Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4274 results about "Bending moment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bending moment is the reaction induced in a structural element when an external force or moment is applied to the element causing the element to bend. The most common or simplest structural element subjected to bending moments is the beam. The diagram shows a beam which is simply supported at both ends. Simply supported means that each end of the beam can rotate; therefore each end support has no bending moment. The ends can only react to the shear loads. Other beams can have both ends fixed; therefore each end support has both bending moment and shear reaction loads. Beams can also have one end fixed and one end simply supported. The simplest type of beam is the cantilever, which is fixed at one end and is free at the other end (neither simple or fixed). In reality, beam supports are usually neither absolutely fixed nor absolutely rotating freely.
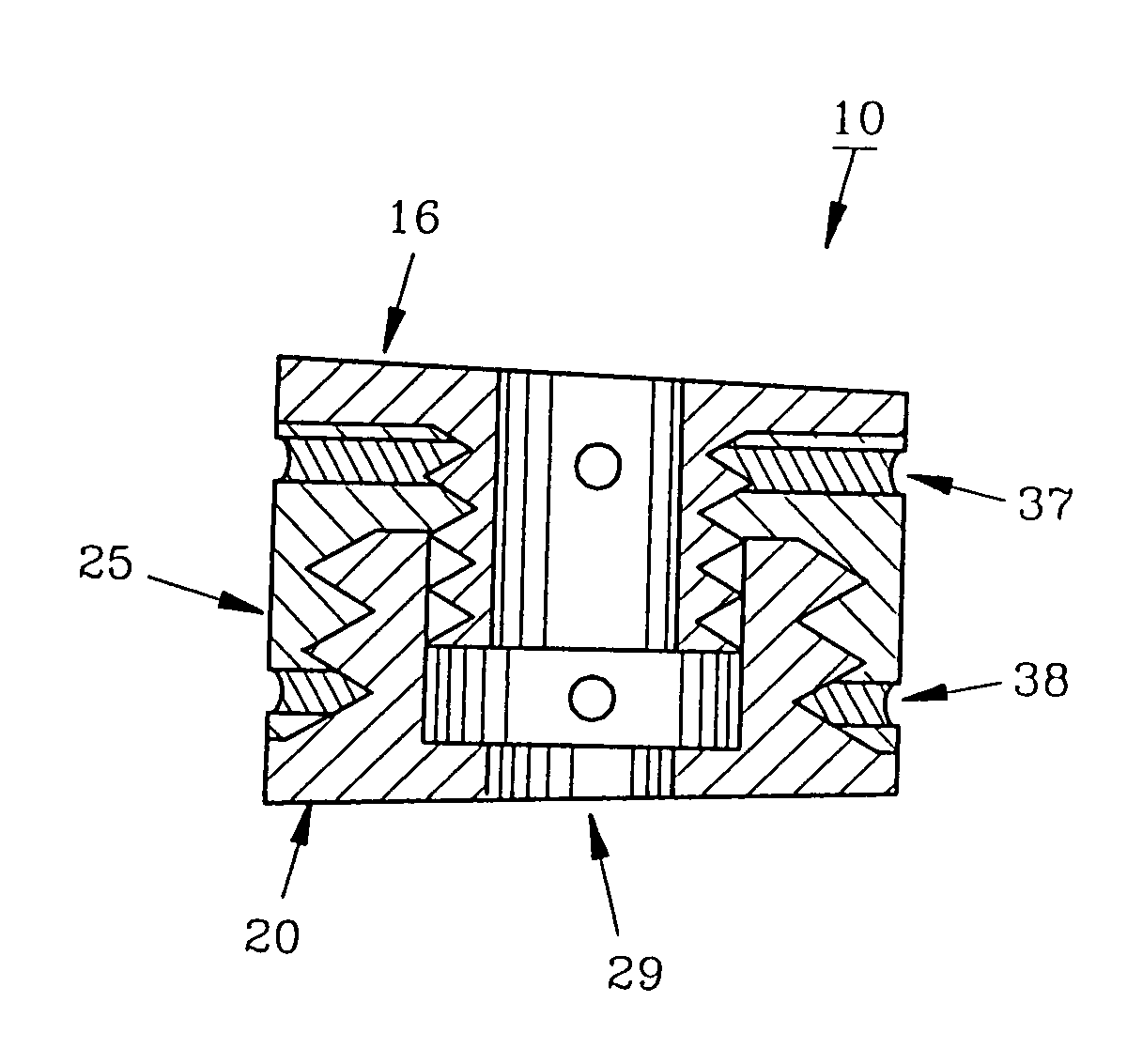
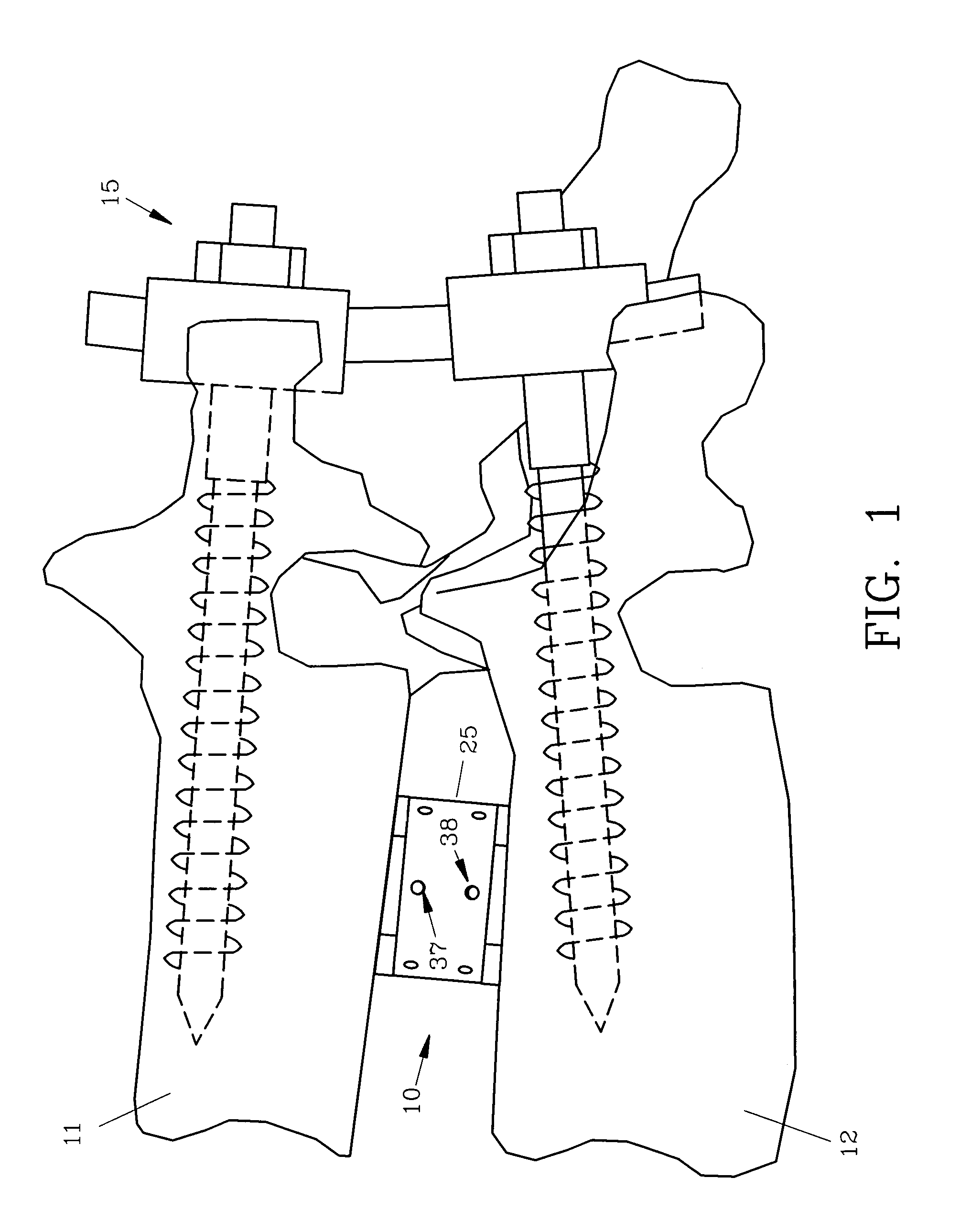
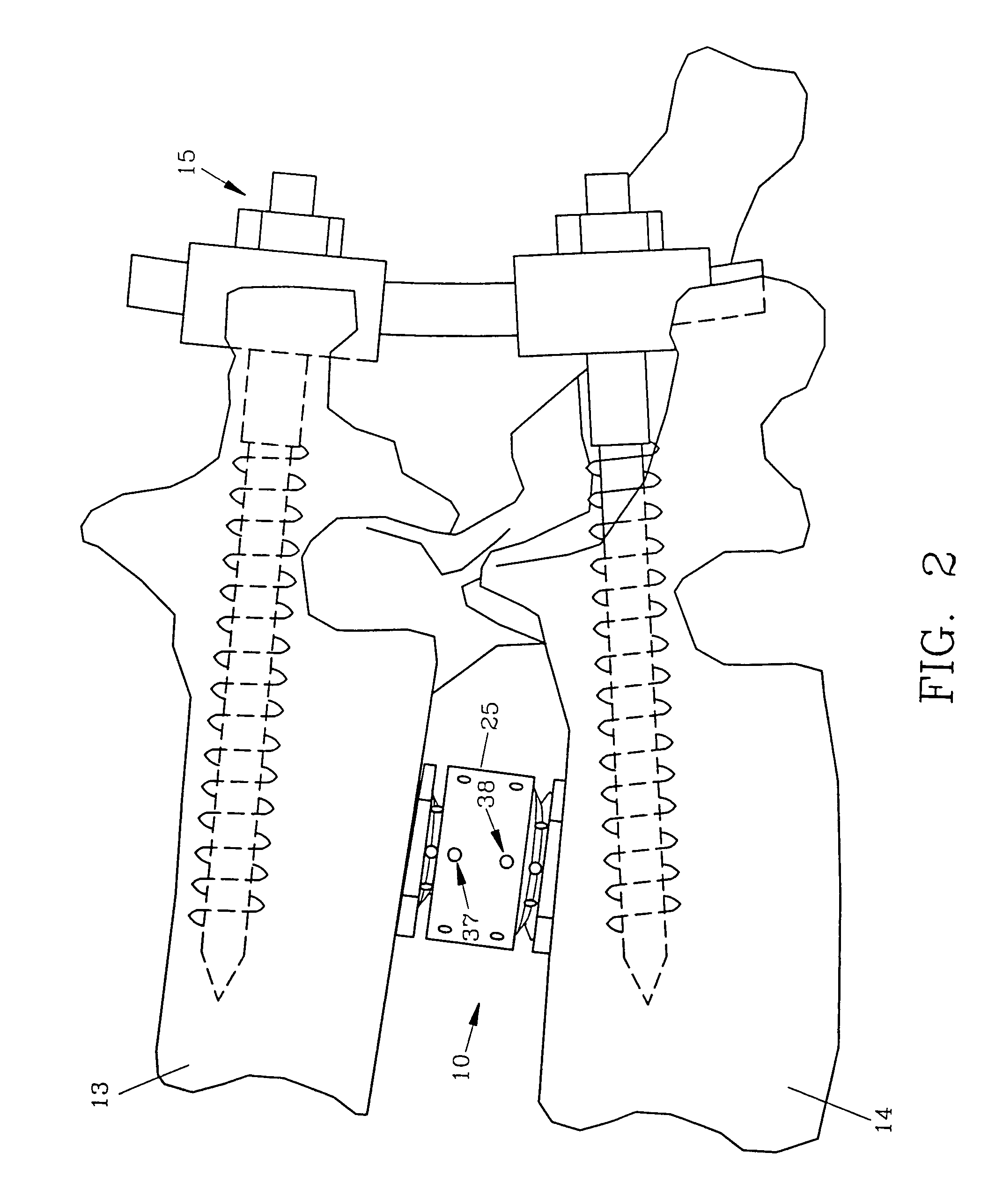
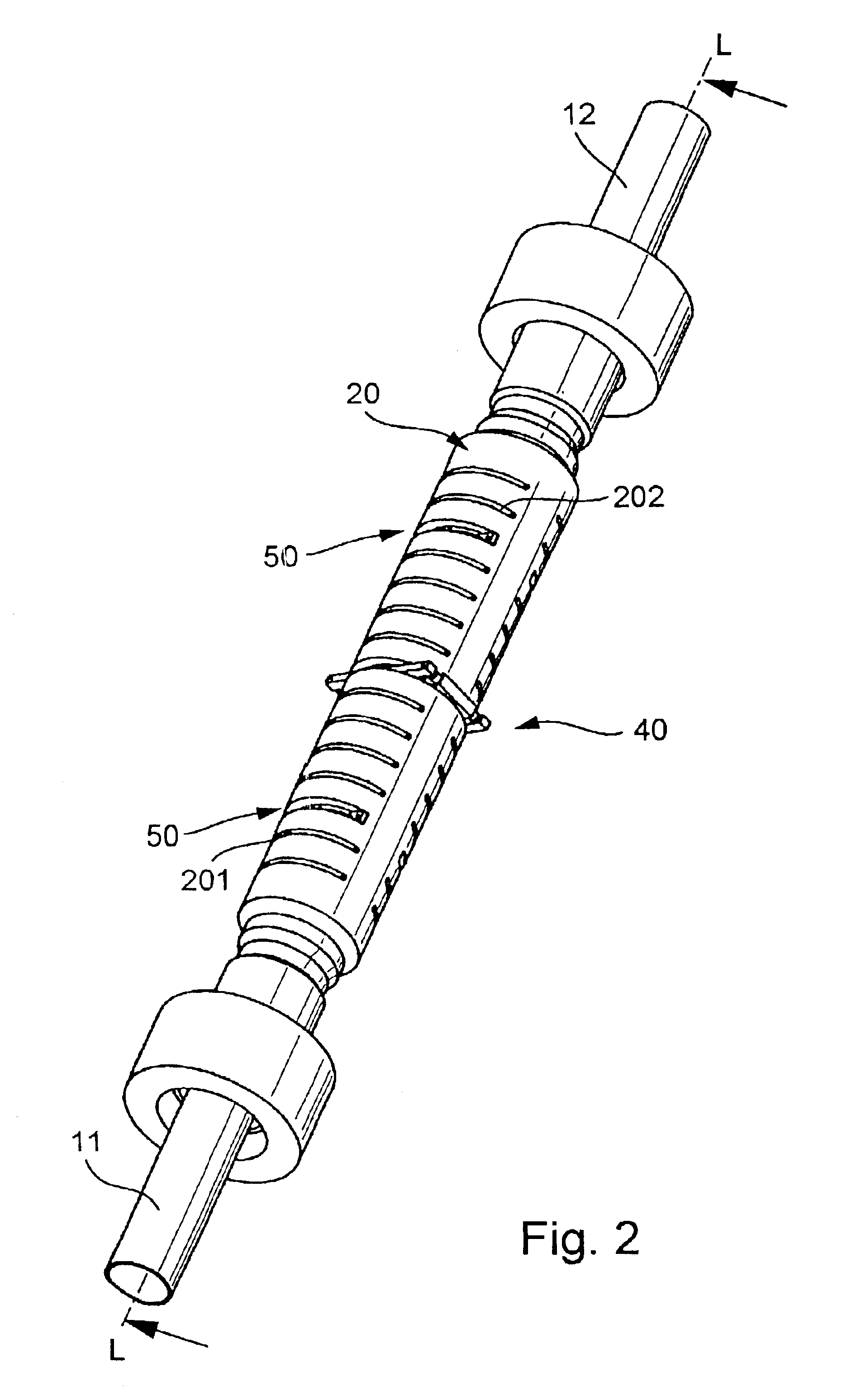
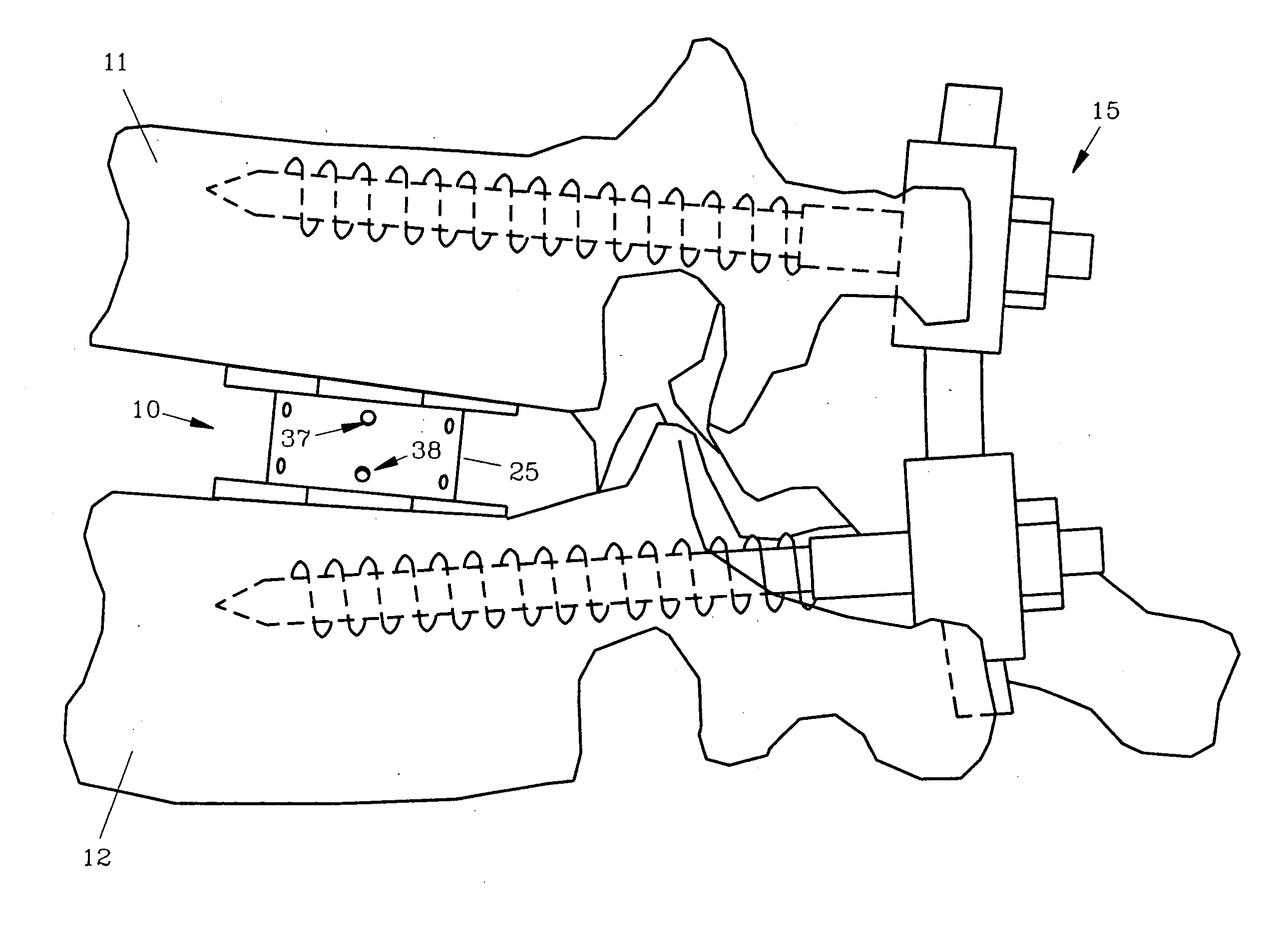
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS7022138B2Easy to copyAvoid injuryInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnIntervertebral disk
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the plate bore. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
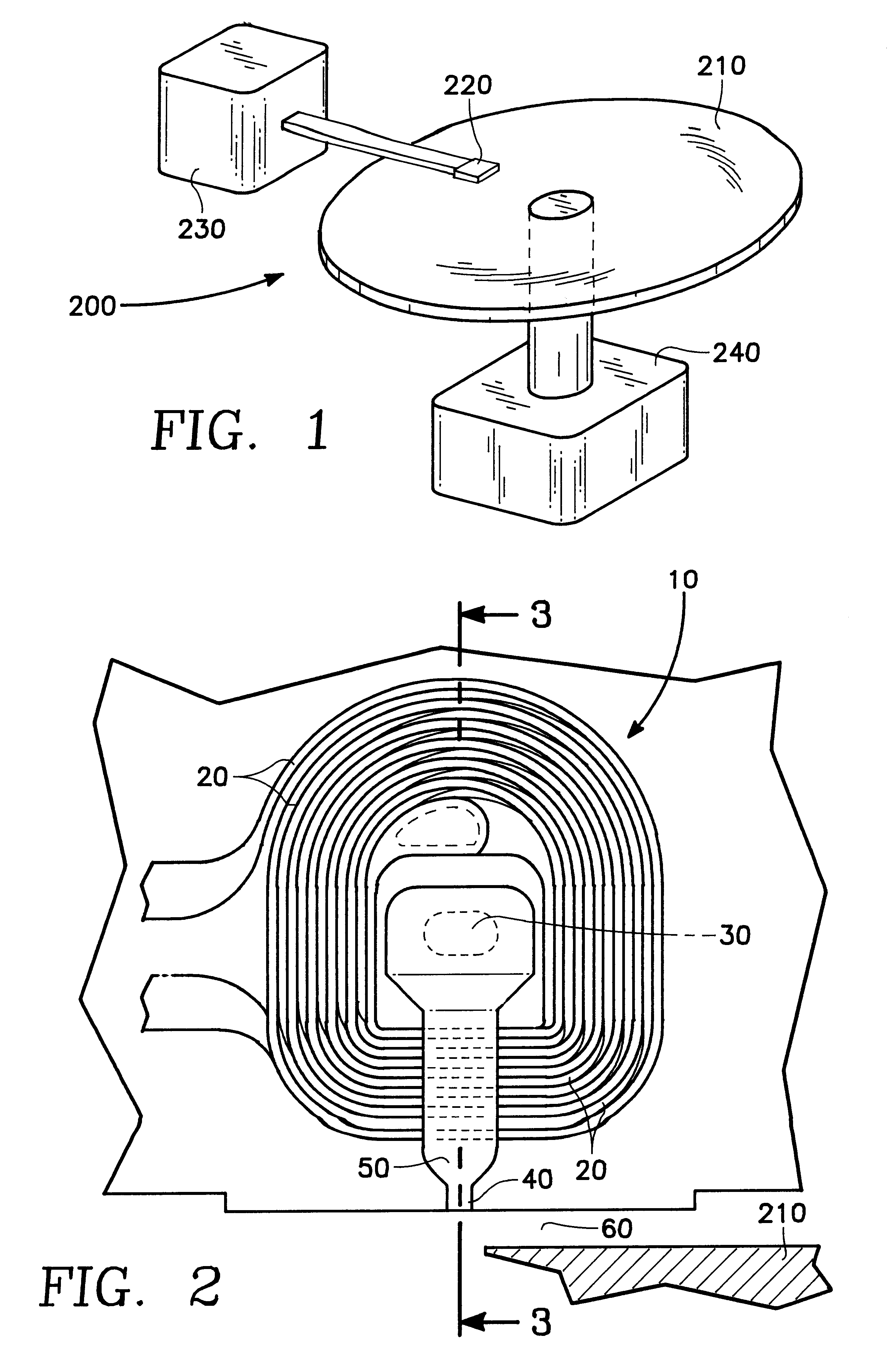
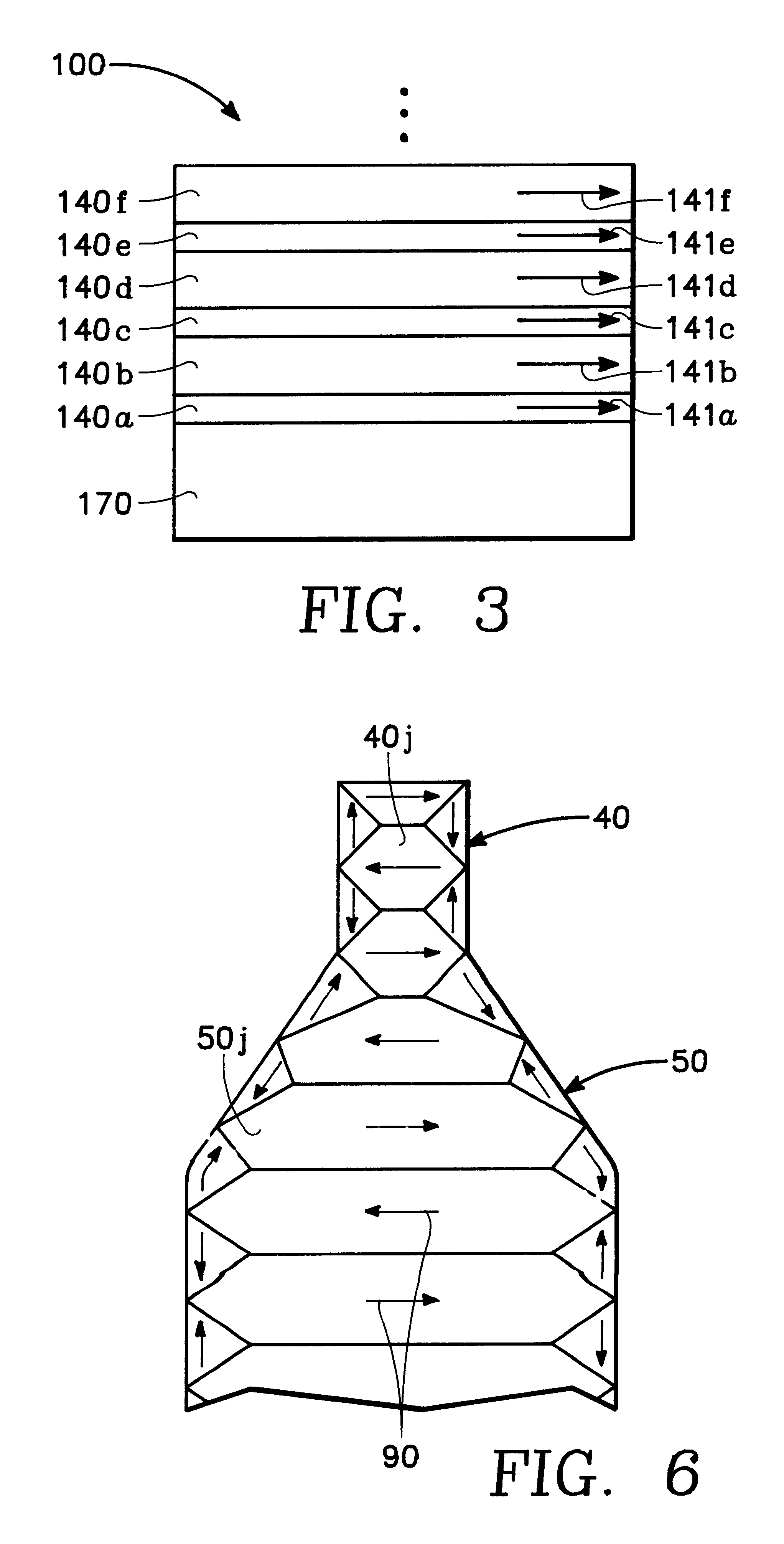
Thin film write head with improved laminated flux carrying structure and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6233116B1High resistivityExcellent soft magnetic propertiesConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsLower poleHigh resistivity
The present invention provides a thin film write head having an improved laminated flux carrying structure and method of fabrication. The preferred embodiment provides laminated layers of: high moment magnetic material, and easily aligned high resistivity magnetic material. In the preferred embodiment, the easily aligned laminating layer induces uniaxial anisotropy, by exchange coupling, to improve uniaxial anisotropy in the high moment material. This allows deposition induced uniaxial anisotropy by DC magnetron sputtering and also provides improved post deposition annealing, if desired. It is preferred to laminate FeXN, such as FeRhN, or other crystalline structure material, with an amorphous alloy material, preferably Co based, such as CoZrCr. In the preferred embodiment, upper and lower pole structures may both be laminated as discussed above. Such laminated structures have higher Bs than structures with insulative laminates, and yokes and pole tips and may be integrally formed, if desired, because flux may travel along or across the laminating layers. The preferred embodiment of the present invention improves soft magnetic properties, reduces eddy currents, improves hard axis alignment while not deleteriously affecting the coercivity, permeability, and magnetostriction of the structure, thus allowing for improved high frequency operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6840109B2Simple and robust mannerSimplifies isolationVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerEngineering
To conduct a fluid, the transducer has a flow tube which in operation vibrated by an excitation assembly. Inlet-side and outlet-side vibrations of the flow tube are sensed by means of a sensor arrangement. To produce shear forces in the fluid, the flow tube is at least intermittently excited into torsional vibrations about a longitudinal flow-tube axis. An internal portion of the transducer, formed at least by the flow tube, an antivibrator, the sensor arrangement, and the excitation assembly and mounted at least on the inlet and outlet tube sections, has a centroid which is located inside the flow tube. The transducer is