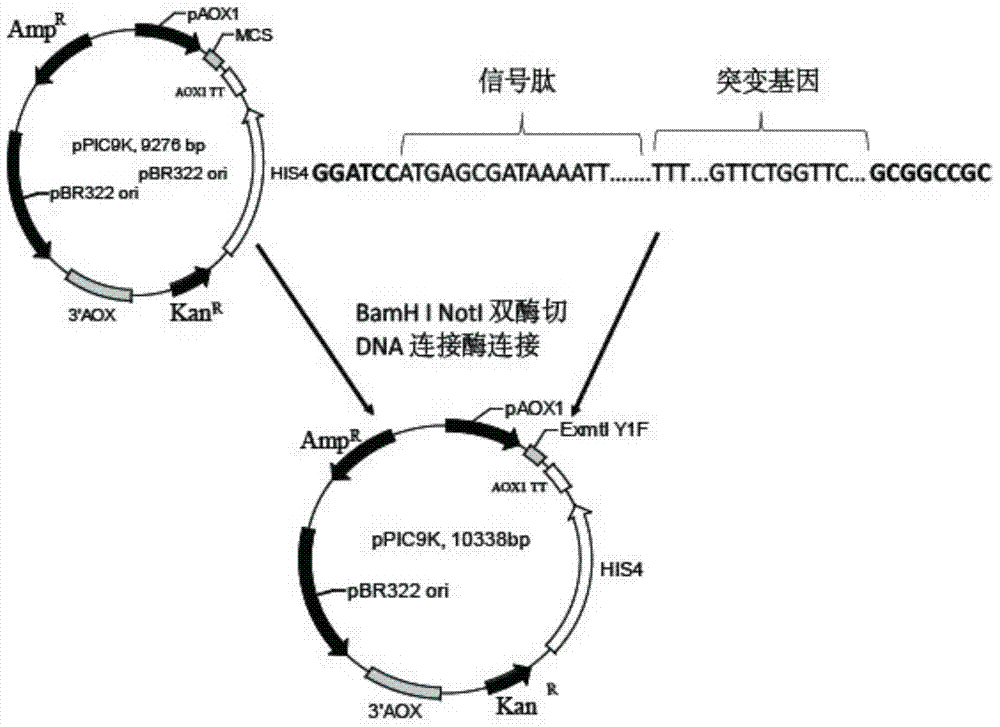
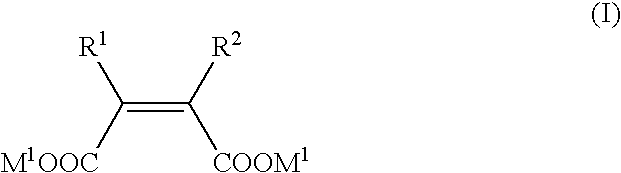Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
140 results about "Amidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, an amidase (EC 3.5.1.4, acylamidase, acylase (misleading), amidohydrolase (ambiguous), deaminase (ambiguous), fatty acylamidase, N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide...
Antifouling composition comprising an enzyme in the absence of its substrate
InactiveUS20050147579A1Trend downReduce adsorptionBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsProteinase activityAmidase
The present invention in one aspect relates to a coating composition comprising at least one enzyme capable of acting on a compound, wherein said action results in the formation of an antifouling species comprising an antifouling activity, and wherein said compound does not form part of said coating composition. The coating composition preferably comprises at least one oxidase capable of acting on a compound, such as a substrate for said oxidase, wherein said action results in the formation of an antifouling species including an antimicrobial species comprising an antimicrobial activity. More preferred, the oxidase comprises an activity which results in the formation of a peroxide. The oxidase can be present in said coating composition in combination with one or more additional enzymes including, but not limited to, an esterase, including a lipase, an amidase, including a protease, and a polysaccharide degrading enzyme, wherein said one or more additional enzyme(s), alone or in any combination, can be included in the presence or absence of one or more substrates for one or more of said enzymes.
Owner:BIOLOCUS
Device and method for detecting antibiotic-inactivating enzymes
ActiveUS20050089947A1Facilitated releaseRobust in vitroMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisΒ lactamasesMicroorganism
A method for determining whether a microorganism produces an AmpC β-lactamase is disclosed in which a culture of a microorganism suspected of producing a β-lactamase that inactivates a β-lactam-containing antibiotic is admixed with an effective amount of each of i) a β-lactam-containing antibiotic, ii) a β-lactamase inhibitor to which AmpC β-lactamase is resistant, and iii) a permeabilizing agent for the microorganism present in a non-growth-inhibiting microorganism-permeabilizing amount to form an assay culture. That assay culture in maintained under appropriate culture conditions and for a time period sufficient to determine the interaction of the microorganism with the AmpC β-lactamase resistant inhibitor and antibacterial compound, and thereby determine the presence of an AmpC β-lactamase, wherein a positive test indicates the presence of an AmpC β-lactamase.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium with amidase gene koucked-out, the construction and the use thereof
