple operation, and is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAHAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
Toughening method of poly(3-hydrox butyrate) and poly(3-hydroxy butyrate-3-hydroxy pentanoate)
The present invention relates to a toughening method of poly(3-hydroxy butyrate) and poly(3-dydroxy butyrate-3-hydroxy pentanoate). The raw material includes the first component of poly(3-hydroxy butyrate) or poly(3-dydroxy butyrate-3-hydroxy pentanoate) with 3-hydroxy pentanoate monomer molar content less than 20%; the second copmonent of p-tert-butylphenol, bisphenol A, bisphenol S or 2,4,6-tri(2'-hydroxy-4'-butoxyphenyl)-1,3,5- triazine; and the optional component including plasticizer and stuffing. The weight ratio between the first component and the second component is 70-90 to 10-30 and the optional component is 0-30 wt% of the first component. By means of solution blending or melting blending, modified material with excellent toughness may be obtained.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polysubstituted indole statin fluorine-containing modifier and use thereof
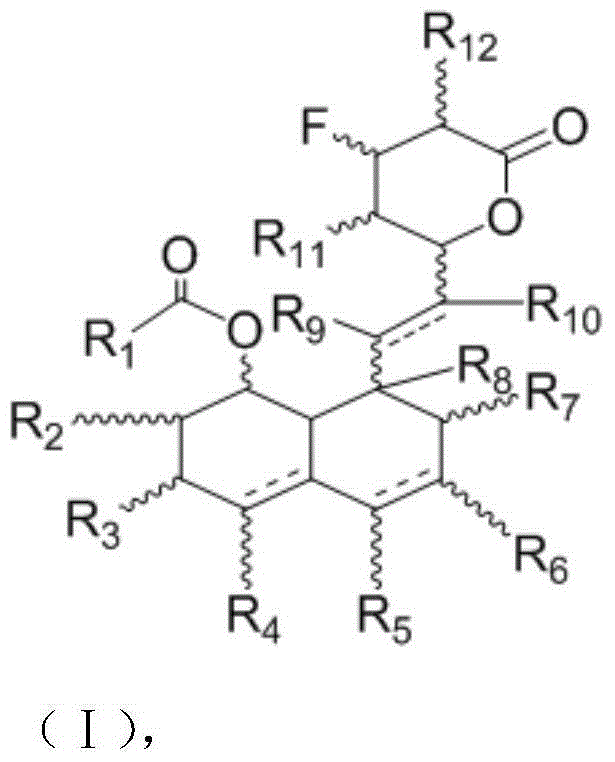
ActiveCN105017231AEliminate or at least reduce toxic side effectsReduce toxic and side effectsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry3-Hydroxypentanoic acidHMG-CoA reductase activity
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and provides a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor is a polysubstituted indole statin fluorine-containing modifier of 1-fluoro-3-hydroxypentanoic acid and its salt or ester formed after ring opening of 3-fluoro-caprolactone fragment and its lactone. The structural formula of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor is shown in the specification. A result of test of like compounds shows that the compounds have an HMG-CoA reductase activity inhibition effect, and can be used as a new-generation latent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
Owner:SHANGHAI ECUST BIOMEDICINE CO LTD
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729BGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acidBiotechnology
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
3-Hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
A kind of renewable resource, biodegradable conductive fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102936761BRealize conductive functionLower percolation thresholdElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberConductive polymer
The invention discloses resource-renewable and biodegradable conductive fiber and a preparation method thereof. The fiber consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-70 parts of polylactic acid (PLA), 30-70 parts of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid-co-3-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) and 0.05-8 parts of conductive filler. The preparation method of the conductive fiber comprises the following steps of: (1) proportionally pre-mixing PHBV (if PLA is not less than 50 parts) or PLA (if PLA is less than 50 parts) and the conductive filler, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA; (2) proportionally pre-mixing the PLA or PHBV and the conductive master batch of the PHBV or PLA, and performing melt blending and granulation to obtain composite conductive mater batches; and (3) spinning and drafting the composite conductive master batches one by one to obtain the conductive fiber. The conductive fiber disclosed by the invention can be used as the material for electrodes, static resistance, low-temperature heating, electromagnetic shielding, thermal sensitivity, gas sensitivity and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Poly-substituted phenanthrene ring statin fluorine-containing derivative and uses thereof
ActiveCN105111173AOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorder3-Hydroxypentanoic acidHMG-CoA reductase activity
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and provides 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, wherein a fragment containing 3-fluoro-caprolactone and a lactone thereof are subjected to ring opening to form a poly-substituted pyrimidine statin fluorine-containing modifier of 1-fluoro-3-hydroxy-pentanoic acid and a salt or ester thereof, ie., the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, and the structure formula is defined in the specification. According to the present invention, the test results show that the compounds have the HMG-CoA reductase activity inhibition effects, and can be used as the new generation of the potential HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