suitable for use in viscometers or Coriolis mass flowmeter-viscometers. In spite of using only a single straight flow tube, it is dynamically well balanced in operation, and the development of bending moments by the torsionally vibrating flow tube is largely prevented. This also effectively prevents the transducer case or the connected pipe from being excited into sympathetic vibration. Measurement signals representative of mass flow rate are readily distinguishable from measurement signals representative of viscosity, particularly if the sensors used for the viscosity measurement are also used for the mass flow measurement.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
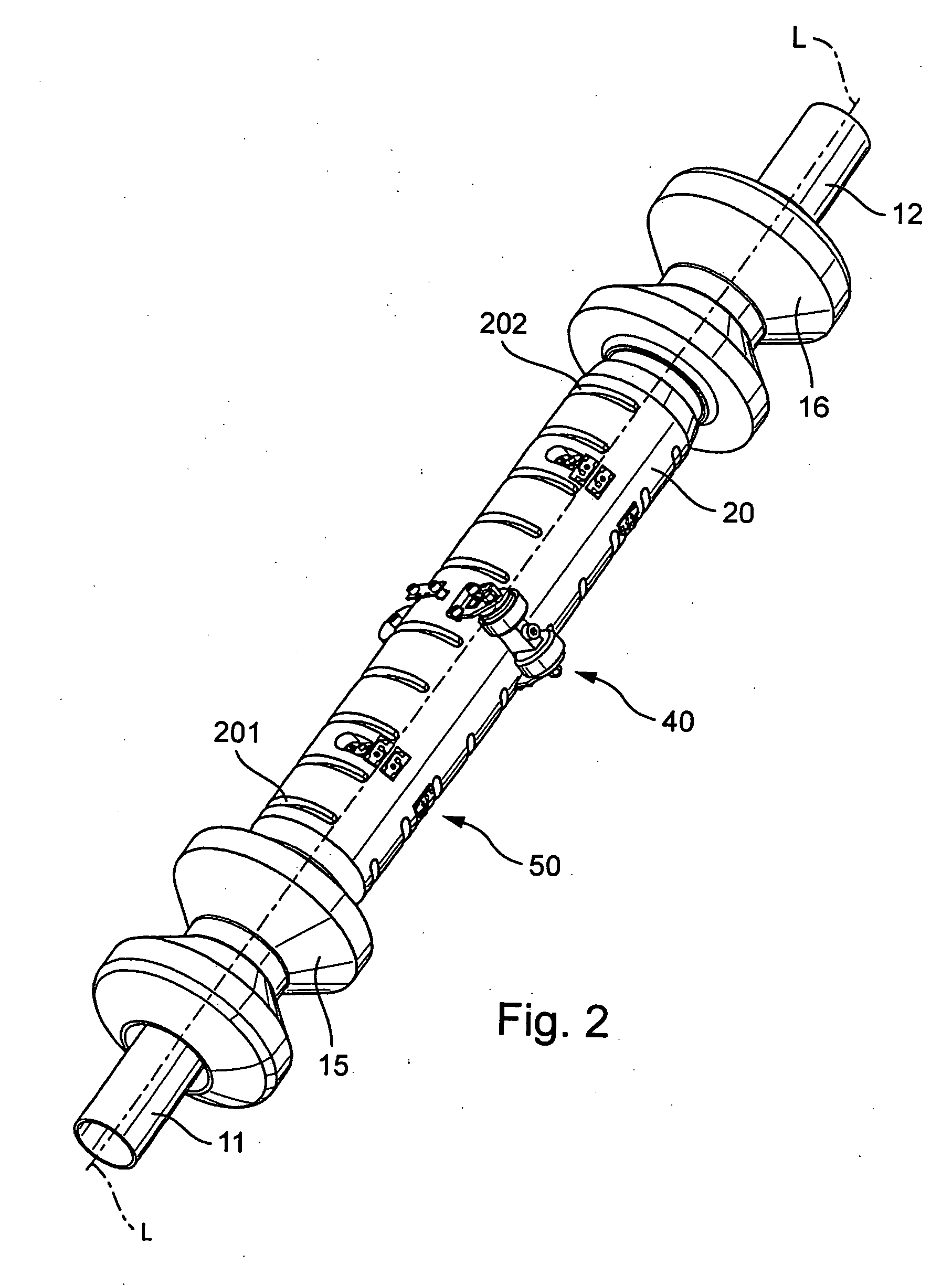
Wind turbine ring/shroud drive system
InactiveUS6951443B1Easy to adaptEliminate structureWind motor controlPump componentsNacelleGear drive
A wind turbine capable of driving multiple electric generators having a ring or shroud structure for reducing blade root bending moments, hub loads, blade fastener loads and pitch bearing loads. The shroud may further incorporate a ring gear for driving an electric generator. In one embodiment, the electric generator may be cantilevered from the nacelle such that the gear on the generator drive shaft is contacted by the ring gear of the shroud. The shroud also provides protection for the gearing and aids in preventing gear lubricant contamination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
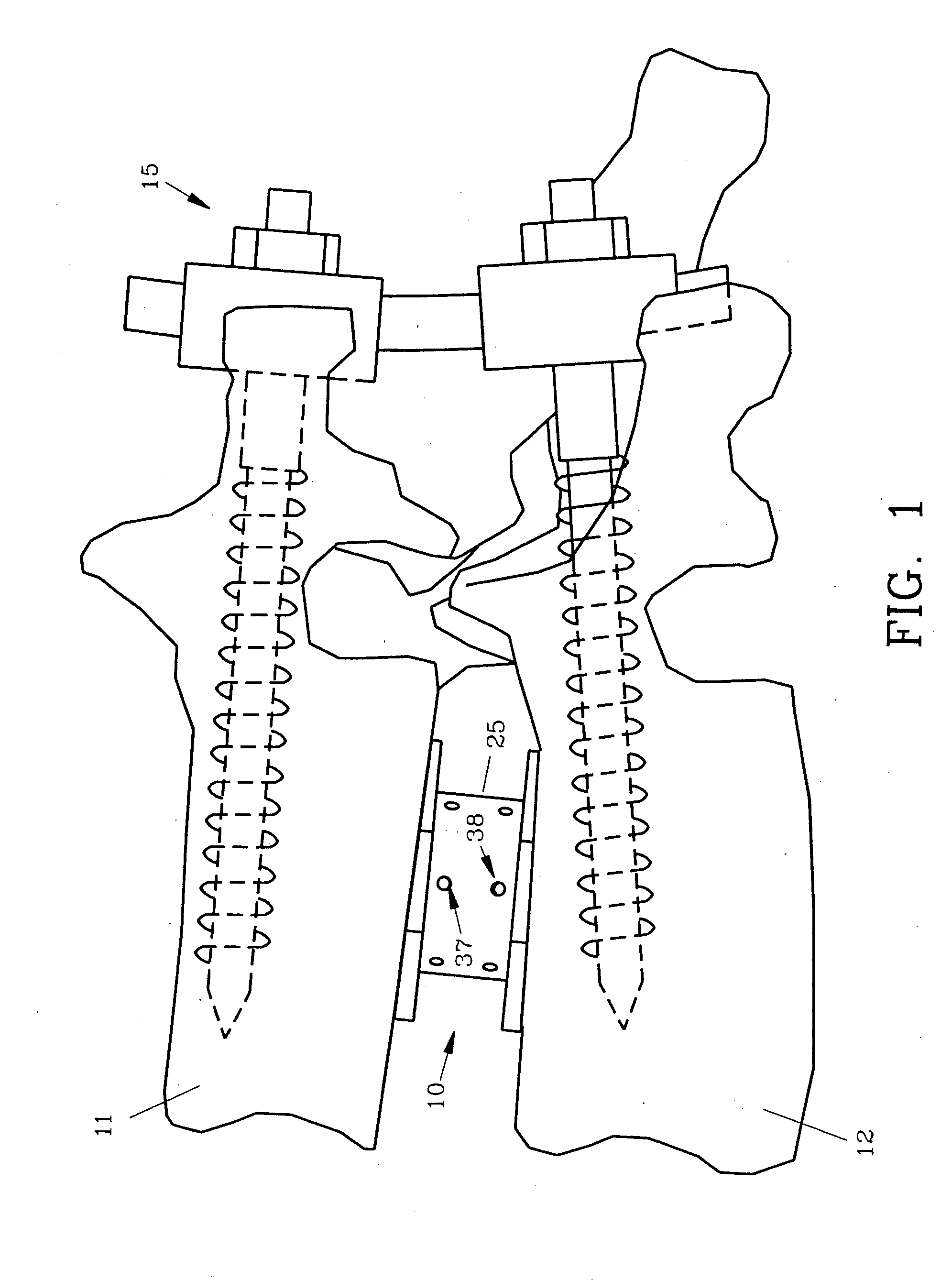
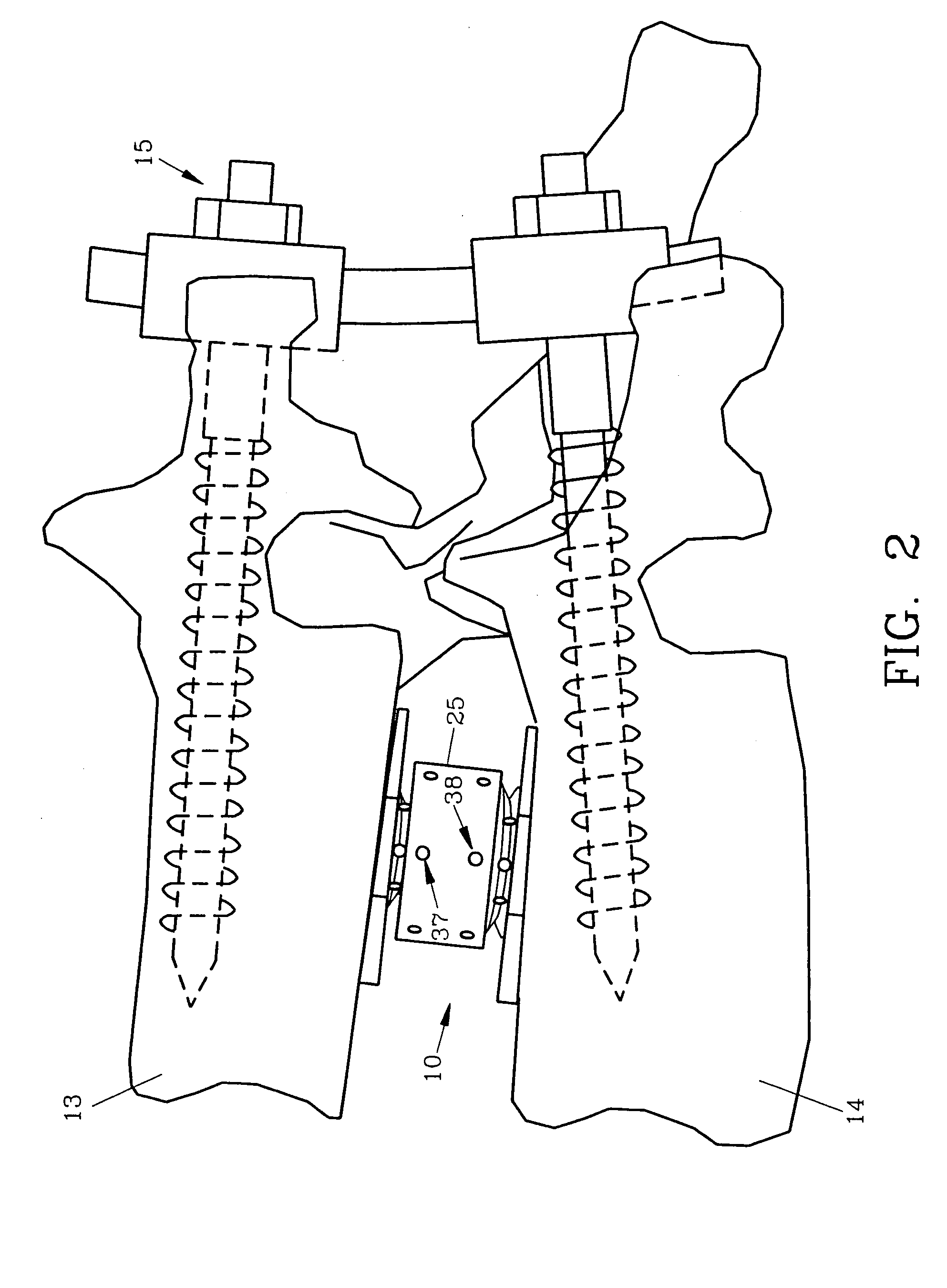
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS20050027359A1Resist translationalResist rotational movementInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnBending of plates
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the shaft bore. The first shaft has external left-hand threads and the second shaft has external right-hand threads, each to mate with different bores of the sleeve. The outside diameter of the first shaft is smaller than the inside diameter of the second shaft, allowing the two shafts to axially engage. The spinal interbody fusion device operates like a turnbuckle, vertically expanding when the sleeve is rotated in one direction and retracting when the sleeve is rotated in the opposite direction. The assembled device defines an open channel axially. Once the fusion device is set at its proper height, set screws are threaded into circumferential apertures of the sleeve to compress against the shaft threads of each plate to maintain a fixed height. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
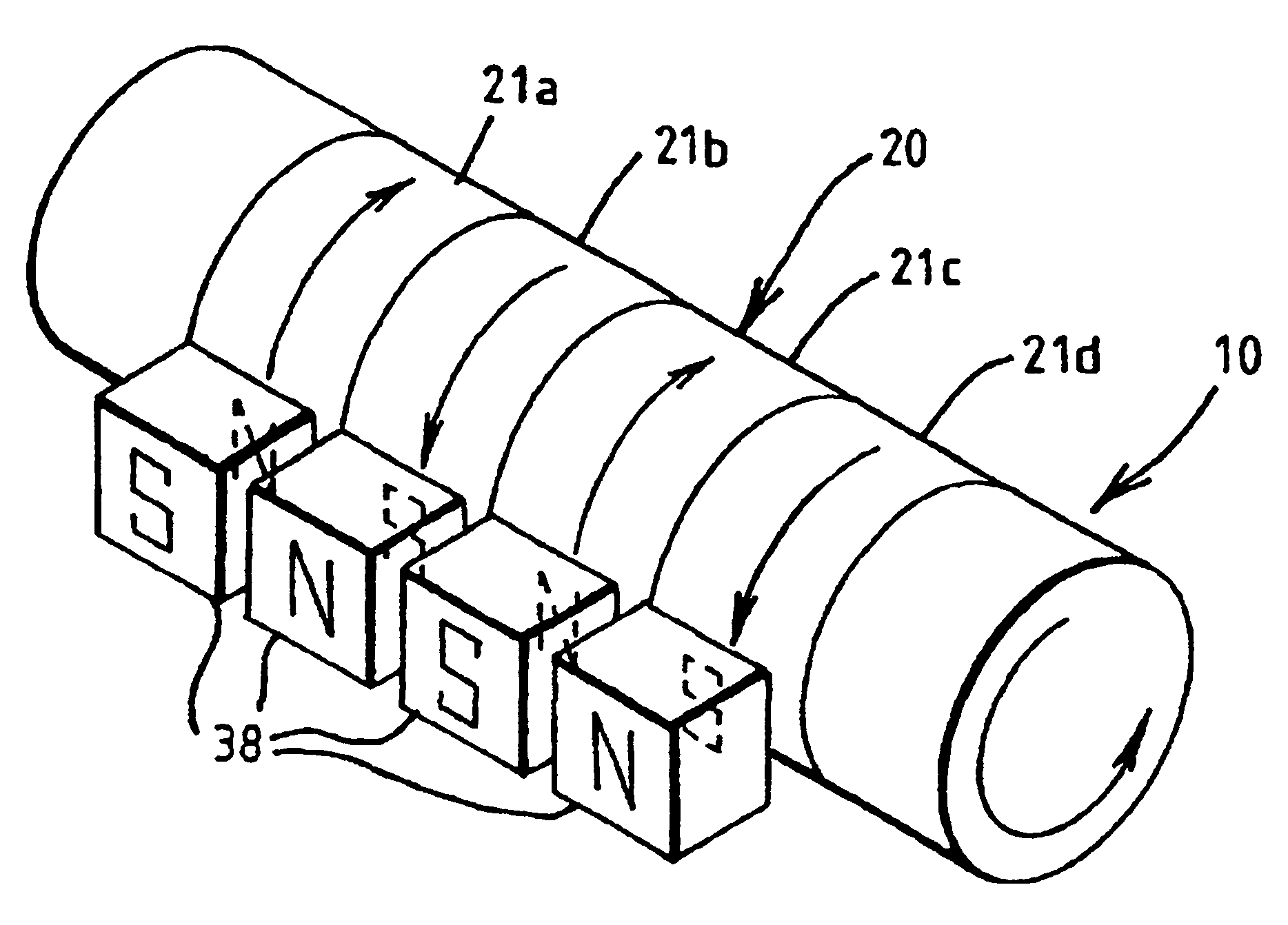
Magnetising arrangements for torque/force sensor
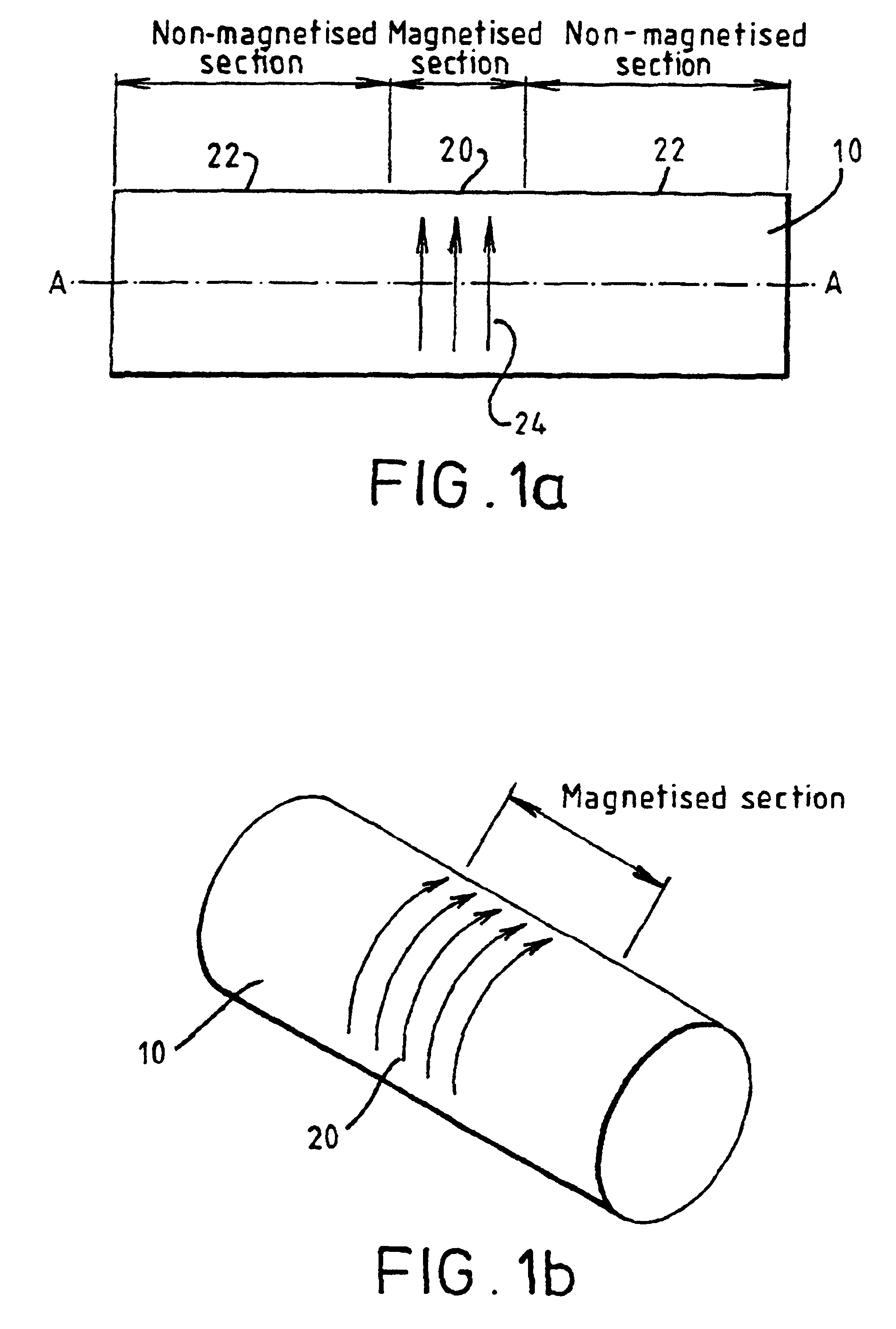
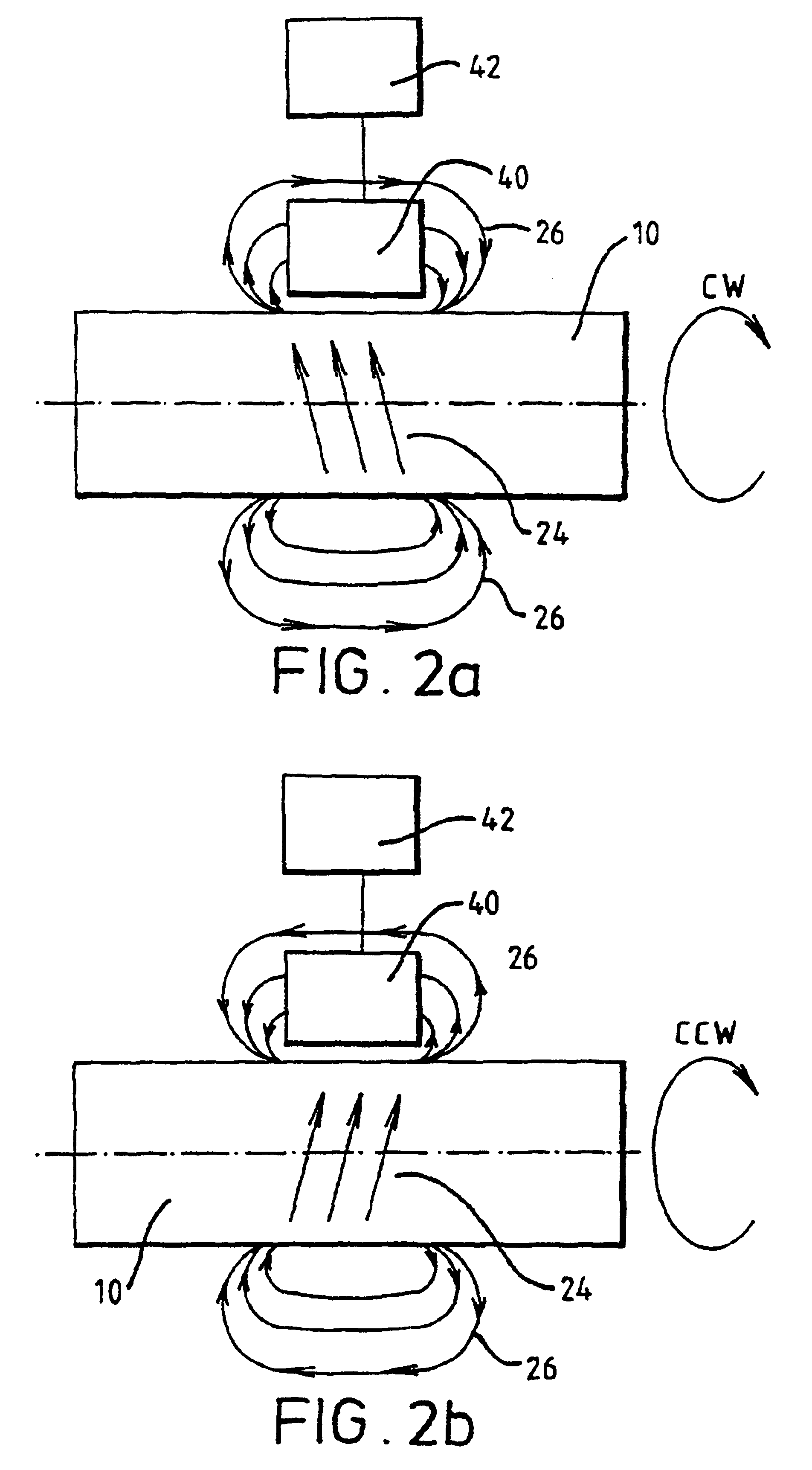
A magnetoclastic transducer for sensing a torque in a shaft (150) is formed by circumferentially magnetising a magnetisable, integral portion (156) of the shaft. To assist in the emanation of a flux-dependent torque, the transducer element portion (156) of the shaft may have further circumferentially magnetised portions (154, 158) to each side. These further portions (154, 158) are of opposite polarity magnetisation to that of the transducer element (156). The external magnetic flux emanated by the transducer (156) is a function of torque and is detectable by a magnetic field sensor (160). An alternative means for the same purpose is to provide the transducer element at a portion (172) of the shaft (170) having an integral annular section of raised profile projecting beyond adjoining portions of the shaft. The shaft may be provided with a series of circumferentially magnetised portions of alternating polarity. A number of ways of achieving circumferential magnetisation are described, together with other directions such as axial. A shaft having the whole or an integral portion of it magnetised can also be used to provide a force transducer sensitive to bending moment induced in the shaft by a force to be measured.
