Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2040 results about "Physiological function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
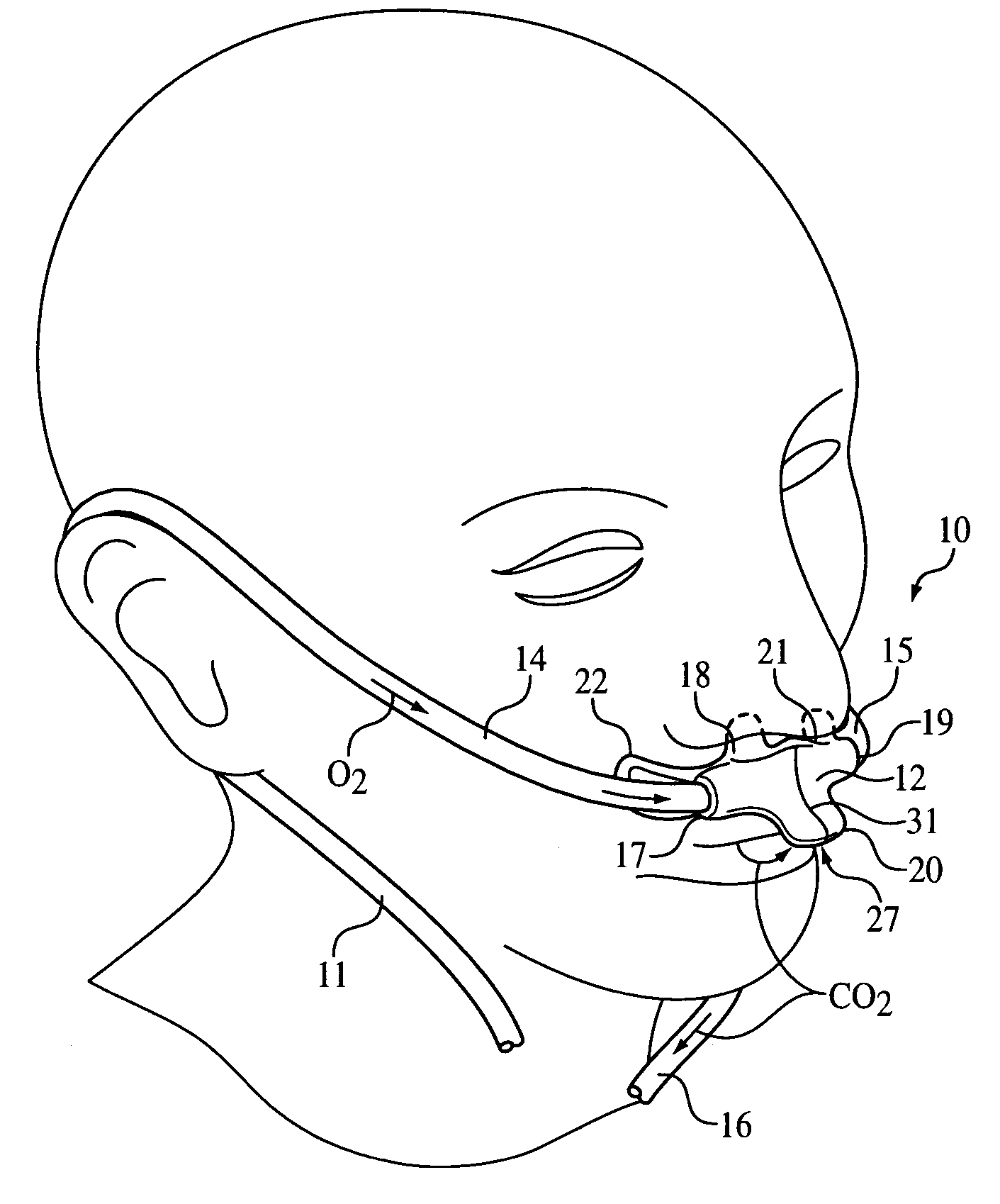
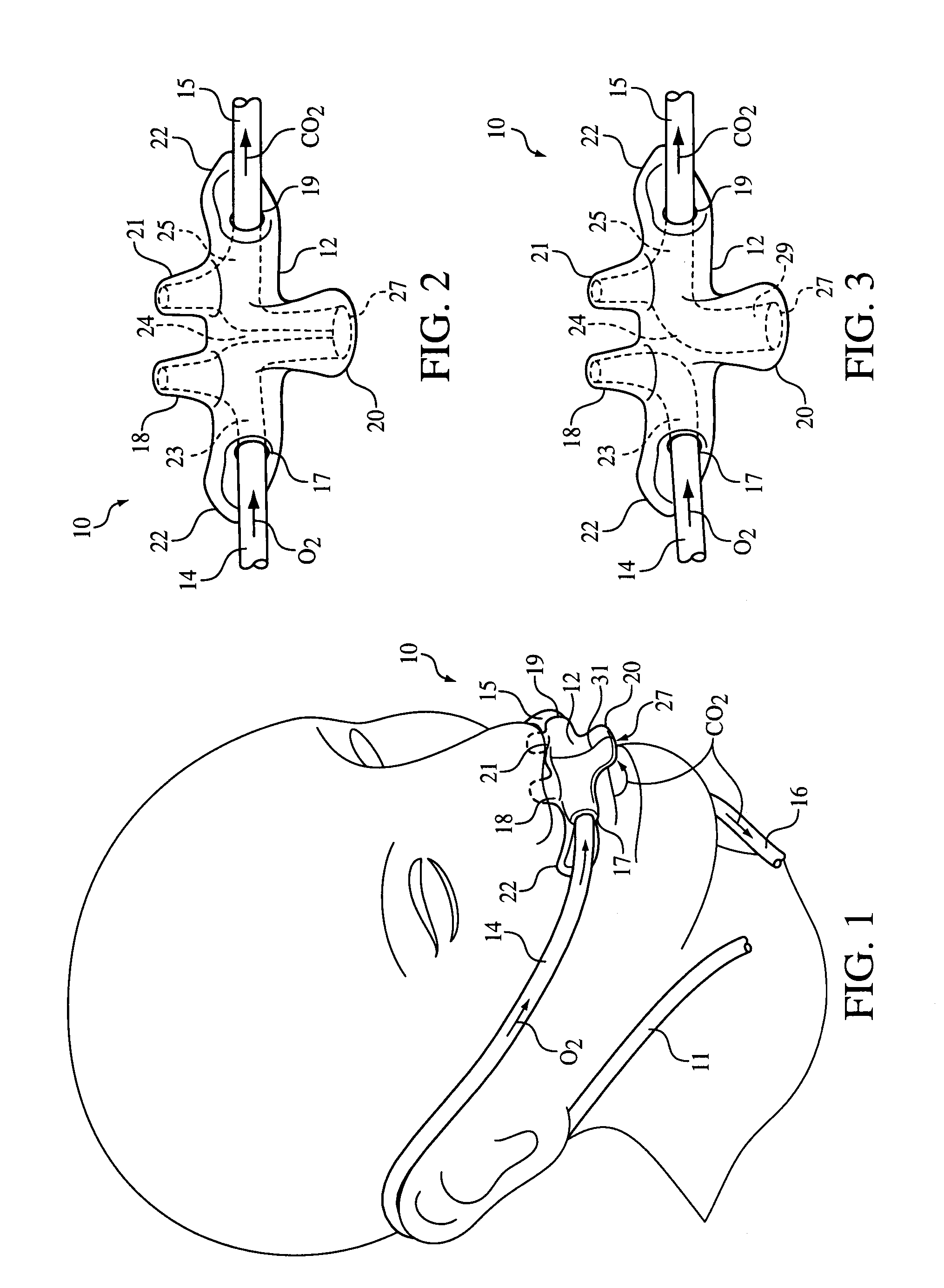
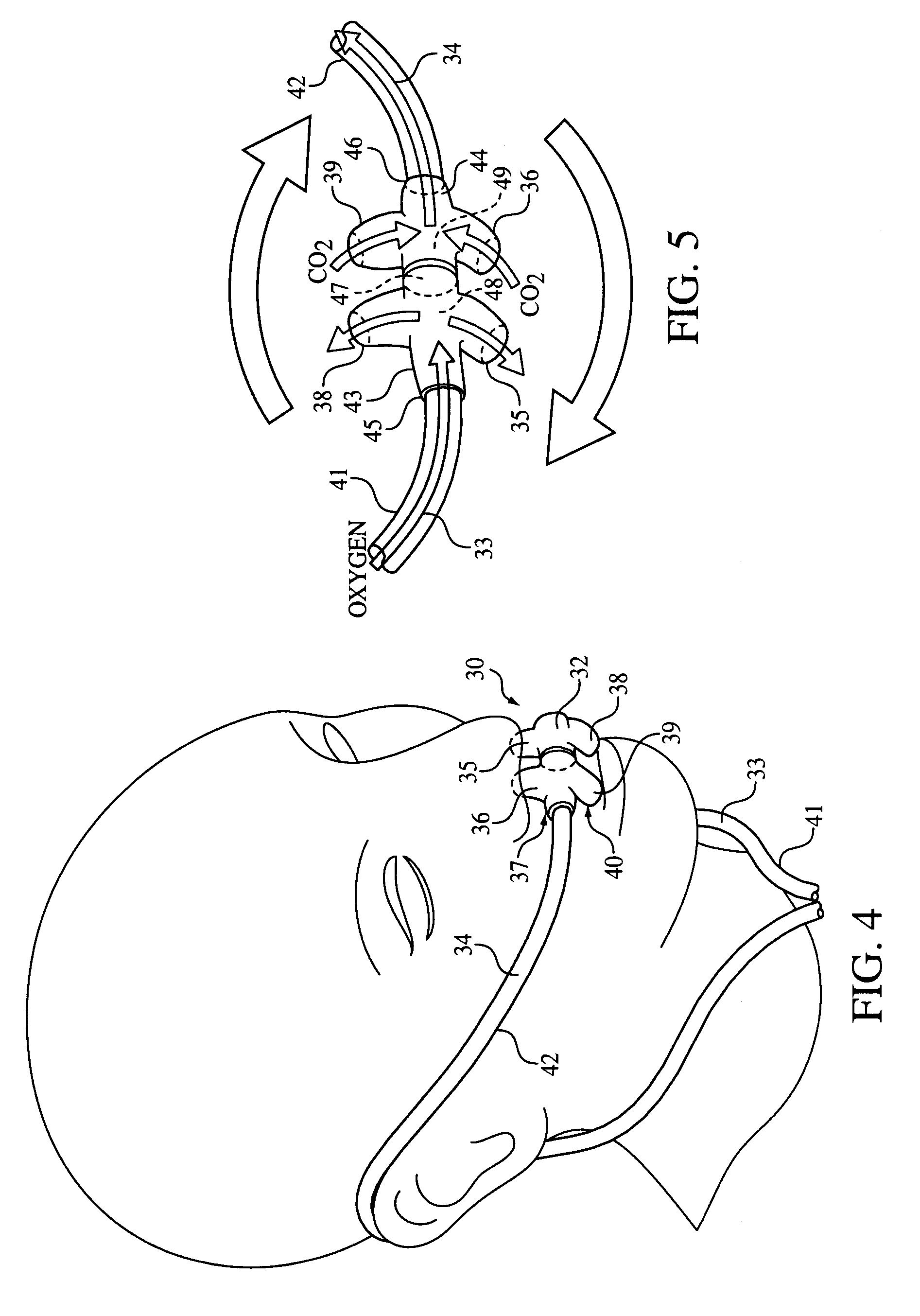
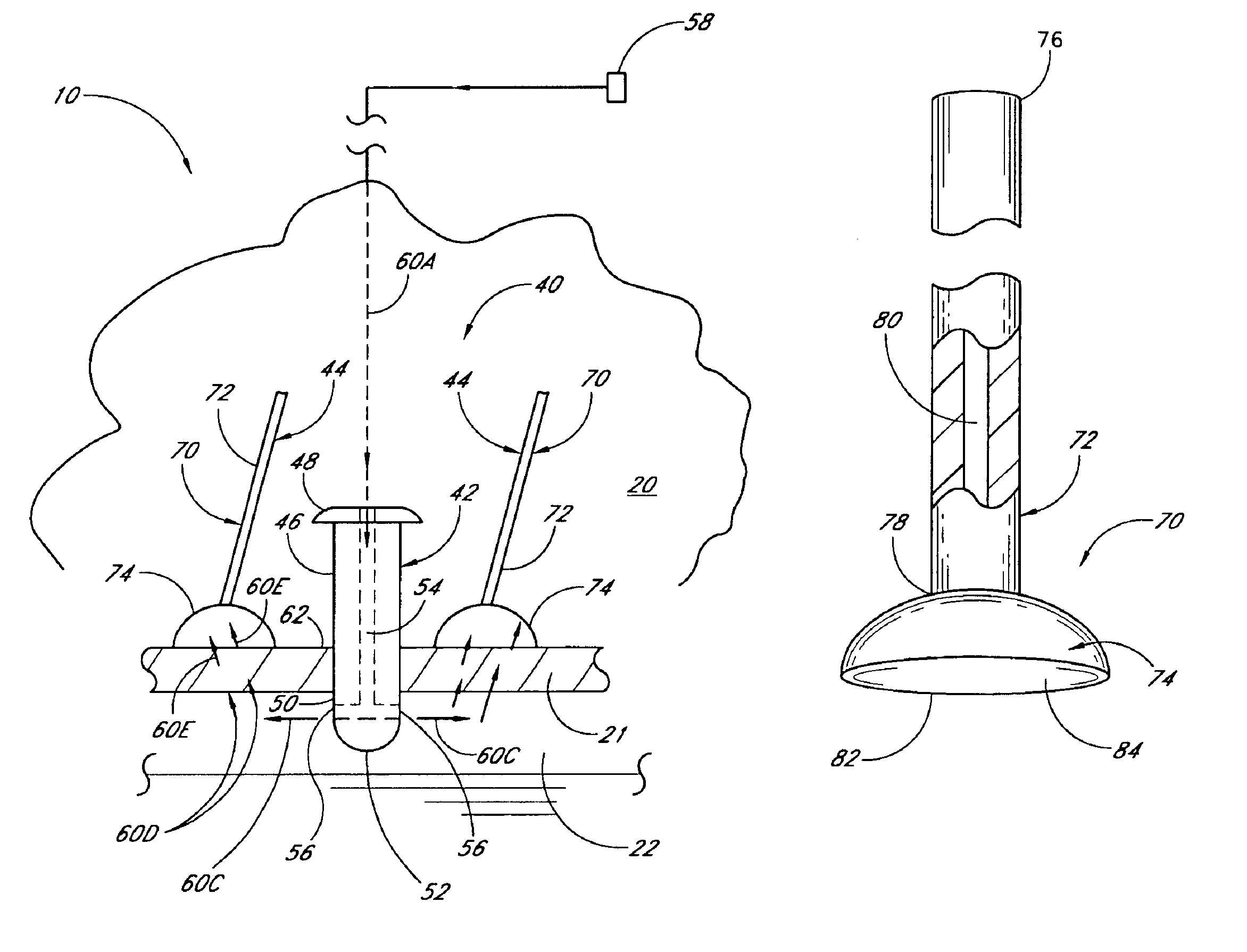
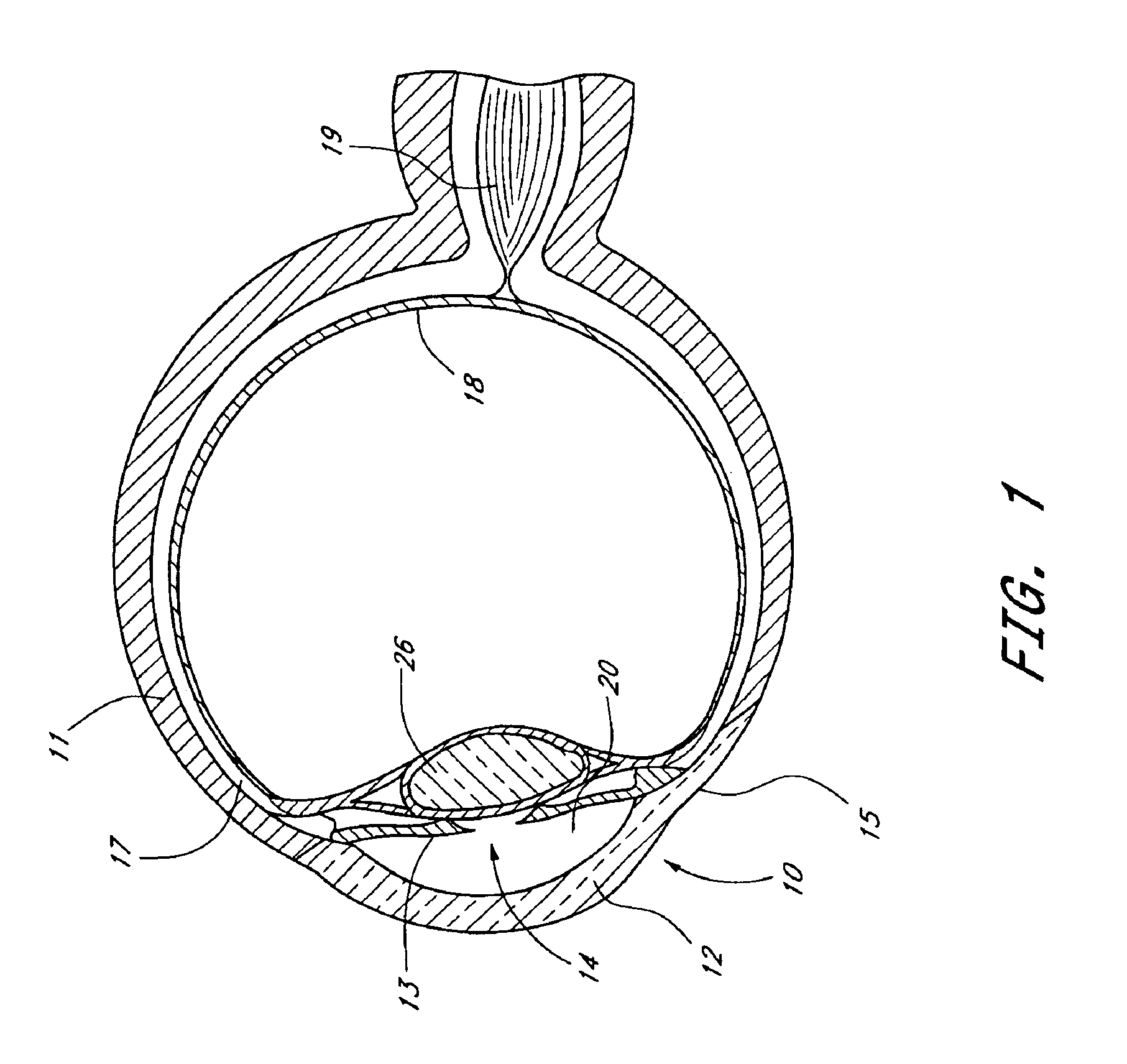
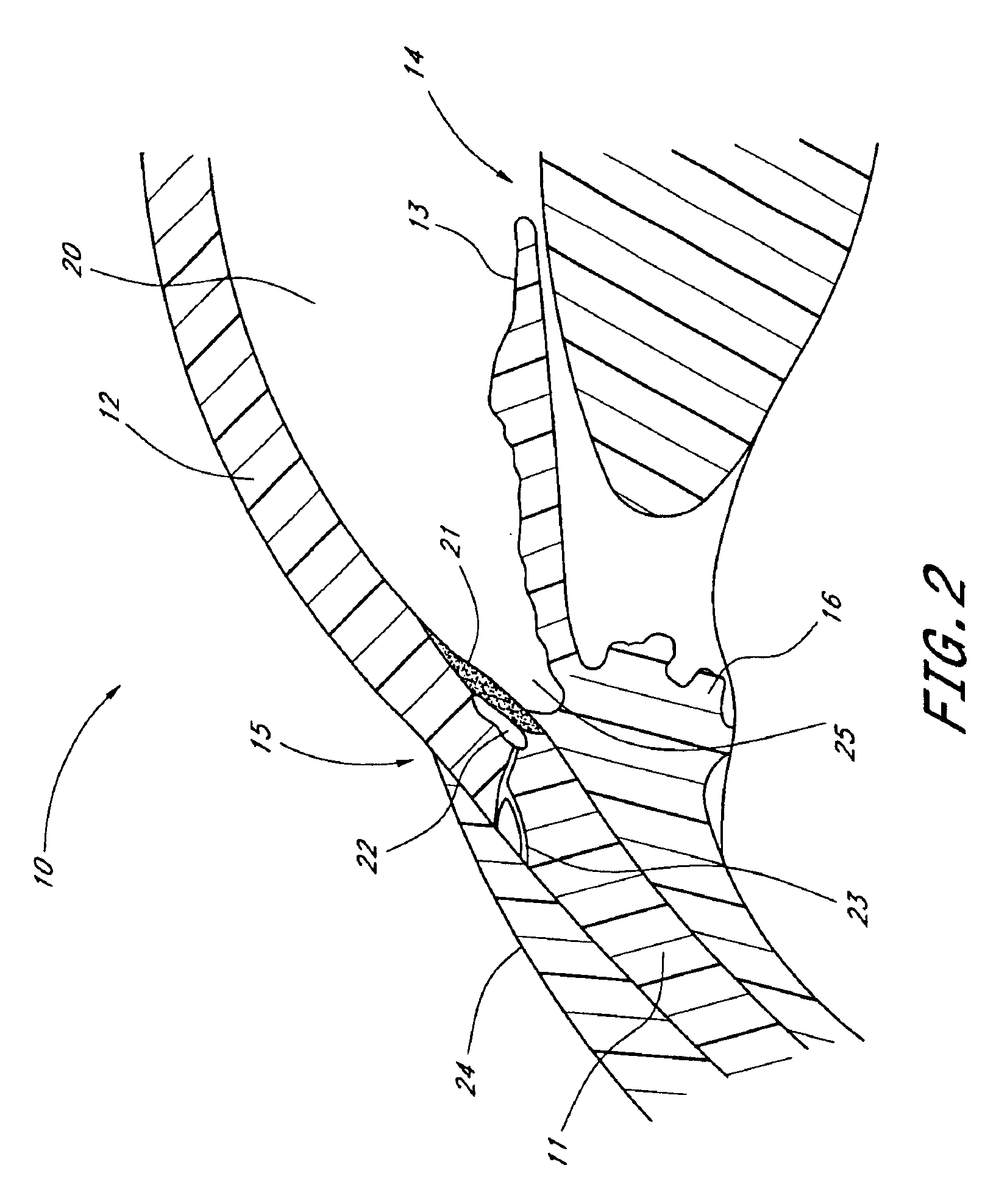
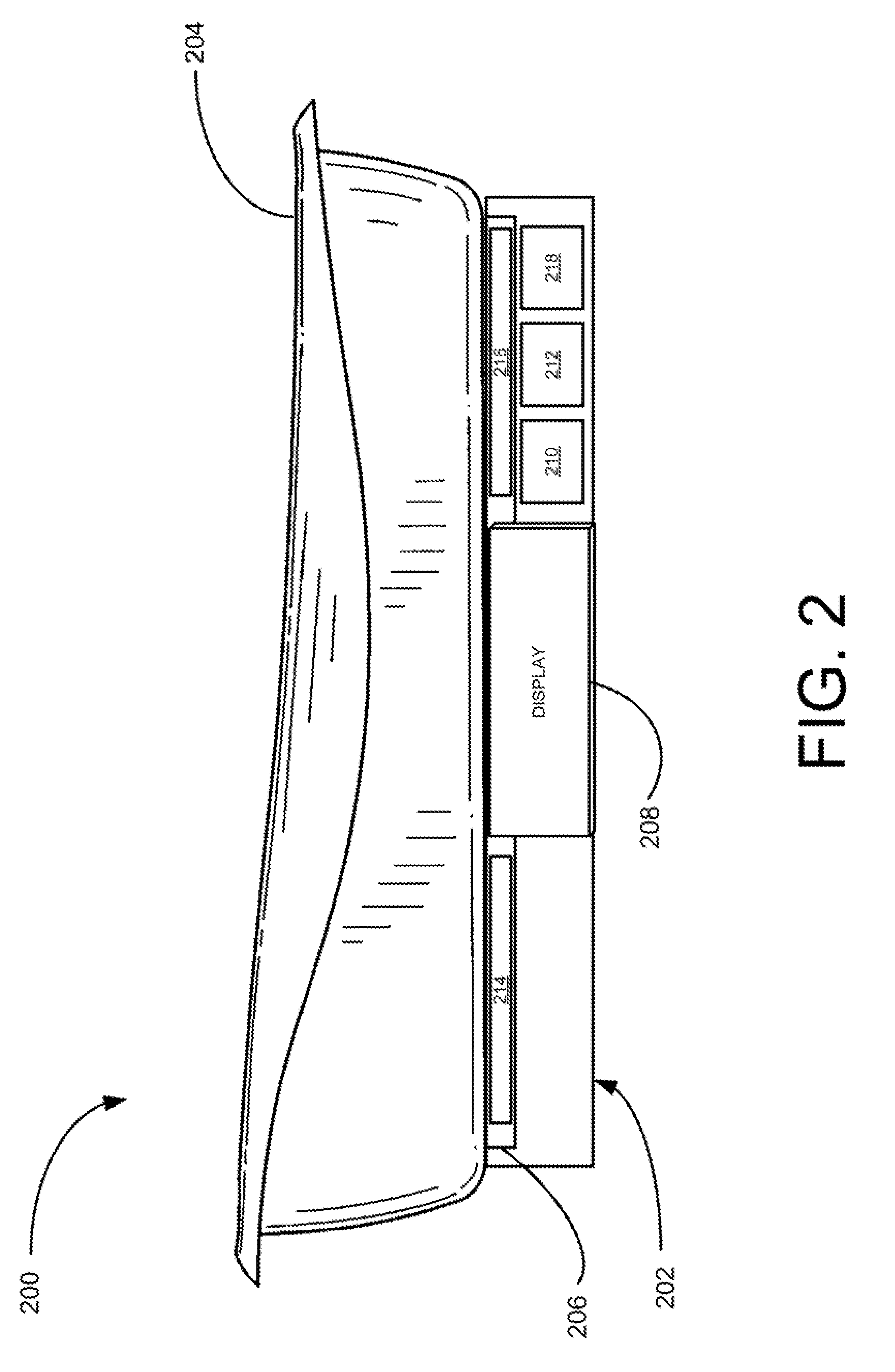
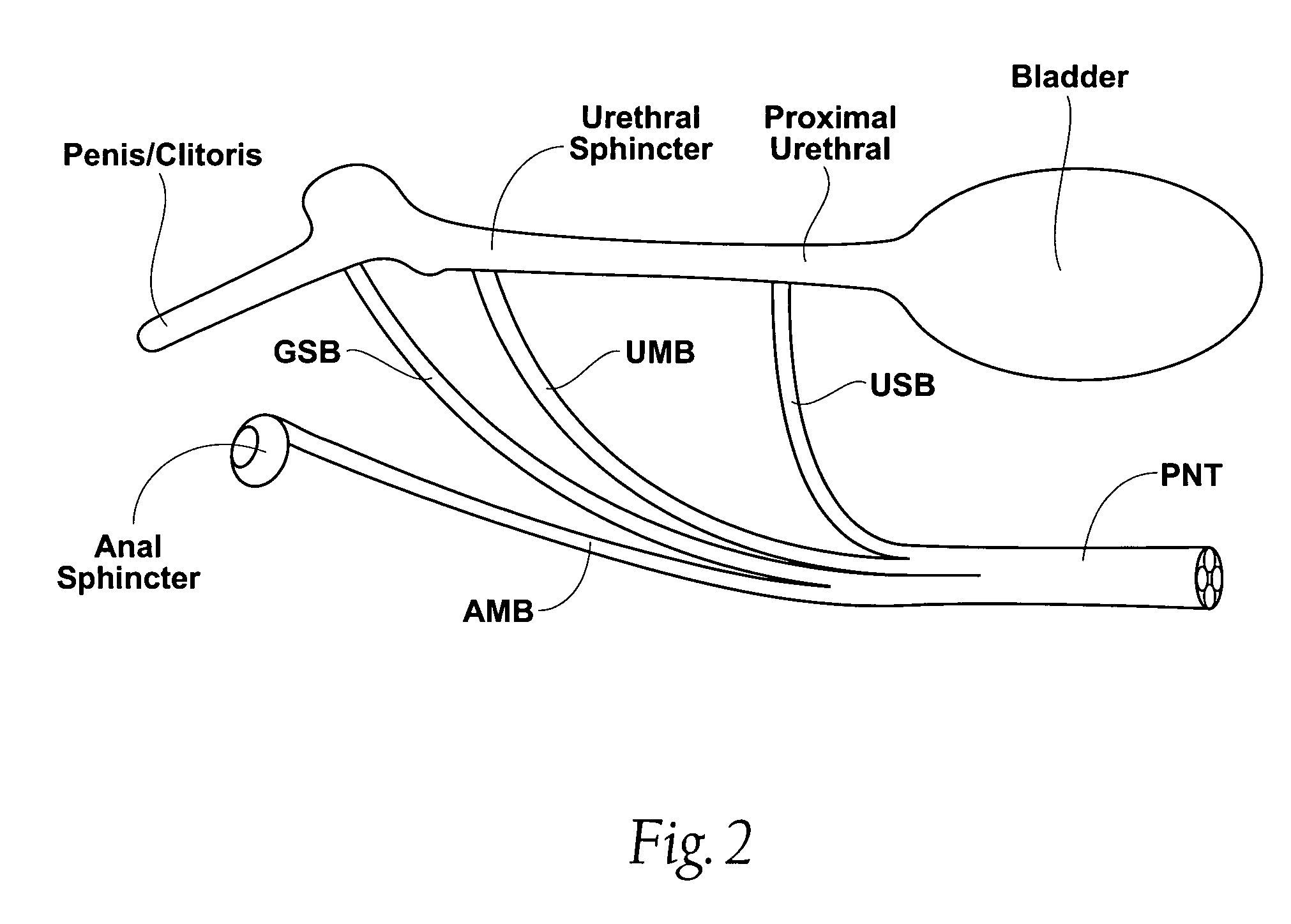
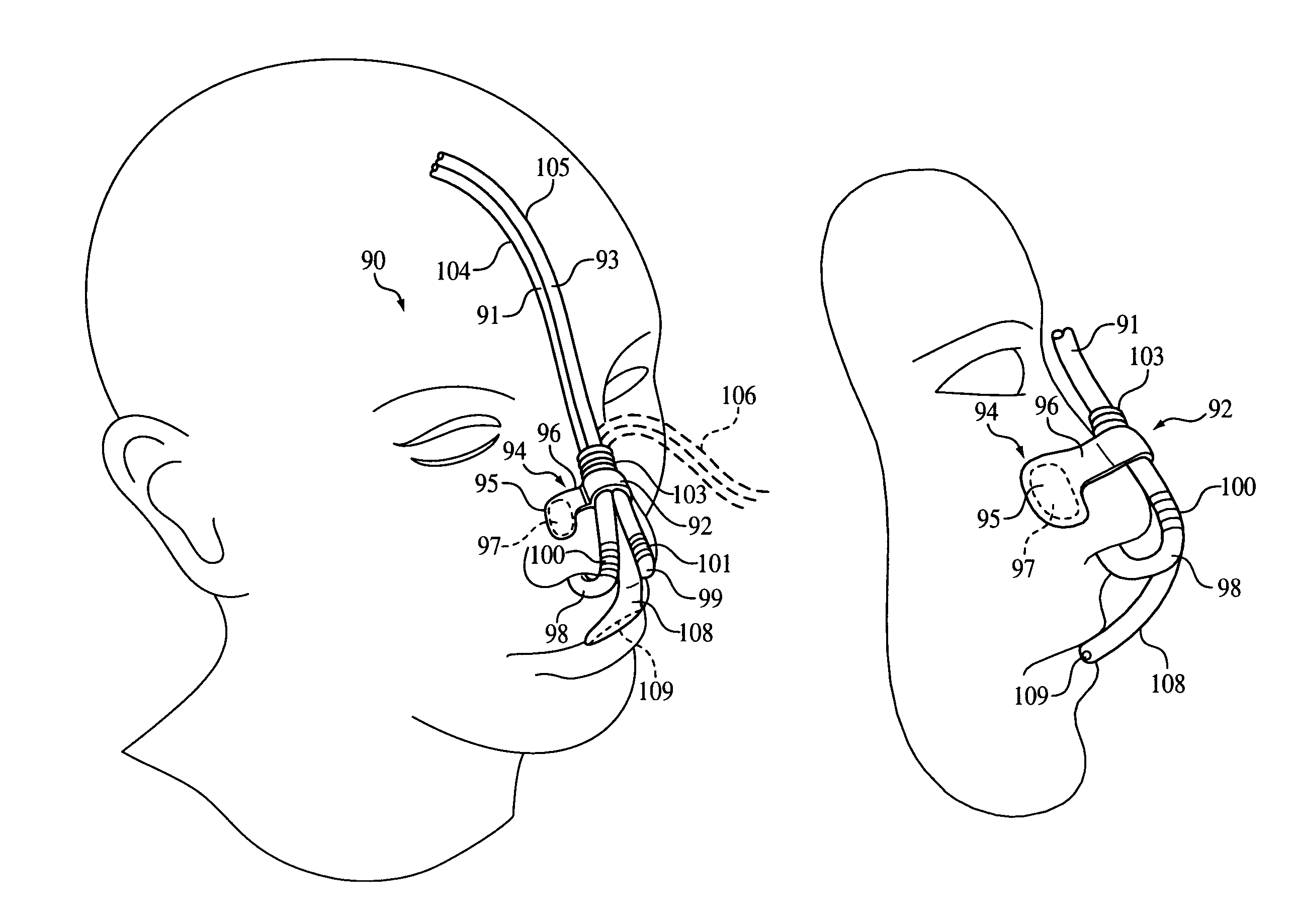
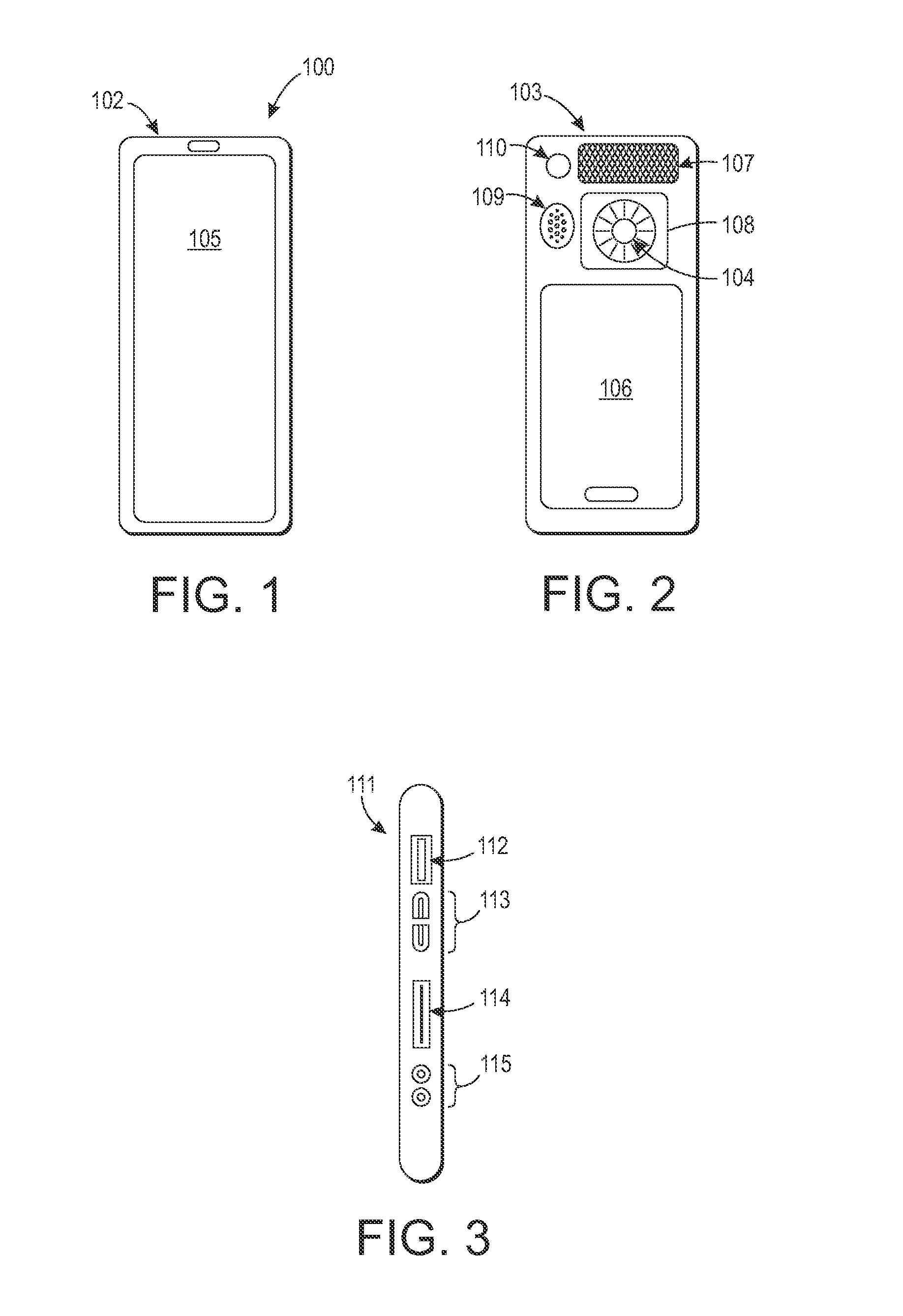
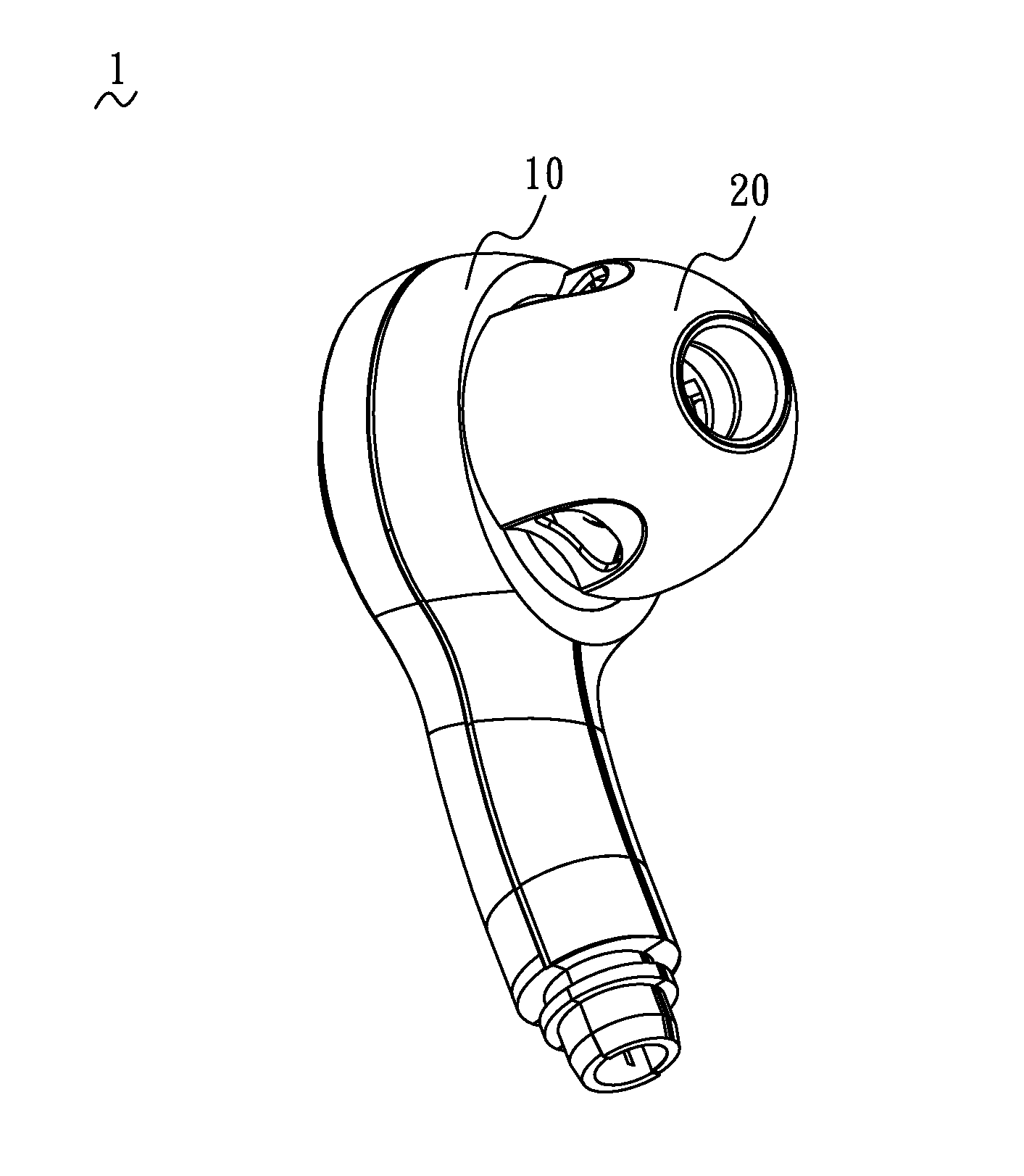
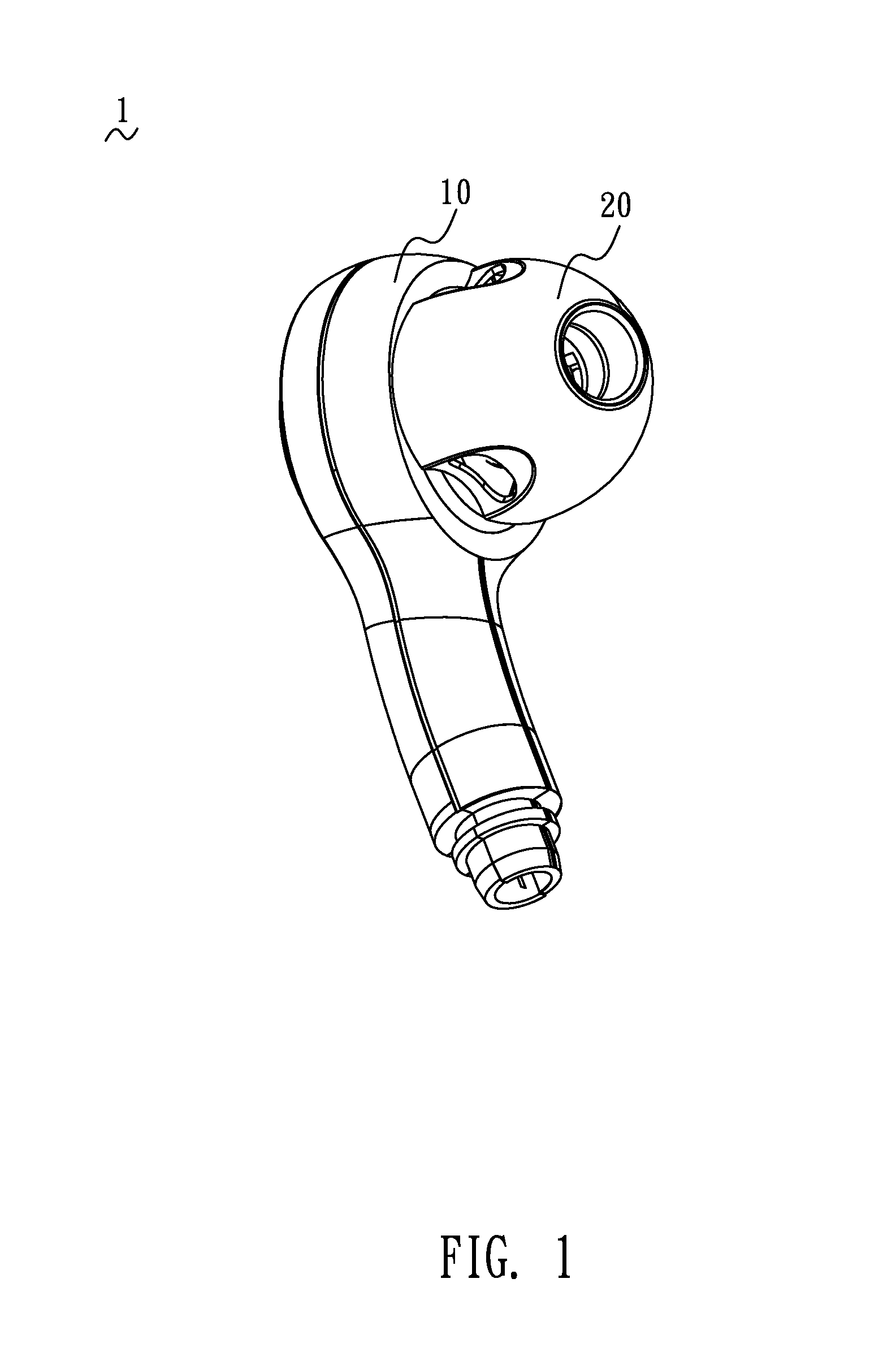
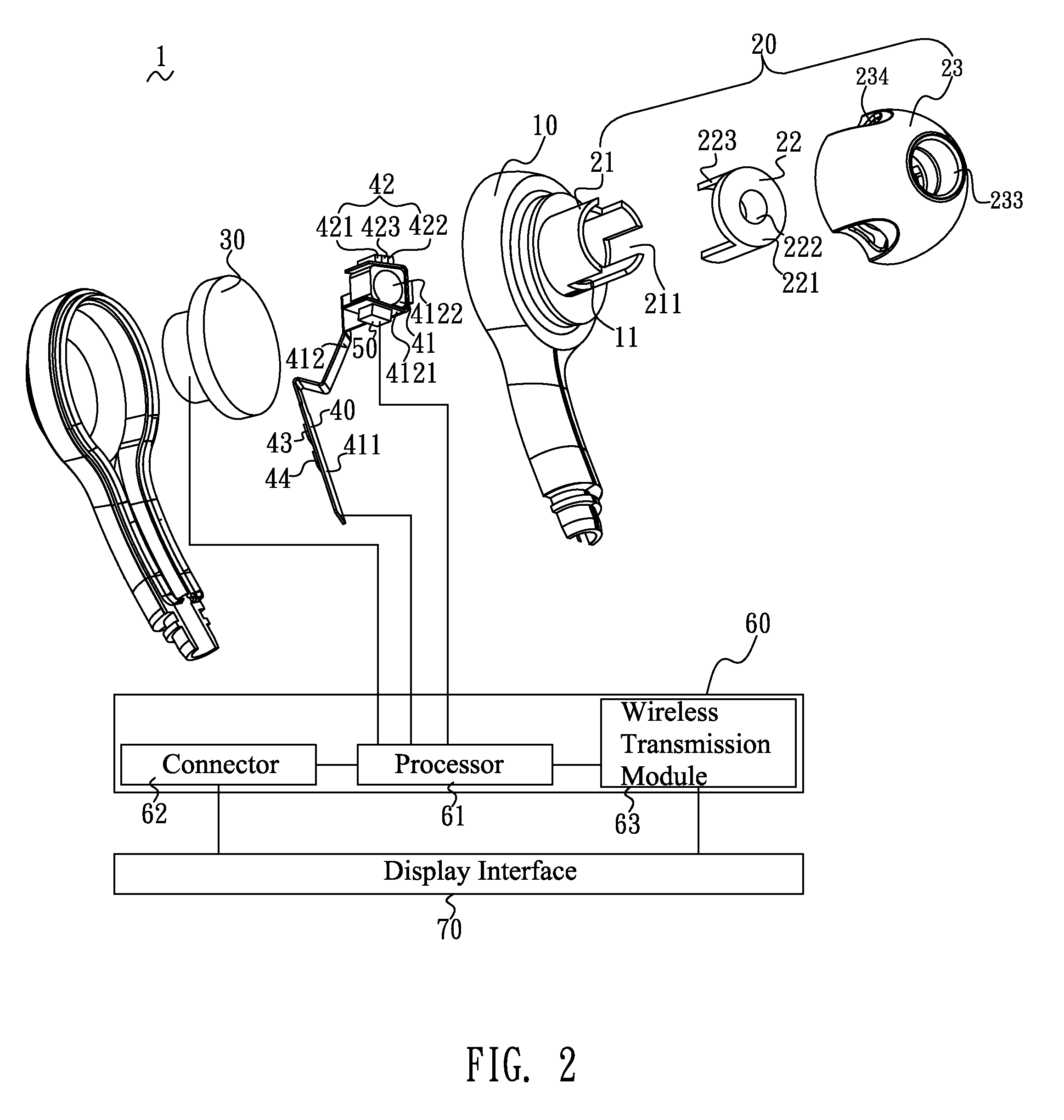
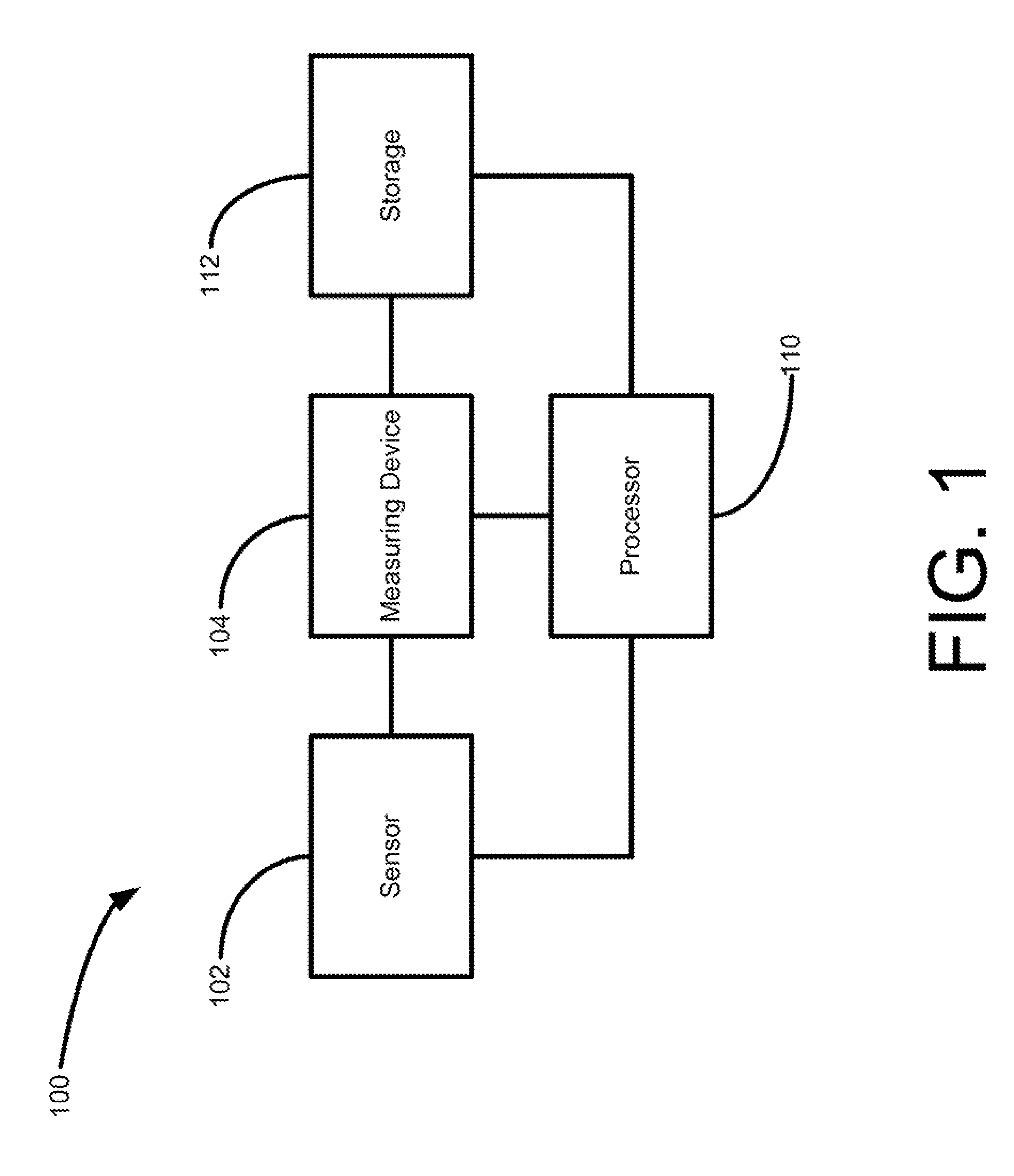
Nasal and oral patient interface
ActiveUS20080190436A1Improve stabilityImprove comfortRespiratorsBreathing filtersNasal cavityProximate
A patient interface for communicating fluids to and / or from a patient's nasal cavity and / or oral cavity is disclosed. In addition, a patient interface for fluid and physiological function monitoring proximate to the patient's nasal cavity and / or oral cavity is disclosed. An apnea monitor and a method for monitoring apnea are also disclosed.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
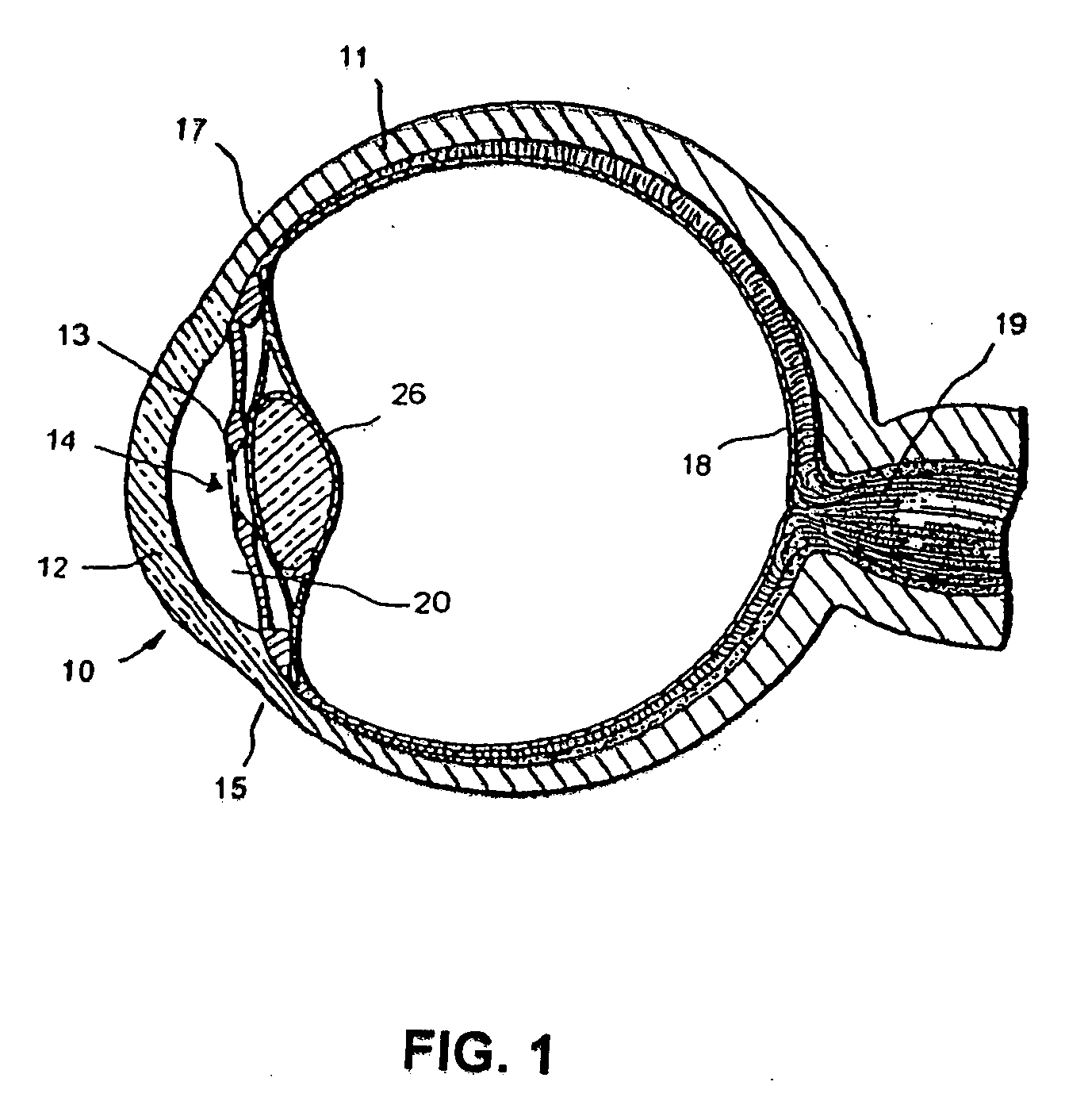
Medical device and methods of use of glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS7094225B2Lower eye pressureThe process is simple and effectiveBiocideSenses disorderAqueous outflowSchlemm's canal
The invention relates generally medical devices and methods for the treatment of glaucoma in an animal eye and, more particularly, to medical devices and methods for treating tissue of the trabecular meshwork and / or Schlemm's canal of the eye to restore or rejuvenate a portion or all of the normal physiological function of directing aqueous outflow for maintaining a normal intraocular pressure in the eye.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
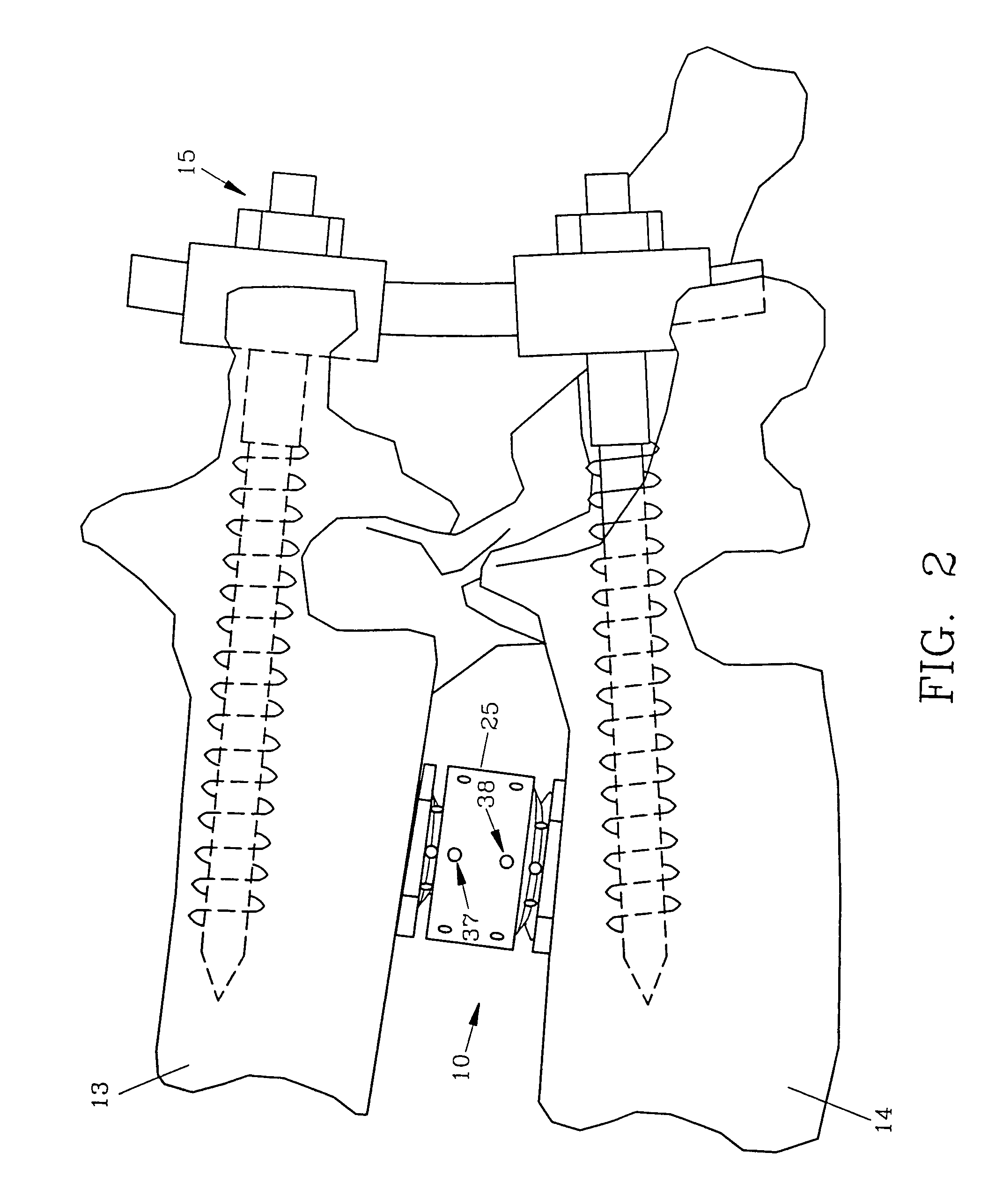
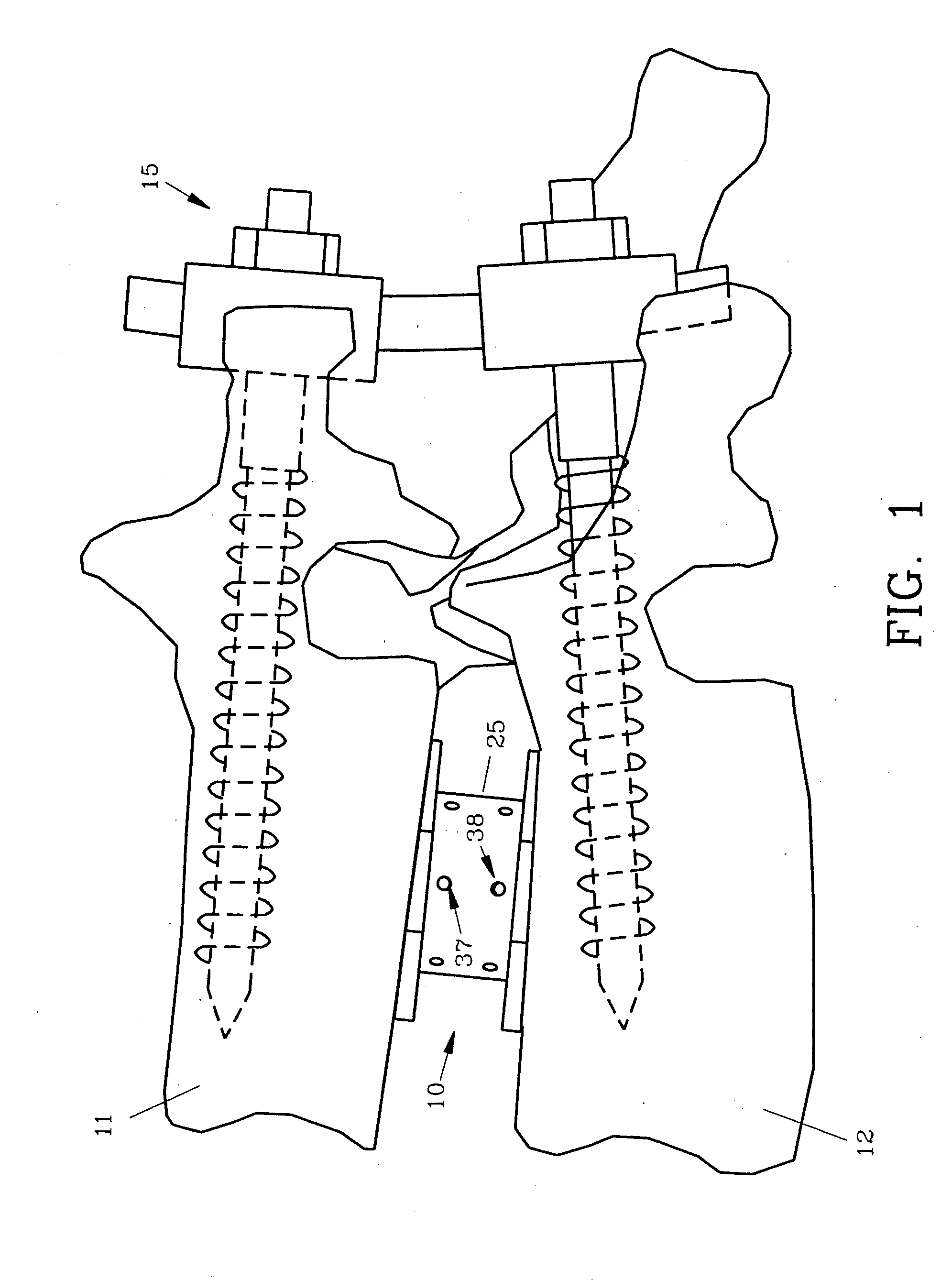
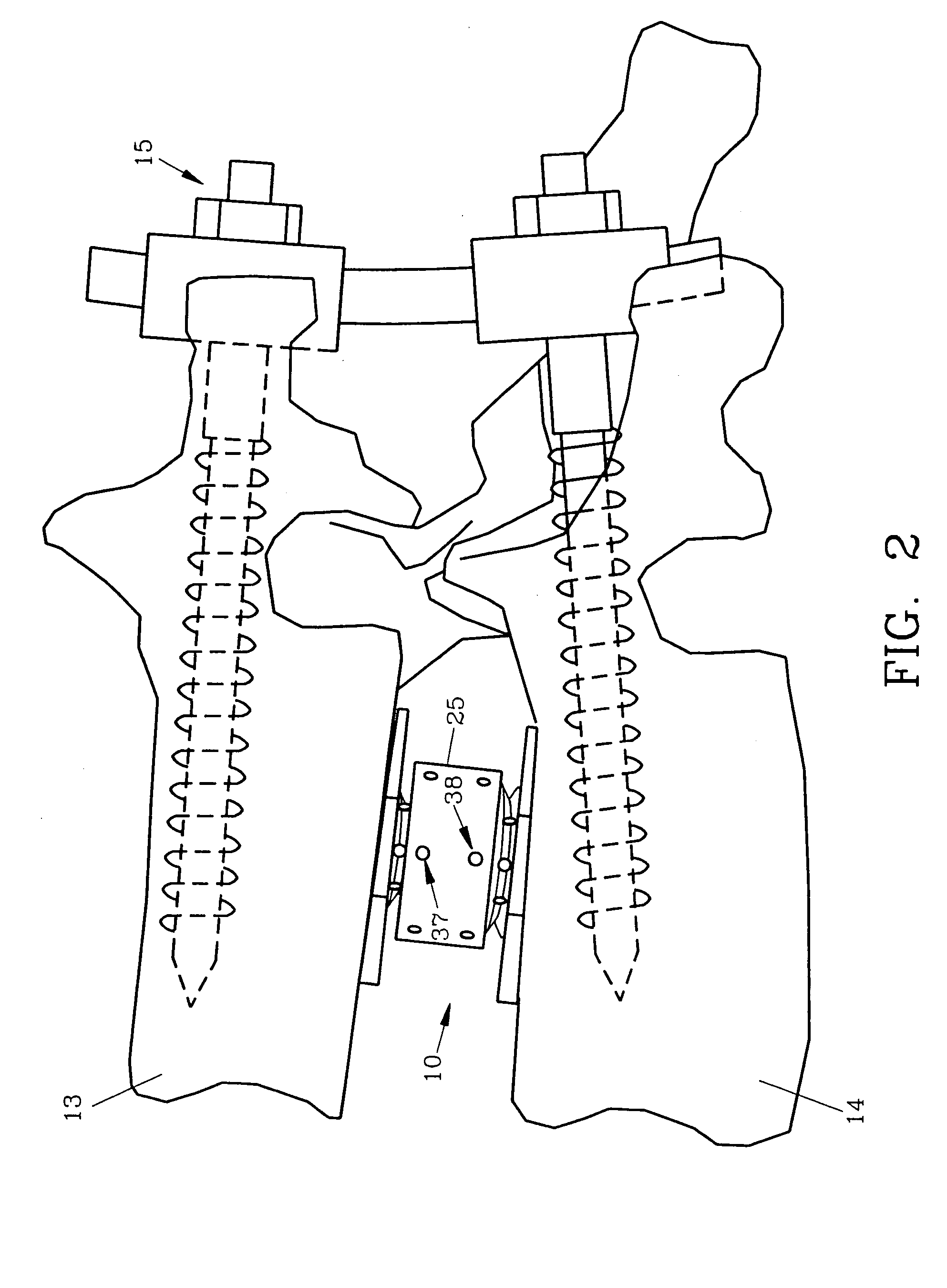
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS7022138B2Easy to copyAvoid injuryInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnIntervertebral disk
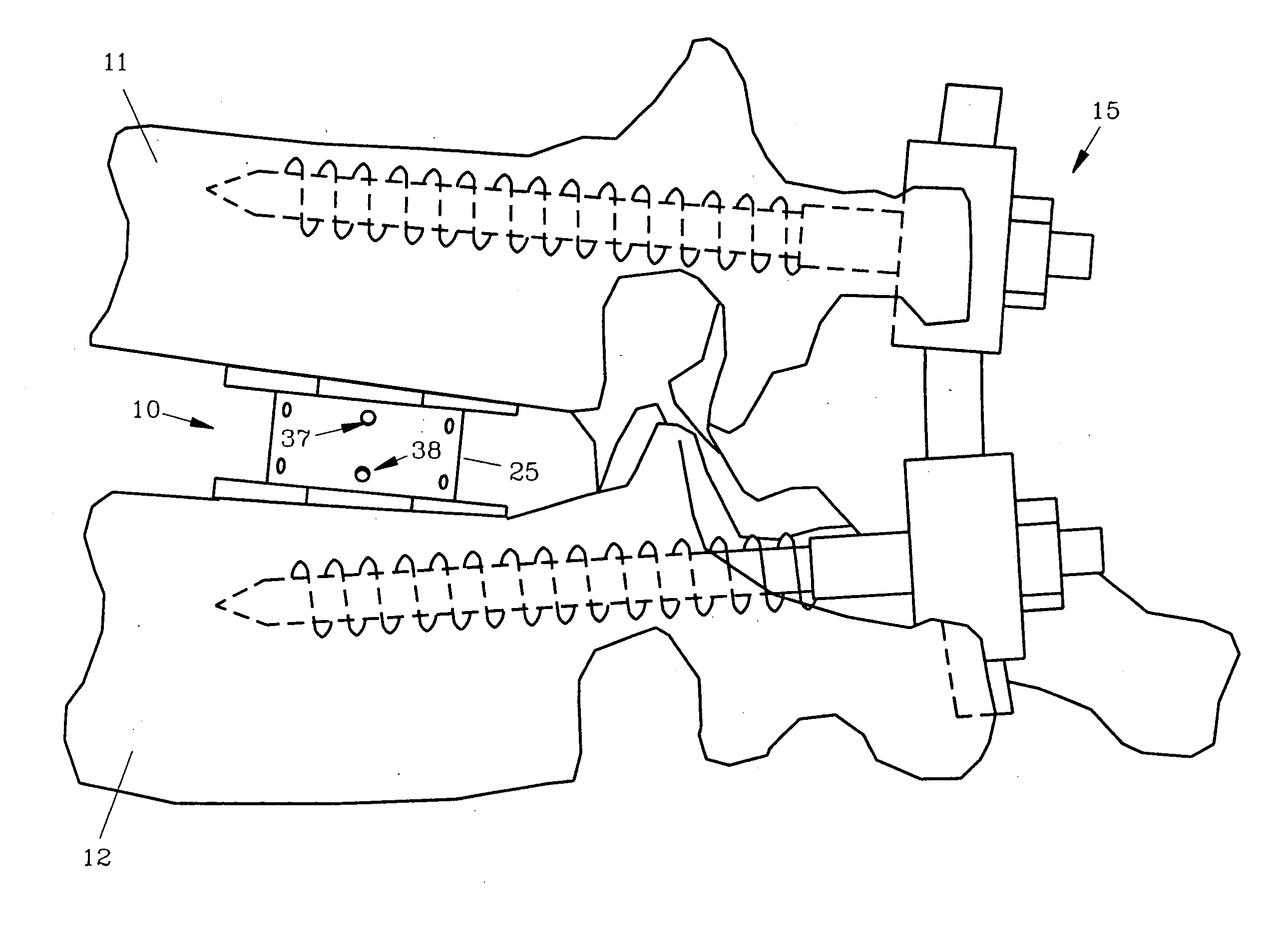
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the plate bore. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
Contrast-enhanced ocular imaging