ActiveUS20110104690A1Inhibit expressionNot affect performance of strainBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesLarge fragment
An engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium and its construction method as well as its applications, wherein the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium is a mutant strain of an original nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium strain obtained by knocking-out or inhibiting the amidase gene in the original strain. The construction method of the engineered bacterium is to block the expression of the amidase gene by inserting the large fragment of a recombinant suicide plasmid carrying an amidase gene fragment into a wild-type strain through the homologous recombination between the recombinant suicide plasmid and the amidase gene of the wild-type strain. Compared to the corresponding wild-type bacterium strain, both the cell growth and the nitrile hydratase expression of the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium according to the invention are increased. In the process of catalyzing the hydration of acrylonitrile to produce acrylamide, the yield of the product, acrylamide, is significantly increased, while the yield of the by-product acrylic acid is significantly decreased. The engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium of the present invention has wide application prospect in the production of acrylamide by microbiological process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Novel rhodococcus, rhodococcus-origin nitrilase gene, nitrilehydratase gene and amidase gene and process for producing carboxylic acids by using the same
InactiveCN1340101AHigh puritySuitable for industrial productionBacteriaHydrolasesChemical compoundCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a novel Rhodococcus bacterium and to a process of hydrolyzing a cyano group of a nitrile compound using a novel Rhodococcus bacterium to produce the corresponding carboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to a process of producing carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids using a transformant transformed with a plasmid containing a nitrilase gene, a nitrile hydratase gene and an amidase gene derived from Rhodococcus bacteria capable of exhibiting particularly excellent position selectivity for the cyano group of aromatic polynitrile compounds, to such a transformant, such a plasmid, to such genes, to a process of producing an enzyme using the transformant, and to enzymes obtained by the process. The carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids obtained by the present invention are useful as starting materials for the synthesis of drugs, agrochemicals, dyestuffand other chemicals.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
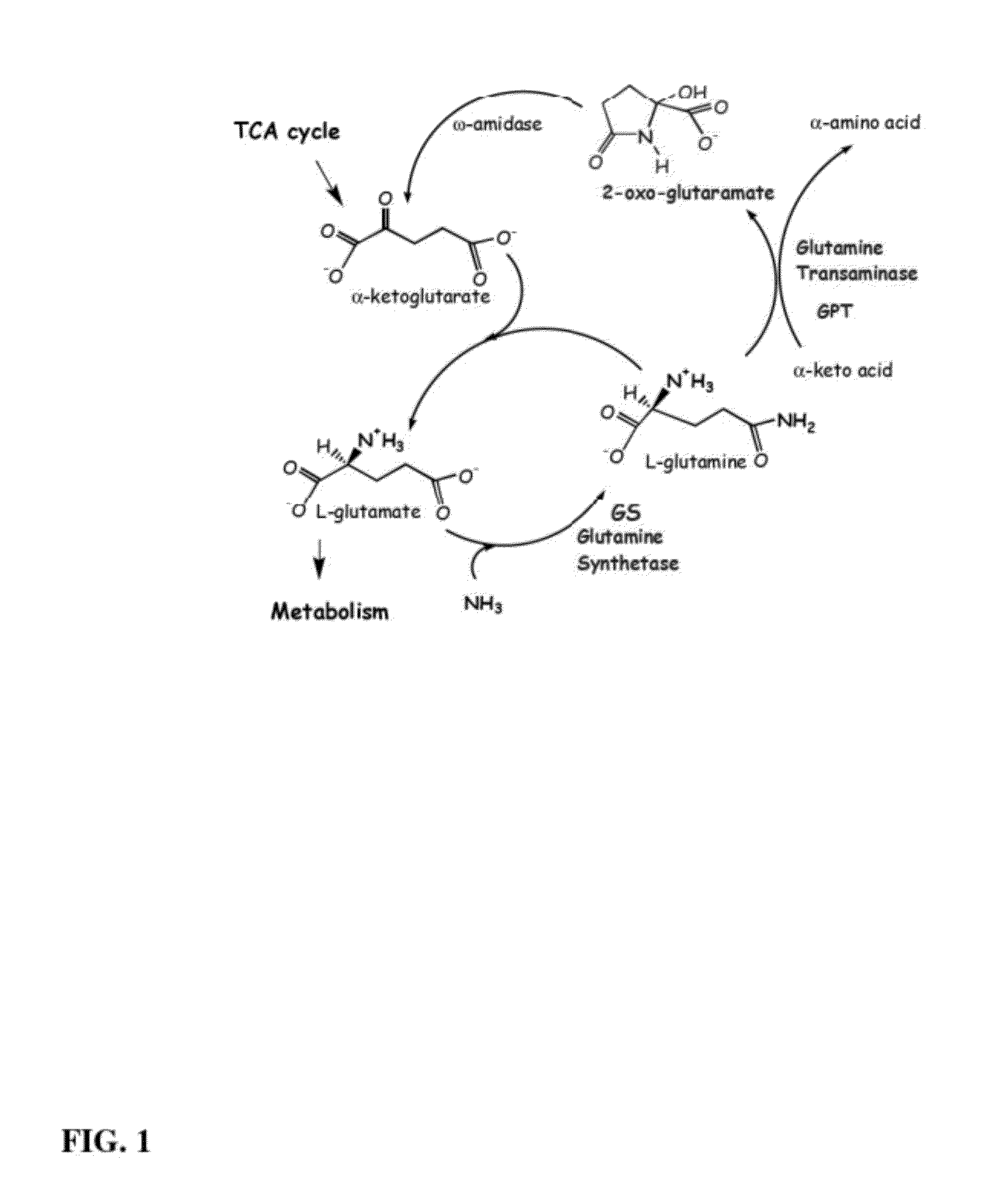
Increasing plant growth by modulating omega-amidase expression in plants