Owner:ABAS
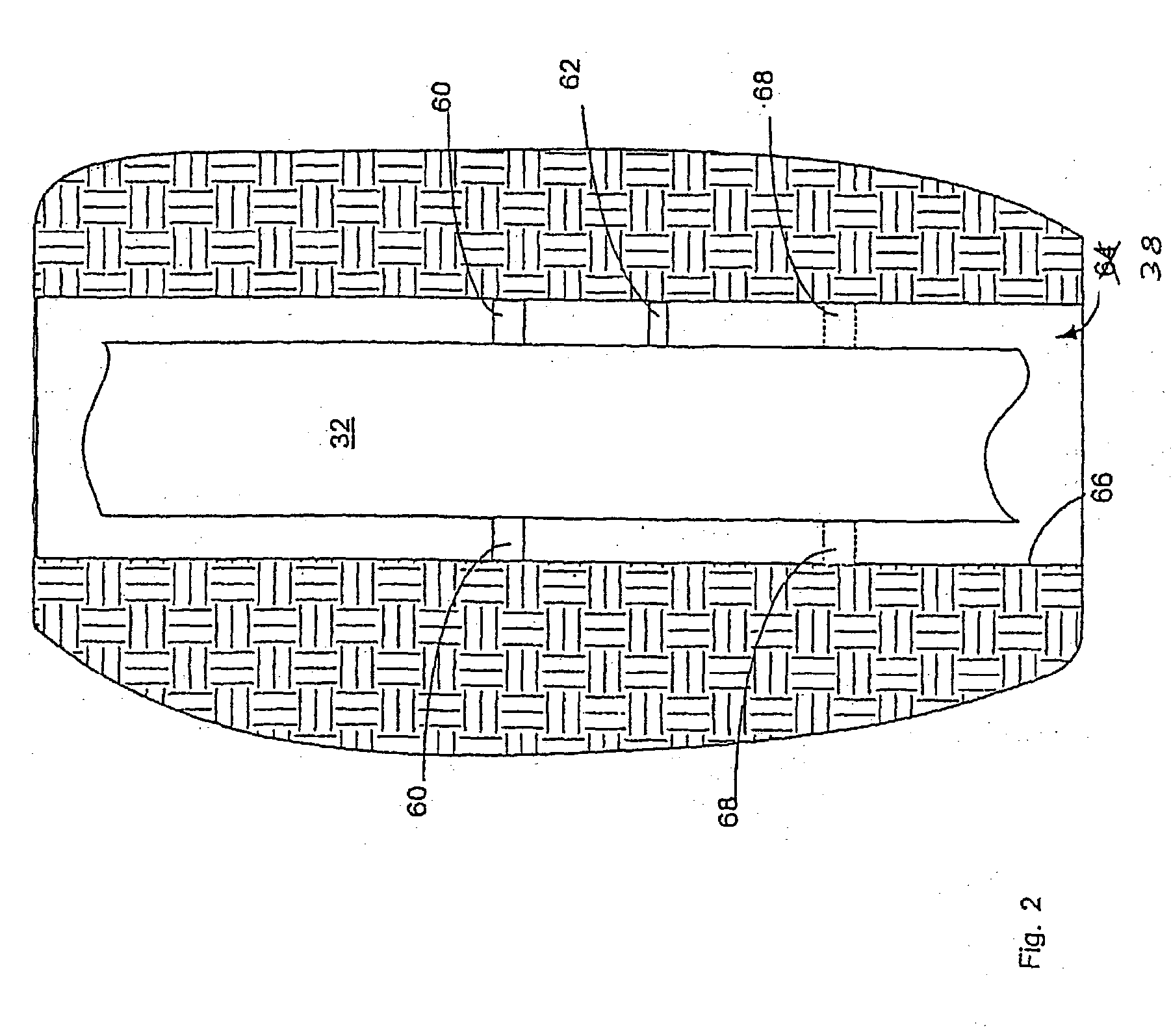
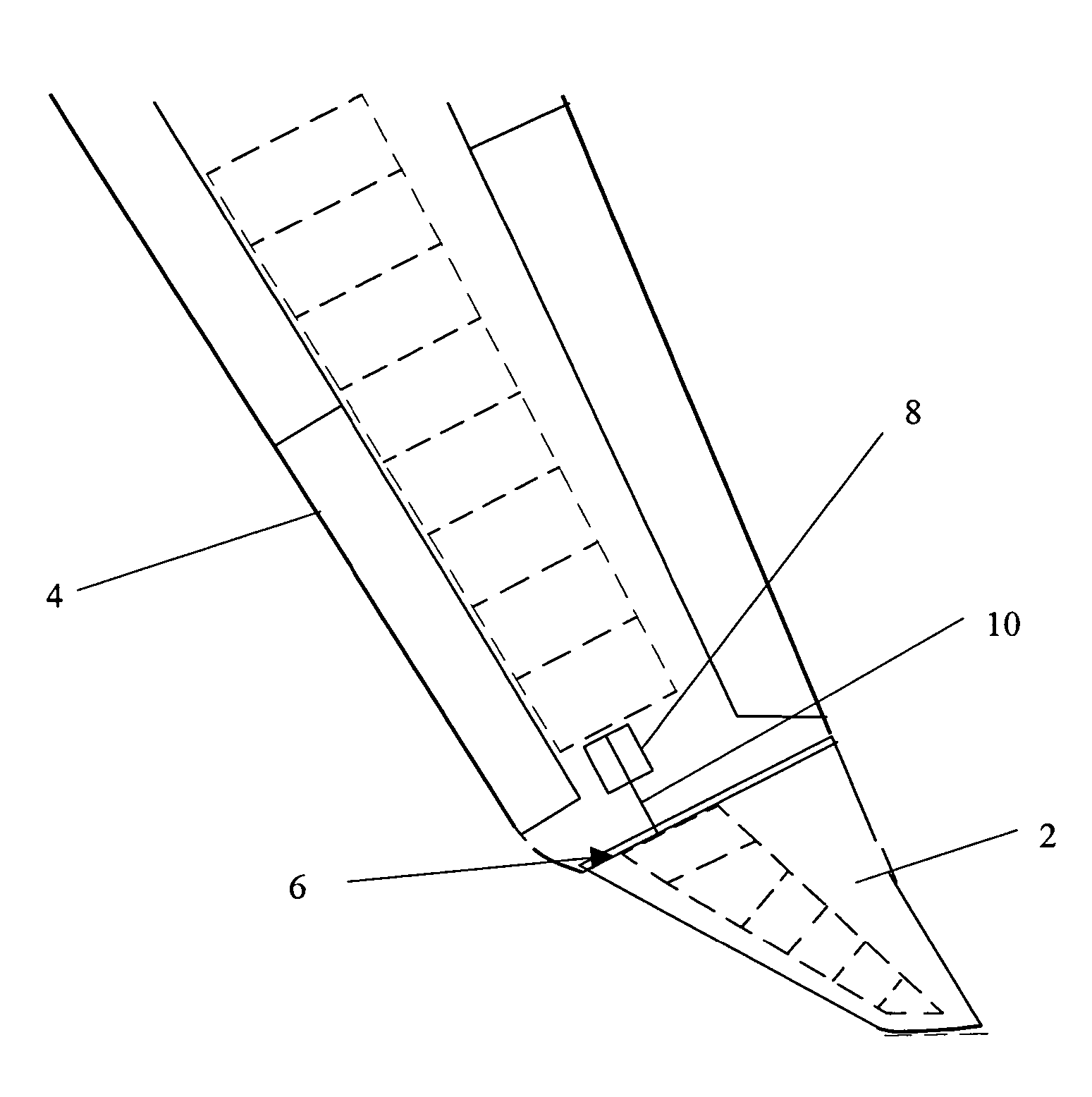
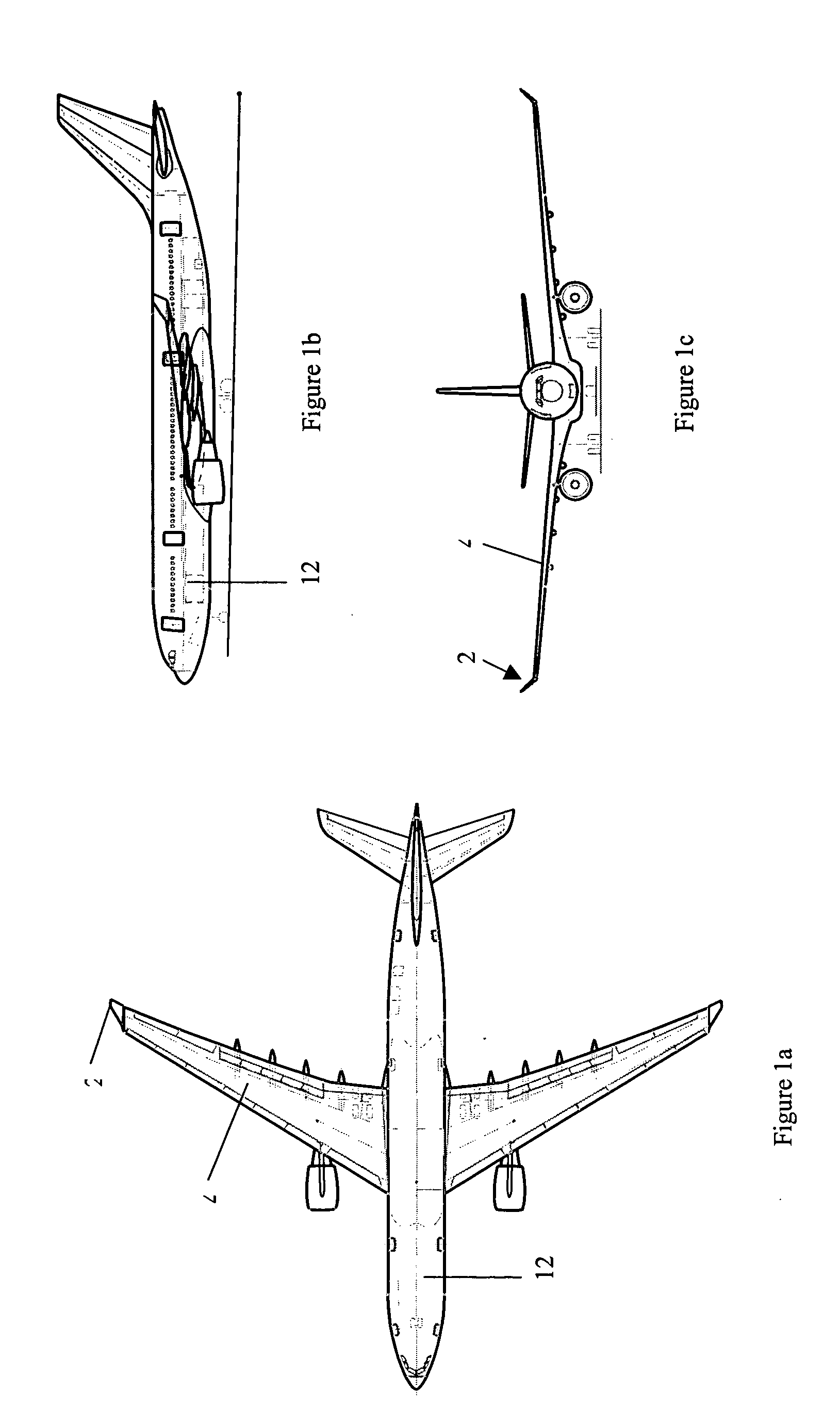
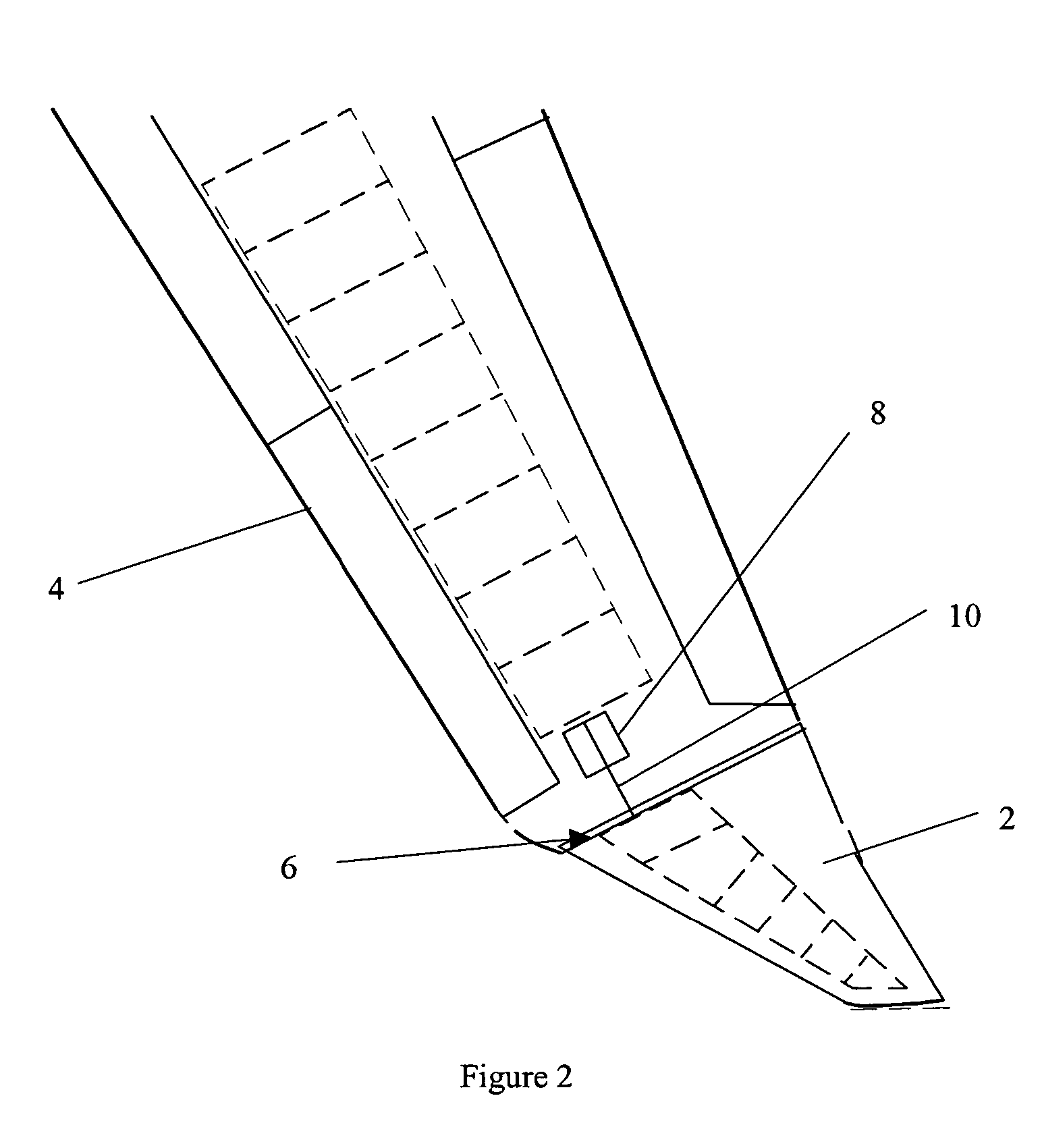
Wing tip device
ActiveUS7275722B2Reduce the total massCareful designInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsHigh loadAirplane
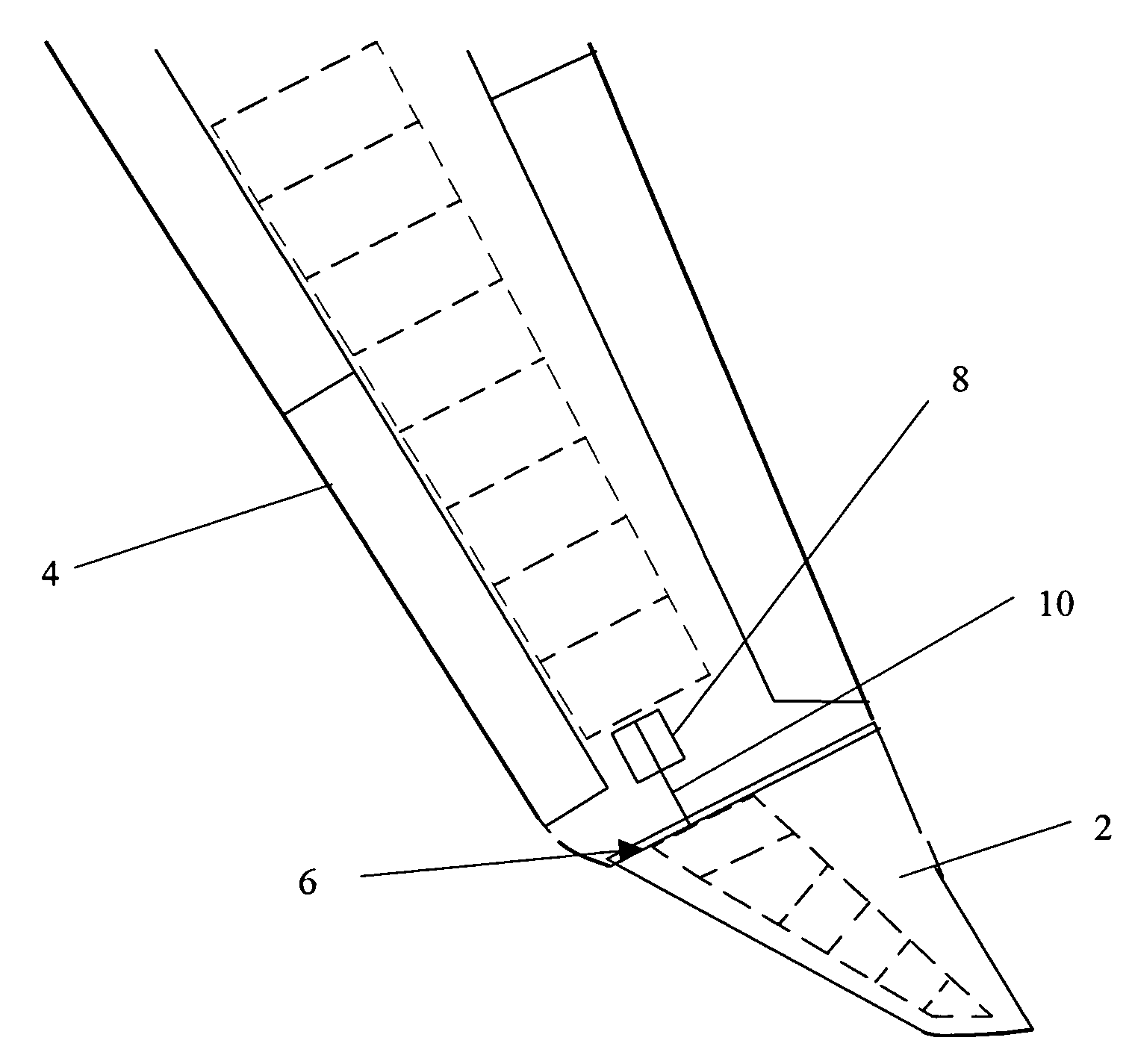
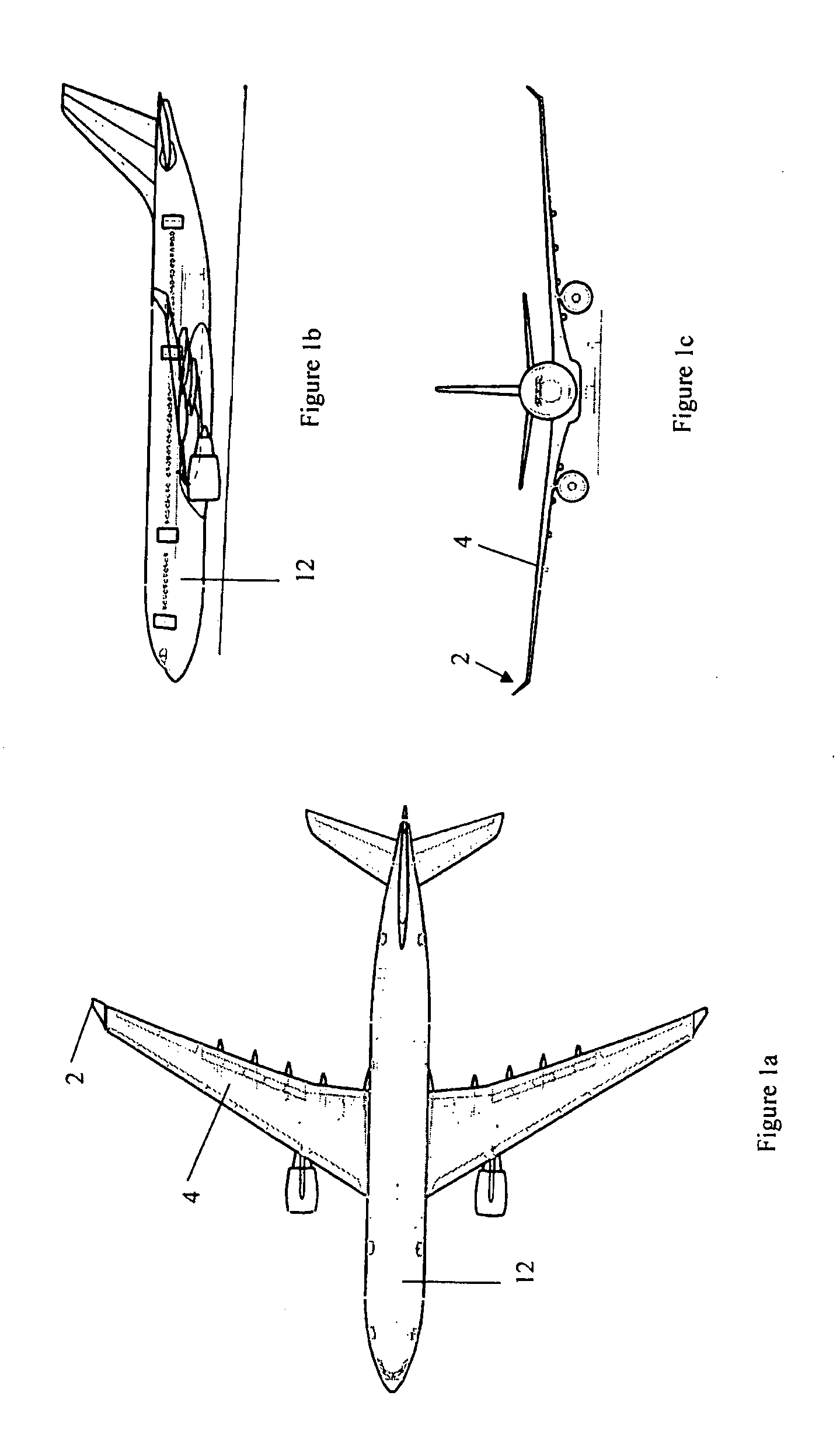
An aircraft comprises a wing tip device, for example a winglet, a raked-tip device, a wing tip fence or a planar wing extension, mounted in the region of the tip of a wing on the aircraft. The wing tip device is rotatably moveable between a first position and a second position, in which the upward lift produced by the wing or the wing tip device is reduced. During flight, the bending moment at the root of the aircraft wing therefore changes in dependence on the position of the wing tip device. The maximum bending moment in the aircraft wing sustained during high-load conditions is thereby reduced, allowing the structural mass of the aircraft to be reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
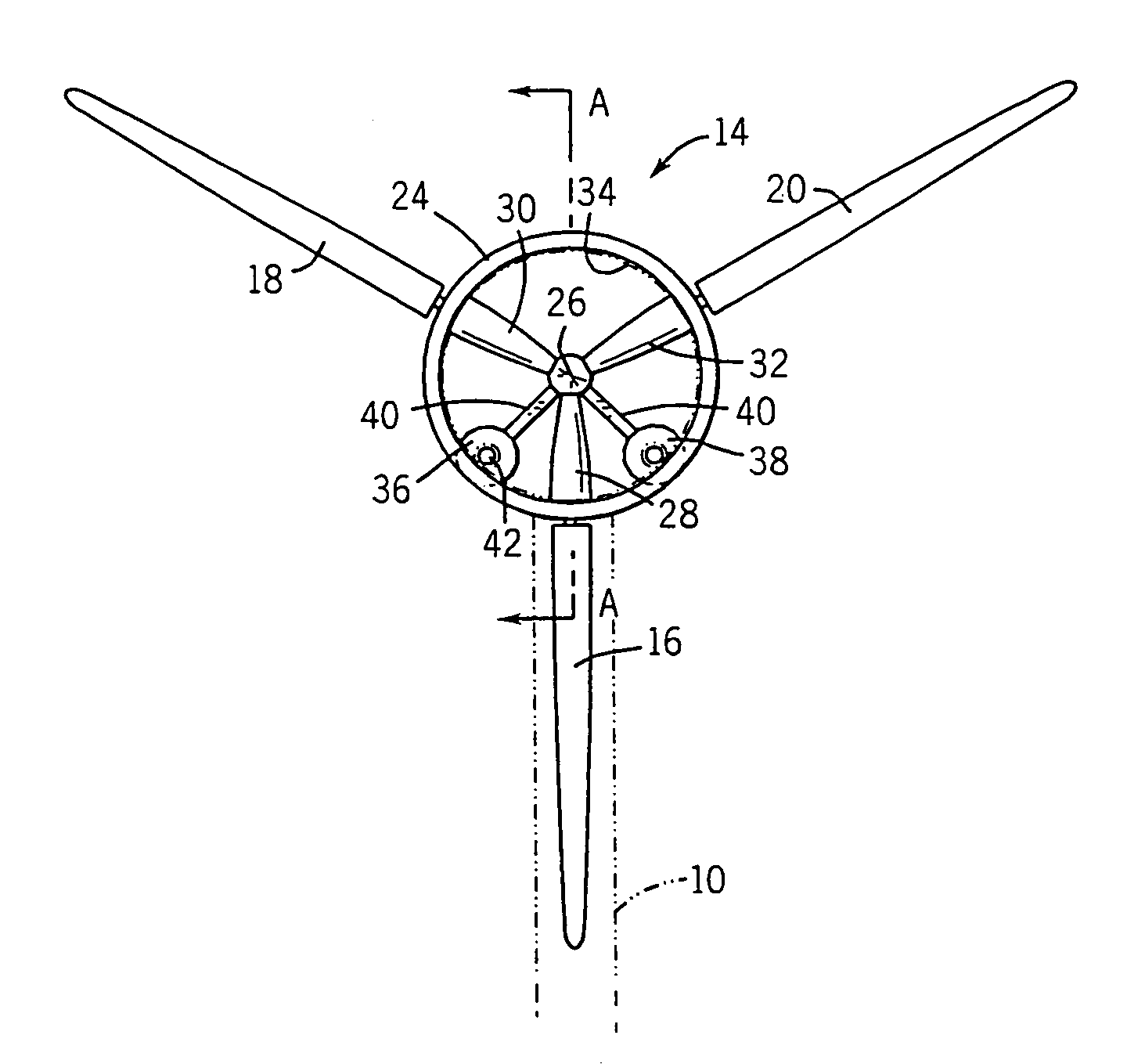
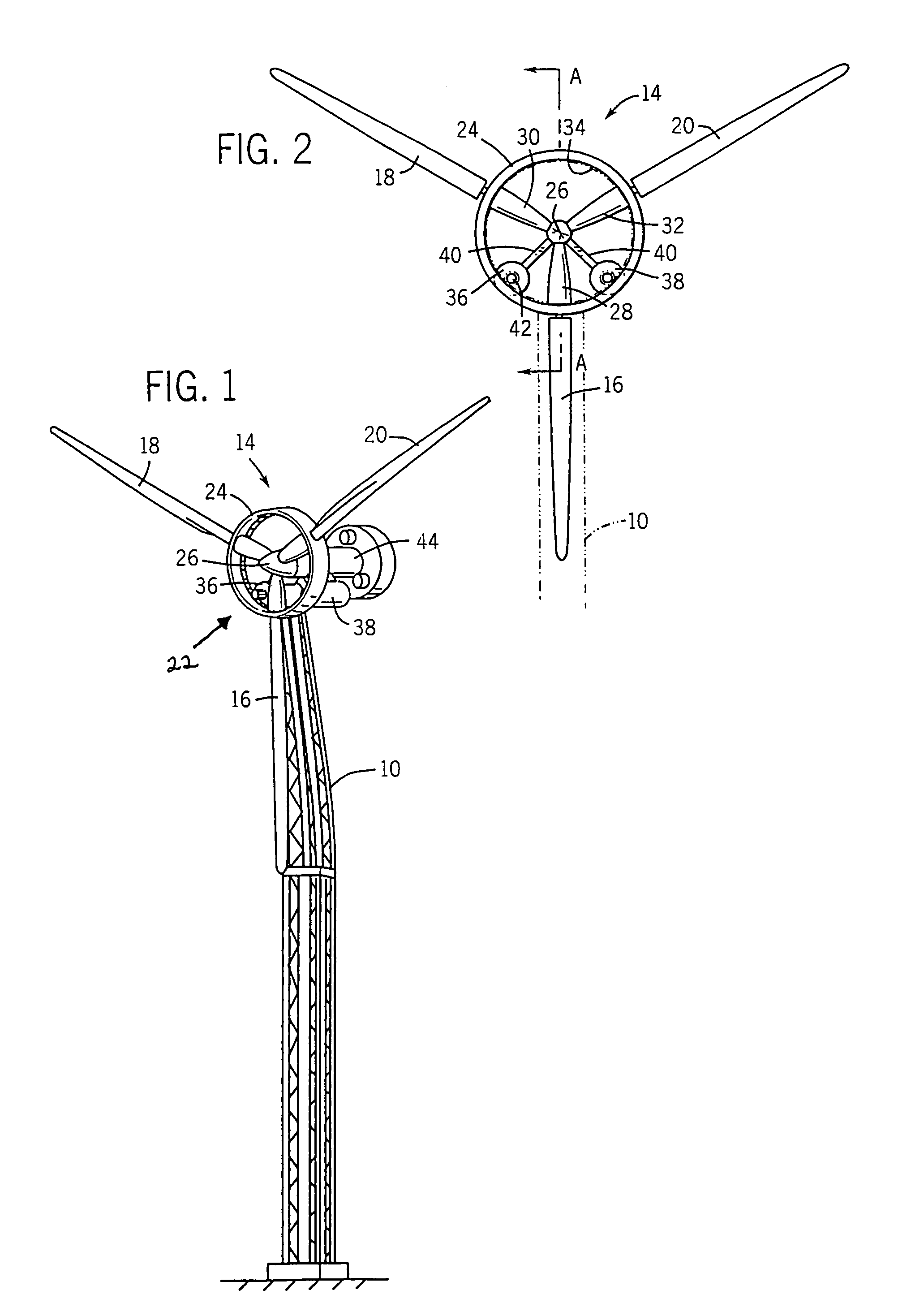
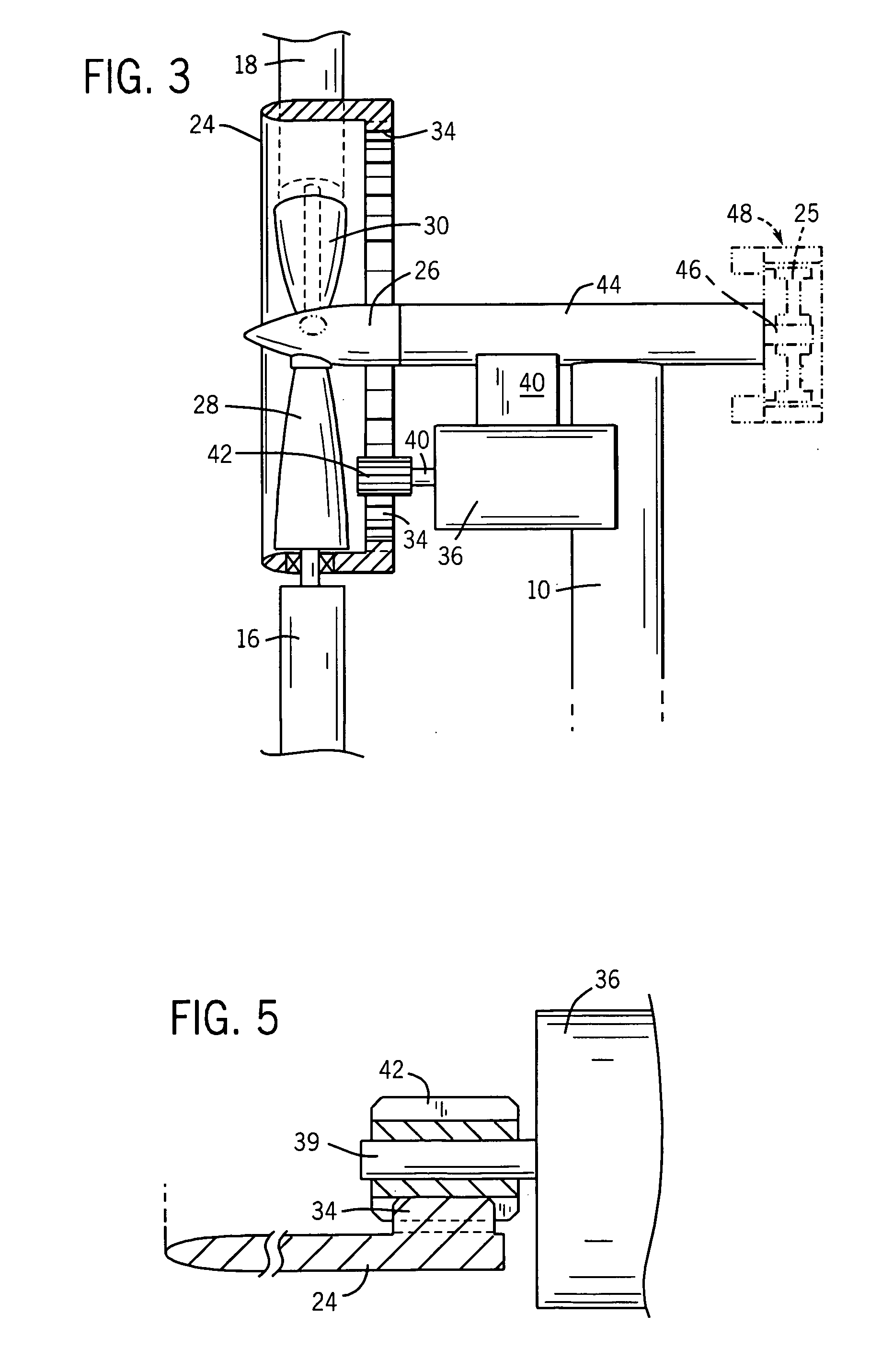
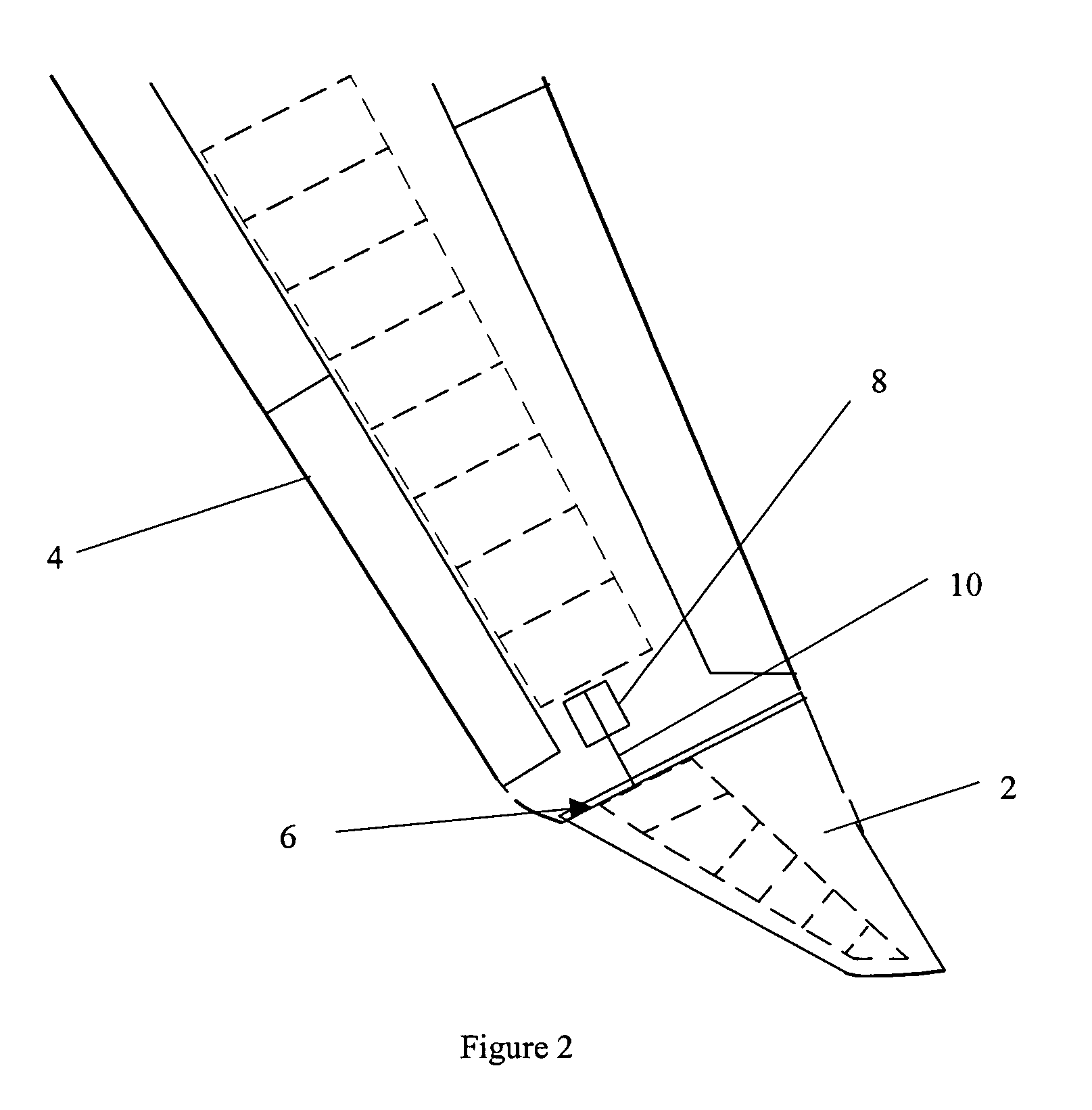
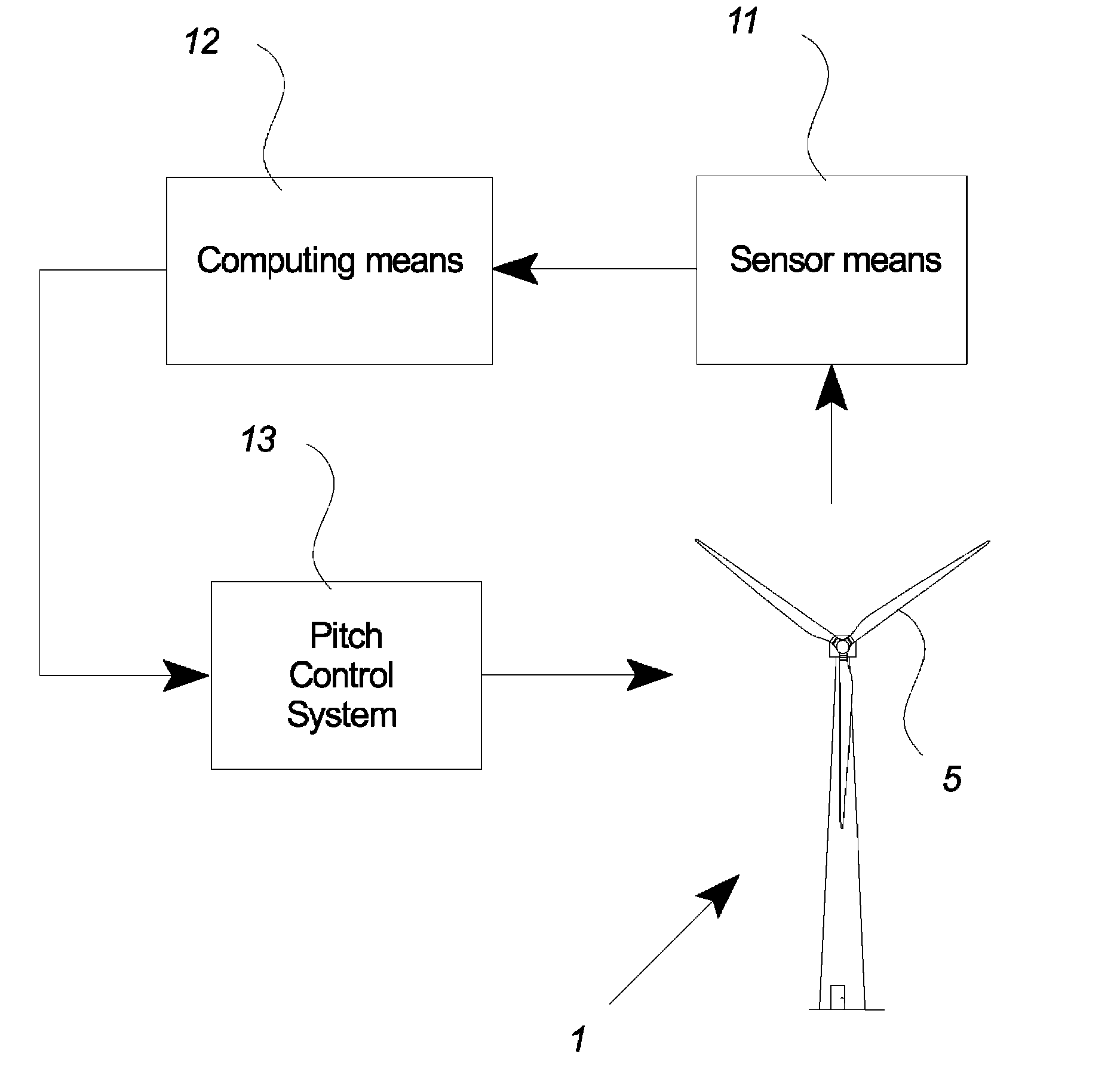
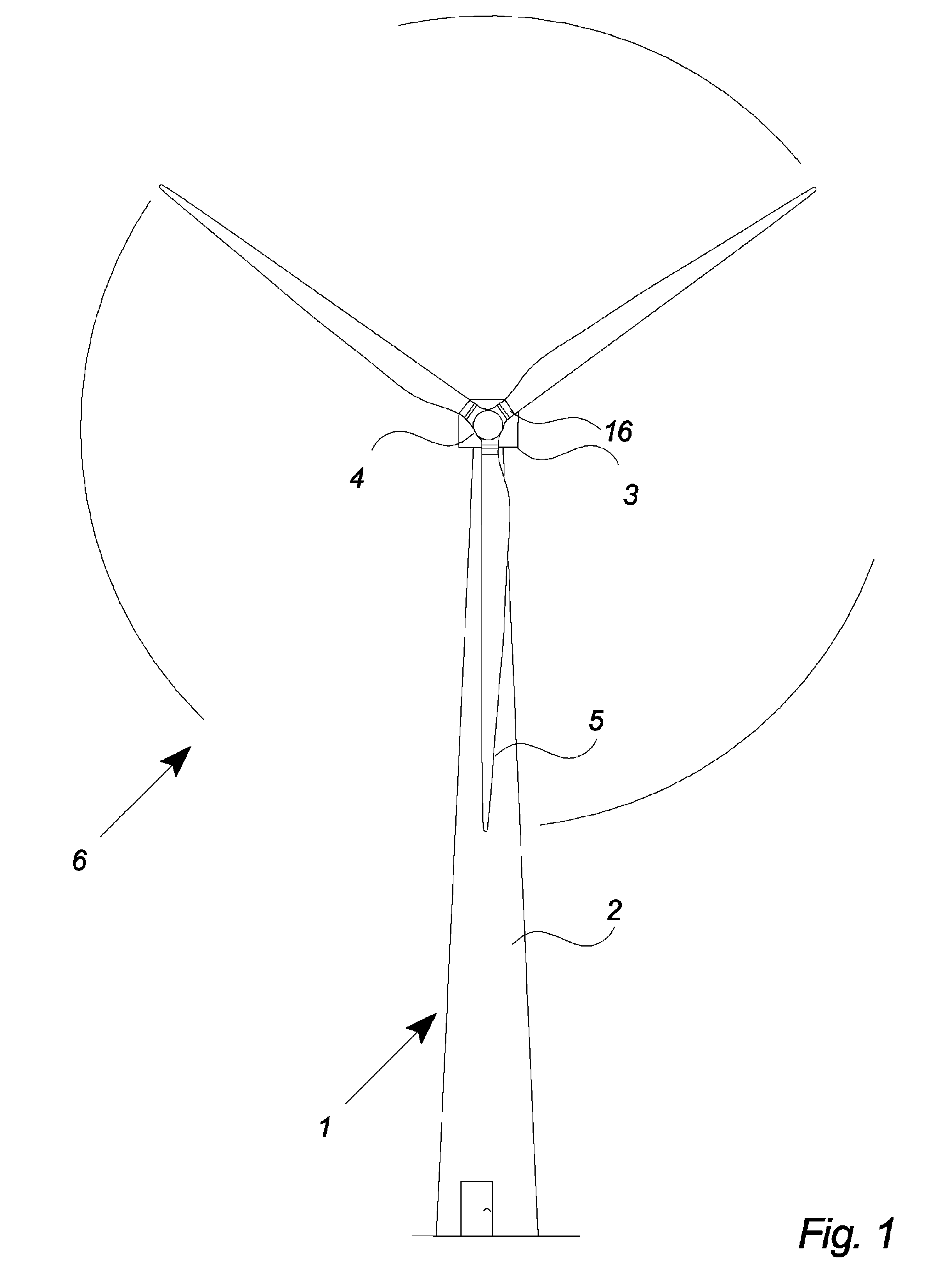
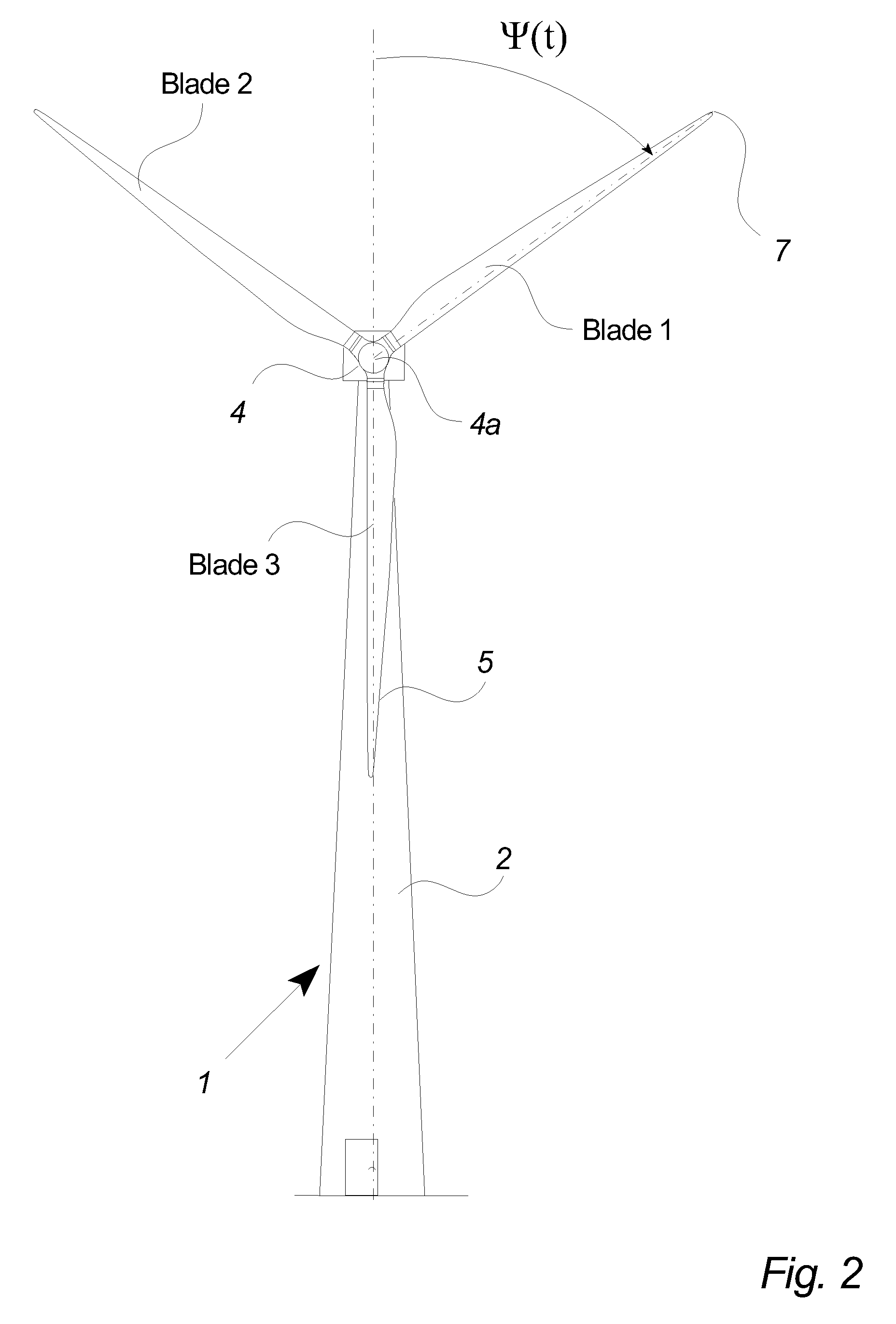
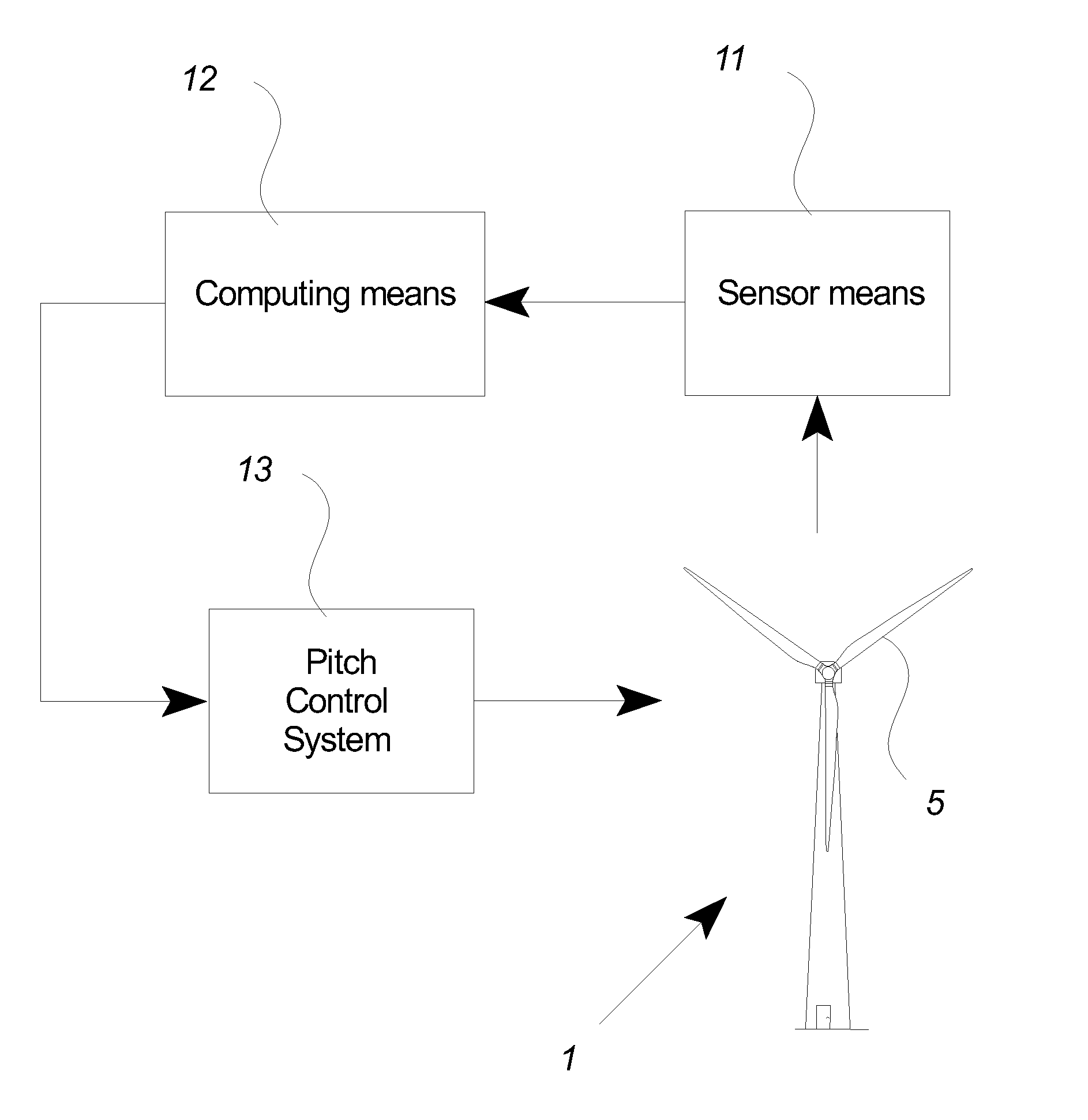
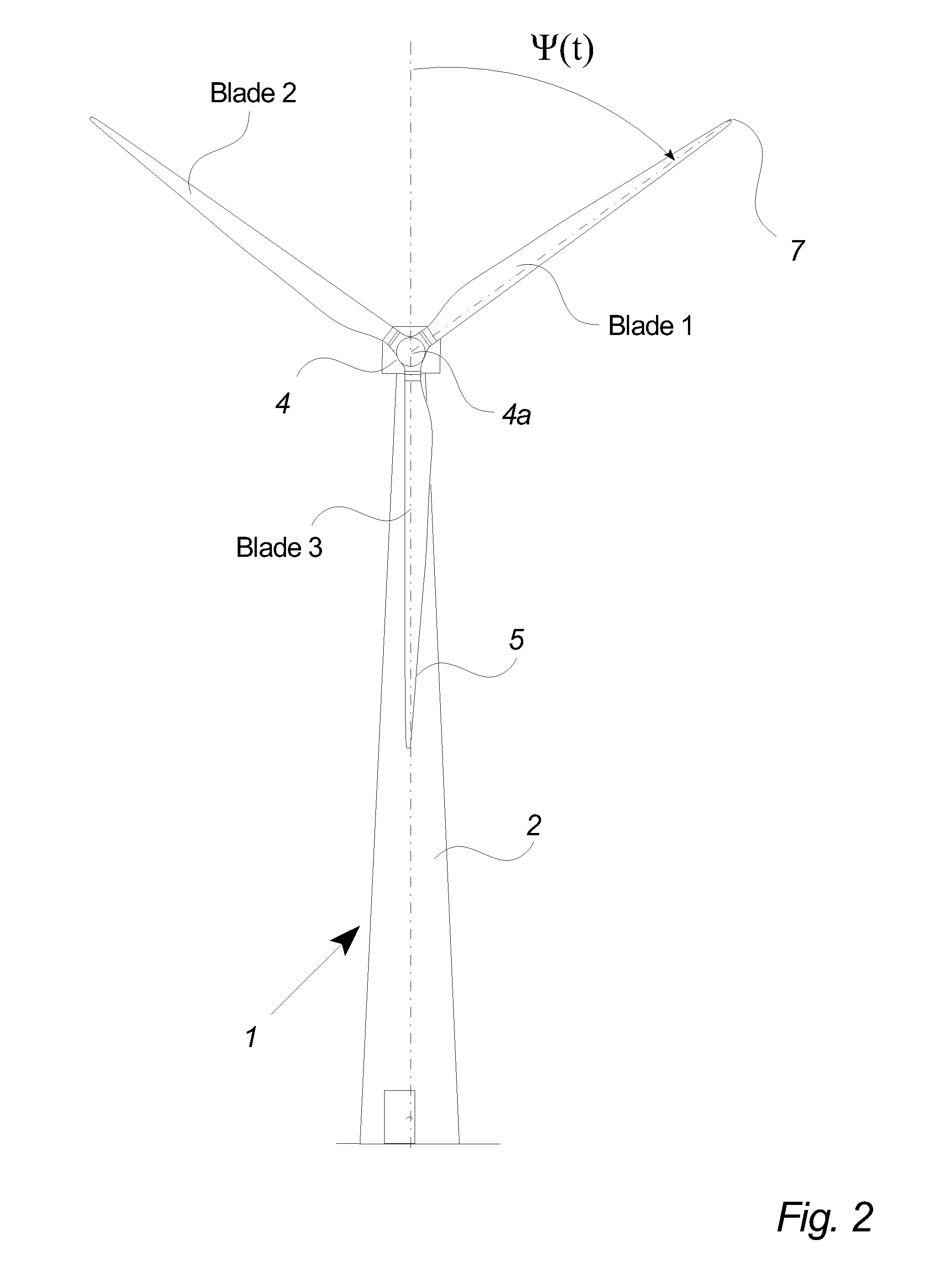
Wind turbine with pitch control arranged to reduce life shortening loads on components thereof
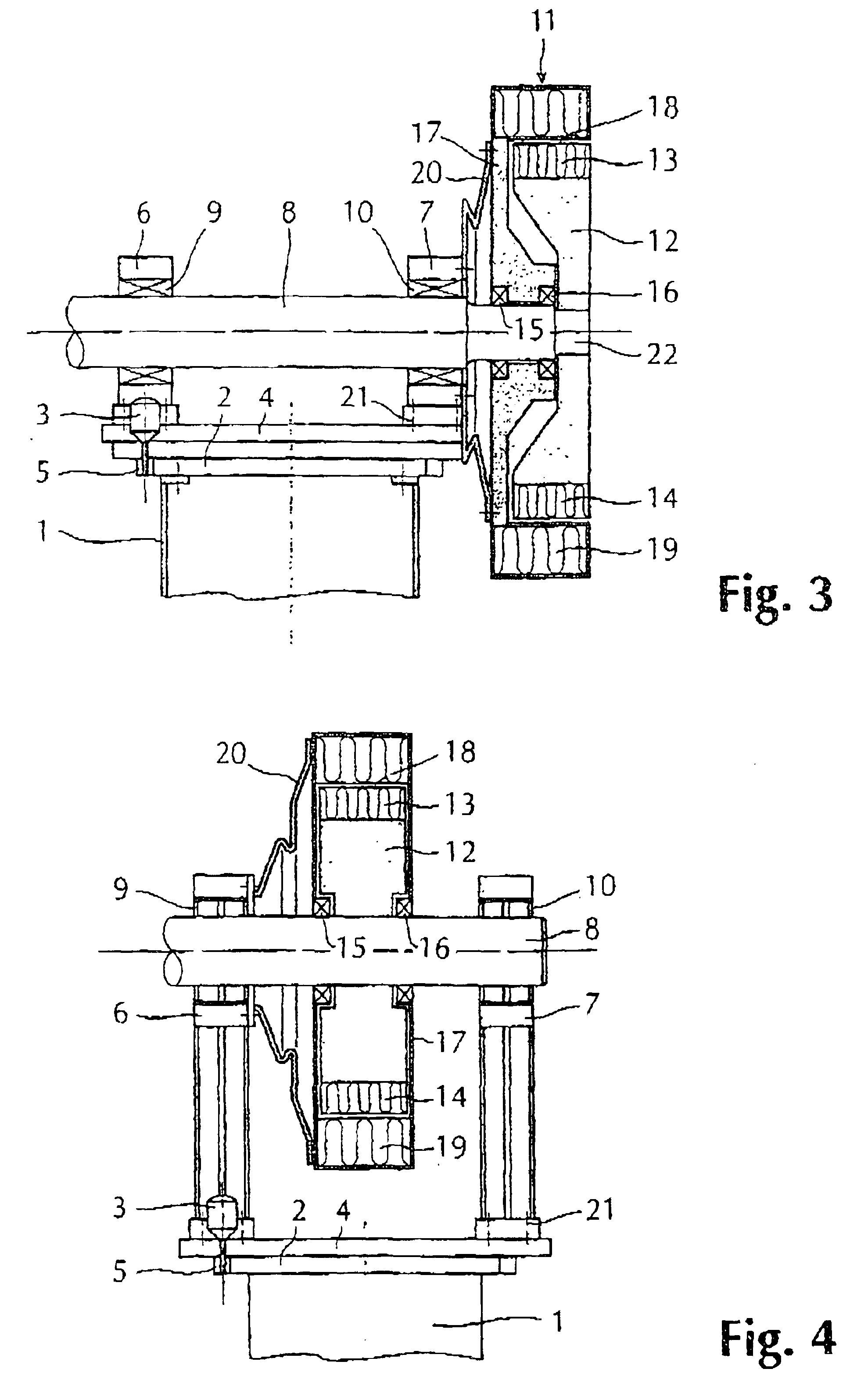
ActiveUS8096762B2Easy to operateReducing the mean bending momentPropellersPump componentsPull forceGravitational force
A wind turbine is presented where the operation lifetime of the main bearing is extended by relieving the main bearing by reducing the mean bending moment on the bearing by means of individual pitch control of the blades of the rotor so as to create an aerodynamic mean tilt moment on the rotor by means of aerodynamic forces on the blades, the tilt moment at least partly counteracting the bending moment caused by the overhang load forces on the main bearing from the gravitational pull on the rotor mass.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Low closure force EMI shielding spacer gasket
InactiveUS6121545AEnhance the imageEnsure electrical continuityEngine sealsScreening gaskets/sealsEdge surfaceBending moment
An EMI shielding spacer gasket assembly for interposition under a predetermined compressive load within an electronics enclosure between a first surface and an oppositely-disposed second surface of the enclosure. The assembly includes a frame member and an electrically conductive, elastomeric member extending along at least a portion of the perimeter of the frame member as retained on a corresponding peripheral edge surface thereof. The elastomeric member has an outboard side which is compressible axially under the compressive load for providing an electrically conductive pathway between the surfaces of the enclosure. In an uncompressed orientation, the outboard side of the elastomeric member exhibits elongate upper and lower bearing portions which are disposed at a spaced-apart radial distance from the frame member to define a corresponding bending moment arm. Each of the bearing portions is angularly deflectable relative to the moment arm to effect the compression of the elastomeric member under a relatively low compressive load.