Owner:SHANGHAI ECUST BIOMEDICINE CO LTD
Composite porous calcium phosphate bone cement and method for making same
The invention relates to a composite porous calcium phosphate bone cement and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of calcium phosphate bone cement preparation. The phosphorus bone cement is composed of calcium phosphate bone cement solid phase powder, 3-hydroxybutyric acid-CO-3-hydroxyvaleric acid copolymer microspheres irradiated with Co60 gamma rays and a solidification solution; the method is to prepare calcium phosphate Bone cement solid phase powder; preparation of simulated body fluid: PHBV microspheres are irradiated with Co60γ rays, washed and dried in water, completely immersed in simulated body fluid, and then washed and dried; then PHBV microspheres are mixed with calcium phosphate bone cement solid phase After powder mixing, compound bone cement slurry is prepared with curing liquid. The composite bone cement of the present invention has high initial curing strength, rapid degradation in the later stage of implantation, and the degradation speed can be adjusted, and the porous structure formed after degradation is beneficial to the growth of new bone tissue and the reconstruction of autogenous bone. It is mainly used for bone defect repair and bone tissue engineering scaffold materials, and can also be used as dental repair materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli and method for applying same to produce poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) by utilizing single carbon source
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli QW102PT and an application thereof in producing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) by utilizing a single carbon source. The recombinant escherichia coli can be used for efficiently utilizing the single carbon source to synthesize the PHBV, and the mole fraction of 3HV (3-hydroxyvaleric acid) is improved from 0.45 percent to 17.5 percent compared with that of recombinant bacteria DH5 alpha (pBHR68), which has obvious significance to commercial production of the PHBV. According to the invention, the problems that the cost is overhigh as propionic acid is used as an auxiliary carbon source and control strategies during the production process are excessively complicated are solved, and a new concept of synthesizing the PHBV byutilizing a simple carbon source is created.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative
InactiveUS7223859B2Easy to produceEasily raw materialCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCholesterylester transfer protein3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The present invention provides a method for easily producing an (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative useful for an intermediate for pharmaceutical products, particularly an inhibitor of a cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) from easily available raw materials. In the present invention, (S)-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-hydroxypentanoic acid amide prepared from easily available raw materials leads a production of (R)-4-ethyl-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-azetidinone to give (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide. Furthermore, (R)-4-ethyl-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-azetidinone is reacted with a carbamic acid ester to give an (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Water treatment chemical for removing chlorobenzene compounds in water
InactiveCN104891624AStrong complexing abilityFast precipitationWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationCarboxylic acidMethylandrostenediol
The invention relates to water treatment chemical for removing chlorobenzene compounds in water. The water treatment chemical is made from 3, 7-dimethyl-6-octenal, 3-amino-2- hydroxypropionic acid, thymopentin, aluminum sulfate, trans, trans-2, 4-nonadienal, 2-hydroxyl-4-isopropyl-2, 4, 6-cycloheptatriene-1-one, alpha-aminoisocaproic acid, sodium alginate, methylandrostenediol, DL-2-amino-3-hydroxyvaleric acid, isoimperatorin, sodium polyacrylate, 3, 7, 11-trimethyl-1, 6, 10-dodecatriene-3-ol, D-acridine-2-carboxylic acid, and 2-ethyl-2, 5-dimethylhexanoic acid. The water treatment chemical has the advantages that the chemical has high ability to complex with the chlorobenzene compounds, complex precipitant forms fast, the removal rate of the phenolic compounds is up to 99%, and the chemical is low in toxicity, low in use amount, free of harm to water and low in treatment cost.