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for increasing the leaf-to-root ratio of the signal metabolite 2-oxoglutaramate and related proline molecules in plants by modulating levels of ω-amidase to increase nitrogen use efficiency, resulting in enhanced growth, faster growth rates, greater seed and fruit / pod yields, earlier and more productive flowering, increased tolerance to high salt conditions, and increased biomass yields.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Food additive comprising an amidase for detoxifying ochratoxin
The present invention relates to amidase enzymes and a feed or food additive comprising the amidase enzyme capable of degrading ochratoxin.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Recombinant amidase Dt-Ami 2, encoding gene, vector, engineering strain and applications of recombinant amidase Dt-Ami 2 and engineering strain
The invention discloses a recombinant amidase Dt-Ami 2, an encoding gene, a vector, an engineering strain and applications of the recombinant amidase Dt-Ami 2 and the engineering strain. The invention provides a Delftia tsuruhatensis (CCTCC No. M 205115)-derived amidase gene, and a recombinant amidase WB encoded by the gene; and the amidase gene can be connected with an expression vector so as to obtain an intracellular expression recombinant plasmid containing the gene, then the intracellular expression recombinant plasmid is transferred to an escherichia coli strain so as to obtain recombinant escherichia coli, the recombinant escherichia coli contains recombinant amidase, and the recombinant amidase can be used as a catalyst for catalyzing the hydrolysis of a series of amide compounds.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
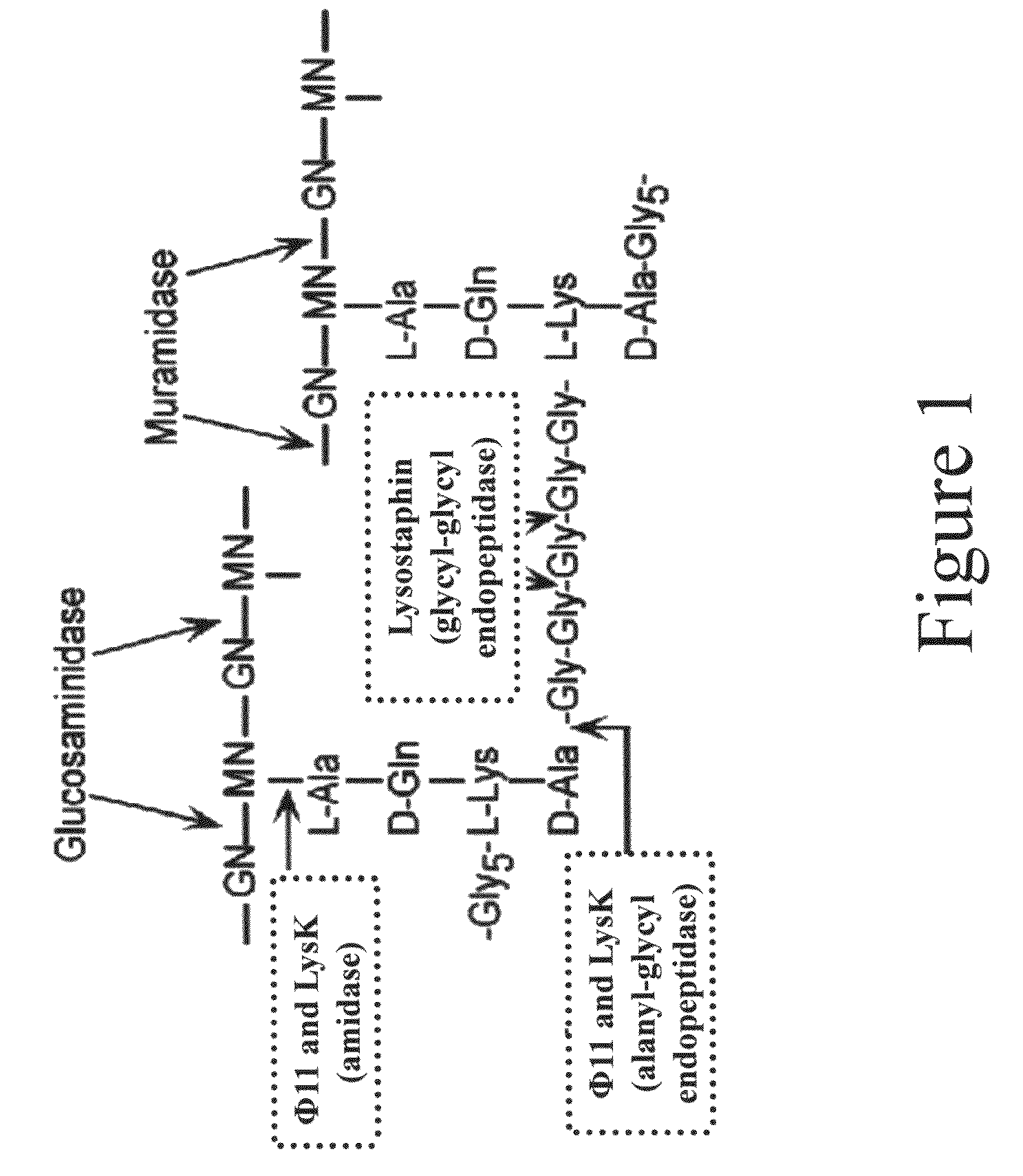
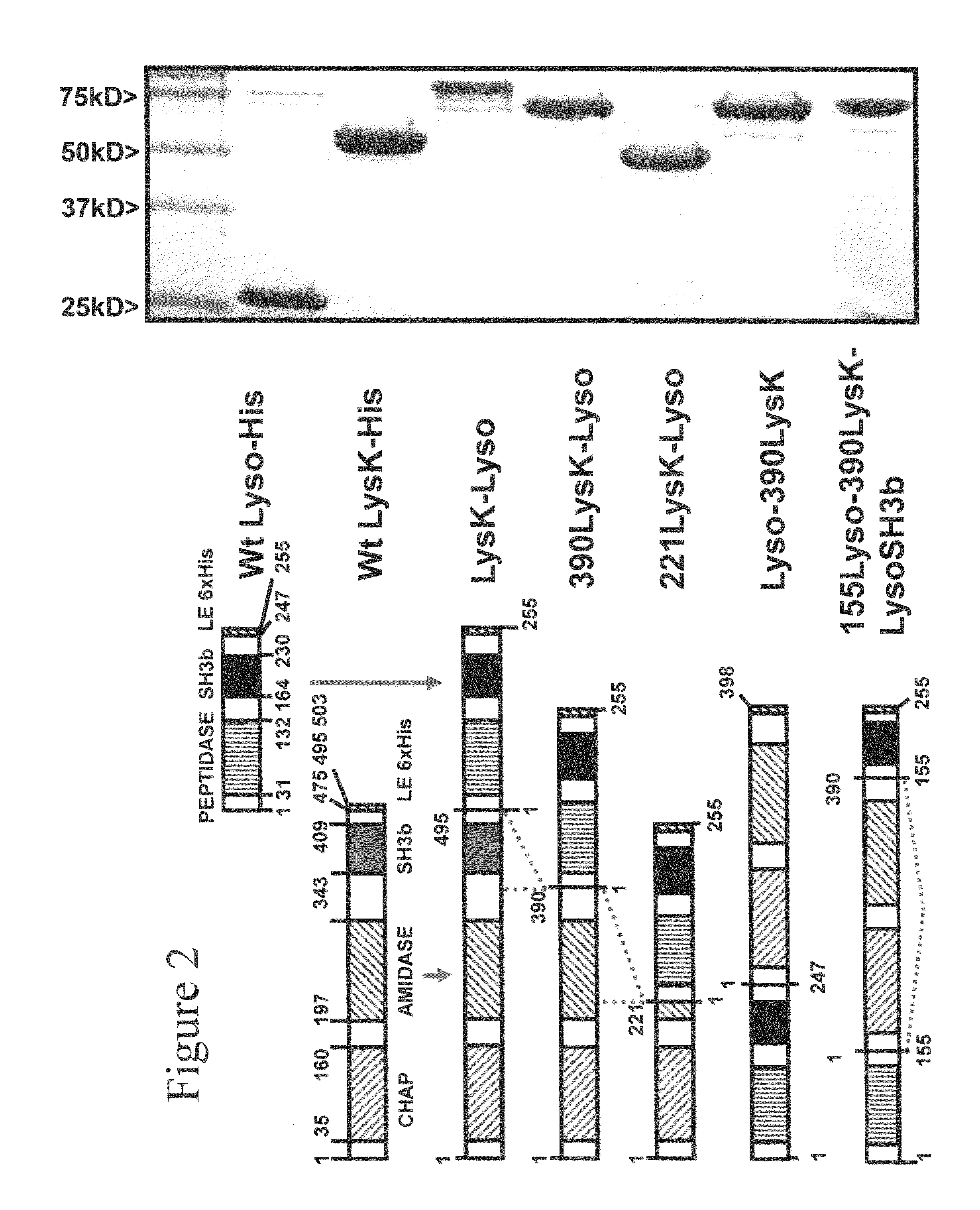
Triple acting antimicrobials that are refractory to resistance development
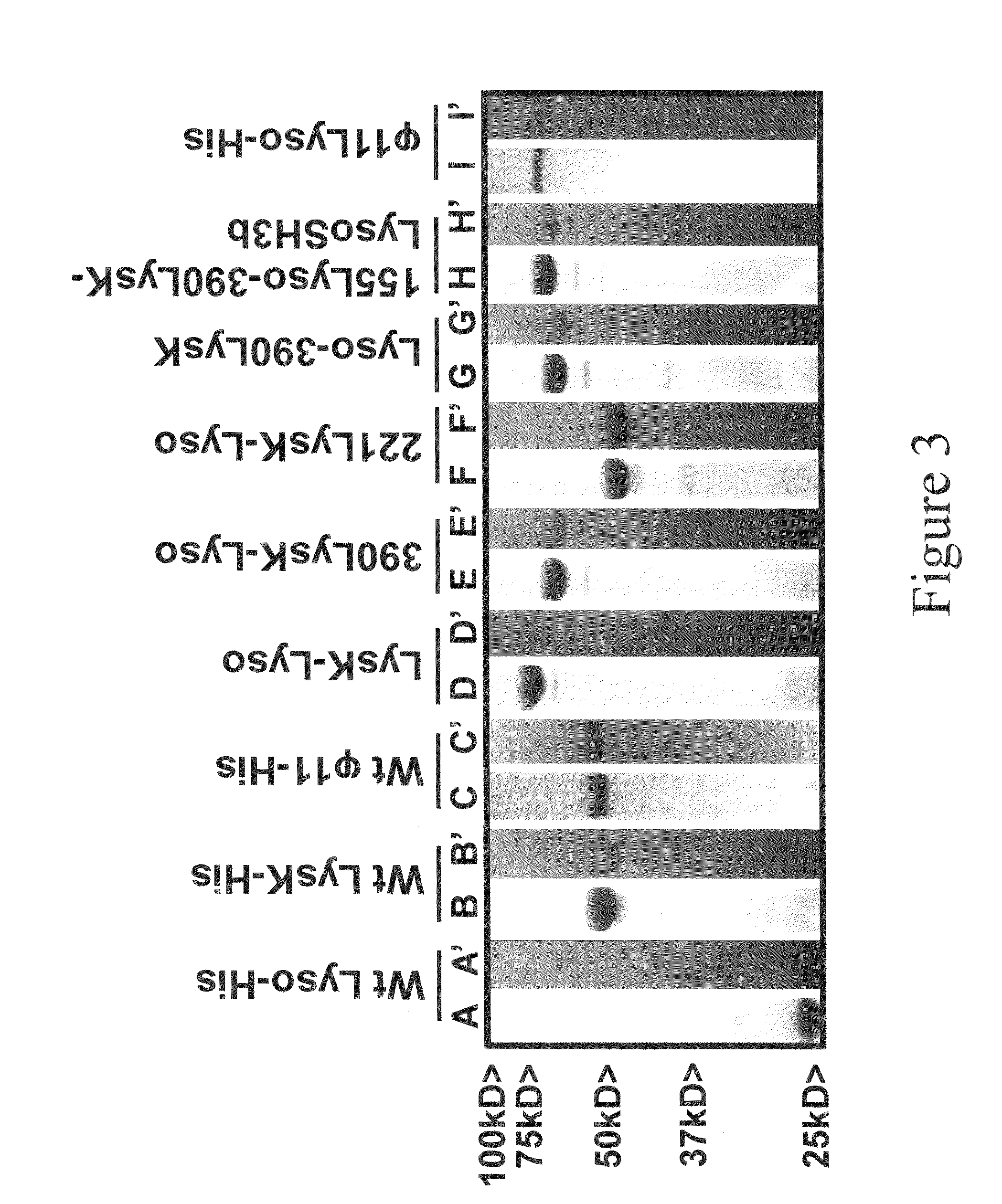
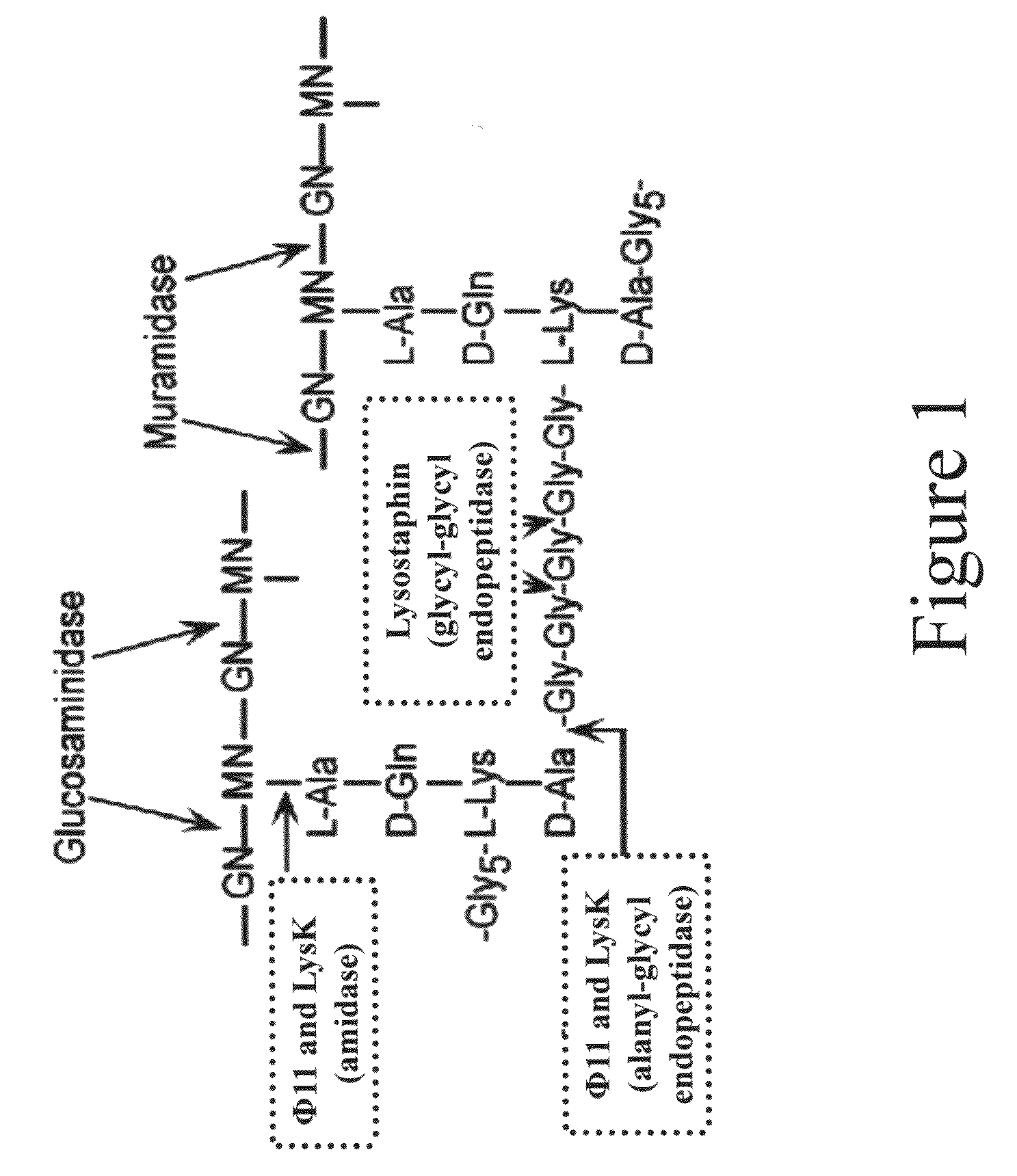
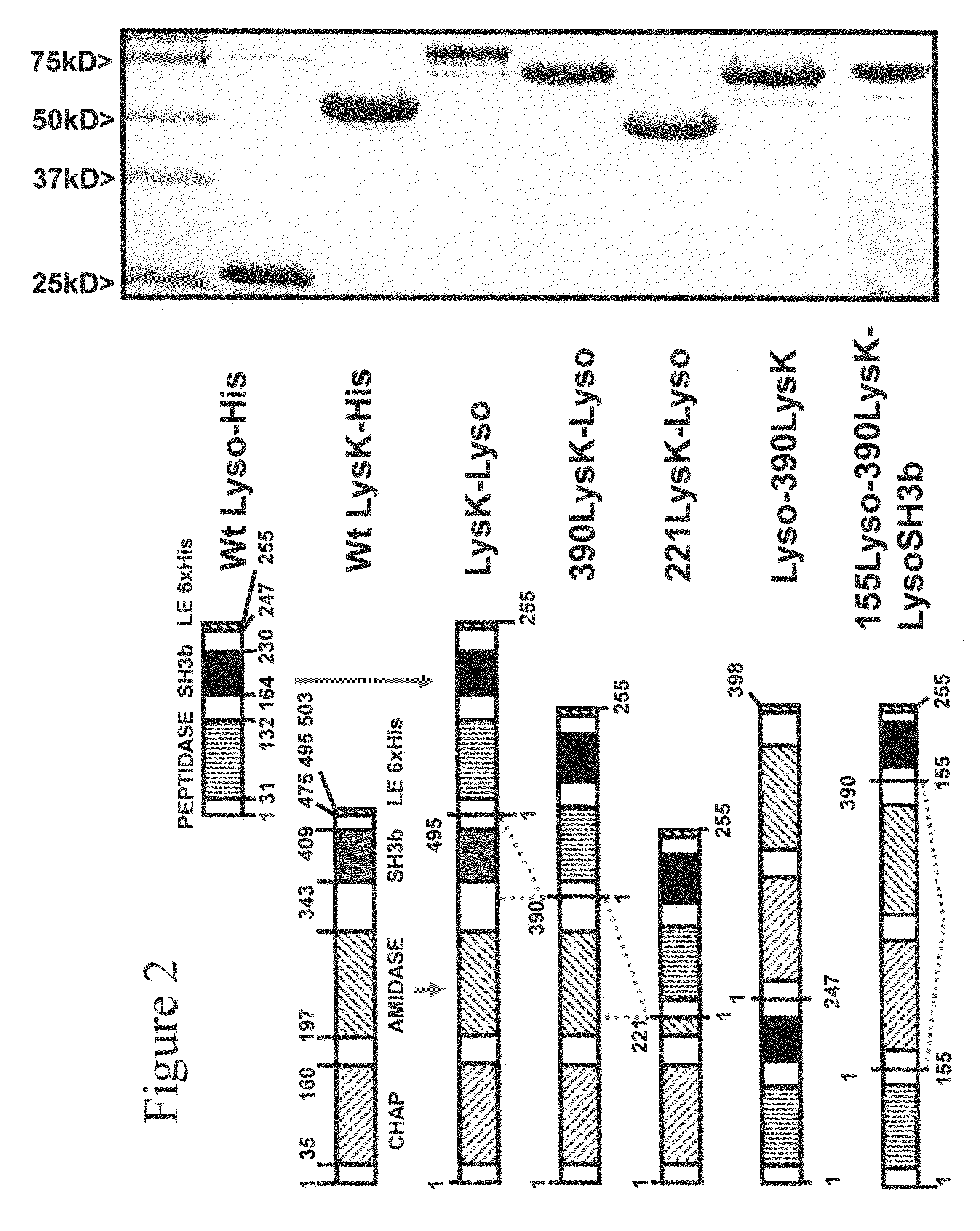
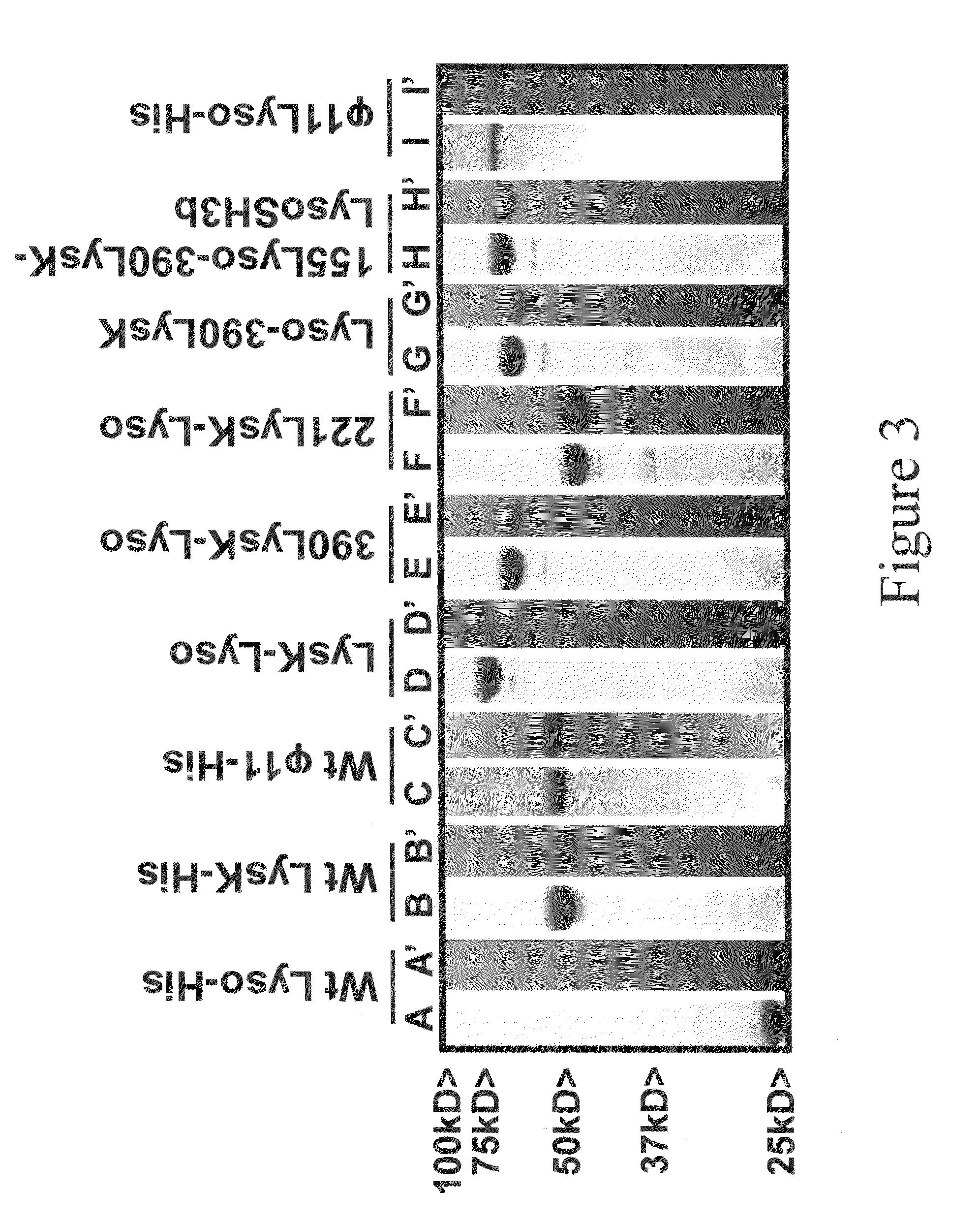
InactiveUS8481289B2Effectively lysingPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesGrowth phaseGlycyl-Glycine
Multi-drug resistant superbugs are a persistent problem in modern health care. This invention provides an antimicrobial endolysin-Lysostaphin triple fusion protein, comprising (1) an endolysin CHAP endopeptidase domain, (2) an endolysin amidase domain, and (3) a Lysostaphin glycyl-glycine endopeptidase domain. The domains are derived from two proteins that show antimicrobial synergy when used in combination. The protein has specificity and exolytic activity for the peptidoglycan cell wall of untreated, live Staphylococcus aureus from many growth phases i.e. stationary, logarithmic and biofilm growth. The recombinant triple fusion protein comprising the three functional antimicrobial domains is designed to be refractory to resistance development.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Primers for Use in Detecting Beta-Lactamases