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Measurement transducer of vibration-type
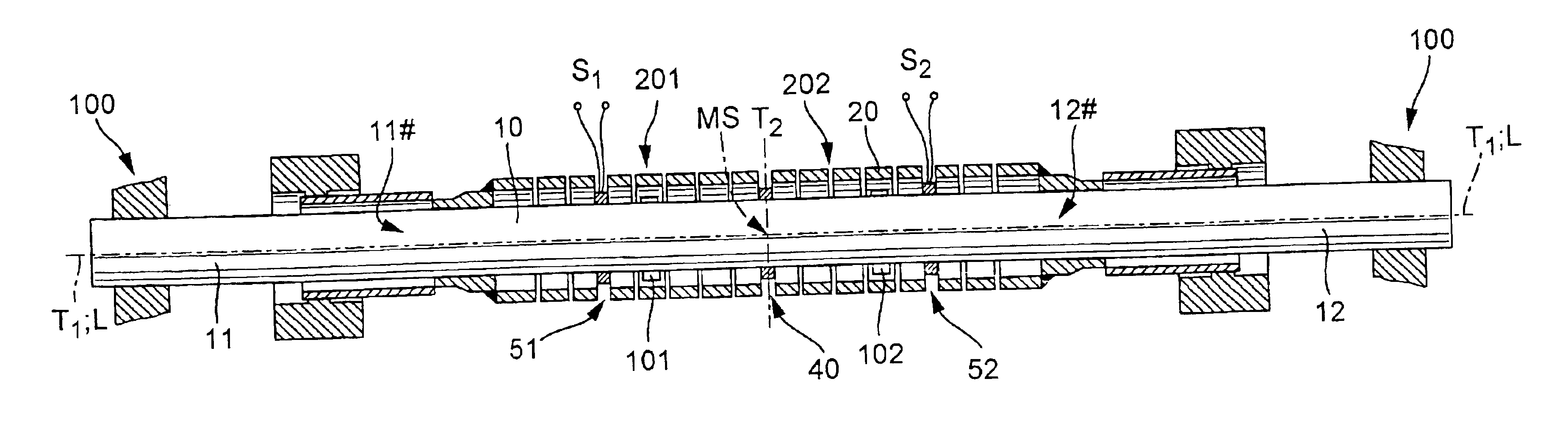
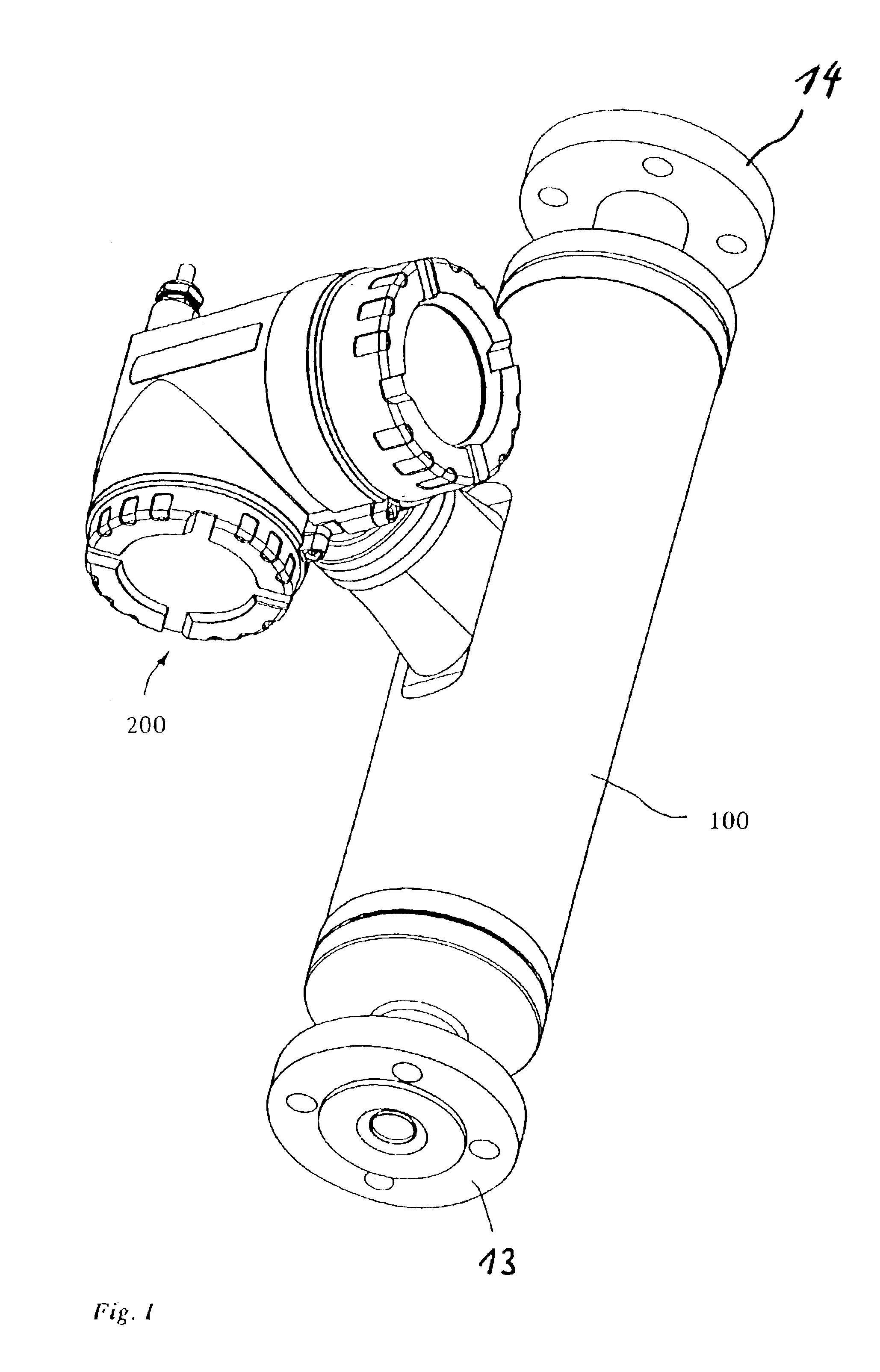
ActiveUS20070119264A1Improve balanceReduce quality problemsDirect mass flowmetersCantilevered beamCoupling
The measurement transducer includes: A measuring tube vibrating at least at times during operation and serving for the conveying of a medium, wherein the measuring tube communicates with a pipeline via an inlet tube piece at an inlet end and an outlet tube piece at an outlet end; a counteroscillator, which is affixed to the measuring tube on the inlet end to form a first coupling zone and affixed to the measuring tube on the outlet end to form a second coupling zone; and a first cantilever for producing bending moments in the inlet tube piece and coupled with the inlet tube piece and the measuring tube essentially rigidly in the area of the first coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the inlet tube piece, as well as a second cantilever for producing bending moments in the outlet tube piece and coupled essentially rigidly with the outlet tube piece and the measuring tube in the region of the second coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the outlet tube piece. The measurement transducer of the invention is especially suited also for measuring tubes having large nominal diameters of more than 50 mm.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Windmill
InactiveUS6911741B2Reduce bendabilityImprove bearing capacityEnergy storageWind motor combinationsVertical axisElectric generator
Wind power plant with a wind turbine with a turbine shaft with which a generator shaft, which can be an extension of the turbine shaft, is connected to the rotor (12) of an electric generator. The rotor is radially surrounded by a stator, the turbine shaft is journalled in two bearing housings with bearings arranged on a base at the top of a tower, the base is pivotable around a vertical axis, and a motor is provided to effect the pivoting. The generator shaft is integrated with or rigidly connected to a flexing turbine shaft, the stator and rotor are carried by the generator shaft, to allow the generator to follow the flexing movement of the turbine shaft and the stator is locked against turning by a non-rotatable coupling which transfers substantially no bending moment or axial force acting against the flexing of the turbine shaft due to the bending moment acting on the turbine shaft from its hub, the bearings being provided to allow flexing of the turbine shaft.
