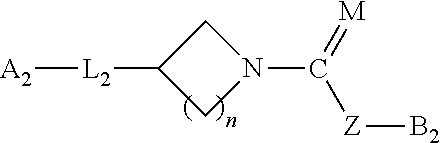
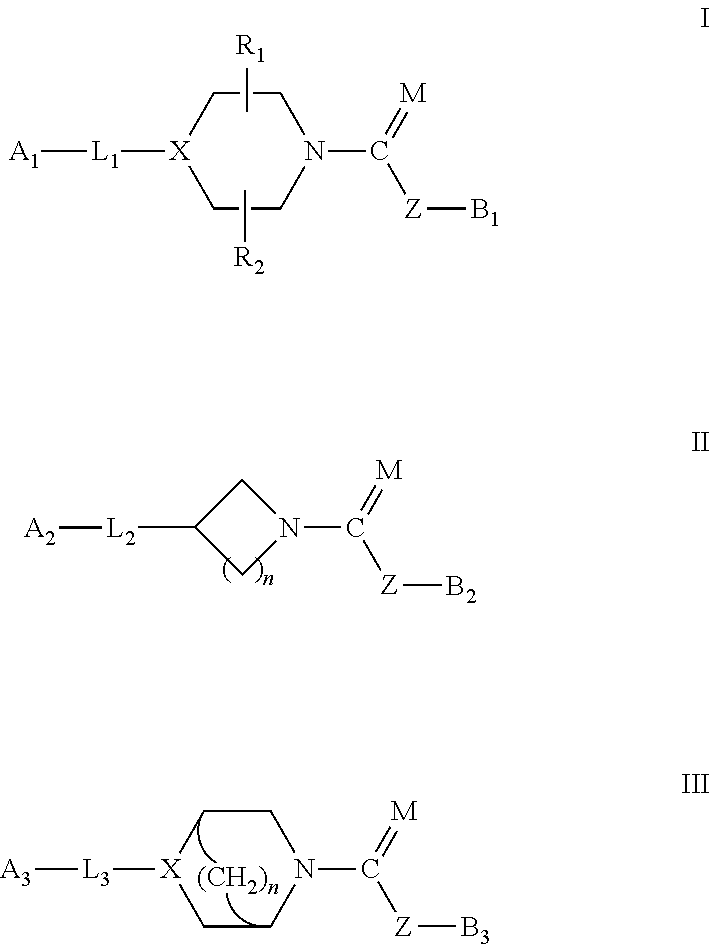
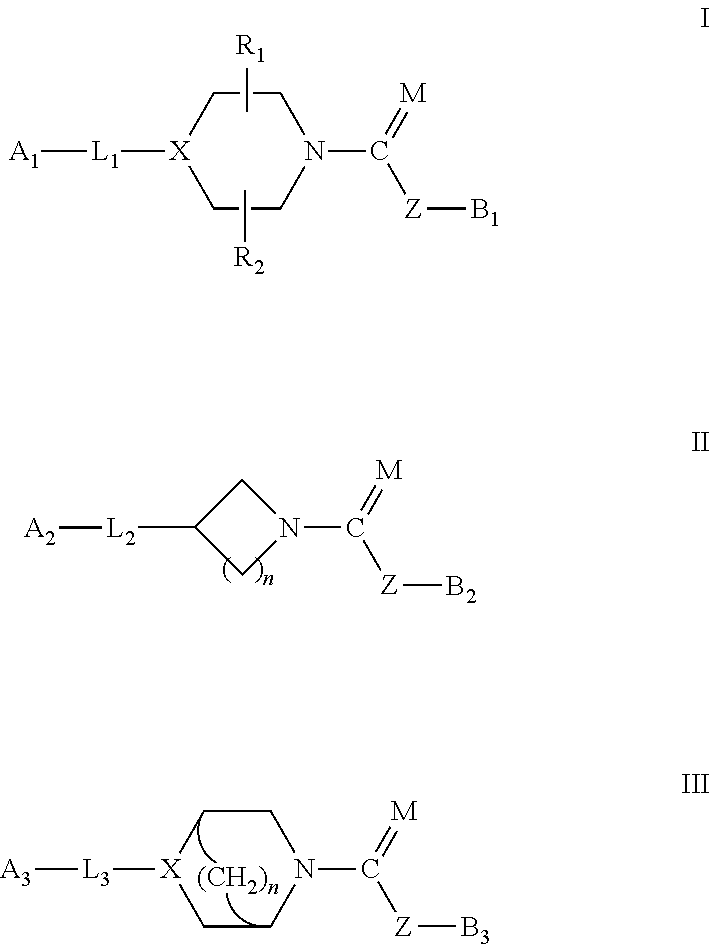
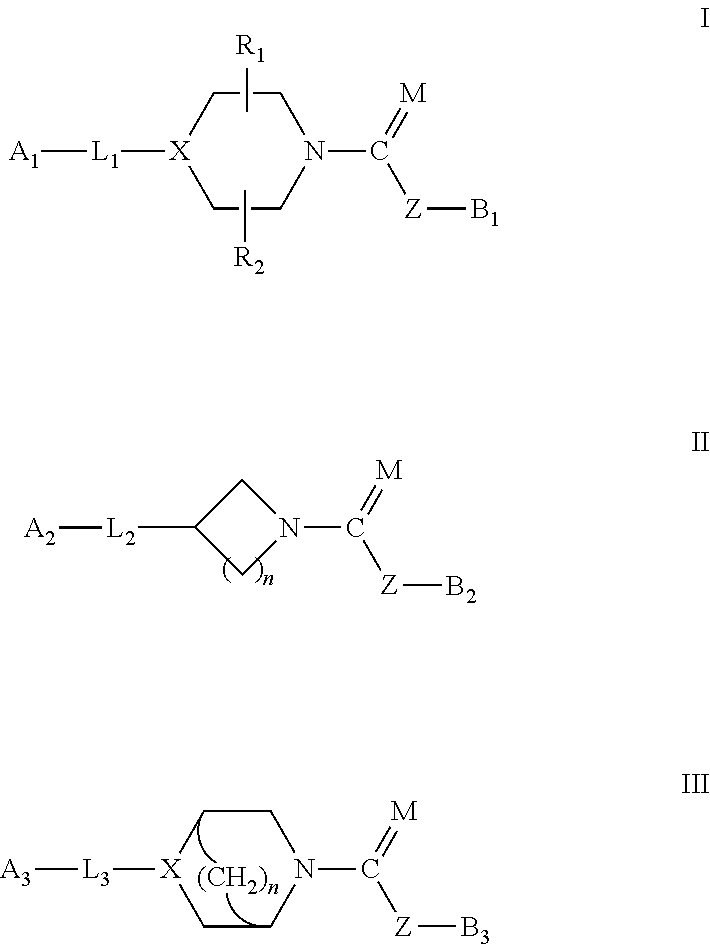
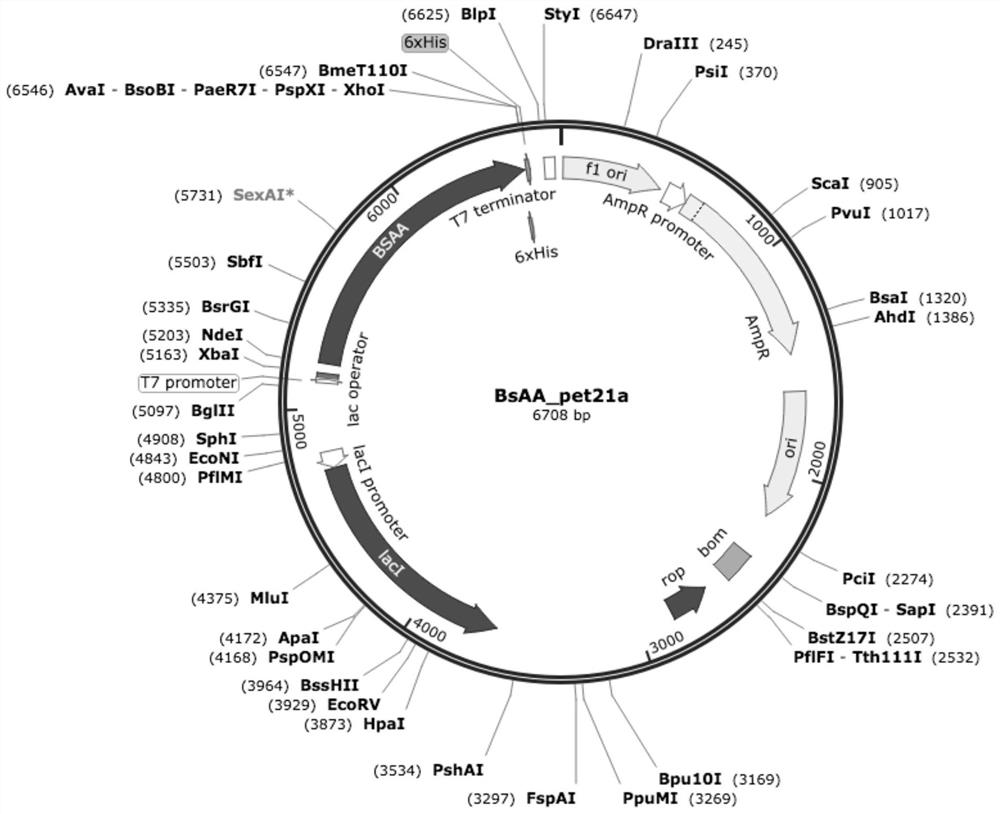
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Amidohydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
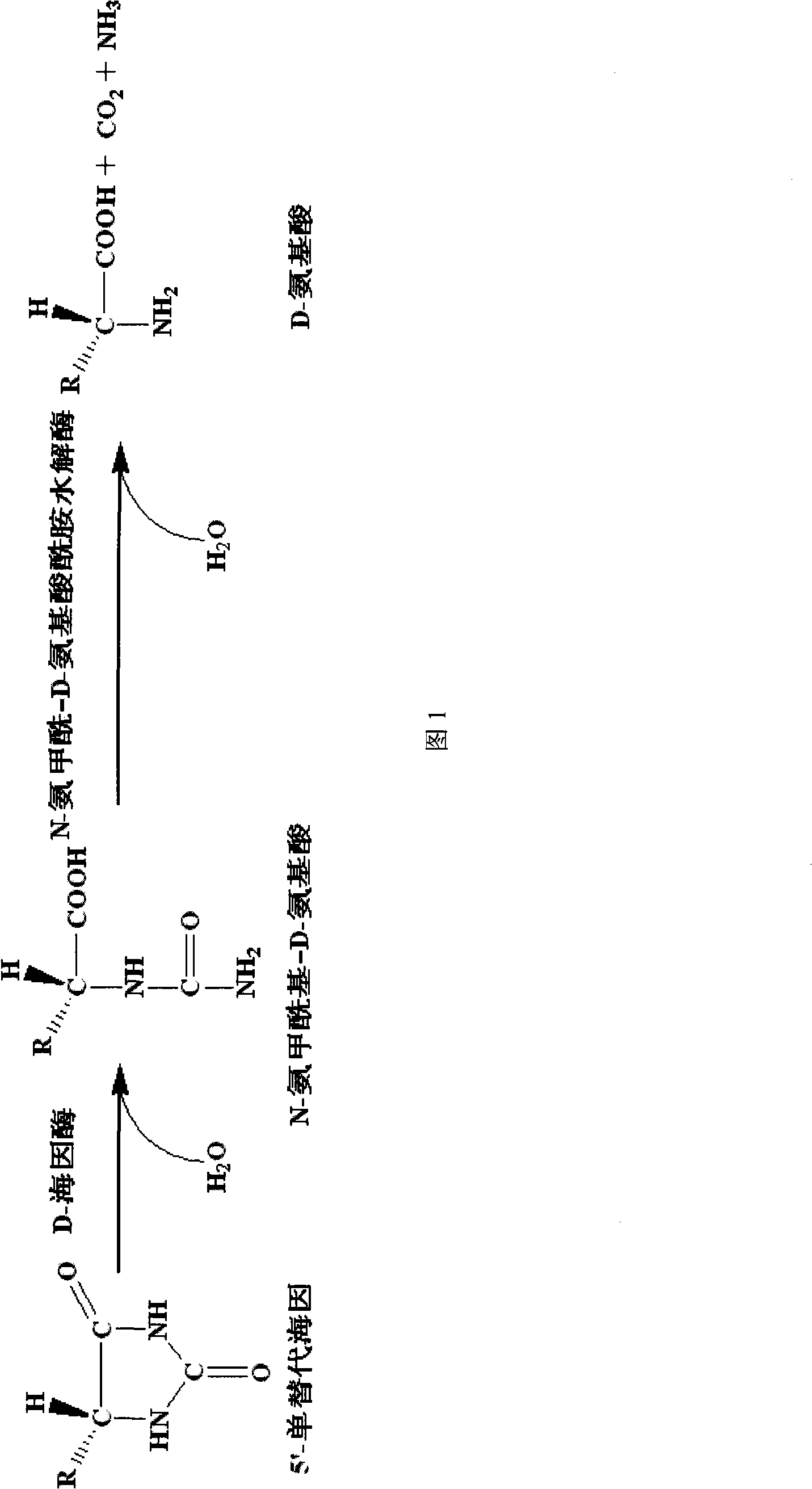
Amidohydrolases (or amidases) are a type of hydrolase that acts upon amide bonds. They are categorized under EC number EC 3.5.1 and 3.5.2.