The invention relates generally to medical devices and methods for ocular imaging and, more particularly, to devices and methods for increasing contrast in an eye in which an imaging contrast agent is introduced into an aqueous humor outflow channel. For example, in one embodiment, the outflow channel may be Schlemm's Canal, or in another embodiment, the outflow channel may be an episcleral vein. Also disclosed are methods for implanting a trabecular stent via an ab extemo procedure with assistance of enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to restore a part or all of the normal physiological function of directing aqueous outflow for maintaining a normal intraocular pressure in an eye.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Device and method or three-dimensional spatial localization and functional interconnection of different types of cells
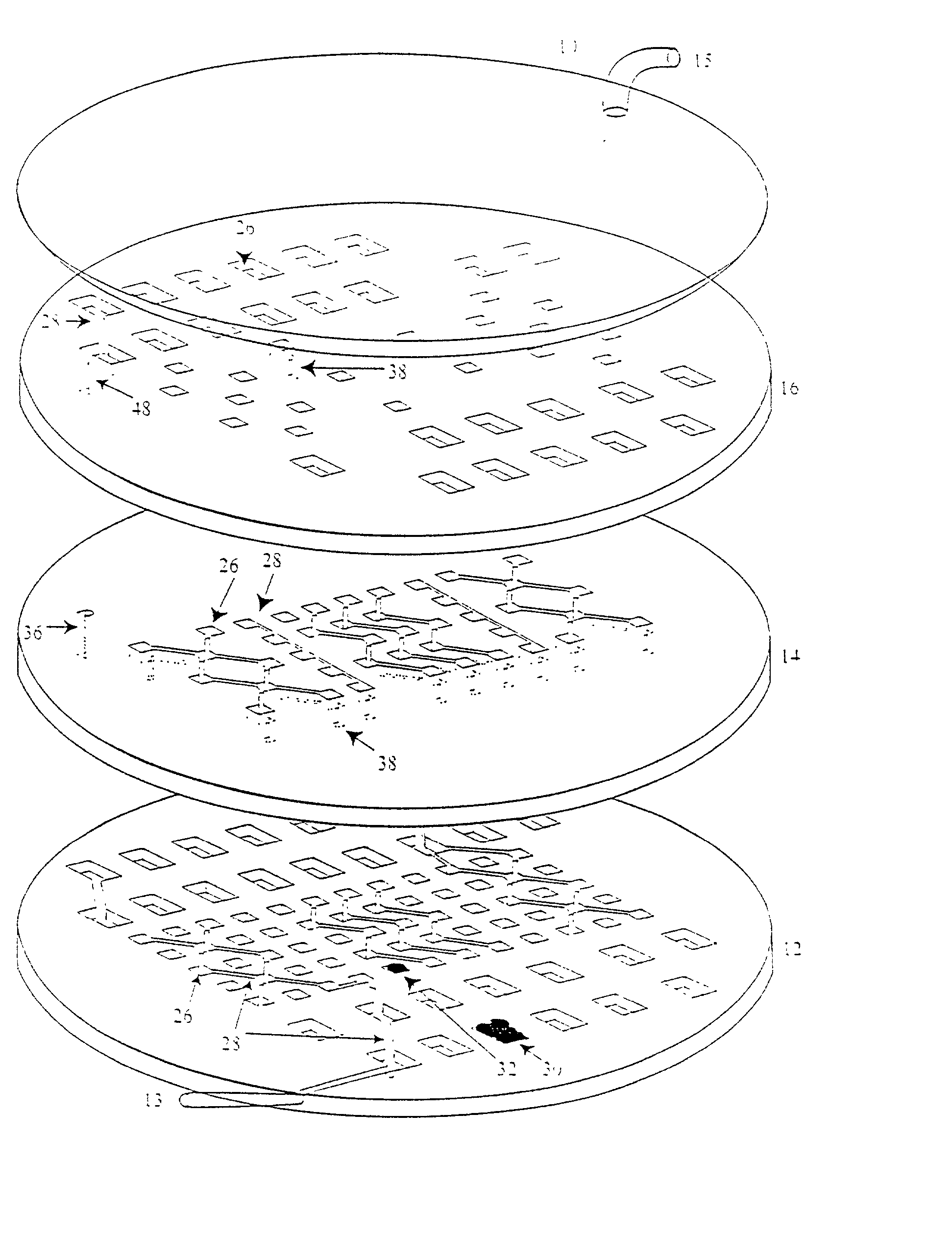
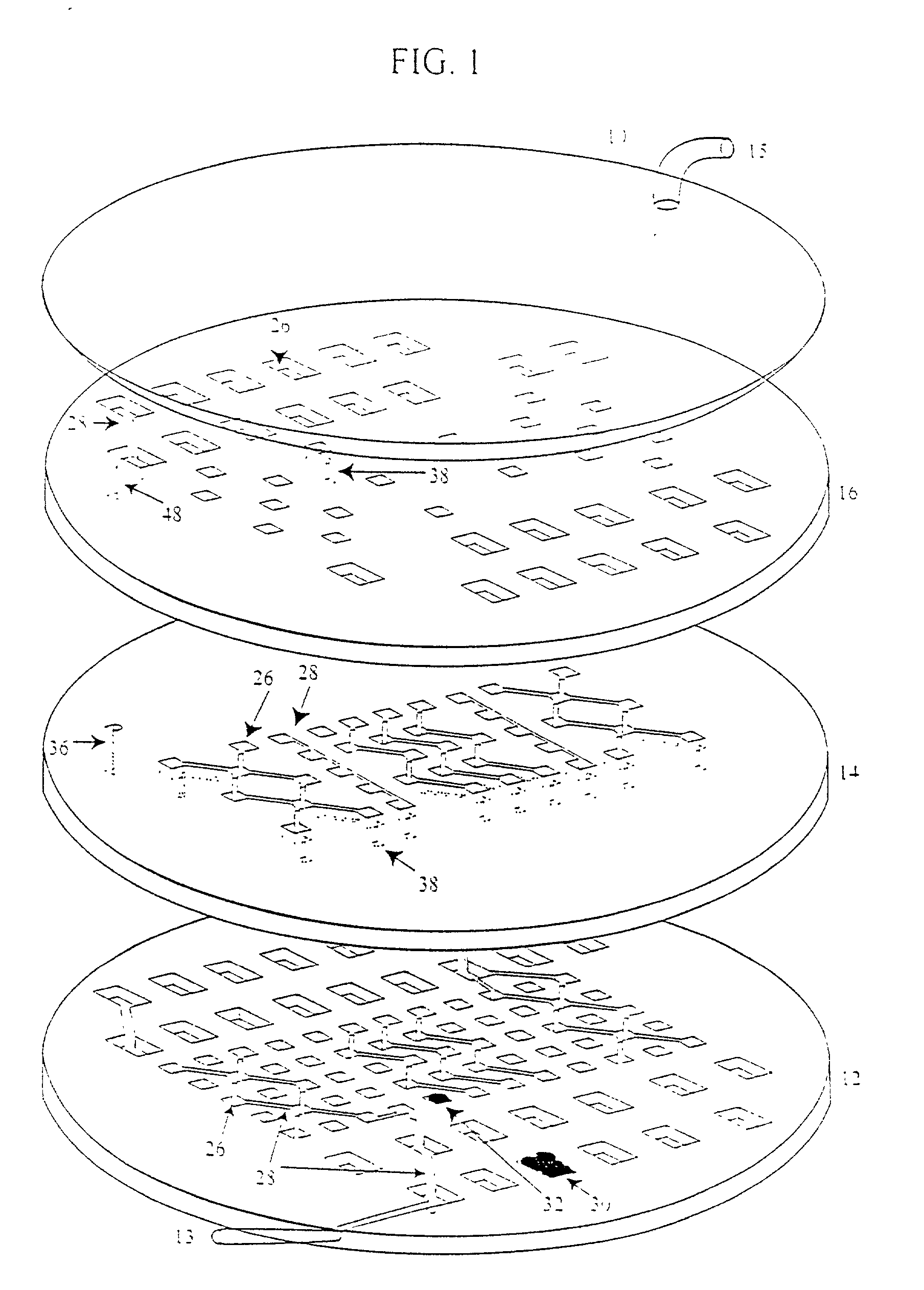
InactiveUS20020173033A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpatial OrientationsMetabolite
A device, method and process for three-dimensional spatial localization and functional interconnection of the same or different types of cells. The two or three-dimensional device comprising multiple layers containing wells for cell deposition where both the wells and layers are interconnected through microfluidic channels. A process for fabricating the three-dimensional device and a method for depositing different types of cells within the device in a functional interdependent spatial orientation thereby mimicking physiological functions. The device is useful for diagnostic assays, determination of dysfunction of certain cells in the system, quantification of production of cellular proteins, metabolites, hormones or other cellular products, for organ or tissue replacement, for co-culturing different cells, for testing pharmaceutical agents and as a bioreactor for production of biologicals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS20050027359A1Resist translationalResist rotational movementInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnBending of plates
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the shaft bore. The first shaft has external left-hand threads and the second shaft has external right-hand threads, each to mate with different bores of the sleeve. The outside diameter of the first shaft is smaller than the inside diameter of the second shaft, allowing the two shafts to axially engage. The spinal interbody fusion device operates like a turnbuckle, vertically expanding when the sleeve is rotated in one direction and retracting when the sleeve is rotated in the opposite direction. The assembled device defines an open channel axially. Once the fusion device is set at its proper height, set screws are threaded into circumferential apertures of the sleeve to compress against the shaft threads of each plate to maintain a fixed height. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