Owner:SCAN WIND GROUP
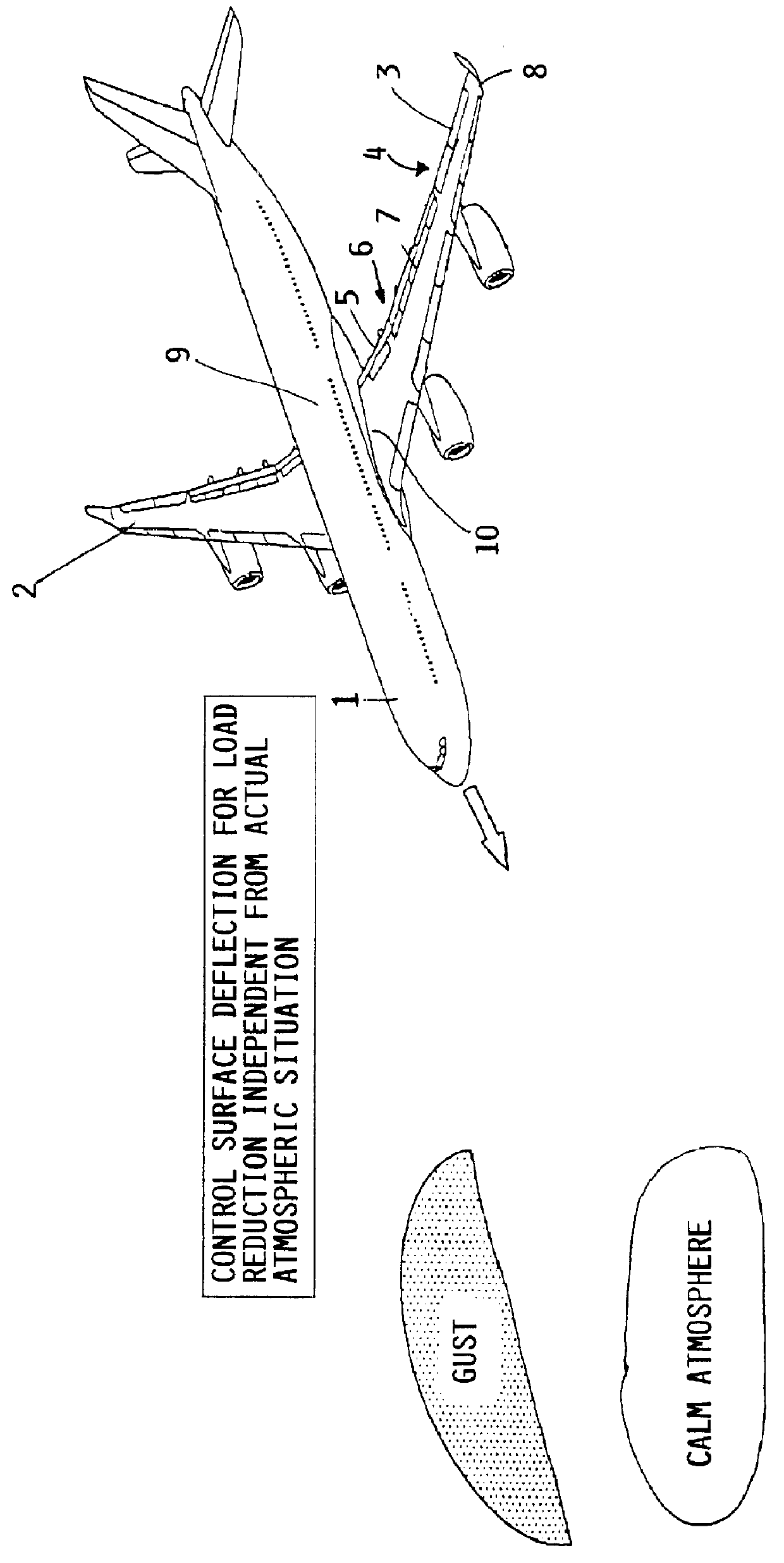
Method of reducing wind gust loads acting on an aircraft
InactiveUS6161801AReduce wing load of wingReduce loadEnergy saving arrangementsActuated automaticallyWing configurationRolling moment
A method of reducing the bending moment effect of wind gust loads acting on the wing of an aircraft involves adjusting the aerodynamic configuration of the wing so as to alter the distribution of lift generated by the wing during phases of flight in which critical wind gusts are expected to occur. Particularly, during climb and descent phases of flight below cruise altitude, the lift generated by outboard portions of the wings is reduced while the lift generated by inboard portions of the wings is increased. Thereby, the 1 g basis load acting on the outboard portions of the wings is reduced, and consequently the total load applied to the outboard portions of the wings, resulting from the 1 g basis load plus the additional wind gust load, is correspondingly reduced. This leads to a reduction of the bending moments effective on the wings, and of any rolling moment effective on the aircraft. The required adjustment of the lift distribution is preferably achieved by deflecting the ailerons of both wings symmetrically upward and / or deflecting the flaps of both wings symmetrically downward during climb and descent. The adjustment of the wing configuration is carried out dependent only on flight parameters such as the altitude, speed and gross weight, and does not require rapid sensing of the occurrence of a wind gust and rapid actuation of control surfaces to try to instantaneously counteract a wind gust as it occurs.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
Method for performing a coplanar connection between a conductor and a contact on an implantable lead
InactiveUS7856707B2Reduce conductor bending momentImprove reliabilityElectrically conductive connectionsInternal electrodesElectrical conductorCoupling
An implantable lead for a medical device with a coplanar coupling for connecting a conductor to a contact reduces conductor bending moments to improve lead reliability. The implantable lead comprises a lead body having a proximal end and a distal end, at least one conductor, at least one contact carried on the proximal end, at least one contact carried on the distal end, and at least one coupling. The lead body has an exterior surface. The conductor is contained in the lead body and extends from the lead proximal end to the distal end. The conductor is also electrically insulated. The contact carried on the proximal end is electrically connected to the conductor. The coupling has a conductor coupling and a contact coupling. The conductor coupling is placed over the conductor and attached to the conductor. The contact coupling exits the lead body and has a weld to connect the contact coupling to the contact. The contact coupling is configured to exit the conductor lumen and mate with the contact while retaining the conductor coplanar to the lead body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
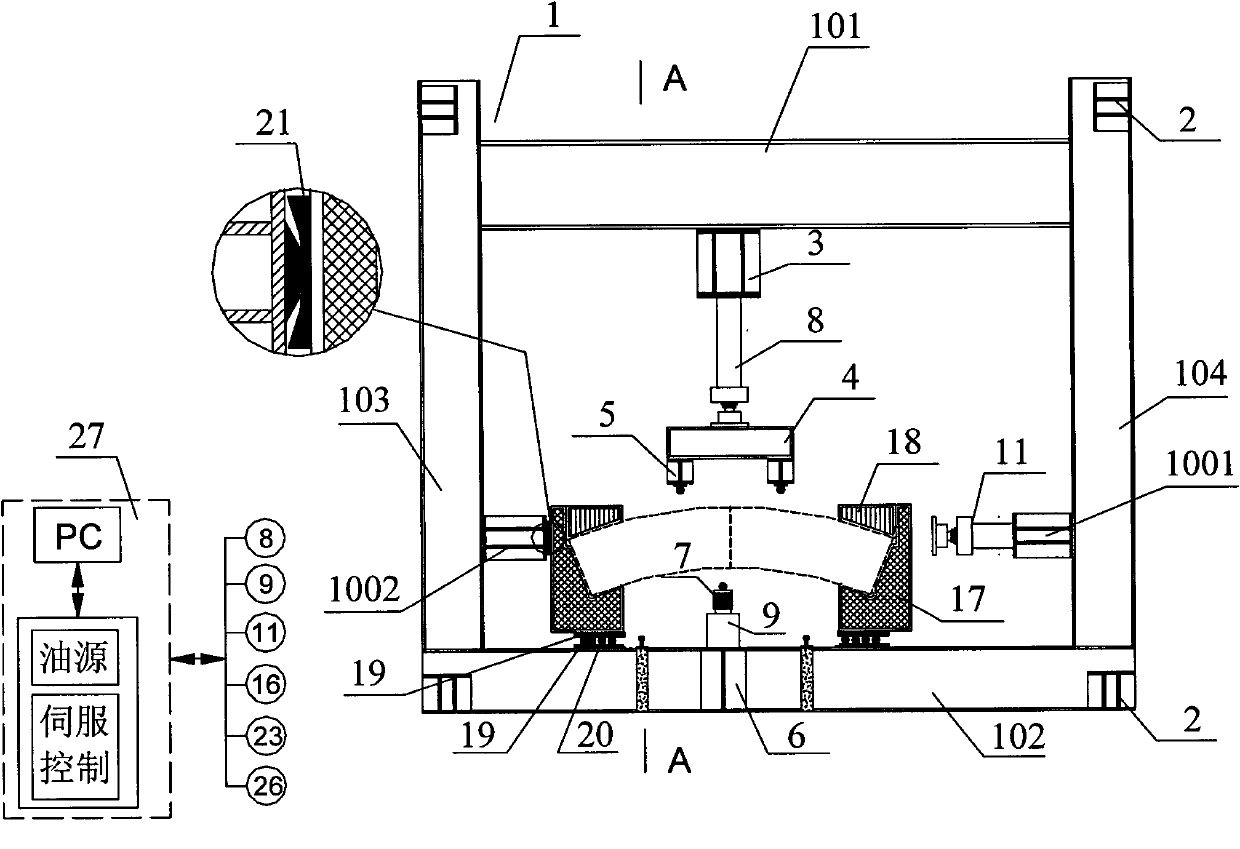
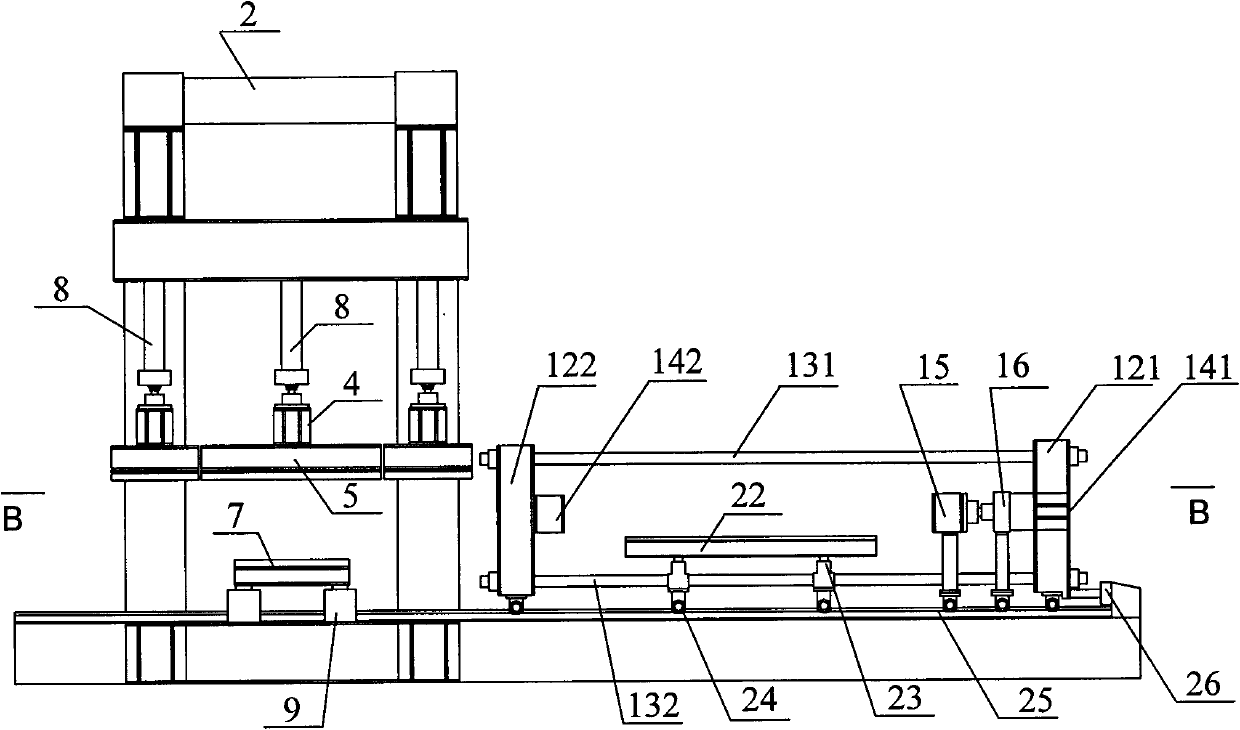
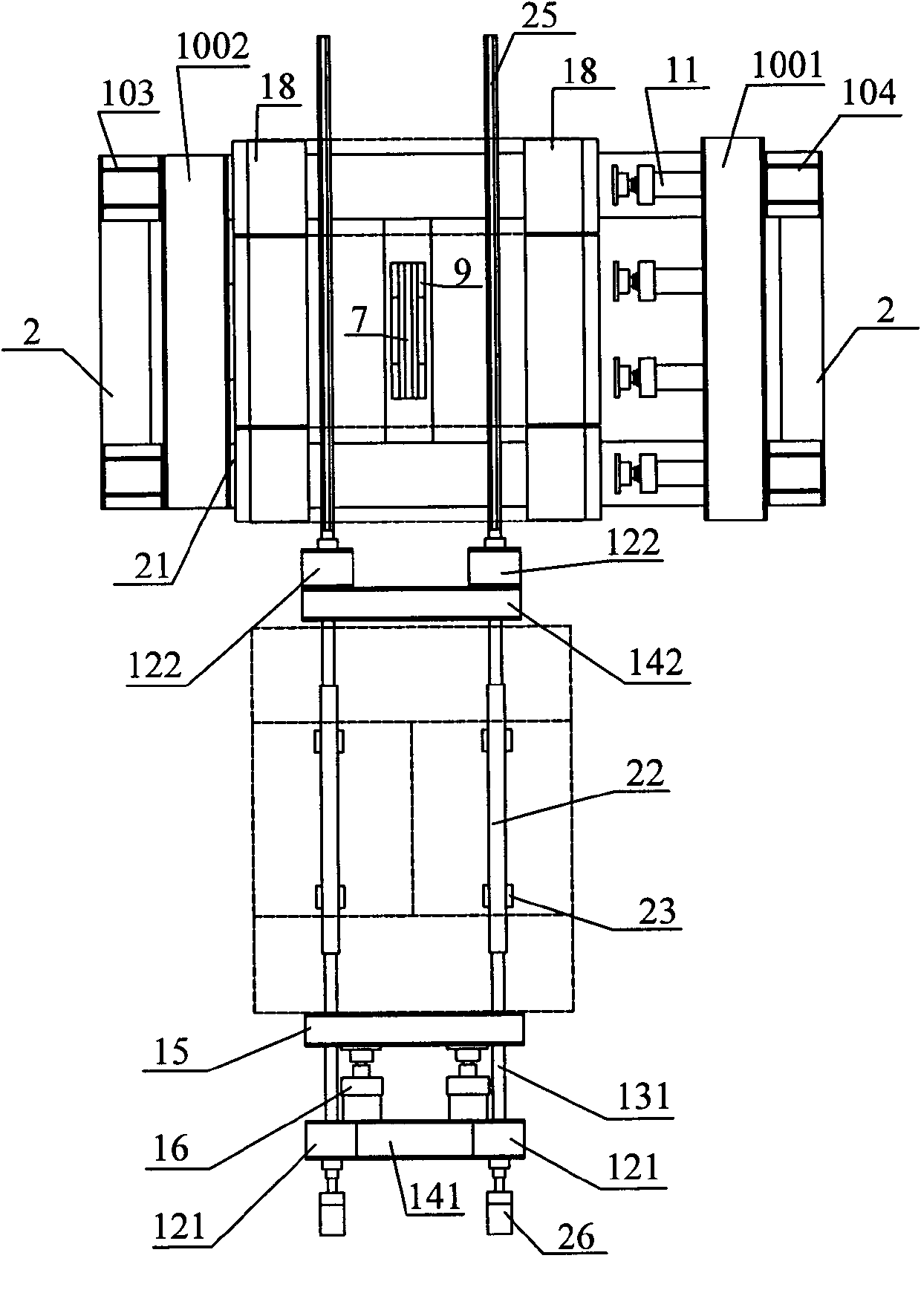
Three-way loading mechanical property test system of multifunctional lining segment joint
ActiveCN102004054AHigh simulationDisplacement boundary conditions are consistentMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesPilot systemModular design
The invention provides a three-way loading mechanical property test system of a multifunctional lining segment joint, which mainly comprises a self-balancing frame sub-system, a loading sub-system, a test-piece support sub-system, a test-piece transporting sub-system, a loading control sub-system and a data acquisition sub-system. The loading sub-system adopts a modular design and can finish a shield tunneling lining segment inter-ring shearing test, a bending moment transferring test, a longitudinal joint corner rigidity test, a longitudinal joint radial shearing test and the like by different combinations. The system of the invention can preferably imitate three-way stress states of the shield tunneling lining segment joint in actual conditions and can finish various different loading modes to obtain mechanical parameters of the shield tunneling lining segment joint and mechanical properties of other similar structures.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Angioplasty stents
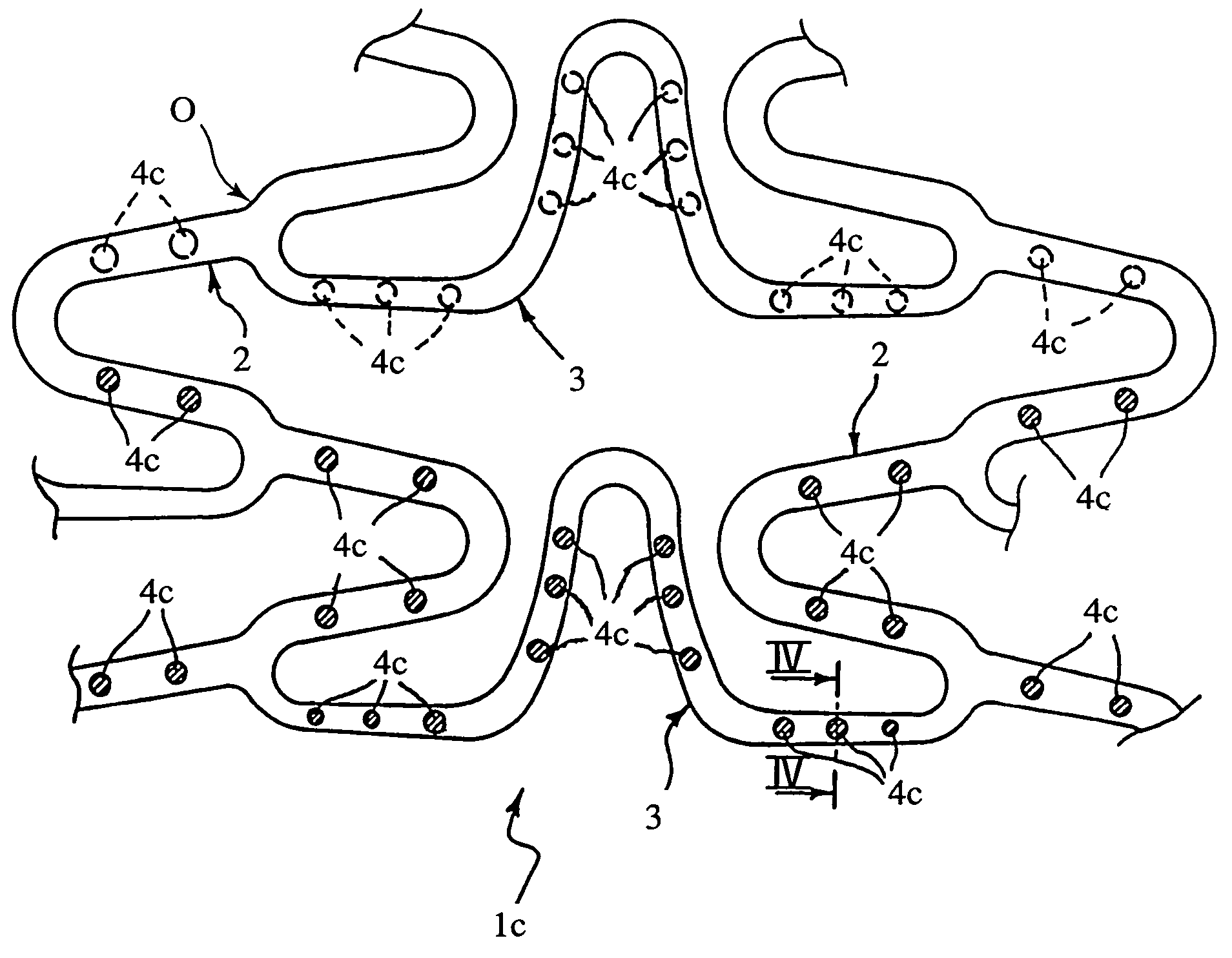
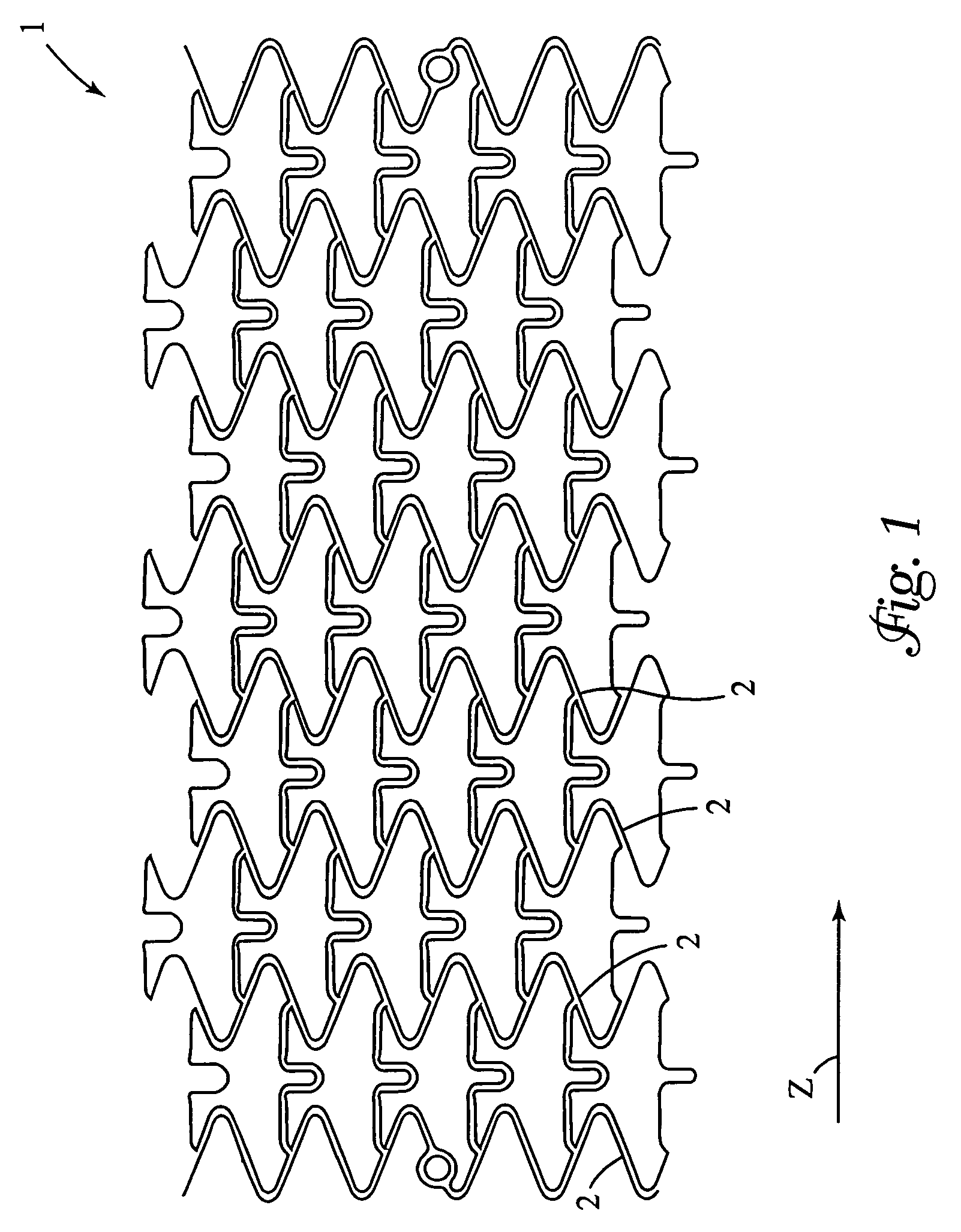
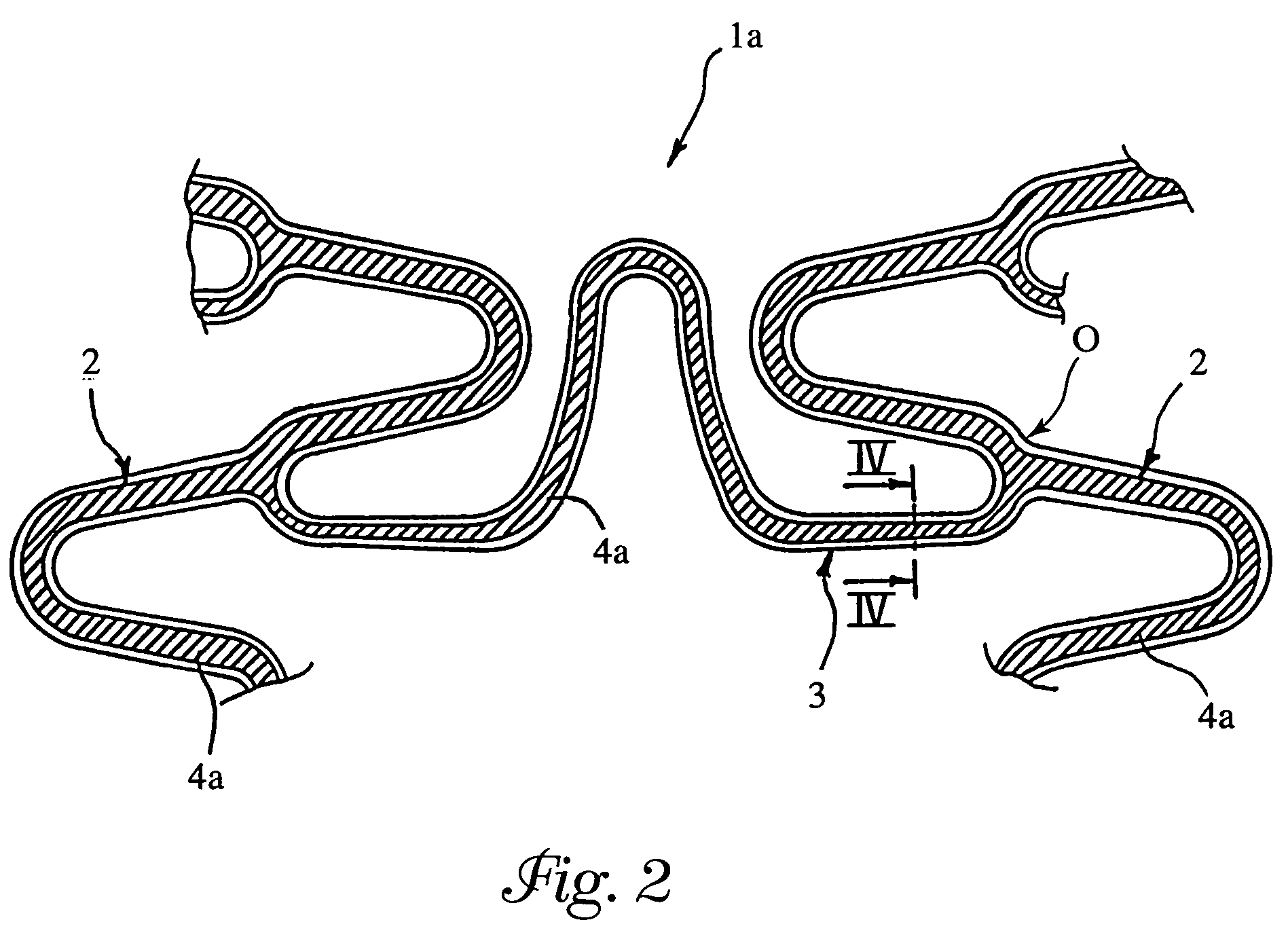
A stent for use at an implant site in a vessel having recesses containing one or more active agents. The stent is a tubular body having a plurality of sinusoidal shaped annular elements and connection elements. The recesses are formed so as to leave substantially unaltered the bending moments of these elements. The recesses may be continuous or discontinuous and may be distributed uniformly or nonuniformly.