InactiveUS20070248954A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementΒ lactamasesGreek letter beta
Oliognucleotide primers are provided that are specific for nucleic acid characteristic of certain β-lactamase genes. The primers can be employed in methods to identify nucleic acid characteristic of family-specific (and even group-specific) β-lactamase enzymes in samples, and particularly, in clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
Compound enzyme, additive, application thereof and method for removal of fungal toxins
Relating to the field of removal of fungal toxins, the invention discloses a compound enzyme, an additive, application thereof and a method for removal of fungal toxins. Specifically, the invention relates to a compound enzyme, which contains amidase and esterase and can remove fungal toxins, especially fumonisins, ochratoxins and T2 toxin, additives containing the compound enzyme and applicationthereof in removal of fungal toxins, especially fumonisins, ochratoxins and T2 toxin, and a method for removal of fungal toxins. According to the technical scheme, combined use of the amidase and esterase can achieve simultaneous removal of ochratoxin A, fumonisins and T2 toxin, the removal efficiency is greatly improved than single use of one enzyme, and vomitoxins, aflatoxins and zearalenone toxin can be removed to certain degree.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Triple acting antimicrobials that are refractory to resistance development
Multi-drug resistant superbugs are a persistent problem in modern health care. This invention provides an antimicrobial endolysin-Lysostaphin triple fusion protein, comprising (1) an endolysin CHAP endopeptidase domain, (2) an endolysin amidase domain, and (3) a Lysostaphin glycyl-glycine endopeptidase domain. The domains are derived from two proteins that show antimicrobial synergy when used in combination. The protein has specificity and exolytic activity for the peptidoglycan cell wall of untreated, live Staphylococcus aureus from many growth phases i.e. stationary, logarithmic and biofilm growth. The recombinant triple fusion protein comprising the three functional antimicrobial domains is designed to be refractory to resistance development.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Detoxifying pre-treated lignocellulose-containing materials
The invention relates to a process of detoxifying pretreated lignocellulose-containing maternal by subjecting pre-treated material to a detoxifying compound capable of binding 1) pre-treated lignocellulose degradation products and / or 2) acetic acid. The detoxifying compound may also be an amidase and / or and anhydrase. The invention also relates to a process of producing a fermentation product including a detoxification process of the invention.