Owner:金双蕾
New preparation method of atorvastatin calcium 1H-pyrrole derivatives
The invention relates to a synthetic route and a method for preparing (R)-5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylamino formyl-1H-pyrrole-1-ethyl)-3-hydroxyvalerate. The (R)-5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-phenylamino formyl-1H-pyrrole-1-ethyl)-3-hydroxyvalerate is obtained through seven steps by using (R)-2,3-dihydroxy-chloropropane as raw material. The method provided bythe invention has low cost, simple operation, and is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAHAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
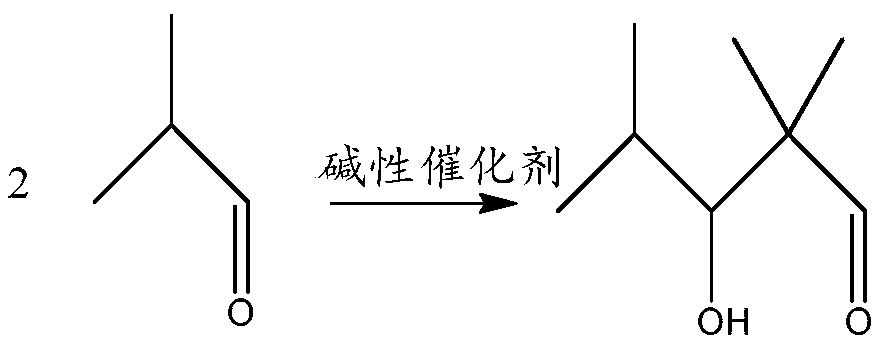
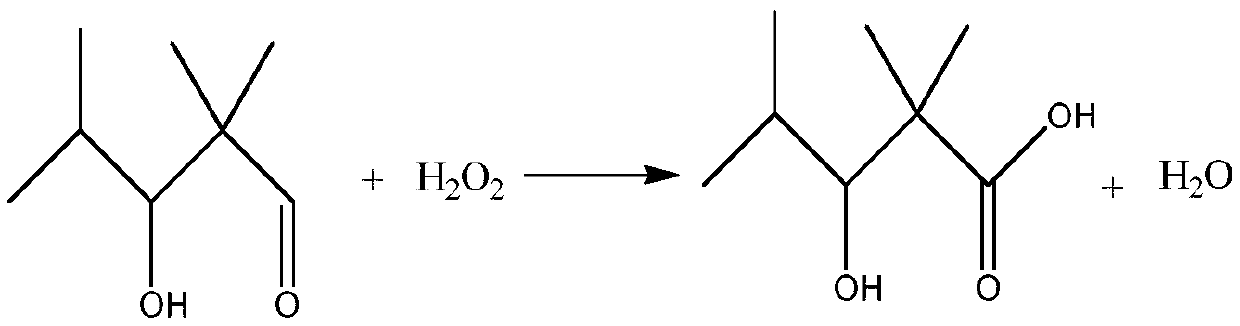
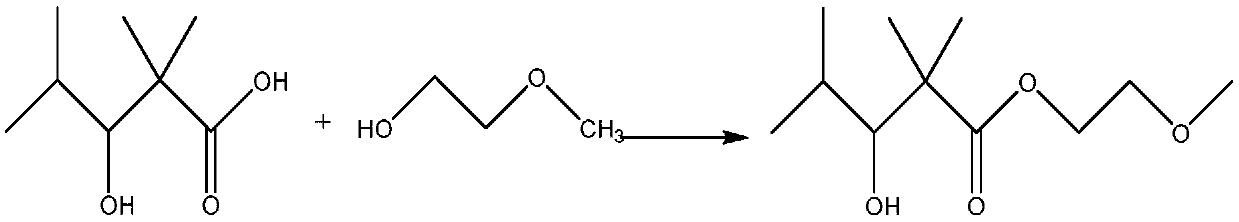
Preparation method of 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 methoxy ethyl hydroxyvalerate and water-borne wood lacquer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110803988AIncrease reaction rateHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention relates to the technical field of organic compound synthesis and application and in particular relates to a preparation method of 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 methoxy ethyl hydroxyvalerate and a water-borne wood lacquer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 methoxy ethyl hydroxyvalerate comprises the following steps: 1) performing a hydroxyaldehyde condensation reaction on iso-butyraldehyde under the action of an alkaline catalyst so as to generate produces 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-hydroxyentanaldehyde, and performing an oxidation reaction on the obtained 2,2,4-trimethyl-3-hydroxyentanaldehyde with H2O2 so as to obtain 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 hydroxypentanoic acid; and 2) enabling the 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 hydroxypentanoic acid prepared in the step 1) to reactwith ethylene glycol monomethyl ether under the action of a strong acid catalyst, so as to obtain the 2,2,4-trimethyl-3 methoxy ethyl hydroxyvalerate. The preparation method of the 2,2,4-trimethyl-3methoxy ethyl hydroxyvalerate, which is provided by the invention, is single in reaction product, needs no multi-step separation and is simple to operate. Meanwhile, the invention further provides thewater-based wood lacquer and the preparation method thereof.