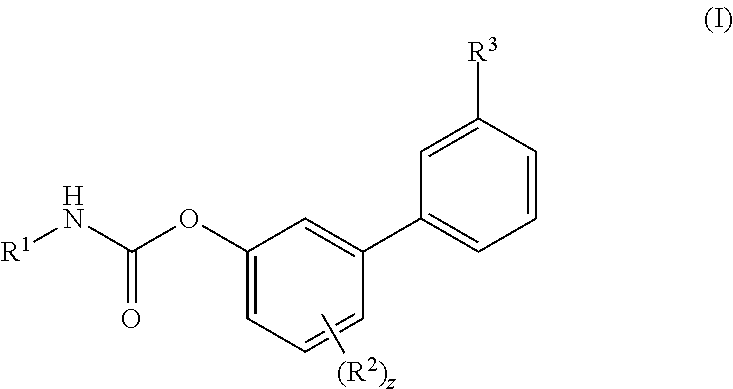
(Oxime)carbamoyl fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
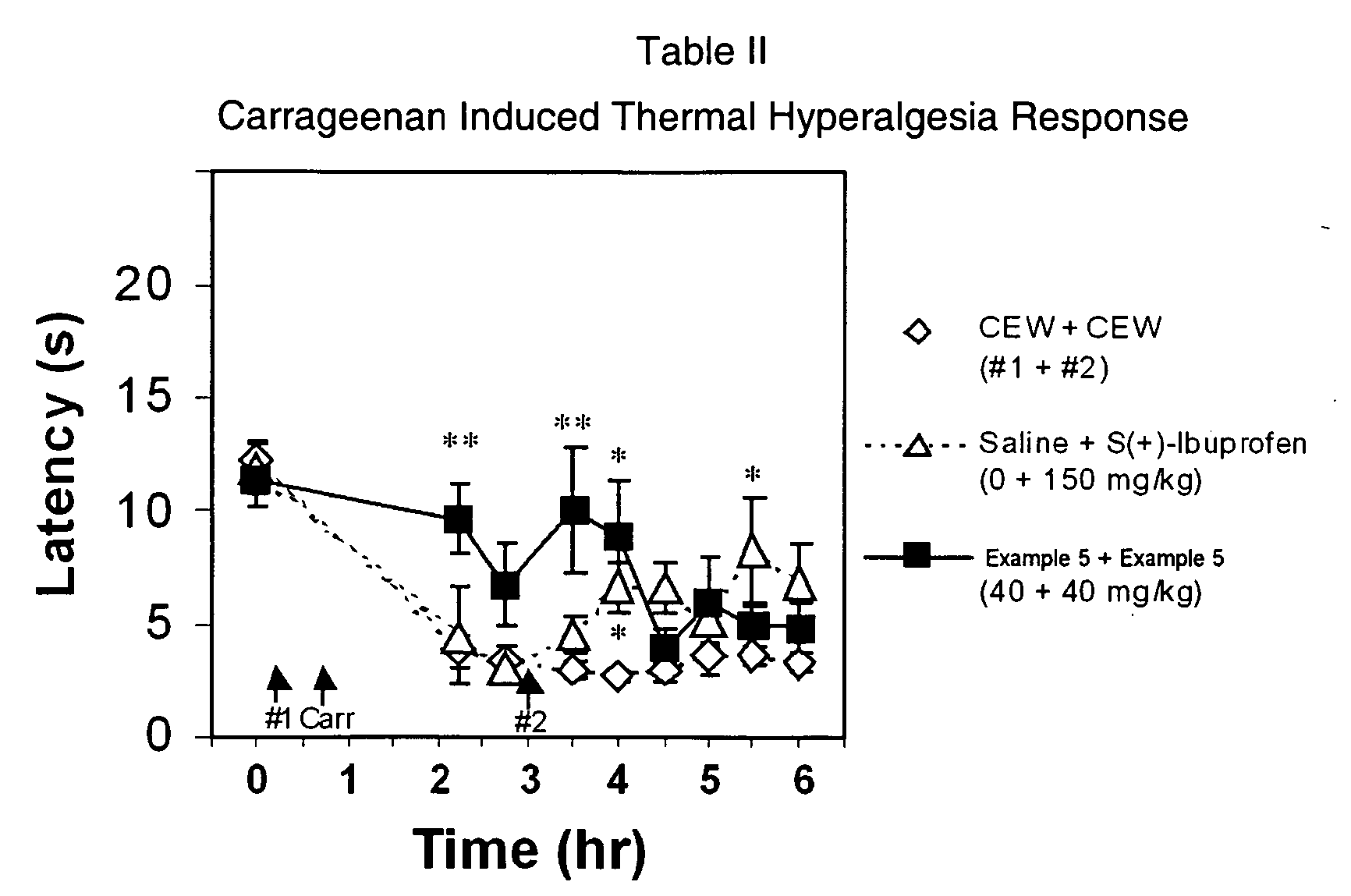
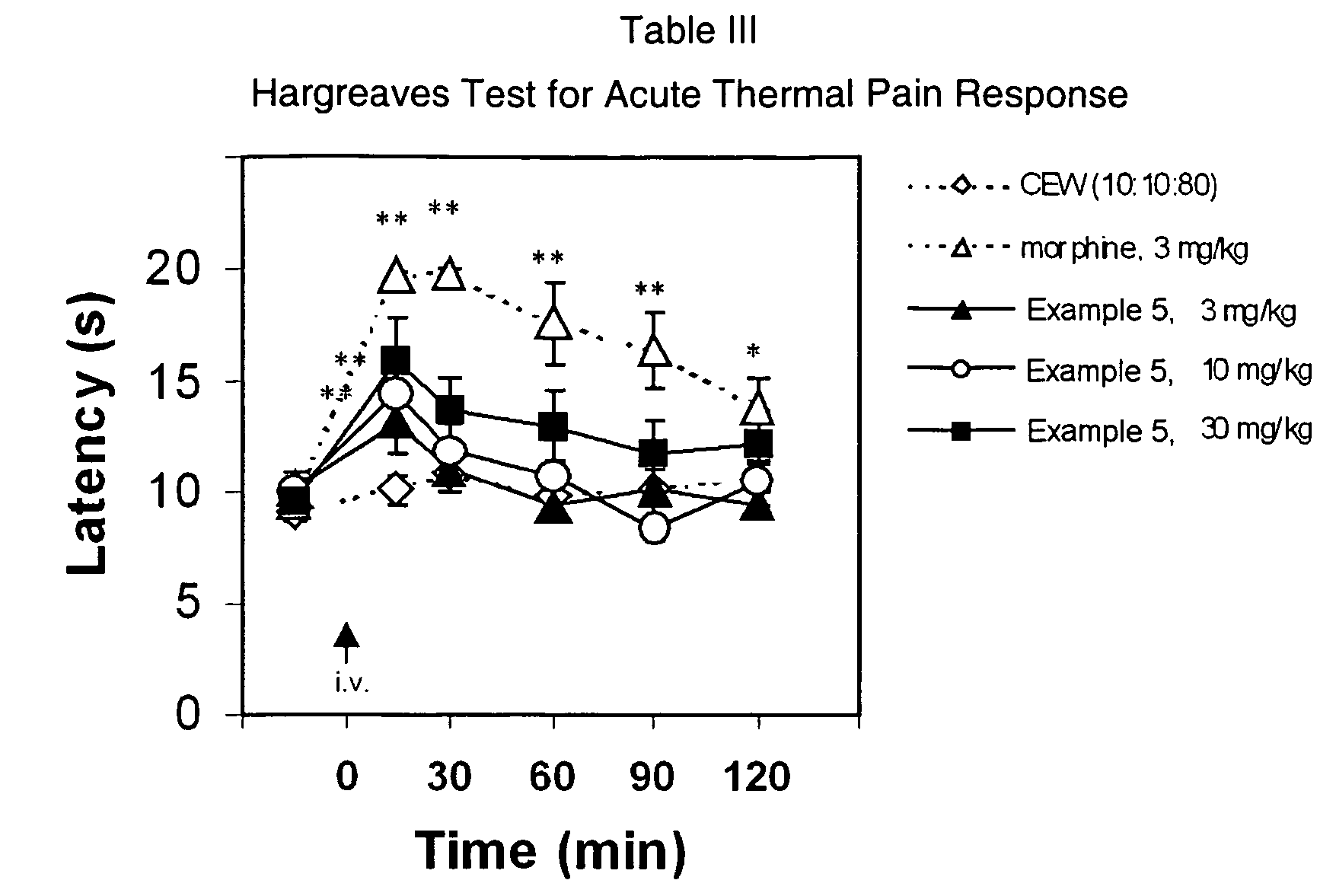
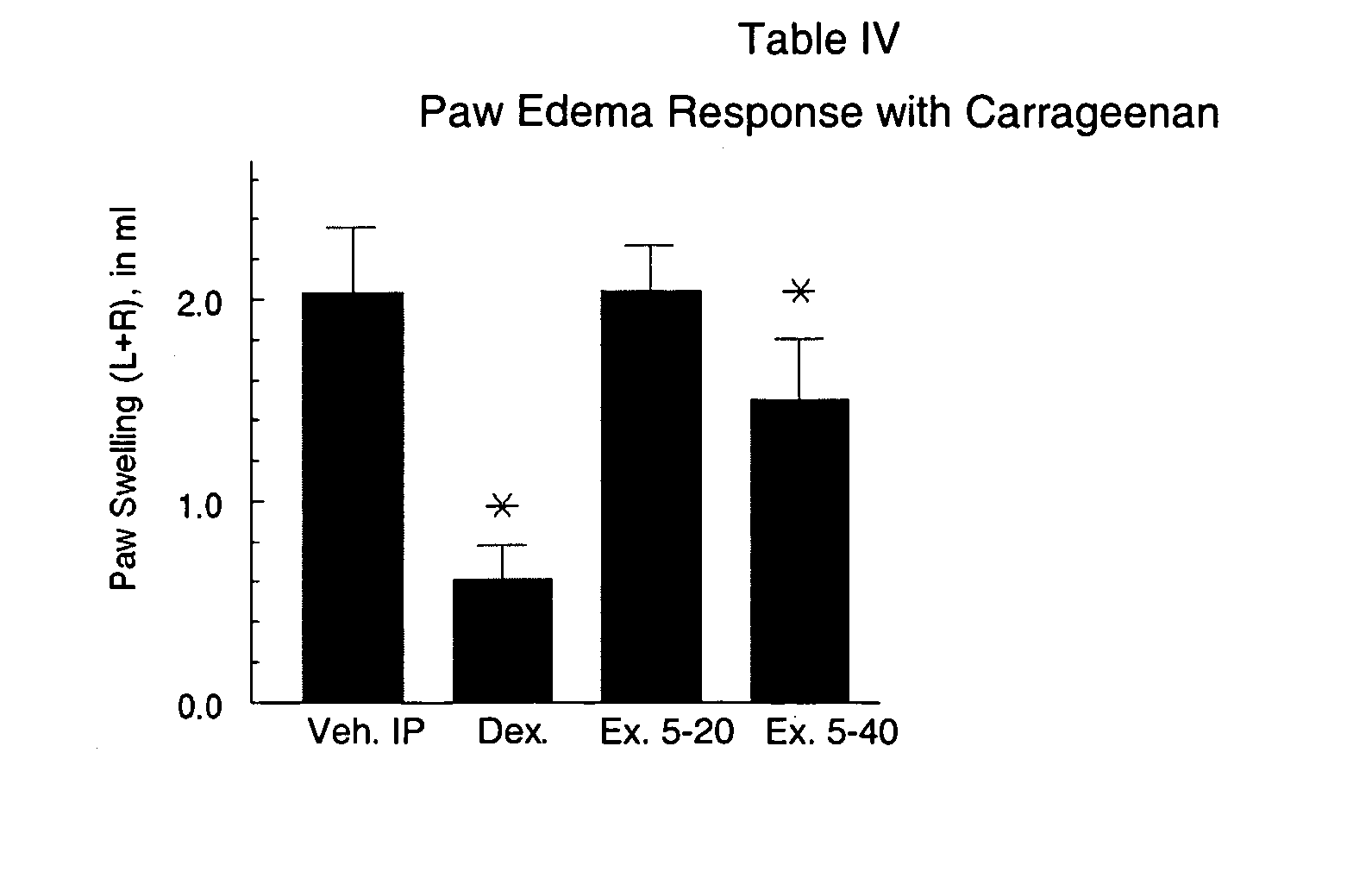
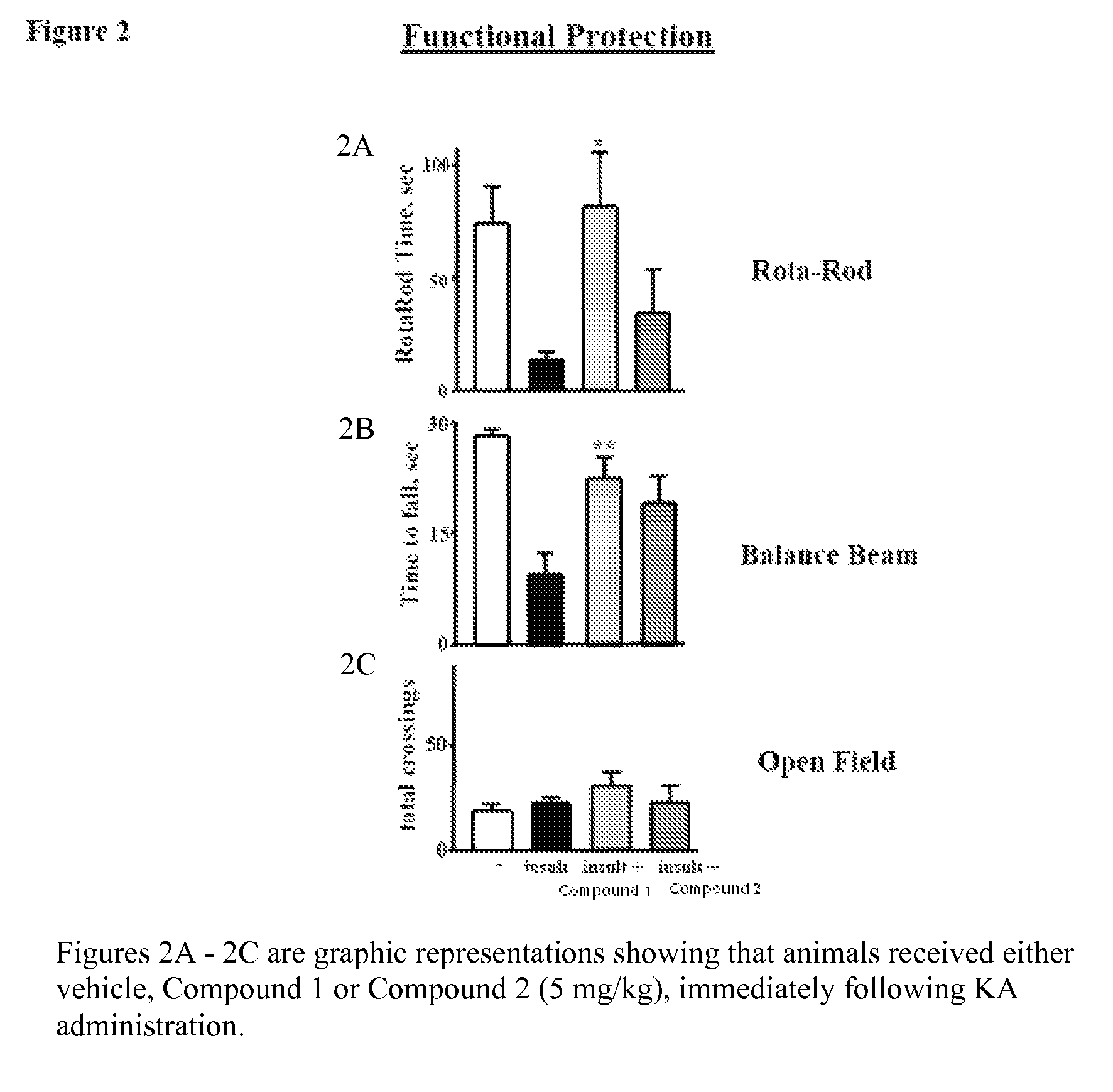
The present invention relates to novel oxime carbamyl derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising said derivatives which inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase. These pharmaceutical compositions are useful for the treatment of conditions which can be effected by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase including, but not limited to, neuropathic pain, emesis, anxiety, altering feeding behaviors, movement disorders, glaucoma, brain injury, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:SIT SING YUEN +2
Detection kit for determining content of creatinine in serum by enzymic method
InactiveCN104198408AImprove stabilityEliminate distractionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsCreatinine riseCreatininase
The invention discloses a detection kit for determining the content of creatinine in serum by an enzymic method. The detection kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 contains 3-10g / L of buffering solution with the pH value being 7.5-8.0, 0.2-0.5g / L of EDTA, 0.5-2g / L of N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxyl-3-sulfopropyl) m-toluidine