Systems, methods and computer program products for monitoring the behavior, health, and/or characteristics of an animal
Systems, methods, and computer code products for monitoring the behavior, health, and / or characteristics of an animal are disclosed herein. In one implementation, the animal is positioned inside a waste container placed on a system that is adapted to determine, record and communicate over a network various animal health parameters. These parameters can be processed to determine trends, statistics and changes of animal physiological functions. The results can be used to access animal health conditions and issue warnings, alarms, messages, and other notifications to designated caretakers. These notifications may be displayed using various means such as computers and / or mobile devices. Data retrieval and review capability can provide improved understanding of an animal's health conditions and facilitate early illness detection.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
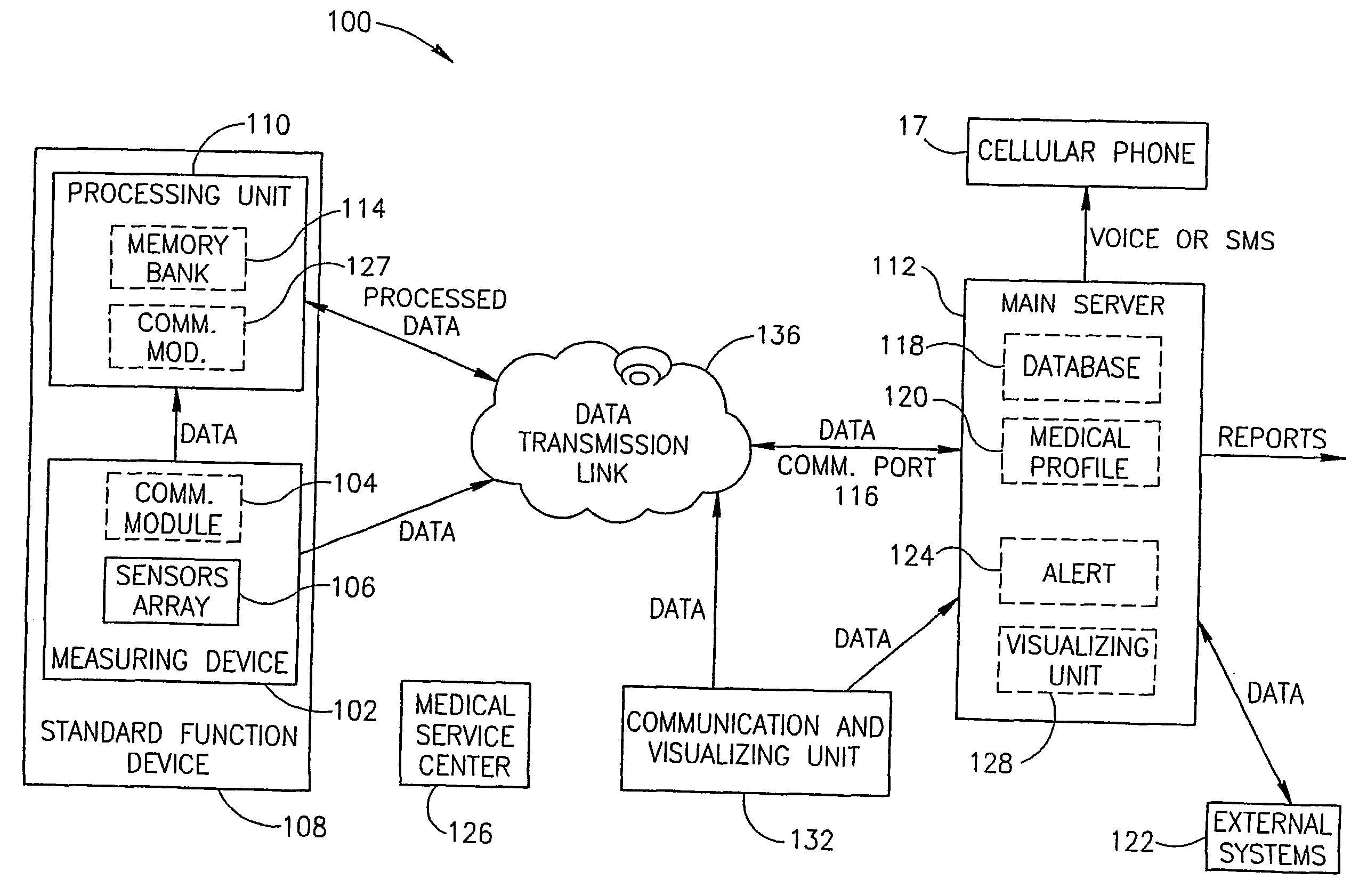
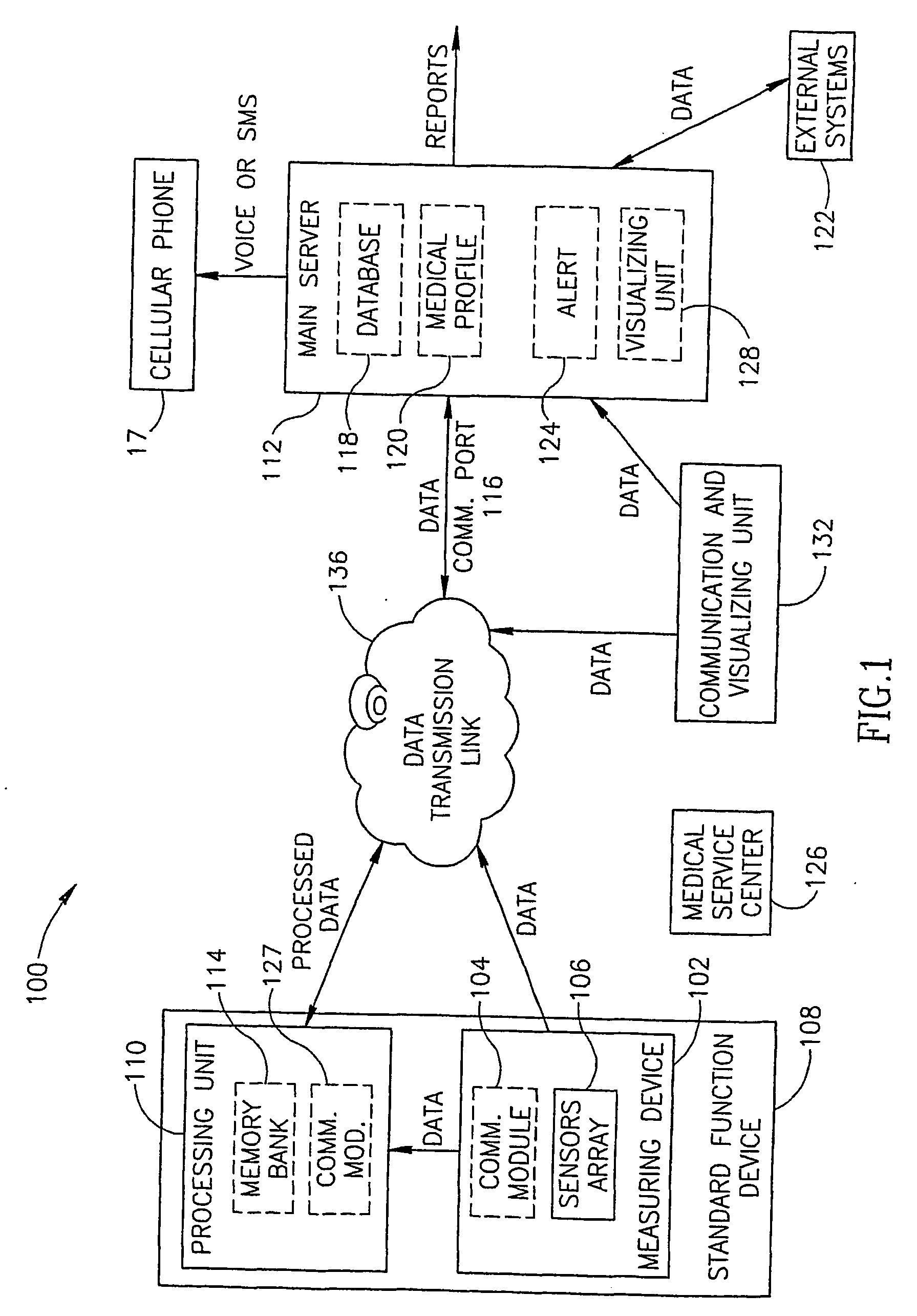
System and method for automatic monitoring of the health of a user
InactiveUS20050075542A1Easy to operateEarly detectionTelemedicineEvaluation of blood vesselsHealth conditionNon invasive
A system and method for automatically monitoring at least one physiological function of the user, without active intervention by the user, in a non-invasive manner. Such monitoring may be used to detect a deterioration in the health of the user. Preferably, the system according to the present invention features at least one physiological sensor for measuring the physiological parameter of the user to obtain the measurement of a physiological function, a local processing unit for extracting medical information from the physiological measurement, and a main server for processing the medical information in order to evaluate the health of the user. Such an evaluation is preferably performed by comparing medical information which has been obtained from a plurality of physiological measurements. Optionally and more preferably, the user is alerted if the evaluation detects a deterioration in at least one physiological function.
