Animal model for fatty acid amide-related neurobehaviors
a neurobehavior and animal model technology, applied in the field of animal model of fatty acid amide-related neurobehaviors, can solve the problems of difficult, if not impossible, to assess the pharmacological and physiological activities of fatty acid amides and related compounds, hindering efforts to characterize the pharmacological and physiological function of this endogenous brain,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Biochemical Characterization of FAAH Knockout Mice
[0060] This example provides biochemical assays useful for characterizing the FAAH knockout mice.
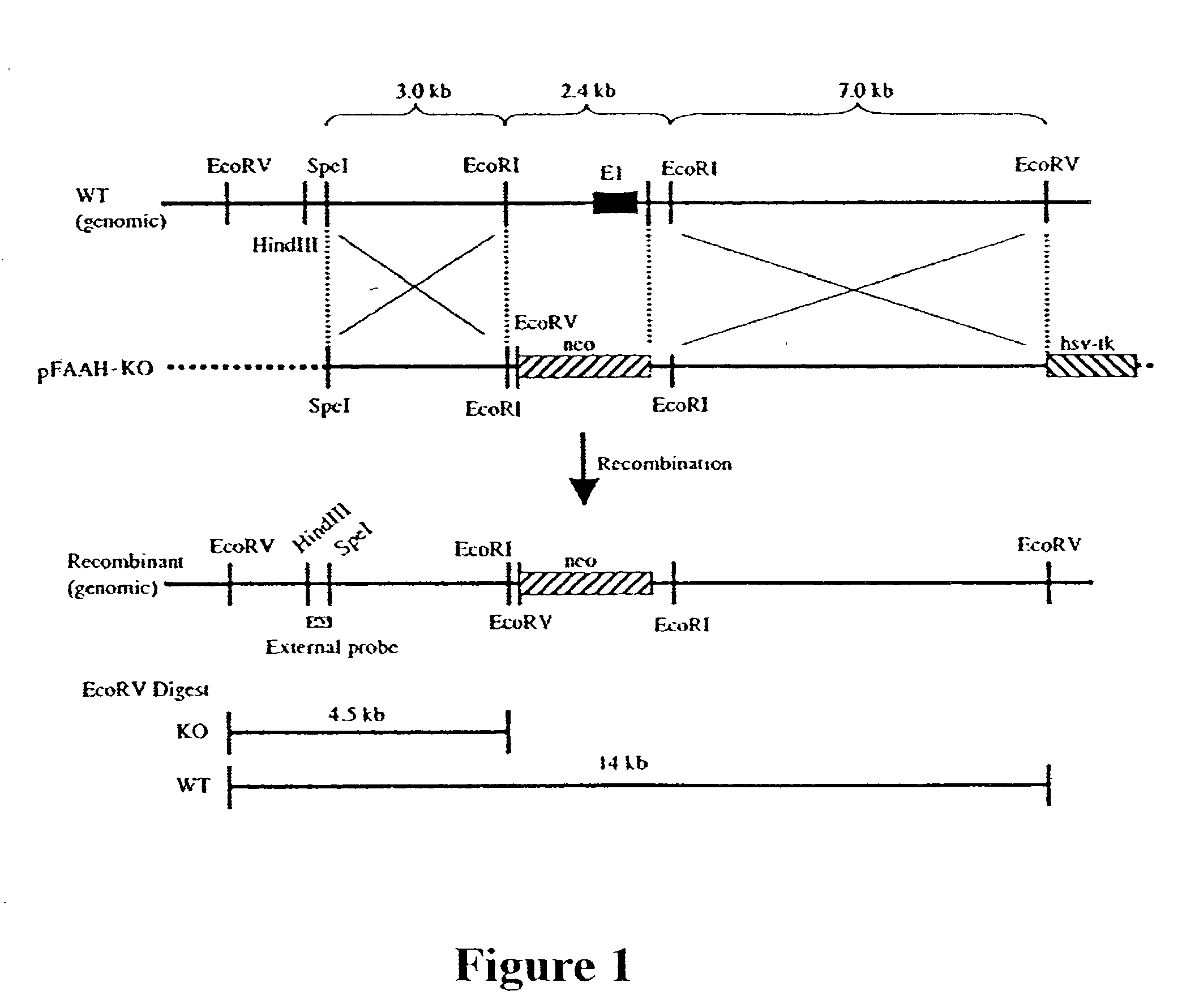
[0061] Brain and liver were isolated from homozygous wild type (FAAH.sup.+ / +), heterozygous (FAAH.sup.+ / -) and homozygous knockout (FAAH.sup.- / -) mice and examined by western blot analysis using polyclonal anti-FAAH antibodies (see Patricelli et al., Biochemistry 37:15177-15187, 1998). No FAAH protein was detectable in the brain or liver of the knockout mice.