sodium salt, 1 per mill-5 per mill of a surface active agent, 0.2-1g / L of sarcosine oxidase, 1-5KU / L of ascorbate oxidase, 2-5KU / L of creatinase and 0.5-1g / L of a stabilizing agent; the reagent R2 contains 3-10g / L of buffering solution with the pH value being 7.5-8.0, 0.1-0.5g / L of 4-aminoantipyrine, 0.1-0.4g / L of potassium ferricyanide, 2-8g / L of creatininase amidohydrolase, 1-6KU / L of peroxidase and 0.5-2g / L of a preservative. The detection kit disclosed by the invention is excellent in stability, strong in interference resistance and high in clinical application value.
Owner:上海睿康生物科技有限公司
Methods, Compositions And Devices For Maintaining Chemical Balance Of Chlorinated Water
InactiveUS20100270228A1Reduce concentrationEfficient use ofImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesAmidohydrolaseEnvironmental chemistry
A composition-of-matter for use in water treatment, composed of a water-insoluble matrix and one or more amidohydrolase, such as cyanuric acid amidohydrolase, incorporated in or on the matrix, is disclosed. Also disclosed are devices containing same and methods utilizing same for water treatment. The water treatment is effected by an enzymatically-catalyzed reduction of the concentration of an amide-containing compound, such as cyanuric acid, found in chlorinated water of swimming polls, spas and other similar structures.