Owner:MEDIC4ALL INC
Uses of dpp-iv inhibitors
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Contrast agent imaging with destruction pulses in diagnostic medical ultrasound
InactiveUS6340348B1Increase the differenceImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryEcg signalUltrasonography
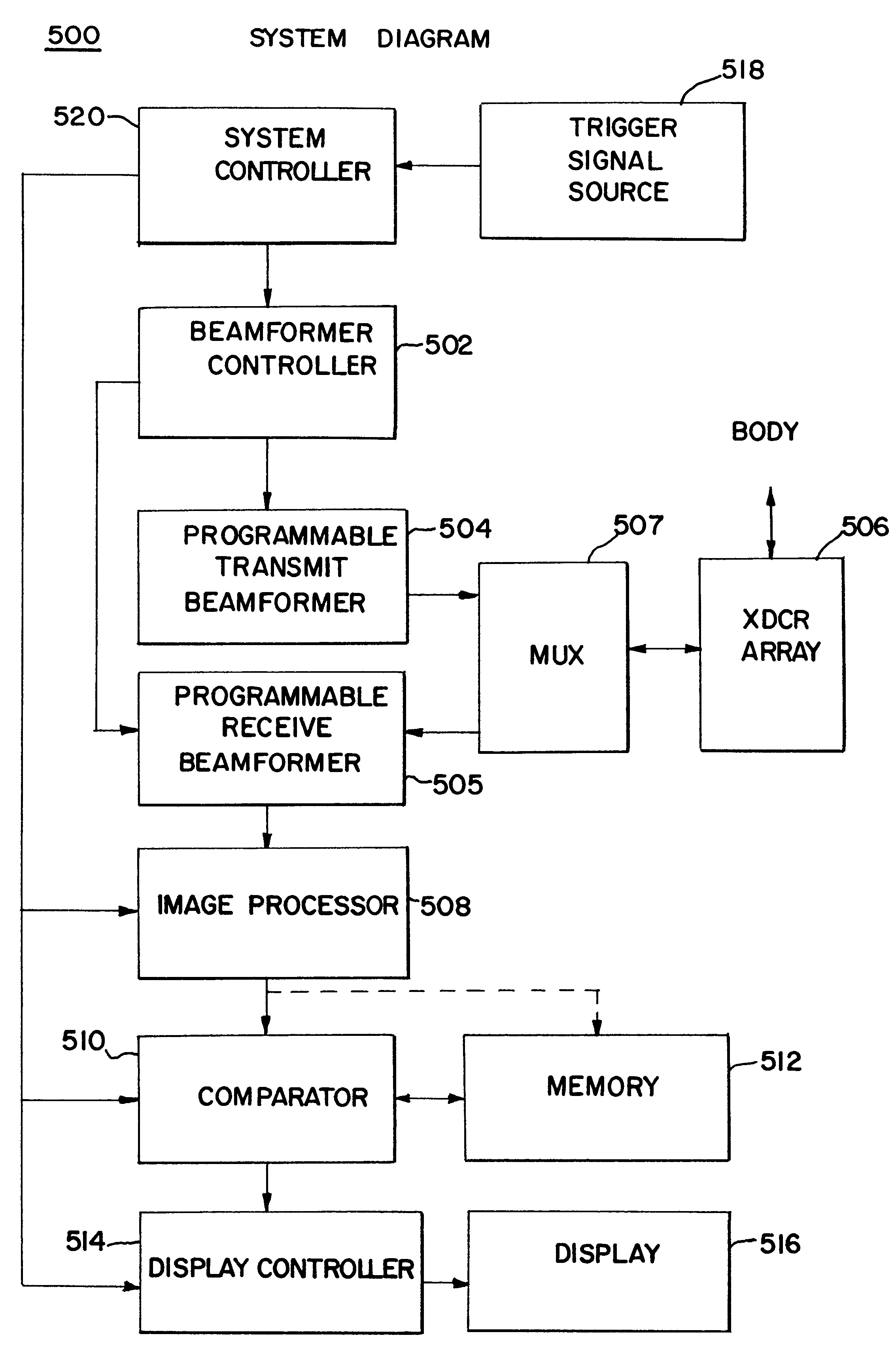
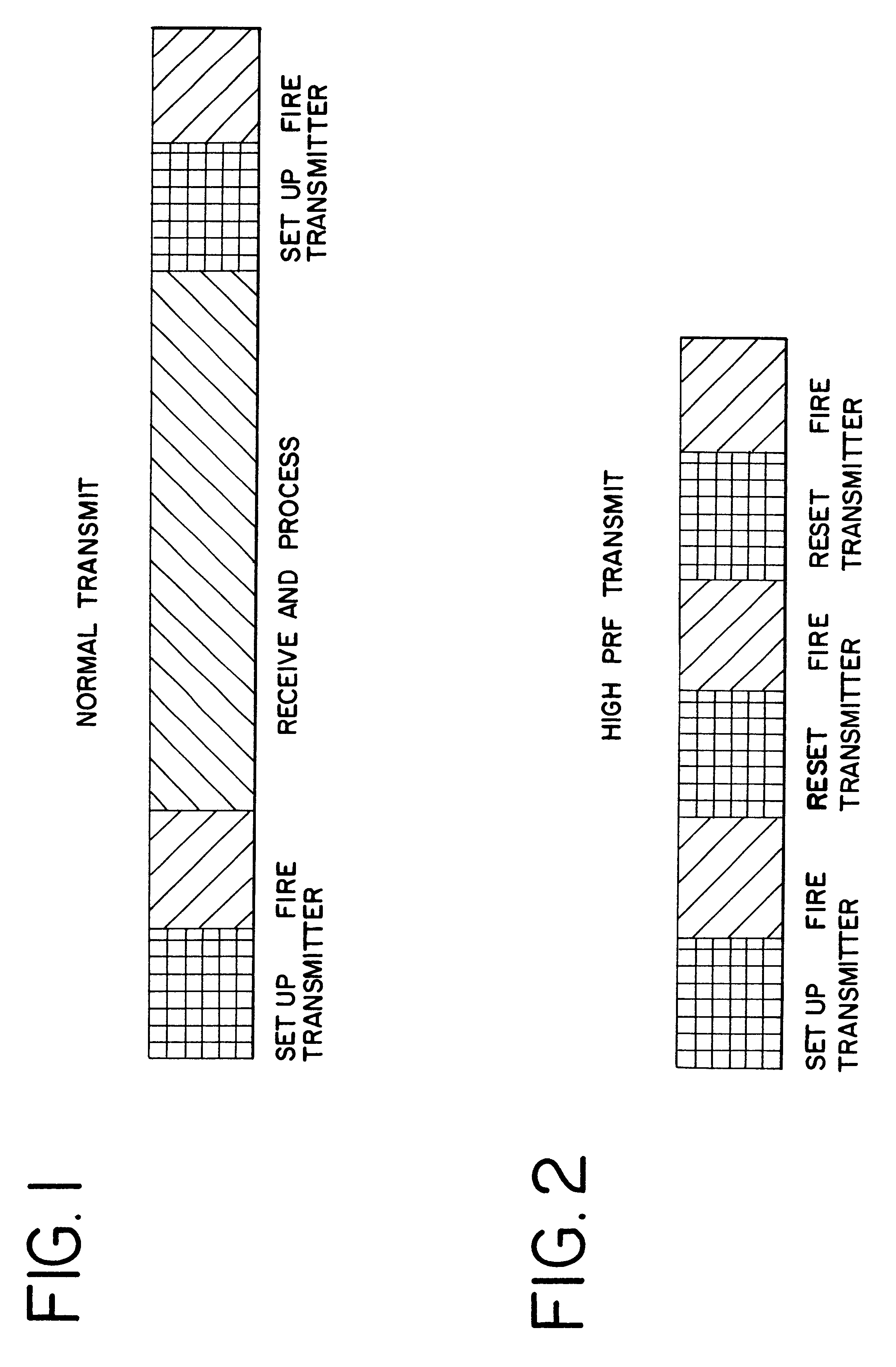
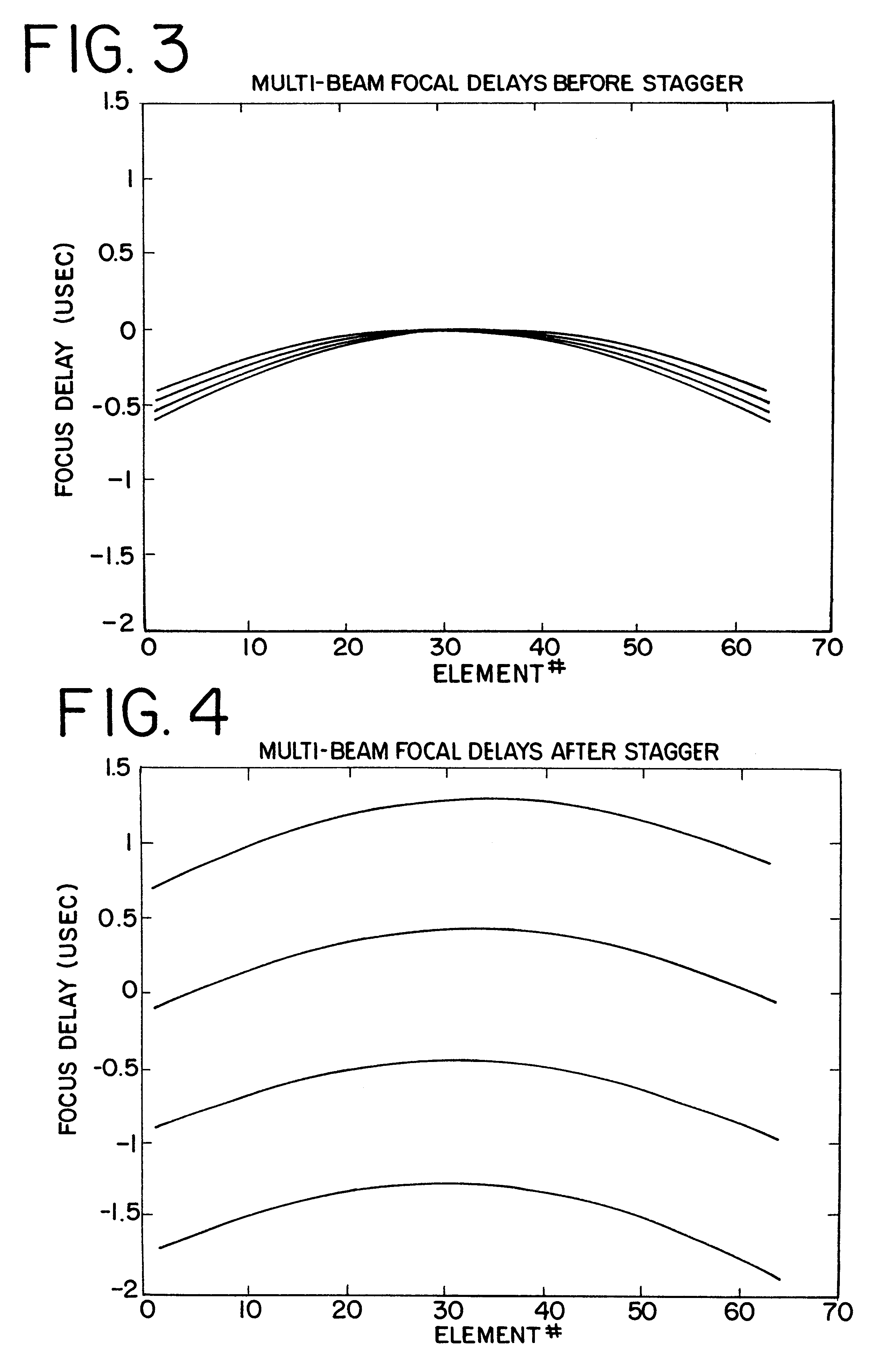
The invention is directed to improvements in diagnostic medical ultrasound contrast agent imaging. In a preferred embodiment, high pulse repetition frequency (HPRF) destruction pulses are fired at a rate higher than necessary for receiving returning echoes. Pulse parameters can also be changed between the plurality of contrast agent-destroying pulses. Other preferred embodiments of the invention are directed to simultaneous transmission of multiple beams of destruction pulses. Destruction frames that consist of a plurality of destruction pulses can be triggered and swept over the entire region of tissue being imaged and at a variety of focal depths from the transmitter. The destruction frames are fired at some time triggered from a timer or some fixed part of a physiological signal, such as an ECG signal. Other preferred embodiments of the invention are directed to continuous low power imaging pulses alternating with destruction pulses triggered at a fixed point of a physiological signal, and a comparison of the received signals from imaging pulses fired before and after the destruction pulses. Alternatively, destruction pulses are triggered at a fixed point on a physiological signal different from the fixed point of a physiological signal used to trigger imaging pulses. In another embodiment, triggered destruction frames are used to enable a comparison of imaging frames in order to determine physiological functions, such as perfusion of blood in cardiac tissue. Finally, in another embodiment, destruction pulses are combined with subharmonic imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
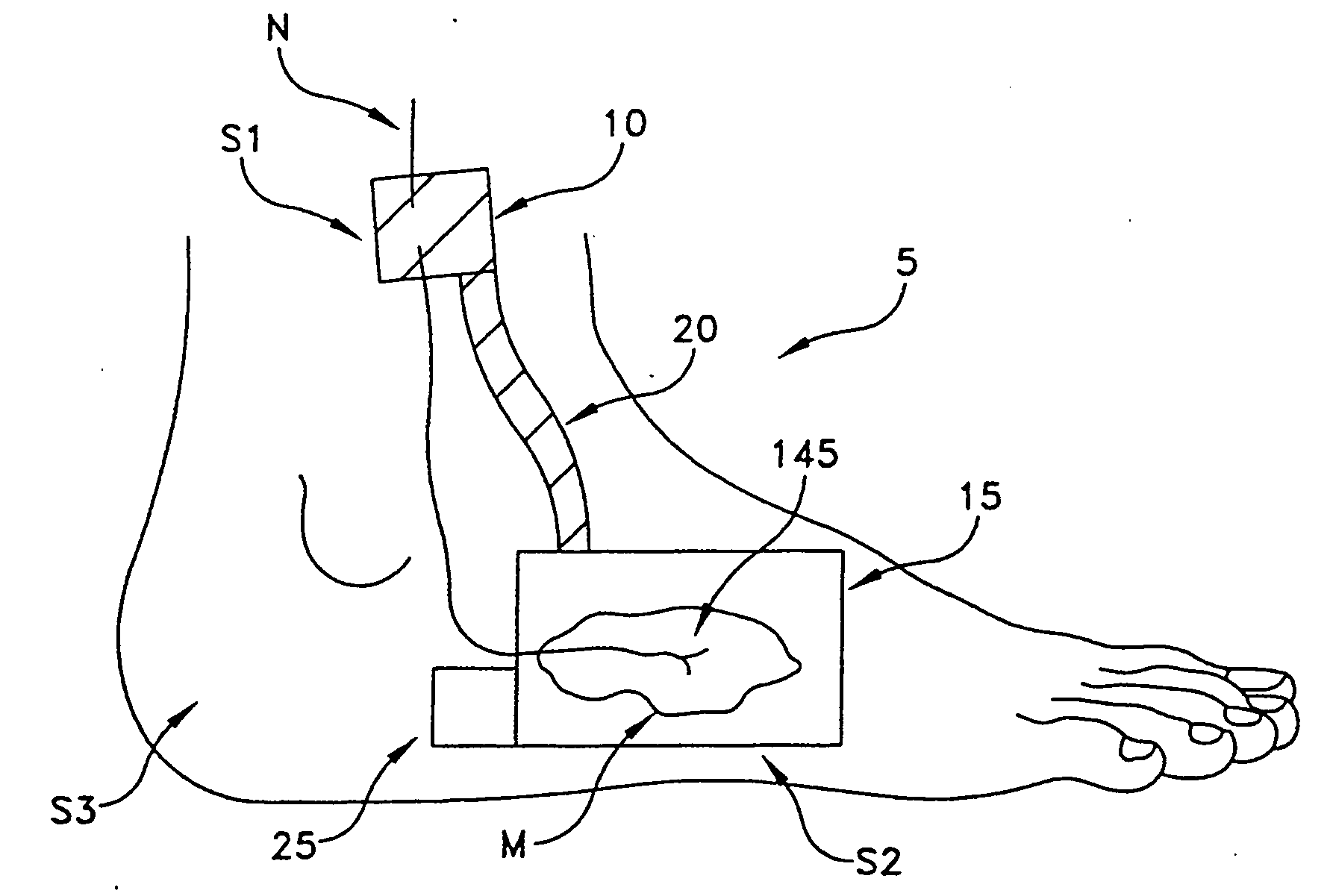
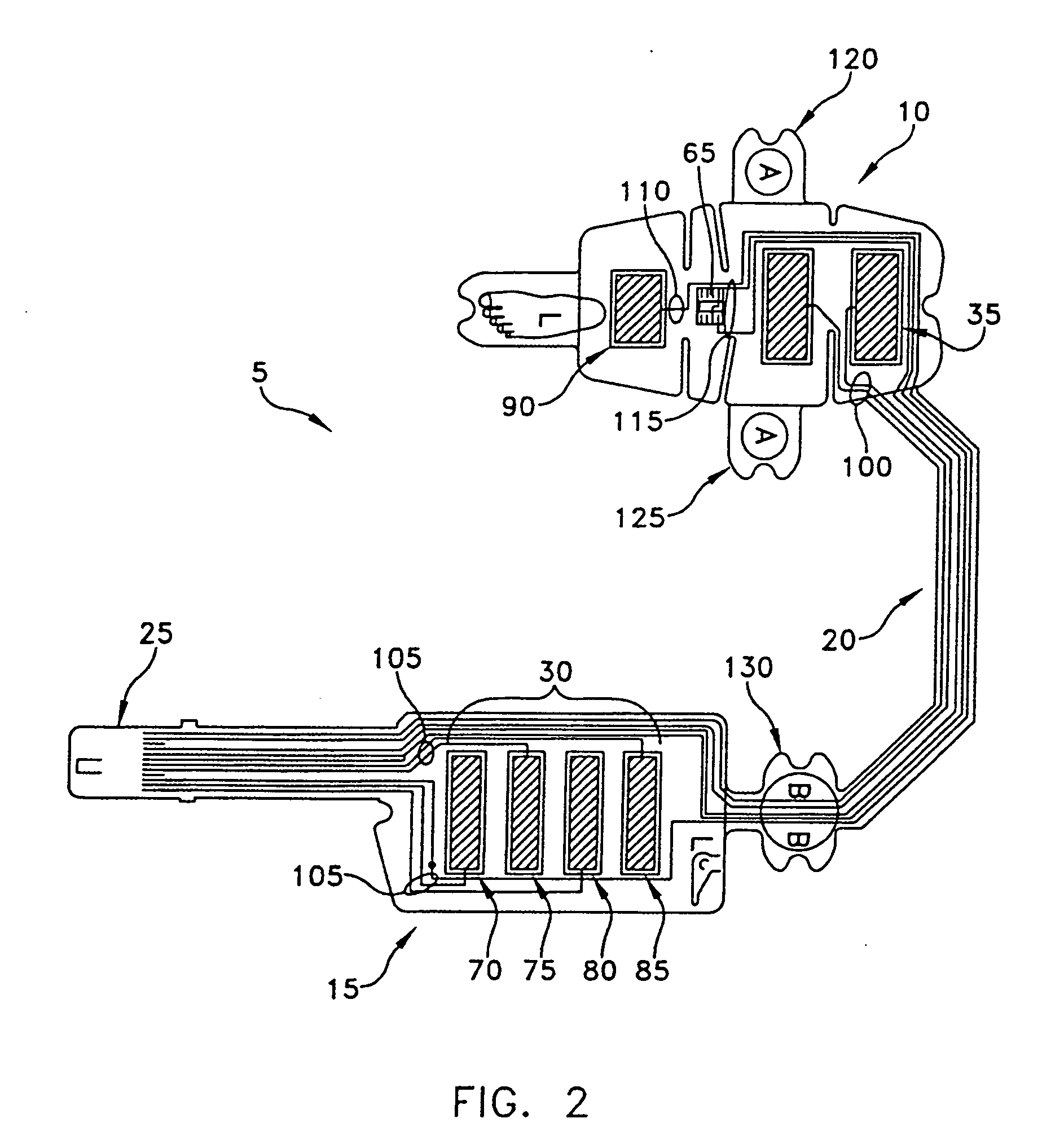
Product, method and system for monitoring physiological function and posture
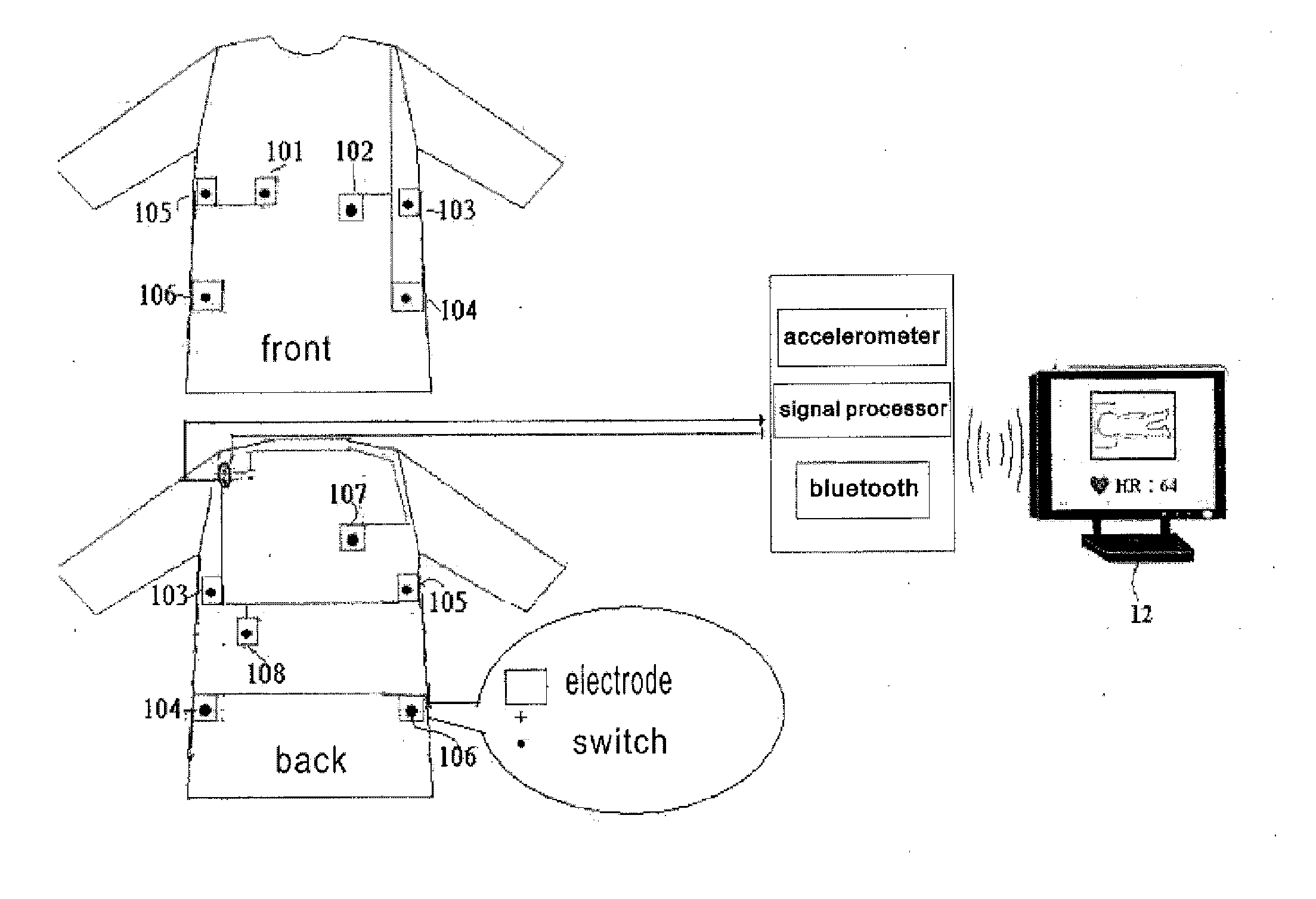
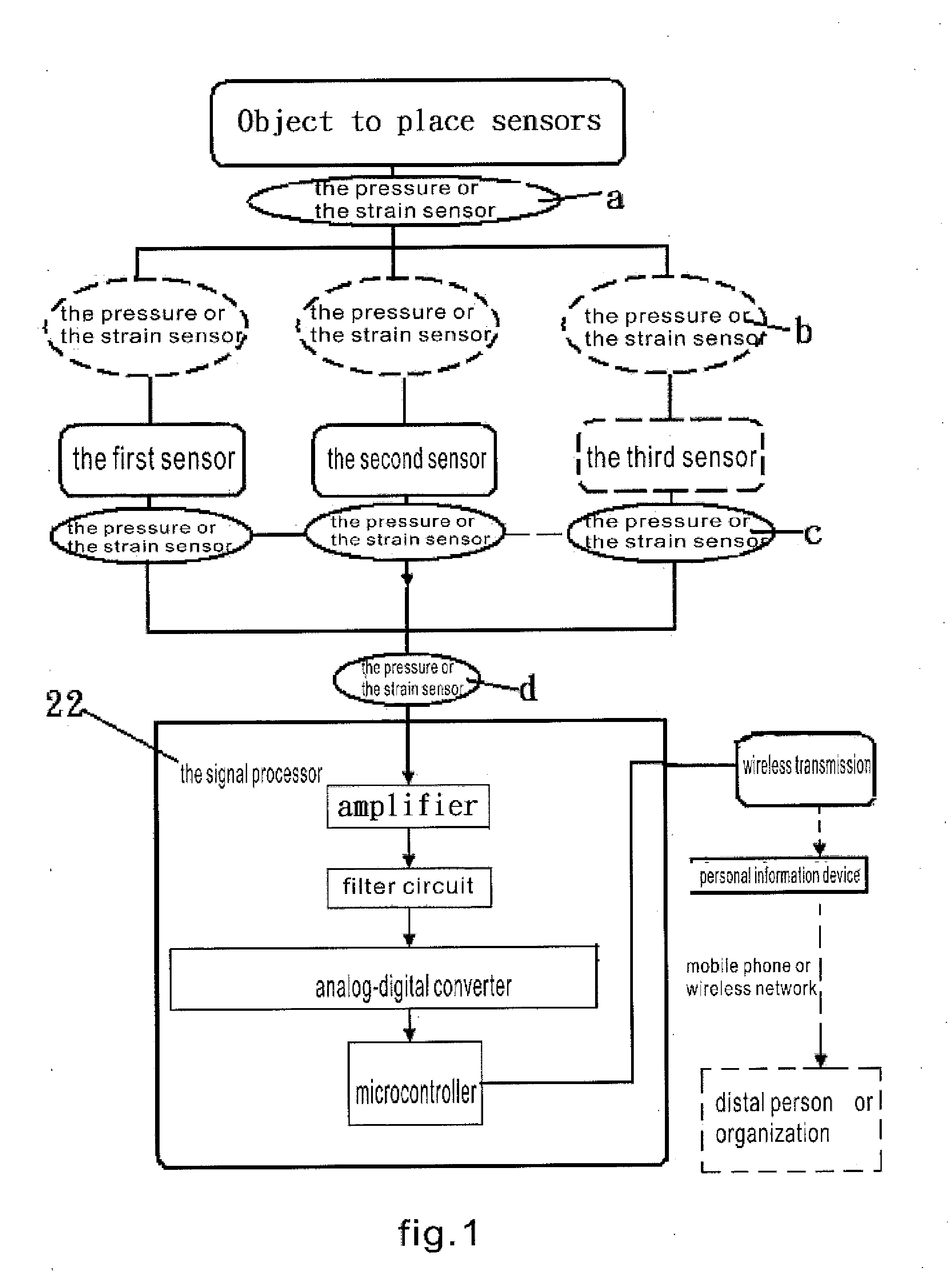
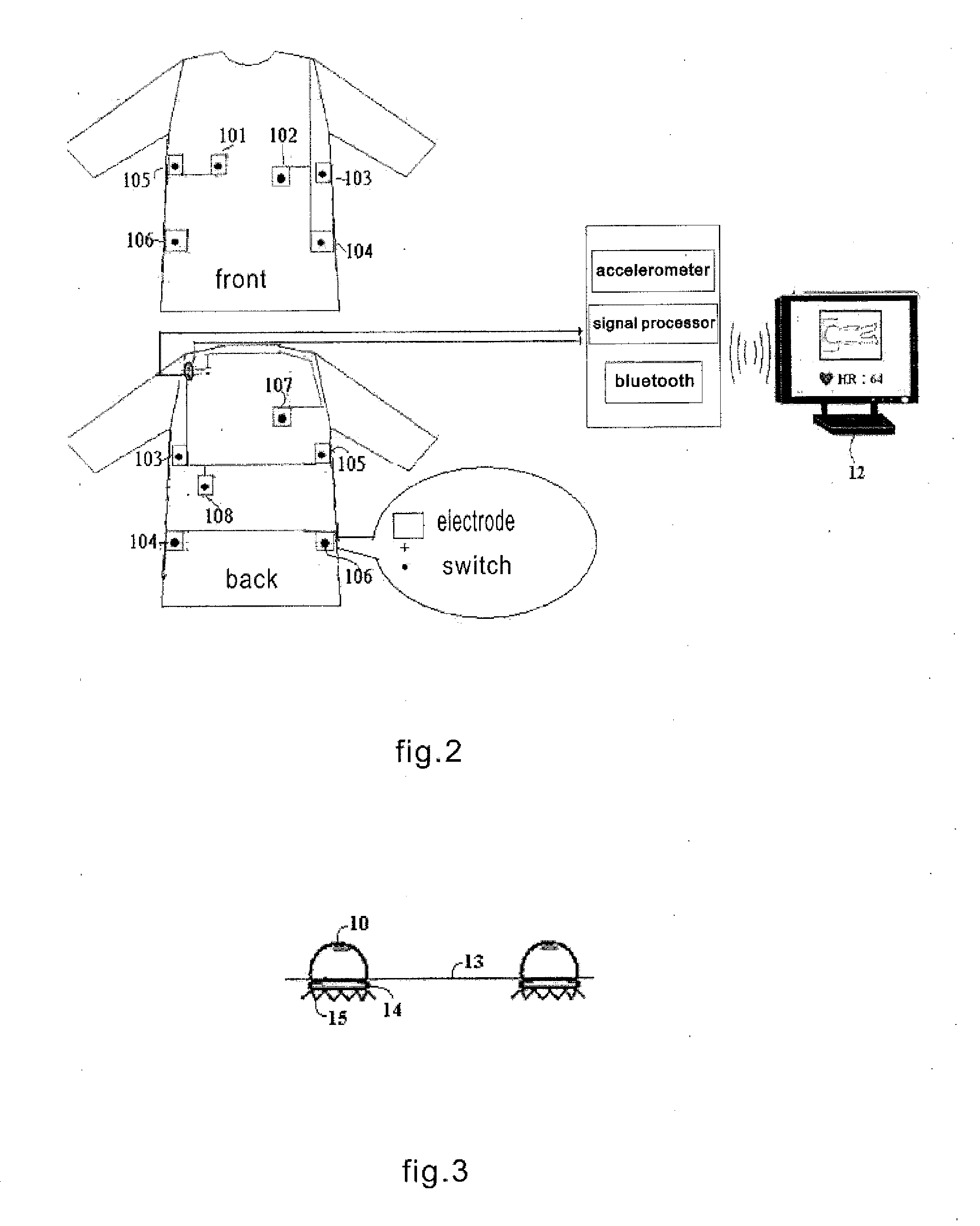
ActiveUS20120215076A1Detection of leakageAccurately detect changeElectrocardiographyHumidity sensorsEngineeringPostural orientation
An article for detecting physiological function and posture status is disclosed. The article touches body directly or indirectly; wherein at least a group of non-posture physiological sensors are configured on this object and at least a switch, tension sensor, pressure sensor or pressure applicator are coupled with or touch this object; the switch, tension sensor, pressure sensor or pressure applicator are configured on a different or the same object with the physiological sensors, or divided into two parts that contact each other while external force applied; the non-posture physiological sensors sense the physiological function and posture status of the user.
