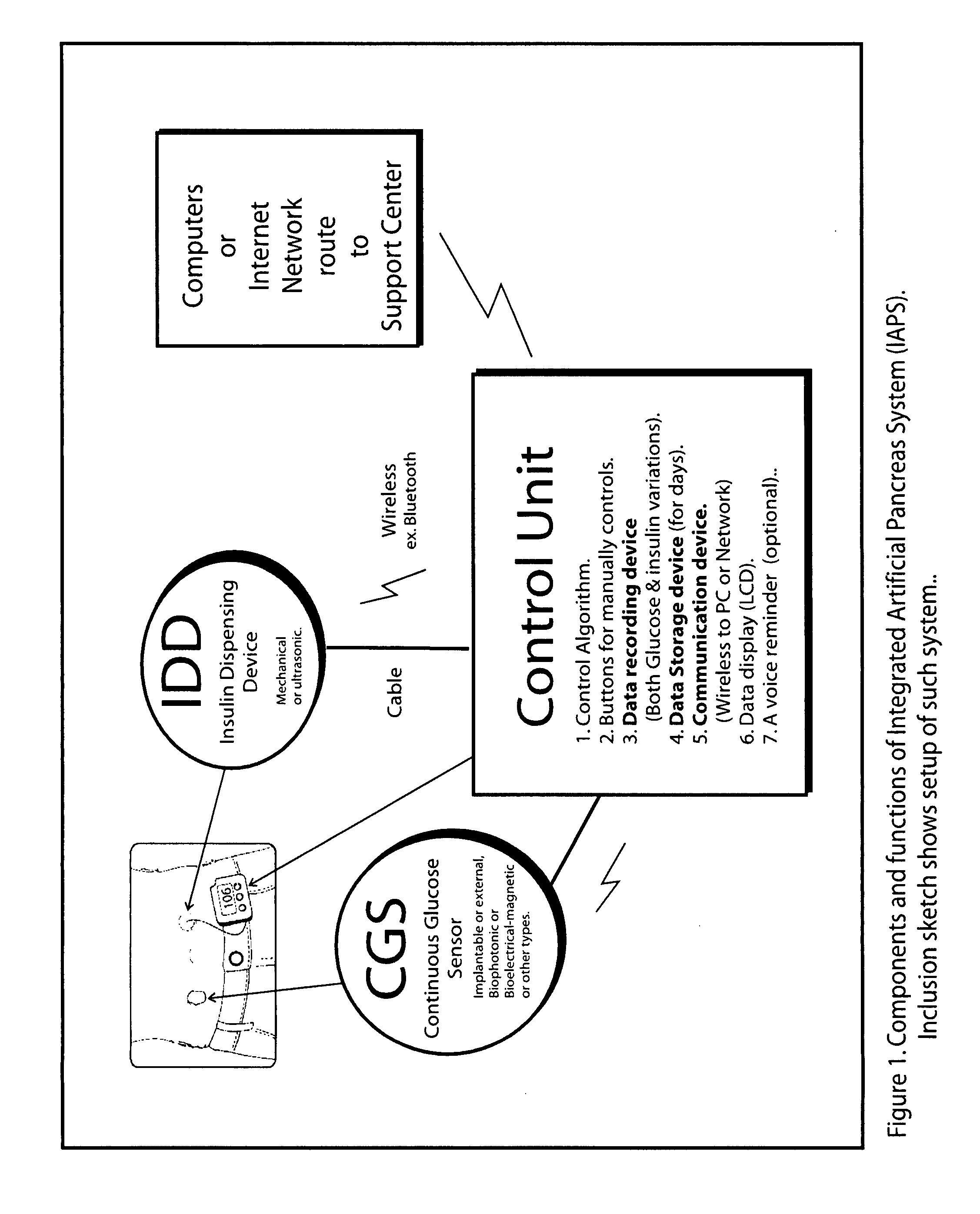
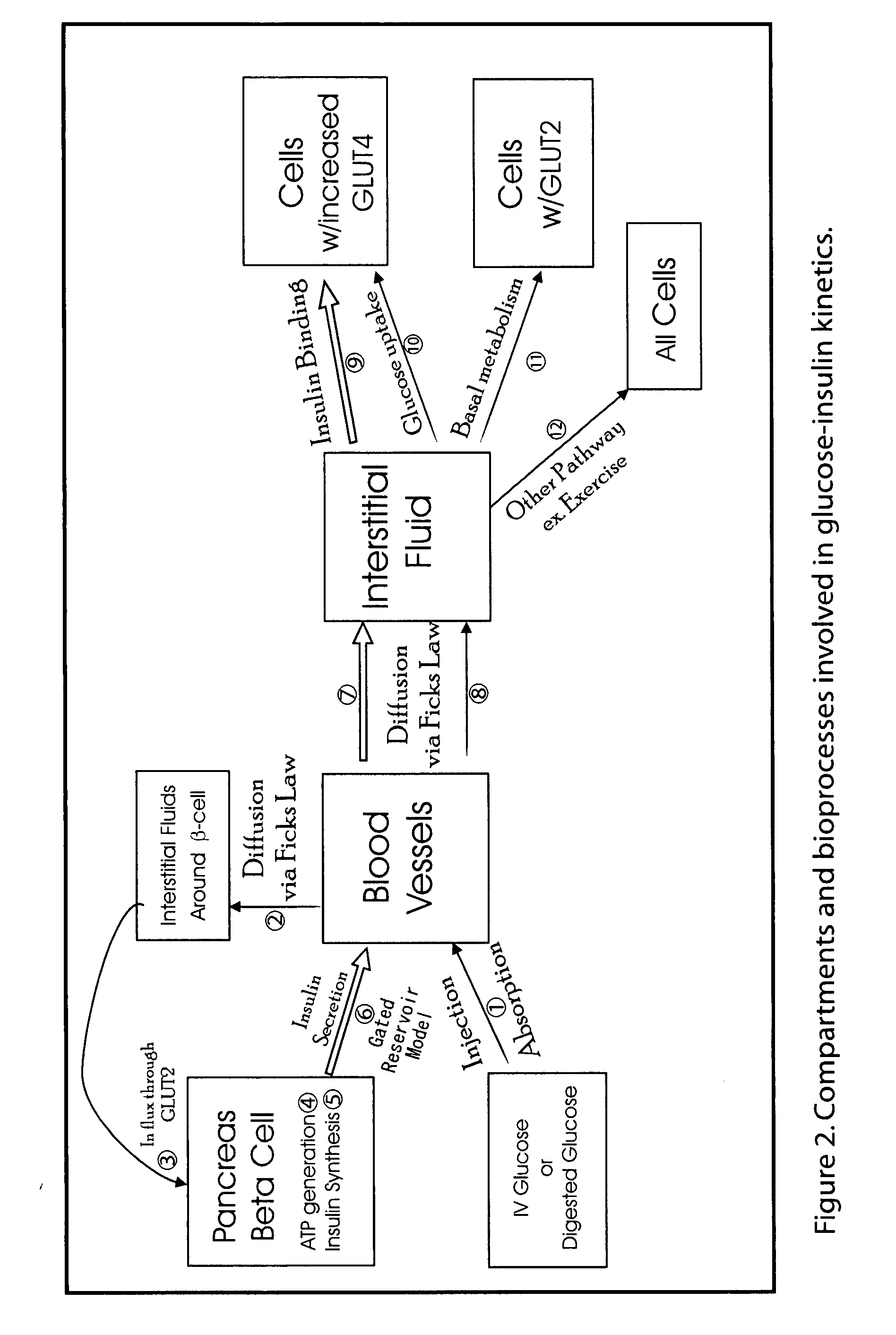
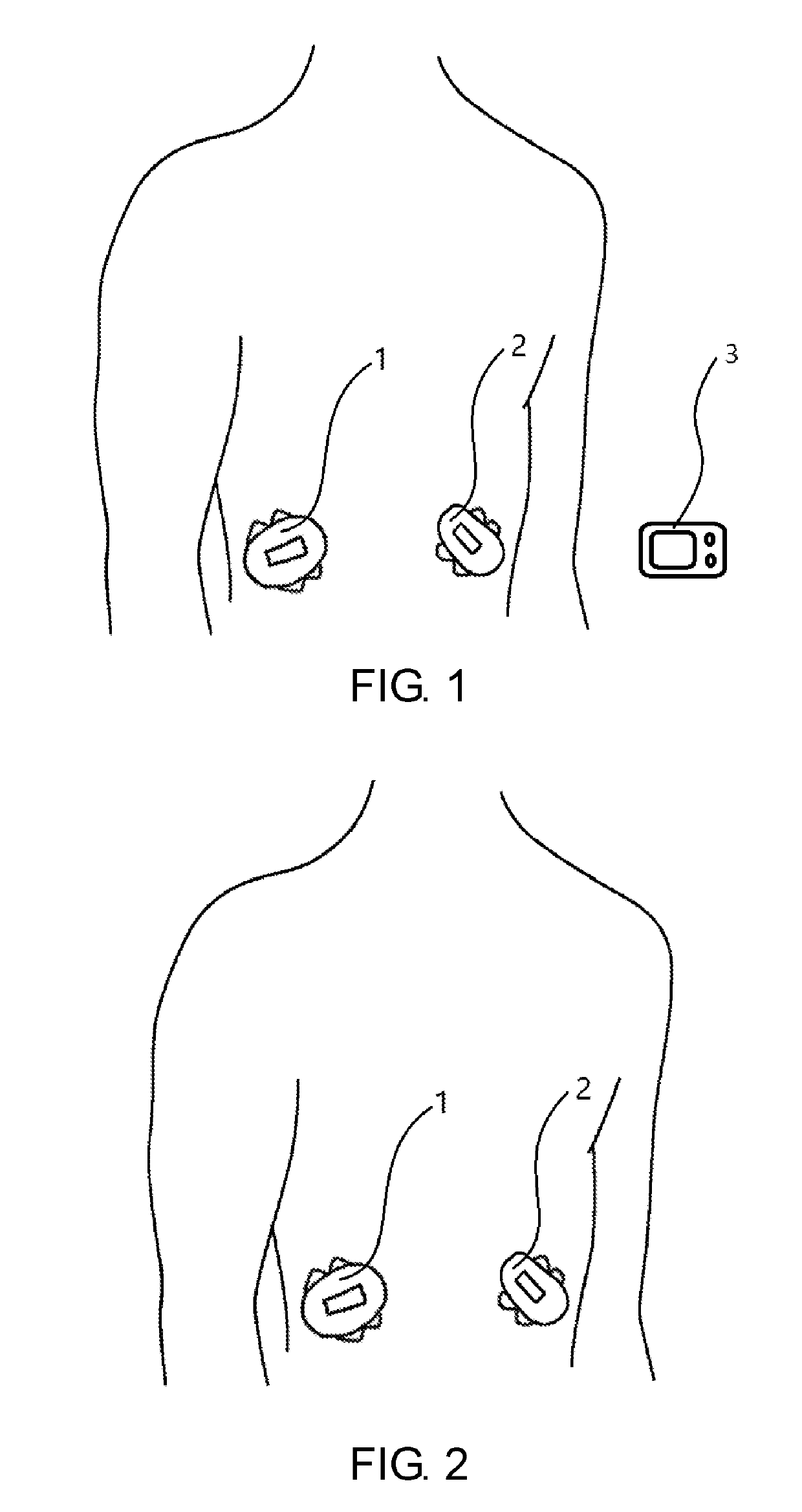
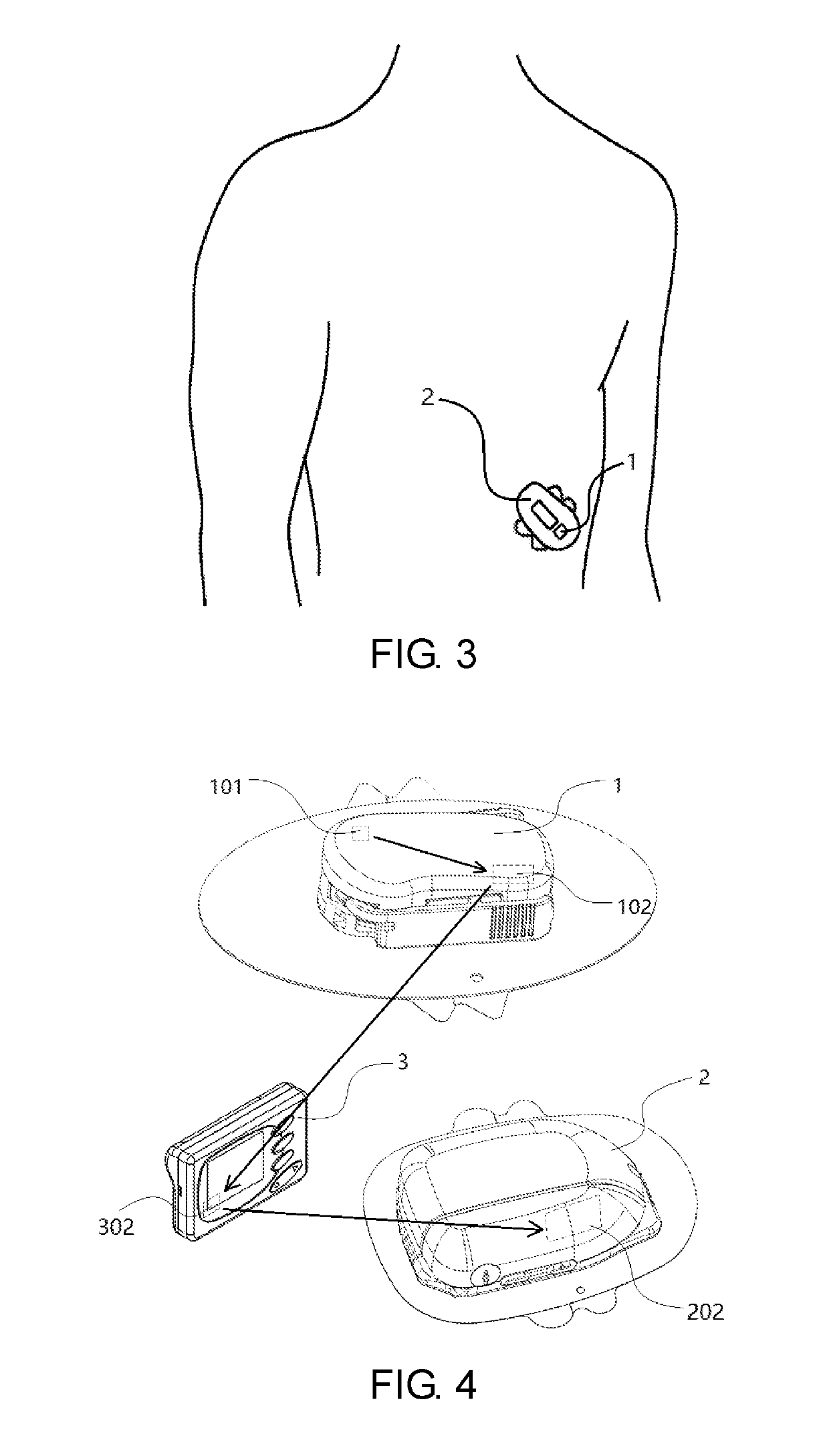
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Artificial pancreas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
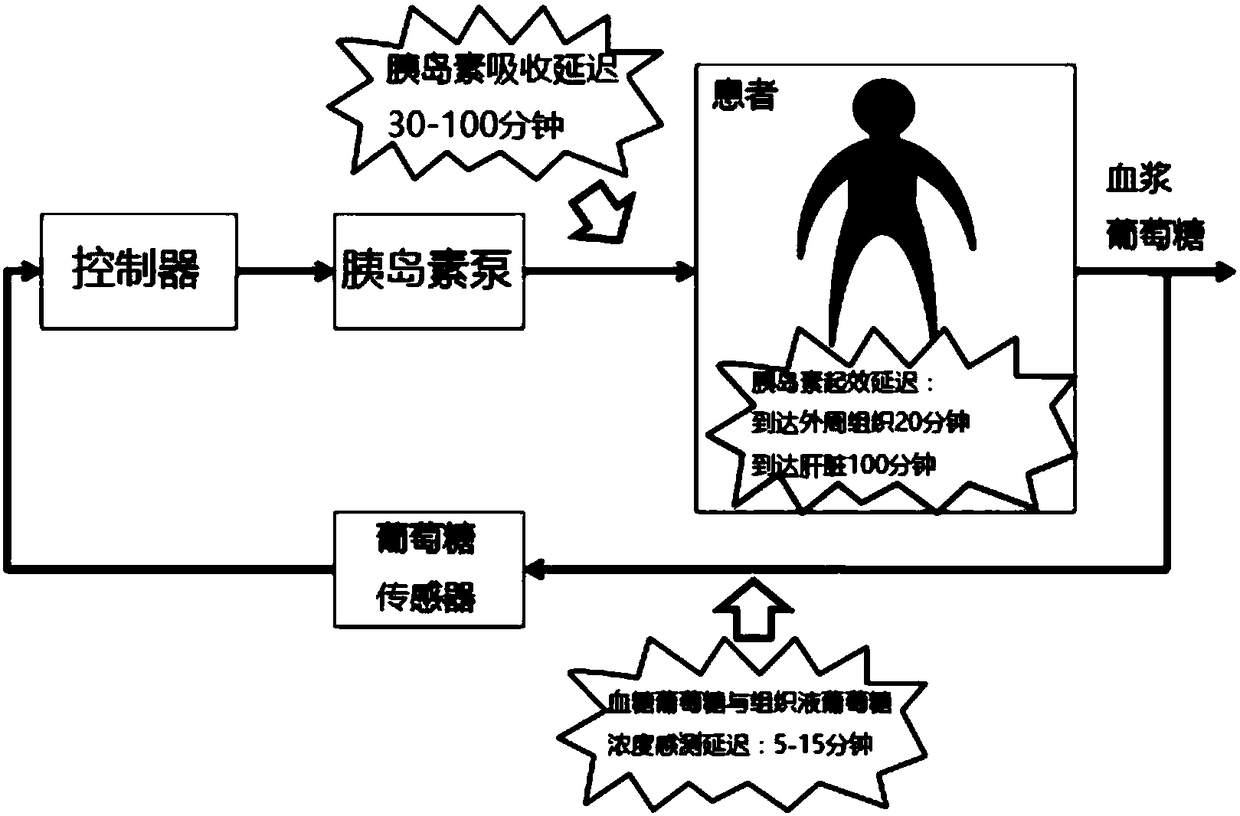
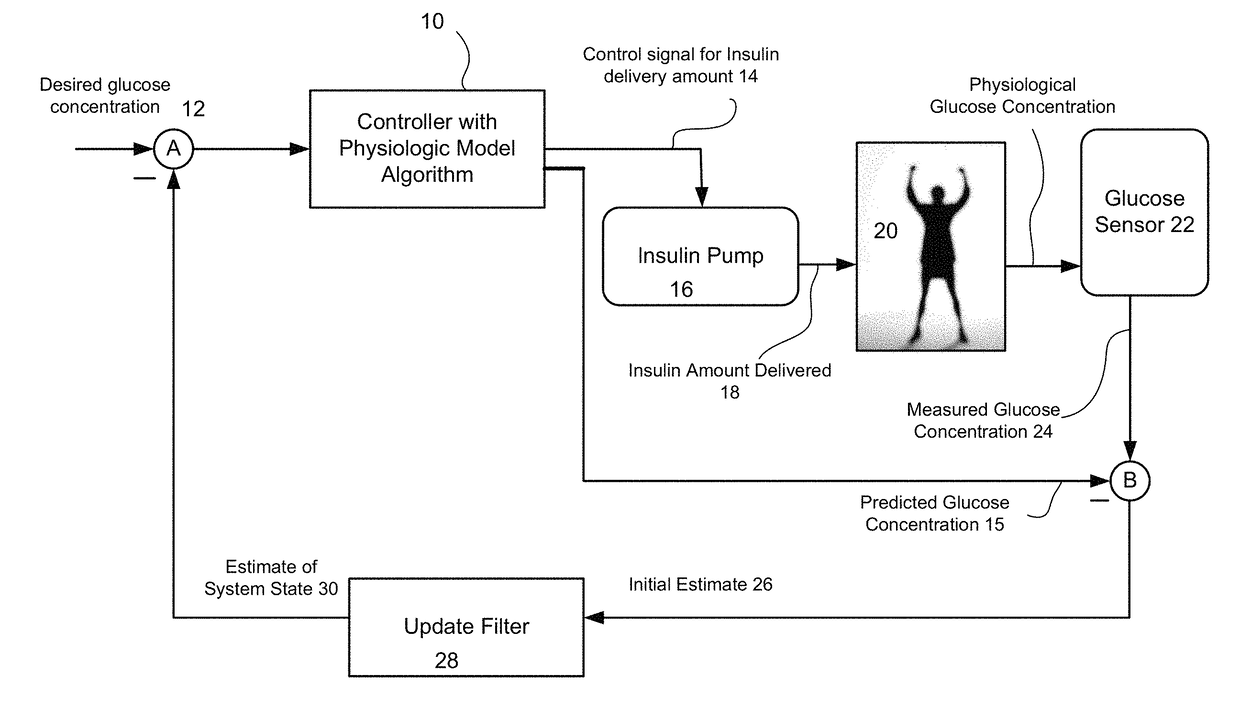
The artificial pancreas is a technology in development to help people with diabetes, primarily type 1, automatically and continuously control their blood glucose level by providing the substitute endocrine functionality of a healthy pancreas.