Owner:TEICHBERG YAAR +2
Engineering bacterium, construction thereof and method for preparing D-valine by using the same
InactiveCN101260381APrevent oxidationImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneValine
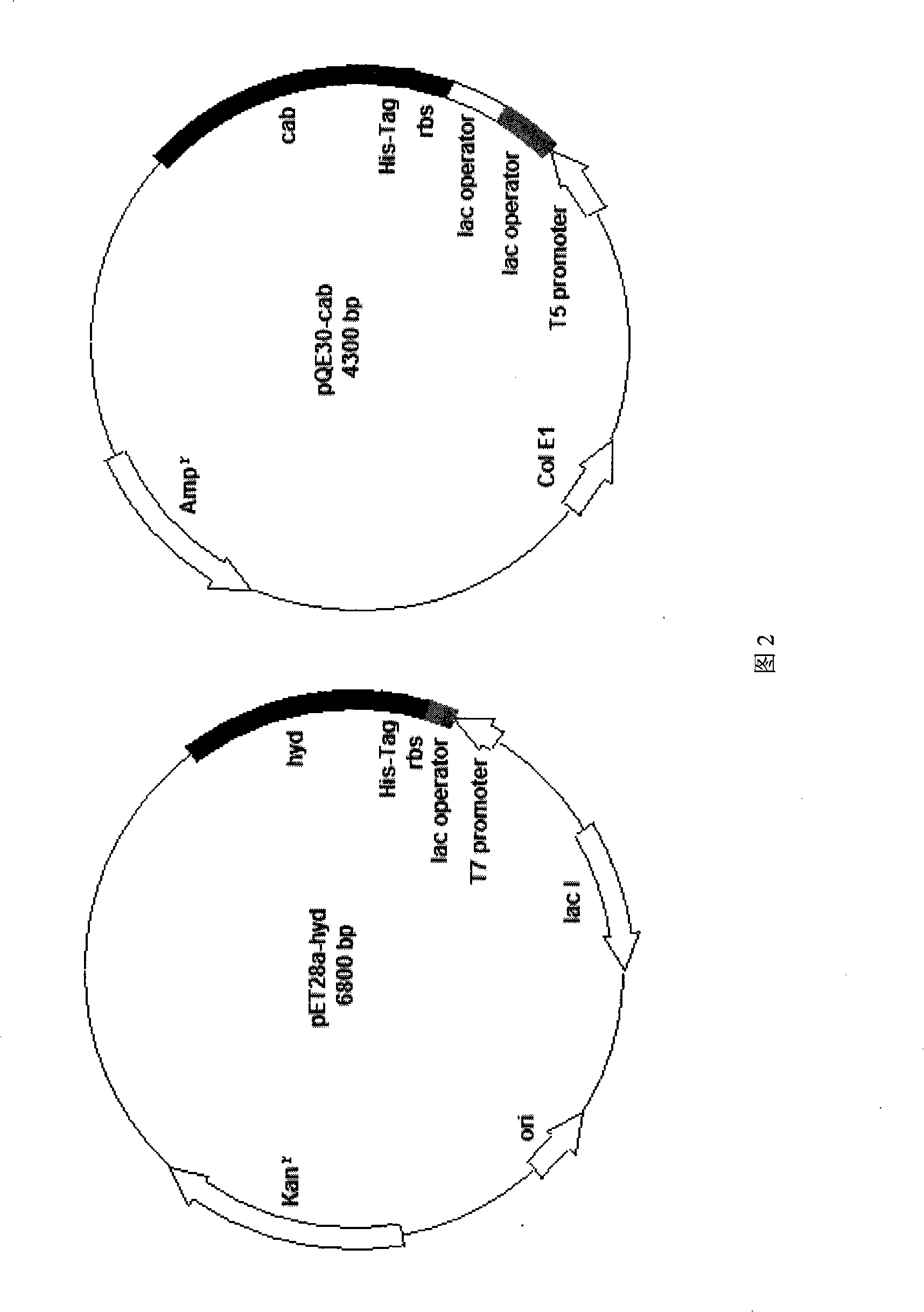
The invention provides an engineering strain, which can simultaneously express D-hydantoin enzyme and N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase. The construction method of the invention is as follows: a D-hydantoin enzyme gene is cloned to a plasmid ET-28a and an N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase gene is cloned to a plasmid pQE-30, and then two recombinant plasmids pET28a-hyd and pQE30-cab are shifted into the same Escherichia coli cell by utilization of a co-conversion technology. The invention also provides a method for producing D-valines by utilization of the engineering strain to convert 5'-opropyl hydantoin. The method is characterized by high optical purity of products, simple manufacturing technique, and environmental protection and so on; moreover, compared with the prior market products, the method is low in production cost.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
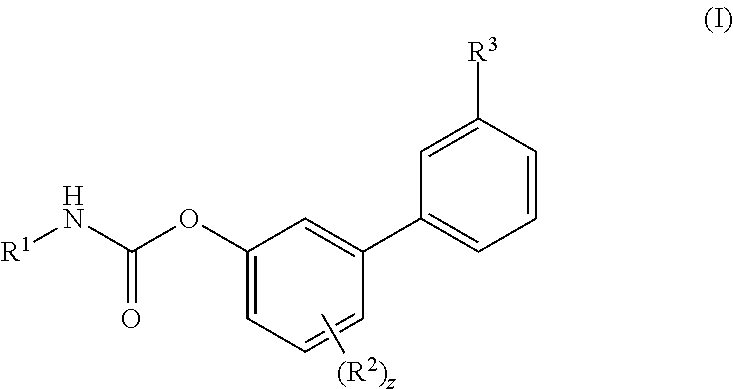
(Oxime)carbamoyl fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel oxime carbamyl derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising said derivatives which inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase. These pharmaceutical compositions are useful for the treatment of conditions which can be effected by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase including, but not limited to, neuropathic pain, emesis, anxiety, altering feeding behaviors, movement disorders, glaucoma, brain injury, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
High-efficient expression and application of amidohydrolase
The invention relates to the clone of amidohydrolase, and the construction, zymoprotein expression and industrial application of engineering bacteria, belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and mainly aims to solve the problems that amidohydrolase produced by natural bacteria is low in enzyme activity, low in bacterial concentration and difficult for production application. On the basis that the hydrolase is produced by fermenting Delftiatsuruhatensis in Delftia, an amidohydrolase gene is cloned to establish a full set of process of the fermentation, and inducible expression, and industrial production of the Escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria. Through the gene engineering modification, the amidase activity is over 3000 u / l, much higher than 300 u / l of the original strain; the actual application shows that the enzyme has a wide application scope, can be applied the production of side chains of statins, the production cost is greatly reduced and the realization of green chemistry is promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Animal model for fatty acid amide-related neurobehaviors
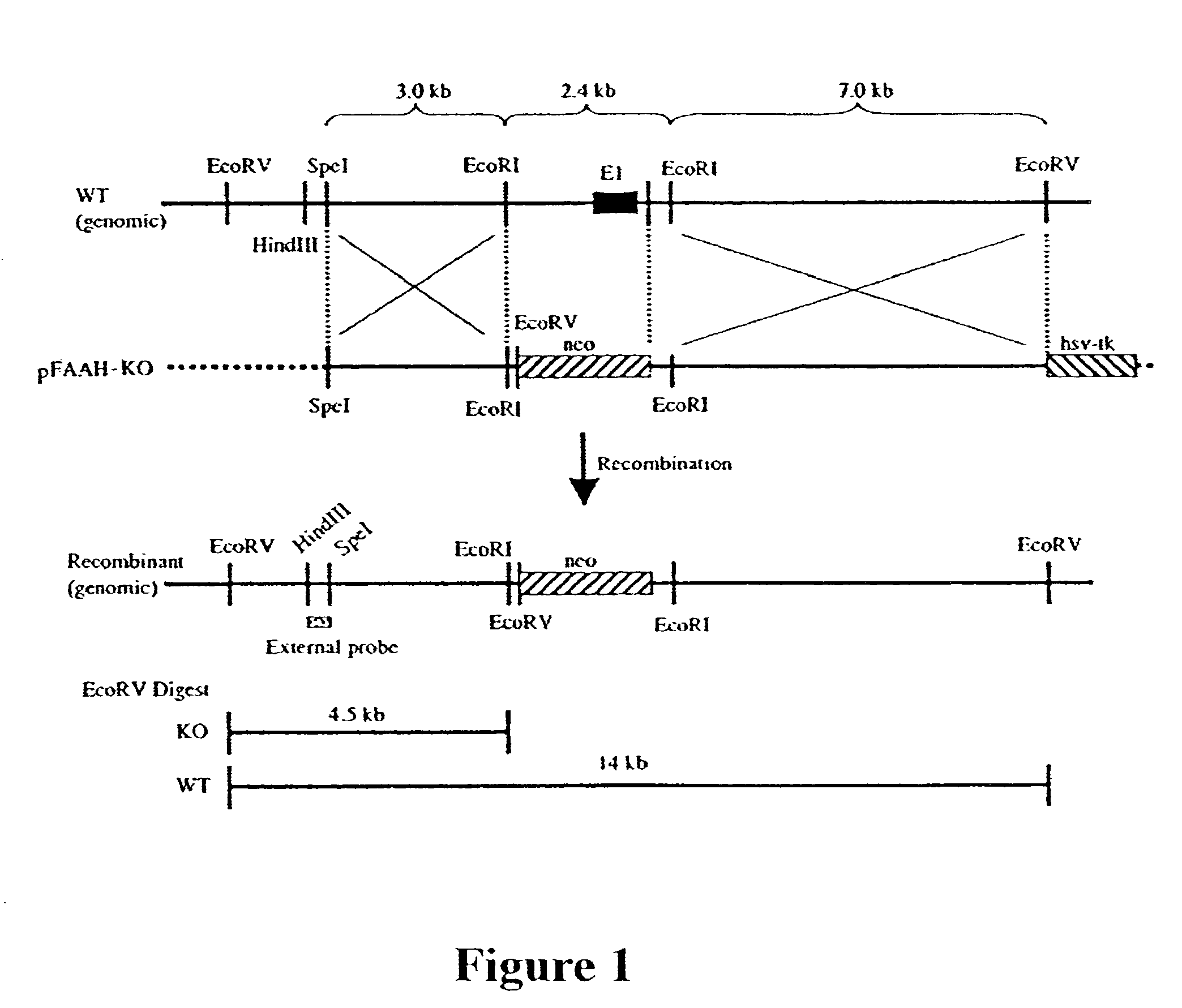
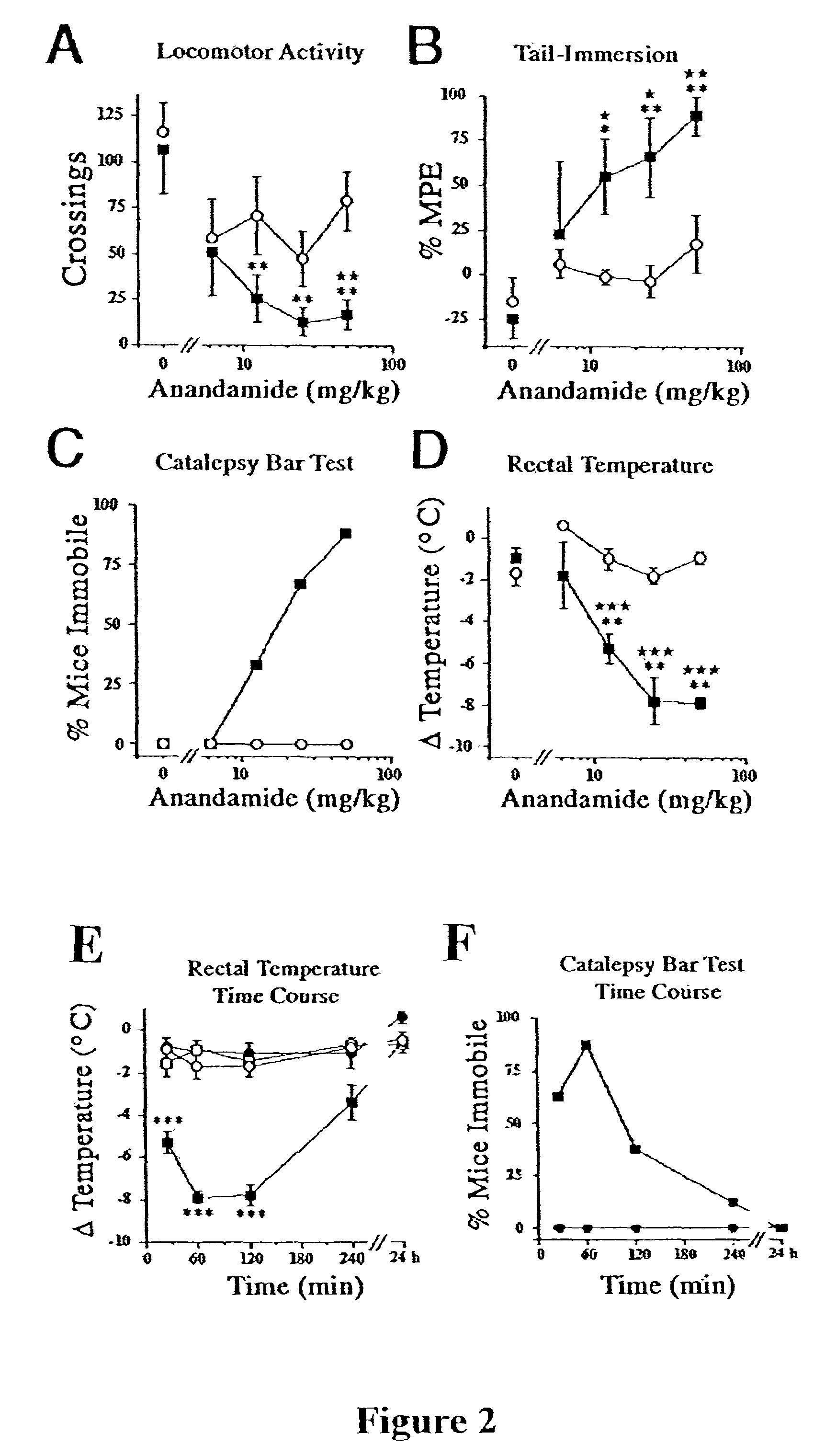
The invention relates to an animal model for studying behavior related to fatty acid amide and hydrolysis of fatty acid amide. The invention provides transgenic animals in which the protein fatty acid amide hydrolase is not expressed, and methods of using such animals.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
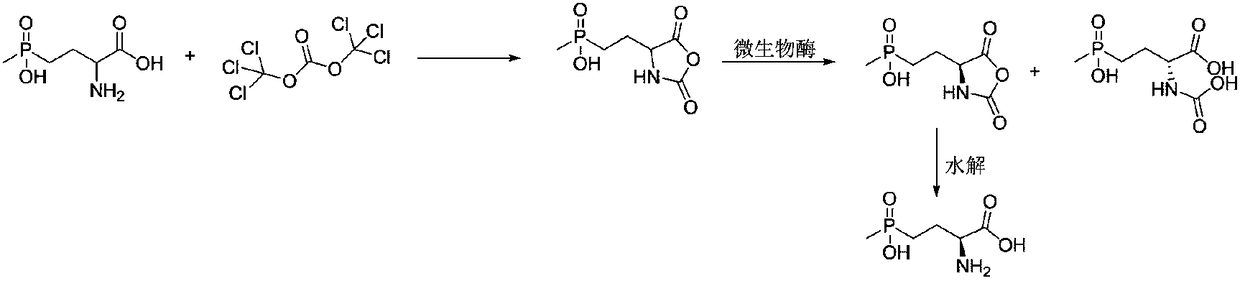
L-glufosinate ammonium preparation method
ActiveCN109384811AEasy to operateLow costGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFermentationGlufosinate-ammoniumHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for obtaining L-glufosinate ammonium with single configuration by catalytically hydrolyzing an inexpensive and easily-available glufosinate ammonium cyanamide intermediate with biological enzyme through a one-pot method, wherein the hydrolyzing process specifically comprises: 1, obtaining a glufosinate ammonium amide racemate from a racemic glufosinate ammonium cyanamide intermediate under the action of non-selective nitrile hydratase; 2, selectively hydrolyzing the L-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate with L-amide hydrolase to obtain L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate while racemizing the unhydrolyzed D-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate under the action of ACL racemase to continuously convert into the L-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate, such that the single L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate is finally obtained through the DKR process; and 3, hydrolyzing the L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate under the action of dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain the L-glufosinate ammonium.