Owner:MING YOUNG BIOMEDICAL CORP
Methods for stimulating components in, on, or near the pudendal nerve or its branches to achieve selective physiologic responses
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Nasal and oral patient interface
A patient interface for communicating fluids to and / or from a patient's nasal cavity and / or oral cavity is disclosed. In addition, a patient interface for fluid and physiological function monitoring proximate to the patient's nasal cavity and / or oral cavity is disclosed. An apnea monitor and a method for monitoring apnea are also disclosed.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Life-nourishing health-care drink
Owner:谌萌 +1
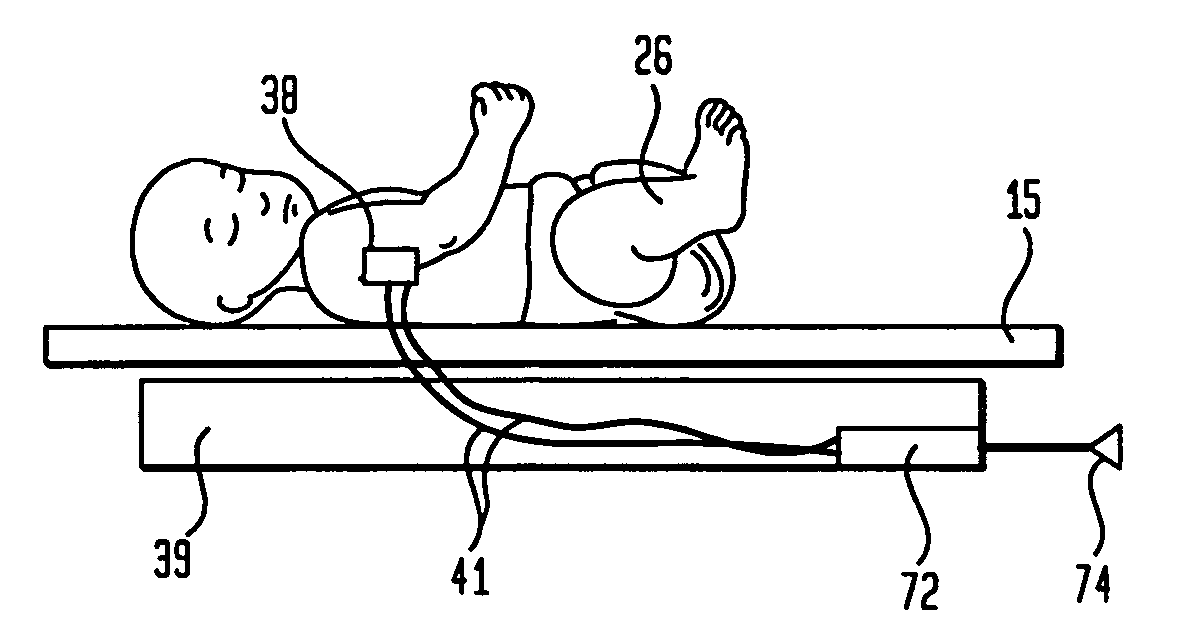
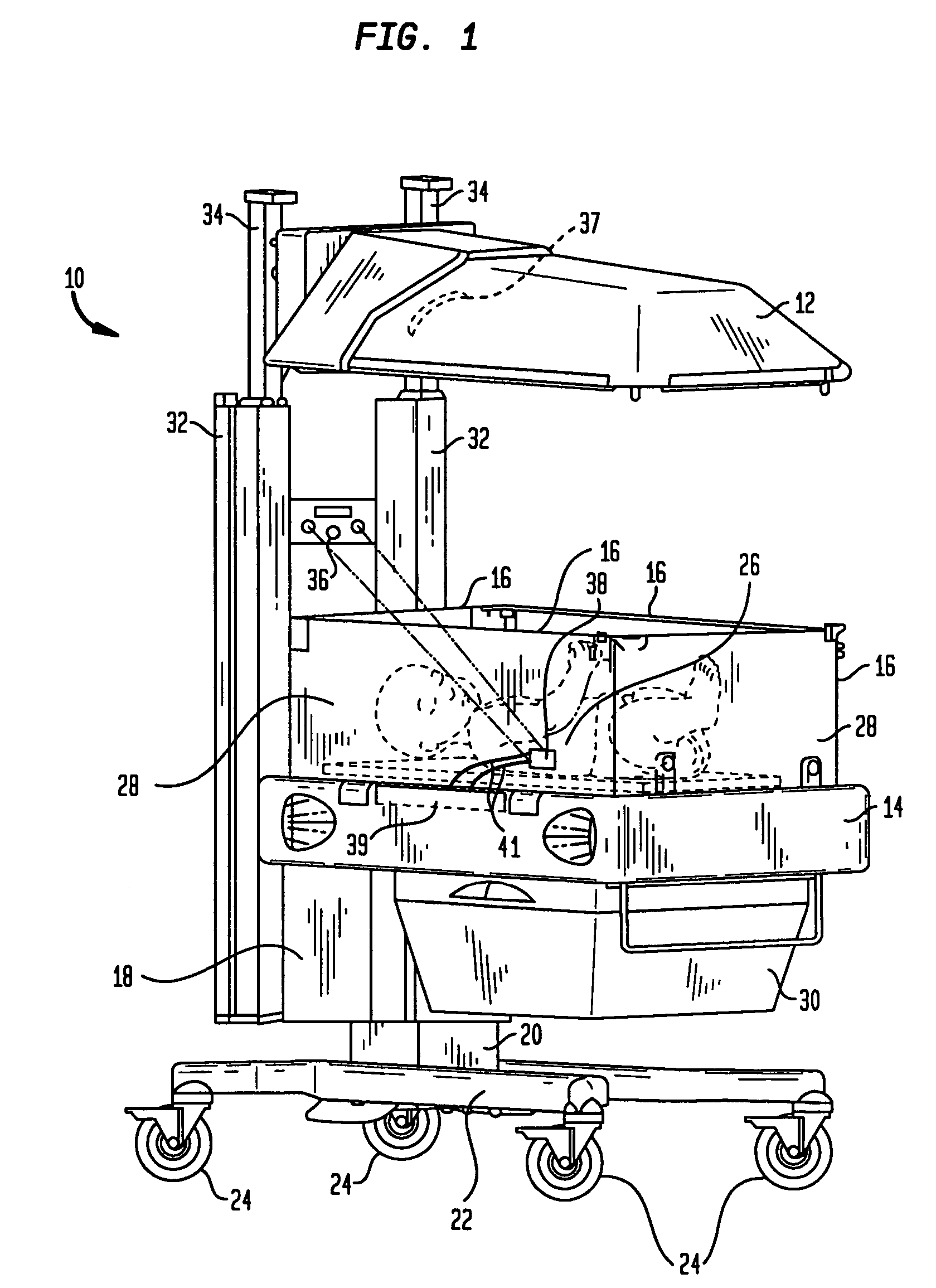
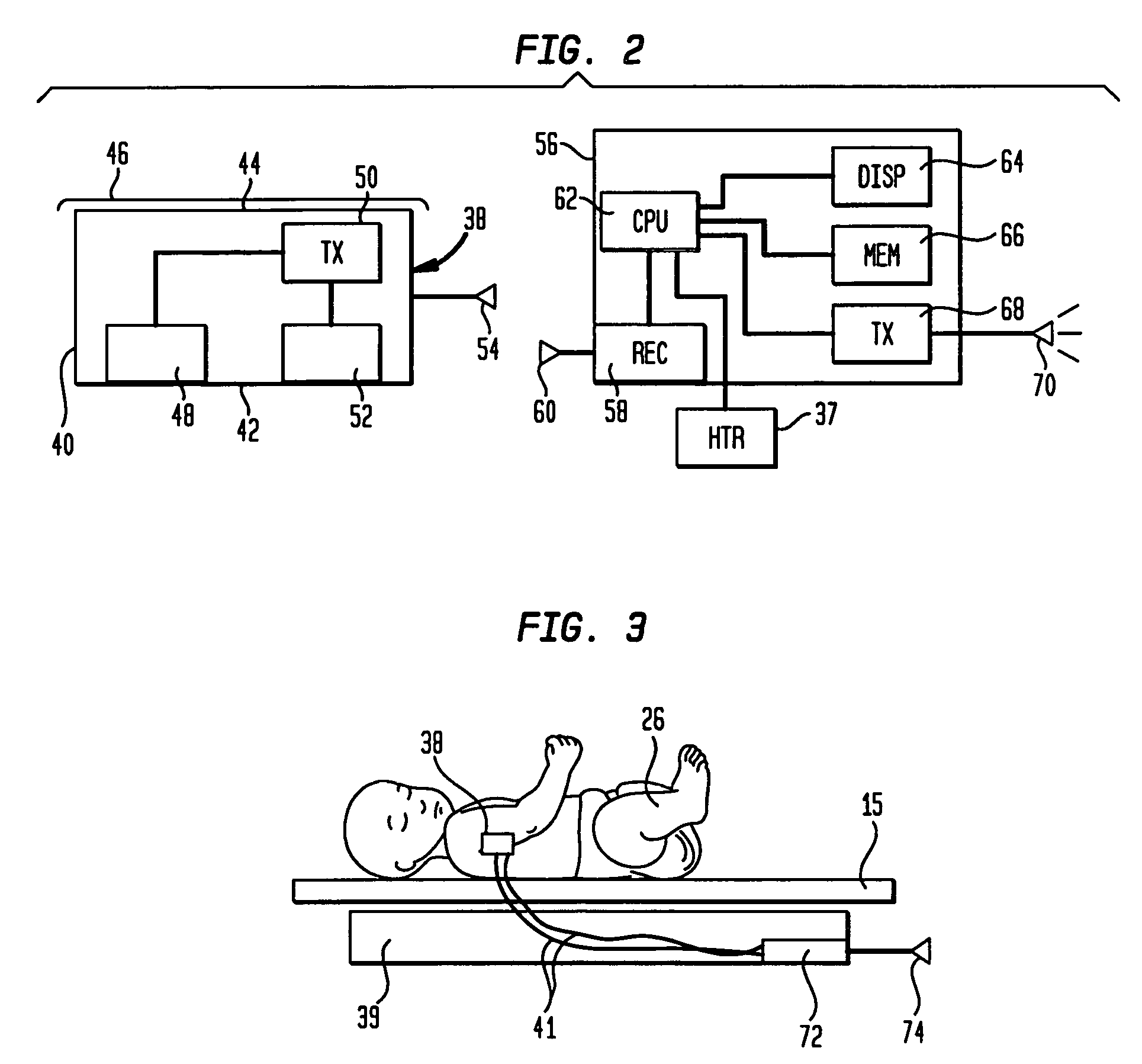
Telemetry sensing system for infant care apparatus
An infant warming apparatus for supporting an infant upon an infant bed. The apparatus has a sensor that is affixed to the skin of the infant to detect one or more physiological functions of the infant. A transmitter is located within the enclosure of the sensor and which transmit the information detected by the physiological sensor to a receiver that is located on the infant care apparatus and which can then convert that information into a recognizable or usable medium. An alternative embodiment includes the transmitter located proximate to the infant within an infant scale located beneath the infant. The sensor is hardwired to the transmitter in the infant scale and signals relating to weight and / or a condition of the infant are transmitted by wireless telemetry to a monitor or other display device to display that information to the caregiver.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fluid sampling, analysis and delivery system
InactiveUS20050228313A1Small volumeMinimal amountMedical devicesPressure infusionMedication monitoringPancreatic hormone
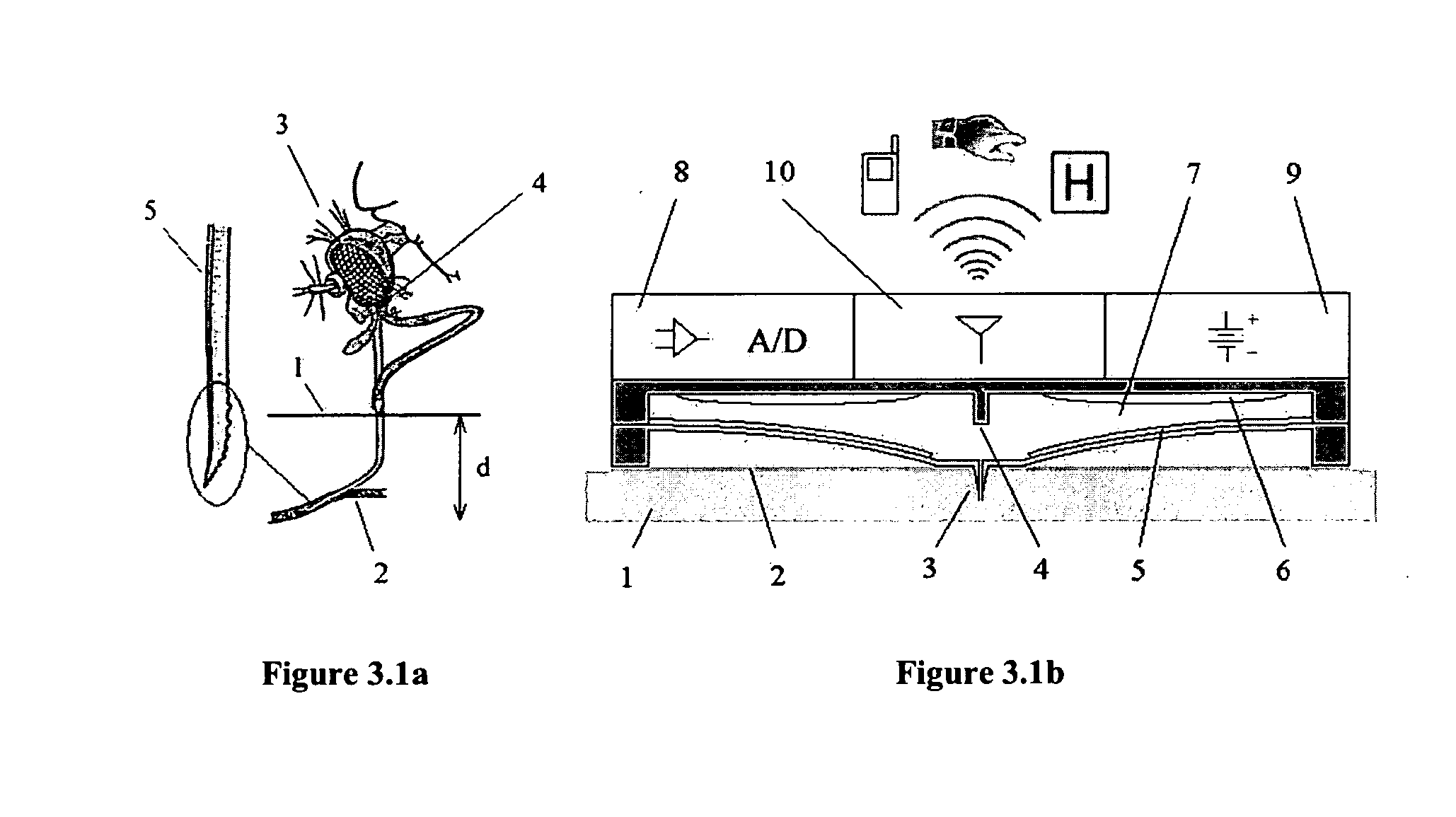
The lack of safe, reliable, automated and clinically acceptable blood sampling has been the main problem precluding the development of real-time systems for blood analysis and subsequent closed-loop physiological function control. While the analysis of a static blood sample in laboratory conditions has been rapidly advancing in reliability and blood volume reduction, non-invasive real-time blood analysis performed in vivo (while the blood is circulating in the body) has been elusive and unreliable. In this study we propose an innovative idea for semi-invasive blood sampling and analysis, which resembles the operation of a mosquito. At a miniature scale the proposed system does penetrate the skin to extract a static blood sample for further analysis, but the extent of this penetration, and the fact that it can be made painless, is particularly attractive for such applications as automated glucose analysis for closed-loop control of insulin infusion (artificial pancreas), continuous drug monitoring, or even periodic DNA analysis for security and identification purposes. These design aspects are described, and a specific implementation, applying MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical Systems) technology, is suggested. The proposed microsystem is a matrix of individually controllable e-Mosquito™ cells, packaged in a disposable patch and attached to the skin, could be an avenue for real-time semi-invasive blood analysis and diagnostics.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT
Dosage forms useful for modifying conditions and functions associated with hearing loss and/or tinnitus
InactiveUS20020061870A1Increased susceptibilityImprove usabilitySalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideWhole bodyActive agent
The invention defines interdependent biofactors and biomolecules, and clinically useful formulations that are comprised of them. The active agents are demonstrated to be complementary in their physiologic functions especially as these relate to the quenching of free radicals and to the support of endothelial physiology, the reduction of hyperinsulinemia and improvements in vascular health. The active components of the invention are selected for inclusion in precise combinations specifically because they improve these various conditions and physiological functions, and by so doing reduce a variety of risks associated with hearing loss and tinnitus. The resulting enhancement of general systemic vascular health, improvement in local VIIIth nerve vascular health, modulation of conditions surrounding blood fluid dynamics, the consequences of hyperinsulinemia, and improvements in free radical defenses, all reduce the potential for cochlear hair cell death and VIIIth nerve atrophy, and the hearing loss and possible deafness that accompany them.