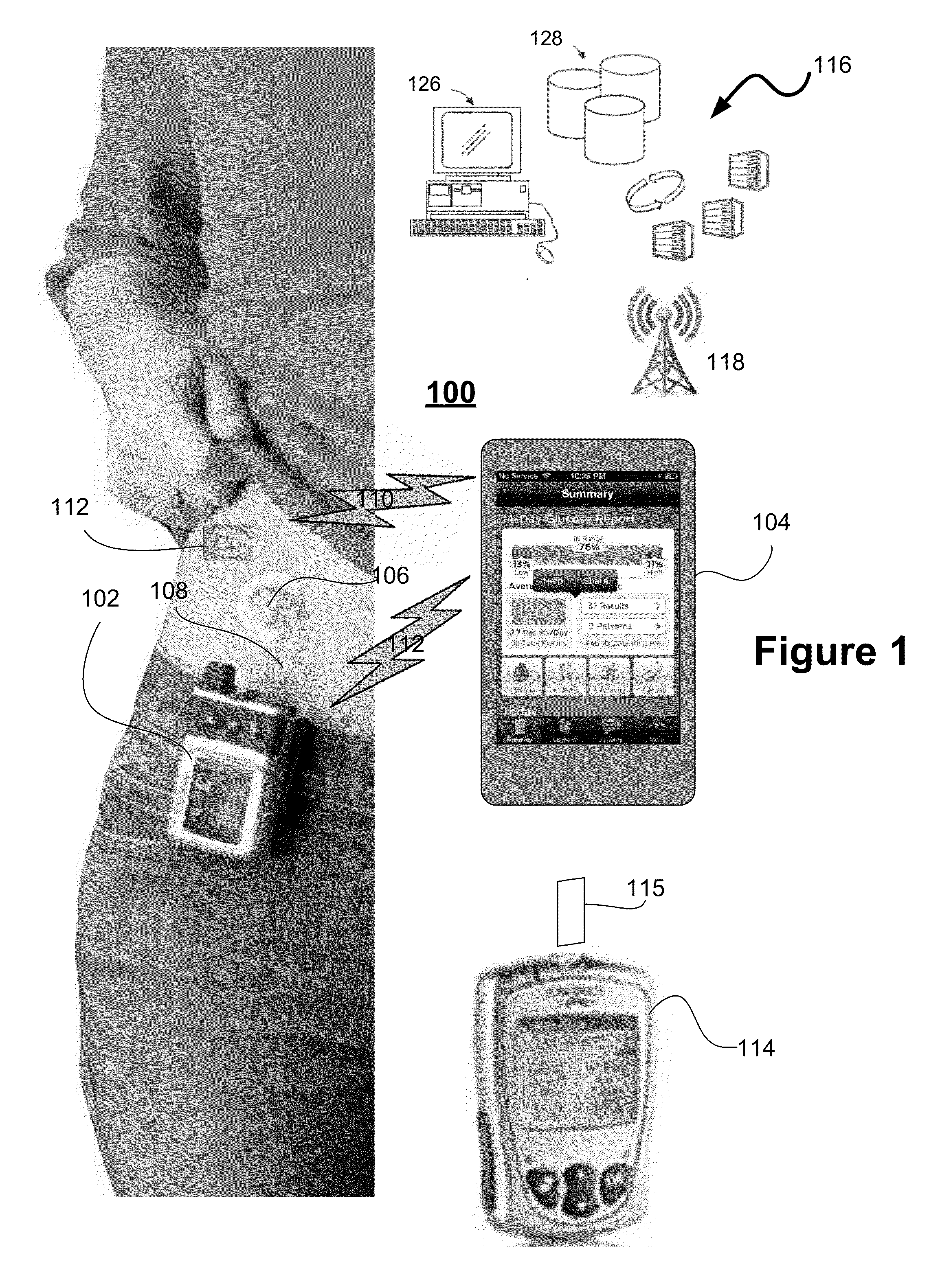
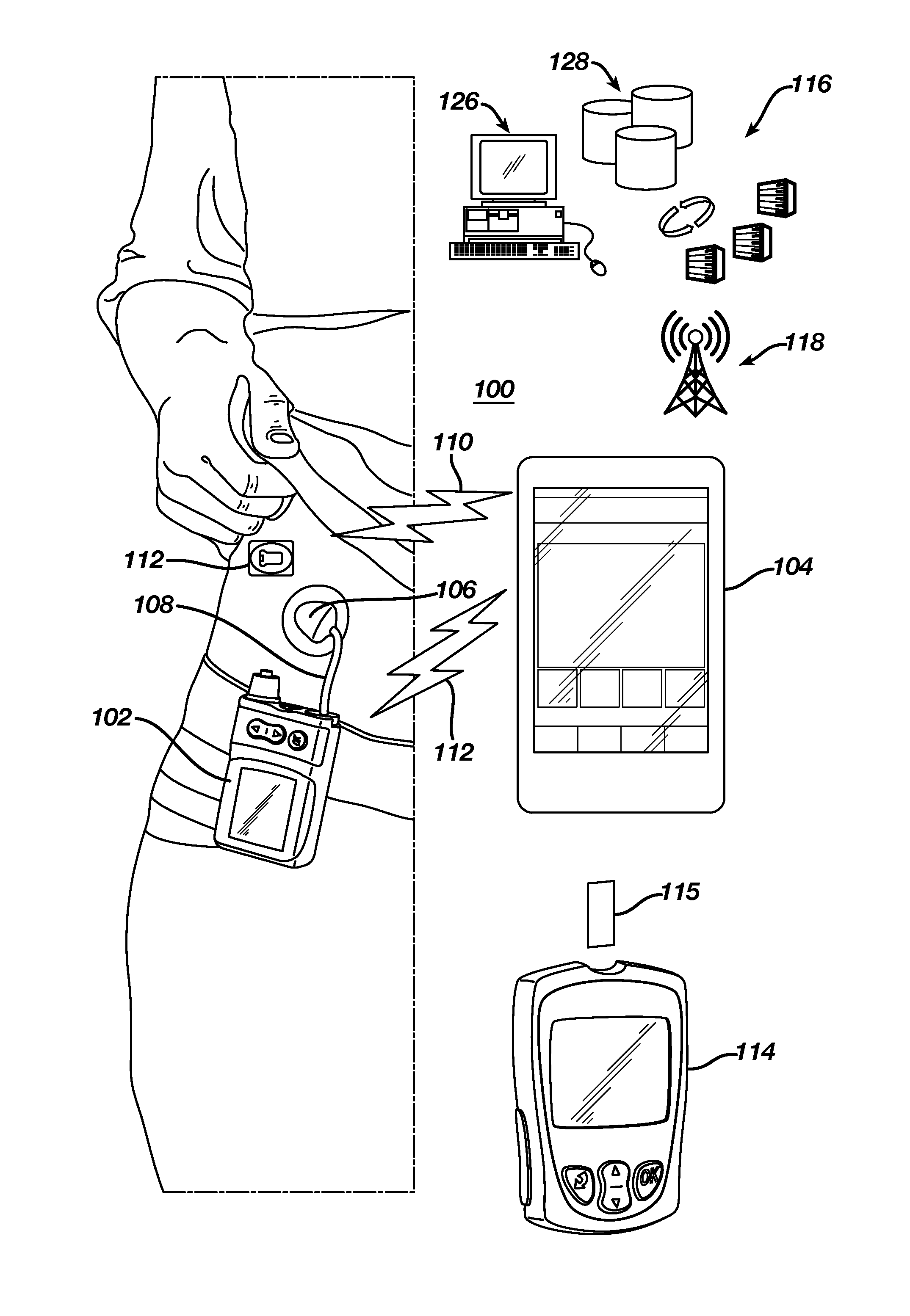
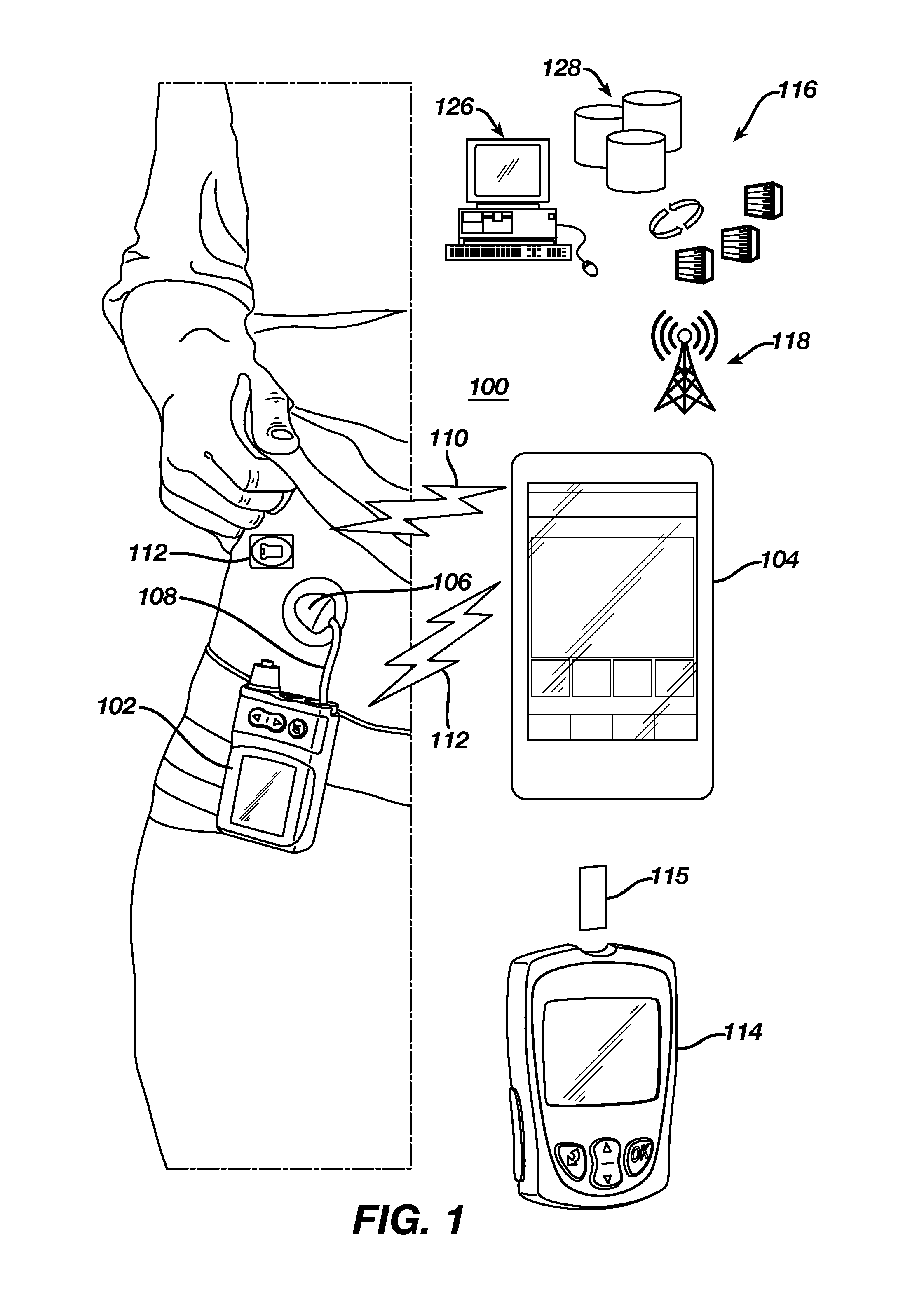
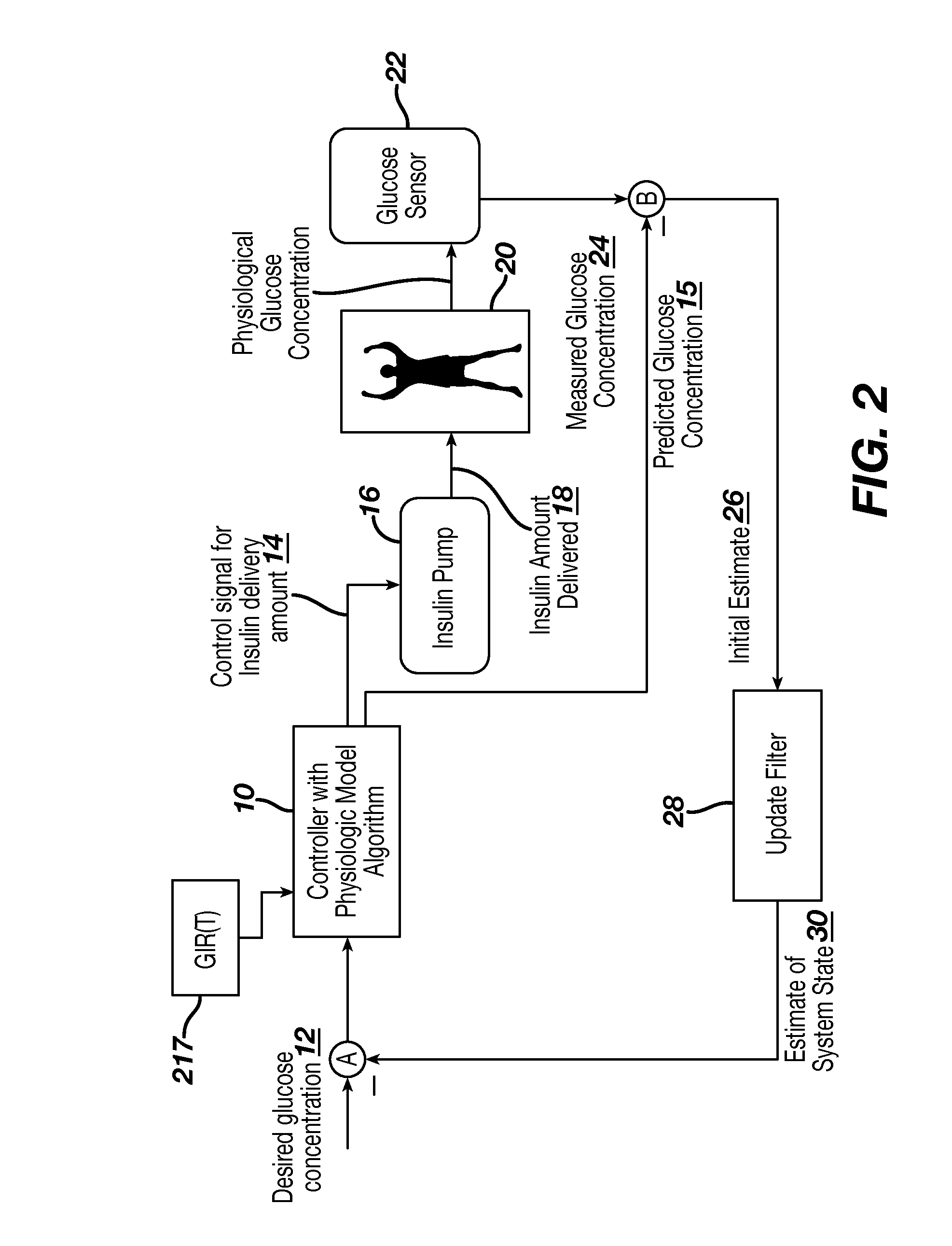
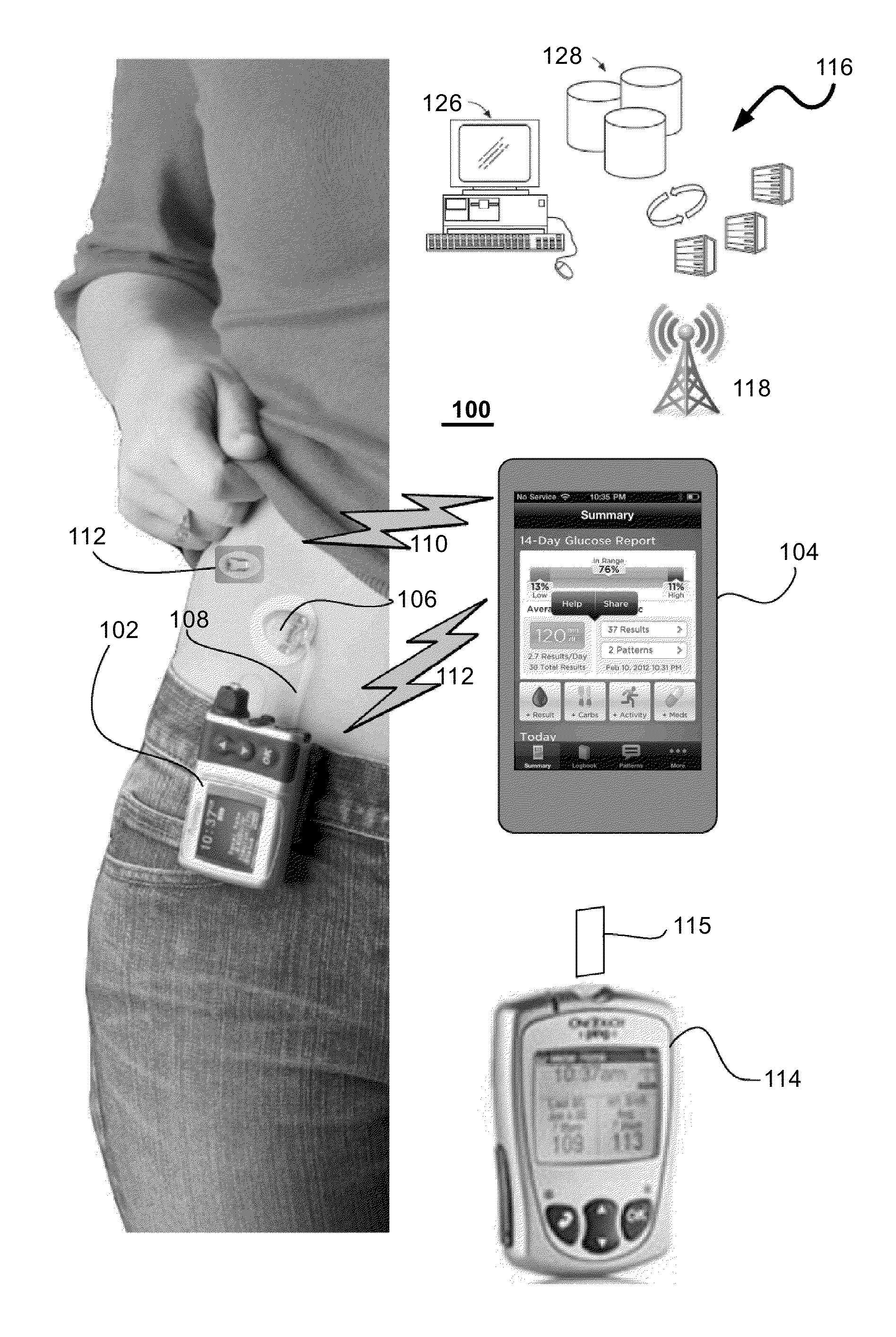
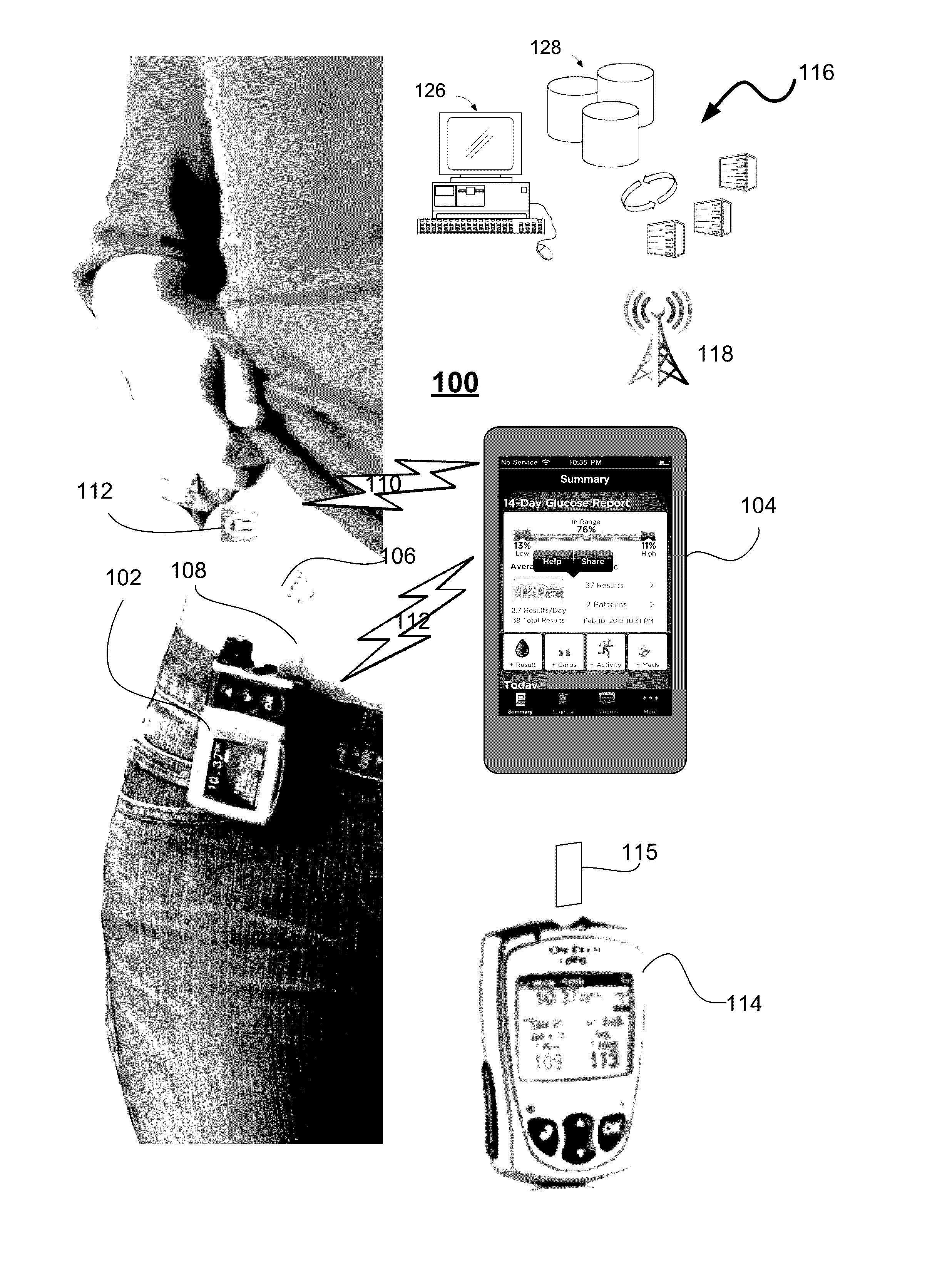
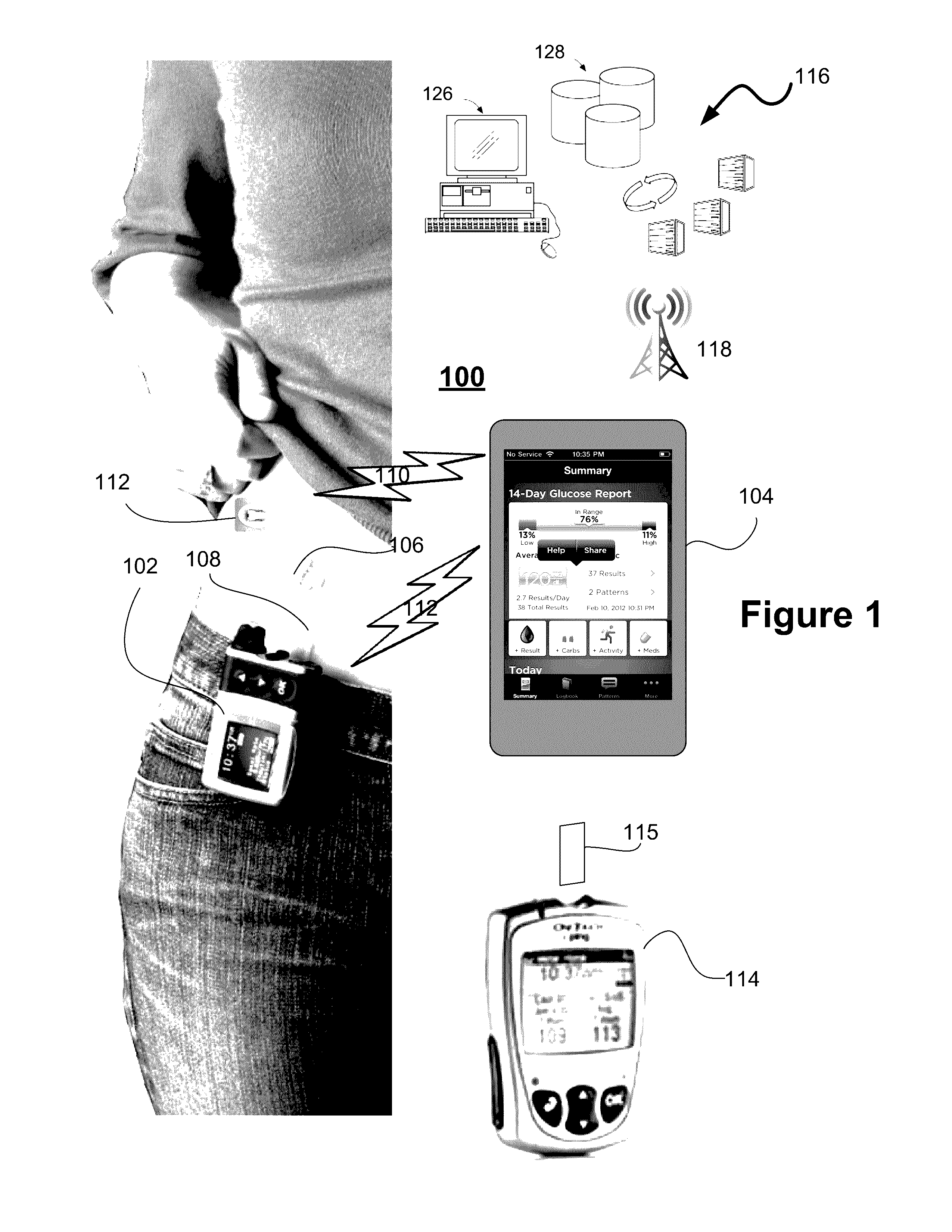
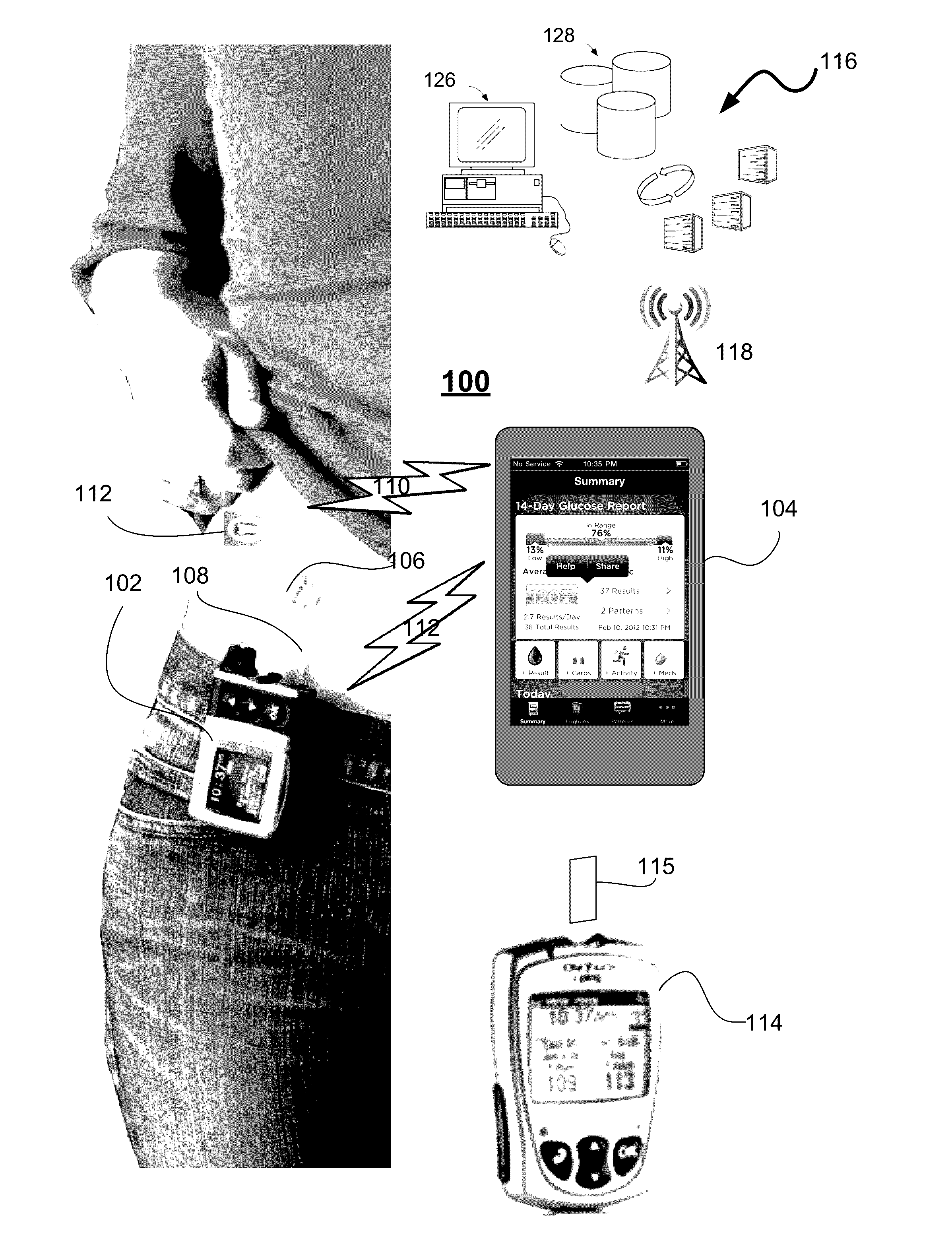
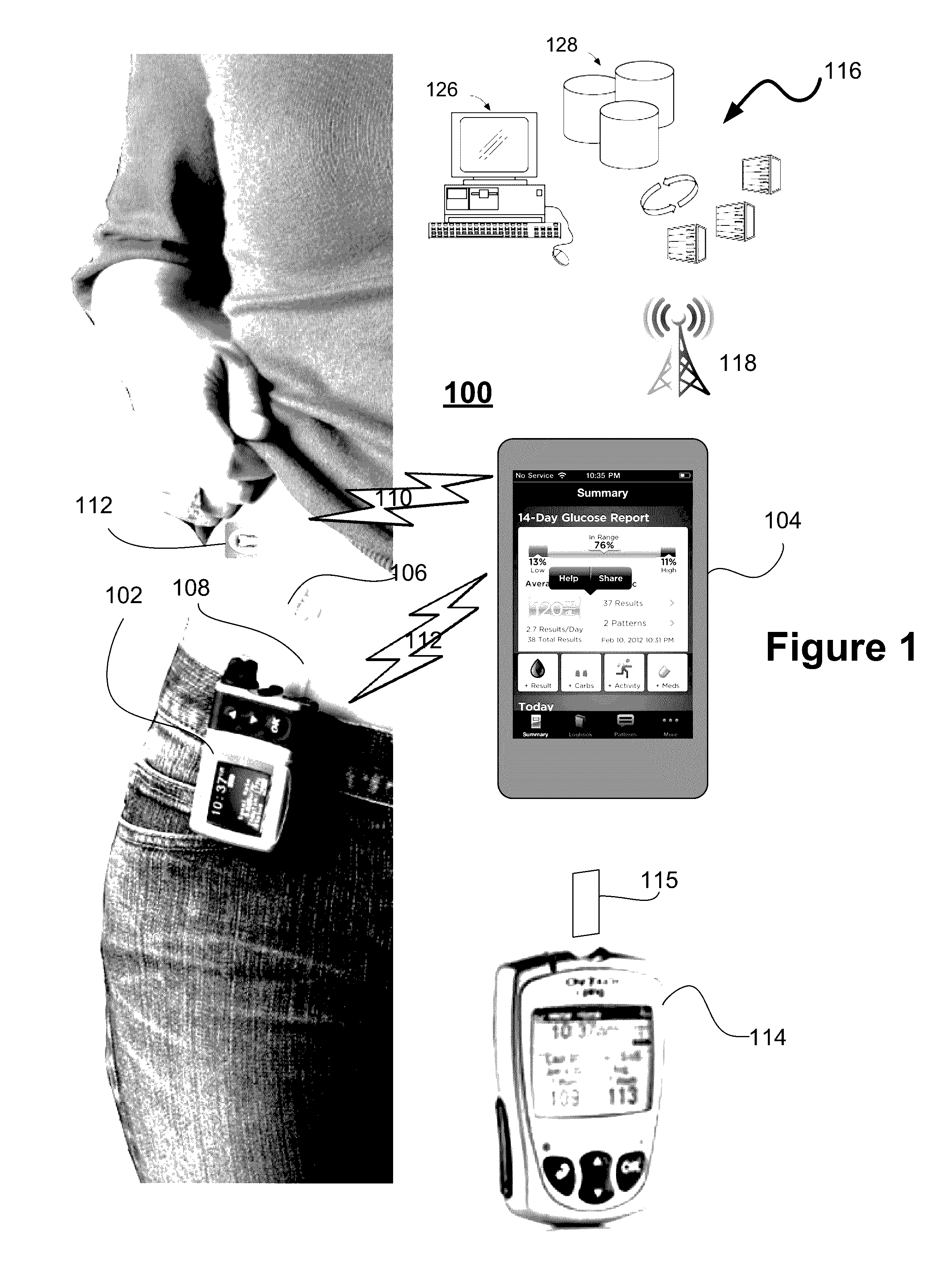
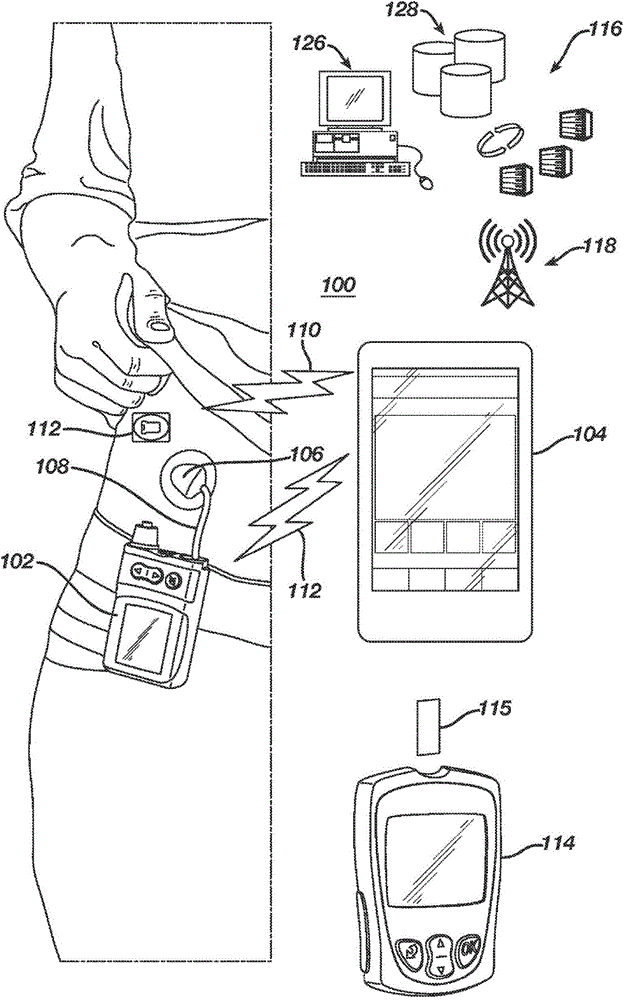
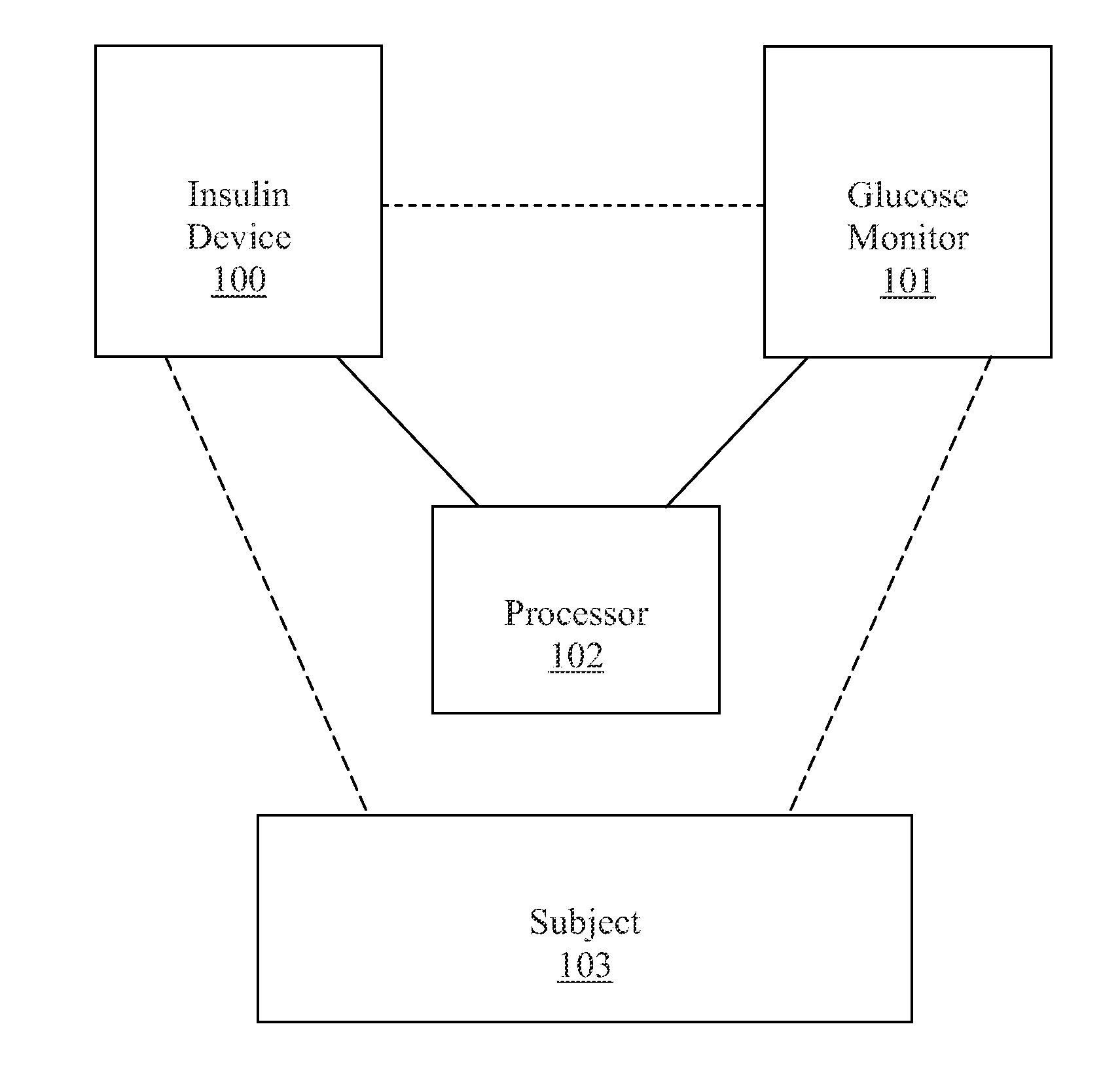
Unified Platform for Monitoring and Control of Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetic Patients
ActiveUS20150018633A1Easy to replaceGuaranteed uptimePeptide/protein ingredientsDrug and medicationsClosed loopSystem call
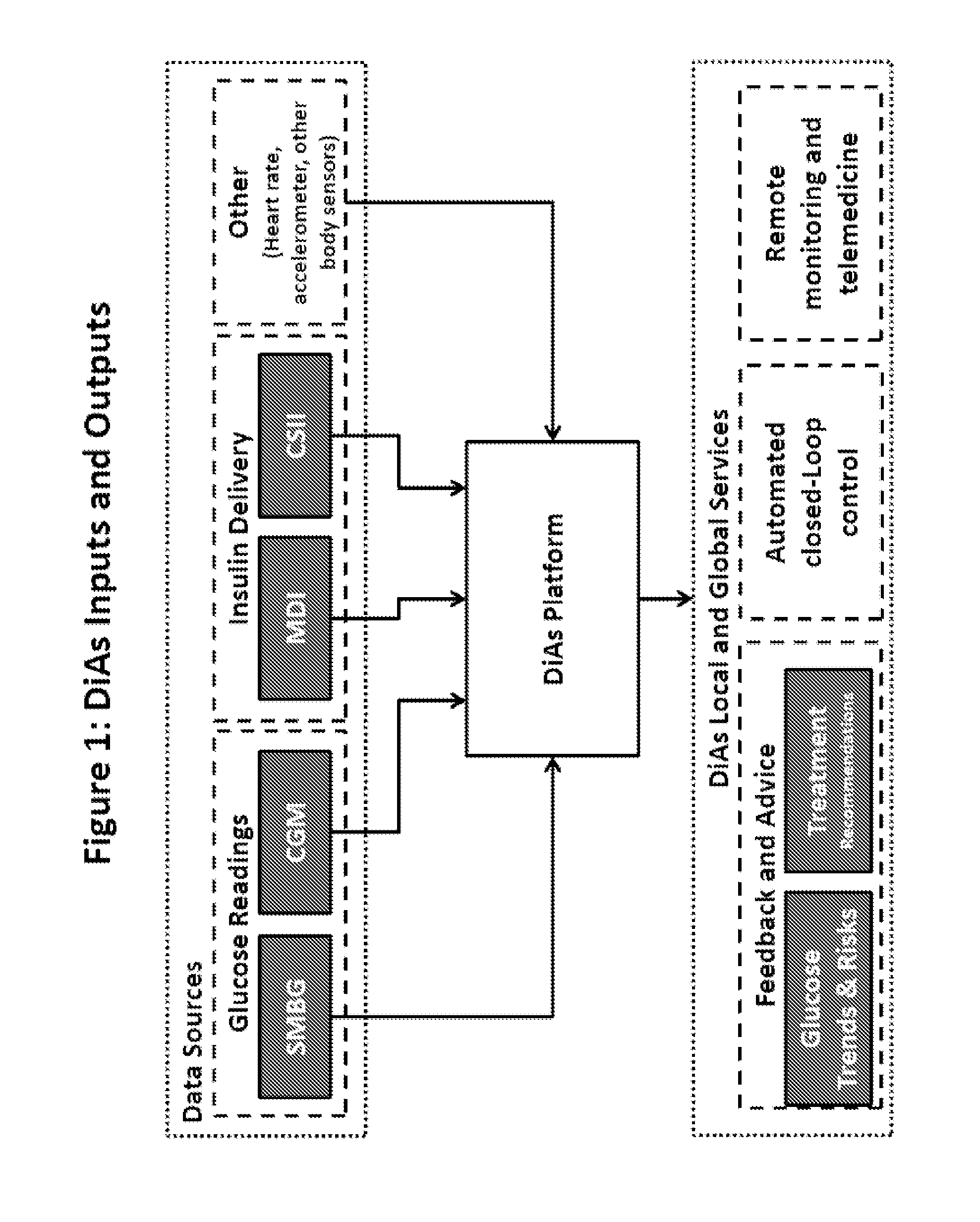
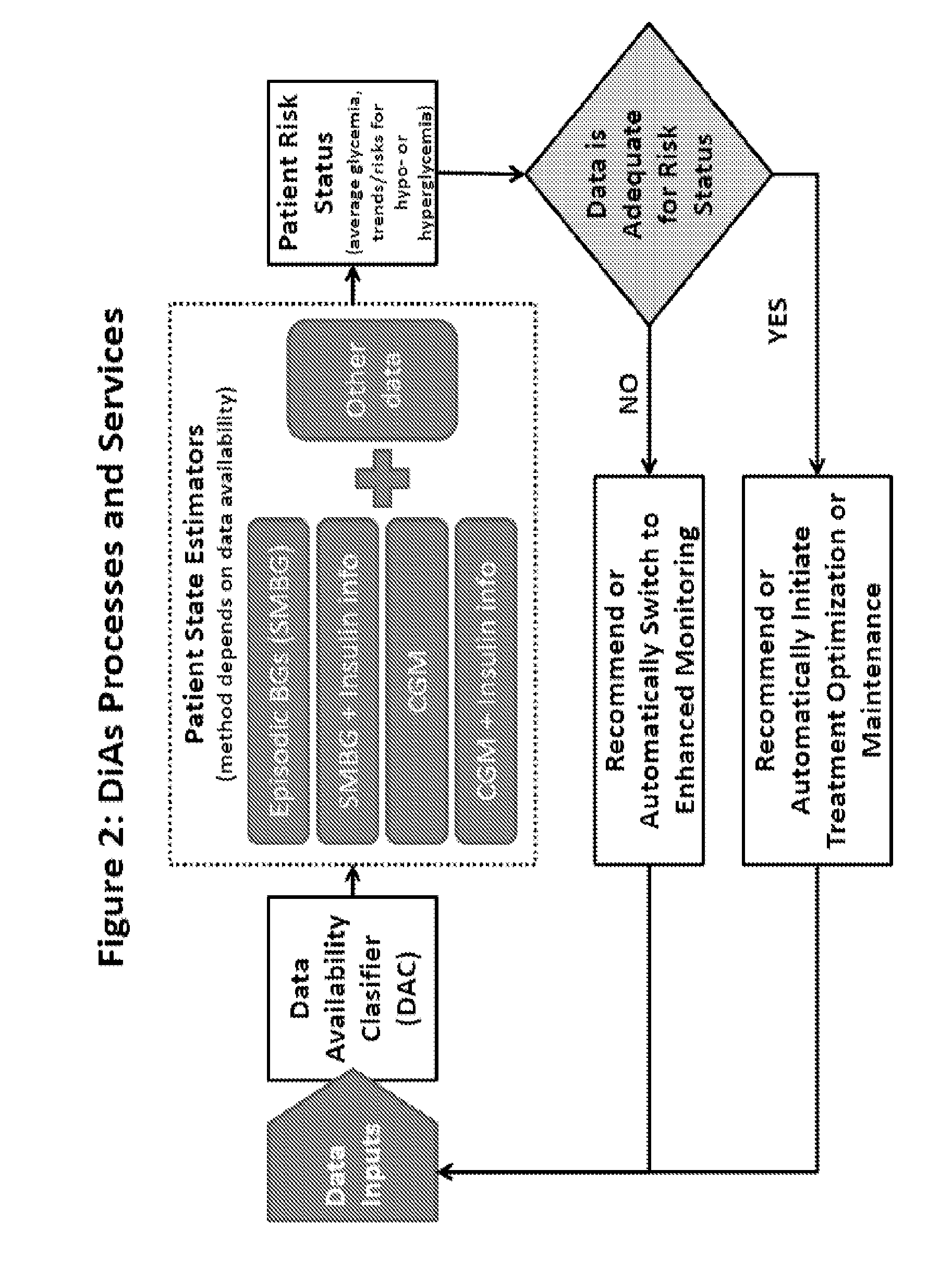
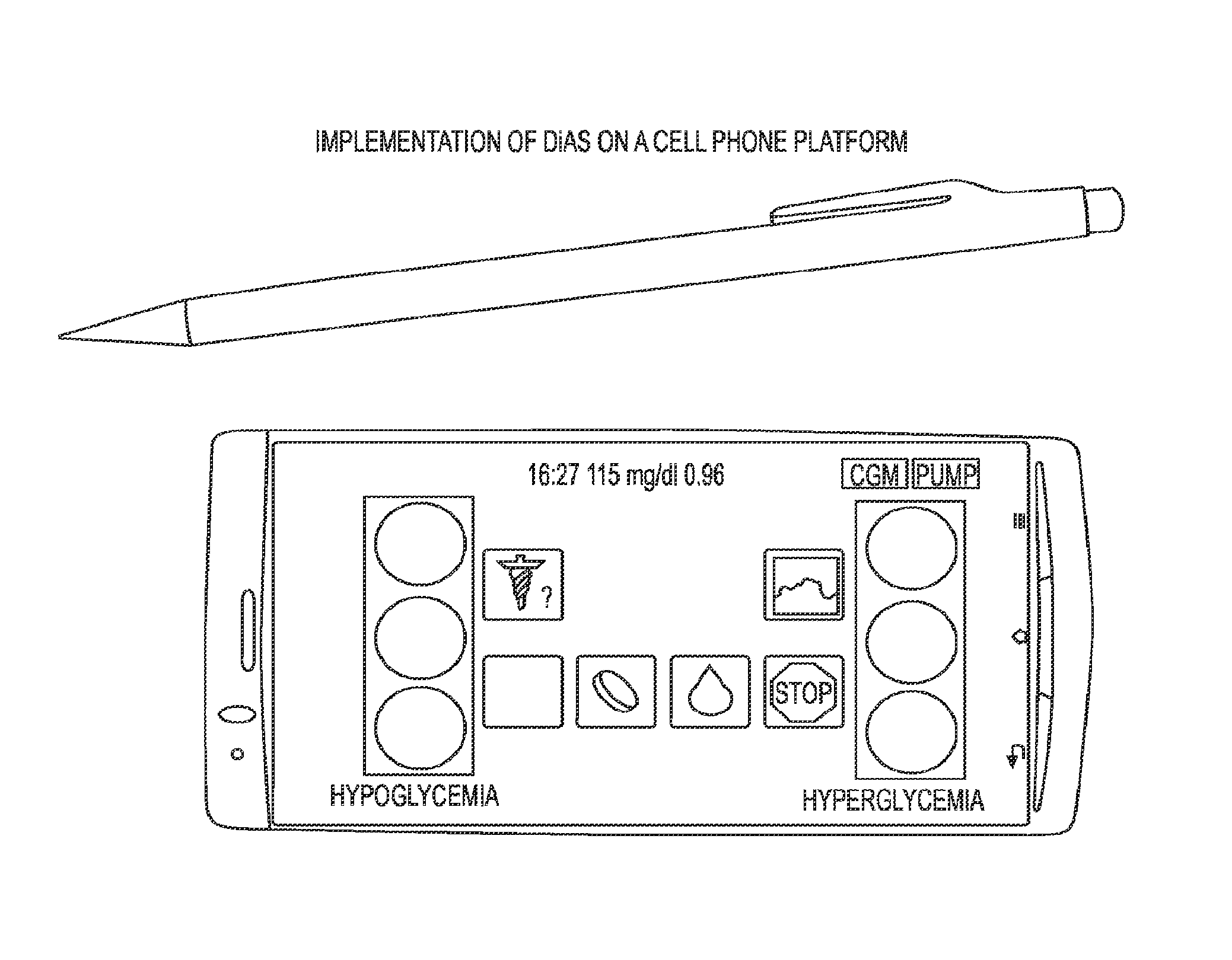
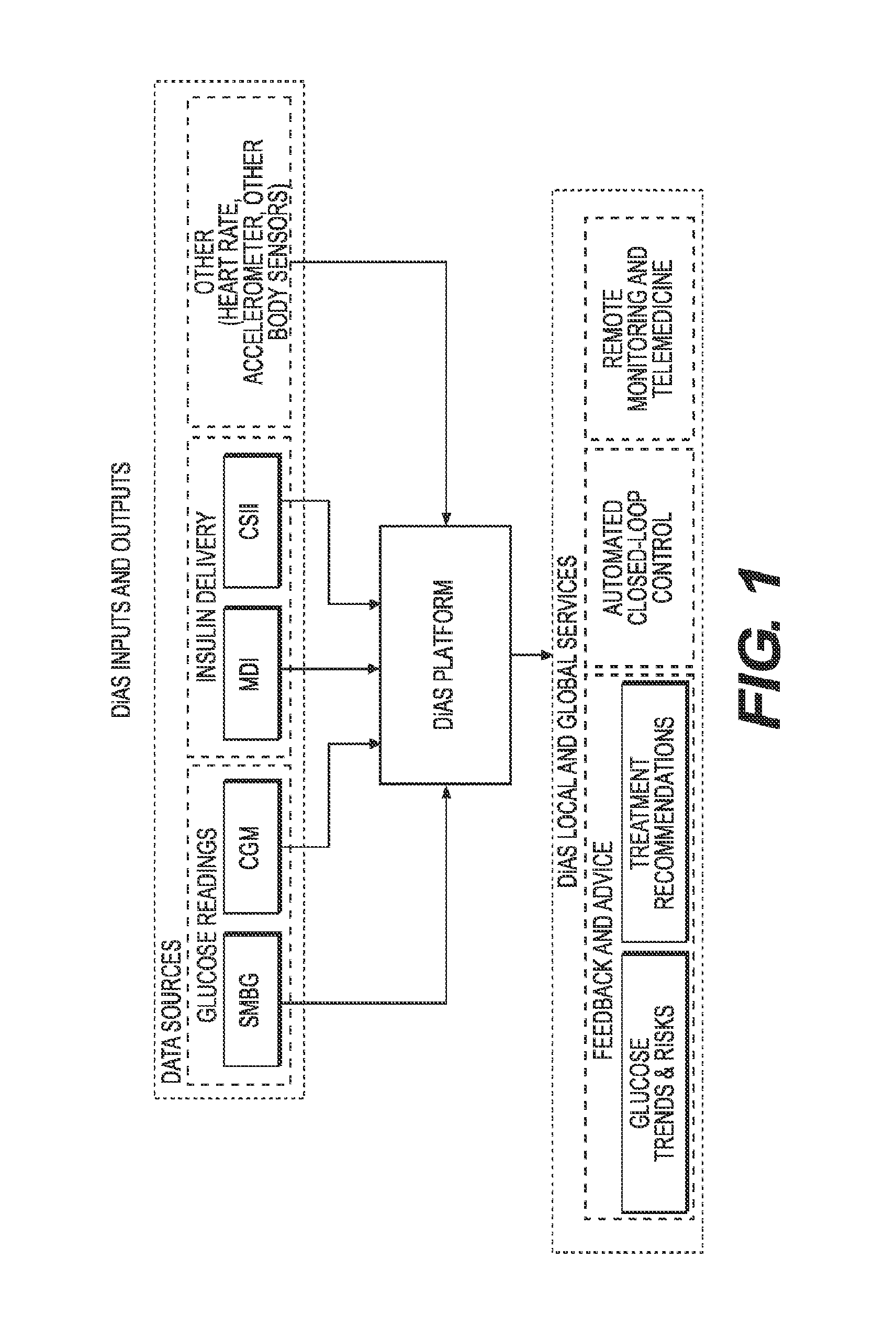
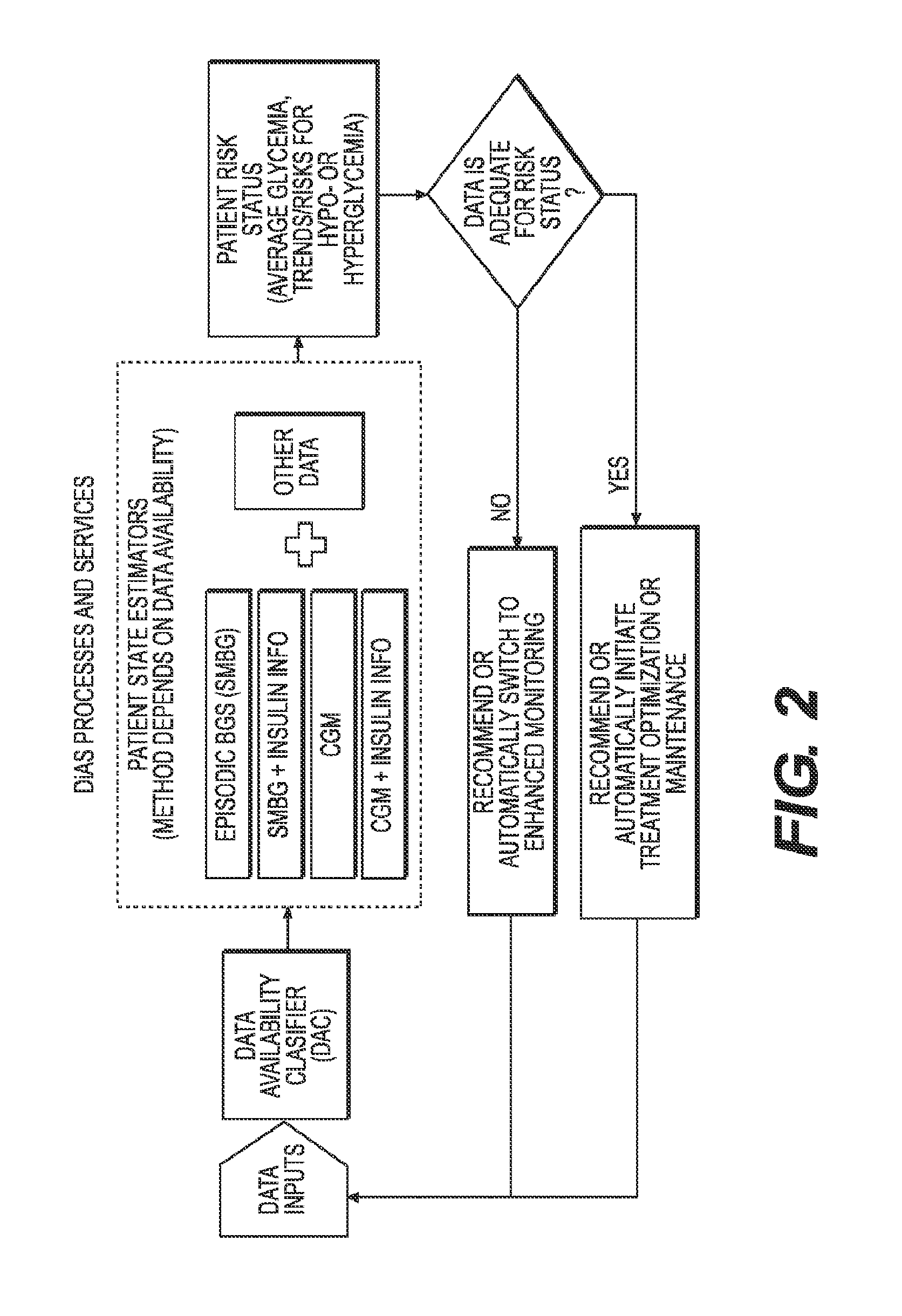
A flexible system capable of utilizing data from different monitoring techniques and capable of providing assistance to patients with diabetes at several scalable levels, ranging from advice about long-term trends and prognosis to real-time automated closed-loop control (artificial pancreas). These