Owner:SICHUAN LIER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
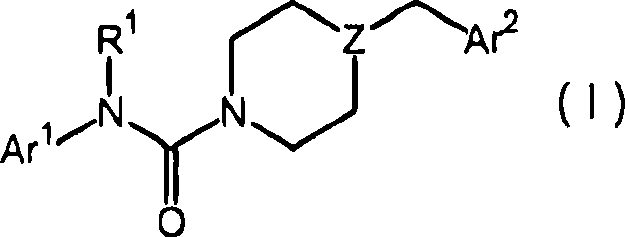
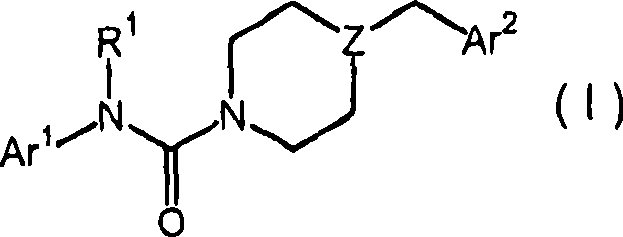
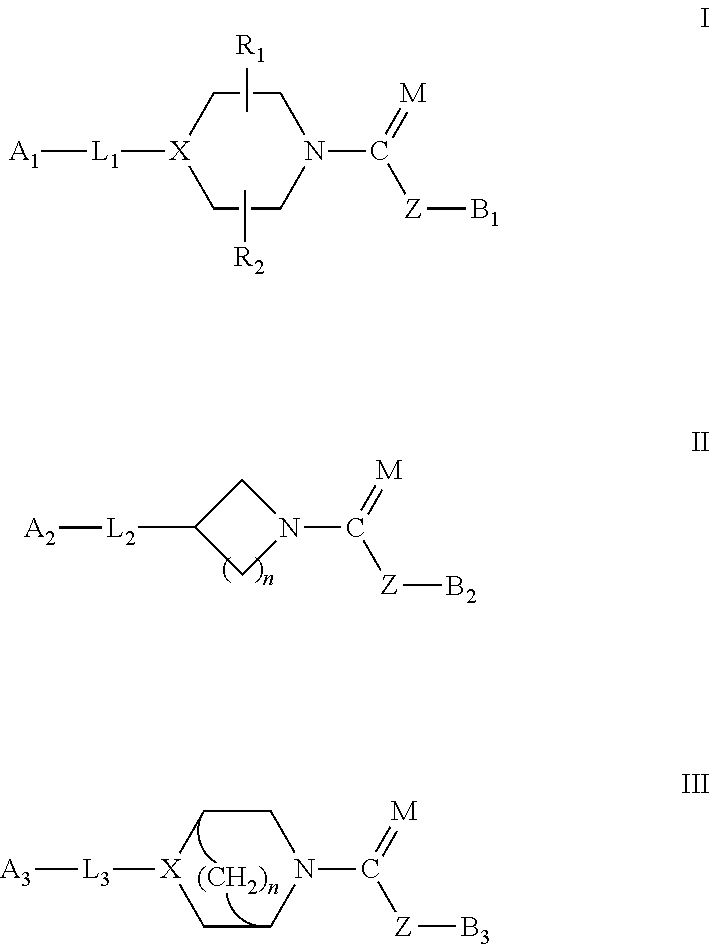
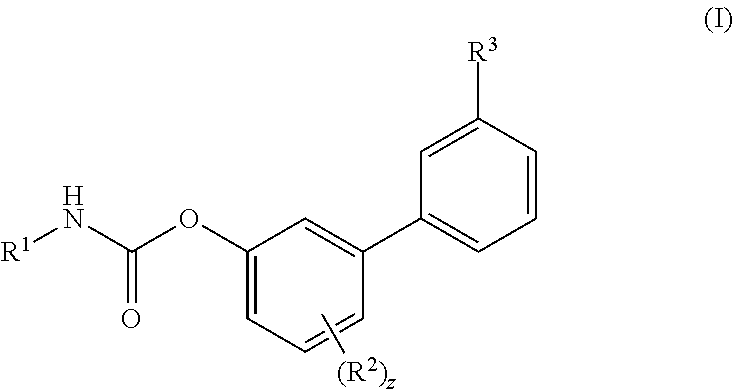
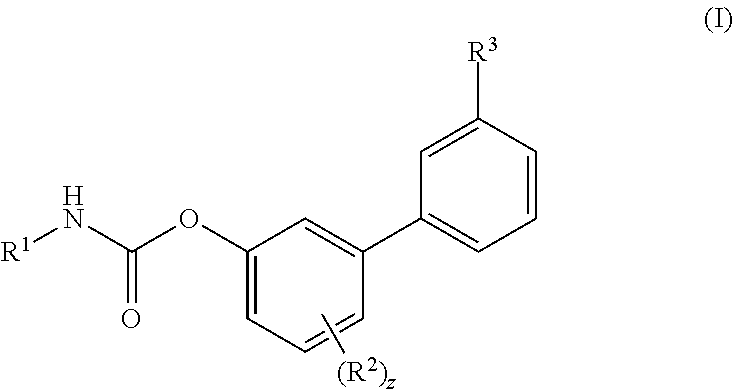
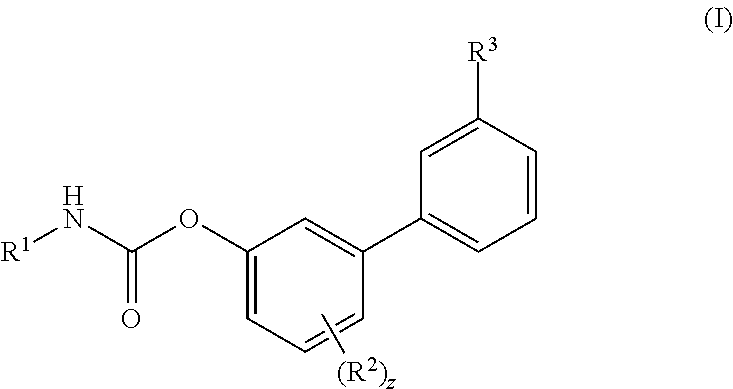
Piperazinyl and piperidinyl ureas as modulators of fatty acid amide hydrolase
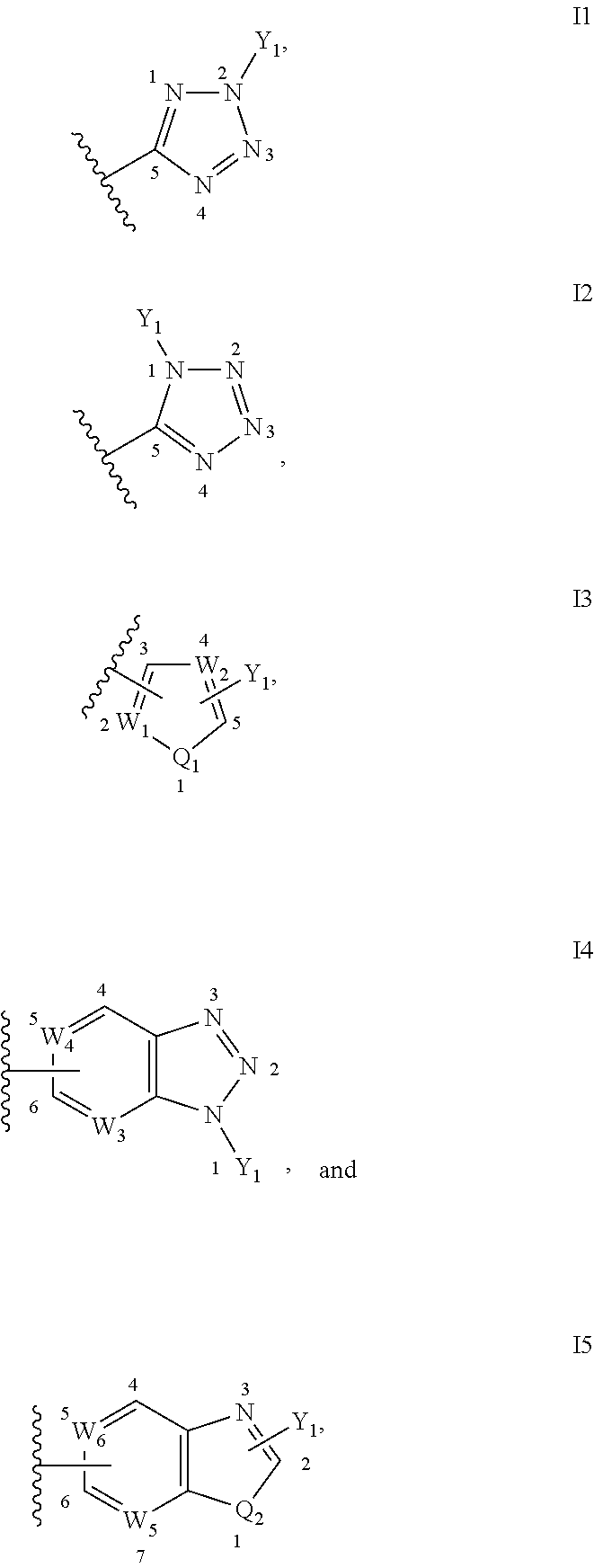
Compounds of formula (I): wherein, Z is -N-or>CH; R<1> is -H or -C1-4alkyl; Ar<1> is 2-thiazolyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, 2-pyrimidinyl, 4-primidinyl, 5-pyrimidinyl, or phenyl, each unsubstituted or substituted at a carbon ring member with one or two R moieties; where each R moiety is independently selected from the group consisting of -C1-4alkyl, -C2-4alkenyl, -OH, -OC1-4alkyl, halo, -CF3, -OCF3, -SCF3, -SH, -S(O)0-2C1-4alkyl, -OSO2C1-4alkyl, -CO2C1-4alkyl, -CO2H, -COC1-4alkyl, -N(R)R<c>, -SO2NRR<c>, -NRSO2R<c>, -C(=O)NRR<c>, -NO2, and -CN, wherein R and R<c> are each independently -H or -C1-4alkyl; and Ar<2> is defined in the claims are useful as FAAH inhibitors. Such compounds may be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of disease states, disorders, and conditions mediated by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity. Thus, the compounds may be administered to treat, e.g., anxiety, pain, inflammation, sleep disorders, eating disorders, or movement disorders (such as multiple sclerosis).