Owner:RUNTAI CHEM TAIXING CO LTD +1
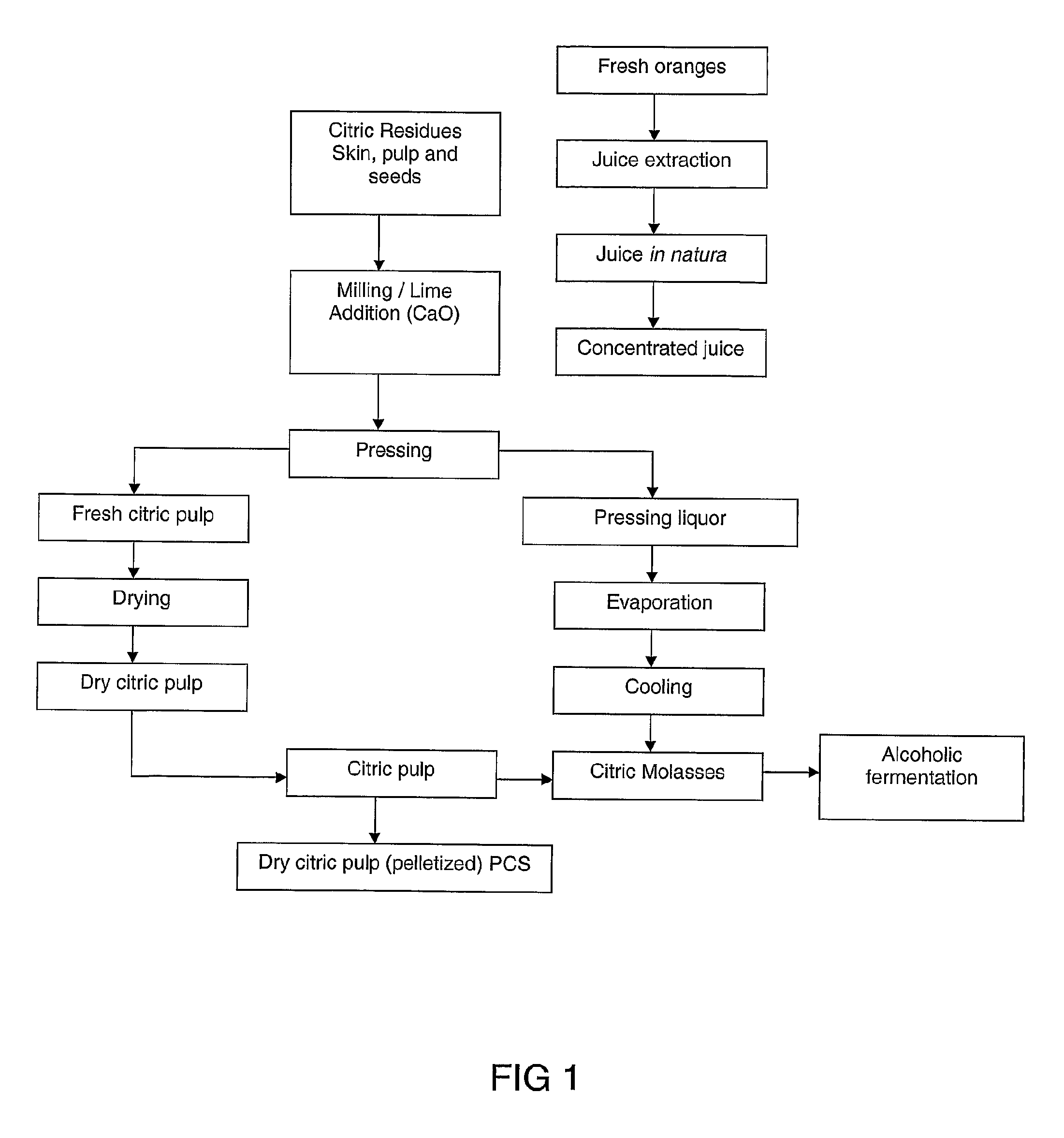
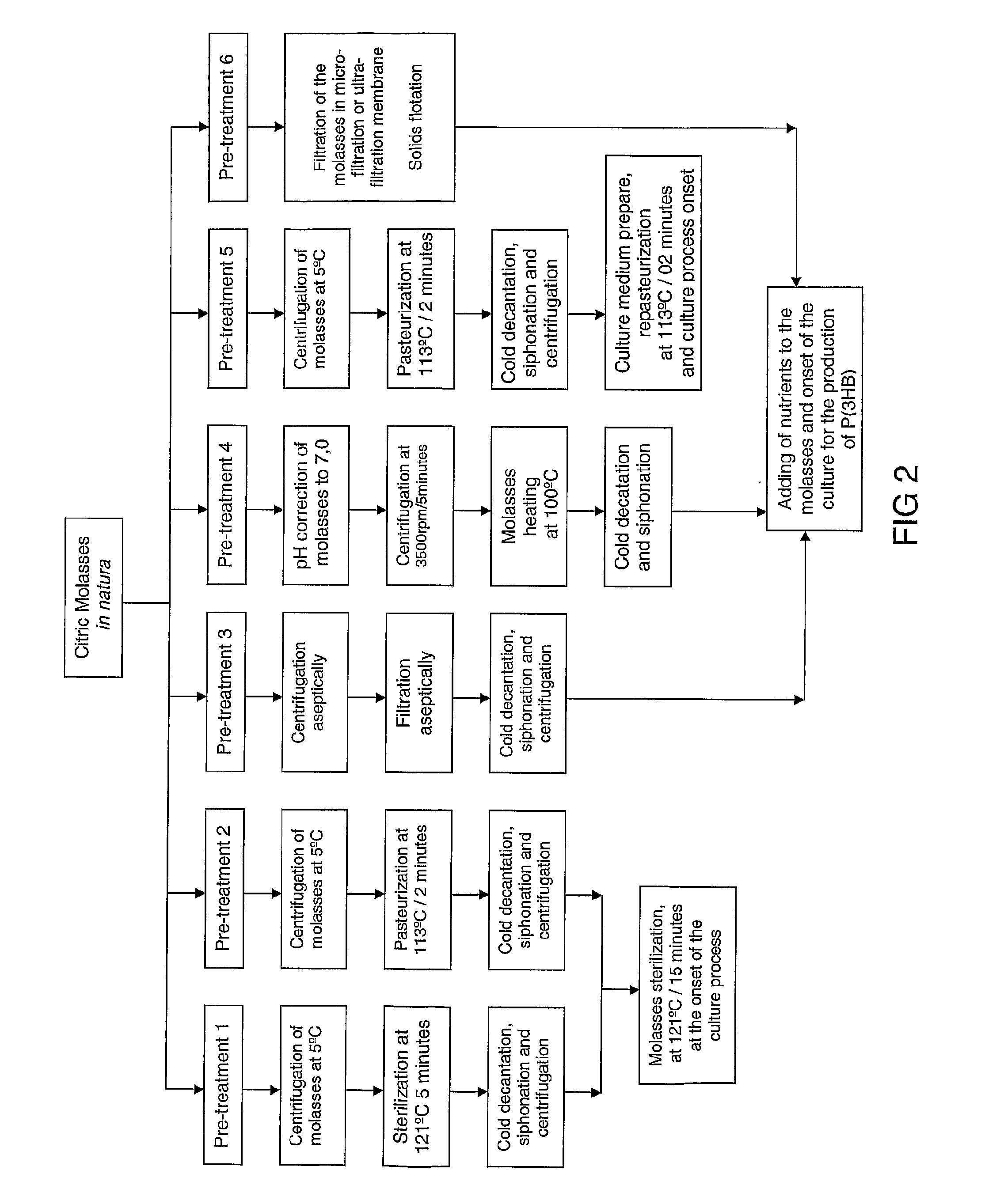
Preparation of PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) from a citric residue
ActiveUS8618245B2Maximum durabilitySimple moldingDyeing processFermentationPolyesterBiodegradable polymer
The present invention relates to an obtainment process of biodegradable polymers from a citric residue resulting from the processing of orange juice. The polymers obtained are polyesters classified as polyhydroxyalkanoates including, among them the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). The biodegradable polymer is obtained from the batch culture process or fed batch culture process with or without recirculation of the cells, using as a carbon source the pre-treated pressing liquor and / or the citric molasses. The polyhydroxyalkanoates, herein described, can be used as substitutes of the synthetic polyesters in different areas, including the food, pharmaceutical, medical, agricultural and other areas.