scalable monitoring and treatment strategies are delivered by a unified system called the Diabetes Assistant (DiAs) platform. The system provides a foundation for implementation of various monitoring, advisory, and automated diabetes treatment algorithms or methods. The DiAs recommendations are tailored to the specifics of an individual patient, and to the patient risk assessment at any given moment.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
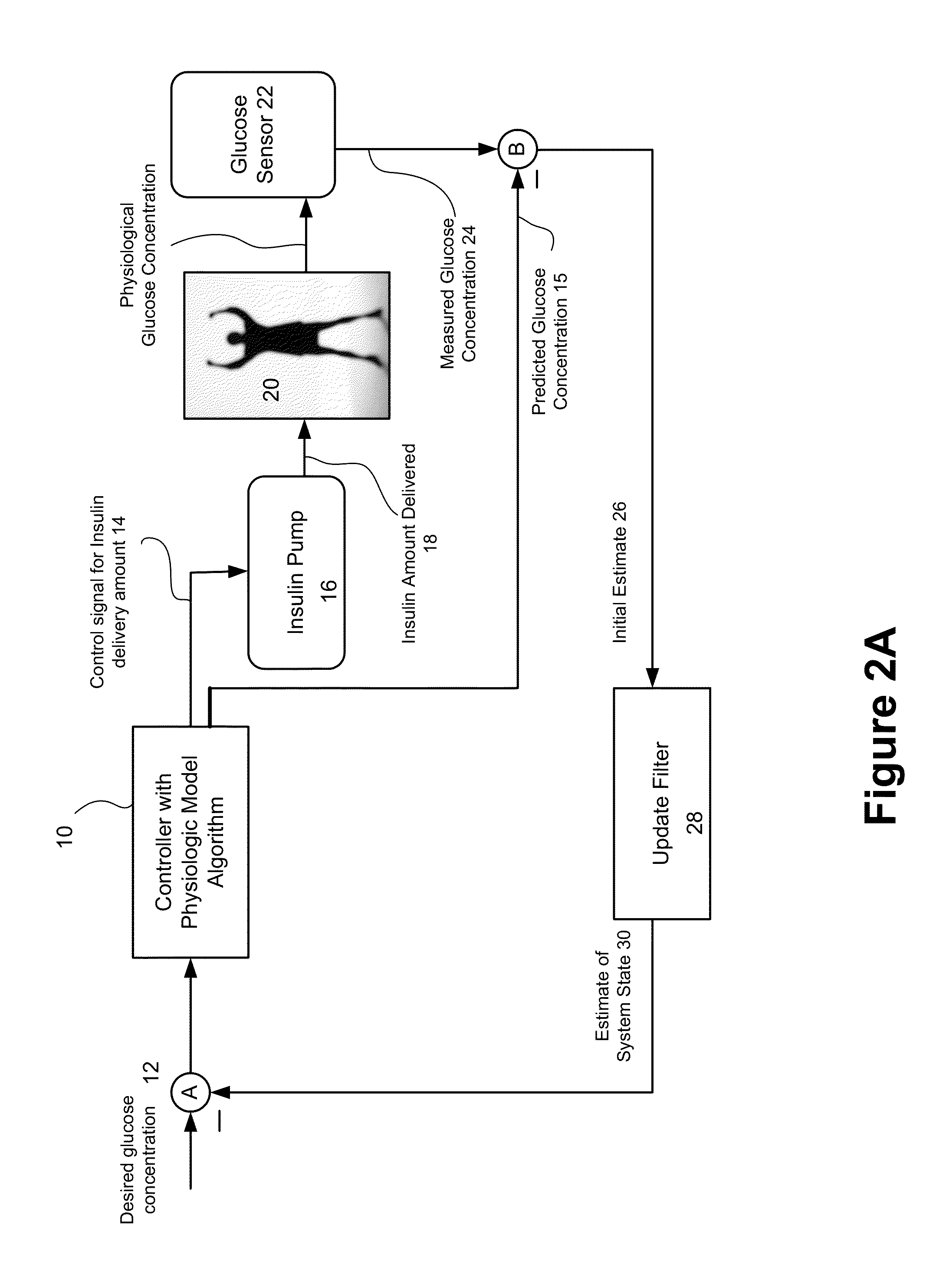
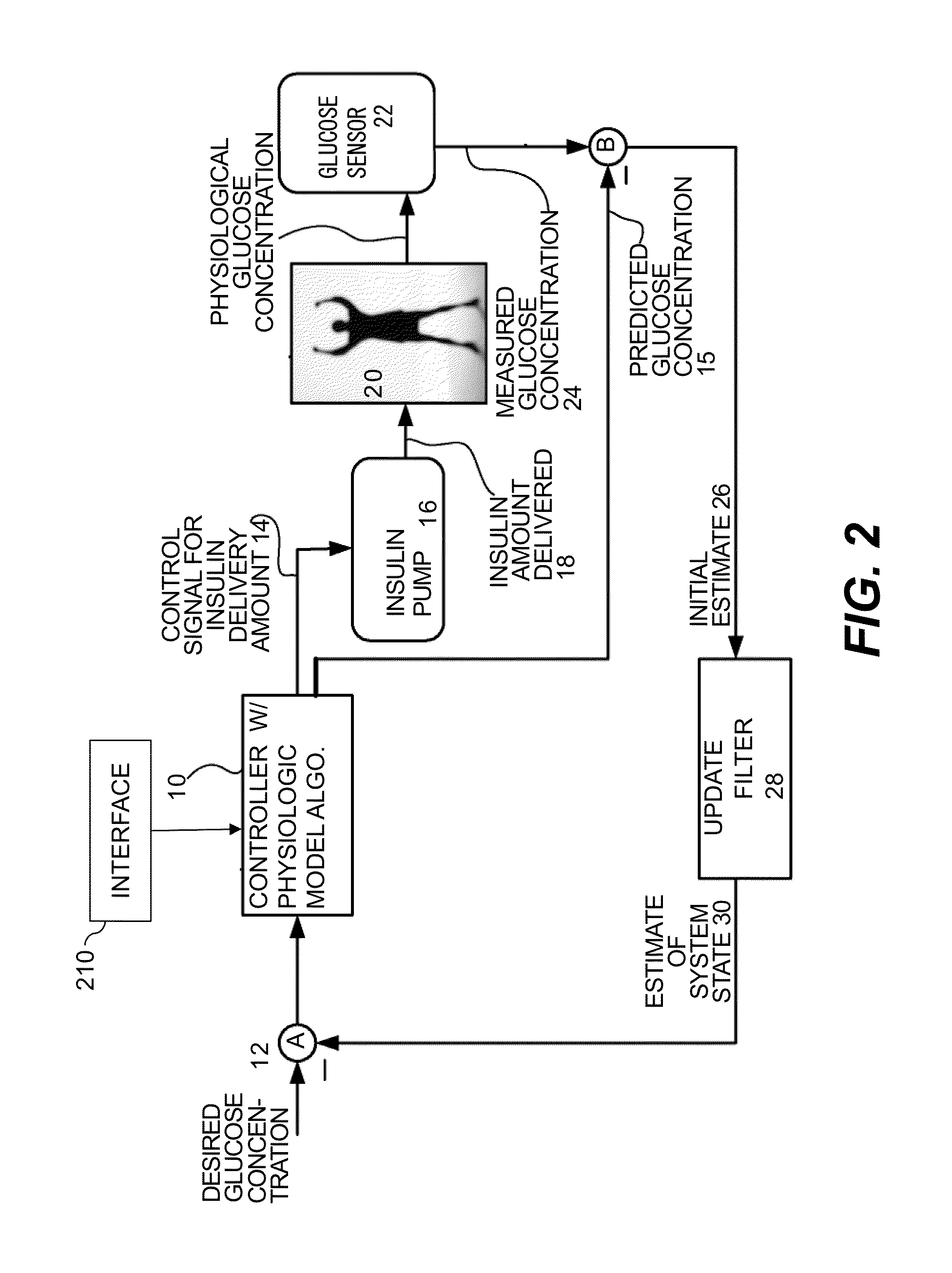
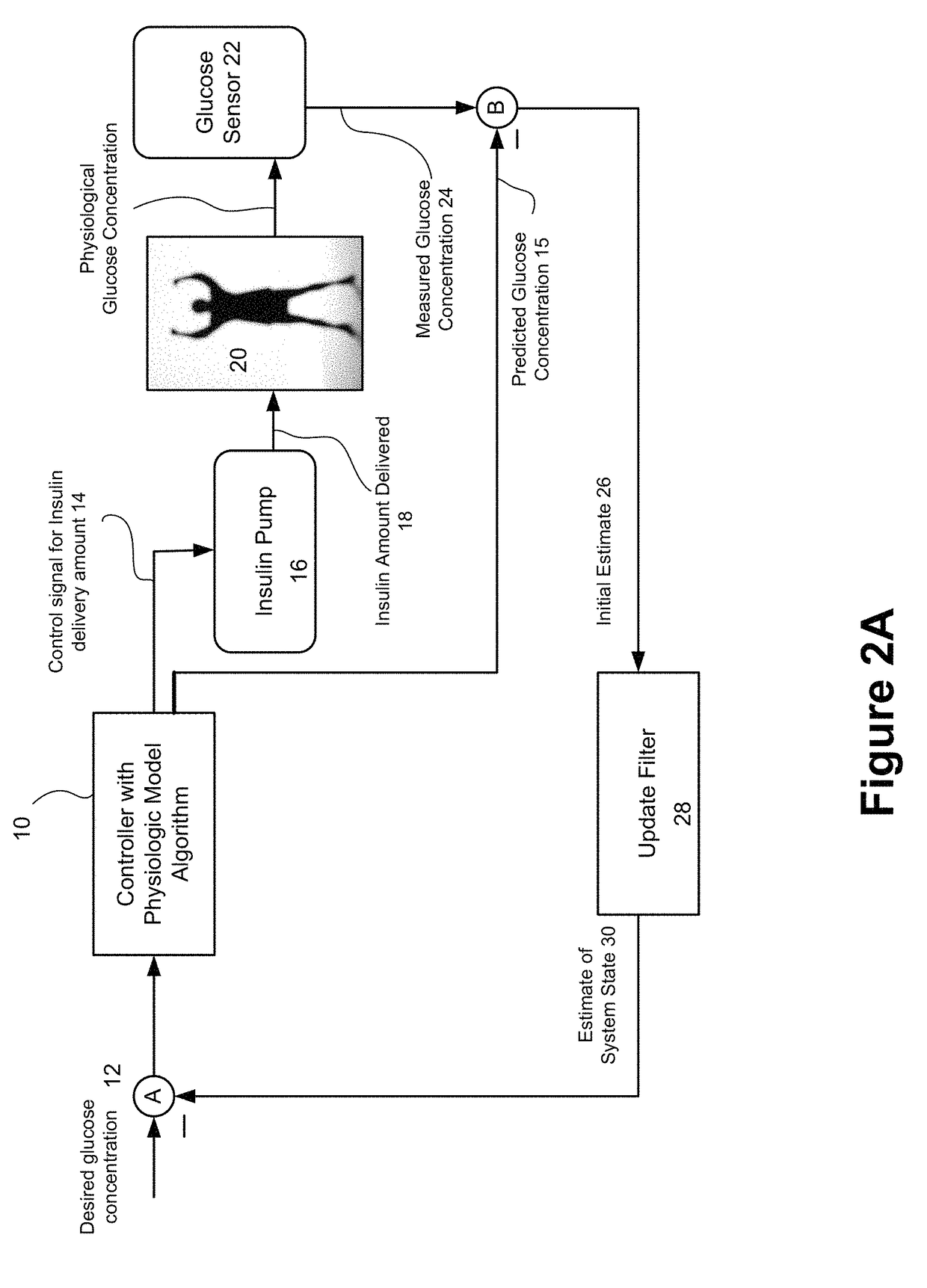
Method and system for a hybrid control-to-target and control-to-range model predictive control of an artificial pancreas
InactiveUS20140180240A1Medical simulationDrug and medicationsGlucose sensorsModel predictive control
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed into the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin to a subject. The glucose sensor is configured to sense glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed to switchover from one mode of MPC control based on a predetermined range of blood glucose values to another MPC mode based on a predetermined target.