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
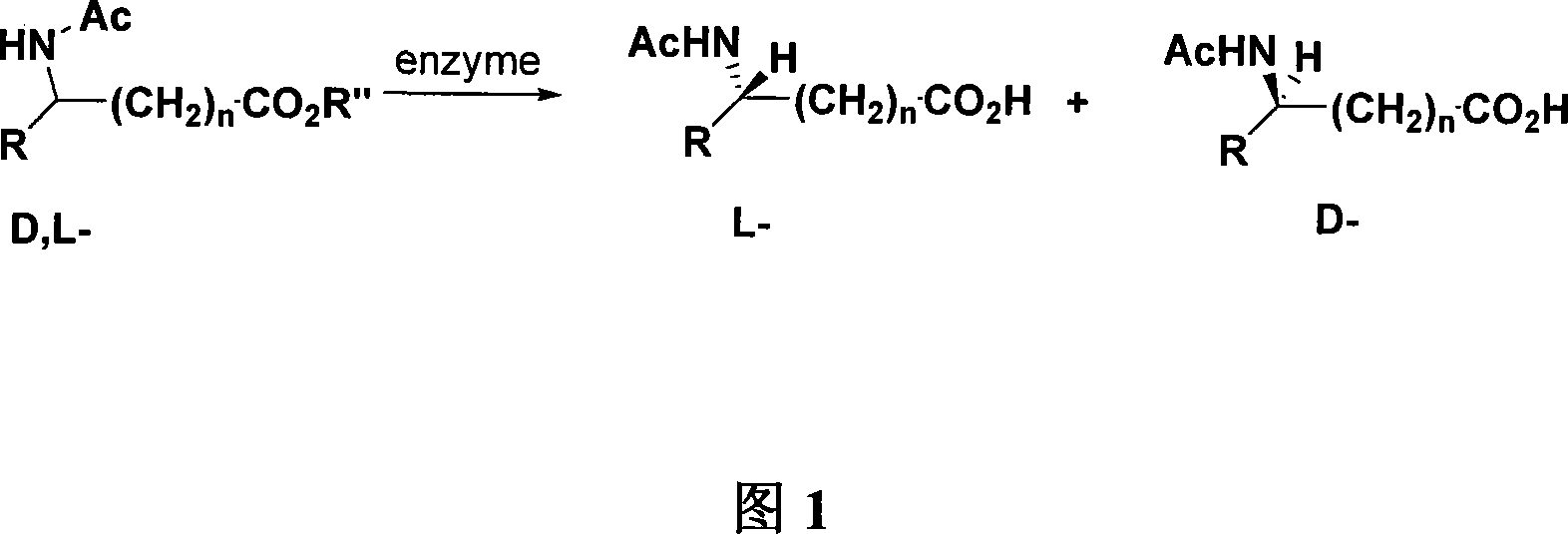
Biological resolution method for amino acid
InactiveCN101186944AAchieve the purpose of splittingReduce intermediate operationsFungiMicroorganism based processesEster hydrolaseAspergillus oryzae
The invention relates to the field of biochemical engineering, in particular to a novel process for preparing L-amino acid and D-amino acid by direct biocatalysis and hydrolysis resolution for DL-N-acetyl amino acid esters. DL-N-acetyl amino acid esters is used as substrate, enzyme including amide hydrolase and ester hydrolase is used as catalyst, wherein the enzyme is achieved by fermenting aspergillus oryzae Lb3085, de-ionized water is utilized as solvent and added in an enzyme catalysis reactor, and L-N-acetyl amino acid esters of the substrate is hydrolyzed into L-amino acid, D-N-acetyl amino acid esters of the substrate is hydrolyzed into D-N-acetyl amino acid, thereby resolution is realized. The resolution technique of 'one bacterium two enzymes' can efficiently reduce operating intermediate process, and achieve purposes of convenience and cleaning.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
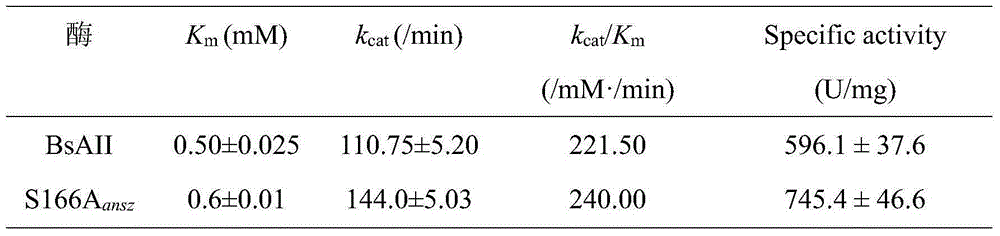
Genetic-engineering L-asparaginase amidohydrolase modified through site-specific mutagenesis
InactiveCN105062998AIncreased potential for industrial applicationsIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesGenetic engineeringL asparaginase
The invention discloses an activity-improved L-asparaginase amidohydrolase mutant and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The mutant is characterized in that the 166th serine is mutated into alanine on the basis of the amino acid shown in SEQ ID No.2. The mutant is expressed in bacillus subtilis, the activity is 657.1 U / ml after flask fermentation is carried out for 24 h, the mutation activity is improved by 23%, the substrate affinity is reduced by 20% compared with original amidohydrolase, the catalytic efficiency is improved by 8.4%, and meanwhile the specific activity is improved by 25%. The mutant and the construction method show that the 166th serine residue has large influences on the catalytic action of the amidohydrolase, a certain foundation is provided for researching the catalytic mechanism of the amidohydrolase, and the industrial application potential of the amidohydrolase is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase and Monoacylglycerol Lipase for Modulation of Cannabinoid Receptors
Disclosed are compounds and compositions that inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), methods of inhibiting FAAH and MGL, methods of modulating cannabinoid receptors, and methods of treating various disorders related to modulation of cannabinoid receptors.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Dry chemical reagent tablet for quantitatively measuring concentration of creatinine and preparation method of dry chemical reagent tablet
InactiveCN109916895ANo preparation requiredEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsHemolysisCreatinine rise
Owner:吉林省汇酉生物技术股份有限公司
Methods for determining effective doses of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors in vivo
InactiveUS20080089845A1Reduction and alleviationRelieve symptomsCompound screeningBiocideHydrolase inhibitorDepressant
Described herein is a method for determining an effective dose of a composition for inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase activity in vivo, by first administering to a subject a dose of a test composition, and subsequently assessing if the level of a fatty acid amide in the subject increases. Also described, is a method for optimizing therapeutic efficacy for treatment of anxiety, depression, pain, or a metabolic disorder by increasing or decreasing a dose of a fatty amide hydrolase inhibitor according to a patient's fatty acid amide levels. In addition, pharmaceutical compositions are described, which contain fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors effective for increasing a FAA level in a patient.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Urea/carbamates FAAH MAGL or dual FAAH/MAGL inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS10570146B2Slow degradationReduce inactivationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCarbamateDepressant
Disclosed are compounds that may be used to inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) or dual FAAH / MAGL. More particularly, compounds of formula IIhave utility in a variety of therapeutic uses such as treatment of pain, inflammation, neuropathy, or appetite disorder.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Urea/carbamates faah magl or dual faah/magl inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170247387A1Slow degradationReduce inactivationOrganic chemistryAmidohydrolaseMonoacylglycerol lipase
Disclosed are compounds that may be used to inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) or dual FAAH / MAGL.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
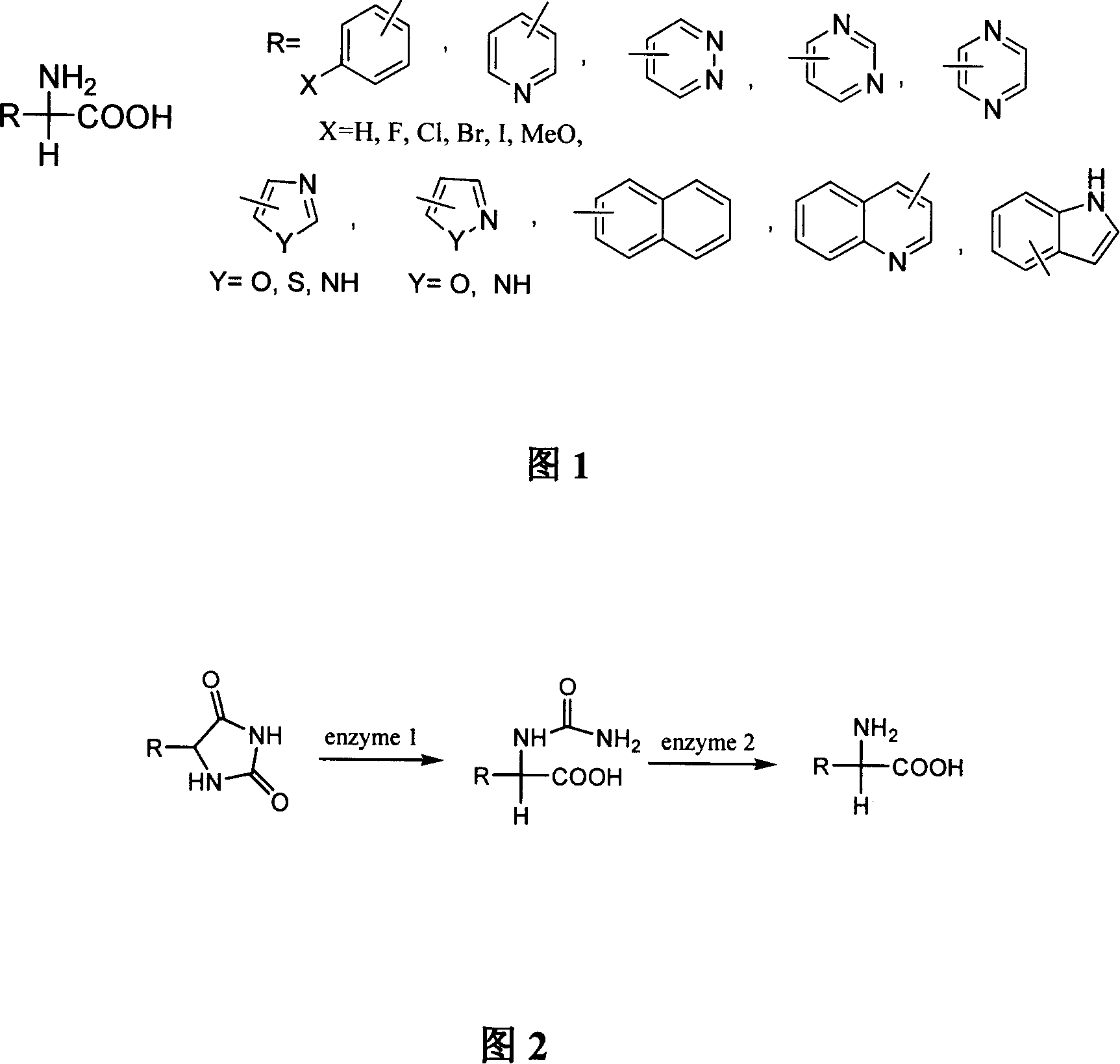
Method for synthesizing D-arylglycine by using heterogeneous enzyme to catalytically hydrolyzing 5-arylhydantoin
ActiveCN101104862AQuick responseReduce consumptionChemical industryMicroorganism based processesArylAgrobacterium radiobacter