Owner:CHRONORX
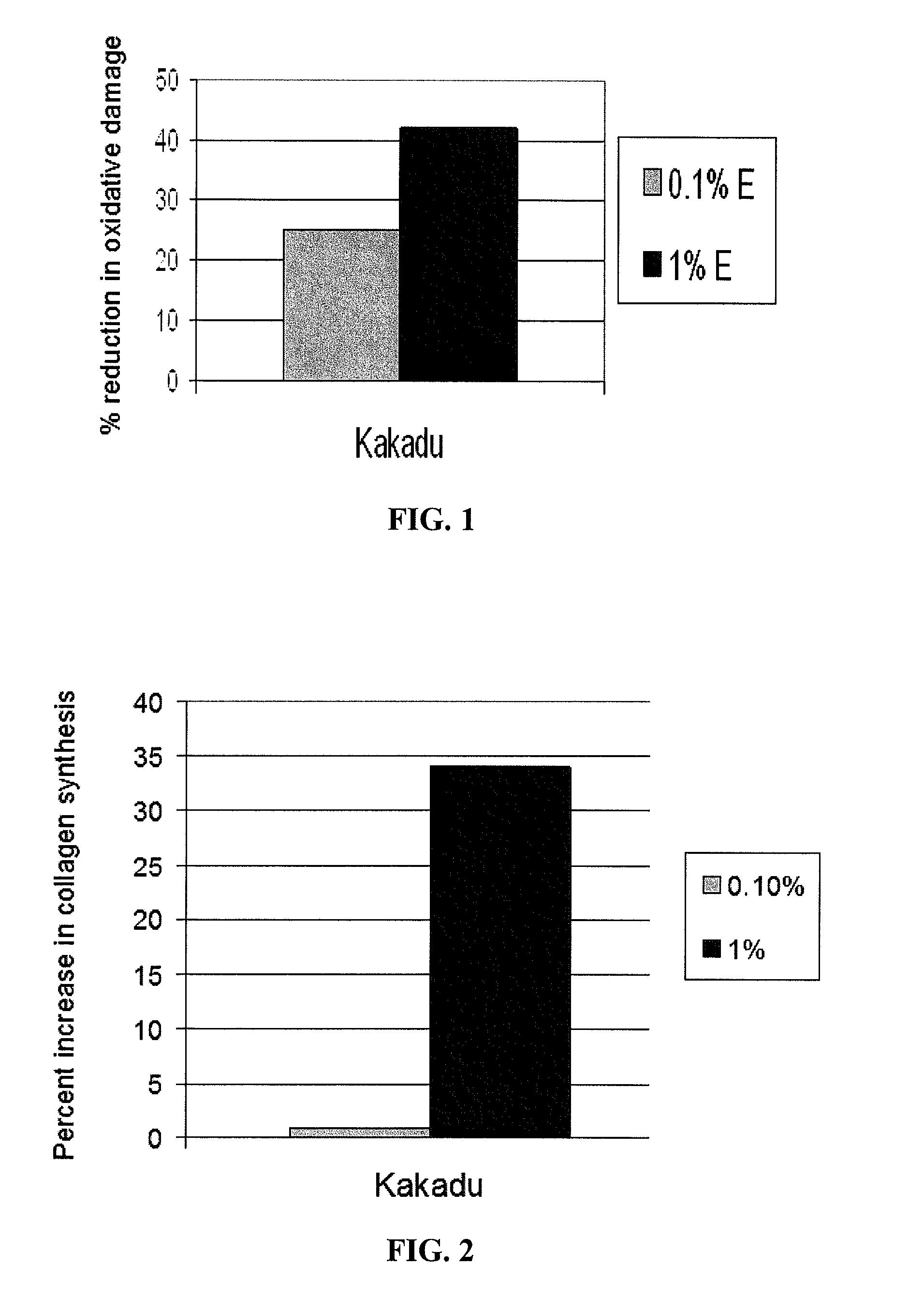
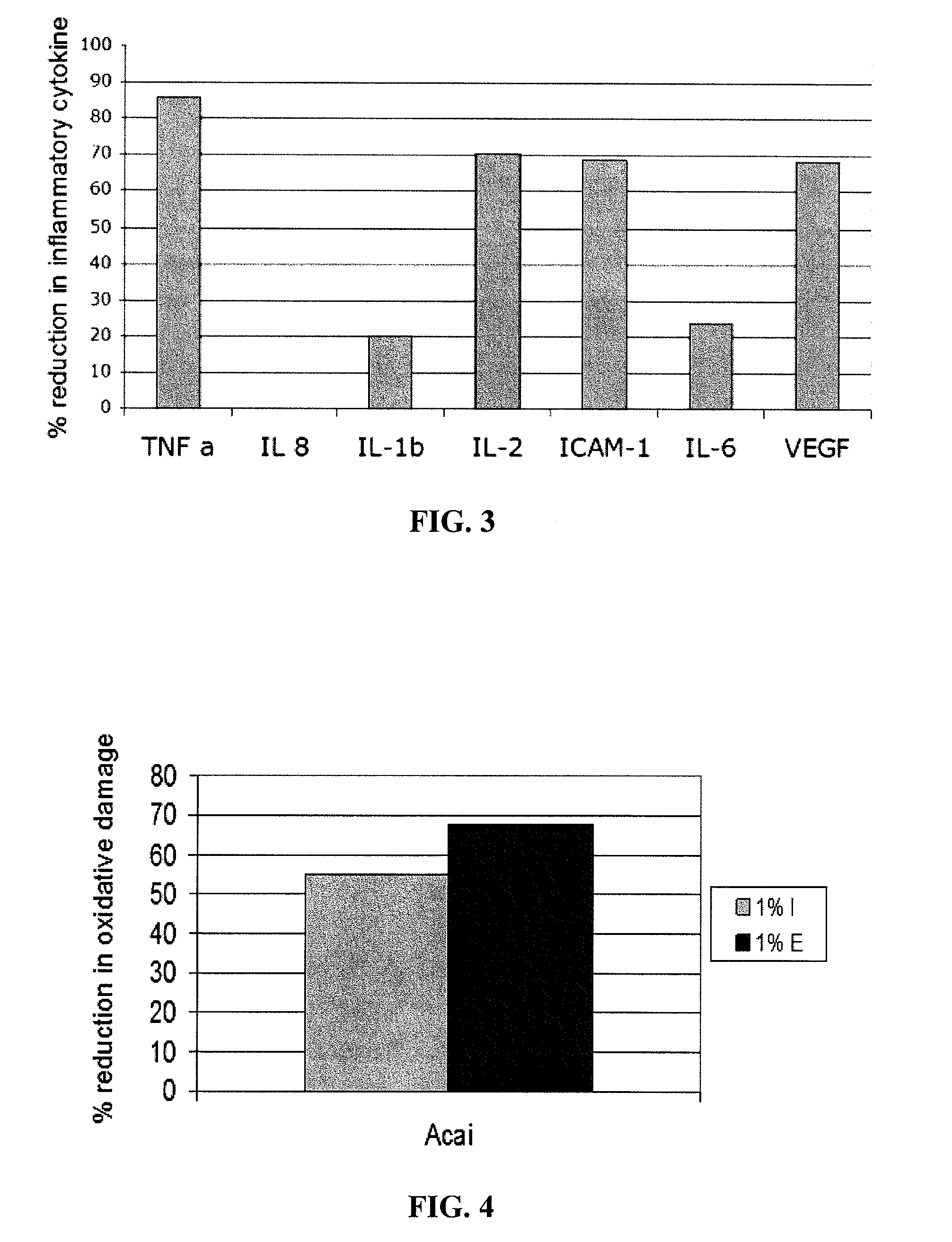
Compositions comprising kakadu plum extract or acai berry extract
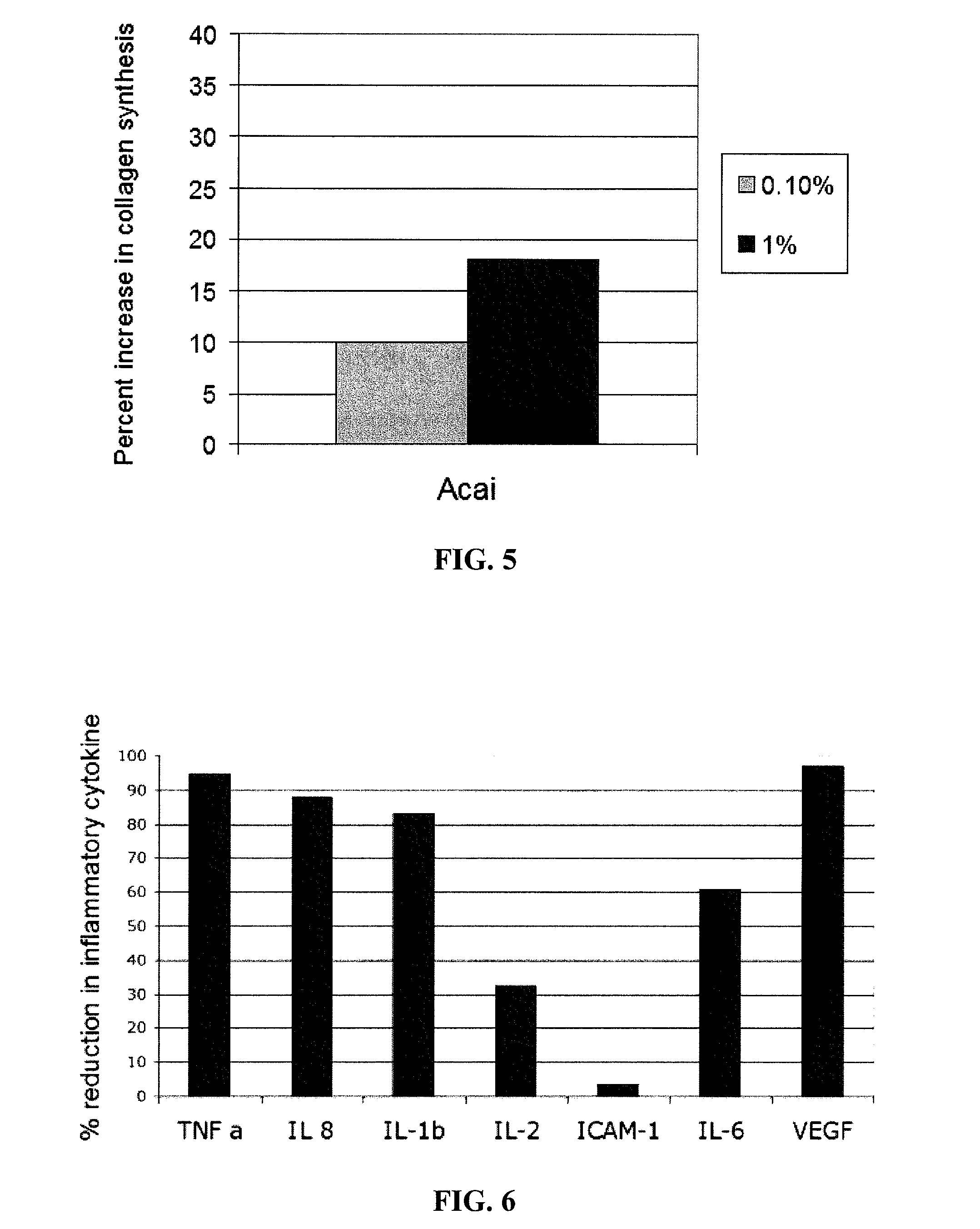
InactiveUS20070166275A1Increase stratum corneum turnover rateIncrease collagen synthesisCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineAcai Berries
A topical skin care composition comprising kakadu plum extract or acai berry extract, or a combination of both, is disclosed. The composition can include a high oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) value. The composition can improve the skin's visual appearance, physiological functions, clinical properties, and / or biophysical properties.
Owner:MARY KAY INC
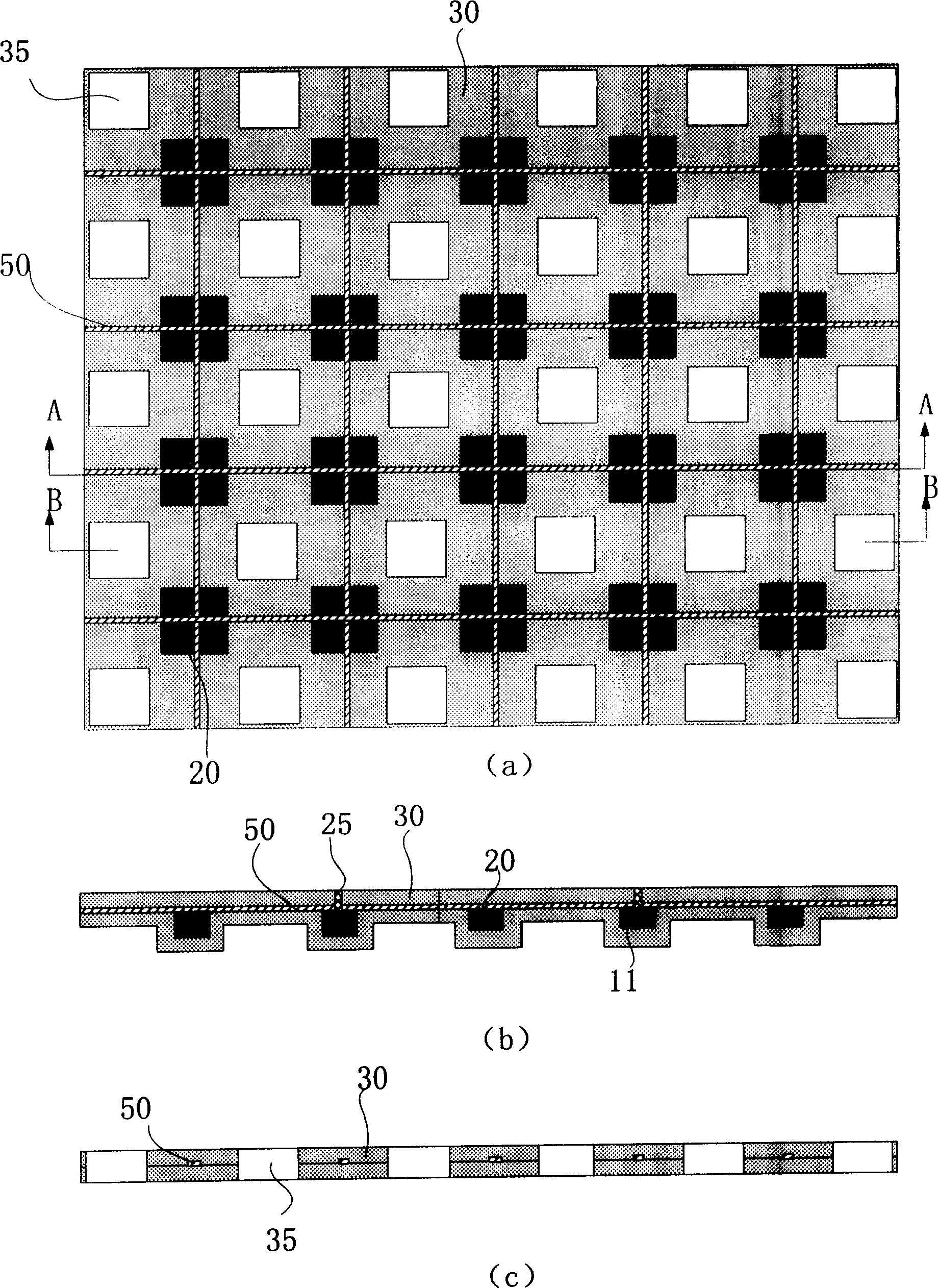
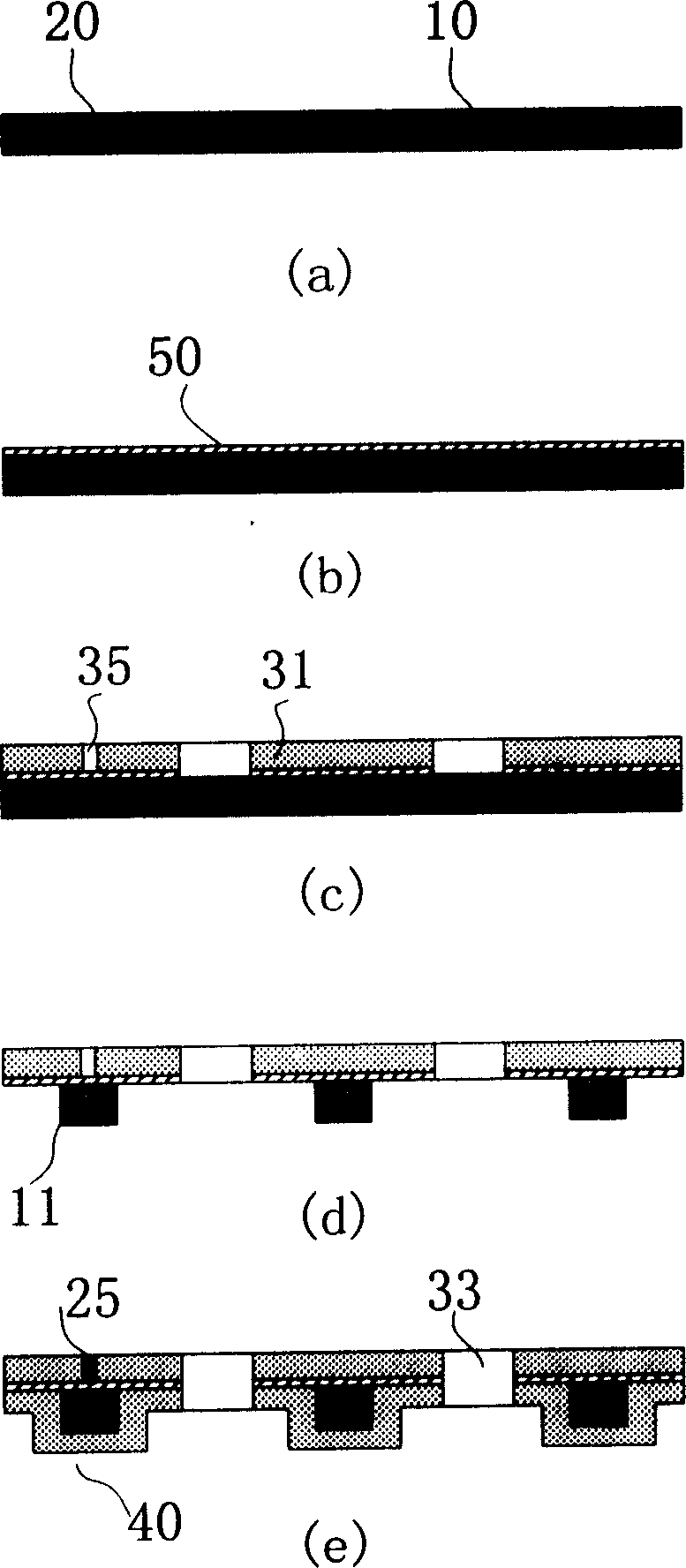
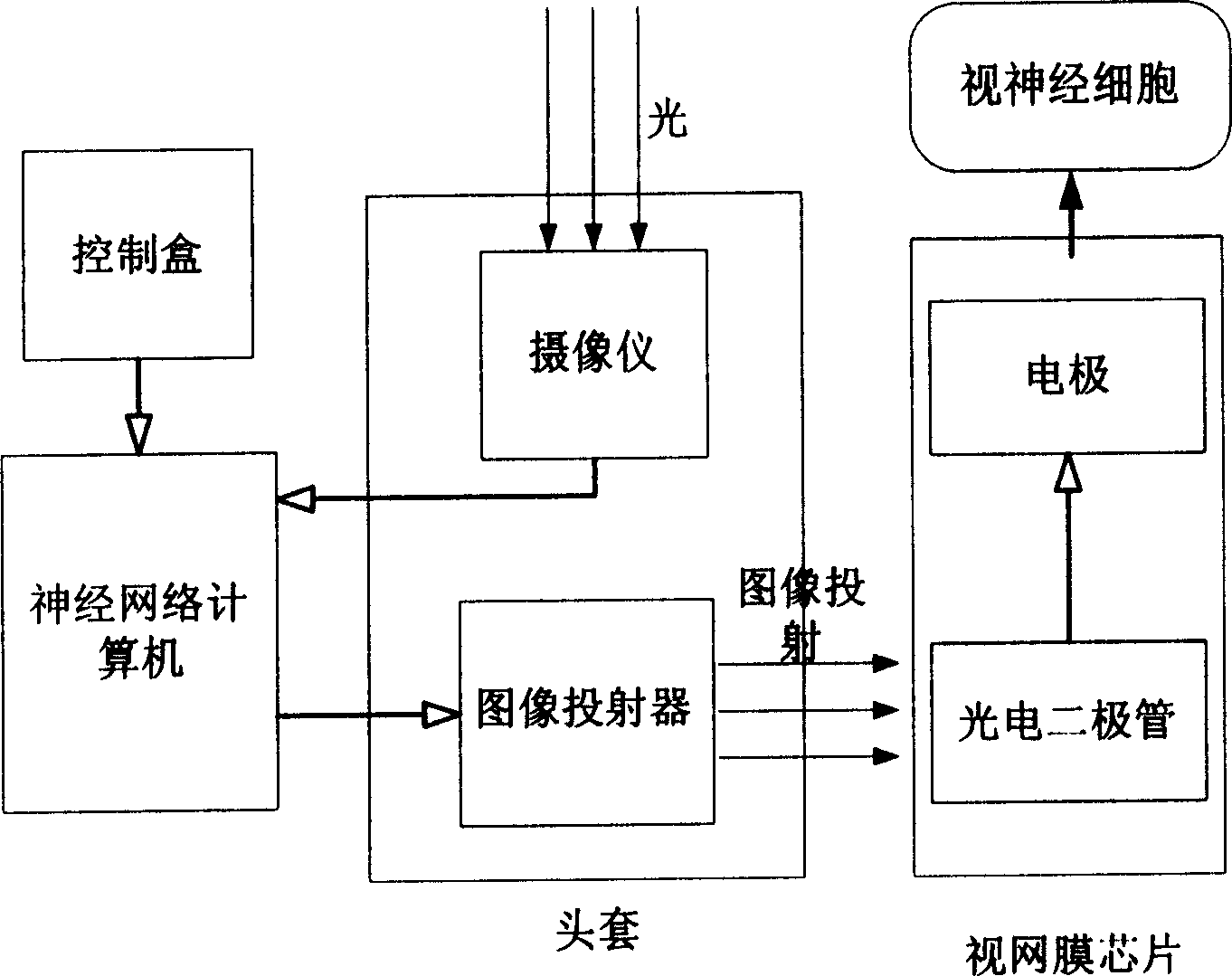
A flexible retina chip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN1875895AImprove flexibilityLittle flexibilityEye implantsDecorative surface effectsBasementMetabolite
The invention discloses the flexible retina chip. Between top layer polymeric film and bottom polymeric film there are silicon islands and via holes, in the silicon island there are function units which is used to simulate physiological function, and the between silicon island and top layer there is lead wire layer; bottom polymeric film is bonded with the top layer polymeric; the electric pole is on the top layer polymeric film or bottom polymeric film. The chip uses the MEMS technology to realize the integration of micro function unit and flexible basement. On the surface of the chip there are holes, so it is easy for nutriment and metabolite to exchange. The invention has the advantages of good biology function perfect ness, good metabolism, and improving the bending property and flexible of chip. The invention is used to high efficiency batch make.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
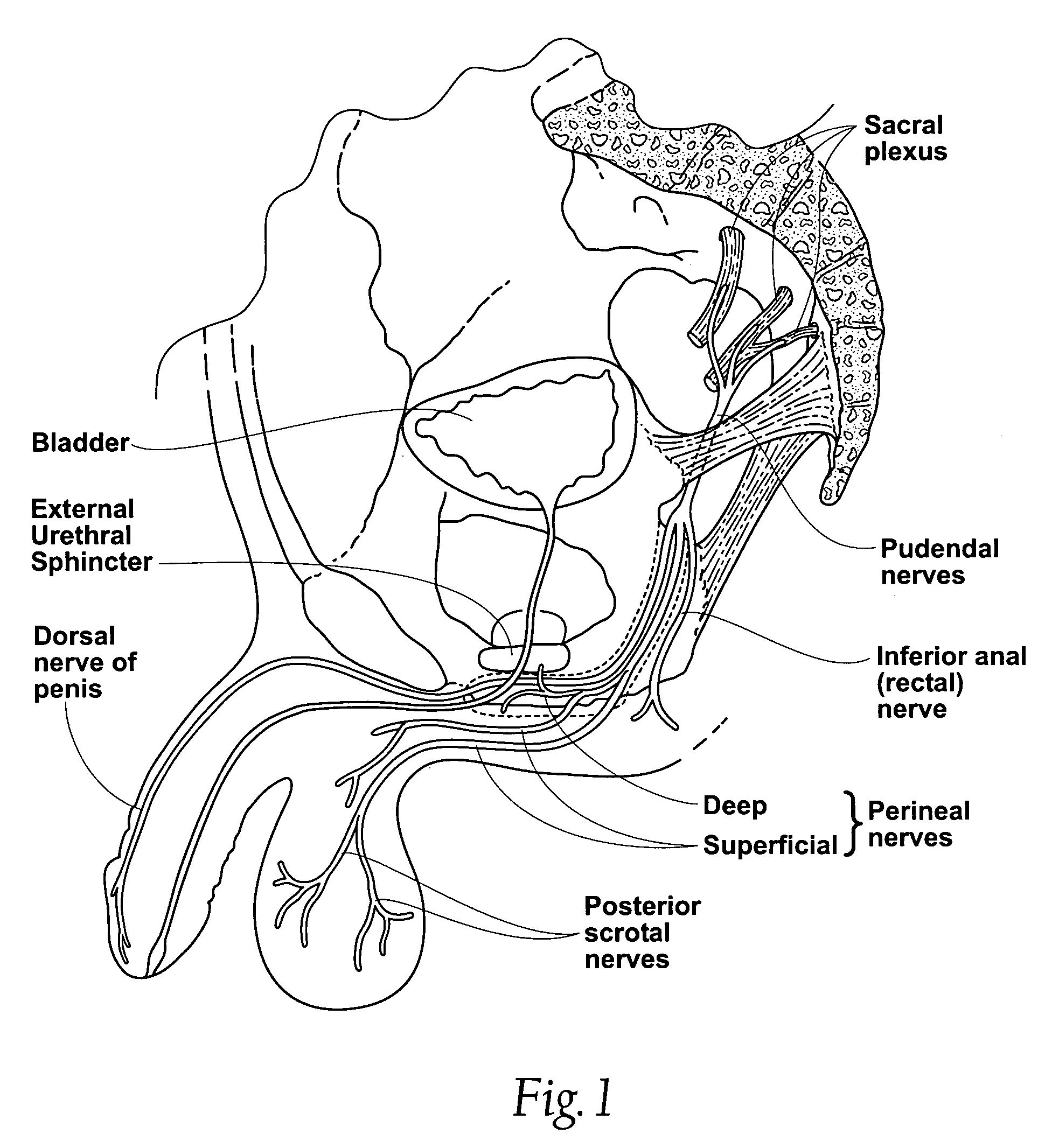
Apparatus and method for performing nerve conduction studies with localization of evoked responses
An apparatus and method for detecting physiological function, for example, nerve conduction, is described. In one embodiment the apparatus includes a housing including a stimulator shaped to fit a first anatomical site and a detector shaped to fit a second anatomical site. The housing automatically positions the detector substantially adjacent to the second anatomical site when the stimulator is positioned substantially adjacent to the first anatomical site. The detector contains a plurality of individual detection elements, whereby the response evoked by stimulation at the first anatomical site is measured using one or more of these detection elements at the second anatomical location.
Owner:GOZANI SHAI N +3
Cosmetic Treatment With Nitric Oxide, Device For Performing Said Treatment And Manufacturing Method Therefor
ActiveUS20080311163A1Increase blood perfusionIncrease supplyAntibacterial agentsBiocideElutionNitric oxide
A cosmetic treatment method, and a device therefor, are provided that allow for cosmetic treatment of cosmetic disorders, caused by chronological age, environmental factors, changes in physiological functions of skin, such as psoriasis, dermatitis, acne, cellulites, and viral and / or bacteriological attacks. The device comprises a nitric oxide (NO) eluting polymer arranged to contact the area to be cosmetically treated, such that a cosmetic dose of nitric oxide is eluted from said nitric oxide eluting polymer to said area. The nitric oxide (NO) eluting polymer is integrated with a carrier material, such that said carrier material, in use, regulates and controls the elution of said cosmetic dosage of nitric oxide (NO). Furthermore, a manufacturing method for said device is provided.
Owner:NAVAN INC
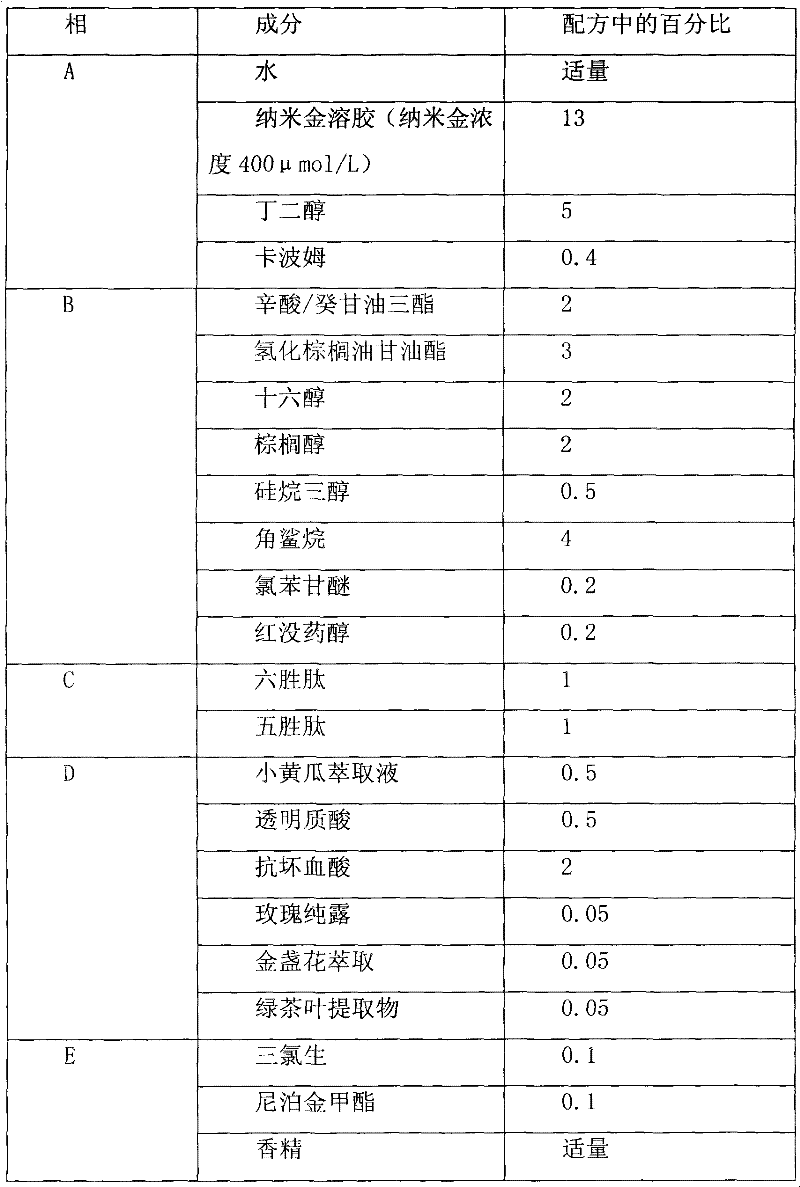
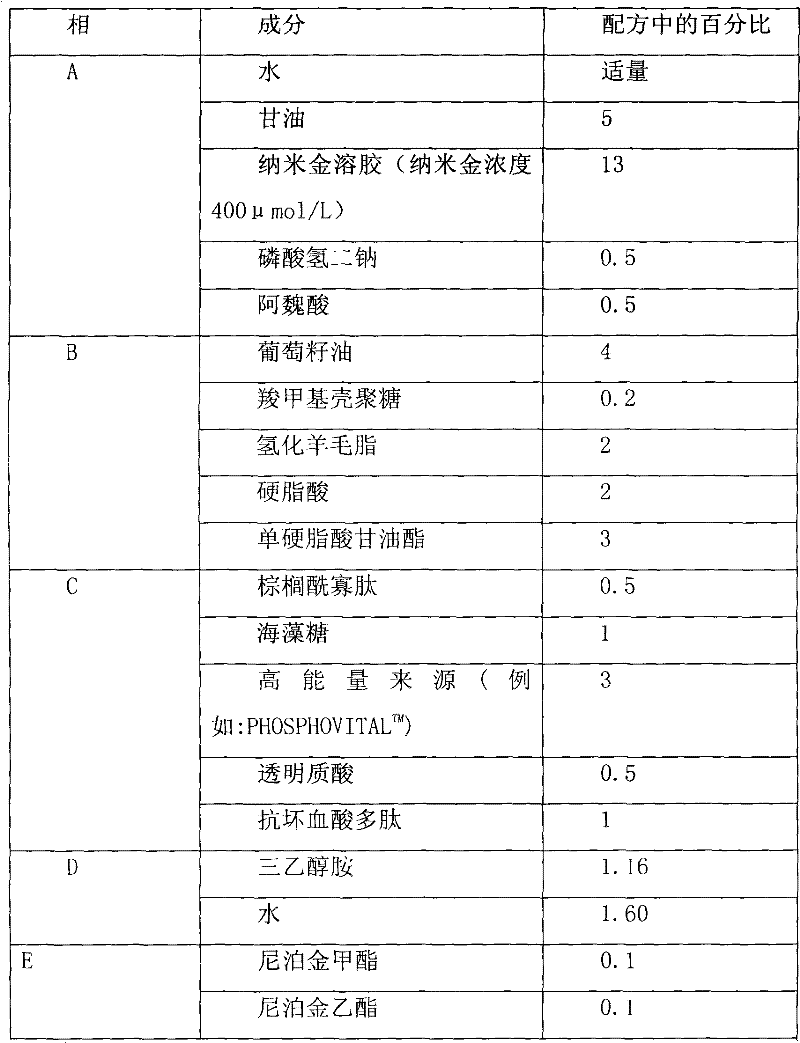
Composition for caring and improving aged or damaged skin
The invention discloses a cosmetic composition for caring and improving aged or nutrient-deficient skin or skin subjected to environmental damage. The composition comprises nanogold, high-energy source and / or peptides for skin cell metabolism, and one or more antioxidants. The components have favorable coordinating actions, and can improve the skin in the aspects of visual appearance, physiological functions, clinical characteristics and biophysical features.