Owner:JDRF INT +1
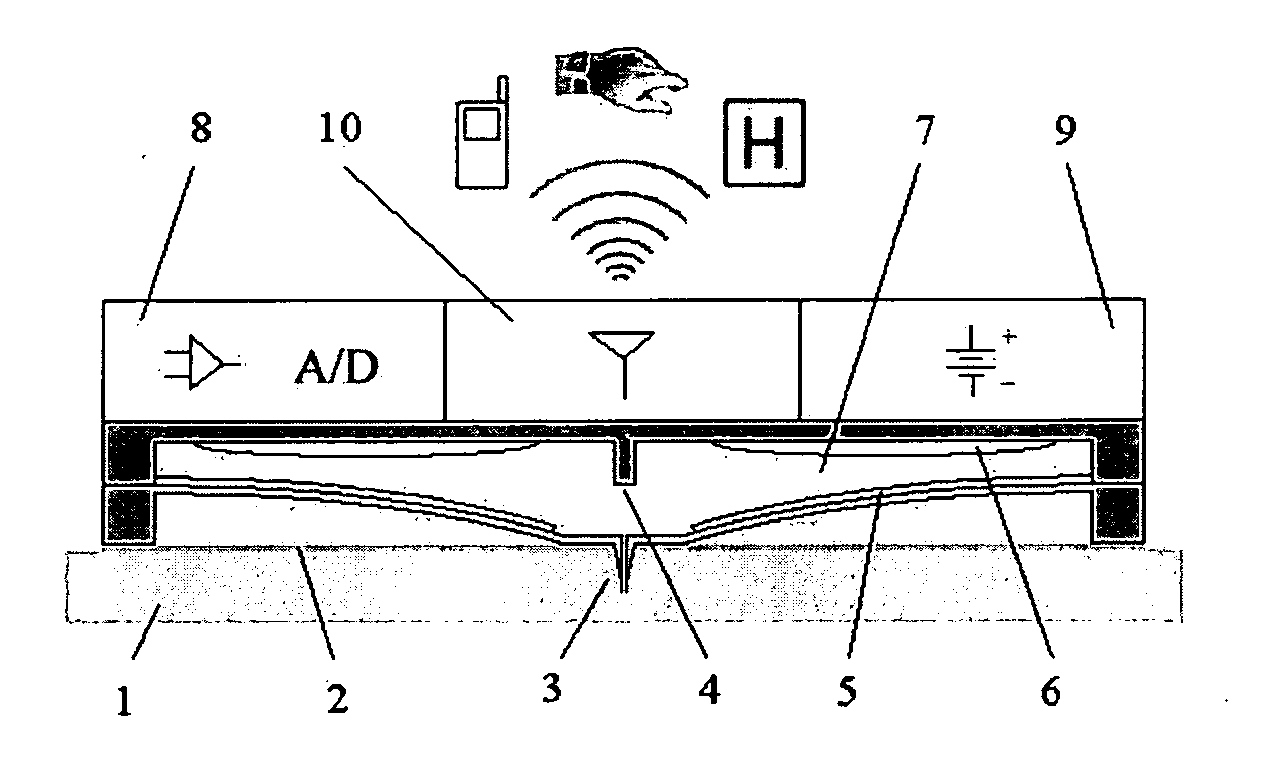
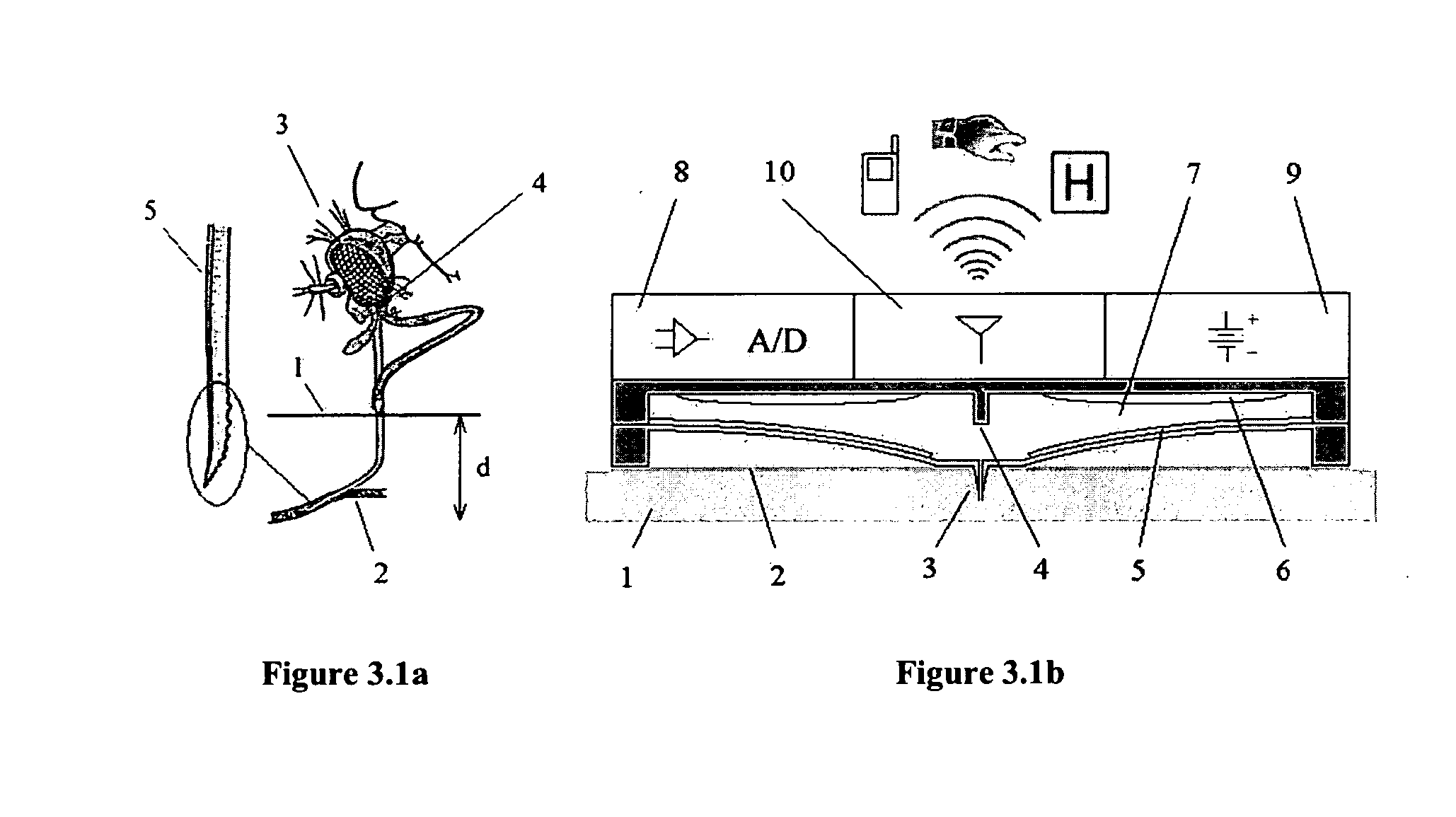
Fluid sampling, analysis and delivery system
InactiveUS20050228313A1Small volumeMinimal amountMedical devicesPressure infusionMedication monitoringPancreatic hormone
The lack of safe, reliable, automated and clinically acceptable blood sampling has been the main problem precluding the development of real-time systems for blood analysis and subsequent closed-loop physiological function control. While the analysis of a static blood sample in laboratory conditions has been rapidly advancing in reliability and blood volume reduction, non-invasive real-time blood analysis performed in vivo (while the blood is circulating in the body) has been elusive and unreliable. In this study we propose an innovative idea for semi-invasive blood sampling and analysis, which resembles the operation of a mosquito. At a miniature scale the proposed system does penetrate the skin to extract a static blood sample for further analysis, but the extent of this penetration, and the fact that it can be made painless, is particularly attractive for such applications as automated glucose analysis for closed-loop control of insulin infusion (artificial pancreas), continuous drug monitoring, or even periodic DNA analysis for security and identification purposes. These design aspects are described, and a specific implementation, applying MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical Systems) technology, is suggested. The proposed microsystem is a matrix of individually controllable e-Mosquito™ cells, packaged in a disposable patch and attached to the skin, could be an avenue for real-time semi-invasive blood analysis and diagnostics.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT
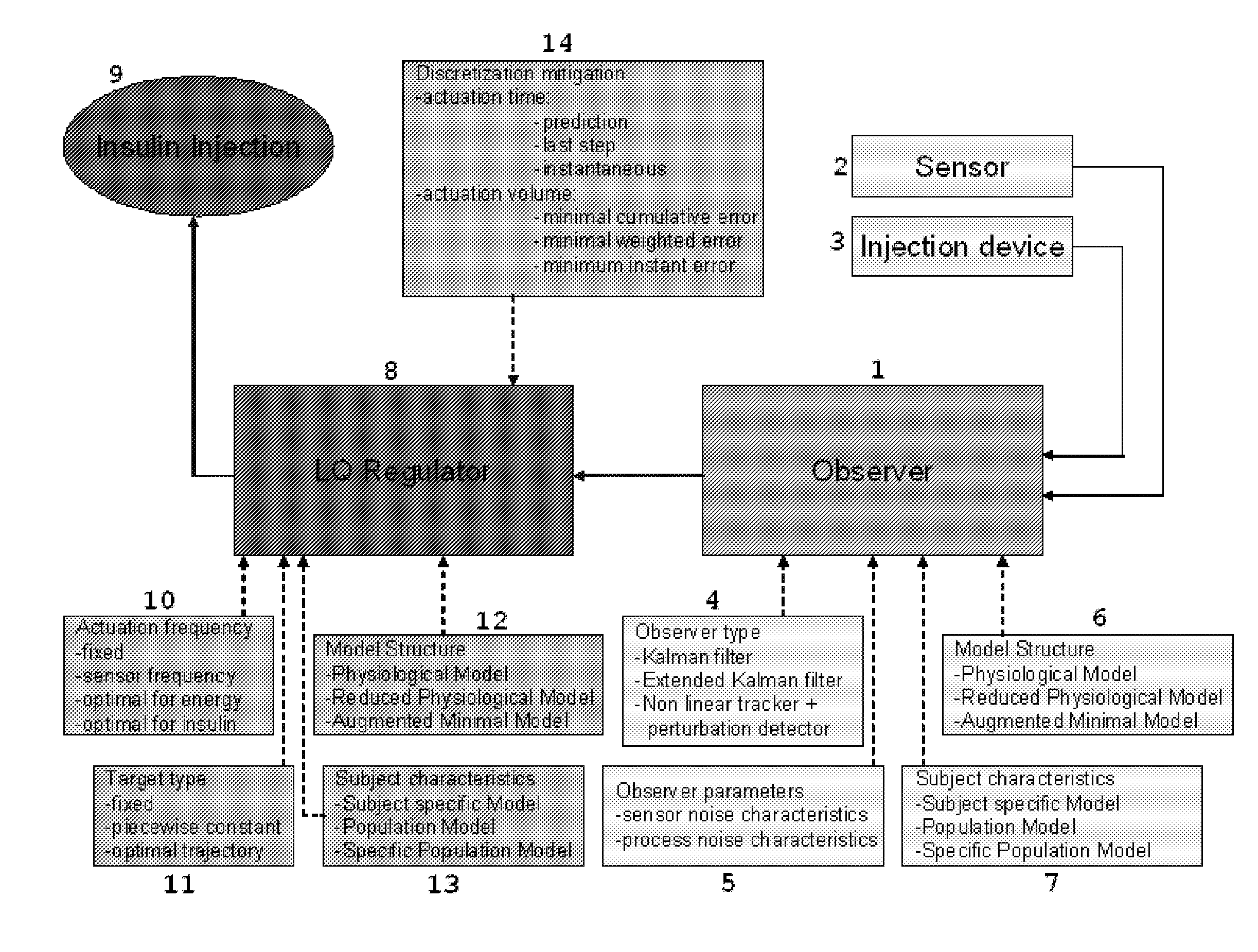
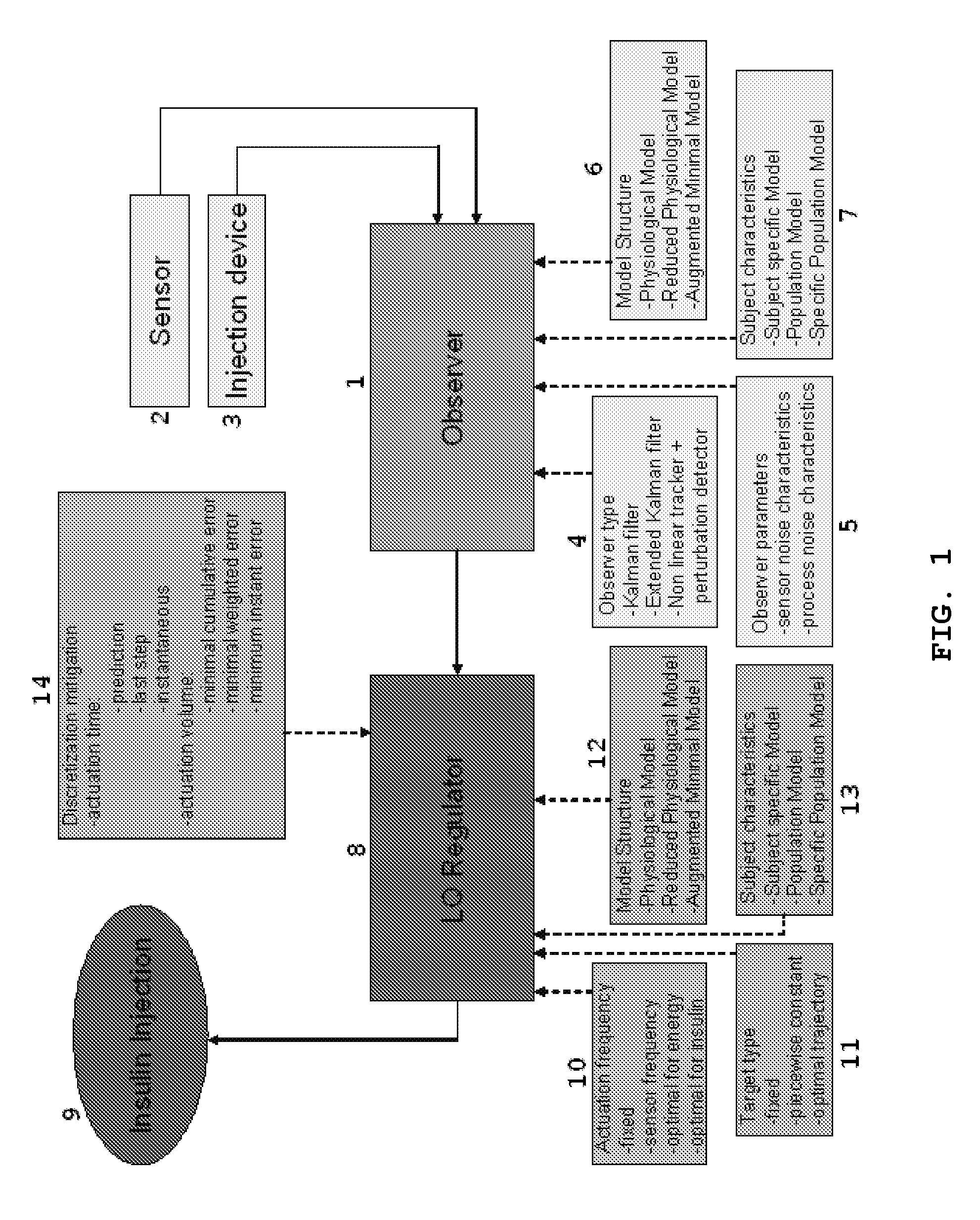
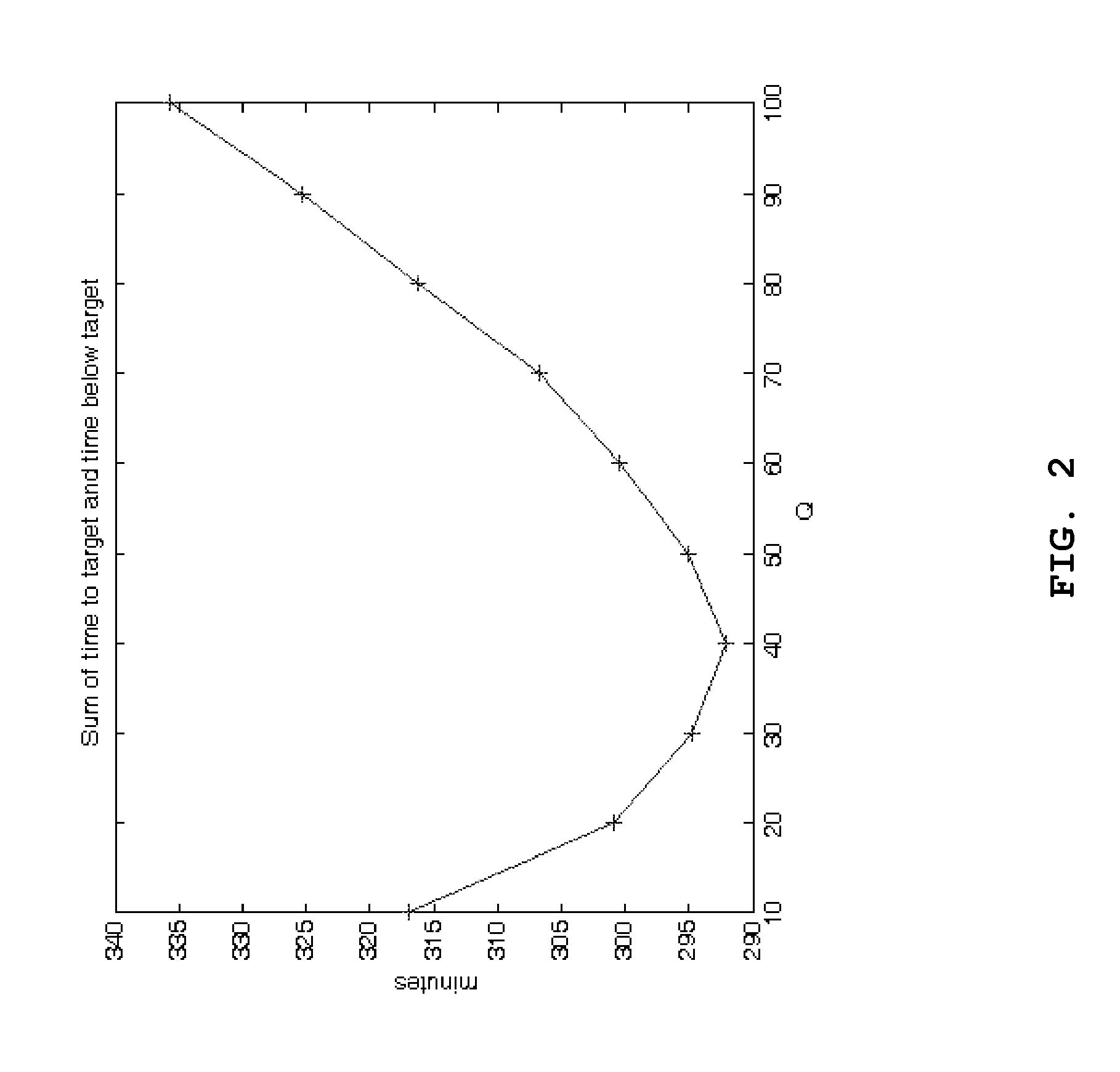
LQG Artificial Pancreas Control System and Related Method
ActiveUS20100249561A1Minimize quadratic cost functionMinimize cost functionMedical simulationDrug and medicationsAdaptive filterControl system
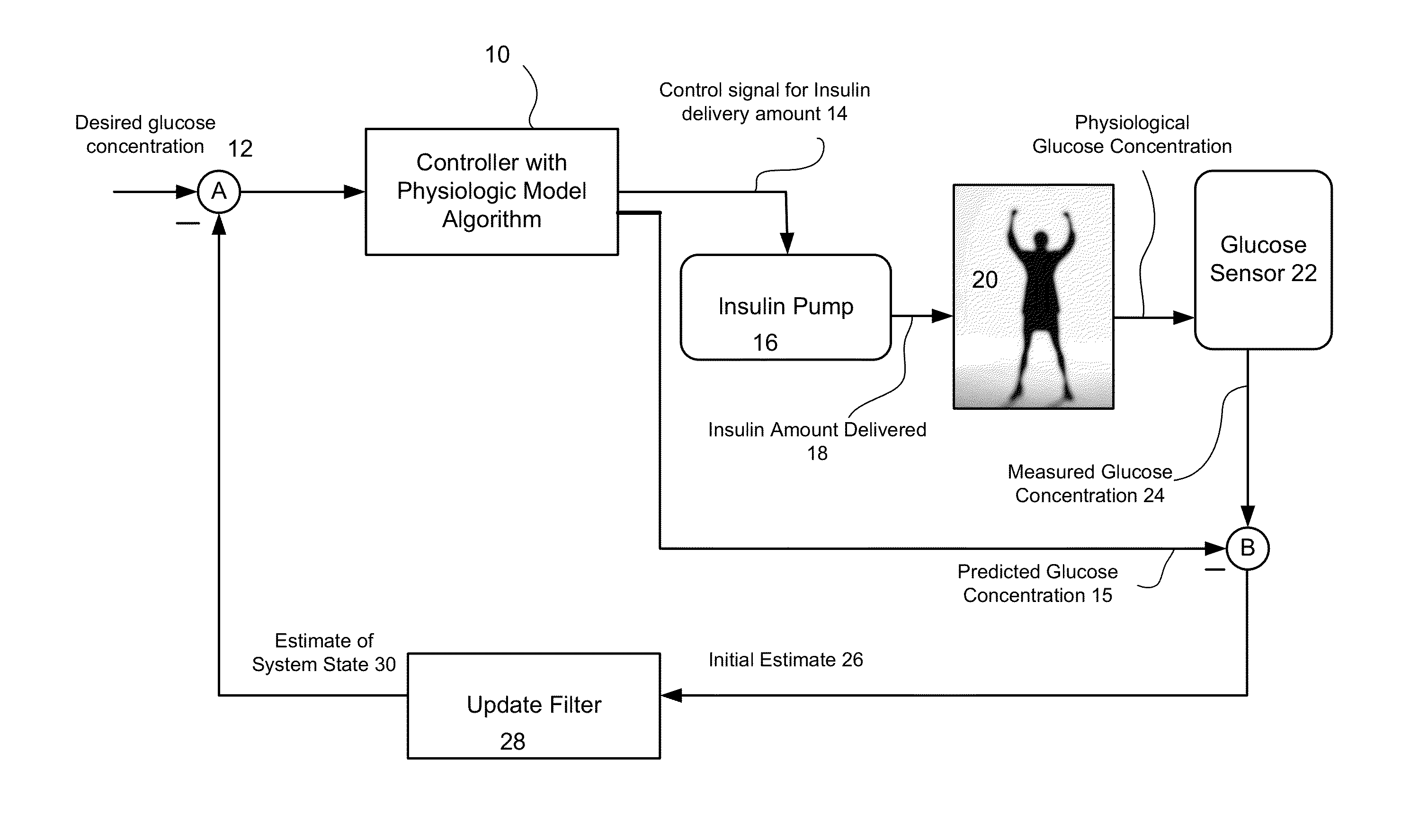
The invention relates to a methods and systems for determining an insulin dosing recommendation. The invention employs Linear Quadratic methodology to determine the insulin dosing recommendation based on a patient's present physiological state, which is estimated by an adaptive filter methodology employing a dynamic model, which utilizes real-time measurements of blood glucose concentration.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
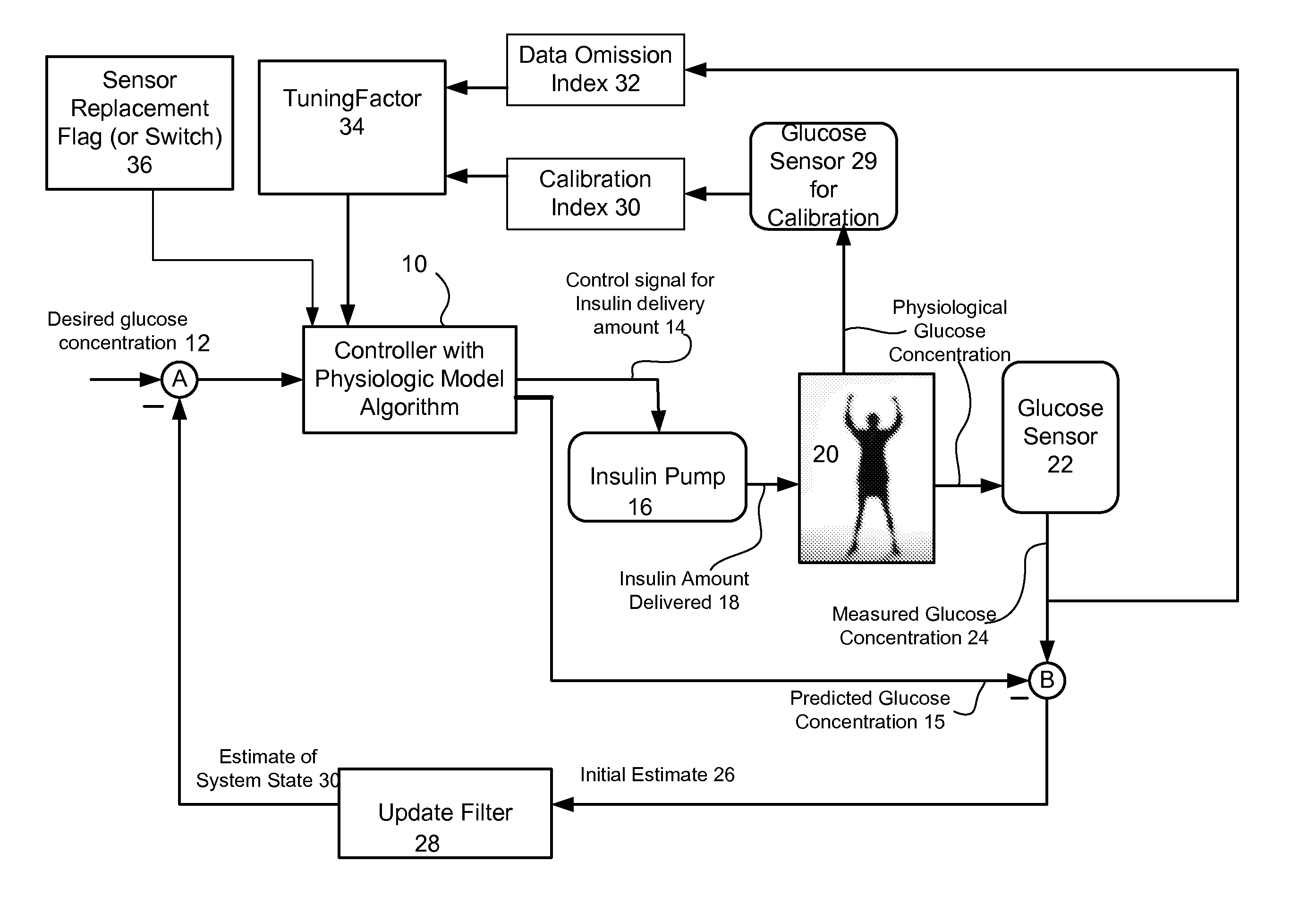
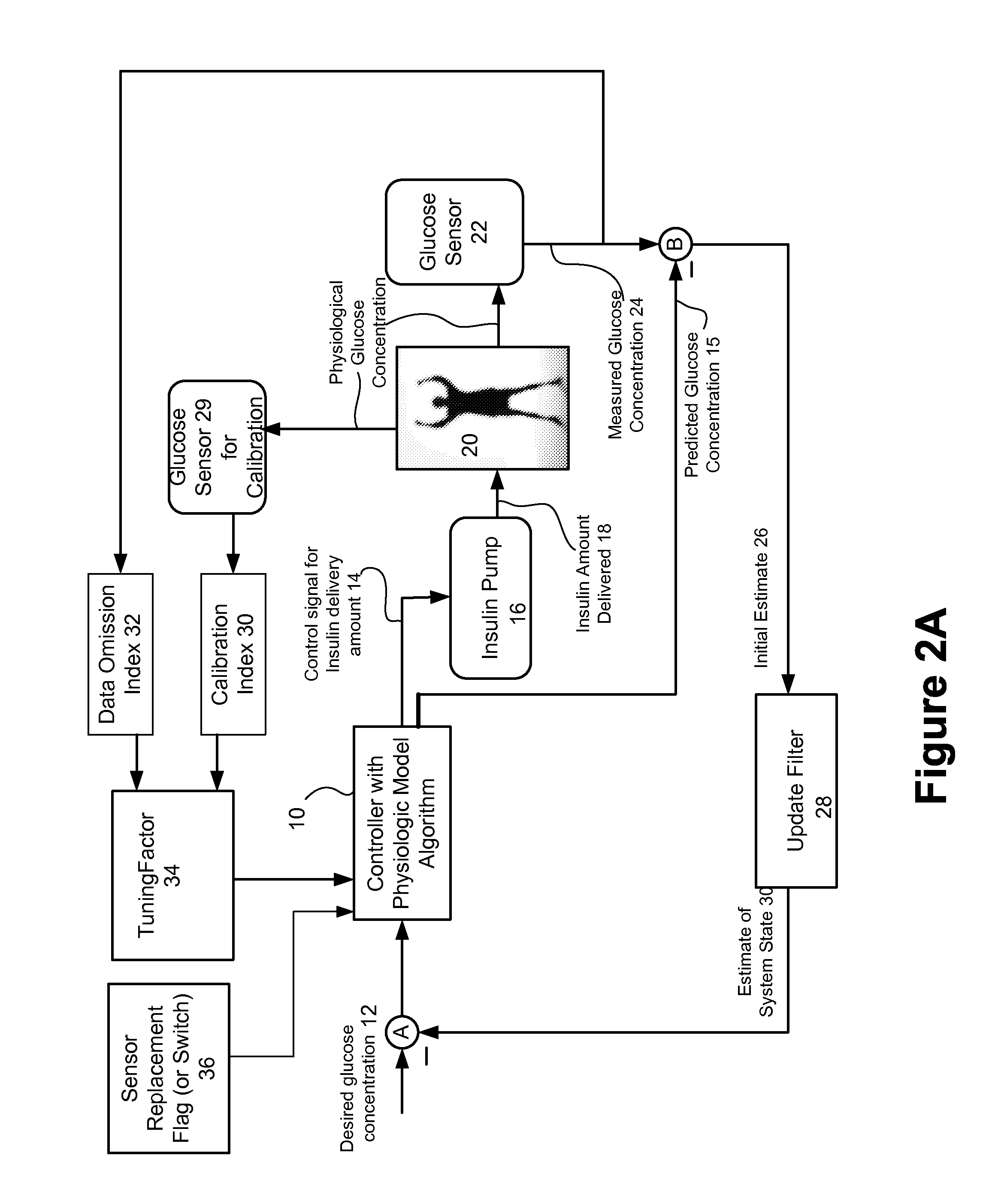
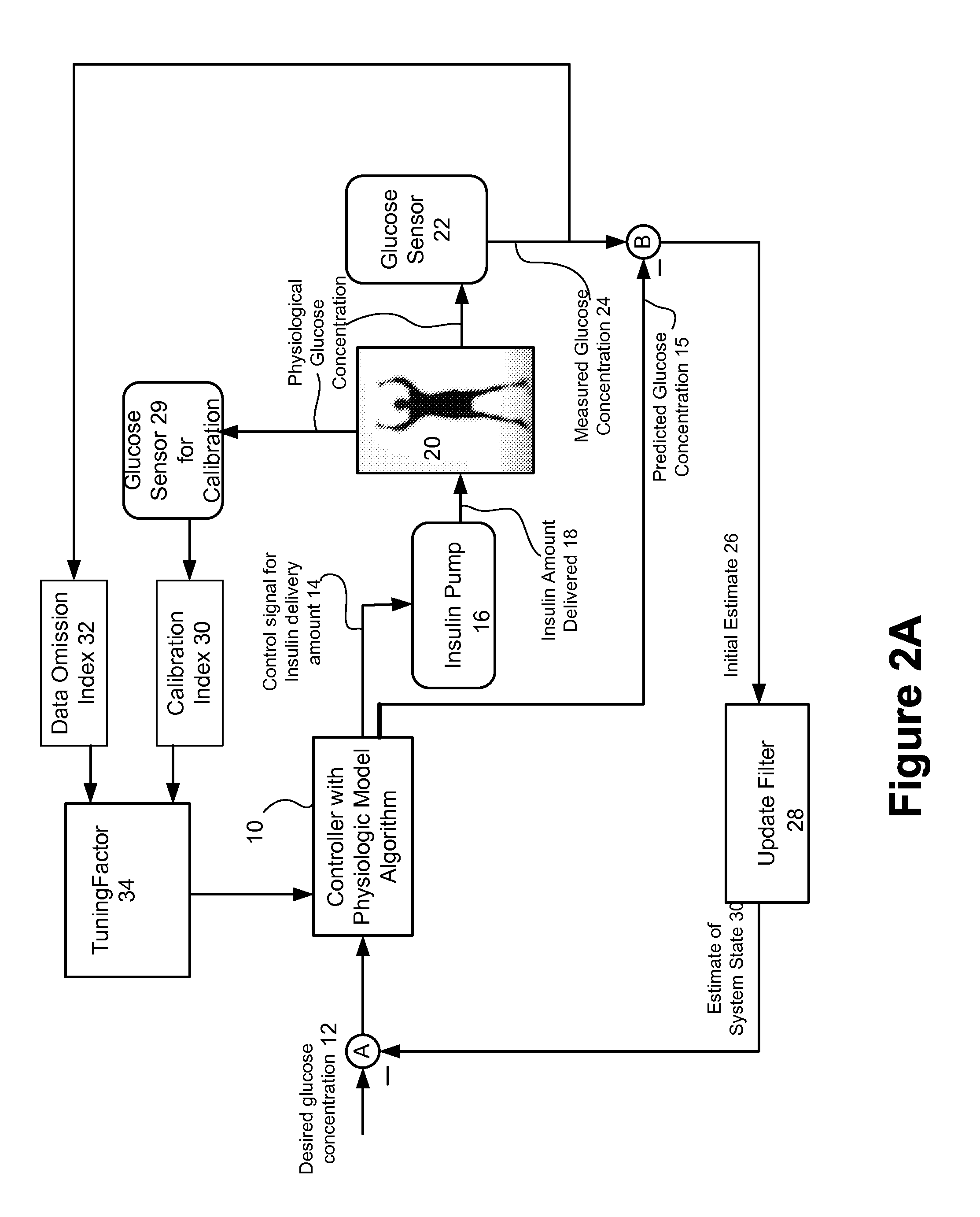
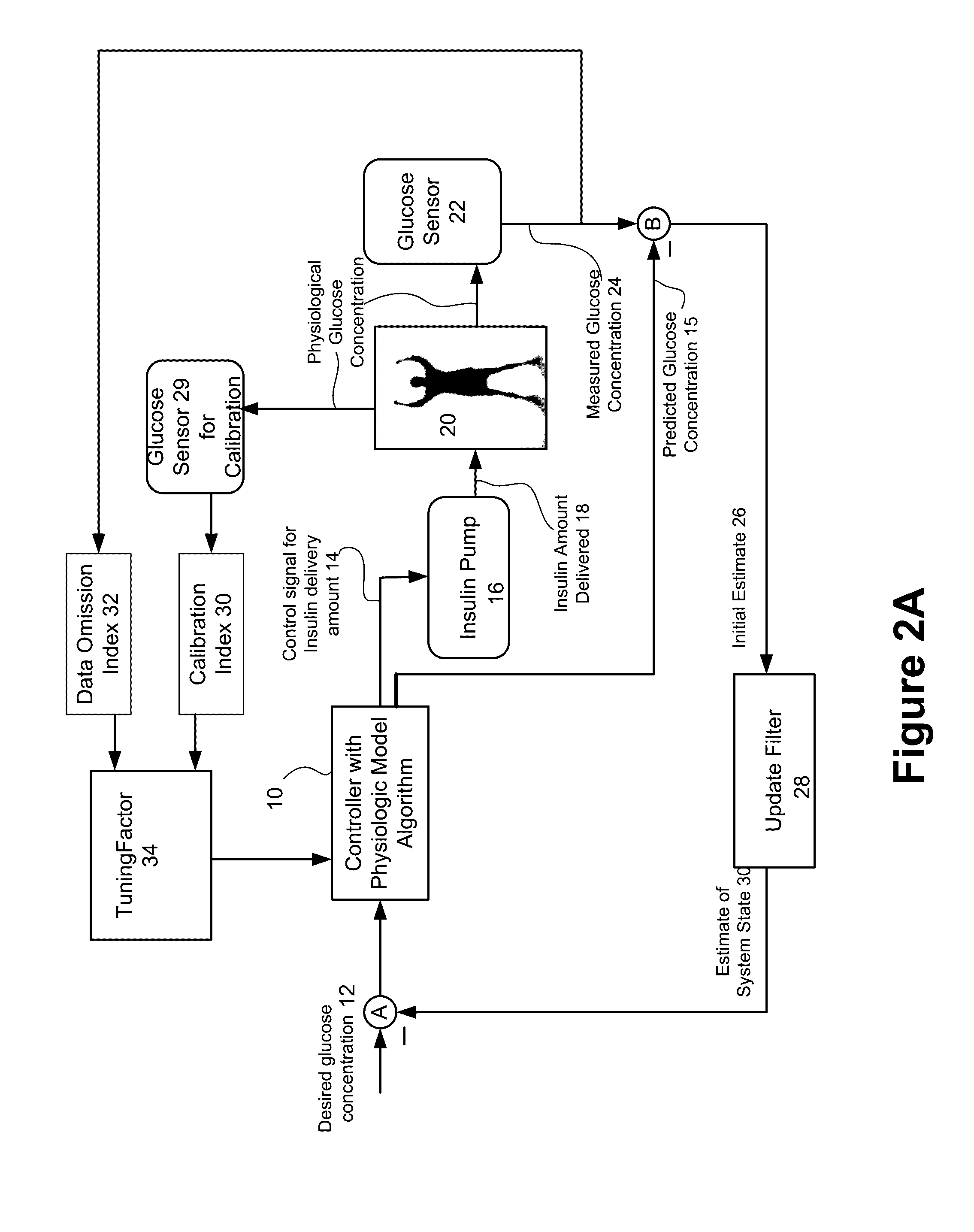
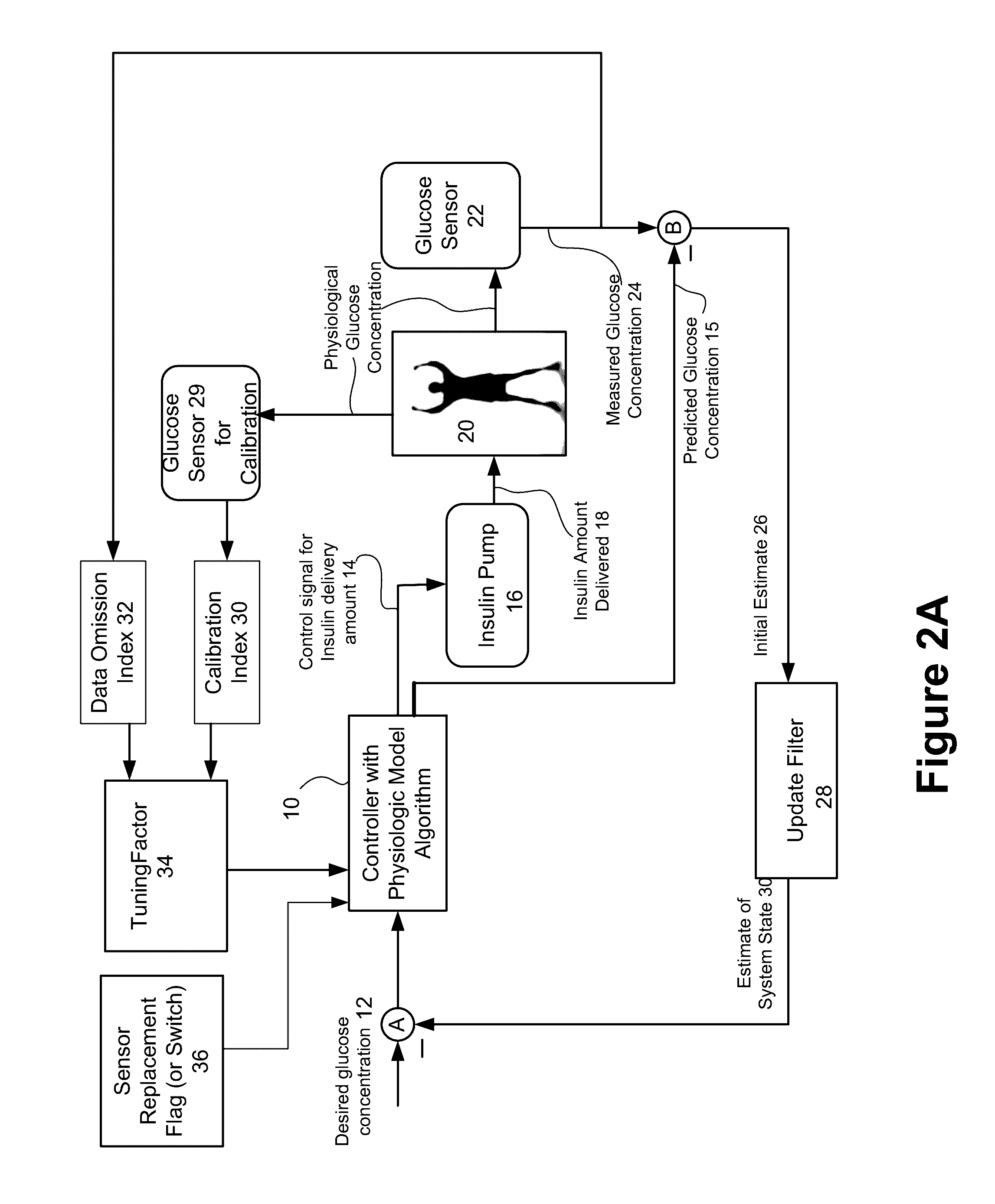
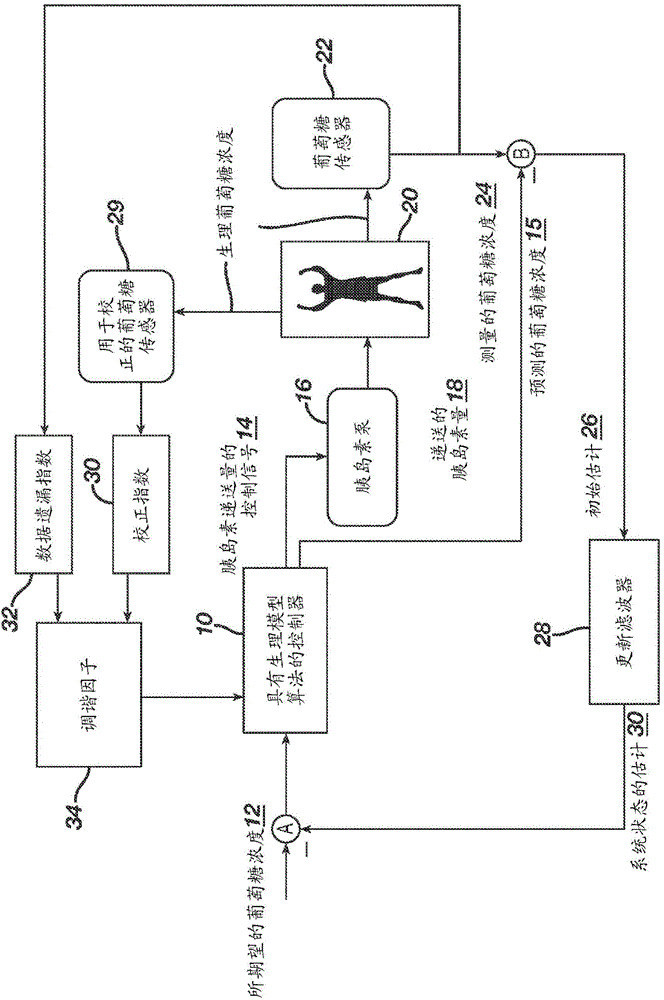
Method and system for controlling a tuning factor due to sensor replacement for closed-loop controller in an artificial pancreas
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed in the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin. The glucose sensor senses glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed receives signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control based on desired glucose levels, insulin amount delivered and measured glucose levels of the subject. The controller is also configured to deliver insulin using a tuning factor (R) for a model predictive controller in the microcontroller as a conservative setting otherwise the system maintains a current tuning factor (R) for the controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
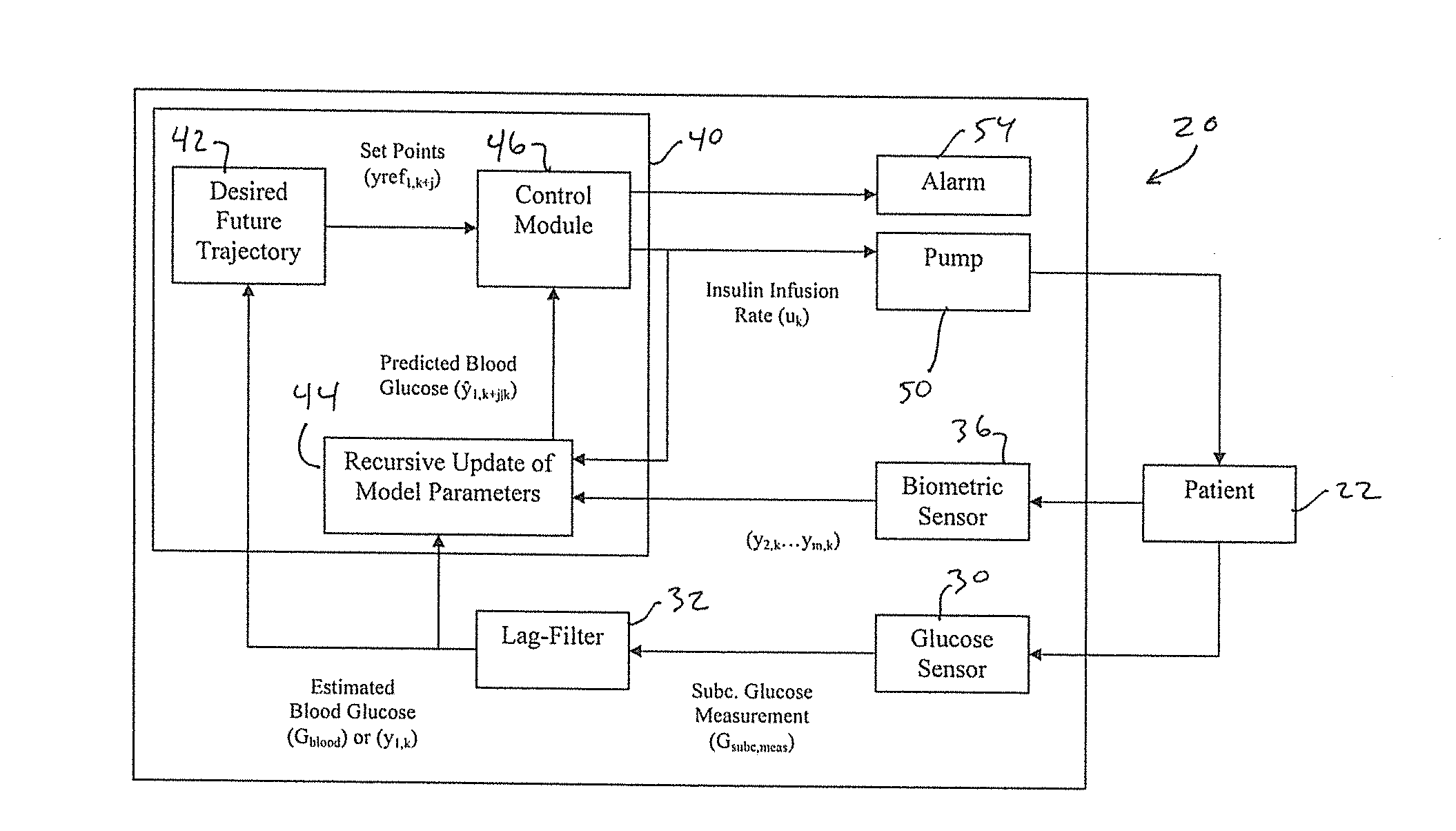
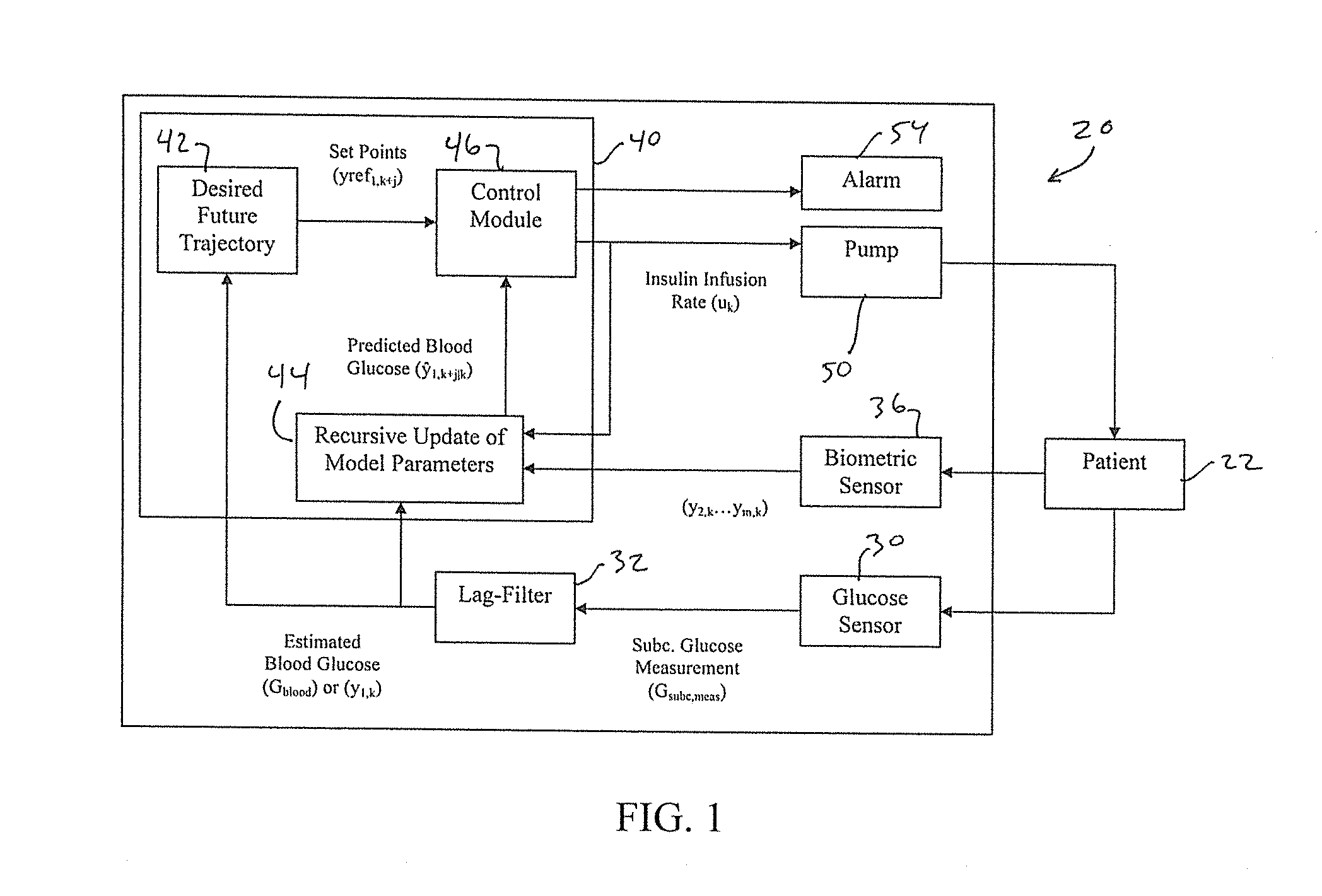
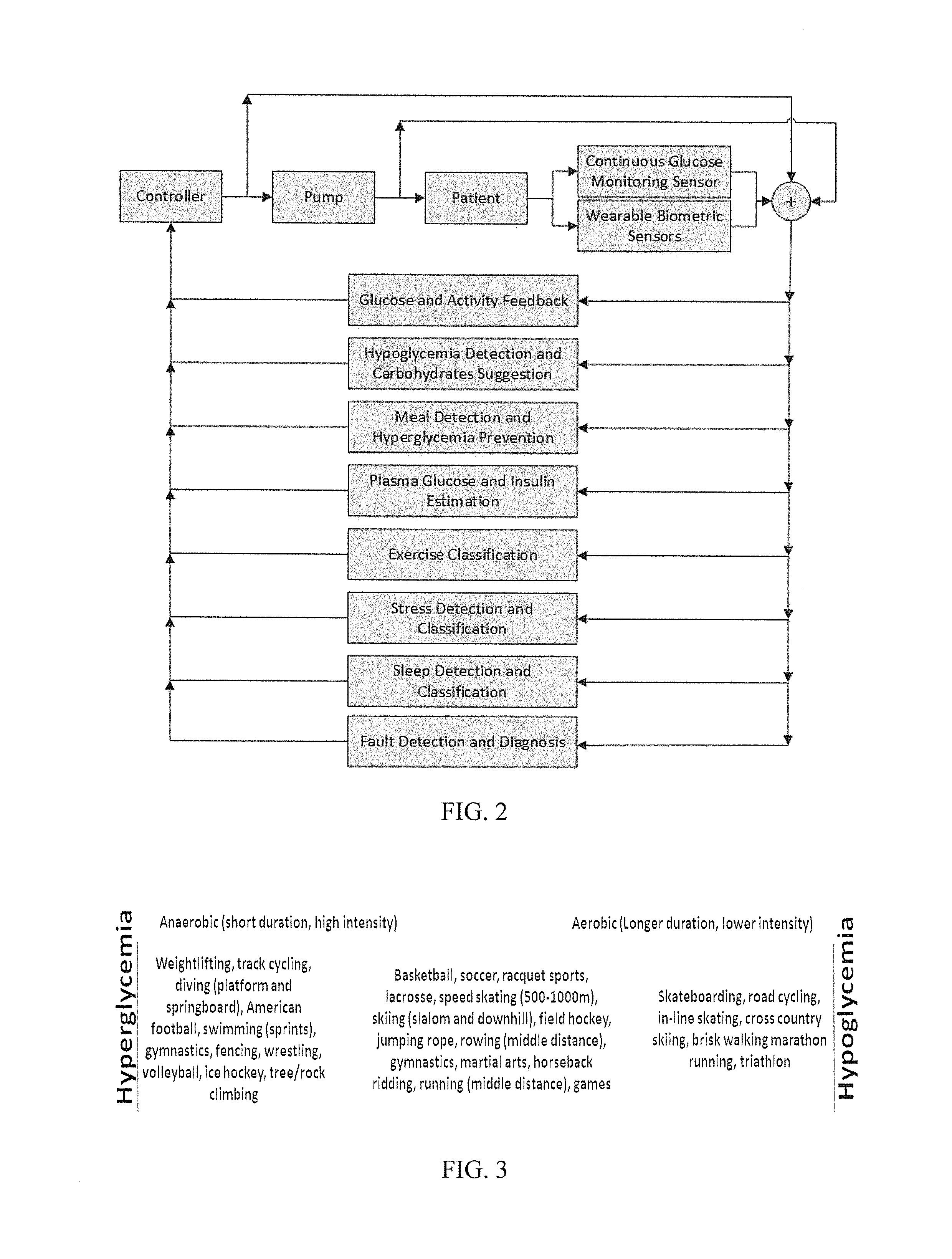
Multivariable artificial pancreas method and system
ActiveUS20160354543A1Easy to controlIncrease heart rateLocal control/monitoringMedical devicesAcute hyperglycaemiaHypoglycemia
Methods and modules for using physiological (biometric) variables to advance the state of the artificial pancreas. The method and system includes one or more modules for recursive model identification, hypoglycemia early alert and alarm, adaptive control, hyperglycemia early alert and alarm, plasma insulin concentration estimation, assessment of physical activity (e.g., presence, type, duration, expected effects on insulin sensitivity and GC), detection of acute stress and assessment of its impact on insulin sensitivity, detection of sleep and its stages and assessment of sleep stages on GC, sensor fault detection and diagnosis, software and controller performance evaluation and adjustment and / or pump fault detection and diagnosis.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
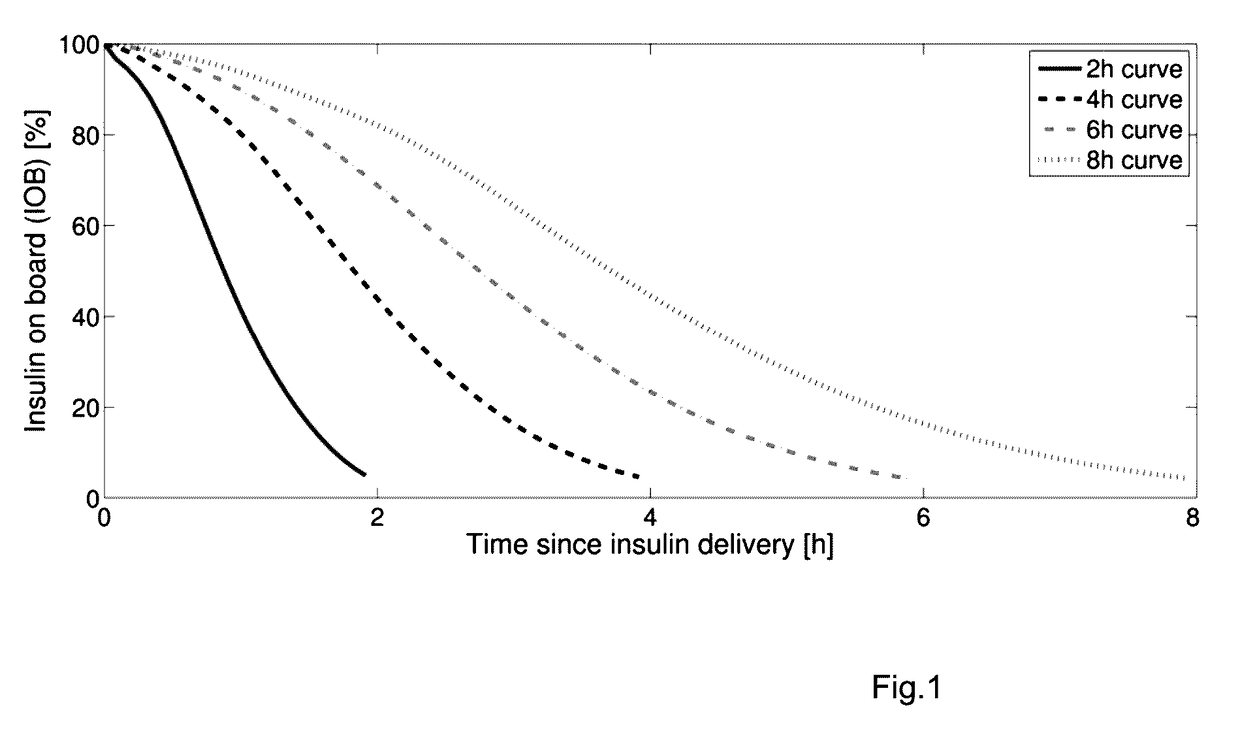
Insulin time-action model
InactiveUS20160038673A1Improve performanceMedical simulationDrug and medicationsRemote controlDynamic models
Described and shown herein is simple dynamic model for insulin time-action profiles. Various aspects are suitable for implementation in an embedded system such as an insulin pump, or a handheld device such as a pump remote control. Various aspects can be used as an off-line modeling tool running on a smartphone to assist patients in their treatment, or can be used as part of a closed-loop control algorithm for an artificial pancreas.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method and system for tuning a closed-loop controller for an artificial pancreas