The invention relates to a chemical pharmaceutical field, in particular to an approach on synthesis of D-aryl glycine by heterogeneous enzyme catalytic hydrolysis of 5-aryl hydantoin. The invention takes an enzyme preparation fermented by a mutant bacteria UV-LZ98 of a hydantoin producing strain Arthrobacter aurescens LZ-98 and a mutant bacteria UV-LZ99 of an ammonia methyl amidohydrolase producing strain Agrobacterium radiobacter LZ99 as a catalyst, and has a heterogeneous catalytic reaction with an input of more than three to ten times of 5-aryl hydantoin than homogeneous reaction to make the D-aryl glycine produced precipitate directly in a solid way during the substrate hydrolysis process, which improves the synthesis efficiency and lowers the evaporation energy consumption with a stable quality.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
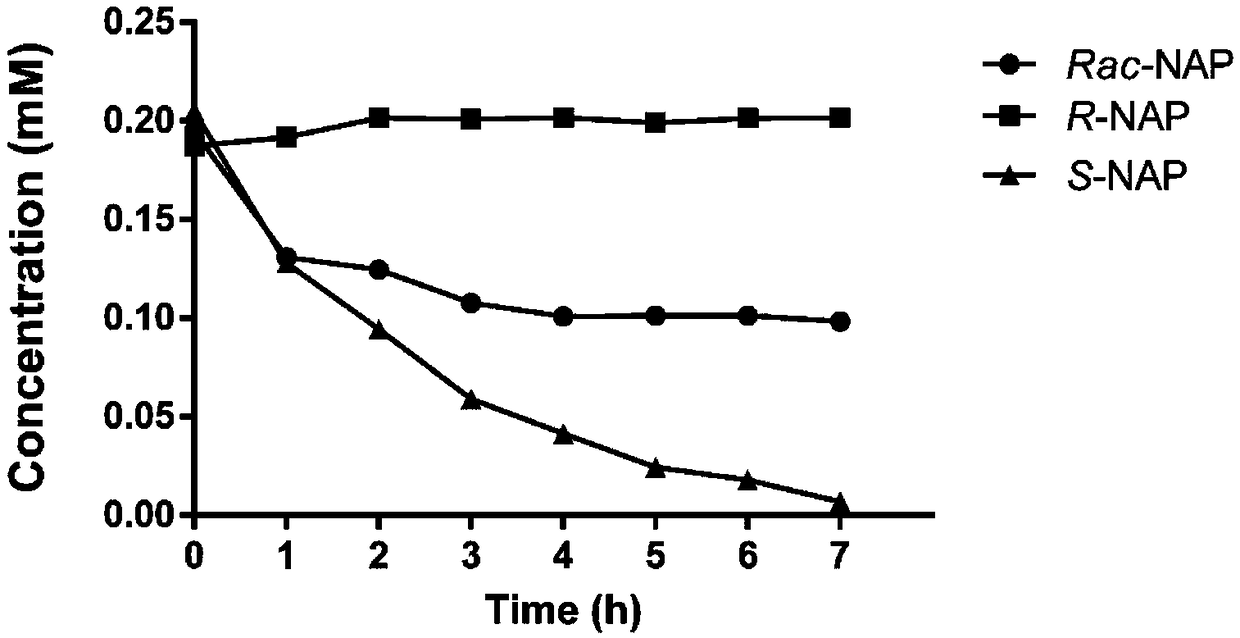
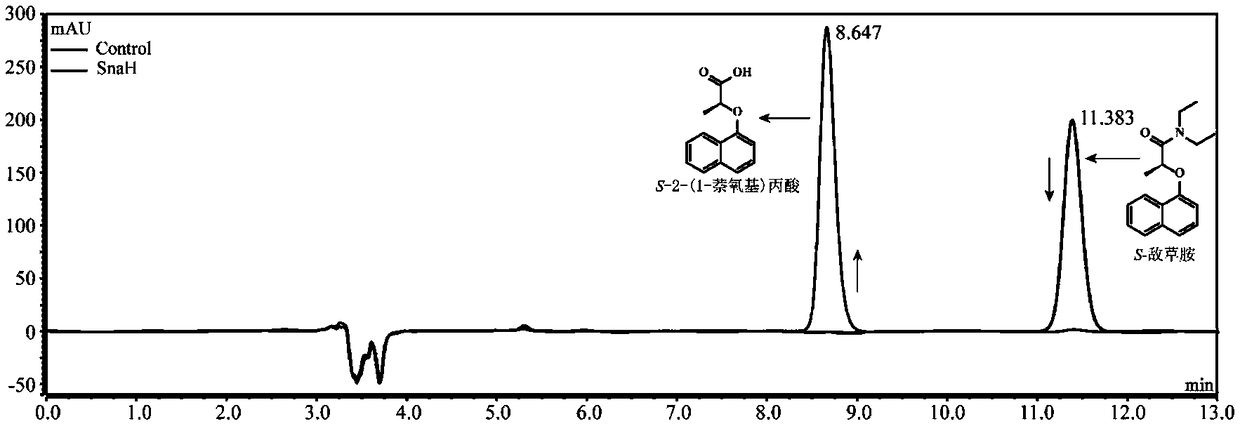
Bacterial strain, amidohydrolase and encoding gene with single conversion function to S-napropamide and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterial strain, an amidohydrolase and an encoding gene with single conversion function to S-napropamide and application thereof. The bacteria strain Sphingobium sp.B2 for degrading napropamide is stored with number of CCTCC NO: M2018684 in China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 16, 2018. The amidohydrolase gene snaH with single conversion function to S-napropamide has the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.1; the encoded protein sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The SnaH pure enzyme can completely degrade 0.4mM S-napropamide within 1h and cannot degrade R-napropamide, so that the SnaH pure enzyme can be used for splitting napropamide raceme in an enzyme method to produce optical pure R-napropamide and can also be used for removing S-napropamide pollution in the environment, so that the theoretical value is high, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for treating energy metabolism disorders by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase activity
Disclosed herein are methods for treating energy metabolism disorders by administering a composition containing a therapeutically effective amount of a fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor. The composition can also be administered to reduce body fat, body weight, or caloric intake.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Recombinant amide hydrolase gene and application thereof
PendingCN113481223AImprove expression efficiencyHigh catalytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolase GeneNucleotide
The invention provides a recombinant amide hydrolase gene and application thereof. The recombinant amide hydrolase gene comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also provides a recombinant vector, a recombinant cell, a preparation method of recombinant amide hydrolase and the recombinant amide hydrolase prepared by the preparation method. The recombinant amide hydrolase gene provided by the invention has high expression efficiency in recipient cells, and provides conditions for industrialized production of amide hydrolase; the preparation and purification method of the amide hydrolase is simple and efficient; and the obtained amide hydrolase has good catalytic activity and stability and has practical application value in production.
Owner:GUANGDONG HEJI BIOTECH CO LTD
Construction and application of ureido amidohydrolase display strain
PendingCN112342148AImprove degradation rateAbility to significantly degrade ureaPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiBiotechnologyProtein target
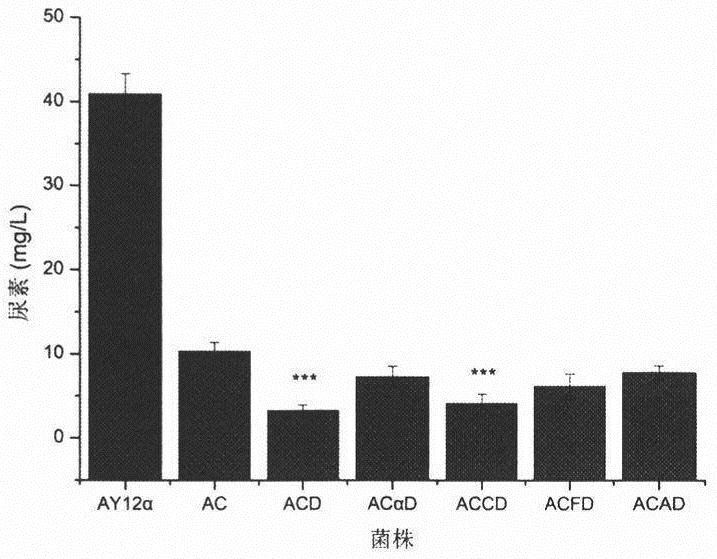
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to breeding of industrial microorganisms, in particular to a strain construction method for displaying ureido amidohydrolaseon the surface of saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by taking cwp2 as anchoring protein and application. The ACCD display strain is constructed by fusing the cwp2 anchoring protein and target protein UA, so that the urea degradation rate of yellow rice wine fermentation liquor reaches 89.9% or above, and the EC degradation rate is 56.4% or above; when the ACCD strain is cultured for 72 hours, the enzyme activity of about 12,000 U / g (stem cells) can be achieved, and compared with commercial urease, displayed enzyme has higher thermal stability and tolerance; and when the ACCD is used as an enzymepreparation to treat the yellow rice wine fermentation liquor, the urea degradation rate and EC degradation rate are highest, the initial urea degradation rate can still be kept at 80% or above afterthe ACCD is repeatedly used ten times, and flavor substances of the yellow rice wine are not obviously changed before and after treatment. Therefore, the ACCD display enzyme strain has a wide marketprospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Pyrazinamide hydrolase, and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107164350AHigh activityGood pH toleranceAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideA-DNA
The invention discloses a pyrazinamide hydrolase, and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The hydrolase has an amino acid sequence represented as the SEQ ID No.1; and the encoding gene is a DNA molecule which has a nucleotide sequence represented as the SEQ ID No.2. The pyrazinamide hydrolase is high in enzyme activity and has good pH tolerance. The invention demonstrates a direction of therapy on patients, which has pyrazinamide resistance in vivo, by combining pyrazinamide with the pyrazinamide hydrolase.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme with improved oral bioavailability and their use as medicaments
ActiveUS20170088510A1Reducing tobacco useReduce appetiteNervous disorderOrganic chemistryBioavailabilityFatty acid
Described herein, inter alia, are compositions and methods useful for inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase.