Owner:AESTHETIC TECH BEIJING
Chinese medicinal herb additive for egg chickens and application
InactiveCN101543262AImprove disease resistanceImprove qualityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseasePhytase
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal herb additive for egg chickens and application. The Chinese medicinal herb additive comprises membranous milkvetch root, eucommia bark, honeysuckle, jiuyue, Weeping Forsythiae Capsule, szechwon tangshen root, sanguisorba, hawthorn, Indian Buead, officinal magnolia bark, Chinese pulsatilla root, giant knotweed rhizome, ricepaperplant pith, largehead atractylodes rhizome, tangerine peel, malt, indigowoad root, swordlike atractylodes rhizome, indigowoad leaf, three immortals, liquorice, cyrtomium fortune, nutgrass galingale rhizome, chatoyancy, calamus and pinellia tuber, and mixture of the compositions is added with calcium bicarbonate, phytase, vitamin E and methionine. The Chinese medicinal herb additive effectively promotes absorption of nutrient, can prevent and control diseases, strengthen quality of eggshells, reduce the broken egg rate and soft-shell eggs, abnormal eggs and sand shell eggs, can effectively prevent bird flu, prevent and control diseases such as laxness, feather pecking, hair shedding, anus pecking, salpingitis, respiratory disease and the like, can achieve good effect with a dosage of about 4 percent, cannot damage physiological functions of the egg chickens, and can prolong egg laying peak season, improve color of the eggshells and the laying rate by 8 to 20 percent, and increase weight of eggs.
Owner:邹振可
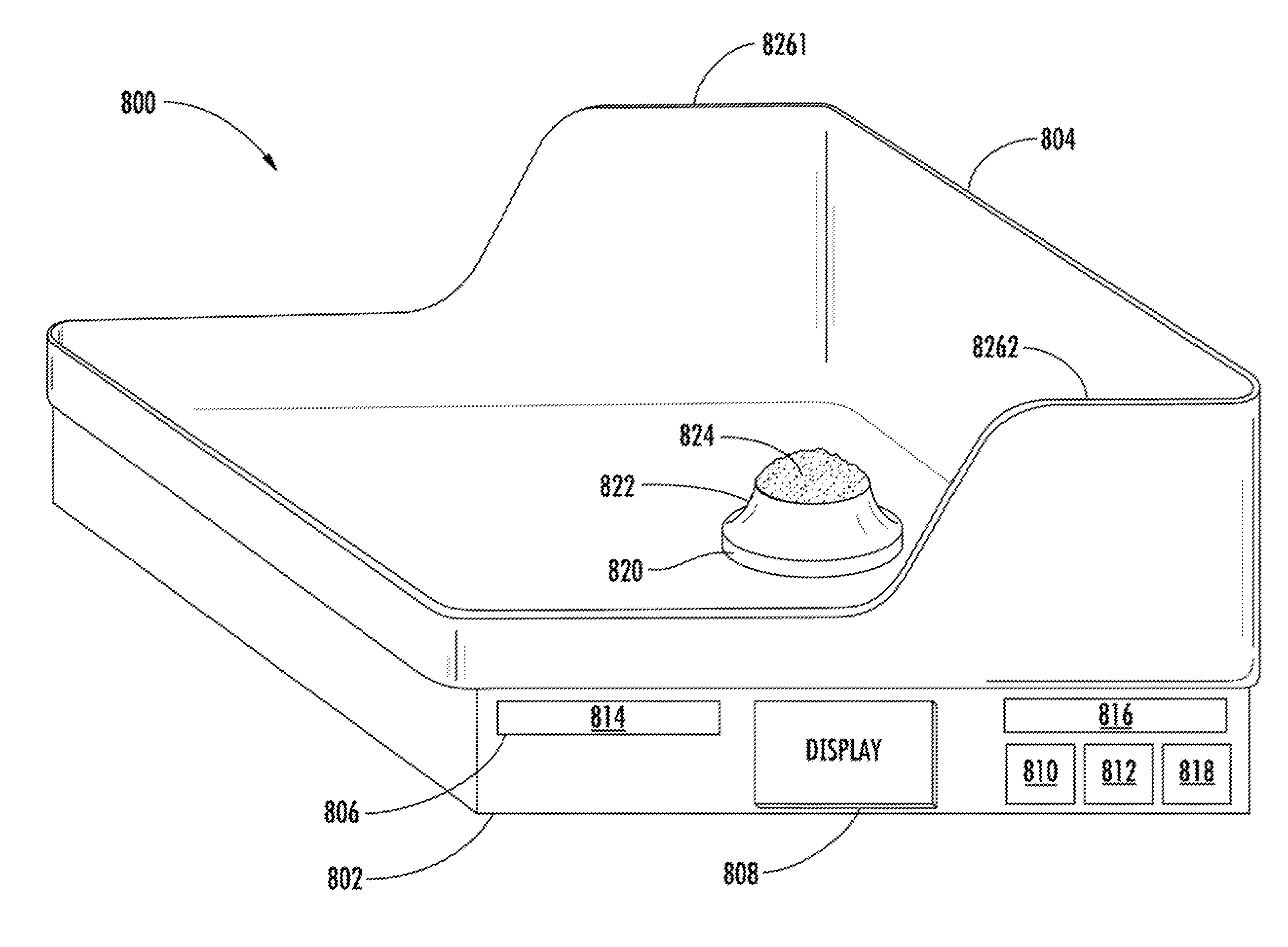
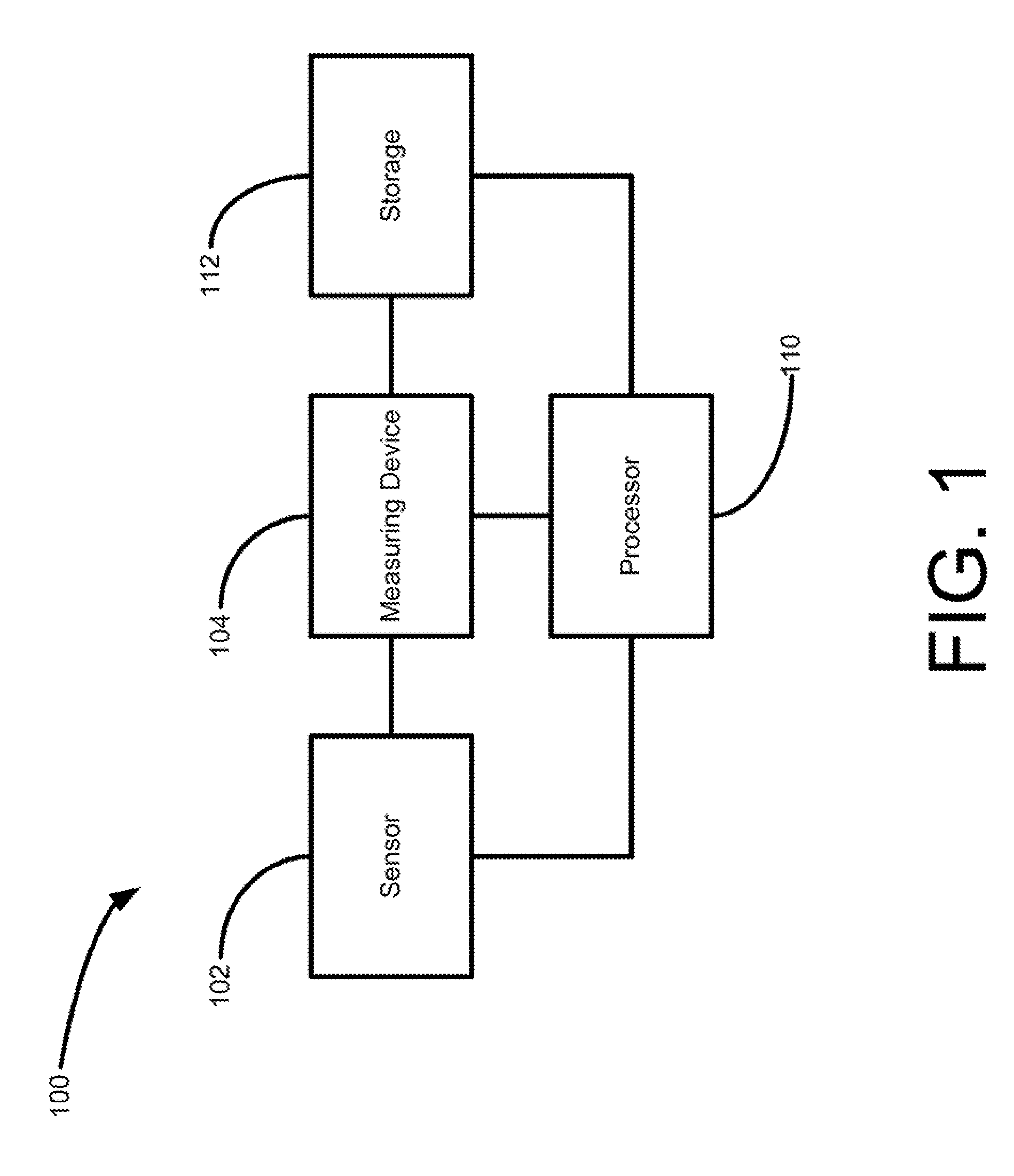
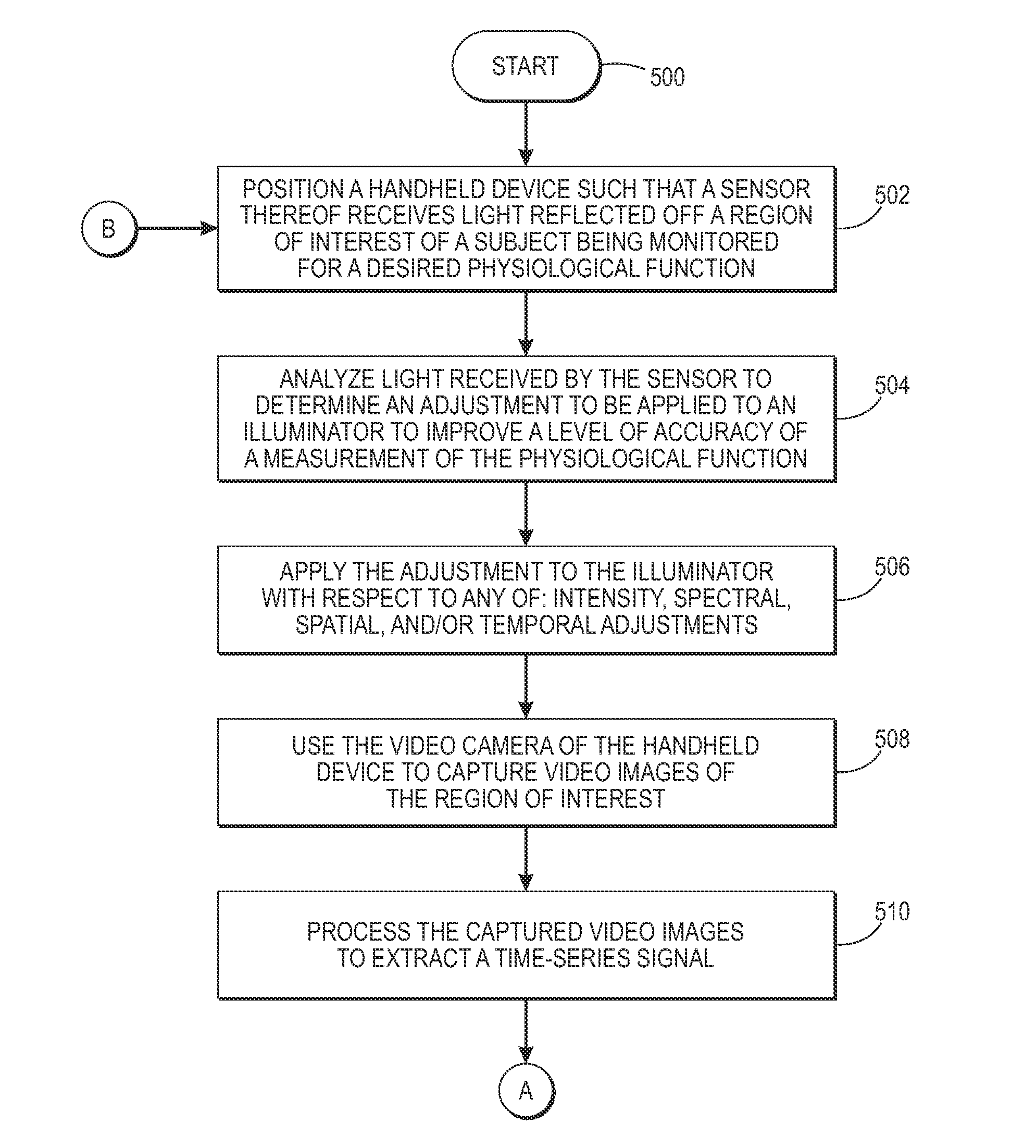
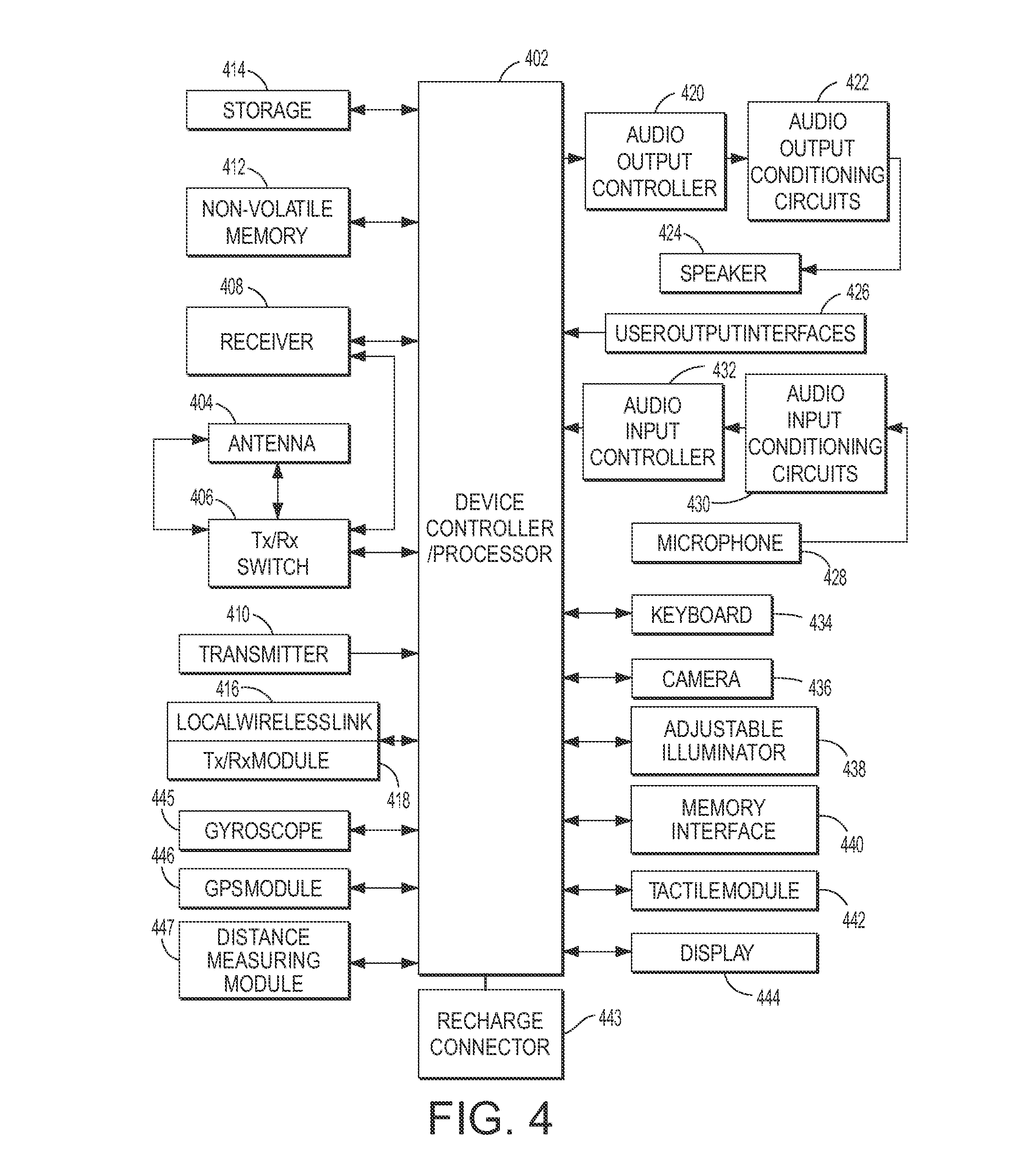
Physiological measurement obtained from video images captured by a camera of a handheld device
InactiveUS20150124067A1Enhanced signalImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsImage analysisVideo imageHandheld equipment
What is disclosed is a handheld device having at least one illuminator for projecting source light and a video camera for capturing images of a region of interest of a subject being monitored for a desired physiological function. The handheld device is positioned such that light reflected off the subject's region of interest is received by a sensor. A determination is then made as to how a physiological signal extracted from video images captured by the video camera can be improved by an adjustment to the illuminator with respect to intensity, spectrally, spatially, and / or temporally, to improve accuracy of a measurement of a desired physiological function. The illuminator is adjusted and video images of a region of interest are captured by the video camera and processed to extract a physiological signal corresponding to that physiological function. That signal is used to monitor the desired physiological function. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
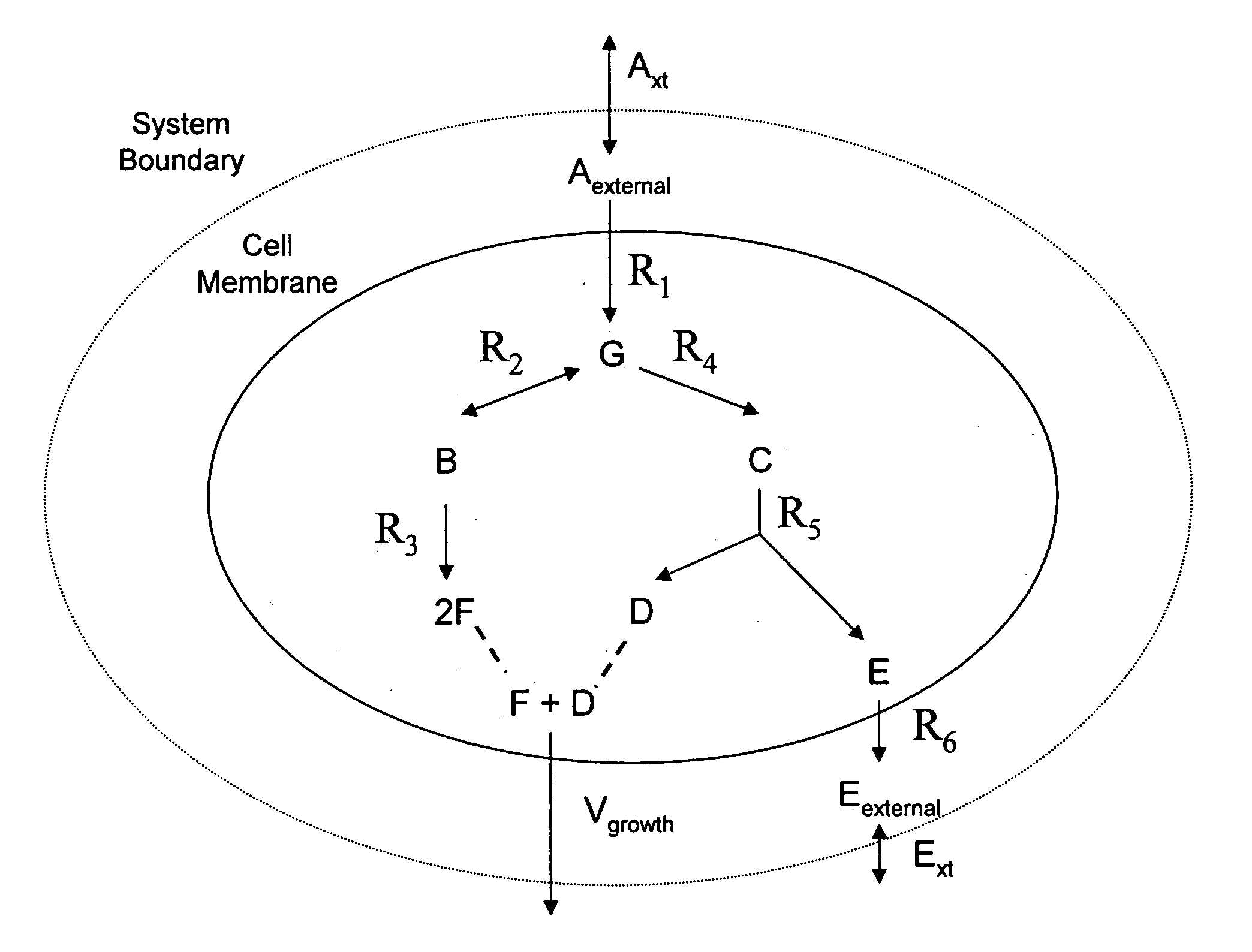
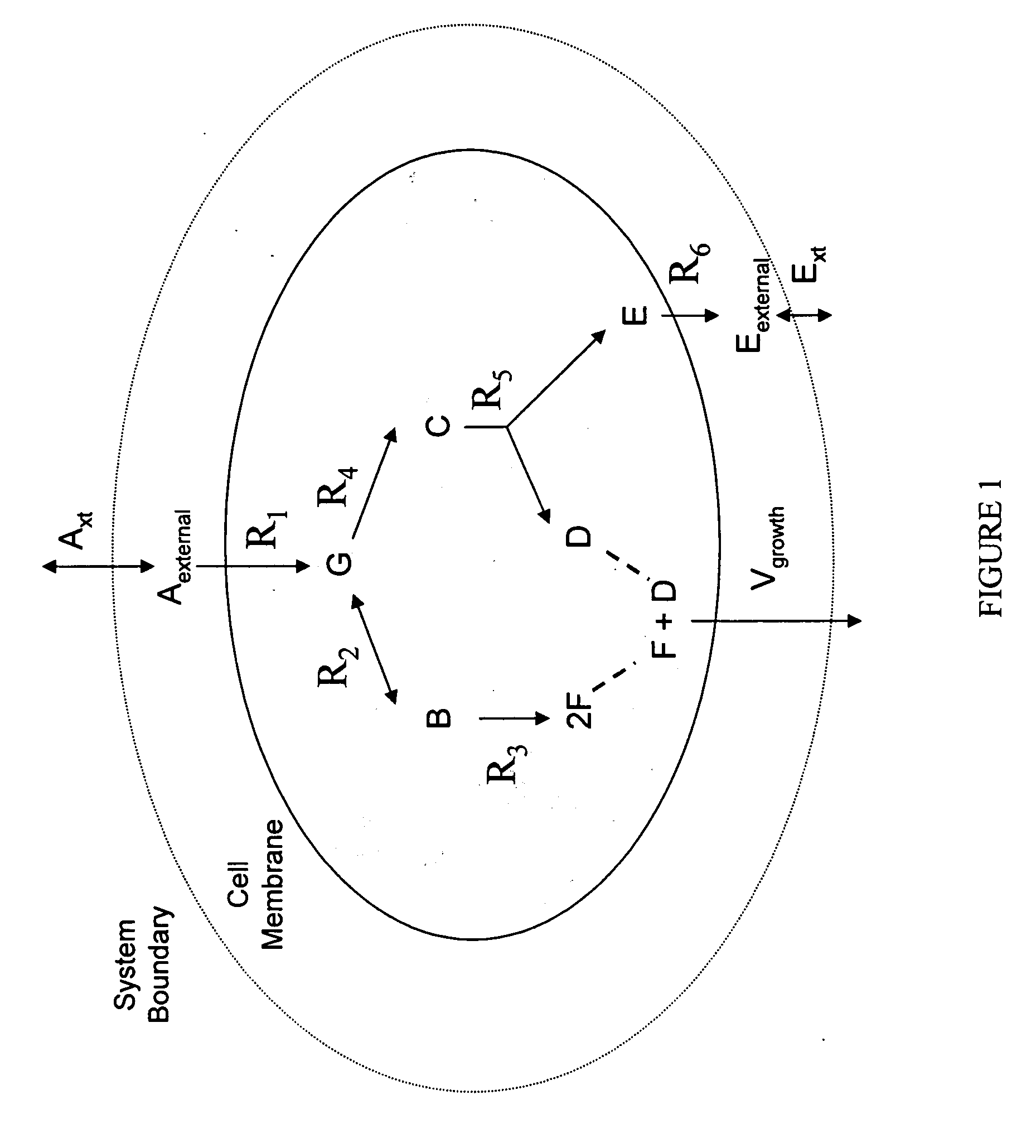
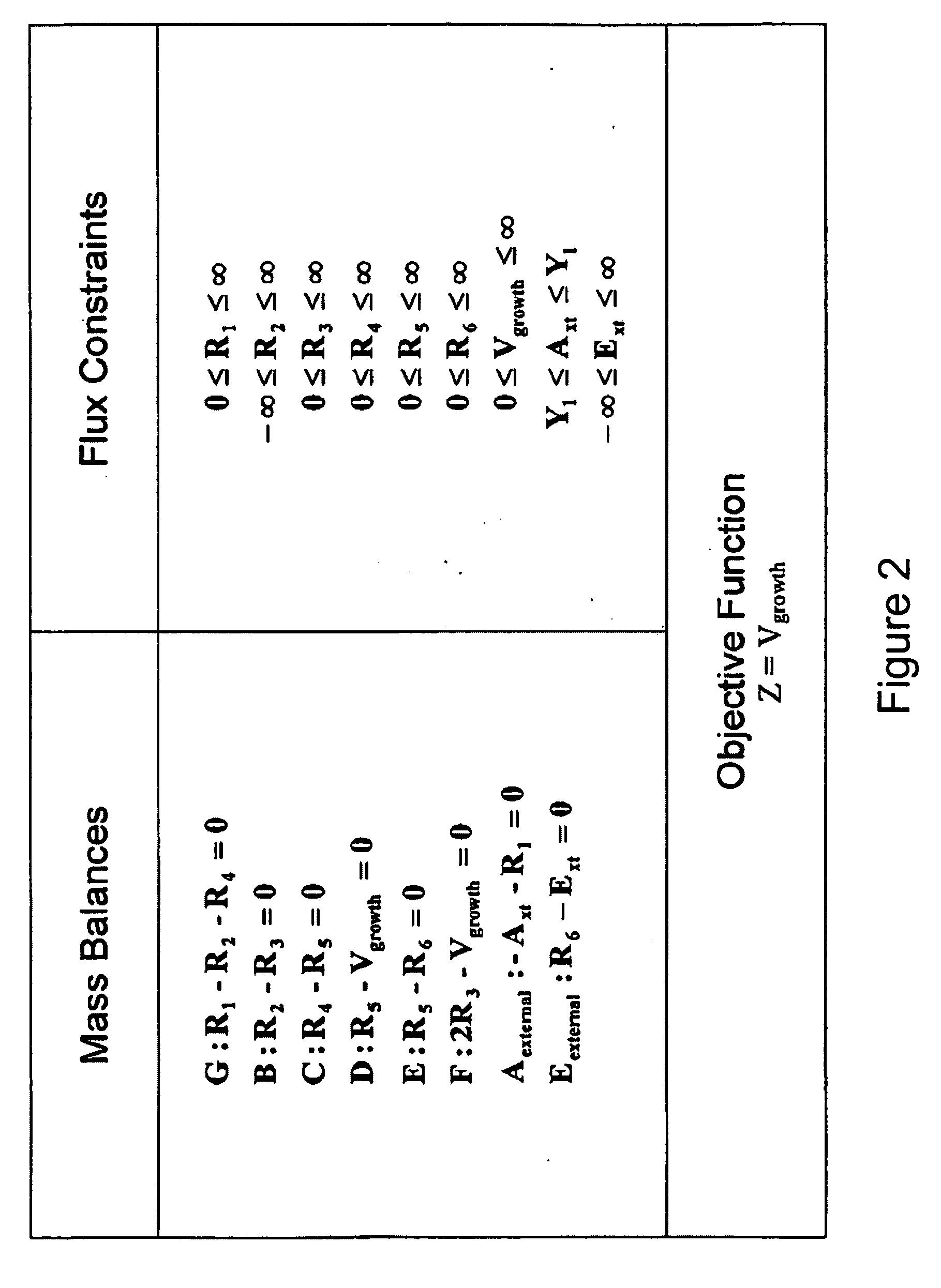
Multicellular metabolic models and methods
ActiveUS20060147899A1Chemical property predictionCompound screeningMulticellular organismMetabolic Model
The invention provides a computer readable medium or media, having: (a) a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures, and (e) commands for determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells. The first, second and third data structures also can include a plurality of data structures. Additionally provided is a method for predicting a physiological function of a multicellular organism. The method includes: (a) providing a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) providing a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) providing a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) providing a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures; (e) providing an objective function, and (f) determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
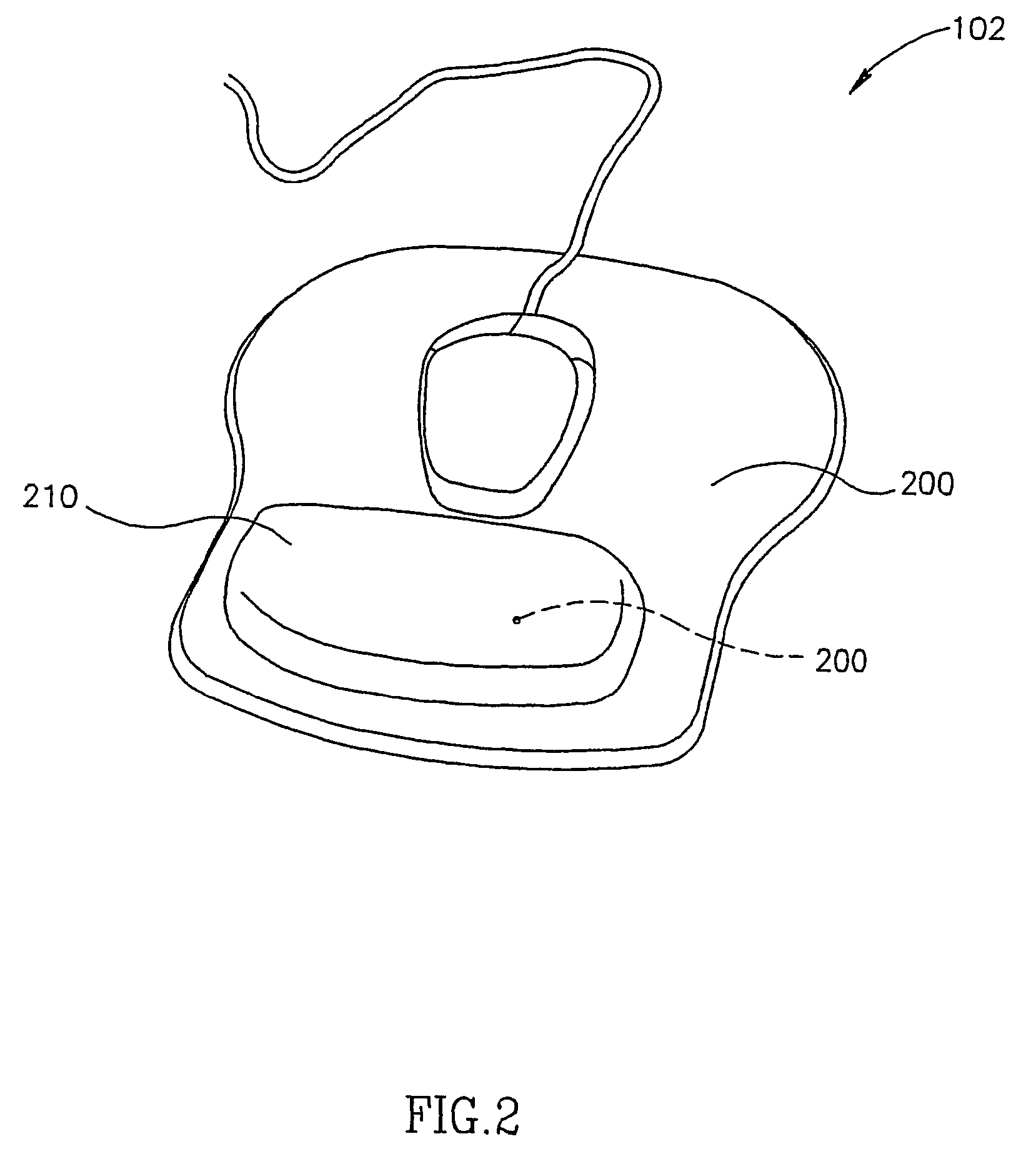
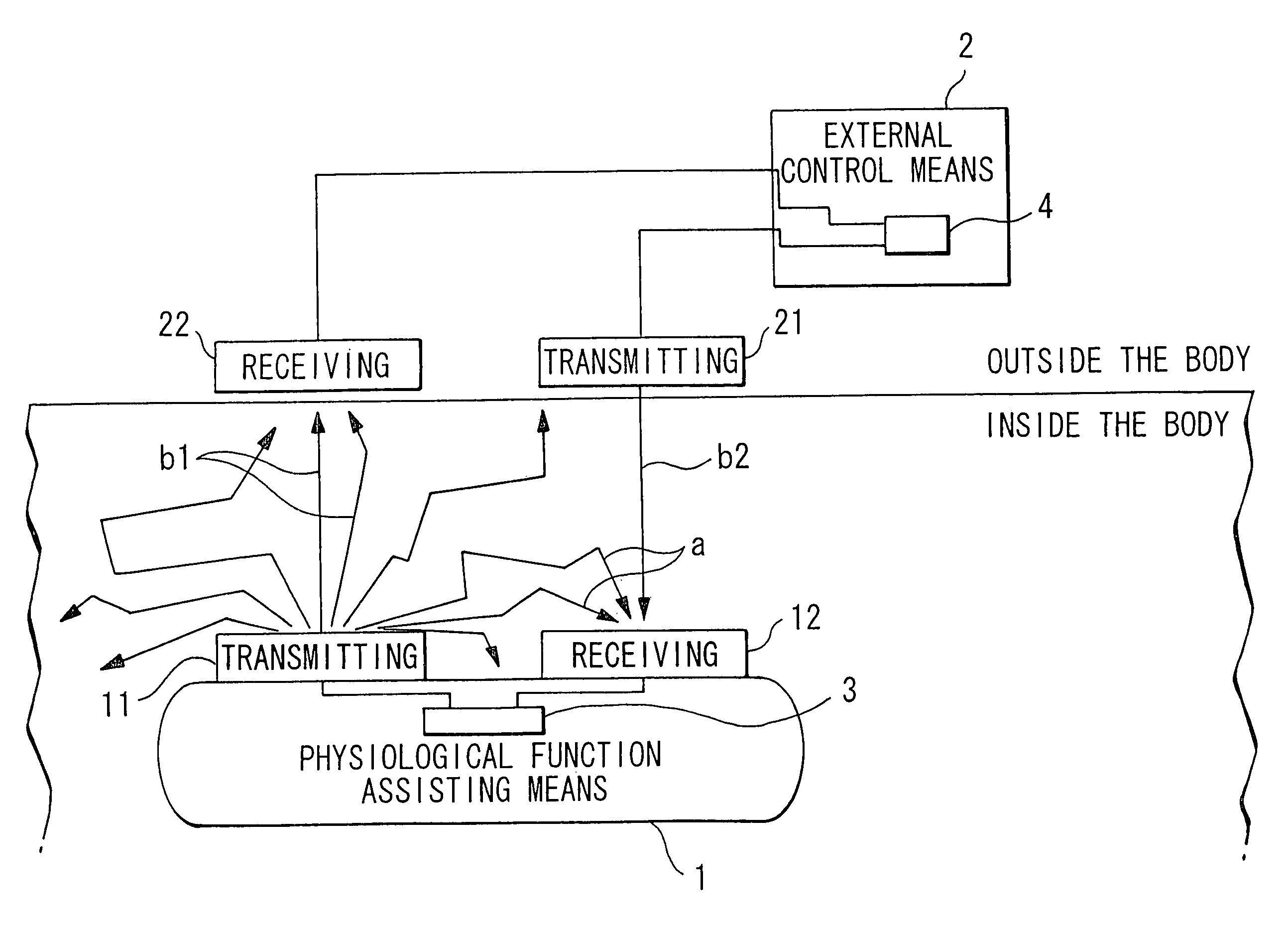
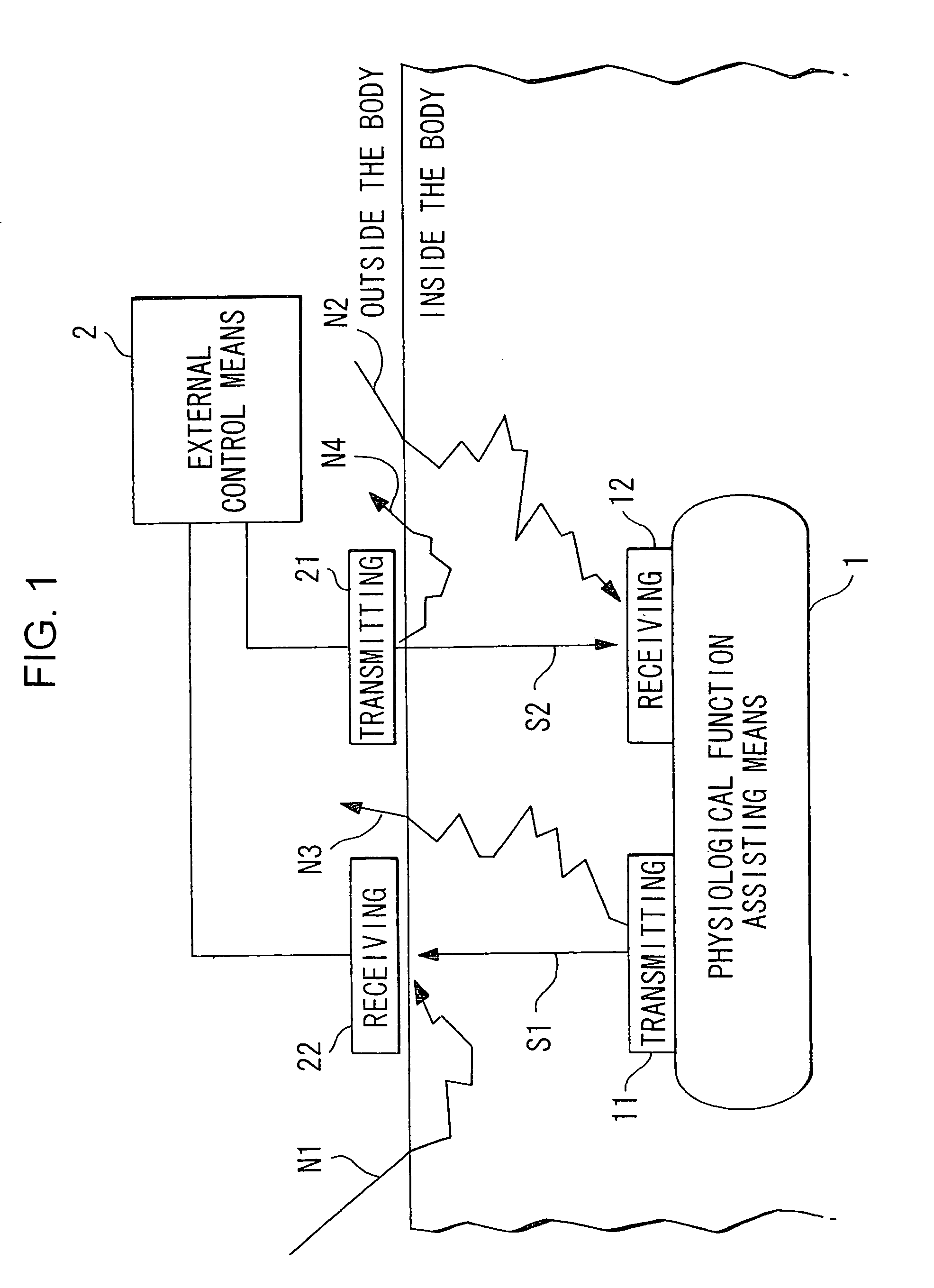
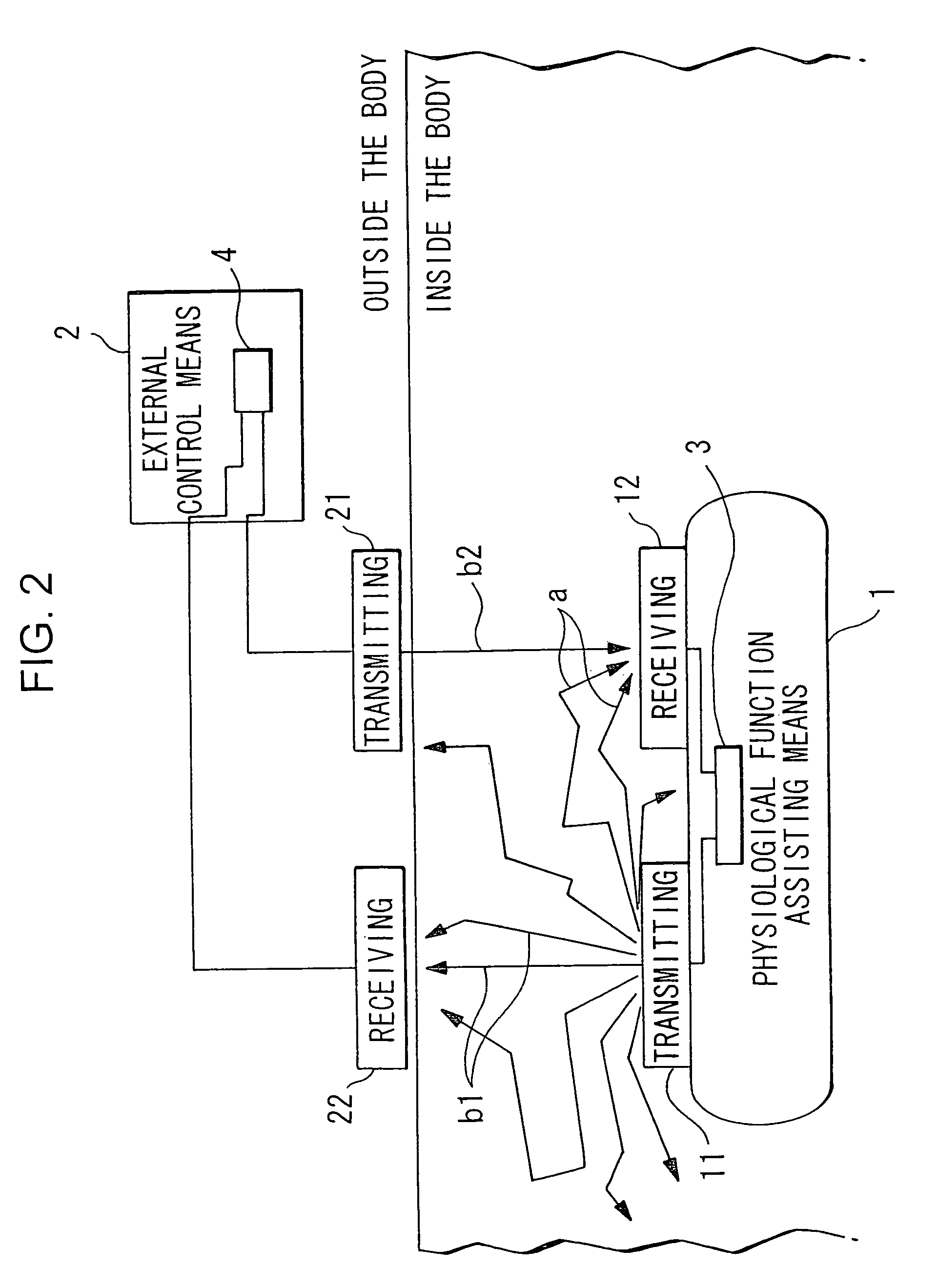
Polarized light communication device, transmitter, laser, polarized light communication device for physiological use, reflected light detector and pulse wave detecting device
InactiveUS6999685B1The overall impact is smallSmall dampingPolarisation multiplex systemsLaser active region structureDispersed mediaEngineering
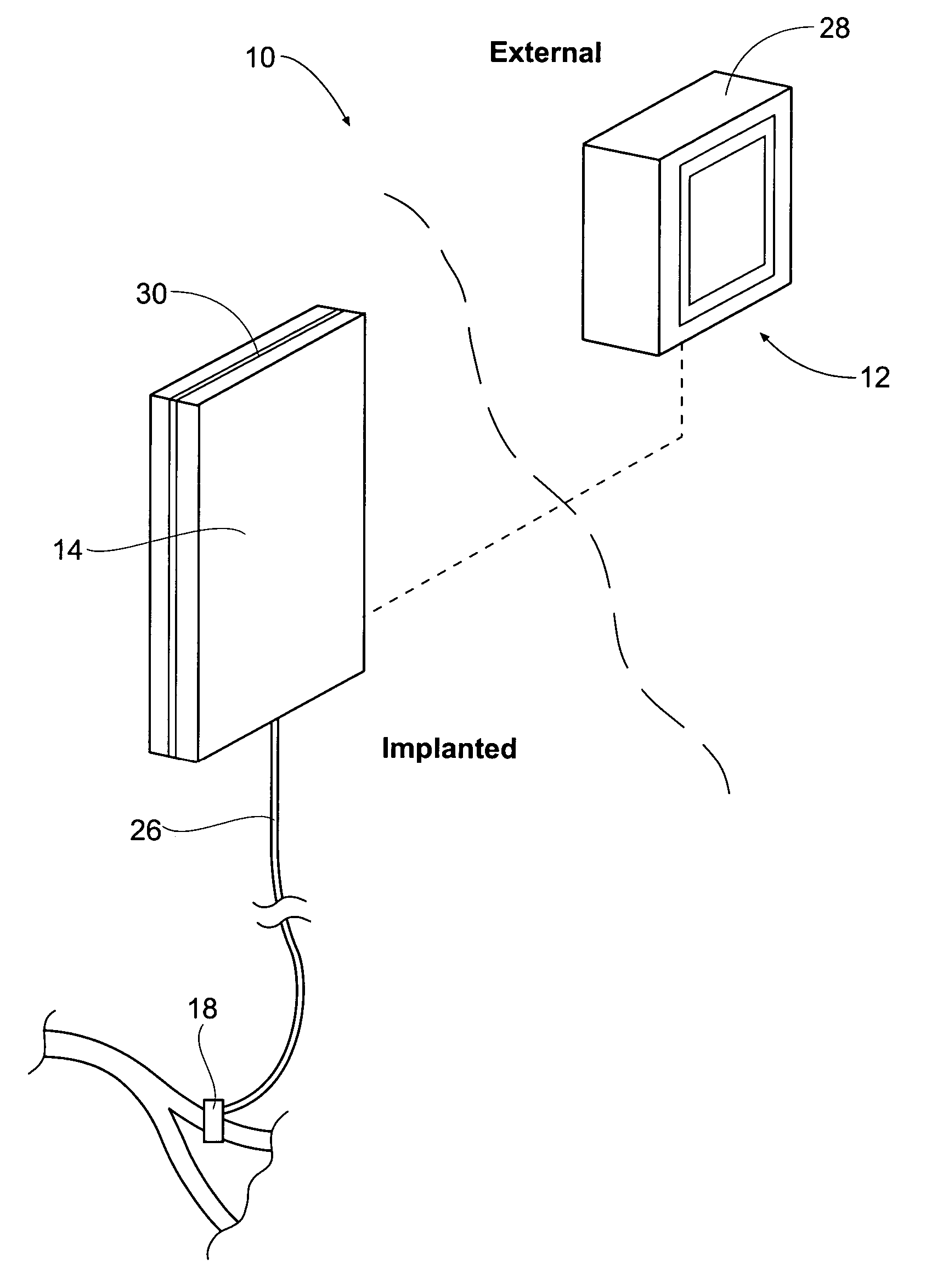