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed into the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin to a subject. The glucose sensor is configured to sense glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed receives signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control of the subject based on desired glucose levels, insulin amount delivered and measured glucose levels of the subject. The controller is also configured to deliver insulin using a tuning factor based on either one of an omission index module or a calibration index module.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP +1
Method and System for Closed-Loop Control of an Artificial Pancreas
ActiveUS20140276555A1Reduce error contributedReduce truncation errorDrug and medicationsMedical devicesInsulin pumpClosed loop
A local extremum of a function ƒ is determined by computing a Jacobian of ƒ at a test point x by adding an imaginary part to x and a Hessian of ƒ by adding two imaginary parts to a multicomplex copy of x and extracting a third imaginary part. Solving a system of equations defined by the Jacobian and Hessian yields a delta; the process is repeated until convergence. This method is used in each of a series of time intervals to compute an insulin-delivery amount for an insulin pump. ƒ is a model-predictive-control cost function; x is a set of successive candidate insulin delivery amounts beginning from a selected time interval. A system includes a glucose monitor and a controller using glucose measurement data therefrom to determine an insulin delivery amount for a time interval by minimizing ƒ; an insulin pump provides insulin corresponding to the delivery amount.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP +1
Method and system for tuning a closed-loop controller for an artificial pancreas
ActiveUS9486578B2Drug and medicationsAnalogue computers for chemical processesGlucose sensorsINSULIN USE
Owner:ANIMAS CORP +1
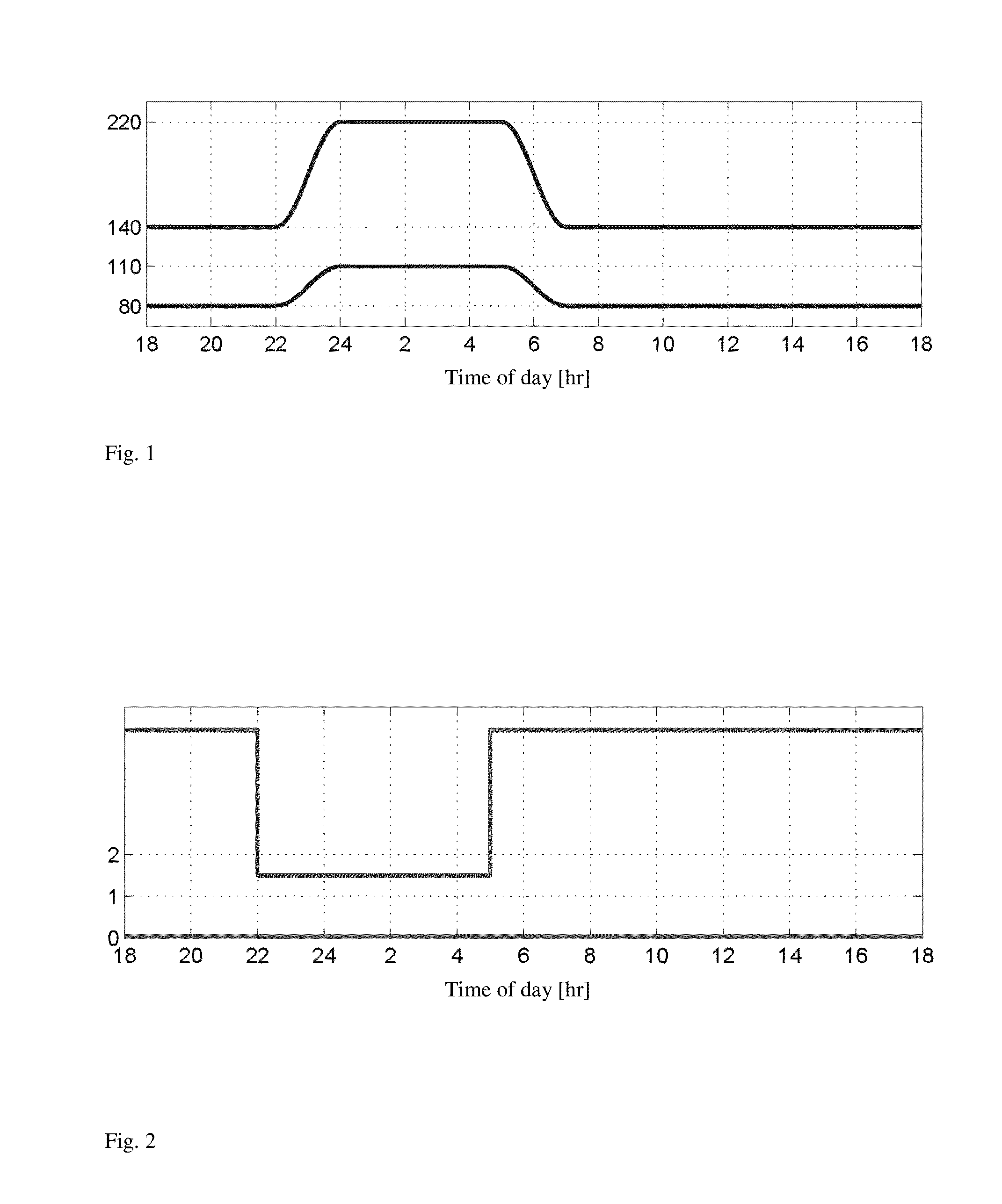
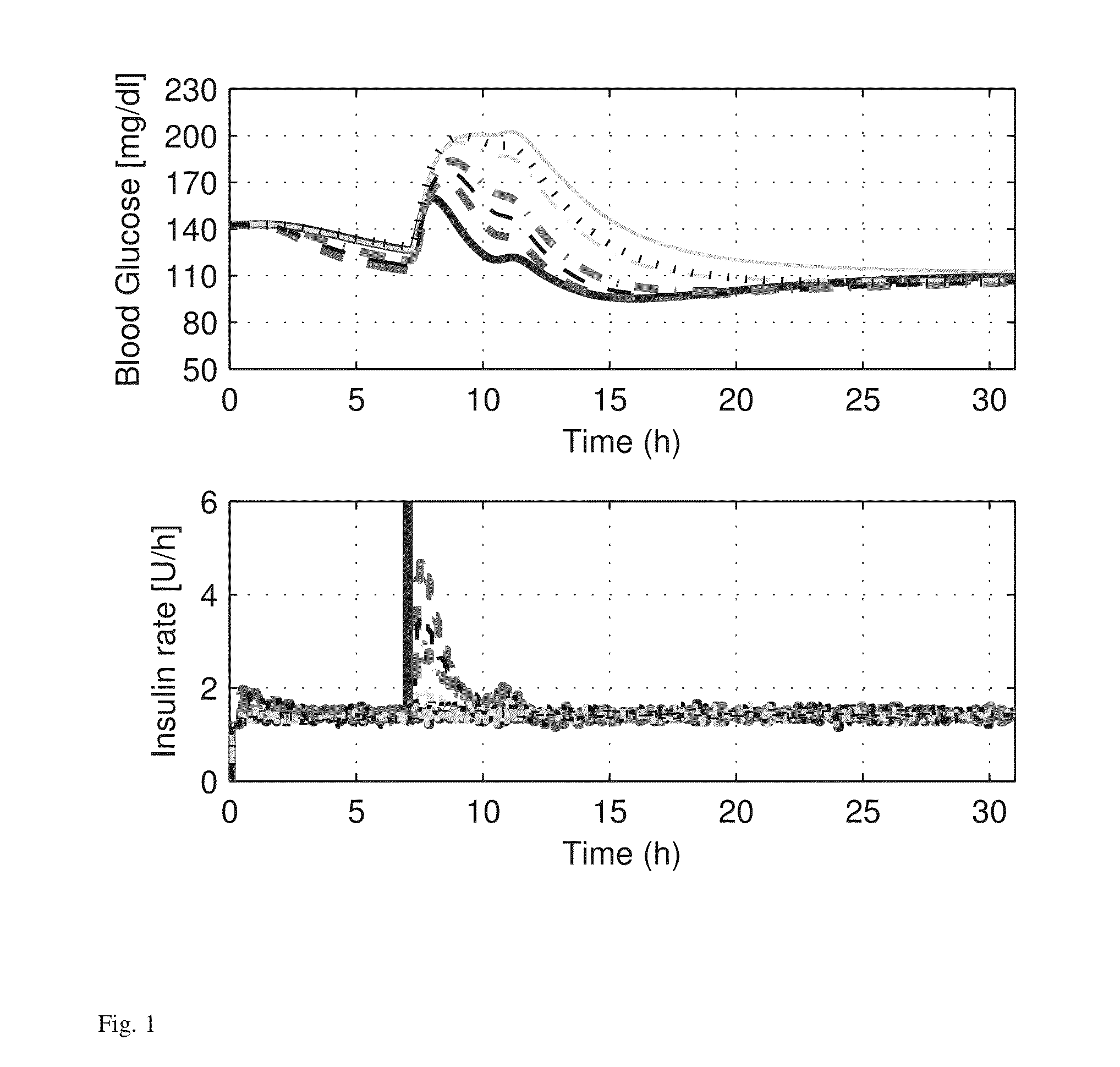
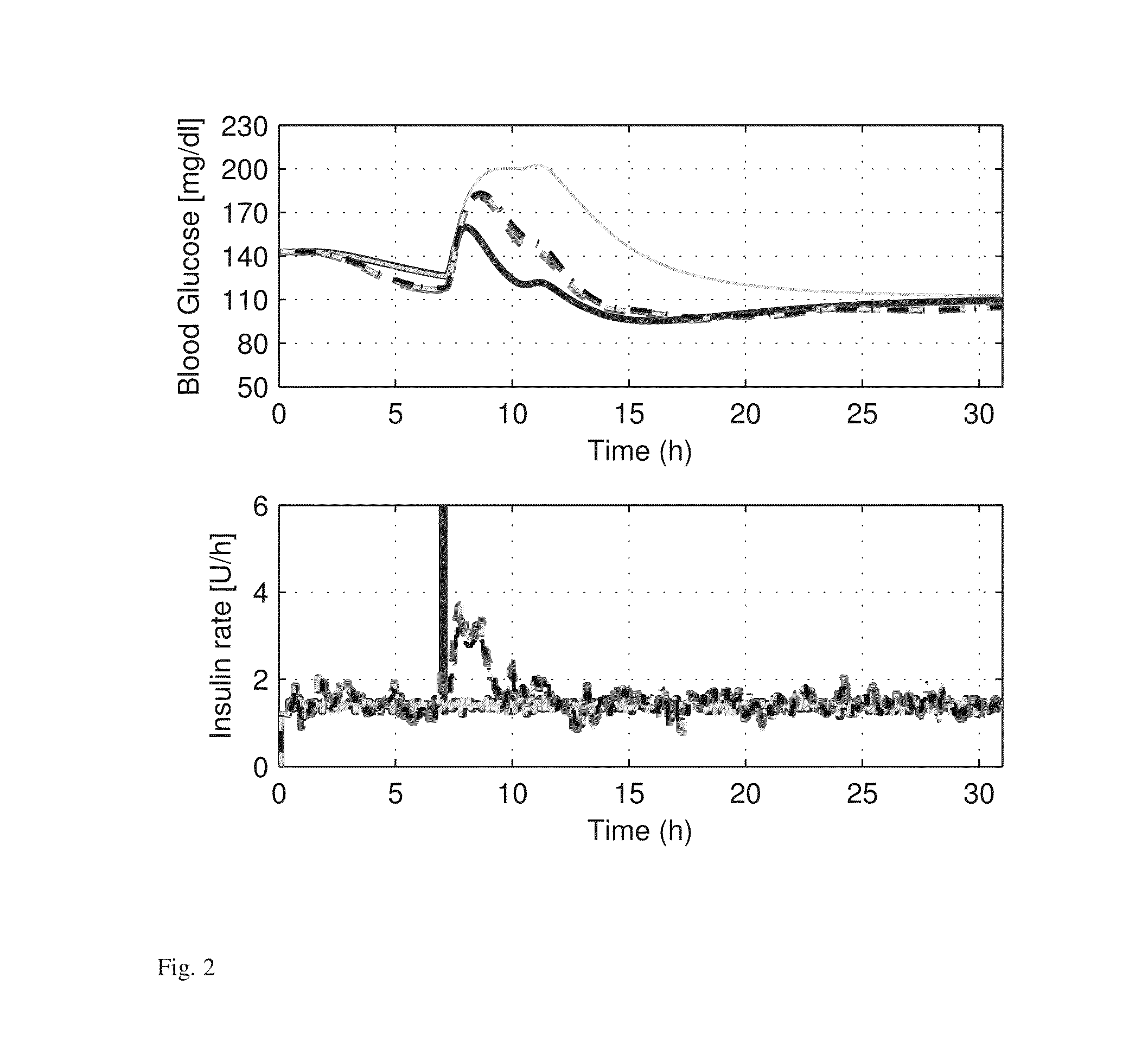
Daily periodic target-zone modulation in the model predictive control problem for artificial pancreas for type I diabetes applications
ActiveUS20140200559A1Easy to testConvenient verificationMedical simulationMetabolism disorderInsulin responseGlycemic
A controller for an artificial pancreas for automated insulin delivery to patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) that enforces safe insulin delivery throughout both day and night, wherein the controller employs zone model predictive control, whereby real-time optimization, based on a model of a human's insulin response, is utilized to regulate blood glucose levels to a safe zone, and time-dependent zones that smoothly modulate the controller correction based on the time of day, wherein the controller strategically strives to maintain an 80-140 mg / dL glucose zone during the day, a 110-220 mg / dL zone at night, and a smooth transition of 2 hour duration in between.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Central data exchange node for system monitoring and control of blood glucose levels in diabetic patients
ActiveUS20160331310A1Easy to replaceGuaranteed uptimeInertial sensorsMedical devicesNODALClosed loop
A flexible system capable of utilizing data from different monitoring techniques and capable of providing assistance to patients with diabetes at several scalable levels, ranging from advice about long-term trends and prognosis to real-time automated closed-loop control (artificial pancreas). These scalable monitoring and treatment strategies are delivered by a unified system called the Diabetes Assistant (DiAs) platform. The system provides a foundation for implementation of various monitoring, advisory, and automated diabetes treatment algorithms or methods. The DiAs recommendations are tailored to the specifics of an individual patient, and to the patient risk assessment at any given moment. A central data exchange node or server collects patient data from individual DiAs devices and provides safety assurance, monitoring, telemedicine and database building for the DiAs system.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Automated detection of a physical behavior event and corresponding adjustment of a medication dispensing system based on historical events
InactiveUS20200135320A1Lower latencyIncreased sensor sampling rateDrug and medicationsMedical automated diagnosisHealth professionalsEmergency medicine
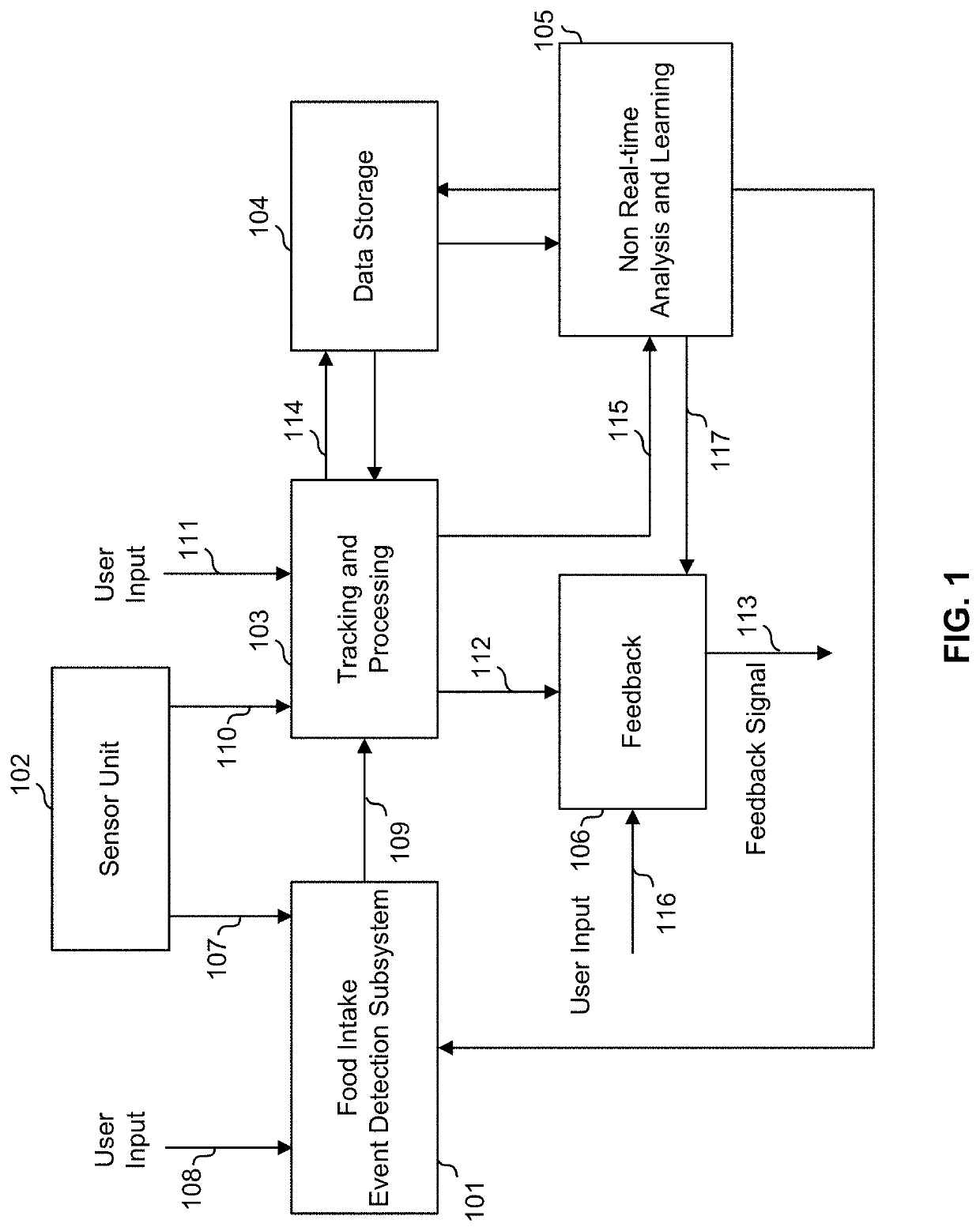
An automated medication dispensing system provides for triggering a medication administration message when an inferred event is detected for which a medication administration message is to be sent. The event might be the start, the beginning, or an anticipation of a start, of an eating event, detected by an event detection module from gestures of a user from a set of sensor readings. The message can be a signal to medication dispensing apparatus, and / or a reminder message to the user, an ancillary message to a caregiver, health professional, or others. The medication administration message might comprise a signal to an input of an insulin management system or an input of a meal-aware artificial pancreas. The events might also include a drinking event, a smoking event, a personal hygiene event, and / or a medication related event.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Model-Based Personalization Scheme of an Artificial Pancreas for Type I Diabetes Applications
ActiveUS20150306314A1Improve performanceImproved profileMedical devicesFlow monitorsPersonalizationMedicine
A model-based control scheme consisting of either a proportional-integral-derivative (IMC-PID) controller or a model predictive controller (MPC), with an insulin feedback (IFB) scheme personalized based on a priori subject characteristics and comprising a lower order control-relevant model to obtain PID or MPC controller for artificial pancreas (AP) applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