Owner:FISCHER AGROINDA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




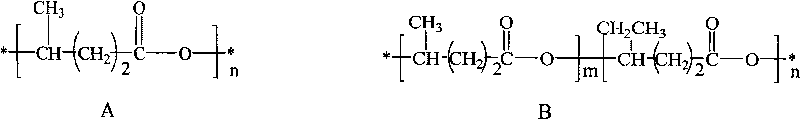
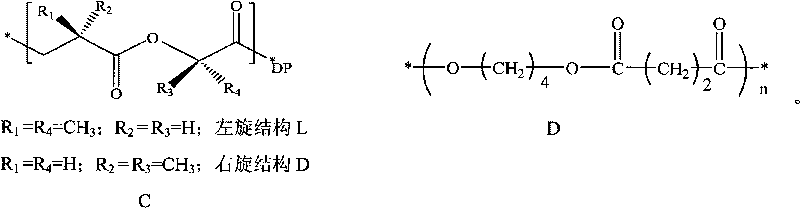
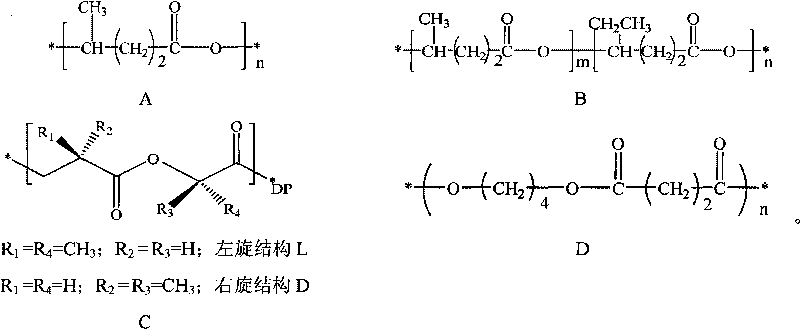







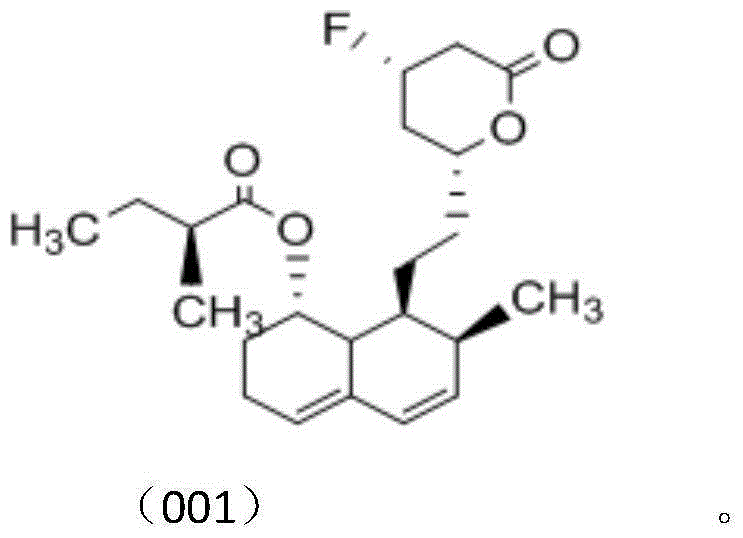



![Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/75d07a2a-26ec-4f42-83cf-e2e9a0845d2e/US07223859-20070529-C00001.png)
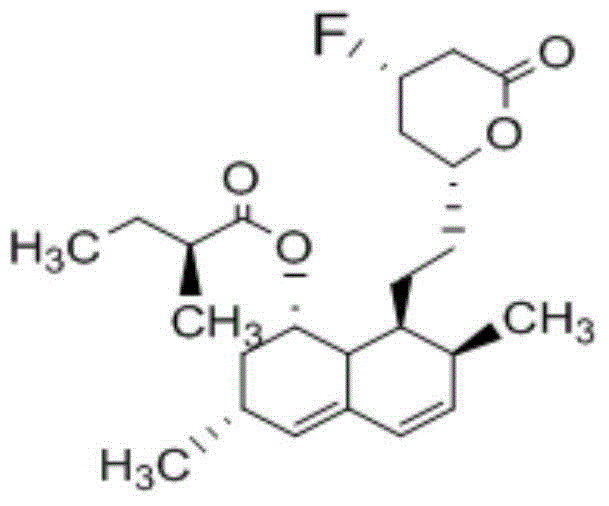
![Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/75d07a2a-26ec-4f42-83cf-e2e9a0845d2e/US07223859-20070529-C00002.png)
![Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative Method for producing (R)-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl) phenylamino]-pentanoic acid amide derivative](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/75d07a2a-26ec-4f42-83cf-e2e9a0845d2e/US07223859-20070529-C00003.png)