Owner:NOVOZYMES NORTH AMERICA INC
Method of deamidation of milk protein and method of denaturation of milk protein
A method for improving the degree of deamidation (%) and the deamidation rate when deamidating a milk protein by an enzyme which exerts a deamidating effect by acting directly on an amide group of a protein without cleaving a peptide bond or crosslinking the protein is provided. A method for denaturing a milk protein enzymatically is also provided.A preliminarily denatured milk protein is deamidated by a protein deamidating enzyme which exerts a deamidating effect by acting directly on an amide group of a protein having a molecular weight of 5,000 or more without cleaving a peptide bond or crosslinking the protein. Such an enzyme can be used also for denaturing a milk protein.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Double knockout recombinant rhodococcus as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105420154AHigh expression activityQuality improvementBacteriaHydrolasesSaccharumLevansucrase
The invention discloses a construction method of double knockout recombinant rhodococcus. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) primers are designed according to nitrile hydratase gene sequence of the rhodococcus for respective amplification of an upstream sequence and a downstream sequence of a nitrile hydratase gene, and an upstream fragment and a downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are obtained; (2) the upstream fragment and the downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are inserted into a suicide plasmid, and a recombinant suicide plasmid is obtained, wherein the suicide plasmid carries a kanamycin resistant gene and a levansucrase gene; (3) competent cells of recombinant rhodococcus of an amidase gene are knocked out through transformation of the recombinant suicide plasmid, and the double knockout recombinant rhodococcus is obtained: first screening is performed through kanamycin resistance, and a first recombinant colony is obtained and subjected to second screening through a sucrose plate. The invention further discloses recombinant rhodococcus with high nitrilase expression, a construction method of the recombinant rhodococcus and a method for preparing acrylamide.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
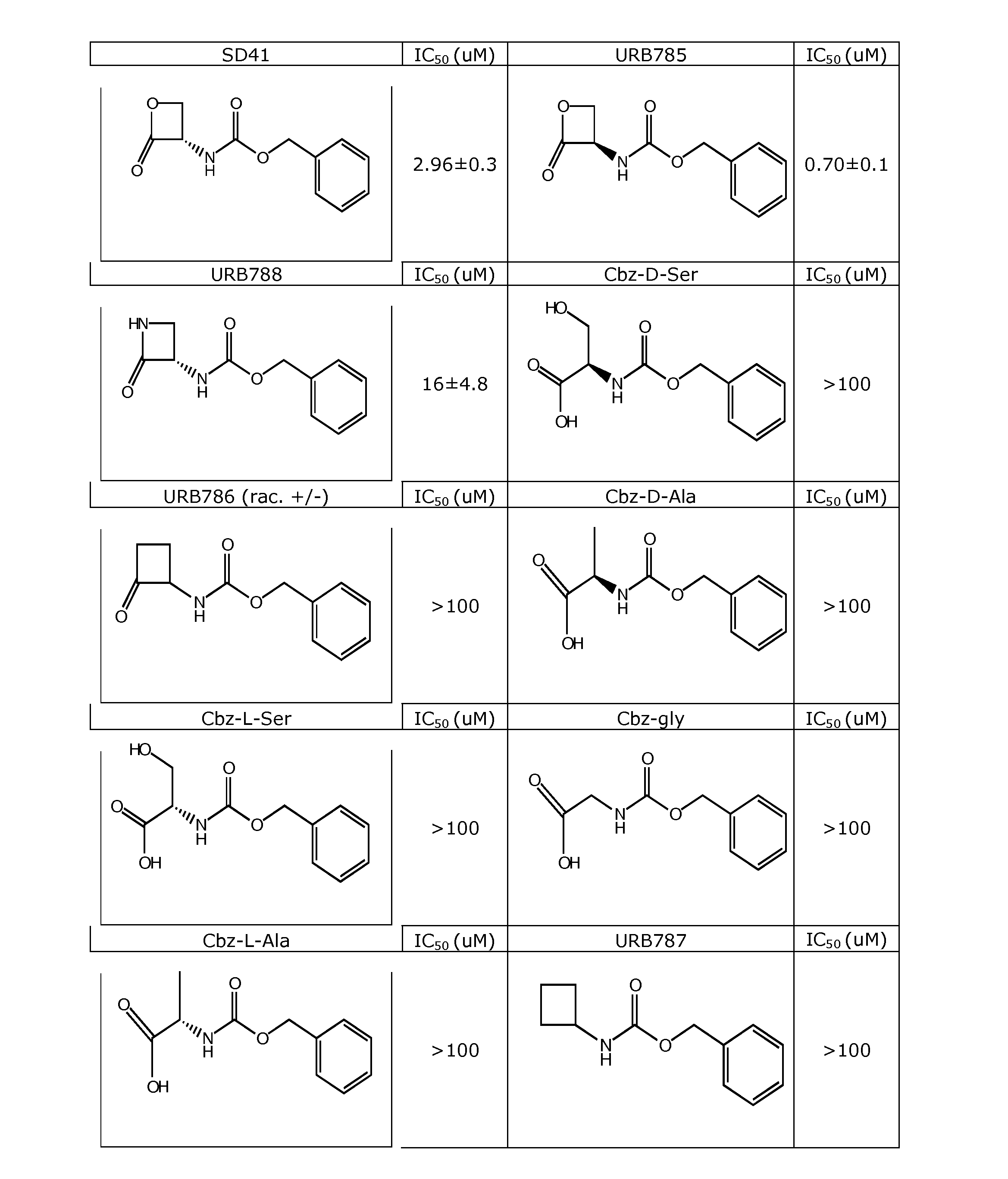
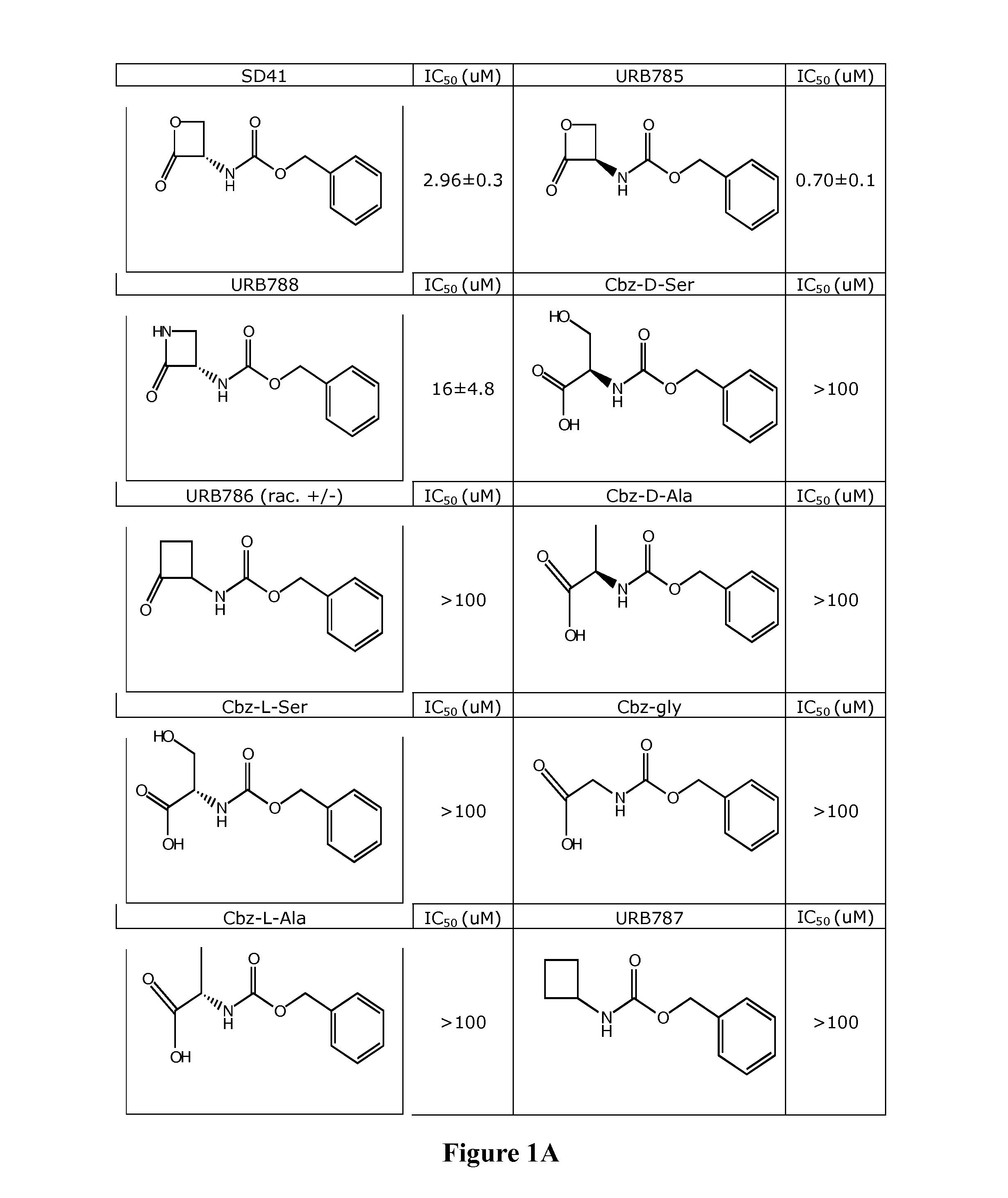
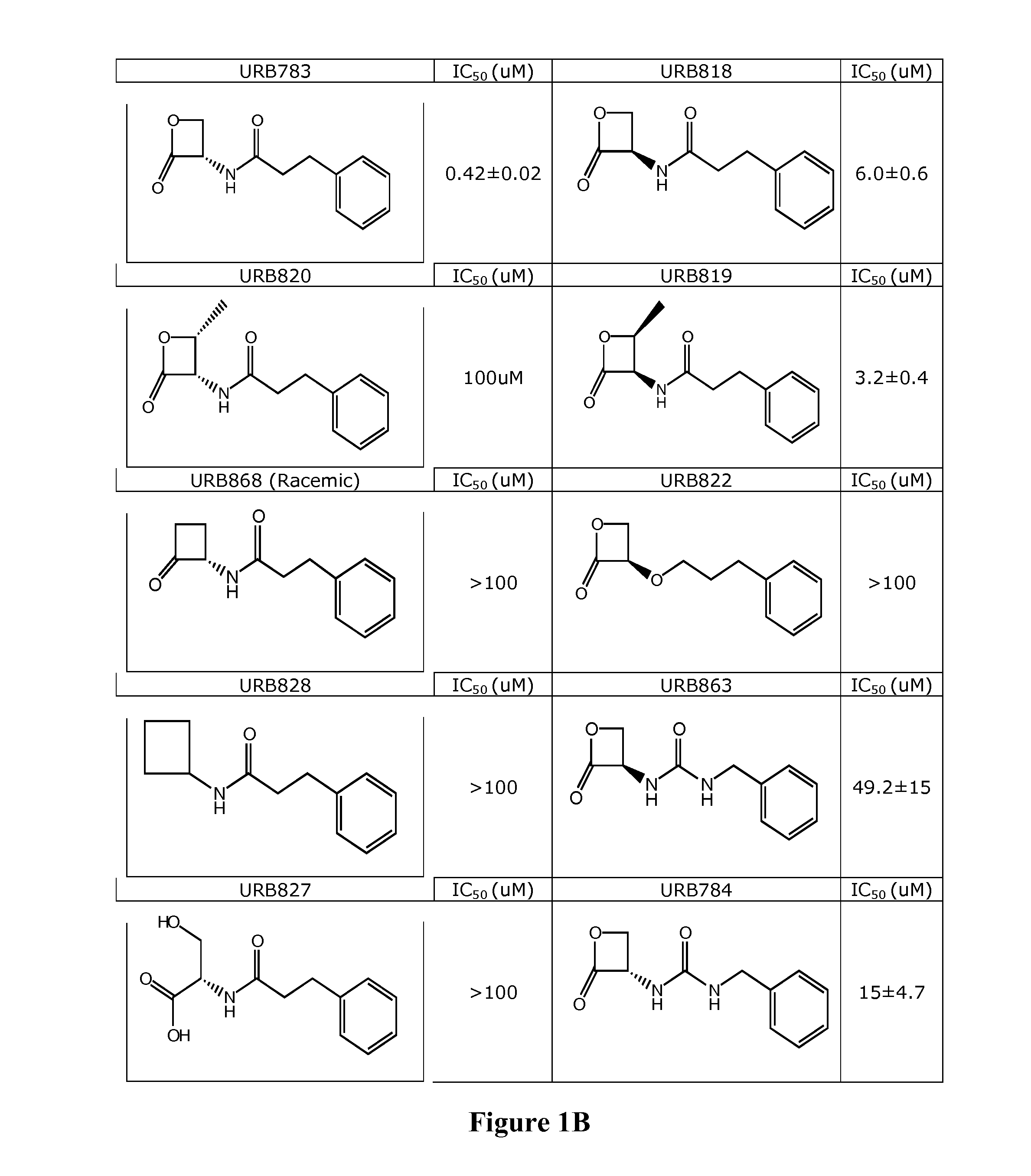
Inhibitors of NAAA and Methods Thereof
Compounds and pharmaceutical compositions are contemplated that inhibit N-acyl-ethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA) to so increase the concentration of the substrate of NAAA, palmitoylethanolamide (PEA). NAAA inhibition is contemplated to be effective to alleviate conditions associated with a reduced concentration of PEA. Among other uses, various NAAA inhibitors are especially contemplated as therapeutic agents in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PARMA +2
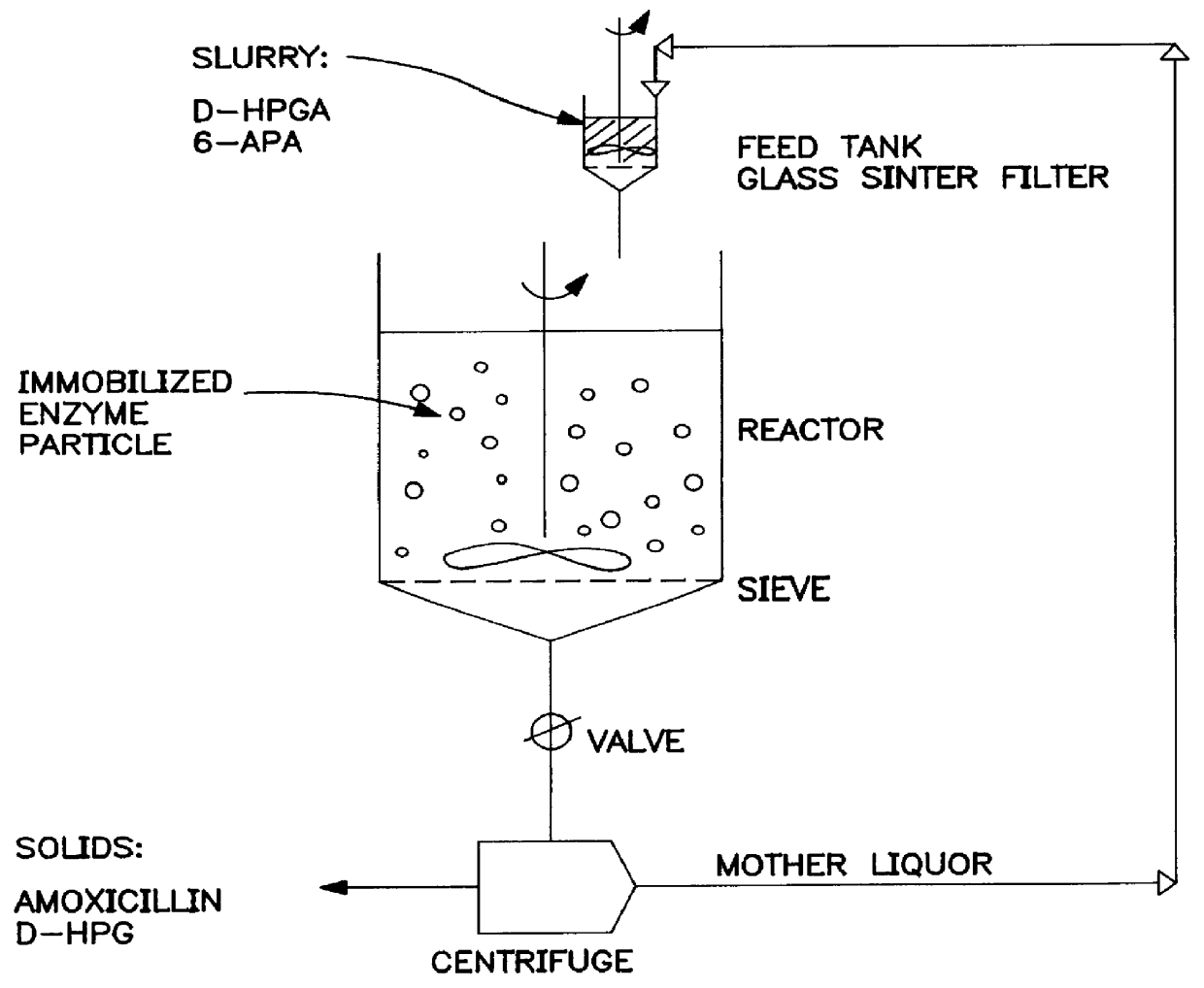
Process for preparation of beta -lactams at constantly high concentration of reactants
InactiveUS6048708AIncrease the molar ratioEconomic impactHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierHigh concentrationAmidase
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 02876 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 19, 1997 PCT Filed Jul. 18, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 02663 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 1, 1996An improvement for enzymatically syhnthesizing a beta -lactam compound is presented. The improvement comprises catalyzing the acylation of an amino beta -lactam with an acylating agent for at least 5 hours with an amidase or acylase, wherein the concentration of each reactant is constantly higher than 70% of the lowest value of the saturated concentration of both reactants.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV
Primers for use in detecting beta-lactamases
Oliognucleotide primers are provided that are specific for nucleic acid characteristic of certain beta-lactamases. The primers can be employed in methods to identify nucleic acid characteristic of family-specific beta-lactamase enzymes in samples, and particularly, in clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
High-efficient expression and application of amidohydrolase
The invention relates to the clone of amidohydrolase, and the construction, zymoprotein expression and industrial application of engineering bacteria, belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and mainly aims to solve the problems that amidohydrolase produced by natural bacteria is low in enzyme activity, low in bacterial concentration and difficult for production application. On the basis that the hydrolase is produced by fermenting Delftiatsuruhatensis in Delftia, an amidohydrolase gene is cloned to establish a full set of process of the fermentation, and inducible expression, and industrial production of the Escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria. Through the gene engineering modification, the amidase activity is over 3000 u / l, much higher than 300 u / l of the original strain; the actual application shows that the enzyme has a wide application scope, can be applied the production of side chains of statins, the production cost is greatly reduced and the realization of green chemistry is promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitors
A new metallo-β-lactamase inhibitor which acts as a medicament for inhibiting the inactivation of β-lactam antibiotics and recovering anti-bacterial activities is disclosed. The maleic acid derivatives having the general formula (I) have metallo-β-lactamase inhibiting activities. It is possible to recover the anti-bacterial activities of β-lactam antibiotics against metallo-β-lactamase producing bacteria by combining the compound of the general formula (I) with β-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Compositions and methods of inhibiting n-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase
Compounds and pharmaceutical compositions are contemplated that inhibit N-acyl-ethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA) to so increase the concentration of the substrate of NAAA, palmitoylethanolamide (PEA). NAAA inhibition is contemplated to be effective to alleviate conditions associated with a reduced concentration of PEA. Among other uses, various NAAA inhibitors are especially contemplated as therapeutic agents in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PARMA +2
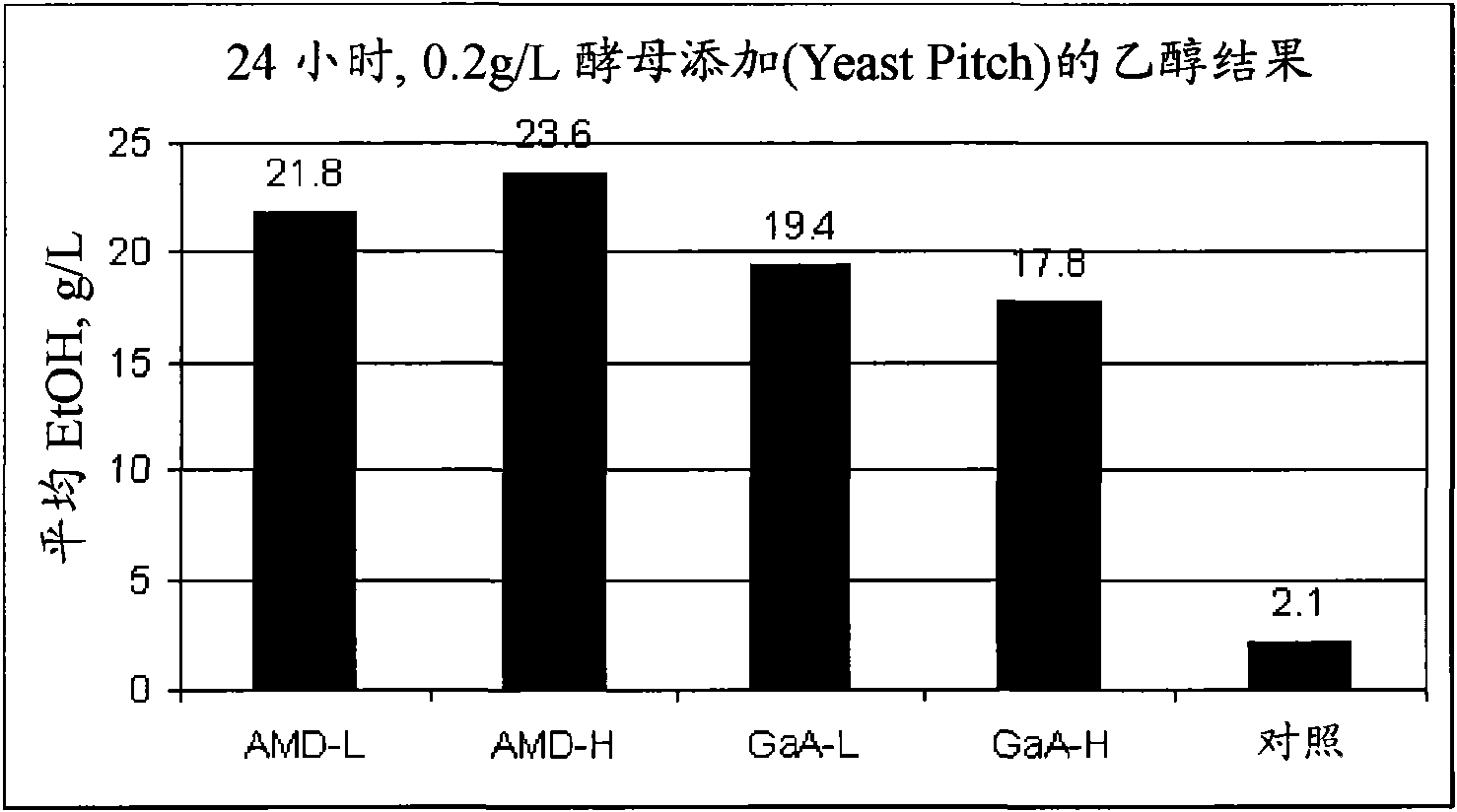
Rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium low in urea yield and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102533573AEnhanced degradation pathwayReduce secretionFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationBiotechnologyFood flavor
The invention discloses a rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium low in urea yield and a construction method thereof. The construction method includes: placing an encoding frame of a carbamido amidase gene DUR 1,2 in control of brewing yeast group forming high-expression thermoplastic polyimide 1 (TPI 1) transcription promoters and TPI 1 transcription terminators, and stably integrating TPI 1p-DUR1,2-TPI1t gene cassette in a bacterial strain rice wine yeast bacterial strain genome through homologous recombination to obtain the rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium. The rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium has the remarkable advantage of being low in urea production level, rice wine produced through fermentation of the rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium is low in ethyl cellulose (EC) content and keeps flavor basically unchanged, and therefore the rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium has wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Detoxifying pre-treated lignocellulose-containing materials