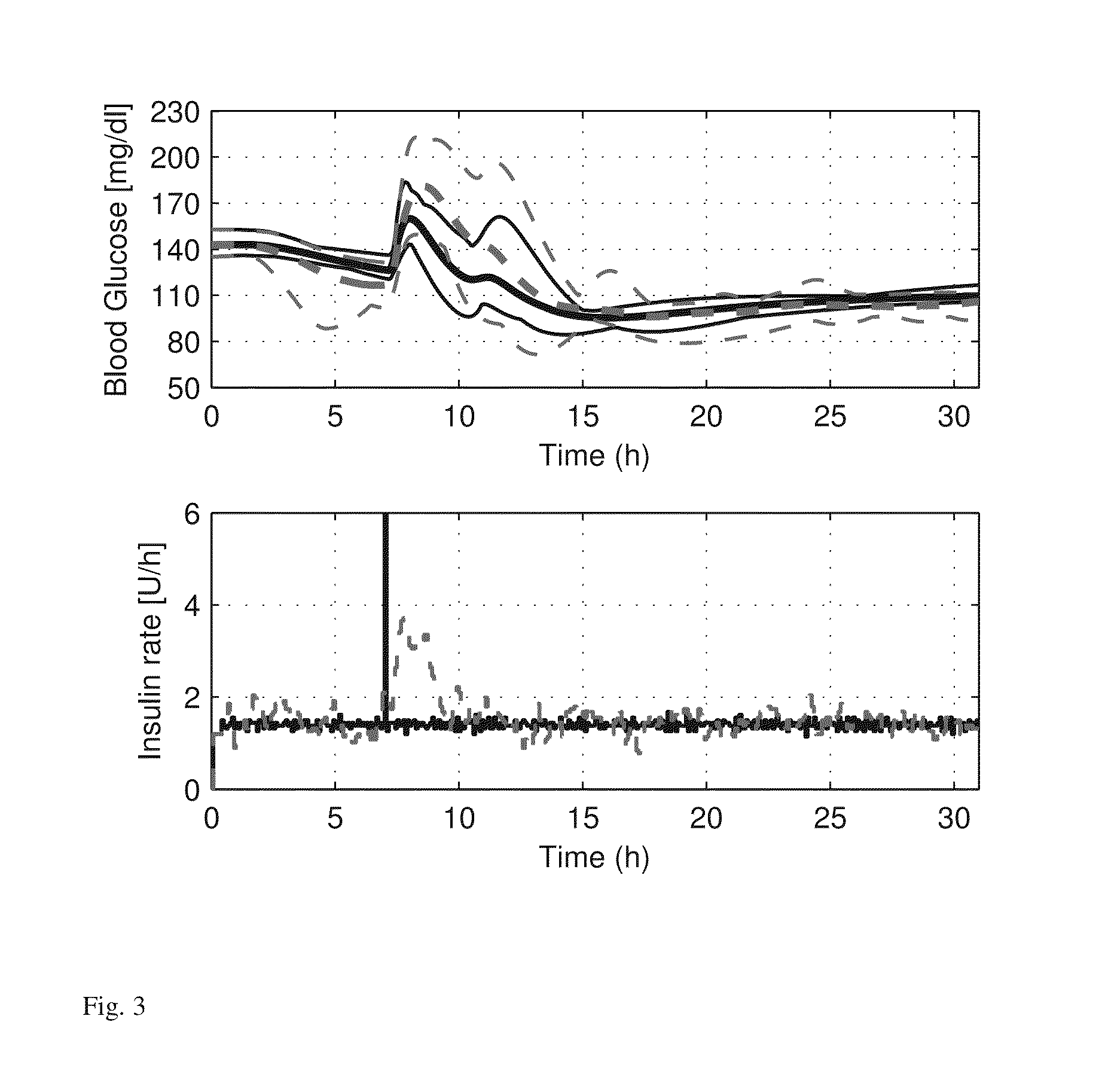
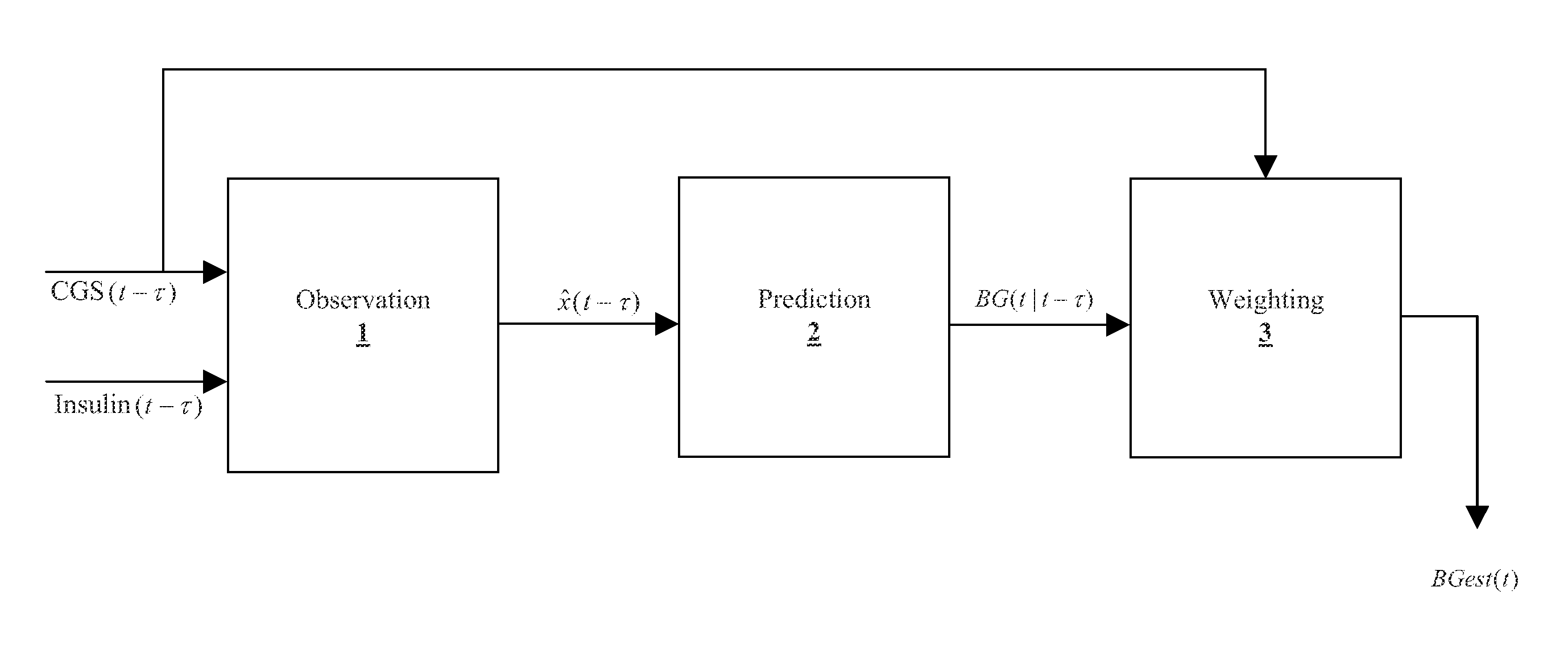
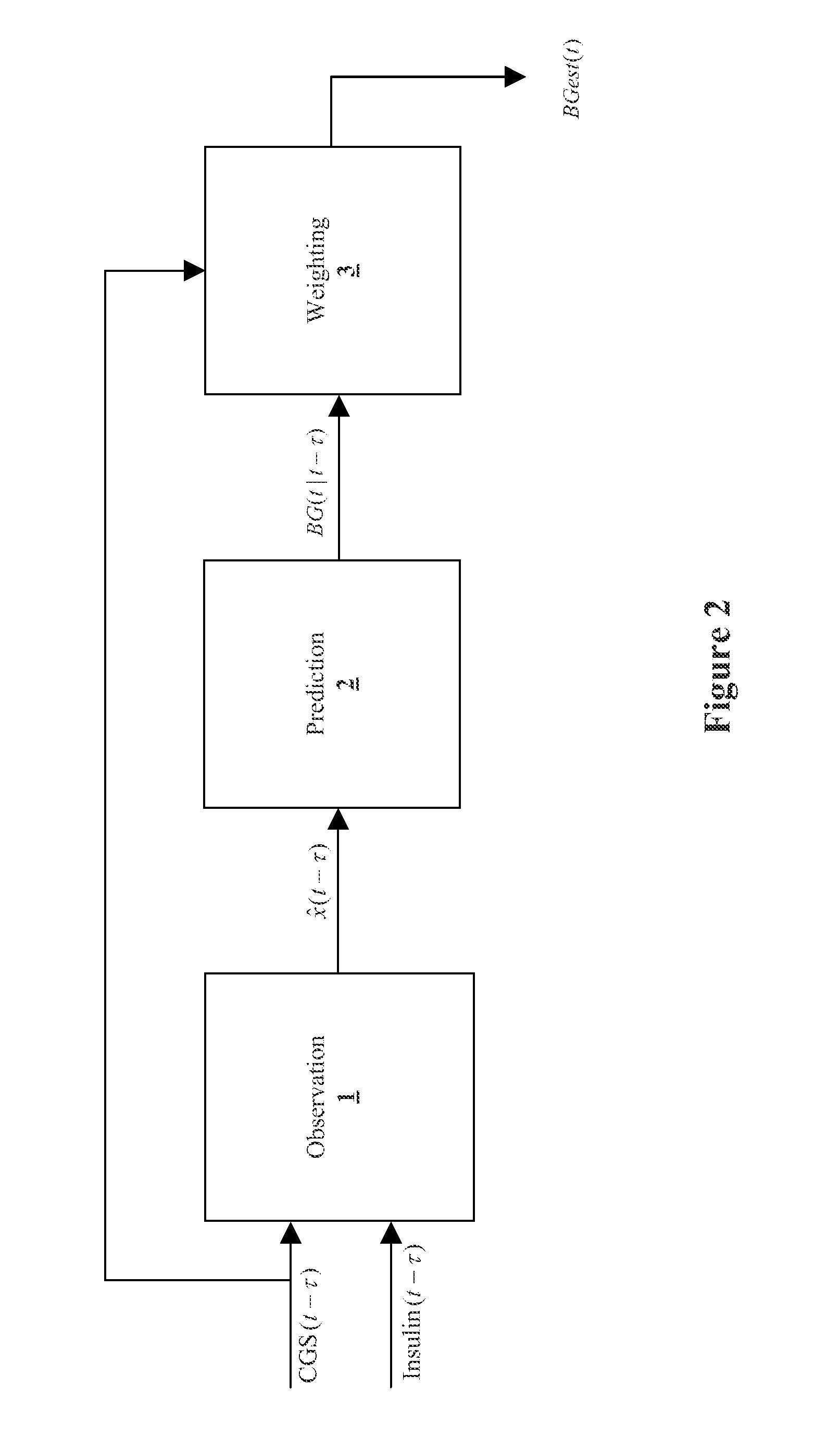
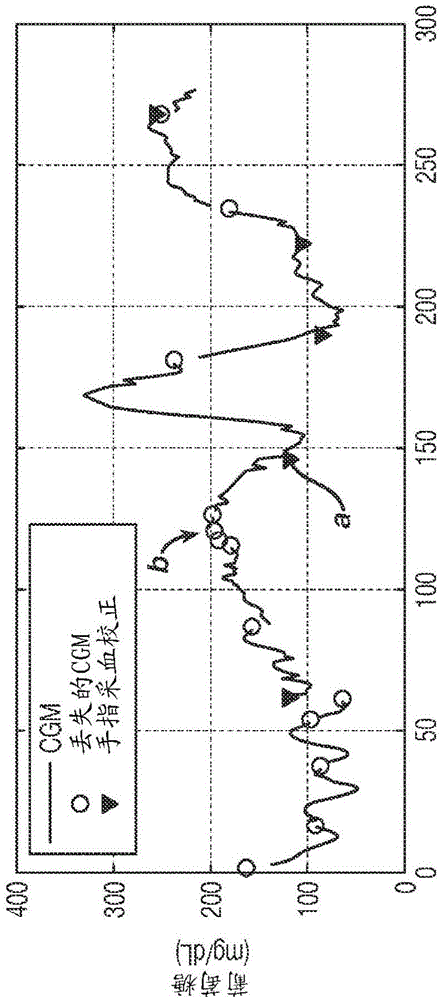
Method, system, and computer program product for improving the accuracy of glucose sensors using insulin delivery observation in diabetes
ActiveUS9398869B2Improve accuracyImprove sensor accuracyOther blood circulation devicesPressure infusionGlucose sensorsInsulin pump
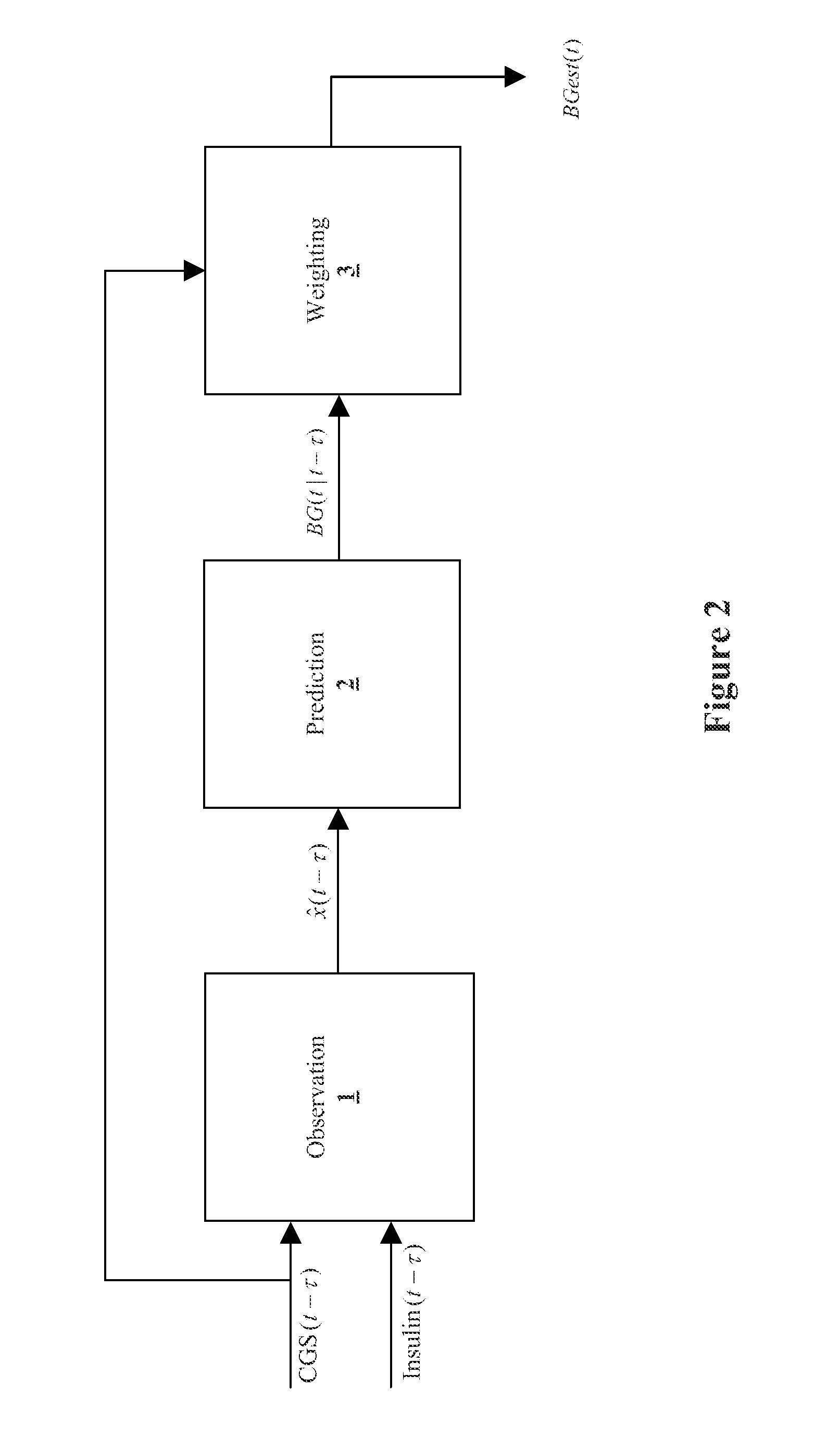
Method and System for providing a signal from an insulin pump, artificial pancreas, or another insulin delivery device as a source of information for improving the accuracy of a continuous glucose sensor (CGS). The effect of using insulin information to enhance sensor accuracy is most prominent at low blood glucose levels, i.e. in the hypoglycemic range, which is critical for any treatment. A system for providing a filtering / state estimation methodology that may be used to determine a glucose state estimate at time t-τ. The estimation may be extrapolated to some future time t and then the extrapolated value is used to extract the blood glucose component. The blood glucose component of the extrapolation and the output of the CGS are weighted and used to estimate the blood glucose level of a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and system for controlling a tuning factor due to sensor replacement for closed-loop controller in an artificial pancreas
ActiveUS9474855B2Analogue computers for chemical processesMedical devicesMicrocontrollerGlucose sensors
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed in the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin. The glucose sensor senses glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed receives signals from at least one of the glucose sensor and the pump and configured to issue signals to the pump to deliver an amount of insulin determined by a feedback controller that utilizes a model predictive control based on desired glucose levels, insulin amount delivered and measured glucose levels of the subject. The controller is also configured to deliver insulin using a tuning factor (R) for a model predictive controller in the microcontroller as a conservative setting otherwise the system maintains a current tuning factor (R) for the controller.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
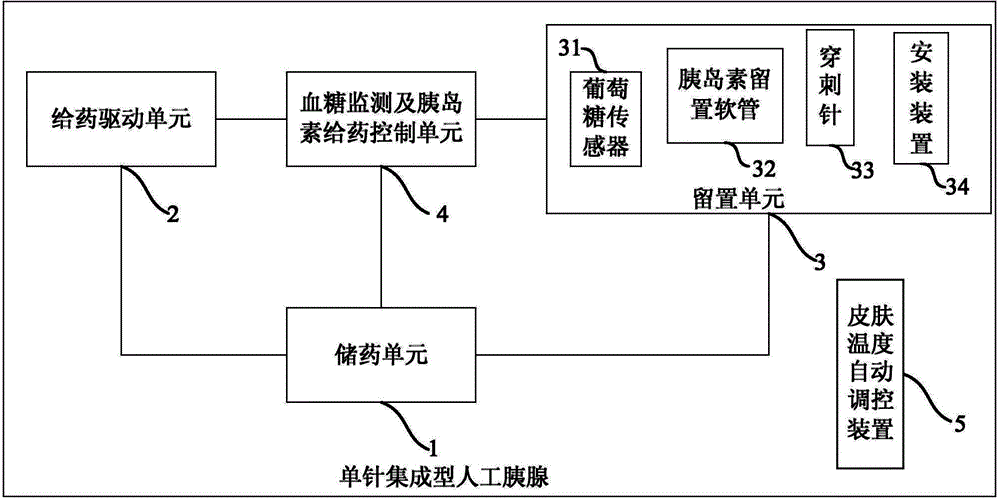
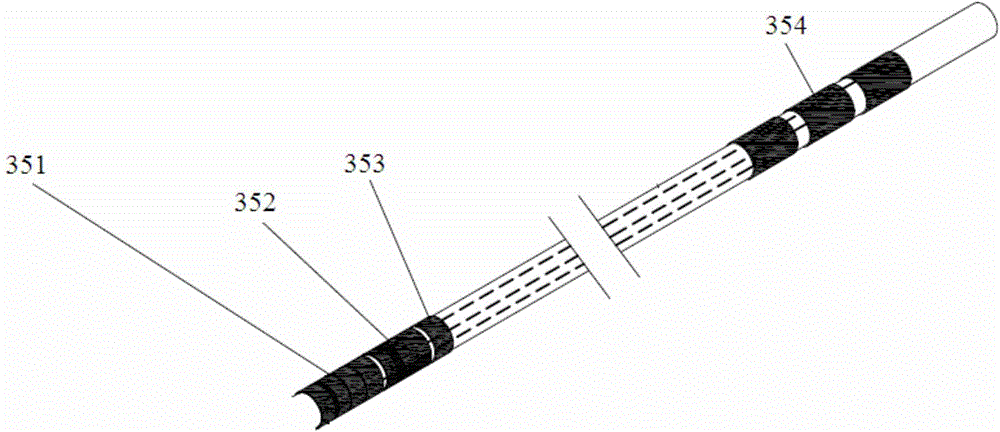
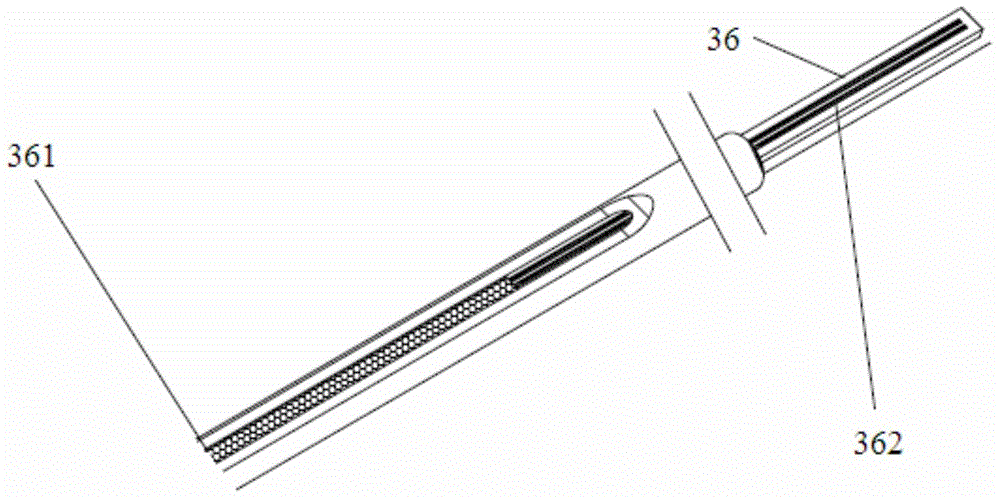
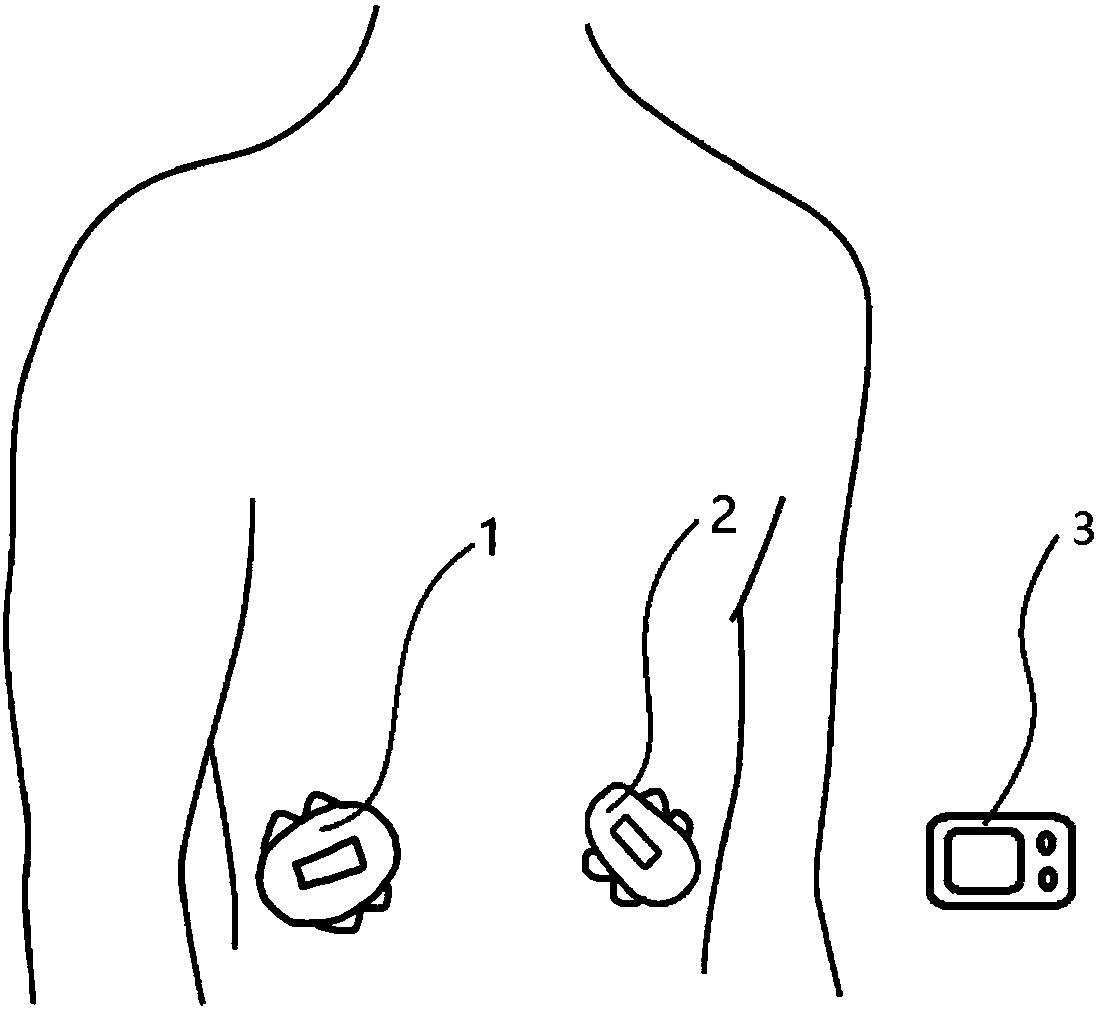
Single-needle integrated artificial pancreas
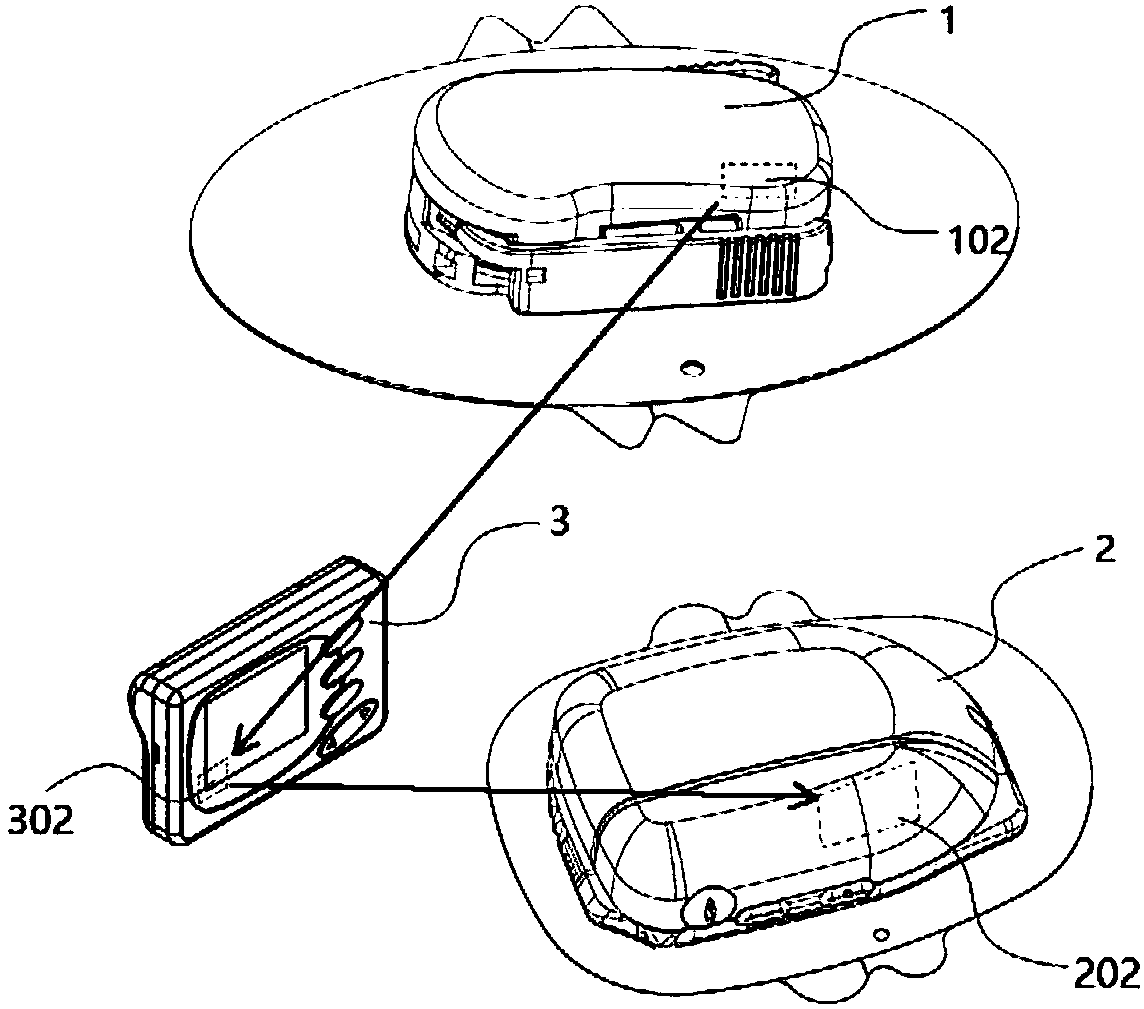
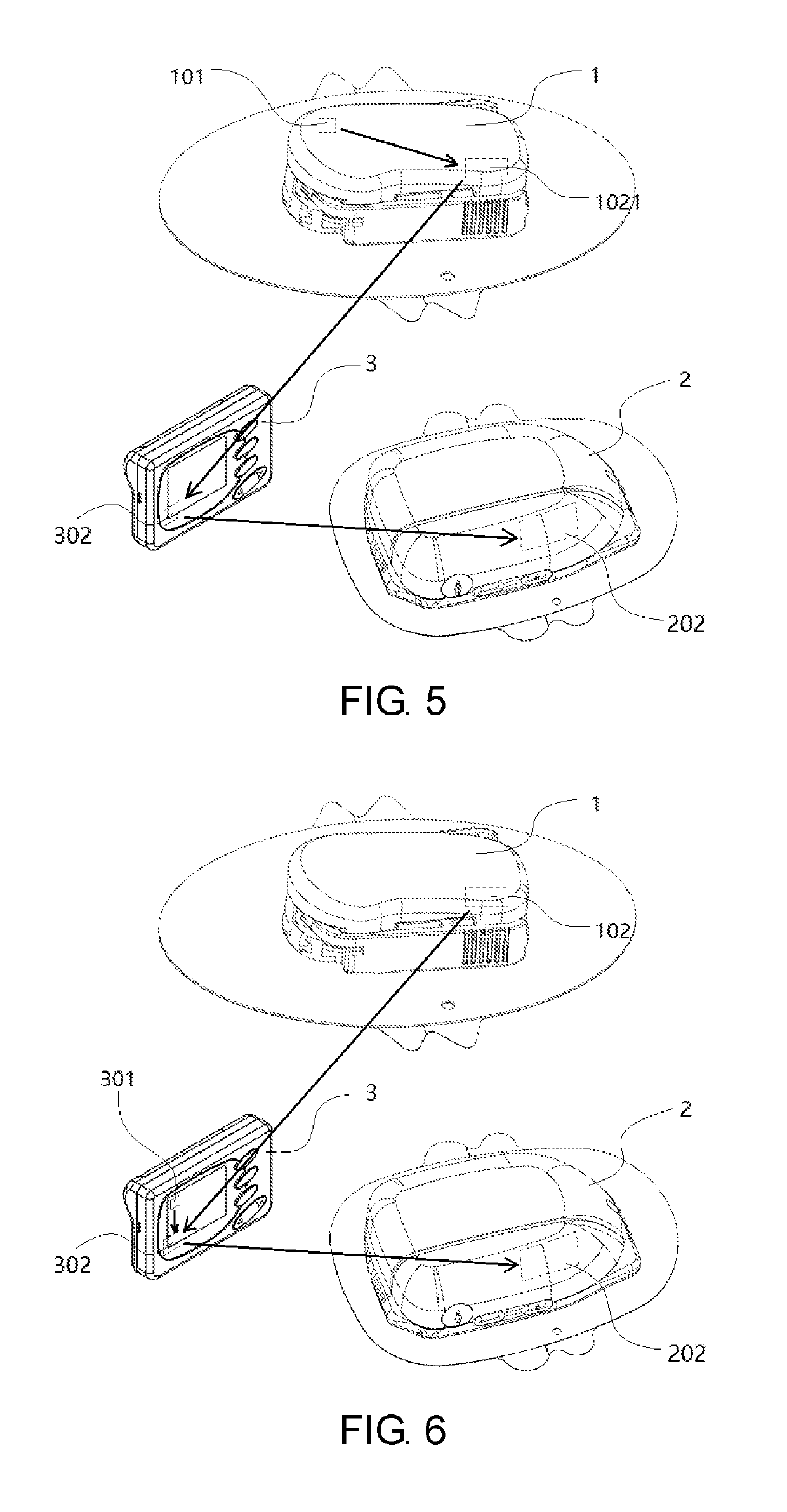
ActiveCN104622480AReduce the chance of infectionEasy to installMedical devicesCatheterDrug reservoirGlucose sensors
Disclosed is a single needle integrated artificial pancreas, wherein the single needle integrated artificial pancreas comprises a drug reservoir unit (1); a dosing drive unit (2) connected to the drug reservoir unit (1); an indwelling unit (3) connected to the drug reservoir unit (1) and comprising a glucose sensor (31), an insulin-indwelling hose (32), a puncture needle (33) and a mounting means (34), wherein the glucose sensor (31) and the insulin-indwelling hose (32) are simultaneously implanted in the same subcutaneous tissue in a patient via the mounting means (34) under the aid of the puncture needle (33), and the puncture needle (33) is a puncture steel needle or groove puncture needle; and a blood glucose monitoring and insulin administration control unit (4) is respectively connected to the drug reservoir unit (1), the dosing drive unit (2) and the indwelling unit (3). The single needle integrated artificial pancreas is able to simultaneously implant the insulin-indwelling hose (32) and the glucose sensor (31) of the artificial pancreas into the same site of a subcutaneous tissue in a patient, thus reducing the chance of a diabetic patient being infected; and is simple in installation and convenient to use.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Loop close control system and method in artificial pancreas
ActiveCN108261585AMaster activity levelReduce distractionsMedical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringLoop closingControl system
The invention provides a loop close control method in artificial pancreas and the artificial pancreas adopting the method. The method comprises the following steps that at least one motion sensor senses the activity level of a patient, and provides a signal to at least one processor; the processor part adjusts a series of related algorithm based on the signal, so that more accurate and more reliable data is provided and taken as the basis for an ideal treatment plan, the processor sends an instruction for enabling the artificial pancreas to automatically carry out the corresponding operation,and thus the loop close control is realized.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Artificial pancreas closed-loop control algorithm
ActiveCN108261591AThe effect of overshoot is obviousStable and reliable outputAutomatic syringesMedical devicesInsulin infusionLoop control
The invention provides an artificial pancreas closed-loop control algorithm and artificial pancreas using the method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: constructing an autoregressive model that an insulin absorption delay factor is actively introduced; calculating required insulin infusion amounts respectively via the autoregressive model and a PID algorithm; and implementing loop optimization of parameters of the two insulin infusion amounts via an average value of calculation results of the two insulin infusion amounts, so as to offer more accurate blood glucose trend prediction and a more appropriate insulin infusion amount.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Preparation method and application method of novel amphipathic copolymerization network