[0062] The mice also were examined for FAAH enzymatic activity. FAAH activity assays for oleamide and anandamide were measured by following the conversion of .sup.14C-labeled substrates using a thin layer chromatography assay essentially as described by Patricelli et al. (Biochemistry 38:9804-9812, 1999), except that enzyme assays were conducted at pH 7.2. Brain and liver from FAAH.sup.- / - mice exhibited greatly reduced FAAH catalytic activity (Table 1). Brain extracts from FAAH.sup.-...
example 3
Neurobehavioral Examination of FAAH Knockout Mice
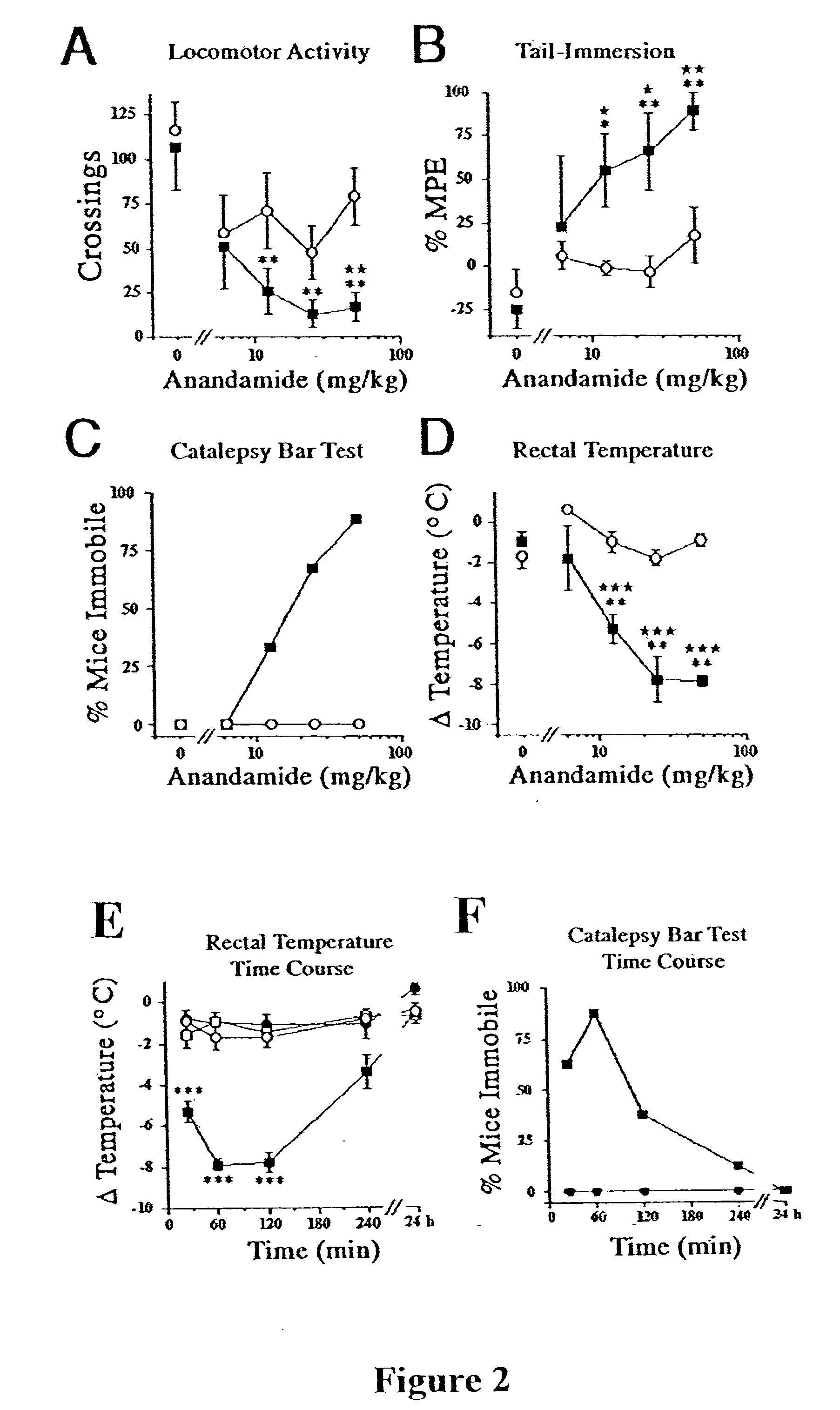
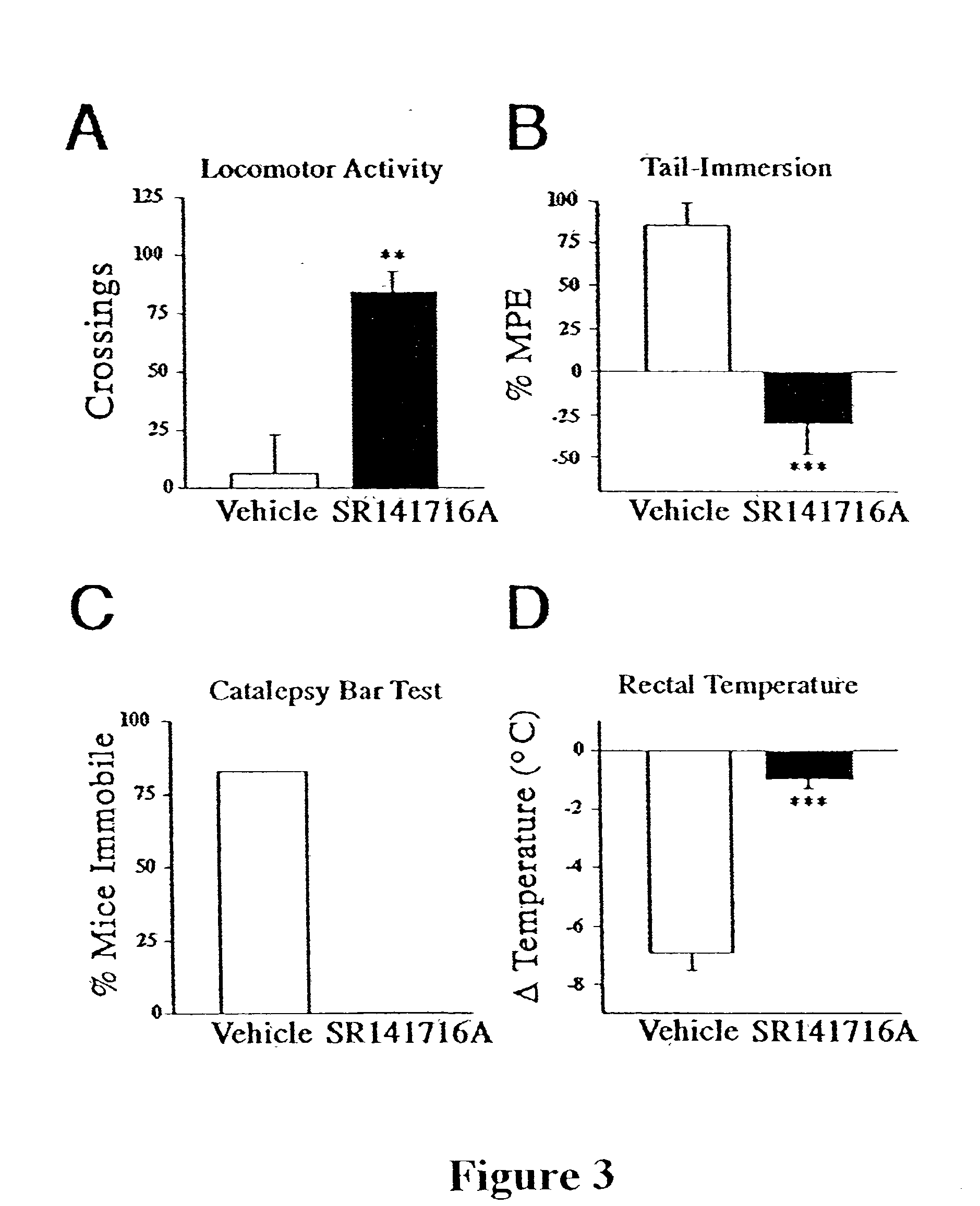
[0063] This example provides neurobehavioral assays that measure spontaneous activity, thermal pain sensation, catalepsy, and rectal temperature, and demonstrates that FAAH regulates anandamide activity in vivo.
[0064] Experiments were performed using a combination of male and female mice (no significant sex differences were observed for either genotype). All drugs were administered intraperitoneal (ip) in a mixture of 1 part ethanol: 1 part EMULPHOR alcohol (GAF Corp.; New York N.Y.): 18 parts saline (10 .mu.l / g body weight), except naloxone was administered ip in saline.
[0065] Locomotor activity was assessed by placing each mouse in a clear plexiglass cage (18.times.10.times.8.5 inches; l.w.h) that was marked in 7 cm square grids on the floor of the cage. The number of grids that were traversed by the hind paws was counted from 15 to 20 min post-injection. Nociception was assessed using the tail immersion assay, wherein each mouse wa...
example 4
Generation of a Mouse Model with FAAH Expression Restricted to the Nervous System
[0077] Exogenously applied and endogenously produced fatty acid amides induce a variety of behavioral effects in mammals, which may reflect either central or peripheral sites of action. In wild type mammals, FAAH is not only expressed in the central and peripheral nervous system, but also in a variety of non-nervous system peripheral tissues, including liver, kidney, and testis. Thus, a standard deletion of the FAAH gene results in an animal model where FAAH is absent from all sites in the organism and therefore does not permit an assignment of phenotypes to central or peripheral modes of action. To address this issue, the mouse FAAH cDNA was placed under the control of the neural specific enolase (NSE) promoter (Forss-Petter et al. (1990) Neuron 5, 187-197) and this construct was used to generate transgenic mice (mixed background of C57Bl / 6 and Balb / c) by pronuclear injection methods following standard...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com