Owner:CID CO LTD
Mechanical scoring and separation of strengthened glass
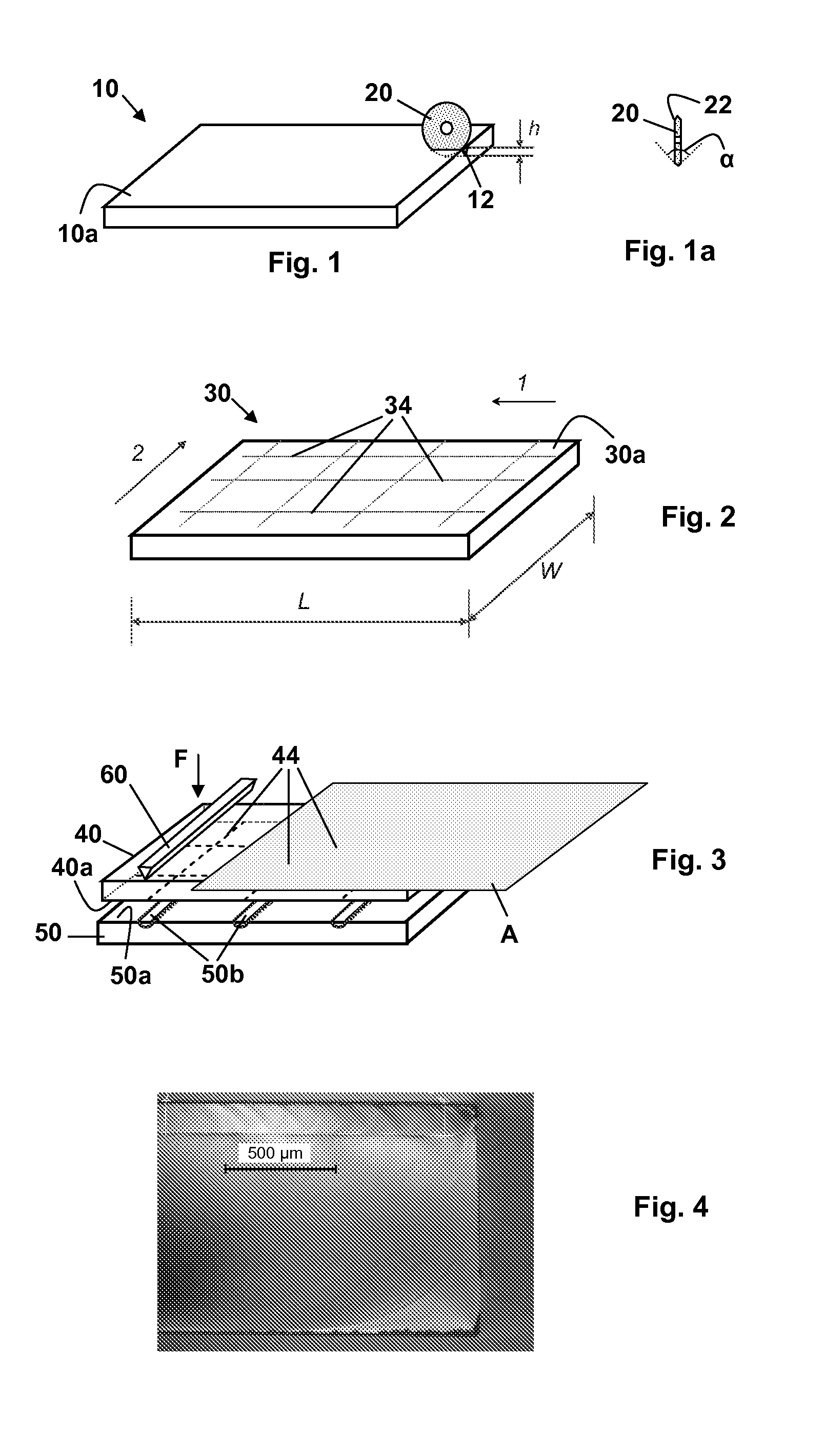
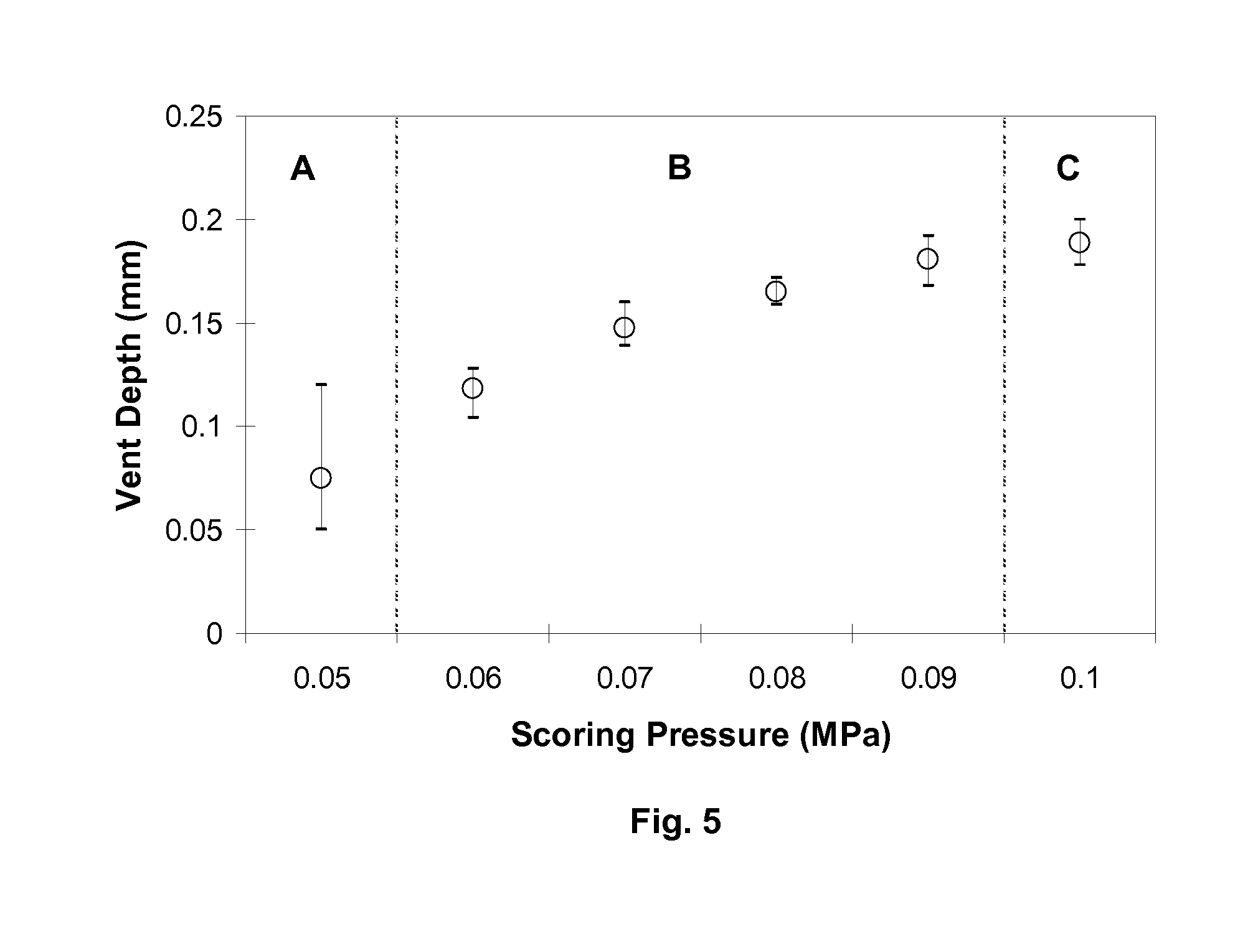
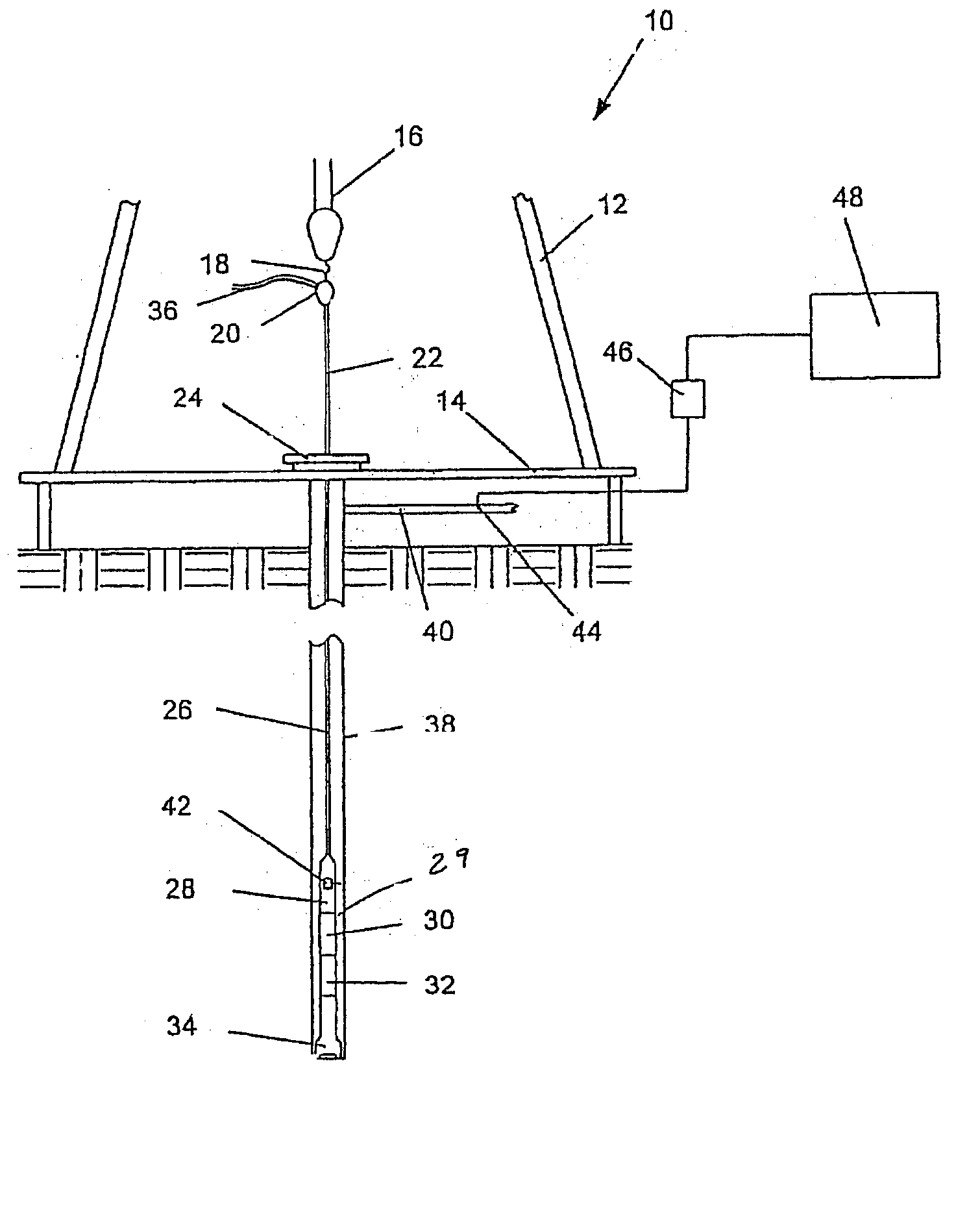
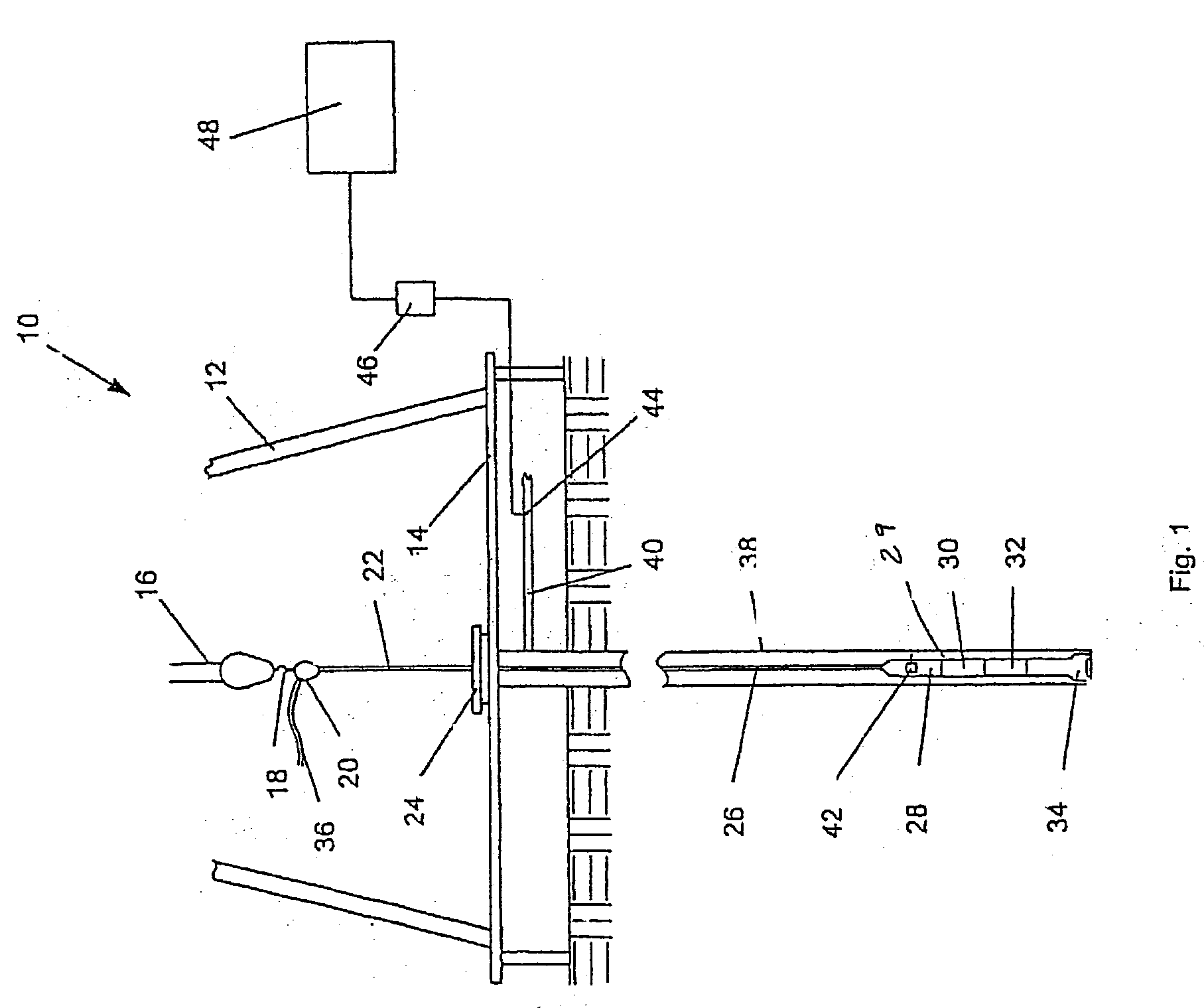
ActiveUS20110226832A1Secure clean sheet separationEasy to adaptFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusLine tubingEngineering
A strengthened glass sheet is separated into undamaged sheet segments by mechanically scribing one or more vent lines of controlled depth into the sheet surface, the depths of the scribed lines being insufficient to effect sheet separation, and then applying a uniform bending moment across the vent lines to effect separation into multiple sheet segments, the vent lines being scribed from crack initiation sites comprising surface indentations formed proximate to the edges of the glass sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
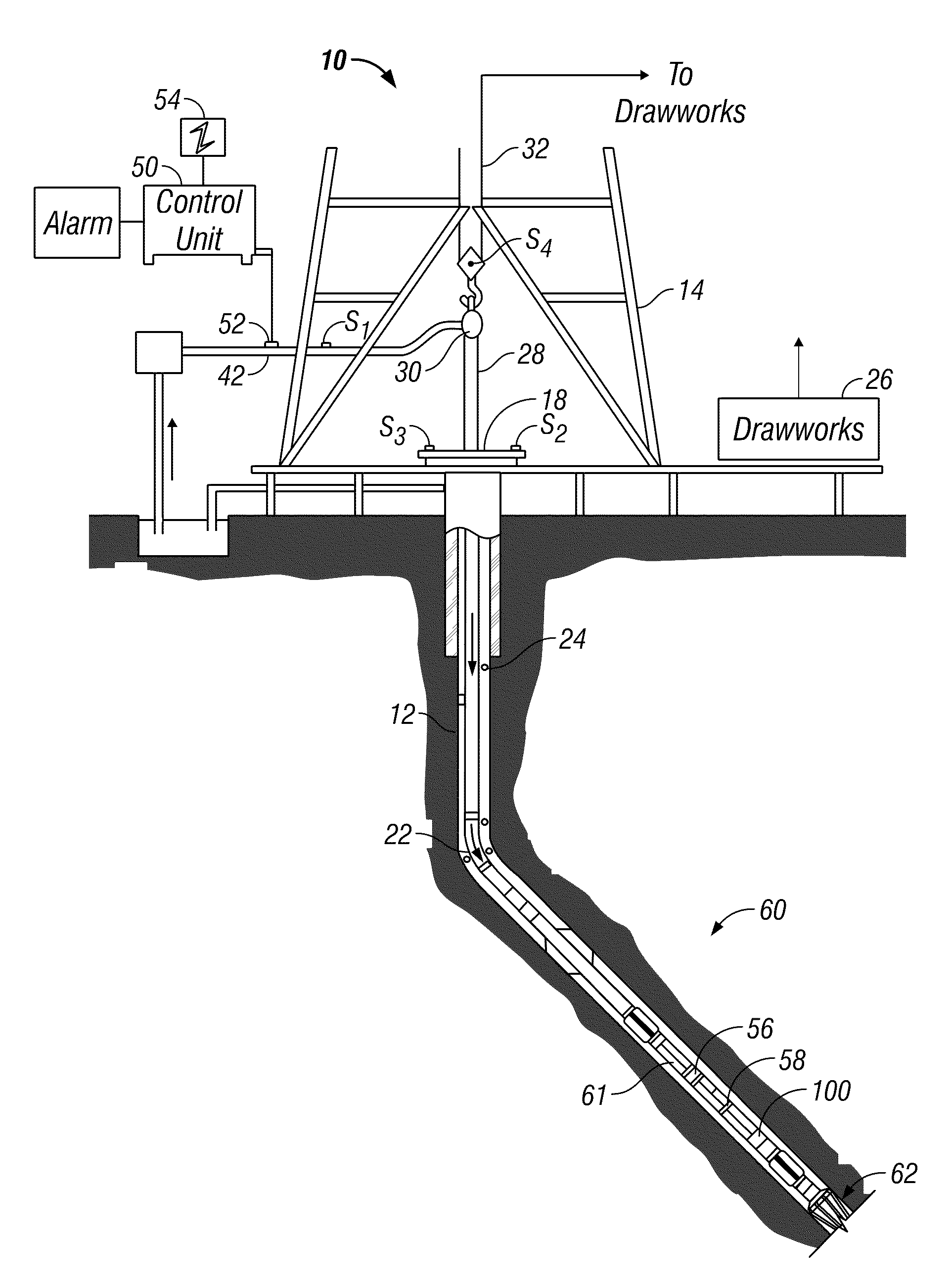
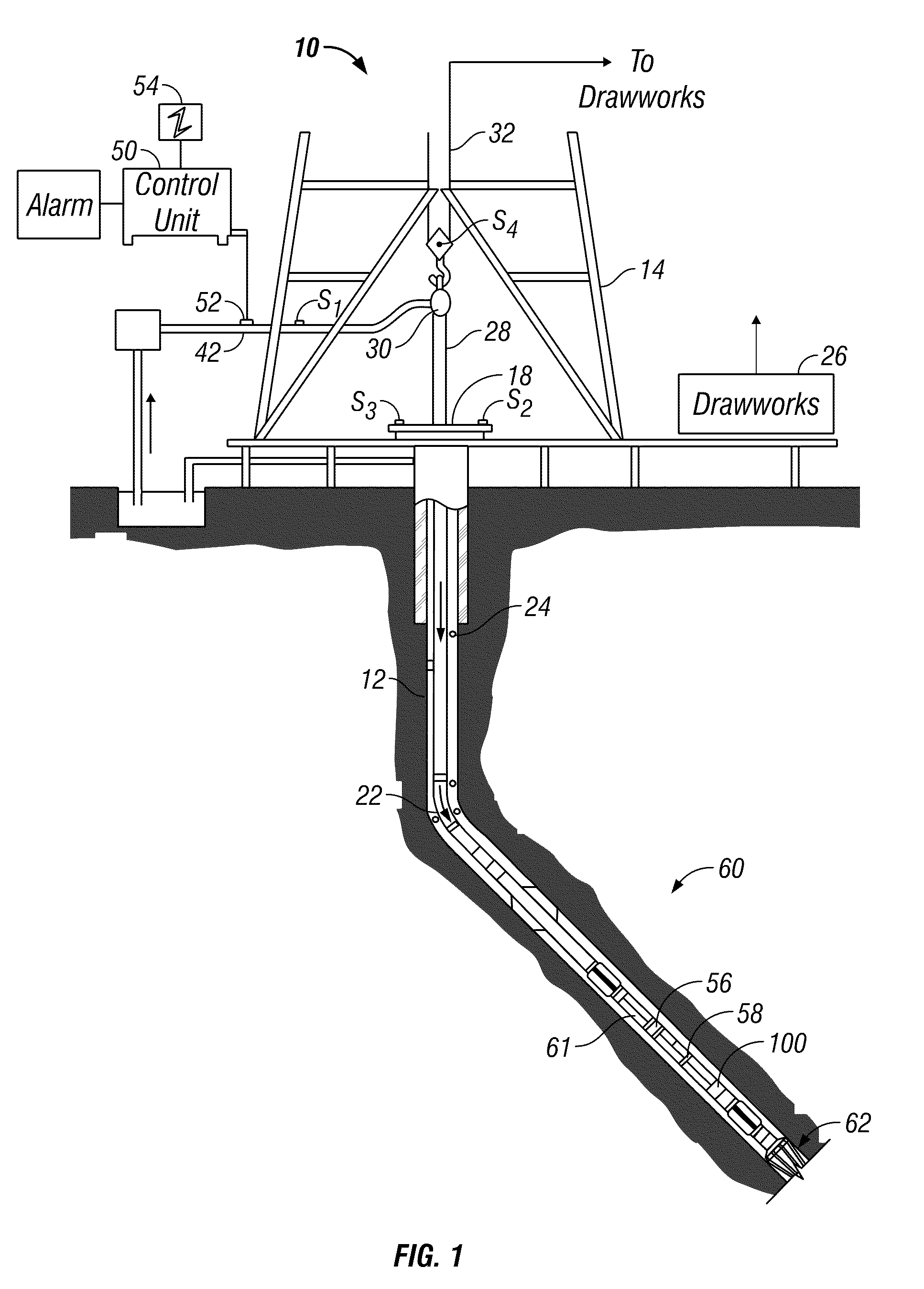
Method and apparatus for MWD formation testing
A method and apparatus for formation testing is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a formation testing tool includes a longitudinal body with a flowbore; a plurality of extendable centralizing pistons coupled to the body; an extendable sample device coupled to the body; and a centralizing hydraulic circuit configured to cause each of the plurality of centralizing pistons to extend at substantially the same rate. The centralizing hydraulic circuit includes a series of flow control and pressure-determining valves configured to extend the centralizing pistons at substantially the same rate, and to help maintain stability in the hydraulic circuit in response to external pressures. In some embodiments, the extendable sample device is preferably configured to be recessed beneath a surface of the body in a first position and to extend beyond the surface in a second position. The extendable sample device is preferably extended to contact the borehole wall substantially normal to the wall, protecting the sample device from excessive bending moments and other excessive forces.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Wing tip device
ActiveUS20050133672A1Reduce the impactUndesirable oscillationInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsFlight vehicleWingtip device
An aircraft comprises a wing tip device, for example a winglet, a raked-tip device, a wing tip fence or a planar wing extension, mounted in the region of the tip of a wing on the aircraft. The wing tip device is rotatably moveable between a first position and a second position, in which the upward lift produced by the wing or the wing tip device is reduced. During flight, the bending moment at the root of the aircraft wing therefore changes in dependence on the position of the wing tip device. The maximum bending moment in the aircraft wing sustained during high-load conditions is thereby reduced, allowing the structural mass of the aircraft to be reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Real Time Misalignment Correction of Inclination and Azimuth Measurements
A method for determining wellbore trajectory includes determining survey parameters in the wellbore; measuring force parameter(s) in the wellbore; and correcting the survey parameters using the measured force parameter(s). The downhole measured force parameters may include forces associated with an operation of a steering device such as an internal reaction force, and / or a bending moment. In variants, the method may include measuring a wellbore temperature; measuring a wellbore parameter in addition to the temperature; and correcting a survey parameter using the measured parameter and the measured temperature. These methods may include correcting survey parameters using measured wellbore diameters. Also, a processor in the wellbore may be programmed to perform the correction while in the wellbore and / or control a steering device using measurements provided by a sensor for measuring internal reaction forces.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
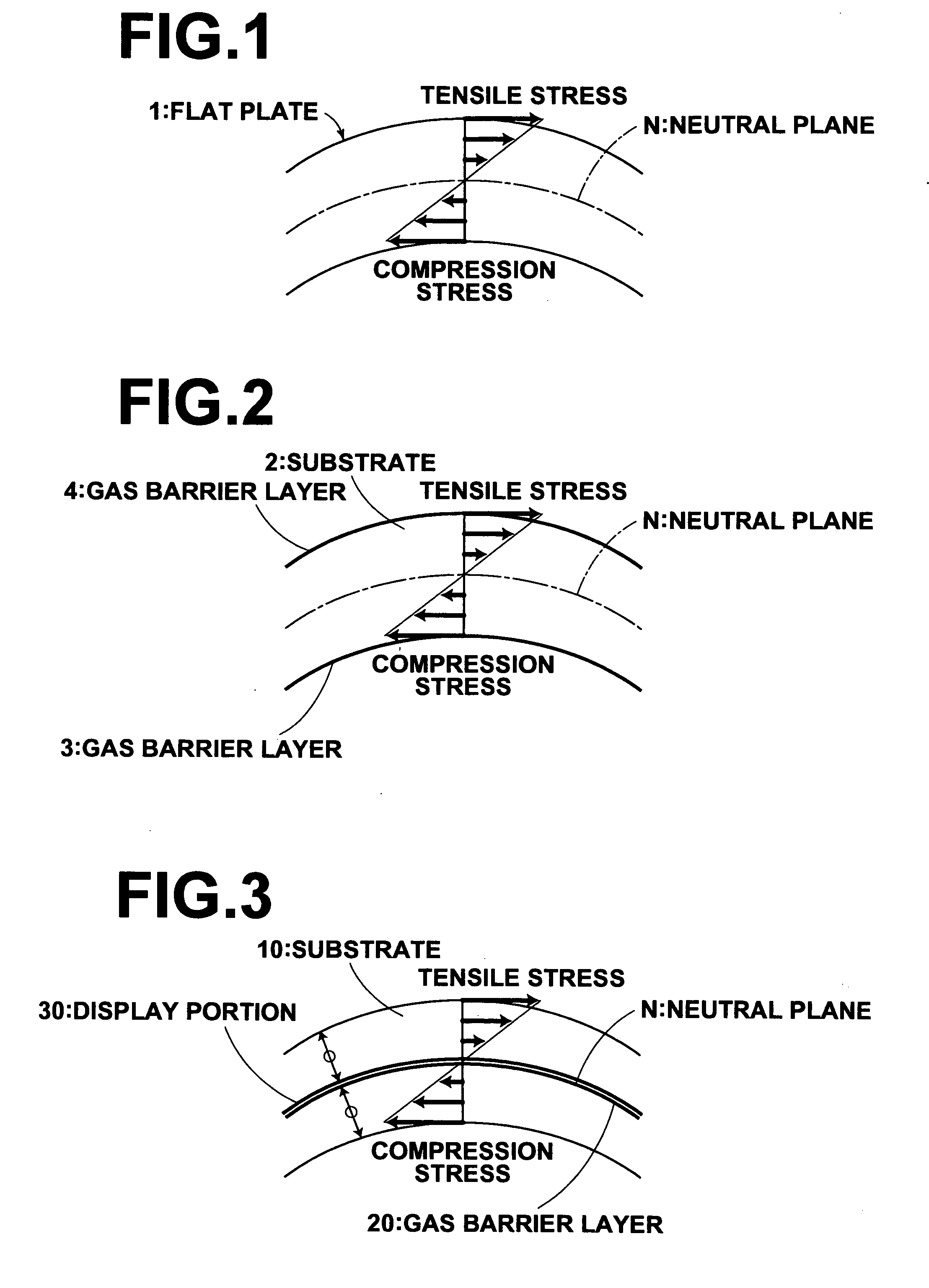
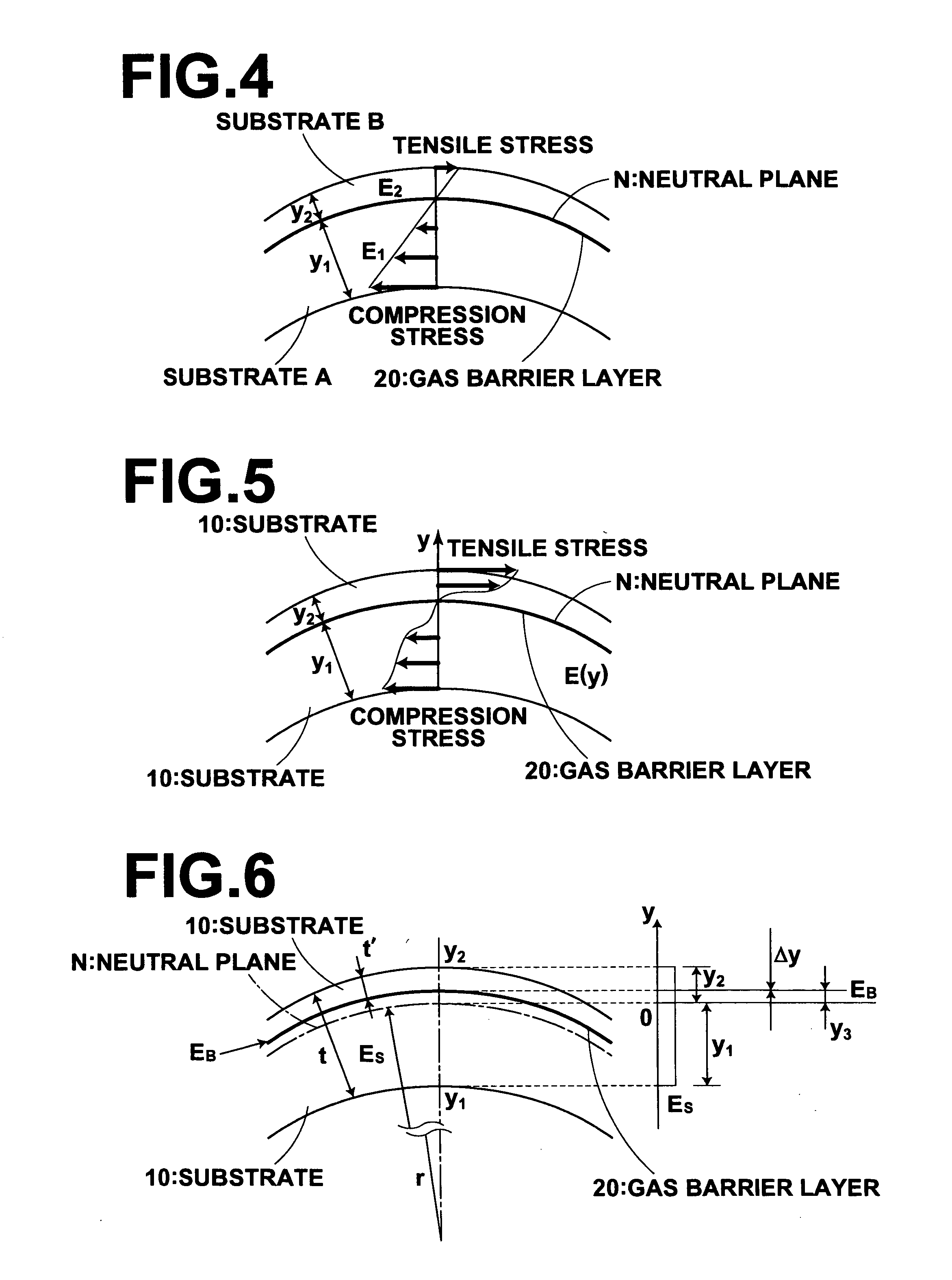
Display device
ActiveUS20060028128A1Avoid damageImprove deteriorationDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceNeutral plane
A display device includes a substrate, a display portion formed on the substrate, an upper layer which covers the display portion, and a gas barrier layer provided between at least a part of the substrate and the display portion. The gas barrier layer is positioned near to the position which forms a neutral plane when bending moment in a direction in which the substrate is warped acts on the overall display device.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Tubular monitor systems and methods
A system for measuring parameters of a structure, the system in certain aspects having a plurality of strain gauges emplaceable on the structure, signal transmission apparatus associated with the plurality of strain gauges for transmitting signals therefrom indicative of gauge measurements to computer apparatus for processing the signals, the gauges, in one aspect, including at least three strain gauge apparatuses for providing axial strain measurements, and computer apparatus for receiving signals from the transmitting apparatus indicative of the measurements and for determining bending moment and bending direction of the structure at a location of the gauge apparatuses, and in one aspect wherein the computer apparatus is programmed to calculate internal pressure and / or bending direction of the structure based on the measurements, and in one aspect to do so in real time.