ActiveCN103214680AGood oxygen transmission rateGood resistance to oxygen degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisHydrophilic monomerDouble bond
The invention provides a preparation method of a novel amphipathic copolymerization network. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the specific steps of: dissolving functionalized polydimethylsiloxane in a solvent to obtain a functionalized polydimethylsiloxane solution, adding an acid-binding agent, dropping a nucleophilic substitution reagent, reacting for 3-24 hours at a temperature of -5-40 DEG C, and purifying to obtain a PDMS-based macroinitiator; mixing a ligand, the PDMS-based macroinitiator, a hydrophilic monomer, a solvent and a first catalyst, reacting for 1-24 hours at a temperature of 10-140 DEG C under an inert atmosphere to obtain an amphipathic segmented copolymer, adding a micromolecule with double bond in the terminal, reacting for 1-24 hours at a temperature of 0-150 DEG C, and purifying to obtain an amphipathic segmented copolymer with allyl in the terminal; and dissolving the amphipathic segmented copolymer with allyl in the terminal and a hydrosilation crosslinking agent in the solvent, and carrying out hydrosilation at a temperature of 65-110 DEG C for 1-36 hours to obtain the amphipathic copolymerization network. The amphipathic copolymerization network is applied to the biomedical fields such as a controlled drug delivery system, an artificial pancreas and contact lenses due to the adoption of a co-continuous structure.
Owner:浙江海富海洋生物科技有限公司
Method, system, and computer program product for improving the accuracy of glucose sensors using insulin delivery observation in diabetes
ActiveUS20130079613A1Improve accuracyImprove sensor accuracyOther blood circulation devicesPressure infusionGlucose sensorsInsulin pump
Method and System for providing a signal from an insulin pump, artificial pancreas, or another insulin delivery device as a source of information for improving the accuracy of a continuous glucose sensor (CGS). The effect of using insulin information to enhance sensor accuracy is most prominent at low blood glucose levels, i.e. in the hypoglycemic range, which is critical for any treatment. A system for providing a filtering / state estimation methodology that may be used to determine a glucose state estimate at time t-τ. The estimation may be extrapolated to some future time t and then the extrapolated value is used to extract the blood glucose component. The blood glucose component of the extrapolation and the output of the CGS are weighted and used to estimate the blood glucose level of a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
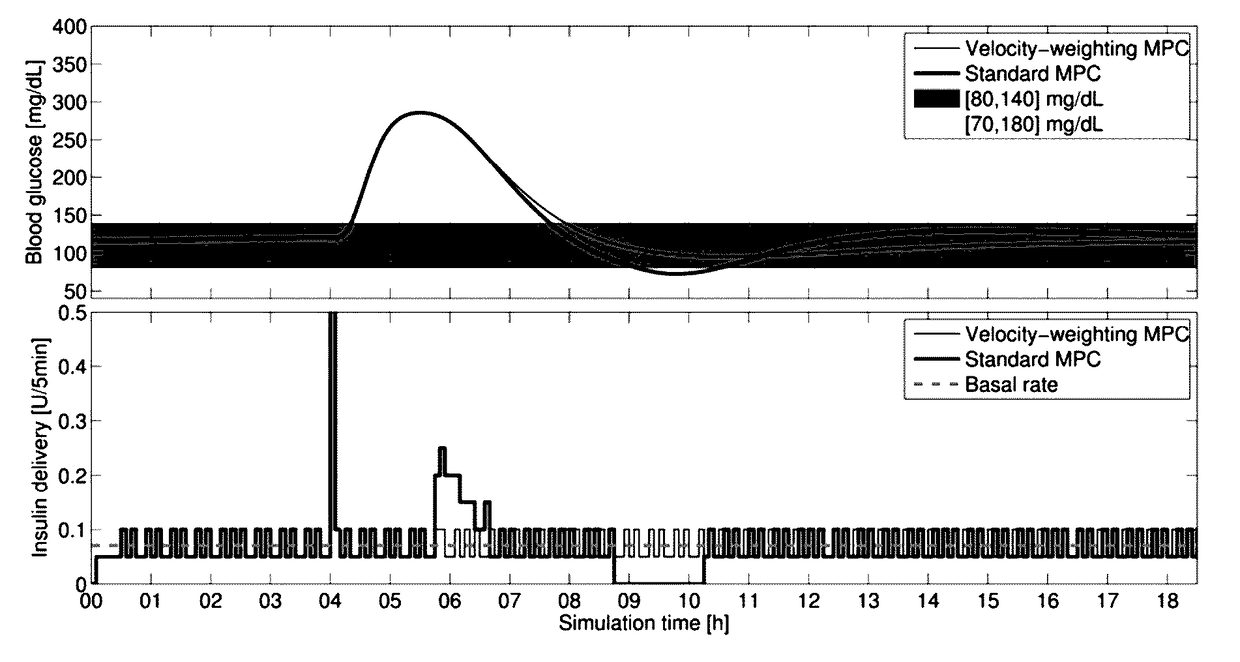
Velocity-weighting model predictive control of an artificial pancreas for type 1 diabetes applications
ActiveUS20170143899A1Reduce generationImprove securityDrug and medicationsMedical devicesGlycemicD-Glucose
Methods, devices, algorithms, and systems controlling insulin delivery employ velocity-weighting. Predicted glucose outcomes are penalized with a cost modulated by a factor that is a function of the glucose velocity, wherein glucose outcomes are penalized increasingly less for increasingly negative glucose velocities, when glucose level is high, and / or wherein a hyperglycemic glucose value that is already converging to the euglycemic zone results in less corrective action by the controller than were the hyperglycemic state steady.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Beta cell mimicking control algorithm for artificial pancreas
The invention is a method of controlling an artificial pancreas. The method includes reading and recording a current plasma glucose level. The method includes computing glucose in beta cell if a current plasma glucose level is greater than a threshold value, and continuing the step of reading and recording a current plasma glucose level if a current plasma glucose level is less than a threshold value. The method includes calling ATP functions for interpolation. The method includes calculating a holding capacity. The method includes calculating a synthesized insulin amount. The method includes comparing amount of insulin with the holding capacity. The method includes releasing insulin if the amount of insulin is greater than the holding capacity, and not releasing insulin if the amount of insulin is less than the holding capacity.
Owner:CHANG SYHHONG
System and method for a closed loop control in an artificial pancreas
ActiveUS20190307958A1Comprehensive graspMore treatmentMedical devicesPressure infusionClosed-loop poleClosed loop
The present invention provides a closed loop control method in an artificial pancreas and a system using the method, comprising sensing an activity level of a patient by at least one motion sensor and providing signals to at least one processer; then adjusting a series of related algorithms depending partly on the signals by the processer to provide more accurate and reliable data that is the basis of desirable treatment plans, and sending corresponding instructions by the processer for automatic operations of the artificial pancreas to realize a closed loop control.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Preparation method of mesenchymal stem cell artificial pancreas islet
InactiveCN109847102AArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsVascular endotheliumAgglutination