A physiological function assisting device 1 is embedded in the body, and is provided with a transmitter 11 and receiver 12 for communicating with an external controller 2. External controller 2 controls embedded physiological function assisting device 1 from the outside. External controller 2 is provided with a transmitter 21 and receiver 22 for communicating with physiological function assisting device 1. Transmitters 11,21 modulate the plane of polarization of laser light, and emit the result as a transmission signal. Receivers 12,22 selectively receive light of a specific polarization state. Receivers 12,22 respectively output electric signals corresponding to the polarization state (polarization angle or ellipticity) of the received light. As a result, full duplex communications between a strongly dispersing medium like the human body and the outside is possible, while the power consumed by the internal device can be reduced.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Physiological function detecting earphone and detecting method thereof
ActiveUS20150257662A1Improve accuracyEliminate the effects ofSignal processingCatheterLight sensingTransmittance
A physiological function detecting earphone includes an earphone body, an earplug mounted at one side of the earphone body and defining a window, a light processing module including a light sensing module towards the window, and a signal processing module. A detecting method includes steps: the participant inserts the earplug in the ear canal thereof; the light sensing module senses the changes of light emitted through the window and then reflected by the wall of the ear canal; the light processing module processes the reflected light of changes to get PPG signals; the signal processing module receives and processes the PPG signals to get physiological information of the participant. The window opened in the earplug can gather the light in a narrow area of the ear canal so that reduces effect of manufacturing material on transmittance of light and improves accuracy of the PPG signals and the physiological information.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Systems, methods and computer program products for monitoring the behavior, health, and/or characteristics of an animal
Systems, methods, and computer code products for monitoring the behavior, health, and / or characteristics of an animal are disclosed herein. In one implementation, the animal is positioned inside a waste container placed on a system that is adapted to determine, record and communicate over a network various animal health parameters. These parameters can be processed to determine trends, statistics and changes of animal physiological functions. The results can be used to access animal health conditions and issue warnings, alarms, messages, and other notifications to designated caretakers. These notifications may be displayed using various means such as computers and / or mobile devices. Data retrieval and review capability can provide improved understanding of an animal's health conditions and facilitate early illness detection.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Methods and compositions for the treatment of skin changes associated with aging and environmental damage
InactiveUS20050158258A1Reduces ultraviolet lightReduces sun exposure damageBiocideCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientUltraviolet lights
The present invention relates to novel methods and compositions comprising a combination of ingredients for treating aged, mature, nutritionally-compromised, or environmentally-damaged skin. These methods and compositions provide improvements in the skin's visual appearance, physiological functions, clinical properties, and biophysical properties. The compositions of the present invention can include, for example, a compound that stimulates microcirculation through the skin, a compound that stimulates the immune system, a compound that reduces ultraviolet light or sun exposure damage, a compound that evens out the pigmentation of the skin, and / or a compound that improves the barrier properties of the skin.
Owner:MARY KAY INC
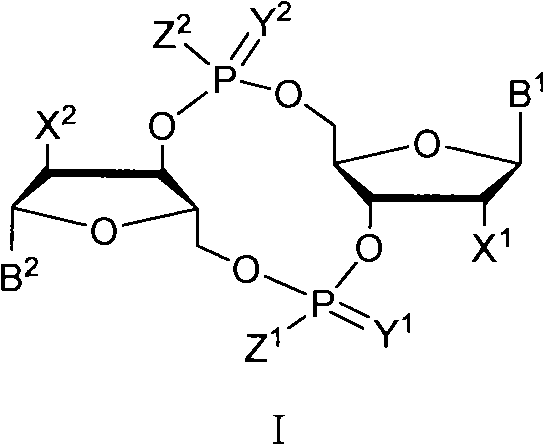
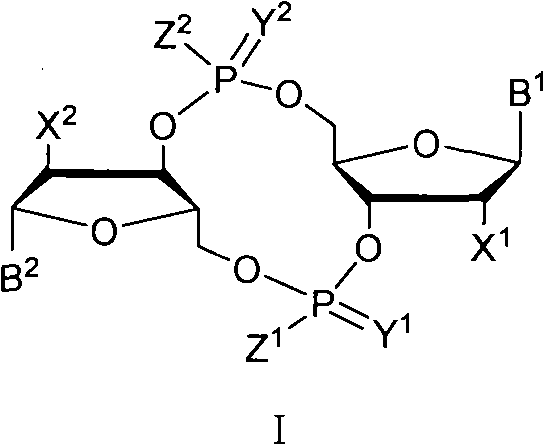
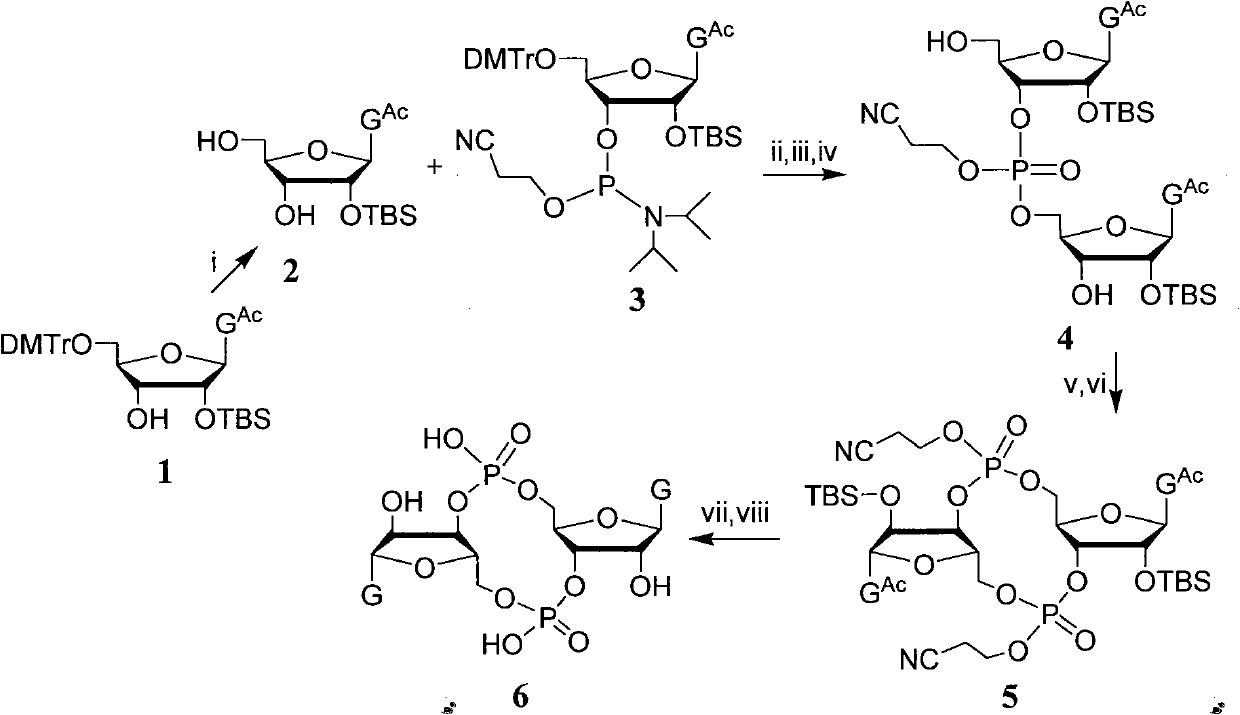
C-di-GMP, analogues thereof and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102199183AInhibition formationPrevent proliferationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationDrug developmentBiological membrane
The invention discloses a c-di-GMP and analogues thereof which have structures of a general formula I. The invention also discloses a novel preparation method-a kettle phosphoramidite method which can be used for rapidly, simply and conveniently preparing c-di-GMP compounds with high yield and low cost on a large scale and at mild conditions. The c-di-GMP is prevalent in bacteria and is a novel second messenger molecular which takes part in regulating multiple physiological functions. The research shows that the c-di-GMP and the analogues thereof can inhibit the formation of bacterium biological membranes and the multiplication of eukaryotic cells; and thereof the c-di-GMP and the analogues thereof have good medicine development prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com