Owner:COILED TUBING ENG SERVICES
Measurement transducer of vibration type
ActiveUS20070186685A1Improve balanceReduce quality problemsDirect mass flowmetersCantilevered beamCoupling
The measurement transducer includes: A measuring tube vibrating at least at times during operation and serving for the conveying of a medium, wherein the measuring tube communicates with a pipeline via an inlet tube piece at an inlet end and an outlet tube piece at an outlet end; a counteroscillator, which is affixed to the measuring tube on the inlet end to form a first coupling zone and affixed to the measuring tube on the outlet end to form a second coupling zone; and a first cantilever for producing bending moments in the inlet tube piece and coupled with the inlet tube piece and the measuring tube essentially rigidly in the area of the first coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the inlet tube piece, as well as a second cantilever for producing bending moments in the outlet tube piece and coupled essentially rigidly with the outlet tube piece and the measuring tube in the region of the second coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the outlet tube piece. The measurement transducer of the invention is especially suited also for measuring tubes having large nominal diameters of more than 50 mm.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
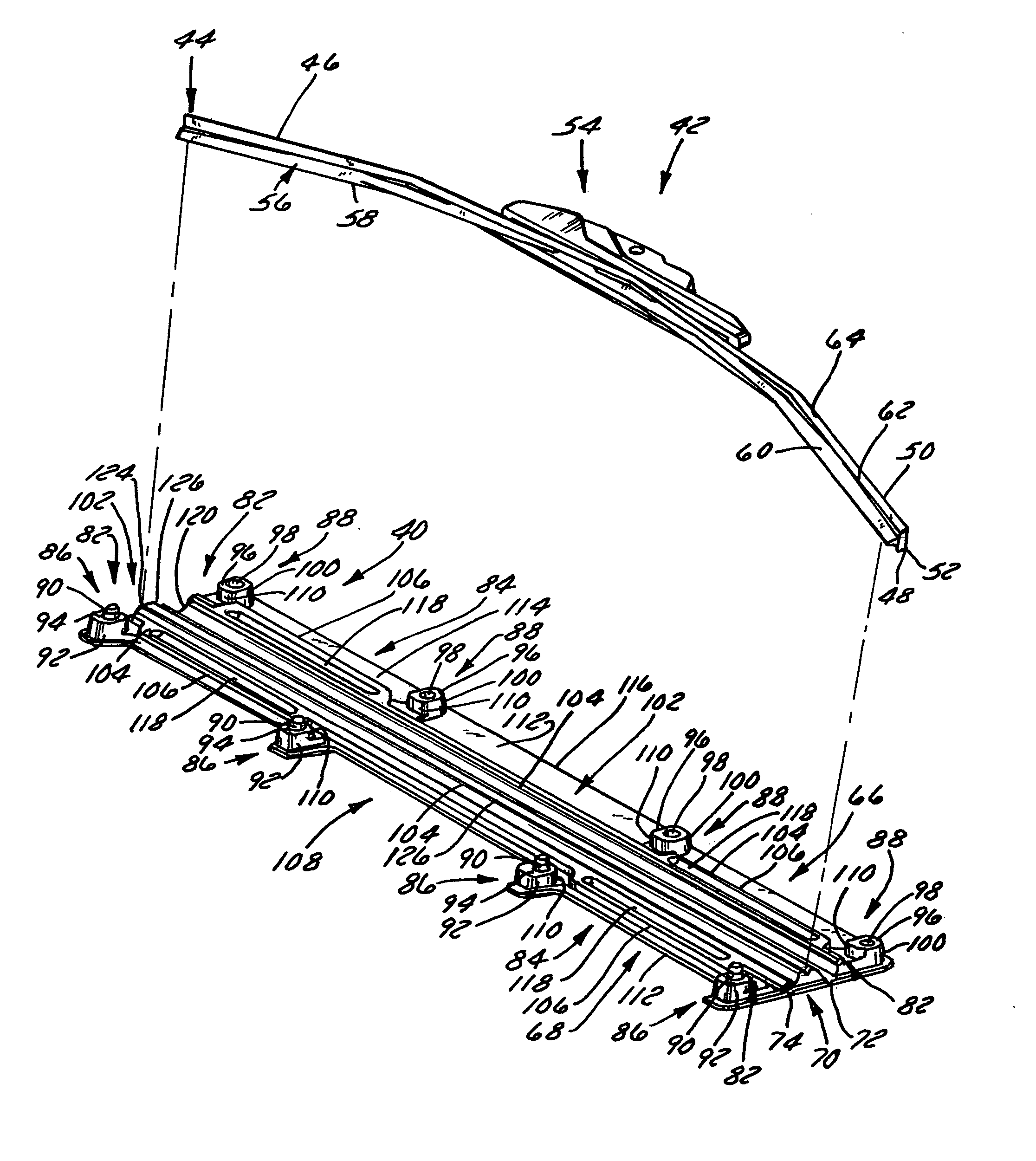
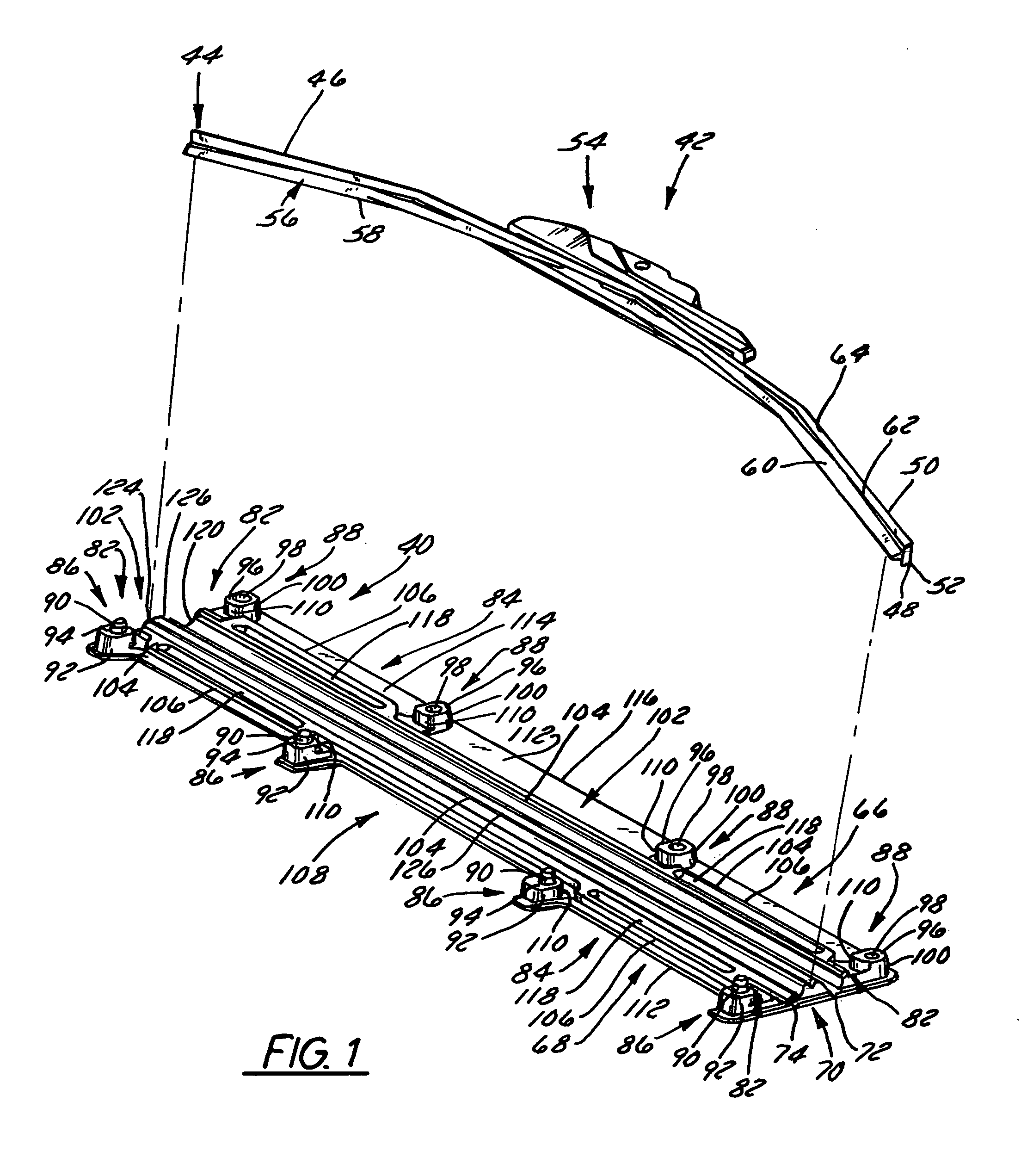
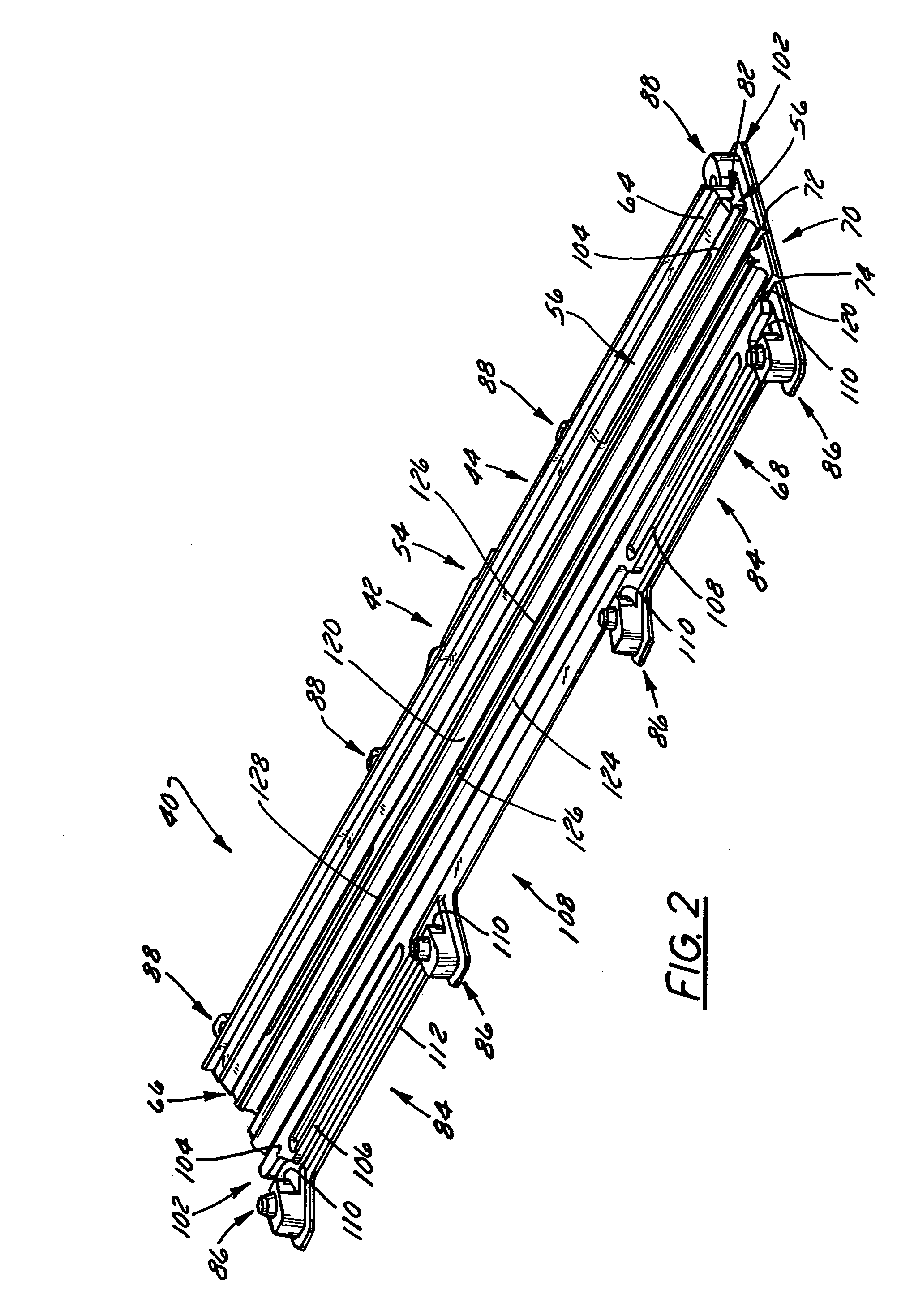
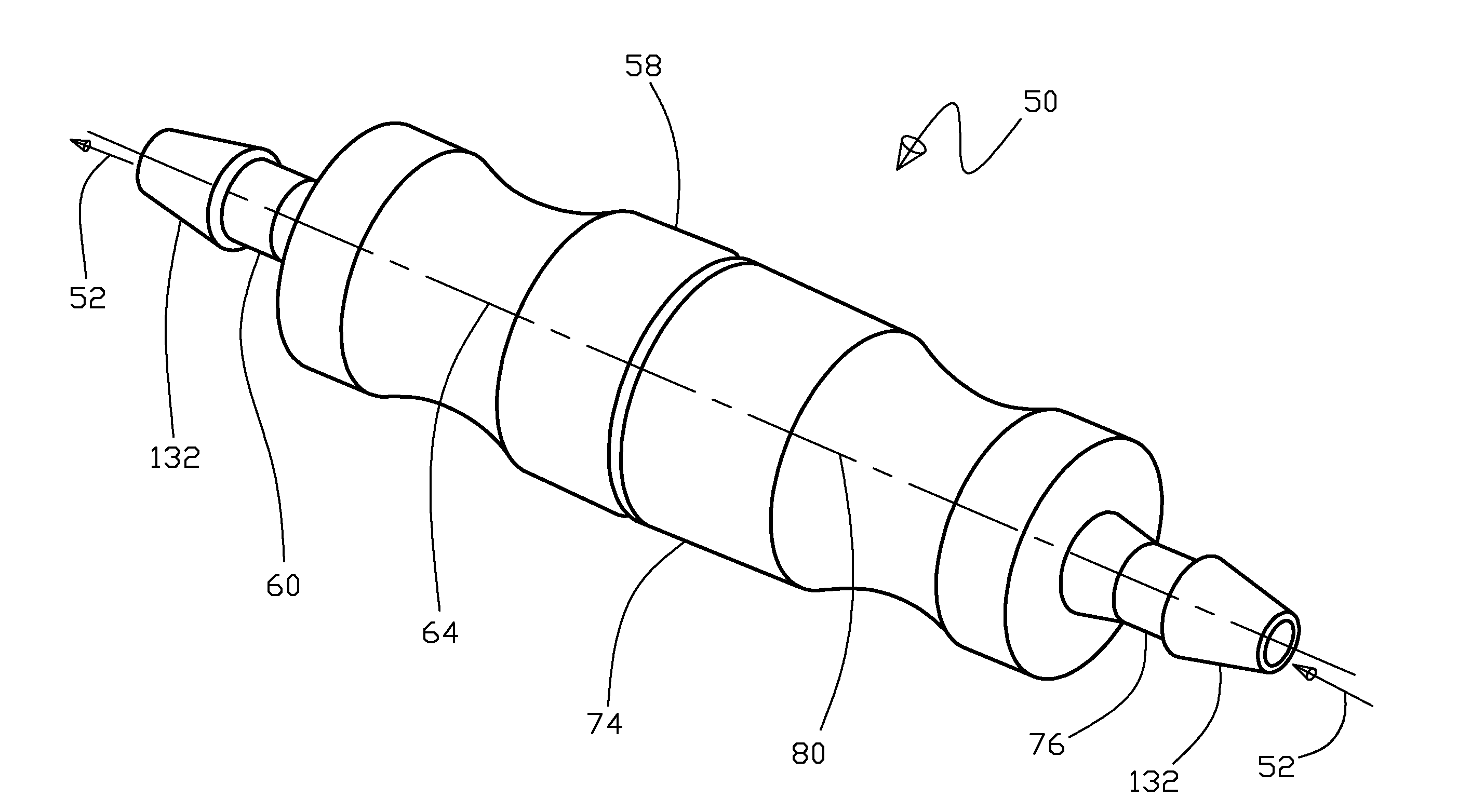
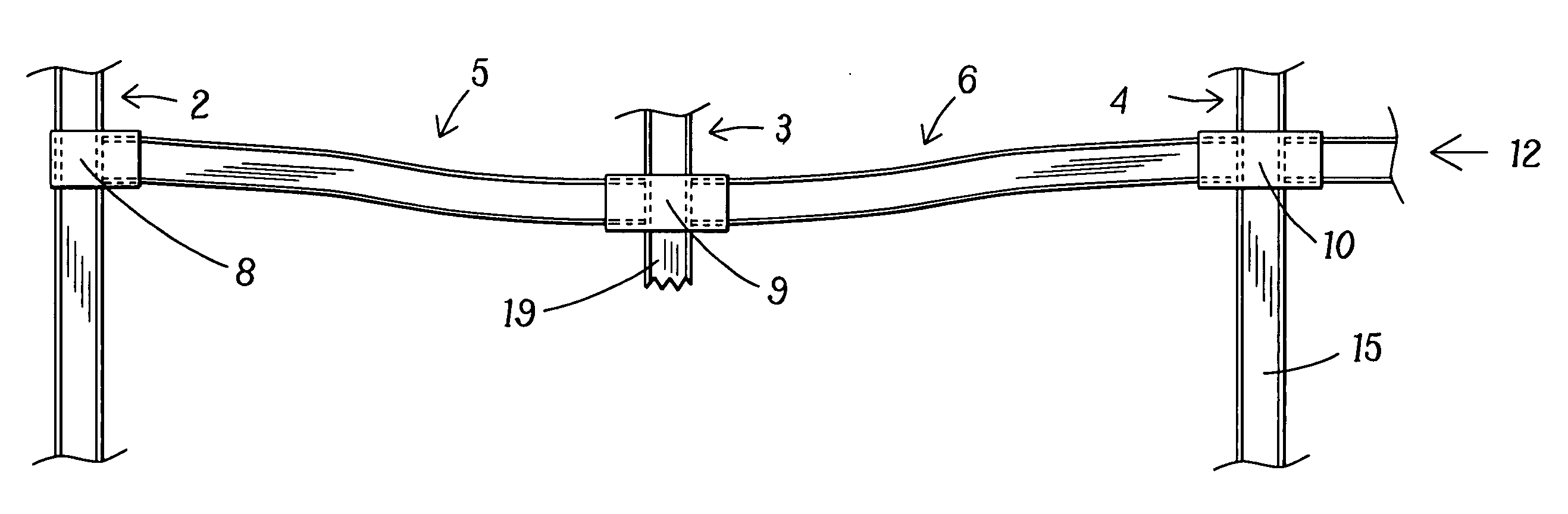
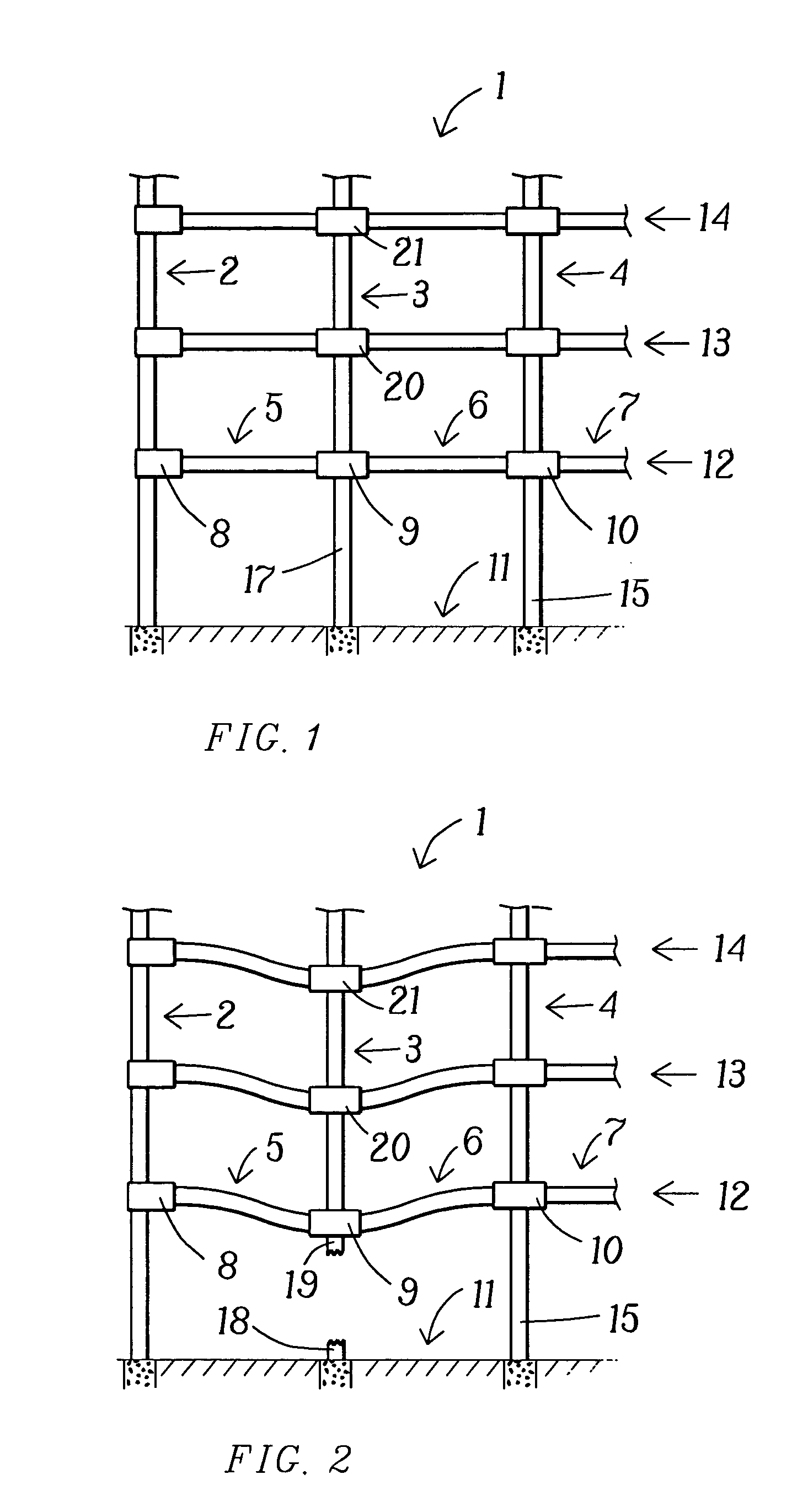
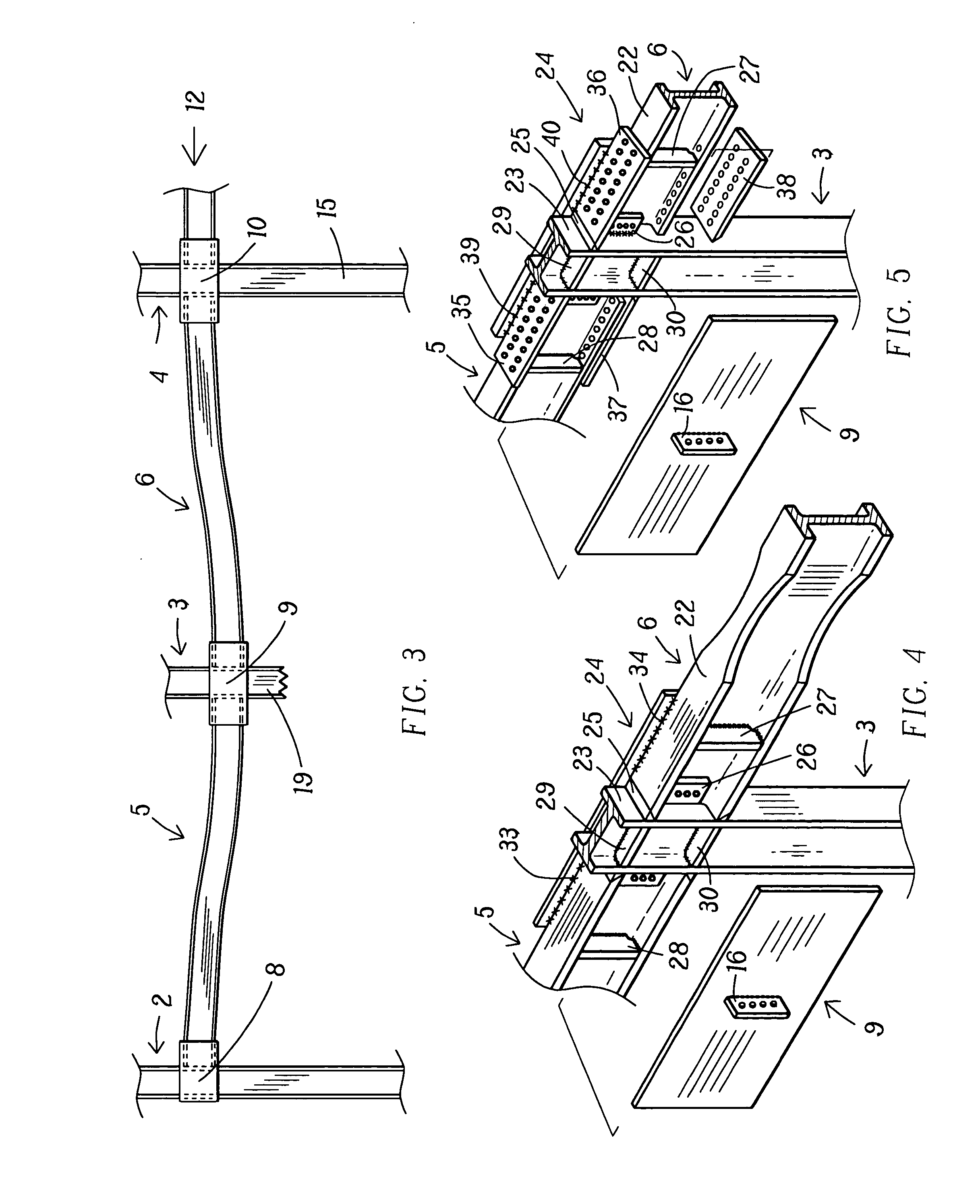
Wiper blade package
InactiveUS20050252812A1Strengthen and structurally rigidifyStrengthen and structurally rigidify the packagePackaging vehiclesContainers for machinesFlangeBending moment
An elongate article holding package for a wiper blade having a pair of package panels with at least one of the panels including a blade beam receiving seat and a support flat upon which part of the blade rests during packaging. When closed, the flats position and can clamp the blade therebetween. In a preferred embodiment, both panels are so configured and preferably include one or more longitudinal stiffeners that oppose bending moments created by force transmitted to the package by the blade beam. The package preferably is of tri-fold construction having a spine that is spaced from and protects the wiper element. The spine preferably includes at least a plurality of spaced apart longitudinally extending stiffeners. One or more stiffening flanges preferably are also provided. When closed, the panels and spine advantageously cooperate with each other to increase package crush and bending resistance.
Owner:PORTAGE PLASTICS
Fluid Connector
ActiveUS20080191466A1Easy to separateFacilitate fluid communicationRespiratorsSleeve/socket jointsEngineeringBending moment
A fluid connector and method of use is disclosed that includes a male housing with a male proximal end portion adapted to be in fluid communication with a first line and a male distal end portion having a resilient ring. Also included is a female housing with a female proximal end portion adapted to be in fluid communication with a second line and a female distal end portion with a resilient annulus that removably engages the ring. Operationally, the male and the female housings are configured at the annulus and ring engagement to have a high separating resistance axially and a low separating resistance transverse to the axial axis by manually applying a bending moment between the male and female engaged housings by a force transverse to the axial axis. Further included is structure for fluid sealing between the male and female housings when the annulus and ring are engaged.
Owner:CUFFCO
Measurement transducer of vibration type
ActiveUS20070119265A1Improve balanceReduce quality problemsDirect mass flowmetersCantilevered beamCoupling
The measurement transducer includes: A measuring tube vibrating at least at times during operation and serving for the conveying of a medium, wherein the measuring tube communicates with a pipeline via an inlet tube piece at an inlet end and an outlet tube piece at an outlet end; a counteroscillator, which is affixed to the measuring tube on the inlet end to form a first coupling zone and affixed to the measuring tube on the outlet end to form a second coupling zone; and a first cantilever for producing bending moments in the inlet tube piece and coupled with the inlet tube piece and the measuring tube essentially rigidly in the area of the first coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the inlet tube piece, as well as a second cantilever for producing bending moments in the outlet tube piece and coupled essentially rigidly with the outlet tube piece and the measuring tube in the region of the second coupling zone and having a center of mass lying in the region of the outlet tube piece. The measurement transducer of the invention is especially suited also for measuring tubes having large nominal diameters of more than 50 mm.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Wind Turbine With Pitch Control Arranged To Reduce Life Shortening Loads On Components Thereof
ActiveUS20100014971A1Maximize power outputMinimizing variation of loadPropellersWind motor controlGravitational forceBlade pitch
A wind turbine is presented where the operation lifetime of the main bearing is extended by relieving the main bearing by reducing the mean bending moment on the bearing by means of individual pitch control of the blades of the rotor so as to create an aerodynamic mean tilt moment on the rotor by means of aerodynamic forces on the blades, the tilt moment at least partly counteracting the bending moment caused by the overhang load forces on the main bearing from the gravitational pull on the rotor mass.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
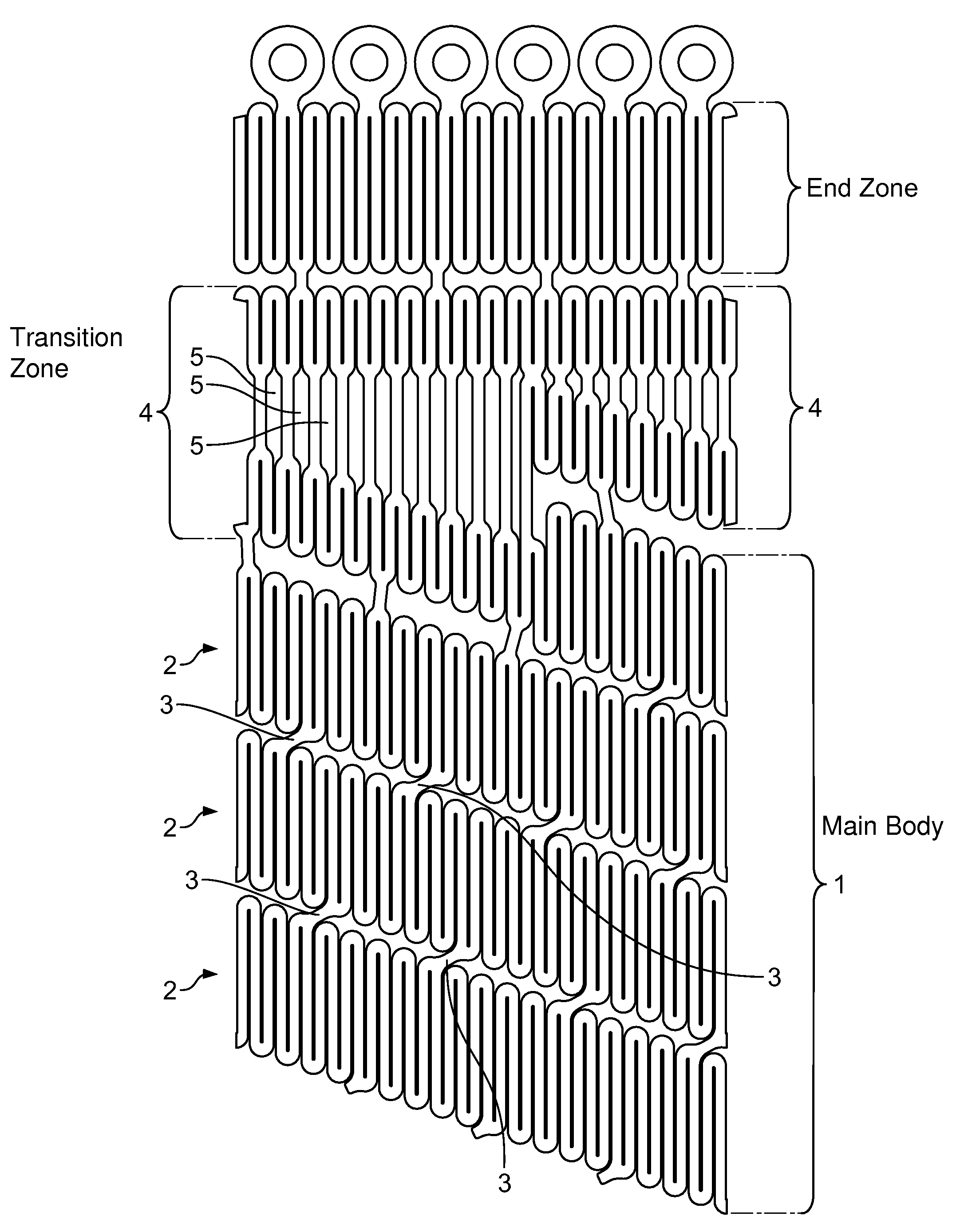
Self-Expanding Stent with Polygon Transition Zone
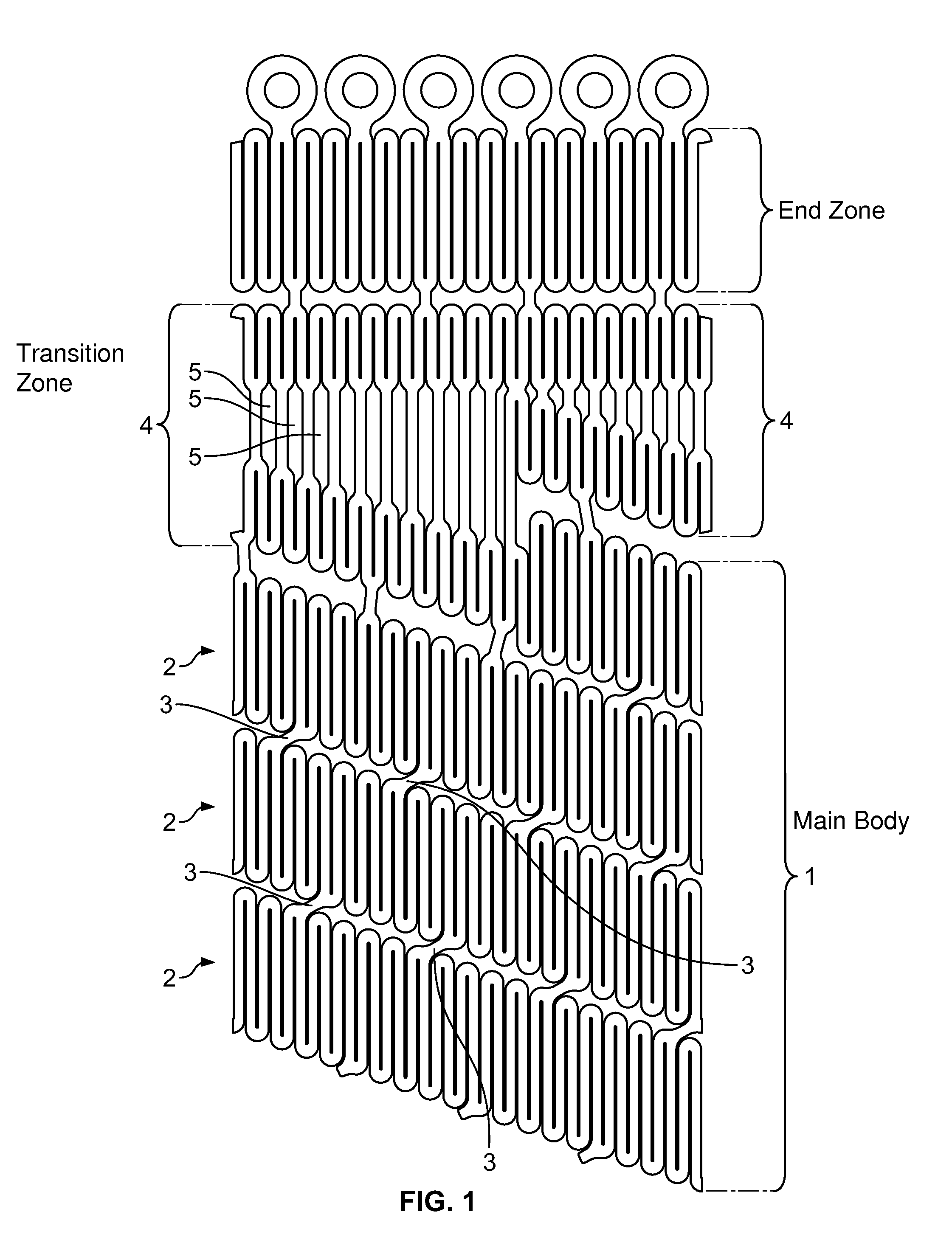
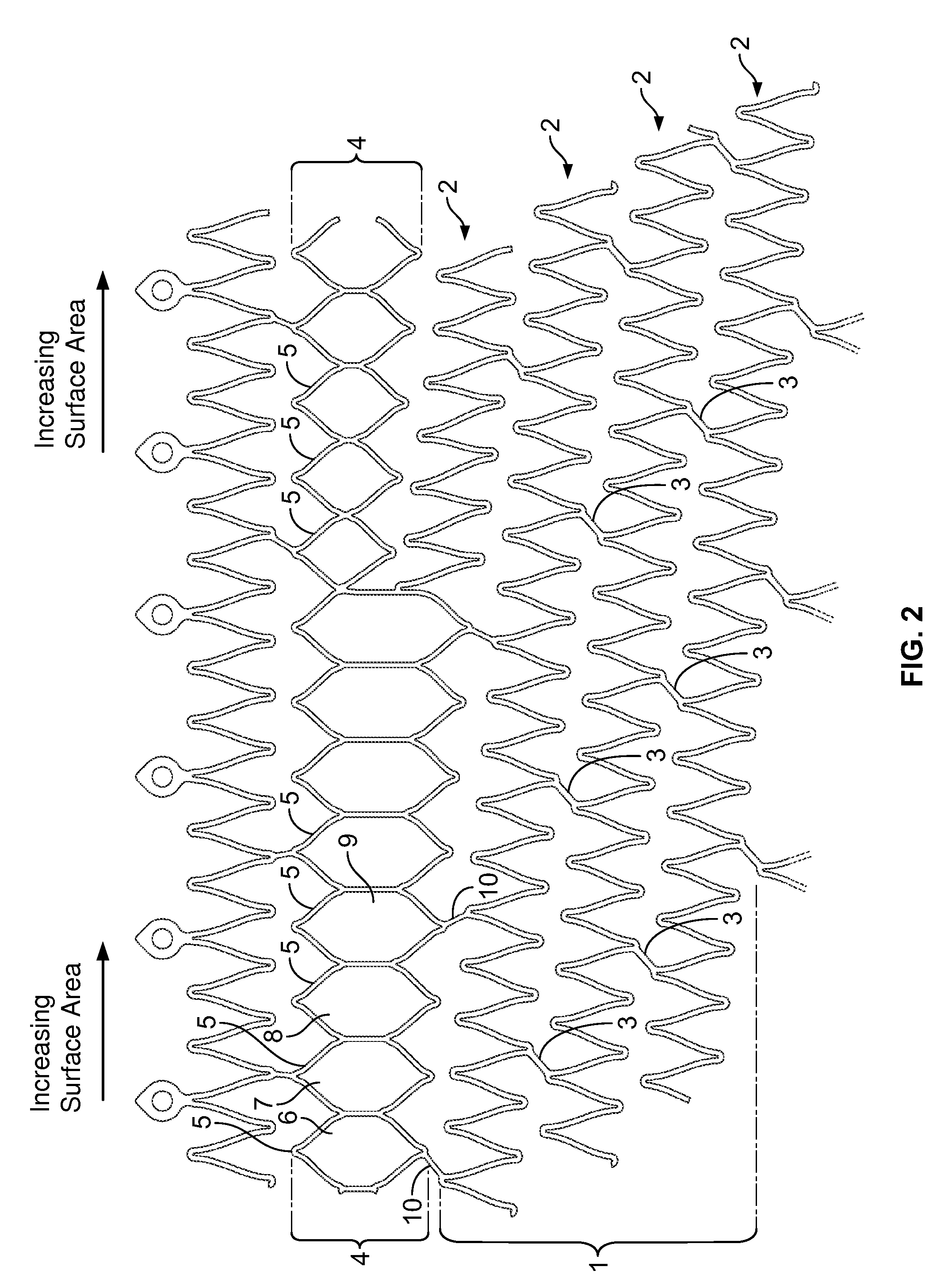
The self-expanding stent of the present invention provides for a transition zone between the main body of the stent and the end zone, comprising a plurality of n-sided polygons where the surface area of the adjacent polygons in the transition zone is unequal. In one embodiment, the surface area of the polygons in the transition zone increases circumferentially across the transition zone in a clockwise or counterclockwise manner. The polygons are formed from two pairs of undulations which are connected by segments. The bending moment of the undulations is equal within each polygon and constant across the transition zone.