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a preparation method of a mesenchymal stem cell artificial pancreas islet. The preparation method of a mesenchymal stem cell artificial pancreas islet comprises the following steps of (1) culturing mesenchymal stem cells, and performing inducing to generate ancreas islet like cells; (2) performing extraction and culture of vascular endothelial cells; (3) preparing temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel; (4) preparing composite hydrogel; and (5) performing partial transplantation on the composite hydrogel obtained in the step(4), and rapidly performing agglutination under the 37 DEG C body temperature environment to form the artificial pancreas islet. According to the preparation method of the mesenchymal stem cell artificial pancreas islet disclosed by the invention, the problems of insulin resistance in the insulin treatment course, large number of pancreas islets required during pancreas islet transplantation and high immunological rejection reactions during pancreas islet transplantation are solved, and new donors are provided for pancreas islet transplantation for treating type I diabetes mellitus.
Owner:山西宾大干细胞生物科技有限公司
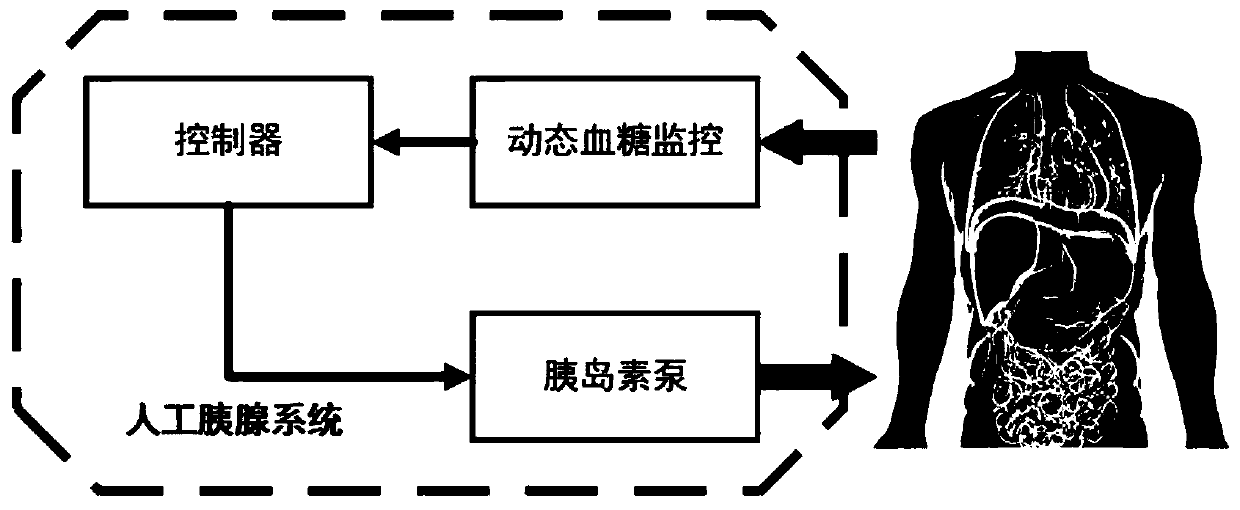
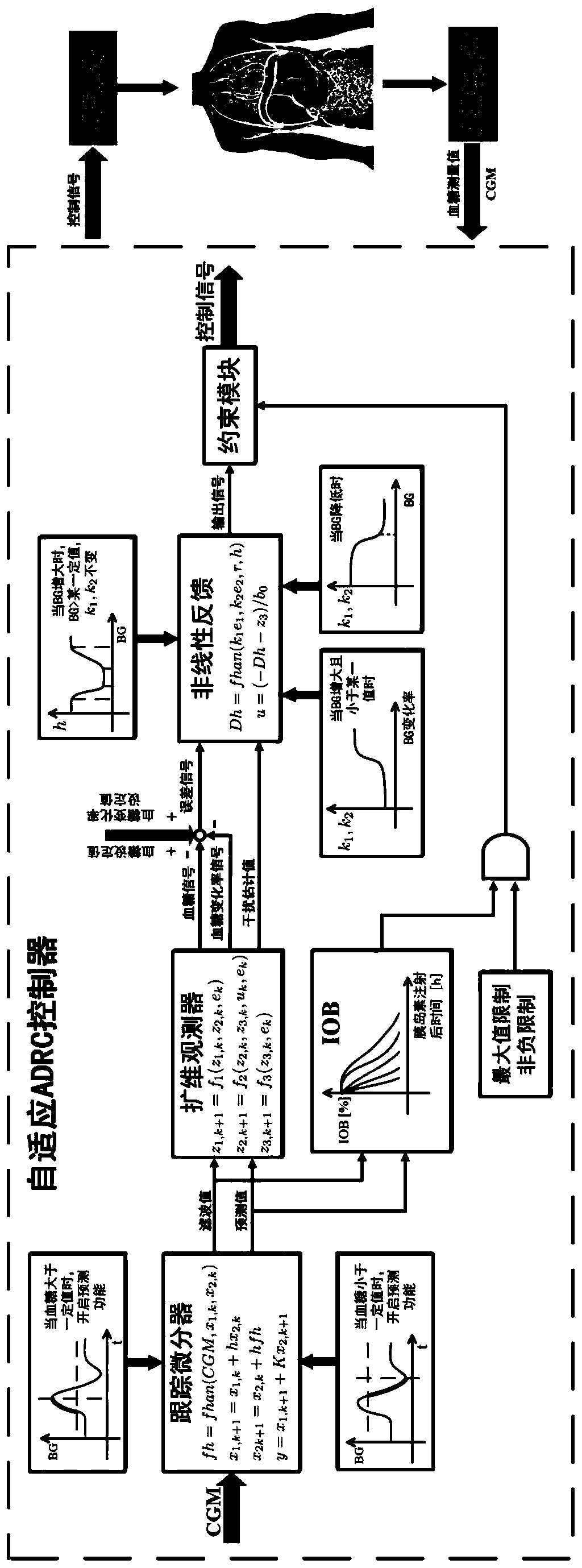
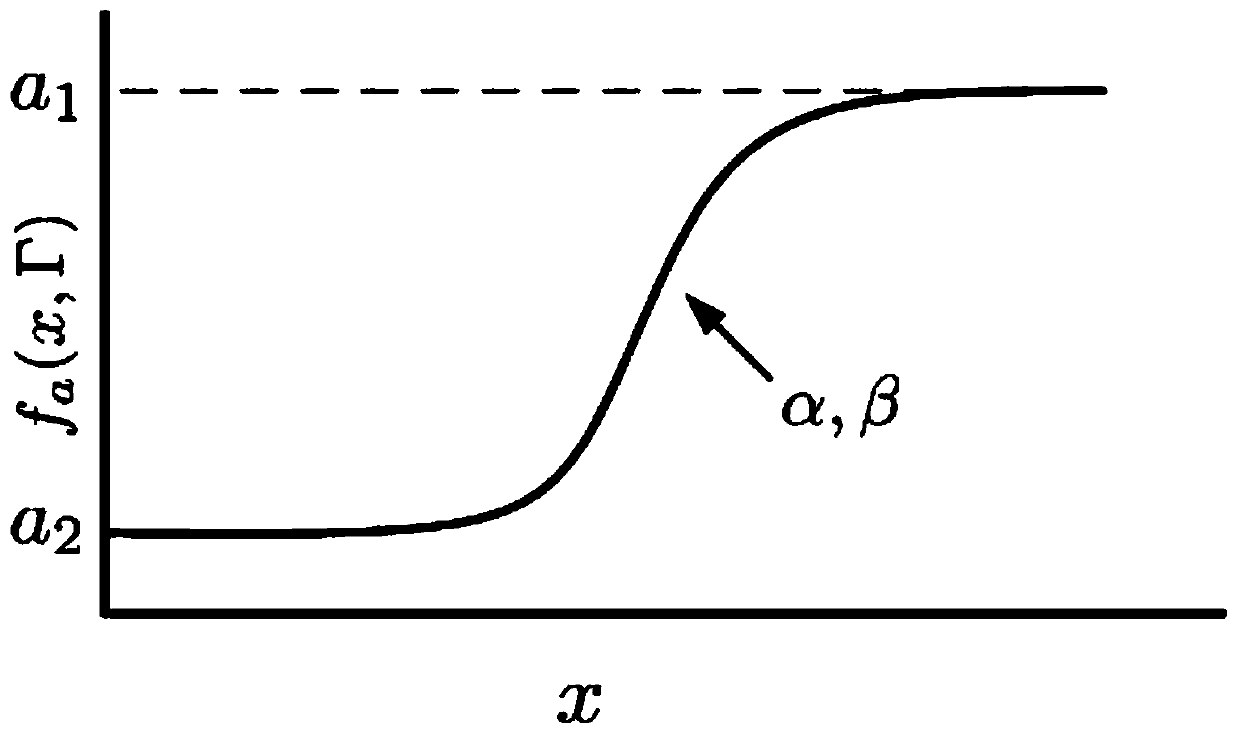
Artificial pancreas self-adaption and active-disturbance-rejection controller based on blood glucose variation trend
ActiveCN109999270AEnsure safetyAddress the risk of high and low blood sugar asymmetryDrug and medicationsMedical devicesDifferentiatorGain coefficient
The invention provides an artificial pancreas self-adaption and active-disturbance-rejection controller based on a blood glucose variation trend. The controller comprises a tracking differentiator module, an extended state observer module, a non-linear feedback module and a constrained module. A non-linear feedback model of the non-linear feedback module is u=(-fhan(k1e1, k2e2, r2, a)-z3) / b0, wherein k1, k2 and a are blood glucose variation trend self-adaption parameters, r2 is named as controlled quantity gain, e1 and e2 are a signal of an error between a blood glucose concentration set valueand a blood glucose concentration estimated value and a signal of an error between a blood glucose concentration variation rate set value and a blood glucose concentration variation rate estimated value respectively, z3 is a total disturbance estimated value, and b0 is a known gain coefficient. According to the controller, all uncertain factor actions on a controlled object come down to unknown disturbances, and the disturbances are estimated by using input and output data of the object and compensated. Therefore, the controller algorithm has certain robustness to the disturbances, such as personal parameter inaccuracy, model uncertainty, eating disturbance and before-meal dose inaccuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Method and system for a hybrid control-to-target and control-to-range model predictive control of an artificial pancreas
Described and illustrated is a system for management of diabetes that includes an infusion pump, glucose sensor and controller with a method programmed into the controller. The infusion pump is configured to deliver insulin to a subject. The glucose sensor is configured to sense glucose levels in the subject and provide output signals representative of the glucose levels in the subject. The controller is programmed to switchover from one mode of MPC control based on a predetermined range of blood glucose values to another MPC mode based on a predetermined target.
Owner:JDRF INT +1
Skin heating type artificial pancreas
ActiveCN103550843APeak action time shortenedMinimize the impact of blood glucose monitoringCatheterPressure infusionHuman bodyGlucose sensors
The invention provides a skin heating type artificial pancreas which comprises a blood sugar monitoring device, a duct-less insulin pump and a skin heating device, wherein the blood sugar monitoring device is used for monitoring the change of the blood sugar in a human body in real time and outputting a blood sugar value; the blood sugar monitoring device comprises a glucose sensor; the duct-less insulin pump is used for simulating the mode and function of a human pancreas for physiologically secreting insulin; the duct-less insulin pump comprises an insulin reserving hose; the skin heating device is used for heating the skin tissues located in the positions buried with the glucose sensor and / or the insulin reserving hose; and the skin heating device comprises a skin heating film, a temperature rising module, a temperature control module, a heat-insulating module and a temperature detecting module. The skin heating type artificial pancreas provided by the invention is capable of controlling the temperature of the skin of the human body, solving the delay problem between target blood sugar concentration and insulin peak acting time, shortening the insulin peak acting time and reducing the influence on the blood sugar monitoring caused by the temperature change.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Bio-artificial pancreas and a procedure for preparation of same
ActiveUS20100150984A1Prevent or diminish an immuno-response and/or rejectionBiocideMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusImplanted device
The present invention generally relates to implantable devices for producing insulin in diabetic animals and to methods of making same. Some embodiments include amphiphilic biomembranes for use in biological applications (e.g., as an alternative and / or supplemental insulin source). Some embodiments also include live insulin-producing cells contained within one or more amphiphilic membranes so as to prevent or diminish an immuno-response and / or rejection by the host.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com