The invention relates to a process of detoxifying pre-treated lignocellulose-containing material by subjecting pre-treated material to a detoxifying compound capable of binding 1) pre-treated lignocellulose degradation products and / or 2) acetic acid. The detoxifying compound may also be an amidase and / or and anhydrase. The invention also relates to a process of producing a fermentation product including a detoxification process of the invention.
Owner:NOVOZYMES NORTH AMERICA INC
Immobilized penicillin amidase carrier and its preparing method
The present invention discloses a kind of immobilized penicillin amidase carrier and its preparation process. The immobilized pencillin amidase carrier is prepared with surfactant as dispersant and vinyl compound as monomer and through crosslinking polymerization in reverse suspension technology. The carrier immobilized pencillin amidase has an apparat enzyme activity in preparing 6-APA with benzyl pencillin potassium as high as 125 IU / g. The polymer bead carrier containing epoxy group of the present invention has high apparent enzyme activity, simple technological process, easy operation andcheap material and may be used in industrial production.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Trypsin mutant capable of improving enzyme activity and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104328102AIncrease extracellular secretionAvoid self-degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisTyrosine
The invention discloses a trypsin mutant capable of improving enzyme activity and a construction method thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the mutant disclosed by the invention, on the basis of an amino acid with a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2, tyrosine on the 1st site is mutated into phenylalanine, meanwhile arginine on the 123rd site is mutated into isoleucine. The mutant disclosed by the invention is expressed in pichia pastoris; the enzyme activity of amidase (BAPNA) fermented in a 3L tank is 85.3U / mL and enzyme activity of esterase (BAEE) is 5954U / mL, which are respectively improved by 3.3 times and 2.7 times in comparison with those of a strain before mutation; therefore, a problem of low extracellular enzyme activity of trypsin is solved. When applied to producing the trypsin, the mutant disclosed by the invention is high in yield, simple in process and convenient for industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
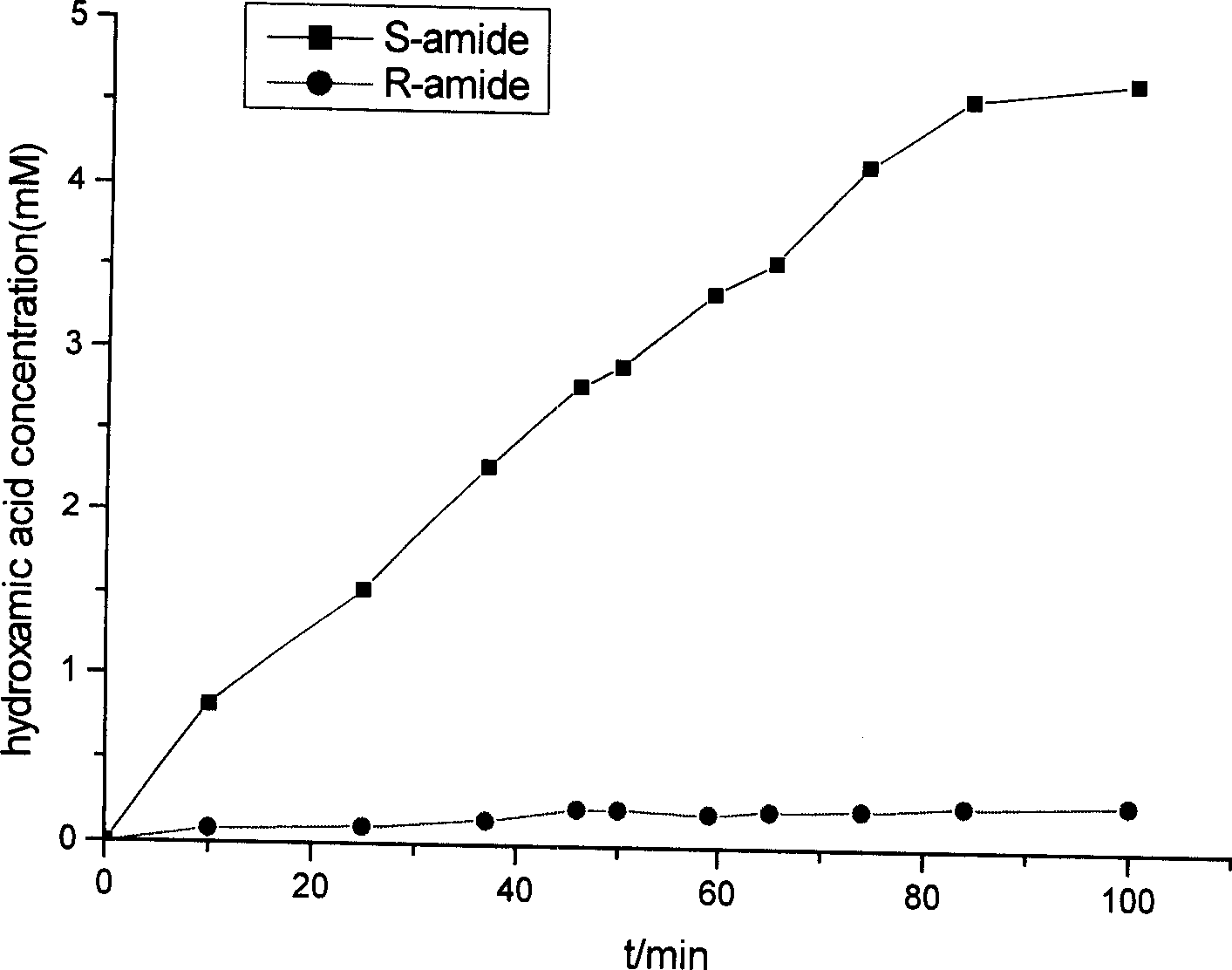
Optical selective screening process for amidase
ActiveCN1824795AEasy to filterOvercoming time-consuming and laboriousMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismHydroxylamine
This invention provides an optical selecting amidase filtration method. The sample detected is dissolved in solution of pH 5 to 9; hydroxylamines are added and make its final concentration between 0.5 to 1M. Then chiral S-amide or R-amide is added as substrate, and make its concentration between 5 to 30mM. They react in water at 20 to 50 degree centigrade, and then the reacted transformation liquor is added solution with Fe<3+> to colored. If it is reddish brown, it reveals that the sample's optical selection is consistent with the substrate spatial configuration, or the amidase didn't have the optical selection. If it is faint yellow, it reveals that the sample's optical selection is not consistent with the substrate spatial configuration. The substrate is don't need derivation, the method can use simple colorimetry to quickly identify the amidase's activity and optical selectivity of the detected microorganism and its extract. Its filtration process is simple, fast, and its equipment request is low, versatility is strong, so it brings great convenience to the optical selecting amidase filtration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for synthesizing pregabalin chiral intermediate through regio-selective and stereo-selective bio-catalytic synthesis
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing a pregabalin chiral intermediate through regio-selective and stereo-selective bio-catalytic synthesis. The method comprises the followingsteps: reacting racemic isobutyl butyronitrile (IBSN) in a reaction medium at a temperature of 20-50 DEG C in presence of nitrilase and amidase catalysis for 4-10 hours, thereby obtaining (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoate. The method is mild in reaction conditions, simple and feasible in operation and excellent in regio-selectivity and stereo-selectivity, the conversion rate of the pregabalin key chiral intermediate, namely (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoate, synthesized from the racemic substrate IBSN through a one-pot process can reach 49.5%, the value e.e. is 99.5%, and the conversion rate is close to a theoretical conversion rate of 50%. Meanwhile, the optical purity exceeds 99%, and the method has obvious application values for simplifying the production process steps of pregabalin and reducing the production cost of the pregabalin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Lactamase amplification substrate
An amplifiable β-lactamase substrate is provided comprising an enzyme donor fragment of β-galactosidase linked to form a ring to a β-lactam ring that is a substrate for lactamase and upon opening of the β-lactam ring the enzyme donor fragment becomes linearized. The cyclic substrate only weakly binds to the enzyme acceptor fragment of β-galactosidase. The substrate finds application for the sensitive detection of β-lactamase for direct detection of the enzyme or when the enzyme is used as a label.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
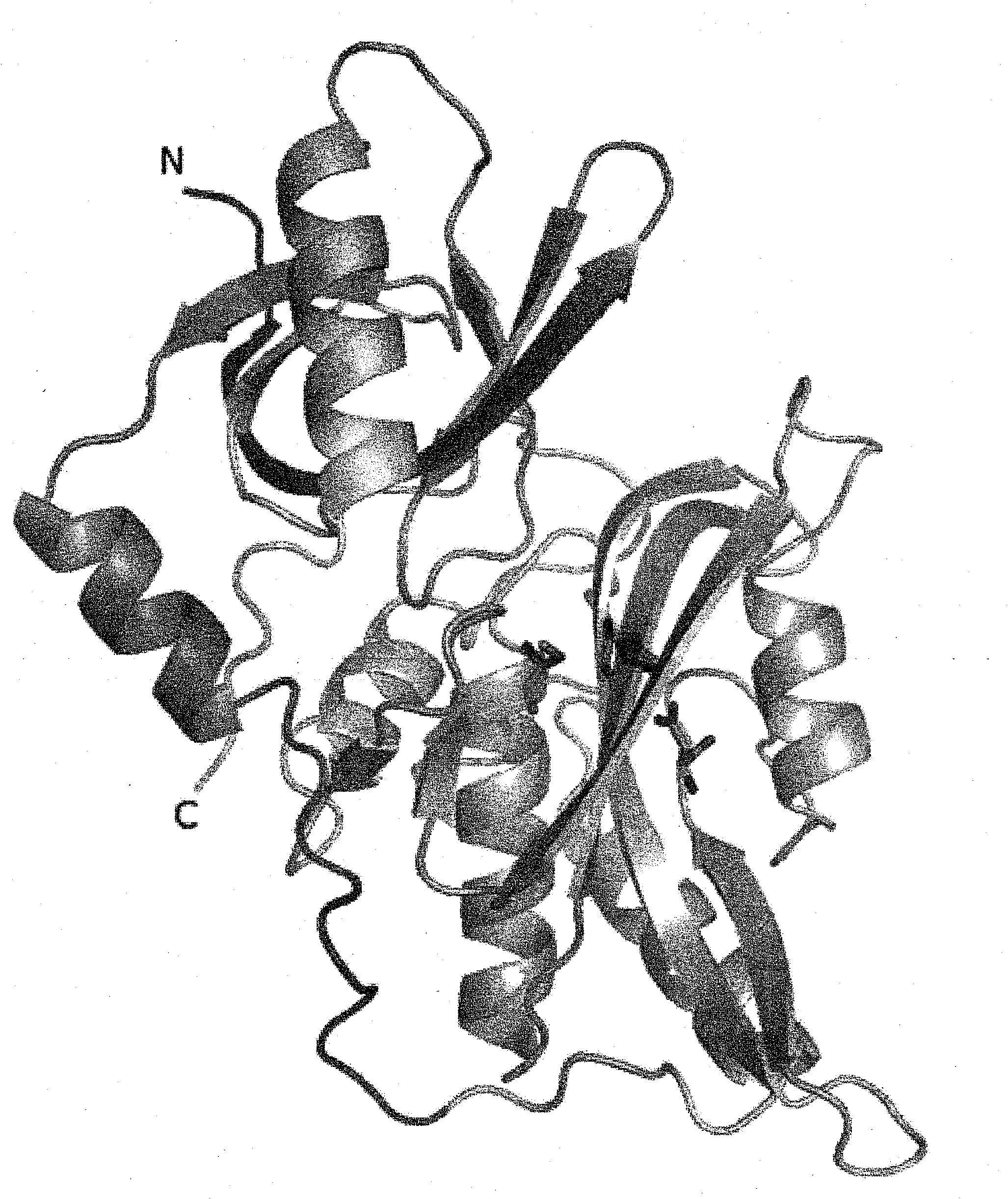
Method for designing mutant enzyme, method for preparing mutant enzyme, and mutant enzyme
Disclosed is a novel method for improving an enzyme capable of deamidating a protein. A mutant enzyme can be designed by the following steps (1) and (2): (1) specifying at least one amino acid residue among amino acid residues corresponding to the amino acid residues located at position-35, position-38, position-39, position-40, position-41, position-42, position-43, position-45, position-46, position-49, position-79, position-80, position-81, position-82, position-83, position-84, position-103, position-104, position-105, position-106, position-117, position-142, position-143, position-146, position-166 and position-185 in the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:2 which is an amino acid sequence for a protein deamidase (an enzyme to be mutated); and (2) constructing an amino acid sequence having the substitution of the amino acid residue specified in step (1) by another amino acid residue or having the deletion of the amino acid residue specified in step (1) by using the amino acid sequence for the enzyme to be mutated as a base sequence.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com