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
Novel amide hydrolase gene
InactiveUS20090215132A1Efficient productionImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesHydrolase GeneEnzyme protein
The present invention relates to an amide hydrolase which is with excellent thermostability and stereoselectively hydrolyzes an α-amino acid amide; a gene encoding the enzyme protein; a novel recombinant vector containing the gene; a transformant containing the recombinant vector; and a process for producing an L-α-amino acid using the transformant.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme with improved oral bioavailability and their use as medicaments
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
Inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase for modulation of cannabinoid receptors
Disclosed are compounds and compositions that inhibit the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), methods of inhibiting FAAH and MGL, methods of modulating cannabinoid receptors, and methods of treating various disorders related to modulation of cannabinoid receptors.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Mouse model for fatty acid amide-related neurobehaviors
The invention relates to an animal model for studying behavior related to fatty acid amide and hydrolysis of fatty acid amide. The invention provides transgenic animals in which the protein fatty acid amide hydrolase is not expressed, and methods of using such animals.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
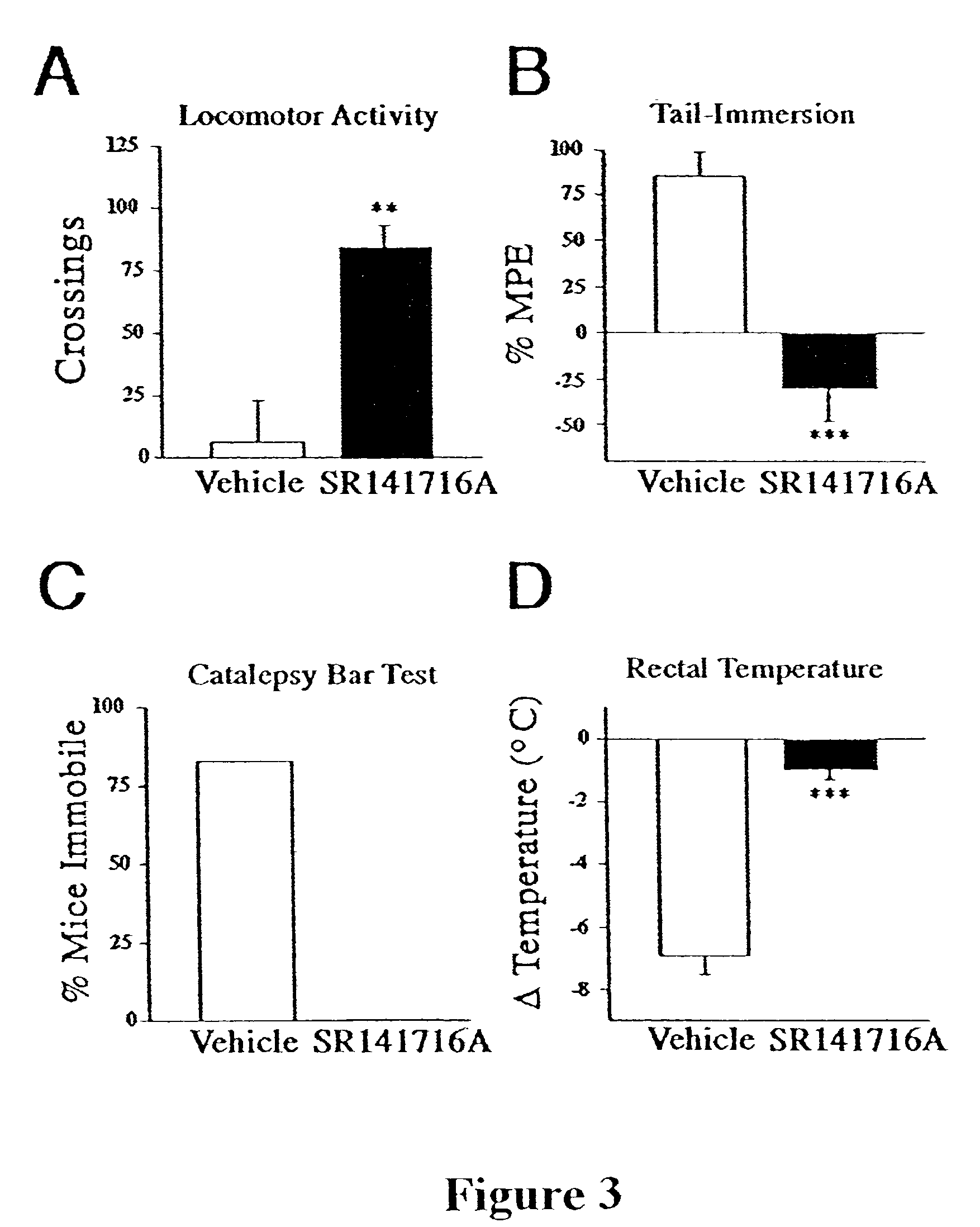
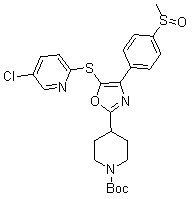
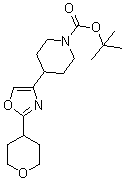
Oxazole derivatives useful as modulators of FAAH
The present invention is directed to certain Oxazole derivatives which are useful as modulators of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) and as FAAH imaging agents. The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzheimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Creatinine detection reagent capable of resisting interference of medicines such as calcium dobesilate
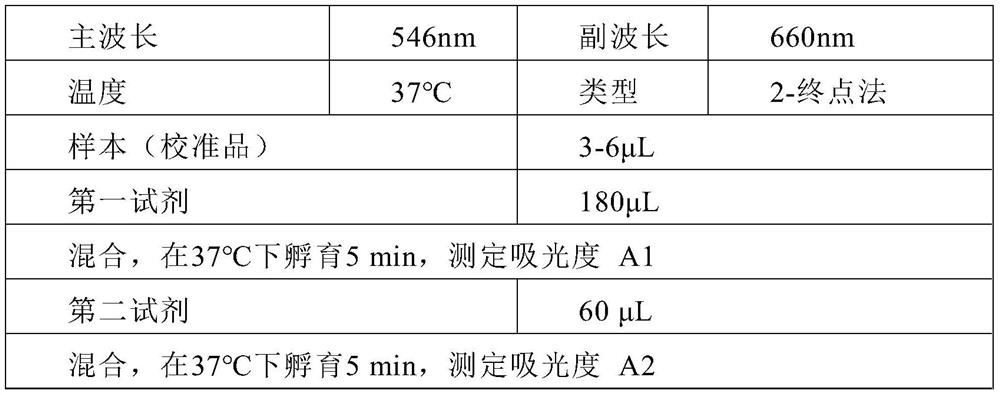
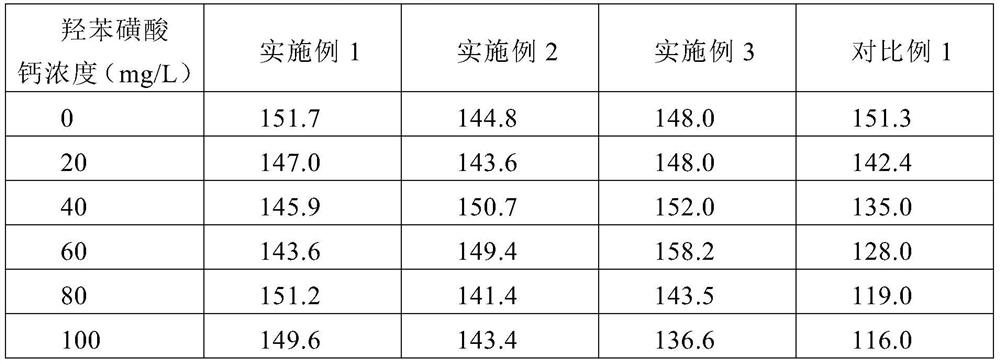
ActiveCN111766234AReduce interferenceImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCreatininasePeroxidase
The invention discloses a creatinine detection reagent capable of resisting interference of medicines such as calcium dobesilate. The creatinine detection reagent comprises a first reagent and a second reagent, wherein the first reagent comprises 3-(N-morpholinyl)propanesulfonic acid, TOOS, gentamicin, sarcosine oxidase, creatinase, ascorbic acid oxidase and catalase, and the second reagent comprises 3-(N-morpholinyl)propanesulfonic acid, 4-AAP, creatininase amidohydrolase, peroxidase, preservative and potassium ferrocyanide; the first reagent and / or the second reagent further comprise / comprises piperidine oxygen radicals. According to the creatinine detection reagent provided by the invention, the interference effect of medicines such as calcium dobesilate can be reduced, the accuracy ofcreatinine detection in clinical detection is ensured, and a creatinine detection method with a wide linear range, strong medicine interference resistance and high accuracy is realized.
Owner:WUHAN HANHAI NEW ENZYMES BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
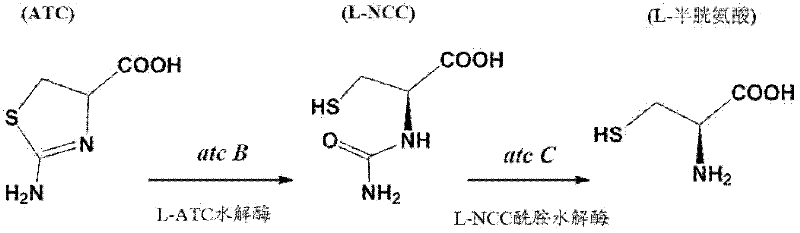
N-carbamyl-L-cysteine (L-NCC) amidohydrolase, encoding gene and application of recombinant expressed protein of L-NCC amidohydrolase
ActiveCN102409033ASingle ingredientHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsHydrolysis
The invention discloses a gene sequence of N-carbamyl-L-cysteine (L-NCC) amidohydrolase, and a preparation and an application of a recombinant expressed protein of the L-NCC amidohydrolase. The L-NCC amidohydrolase derived from pseudomonad with preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.5315 is an amino acid residue sequence in SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table, or is a protein which is derived from SEQ ID No.1 by substituting, deleting or adding one or more amino acid residues to the amino acid residue sequence in SEQ ID No.1 and has the same activity asSEQ ID No.1. According to the invention, the pseudomonad-derived L-NCC amidohydrolase is subjected to gene cloning and expression to prepare a recombinant enzyme, and the obtained recombinant enzyme can be used for biological hydrolysis of L-NCC to obtain L-cysteine, thus the L-NCC amidohydrolase can be used for enzymatic production of L-cysteine.
Owner:天津世纪伟康生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com