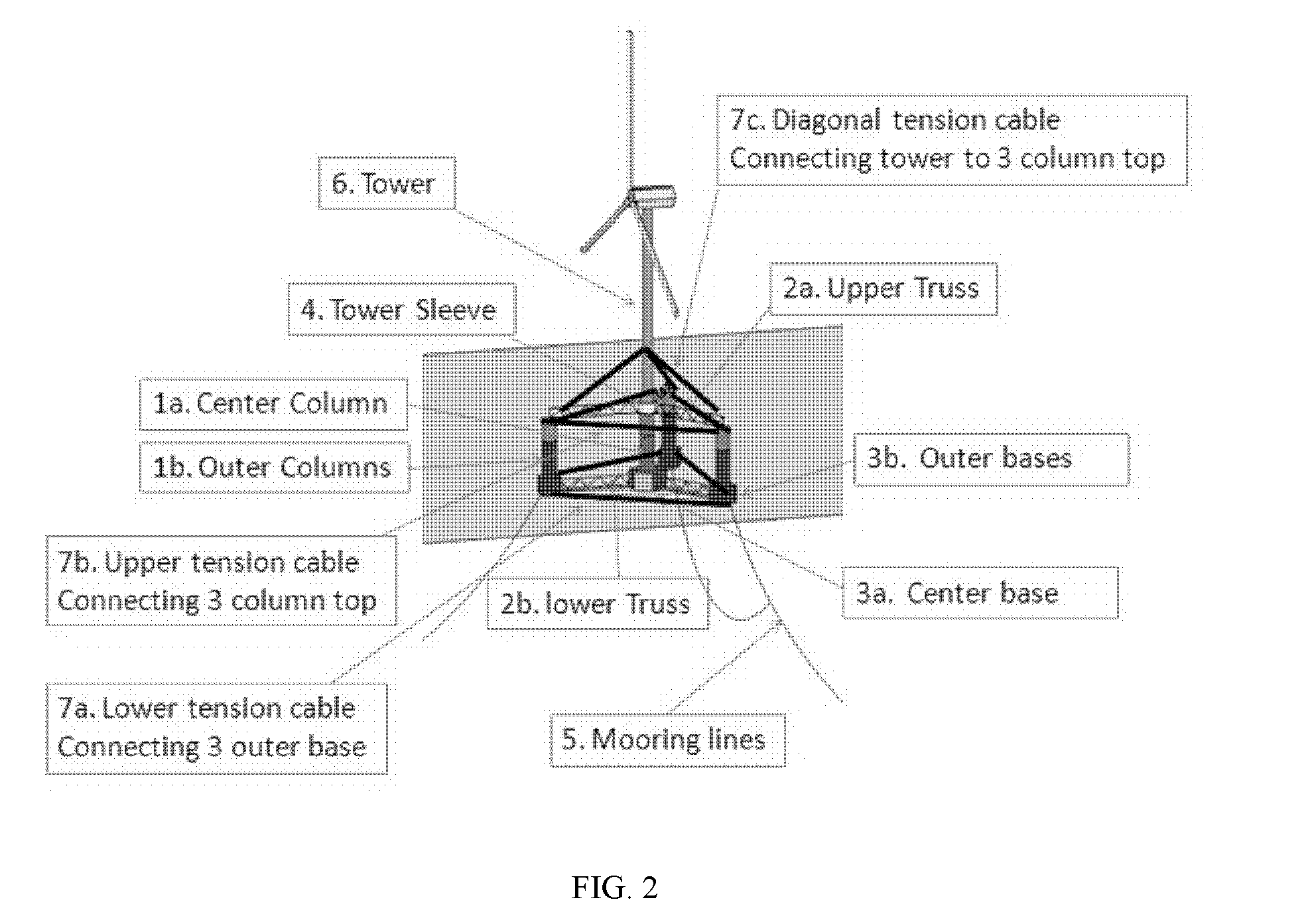
Truss Cable Semi-submersible Floater for Offshore Wind Turbines and Construction Methods
InactiveUS20120103244A1Improve dynamic performanceImprove stabilityWind energy generationFloating buildingsHull structureHybrid material
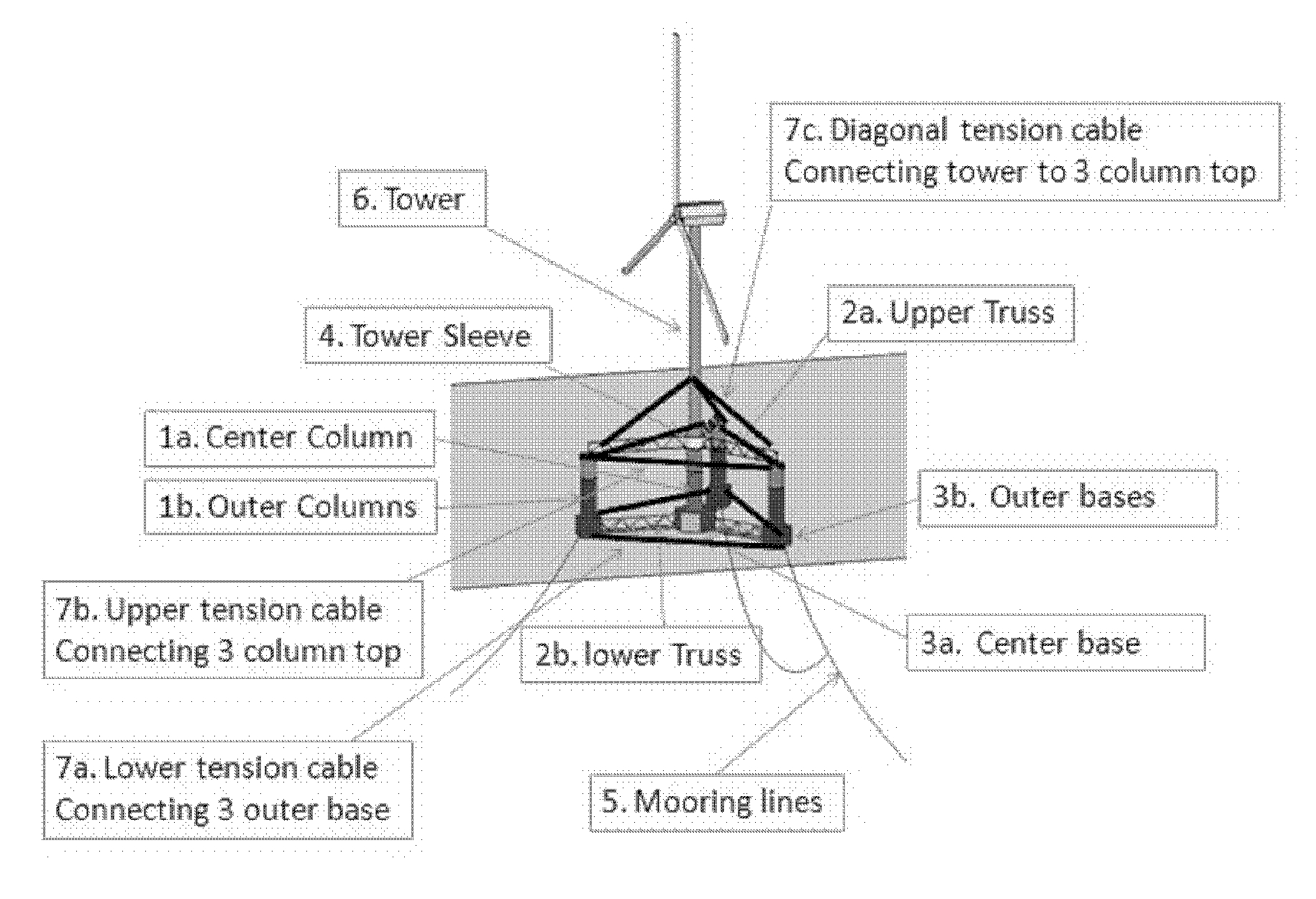
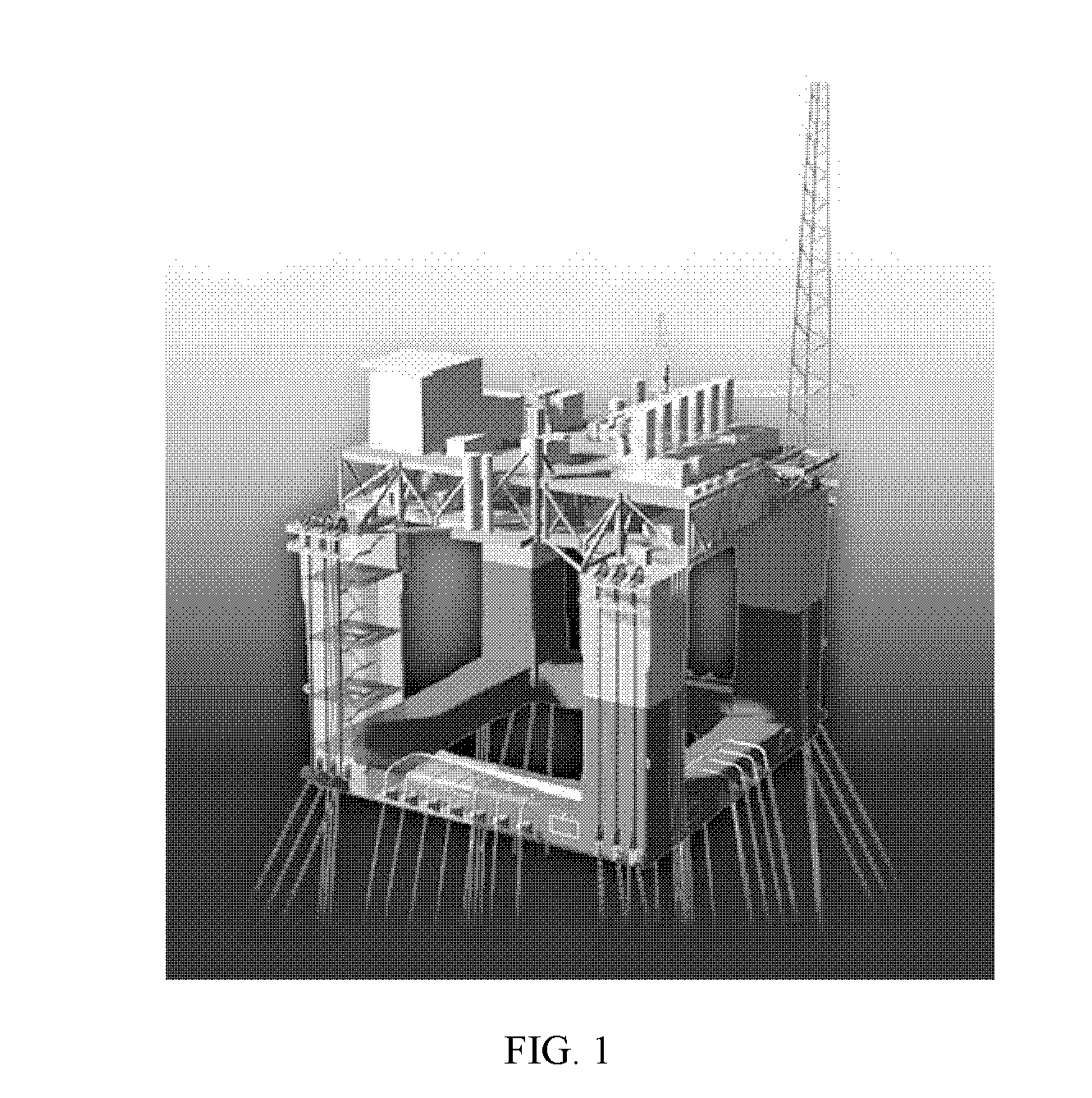
Truss cable semi-submersible floater for offshore wind turbines and construction methods are provided. A floating system includes a hull, a tensioned cable system, and a tower. The hull includes vertical buoyant columns with one column at the center of the pattern, larger size column base tanks, and a truss system, all of which are coupled to each other for supporting the tower and wind turbines. The column can be made of hybrid materials, including steel and composite-concrete. The steel section and the composite-concrete section of the column can be connected by grouting. The tensioned cable system including upper, lower, and diagonal tensioned cables to connect the column, the column base, and the tower to reduce the bending moments and improve stability, strength and dynamic performance of the hull structure.
Owner:WANG JIN +1
Structural joint connection providing blast resistance and a beam-to-beam connection resistant to moments, tension and torsion across a column
ActiveUS20050204684A1Mitigates likelihood of progressive collapseTremendous tensile pull and vertical moment demandBuilding roofsFloorsGusset plateEngineering
At a beams-to-column joint connection of two beams to a column, in which the joint connection comprises both a gravity load-carrying connection and a moment-resisting connection, there is added a beam-to-beam connection across the column, using two gusset plates, facing each other, on opposite sides of the joint connection. The gusset plates, which are not connected to the column in a moment-resisting connection, connect the two beams, in a tension and moment-resisting connection with respect to each other, by longitudinal welds between the gusset plates and the beams, and provide the capability of withstanding disastrous events, including loss of column support and / or loss of integrity of the beams-to-column joint connection and severe torsional and lateral inelastic deformation due to direct blast pressure. When subjected to such violent conditions and upon loss of column support, and, the likely loss of integrity of the beams-to-column joint connection, the two beams and two gusset plates provide independent beam-to-beam structural continuity, causing the two beams to act as one long beam, or, in other words, a “double-span” condition is created. Such beam-to-beam connection is capable of carrying the tension, torsional and moment loads placed upon the beams, to the ultimate capacity of the beams. Inasmuch as a gusset plate is disposed on each side of the beams-to-column joint connections, substantial shielding of those connections against blast and impact forces is also achieved.
Owner:MITEK HLDG INC
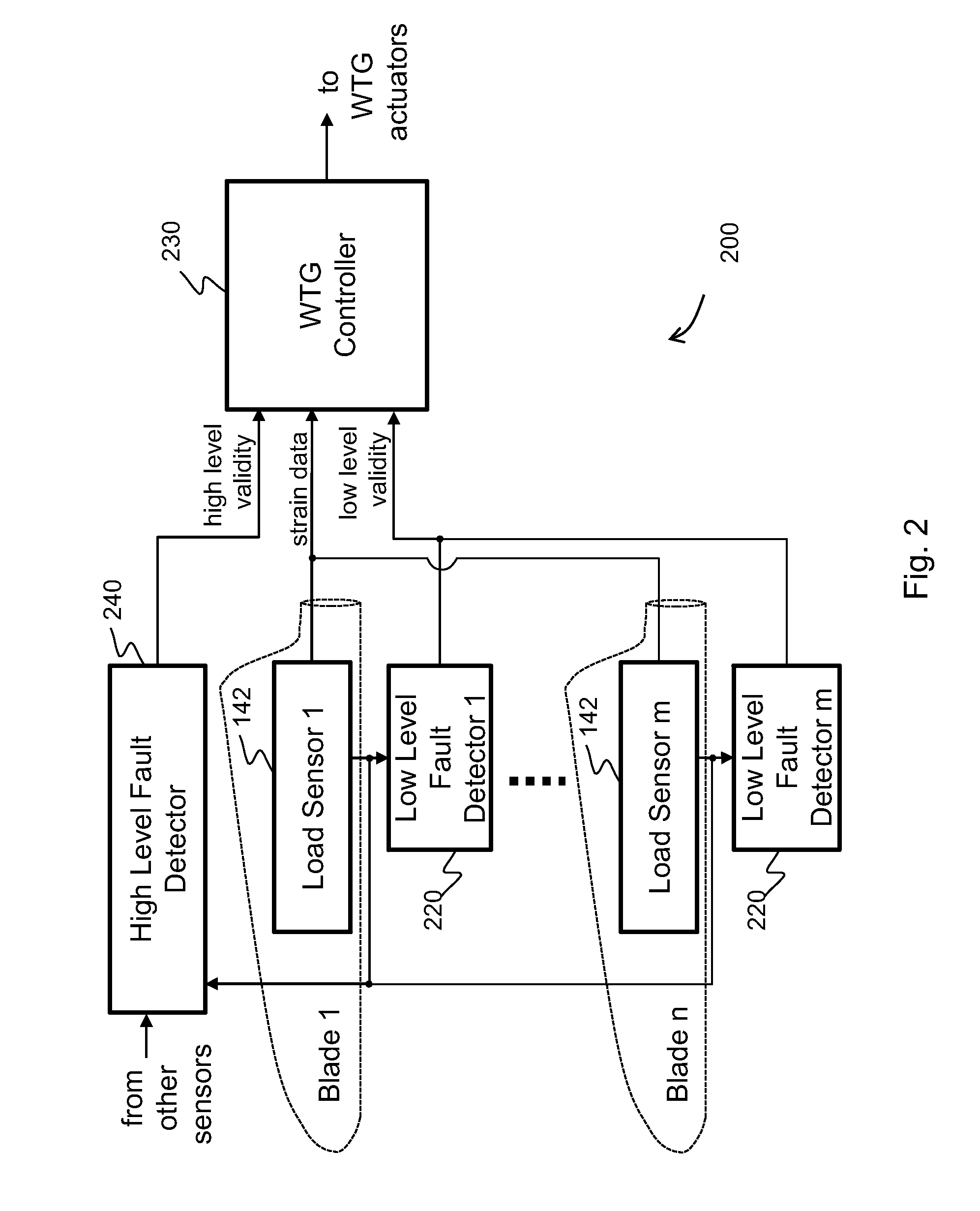
Methods and systems for detecting sensor fault modes
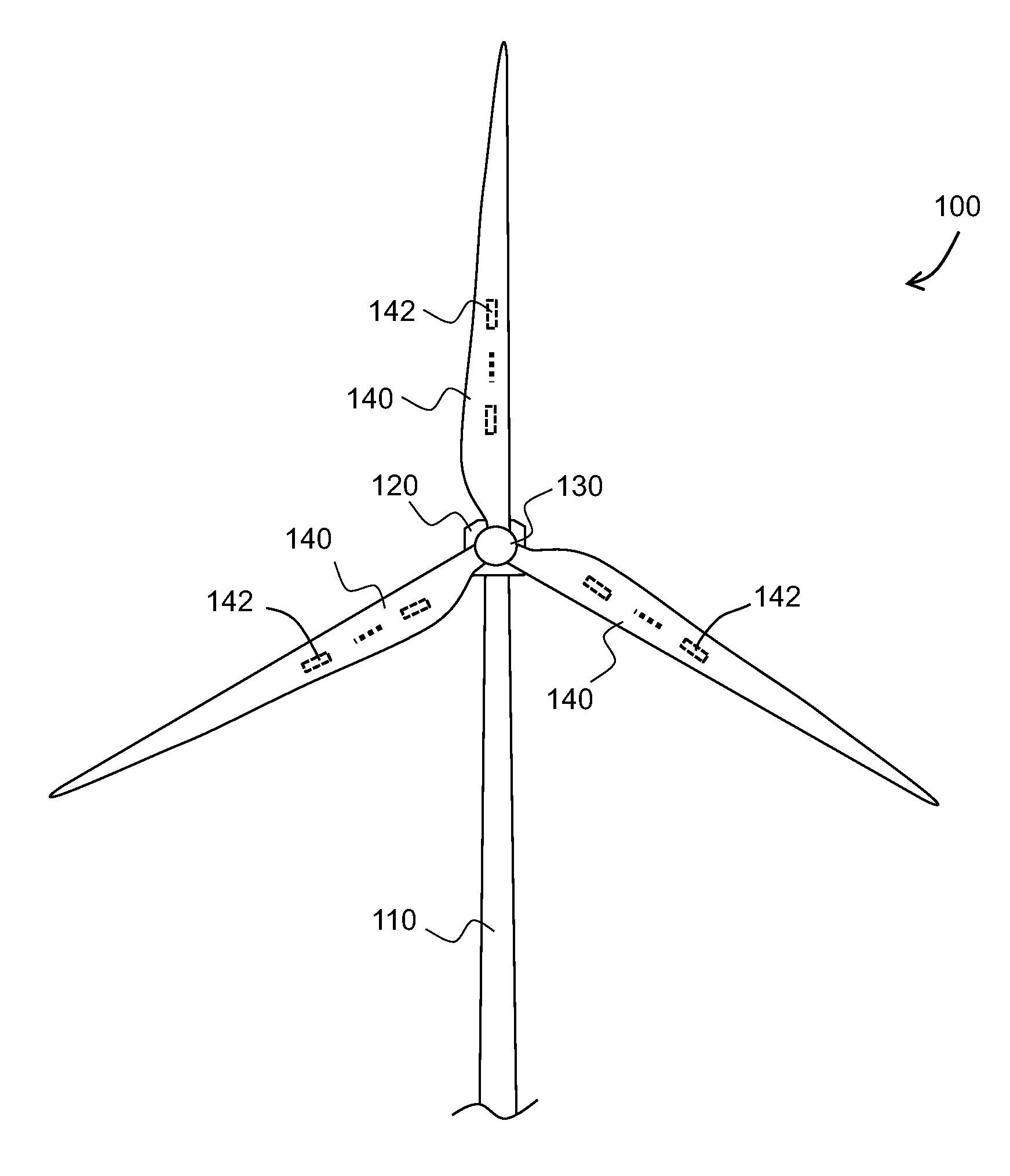
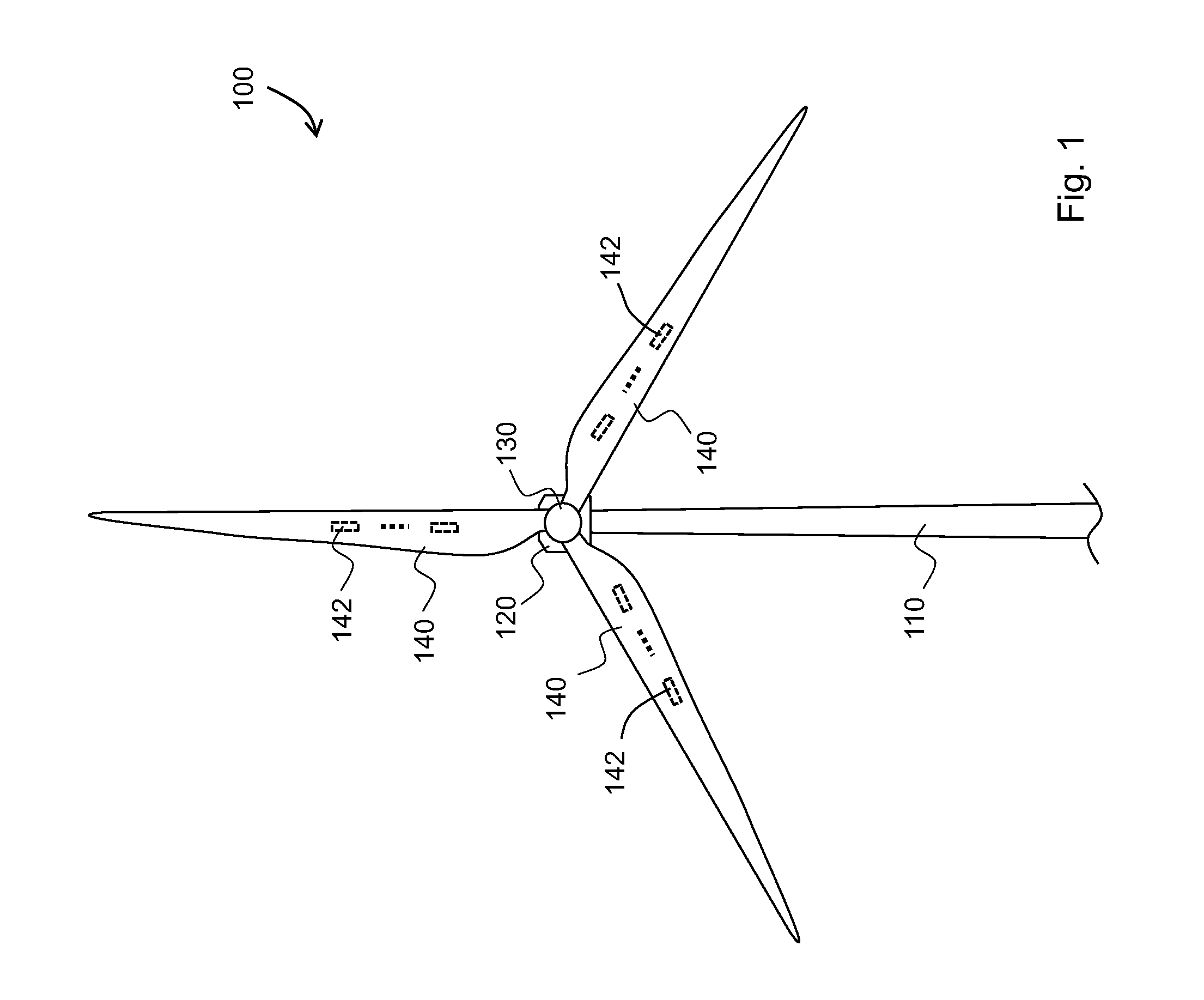
A method of detecting a fault mode of a sensor is provided. The sensor may be, for example, a bending moment sensor and may sense a bending moment of a blade on a wind turbine generator (WTG). The method includes comparing data output by a first sensor with reference data indicating what is expected to be output by the first sensor to produce a first comparison result and comparing data output by the first sensor with data output by a second sensor to produce a second comparison result. A determination of whether the first sensor has entered a fault mode is made based at least in part on the first and second comparison results.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com